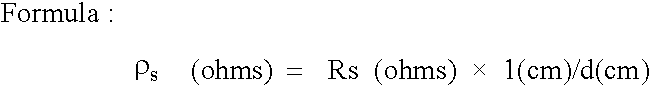Patents
Literature
113 results about "Standard technique" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
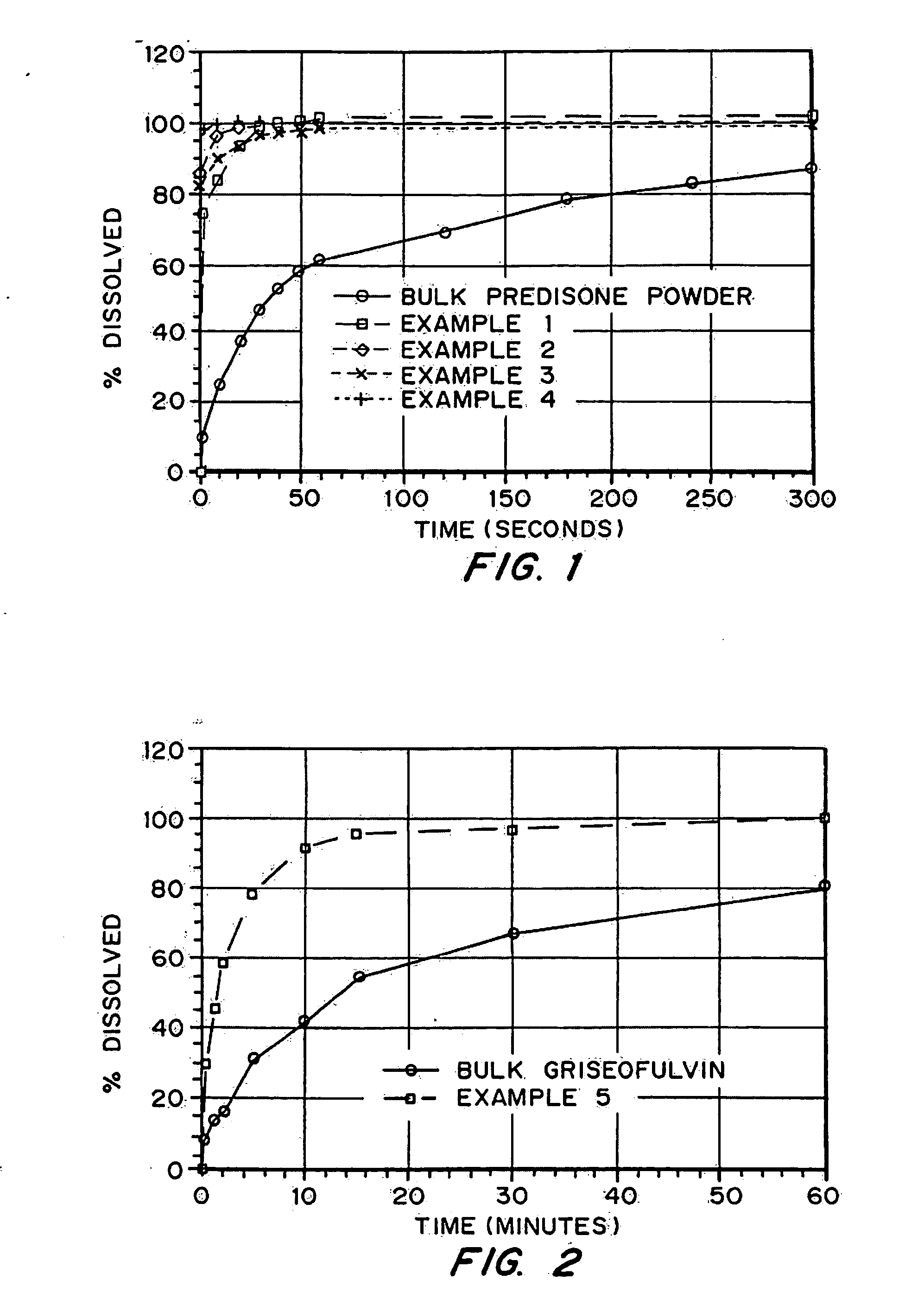
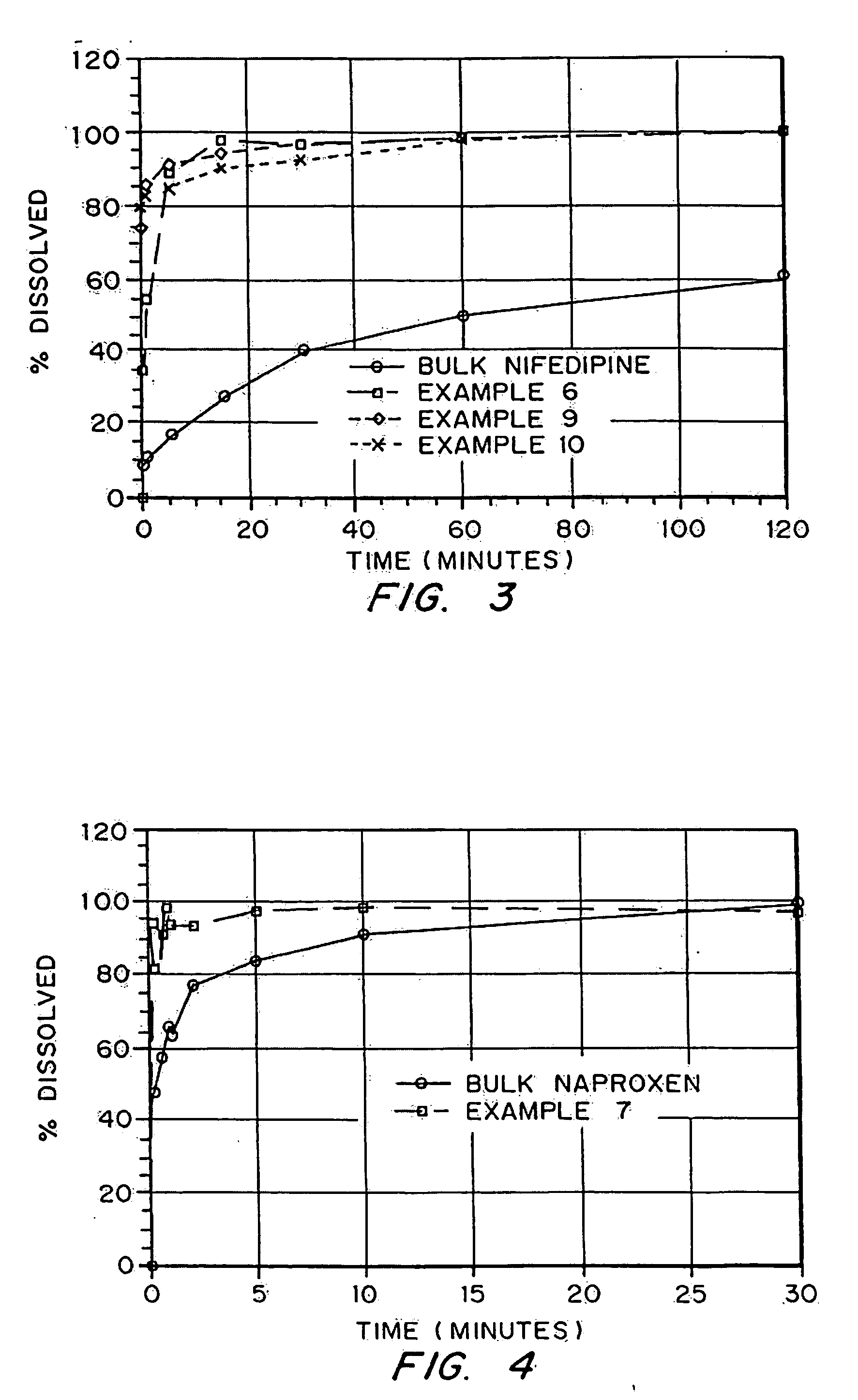
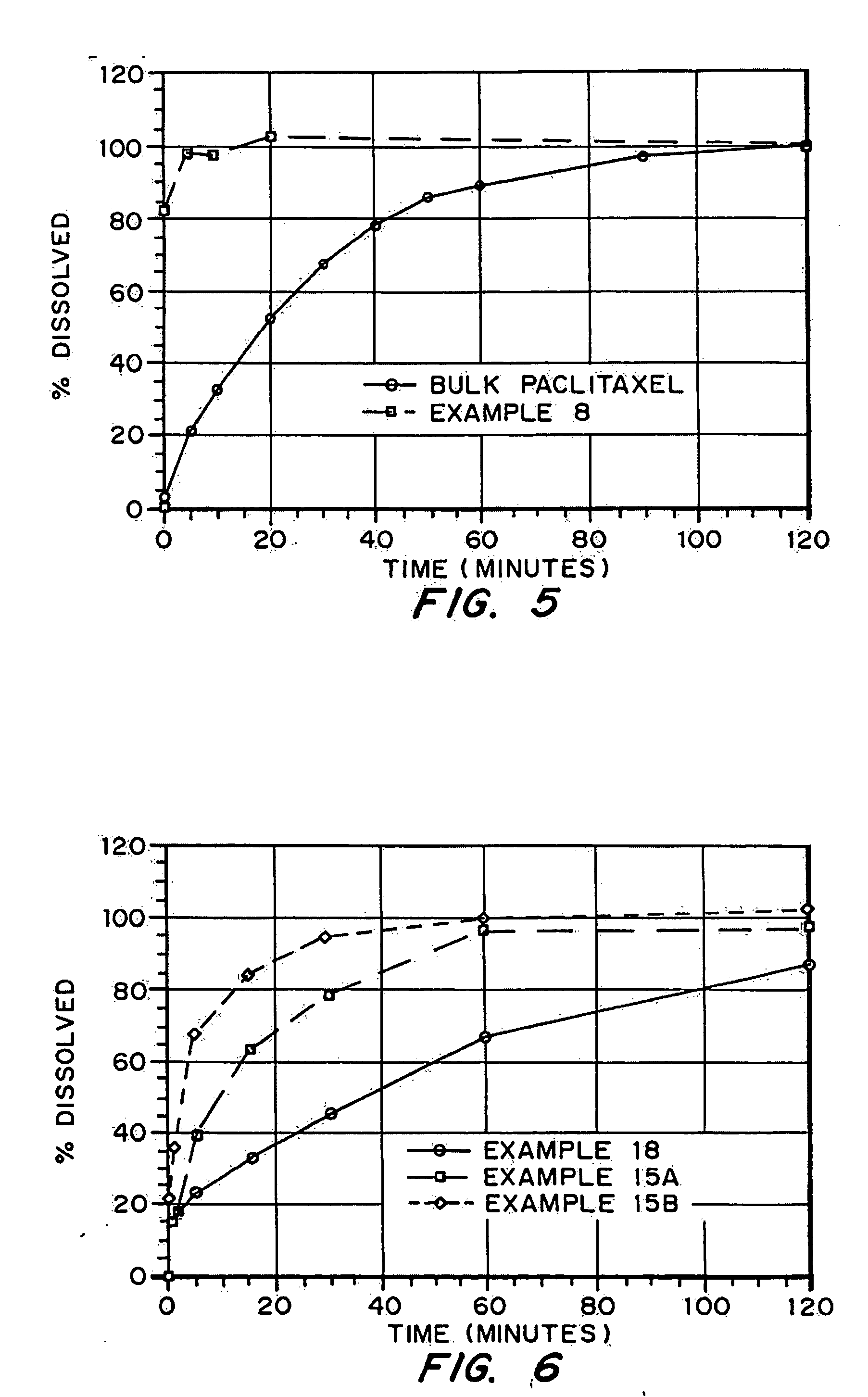
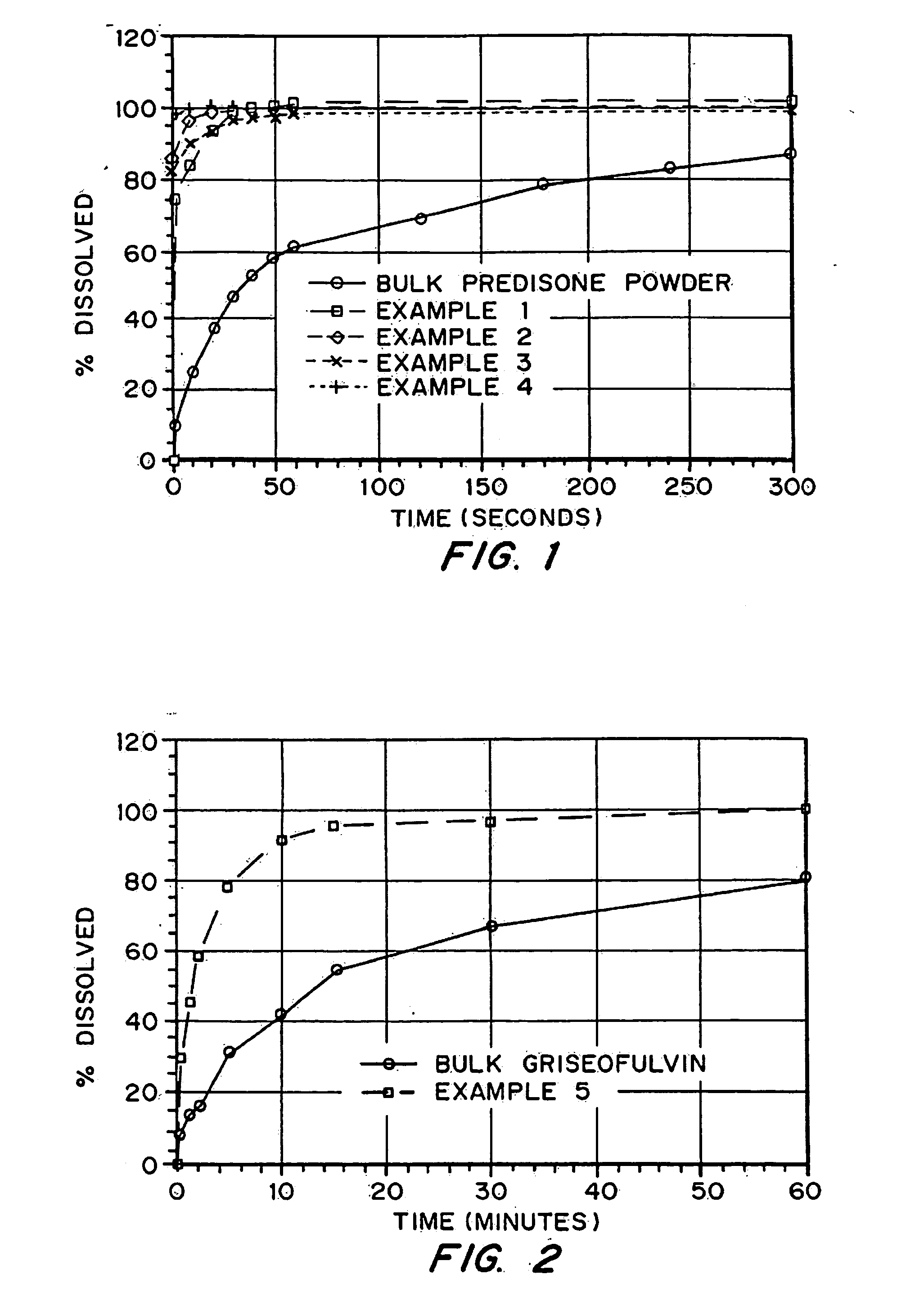
Porous drug matrices and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6932983B1Lower the volumePrevent precipitationPowder deliveryNanotechDrugs solutionWater soluble drug
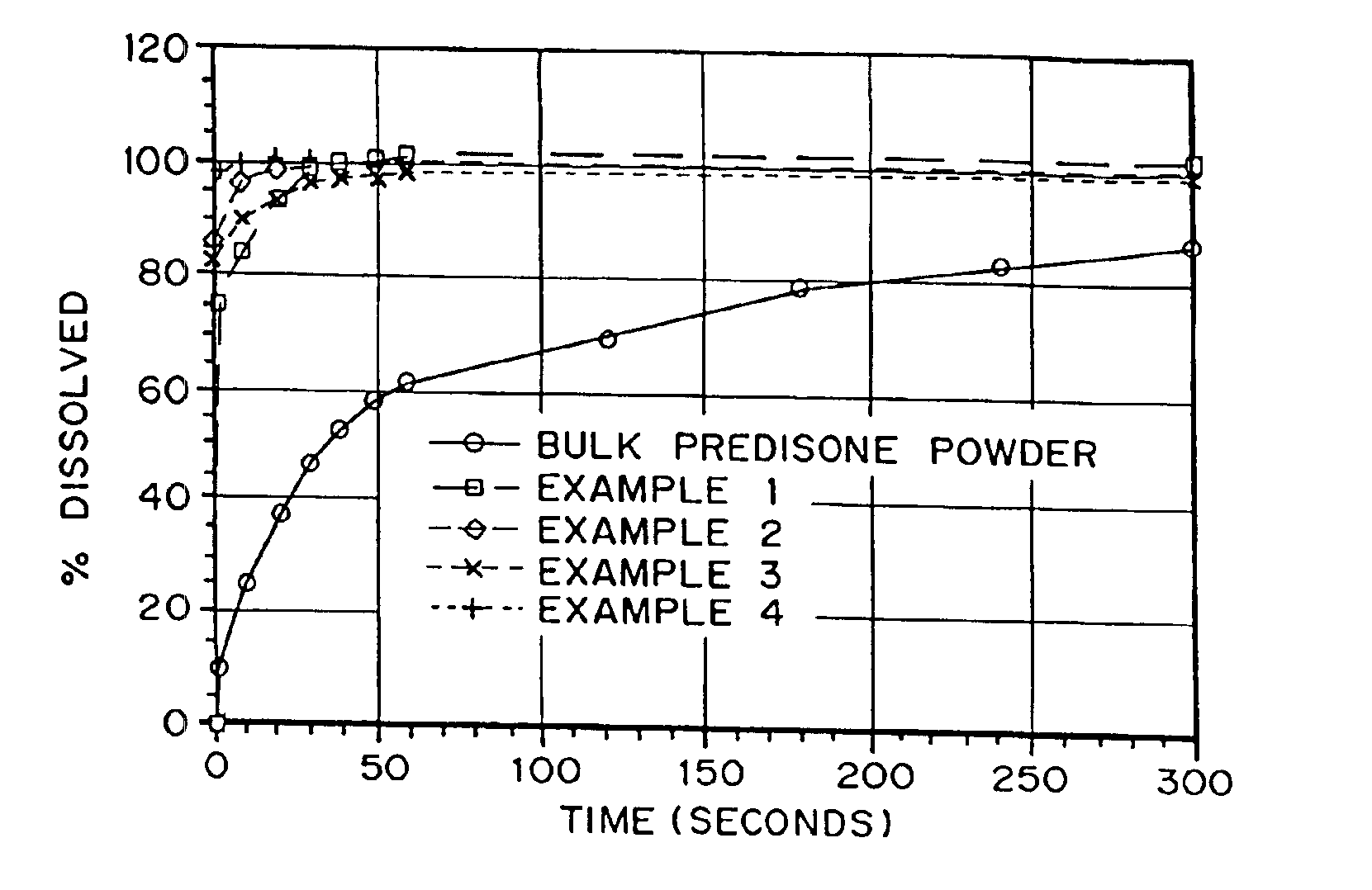
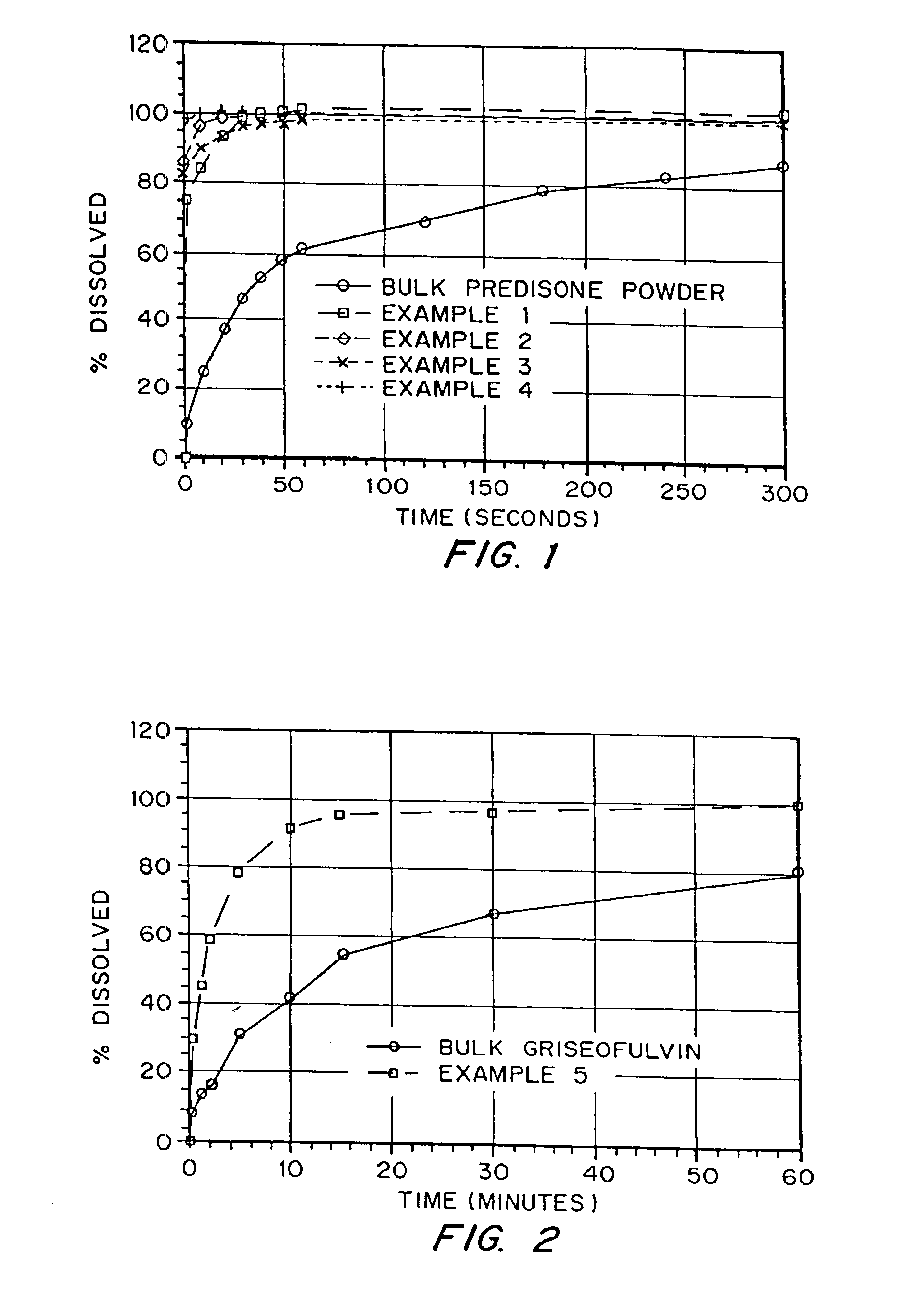
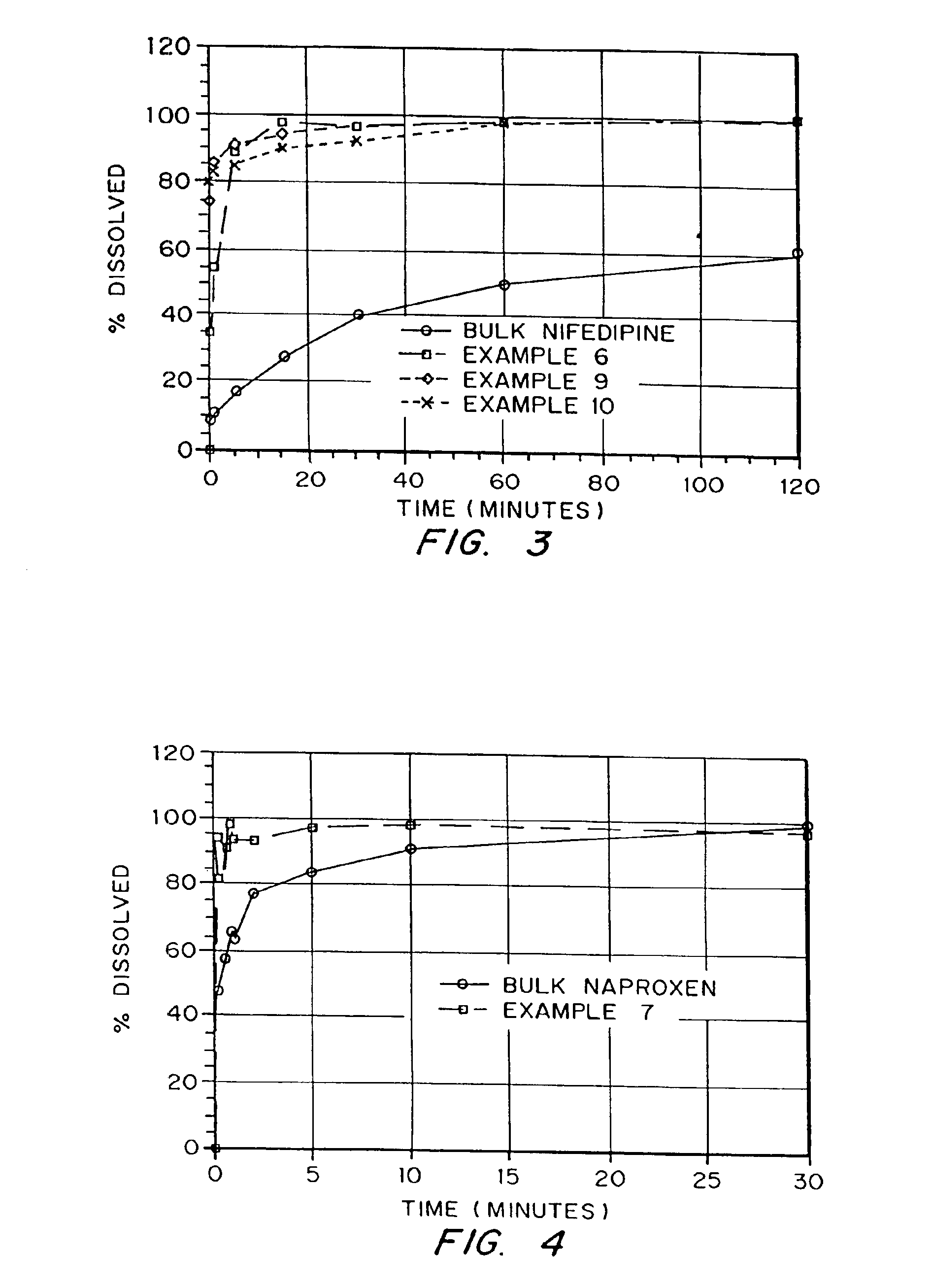
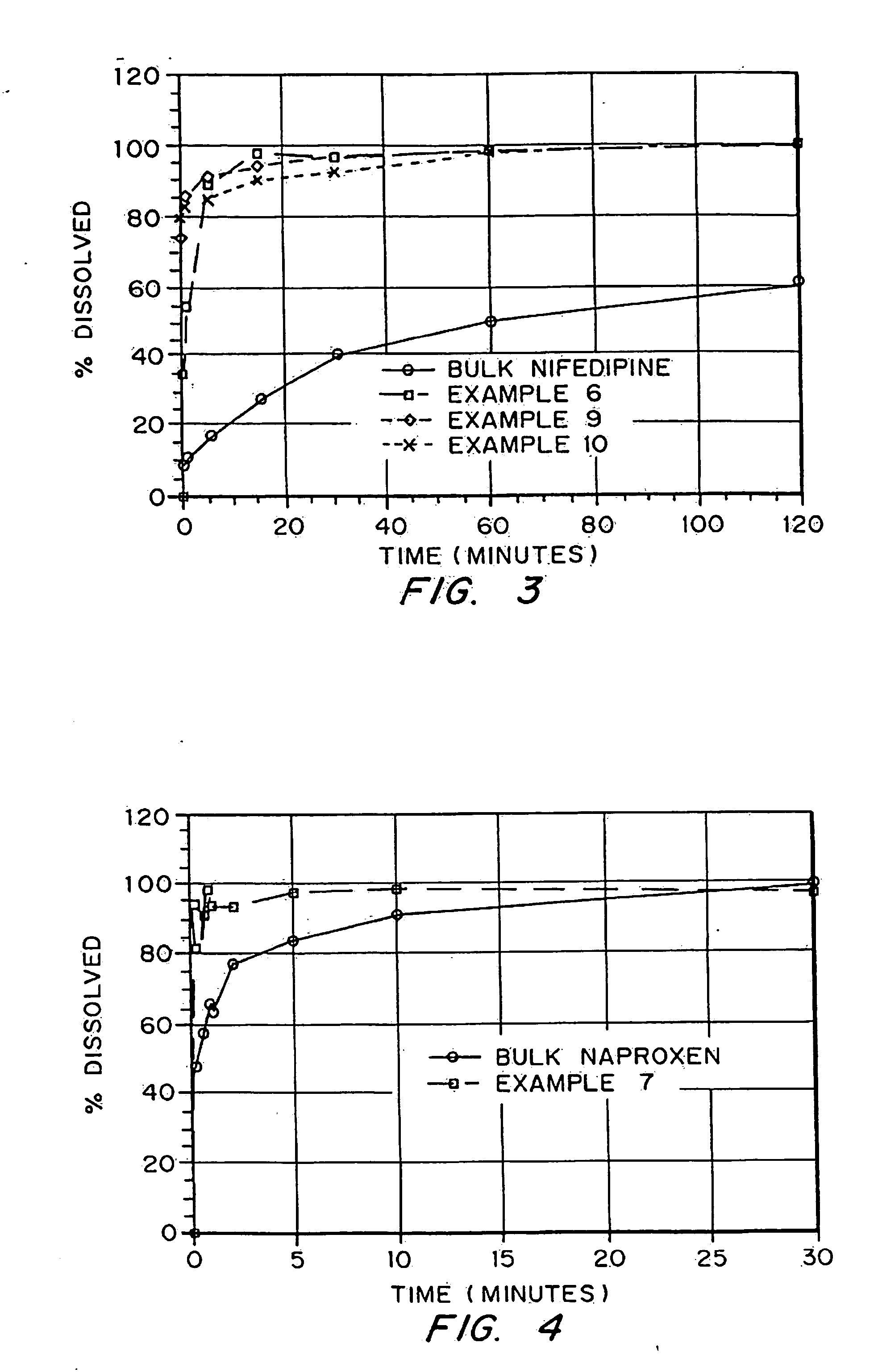
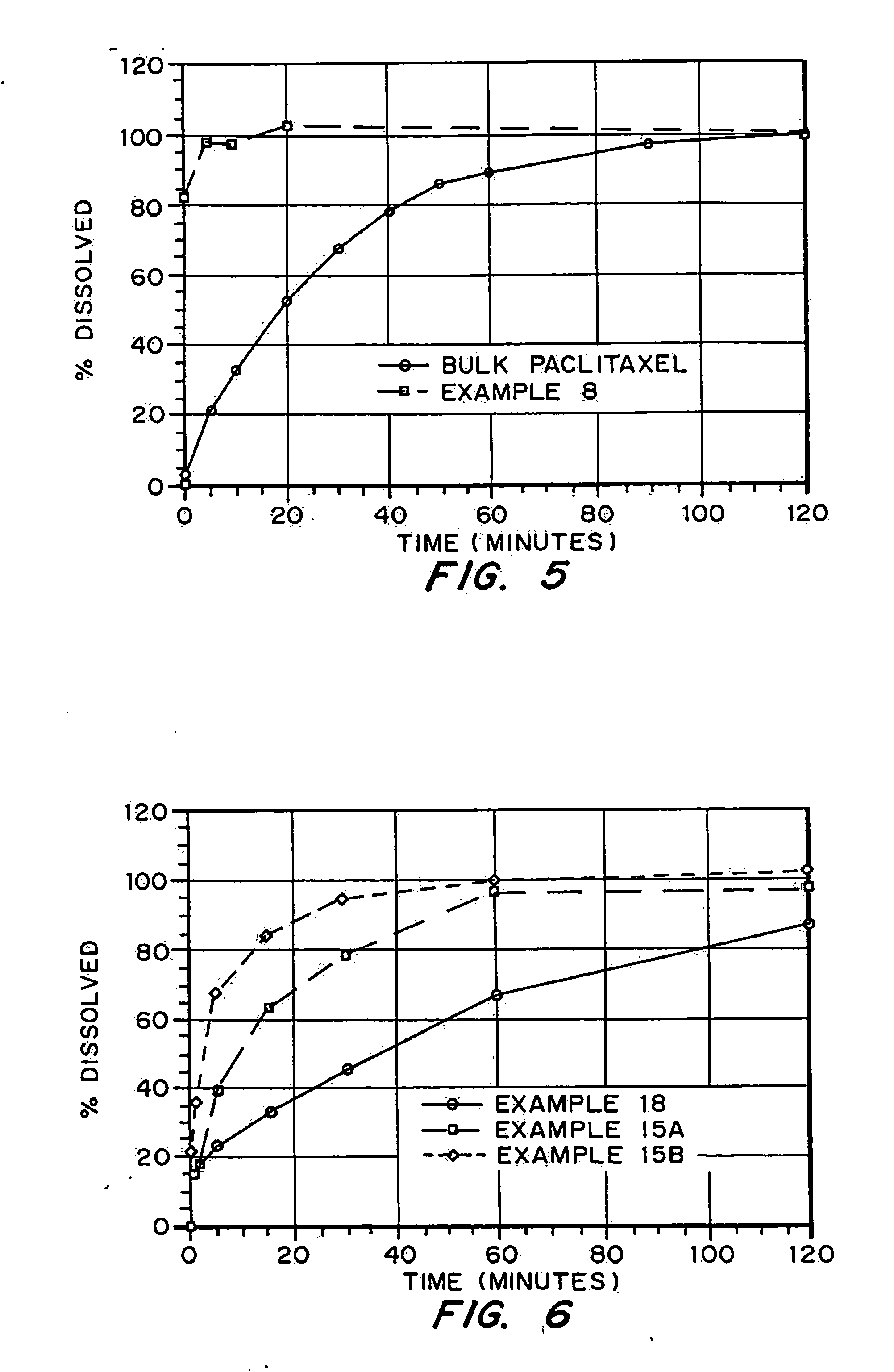
Drugs, especially low aqueous solubility drugs, are provided in a porous matrix form, preferably microparticles, which enhances dissolution of the drug in aqueous media. The drug matrices preferably are made using a process that includes (i) dissolving a drug, preferably a drug having low aqueous solubility, in a volatile solvent to form a drug solution, (ii) combining at least one pore forming agent with the drug solution to form an emulsion, suspension, or second solution, and (iii) removing the volatile solvent and pore forming agent from the emulsion, suspension, or second solution to yield the porous matrix of drug. The pore forming agent can be either a volatile liquid that is immiscible with the drug solvent or a volatile solid compound, preferably a volatile salt. In a preferred embodiment, spray drying is used to remove the solvents and the pore forming agent. The resulting porous matrix has a faster rate of dissolution following administration to a patient, as compared to non-porous matrix forms of the drug. In a preferred embodiment, microparticles of the porous drug matrix are reconstituted with an aqueous medium and administered parenterally, or processed using standard techniques into tablets or capsules for oral administration.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
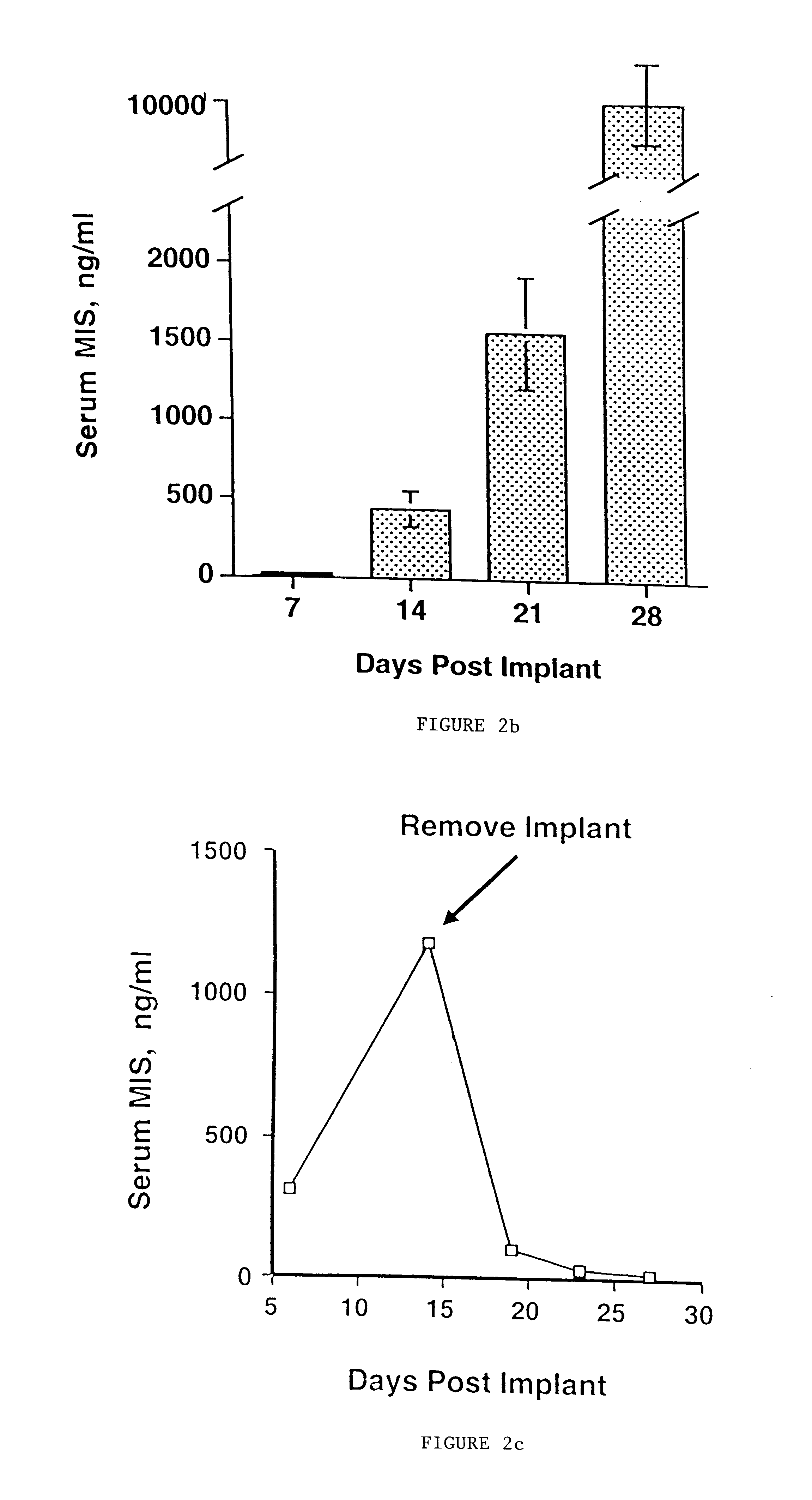
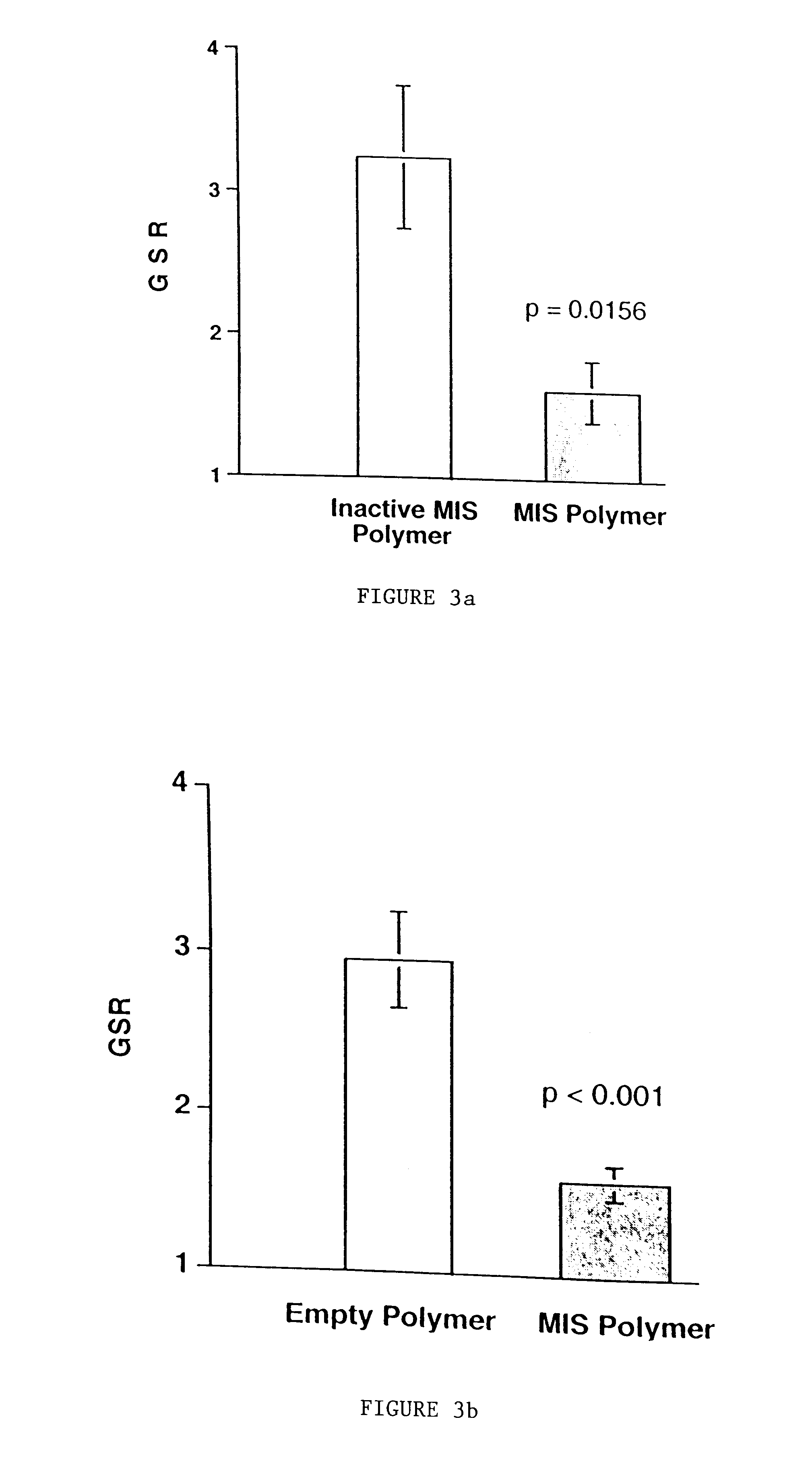
Delivery of therapeutic biologicals from implantable tissue matrices
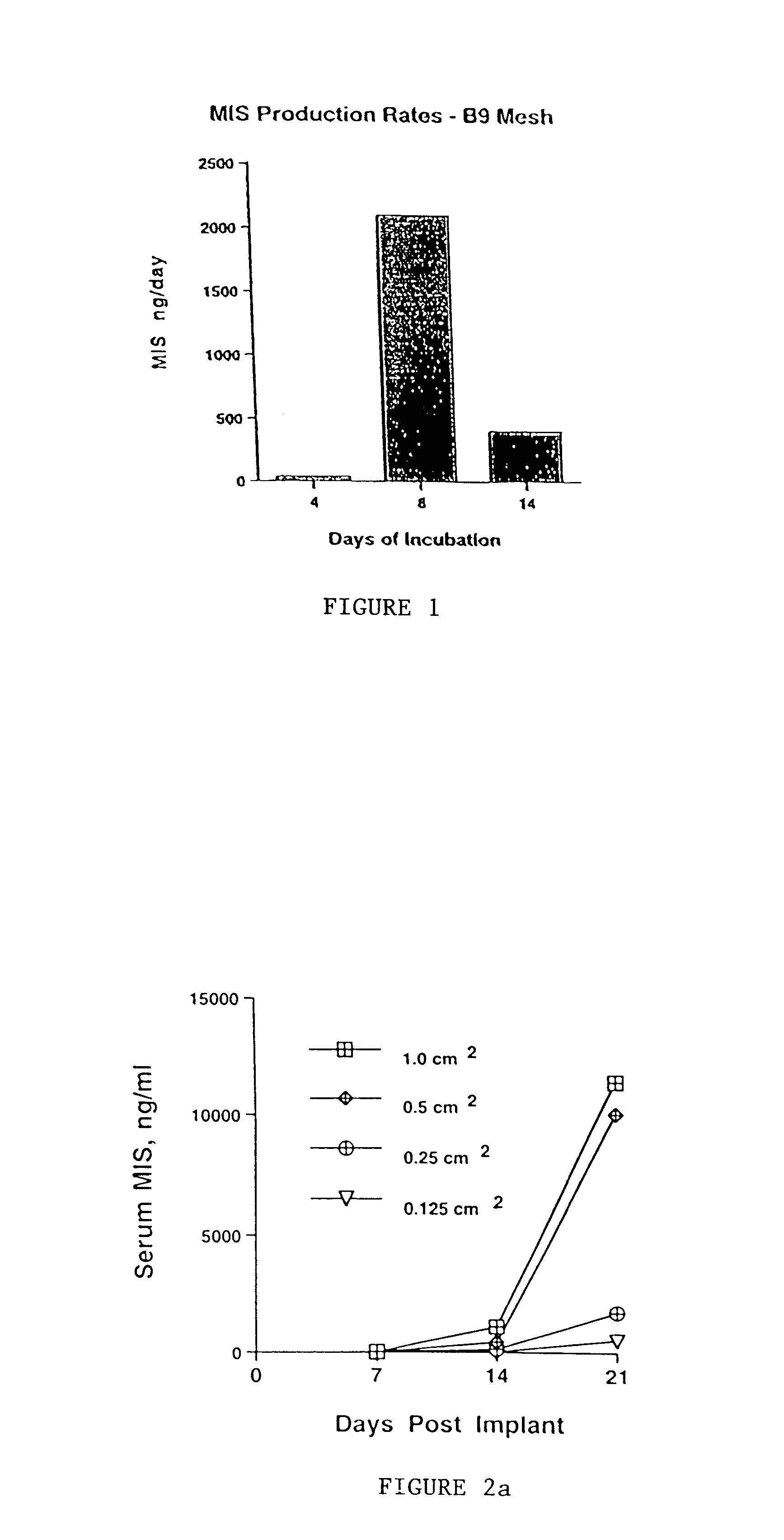
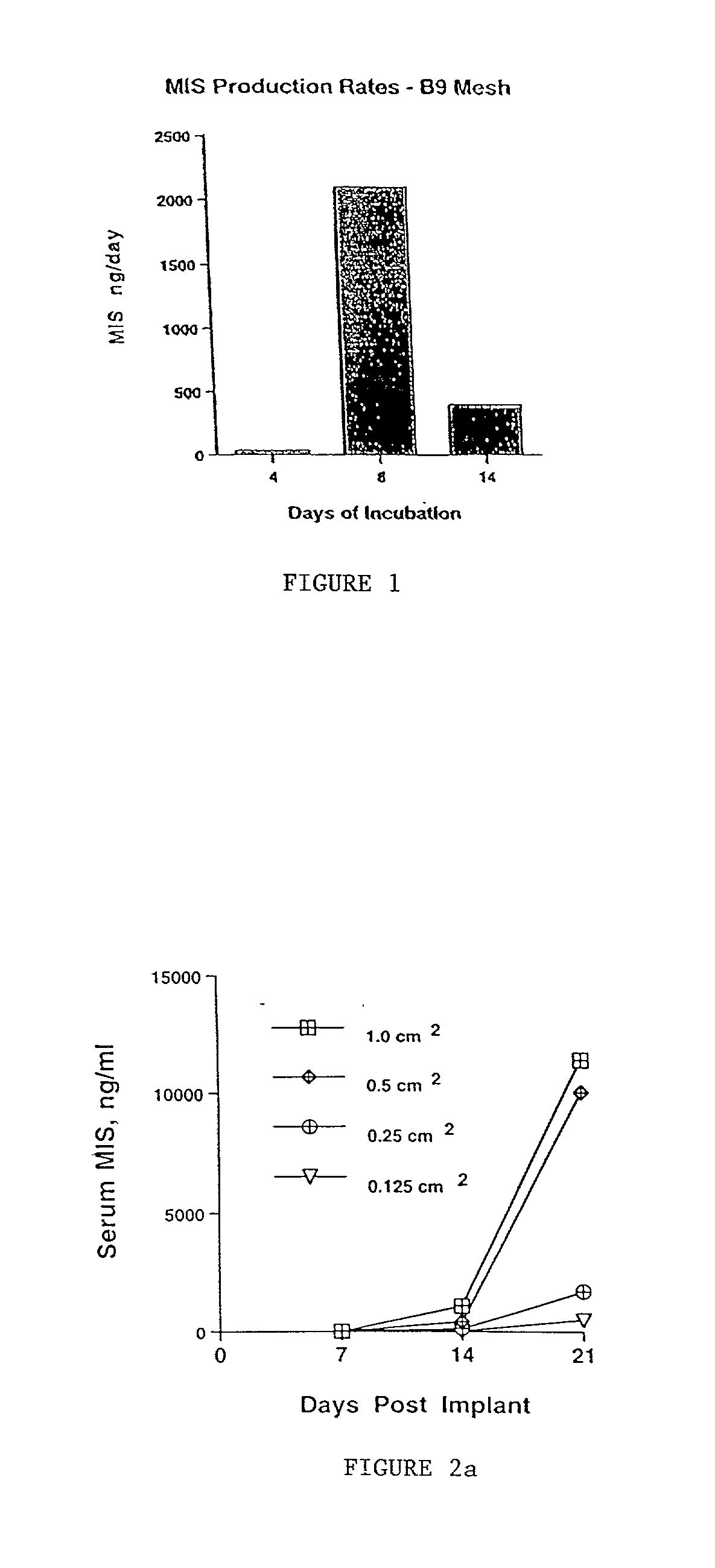
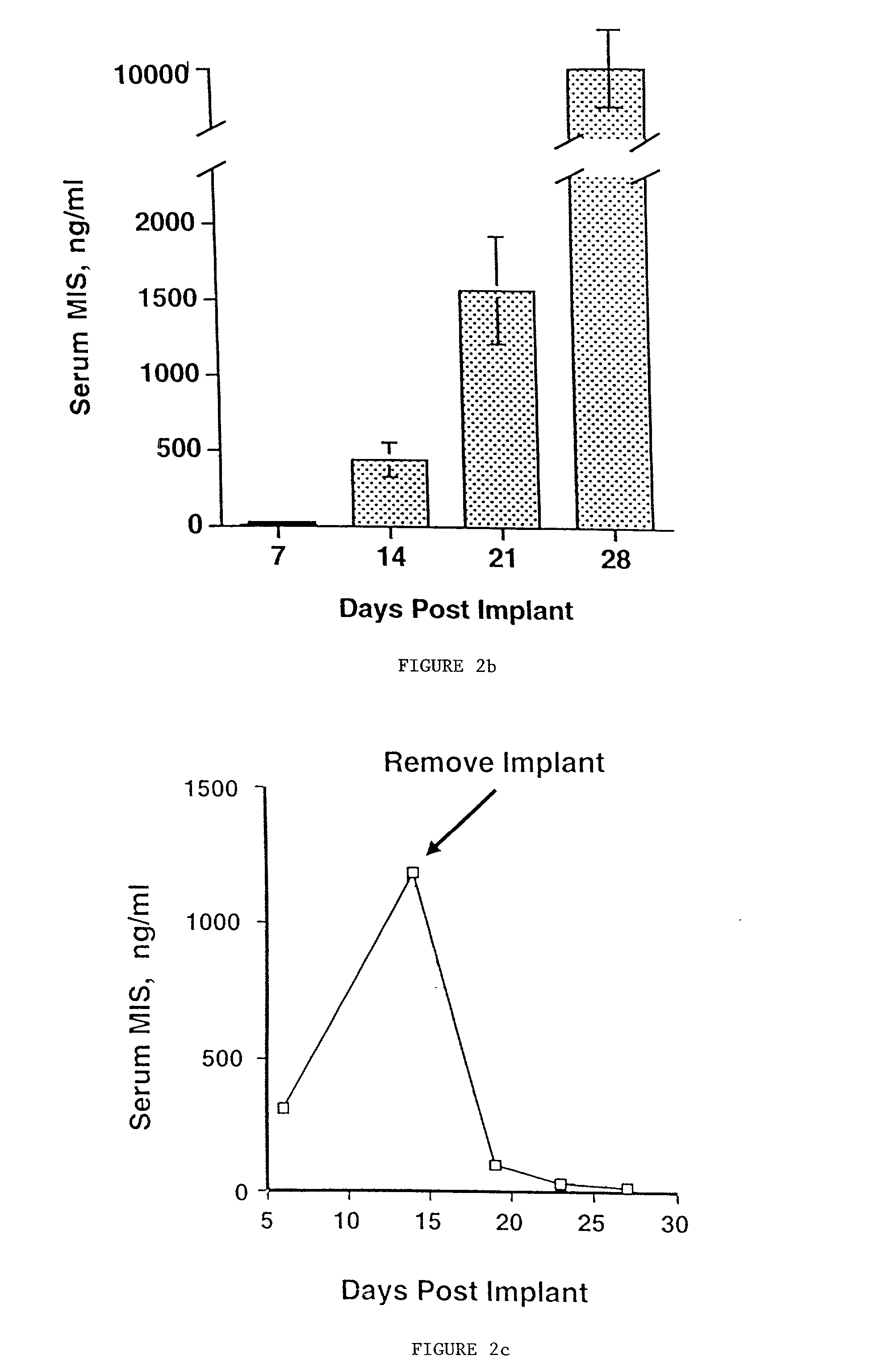
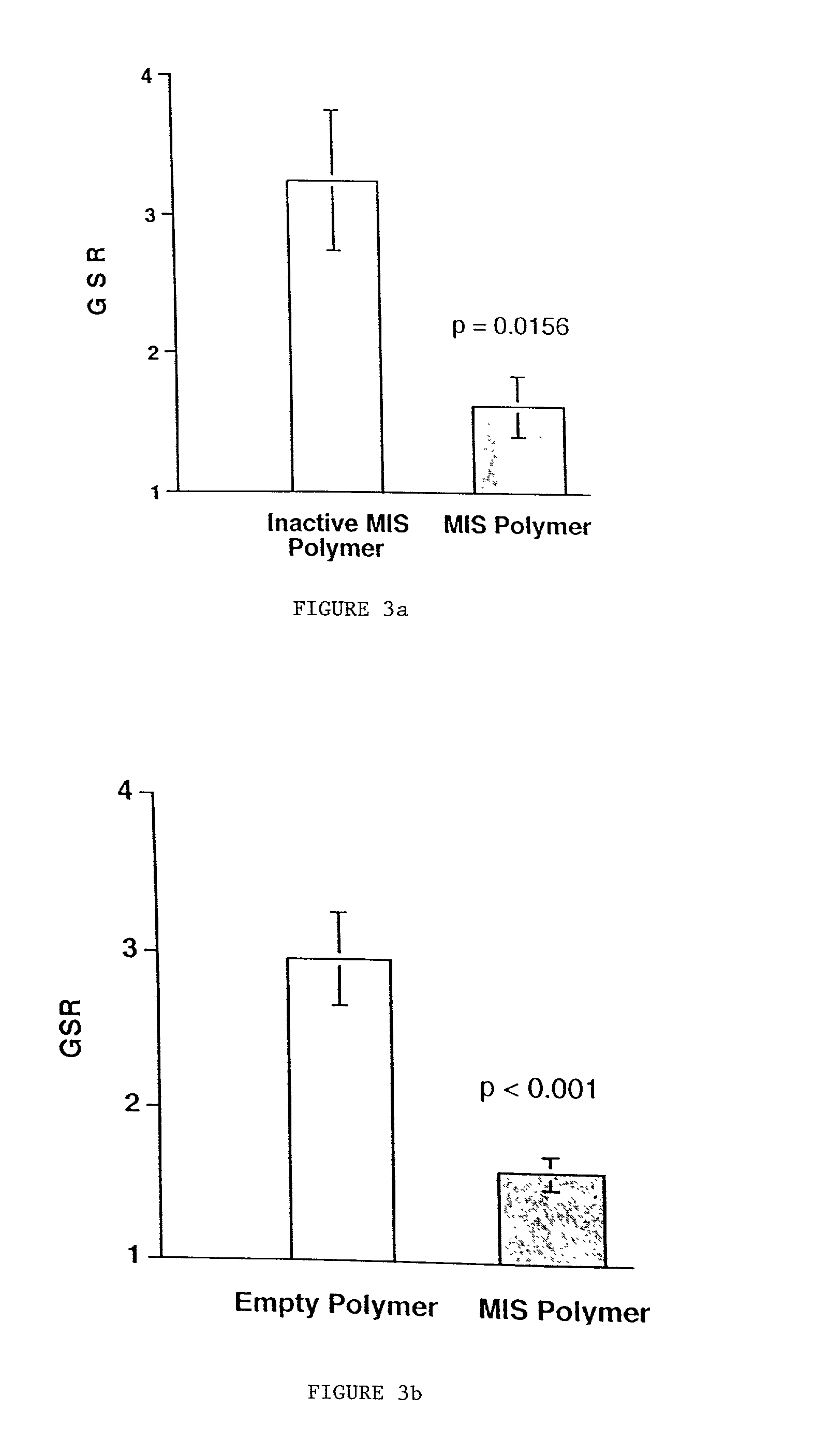
Normal cells, such as fibroblasts or other tissue or organ cell types, are genetically engineered to express biologically active, therapeutic agents, such as proteins that are normally produced in small amounts, for example, MIS, or other members of the TGF-beta family Herceptin(TM), interferons, andanti-angiogenic factors. These cells are seeded into a matrix for implantation into the patient to be treated. Cells may also be engineered to include a lethal gene, so that implanted cells can be destroyed once treatment is completed. Cells can be implanted in a variety of different matrices. In a preferred embodiment, these matrices are implantable and biodegradable over a period of time equal to or less than the expected period of treatment, when cells engraft to form a functional tissue producing the desired biologically active agent. Implantation may be ectopic or in some cases orthotopic. Representative cell types include tissue specific cells, progenitor cells, and stem cells. Matrices can be formed of synthetic or natural materials, by chemical coupling at the time of implantation, using standard techniques for formation of fibrous matrices from polymeric fibers, and using micromachining or microfabrication techniques. These devices and strategies are used as delivery systems via standard or minimally invasive implantation techniques for any number of parenterally deliverable recombinant proteins, particularly those that are difficult to produce in large amounts and / or active forms using conventional methods of purification, for the treatment of a variety of conditions that produce abnormal growth, including treatment of malignant and benign neoplasias, vascular malformations (hemangiomas), inflammatory conditions, keloid formation, abdominal or plural adhesions, endometriosis, congenital or endocrine abnormalities, and other conditions that can produce abnormal growth such as infection. Efficacy of treatment with the therapeutic biologicals is detected by determining specific criteria, for example, cessation of cell proliferation, regression of abnormal tissue, or cell death, or expression of genes or proteins reflecting the above.