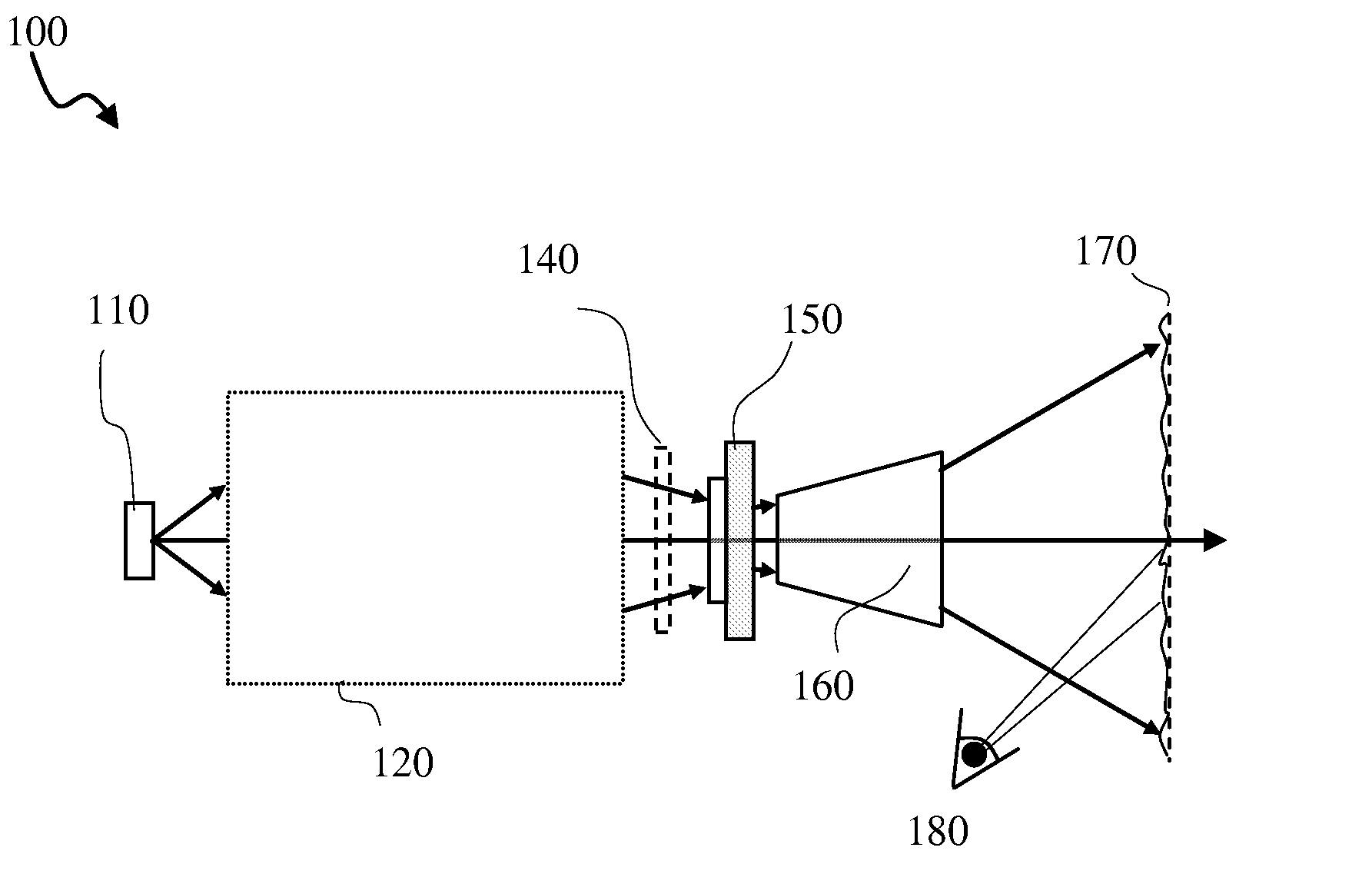
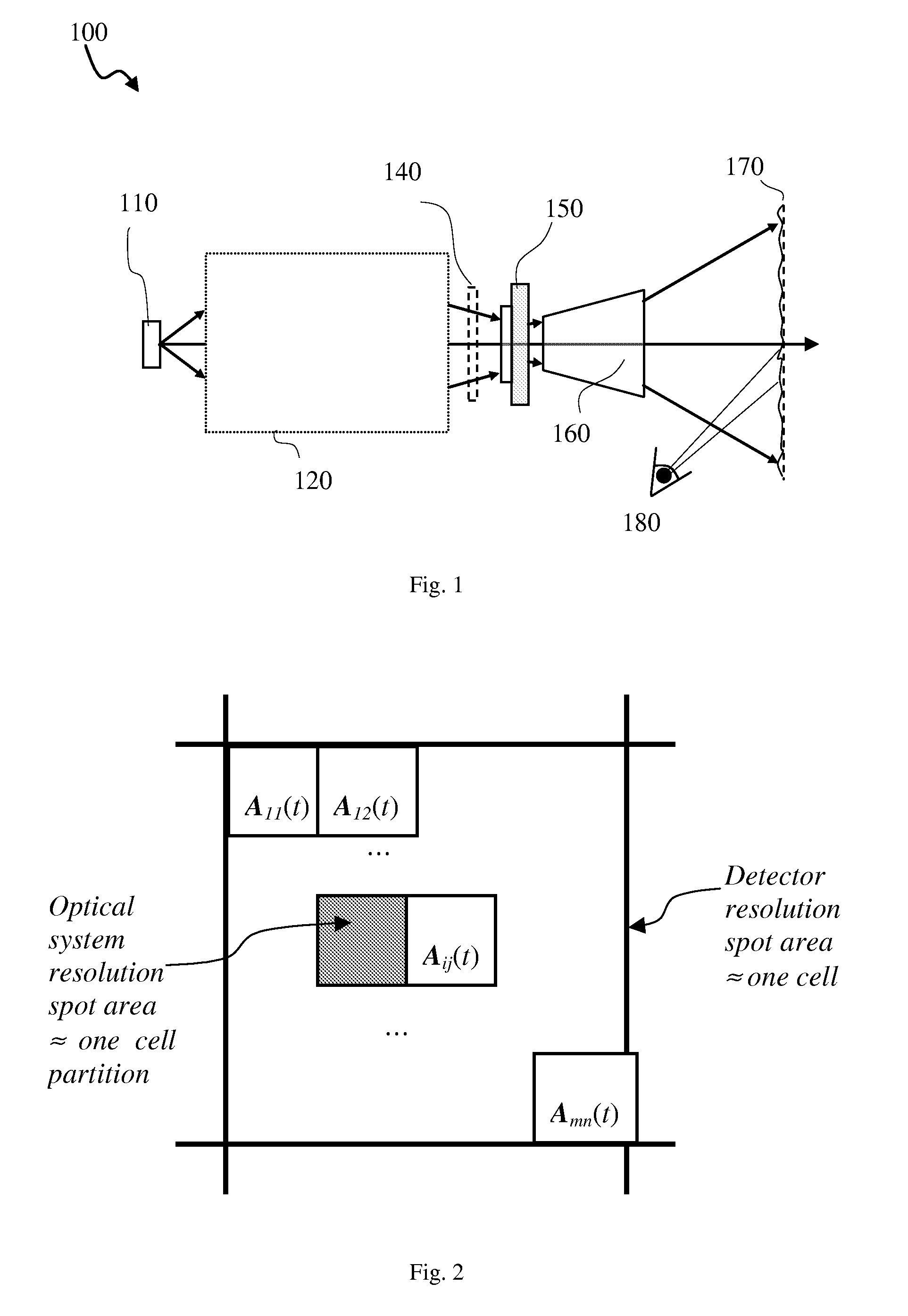
Patents
Literature
380 results about "Spatial change" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
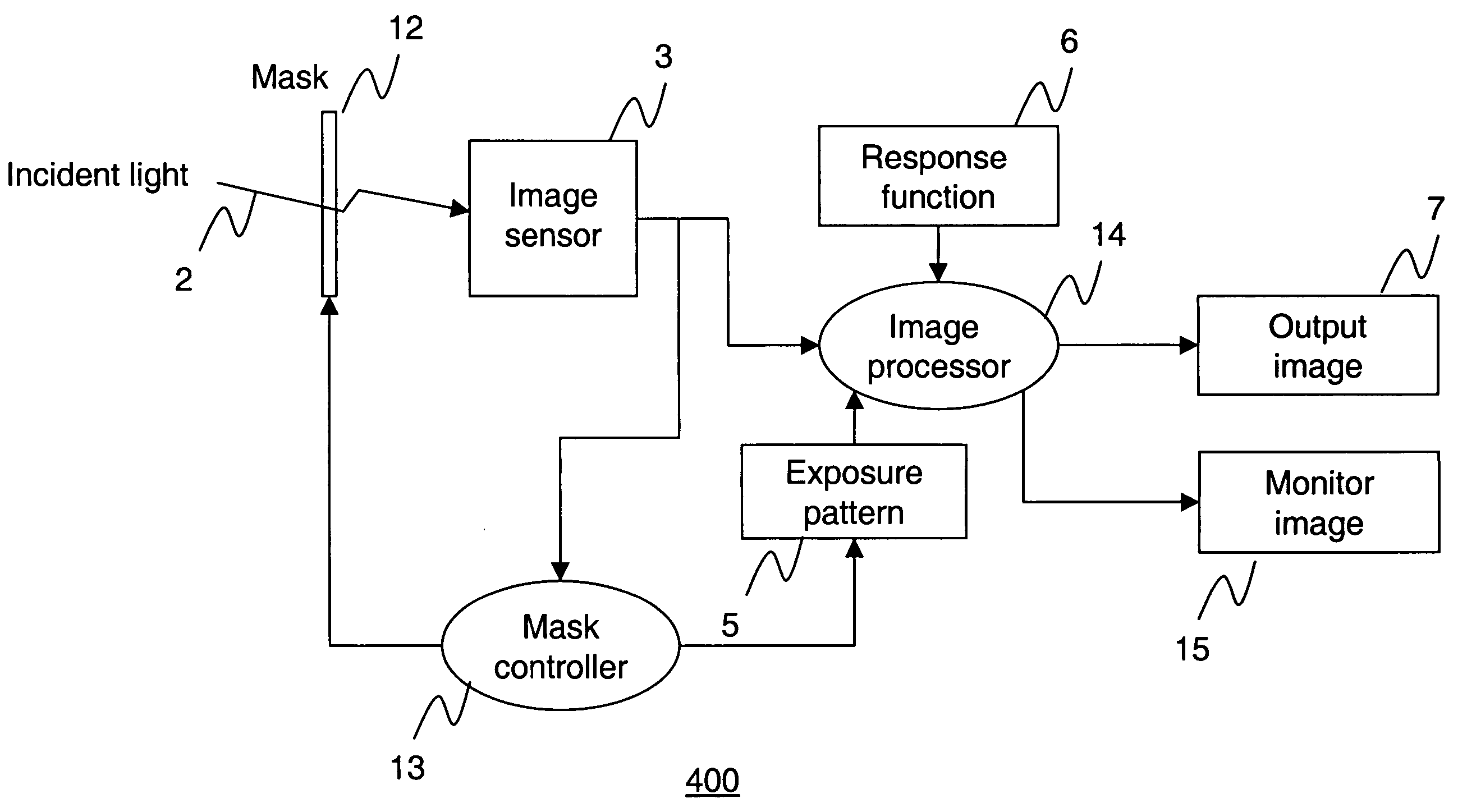
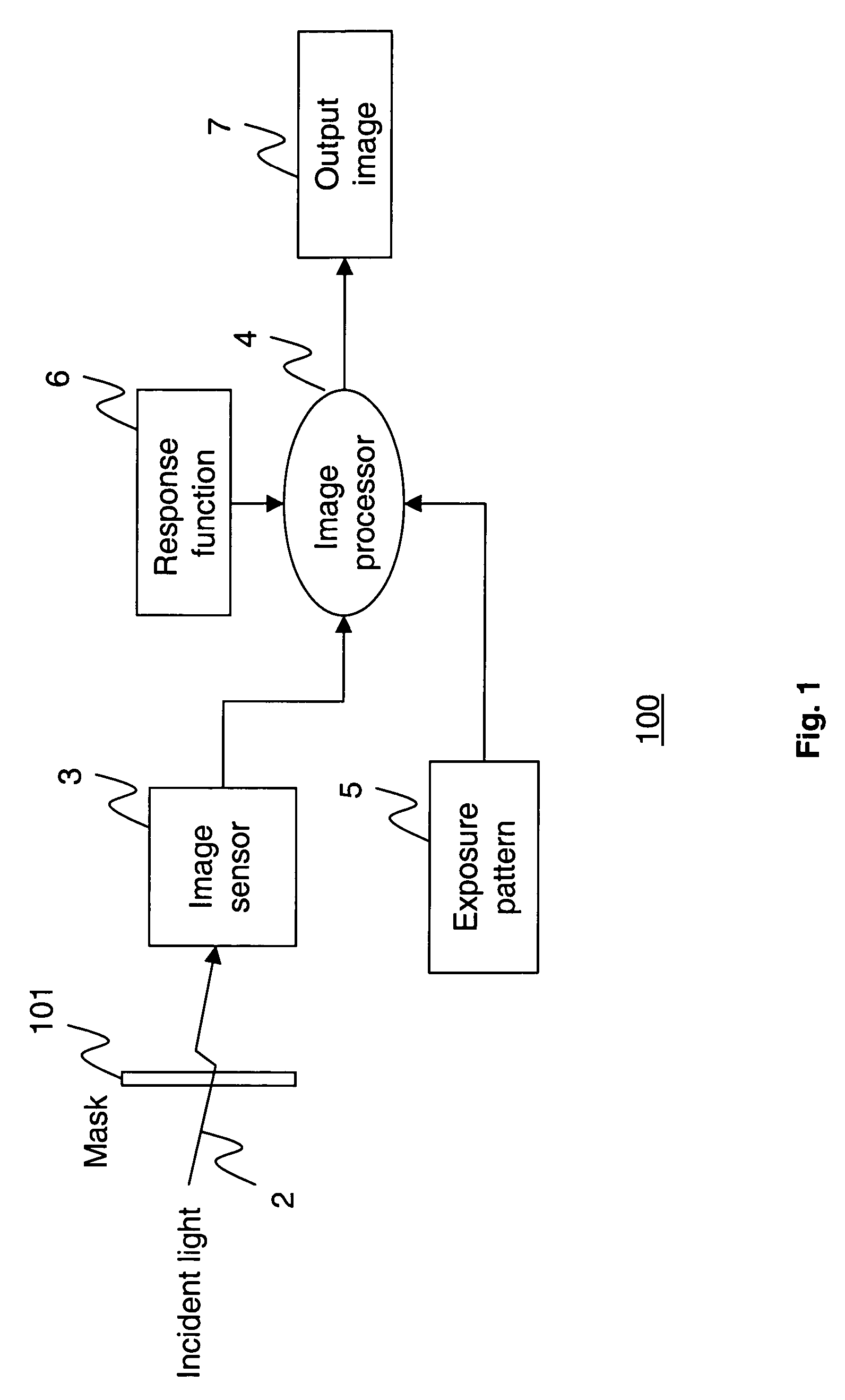
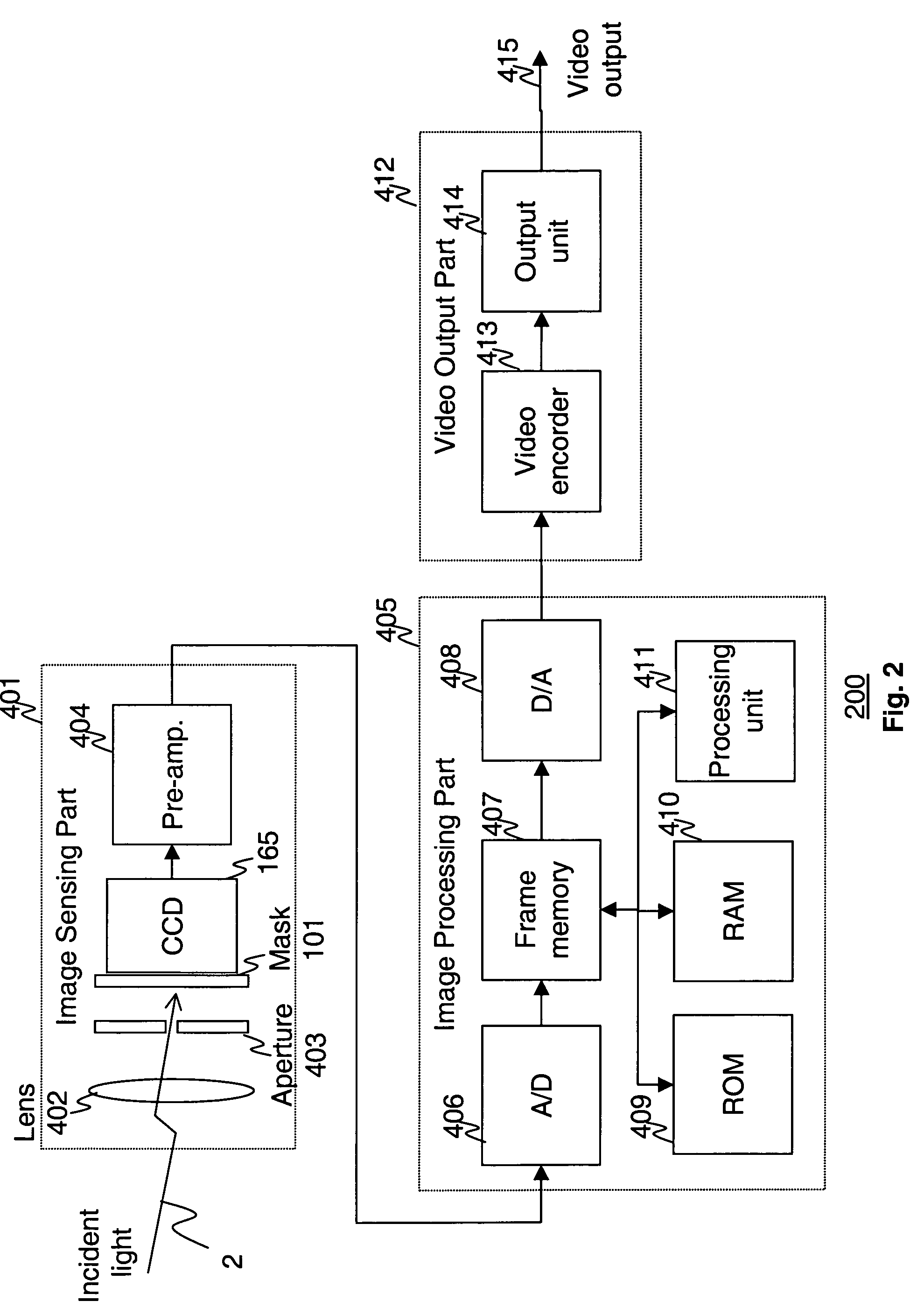
Apparatus and method for high dynamic range imaging using spatially varying exposures
InactiveUS6864916B1Minimize the numberSubstantial lossTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsHigh-dynamic-range imagingUltrasound attenuation
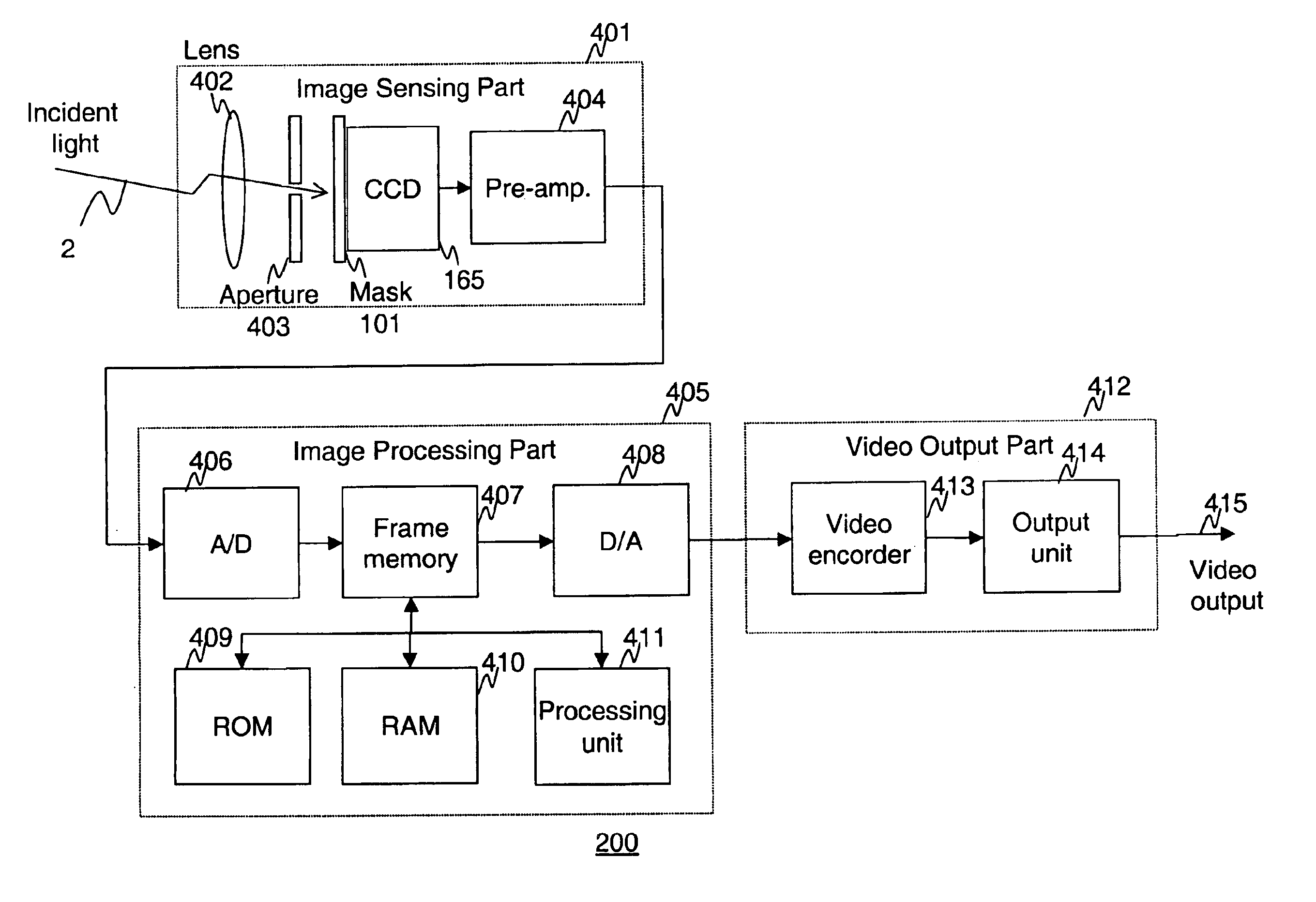
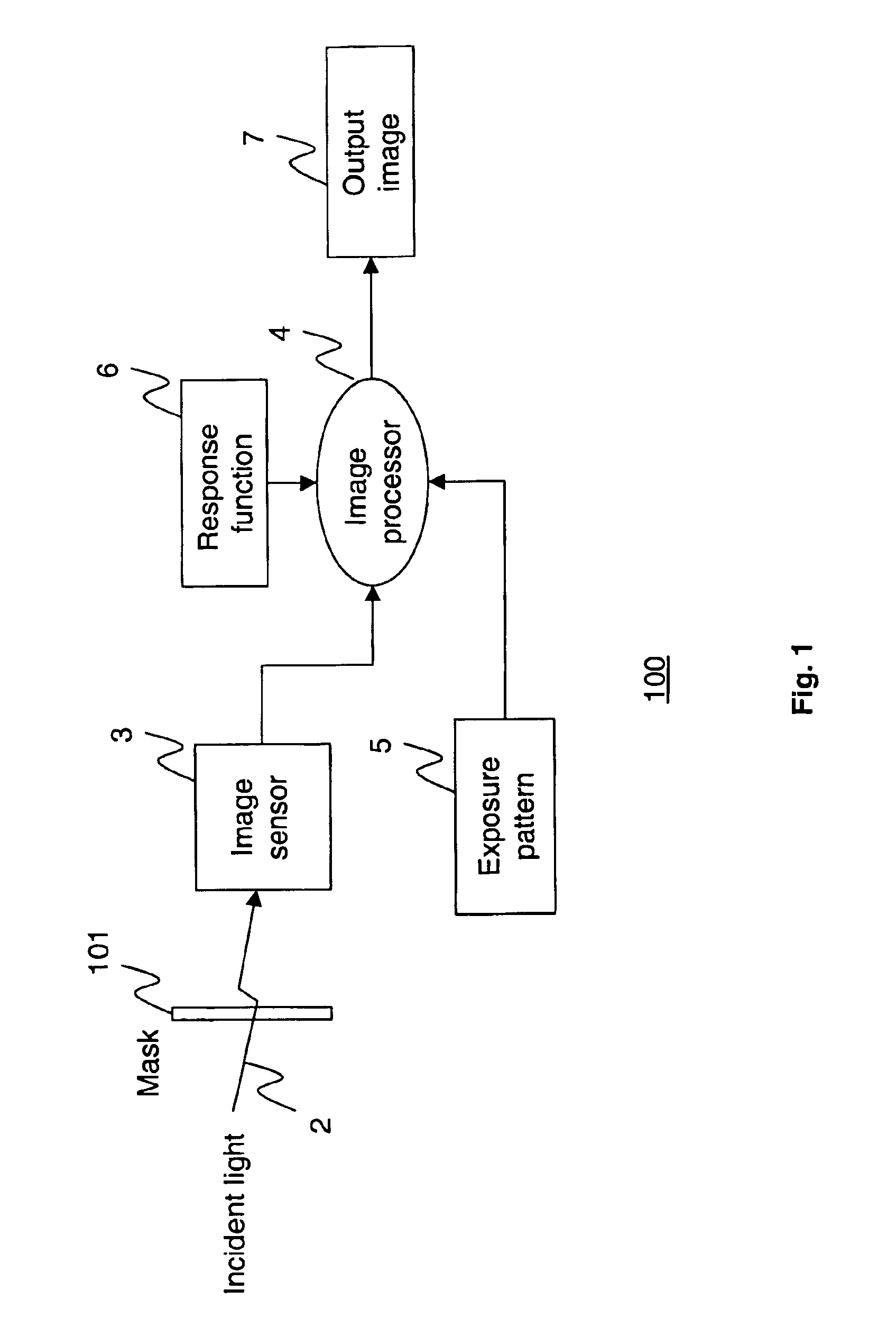
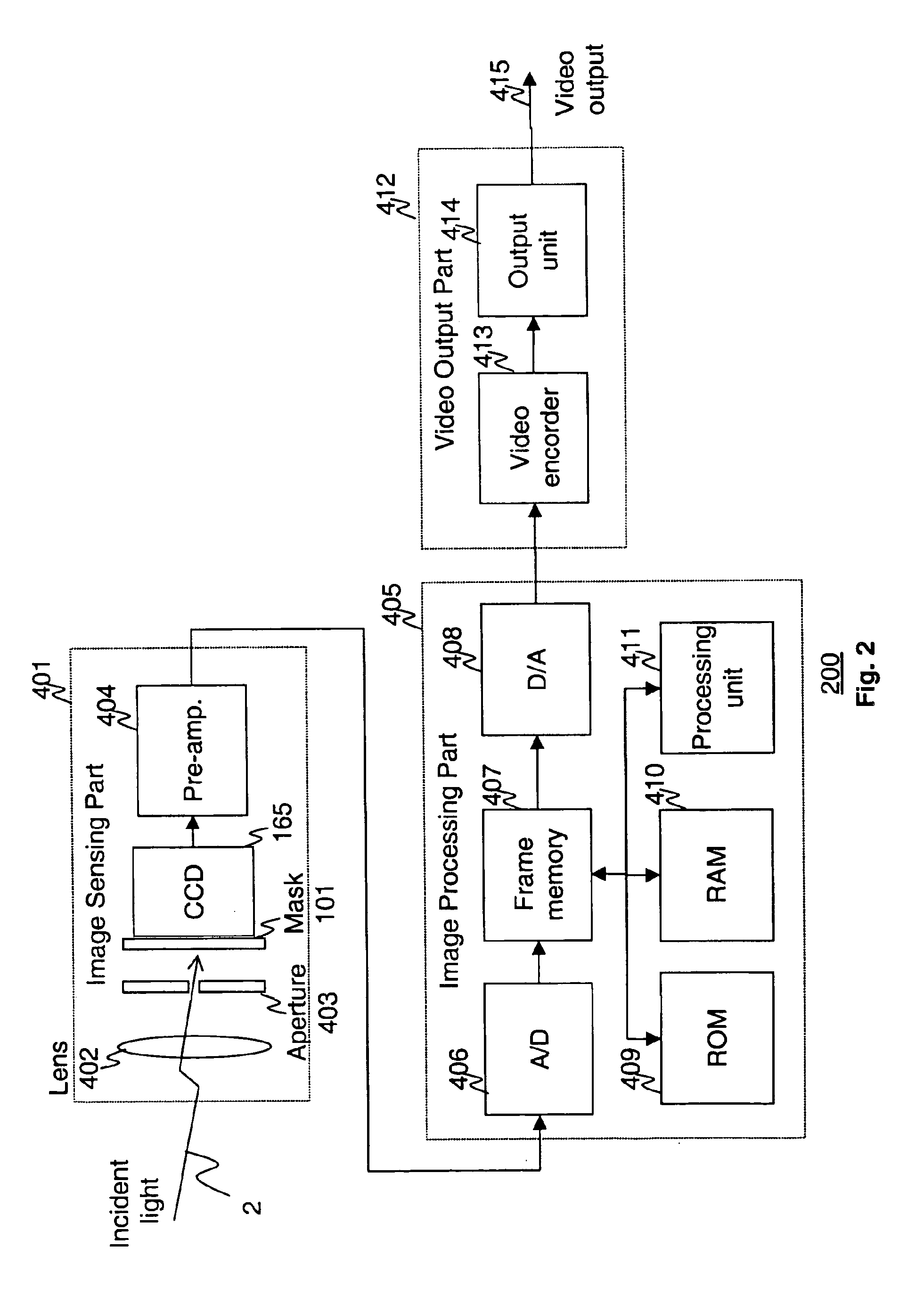
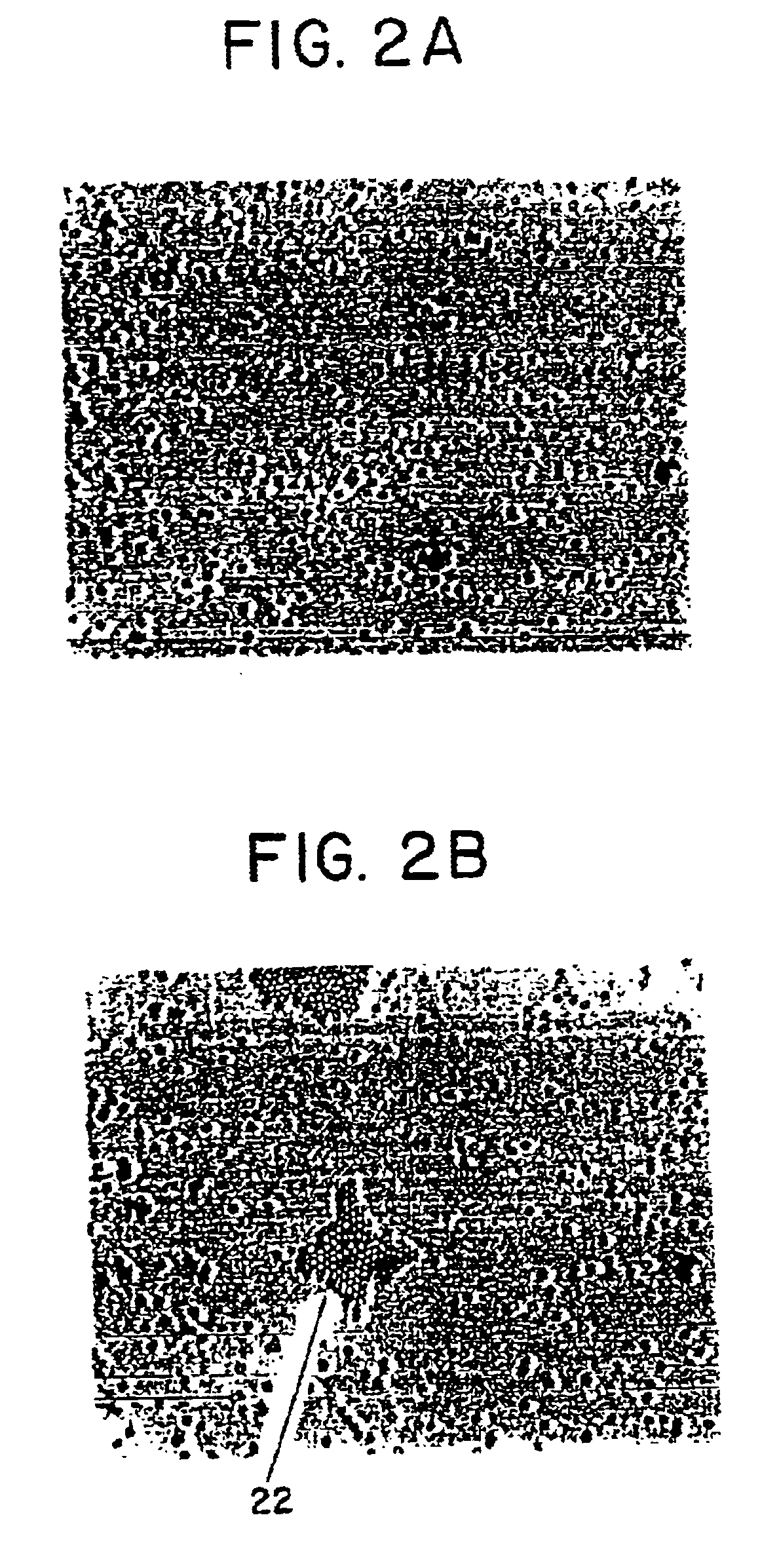
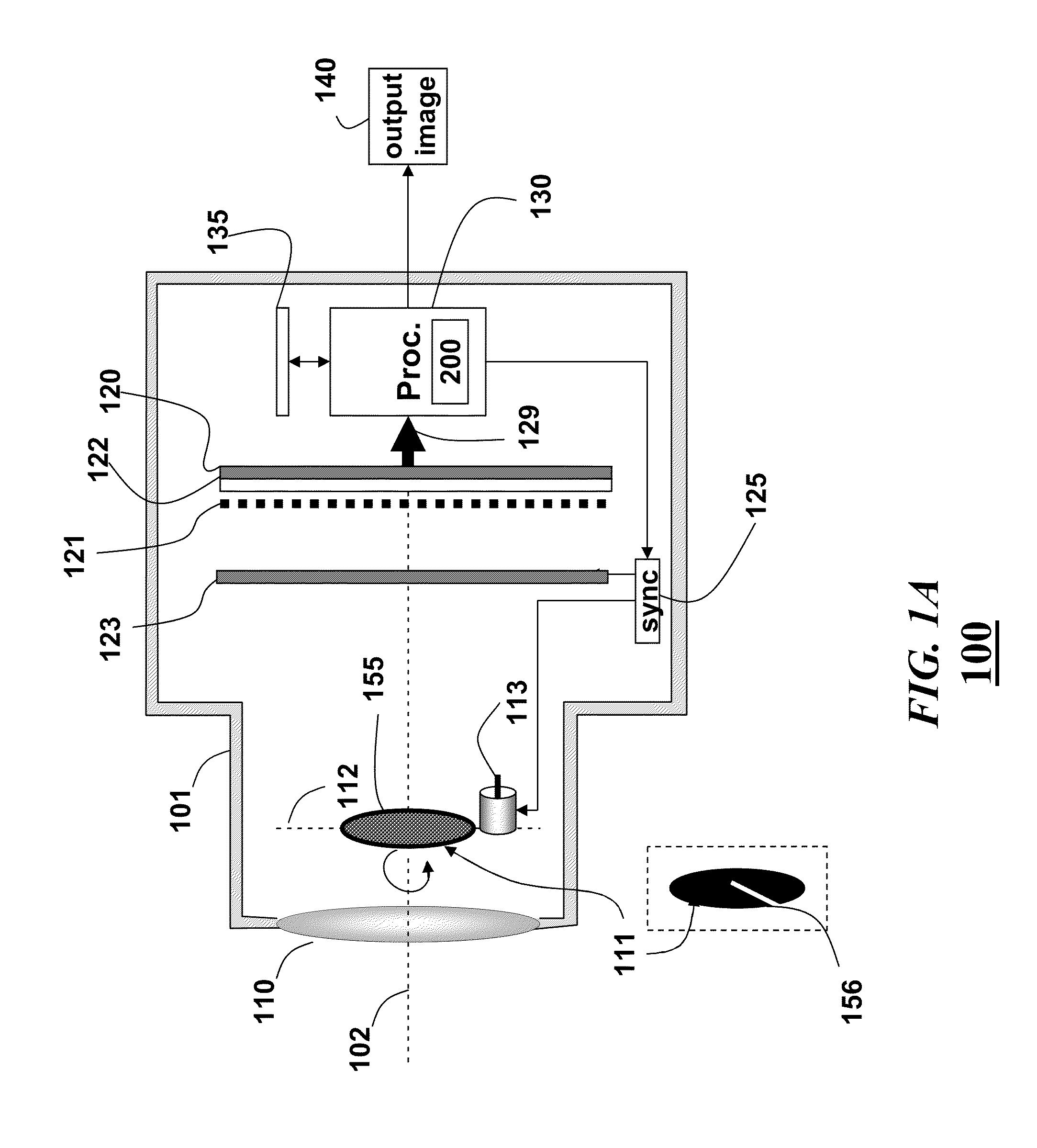
Apparatus and methods are provided for obtaining high dynamic range images using a low dynamic range image sensor. The image of a scene is captured with an image sensor using a spatially varying exposure function. The spatially varying exposure function can be implemented in a number of ways, such as by using as an optical mask with a fixed spatial attenuation pattern or by using an array of light sensing elements having spatially varying photosensitivities. The captured image is then normalized with respect to the spatially varying exposure function. The normalized image data can be interpolated to account for pixels that are either saturated or blackened to enhance the dynamic range of the image sensor.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Space-variant waveplate for polarization conversion, methods and applications
InactiveUS20070115551A1Improve optical qualityPhotomechanical apparatusPolarising elementsPupilOptical polarization
