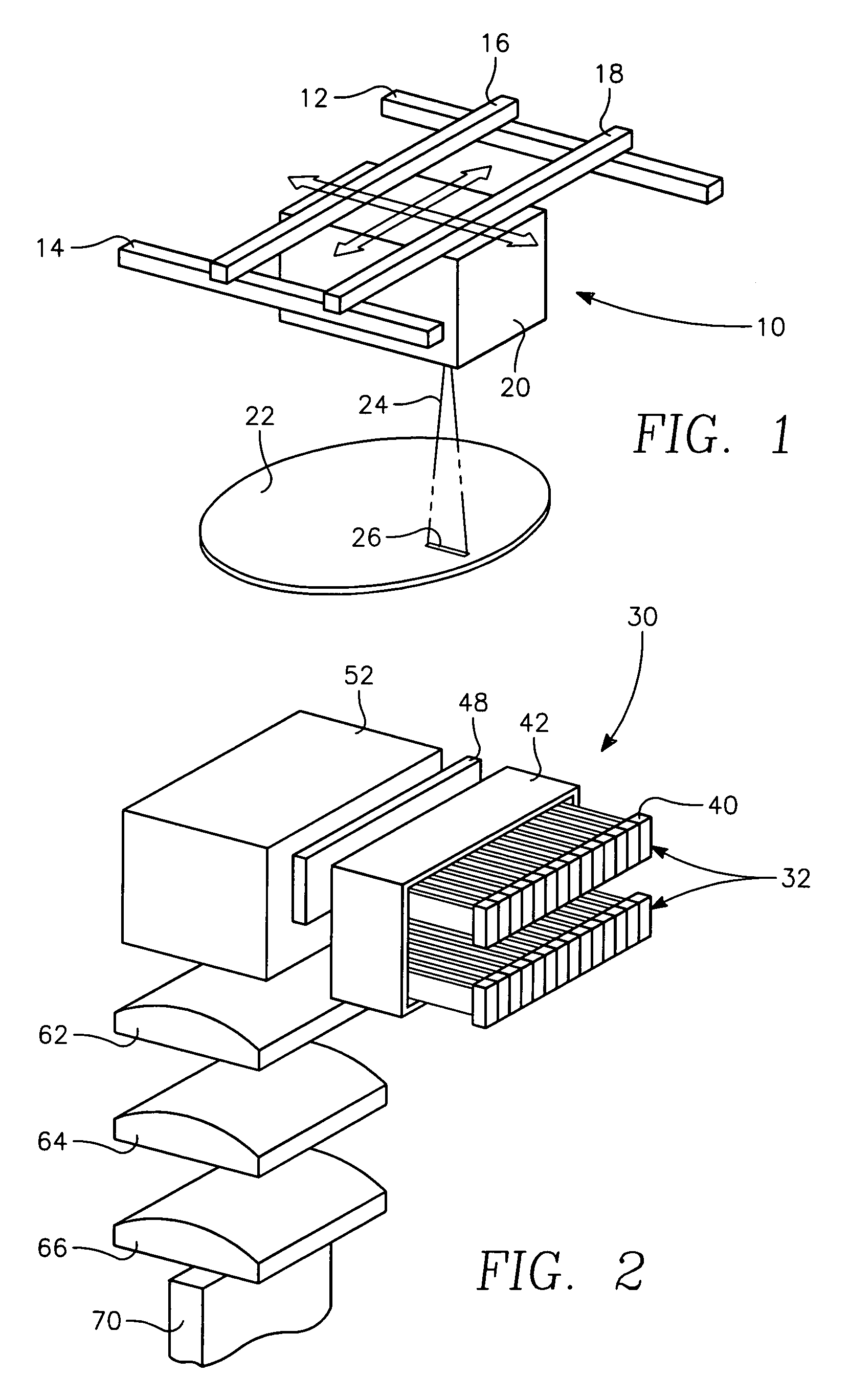
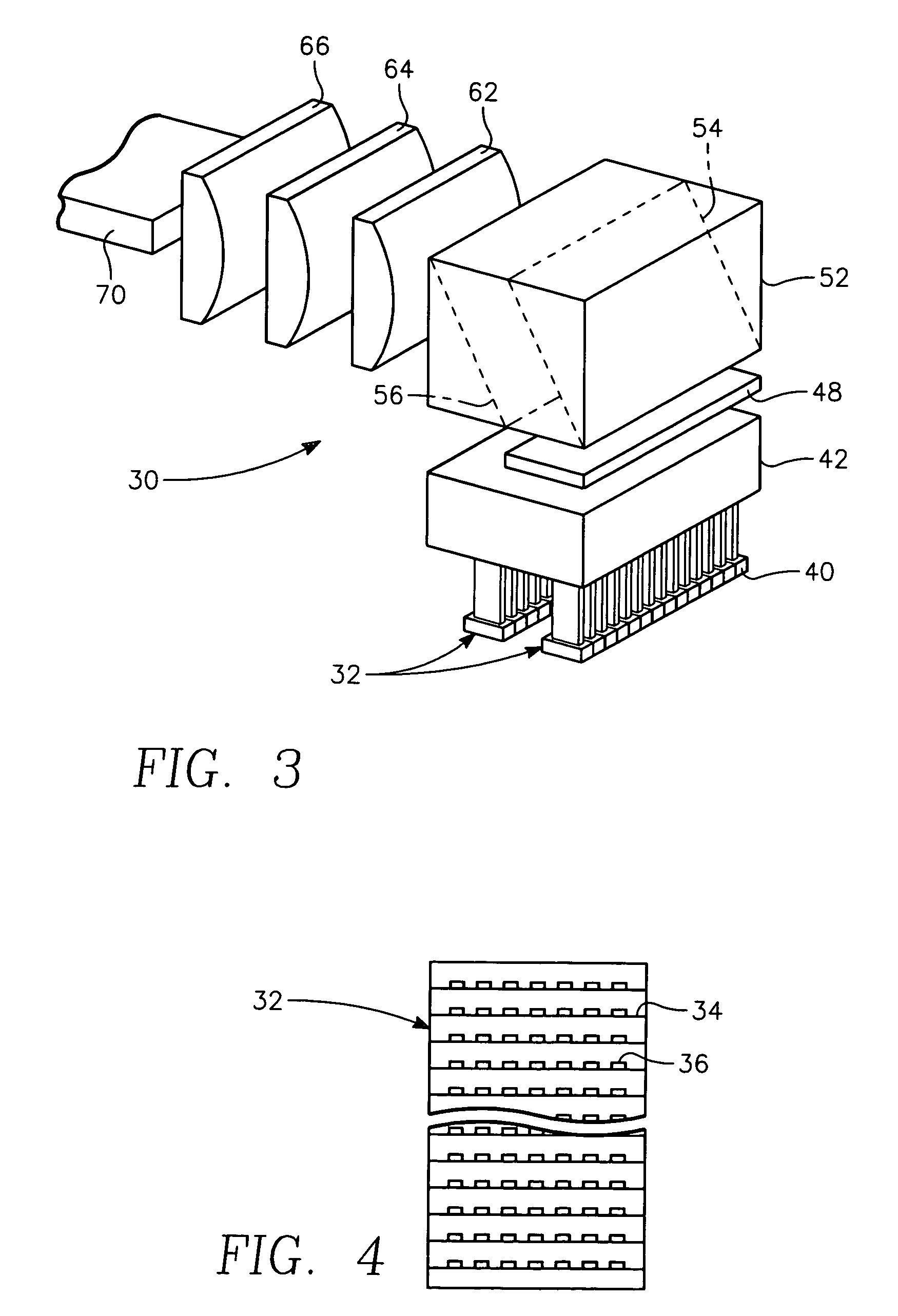
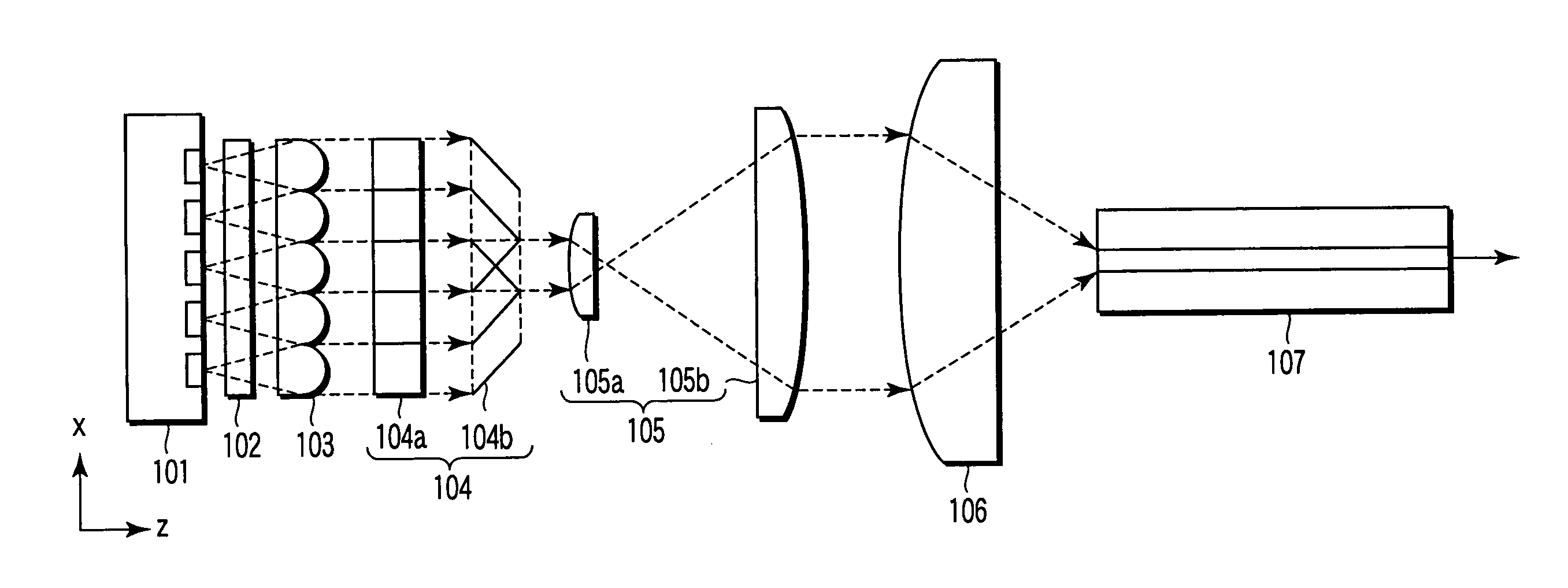
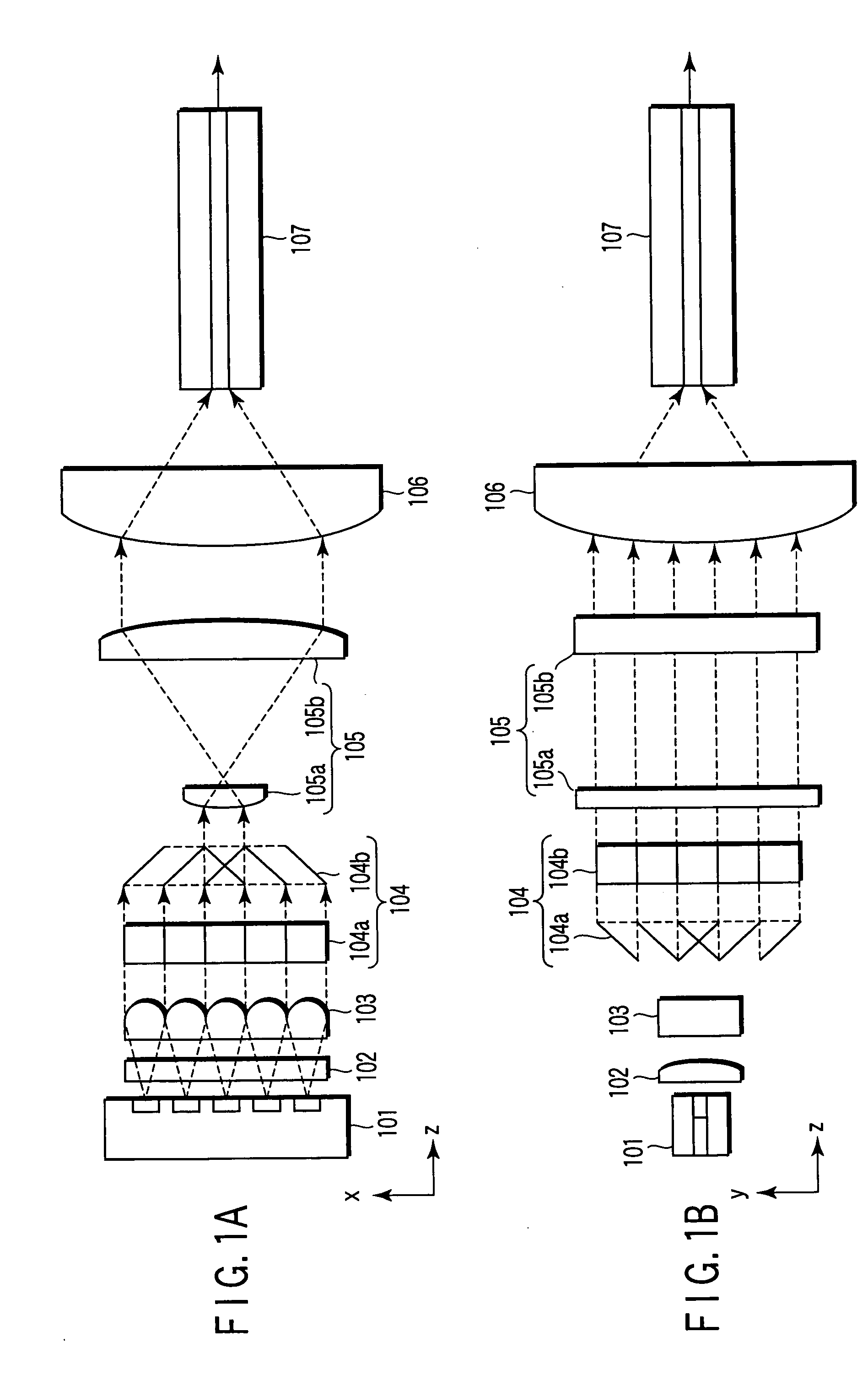
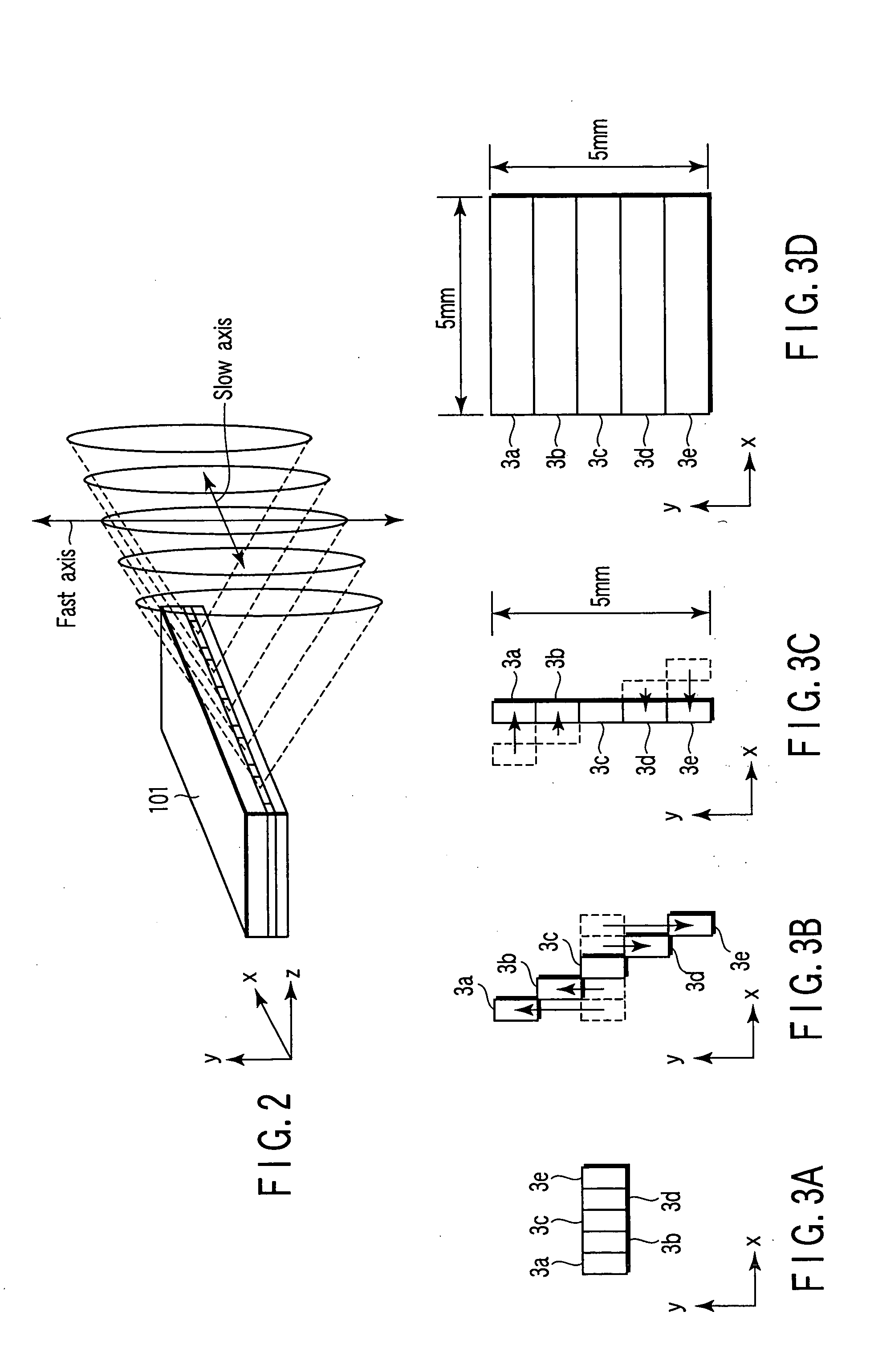
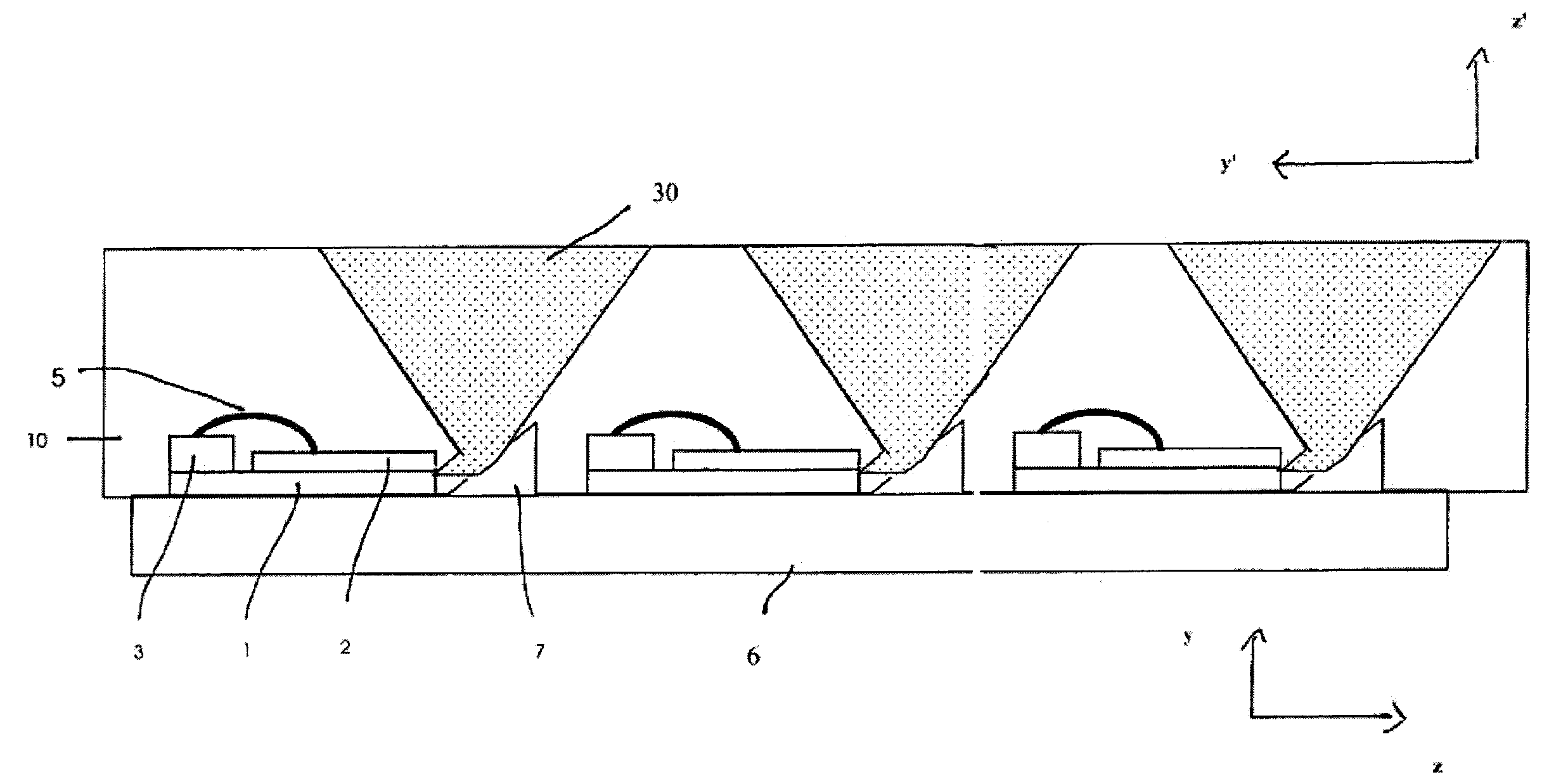
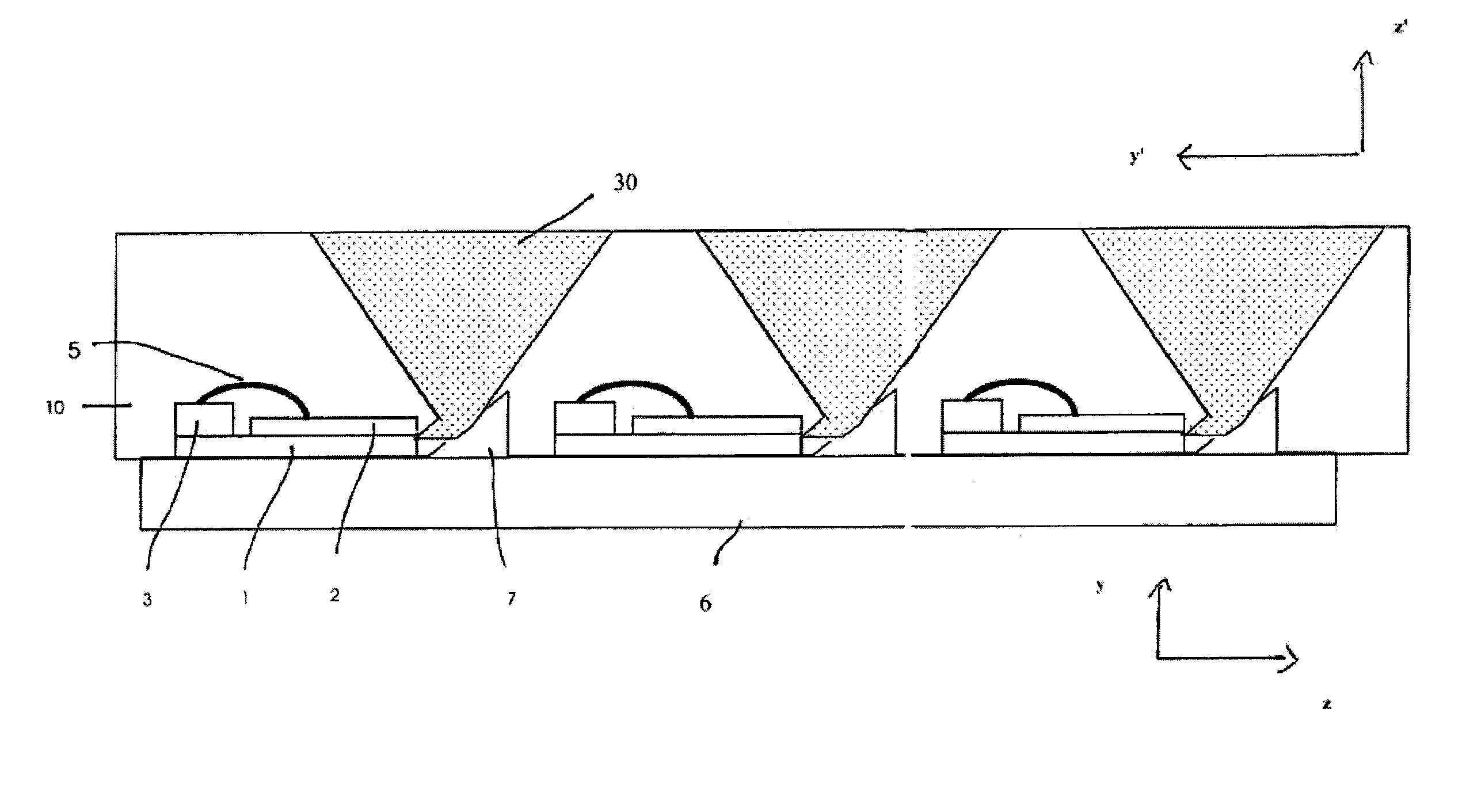
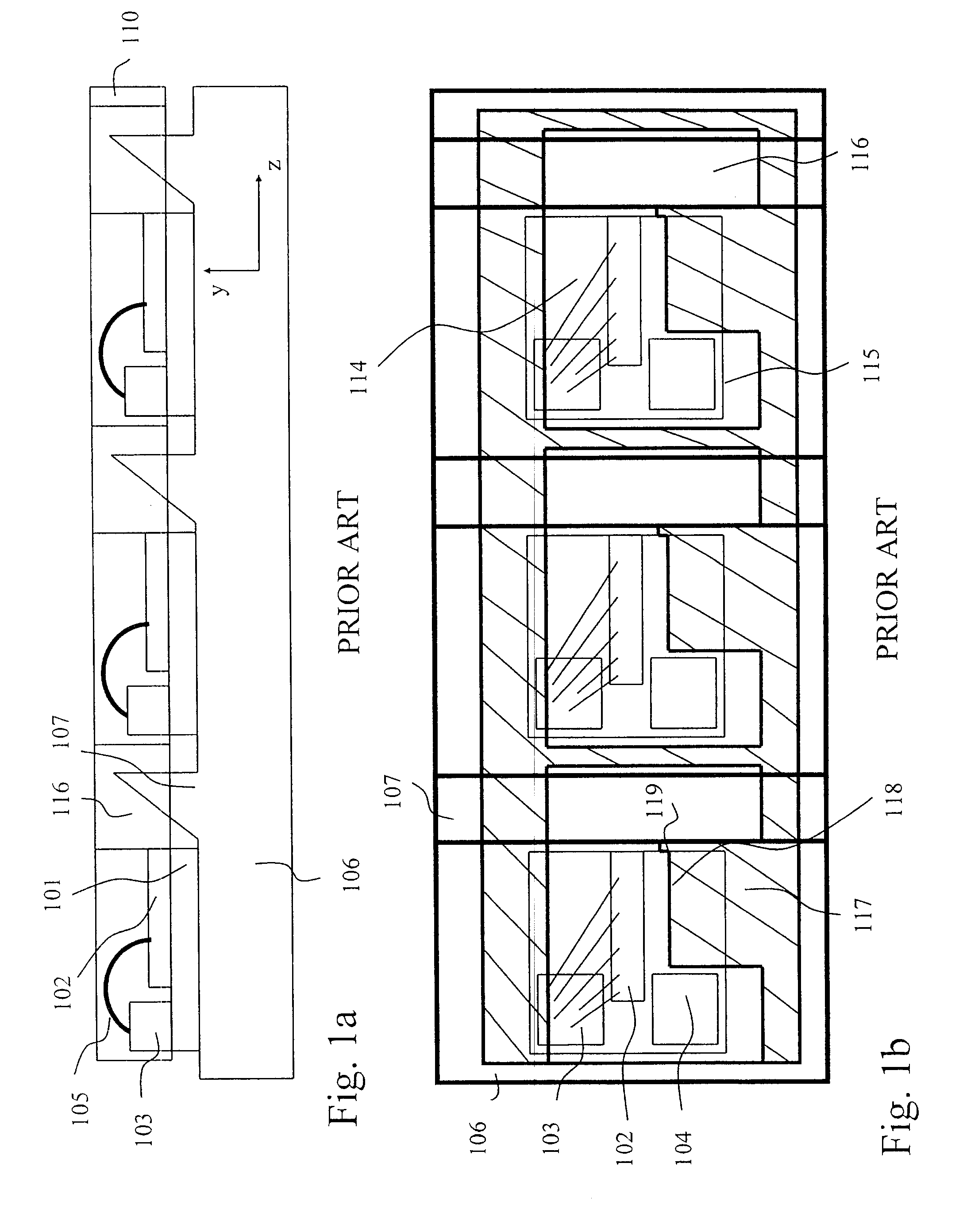
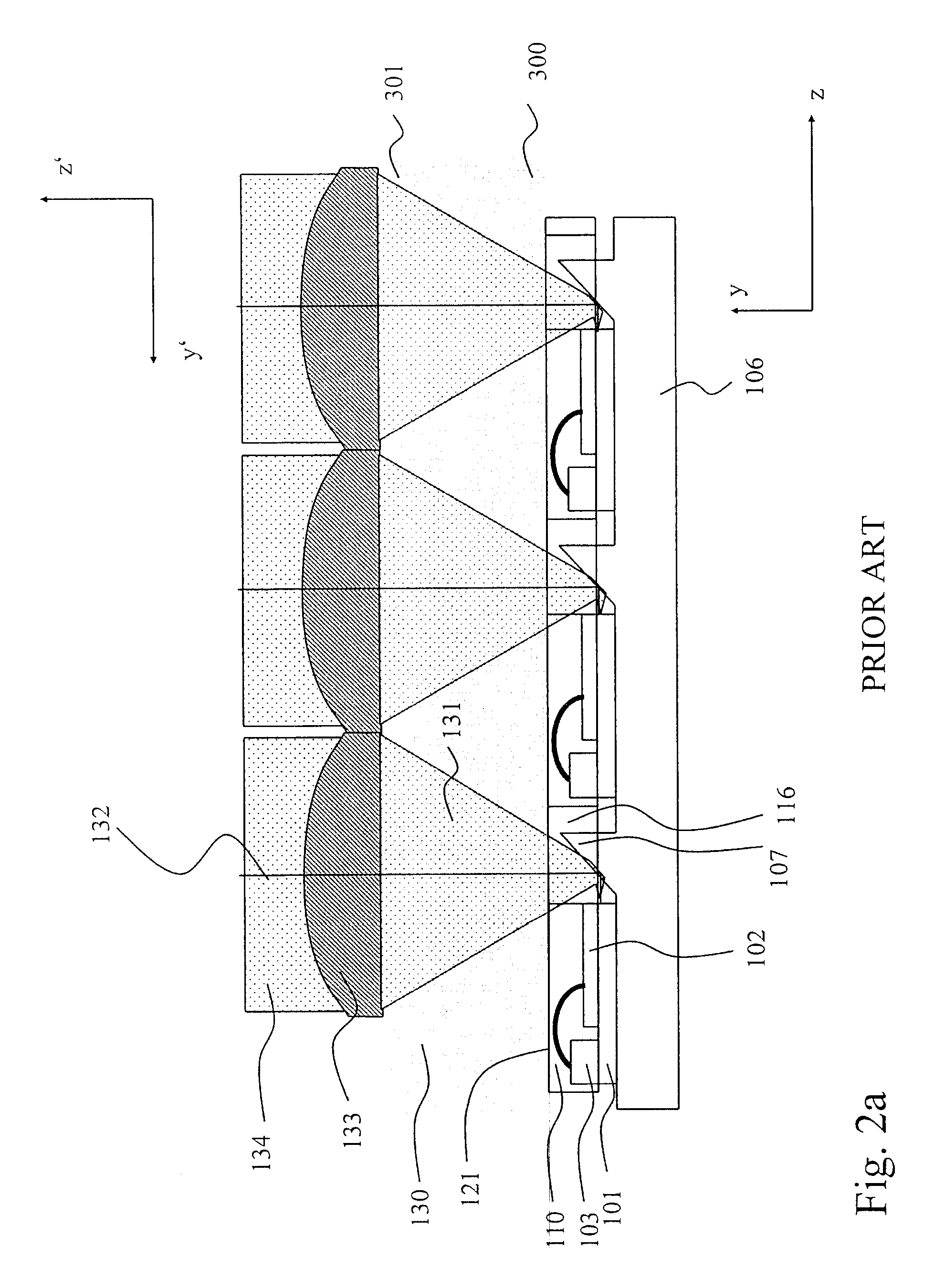
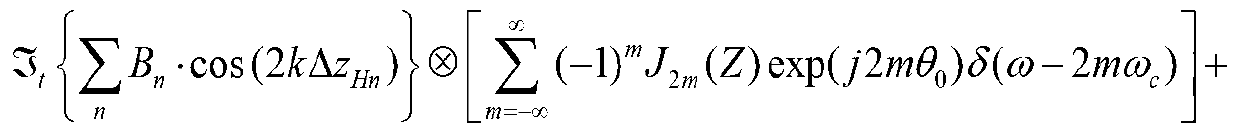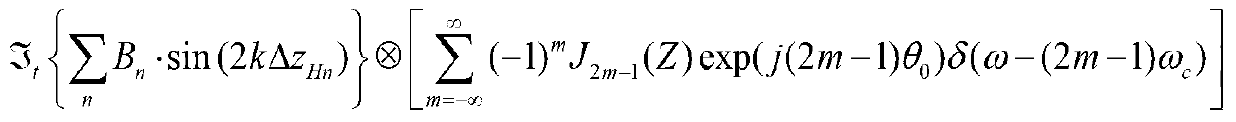Patents
Literature
791 results about "Fast axis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
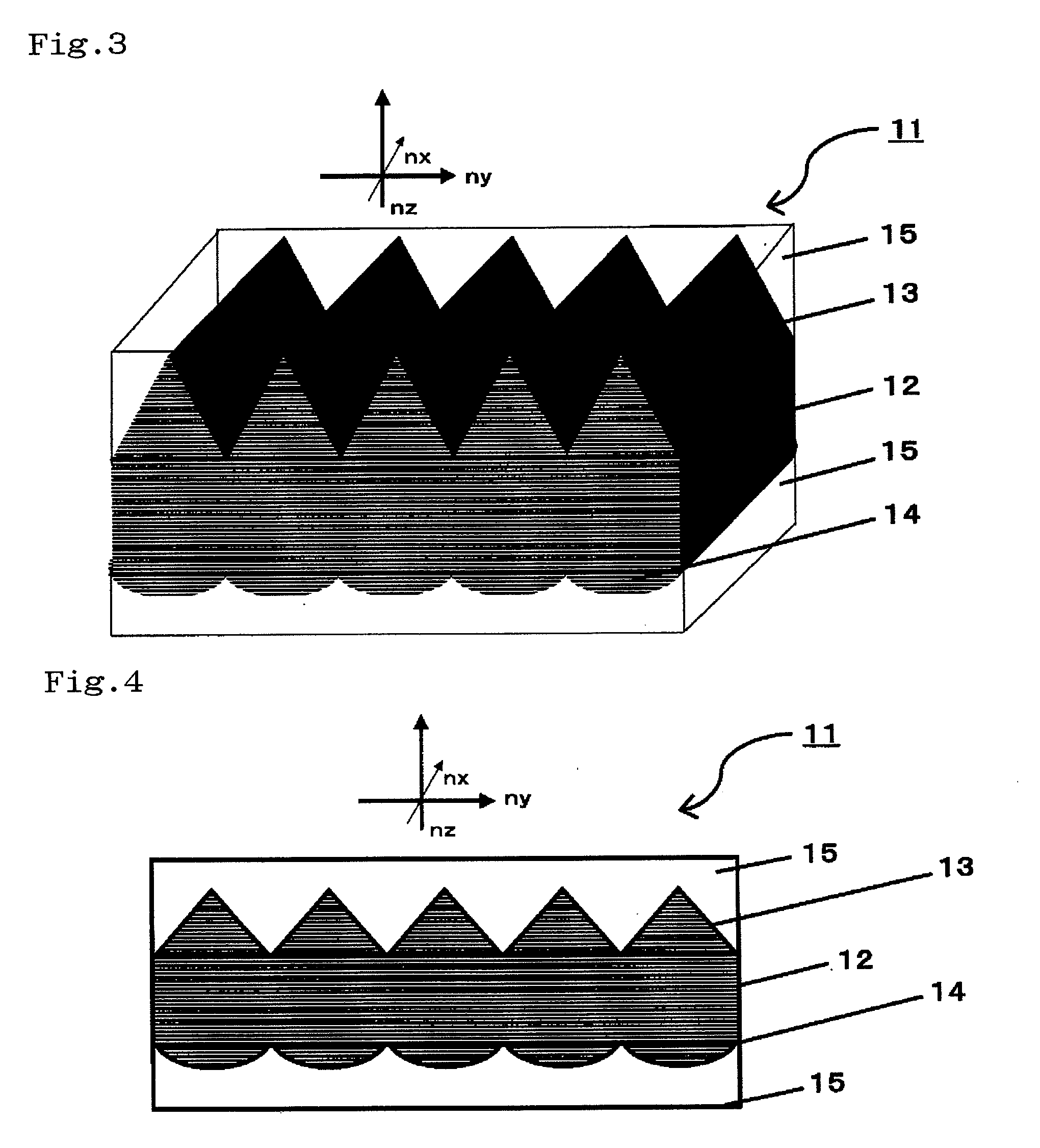
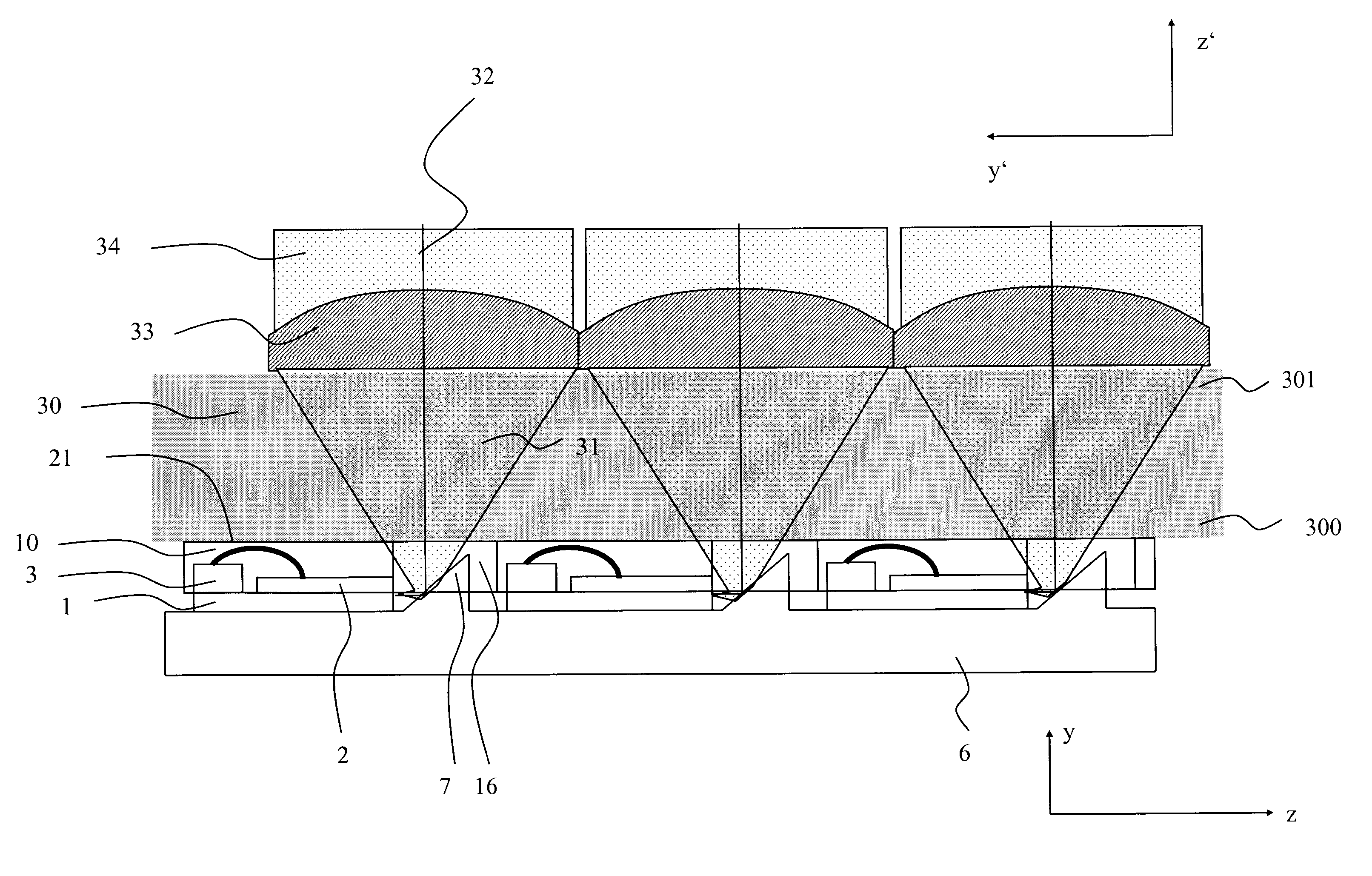
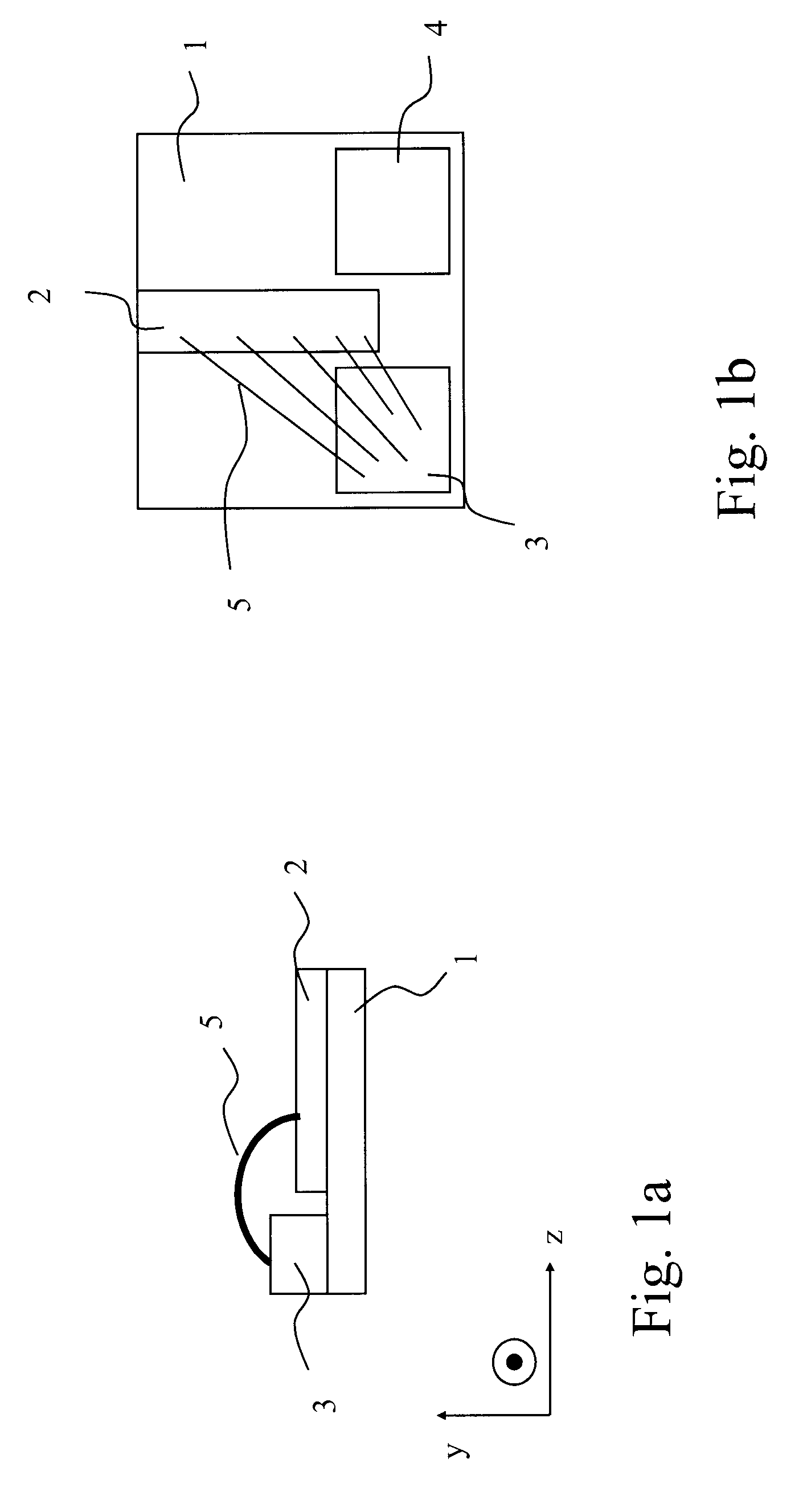
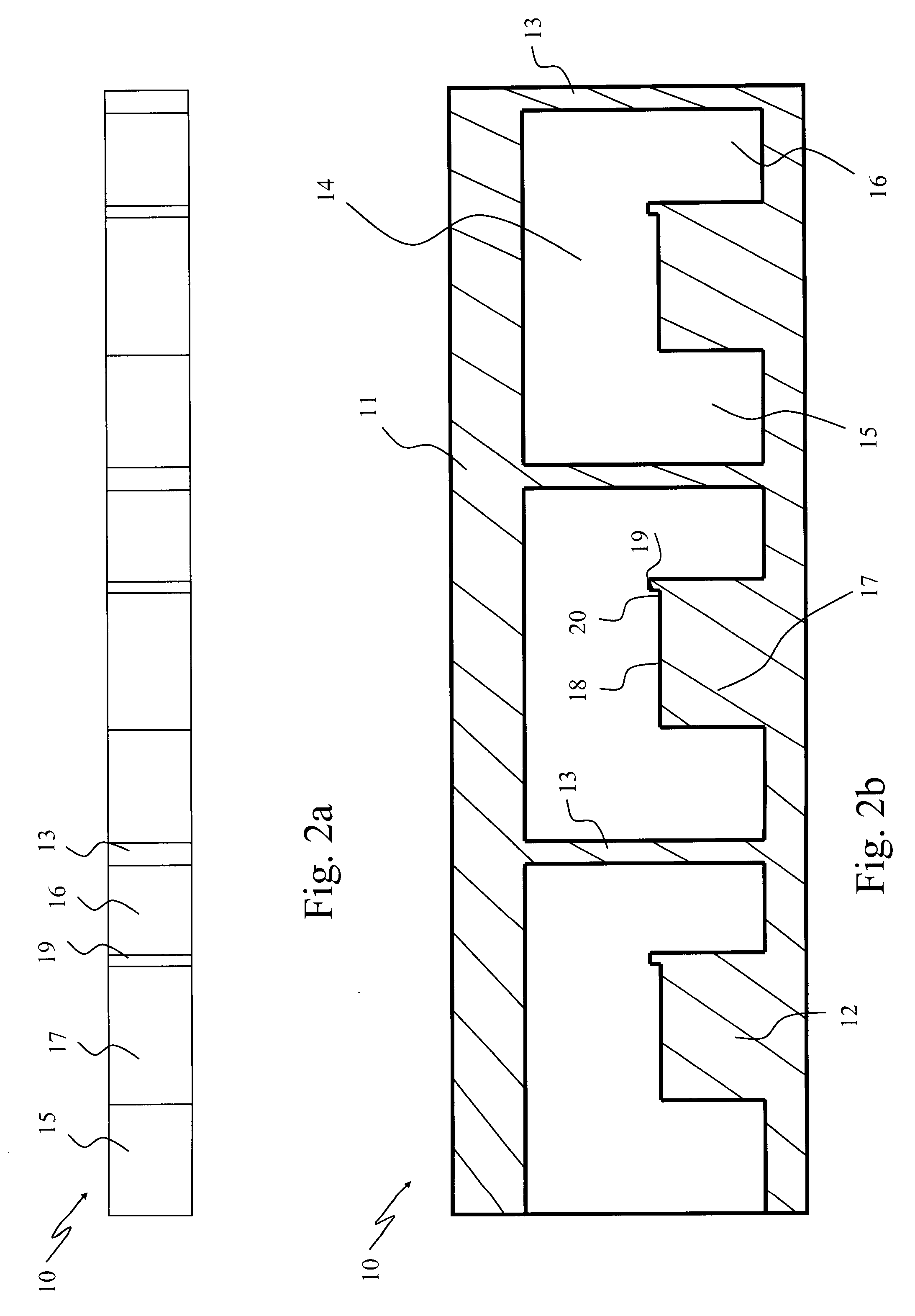
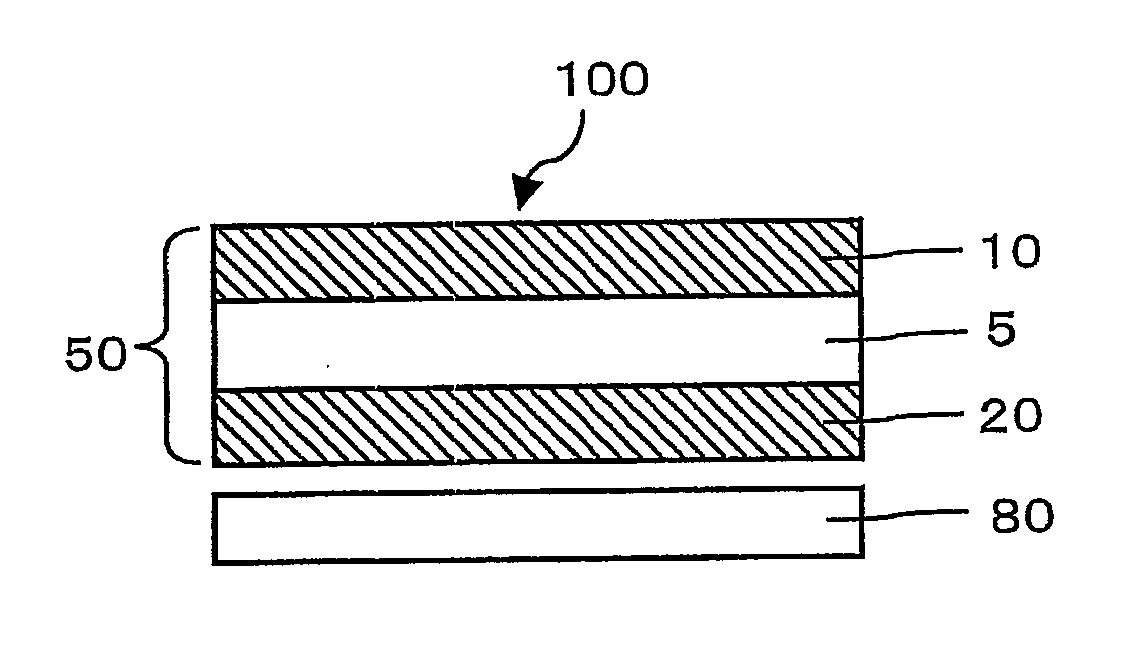
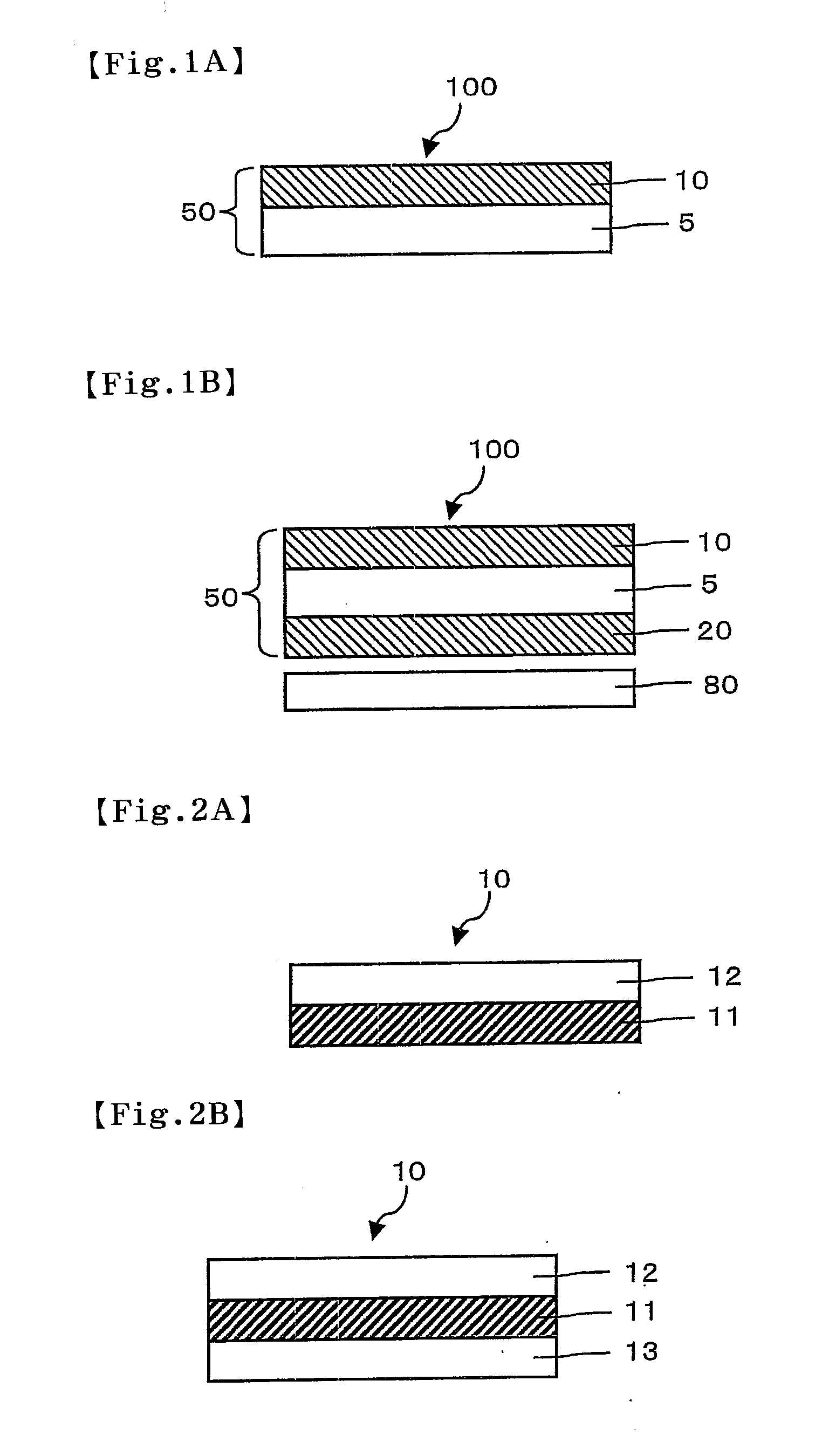