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Porous drug matrices and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20050048116A1Fast dissolutionHigh dissolution ratePowder deliveryGranular deliveryDrugs solutionMicroparticle
Drugs, especially low aqueous solubility drugs, are provided in a porous matrix form, preferably microparticles, which enhances dissolution of the drug in aqueous media. The drug matrices preferably are made using a process that includes (i) dissolving a drug, preferably a drug having low aqueous solubility, in a volatile solvent to form a drug solution, (ii) combining at least one pore forming agent with the drug solution to form an emulsion, suspension, or second solution and hydrophilic or hydrophobic excipients that stabilize the drug and inhibit crystallization, and (iii) removing the volatile solvent and pore forming agent from the emulsion, suspension, or second solution to yield the porous matrix of drug. Hydrophobic or hydrophilic excipients may be selected to stabilize the drug in crystalline form by inhibiting crystal growth or to stabilize the drug in amorphous form by preventing crystallization. The pore forming agent can be either a volatile liquid that is immiscible with the drug solvent or a volatile solid-compound, preferably a volatile salt. In a preferred embodiment, spray drying is used to remove the solvents and the pore forming agent. The resulting porous matrix has a faster rate of dissolution following administration to a patient, as compared to non-porous matrix forms of the drug. In a preferred embodiment, microparticles of the porous drug matrix are reconstituted with an aqueous medium and administered parenterally, or processed using standard techniques into tablets or capsules for oral administration.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
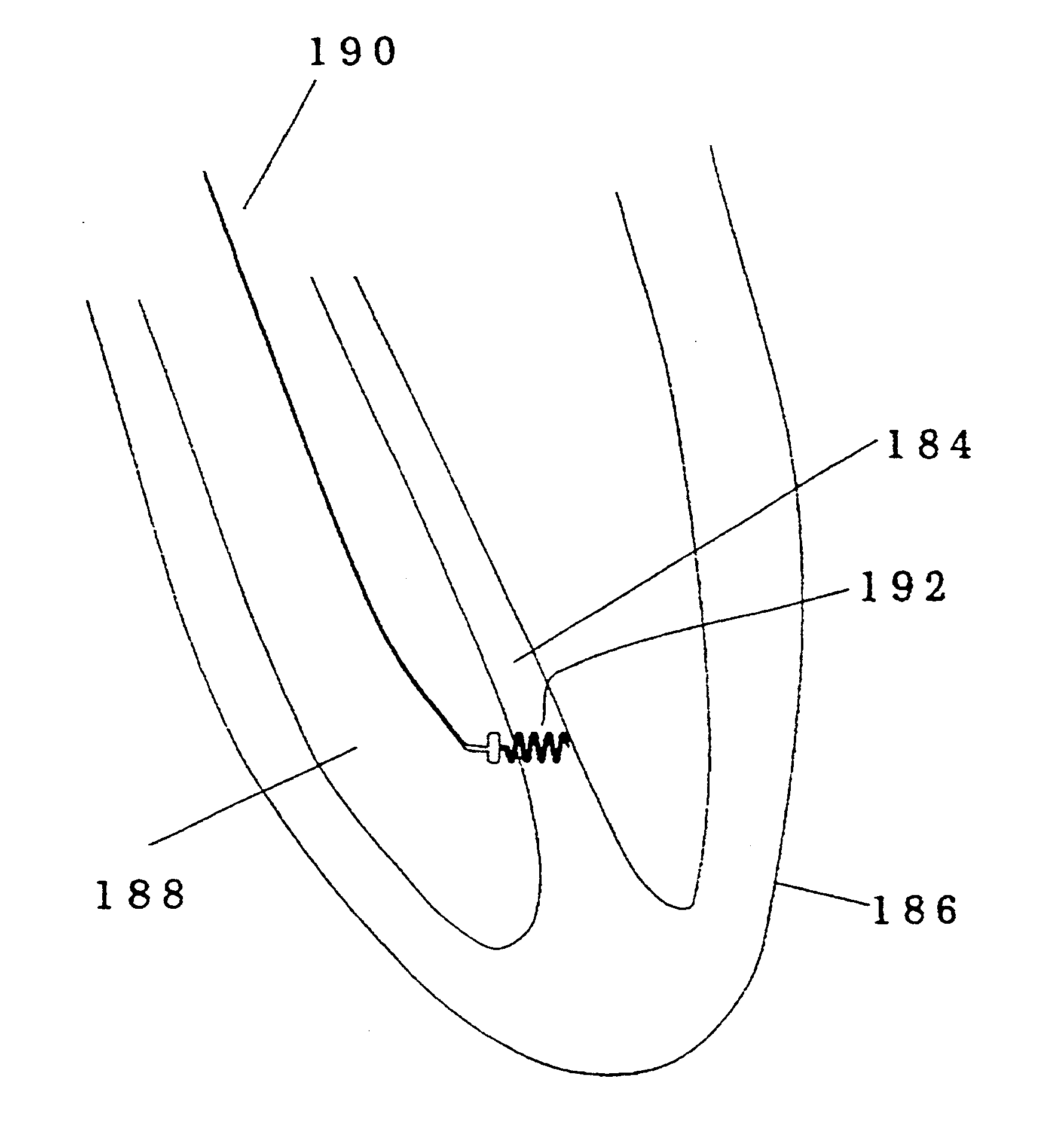
Implantable device for penetrating and delivering agents to cardiac tissue
InactiveUSRE37463E1Avoid damageEliminate the effects ofTransvascular endocardial electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical conductorCardiac wall
An implantable devices for the effective elimination of an arrhythmogenic site from the myocardium is presented. By inserting small biocompatible conductors and / or insulators into the heart tissue at the arrhythmogenic site, it is possible to effectively eliminate a portion of the tissue from the electric field and current paths within the heart. The device would act as an alternative to the standard techniques for the removal of tissue from the effective contribution to the hearts electrical action which require the destruction of tissue via energy transfer (RF, microwave, cryogenic, etc.). This device is a significant improvement in the state of the art in that it does not require tissue necrosis.In one preferred embodiment the device is a non conductive helix that is permanently implanted into the heart wall around the arrhythmogenic site. In variations on the embodiment, the structure is wholly or partially conductive, the structure is used as an implantable substrate for anti arrhythmic, inflammatory, or angiogenic pharmacological agents, and the structure is deliverable by a catheter with a disengaging stylet. In other preferred embodiments that may incorporate the same variations, the device is a straight or curved stake, or a group of such stakes that are inserted simultaneously.