Embodiments of the invention are directed to apparatus and methods for converting spatially homogeneously polarized light into spatially inhomogeneously polarized light having a fast axis orientation that varies in a smooth and continuous manner over a pupil aperture. A space-variant waveplate referred to herein as a polarization converter includes an optically transmissive window characterized by a symmetric stress birefringence that provides at least λ / 4 retardance and, more particularly, λ / 2 retardance over an annular region centered about the optical axis of the window. Structural embodiments of the polarization converter include a mechanical compression housing and a thermal compression housing. Radially and azimuthally polarized vortex beams including cylindrical vector beams and counter-rotating beams can be generated from uniformly plane polarized input beams propagating through the polarization converter. Low-order polarization vortex beams can be optically combined to produce higher-order scalar vortex beams. Embodiments of the invention are also directed to various optical illumination and imaging systems utilizing the apparatus and methods described herein.
Owner:SPILMAN ALEXIS +1
Diffraction Grating With a Spatially Varying Duty-Cycle
InactiveUS20090128911A1Diffraction gratingsPlanar/plate-like light guidesSpatial changeDiffraction optics
A diffractive optical element is disclosed. The optical element comprises a grating having a periodic linear structure in at least one direction. The linear structure is characterized by non-uniform duty cycle selected to ensure non-uniform diffraction efficiency.
