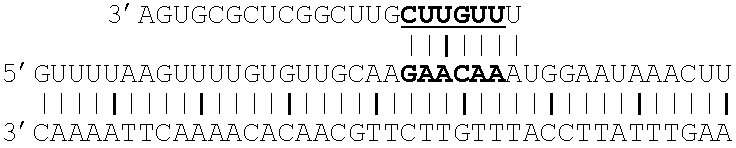Patents
Literature
154 results about "RNase H" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
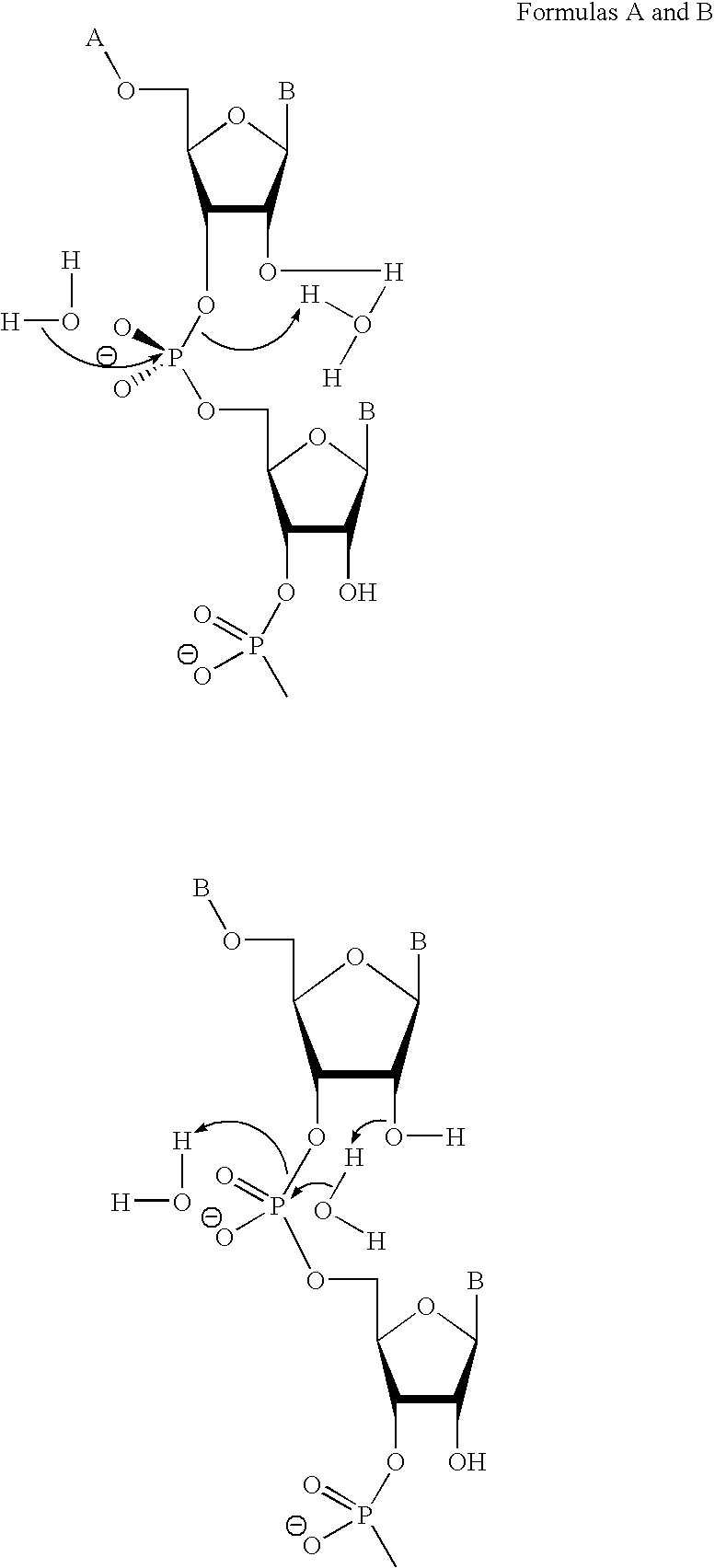
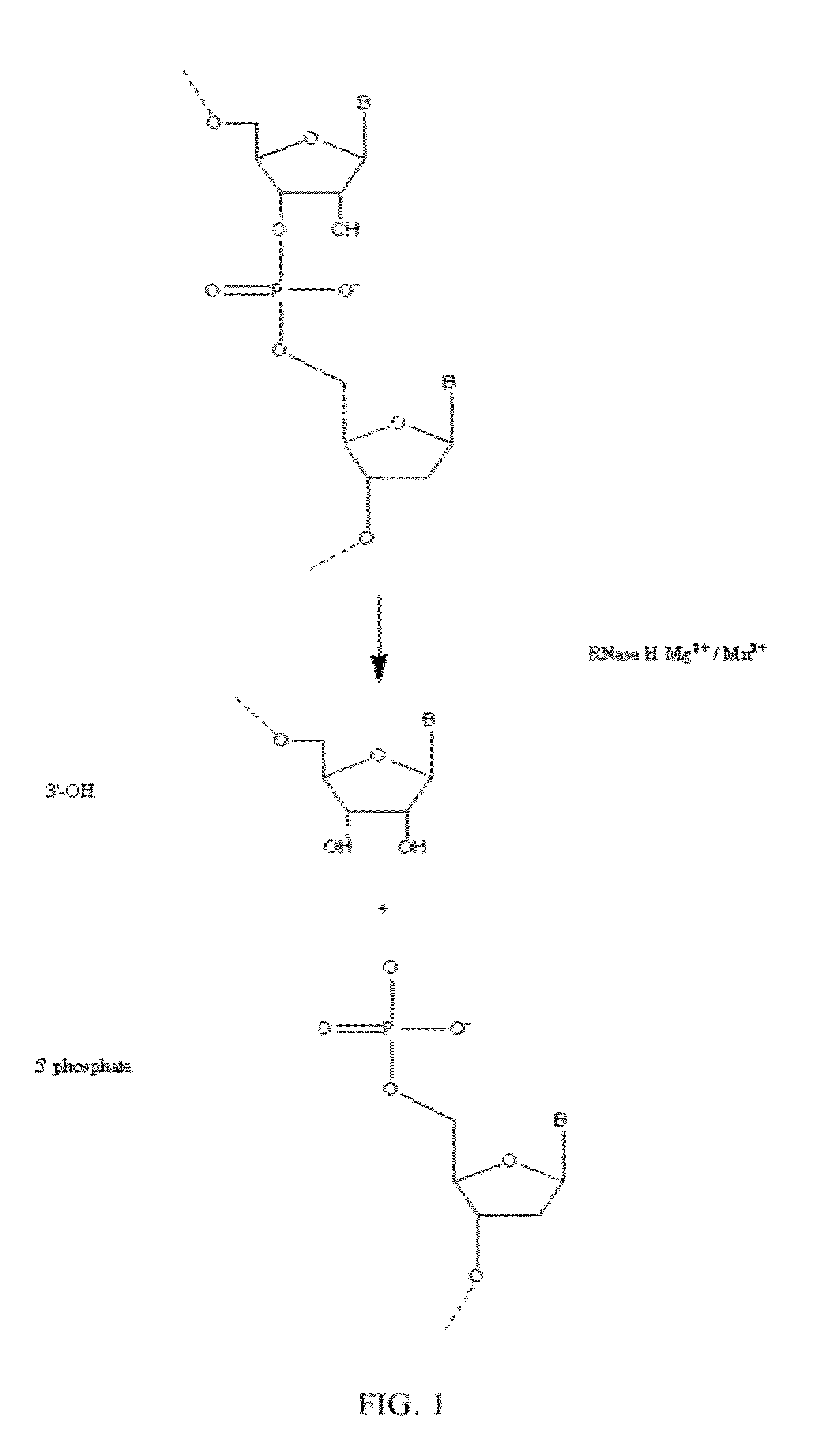
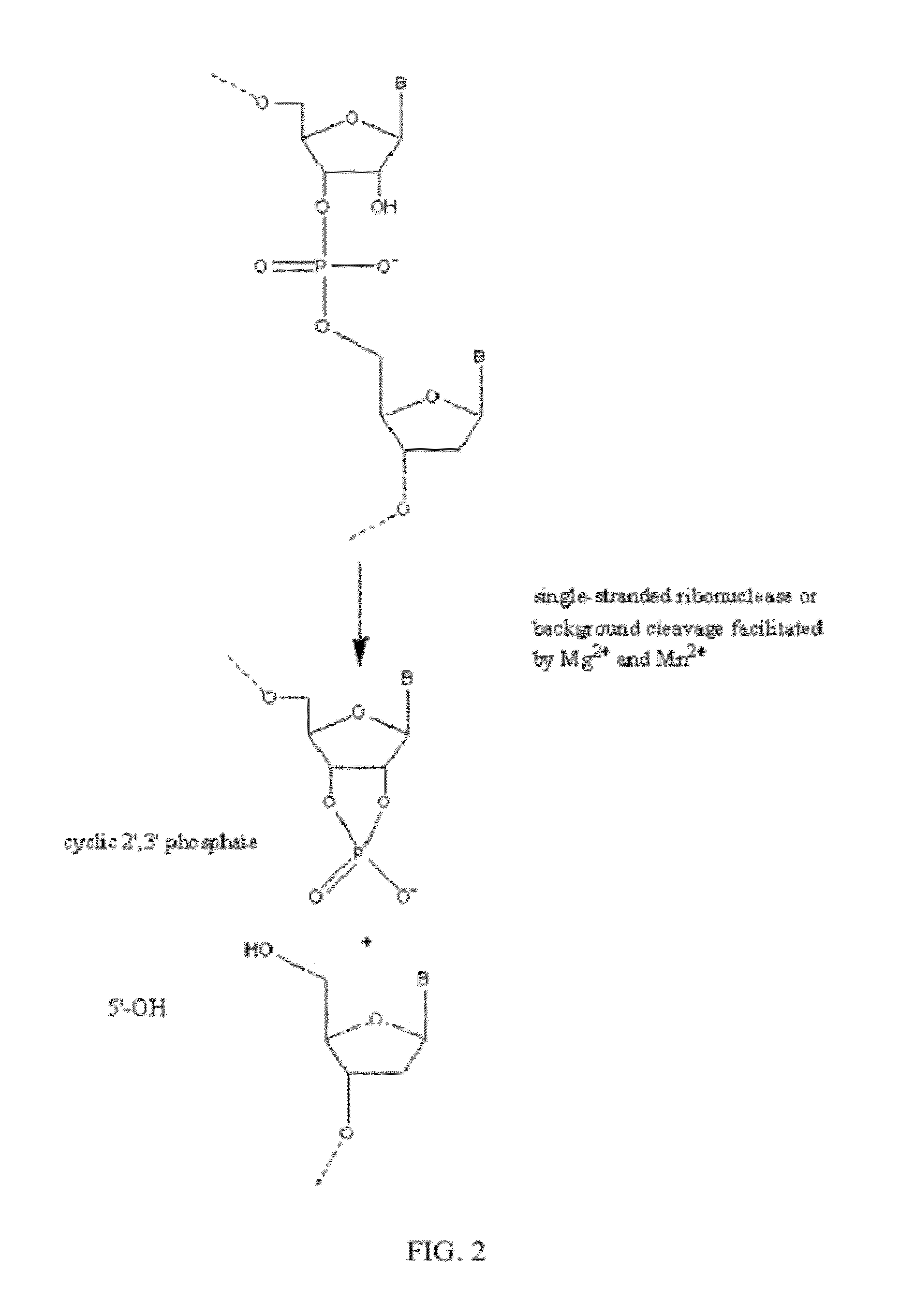
Ribonuclease H (abbreviated RNase H or RNH) is a family of non-sequence-specific endonuclease enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of RNA in an RNA/DNA substrate via a hydrolytic mechanism. Members of the RNase H family can be found in nearly all organisms, from bacteria to archaea to eukaryotes.
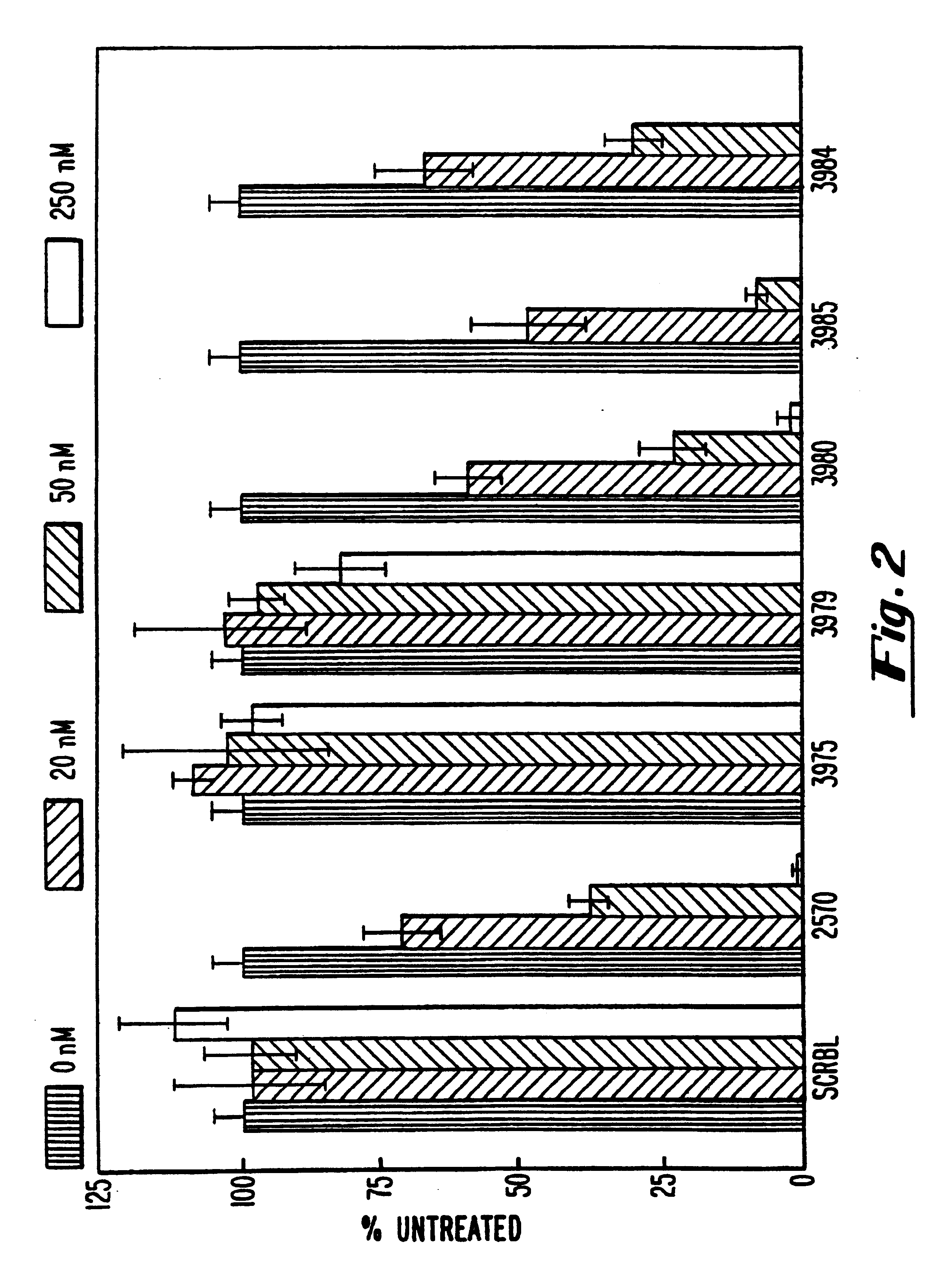
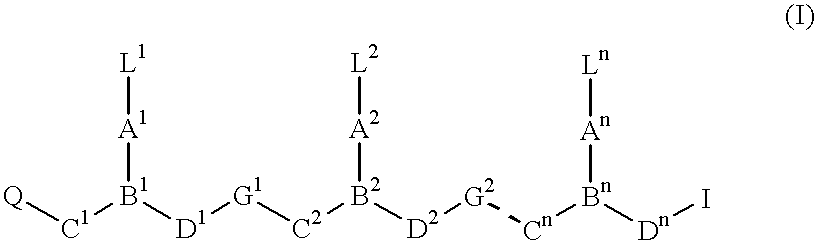
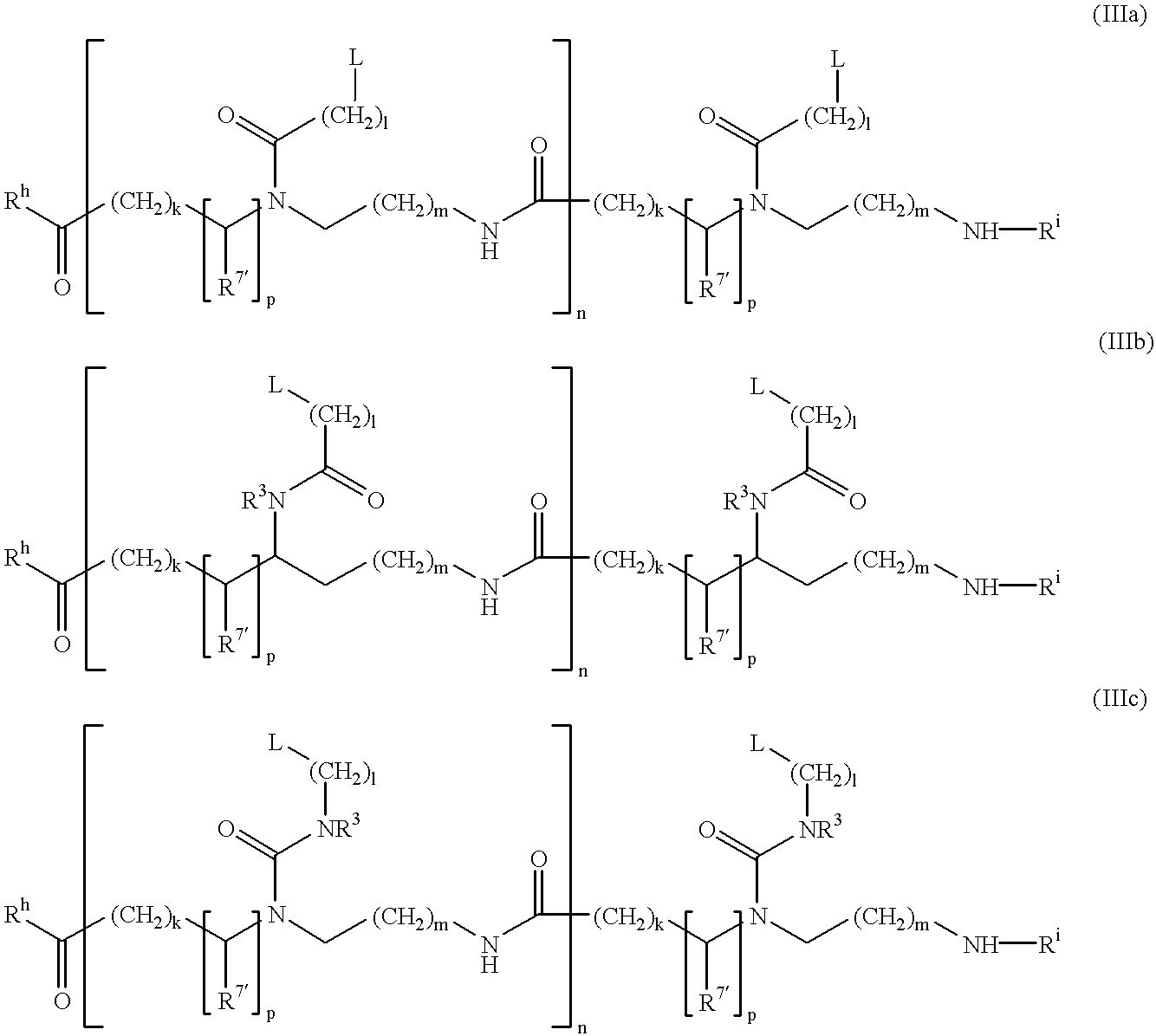
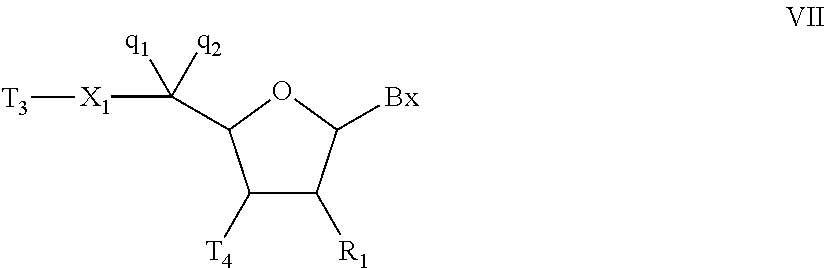
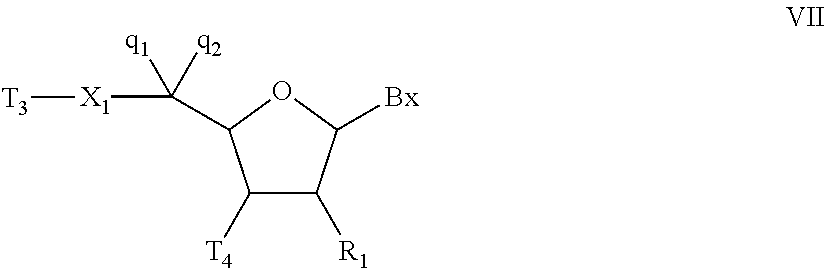
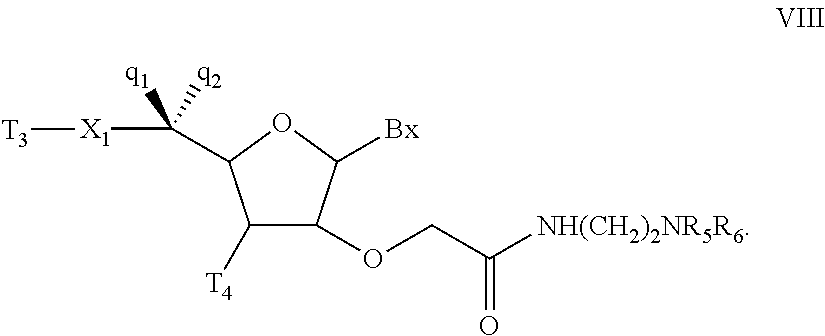
Gapped oligonucleotides
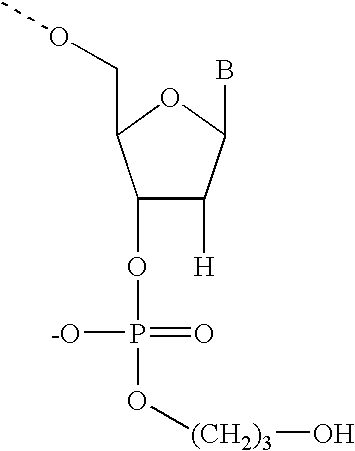
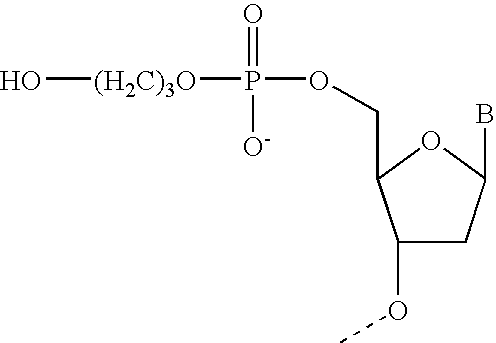
InactiveUS7015315B1Increased nuclease resistanceHigh binding affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsNuclease
Oligonucleotides and other macromolecules are provided which have increased nuclease resistance, substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary strand, and subsequences of 2′-deoxy-erythro-pentofuranosyl nucleotides that activate RNase H. Such oligonucleotides and macromolecules are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Gapped 2' modified oligonucleotides
InactiveUS6326199B1High affinityAvoid degradationHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideNuclease
Oligonucleotides and other macromolecules are provided that have increased nuclease resistance, substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary strand, and sub-sequences of 2'-deoxy-erythro-pentofuranosyl nucleotides that activate RNase H enzyme. Such oligonucleotides and macromolecules are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to antisense therapeutics.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
