Patents
Literature
54results about How to "Space is required" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
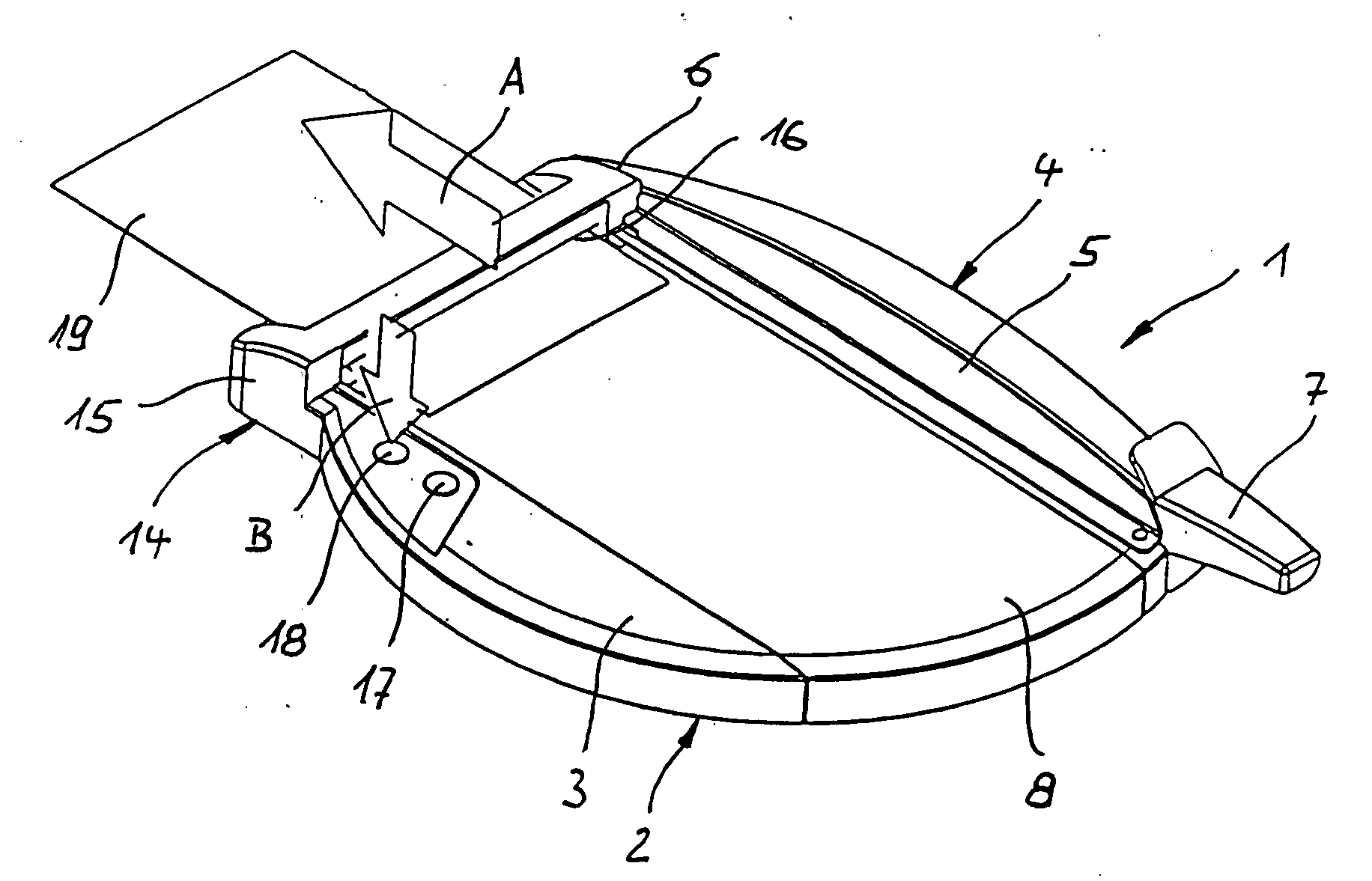
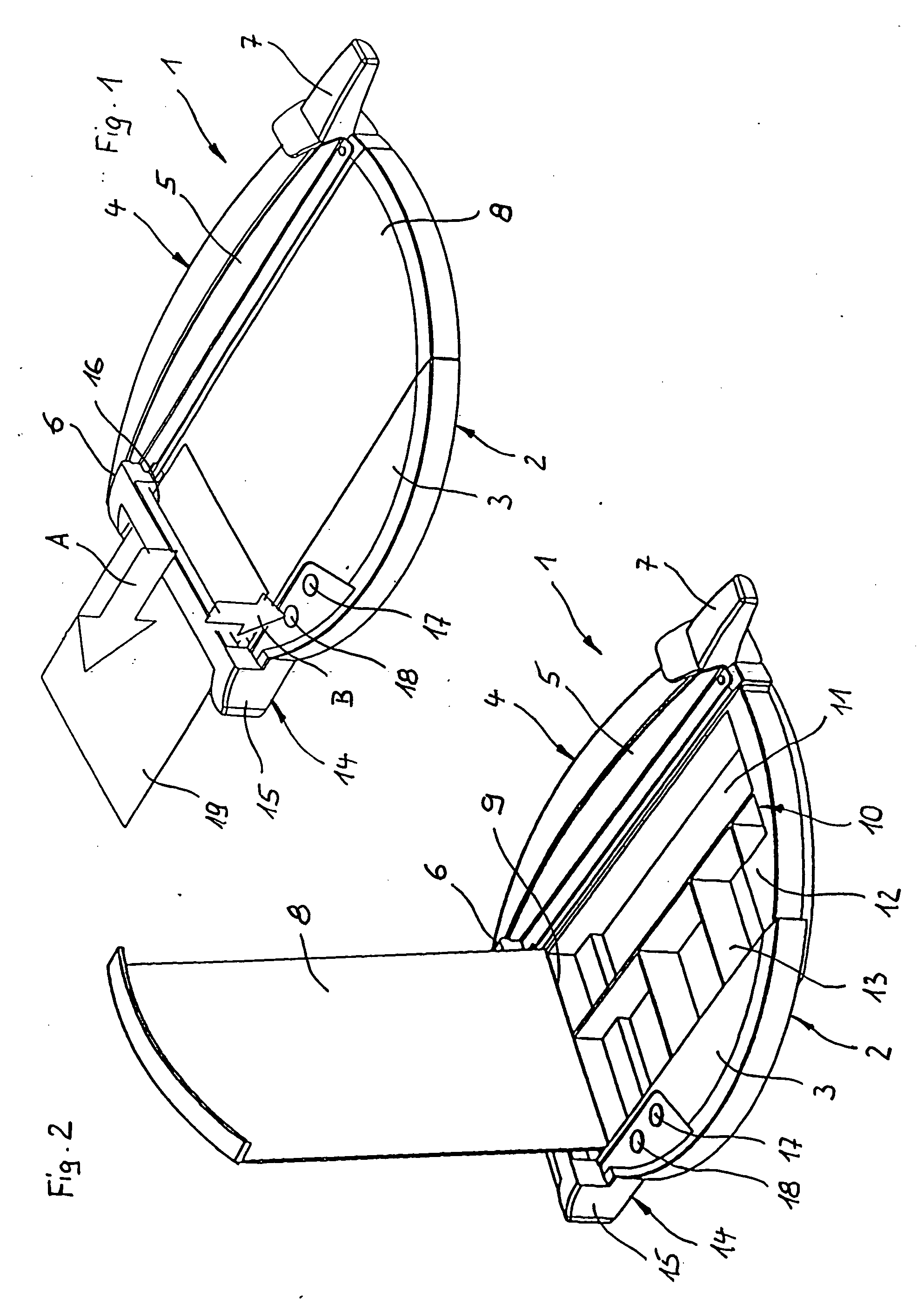
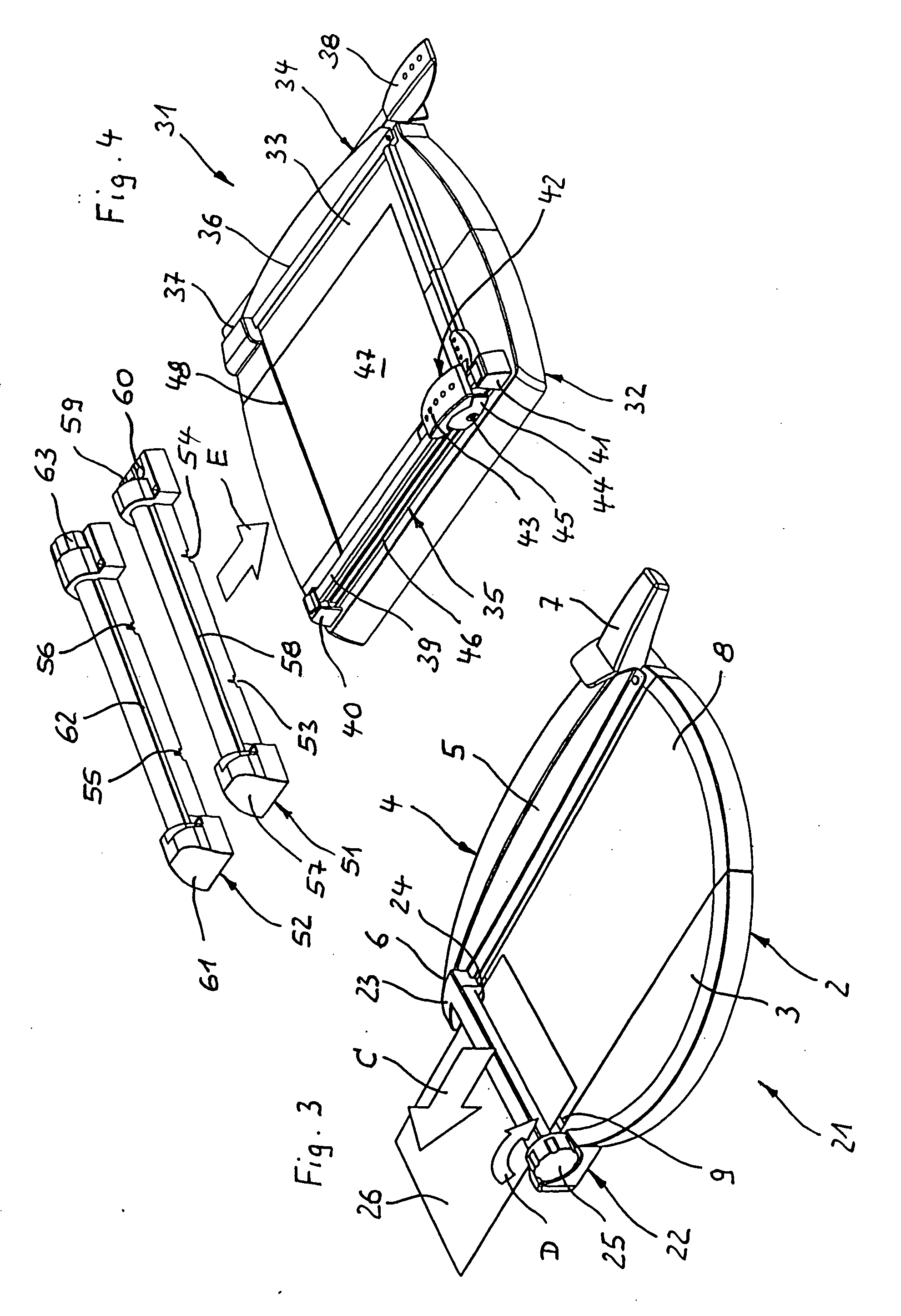
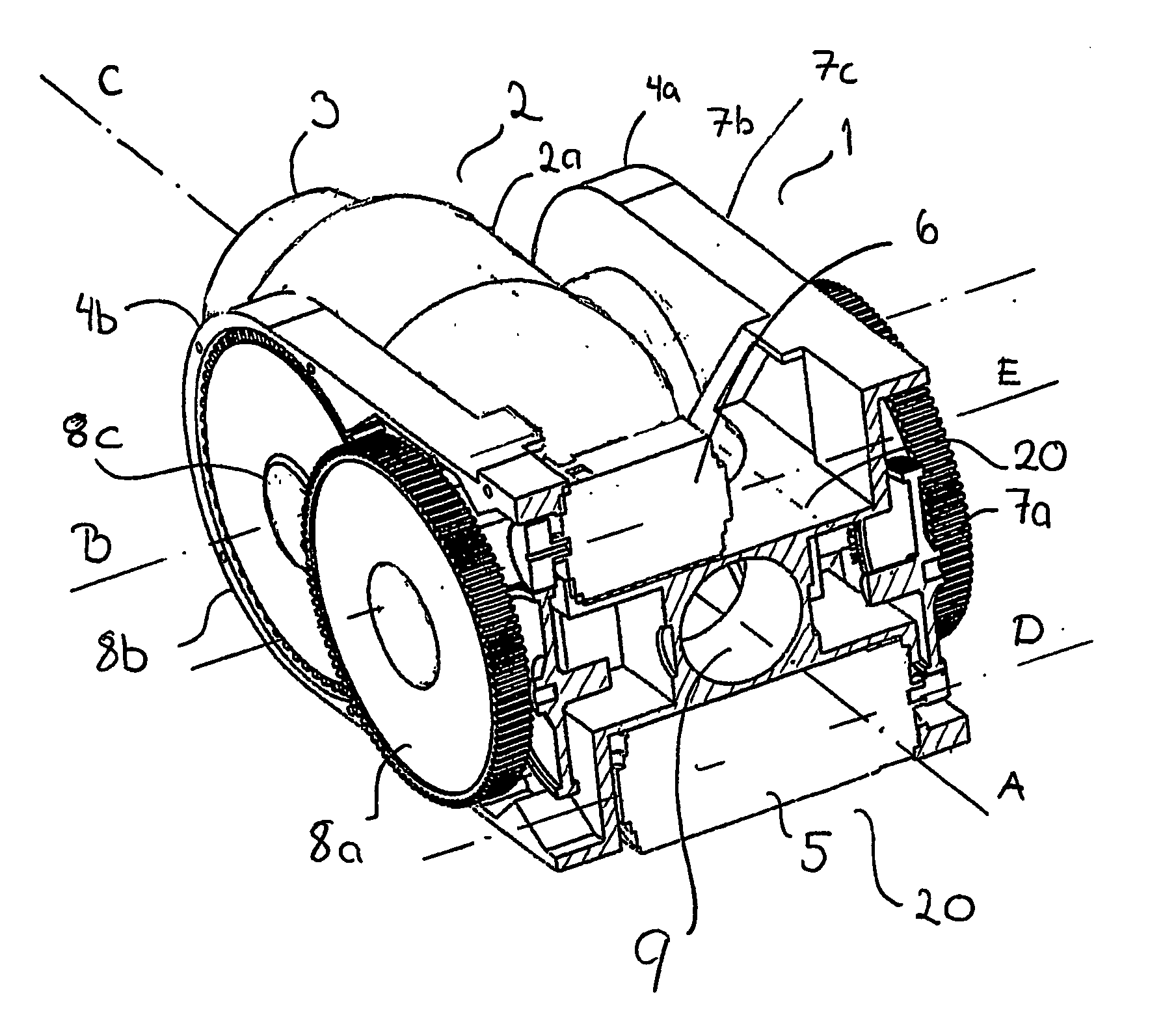
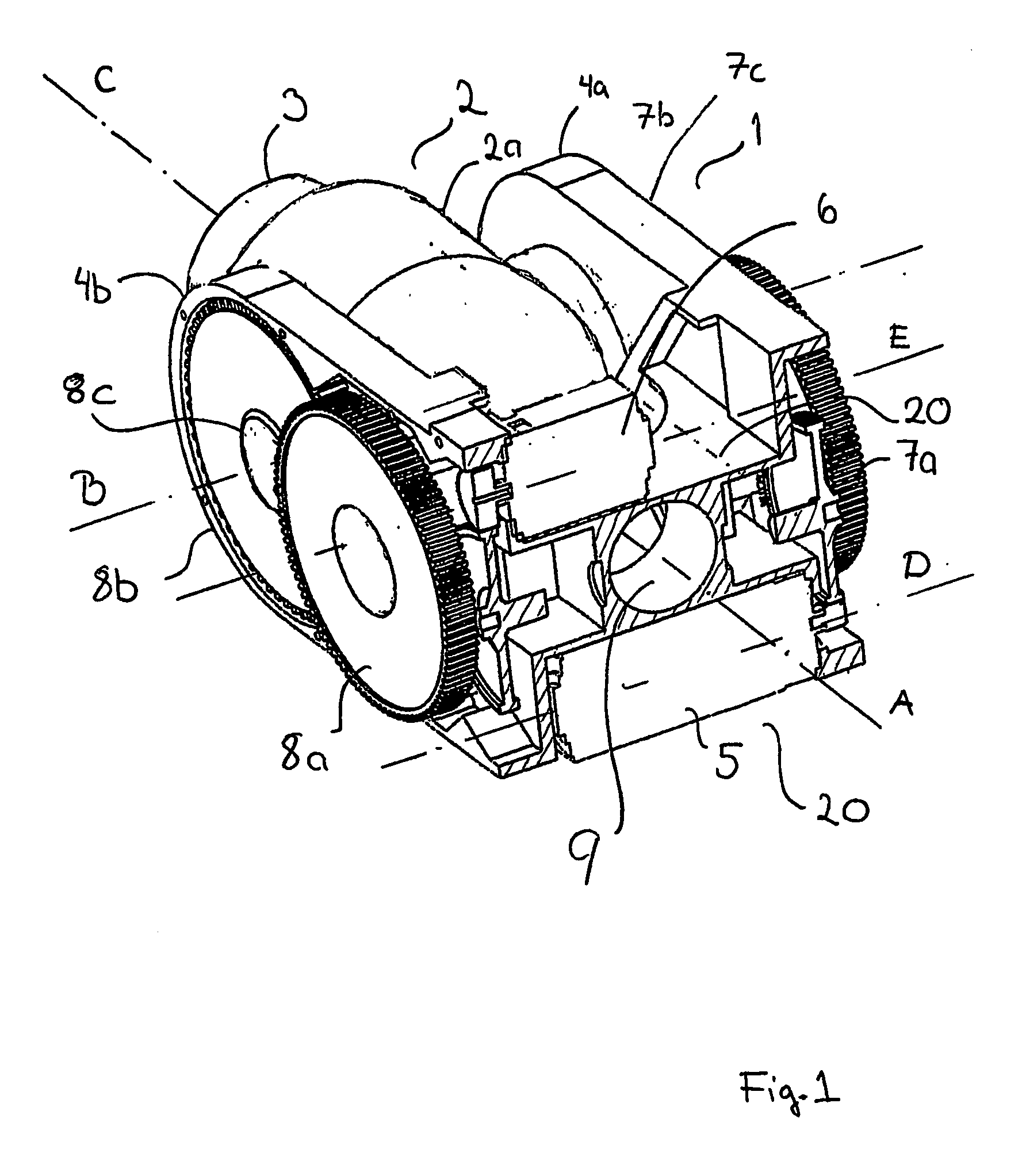
Starter/generator for an internal combustion engine, especially an engine of a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6365983B1Improve overall utilizationReduce the overall diameterRotating vibration suppressionBraking element arrangementsExternal combustion engineElectric machine
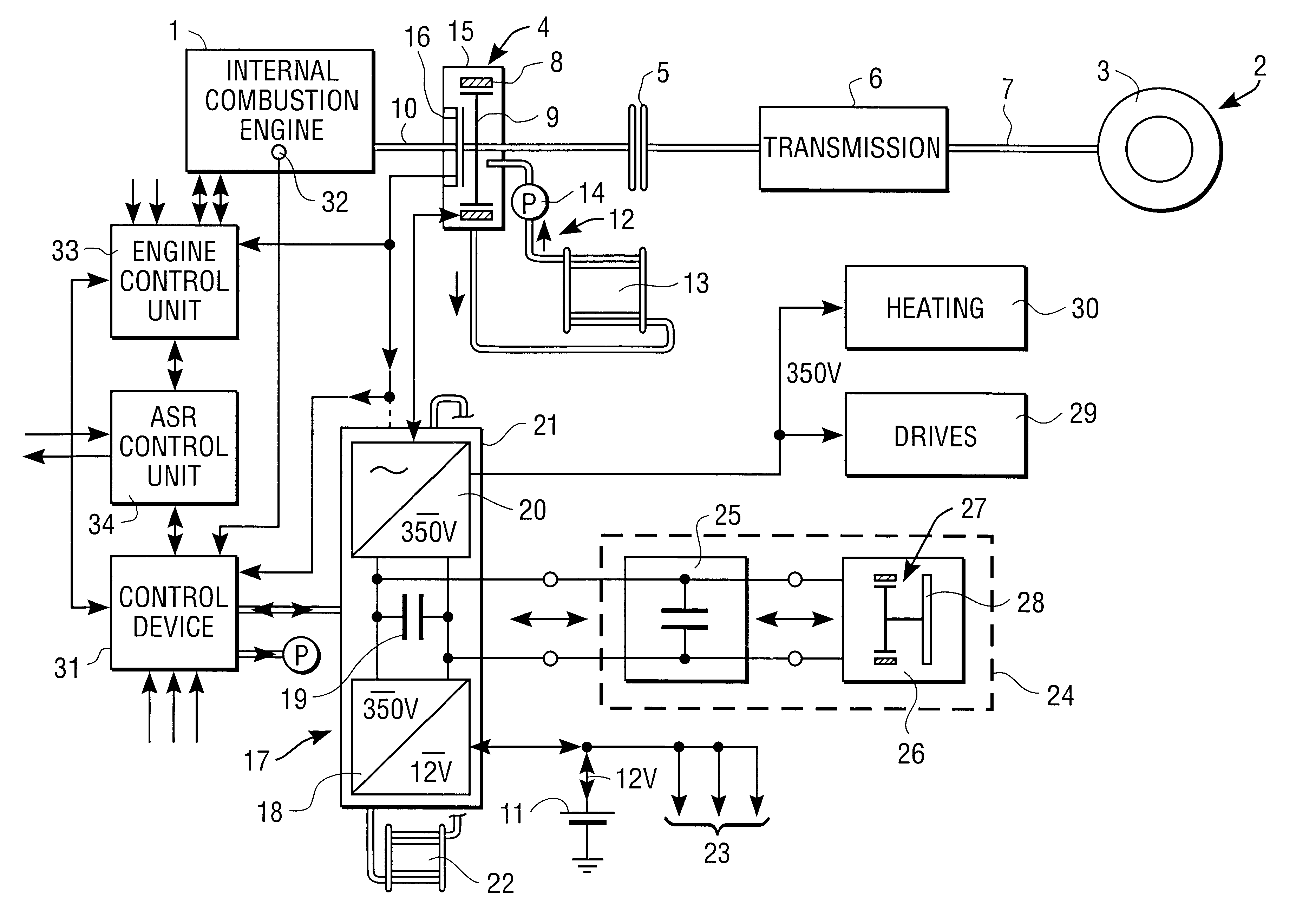
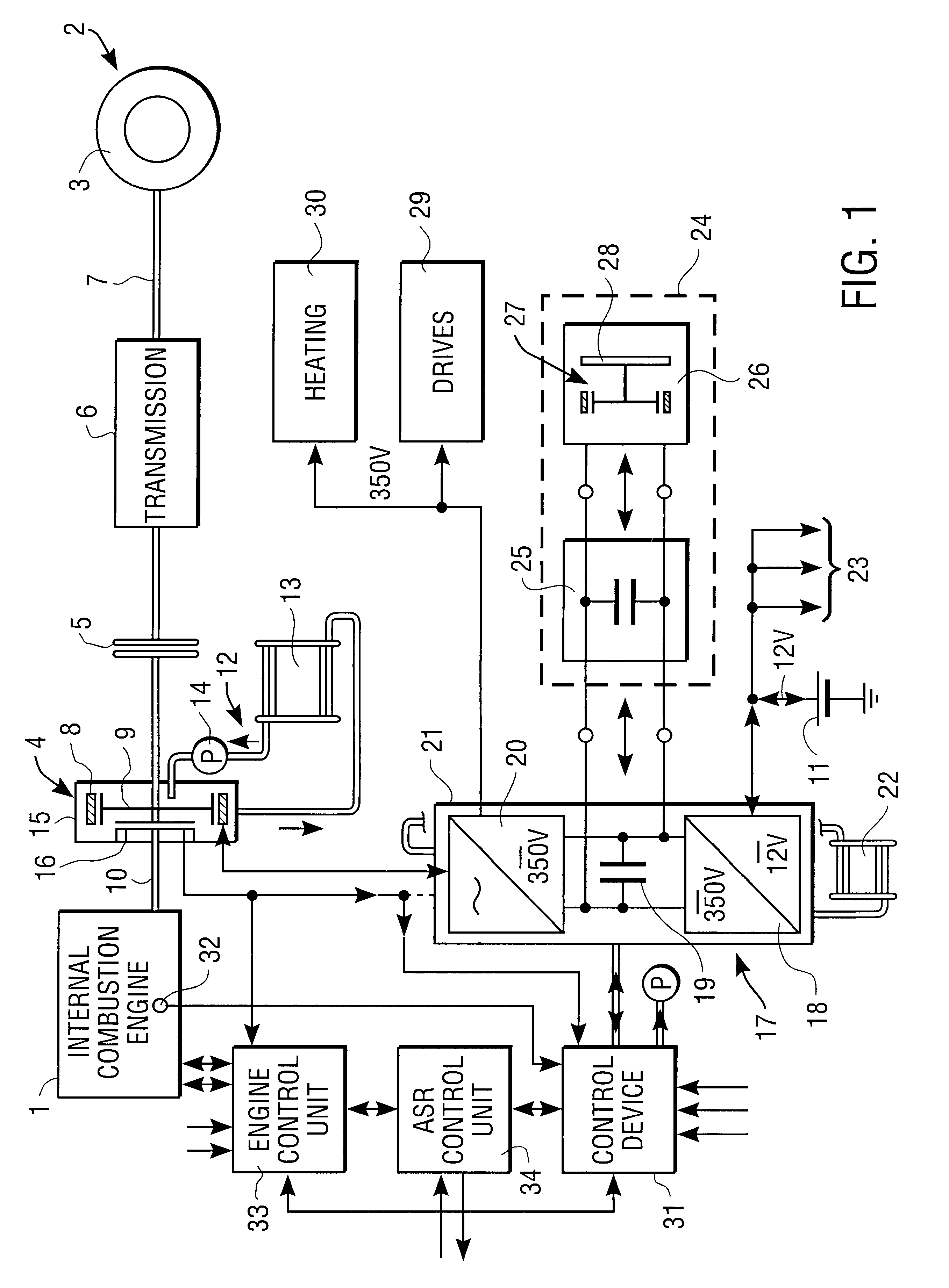
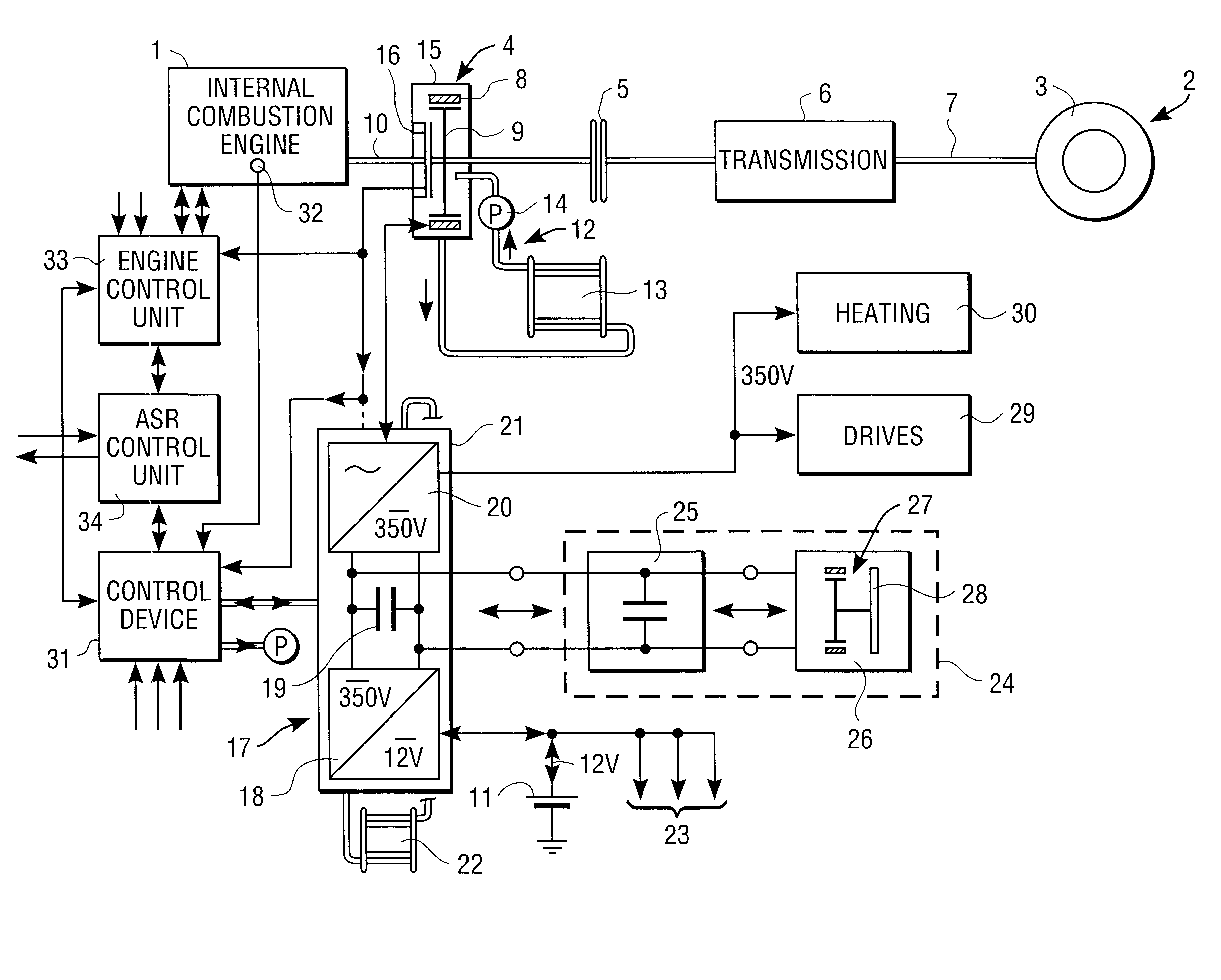
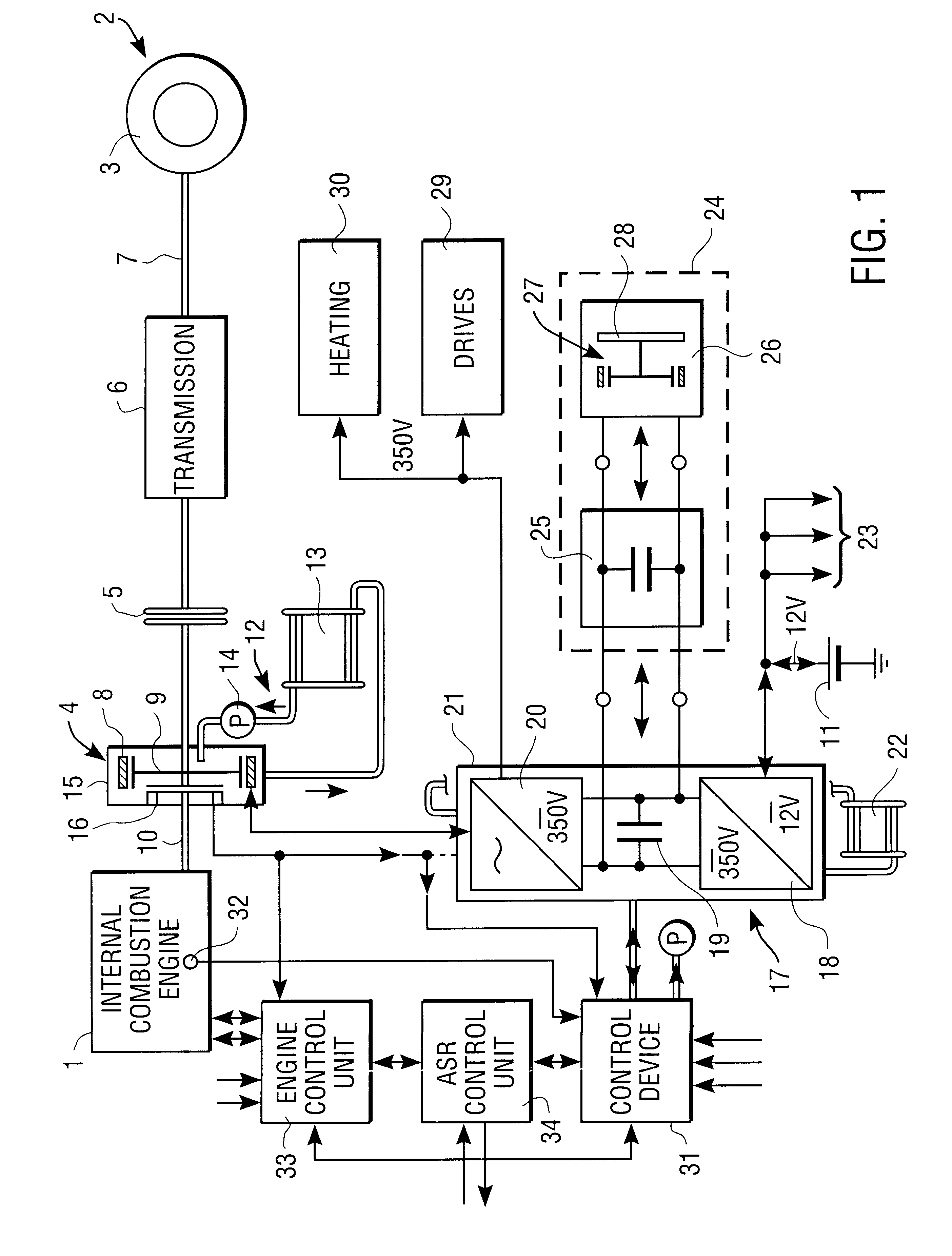
The invention concerns a starter / generator for an internal combustion engine (1), especially that of a motor vehicle, with an electric rotary-field machine (4), which exercises the starter and generator function; and at least one invertor (17) for generating the voltages and / or currents of variable frequency, amplitude and / or phase required for the magnetic fields of the electric machine (4); wherein the electric machine (4) starts the internal combustion engine (1) by merging in from standstill.
Owner:GRUNDL ANDREAS +2
Starter/generator for an internal combustion engine, especially an engine of a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6177734B1Improve overall utilizationReduce the overall diameterRotating vibration suppressionBraking element arrangementsElectric machineExternal combustion engine
The invention concerns a starter / generator for an internal combustion engine (1), especially that of a motor vehicle, with an electric rotary-field machine (4), which exercises the starter and generator function; and at least one invertor (17) for generating the voltages and / or currents of variable frequency, amplitude and / or phase required for the magnetic fields of the electric machine (4); wherein the electric machine (4) starts the internal combustion engine (1) by merging in from standstill.
Owner:GRUNDL ANDREAS +2
Low profile active electronically scanned antenna (AESA) for Ka-band radar systems
InactiveUS6975267B2Space is requiredRadiating element housingsAntenna arrays manufactureTransceiverRadar systems
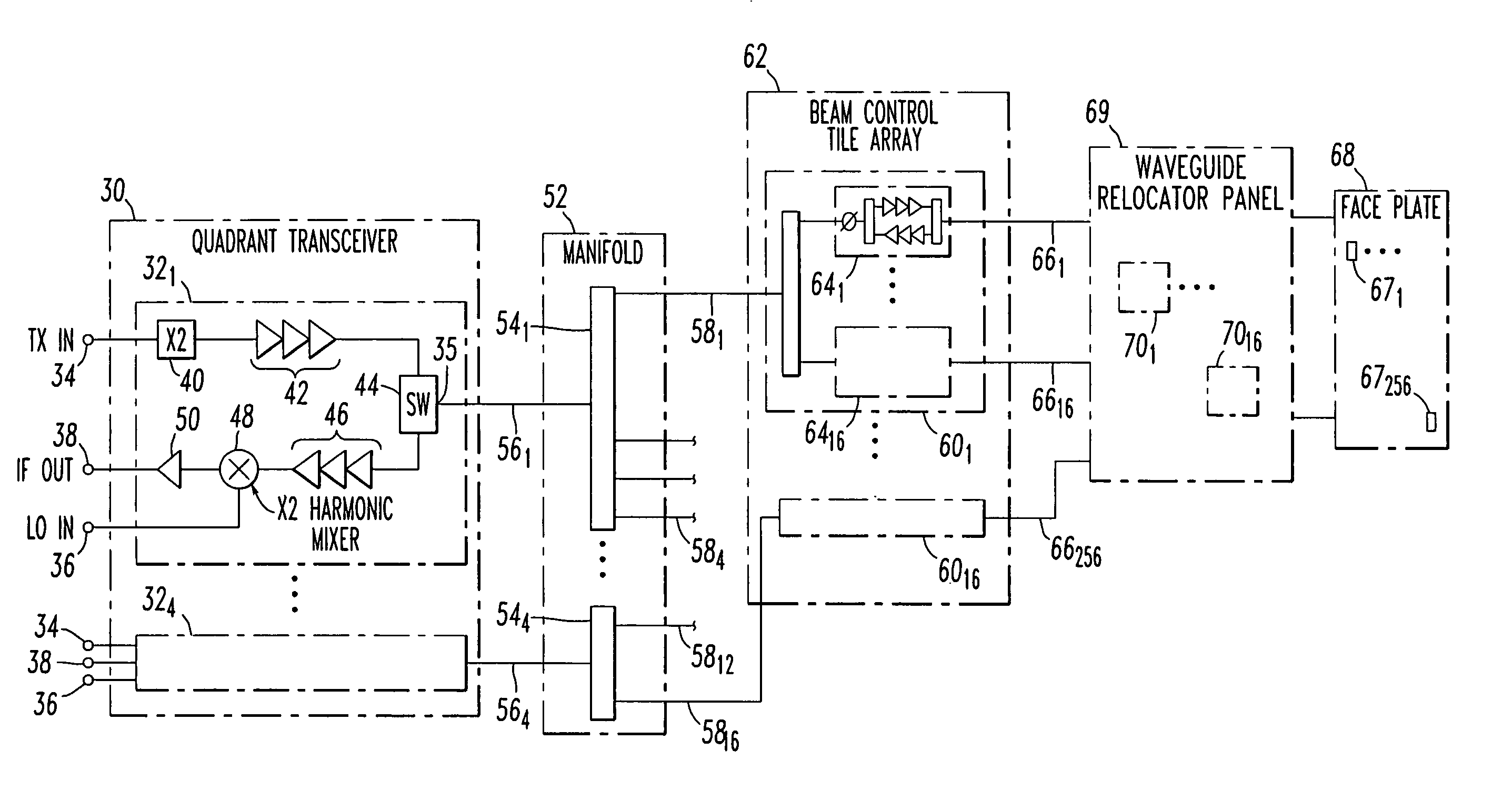
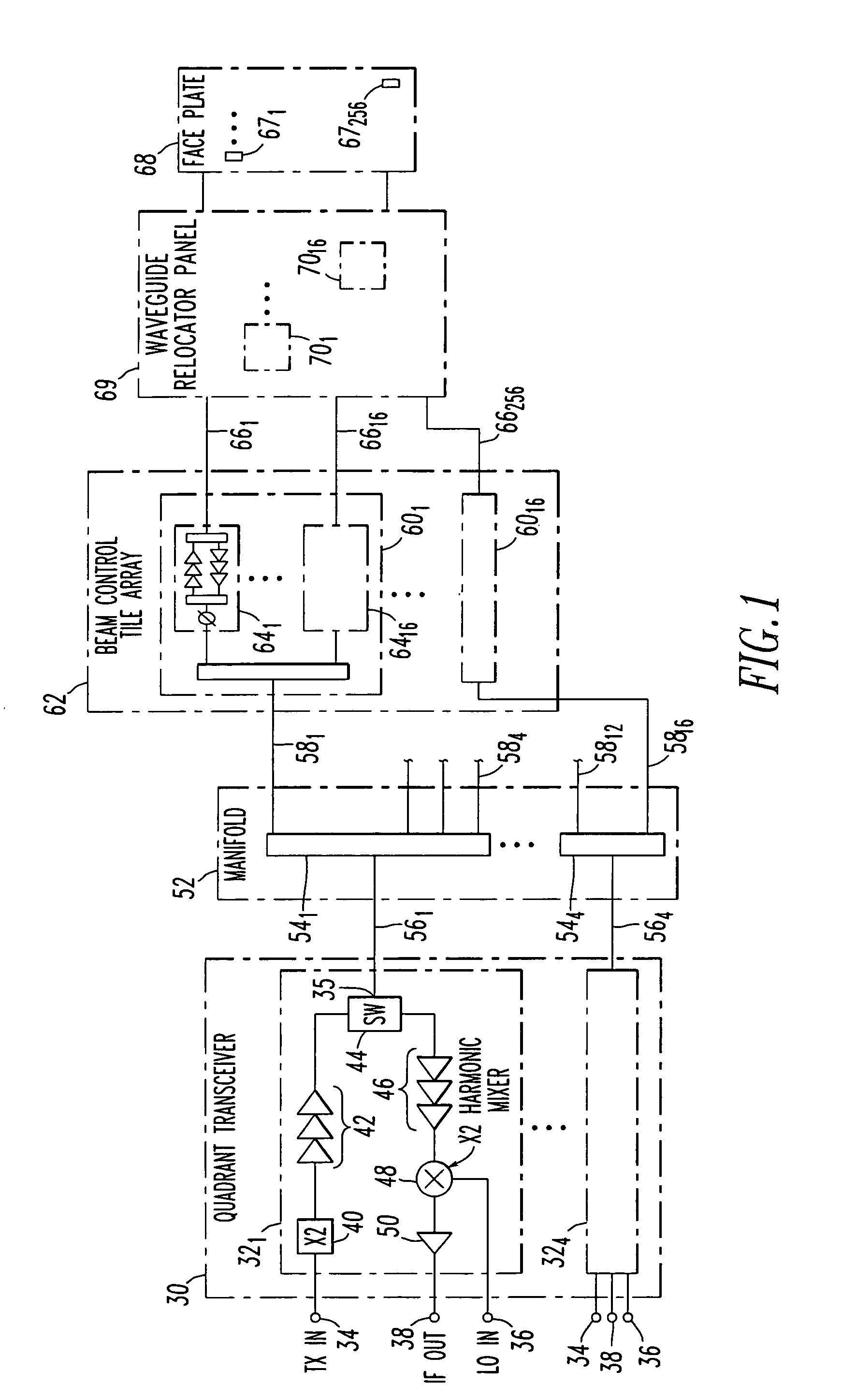
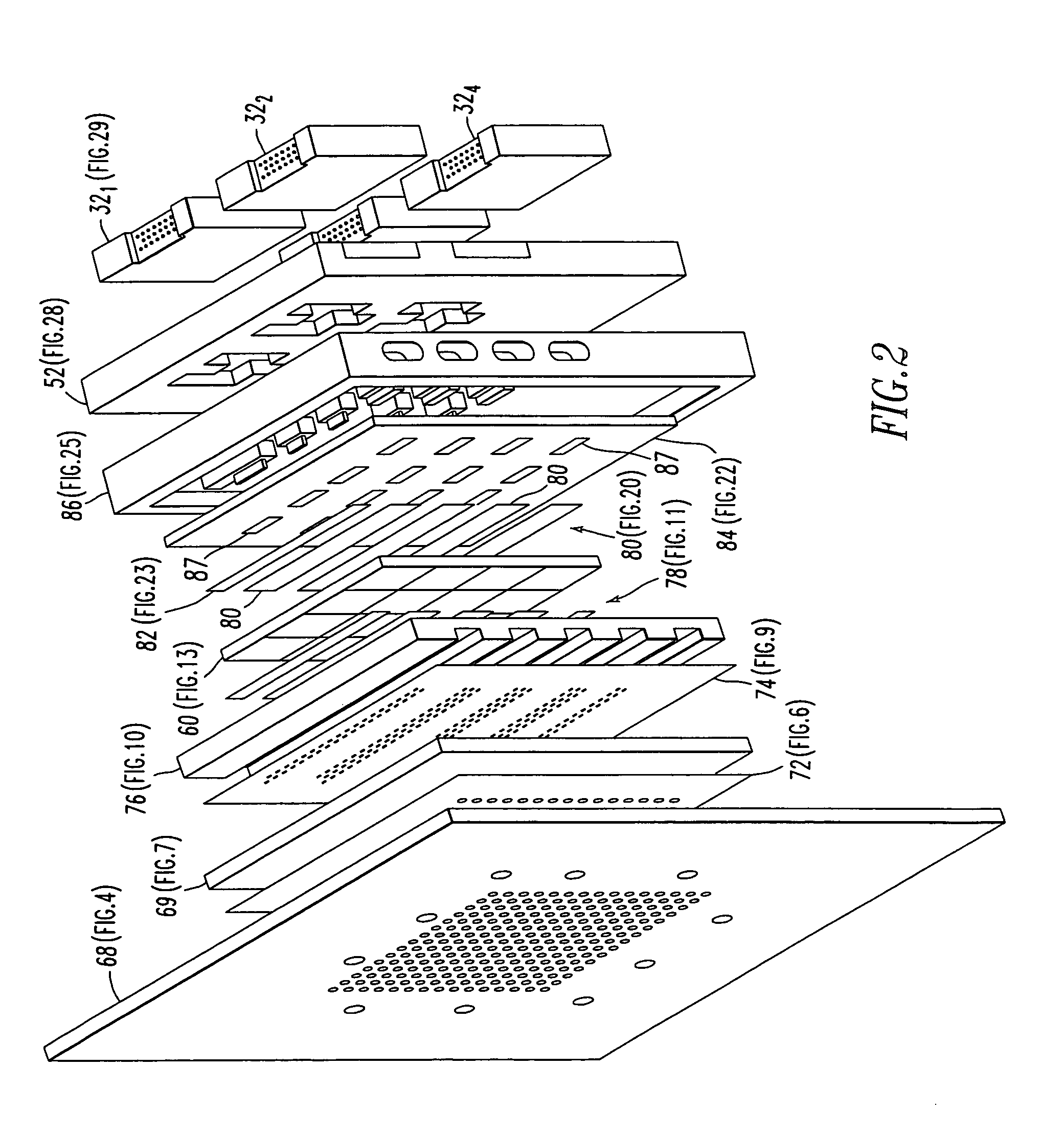