Owner:MIRAGE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method and apparatus for obtaining high dynamic range images
InactiveUS7084905B1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLight sensingImage resolution
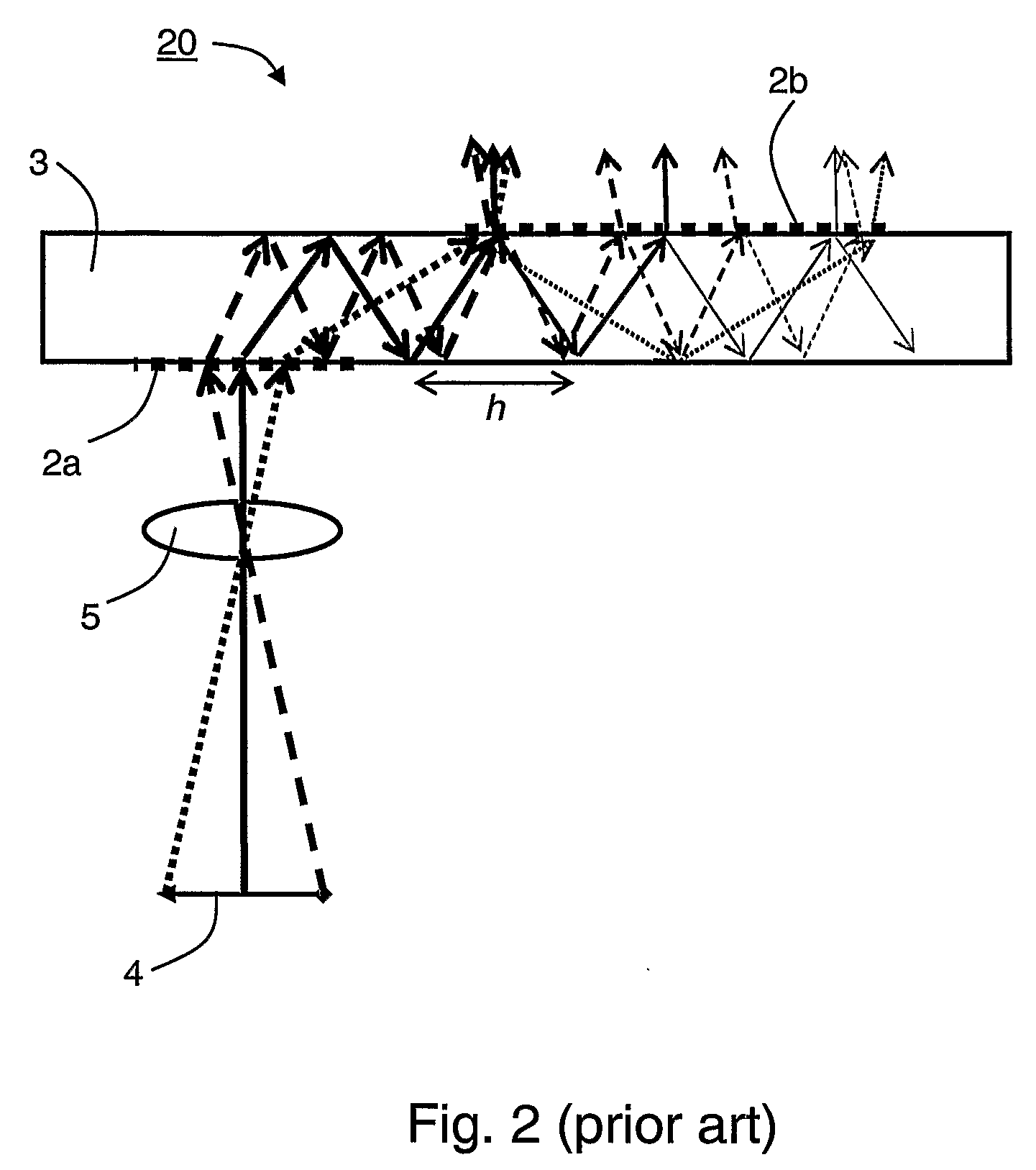
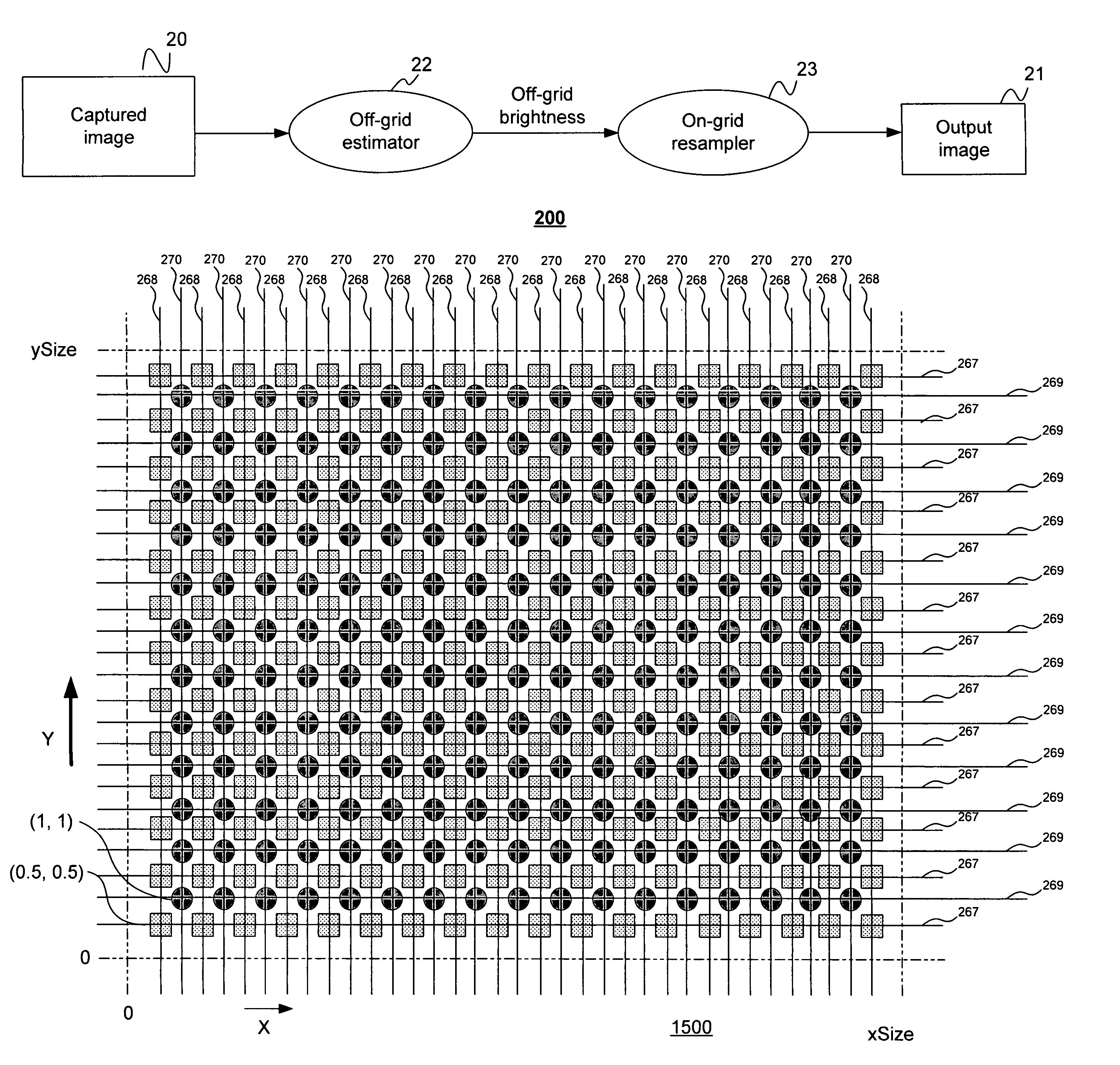
Disclosed are method and apparatus for obtaining relatively high dynamic range images using a relatively low dynamic range image sensor without significant loss of resolution. The image sensor has an array of light-sensing elements with different sensitivity levels in accordance with a predetermined spatially varying sensitivity pattern for the array of light-sensing elements. An image of a scene is captured with the image sensor and stored as brightness values at respective pixel positions in a linear or two-dimensional uniform grid. The brightness values of the captured image at the pixel positions are then used to estimate the brightness values at off-grid positions of a uniform off-grid array located at respective interstices of the pixel position grid. The estimated off-grid brightness values are either used directly as the pixel brightness values of a relatively high dynamic output image or interpolated to derive resampled on-grid brightness values at the pixel positions of the pixel position grid to provide a relatively high dynamic range output image. Alternatively, the brightness values of the captured image are interpolated by an on-grid interpolation filter to derive pixel brightness values of a relatively high dynamic range output image, each pixel brightness value of the output image being derived from a corresponding plurality of the captured image brightness values. In each instance, either the captured image brightness values or the pixel brightness values of the output image may be compensated for non-linearities of the radiometric response function of the light-sensing elements of the image sensor.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Method and apparatus for generating structural pattern illumination
InactiveUS6937348B2High measurement accuracyImprove resolution accuracyImage analysisHearing aid design aspectsLighting spectrumSpatial change
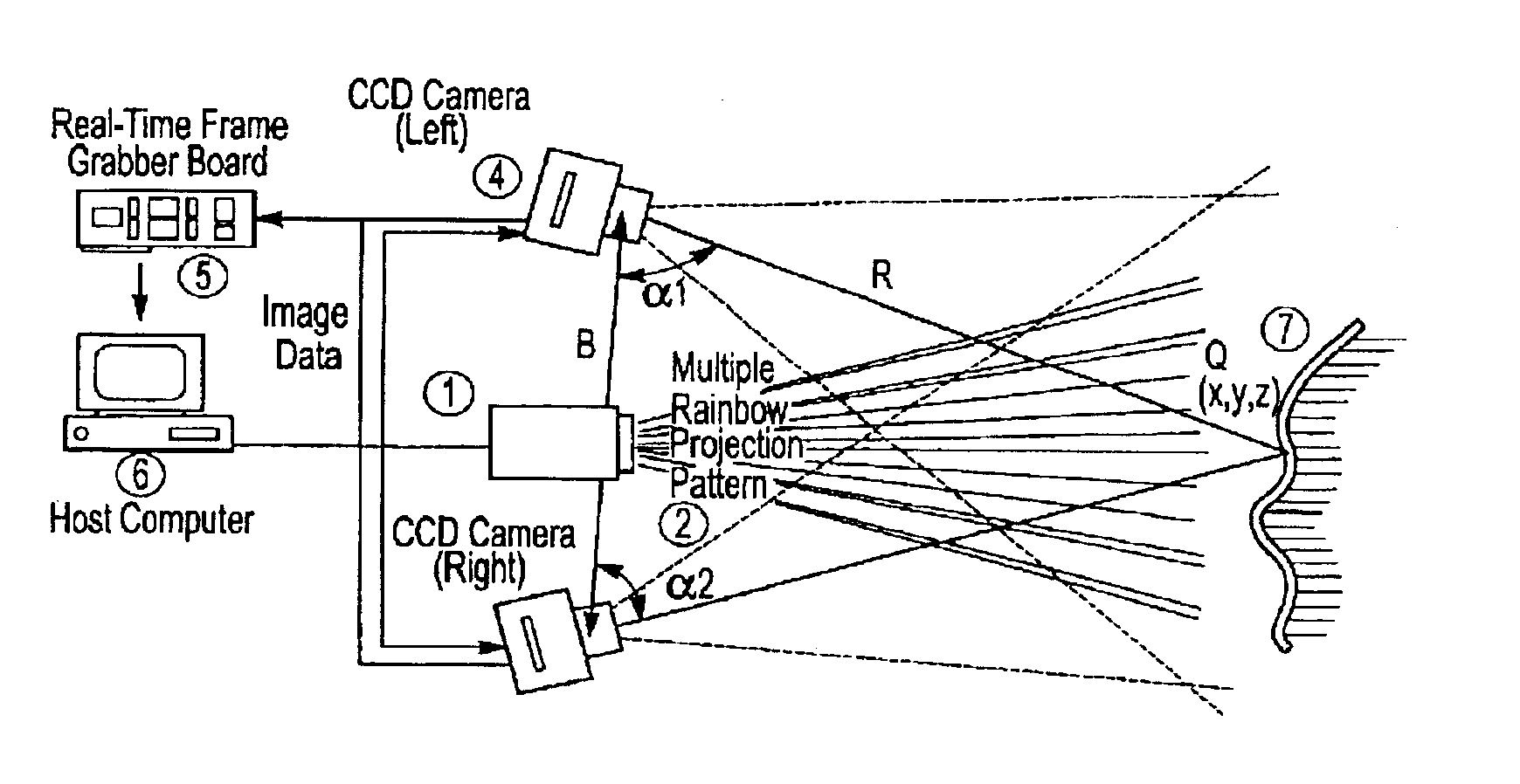
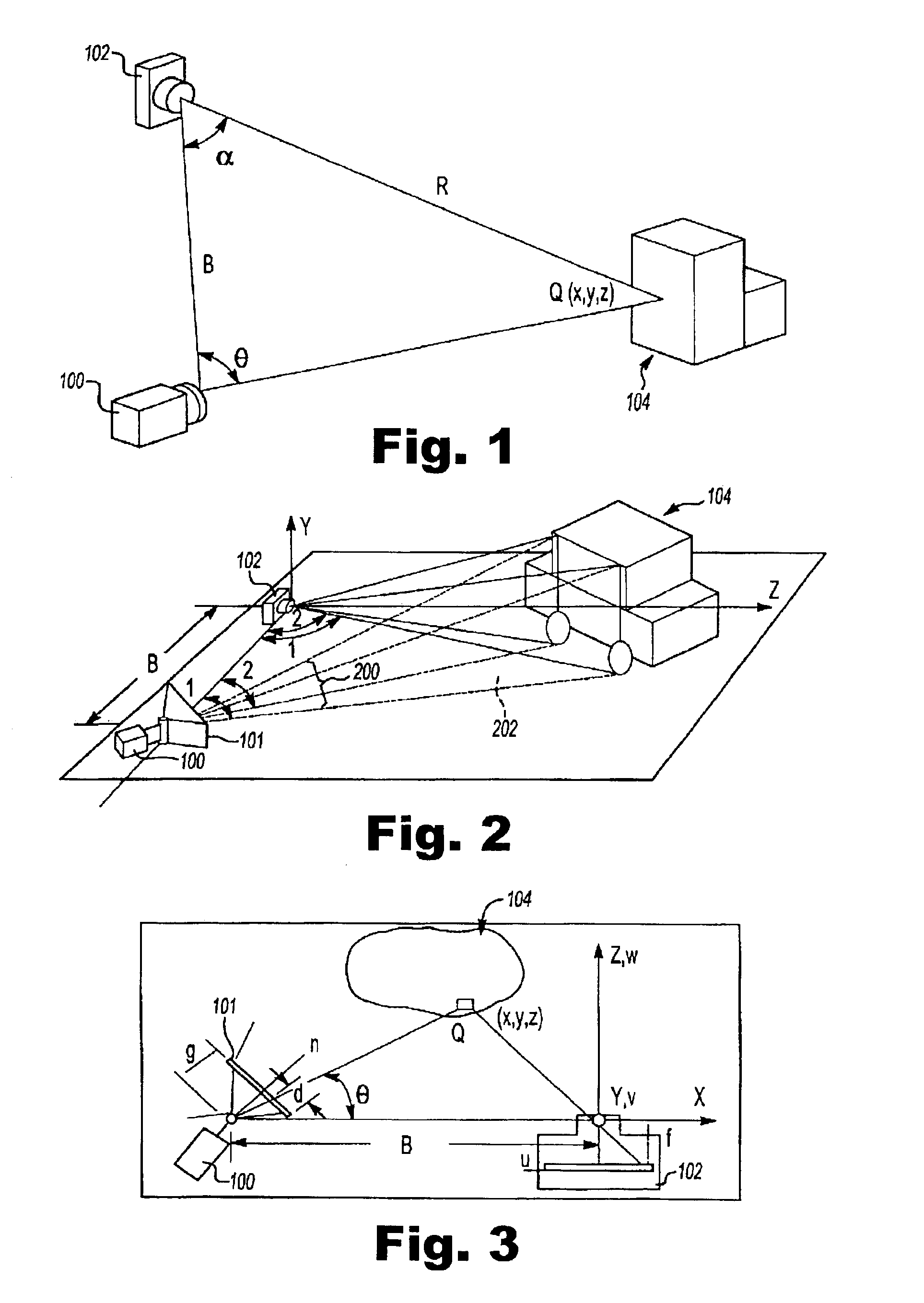
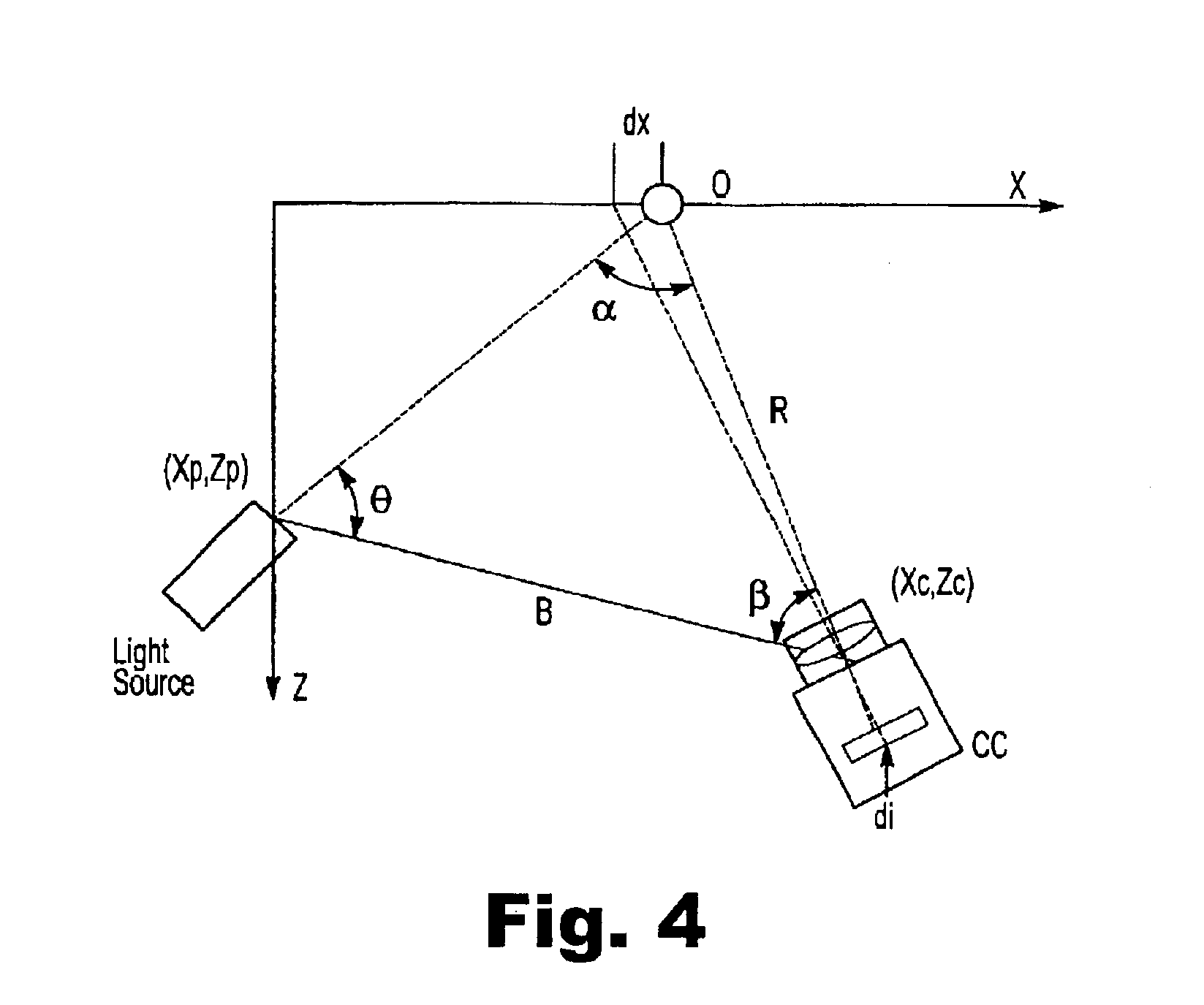
A three-dimensional imaging method and system illuminates an object to be imaged with a light pattern that is formed from two or more light sub-patterns. The sub-patterns can each encompass the visible light spectrum or can be spatially varying intensity sub-patterns that each correspond to a red, green, or blue component. The light pattern is generated by a slotted planar member or an optical filter.
