Patents
Literature
13808 results about "Spray drying" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
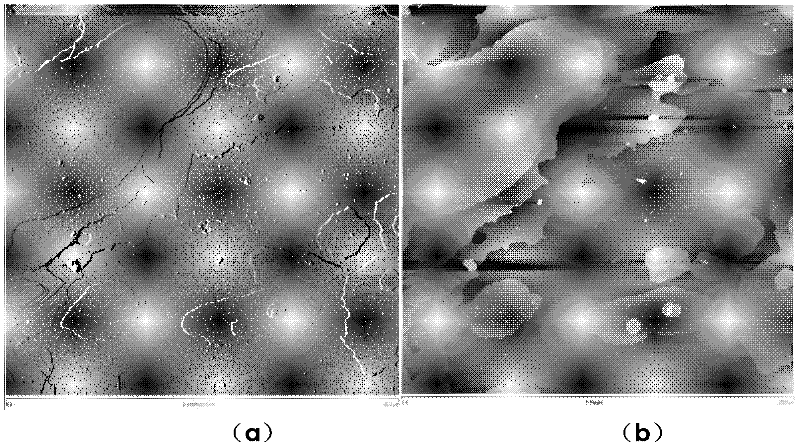
Spray drying is a method of producing a dry powder from a liquid or slurry by rapidly drying with a hot gas. This is the preferred method of drying of many thermally-sensitive materials such as foods and pharmaceuticals. A consistent particle size distribution is a reason for spray drying some industrial products such as catalysts. Air is the heated drying medium; however, if the liquid is a flammable solvent such as ethanol or the product is oxygen-sensitive then nitrogen is used.
Porous drug matrices and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6932983B1Lower the volumePrevent precipitationPowder deliveryNanotechDrugs solutionWater soluble drug
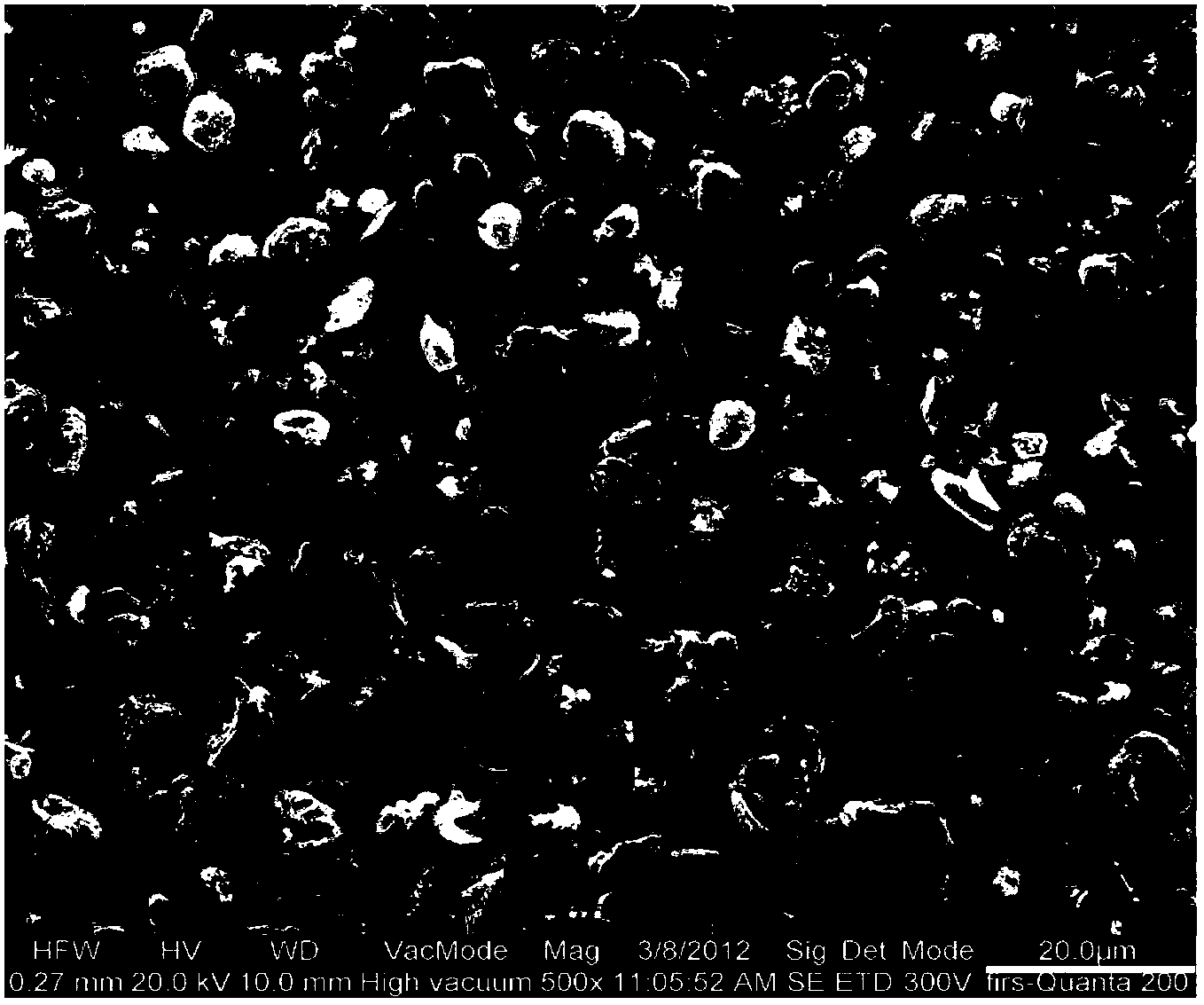
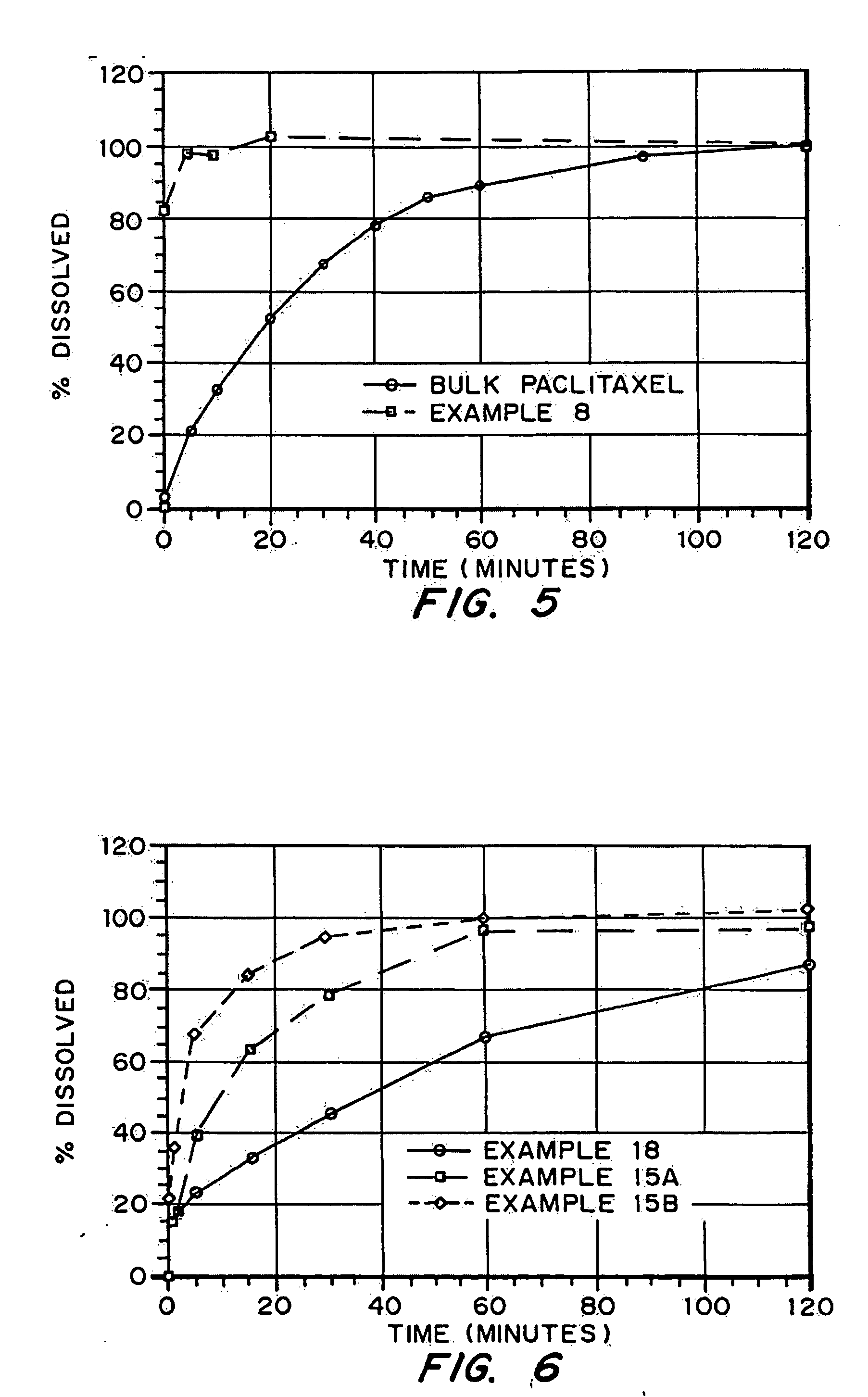
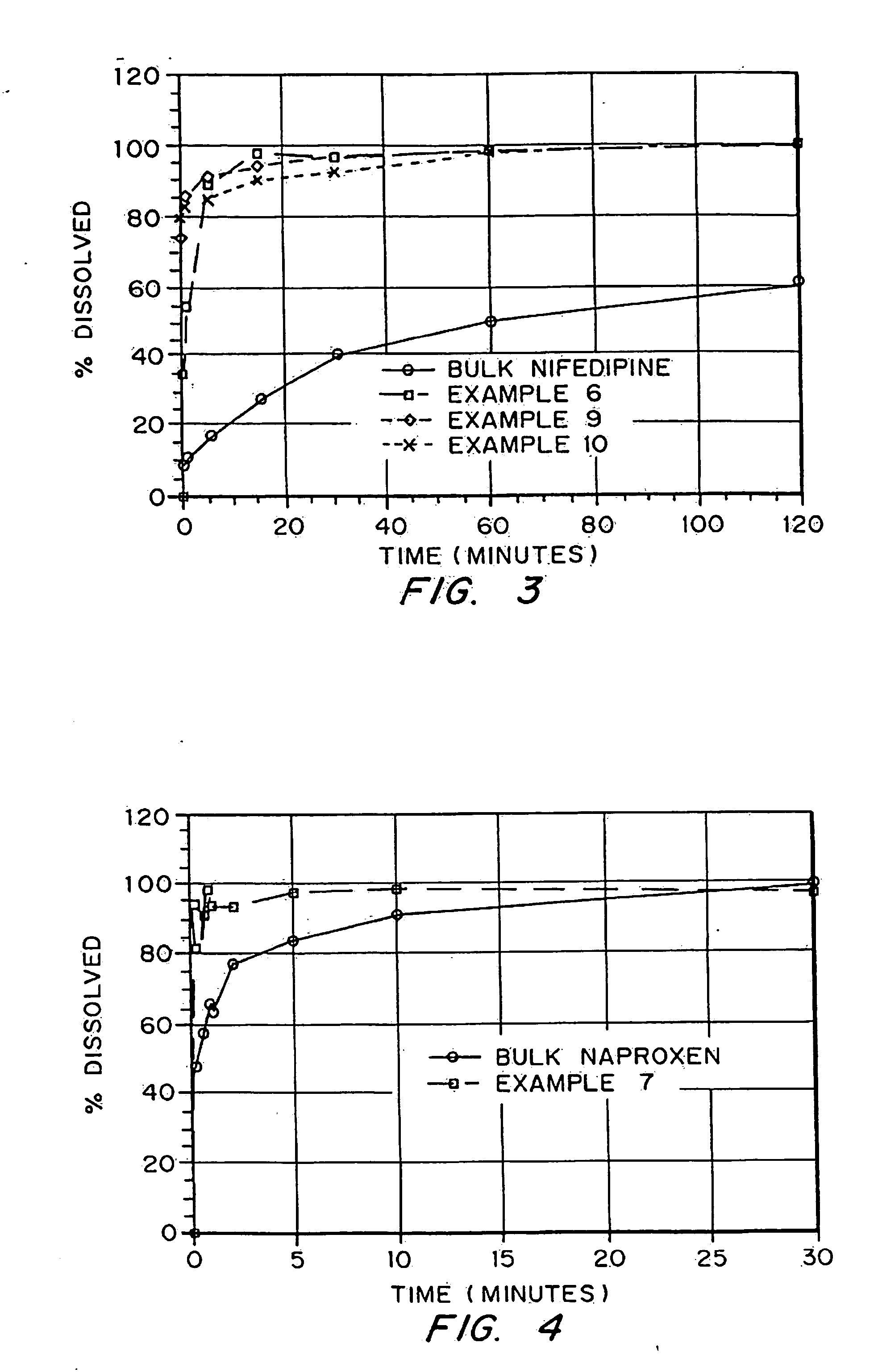
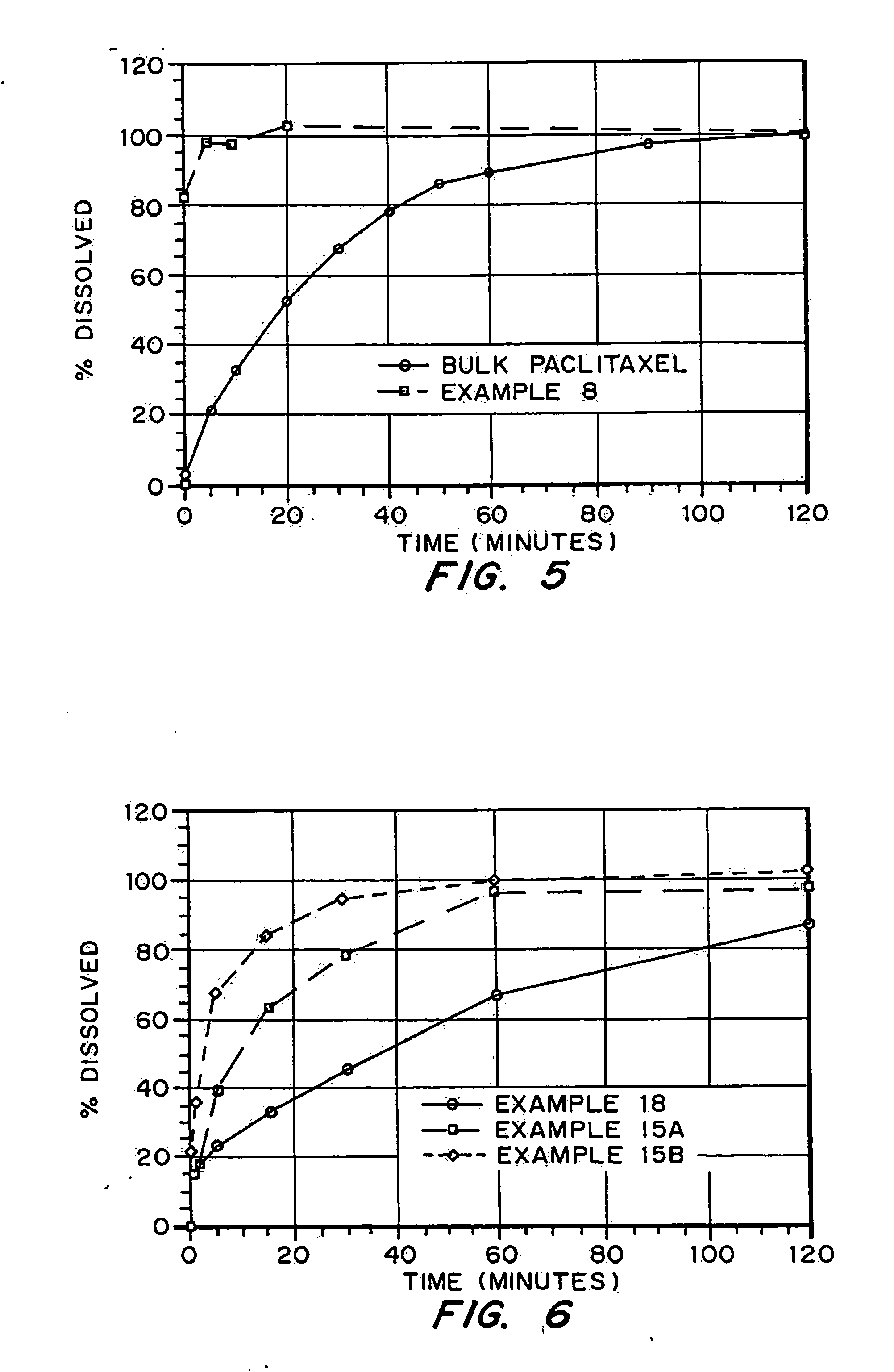
Drugs, especially low aqueous solubility drugs, are provided in a porous matrix form, preferably microparticles, which enhances dissolution of the drug in aqueous media. The drug matrices preferably are made using a process that includes (i) dissolving a drug, preferably a drug having low aqueous solubility, in a volatile solvent to form a drug solution, (ii) combining at least one pore forming agent with the drug solution to form an emulsion, suspension, or second solution, and (iii) removing the volatile solvent and pore forming agent from the emulsion, suspension, or second solution to yield the porous matrix of drug. The pore forming agent can be either a volatile liquid that is immiscible with the drug solvent or a volatile solid compound, preferably a volatile salt. In a preferred embodiment, spray drying is used to remove the solvents and the pore forming agent. The resulting porous matrix has a faster rate of dissolution following administration to a patient, as compared to non-porous matrix forms of the drug. In a preferred embodiment, microparticles of the porous drug matrix are reconstituted with an aqueous medium and administered parenterally, or processed using standard techniques into tablets or capsules for oral administration.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
Powdered protein compositions and methods of making same
InactiveUS20090226530A1Easy to moveWide concentration rangeAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryBiotechnologyProtein composition
Owner:ABBVIE DEUTSHLAND GMBH & CO KG
Methods of spray-drying a drug and a hydrophobic amino acid
InactiveUS6372258B1High level of stabilityEasy to manufacturePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsMoistureParticle-size distribution
According to the subject invention, dispersible dry powder pharmaceutical-based compositions are provided, including methods for their manufacture and dry powder dispersion devices. A dispersible dry powder pharmaceutical-based composition is one having a moisture content of less than about 10% by weight (% w) water, usually below about 5% w and preferably less than about 3% w; a particle size of about 1.0-5.0 mum mass median diameter (MMD), usually 1.0-4.0 mum MMD, and preferably 1.0-3.0 mum MMD; a delivered dose of about >30%, usually >40%, preferably >50%, and most preferred >60%; and an aerosol particle size distribution of about 1.0-5.0 mum mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD), usually 1.5-4.5 mum MMAD, and preferably 1.5-4.0 MMAD. Such composition are of pharmaceutical grade purity.
