Patents
Literature
1662 results about "Beam shape" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
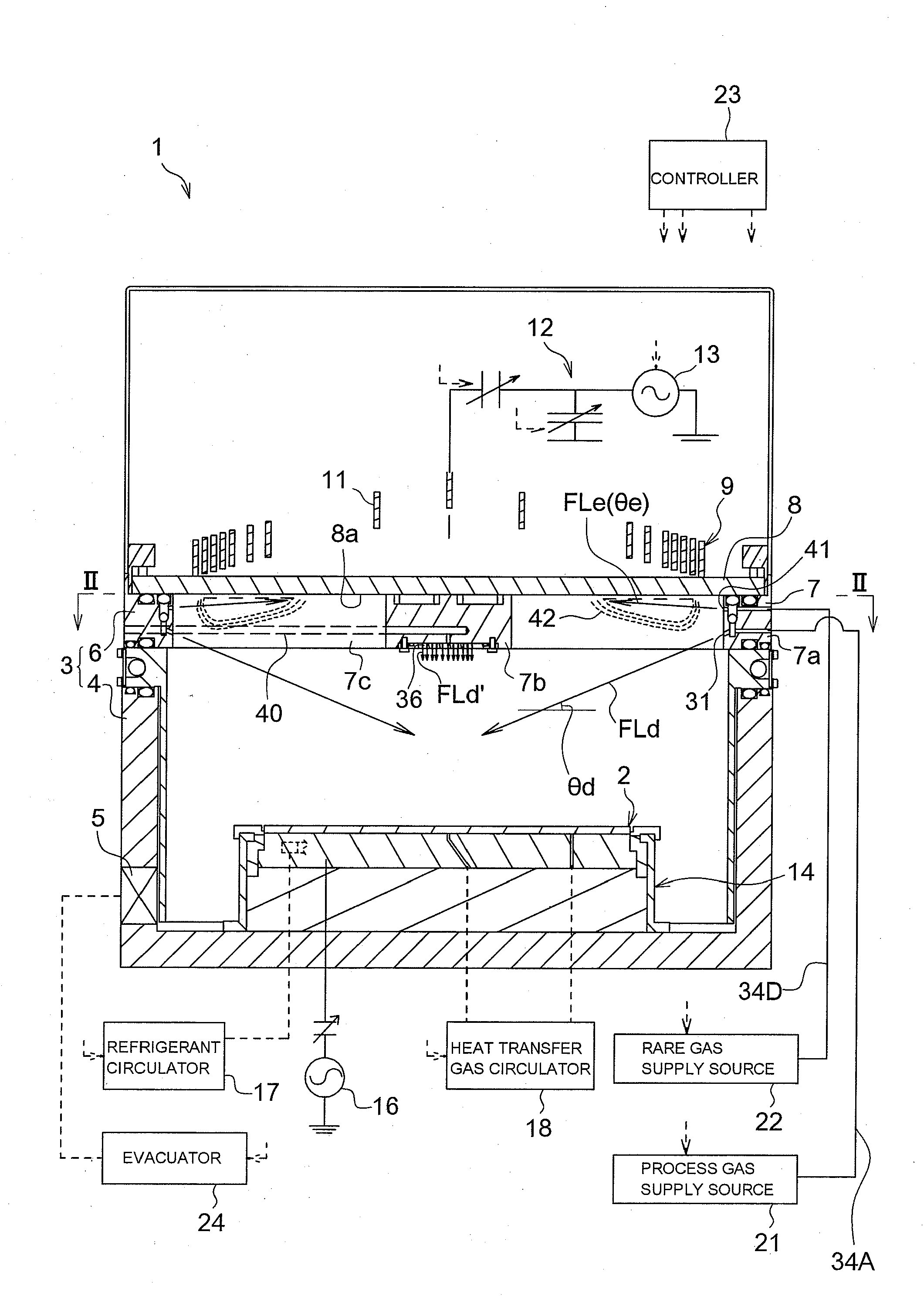
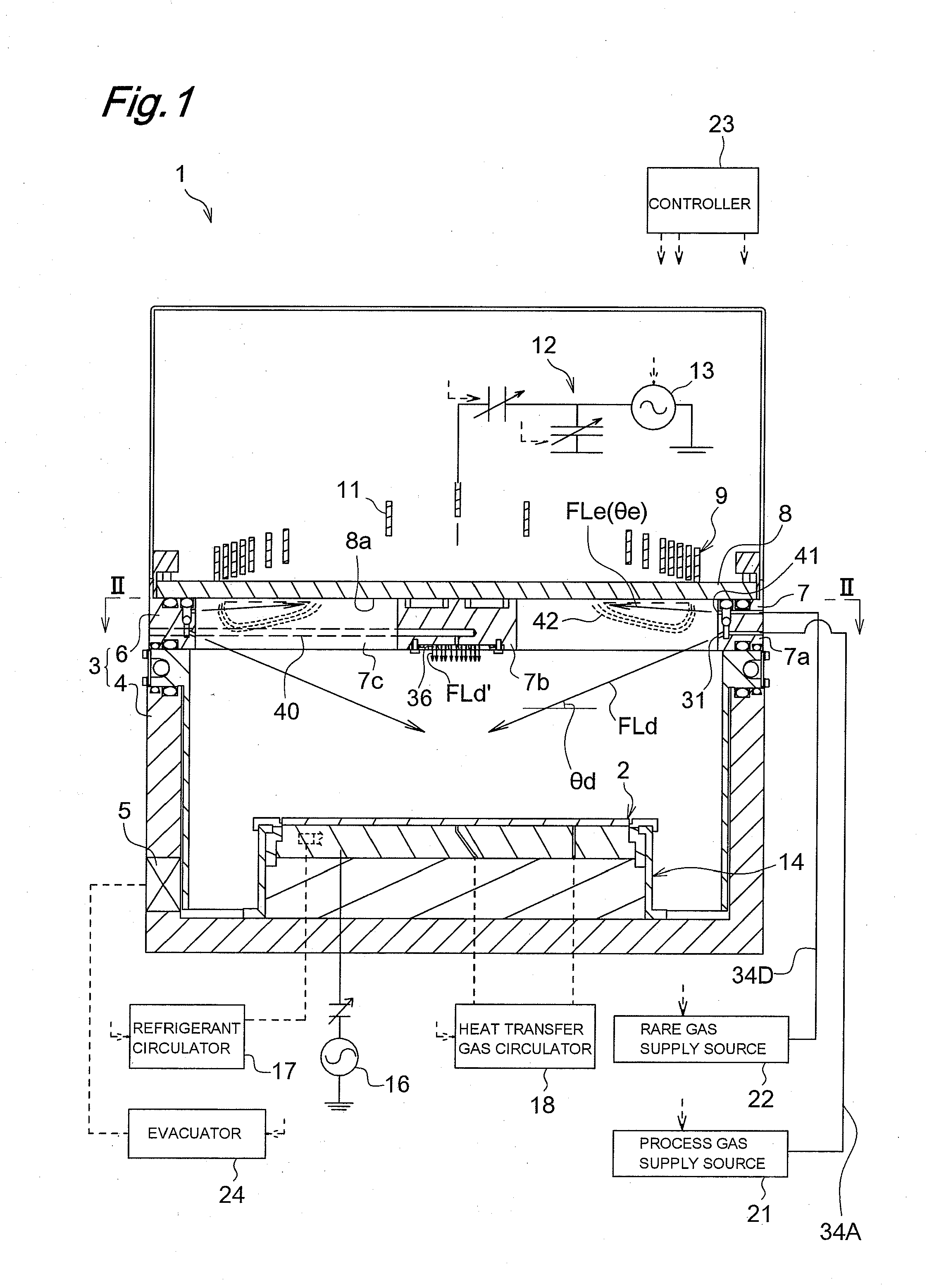
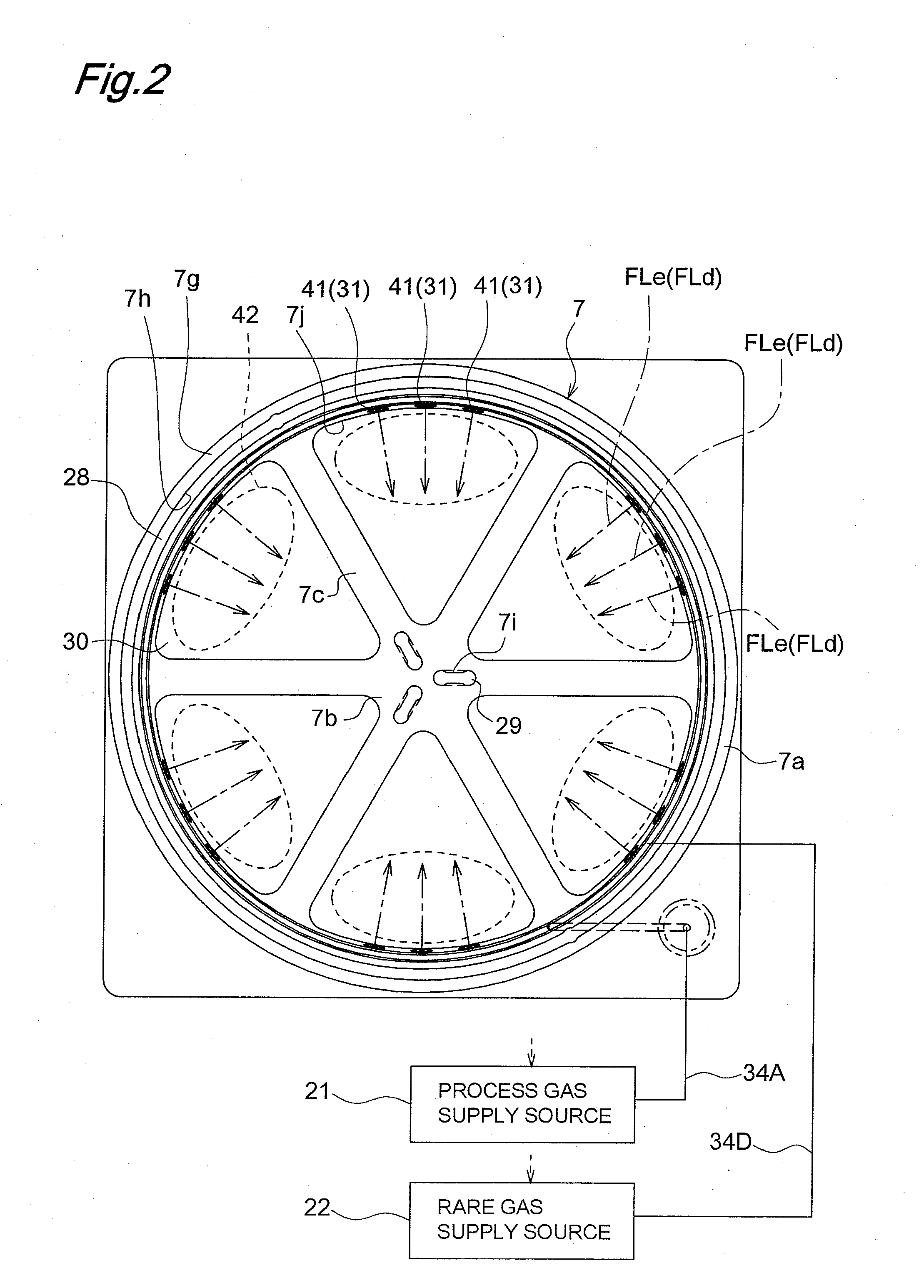
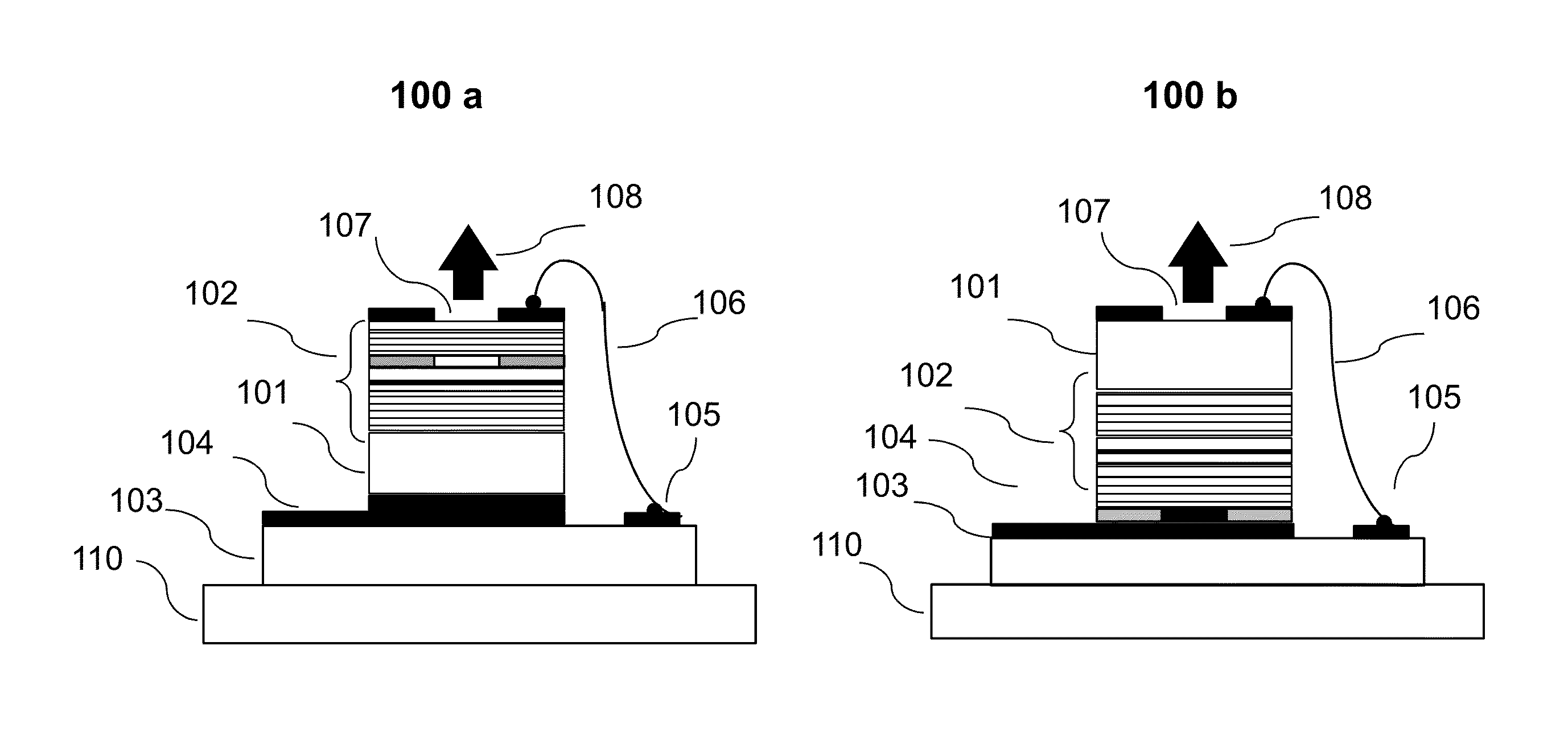
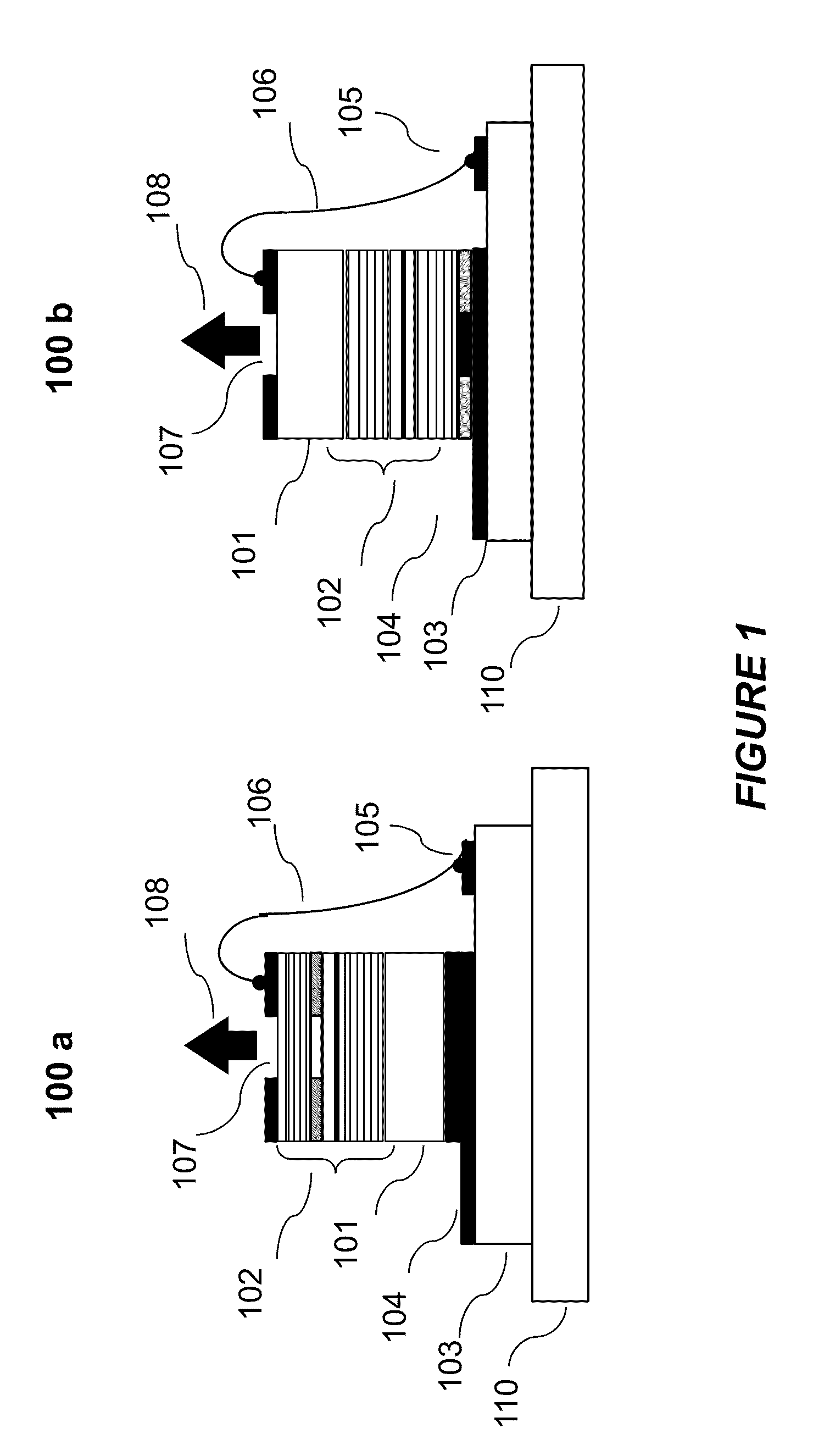
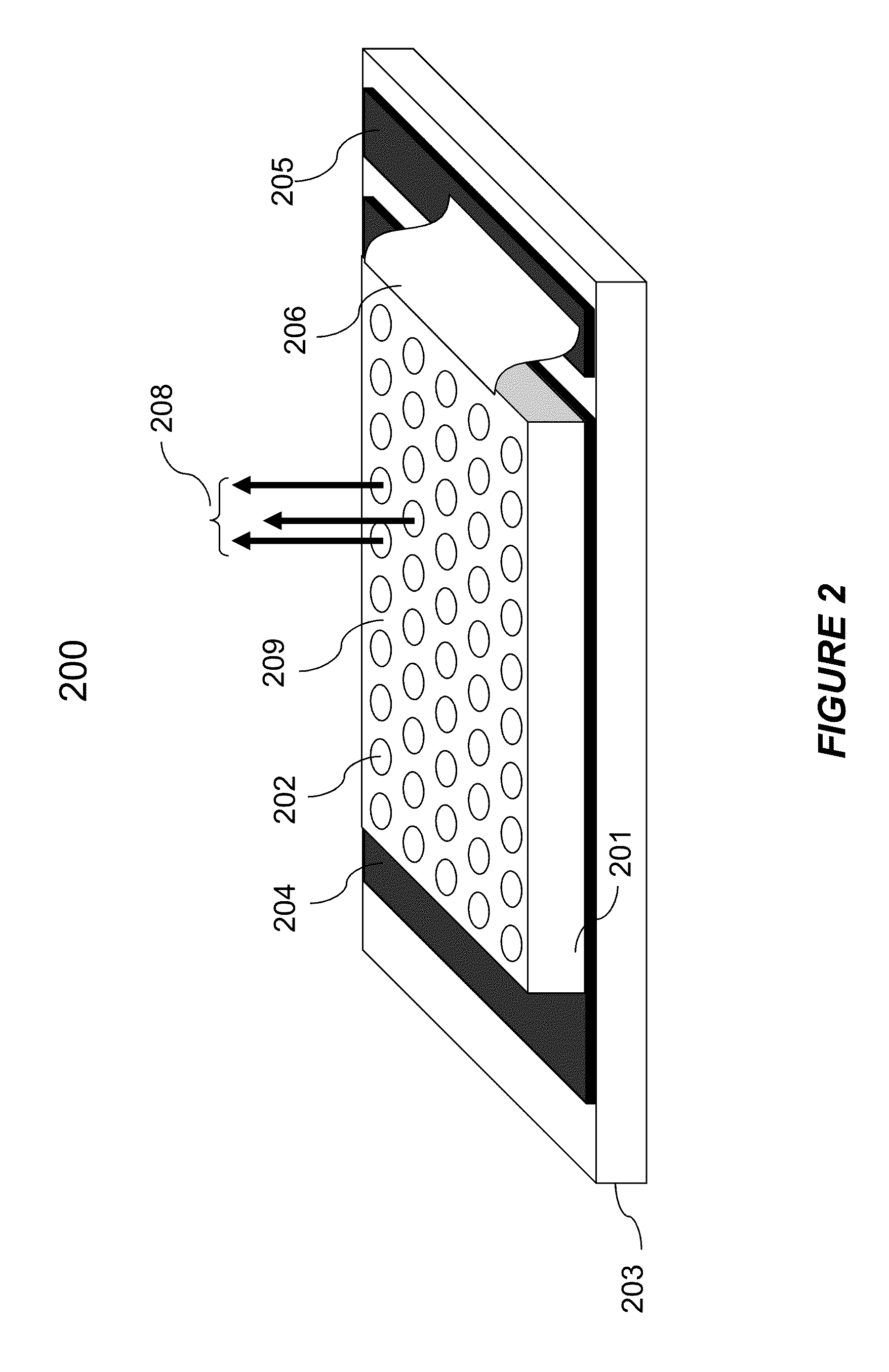
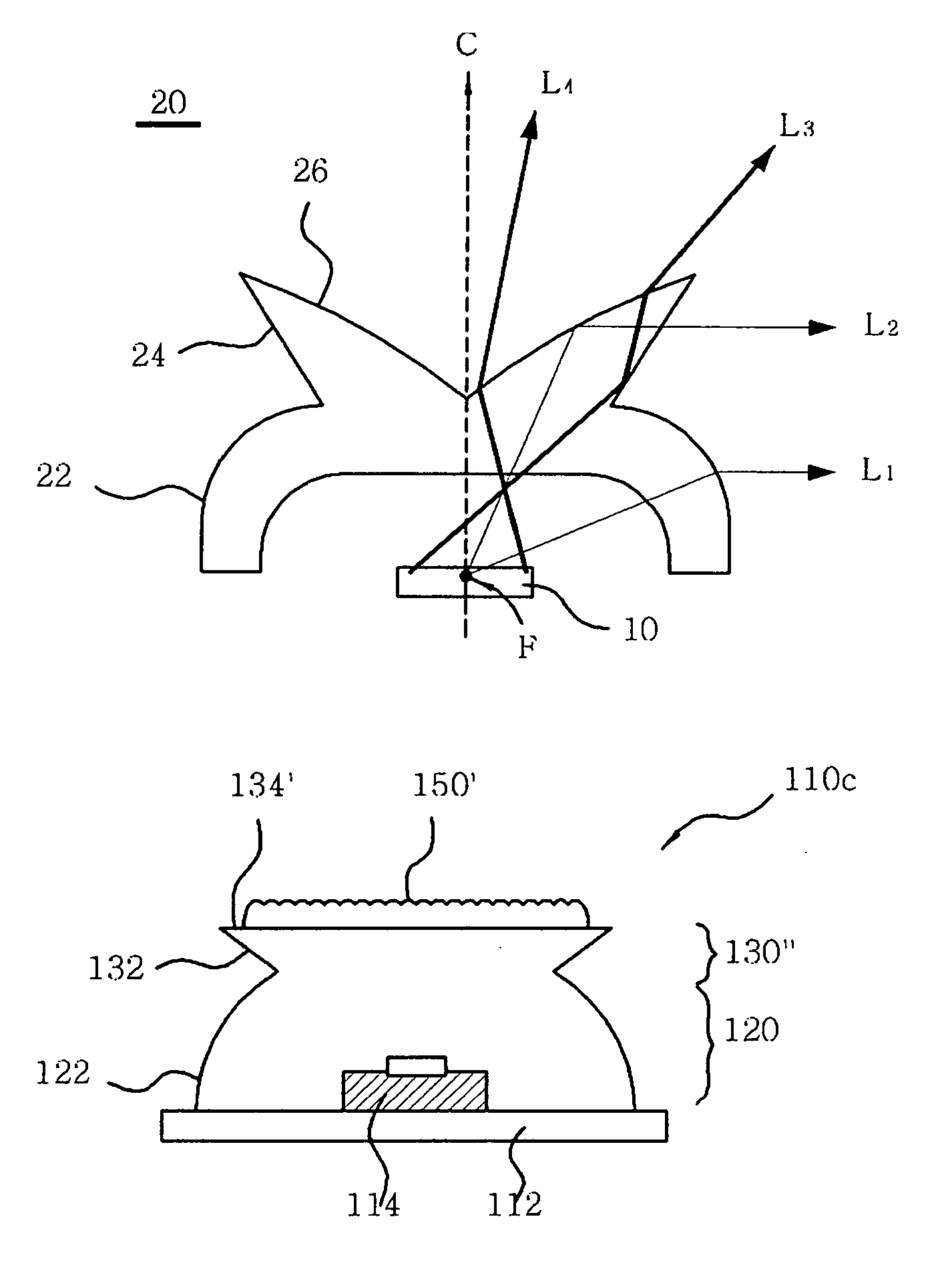
Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method
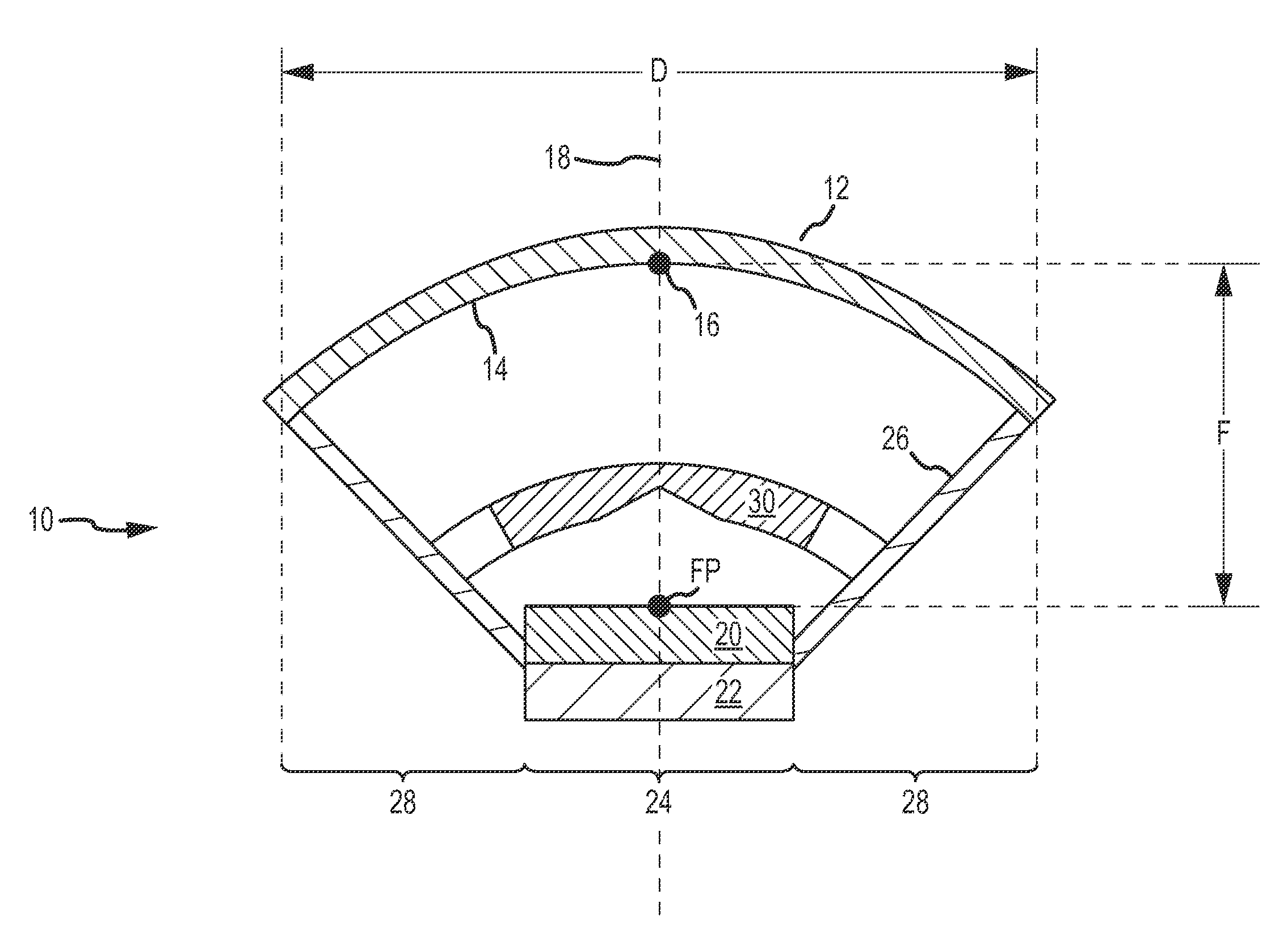
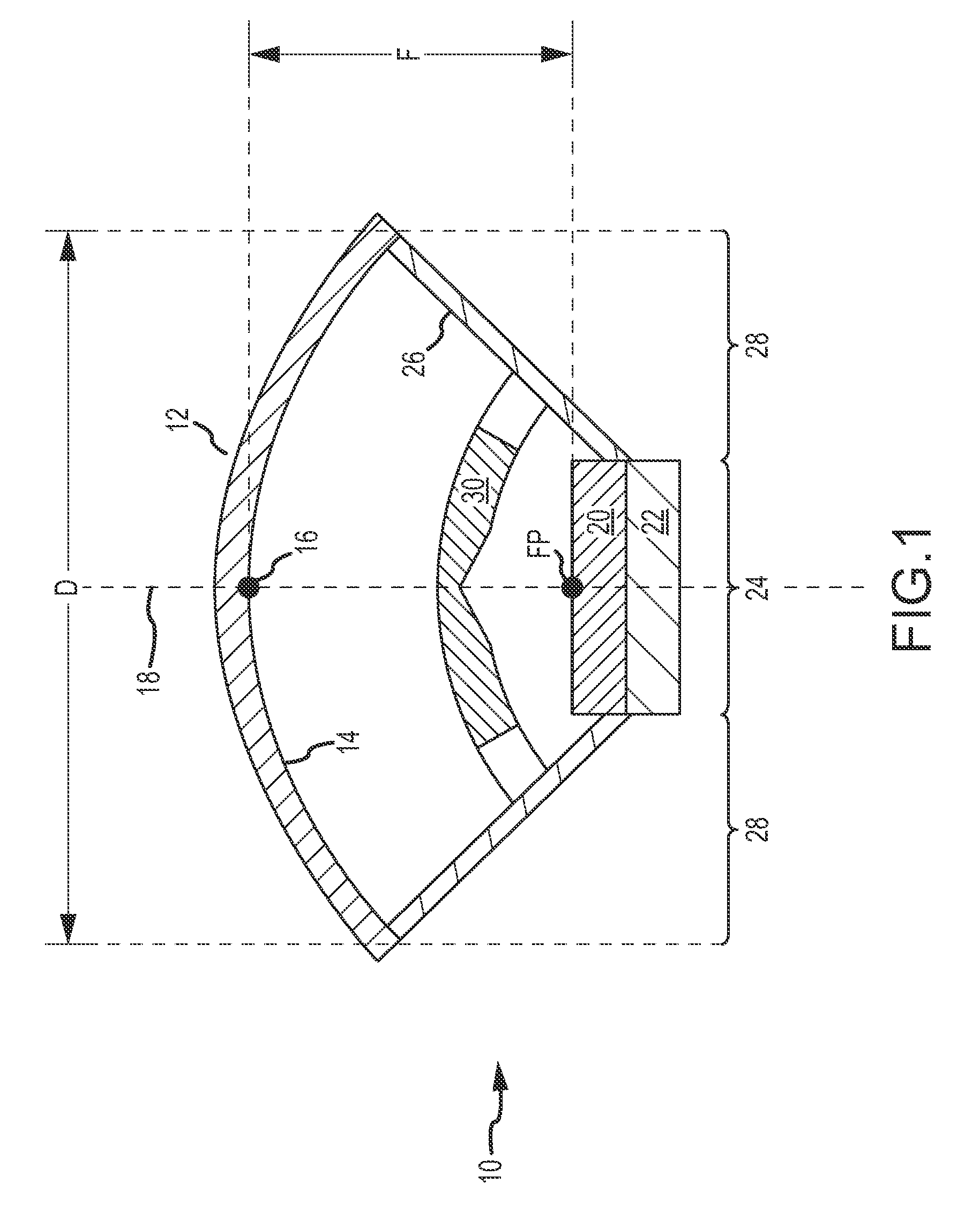
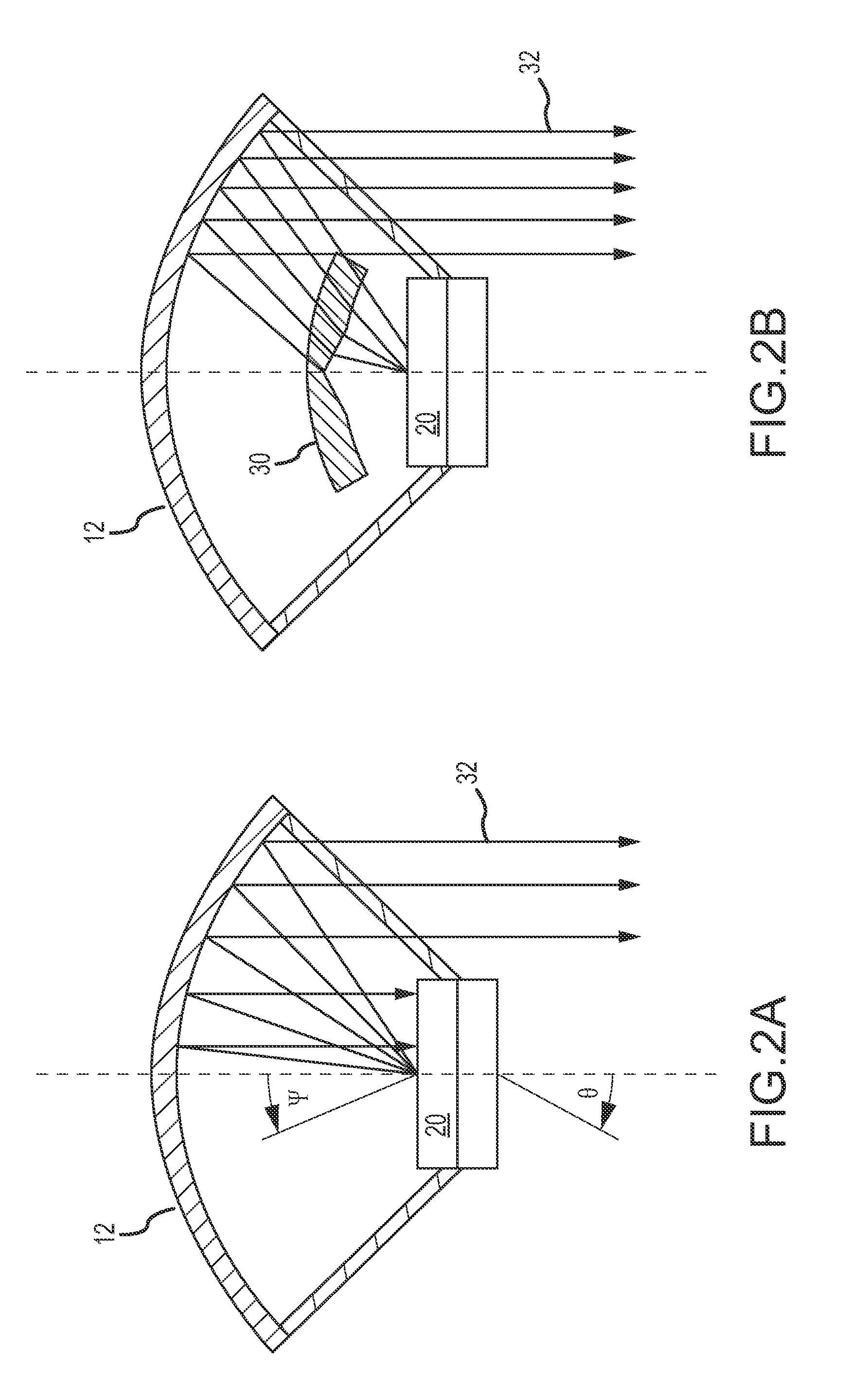
ActiveUS20100089870A1Improve processing speedEffective suppression of wearElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsElevation angleNoble gas
A plasma processing apparatus includes a beam-shaped spacer 7 which is placed at an upper opening of a chamber 3 opposed to a substrate 2 to support a dielectric plate 8. The dielectric plate 8 is supported by the beam-shaped spacer 7. In the beam-shaped spacer 7 are provided a plurality of process gas introducing ports 31, 36 which have a depression angle θd and which are provided downward and directed toward the substrate 2, as well as a plurality of rare gas introducing ports 41 having a elevation angle θe directed toward the dielectric plate 8. Improvement of processing rates such as etching rate as well as effective suppression of wear of the dielectric plate 8 can be achieved.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Bicone pattern shaping device
ActiveUS7525501B2Low costHigh gainAntenna feed intermediatesElectromagnetic radiationOmni directional
A broadband omni-directional bicone antenna. The antenna can comprise conductive surfaces of conical voids provided within a solid dielectric structure. The outside surface of the solid structure can support a radio frequency (RF) lens geometry operable for beam forming. The beam forming can modify the elevation pattern of the electromagnetic radiation from the bicone antenna. The solid dielectric structure may be machined or molded from a single piece of material. The conical voids provided within the solid structure can be metallized to provide conductive bicone radiators. The outer surface beam shaping lenses can be zoned or continuous and can provide elevation patterns with increased gain, cosecant squared falloff, or various other patterns. The beam shaping lens may be formed from any low-loss dielectric. Alternatively, the lens may be formed from a less dense material such as dielectric foam that can support radial conductive beam forming vanes.
Owner:EMS TECHNOLOGIES
Dielectric-resonator array antenna system
InactiveUS20060082516A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesDielectric resonator antennaLight beam
A dielectric resonator element array (DRA) antenna system and method for using same is disclosed. The dielectric resonator antenna system includes a ground plain, a feed structure, an array of dielectric resonator elements electrically coupled to the feed structure, each dielectric element having a relatively high permittivity, a radome close to or in contact with the array of dielectric resonator elements, an object mounting apparatus for mounting the antenna system on an object, and a beam shaping and steering controller, the beam shaping and steering controller controlling the feed structure to thereby control excitation phases of the dielectric resonator elements.
Owner:STRICKLAND PETER C
Laser Illuminator System
InactiveUS20130163627A1Improve thermal conductivityHeat dissipation fastSolid-state devicesSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserLow inductance