Owner:TECHNEST HLDG
Microfabricated ultrasonic transducers with bias polarity beam profile control and method of operating the same
InactiveUS7087023B2Increased complexityIncrease expensesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCapacitanceSlice thickness
A capacitive microfabricated ultrasonic transducer with control of elevation phase through alternating bias polarity is disclosed. Such control of elevation phase results in simple ultrasonic probes with excellent slice thickness attributes. Furthermore, tight spatial variation of phase results in an effective way to achieve transmit aperture and apodization control. Further still, such capacitive microfabricated ultrasonic transducers can achieve elevation focus without the need of a lossy mechanical lens.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Array cytometry
InactiveUS6958245B2Easy to disassembleMinimize Faradaic processImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsParticulatesSilicon oxide
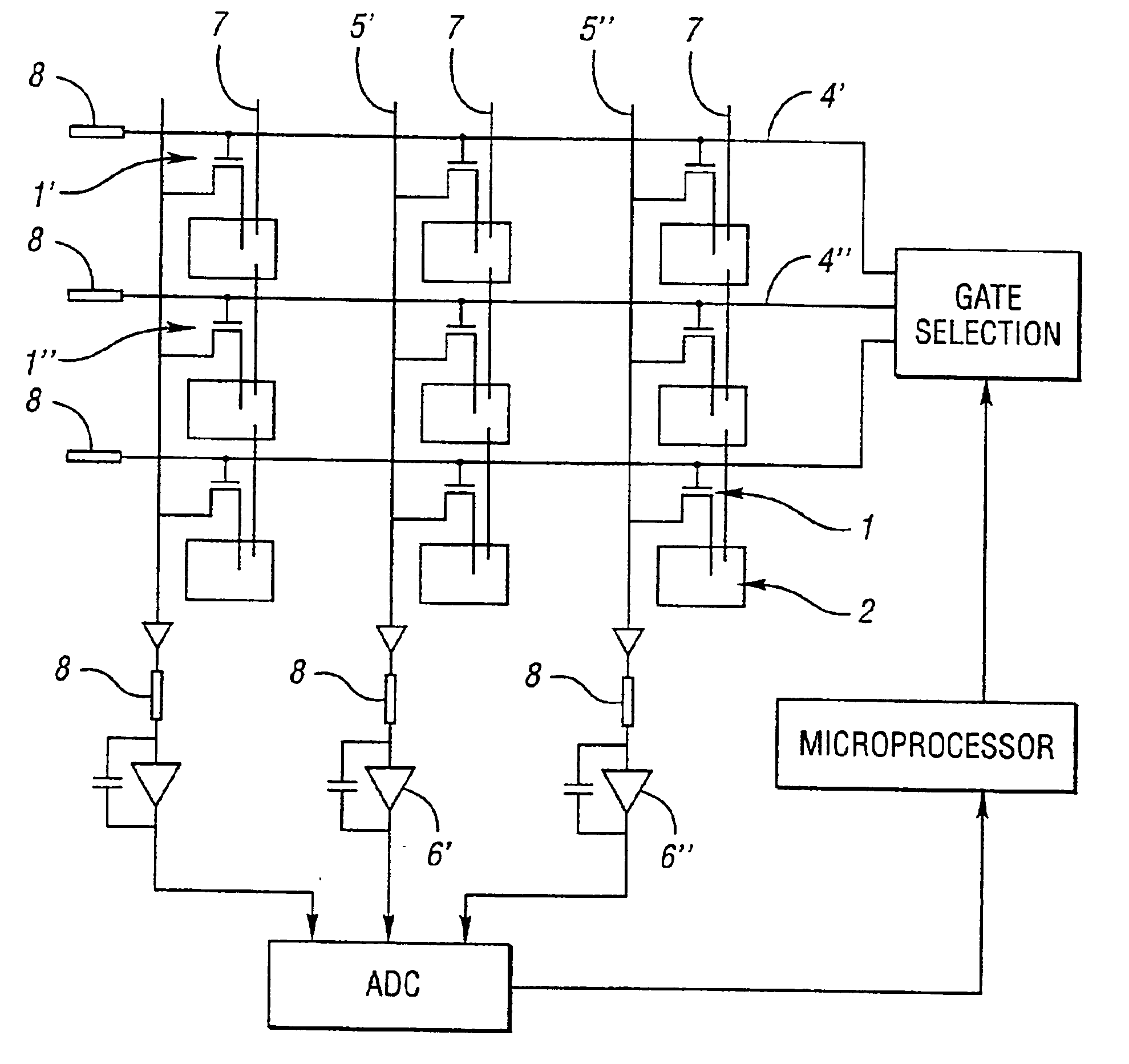
A method and apparatus for the manipulation of colloidal particulates and biomolecules at the interface between an insulating electrode such as silicon oxide and an electrolyte solution. Light-controlled elektrokinetic assembly of particles near surfaces relies on the combination of three functional elements, the AC electric field-induced assembly of planar aggregates; the patterning of the electrolyte / silicon oxide / silicon interface to exert spatial control over the assembly process; and the real-time control of the assembly process via external illumination. The present invention provides a set of fundamental operations enabling interactive control over the creation and placement of planar arrays of several types of particles and biomolecules and the manipulation of array shape and size. The present invention enables sample preparation and handling for diagnostic assays and biochemical analysis in an array format, and the functional integration of these operations. In addition, the present invention provides a procedure for the creation of material surfaces with desired properties and for the fabrication of surface-mounted optical components. This invention is also for a method and apparatus to direct the lateral motion and induce the assembly into planar arrays of cells on semiconductor surfaces in response to temporally and spatially varying electric fields and to projected patterns of illumination.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
Apparatus and method for high dynamic range imaging using spatially varying exposures
InactiveUS7924321B2Minimize the numberSubstantial lossTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsHigh-dynamic-range imagingUltrasound attenuation
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
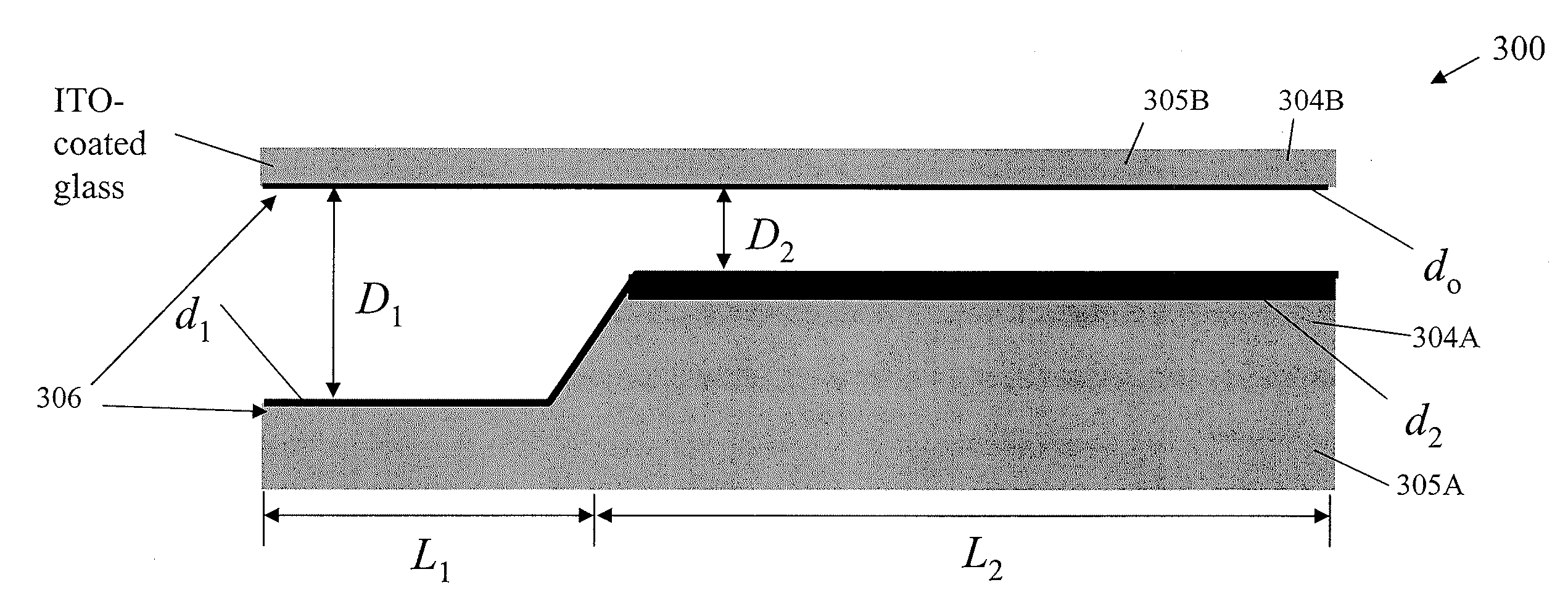
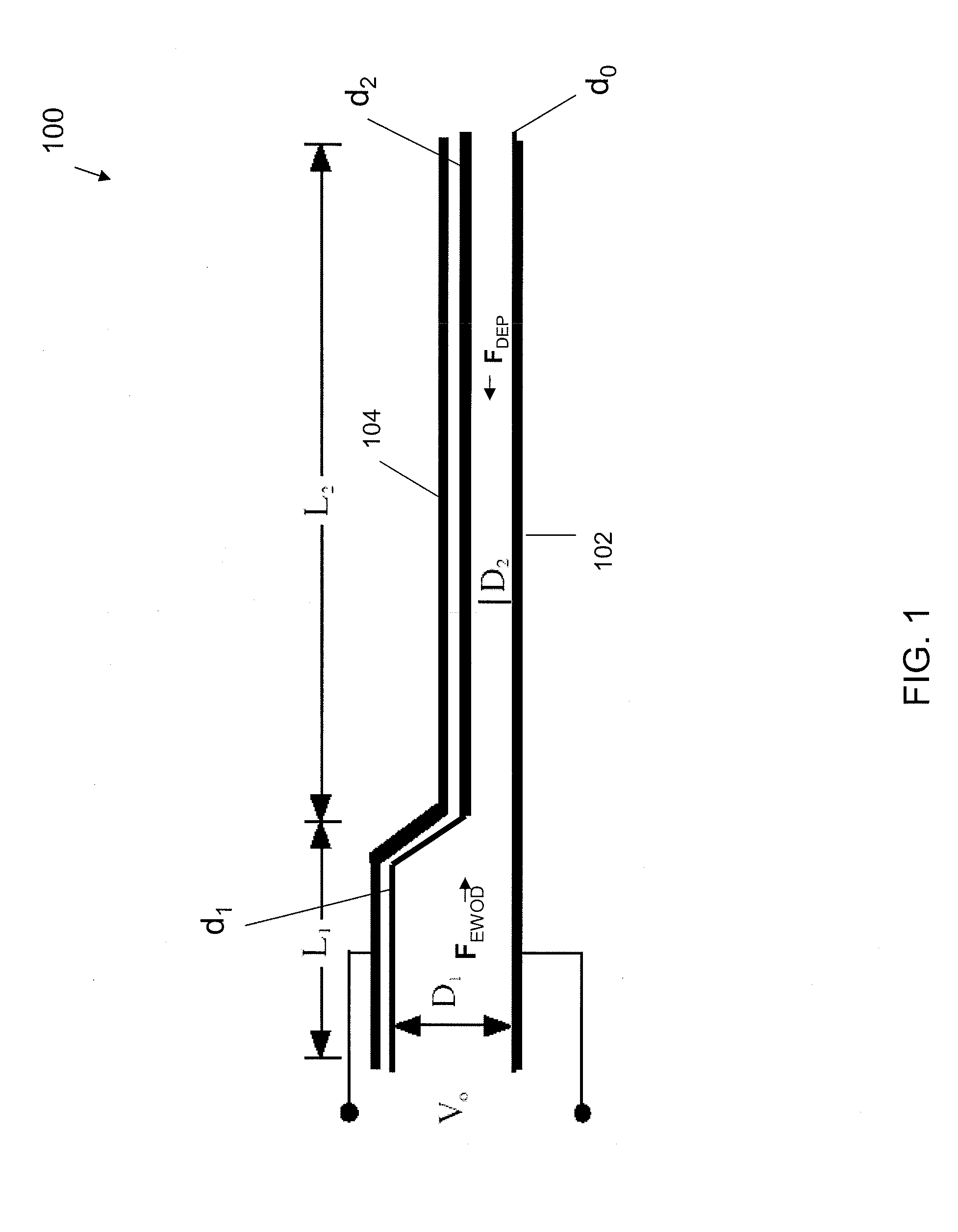
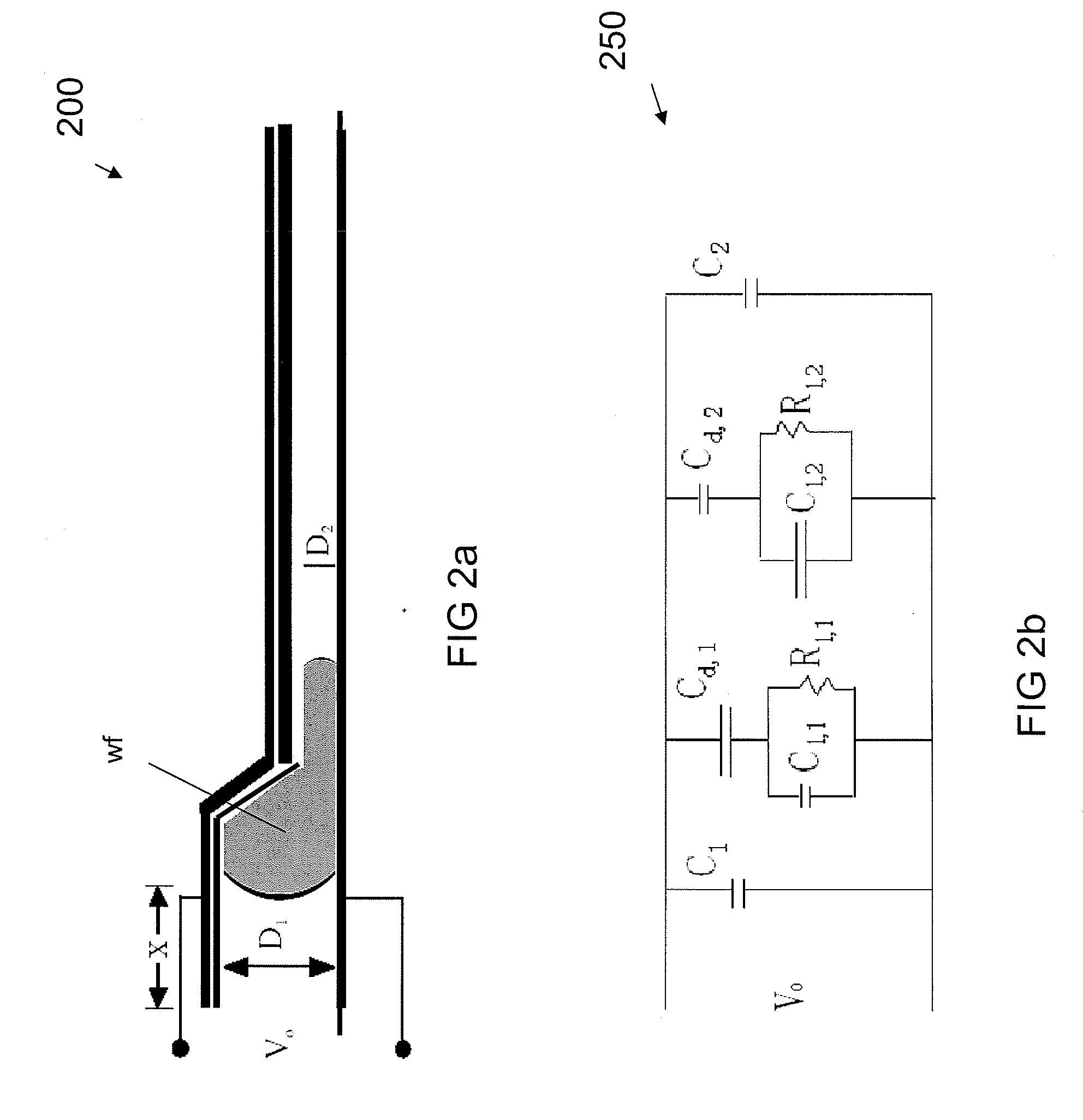
Frequency-addressable Apparatus and Methods for Actuation of Liquids
InactiveUS20080169195A1Uniform thicknessSludge treatmentElectrostatic separatorsDielectricWorking fluid
Embodiments of the invention are directed to apparatus, methods, and applications involving the actuation of a semi-insulative working fluid by electromechanical forces based on electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD) and liquid dielectrophoresis (liquid DEP) mechanisms that are controlled by the frequency, but not the magnitude, of an AC voltage (i.e., ‘frequency-addressable). In the various apparatus embodiments of the invention, a single, frequency-addressable electrode pair includes at least one electrode that has a spatially-varying dielectric coating thickness and thus a spatially-varying electrode gap wherein at least a portion of which a volume of a working fluid can stably reside under no influence of an applied voltage. In an exemplary aspect, a frequency-addressable, bistable apparatus includes at least one wider gap and one narrower gap associated, respectively, with a thicker and a thinner dielectric coating thickness of the electrode(s). The working fluid resides in only one of the at least two gap regions only under the influence of capillary force. A brief burst of AC voltage at a selected high frequency or low frequency will move the liquid from one gap region to another (and back) by one of an EWOD-based and a DEP-based force. In an alternative aspect, an analog apparatus has a continuous, spatially-varying electrode gap in which the dielectric coating thickness on the electrodes varies smoothly in an inverse manner. Various applications to a display device, fiber optic coupler and attenuator, controlled liquid volume dispensers, spotting arrays, well plate apparatus, and others are presented, along with control methods.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Array cytometry