A vertically integrated Ka-band active electronically scanned antenna including, among other things, a transitioning RF waveguide relocator panel located behind a radiator faceplate and an array of beam control tiles respectively coupled to one of a plurality of transceiver modules via an RF manifold. Each of the beam control tiles includes a respective plurality of high power transmit / receive (T / R) cells as well as dielectric waveguides, RF stripline and coaxial transmission line elements. The waveguide relocator panel is preferably fabricated by a diffusion bonded copper laminate stack up with dielectric filling. The beam control tiles are preferably fabricated by the use of multiple layers of low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) material laminated together. The waveguide relocator panel and the beam control tiles are designed to route RF signals to and from a respective transceiver module of four transceiver modules and a quadrature array of antenna radiators matched to free space formed in the faceplate. Planar type metal spring gaskets are provided between the interfacing layers so as to provide and ensure interconnection between mutually facing waveguide ports and to prevent RF leakage from around the perimeter of the waveguide ports. Cooling of the various components is achieved by a pair of planar forced air heat sink members which are located on either side of the array of beam control tiles. DC power and control of the T / R cells is provided by a printed circuit wiring board assembly located adjacent to the array of beam controlled tiles with solderless DC connections being provided by an arrangement of “fuzz button” electrical connector elements.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Clip device for attaching structural member to a supporting structure
ActiveUS20130104493A1Easy to installEliminate needBuilding reinforcementsFlooringClip deviceStructural element
Owner:PAN AMERICAN SCREW
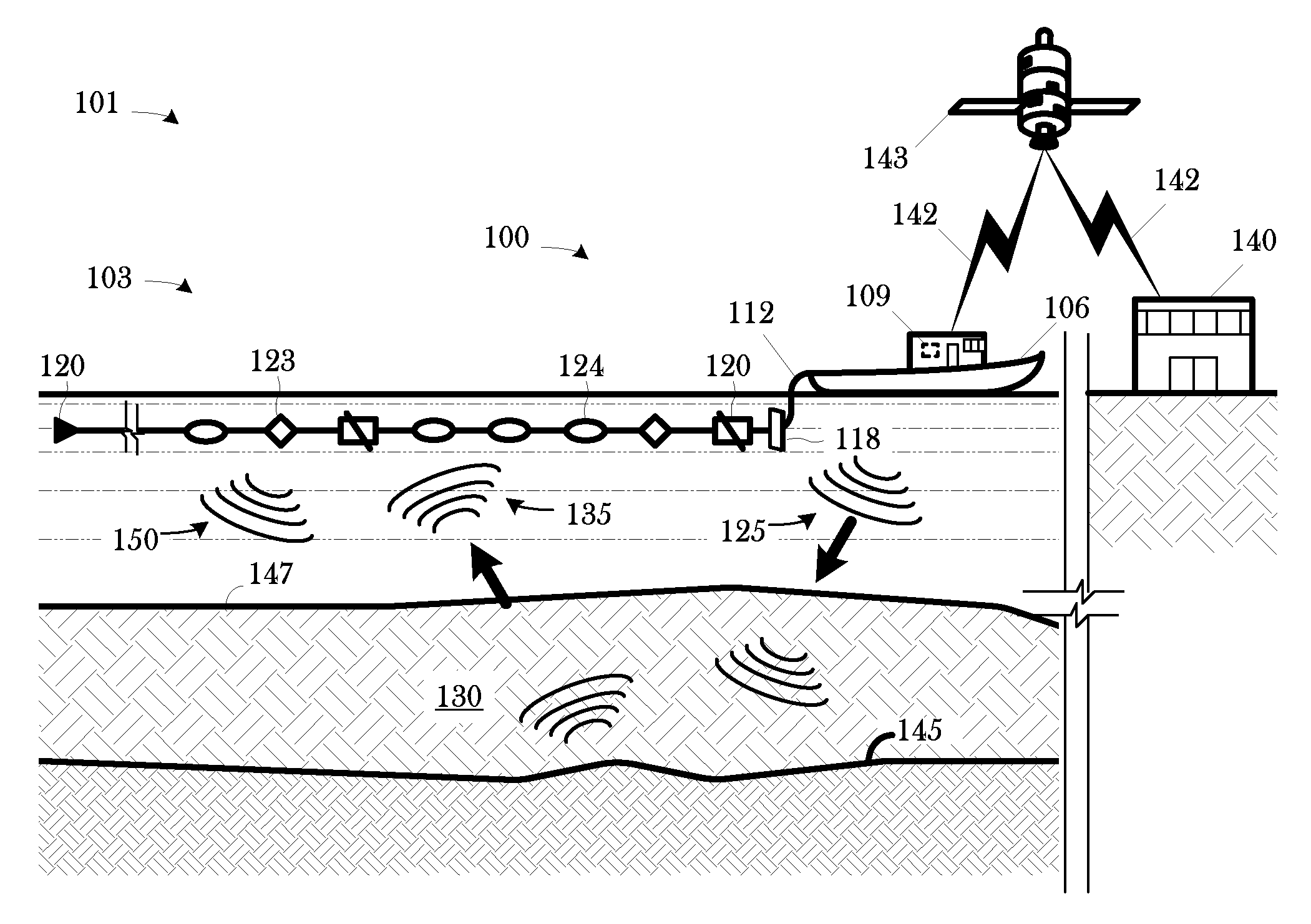
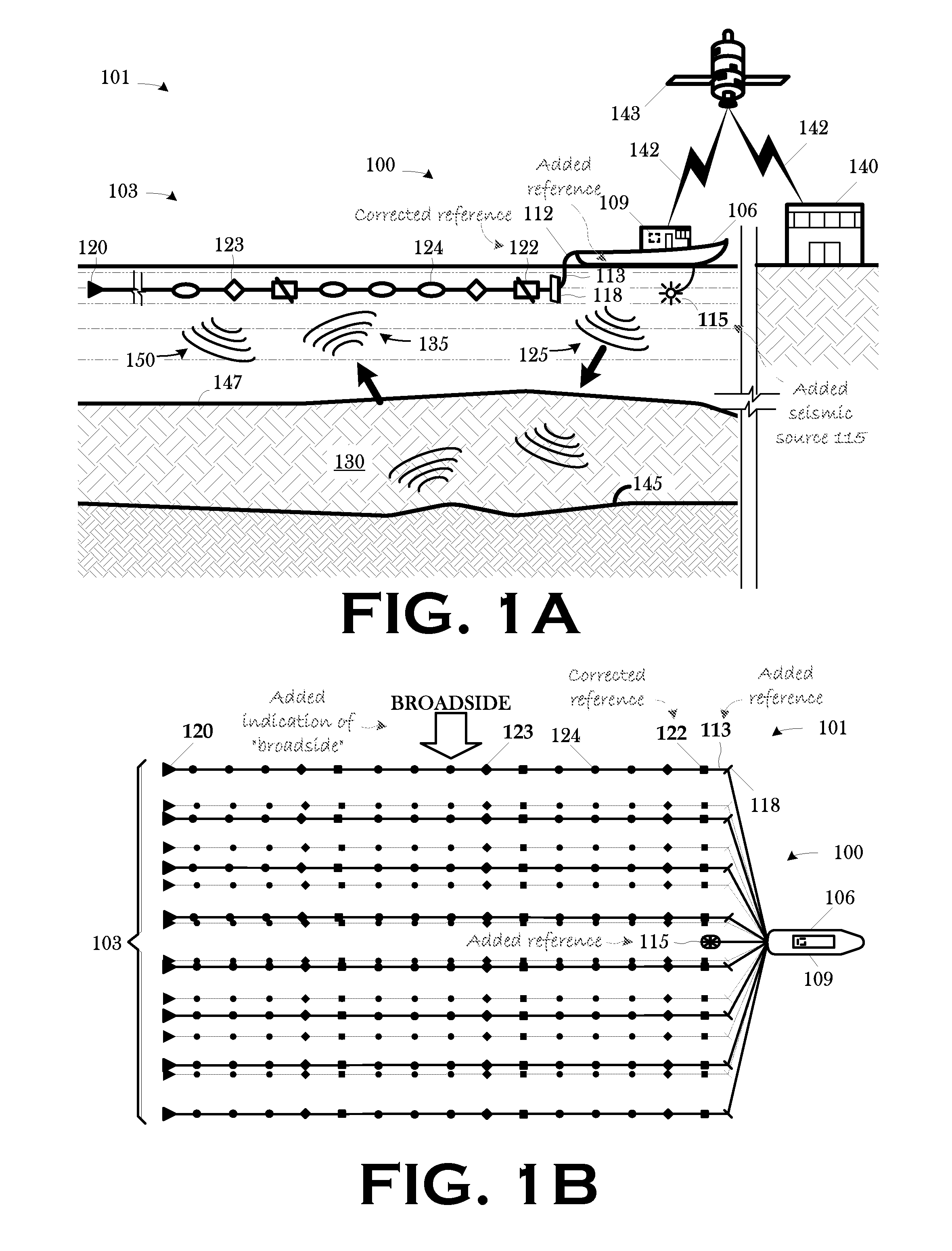
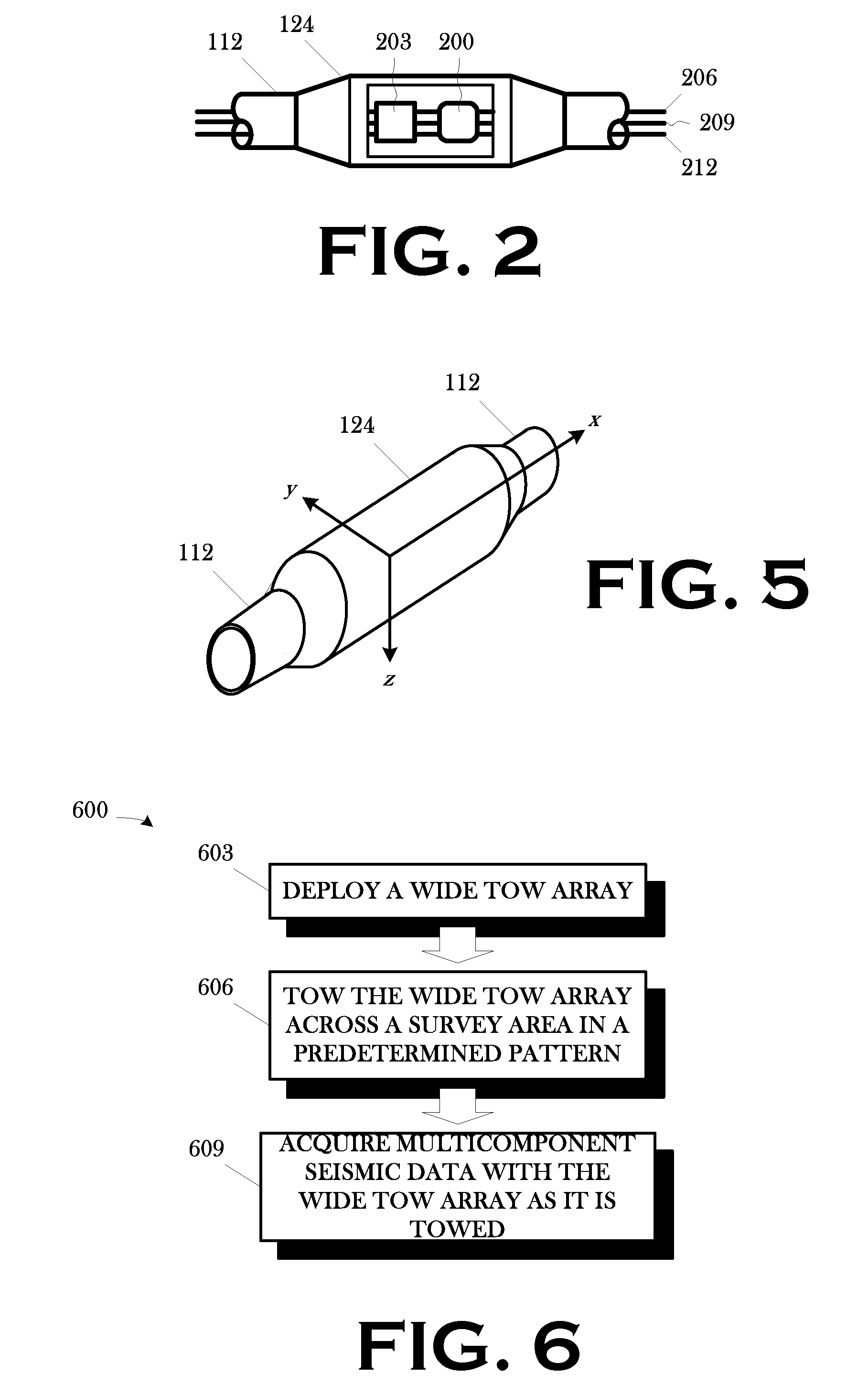
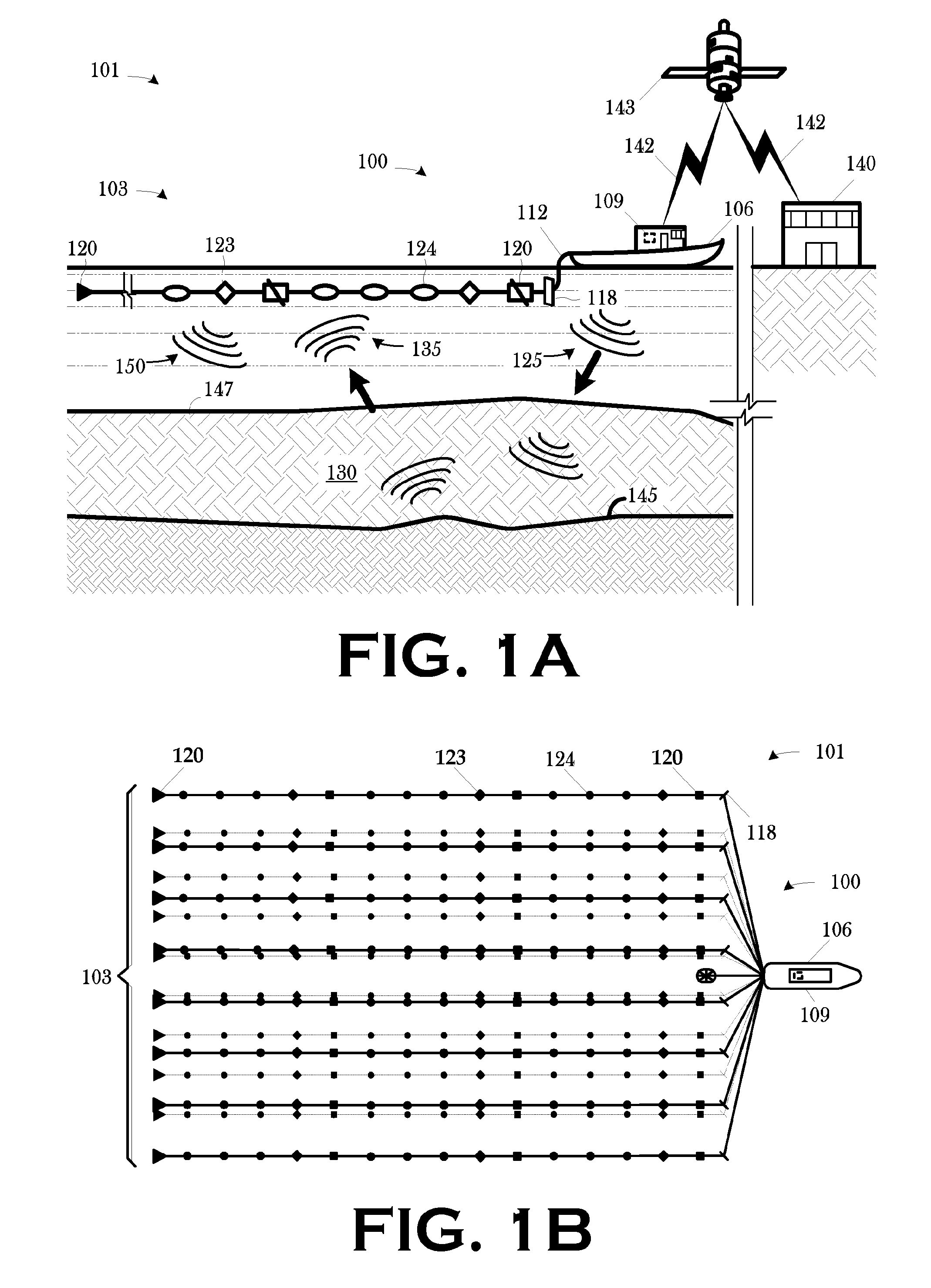
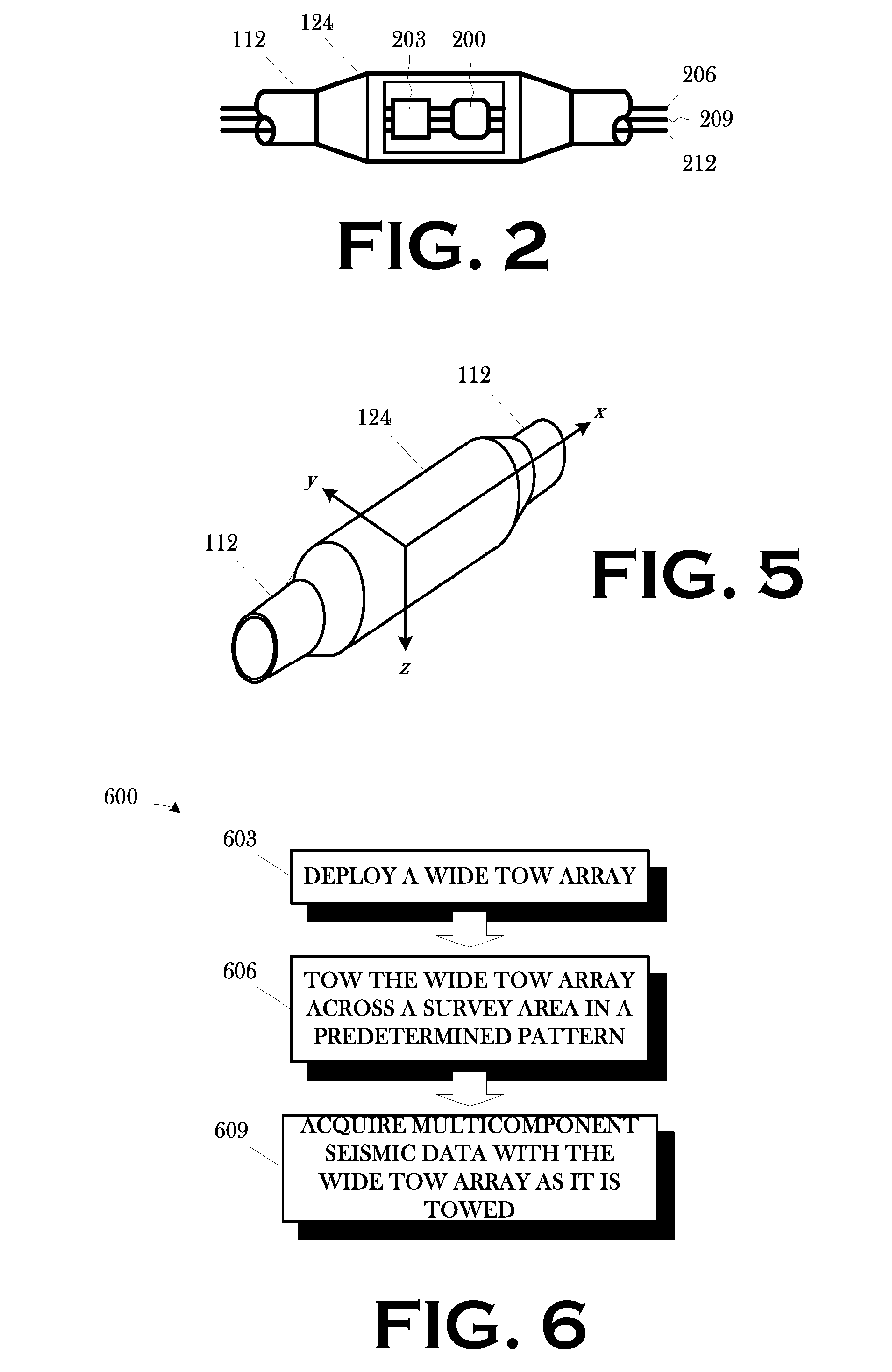
Wide tow enabled by multicomponent marine seismic cable
InactiveUS20080008036A1Space is requiredSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyGeophysics
A technique for use in towed-array, marine seismic surveys includes a method and an apparatus. The method includes accessing a set of multicomponent seismic data acquired in a wide tow, marine seismic survey; and interpolating a set of seismic data from the acquired seismic data in the crossline direction such that the combined acquired and interpolated seismic data meet the discrete spatial sampling theory requirements for array detection of broadside seismic signal and the discrimination and suppression of broadside linear noise. In some aspects, the technique includes programmed storage media and / or programmed computers for use in executing such a method. The apparatus is a wide tow array, including a plurality of streamers spaced apart by a cable separation exceeding the maximum cable spacing for array detection of broadside seismic signal and the discrimination and suppression of broadside linear noise as determined by discrete spatial sampling theory.