Patents
Literature
930results about "Antenna arrays manufacture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
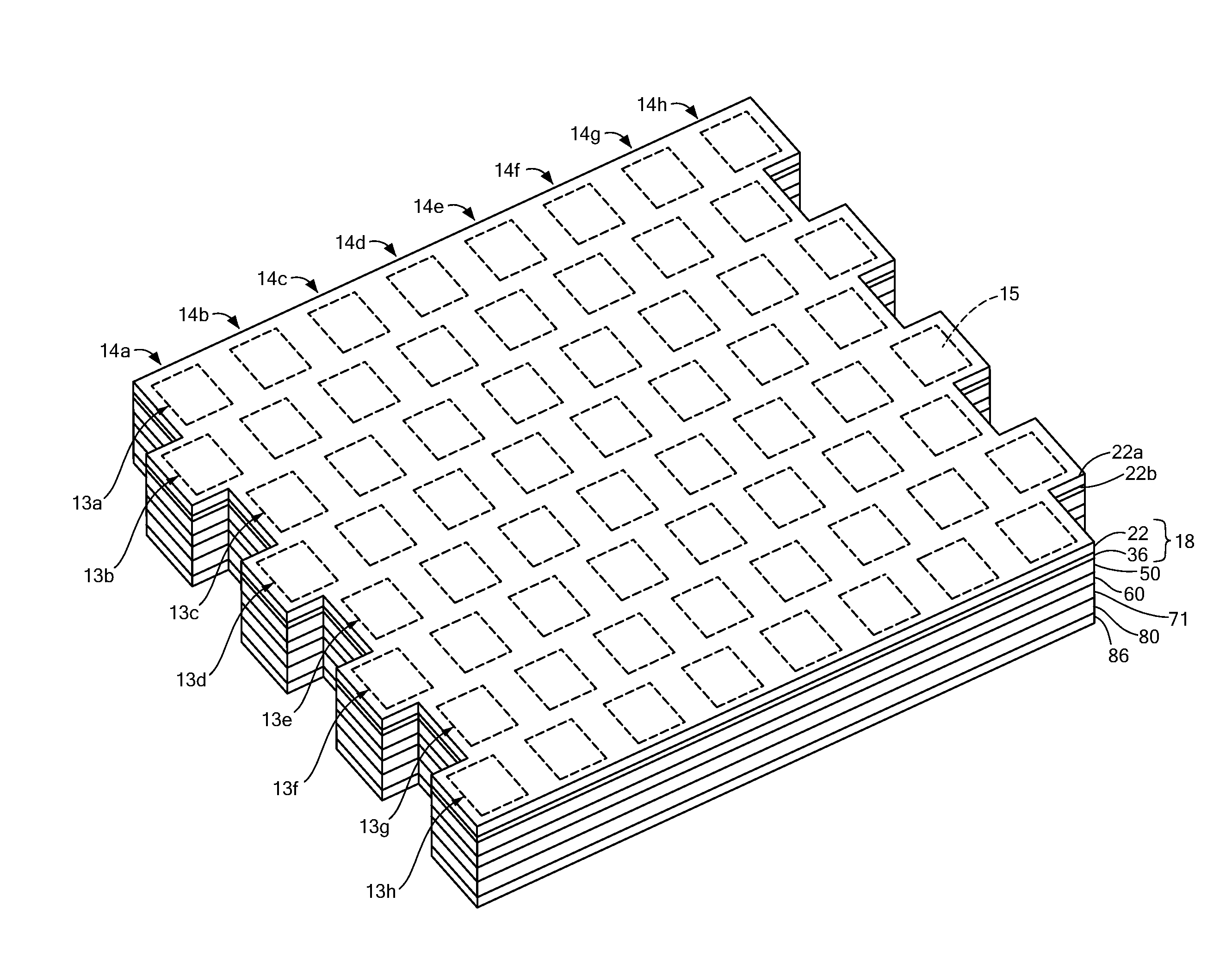
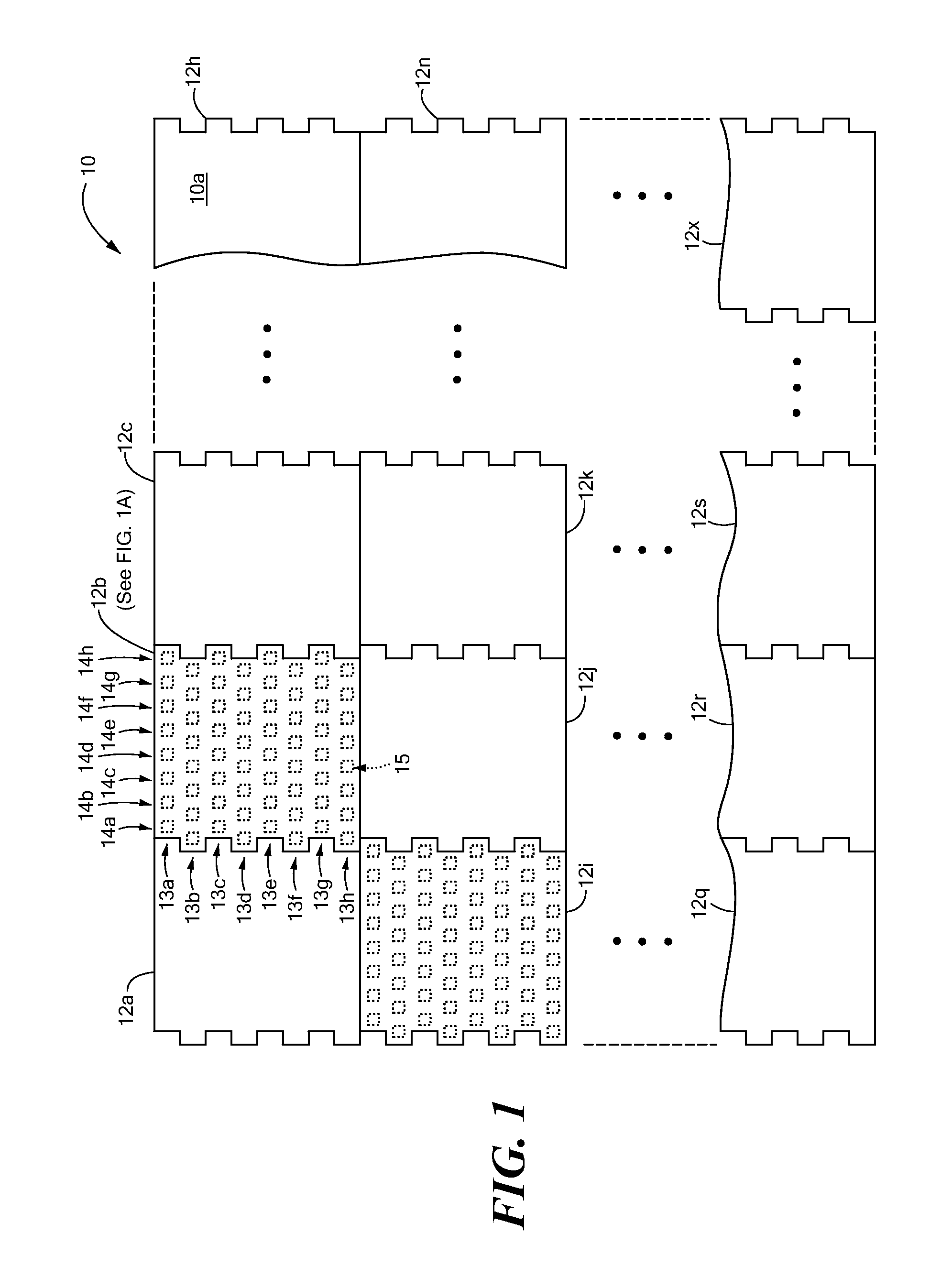
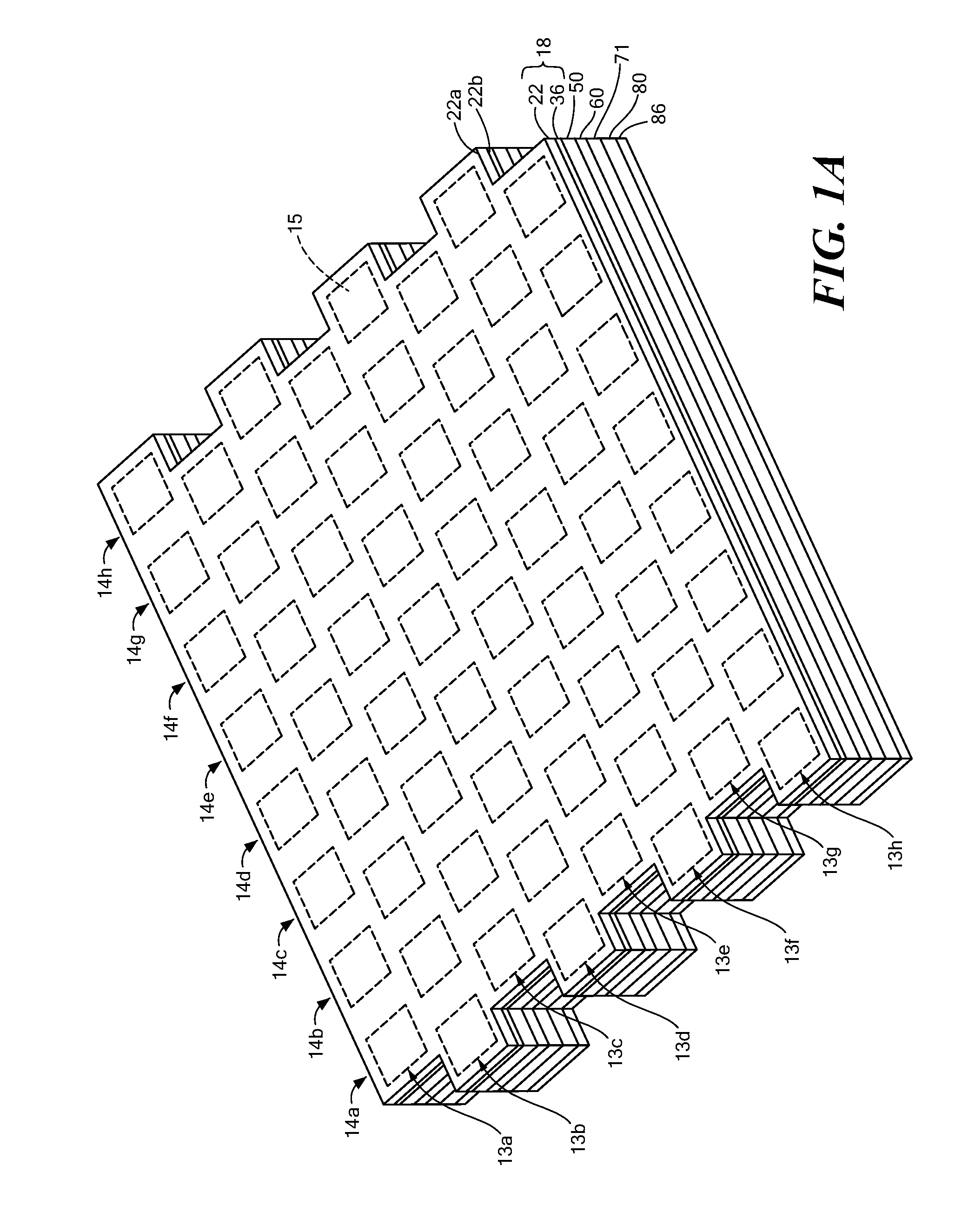
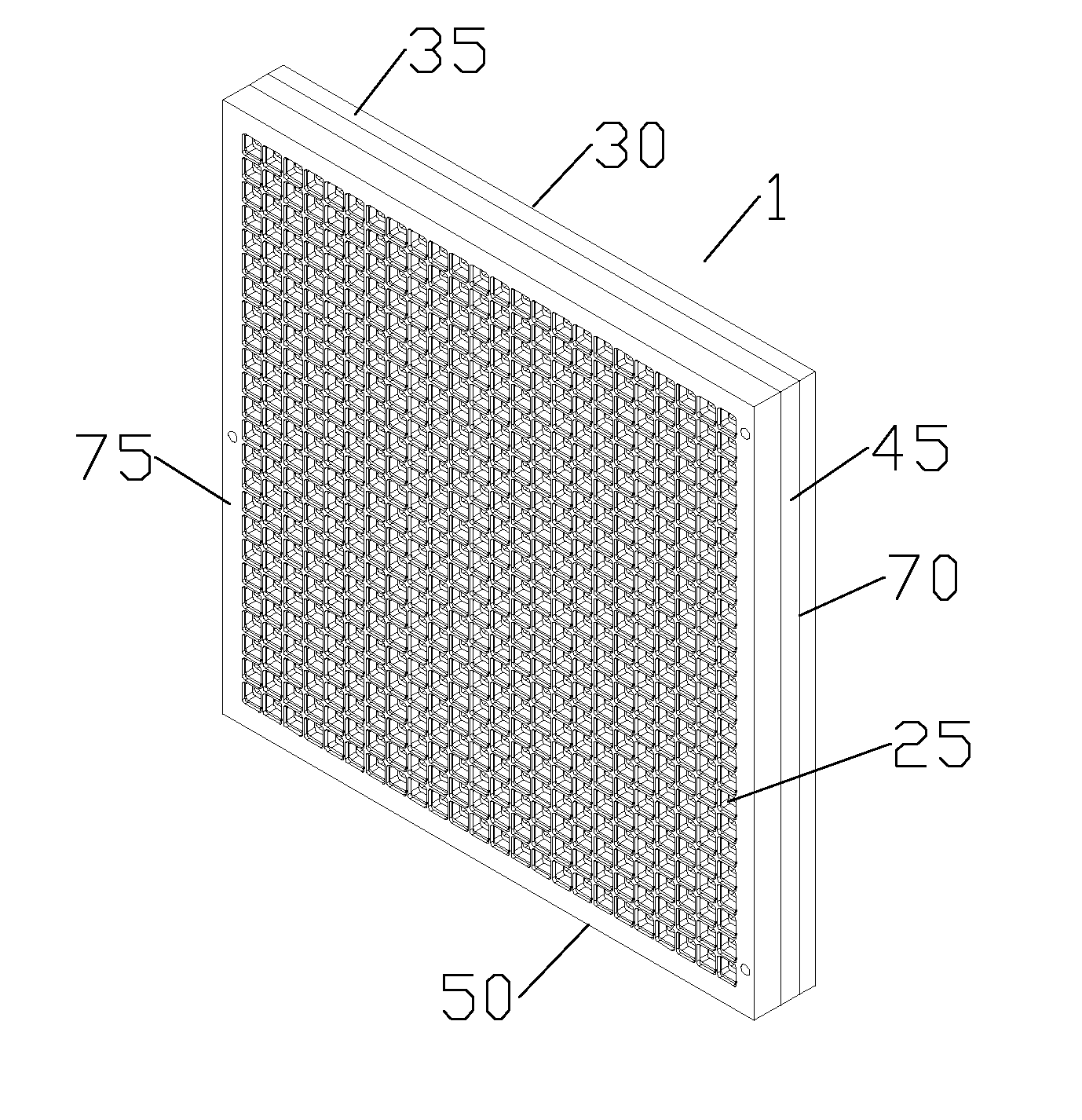
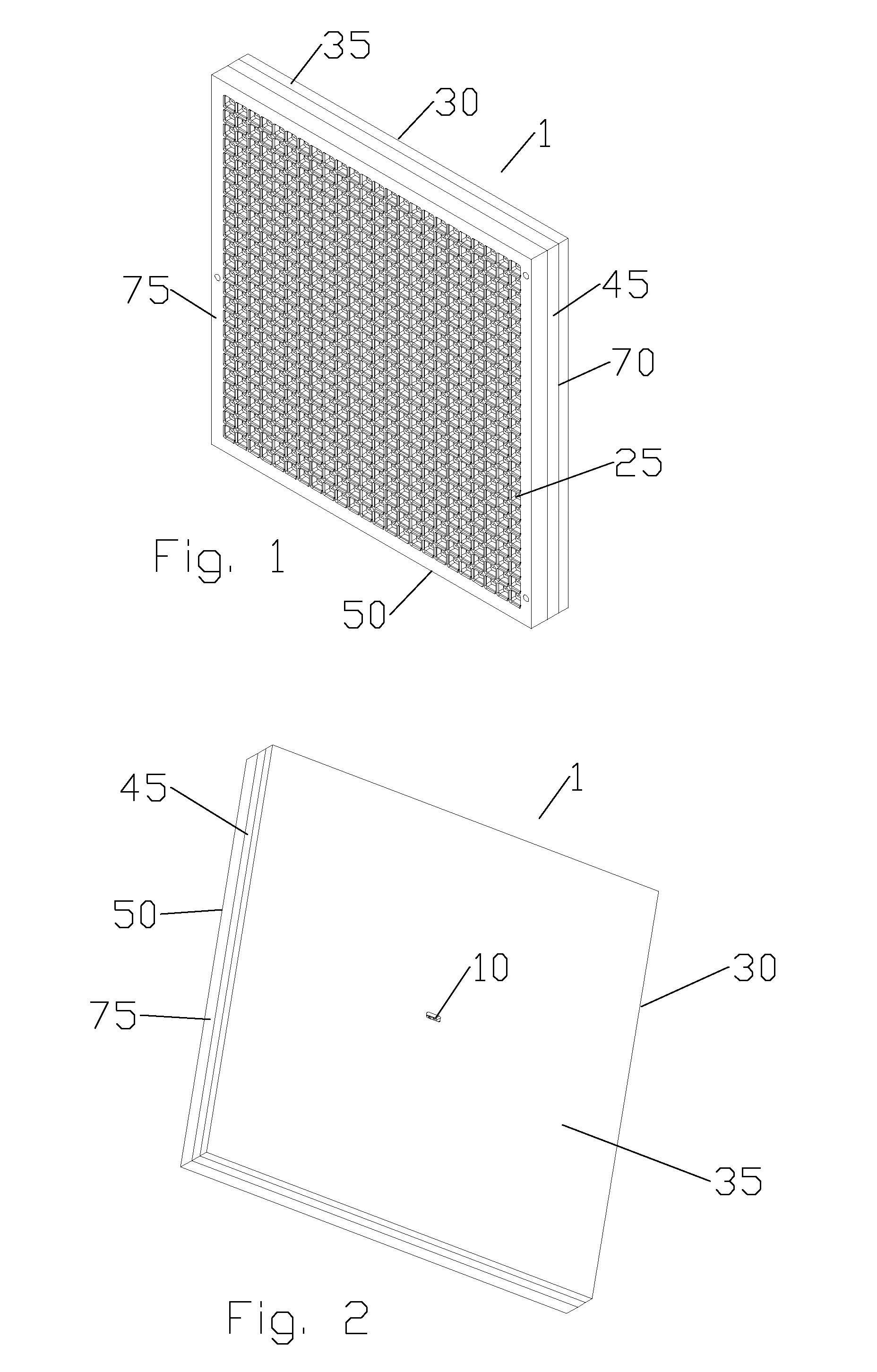
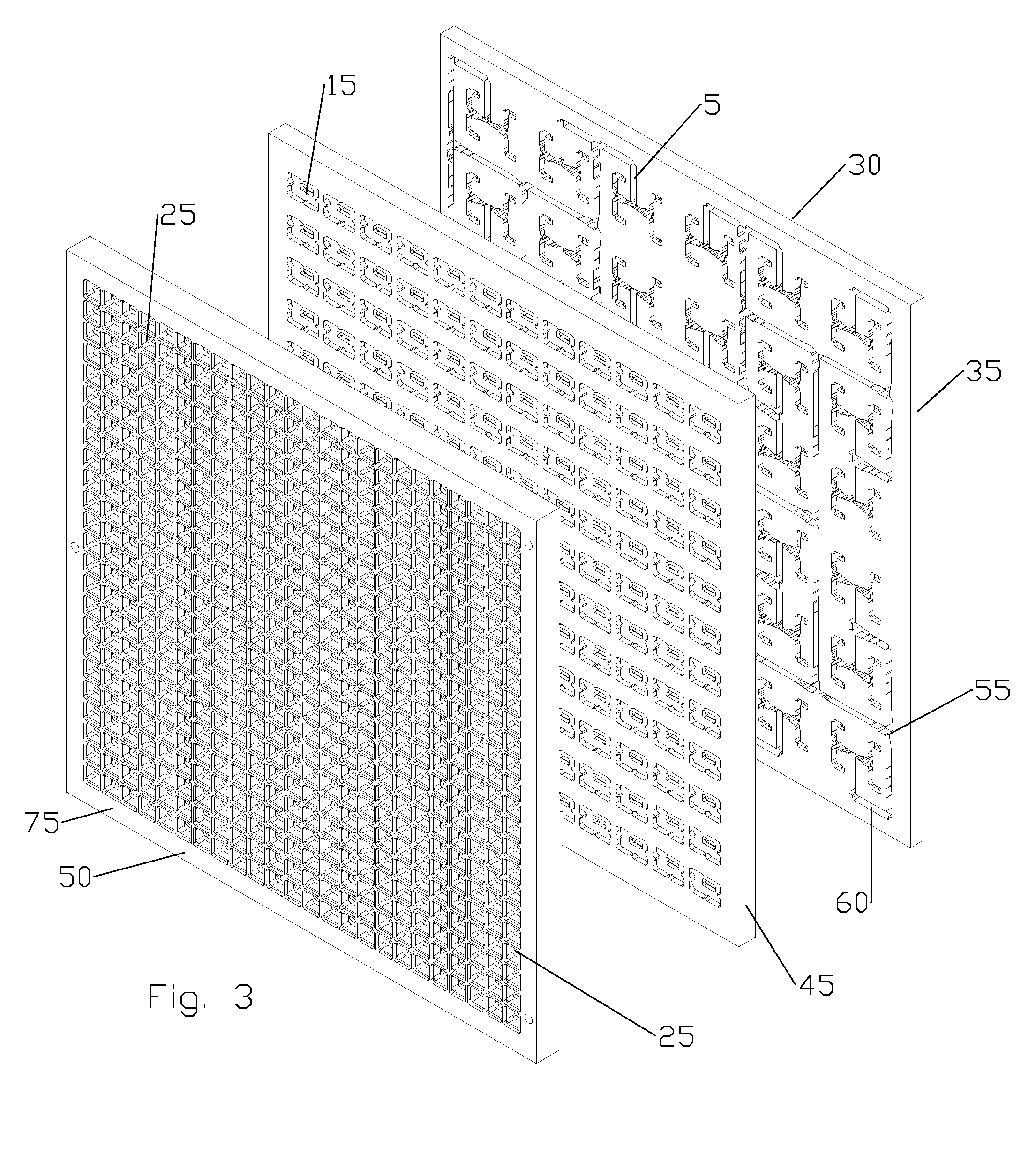
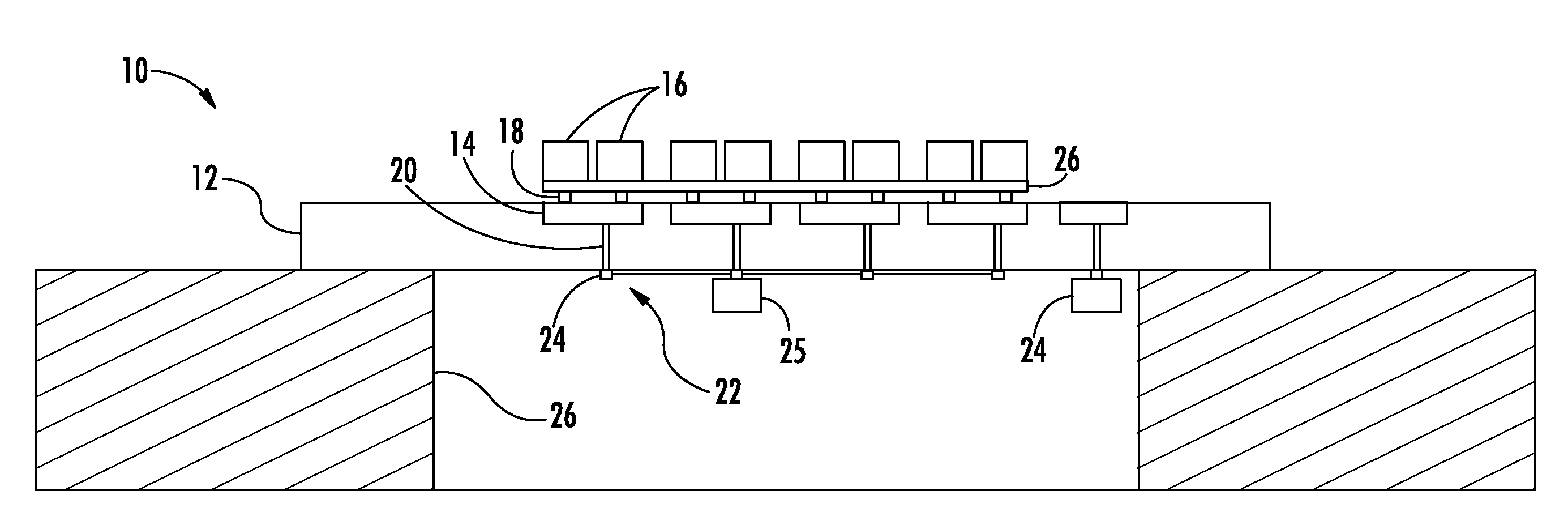
Panel Array
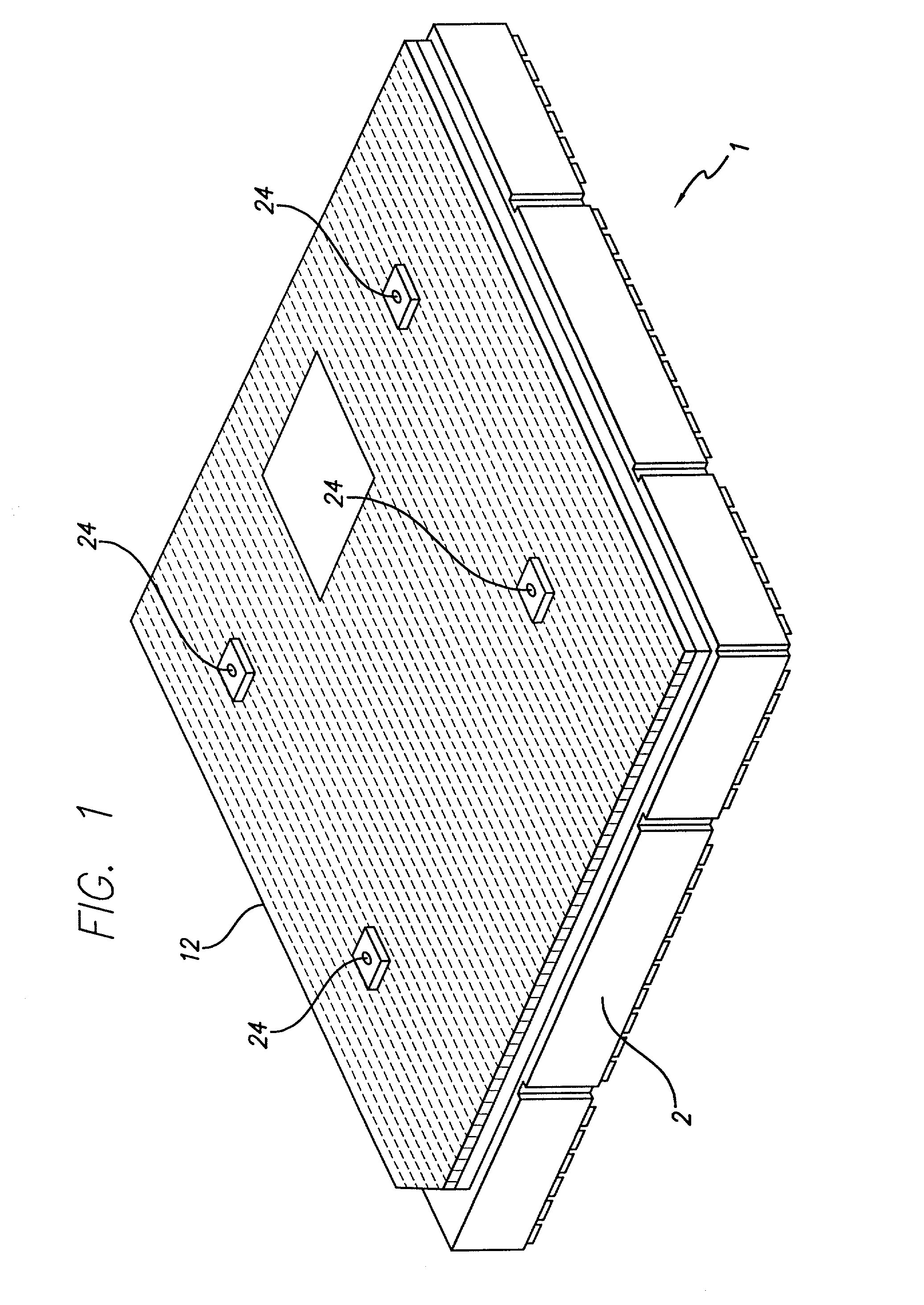
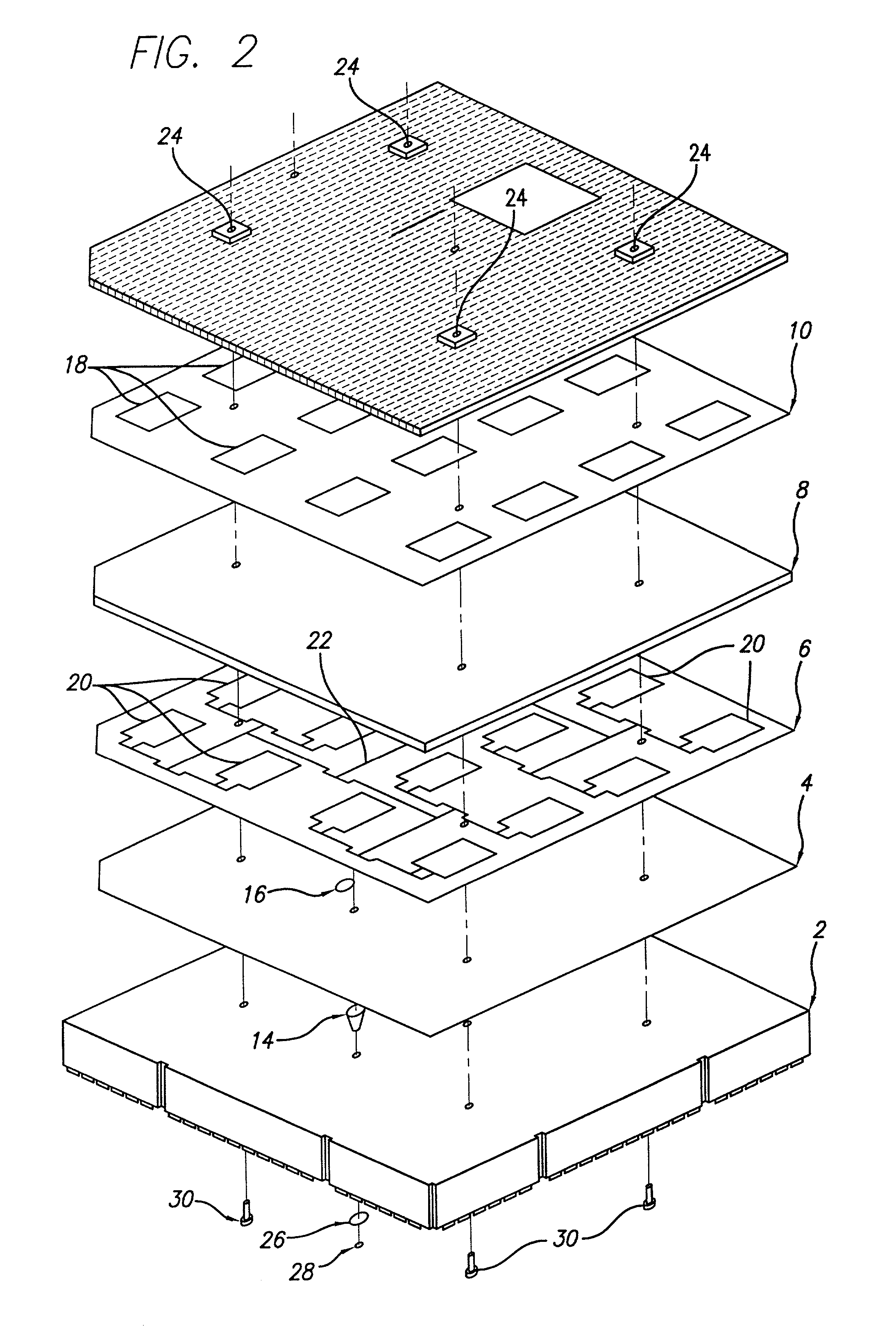
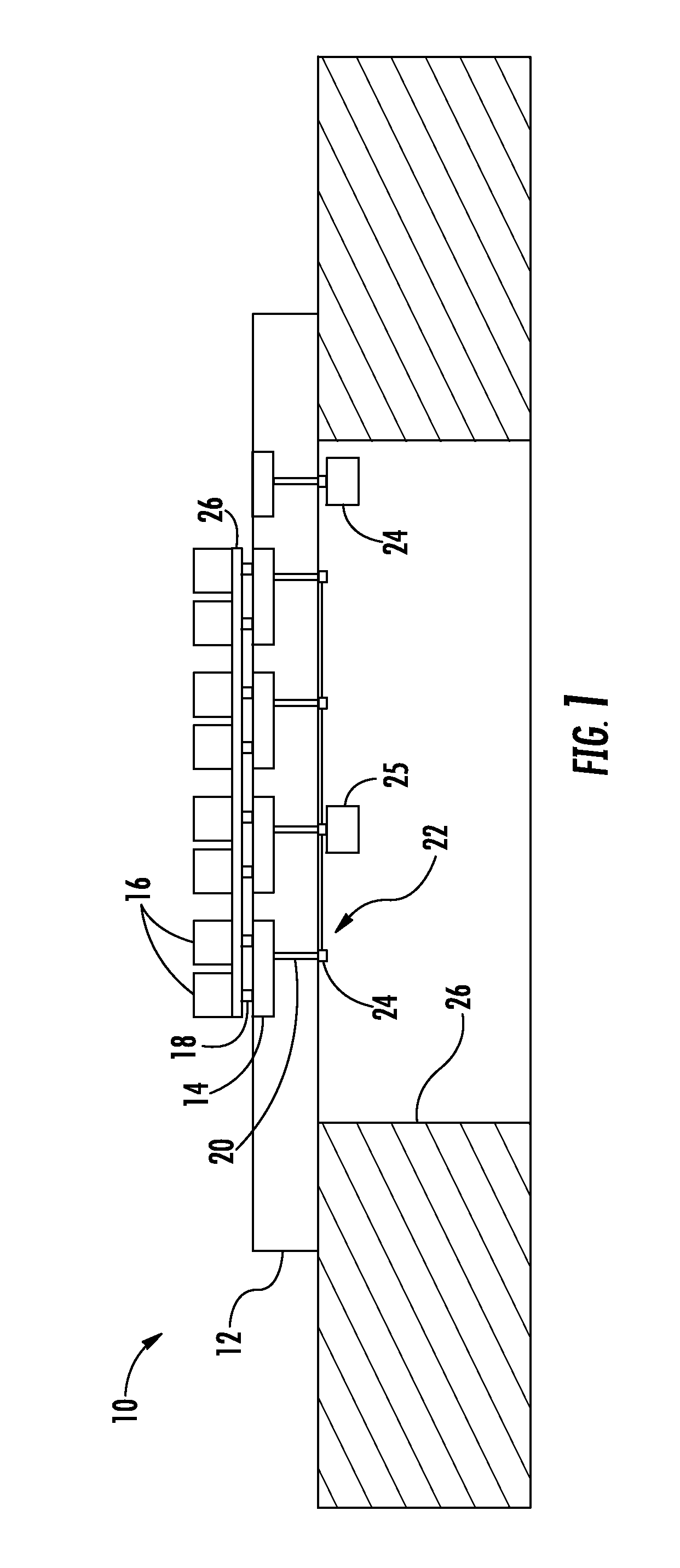
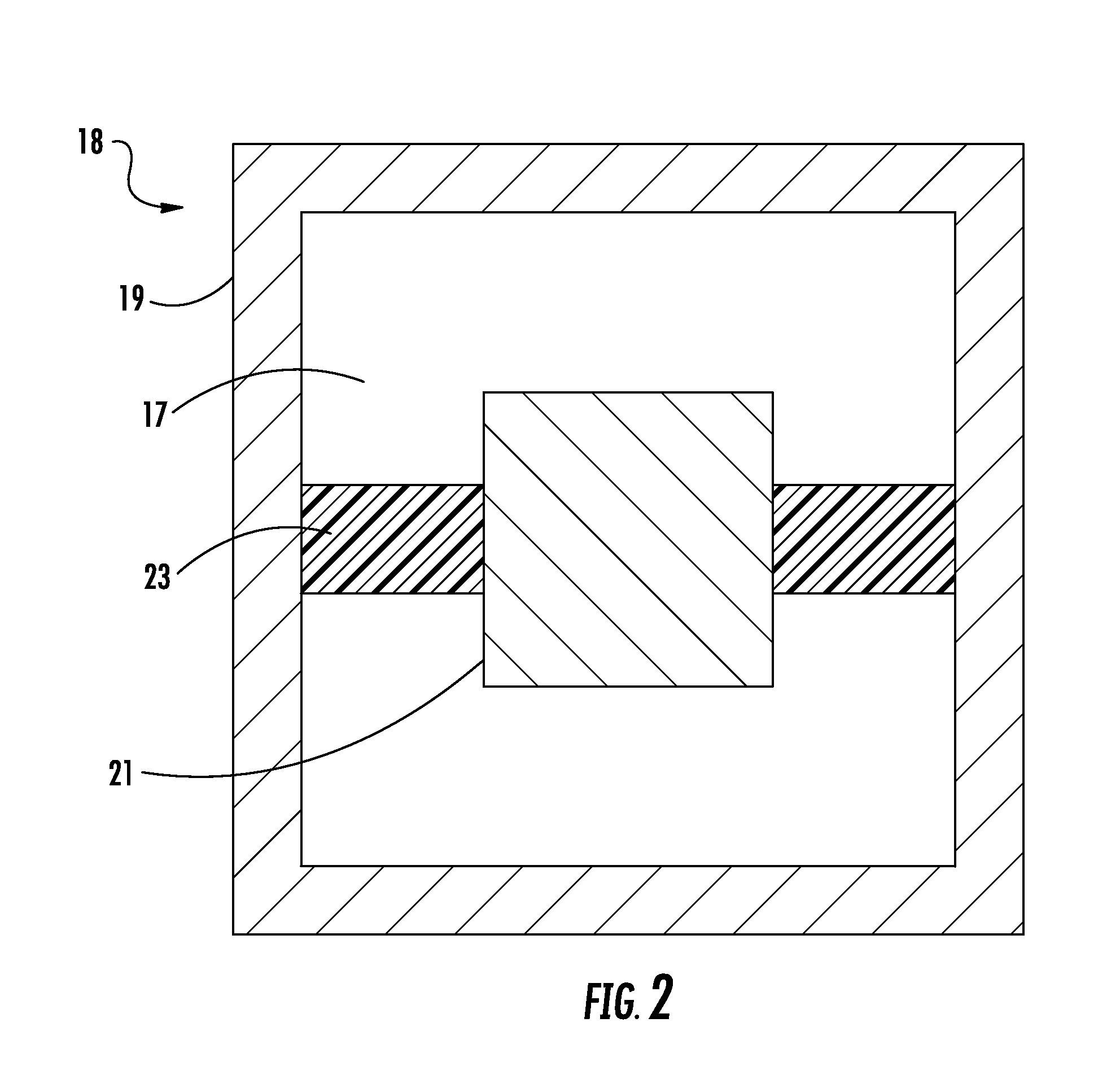
ActiveUS20100066631A1Low insertion lossEliminate needAntenna arrays manufactureModular arraysHemt circuitsChipset
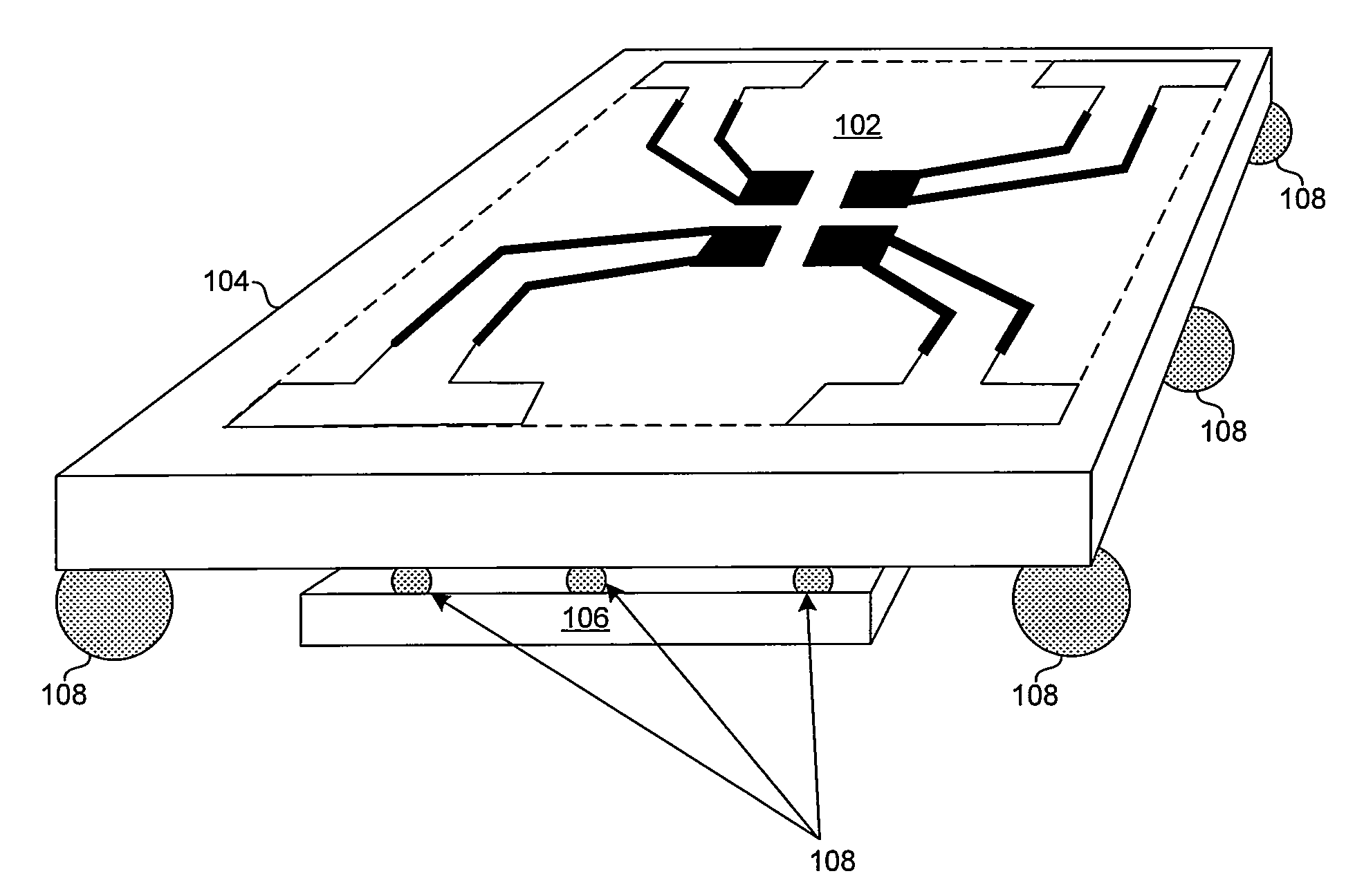
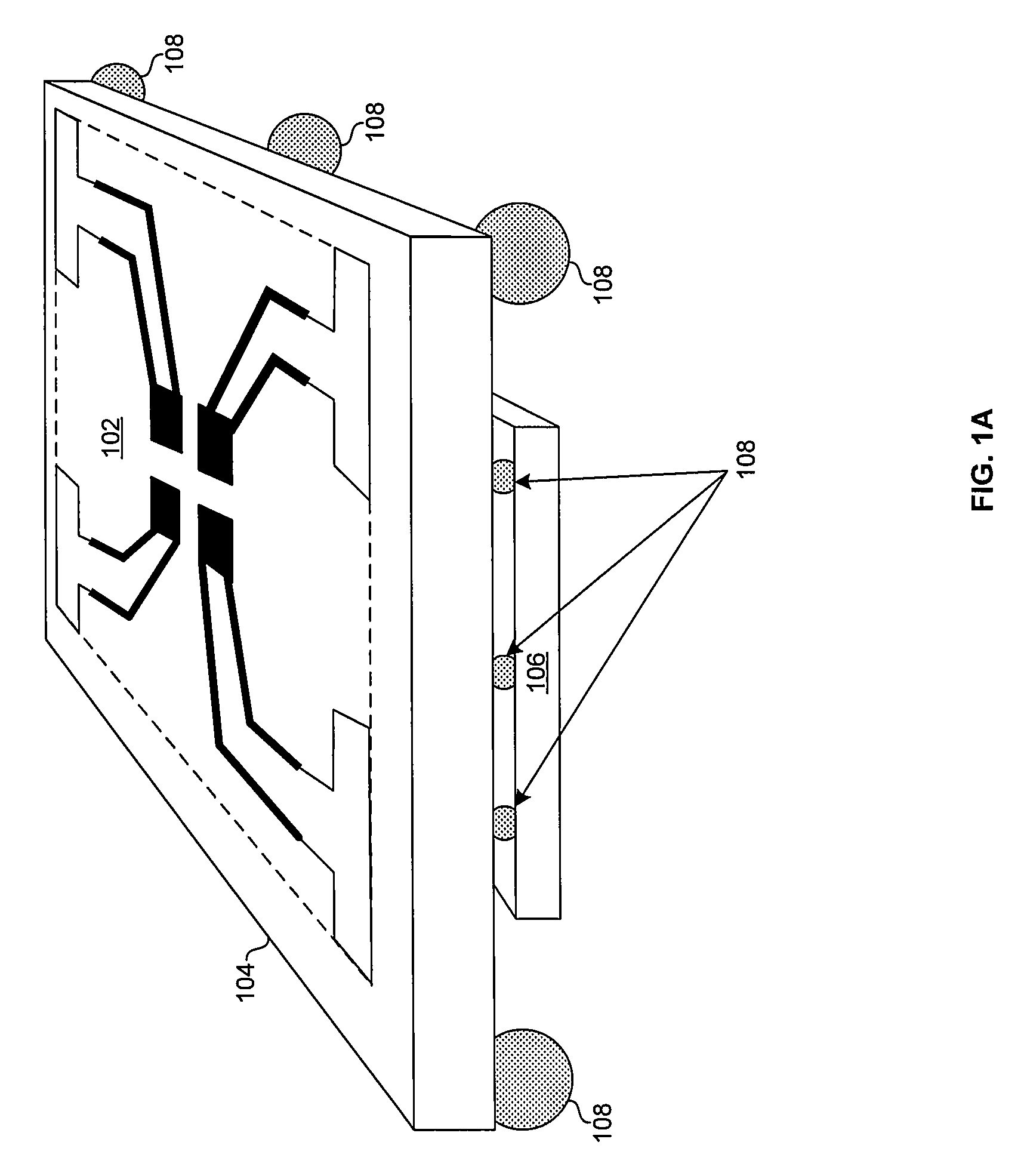
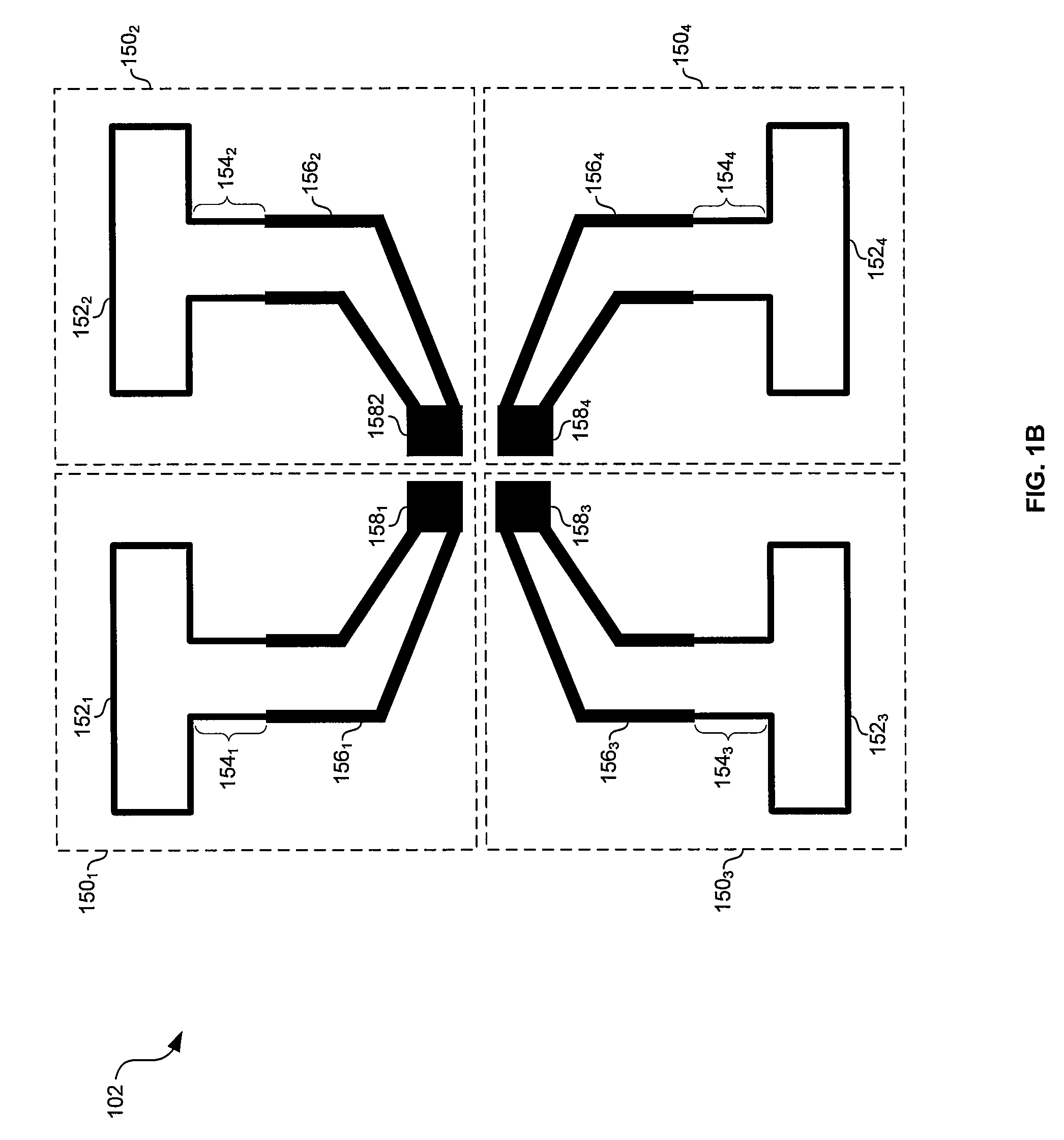
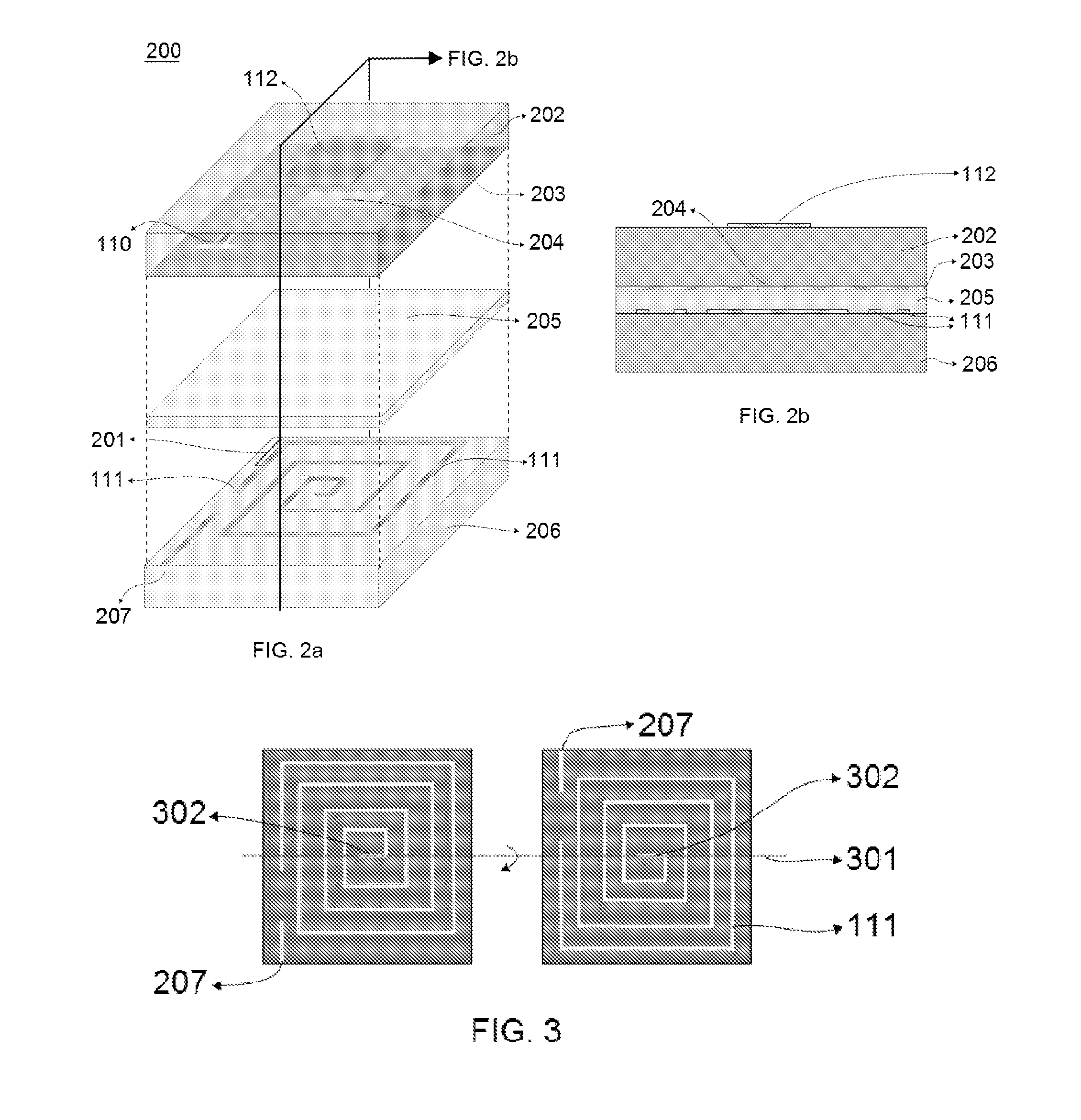
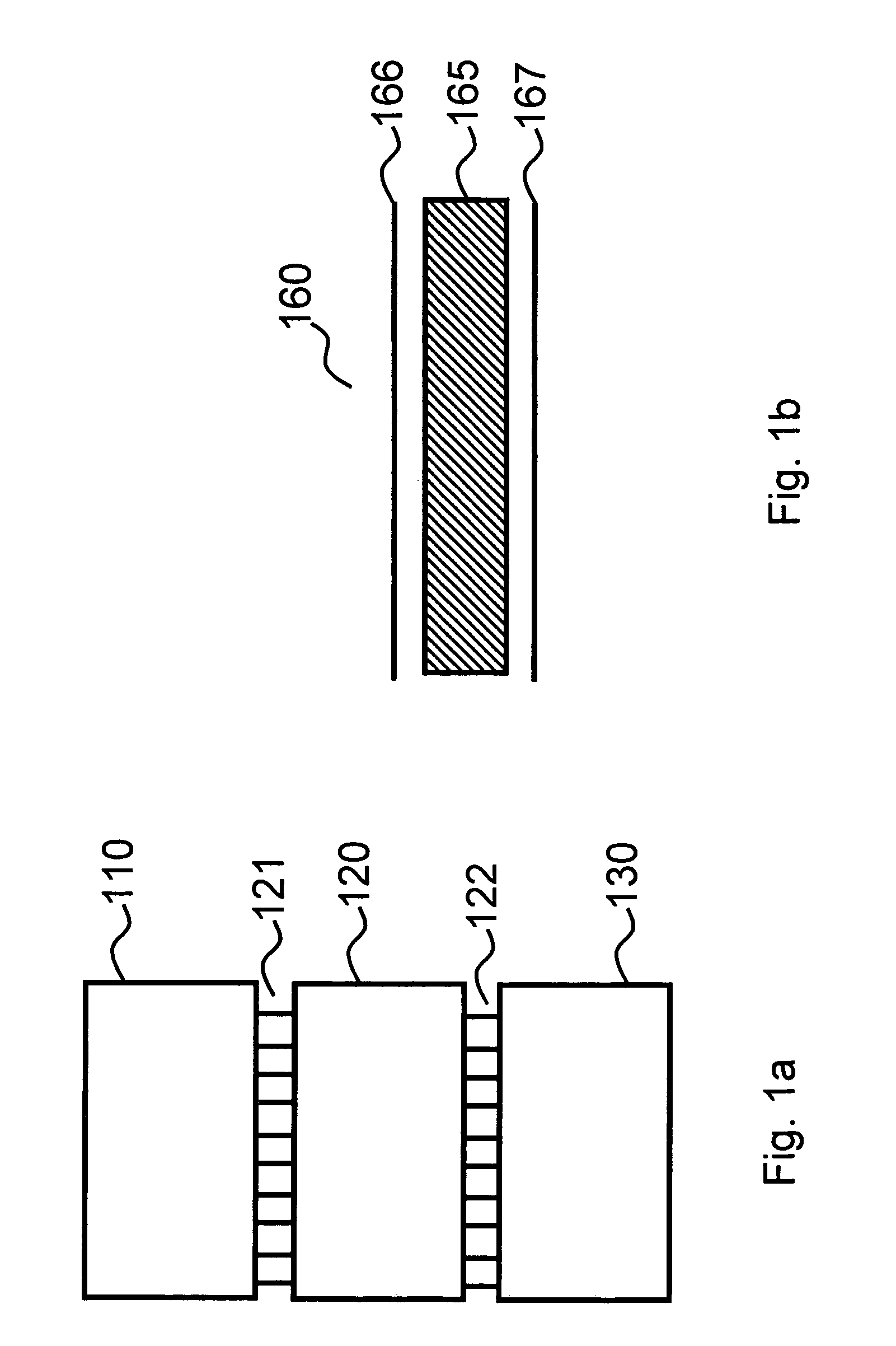
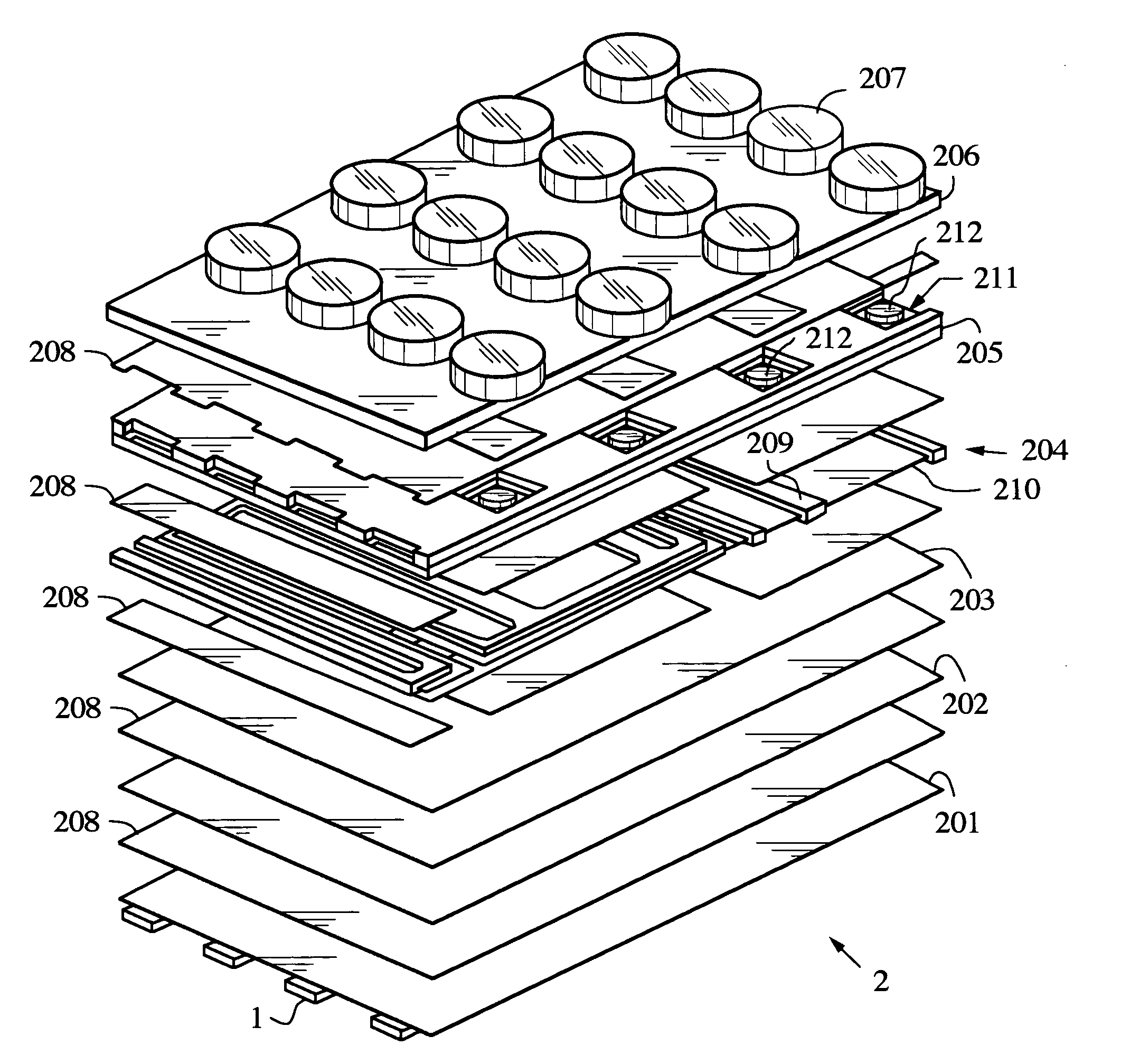
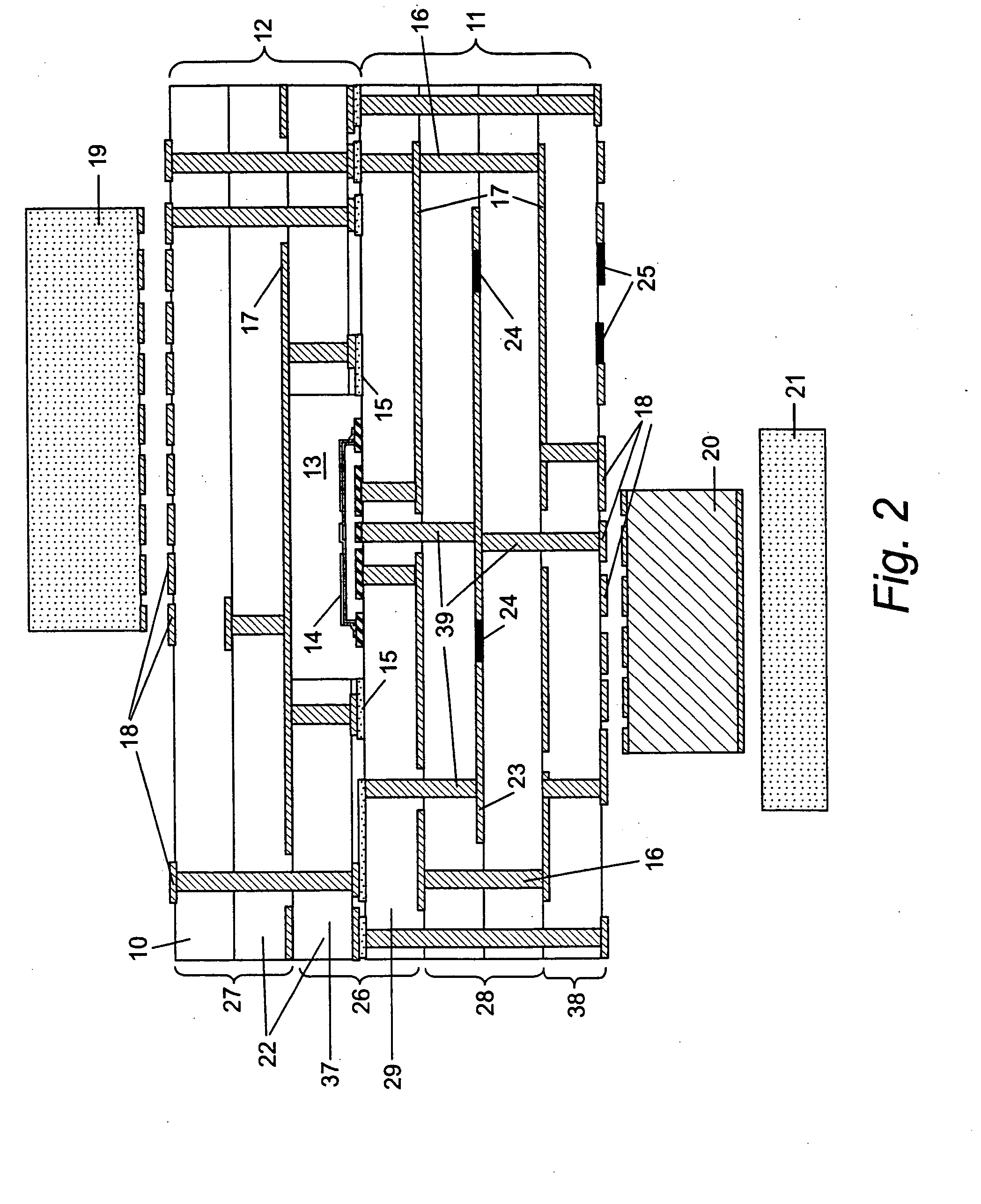