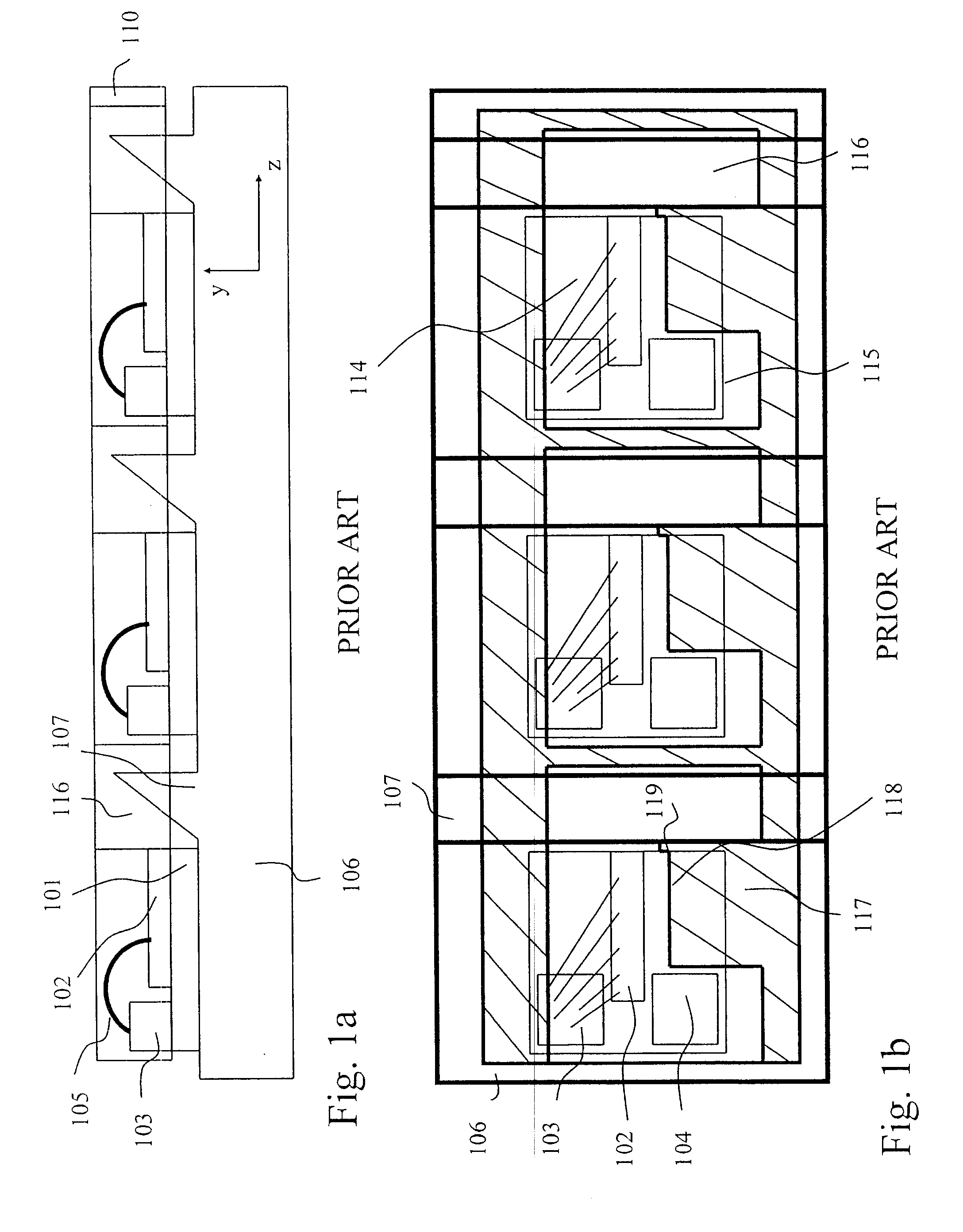
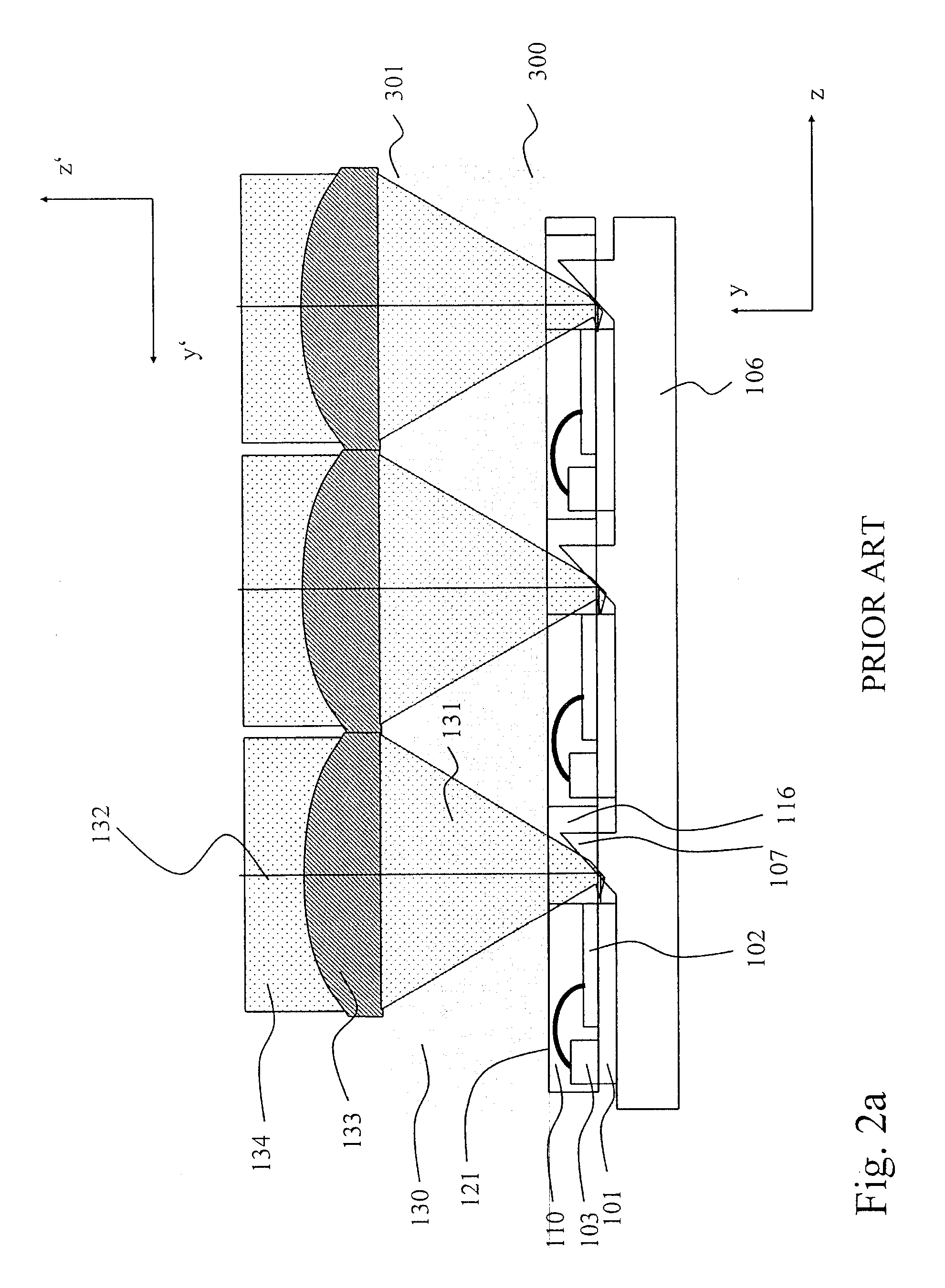
Space-variant waveplate for polarization conversion, methods and applications
InactiveUS20070115551A1Improve optical qualityPhotomechanical apparatusPolarising elementsPupilOptical polarization
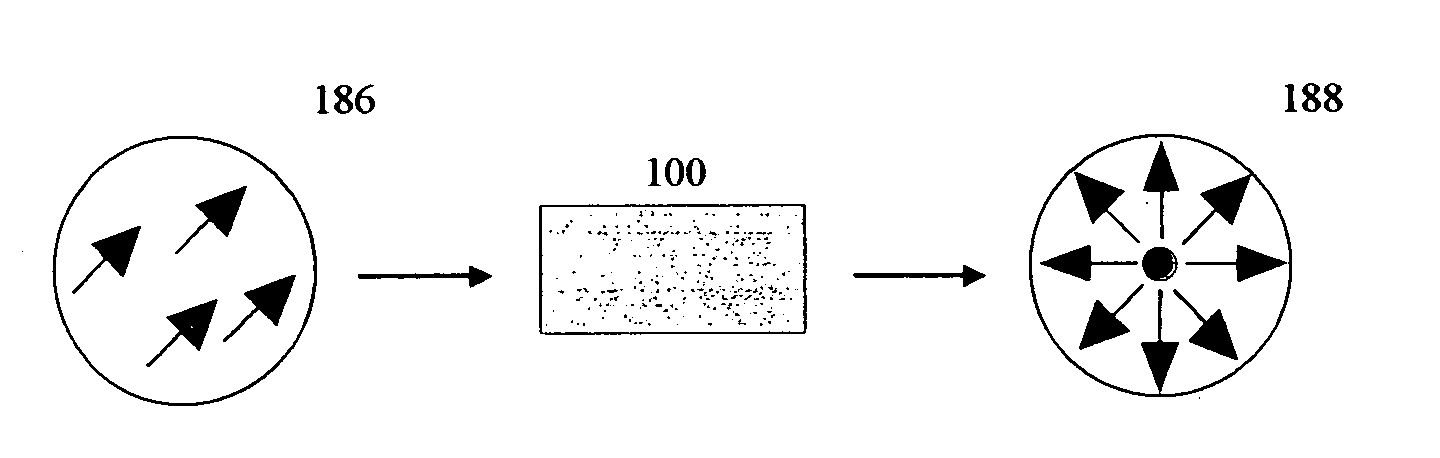
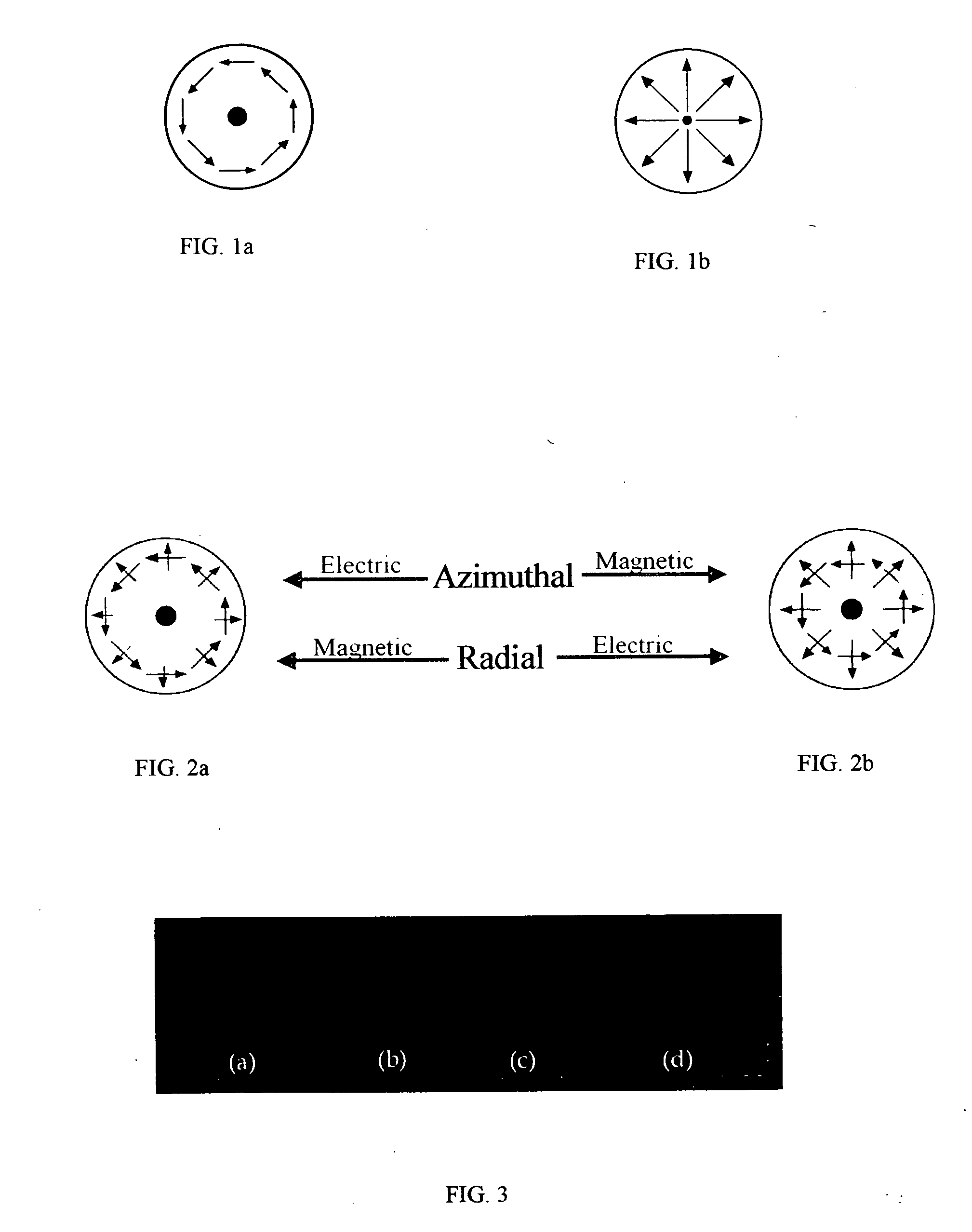
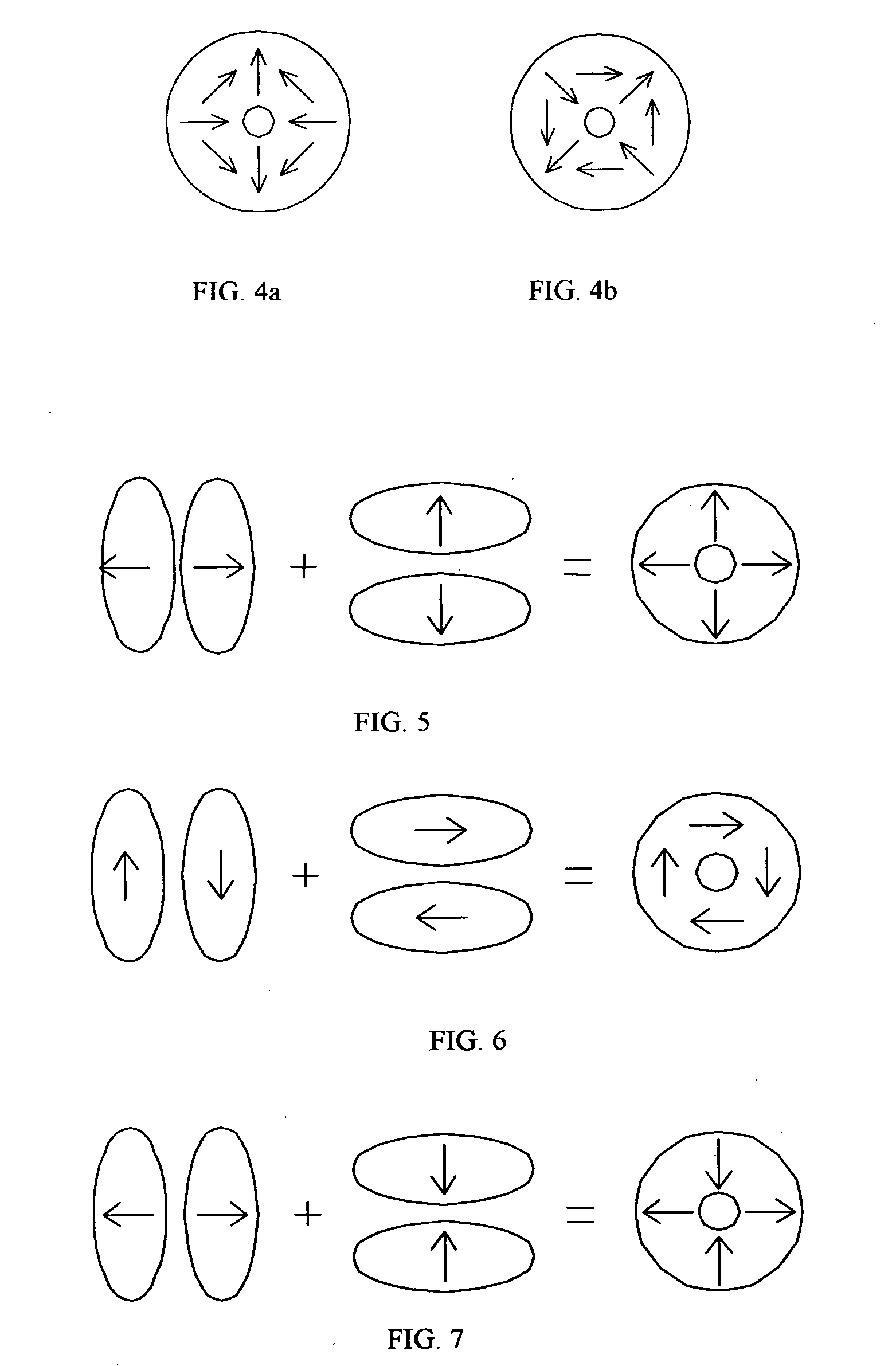
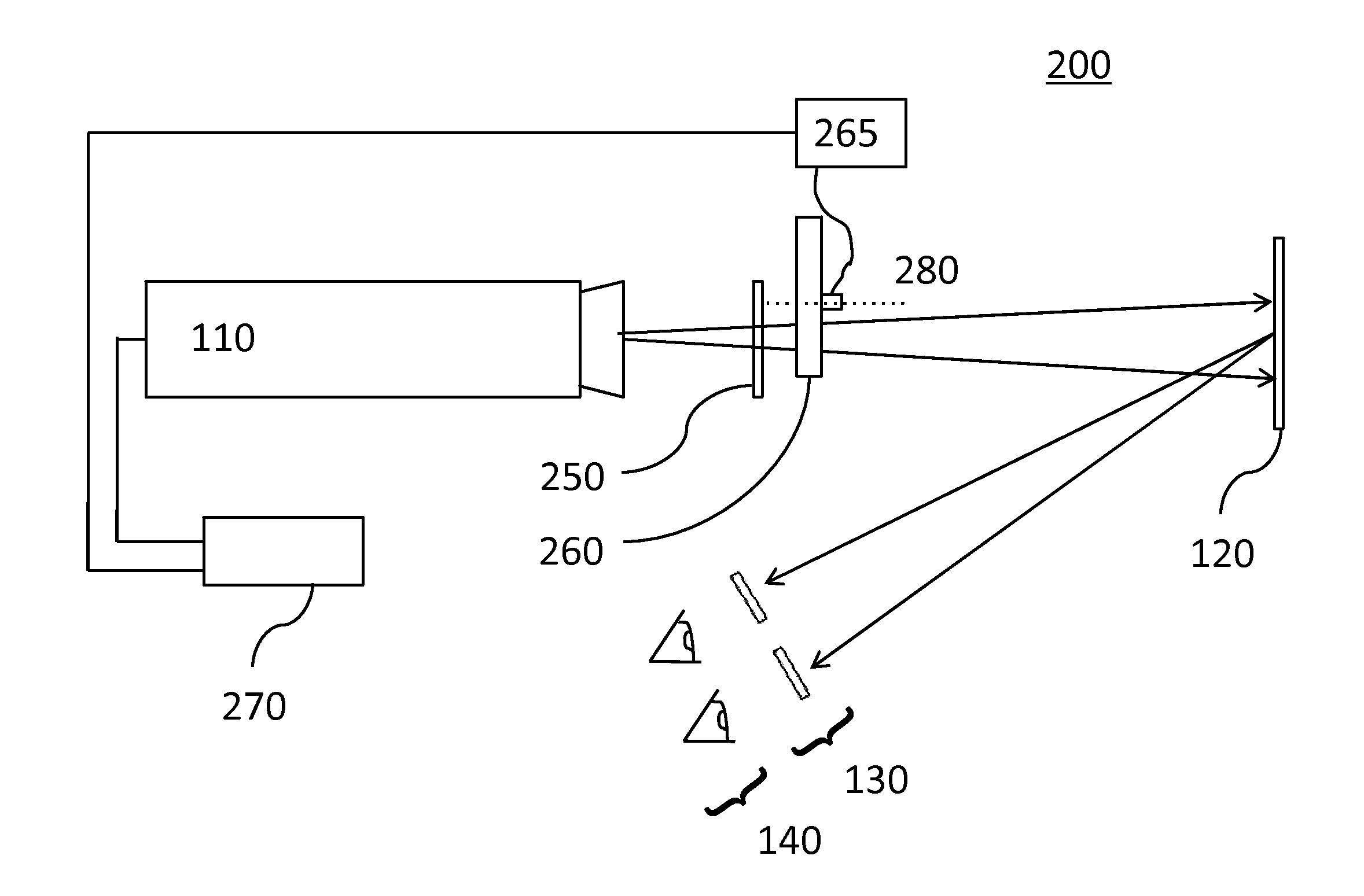
Embodiments of the invention are directed to apparatus and methods for converting spatially homogeneously polarized light into spatially inhomogeneously polarized light having a fast axis orientation that varies in a smooth and continuous manner over a pupil aperture. A space-variant waveplate referred to herein as a polarization converter includes an optically transmissive window characterized by a symmetric stress birefringence that provides at least λ / 4 retardance and, more particularly, λ / 2 retardance over an annular region centered about the optical axis of the window. Structural embodiments of the polarization converter include a mechanical compression housing and a thermal compression housing. Radially and azimuthally polarized vortex beams including cylindrical vector beams and counter-rotating beams can be generated from uniformly plane polarized input beams propagating through the polarization converter. Low-order polarization vortex beams can be optically combined to produce higher-order scalar vortex beams. Embodiments of the invention are also directed to various optical illumination and imaging systems utilizing the apparatus and methods described herein.