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Clip device for attaching structural member to a supporting structure
Owner:PAN AMERICAN SCREW
Amplifier with low pass filter feedback
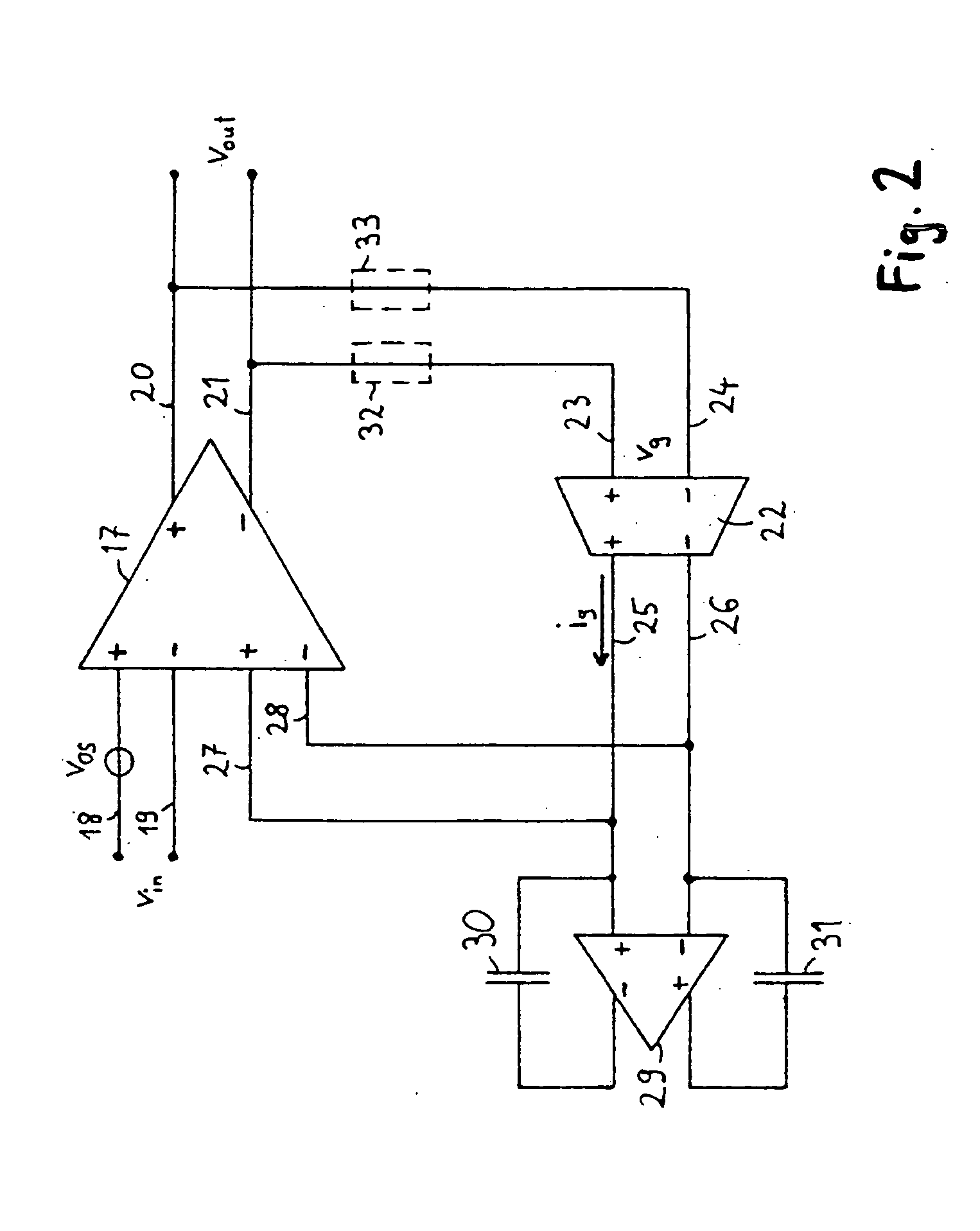
ActiveUS20060097782A1High voltageLarge capacitanceNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPulse automatic controlCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
An amplifier is described which amplifies an input signal according to a defined amplification factor, and which generates an output signal. To reduce an offset fraction of the output signal the amplifier comprises a feedback path which has lowpass characteristics and which returns the output signal in a lowpass-filtered state to an input of the amplifier. The feedback path comprises an amplifier stage as well as at least one Miller capacitance connected between an input and an output of the amplifier stage.
Owner:NAT SEMICON GERMANY
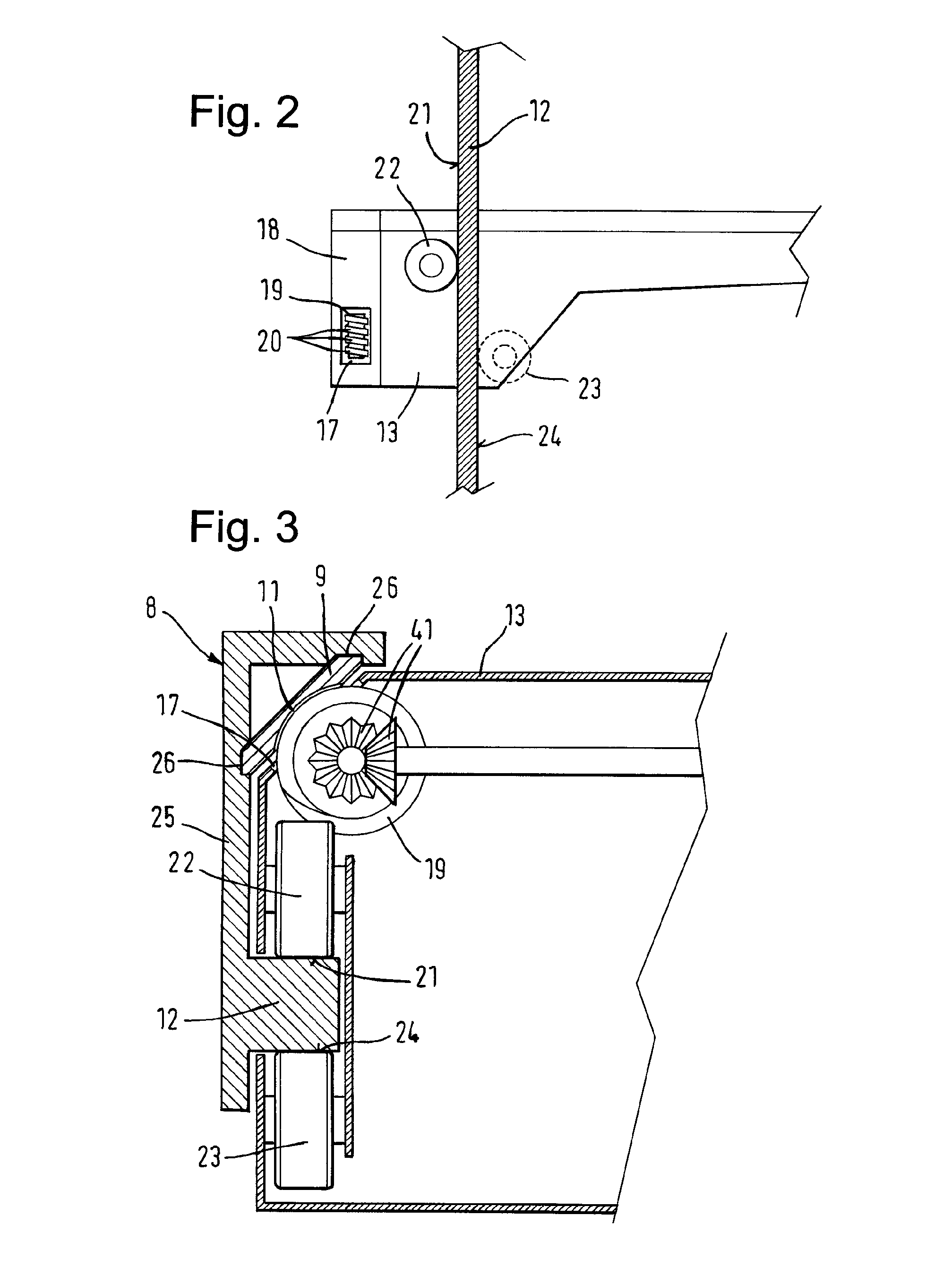
Freewheel bearing device with torque limiter
InactiveUS20070074945A1Run economyReduced risk of breakageBearing assemblyMechanical actuated clutchesFreewheelRadial plane
The invention concerns a freewheel bearing device including an outer element and inner element arranged inside the outer element, and a free wheel provided with at least a wedging element, arranged between the inner element and the outer element to allow a free rotational movement in one direction between the outer element and the inner element and for transmission of a torque in the other direction between the outer element and the inner element, the free wheel including a ring provided with a cylindrical inner surface and a cylindrical outer surface, substantially aligned on a radial plane perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the device, and a torque limiting member adapted to limit the torque transmitted by the free wheel, the torque limiting member being arranged radially between said ring and the outer element or the inner element in contact with said ring and said element.
Owner:SKF FRANCE
Tactile display device
ActiveUS20130004922A1Small thicknessEasy to handleTeaching apparatusInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceTactile display