InactiveUS7056746B2Easy to disassembleMinimize Faradaic processSequential/parallel process reactionsOrganic chemistry methodsParticulatesEngineering
A method and apparatus for the manipulation of colloidal particulates and biomolecules at the interface between an insulating electrode such as silicon oxide and an electrolyte solution. Light-controlled electrokinetic assembly of particles near surfaces relies on the combination of three functional elements: the AC electric field-induced assembly of planar aggregates; the patterning of the electrolyte / silicon oxide / silicon interface to exert spatial control over the assembly process; and the real-time control of the assembly process via external illumination. The present invention provides a set of fundamental operations enabling interactive control over the creation and placement of planar arrays of several types of particles and biomolecules and the manipulation of array shape and size. The present invention enables sample preparation and handling for diagnostic assays and biochemical analysis in an array format, and the functional integration of these operations. In addition, the present invention provides a procedure for the creation of material surfaces with desired properties and for the fabrication of surface-mounted optical components. This invention is also for a method and apparatus to direct the lateral motion and induce the assembly into planar arrays of cells on semiconductor surfaces in response to temporally and spatially varying electric fields and to projected patterns of illumination.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
Retarder-based despeckle device for laser illumination systems
ActiveUS20090257106A1Reducing perceived speckleHigh degreeLaser detailsColor television detailsImage resolutionLight beam
A method and apparatus for reducing speckle in a laser illumination system uses a despeckle device including an optical retarder providing an odd integer multiple of substantially half-wave retardation for light emitted from a coherent laser in the laser illumination system. The near half-wave optical retarder has a substantially constant retardance and a spatially varied slow axis. The spatially varied slow axis imposes a phase mask on the beam of light, which provides sub-resolution optical phase modulation to a resolution spot on the detector. The near half-wave optical retarder is actuated mechanically or electrically to vary the sub-resolution optical phase modulation within an integration time of the detector.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
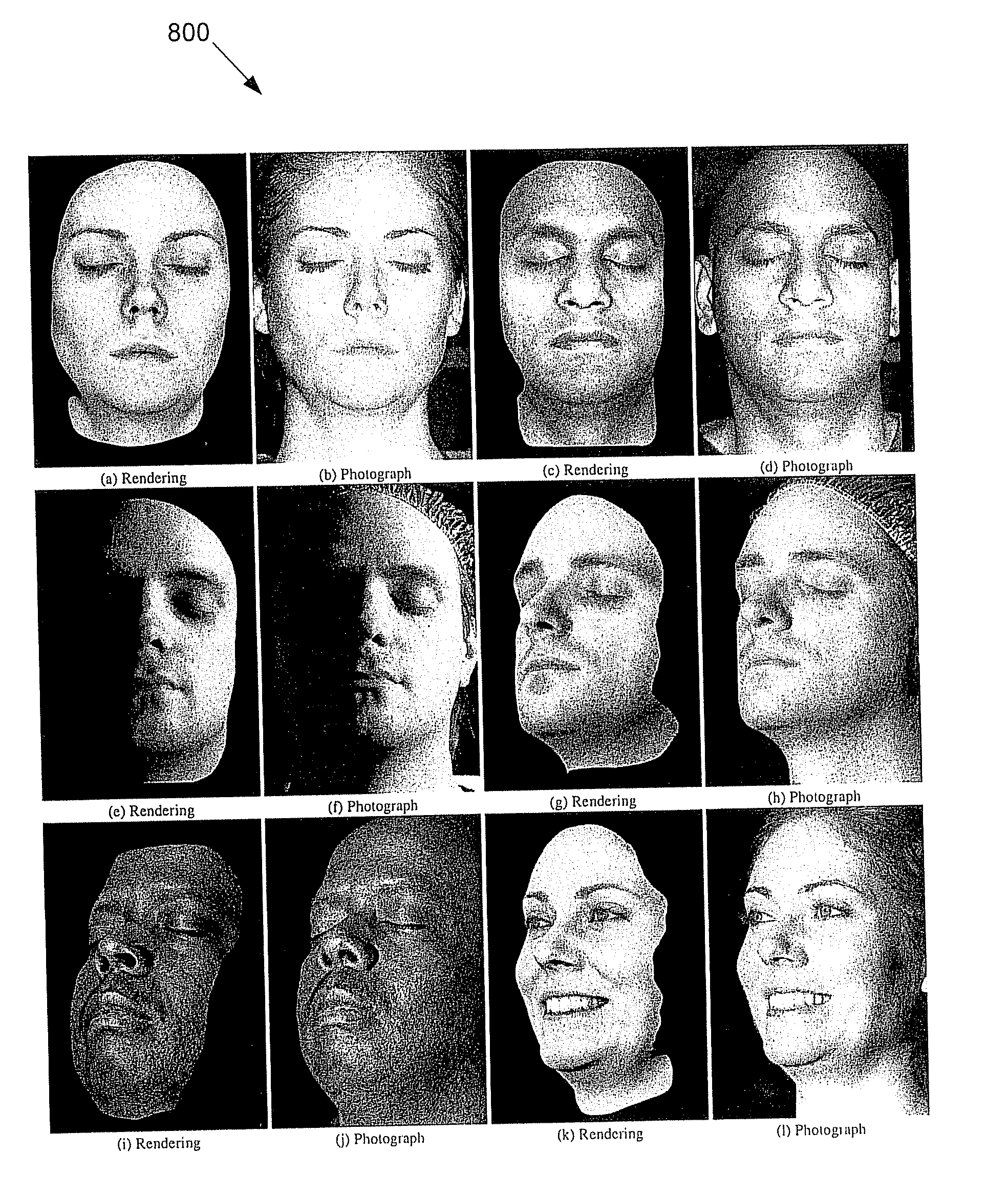
Practical Modeling and Acquisition of Layered Facial Reflectance
ActiveUS20090226049A1Easy to mergeConvenience to workCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsViewpointsDeep level
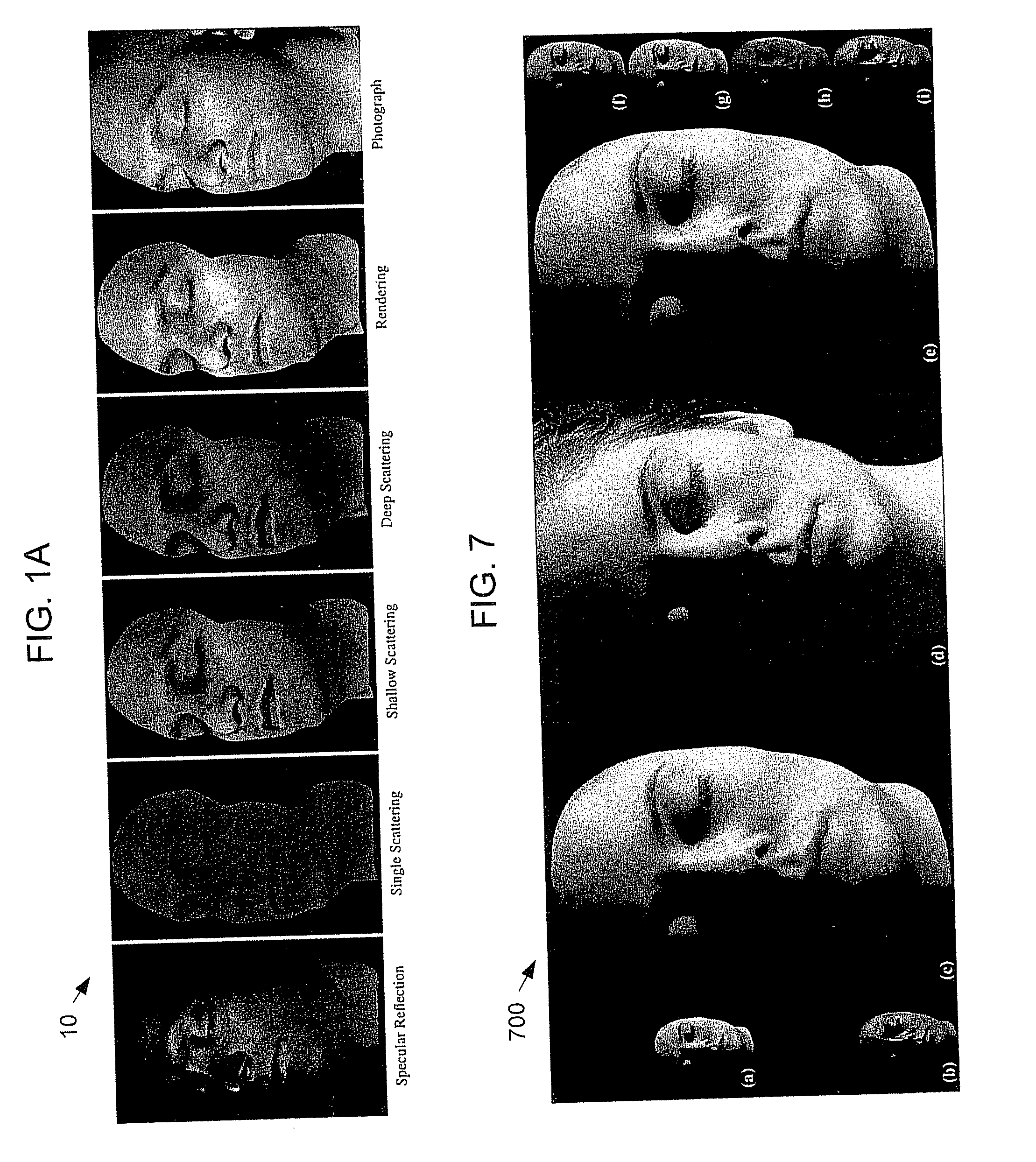
Techniques are described for modeling layered facial reflectance consisting of specular reflectance, single scattering, and shallow and deep subsurface scattering. Parameters of appropriate reflectance models can be estimated for each of these layers, e.g., from just 20 photographs recorded in a few seconds from a single view-point. Spatially-varying specular reflectance and single-scattering parameters can be extracted from polarization-difference images under spherical and point source illumination. Direct-indirect separation can be employed to decompose the remaining multiple scattering observed under cross-polarization into shallow and deep scattering components to model the light transport through multiple layers of skin. Appropriate diffusion models can be matched to the extracted shallow and deep scattering components for different regions on the face. The techniques were validated by comparing renderings of subjects to reference photographs recorded from novel viewpoints and under novel illumination conditions. Related geometry acquisition systems and software products are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Method, processor and computed tomography (CT) machine for generating images utilizing high and low sensitivity data collected from a flat panel detector having an extended dynamic range
