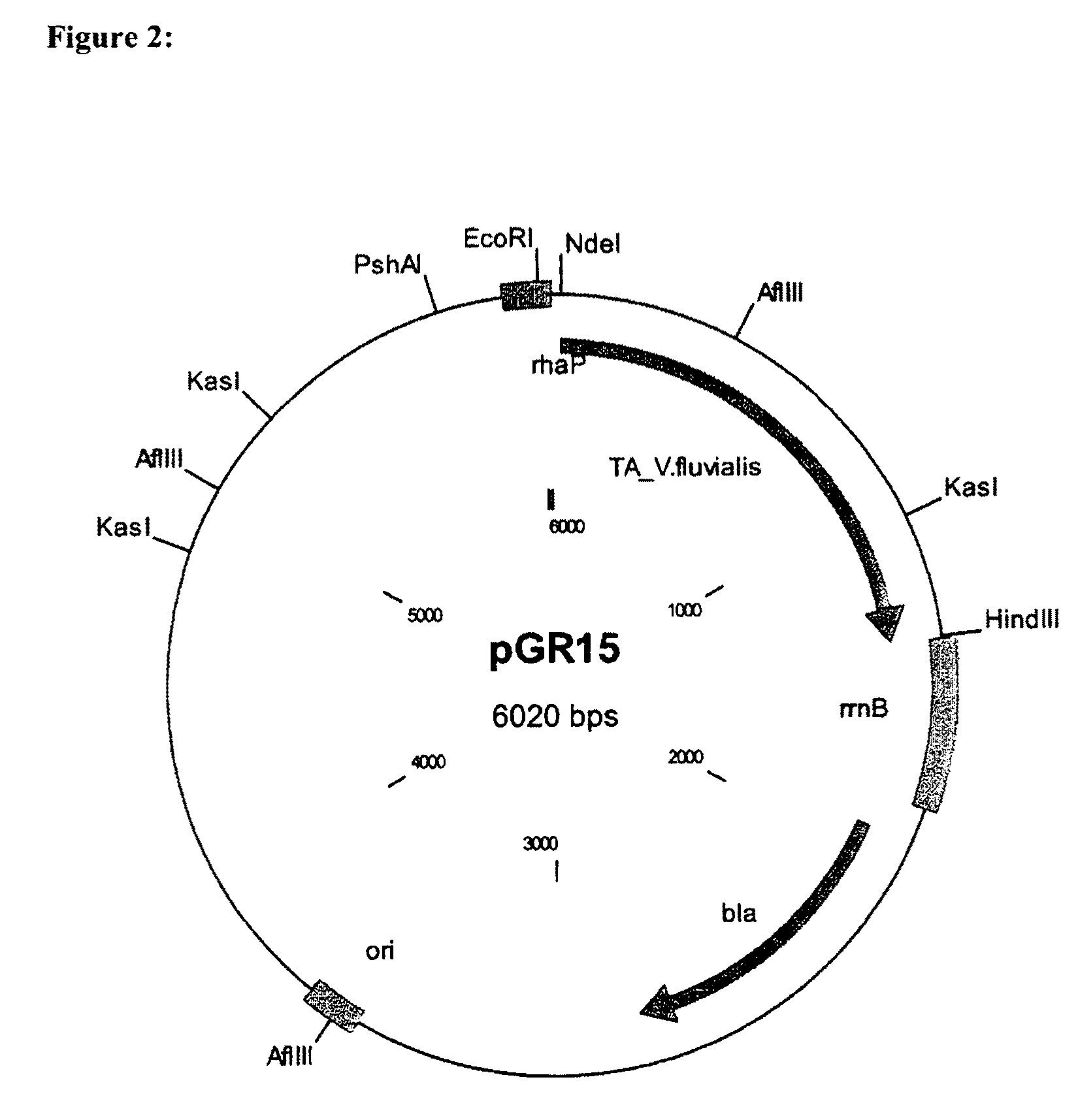
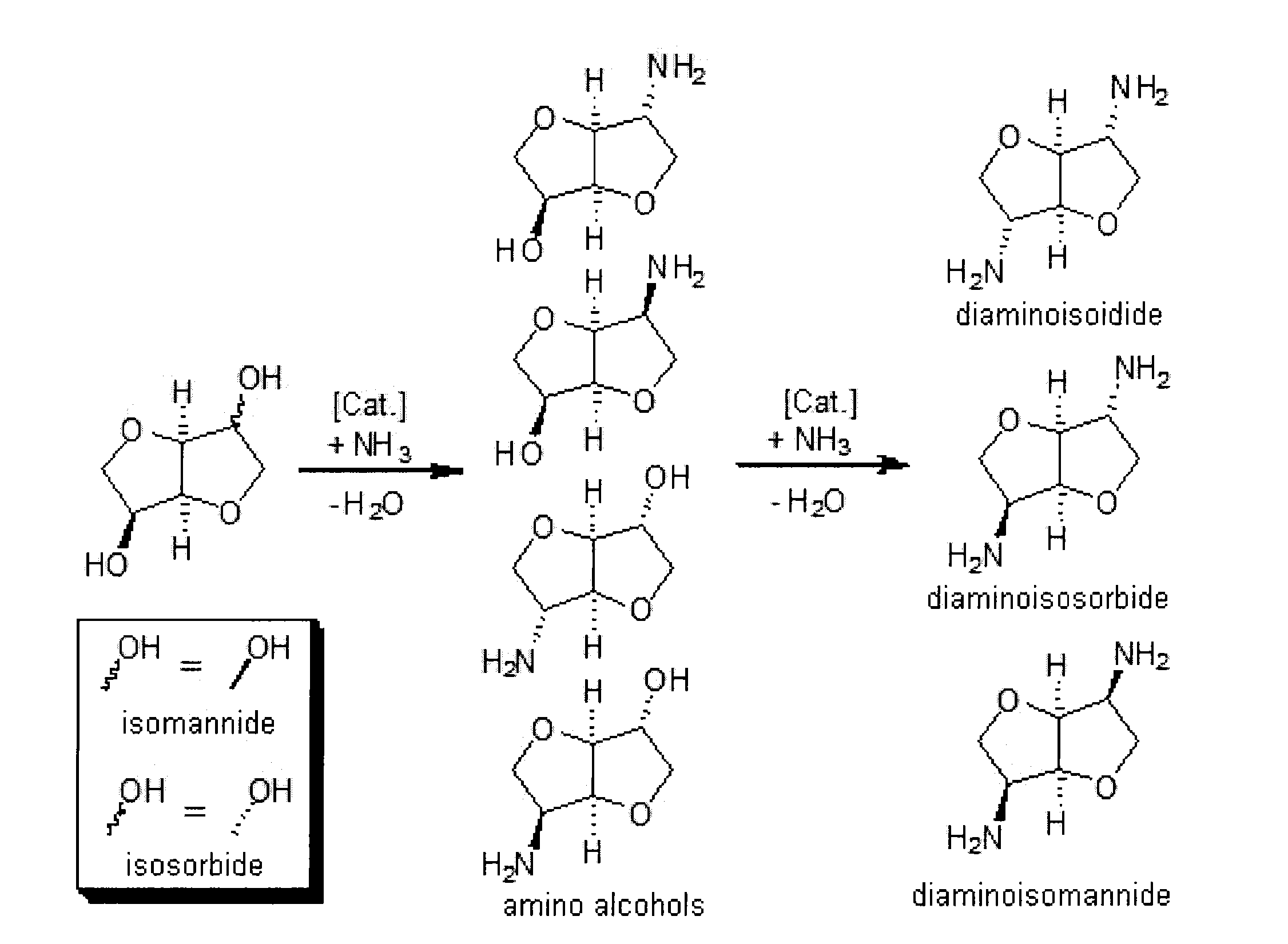
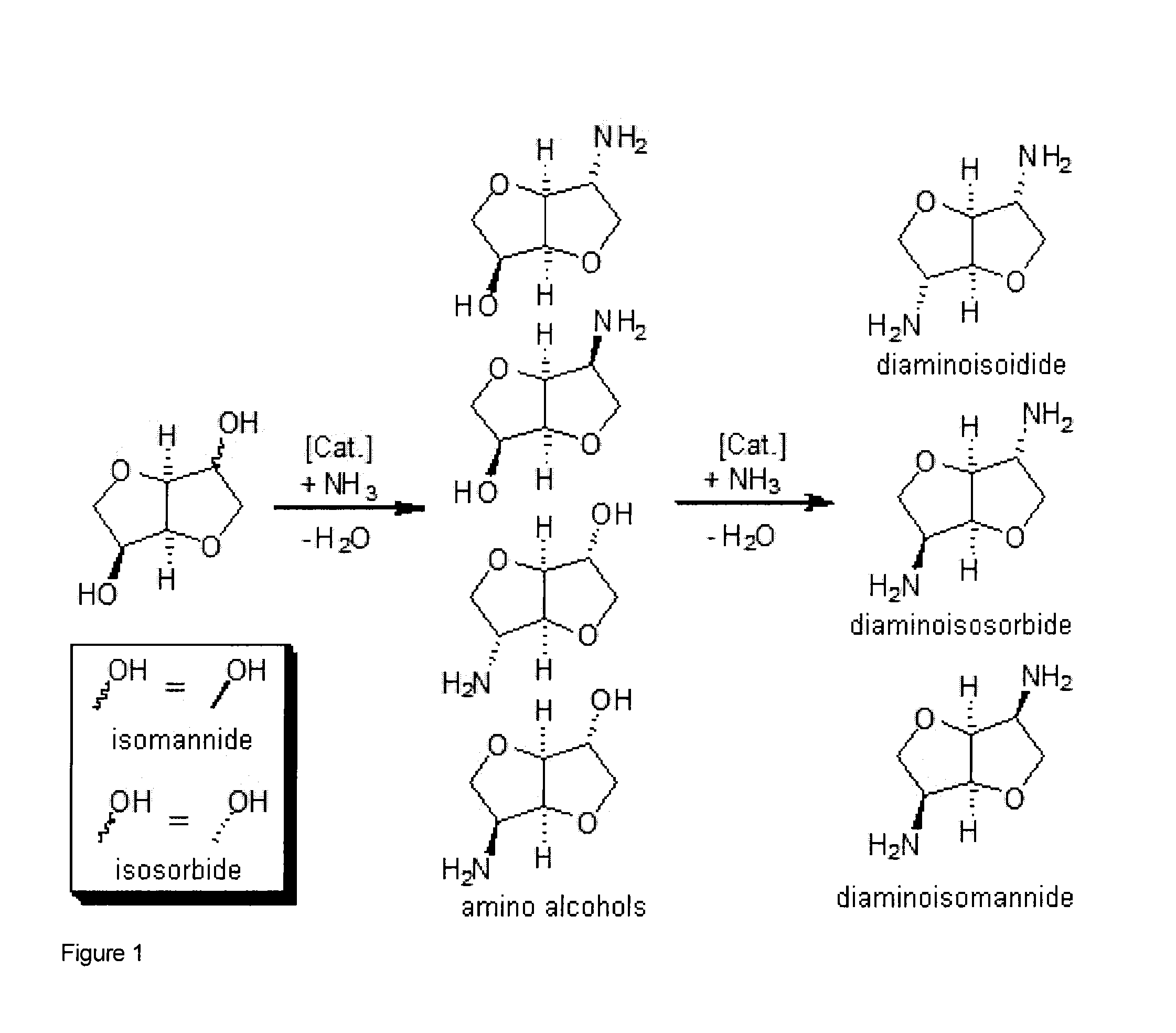
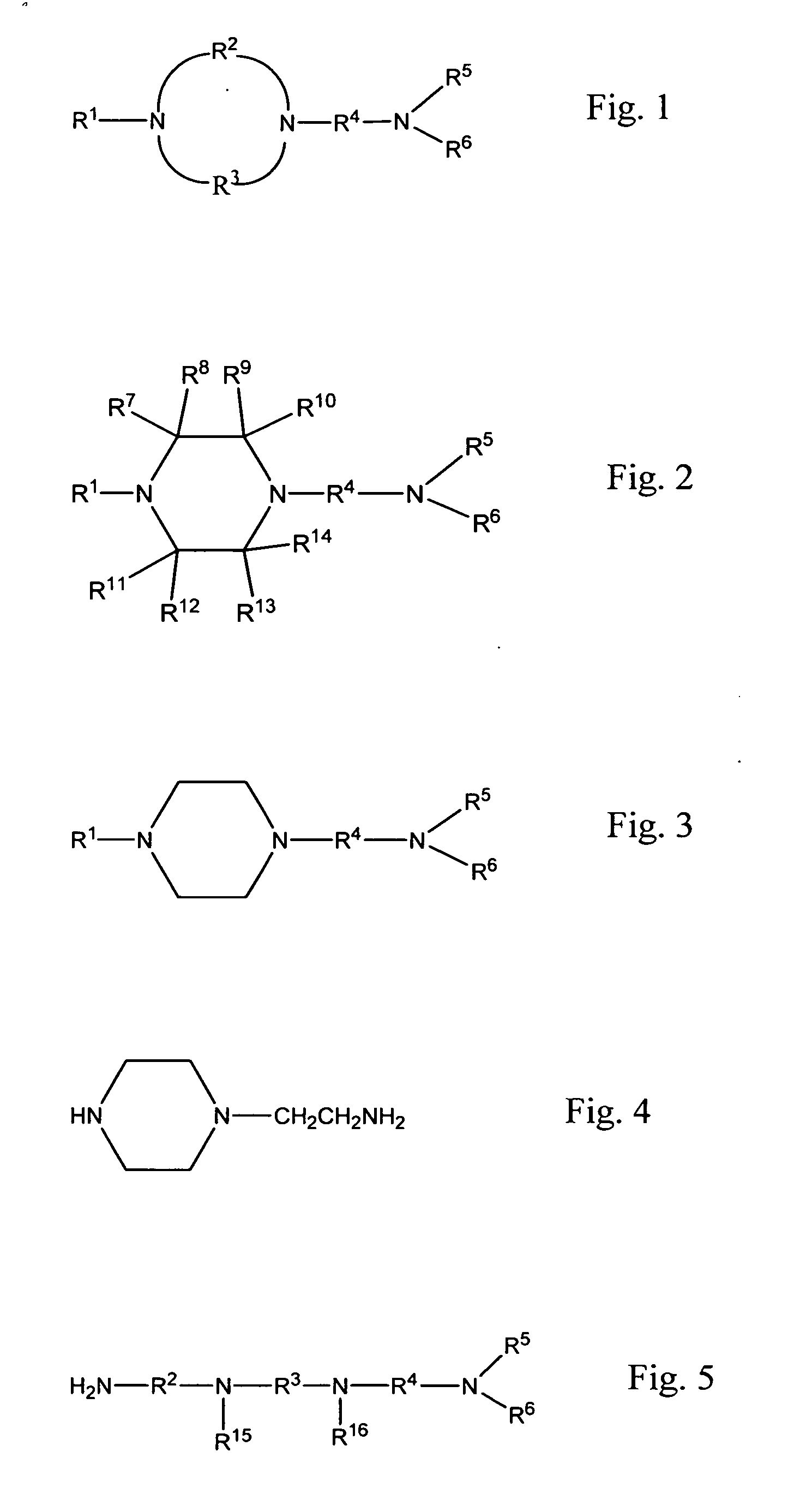
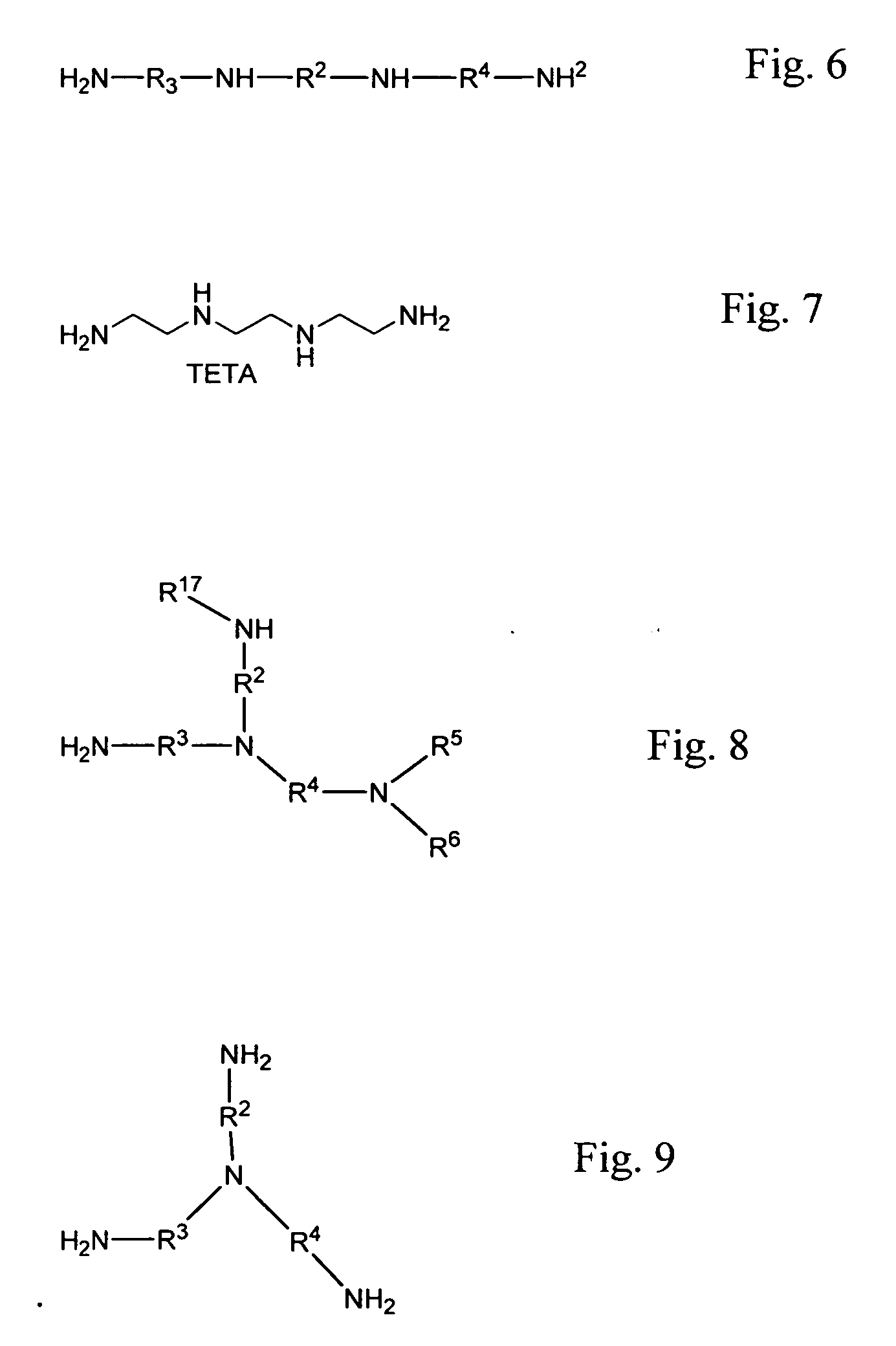
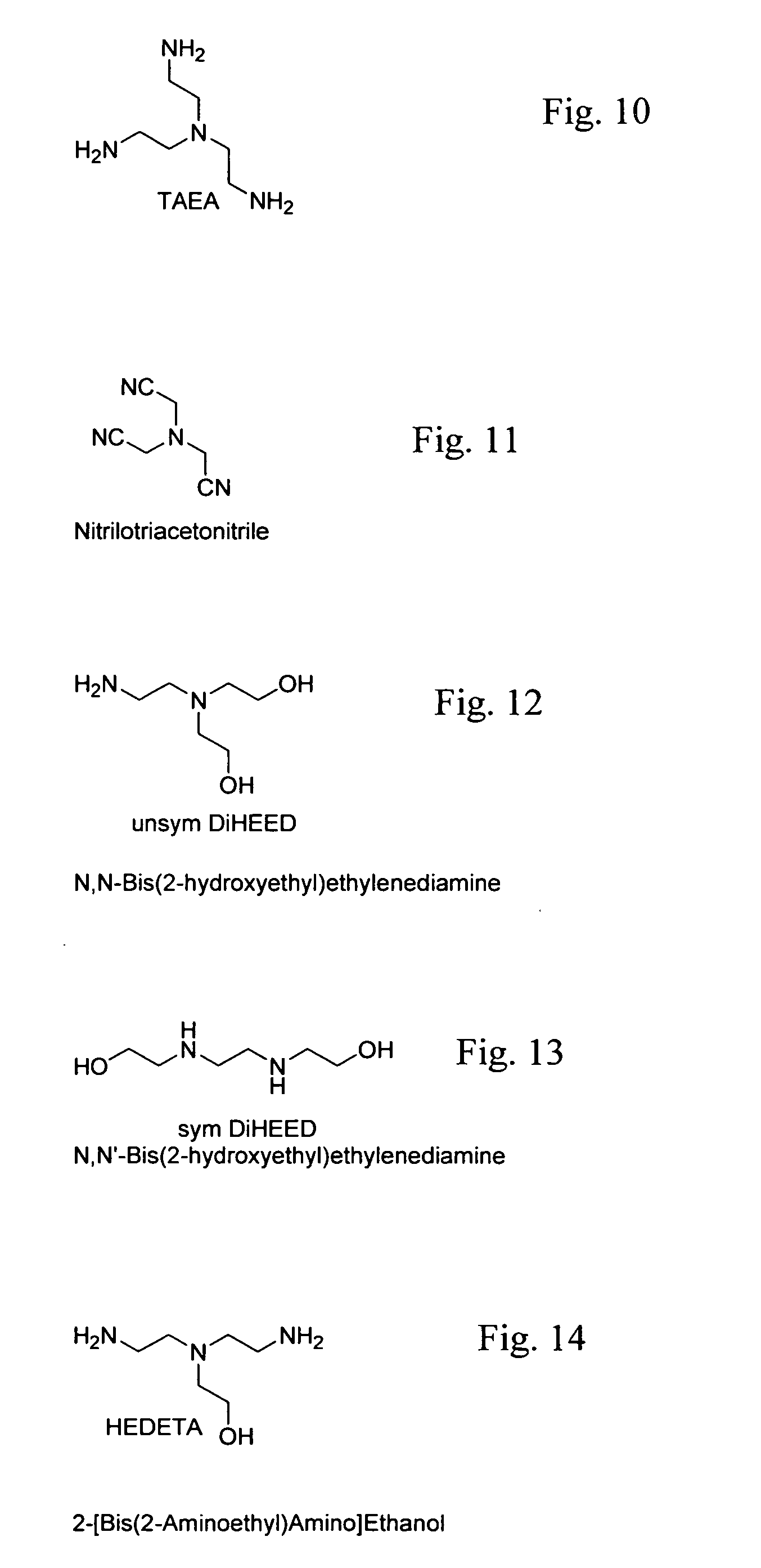
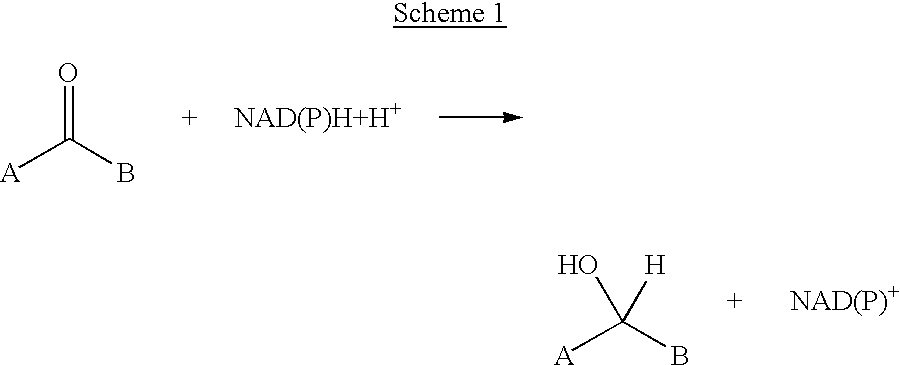
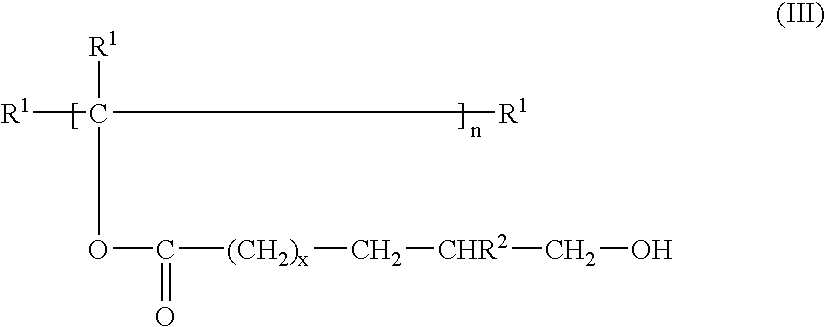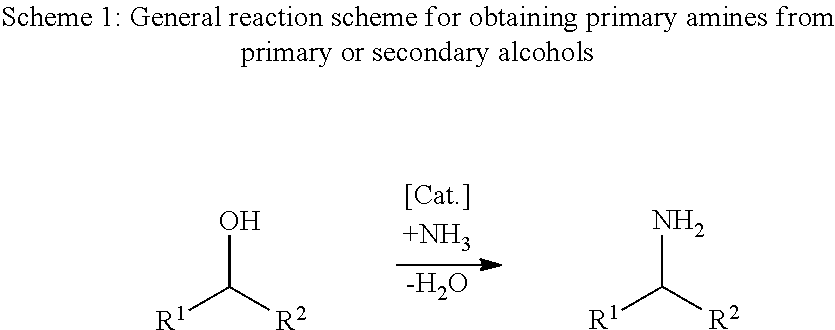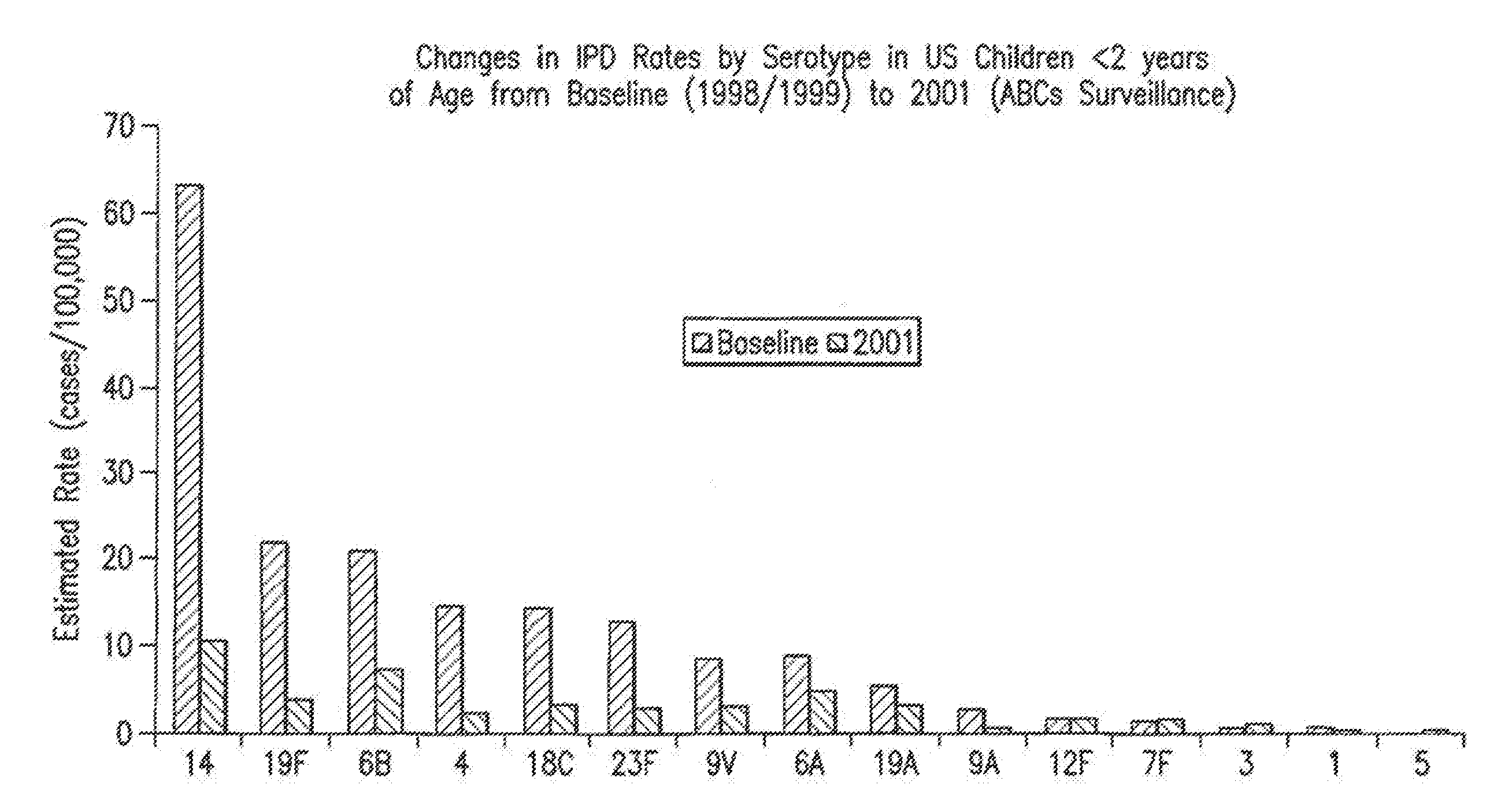Patents
Literature
639 results about "Reductive amination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