Actuators are disposed between a lower wiring substrate and an upper wiring substrate. The actuators, the lower wiring substrate, and the upper wiring substrate are interposed between a lower frame and an upper frame. The end of each actuator is held between pushing parts of the lower frame and upper frame. The free ends of the actuators move projections upward that are displayed in a tactile display.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Wide tow enabled by multicomponent marine seismic cable
ActiveUS20090040871A1Space is requiredSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyGeophysics
A technique for use in towed-array, marine seismic surveys includes a method and an apparatus. The method includes accessing a set of multicomponent seismic data acquired in a wide tow, marine seismic survey; and interpolating a set of seismic data from the acquired seismic data in the crossline direction such that the combined acquired and interpolated seismic data meet the discrete spatial sampling theory requirements for array detection of broadside seismic signal and the discrimination and suppression of broadside linear noise. In some aspects, the technique includes programmed storage media and / or programmed computers for use in executing such a method. The apparatus is a wide tow array, including a plurality of streamers spaced apart by a cable separation exceeding the maximum cable spacing for array detection of broadside seismic signal and the discrimination and suppression of broadside linear noise as determined by discrete spatial sampling theory.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Elevator door system
InactiveUS7246688B2Space is requiredMan-operated mechanismPower-operated mechanismSimulationDrive motor
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
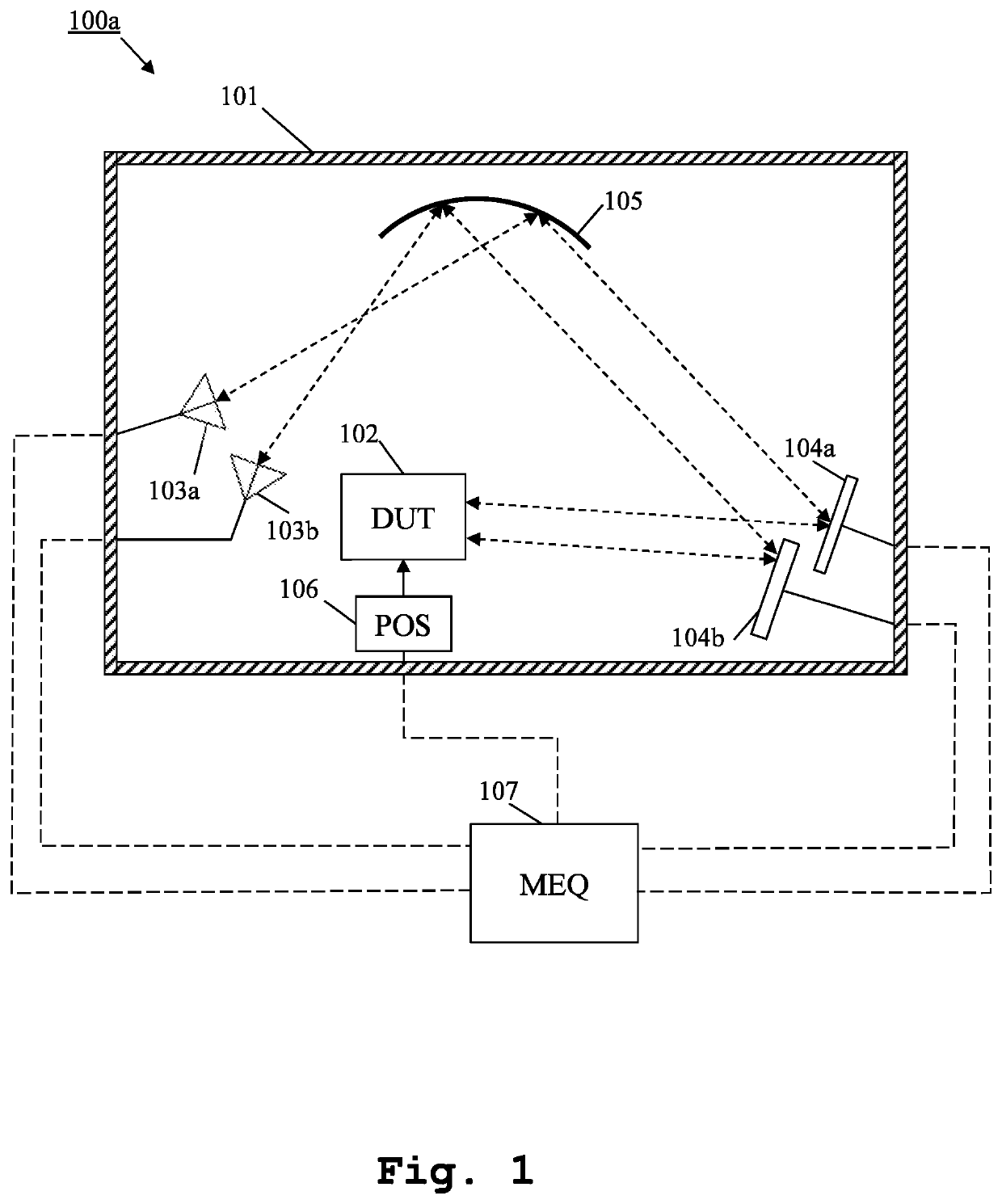
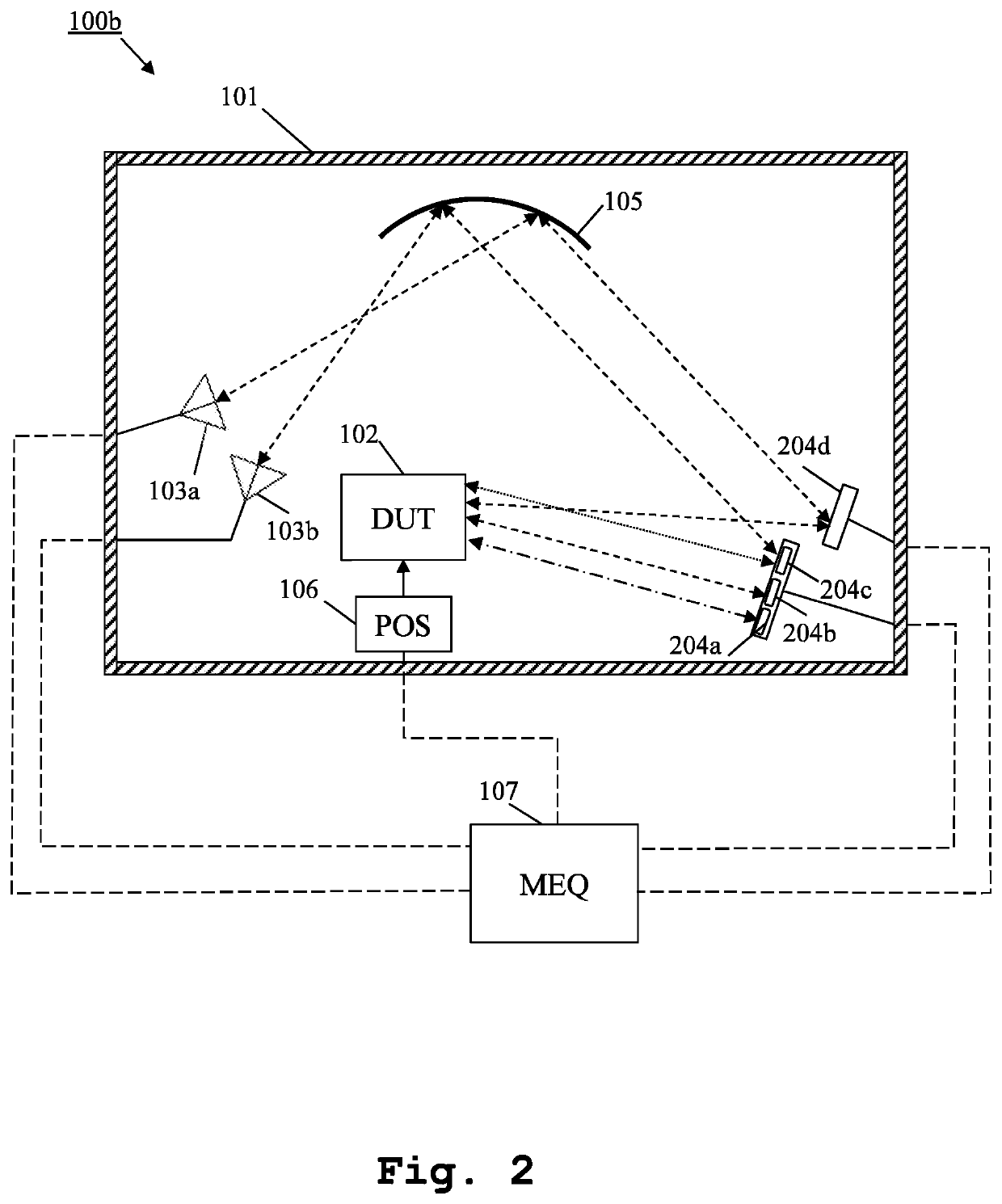
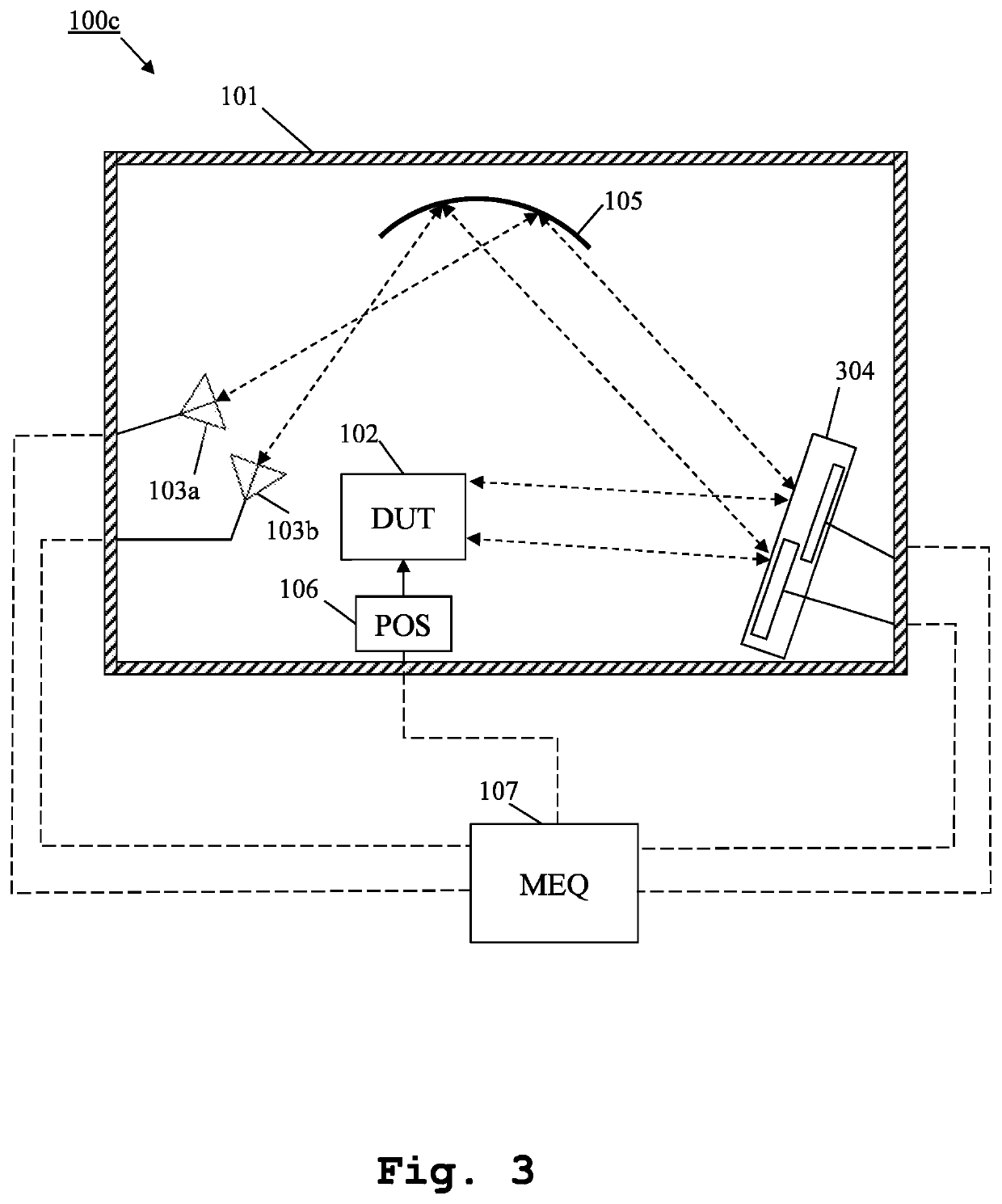
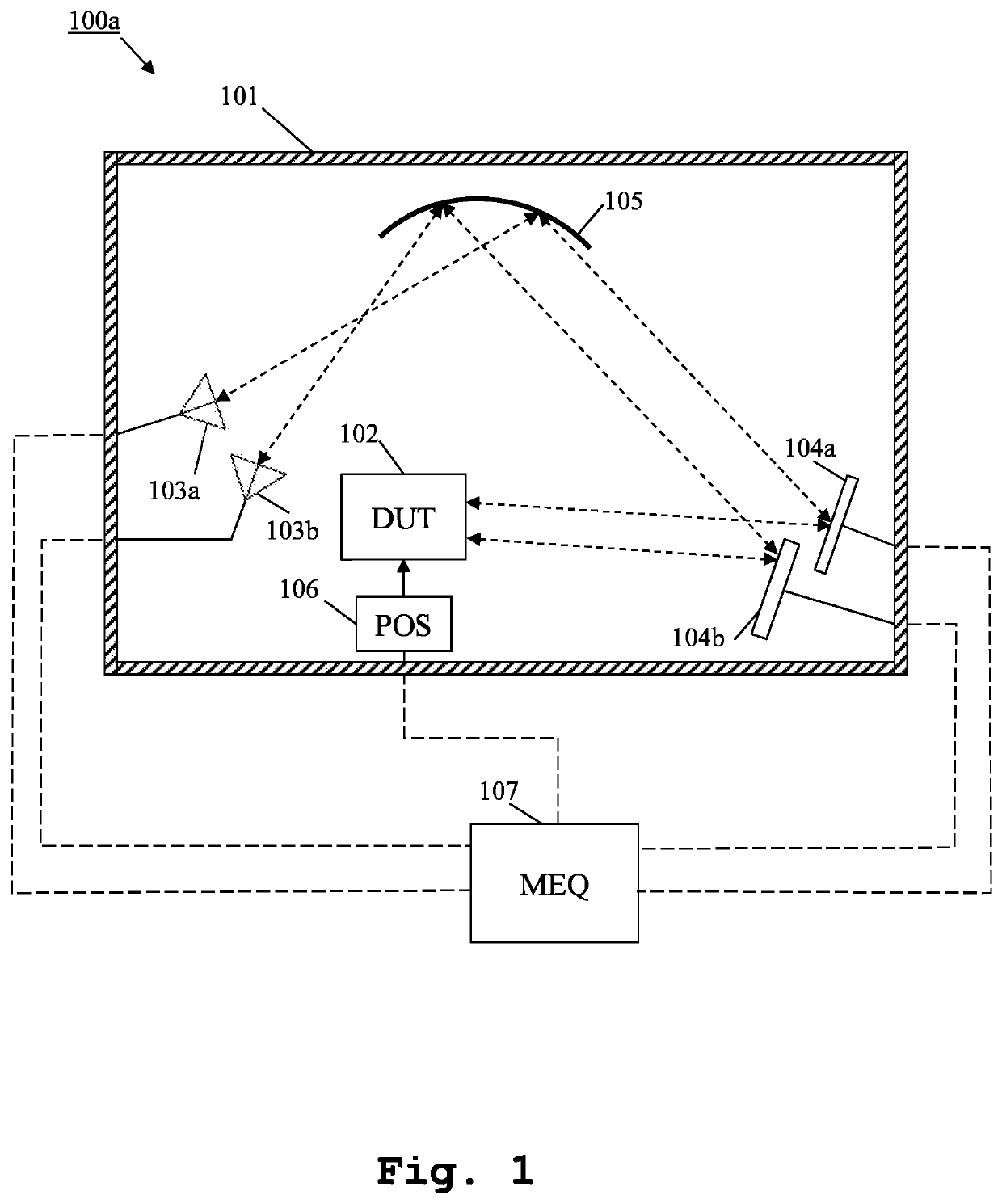
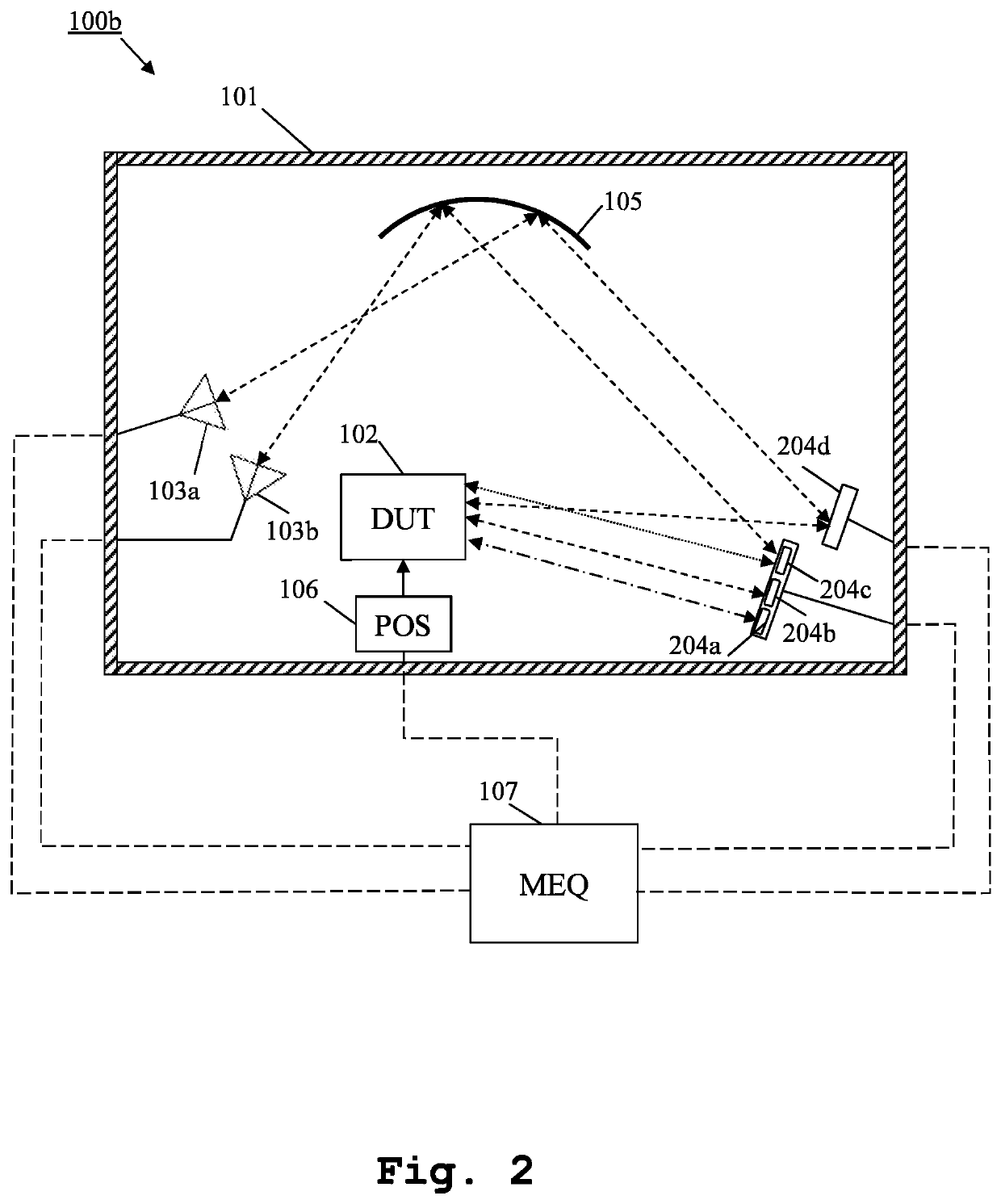
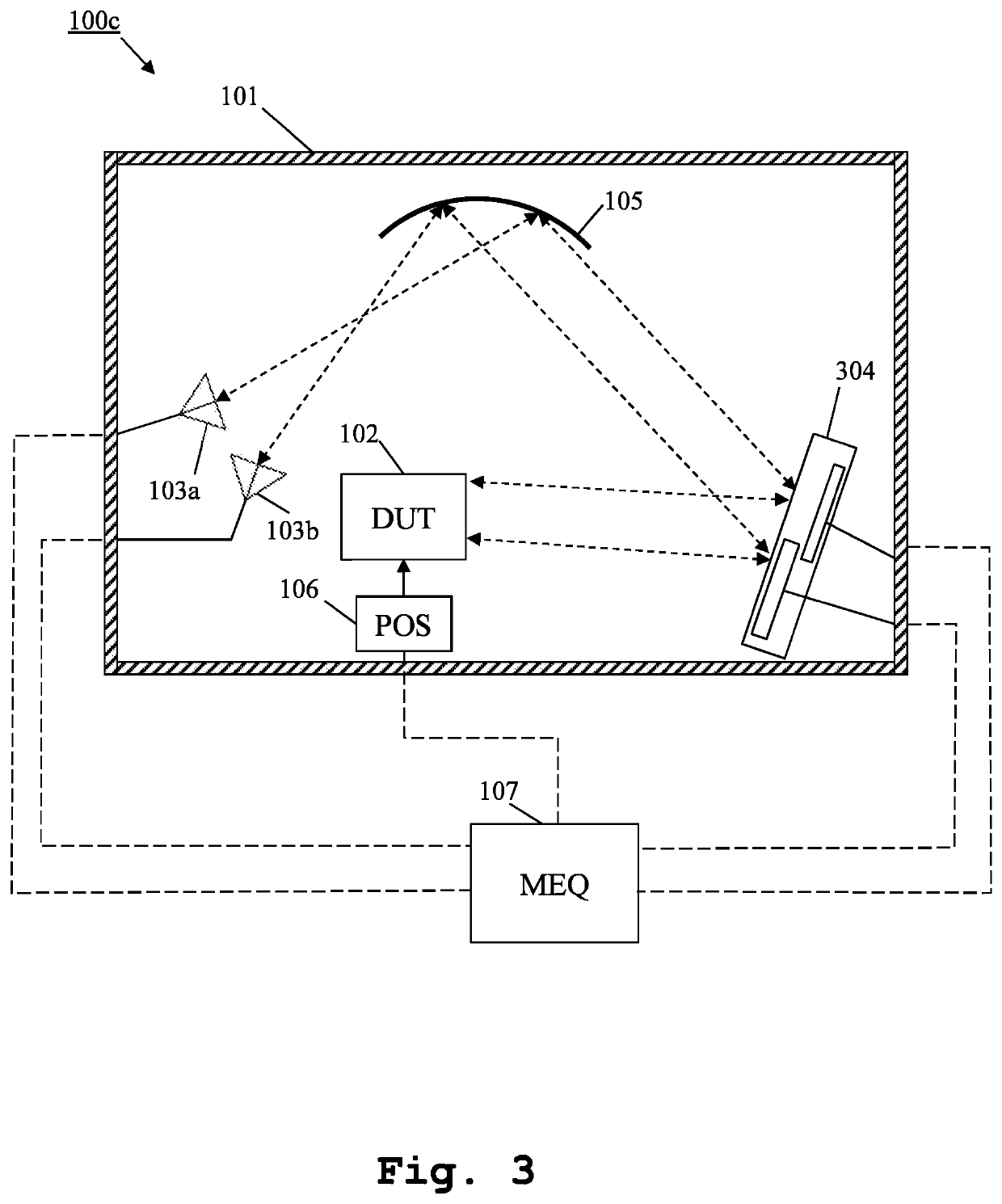
Measurement system and method for multiple antenna measurements with different angles of arrival
ActiveUS20200217885A1Quick switchImprove accuracySolid-state devicesRadiofrequency circuit testingEquipment under testEngineering
A measurement system and method for over the air multiple antennas measurements are provided. The measurement system comprises, inside an anechoic chamber, a device under test, several measurement antennas, several mirrors and at least one shaped reflector. The measurement antennas are placed pointing at the shaped reflector. Each of the mirrors is placed along fields reflected by the shaped reflector. The mirrors reflect fields that form different angles of arrival at the device under test.