A mixed-signal, multilayer printed wiring board fabricated in a single lamination step is described. The PWB includes one or more radio frequency (RF) interconnects between different circuit layers on different circuit boards which make up the PWB. The PWB includes a number of unit cells with radiating elements and an RF cage disposed around each unit cell to isolate the unit cell. A plurality of flip-chip circuits are disposed on an external surface of the PWB and a heat sink can be disposed over the flip chip components.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Antenna arrays formed of spiral sub-array lattices
InactiveUS6842157B2Improve bindingWider antenna bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringGrating lobe
A antenna array (20) includes a plurality of periodic or aperiodic arranged sub-arrays (22). Each sub-array (22) includes a plurality of antenna elements (32) arranged in the form of a spiral (30). The sub-arrays (22) can comprise various spiral shapes to provide the required physical configuration and operational parameters to the antenna array (20). The elements (32) of each sub-array (22) are arranged to minimize the number of such elements (32) that intersect imaginary planes perpendicular to the spiral and passing through the spiral center. Such an orientation of the elements (32) minimizes grating lobes in the antenna pattern.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
High dielectric antenna array
InactiveUS20150042526A1Small sizeReduce distanceNear-field transmissionCircuit arrangementsDielectricPhased array
A system and method for wirelessly transmitting signals via antenna phased array. In order to decrease the distance between individual antennae in the array, the antennae are submersed in a high dielectric material in addition to being arranged at right angles to one another, both features precluding one or more antennae from coupling. Furthermore, wires are covered in high dielectric material in order to refract RF signals around them, allowing antennae towards the center of the array to successfully transmit signals past other layers.