InactiveUS6868138B2Television system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayFlat panel detector
A method, processor and computed tomography (CT) machine for generating images utilizing high and low sensitivity data collected from a flat panel detector having an extended dynamic range. Hardware modifications for extending the dynamic range include grouping pixel rows and pixel columns into clusters of two. The sensitivity of the rows / columns is modified by positioning optical masks that have different transparencies for different rows / columns. Software modifications for extending the dynamic range include taking two correlated exposure scan measurements at each angle and combining the two data sets into one scan prior to image reconstruction. This method uses a spatially varying pixel exposure method where several adjacent pixels are clustered and each cluster has a different sensitivity. The signals of these clusters are combined to form one image effectively producing an increased dynamic range. The flat panel imager may be an a-Si:H based flat panel detector for use in X-ray imaging, including cone beam computer tomography (CBCT).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Radiation imaging system and method
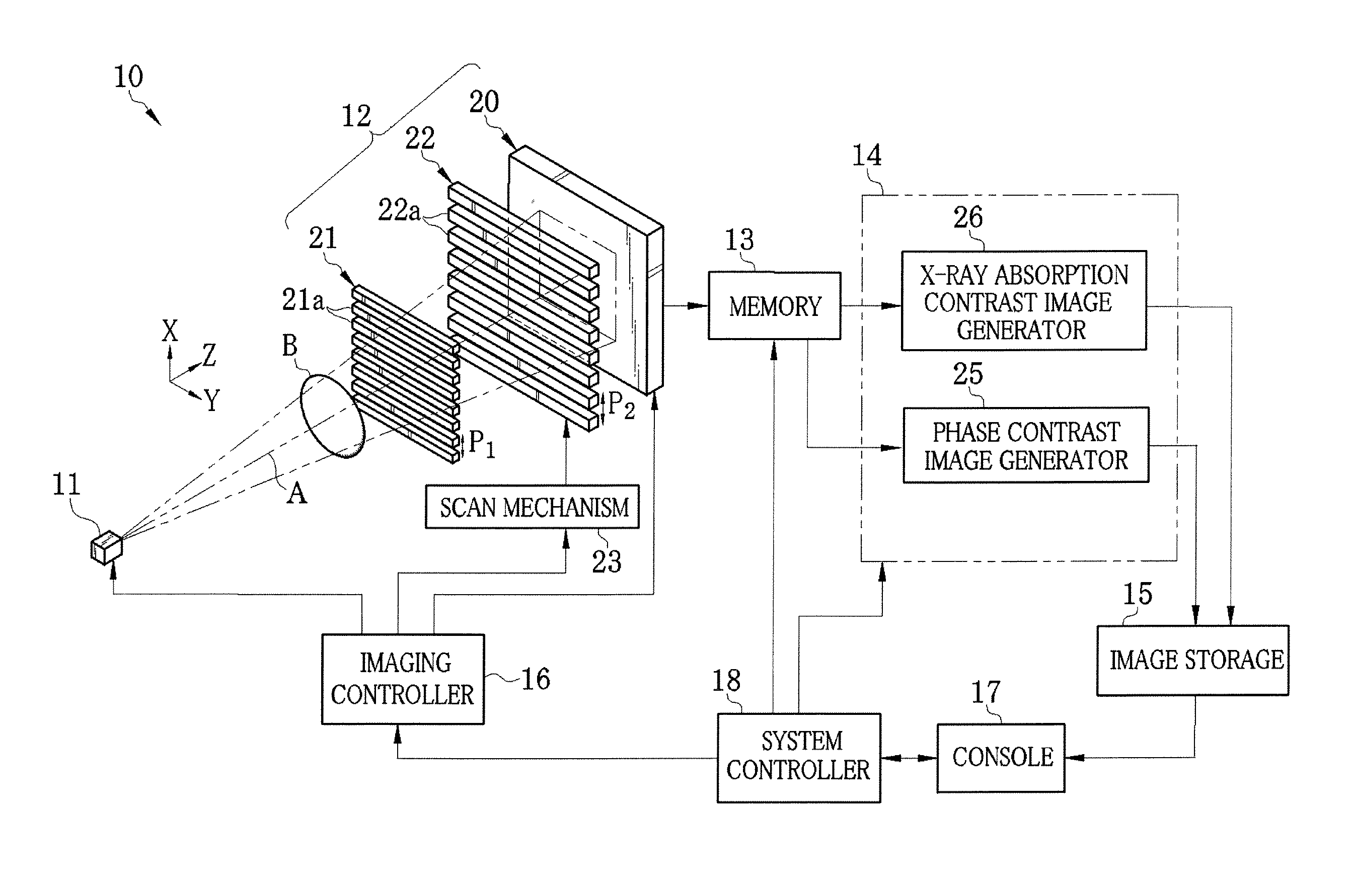
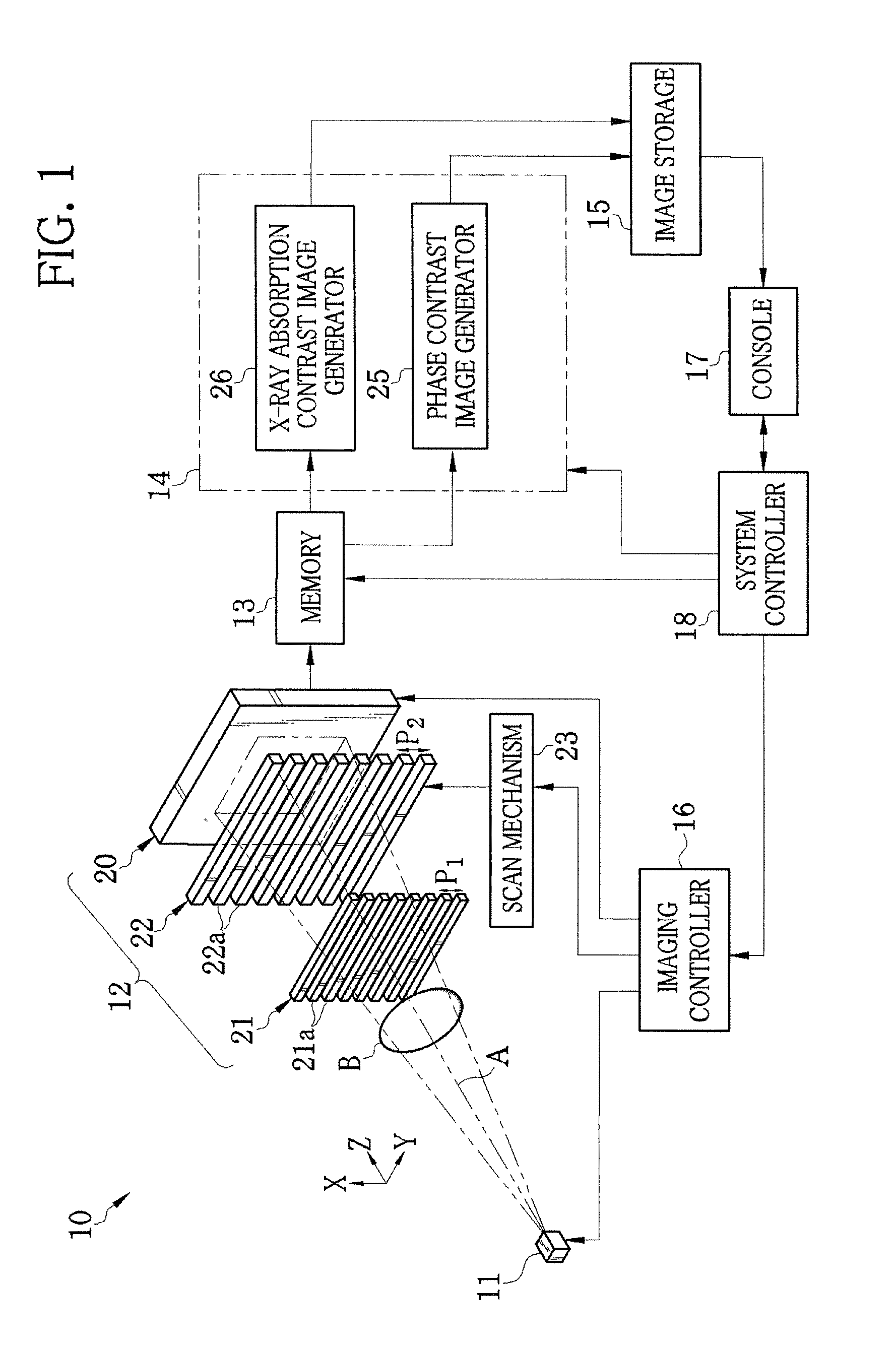
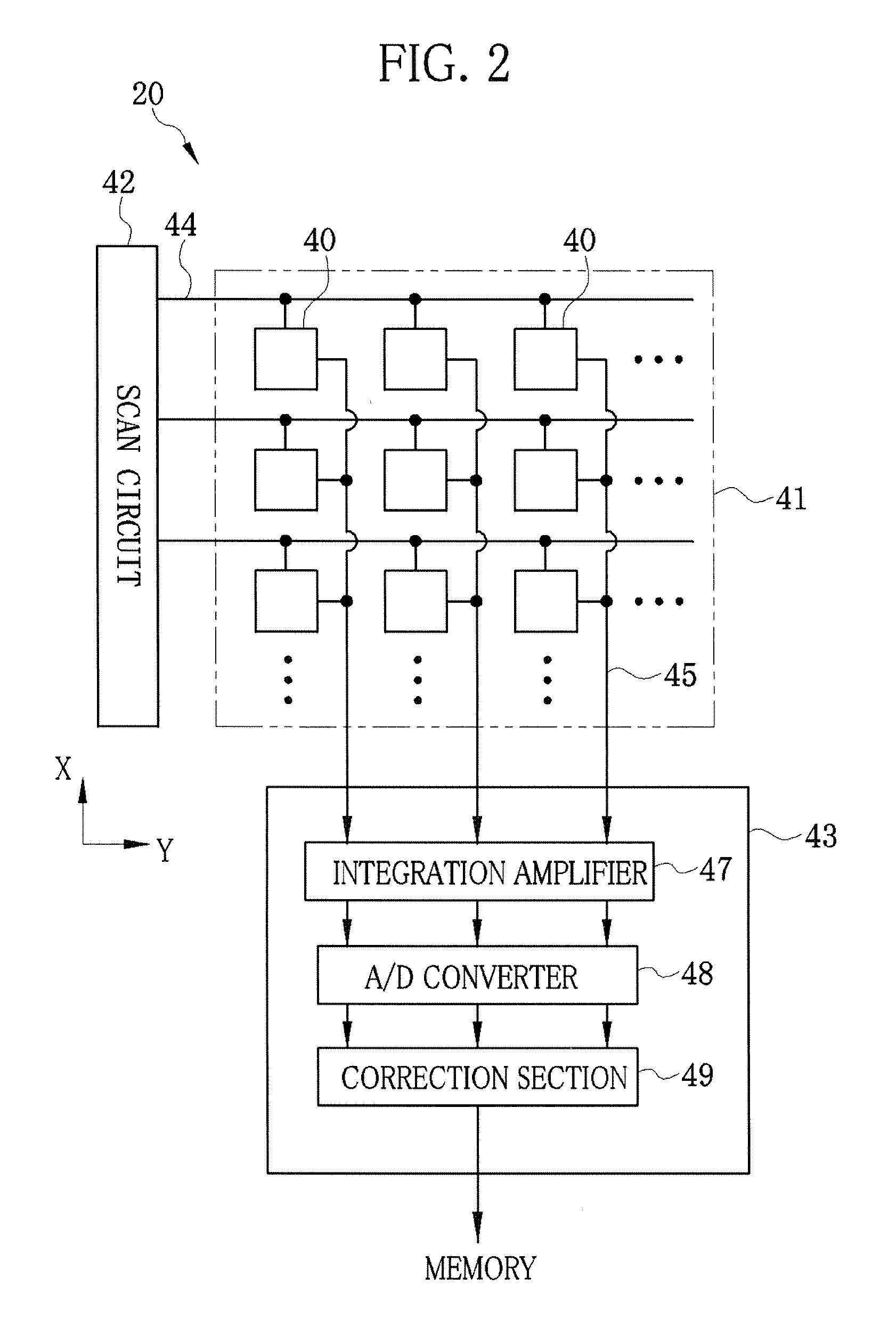
InactiveUS20110243302A1Eliminate the effects ofEnhance the imageImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingGratingAbsorption contrast
A radiation imaging system includes an X-ray source, first and second absorption gratins disposed in a path of X-rays emitted from the X-ray source, and an FPD. The second absorption grating is stepwise slid in an X direction relatively against the first absorption grating. Whenever the second absorption grating is slid, the FPD captures a fringe image and produces image data. A correction section corrects the image data for spatial variation of X-ray transmittance of the first and second absorption gratings. A phase contrast image generator produces a phase contrast image from the corrected image data. An X-ray absorption contrast image generator calculates a value related to an average of the corrected image data on a pixel-by-pixel basis, and produces an X-ray absorption contrast image from the value.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
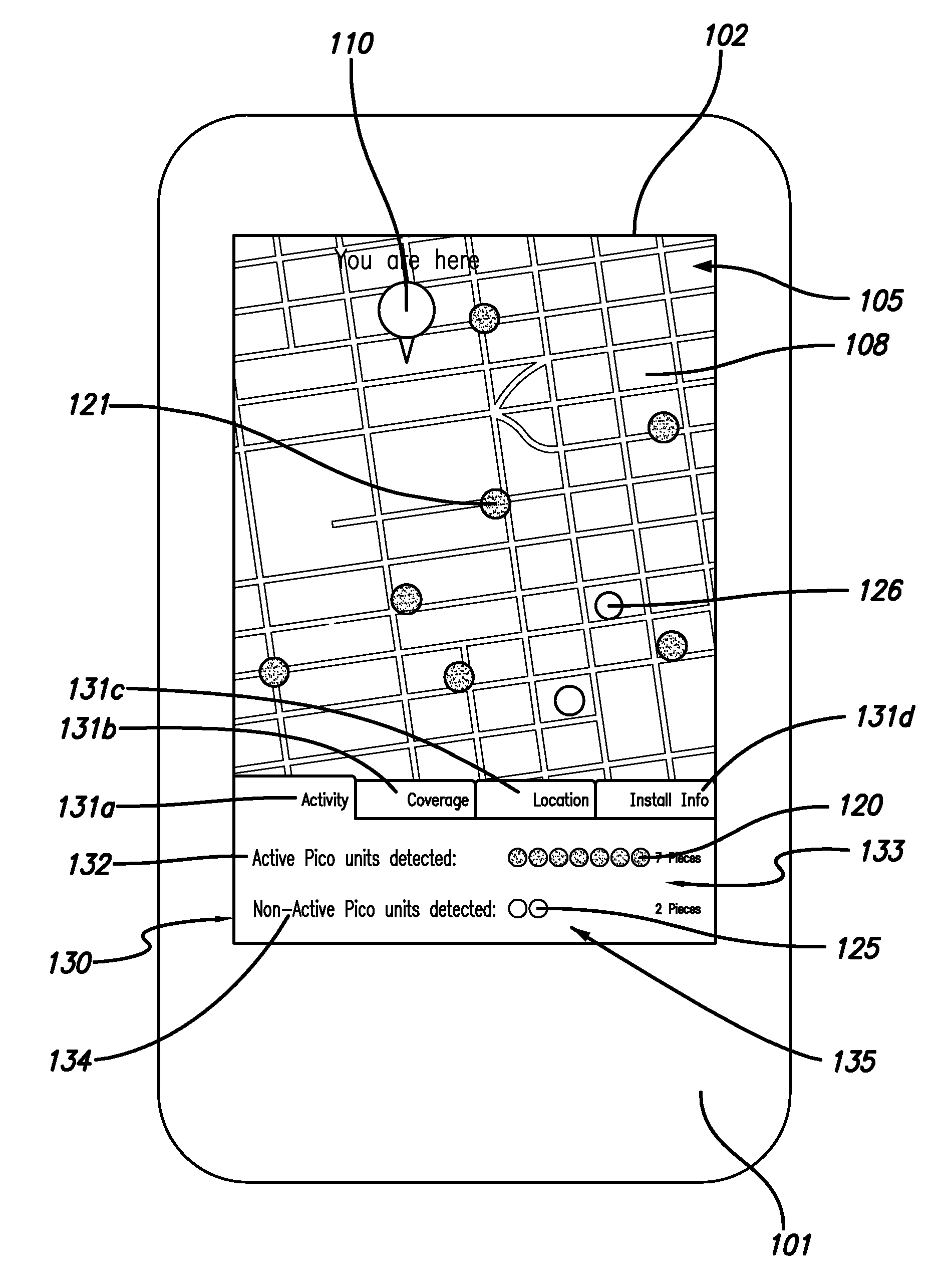
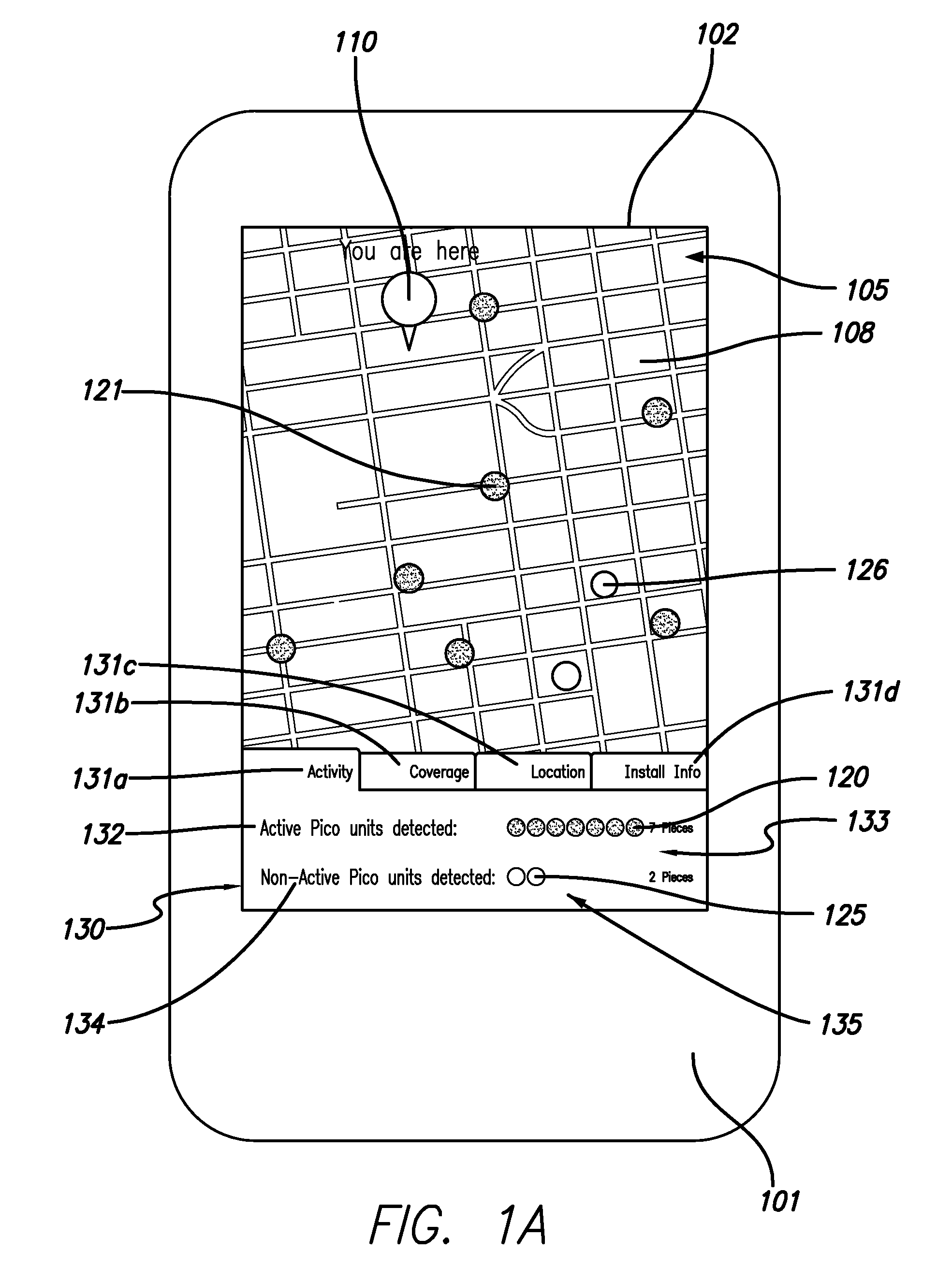
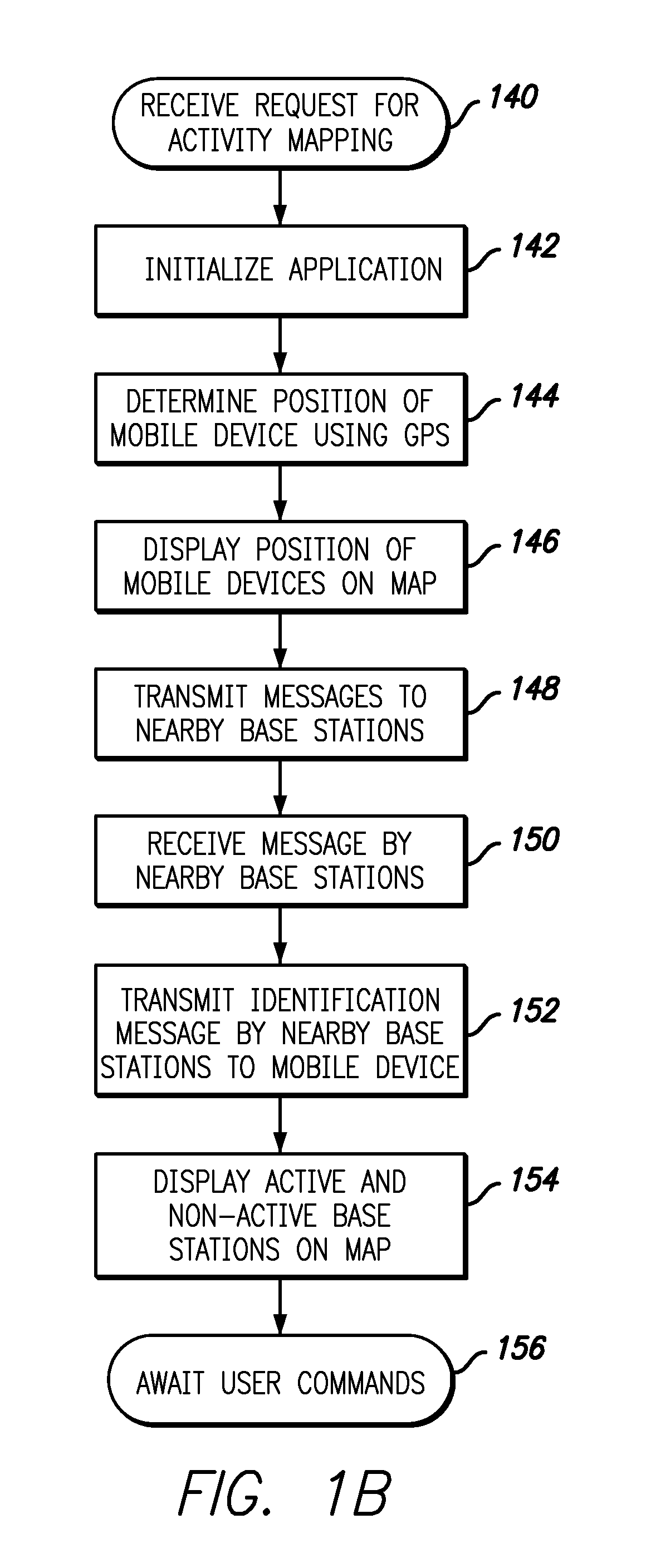
Pico base station location and analysis using mobile devices
A base station analysis system and method that may employ commercially-available mobile device platforms is disclosed. The base station analysis application enables a service technician to locate nearby base stations in the field, determine which base stations are functioning properly, and retrieve information associated with the base stations. The mobile device displays nearby base stations on a street map relative to the location of the mobile device in an embodiment. The mobile device preferably displays the spatially-varying signal strength for the active base stations to enable the service technician to locate dead spots in the coverage. The mobile device displays a reality augmented view having graphical icons which represent base stations embedded within a street-view image obtained by the mobile device camera in a preferred embodiment. When a service technician selects a base station icon, installation information describing the base station is provided.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and methods for obstacle mapping and navigation
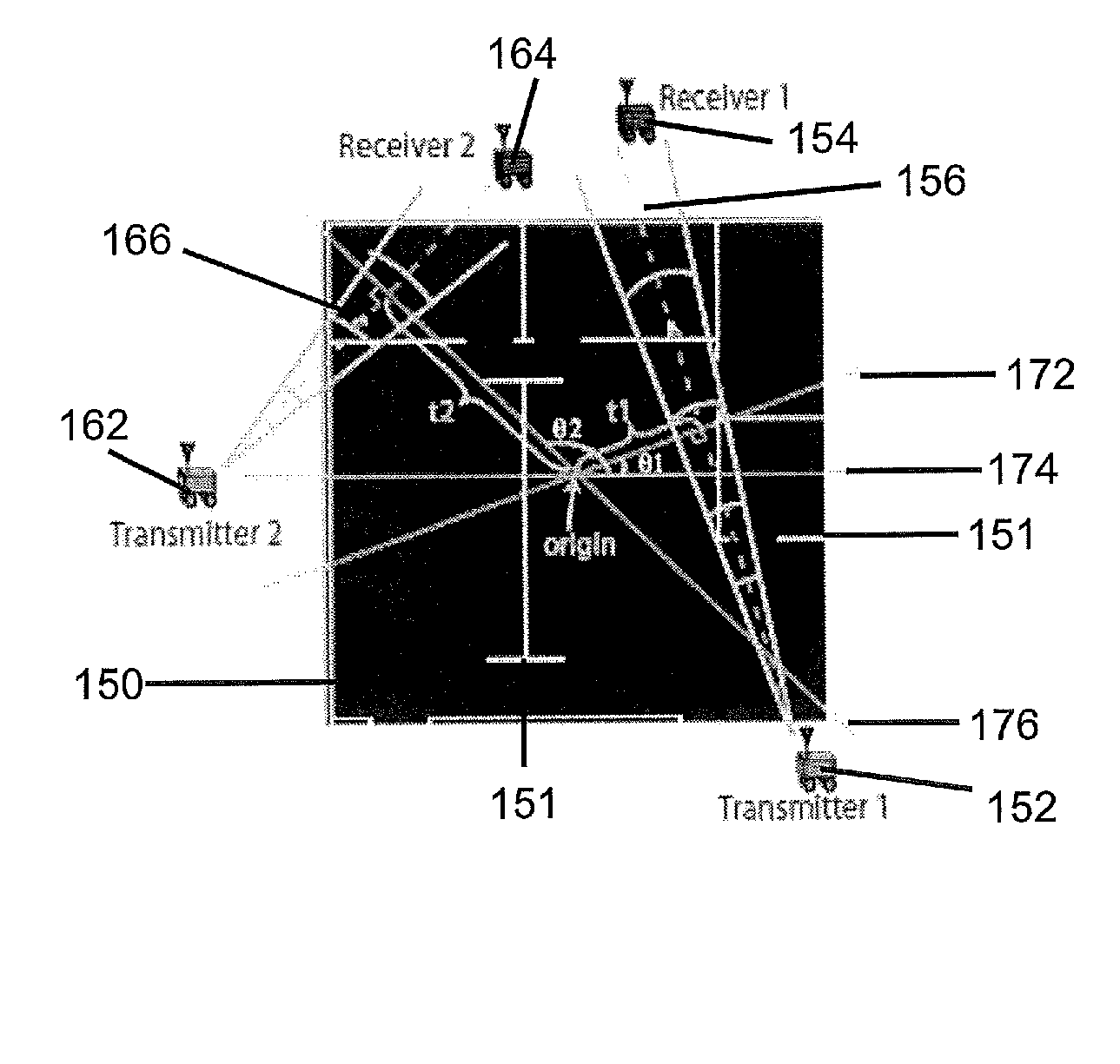
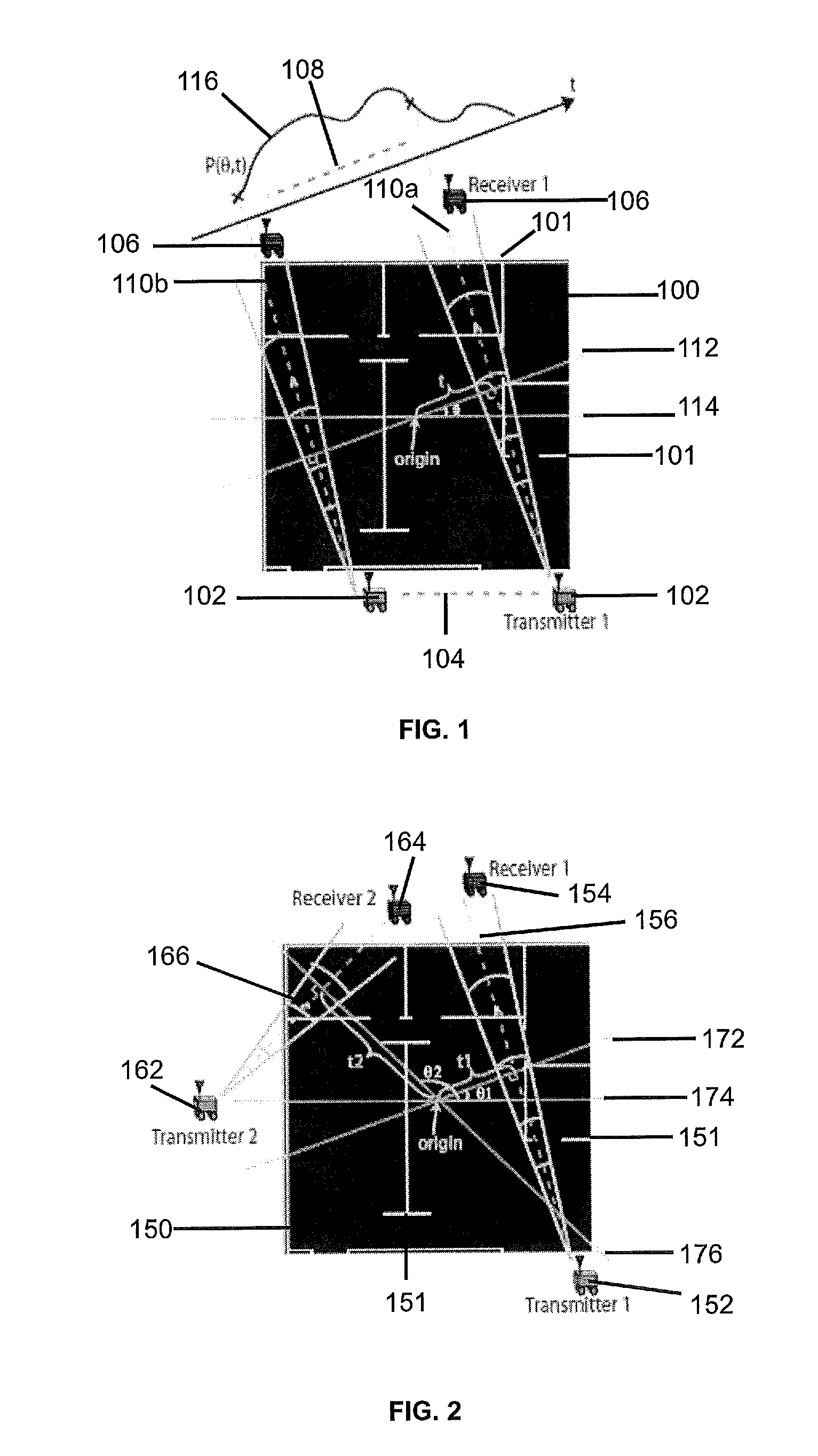
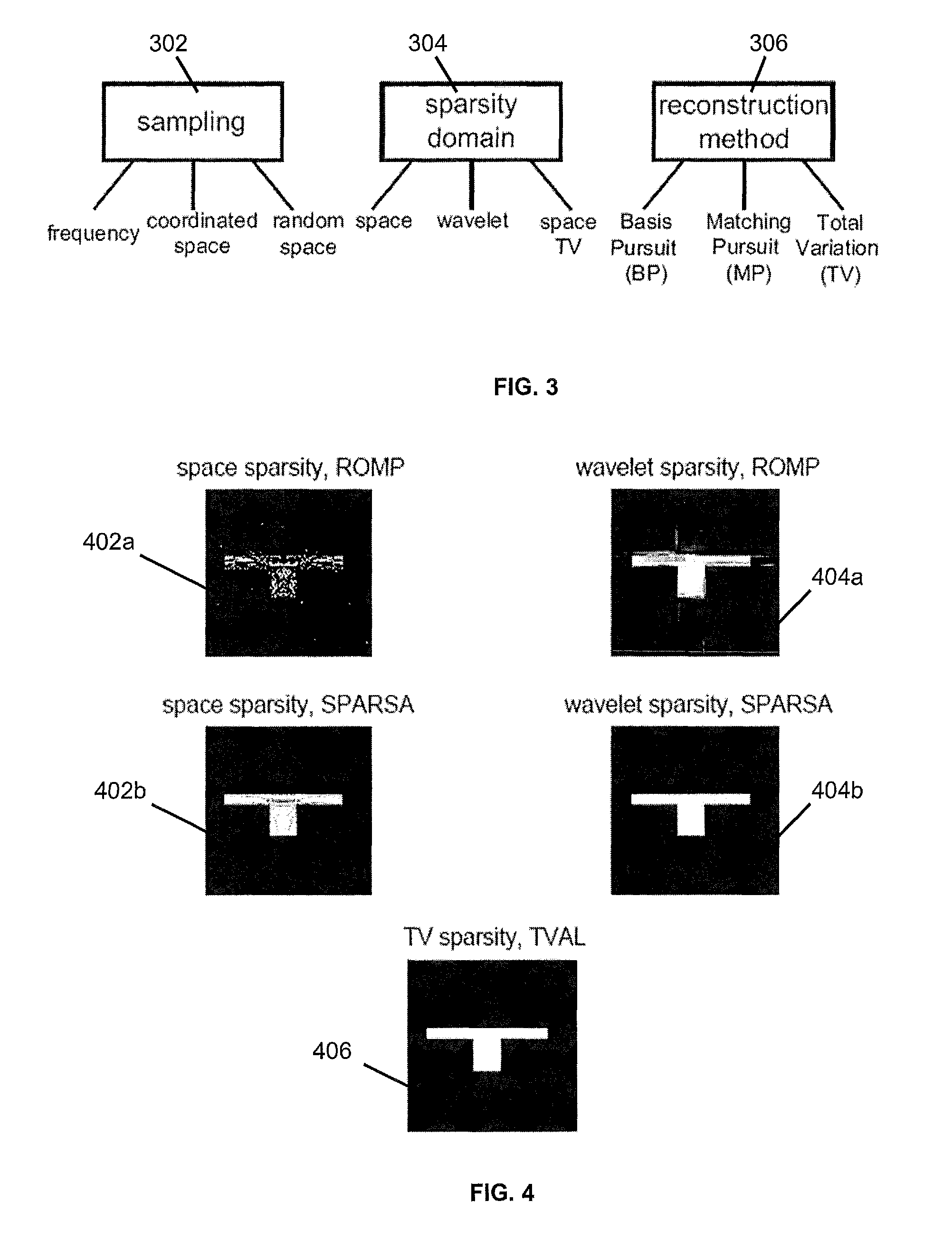
InactiveUS8712679B1Facilitates “ ”Improve abilitiesDirection finders using radio wavesComputer controlSpatial changeComputer science
A system and methods for building a map non-invasively (i.e. mapping of occluded and non-occluded obstacles) based on a small number of wireless channel measurements. Approaches for building an obstacle map are based on coordinated space, random space and frequency sampling, such that the sparse representation of the map in space, wavelet or spatial variations, are exploited in order to build the map with minimal sensing.