Owner:SPILMAN ALEXIS +1
Multi-segment optical retarder for creating 3D images
A multi-segment optical retarder that can be used with or within a single projector for creating 3D images. The multi-segment optical retarder is coupled to an actuator used to effect some predetermined linear, rotary, or oscillating movement of the multi-segment optical retarder such that a fast axis orientation of each segment is substantially constant relative to itself over time and for a given area of incidence.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Polarizing element and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20100045902A1Improve efficiencyNot problematicPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsIn planeLiquid-crystal display
A polarizing element is provided that can serve as a reflective polarizing element, can be produced with relative ease, and is not problematic in terms of strength. Further, the polarizing element can maintain the intensity and the propagation direction of the light that has passed through the polarizing element. Further, a liquid crystal display device is provided that can use light with improved efficiency with the use of the polarizing element. Specifically, the polarizing element includes a plurality of specifically angled, polygonal prisms on a surface of a substantially uniaxial sheet having an in-plane optical axis, and an optically transparent resin layer having a refractive index substantially the same as the fast-axis refractive index of the sheet, and that coats the prisms.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
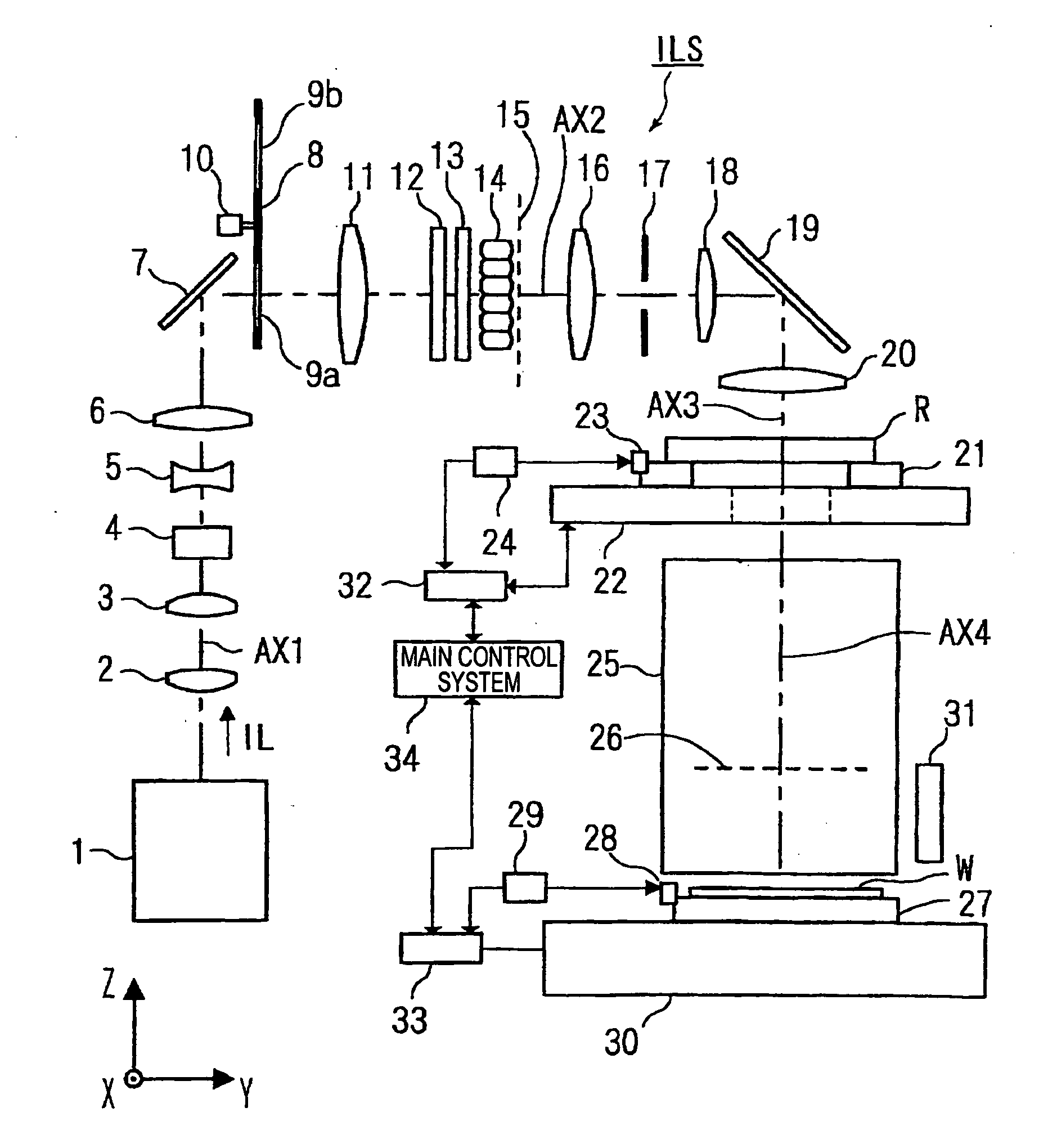
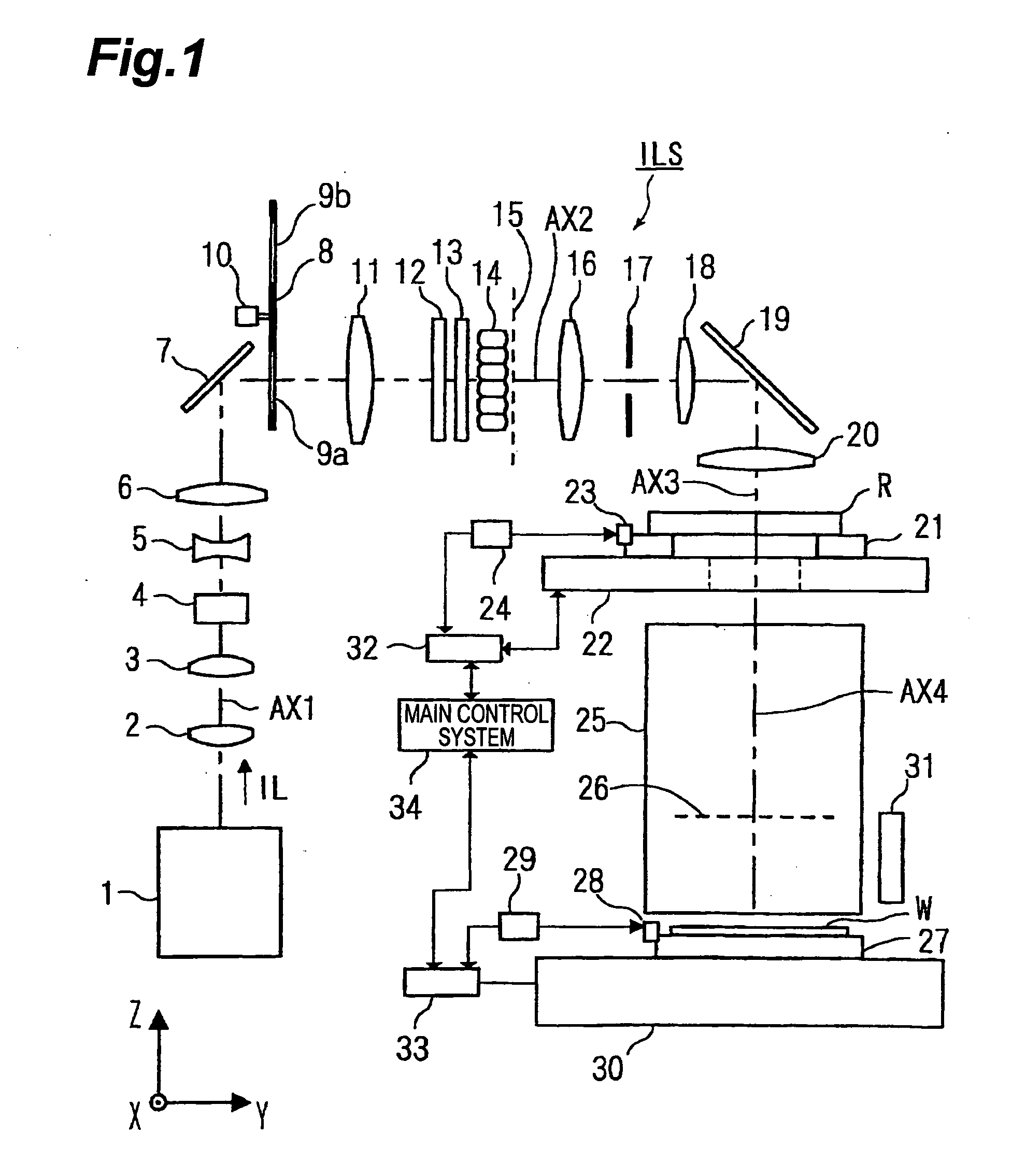
Illumination optical apparatus and projection exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20090122292A1Little lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOptical axisOptoelectronics
An illumination optical apparatus and projection exposure apparatus capable of reducing a light quantity loss when a mask is illuminated with a polarized illumination light. An illumination optical system for illuminating a reticle with an illumination light and a projection optical system for projecting the pattern image of the reticle onto a wafer are provided. An illumination light emitted from an exposure light source in a linearly polarized state in the illumination optical system passes through first and second birefringent members having different fast axis directions and is converted into a polarized state that is substantially linearly polarized in a circumferential direction with the optical axis as the center in an almost specific annular area, and them illuminates the reticle under an annular illuminating condition after passing through a fly-eye lens.
Owner:GEARBOX
Retardation film, process for producing the same, optical film, image display, liquid crystal panel and liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20060028601A1Retardation valueHard to cause a shift or an unevenness of a retardation valueOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsRefractive indexDisplay device
A retardation film of the present invention comprises a stretched film of a polymer film containing a norbornene-based resin, wherein the stretched film satisfies the following equation (1) and the equation (2); 100 nm≦(nx−ny)·d≦350 nm . . . (1),0.1≦(nx−nz) / (nx−ny)≦0.9 . . . (2), where the refractive indices in the slow axis direction, the fast axis direction and the thickness direction of the film are nx, ny and nz, respectively, d(nm) is thickness of the film, and the slow axis direction is a direction that the refractive index in film plane is maximum. The retardation film is hard to cause a shift or an unevenness of a retardation value due to a stress.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
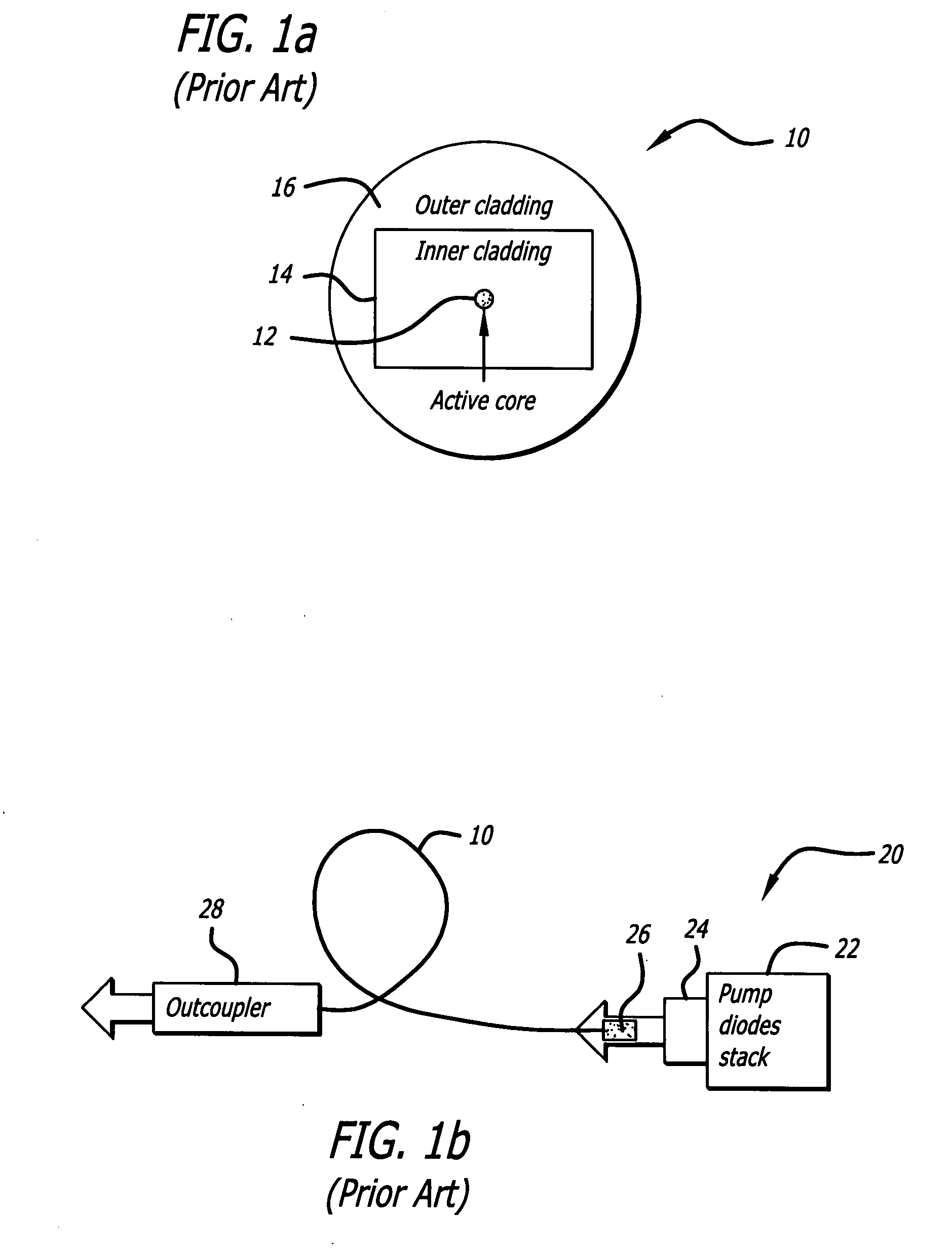
Method and apparatus for generation and amplification of light in a semi-guiding high aspect ratio core fiber
ActiveUS20090041061A1High aspect ratioHigh beam qualityGlass making apparatusLaser using scattering effectsFiberActive core
A planar laser gain medium and laser system. The novel laser gain medium includes an active core having a high aspect ratio cross-section with a fast-axis dimension and a slow-axis dimension, signal claddings adapted to form reflective boundaries at fast-axis boundaries of the core, and a material adapted to minimize reflections at slow-axis boundaries of the core. In an illustrative embodiment, the laser gain medium is an optical fiber. The core and claddings form a waveguide adapted to control modes propagating in the fast-axis direction. When the laser gain medium is employed as a laser oscillator, a high reflectivity mirror and an outcoupler are positioned at opposite ends of the core to form a laser resonator adapted to control modes in the slow-axis direction.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Illumination optical apparatus and projection exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20090284729A1Little lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOptical axisOptoelectronics
An illumination optical apparatus and projection exposure apparatus capable of reducing a light quantity loss when a mask is illuminated with a polarized illumination light. An illumination optical system for illuminating a reticle with an illumination light and a projection optical system for projecting the pattern image of the reticle onto a wafer are provided. An illumination light emitted from an exposure light source in a linearly polarized state in the illumination optical system passes through first and second birefringent members having different fast axis directions and is converted into a polarized state that is substantially linearly polarized in a circumferential direction with the optical axis as the center in an almost specific annular area, and them illuminates the reticle under an annular illuminating condition after passing through a fly-eye lens.