Owner:BIOCARDIA
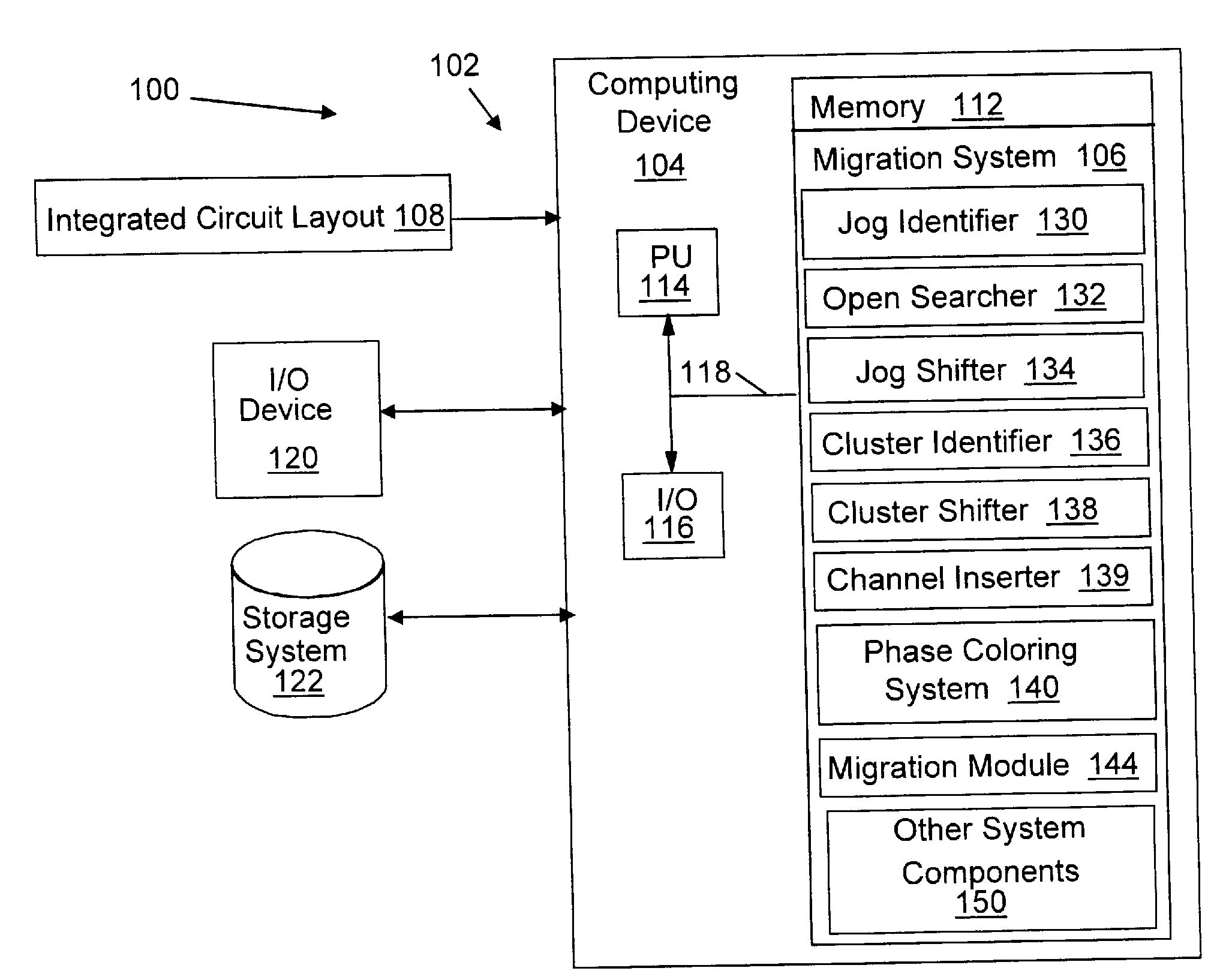
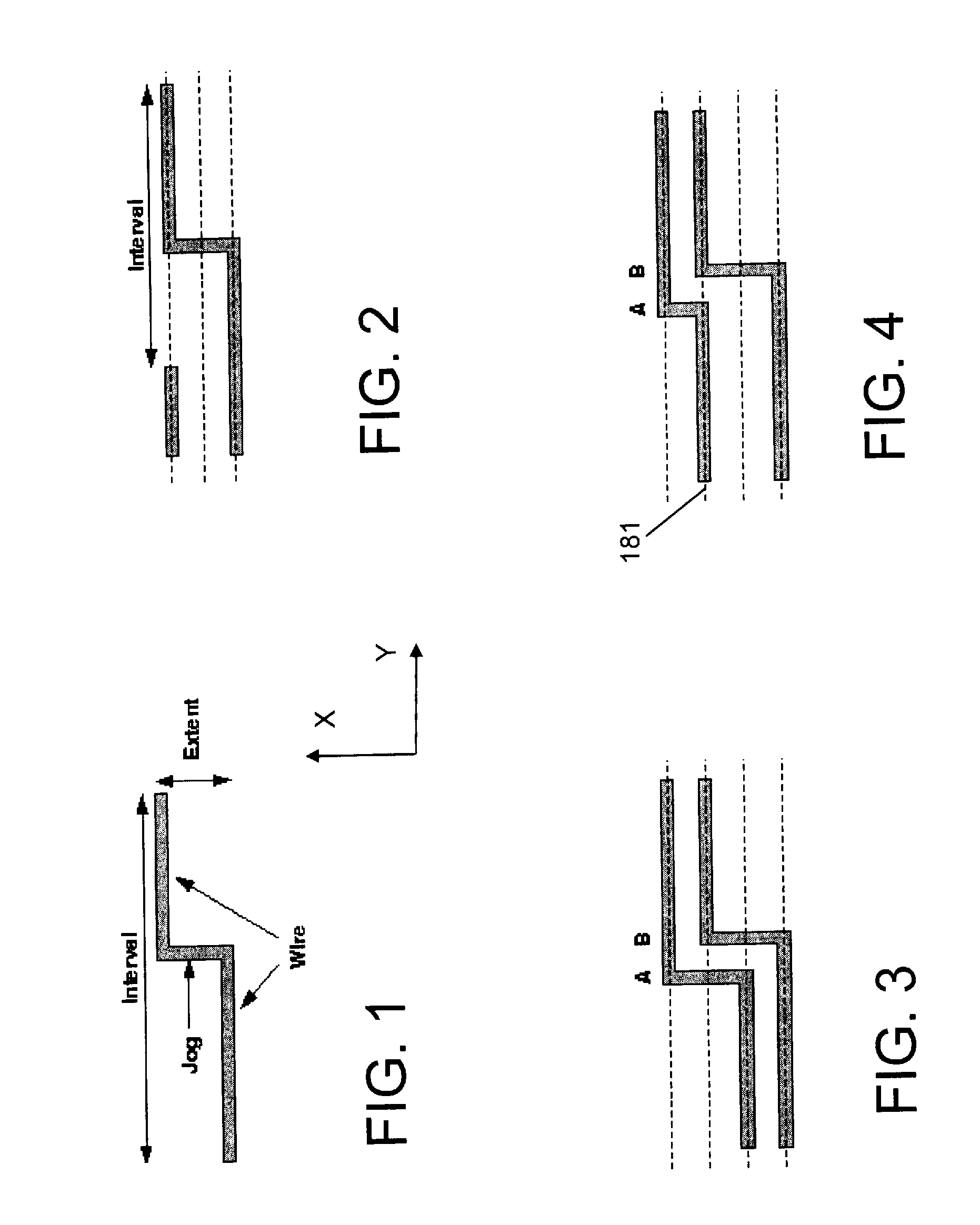
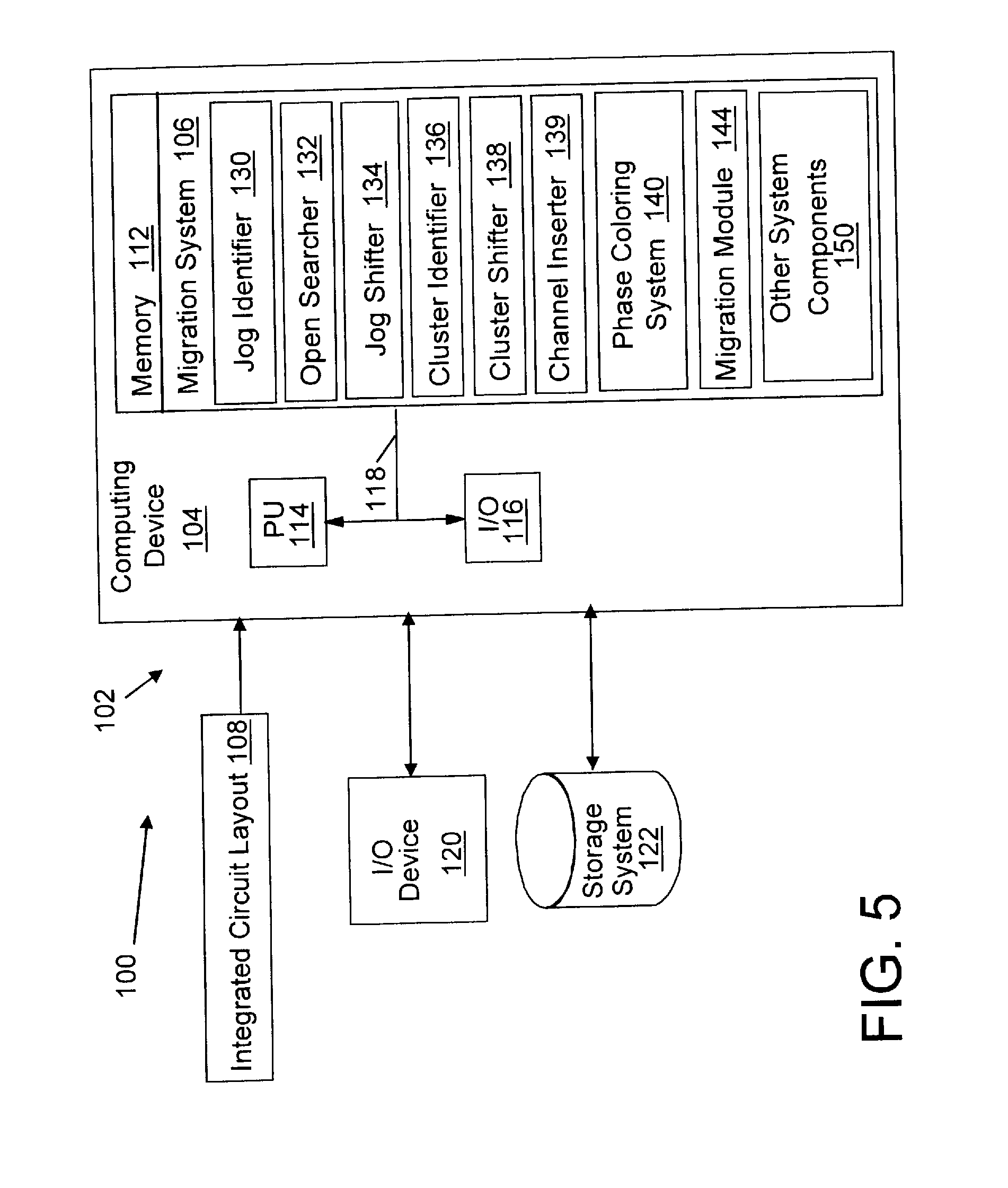
Migration of integrated circuit layout for alternating phase shift masks
InactiveUS20080244494A1Space is requiredCAD circuit designOriginals for photomechanical treatmentPhase shiftedProbable Case
Method, system and program product for migrating an integrated circuit (IC) layout for, for example, alternating aperture phase shift masks (AltPSM), are disclosed. In order to migrate a layout to phase compliance, jogs are identified on a first (AltPSM) layer and shifted to another second layer. Isolated or clustered jogs are shifted into an open channel portions on the second layer where possible. Remaining clustered jogs are shifted into as few new channels as possible on the second layer. The jog removal process leaves unidirectional wires that can be trivially phase colored. Standard technology migration techniques are then used to legalize the results on the layers.
Owner:IBM CORP
Porous drug matrices and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20050058710A1Fast dissolutionExtended half-lifePowder deliveryGranular deliveryDrugs solutionMicroparticle
Drugs, especially low aqueous solubility drugs, are provided in a porous matrix form, preferably microparticles, which enhances dissolution of the drug in aqueous media. The drug matrices preferably are made using a process that includes (i) dissolving a drug, preferably a drug having low aqueous solubility, in a volatile solvent to form a drug solution, (ii) combining at least one pore forming agent with the drug solution to form an emulsion, suspension, or second solution and hydrophilic or hydrophobic excipients that stabilize the drug and inhibit crystallization, and (iii) removing the volatile solvent and pore forming agent from the emulsion, suspension, or second solution to yield the porous matrix of drug. Hydrophobic or hydrophilic excipients may be selected to stabilize the drug in crystalline form by inhibiting crystal growth or to stabilize the drug in amorphous form by preventing crystallization. The pore forming agent can be either a volatile liquid that is immiscible with the drug solvent or a volatile solid compound, preferably a volatile salt. In a preferred embodiment, spray drying is used to remove the solvents and the pore forming agent. The resulting porous matrix has a faster rate of dissolution following administration to a patient, as compared to non-porous matrix forms of the drug. In a preferred embodiment, microparticles of the porous drug matrix are reconstituted with an aqueous medium and administered parenterally, or processed using standard techniques into tablets or capsules for oral administration.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
