Patents
Literature
42results about "Hormones" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cancer biomarkers
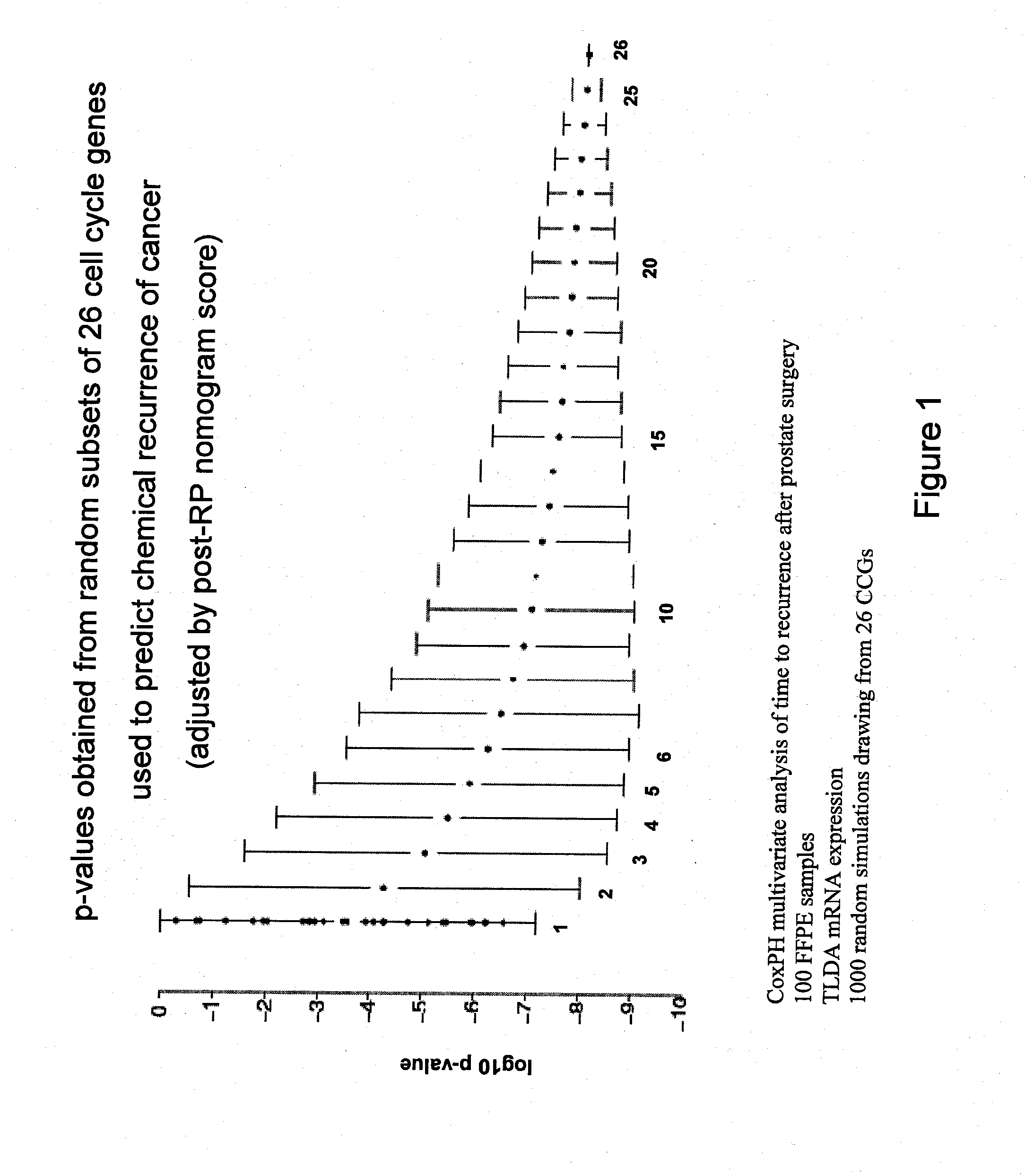
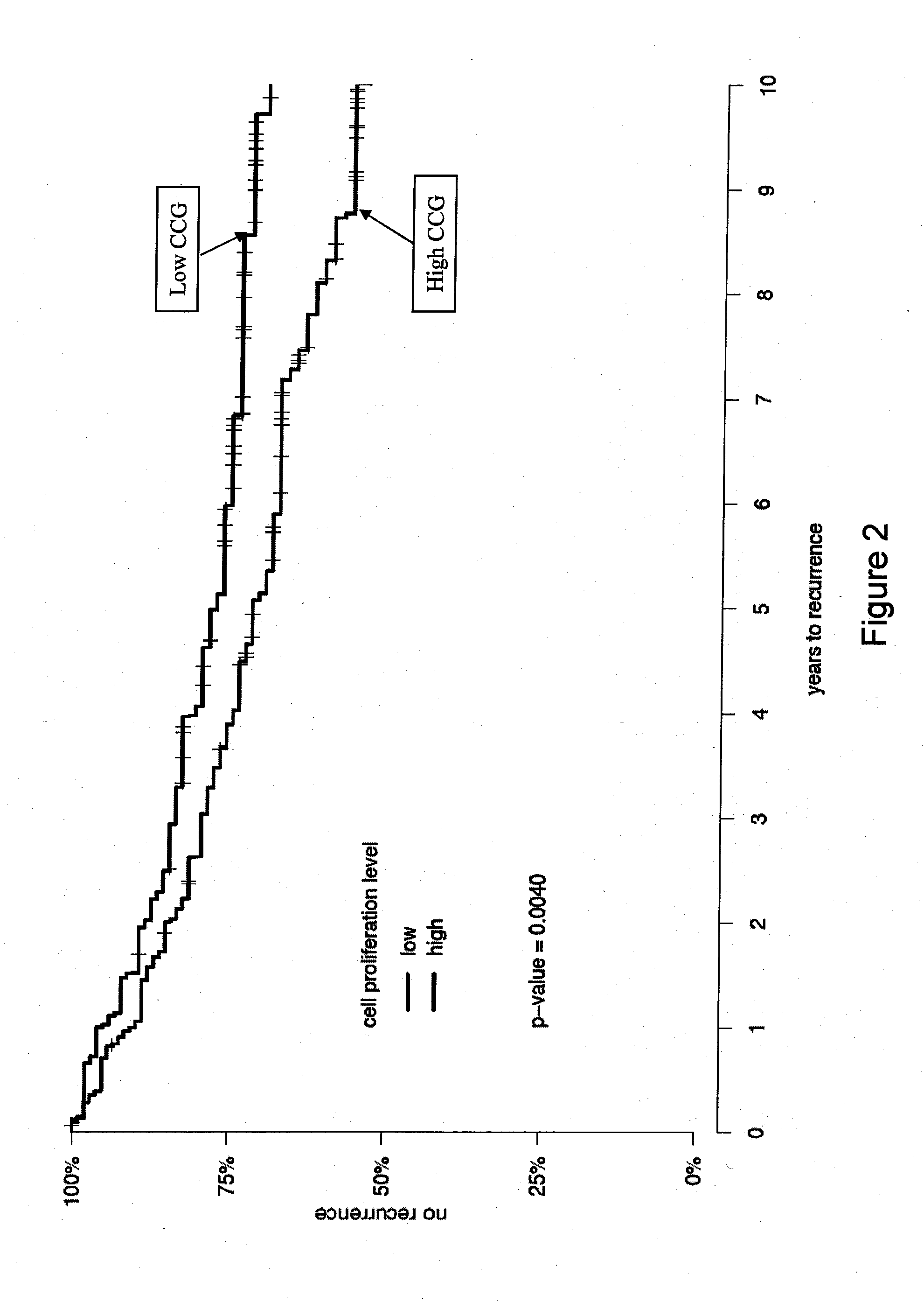
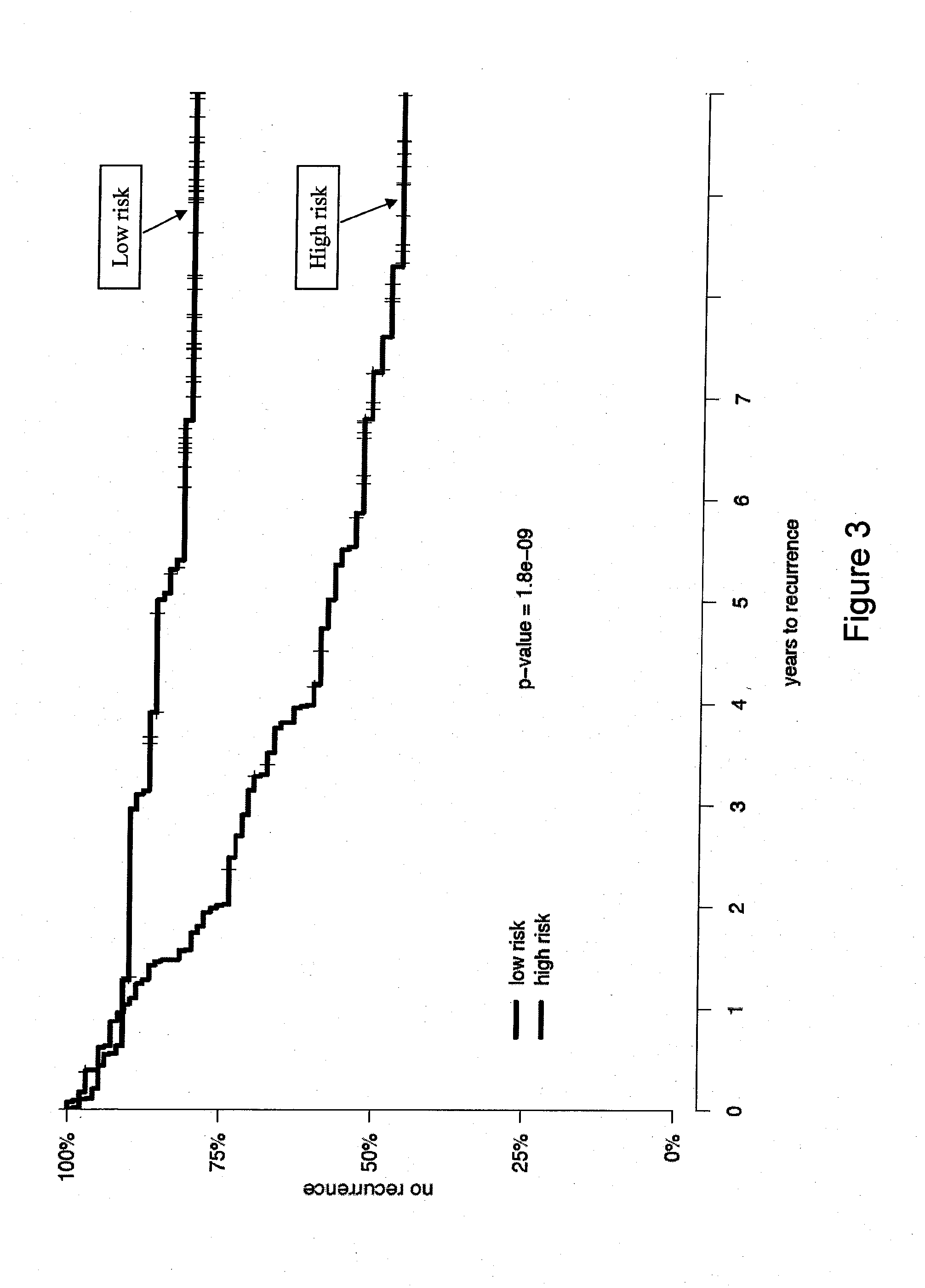
InactiveUS20120041274A1Improve predictive performanceIncreased likelihood of recurrenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTumor BiomarkersBiologic marker
Biomarkers and methods using the biomarkers for the prediction of the recurrence risk of cancer in a patient are provided.
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS
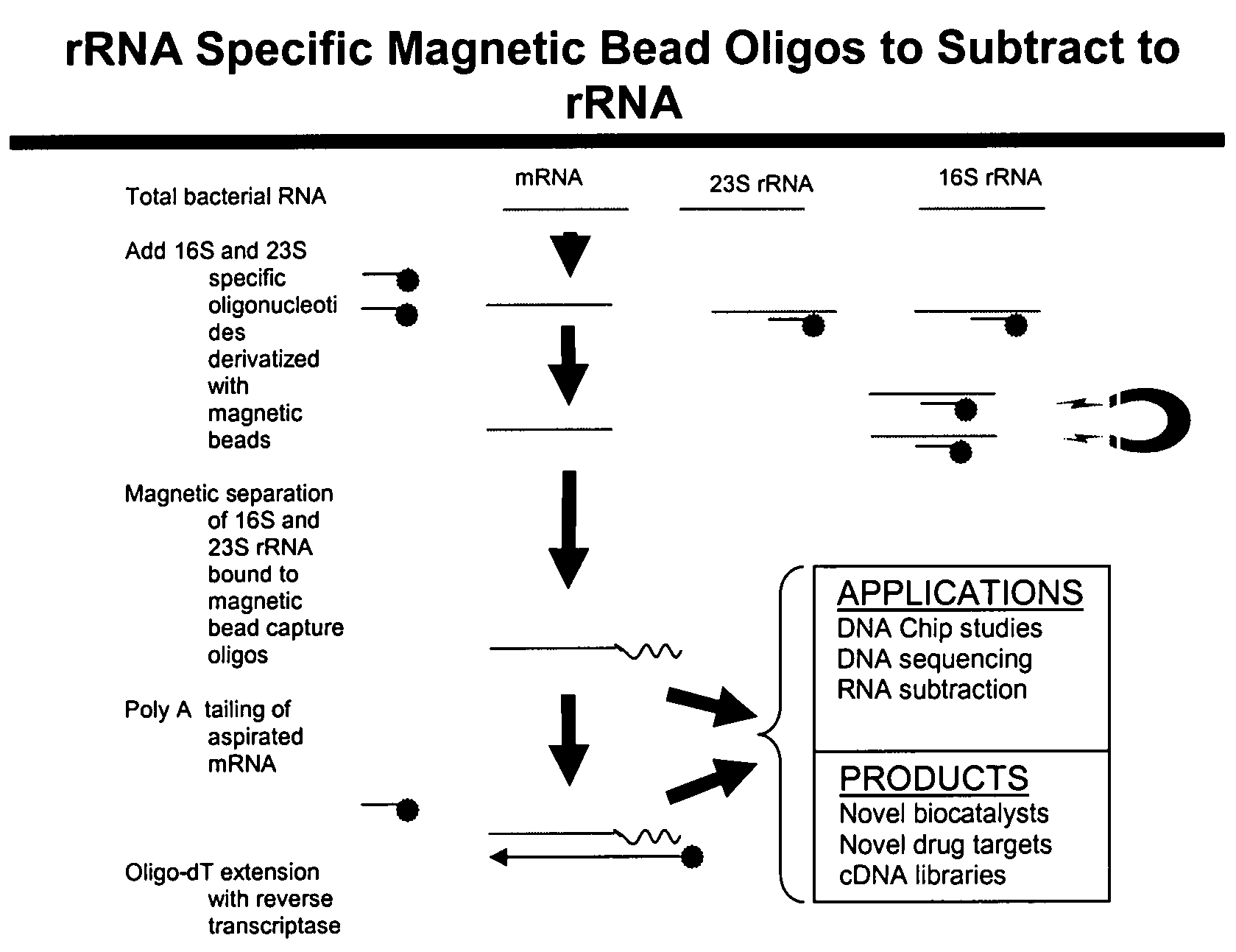
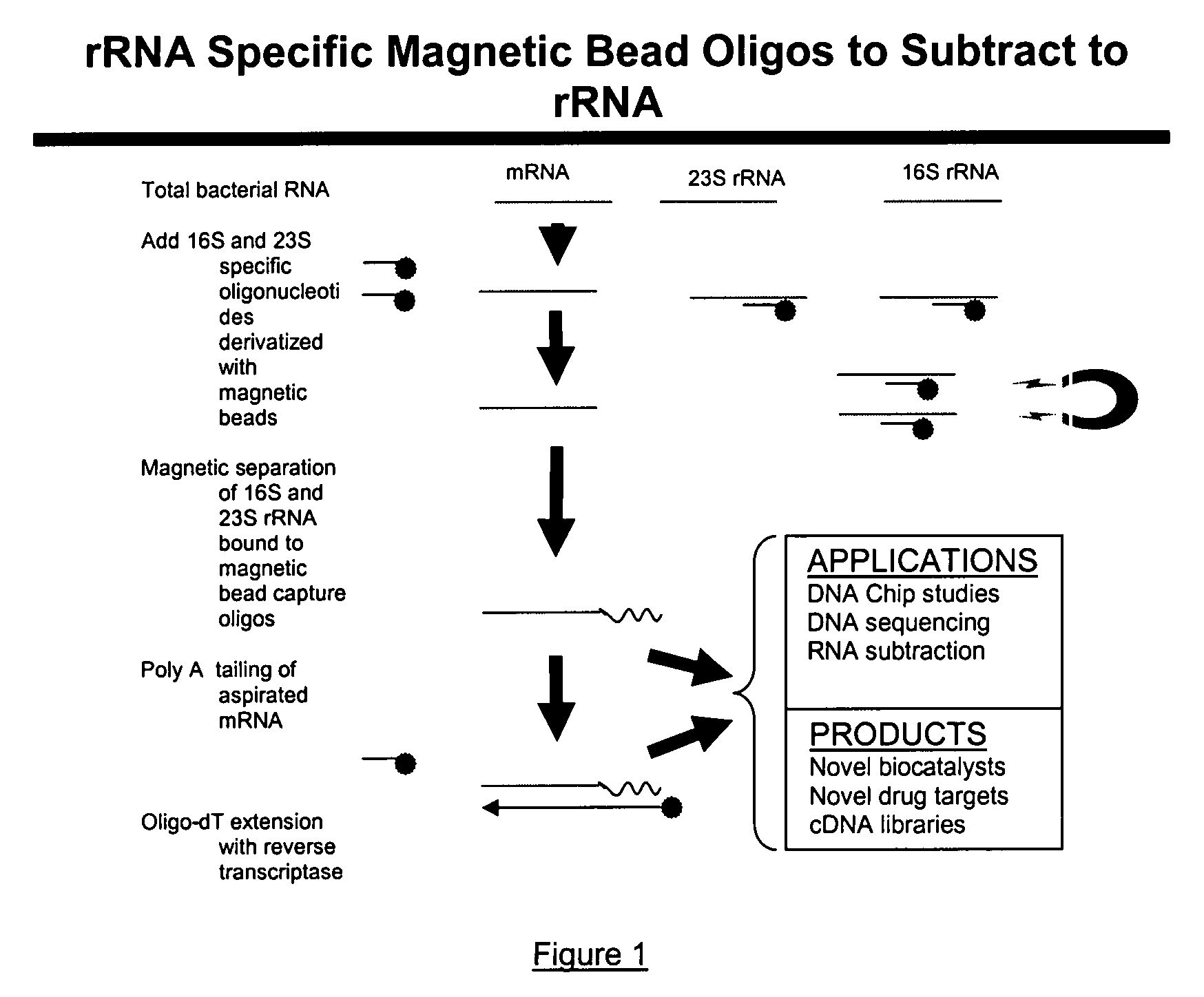
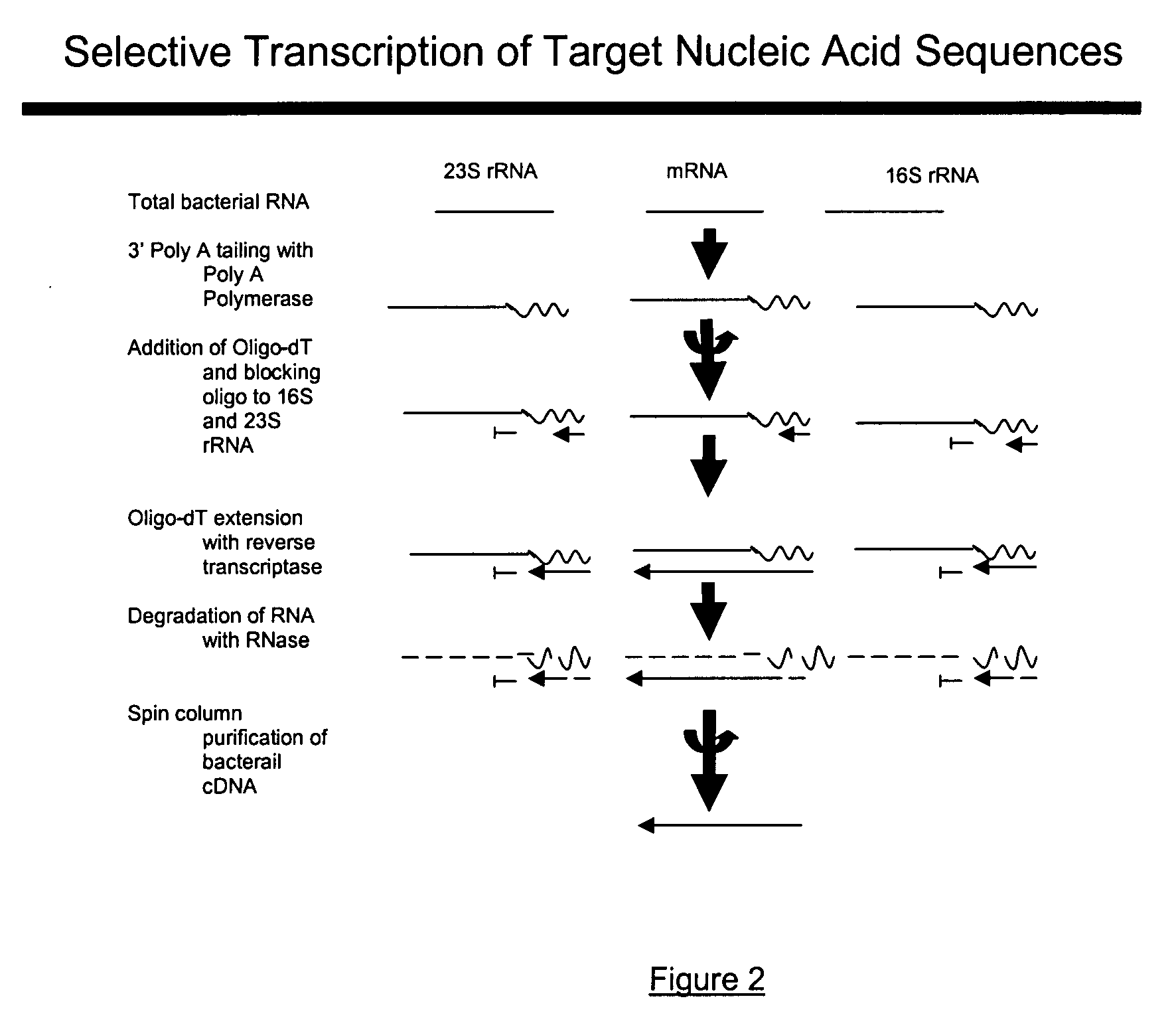
Methods and kits for negative selection of desired nucleic acid sequences
The present invention pertains to a method to isolate, separate, enrich or amplify a targeted nucleotide polymer such as mRNA through selective reverse transcription of the targeted polymer into cDNA from a sample comprising of chemically identical or similar polynucleotide polymers such as rRNA. The enrichment of the targeted nucleic acid such as mRNA is accomplished by blocking the reverse transcription of undesired rRNA while allowing unrestricted reverse transcription of the targeted polymer. The invention also embodies that the cleavage of the non-targeted nucleic acid such as rRNA bound to an oligonucleotide through enzymatic activity (RNase H). The invention further embodies methods and kits to accomplish the utility of the invention through the following steps 1) 3′ tailing of chemically identical or similar nucleotide polymers in a sample that includes bacterial mRNA 2) a 3′ tail capable of binding to a oligo-dN primer 3) at least one oligonucleotide capable of preventing the extension of oligo-dN bound to at least one non-targeted nucleotide polymers by a DNA polymerase such as a reverse transcriptase without restricting conversion of bacterial mRNA into cDNA 4) where the non-targeted molecule is prevented as a template for cDNA synthesis by enzymatic cleavage (RNase H) of template (rRNA)-oligonucleotide hybrid 5) where the reverse transcriptase is physically blocked by the oligonucleotide bound to the non-targeted nucleic acids such as rRNA 5) purification of the selectively transcribed cDNA. In further embodiments of the present invention, methods and composition to enable the study of bacterial transcriptomics-an analysis of genes expressed by a bacterial infection of a host, an isolated bacterial culture or a bacterial community, such as recovered from soil, intestine, mouth, biofilm, water etc are also included for use in DNA-chip or sequencing analyses.