Owner:ROHDE & SCHWARZ GMBH & CO KG
Method and apparatus of growing a thin film
InactiveUS7060132B2Improve throughputSimple requirementsPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesSurface reactionEngineering
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Refrigerator with height-adjustable shelf for refrigerated goods
InactiveUS8529001B2Space is requiredReduced drive mechanismLighting and heating apparatusFurniture partsEngineeringHorizontal orientation
A refrigeration appliance includes a housing and toothed profiles which are fixed to the housing. A height-adjustable shelf for refrigerated goods is received in the housing. The shelf has two rotatably drivable screws in engagement with the toothed profiles such that a storage surface of the shelf is held at least approximately in a horizontal orientation.
Owner:BSH BOSCH & SIEMENS HAUSGERAETE GMBH
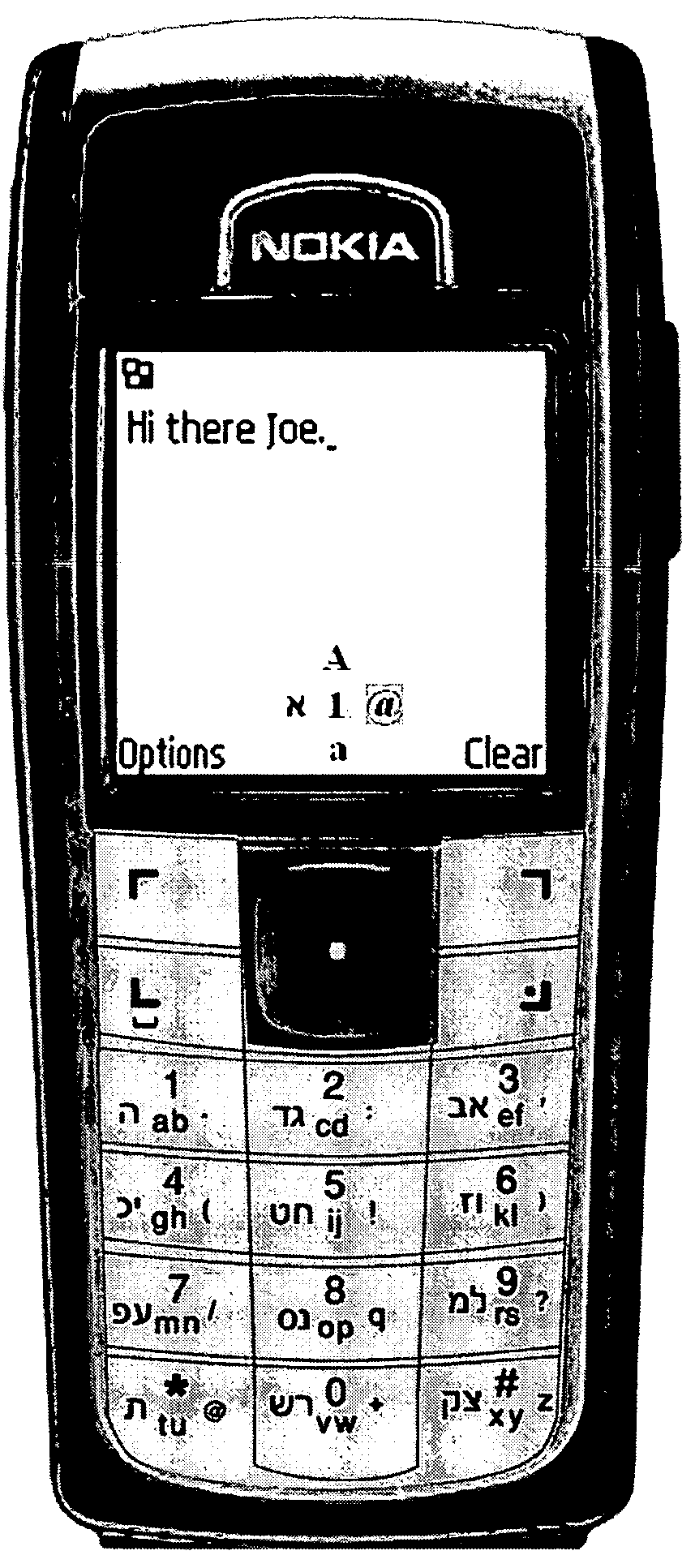
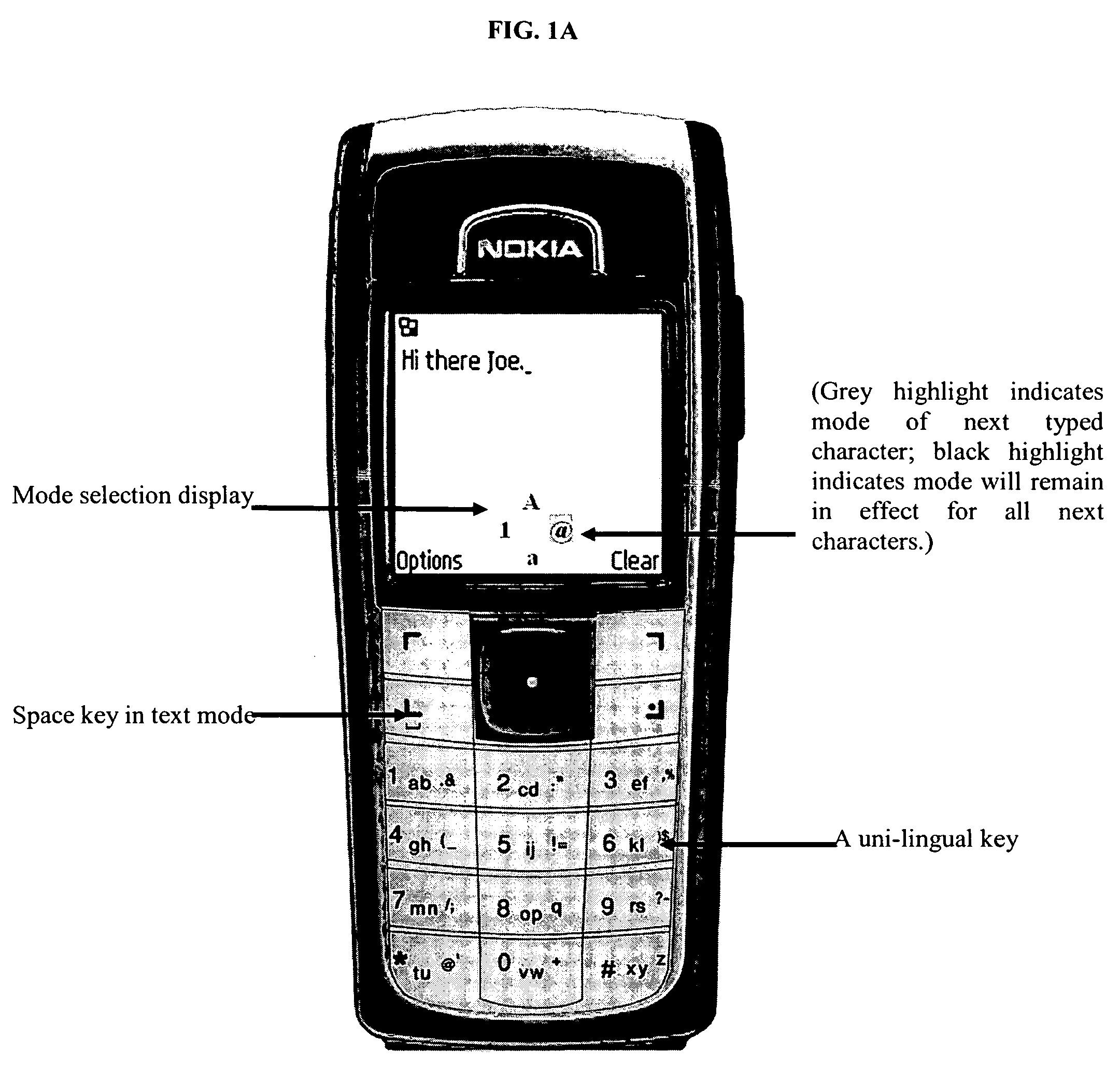
Method for assigning large sets of characters in different modes to keys of a number keypad for low keypress-data-entry ratio
InactiveUS7320111B2Easy to operateEasy to useAlphabetical characters enteringTelephone set constructionsKey assignmentMulti language
A key assignment method assigns large sets of alphabetic and other characters and functions to the keys of a standard numeric keypad for text / data entry on an electronic device. Two letters are assigned in pairs to each key of the standard 12-key keypad in a first character mode, and other symbols, characters, or infrequently used letters are assigned in a second or more optional character modes. A mode selection key is provided to select between the modes. In the first character mode, a keypress of a key selects the first letter of the pair and two keypresses in succession selects the second letter. The letter pairs may be assigned in alphabetic order, except for infrequently used letters, such as ‘Q’ and ‘Z’, or in QWERTY order, or in pairs of a more frequently-used letter with a less frequently-used letter. By comparison to the standard phone keypad layout having an average KPD=2.2, this method can achieve a KPD=1.4 or lower. The standard directional arrow keys (RDI keys) may be used for mode selection in multiple character modes. Using the RDI mode selector can transform the conventional 12-key telephone keypad into the equivalent of a 60-key data entry layout (or expandable by 48 more keys for each additional mode keystroke used), thereby allowing operation comparable to a full QWERTY keyboard of characters, with enhanced symbols and functions, and / or with multi-language character sets.
