Patents
Literature
64 results about "Magic angle spinning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In nuclear magnetic resonance, magic-angle spinning (MAS) is a technique often used to perform experiments in solid-state NMR spectroscopy and, more recently, liquid Proton nuclear magnetic resonance.
NMR CryoMAS probe for high-field wide-bore magnets
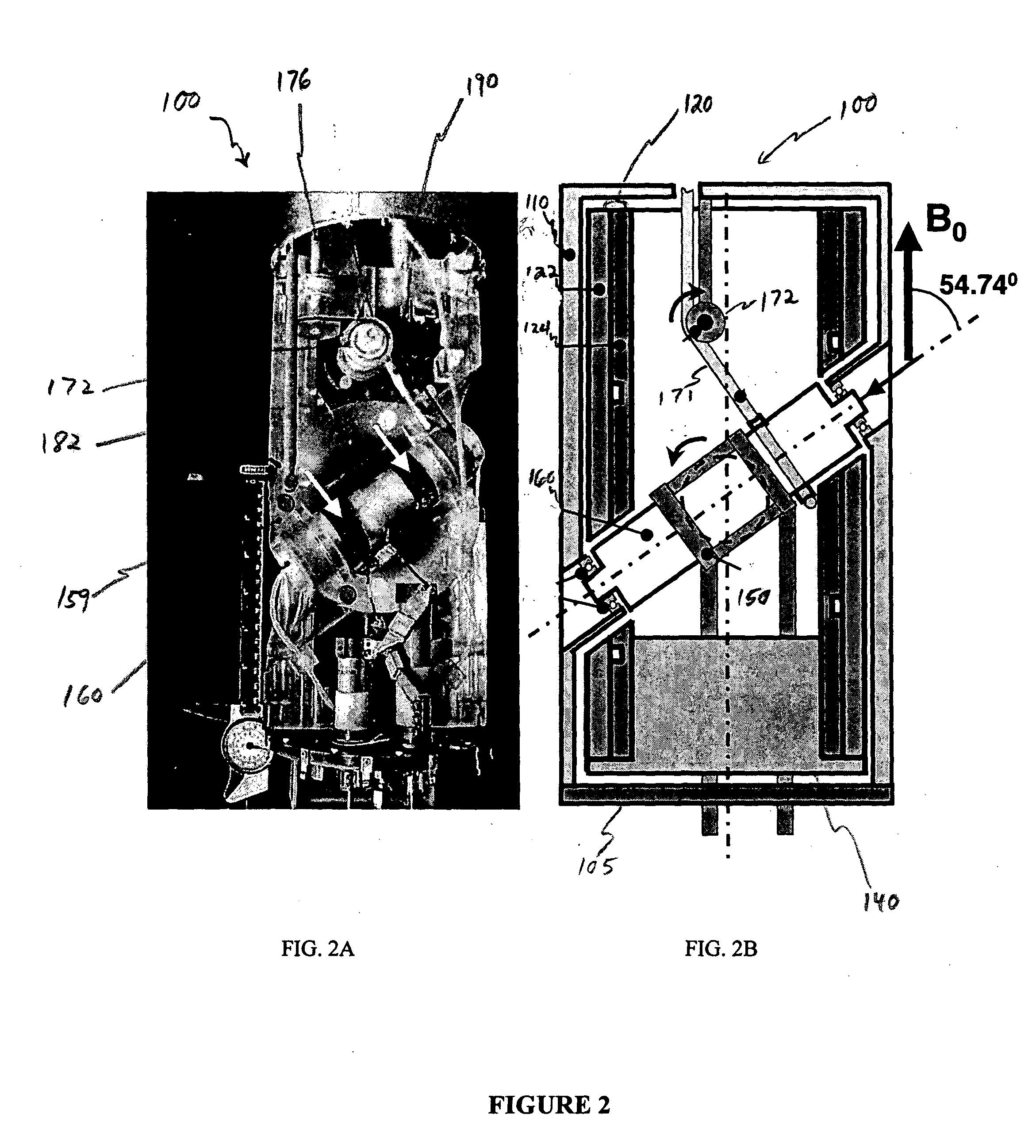
InactiveUS7282919B2Reduce riskAvoid flowElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagic angle spinningNitrogen gas
Owner:DOTY SCI
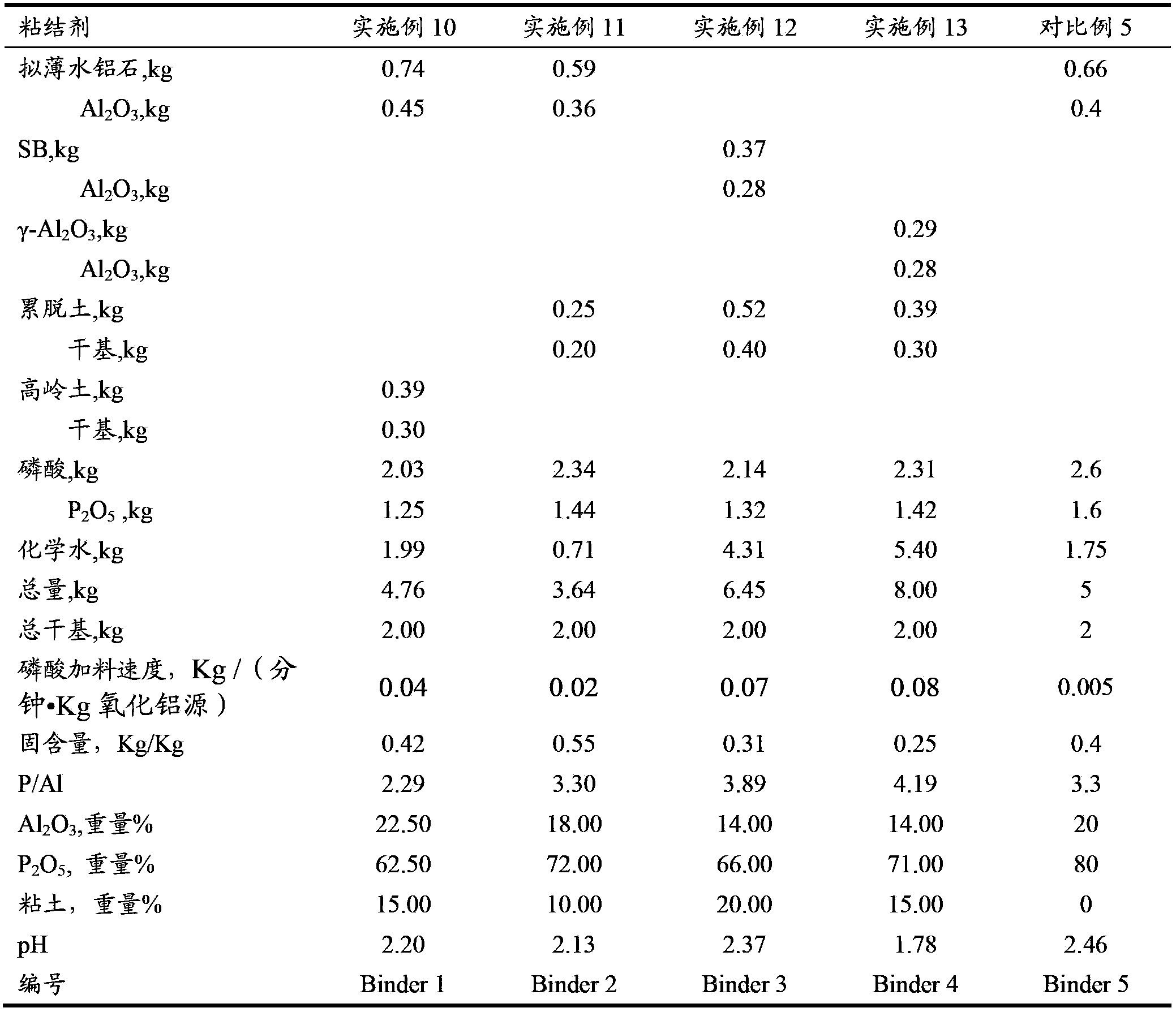
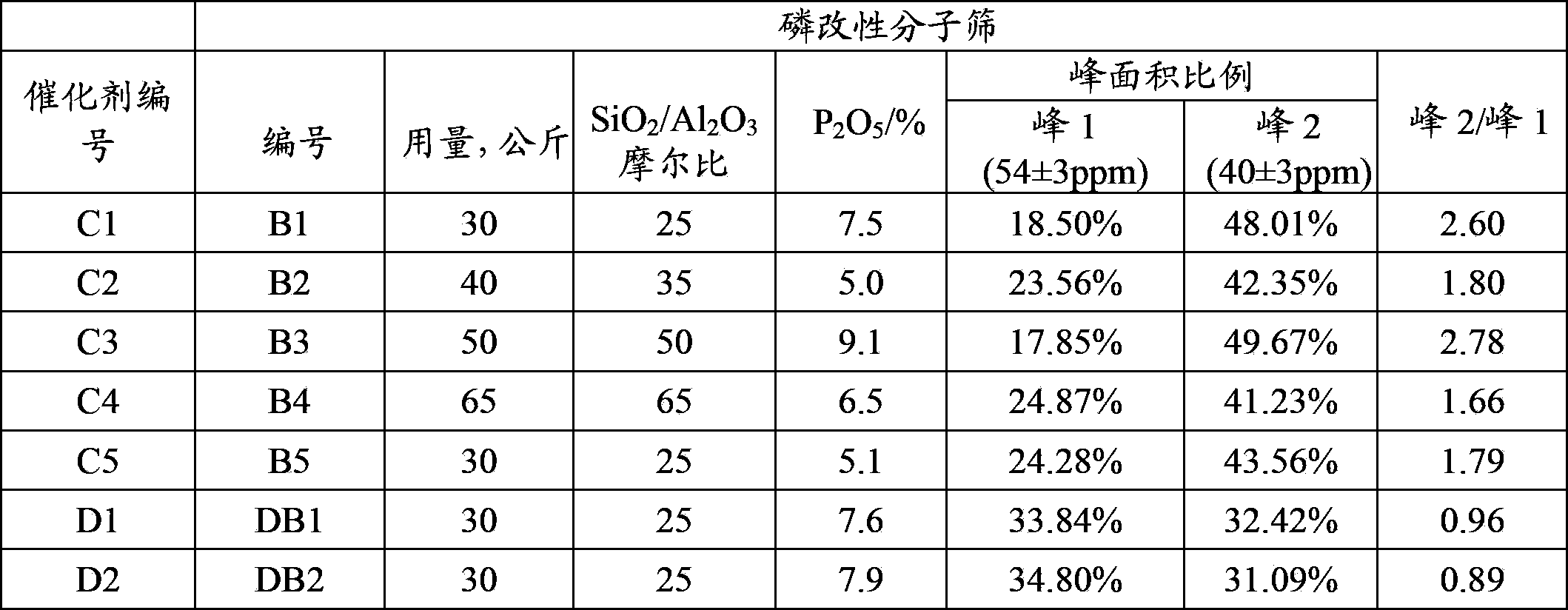
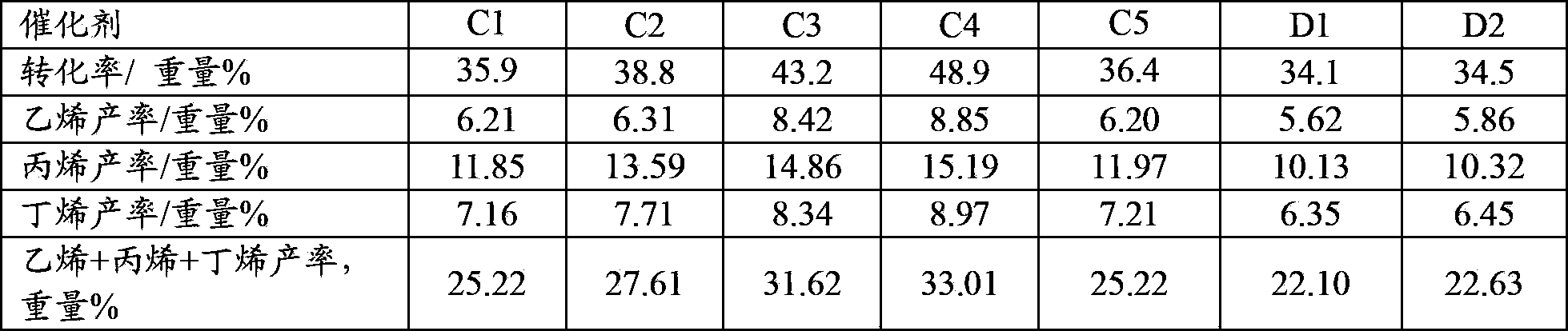
Catalytic cracking catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103785460AGood choiceHigh yieldCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMagic angle spinningAdhesive
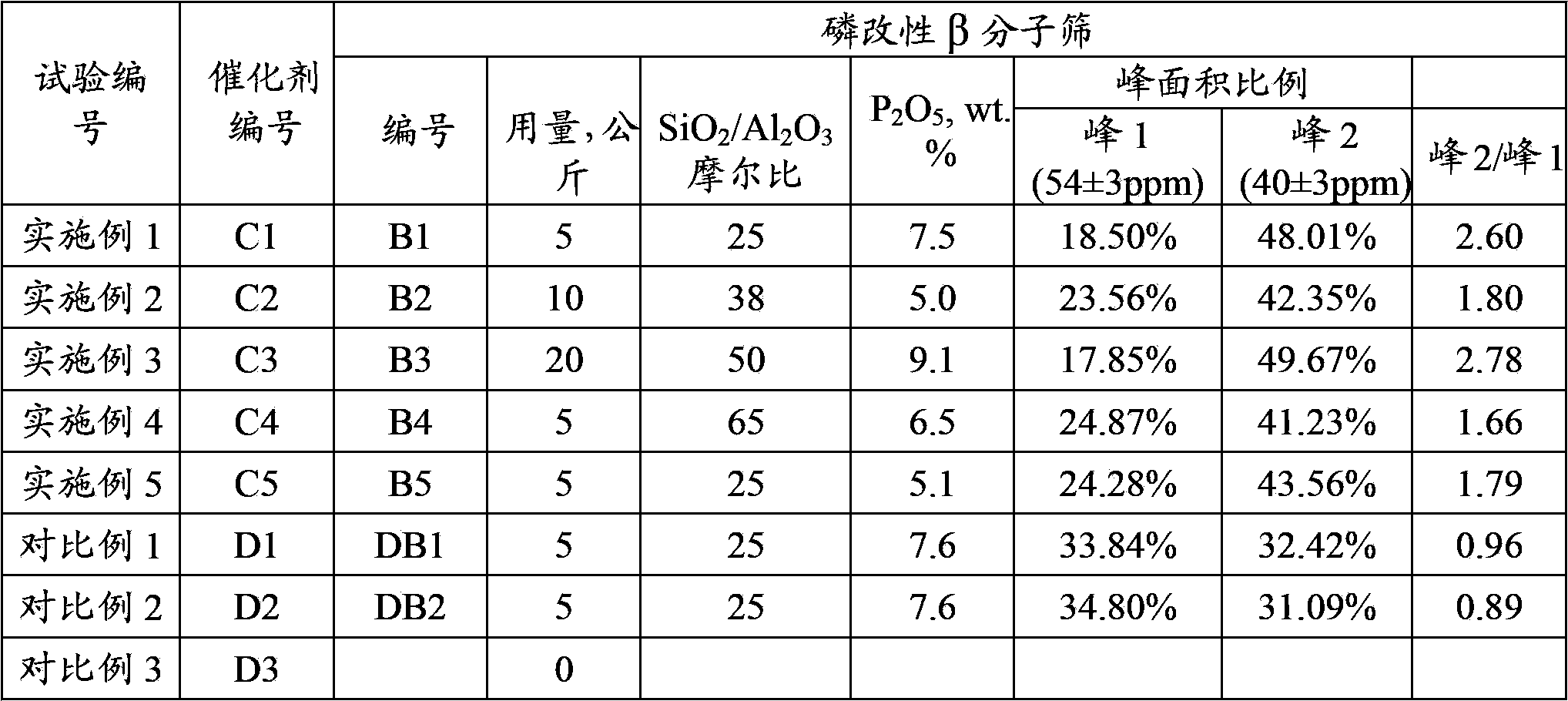
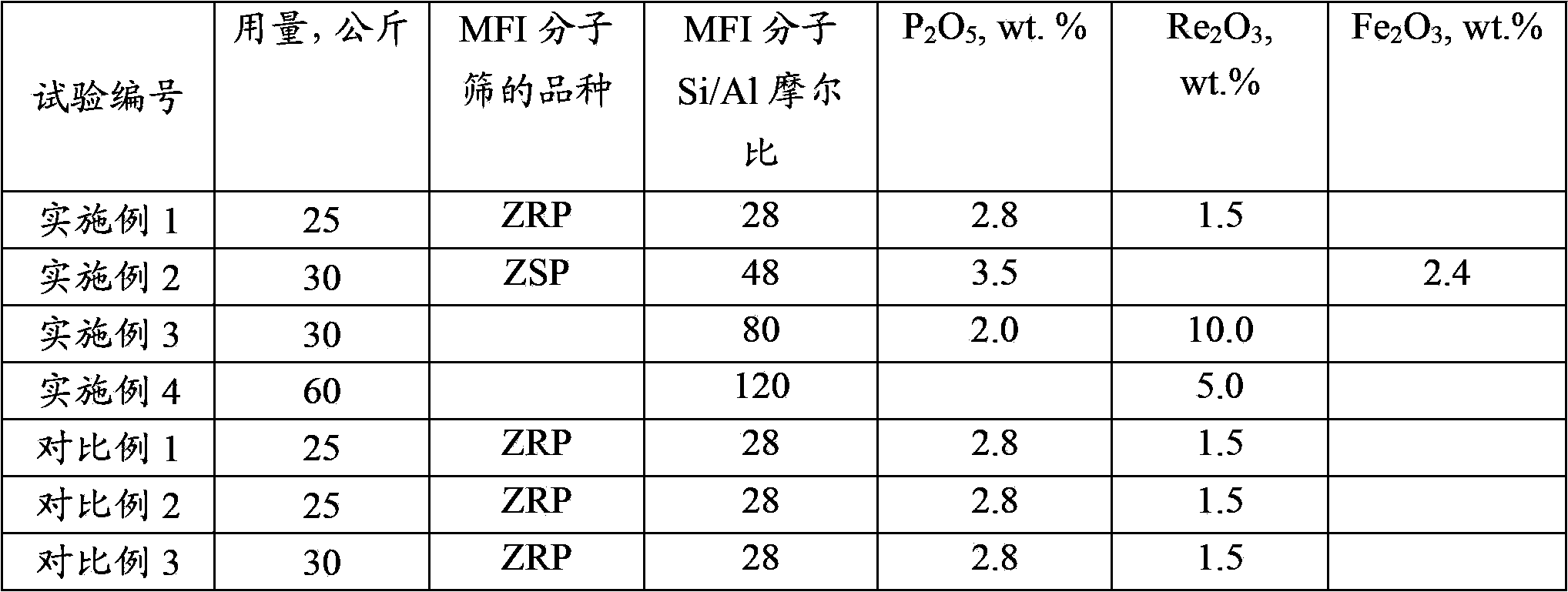
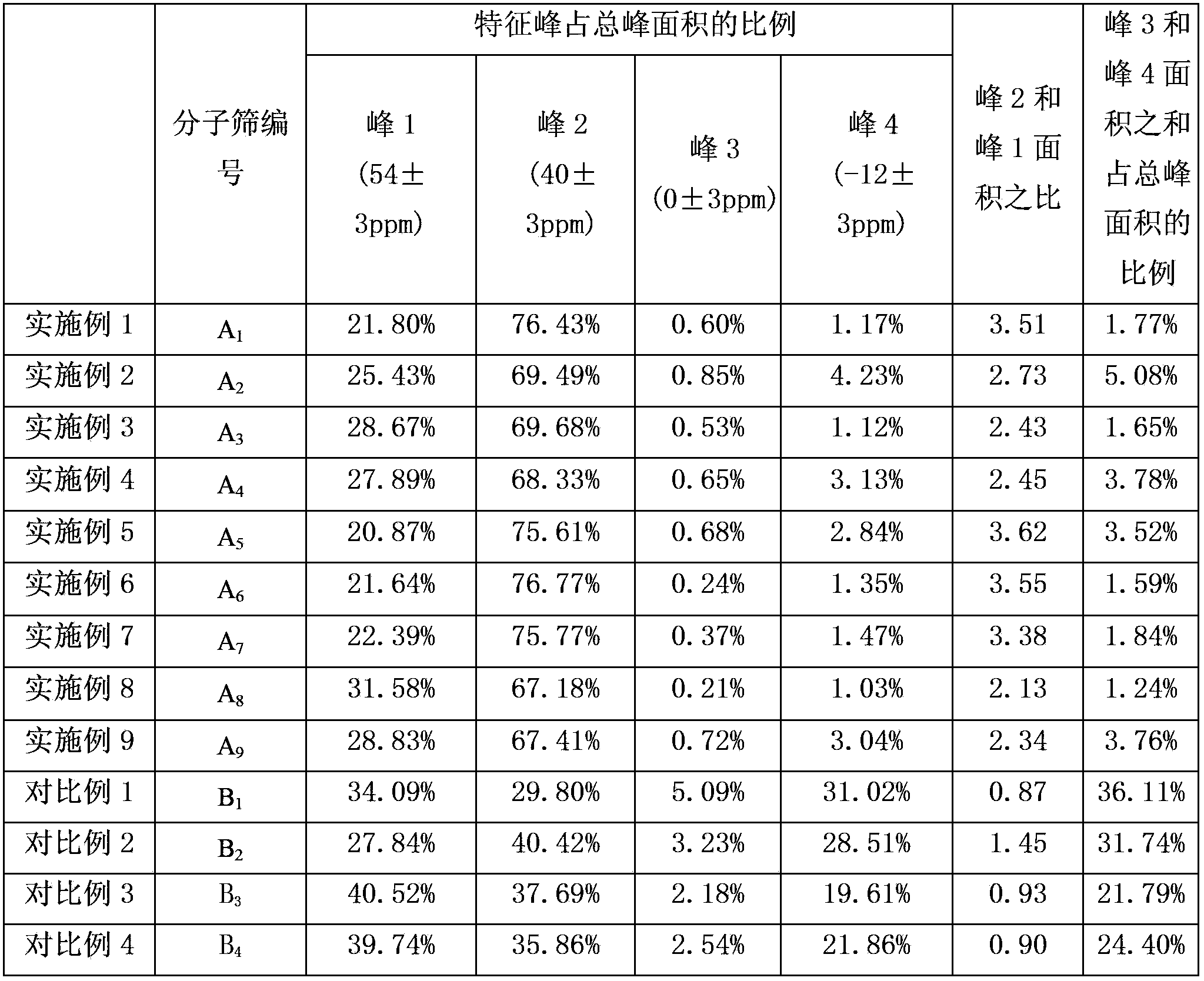
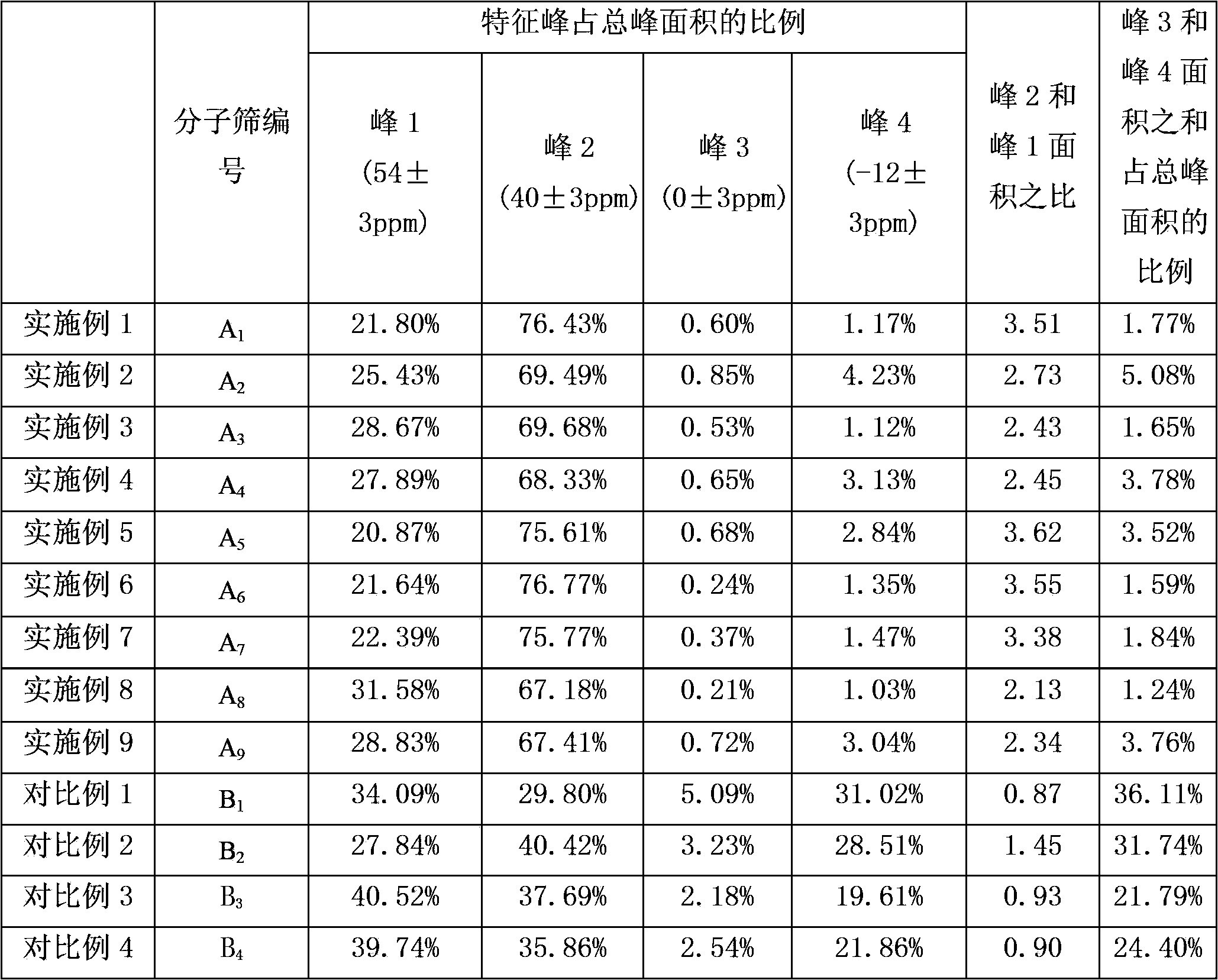
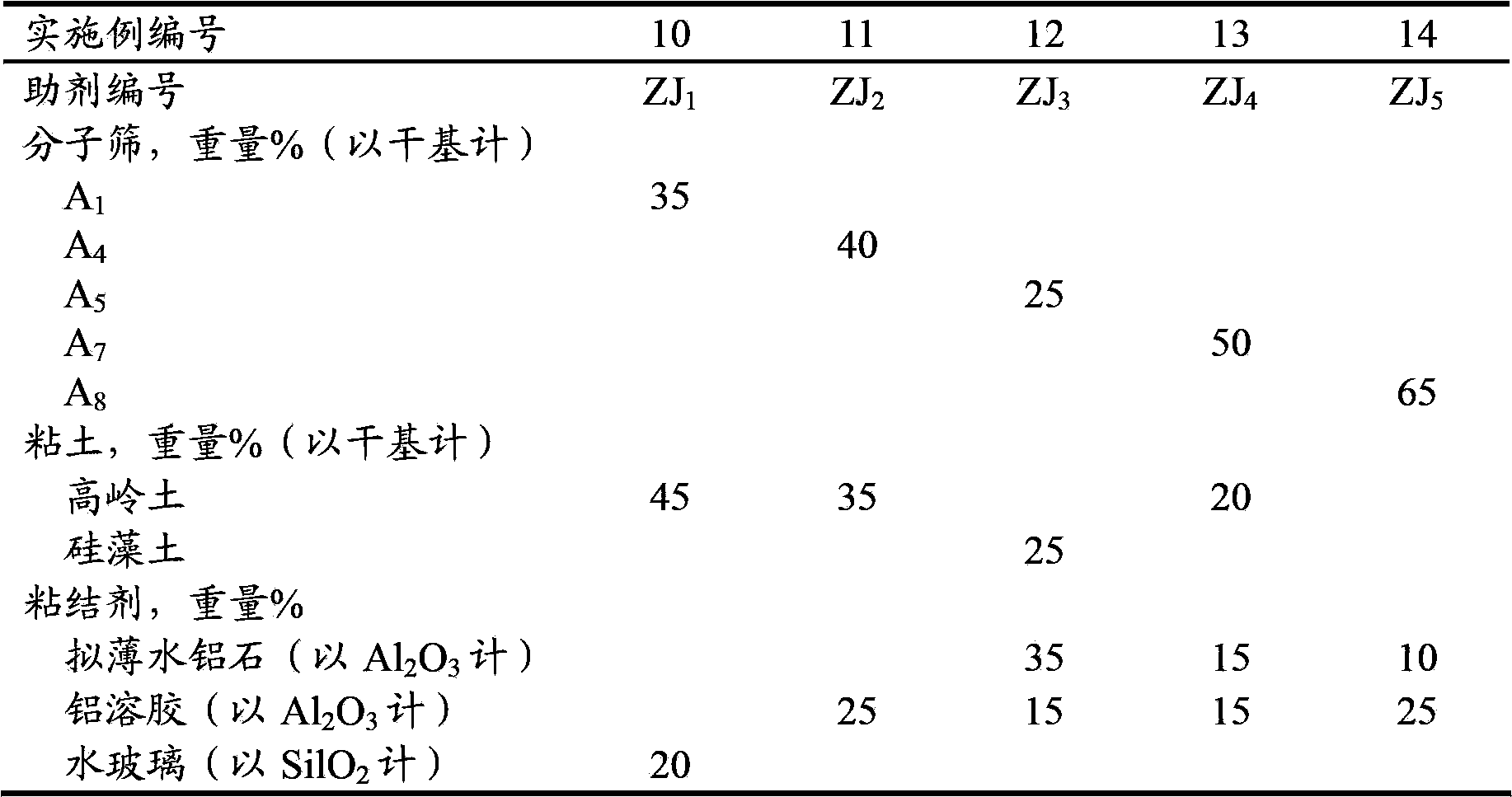
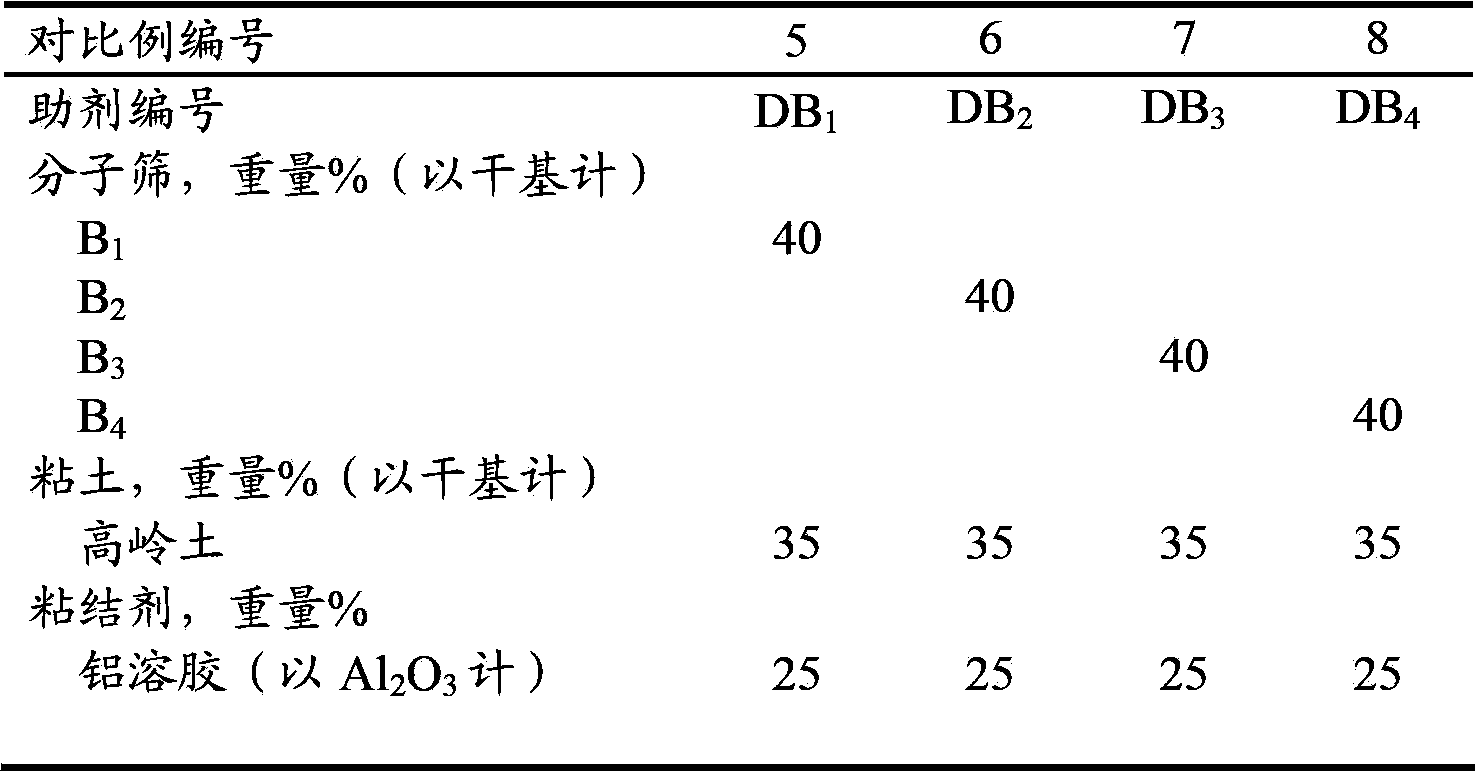
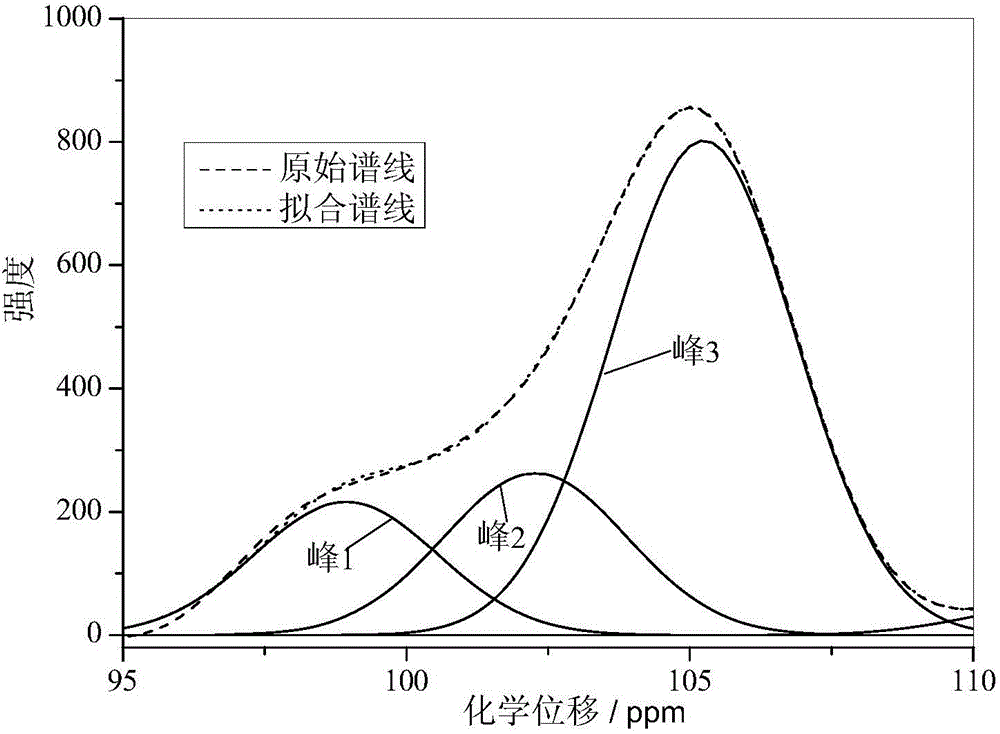
The invention discloses a catalytic cracking catalyst and a preparation method thereof, the catalytic cracking catalyst includes (a)15%-65% of a natural mineral, (b) 10%-30% of an oxide and (c) 25%-75% of a mixture of a MFI structure molecular sieve and a phosphorus-modified beta molecular sieve; the phosphorus-modified beta molecular sieve comprises 3-10 wt% by P2O5 of phosphorus, and in the 27Al MAS NMR (Magic Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) of the molecular sieve, the ratio of resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 40+-3ppm to resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 54+-3ppm is greater than or equal to 1. The preparation method of the catalyst comprises the steps of mixing and pulping of the phosphorus-modified beta molecular sieve, the natural mineral and a non-polar oxide adhesive, and spray drying, and the preparation method of the phosphorus-modified beta molecular sieve is as follows: programmed heating of beta molecular sieve raw powder to bake to remove a template agent, and then phosphorus modification. The catalytic cracking catalyst is applied to preparation of propylene by catalytic cracking of naphtha, and the low-carbon olefin production rate is higher.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Campylobacter glycans and glycopeptides
ActiveUS20060165728A1Prevent groundwater pollutionEliminating and reducing presenceAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaMagic angle spinningGlycopeptide
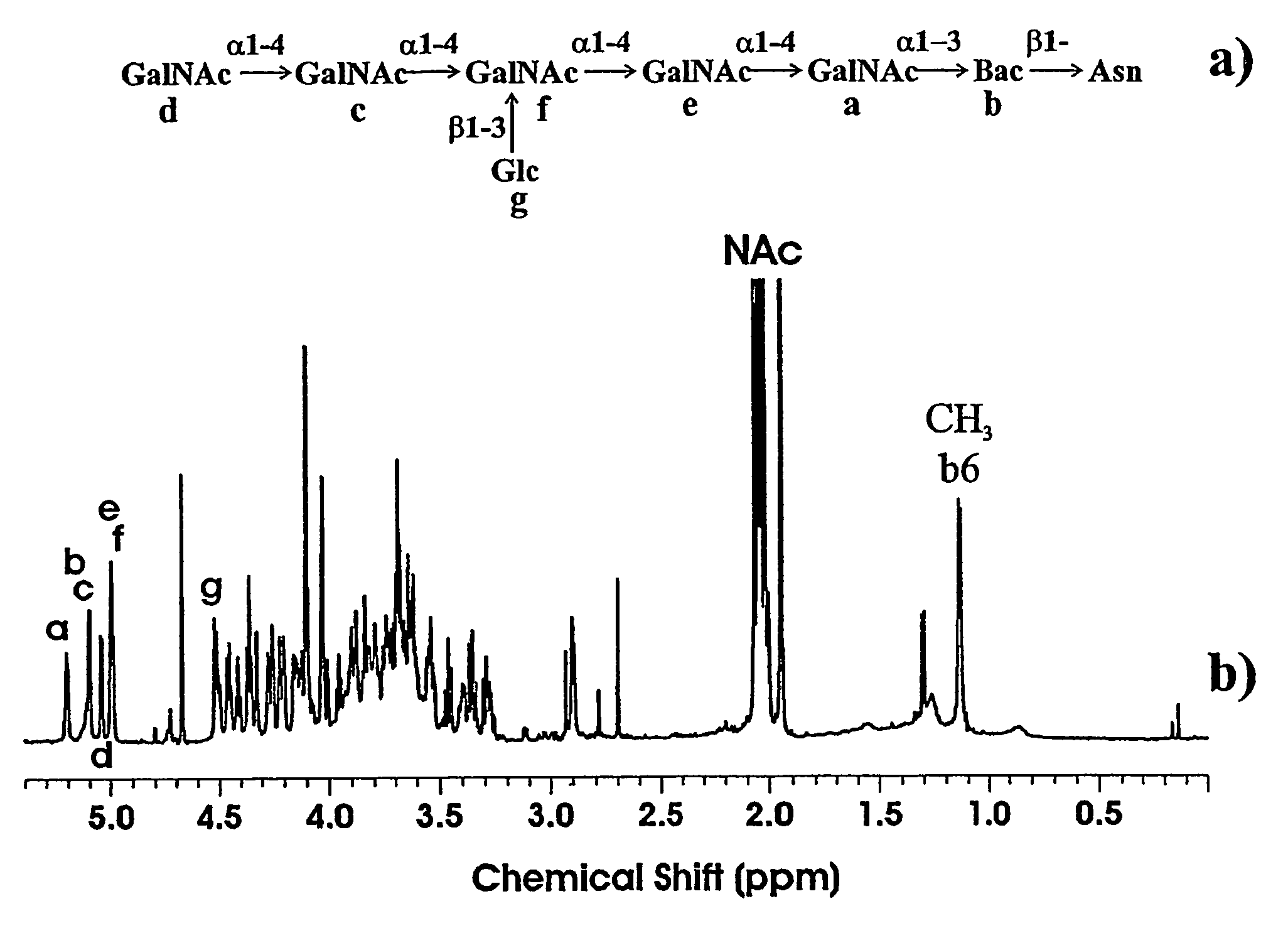
Multiple strains and species of Campylobacter were found to share a common glycan moitie which is present in a plurality of surface-exposed glycoproteins. This glycan has the formula: GalNAc-a1,4-GalNAc-a1,4-[Glc-β1,3]GalNAc-a1,4-GalNAc-a1,4-GalNAc-a1,3-Bac, wherein Bac is 2,4-diacetamido-2,4,6-trideoxy-D-glucopyranose. This glycan and immunologically active fragments of it have use as vaccines against campylobacter infection in humans and animals. As well, antibodies which specifically bind these compounds may be provided. Such antibodies and vaccines may be used to prevent or neutralize campylobacter infections in livestock thereby preventing this pathogen from entering the human food chain. The glycan may be linked to one or more amino acids to form a glycopeptide. As well, a method for determining the glycan structure of an intact glycoprotein consists of subjecting a sample to high resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (HR-MAS-NMR) spectroscopy.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
NMR CryoMAS Probe for High-field Wide-bore Magnets
InactiveUS20060176056A1Reduce riskImprovement factorElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonancePartial solutionNitrogen gas
An MAS probe is disclosed for obtaining a substantial improvement in signal to noise (S / N) in triple-resonance high-resolution (HR) magic-angle-spinning (MAS) NMR of samples near room temperature (RT) in high-field magnets where the magnet's RT shim bore is greater than 60 mm. All critical circuit components, including the sample coils, are located along with the spinner assembly in a thermally insulated cold zone pressurized with helium gas. The spinner assembly attaches to a sealed, curved, rotor-loading tube to permit automatic sample change, and it is surrounded by a partially insulated jacket cooled with a cryogenic fluid, generally nitrogen gas. The MAS probe is also compatible with magic angle gradients, variable temperature operation, field locking, and commonly available closed-cycle cold fingers. One major challenge in implementing CryoMAS is solving the problem of gas leakage from the spinner bearing, drive, and exhaust nitrogen into the cold zone, as some components will necessarily be ceramic, some plastic, and some metal. It is not desirable to use helium for the spinner bearing and drive gases for cost reasons and to prevent risk of degradation of o-ring-sealed magnet cryostats. A pressurized helium atmosphere in the cold zone may be utilized to prevent nitrogen flow from the spinner exhaust streams or atmosphere into the cold zone. The drawback to a pressurized cold zone is that the heat transfer coefficient in dense helium at low temperatures is very high, making it challenging to cool the sample coils and all the large, critical, circuit components in a practical manner. Part of the solution here is to use a first-stage cooling-jacket around the major heat leaks near the spinner exhaust flows. The critical components may be insulated with fine glass wool or teflon foam and conduction cooled without cooling much of the cold zone below the temperature of the first-stage cooling. The use of coaxial sapphire capacitors allows the noise contributions from the most critical capacitors to be reduced to a minor fraction of the total.
