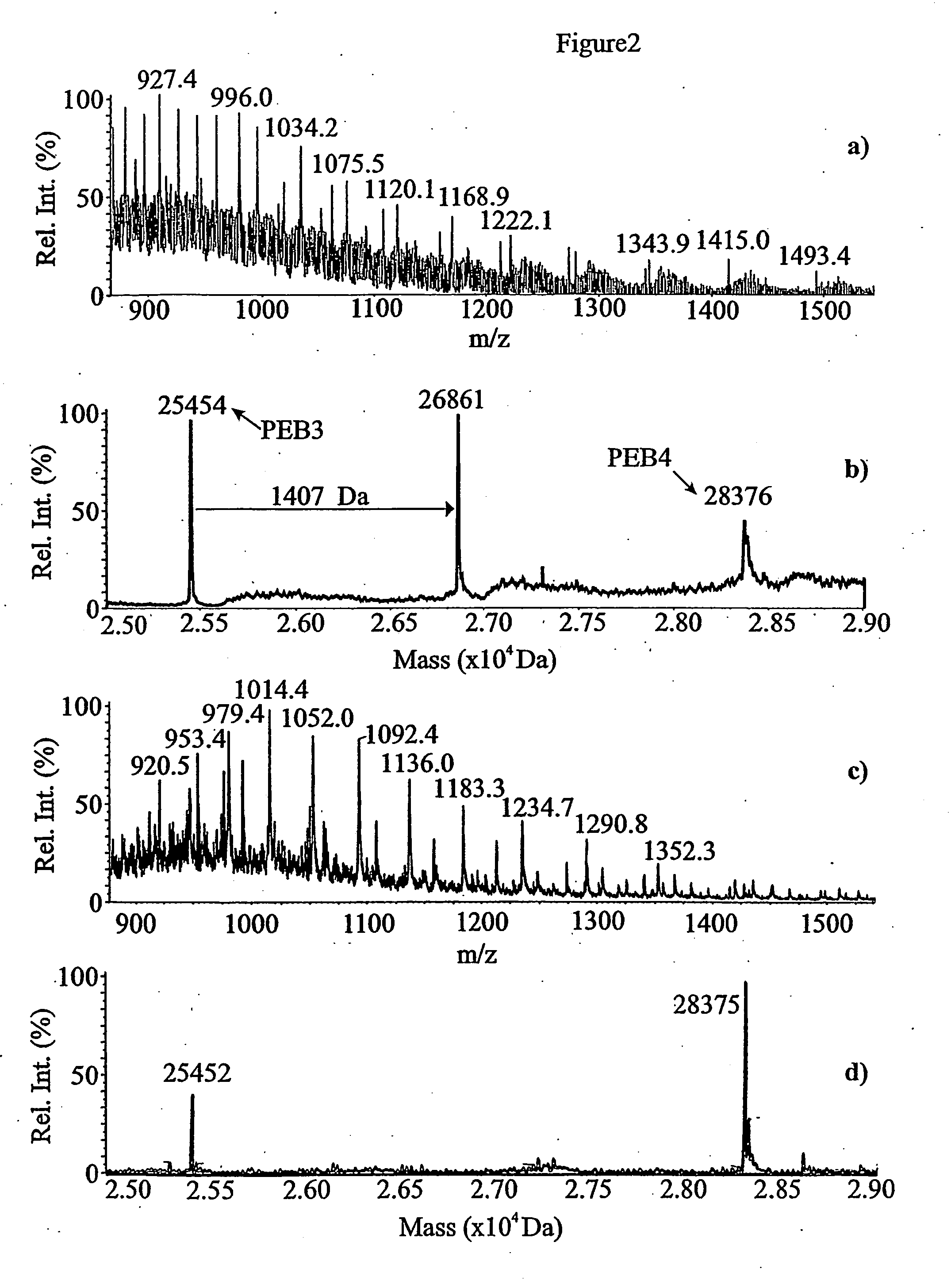
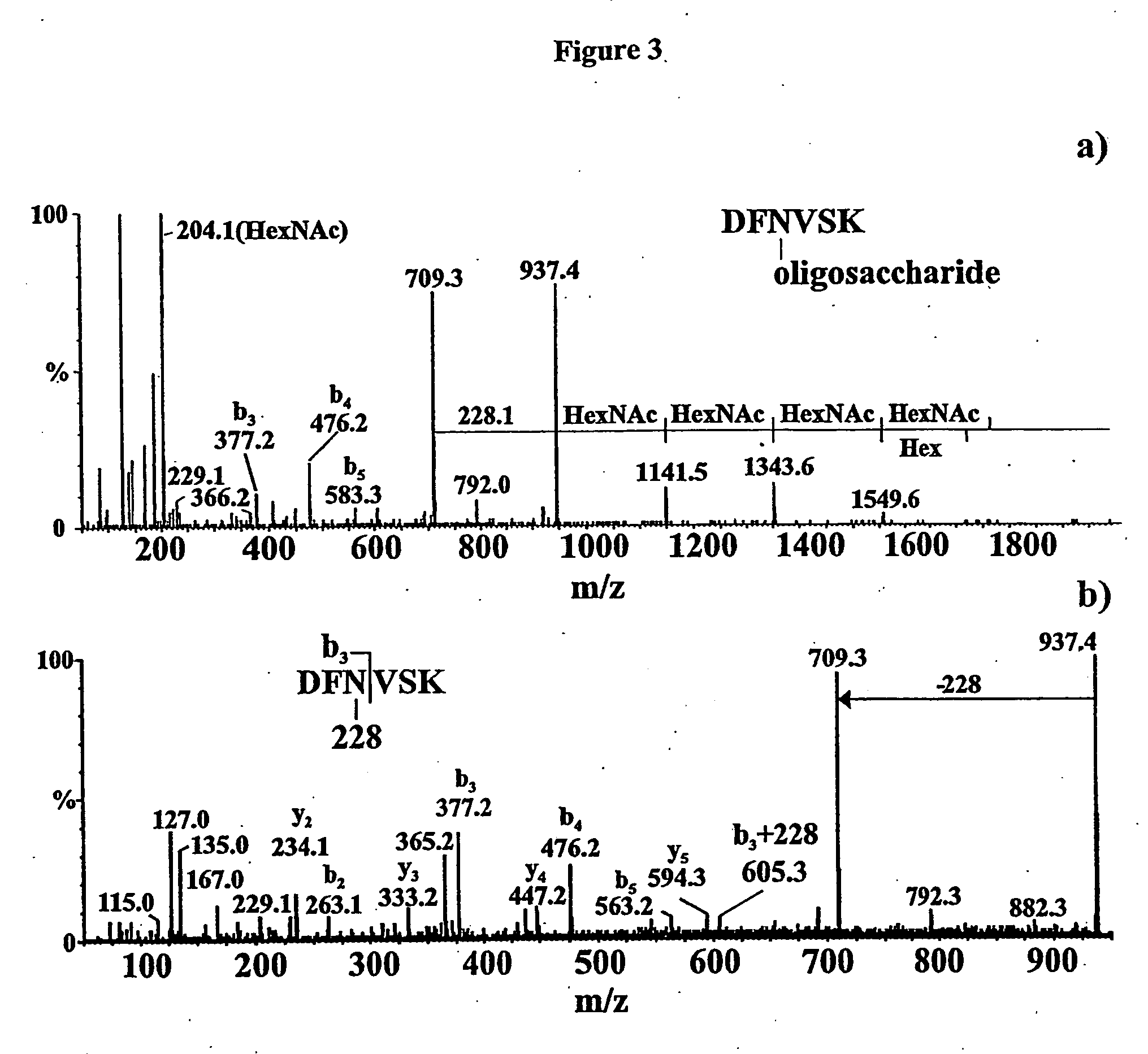
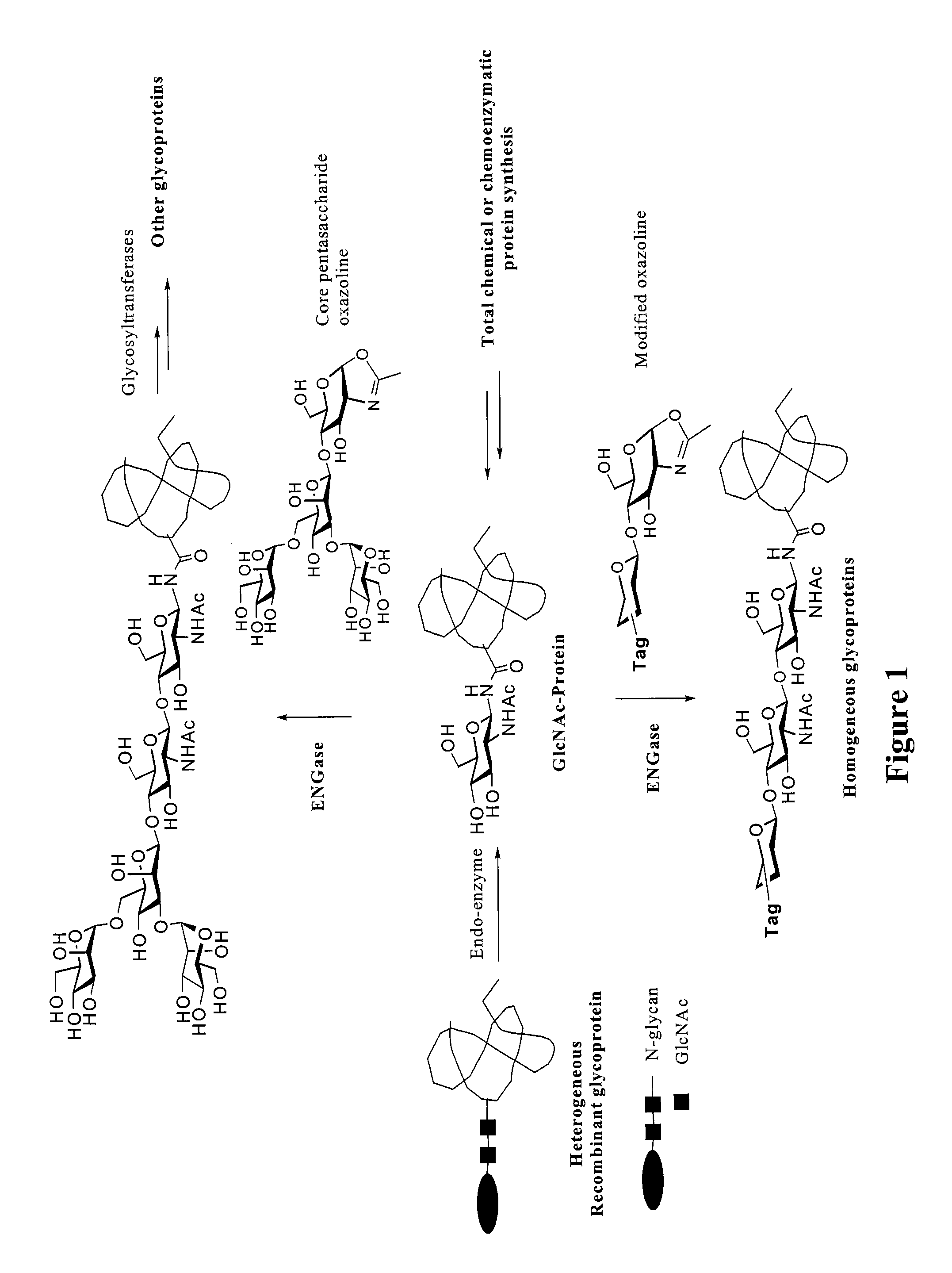
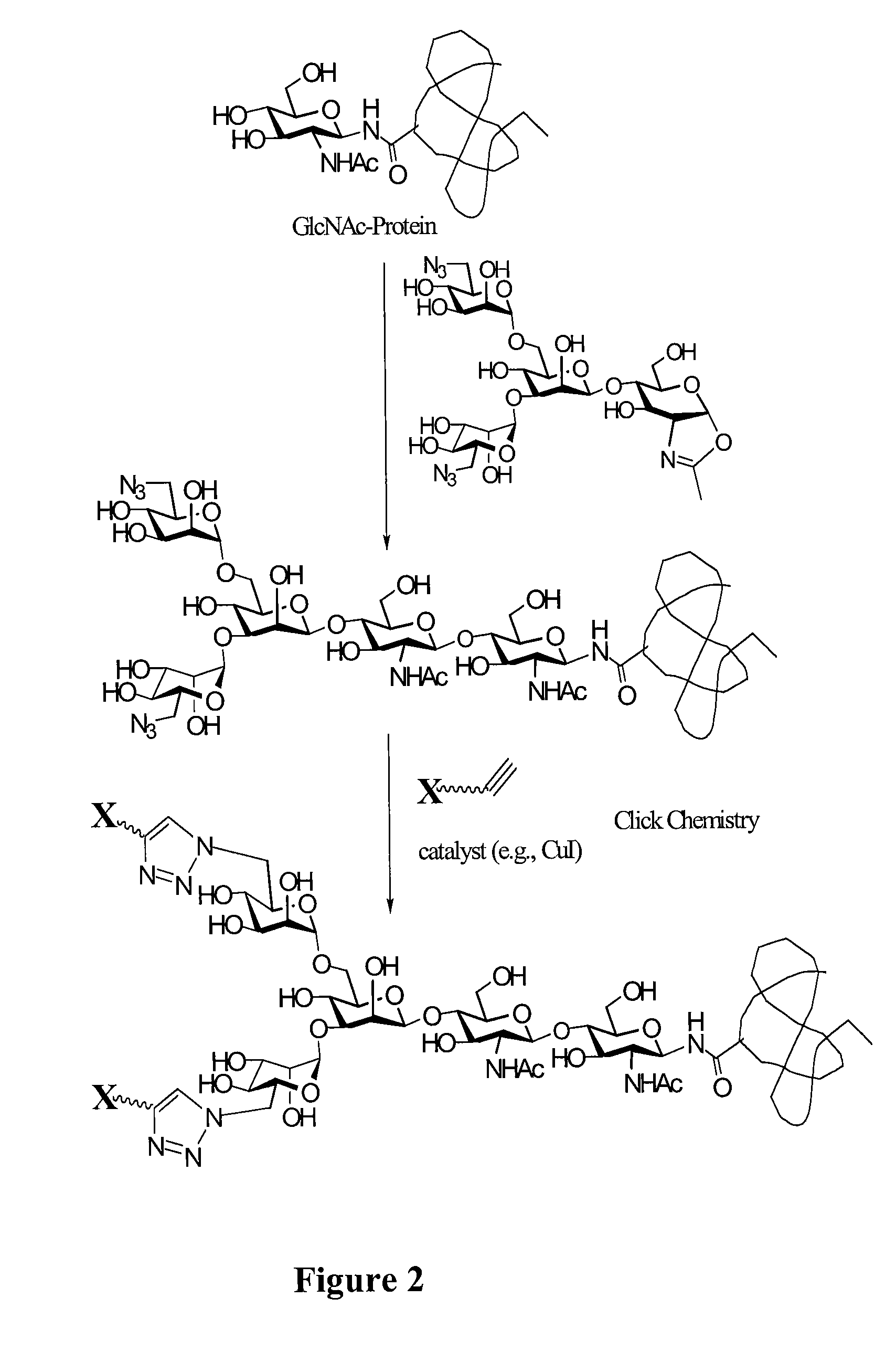
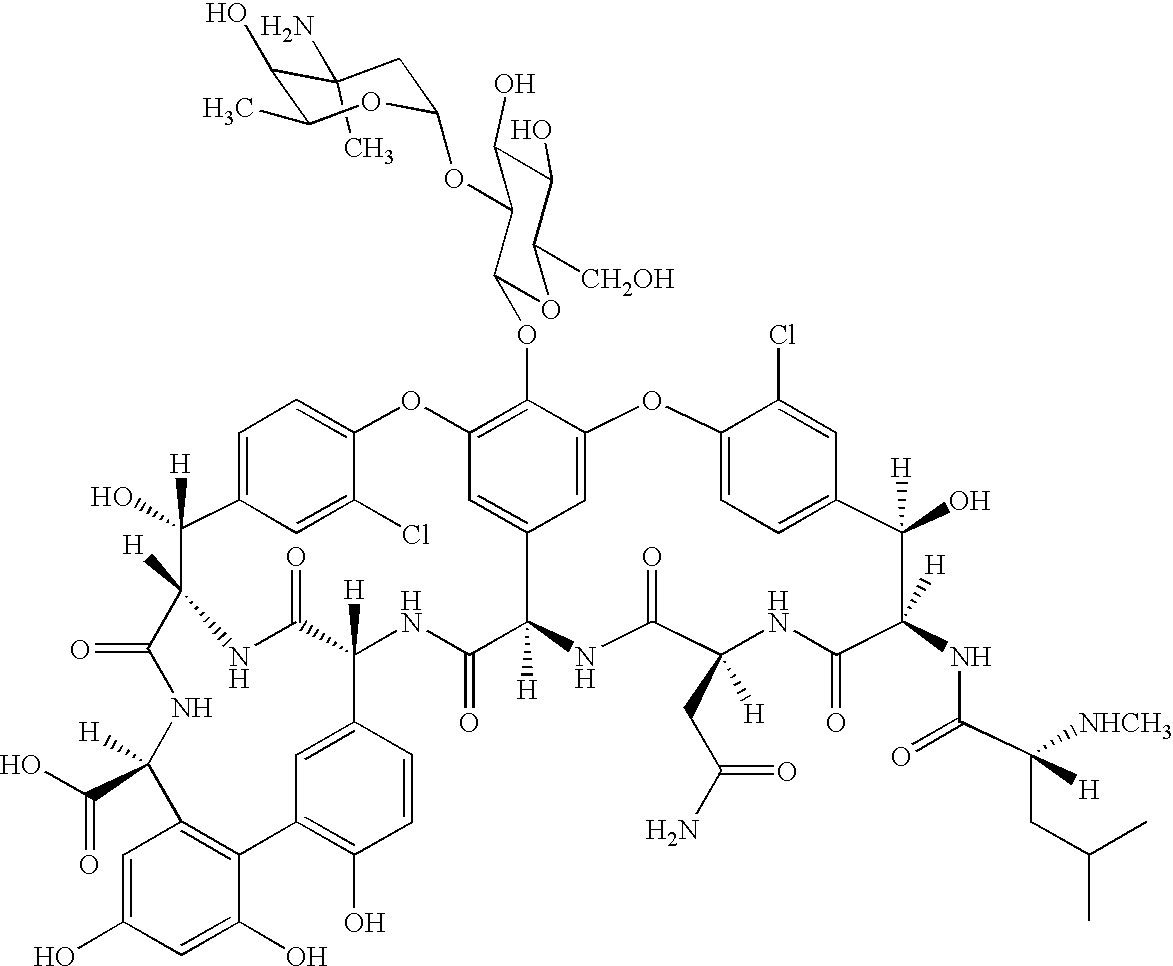
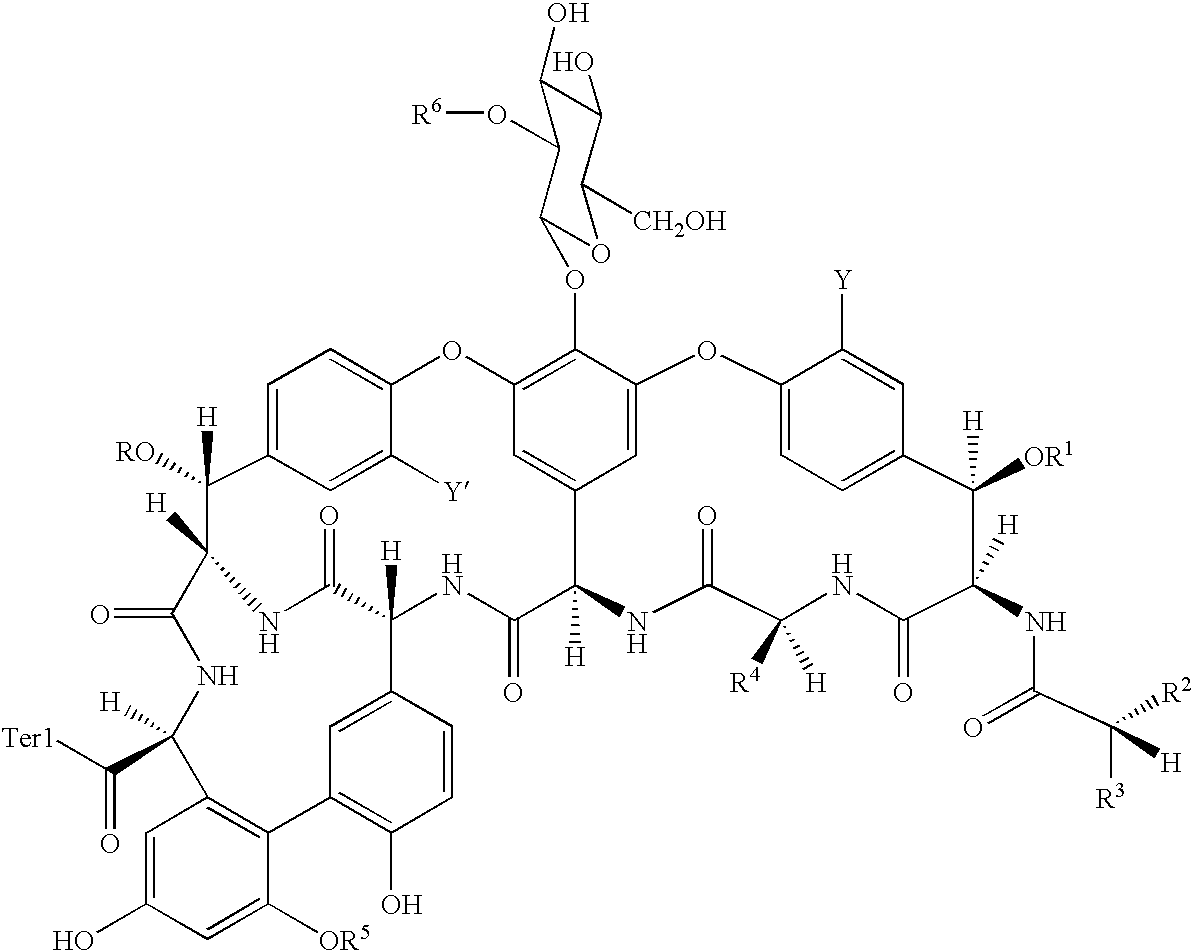
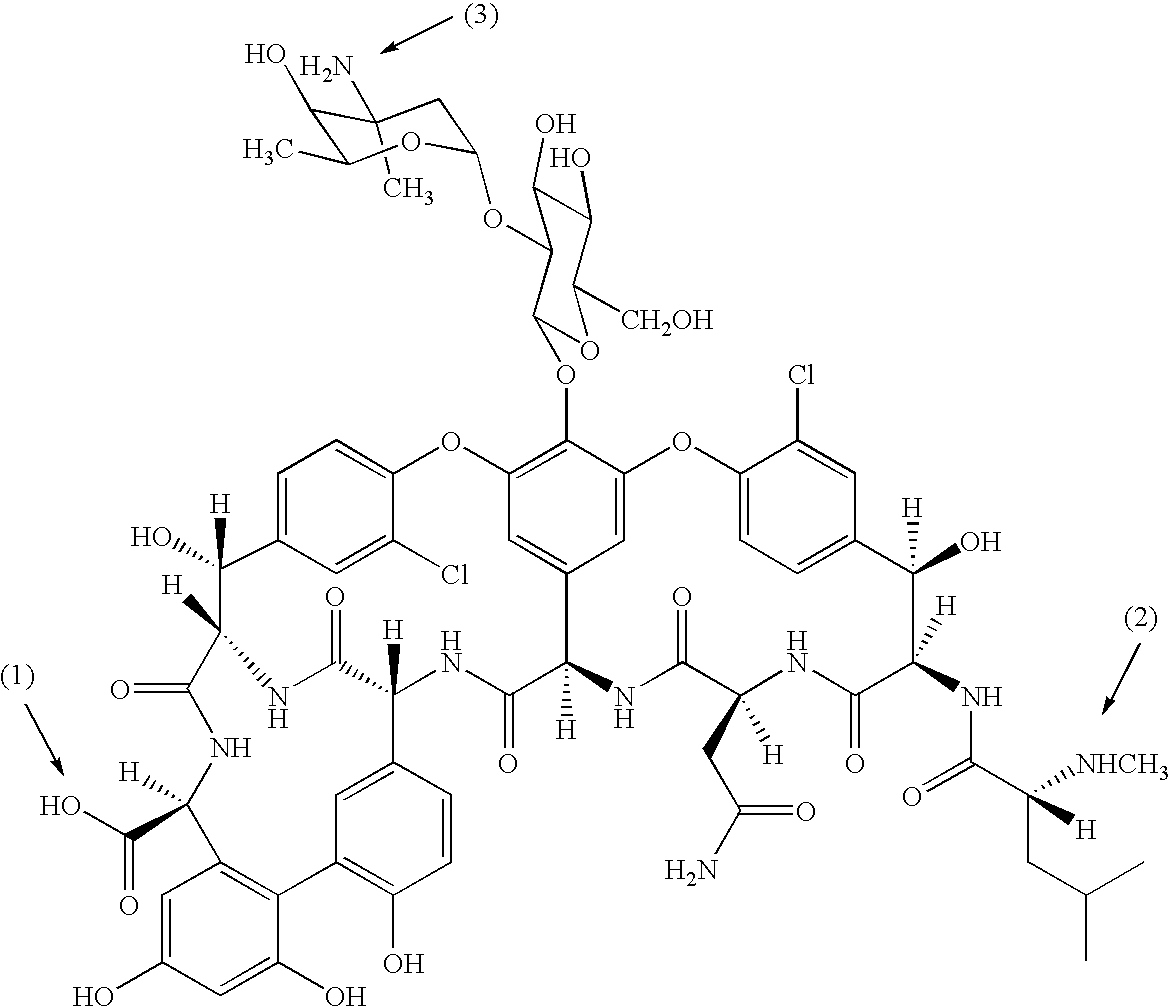
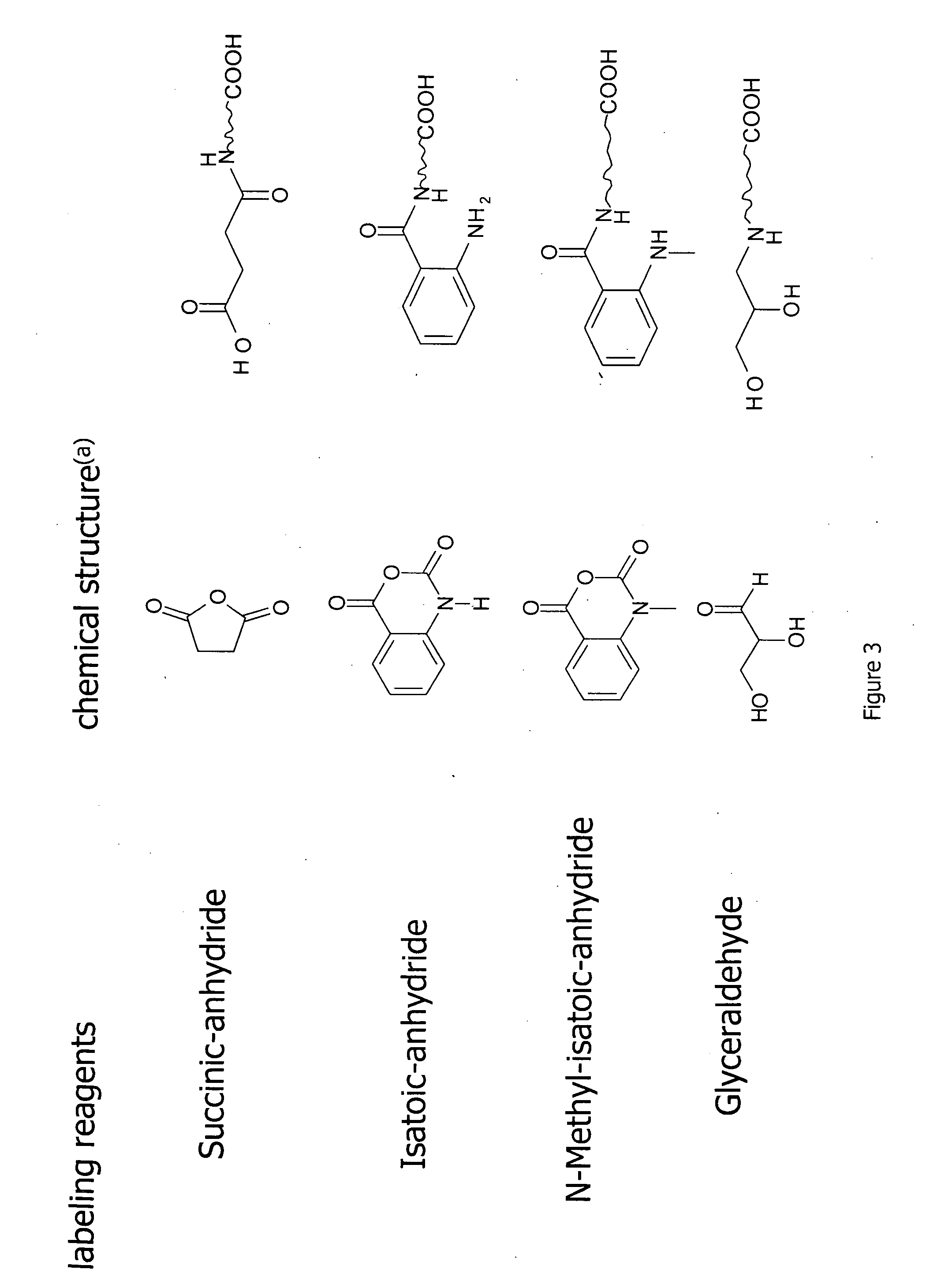
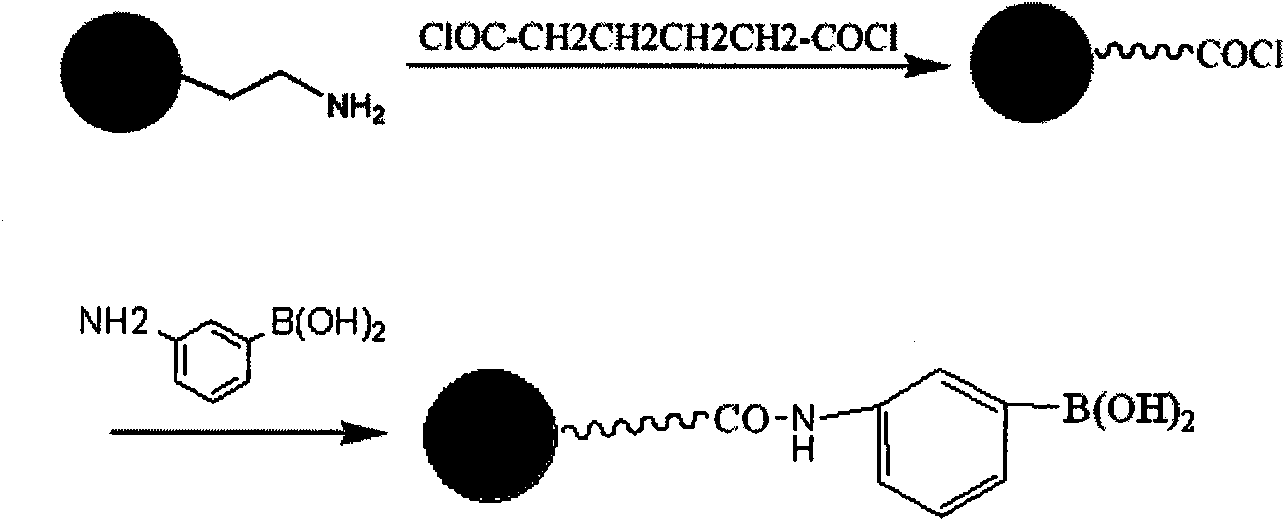
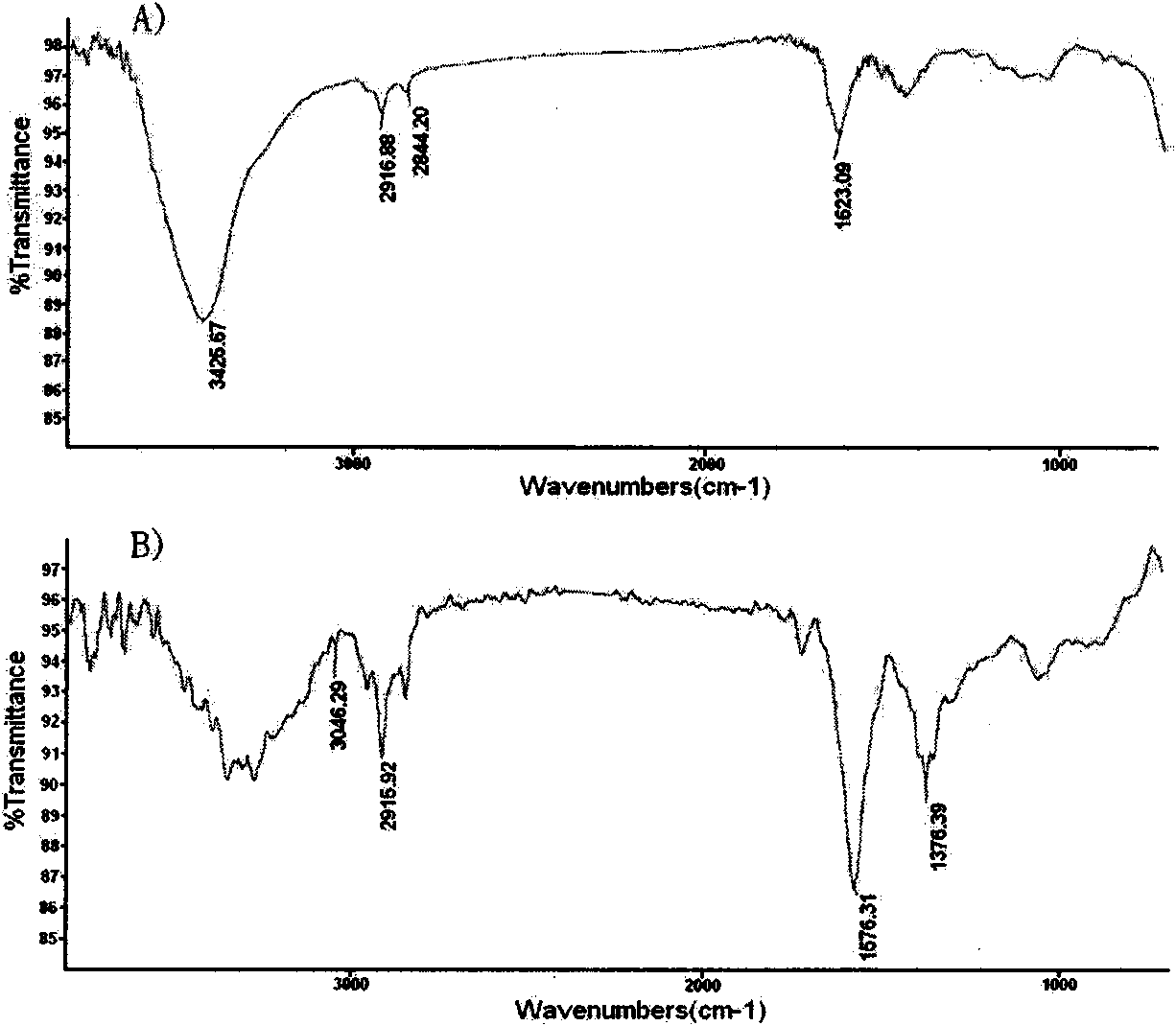
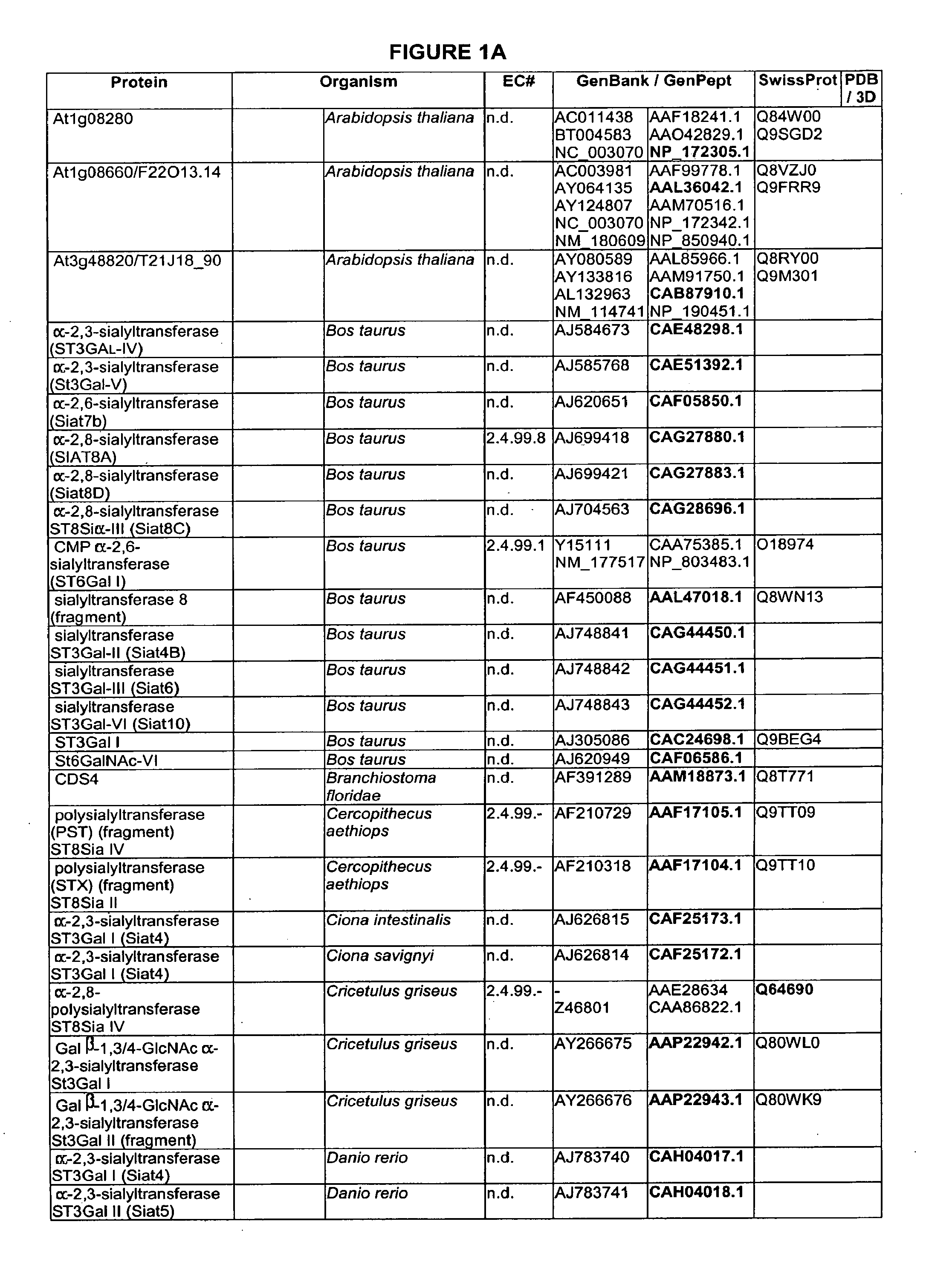
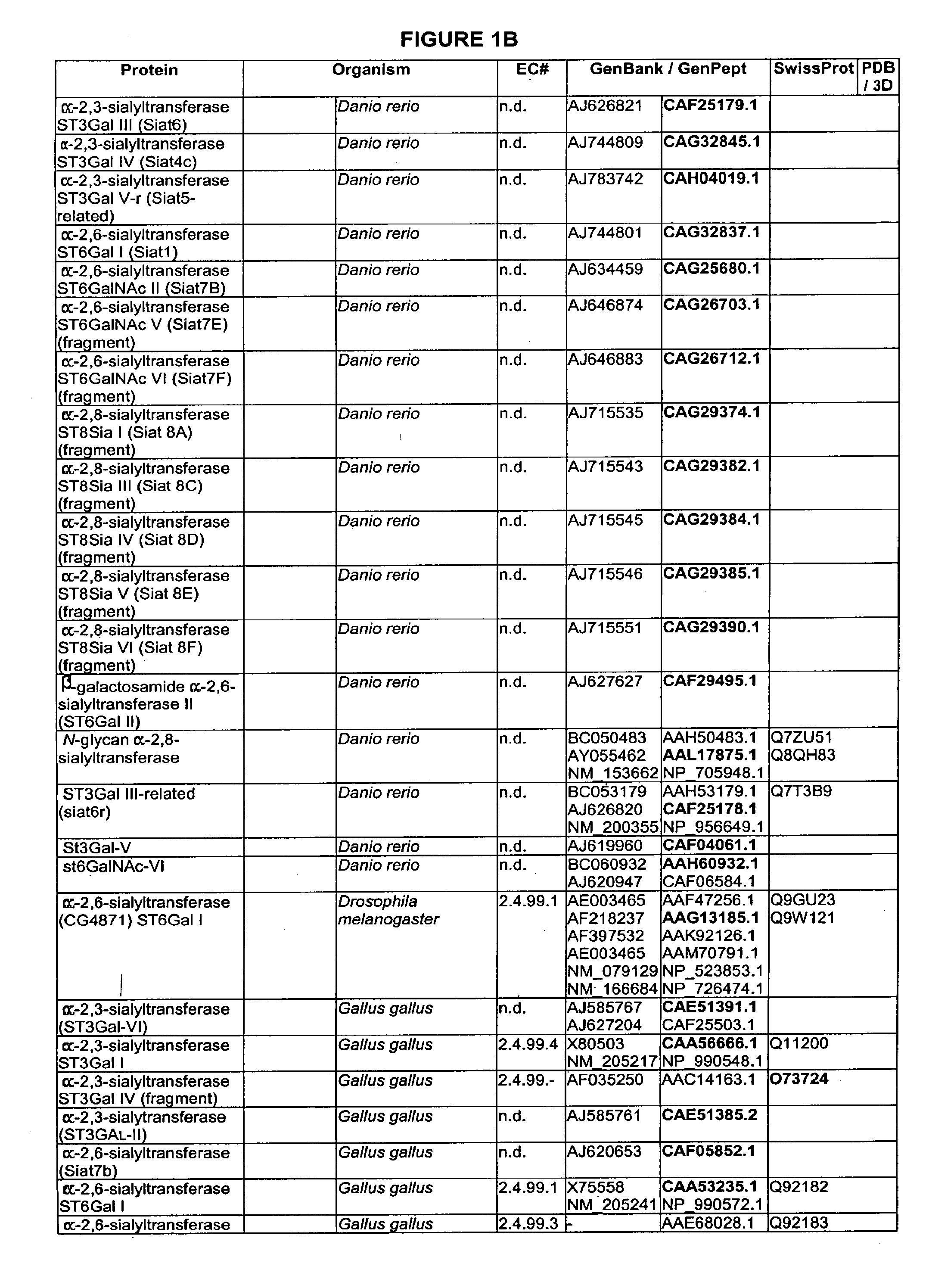
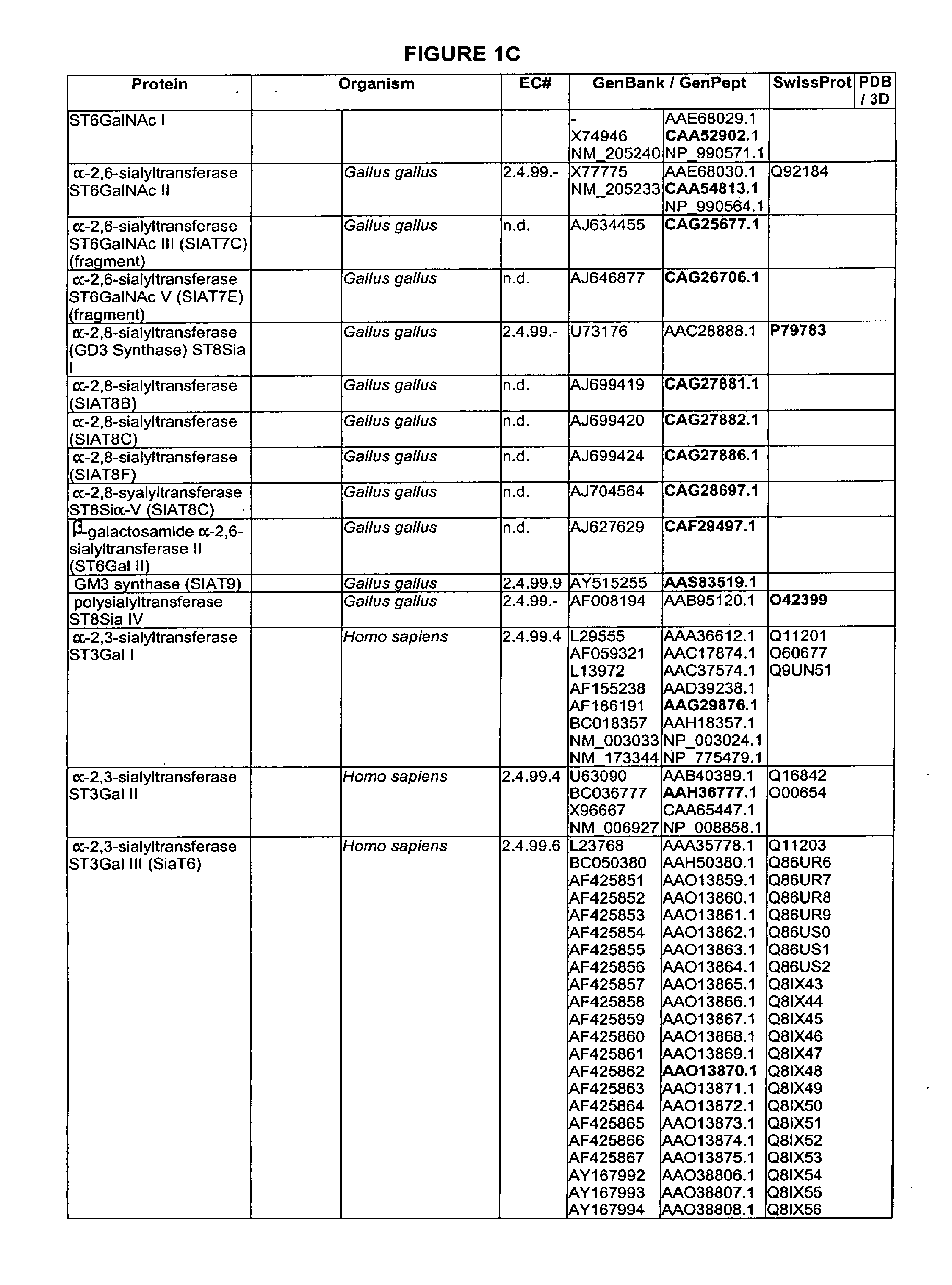
Patents
Literature
794 results about "Glycopeptide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