PNA-DNA-PNA chimeric macromolecules
InactiveUS6277603B1Increase resistanceHigh affinitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological bodyResearch purpose
Macromolecules are provided that have increased nuclease resistance, increasing binding affinity to a complementary strand, and that activate RNase H enzyme. The macromolecules have the structure PNA-DNA-PNA where the DNA portion is composed of subunits of 2'-deoxy-erythro-pento-furanosyl nucleotides and the PNA portions are composed of subunits of peptide nucleic acids. Such macromolecules are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to therapeutics.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Rnase h-based assays utilizing modified RNA monomers
InactiveUS20090325169A1Strong specificityConvenient ligationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRNase PHOligonucleotide
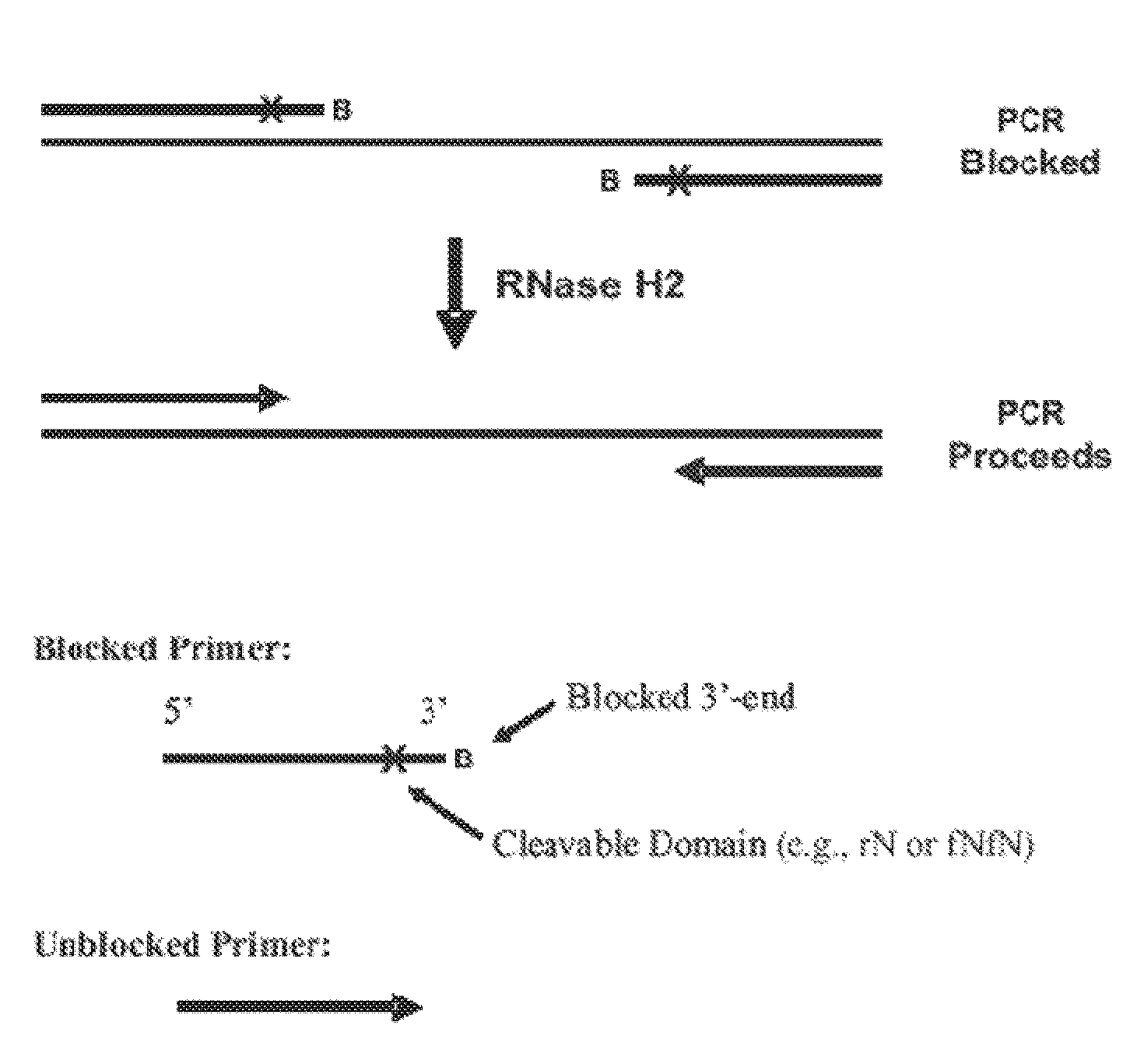
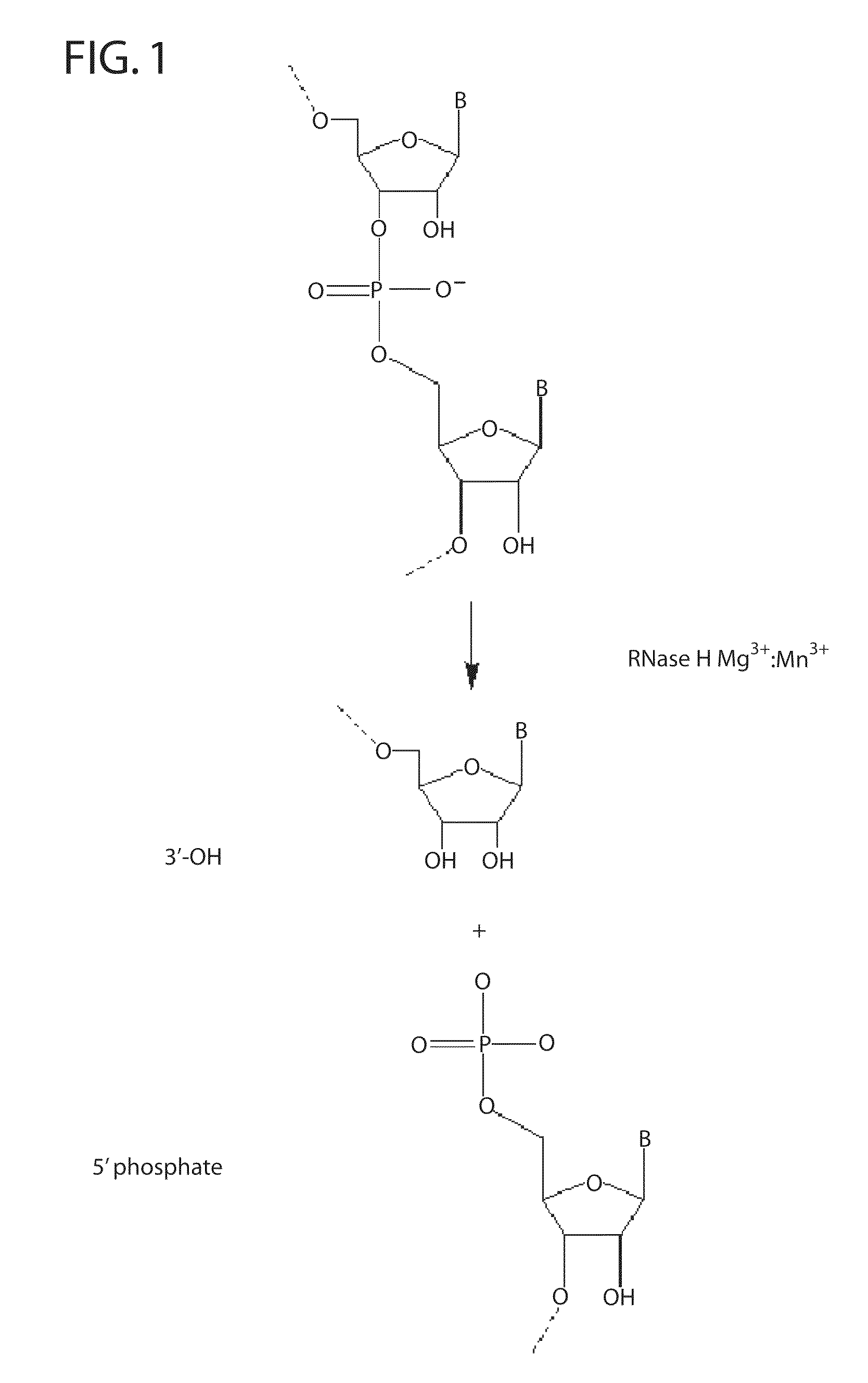
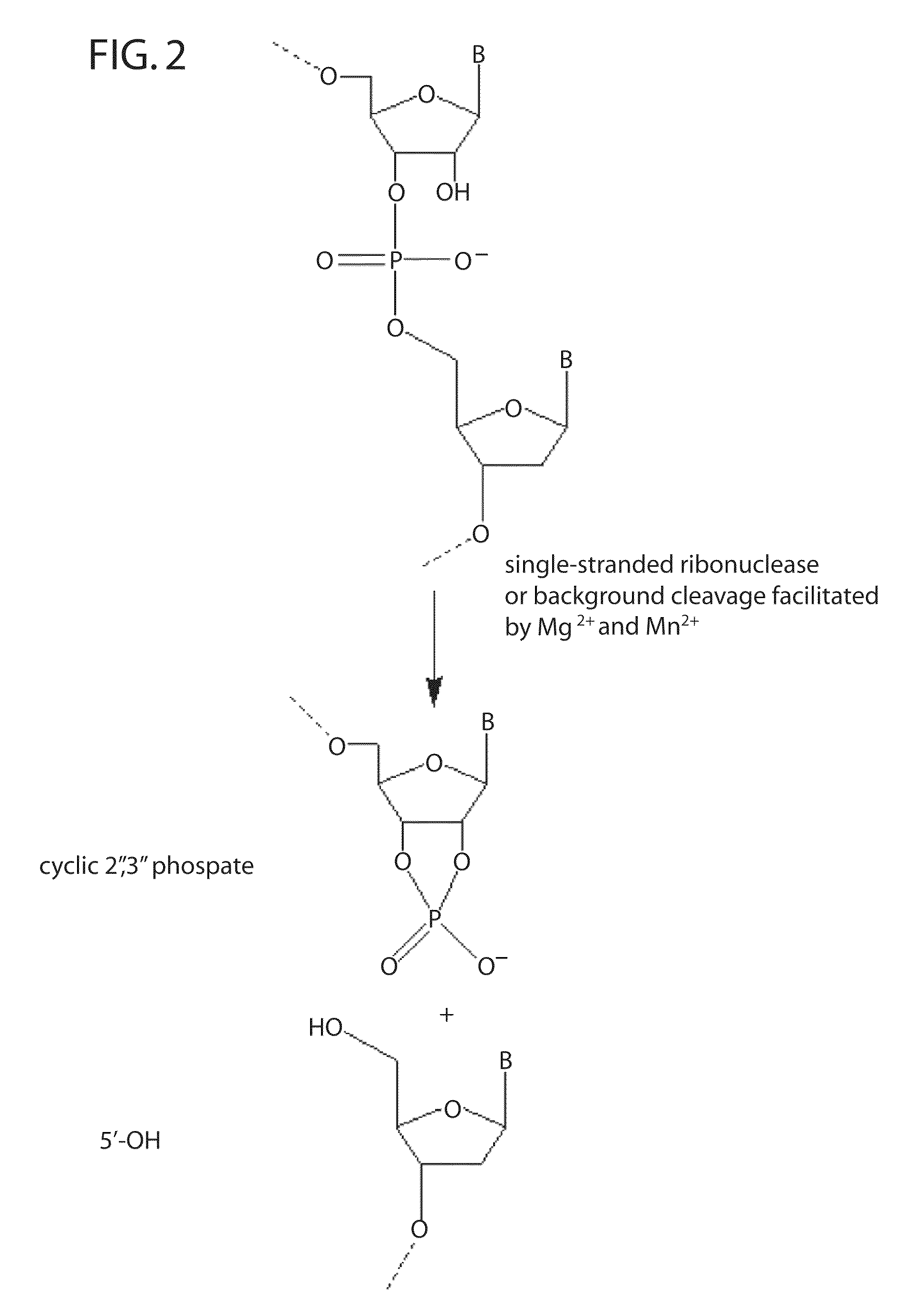
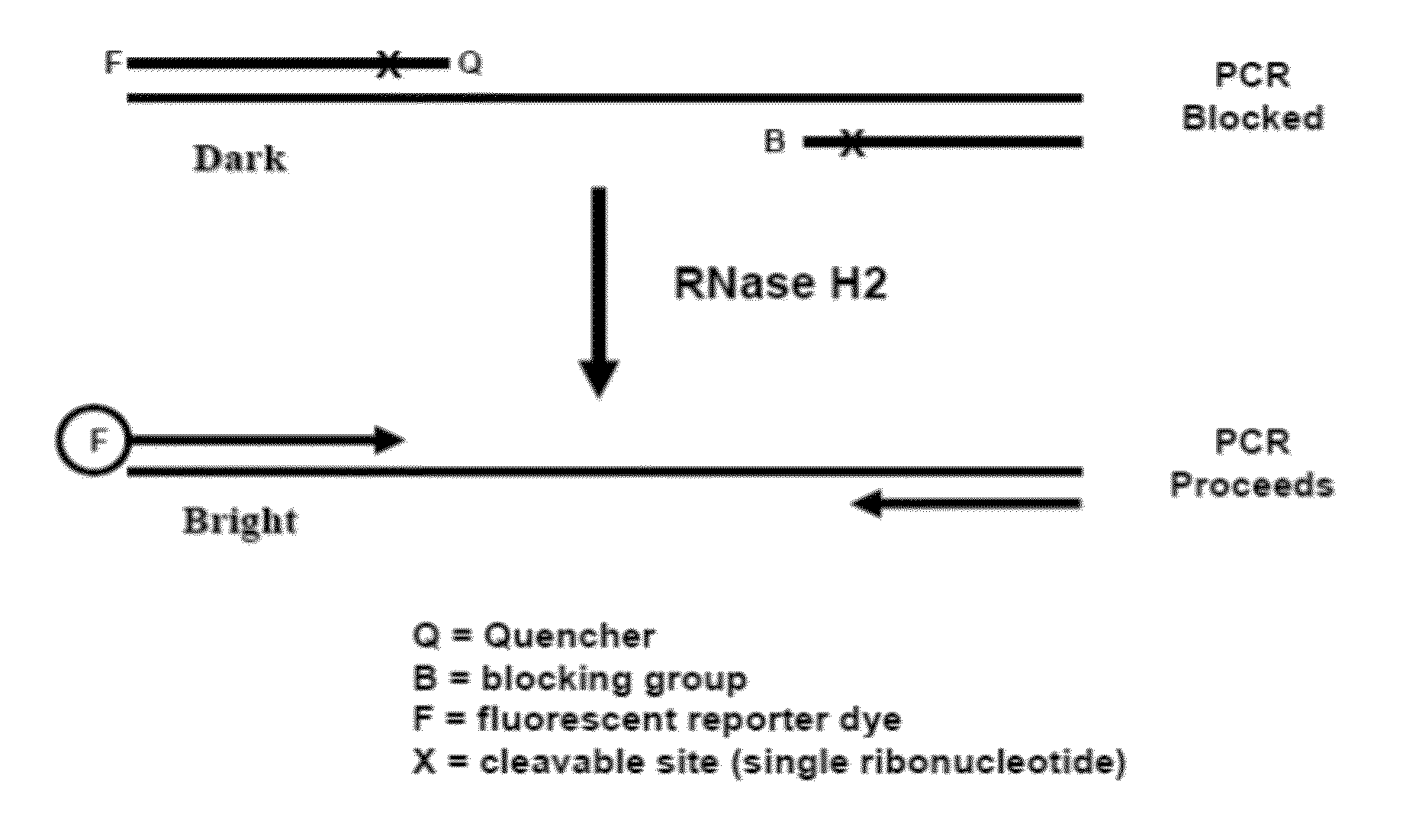
The present invention pertains to novel oligonucleotide compounds for use in various biological assays, such as nucleic acid amplification, ligation and sequencing reactions. The novel oligonucleotides comprise a ribonucleic acid domain and a blocking group at or near the 3′ end of the oligonucleotide. These compounds offer an added level of specificity previously unseen. Methods for performing nucleic acid amplification, ligation and sequencing are also provided. Additionally, kits containing the oligonucleotides are also disclosed herein.