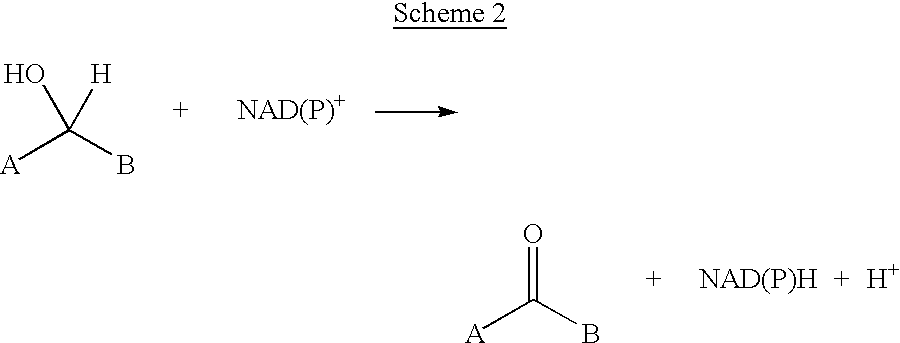
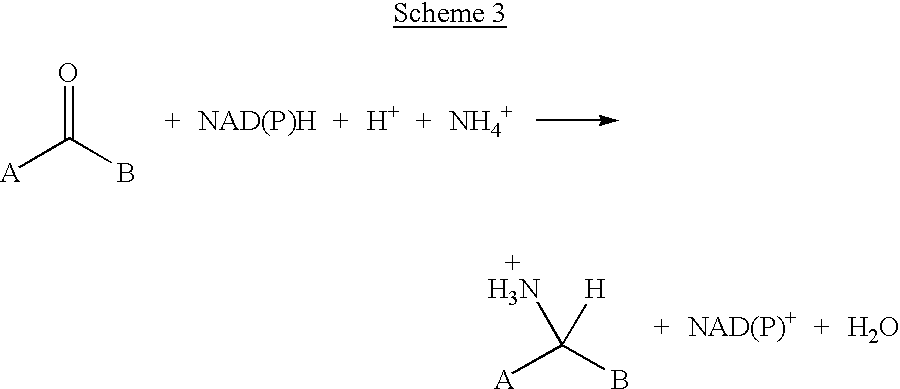
Reductive amination (also known as reductive alkylation) is a form of amination that involves the conversion of a carbonyl group to an amine via an intermediate imine. The carbonyl group is most commonly a ketone or an aldehyde. It is considered the most important way to make amines, and a majority of amines made in the pharmaceutical industry are made this way.