Owner:SOWLAY MOHANKUMAR R
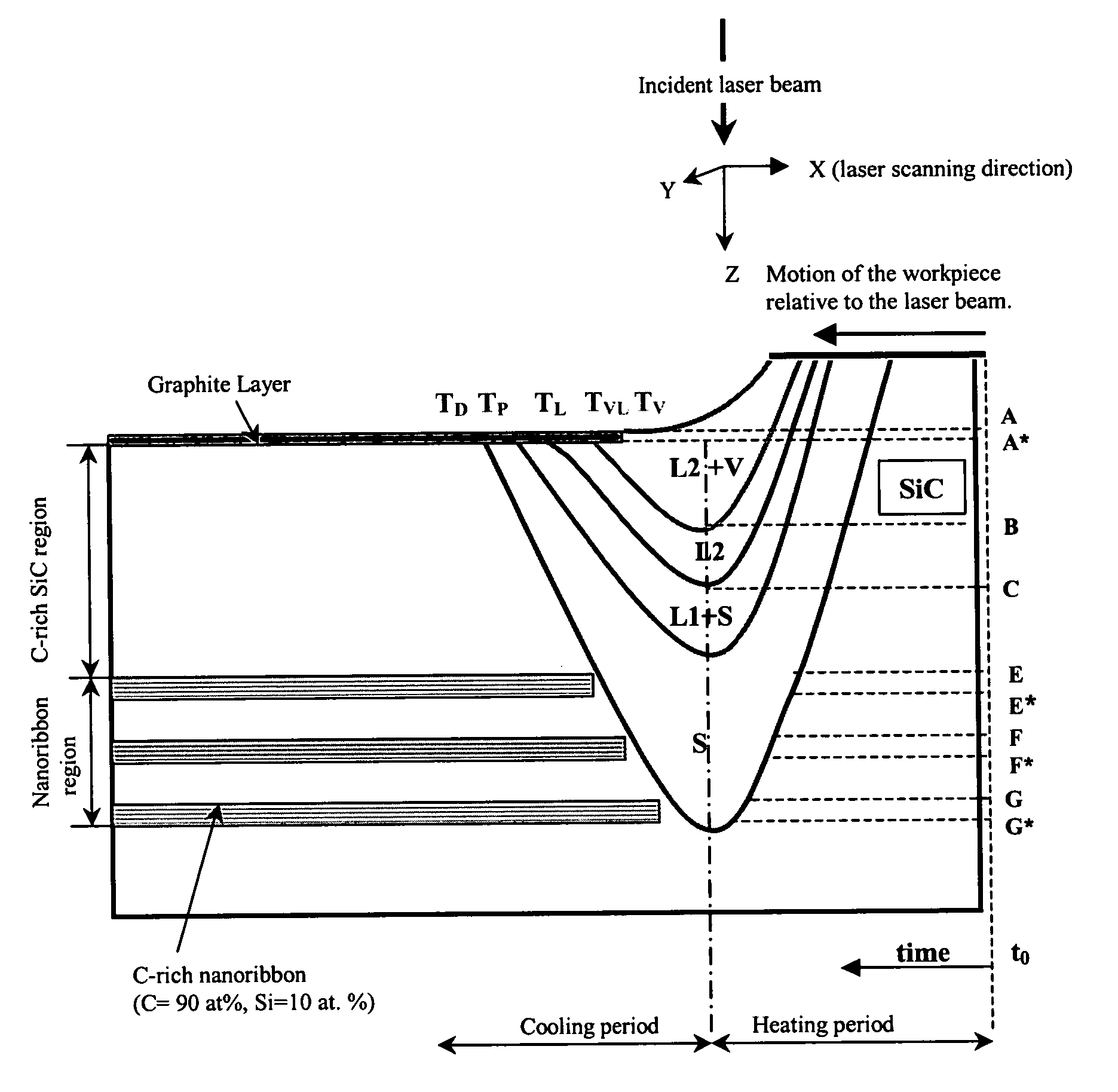
Nano-size semiconductor component and method of making
A method is disclosed for making a nano-size semiconductor component within a wide-bandgap semiconductor substrate. A first thermal energy beam is directed onto a first portion of the wide-bandgap semiconductor substrate to change the structure of the wide-bandgap semiconductor substrate into a first element of the semiconductor component. A second thermal energy beam is directed onto a second portion of the wide-bandgap semiconductor substrate adjacent to the first portion to form a second element of the semiconductor component.
Owner:ROBERT F FRIJOUF +1
Method of treating biomass, compost, mulching material for livestock and agent for treating biomass
ActiveUS20090241623A1Inhibit productionReduce nitrogen contentBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaMicroorganismMedicine
The present invention provides a method of treating biomass that reduces water-polluting substances, suppresses the production of malodorous gases and greenhouse gases, decreases the nitrogen content in the compost or livestock bedding thus prepared, and furthermore, easily treats nitrogen-containing biomass in a short time at high temperature. The present invention also provides compost and livestock bedding produced by the method and a biomass treating agent. The method of treating biomass includes blending, with nitrogen-containing biomass, a Geobacillus microorganism having denitrification capability and a fermentation promoter that promotes the fermentation of the nitrogen-containing biomass by the Geobacillus microorganism.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
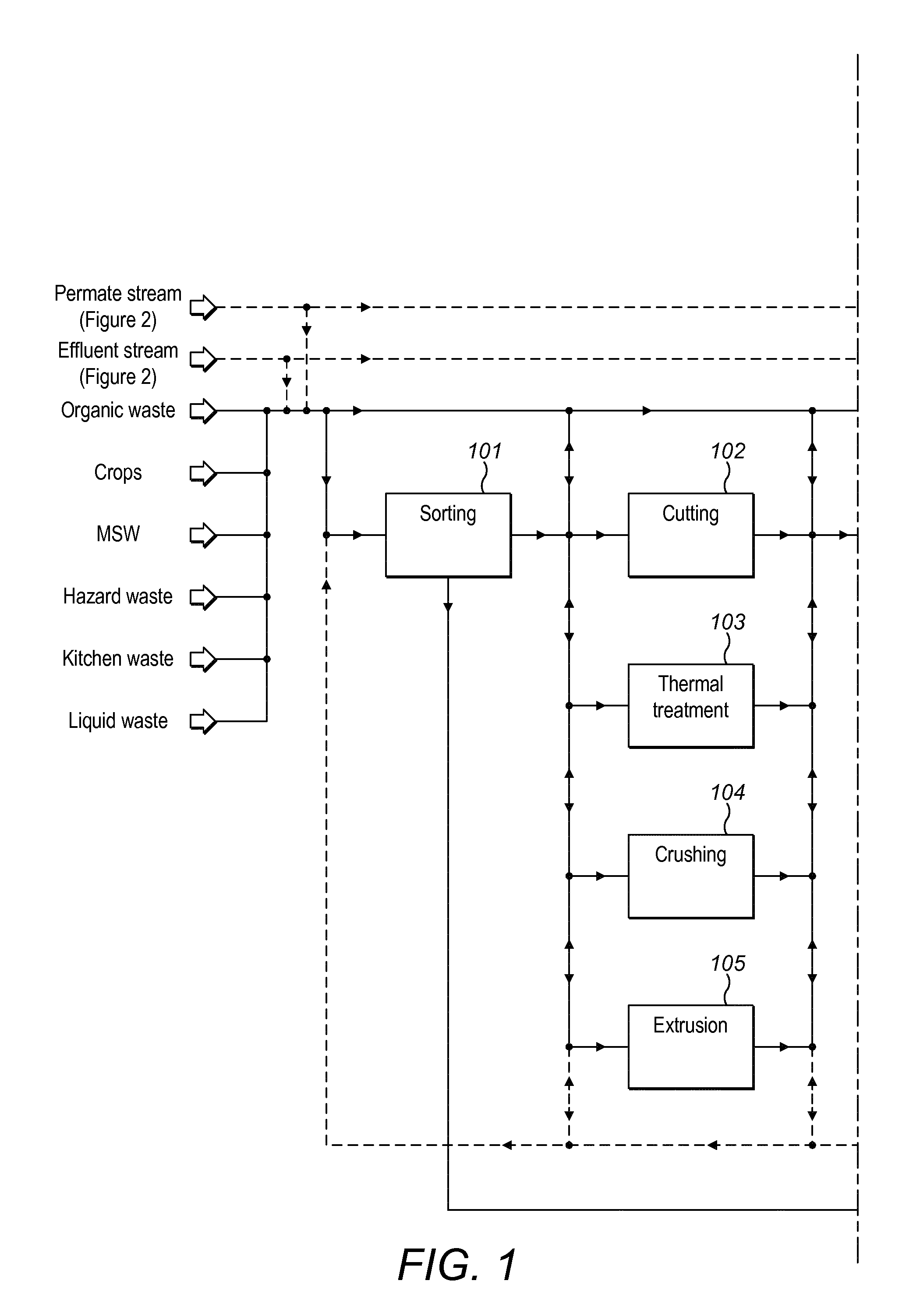
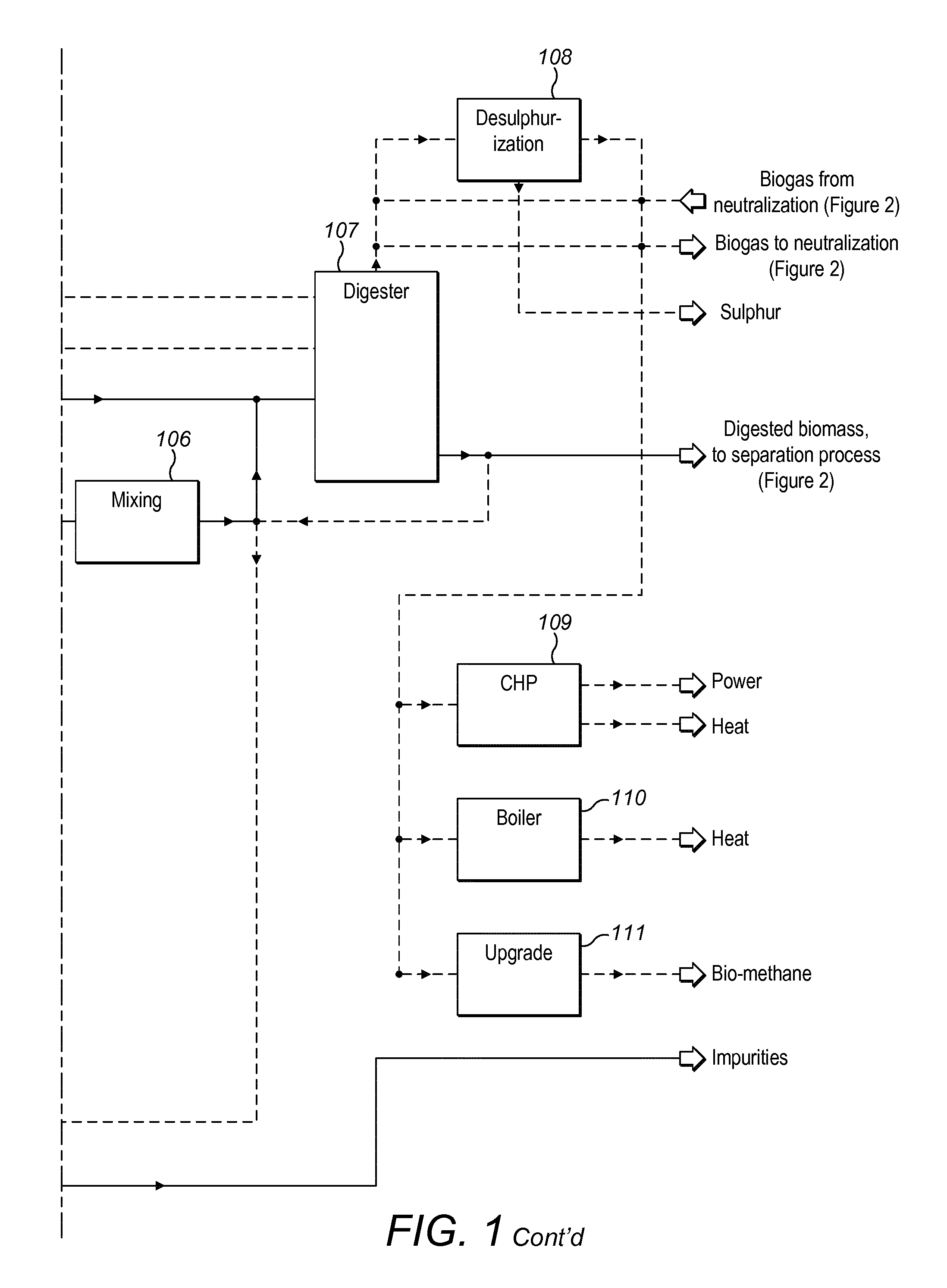
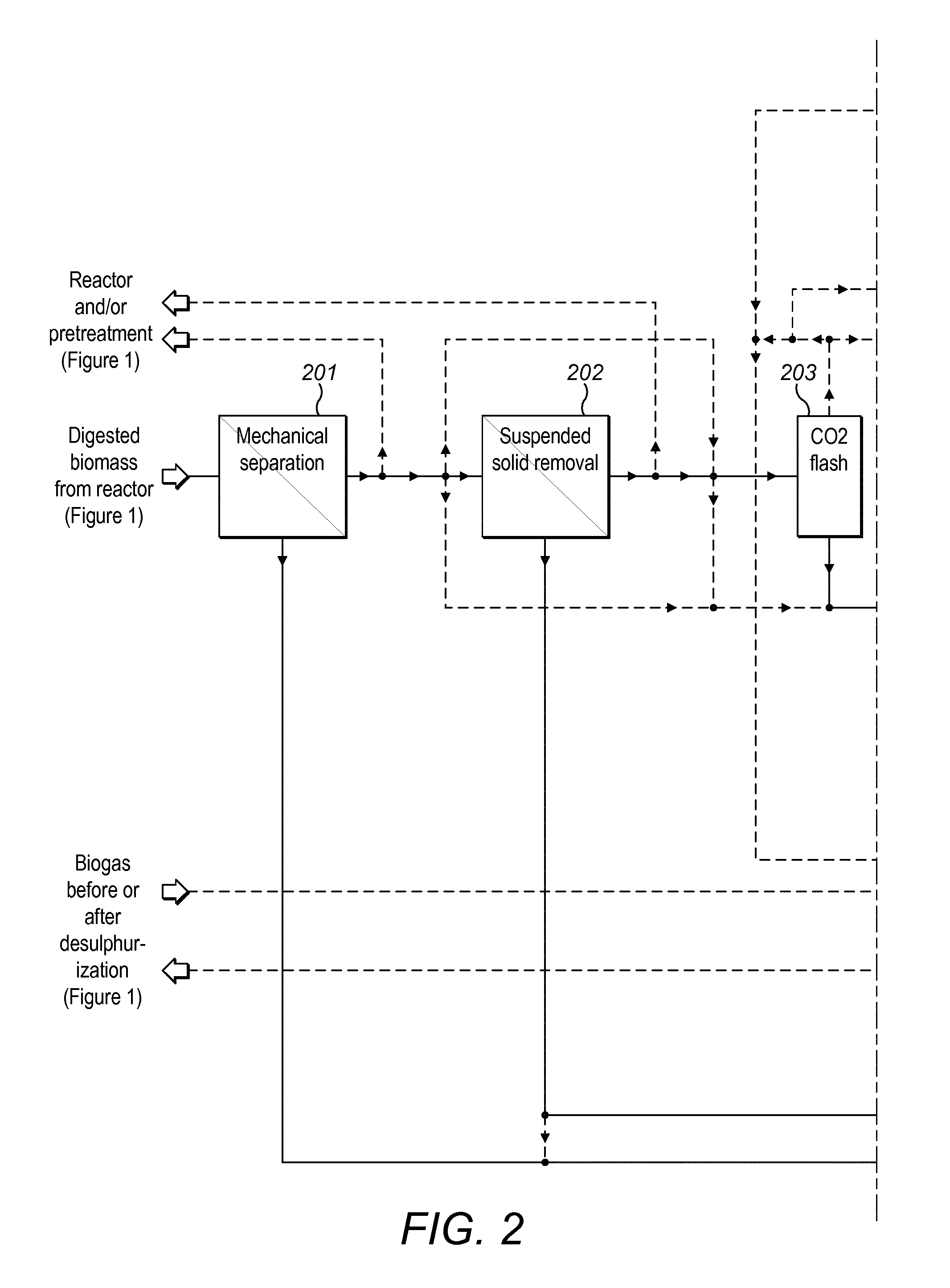
Method and plant for treatment of organic waste
ActiveUS20160176768A1Increasing biogasCost effectiveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingBoiling pointAmmonia
The present invention relates to methods and plants for the treatment of an organic waste material, wherein waste is subjected to anaerobic fermentation in a biogas digester; effluent is mechanically separated from the biogas digester into a concentrated fraction and a liquid fraction; the liquid fraction is heated to a high temperature below the boiling point of the liquid; the heated liquid is introduced to a flash column to partially remove volatile carbon dioxide, the pH of the liquid is elevated and ammonia is removed from the liquid.
Owner:RENEW ENERGY USA LLC +1
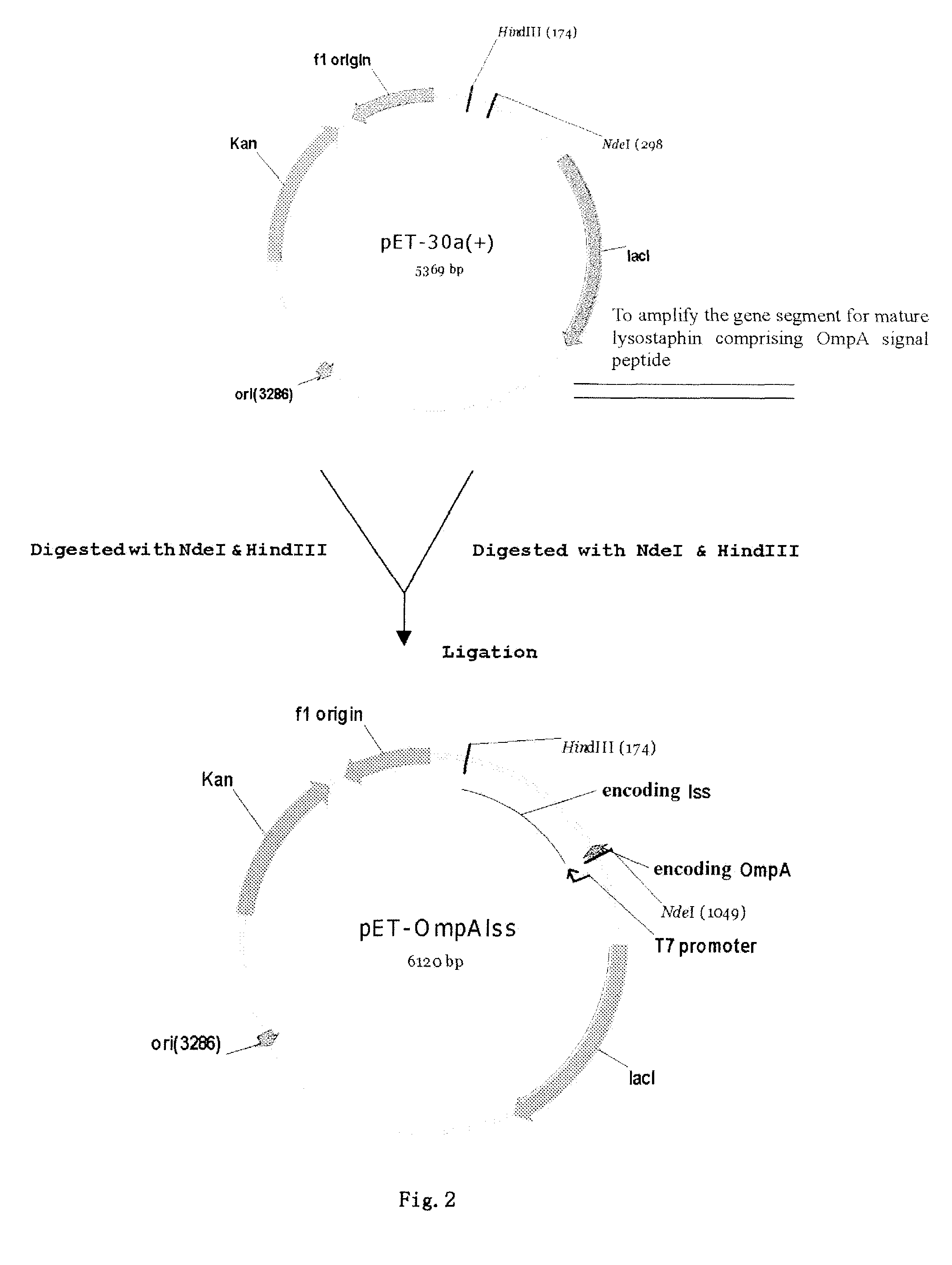
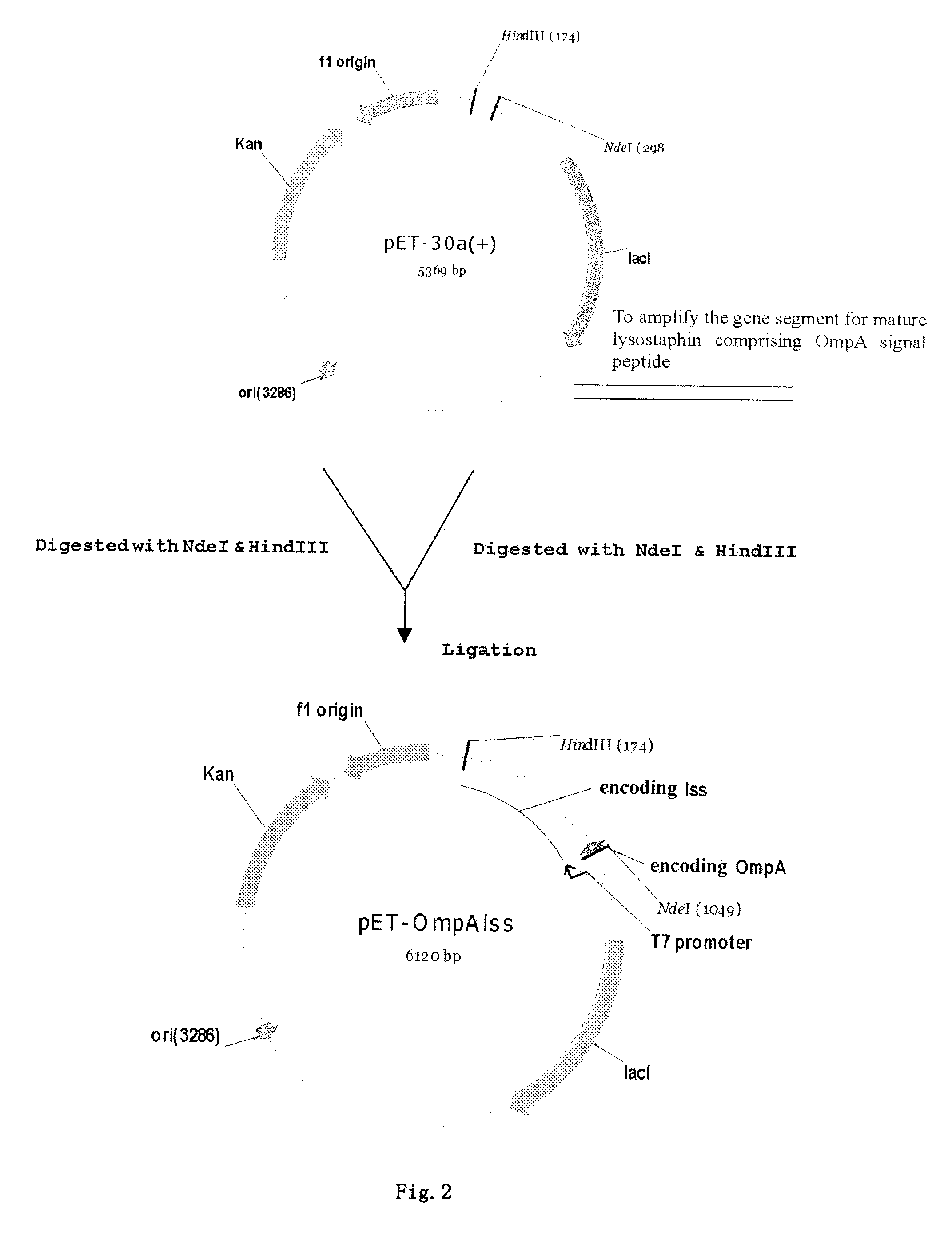
Method of secretory expression of lysostaphin in Escherichia coli at high level
ActiveUS8241901B2Economical and social benefitSpeed up the processBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
A method of secretory expression of lysostaphin in Escherichia coli at high level, which comprises constructing a expression vector by cloning a sequence encoding a signal peptide which is suitable for secretory expression in Escherichia coli before part or whole gene sequence which encodes mature lysostaphin, and ligating the cloned sequence with a promoter; and transforming Escherichia coli with the expression vector, culturing and fermenting, and then isolating lysostaphin from the supernatant of the fermentation broth. The advantage of secretory expression is that the expression product can exist in the medium in an active form, and thus does not need the process for renaturation of the inclusion body; it is more easily to purify from the supernatant of the fermentation broth with high rate of recovery; and there is less contamination from the host's proteins.