Owner:DIAMOND DISTRIBUTORS
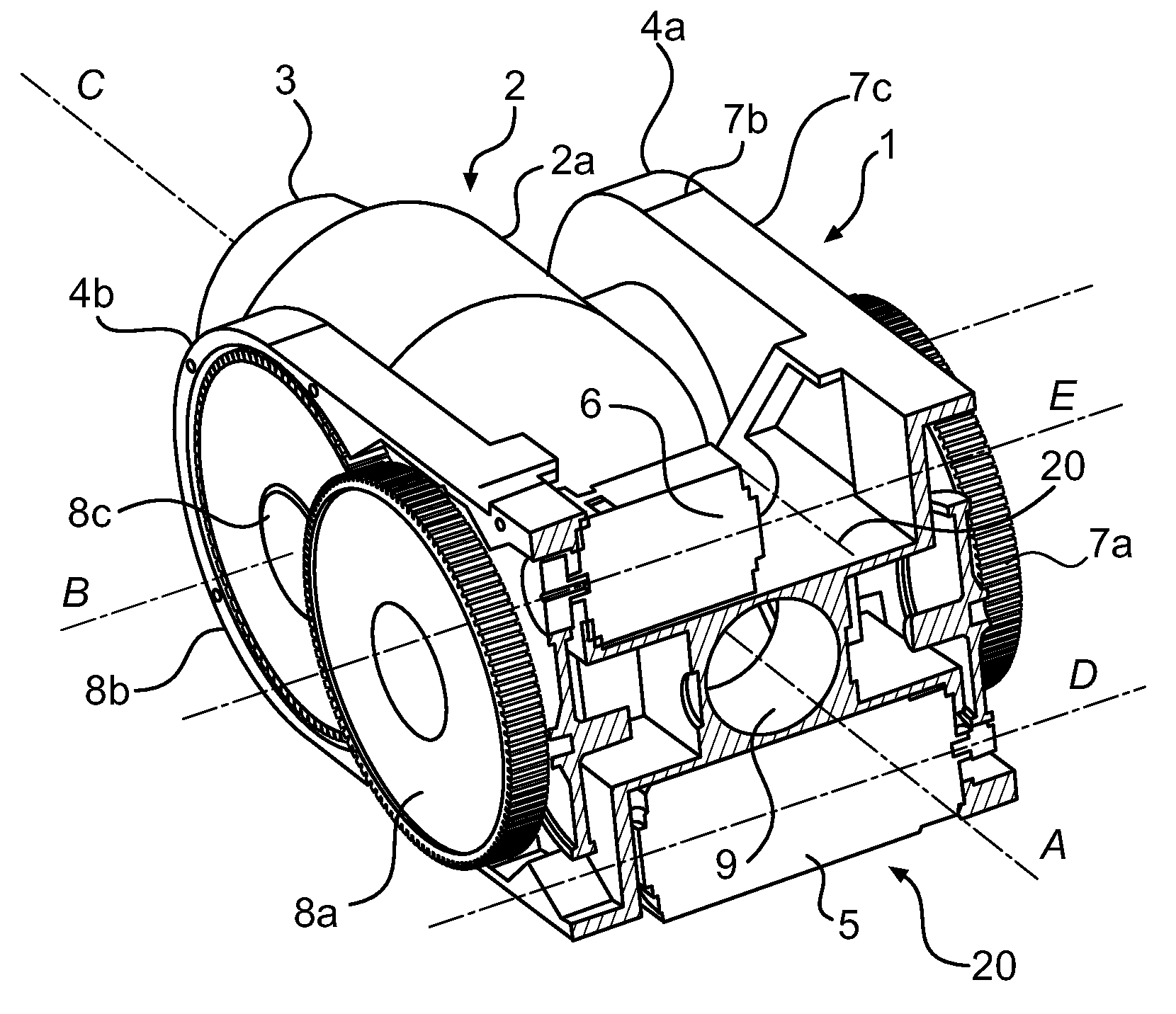
Industrial robot
ActiveUS7806020B2Improve accessibilityMinimized dimensionProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusMotor driveControl theory
A robot arm for an industrial robot. The robot arm includes a wrist housing, a wrist, and a turn disc. The wrist is rotatably connected to the wrist housing and the turn disc is rotatably connected to the wrist. A first motor drives the wrist and a second motor drives the turn disc. A first driving rope transmits the motor rotation to the wrist, and a second driving rope transmits the motor rotation to the drive pulley.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
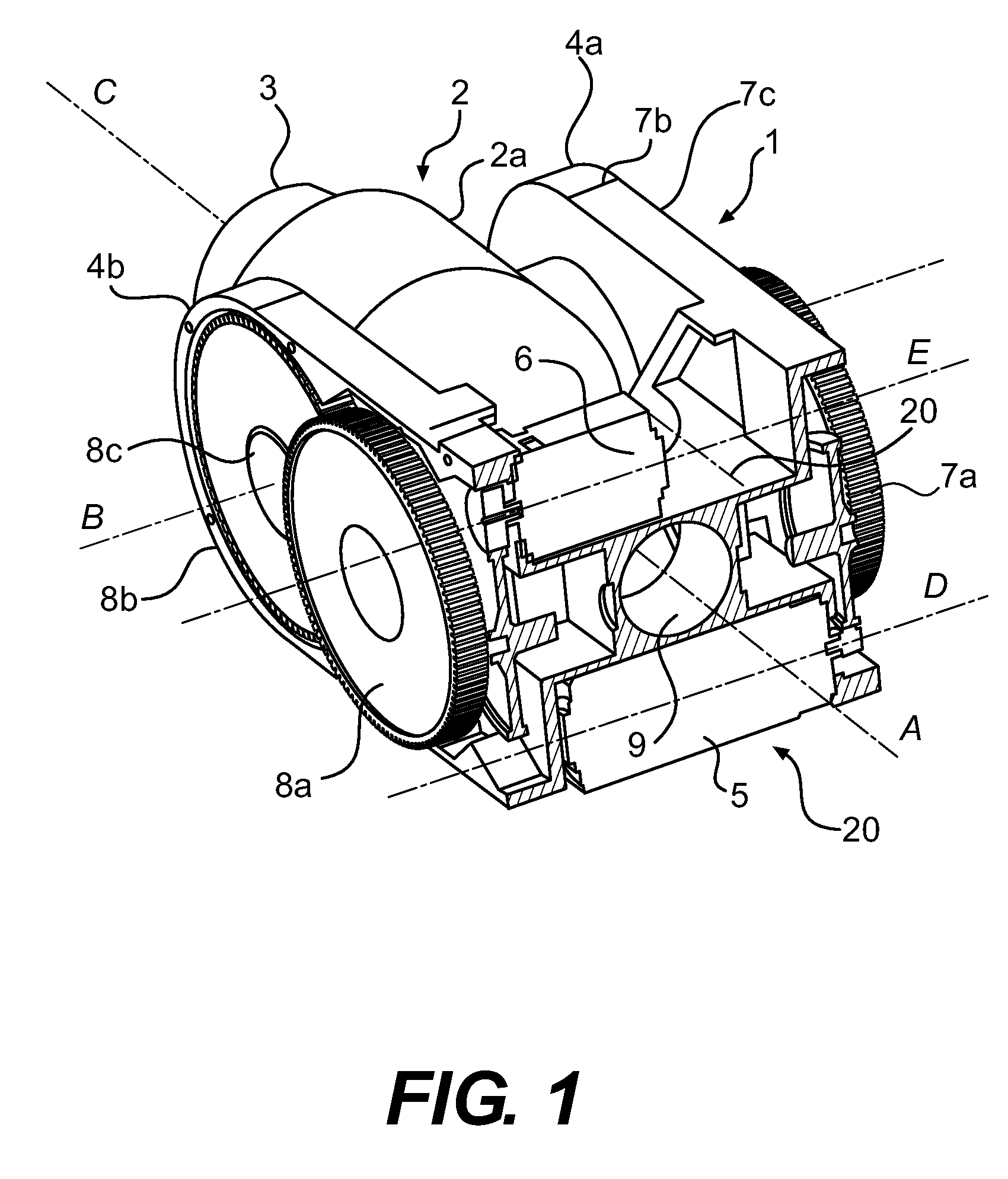
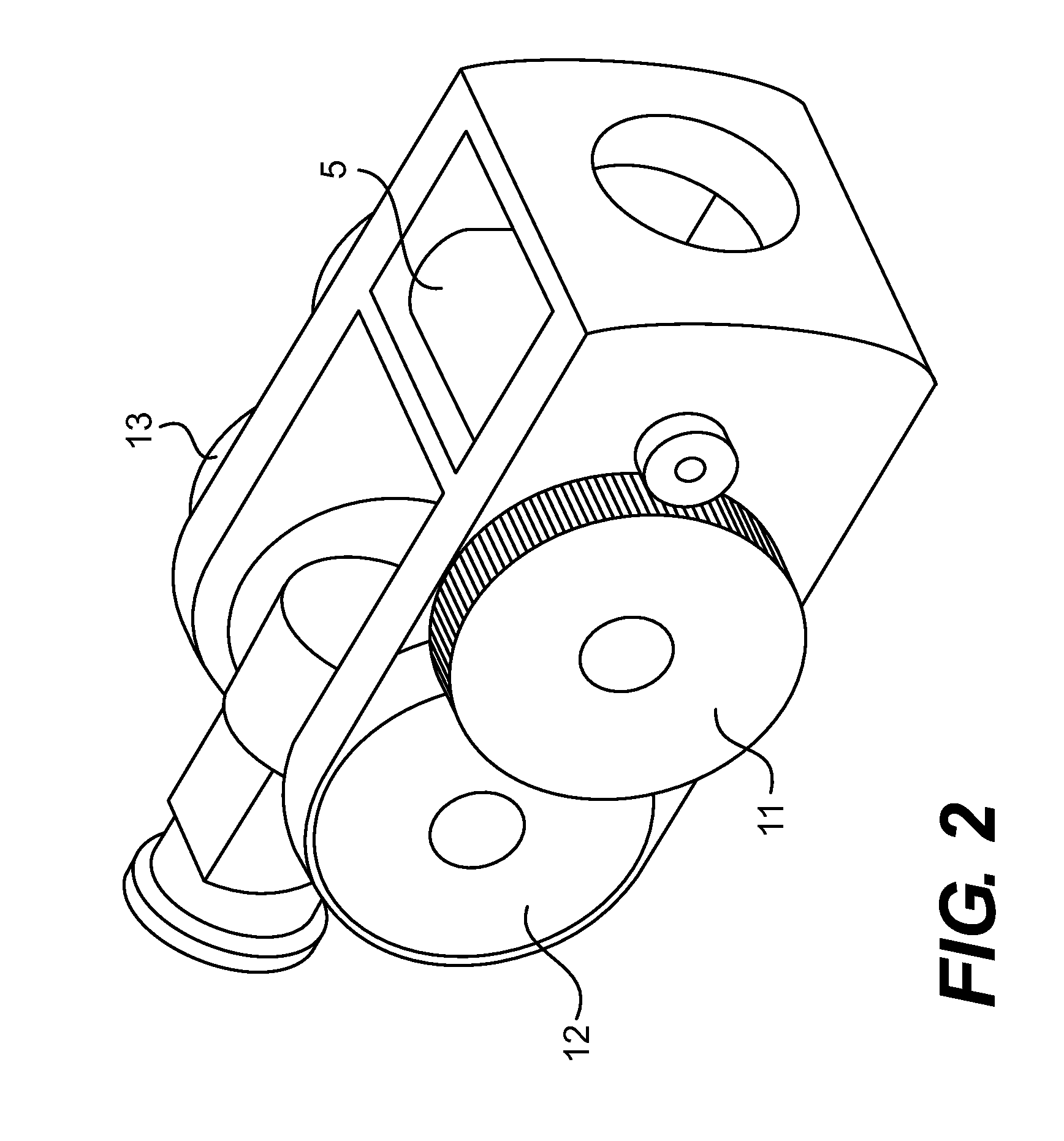
Lifting column and drive system for a lifting system of a furniture
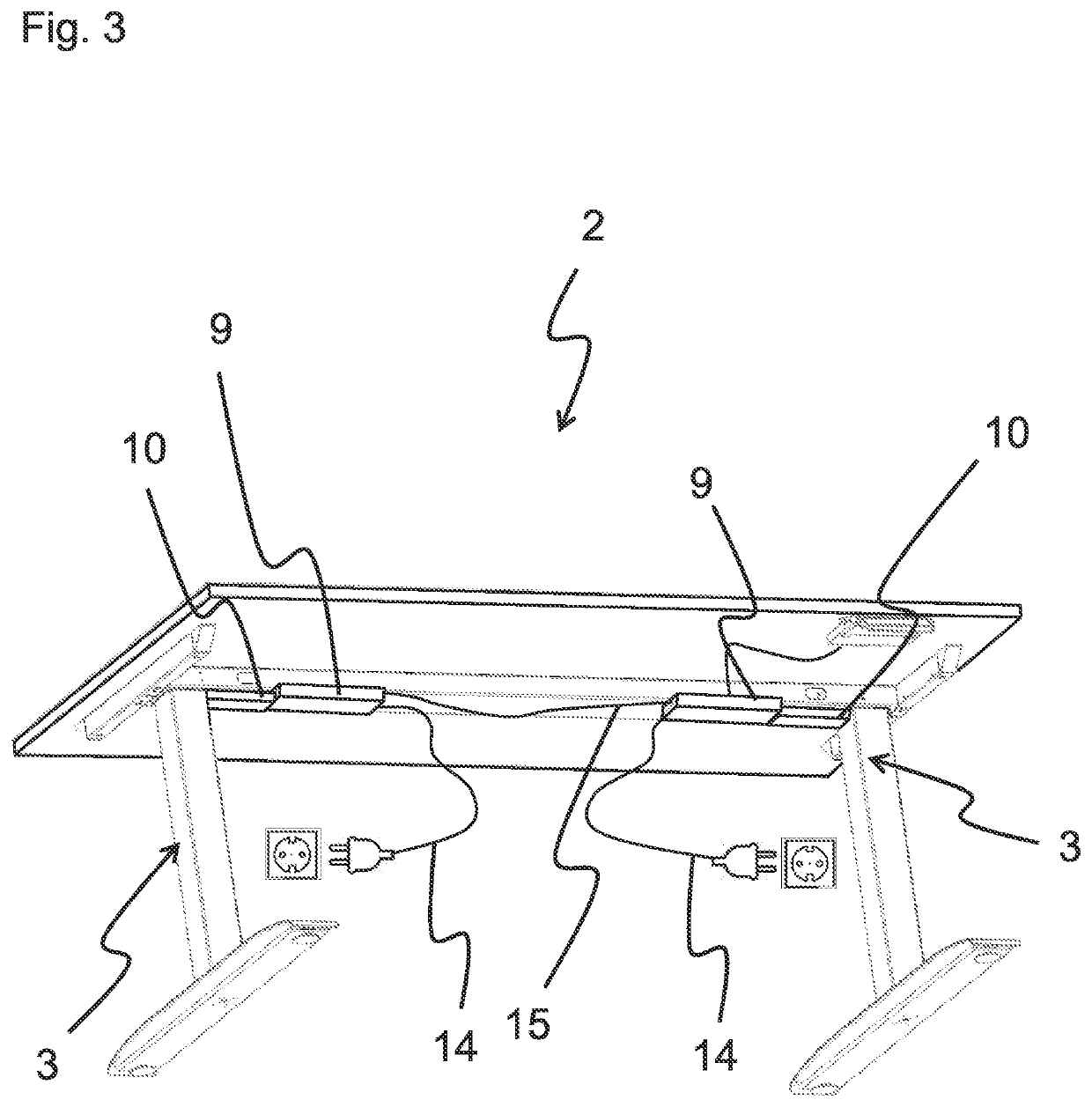
PendingUS20220031062A1Easy to set upEnsure normal communicationLifting devicesFurniture partsLinear motionHigh-voltage direct current
A lifting column (3) for a lifting system (2) of a furniture is provided. The lifting column (3) comprises at least two tube portions (4, 5) displaceable with respect to one another like a telescope, a high-voltage direct-current motor (6) and a transmission (7) for transforming a rotational motion into a linear motion, wherein the high-voltage direct-current motor (6) and the transmission (7) are arranged inside at least one of the at least two tube portions (4, 5) displaceable with respect to one another like a telescope.