Owner:NOVARTIS FARMA
Porous drug matrices and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20050048116A1Fast dissolutionHigh dissolution ratePowder deliveryGranular deliveryDrugs solutionMicroparticle
Drugs, especially low aqueous solubility drugs, are provided in a porous matrix form, preferably microparticles, which enhances dissolution of the drug in aqueous media. The drug matrices preferably are made using a process that includes (i) dissolving a drug, preferably a drug having low aqueous solubility, in a volatile solvent to form a drug solution, (ii) combining at least one pore forming agent with the drug solution to form an emulsion, suspension, or second solution and hydrophilic or hydrophobic excipients that stabilize the drug and inhibit crystallization, and (iii) removing the volatile solvent and pore forming agent from the emulsion, suspension, or second solution to yield the porous matrix of drug. Hydrophobic or hydrophilic excipients may be selected to stabilize the drug in crystalline form by inhibiting crystal growth or to stabilize the drug in amorphous form by preventing crystallization. The pore forming agent can be either a volatile liquid that is immiscible with the drug solvent or a volatile solid-compound, preferably a volatile salt. In a preferred embodiment, spray drying is used to remove the solvents and the pore forming agent. The resulting porous matrix has a faster rate of dissolution following administration to a patient, as compared to non-porous matrix forms of the drug. In a preferred embodiment, microparticles of the porous drug matrix are reconstituted with an aqueous medium and administered parenterally, or processed using standard techniques into tablets or capsules for oral administration.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
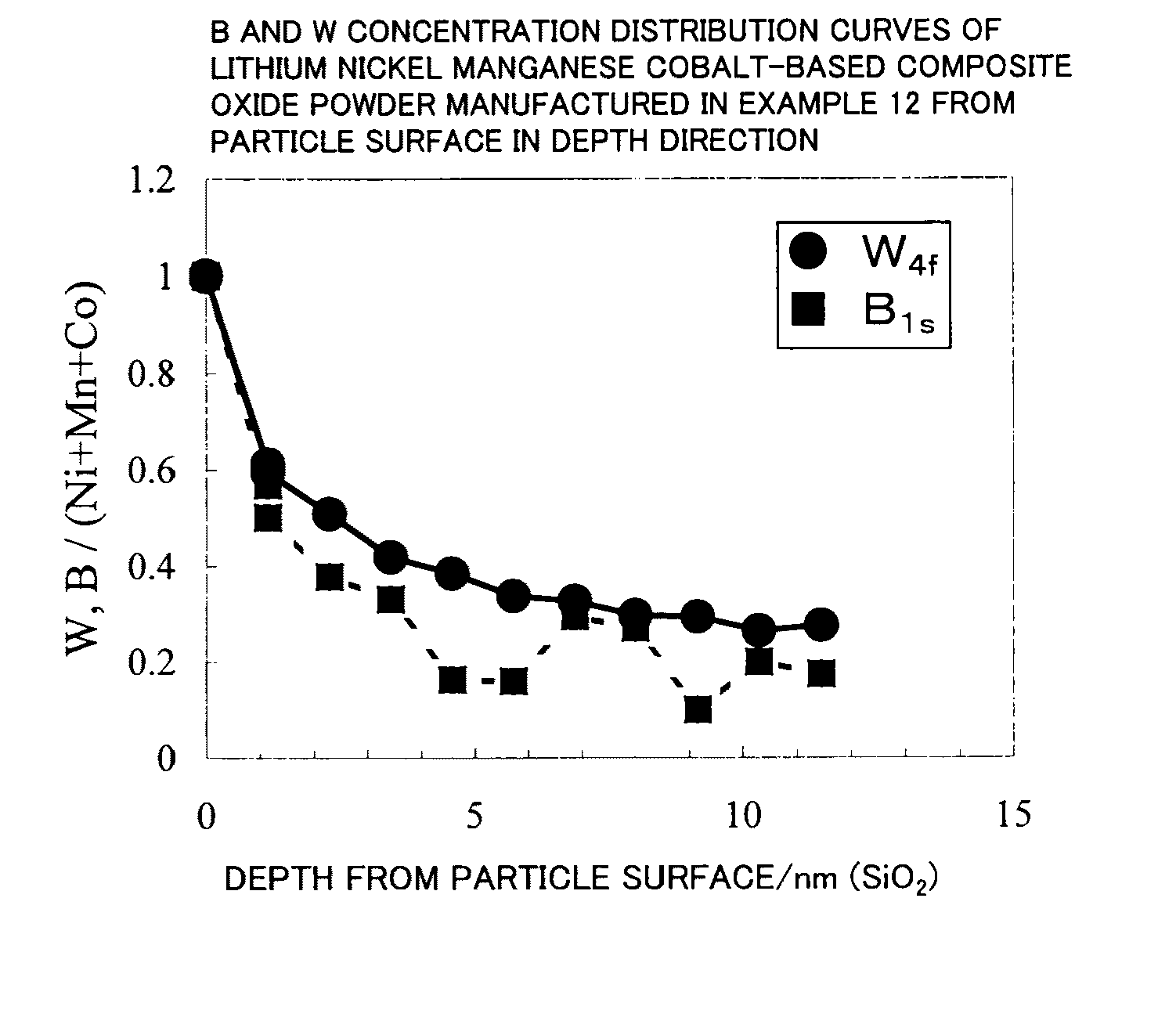
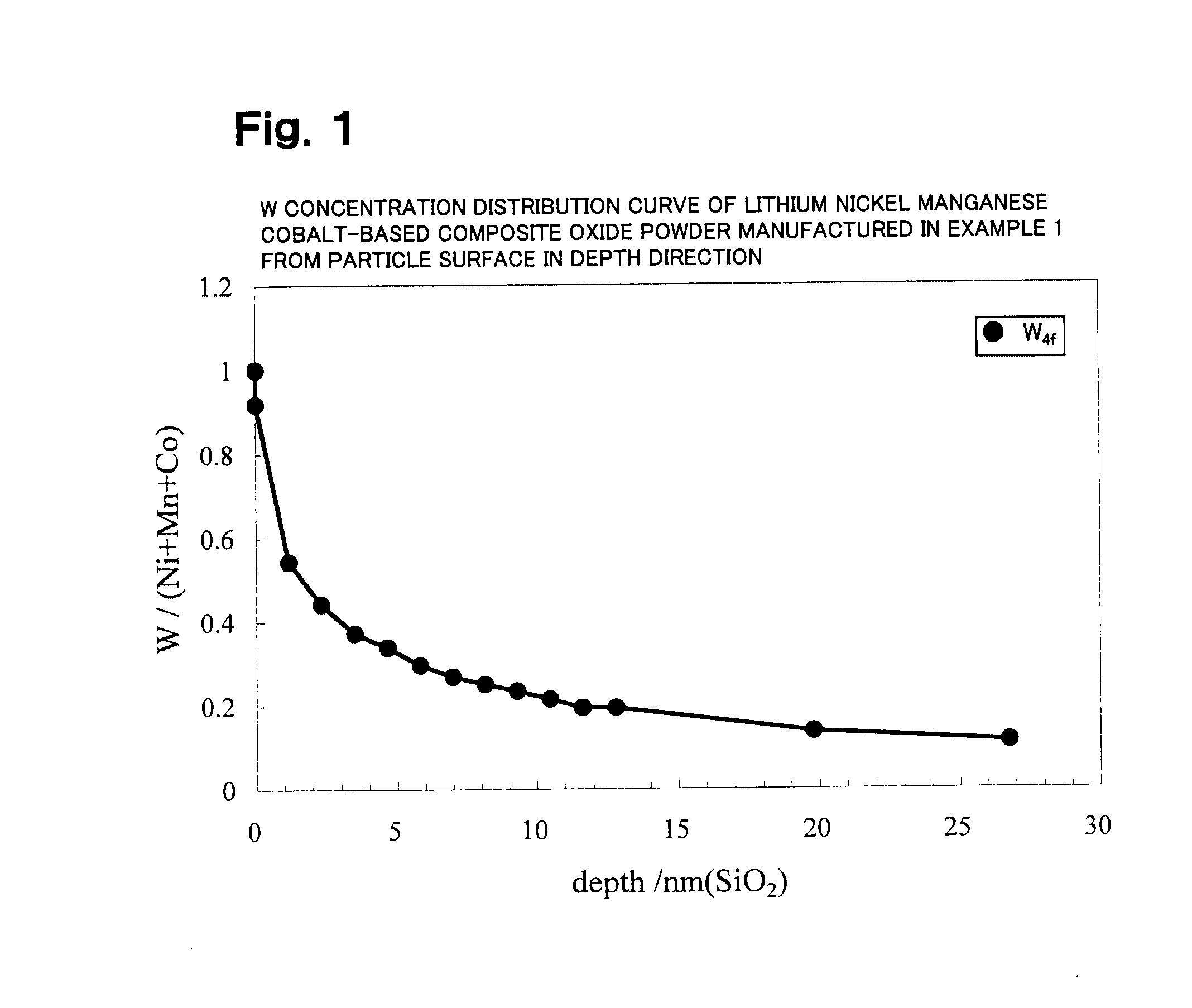
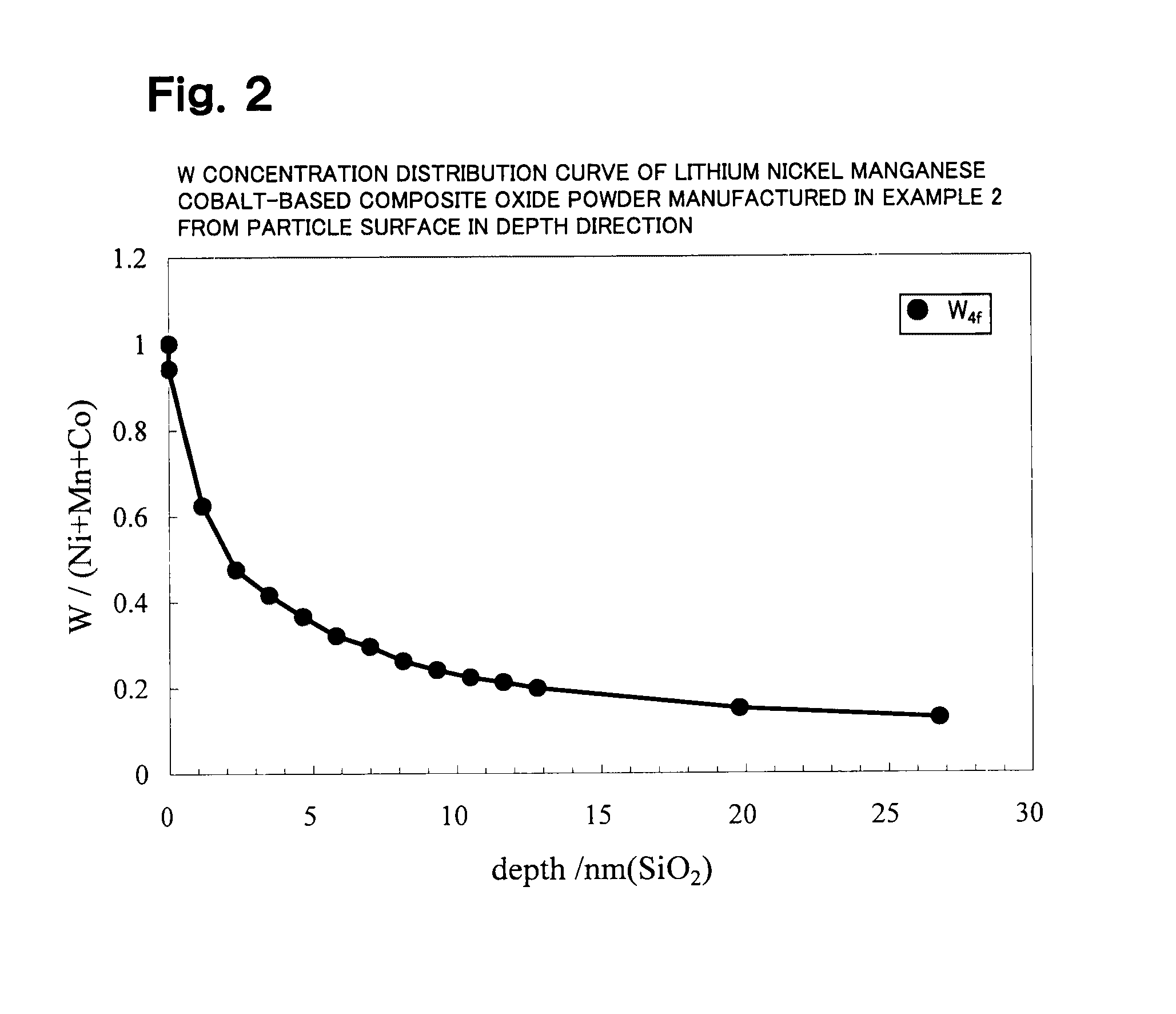
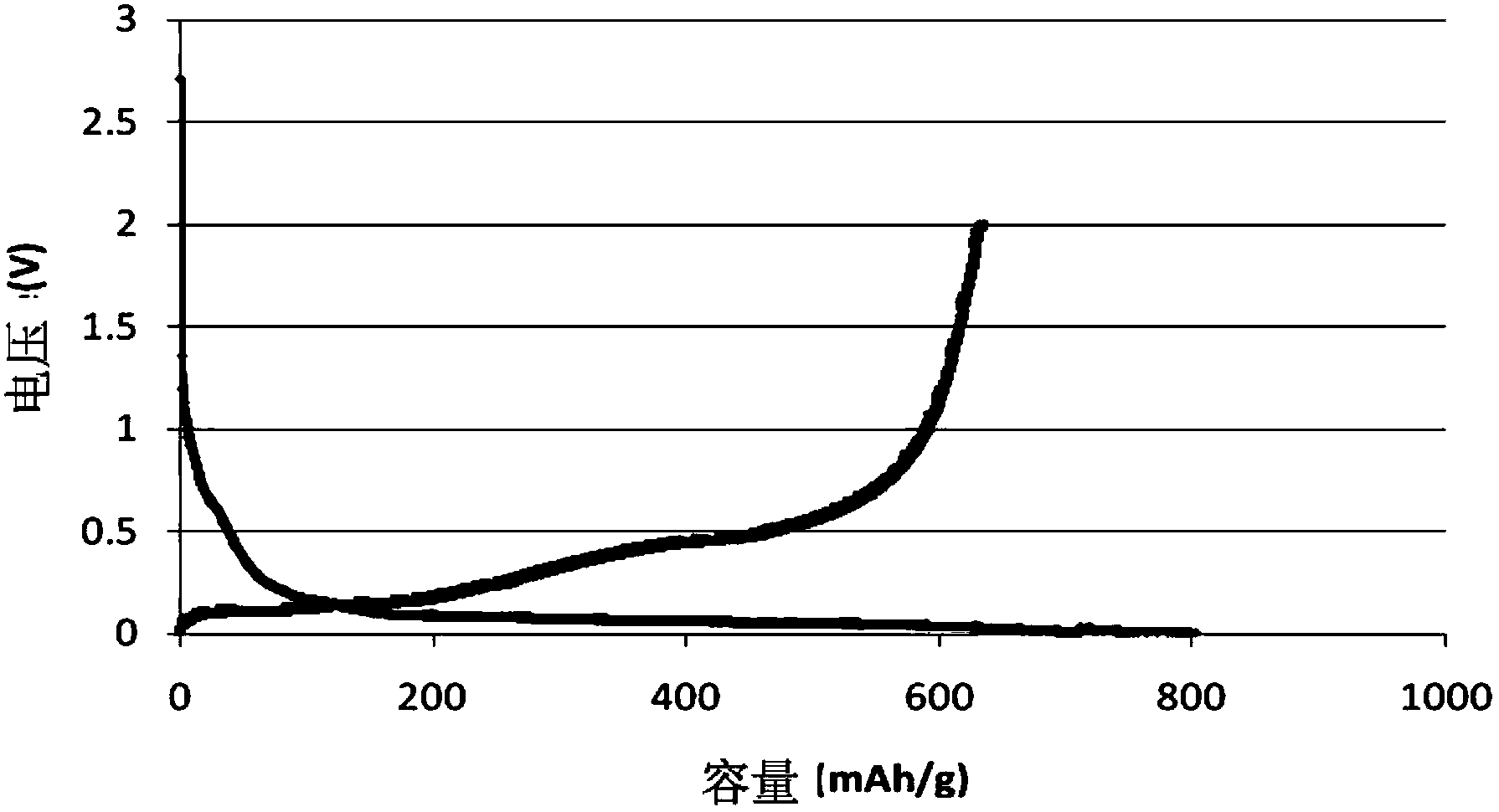
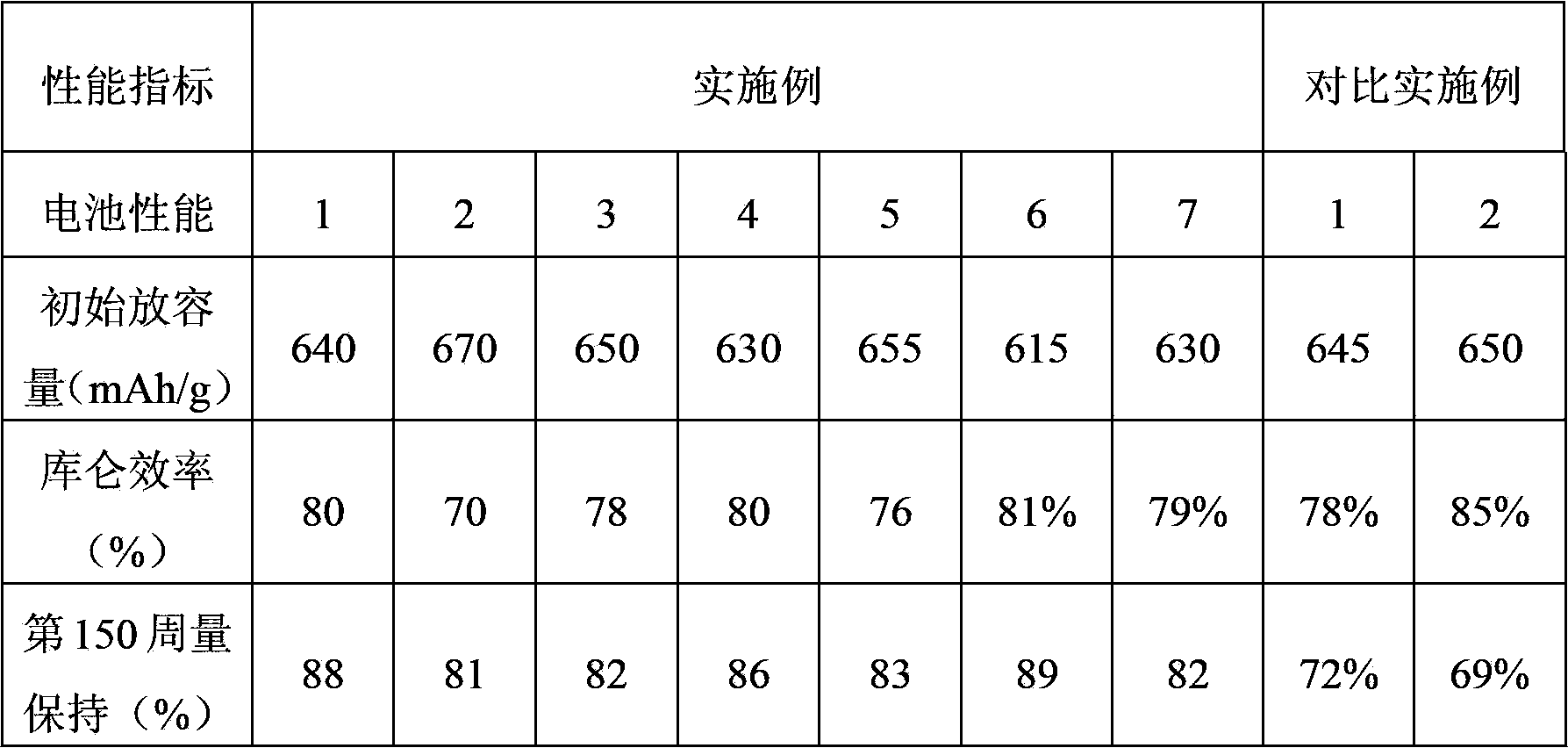
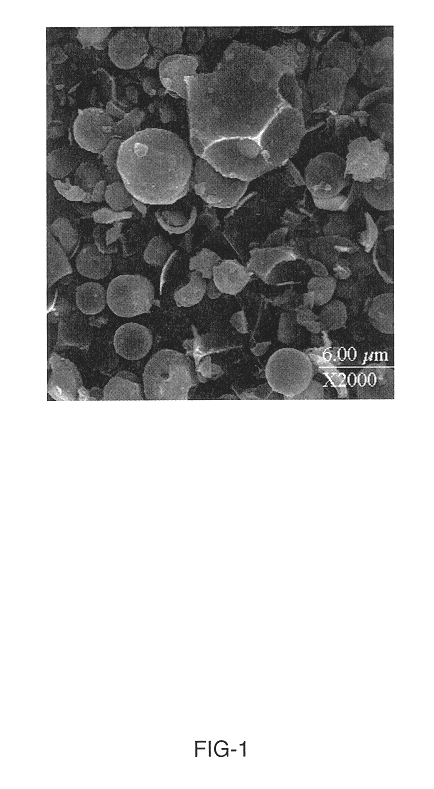
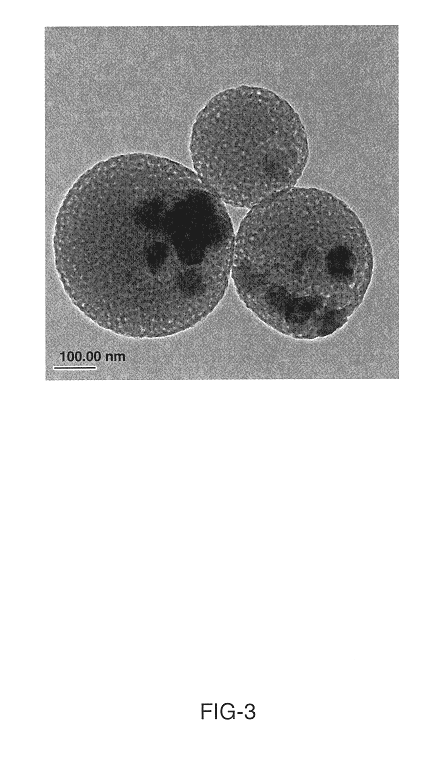
Lithium transition metal-based compound powder for positive electrode material in lithium rechargeable battery, method for manufacturing the powder, spray dried product of the powder, firing precursor of the powder, and positive electrode for lithium rechargeable battery and lithium rechargeable battery using the powder
ActiveUS20090104530A1Low costImprove security levelElectrode manufacturing processesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesMetalHigh voltage
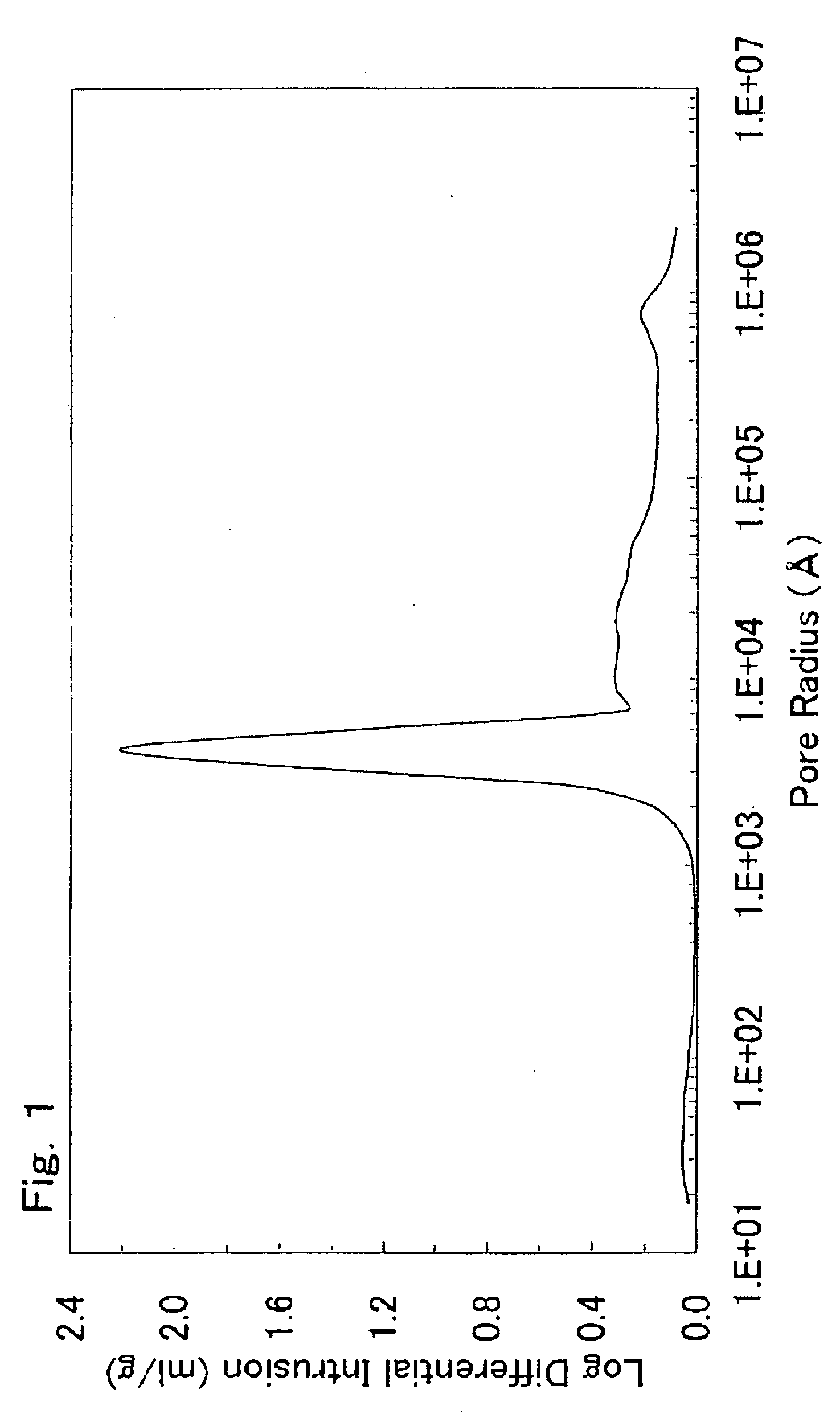
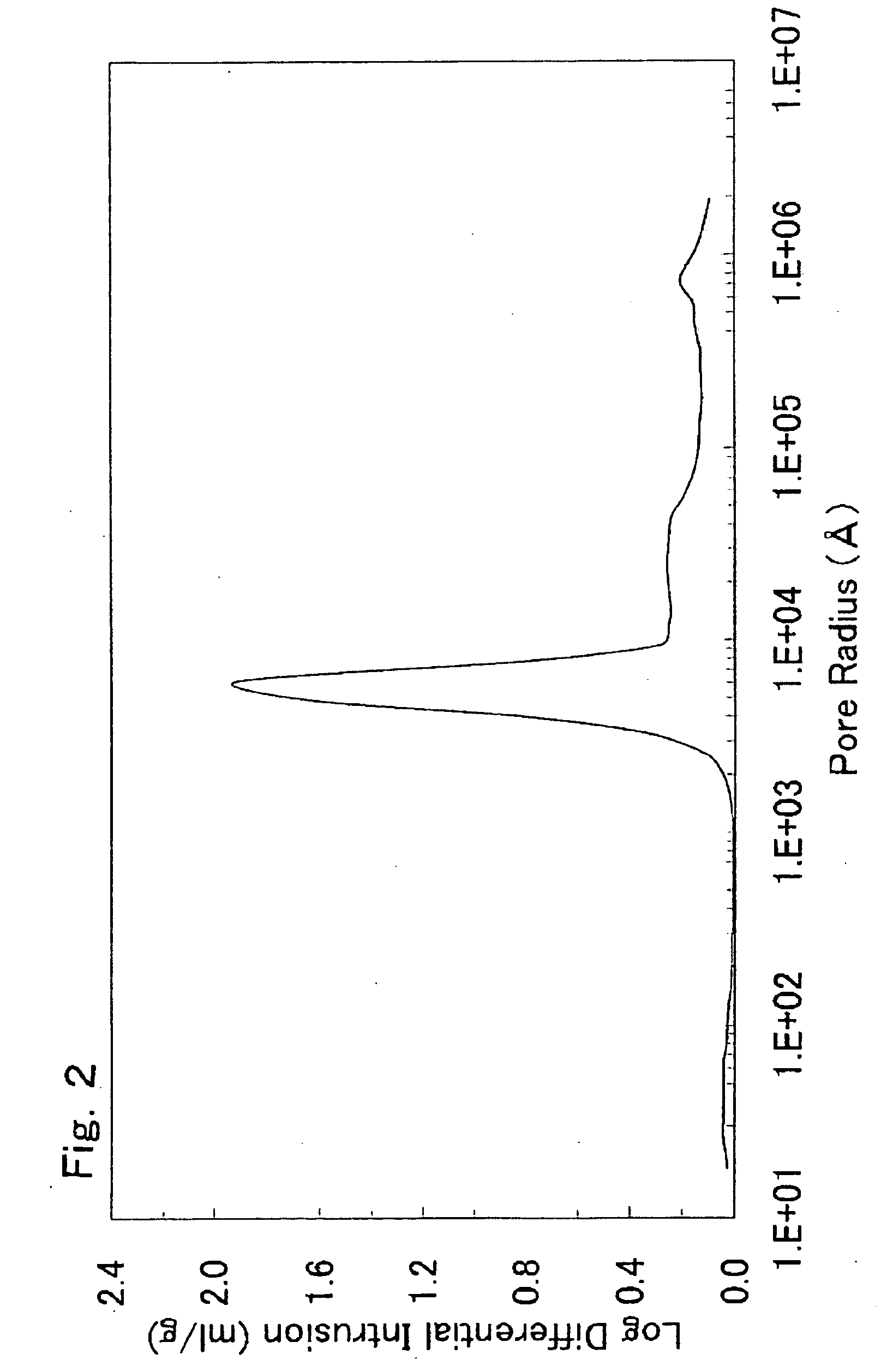
There is provided a powder of a lithium transition-metal compound for a positive-electrode material in a lithium secondary battery, in which the use of the powder as that of a positive-electrode material in a lithium secondary battery achieves a good balance among improvement in battery performance, cost reduction, resistance to a higher voltage, and a higher level of safety. The powder of the lithium transition-metal compound for a positive-electrode material in a lithium secondary battery is characterized in that in a mercury intrusion curve obtained by mercury intrusion porosimetry, the amount of mercury intruded is in the range of 0.8 cm3 / g to 3 cm3 / g when the pressure is increased from 3.86 kPa to 413 MPa.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
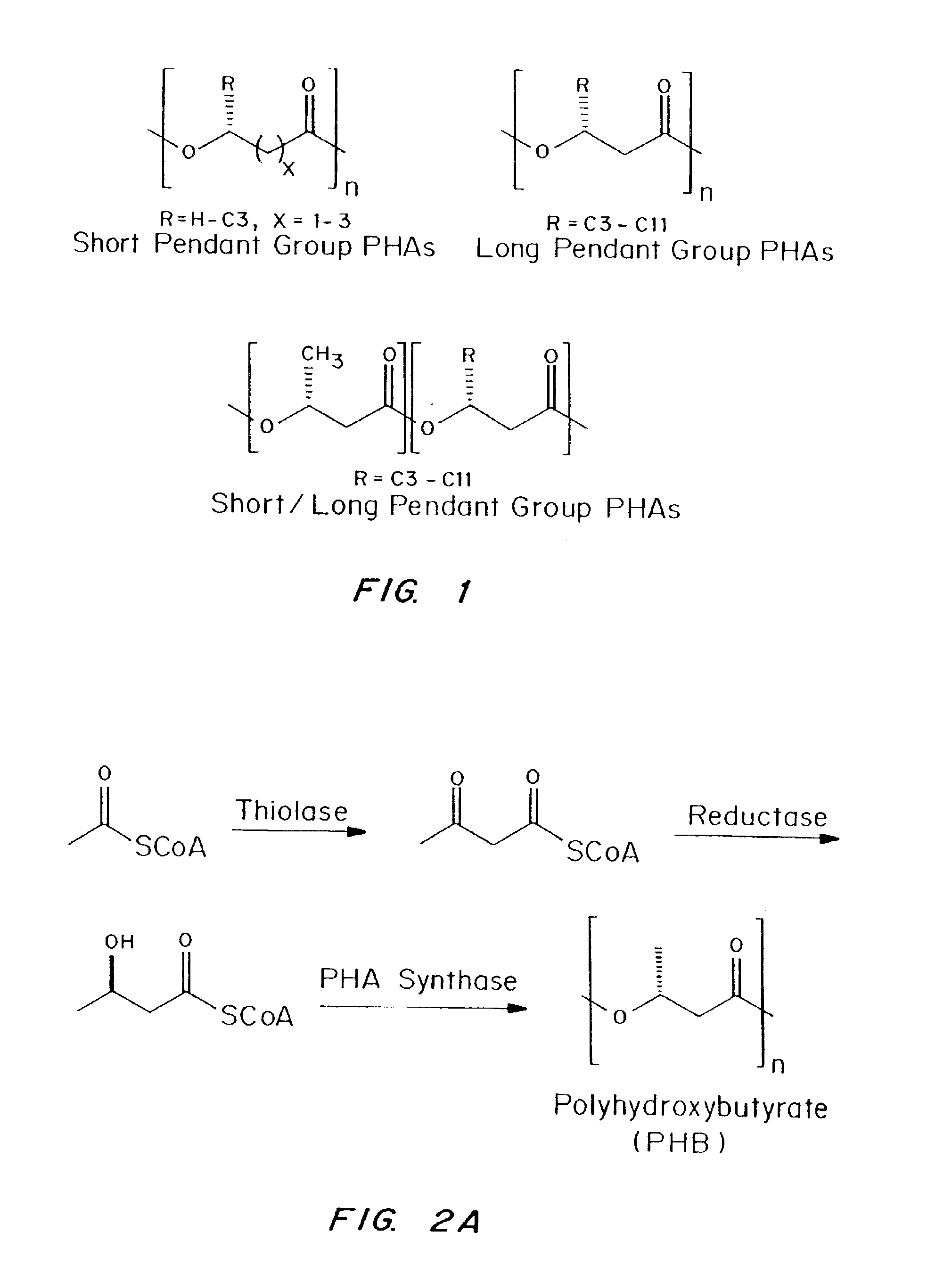
Polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions having controlled degradation rates
Biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions with controlled degradation rates have been developed. In one embodiment, the polyhydroxyalkanoates contain additives to alter the degradation rates. In another embodiment, the polyhydroxyalkanoates are formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones to alter their degradation rates. In still another embodiment, the polyhydroxyalkanoates are chemically modified. Methods for manufacturing the devices which increase porosity or exposed surface area can be used to alter degradability. For example, as demonstrated by the examples, porous polyhydroxyalkanoates can be made using methods that creates pores, voids, or interstitial spacing, such as an emulsion or spray drying technique, or which incorporate leachable or lyophilizable particles within the polymer. Examples describe poly(4HB) compositions including foams, coatings, meshes, and microparticles. As demonstrated by the examples, these polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions have extremely favorable mechanical properties, as well as are biocompatible and degrade within desirable time frames under physioogical conditions. These polyhydroxyalkanoate materials provide a wider range of polyhydroxyalkanoate degradation rates than are currently available. Methods for processing these materials, particularly for therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic applications, or into devices which can be implanted or injected, are also described.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Lithium transition metal-based compound powder, method for manufacturing the same, spray-dried substance serving as firing precursor thereof, and lithium secondary battery positive electrode and lithium secondary battery using the same