Owner:INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES
Hybrid oligonucleotide phosphorothioates
The invention provides hybrid oligonucleotides having phosphorothioate or phosphorodithioate internucleotide linkages, and both deoxyribonucleosides and ribonucleosides or 2′-substituted ribonucleosides. Such hybrid oligonucleotides have superior properties of duplex formation with RNA, nuclease resistance, and RNase H activation.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS WORCESTER
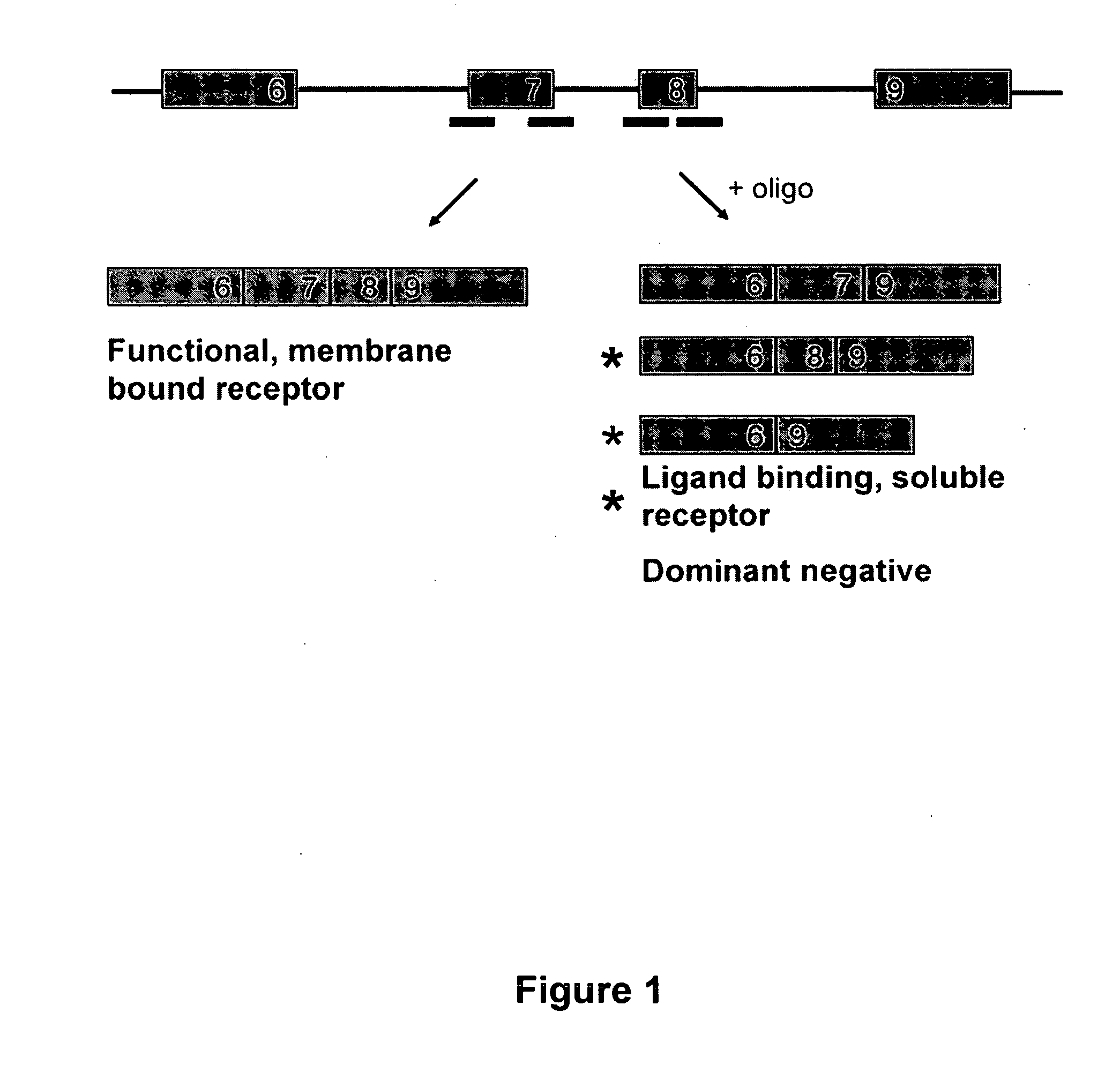
Splice switch oligomers for TNF superfamily receptors and their use in treatment of disease
InactiveUS20070105807A1High expressionReduce expressionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSplice switchingPrecursor mRNA
Methods and compositions are disclosed for controlling expression of TNF receptors (TNFR1 and TNFR2) and of other receptors in the TNFR superfamily using compounds that modulate splicing of pre-mRNA encoding these receptors. More specifically these compounds cause the removal of the transmembrane domains of these receptors and produce soluble forms of the receptor which act as an antagonist to reduce TNF-α activity or activity of the relevant ligand. Reducing TNF-α activity provides a method of treating or ameliorating inflammatory diseases or conditions associated with TNF-α activity. Similarly, diseases associated with other ligands can be treated in like manner. In particular, the compounds of the invention are splice-splice switching oligomers (SSOs) which are small molecules that are stable in vivo, hybridize to the RNA in a sequence specific manner and, in conjunction with their target, are not degraded by RNAse H.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS +3
Gapped 2' modified oligonucleotides
InactiveUS6146829AHigh affinityAvoid degradationSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleaseOrganism
Oligonucleotides and other macromolecules are provided that have increased nuclease resistance, substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary strand, and sub-sequences of 2'-deoxy-erythro-pentofuranosyl nucleotides that activate RNase H enzyme. Such oligonucleotides and macromolecules are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to antisense therapeutics.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
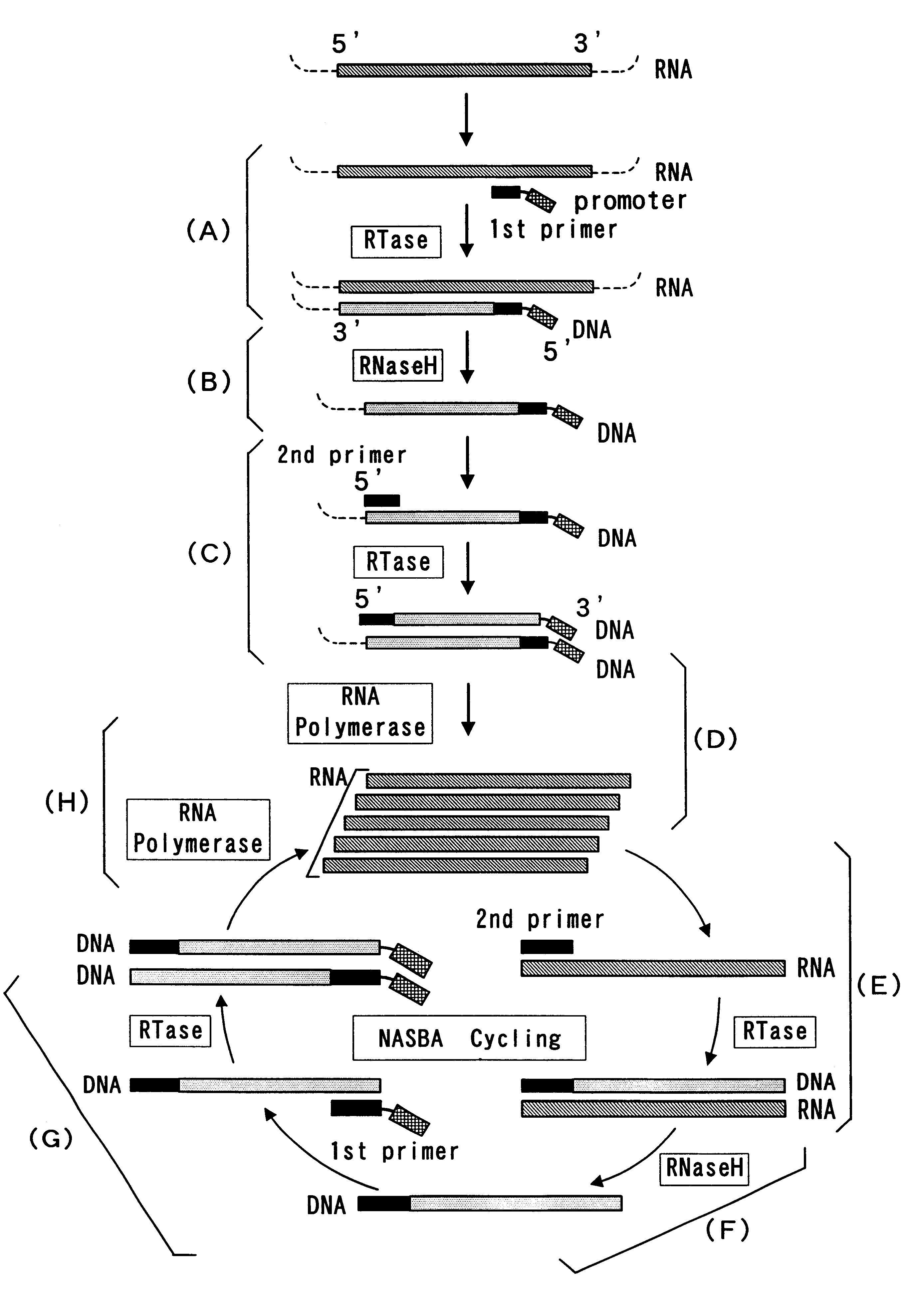
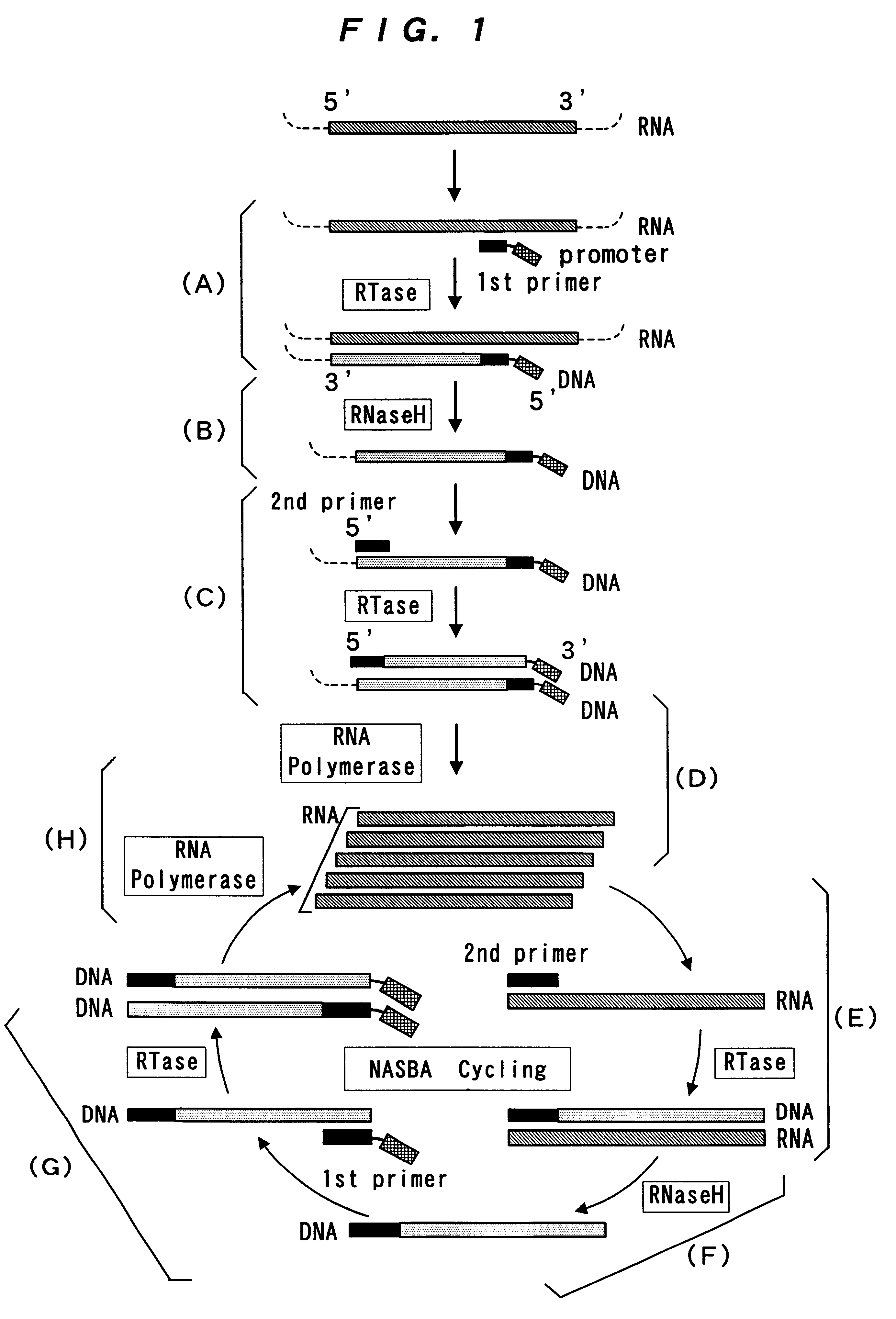
Method for generating amplified RNA
InactiveUS7354742B2Improve efficiencyShorten the time periodSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyDNA
The present invention provides a new method for producing amplified RNA from a selected set of cells. This method combines and utilizes known methods in a novel way to produce the gene expression profiles. The methods of the present invention utilize thermostable DNA polymerases and RNase H to produce high fidelity second strand synthesis of nucleic acids from selected cells in a highly efficient mariner and in substantially reduced time.
Owner:ORTHO MCNEIL PHARM INC
Gapped 2' modified oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20070032446A1High affinityAvoid degradationSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological bodyNuclease
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Rnase h-based assays utilizing modified RNA monomers
InactiveUS20150225782A1Strong specificityConvenient ligationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationOligonucleotideMonomer
The present invention pertains to novel oligonucleotide compounds for use in various biological assays, such as nucleic acid amplification, ligation and sequencing reactions. The novel oligonucleotides comprise a ribonucleic acid domain and a blocking group at or near the 3′ end of the oligonucleotide. These compounds offer an added level of specificity previously unseen. Methods for performing nucleic acid amplification, ligation and sequencing are also provided. Additionally, kits containing the oligonucleotides are also disclosed herein.