Owner:OSSIA
Phased array antenna and method for producing thereof
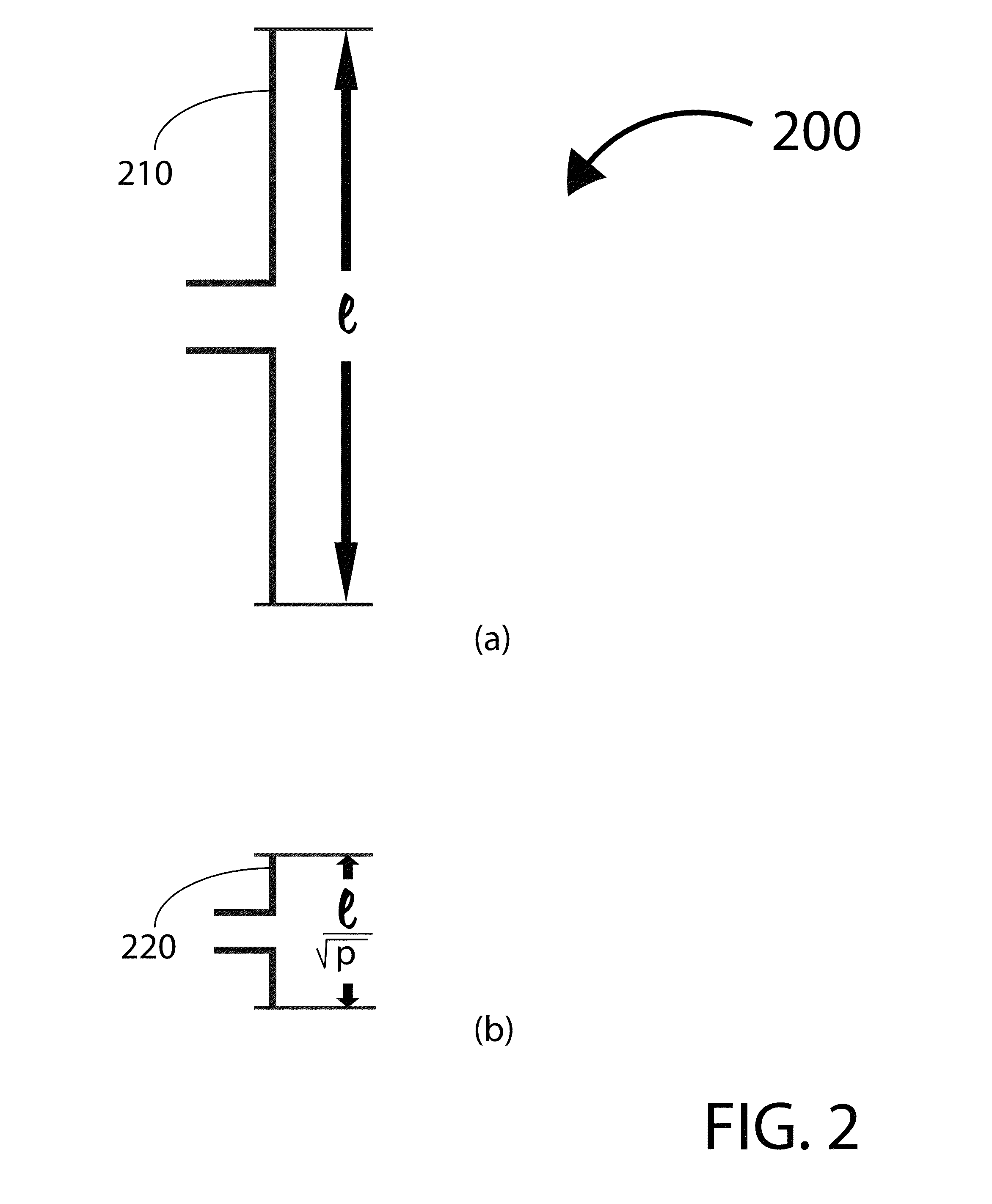
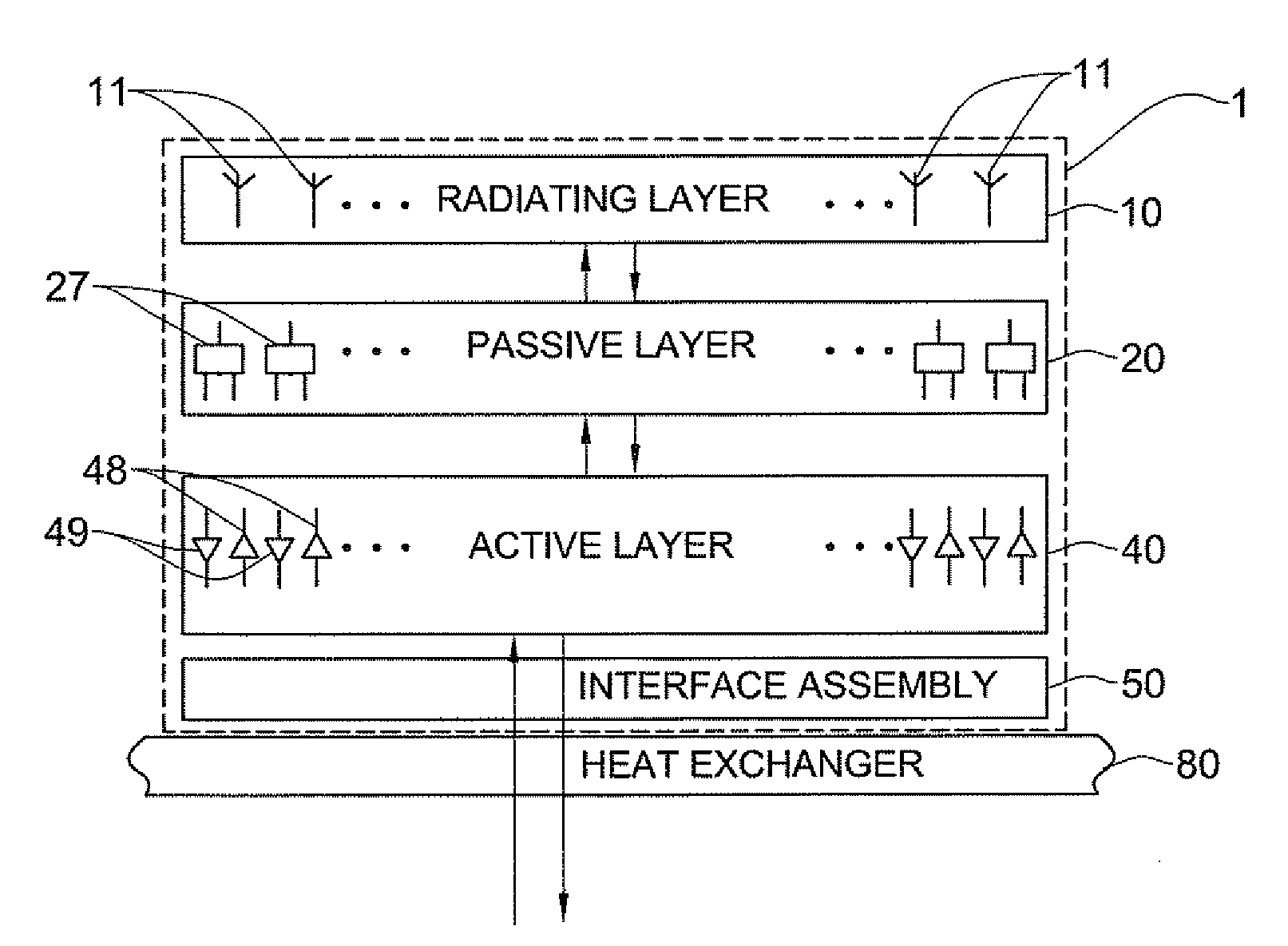
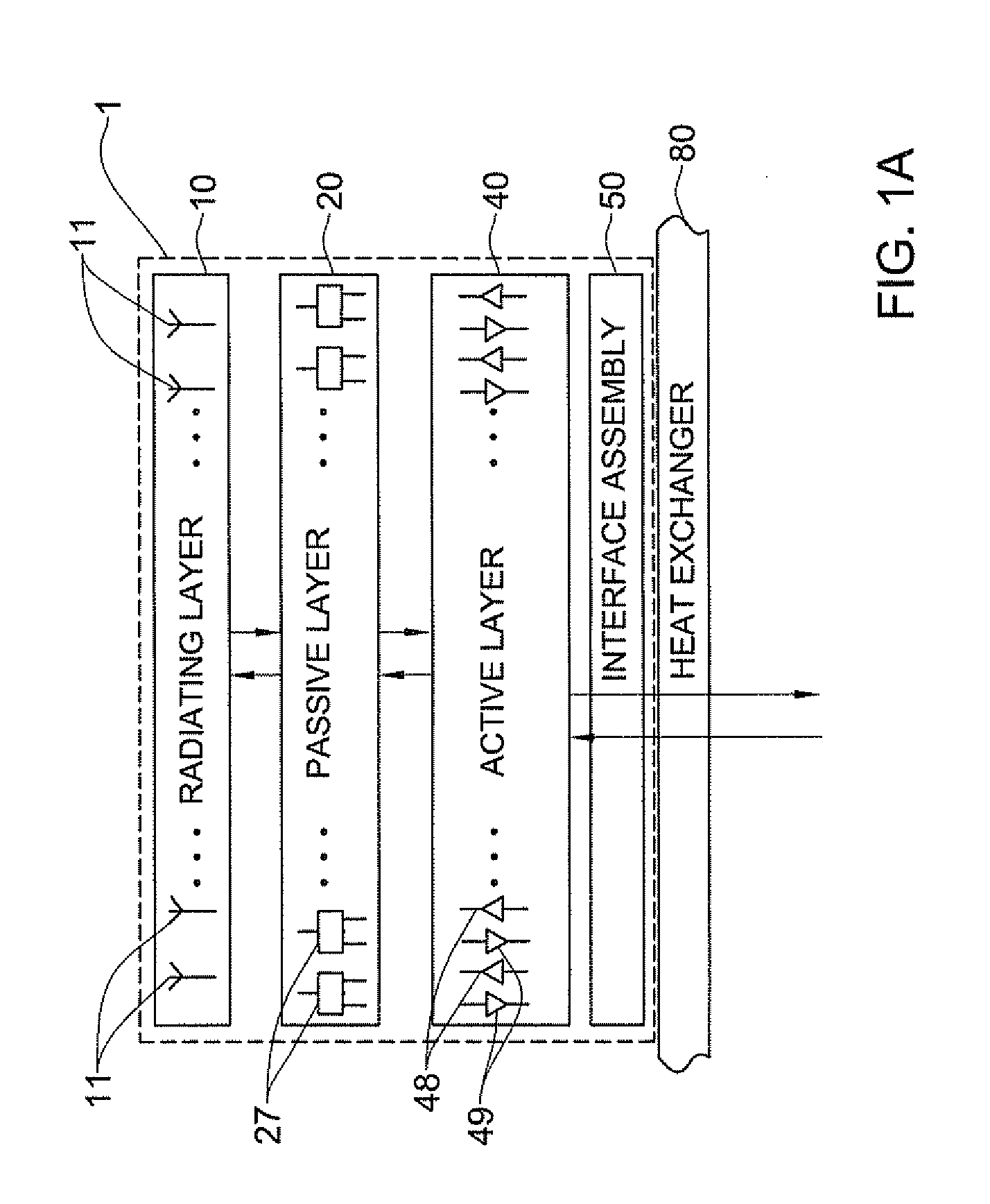
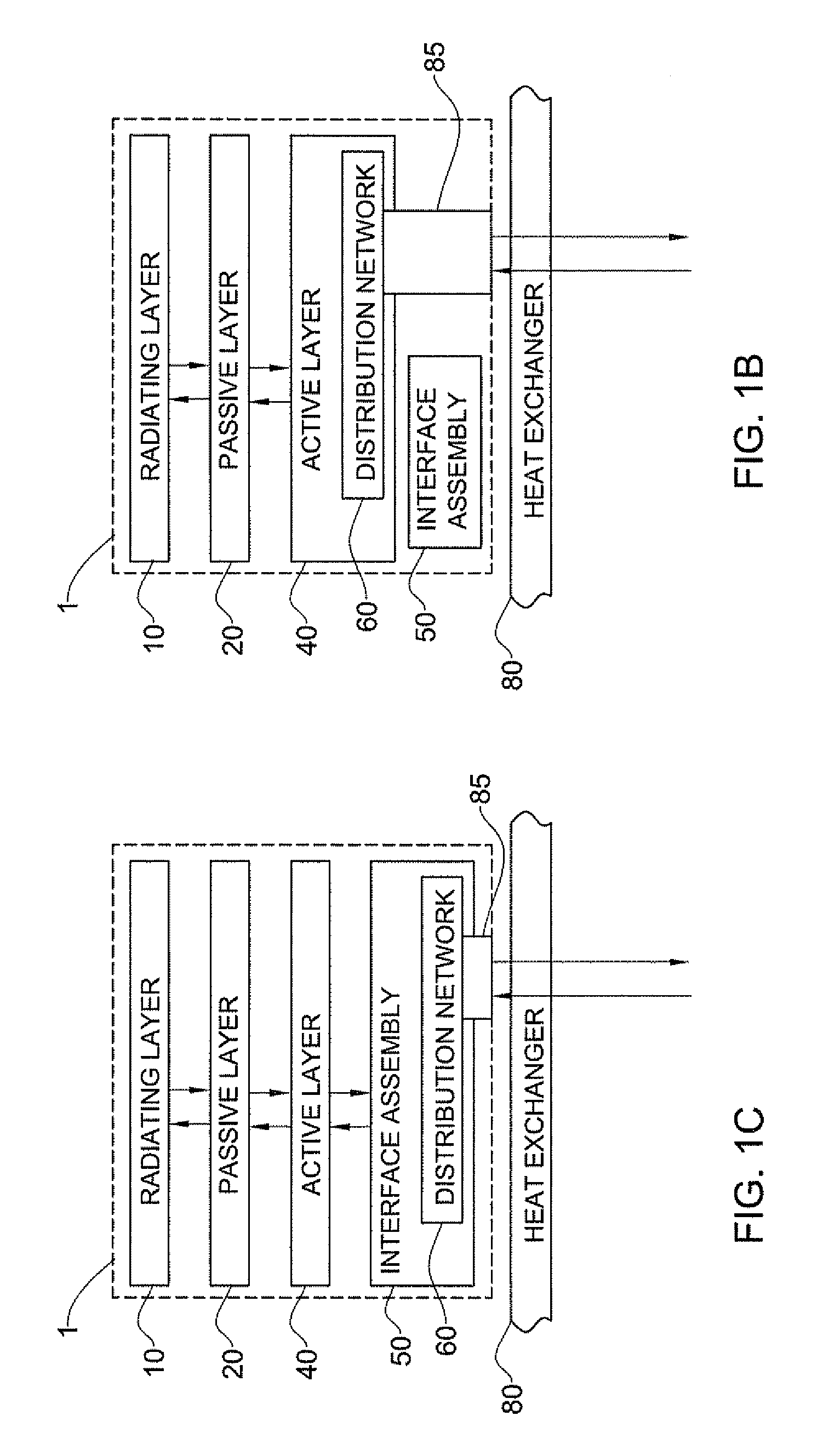
A vertically stacked array antenna structure is described. The structure comprises a radiating layer, a passive layer disposed under said radiating layer, an active layer disposed under said passive layer, and an interface assembly. The radiating layer comprises an array of radiating elements. The passive layer has only passive components. At least a part of the passive components includes an array of RF duplexers corresponding to the array of radiating elements. The active layer comprises RF amplifiers. The interface assembly comprises at least one metallic frame which is in direct thermal coupling with the RF amplifiers. The interface assembly is configured for providing thermal communication of the active layer with a heat exchanger.
Owner:ELTA SYST LTD
Radar system and method of manufacturing same
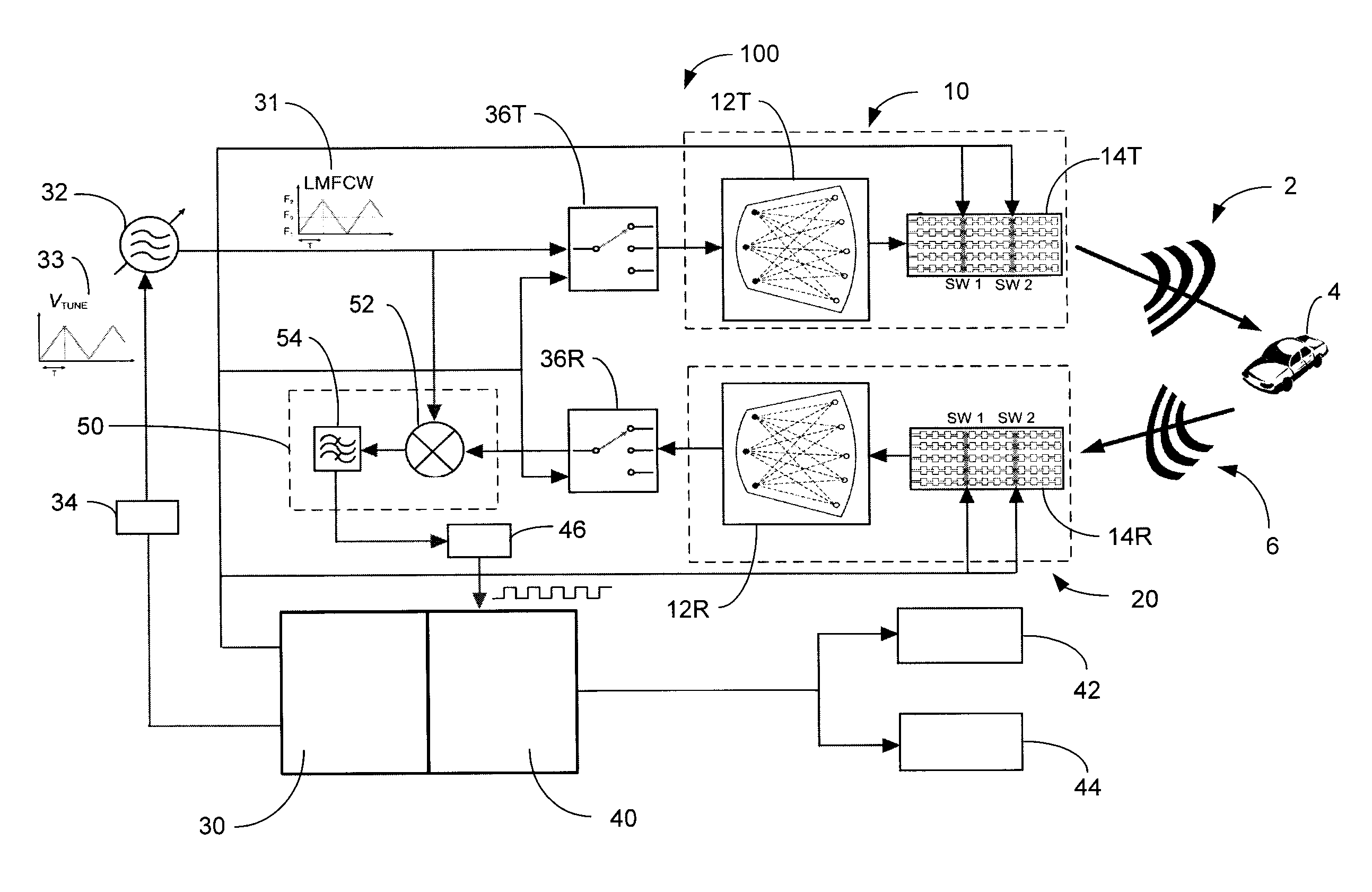
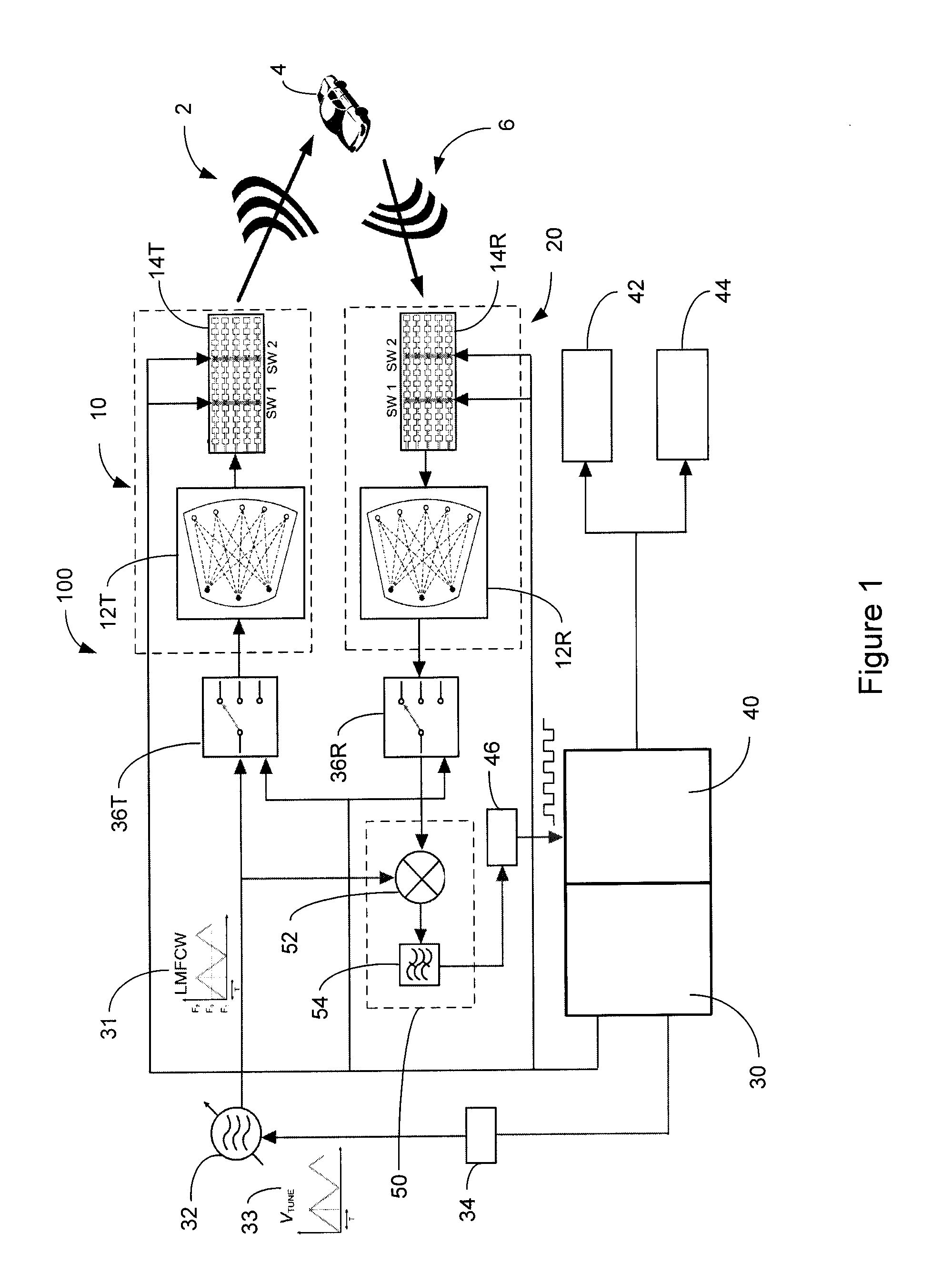
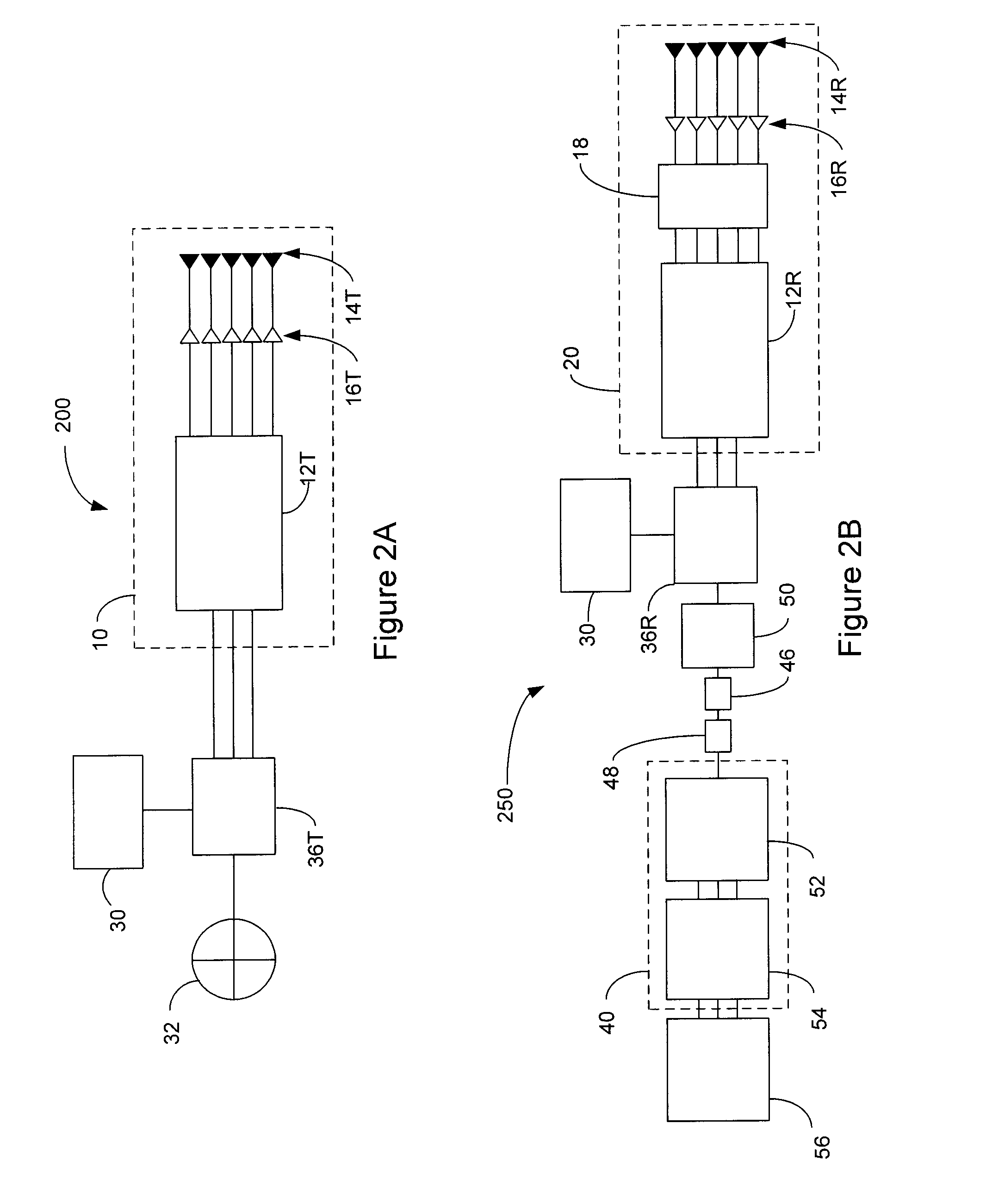
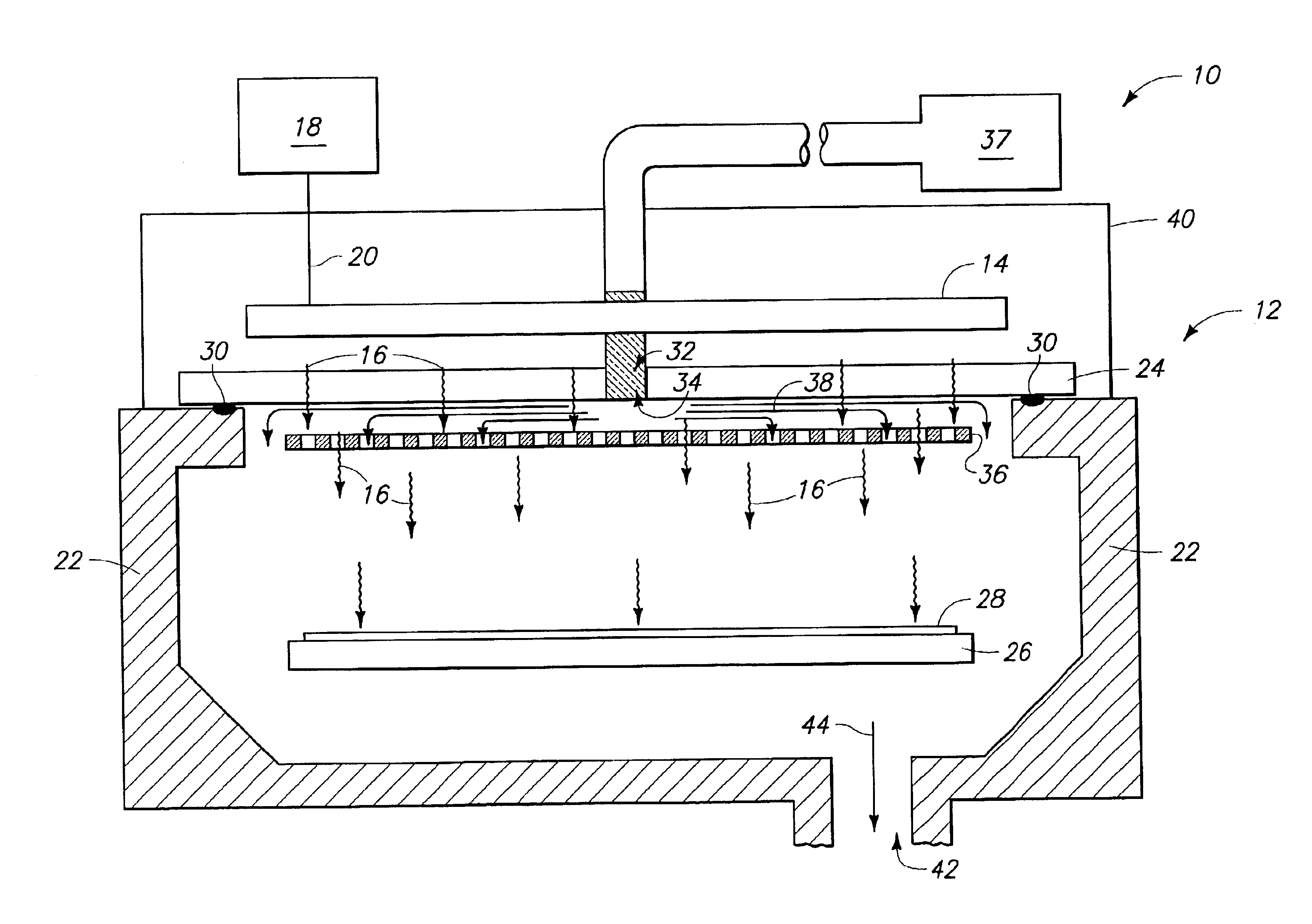
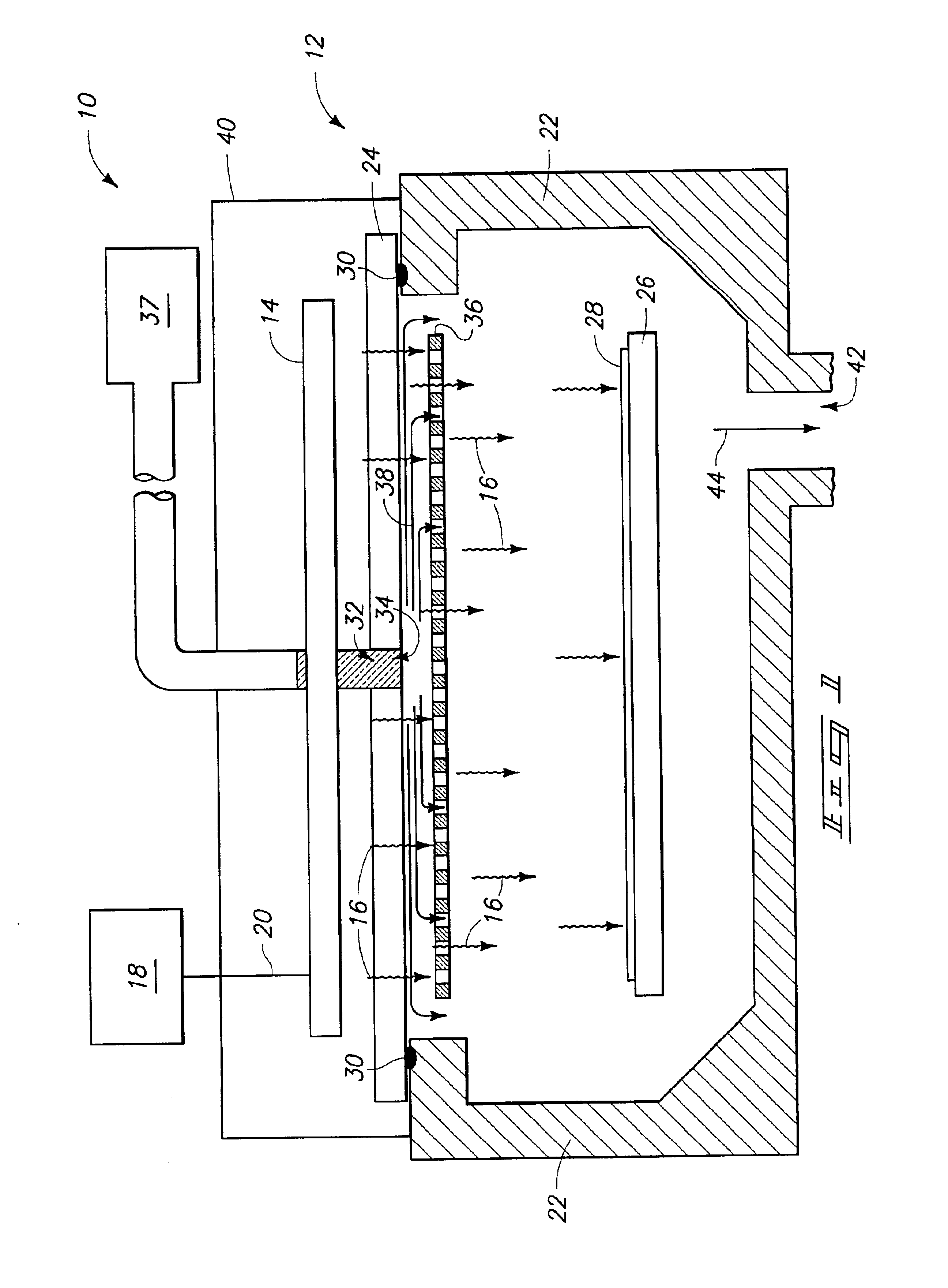
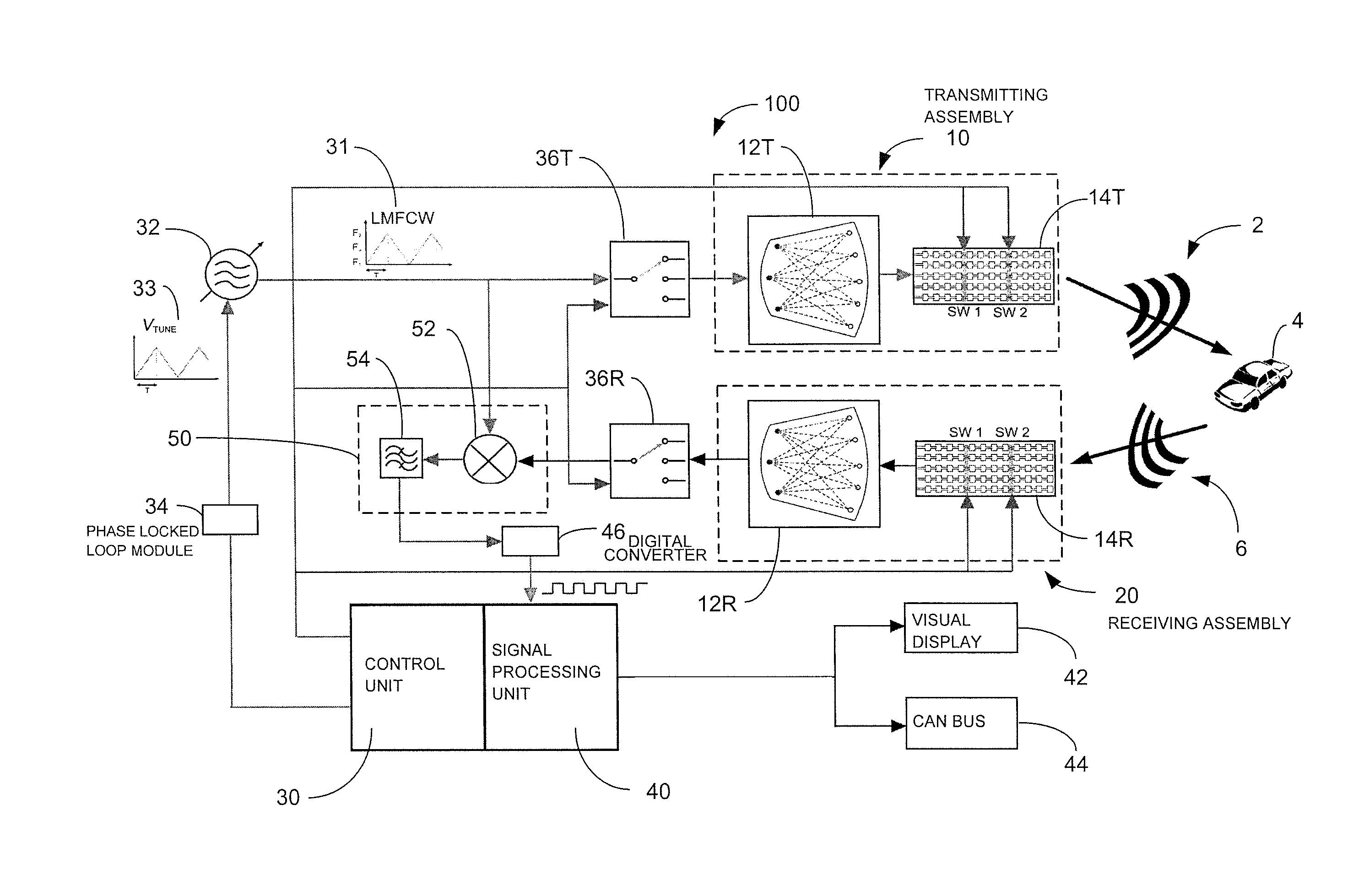
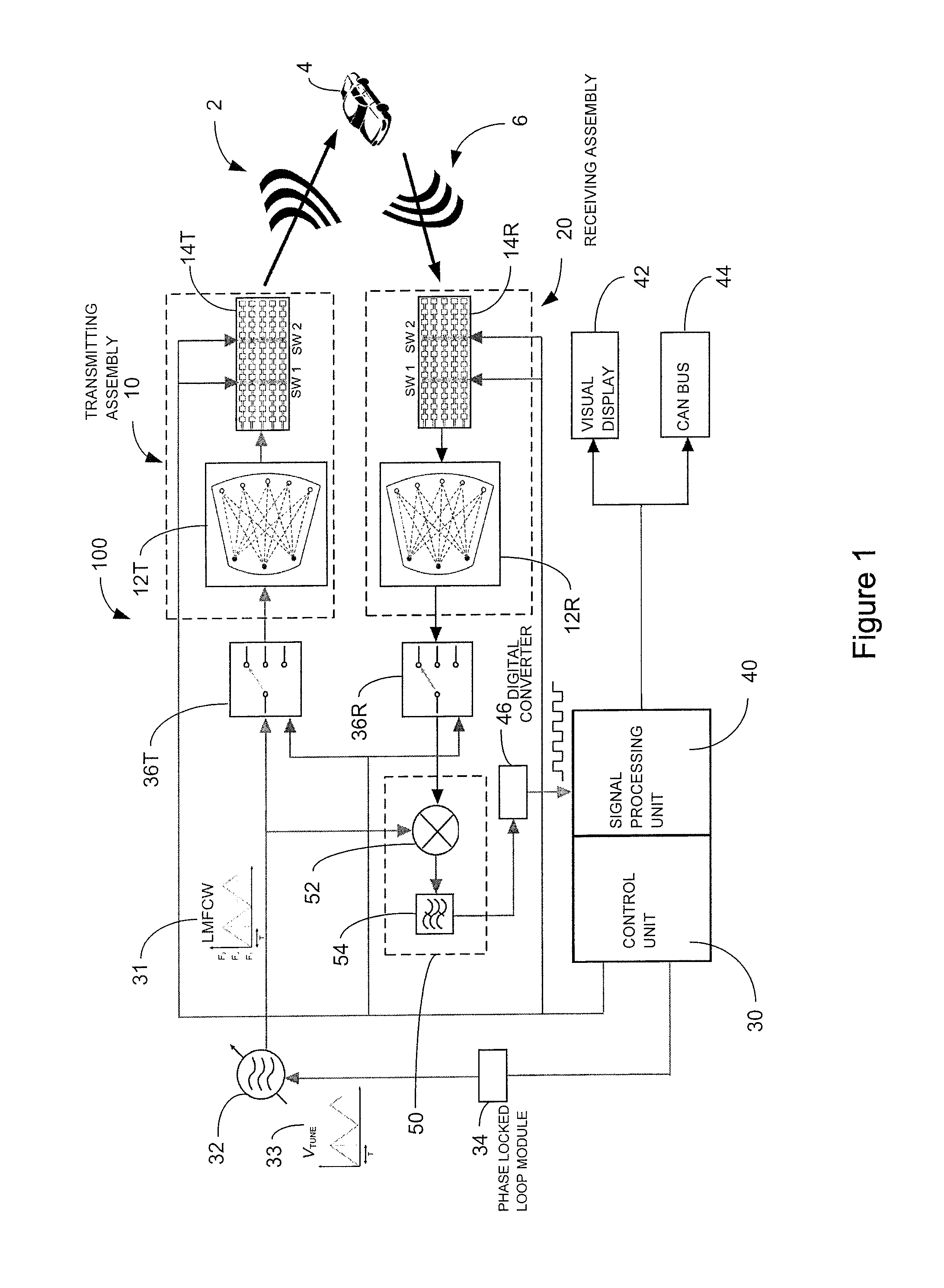
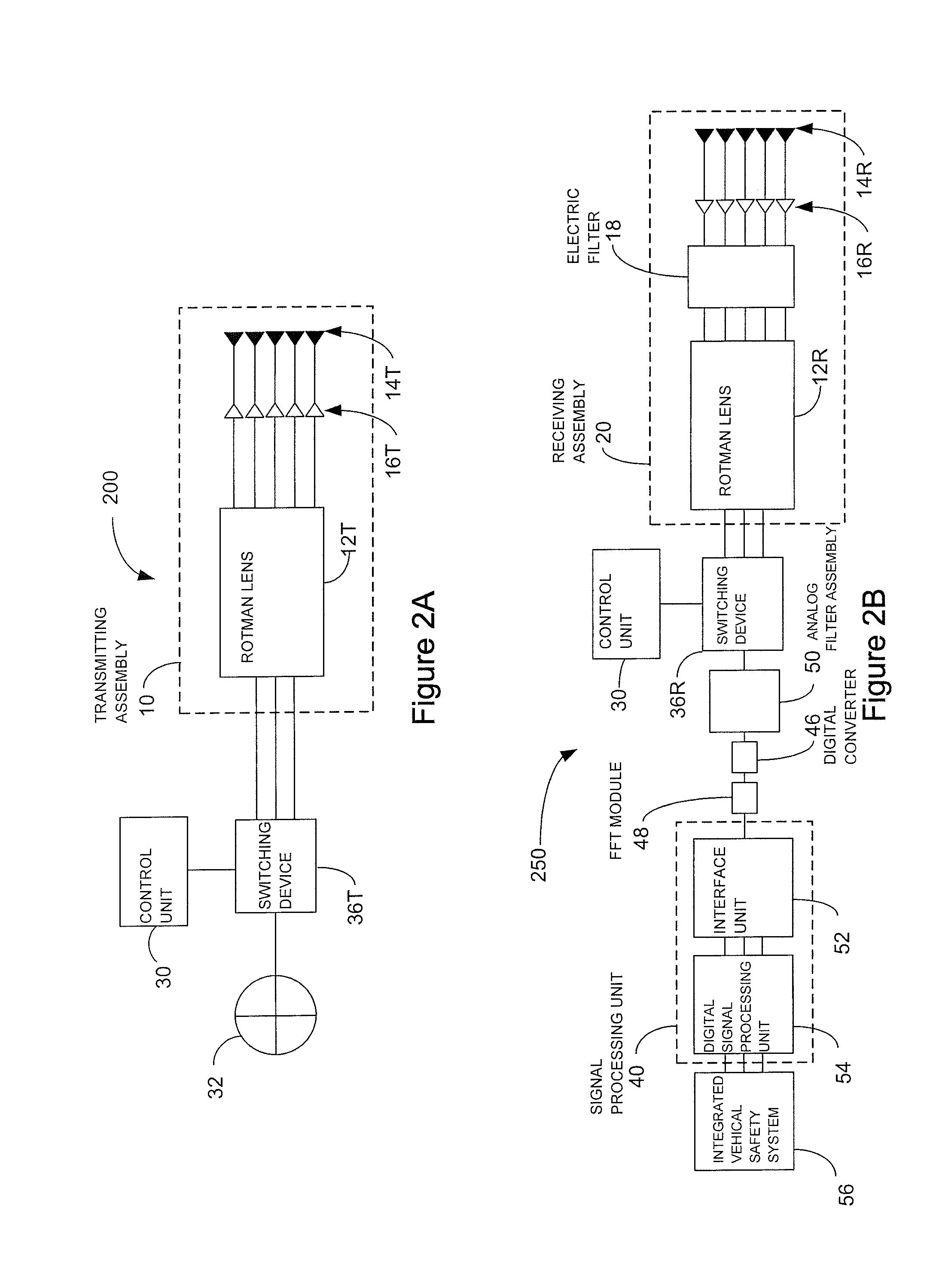
ActiveUS20130027240A1Increase speedThe signal is accurate and reliableAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesParallel-plate/lens fed arraysRadar systemsEngineering
A radar system (100) is described including a transmitting assembly (10), a receiving assembly (20), a control unit (30) and a signal processing unit (40). The transmitting assembly (10) receives an input signal (31) and transmits an incident radar signal (2). The transmitting assembly (10) includes a Rotman lens (12) having a lens cavity (74), a plurality of beam ports (60), a plurality of array ports (62) and a patch antenna assembly (14). The lens cavity (74) has a lens gap (h) between 10 microns to 120 microns, and preferably 40 microns to 60 microns. The patch antenna assembly (14) includes a plurality of antenna arrays (130) operable to receive a plurality of time-delayed, in-phase signals from the Rotman lens (12) and to transmit the incident radar signal (2) towards a target (4). The receiving assembly (20) receives a reflected radar signal (6) and produces an output signal. The signal processing unit (40) compares the input signal (31) to the output signal and implements an algorithm determining the range, velocity and position of the target (4).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WINDSOR
Wideband antenna array
InactiveUS7109939B2Increased frequency rangeEfficient connectionParticular array feeding systemsAntenna arrays manufactureEngineeringWide band
An antenna array comprises a substrate; a plurality of projecting, tapering structures disposed in an array and attached to a first major surface of said substrate, the plurality of projecting, tapering structures defining a plurality of waveguides therebetween; and a plurality of box-shaped structures disposed in an array and attached to a second major surface of the substrate, the plurality of box-shaped structures defining a plurality of waveguides therebetween, the plurality of waveguides defined by the plurality of projecting, tapering structures aligning with the plurality of waveguides defined by the plurality of box-shaped structures. The substrate includes a plurality of probes for feeding the plurality waveguides.
Owner:HRL LAB
Reflect array antennas having monolithic sub-arrays with improved DC bias current paths
ActiveUS20070090997A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsHeat spreaderActive array
Embodiments of active array antennas are generally described herein. Other embodiments may be described and claimed. In some embodiments, a reflect array antenna includes an array of rectangular monolithic sub-array modules arranged in a non-uniform pattern to leave a plurality of rectangular gaps in the pattern. A DC feed pin located within each gap may provide DC bias current to the sub-array modules. The sub-array modules may be mounted on a heat sink in the non-uniform pattern. The heat sink may have holes aligned with the gaps to allow passage of the DC feed pins. In some embodiments, an array cooling assembly may be coupled to the back of the heat sink to cool the reflect array antenna with a coolant.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Wireless antennas, networks, methods, software, and services