Owner:NIKON CORP
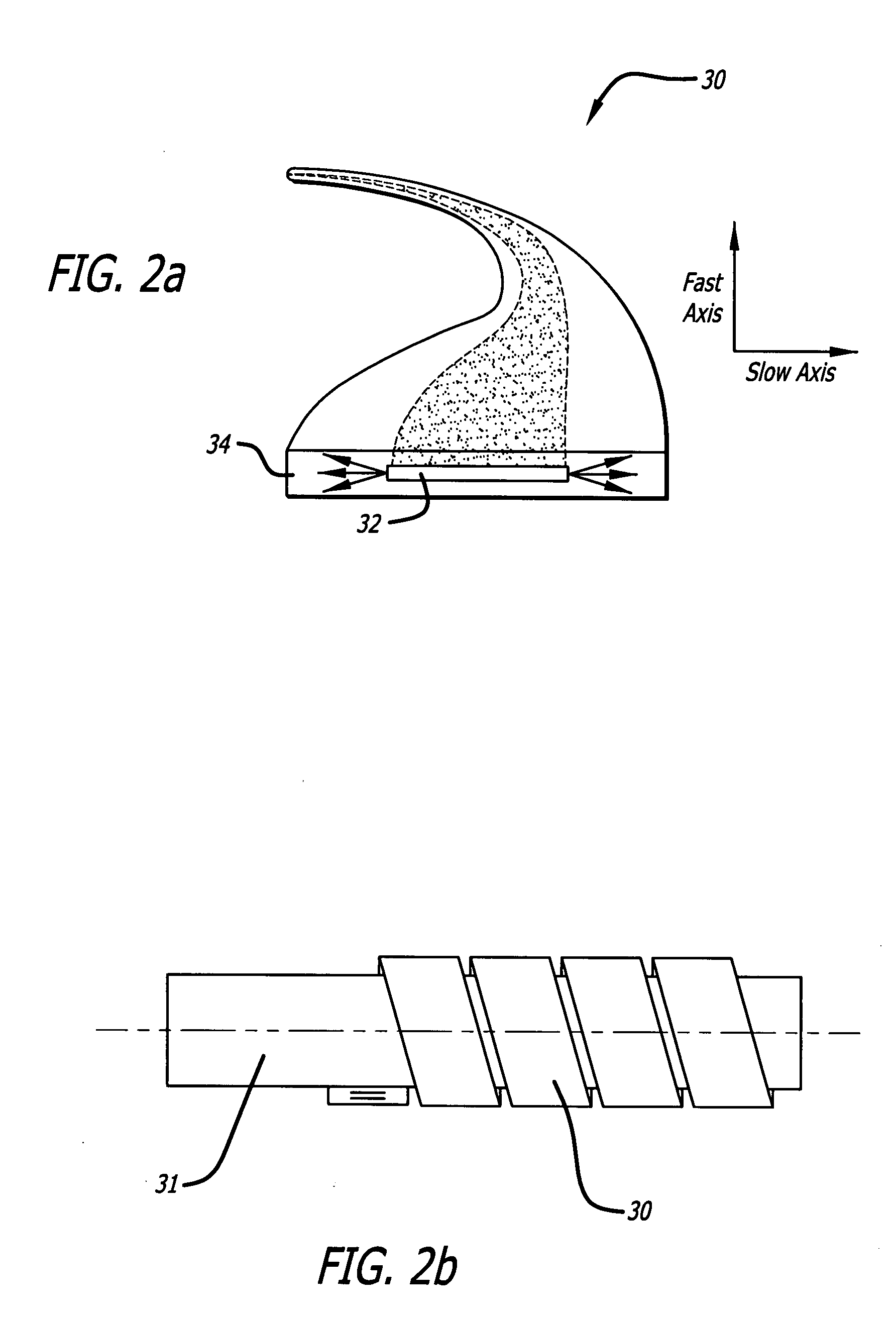
Surface array semiconductor laser light beam shaping device
InactiveCN101144909AEasy to manufactureSimple structureLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersDivergence angleLight beam
The present invention relates to a beam reshaping device for a plane array semiconductor laser. The device includes a fast axis collimating lens, a slow axis collimating lens, a ladder lens, a first parallelepiped prism unit, and a second parallelepiped prism unit. The beam emitted by the plane array semiconductor laser passes through the fast axis collimating lens and the slow axis collimating lens, and lowers the divergence angle of the fast axis and the divergence angle of the slow axis. The irradiance interspace between bars can be eliminated by the ladder lens and can be compressed in the direction of the fast axis. Finally, part of beam can be moved parallel along the fast axis direction by the first parallelepiped prism unit and the second parallelepiped prism unit, and then be moved along the slow axis direction. Through the above process, the beam is realigned, and the purpose that the quality of the fast axis beam and the quality of the slow axis beam tend to be coincident is reached. The realigned beam can get high-power high-brightness facula after being focused. The optical apparatus used in the present invention is easy to be produced and convenient to be adjusted with simple structure.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
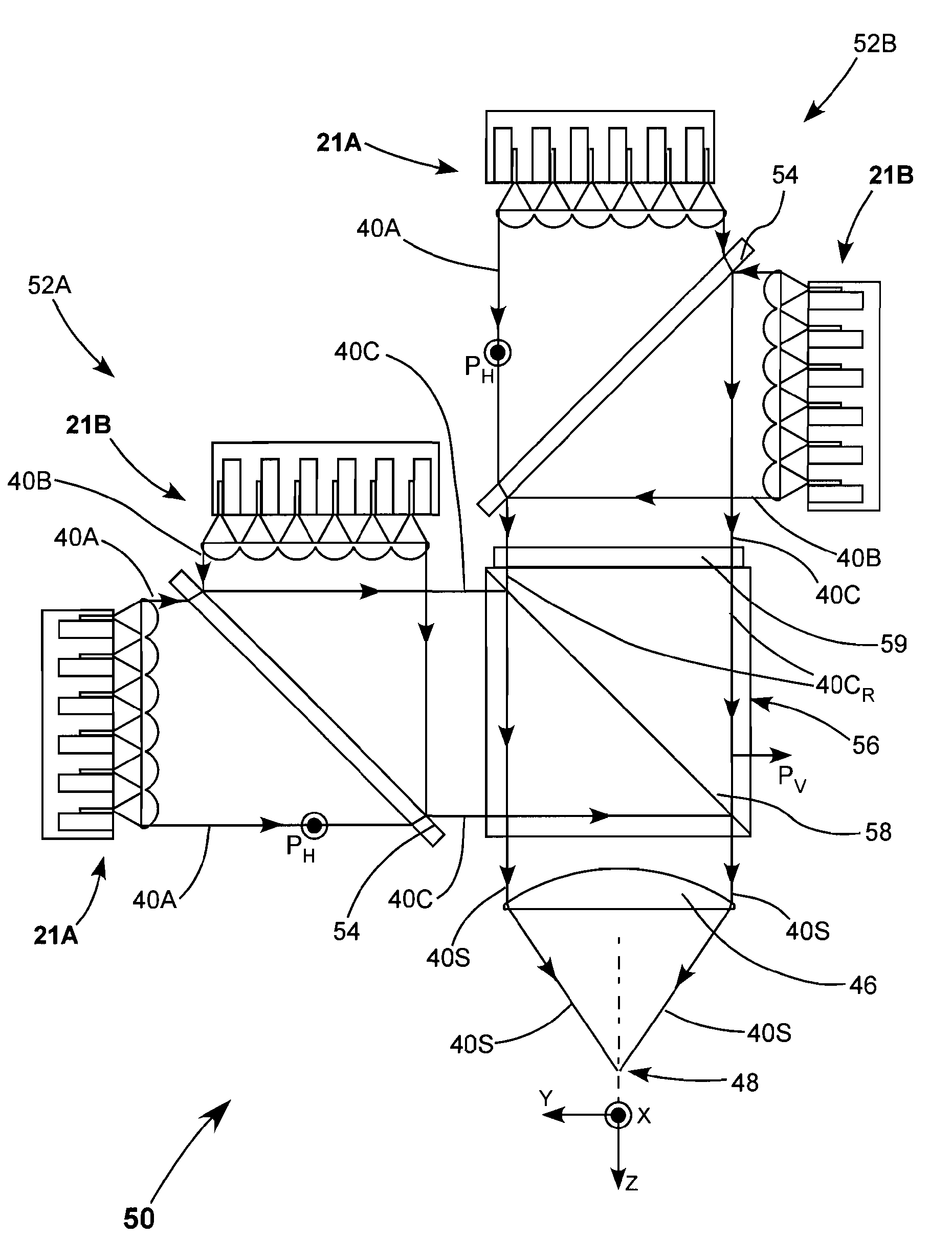
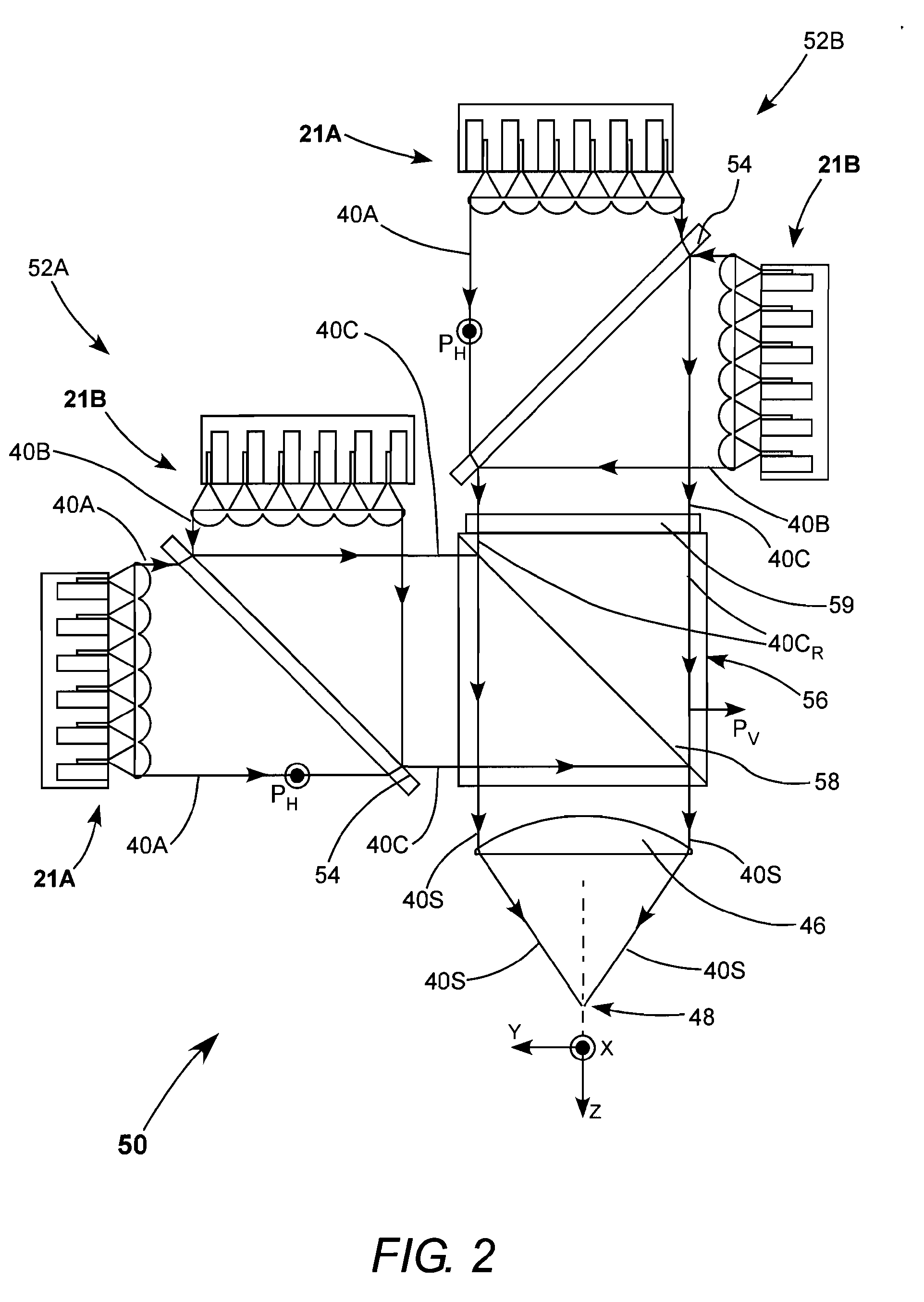
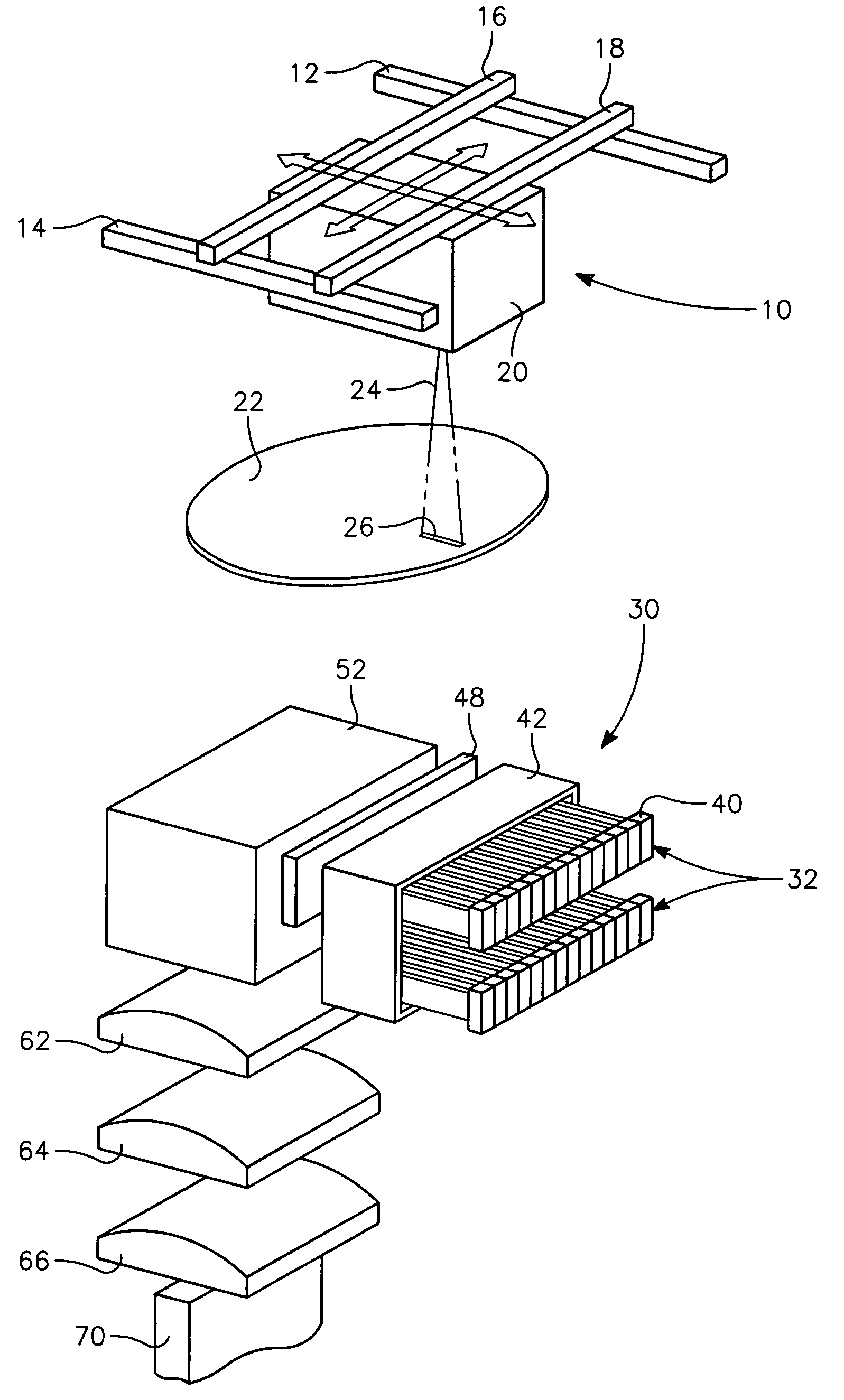
High power and high brightness diode-laser array for material processing applications
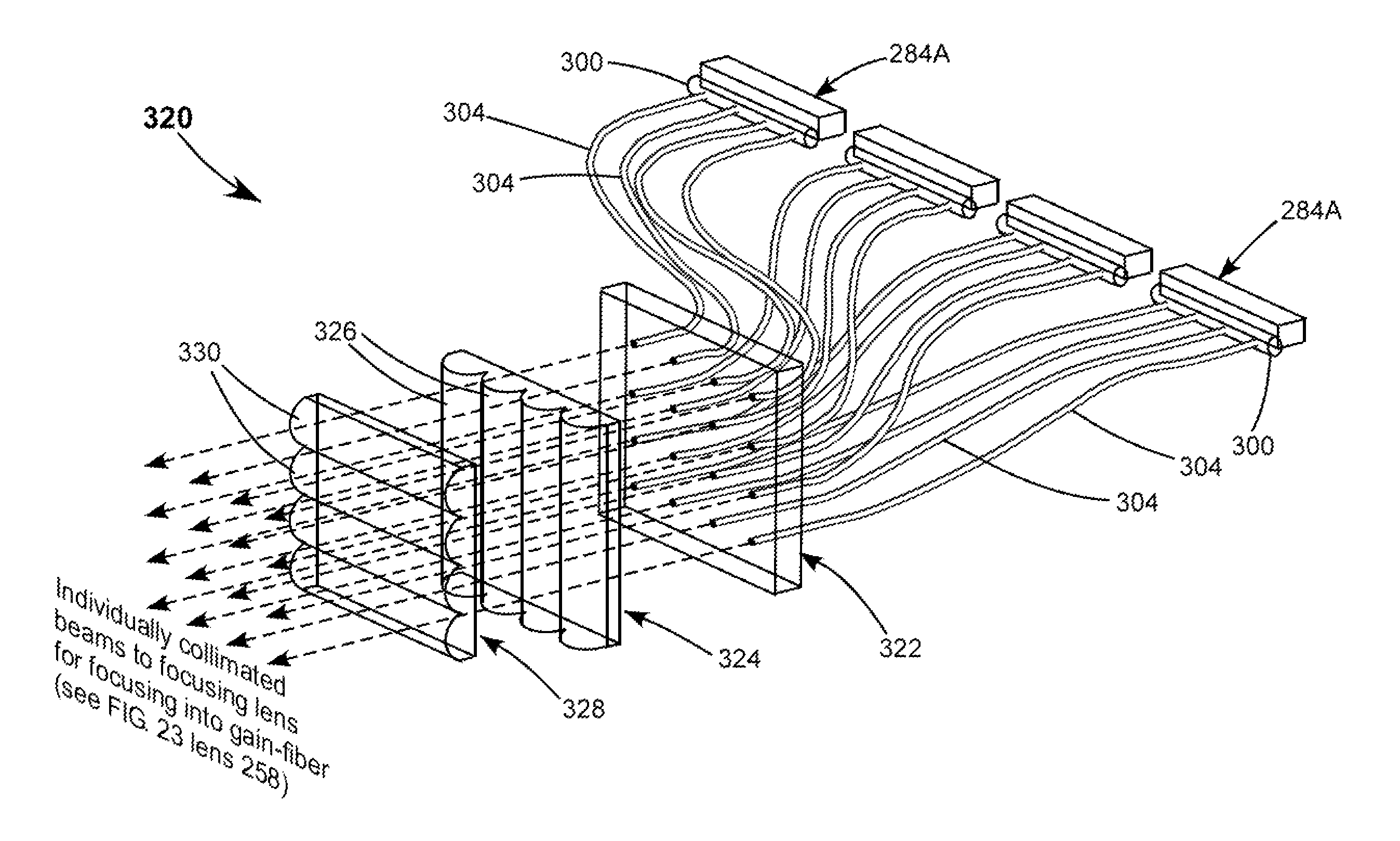
Arrangements for combination and fast-axis alignment of fast-axes of diode-laser beams are disclosed. Alignment arrangements include providing each diode-laser with a corresponding alignable fast-axis collimating lens, providing individually alignable mirrors for steering an re-orienting beams from each diode-laser, and providing single diode-laser slab-modules in which the diode-laser beams can be pre-aligned to a common propagation-axis direction, and in which edges and surfaces of the slabs can be used to align the fast and slow-axes of the beams. Beam combination methods include combination by dichroic elements, polarization-sensitive elements, and optical fiber bundles.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Thermal flux laser annealing for ion implantation of semiconductor P-N junctions
ActiveUS7135392B1Facilitate multiple reflectionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor lasersLaser transmitterHeat flux
A method for forming P-N junctions in a semiconductor wafer includes ion implanting dopant impurities into the wafer and annealing the wafer using a thermal flux laser annealing apparatus that includes an array of semiconductor laser emitters arranged in plural parallel rows extending along a slow axis, plural respective cylindrical lenses overlying respective ones of the rows of laser emitters for collimating light from the respective rows along a fast axis generally perpendicular to the slow axis, a homogenizing light pipe having an input face at a first end for receiving light from the plural cylindrical lenses and an output face at an opposite end, the light pipe comprising a pair of reflective walls extending between the input and output faces and separated from one another along the direction of the slow axis, and scanning apparatus for scanning light emitted from the homogenizing light pipe across the wafer in a scanning direction parallel to the fast axis.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Optical coherence tomography method and optical coherence tomography system for complex polarization frequency domain
ActiveCN103344569AEliminate complex conjugate mirror imagesCancel noisePolarisation-affecting propertiesPlane mirrorDelayed imaging
The invention discloses an optical coherence tomography method and an optical coherence tomography system for a complex polarization frequency domain. The method comprises the following steps of: on the basis of optical coherence tomography of a polarization frequency domain, driving a reference plane mirror of a reference arm to vibrate by a phase modulation device, introducing sinusoidal phase modulation while transversely scanning a sample, performing processing such as Fourier transform on acquired interference signals of horizontal and vertical polarization channels to obtain chromatography signals of the horizontal and vertical polarization channels without parasitic images, extracting magnitudes and phases of the chromatography signals respectively, and calculating to obtain an intensity image, a fast axis image and a delay image of the sample with double refraction properties within a full-depth range. According to the method, the imaging speed is high, a complex conjugate mirror image, a direct-current background and the self-coherence noise in the coherent tomography of the polarization frequency domain are removed, the sensitivity cannot be reduced along with the prolonging of a transverse scanning distance, and the method is not sensitive to motion blur in the sample.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-power CW fiber-laser
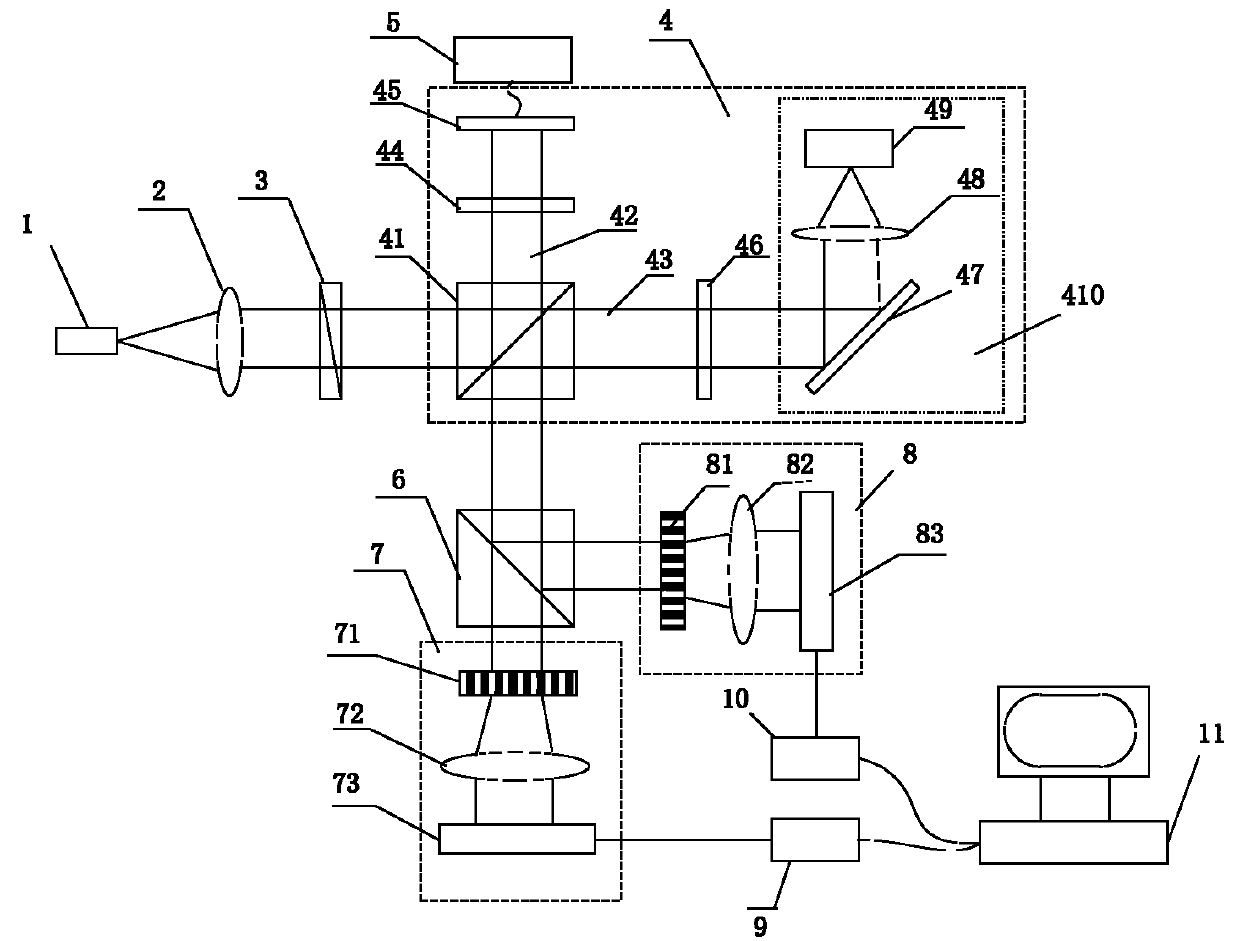
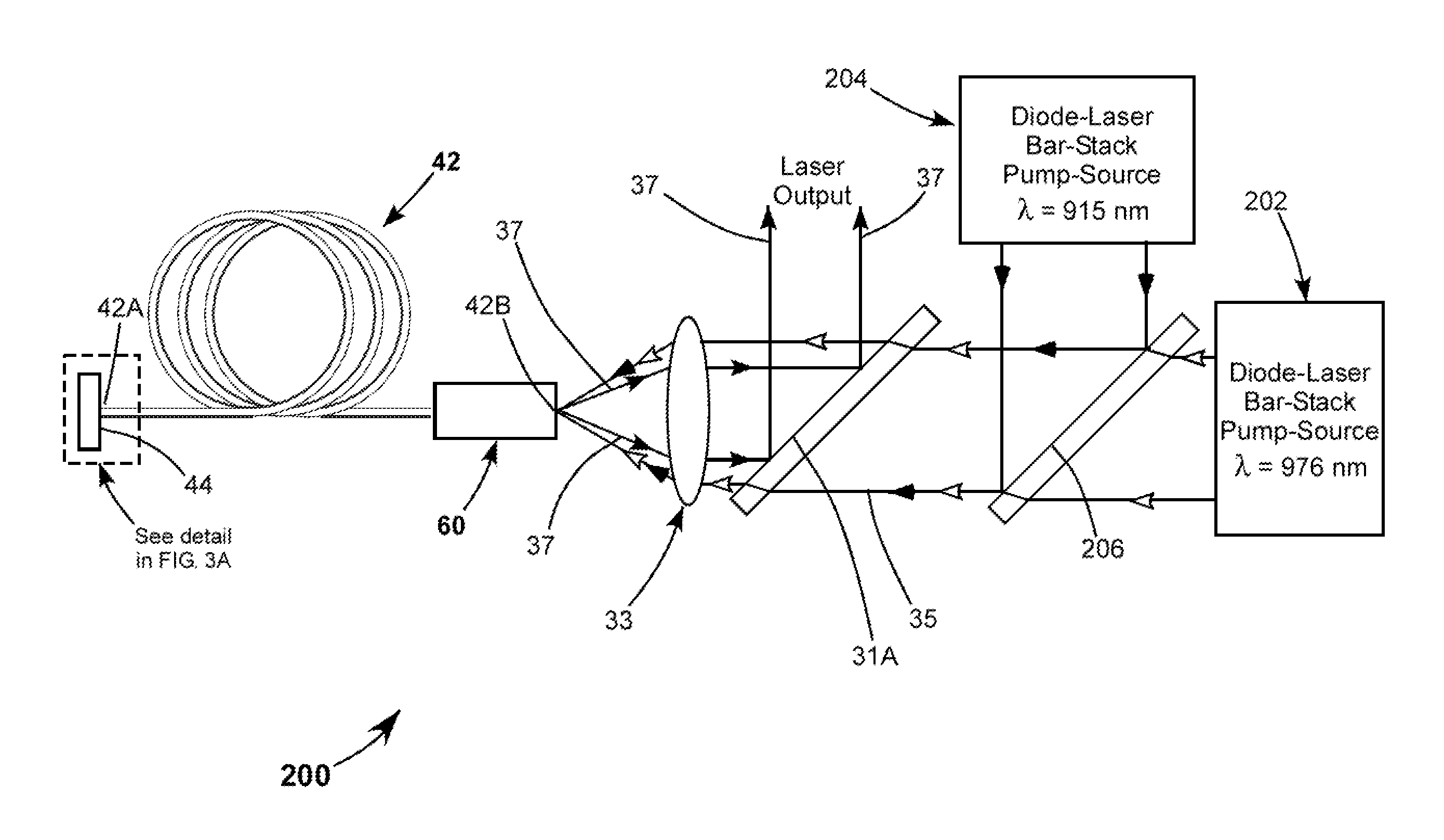
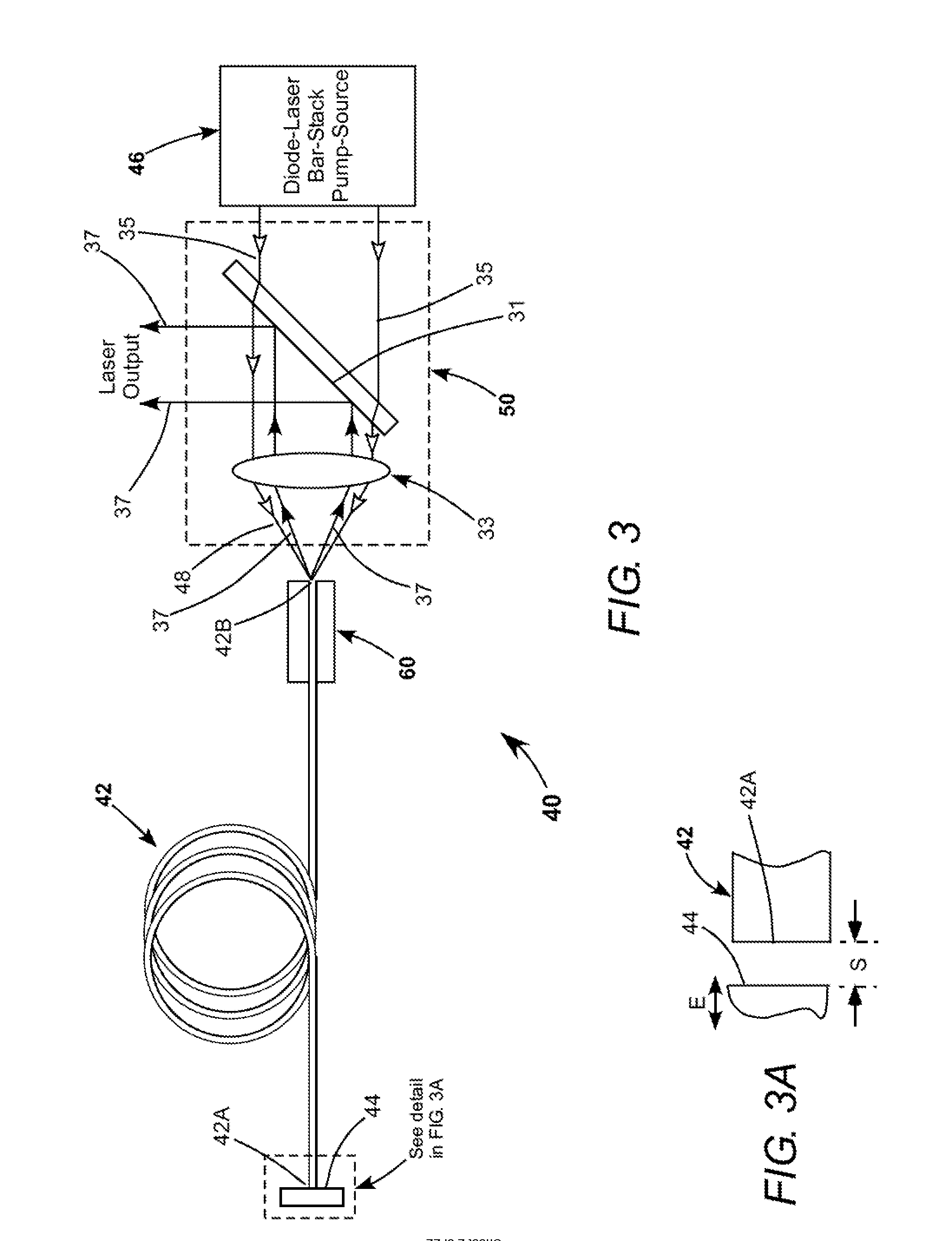
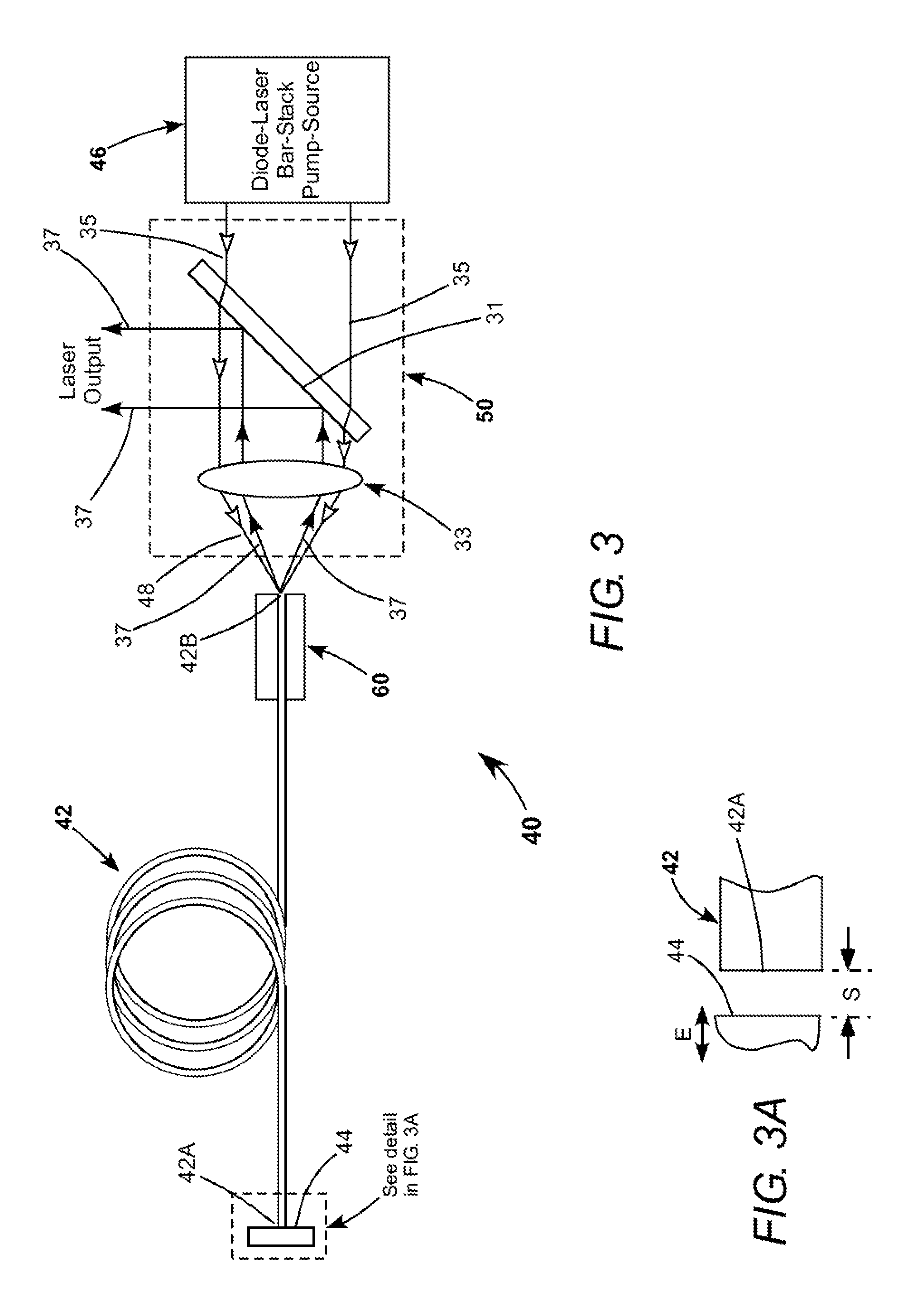
InactiveUS20130028276A1Improve transmittanceMinimizationLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor laser optical deviceResonatorFast axis
A CW ytterbium-doped fiber-laser includes a gain-fiber having a reflector proximity-coupled to one end, with the other end left uncoated. A laser resonator is defined by the reflector and the uncoated end of the gain-fiber. Pump-radiation from fast-axis diode-laser bar-stacks emitting at 915 nm and 976 nm is combined and focused into the uncoated end of the gain-fiber for energizing the fiber. Laser radiation resulting from the energizing is delivered from the uncoated end of the gain-fiber and separated from the pump-radiation by a dichroic minor.