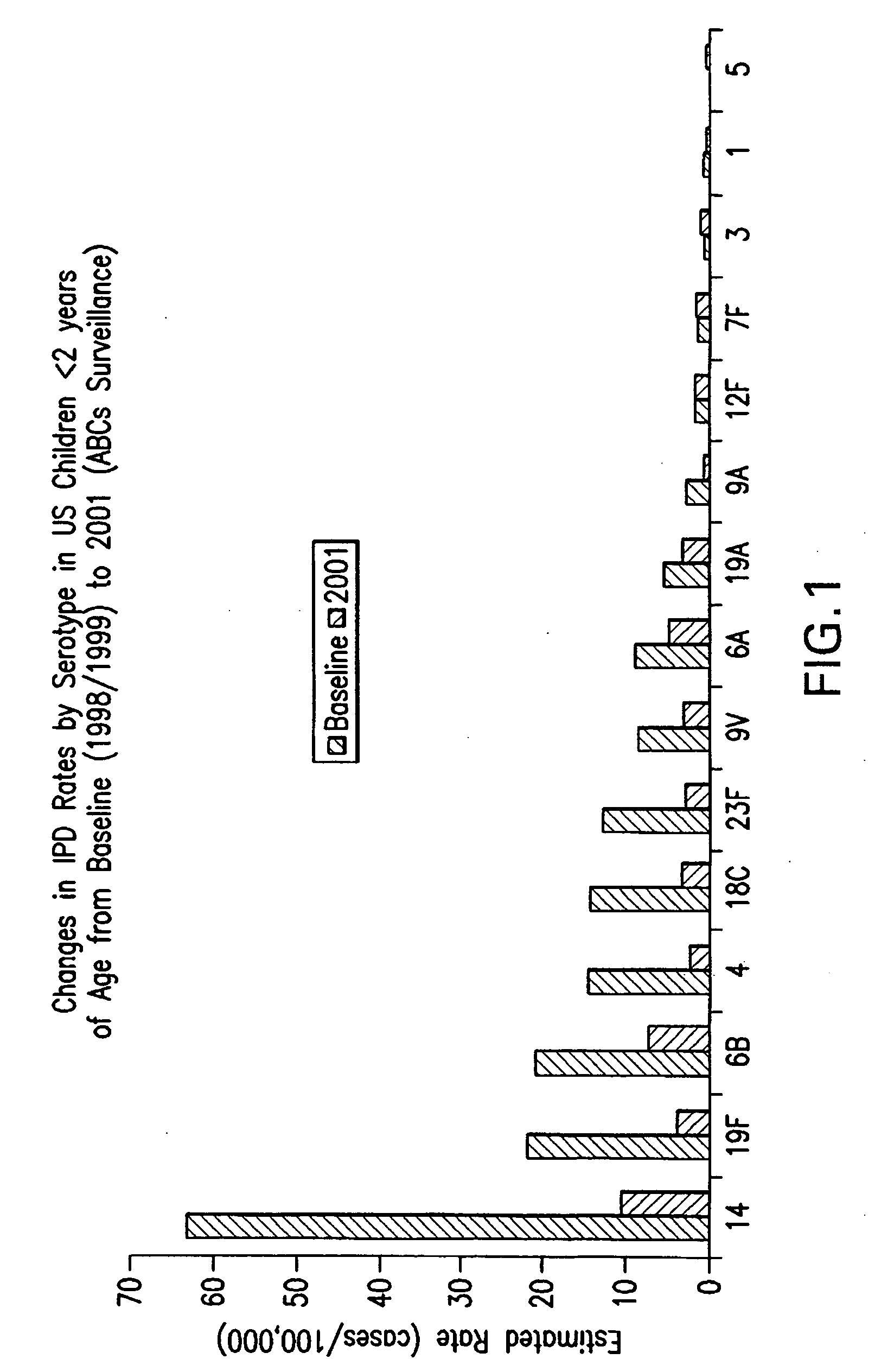
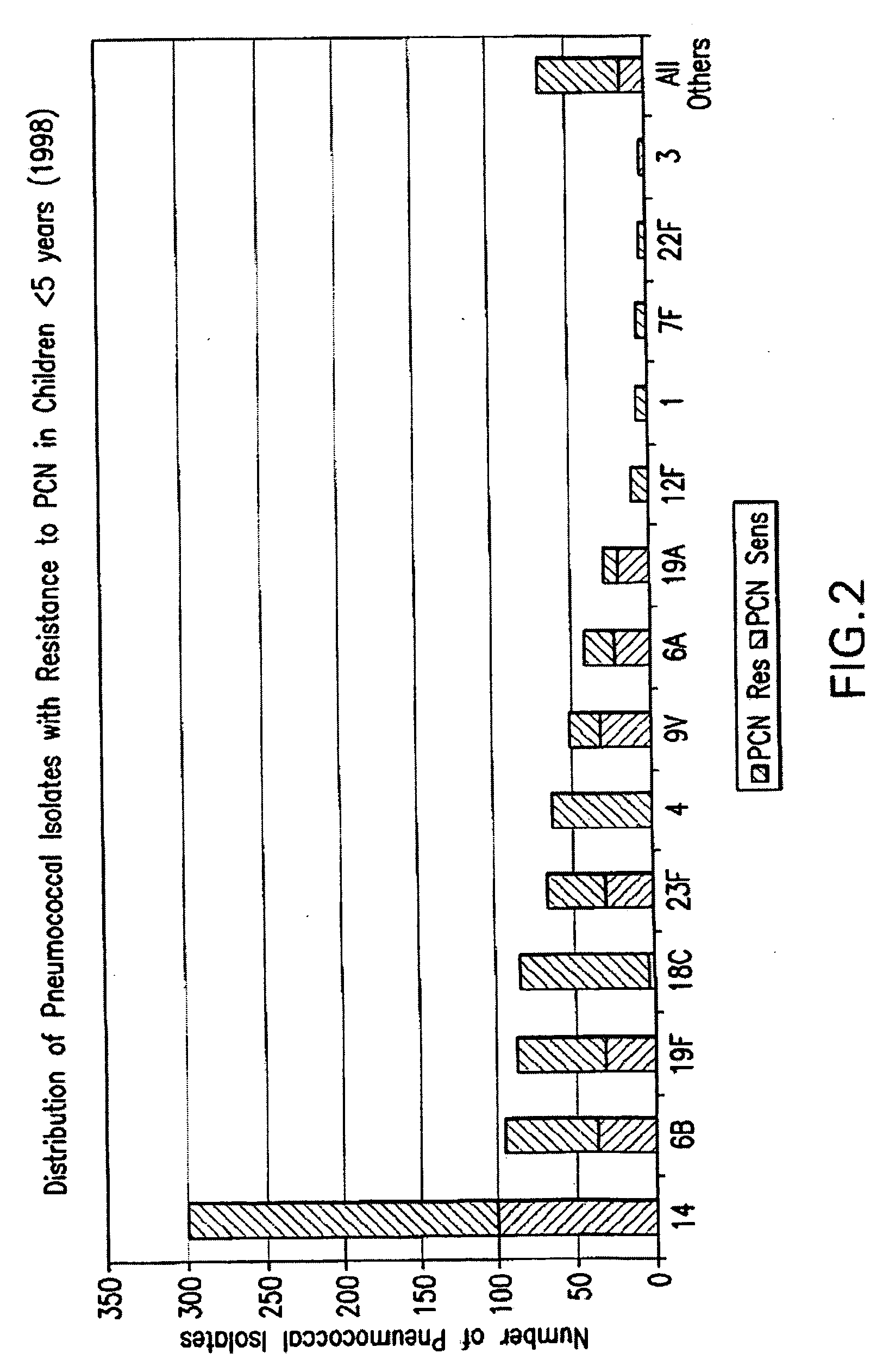
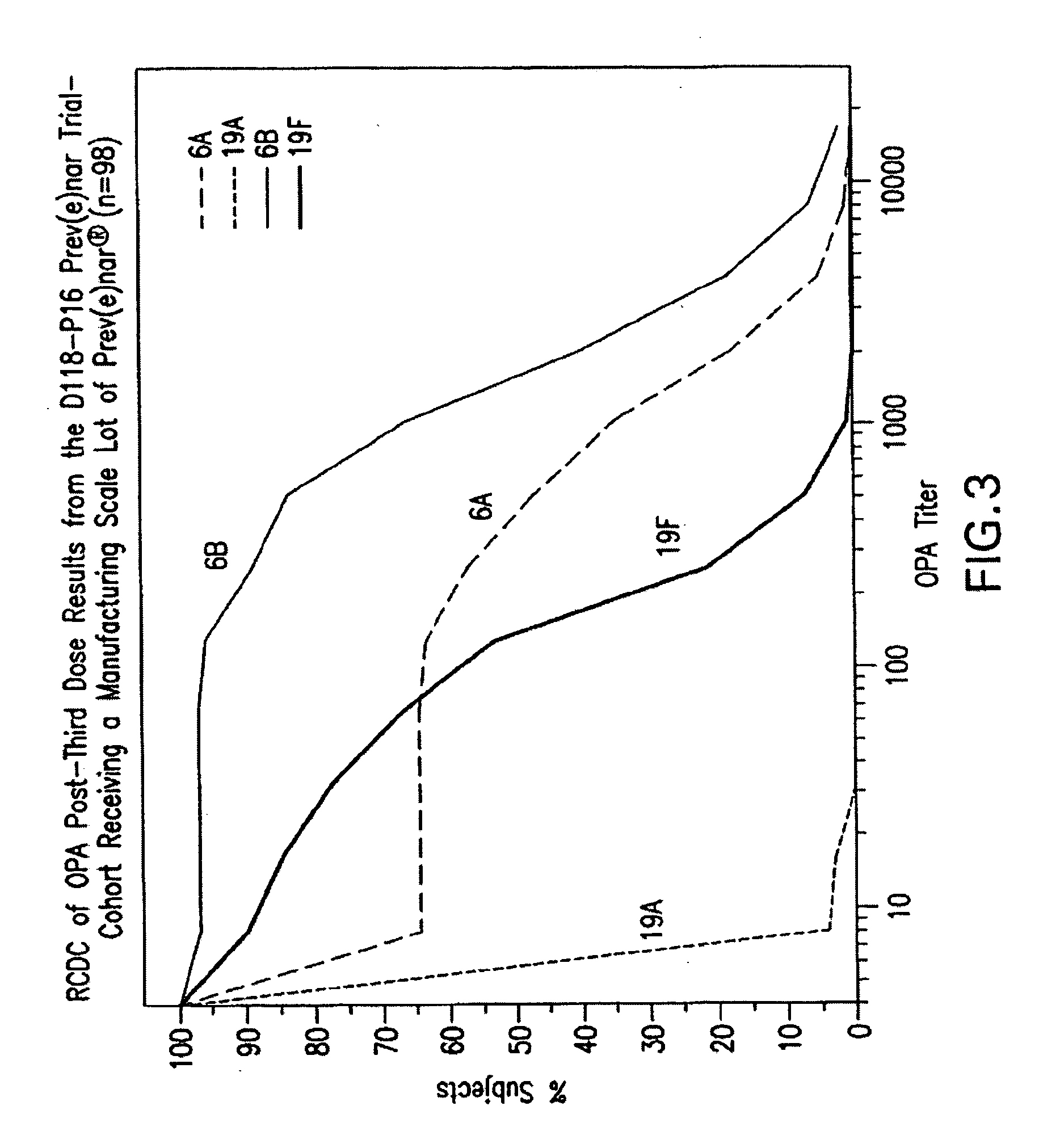
Multivalent pneumococcal polysaccharide-protein conjugate composition
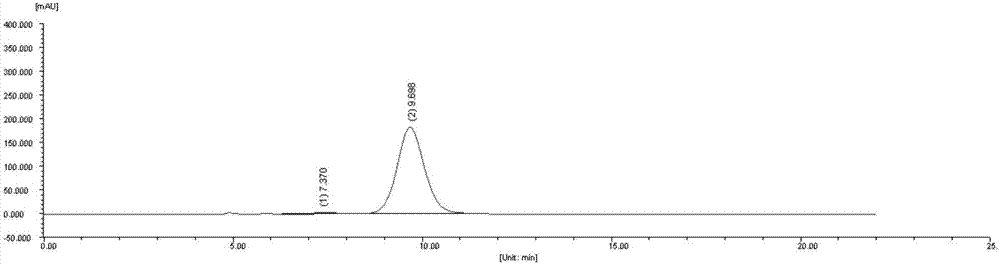
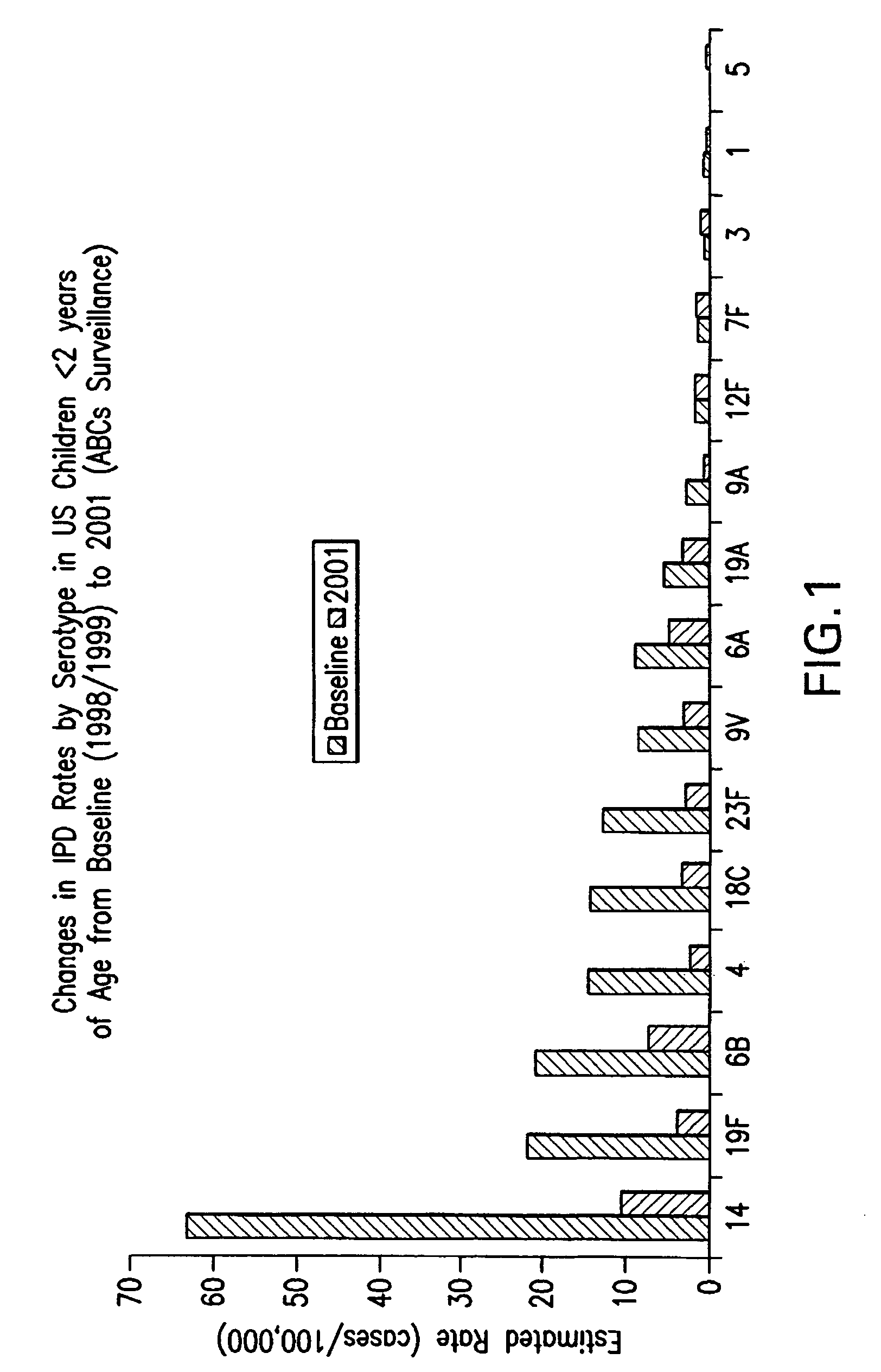
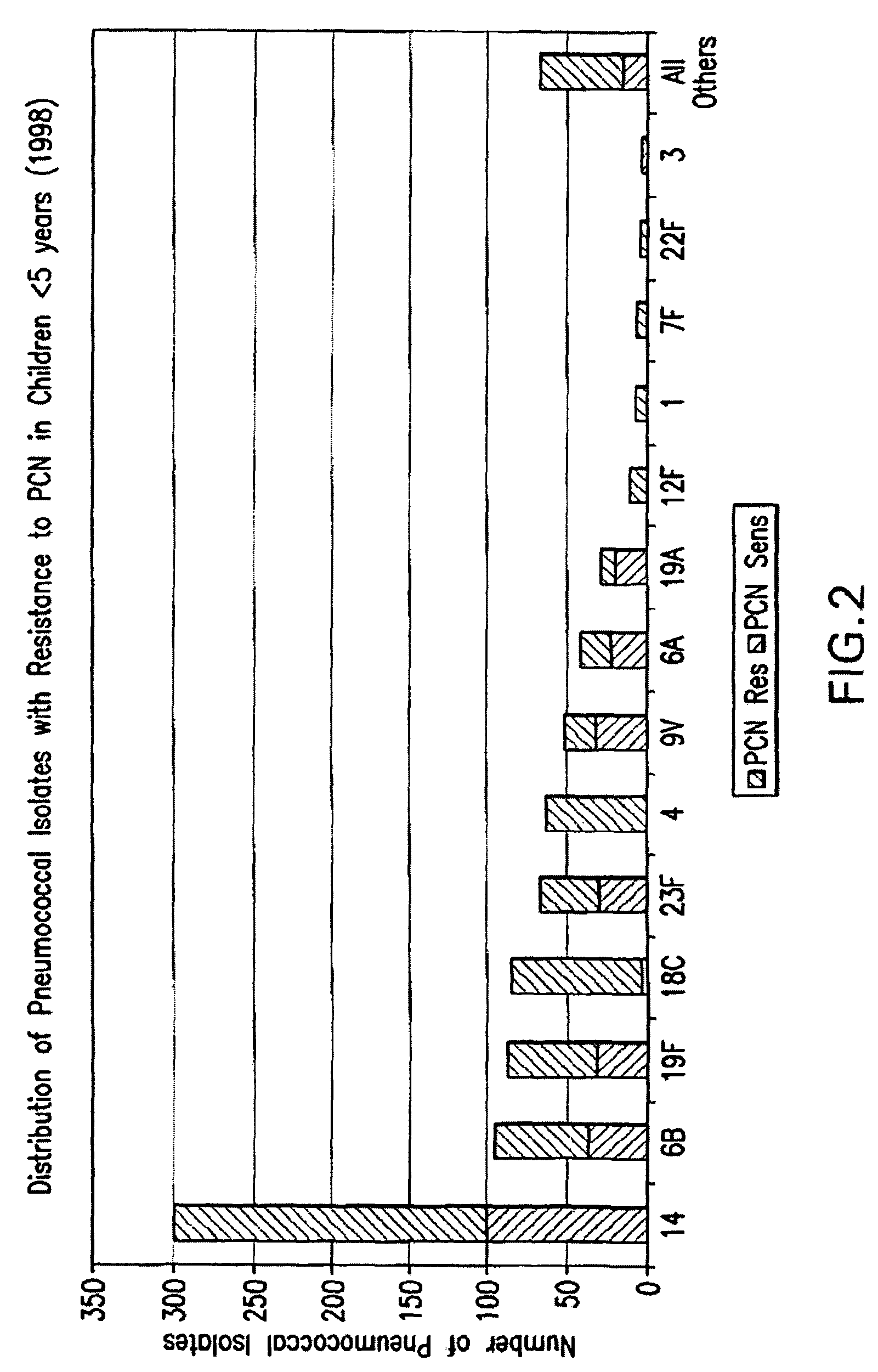
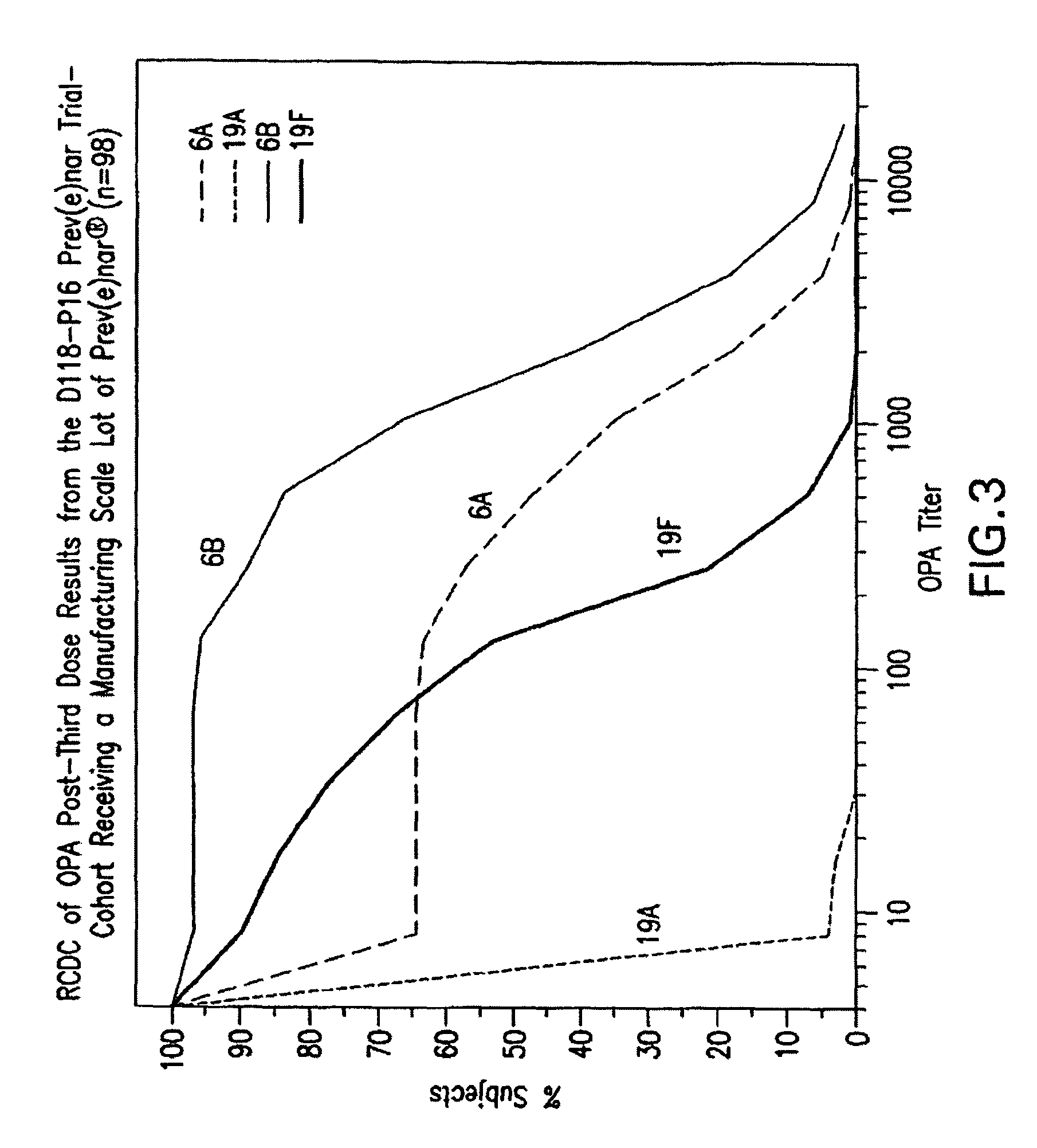
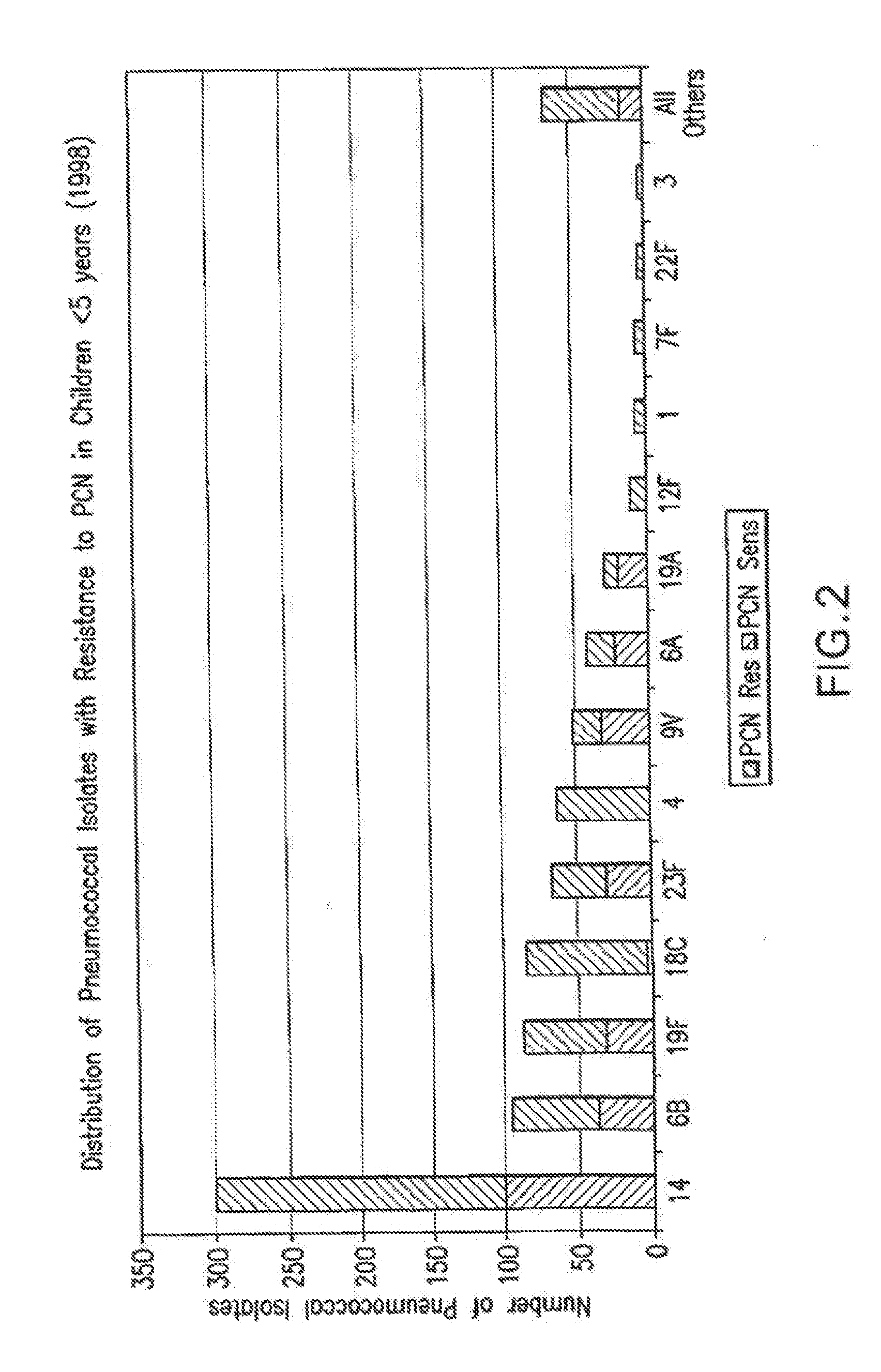
An immunogenic composition having 13 distinct polysaccharide-protein conjugates and optionally, an aluminum-based adjuvant, is described. Each conjugate contains a capsular polysaccharide prepared from a different serotype of Streptococcus pneumoniae (1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C, 19A, 19F and 23F) conjugated to a carrier protein. The immunogenic composition, formulated as a vaccine, increases coverage against pneumococcal disease in infants and young children globally, and provides coverage for serotypes 6A and 19A that is not dependent on the limitations of serogroup cross-protection. Methods for making an immunogenic conjugate comprising Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A polysaccharide are also provided in which the serotype 19A polysaccharide is co-lyophilized with a carrier protein and conjugation is carried out in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) via a reductive amination mechanism.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Integrate chemical processes for industrial utilization of seed oils
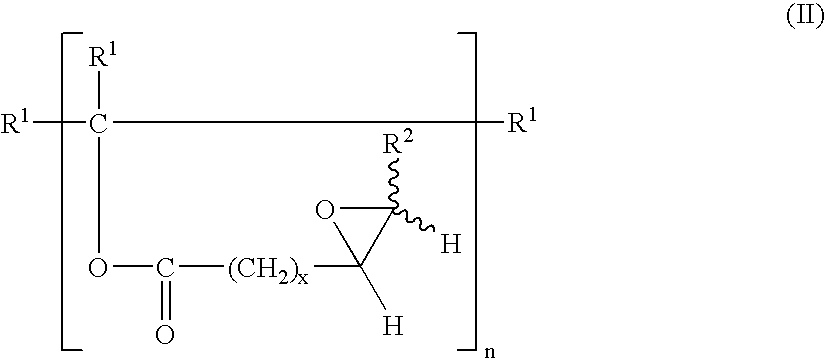
ActiveUS20050154221A1Easy to operateHigh olefin conversionFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOxygen-containing compound preparationPolyesterAmino esters
Integrated processes of preparing industrial chemicals starting from seed oil feedstock compositions containing one or more unsaturated fatty acids or unsaturated fatty acid esters, which are essentially free of metathesis catalyst poisons, particularly hydroperoxides; metathesis of the feedstock composition with a lower olefin, such as ethylene, to form a reduced chain olefin, preferably, a reduced chain α-olefin, and a reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester, preferably, a reduced chain α,Ω-unsaturated acid or ester. The reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be (trans)esterified to form a polyester polyolefin, which may be epoxidized to form a polyester polyepoxide. The reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be hydroformylated with reduction to produce an α,Ω-hydroxy acid or α,Ω-hydroxy ester, which may be (trans)esterified with a polyol to form an α,Ωpolyester polyol. Alternatively, the reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be hydroformylated with reductive amination to produce an α,Ω-amino acid or α,Ω-amino ester, which may be (trans)esterified to form an α,Ωpolyester polyamine.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Metal catalysts
InactiveUS6747180B2Low bulk densityHigh activityOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationHydration reactionAlkyl transfer
Owner:DEGUSSA AG +1
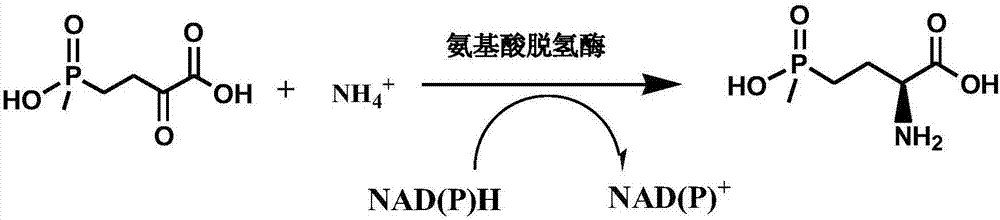
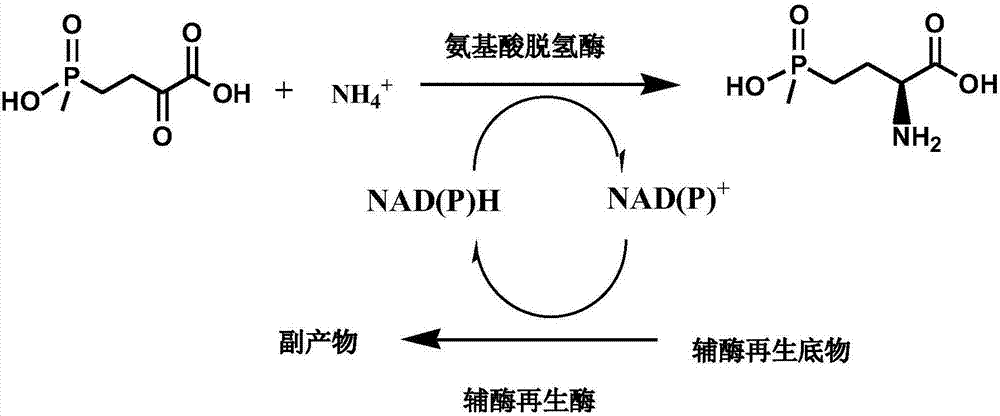
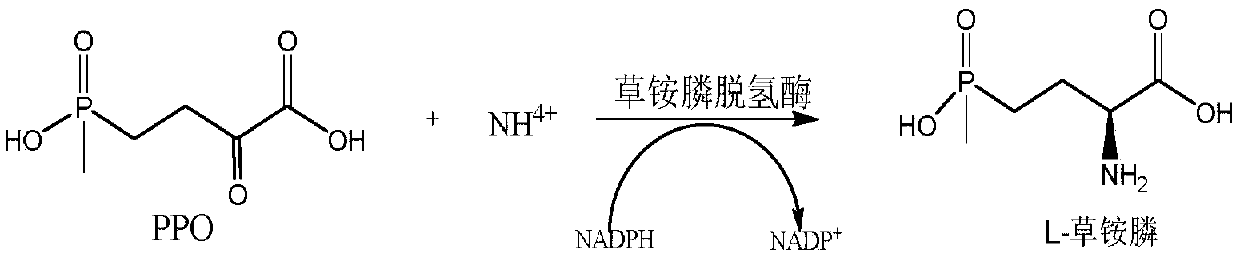
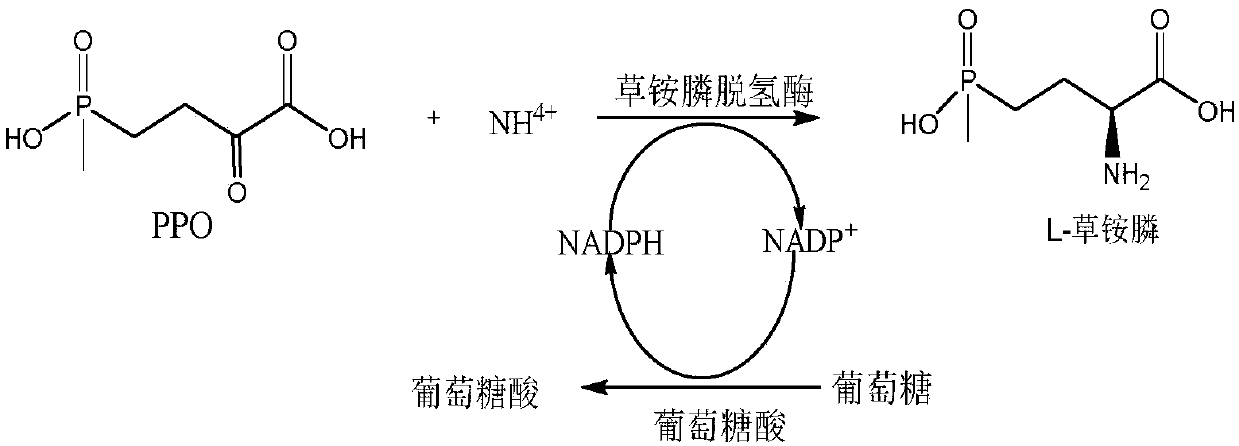
Method for preparing L-glufosinate-ammonium by use of amino acid dehydrogenase
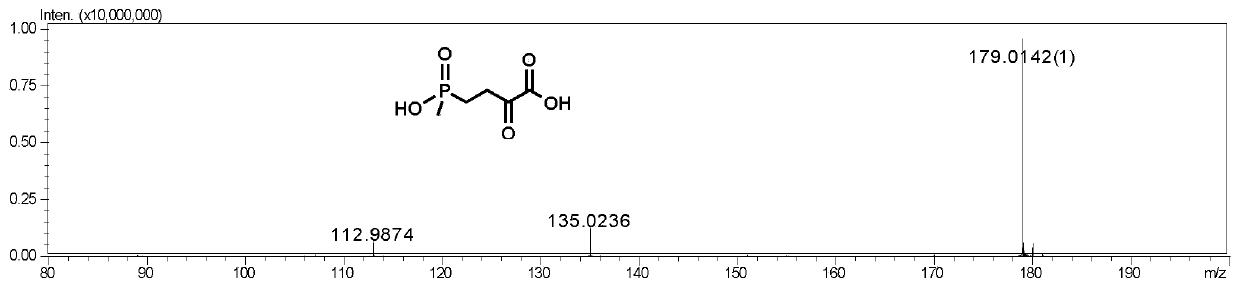
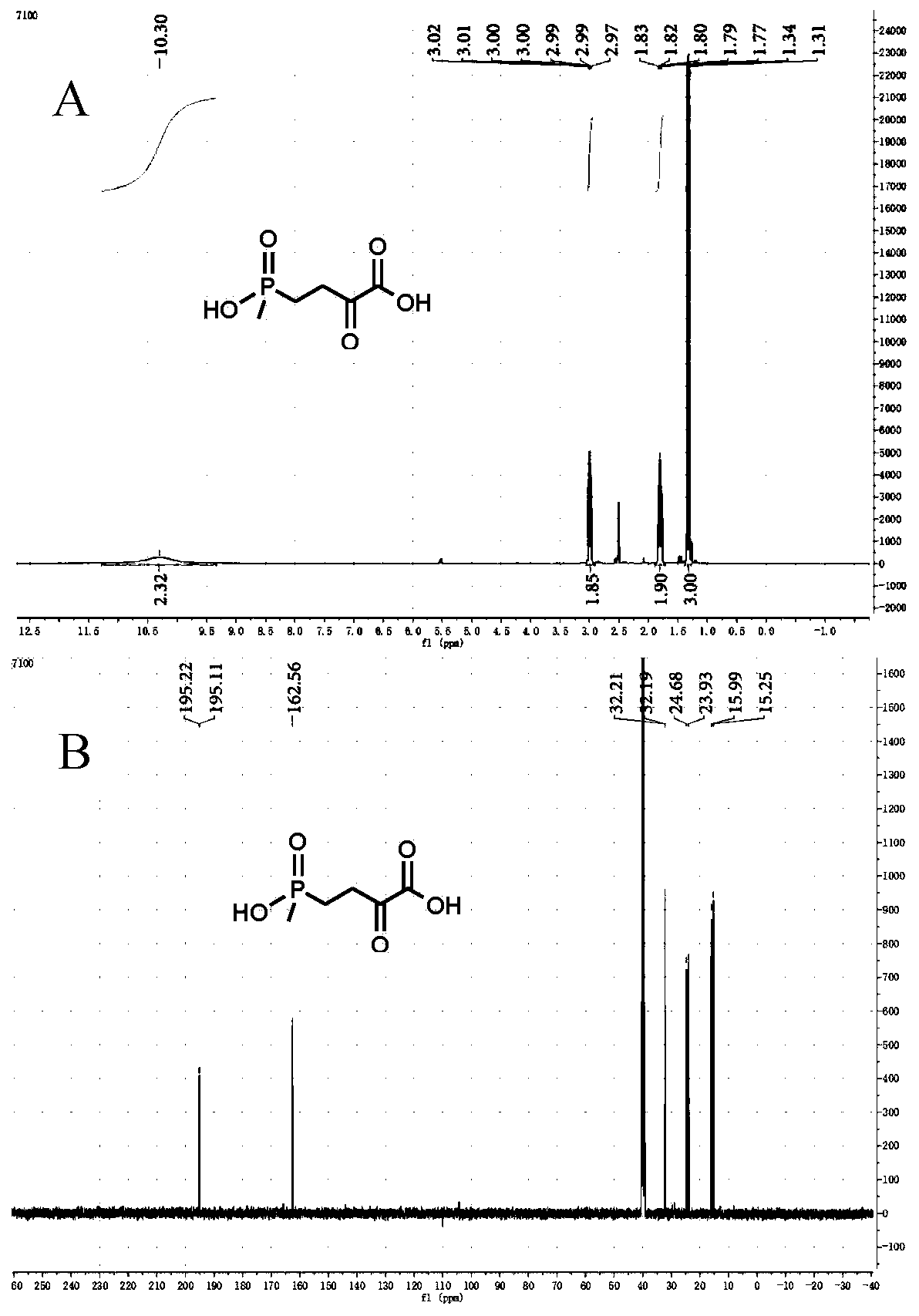
The invention discloses a method for preparing L-glufosinate-ammonium by use of amino acid dehydrogenase. The method comprises the following steps: taking 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxymethylphosphonyl)butyric acid or a salt thereof as a substrate, taking a cell of the isolated glutamate dehydrogenase or in vitro expression glutamate dehydrogenase as a catalyst to perform reductive amination reaction under the condition of the existence of inorganic amino donor and reduced coenzyme, thereby acquiring the L-glufosinate-ammonium. The method disclosed by the invention is high in raw material conversion rate and high in yield, the product is easy to separate and purify, and the chirality purity is high; compared with the transaminase and like catalysis technology, the process is relatively simple, and the raw material conversion rate reaches up to 100%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Metal catalysts
InactiveUS6573213B1Low bulk densityHigh activityOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationHydration reactionAlkyl transfer