ActiveUS20100209771A1Improve load characteristicsHigh densityMaterial nanotechnologyAlkaline accumulatorsLithiumHigh density
A lithium transition metal-based compound powder for a lithium secondary battery positive electrode material that can achieve both improvements of load characteristics such as rate and output characteristics and a higher density is a lithium transition metal-based compound powder containing, as a main component, a lithium transition metal-based compound that has a function of allowing elimination and insertion of lithium ions, and including a crystal structure belonging to a layer structure, wherein primary particles are aggregated to form secondary particles, the ratio A / B of a median diameter A of the secondary particles to an average diameter (average primary particle diameter B) is in the range of 8 to 100, and 0.01≦FWHM(110)≦0.5 where FWHM(110) is the half width of a (110) diffraction peak present near a diffraction angle 2θ of 64.5° in a powder X-ray diffraction analysis using a CuKα line.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Spray dry capsule products and methods for preparing and using same
Owner:LEE KAIPING +1
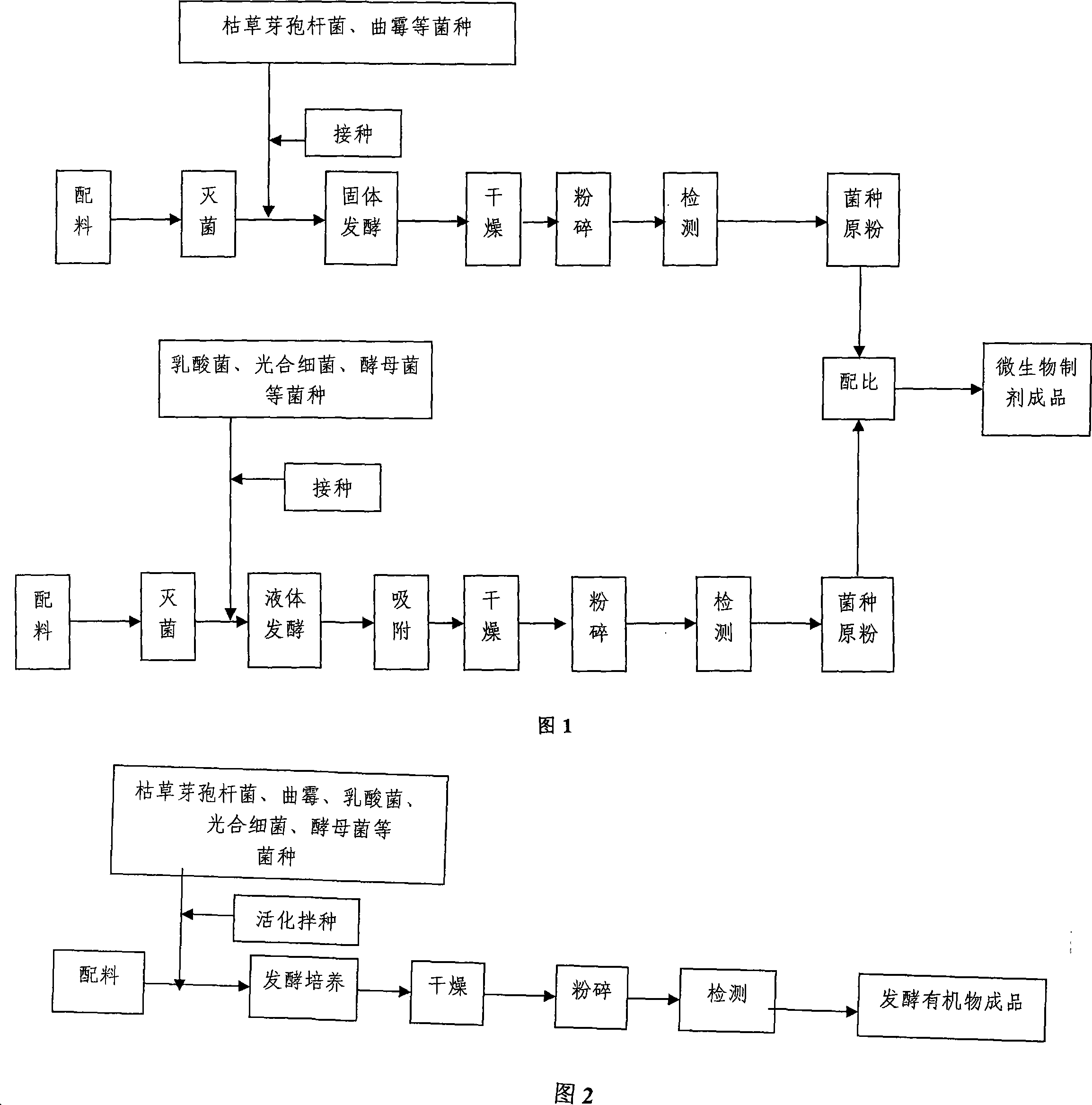
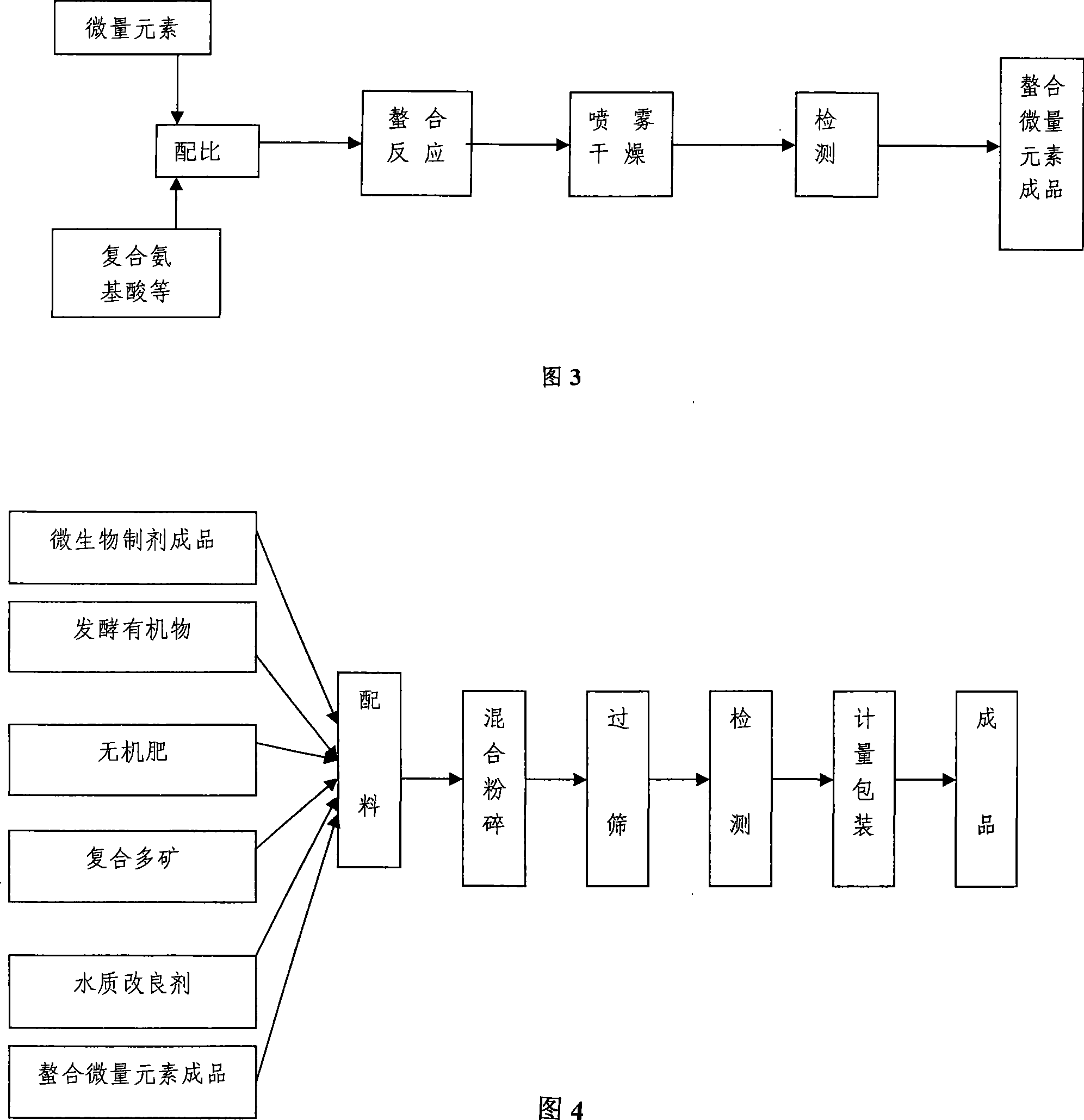
Special biological fish-fertilizer for aquaculture and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101225007AMatching scienceIncrease profitClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseWater quality
The invention discloses a special biological fish fertilizer and a preparation method for the fertilizer used in aquiculture; wherein, the biological fish fertilizer mainly comprises raw materials as follows: microbiological preparation, inorganic fertilizers, fermentation organics, micro-mineral amino acid chelate, mineral composites, and water quality improver. The preparation method for the special biological fish fertilizer in aquiculture comprises steps as follows: microbiological preparation is produced; fermentation organics is then produced, and the micro-mineral amino acid chelate is produced, eventually the finished products are made. The special biological fish fertilizer has the advantages of limiting the growth and reproduction of the harmful algae, promoting the large-scale growth and reproduction of the suitable food for fish, effectively improving the water quality and purifying the water environment, strengthening the fish immunity, reducing the diseases, reducing cost due to the small use level, convenient use, mild odor, no pollution to the water, and environment protection. By combining the modern bioengineering technique, low-temperature drying technique, spray-drying technique, and super-fine crushing techniques, the preparation method has the advantages of stable quality for the fish fertilizers and lower overall cost.
Owner:WUHAN KEYANG BIOTECH
Porous drug matrices and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20050058710A1Fast dissolutionExtended half-lifePowder deliveryGranular deliveryDrugs solutionMicroparticle
Drugs, especially low aqueous solubility drugs, are provided in a porous matrix form, preferably microparticles, which enhances dissolution of the drug in aqueous media. The drug matrices preferably are made using a process that includes (i) dissolving a drug, preferably a drug having low aqueous solubility, in a volatile solvent to form a drug solution, (ii) combining at least one pore forming agent with the drug solution to form an emulsion, suspension, or second solution and hydrophilic or hydrophobic excipients that stabilize the drug and inhibit crystallization, and (iii) removing the volatile solvent and pore forming agent from the emulsion, suspension, or second solution to yield the porous matrix of drug. Hydrophobic or hydrophilic excipients may be selected to stabilize the drug in crystalline form by inhibiting crystal growth or to stabilize the drug in amorphous form by preventing crystallization. The pore forming agent can be either a volatile liquid that is immiscible with the drug solvent or a volatile solid compound, preferably a volatile salt. In a preferred embodiment, spray drying is used to remove the solvents and the pore forming agent. The resulting porous matrix has a faster rate of dissolution following administration to a patient, as compared to non-porous matrix forms of the drug. In a preferred embodiment, microparticles of the porous drug matrix are reconstituted with an aqueous medium and administered parenterally, or processed using standard techniques into tablets or capsules for oral administration.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