InactiveUS20040162115A1Reduce complexityLow costAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentBeam patternMulti beam
The invention is directed to a wireless network arrangement in which nodes comprise multi-faceted multi-beam antennas and in which wireless backhaul is provided using those multi-faceted multi-beam antennas. In particular, the invention is directed to a wireless communication node comprising: an antenna defining a first wireless coverage area and a second wireless coverage area. The first wireless coverage area extends in a first beam pattern and the second wireless coverage area extends in a second beam pattern and the second beam pattern comprises at least one directional beam having a direction which is variable. Associated apparatus, methods, programs, and subscriber services are also provided.
Owner:APPLE INC +1
Method and apparatus for automotive radar sensor
InactiveUS20050225481A1Low costAdditional imaging capabilityAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesSolid-state devicesEngineeringWaveguide
Methods and apparatus are presented which reduce the overall cost and increase the imaging capability for medium and long range automotive radar sensing applications through the combination of a high signal-to-noise ratio and wide dynamic range radar waveform and architecture, antenna arrangement, and a low cost packaging and interconnection method. In accordance with aspects of the present invention, one way a high signal-to-noise ratio and wide dynamic range imaging radar with reduced cost can be achieved is through the combination of a pulsed stepped-frequency-continuous-wave waveform and electrically beam-switched radar architecture, utilizing a planar package containing high-frequency integrated circuits as well as integrated high-frequency waveguide coupling ports, coupled to a multi-beam waveguide-fed twist-reflector narrow beam-width antenna. Other methods and apparatus are presented.
Owner:GHZ TR CORP
System, method and computer-accessible medium for depth of field imaging for three-dimensional sensing utilizing a spatial light modulator microscope arrangement
ActiveUS20150369660A1Efficiently modulate the intensity, phase, and/or polarization of incident radiationSolid-state devicesRadiating elements structural formsElectrical conductorPlanar antennas
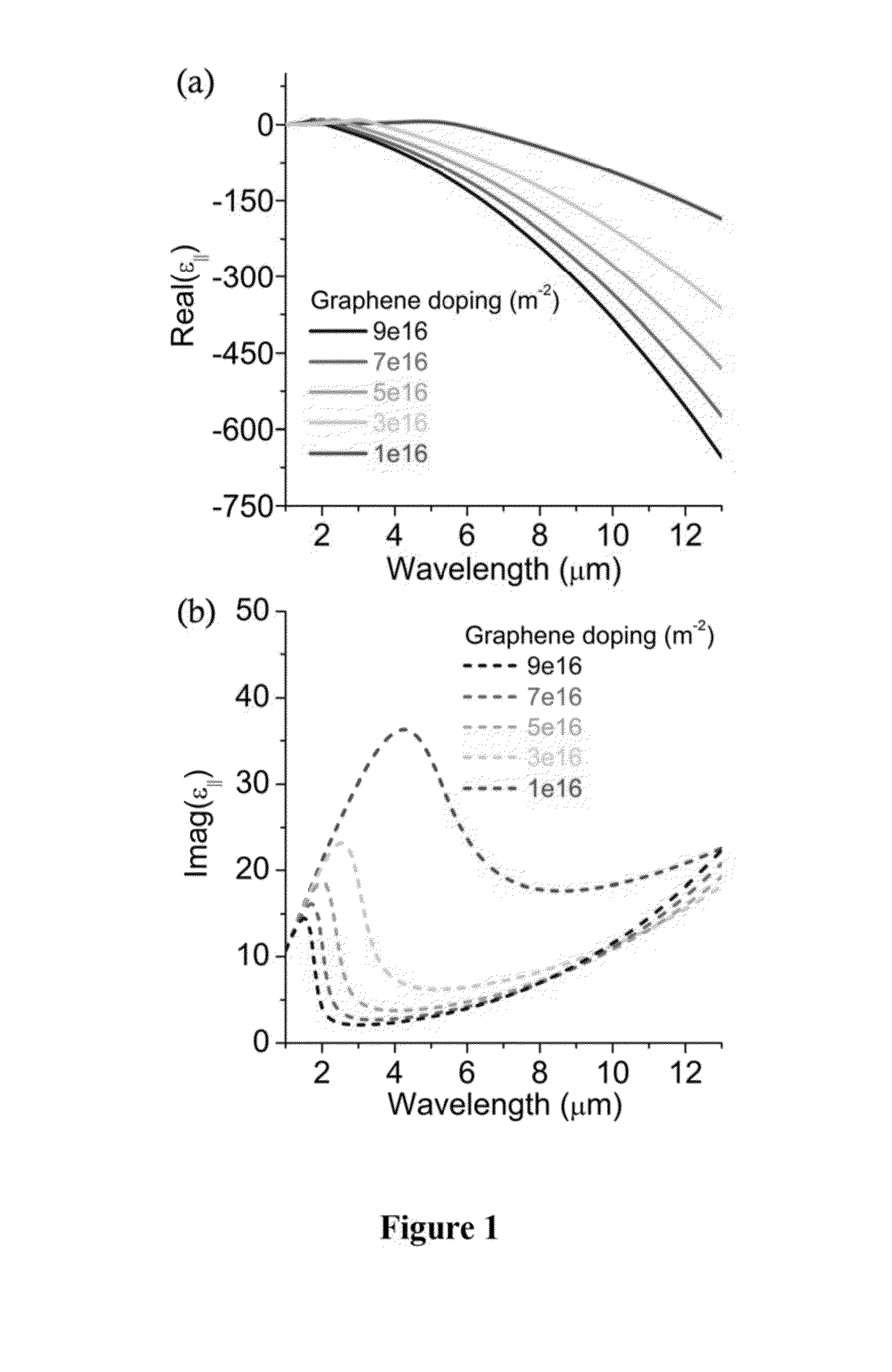
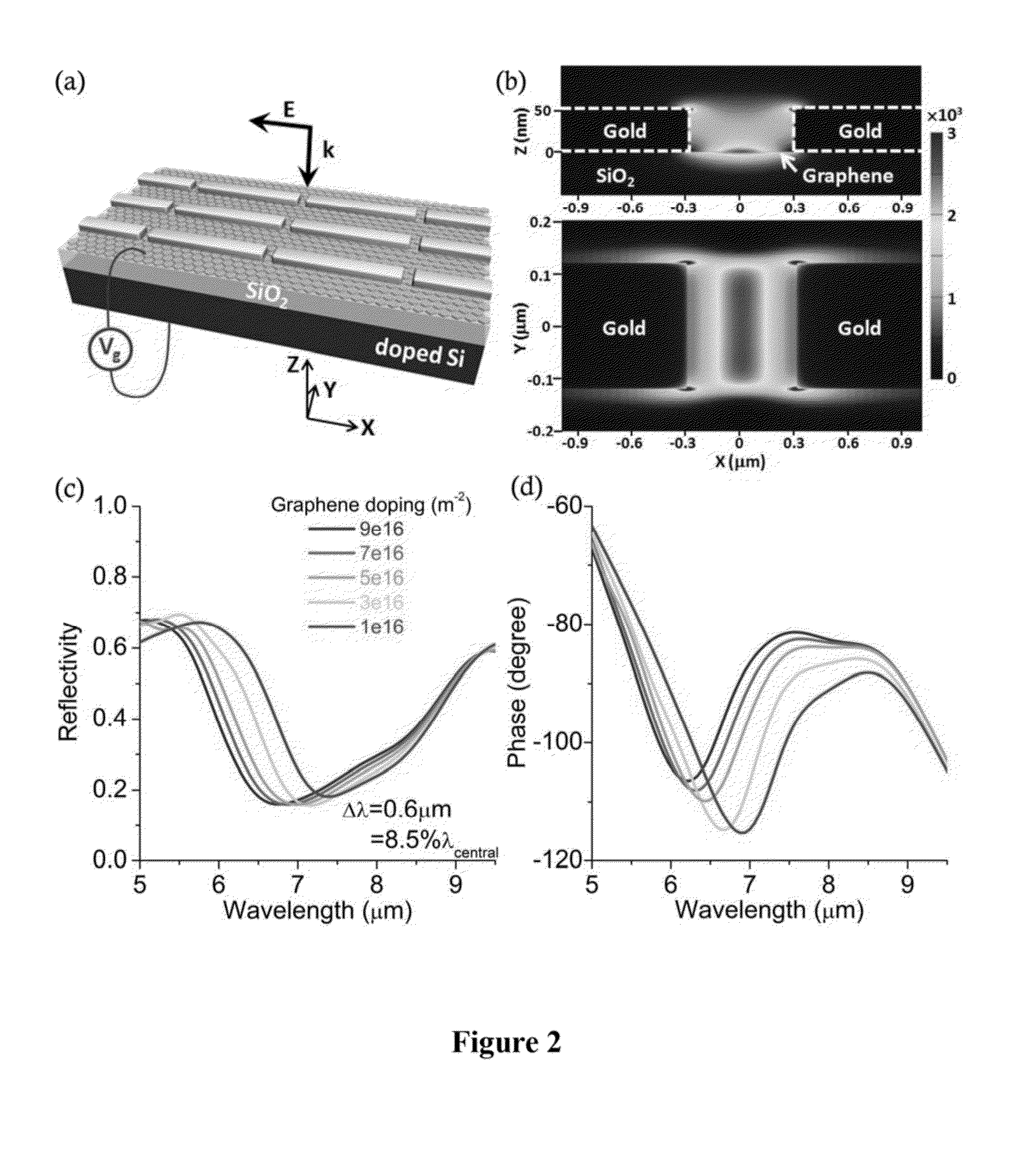
Exemplary embodiment can utilize the properties of tunable thin-film, material (e.g., graphene) to efficiently modulate the intensity, phase, and / or polarization of transmitted and / or reflected radiation, including mid-infrared (“mid-IR”) radiation. Exemplary embodiments include planar antennas comprising tunable thin-film material sections and metallic sections disposed in contact with the tunable thin-film material sections, each metallic section having a gap with at least one dimension related to a wavelength of the radiation, which in some embodiments may be less than the wavelength. The metallic layer may comprise rods arrange in one or more shapes, or one or more apertures of one or more shapes. Embodiments of the antenna may also comprise a substrate, which may be a semiconductor or conductor in various embodiments. Embodiments also include systems, computer-implemented methods, devices, and computer-readable media for effectuating desired modulation of incident radiation by, e.g., varying the doping level of the tunable thin-film material.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Antenna
InactiveUS20150349415A1Excellent side-lobe suppression characteristicWaveguide hornsParticular array feeding systemsCouplingAntenna element
An antenna includes an antenna layer, a coupling layer, and a feeder circuit layer. The antenna layer includes antennas elements. First and second antennas elements are arranged in such a manner that the centers thereof are aligned in a first direction. A third antenna element is arranged in such a manner that the third antenna element is separated from the first antenna element in a second direction and centers of the antennas elements are not aligned in the second direction. A waveguide is formed in the coupling layer.