Metal catalysts comprising hollow forms or spheres are made of metal alloy and optionally activated. The metal catalysts can be used for the hydrogenation, dehydrogenation, isomerization reductive alkylation, reductive amination, and / or hydration reaction of organic compounds.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Nitrogen-doped carbon material supporting cobalt catalyst and method therewith of catalytic hydrogenation reductive amination to produce amine compounds
InactiveCN106552661AEasy to prepareReduce manufacturing costOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationReaction temperatureNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a nitrogen-doped carbon material supporting cobalt catalyst and a method therewith of catalytic hydrogenation reductive amination to produce primary amine compounds. The catalyst is prepared through the steps of: 1) preparing a MOF material ZIF-67; and 2) under protection of nitrogen gas, calcining the MOF material ZIF-67 at 200-1000 DEG C for 1-10 h to produce the nitrogen-doped carbon material supporting cobalt catalyst Co / N-C. The method of catalytic hydrogenation reductive amination to produce the primary amine compounds with the catalyst includes the steps of: in an organic solvent, adding a carbonyl compound, ammonia water and the nitrogen-doped carbon material supporting cobalt catalyst, feeding hydrogen gas, and performing a reaction at 50-150 DEG C under 0.1-5 MPa for 0.5-20.0 h to produce the amine compounds. The preparation method of the catalyst is simple in operations. The catalyst can be used for producing the primary amine compounds in a manner of catalytic hydrogenation reductive amination. In the method, the primary amine compounds are produced with the carbonyl compound as a raw material through catalytic hydrogenation by means of the catalyst, so that the method has mild reaction conditions and is high in yield.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Integrated chemical processes for industrial utilization of seed oils
InactiveUS20090143544A1Easy to operateImprove productivityFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOrganic compound preparationPolyesterPolymer science
Integrated processes of preparing industrial chemicals starting from seed oil feedstock compositions containing one or more unsaturated fatty acids or unsaturated fatty acid esters, which are essentially free of metathesis catalyst poisons, particularly hydroperoxides; metathesis of the feedstock composition with a lower olefin, such as ethylene, to form a reduced chain olefin, preferably, a reduced chain α-olefin, and a reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester, preferably, a reduced chain α,ω-unsaturated acid or ester. The reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be (trans)esterified to form a polyester polyolefin, which may be epoxidized to form a polyester polyepoxide. The reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be hydroformylated with reduction to produce an α,ω-hydroxy acid or α,ω-hydroxy ester, which may be (trans)esterified with a polyol to form an α,ωpolyester polyol. Alternatively, the reduced chain unsaturated acid or ester may be hydroformylated with reductive amination to produce an α,ω-amino acid or α,ω-amino ester, which may be (trans)esterified to form an α,ω-polyester polyamine.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Process for preparing enantiomerically enriched amines
A process for preparing enantiomerically enriched amines by reacting a ketone with ammonia or an ammonium salt and a reducing agent in the presence of a catalytic system comprising the components:a) an amino acid transaminase,b) an alpha-amino acid which is a substrate of the amino acid transaminase,c) an amino acid dehydrogenase suitable for preparing the alpha-amino acid,d) NAD(P)+ ande) an NAD(P)+-reducing enzyme, which reacts NAD(P)+ with the reducing agent to give NAD(P)H.The process can be carried out with catalytic amounts of alpha-amino acid and NAD(P)+, and enables an enantioselective reductive amination of ketones.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Process for the direct amination of secondary alcohols with ammonia to give primary amines
InactiveUS20130165672A1Isolation and purification of intermediatesAvoid isolationOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationAlcoholGas phase
The invention relates to a process for preparing primary amines which comprises the process stepsA) provision of a solution of a secondary alcohol in a fluid, nongaseous phase,B) contacting of the phase with free ammonia and / or at least one ammonia-releasing compound and a homogeneous catalyst and optionallyC) isolation of the primary amine formed in process step B),characterized in that the volume ratio of the volume of the liquid phase to the volume of the gas phase in process step B is greater than or equal to 0.25, and / or in that the ammonia is used in process step B) in a molar ratio based on the hydroxyl groups in the secondary alcohol of at least 5:1.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Methods of making cyclic, n-amino functional triamines