Owner:DOTY SCI
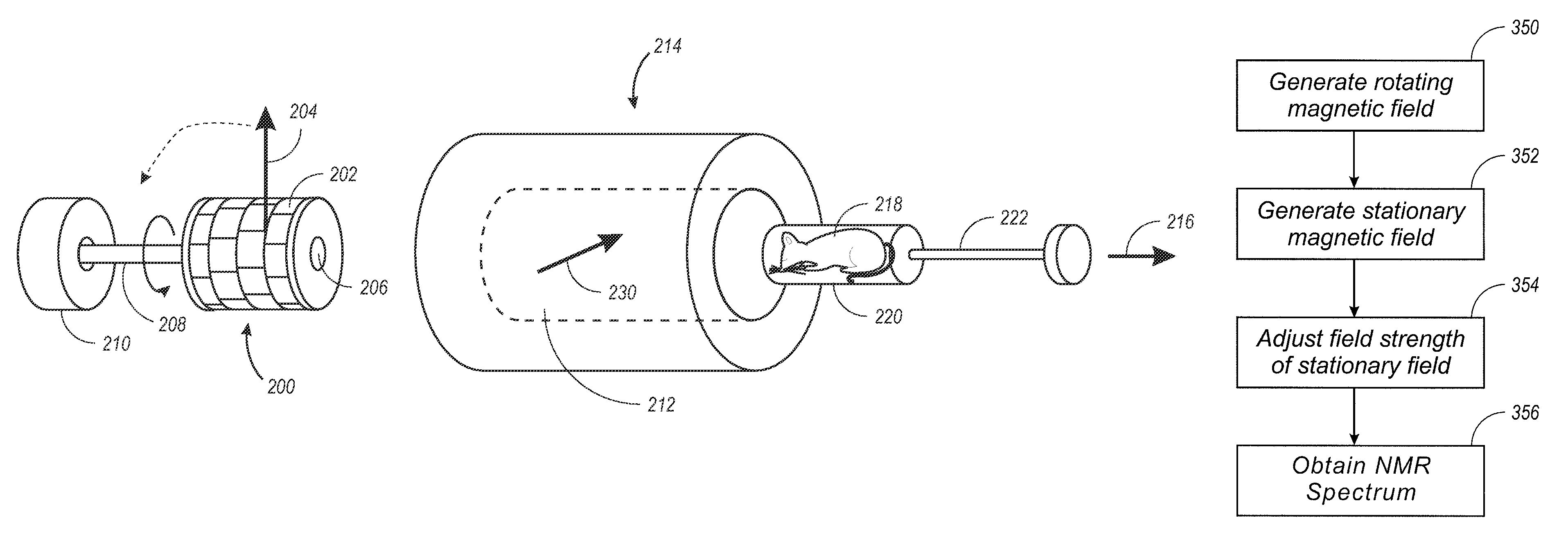
System and method for providing a rotating magnetic field
InactiveUS20080024130A1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagic angle spinningLive animal
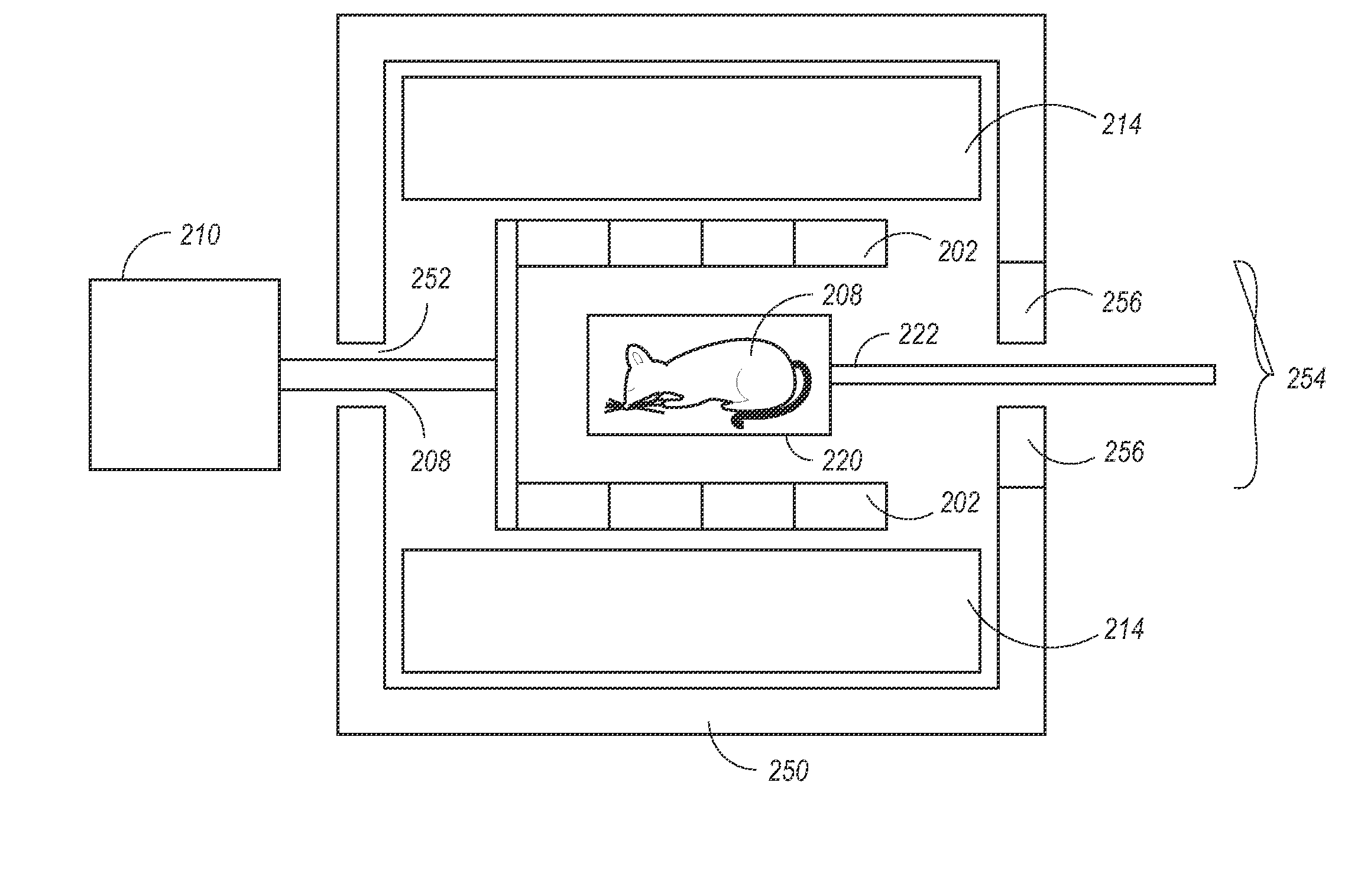
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for generating a rotating magnetic field. The rotating magnetic field can be used to obtain rotating-field NMR spectra, such as magic angle spinning spectra, without having to physically rotated the sample. This result allows magic angle spinning NMR to be conducted on biological samples such as live animals, including humans.
Owner:SCHLUETER ROSS D +1
Cracking assistant for improving low-carbon olefin concentration
ActiveCN103785458AImprove wear resistanceGood catalytic cracking performanceCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMagic angle spinningPeak area
The invention discloses a cracking assistant for improving the low-carbon olefin concentration. The cracking assistant comprises a phosphorus and transition metal-containing beta molecular sieve, a first-clay-containing phosphorus aluminum inorganic binder, other inorganic binder and second clay; the first-clay-containing phosphorus aluminum inorganic binder comprises 15-40 wt% by Al2O3 of an aluminum component, 45-80 wt % by P2O5 of a phosphorus component and 1-40 wt % by dry basis of first clay, the weight ratio of P to Al is 1-6; the phosphorus and transition metal-containing beta molecular sieve comprises 1-10wt% by P2O5 of phosphorus and 0.5-10 wt % by metallic oxide of a metal; and in the 27Al MAS NMR (Magic Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) of the phosphorus and transition metal-containing beta molecular sieve, the ratio of resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 40+-3ppm to resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 54+-3ppm is greater than 1, and the percentage of the sun of the resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 0+-3ppm and the resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of-12+-3ppm to the total peak area is less than 10%. The cracking assistant is used for catalytic cracking, and can improve ethylene concentrations in a catalytic cracking dry gas, and improve propylene and isobutylene concentration in a liquefied gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
NMR MAS probe with cryogenically cooled critical circuit components
ActiveUS7151374B2Enhanced signalReduce noiseElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagic angle spinningHigh field
A MAS probe offers a substantial improvement in signal to noise (S / N) in triple-resonance high-resolution (HR) magic-angle-spinning (MAS) NMR of samples near room temperature (RT) in high field magnets, especially where the RT shim bore is less than 55 mm. Critical circuit components other than the sample coils, including both high-power capacitors and inductors for one or more channels are located in a small, thermally insulated, cold zone immediately below the sample spinner assembly. Cooling these components to 100 K allows their thermal noise power to be conveniently reduced by a factor of three or more. Variable capacitors for fine tuning are located in an RT tuning zone below the cold zone. The circuit is designed such that the currents, voltages, and standing wave ratio (SWR) in circuit tuning elements in the RT tuning zone are relatively low, so rf losses and noise contributions below the cold zone may be only a few percent. The MAS probe is also compatible with magic angle gradients, automatic sample change, multi-nuclear tuning, variable temperature operation, field locking, and optical spin rate detection.
Owner:DOTY SCI
Magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus and process for high-resolution in situ investigations
ActiveUS20140099730A1Short timeRaise the ratioMeasurements using NMR spectroscopySupporting apparatusMagic angle spinningContinuous flow
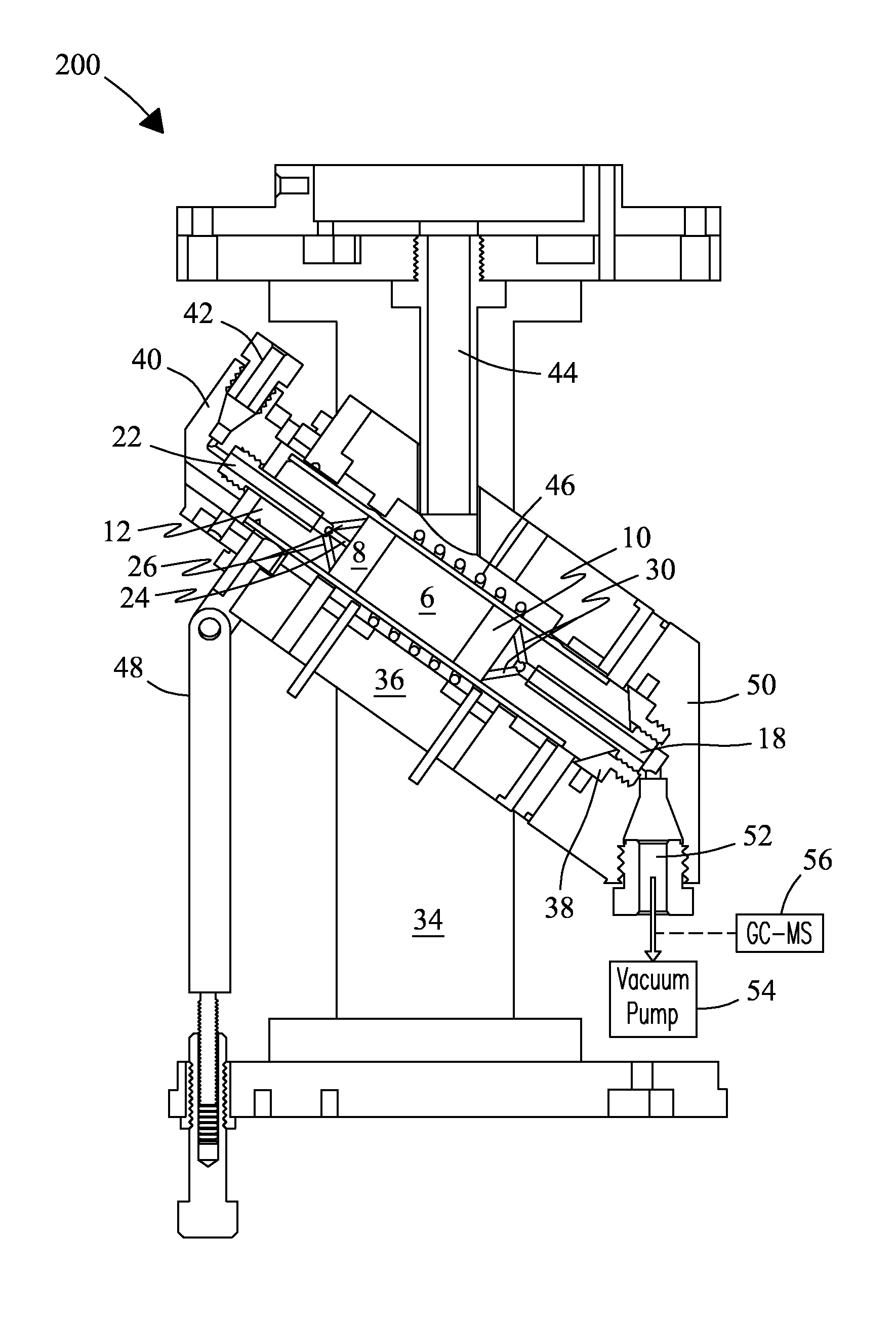
A continuous-flow (CF) magic angle sample spinning (CF-MAS) NMR rotor and probe are described for investigating reaction dynamics, stable intermediates / transition states, and mechanisms of catalytic reactions in situ. The rotor includes a sample chamber of a flow-through design with a large sample volume that delivers a flow of reactants through a catalyst bed contained within the sample cell allowing in-situ investigations of reactants and products. Flow through the sample chamber improves diffusion of reactants and products through the catalyst. The large volume of the sample chamber enhances sensitivity permitting in situ 13C CF-MAS studies at natural abundance.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Multiphase catalytic reaction device for testing in situ solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance
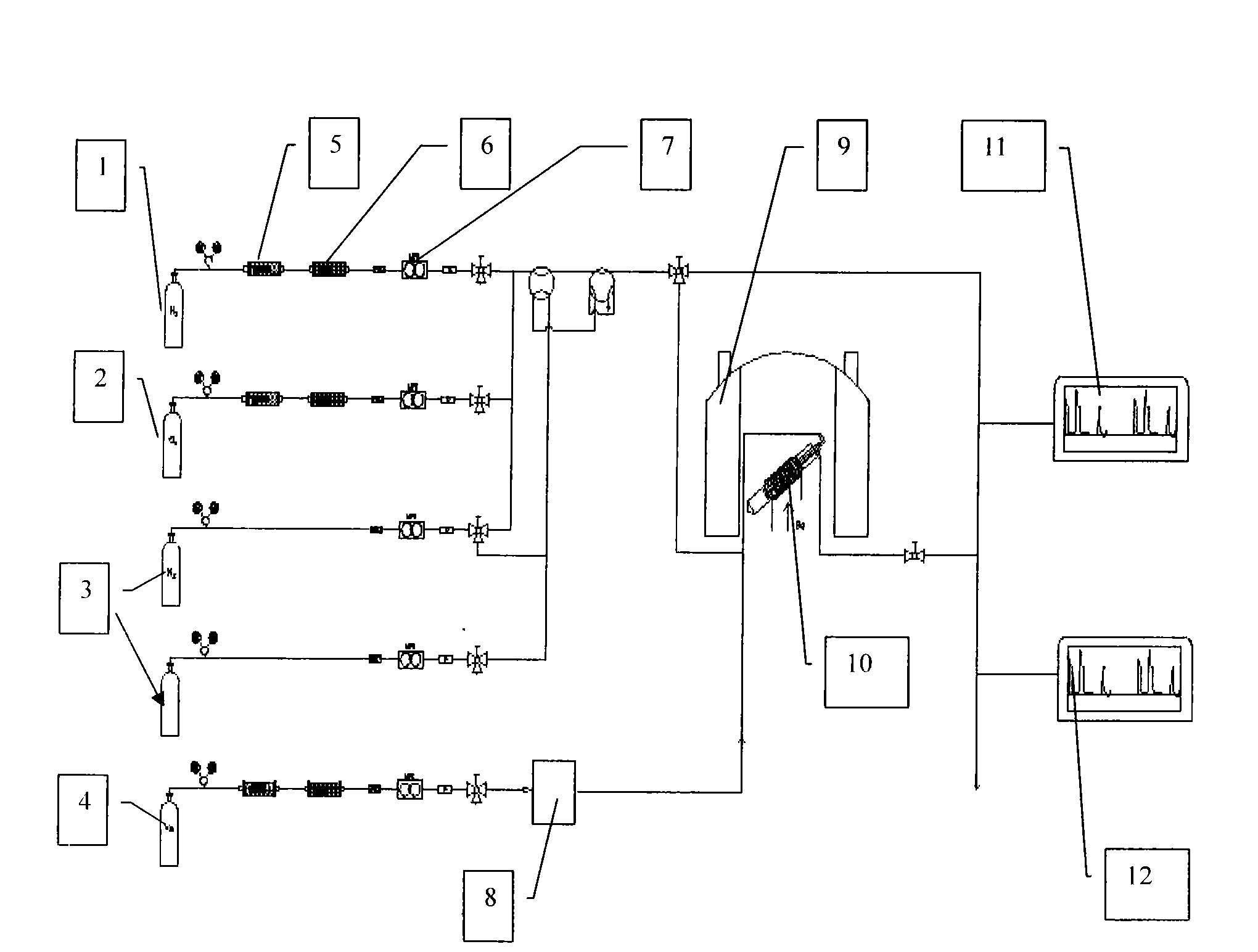
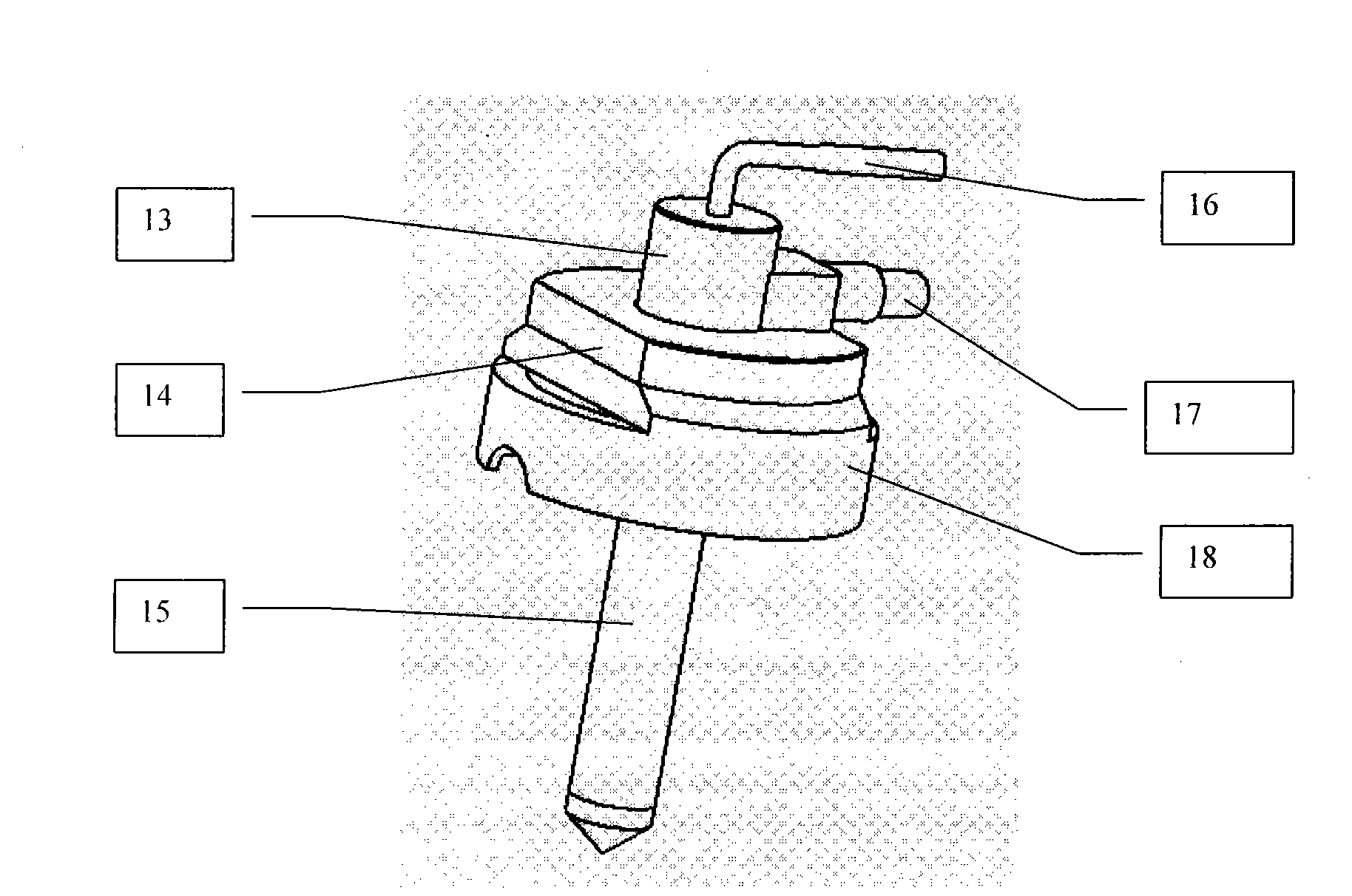
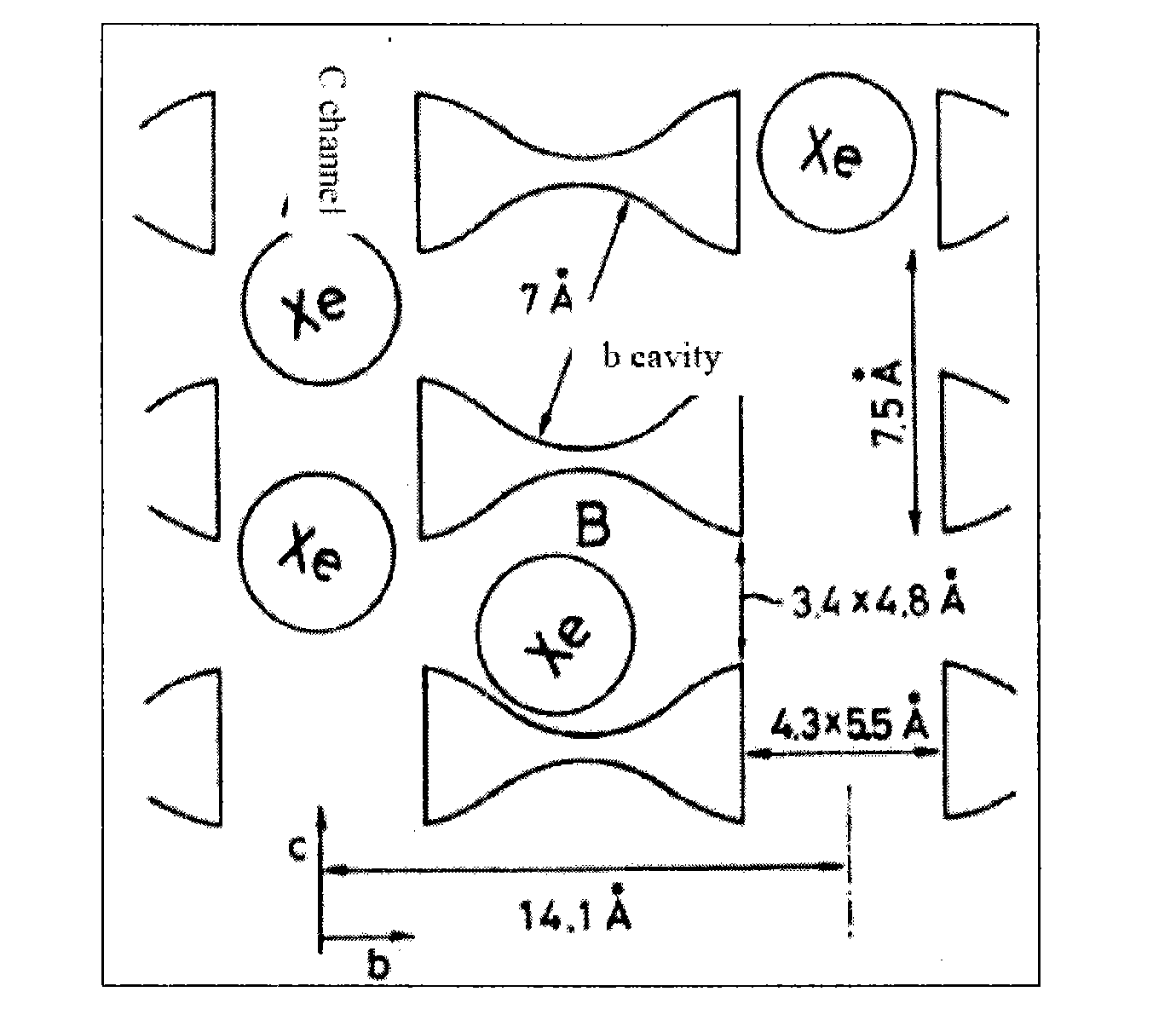
InactiveCN101634651AChemical analysis using catalysisComponent separationMagic angle spinningGas phase
The invention relates to a multiphase catalytic reaction device for testing in situ solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance, which is a magic angle spinning multiphase catalytic reactor in which an online solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance system, a quadrupole mass-spectrometer, a gas chromatograph and a laser-induced hyperpolarized 129Xe isotope probe are linked for use. The reactor can apply various solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance techniques to track and detect a catalyst structure, reaction intermediates and species with catalyst activity in the catalytic reaction process; reaction products are qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed by the quadrupole mass-spectrometer and the gas chromatograph, so that the performance of the catalyst is evaluated; simultaneously, laser-induced hyperpolarized 129Xe isotope is used as a probe molecule to study the change of the catalyst structure, adsorption positions and diffusion behaviors of various species in the reaction process and the like. In-situ tracking in the catalytic reaction process and the mechanism of the catalytic reaction can be systematically studied through the various techniques.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
NMR system and method having a permanent magnet providing a rotating magnetic field
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for generating a rotating magnetic field. The rotating magnetic field can be used to obtain rotating-field NMR spectra, such as magic angle spinning spectra, without having to physically rotate the sample. This result allows magic angle spinning NMR to be conducted on biological samples such as live animals, including humans.