Owner:NEC CORP
Phase shifters deposited en masse for an electronically scanned antenna
ActiveUS7324043B2Increase processing costPatterning of backsideSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectricEngineering
A system and method for an electronically scanned antenna is provided in which phase shifters are deposited en masse along with other electronically scanned antenna components on a wafer scale substrate using a thin film process. Alternative wafer scale sizes may be utilized to furnish a required antenna aperture area. Significant processing costs for radar and communication systems are saved utilizing the present invention as compared with contemporary discrete phase shifters that are individually mounted on an antenna. In an aspect, the phase shifter is made up of a base electrode, a barium strontanate titanate (BST) ferroelectric varactor and a top electrode. The BST ferroelectric material is a voltage variable dielectric, which generates a radiation phase. The radiation phase is regulated by a phase shifter control. The radiation phase generates an electromagnetic field about a radiating element and electromagnetic radio waves are radiated from the radiating element.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Method and system for a phased array antenna embedded in an integrated circuit package
ActiveUS7880677B2Simultaneous aerial operationsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPhase shiftedTransformer
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Low cost microstrip antenna
InactiveUS20020109633A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsElectricityDielectric
An low cost stacked microstrip antenna and low cost method of making the same are disclosed. By using specially designed bandwidth and directivity parameters in conjunction with lower cost dielectric, materials economies of production are realized. In particular, dielectric support layers made from fine cell foam sheet material that is mass produced for primary purposes other than electrical insulation materials, are used to reduce cost. A stackable design used in conjunction with a capacitively coupled feedline connector reduce assembly costs as well.
Owner:MAXRAD +1
Electronically steerable planar phase array antenna
InactiveUS20140266897A1Low profileRadiating elements structural formsAntenna arrays manufactureManufacturing technologyLight beam
A two-dimensional (2-D) beam steerable phased array antenna is presented comprising a continuously electronically steerable material including a tunable material or a variable dielectric material, preferred a liquid crystal material. A compact antenna architecture including a patch antenna array, tunable phase shifters, a feed network and a bias network is proposed. Similar to the LC display, the proposed antenna is fabricated by using automated manufacturing techniques and therefore the fabrication costs are reduced considerably.
Owner:ALCAN SYST GMBH
Wireless network communication apparatus, methods, and integrated antenna structures
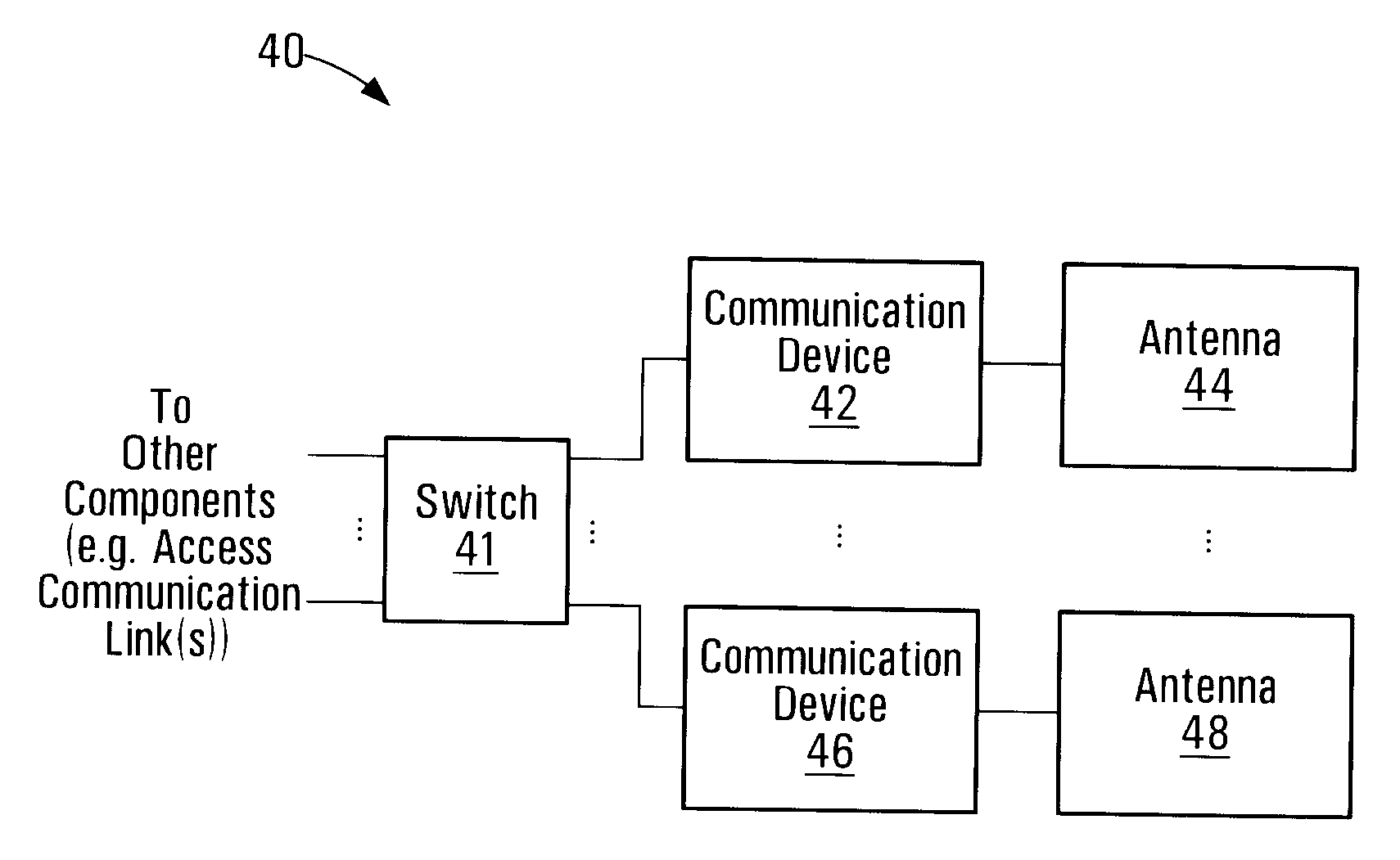
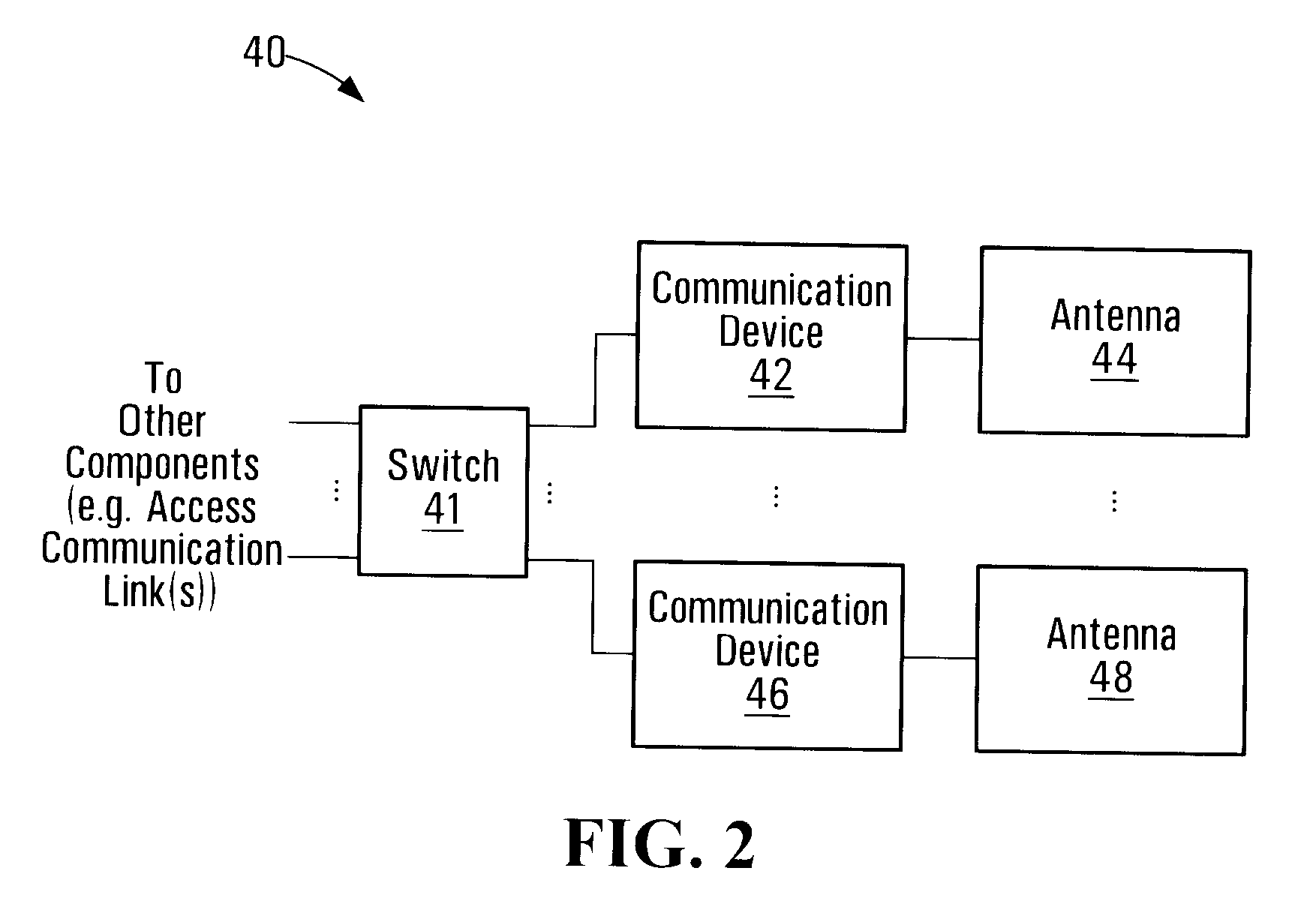
ActiveUS20090274130A1Radiating element housingsSubstation equipmentTelecommunications linkWireless mesh network
Wireless mesh network communication apparatus and methods are disclosed. Directional antennas are respectively operatively coupled to dedicated communication devices to provide multiple independent wireless communication links. Exchange of communication traffic through the wireless communication links provided by the communication devices and the antennas is controlled by a switch. Any or all of the antennas may be adjustable so as to provide for flexibility in antenna beam alignment. Beam alignment may be physically or electronically adjustable. Radio units including the communication devices and the antennas, and possibly also the switch, may be enclosed in a single housing. The housing may be shared with other components such as wireless communication network base station antennas.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
Transmit/Receive Daughter Card With Integral Circulator
ActiveUS20150015453A1Low insertion lossEliminate needSolid-state devicesAntenna arrays manufactureRadio frequencyDaughterboard
A mixed-signal, multilayer printed wiring board fabricated in a single lamination step is described. The PWB includes one or more radio frequency (RF) interconnects between different circuit layers on different circuit boards which make up the PWB. The PWB includes a number of unit cells with radiating elements and an RF cage disposed around each unit cell to isolate the unit cell. A plurality of flip-chip circuits are disposed on an external surface of the PWB and a heat sink can be disposed over the flip chip components.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method and system for a phased array antenna embedded in an integrated circuit package
ActiveUS20090153428A1Antenna supports/mountingsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPhase shiftedTransformer
Aspects of a method and system for configurable antenna in an integrated circuit package are provided. In this regard, a phased array antenna embedded in a multi-layer integrated circuit (IC) package may be utilized for transmitting and / or receiving signals. An IC enabled to transmit and / or receive signals may be bonded to the multi-layer IC package and may communicate a reference signal and / or one or more phase shifted versions of said reference signal to the antenna. One or more phase shifters (fabricated, for example, in planar transmission line) may be embedded in the multi-layer IC package and may be controlled via an IC bonded to the multi-layer IC package. The phased array antenna may comprise a plurality of antenna elements which may each comprise an interconnection for communicatively coupling to an associated transmitter and / or receiver, a feeder line, a quarter wavelength transformer, and a radiating portion (e.g., a folded dipole).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Mm-wave/IR monolithically integrated focal plane array