The present invention provides strategies for making cyclic triamines. Reactant media including certain precursors and / or certain types of catalysts can be converted into cyclic triamines with improved conversion and selectivity. The strategies can be incorporated into reactions that involve transamination schemes and / or reductive amination schemes. In the case of transamination, for instance, using transamination to cause ring closure of higher amines in the presence of a suitable catalyst leads to desired cyclic triamines with notable conversion and yield. In the case of reductive amination, reacting suitable polyfunctional precursors in the presence of a suitable catalyst also yields cyclic triamines via ring closure with notable selectivity and conversion. Both transamination and reductive amination methodologies can be practiced under much milder temperatures than are used when solely acid catalysts are used. Preferred embodiments can produce reaction mixtures that are generally free of salt by-products.
Owner:UNION CARBIDE CORP
Method for reductive amination of a ketone using a mutated enzyme
Methods for chemically transforming compounds using a mutated enzyme are provided, and more particularly a method for the production of an amino acid from a target 2-ketoacid, the production of an amine from a target ketone and the production of an alcohol from a target ketone. The methods comprise creating a mutated enzyme that catalyzes the reductive amination or transamination of the target 2-ketoacid or ketone or the reduction of the ketone and providing the mutated enzyme in a reaction mixture comprising the target 2-ketoacid or ketone under conditions sufficient to permit the formation of the desired amino acid, amine or alcohol to thereby produce the amino acid, amine or alcohol.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
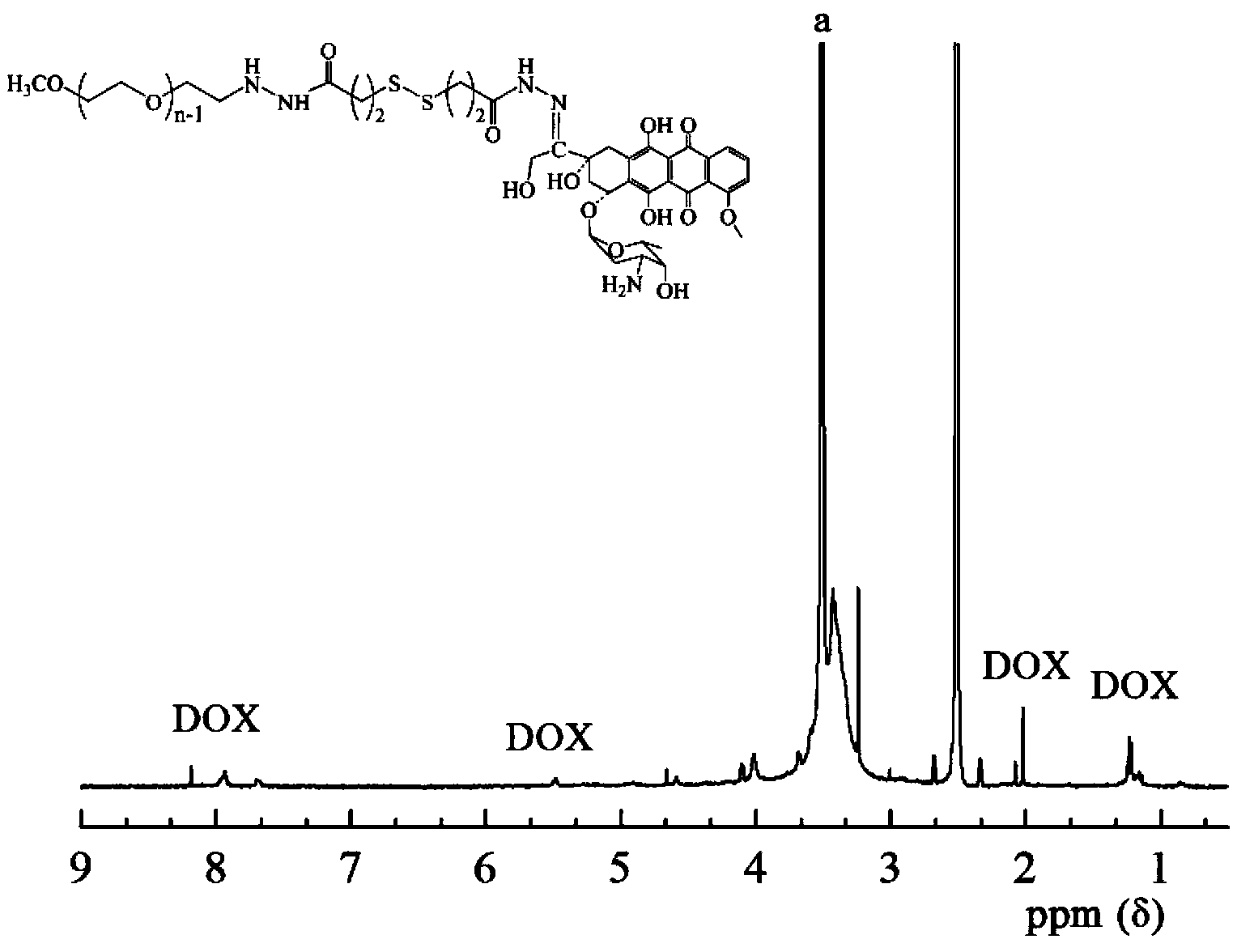
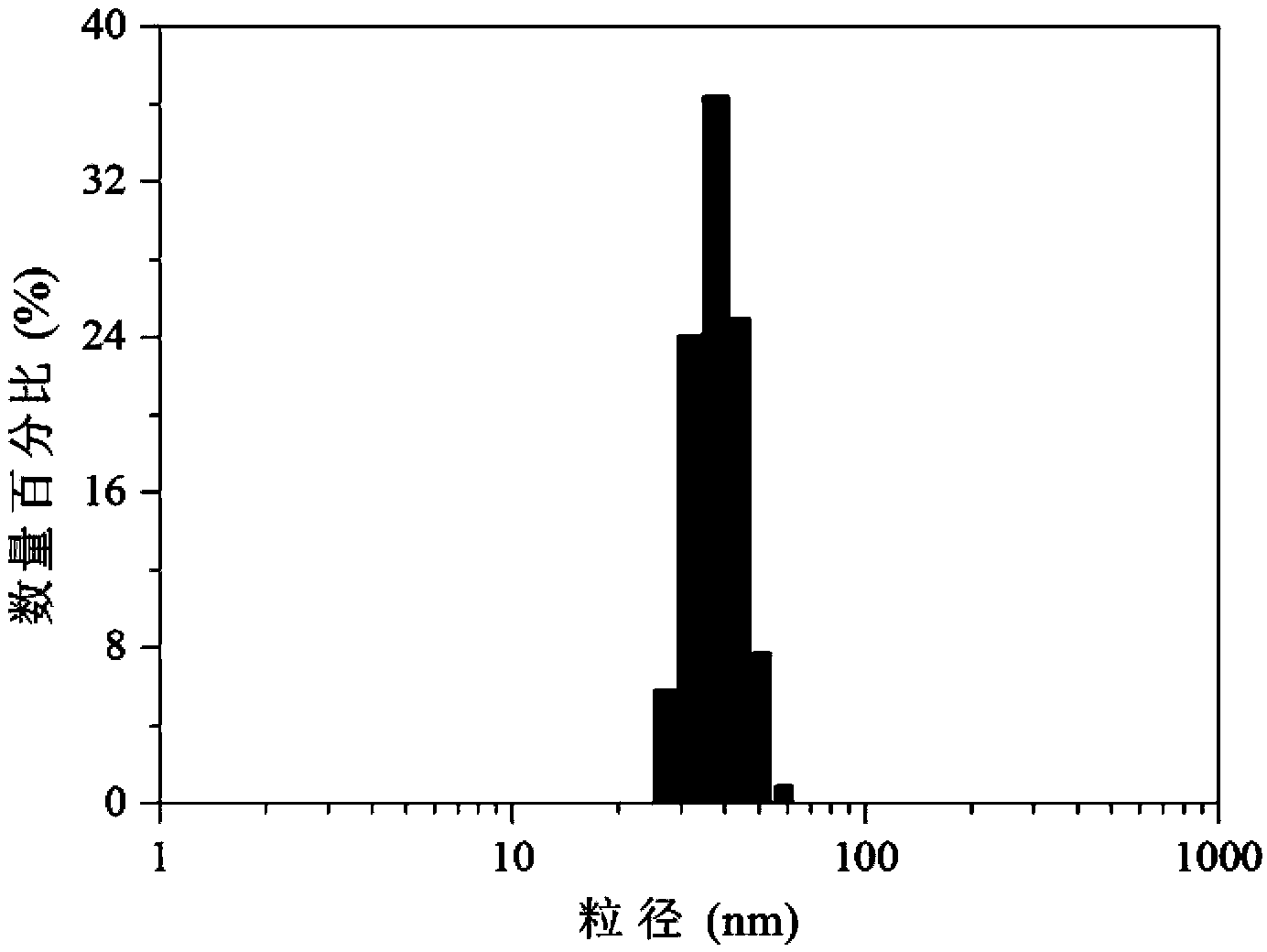
Bifunctional polyethylene glycol and adriamycin conjugate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103357022ASmall toxicityGood water solubilityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCancer cellKetone
The invention relates to a bifunctional polyethylene glycol and adriamycin conjugate and a preparation method thereof. The bifunctional polyethylene glycol and adriamycin conjugate is prepared in the following steps: modifying methoxy polyethylene glycol which serves as a raw material through hydroformylation, carrying out a reductive amination reaction on the modified methoxy polyethylene glycol and disulfide-bond containing dihydrazide to generate terminal-hydrazide polyethylene glycol, and carrying out a reaction on the terminal hydrazide of the terminal-hydrazide polyethylene glycol and the ketone carbonyl of the adriamycin to generate a hydrazone bond to obtain the bifunctional polyethylene glycol and adriamycin conjugate. The bifunctional polyethylene glycol and adriamycin conjugate provided by the invention can adapt to the reductive acidic environment in a cancer cell to release drugs rapidly to improve the cancer treatment effect and reduce the drug resisting possibility of the cancer cell, and in addition, the bifunctional polyethylene glycol and adriamycin conjugate can be self-assembled into a nano particle in a water phase to be able to circulate for a long time in blood to improve the pharmacokinetics of the doxorubicin. The method for preparing the bifunctional polyethylene glycol and adriamycin conjugate has the advantages of simple process, mild reaction conditions, high drug carrying rate and low cost, and the raw materials are easy to obtain. The bifunctional polyethylene glycol and adriamycin conjugate has potential application values in the aspects of targeted delivery of drugs, controlled release of drugs and improvement of clinical cancer resisting and treating effects.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
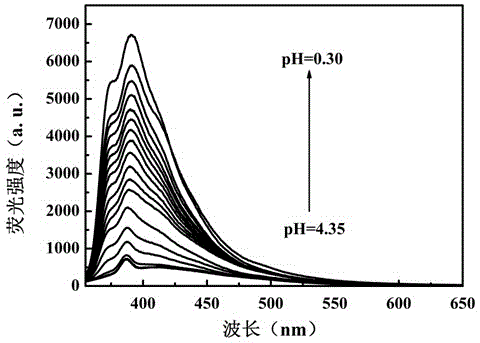
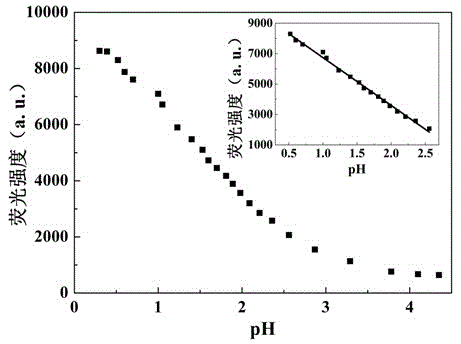
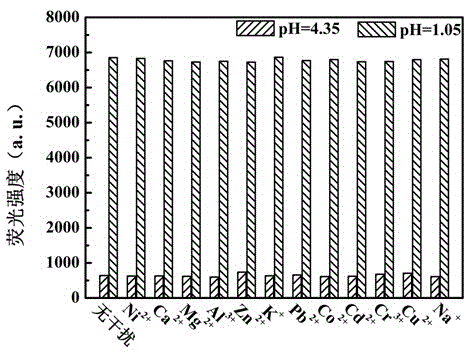
Benzothiazole-aniline compound used as pH fluorescent probe and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102942537ASimple preparation processConjugate plane largeOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceAlkaneSolubility
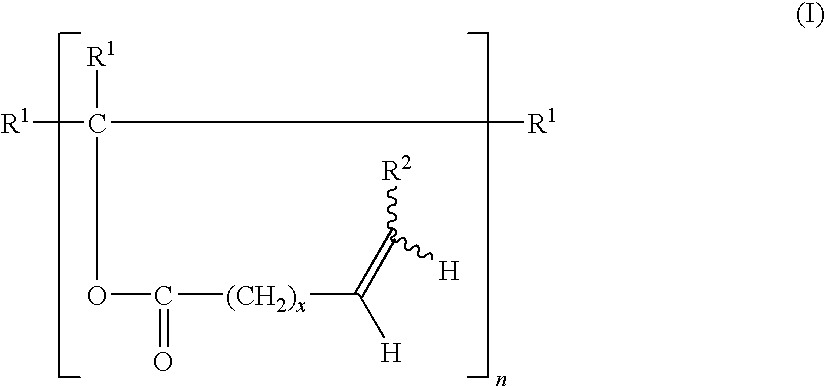