Owner:SCHLUETER ROSS D +1
Sealed magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance probe and process for spectroscopy of hazardous samples
ActiveUS20140167756A1Prevent proliferationEasy to controlAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionMagic angle spinningNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A magic-angle-spinning (MAS) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) probe is described that includes double containment enclosures configured to seal and contain hazardous samples for analysis. The probe is of a modular design that ensures containment of hazardous samples during sample analysis while preserving spin speeds for superior NMR performance and convenience of operation.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Cracking assistant for improving low-carbon olefin concentration
ActiveCN103785457AHigh yieldGood hydrothermal stabilityCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMagic angle spinningPeak area
The invention discloses a cracking assistant for improving the low-carbon olefin concentration. The cracking assistant comprises 10 to 75wt% of a phosphorus and transition metal-containing beta molecular sieve, 0 to 60wt% of clay and 15 to 60wt% of an inorganic oxide binder; the phosphorus and transition metal-containing beta molecular sieve comprises 1-10wt% by P2O5 of phosphorus and 0.5-10 wt % by metallic oxide of a metal; and in the 27Al MAS NMR (Magic Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) of the phosphorus and transition metal-containing beta molecular sieve, the ratio of resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 40+-3ppm to resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 54+-3ppm is greater than 1, and the percentage of the sun of the resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 0+-3ppm and the resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of-12+-3ppm to the total peak area is less than 10%. The cracking assistant is used for catalytic cracking, and can improve ethylene concentration in a catalytic cracking dry gas, and improve propylene and isobutylene concentration in a liquefied gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
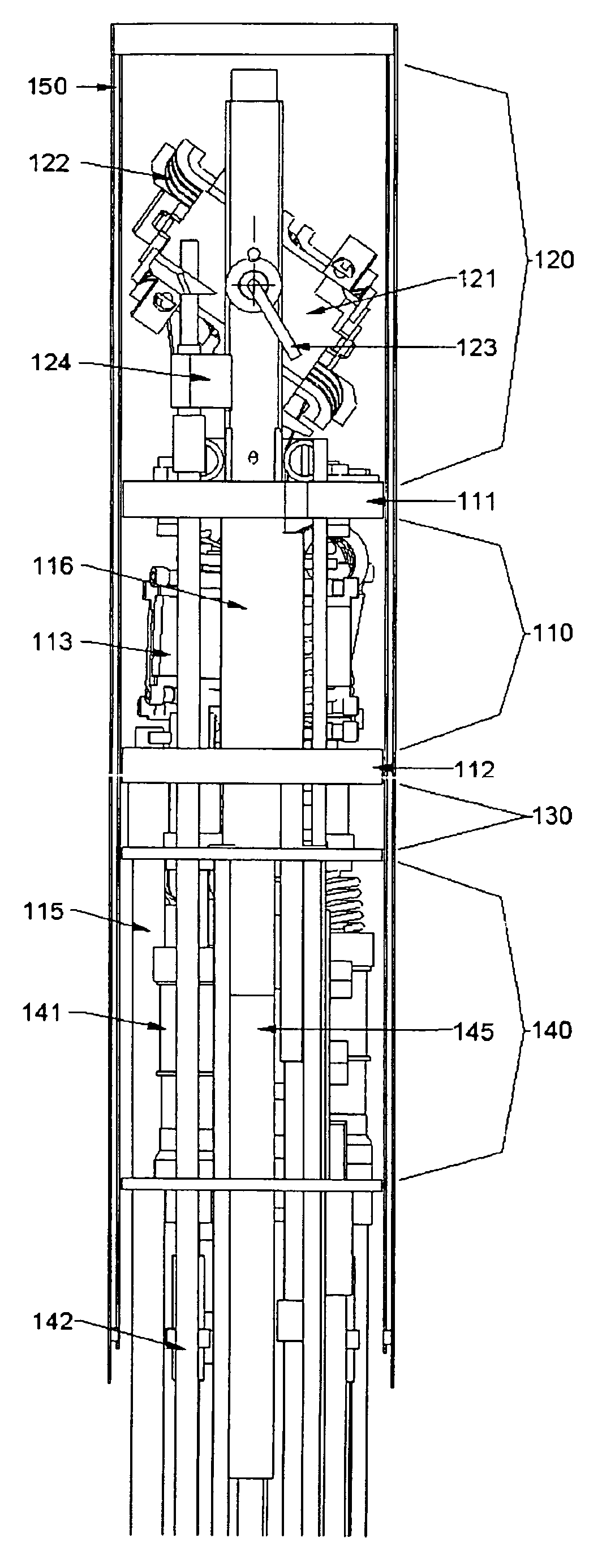
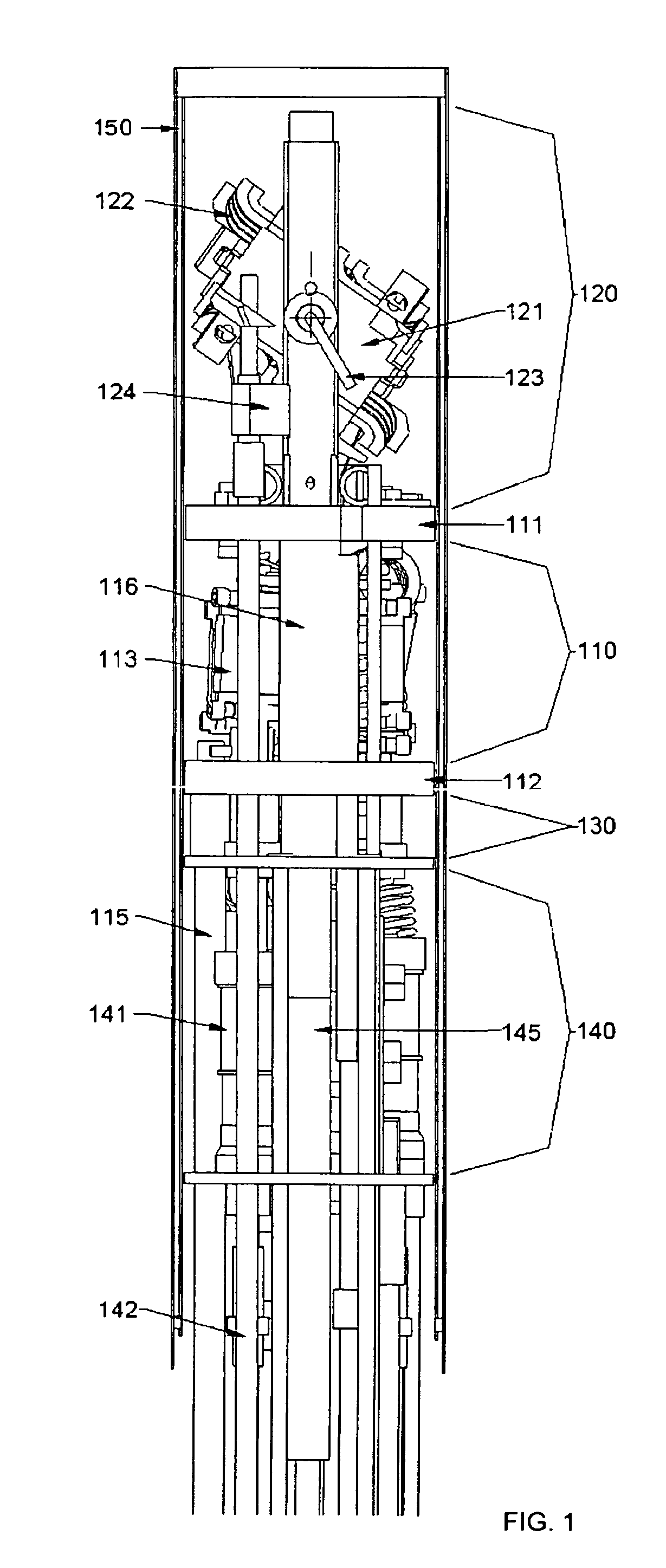
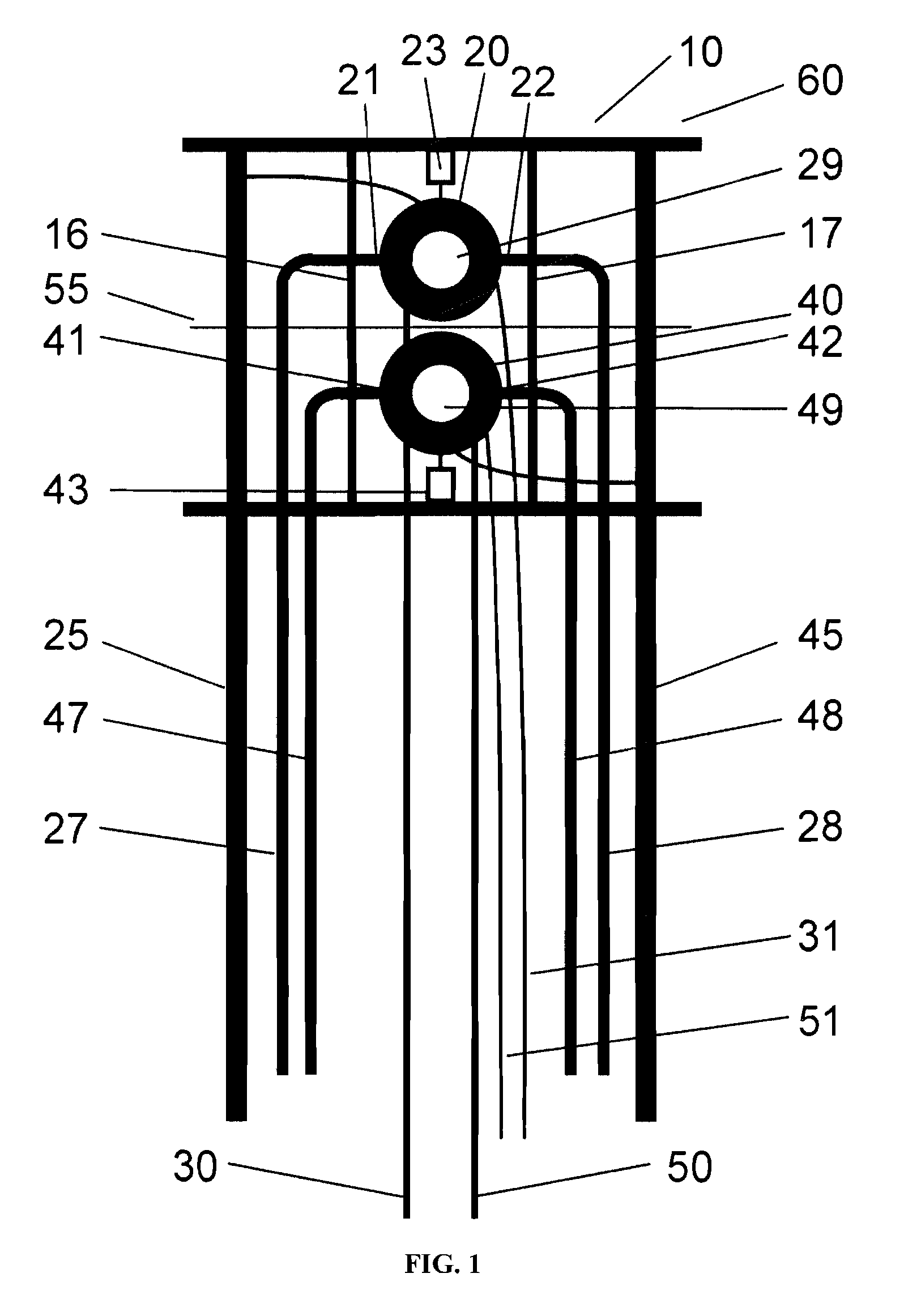
Completely automatic MAS-NMR apparatus
InactiveUS20080088312A1Accelerates automatic sample preparationSamplingElectric/magnetic detectionMagic angle spinningNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
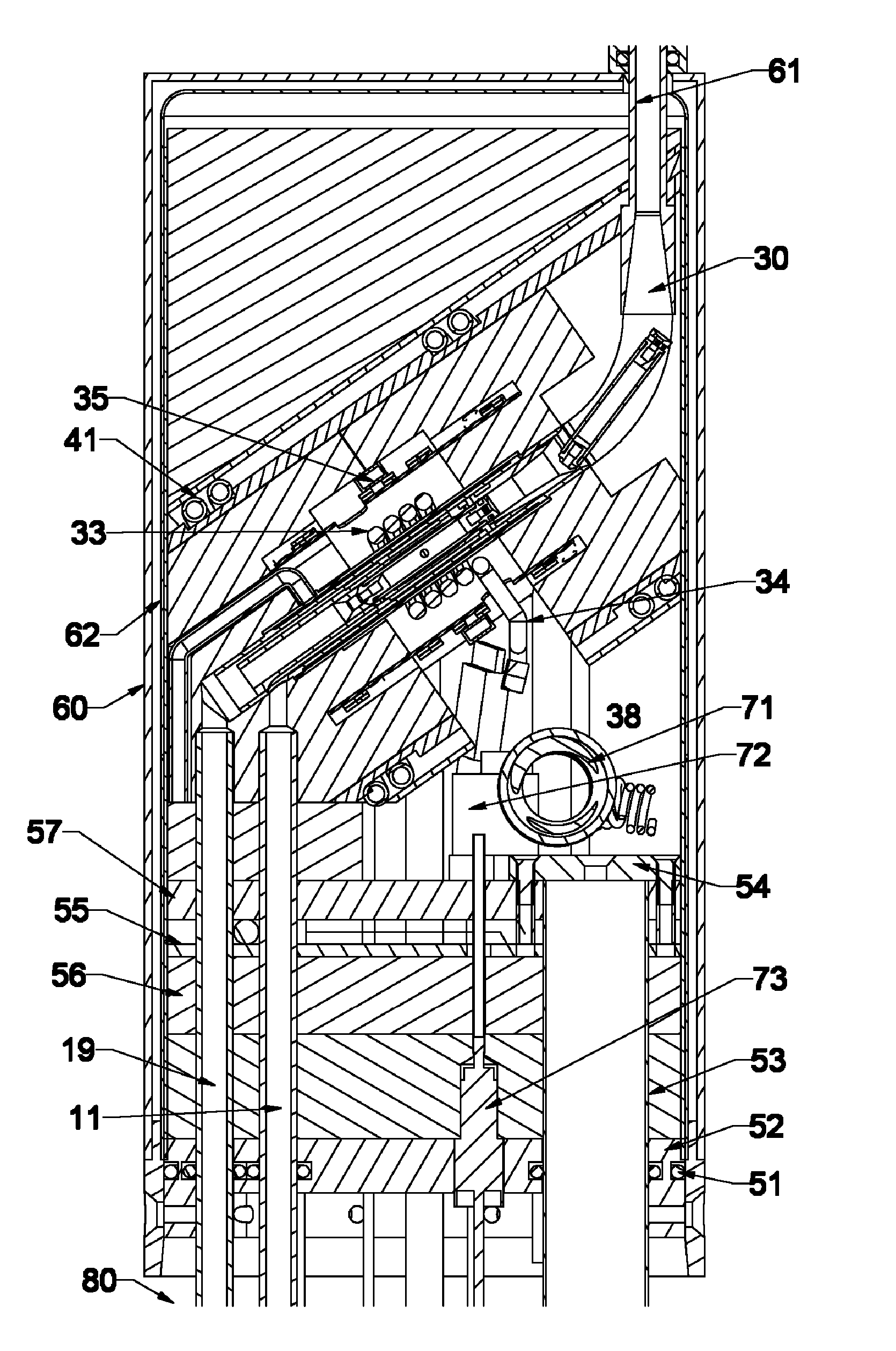
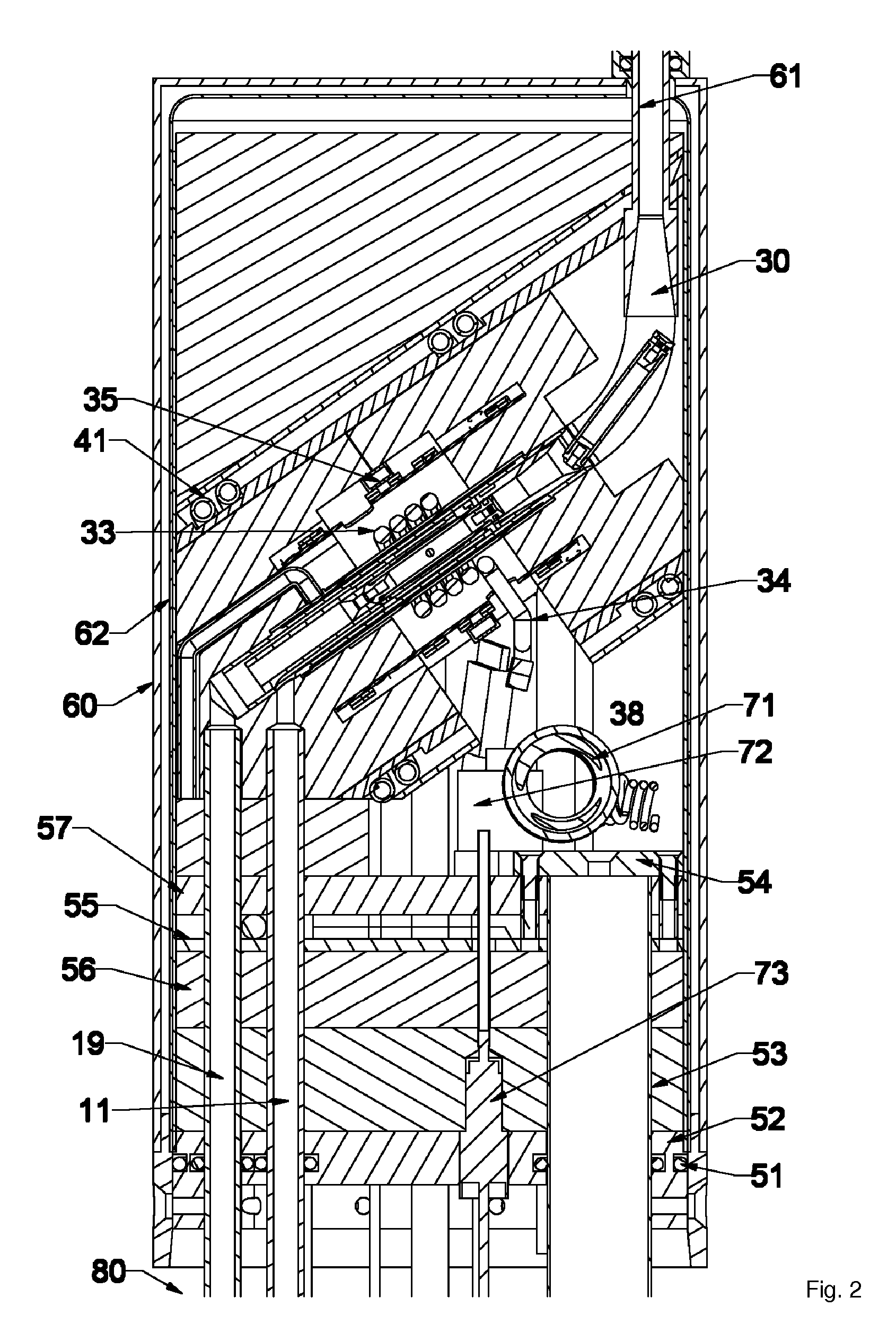
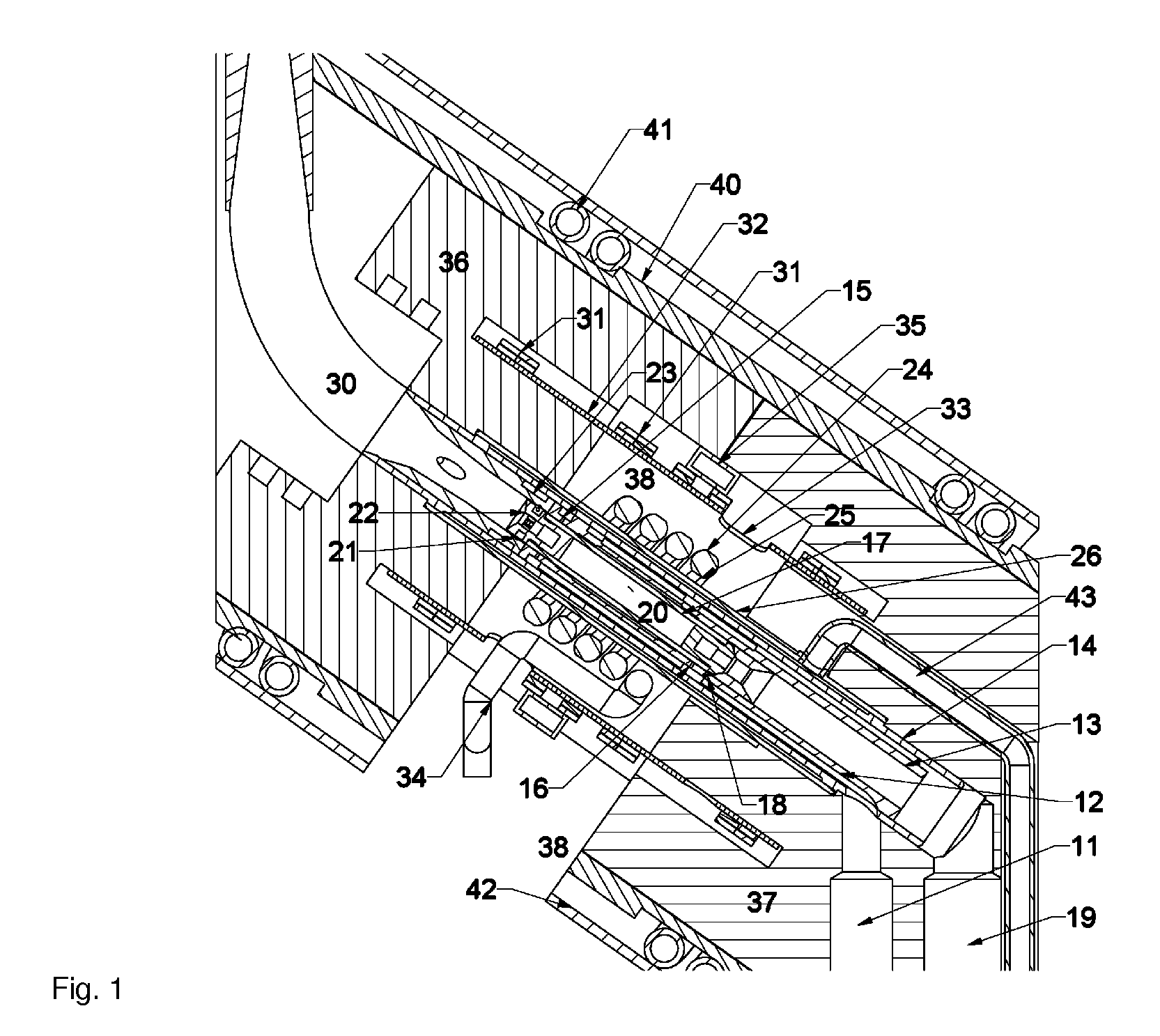
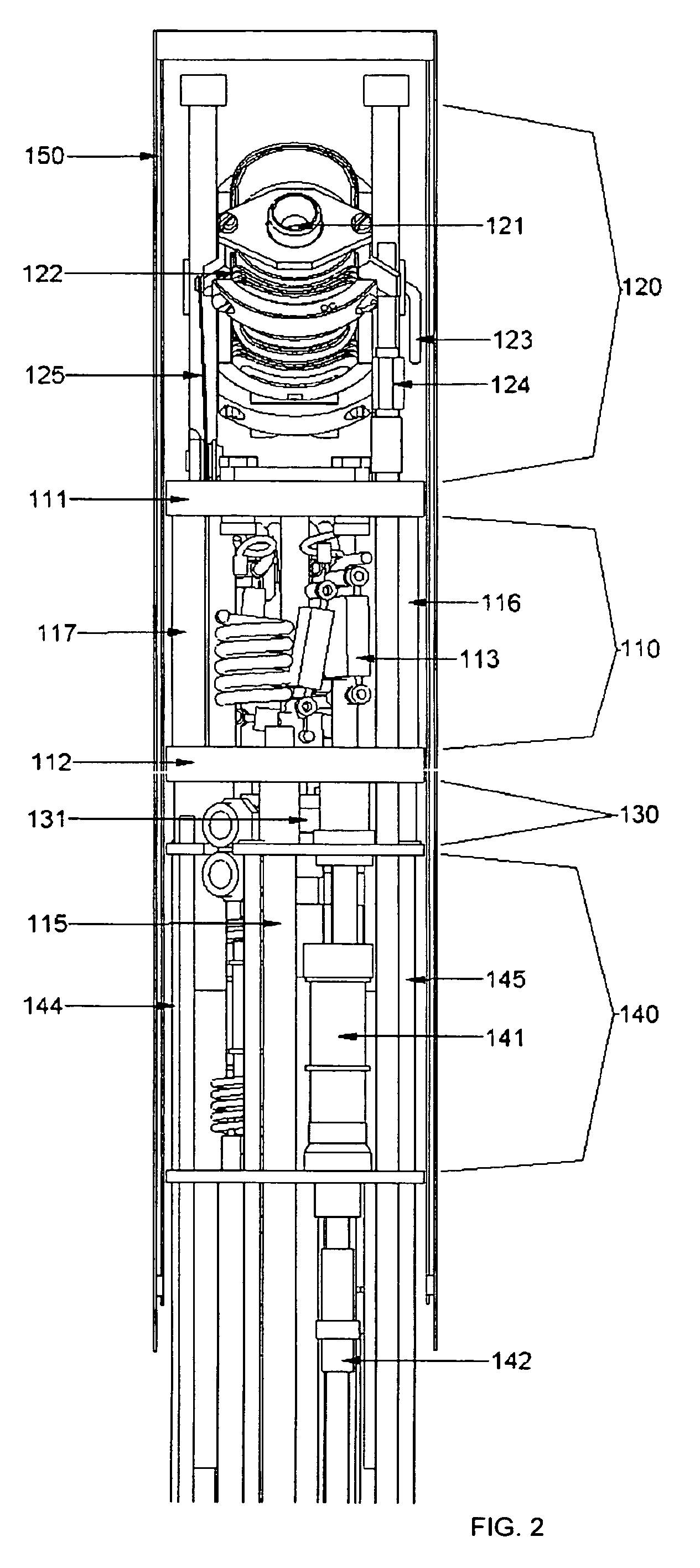
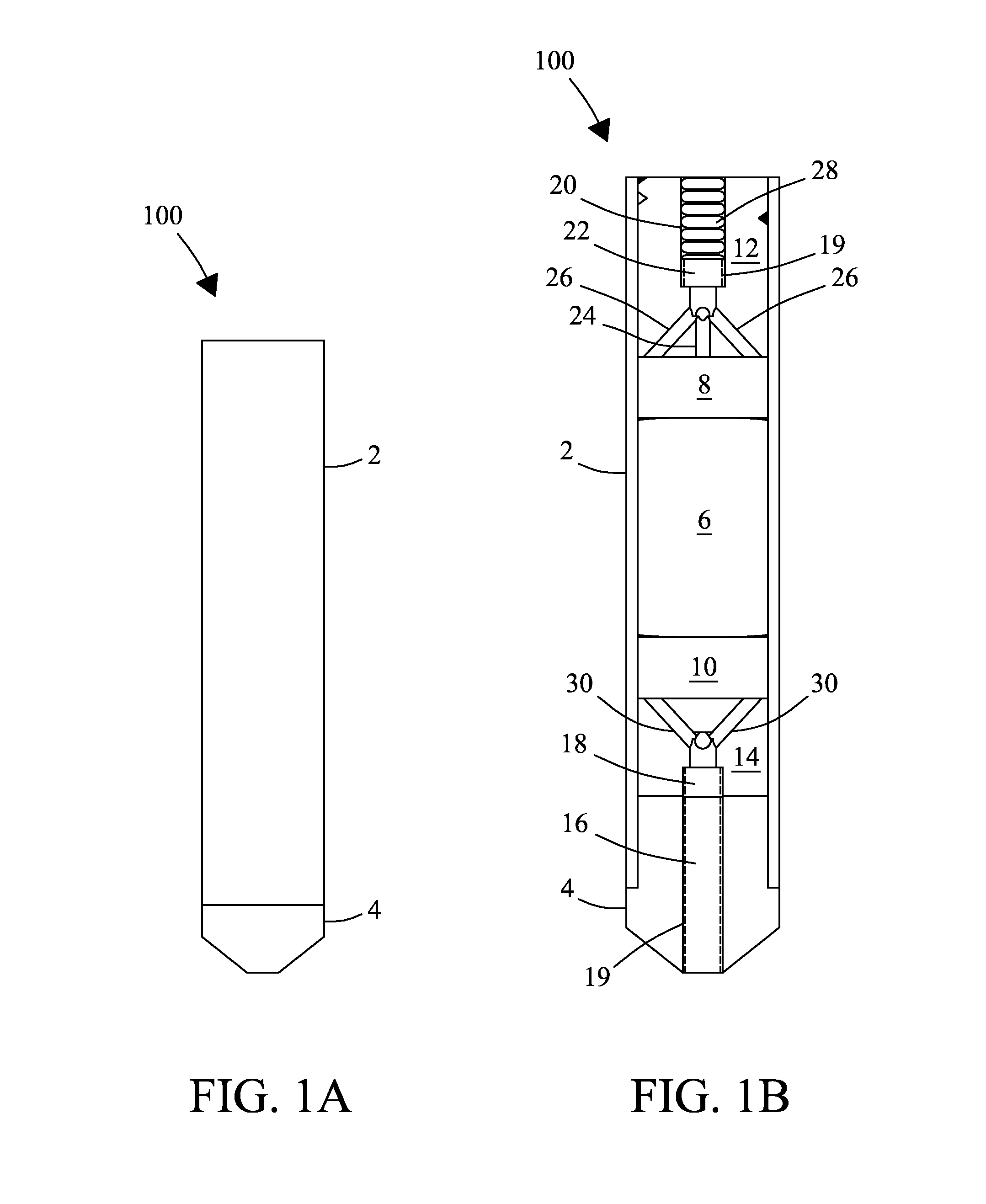
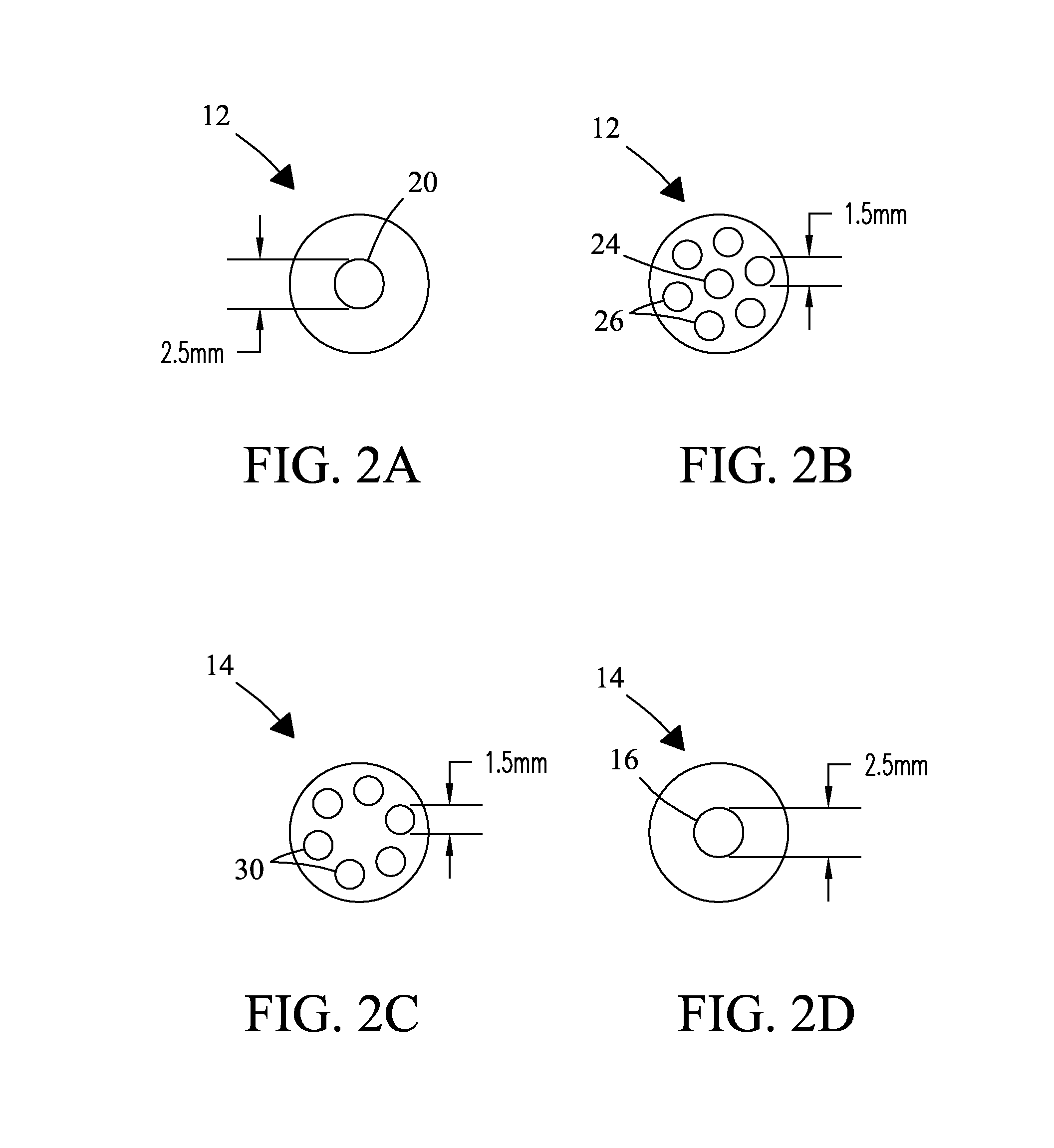
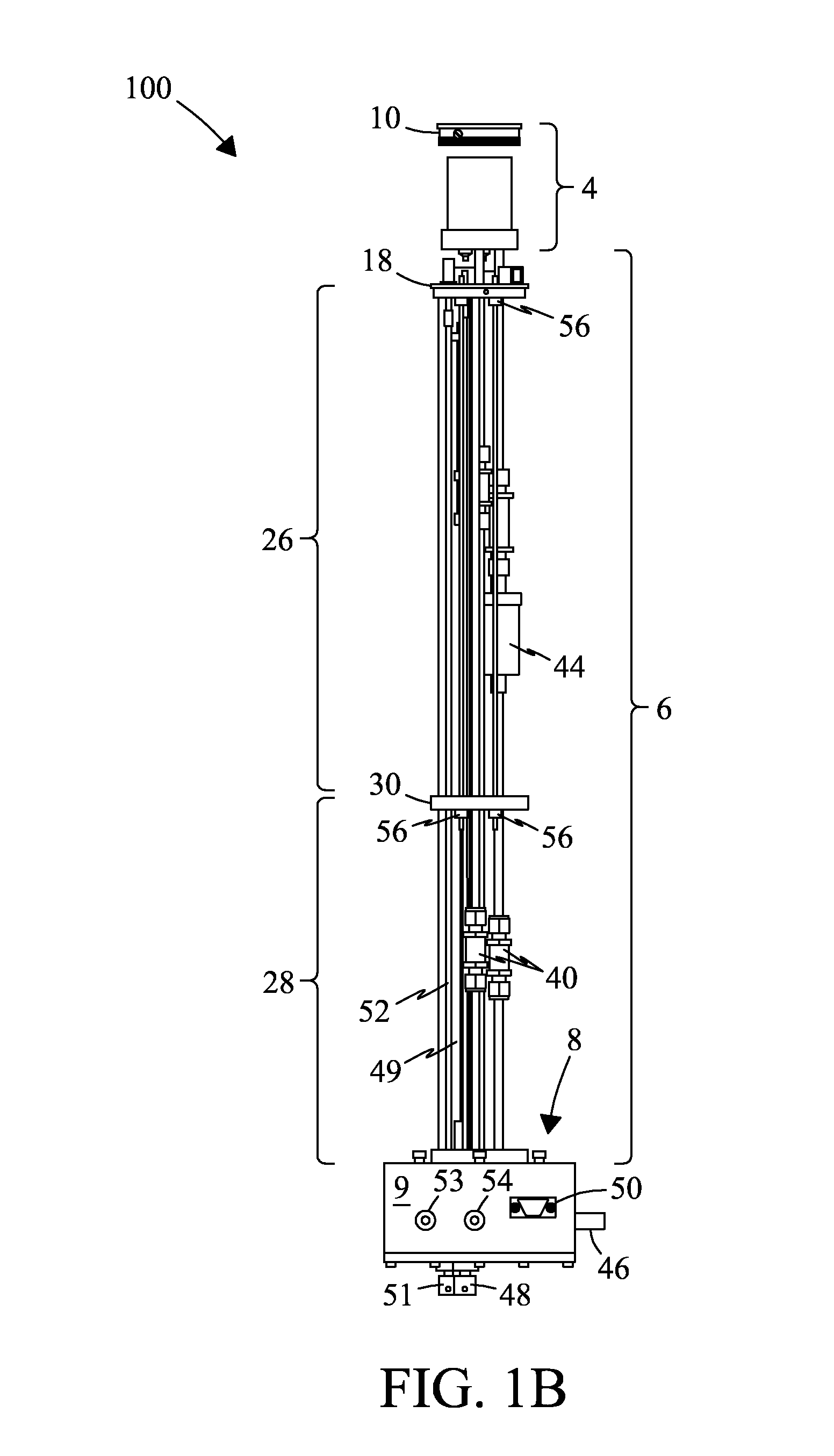
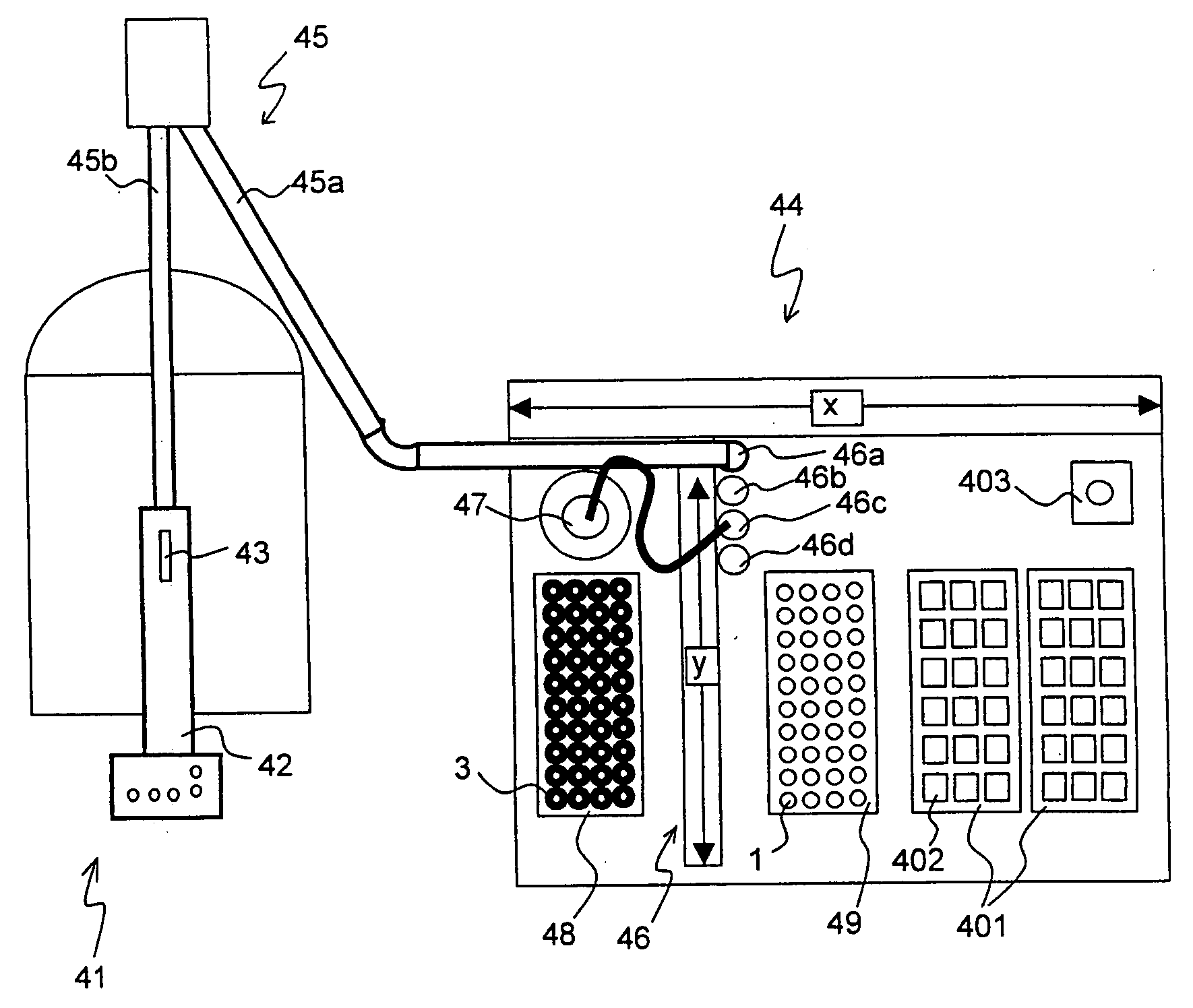
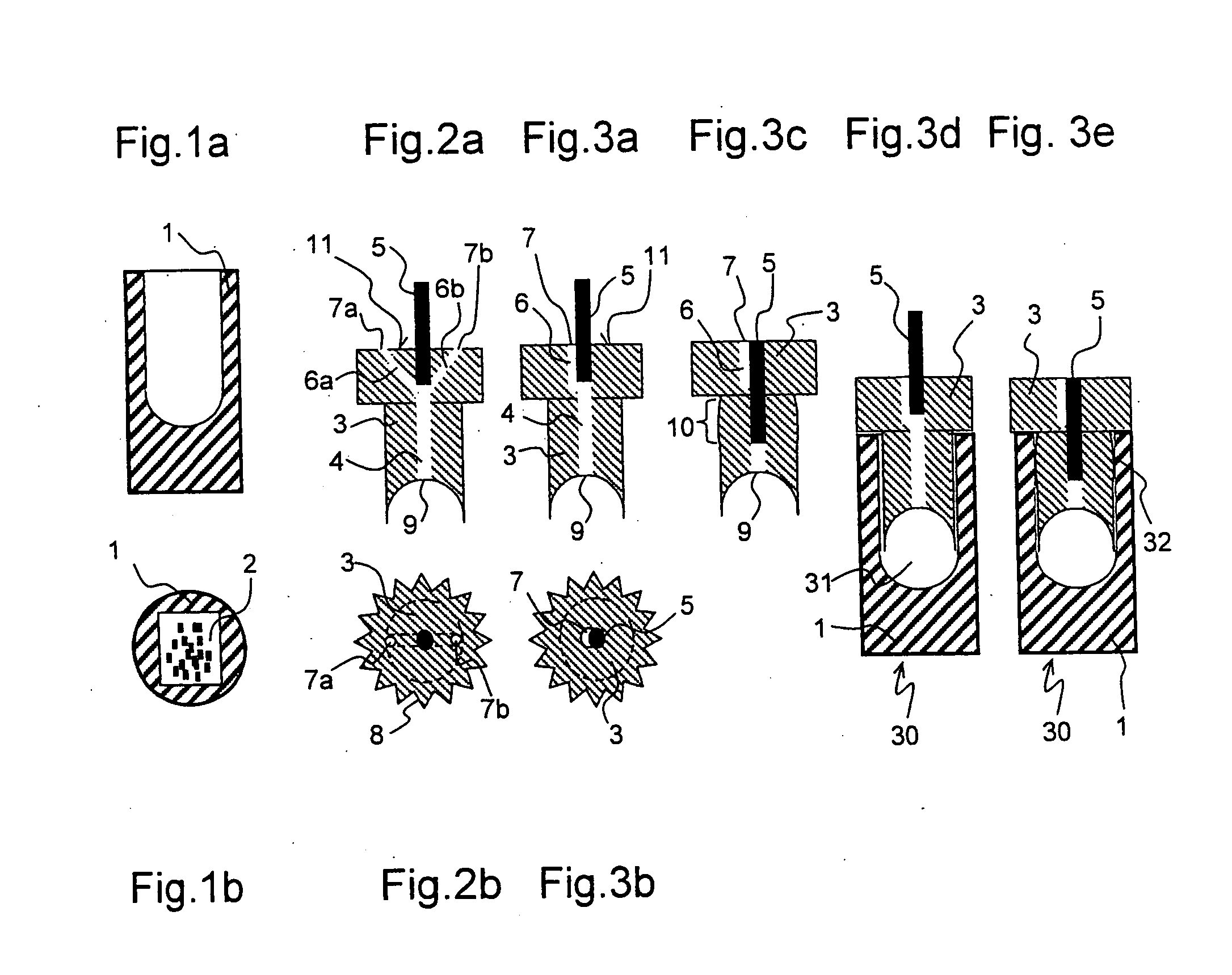
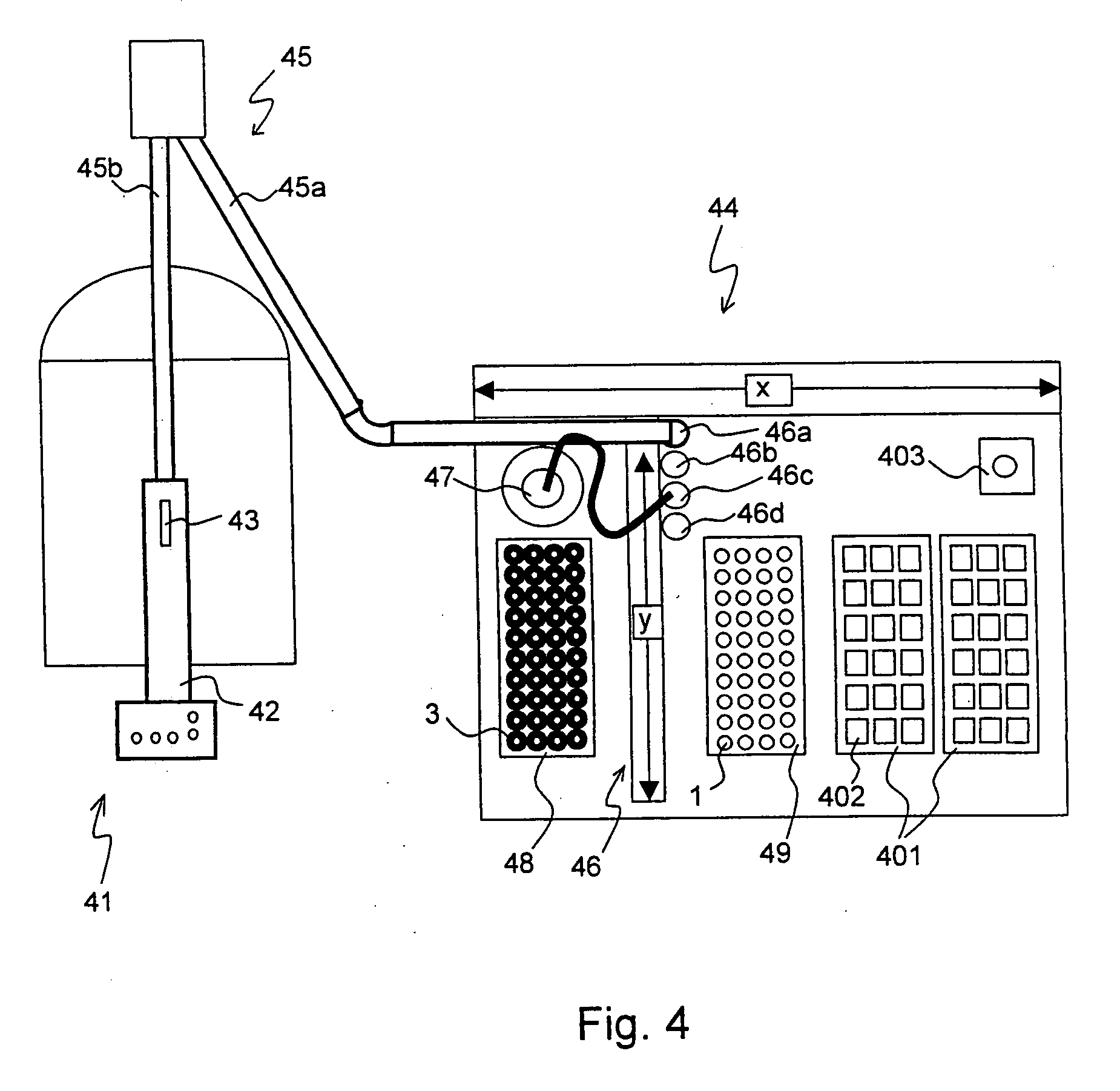
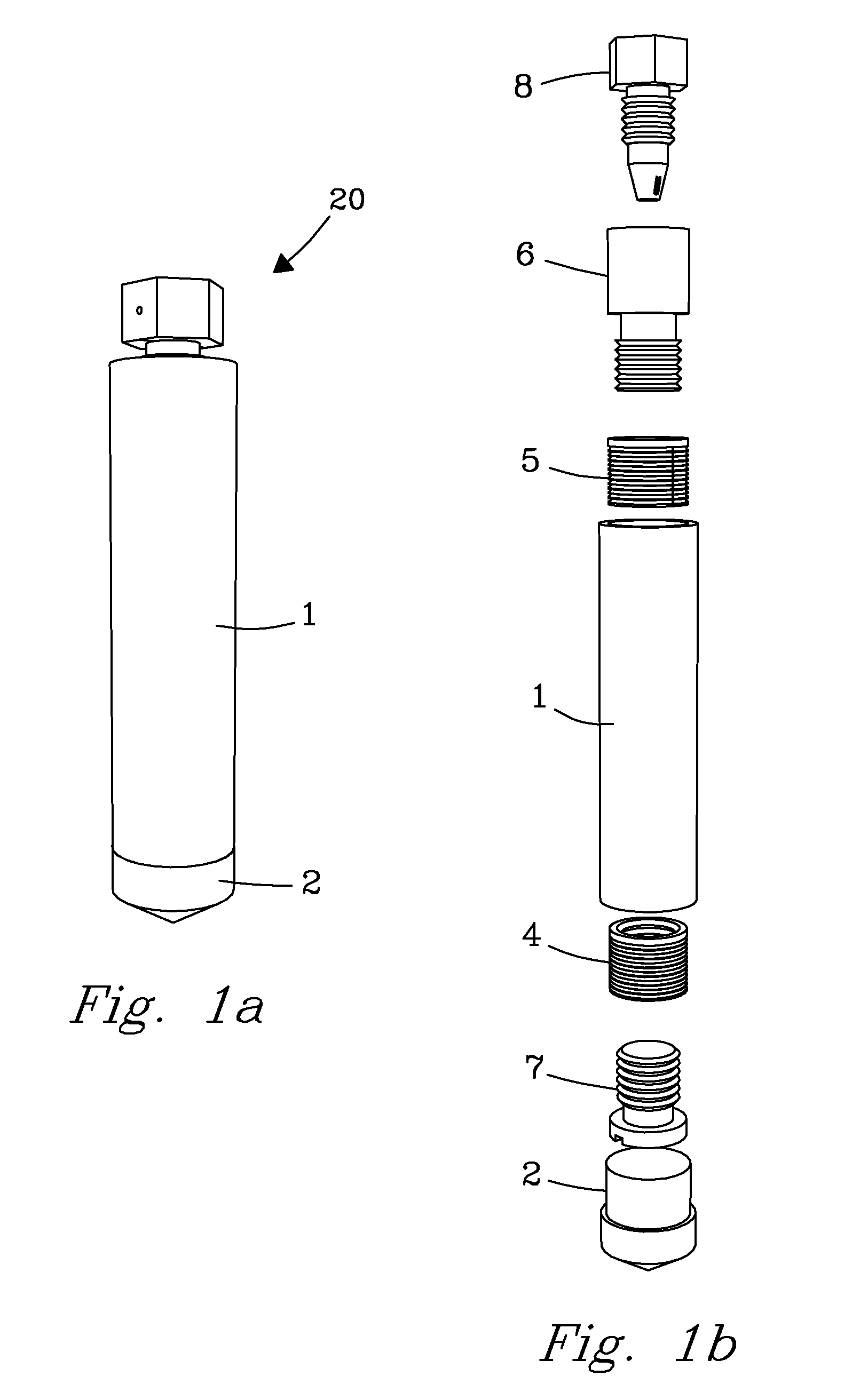
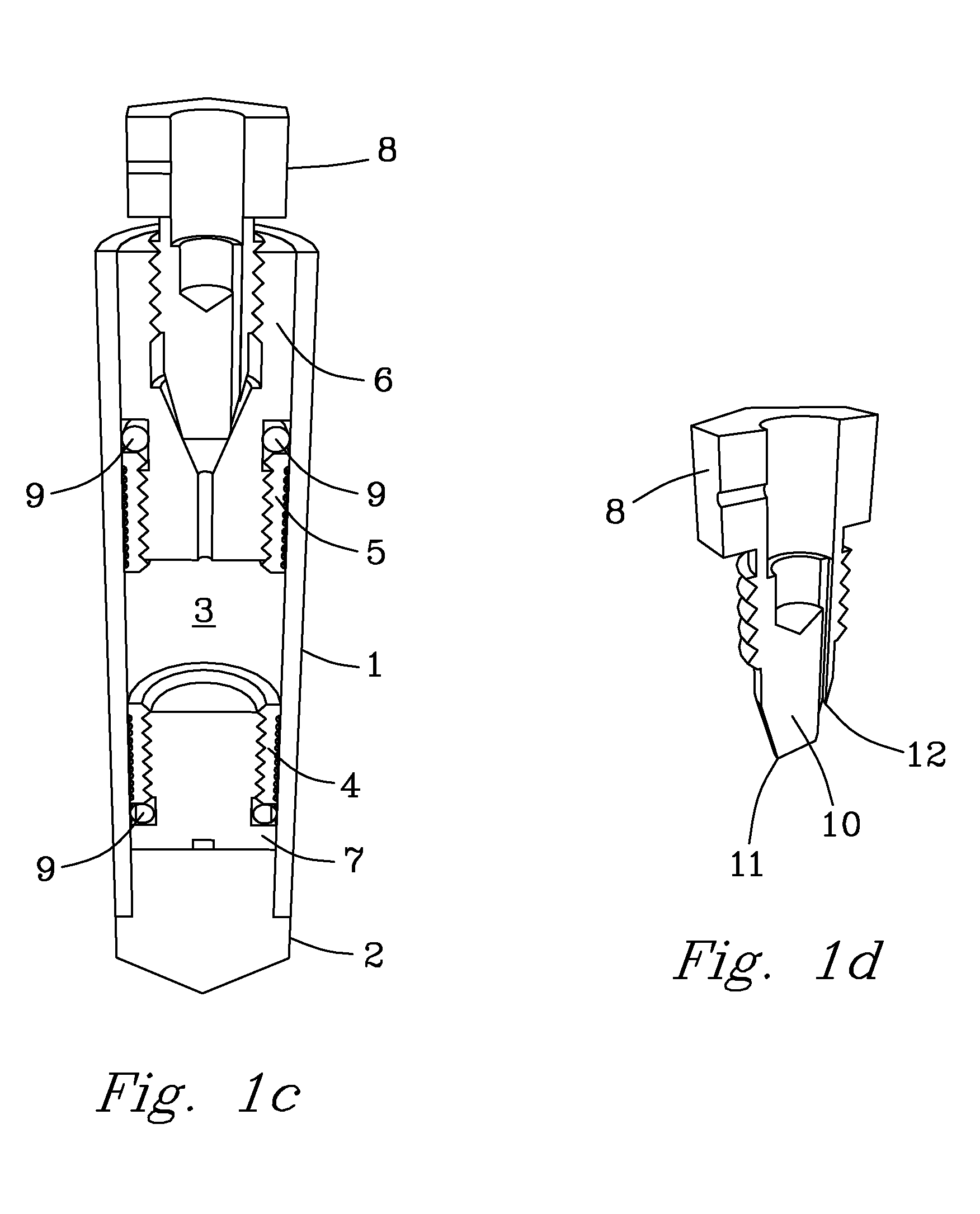
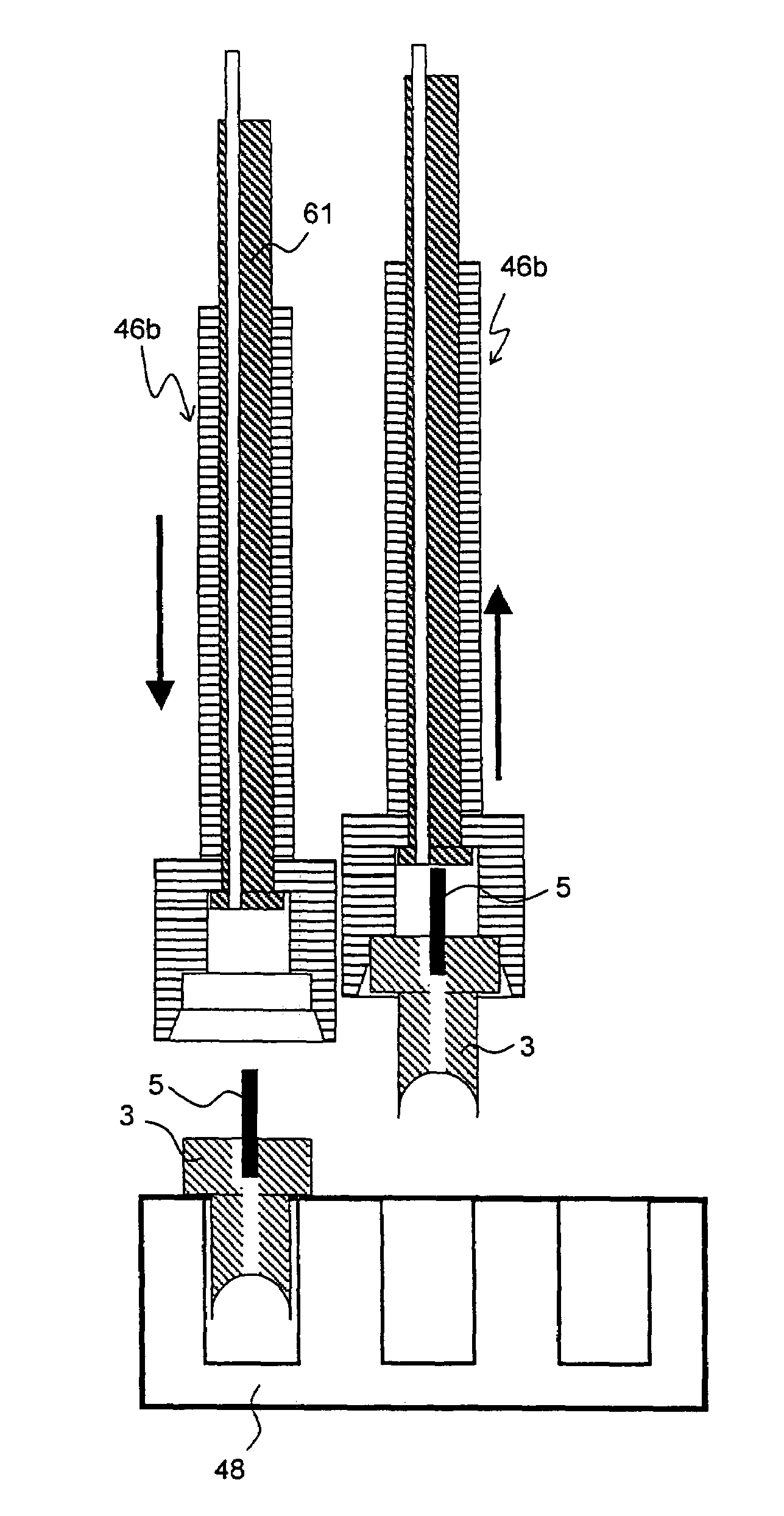
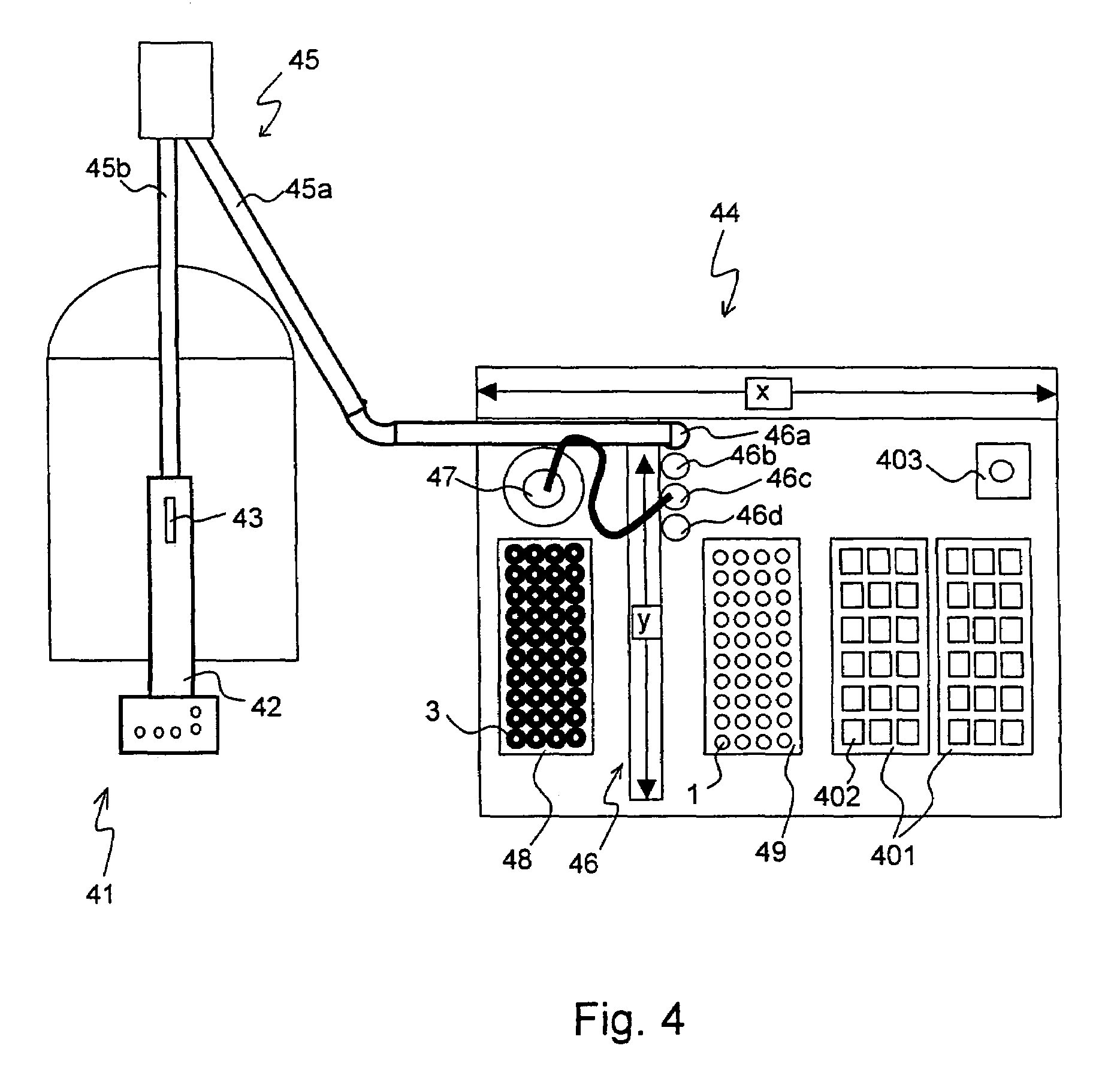
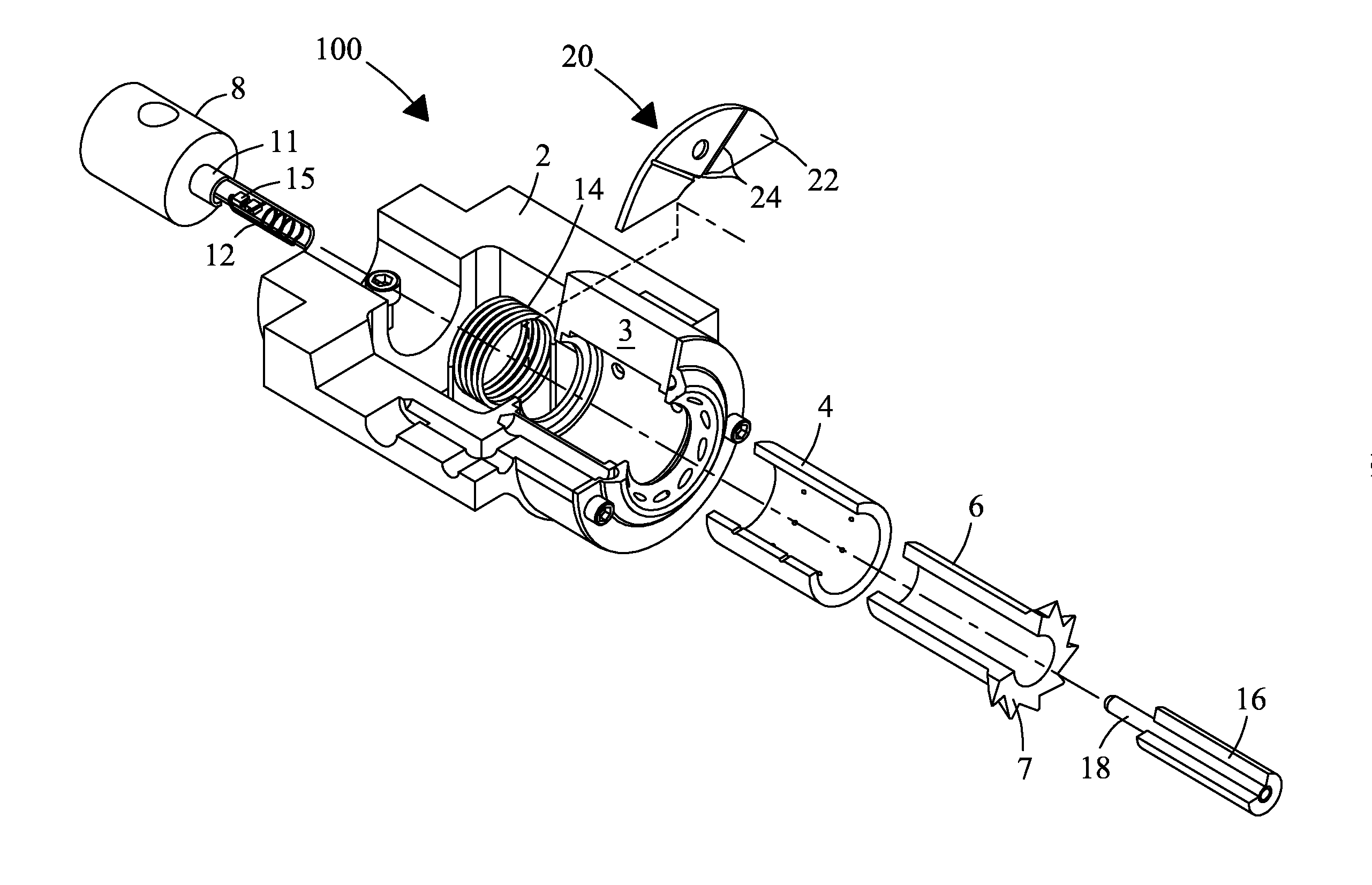
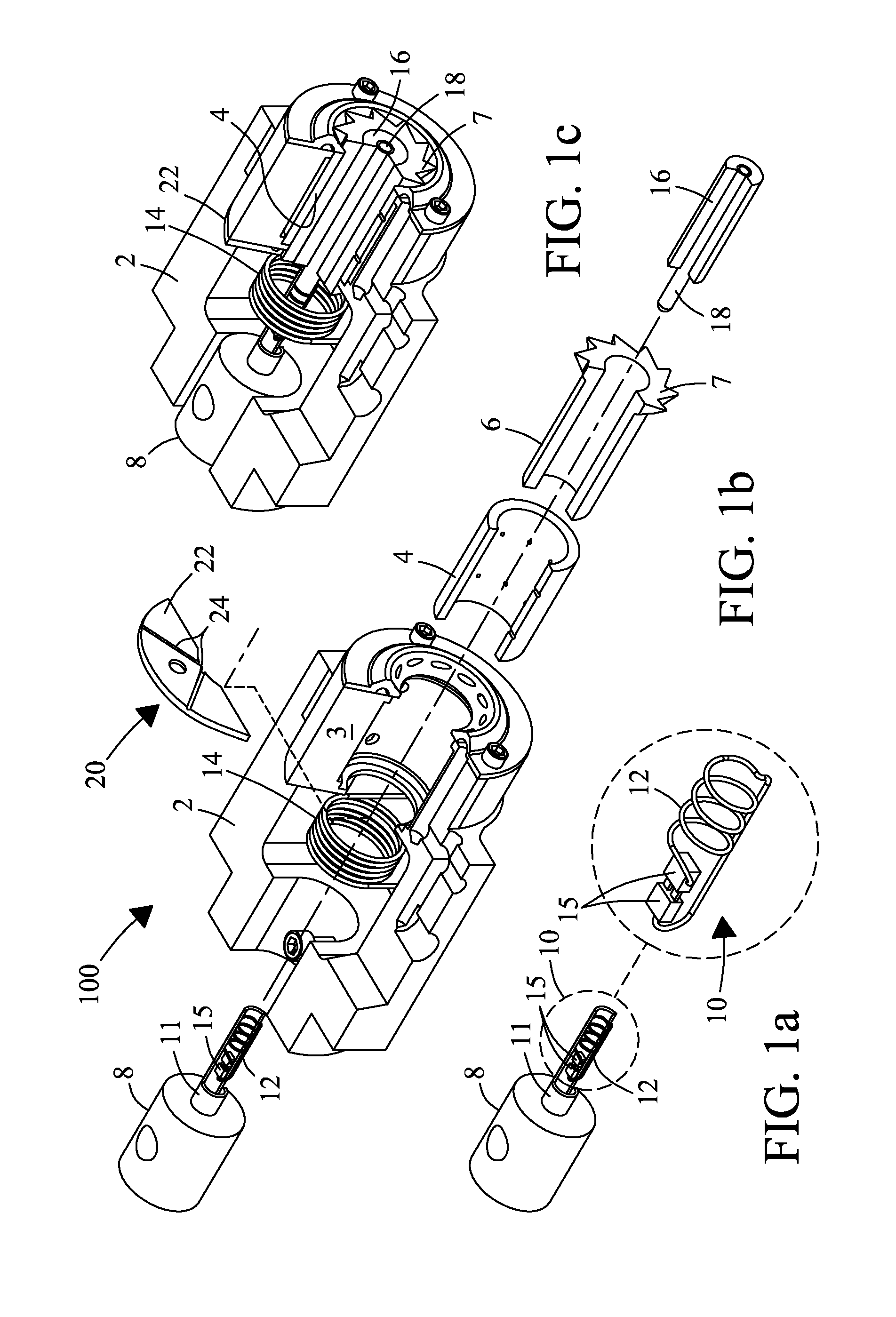
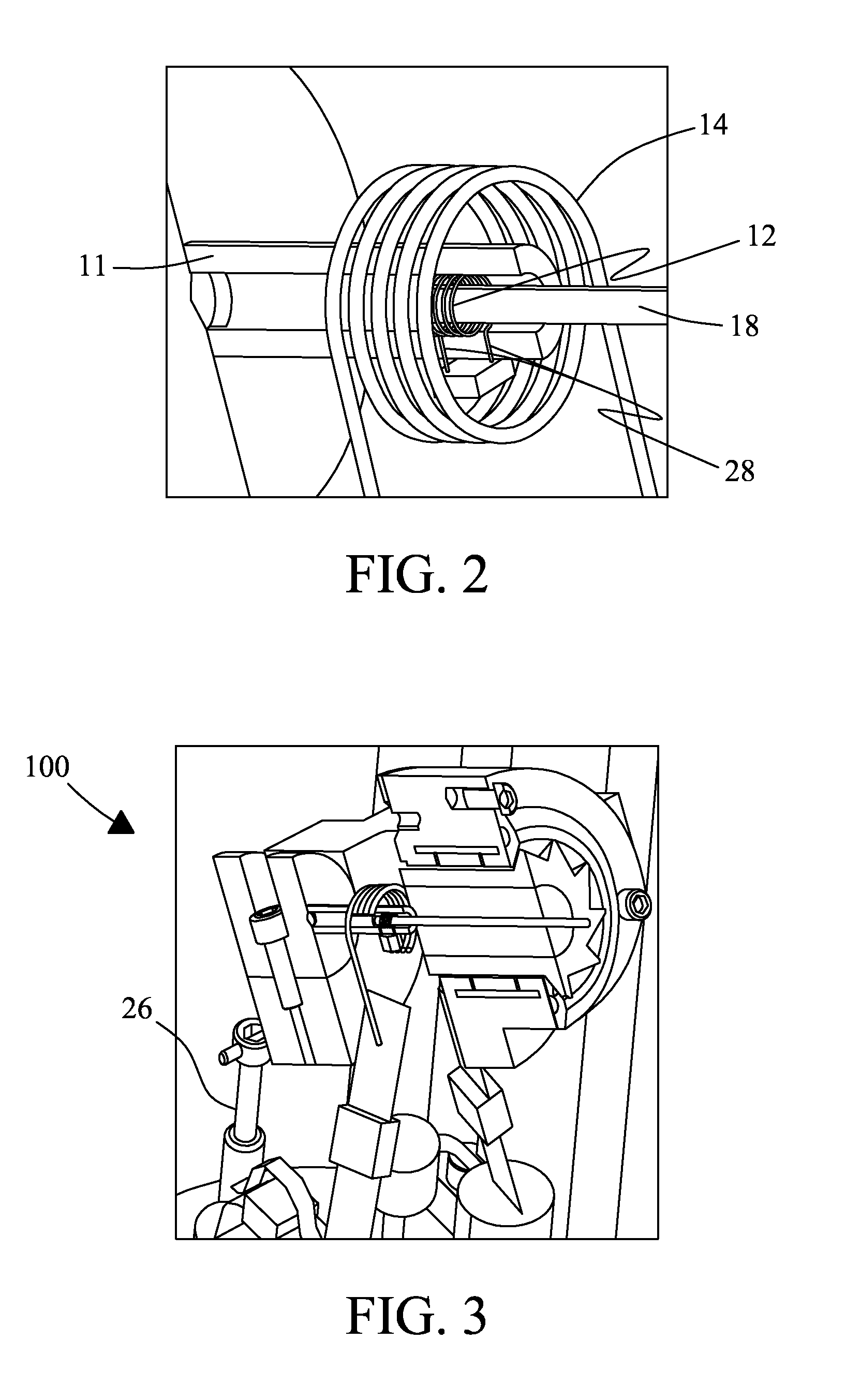
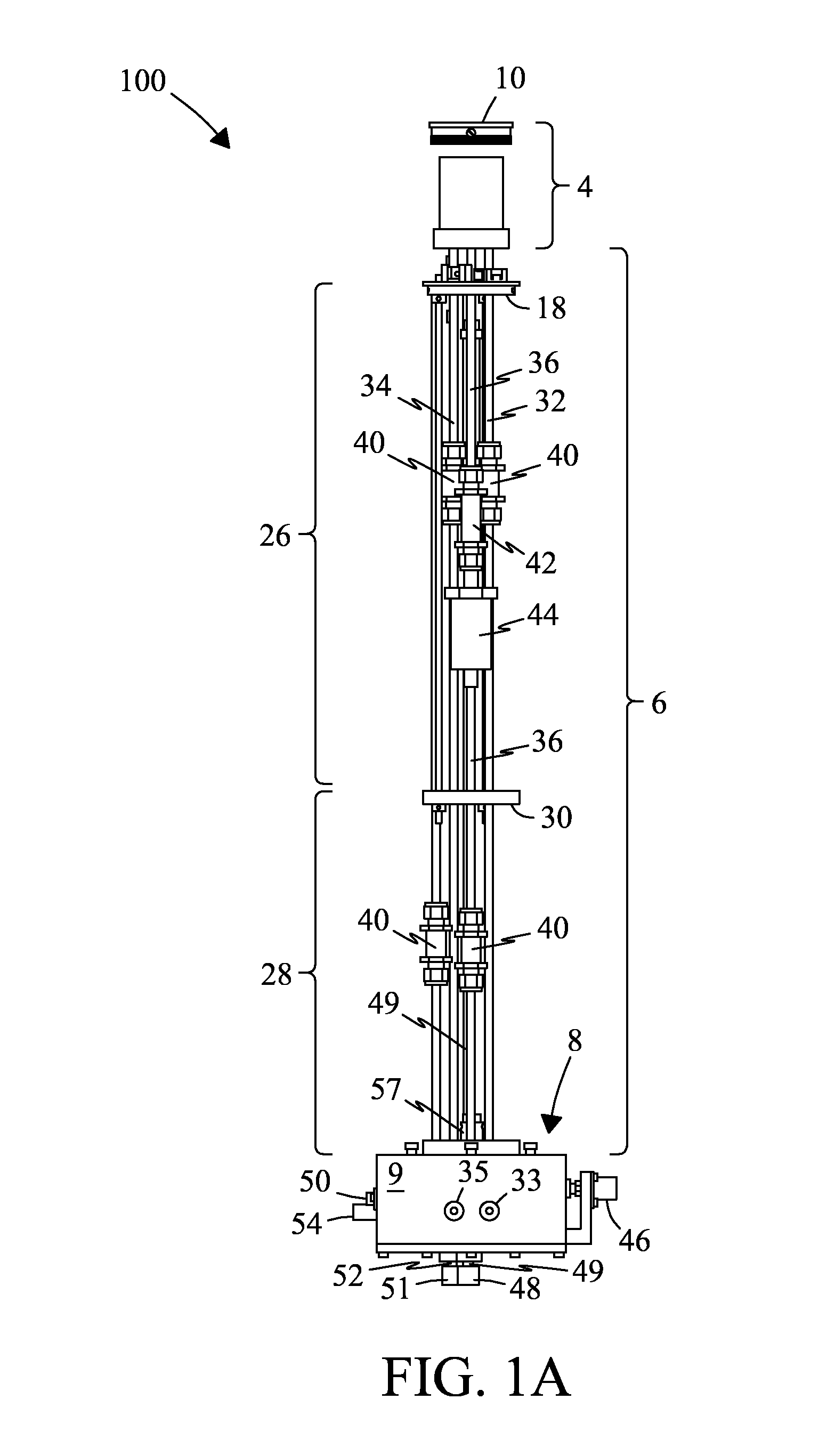
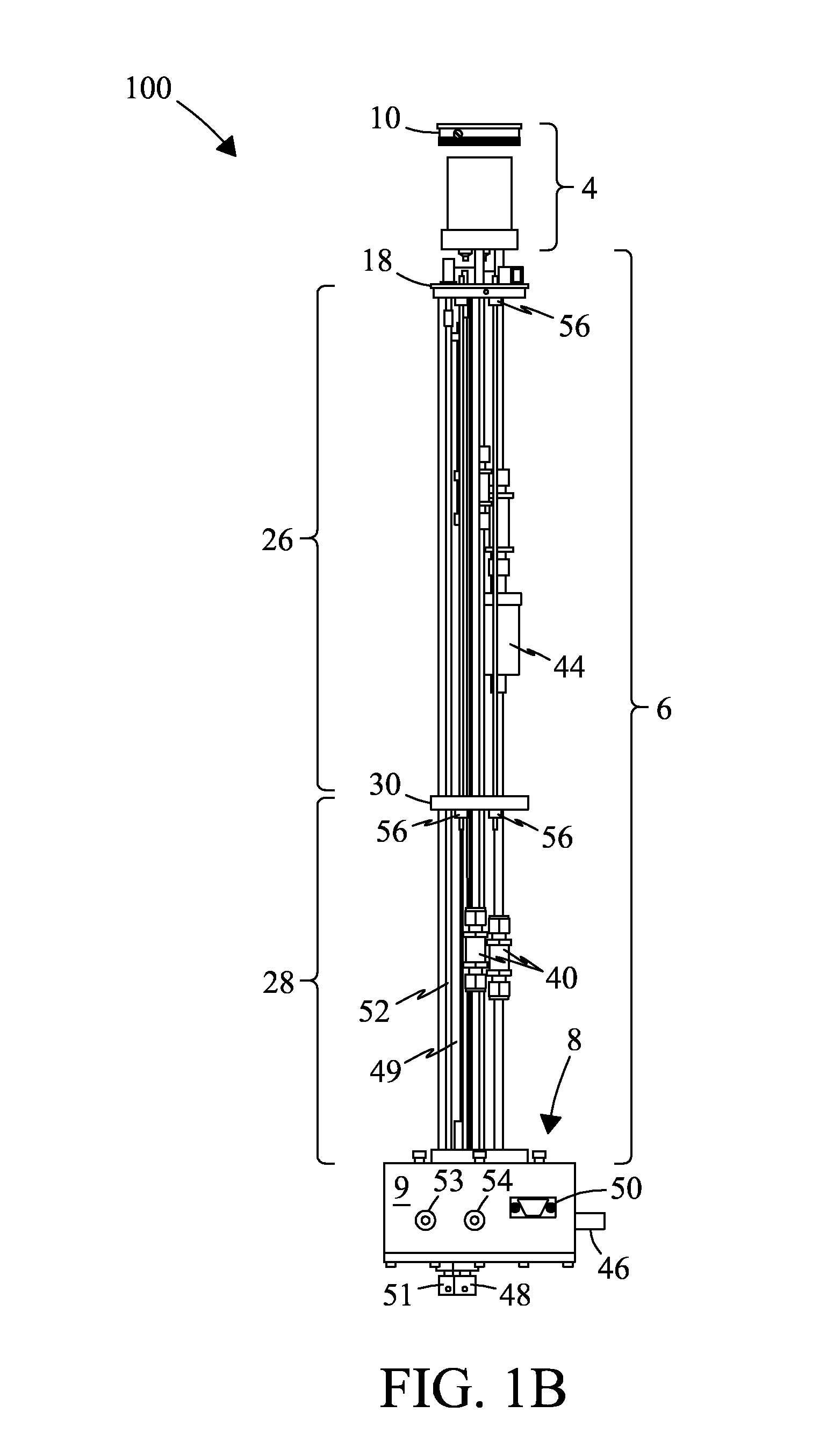
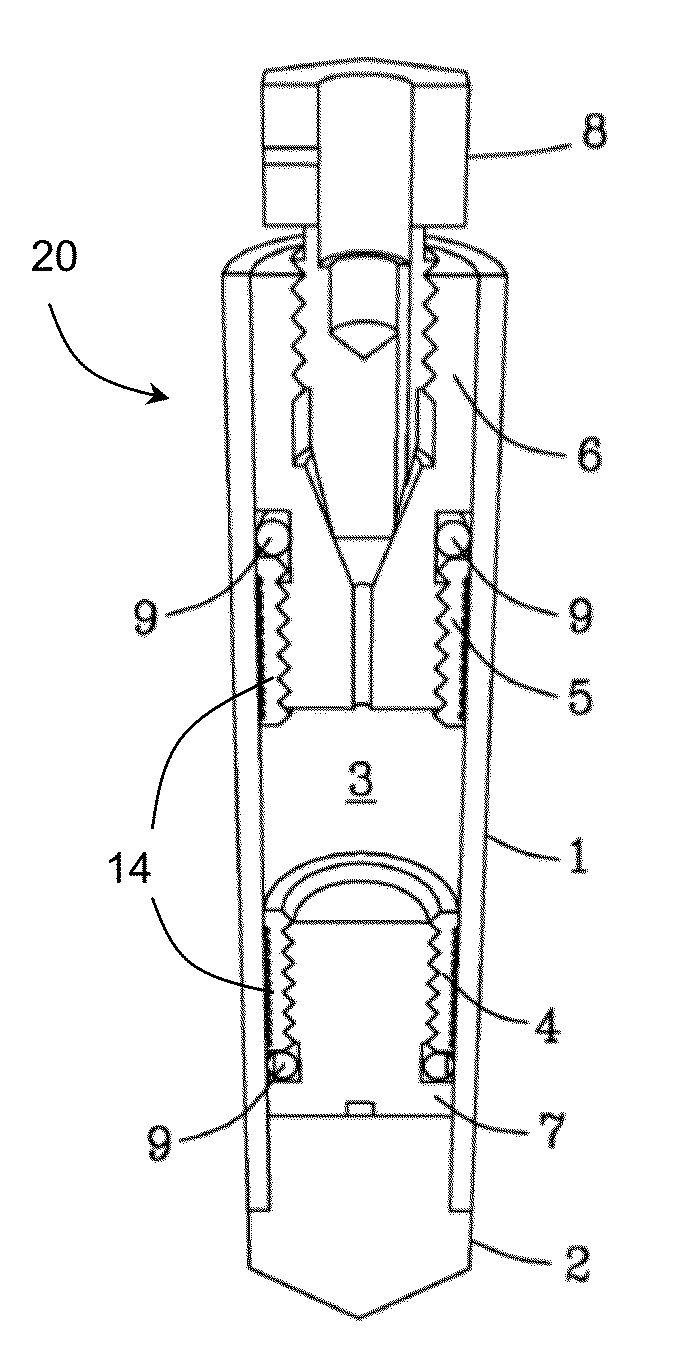
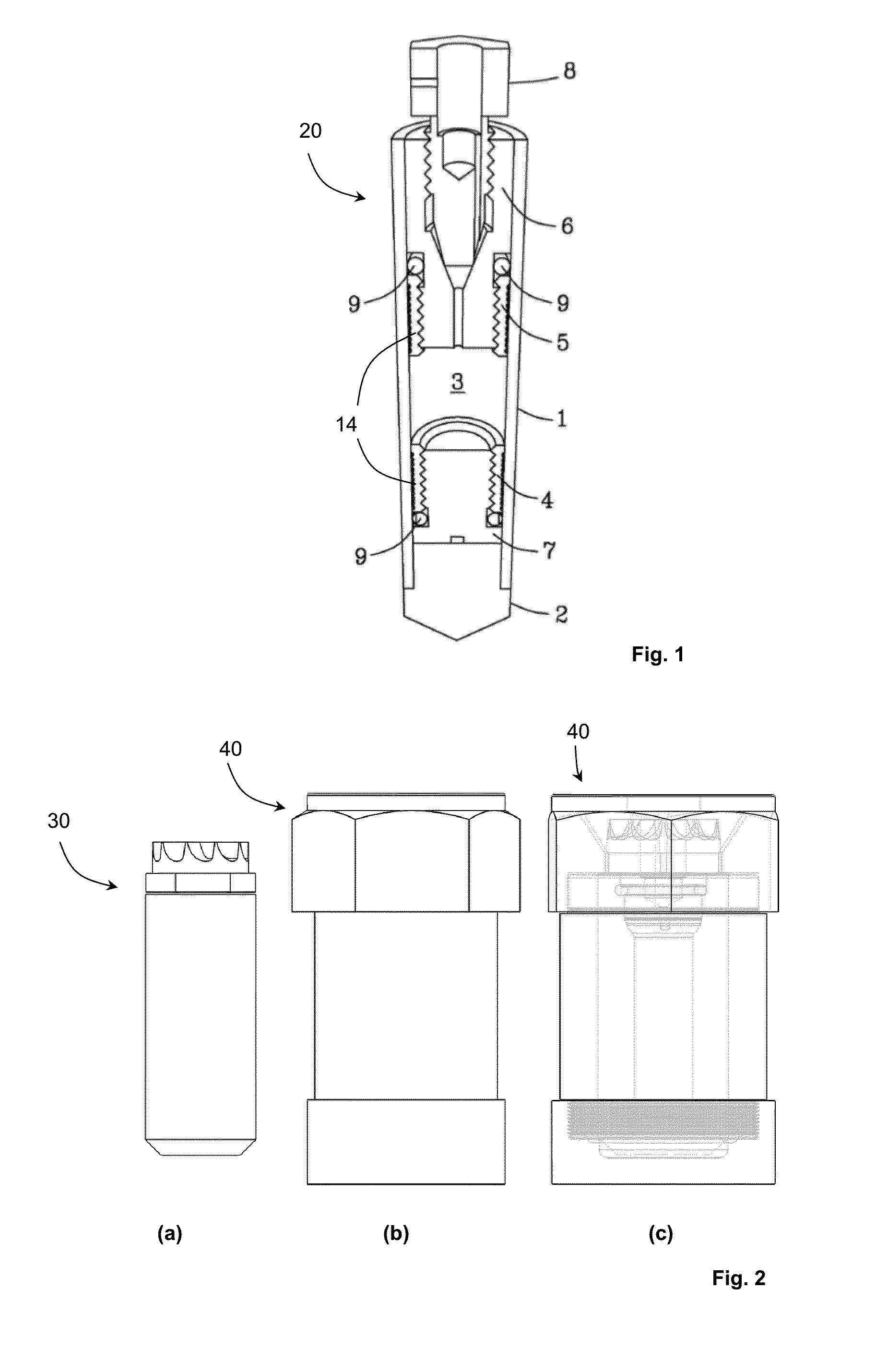
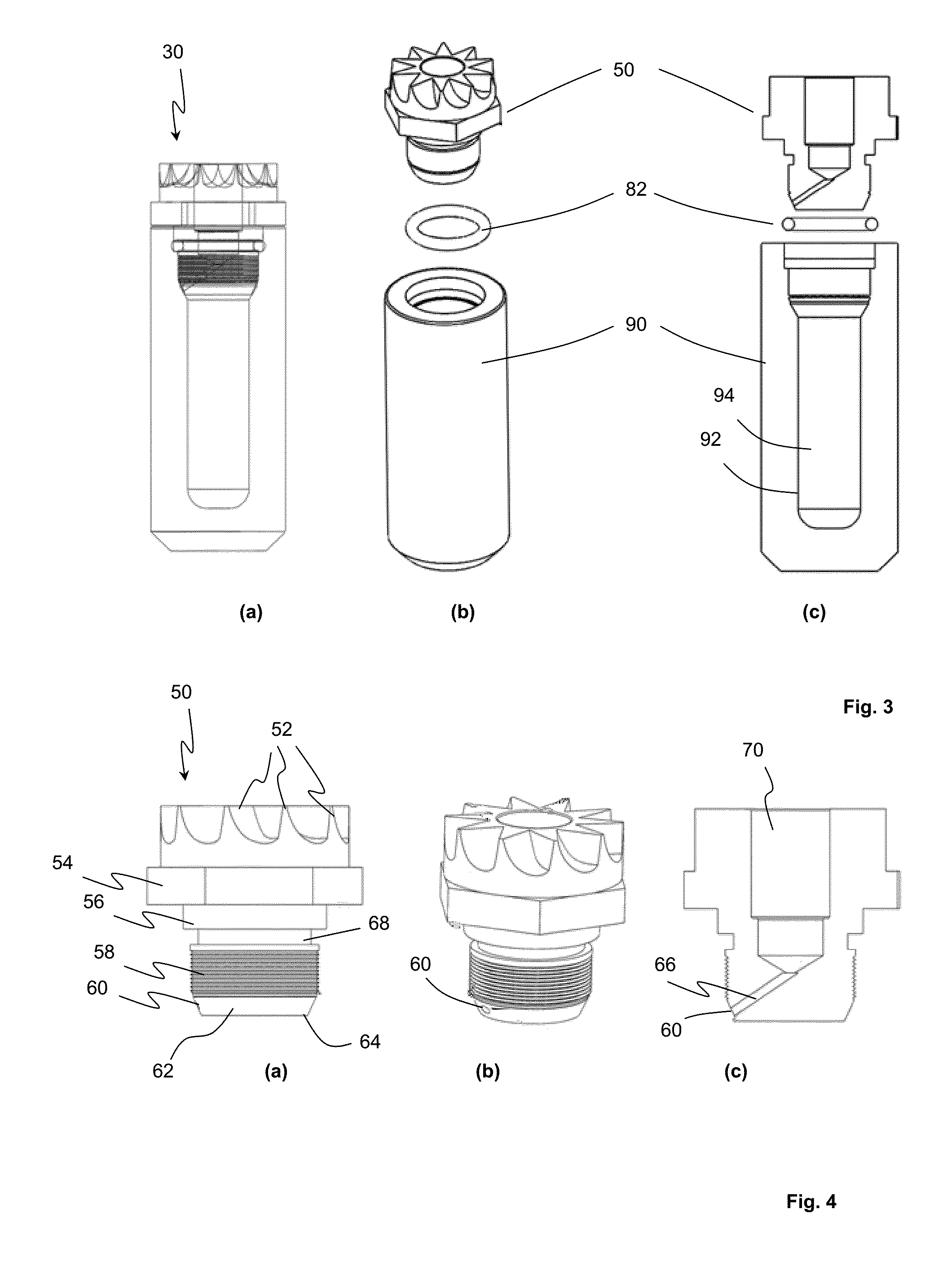