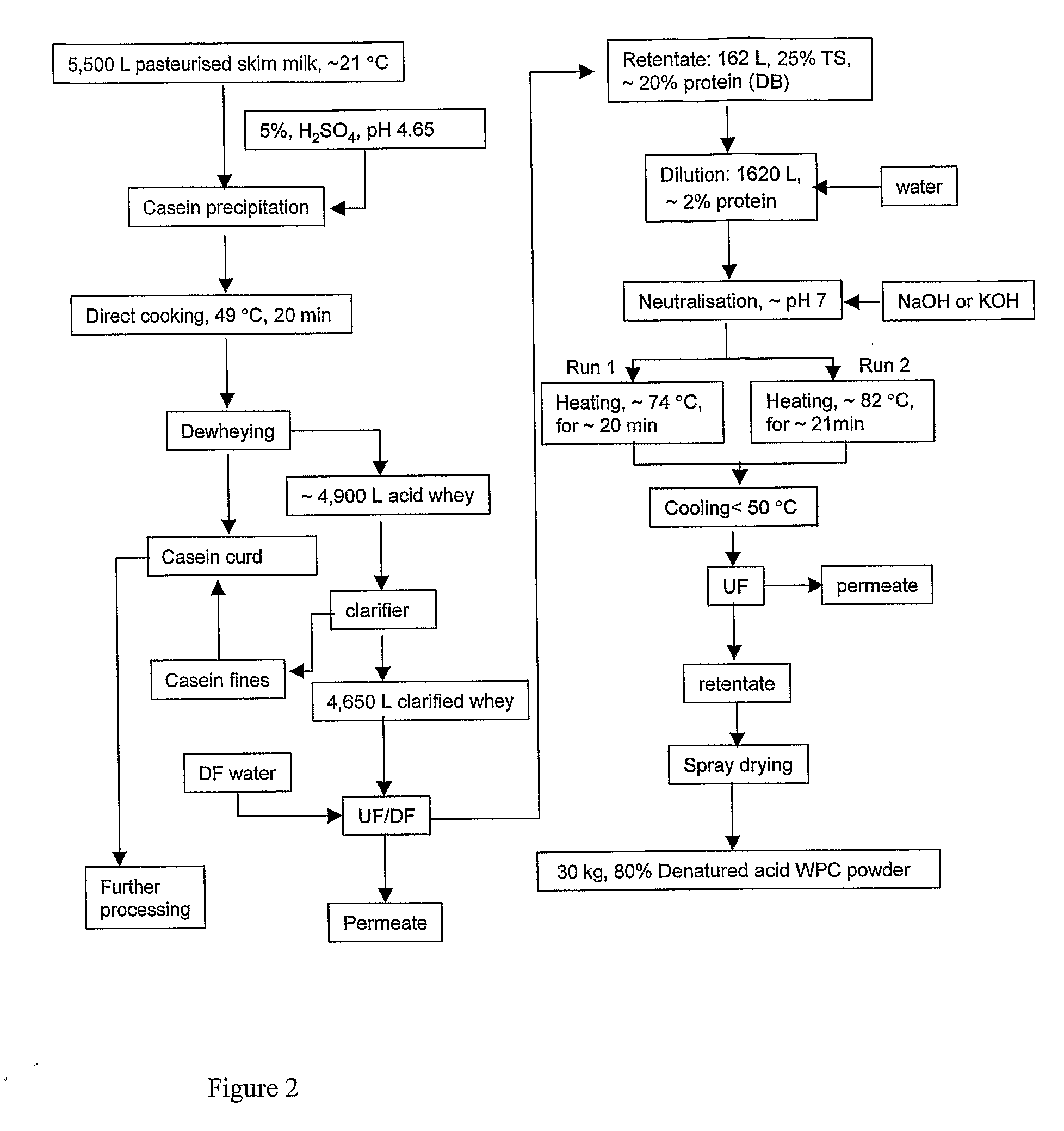
Whey Product and Process
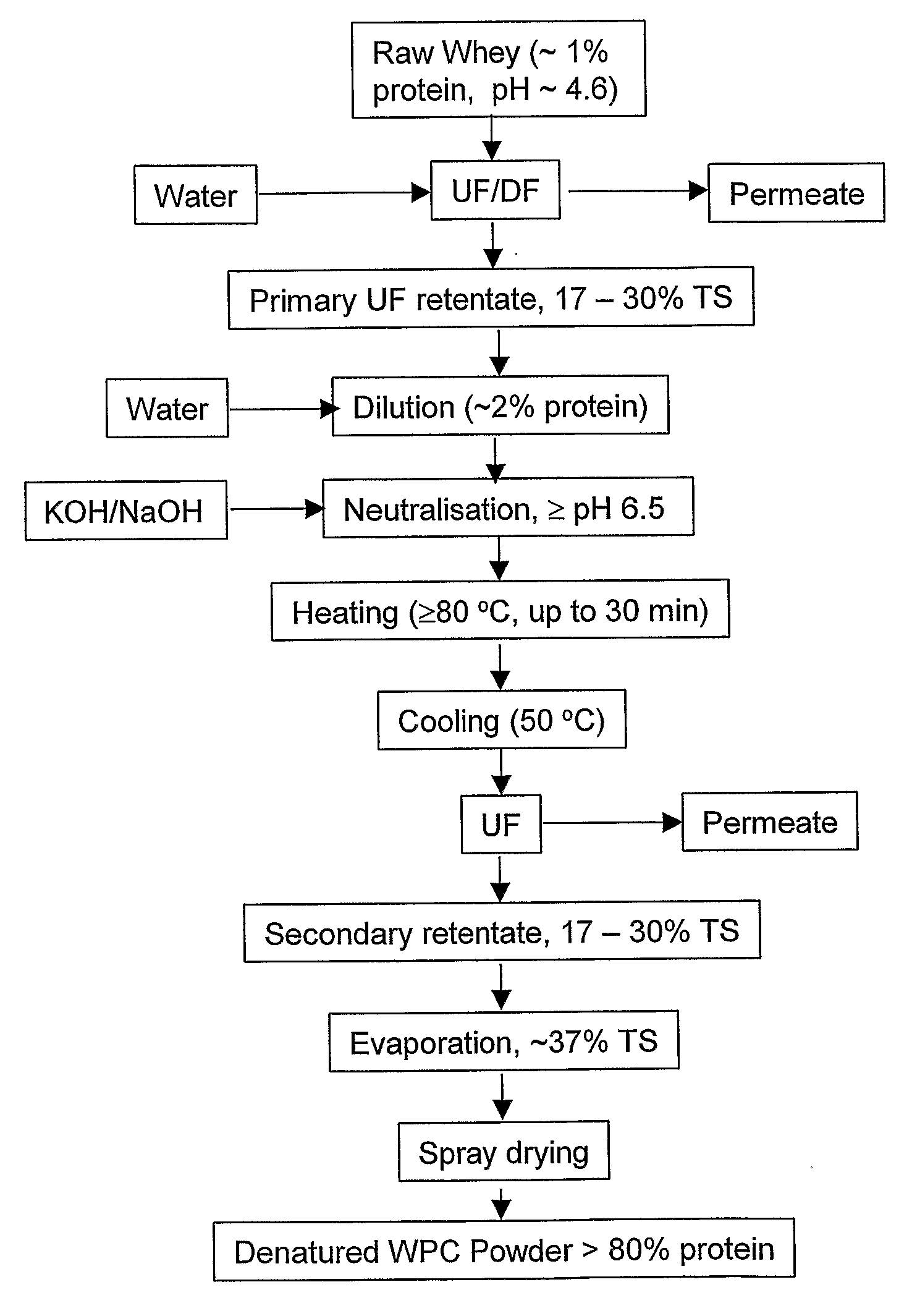
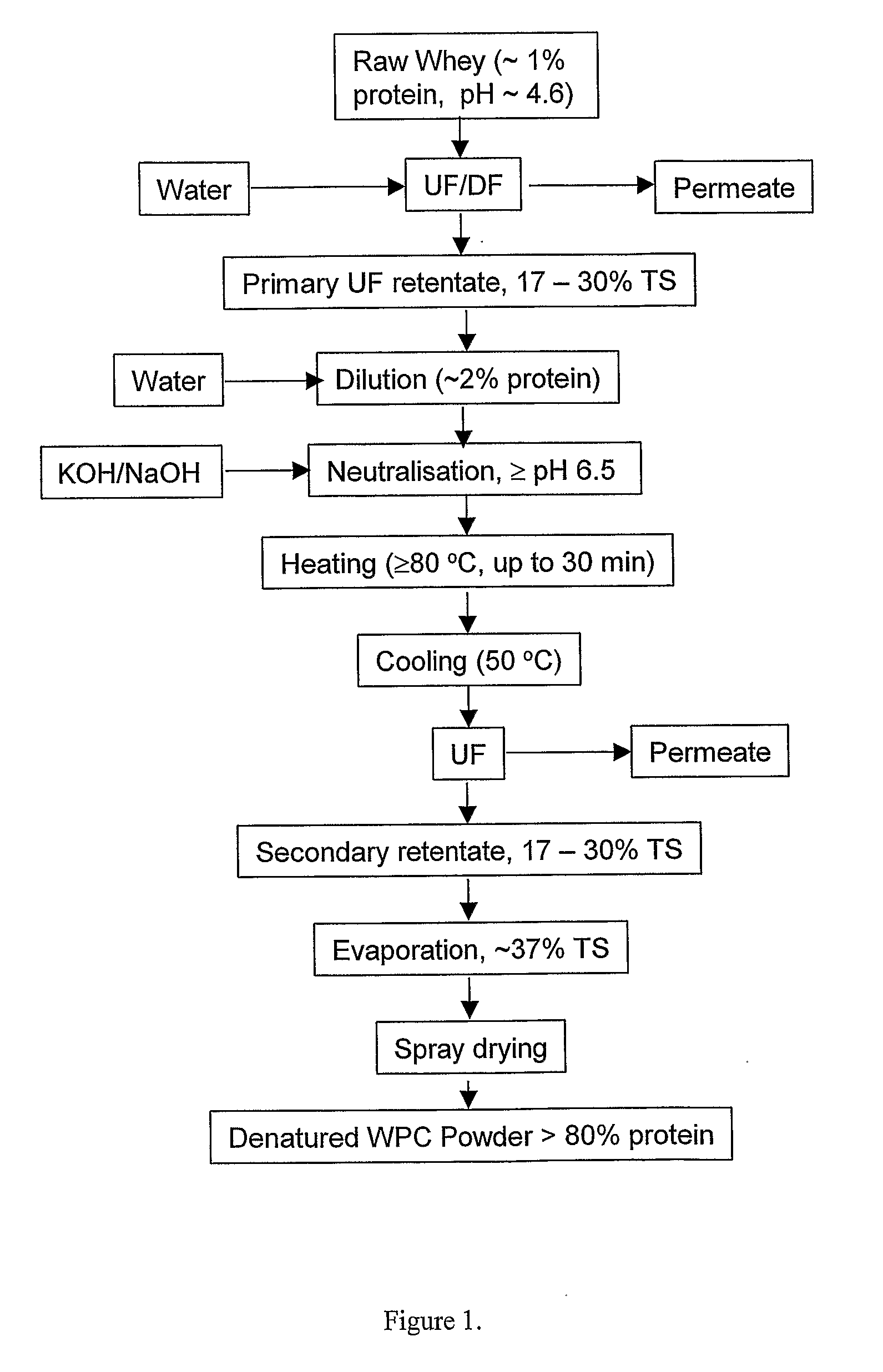
InactiveUS20080305235A1High viscosityHigh in proteinMilk preparationFood ingredient as viscosity modification agentWhey proteinSurface heat
The invention provides a process for preparing a dried modified whey protein concentrate. A whey protein solution is used having less than 5% total solids and a combined calcium and magnesium concentration of less than 70 mmol / kg on a dry basis and a pH of 6.0-7.5. It is heated to greater than 70° C. for up to 60 minutes to denature the whey protein. The solution is then cooled to 40° C.-60° C.; and subsequently spray dried. Alternatively a higher initial concentration of total solids may be used in an embodiment where the heating is carried out on a scraped surface heat exchanger.
Owner:FONTERRA COOP GRP LTD
Titanium-series cathode active material and preparation method thereof, titanium-series lithium ion power battery
ActiveCN101373829AIncrease capacityHigh bulk densityElectrode manufacturing processesLi-accumulatorsHigh rateLithium titanate
The invention discloses a titanium cathode active substance, a preparation method thereof and a titanium lithium ion power battery, and aims to solve the technical problem of enhancing the rate performance of a lithium ion power battery. The formula of the titanium cathode active substance is Li4Ti5O12 / Mx, wherein Li4Ti5O12 is spinel lithium titanate, M is a dopant such as a metal simple substance, a metal compound, a nonmetallic simple substance or a nonmetallic compound; the elements or the ions contained in the dopant enter the Li4Ti5O12 crystal lattice or are compounded with the Li4Ti5O12 crystal lattice; and the preparation method comprises the following steps: the precursor mixture of compound lithium titanate is prepared, and spray drying and heat treatment are performed. The cathode of the titanium lithium ion power battery adopts Li4Ti5O12 / Mx. Compared with the prior art, the titanium cathode active substance has the advantages of high capacity, high bulk density, high volume specific capacity, good high-rate performance, good product uniformity, good battery processability, low possibility of air bulking of the battery, and low cost.
Owner:BTR NEW MATERIAL GRP CO LTD
Tea making method and application thereof in other plant stem-leaf products
InactiveCN101480208AQuality assuranceNo pesticide residuePre-extraction tea treatmentFood preparationPesticide residueEngineering
The invention relates to a tea-making method which scientifically, reasonably and integrally applies prior mature application technologies to a tea-making process, in particular to applications of an ozone sterilization strong oxidation technology, a microwave enzyme and germ deactivation technology, a low-temperature freezing, shredding and crushing technology, a vacuum freezing and drying technology, a colloid milling micronization technology and a spray drying technology to the processing and the production of tea. The invention effectively solves the traditional problems influencing the quality of tea products by agriculture residue, pesticide residue, overproof heavy metal content and overproof total bacterial count, enables the quality of tea products to reach the standard of organic tea, effectively improves the quality of the tea products and the utilization rate of tea raw material and can be applied to other plant stem leaf products.
Owner:刘川汶
Polymeric drug delivery system for hydrophobic drugs
InactiveUS20050249799A1Low oral bioavailabilityStable against aggregationAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryHydrophobic polymerImmediate release