An optical illuminator using Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser (VCSEL) is disclosed. Optical modules configured using single VCSEL and VCSEL arrays bonded to a thermal submount to conduct heat away from the VCSEL array, are suited for high power and high speed operation. High speed optical modules are configured using single VCSEL or VCSEL arrays connected to a high speed electronic module on a common thermal submount or on a common Printed Circuit Board (PCB) platform including transmission lines. The electronic module provides low inductance current drive and control functions to operate the VCSEL and VCSEL array. VCSEL apertures are designed for a desired beam shape. Additional beam shaping elements are provided for VCSELs or VCSEL arrays, for desired output beam shapes and / or emission patterns. VCSEL arrays may be operated in continuous wave (CW) or pulse operation modes in a programmable fashion using a built-in or an external controller.
Owner:PRINCETON OPTRONICS
Beam shaping of RF feed energy for reflector-based antennas
A beam-shaping element is provided to shape RF feed energy for reflector-based antennas. The RF beam-shaping element is located between the primary reflector and the antenna feed and configured to direct RF energy from the feed away from a blockage created by the feed itself towards unblocked regions of the primary reflector. The beam-shaping element allows for a simplified feed design. The feed may comprise one or more feed elements, each comprising a radiating element and a feed to the radiating element such as a cavity-backed slot radiator and stripline trace. In a monopulse tracking system, each quadrant may include only a single feed element. In common aperture systems, the RF beam-shaping element may be formed on only the rear surface of the secondary reflector that allows transmission at the predefined RF wavelength while reflecting energy of a second predetermined wavelength to another sensor.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Beam controller for aperture antenna, and aperture antenna therewith
The present invention relates to an aperture antenna capable of controlling a shape of a radiated beam without changing a structure of an aperture antenna by connecting a beam controller with a single aperture antenna. the aperture antenna including a beam controller according to the present invention includes: a waveguide; an aperture horn of which one end is connected to the waveguide and the other end is provided with an opening; and a beam controller including a feeding unit connected to the opening and provided with a plurality of slits, a dielectric layer connected to the feeding unit, and a plurality of patches connected to the dielectric layer to control a beam shape of a signal introduced into the feeding unit and radiated through the patches.
Owner:LIG NEX1 CO LTD
Laser depilator
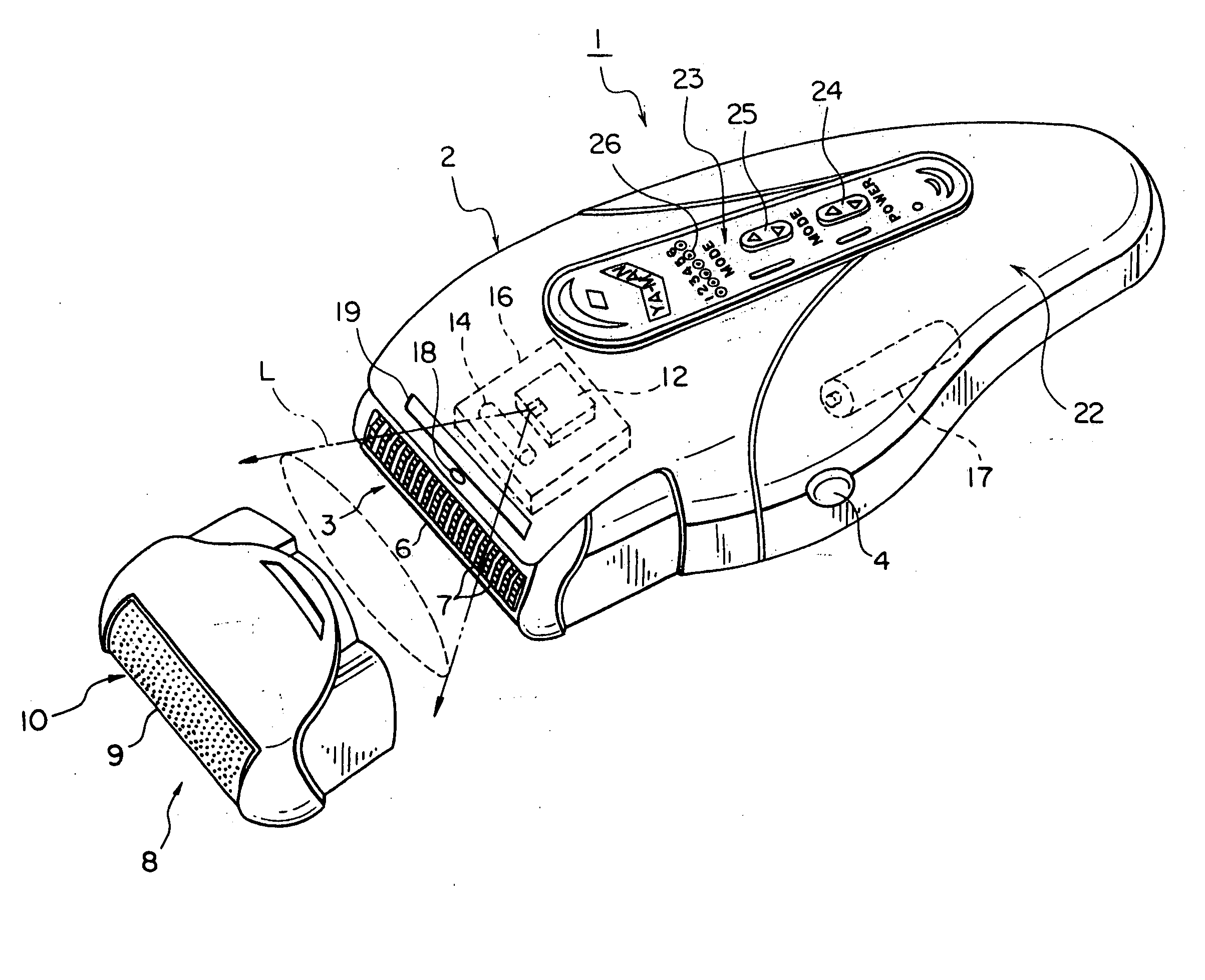
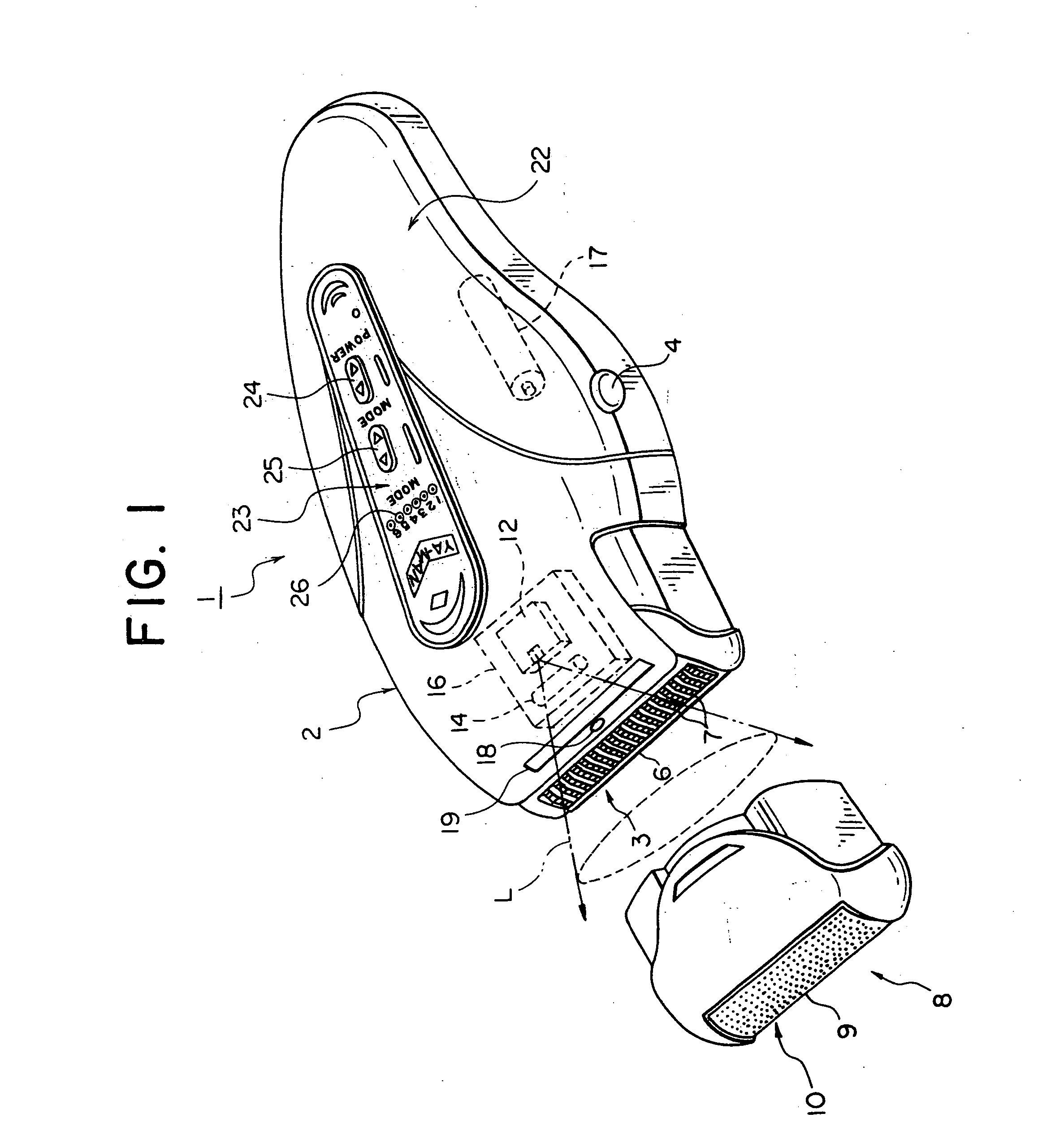
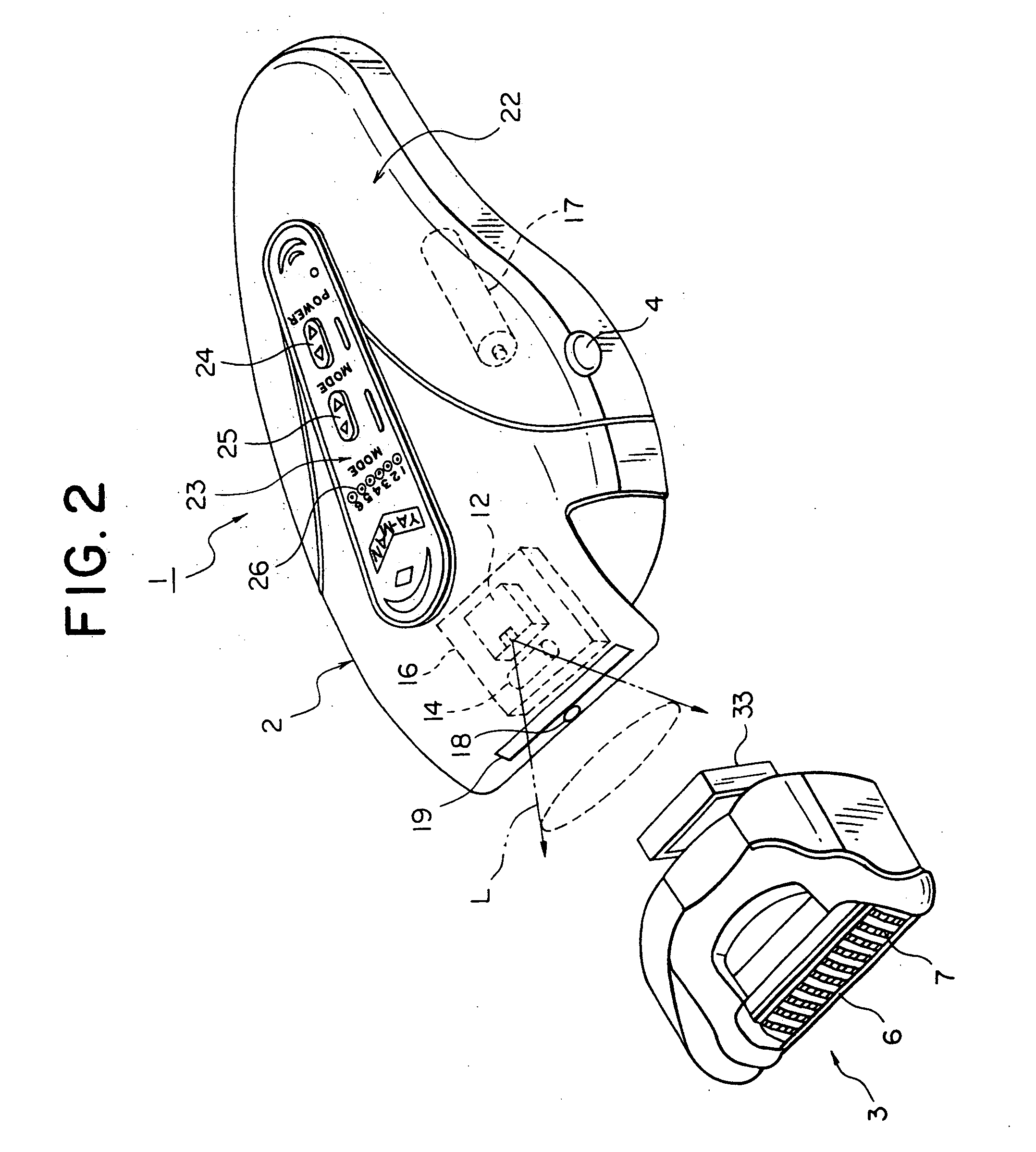
InactiveUS20050177139A1Troublesome to performHigh-efficiency laser depilationHair-singeingDiagnosticsHair rootsLaser hair removal
A laser depilator comprising a unit for removing hairs from the skin, a light source for irradiating laser light, and a lens for irradiating the skin with the laser light irradiated from the light source while deforming the beam shape so as to conform to the shape of a region of the skin from which hairs are removed by the hair removing unit. Since removal of hairs shielding the laser light and irradiation of laser light for damaging hair roots can be carried out continuously, efficiency of depilation treatment can be enhanced. Furthermore, depilation can be carried out effectively through a simple arrangement because a shaved skin surface can be irradiated with laser light over a relatively wide range using a lens.