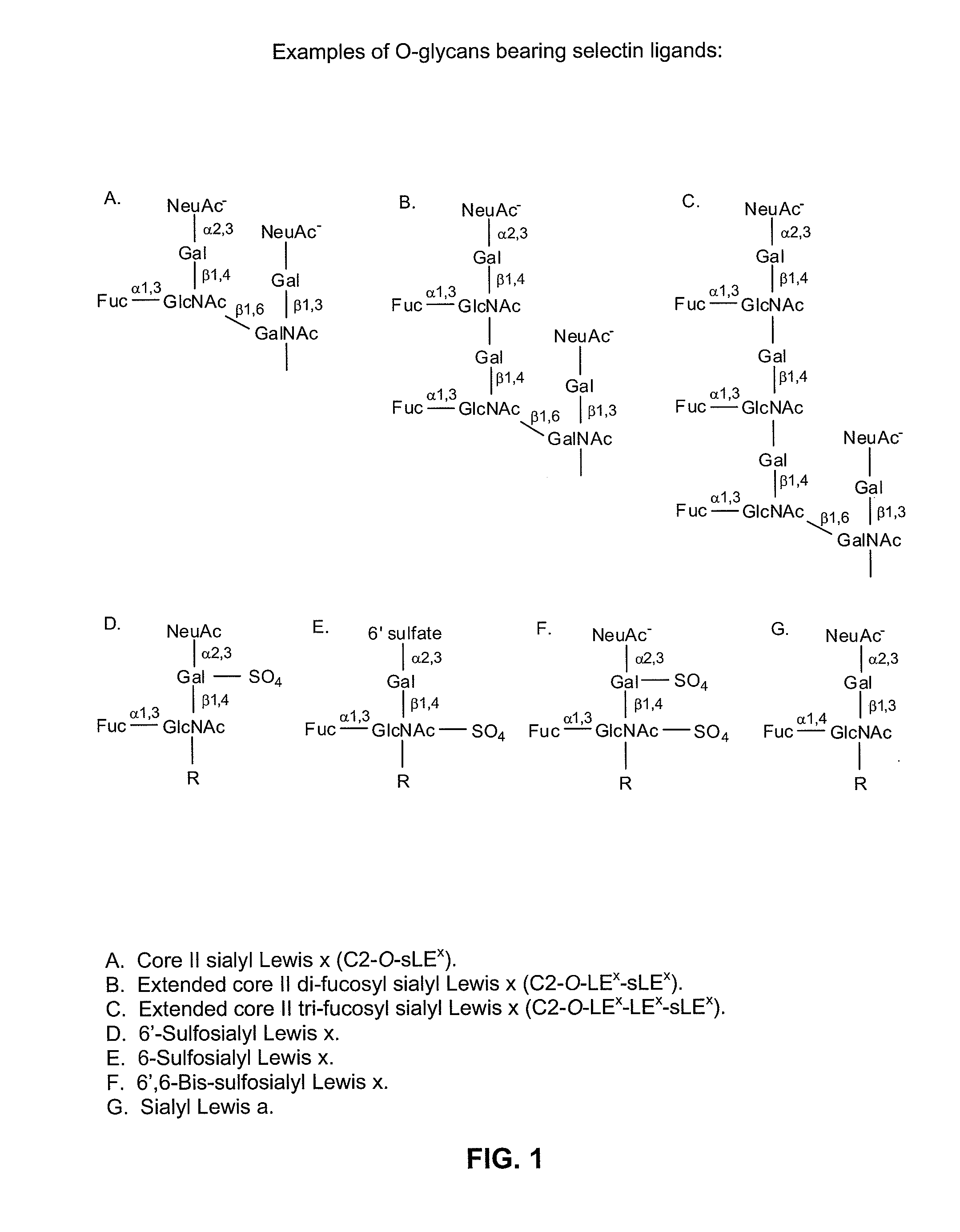
Glycopeptides are peptides that contain carbohydrate moieties (glycans) covalently attached to the side chains of the amino acid residues that constitute the peptide. Over the past few decades it has been recognised that glycans on cell surface (attached to membrane proteins or lipids) and those bound to proteins (glycoproteins) play a critical role in biology. For example, these constructs have been shown to play important roles in fertilization, the immune system, brain development, the endocrine system, and inflammation.