A MAS (magic angle spinning) NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) apparatus, with automatic sample supply by a supply unit (45), is characterized in that an automatic preparation station (44) for samples is provided, with a rotor storage (49) having several rotors (1) for receiving sample material (53) soaked with NMR solution (55), a cap storage (48) with several caps (3), each cap (3) being suited for closing a rotor (1), wherein each cap (3) has a central axial bore (4), several movable pins (5), each being insertable into the central axial bore (4) of a cap (3) to close the bore (4) in the inserted state, a cap handling unit (46b) which can grip a cap (3) from the cap storage (48), move it, and dispose it onto a rotor (1), a plunger (61) for inserting a pin (5) into the bore (4) of the cap (3), and a suctioning device (62) for suctioning excess NMR solution (55) that escapes from the bore (4). The apparatus provides simple and automatic preparation of sample units, in particular, closure of rotors with caps.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Devices and process for high-pressure magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance
ActiveUS8692548B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagic angle spinningNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A high-pressure magic angle spinning (MAS) rotor is detailed that includes a high-pressure sample cell that maintains high pressures exceeding 150 bar. The sample cell design minimizes pressure losses due to penetration over an extended period of time.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
NMR-MAS probehead with integral transport conduit for an MAS-rotor
ActiveUS8212559B2Easy constructionEasy to changeElectrical testingMeasurement leads/probesMagic angle spinningNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
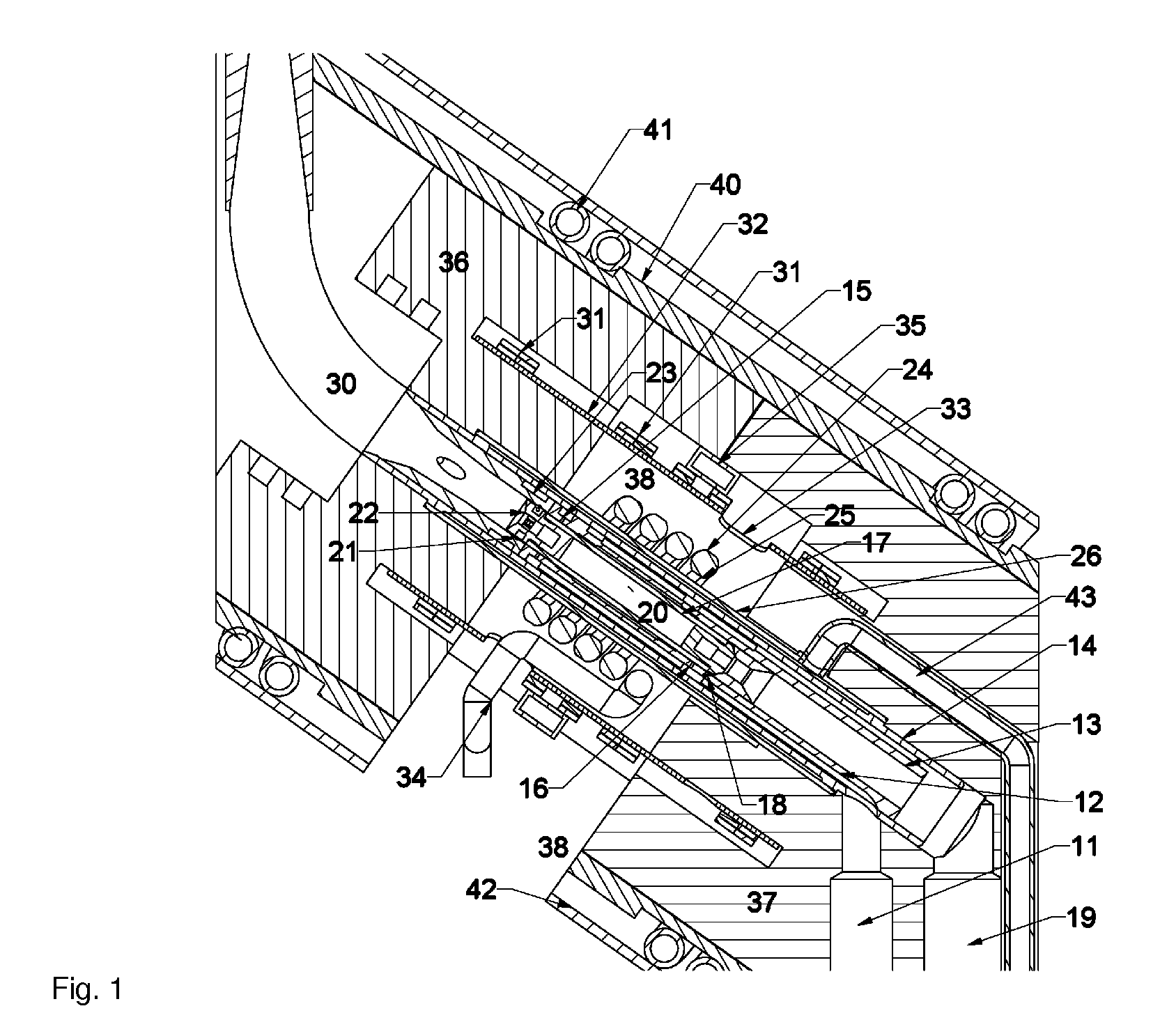
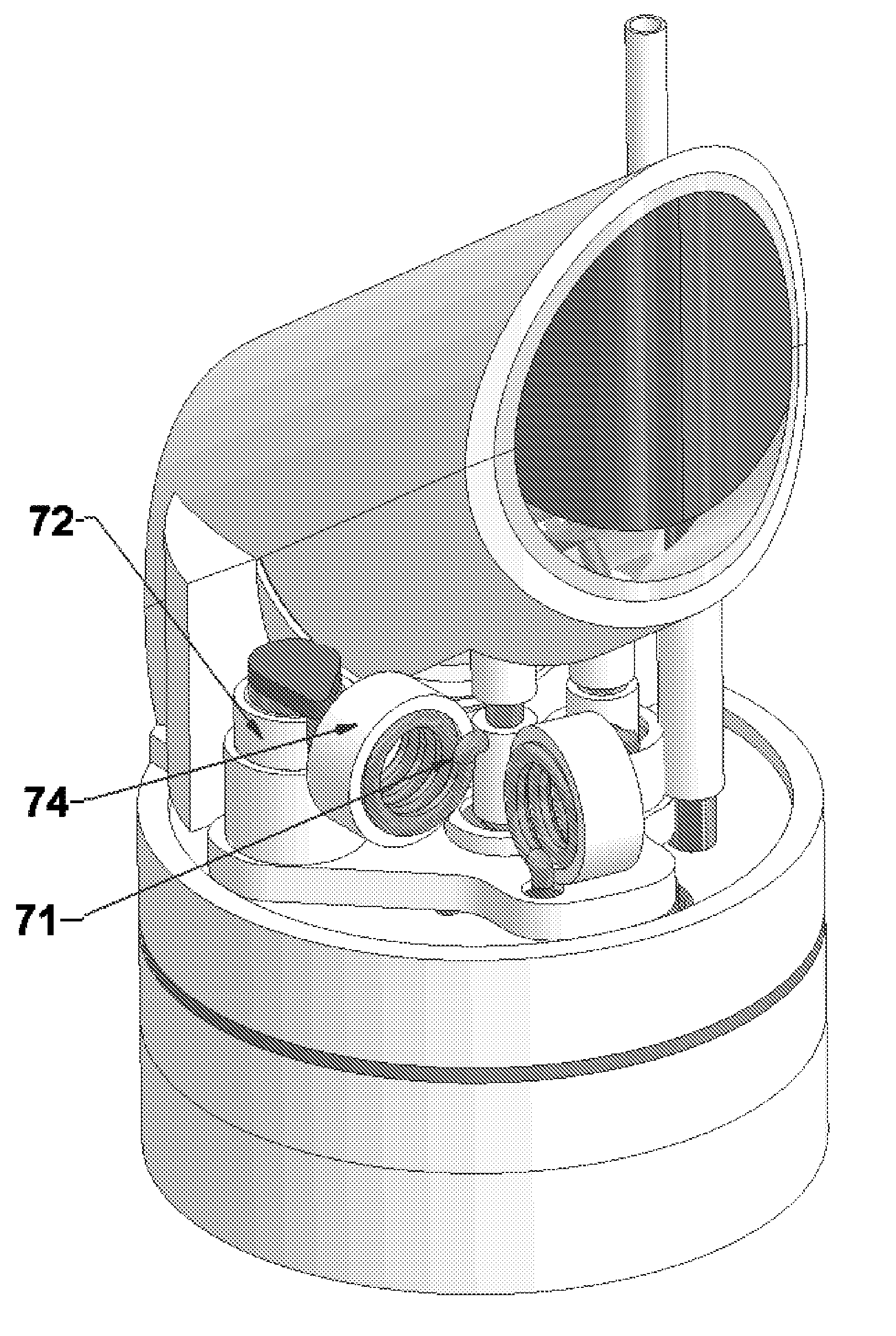
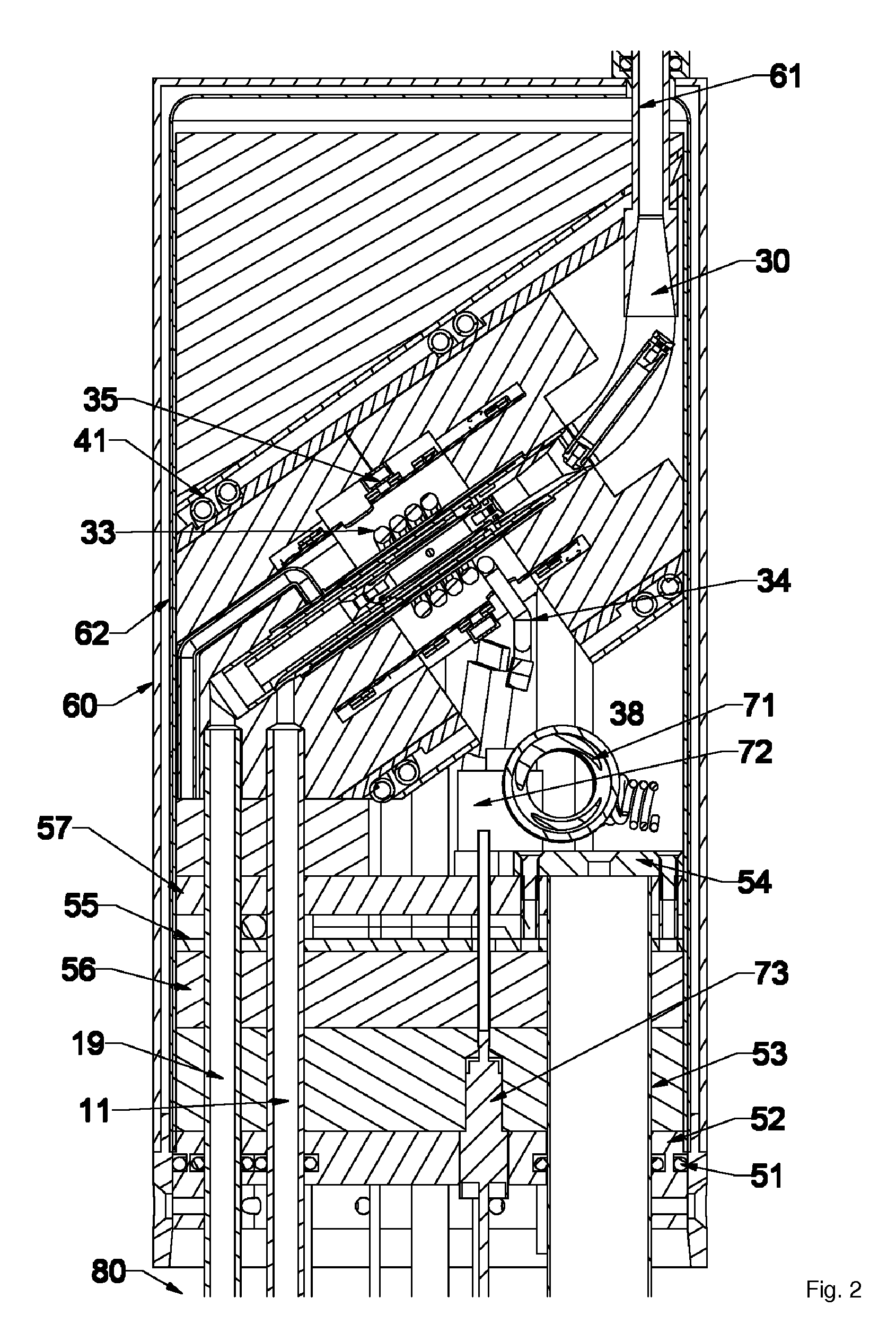
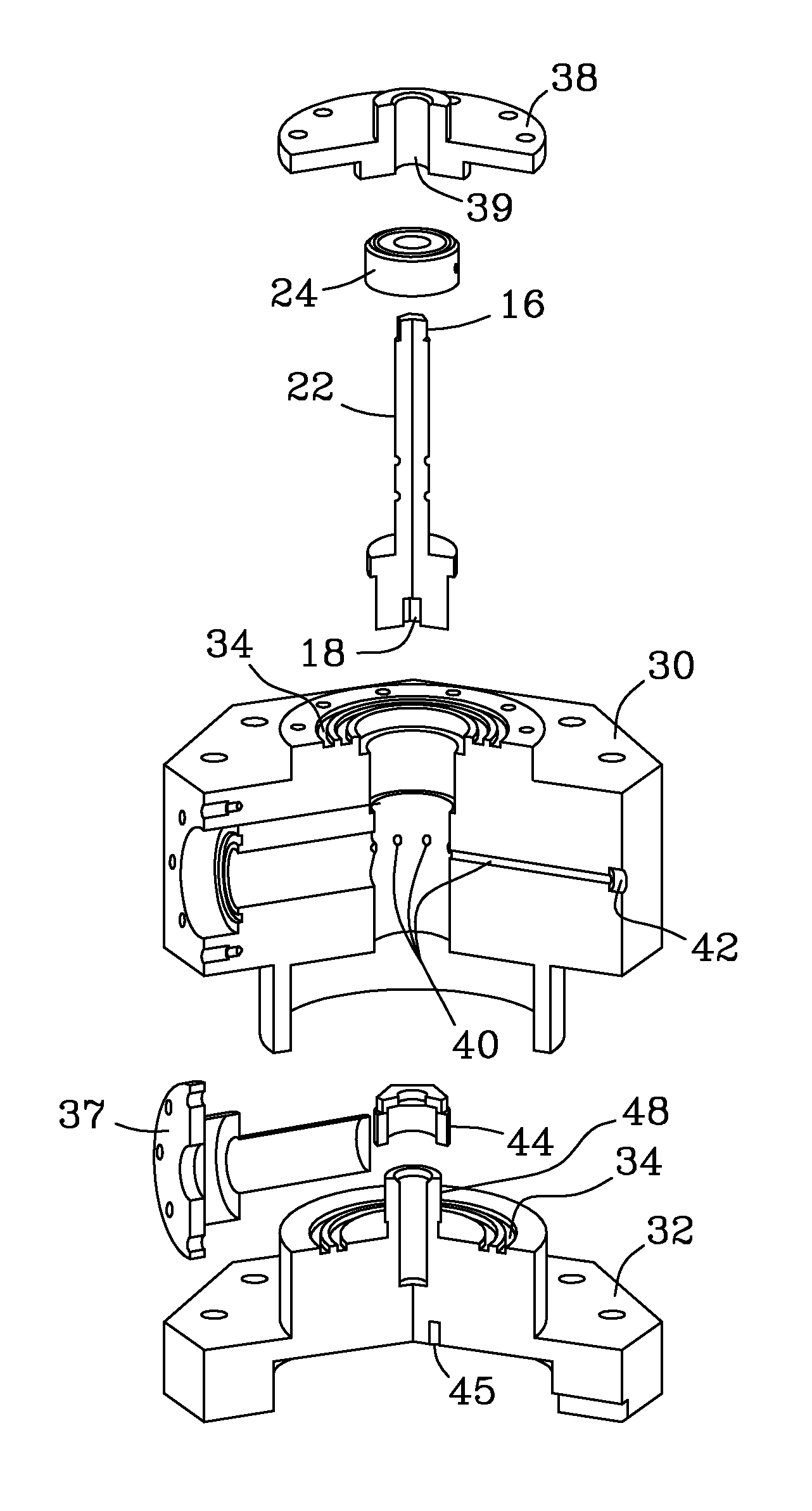
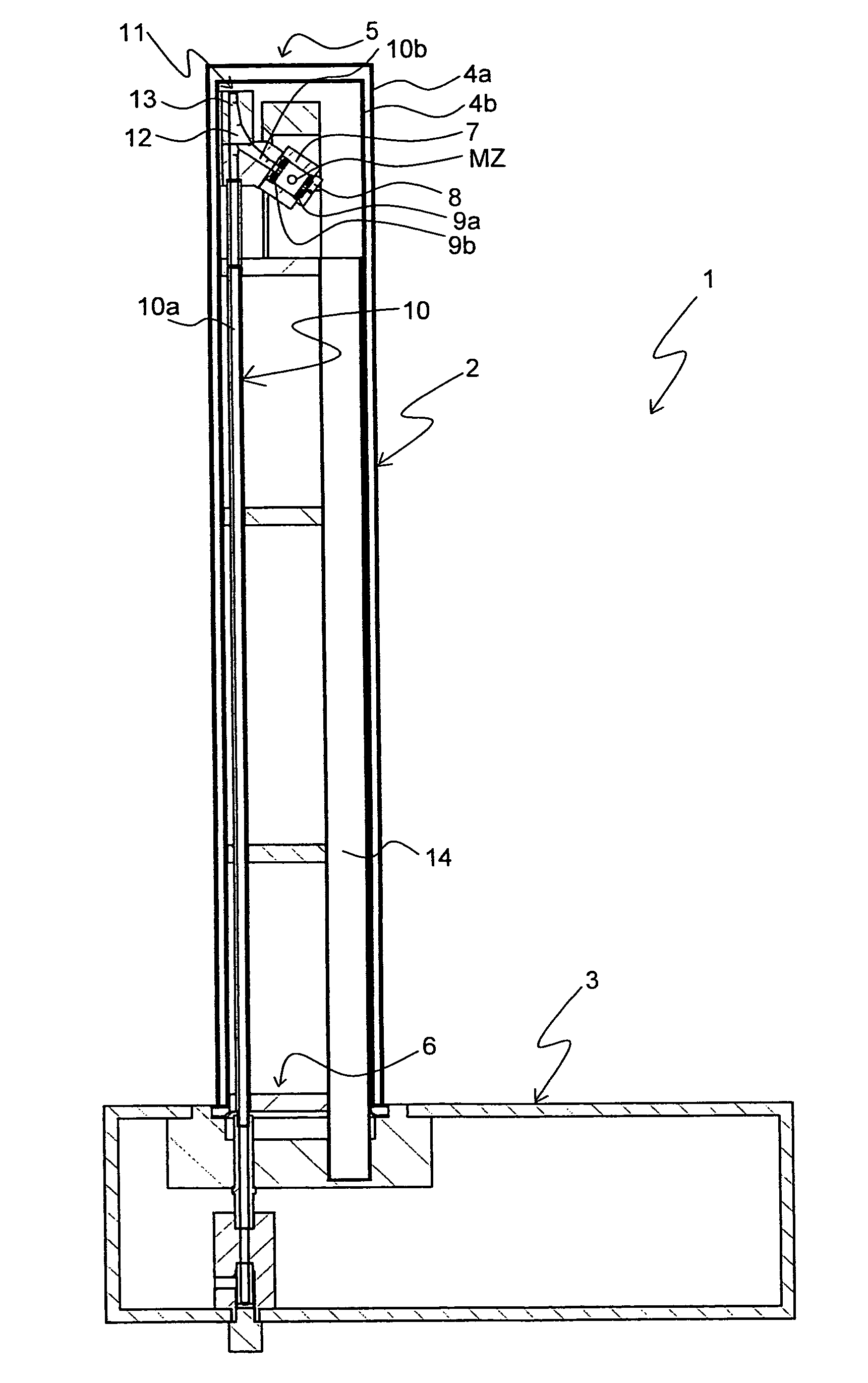
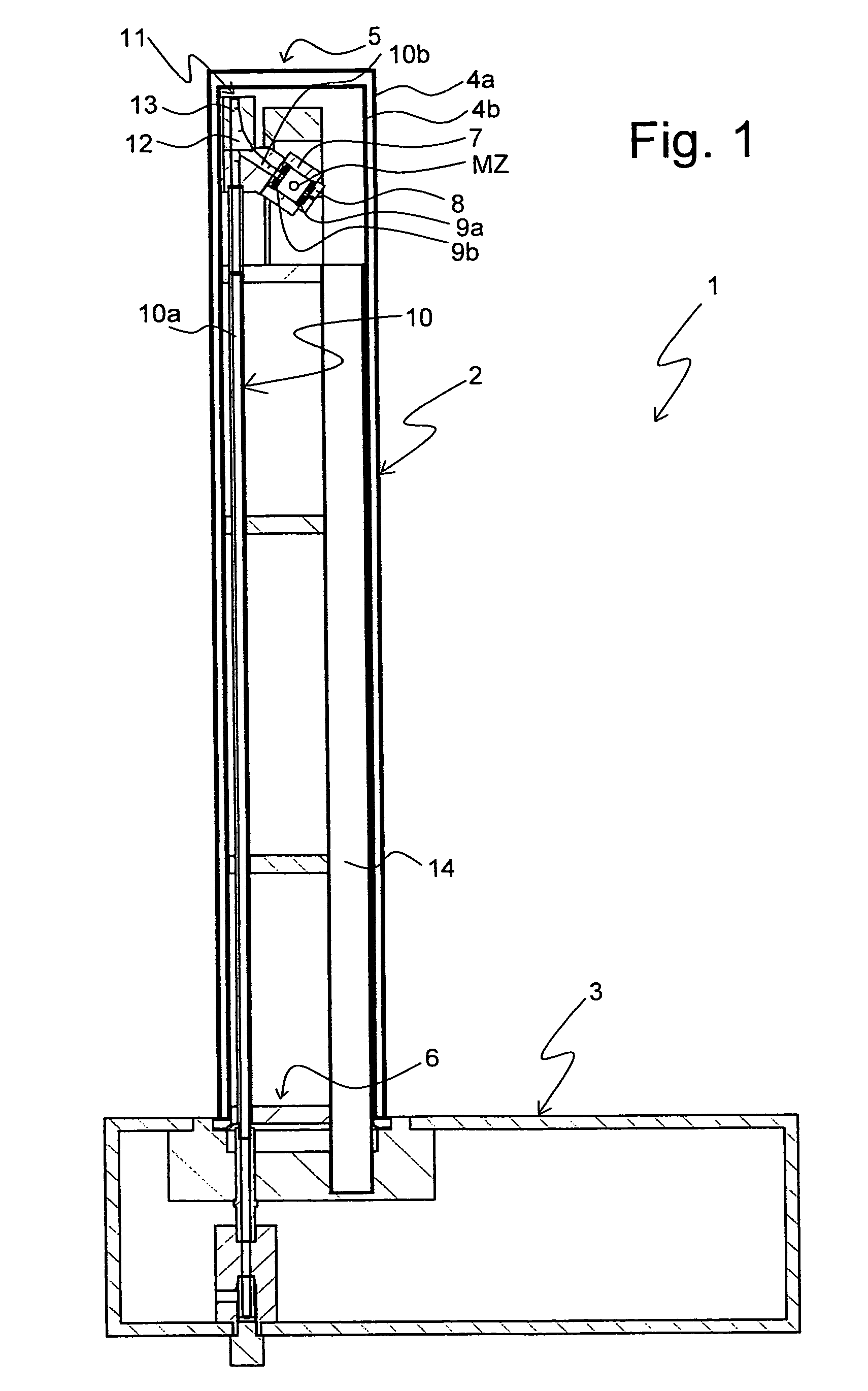
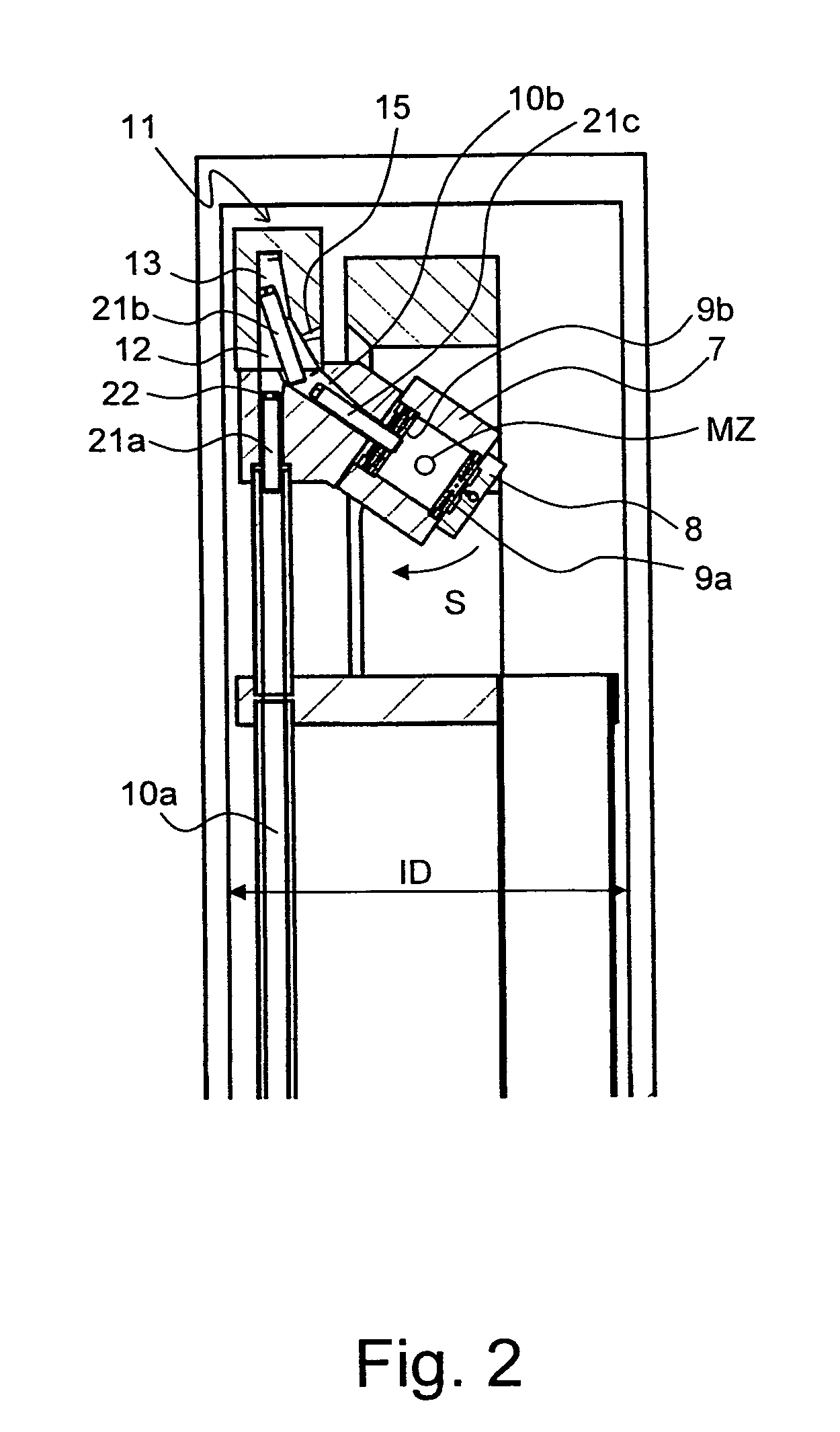
A nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) magic angle spinning (MAS) probe head (1; 61) for measuring a measuring substance in an MAS rotor (21a-21c), comprises a bottom box (3) and a tube (2) mounted to the bottom box (3) and projecting from the bottom box, wherein, in the area of the end (5) of the tube (2) facing away from the bottom box (3), an MAS stator (7; 62) is disposed within the tube (2) for receiving an MAS rotor (21a-21c), and with a pneumatic sample changing system for supplying and discharging an MAS rotor (21a-21c) to / from the MAS stator (7; 62). A transport conduit (10) is provided for pneumatically transferring an MAS rotor (21a-21c) within the transport conduit (10), wherein the transport conduit (10) extends in the inside of the tube (2) from the bottom box (3) to the MAS stator (7; 62). The probe head realizes fast change between different MAS rotors and facilitates RF shielding and keeping of defined extreme temperature conditions.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Advanced slow-magic angle spinning probe for magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy
InactiveUS6989674B2Additive manufacturing apparatusMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMagic angle spinningMetabolite
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Lithium composite metal oxide
InactiveUS20090309062A1Good capacity retentionCell electrodesCobalt compoundsMagic angle spinningSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonance
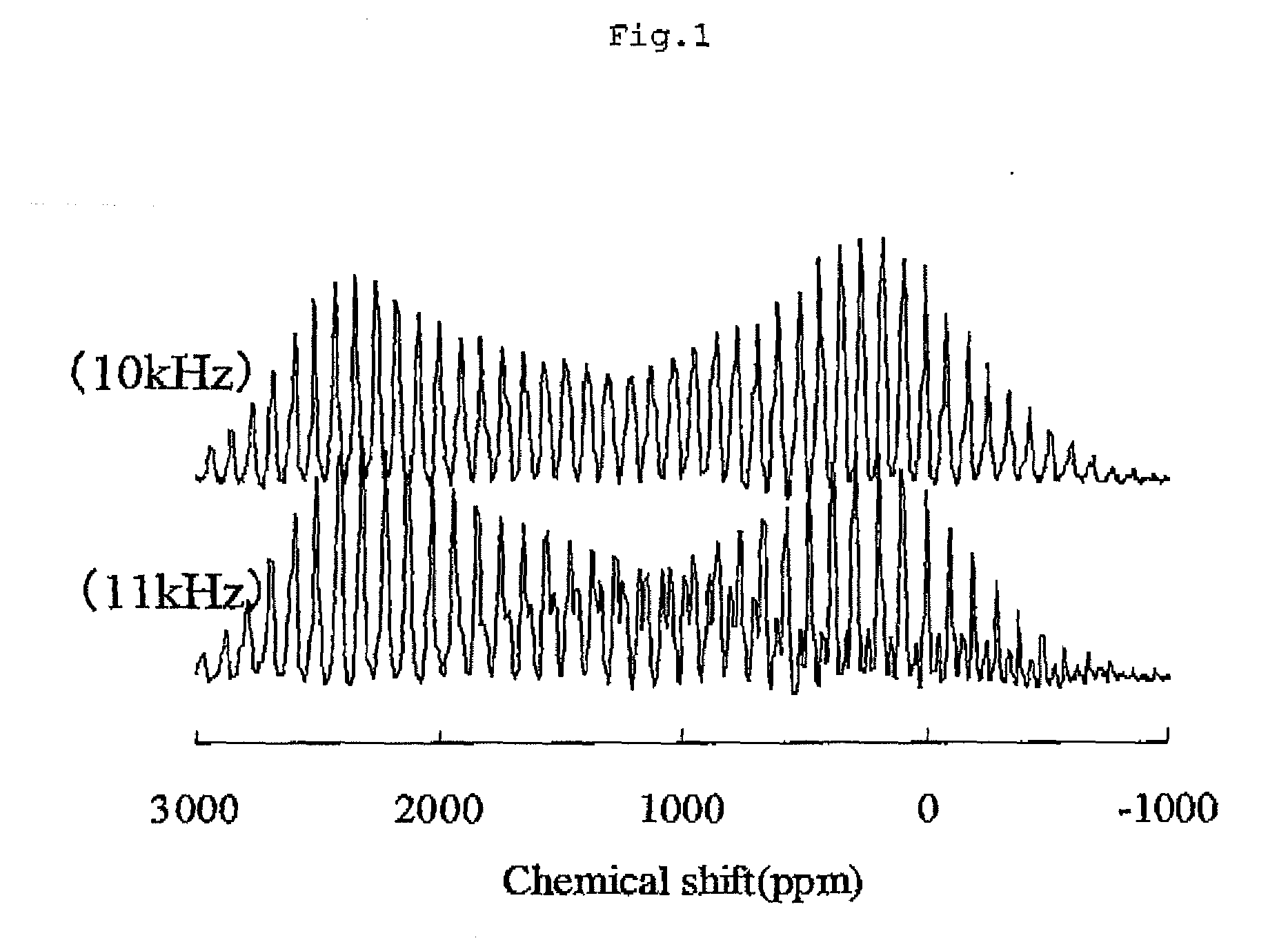
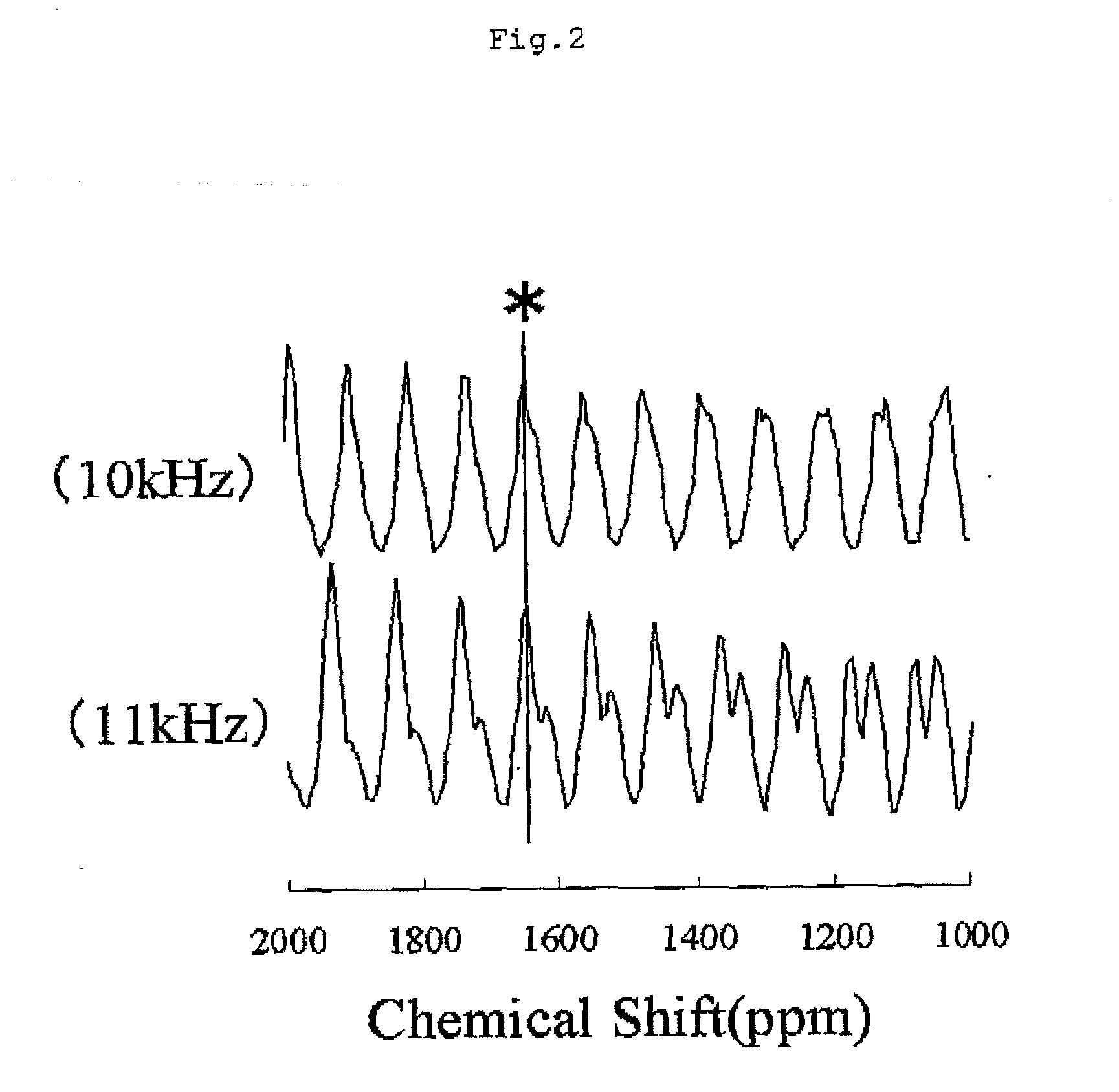
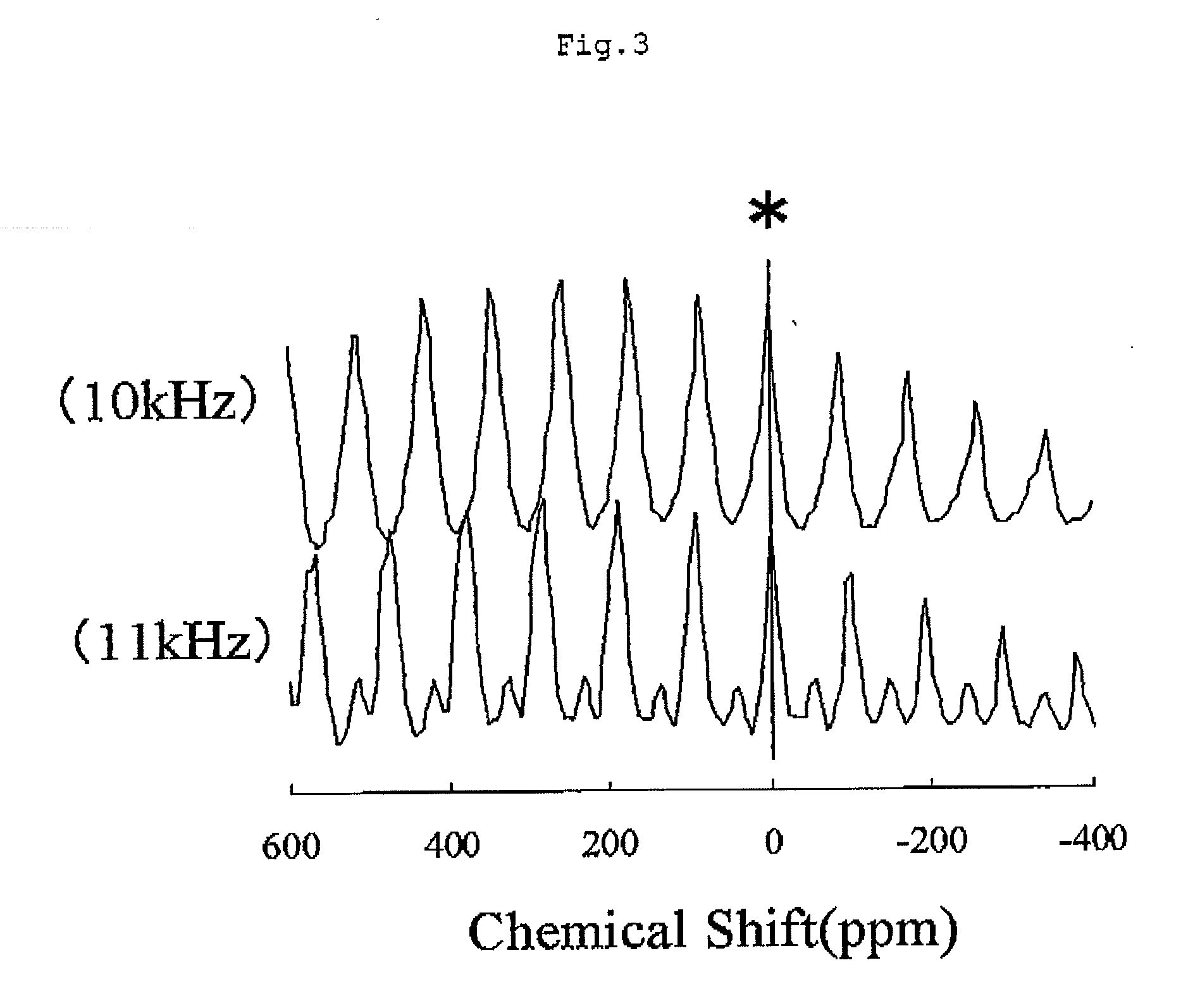