Owner:INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES
Isothermal chimeric primer nucleic acid amplification methods using blocking oglionucleotide
InactiveUS7056671B2Improve targeting efficiencyHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolymerase LRibonucleotide synthesis
Methods of amplifying a target nucleic acid whereby the target nucleic acid is amplified in the presence of a deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate, a DNA polymerase having strand displacement activity, at least one chimeric oligonucleotide primer, at least one upstream block oligonucleotide and a RNase H; wherein the chimeric oligonucleotide primer contains a ribonucleotide positioned at the 3′-terminus; wherein the upstream block oligonucleotide is capable of annealing to a region 3′ to a portion in the nucleic acid as the template to which the chimeric oligonucleotide primer anneals; and compositions and kits thereof.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
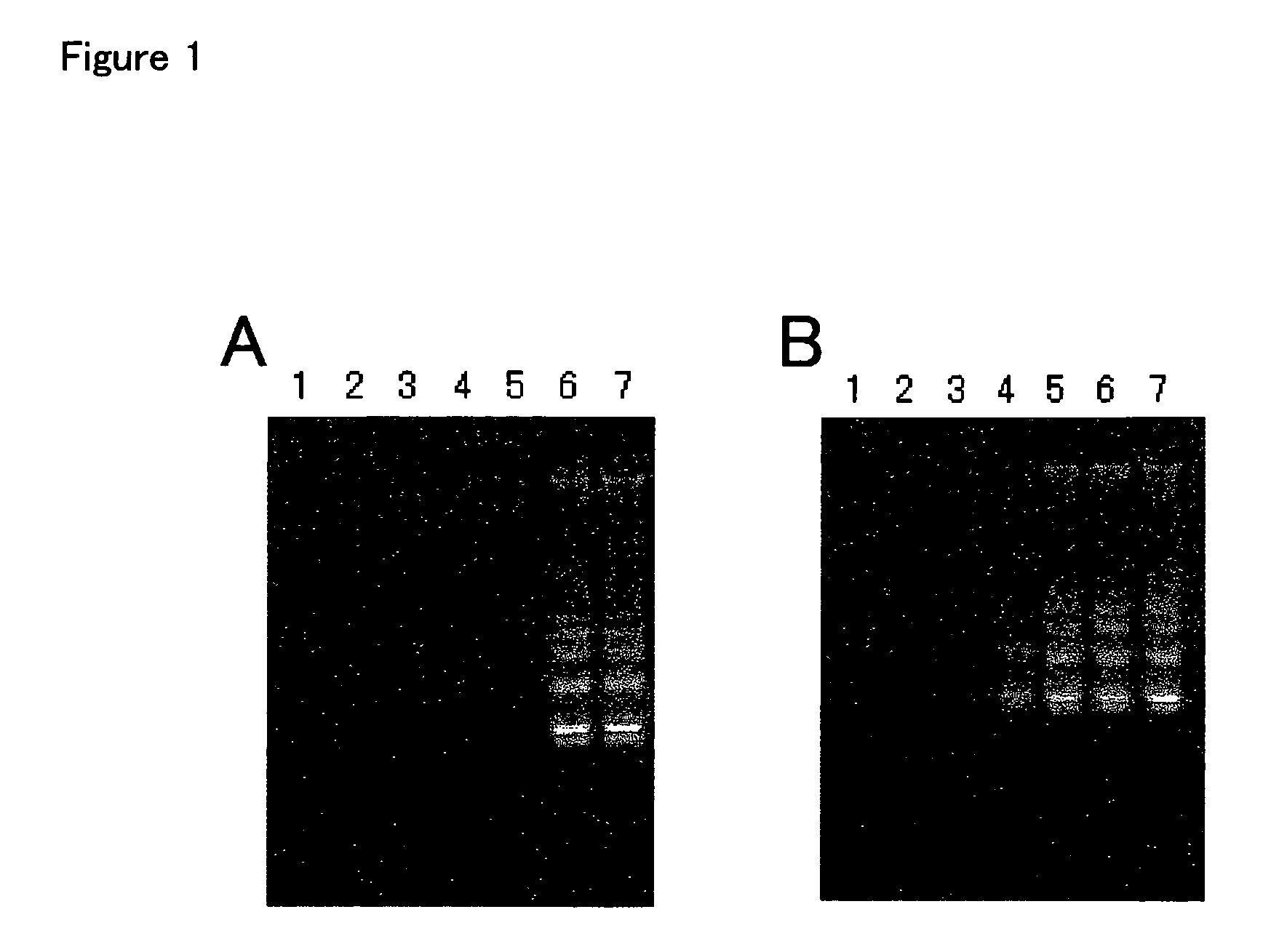
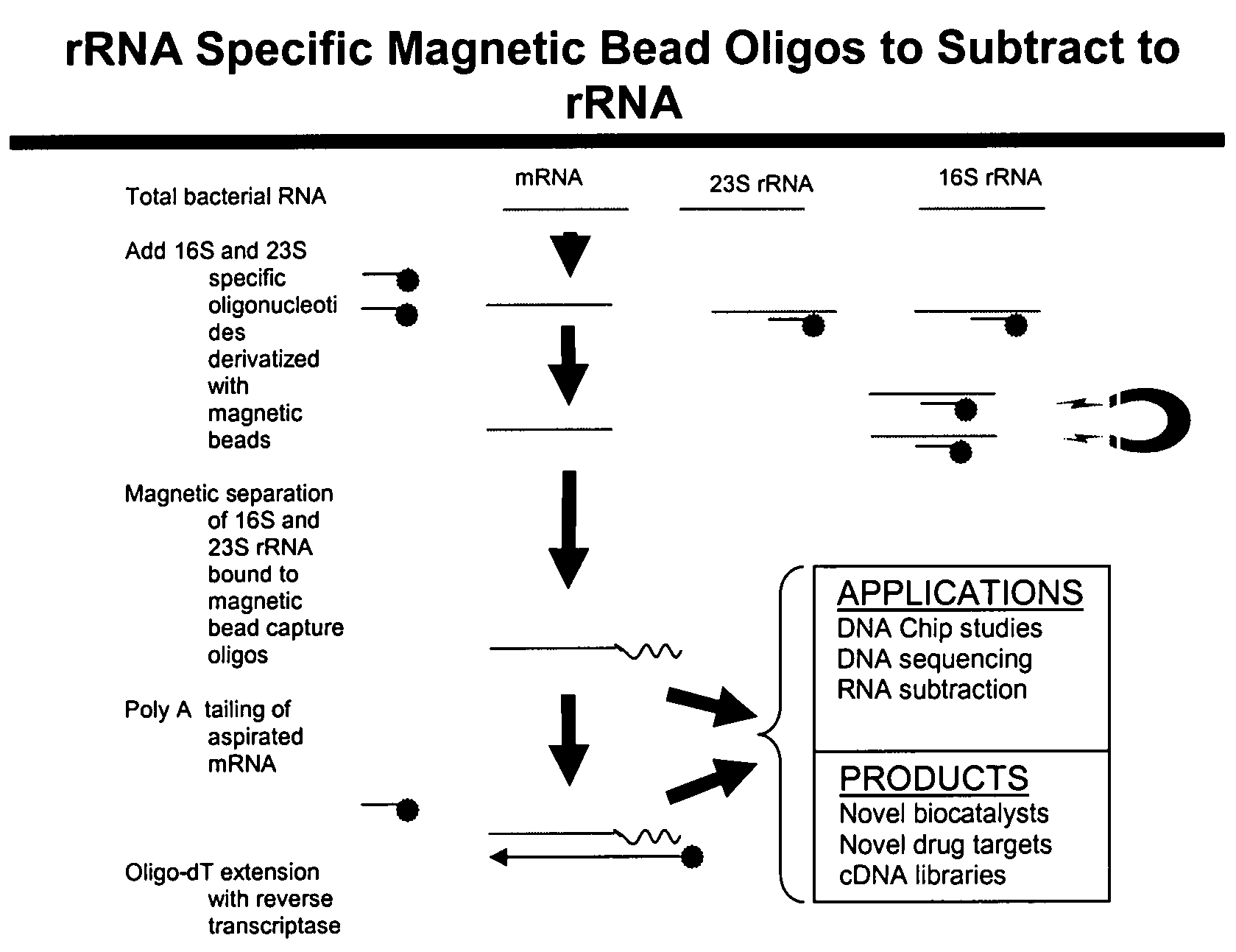
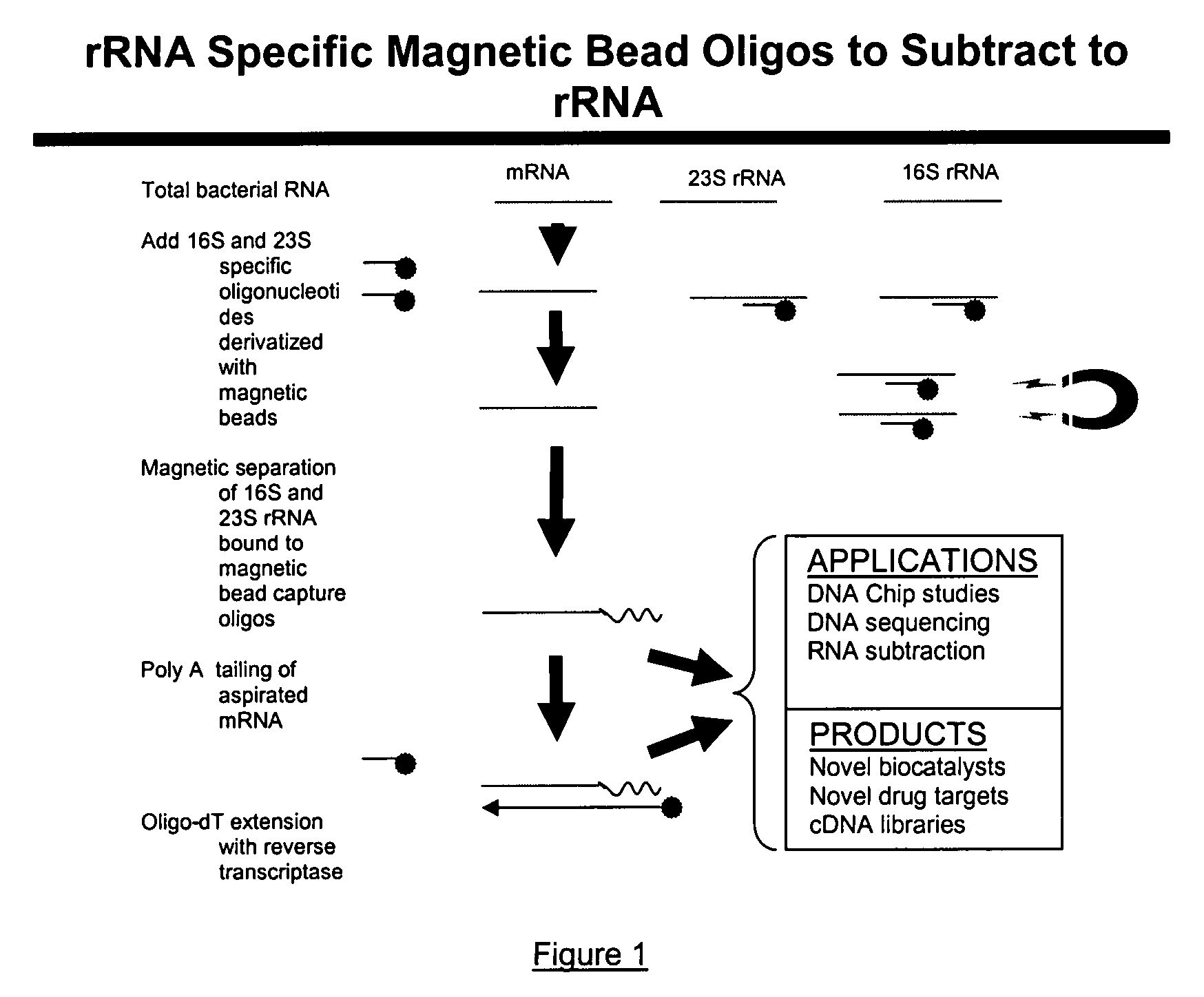
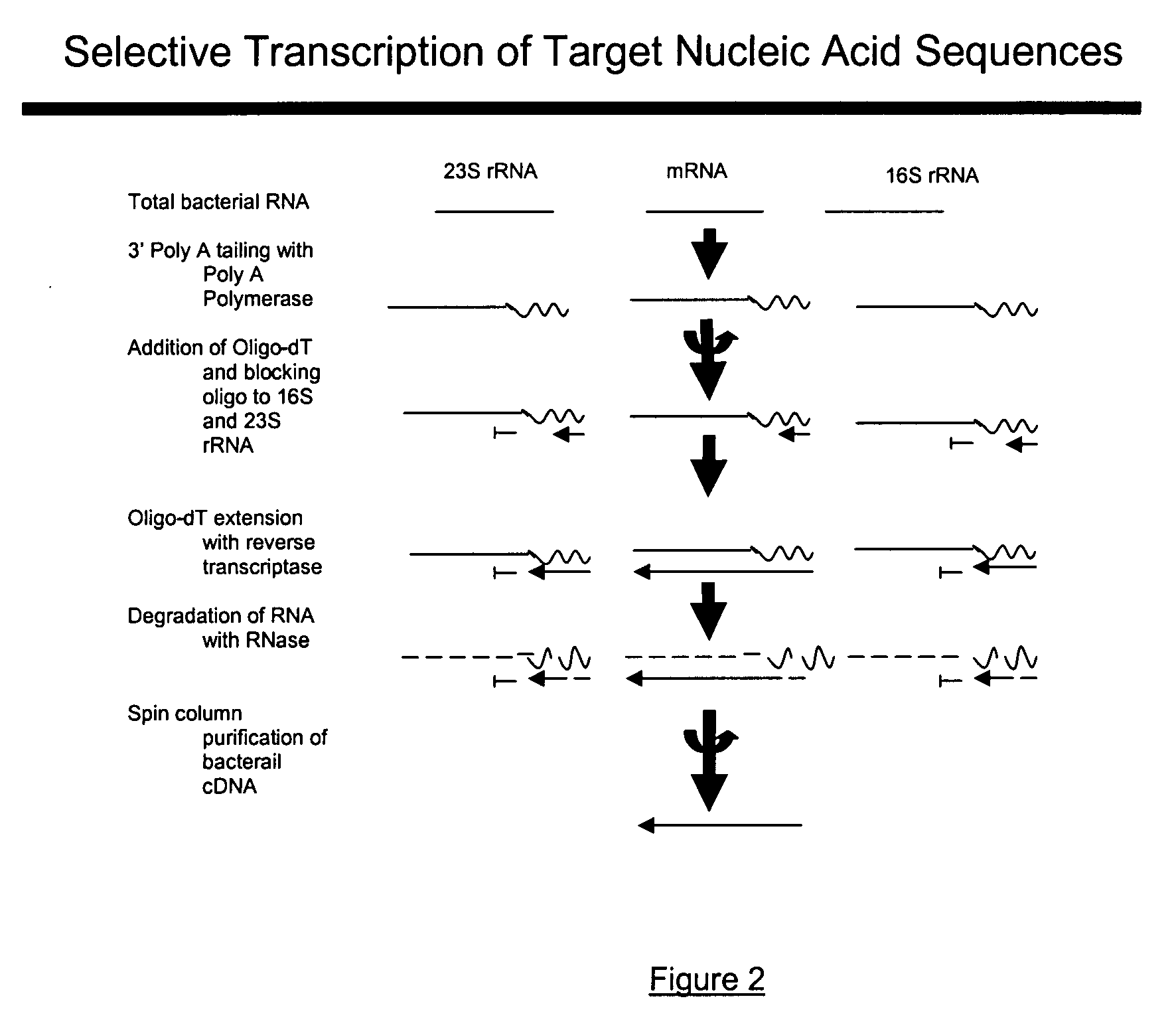
Methods and kits for negative selection of desired nucleic acid sequences
The present invention pertains to a method to isolate, separate, enrich or amplify a targeted nucleotide polymer such as mRNA through selective reverse transcription of the targeted polymer into cDNA from a sample comprising of chemically identical or similar polynucleotide polymers such as rRNA. The enrichment of the targeted nucleic acid such as mRNA is accomplished by blocking the reverse transcription of undesired rRNA while allowing unrestricted reverse transcription of the targeted polymer. The invention also embodies that the cleavage of the non-targeted nucleic acid such as rRNA bound to an oligonucleotide through enzymatic activity (RNase H). The invention further embodies methods and kits to accomplish the utility of the invention through the following steps 1) 3′ tailing of chemically identical or similar nucleotide polymers in a sample that includes bacterial mRNA 2) a 3′ tail capable of binding to a oligo-dN primer 3) at least one oligonucleotide capable of preventing the extension of oligo-dN bound to at least one non-targeted nucleotide polymers by a DNA polymerase such as a reverse transcriptase without restricting conversion of bacterial mRNA into cDNA 4) where the non-targeted molecule is prevented as a template for cDNA synthesis by enzymatic cleavage (RNase H) of template (rRNA)-oligonucleotide hybrid 5) where the reverse transcriptase is physically blocked by the oligonucleotide bound to the non-targeted nucleic acids such as rRNA 5) purification of the selectively transcribed cDNA. In further embodiments of the present invention, methods and composition to enable the study of bacterial transcriptomics-an analysis of genes expressed by a bacterial infection of a host, an isolated bacterial culture or a bacterial community, such as recovered from soil, intestine, mouth, biofilm, water etc are also included for use in DNA-chip or sequencing analyses.