Data throughput over lossy communication links
InactiveUS7061856B2Promote recoveryError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsData connectionTelecommunications link
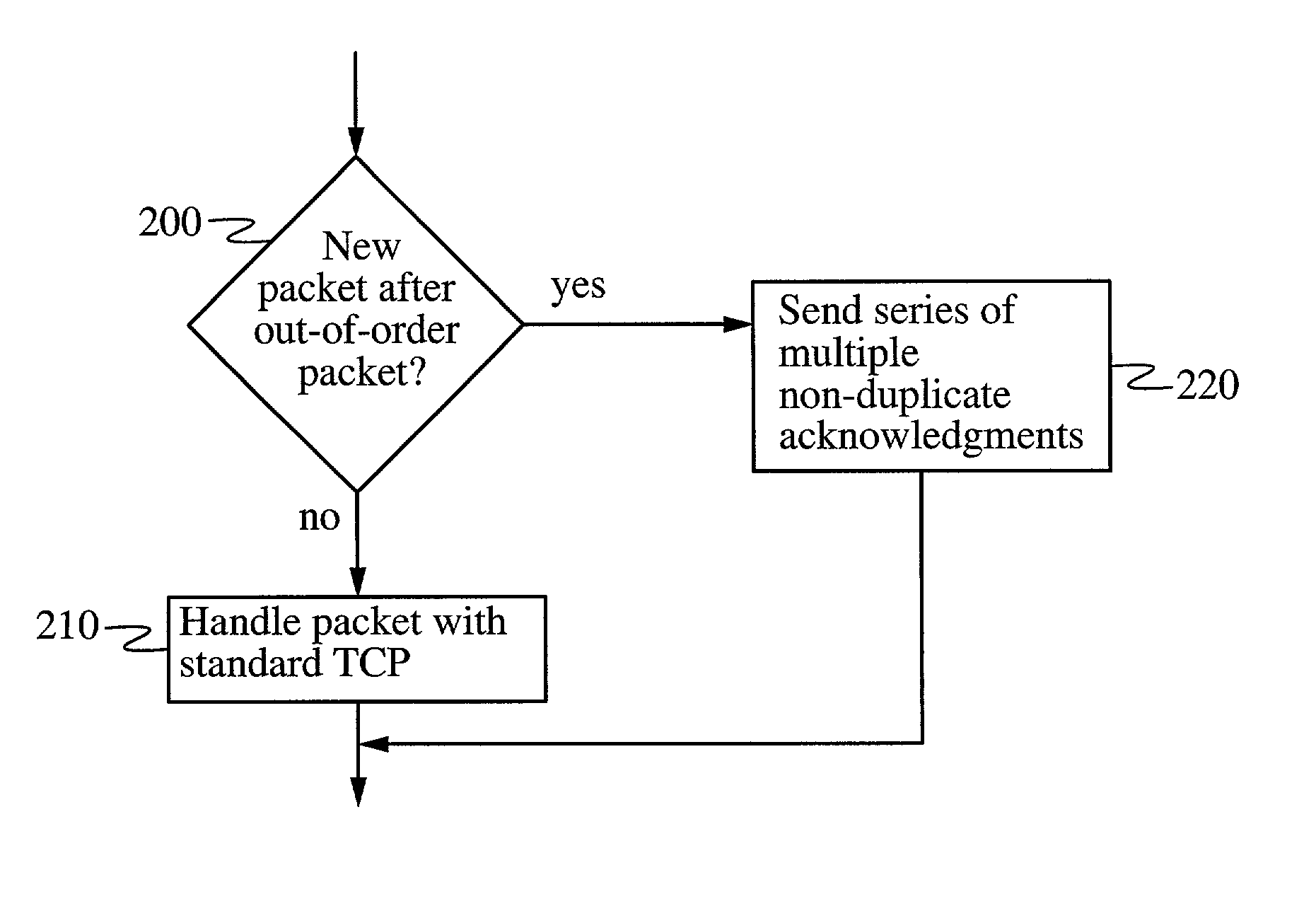
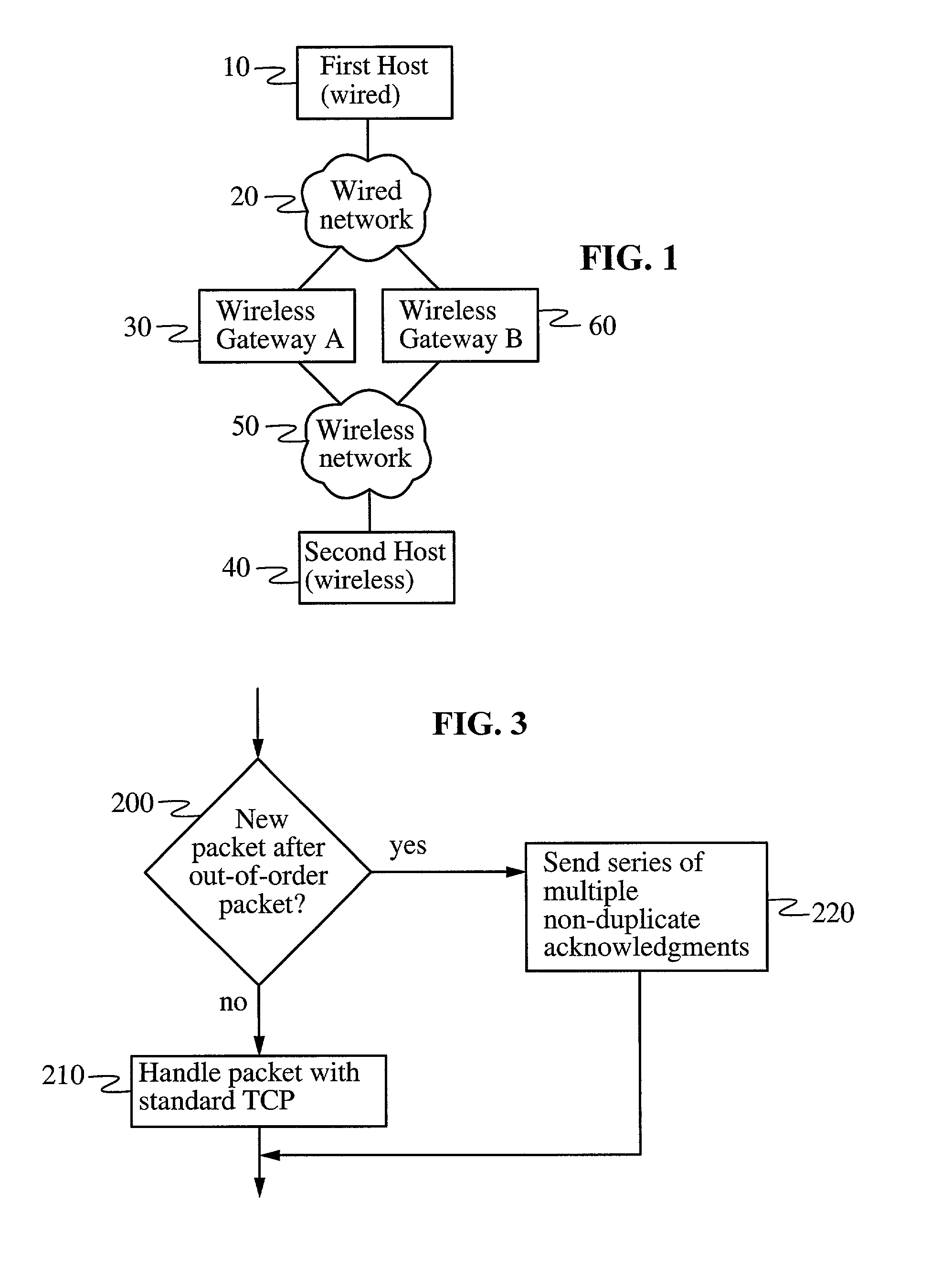
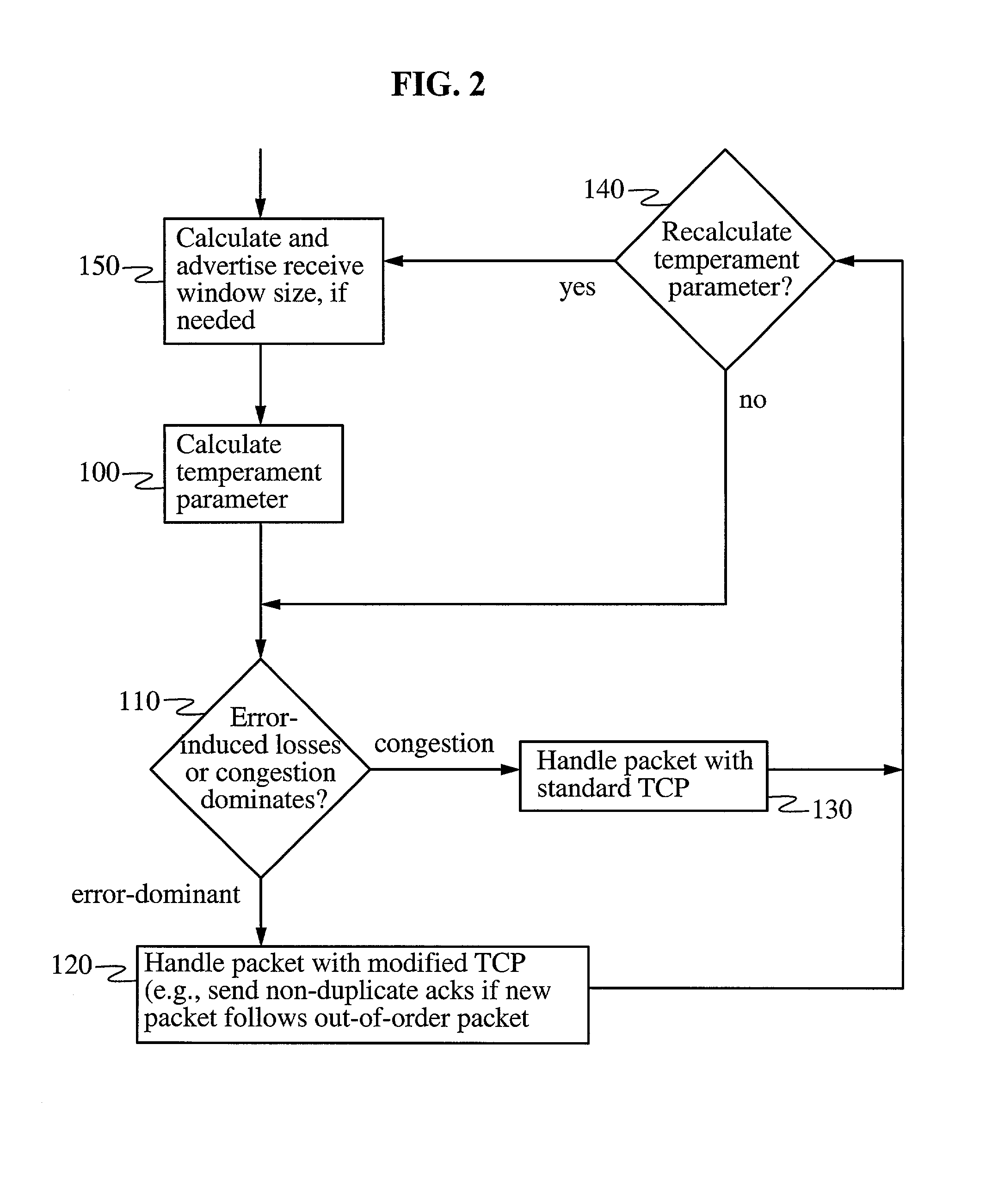
In a heterogeneous data network including both wired and wireless / lossy links, a transport protocol method implemented at the wireless host is fully compatible with existing wired networks and wireless gateways, and requires no modification to transport protocols at existing wired hosts. The wireless host calculates a temperament parameter [100] characterizing the error-proneness of the data connection and uses this parameter to determine whether error-induced losses or congestion-losses dominate the data connection [110]. If congestion-losses dominate the data connection, then the host uses a standard technique for acknowledging data packets [130]. If, on the other hand, error-induced losses dominate the connection, the host uses a modified technique for acknowledging data packets [120]. According to this modified technique, the wireless host sends a plurality of non-duplicate acknowledgements of a single packet whenever a packet is received after an out-of-order packet is received. By acknowledging distinct fragments of the packet, rather than identical (i.e., duplicate) acknowledgments of the packet, the acknowledgments have the effect of accelerating recovery of maximal window size at the wired host and increasing data throughput.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
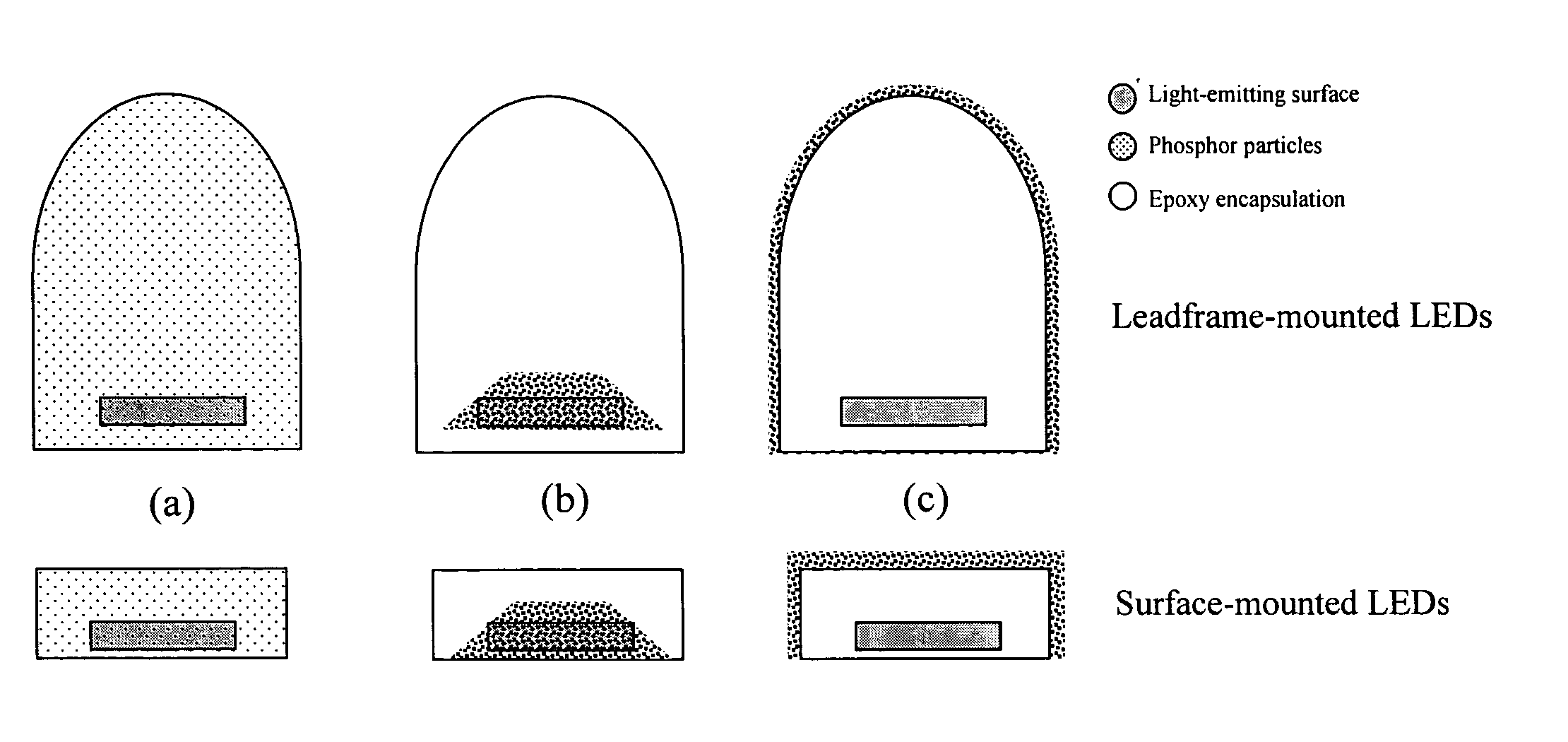
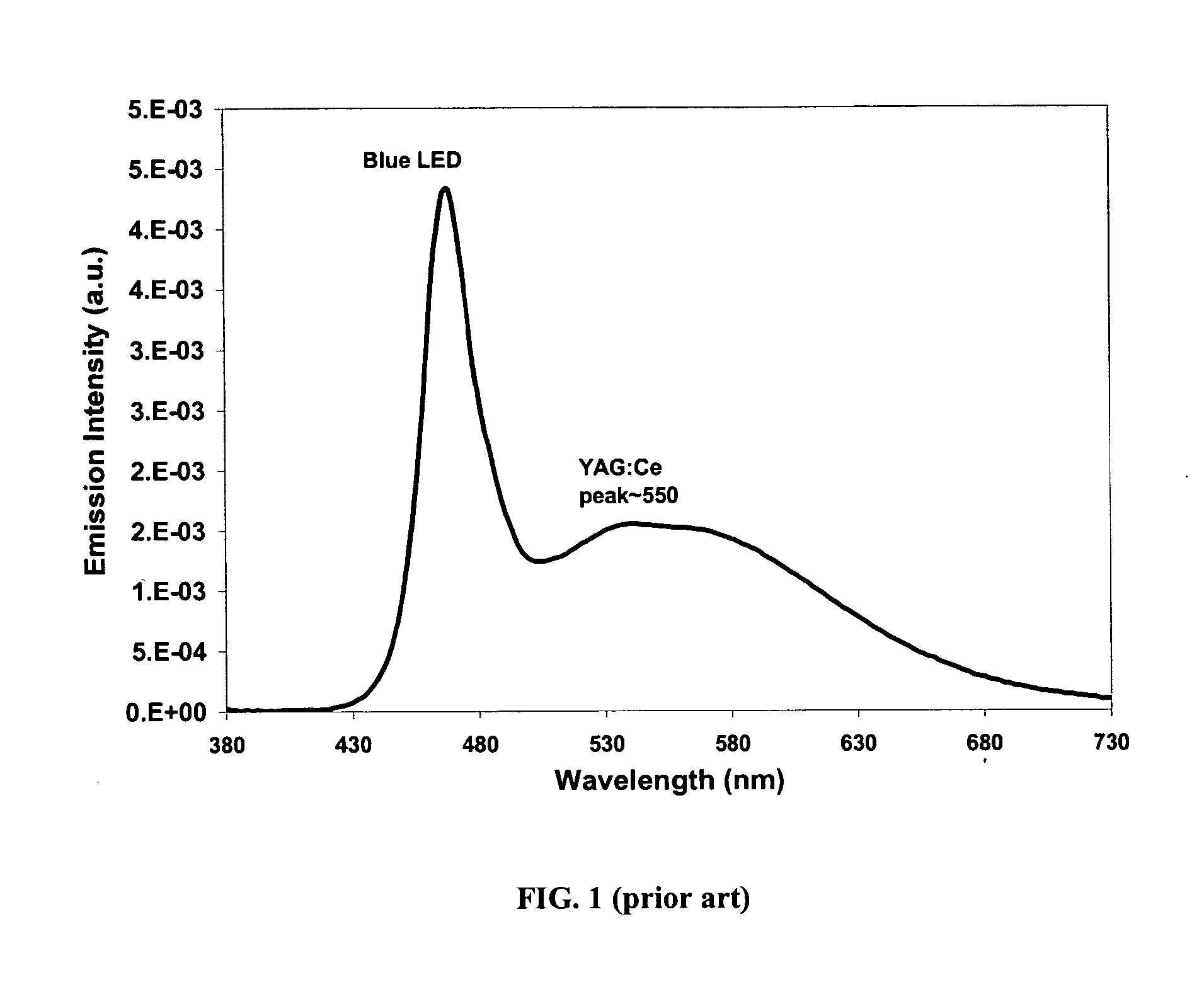
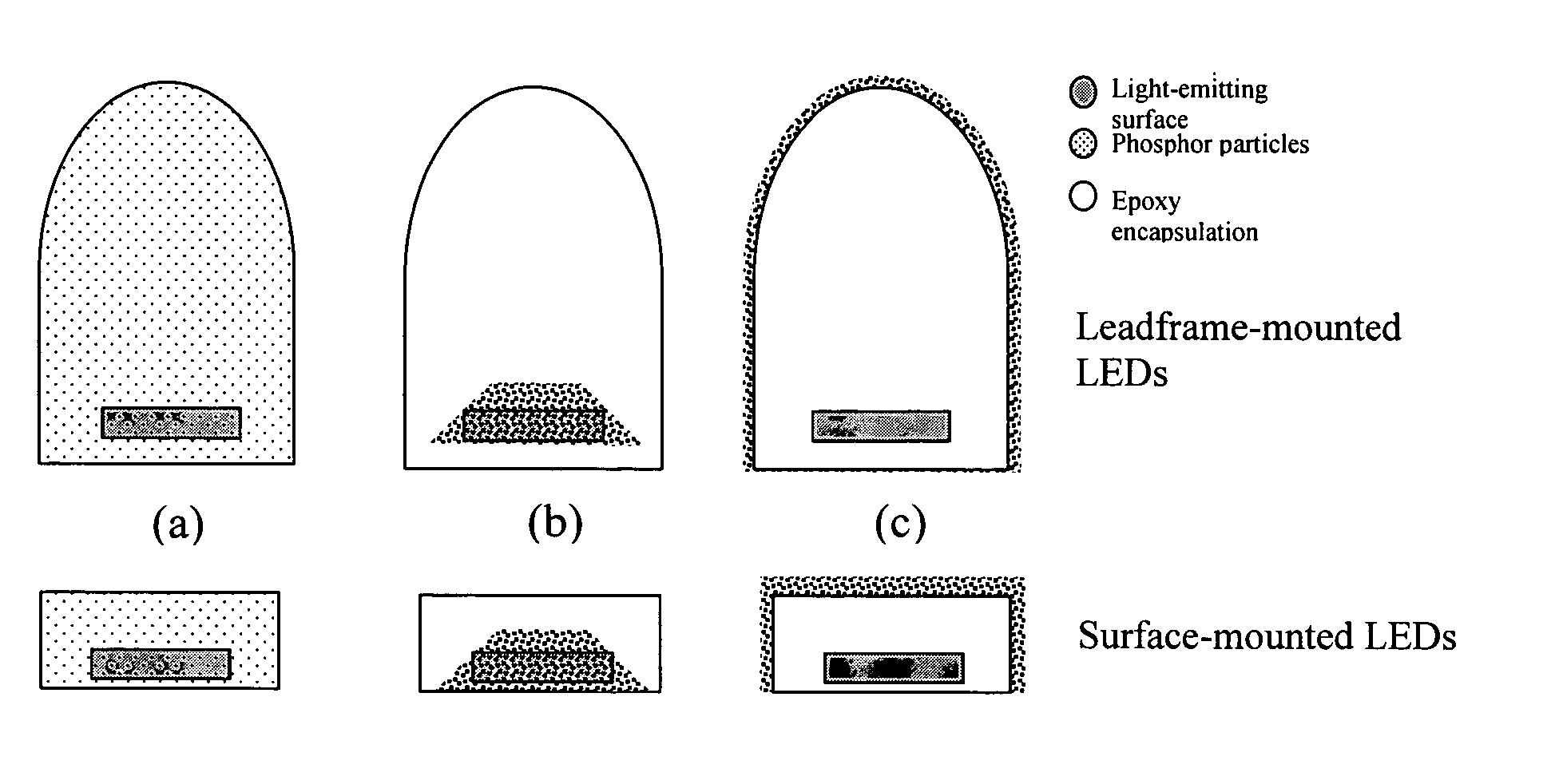
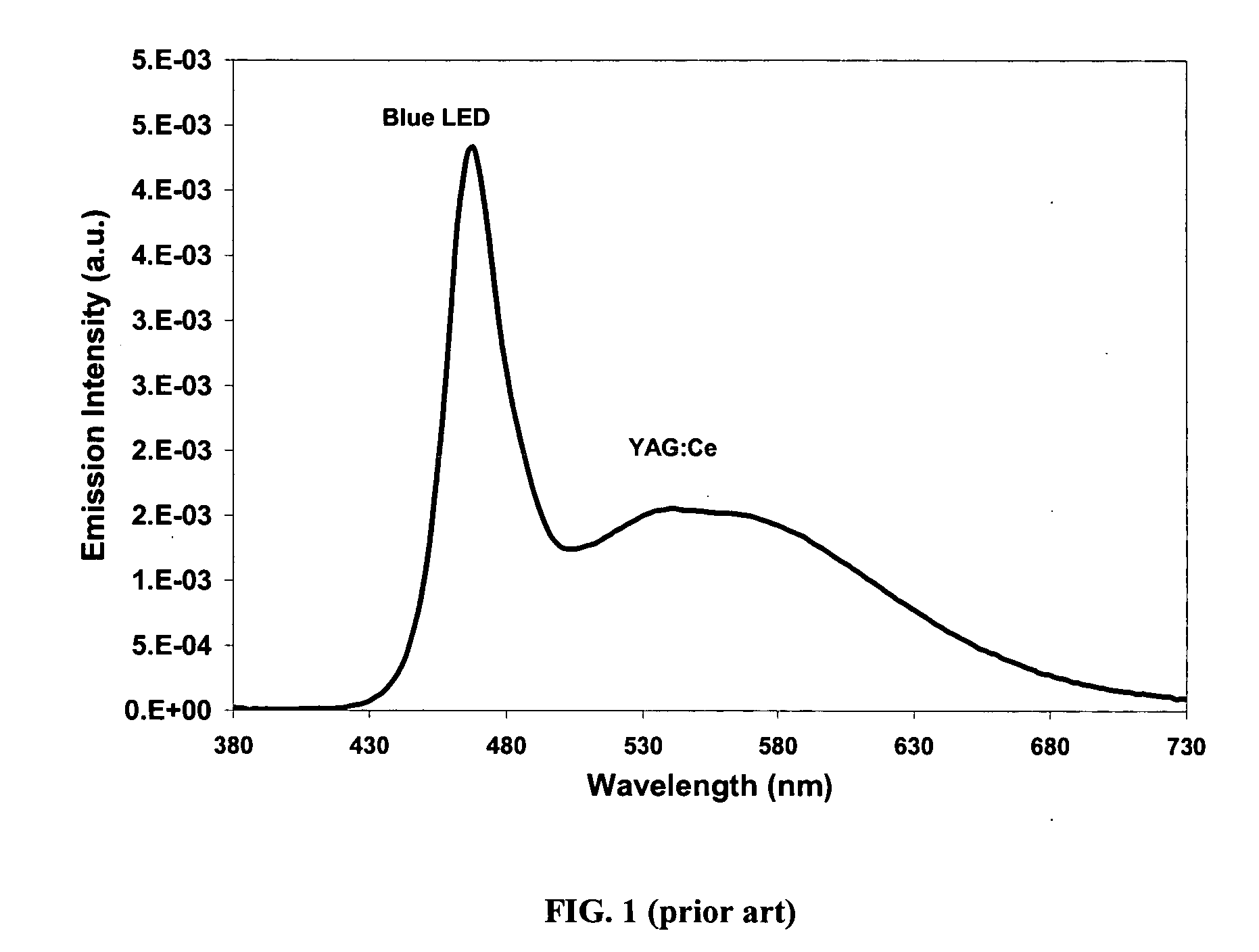
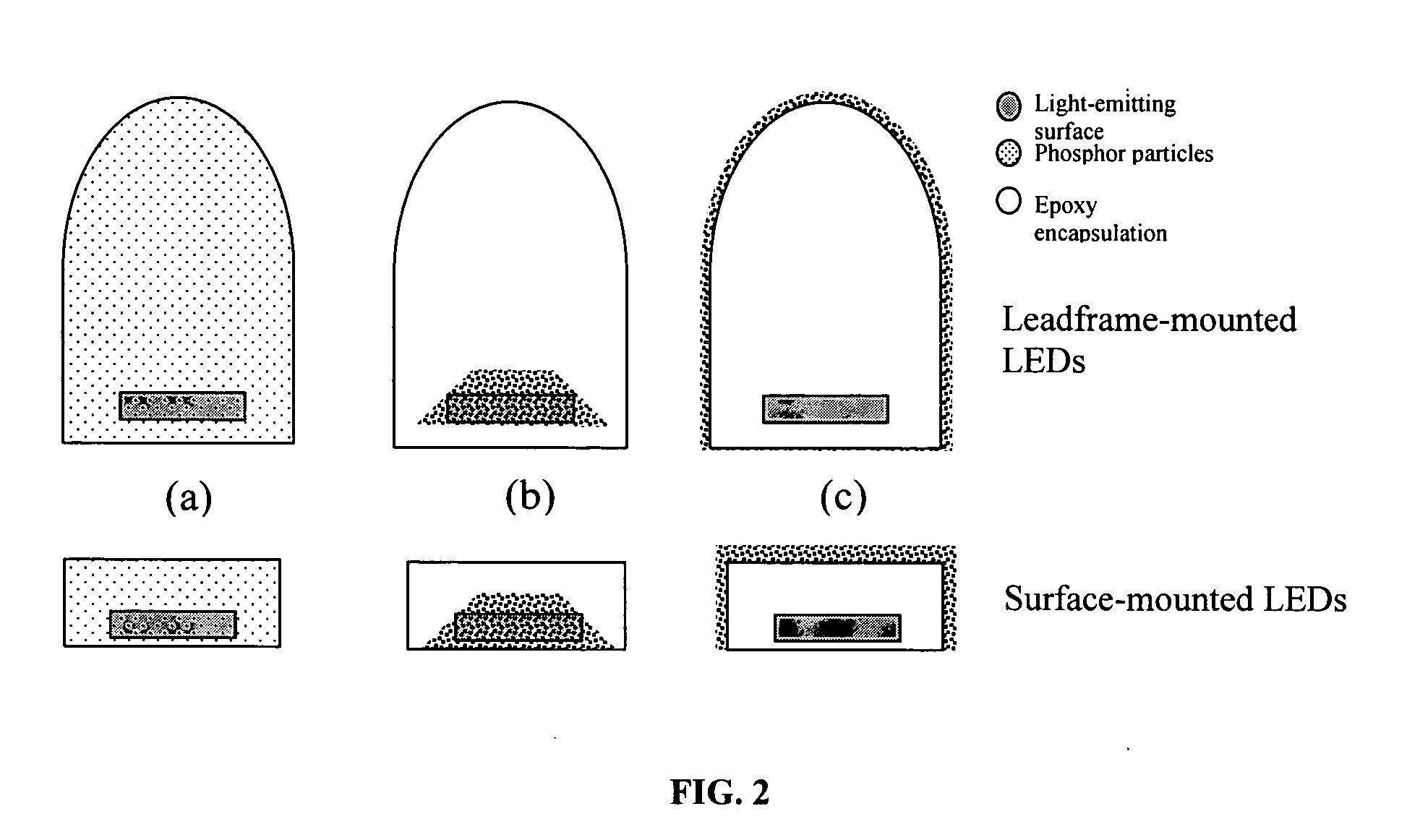
Light emitting device having silicate fluorescent phosphor
InactiveUS6982045B2Improve efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsFluorescenceProviding material
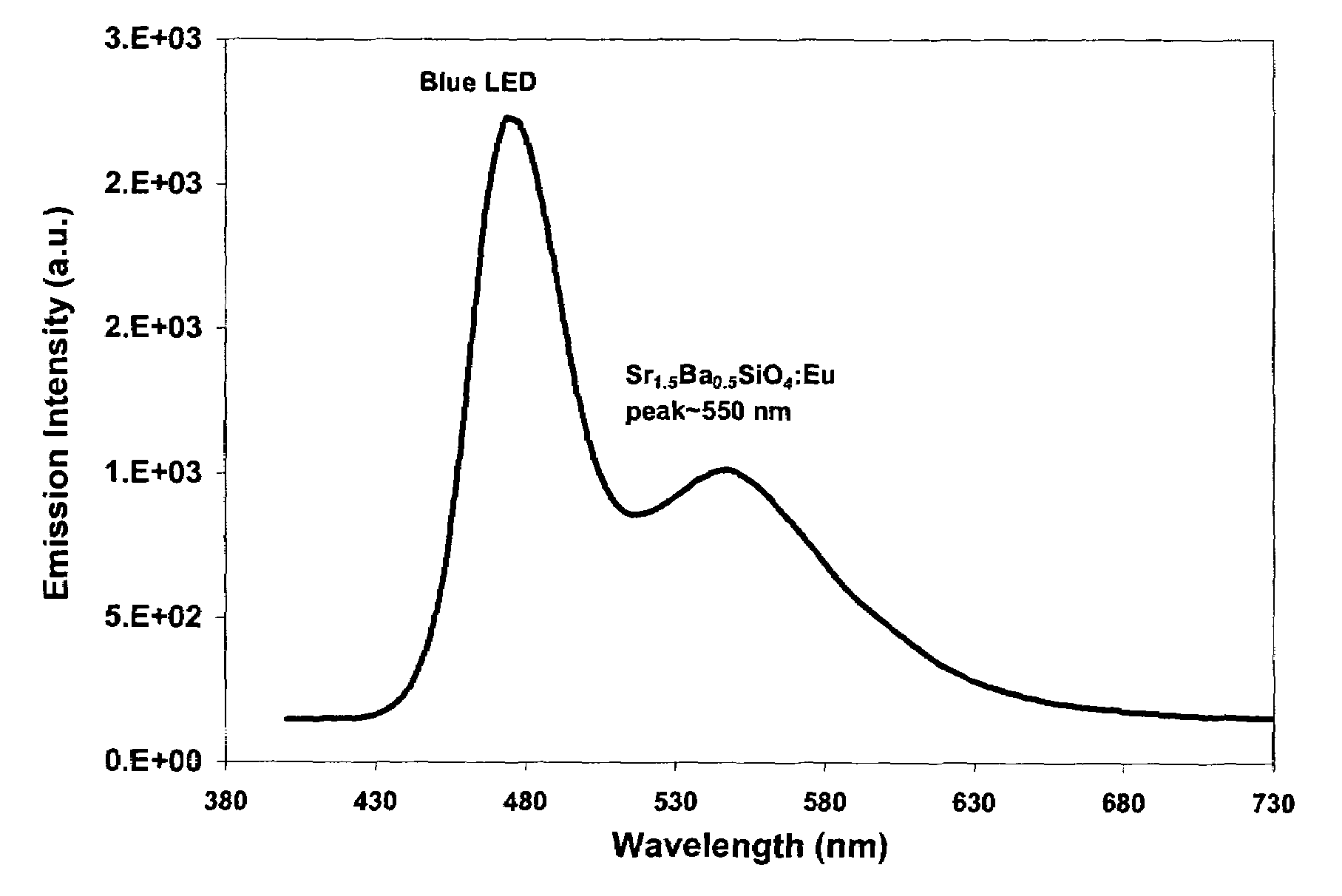
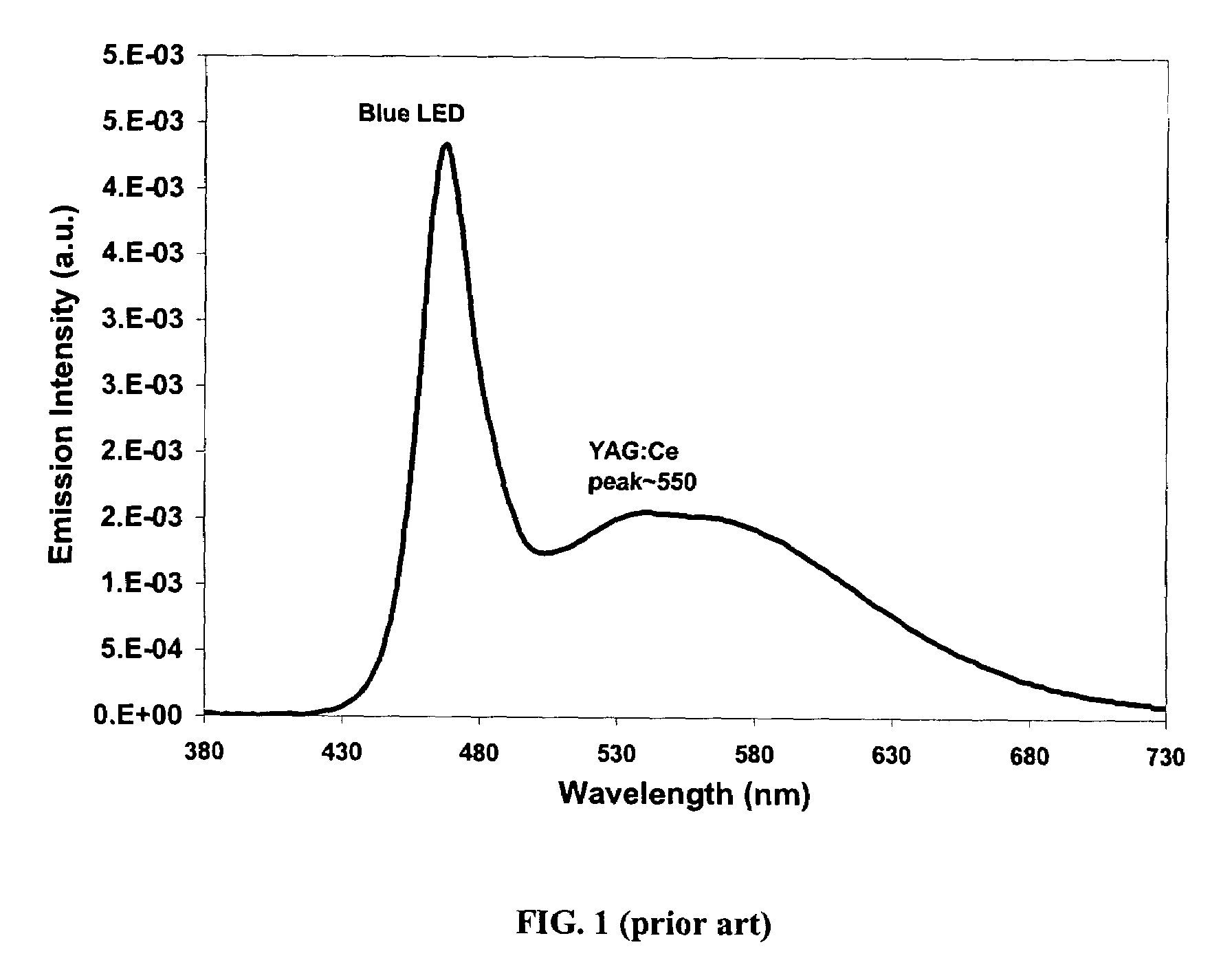
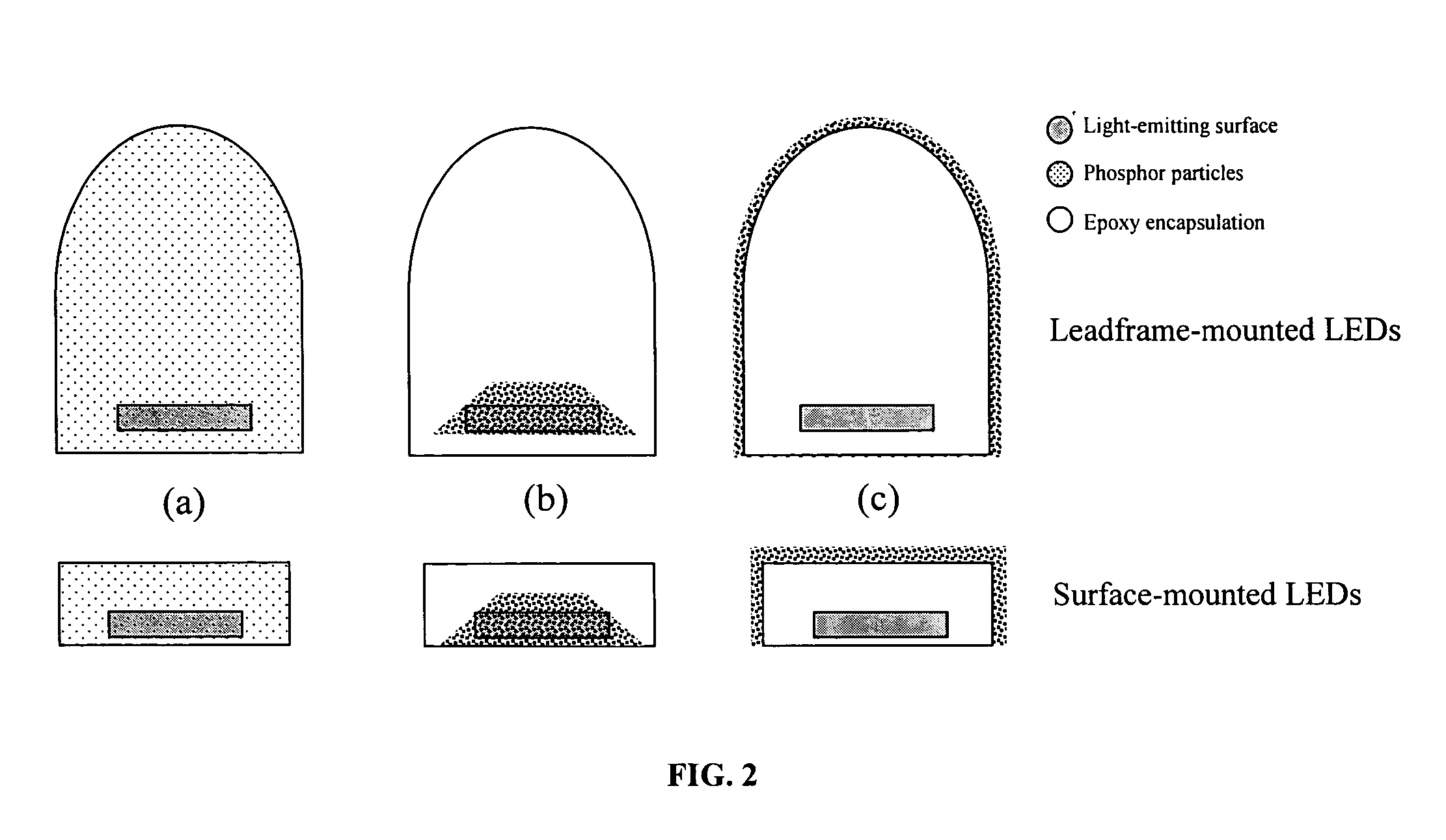
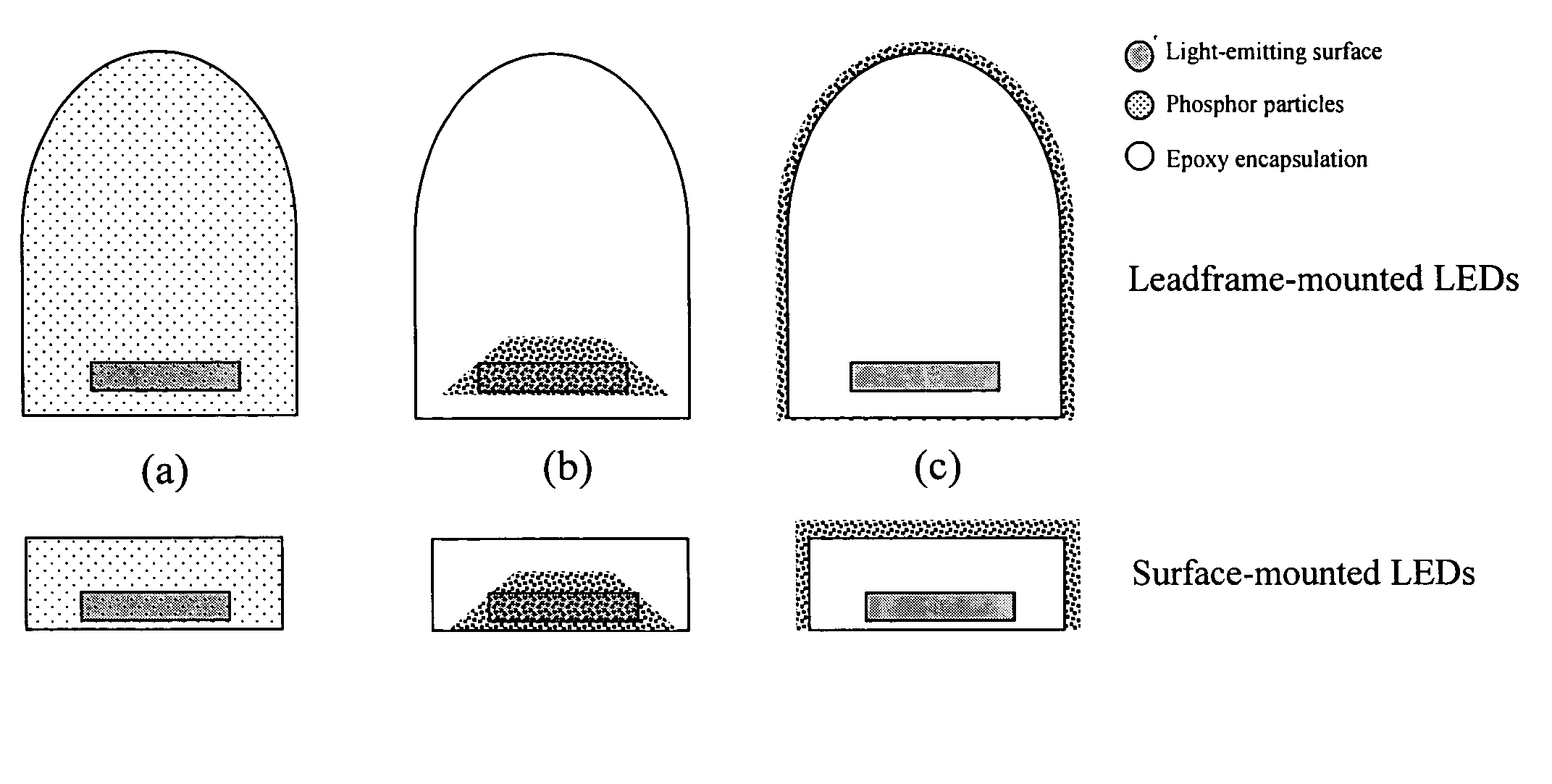
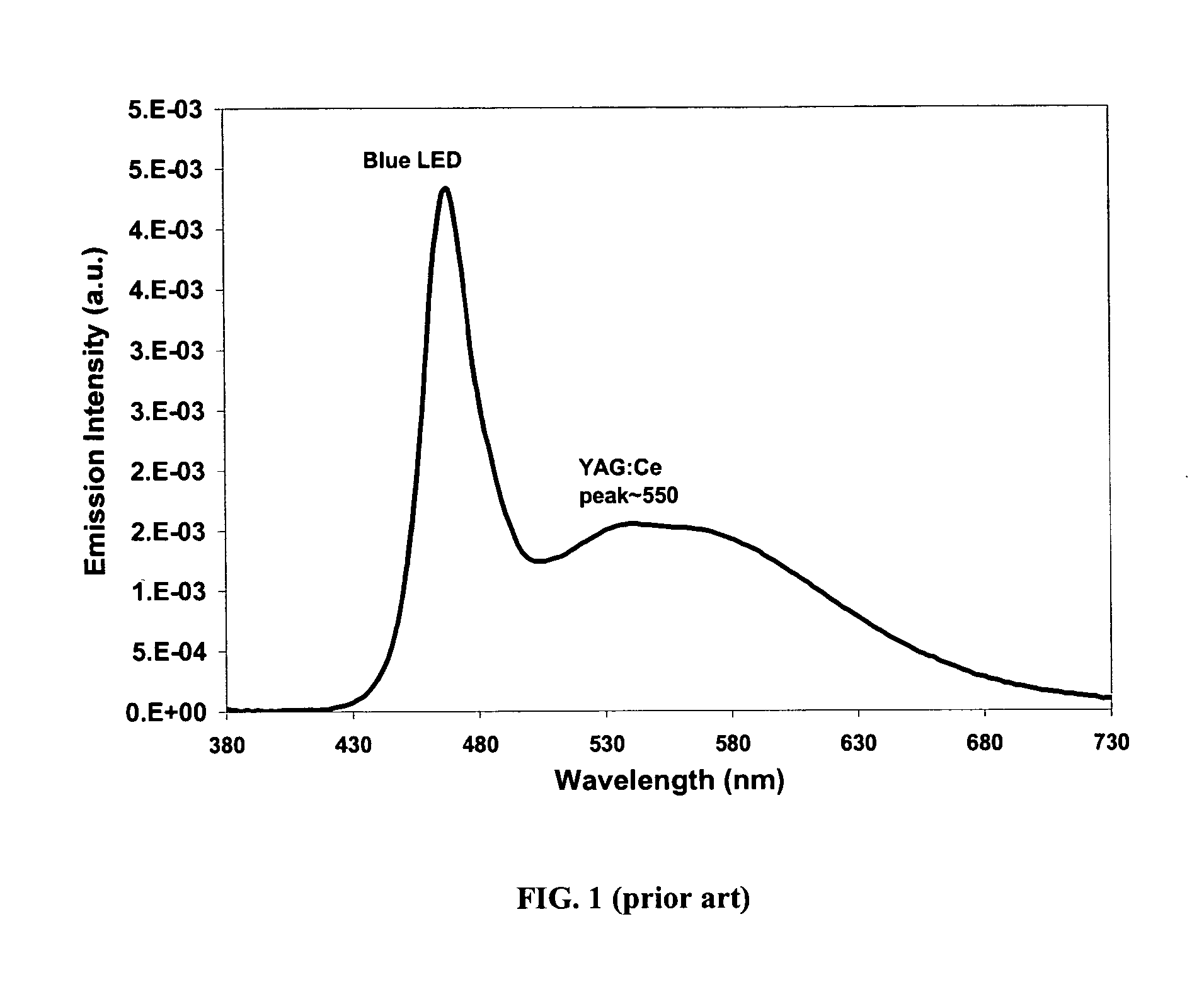
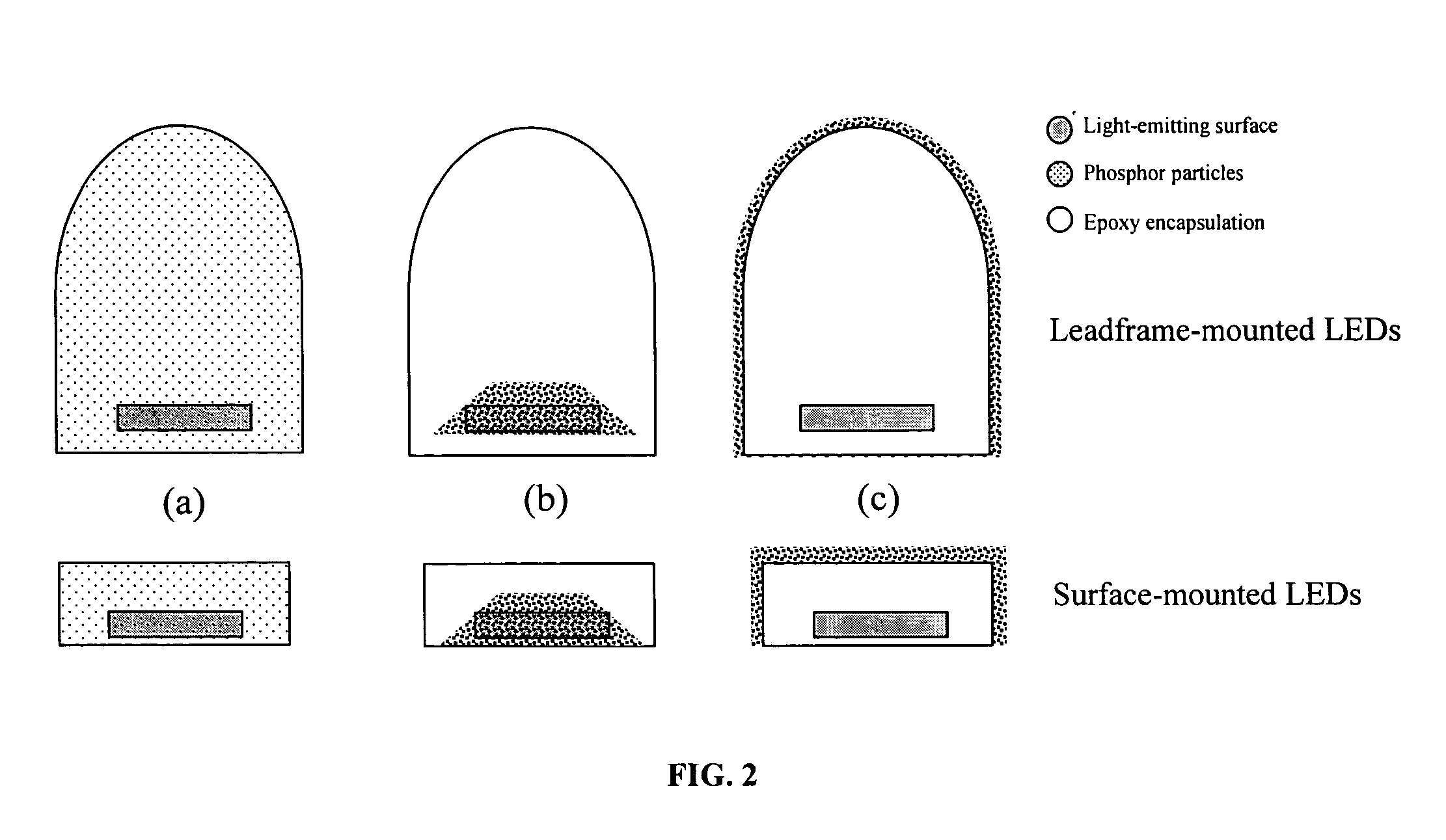
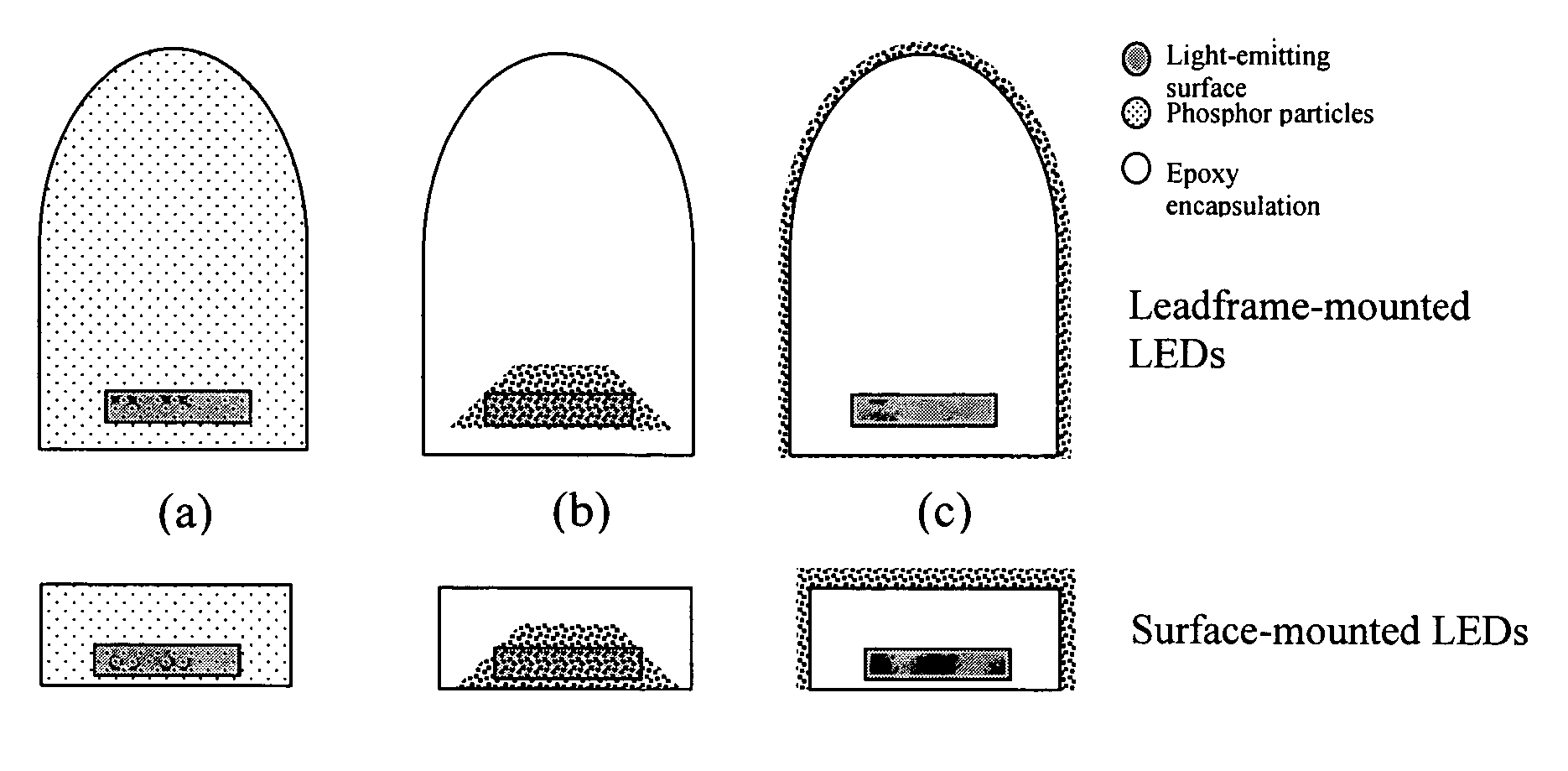
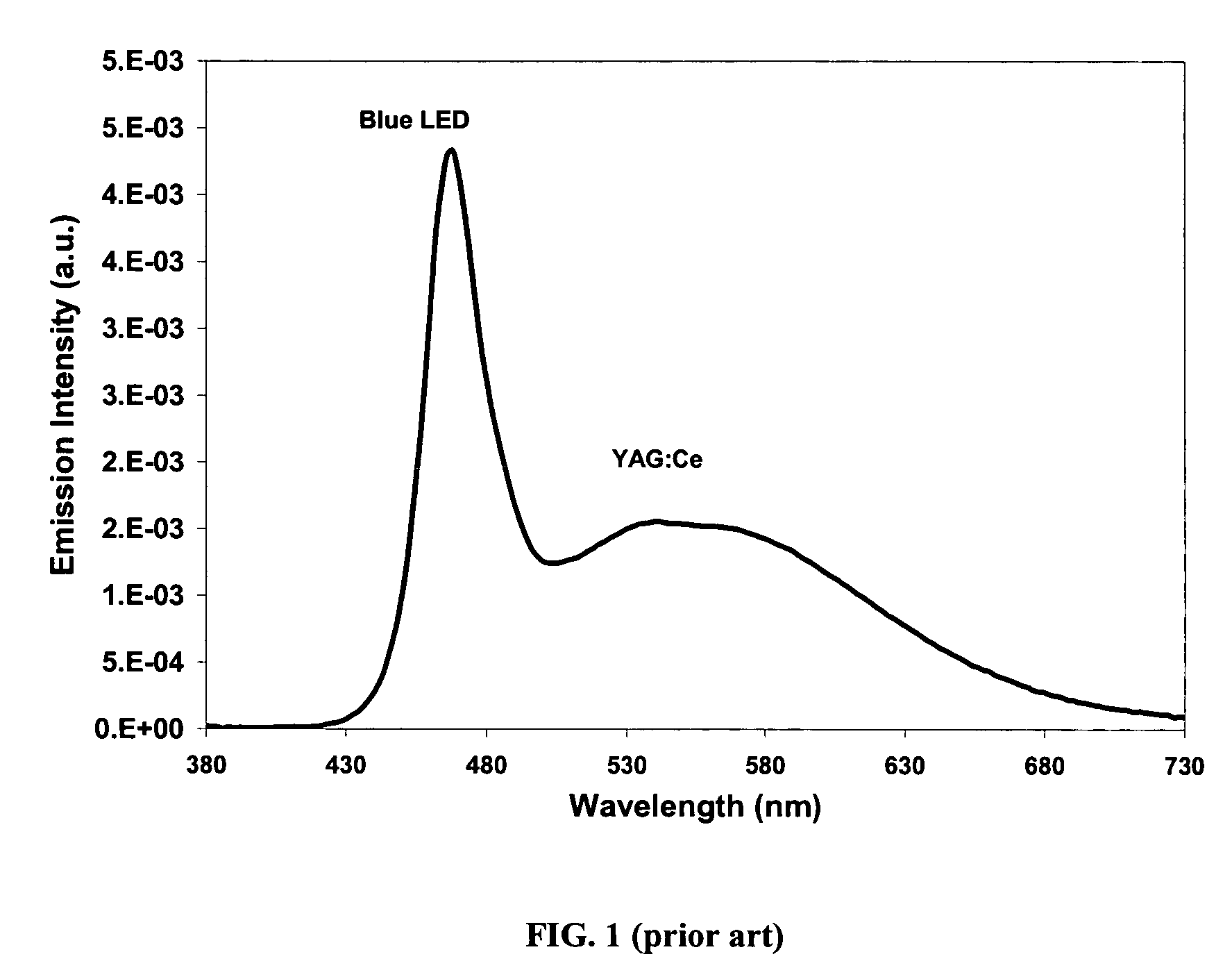