Owner:YA MAN LTD
Thin illumination system
ActiveUS20100315833A1Without compromise in sharpnessModerate brightnessPlanar light sourcesMechanical apparatusLight beamEffect light
The present invention introduces a new class of thin doubly collimating light distributing engines for use in a variety of general lighting applications, especially those benefiting from thinness. Output illumination from these slim-profile illumination systems whether square, rectangular or circular in physical aperture shape is directional, square, rectangular or circular in beam cross-section, and spatially uniform and sharply cutoff outside the system's adjustable far-field angular cone. Field coverage extends from + / −5- to + / −60-degrees and more in each meridian, including all asymmetric combinations in between, both by internal design, by addition of angle spreading film sheets, and angular tilts. Engine brightness is held to safe levels by expanding the size of the engine's output-aperture without sacrifice in the directionality of illumination. One form of the present invention has a single input light emitter, a square output aperture and the capacity to supply hundreds of lumens per engine. A second multi-segment form of the invention deploys one light emitter in each engine segment, so that total output lumens is determined by the number of segments. Both types of thin light distributing engines provide input light collimated in one meridian and a light distributing element that maintains input collimation while collimating output light in the un-collimated orthogonal meridian, in such a manner that the system's far-field output light is collimated in both its orthogonal output meridians. The present invention also includes especially structured optical films that process the engine's doubly collimated output illumination so as to increase its angular extent one or both output meridians without changing beam shape or uniformity.
Owner:SNAPTRACK +1
Micro-projector
InactiveUS20110037953A1Increase brightnessQuality improvementTelevision system detailsPrismsDisplay deviceLaser source
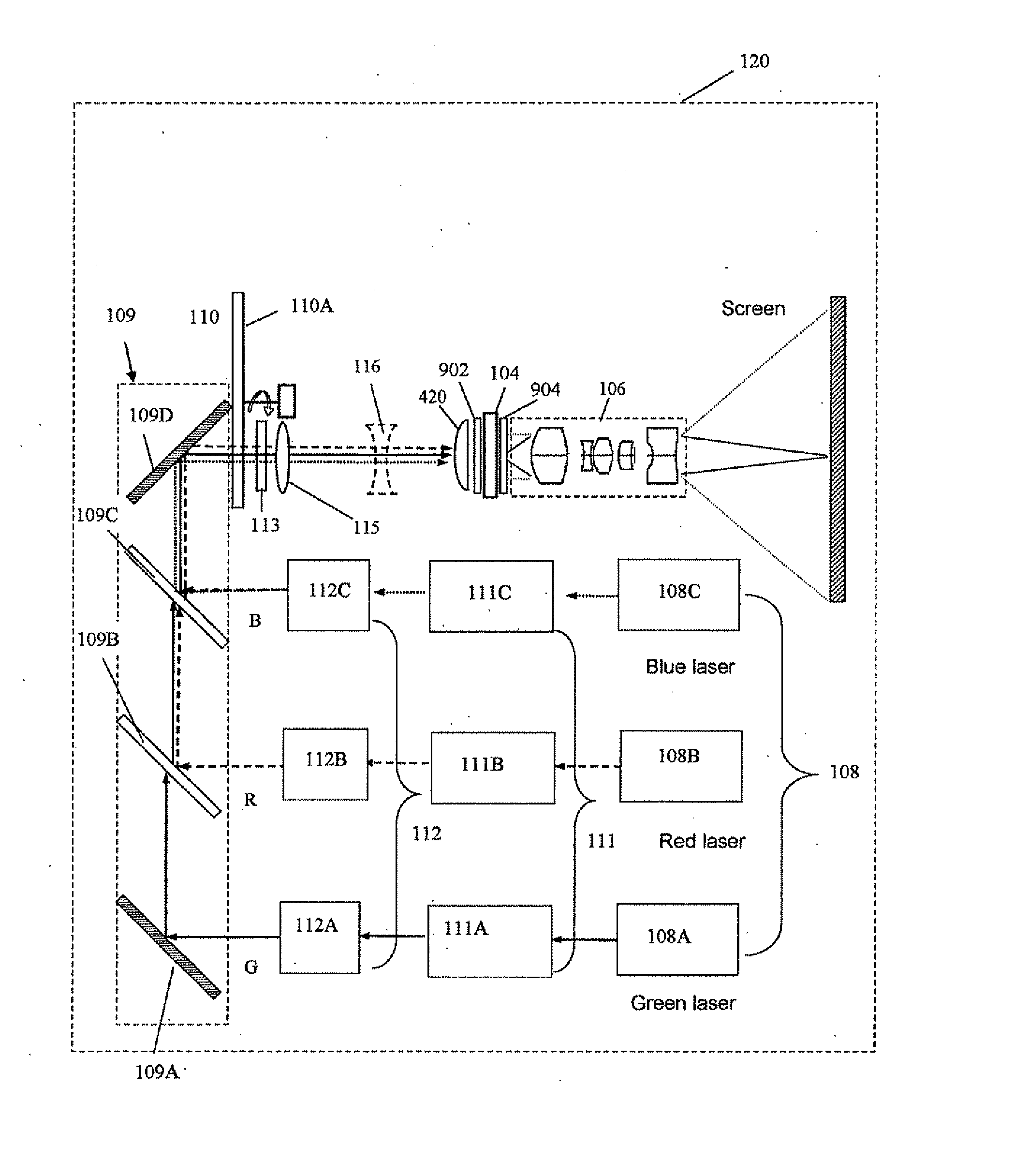
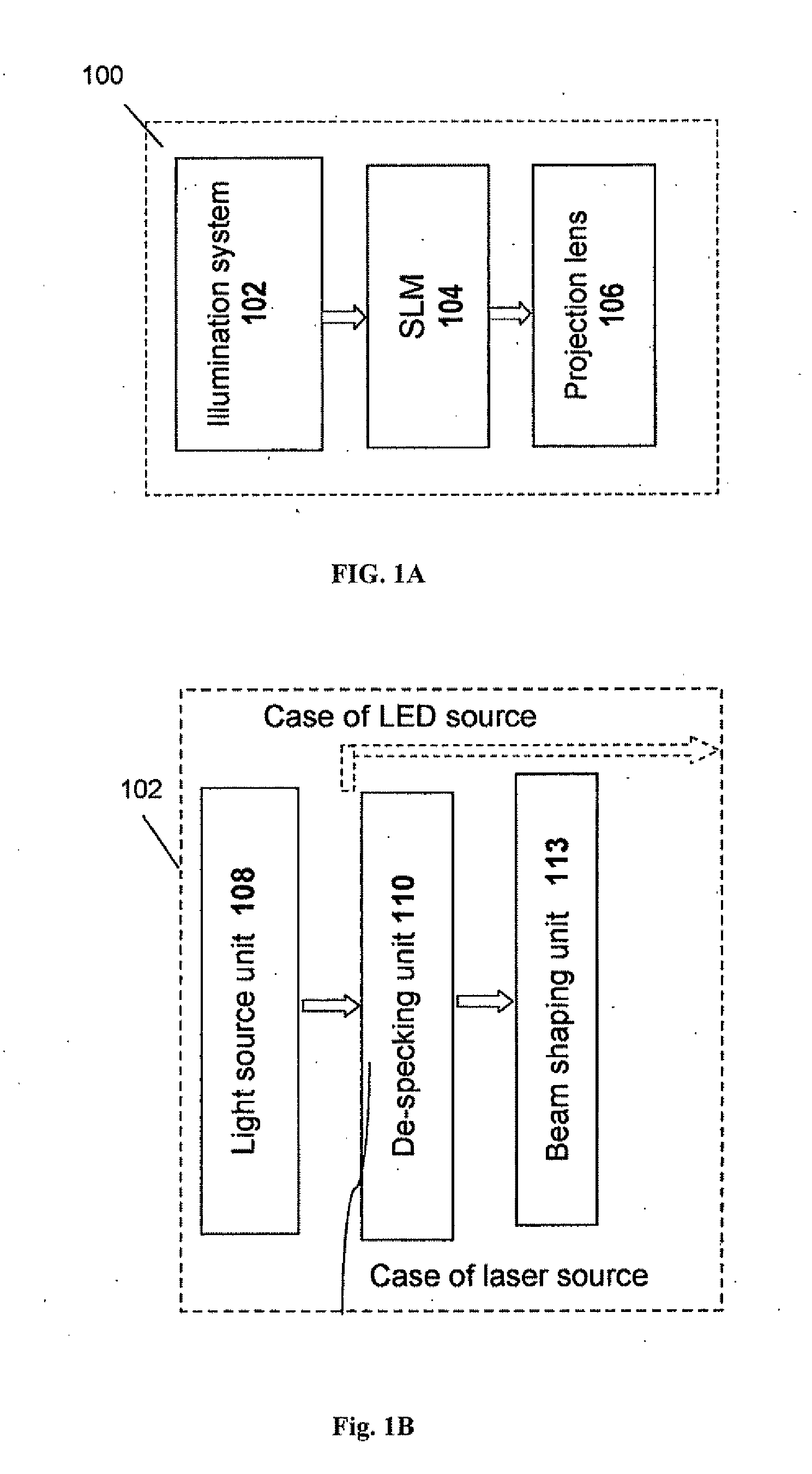
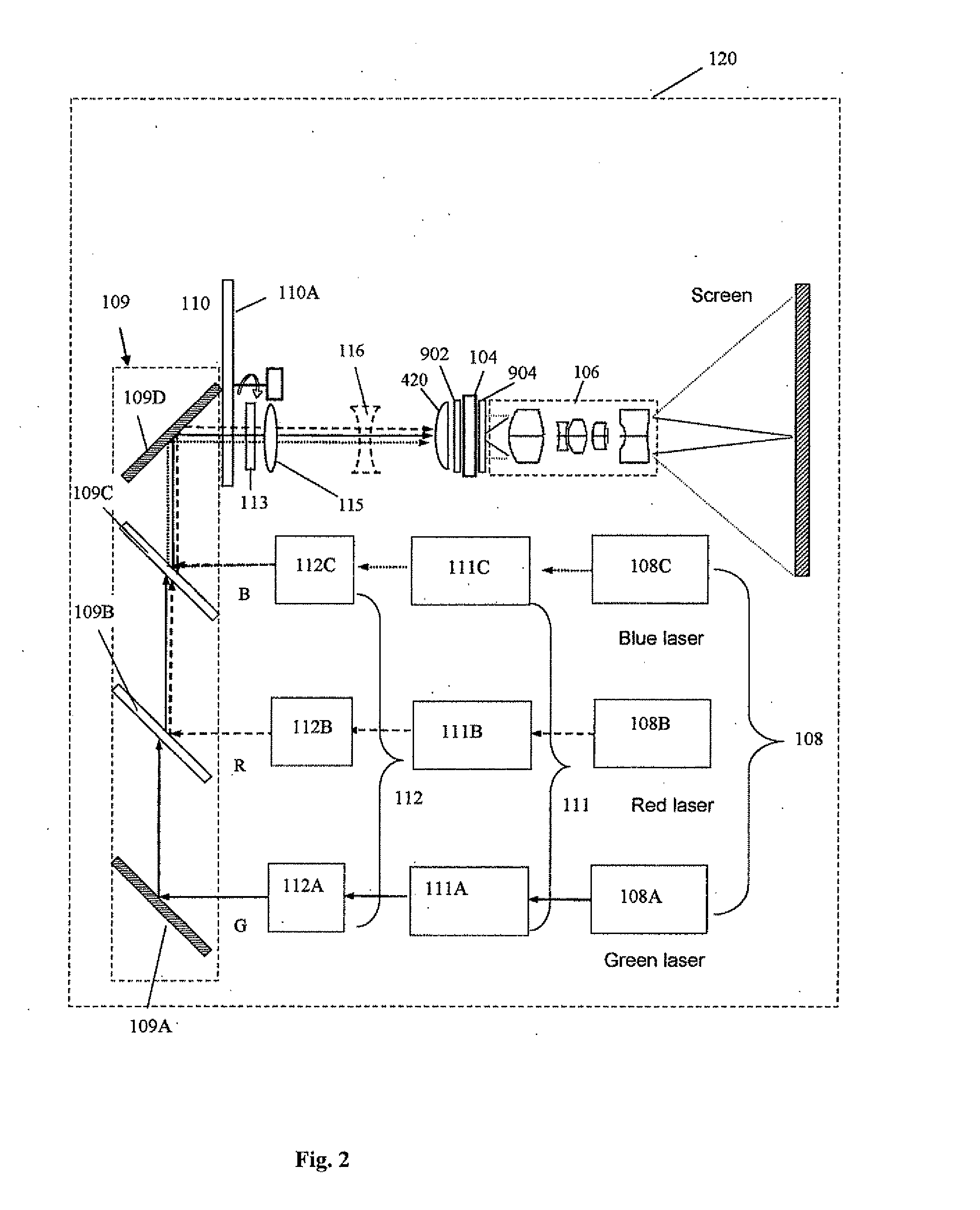
The present invention provides a projection display comprising an illumination system comprising at least one laser source unit and configured and operable for producing one or more light beams; a spatial light modulating (SLM) system accommodated at output of the illumination system and comprising one or more SLM units for modulating light incident thereon in accordance with image data; and a light projection optics for imaging modulated light onto a projection surface. The illumination system comprises at least one beam shaping unit comprising a Dual Micro-lens Array (DMLA) arrangement formed by front and rear micro-lens arrays (MLA) located in front and rear parallel planes spaced-apart along an optical path of light propagating towards the SLM unit, the DMLA arrangement being configured such that each lenslet of the DMLA directs light incident thereon onto the entire active surface of the SLM unit, each lenslet having a geometrical aspect ratio corresponding to an aspect ratio of said active surface of the SLM unit.
Owner:EXPLAY
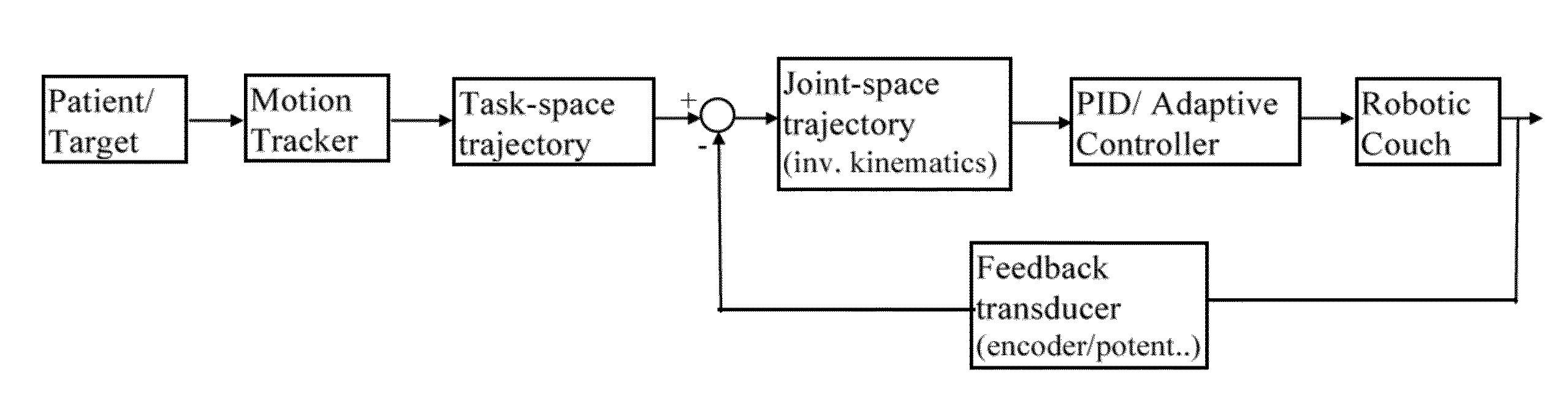
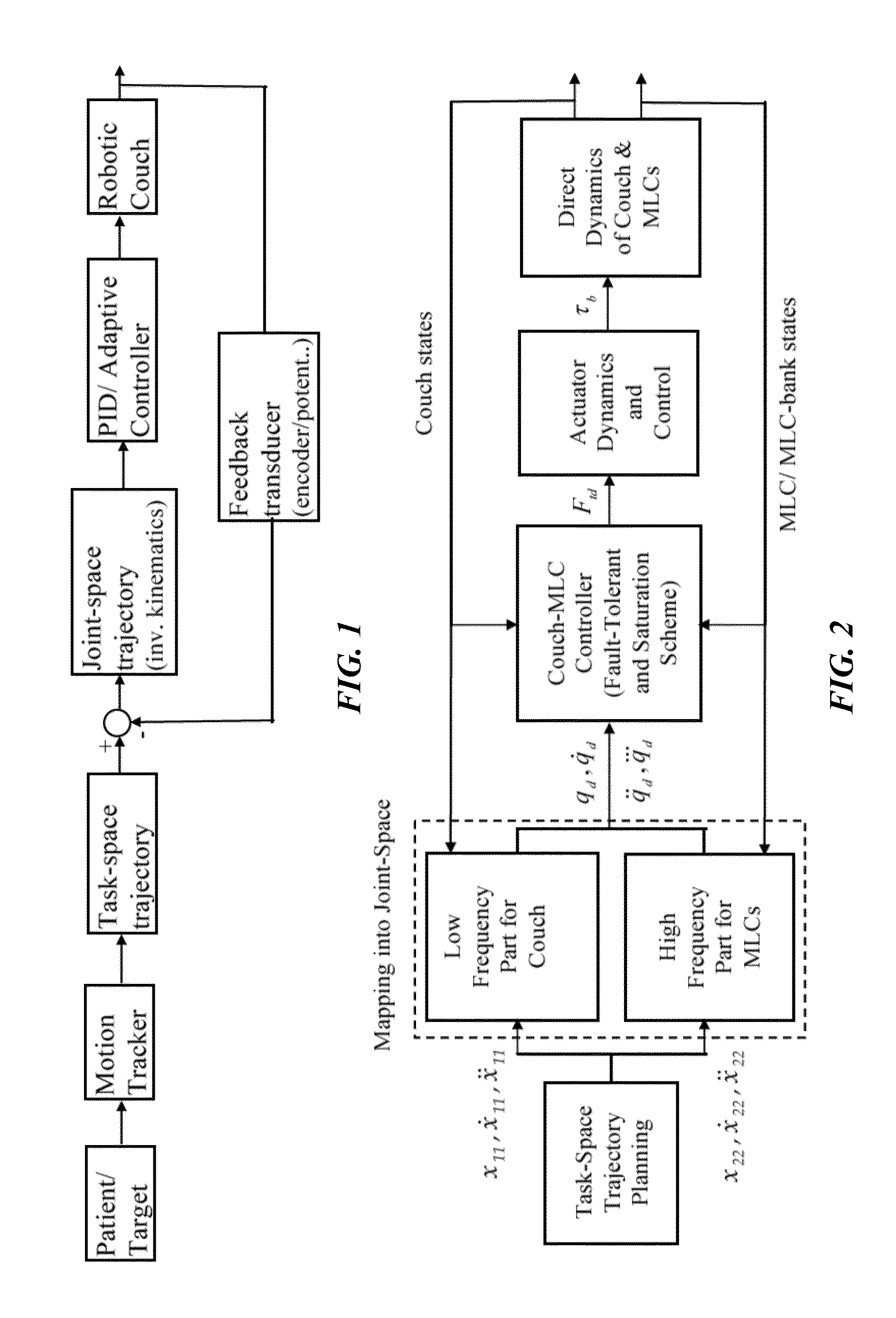
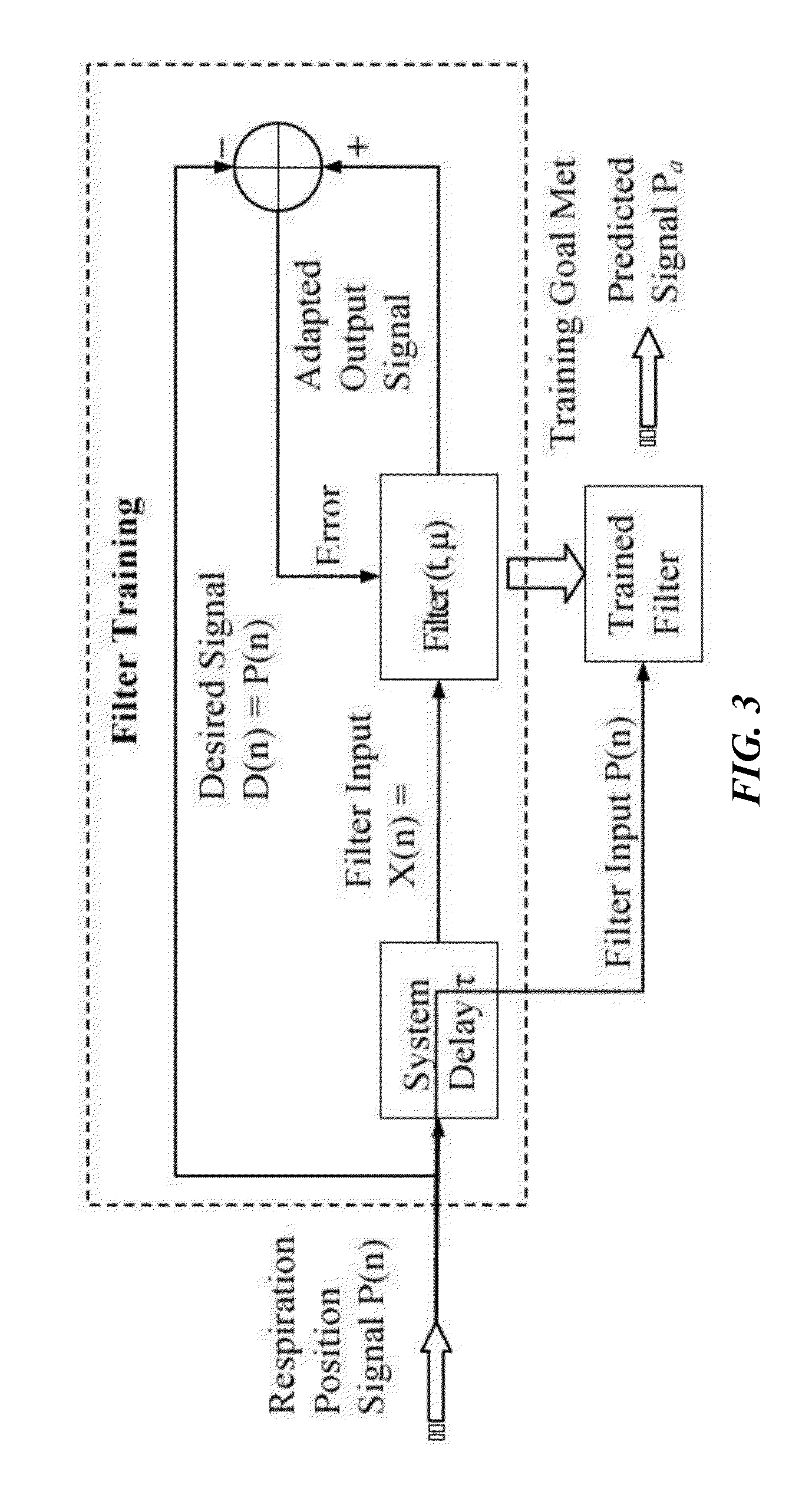
Implementation and experimental results of real-time 4d tumor tracking using multi-leaf collimator (MLC), and/or mlc-carriage (mlc-bank), and/or treatment table (COUCH)
InactiveUS20140107390A1Reduce radiationEasy to optimizeMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesVehicle frameControl system
Methods and systems of operating a support structure and beam shaping mechanism in a manner that compensates for motion patterns exhibited by a patient, promotes comfort of the patient, and optimizes accuracy of delivery of radiotherapy to a targeted location within the patient. The support structure can be a treatment table or couch and the beam shaping mechanism can be a multi-leaf collimator (MLC), and / or an MLC-bank / -carriage. The control system can utilize algorithms for predicting tumor motion and loading condition on the table / couch during radiation therapy.