Provided is a lithium composite metal oxide containing Li, Ni and M (wherein, M is Mn and / or Co), characterized by exhibiting Signal B below in a spectrum at a rotational speed of 10 kHz among the solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of 7Li of a lithium composite metal oxide obtained by the nuclear magnetic resonance measuring method 1,<Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Measuring Method 1>A lithium composite metal oxide is rotated at each of rotational speeds of 10 kHz and 11 kHz by the magic angle-spinning method using a nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus with a magnetic field strength of 7.05 teslas, a solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance of 7Li of the lithium composite metal oxide is measured at each rotational speed, and a chemical shift of a central peak is evaluated from two resulting solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectra (wherein the chemical shift value is a value corrected by taking a position of a central peak of lithium chloride as 0 ppm using lithium chloride as an external standard substance);<Signal B>A signal having a central peak and its spinning side bands, wherein the central peak has a chemical shift in the range of +1100 to +1900 ppm and the largest peak has a chemical shift in the range of +2100 to +2600 ppm.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Tobacco cellulose content determination method
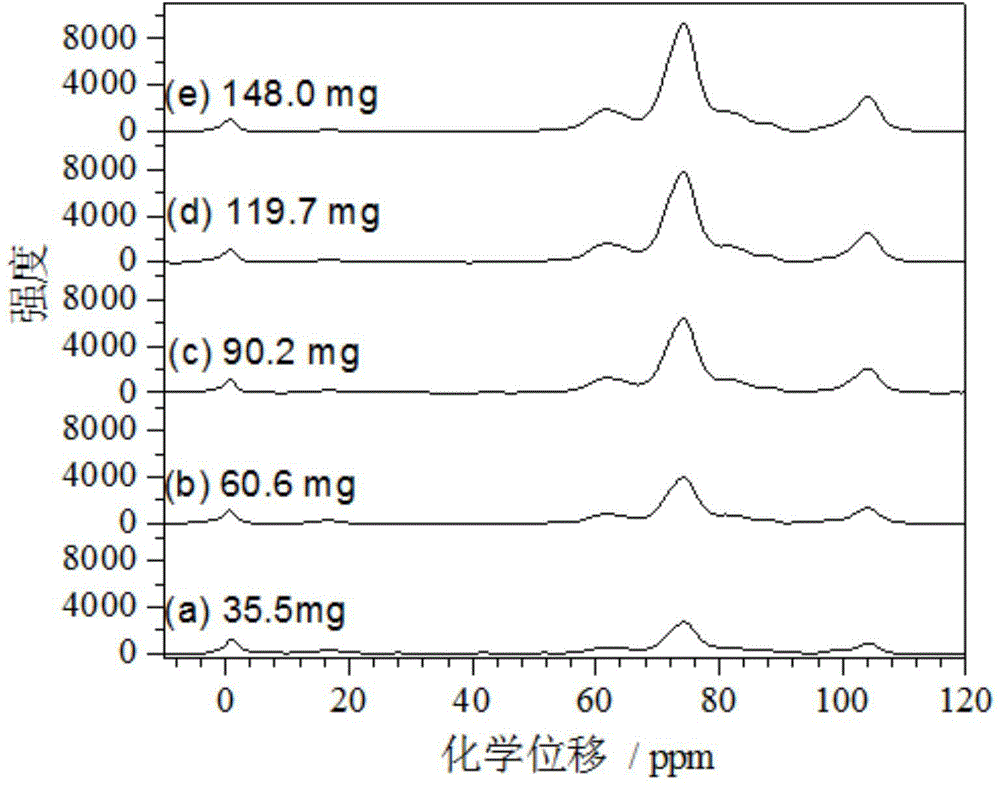
ActiveCN104614393AThe testing process is simpleAccurate and reliable measurement resultsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMagic angle spinningCellulose
The invention discloses a tobacco cellulose content determination method, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, weighing different mass of cellulose standard sample powder, adding the powder into sample tubes which use silicone tubes as internal standard substance, testing in a carbon 13 cross polarization magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, and thus obtaining wave spectrogram of each cellulose standard sample, processing with FeakFit software to obtain a ratio of quantitative peak area of the standard sample in the same wave spectrogram to the quantitative peak area of the internal standard substance, by taking absolute mass of the cellulose in the standard sample as abscissa and taking the ratio as ordinate for drawing, obtaining a standard work curve; then, repeating the steps above, obtaining the ratio of the quantitative peak area of a to-be-determined sample in a to-be-determined tobacco sample wave spectrogram to the quantitative peak area of the internal standard substance, further obtaining absolute mass of the cellulose in the to-be-determined tobacco sample according to the standard work curve, thereby obtaining the cellulose content in the to-be-determined tobacco sample. The determination method needs no pretreatment, is accurate in quantification, and is applicable to determination of tobacco cellulose content in batches.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO ANHUI IND CO LTD +1
Completely automatic MAS-NMR apparatus
InactiveUS7518371B2Magnetic measurementsSamplingMagic angle spinningNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A MAS (magic angle spinning) NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) apparatus, with automatic sample supply by a supply unit (45), is characterized in that an automatic preparation station (44) for samples is provided, with a rotor storage (49) having several rotors (1) for receiving sample material (53) soaked with NMR solution (55), a cap storage (48) with several caps (3), each cap (3) being suited for closing a rotor (1), wherein each cap (3) has a central axial bore (4), several movable pins (5), each being insertable into the central axial bore (4) of a cap (3) to close the bore (4) in the inserted state, a cap handling unit (46b) which can grip a cap (3) from the cap storage (48), move it, and dispose it onto a rotor (1), a plunger (61) for inserting a pin (5) into the bore (4) of the cap (3), and a suctioning device (62) for suctioning excess NMR solution (55) that escapes from the bore (4). The apparatus provides simple and automatic preparation of sample units, in particular, closure of rotors with caps.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Slow magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance device and process for metabolomics profiling of tissues and biofluids