Owner:STC UNM
Cameras with Varying Spatio-Angular-Temporal Resolutions
A camera includes a lens and a sensor. A dynamic mask is arranged at an aperture plane between the lens and the sensor, and a static mask is arranged immediately adjacent to the sensor. Angular, temporal or spatial variations in light rays acquired of a scene by the sensor are mapped to individual pixels of the sensor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Apodized diffraction grating with improved dynamic range
InactiveUS20060056028A1Diffraction efficiencySpectrum investigationDiffraction gratingsOptical diffractionOptical property
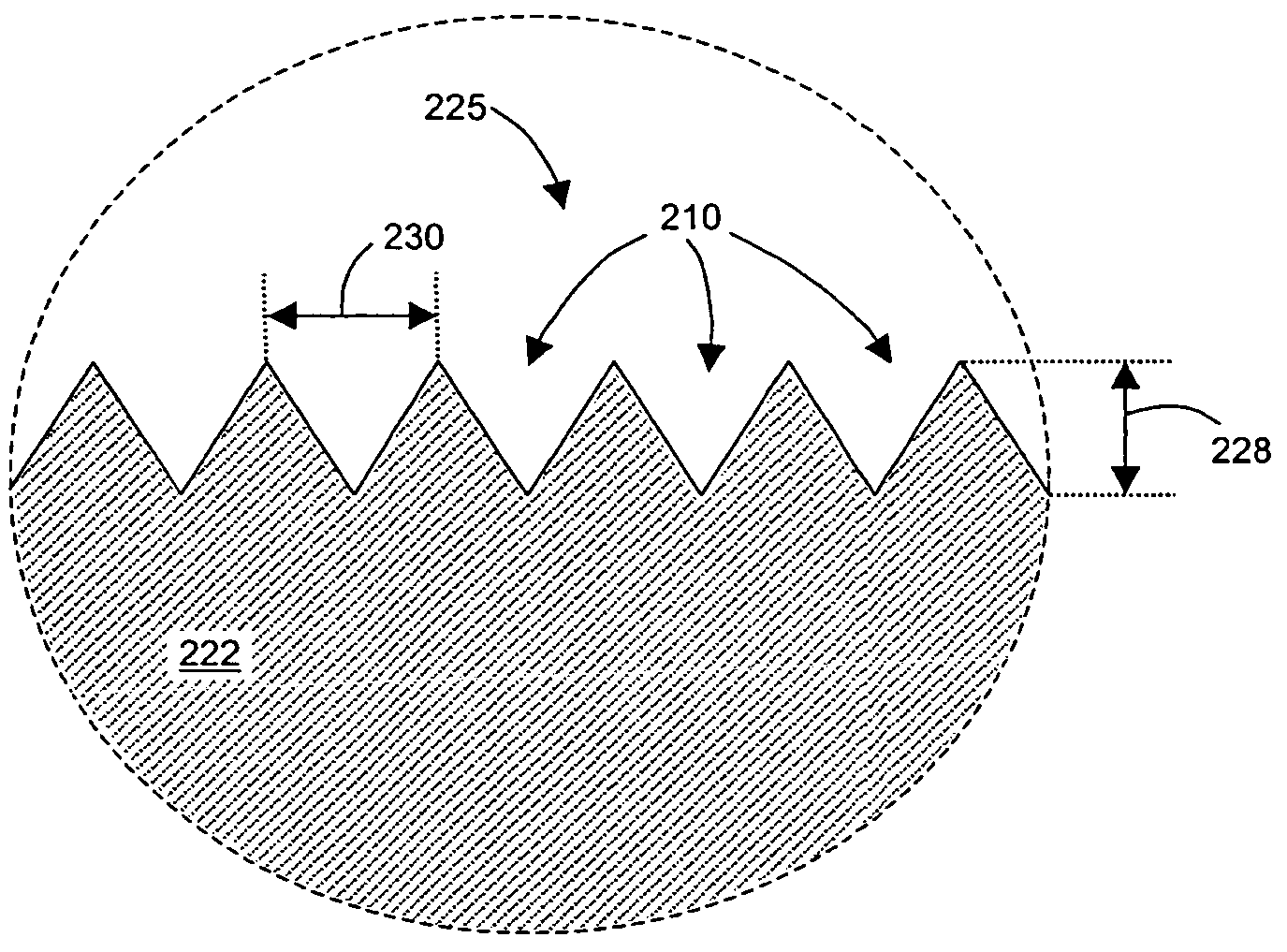
An optical diffraction grating includes a substrate and a diffraction surface comprising, for example, diffraction grooves. The diffraction grating has a spatially varying diffraction efficiency which increases or decreases as a function of distance from a reference location at which an incident light beam is received at the grating. Spatially varying the diffraction efficiency of the grating may be accomplished by selectively changing or modifying one or more grating design parameters such as the shape, size, depth, profile, pitch, and optical properties of the diffraction grooves at predetermined locations on the grating.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
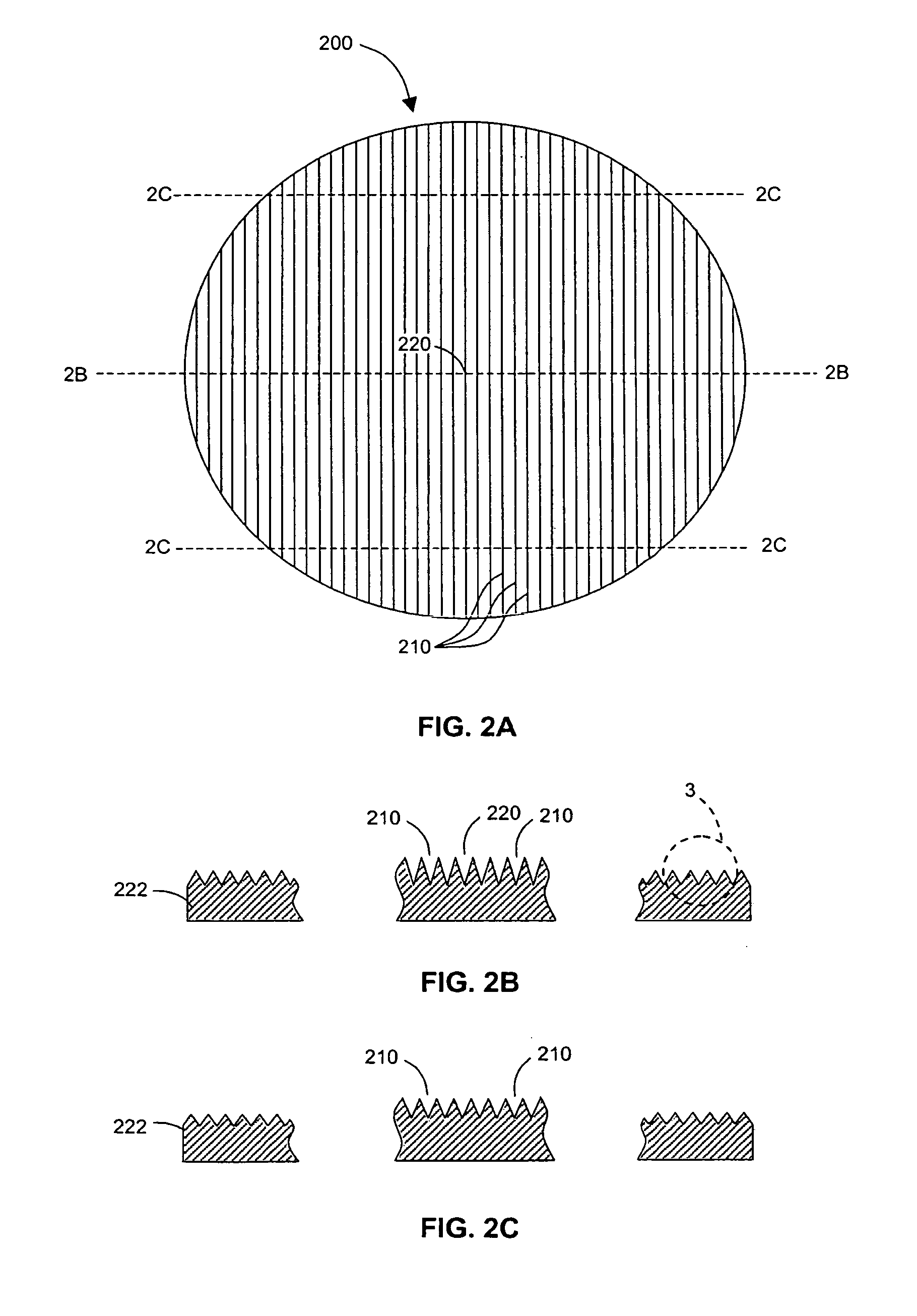
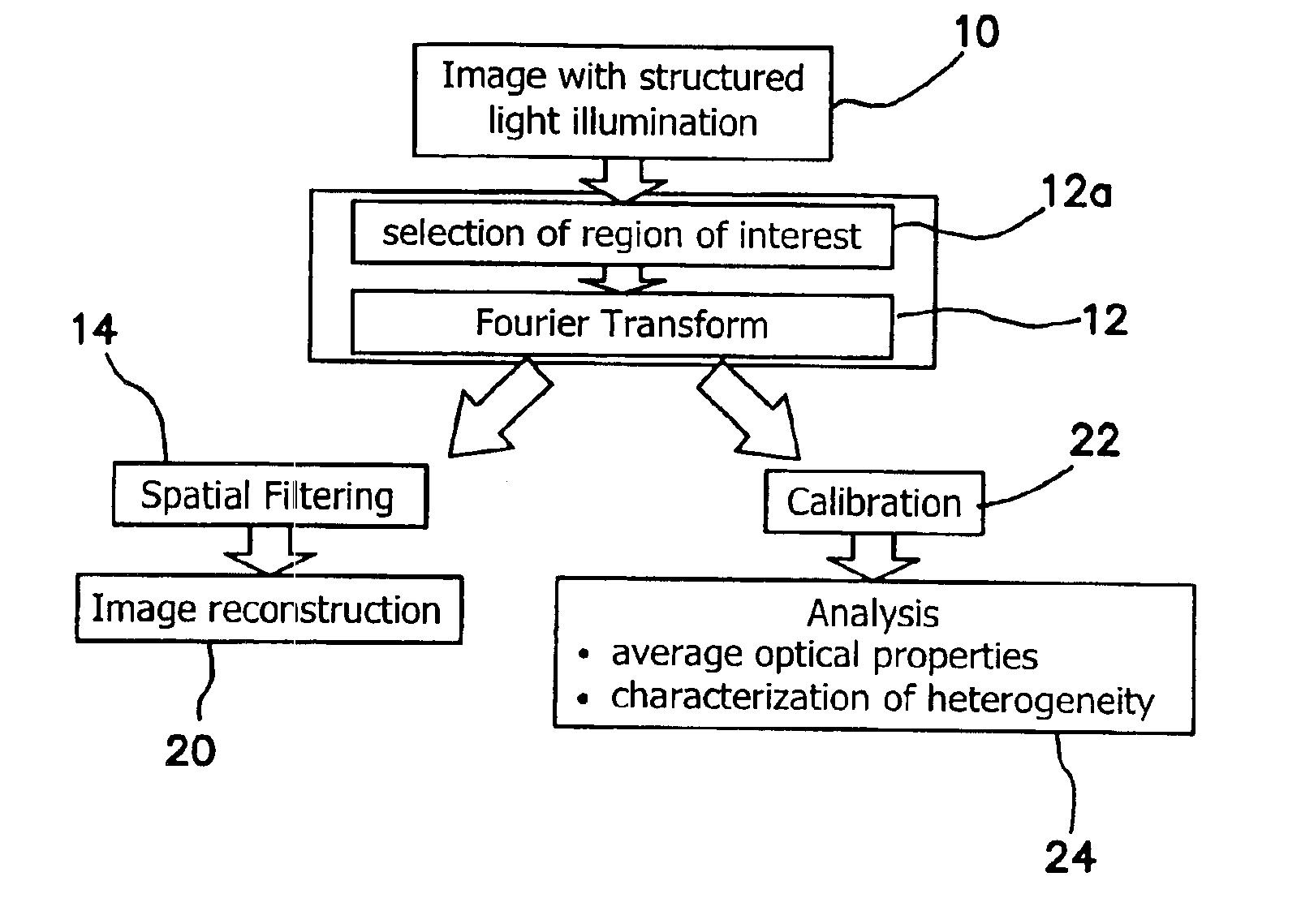
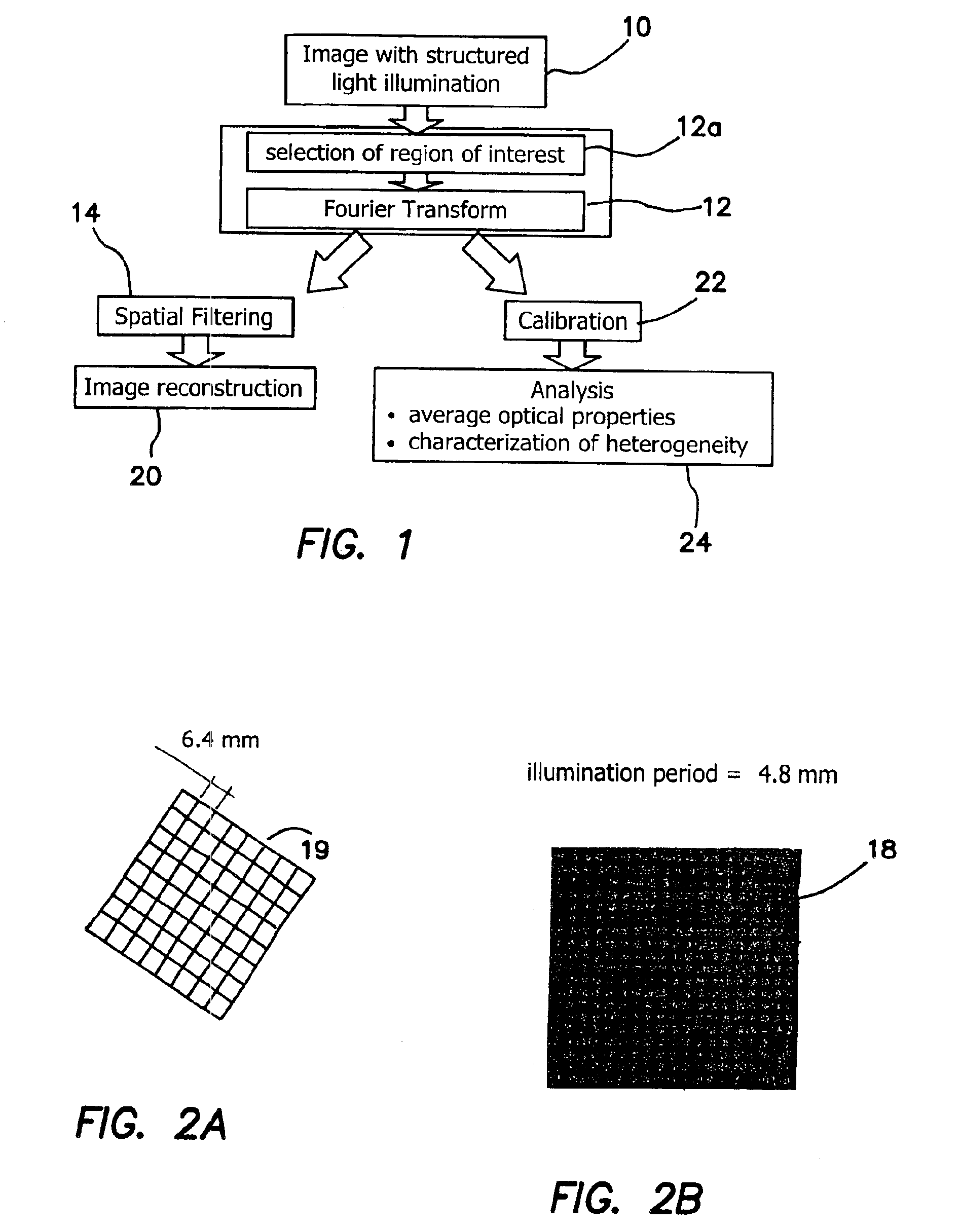
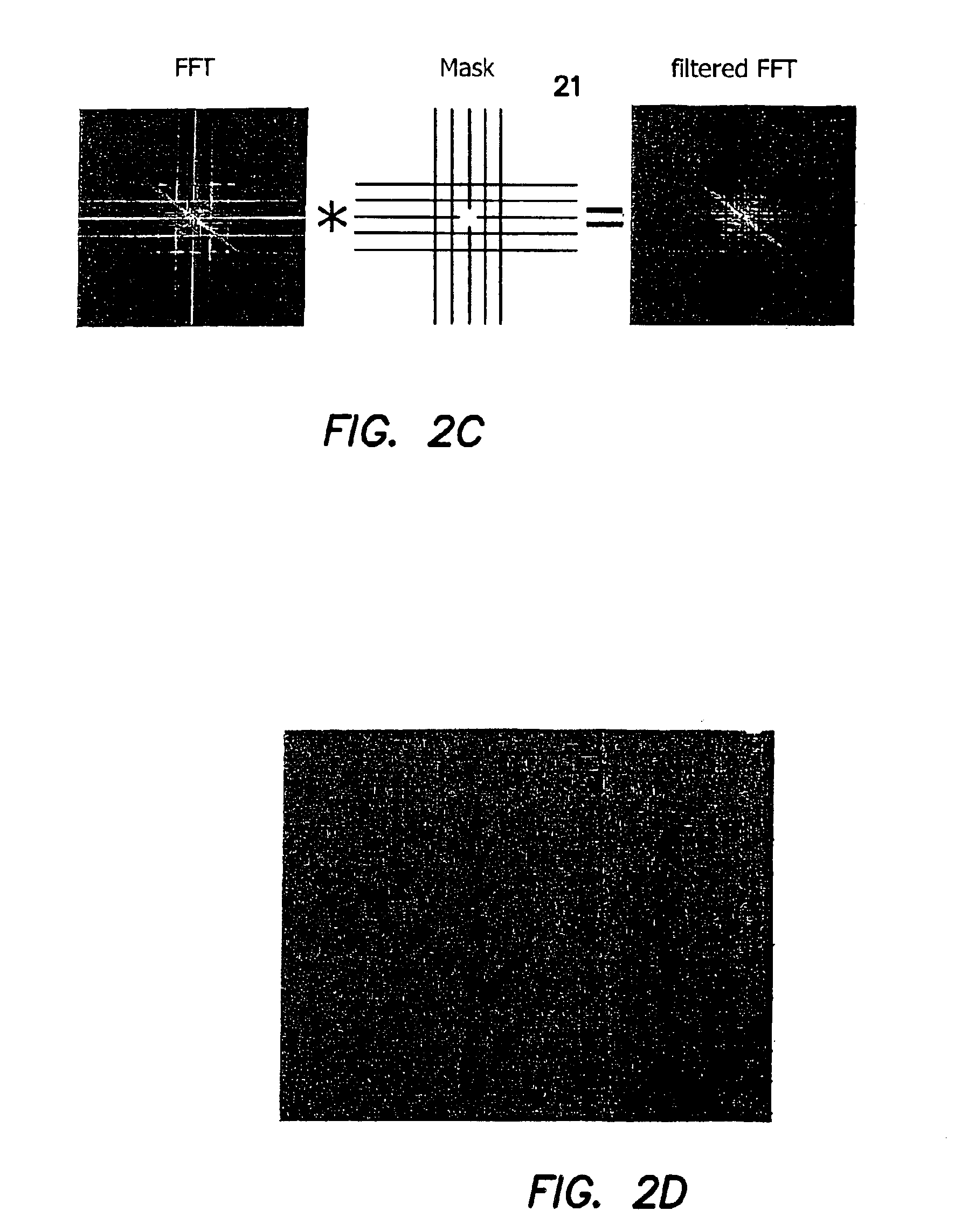
Method and apparatus for performing quantitative analysis and imaging surfaces and subsurfaces of turbid media using spatially structured illumination
ActiveUS6958815B2Recover optical propertyScattering properties measurementsOptical propertySpatial structure
Illumination with a pattern of light allows for subsurface imaging of a turbid medium or tissue, and for the determination of the optical properties over a large area. Both the average and the spatial variation of the optical properties can be noninvasively determined. Contact with the sample or scanning is not required but may be desired. Subsurface imaging is performed by filtering the spectrum of the illumination in the Fourier domain but other filtering approaches, such as wavelet transform, principle component filter, etc may be viable as well. The depth sensitivity is optimized by changing the spatial frequency of illumination. A quantitative analysis of the average optical properties and the spatial variation of the optical properties is obtained. The optical properties, i.e. reduced scattering and absorption coefficients are determined from the modulated transfer function, MTF.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Digital image compression with spatially varying quality levels determined by identifying areas of interest
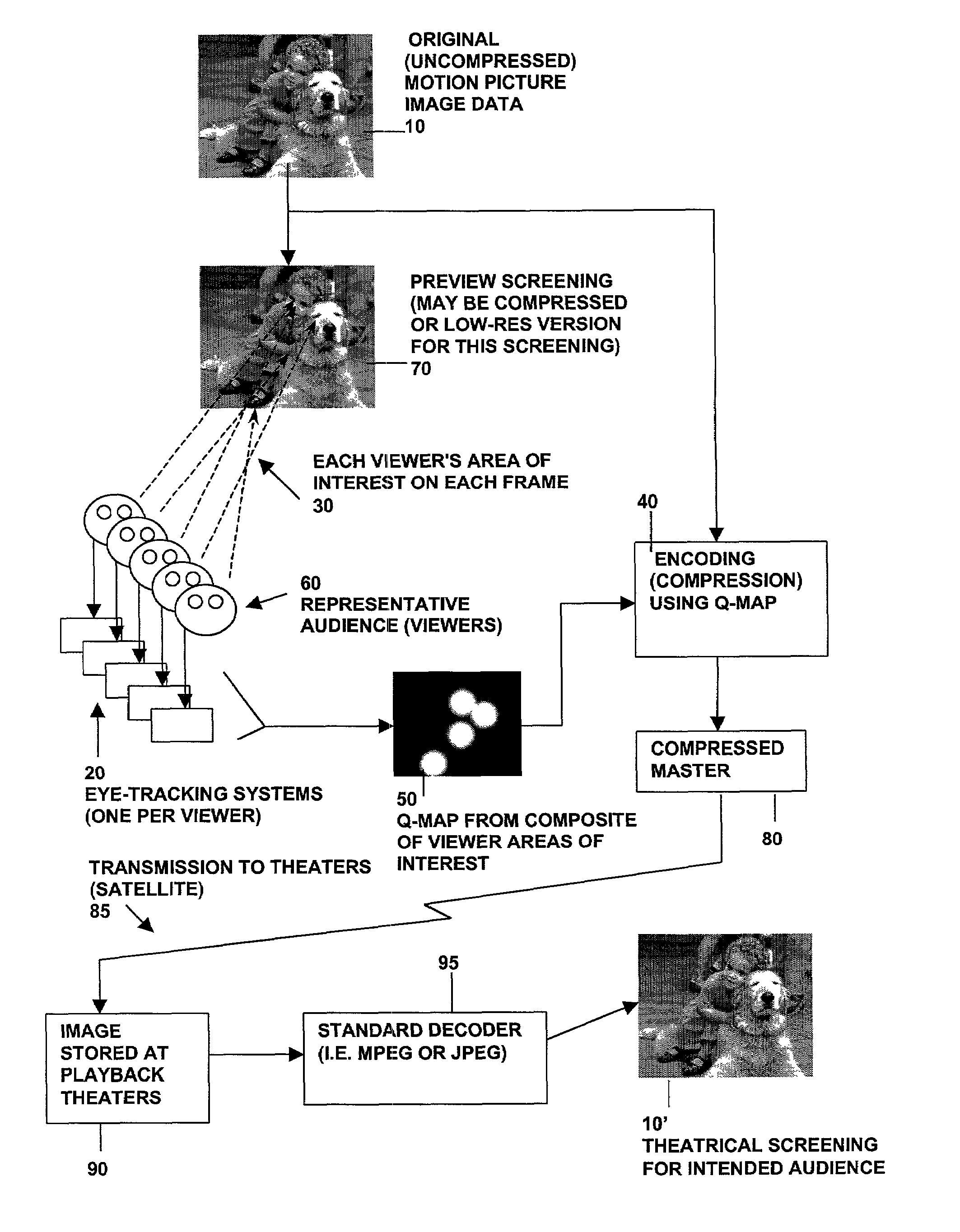
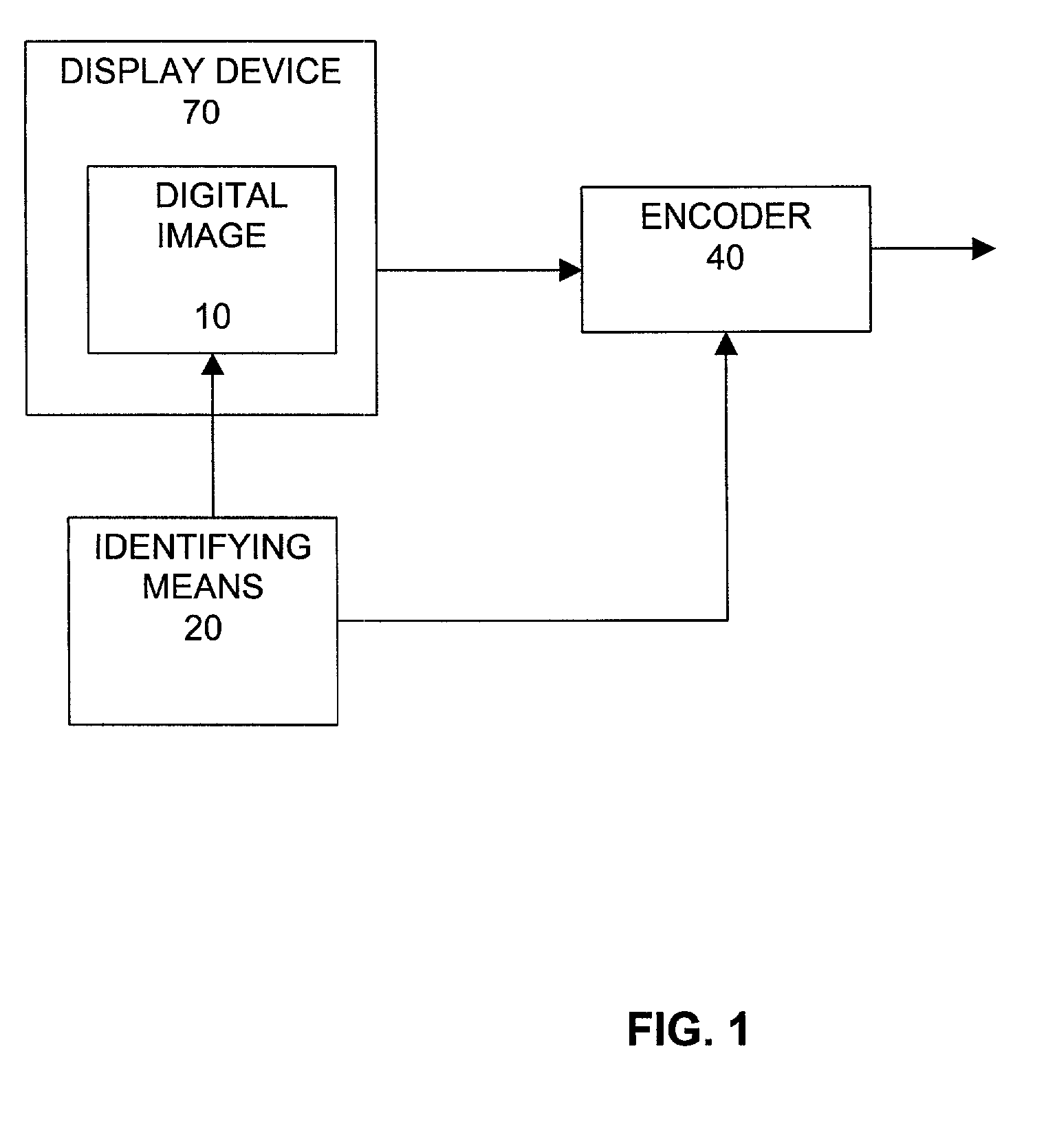
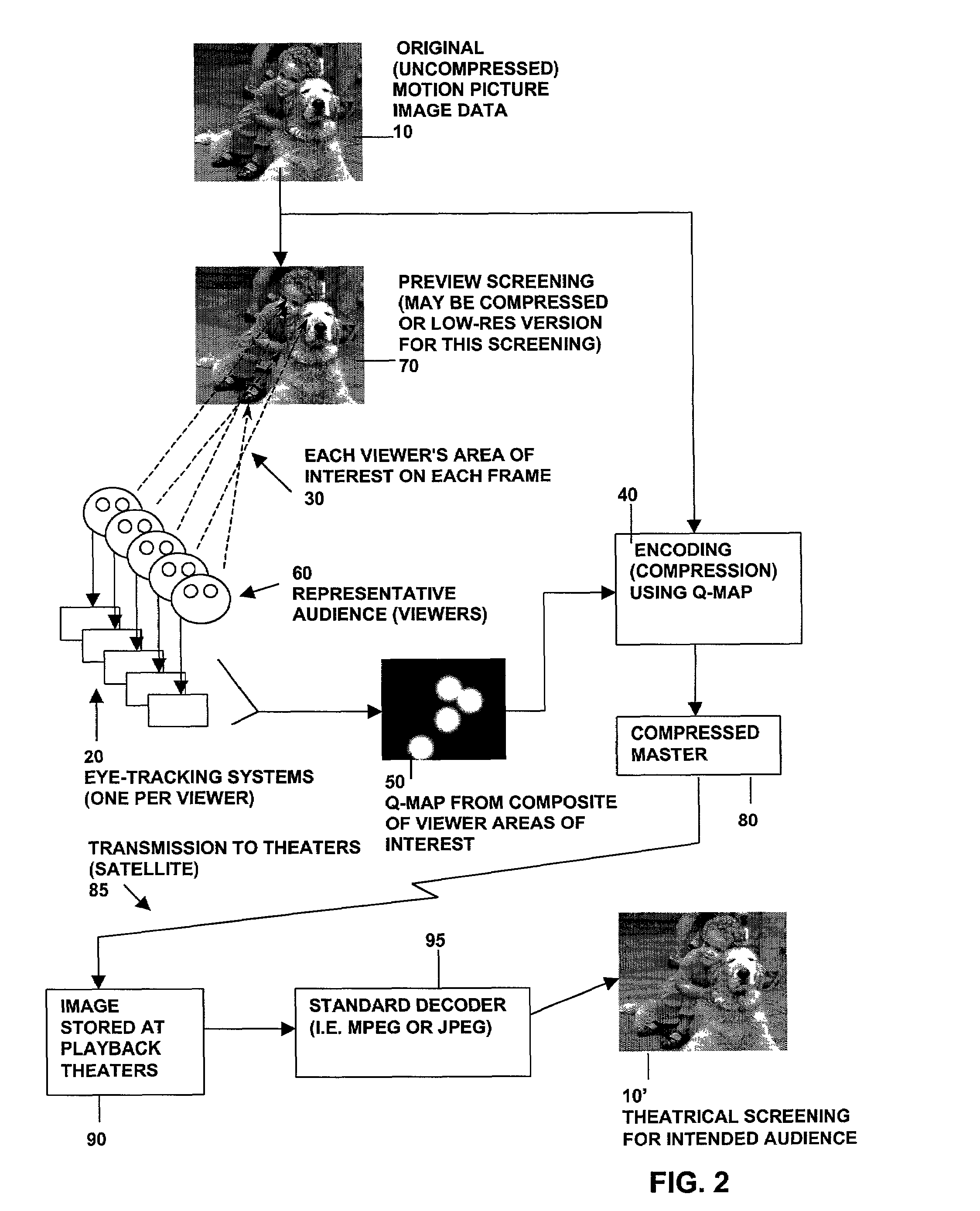
InactiveUS7027655B2Low bit rateLower quality factorAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionQuality levelDigital image compression
Methods and systems for compression of digital images (still or motion sequences) are provided wherein predetermined criteria may be used to identify a plurality of areas of interest in the image, and each area of interest is encoded with a corresponding quality level (Q-factor). In particular, the predetermined criteria may be derived from measurements of where a viewing audience is focusing their gaze (area of interest). In addition, the predetermined criteria may be used to create areas of interest in an image in order to focus an observer's attention to that area. Portions of the image outside of the areas of interest are encoded at a lower quality factor and bit rate. The result is higher compression ratios without adversely affecting a viewer's perception of the overall quality of the image.