An oral delivery system for Class II drugs that have low oral bioavailability due to their insolubility in water and slow dissolution kinetics and method for making such a drug delivery system are disclosed herein. The formulation may be a controlled release or immediate release formulation. The immediate release formulation contains a Class II drug, together with a hydrophobic polymer, preferably a bioadhesive polymer. In one embodiment, the drug and polymer are co-dissolved in a common solvent. The solution is formed into small solid particles by any convenient method, particularly by spray drying. The resulting particles contain drug dispersed as small particles in a polymeric matrix. The particles are stable against aggregation, and can be put into capsules or tableted for administration. The controlled release formulations contain a BCS Class II drug and a bioadhesive polymer. The controlled release formulations may be in the form of a tablet, capsules, mini-tab, microparticulate, or osmotic pump. Enhancement of oral uptake of the drug from use of bioadhesive polymers occurs through (1) increased dissolution kinetics due to stable micronization of the drug, (2) rapid release of the drug from the polymer in the GI tract; and (3) prolonged GI transit due to bioadhesive properties of the polymers. The combination of these effects allows the preparation of a compact, stable dosage form suitable for oral administration of many class II drugs.
Owner:SPHERICS
Preparation method of completely peeled oxidation graphene/ rubber nanometer composite material
A preparation method of completely peeled oxidation graphene / rubber nanometer composite material adopts combination of emulsion compounding and flocculation processes or combination of emulsion compounding and spraying drying processes. The preparation method retains the phase state structure of the oxidation grapheme / rubber composite emulation in the liquid state and obtains the phase-state structure which is highly dispersed, highly peeled and dispersed in nanometer scale dispersion. Simultaneously, substances capable of acting with generating ionic bond effect or chemical bond effect with an oxidation graphene surface functional group are added into the oxidation graphene / hydrosol to serve as an interface agent, thereby improving interface combination effect of oxidation graphene and rubber. Vulcanized rubber prepared by the composite material of the preparation method through follow-up mixing and vulcanizing has mechanical property such as high tensile strength, stretching stress and tearing strength and is capable of greatly improving abrasion resistance and gas separation performance of the vulcanized rubber. The preparation method is simple, easy, low in cost, apt to industrialization and wide in suitable aspect, saves energy and has better economical and social benefits.
Owner:JIANGSU LVYUAN RUBBER RESOURCE RECYCLING INNOVATION CENT CO LTD
Method for preparing graphene powder
The invention relates to a method for preparing graphene powder in large scale, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly, uniformly peeling graphene oxide into a graphene oxide suspension solution; then, atomizing the graphene oxide solution by using the spray drying technology comprising spray pyrolysis drying and spray freeze drying, and removing a solvent to obtain graphene oxide powder; and finally, oxidizing grapheme by using the non-expansion heat treatment process to obtain non-agglomerative graphene powder. The continuous preparation process of the spray technology and the non-expansion heat treatment process ensure the large-scale preparation of the graphene powder. The prepared graphene powder comprising intermediate product graphene oxide powder does not have agglomeration and has good dispersivity in the solvent. The graphene powder is used as a filling material to prepare high strength composite materials, conductive composite materials, novel air-tight flame-retardant composite materials, novel nanodevices and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spray-Dried Compositions Capable of Retaining Volatile Compounds and Methods of Producing the Same
InactiveUS20130022728A1Stable spray-dried flavor compositionComposition is stableChewing gumFood preparationSpray drying
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
Pulmonary insulin crystals
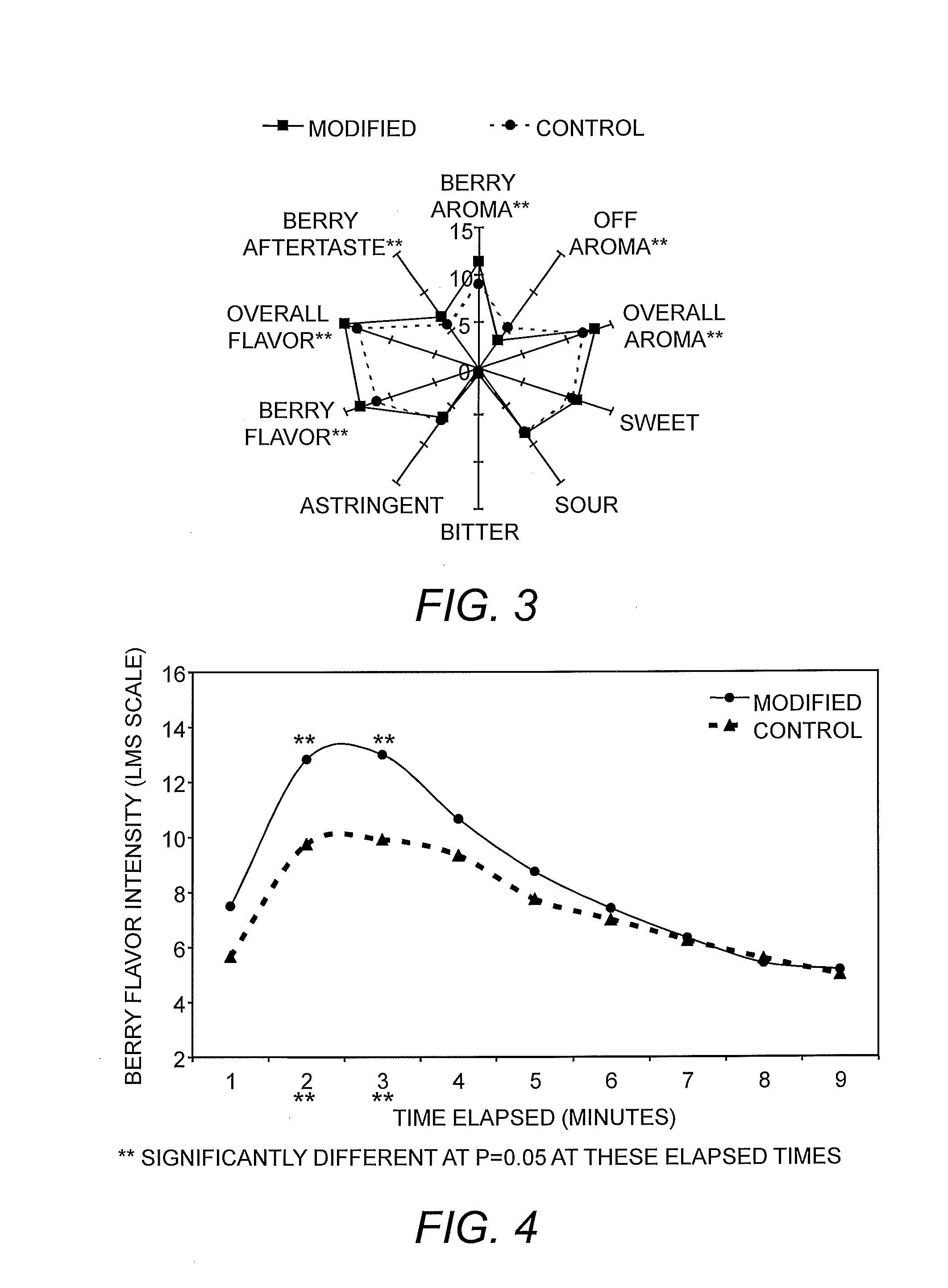
The present invention relates to zinc free insulin crystals having a diameter below 10 mum and to therapeutic powder formulations suitable for pulmonary administration containing such insulin crystals. The crystals of the present invention exhibit a better stability profile than powders of essentially the same composition prepared by spray drying, freeze-drying, vacuum drying and open drying. The therapeutic powder formulations elucidate better flowing properties than corresponding amorphous powder formulations.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Diketopiperazine salts for drug delivery and related methods