Owner:SOWLAY MOHANKUMAR R
Reagent for nucleic acid amplification and process for nucleic acid amplification
InactiveUS6261773B1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyForward primerPolymerase L
The present invention provide a process for sequence-specific nucleic acid amplification capable of improving the detection sensitivity and increasing the signal. In particular, the present invention provides a reagent for nucleic acid amplification containing at least one member selected from the group consisting of EDTA, NTA, UDA, CyDTA, DTPA, GEDTA, TTHA and their salts, specifically a reagent for nucleic acid amplification comprising, in addition to the at least one compound, a forward primer having a DNA sequence homologous to a sequence of a target RNA; a reverse primer having a DNA sequence complementary to a sequence of the target RNA and having a promoter for RNA polymerase attached to its 5' end; ribonucleotides; deoxyribonucleotides; a reverse transcriptase or RNA-directed DNA polymerase; a RNase H; a DNA polymerase or a reverse transcriptase having DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity; and a RNA polymerase. The present invention also provides a process for nucleic acid amplification characterized by carrying out a nucleic acid amplification reaction in the presence of at least one member selected from the group consisting of EDTA, NTA, UDA, CyDTA, DTPA, GEDTA, TTHA and their salts.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Oligonucleotides having A-DNA form and B-DNA form conformational geometry
InactiveUS6737520B2High affinityImproved nuclease resistanceSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideA-DNA
Modified oligonucleotides containing both A-form conformation geometry and B-from conformation geometry nucleotides are disclosed. The B-form geometry allows the oligonucleotide to serve as substrates for RNase H when bound to a target nucleic acid strand. The A-form geometry imparts properties to the oligonucleotide that modulate binding affinity and nuclease resistance. By utilizing C2' endo sugars or O4' endo sugars, the B-form characteristics are imparted to a portion of the oligonucleotide. The A-form characteristics are imparted via use of either 2'-O-modified nucleotides that have 3' endo geometries or use of end caps having particular nuclease stability or by use of both of these in conjunction with each other.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Oligonucleotides having A-DNA form and B-DNA form conformational geometry
InactiveUS7119184B2High affinityImproved nuclease resistanceSugar derivativesPhosphorus organic compoundsNucleotideA-DNA
Modified oligonucleotides containing both A-form conformation geometry and B-from conformation geometry nucleotides are disclosed. The B-form geometry allows the oligonucleotide to serve as substrates for RNase H when bound to a target nucleic acid strand. The A-form geometry imparts properties to the oligonucleotide that modulate binding affinity and nuclease resistance. By utilizing C2′ endo sugars or O4′ endo sugars, the B-form characteristics are imparted to a portion of the oligonucleotide. The A-form characteristics are imparted via use of either 2′-O-modified nucleotides that have 3′ endo geometries or use of end caps having particular nuclease stability or by use of both of these in conjunction with each other.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
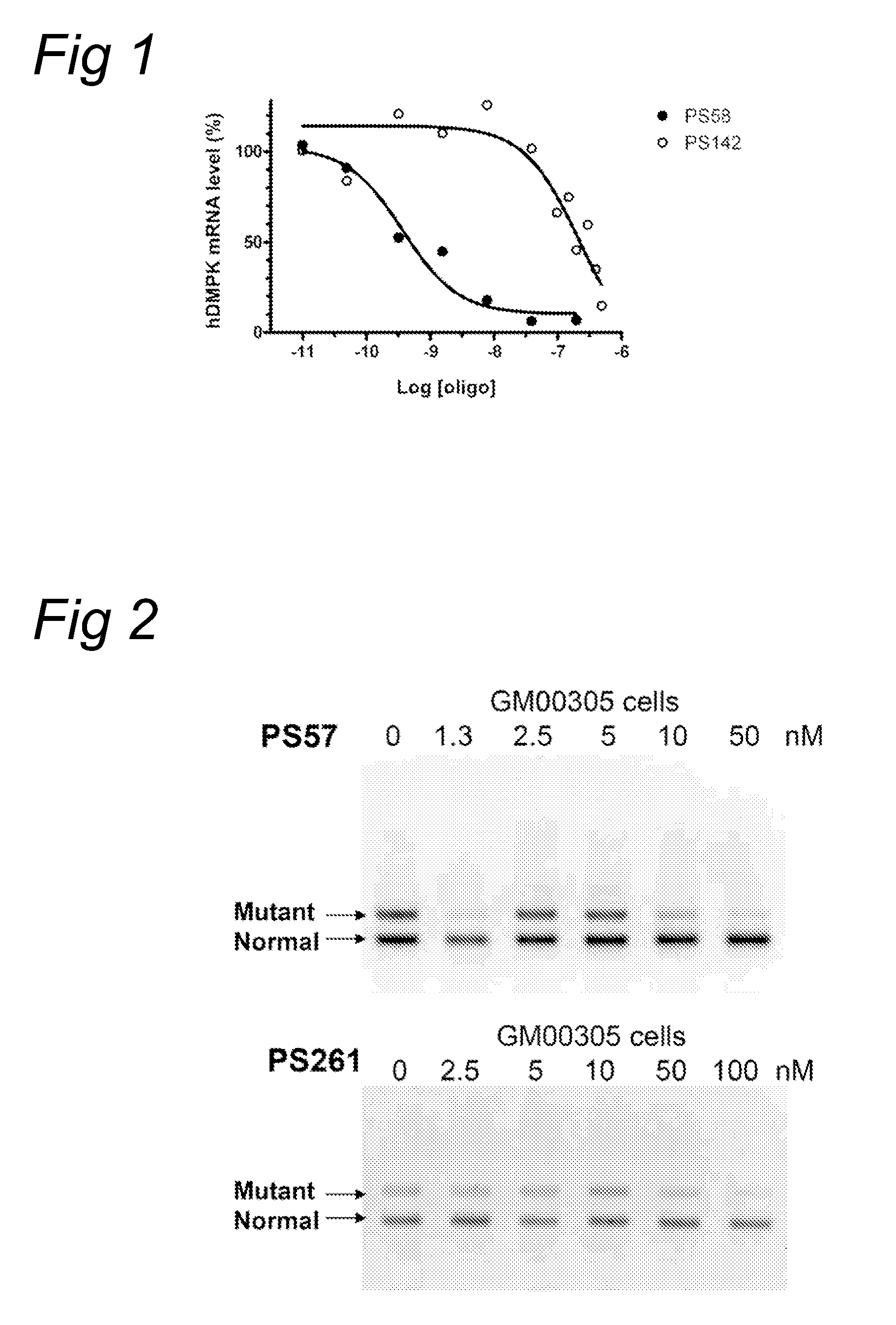
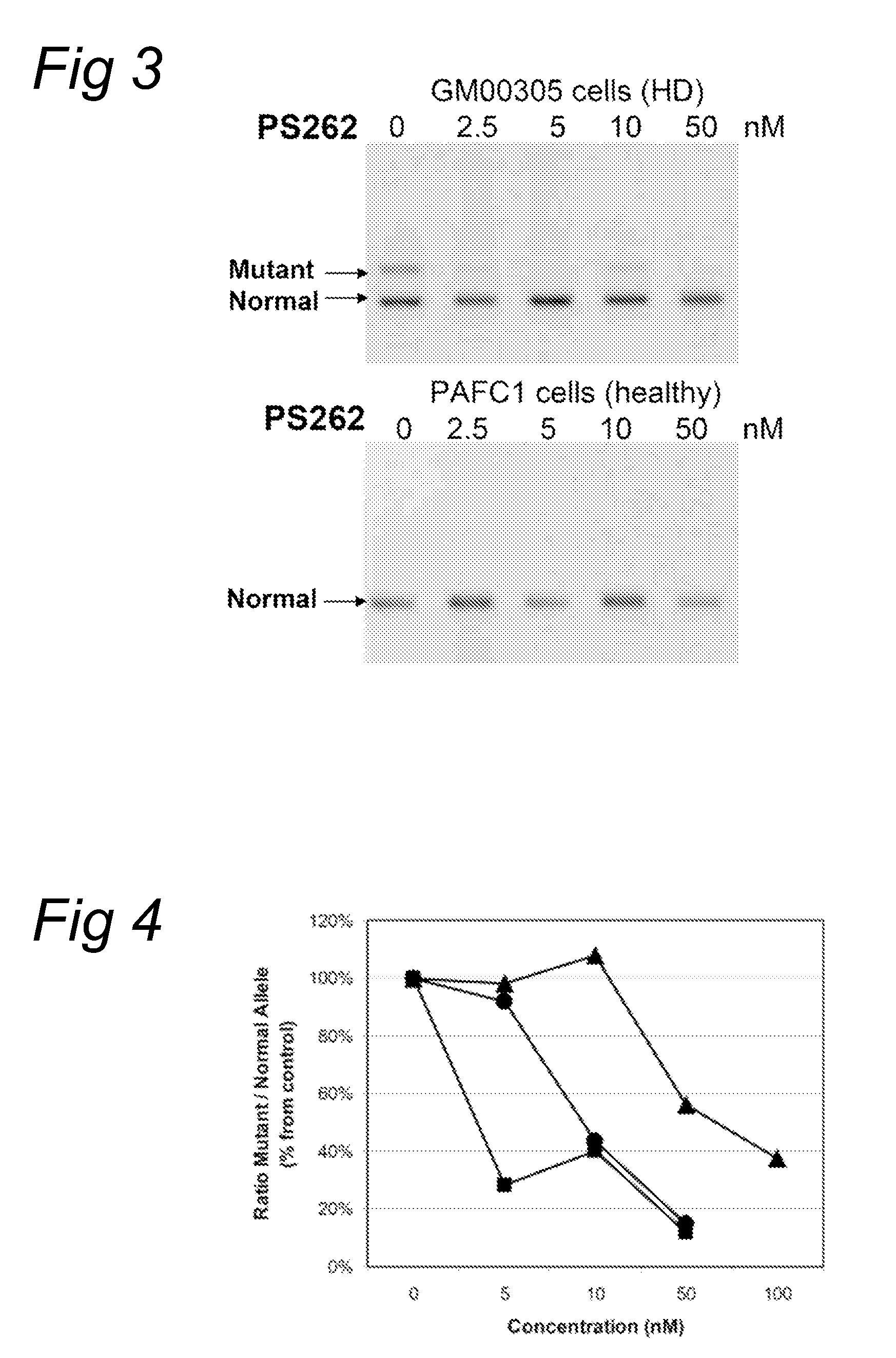
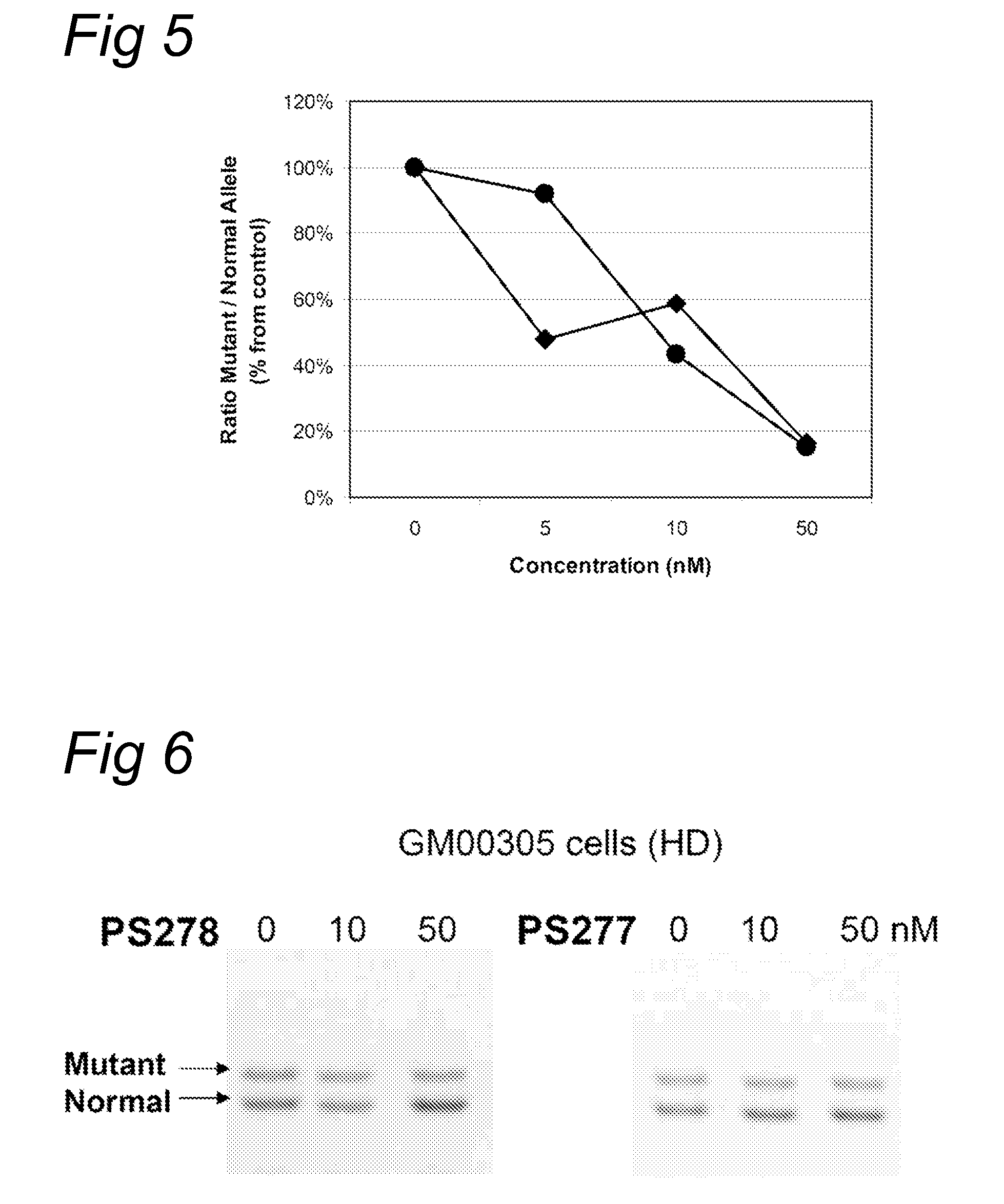
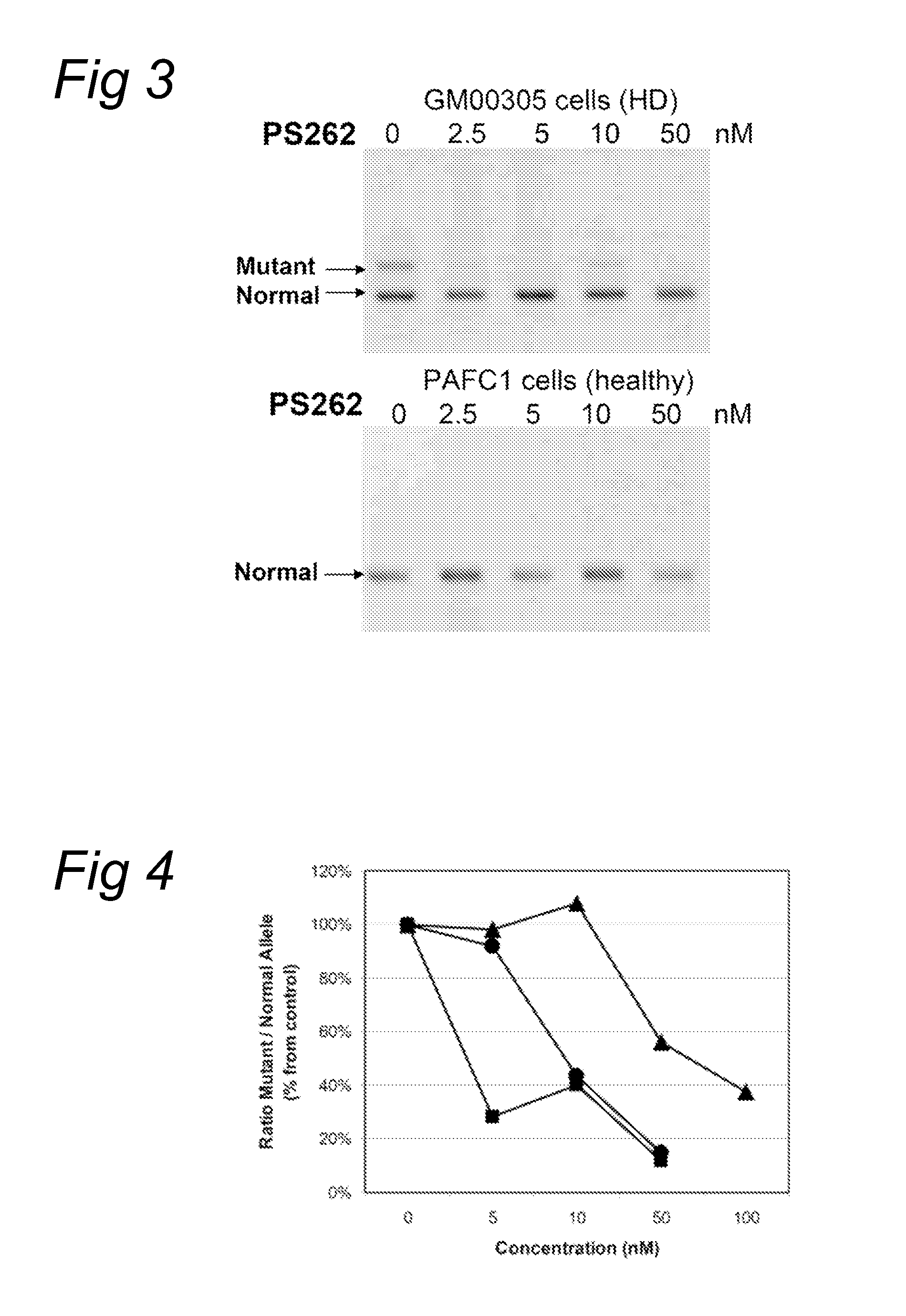
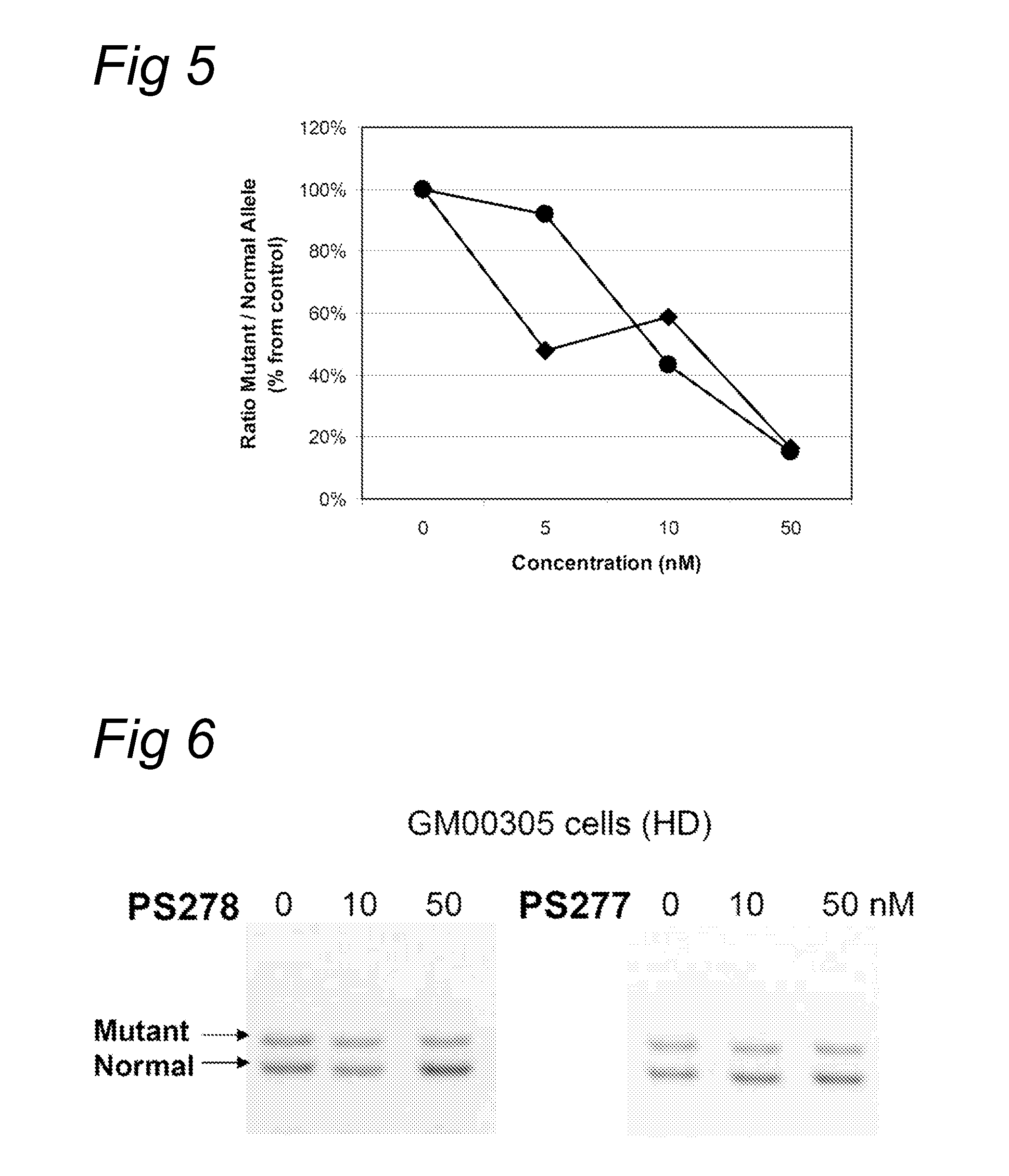
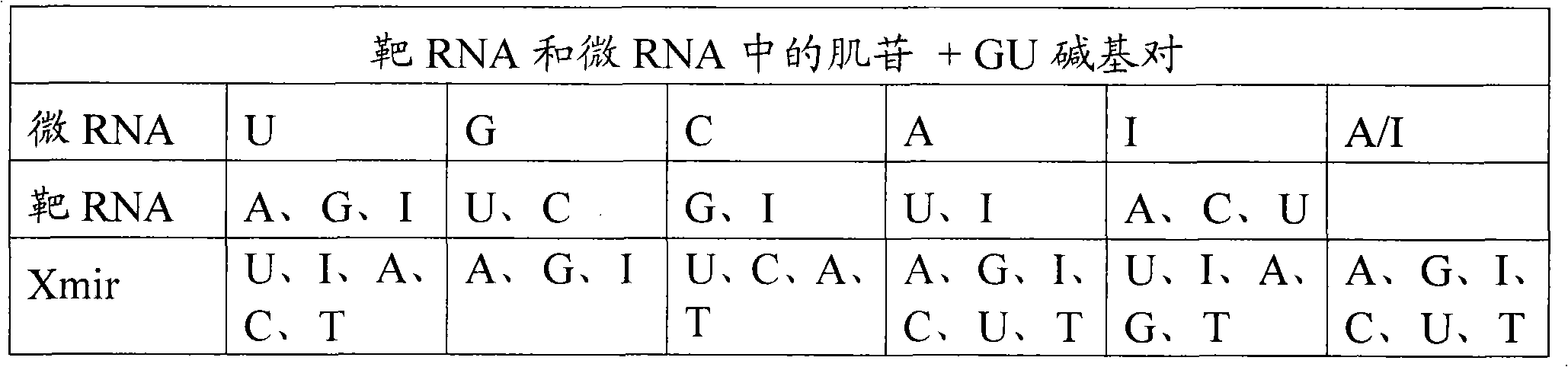
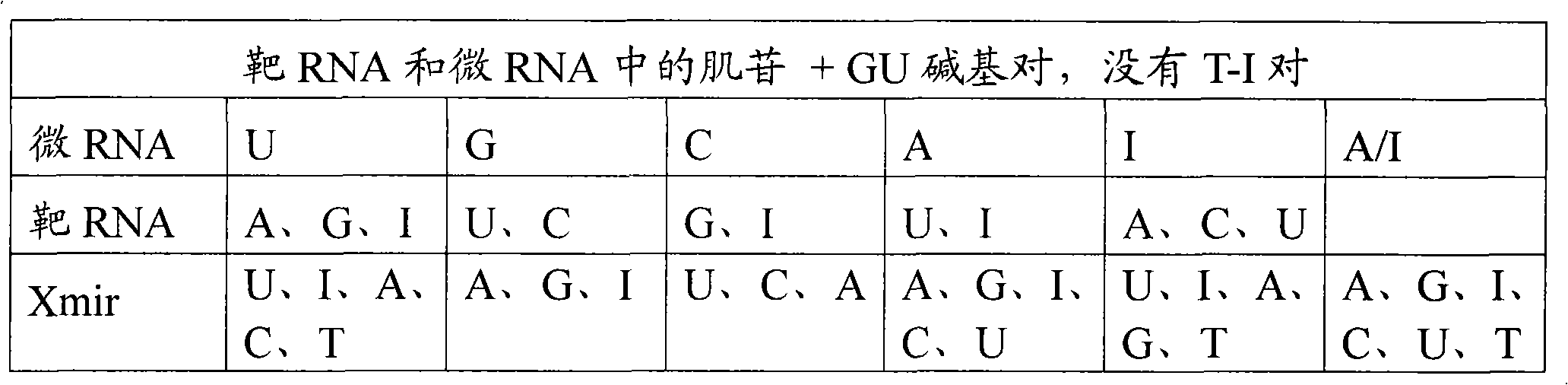
Methods and means for treating DNA repeat instability associated genetic disorders
InactiveUS8263760B2Lower Level RequirementsReduced stabilityNervous disorderSugar derivativesUracilInstability