The invention discloses a benzothiazole-aniline compound used as a pH fluorescent probe and a preparation method thereof. The structural formula is shown as a chemical formula (shown in the description) (I), wherein in the formula, R1 is vinyl, acetenyl, styryl, phenylethynyl, biphenyl or perylene base; and R2 and R3 are both hydrogen, methyl or ethyl alkane. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: taking p-bromobenzaldehyde and 2-aminothiophenol as raw materials, and connecting with iodine-containing nitrobenzene derivative through dehydration cyclization reaction and coupling reaction; and generating the pH fluorescent probe benzothiazole-aniline derivative through reductive amination. Rigid structures, such as benzothiazole and phenylethynyl, are introduced into the fluorescent probe; the fluorescent probe is high in fluorescence quantum efficiency, and high in thermal stability and solubility. The probe can detect pH value under strong acid condition by adopting a photoinduced charge transfer mechanism and a conjugate passivation mechanism; and the probe has the characteristics of rapid response, high sensitivity and high selectivity, and has wide application prospect in environment monitoring, ecological protection, disease diagnosis, industrial production and sewage inspection.
Owner:浙江富昇科技有限公司
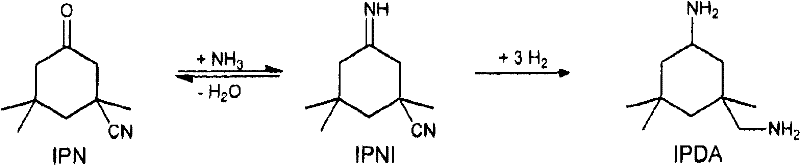
Process for preparing 3-aminomethyl-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohexylamine
InactiveCN102531916AIncrease concentrationOrganic compound preparationWater/sewage treatment by heatingIsophoroneAsymmetric hydrogenation
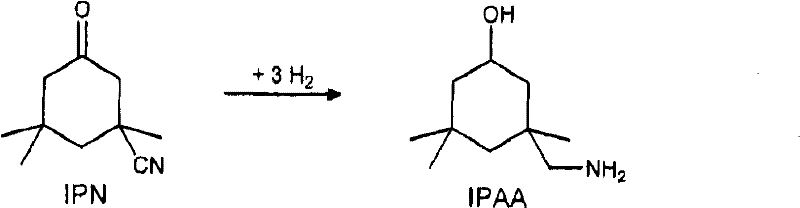
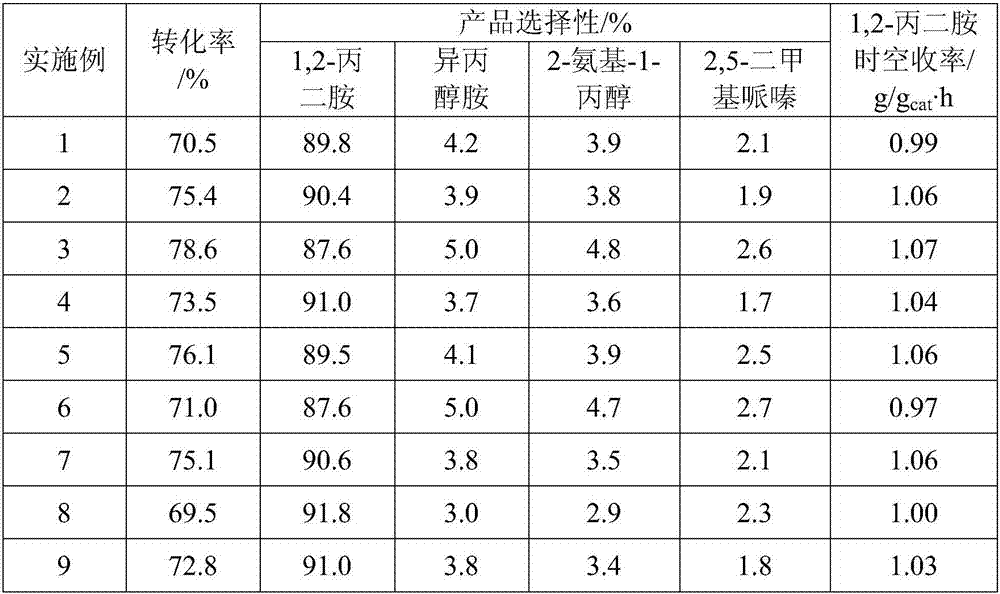
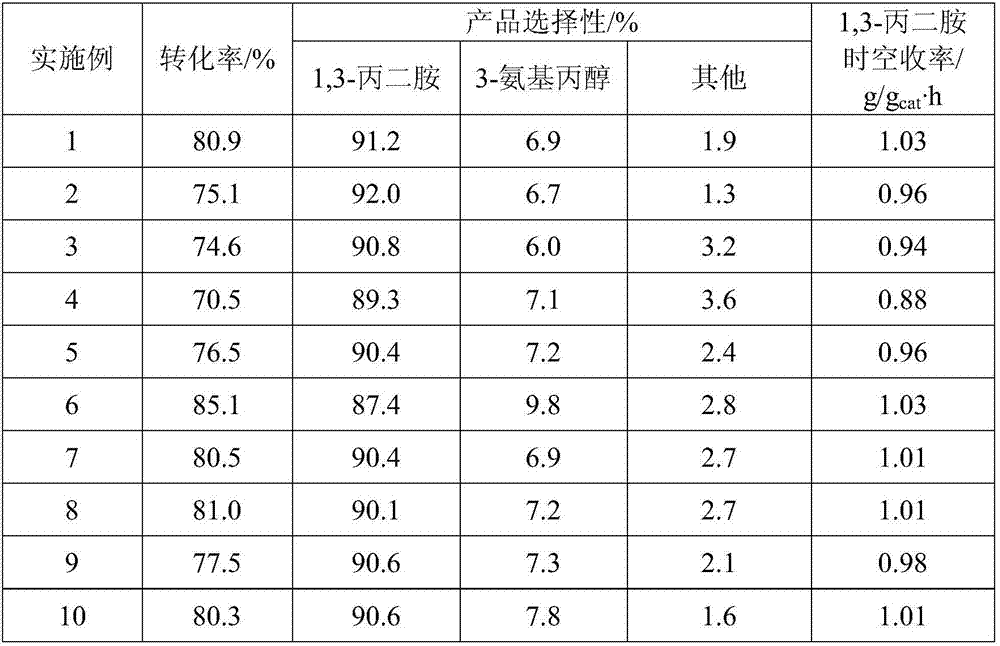
The invention relates to an improved process for preparing 3-aminomethyl-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohexylamine, referred to hereinafter as isophoronediamine or, in abbreviated form, IPDA, by: I. preparation of isophorone by catalyzed aldol condensations with acetone as reactant; II. Reaction of isophorone with HCN to form isophoronenitrile (IPN, 3-cyano-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohexanone); III. catalytic hydrogenation and / or catalytic reductive amination (also referred to as aminative hydrogenation) of 3-cyano-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohexanone, hereinafter called isophoronenitrile or, in abbreviated form, IPN, to give the isophoronediamine.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Method for preparing 2, 5-dimethylamino furan from 2, 5-diformyl furan
ActiveCN104277018AEfficient reductionStrong reductionOrganic chemistryChemical recyclingFuranHydrogen
The invention discloses a method for preparing 2, 5-dimethylamino furan by catalytic reductive amination of 2, 5-diformyl furan, according the method, ammonia is used as an amine source, hydrogen is used as a hydrogen source, a loading type metal is used as a catalyst, and the 2, 5-dimethylamino furan is prepared by selective reductive amination of the 2, 5-diformyl furan at 30-220 DEG C. The method has the advantages that reaction conditions are mild, product yield is high, the catalyst is easy to separate and recycle, and the product is easy to separate and purify, the purity of the product reaches more than 99%, and the product has a good application prospect.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
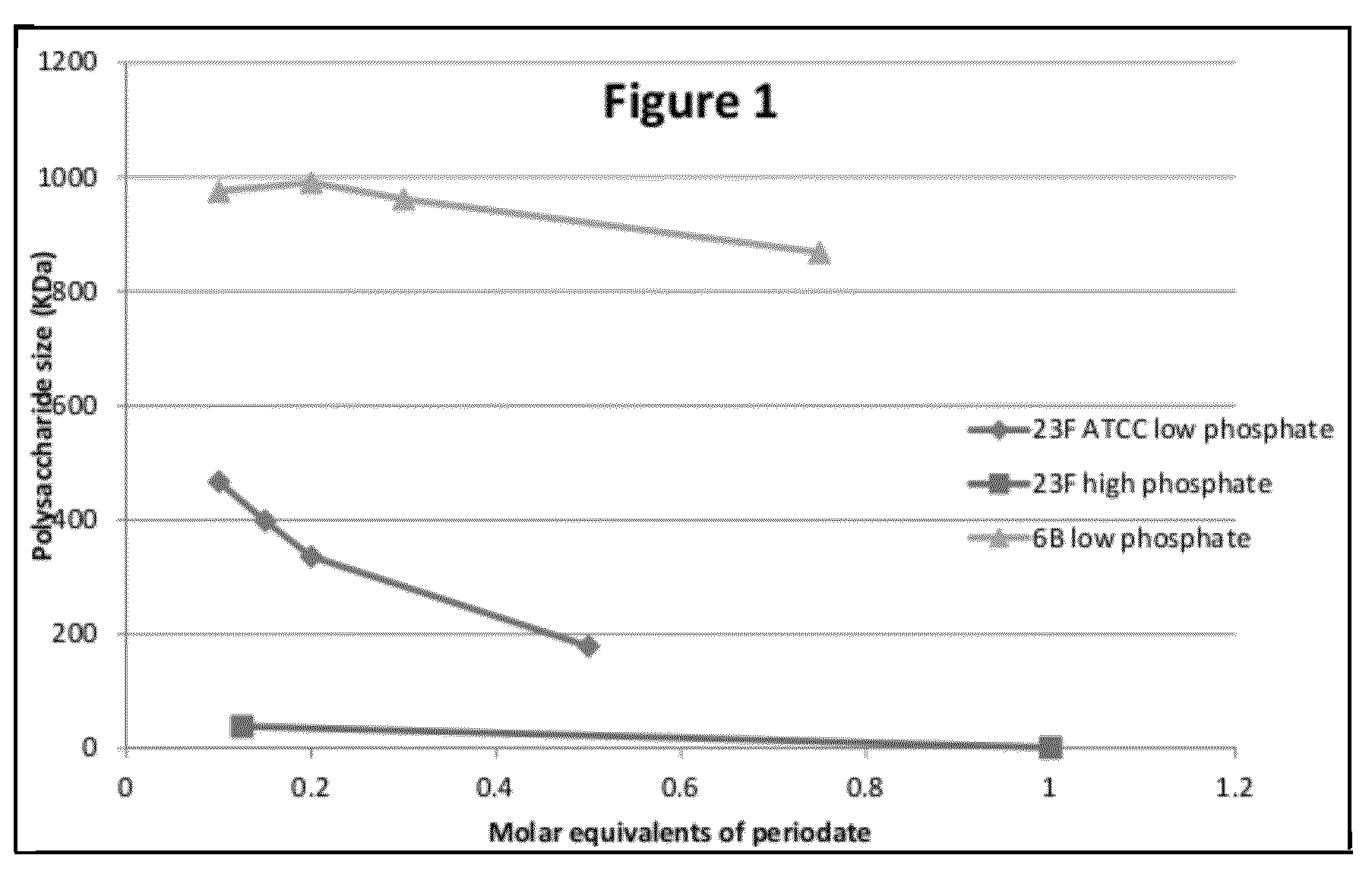
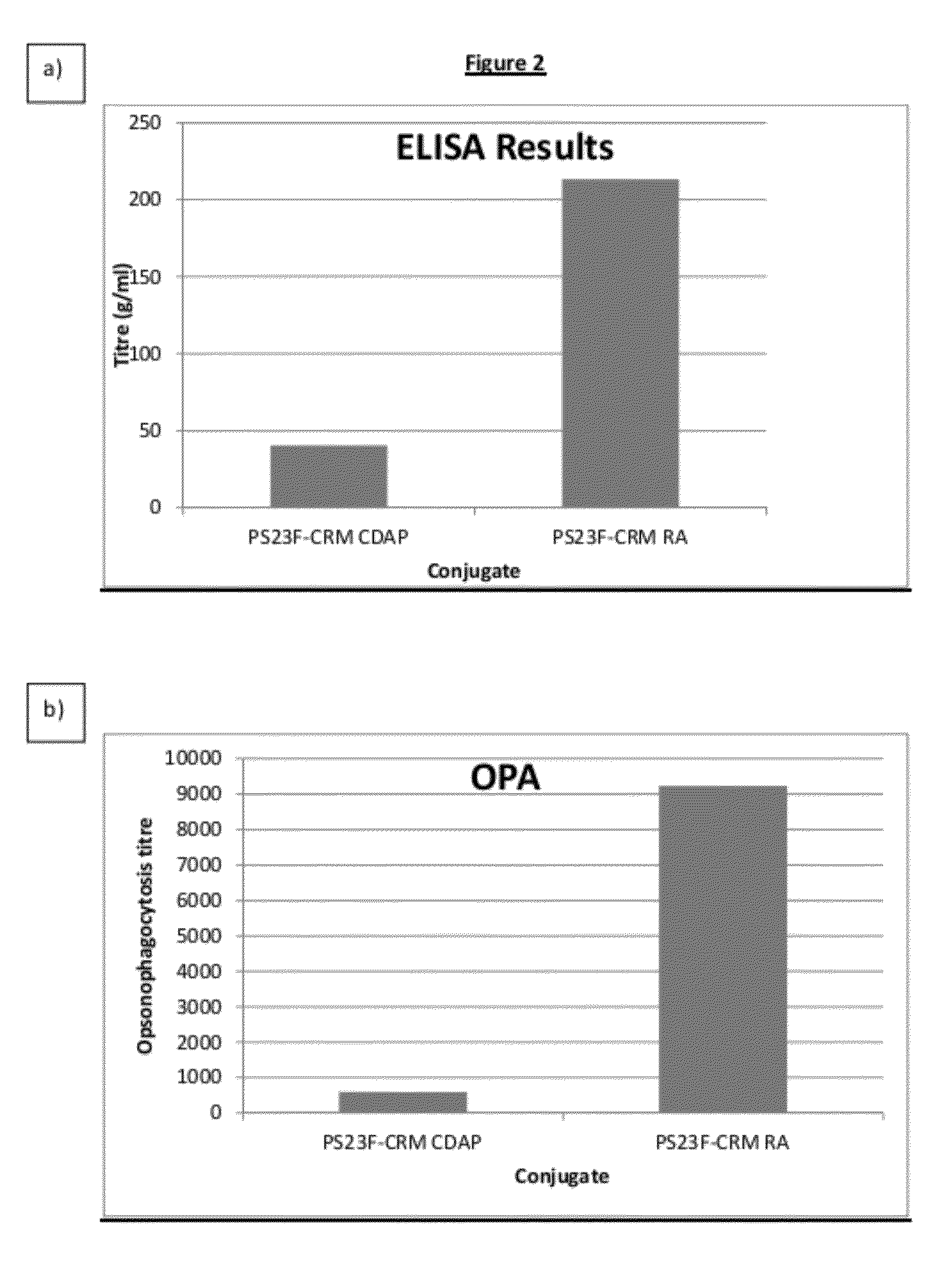
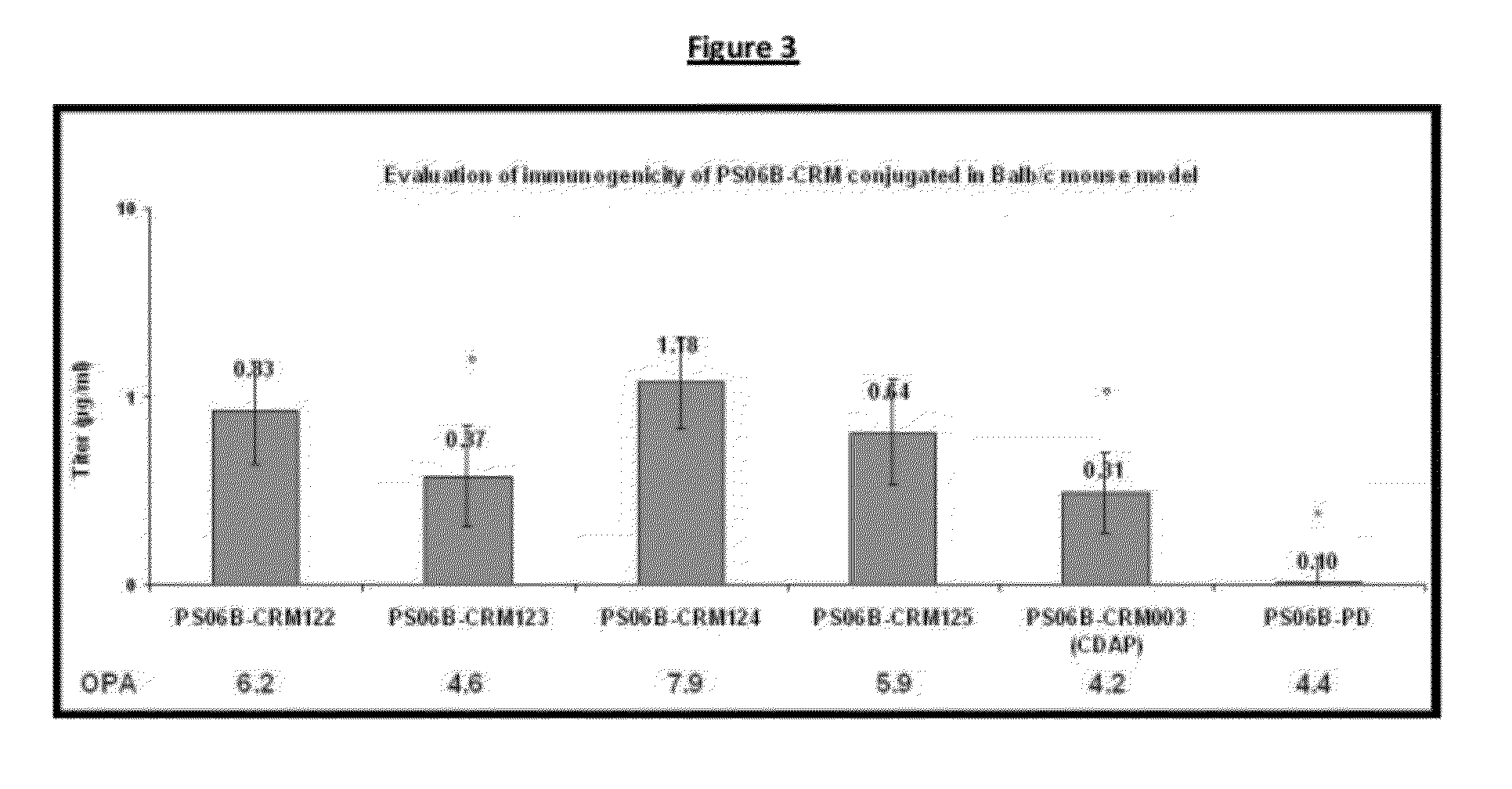
Conjugation process of bacterial polysaccharides to carrier proteins
ActiveUS8753645B2Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesStreptococcus pneumoniae
Process for conjugation of bacterial saccharides including Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae saccharides by reductive amination are provided herein.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
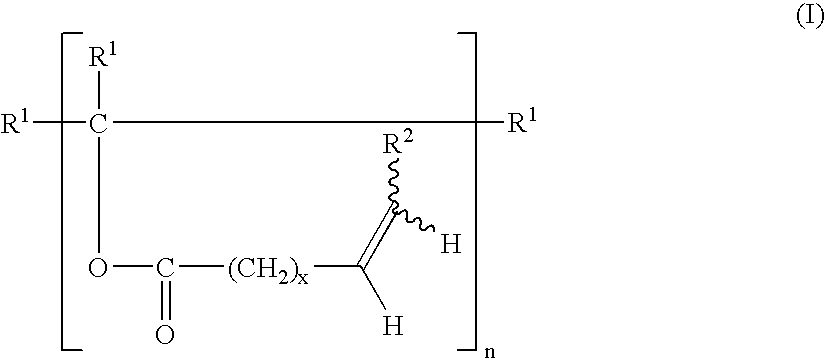
Alicyclic polyamines and process for the preparation thereof
InactiveUS6100430AImprove isolationEasy to purifyPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationArylHydrogen atom
PCT No. PCT / JP98 / 00192 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 10, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 10, 1998 PCT Filed Jan. 20, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 32729 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 30, 1998An alicyclic polyamine of the formula (1) wherein Y1 represents a saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon group and R1 through R4 are the same or different and each represents hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group, an aryl group, or an aralkyl group. The alicyclic polyamine can be obtained by subjecting a 3-formylcycloalkanone or 3-formylcycloalkenone to reductive amination reaction.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Method for selective enrichment and identification of N-linked glycopeptide