Drug delivery systems have been developed based on the formation of diketopiperazine carboxylate salts and microparticles containing the same. The systems may further comprise a bioactive agent. Related methods for making and using the biologically active agent delivery compositions are also provided. In certain embodiments, the pharmaceutically acceptable salts described can be formed by removal of solvent by methods including distillation, evaporation, spray drying or lyophilization.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Preservation of bioactive materials by spray drying
ActiveUS7258873B2Reduce materialIncrease surface areaSsRNA viruses negative-sensePowder deliveryMetallurgyHigh pressure
This invention provides methods and compositions to preserve bioactive materials in a matrix of powder particles. Methods provide high-pressure gas spraying and / or near supercritical spraying of formulations followed by drying in a stream of conditioned gas to form stable powder particles containing bioactive materials.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
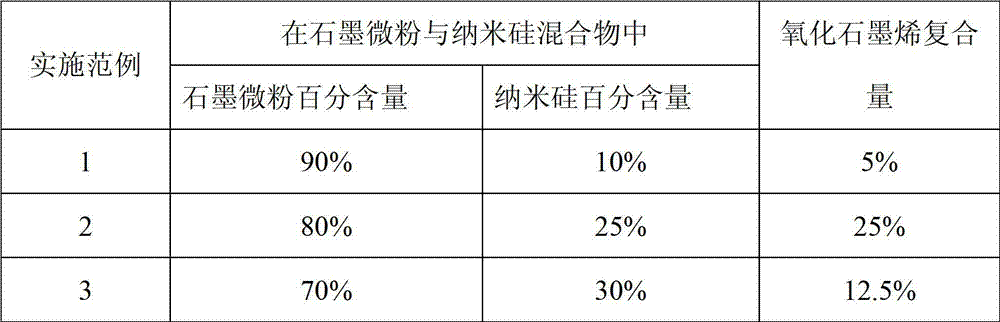
Preparation method of silicon and carbon-coated graphene composite cathode material
ActiveCN103050666ARealize in situ restorationThe preparation process is simple, convenient and practicalMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesCarbon coatedStructural stability
The invention discloses a preparation method of a silicon and carbon-coated graphene composite cathode material. The technical problem to be solved is to enhance the electronic conductivity of the silicon-based cathode material, buffer the volume effect produced in the process of deintercalation of the lithium in the silicon-based cathode material and enhance the structure stability in the circulation process of the material at the same time. The material is prepared by using a spray drying-thermally decomposing treatment process in the invention. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: evenly dispersing nano silicon and graphite micro powder in a dispersion solution of oxidized graphene, carrying out thermal treatment under an inert protection atmosphere after spray drying, subsequently cooling along a furnace to obtain the silicon and carbon-coated graphene composite cathode material. The extra binder does not need to add in the process of manufacturing balls in the invention and the outer oxidized graphene is thermally reduced in situ to graphene in the thermal treatment process of the composite precursor, so that the process is simple and easy to operate; and the practical degree is high. The prepared composite material has the advantages of great reversible capacity, designable capacity, good cycling performance and high-current discharging performance, high tap density and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Nutrition bar
InactiveUS20050181019A1Stable and goodExtended shelf lifeBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsRice proteinIngested food
A nutrition bar comprising about 10% wt or more of soy and / or rice protein, at least one transition metal or transition metal compound, and about 2% wt or more of a humectant, and wherein the at least one transition metal or transition metal compound is in a substantially water insoluble form at 20° C. or the nutrition bar has an Aw of 0.45 or less or about 1% wt or more of the soy and / or rice protein is in the form of nuggets and the humectant is selected from polyols. The bars have elevated levels of soy and / or rice protein, yet do not suffer unacceptable from a deterioration in taste or other organoleptic properties over time. In other aspects, a nutrition bar or other food which incorporates pro-oxidants and / or polyunsaturated fatty acids or their sources in encapsulated form, especially as microcapsules. The pro-oxidants may be metal salts such as copper, manganese, iron and / or zinc salts. Sources of omega-3 fatty acids include fish oil. Processes for preparing the polyunsaturated fatty acid capsules are also disclosed. The polyunsaturated fatty acid capsules / microcapsules are prepared by forming an emulsion of the unsaturated fatty acid with a carrier, spray drying the emulsion to form a powder and encapsulating powder, especially with a fluid bed. The invention is especially useful for encapsulating polyunsaturated fatty acids, or oil sources thereof, most preferably omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, such as arachidonic acid, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), lineoleic acid, linolenic acid (alpha linolenic acid), and gamma-linolenic acids, fish oil, and oil sources of C18:2 and C18:3 fatty acids such as canola oil, soybean oil or blends thereof.