An integrated infrared and millimeter-wave monolithic focal plane sensor array having a substrate upon which an integrated array of infrared sensors and mm-wave sensors are provided at a first planar level on the same side of the substrate, and a planar antenna for receiving incident millimeter-wave radiation located at a second planar level located between the integrated array of sensors and the surface of the substrates for coupling the mm-wave radiation field to the mm-wave sensor. The antenna receiver of electromagnetic radiation, in one embodiment, is an antenna having a crossed bowtie configuration which efficiently couples the radiation field to the mm-wave sensor. The invention also is directed to a method of fabricating such a radiation sensor.
Owner:HRL LAB
Semiconductor package having an antenna and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20140035097A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipSemiconductor package
A semiconductor package and a manufacturing method thereof are provided. The semiconductor package includes a first substrate, a second substrate, an interposer substrate, a semiconductor chip, a package body and a first antenna layer. The first substrate comprises a grounding segment. The interposer substrate is disposed between the second substrate and the first substrate. The semiconductor chip is disposed on the second substrate. The package body encapsulates the second substrate, the semiconductor chip and the interposer substrate, and has a lateral surface and an upper surface. The first antenna layer is formed on the lateral surface and the upper surface of the package body, and electrically connected to the grounding segment.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
Modular Feed Network
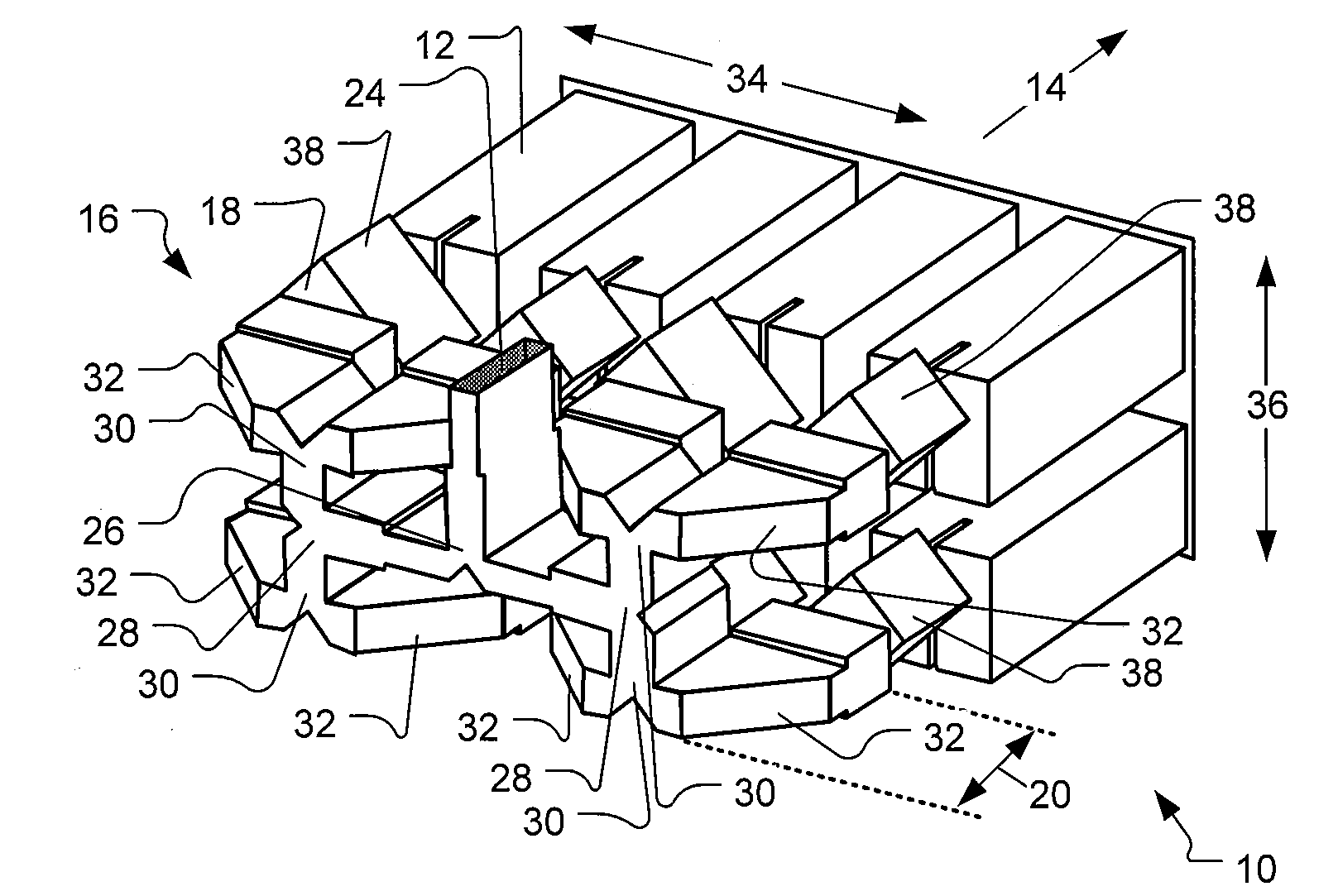
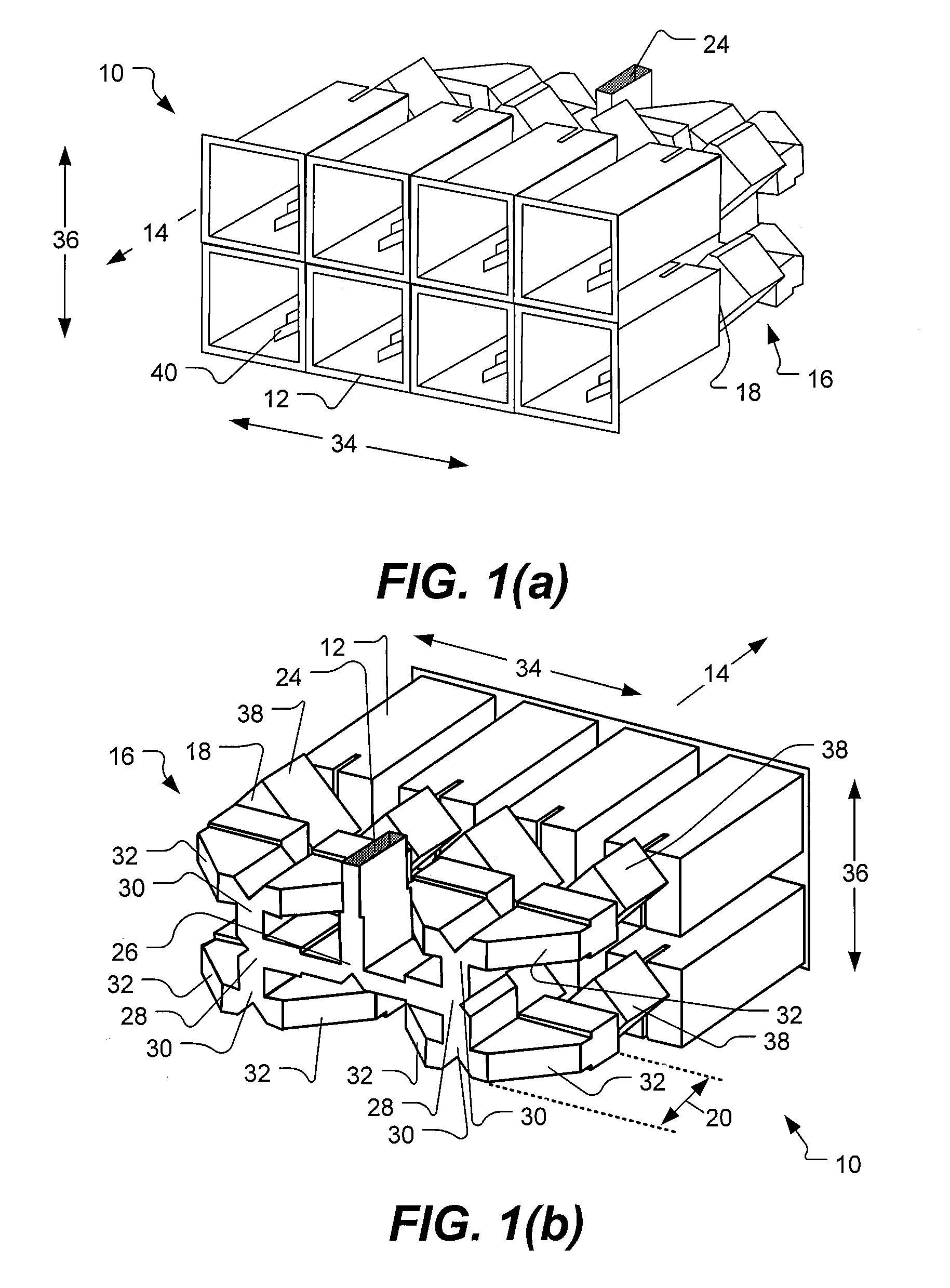
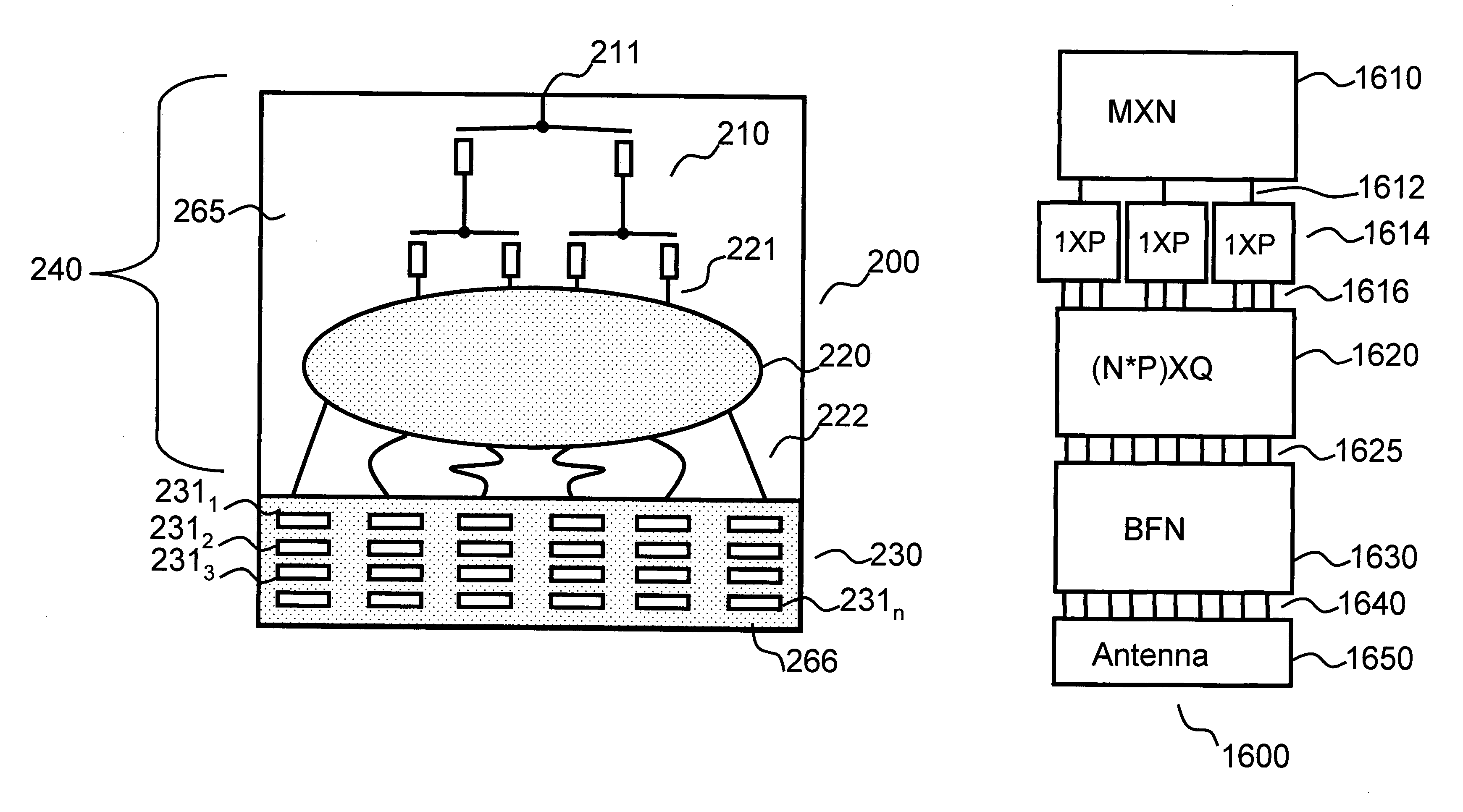
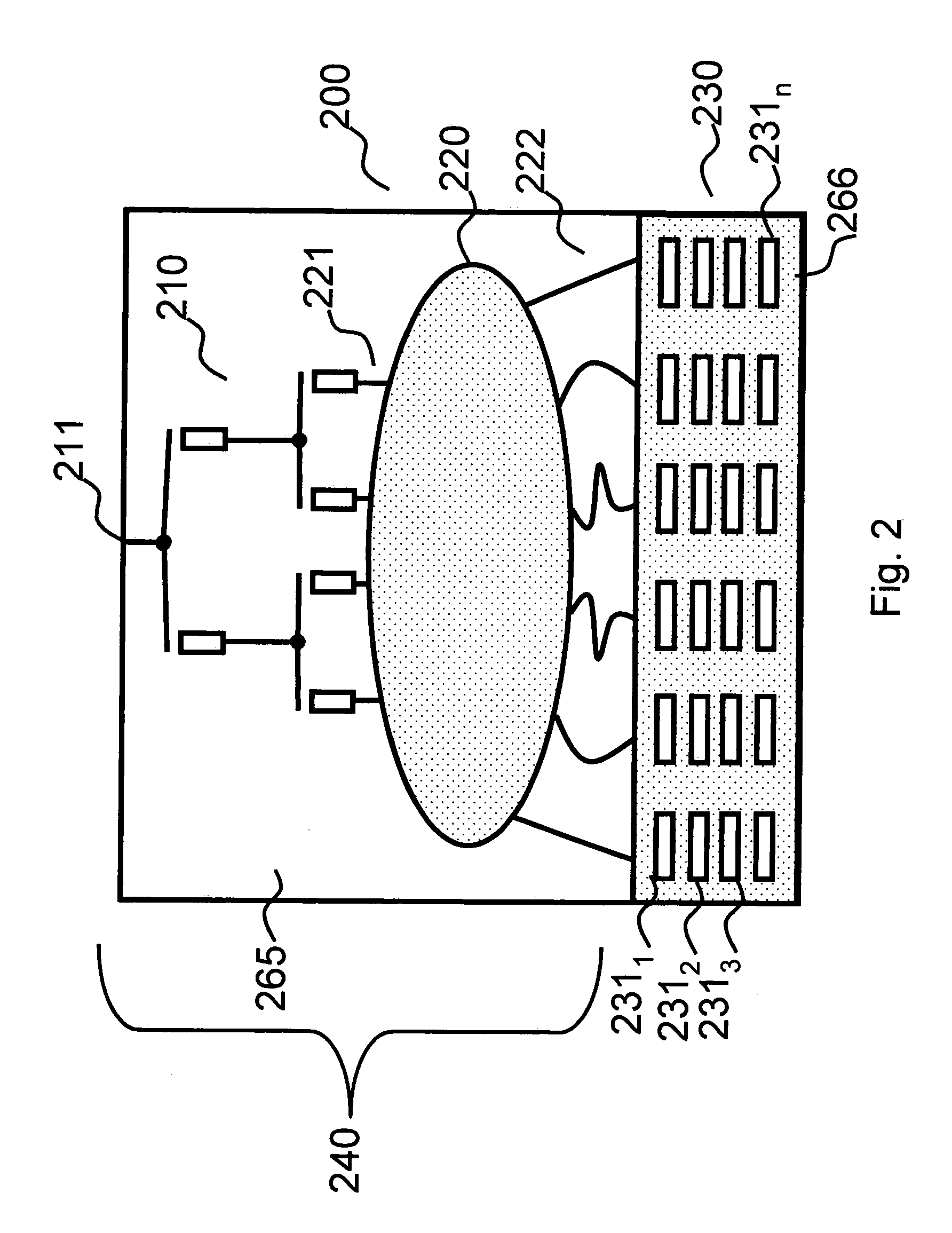
ActiveUS20130120206A1Simple requirementsReduce couplingAntenna arrays manufactureModular arraysModularityEngineering
A modular feed network is provided with a segment base provided with a feed aperture, a corner cavity at each corner and a tap cavity at a mid-section of each of two opposite sides. A segment top is provided with a plurality of output ports. The segment top is dimensioned to seat upon the segment base to form a segment pair. the segment base provided with a plurality of waveguides between cavities of the segment base. The modular feed network is configurable via a range of feed, bypass and / or power divider taps seated in the apertures and / or cavities to form a waveguide network of varied numbers of output ports by routing across one or more of the segment tops. For example, the modular feed network may comprise 1, 4 or 16 of the segment bases retained side to side.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Phased array antenna module and method of making same
ActiveUS20130050055A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAntenna arrays manufactureElectrical conductorCoupling
A phased array antenna includes a semiconductor wafer, with radio frequency (RF) circuitry fabricated on top side of the semiconductor wafer. There is an array of antenna elements above the top side of the semiconductor wafer, and a coaxial coupling arrangement coupling the RF circuitry and the array of antenna elements. The coaxial coupling arrangement may include a plurality of coaxial connections, each having an outer conductor, an inner conductor, and a dielectric material therebetween. The dielectric material may be air.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
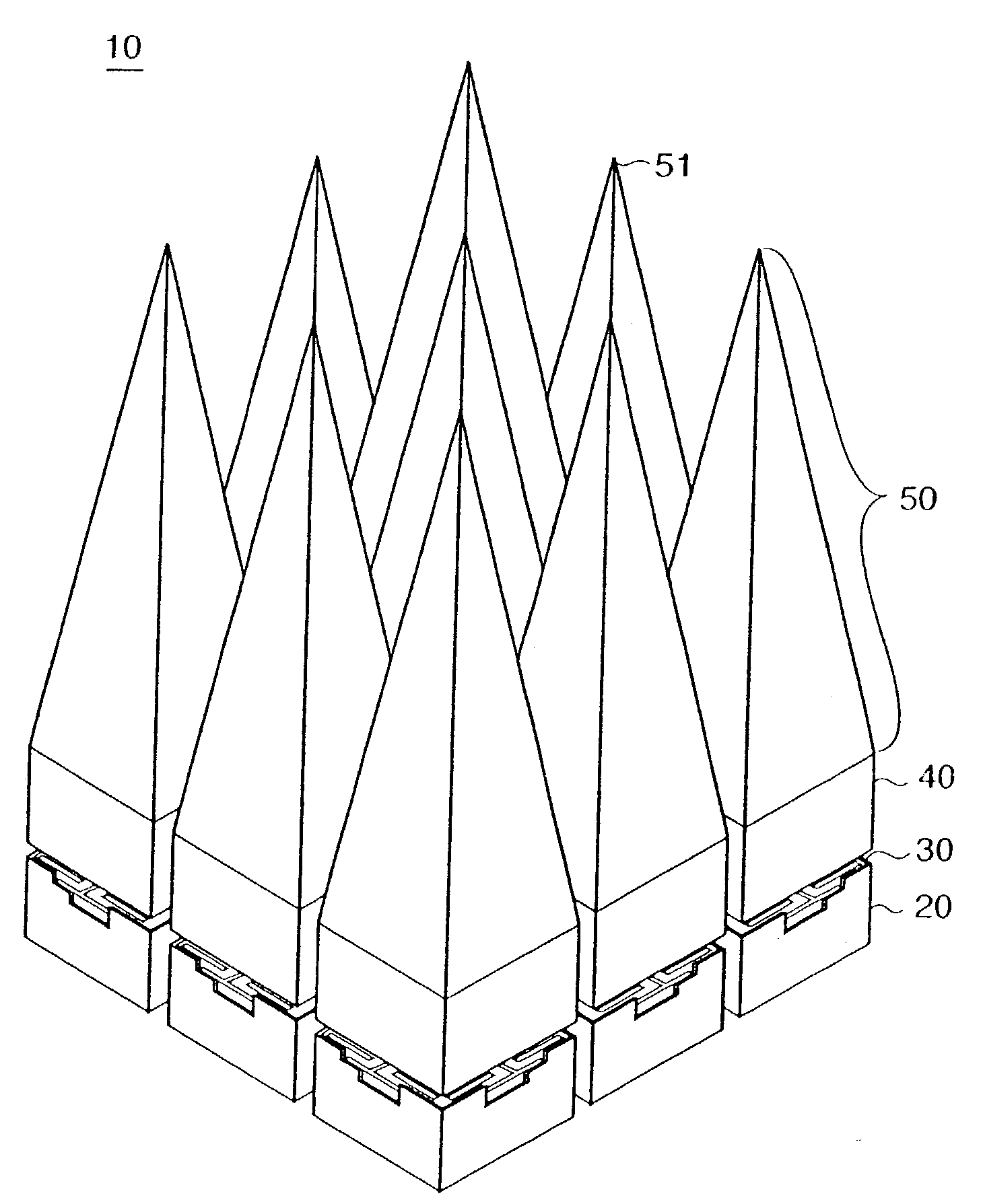
Compact waveguide antenna array and feed
A compact waveguide antenna array feed system provides antenna element ports spaced along an array face by less than one free-space wavelength in at least one dimension, while retaining a thickness in a direction perpendicular to the array face of less than one and one-half free-space wavelength.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
Steerable antenna
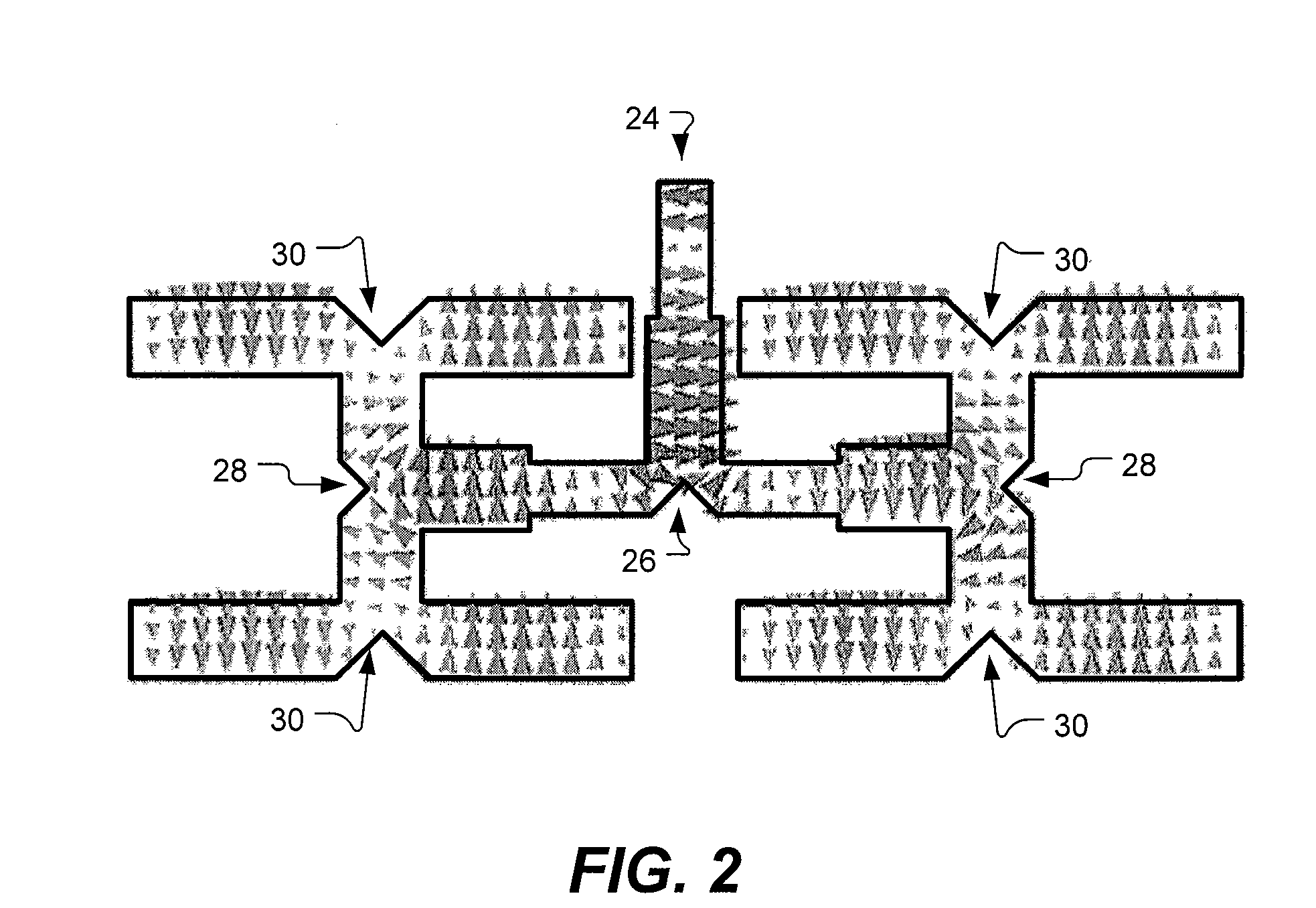
InactiveUS8604989B1Improve reliabilityLow costSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsWaveguidePhased array
An integrated phased array including an array of antenna elements (130), a plurality of waveguides (122), a beam forming network (120), and an RF switch (110). The phased array may further comprise a monolithic integration module (160) comprising a dielectric layer (165) sandwiched between two conductive layers (166, 167).
Owner:OLSEN RANDALL B
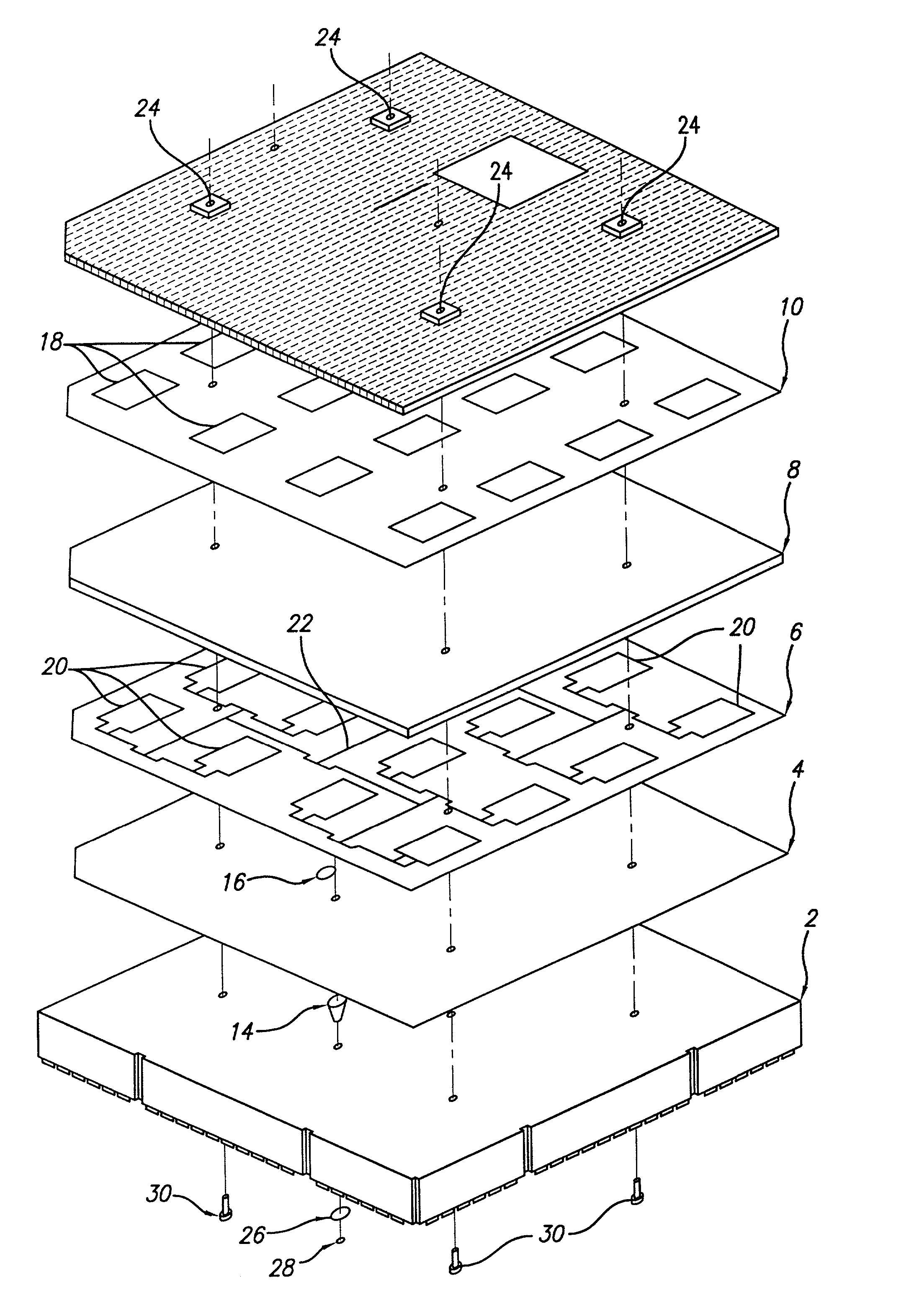
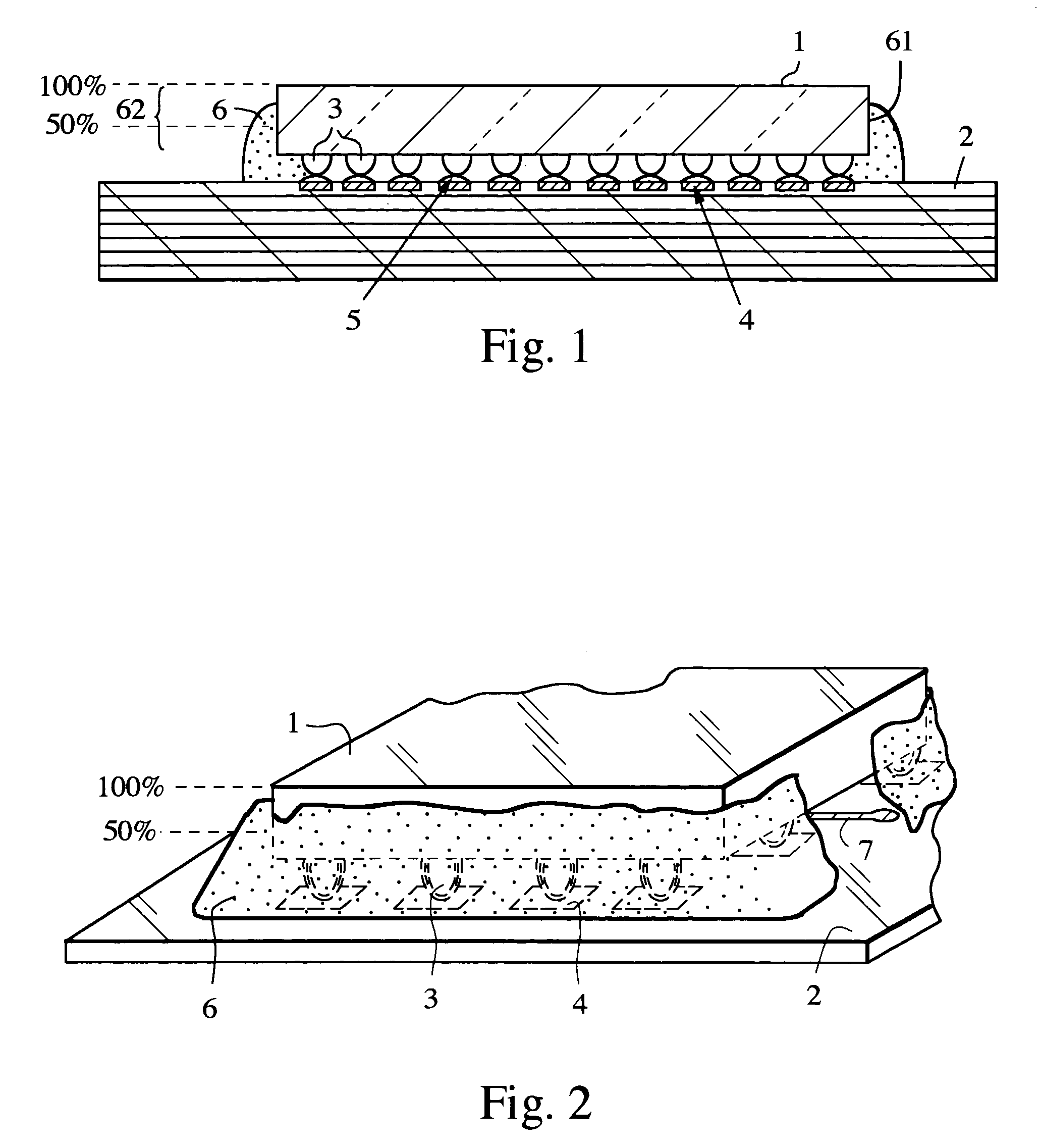
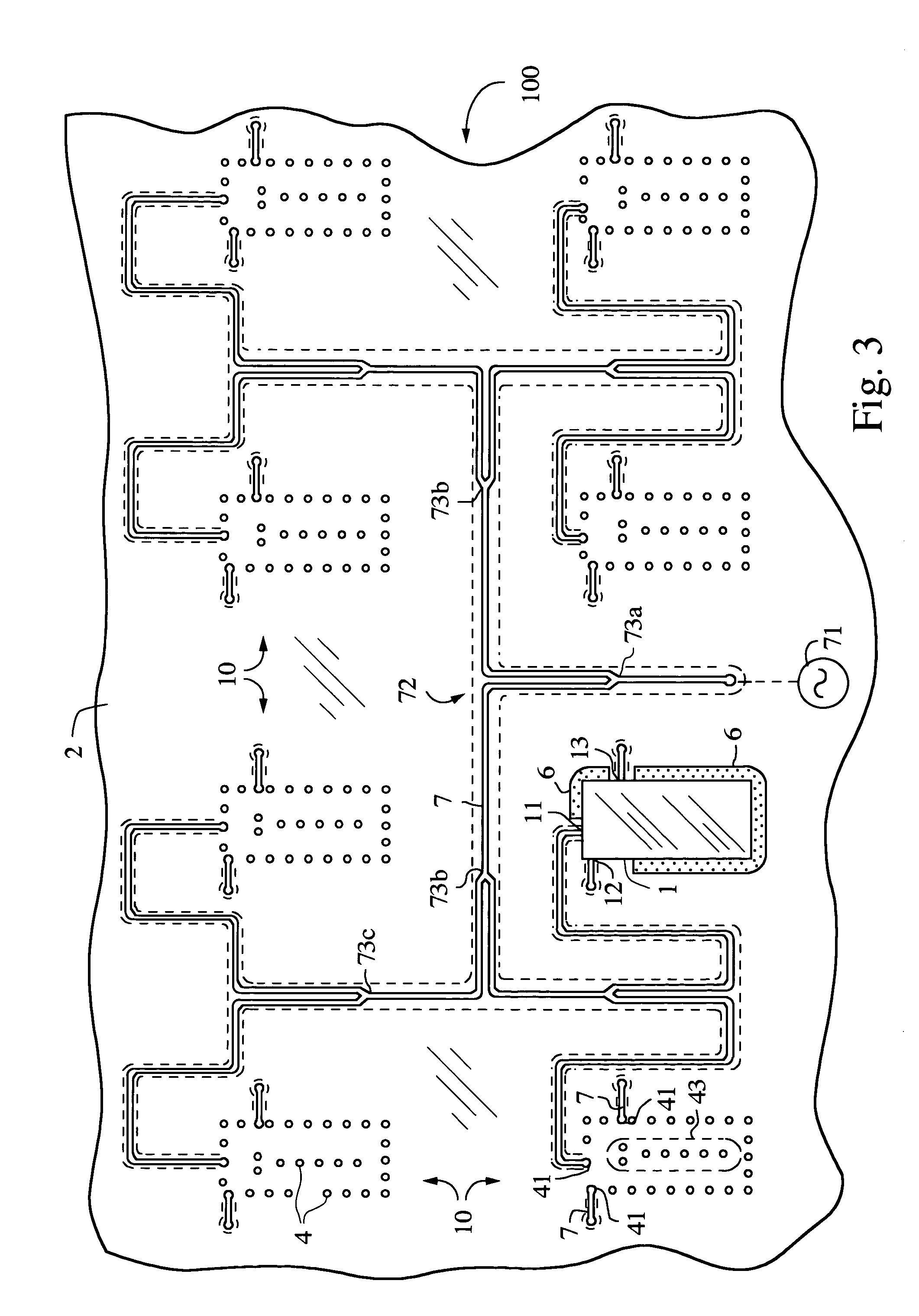
Circuit board assembly and method of attaching a chip to a circuit board
An antenna array is assembled by direct attaching a flip chip transmit / receive (T / R) module to an antenna circuit board. A fillet bond is applied to the circuit board and the flip chip T / R module around at least a portion of the periphery of the flip chip T / R module.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
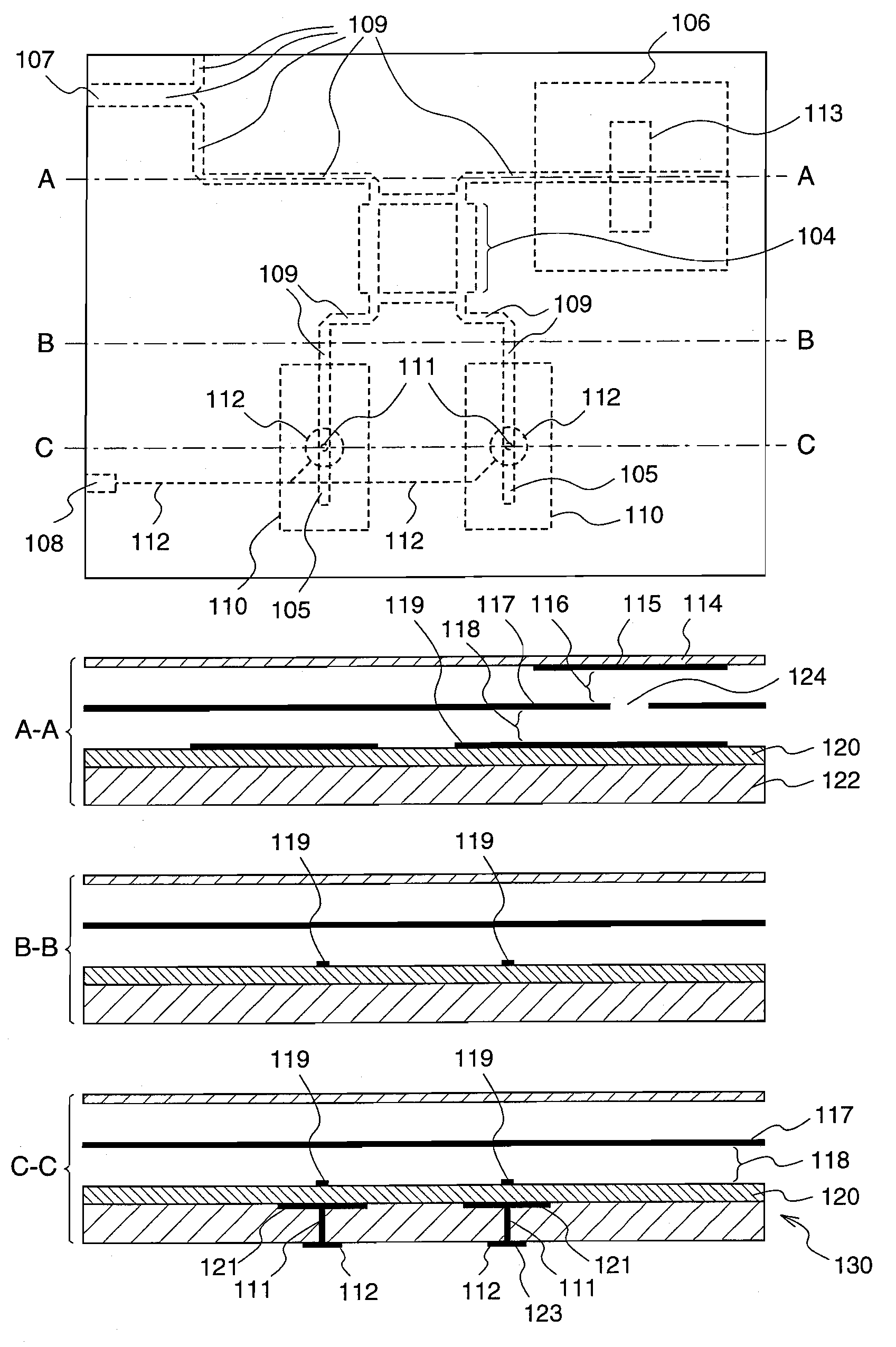
Phased array antenna
InactiveUS20090278744A1High directional gainLess deformationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsPhase shiftedElectrical conductor