InactiveCN106483294AMaterials are cheap and readily availableGood dispersionPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingMicrosphereSide chain
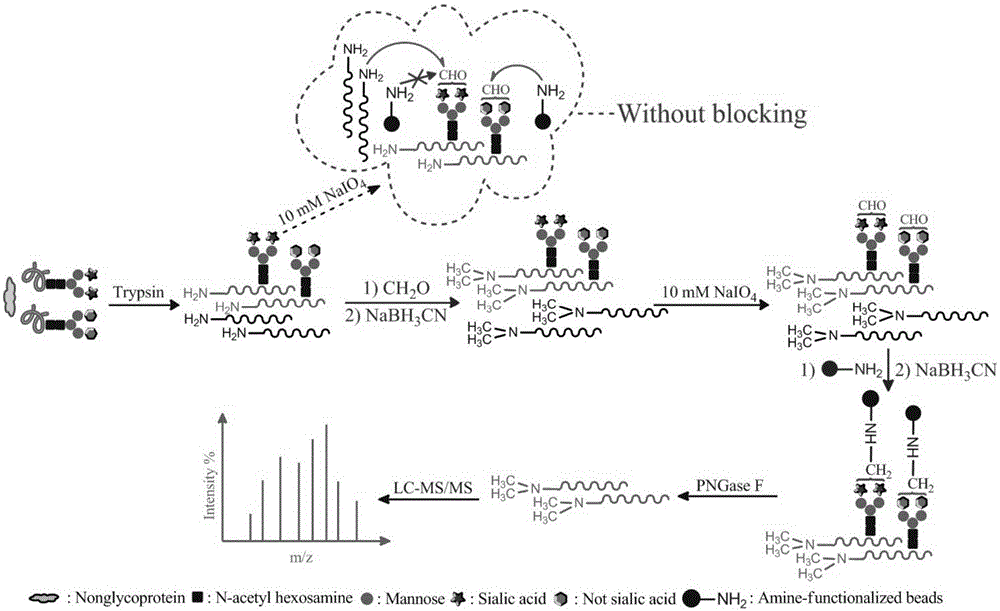
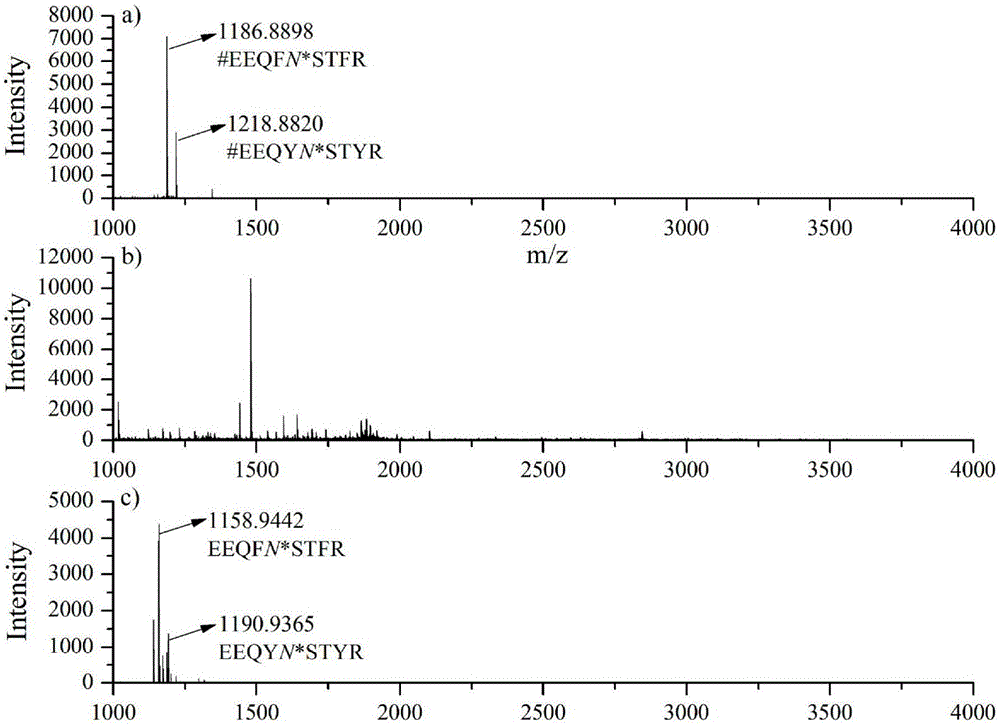
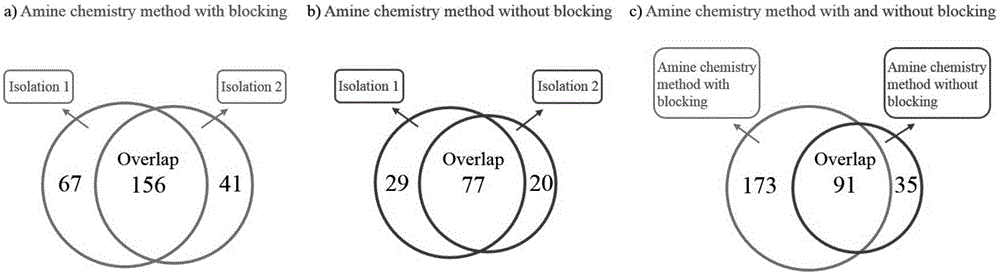
The invention relates to a method for selective enrichment and identification of N-glycosylation sites in a biological sample based on a reductive amination reaction of amino and aldehyde groups and application of the method to proteomic analysis of N-glycoprotein. The method comprises the following steps: taking a biological sample containing glycoprotein, carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis by using trypsin and then blocking the terminated amino group and side-chain amino group of a peptide fragment by using formaldehyde; then oxidizing a sugar chain on glycopeptide by using a sodium periodate solution so as to produce an aldehyde group; then enriching oxidized glycopeptide with amino microspheres and carrying out treatment with peptide glycosidase PNGase F; and carrying out mass spectrometry on released N-glycopeptide so as to obtain proteome information of N-glycoprotein in the sample. The method can be used for proteomic analysis of glycosylation and can acquire identification results of corresponding glycoprotein, glycopeptide and glycosylation sites at the same time. The method is simple and highly efficient and has high throughput in identification of N-glycosylation sites on glycoprotein.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
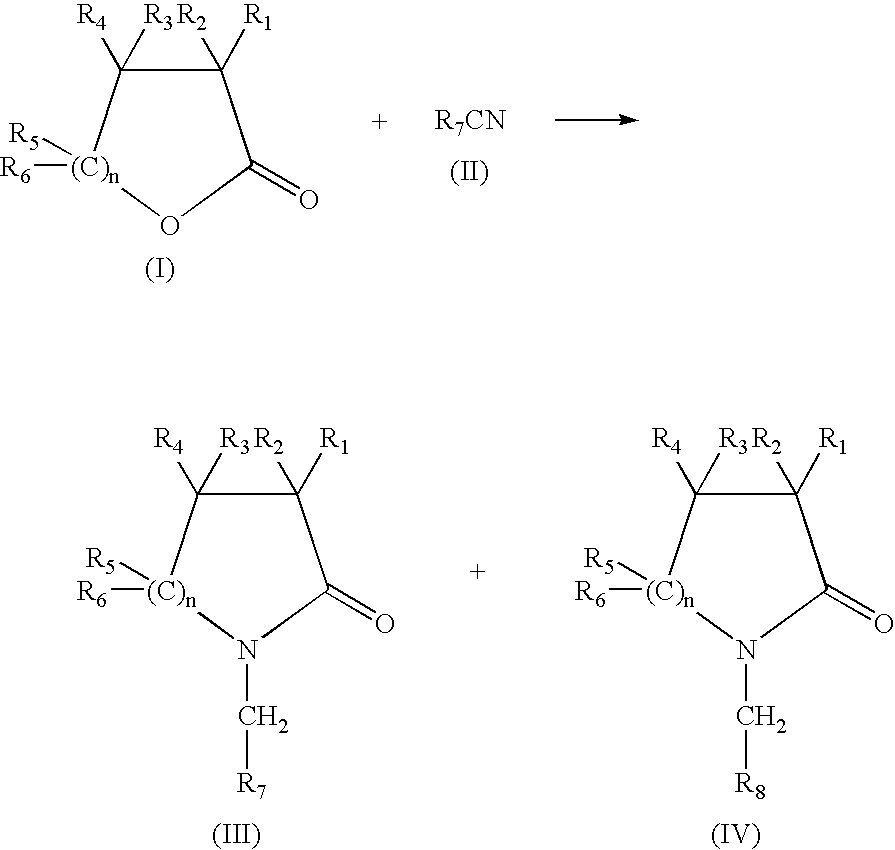
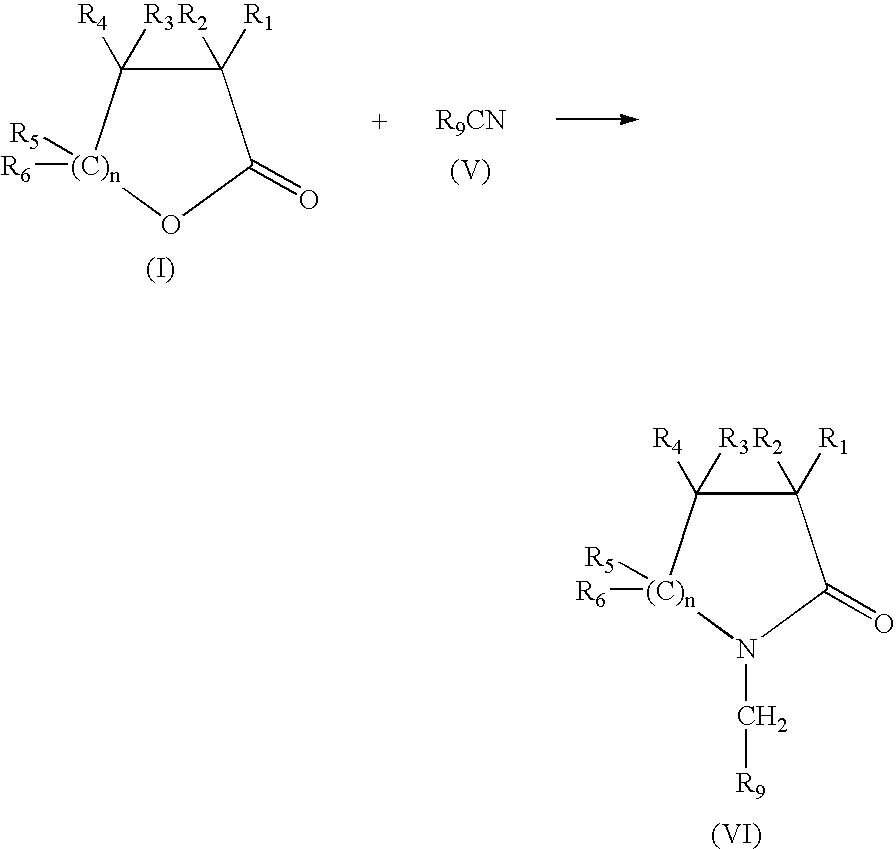
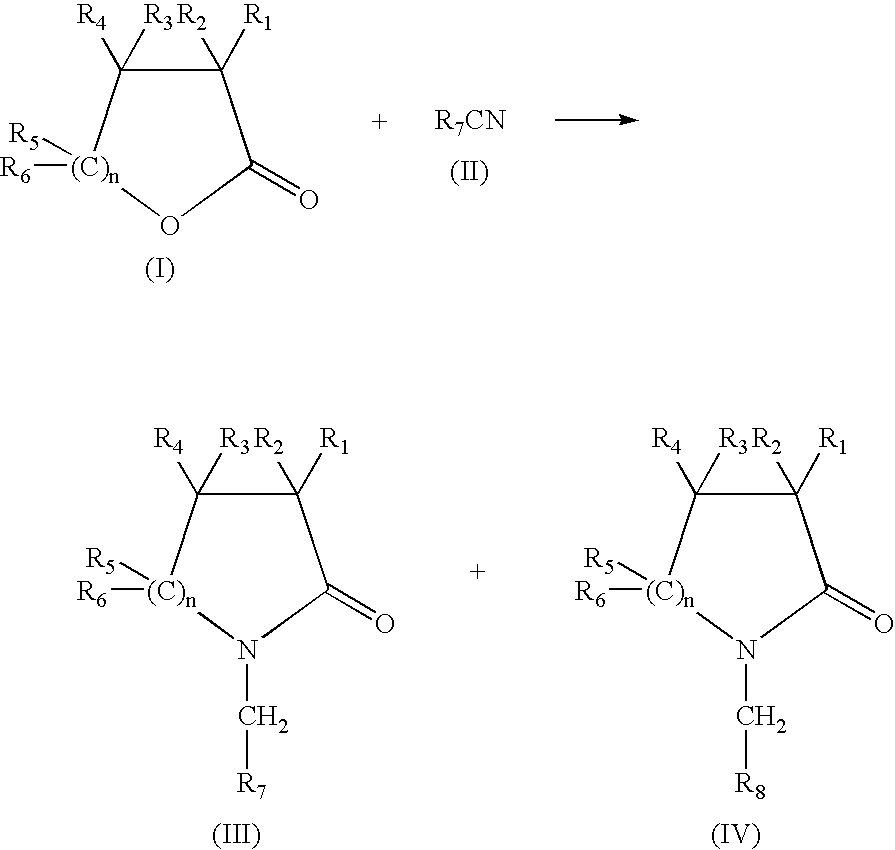
Production of N-(methyl aryl)-2-lactam, N-(methyl cycloalkyl)-2-lactam and N-alkyl-2-lactam by reductive amination of lactones with aryl and alkyl cyano compounds
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Multivalent pneumococcal polysaccharide-protein conjugate composition
An immunogenic composition having 13 distinct polysaccharide-protein conjugates and optionally, an aluminum-based adjuvant, is described. Each conjugate contains a capsular polysaccharide prepared from a different serotype of Streptococcus pneumoniae (1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C, 19A, 19F and 23F) conjugated to a carrier protein. The immunogenic composition, formulated as a vaccine, increases coverage against pneumococcal disease in infants and young children globally, and provides coverage for serotypes 6A and 19A that is not dependent on the limitations of serogroup cross-protection. Methods for making an immunogenic conjugate comprising Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A polysaccharide are also provided in which the serotype 19A polysaccharide is co-lyophilized with a carrier protein and conjugation is carried out in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) via a reductive amination mechanism.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Method for the production of amines by reductive amination of carbonyl compounds under transfer-hydrogenation conditions
InactiveUS7230134B2Efficiently obtainedOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogenMetal catalyst
This application claims the benefit of German priority Application No. 10138140.9, filed on Aug. 9, 2001, and International Application No. PCT / EP02 / 08748, filed on Aug. 6, 2002. The invention relates to the production of amines by the reaction of aldehydes or ketones with ammonia or primary or secondary amines in the presence of a hydrogen-donor and the presence of homogeneous metal catalysts of the eighth sub-group under mild conditions.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Process for the direct amination of alcohols using ammonia to form primary amines by means of a xantphos catalyst system
The present invention relates to a chemocatalytic liquid-phase process for the direct one-stage amination of alcohols to primary amines by means of ammonia in high yields using a catalyst system containing at least one transition metal compound and a xantphos ligand.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof to synthetizing L- glufosinate-ammonium
ActiveCN109609475AIncrease concentrationHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlufosinate-ammoniumMutant
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
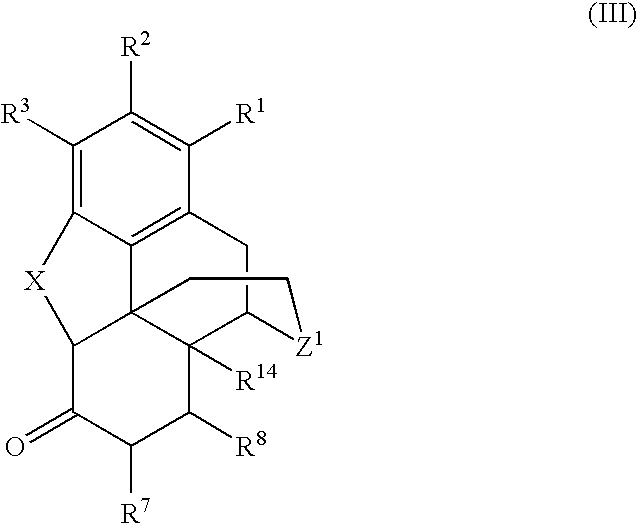
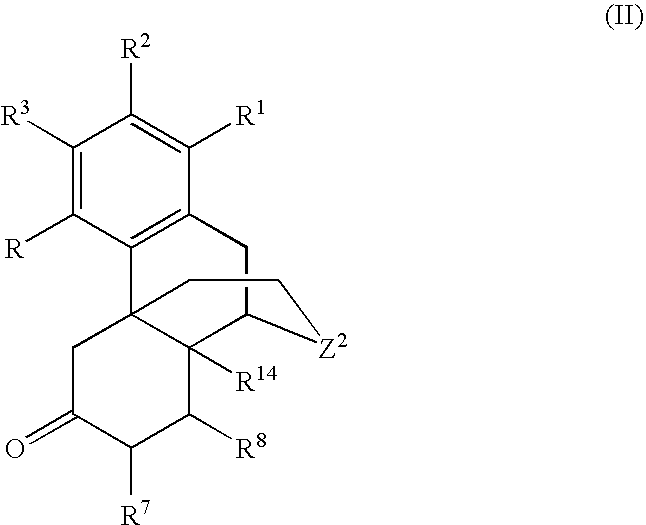