Owner:SHANGHAI HI TECH UNITED BIO TECHCAL RES
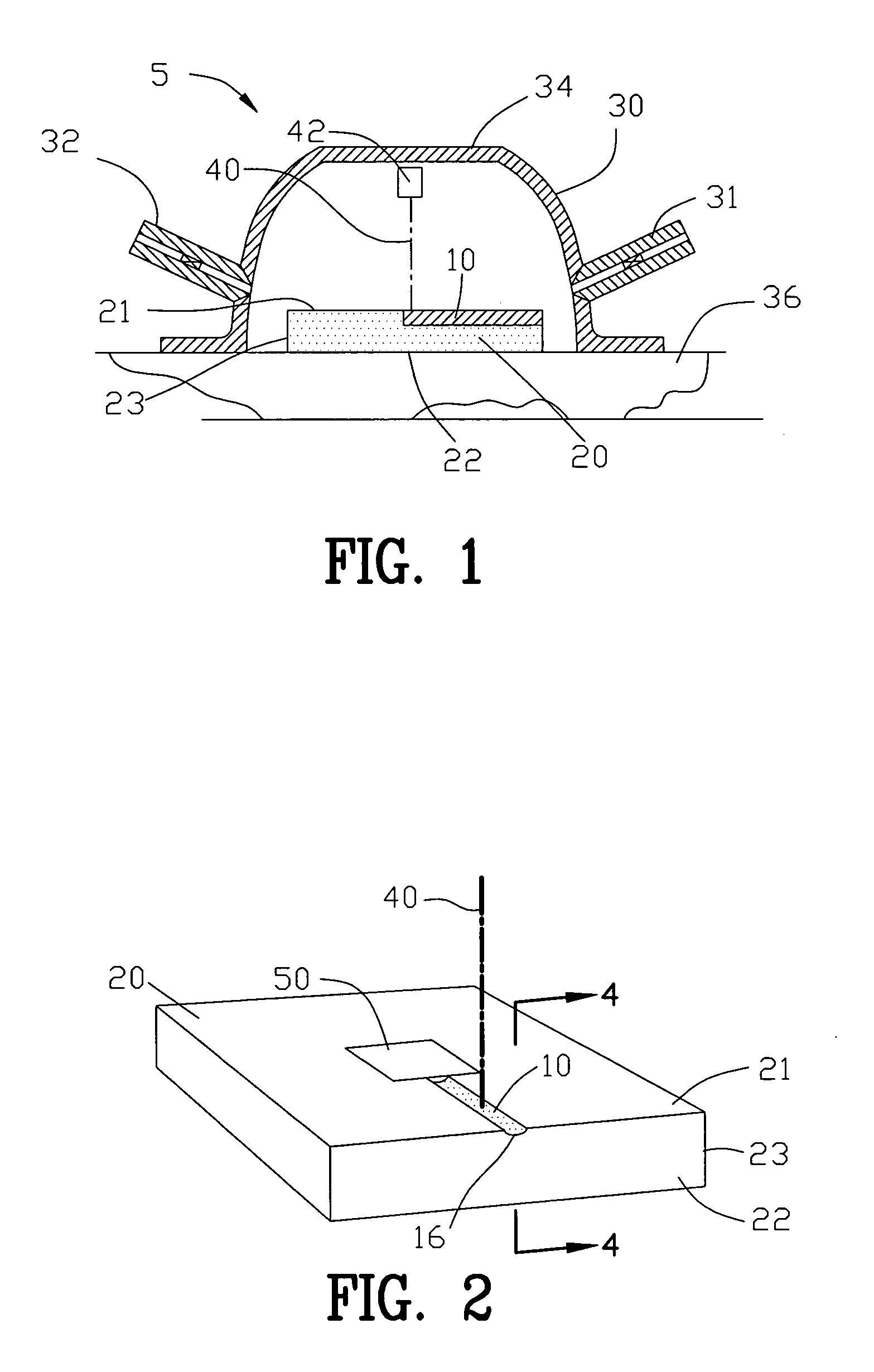
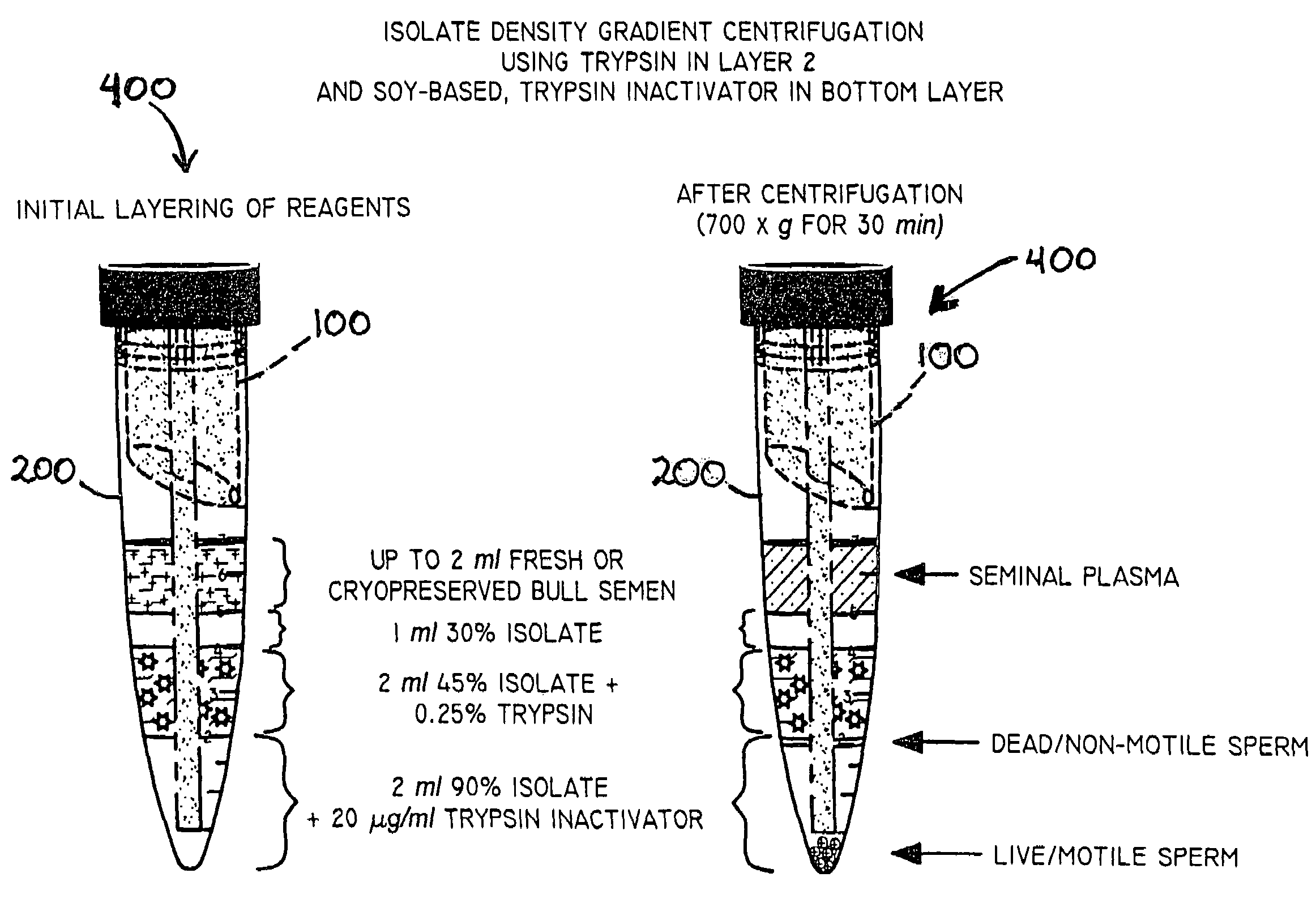
Apparatus and process for reducing pathogens in a biological sample and removing a sample pellet from a sample tube
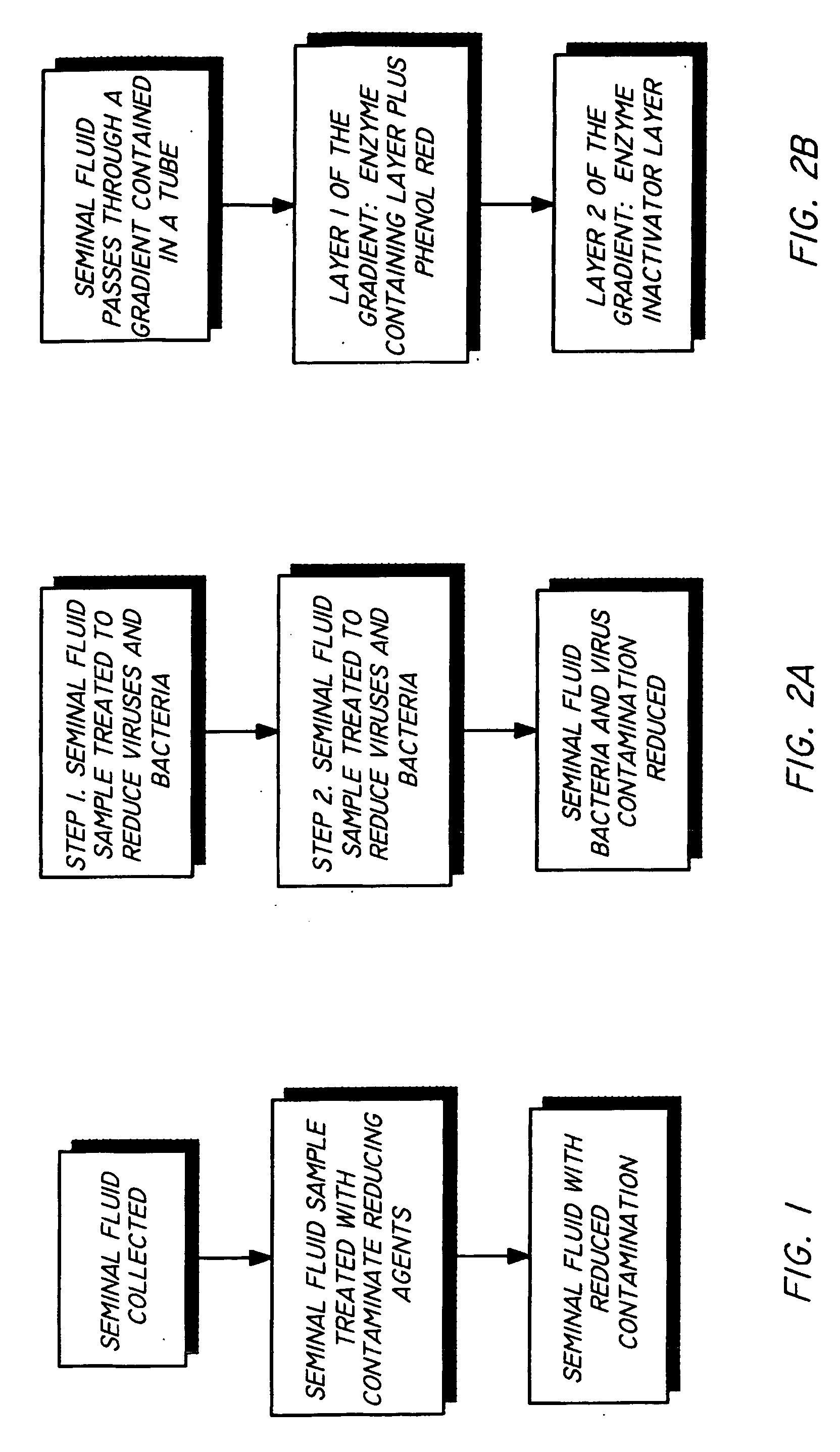
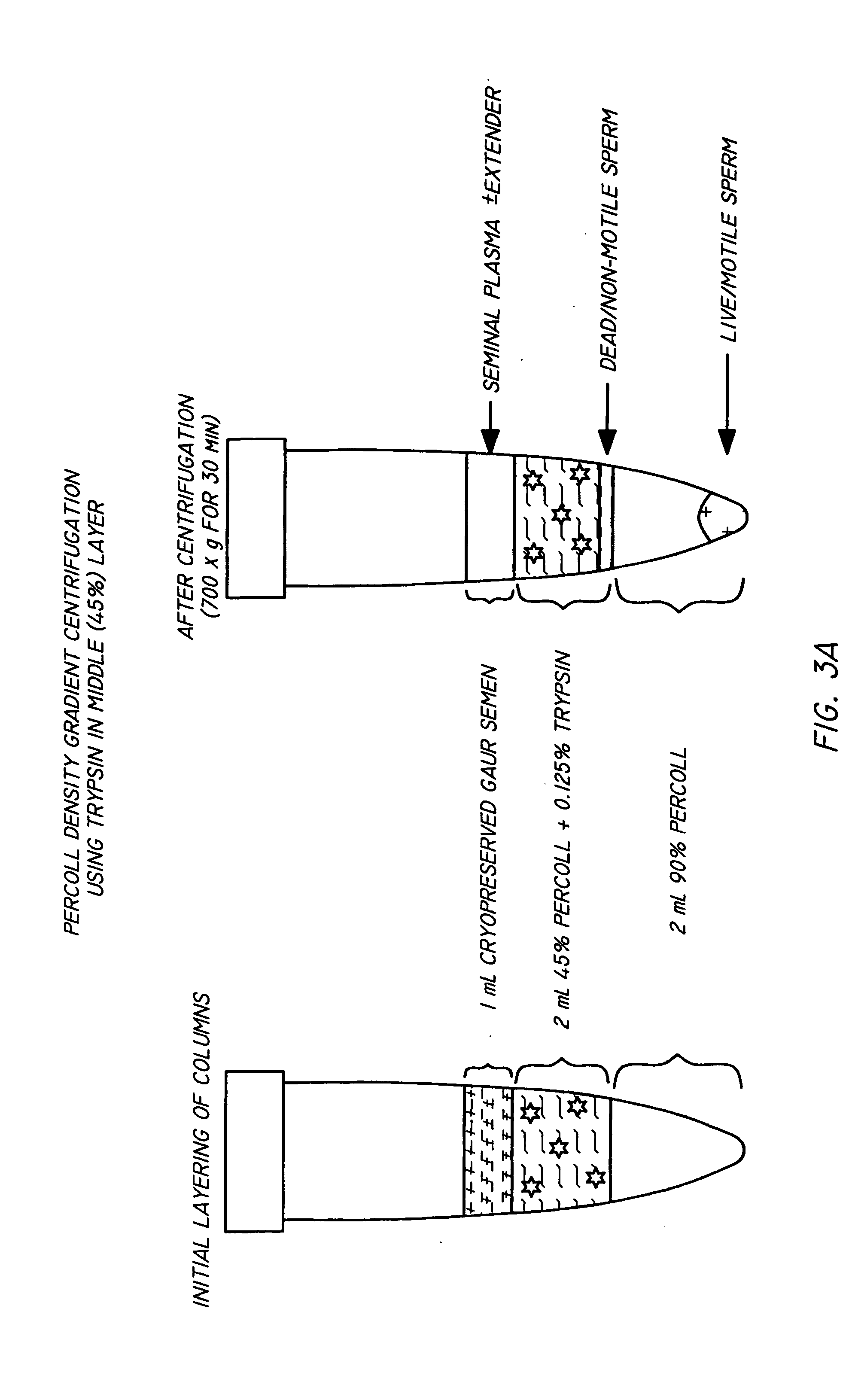
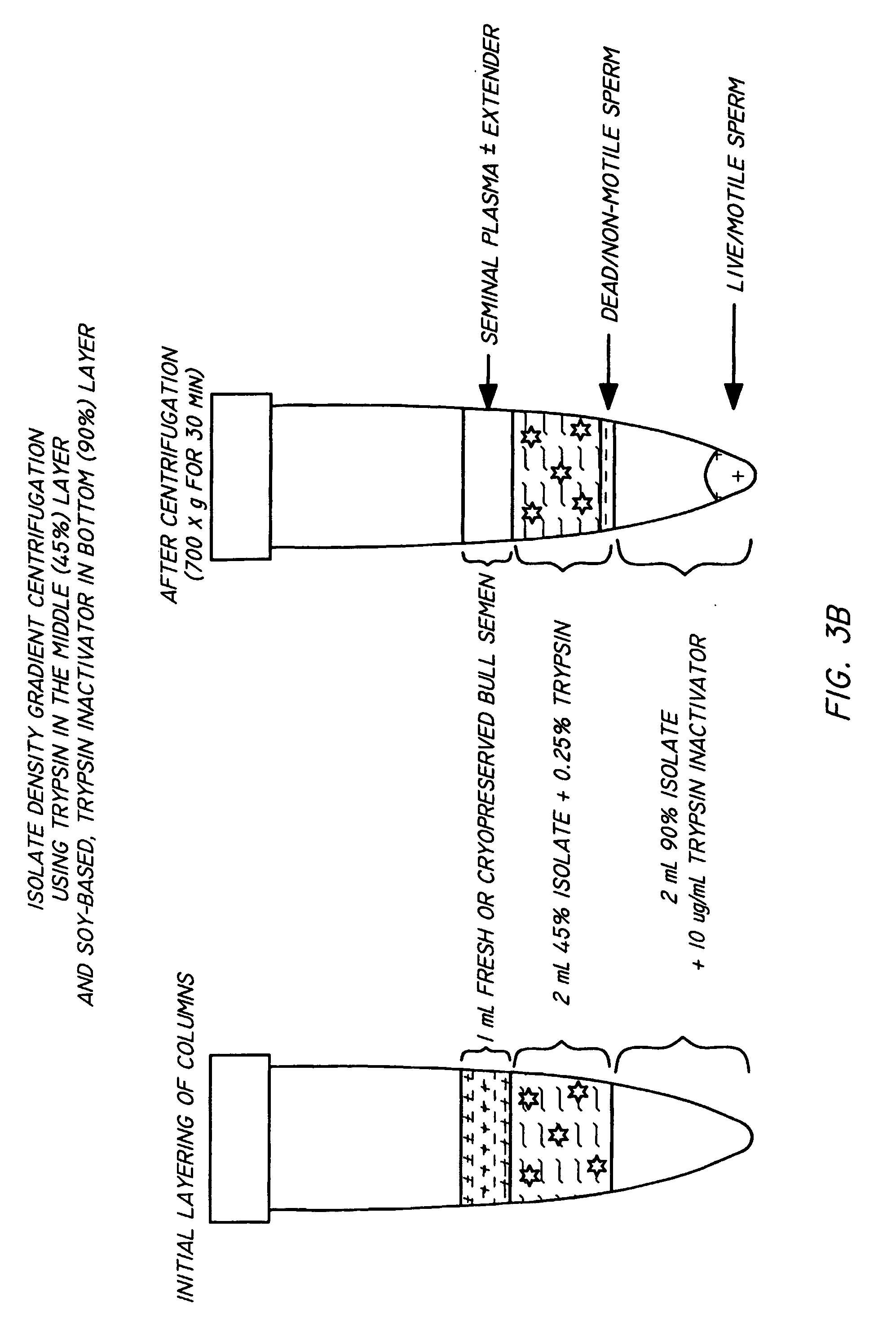
InactiveUS20050064579A1Reducing and eliminating riskBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringSemen
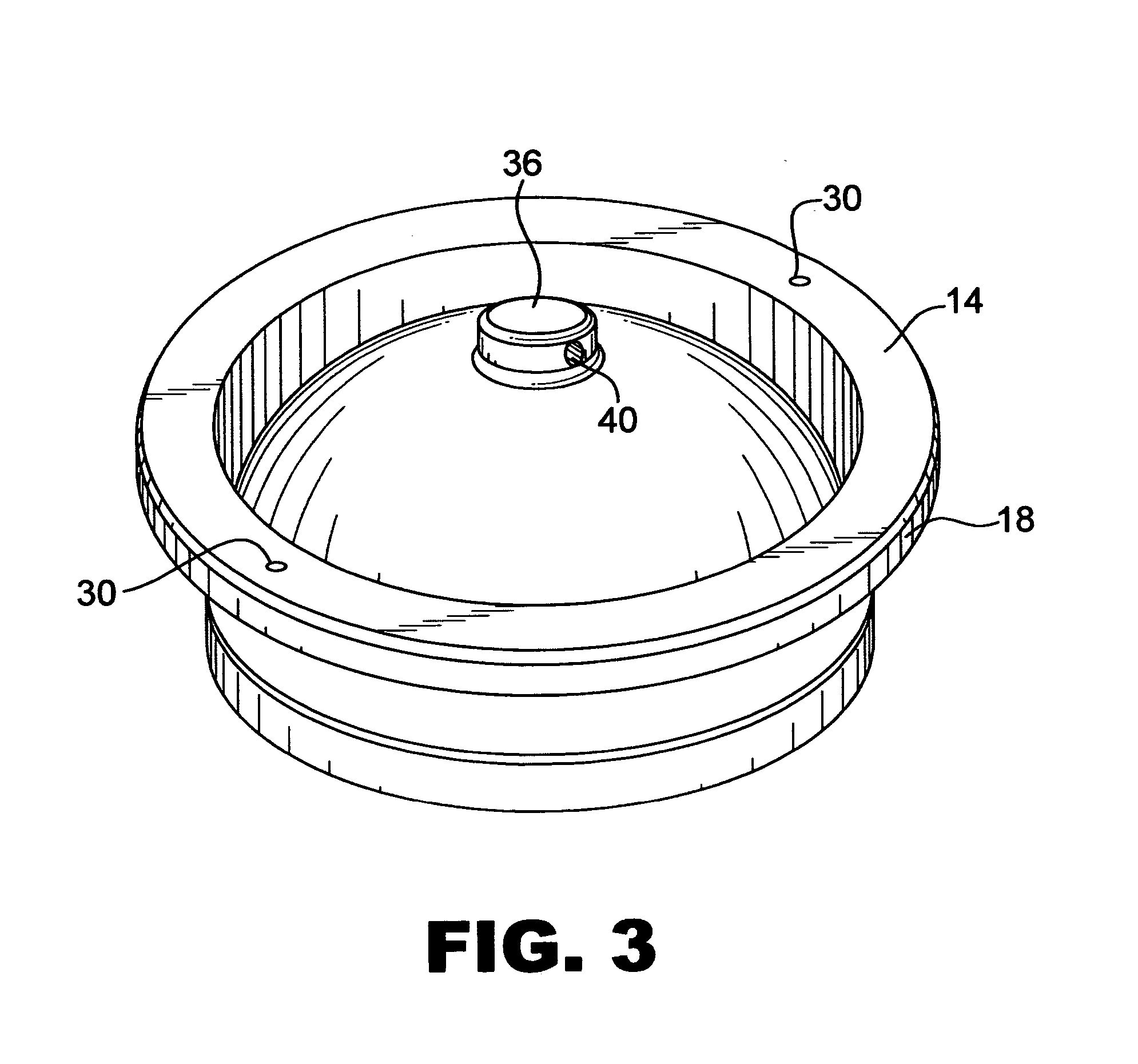
The present invention is directed towards an apparatus and method for disinfecting biological samples, including semen and the like, and for removing a biological sample pellet from surrounding media while reducing the risk of recontamination of the pellet with said media. An insert receptacle includes a receiving cylinder having a drain in a floor which allows the fluids to decant slowly down the side of a tube. The insert receptacle further includes an aspiration channel which allows an aspiration device, such as a modified micro-pipette, to be utilized for extracting a sample pellet from the bottom of the tube. Utilizing the novel apparatus, a method for reducing pathogens in a biological sample includes decanting the biological sample through the receiving cylinder and into a tube where it passes through a multi-layer gradient including an enzyme suitable for removal of at least one pathogen from the biological sample. Centrifuging of the insert receptacle, tube, and sample, isolates a sample pellet of the biological sample from the surrounding at least one pathogen. After the sample pellet is isolated it is aspirated via the aspiration device without re-contaminating the sample pellet through contact with the surrounding at least one pathogen.