Bioactive Complexes Compositions and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20070085059A1Enhanced soluble complexesGood fluidityCosmetic preparationsNervous disorderDiseaseCholesterol blood
A bioactive complex composition having enhanced oxidative stability, emulsion stability, mineral rich transparent beverages and a wide range of functional health benefits. The composition may include as a base composition individual ingredients or a synergistic blend of mineral salts, Omega-3 rich oils, phospholipids, chitosan, and alpha-casein, beta-casein, kappa-casein or protein fragments, glycopeptides, phosphopeptides. The composition may optionally be further utilized for the prevention of hypercholesterolemia, bone (and teeth) mineral loss, treatment of mental health diseases, heart health, additional nutritional supplementation, and treatment of additional medical conditions.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
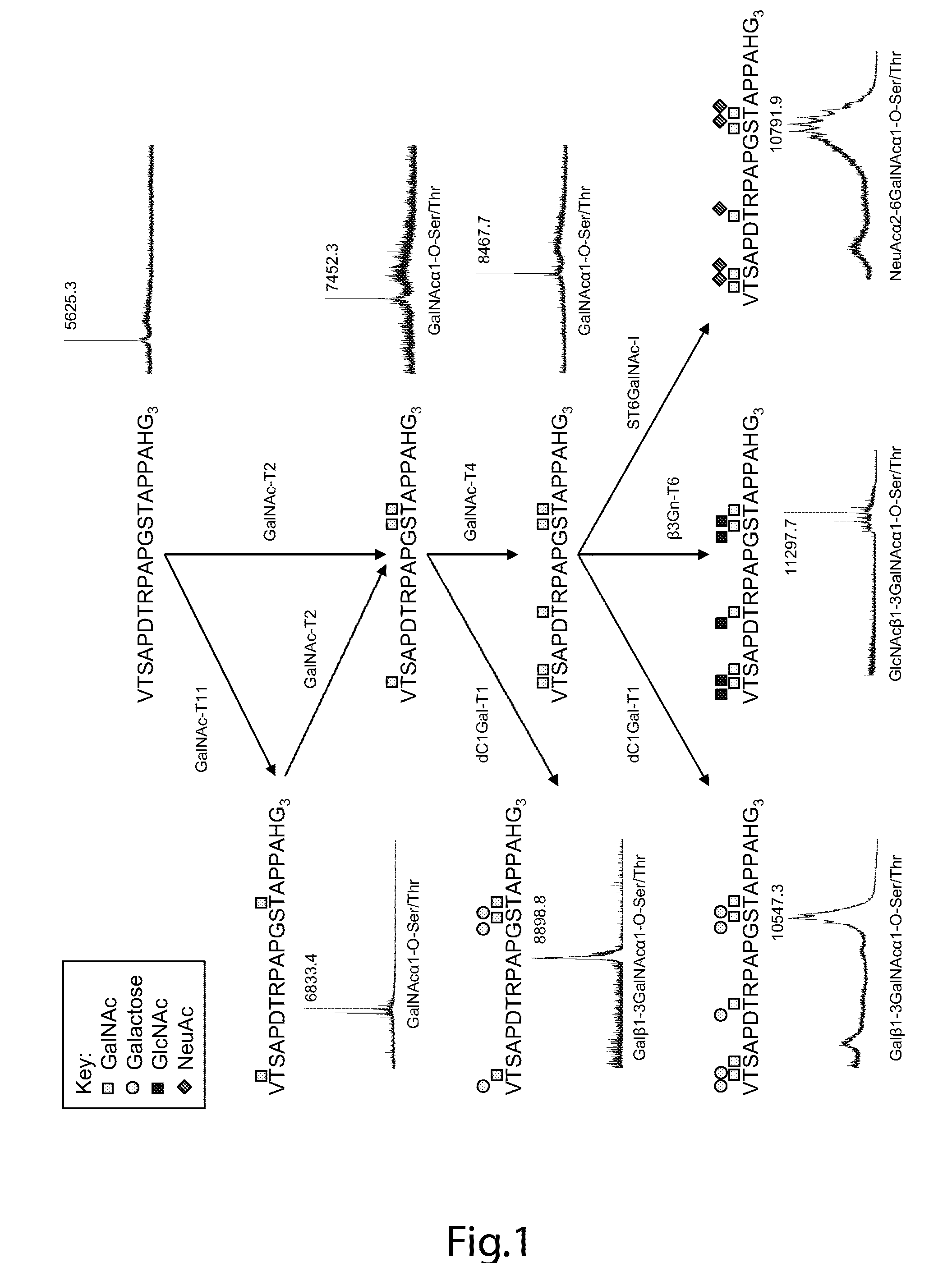
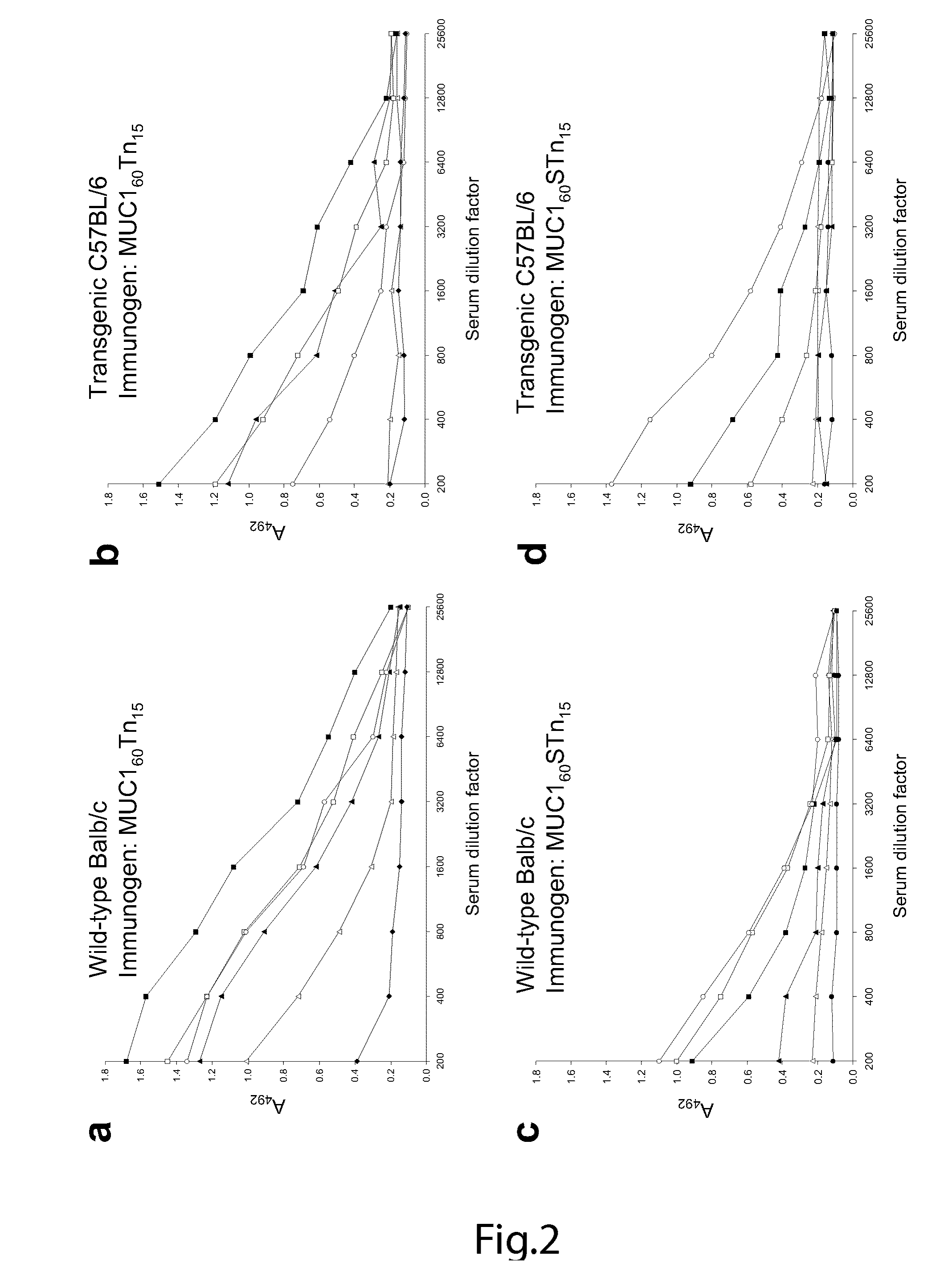
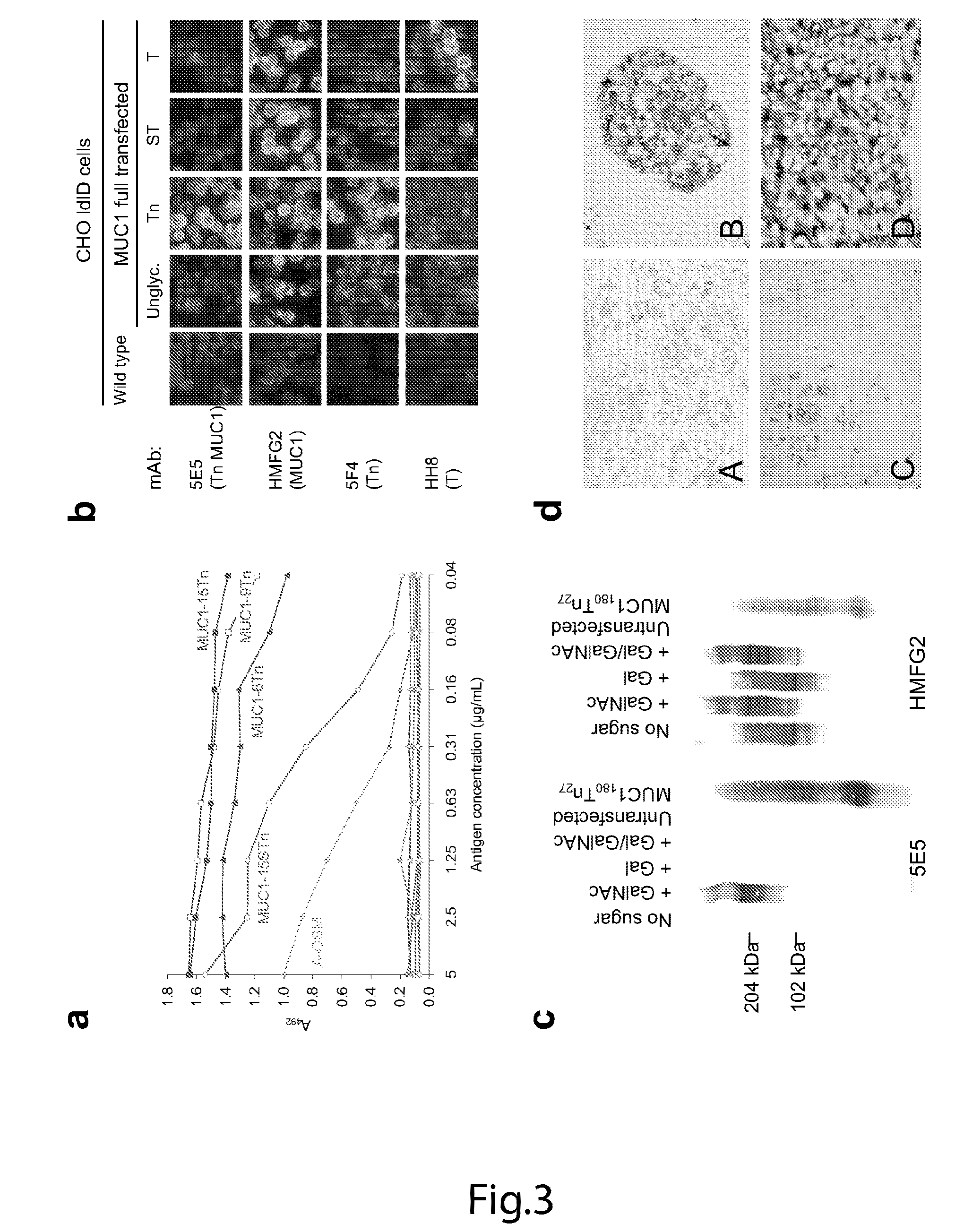
Generation of a cancer-specific immune response toward MUC1 and cancer specific MUC1 antibodies
The present invention provides a method for inducing a cancer specific immune response against MUC1 using an immunogenic glycopeptide. Other aspects of the invention are a pharmaceutical composition comprising the immunogenic glycopeptide and a cancer vaccine comprising the immunogenic glycopeptide. Another aspect is an antibody generated using the immunogenic glycopeptide and the use of said antibody in therapy and diagnosis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN +1
Treatment of pulmonary disorders with aerosolized medicaments such as vancomycin
InactiveUS20100282247A1Reduce in quantityReduce the amount requiredAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseGlycopeptide
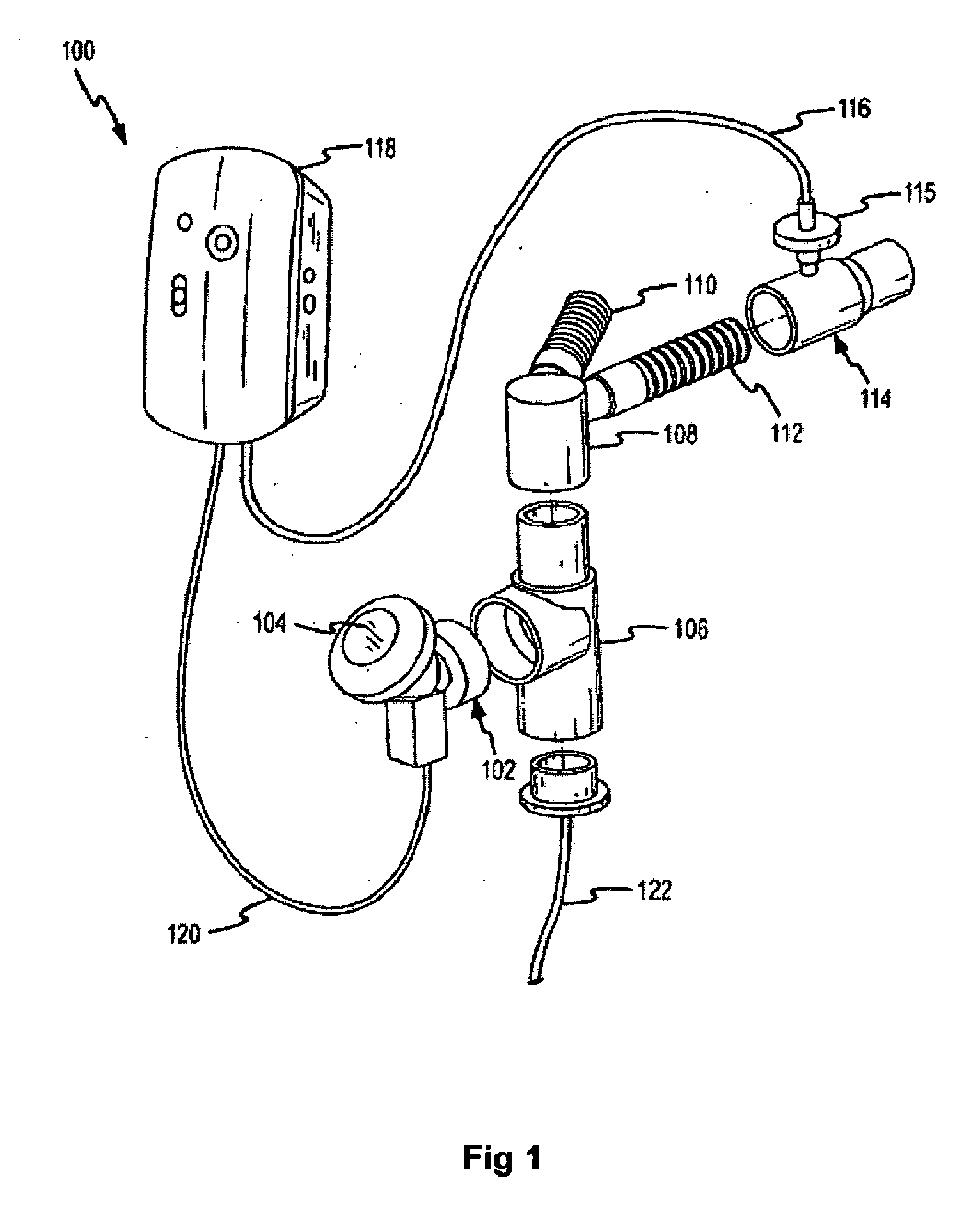
A method of administering an aerosolized anti-infective, such as a glycopeptide, to the respiratory system of a patient. A ratio of an amount of the glycopeptide, such as vancomycin, delivered to the pulmonary system of the patient in a 24 hour period to a minimum inhibitory amount for the target organ for the same period is about 2 or more. A system to introduce aerosolized medicament to a patient may include a humidifier coupled to an inspiratory limb of a ventilator circuit wye, where the humidifier supplies heated and humidified air to the patient, and an endotracheal tube having a proximal end coupled to a distal end of the ventilator circuit wye. The system may also include a nebulizer coupled to the endotracheal tube, where the nebulizer generates the aerosolized medicament.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Manufacturing process for the production of polypeptides expressed in insect cell-lines
InactiveUS20080207487A1Promote recoveryReduce manufacturing costPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesFiberCulture fluid
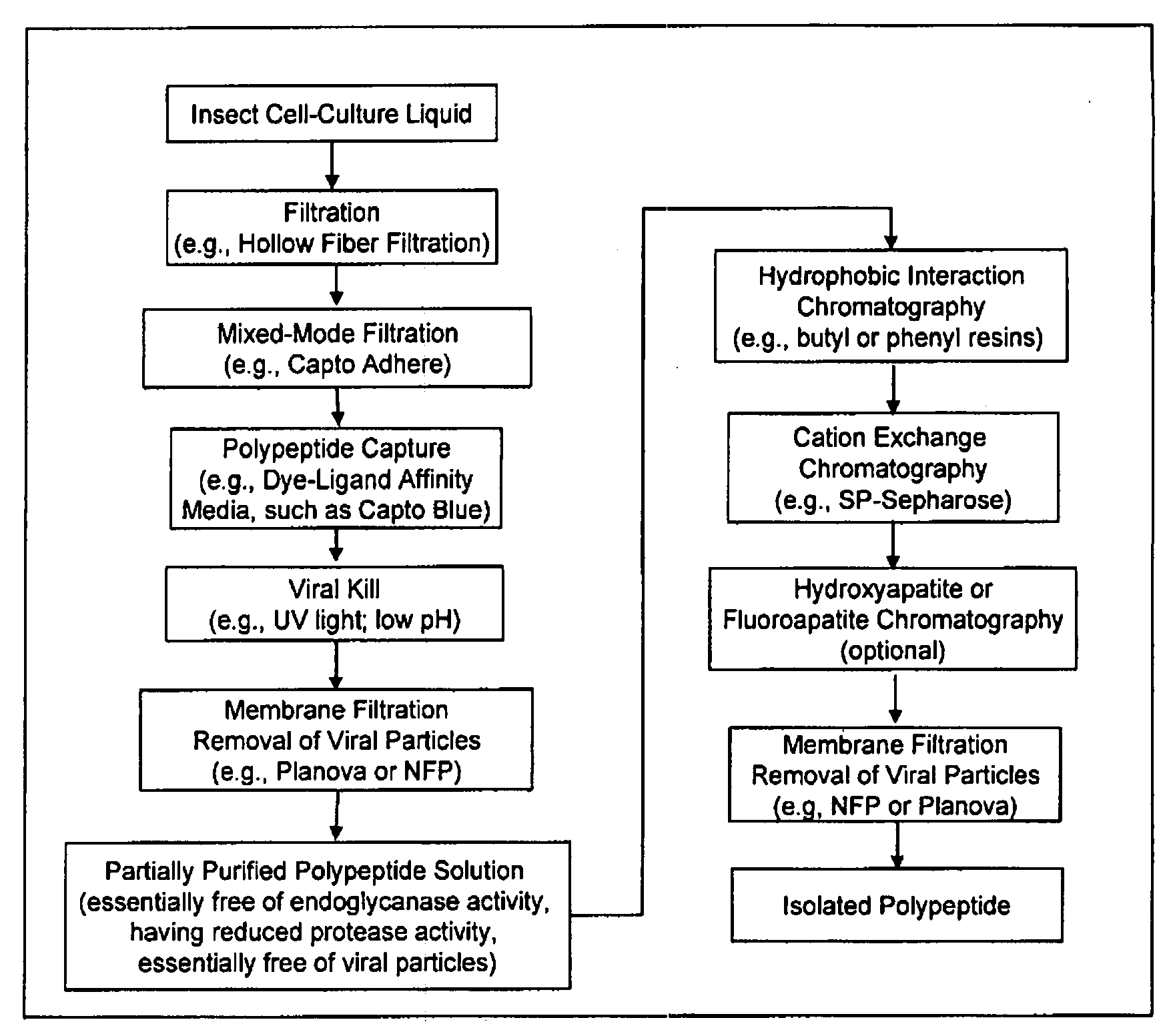
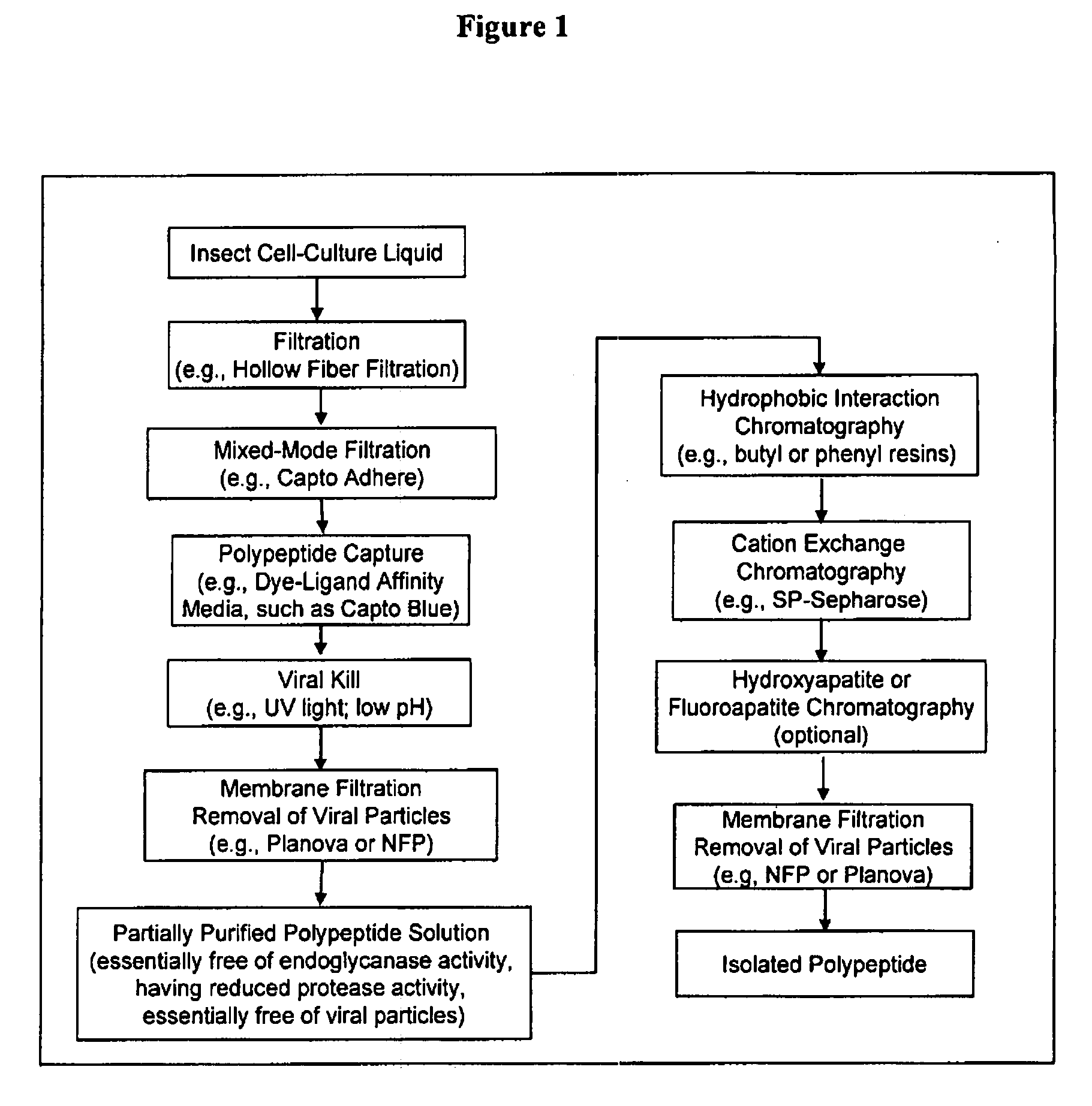
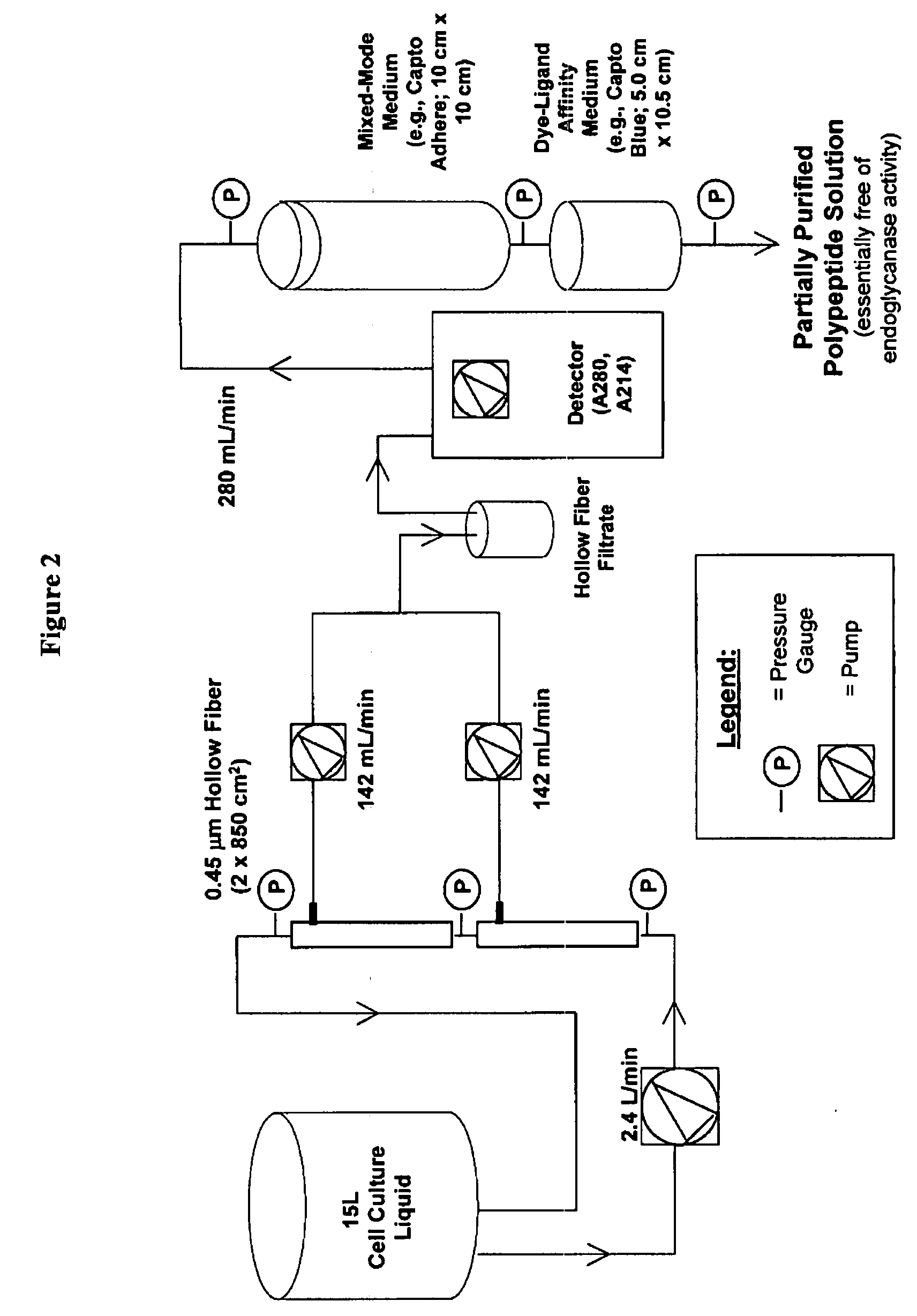
The present invention provides a manufacturing method for polypeptides that are produced in insect cells using a baculoviral expression system. In one example, the insect cell culture is supplemented with a lipid mixture immediately prior to infection (e.g., one hour prior to infection). The polypeptides are isolated from the insect cell culture using a method that employs anion exchange or mixed-mode chromatography early in the purification process. This process step is useful to remove insect-cell derived endoglycanases and proteases and thus reduces the loss of desired polypeptide due to enzymatic degradation. In another example, mixed-mode chromatography is combined with dye-ligand affinity chromatography in a continuous-flow manner to allow for rapid processing of the insect-cell culture liquid and capture of the polypeptide. In yet another example, a polypeptide is isolated from an insect cell culture liquid using a process that combines hollow fiber filtration, mixed-mode chromatography and dye-ligand affinity in a single unit operation producing a polypeptide solution that is essentially free of endoglycanase and proteolytic activities. In a further example, the isolated polypeptides are glycopeptides having an insect specific glycosylation pattern, which are optionally conjugated to a modifying group, such as a polymer (e.g., PEG) using a glycosyltransferase and a modified nucleotide sugar.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Glycoconjugation Using Saccharyl Fragments