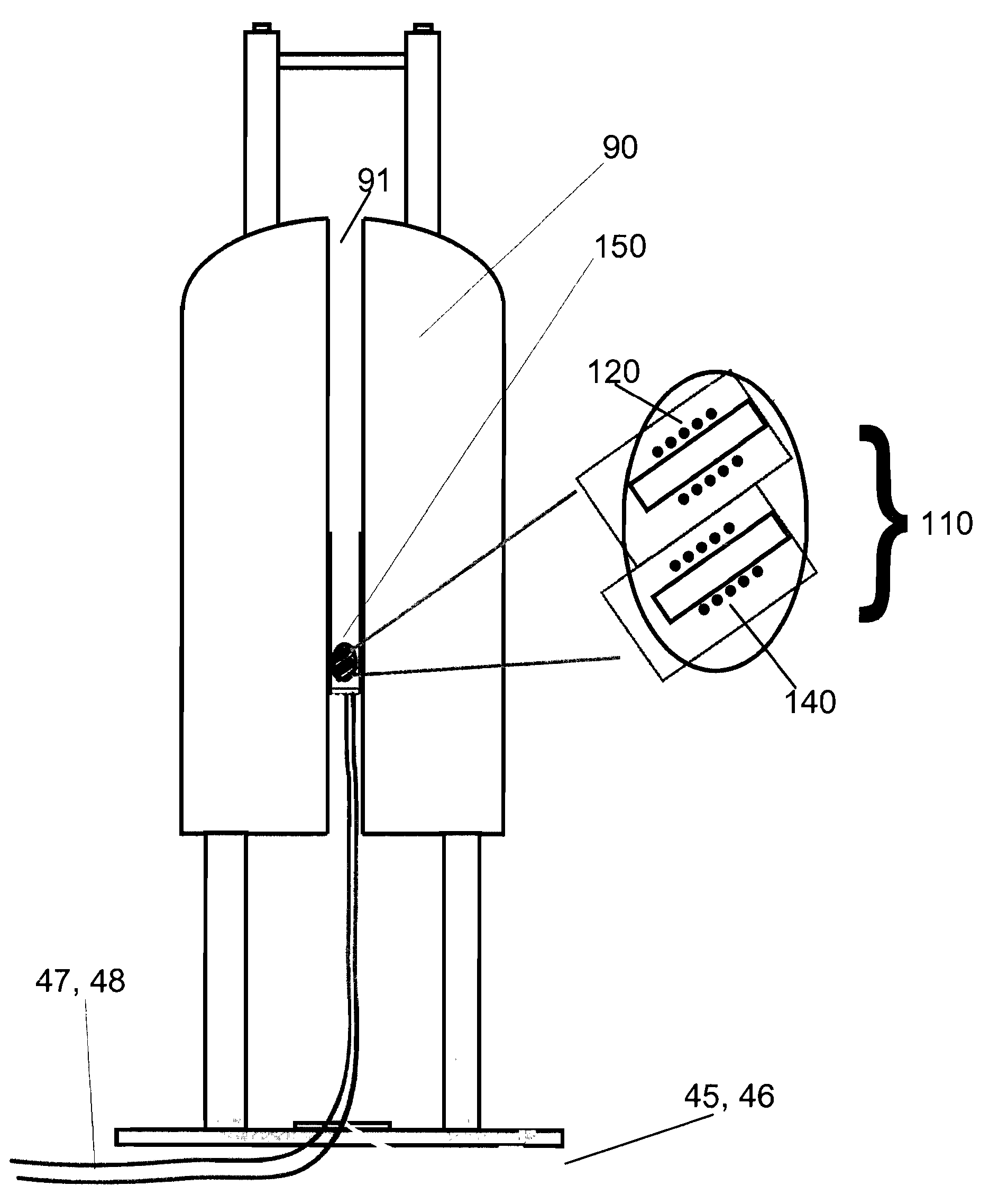
ActiveUS20130257432A1Enhances sample filling factorEliminate the effects ofManufacture of electrical instrumentsElectric/magnetic detectionMagic angle spinningTissue biopsy
A slow Magic-Angle Spinning NMR device and method are detailed that provide high resolution and high sensitivity metabolic profiling of biological samples. A new 1H-PASS sequence suppresses line broadening in the various biological samples. The device and method allow metabolic changes in small animals to be tracked through continuous investigations of minimally-invasive blood and tissue biopsy samples over a sustained period and allow intact biological objects with sizes up to a few centimeters to be studied.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
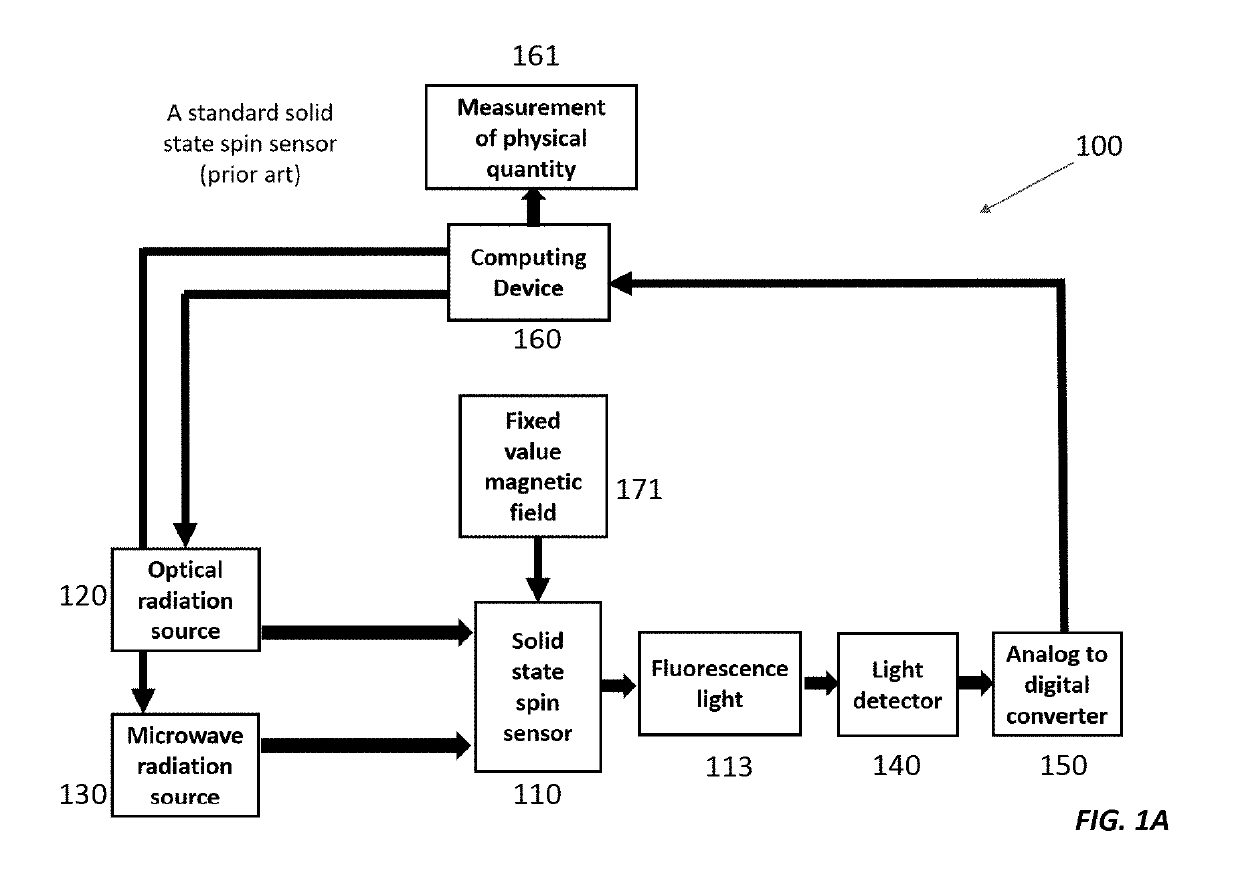
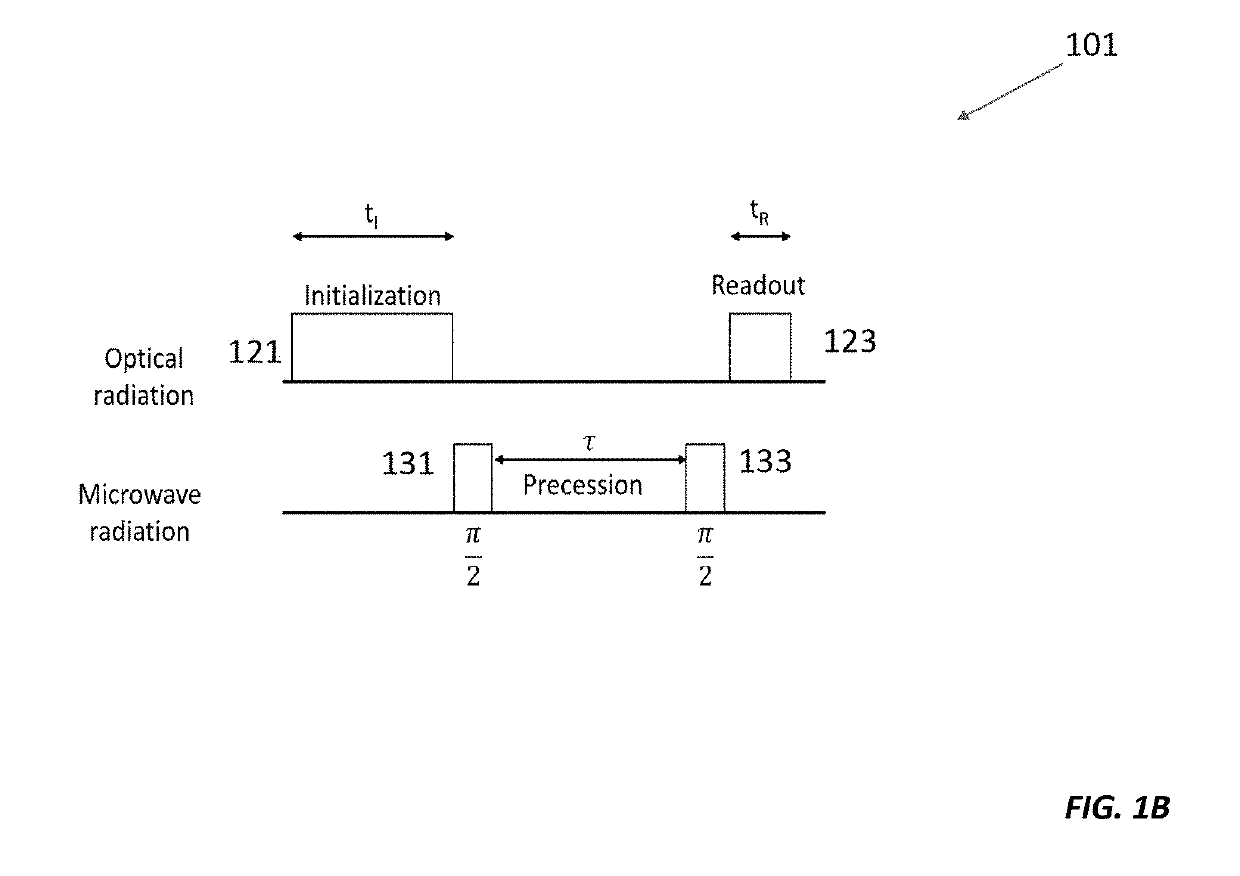
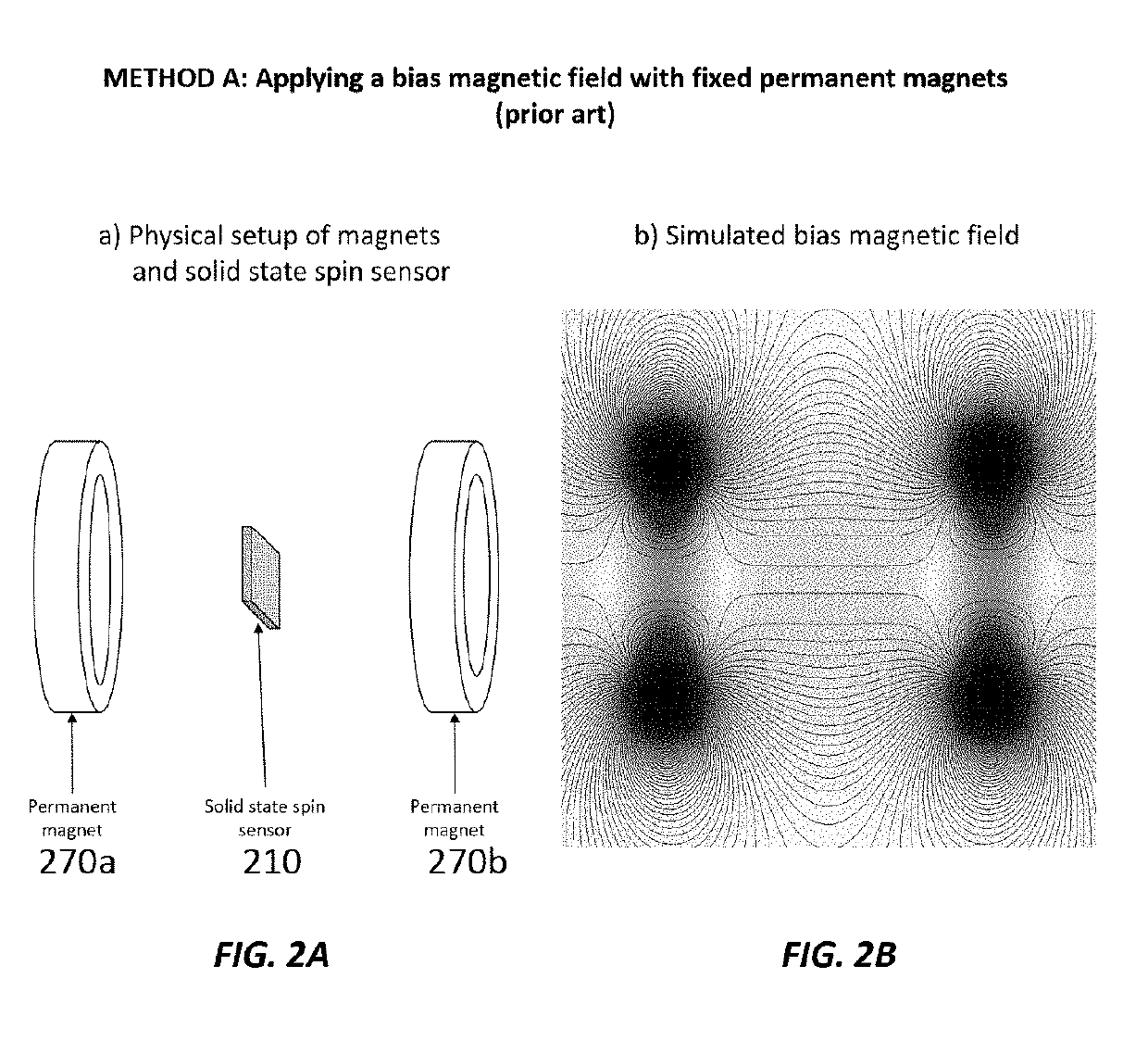
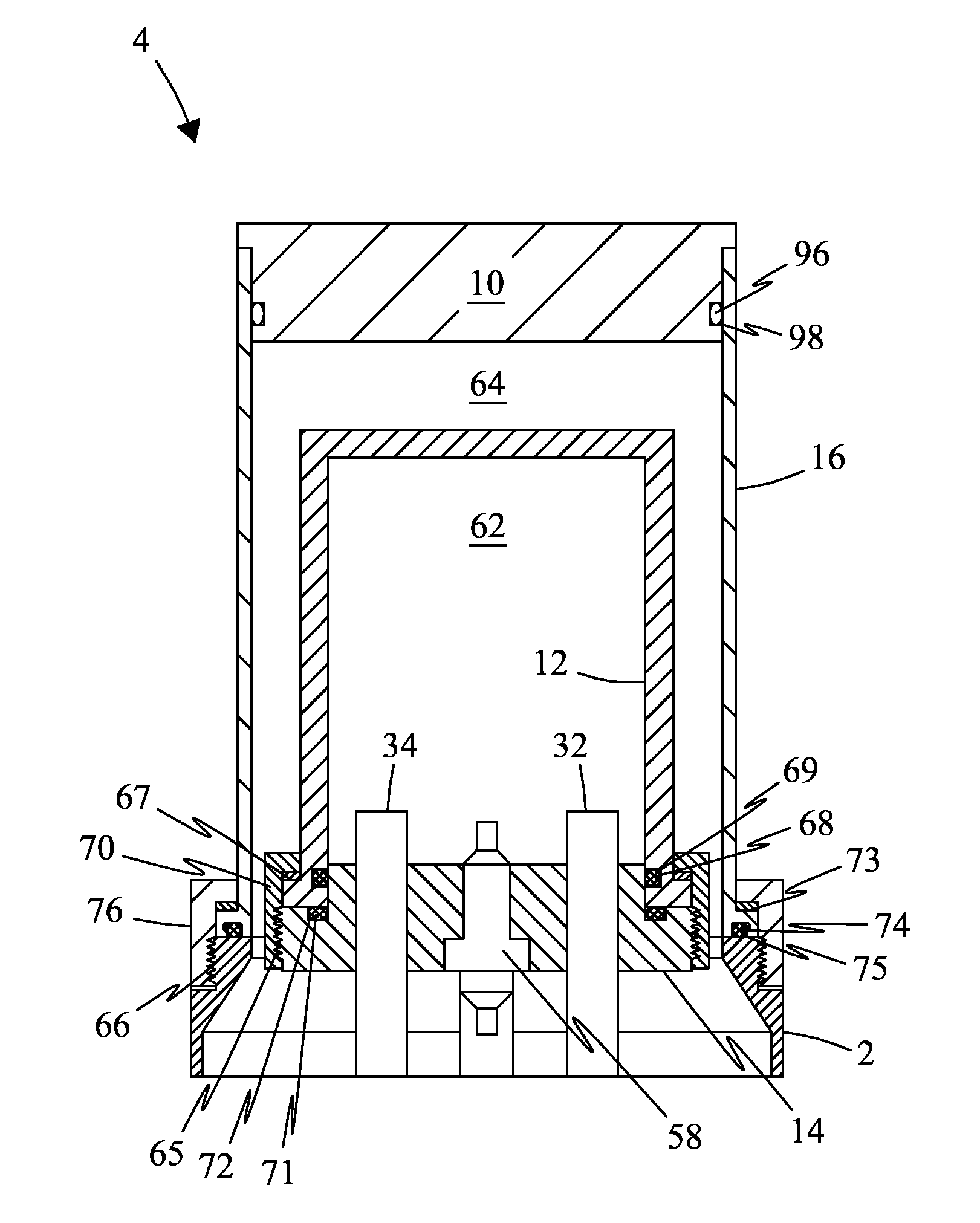
Stationary Magic Angle Spinning Enhanced Solid State Spin Sensor
ActiveUS20190178958A1Increases dephasing timeAnalysis using double resonanceMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagic angle spinningTime extension
Here we present a solid-state spin sensor with enhanced sensitivity. The enhanced sensitivity is achieved by increasing the T2* dephasing time of the color center defects within the solid-state spin sensor. The T2* dephasing time extension is achieved by mitigating dipolar coupling between paramagnetic defects within the solid-state spin sensor. The mitigation of the dipolar coupling is achieved by applying a magic-angle-spinning magnetic field to the color center defects. This field is generated by driving a magnetic field generator (e.g., Helmholtz coils) with phase-shifted sinusoidal waveforms from current source impedance-matched to the magnetic field generator. The waveforms may oscillate (and the field may rotate) at a frequency based on the precession period of the color center defects to reduce color center defect dephasing and further enhance measurement sensitivity.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Sealed magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance probe and process for spectroscopy of hazardous samples
ActiveUS9366736B2Prevent proliferationEasy to controlAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionMagic angle spinningNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A magic-angle-spinning (MAS) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) probe is described that includes double containment enclosures configured to seal and contain hazardous samples for analysis. The probe is of a modular design that ensures containment of hazardous samples during sample analysis while preserving spin speeds for superior NMR performance and convenience of operation.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Advanced slow-magic angle spinning probe for magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy
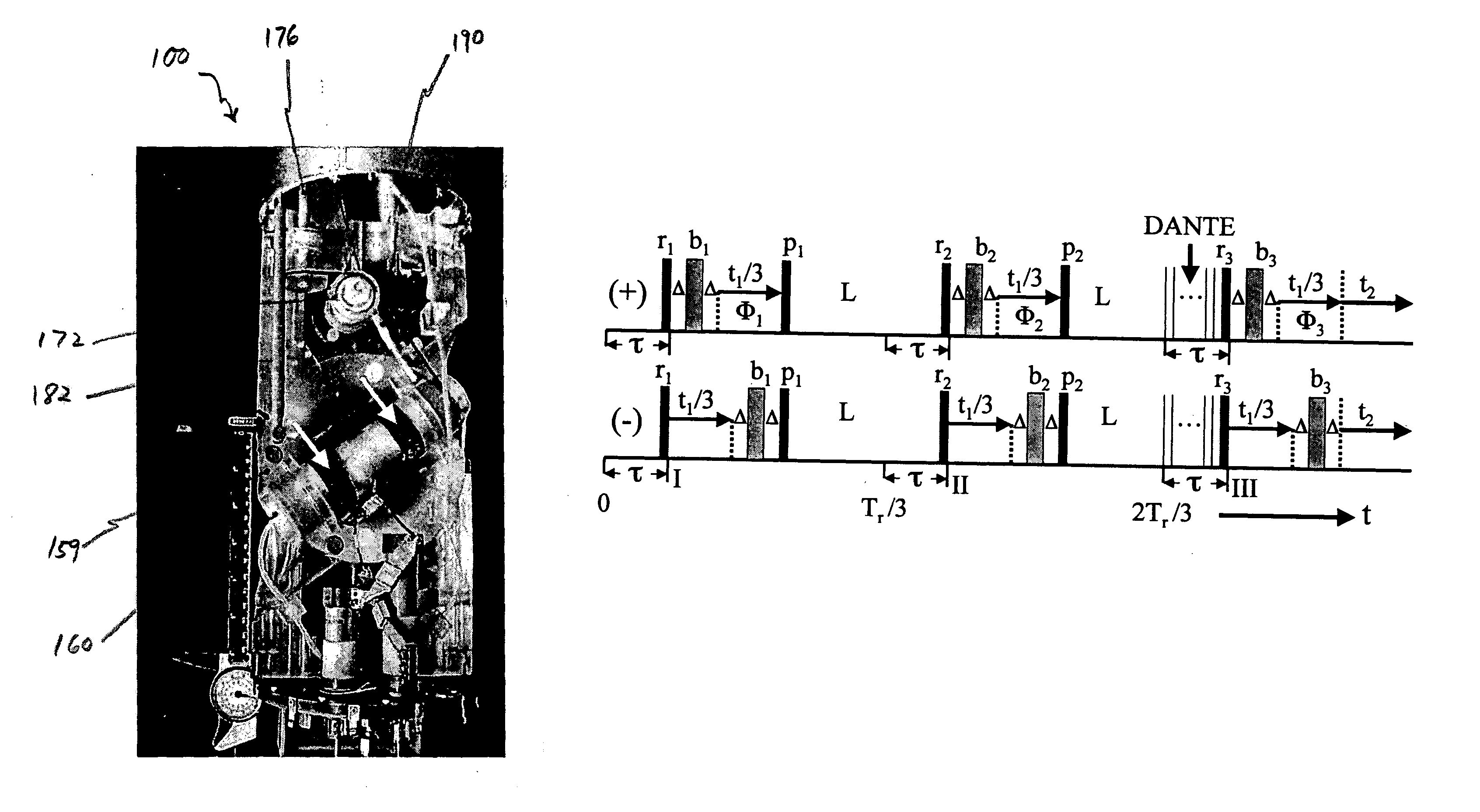
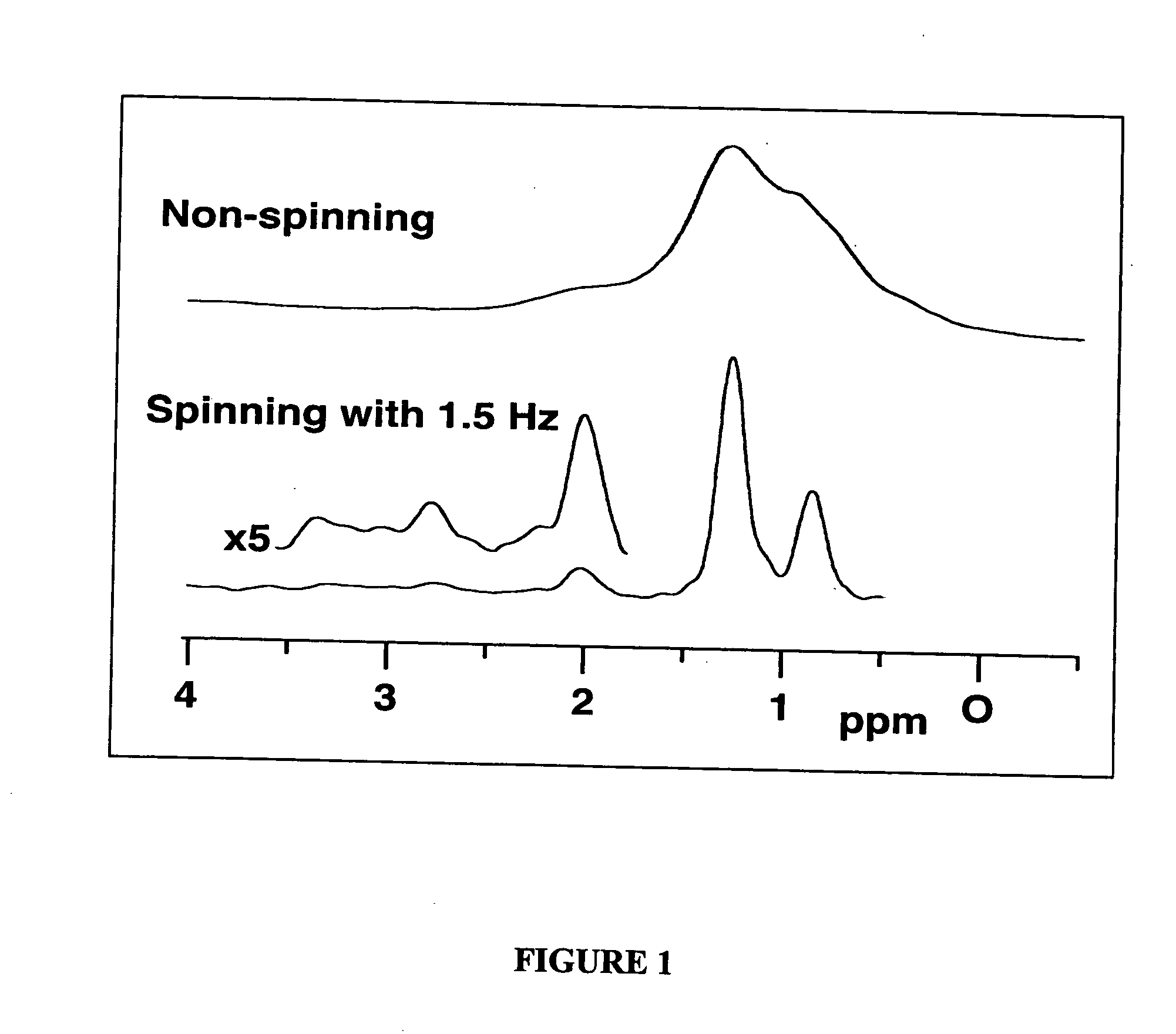
InactiveUS20050035766A1Additive manufacturing apparatusMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMagic angle spinningMetabolite
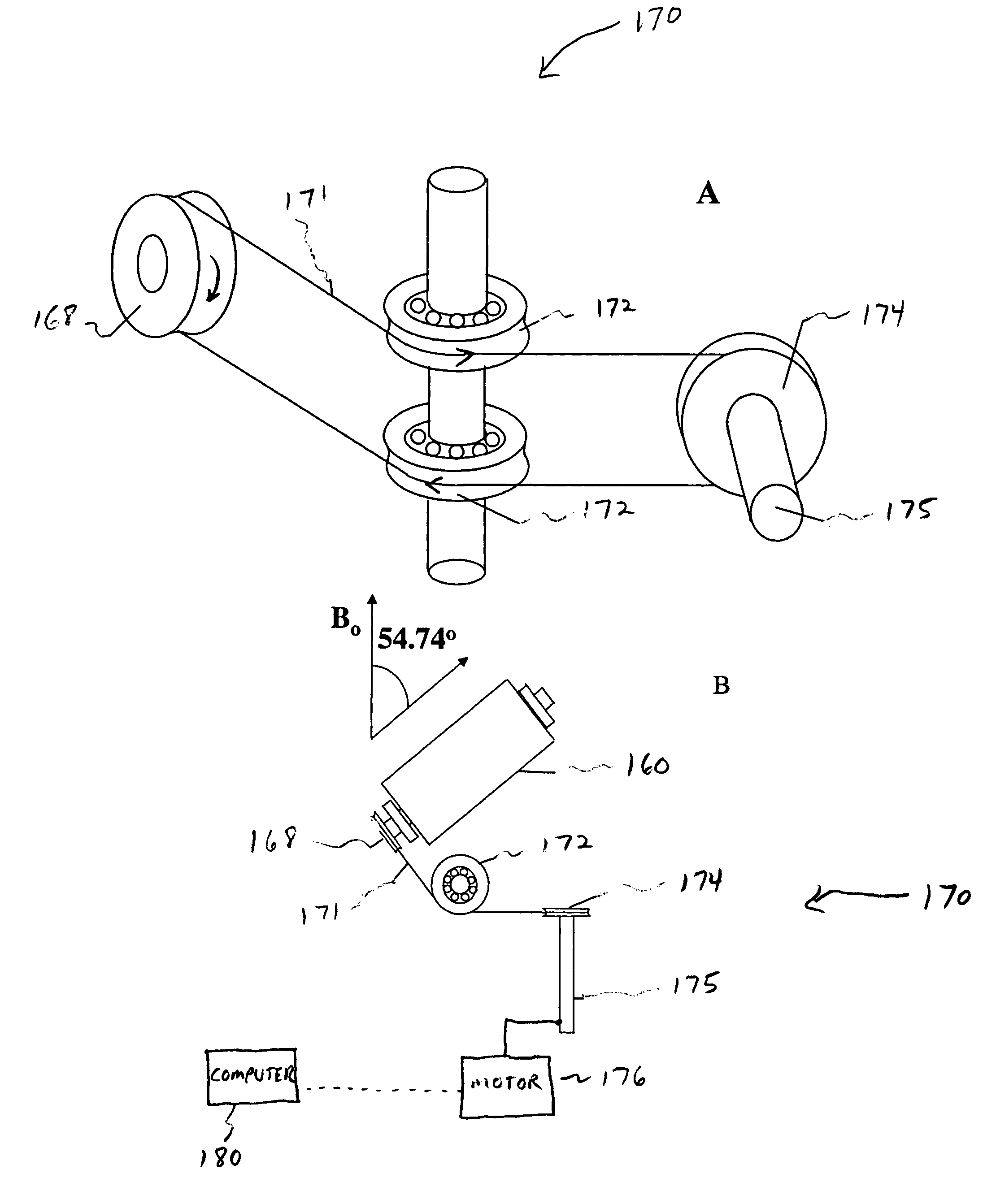
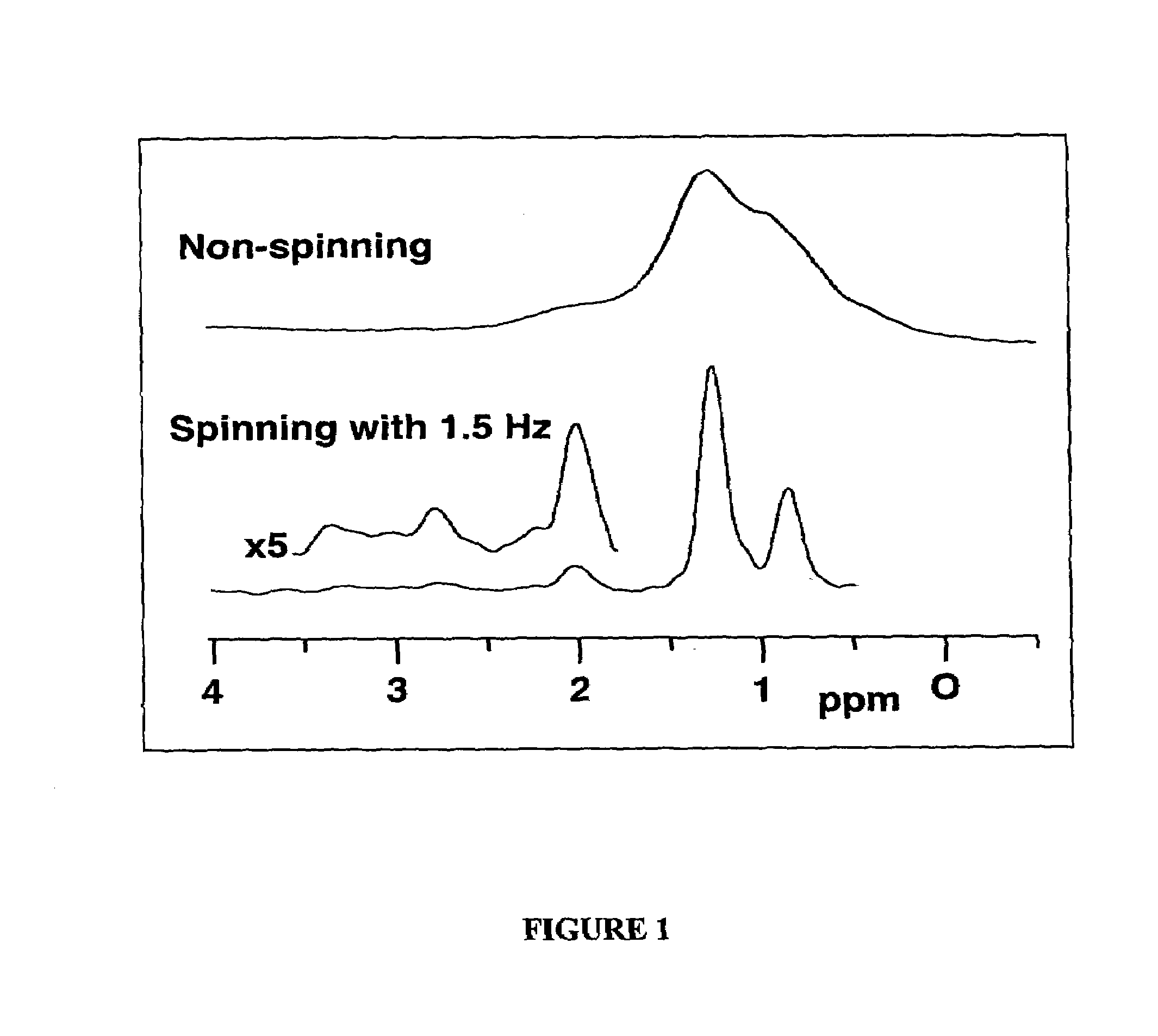
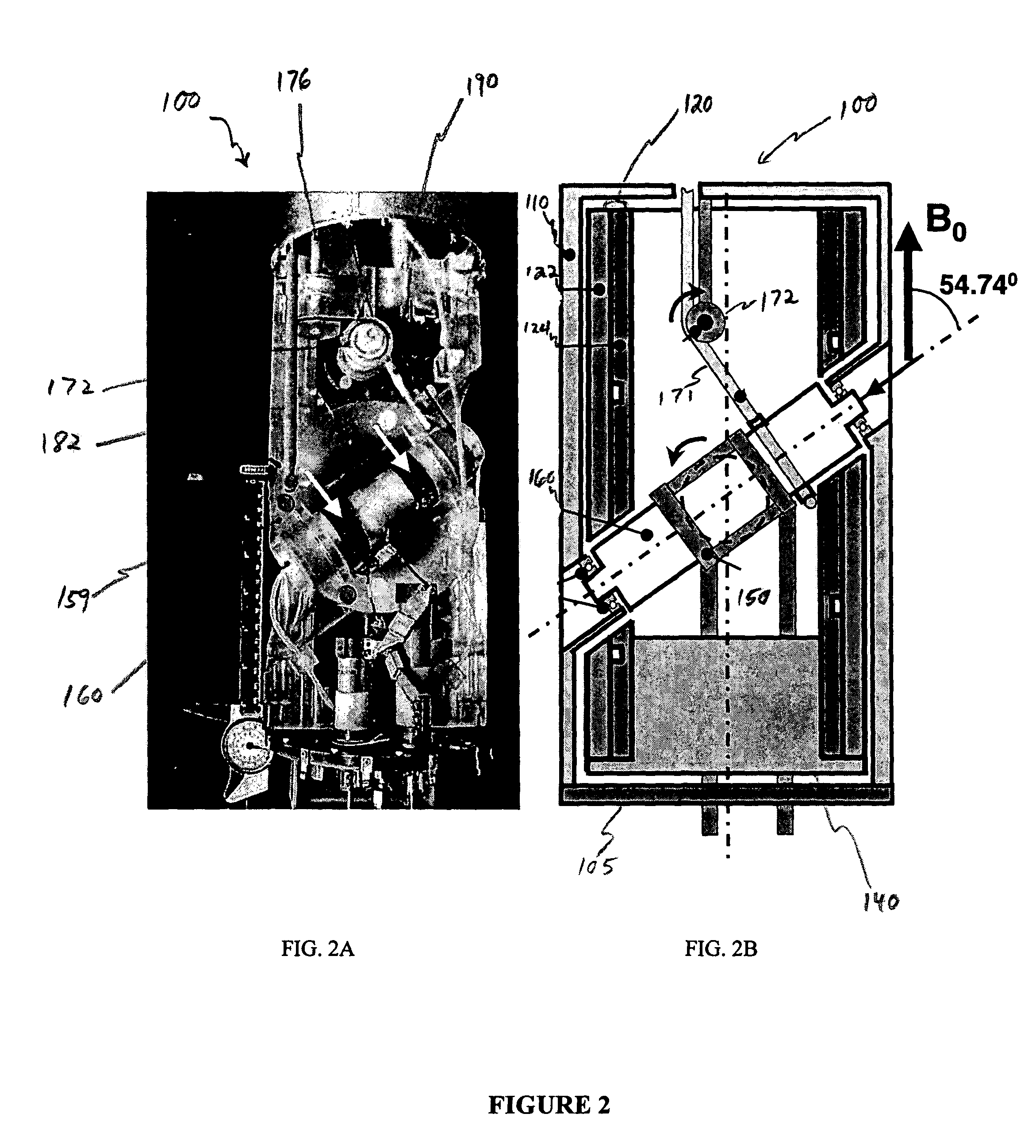