Owner:SLIM FAST FOODS COMPANY A DIV OF CONOPCO
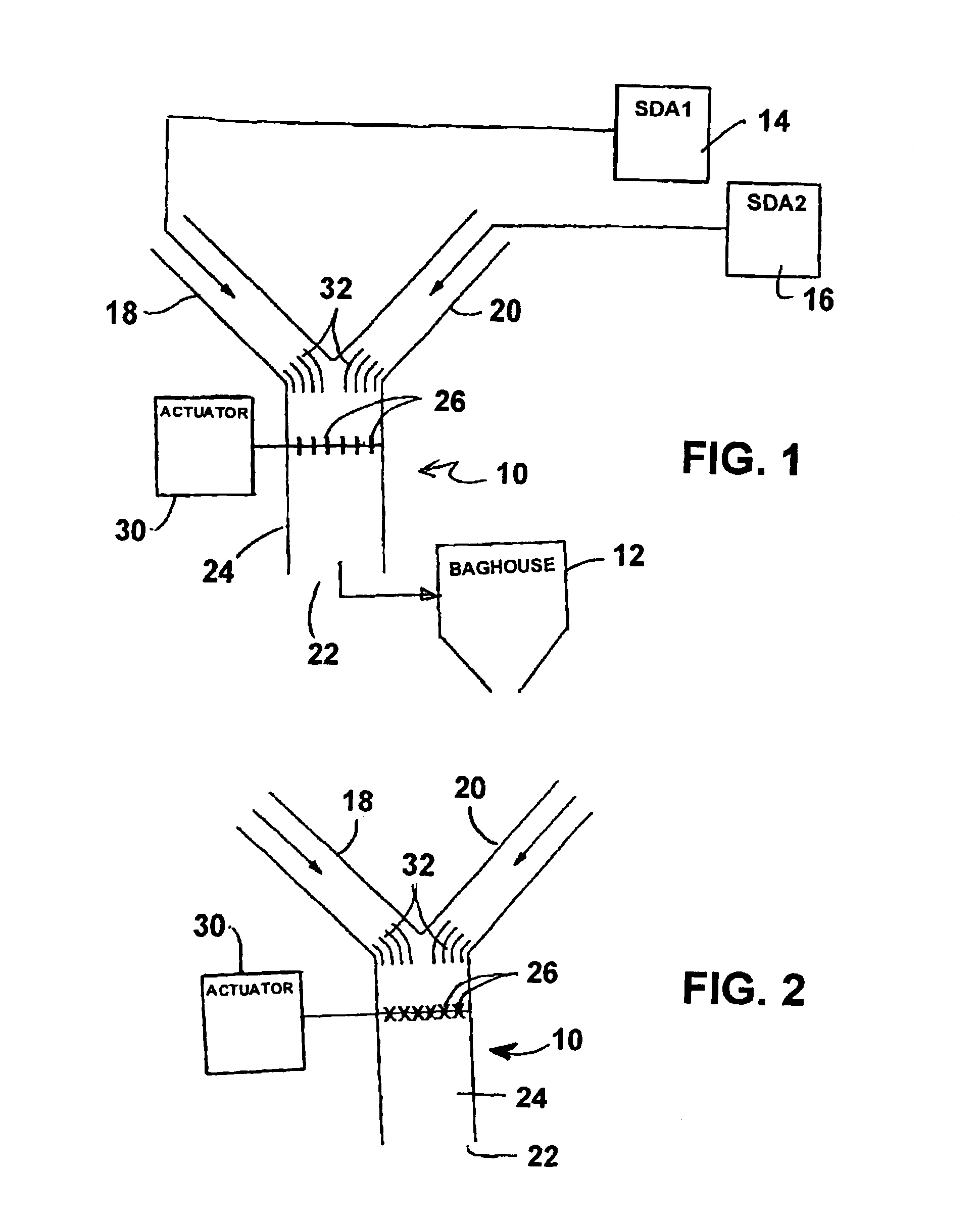
Intermittent mixer with low pressure drop
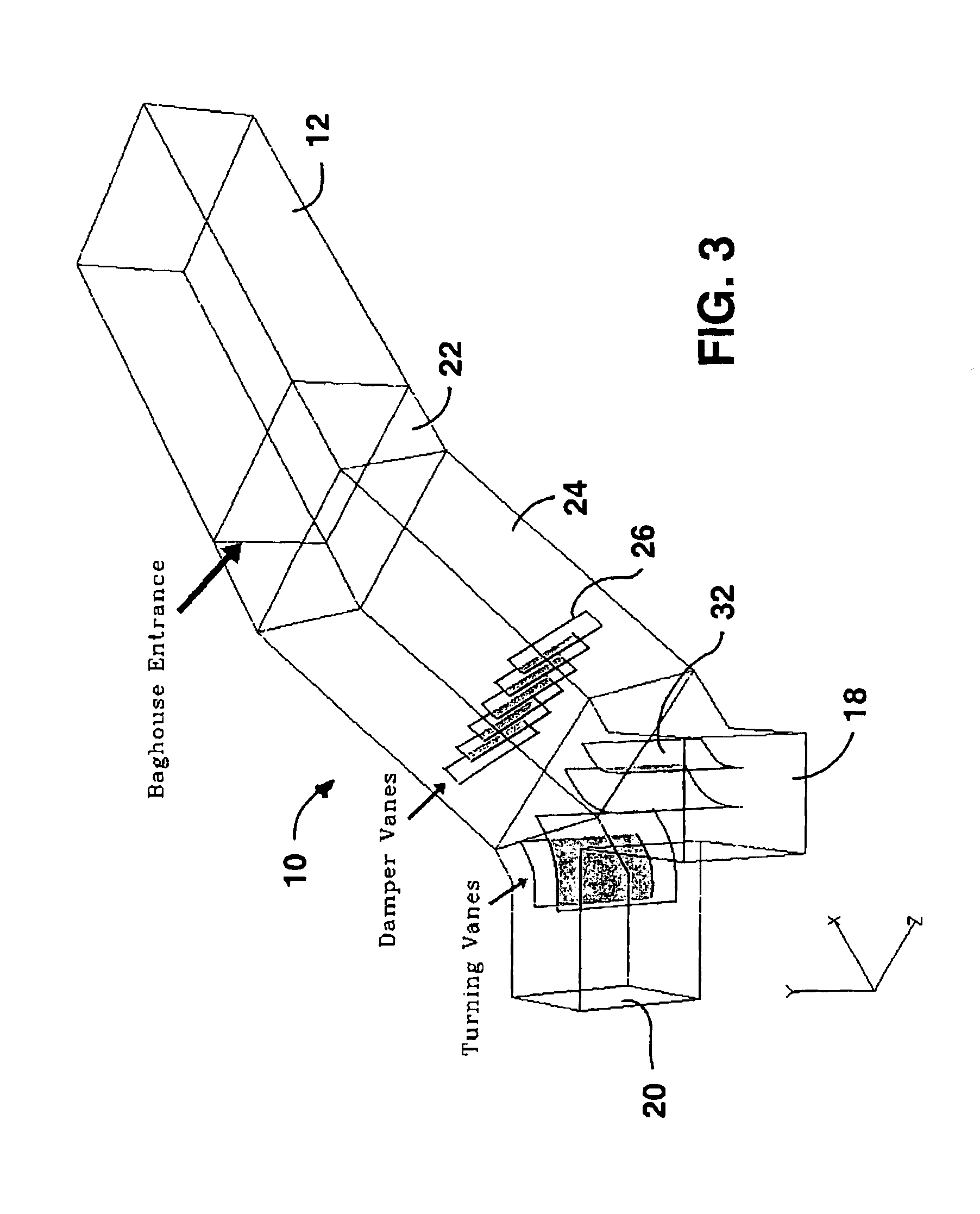
InactiveUS6946011B2Reduce the temperatureAuxillary pretreatmentOther chemical processesChemical compositionFlue gas
A thermal mixer reduces the temperature of flue gas supplied to a fabric filter. Two spray dry absorbers are operable to cool flue gas. A housing of the mixer has first and second inlet passages for gas from the absorbers, an outlet passage for gas to the fabric filter, and a mixing passage. A set of damper vanes extends in the mixing passage and has a mixing position for mixing the flue gases from the inlet passages to supply mixed gas to the outlet passage at relatively high pressure drop but lower temperature if one of the absorbers in not operating. They have a non-mixing position for passage of gases without mixing and at low pressure drop when both absorbers are operating. The invention can also be used to improve mixing of combined gas streams initially having different chemical compositions or amounts of particle loading.
Owner:THE BABCOCK & WILCOX CO
Method of synthesizing electrochemically active materials from a slurry of precursors
InactiveUS6913855B2Quality improvementHigh-quality materialPhosphatesElectrode thermal treatmentCompound (substance)Slurry
A method for making an active material comprises the steps of forming a slurry, spray drying the slurry to form a powdered precursor composition, and heating the powdered precursor composition at a temperature and for a time sufficient to form a reaction product. The slurry has a liquid phase and a solid phase, and contains at least an alkali metal compound and a transition metal compound. Preferably the liquid phase contains dissolved alkali metal compound, and the solid phase contains an insoluble transition metal compound, an insoluble carbonaceous material compound, or both. Electrodes and batteries are provided that contain the active materials.