Provided herein are novel phosphors useful in the manufacture of white light emitting diodes. The phosphors provided by the invention are described by the formula:SrxBayCazSiO4:Euin which x, y, and z are each independently variable to be any value between about 0 and about 2, including without limitation 0.001 and 2, and every thousandth therebetween, subject to the proviso that the sum of x, y, or z is equal to at least 1, and in which Eu is present in any amount between about 0.0001% and about 5% by weight based upon the phosphor's total weight, wherein substantially all of the europium present is present in the divalent state. A phosphor according to the invention may optionally further comprise an element selected from the group consisting of: Ce, Mn, Ti, Pb, and Sn and is present in any amount between about 0.0001% and about 5% by weight based on the phosphor's total weight. The silicate phosphor materials provided by the present invention do not require the addition of dissimilar blue and red phosphor compounds, and do not contain zinc and / or magnesium. In addition, the present invention provides materials which emit a broad yellowish color containing both green and red emissions.Standard techniques used in phosphor deposition for the manufacture of light emitting diodes which comprise phosphors may be employed to produce LED's having a white light output when the phosphors of the invention are utilized.
Owner:PHOSPHORTECH
Content distribution using CD/DVD burners, high speed interconnects, and a burn and return policy
InactiveUS20050204019A1Additional revenue opportunityIncrease opportunitiesRecord information storageMultiple digital computer combinationsContent distributionHard disc drive
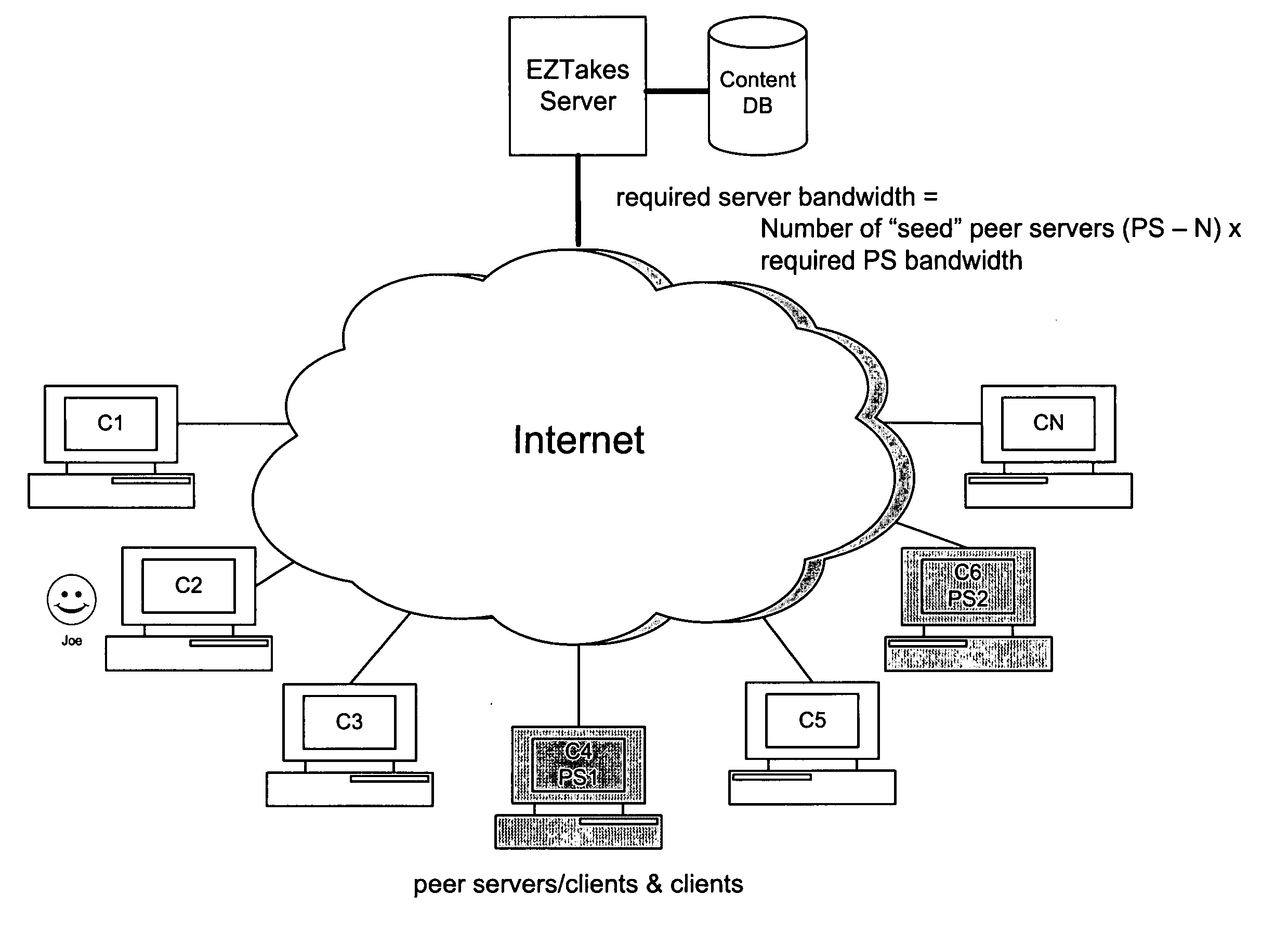
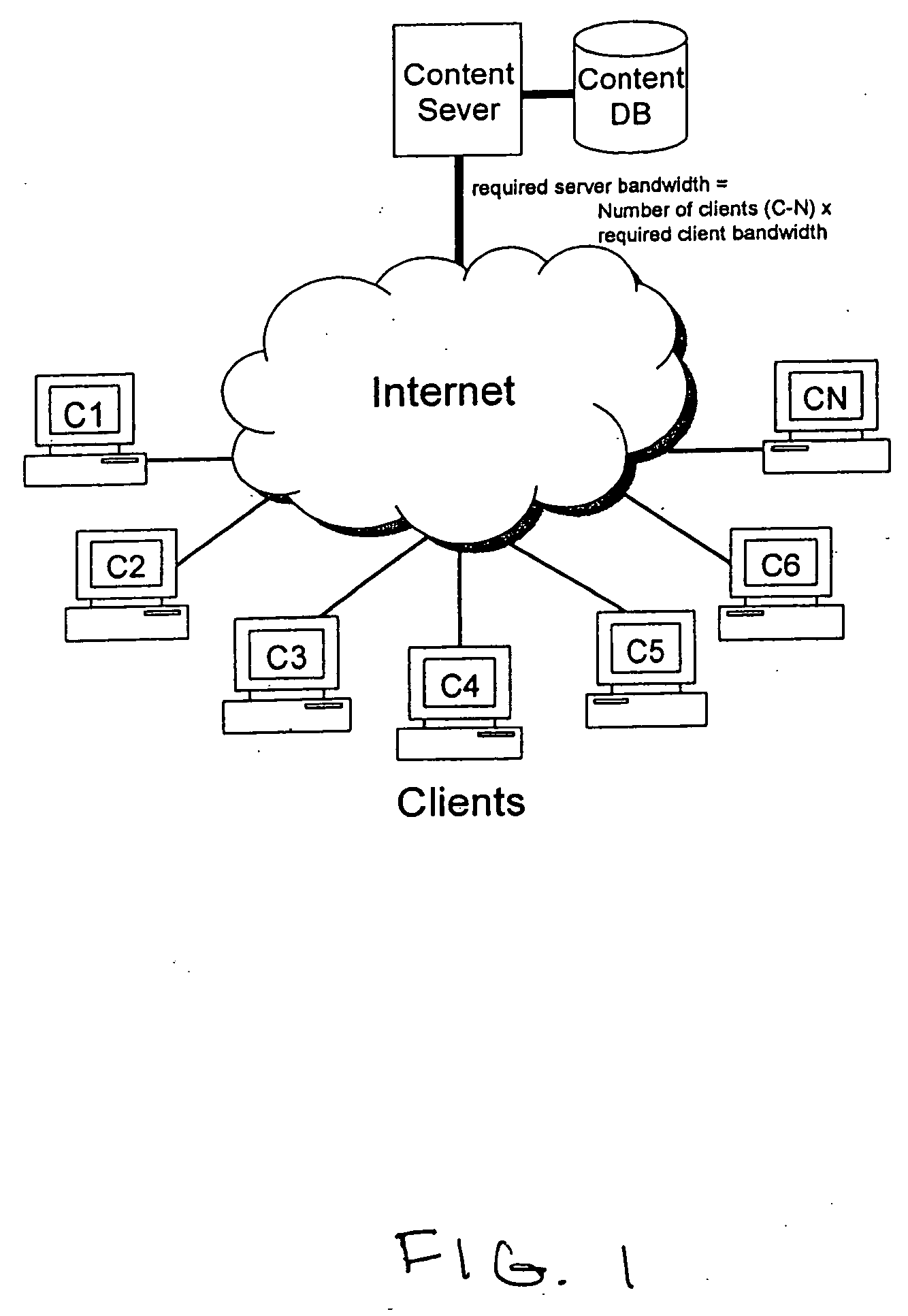
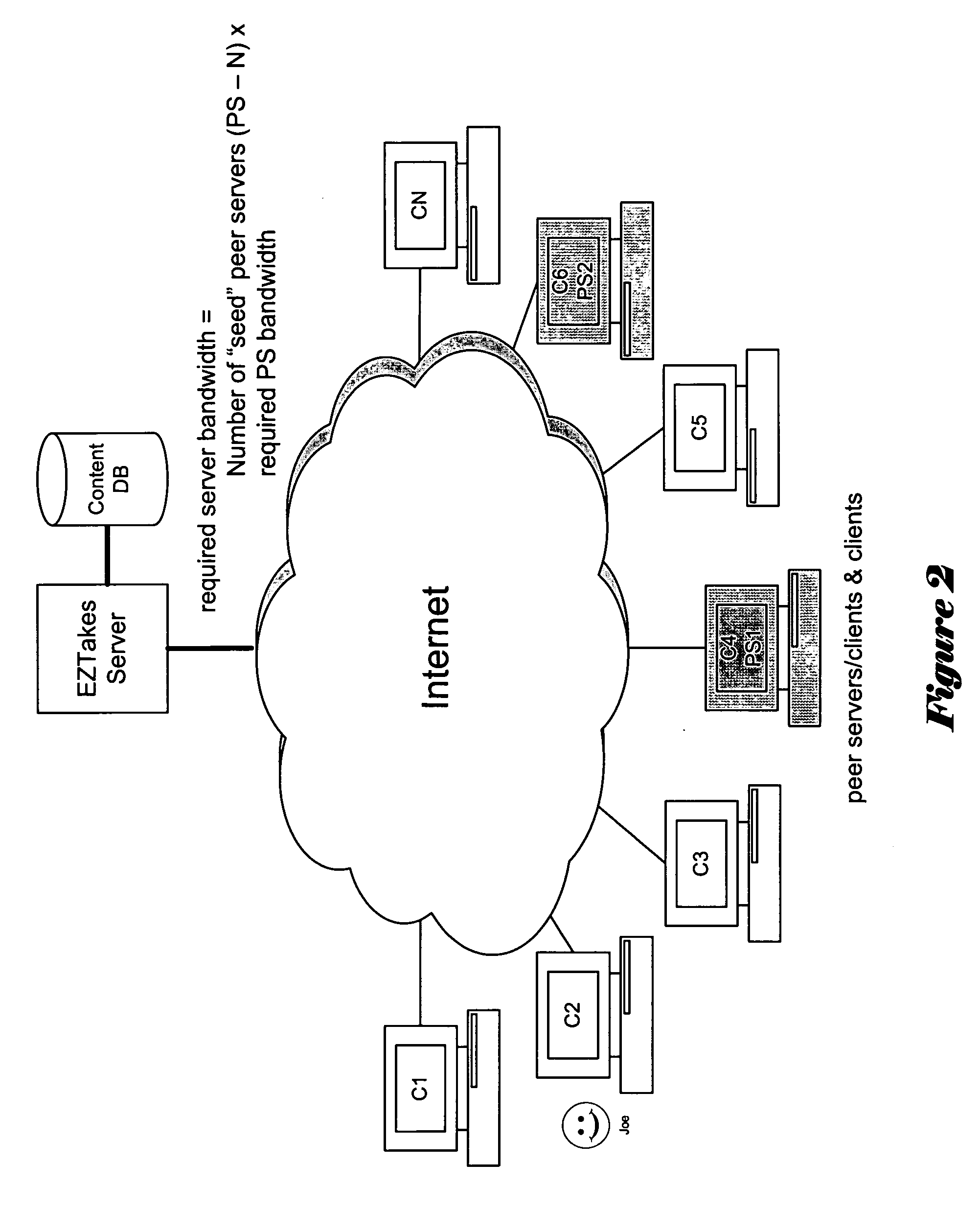
Embodiments of the present invention provide services that enable individuals to rent and / or purchase content over the Internet and to receive it electronically, referred to below as “EZTakes.” This content may include movies, TV shows, music, games and other information typically distributed on CD / DVD. EZTakes leverages high-speed broadband Internet connections, peer-to-peer networking, digital rights management (DRM) and the growing prevalence of home computers that now typically feature large hard drives (e.g. 180+gigabytes) and have the capability to “burn” (i.e. create) DVDs and / or CDs. EZTakes bridges the gap between the home computer and the living room by using standard technologies that consumers already own and are already familiar with: home computers, DVD media, DVD players and the Internet. EZTakes also promotes the interests of content owners (e.g. movie production companies) by expanding their revenue opportunities through enabling them to distribute their content assets over the Internet. EZTakes also includes technical control mechanisms, such as digital watermarking, that could not easily be exploited when using physical DVD / CD distribution channels.