InactiveUS20100009902A1Lower potential for exposureImprove homogeneitySugar derivativesPeptidesLipid formationGlycopeptide
The present invention provides conjugates between a substrate, e.g., peptide, glycopeptide, lipid, etc., and a modified saccharyl fragment bearing a modifying group such as a water-soluble polymer, therapeutic moiety or a biomolecule. The conjugates are linked via the enzymatic conversion of the activated modified saccharyl fragment into a glycosyl linking group that is interposed between and covalently attached to the substrate and the modifying group. The conjugates are formed from substrates by the action of a sugar transferring enzyme, e.g., a glycosyltransferase. For example, when the substrate is a peptide, the enzyme conjugates a modified saccharyl fragment moiety onto either an amino acid or glycosyl residue of the peptide. Also provided are pharmaceutical formulations that include the conjugates. Methods for preparing the conjugates are also within the scope of the invention.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Antioxidant compositions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20050184275A1Growth inhibitionPreventing bone mineral lossCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAdditive ingredientPhospholipid
An antioxidant composition having enhanced oxidative stability, emulsion stability, and health benefits. The composition may include individual ingredients or a synergistic blend of non-reducing sugars, sugar polyols, medium-chain triglycerides, polysaccharides, polyphenols, phospholipids, chitosan, and alpha-casein, beta-casein, kappa-casein or protein fragments, glycopeptides, phosphopeptides. The composition may optionally be further utilized for the prevention of hypercholesterolemia or bone mineral loss.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
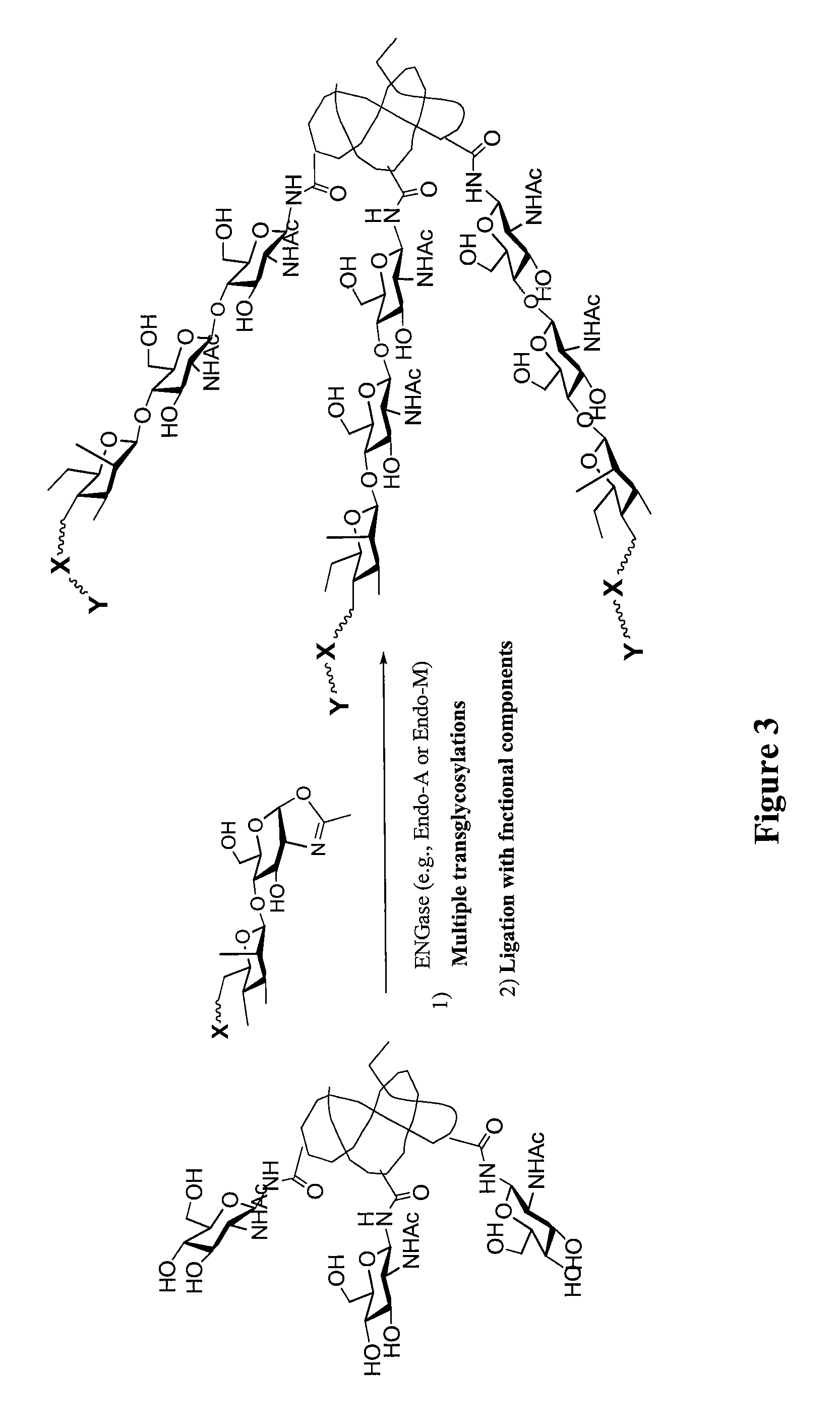
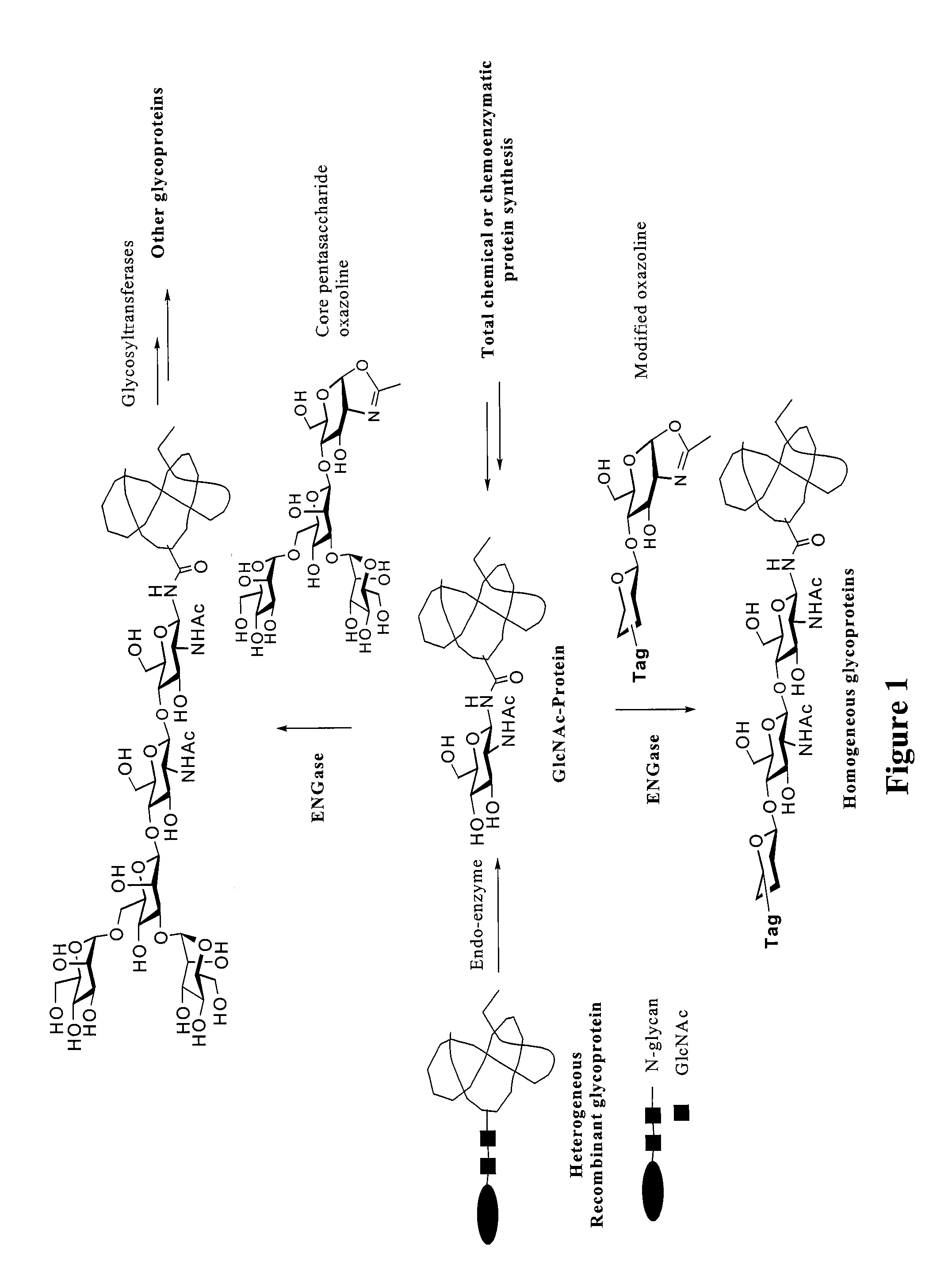
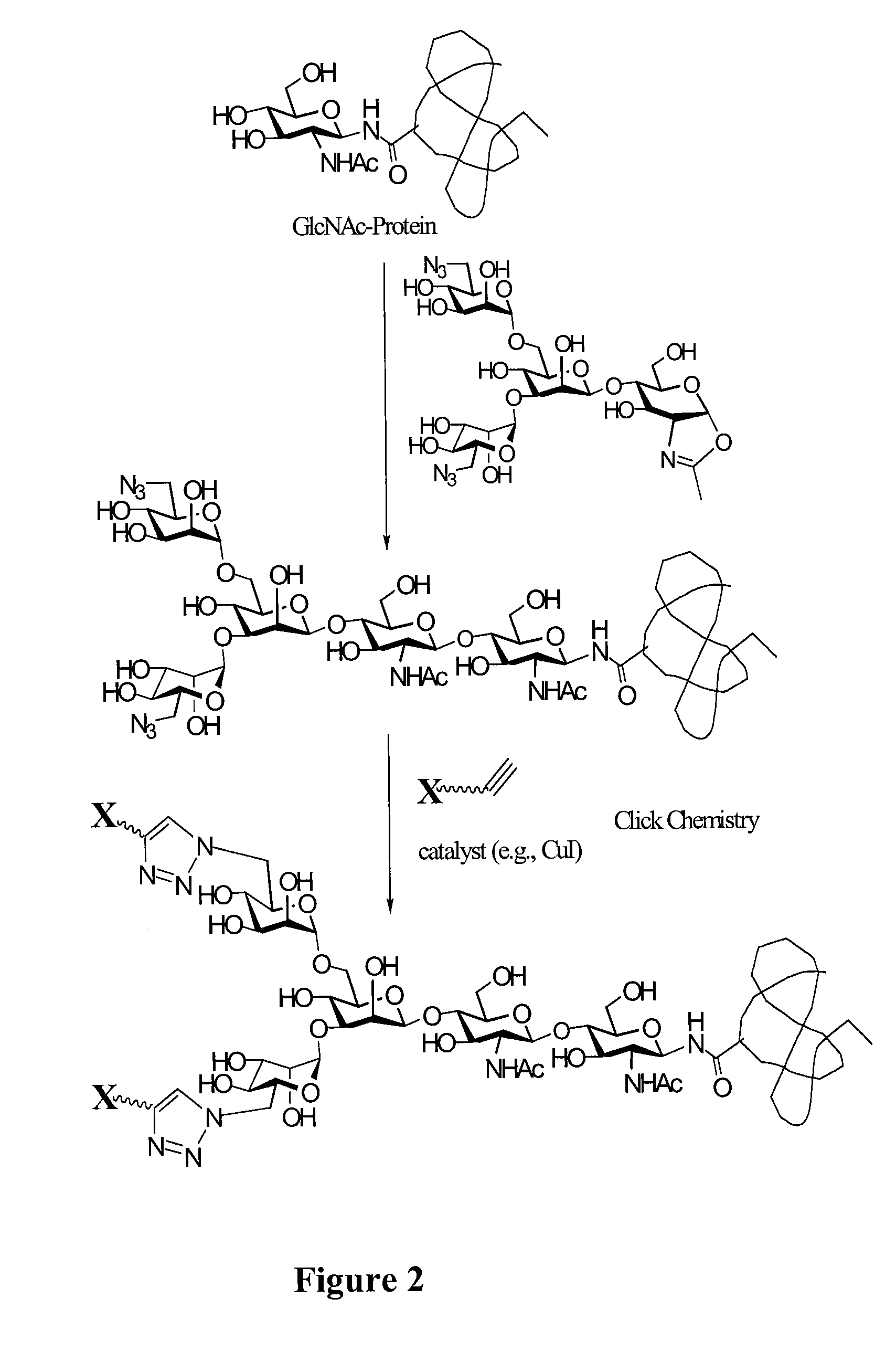
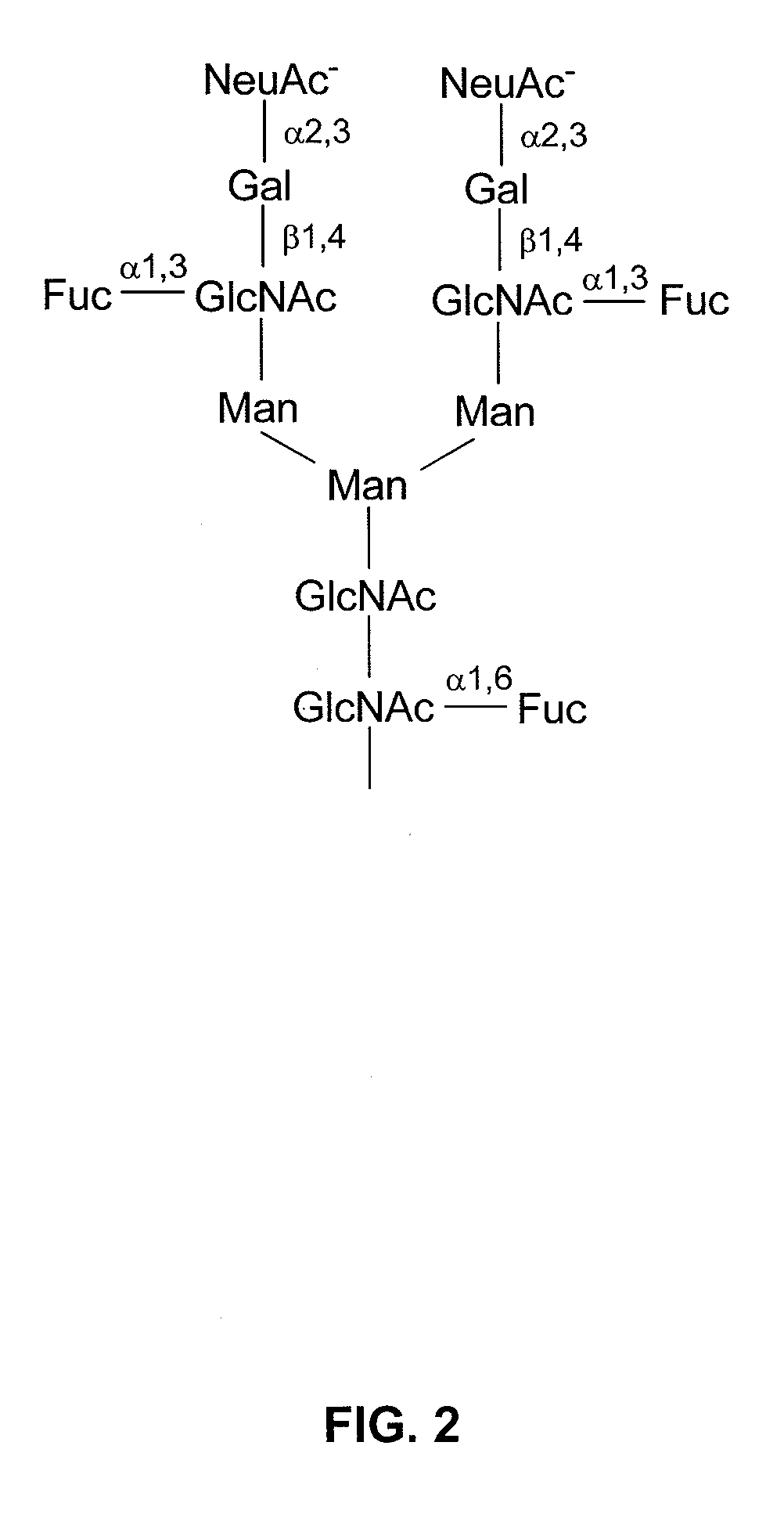
Core fucosylated glycopeptides and glycoproteins: chemoenzymatic synthesis and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120226024A1Prolonged half-life-timeLess immunogenicityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansEnzymesFucosylationEndorhamnosidase
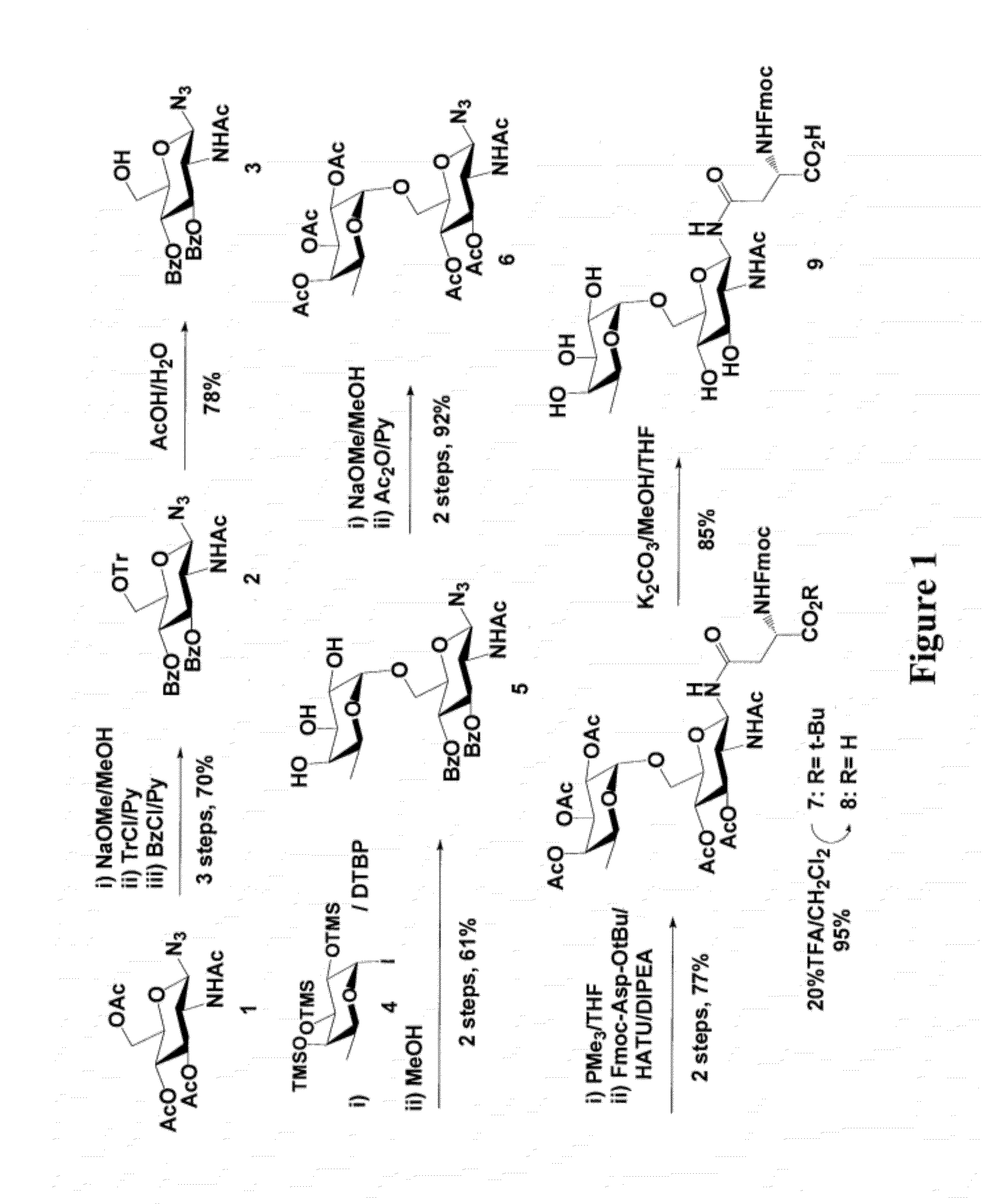
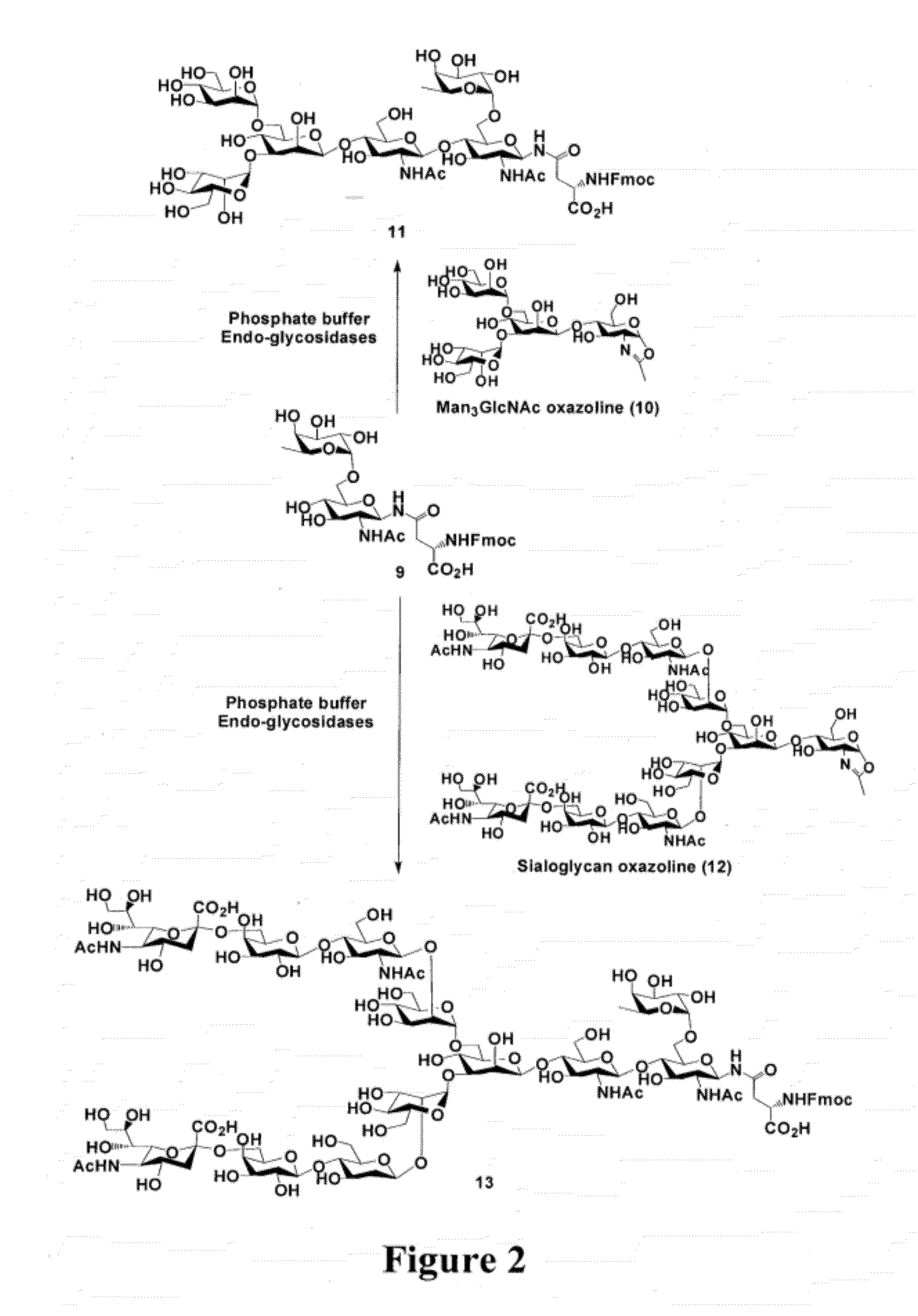
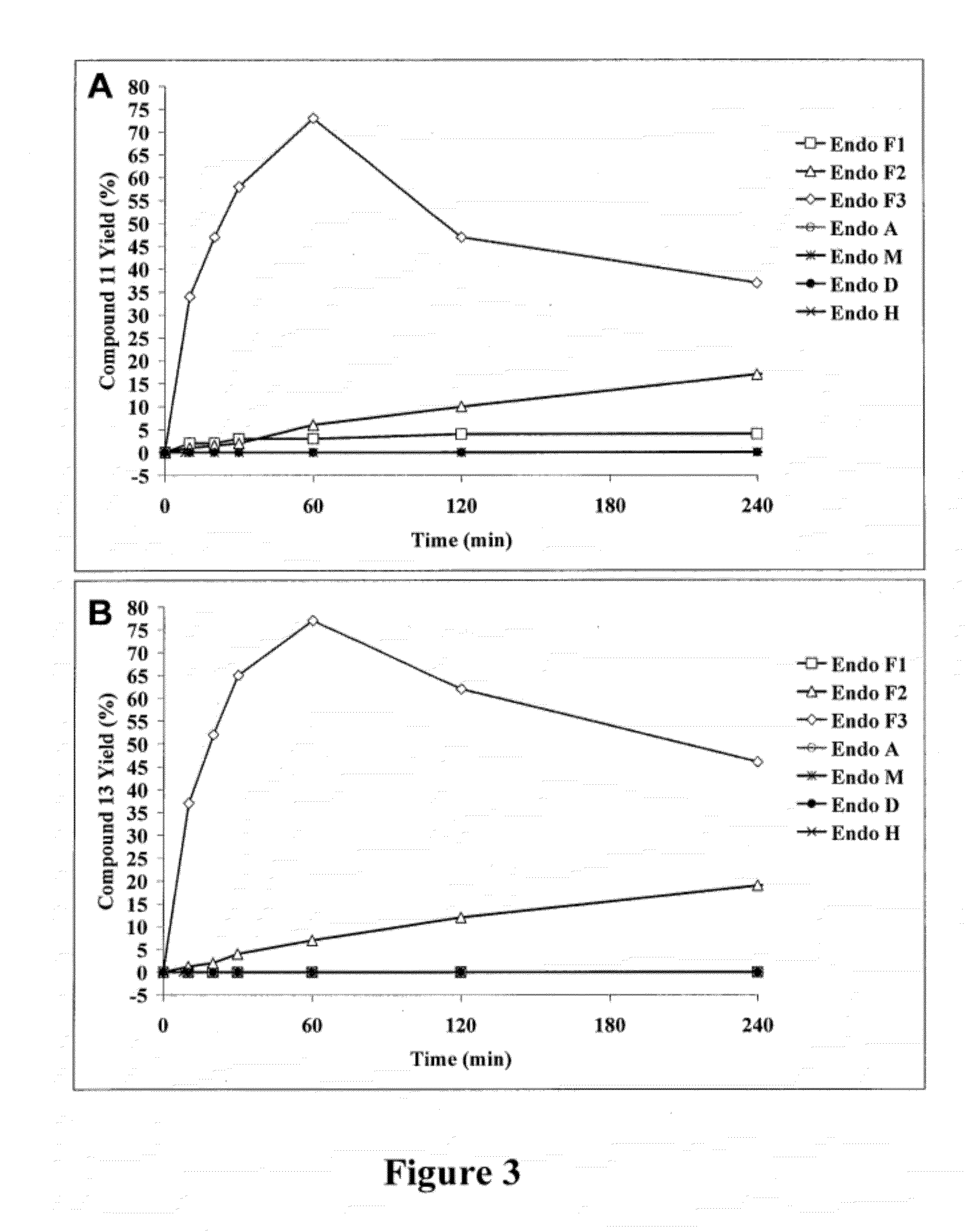
A chemoenzymatic method for the preparation of a core-fucoslyated glycoprotein or glycopeptide, including (a) providing an acceptor selected from the group consisting of a fucosylated GlcNAc-protein and fucosylated GlcNAc-peptide; and (b) reacting the acceptor with a donor substrate including an activated oligosaccharide moiety, in the presence of an endoglycosidase (ENGase) selected from Endo;F1, Endo-F2, Endo-F3, Endo-D and related glycosynthase mutants to transfer the oligosaccharide moiety to the acceptor and yield the structure defined core-fucosylated glycoprotein or glycopeptide. The donor substrate includes, in a specific implementation, a synthetic oligosaccharide oxazoline. A related method of fucosylated glycoprotein or fucosylated glycopeptide remodeling with a predetermined natural N-glycan or a tailor-made oligosaccharide moiety, and a method of remodeling an antibody to include a predetermined sugar chain to replace a heterogeneous sugar chain, are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
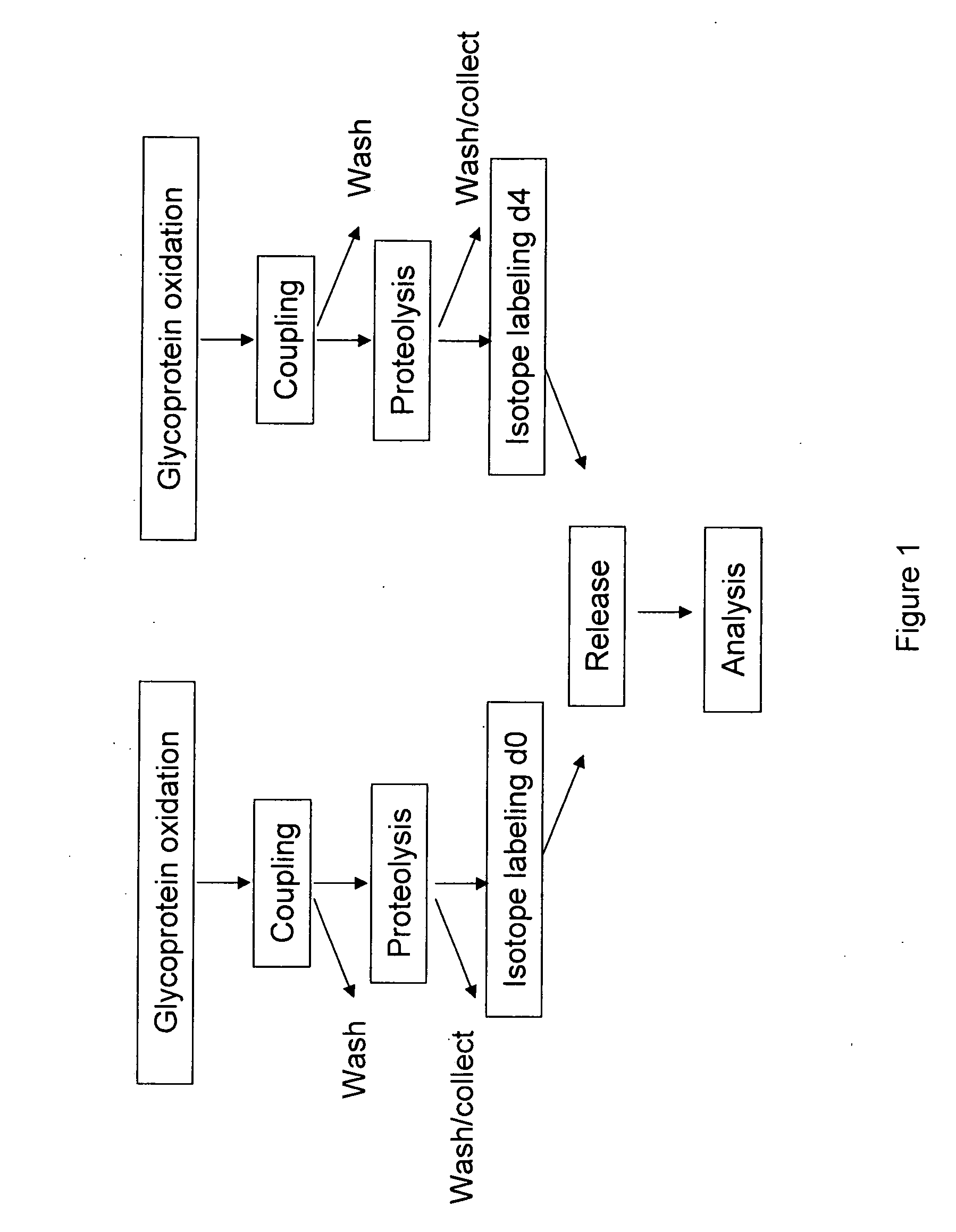
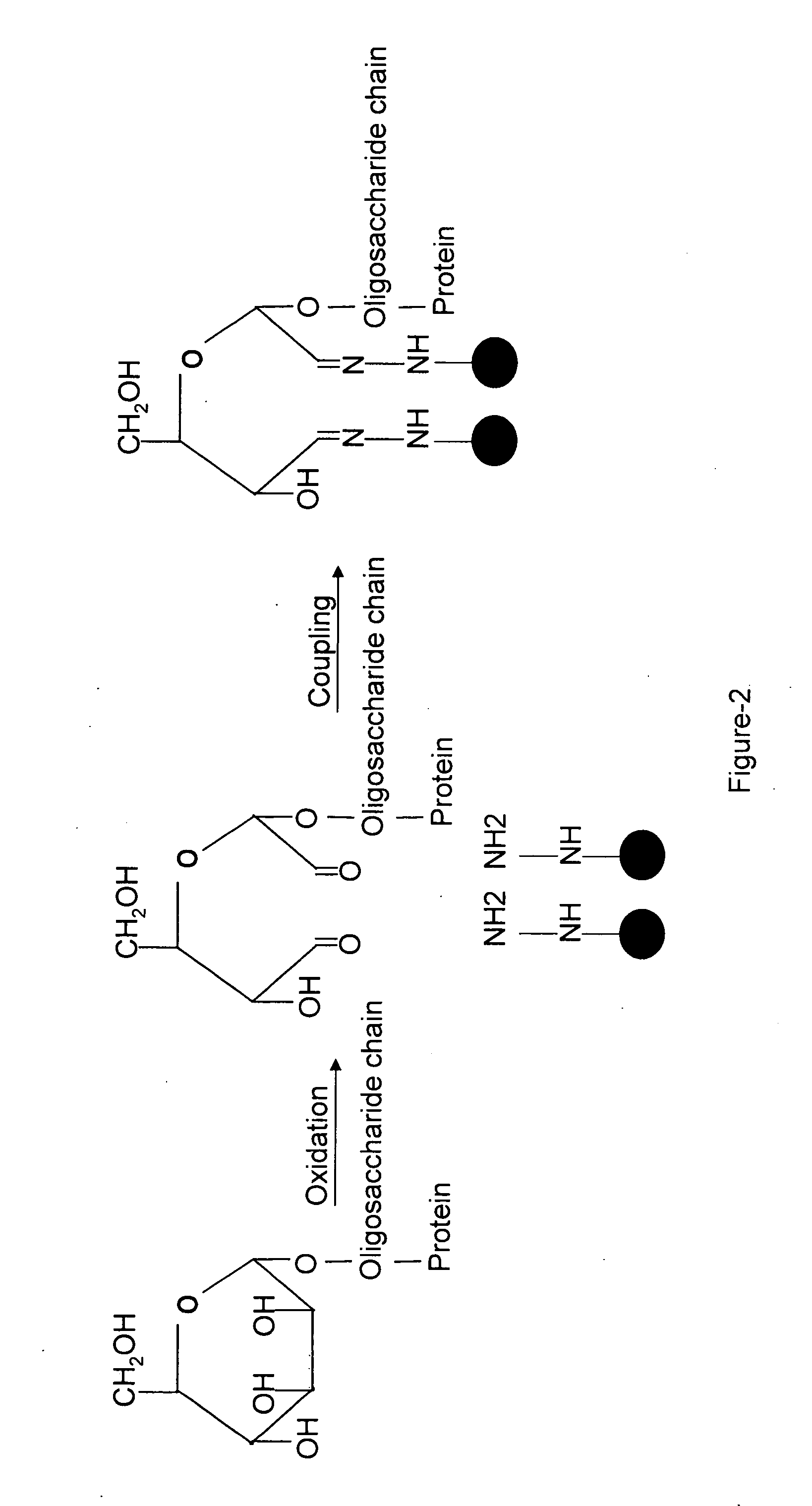