The present invention relates to a probe and processes useful for magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy instruments. More particularly, the invention relates to a MR probe and processes for obtaining resolution enhancements of fluid objects, including live specimens, using an ultra-slow (magic angle) spinning (MAS) of the specimen combined with a modified phase-corrected magic angle turning (PHORMAT) pulse sequence. Proton NMR spectra were measured of the torso and the top part of the belly of a female BALBc mouse in a 2 T field, while spinning the animal at a speed of 1.5 Hz. Results show that even in this relatively low field with PHORMAT, an isotropic spectrum is obtained with line widths that are a factor 4.6 smaller than those obtained in a stationary mouse. Resolution of 1H NMR metabolite spectra are thus significantly enhanced. Results indicate that PHORMAT has the potential to significantly increase the utility of 1H NMR spectroscopy for in vivo biochemical, biomedical and / or medical applications involving large-sized biological objects such as mice, rats and even humans within a hospital setting. For small-sized objects, including biological objects, such as excised tissues, organs, live bacterial cells, and biofilms, use of PASS at a spinning rate of 30 Hz and above is preferred.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Campylobacter glycans and glycopeptides
ActiveUS7598354B2Avoid pollutionEliminating and reducing presenceAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaMagic angle spinningGlycopeptide
Multiple strains and species of Campylobacter share a common glycan moiety which is present in a plurality of surface-exposed glycoproteins. This glycan has the formula: GalNAc-a1, 4-GalNAc-a1,4-[Glc-β1,3]GalNAc-a1,4-GalNAc-a1,4-GalNAc-a1,3-Bac, wherein Bac is 2, 4-diacetamido-2,4,6-trideoxy-D-glucopyranose. This glycan and immunologically active fragments of it have use as vaccines against campylobacter infection in humans and animals. As well, antibodies which specifically bind these compounds may be provided. Such antibodies and vaccines may be used to prevent or neutralize campylobacter infections in livestock thereby preventing this pathogen from entering the human food chain. The glycan may be linked to one or more amino acids to form a glycopeptide. As well, a method for determining the glycan structure of an intact glycoprotein consists of subjecting a sample to high resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (HR-MAS-NMR) spectroscopy.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
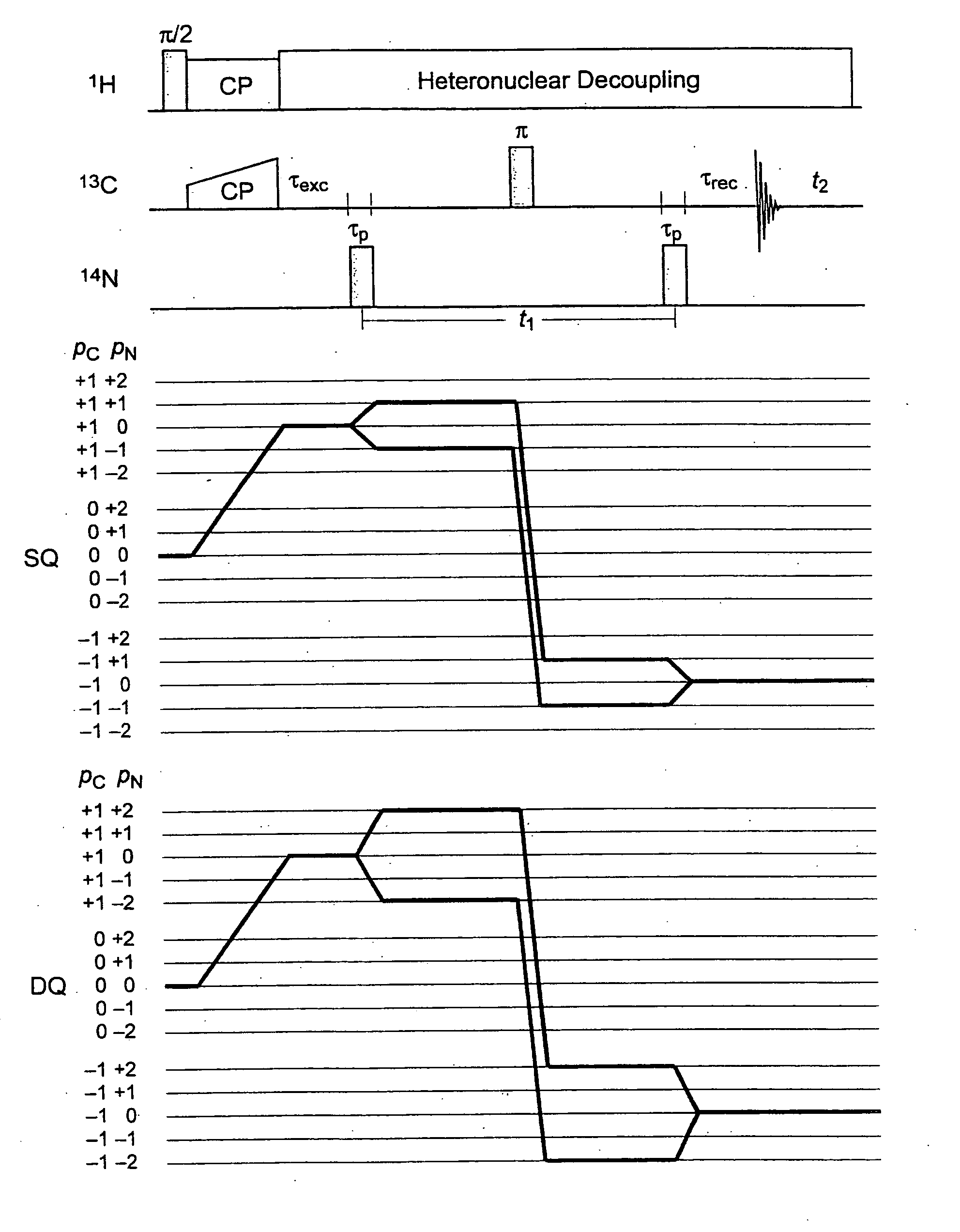
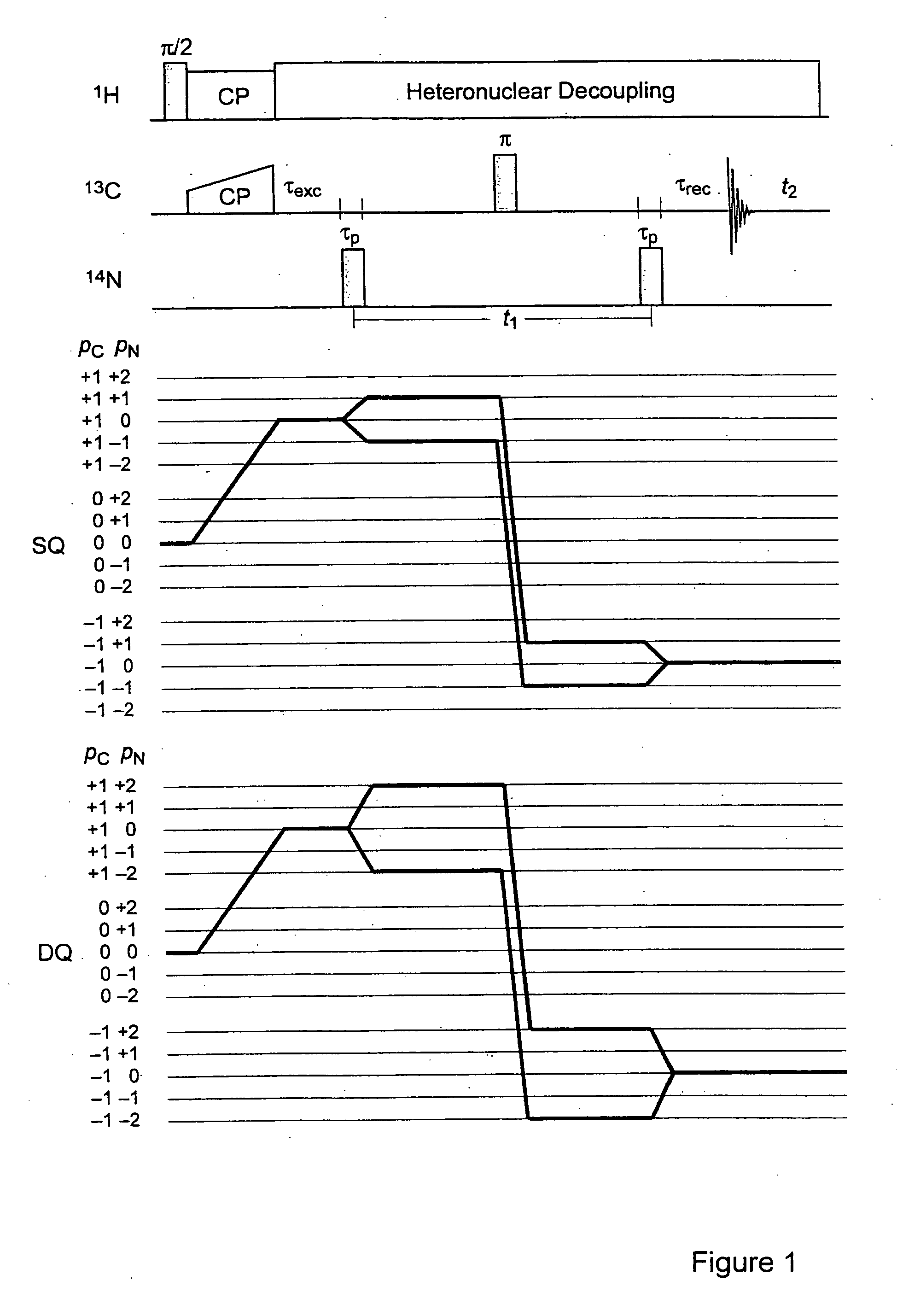
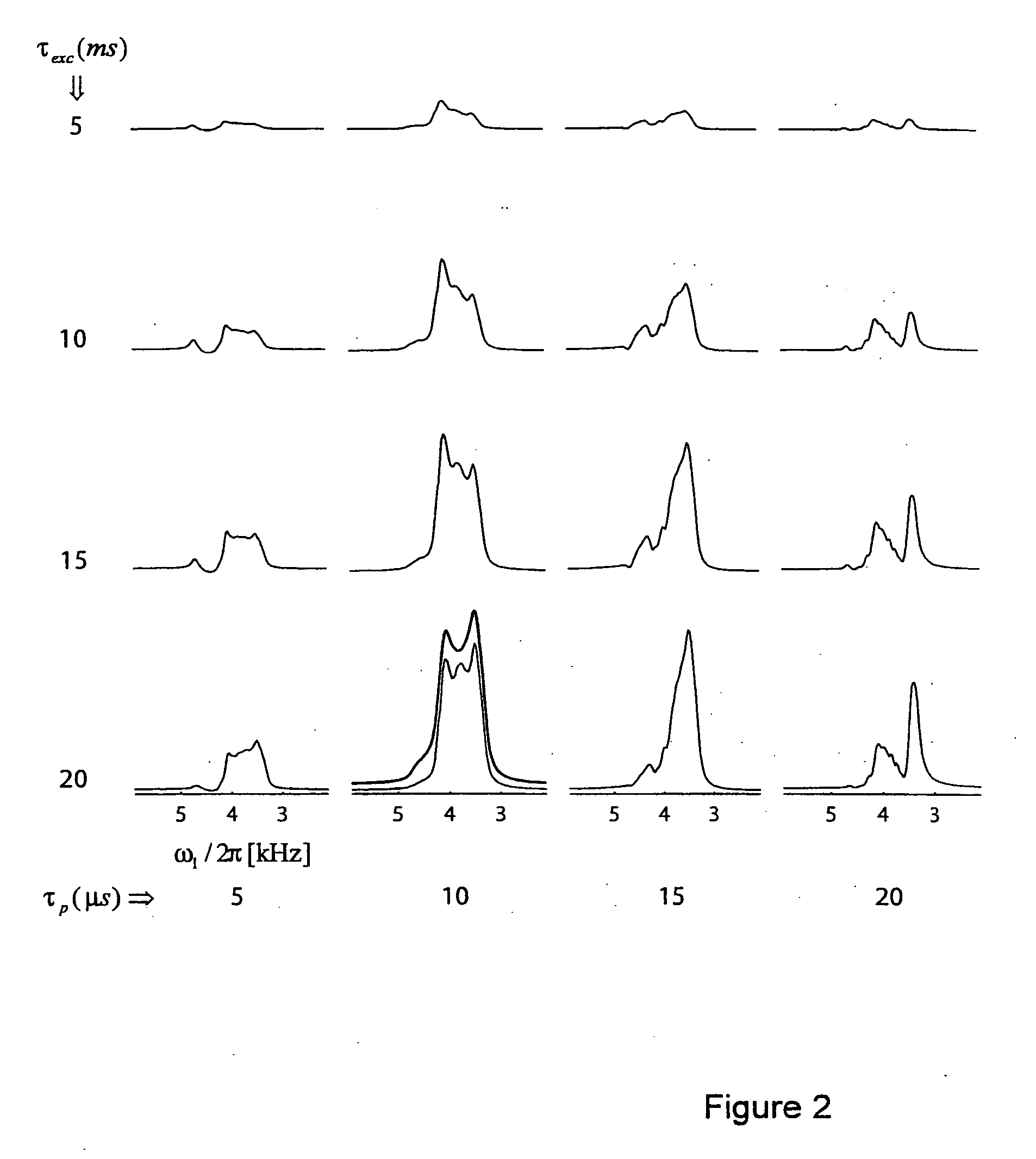
Quadrupolar nuclei NMR using residual dipolar splittings in solids
ActiveUS7276903B2Broaden spectrumMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagic angle spinningNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
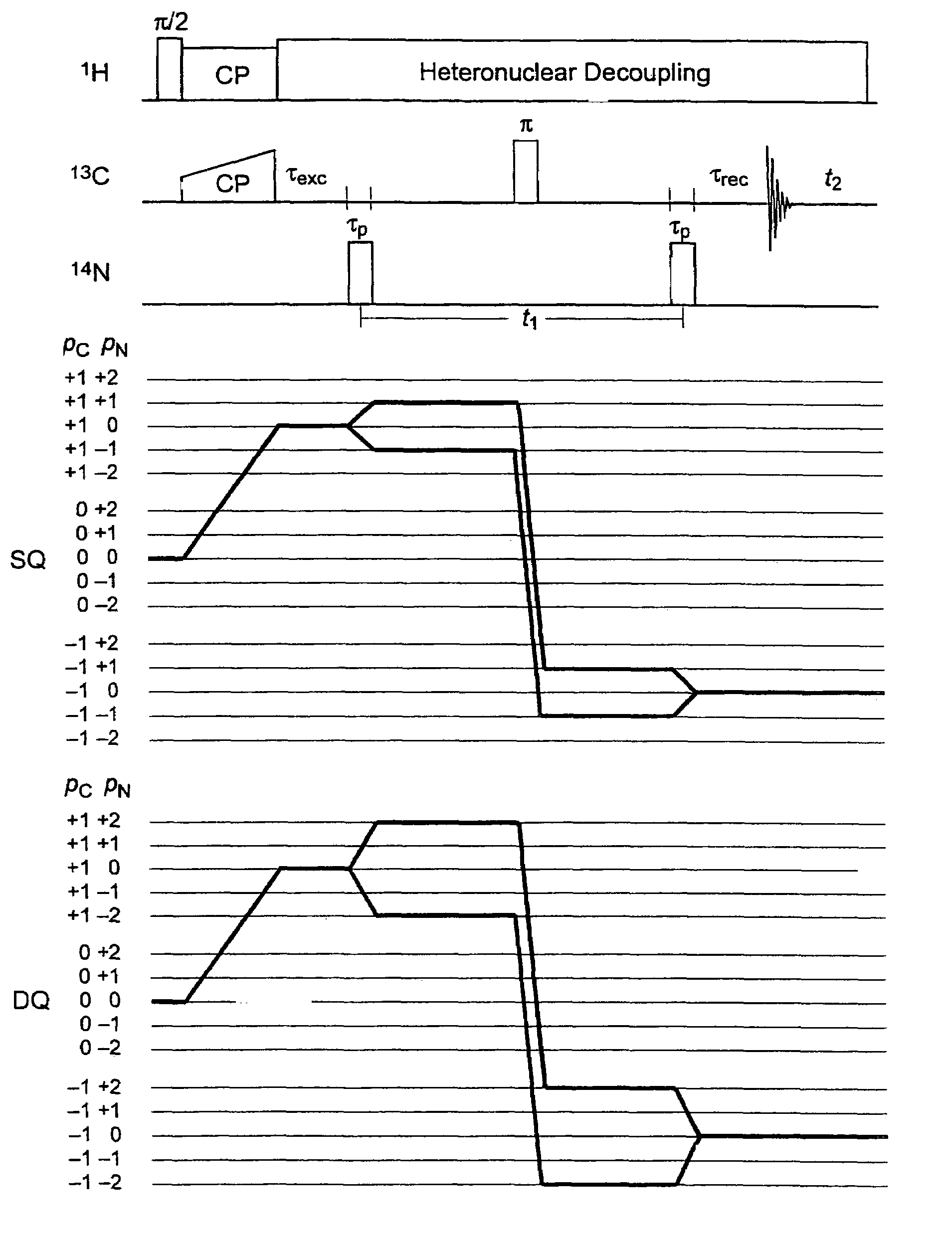
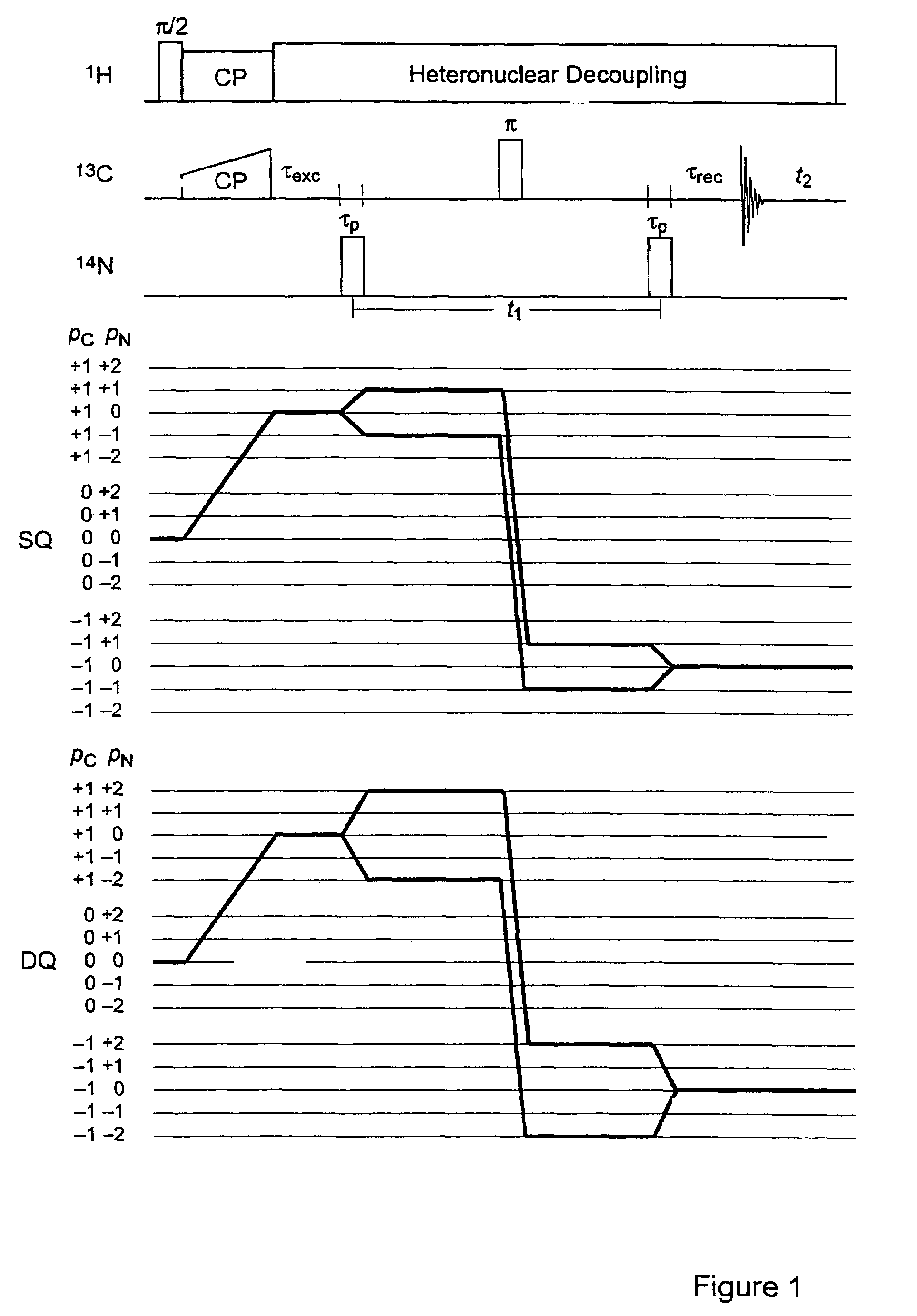
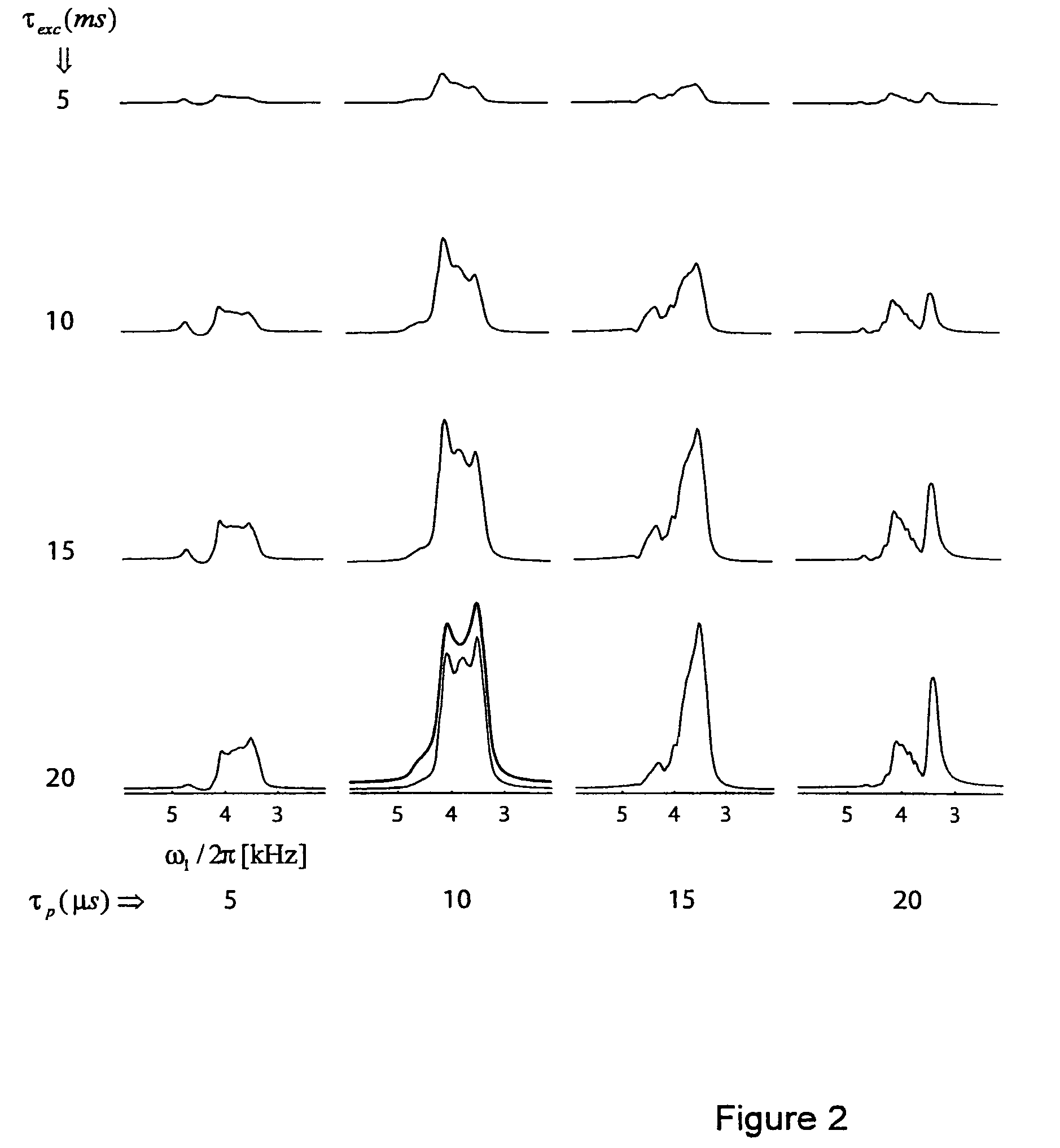
A method for obtaining NMR (=nuclear magnetic resonance) spectra of quadrupolar nuclei having spin I>½ using magic angle spinning (=MAS) in solid powders and transfer of coherences from a neighboring nucleus with spin S= 1 / 2 to single- or double-quantum transitions of quadrupolar nuclei having spin I>½, is characterized in that the transfer of coherences occurs through a combination of scalar and residual dipolar splittings. With the inventive method improved NMR-spectra can be obtained from which parameters can be extracted, which can be related to the structure and internal dynamics of solids containing the quadrupolar nuclei.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Sample holder and method
InactiveUS20160047867A1Easy to useImprove abilitiesElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagic angle spinningResonance analysis