Owner:EZTAKES
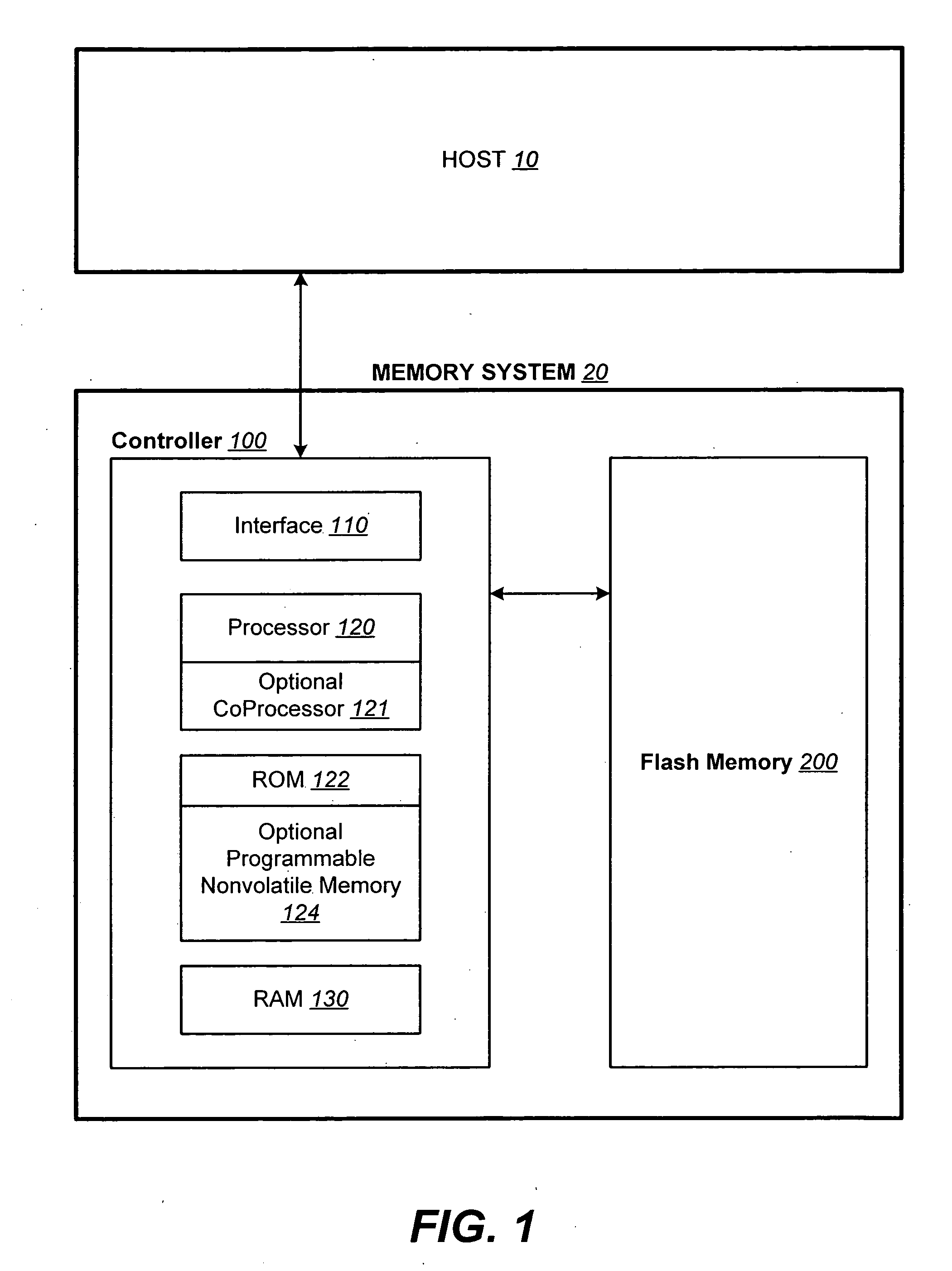
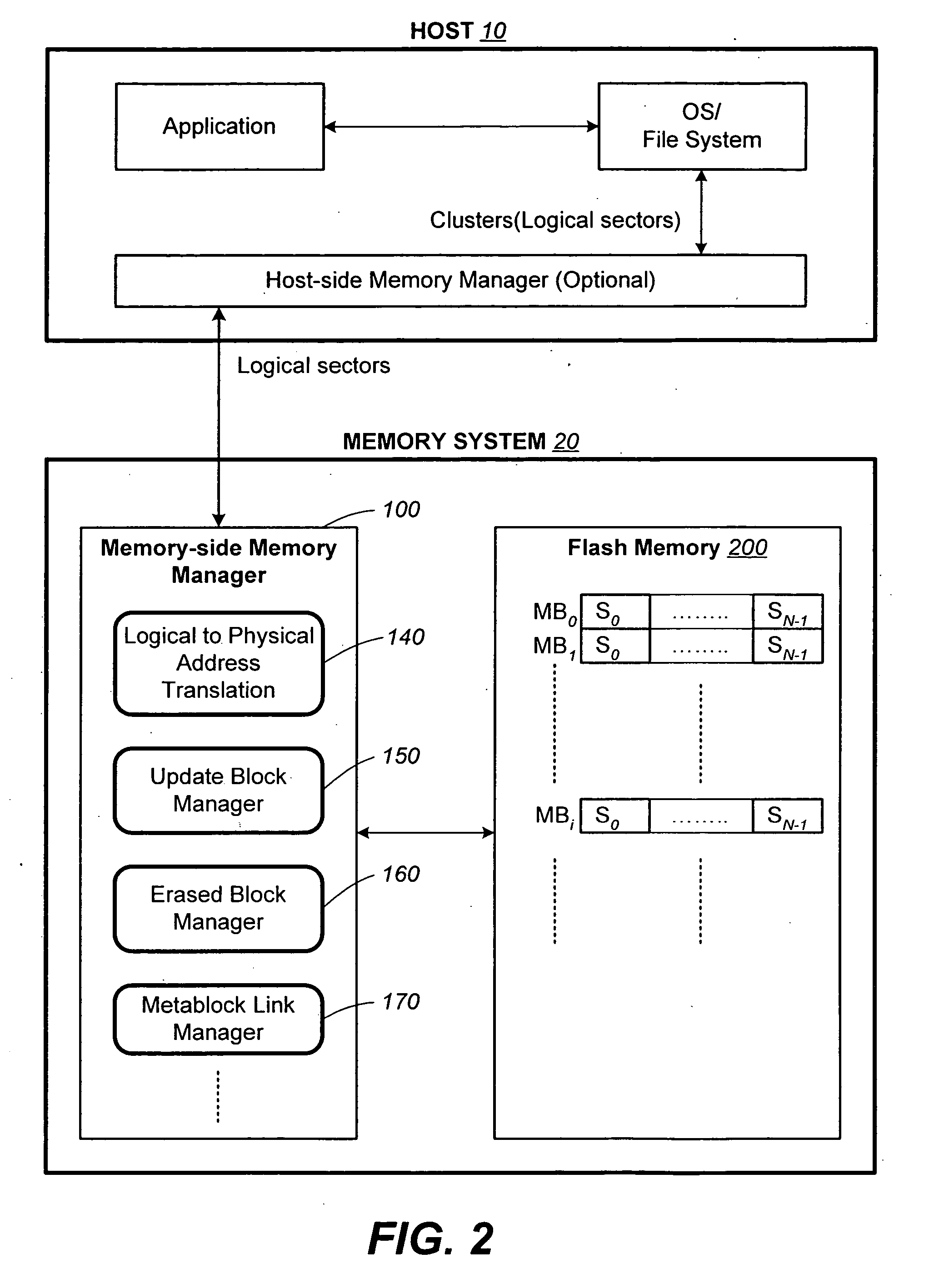
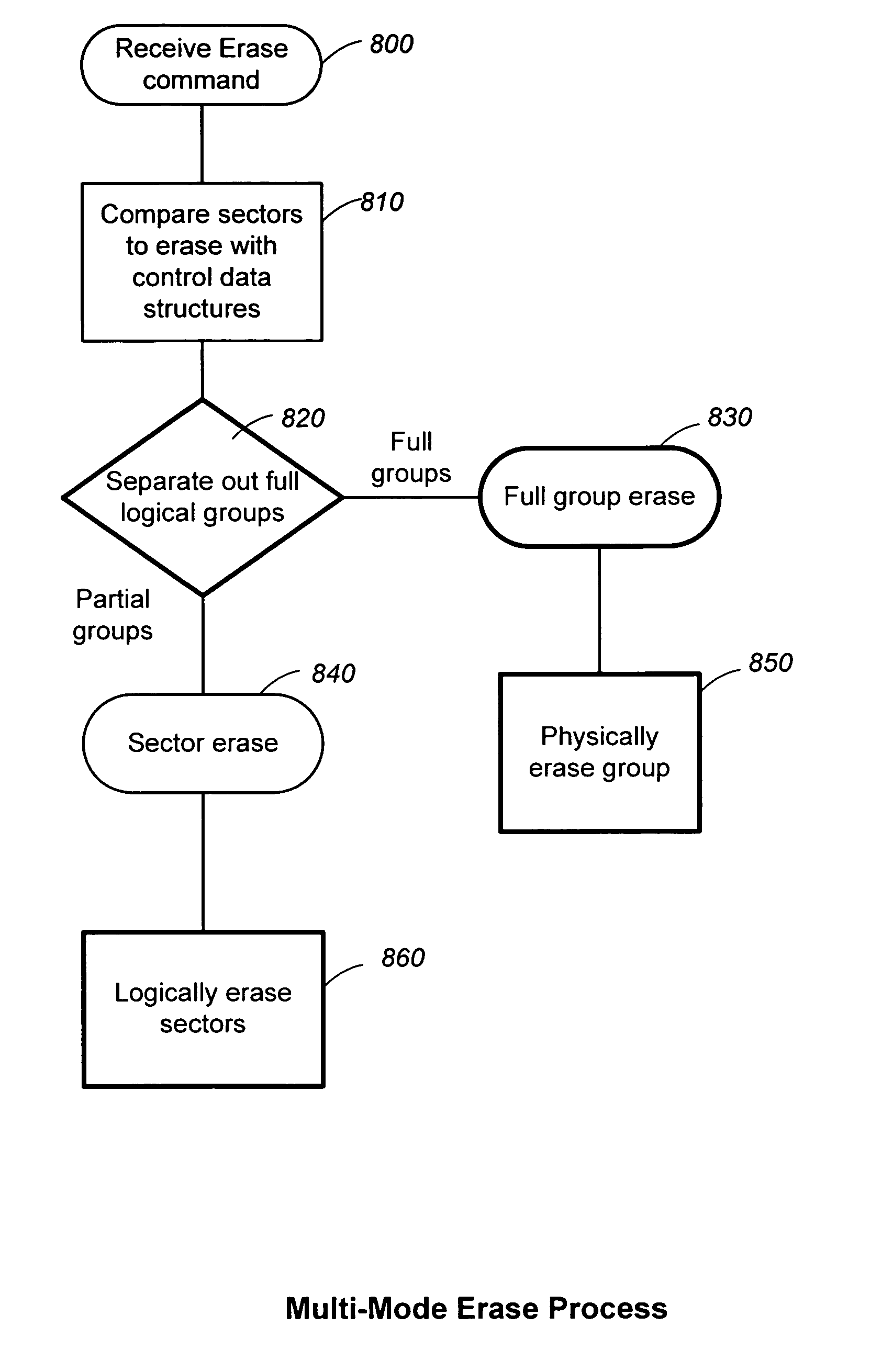
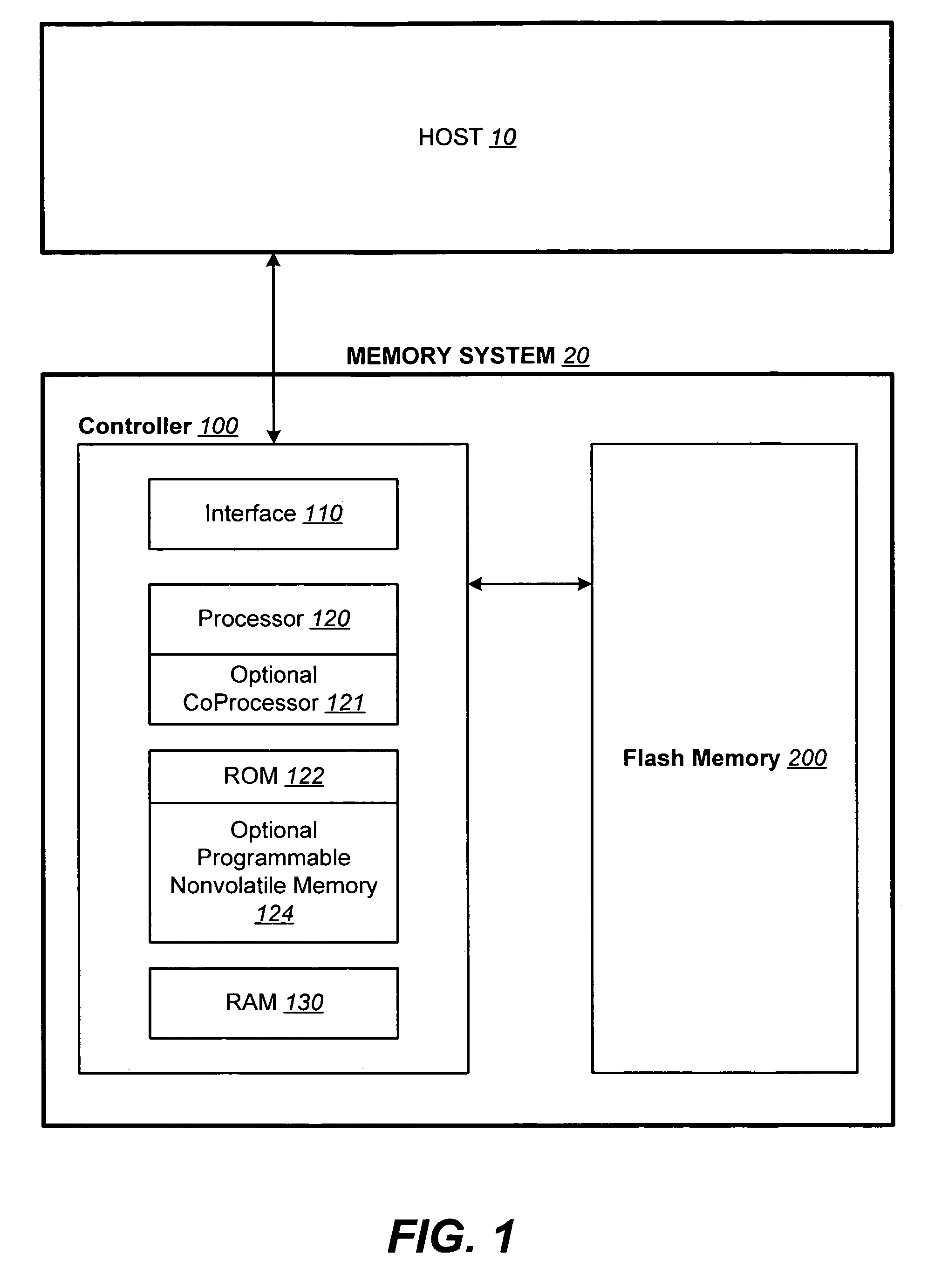
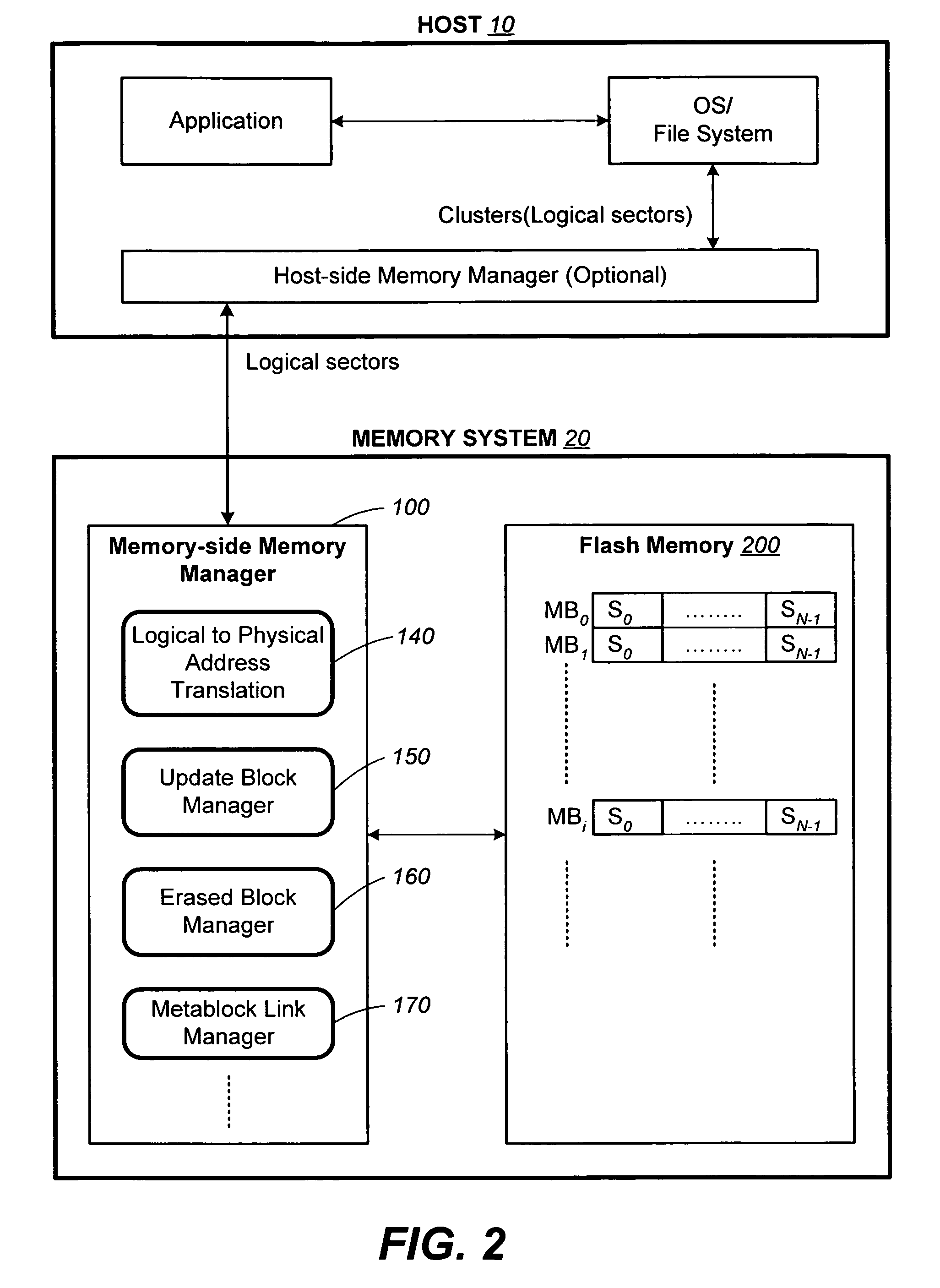
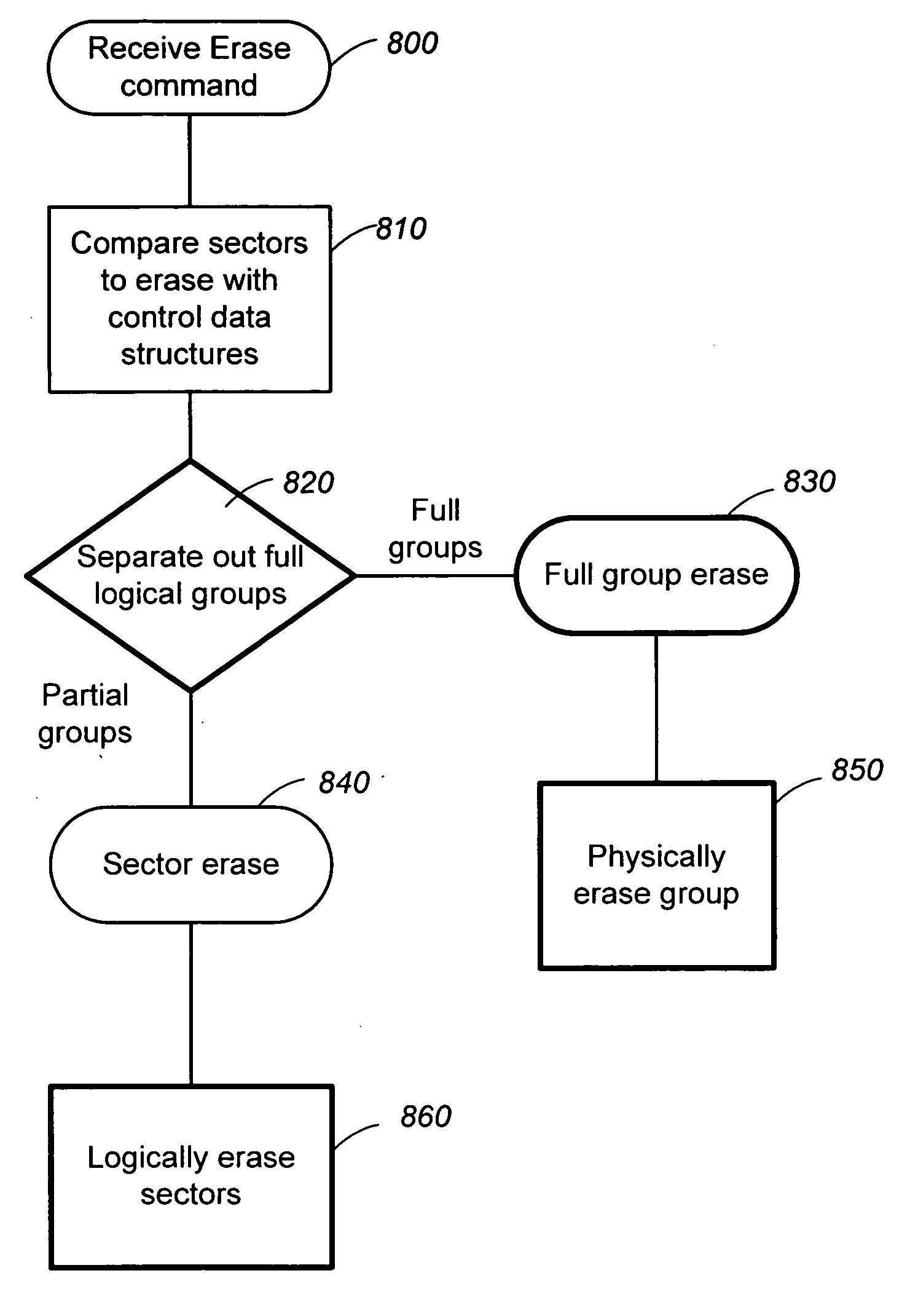
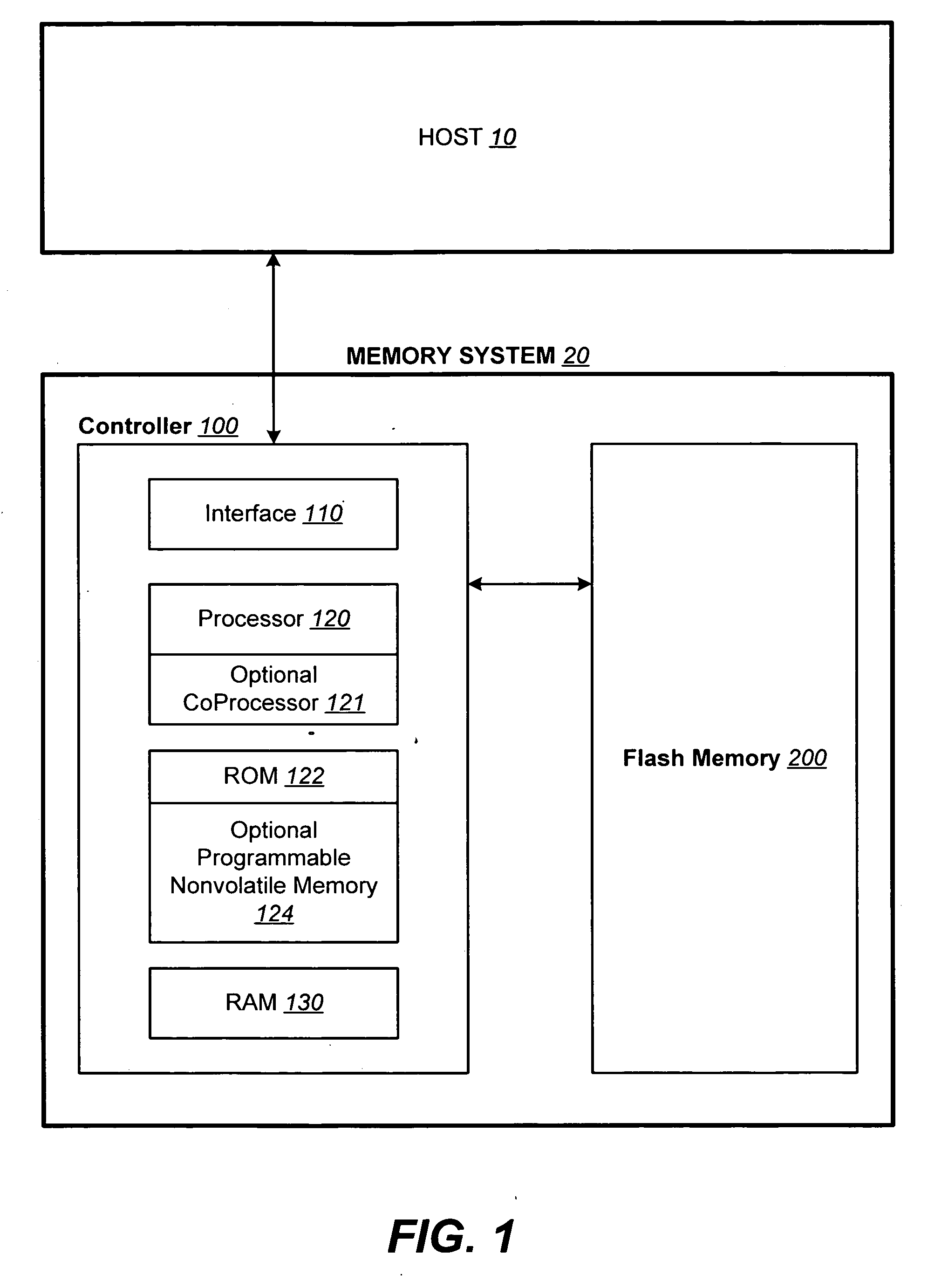
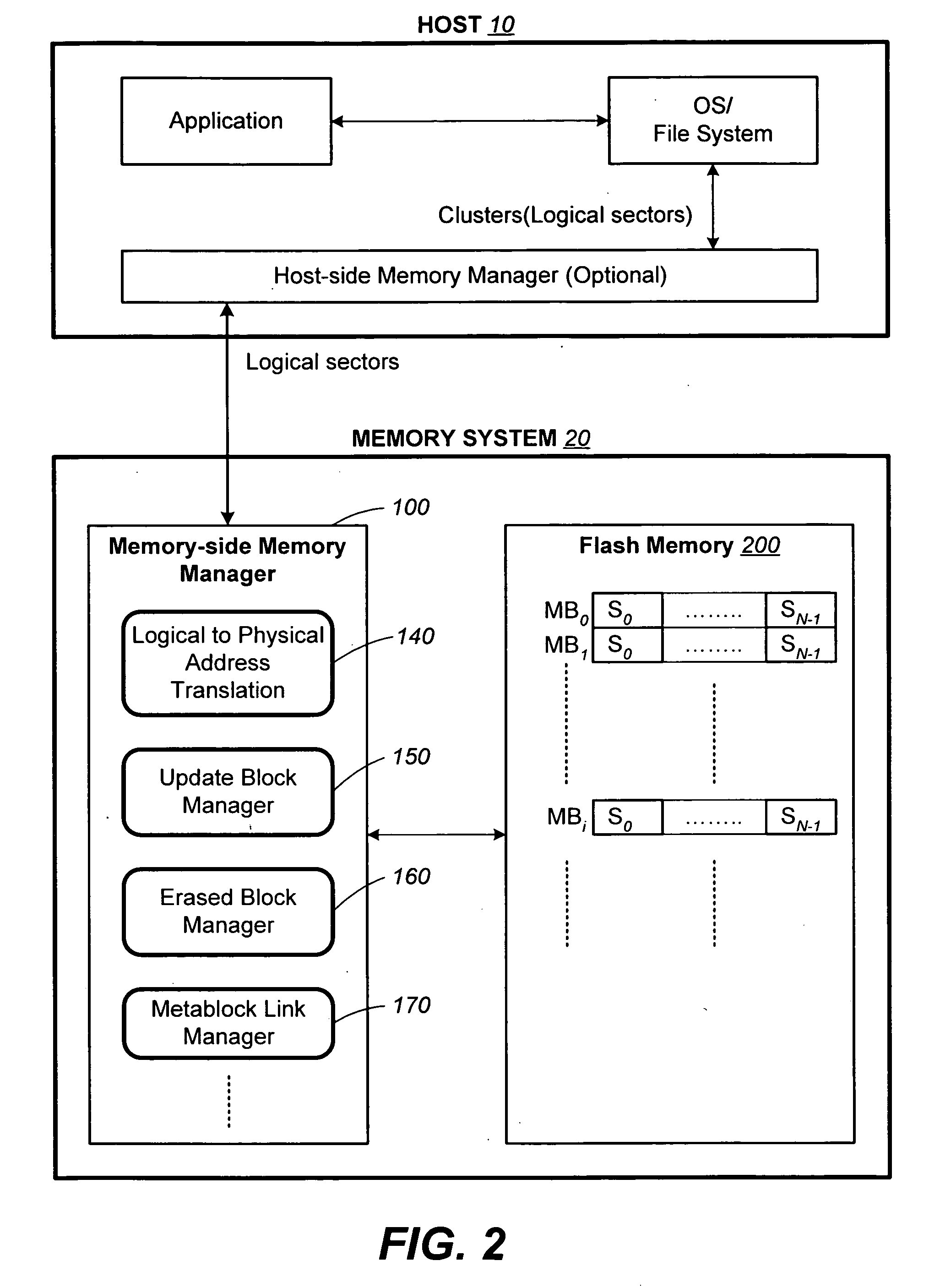
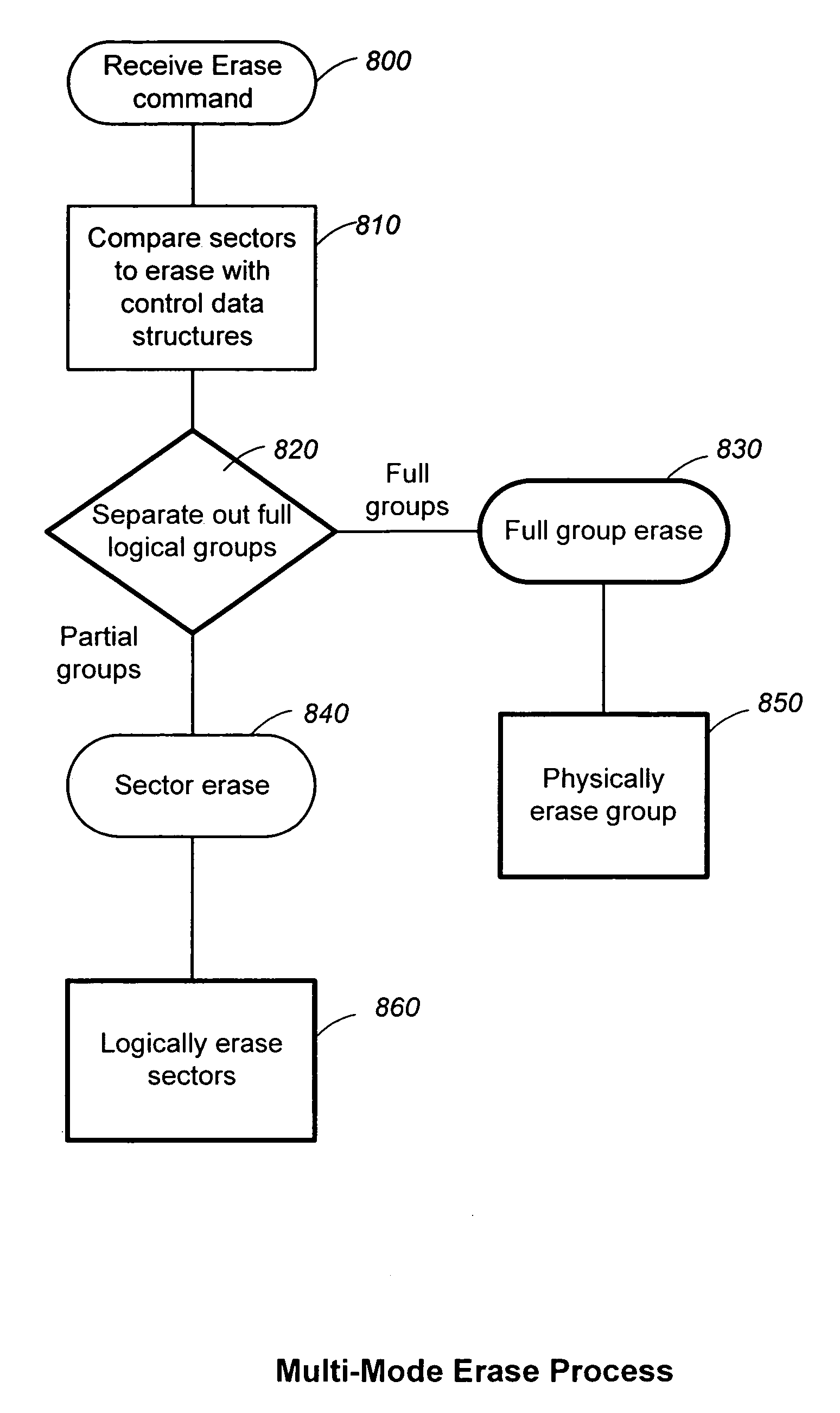
Structures for the management of erase operations in non-volatile memories
ActiveUS20070113029A1Easy to eraseExecution time can be made muchMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsControl dataOperating system
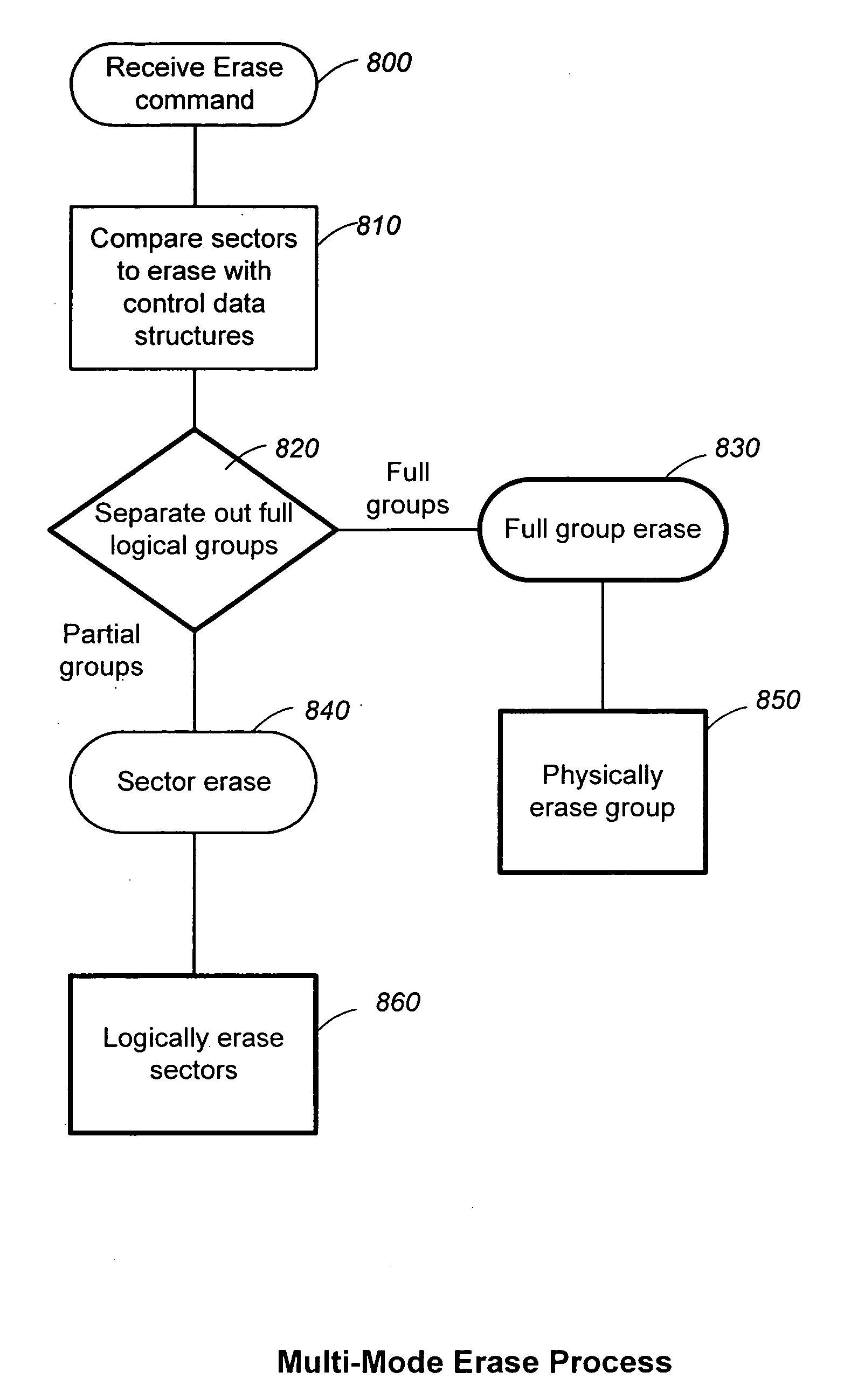
The present invention presents a number of improvements for managing erase processes in non-volatile memory. Such memory systems typically manage the memory by logically organize the basic unit of physical erase (erase block) into composite logical groupings (meta-blocks or logical group), where an erase block generally consists of a number of sectors. When an erase command is received, the specified sectors are checked against the memory system's control data. If the specified sectors span any full logical grouping, the full logical groupings can each be treated a whole and erased according to one process (such as performing a true, physical erase), while other sectors are “logically” erased at the sector level by standard techniques.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Light emitting device having sulfoselenide fluorescent phosphor
InactiveUS20050023962A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesFluorescencePhosphor
Provided herein are novel phosphors useful in the manufacture of white light emitting diodes. The phosphors provided by the invention are described by the formula: described by the formula: ZnSxSey:Cu,A in which x and y are each independently any value between 0 and about 1, subject to the proviso that the sum of x and y is equal to any number in the range of between about 0.75 and about 1.25; wherein A is optional and comprises at least one additional element selected from the group consisting of: Ag, Al, Ce, Tb, Cl, I, Mg, and Mn, including mixtures thereof, and wherein Cu is present in any amount between about 0.0001% and about 5% in mole percent based on the total molar weight of said composition. Standard techniques used in phosphor deposition for the manufacture of light emitting diodes which comprise phosphors may be employed to produce LED's having a white light output when the phosphors of the invention are utilized.