Methods for quantitative proteome analysis of glycoproteins
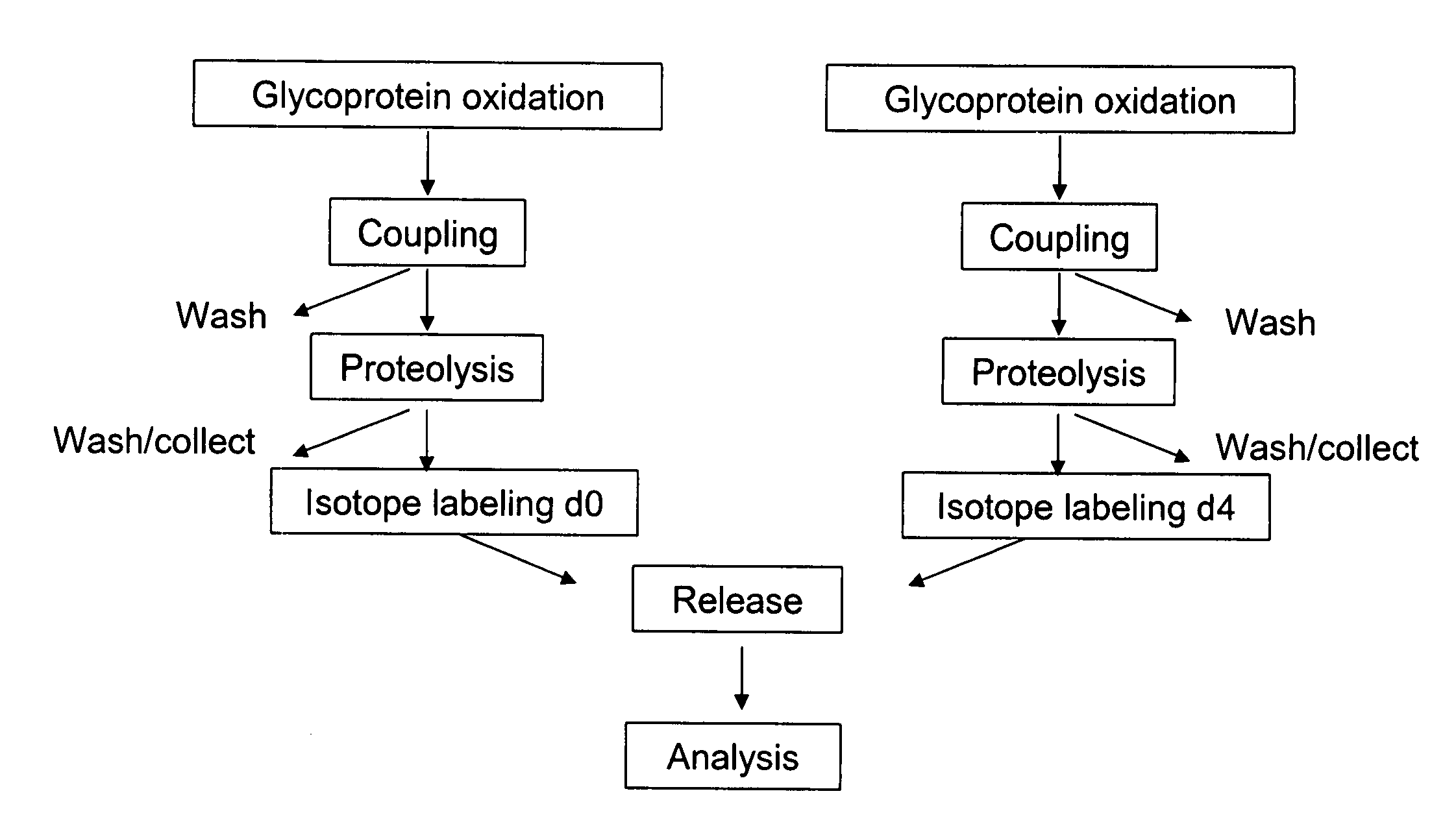
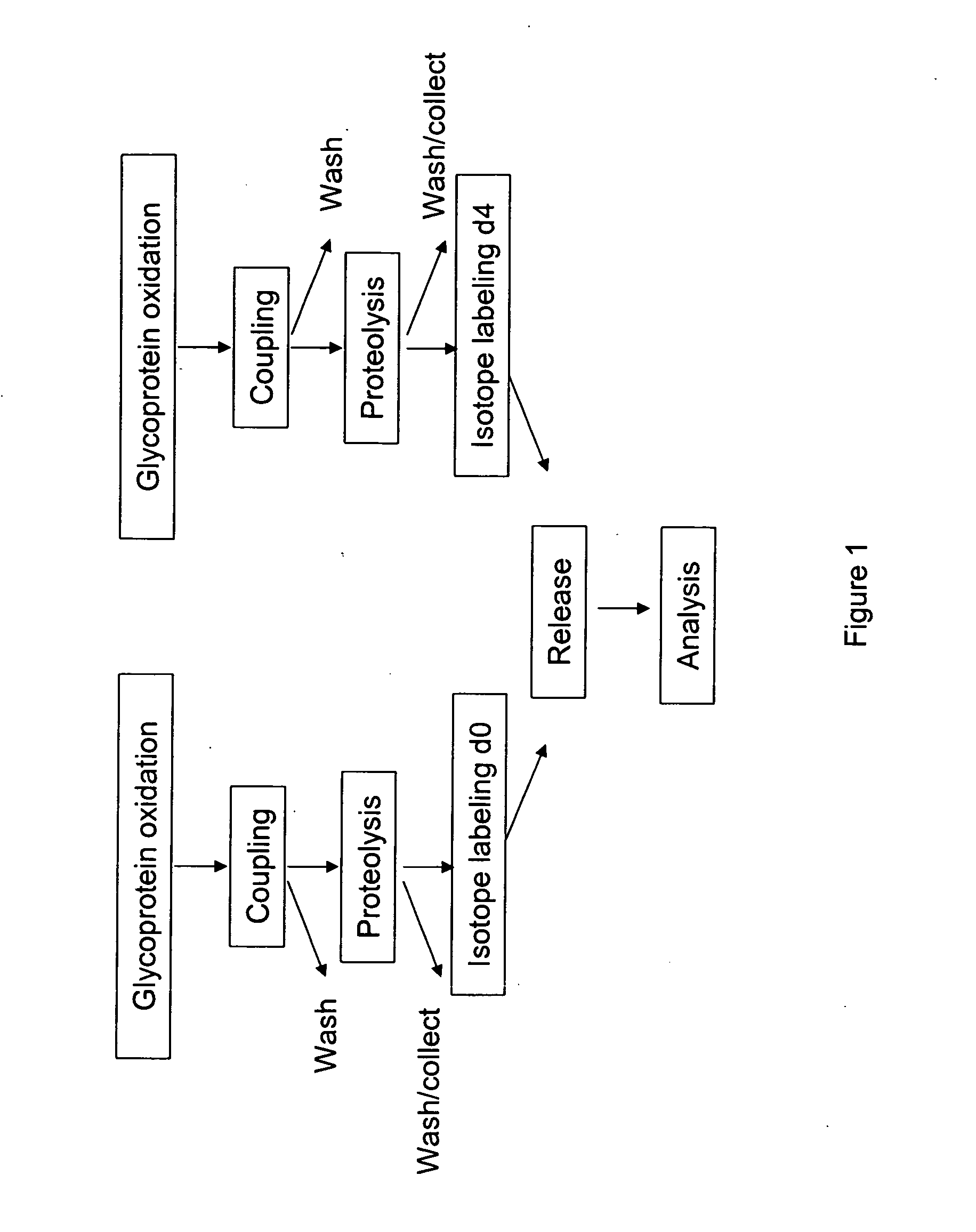
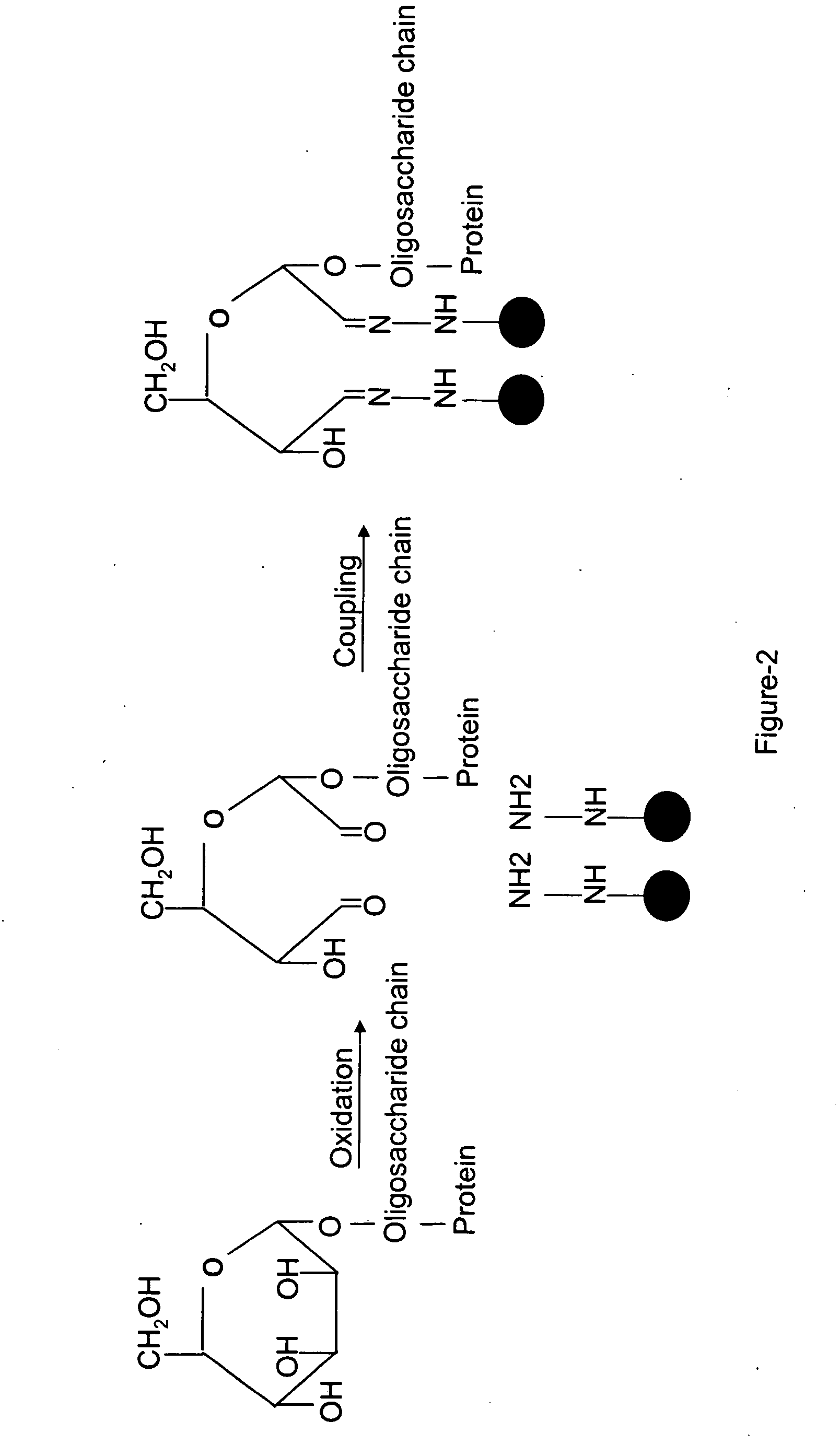
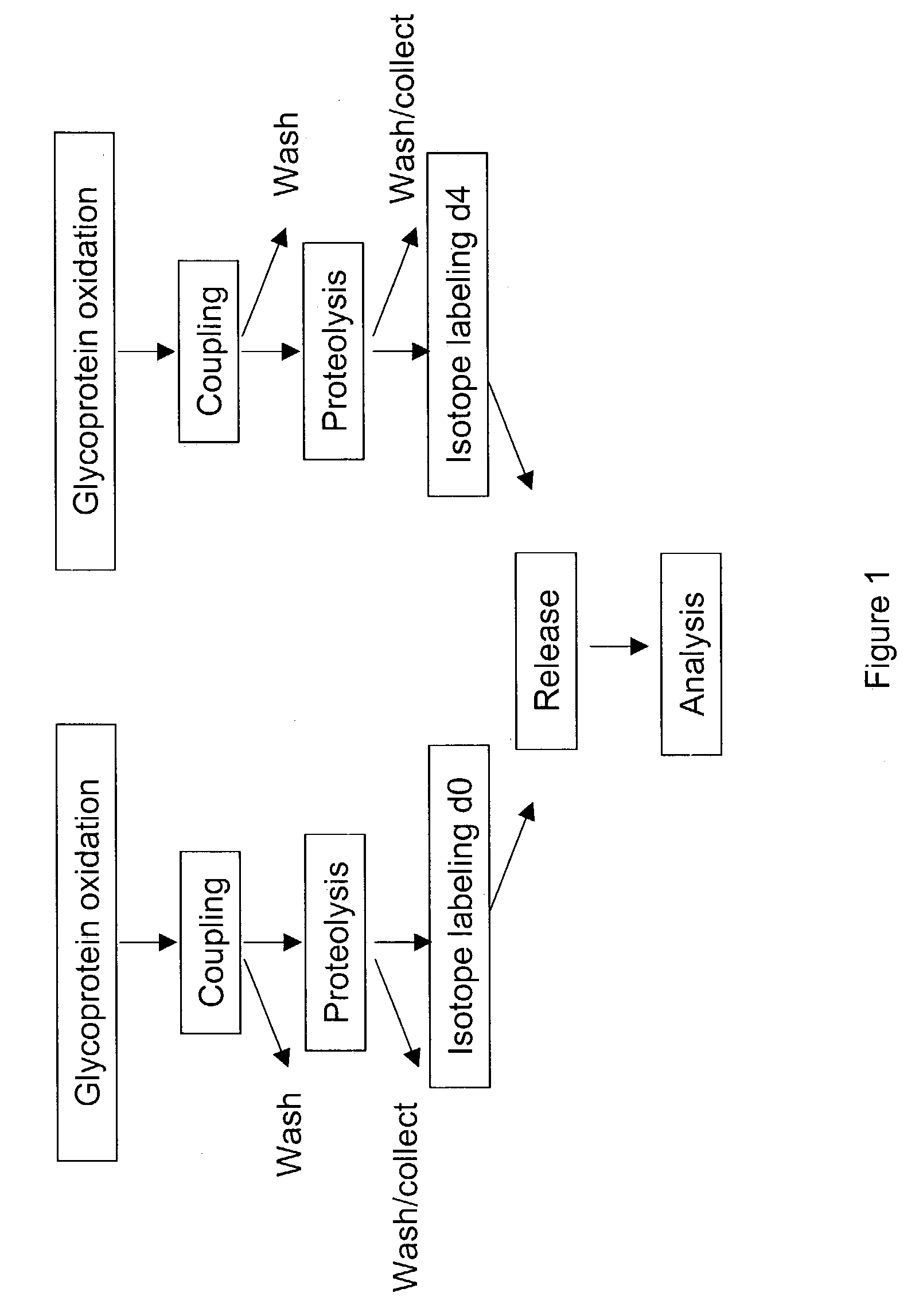
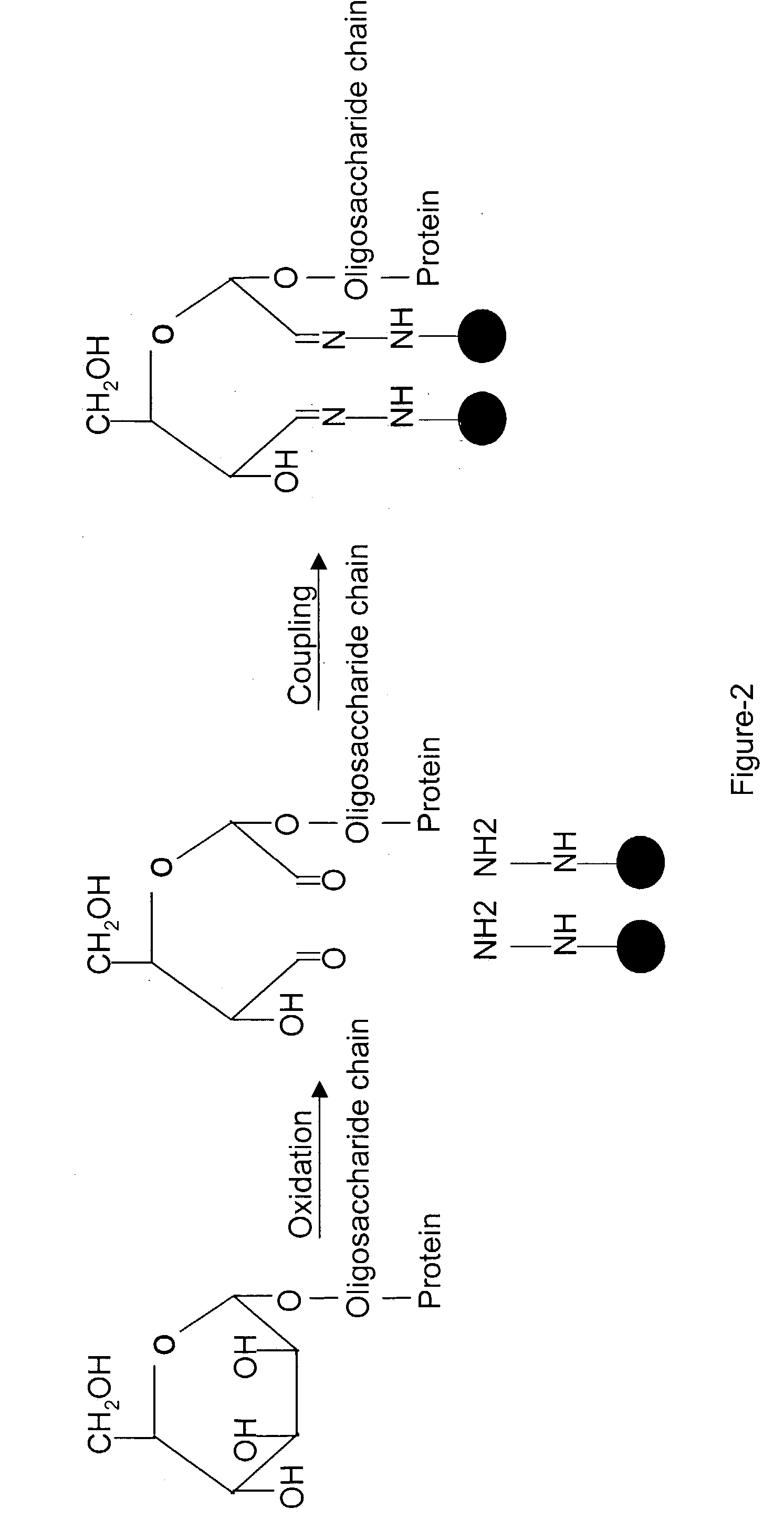
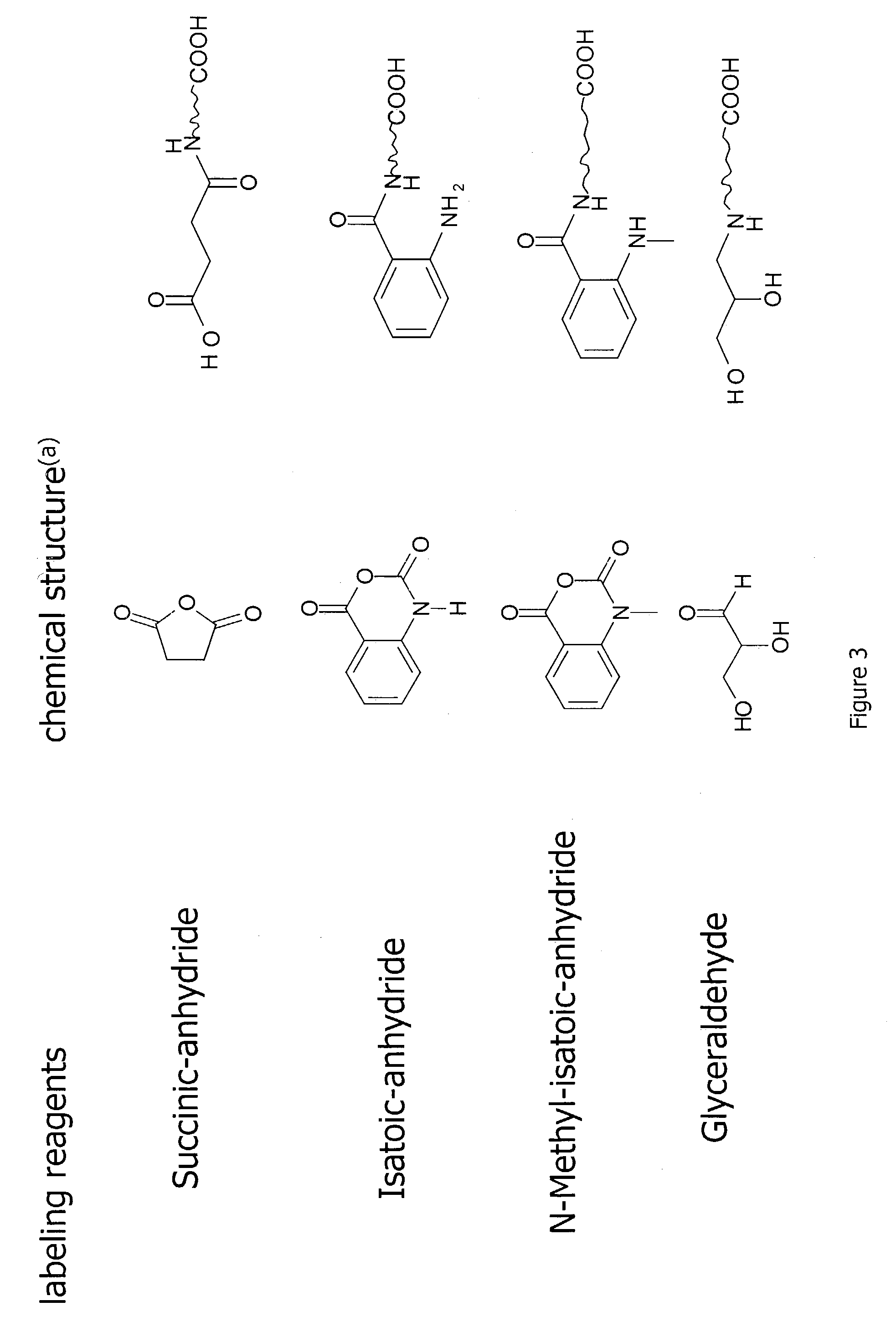
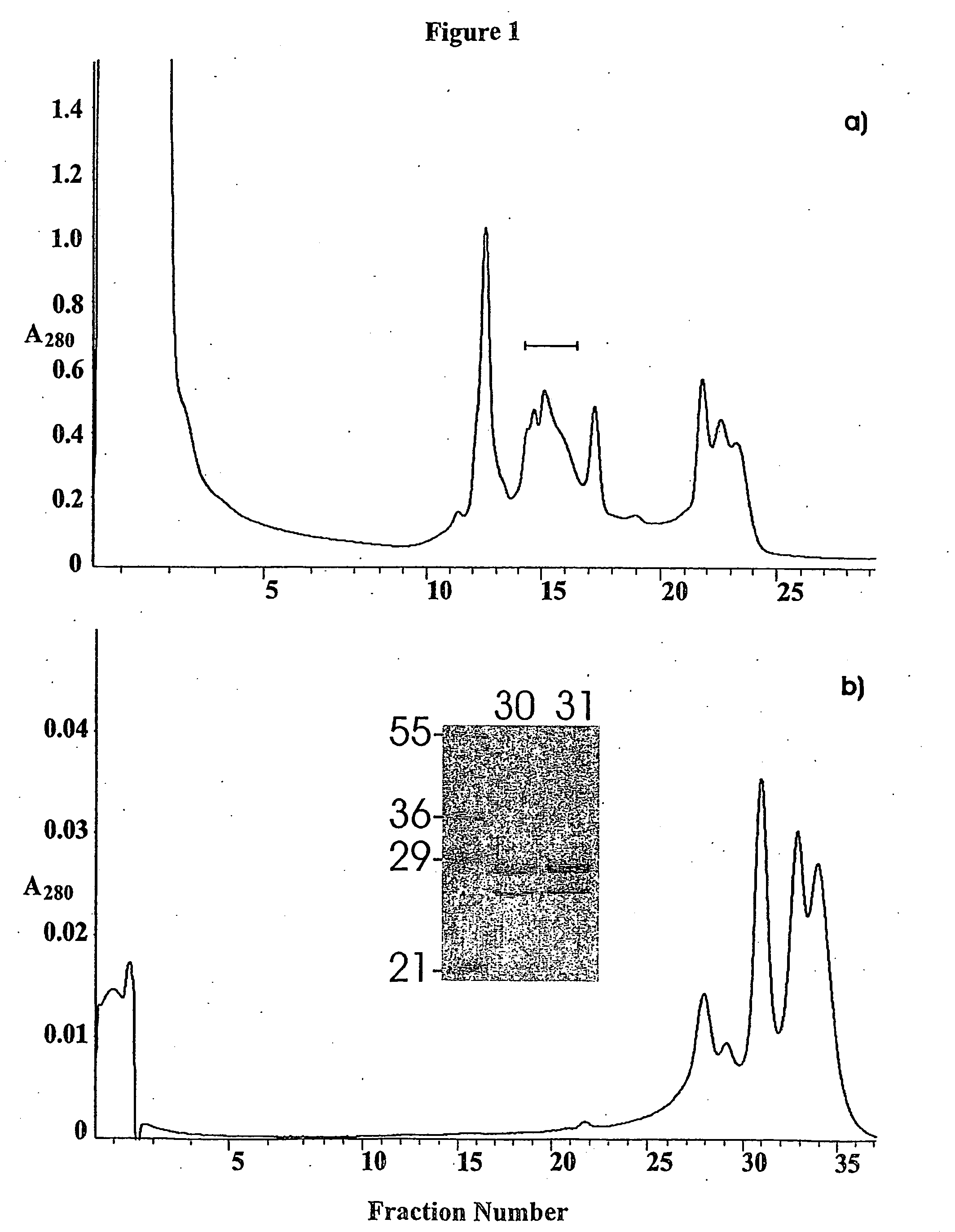
InactiveUS20070269895A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingGlycopeptideGlycoprotein i
The invention provides a method for identifying and quantifying polyglycopeptides in a sample. The method can include the steps of immobilizing glycopolypeptides to a solid support; cleaving the immobilized glycopolypeptides, thereby releasing non-glycosylated peptides and retaining immobilized glycopeptides; releasing the glycopeptides from the solid support; and analyzing the released glycopeptides. The method can further include the step of identifying one or more glycopeptides, for example, using mass spectrometry.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY
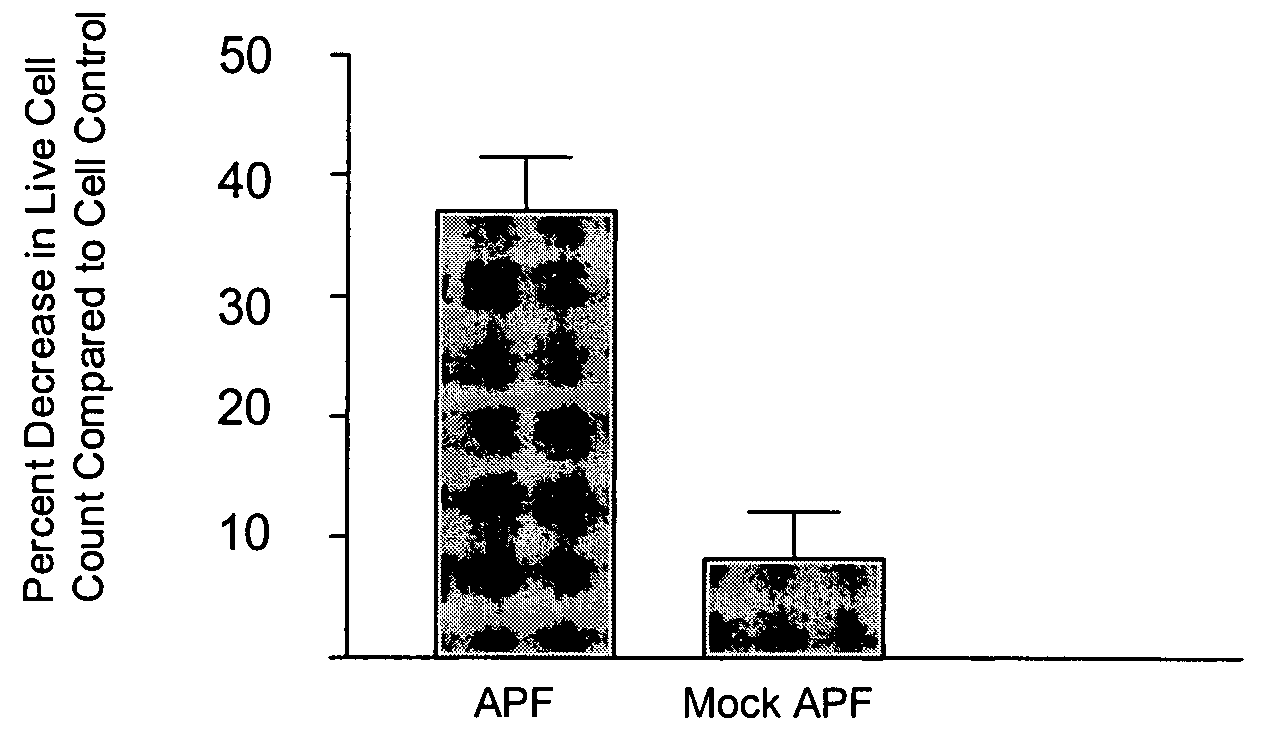
Novel antiproliferative factor and methods of use
InactiveUS20050096263A1Improved and facilitatedAssist in resistanceAntipyreticAnalgesicsInterstitial cystitisCompound (substance)
A novel antiproliferative factor comprising a glycopeptide is disclosed. In specific embodiments, the novel antiproliferative factor is associated with the bladder. Compositions, diagnostic kits and reagents, and methods of using the compounds for identifying and / or treating interstitial cystitis and cancer are disclosed.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE DEPT OF +1
Glycopeptide phosphonate derivatives
Disclosed are glycopeptides that are substituted with one or more substituents each comprising one or more phosphono groups; and pharmaceutical compositions containing such glycopeptide derivatives. The disclosed glycopeptide derivatives are useful as antibacterial agents.
Owner:CUMBERLAND PHARM INC
Processing method of sea cucumber glycopeptides chelated calcium
The invention relates to a processing method of sea cucumber glycopeptides chelated calcium. The method comprises the following steps: A. material treatment: cleaning sea cucumber mouthparts, cooking, soaking, beating, and homogenizing; B. biological enzymatic hydrolysis: choosing a variety of protease for composite segmented enzymatic hydrolysis; C. centrifugal separation: conducting continuous centrifugal separation on an enzymolysis liquid to obtain the sea cucumber glycopeptides solution and sea cucumber calcium precipitate; D. filtration, concentration and grading: subjecting the enzyme liquid to ultrafiltration fractionation concentration, and desalinating small peptide filtered solution by nanofiltration; E. preparation of sea cucumber calcium by organic acidolysis; G. chelating reaction: promoting the chelating of sea cucumber calcium and glycopeptides of sea cucumber by microwave assistance; and H. after the reaction, carrying out centrifuging separation, and drying the precipitate and supernatant respectively. The present invention comprehensively utilizes the sea cucumber processing waste to prepare sea cucumber autologous calcium and autologous glycopeptides for chelation. The method on the one hand is beneficial to playing their biological effects, and on the other hand can also obtain five products with different specific biological functions.
Owner:烟台参福元海洋科技有限公司
Methods for quantitative proteome analysis of glycoproteins
ActiveUS7183118B2SamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryGlycoprotein i
The invention provides a method for identifying and quantifying polyglycopeptides in a sample. The method can include the steps of immobilizing glycopolypeptides to a solid support; cleaving the immobilized glycopolypeptides, thereby releasing non-glycosylated peptides and retaining immobilized glycopeptides; releasing the glycopeptides from the solid support; and analyzing the released glycopeptides. The method can further include the step of identifying one or more glycopeptides, for example, using mass spectrometry.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY
Nanoemulsion compositions and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070085058A1Improve bioavailabilityEnhanced soluble complexesCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAdditive ingredientCholesterol blood
A nanoemulsion composition having enhanced oxidative stability, emulsion stability, and health benefits. The composition may include individual ingredients or a synergistic blend of non-reducing sugars, sugar polyols, medium-chain triglycerides, polysaccharides, polyphenols, phospholipids, chitosan, and alpha-casein, beta-casein, kappa-casein or protein fragments, glycopeptides, phosphopeptides. The composition may optionally be further utilized for the prevention of hypercholesterolemia or bone (and teeth) mineral loss.
Owner:PETTY BLAKE
Campylobacter glycans and glycopeptides
ActiveUS20060165728A1Prevent groundwater pollutionEliminating and reducing presenceAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaMagic angle spinningGlycopeptide
Multiple strains and species of Campylobacter were found to share a common glycan moitie which is present in a plurality of surface-exposed glycoproteins. This glycan has the formula: GalNAc-a1,4-GalNAc-a1,4-[Glc-β1,3]GalNAc-a1,4-GalNAc-a1,4-GalNAc-a1,3-Bac, wherein Bac is 2,4-diacetamido-2,4,6-trideoxy-D-glucopyranose. This glycan and immunologically active fragments of it have use as vaccines against campylobacter infection in humans and animals. As well, antibodies which specifically bind these compounds may be provided. Such antibodies and vaccines may be used to prevent or neutralize campylobacter infections in livestock thereby preventing this pathogen from entering the human food chain. The glycan may be linked to one or more amino acids to form a glycopeptide. As well, a method for determining the glycan structure of an intact glycoprotein consists of subjecting a sample to high resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (HR-MAS-NMR) spectroscopy.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
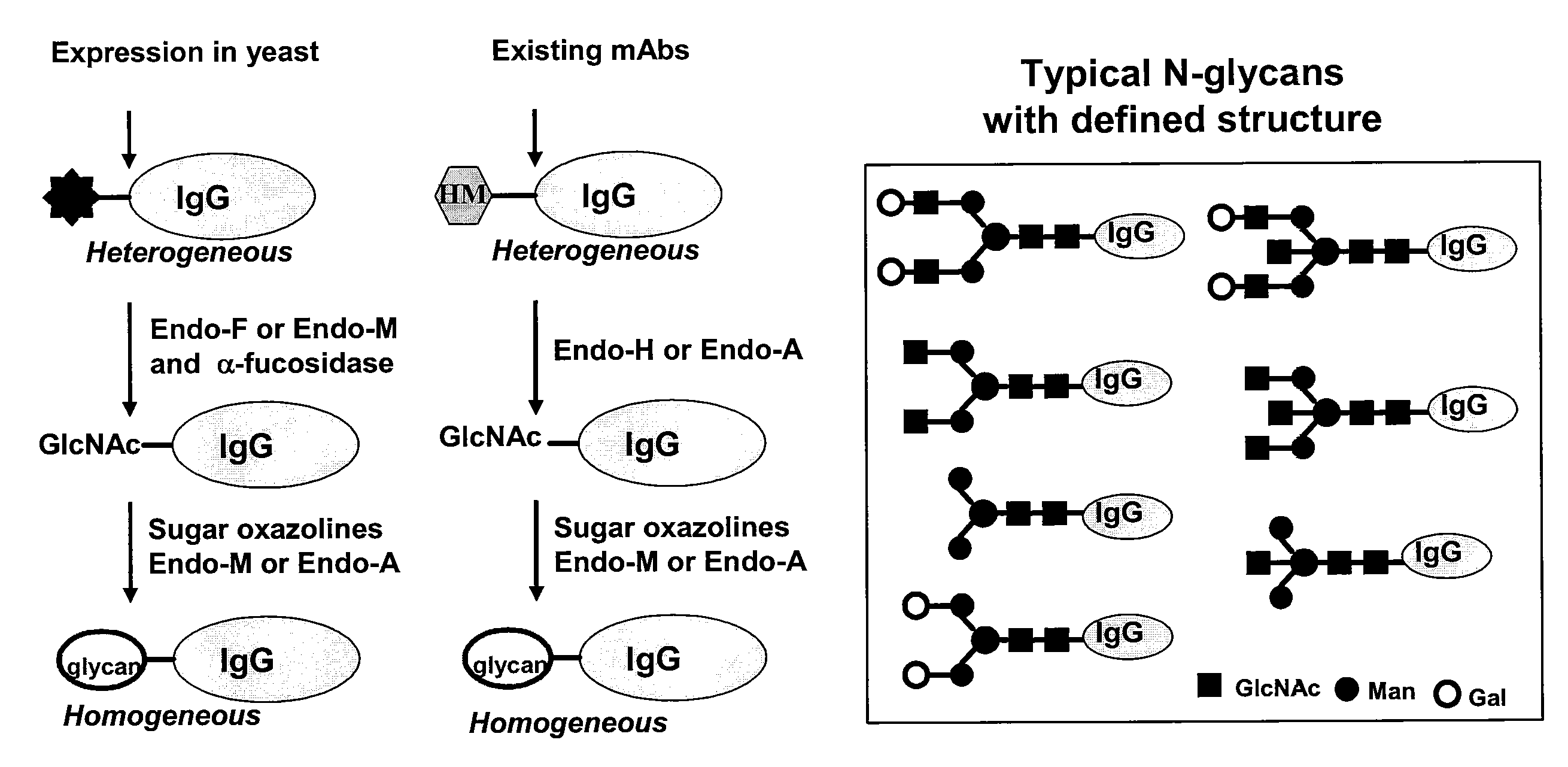
Glycoprotein synthesis and remodeling by enzymatic transglycosylation
ActiveUS7807405B2Prolonged half-life-timeLess immunogenicVirus peptidesPeptide preparation methodsHalf-lifeGlycopeptide
A chemoenzymatic method for the preparation of a homogeneous glycoprotein or glycopeptide, including (a) providing an acceptor selected from the group consisting of GlcNAc-protein and GlcNAc-peptide; and (b) reacting the acceptor with a donor substrate including an activated oligosaccharide moiety, in the presence of a catalyst comprising endoglycosidase (ENGase), to transfer the oligosaccharide moiety to the acceptor and yield the homogeneous glycoprotein or glycopeptide. The donor substrate includes, in a specific implementation, a synthetic oligosaccharide oxazoline. A related method of glycoprotein or glycopeptide remodeling with a predetermined natural N-glycan or a tailor-made oligosaccharide moiety, and a method of remodeling an antibody including a heterogeneous sugar chain, are also described. The disclosed methodology enables glycoprotein drugs to be modified for prolonged half-life in vivo, reduced immunogenicity, and enhanced in vivo activity, and for targeting and drug delivery.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Enzymatic modification of glycopeptides
InactiveUS20090292110A1Lower potential for exposureImprove homogeneityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsAcyl residueGlycopeptide
The present invention provides glycoconjugates that are formed through the enzymatically-mediated coupling of a glycosyl moiety, e.g., on a peptide or lipid, and a modifying group that includes an acyl group. The conjugates include the modifying group tethered to the glycosyl moiety through a linking moiety that includes an acyl residue. Also provided are methods for preparing the conjugates of the invention
Owner:RATIOPHARM GMBH