Owner:ELEKTA AB +1
High density electrical connector with variable insertion and retention force
ActiveUS8182289B2Lower insertion forceImprove retentionTwo-part coupling devicesCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsElectricityHigh density
An interconnection system that includes a daughter card and backplane electrical connectors mounted to printed circuit boards at connector footprints. The spring rate of beam-shaped contacts in the daughter card connector increases while mating with the backplane connector so that the retention force may be greater than the insertion force. Such a change in spring rate may be achieved by positioning the beam-shaped contacts adjacent a surface of a connector housing. That surface may include a projection that aligns with the beam-shaped contact. When the connectors are unmated, the beam-shaped contact may be spaced from the projection. As the connectors begin to mate, a central portion of the beam-shaped contact may be pressed against the projection, which has the effect of shortening the beam length and increasing its stiffness.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
LED lens for backlight
ActiveUS7549769B2Color andLuminous overallNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceLight beamLight-emitting diode
Disclosed herein is a Light Emitting Diode (LED) lens for a backlight. The LED lens includes an LED light source, a lens body, and a beam shaping element. The lens body is configured such that the LED light source is accommodated in the lower portion thereof, and light emitted from the LED light source is radiated in vertical and lateral directions of the lens body. The beam shaping element is fastened to the top of the lens body and is configured to adjust light beams radiated through the upper surface of the lens body. Accordingly, the uniformity of luminance and color can be increased and, at the same time, the overall performance of the system can be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multiple Pixel Scanning LIDAR
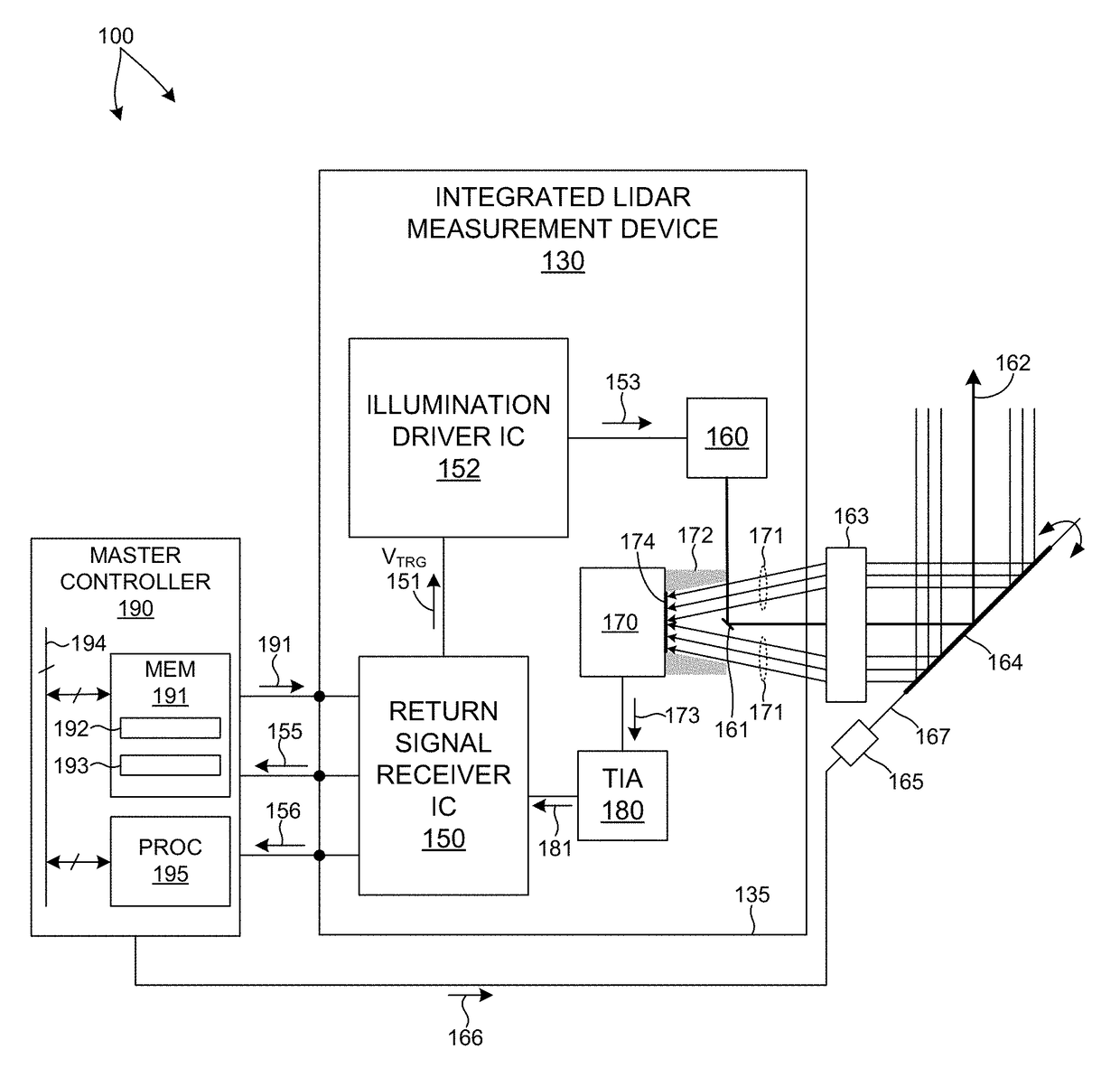
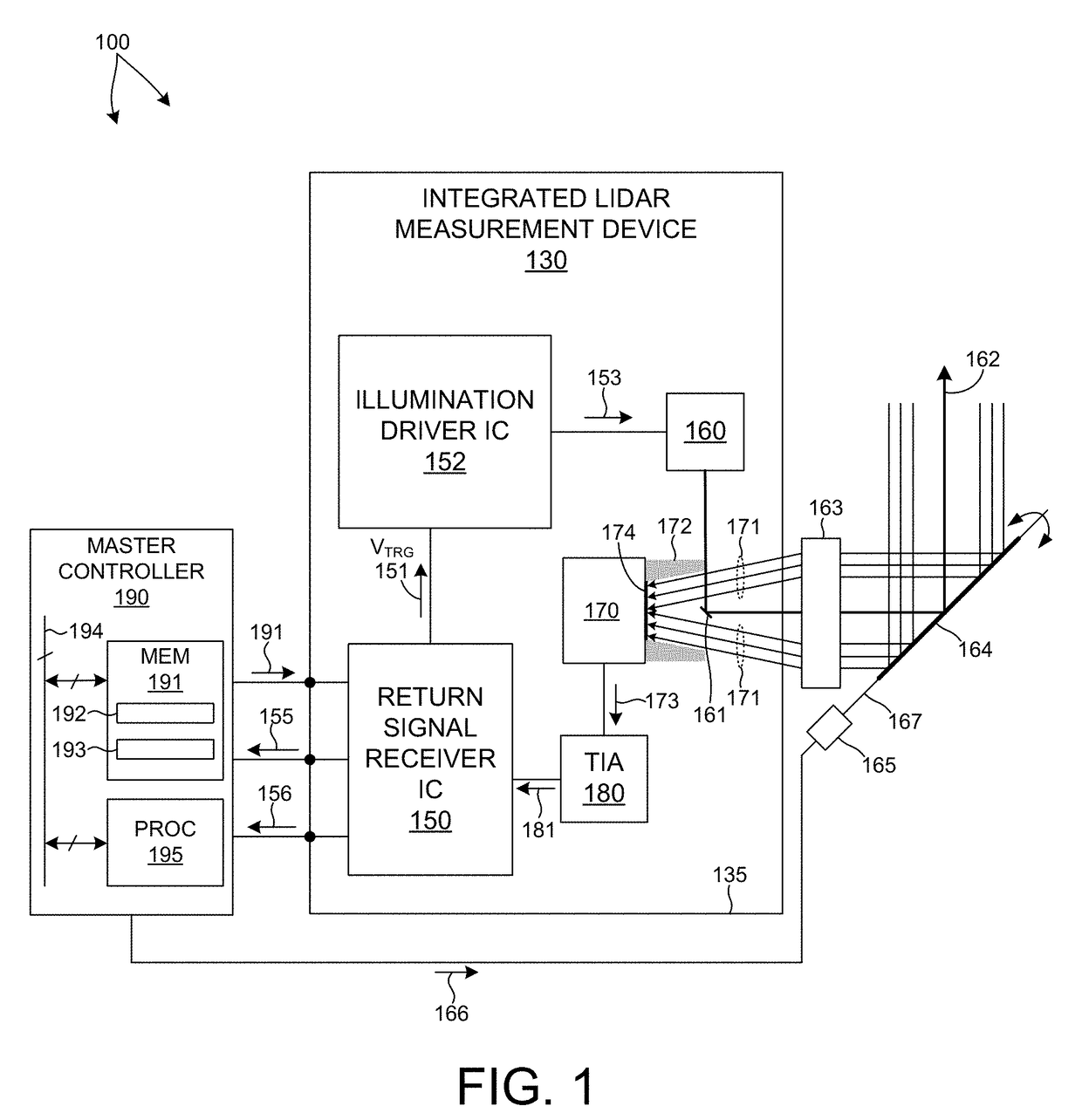
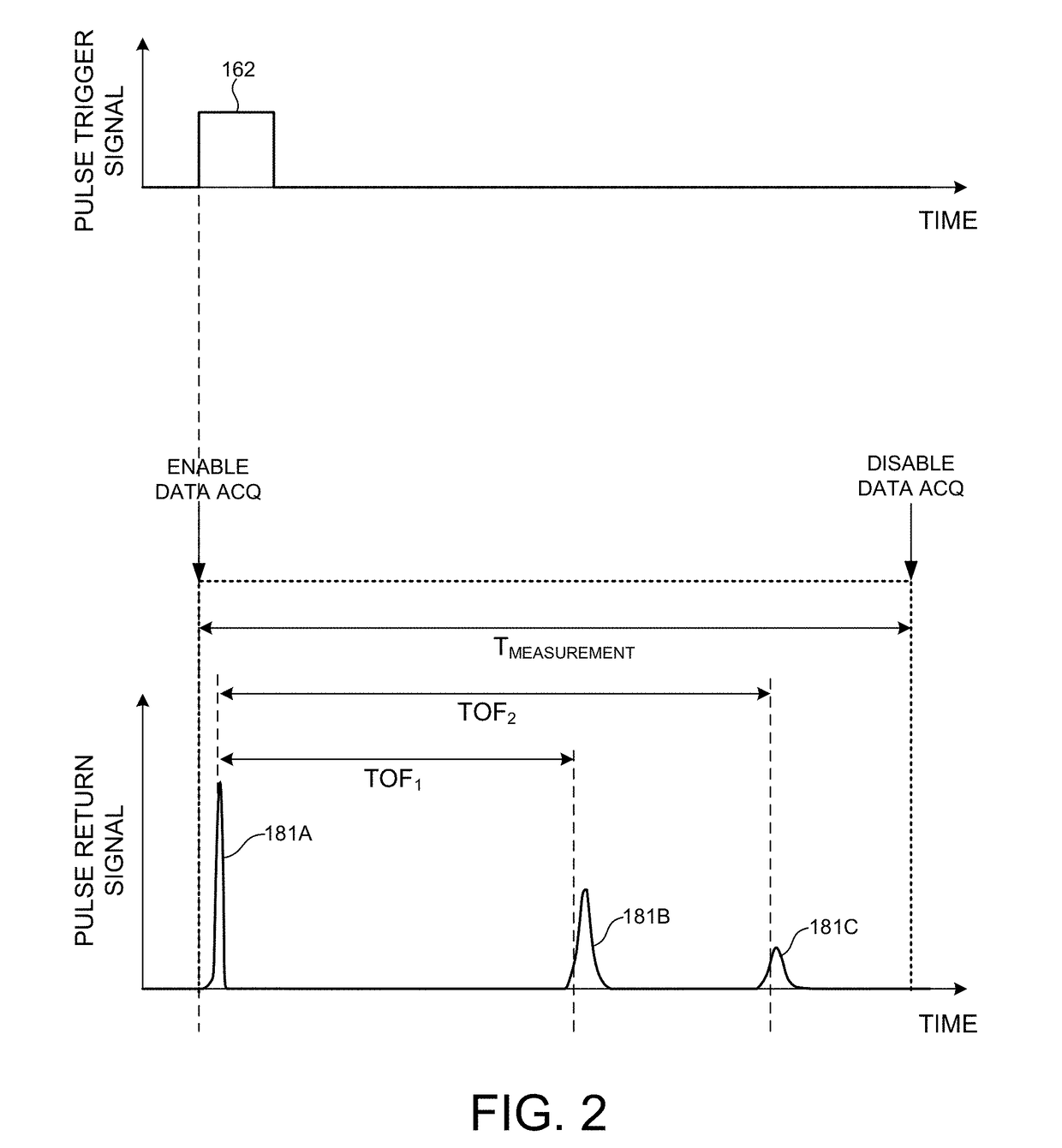
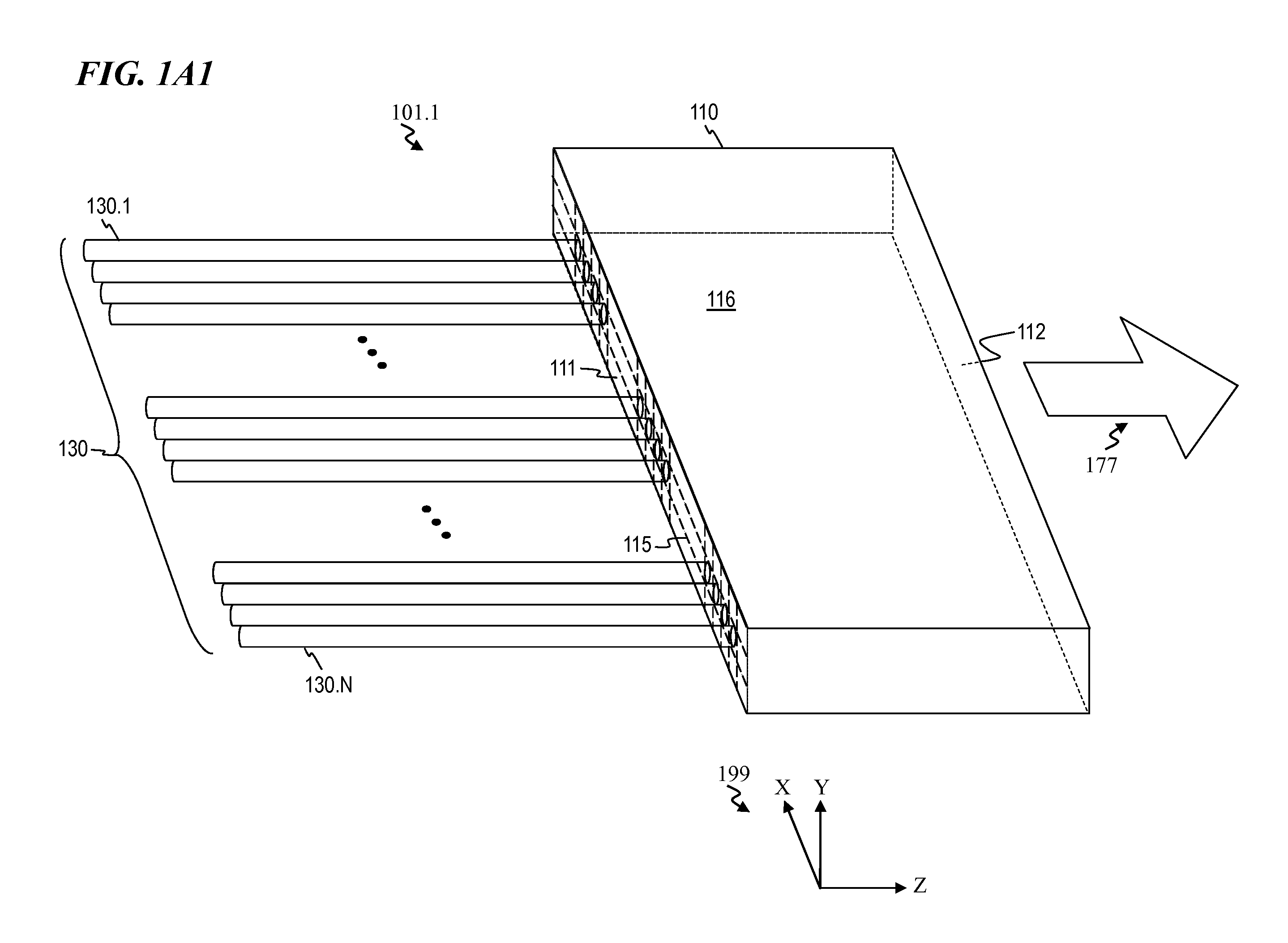
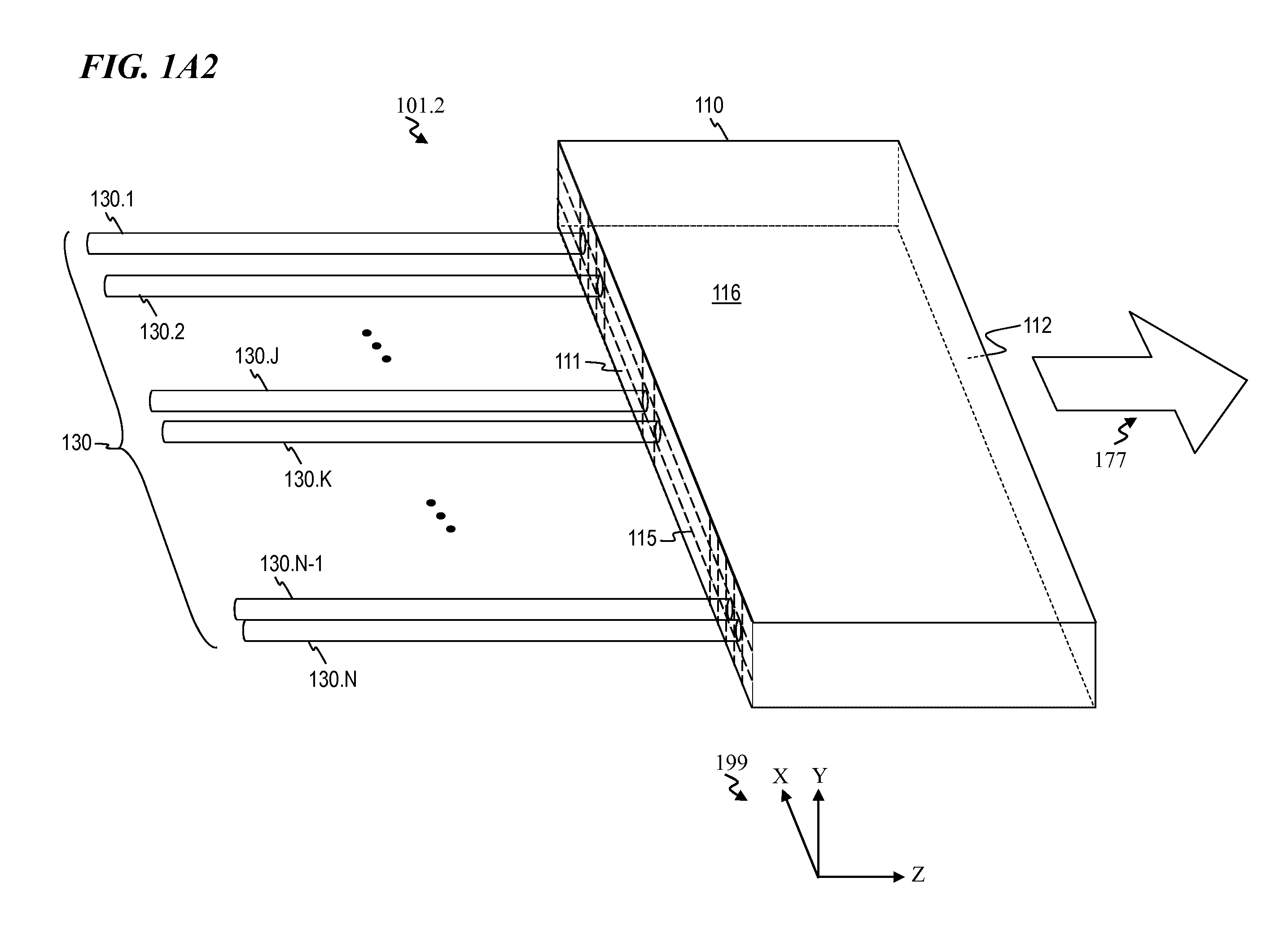
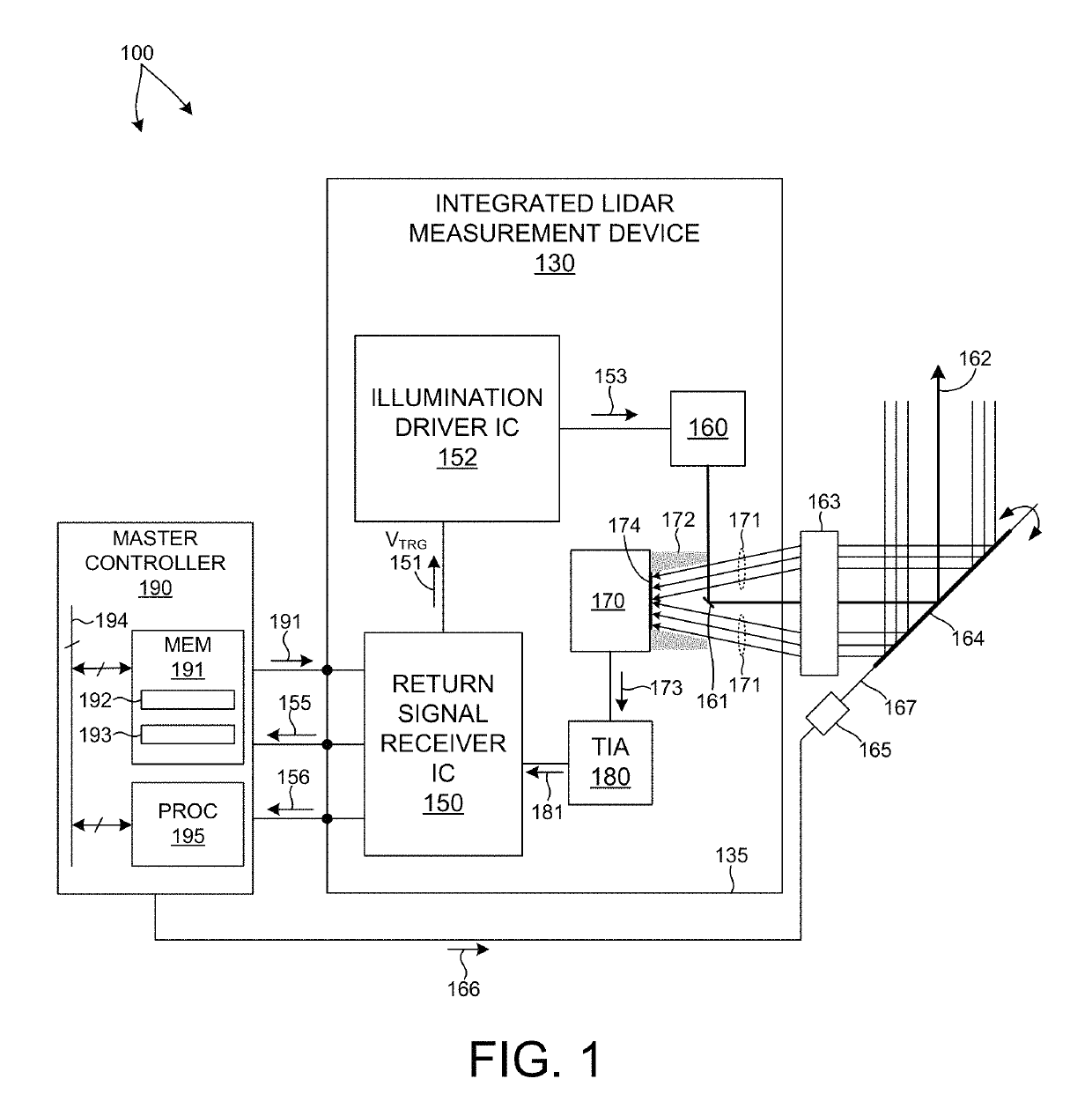
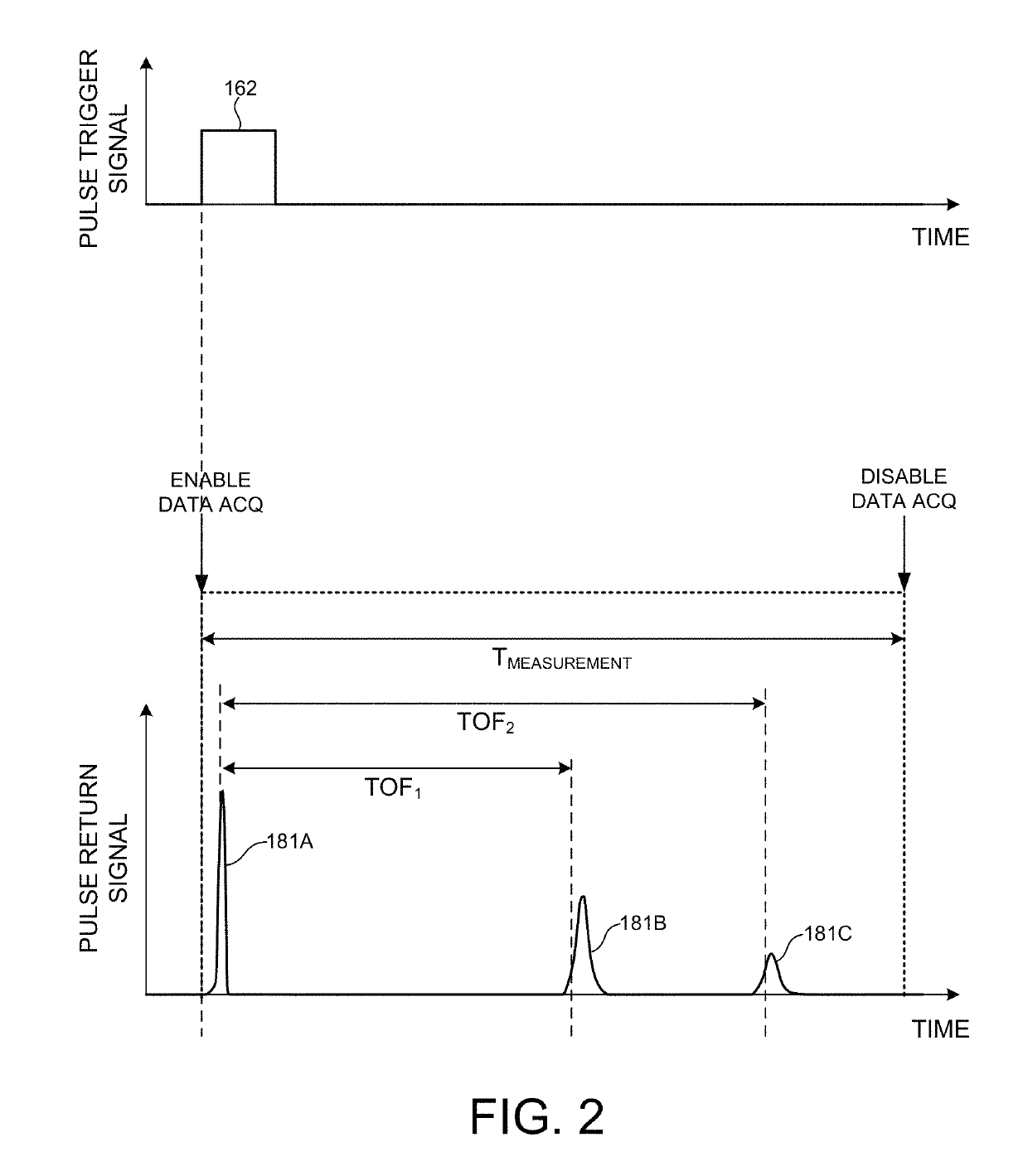
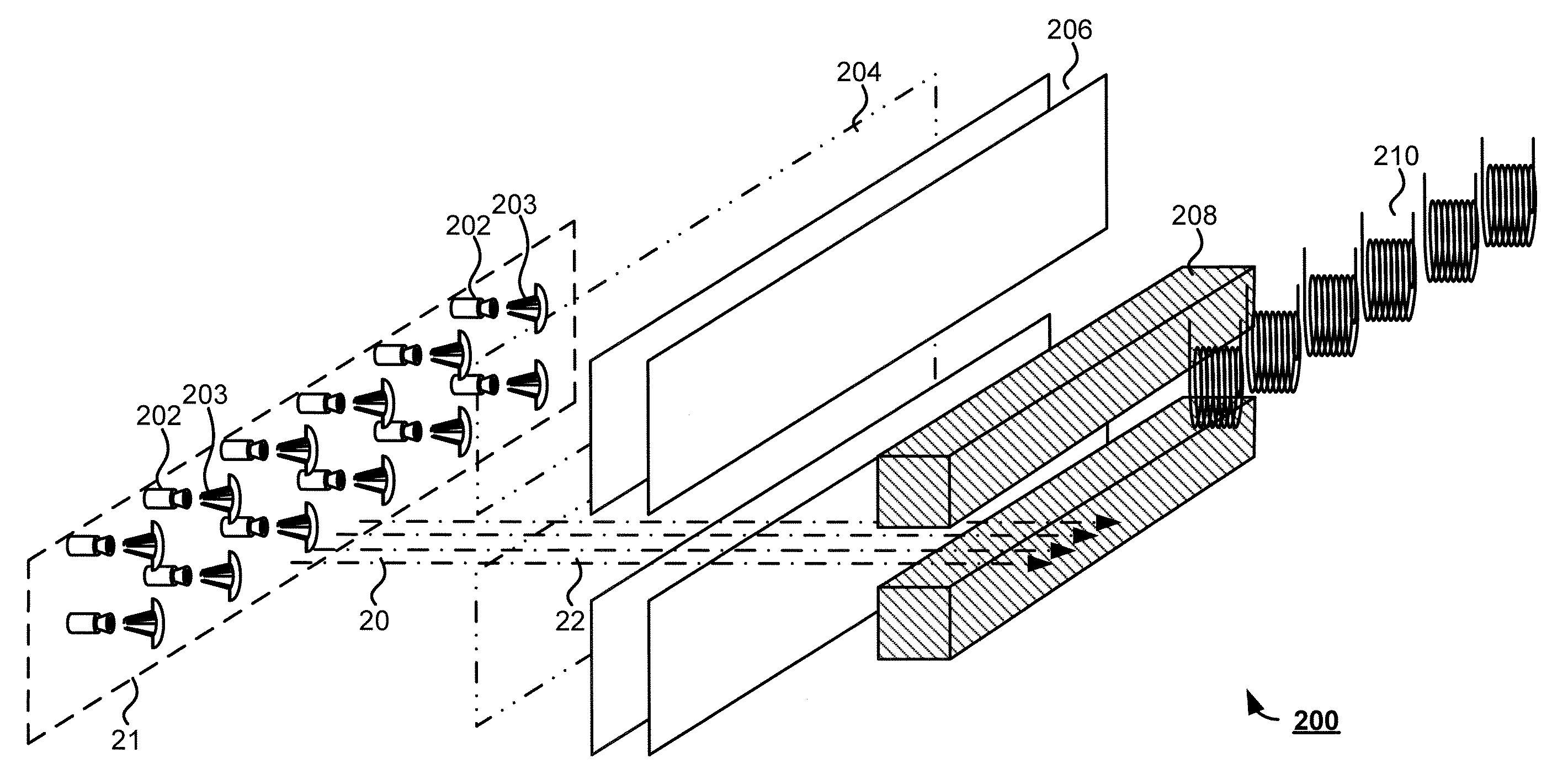
ActiveUS20170350983A1Expand field of viewIncrease sampling densityOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhotodetectorBeam scanning
Methods and systems for performing three dimensional LIDAR measurements with multiple illumination beams scanned over a three dimensional environment are described herein. In one aspect, illumination light from each LIDAR measurement channel is emitted to the surrounding environment in a different direction by a beam scanning device. The beam scanning device also directs each amount of return measurement light onto a corresponding photodetector. In some embodiments, a beam scanning device includes a scanning mirror rotated in an oscillatory manner about an axis of rotation by an actuator in accordance with command signals generated by a master controller. In some embodiments, the light source and photodetector associated with each LIDAR measurement channel are moved in two dimensions relative to beam shaping optics employed to collimate light emitted from the light source. The relative motion causes the illumination beams to sweep over a range of the three dimensional environment under measurement.
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
Thin illumination system
The present invention introduces a new class of thin doubly collimating light distributing engines for use in a variety of general lighting applications, especially those benefiting from thinness. Output illumination from these slim-profile illumination systems whether square, rectangular or circular in physical aperture shape is directional, square, rectangular or circular in beam cross-section, and spatially uniform and sharply cutoff outside the system's adjustable far-field angular cone. Field coverage extends from + / −5- to + / −60-degrees and more in each meridian, including all asymmetric combinations in between, both by internal design, by addition of angle spreading film sheets, and angular tilts. Engine brightness is held to safe levels by expanding the size of the engine's output-aperture without sacrifice in the directionality of illumination. One form of the present invention has a single input light emitter, a square output aperture and the capacity to supply hundreds of lumens per engine. A second multi-segment form of the invention deploys one light emitter in each engine segment, so that total output lumens is determined by the number of segments. Both types of thin light distributing engines provide input light collimated in one meridian and a light distributing element that maintains input collimation while collimating output light in the un-collimated orthogonal meridian, in such a manner that the system's far-field output light is collimated in both its orthogonal output meridians. The present invention also includes especially structured optical films that process the engine's doubly collimated output illumination so as to increase its angular extent one or both output meridians without changing beam shape or uniformity.