Owner:SAFETY ART +1
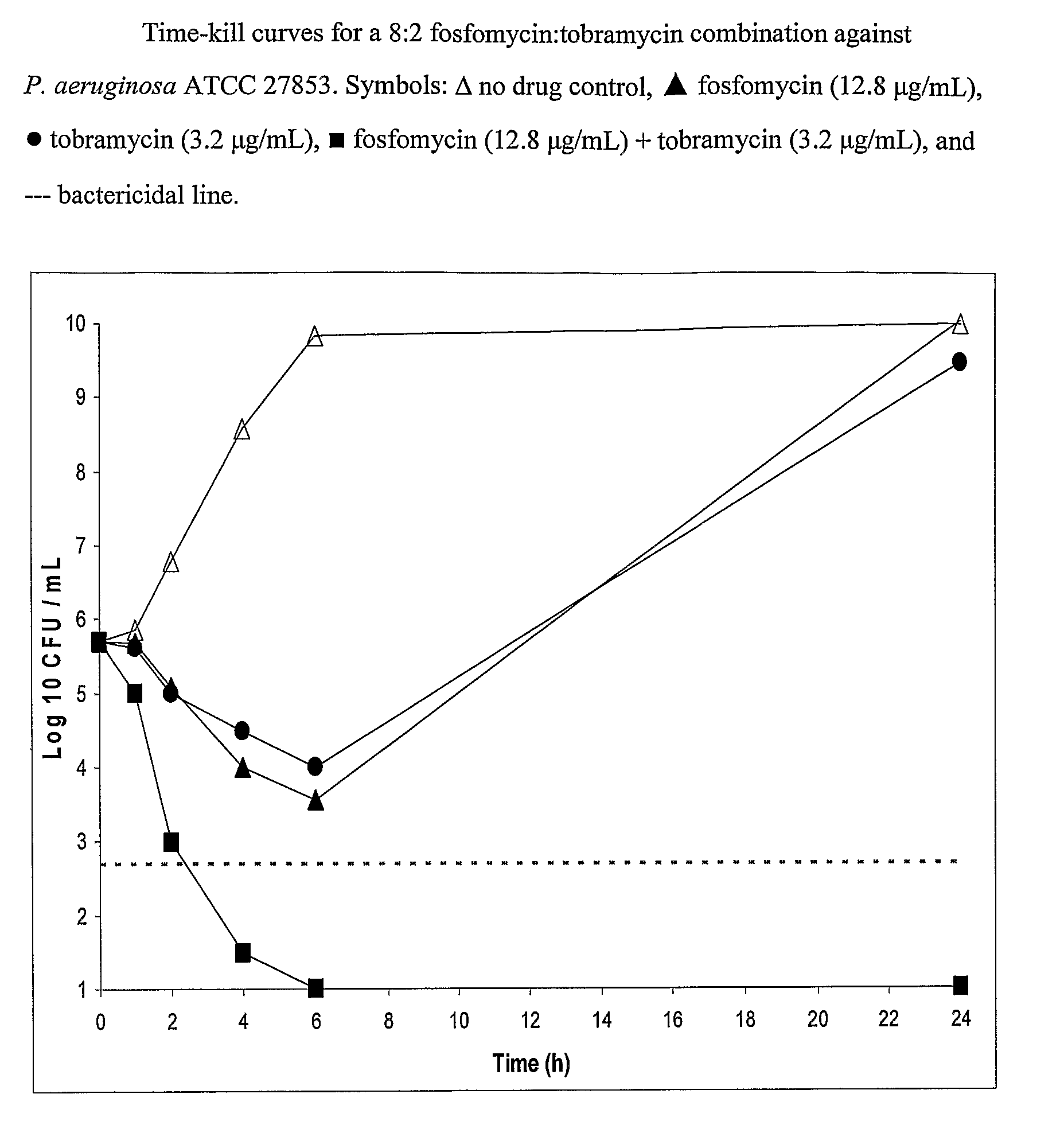
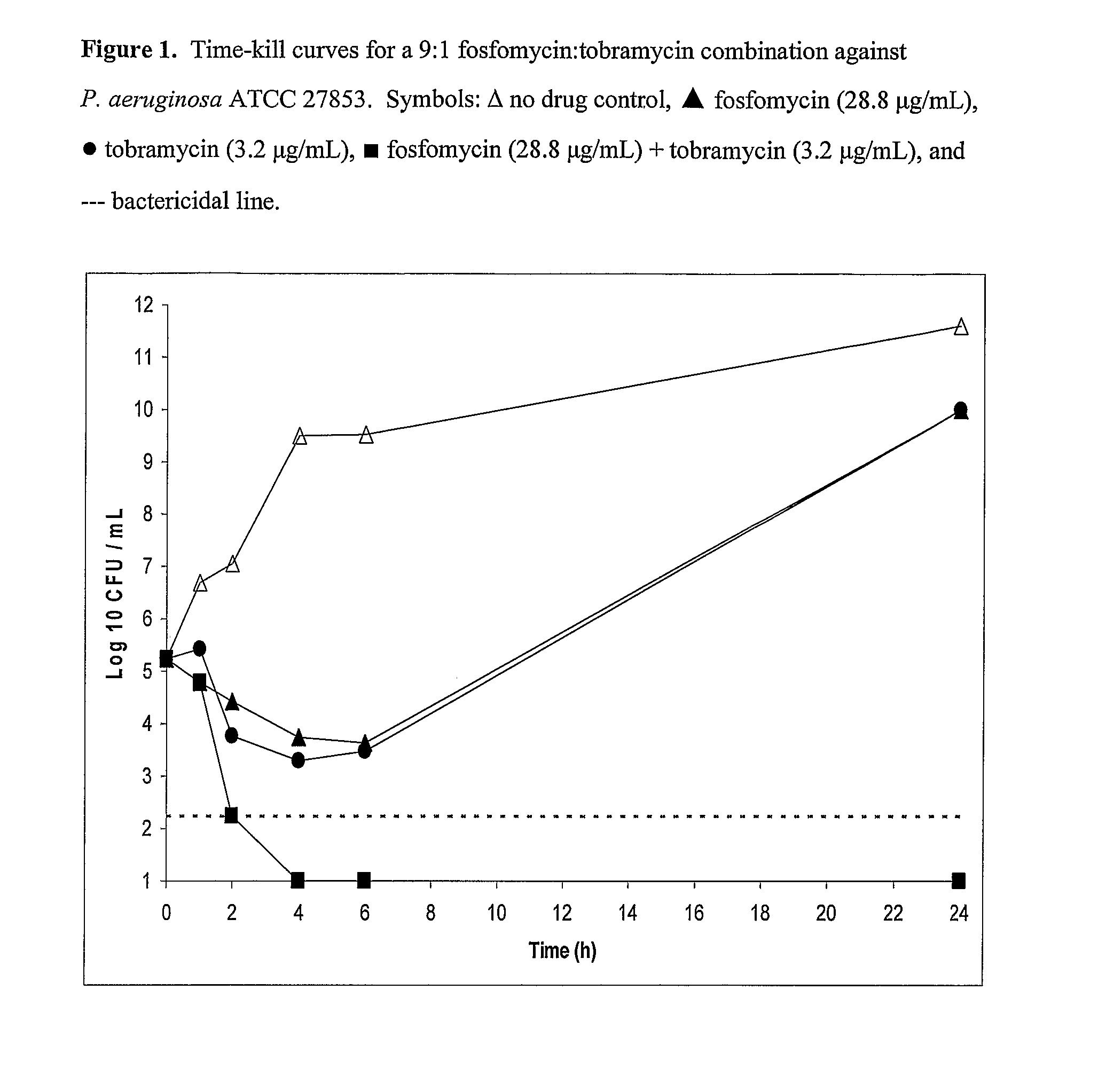
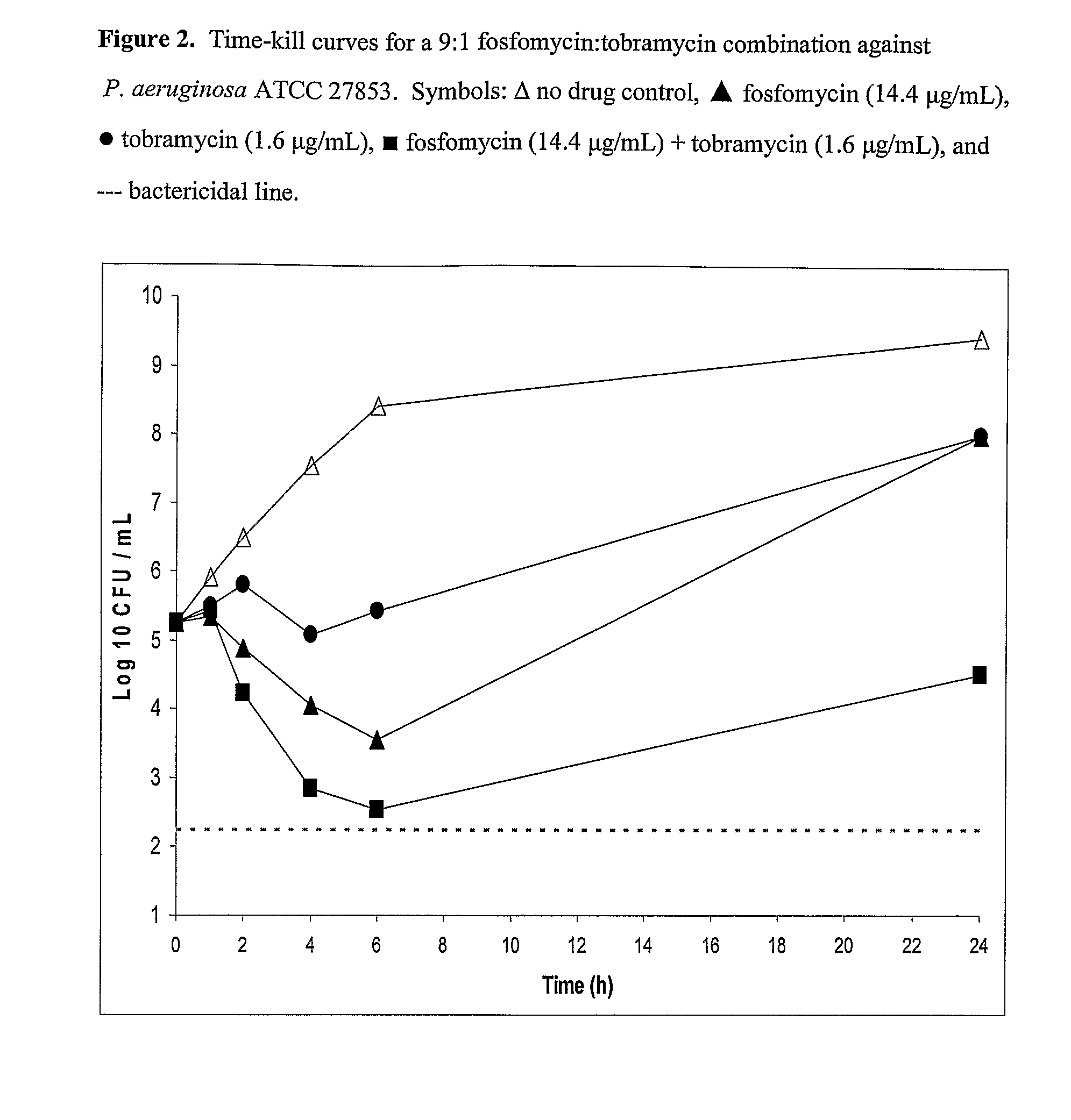
Aerosolized fosfomycin/aminoglycoside combination for the treatment of bacterial respiratory infections
InactiveUS7943118B2Reduce developmentIncreases the post antibiotic affect (PAE)Antibacterial agentsBiocideBacterial respiratory infectionTobramycin
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
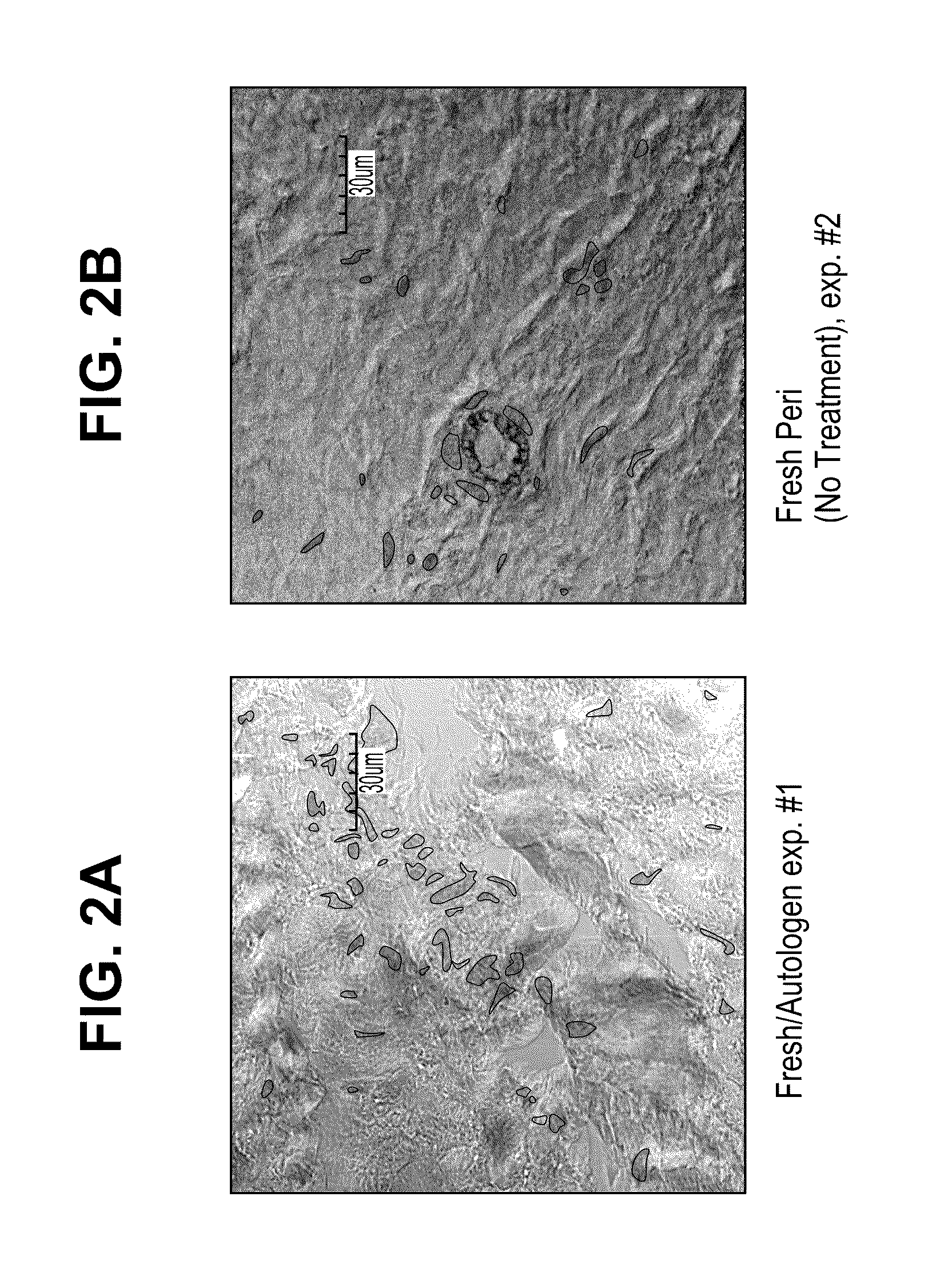
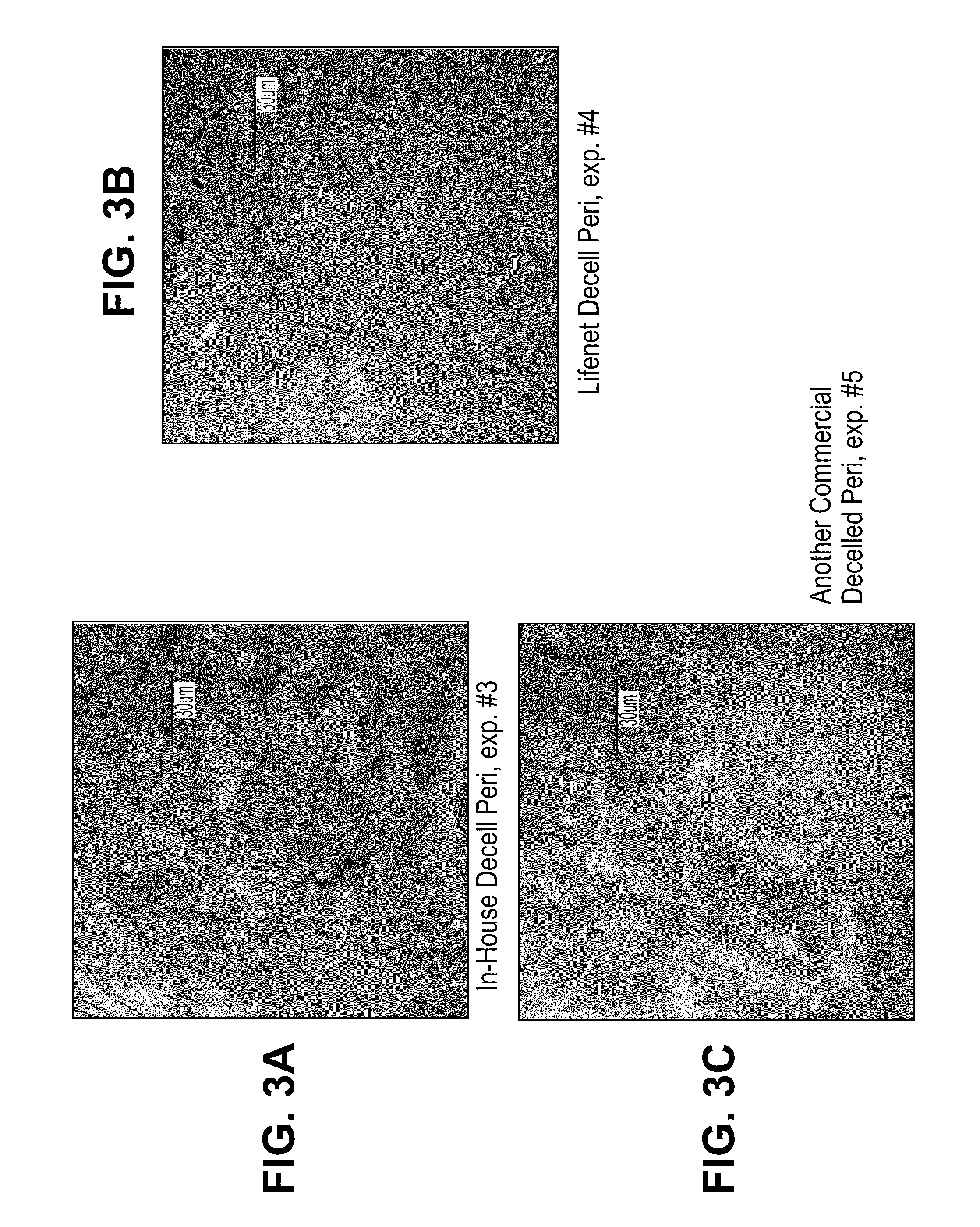
Method for processing porcine cornea for decellularization
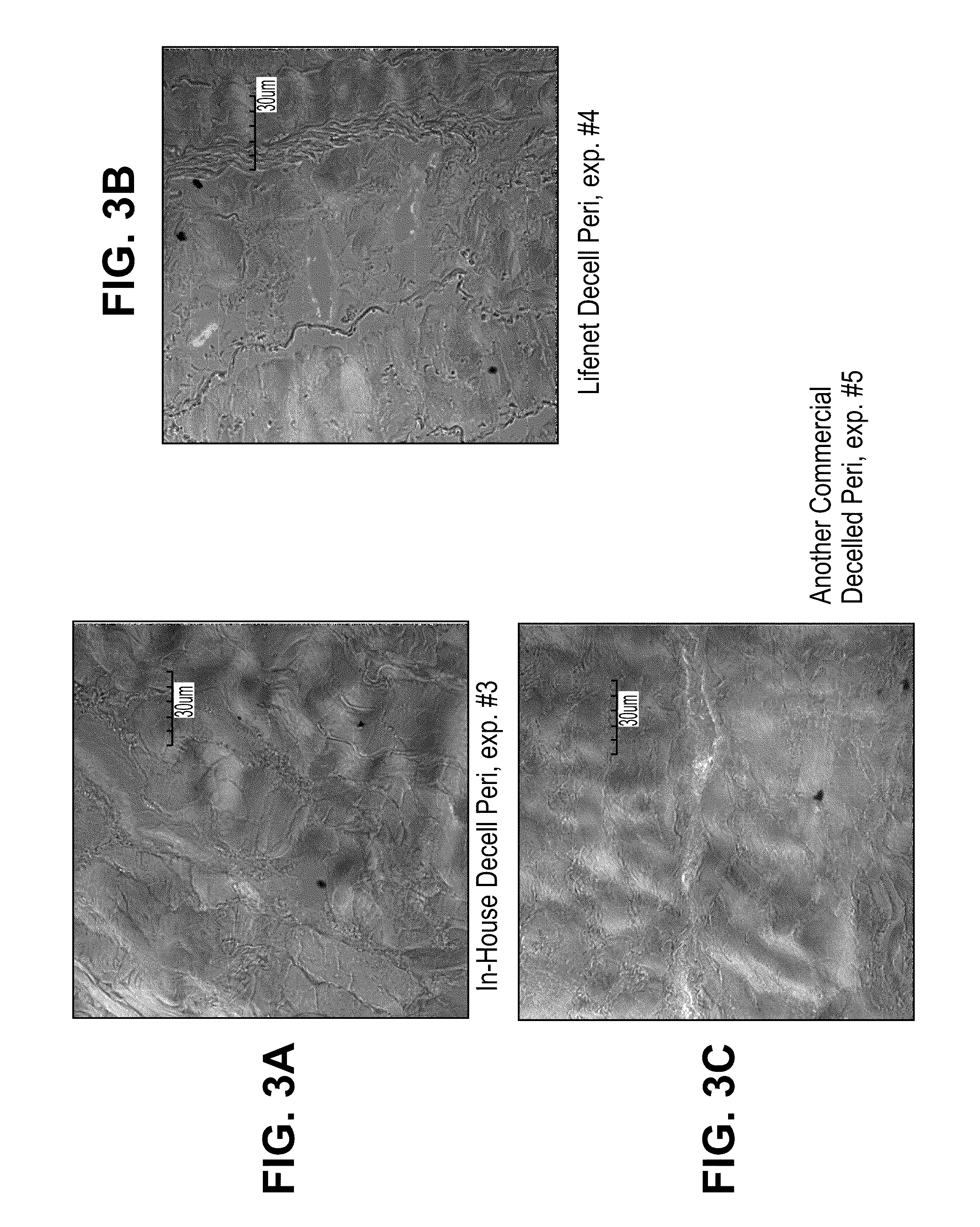
ActiveUS20110183404A1Efficient processingMinimizing immune responseHormonesEye implantsMedicineDecellularization
Disclosed is a method for processing porcine cornea using an aqueous NaCl solution and an aqueous trypsin / EDTA solution to decellularize enucleated porcine cornea. The porcine cornea processed by the method causes neither inflammation nor immune rejection. The porcine corneal stroma decellularized by the method can be recellularized together with host keratocytes after transplantation.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
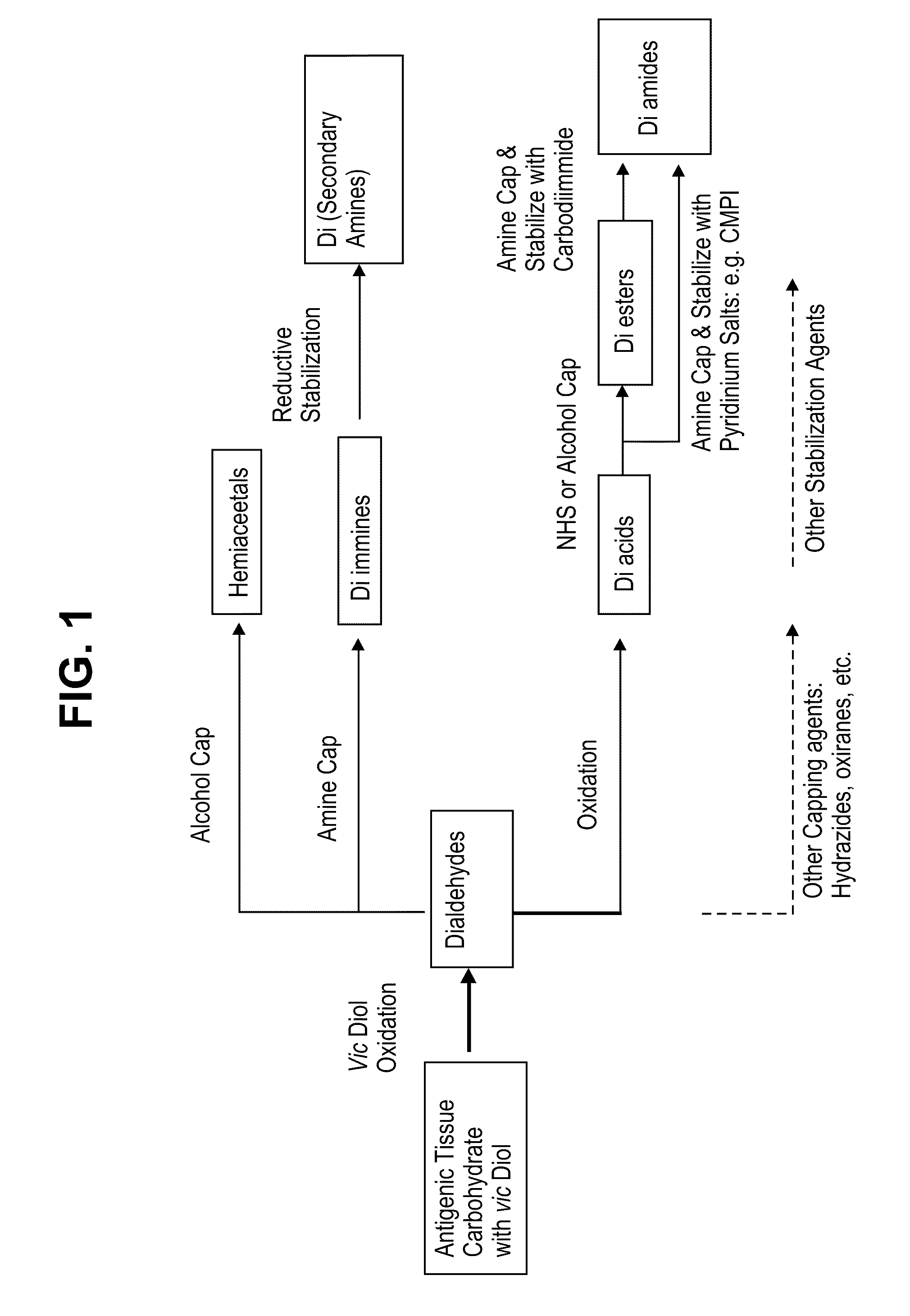
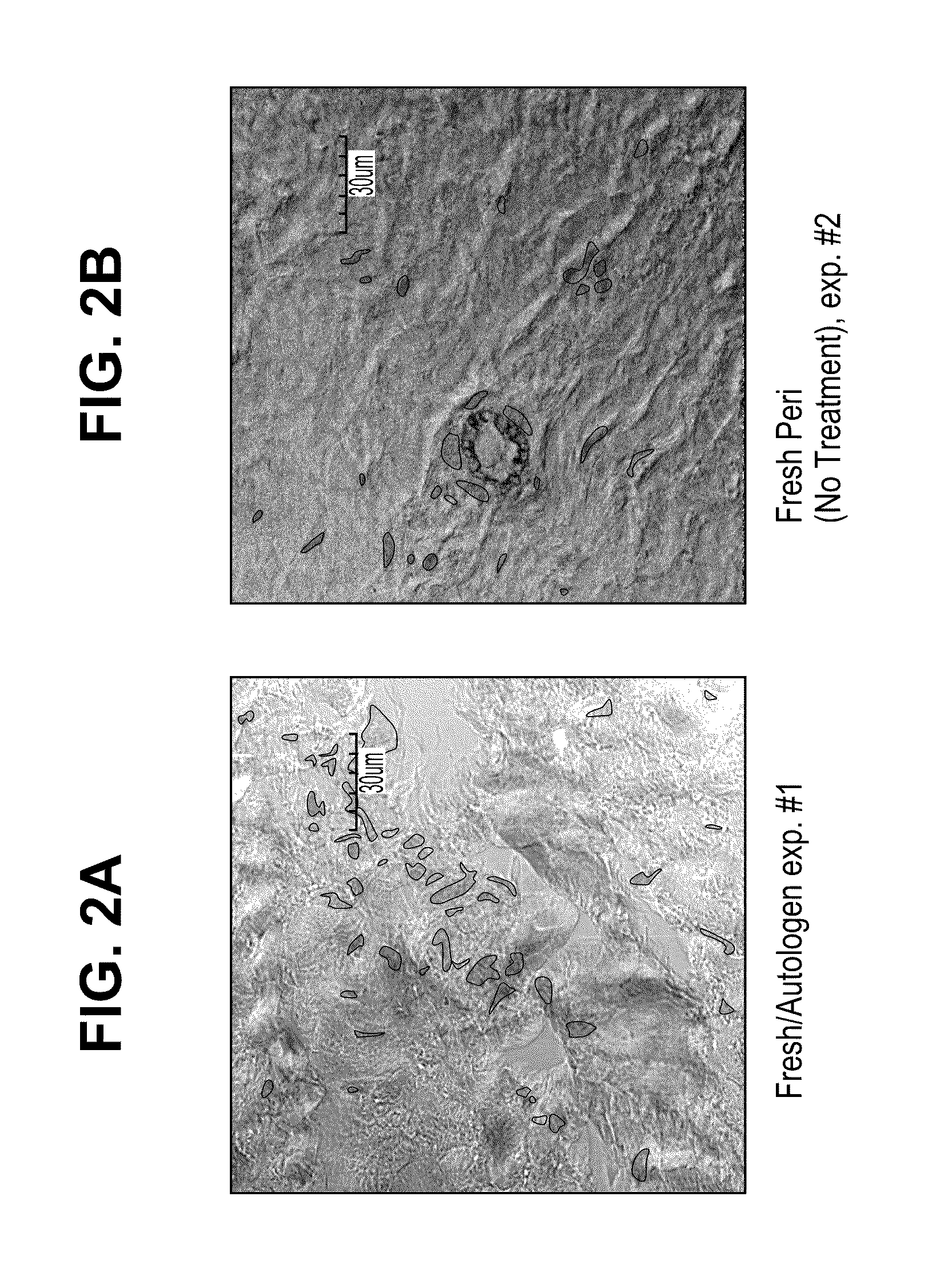
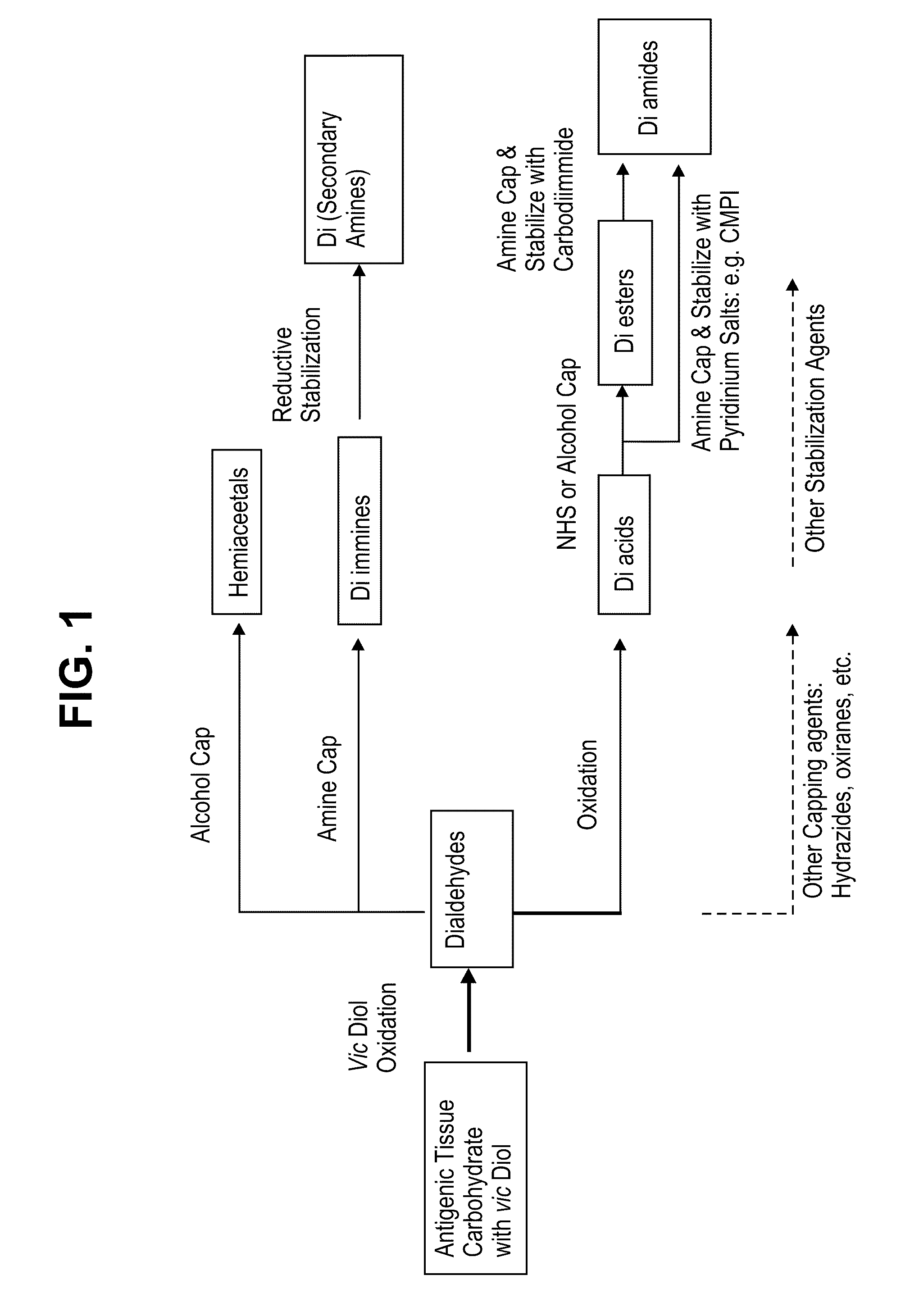
Methods for stabilizing a bioprosthetic tissue by chemical modification of antigenic carbohydrates
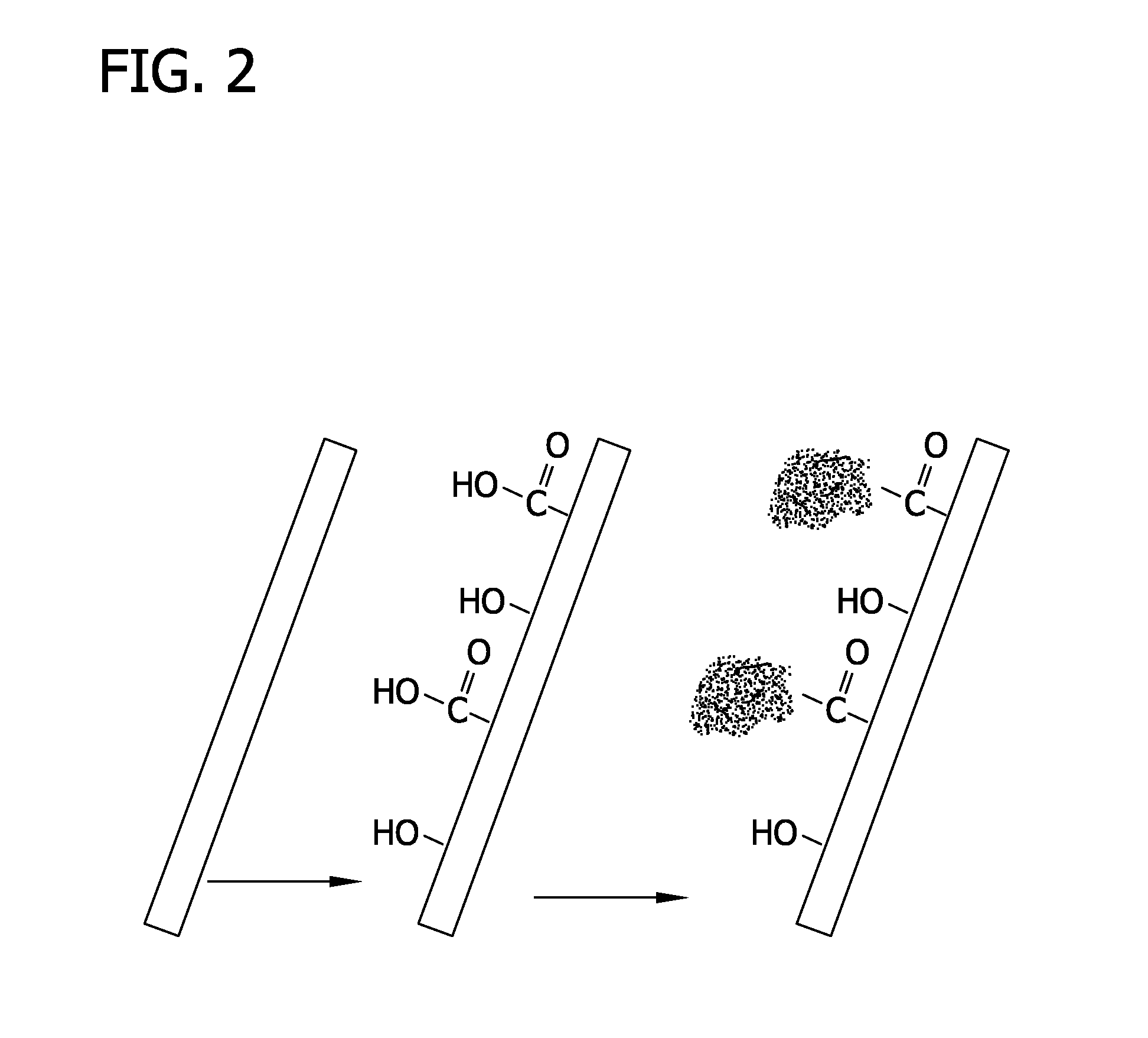