Owner:PHOSPHORTECH
Light emitting device having sulfoselenide fluorescent phosphor
InactiveUS6987353B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesFluorescencePhosphor
Provided herein are novel phosphors useful in the manufacture of white light emitting diodes. The phosphors provided by the invention are described by the formula: described by the formula:ZnSxSey:Cu,Ain which x and y are each independently any value between 0 and about 1, subject to the proviso that the sum of x and y is equal to any number in the range of between about 0.75 and about 1.25; wherein A is optional and comprises at least one additional element selected from the group consisting of: Ag, Al, Ce, Tb, Cl, I, Mg, and Mn, including mixtures thereof, and wherein Cu is present in any amount between about 0.0001% and about 5% in mole percent based on the total molar weight of said composition.Standard techniques used in phosphor deposition for the manufacture of light emitting diodes which comprise phosphors may be employed to produce LED's having a white light output when the phosphors of the invention are utilized.
Owner:PHOSPHORTECH
Transgenic microbial polyhydroxyalkanoate producers
InactiveUS6913911B2Simple production processInduce expressionSugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyTransposon mutagenesis
Transgenic microbial strains are provided which contain the genes required for PHA formation integrated on the chromosome. The strains are advantageous in PHA production processes, because (1) no plasmids need to be maintained, generally obviating the required use of antibiotics or other stabilizing pressures, and (2) no plasmid loss occurs, thereby stabilizing the number of gene copies per cell throughout the fermentation process, resulting in homogeneous PHA product formation throughout the production process. Genes are integrated using standard techniques, preferably transposon mutagenesis. In a preferred embodiment wherein mutiple genes are incorporated, these are incorporated as an operon. Sequences are used to stabilize mRNA, to induce expression as a function of culture conditions (such as phosphate concentration), temperature, and stress, and to aid in selection, through the incorporation of selection markers such as markers conferring antibiotic resistance.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Methods for the management of erase operations in non-volatile memories
InactiveUS7624239B2Easy to eraseMany timesMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesMemory systemsVolatile memory
The present invention presents a number of improvements for managing erase processes in non-volatile memory. Such memory systems typically manage the memory by logically organize the basic unit of physical erase (erase block) into composite logical groupings (meta-blocks or logical group), where an erase block generally consists of a number of sectors. When an erase command is received, the specified sectors are checked against the memory system's control data. If the specified sectors span any full logical grouping, the full logical groupings can each be treated as a whole and erased according to one process (such as performing a true, physical erase), while other sectors are “logically” erased at the sector level by standard techniques.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
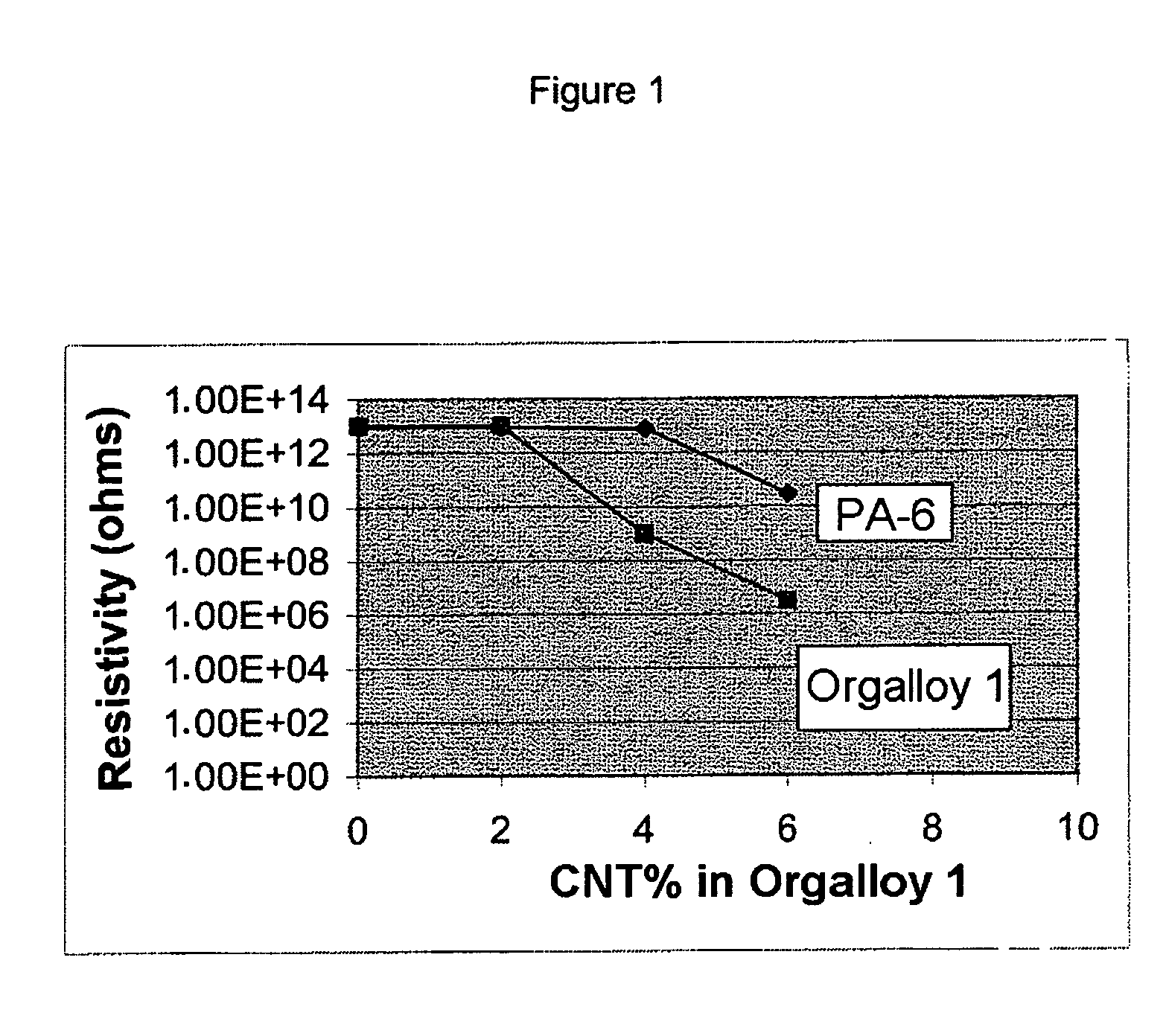
Polyamide/polyolefin blends containing carbon nanotubes
The present invention relates to polyamide / polyolefin blends containing carbon nanotubes. The invention also relates to structures comprising at least one layer of these blends and optionally at least one layer of another material. These structures may be in the form of bottles, tanks, containers, hoses, pipes and vessels of any kind. These structures may be manufactured using the standard techniques for thermoplastics, such as injection moulding, extrusion-blow moulding and coextrusion. The present invention, according to one embodiment, relates to a multilayer tube comprising, in its radial direction from the outside inwards: an outer layer (1) formed from a polyamide chosen from PA-11 and PA-12; a layer (2) formed from a tie; an optional layer (3) formed from an EVOH; optionally, a tie layer (this does not exist if no layer (3) is present); an inner layer (4) formed from a polyamide (A) / polyolefin (B) blend having a polyamide matrix and containing carbon nanotubes; with the layers being successive and adhering to one another in their respective areas of contact.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Delivery of therapeutic biologicals from implantable tissue matrices
InactiveUS20020031500A1Many of effectMany of inconveniencePowder deliveryBiocideProgenitorActive agent
Normal cells, such as fibroblasts or other tissue or organ cell types, are genetically engineered to express biologically active, therapeutic agents, such as proteins that are normally produced in small amounts, for example, MIS, or other members of the TGF-beta family Herceptin(TM), interferons, andanti-angiogenic factors. These cells are seeded into a matrix for implantation into the patient to be treated. Cells may also be engineered to include a lethal gene, so that implanted cells can be destroyed once treatment is completed. Cells can be implanted in a variety of different matrices. In a preferred embodiment, these matrices are implantable and biodegradable over a period of time equal to or less than the expected period of treatment, when cells engraft to form a functional tissue producing the desired biologically active agent. Implantation may be ectopic or in some cases orthotopic. Representative cell types include tissue specific cells, progenitor cells, and stem cells. Matrices can be formed of synthetic or natural materials, by chemical coupling at the time of implantation, using standard techniques for formation of fibrous matrices from polymeric fibers, and using micromachining or microfabrication techniques. These devices and strategies are used as delivery systems via standard or minimally invasive implantation techniques for any number of parenterally deliverable recombinant proteins, particularly those that are difficult to produce in large amounts and / or active forms using conventional methods of purification, for the treatment of a variety of conditions that produce abnormal growth, including treatment of malignant and benign neoplasias, vascular malformations (hemangiomas), inflammatory conditions, keloid formation, abdominal or plural adhesions, endometriosis, congenital or endocrine abnormalities, and other conditions that can produce abnormal growth such as infection. Efficacy of treatment with the therapeutic biologicals is detected by determining specific criteria, for example, cessation of cell proliferation, regression of abnormal tissue, or cell death, or expression of genes or proteins reflecting the above.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Methods for the management of erase operations in non-volatile memories
InactiveUS20070113030A1Easy to eraseExecution time can be made muchMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesControl dataOperating system
The present invention presents a number of improvements for managing erase processes in non-volatile memory. Such memory systems typically manage the memory by logically organize the basic unit of physical erase (erase block) into composite logical groupings (meta-blocks or logical group), where an erase block generally consists of a number of sectors. When an erase command is received, the specified sectors are checked against the memory system's control data. If the specified sectors span any full logical grouping, the full logical groupings can each be treated a whole and erased according to one process (such as performing a true, physical erase), while other sectors are “logically” erased at the sector level by standard techniques.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Use of novel draw solutes and combinations thereof to improve performance of a forward osmosis system and process
This disclosure describes draw solution compositions for FO processes which increase the available membrane area for permeation and are also amenable to reconcentration with standard techniques, such as membrane filtration and evaporative technologies. The composition are comprised of a water soluble draw solute having surface active properties, i.e., a surfactant.
Owner:HYDRATION SYST
Transgenic microbial polyhydroxyalkanoate producers
Transgenic microbial strains are provided which contain the genes required for PHA formation integrated on the chromosome. The strains are advantageous in PHA production processes, because (1) no plasmids need to be maintained, generally obviating the required use of antibiotics or other stabilizing pressures, and (2) no plasmid loss occurs, thereby stabilizing the number of gene copies per cell throughout the fermentation process, resulting in homogeneous PHA product formation throughout the production process. Genes are integrated using standard techniques, preferably transposon mutagenesis. In a preferred embodiment wherein mutiple genes are incorporated, these are incorporated as an operon. Sequences are used to stabilize mRNA, to induce expression as a function of culture conditions (such as phosphate concentration), temperature, and stress, and to aid in selection, through the incorporation of selection markers such as markers conferring antibiotic resistance.
Owner:METABOLIX
Electronic device package with an integrated evaporator
ActiveUS7505268B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsManufacturing technologyThermal management system
The present invention provides an electronic device package that can be fabricated using standard package fabrication technologies while providing a desired level of thermal transfer capability to an attachable thermal management system. The electronic device package according to the present invention comprises a housing that is specifically designed to couple with an evaporator portion of a thermal management system, for example a heat pipe. One or more electronic devices are mounted in thermal contact with the evaporator portion of the thermal management system. Upon completion of the fabrication of the package using standard techniques, the evaporator portion of the electronic device package is operatively coupled with a secondary portion of the thermal management system. In this manner the electronic device package can be fabricated to incorporate a desired thermal management system, while being fabricated using standard package fabrication processes and machinery.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Method for producing stereoscopic images from monoscopic images
Owner:STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG (A R O) (VOLCANI CENT)
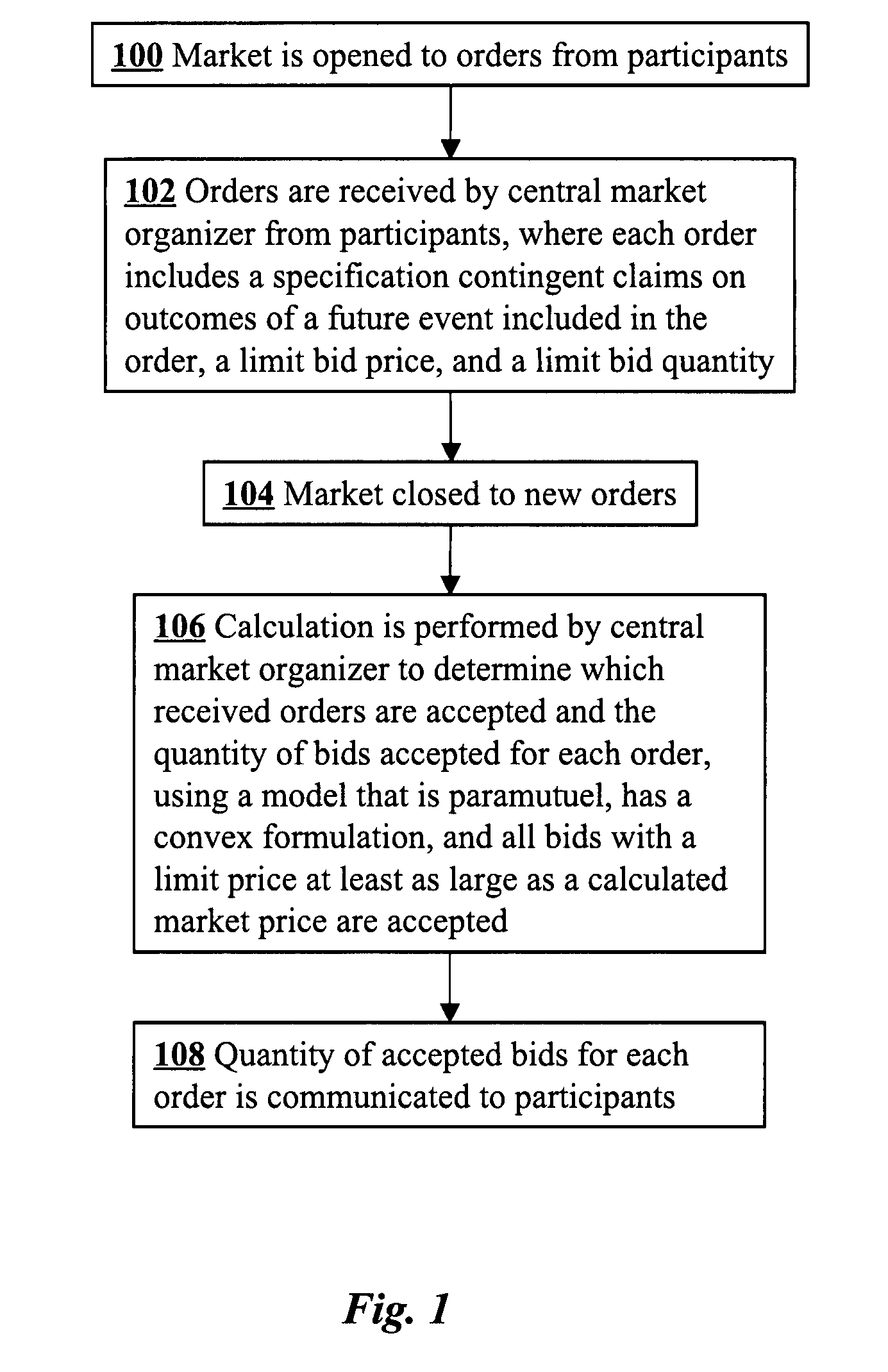
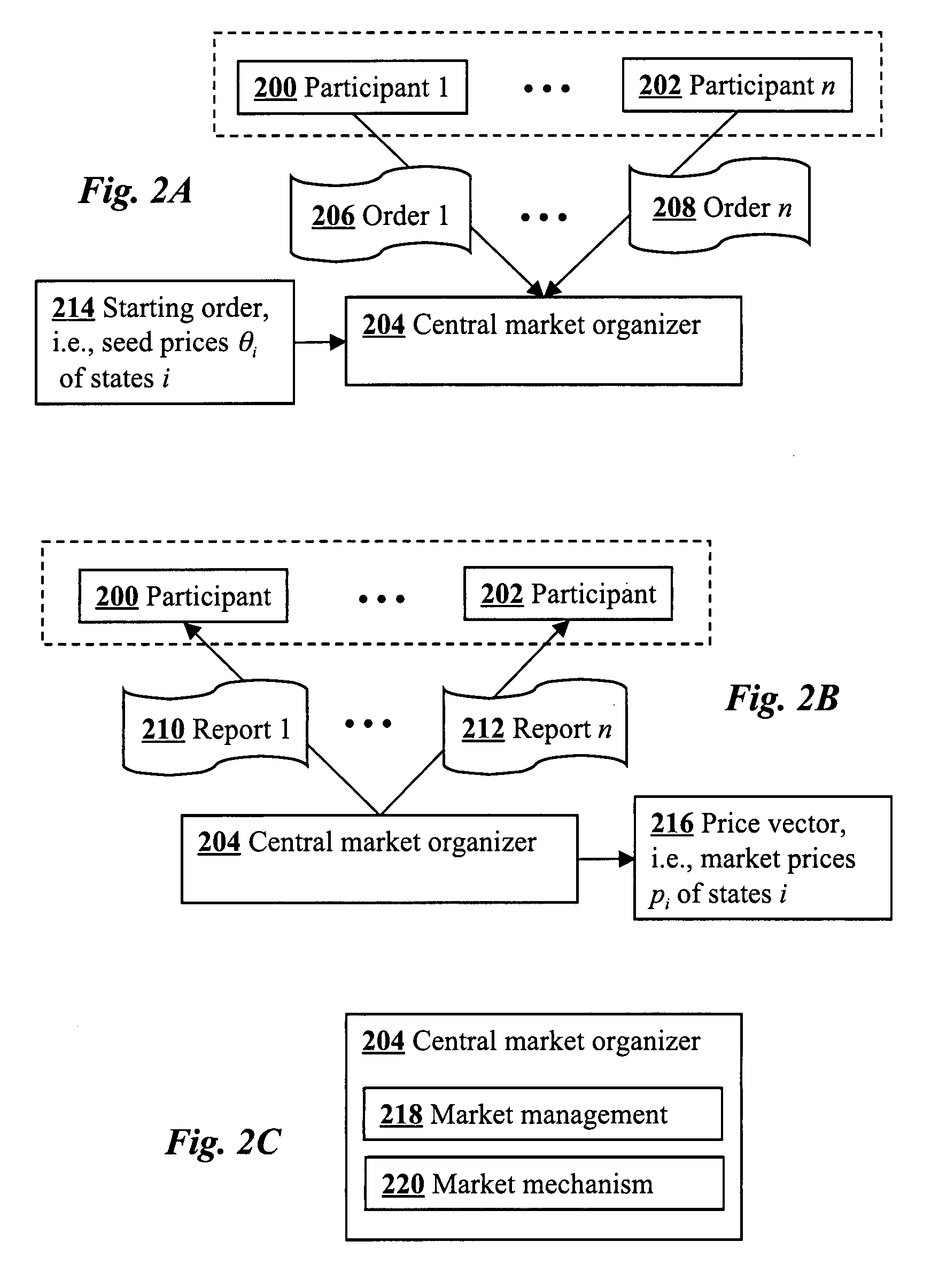
Convex parimutuel contingent claim market mechanism
InactiveUS20090099955A1Easy to solveEfficient priceFinanceCommercePath following algorithmComputer science
A convex paramutuel call auction implemented at a central market organizer computer includes receiving orders from market participants, calculating a quantity of accepted bids for each of the orders, and communicating to the participants the calculated quantity of accepted bids for each of the orders. Each order includes a specification by a participant of contingent claims on outcomes of a future event, a limit bid price, and a limit bid quantity. The calculation involves maximizing an objective function given by an approximate profit to the market organizer plus a weighted logarithmic penalty function. Because the formulation is convex, the solution may be computed in polynomial time using standard techniques, such as a path-following algorithm.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Light emitting device having selenium-based fluorescent phosphor
InactiveUS7112921B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesFluorescencePhosphor
Provided herein are novel phosphors useful in the manufacture of white light emitting diodes. The phosphors provided by the invention are described by the formulae:MSxSey: Bin which x, and y are each independently any value between about 0 and about 1, subject to the proviso that the sum of x and y is equal to any number in the range of between about 0.75 and about 1.25; M is at least one of Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Zn, excepting Zn alone; and wherein the activator(s) B comprises one or more elements selected from the group consisting of: Eu, Ce, Cu, Ag, Al, Tb, Sb, Bi, K, Na, Cl, F, Br, I, Mg, Pr, and Mn, including mixtures comprising any two, any three, any four, any five, any six, any seven, or more of these elements in any proportion, and wherein the elements in these mixtures may each independently be present in any amount between 0.0001% and about 10% in mole percent based on the total molar weight of said composition.Standard techniques used in conventional phosphor deposition for the manufacture of light emitting diodes which comprise phosphors according to the invention may be employed to produce LED's having a white light output.