Owner:SNAPTRACK +1
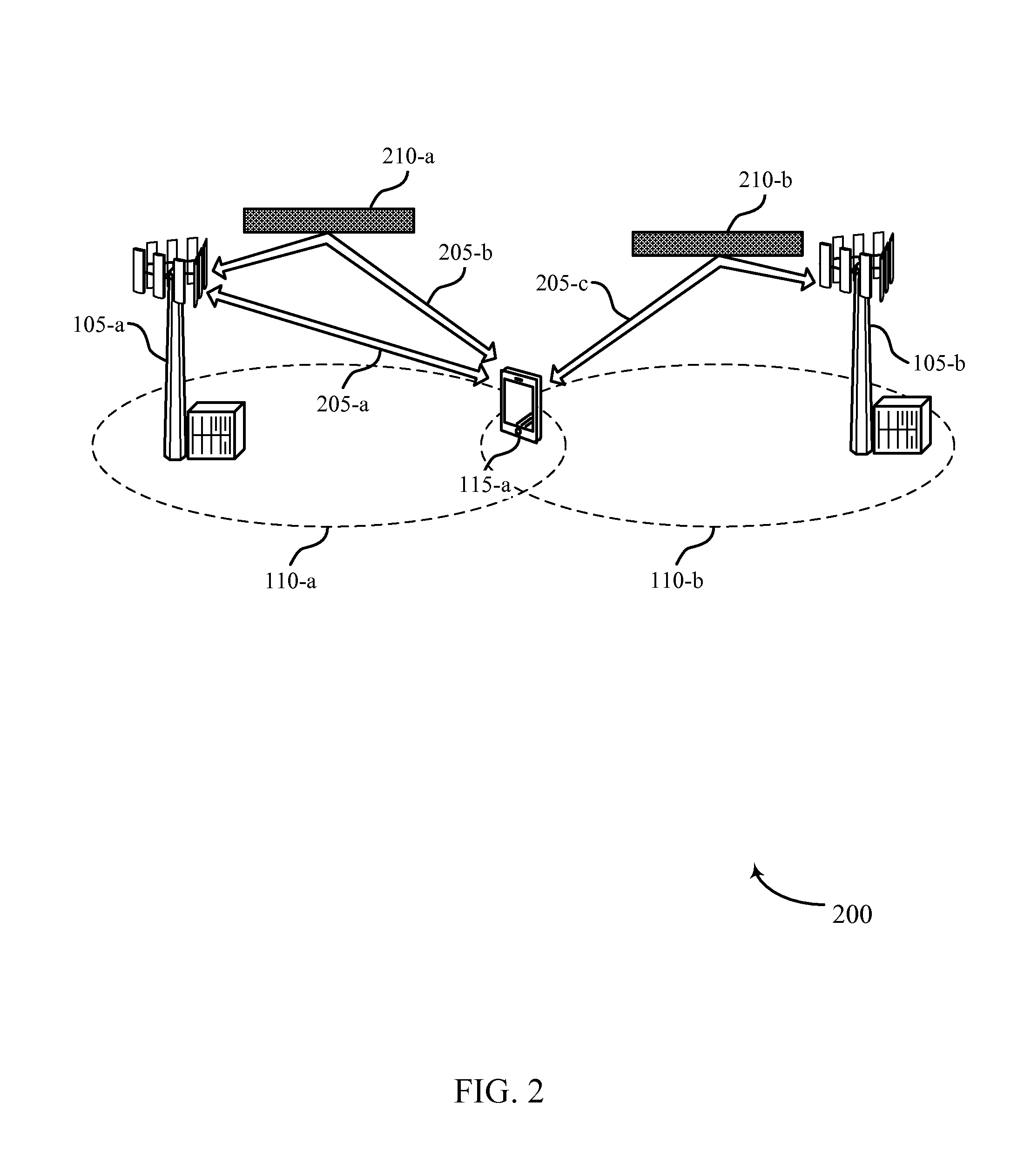
Techniques for beam shaping at a millimeter wave base station and a wireless device and fast antenna subarray selection at a wireless device
ActiveUS20160198474A1Improve latencyQuick selectionSpatial transmit diversityWireless communicationCommunications systemLink margin
Methods, systems, and devices are described for wireless communication at a user equipment (UE). A wireless communications system may improve UE discovery latency by dynamically selecting and switching beam forming codebooks at the millimeter wave base station and the wireless device. Selecting an optimal beam forming codebook may allow the wireless communication system to improve link margins between the base station without compromising resources. In some examples, a wireless device may determine whether the received signals from the millimeter wave base station satisfy established signal to noise (SNR) thresholds, and select an optimal beam codebook to establish communication. Additionally or alternately, the wireless device may further signal the selected beam codebook to the millimeter wave base station and direct the millimeter wave base station to adjust its codebook based on the selection.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
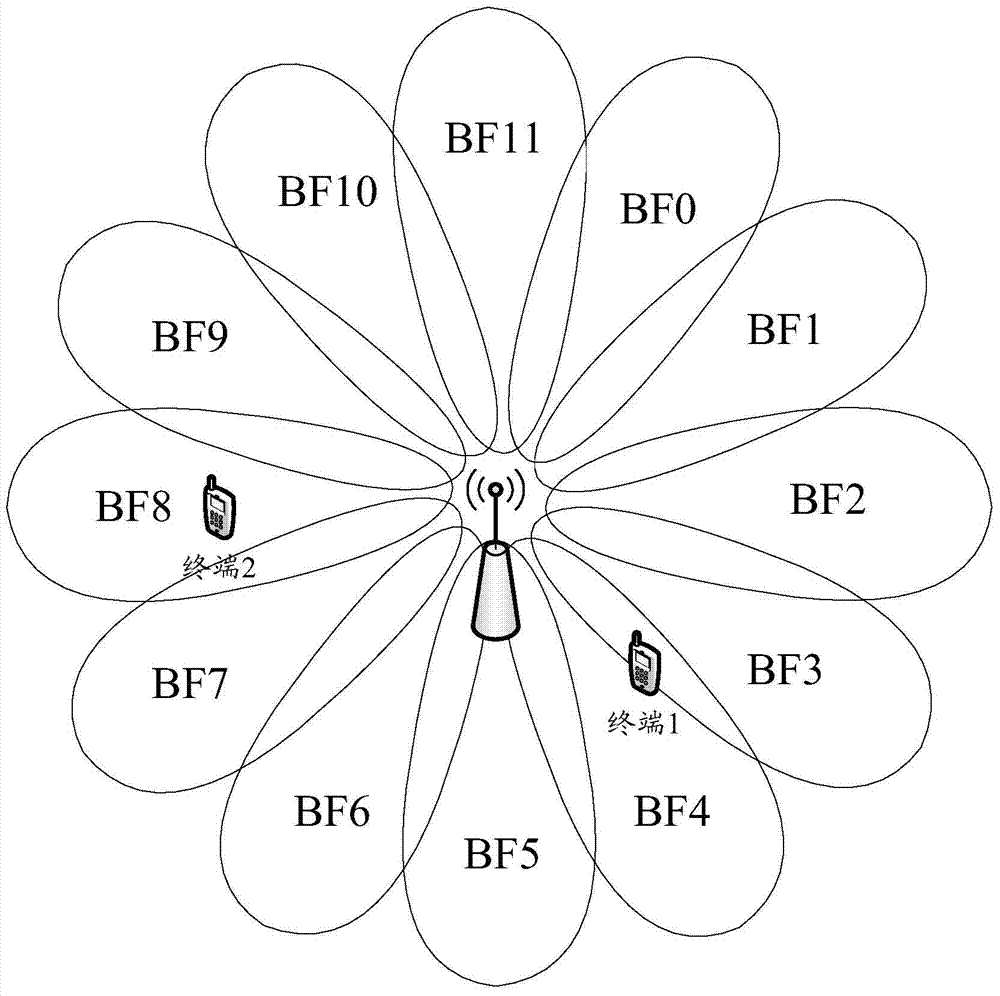
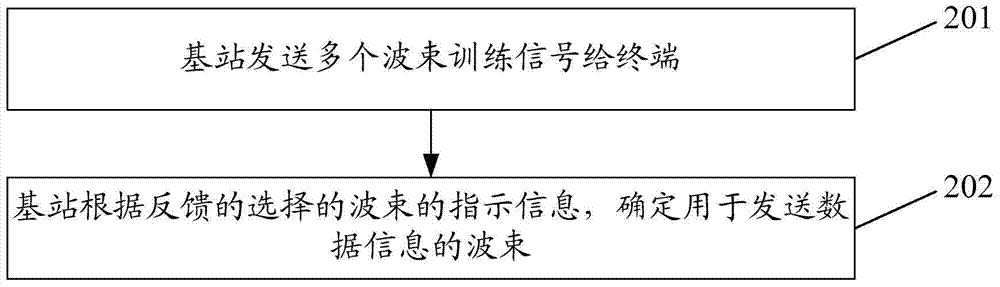
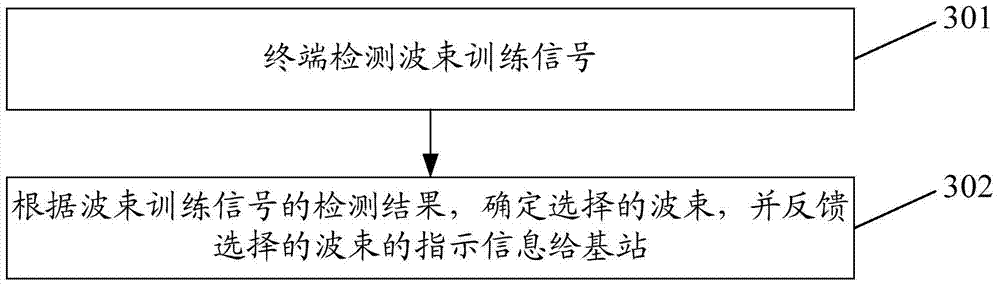
Wave beam recognition method, related device and system for MIMO beam forming communication system
ActiveCN104734759ASpatial transmit diversityWireless communicationCommunications systemData information
Disclosed is a beam identification method in a MIMO beam forming communications system. The method comprises: a base station sending multiple beam training signals to a terminal, each beam training signal corresponding to one beam, and each beam covering a different direction; the terminal detecting the beam training signals, determining a selected beam according to a result of the detection, and feeding back information indicating the selected beam to the base station; the base station determining, according to the information indicating the selected beam fed back by the terminal, a beam used for sending data information. Also disclosed are a related beam identification device and system in a MIMO beam shaping communications system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Led lens for backlight
ActiveUS20070047232A1Reduce thicknessImprove efficiencyNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceLight beamLight-emitting diode
Disclosed herein is a Light Emitting Diode (LED) lens for a backlight. The LED lens includes an LED light source, a lens body, and a beam shaping element. The lens body is configured such that the LED light source is accommodated in the lower portion thereof, and light emitted from the LED light source is radiated in vertical and lateral directions of the lens body. The beam shaping element is fastened to the top of the lens body and is configured to adjust light beams radiated through the upper surface of the lens body. Accordingly, the uniformity of luminance and color can be increased and, at the same time, the overall performance of the system can be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
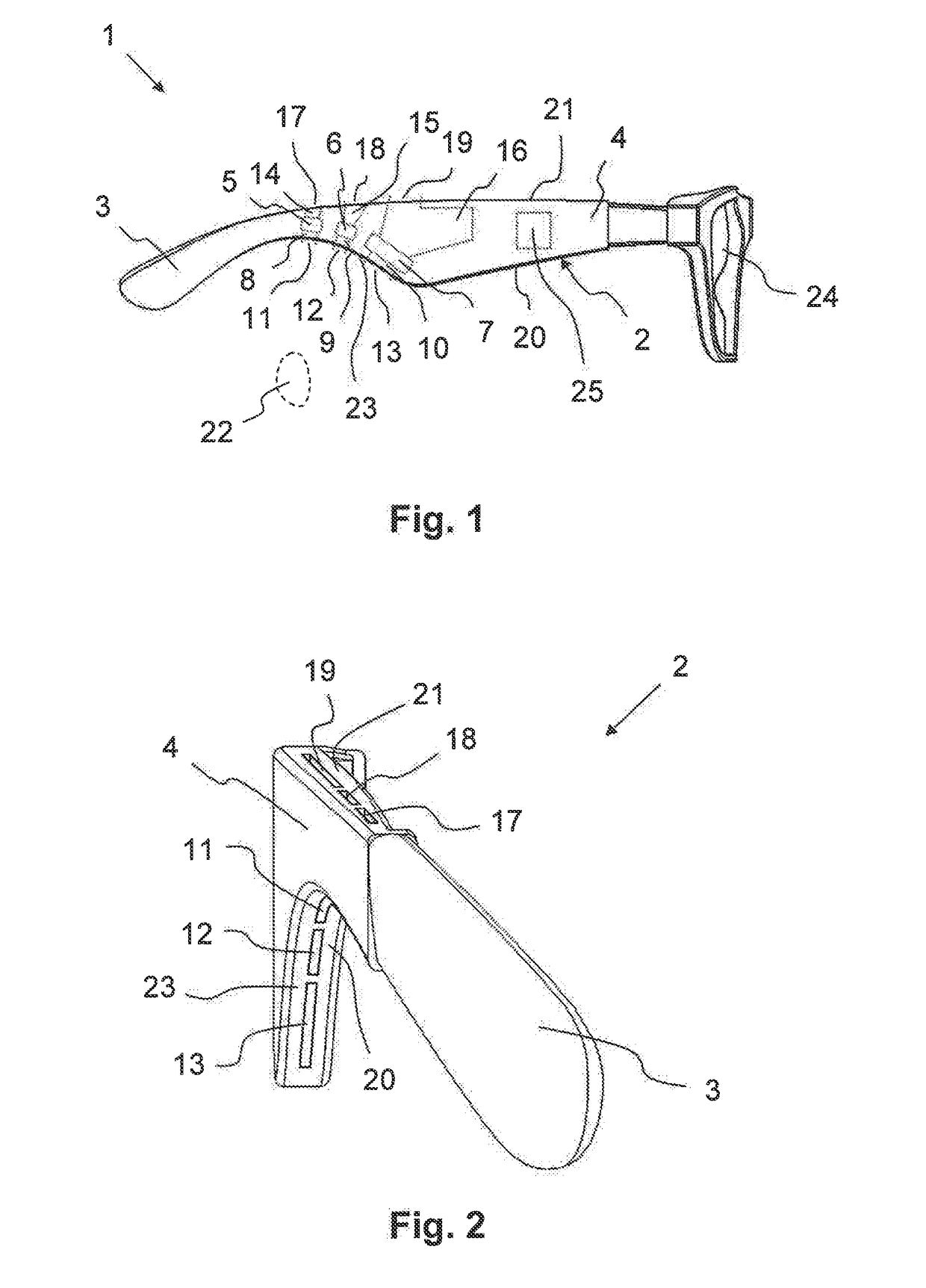
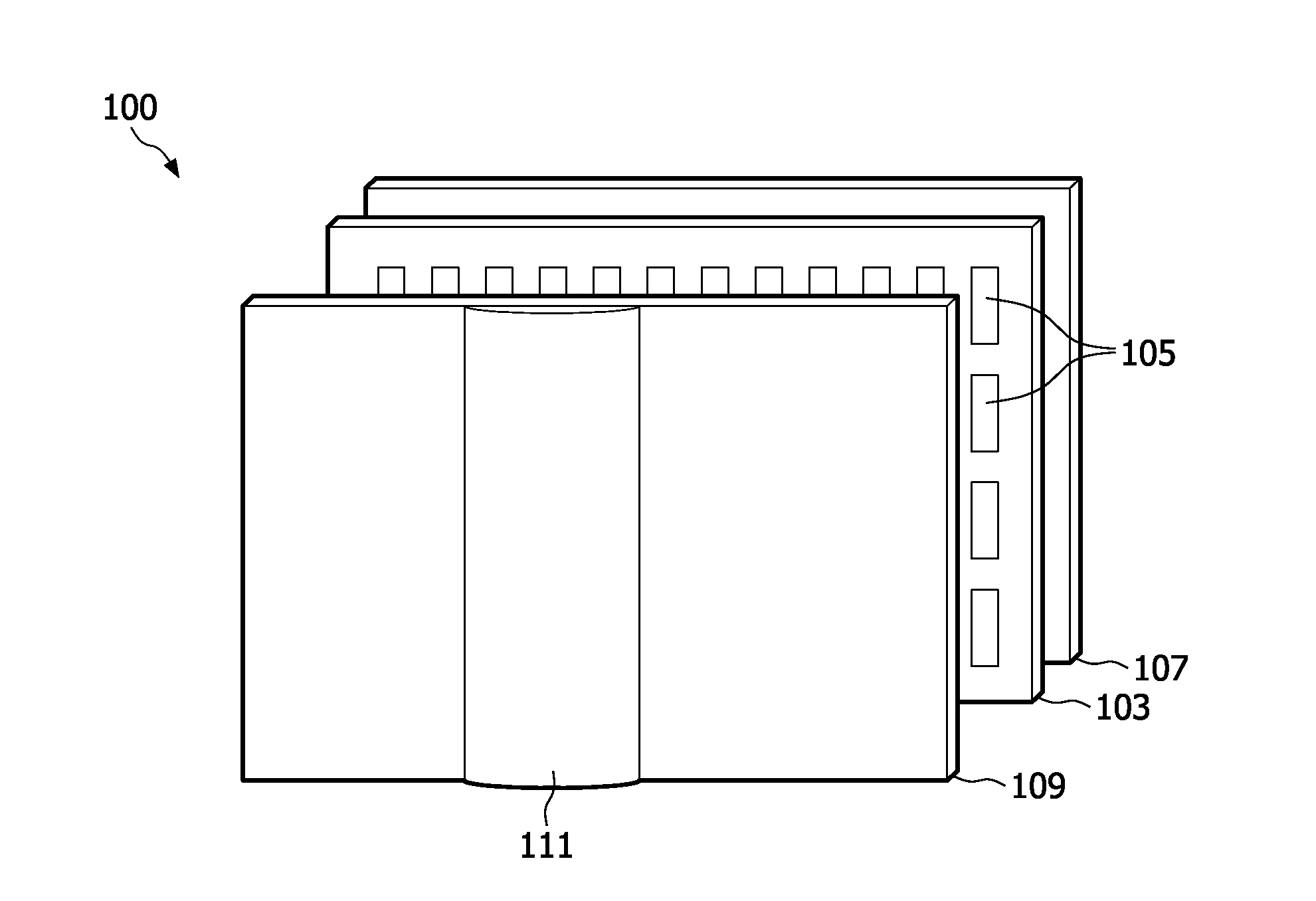
Audio system having beam-shaping speakers and eyewear having such an audio system
ActiveUS20190052954A1Improve wearing comfortSupra/circum aural earpiecesSound producing devicesEyewearAcoustic wave
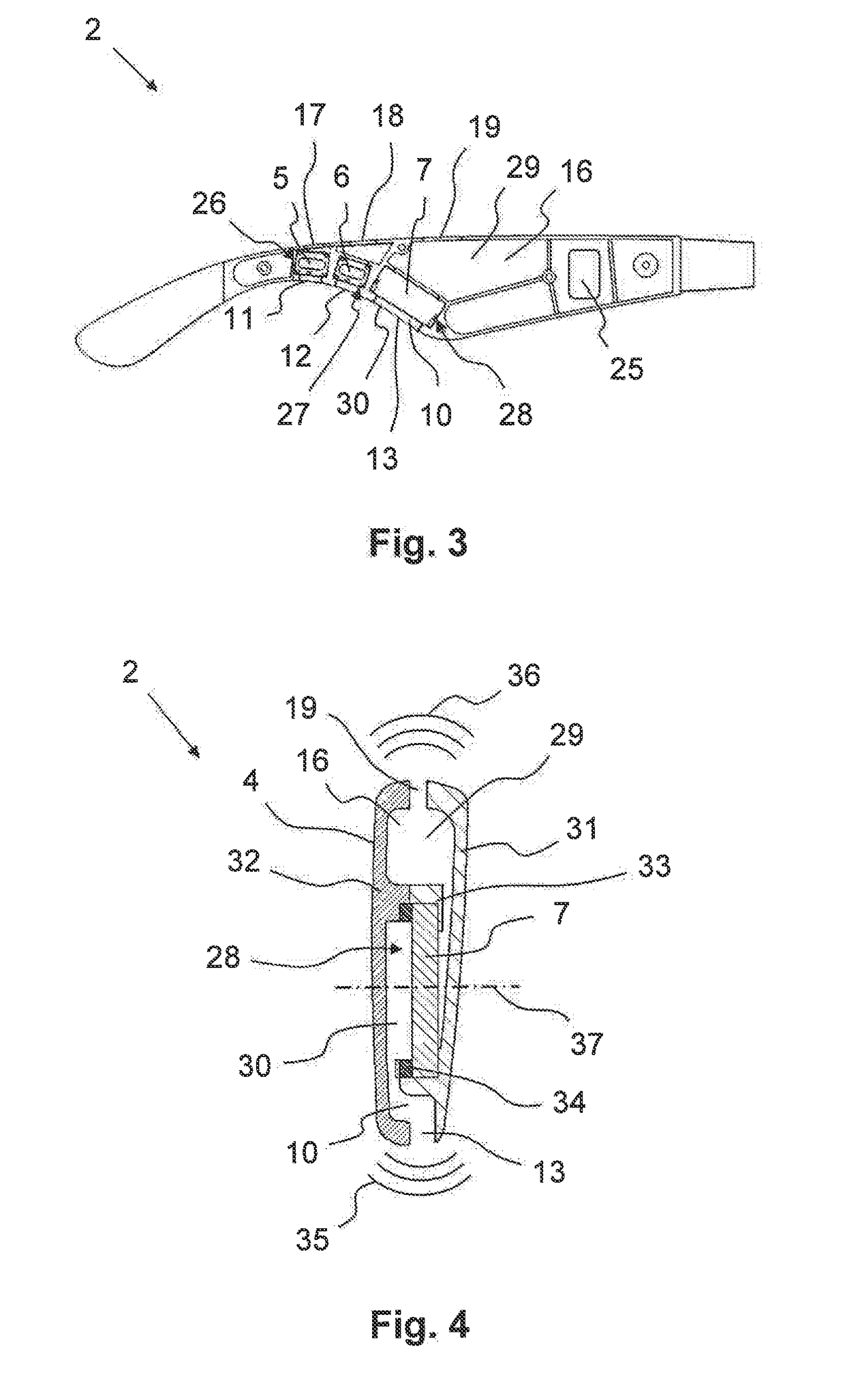
The invention relates to an audio system (2) for disposing in the external region of an ear, having a carrier element (4) for affixing to the head of the user and comprising at least one hollow space (26, 27, 28) having a primary opening (11, 12, 13) oriented in the direction of an ear opening (22) of the intended ear when the carrier element (4) is disposed as intended, and having at least one speaker (5, 6, 7) disposed in the hollow space (26, 27, 28), the cavity (14, 15, 16) thereof being at least partially formed by a first hollow space region (29) and by means of which first sound waves (35) can be emitted through the primary opening (11, 12, 13) in the direction of the ear spaced apart from said opening. According to the invention, the hollow space (26, 27, 28) comprises a secondary opening (17, 18, 19) disposed in the first hollow space region (29) such that said opening is oriented away from the ear toward the surrounding area when the carrier element (4) is disposed as intended so that second sound waves (36) can be emitted through the secondary opening (17, 18, 19) by means of the speaker (5, 6, 7), said waves being offset in phase from the first sound waves (35) such that the volume of the sound waves emitted by the audio system (2) into the surrounding area can be reduced.
Owner:USOUND
Beam light source and lighting device using same