Processes for the selective amination of ketomorphinans
The present invention is generally directed to a process for the preparation of a ketomorphinan comprising maintaining a ketone group as unprotected and performing reductive amination using a hydrogen source and a catalyst.
Owner:SPECGX LLC
Synthesis method of mirabegron
InactiveCN103193730ALow costRealize safe and clean productionOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionSynthesis methodsPhenethyl alcohol
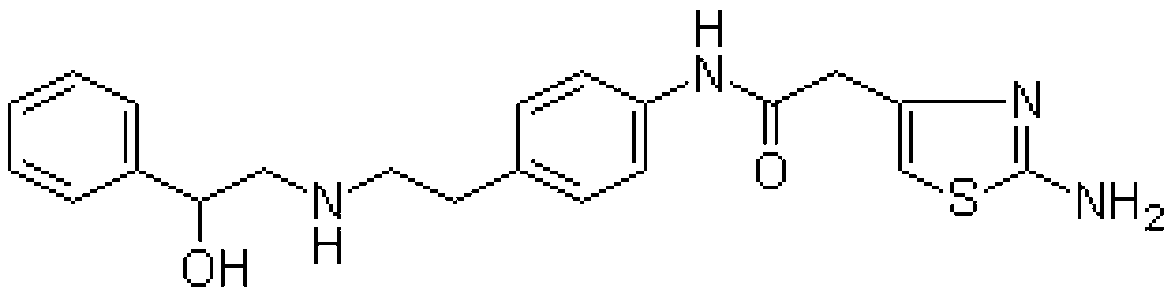
The invention provides a synthesis method of mirabegron and belongs to the technical field of medicine synthesis. The synthesis method solves the problems that the synthesis method of the mirabegron is low in product yield and is not suitable for large-scale industrialized production in the prior art. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: 1) amino protection: reacting 2-aminothiazole-5-acetic acid with an amino protective agent to obtain a mirabegron intermediate product A; 2) condensation reaction: performing condensation reaction on the mirabegron intermediate product A and 4-amino phenethyl alcohol to obtain a mirabegron intermediate product B; 3) oxidation reaction: performing oxidation reaction on the mirabegron intermediate product B and an oxidant to obtain a mirabegron intermediate product C; and 4) reductive amination and protecting group removal: reacting the mirabegron intermediate product C with (R)-2-amino-1-phenethyl alcohol and removing the protecting group from the mirabegron intermediate product C to obtain the mirabegron. The synthesis method of the mirabegron is low in cost, high in product yield and suitable for large-scale industrialized production.
Owner:SUZHOU UUGENE BIOPHARMA
Cyclohexanedimethanamine by direct amination of cyclohexanedimethanol
InactiveUS20110009670A1Easy to useOrganic compound preparationAmino preparation by functional substitutionCyclohexanedimethanolAmination
Embodiments of the present invention include methods for producing a cyclohexanedimethanamine by a reductive amination process.
Owner:HUNTSMAN PETROCHEMICAL LLC
Reductive amination catalyst and preparation method
ActiveCN107983400AFacilitated DiffusionHigh activityMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationHydrogenAlcohol
The invention relates to a reductive amination catalyst and a preparation method. The reductive amination catalyst consists of aM*bA*cX1*(100-a-b-c)X2, in the formula, M represents an active componentmetal and / or an oxide thereof; A represents an auxiliary active component; X1 and X2 represent two carriers; a, b and c respectively represent mass percentages of M, A and X1; a is greater than or equal to 0.1 and less than or equal to 50; b is greater than or equal to 0.1 and less than or equal to 50; c is greater than or equal to 0.1 and less than or equal to 90. The preparation method of the catalyst comprises the following steps: mixing an alcohol with water so as to obtain a mixed solvent; adding ethanol amine; dissolving soluble salts of the active component M and the auxiliary active component A in the mixed solution; leaving to stand, depressurizing to remove the solvent, drying, molding, and roasting so as to obtain a catalyst precursor; performing reduction in the presence of hydrogen, thereby obtaining the catalyst. The catalyst provided by the invention has activity and stability prior to those of the prior art, and has remarkable industrial application values.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Glutamate dehydrogenase mutants and application thereof
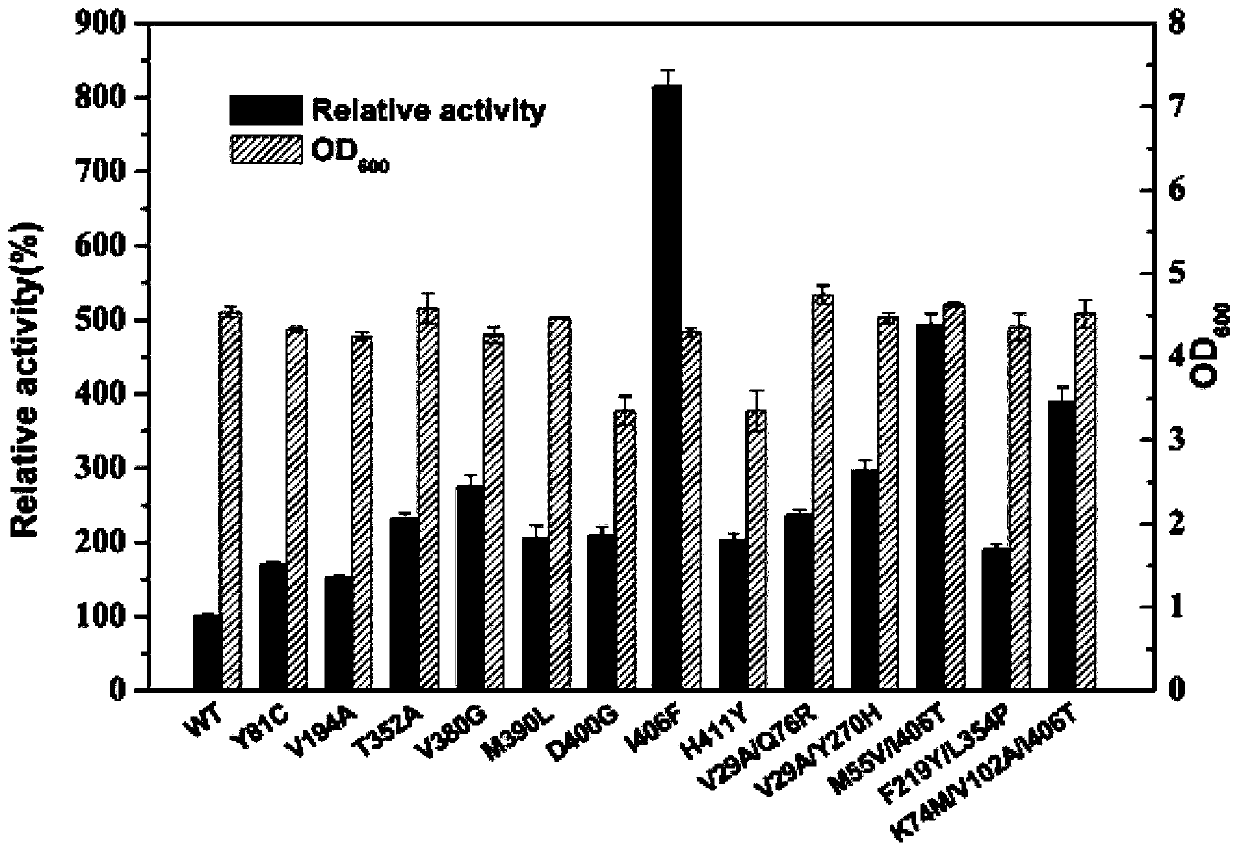
ActiveCN110184246AHigh catalytic activitySolve the problem of low enzyme activityOxidoreductasesFermentationPseudomonas putidaThreonine
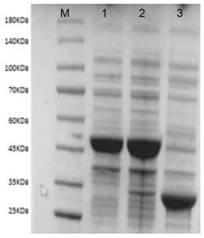
The present invention discloses glutamate dehydrogenase mutants and an application thereof. The glutamate dehydrogenase mutants are one of the following: mutating 402th lysine of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 to phenylalanine or aspartic acid; mutating 406th isoleucine to phenylalanine or threonine; conducting combined mutation of 121th threonine and 123th leucine; and conducting combined mutation of 379th alanine and 383th leucine. A molecular transformation method combining directed evolution with semi-rational design significantly improves catalytic activity of glutamate dehydrogenase derived from pseudomonas putida to 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxymethylphosphono)butyric acid (PPO) and solves a problem of low glutamate dehydrogenase activity in preparation of L-glufosinate by a reductive amination method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com