Owner:COHERENT INC
High power diode laser having multiple emitters and method for its production
InactiveUS20080084905A1Simple and cost-efficient configurationIncrease powerSolid-state devicesSemiconductor laser optical deviceLaser transmitterHigh power lasers
The invention discloses a high power laser diode comprising a plurality of laser light emitters (2) and a plurality of light collimating means (33), wherein each of the laser light emitters (2) defines, in a direction perpendicular to a direction of propagation (32) of an output laser beam, a fast axis (y) and a slow axis (x), and wherein each of the light collimating means is associated with a laser light emitter and configured for collimating the output laser beam at least in a fast axis (y) direction. In order to enable a simple and cost-efficient assembly of the diode laser with collimating means, having a layered structure consisting of a plurality of plane-parallel substrates. For this purpose, the diode laser comprises planar substrate means (10, 30) which serves to precisely define a distance between a respective laser light emitter (2) and an associated light collimating means to the order of one or several millimetres and to support the collimating means (33) such that the optical axis of said laser light emitters are parallel to each other and for defining a precise location of emitters on the planar substrate (10), preferably at predetermined distance in fast axis direction between said laser light emitters. The collimating means is an array or multiple single of micro-optical lenses having a rear side which is bonded to the upper surface of the planar spacer means. The submounts of the light emitters (2) are mounted to the planar substrate means (10, 30) and to a heatsink (6).
Owner:FRAUNHOFER USA
Image display device
ActiveUS20110128477A1Increase awarenessPrevented from suffering from iridescent unevennessSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsIn planeRefractive index
Provided is an image display device including an image display cell and a polarizing plate placed on a viewer side of the image display cell. The first polarizing plate includes a polarizer and a first protective film. The first protective film is placed on a viewer-side principal surface of the polarizer and satisfies following relations: (i) 0 nm≦Re1≦3000 nm; (ii) Nz1≧7; and (iii) Rth1>2500 nm. Re1, Rth1 and Nz1 are defined by following equations: Re1=(nx1−ny1)d1; Rth1=(nx1−nz1)d1; and Nz1=Rth1 / Re1, wherein d1 represents a thickness of the first protective film, nx1 represents a refractive index in a direction of an in-plane slow axis of the protective film, ny1 represents a refractive index in a direction of an in-plane fast axis of the protective film, and nz1 represents a refractive index in a direction of the thickness of the protective film.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
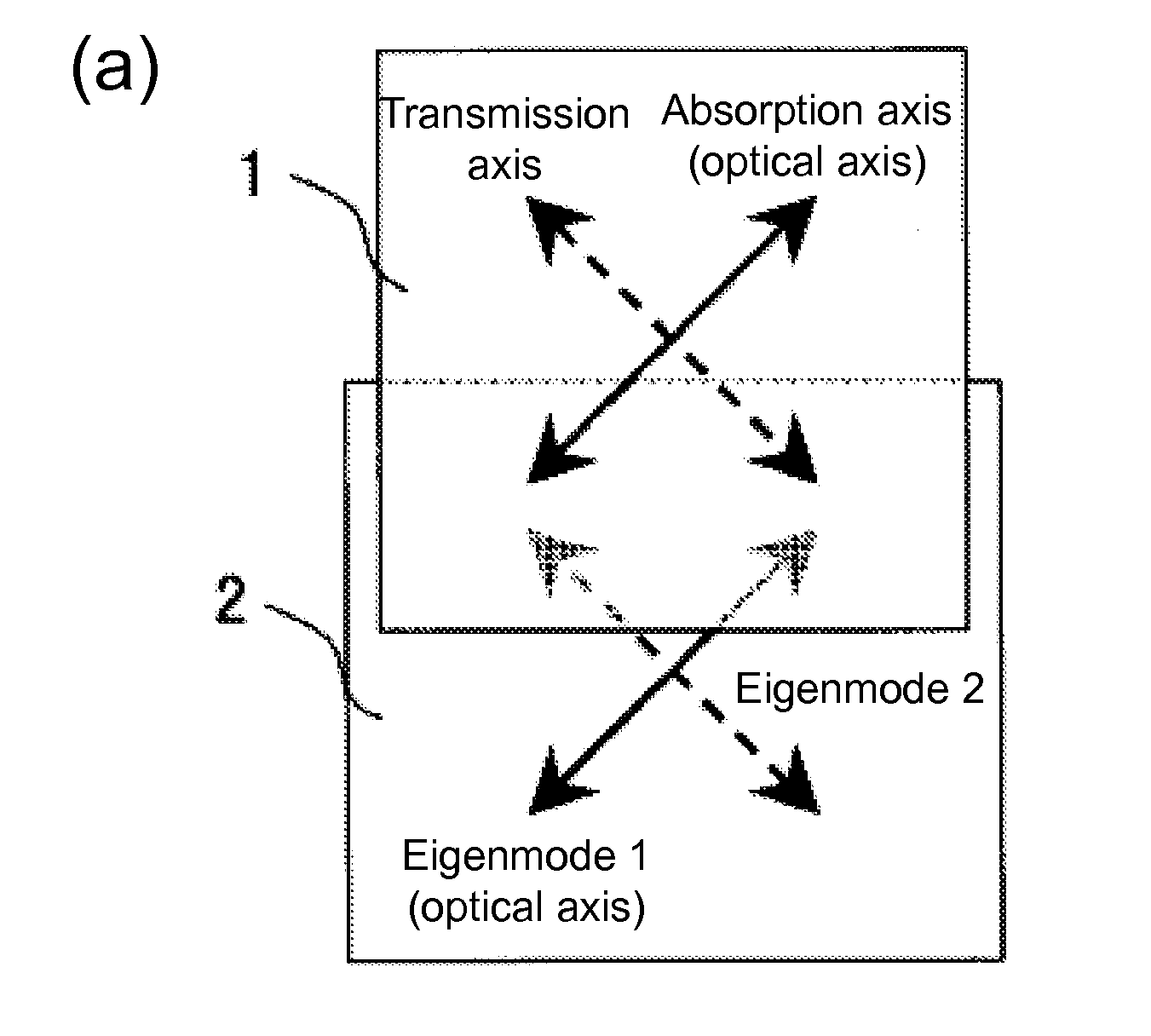
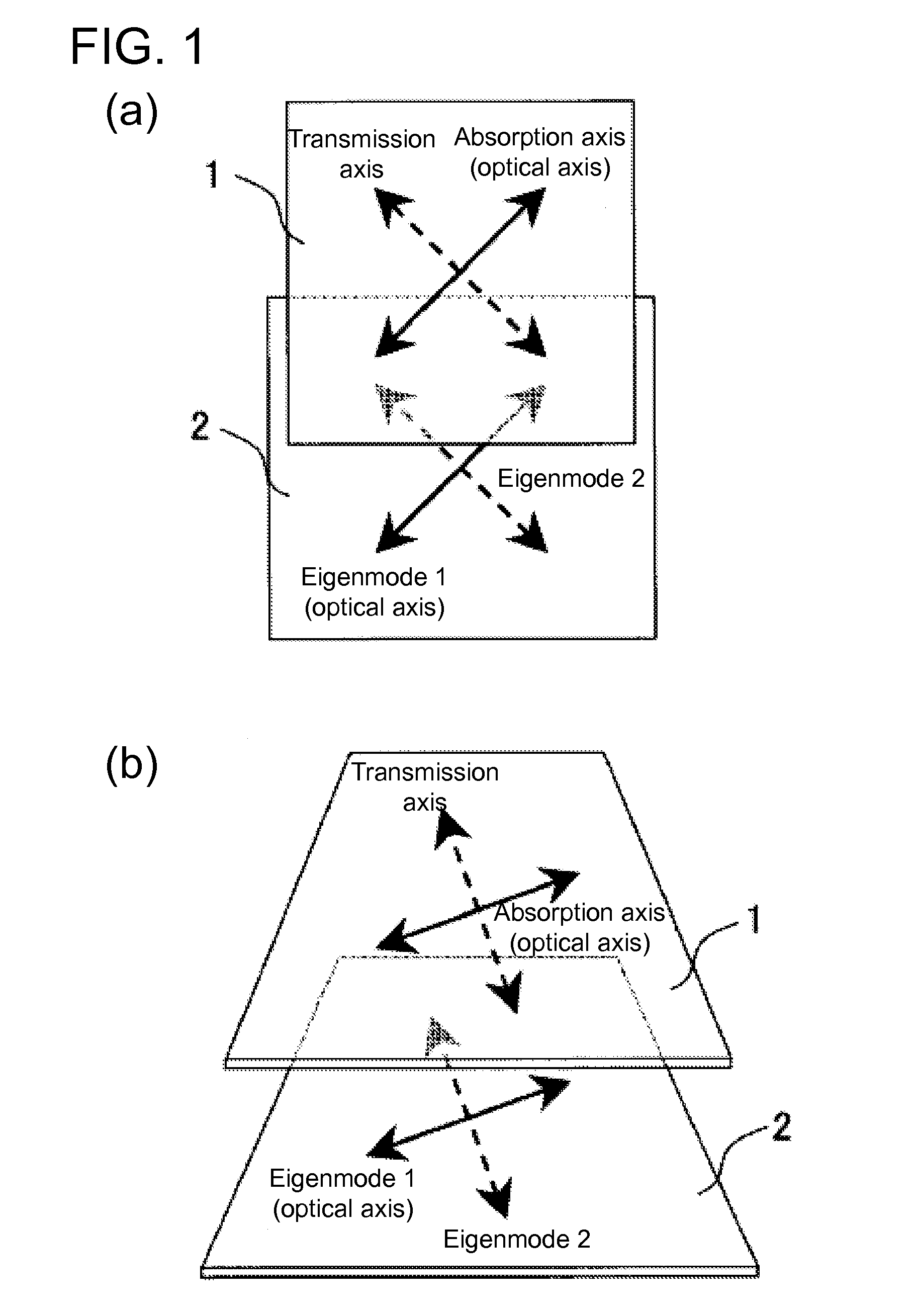
Circularly polarizing plate and display device
ActiveUS20110222155A1Improve visibilityIncrease contrastPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsIn planeVisibility
The present invention provides at low cost a display device with superior visibility and high contrast ratio even in a bright room environment through a reduction in the undesired reflection, not only of the incident outside light from the normal direction, but also of the outside incident light from an oblique direction. The present invention is a circularly polarizing plate including a polarizer and a λ / 4 plate, and the aforementioned circularly polarizing plate includes an anti-reflective layer, the aforementioned polarizer, a birefringent layer, and the aforementioned λ / 4 plate which are laminated in this order, the NZ coefficient of the aforementioned birefringent layer satisfies NZ<0.1, the in-plane fast axis of the aforementioned birefringent layer is orthogonal to the absorption axis of the aforementioned polarizer, the NZ coefficient of the aforementioned λ / 4 plate satisfies NZ>0.9, and the in-plane slow axis of the aforementioned λ / 4 plate intersects the absorption axis of the aforementioned polarizer.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display device for vehicle
ActiveUS20140184996A1Low costSmall sizePolarising elementsNon-linear opticsPhase differenceDisplay device
A display device for a vehicle according to the present invention includes a display which emits an emission display light having a polarization plane in a specific direction, an illumination light source which illuminates the display, and a phase difference plate which is disposed facing the display in a state where a fast axis is shifted by a predetermined angle with respect to the polarization plane of the emission display light emitted by the display.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
Optical layered body, polarizer and image display device
ActiveUS20130194211A1AdhesivenessImprove adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsPolarising elementsPolyesterRefractive index
Provided is an optical layered body that includes a polyester base, a primer layer formed thereon, and a hard coat layer formed on the primer. The polyester has a retardation of not less than 8000 nm, and a difference (nx−ny) of 0.07 to 0.20 between a refractive index (nx) in a slow axis direction that is a high refractive index direction and a refractive index (ny) of a fast axis direction that is orthogonal to the slow axis direction, a refractive index (np) of the primer, the refractive index (nx) in the slow axis direction of the polyester, and the refractive index (ny) in the fast axis direction of the polyester satisfy ny<np<nx, and a refractive index (nh) of the hard coat, the refractive index (nx) in the slow axis direction of the polyester, and the refractive index (ny) in the fast axis direction of the polyester satisfy ny<nh<nx.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
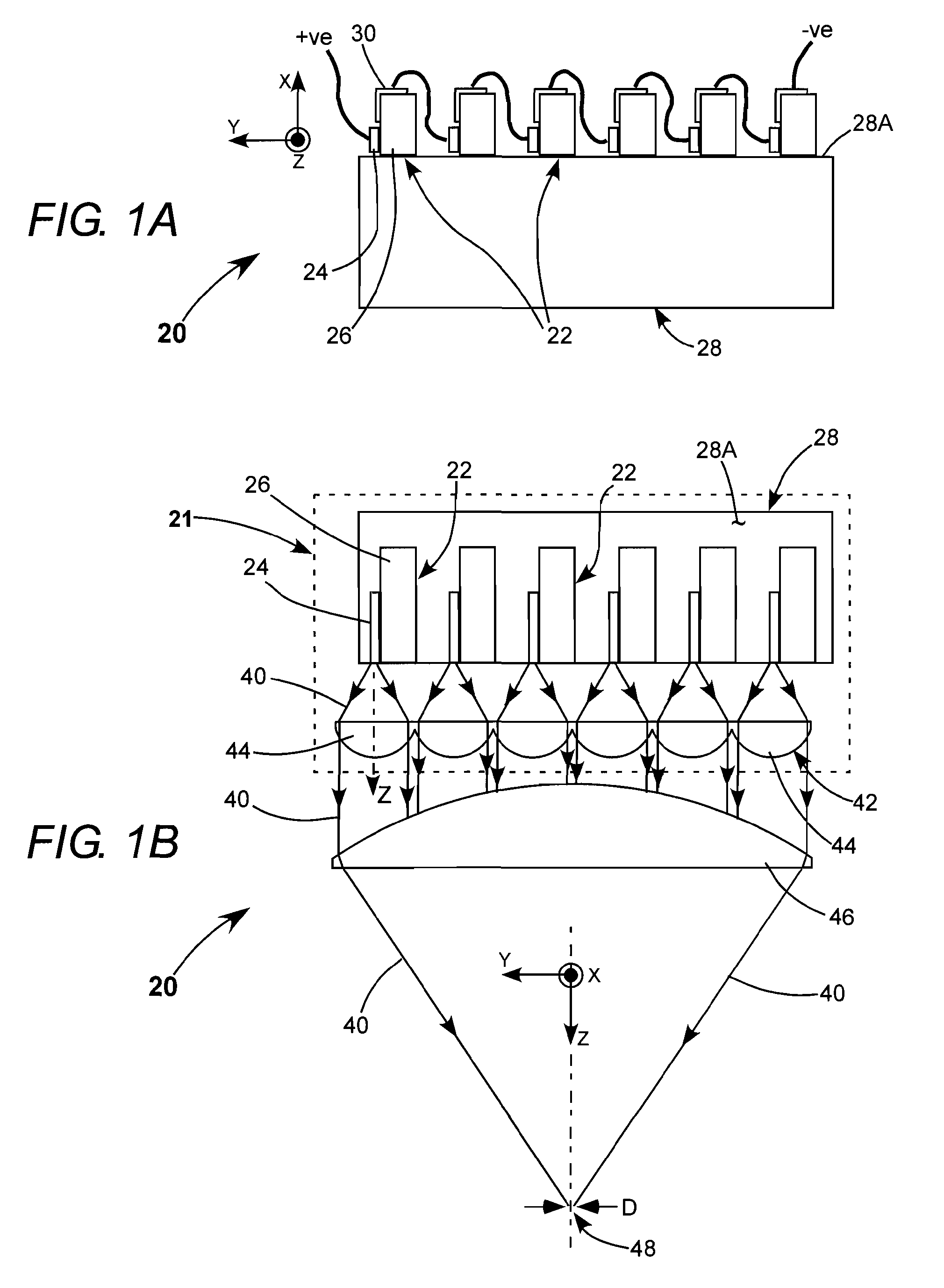
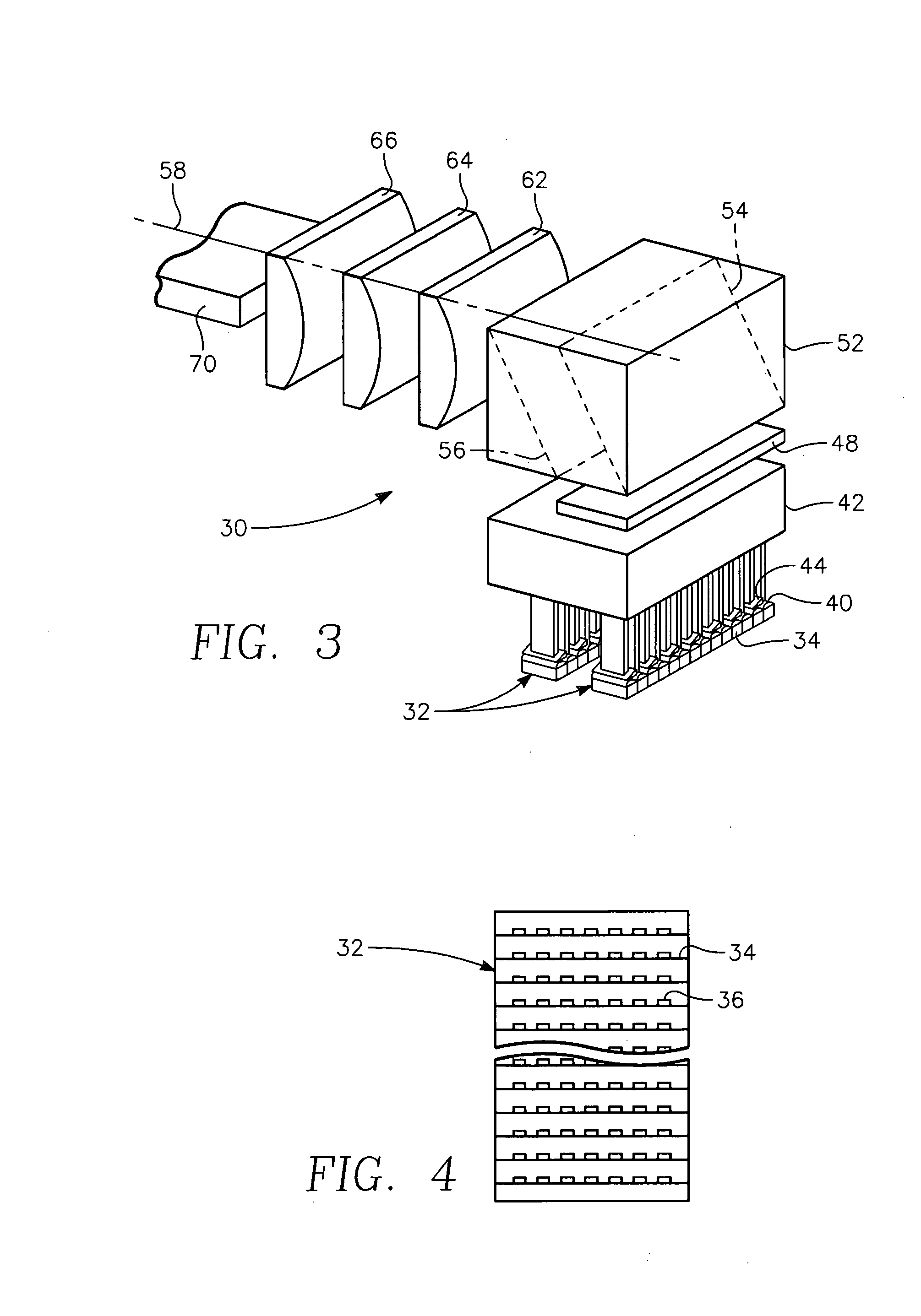
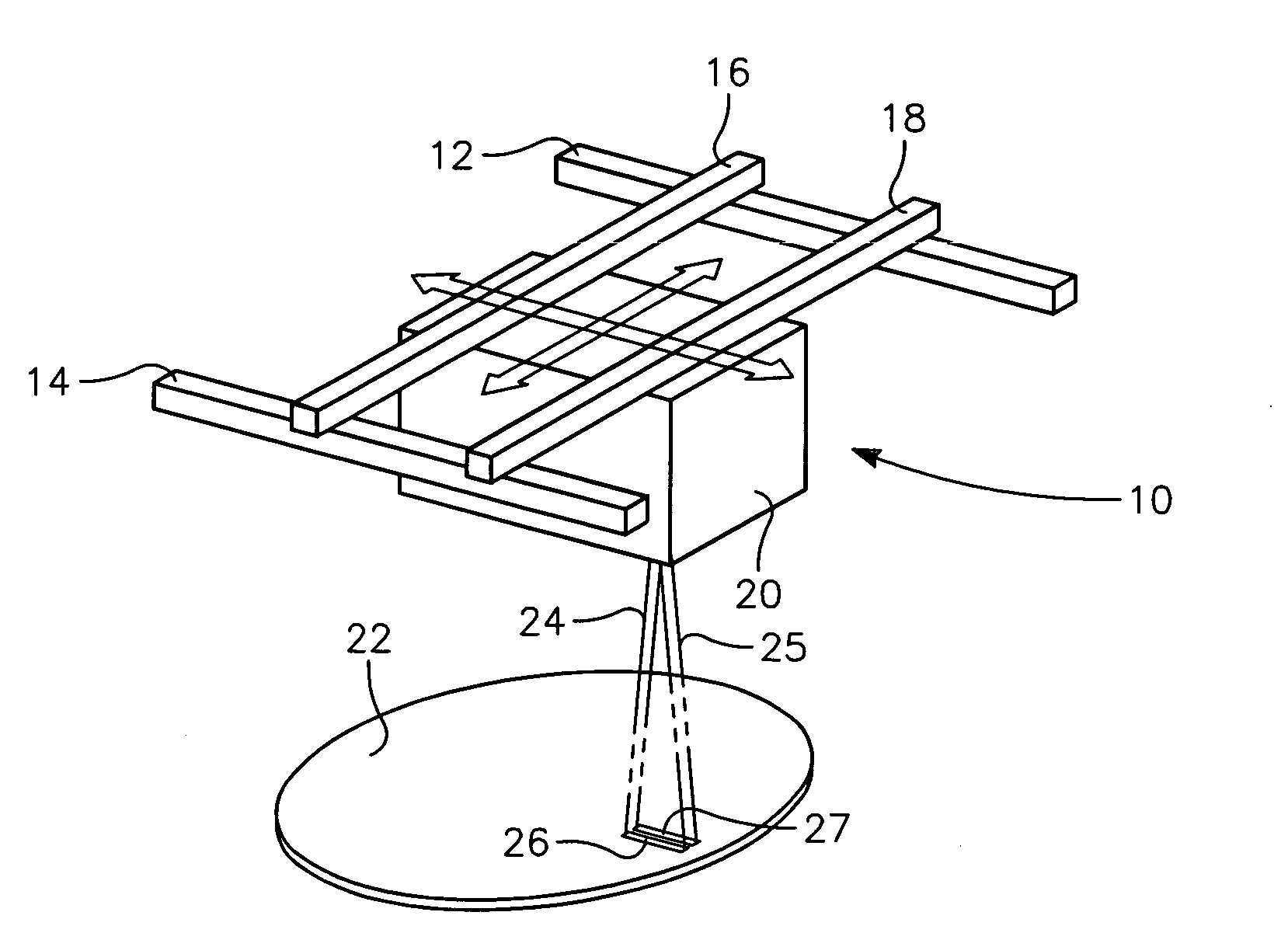
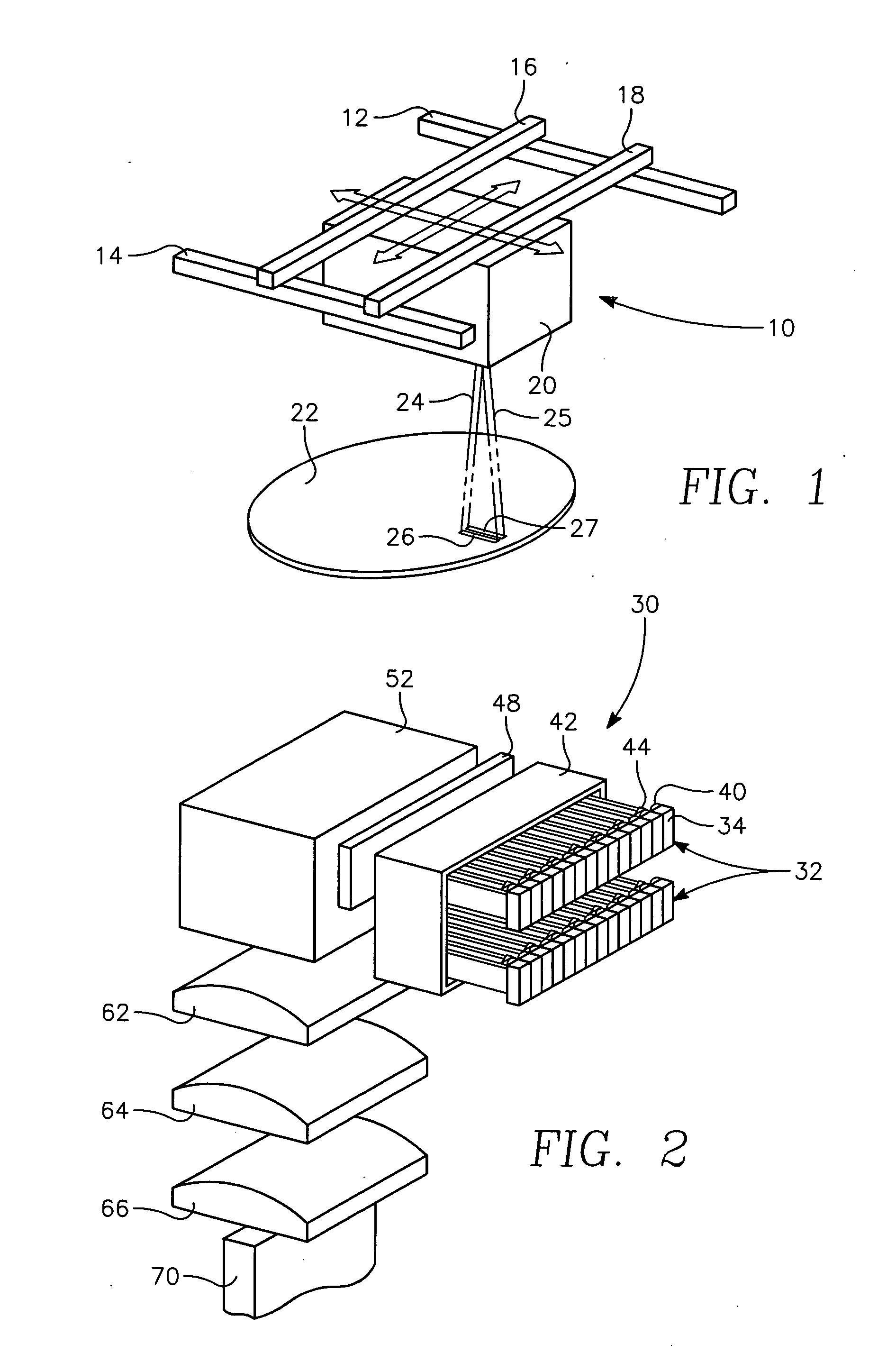
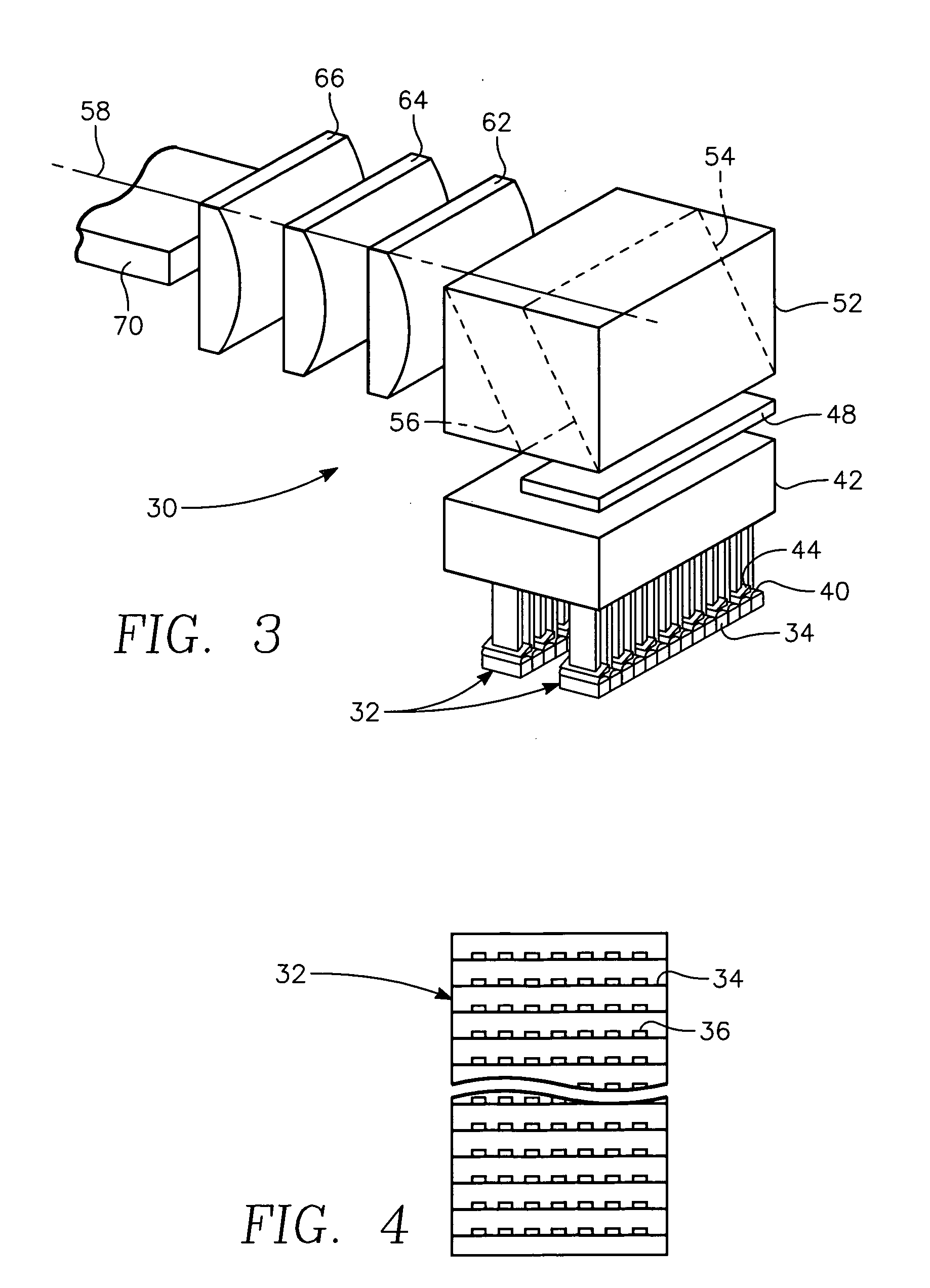
Fast axis beam profile shaping by collimation lenslets for high power laser diode based annealing system
ActiveUS20080210671A1Laser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser transmitterHigh power lasers