This invention provides a beam light source which enables a light guide plate for receiving light to have a smooth end surface. A light emitting surface of the beam-shaped light guide for dispersing and emitting light emitted from a point light source in a form of beam light faces to a channel bottom surface as a scattering reflecting surface of a reflecting member. The light emitted from the light emitting surface is irregularly reflected on the channel bottom surface of the reflecting member so as to make viewing angle characteristics uniform. The light having the uniform viewing angle characteristics is transmitted from the light emitting surface of the beam-shaped light guide through a side surface opposite to the light emitting surface, and is emitted from another side surface opposite to the above side surface.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Particle-beam exposure apparatus with overall-modulation of a patterned beam
ActiveUS7781748B2Avoid placement errorsStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsProjection opticsParticle beam
In a charged-particle exposure apparatus for exposure of a target with a beam of electrically charged particles, the illumination system includes a deflector device adapted to vary the direction of incidence of the illuminating beam upon the pattern definition device, the pattern definition device forms the shape of the illuminating beam into a desired pattern, and the projection optics system projects an image of the beam shape defined in the pattern definition device onto the target; the projection optics system includes a blocking aperture device having an opening and being adapted to block passage of beams traversing outside the opening, namely when the deflector device is activated to tilt the beamlet by a sufficient angle from its non-deflected path, e.g., for blanking out during the process of loading a pattern into the pattern definition device.
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
Antenna array, network planning system, communication network and method for relaying radio signals with independently configurable beam pattern shapes using a local knowledge
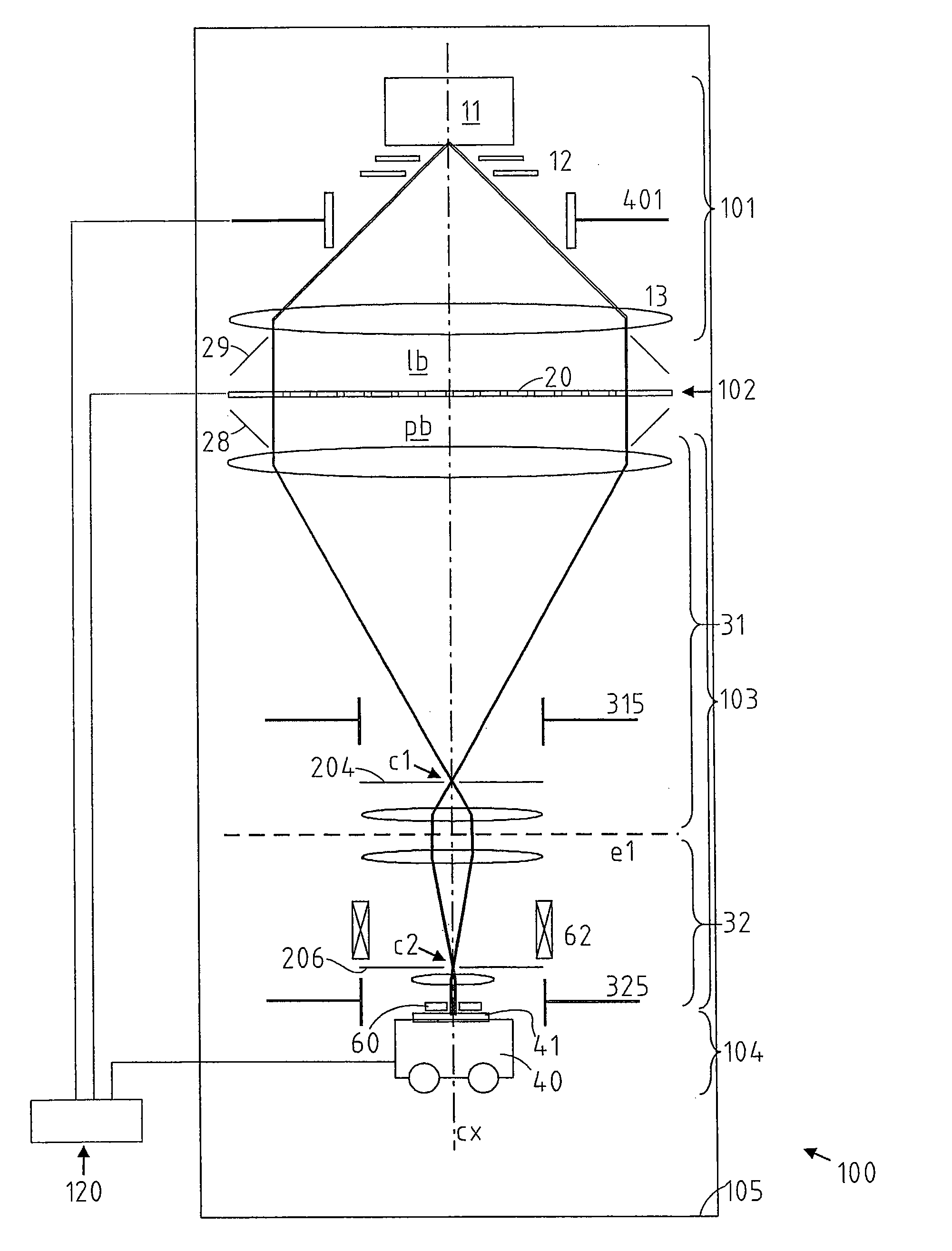
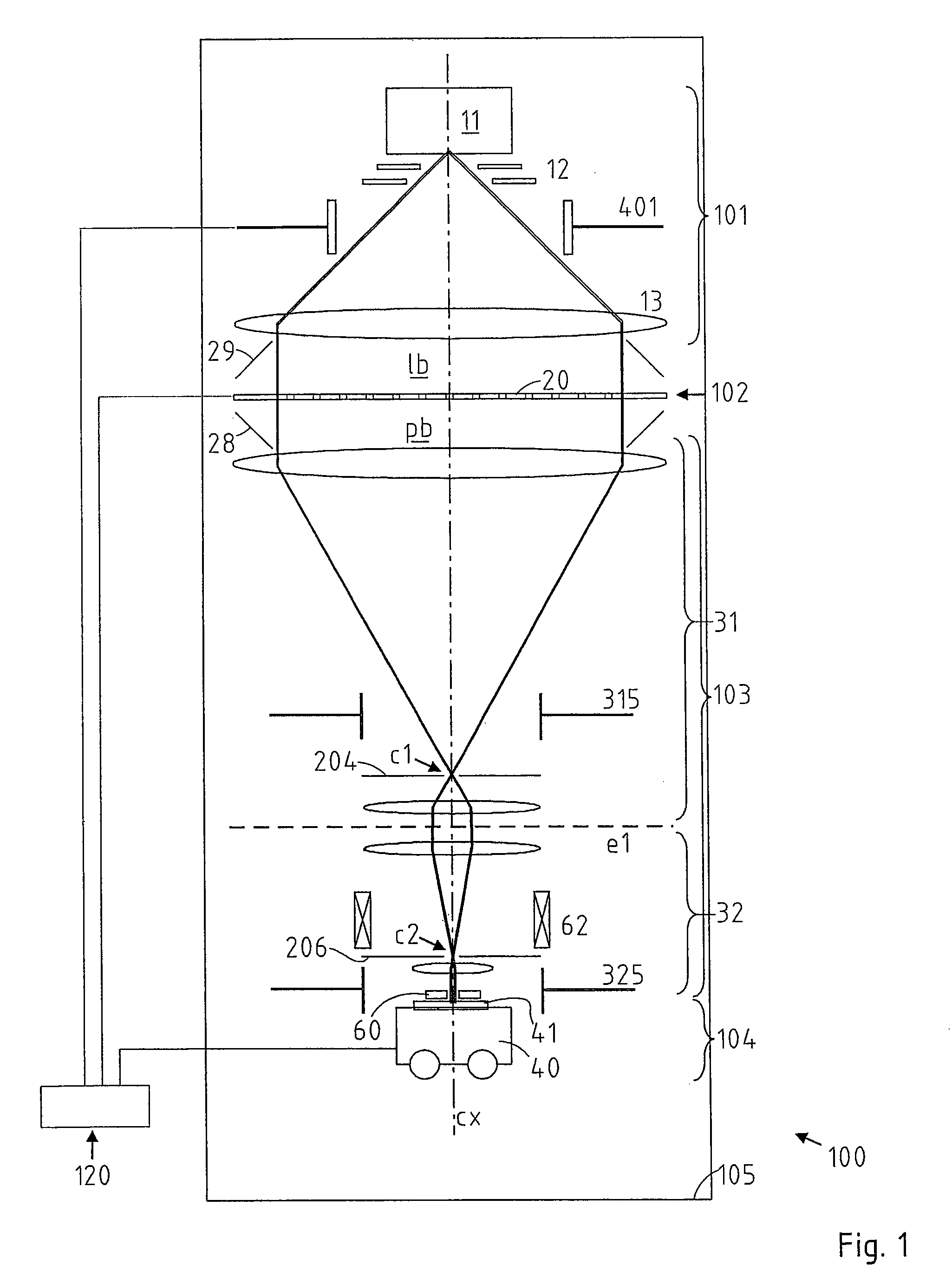
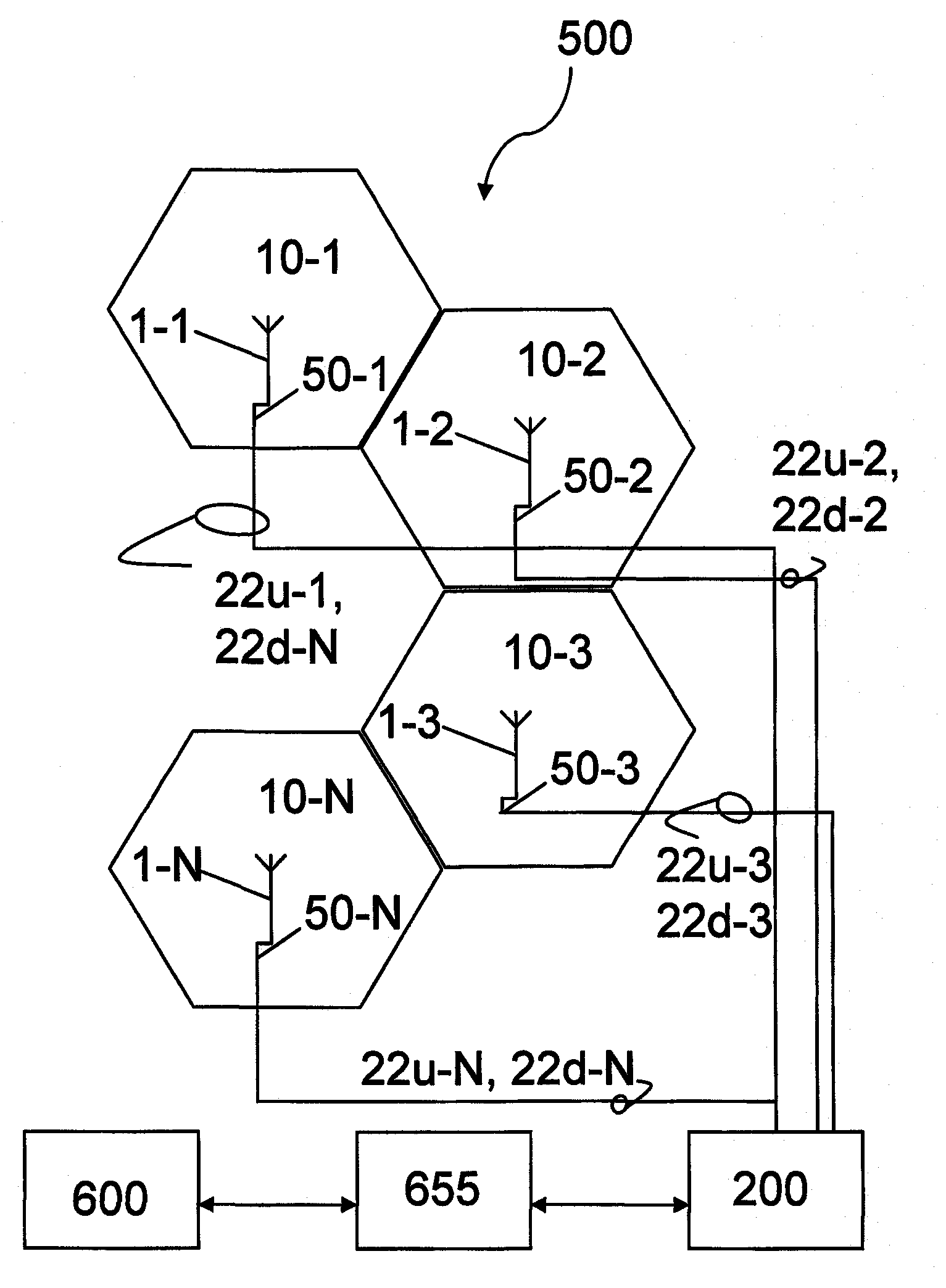
The present disclosure provides an antenna array (1) for relaying radio signals into a cell (10) of a communication network (500). The antenna array (1) comprises a plurality of uplink beam forming vectors (20u) selectable as an uplink beam shape for an uplink relaying and a plurality of downlink beam forming vectors (20d) selectable as a down link beam shape for a down link relaying. The plurality of uplink beam forming vectors (20u) and / or the plurality of the downlink beam forming vectors (20d) may be adjusted at a digital radio interface and forwarded from the digital radio interface to the antenna array (1). An individual one (22u) of the plurality of uplink beam forming vectors (20u) and an individual one (22d) of the plurality of downlink beam forming vectors (20d) are independently selectable using a local knowledge (60) about the cell 10. The present disclosure further provides a communication network (500) comprising a plurality of the antenna arrays (1-1, 1-2, . . . , 1-N) for relaying radio signals into the communication network (500). The communication network (500) further comprises a network playing system (200) adapted to independently select an individual one (22u-1, 22u-2, . . . , 22u-N) of the plurality of uplink beam forming vectors (20u-1, 20u-2, . . . , 20u-N) and an individual one (22d-1, 22d-2, . . . , 22d-N) of the plurality of downlink beam forming vectors (20d-1, 20d-2, . . . , 20d-N) for at least one of the antenna arrays (1-1, 1-2, . . . , 1-N) using a local knowledge (600) about the communication network (500). The present disclosure further provides a method for relaying radio signals into a cell (10) of the communication network (500), a method (2000) for planning the communication network (500), and a method (5000) for relaying radio signals into cells (10-1, 10-2, . . . , 10-N) of the communication network (500); all methods (1000, 2000, 5000) using a local knowledge (600) about the network (500) and or a local knowledge (60-1, 60-2, . . . , 60-N) about the cells (10-1, 10-2, 10-3 . . . , 10-N).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Rectangular flat-top beam shaper
The invention relates to a beam shaping system for providing a square or rectangular laser beam having a controlled intensity profile (uniform, super gaussian or cosine corrected for example) from an incident non-uniform beam intensity profile laser beam source (a Gaussian profile, a profile with astigmatism or any non-rotationally symmetric and non-uniform profile for example). The beam shaping system uses a first acylindrical lens for shaping the incident laser beam along a first axis and a second acylindrical lens orthogonally disposed relative to the first acylindrical lens and for shaping the incident beam along a second axis. The thereby provided light beam is a rectangular beam having a controlled intensity distribution in the far field.