The current invention provides for methods and medicaments that apply an oligonucleotide comprising aninosine and / or an uracile and / or a nucleotide containing a base able to form a wobble base pair, said oligonucleotide being preferably RNAse H substantially independent and being complementary only to a repetitive sequence in a human gene transcript, for the manufacture of a medicament for the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of a cis-element repeat instability associated genetic disorders in humans. The invention hence provides a method of treatment for cis-element repeat instability associated genetic disorders. The invention also pertains to a modified oligonucleotide which can be applied in a method of the invention to prevent the accumulation and / or translation of repeat expanded transcripts in cells.
Owner:PROSENSA HLDG BV +1
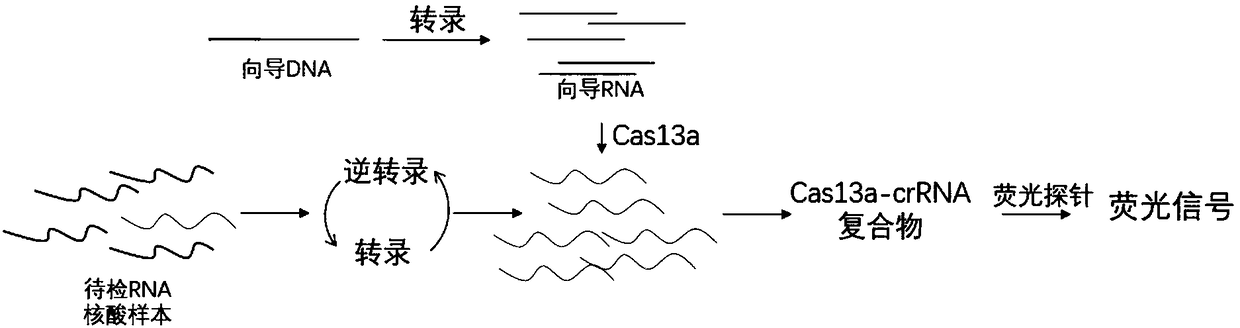
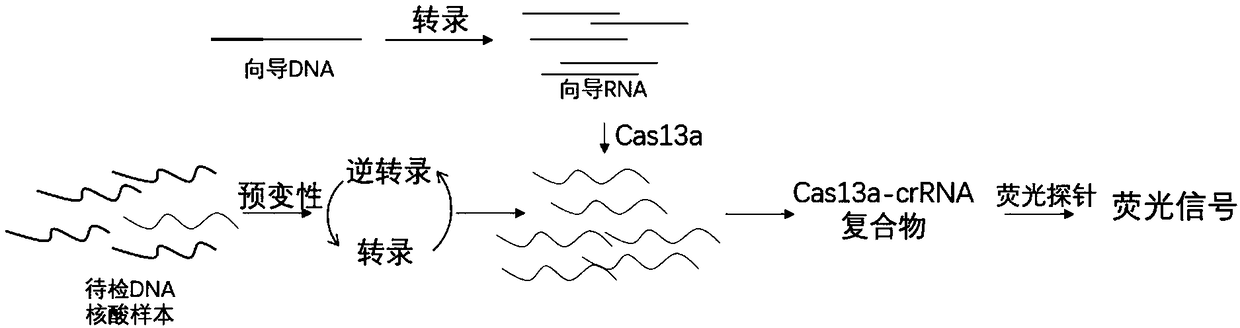
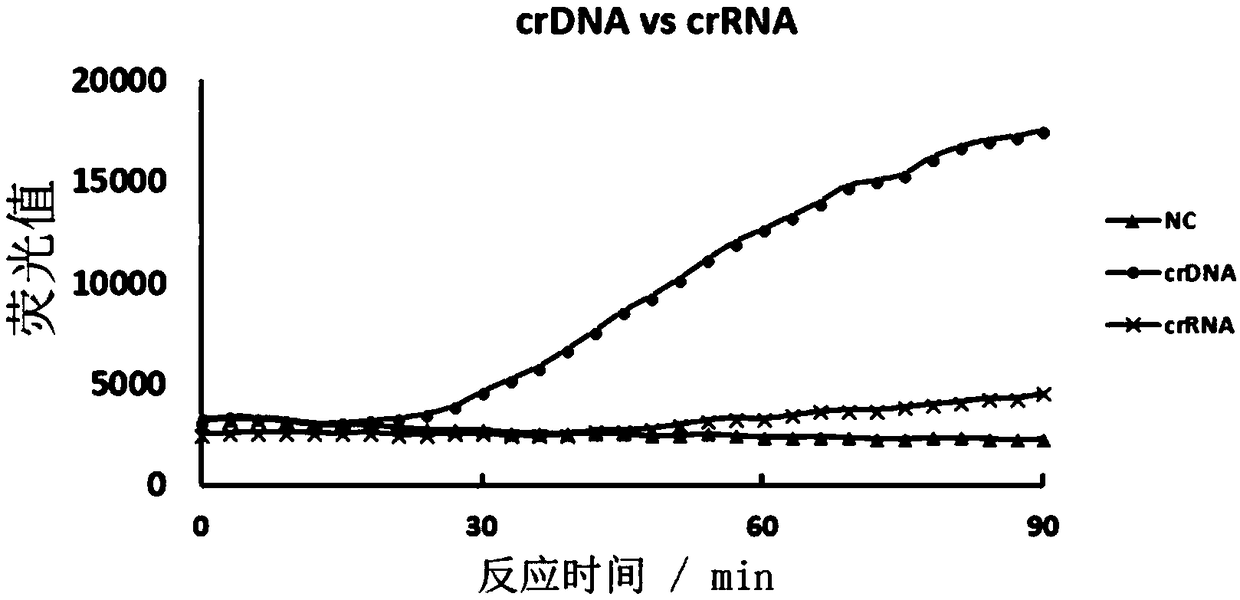
CRISPR-Cas based isothermal nucleic acid detection method and kit
ActiveCN109055499AQuick upgradeRapid responseMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceReverse transcriptase
The invention discloses a CRISPR-Cas based technology for normal-temperature / isothermal rapid detection of ribonucleic acid and a detection method. The invention aims to perform in-vitro ribonucleic acid amplification on multiple disclosed gentically engineered enzymes and chemical components and to realize amplification and detection of specific ribonucleic acid (RNA) or desoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) quickly in one step or two steps in normal-temperature / isothermal condition so that the detection of each nucleic acid is faster and more convenient. The method comprises the following steps: (1)performing nucleic acid extraction to obtain the RNA, single-stranded DNA or double-stranded DNA of a to-be-detected sample; (2) conducting a reaction with to-be-detected nucleic acid by using the combined enzyme of reverse transcriptase, transcriptase, ribonuclease H and CRISPR-associated protein 13 as well as a nucleic acid fluorescent probe in an isothermal condition, wherein if the to-be-detected nucleic acid is DNA, a pre-denaturation step is added before the reaction; (3) detecting the fluorescence signal to judge whether target nucleic acid exists in the to-be-detected sample.
Owner:HANGZHOU MATRIDX BIOTECH CO LTD
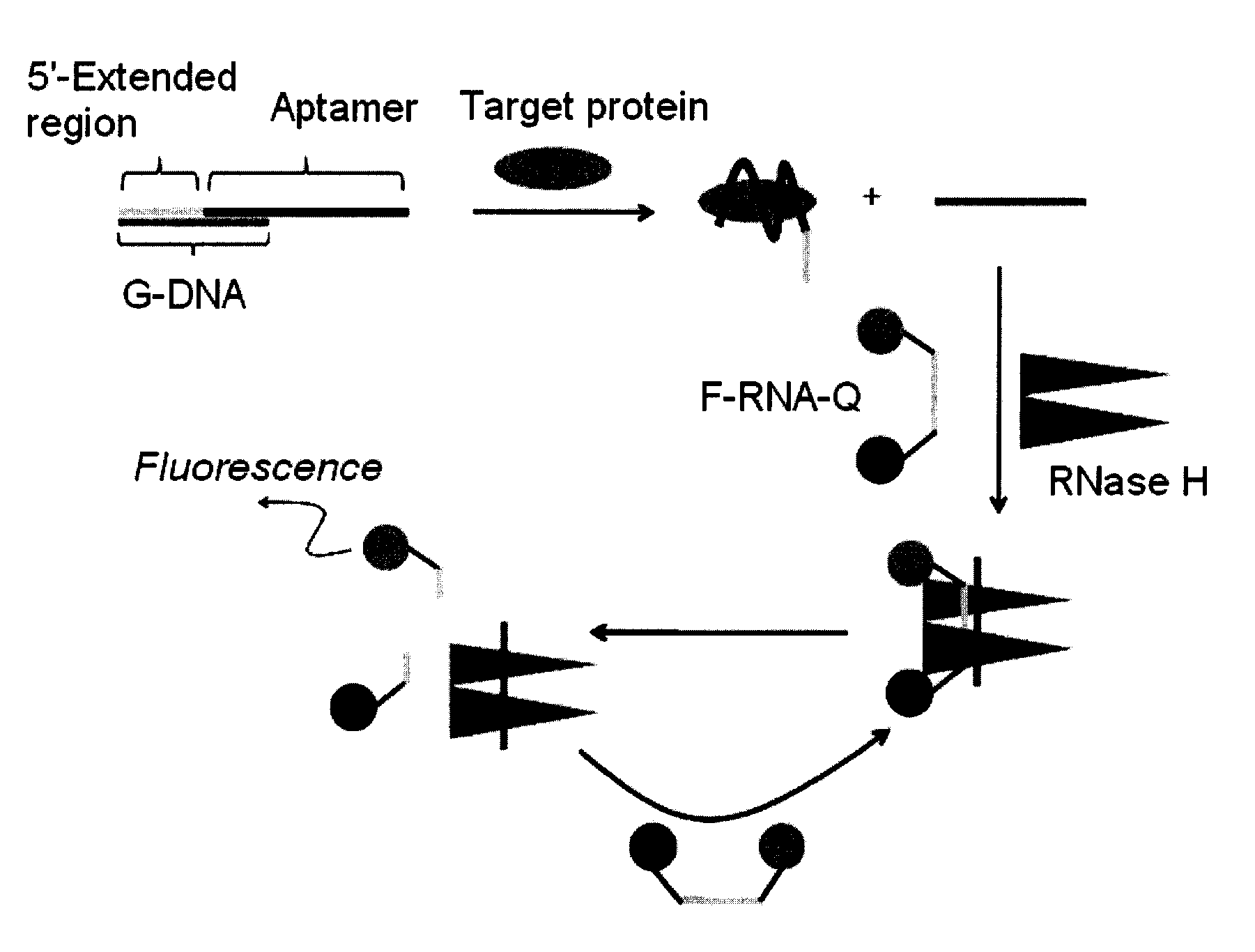
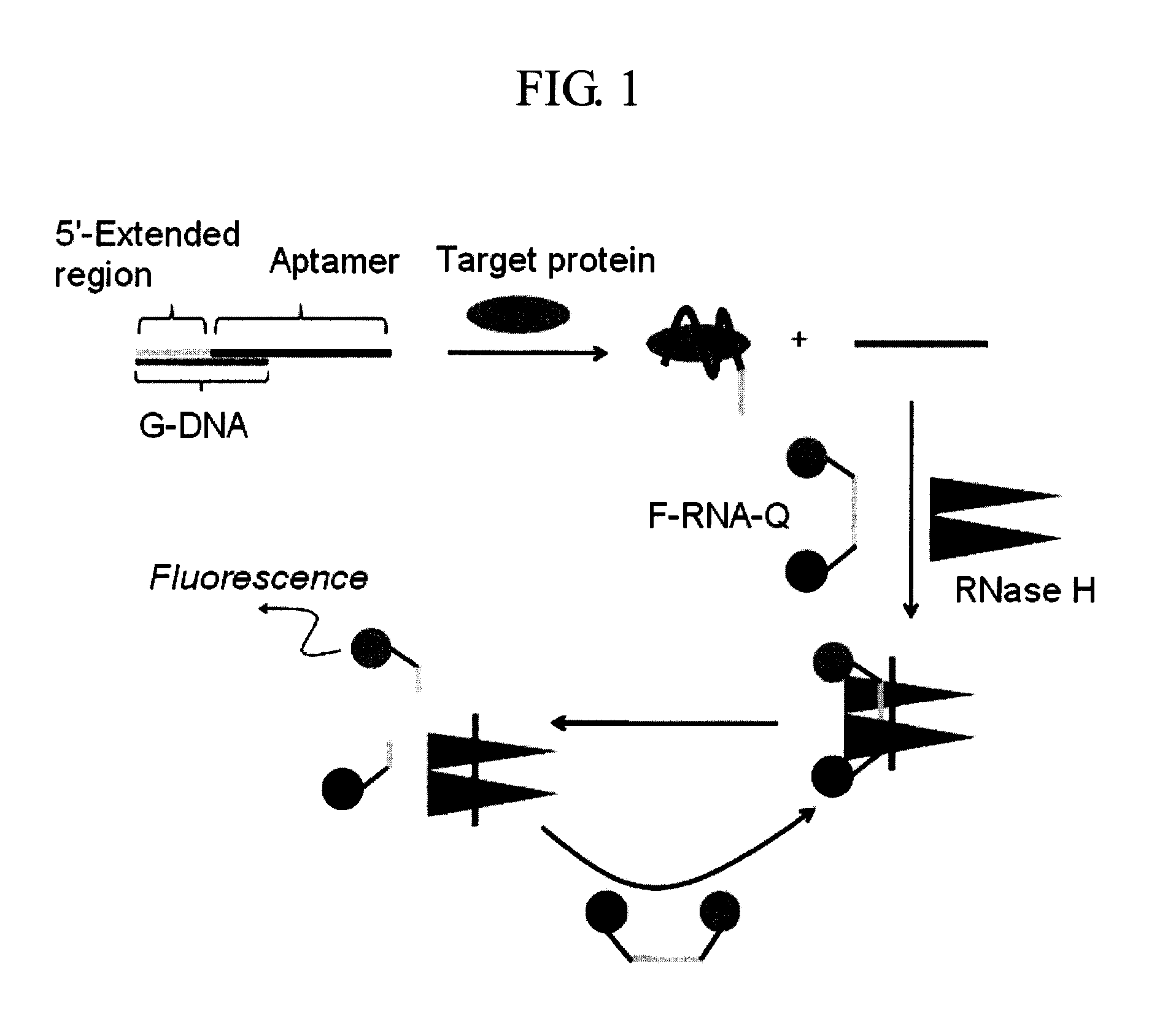
Method and kit for detecting a target protein using a DNA aptamer
A method and a kit for detecting a target protein in a sample with a signal amplification strategy are provided. The signal amplification strategy is established for the aptamer-based molecular recognition of a target protein with concomitant release of single-stranded DNA (G-DNA), which binds complementarily to a single-stranded RNA comprising a fluorophore and a quencher (“F-RNA-Q”). The fluorescence-quenched RNA is then degraded by RNase H to result in a fluorescence signal, and the undamaged G-DNA is recycled to yield fluorescence amplification.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
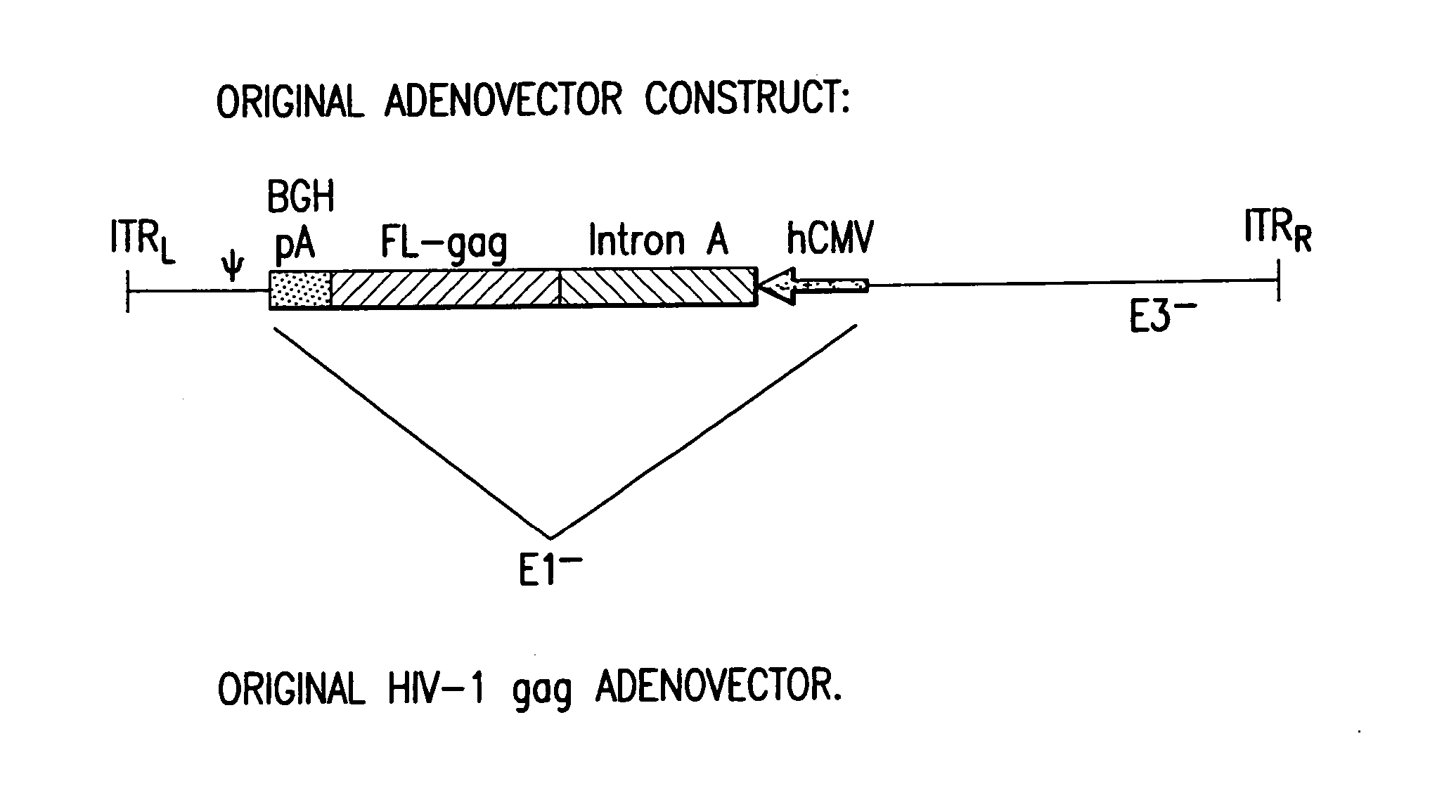
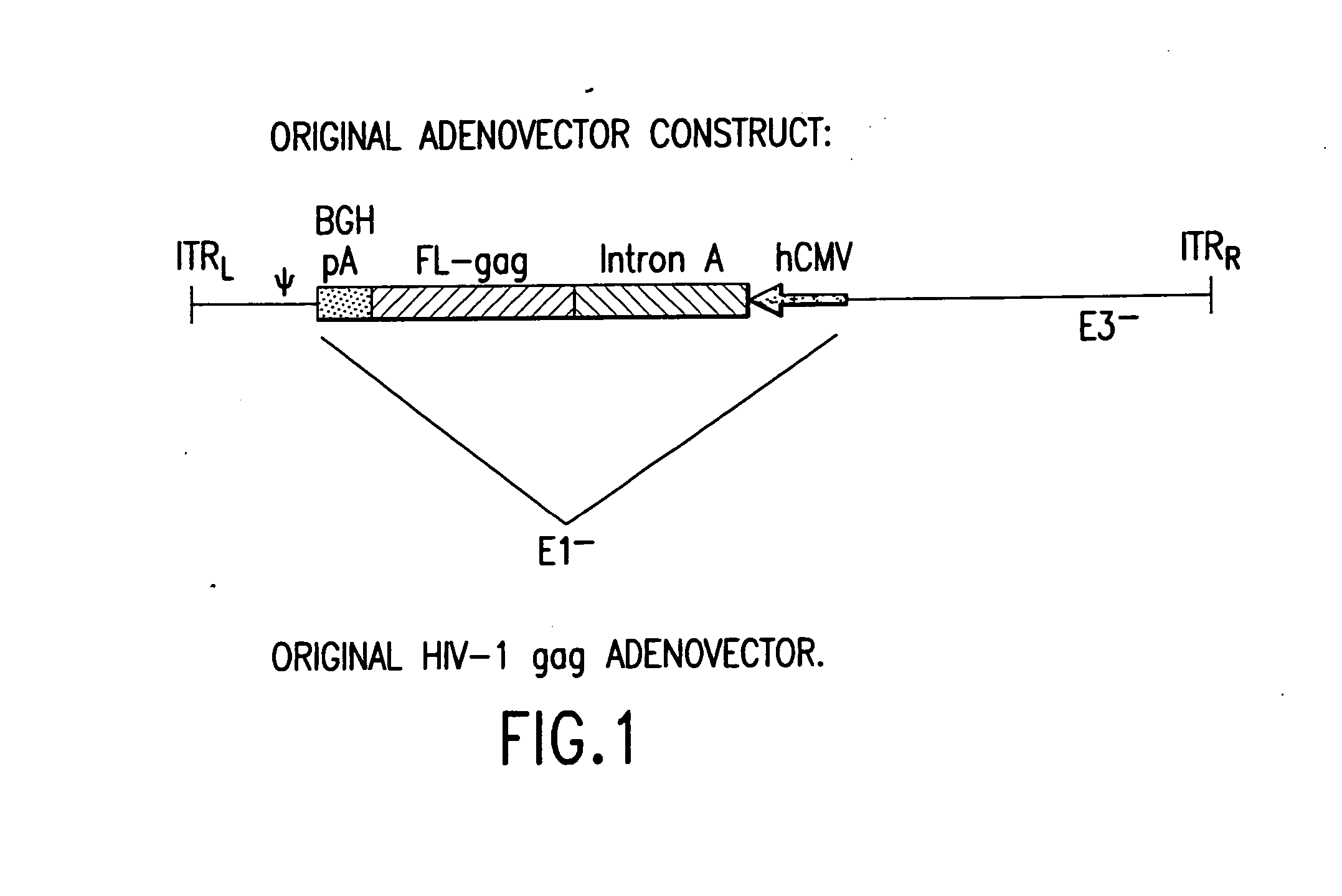
Enhanced first generation adenovirus vaccines expressing codon optimized HIV1-Gag, Pol, Nef and modifications
InactiveUS20070054395A1Genetically stableImprove featuresVectorsViral antigen ingredientsMammalReverse transcriptase
First generation adenoviral vectors and associated recombinant adenovirus-based HIV vaccines which show enhanced stability and growth properties and greater cellular-mediated immunity are described within this specification. These adenoviral vectors are utilized to generate and produce through cell culture various adenoviral-based HIV-1 vaccines which contain HIV-1 gag, HIV-1 pol and / or HIV-1 nef polynucleotide pharmaceutical products, and biologically relevant modifications thereof. These adenovirus vaccines, when directly introduced into living vertebrate tissue, preferably a mammalian host such as a human or a non-human mammal of commercial or domestic veterinary importance, express the HIV1-Gag, Pol and / or Nef protein or biologically modification thereof, inducing a cellular immune response which specifically recognizes HIV-1. The exemplified polynucleotides of the present invention are synthetic DNA molecules encoding HIV-1 Gag, encoding codon optimized HIV-1 Pol, derivatives of optimized HIV-1 Pol (including constructs wherein protease, reverse transcriptase, RNAse H and integrase activity of HIV-1 Pol is inactivated), HIV-1 Nef and derivatives of optimized HIV-1 Nef, including nef mutants which effect wild type characteristics of Nef, such as myristylation and down regulation of host CD4. The adenoviral vaccines of the present invention, when administered alone or in a combined modality regime, will offer a prophylactic advantage to previously uninfected individuals and / or provide a therapeutic effect by reducing viral load levels within an infected individual, thus prolonging the asymptomatic phase of HIV-1 infection.