A dynamic surface anneal apparatus for annealing a semiconductor workpiece has a workpiece support for supporting a workpiece, an optical source and scanning apparatus for scanning the optical source and the workpiece support relative to one another along a fast axis. The optical source includes an array of laser emitters arranged generally in successive rows of the emitters, the rows being transverse to the fast axis. Plural collimating lenslets overlie respective ones of the rows of emitters and provide collimation along the fast axis. The selected lenslets have one or a succession of optical deflection angles corresponding to beam deflections along the fast axis for respective rows of emitters. Optics focus light from the array of laser emitters onto a surface of the workpiece to form a succession of line beams transverse to the fast axis spaced along the fast axis in accordance with the succession of deflection angles.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Fast axis beam profile shaping for high power laser diode based annealing system
ActiveUS20090152247A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusLaser transmitterHigh power lasers
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Optical module, optical fiber laser device and image display device
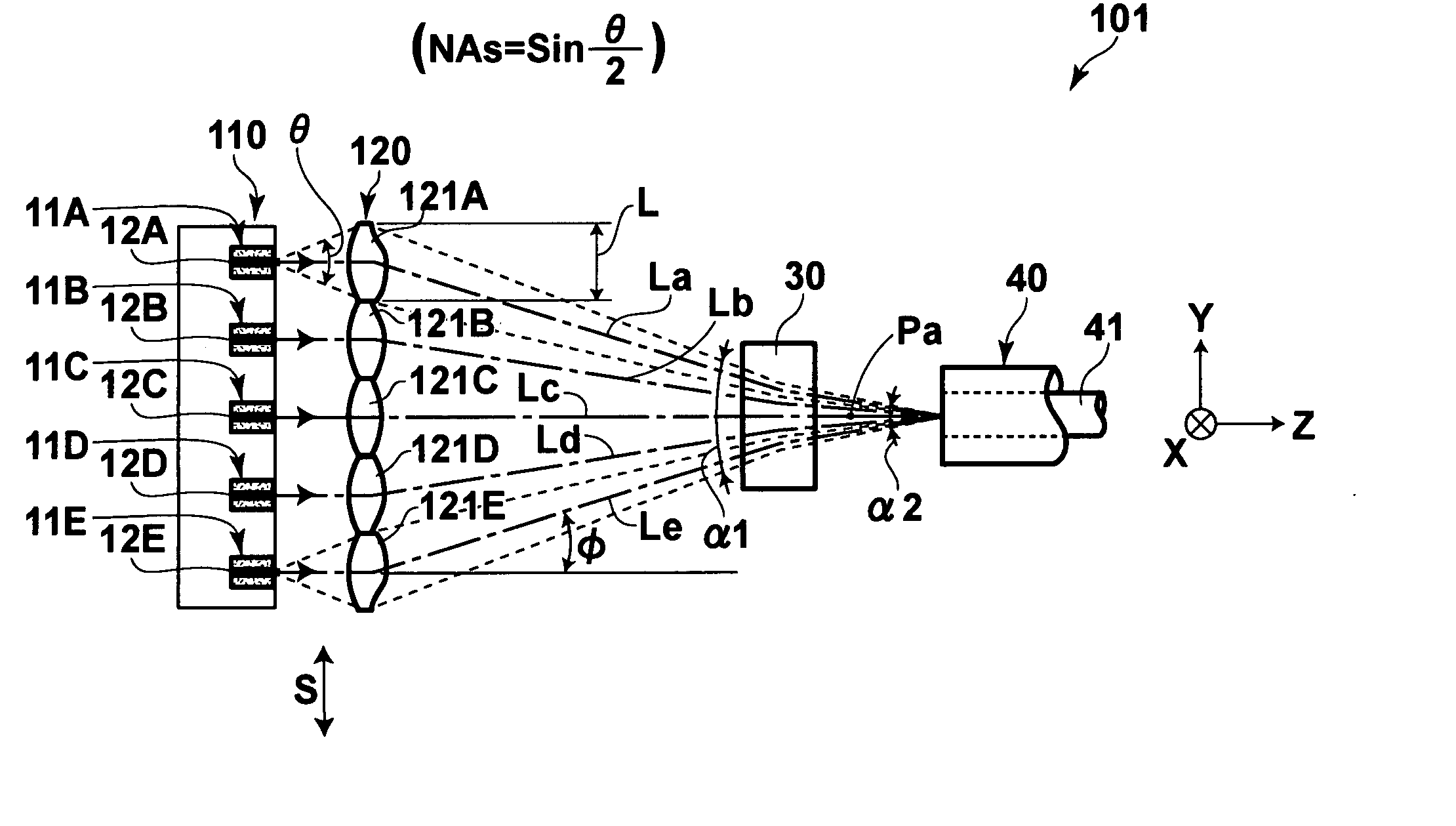
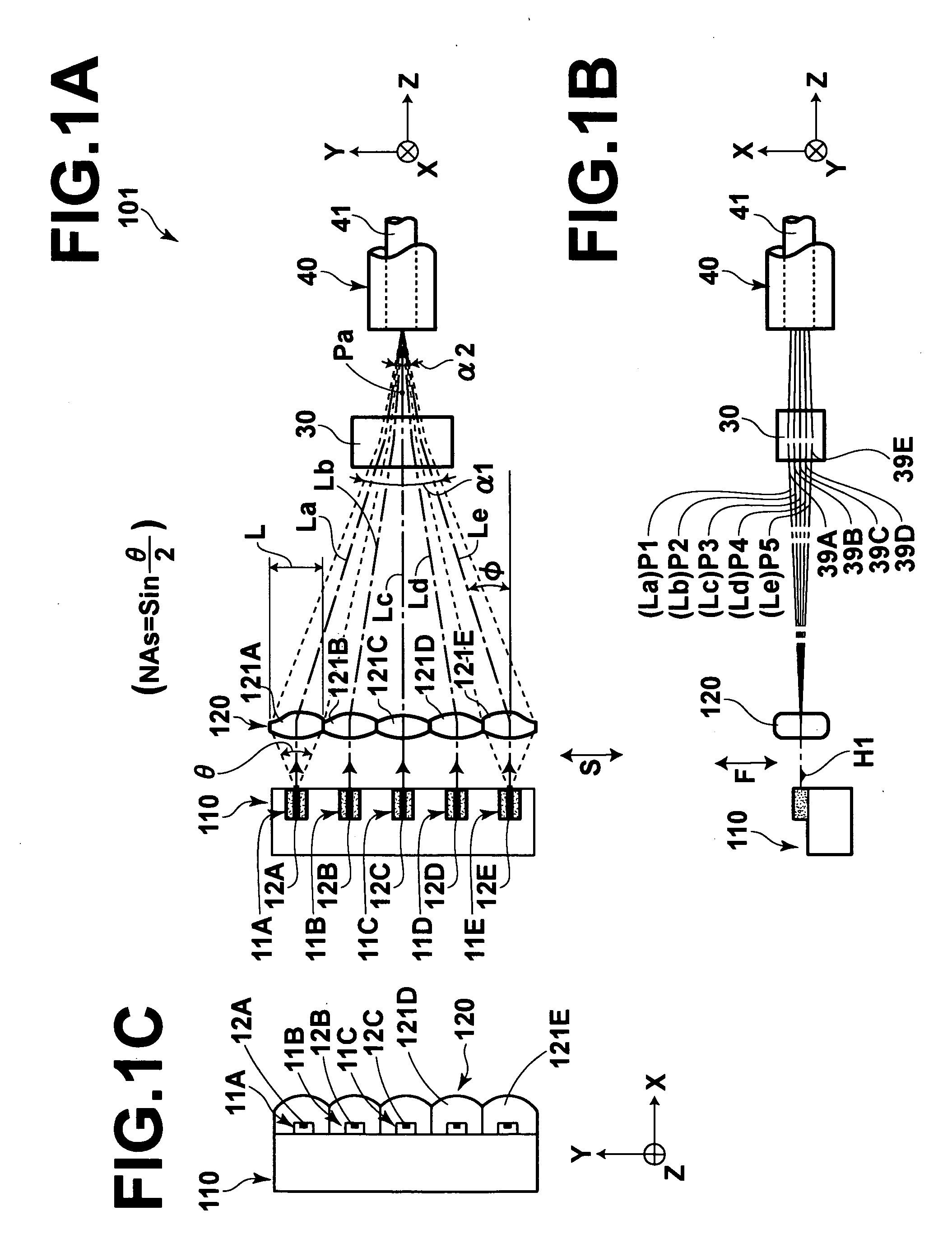
The fast-axis and slow-axis direction components of light exited from any light emitting sections are respectively independently collimated to allow the light beams which are collimated in both the fast-axis and slow-axis directions to be shaped and / or image-converted to a predetermined cross-sectional configuration at least relative to the slow-axis direction components and allow the light beams which are given the predetermined cross-sectional configuration to be condensed to a predetermined position. By doing so it is possible to reduce any loss involved upon the optical coupling of a laser array to an optical fiber.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
High power laser diode array comprising at least one high power diode laser and laser light source comprising the same
InactiveUS20090129420A1Enhance the imageEnhance optical loss characteristicSemiconductor laser optical deviceOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser transmitterHigh power lasers
Array comprising high power laser diode comprising laser light emitters, each defining, in a direction perpendicular to direction of propagation of an output laser beam, a fast axis and a slow axis; fast axis collimating means for collimating output laser beams in fast axis direction; and slow axis beam shaping means for collimating or focussing output laser beams in slow axis direction, said slow axis beam shaping means disposed external to said high power laser diode; wherein said laser light emitters are displaced relative to each other in fast axis direction or in fast and slow axis direction by equidistant spacings, respectively; and including optical means for forming output laser beam profile in far field of all laser light emitters consisting of said fast and slow axis collimated or focussed output laser beams arranged adjacently in seamless manner in one or two dimensions with optical fill factor of about 100%.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER USA CENT FOR LASER TECH
Method and apparatus for use of beam control prisms with diode laser arrays
InactiveUS6975465B1Shorten physical lengthHigh densityPrismsLaser optical resonator constructionLaser arrayPrism
The subject invention relates to beam control prisms and the use of a beam control prism to modify the beam properties of light emitted from an edge emitting diode laser. The subject invention can utilize a beam control prism placed next to a diode laser bar. The subject beam control prism can have, for example, a curved surface and / or a high reflective coated surface for a diode laser wavelength. The curved surface can collimate the fast axis divergence and the mirror surface can change the beam direction. The subject curved surface beam control prisms can incorporate one or more features, such as parabolic reflecting surface, elliptical exit surface with flat reflecting surface, and a hyperbolic entrance surface with flat reflecting surface.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Retardation film, process for producing the same, optical film, image display, liquid crystal panel and liquid crystal display
ActiveUS7215839B2Hard to cause a shift or an unevenness of a retardation valueOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayFilm plane
A retardation film of the present invention comprises a stretched film of a polymer film containing a norbornene-based resin, wherein the stretched film satisfies the following equation (1) and the equation (2); 100 nm≦(nx−ny)·d≦350 nm . . . (1), 0.1≦(nx−nz) / (nx−ny)≦0.9 . . . (2), where the refractive indices in the slow axis direction, the fast axis direction and the thickness direction of the film are nx, ny and nz, respectively, d(nm) is thickness of the film, and the slow axis direction is a direction that the refractive index in film plane is maximum. The retardation film is hard to cause a shift or an unevenness of a retardation value due to a stress.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
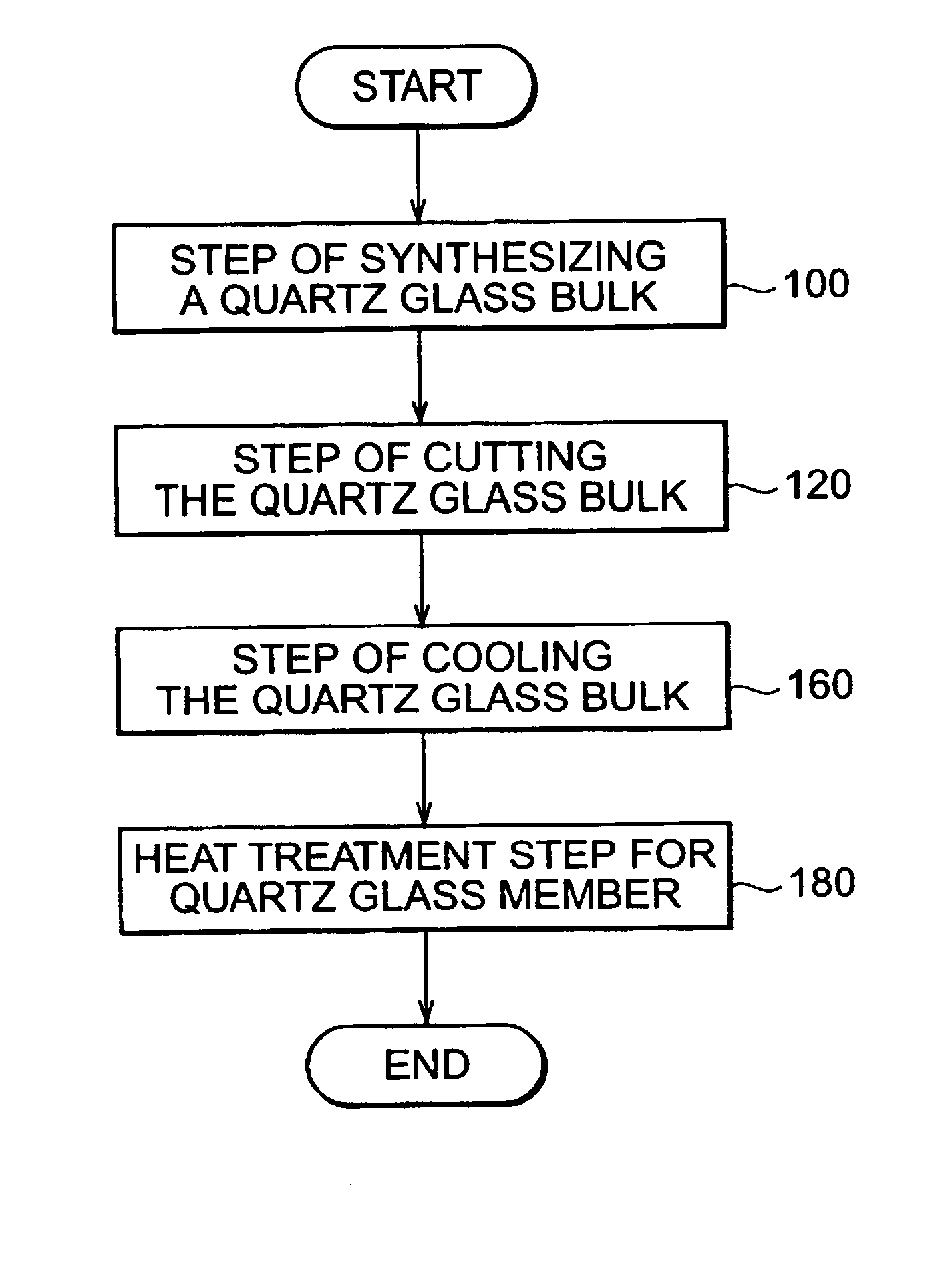
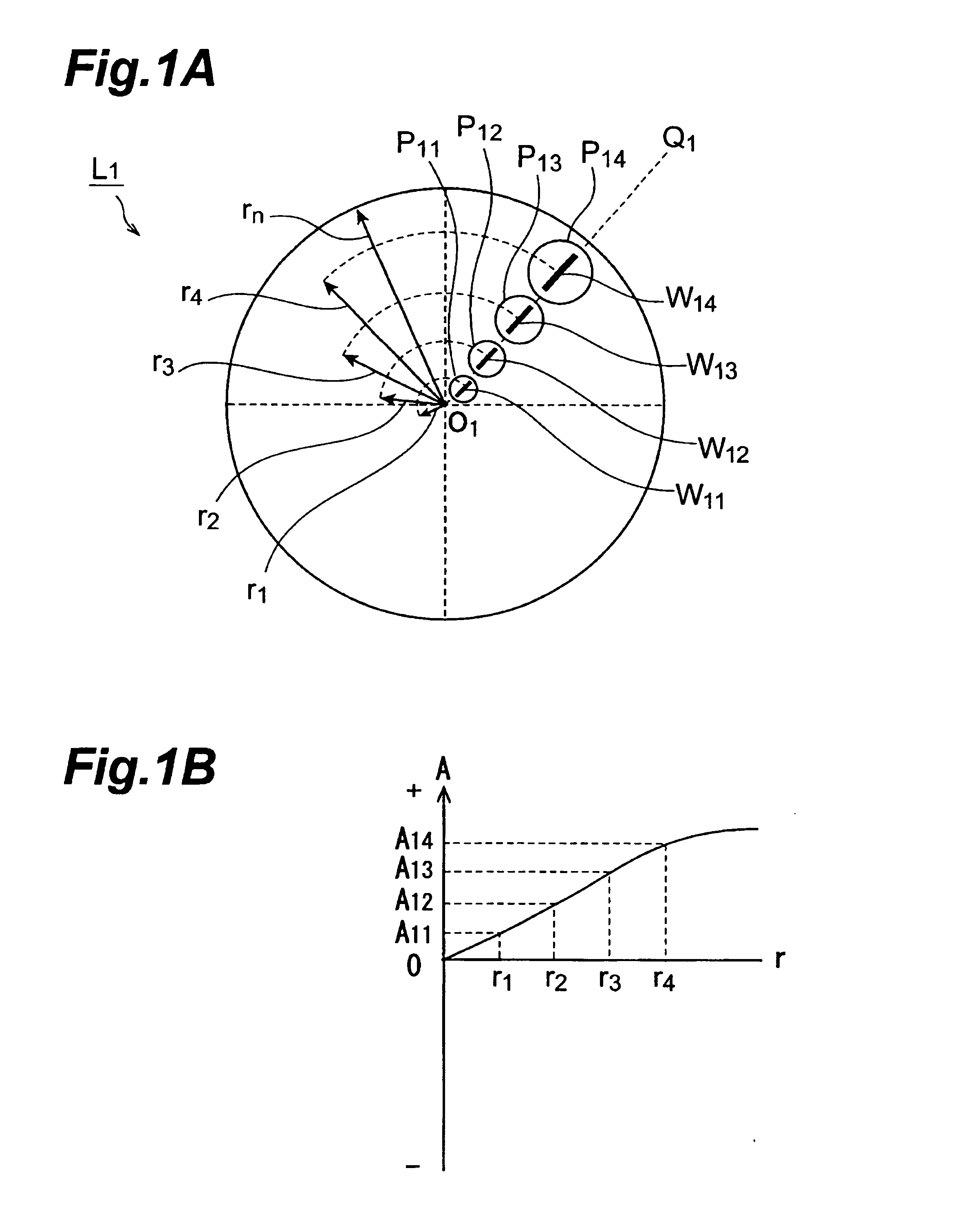
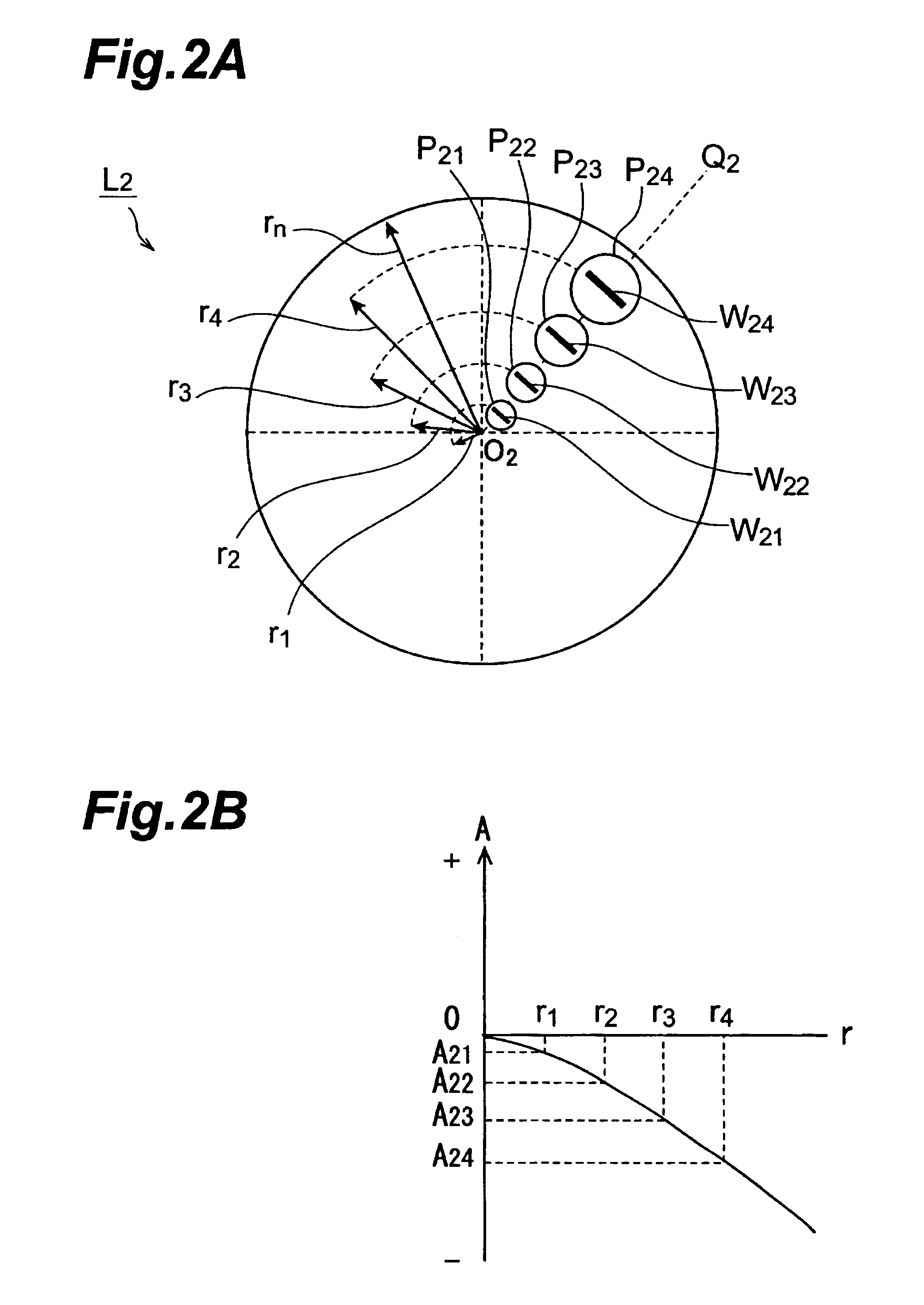
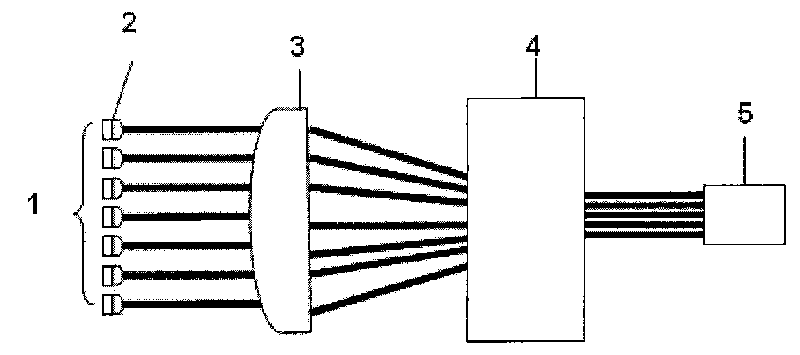
Silica glass member, method for producing the same, and projection aligners using the same
InactiveUS6672109B1Efficient HomogenizationEvenly dispersedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusHigh resistanceOptical axis
A silica glass member for use with a light having a specific wavelength of 250 nm or shorter, in which the difference in the maximum and the minimum values of hydroxyl group concentration as measured in a plurality of points within a plane vertical to an optical axis whose center is the crossing point of its optical axis with the optical axis of the silica glass member is 50 ppm or lower; and in which the plurality of signed birefringence values obtained based on the birefringence values measured on several points within a plane vertical to an optical axis whose center is the crossing point of its optical axis with the optical axis of the silica glass member and the direction of the fast axis fall within a range of from -2.0 to +2.0 nm / cm. Thus, a silica glass member having high optical transmittance and a high resistance against ultraviolet radiations is provided.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Multi-single pipe light beam coupling type high-power semiconductor laser