Methods are provided herein for modifying antigenic carbohydrate epitopes within a xenographic bioprosthetic tissue by oxidation of vicinal diols to form aldehydes or acids and subsequence reductive amination of aldehydes to form stable secondary amines, or amidation or esterification of acids to form stable amides or esters. Advantageously, methods provided herein mitigate the antigenicity of the bioprosthetic tissue while leaving the overall tissue structure substantially undisturbed, and thereby enhance the durability, safety and performance of the bioprosthetic implant.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
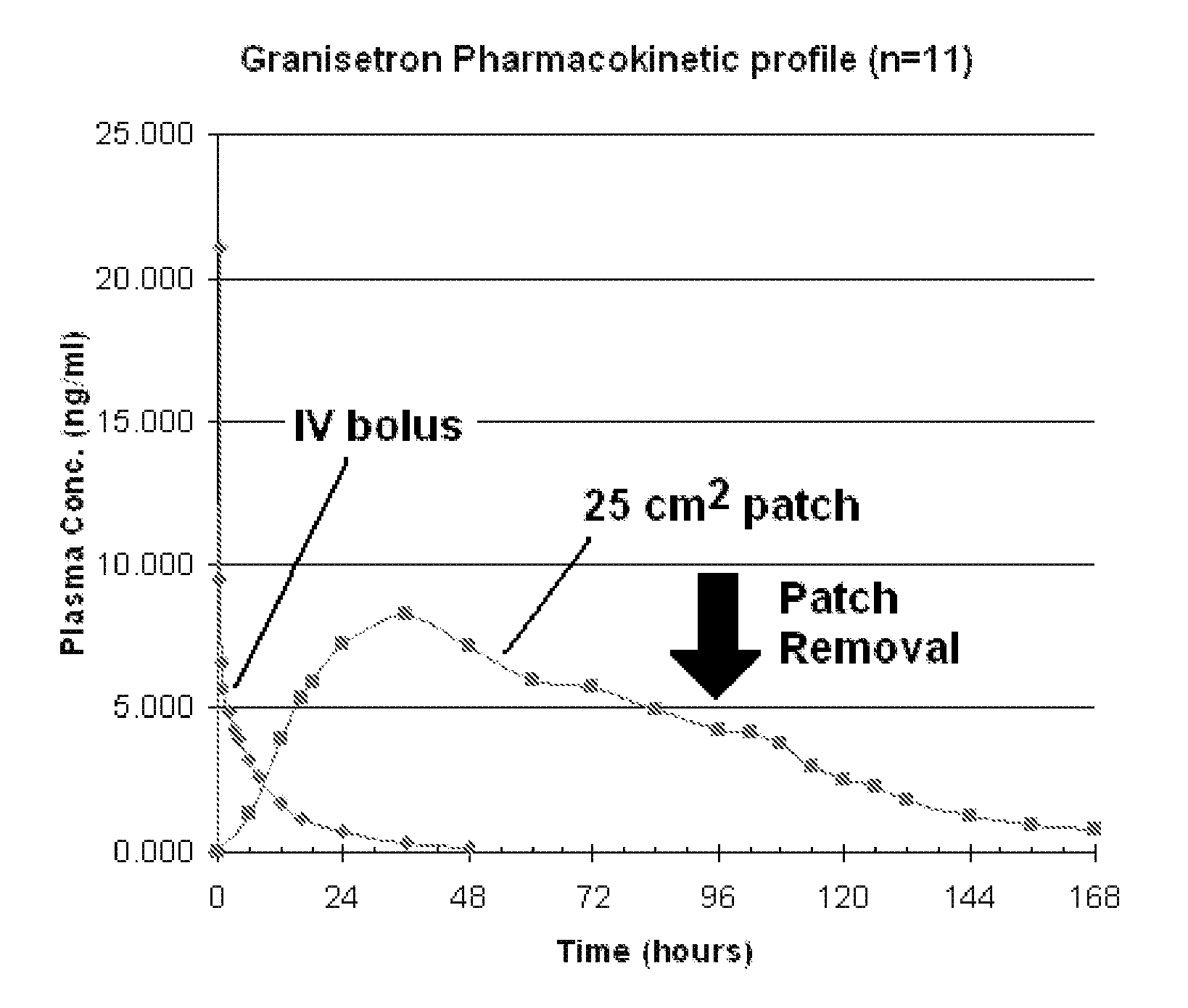
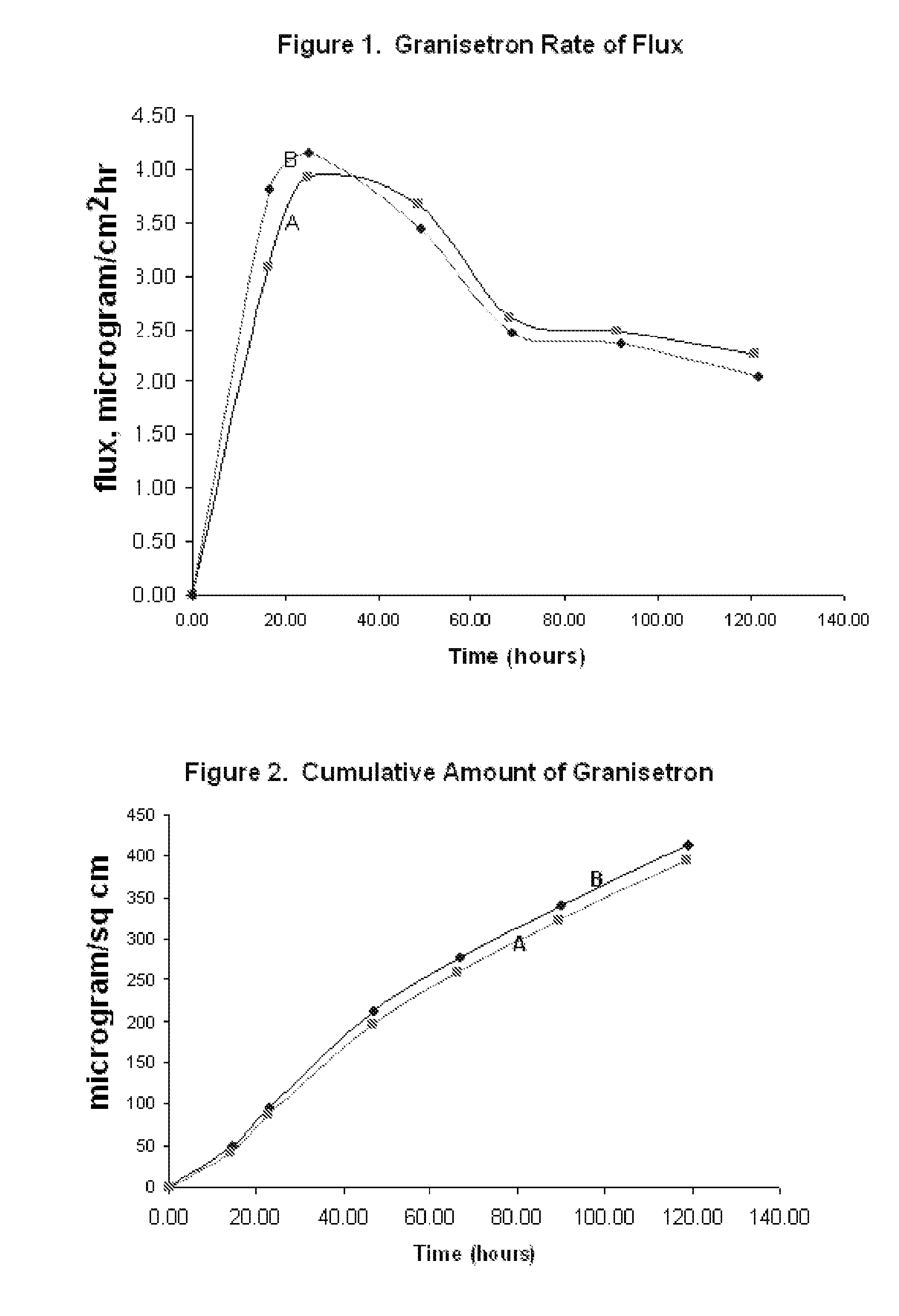
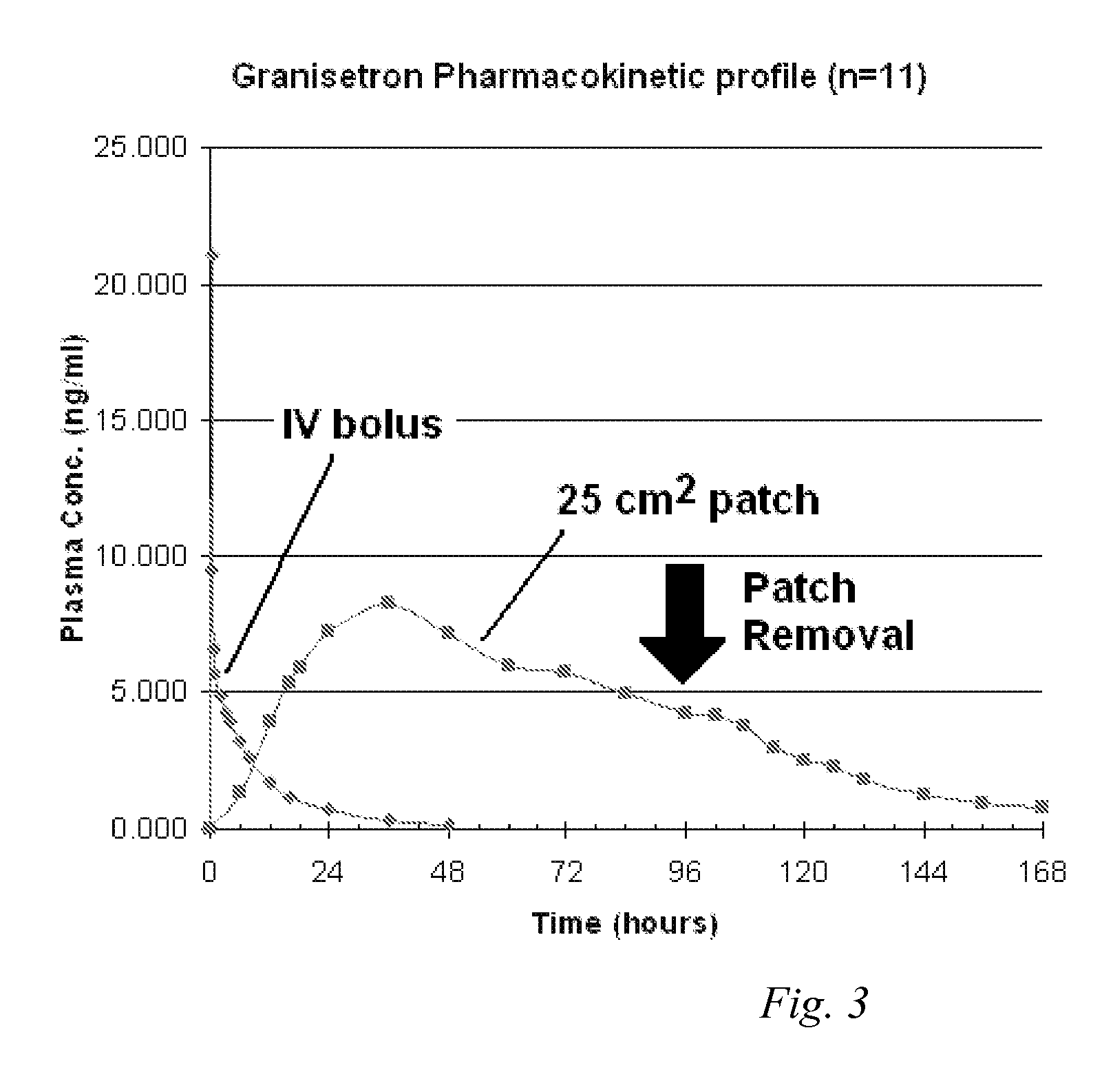
Transdermal Method and Patch for Nausea
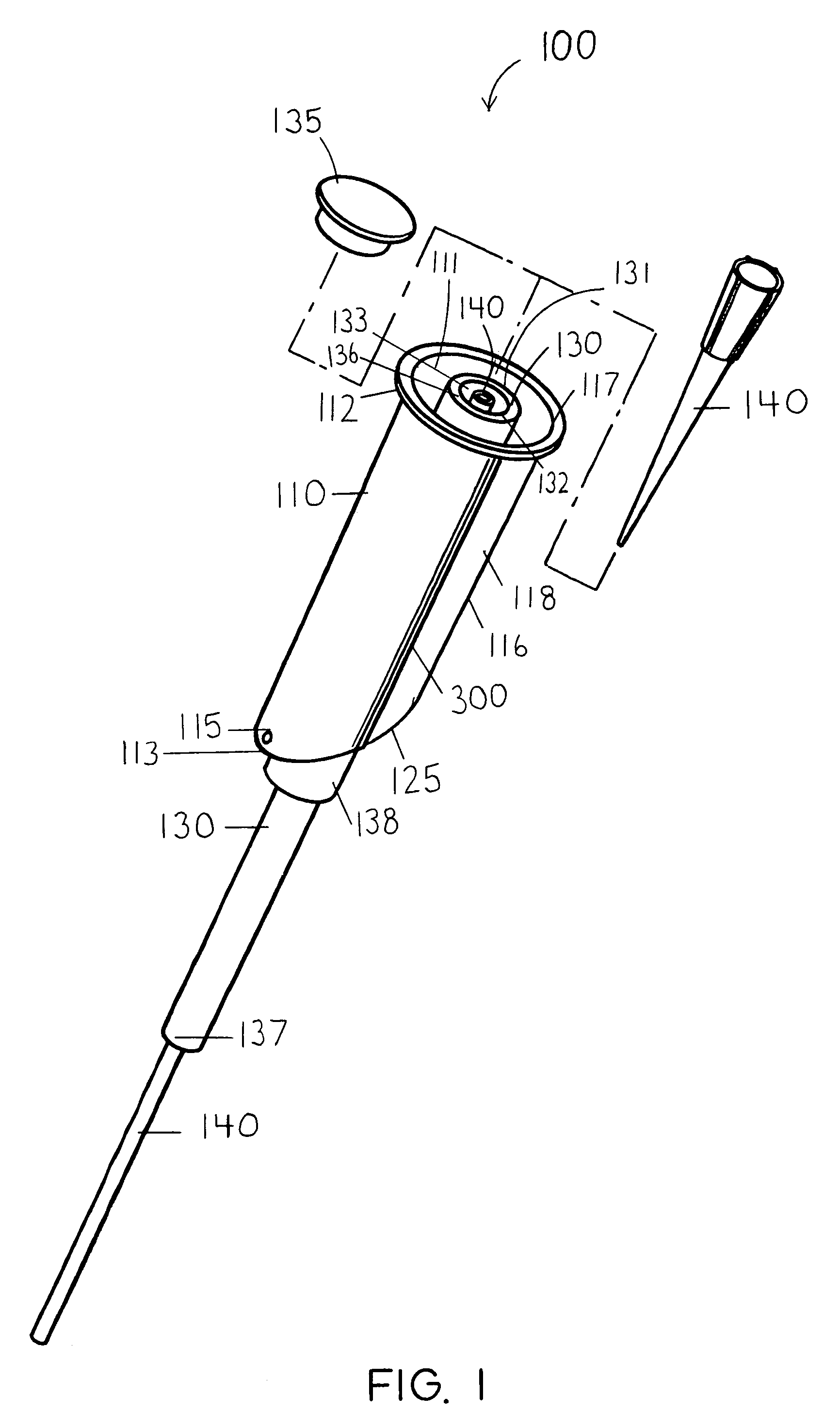
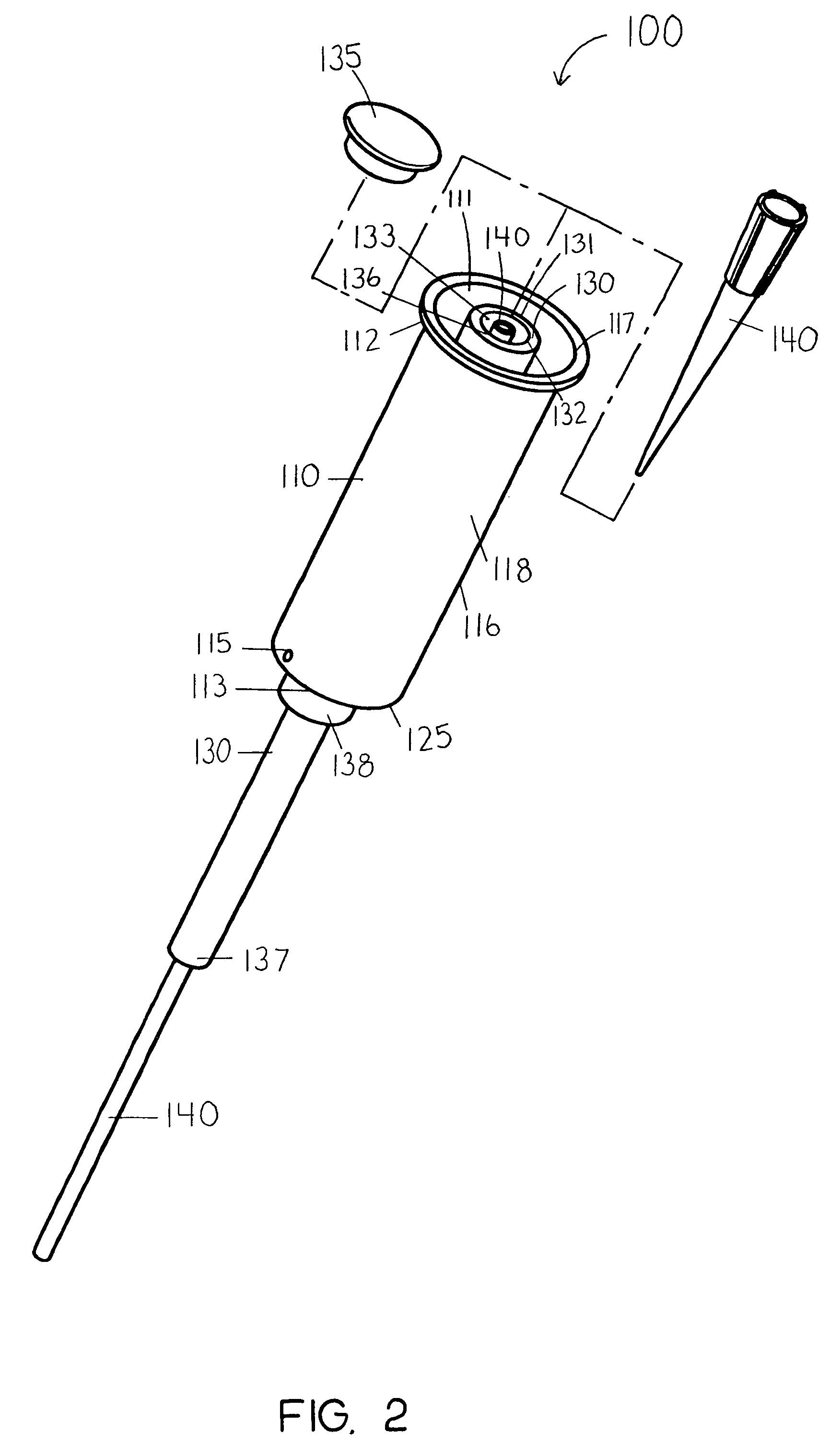
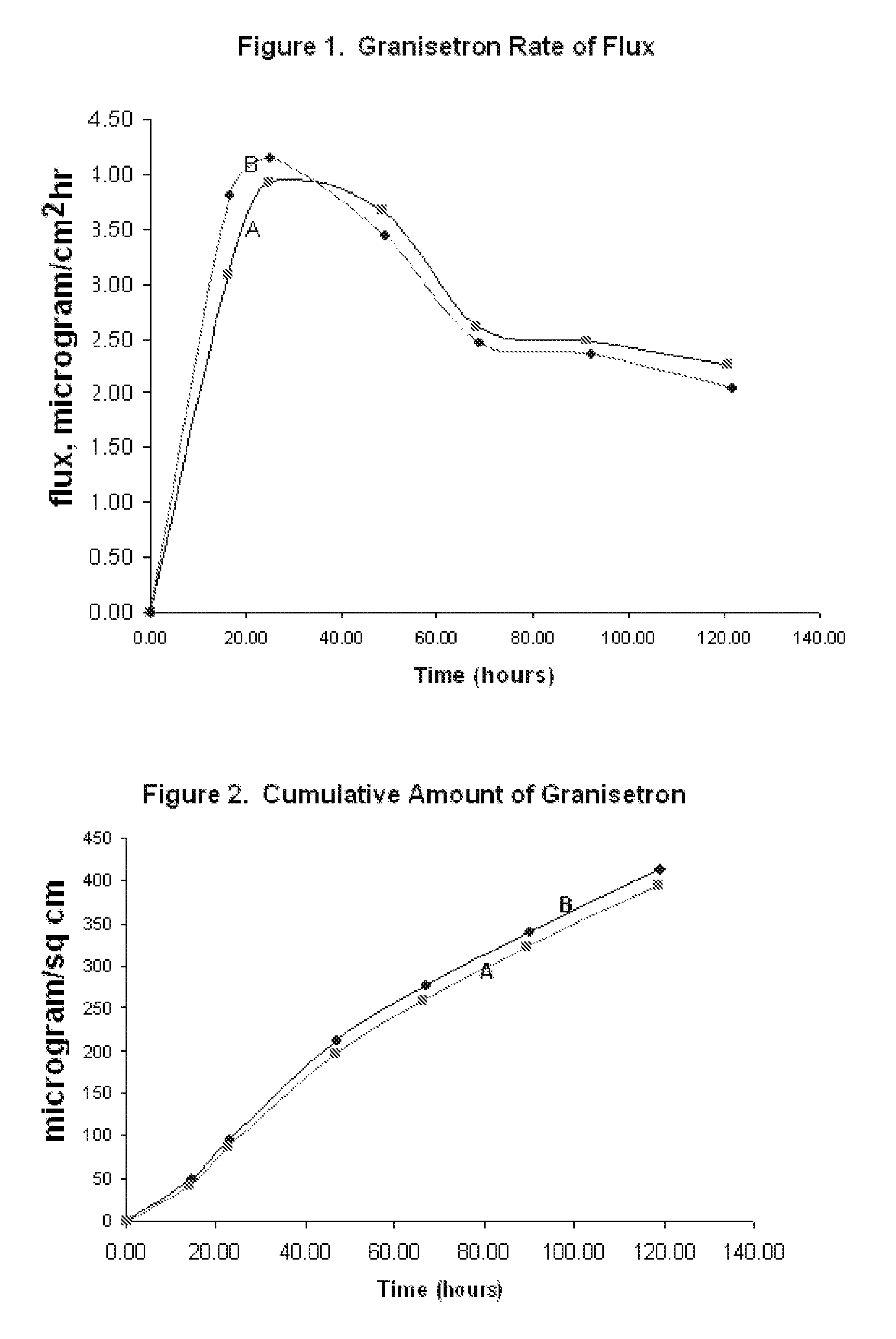
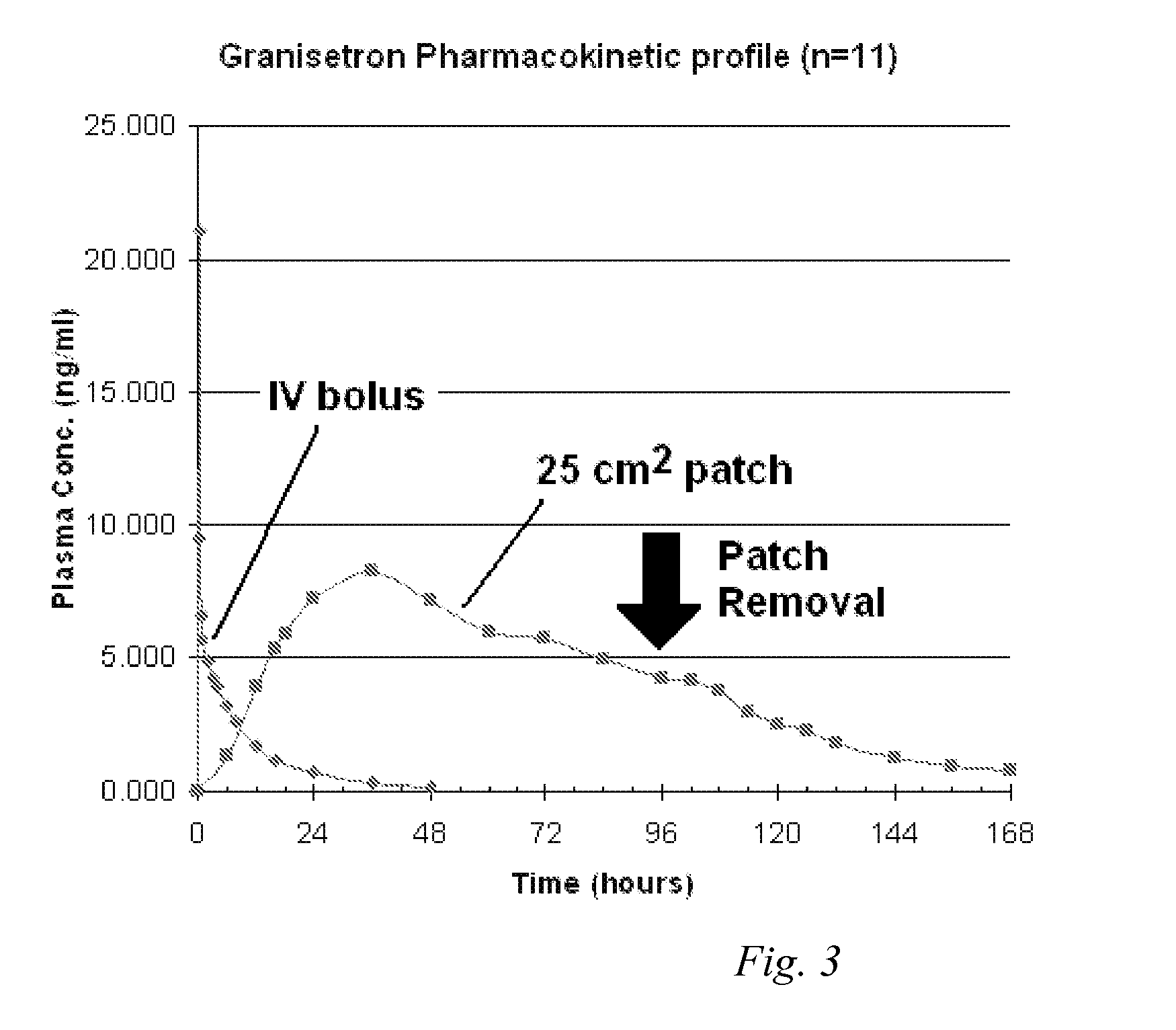
InactiveUS20060263421A1Induce skin irritationLow viscosityBiocideHormonesTransdermal patchIntact skin
Provided, among other things, is a method of treating acute, delayed or anticipatory emesis for a sustained period in an individual, which involves applying to a portion of intact skin on the individual a composition of i. an antiemetically effective amount of a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist; ii. a permeation enhancing amount of permeation enhancer comprising 0.5% to 15% by weight of the skin-contacting layer; and iii. an adhesive, wherein a plasma concentration of the 5-HT3 receptor antagonist in a therapeutically effective range is provided for period of time from an onset time to 12 hours or more after the composition is removed.