A sample holder for use with magic angle spinning NMR and similar magnetic resonance analysis techniques which includes a sample holder sealed by an O-ring and a contact seal. The O-ring seals the sample volume during pressurization whereas the contact seal is active during analysis. The O-ring and the contact seal are disposed so that rotation of a plug selective engages one or both of the seals.
Owner:UB2 INSTR SRL
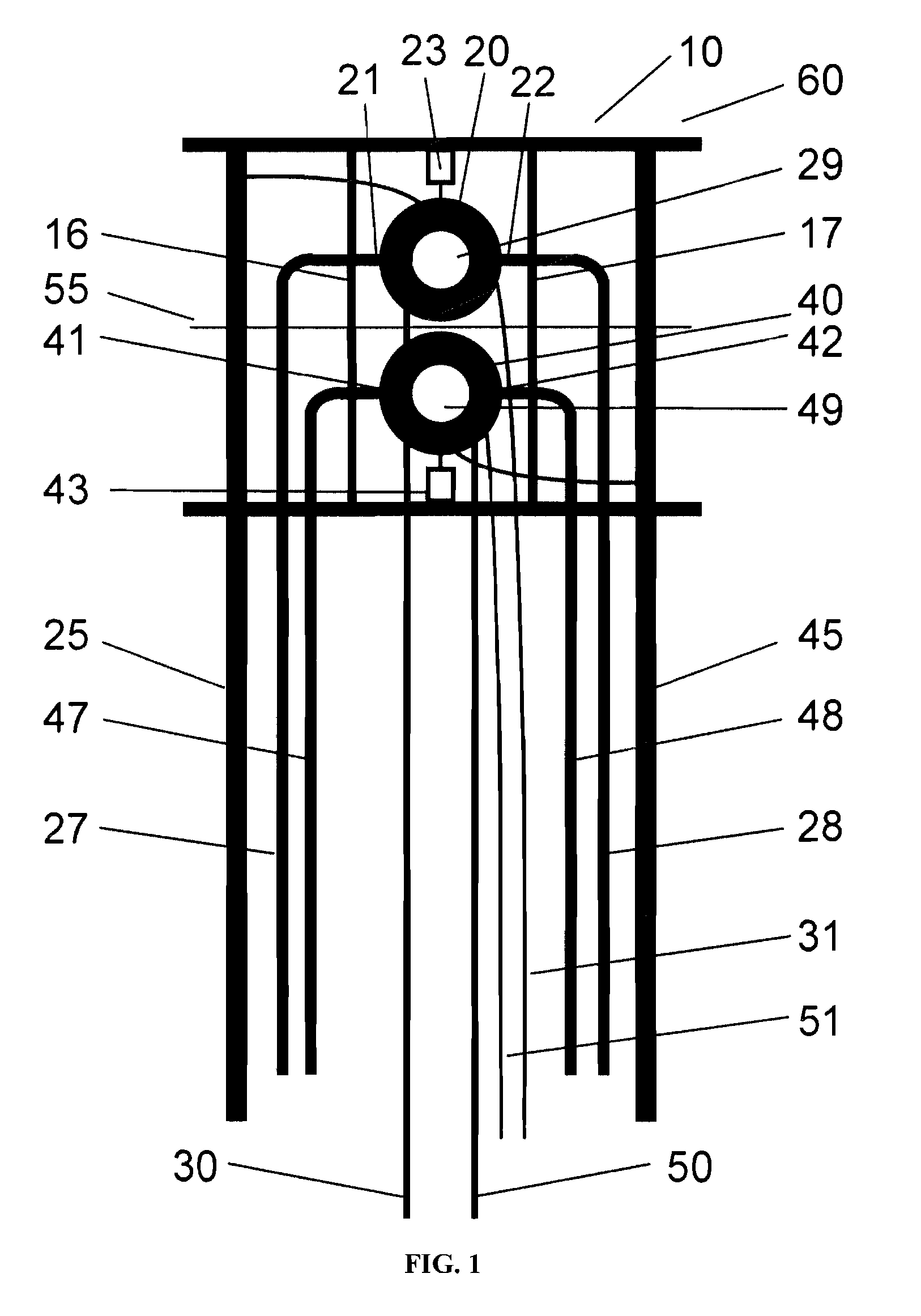
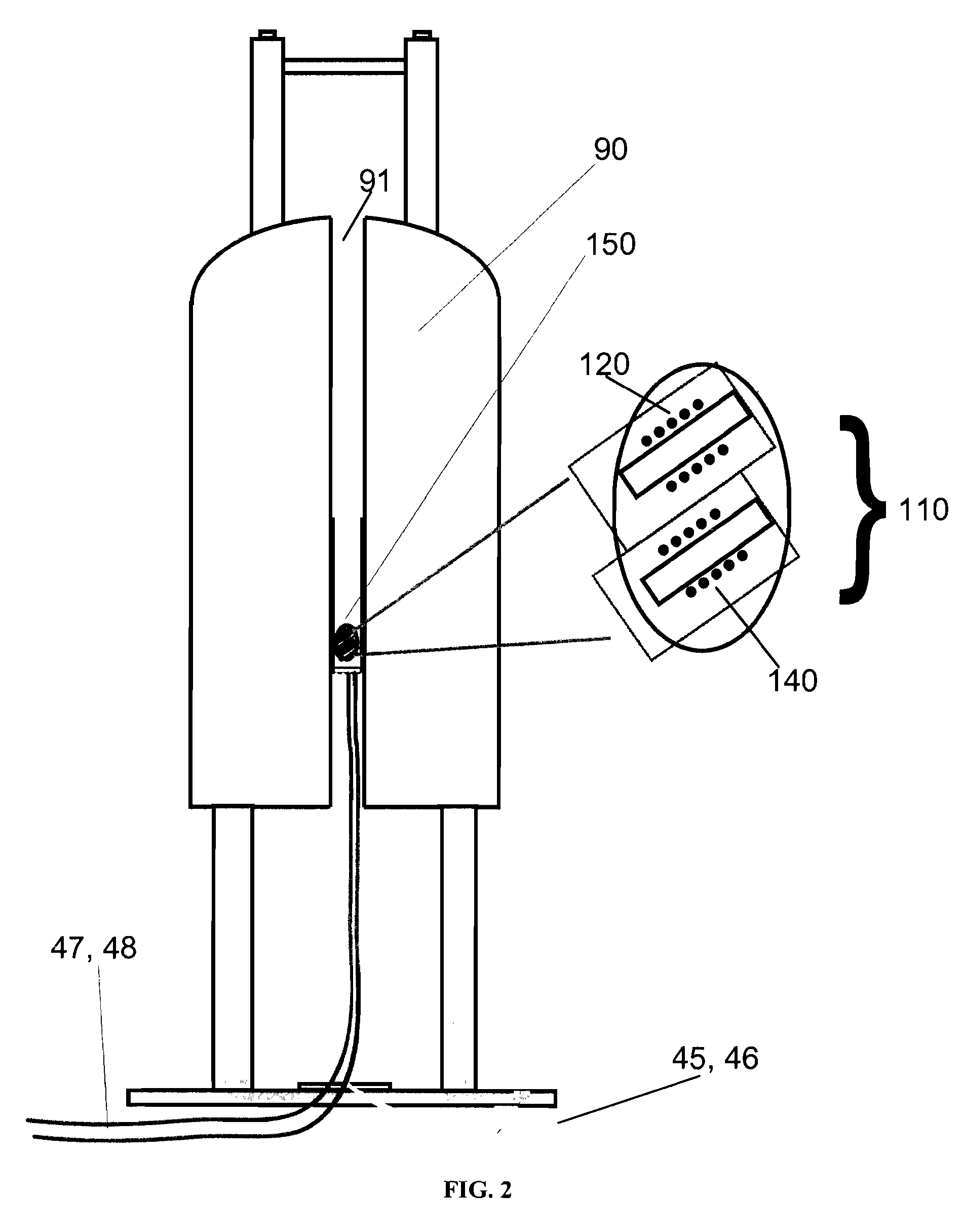
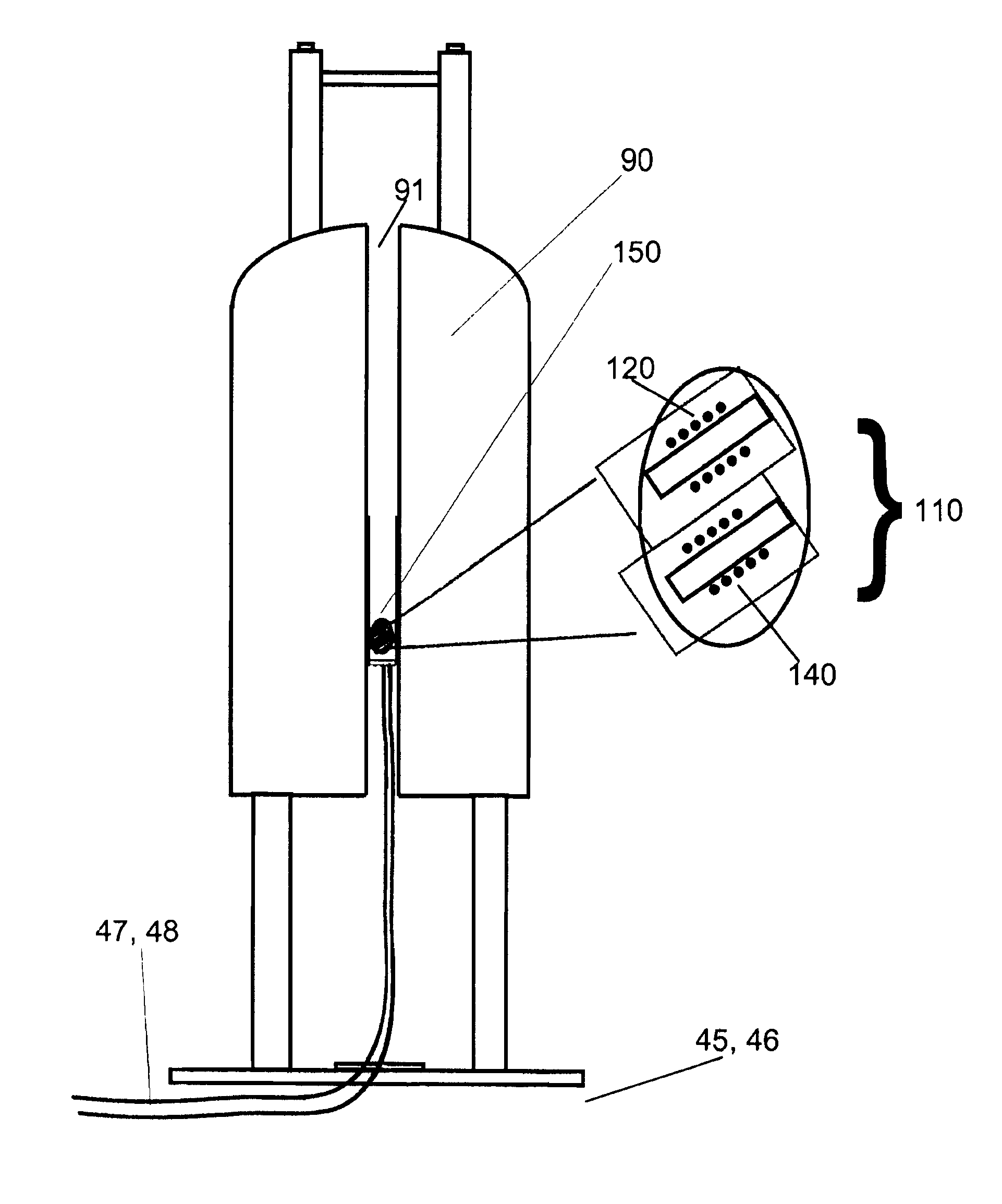
High-Throughput Systems for Magic-Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
InactiveUS20080169814A1Reduce crosstalkMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagic angle spinningSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonance
A solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance probe for use in a magnetic field having a plurality of isolated magic angle spinning modules positioned within the housing is disclosed. The housing is configured so that the plurality of magic angle spinning modules are located in a stationary position within a homogenous region of said magnetic field during use.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Catalytic cracking catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103785453AGood hydrothermal stabilityGood choiceCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMagic angle spinningPeak area
The invention discloses a catalytic cracking catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The catalytic cracking catalyst includes 15%-65% of a natural mineral, 10%-30% of an oxide and 25%-75% of a phosphorus-modified beta molecular sieve; the phosphorus-modified beta molecular sieve comprises 3-10 wt% of phosphorus by P2O5, and in the 27Al MAS NMR (Magic Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) of the molecular sieve, the ratio of peak area of a resonance signal at the chemical shift of 40+ / -3ppm to peak area of a resonance signal at the chemical shift of 54+ / -3ppm is greater than or equal to 1. The catalyst has excellent hydrothermal stability and better product selectivity, and is applied to ethylene, propylene and butylene production by using naphtha as a raw material through a catalytic cracking process.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Quadrupolar nuclei NMR using residual dipolar splittings in solids
ActiveUS20070013373A1Broaden spectrumMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagic angle spinningNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method for obtaining NMR (=nuclear magnetic resonance) spectra of quadrupolar nuclei having spin l>½ using magic angle spinning (=MAS) in solid powders and transfer of coherences from a neighboring nucleus with spin S= 1 / 2 to single- or double-quantum transitions of quadrupolar nuclei having spin l>½, is characterized in that the transfer of coherences occurs through a combination of scalar and residual dipolar splittings. With the inventive method improved NMR-spectra can be obtained from which parameters can be extracted, which can be related to the structure and internal dynamics of solids containing the quadrupolar nuclei.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
High-throughput systems for magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveUS7626391B2Reduce crosstalkMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagic angle spinningSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonance
A solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance probe for use in a magnetic field having a plurality of isolated magic angle spinning modules positioned within the housing is disclosed. The housing is configured so that the plurality of magic angle spinning modules are located in a stationary position within a homogenous region of said magnetic field during use.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com