Owner:KESSEBOHMER HLDG KG
Carbon NANO tube coating apparatus and method thereof
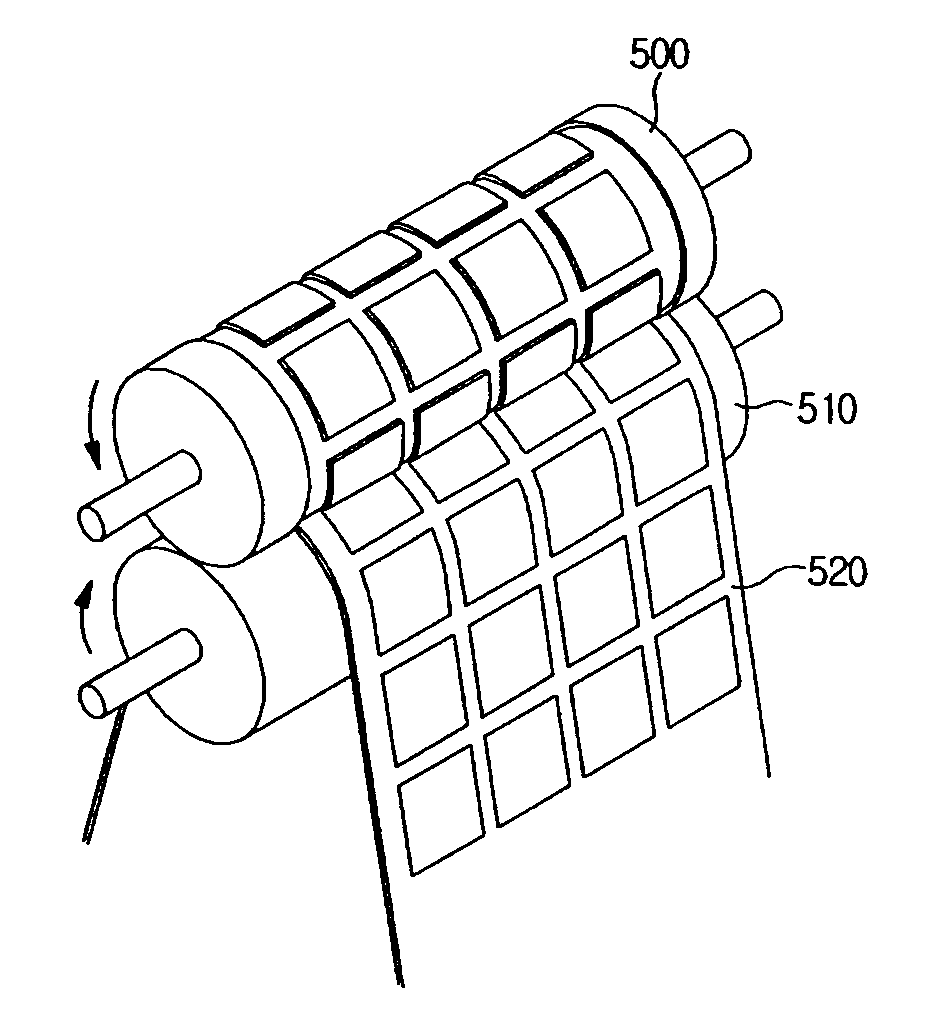
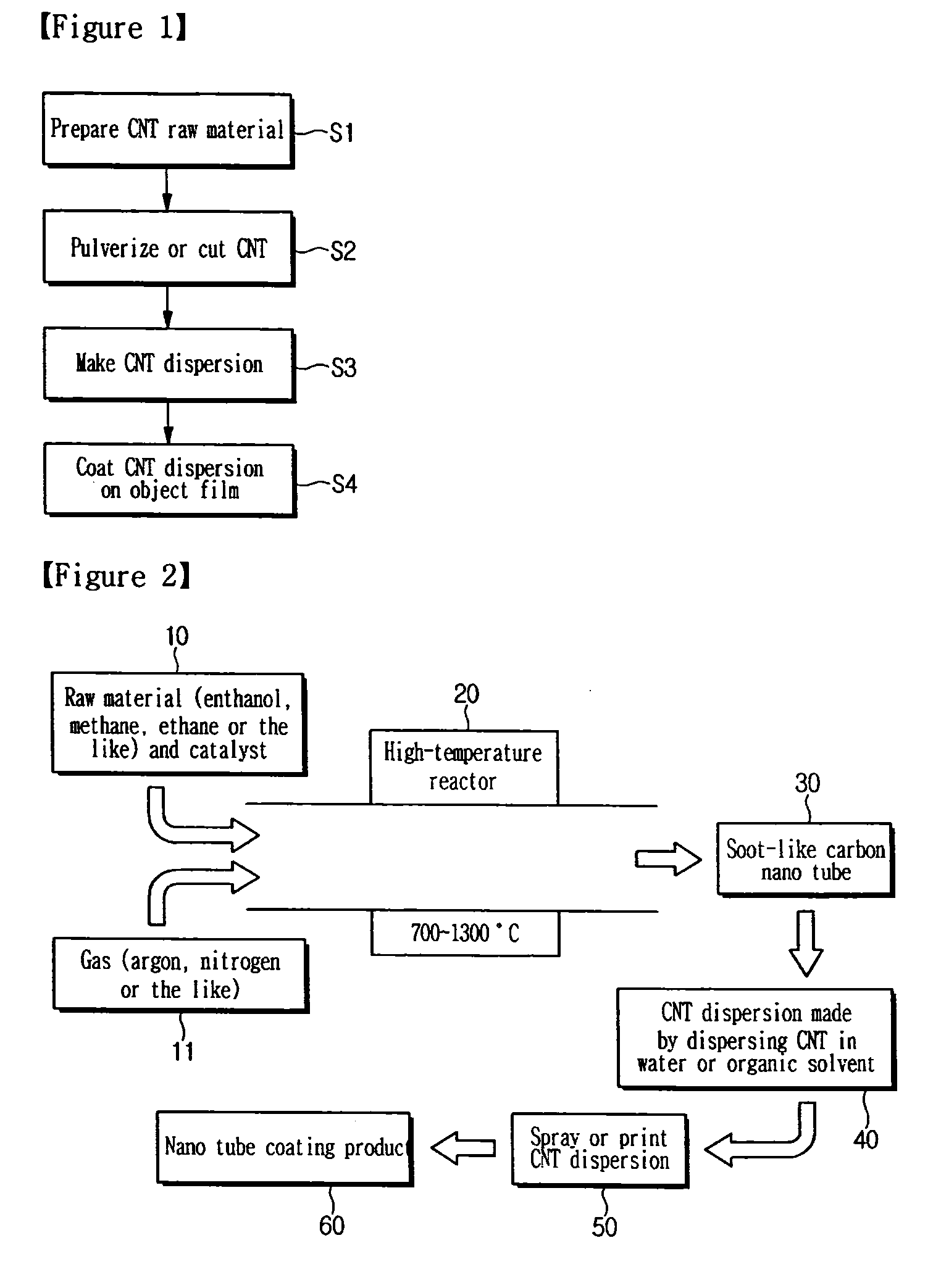
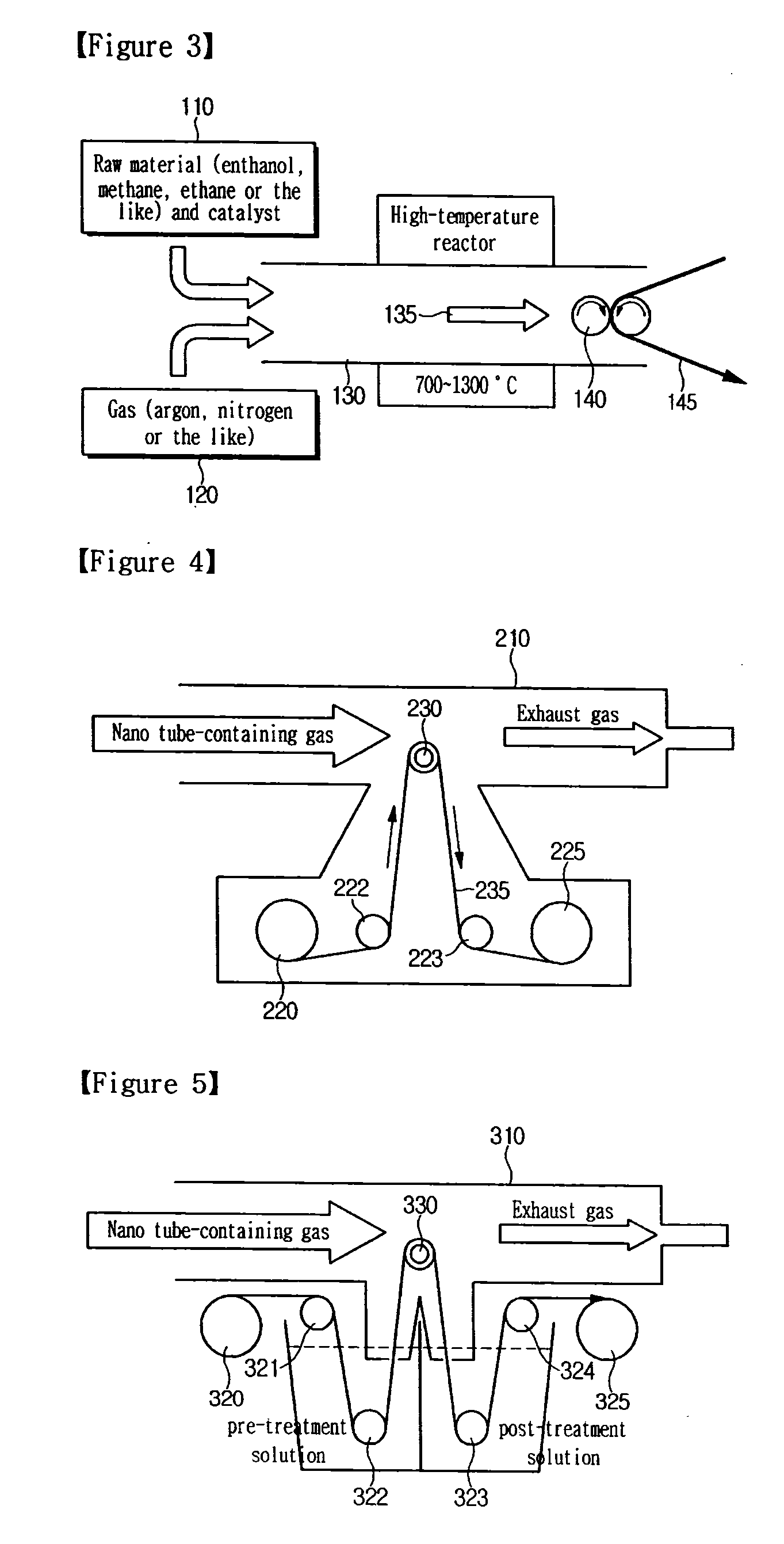
InactiveUS20110183067A1Reduce number of processHigh qualityMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureProduct gasNano tube
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for coating carbon nano tubes, which is capable of coating carbon nano tubes on a film at the same time when the carbon nano tubes are produced, unlike a wet method, thereby reducing the number of processes and costs and improving performance. The apparatus and method has an advantage of directly applying a CNT-containing gas obtained by thermal chemical vapor deposition to a film to obtain a CNT coating film with the reduced numbers of processes and high quality through improvement of an electrical property by maintenance of dispersibility and CNT length, as compared to a conventional wet process.
Owner:NANOBASE
Office accessory
InactiveUS20060254720A1Shorten the timeSpace is requiredLamination plant layoutLamination ancillary operationsPaper sheetEngineering
An office accessory for processing sheet material such as paper and / or films has a support plate to support the sheet material during the processing operation. At least one cutting device is associated with the support plate. The office accessory additionally comprises at least one laminating device for laminating sheet material to at least one film.
Owner:LOIBL BERND
Industrial Robot
ActiveUS20070256513A1Improve accessibilityCompact wrist housingProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsMotor driveControl theory
A robot arm for an industrial robot. The robot arm includes a wrist housing, a wrist, and a turn disc. The wrist is rotatably connected to the wrist housing and the turn disc is rotatably connected to the wrist. A first motor drives the wrist and a second motor drives the turn disc. A first driving rope transmits the motor rotation to the wrist, and a second driving rope transmits the motor rotation to the drive pulley.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Business Card Holder and Dispenser
InactiveUS20110108565A1Space is requiredSmall dead spaceFlat article dispensingOther accessoriesBusiness cardEngineering
Embodiments of the invention are concerned with a business card dispenser that presents a single card to the user, when the front of the dispenser is pushed. The dispenser can hold over one hundred cards, plus one protected display card to show the contents of the dispenser. This dispenser provides a large quantity of cards in a compact volume and eliminates “dry finger” syndrome that affects many other business card dispensers. This is accomplished by use of a plunger, which pushes through a slot a single card, partially exposing it outside of the dispenser. Hence, allowing the user to grab the card with two fingers and pull it to retrieve the card.
Owner:GEORGE PATTON ASSOC
Magnetic tape cartridge library apparatus having vertically oriented stages
InactiveUS7130148B2Increase the number ofEfficient use ofRecord information storageAutomatic cassette changing arrangementsMagnetic tapeEngineering
Owner:NEC PLATFORMS LTD
Measurement system and method for multiple antenna measurements with different angles of arrival
ActiveUS10969427B2Quick switchImprove accuracySolid-state devicesRadiofrequency circuit testingEquipment under testEngineering
A measurement system and method for over the air multiple antennas measurements are provided. The measurement system comprises, inside an anechoic chamber, a device under test, several measurement antennas, several mirrors and at least one shaped reflector. The measurement antennas are placed pointing at the shaped reflector. Each of the mirrors is placed along fields reflected by the shaped reflector. The mirrors reflect fields that form different angles of arrival at the device under test.
Owner:ROHDE & SCHWARZ GMBH & CO KG
Network processor for forwarding packets in an IP network
ActiveUS7583673B2High flexibility and reliabilityImpact performanceTime-division multiplexGeneral purpose stored program computerNetwork processorApplication-specific integrated circuit
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Freewheel bearing device with torque limiter
InactiveUS7766140B2Torque is limitedSimple and compact mannerBearing assemblySlip couplingFreewheelRadial plane
Owner:SKF FRANCE
Device for taking over, temporarily storing and passing on elongated, hollow cylindrical product units and a method for the operation of such a device
InactiveUS8590690B2Increase storage capacitySpace is requiredComputer controlSimulator controlProduction lineConveyor belt
A device for taking over, temporarily storing and passing on elongated, hollow-cylindrical product units, preferably tubes, sleeves or cans, which come from a production line, has a first supplying conveyor belt and a continuously delivering second conveyor belt. The first and the second conveyor belts are disposed horizontally lying one above the other in a transfer zone. An intermediate storage arrangement is designed as a high-rack storage arrangement or as a paternoster storage arrangement. At least one handling robot is also located in the region of the transfer zone between the conveyor belts and the intermediate storage arrangement. This handling robot is designed either (a) to take a number of product units from the first conveyor belt and to feed them to the second conveyor belt or the intermediate storage arrangement, or (b) to remove a number of product units from the intermediate storage arrangement and to feed them to the second conveyor belt.
Owner:TEXA
Planar transmitter with a layered structure
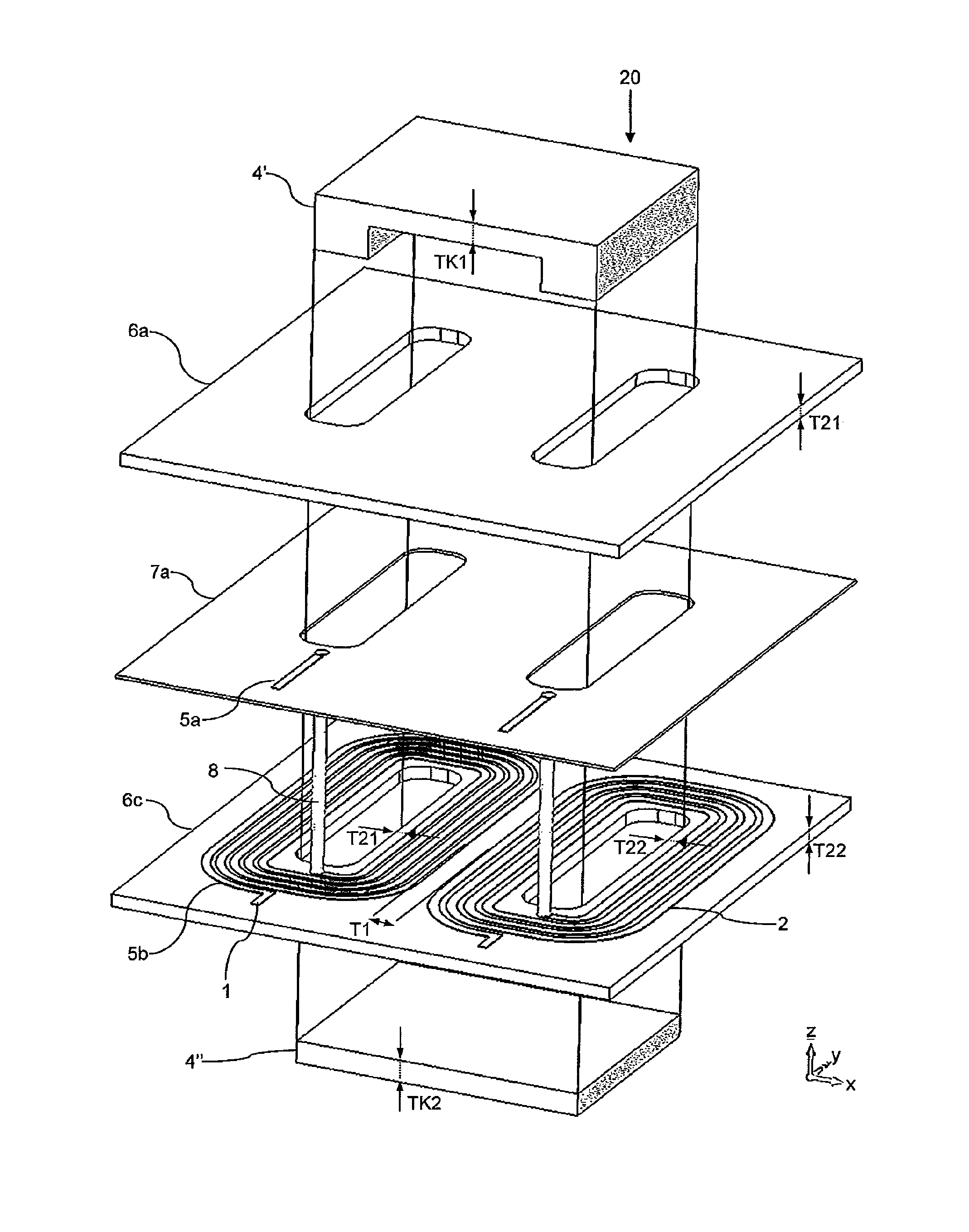
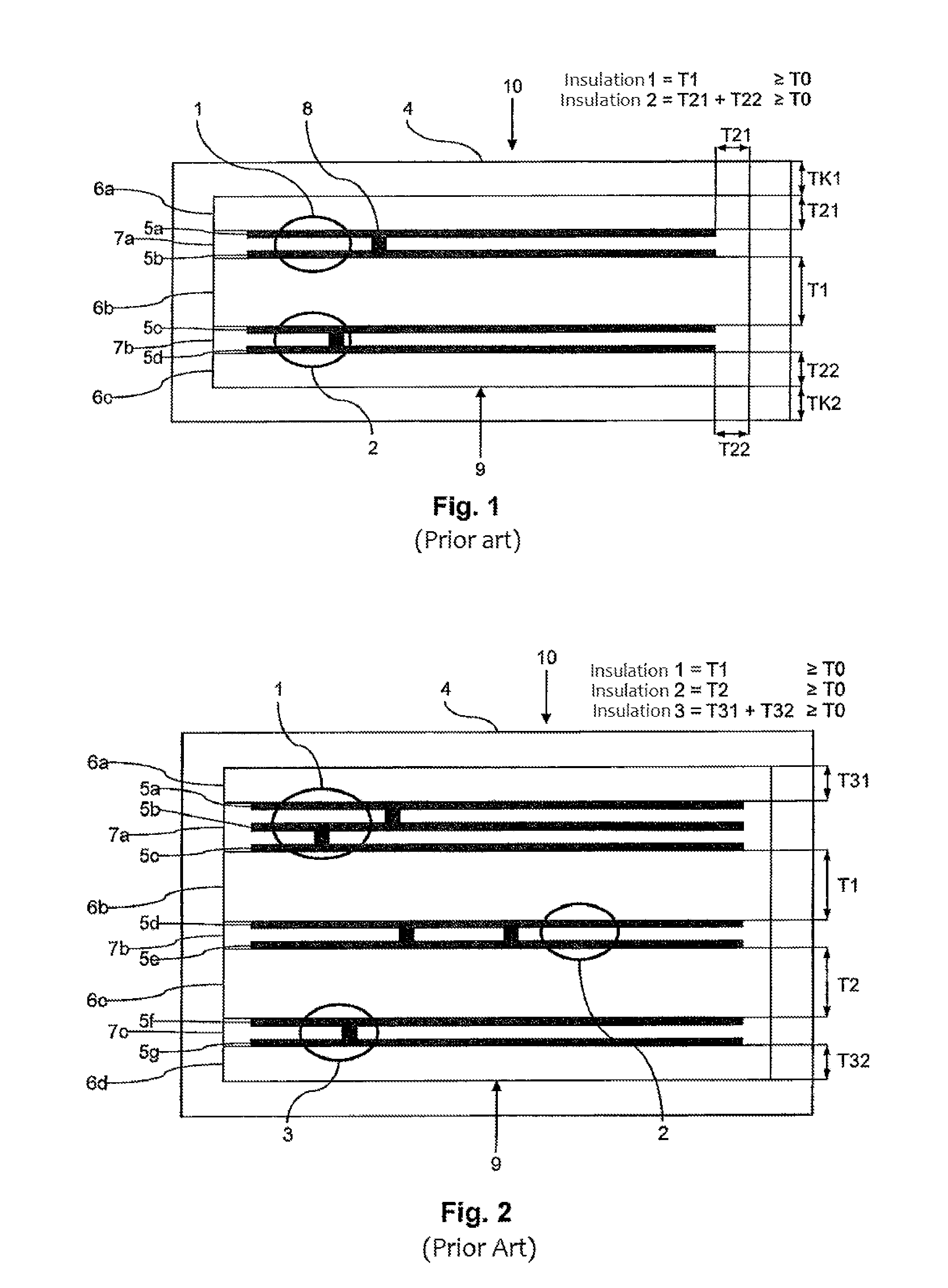
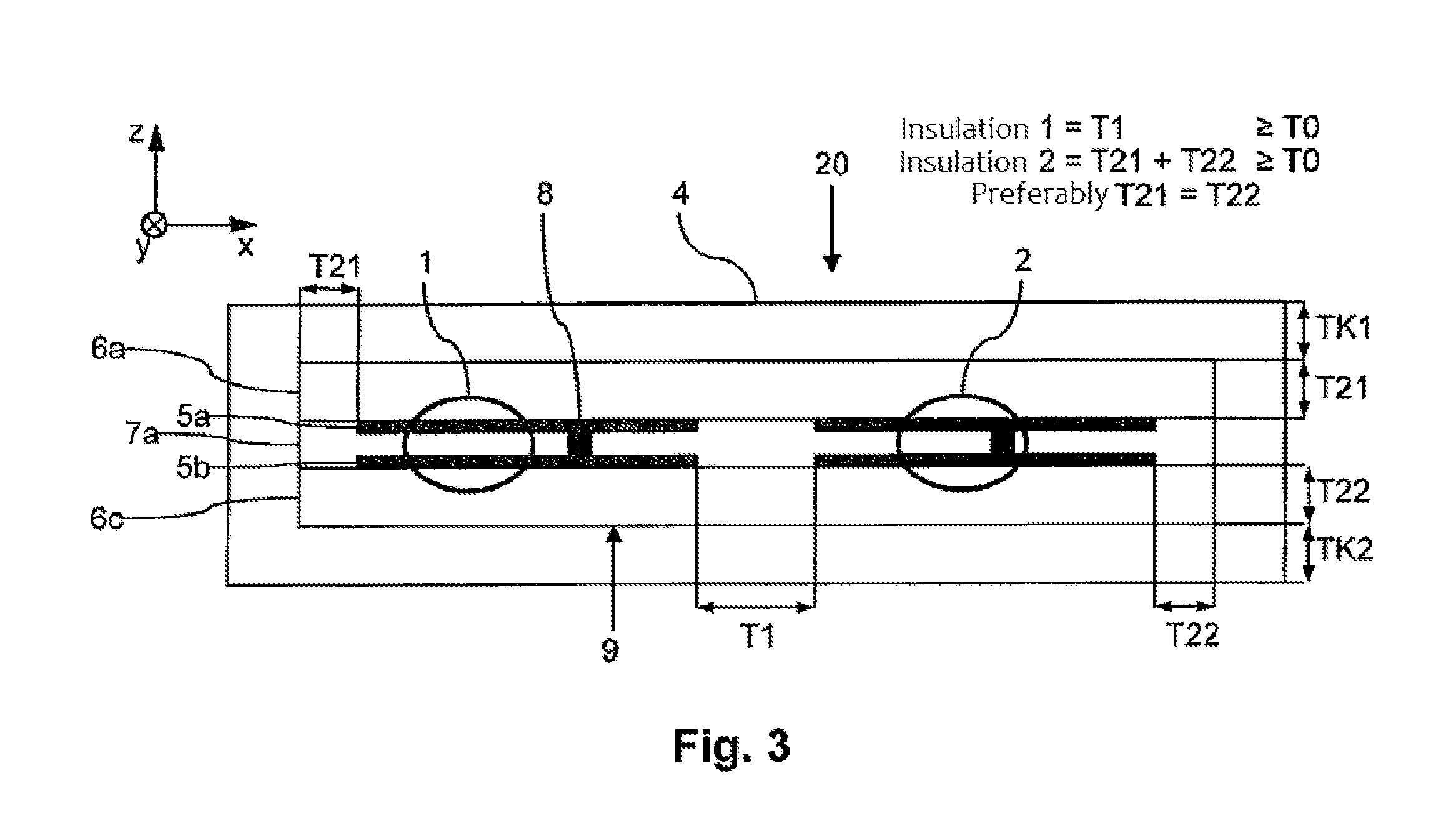
ActiveUS20150022306A1Safely galvanically isolatedSpace is requiredTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsPrinted circuit aspectsPower flowTransducer
A planar intrinsically safe transducer having a vertical extension and a horizontal extension having a layer structure with a plurality of circuits, wherein a first circuit and a second circuit are galvanically isolated from one another. Further, the transducer has a magnetic core 4, which at least partially encompasses the layer structure and acts at least on the first circuit and on the second circuit, wherein the first circuit and the second circuit lie in one plane and form a layer of the layer structure.