Owner:PHOSPHORTECH
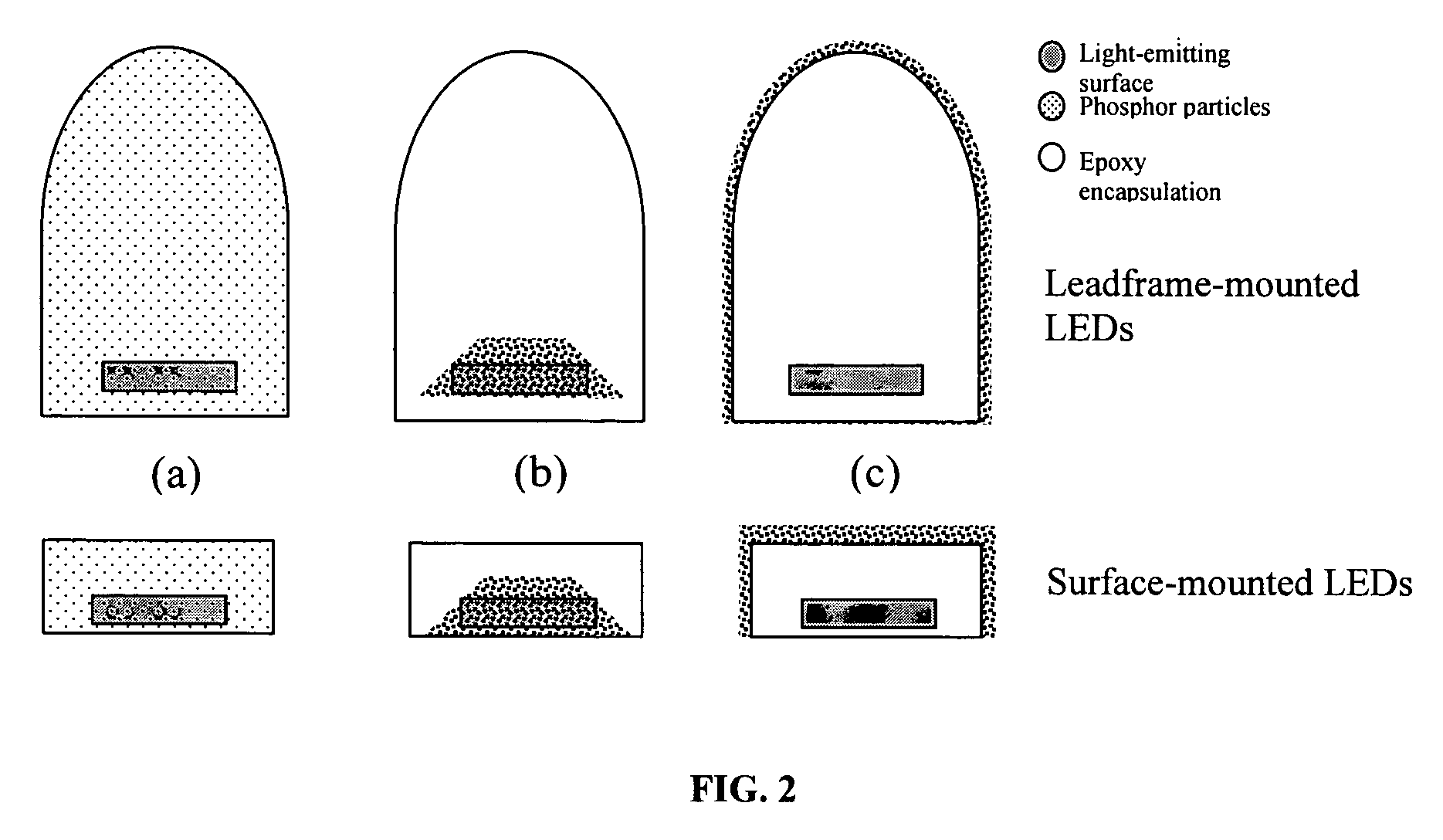
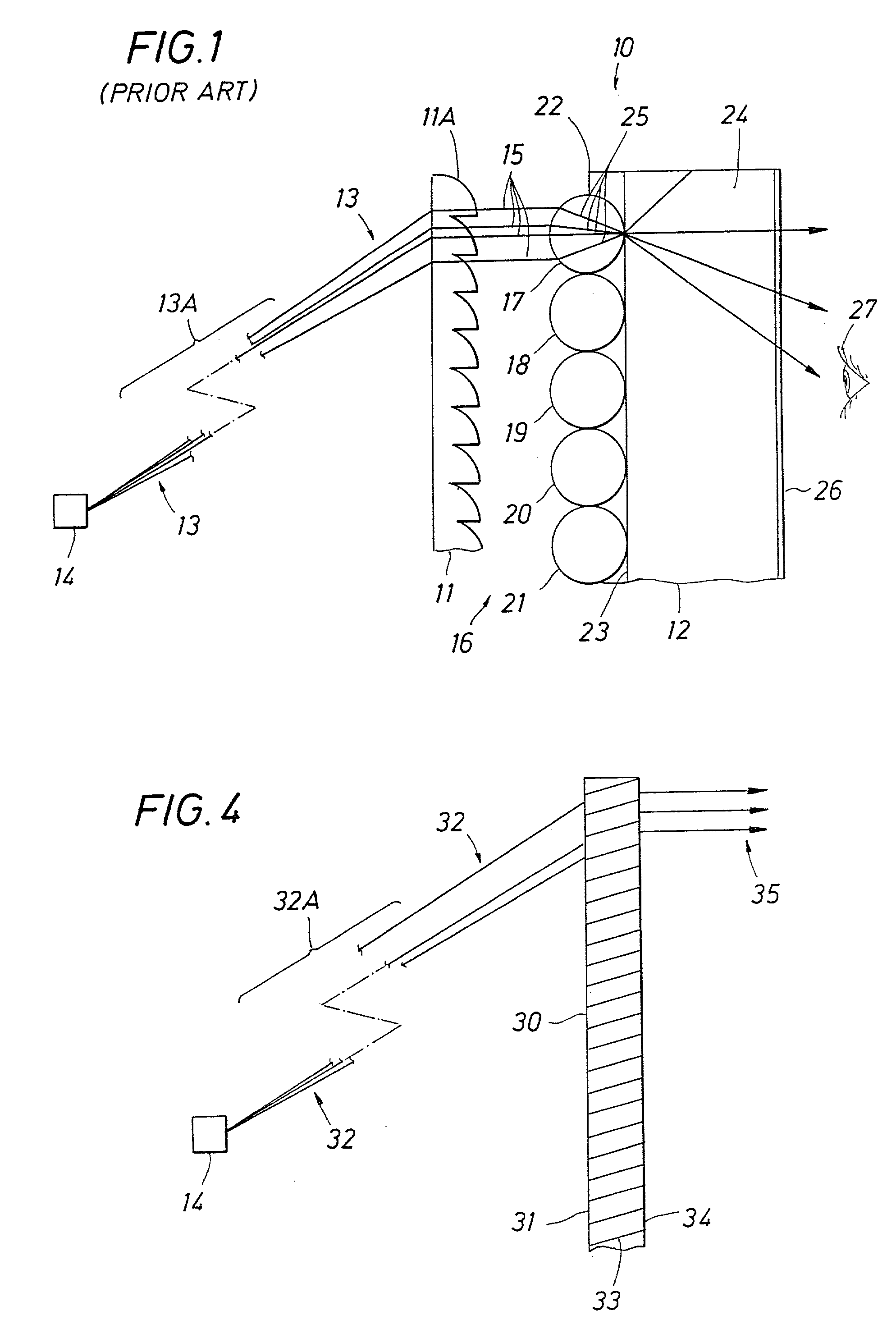
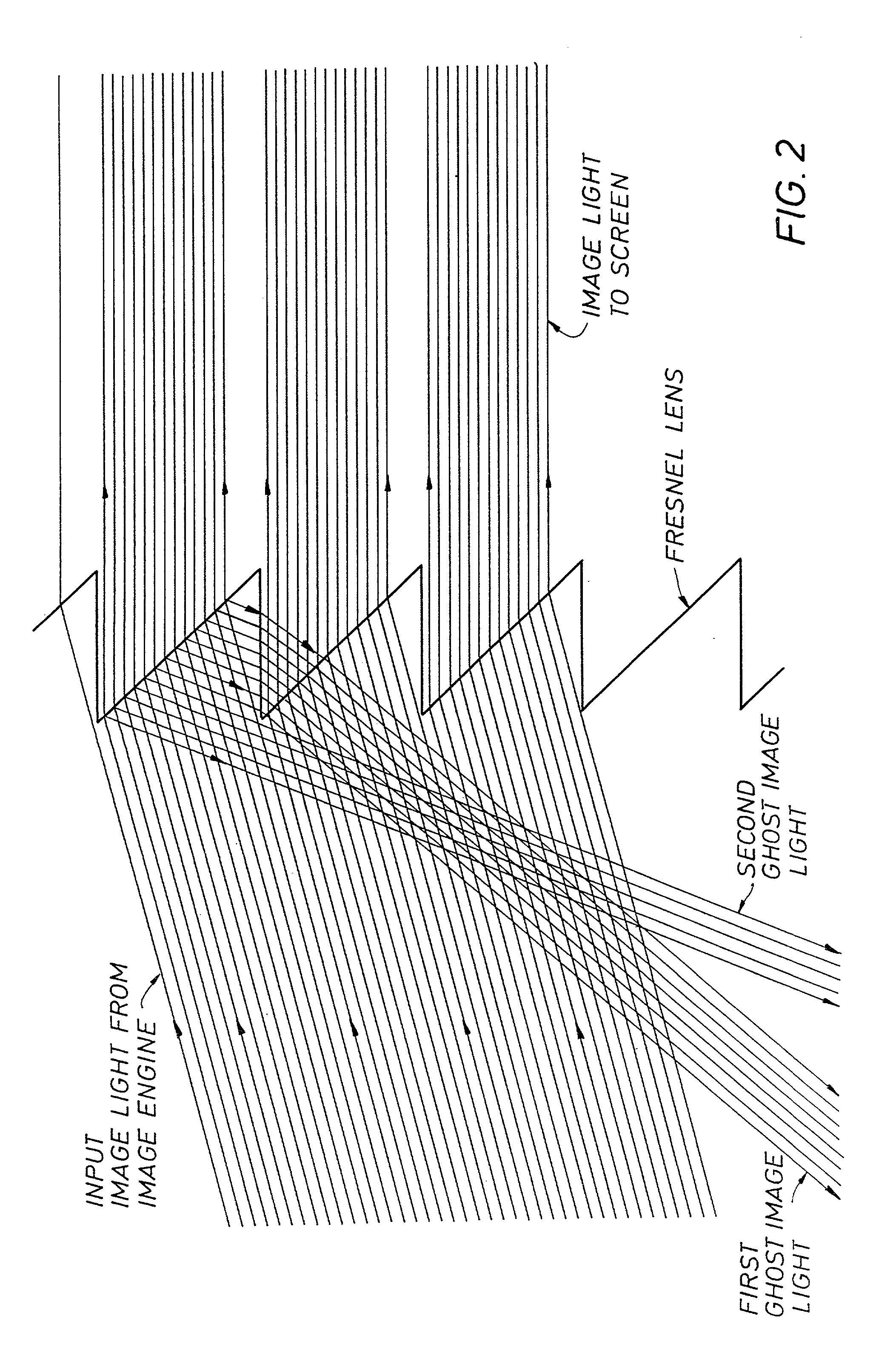
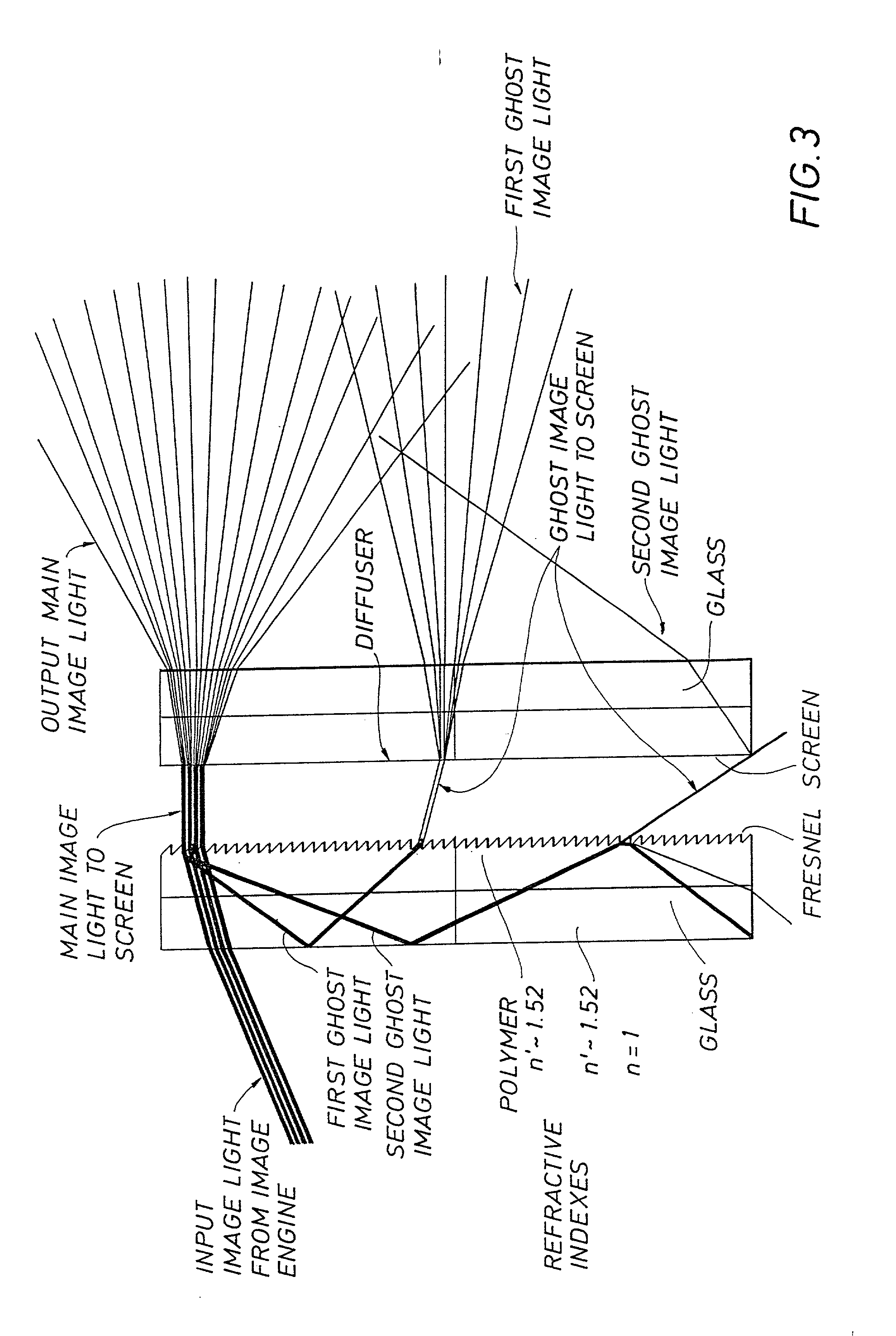
Projection screen apparatus including holographic optical element
A screen apparatus includes a holographic optical element and a diffuser. The holographic optical element may be constructed using standard techniques known in the field of holography. The holographic optical element may be used to replace a typical Fresnel lens used in projection screen apparatuses. In operation, the holographic optical element receives image light from an image engine or projector and redirects the image light to the diffuser for scattering. The holographic optical element can be designed to substantially collimate. converge, or diverge the image light. The combination of the holographic optical element and the diffuser provides improved illumination uniformity that can be perceived by a viewer as the viewer moves in directions transverse to the screen apparatus. The screen apparatus may be designed to provide improved illumination uniformity to optimized or optimal locations in a viewing region. The screen apparatus may be advantageously employed in display apparatuses.
Owner:CHI MEI MATERIALS TECH CORP
Structures for the management of erase operations in non-volatile memories
ActiveUS7783845B2Easy to eraseMany timesMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsControl dataComputer science
The present invention presents a number of improvements for managing erase processes in non-volatile memory. Such memory systems typically manage the memory by logically organize the basic unit of physical erase (erase block) into composite logical groupings (meta-blocks or logical group), where an erase block generally consists of a number of sectors. When an erase command is received, the specified sectors are checked against the memory system's control data. If the specified sectors span any full logical grouping, the full logical groupings can each be treated as a whole and erased according to one process (such as performing a true, physical erase), while other sectors are “logically” erased at the sector level by standard techniques.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
NVME interface-based Intel SSD management method
The invention provides an optical fiber communication method and relates to the technical field of NVME interface standards. The method mainly comprises the three steps of firstly installing device drivers; secondly performing device management based on an NVMe SSD user space management tool Nvme-cli hosted and developed by a maintainer Keitch Busch; and finally performing pressure testing on a device to detect device performance and viewing smart information through the Nvme-cli to view a device state. The invention provides a series of management methods from device driver installation to device detection, thereby filling the technical blanks.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
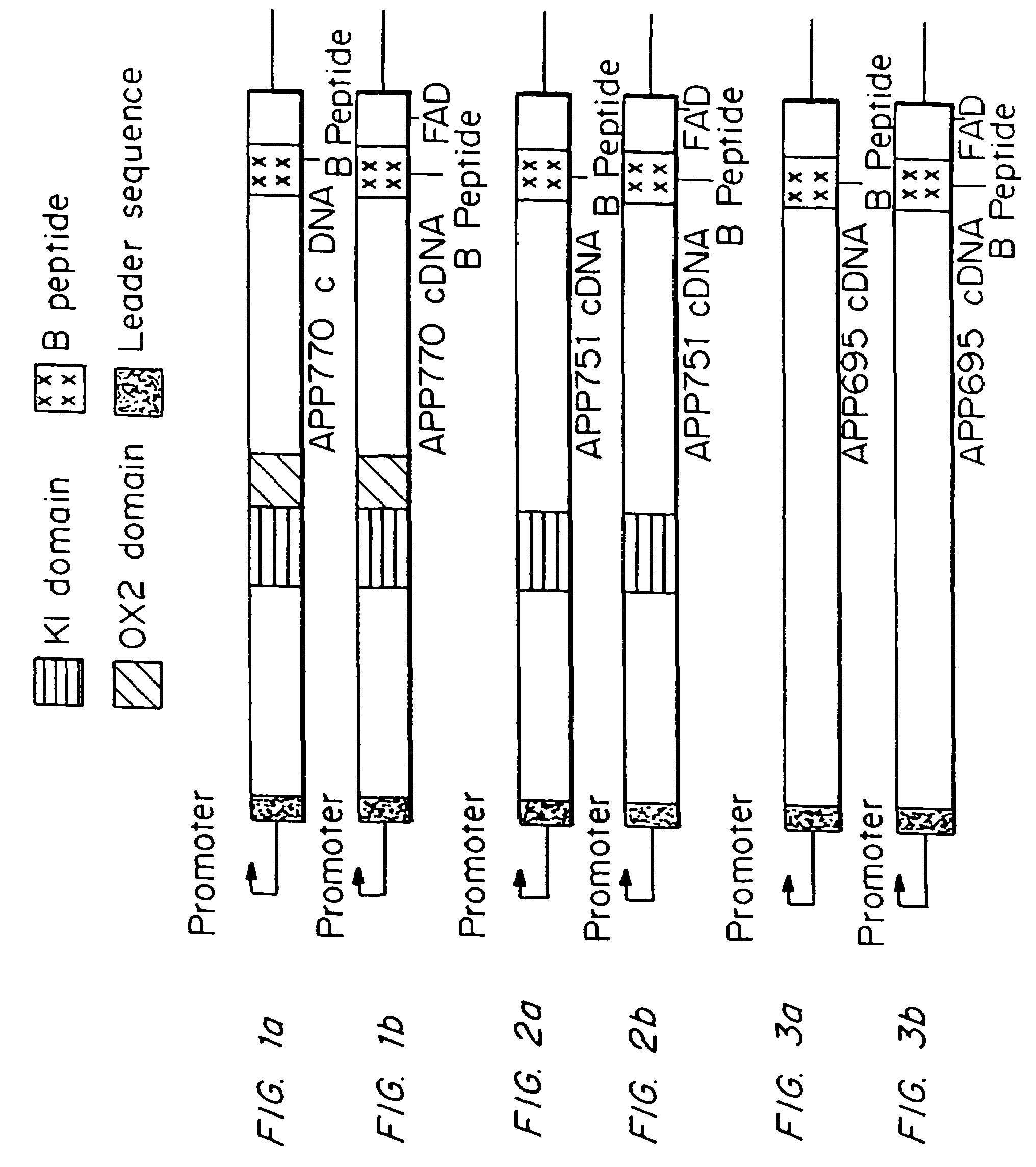
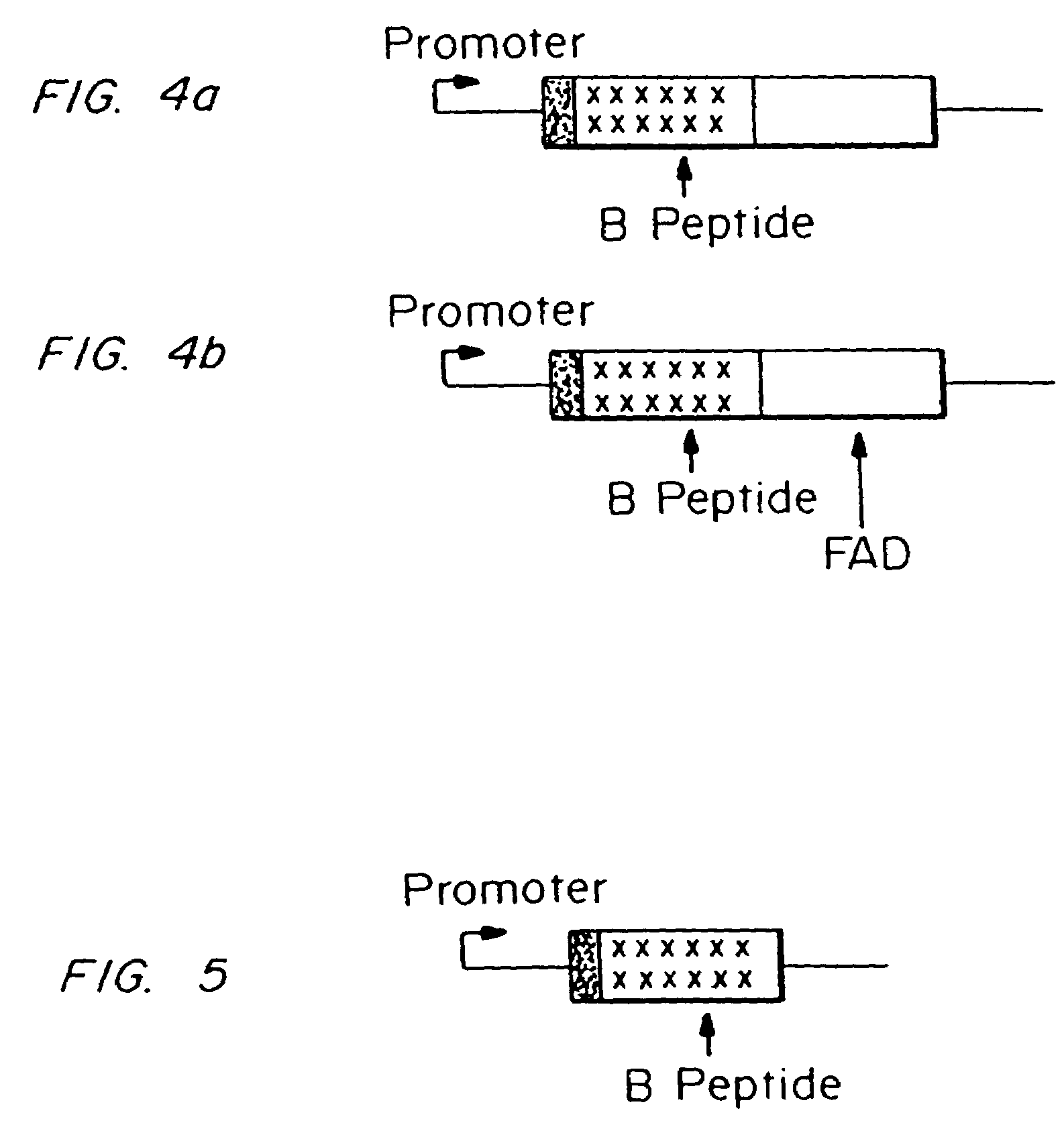
Testing compounds for effects on synaptophysin in transgenic mice expressing an Alzheimer's disease FAD DNA sequence
InactiveUS7186881B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAnimals/human peptidesSynaptophysinElectroporation
The construction of transgenic animal models of human Alzheimer's disease, and methods of using the models to screen potential Alzhe## disease therapeutics, are described. The models are characterized by pathologies similar to pathologies observed in Alzheimer's disease, based on expression of all three forms of the β-amyloid precursor protein (APP), APP695, APP751, and APP770, as well as various point mutations based on naturally occurring mutations, such as the London and Indiana familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD) mutations at amino acid 717, predicted mutations in the APP gene, and truncated forms of APP that contain the Aβ region. Animal cells can be isolated from the transgenic animals or prepared using the same constructs with standard techniques such as lipofection or electroporation. The transgenic animals, or animal cells, are used to screen for compounds altering the pathological course of Alzheimer's disease as measured by their effect on the amount of APP, β-amyloid peptide, and numerous other Alzheimer's disease markers in the animals, the neuropathology of the animals, as well as by behavioral alterations in the animals.
Owner:ELAN PHARM INC
Detection of surface-associated human leukocyte elastase
InactiveUS6858400B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPhagocyteBinding site
In order to accurately and reliably quantitate HLE on the plasma membranes of the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes, a test sample containing the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes is initially treated with a first antiserum specific for CD4 receptors on the plasma membrane or with a second antiserum specific for chemokine receptors on the plasma membrane. Once the CD4 or chemokine receptors have been rendered non-reactive (competitive) relative to the HLE receptors (also “binding sites”) on the plasma membrane, the test sample is contacted with an immunoreagent specific for interaction with one or more of the HLE receptors on the plasma membranes of the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes. The immunoreagent forms a complex with the HLE binding sites and produces a characteristic physical change in the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes that can be monitored by any one of a number of standard techniques, (e.g., confocal laser scanning microscopy and flow cytometry).
Owner:BRISTOW CYNTHIA L
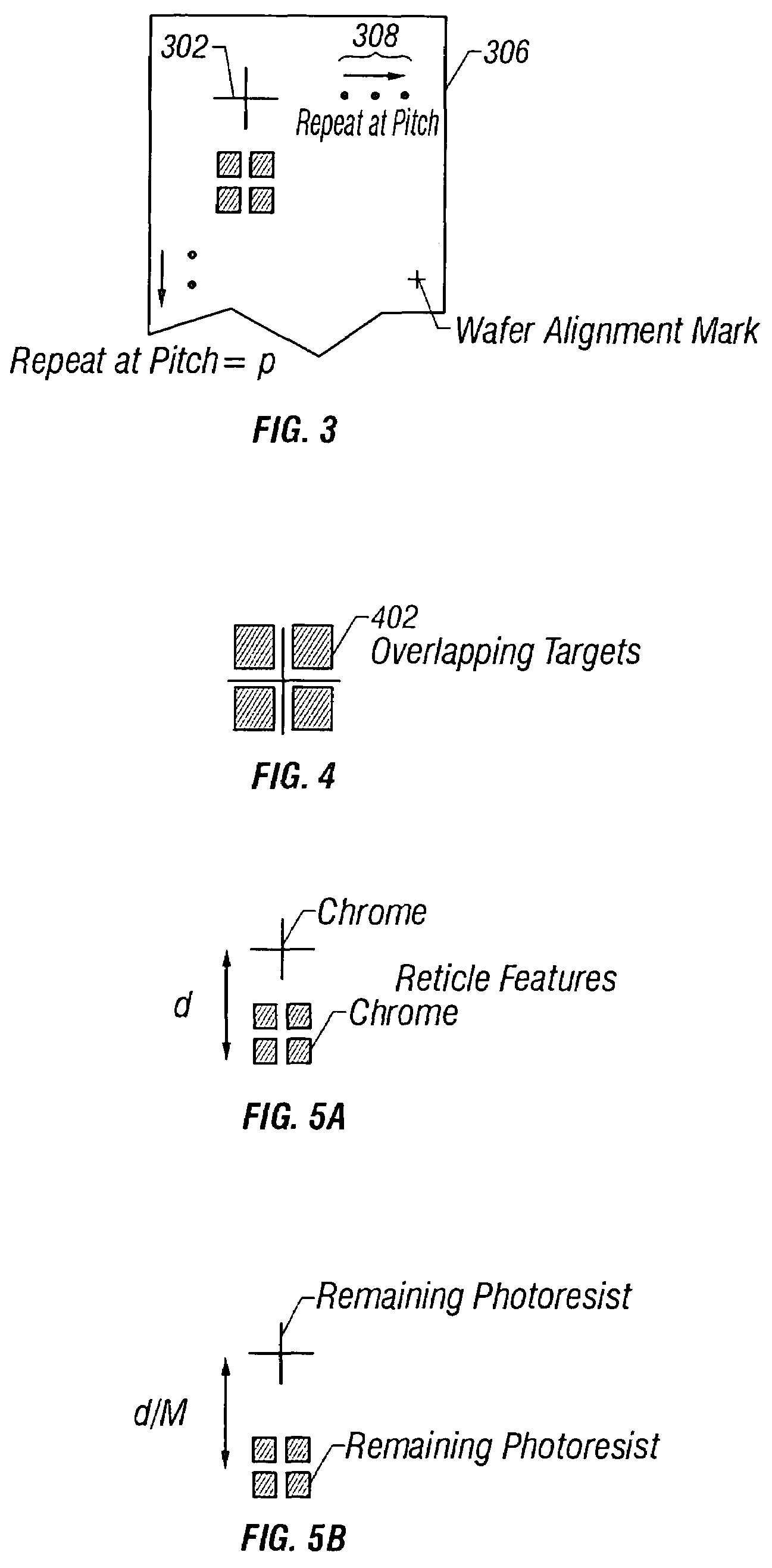
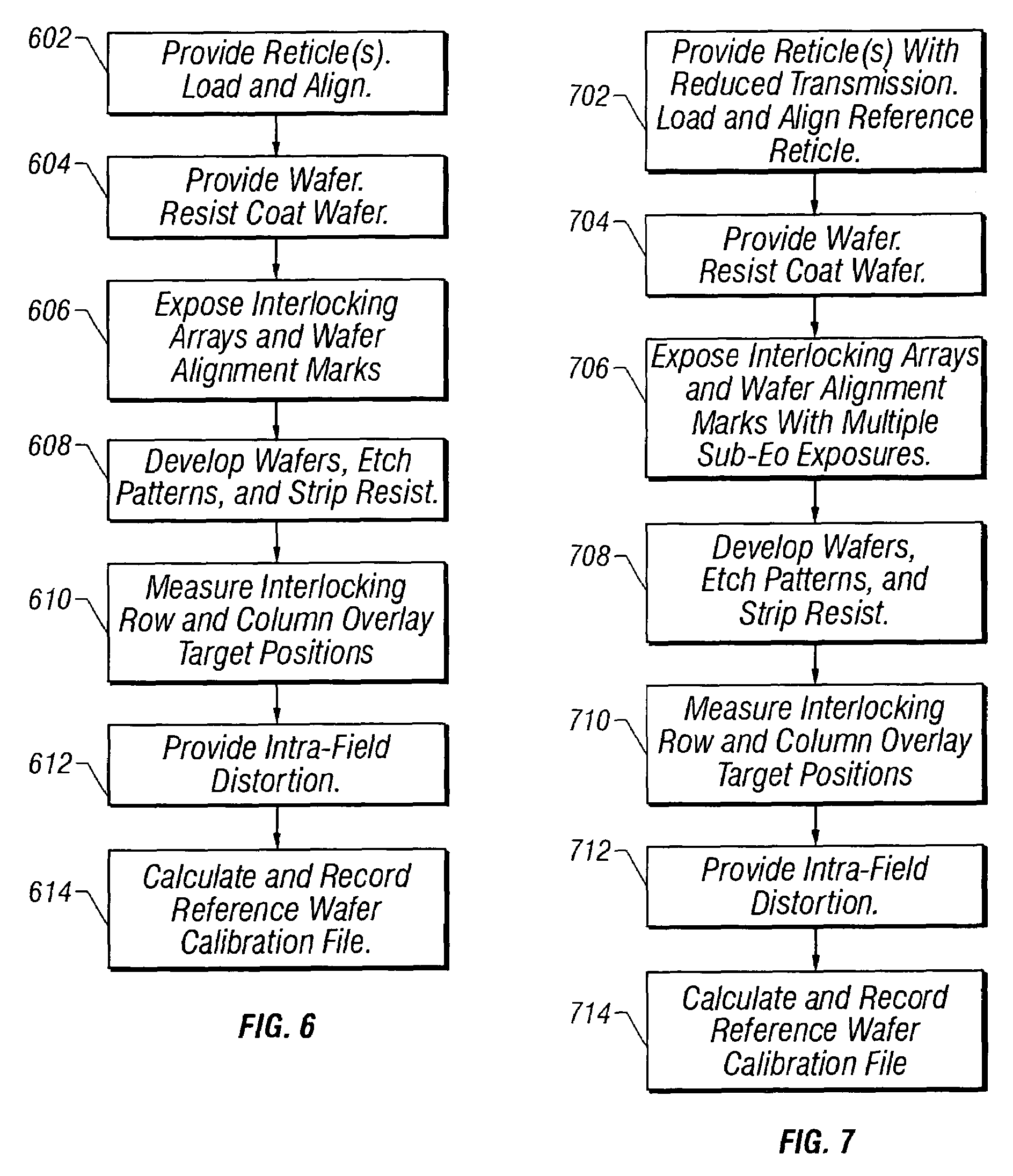
Reference wafer and process for manufacturing same
InactiveUS7160657B2Accurately determinePrecise positioningElectric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsResistMetrology
An apparatus and method for manufacturing and using a calibrated registration reference wafer in a semiconductor manufacturing facility. A reference reticle consisting of a 2-dimensional array of standard alignment attributes is exposed several times onto a photoresist coated semiconductor wafer using a photolithographic exposure tool. After the final steps of the lithographic development process the resist patterned wafer is physically etched using standard techniques to create a permanent record of the alignment attribute exposure pattern. The permanently recorded alignment attributes are measured for placement error using a conventional overlay metrology tool. The resulting overlay error data is used to generate a calibration file that contains the positions of the alignment attributes on the reference wafer. The reference wafer and calibration file can be used to determine the wafer stage registration performance for any photolithographic exposure tool.
Owner:LITEL INSTR
Light emitting device having selenium-based fluorescent phosphor
InactiveUS20050023546A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesFluorescencePhosphor
Provided herein are novel phosphors useful in the manufacture of white light emitting diodes. The phosphors provided by the invention are described by the formulae:MSxSey: Bin which x, and y are each independently any value between about 0 and about 1, subject to the proviso that the sum of x and y is equal to any number in the range of between about 0.75 and about 1.25; M is at least one of Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Zn, excepting Zn alone; and wherein the activator(s) B comprises one or more elements selected from the group consisting of: Eu, Ce, Cu, Ag, Al, Tb, Sb, Bi, K, Na, Cl, F, Br, I, Mg, Pr, and Mn, including mixtures comprising any two, any three, any four, any five, any six, any seven, or more of these elements in any proportion, and wherein the elements in these mixtures may each independently be present in any amount between 0.0001% and about 10% in mole percent based on the total molar weight of said composition. Standard techniques used in conventional phosphor deposition for the manufacture of light emitting diodes which comprise phosphors according to the invention may be employed to produce LED's having a white light output.
Owner:PHOSPHORTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com