Owner:EMINI EMILIO A +7
Oligonucleotides for modulating target RNA activity
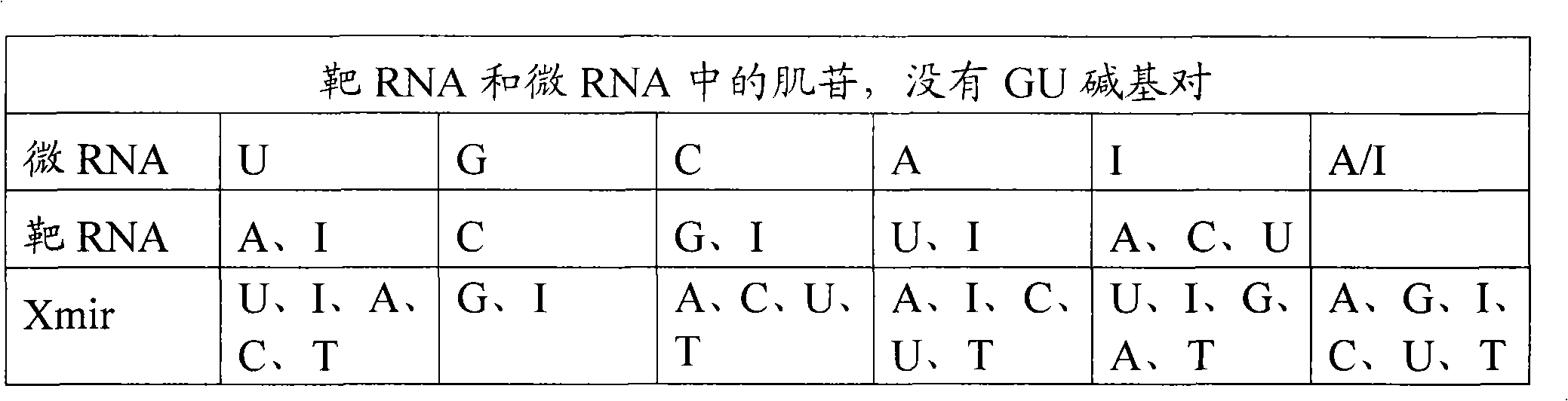
ActiveUS20100256223A1Few and no effectPrevents microRNA regulationOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesBinding siteMicroRNA binding
The present invention relates to oligonucleotides for modulation of target RNA activity. Thus, the invention provides oligonucleotides that bind to microRNA binding sites of target RNA. The oligonucleotides may activate RNase H or RNAi. In a preferred embodiment, the oligonucleotides prevents a microRNA from binding to its binding site of the target RNA and thereby prevent the microRNA from regulating the target RNA. Such oligonucleotides have uses in research and development of new therapeutics.
Owner:GUANGDONG MAIJINJIA BIOTECH CO LTD
Oligomeric compounds and methods
ActiveUS20110313019A1Improve propertiesLoss of normal functionAnimal cellsOrganic active ingredientsBiochemistryOrganic chemistry
The present invention provides oligomeric compounds and uses thereof. In certain embodiments, such oligomeric compounds are useful as antisense compounds. Certain such antisense compounds are useful as RNase H antisense compounds or as RNAi compounds.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Three component chimeric antisense oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20030083477A1Reduce errorsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEucaryotic cellBiological activation
The invention provides a class of oligonucleotide that is optimized to target a specific RNA for RNAse H degradation and to be itself resistant to degradation within in plasma and within eukaryotic, especially mammalian cells. The oligonucleotides of the invention contain no naturally occurring 5'->3'-linked nucleotides. Rather, the invention provides oligonucleotides having two types of nucleotides: 2'-deoxyphosphorothioate, which activate RNase H, and 2'-modified nucleotides, which do not. The linkages between the 2'-modified nucleotides can be phosphodiesters, phosphorothioate or P-ethoxyphosphodiester. Activation of RNAse H is accomplished by a contiguous, RNAse H-activating region, which contains between three and five 2'-deoxyphosphorothioate nucleotides to activate bacterial RNAse H and between five and ten 2'-deoxyphosphorothioate nucleotides to activate eukaryotic and, particularly, mammalian RNAse H. Protection from degradation is accomplished by making the 5' and 3' terminal bases highly nuclease resistant and, optionally, by placing a 3' terminal blocking group.
Owner:WOOLF TOD MITCHELL +1
RNase H-based assays utilizing modified RNA monomers
ActiveUS8911948B2Strong specificityConvenient ligationSugar derivativesHydrolasesOligonucleotideMonomer
The present invention pertains to novel oligonucleotide compounds for use in various biological assays, such as nucleic acid amplification, ligation and sequencing reactions. The novel oligonucleotides comprise a ribonucleic acid domain and a blocking group at or near the 3′ end of the oligonucleotide. These compounds offer an added level of specificity previously unseen. Methods for performing nucleic acid amplification, ligation and sequencing are also provided. Additionally, kits containing the oligonucleotides are also disclosed herein.
Owner:INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES
RNase H-Based Assays Utilizing Modified RNA Monomers
ActiveUS20120258455A1Improve abilitiesEfficient cuttingMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFibrin MonomerMonomer
The present invention provides methods of cleaving a nucleic acid strand to initiate, assist, monitor or perform biological assays.