There is provided a phased array antenna having variable phase shifters constituted by using a variable dielectric-constant dielectric substance whose dielectric constant varies according to an applied electric field, which antenna can dispense with a DC blocking element that causes mismatch, and reduce deformation of the beam shape even when beam tilt occurs, in the case where the variable phase shifters are divided into those for right-side tilt and those for left-side tilt and the phase shift amounts thereof are independently controlled.The phased array antenna is provided with a feeding phase shift unit (130) having a laminated structure obtained by laminating at least a ground conductor layer (117), an insulator layer (118), a main conductor layer (119), a variable dielectric-constant dielectric layer (120), and a sub conductor layer (121) in this order, and a propagation characteristic variable line (105) having a line on the sub conductor layer in an area which planarly overlaps a line on the main conductor layer is provided on the feeding phase shift unit. By applying a bias voltage between the main conductor layer and the sub conductor layer, the dielectric constant of the variable dielectric-constant dielectric substance in the propagation characteristic variable line area is varied to control the propagation characteristics. Thereby, a DC blocking element to be inserted in series into the feeding line can be dispensed with.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
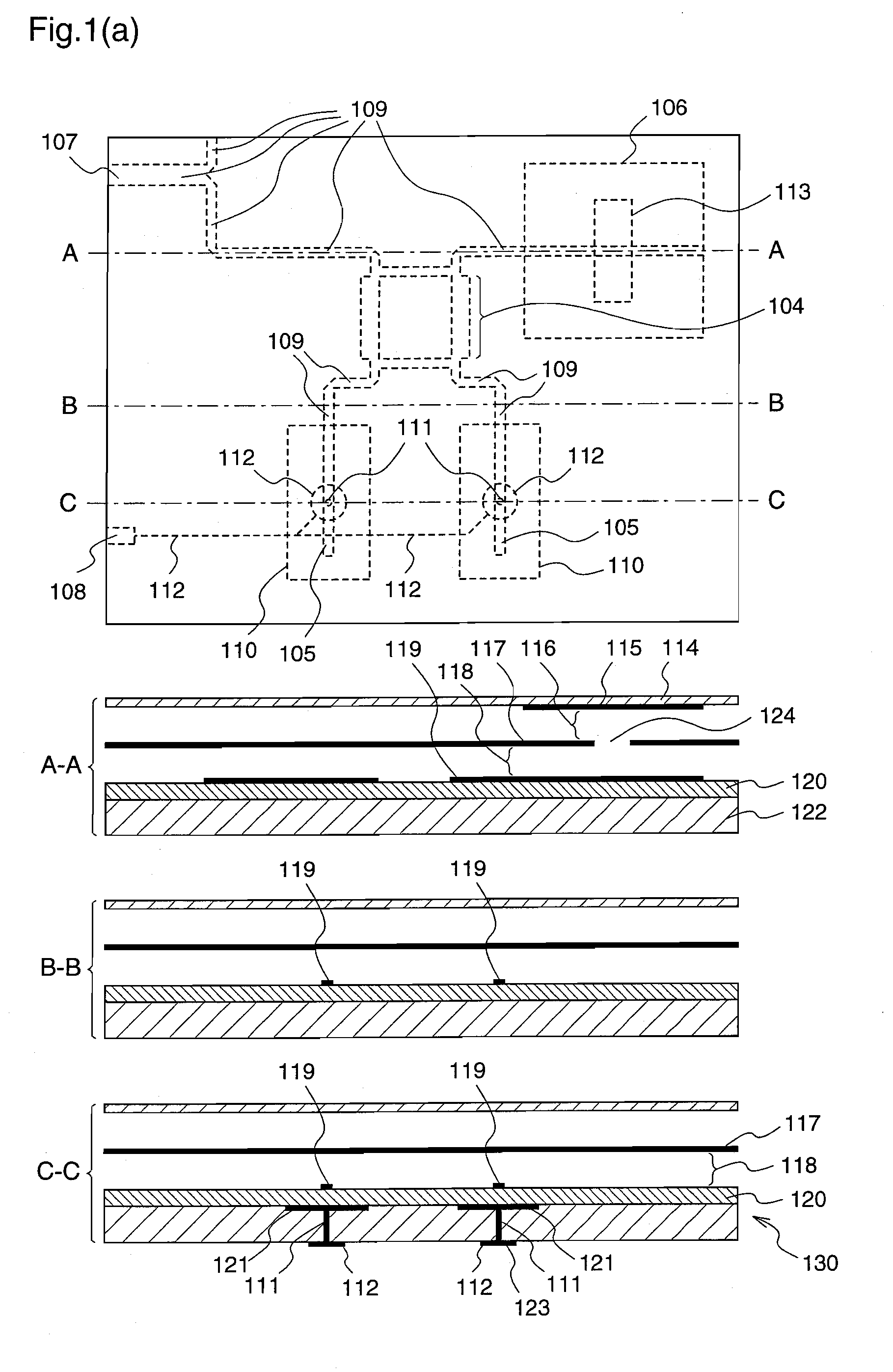
Method of fabricating radio frequency microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) devices on low-temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) substrates
InactiveUS20050161753A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricRadio frequency microelectromechanical system
A phased-array antenna system and other types of radio frequency (RF) devices and systems using microelectromechanical switches (“MEMS”) and low-temperature co-fired ceramic (“LTCC”) technology and a method of fabricating such phased-array antenna system and other types of radio frequency (RF) devices are disclosed. Each antenna or other type of device includes at least two multilayer ceramic modules and a MEMS device fabricated on one of the modules. Once fabrication of the MEMS device is completed, the two ceramic modules are bonded together, hermetically sealing the MEMS device, as well as allowing electrical connections between all device layers. The bottom ceramic module has also cavities at the backside for mounting integrated circuits. The internal layers are formed using conducting, resistive and high-k dielectric pastes available in standard LTCC fabrication and low-loss dielectric LTCC tape materials.
Owner:FOR NAT RES INITIATIVES
Highly integrated microwave outdoor unit (ODU)
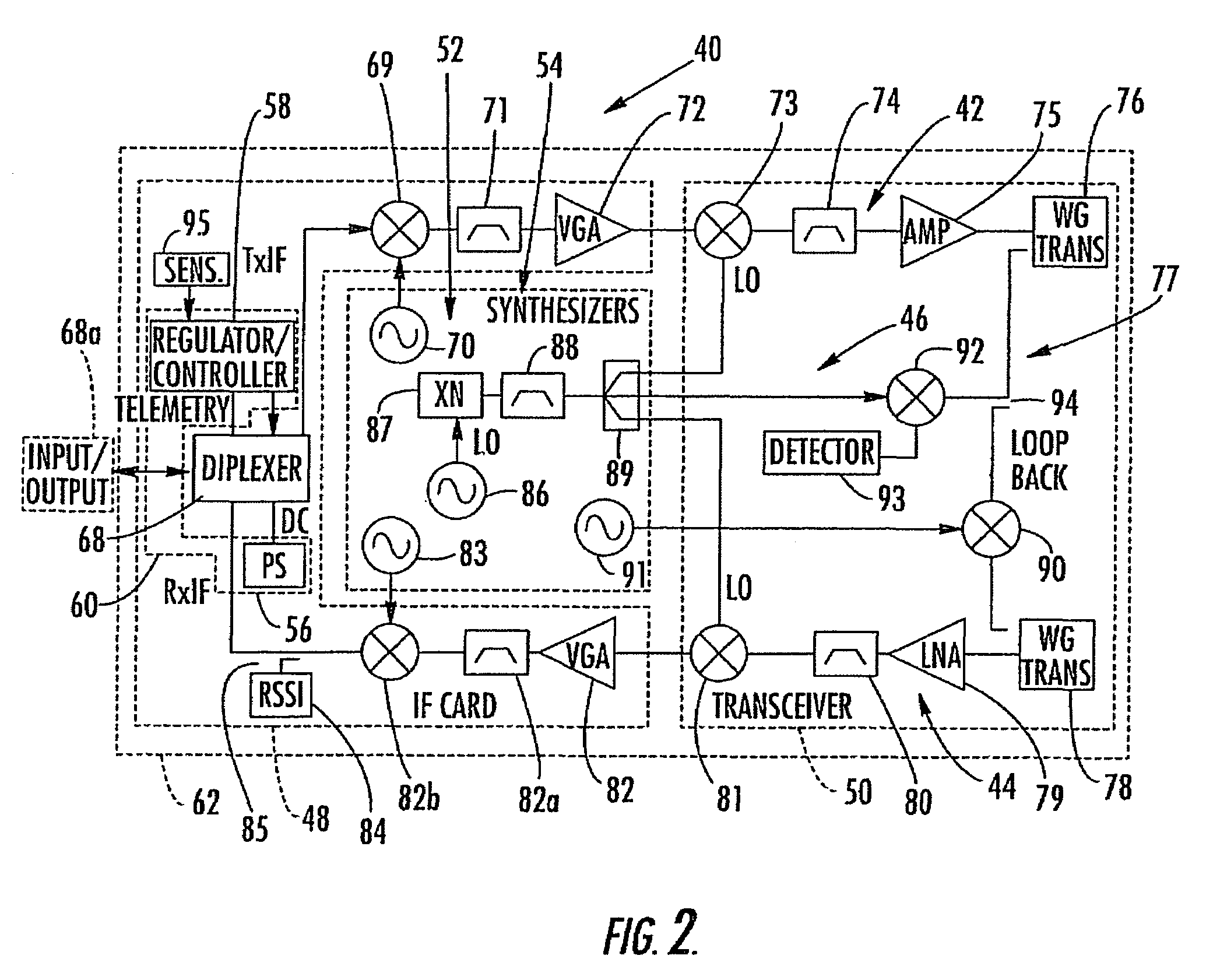
InactiveUS7050765B2Fast disconnectionUse minimizedActive radio relay systemsRadiating element housingsLocal oscillator signalTransceiver
A lightweight millimeter wave outdoor unit includes a lightweight housing with a heat sink and mounting member configured for mounting on the antenna to form a wireless link. A millimeter wave transceiver board is formed of ceramic material and mounted within the housing. It includes a millimeter wave transceiver circuit that has microwave monolithic integrated circuit (MMIC) chips and operable with the transmit and receive boards. An intermediate frequency (IF) board has components forming an intermediate frequency circuit operable with the millimeter wave transceiver circuit. A frequency synthesizer board has a signal generating circuit for generating local oscillator signals to the transceiver circuit. A controller board has surface mounted DC and low frequency discrete devices thereon forming power and control circuits that supply respective power and control signals to other circuits on other boards. A quick connect / disconnect assembly is operative with the housing for allowing the housing to be rapidly connected and disconnected to the antenna circuit contact members interconnect circuits between boards.
Owner:REVEAL IMAGING
Deposition apparatuses configured for utilizing phased microwave radiation
InactiveUS6845734B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrowave irradiationReaction chamber
The invention includes a deposition apparatus having a reaction chamber, and a microwave source external to the chamber. The microwave source is configured to direct microwave radiation toward the chamber. The chamber includes a window through which microwave radiation from the microwave source can pass into the chamber. The invention also includes deposition methods (such as CVD or ALD methods) in which microwave radiation is utilized to activate at least one component within a reaction chamber during deposition of a material over a substrate within the reaction chamber.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Radar system and method of manufacturing same
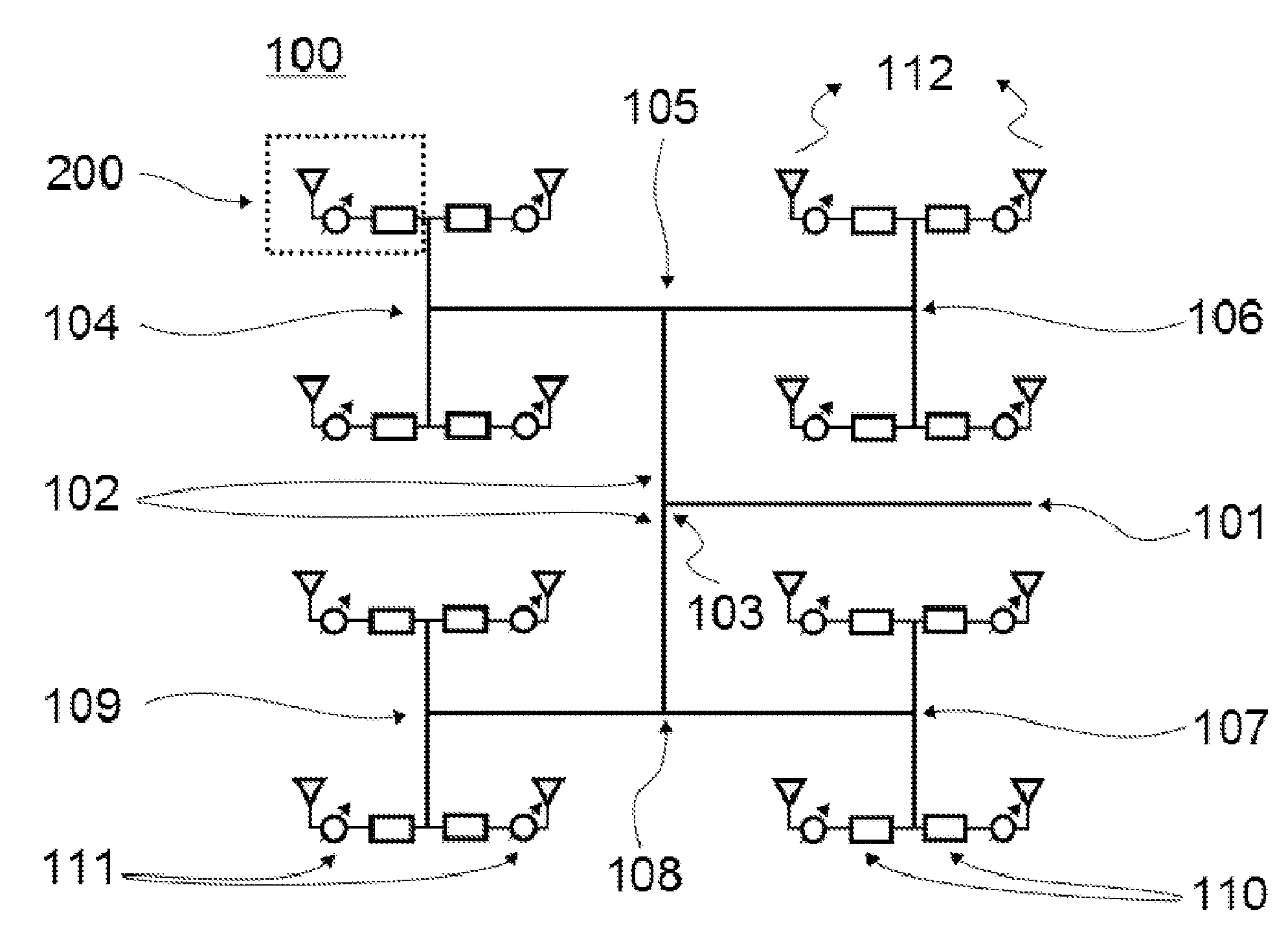
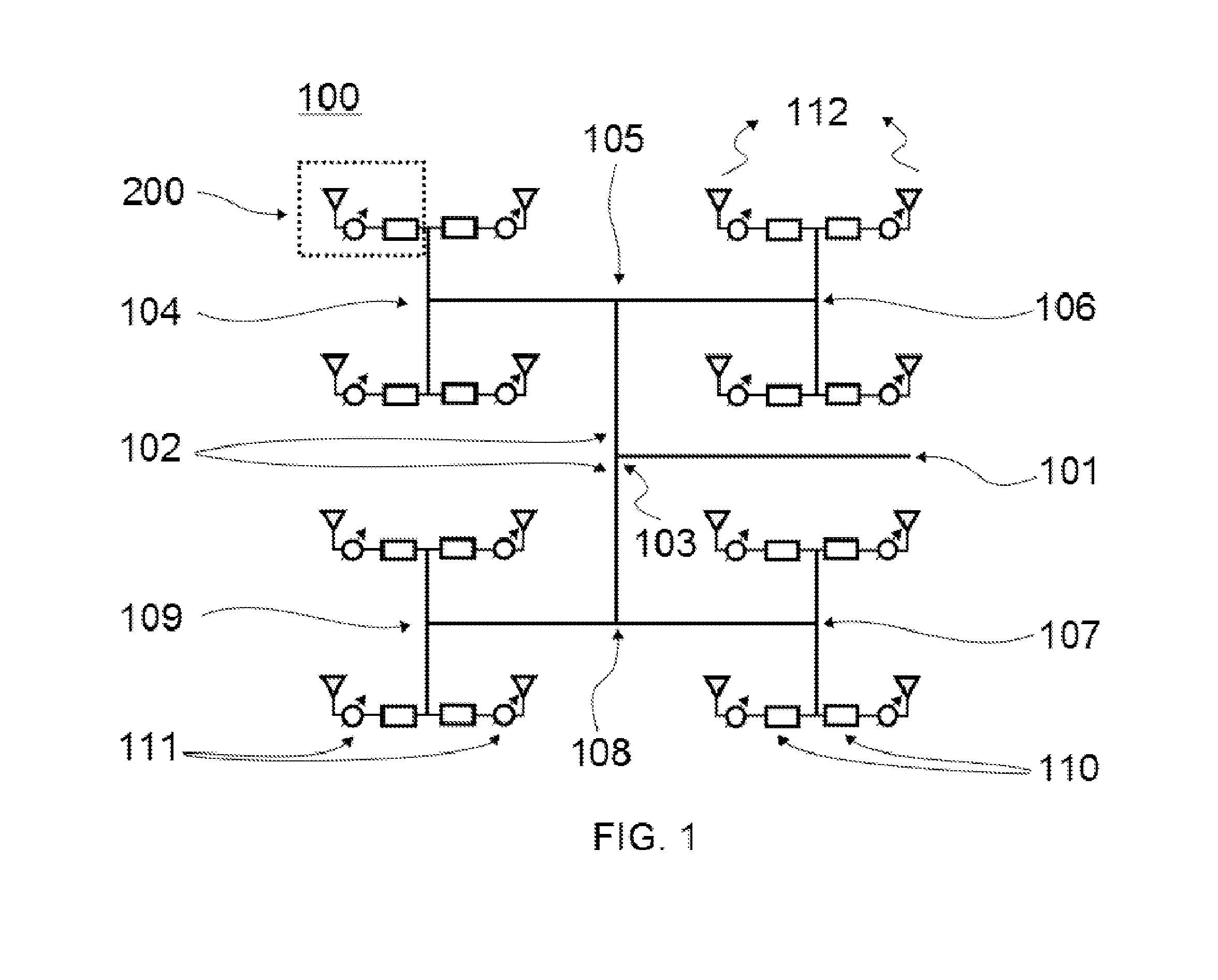
ActiveUS8976061B2Increase speedThe signal is accurate and reliableAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadiating elements structural formsRadar systemsEngineering
A radar system (100) is described including a transmitting assembly (10), a receiving assembly (20), a control unit (30) and a signal processing unit (40). The transmitting assembly (10) receives an input signal (31) and transmits an incident radar signal (2). The transmitting assembly (10) includes a Rotman lens (12) having a lens cavity (74), a plurality of beam ports (60), a plurality of array ports (62) and a patch antenna assembly (14). The lens cavity (74) has a lens gap (h) between 10 microns to 120 microns, and preferably 40 microns to 60 microns. The patch antenna assembly (14) includes a plurality of antenna arrays (130) operable to receive a plurality of time-delayed, in-phase signals from the Rotman lens (12) and to transmit the incident radar signal (2) towards a target (4). The receiving assembly (20) receives a reflected radar signal (6) and produces an output signal. The signal processing unit (40) compares the input signal (31) to the output signal and implements an algorithm determining the range, velocity and position of the target (4).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WINDSOR
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com