Owner:ABEILLE PHARMA
Remediation of sulfur-containing pollutants with hydrocarbon-utilizing bacteria
InactiveUS7329532B2Reducing sulfur-containing compoundEncouraging growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAlkaneSulfolane
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for remediating sulfur-containing pollutants with a hydrocarbon that is used to stimulate the growth of hydrocarbon-utilizing bacteria. The hydrocarbon is preferably an alkane such as butane. The sulfur-containing pollutant may comprise sulfate, sulfite, sulfide, disulfides, mercaptans, alkanesulfonates, dialkyl sulfides, thiosulfate, thiofurans, thiocyanates, isothiocyanates, thioureas, thiols, thiophenols, thioethers, thiophene, tetrathionate, dithionite, dialkyl disulfides, sulfones, sulfoxides, sulfolanes, sulfonic acid, dimethylsulfoniopropionate, sulfonic esters, hydrogen sulfide, sulfate esters, sulfur dioxide and any other sour gases, elemental sulfur and any other sulfur-containing material considered to be a contaminant or pollutant.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
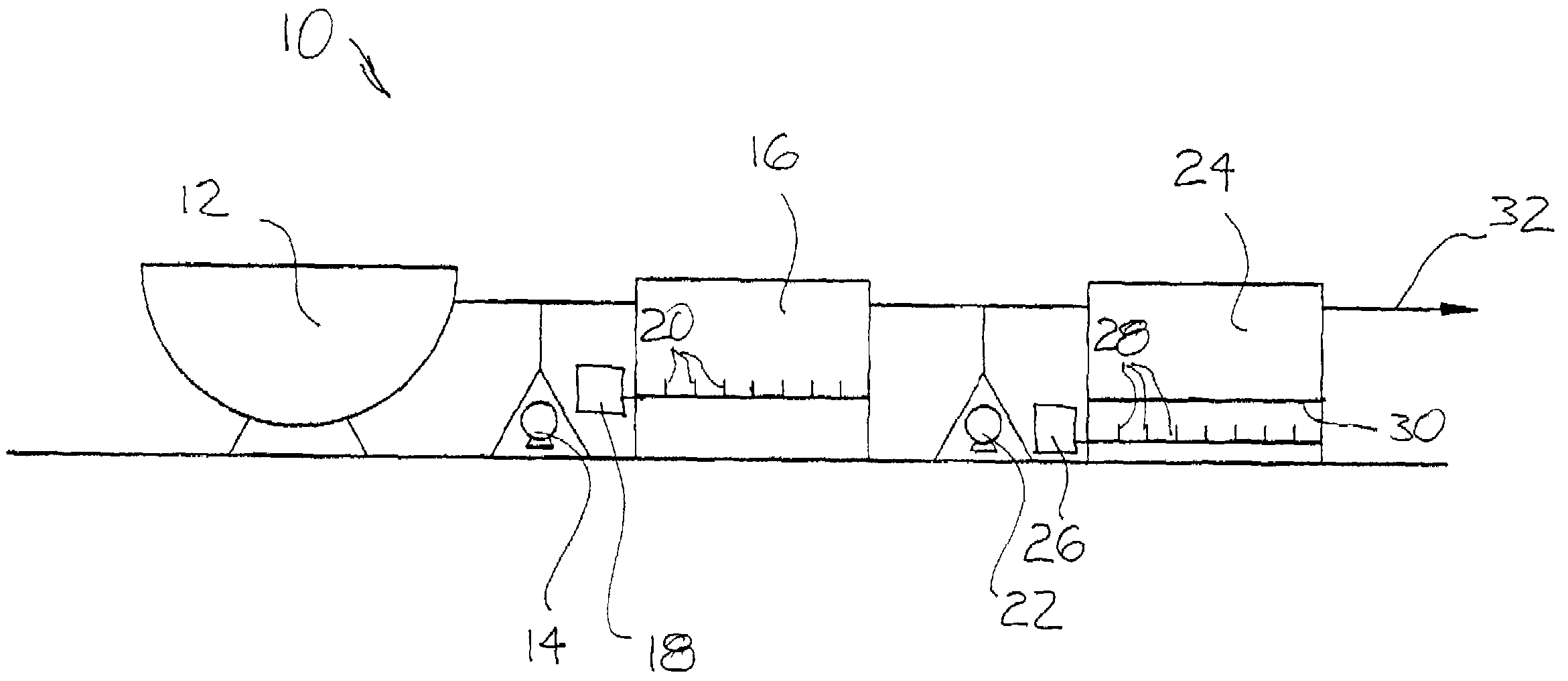
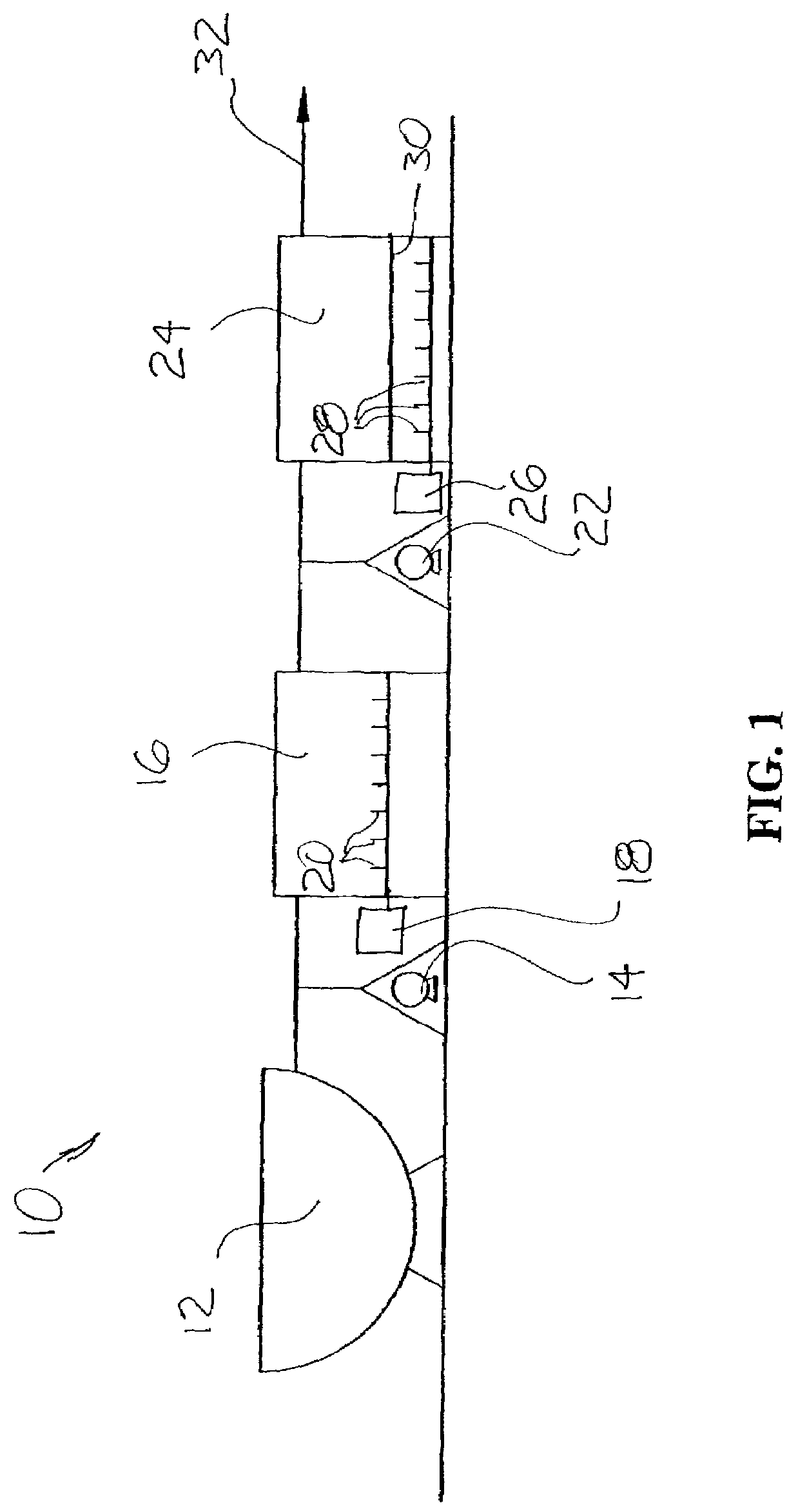
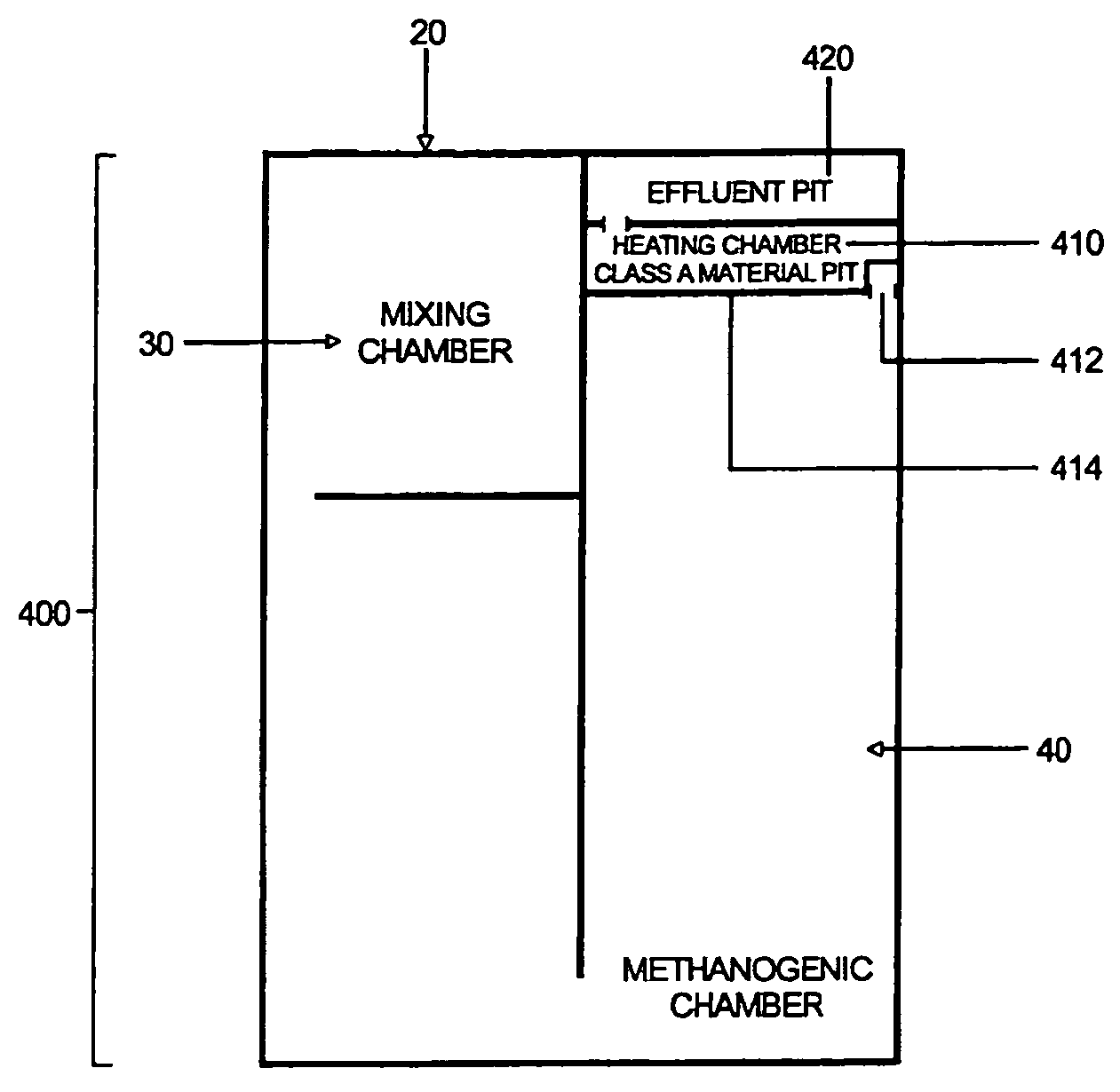
Biosolids digester and process for biosolids production
ActiveUS8835155B2Enhanced convectionOptimizing Flow PathsBio-organic fraction processingGas production bioreactorsPulp and paper industryBiosolids
The invention relates to methods and apparatuses for producing Class A biosolids. In yet another embodiment, the invention relates to a method comprising digesting waste material by anaerobic digestion, and yielding Class A biosolids. In still yet another embodiment, the invention relates to a system for anaerobic digestion of waste material to produce Class A biosolids. In still yet another embodiment, the invention relates to a system for anaerobic digestion of waste material comprising a mixing chamber, a digester, a heating pit, and an effluent pit.