Owner:INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES
Antisense Polynucleotides to Induce Exon Skipping and Methods of Treating Dystrophies
ActiveUS20150225718A1Inhibit progressImprove muscle functionSplicing alterationSugar derivativesDiseasePolynucleotide
Antisense polynucleotides and their use in pharmaceutical compositions to induce exon skipping in targeted exons of the gamma sarcoglycan gene are provided, along with methods of preventing or treating dystrophic diseases such as Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy. One aspect the disclosure provides an isolated antisense polynucleotide wherein the polynucleotide specifically hybridizes to an exon target region of a gamma sarcoglycan RNA, wherein the exon is selected from the group consisting of exon 4 (SEQ ID NO:1), exon 5 (SEQ ID NO: 2), exon 6 (SEQ ID NO: 3), exon 7 (SEQ ID NO: 4) and a combination thereof. In some embodiments, the antisense polynucleotide cannot form an RNase H substrate, and in further embodiments the antisense polynucleotide comprises a modified polynucleotide backbone.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
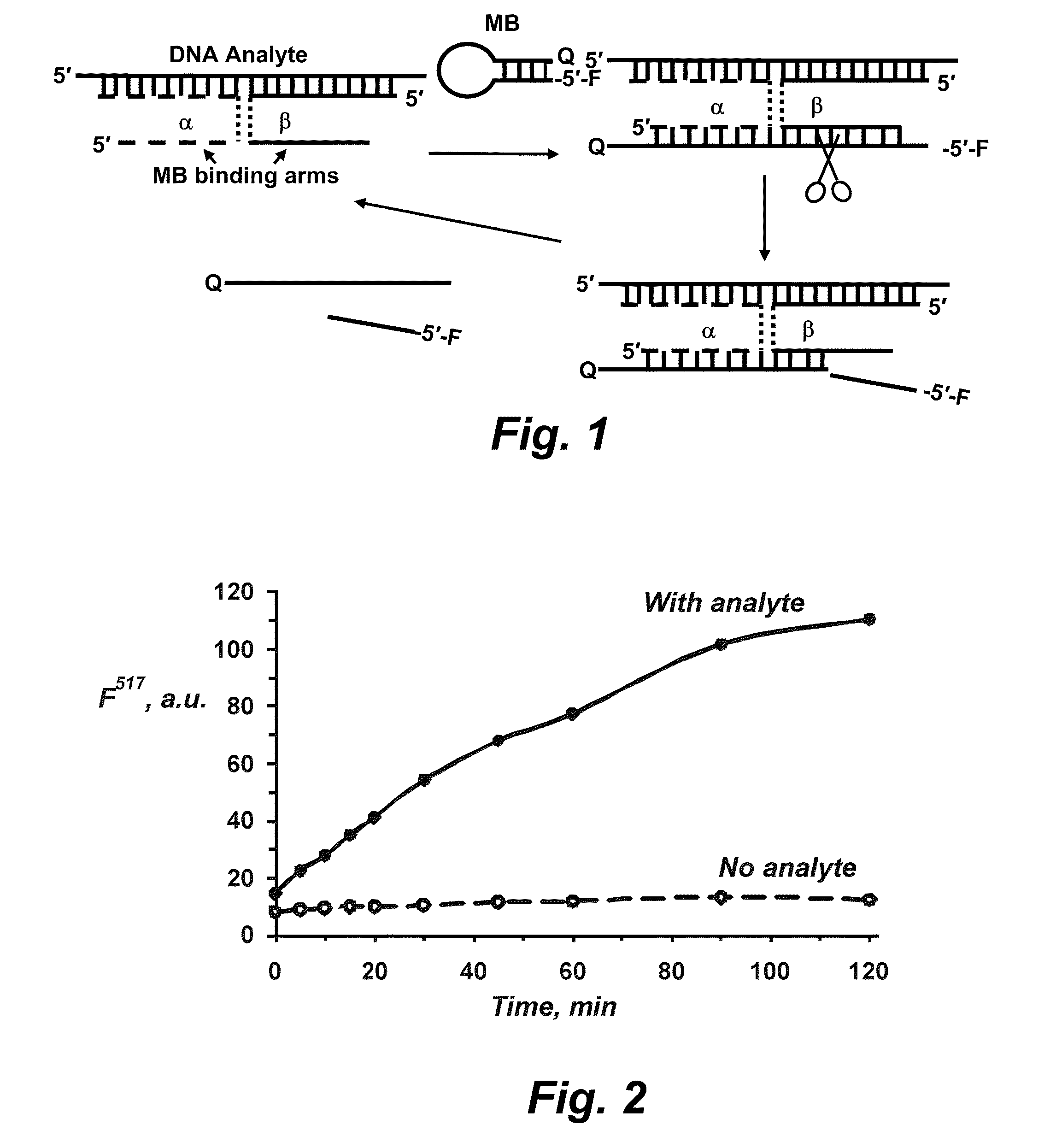
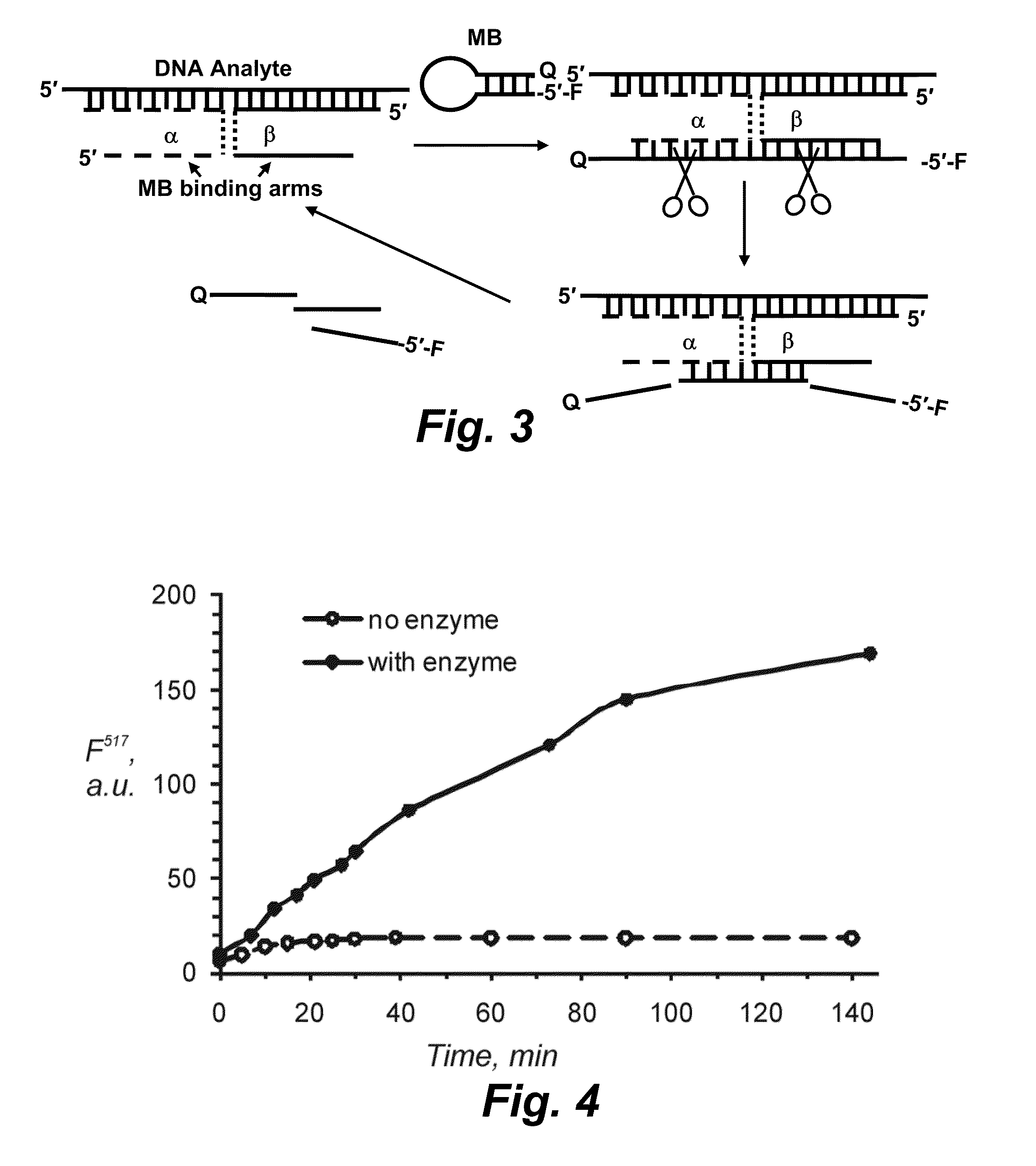
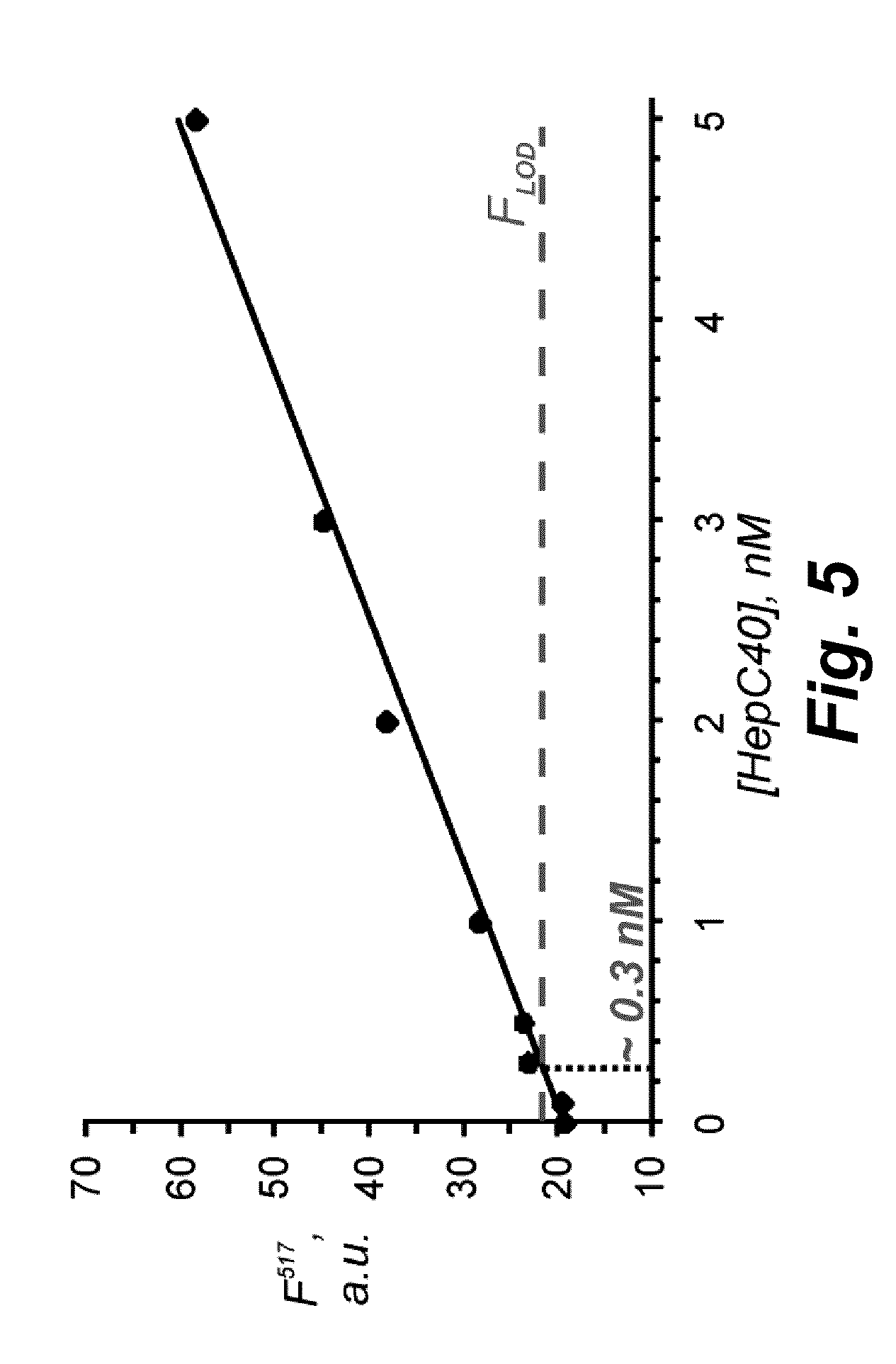
Binary probe system for sensitive detection of target analytes
The present disclosure encompasses systems, and their methods of use, for detecting a target analyte, the systems comprising: (a) a first oligonucleotide probe comprising a reporter oligonucleotide-binding arm complementary to the nucleotide sequence of a first region of a reporter oligonucleotide and an analyte-binding arm selectively binding to a first region of a target analyte, a second oligonucleotide probe comprising a reporter oligonucleotide-binding arm having a nucleotide sequence complementary to the nucleotide sequence of a second region of a reporter oligonucleotide, and an analyte-binding arm having a nucleotide sequence characterized as selectively binding to a second region of a target analyte; and a reporter oligonucleotide comprising a region complementary to the reporter oligonucleotide-binding arm of the first oligonucleotide probe, a second region complementary to the reporter oligonucleotide-binding arm of the second oligonucleotide probe, a fluorophore and a quencher disposed on the reporter oligonucleotide and a cleavable site disposed between the fluorescent label and the quencher. The cleavable site of the reporter oligonucleotide when in the presence of a target analyte can be cleaved by an enzyme such as a restriction endonuclease, an RNase H, a Flap-endonuclease-1 (FEN-1), and a DNA glycosylase.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Method of detecting UDG activity by enzyme-mediated two-step serial signal amplification based on excision repair
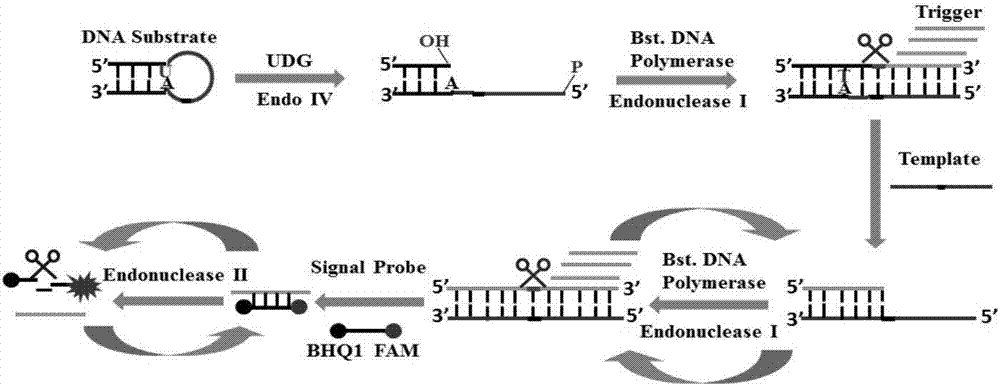
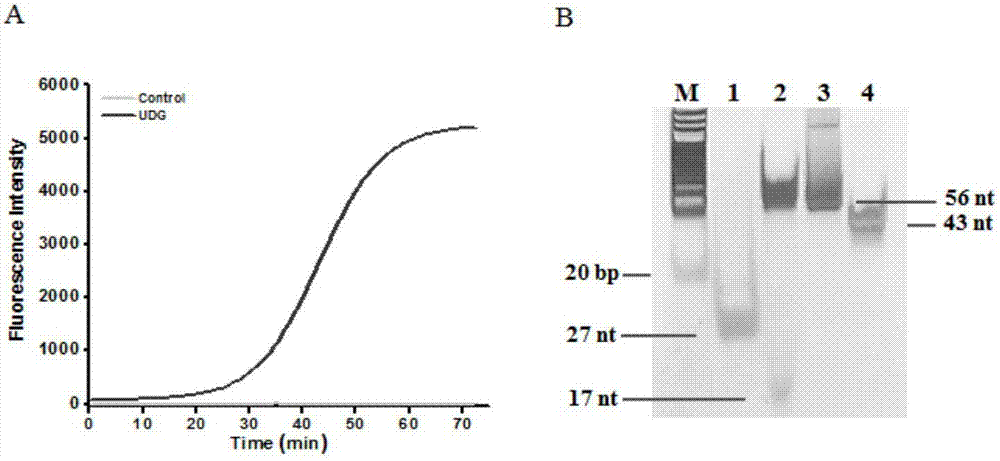
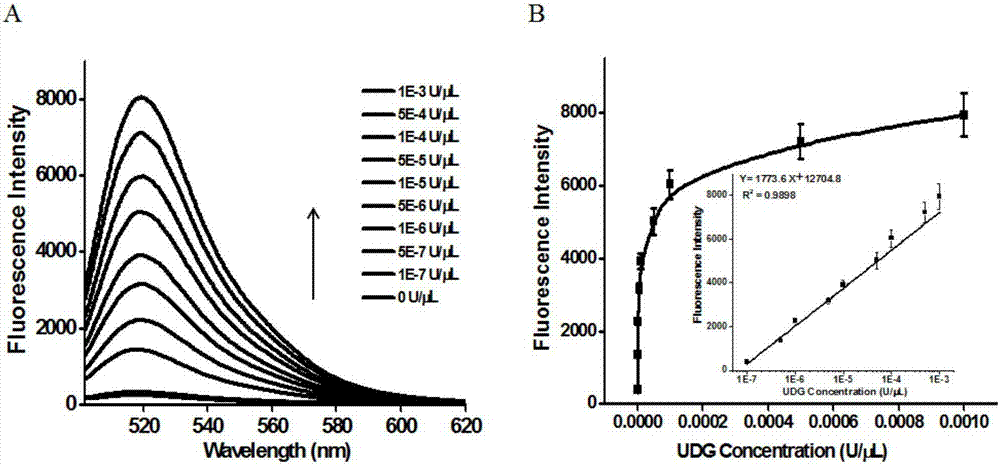
ActiveCN106929563AHigh sensitivityHigh resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceDisplacement reactions
The invention discloses a method of detecting the UDG activity by enzyme-mediated two-step serial signal amplification based on excision repair. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding a UDG active substrate in an excision reaction buffer solution to carry out excision repair reaction, excising a uracil base of the UDG active substrate, and leaving an abasic site; and (2) adding an excision repair reaction product in an amplification reaction buffer solution to carry out enzyme-assisted two-step serial signal amplification reaction, namely inducing strand displacement reaction and index amplification reaction, generating strengthened fluorescence signals in a circulation manner, and determining the UDG activity through weakness of the fluorescence signals. According to the method provided by the invention, ultrahigh sensitive detection to the activity of uracil DNA glycosylase (UDG) is realized by utilizing high amplification efficiency of constant-temperature index amplification reaction and specific circulation digestion of ribonuclease H.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Methods and means for treating DNA repeat instability associated genetic disorders
InactiveUS20110184050A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced stabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderRepetitive SequencesNucleotide
The current invention provides for methods and medicaments that apply an oligonucleotide comprising aninosine and / or an uracile and / or a nucleotide containing a base able to form a wobble base pair, said oligonucleotide being preferably RNAse H substantially independent and being complementary only to a repetitive sequence in a human gene transcript, for the manufacture of a medicament for the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of a cis-element repeat instability associated genetic disorders in humans. The invention hence provides a method of treatment for cis-element repeat instability associated genetic disorders. The invention also pertains to a modified oligonucleotide which can be applied in a method of the invention to prevent the accumulation and / or translation of repeat expanded transcripts in cells.
Owner:PROSENSA HLDG BV +1
Oligonucleotides for modulating target rna activity
The present invention describes oligonucleotides that bind to microRNA target sites in target RNAs, such as mRNAs. The oligonucleotides of the invention may mediate RNase H degradation of the target RNA, mediate RNAi of the target RNA or prevent microRNA regulation of the target RNA. The oligonucleotides of the invention are useful e.g. as research tools for studying microRNA:mRNA interactions andfor therapeutic development. The present invention also describes methods of identifying microRNA target sites, methods of validating microRNA target sites, methods of identifying oligonucleotides ofthe invention and methods of modulating the activity of a target RNA using the oligonucleotides of the invention.
Owner:米尔克斯治疗有限责任公司
Oligomeric compounds and methods
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com