Antibacterial agents comprising conjugates of glycopeptides and peptidic membrane associating elements
InactiveUS7078380B2Improve bindingHigh proportionAntibacterial agentsBiocideGlycopeptideAntibacterial activity
The invention concerns agents with anti-bacterial activity and methods and intermediates for their production. The present invention further concerns the use of such agents for the treatment of bacterial infections in animals, including man. The agents are derivatives of vancomycin-type antibiotics, of structure: V-L-W-X; wherein V is a glycopeptide moiety which inhibits peptidoglycan biosynthesis in bacteria; L is a linking group; W is a peptidic membrane-associating element such as an element based on naturally-occurring animal or bacterial peptide antibiotics; and X is hydrogen or a membrane-insertive element.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
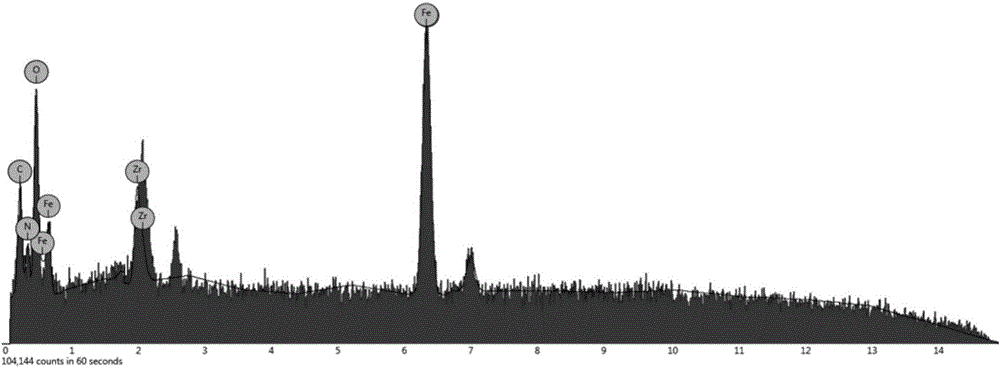
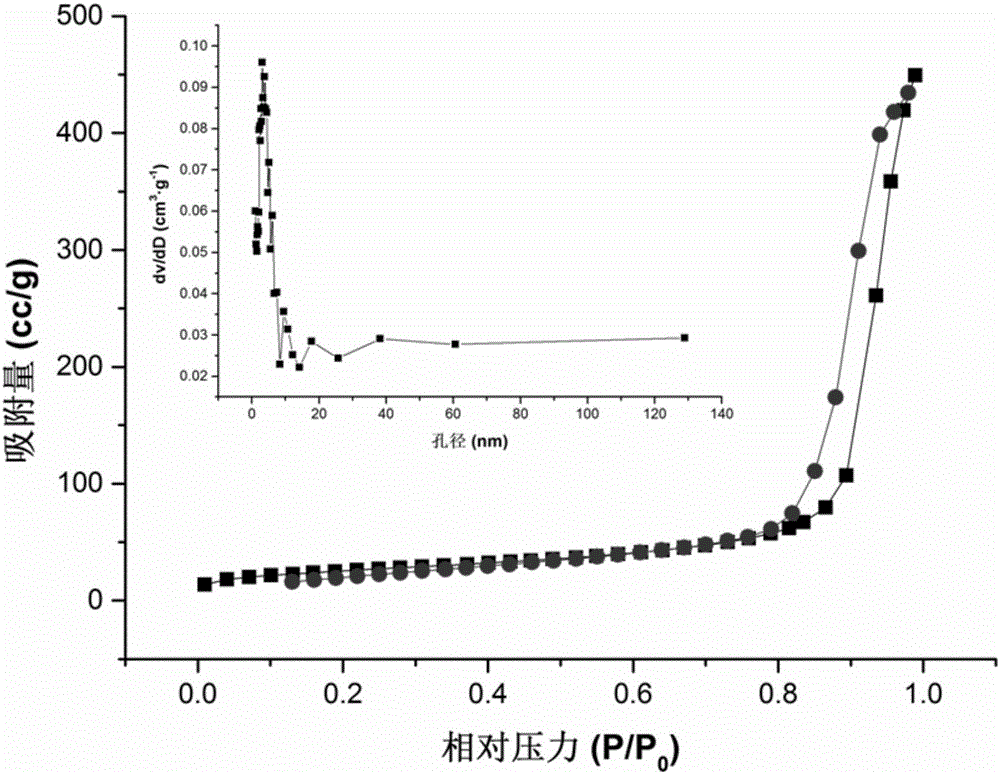
Synthetic method and application of metal-organic framework composite nanomaterial
InactiveCN106512965AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesSynthesis methodsMetal-organic framework
The invention provides a synthetic method and application of a metal-organic framework (MOF) composite nanomaterial. The method comprises the following steps: dispersing ferriferrous oxide magnetic spheres which are synthesized through a traditional hydrothermal technology in a weakly alkaline solution of dopamine hydrochloride to carry out self-polymerization of dopamine on the surfaces of the magnetic spheres; and sequentially dispersing polydopamine coated magnetic spheres in a dimethylformamide solution of zirconium chloride and a dimethylformamide solution of 2-amino-terephthalic acid to obtain the MOF composite nanomaterial with the magnetic sphere surfaces coated with polydopamine and modified with an amino group and with zirconium as a center metal ion. The material has the advantages of large specific surface area, good hydrophilicity and suitable pore structure, can be applied to further researches of the proteomics, and can specifically enrich Which can specifically enrich phosphorylated peptide segments and glycopeptides; the synthetic method is simple and quick; and the synthesized material has good hydrophilicity and biocompatibility, and can be used for selectively enriching endogenous phosphorylation peptide segments and glycopeptide in complex biological samples.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Glycoprotein synthesis and remodeling by enzymatic transglycosylation
ActiveUS20080138855A1Prolonged half-life-timeLess immunogenicImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDepsipeptidesHalf-lifeGlycopeptide
A chemoenzymatic method for the preparation of a homogeneous glycoprotein or glycopeptide, including (a) providing an acceptor selected from the group consisting of GlcNAc-protein and GlcNAc-peptide; and (b) reacting the acceptor with a donor substrate including an activated oligosaccharide moiety, in the presence of a catalyst comprising endoglycosidase (ENGase), to transfer the oligosaccharide moiety to the acceptor and yield the homogeneous glycoprotein or glycopeptide. The donor substrate includes, in a specific implementation, a synthetic oligosaccharide oxazoline. A related method of glycoprotein or glycopeptide remodeling with a predetermined natural N-glycan or a tailor-made oligosaccharide moiety, and a method of remodeling an antibody including a heterogeneous sugar chain, are also described. The disclosed methodology enables glycoprotein drugs to be modified for prolonged half-life in vivo, reduced immunogenicity, and enhanced in vivo activity, and for targeting and drug delivery.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
In vitro modification of glycosylation patterns of recombinant glycopeptides
This invention provides methods for modifying glycosylation patterns of glycopeptides, including recombinantly produced glycopeptides. Also provided are glycopeptide compositions in which the glycopeptides have a uniform glycosylation pattern.