Owner:DVO LICENSING
Method for preparing the decellularized matrix
InactiveUS20110045566A1Increase speedIncrease biological functionHormonesElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentPhospholipaseOrganic chemistry
A method for preparing the decellularized matrix using the phospholipase includes the following steps: pretreating the standby tissue and organ; putting the standby tissue and organ into the solution containing the phospholipase; preparing the decellularized matrix in the control condition; washing the prepared decellularized matrix.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN OPHTHALMIC CENT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method of using endophytic fungi to decontaminate and decompose human and animal wastes
InactiveUS20090017526A1Good curative effectSafely treating human and animal wastesBio-organic fraction processingFungiFusarium culmorumBuffering agent
A method of treating human and / or animal waste products comprising contacting the waste products with an effective amount of Fusarium culmorum and Muscodor albus, together with a buffering agent and starch. The treatment process covered by the present invention can be employed in connection with pit toilets, portal a toilets, disposable waste bags, or any other environment in which the treatment of human and / or animal wastes is desired. Both the Fusarium culmorum and the Muscodor albus can be stored on infested seed grains, including, but not limited to, barley, rye, rice, wheat, mustard and grass. A method or preparing Fusarium culmorum for use in the treatment of human and / or animal wastes. An isolated culture of Fusarium culmorum. A composition comprising the same four elements used in the treatment process. A method for controlling the pH of a mixture of human liquid and sold wastes.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
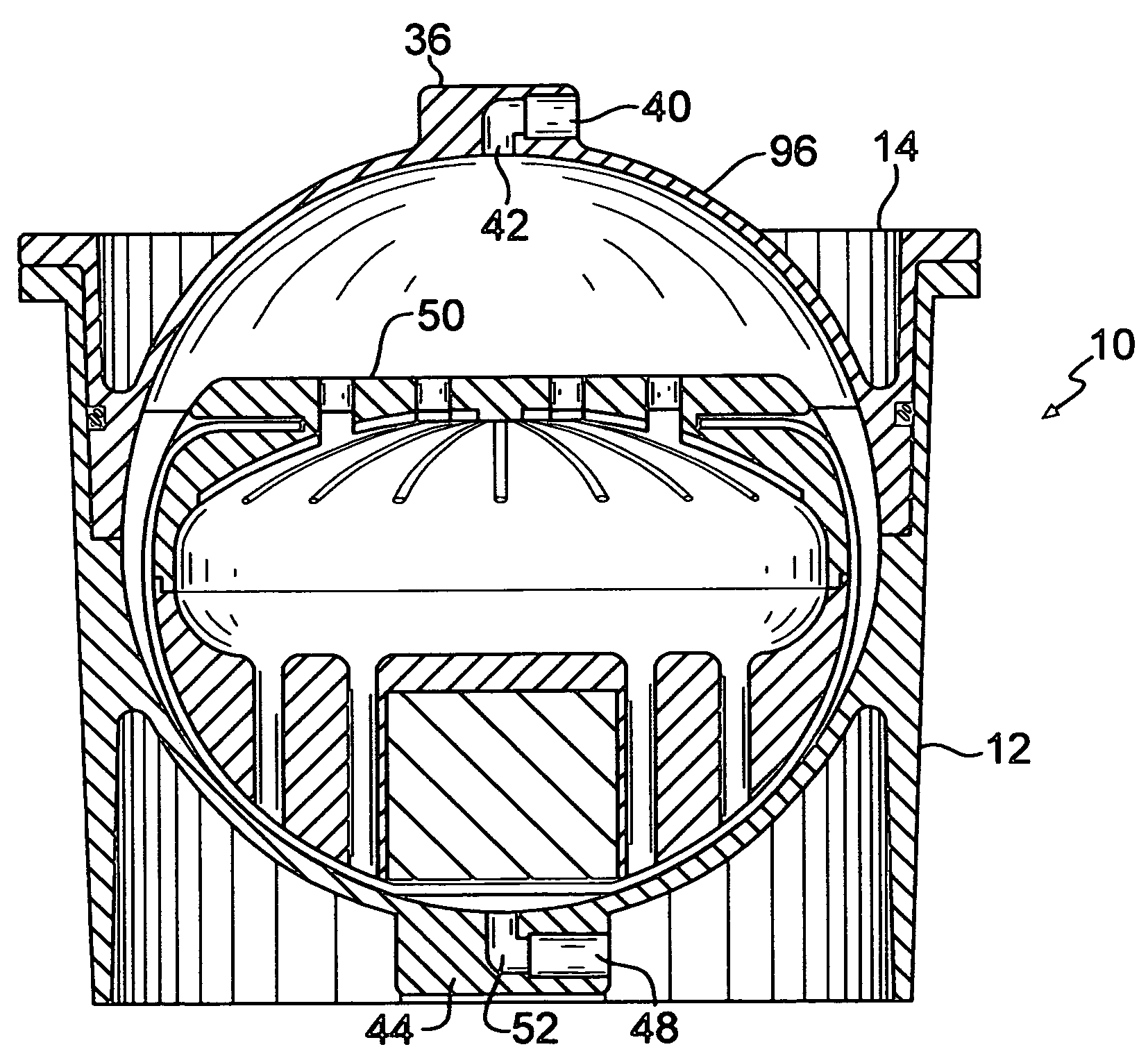
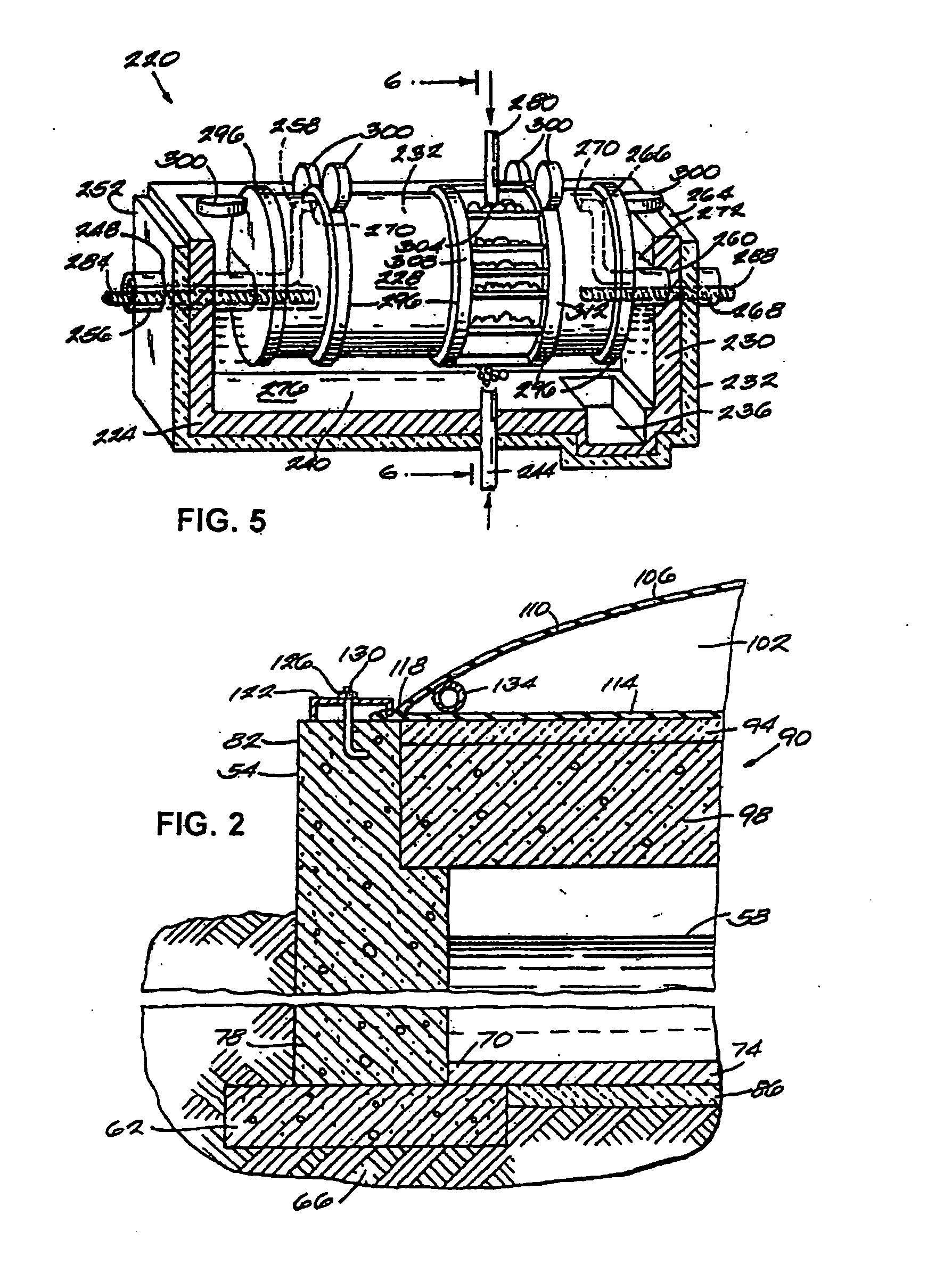
Organ preservation container and method
InactiveUS20060121437A1Facilitate maintaining contactIncrease contactHormonesDead animal preservationHermetic sealEngineering
An organ preservation container includes a gas impermeable housing for containing an organ. At least two liquids having different densities and forming a liquid-liquid interface are also contained in the housing. A closure for hermetically sealing the housing is provided. A structure is provided within the housing for engaging the organ and for maintaining a portion of the organ at the liquid-liquid interface such that the organ will be maintained partially in both of the liquids. A method for preserving the organ is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI +1
Altering protein concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid and/or brain interstitial fluid
Devices and methods of altering protein concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid and / or brain interstitial fluid are disclosed. Devices include a support having at least one protease attached to the support. The device may further include a housing. Devices may be implantable for use in an in vivo active flow system or for use in an in vivo passive system. Devices may also be used in an ex vivo active flow system. Devices may also be used in a passive system to treat cerebrospinal fluid and / or brain interstitial fluid that is withdrawn, or in a passive system that is implanted surgically. Methods include contacting cerebrospinal fluid and / or brain interstitial fluid with a support including at least one protease attached to the support. Proteins contained in the cerebrospinal fluid and / or brain interstitial fluid are cleaved by the protease resulting in the reduction of protein in cerebrospinal fluid and / or brain interstitial fluid. Additionally, methods are disclosed for treating neurodegenerative diseases and neurological disorders.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Method and apparatus for reducing pathogens in a biological sample
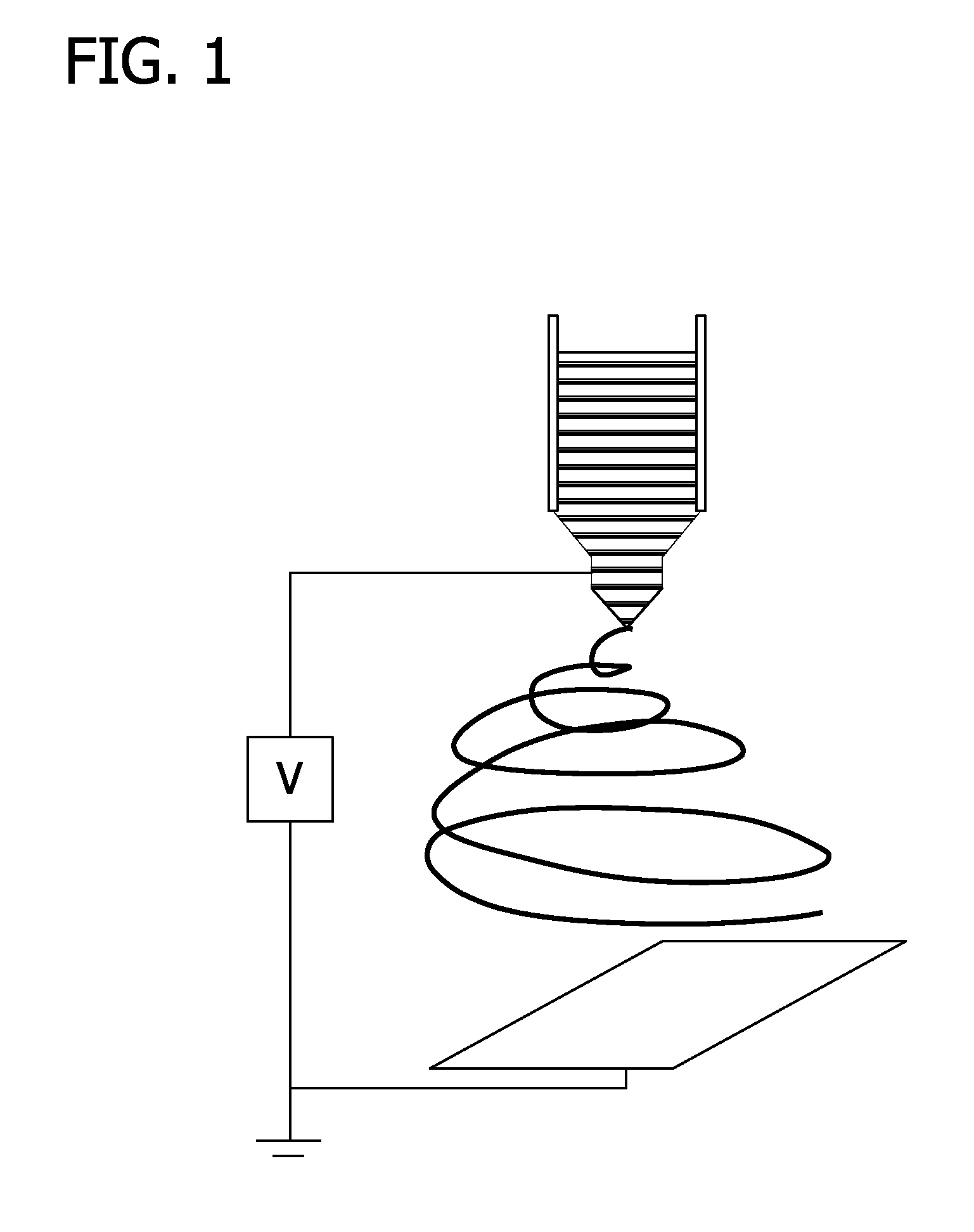
ActiveUS20050079480A1Reduce pollutionWide of utilityHormonesMammal material medical ingredientsSemenEnzyme
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for disinfection of biological samples, including semen and the like. In a first aspect of the present invention, a method for reducing pathogens in a biological sample includes passing the biological sample through a gradient including an enzyme suitable for removal of at least one pathogen from the sample. In an additional aspect of the present invention, an apparatus for removing pathogens from a biological sample includes a container including a gradient having at least one layer that is suitable for having the biological sample pass through the layer, the at least one layer including an enzyme suitable for removing at least one pathogen from the biological sample.
Owner:SAFETY ART +1
Method of secretory expression of lysostaphin in escherichia coli at high level
ActiveUS20090186380A1Easy to purifyLess protein contaminantBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
A method of secretory expression of lysostaphin in Escherichia coli at high level, which comprises constructing a expression vector by cloning a sequence encoding a signal peptide which is suitable for secretory expression in Escherichia coli before part or whole gene sequence which encodes mature lysostaphin, and ligating the cloned sequence with a promoter; and transforming Escherichia coli with the expression vector, culturing and fermenting, and then isolating lysostaphin from the supernatant of the fermentation broth. The advantage of secretory expression is that the expression product can exist in the medium in an active form, and thus does not need the process for renaturation of the inclusion body; it is more easily to purify from the supernatant of the fermentation broth with high rate of recovery; and there is less contamination from the host's proteins.
Owner:SHANGHAI HI TECH UNITED BIO TECHCAL RES
Method for Promoting Production of Biogas Using Pancreatin in an Anaerobic Digestion Process
InactiveUS20150175462A1Promote degradationImprove hydrolysis efficiencyHormonesWaste based fuelBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Disclosed is a method for promoting production of biogas using pancreatin in an anaerobic digestion process. In addition, disclosed are a composition for improving hydrolysis efficiency or promoting production of biogas, which includes pancreatin as an active ingredient, and a method for promoting (or increasing) production of biogas from organic manure of livestock using the same. The composition for improving hydrolysis efficiency or for promoting production of biogas in an anaerobic digestion process for treatment of organic waste, includes pancreatin as an active ingredient. The organic waste is livestock manure, and the composition has optimum activity at pH 7.0 to pH 8.0. The composition further includes a microorganism with excellent degradability of degradation resistant organic compounds.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Organ preservation container and method
An organ preservation container includes a gas impermeable housing for containing an organ. At least two liquids having different densities and forming a liquid-liquid interface are also contained in the housing. A closure for hermetically sealing the housing is provided. A structure is provided within the housing for engaging the organ and for maintaining a portion of the organ at the liquid-liquid interface such that the organ will be maintained partially in both of the liquids. A method for preserving the organ is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI +1
Biosolids digester and process for biosolids production
ActiveUS20120329139A1Energy efficiencyEnhanced convectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingPulp and paper industryBiosolids
The invention relates to methods and apparatuses for producing Class A biosolids. In yet another embodiment, the invention relates to a method comprising digesting waste material by anaerobic digestion, and yielding Class A biosolids. In still yet another embodiment, the invention relates to a system for anaerobic digestion of waste material to produce Class A biosolids. In still yet another embodiment, the invention relates to a system for anaerobic digestion of waste material comprising a mixing chamber, a digester, a heating pit, and an effluent pit.
Owner:DVO LICENSING
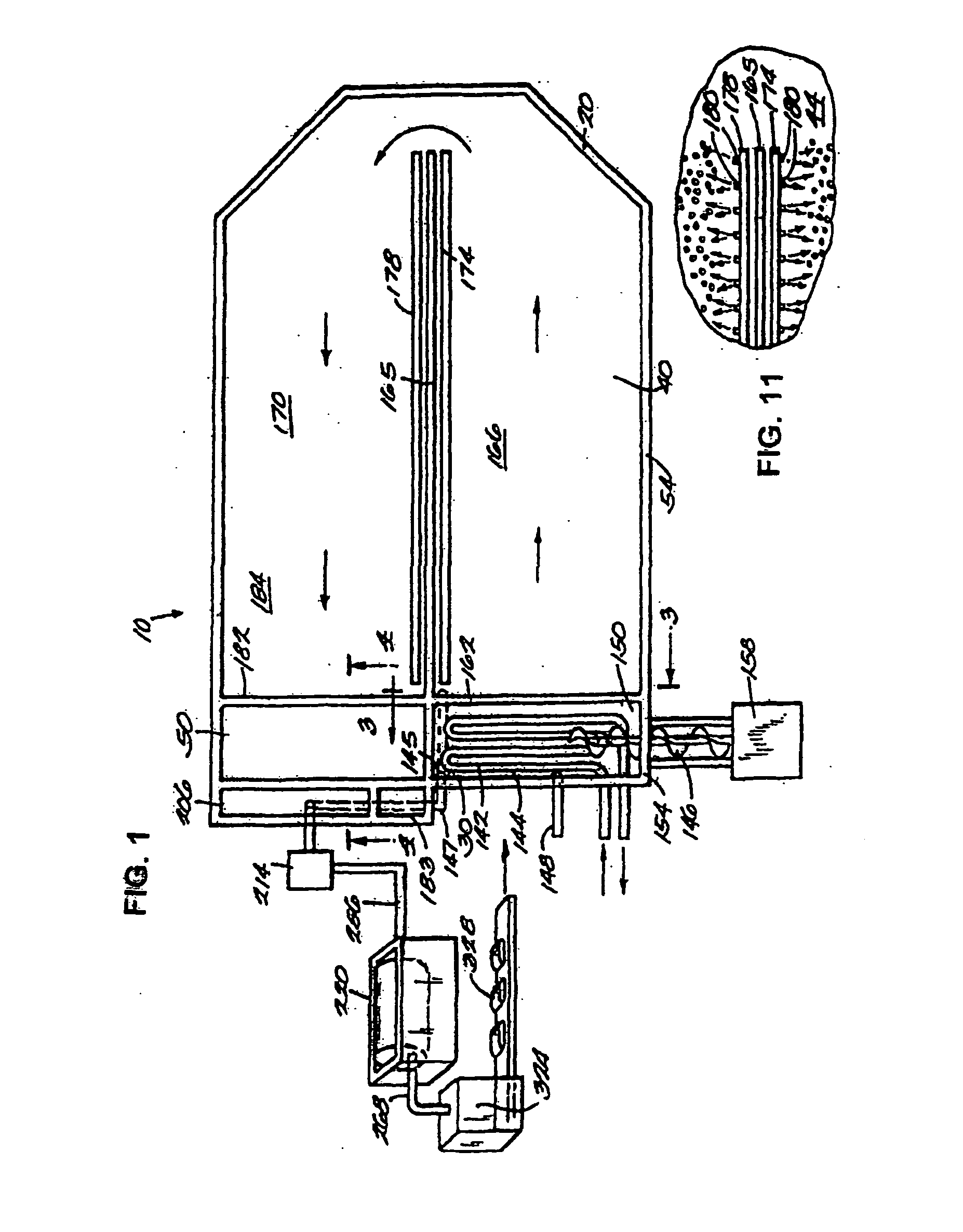
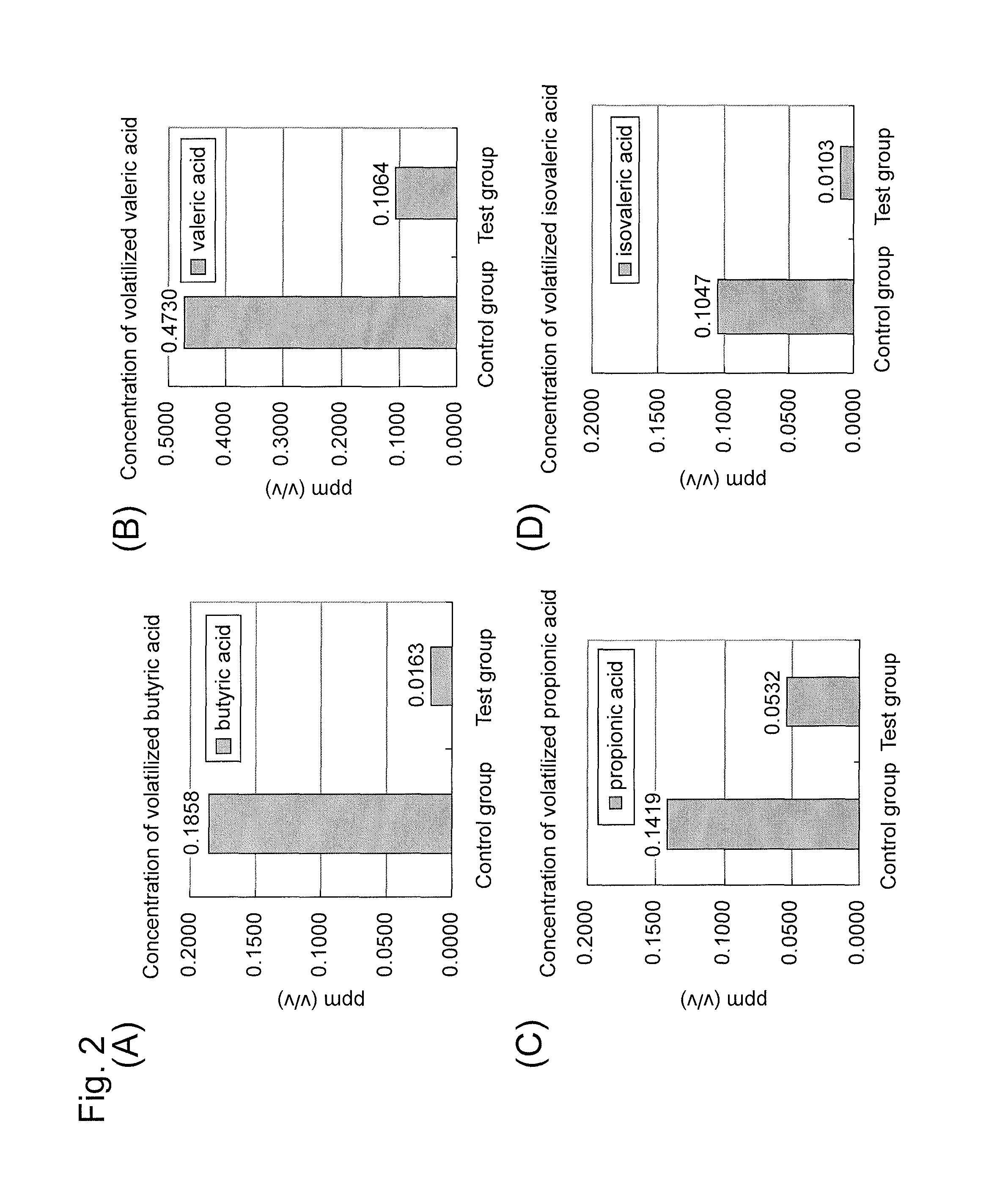
Microorganism and deodorizer containing the same
ActiveUS8741625B2Production of short chain fatty acidReduce productionHormonesBacteriaMicroorganismBacillus licheniformis
Thermophilic microorganisms having a deodorizing ability for short chain fatty acids, which are the offensive odor components, are provided. Disclosed are thermophilic microorganisms having a deodorizing ability for short chain fatty acids, which belong to Bacillus licheniformis.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method of decellularizing porcine cornea
ActiveUS8313893B2Efficient processingMinimizing immune responseHormonesEye implantsMedicinePorcine cornea
Disclosed is a method for processing porcine cornea using an aqueous NaCl solution and an aqueous trypsin / EDTA solution to decellularize enucleated porcine cornea. The porcine cornea processed by the method causes neither inflammation nor immune rejection. The porcine corneal stroma decellularized by the method can be recellularized together with host keratocytes after transplantation.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
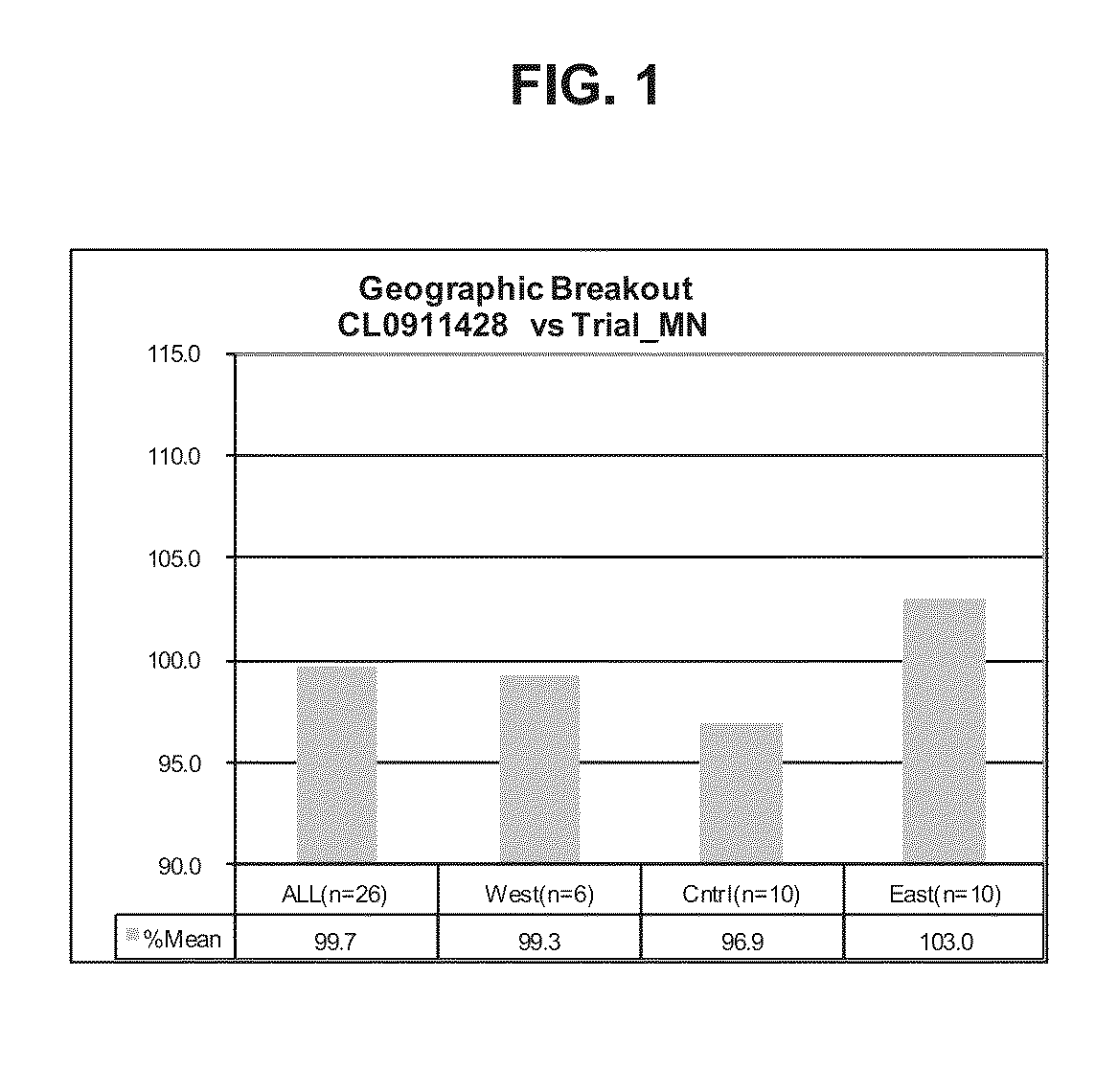
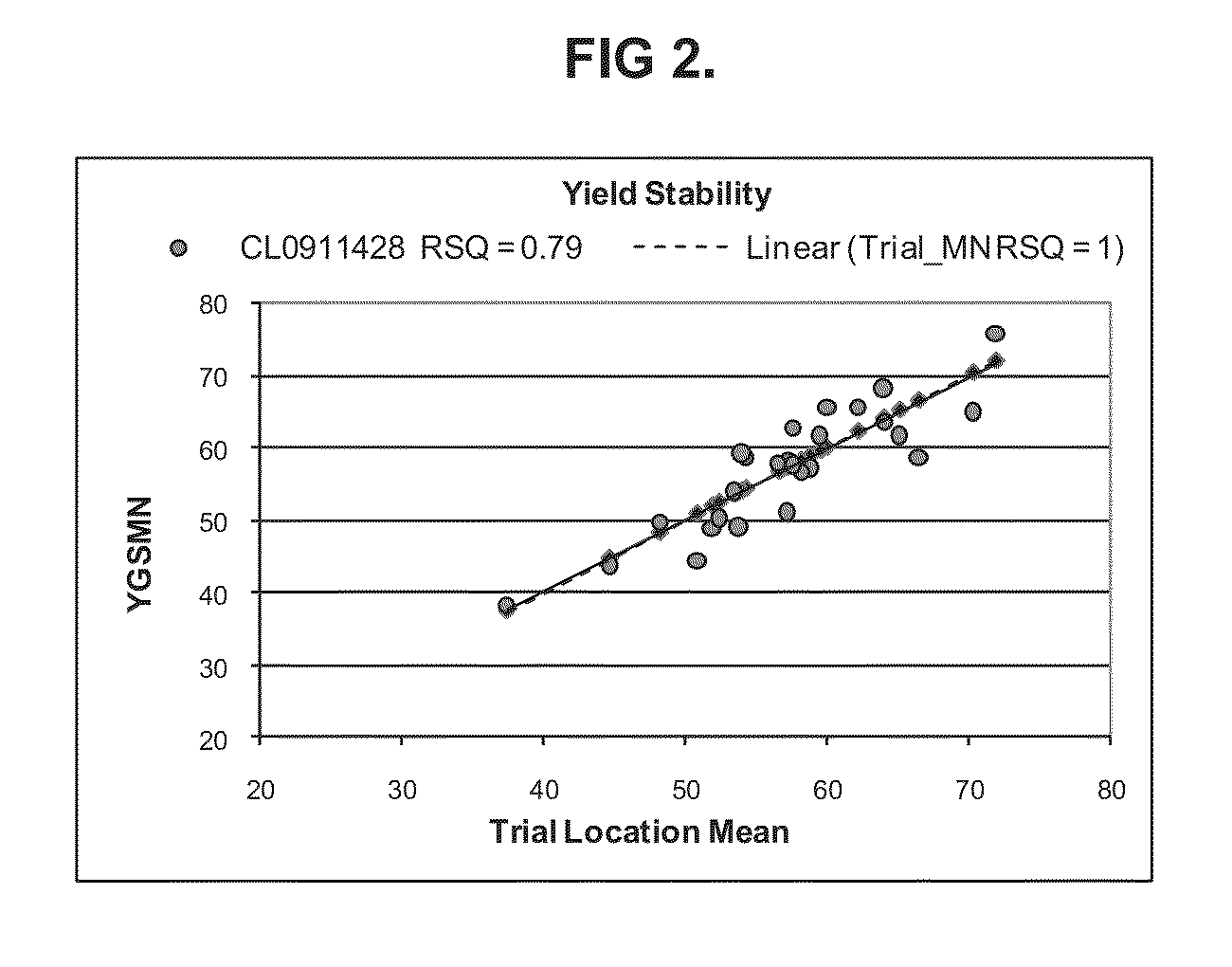
Soybean cultivar CL0911428
InactiveUS8541662B1High yieldAchieving yieldHormonesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyCultivar
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Methods for stabilizing a bioprosthetic tissue by chemical modification of antigenic carbohydrates
ActiveUS8906601B2Improve stabilityIncreased durabilityElectrolysis componentsHeart valvesEpitopeDiol
Methods are provided herein for modifying antigenic carbohydrate epitopes within a xenographic bioprosthetic tissue by oxidation of vicinal diols to form aldehydes or acids and subsequence reductive amination of aldehydes to form stable secondary amines, or amidation or esterification of acids to form stable amides or esters. Advantageously, methods provided herein mitigate the antigenicity of the bioprosthetic tissue while leaving the overall tissue structure substantially undisturbed, and thereby enhance the durability, safety and performance of the bioprosthetic implant.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Process for reducing pathogens in a biological sample and removing a sample pellet from a sample tube
InactiveUS7405036B2Reducing and eliminating riskWide range of applicability and utilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyEngineering
The present invention is directed towards an apparatus and method for disinfecting biological samples, including semen and the like, and for removing a biological sample pellet from surrounding media while reducing the risk of recontamination of the pellet with said media. An insert receptacle includes a receiving cylinder having a drain in a floor which allows the fluids to decant slowly down the side of a tube. The insert receptacle further includes an aspiration channel which allows an aspiration device, such as a modified micro-pipette, to be utilized for extracting a sample pellet from the bottom of the tube. Utilizing the novel apparatus, a method for reducing pathogens in a biological sample includes decanting the biological sample through the receiving cylinder and into a tube where it passes through a multi-layer gradient including an enzyme suitable for removal of at least one pathogen from the biological sample. Centrifuging of the insert receptacle, tube, and sample, isolates a sample pellet of the biological sample from the surrounding at least one pathogen. After the sample pellet is isolated it is aspirated via the aspiration device without re-contaminating the sample pellet through contact with the surrounding at least one pathogen.