Owner:COHERENT INC
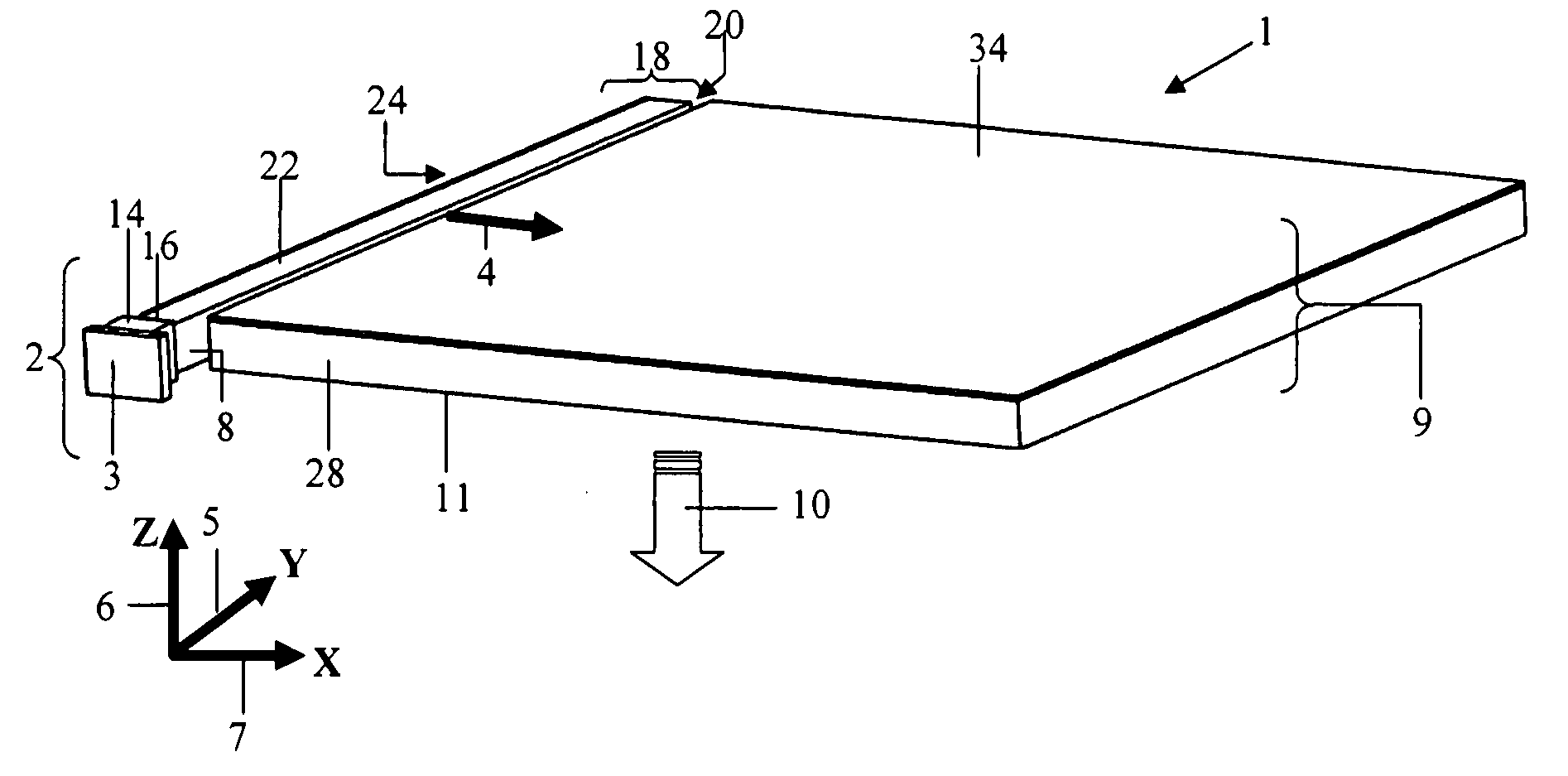
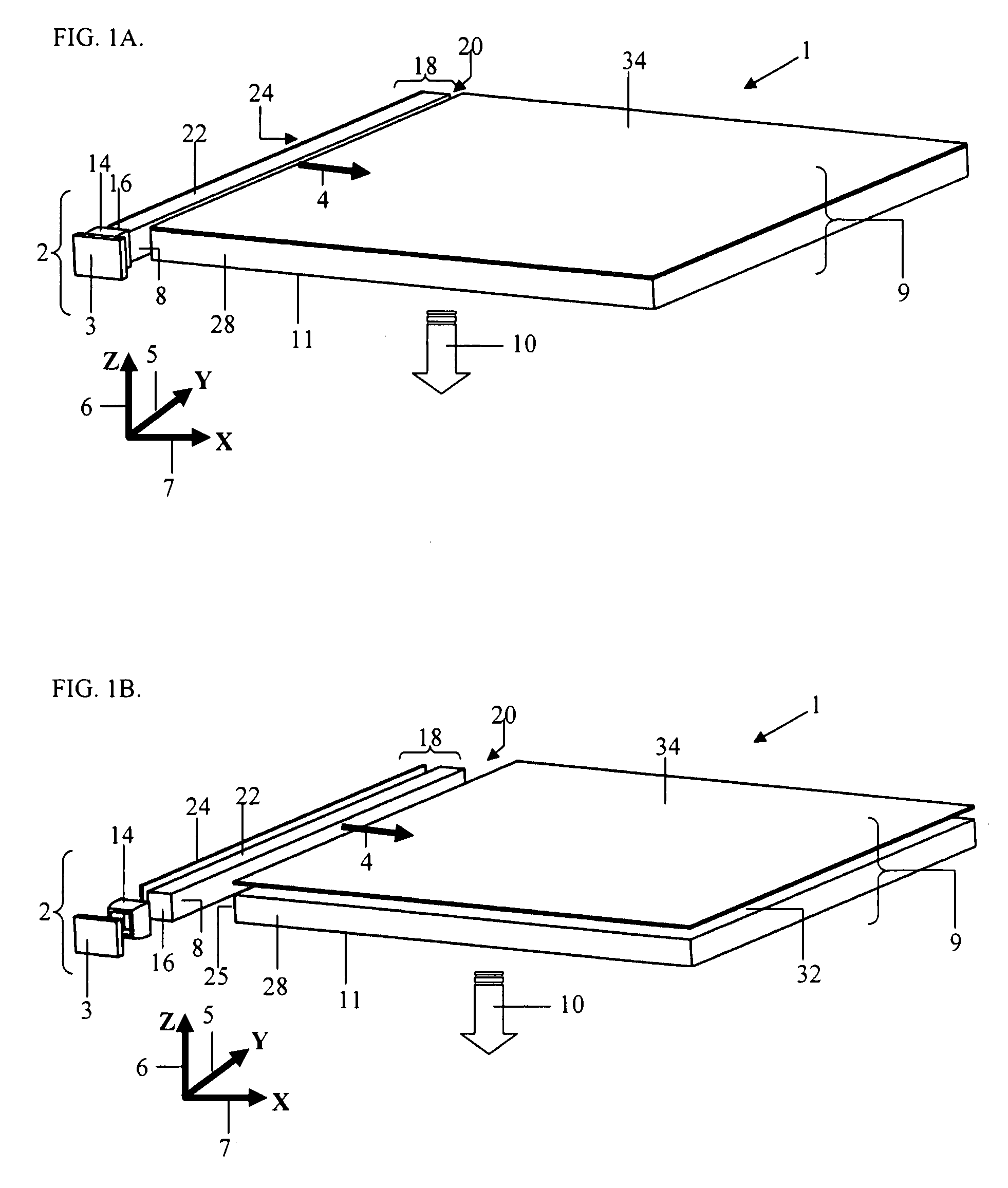
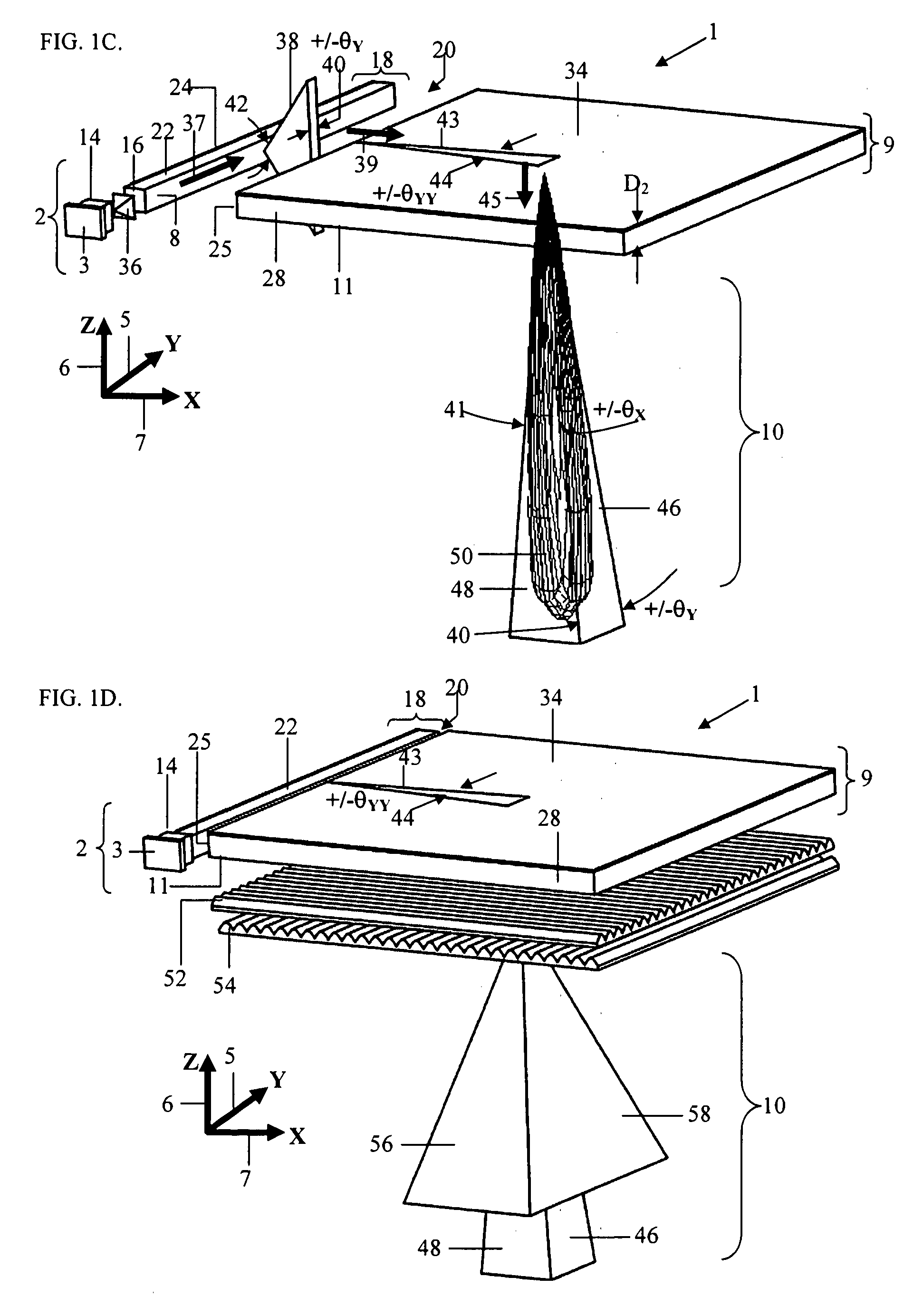
Beam-shaping device
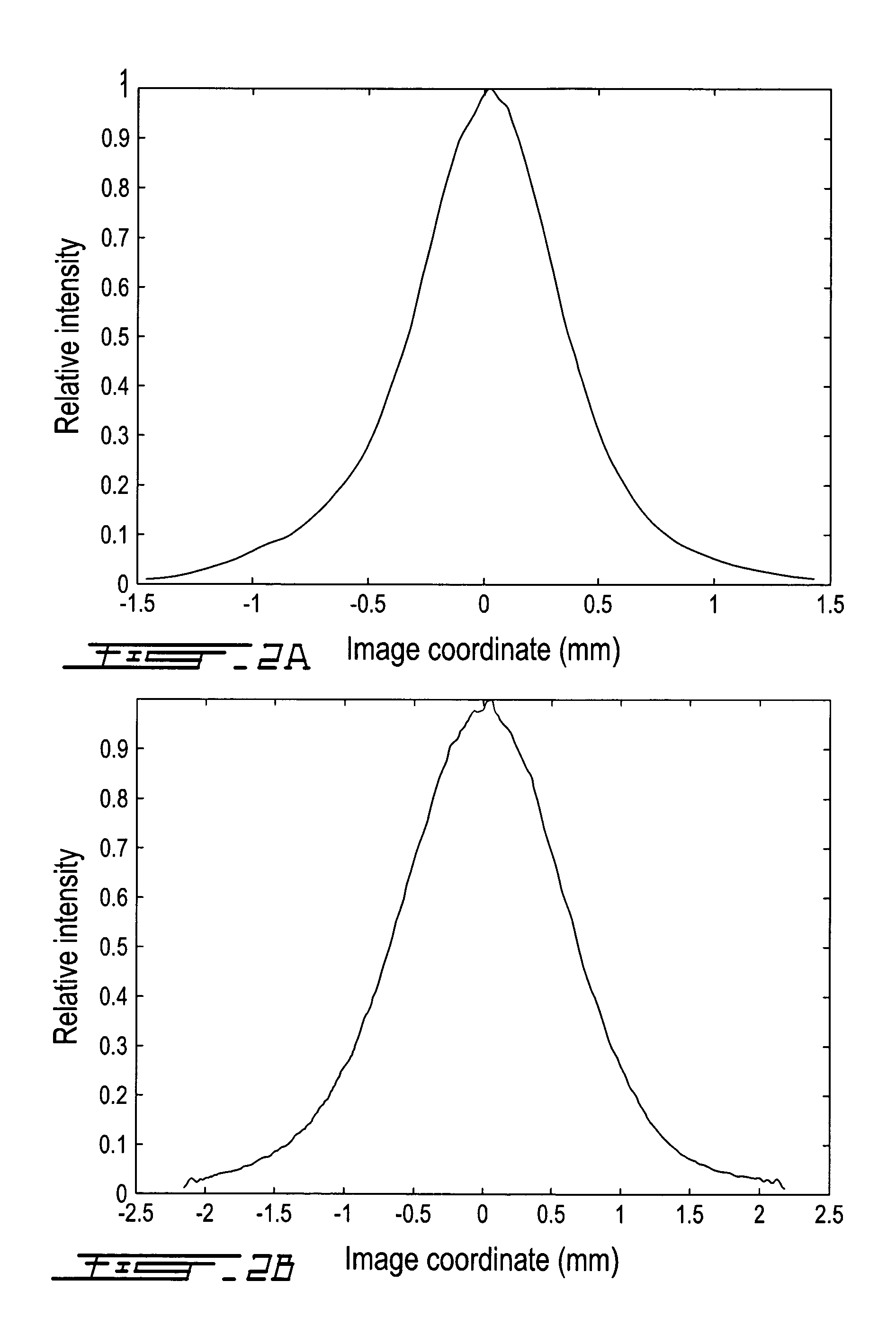
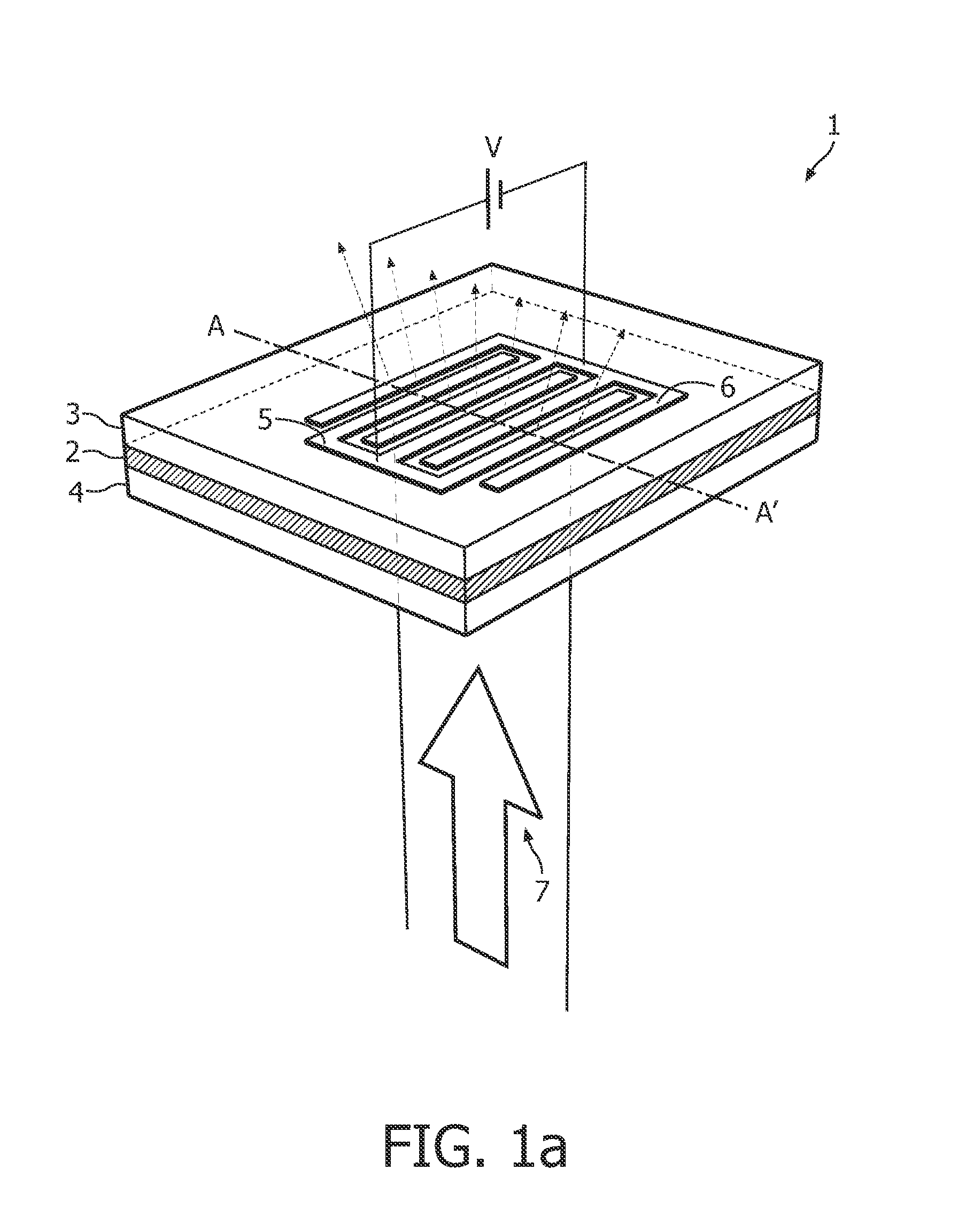
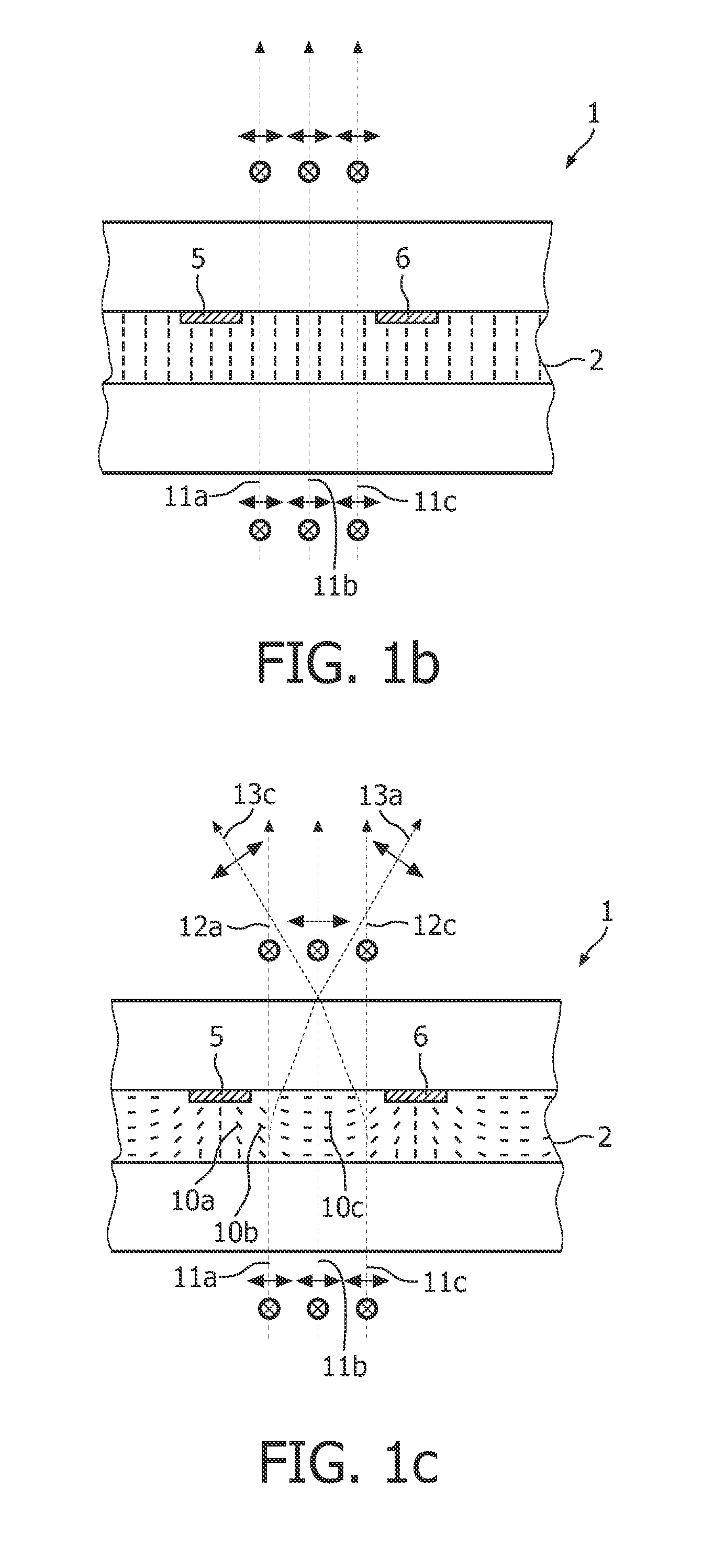
InactiveUS20100149444A1Efficiently divergingEffective convergenceStatic indicating devicesSteroscopic systemsIn planeShortest distance
A beam shaping device (1; 31) comprising first (3; 33) and second (4; 37) optically transparent substrates, a liquid crystal layer (2; 36) sandwiched there between, and first (5; 34) and second (6; 35) electrodes arranged on a side of the liquid crystal layer (2; 36) facing the first substrate (3; 34). The beam shaping device (1; 31) is controllable between beam-shaping states, each permitting passage of light through the beam-shaping device in a direction perpendicular thereto. The beam shaping device (1; 31) is configured in such a way that application of a voltage (V) across the first (5; 34) and second (6; 35) electrodes results in an electric field having a portion essentially parallel to the liquid crystal layer (2; 36) in a segment thereof between neighboring portions of the electrodes (5, 6; 34; 35) and extending substantially from the first substrate (3; 34) to the second (4; 35) substrate. In this way a relatively high refractive index gradient can be obtained across short distances, which enables a very efficient beam shaping. The electric field can be achieved by utilizing electrodes provided on one side of the liquid crystal layer, in a so-called in-plane configuration. The device can be used in an autostereoscopic display device, for switching between 2D and 3D modes.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Phased array antenna
InactiveUS20090278744A1High directional gainLess deformationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsPhase shiftedElectrical conductor
There is provided a phased array antenna having variable phase shifters constituted by using a variable dielectric-constant dielectric substance whose dielectric constant varies according to an applied electric field, which antenna can dispense with a DC blocking element that causes mismatch, and reduce deformation of the beam shape even when beam tilt occurs, in the case where the variable phase shifters are divided into those for right-side tilt and those for left-side tilt and the phase shift amounts thereof are independently controlled.The phased array antenna is provided with a feeding phase shift unit (130) having a laminated structure obtained by laminating at least a ground conductor layer (117), an insulator layer (118), a main conductor layer (119), a variable dielectric-constant dielectric layer (120), and a sub conductor layer (121) in this order, and a propagation characteristic variable line (105) having a line on the sub conductor layer in an area which planarly overlaps a line on the main conductor layer is provided on the feeding phase shift unit. By applying a bias voltage between the main conductor layer and the sub conductor layer, the dielectric constant of the variable dielectric-constant dielectric substance in the propagation characteristic variable line area is varied to control the propagation characteristics. Thereby, a DC blocking element to be inserted in series into the feeding line can be dispensed with.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
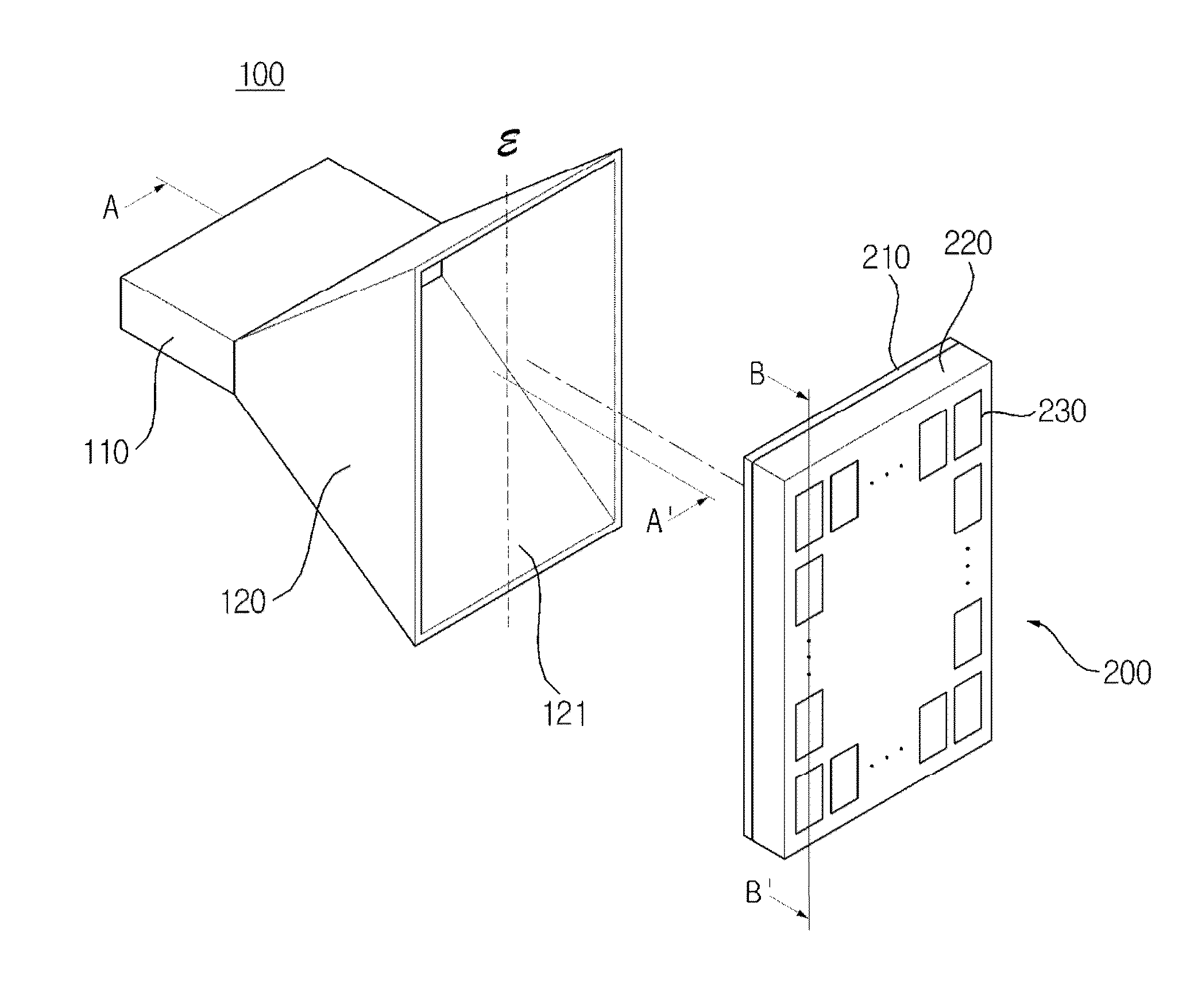
Optical-fiber array method and apparatus
Method and apparatus for forming an optical-fiber-array assembly, which include providing a plurality of optical fibers including a first optical fiber and a second optical fiber, providing a fiber-array plate that includes a first surface and a second surface, connecting the plurality of optical fibers to the first surface of the fiber-array plate, transmitting a plurality of optical signals through the optical fibers into the fiber-array plate at the first surface of the fiber-array plate, and emitting from the second surface of the fiber-array plate a composite output beam having light from the plurality of optical signals. Optionally, the first surface of the fiber-array plate includes indicia configured to assist in the alignment of the plurality of optical fibers on the first surface of the fiber-array plate. In some embodiments, the second surface of the fiber-array plate includes a plurality of beam-shaping optics configured to shape the composite output beam.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Multiple pixel scanning LIDAR
ActiveUS10393877B2Expand field of viewIncrease sampling densityOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhotodetectorBeam scanning
Methods and systems for performing three dimensional LIDAR measurements with multiple illumination beams scanned over a three dimensional environment are described herein. In one aspect, illumination light from each LIDAR measurement channel is emitted to the surrounding environment in a different direction by a beam scanning device. The beam scanning device also directs each amount of return measurement light onto a corresponding photodetector. In some embodiments, a beam scanning device includes a scanning mirror rotated in an oscillatory manner about an axis of rotation by an actuator in accordance with command signals generated by a master controller. In some embodiments, the light source and photodetector associated with each LIDAR measurement channel are moved in two dimensions relative to beam shaping optics employed to collimate light emitted from the light source. The relative motion causes the illumination beams to sweep over a range of the three dimensional environment under measurement.