Owner:RATIOPHARM GMBH
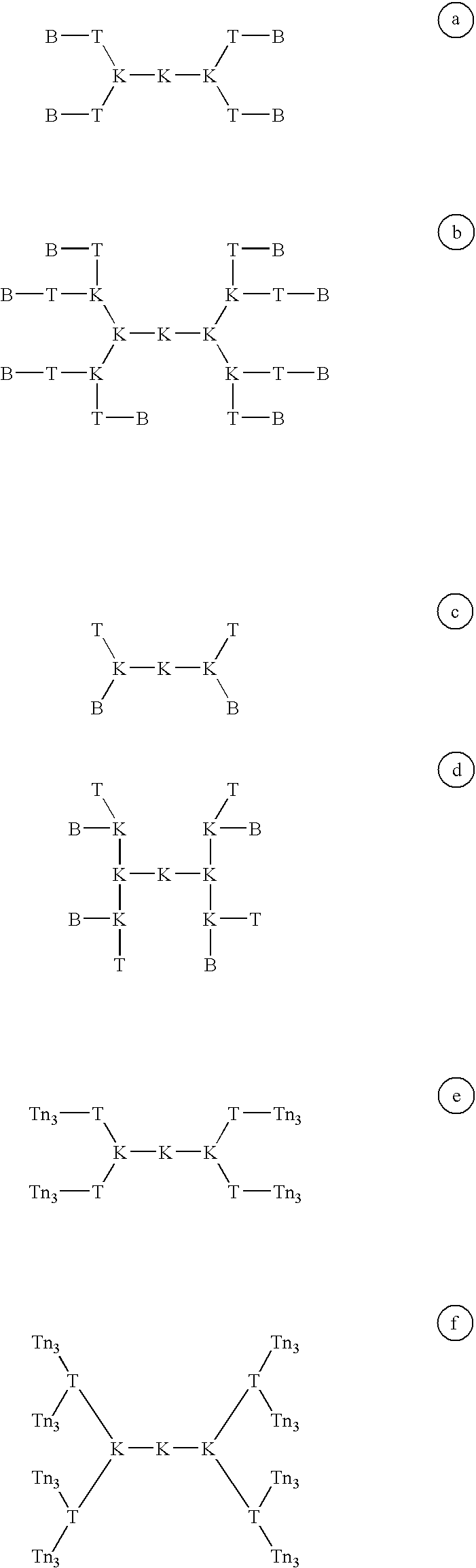
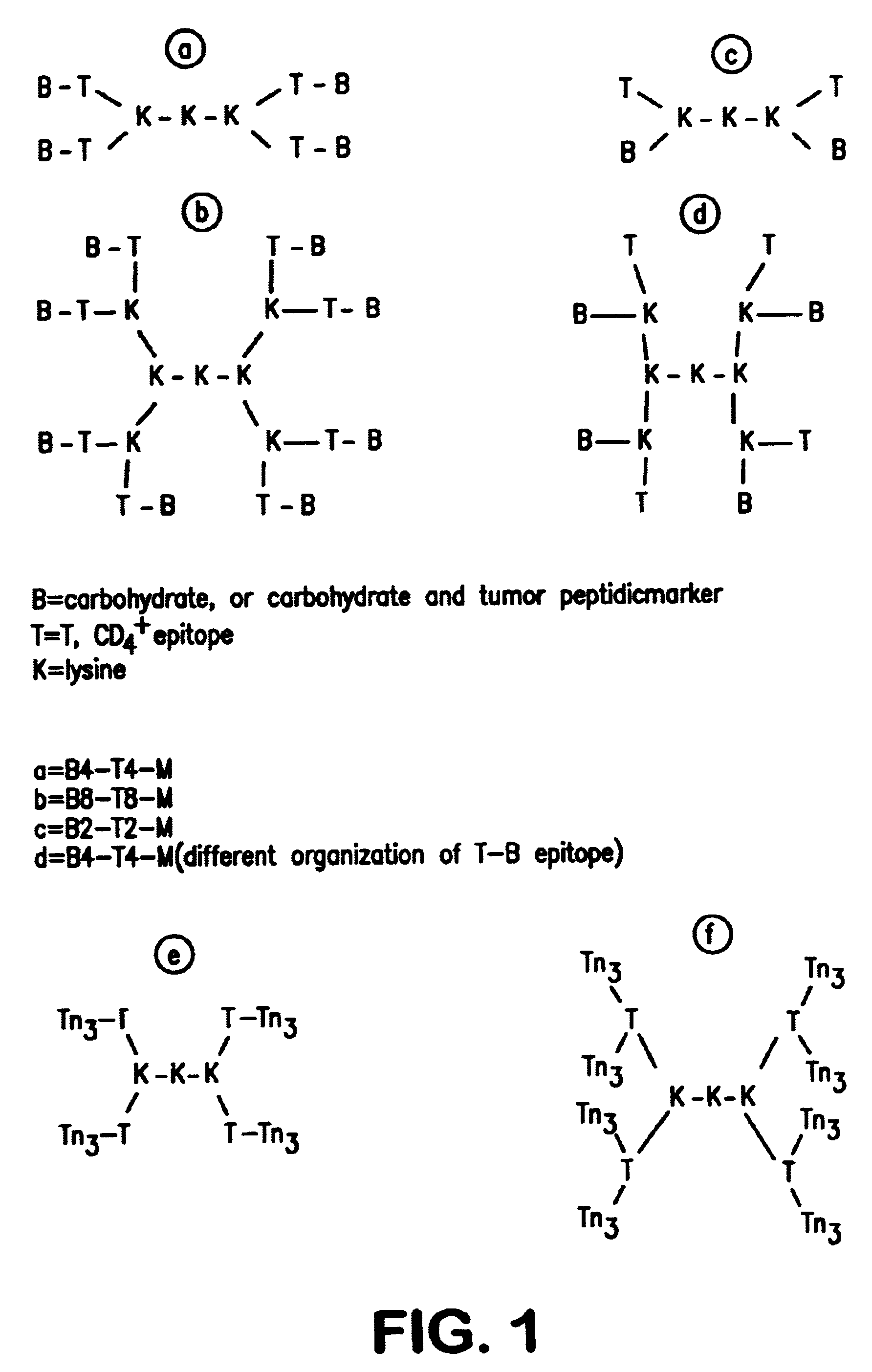
Multiple antigen glycopeptide carbohydrate vaccine comprising the same and use thereof
InactiveUS6676946B2Enhance antibody responseEfficient T cell helpPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteria peptidesT epitopeGlycopeptide
A carbohydrate peptide conjugate containing:(i) a carrier containing a dendrimeric poly-lysine enabling multiple epitopes to be covalently attached thereto,(ii) at least one peptide containing one T epitope or several identical or different T-epitopes,(iii) at least one carbohydrate moiety which is tumor antigen, or a derivative thereof, containing a B epitope, provided it is not a sialoside, or several identical or different epitopes, wherein said conjugate containing at least 3-lysines and up to 15 lysine covalently linked to one another, and wherein:(a) to the NH2 and of at least two lysine residues is bound at least one carbohydrate residue being not a sialoside, optionally substituted and containing an epitope and wherein the peptide containing one T epitope is covalently bound to the end of said carbohydrate which induces immune responses.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Methods for quantitative proteome analysis of glycoproteins
InactiveUS20070202539A1Microbiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryGlycopeptide
The invention provides a method for identifying and quantifying polyglycopeptides in a sample. The method can include the steps of immobilizing glycopolypeptides to a solid support; cleaving the immobilized glycopolypeptides, thereby releasing non-glycosylated peptides and retaining immobilized glycopeptides; releasing the glycopeptides from the solid support; and analyzing the released glycopeptides. The method can further include the step of identifying one or more glycopeptides, for example, using mass spectrometry.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY
Pharmaceutical compositions and use thereof
InactiveUS20090169635A1Efficient curingIncrease loopAntiinfectivesGranular deliveryAntibacterial activityAntibiotic Y
Colloidal compositions, loaded with non-covalently bonded antibiotics, can be efficiently used for the treatment of severe bacterial pneumonia and other serious lung infections such as tuberculosis. Such formulations, comprised of biodegradable nanoparticles or nanocapsules with incorporated antibiotics, show a significant increase in antibacterial activity, extended and sustained drug release and a decrease in frequency of the drug administration. Antibiotics of various types, such as aminoglycosides, glycopeptides and others can be successfully incorporated into a nanoparticulate colloidal delivery system.
Owner:ALPHARX
Method for preparing gingko protein peptide
ActiveCN103609831AIncrease contentHigh extraction rateProtein composition from vegetable seedsVegetable proteins working-upFood additiveSide effect
The invention relates to a method for deeply processing gingko, and particularly discloses a method for preparing gingko protein peptide. The method mainly comprises the following steps: (1), processing raw materials; (2), preparing gingko powder; (3), preparing gingko protein powder; (4), carrying out primary enzymolysis; and (5), carrying out secondary enzymolysis to obtain gingko glycopeptides, amino acid balance peptide and gingko polypeptide products. The utilization of gingko resources is expanded, and new resources are provided for developing products with special functions. The method is special and simple in process, and low in production cost; the gingko protein peptide is safe without toxic and side effects; the novel preparation process of the gingko polypeptide product is developed, a new utilization field of the gingko is opened up. The gingko polypeptide prepared by adopting the method provided by the invention can be used as raw material for developing health care foods, food additives and medicine raw materials and excipients.
Owner:徐州绿之野生物食品有限公司
Nano magnetic material of surface modified boric acid base group, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101684005ATroubleshooting Analytical DifficultiesThe synthesis method is simpleFerric oxidesSynthesis methodsGlycopeptide
The invention belongs to the technical fields of inorganic materials and analysis, which relates to a magnetic material of surface modified aminobenzene boric acid, a preparation method and an application thereof. In the invention, a magnetic nano material of ferroferric oxide of which the surface is rich in amino groups is synthesized firstly, and surface chemical modification is carried out on the magnetic nano material by aminobenzene boric acid. The synthesis method of the invention is simple and effective, the prepared magnetic material has very good magnetic field inductivity, large specific surface area and strong specificity, is used as a micro-adsorbent and can be directly put into a peptide section without special processing, and the specific separation and enrichment of glycoprotein and glycopeptide can be realized by a simple magnetic field action without centrifugal separation after being complexed on the magnetic nano material. The material has favorable practical value and application prospect in the fields of protein group science and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Antioxidant compositions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS7118688B2Preventing bone mineral lossImproves antioxidant activityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCholesterol bloodAdditive ingredient
An antioxidant composition having enhanced oxidative stability, emulsion stability, and health benefits. The composition may include individual ingredients or a synergistic blend of non-reducing sugars, sugar polyols, medium-chain triglycerides, polysaccharides, polyphenols, phospholipids, chitosan, and alpha-casein, beta-casein, kappa-casein or protein fragments, glycopeptides, phosphopeptides. The composition may optionally be further utilized for the prevention of hypercholesterolemia or bone mineral loss.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Enzymatic modification of glycopeptides
InactiveUS20110318780A1Improve homogeneityHigh degree of homogeneityFermentationLipid formationGlycopeptide
The present invention provides glycoconjugates that are formed through the enzymatically-mediated coupling of a glycosyl moiety, e.g., on a peptide or lipid, and a modifying group that includes an acyl group. The conjugates include the modifying group tethered to the glycosyl moiety through a linking moiety that includes an acyl residue. Also provided are methods for preparing the conjugates of the invention
Owner:RATIOPHARM GMBH
Process for producing soybean protein peptide using soybean as raw material
InactiveCN1500881AIncrease methionine contentNutrition scienceFermentationGlycopeptideTherapeutic effect
The present invention is the technological process of preparing soybean protein peptide with soybean as material. The technological process includes dissolving soybean protein, the first enzymolysis, centrifugal separation to obtain supernatant and precipitate; separating and enzymolyzing the supernatant and the precipitate, with soybean glycopeptide being obtained via enzymolyzing the supernatant; centrifugally separating the precipitate enzymolyzing product to obtain supernatant and precipitate for the second time; separately drying the the supernatant and the precipitate to obtain amino acid balanced peptide and soybean polypeptide separately. The technological process is unique and low in cost, and the products have nourishing and auxiliary treatment effects and no toxic side effect and may be used widely in medicine and health food.
Owner:陆晓民
Method for enriching glycopeptide by phenylboronic acid material
ActiveCN104374848AEfficient enrichmentHigh selectivityComponent separationPhenylboronic acidOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a method for enriching glycopeptide by a phenylboronic acid material. The glycopeptide is selectively enriched through optimizing the kind and concentration of an organic solvent, the kind and concentration of a buffer salt, the enrichment temperature and other parameters with phenylboronic acid modified silicon spheres as an enrichment material. The method has the characteristics of high selectivity, high adsorption amount, simple and controllable operation and the like, and is suitable for the selective enrichment of glycopeptides in a biological sample.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Method for selective enrichment and identification of N-linked glycopeptide
InactiveCN106483294AMaterials are cheap and readily availableGood dispersionPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingMicrosphereSide chain
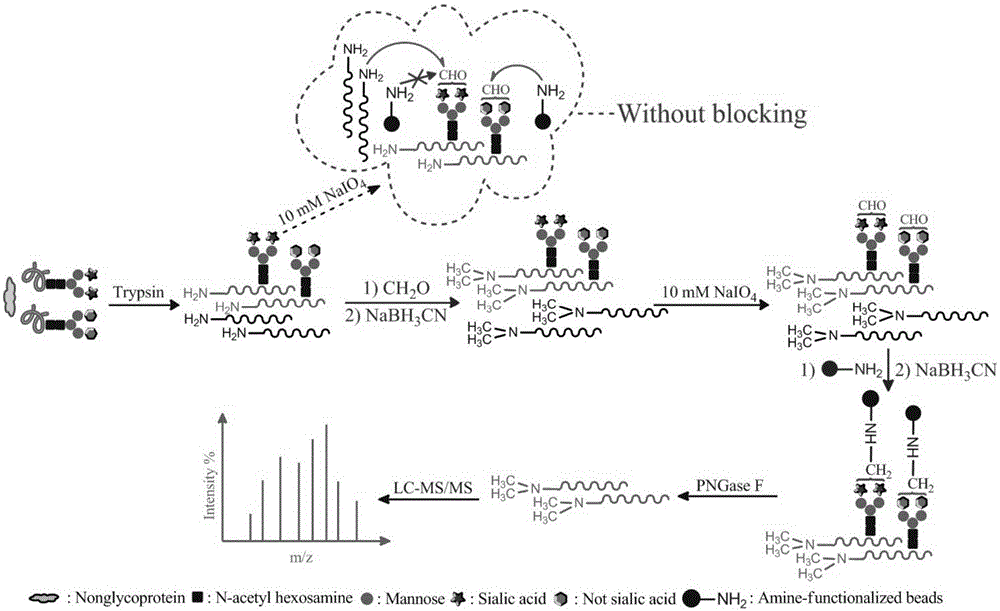
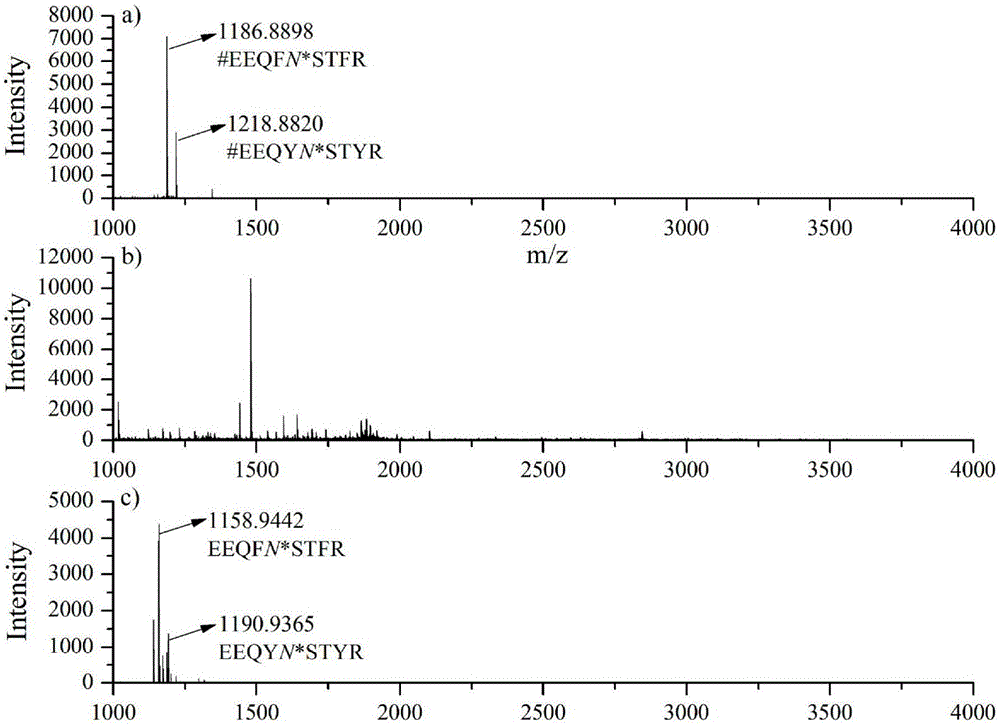
The invention relates to a method for selective enrichment and identification of N-glycosylation sites in a biological sample based on a reductive amination reaction of amino and aldehyde groups and application of the method to proteomic analysis of N-glycoprotein. The method comprises the following steps: taking a biological sample containing glycoprotein, carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis by using trypsin and then blocking the terminated amino group and side-chain amino group of a peptide fragment by using formaldehyde; then oxidizing a sugar chain on glycopeptide by using a sodium periodate solution so as to produce an aldehyde group; then enriching oxidized glycopeptide with amino microspheres and carrying out treatment with peptide glycosidase PNGase F; and carrying out mass spectrometry on released N-glycopeptide so as to obtain proteome information of N-glycoprotein in the sample. The method can be used for proteomic analysis of glycosylation and can acquire identification results of corresponding glycoprotein, glycopeptide and glycosylation sites at the same time. The method is simple and highly efficient and has high throughput in identification of N-glycosylation sites on glycoprotein.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com