Owner:SAFETY ART +1
Transdermal method and patch for emesis
InactiveUS8246981B2Induce skin irritationLow viscosityHormonesDigestive systemTransdermal patchAdhesive
Provided, among other things, is a method of treating acute, delayed or anticipatory emesis for a sustained period in an individual, which involves applying to a portion of intact skin on the individual a composition ofi. an antiemetically effective amount of a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist;ii. a permeation enhancing amount of permeation enhancer comprising 0.5% to 15% by weight of the skin-contacting layer; andiii. an adhesive.
Owner:ABEILLE PHARMA
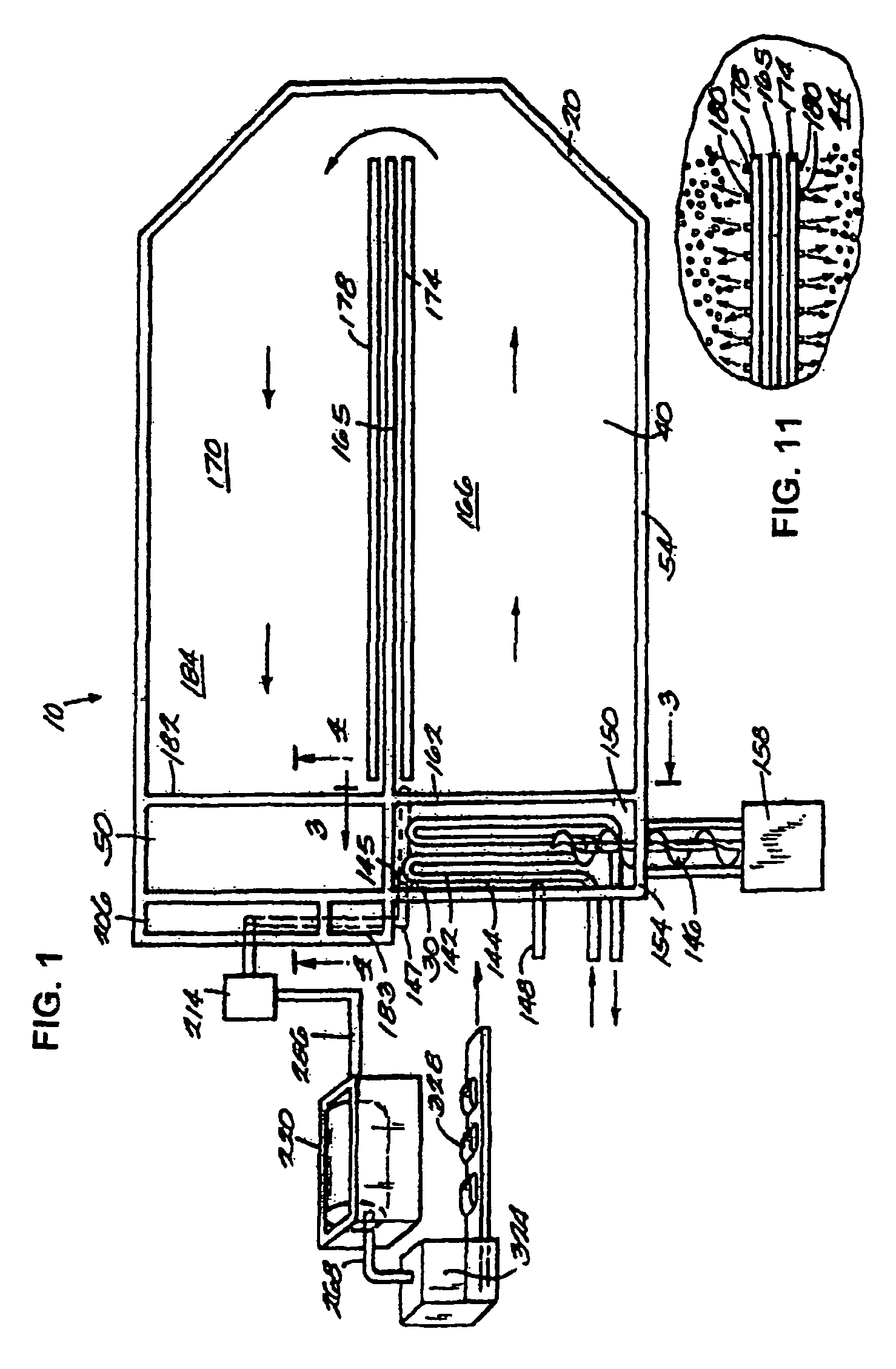
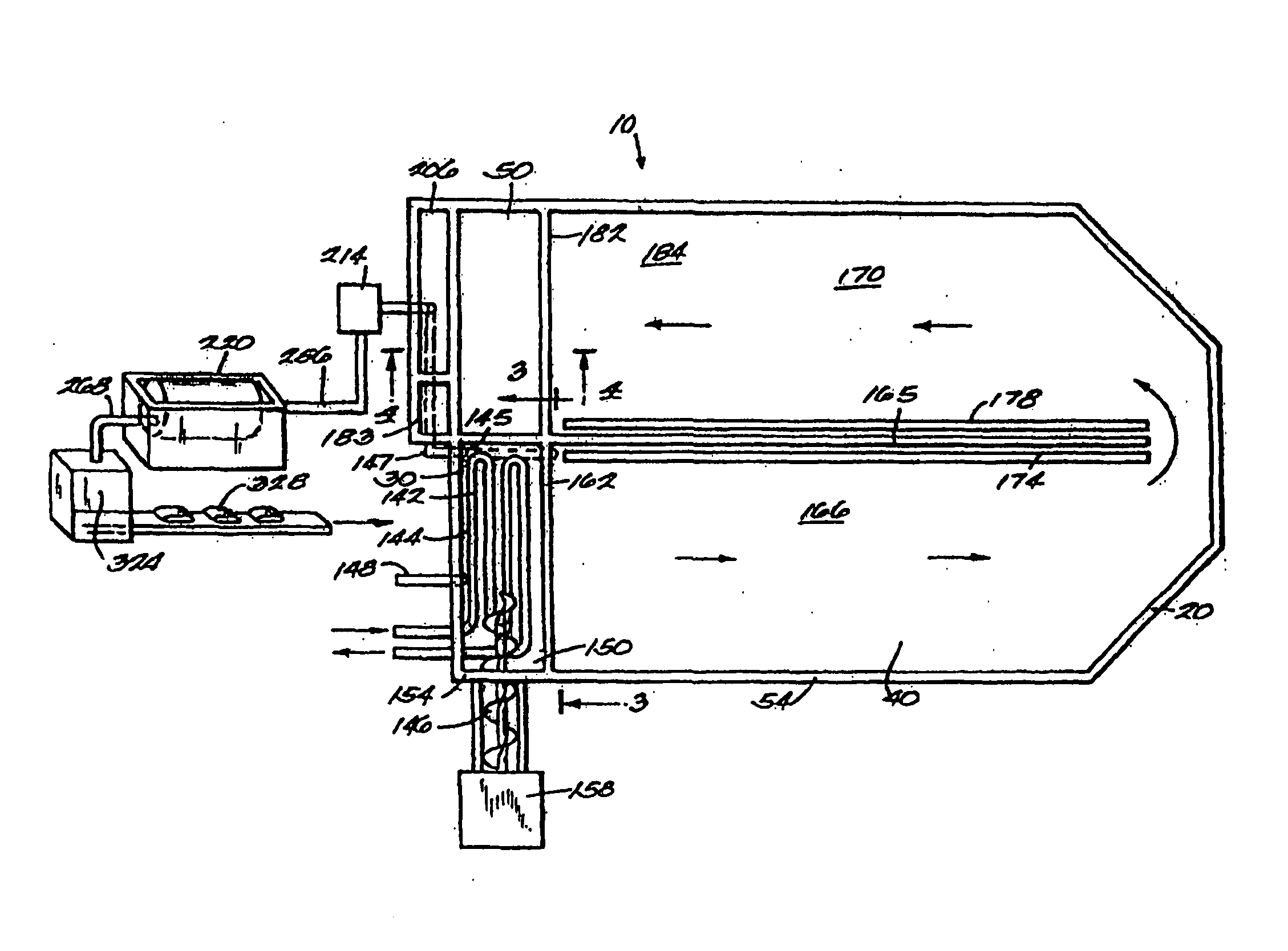
Biological process for converting organic by-products or wastes into renewable energy and usable products
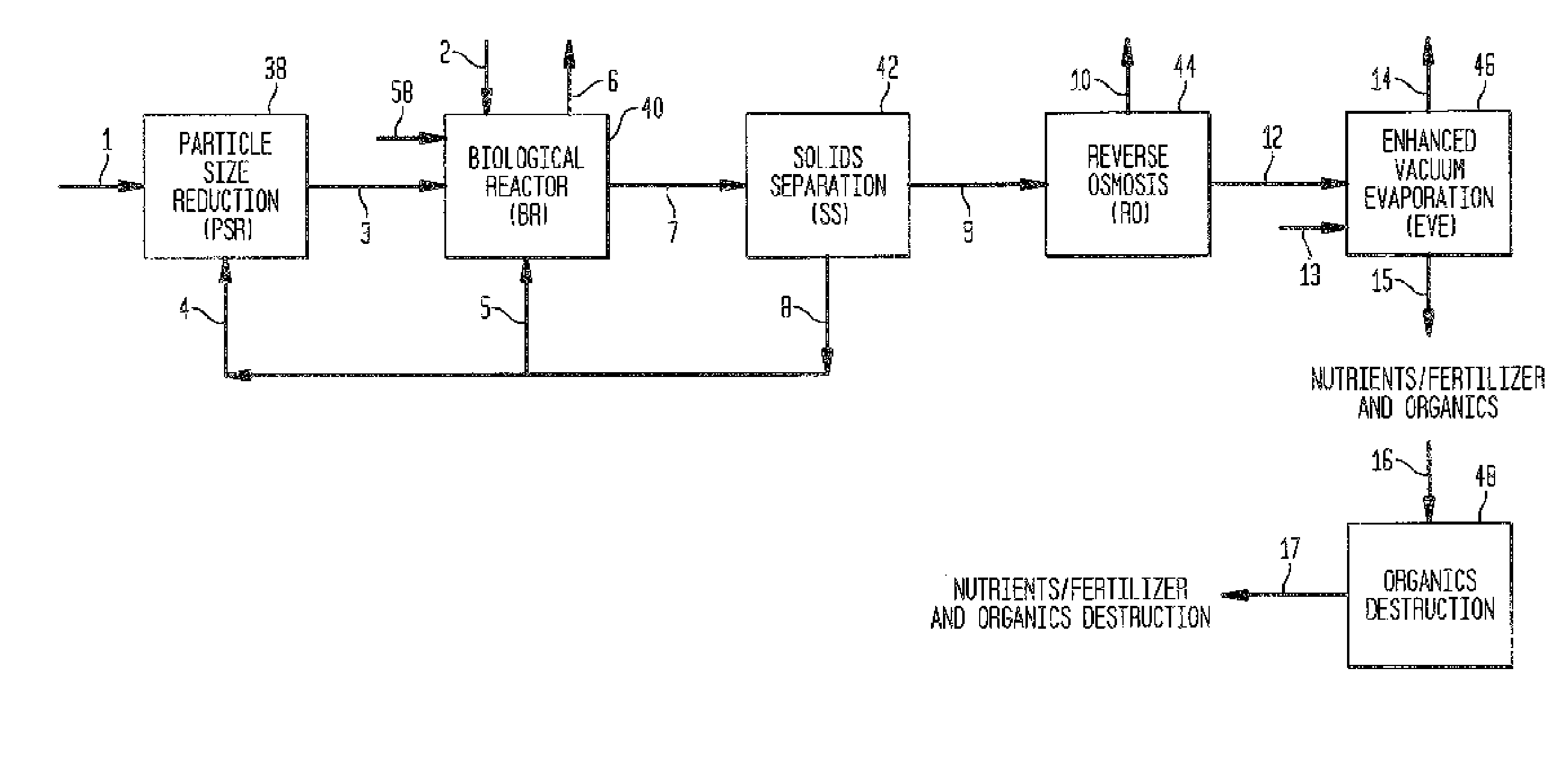
InactiveUS20110281341A1Small particle sizeHigh biological efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingOrganismal ProcessWaste stream
Apparatus for the treatment of organic waste streams is disclosed, in which the organic waste stream is treated in order to reduce the average particle size prior to entry into a biological reactor. The use of a mechanical device to reduce this average particle size while simultaneously mixing the organic waste stream increases the efficiency of the biological reactor. The mechanical device is preferably one which causes attrition and reduction in the average particle size of the organic waste stream. This results in a lower viscosity feed to the biological reactor, and therefore a far more efficient process, which can therefore handle a feed stream of greater concentration than was previously thought to be possible.
Owner:PMC BIOTEC
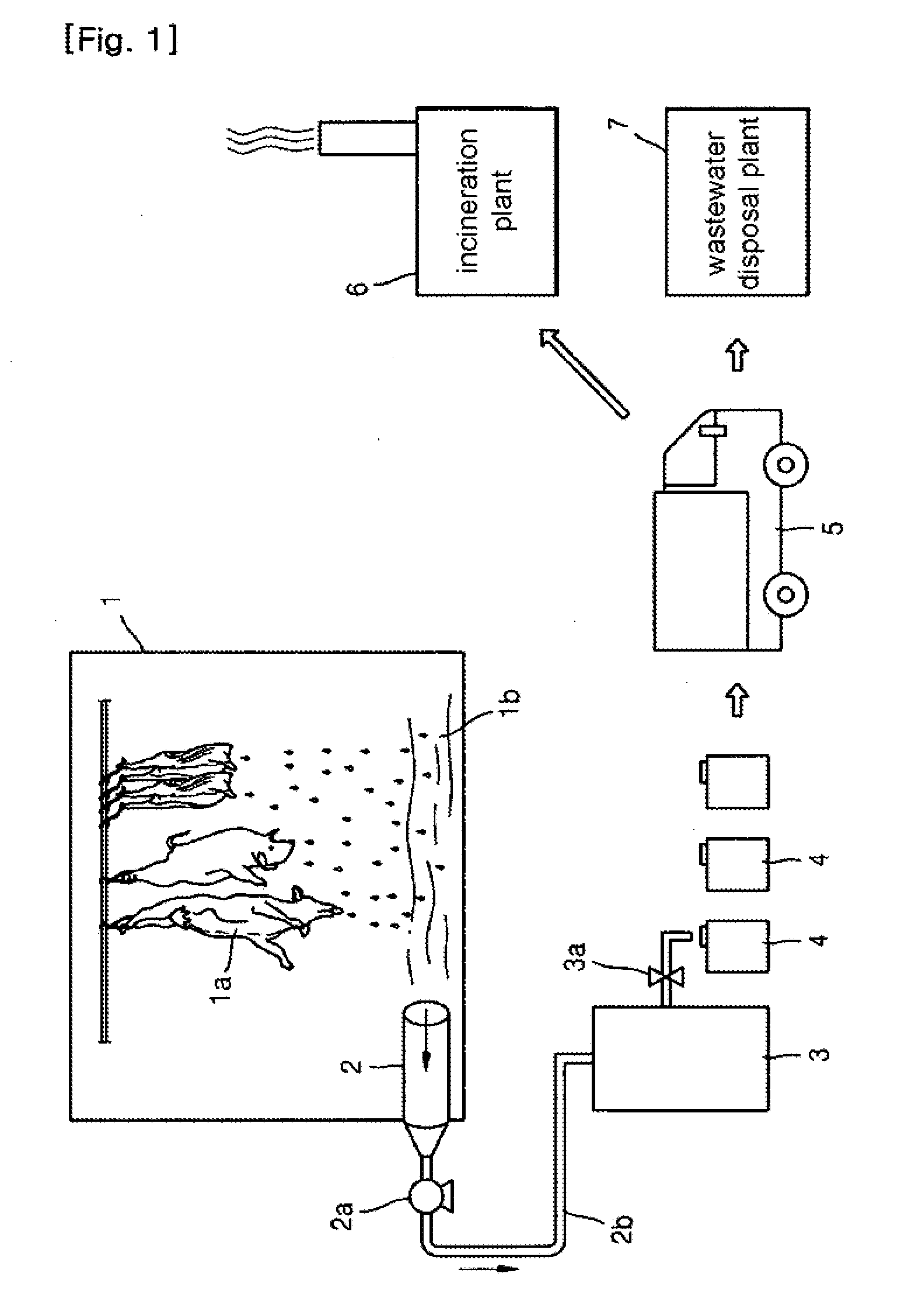
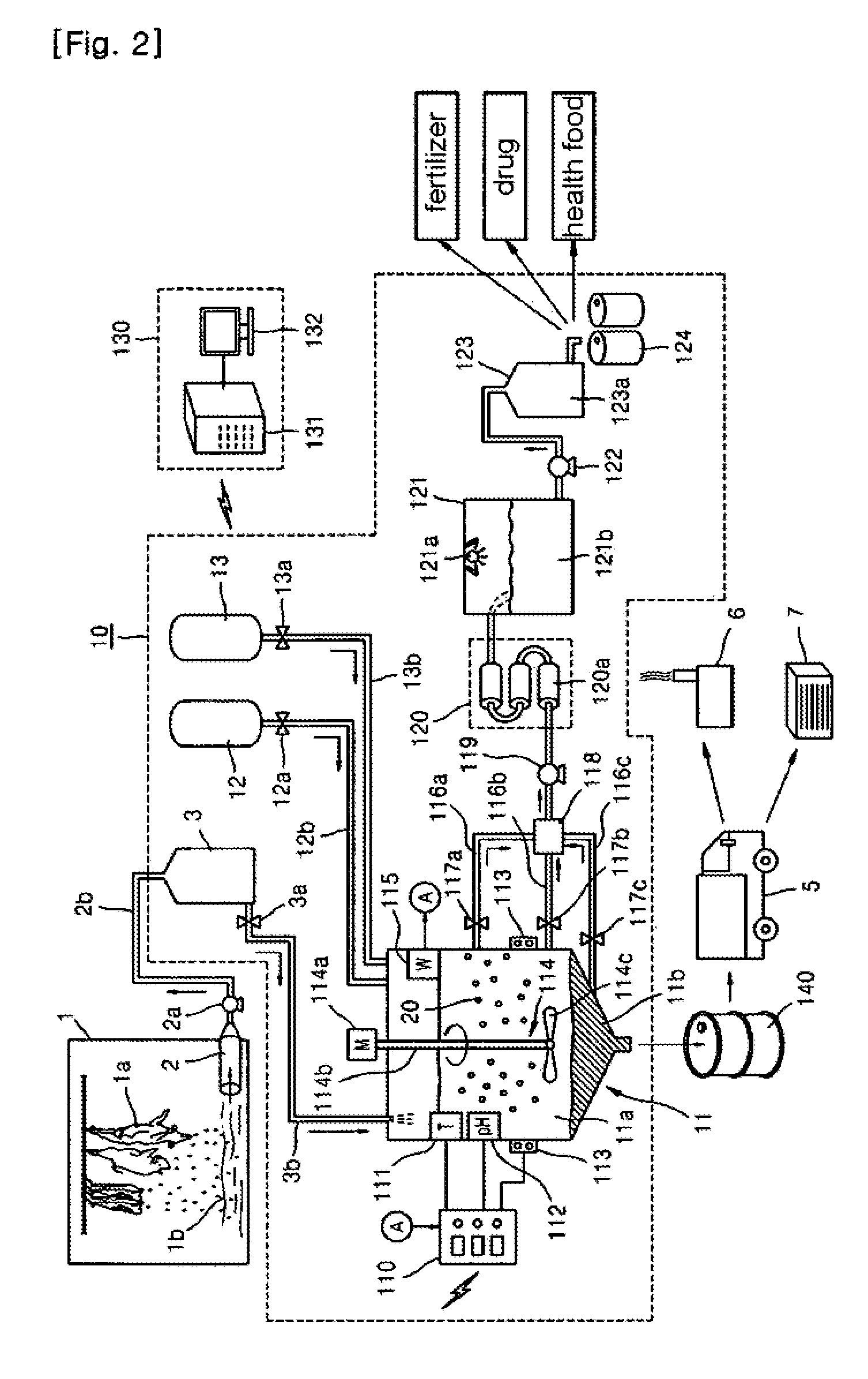
System for Treating Blood of Slaughtered Animals and Method for Producing High-Quality Amino Acid Solution Using Blood of Slaughtered Animals
InactiveUS20110300607A1Avoid polluting the environmentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSludgeMicrobial agent
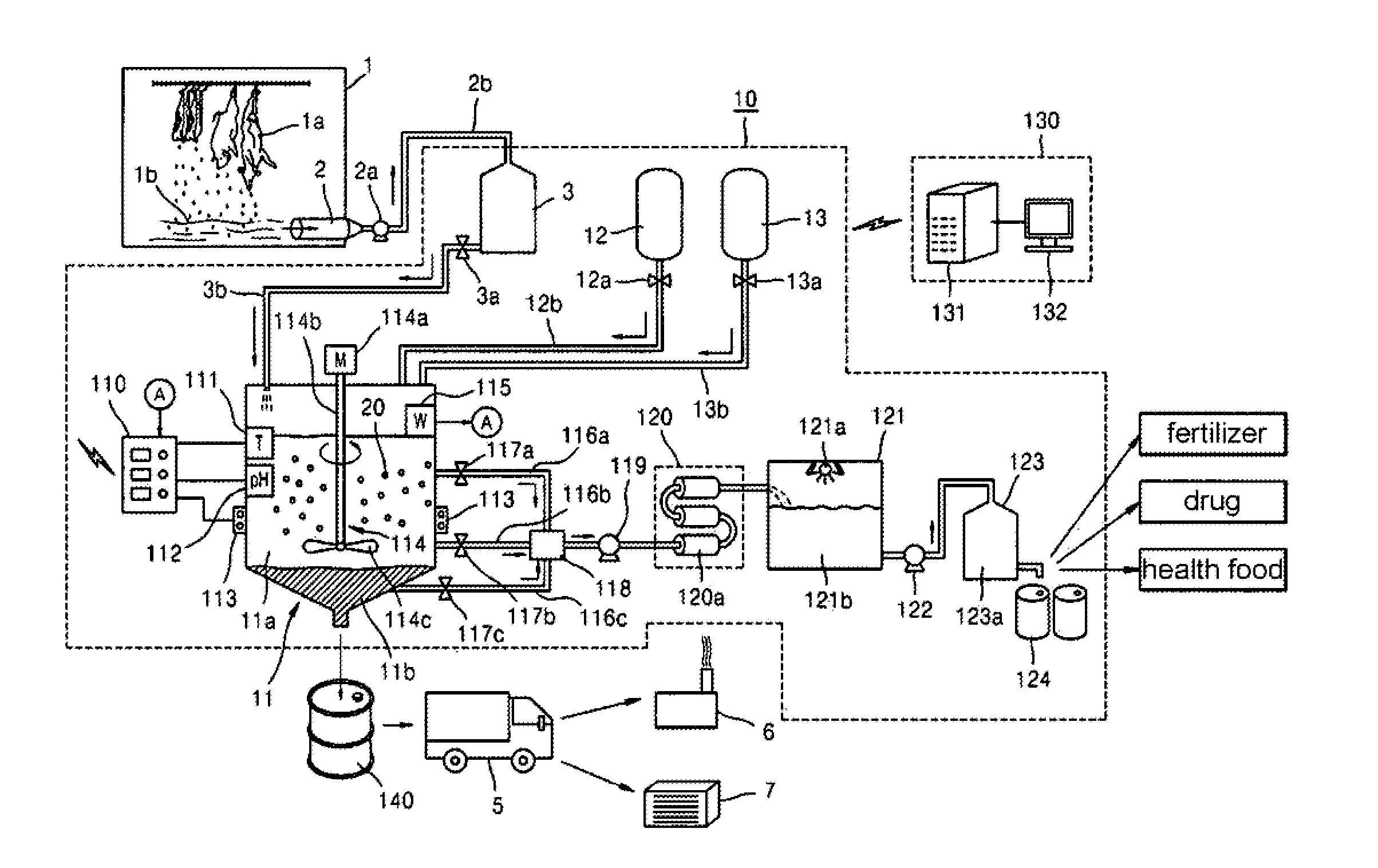
The present invention provides a system for treating the blood of slaughtered animals, the system comprising: a storage tank for collecting and storing the blood of animals slaughtered in a slaughter plant; a blood treatment tank in which the animal blood is received and stored from the blood storage tank and into which a liquid microbial agent for treating blood is introduced so that microorganisms of the liquid microbial agent are allowed to react at a temperature of 25˜35° C. for 8-12 hours, thereby separating the animal blood into an amino acid solution and a waste blood sludge; a blood-treating agent supply unit for supplying the liquid microbial agent to the blood treatment tank; a water supply unit for supplying water to the blood treatment tank; a filtering means for filtering the amino acid solution discharged from the blood treatment tank to remove impurities; a heater for maintaining the blood treatment tank at a temperature of 25˜35° C.; and a temperature sensor for sensing the internal temperature of the blood treatment tank. According to the invention, microorganisms are used to degrade waste animal blood and produce high-quality environmentally friendly amino acids, thereby providing the effects of recycling resources and preventing environmental contamination.
Owner:SHINN TAE YONG +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com