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
Surface array semiconductor laser light beam shaping device
InactiveCN101144909AEasy to manufactureSimple structureLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersDivergence angleLight beam
The present invention relates to a beam reshaping device for a plane array semiconductor laser. The device includes a fast axis collimating lens, a slow axis collimating lens, a ladder lens, a first parallelepiped prism unit, and a second parallelepiped prism unit. The beam emitted by the plane array semiconductor laser passes through the fast axis collimating lens and the slow axis collimating lens, and lowers the divergence angle of the fast axis and the divergence angle of the slow axis. The irradiance interspace between bars can be eliminated by the ladder lens and can be compressed in the direction of the fast axis. Finally, part of beam can be moved parallel along the fast axis direction by the first parallelepiped prism unit and the second parallelepiped prism unit, and then be moved along the slow axis direction. Through the above process, the beam is realigned, and the purpose that the quality of the fast axis beam and the quality of the slow axis beam tend to be coincident is reached. The realigned beam can get high-power high-brightness facula after being focused. The optical apparatus used in the present invention is easy to be produced and convenient to be adjusted with simple structure.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
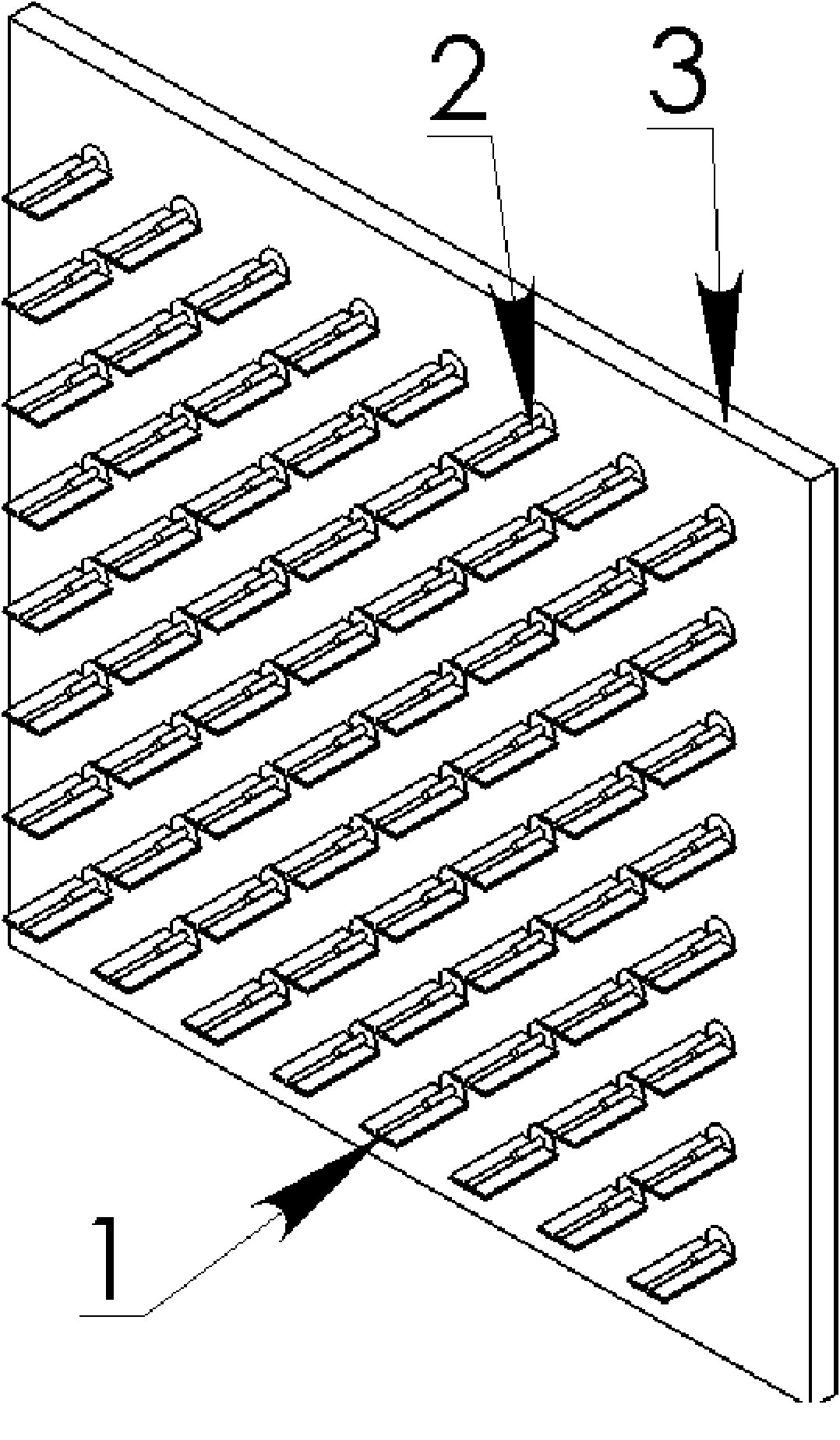
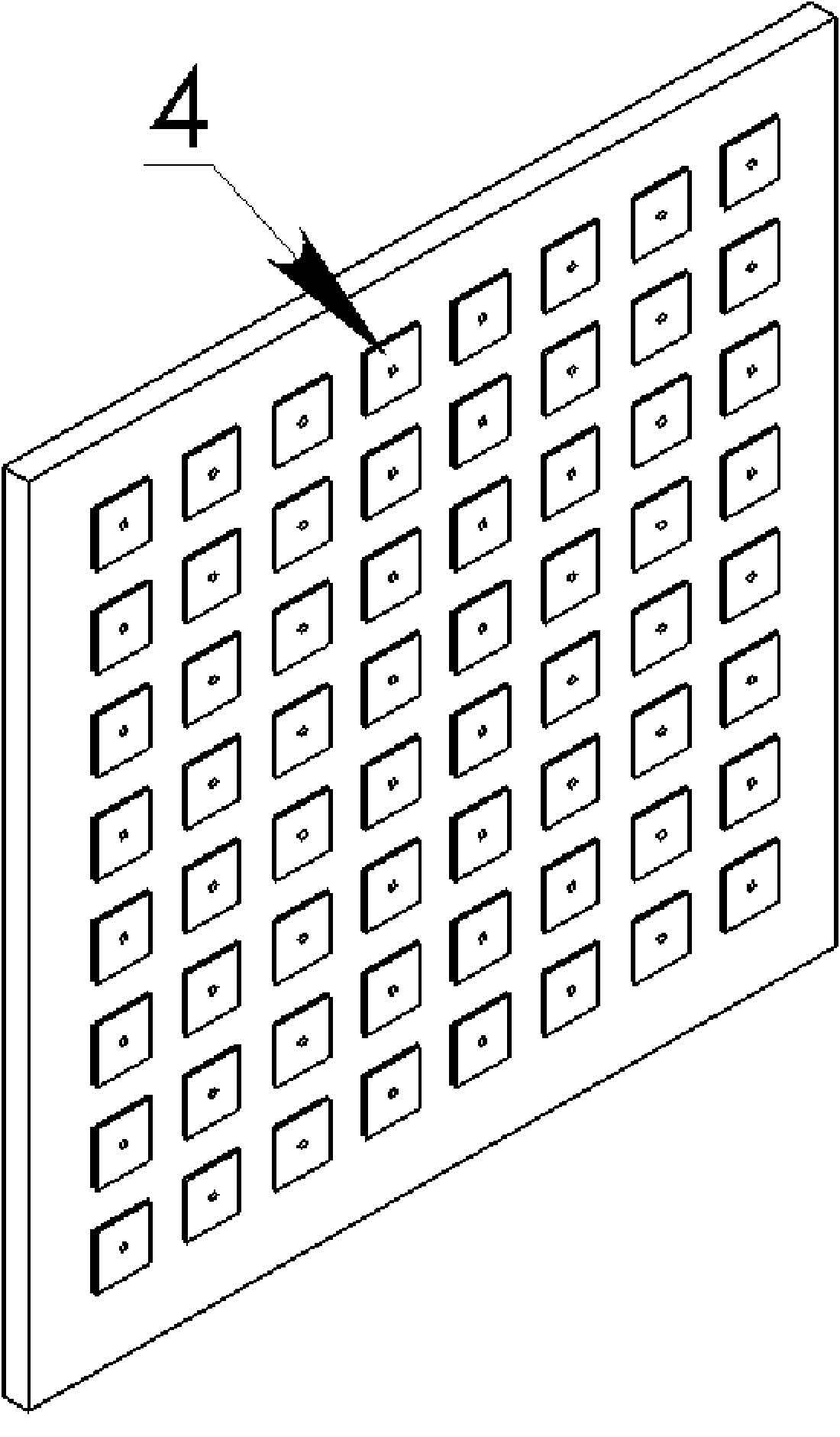
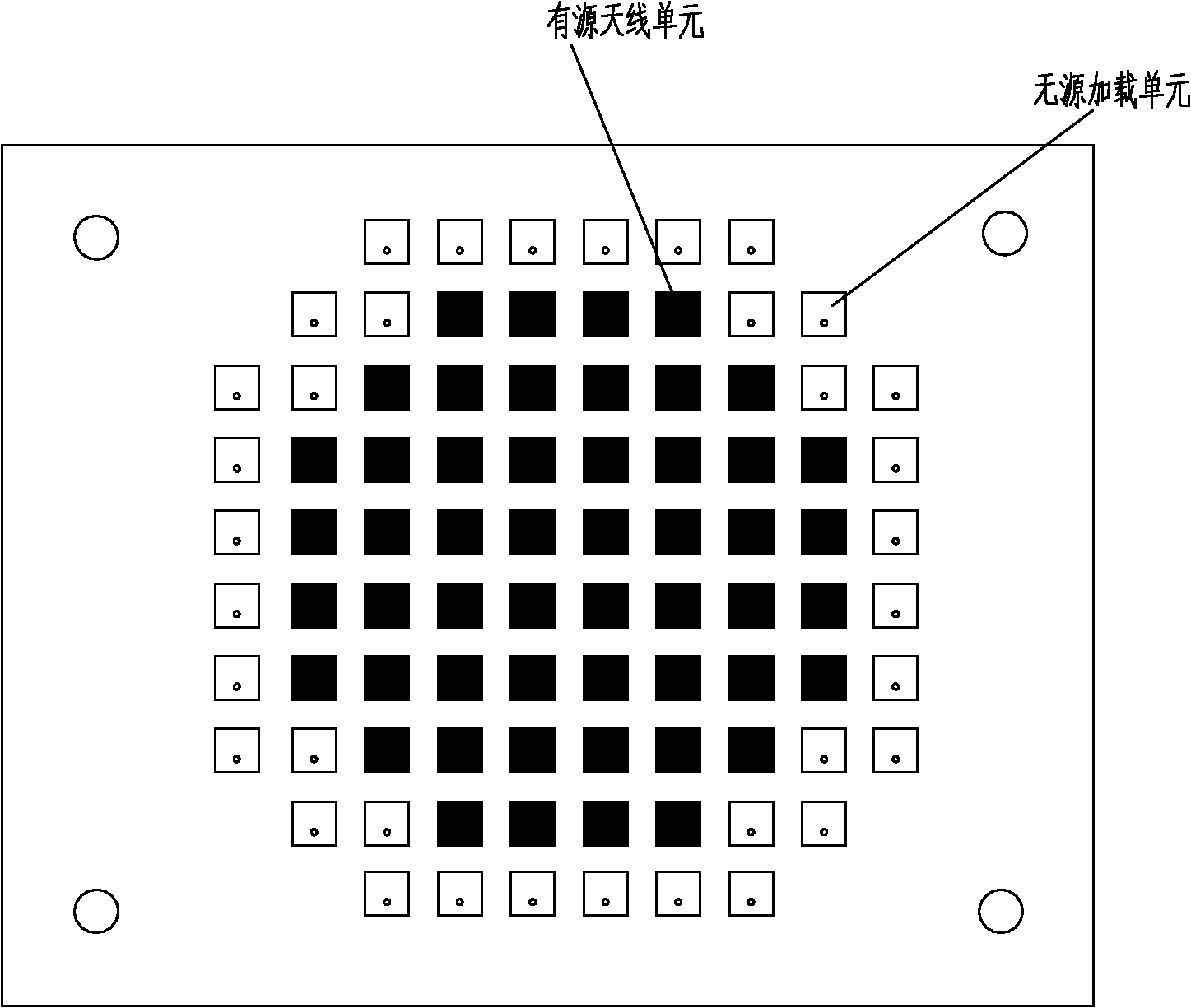
Active phased array antenna adopting passive loading way to control sidelobe level
The invention relates to an active phased array antenna adopting the passive loading way to control sidelobe level, which is characterized in that the array surface of the active phased array antenna is jointly constituted by active loading units and passive loading units, and the passive loading units are positioned on the periphery of the active loading units; each active loading unit channel is controlled by an independent vector modulator and a low-noise amplifier, and each vector modulator simultaneously controls the amplitude and the phase of a feed source, thereby further changing the amplitude and the phase of surface current of the antenna units, and finally controlling the scanning angel of a wave beam and inhibiting the sidelobe level of the wave beam, wherein the active phasedarray transmitting antenna comprises 64 radiating units, the excitation way through a coaxial connector is adopted, the scanning of the spatial wave beam is realized by changing the phase distribution of the antenna on the pore diameter, and the required wave beam shape is obtained by changing the amplitude of the surface current on each radiation unit. The mutual coupling among array elements isutilized, thereby reducing the sidelobe level of the antenna in the pitching direction by 5dB in comparison with square fully array caliber feed on the basis of reducing the cost of the feed source.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Techniques for providing a ribbon-shaped gas cluster ion beam
ActiveUS20080149826A1Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsForming gasGas cluster ion beam
Techniques for providing a ribbon-shaped gas cluster ion beam are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the techniques may be realized as an apparatus for providing a ribbon-shaped gas cluster ion beam. The apparatus may comprise at least one nozzle configured to inject a source gas at a sufficient speed into a low-pressure vacuum space to form gas clusters. The apparatus may also comprise at least one ionizer that causes at least a portion of the gas clusters to be ionized. The apparatus may further comprise a beam-shaping mechanism that forms a ribbon-shaped gas cluster ion beam based on the ionized gas clusters.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
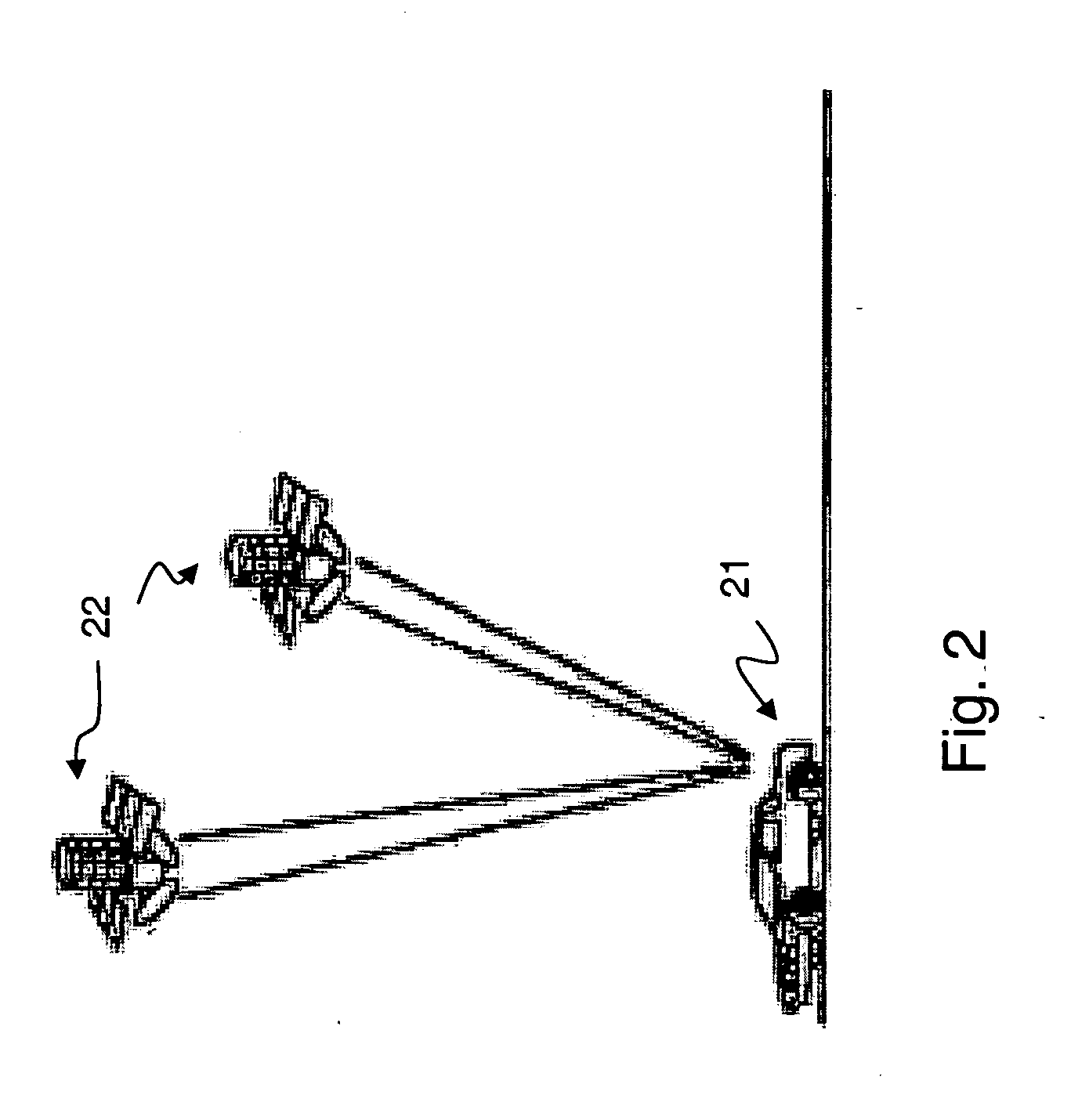
Horizontal emitting, vertical emitting, beam shaped, distributed feedback (DFB) lasers fabricated by growth over a patterned substrate with multiple overgrowth
InactiveUS20070125995A1Improve propertiesEffective limitOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionDistributed feedback laserGrating
A structure using integrated optical elements is comprised of a substrate, a buffer layer grown on the substrate, one or more first patterned layers deposited on top of the buffer layer, wherein each of the first patterned layers is comprised of a bottom lateral epitaxial overgrowth (LEO) mask layer and a LEO nitride layer filling holes in the bottom LEO mask layer, one or more active layers formed on the first patterned layers, and one or more second patterned layers deposited on top of the active layer, wherein each of the second patterned layers is comprised of a top LEO mask layer and a LEO nitride layer filling holes in the top LEO mask layer, wherein the top and / or bottom LEO mask layers act as a mirror, optical confinement layer, grating, wavelength selective element, beam shaping element or beam directing element for the active layers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com