Owner:PHOENIX CONTACT GMBH & CO KG
Method and device for electrostatic cleaners
InactiveUS20090007788A1Improve efficiencyIncreased uninterrupted production timeParticle charging/ionising stationsExternal electric electrostatic seperatorFilter systemEngineering
An electrostatically charged rotating plate or cylinder is used to attract electrostatically charged particles in smoke to avoid pollution and improve the efficiency of the filtering process. The rotating plate is constantly cleaned from the ionized particles adhering to it and the particles so collected are removed without polluting the environment. This filtering system reduces capital and running costs compared with the present filtering systems.
Owner:ARYE NOAM +3
Aperture engine
InactiveUS20100301610A1Reduce weightEasy to handleFluid couplingsEngine fuctionsSurface oceanBasement
A hydro pneumatic engine, providing rotational energy at very low RPM, proper to drive an electric generator directly coupled, using as power supply atmospheric pressure variations, originated by vacuum coming from an oscillating wave chamber. With dynamic variable resonance for marine working environment, low internal friction, few mechanical internal reactions and low level noise, this devise operates with potential / kinetic energy multiple conversions and uses as torsion converter a similar unbalanced turbine mechanism, with modified movement, of external zero flow and outstanding minimum head pressure with non corrosive recycling liquid; works offshore or shore line, including also indoor or basement locations, even works with some lakes and with some rivers also without any dam requirement, being as such an environmentally low impact design.
Owner:LEON ENRIQUE H
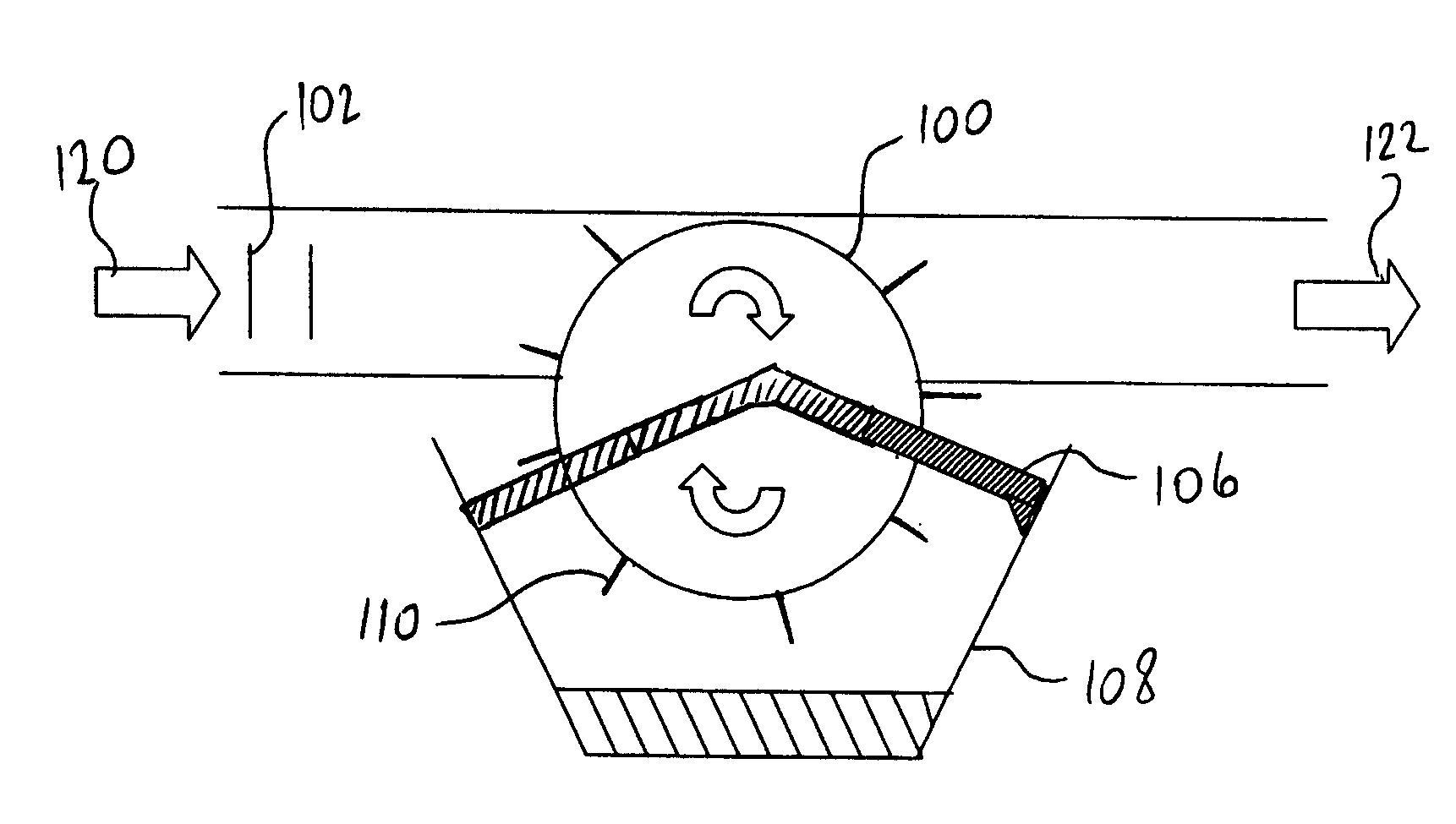
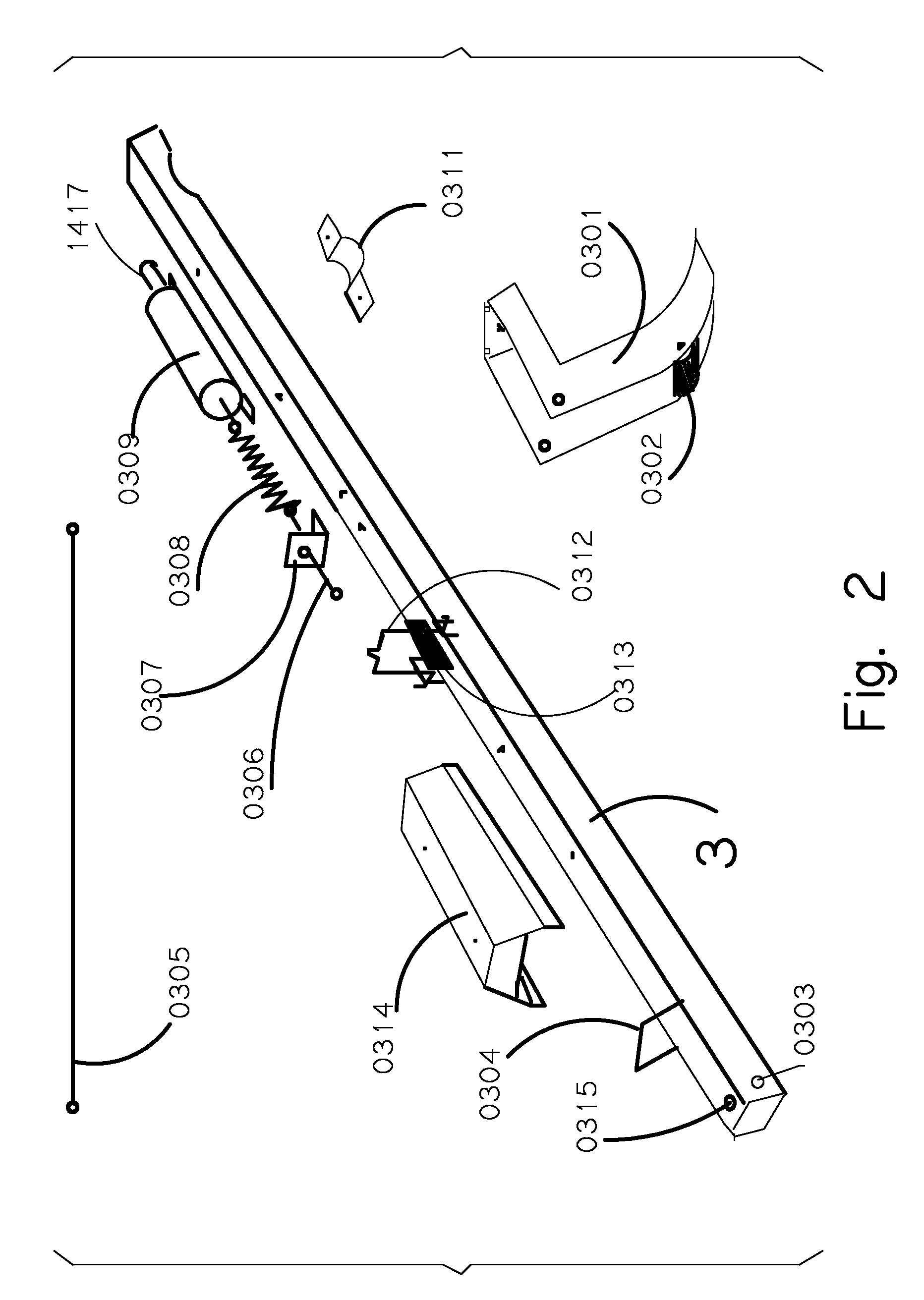
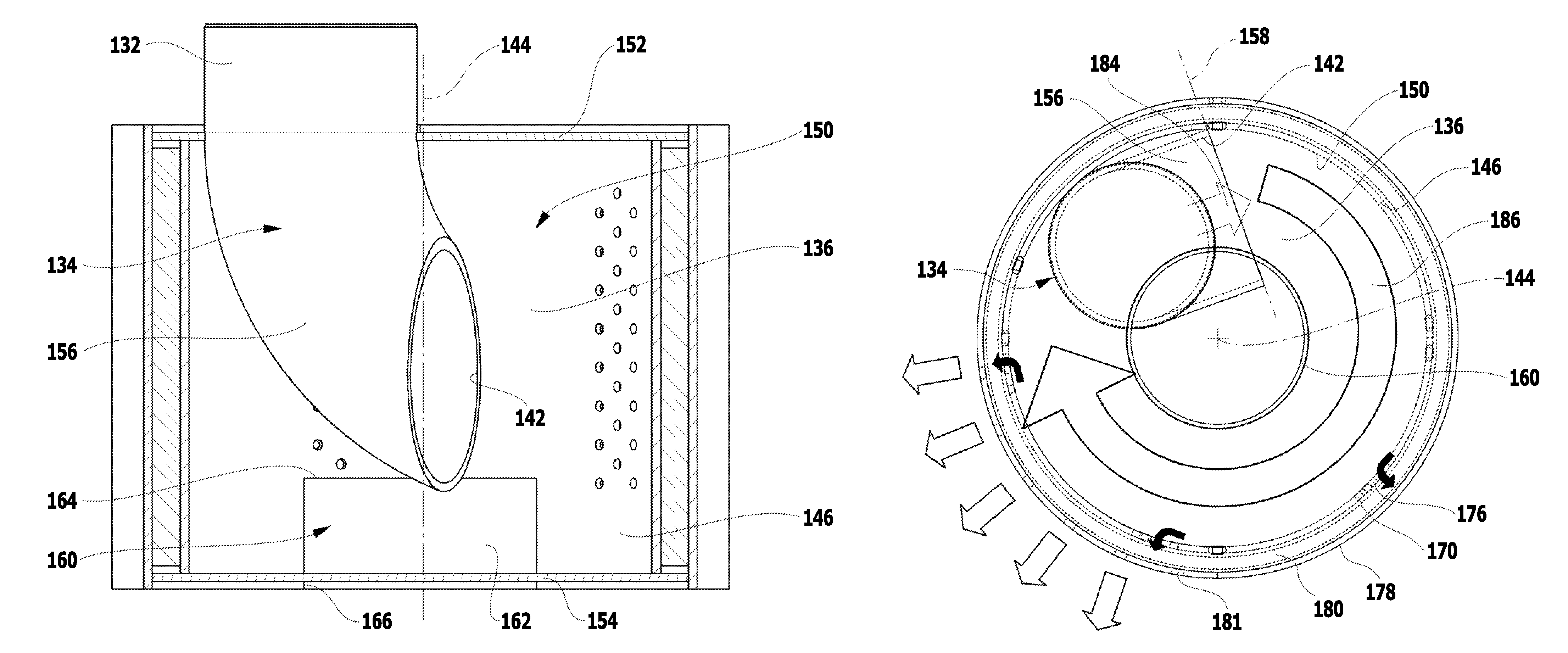
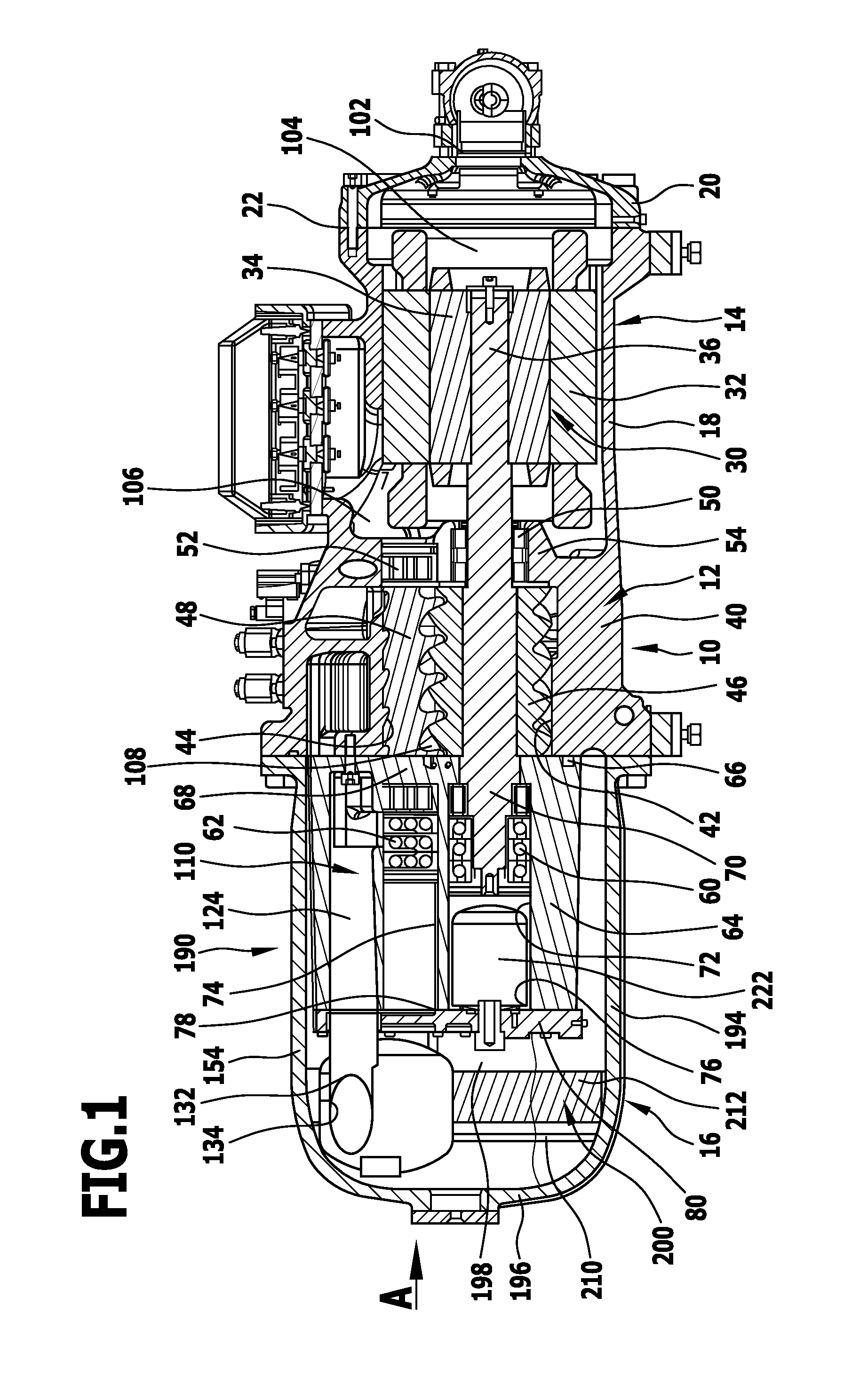
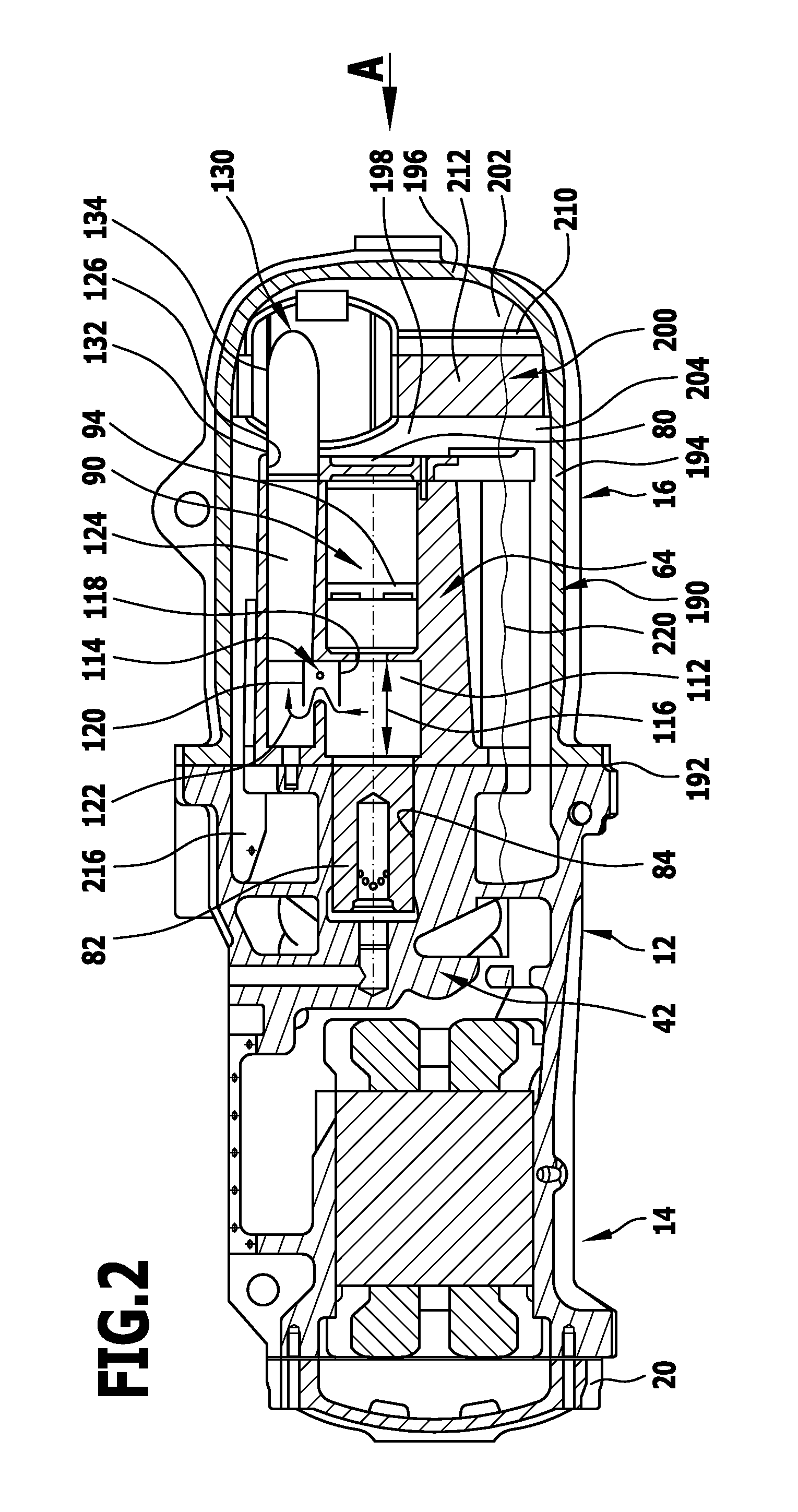
Screw compressor with a sound dampening device that separates lubricant
ActiveUS8500424B2Space is requiredReduce trafficOscillating piston enginesEngine of counter-engagement typeInterior spaceCentrifugal force
In order to improve a screw compressor comprising an outer housing, a compressor screw housing which is arranged in the outer housing and in which rotor bores for screw rotors are arranged, a drive arranged in the outer housing on one side of the compressor screw housing, a bearing housing arranged in the outer housing on a side of the compressor screw housing located opposite the drive and a sound damping device which is arranged within the outer housing and has compressed working medium flowing through it, in such a manner that the working medium leaving the screw compressor carries as little lubricant as possible along with it, it is suggested that the sound damping device guide the compressed working medium by means of a flow guide in an interior space as a circulating flow circulating around an axis and that lubricant be separated from the circulating flow of the working medium as a result of centrifugal forces.
Owner:BITZER KUEHLMASCHINENBAU GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com