Owner:RIL USA INC +1
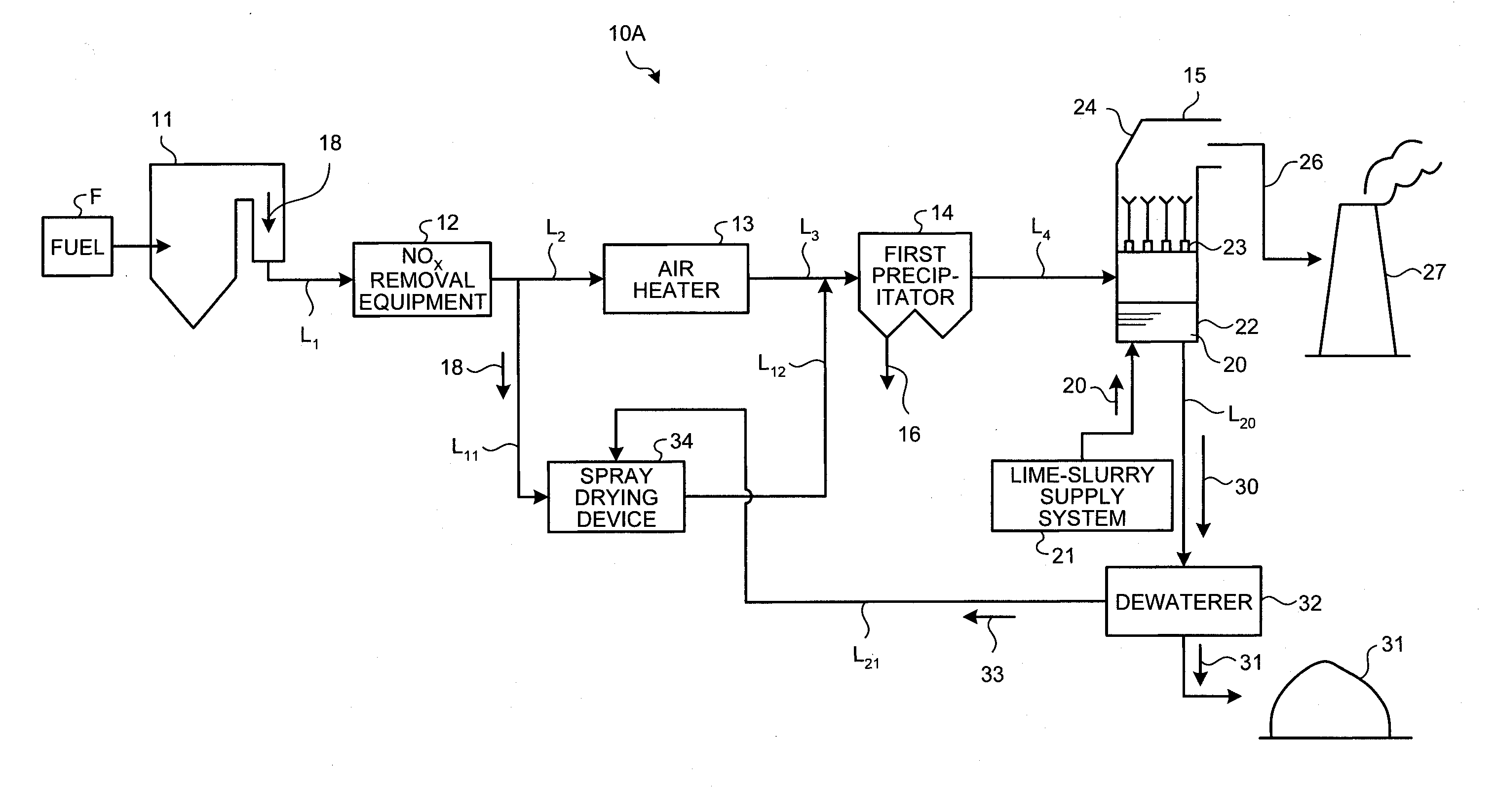
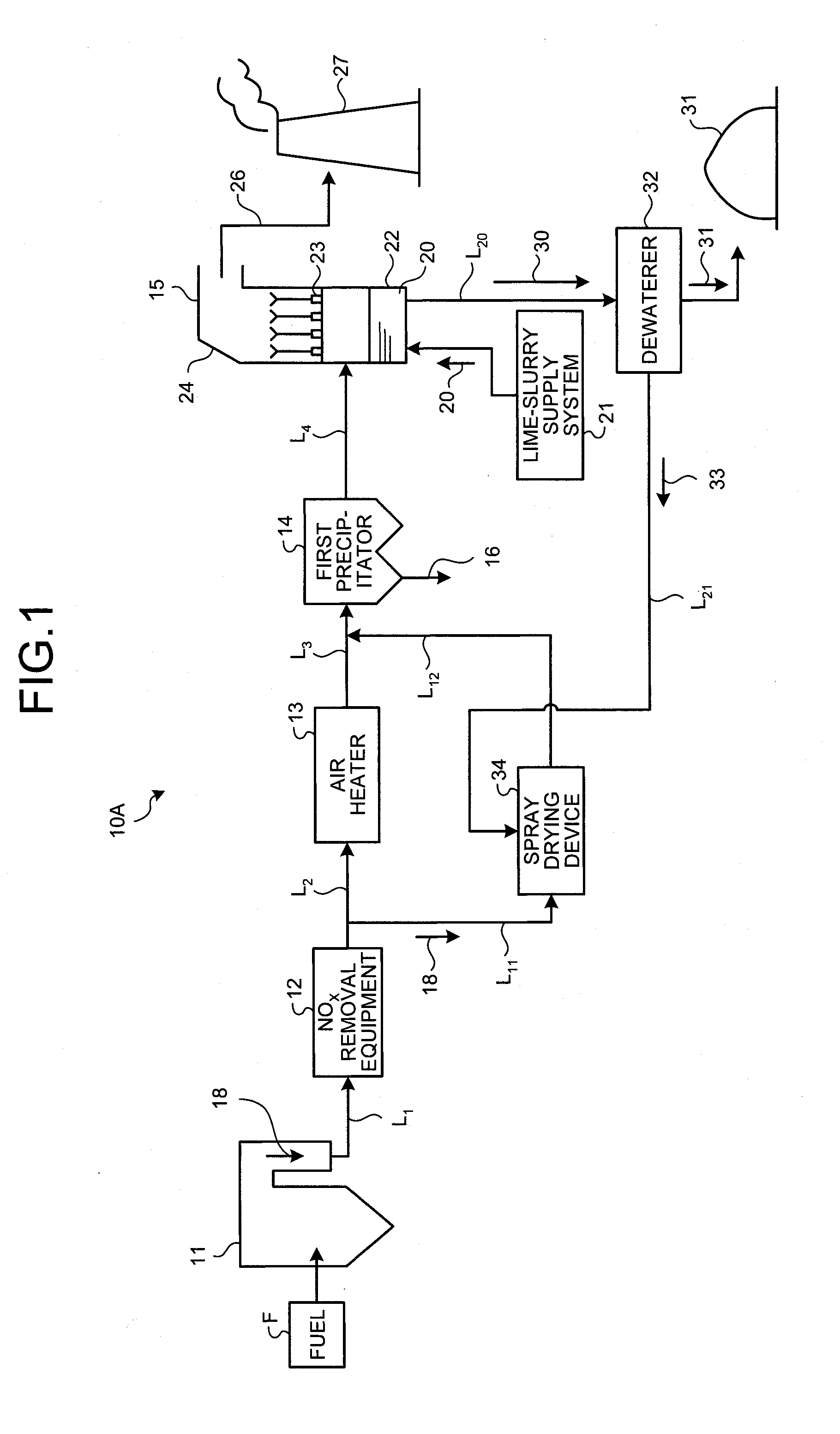
Air pollution control system and air pollution control method, spray drying device of dewatering filtration fluid from desulfurization discharged water, and method thereof
ActiveUS20120240761A1Improve performanceStable atomizationGas treatmentLiquid degasificationControl systemFlue gas
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Silicon-carbon composite material, lithium ion battery, and preparation method and application of silicon-carbon composite material
ActiveCN103633295AAlleviate volume expansionAvoid direct contactCell electrodesSecondary cellsCarbon compositesSilicon monoxide
The invention discloses a silicon-carbon composite material, a lithium ion battery, and a preparation method and application of the silicon-carbon composite material. The preparation method of the silicon-carbon composite material comprises the steps: uniformly mixing silicon powder and silicon monoxide powder, then mixing with a solution containing an organic carbon source dispersant, and performing wet-process ball milling to obtain a slurry; uniformly mixing the slurry, graphite and a conductive agent, and performing spray drying to obtain spherical-like particles, wherein graphite is synthetic graphite and / or intermediate-phase graphite; mixing the spherical-like particles and asphalt, performing cladding processing under the inert atmosphere to obtain a cladded material; and then performing carbonizing processing to obtain the silicon-carbon composite material, wherein silicon powder, silicon monoxide powder, graphite and asphalt respectively accounts for 5-15%, 3-10%, 45-75% and 5-40% by weight of the sum of the above materials, and the organic carbon source dispersant and the conductive agent both accounts for 0.1-2% by weight of the sum of silicon powder, silicon monoxide powder and graphite. The silicon-carbon composite material has relatively good cycle performance, and can be directly used as a cathode material of the lithium ion battery. The preparation method is simple in technology, low in cost and applicable to industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHANSHAN TECH CO LTD
Process for preparing novel formulation of integrative traditional Chinese medicine and production method thereof
InactiveCN102100661AWide distribution of targetsStrong slow and controlled release performancePharmaceutical delivery mechanismPlant ingredientsHigh pressureIndustrial scale
The invention relates to a process for preparing a novel formulation of an integrative traditional Chinese medicine and a production method thereof. Traditional Chinese medicine simple recipe, traditional Chinese medicine compound recipe, integrated Chinese and western medicine compound recipe and integrated Chinese and western medicine composition are prepared by utilizing a nanometer vector combination process. The production method comprises the following steps of extracting with alcohol-water, crushing and extracting in an ultrasonic manner, extracting in a microwave manner, decocting in water and condensing, spraying and drying, homogenizing under high pressure, grinding to be nanometer particles, preparing the nanometer particles and the like. The invention pays attention to the advantages of nanometer traditional Chinese medicine, such as multiple synergism, multiple targets and the like. After the novel formulation disclosed by the invention is produced in an industrial scale, the production cost can be greatly reduced, the quality of the product can be improved, and the target performance and the controlled release performance of the medicines are stronger.
Owner:SUZHOU ZHIWEITANG BIOLOGICAL TECH +1
Synthesis of attrition-resistant heterogeneous catalysts using templated mesoporous silica
The present invention relates to catalysts in mesoporous structures. In a preferred embodiment, the invention comprises a method for encapsulating a dispersed insoluble compound in a mesoporous structure comprising combining a soluble oxide precursor, a solvent, and a surfactant to form a mixture; dispersing an insoluble compound in the mixture; spray-drying the mixture to produce dry powder; and calcining the powder to yield a porous structure comprising the dispersed insoluble compound.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Electrode active composite materials and methods of making thereof
ActiveUS20100279117A1PhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesNanoparticleLithium metal
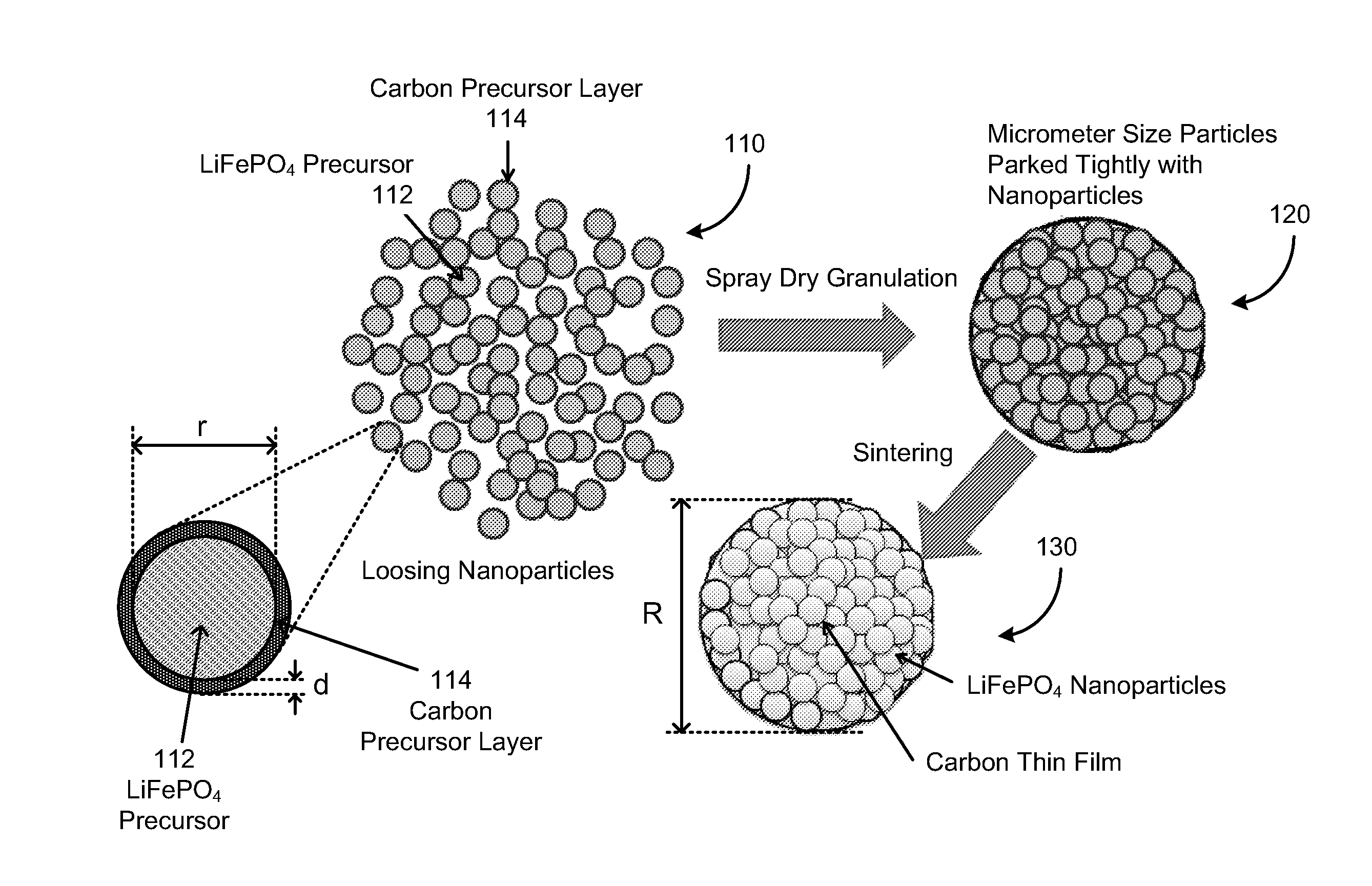
In one aspect of the invention, a method of synthesizing a lithium metal phosphate composite usable for a lithium secondary battery includes the steps of forming a nanometer-size precursor comprising lithium source and metal phosphate nanoparticles having each nanoparticle at least partially coated a layer of carbon precursor, spray drying the nanometer-size precursor at a first desired temperature to form micron-size particles packed with the lithium metal phosphate precursor nanoparticles, and sintering the micron-size particles at a second desired temperature under an inert and / or reduction atmosphere to form a micron-size lithium metal phosphate composite.
Owner:MEECOTECH
Silicone containing powders
A spray-dried, granular powder comprising: (i) from about 50% to about 99% of a water-soluble carrier, (ii) from about 1% to about 50% of a hydrophobic silicone oil dispersed within the carrier, wherein the spray-dried powder has a volume average particle size in the range from about 20 .mu.m to about 500 .mu.m, the powder being prepared by spray-drying an aqueous dispersion of the silicone oil and the water-soluble carrier, characterized in that the silicone oil is present in the dispersion in the form of discrete droplets having a volume average droplet size in the range from about 0.5 .mu.m to about 20 .mu.m and that the ratio of the average spray-dried particle size to the average droplet size is at least about 2.5:1. The powder is dry, free-flowing and processable into a punched tablet or other compressed forms, yet efficiently delivers the silicone oil on subsequent dissolution in water.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com