InactiveCN101707326AAvoid pitfalls that reduce overall efficiencyEasy to processSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser output parameters controlHigh power lasersCoupling
The invention relates to a high-power semiconductor laser, in particular to a multi-single pipe light beam coupling type high-power semiconductor laser. A plurality of single pipe semiconductor lasers, the emitting ends of which are provided with fast axis collimation cylindrical lenses, are arranged in parallel in the same direction; a cylindrical lens, a slow axis collimation lens perpendicular to a normal line of the cylindrical lens, and an optical fiber for receiving a focused light beam are sequentially arranged along the optical path transmission direction of the single pipe semiconductor lasers; the cylindrical lens further compresses the light beam fast axis of each single pipe semiconductor laser, and the slow axis collimation lens collimates the slow axis and focuses light beams; and finally, the light beams are output after focused and coupled into the optical fiber. The laser has simple structure and easy processing of elements, overcomes the defects existing in the prior art for manufacturing the high-power laser and is easy to realize higher power and luminance output.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus for synthesizing laser beams
InactiveUS20040233964A1Semiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser structural detailsOptical axisLight beam
Laser beams are synthesized by offsetting in different positions in the direction of the fast axis beam bundles radiated from semiconductor lasers, converging the optical axes of the beam bundles in the fast axis view, and introducing the beam bundles into an optical fiber after converging them in the directions of the fast and slow axes. A convergent angle transforming optical system is disposed further upstream of the upstream-most position in the positions where the optical axes of the beam bundles converged in the fast axis view intersect in the fast axis view. The whole beam bundle formed of the beam bundles converged in the fast axis view is passed through the convergent angle transforming optical system so that the angle of convergence of the whole beam bundle or part of the beam bundles is made smaller in the fast axis view, and introduced into the optical fiber.
Owner:ADTEC ENG +1
Laser multiplexing apparatus
InactiveUS6922288B2Small device sizeImprove space utilization efficiencyOptical wave guidancePrismsMultiplexingOptical axis
In a laser light multiplexing apparatus: a collimating optical system collimates light beams emitted from semiconductor lasers so that the slow axes of the light beams become coplanar, and optical axes of the light beams become parallel to each other; a light beam rearrangement optical system constituted by prisms respectively arranged in correspondence with the light beams rearranges the light beams in such a manner that directions of the fast axes of the light beams are changed at different locations along a direction in which the light beams propagate, and the fast axes of the light beams become coplanar; and a convergence optical system converges a bundle of the light beams rearranged by the light beam rearrangement optical system, in directions of the fast axes and the slow axes of the light beams, and makes the converged bundle of the light beams enter an optical fiber.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
High power laser diode array comprising at least one high power diode laser and laser light source comprising the same
InactiveUS7751458B2Enhance imaging and optical loss characteristicSimple configurationSemiconductor laser optical deviceOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser transmitterHigh power lasers
Array comprising high power laser diode comprising laser light emitters, each defining, in a direction perpendicular to direction of propagation of an output laser beam, a fast axis and a slow axis; fast axis collimating means for collimating output laser beams in fast axis direction; and slow axis beam shaping means for collimating or focussing output laser beams in slow axis direction, said slow axis beam shaping means disposed external to said high power laser diode; wherein said laser light emitters are displaced relative to each other in fast axis direction or in fast and slow axis direction by equidistant spacings, respectively; and including optical means for forming output laser beam profile in far field of all laser light emitters consisting of said fast and slow axis collimated or focussed output laser beams arranged adjacently in seamless manner in one or two dimensions with optical fill factor of about 100%.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER USA CENT FOR LASER TECH
Cellulose ester film, polarizing plate and display
InactiveUS20070092663A1Reduced optical anisotropyImprove visibilityLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsCelluloseRefractive index
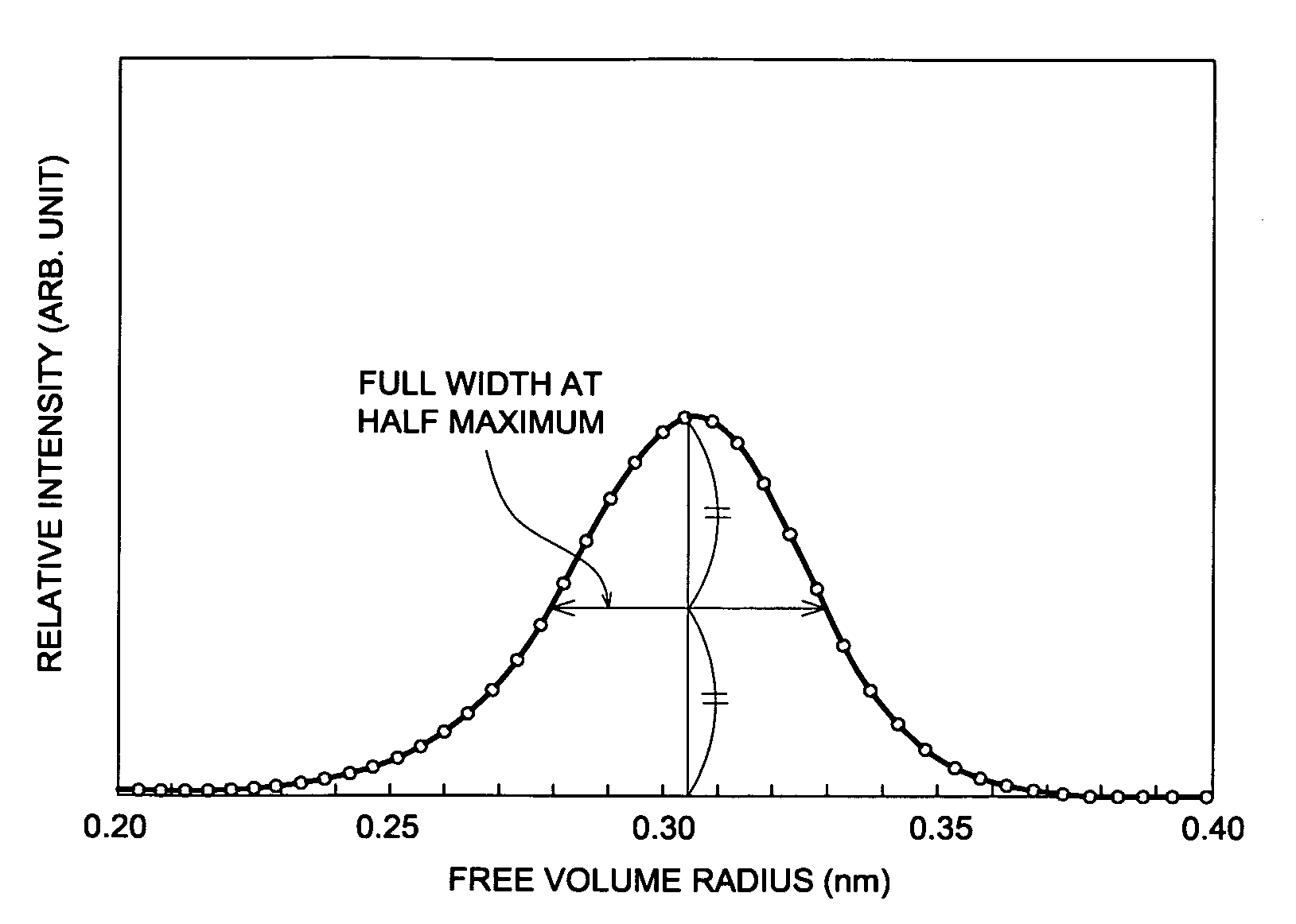
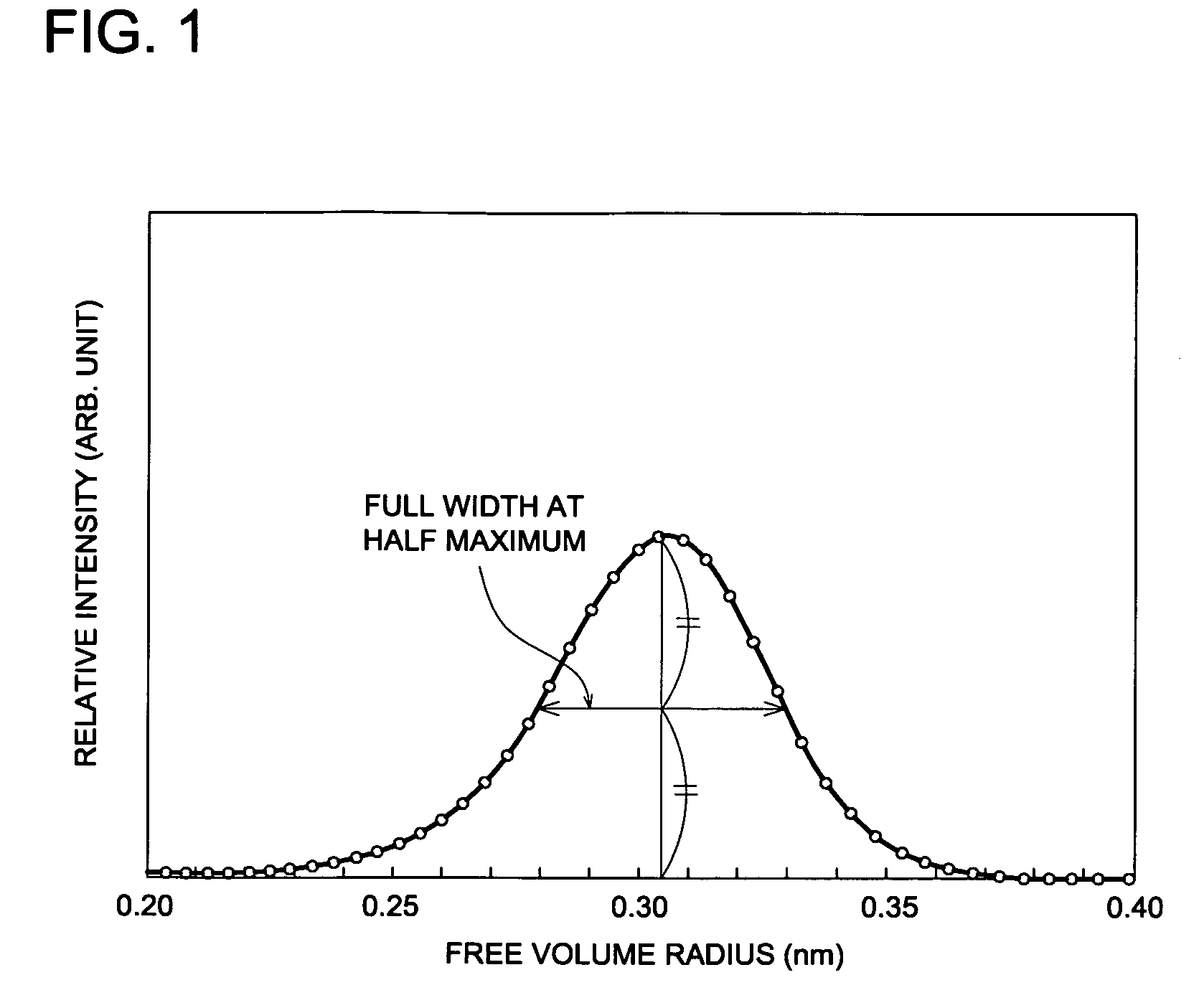
A cellulose ester film exhibiting: a free volume radius of 0.25 to 0.31 nm and a half-width of 0.04 to 0.1 nm, the free volume radius and the half-width being determined by positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy; and Ro of 0 to 10 nm and Rt of −30 to ⇄20 nm, Ro and Rt being defined by the following equations: Equation (a): Ro=(nx−ny)×d; Equation (b): Rt=((nx+ny) / 2−nz)×d (Ro: in-plane retardation, Rt: retardation in the thickness direction of the film, nx: in-plane refractive index in slow axis direction, ny: in-plane refractive index in fast axis direction, nz: refractive index in the thickness direction of the film (refractive indexes being measured at wavelength of 590 nm), d: thickness of the film (nm)).
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
High-power CW fiber-laser
InactiveUS9014220B2Improve transmittanceStimulated Raman scattering is minimizedLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor laser arrangementsResonatorFast axis
A CW ytterbium-doped fiber-laser includes a gain-fiber having a reflector proximity-coupled to one end, with the other end left uncoated. A laser resonator is defined by the reflector and the uncoated end of the gain-fiber. Pump-radiation from fast-axis diode-laser bar-stacks emitting at 915 nm and 976 nm is combined and focused into the uncoated end of the gain-fiber for energizing the fiber. Laser radiation resulting from the energizing is delivered from the uncoated end of the gain-fiber and separated from the pump-radiation by a dichroic mirror.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com