Owner:ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING
Method and apparatus for recording a sequence of images using a moving optical element
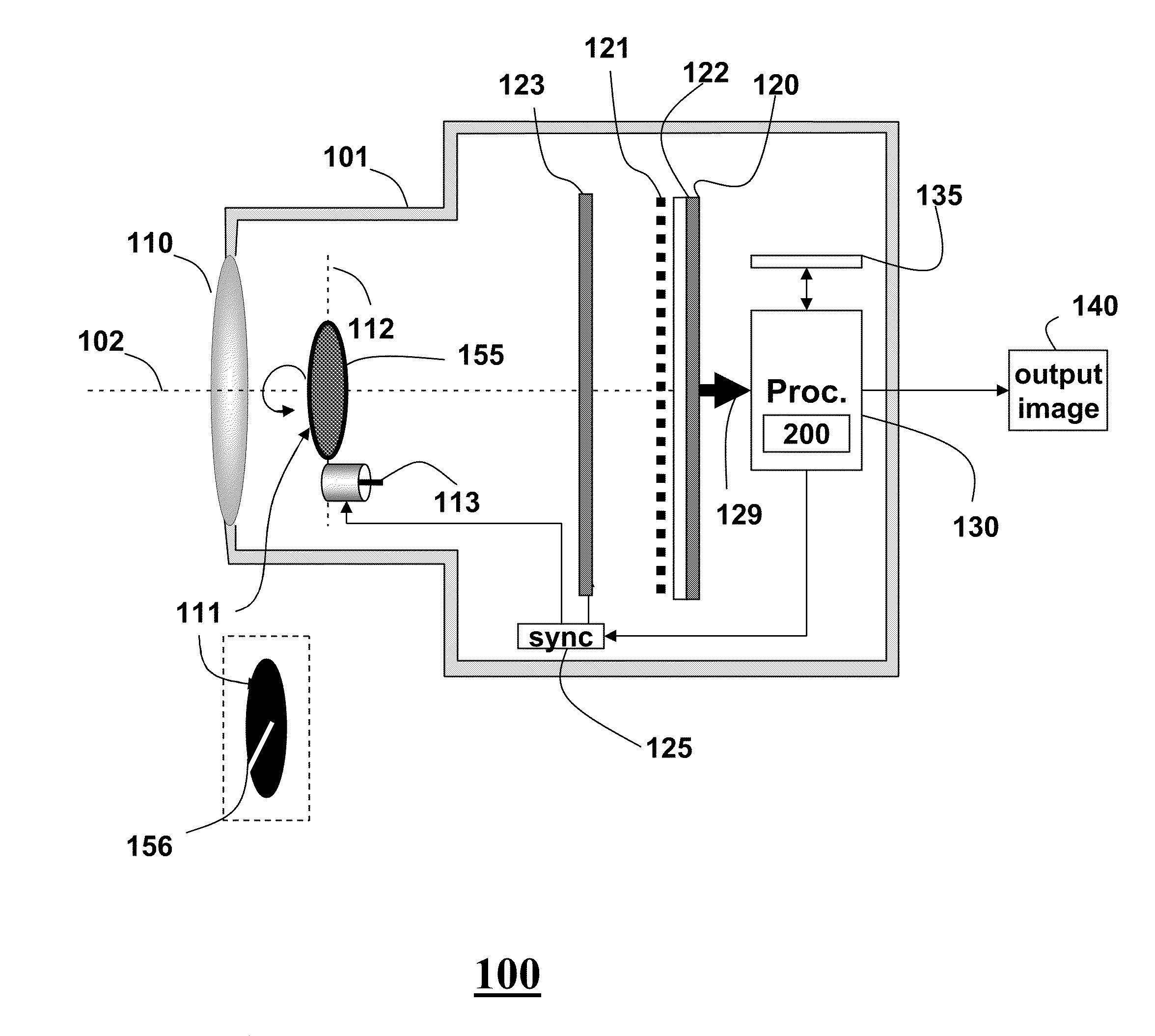
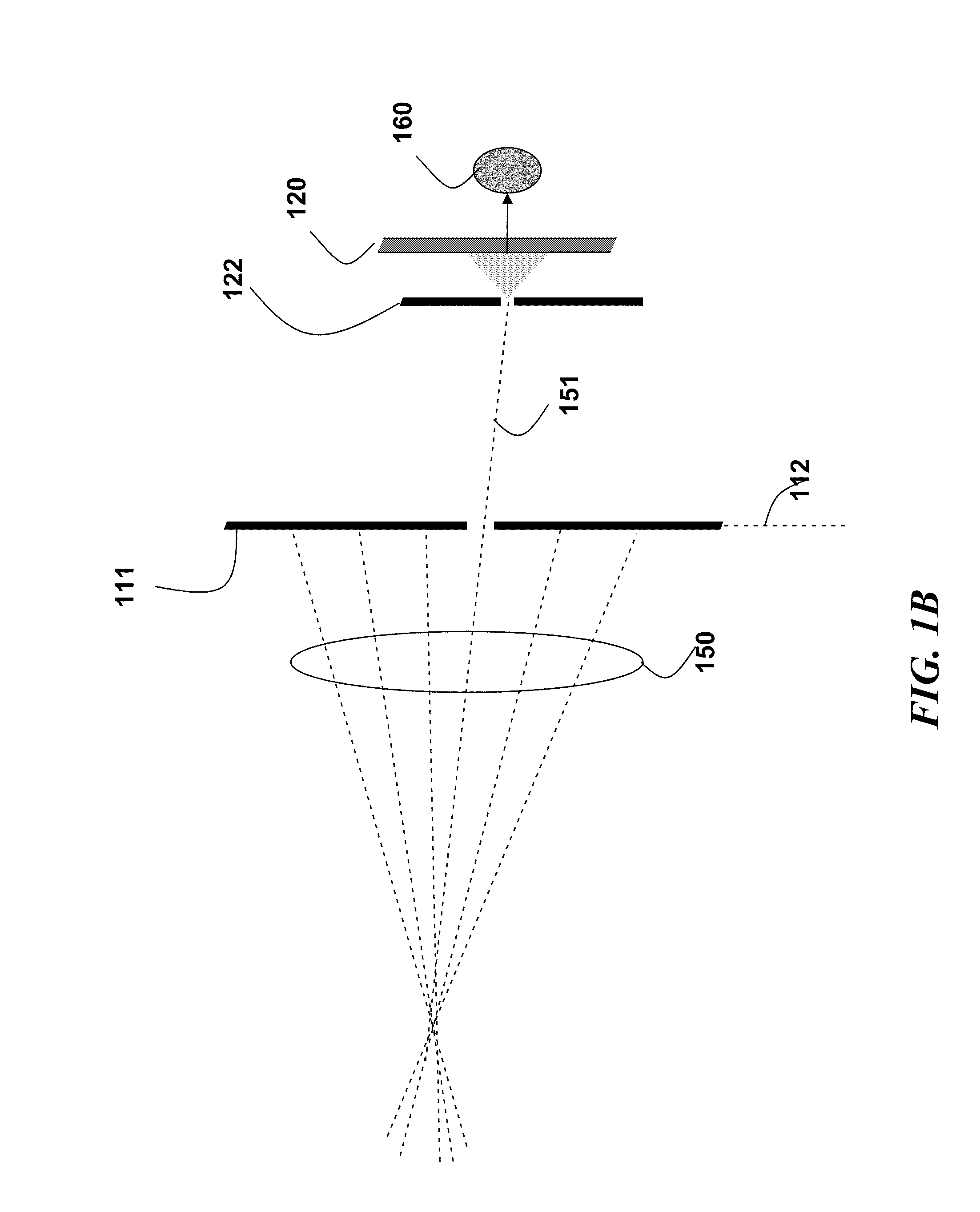
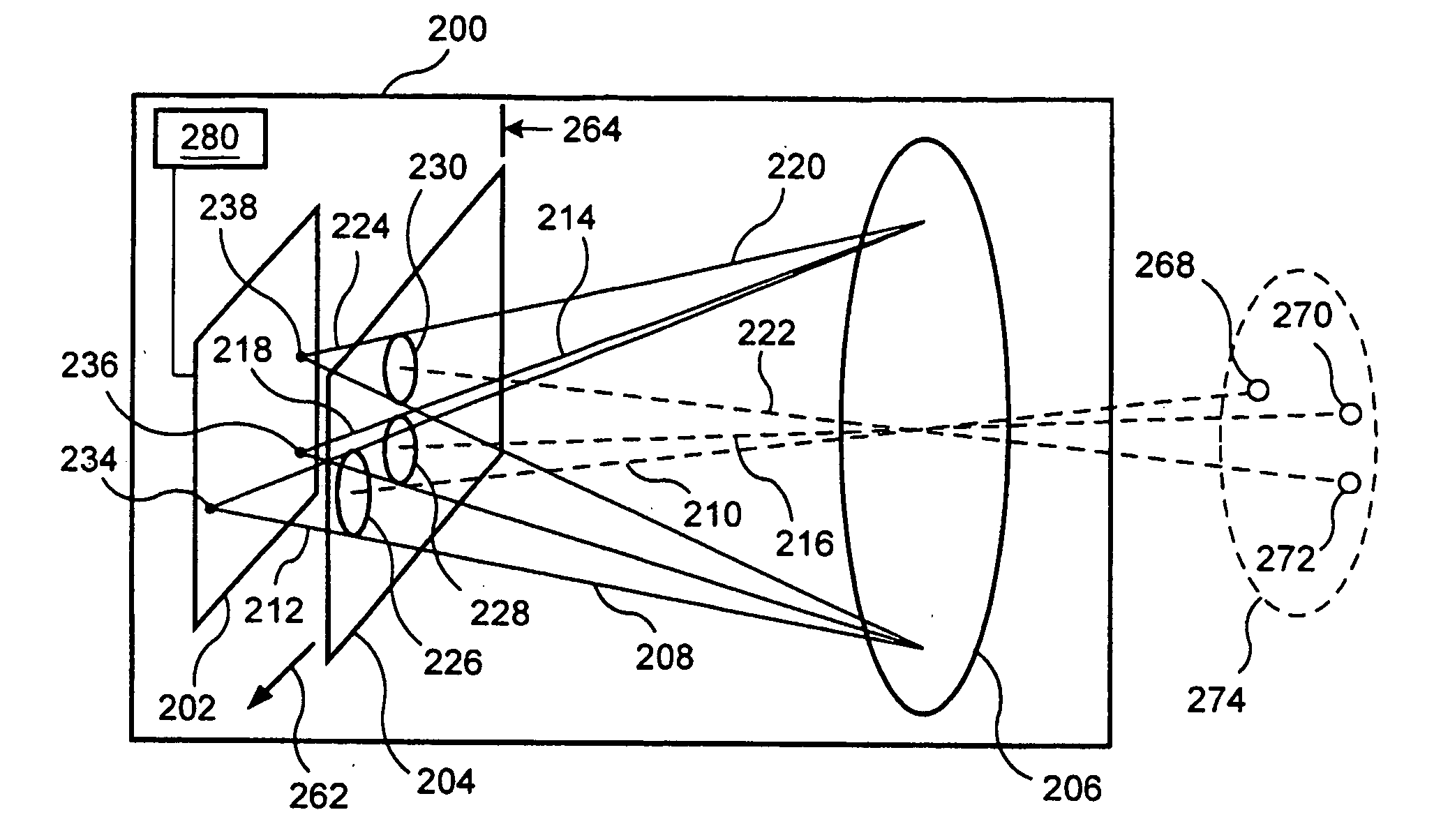
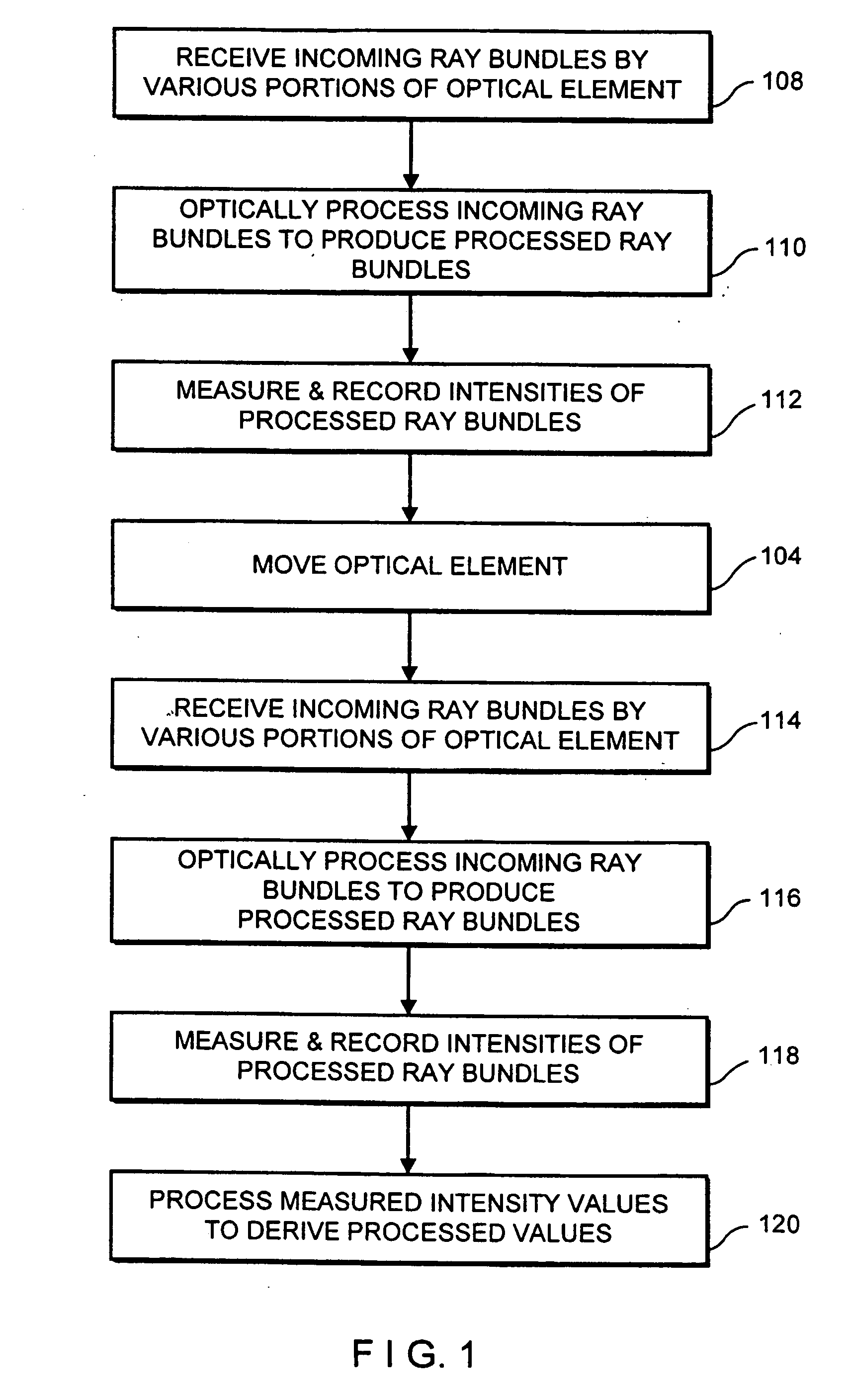
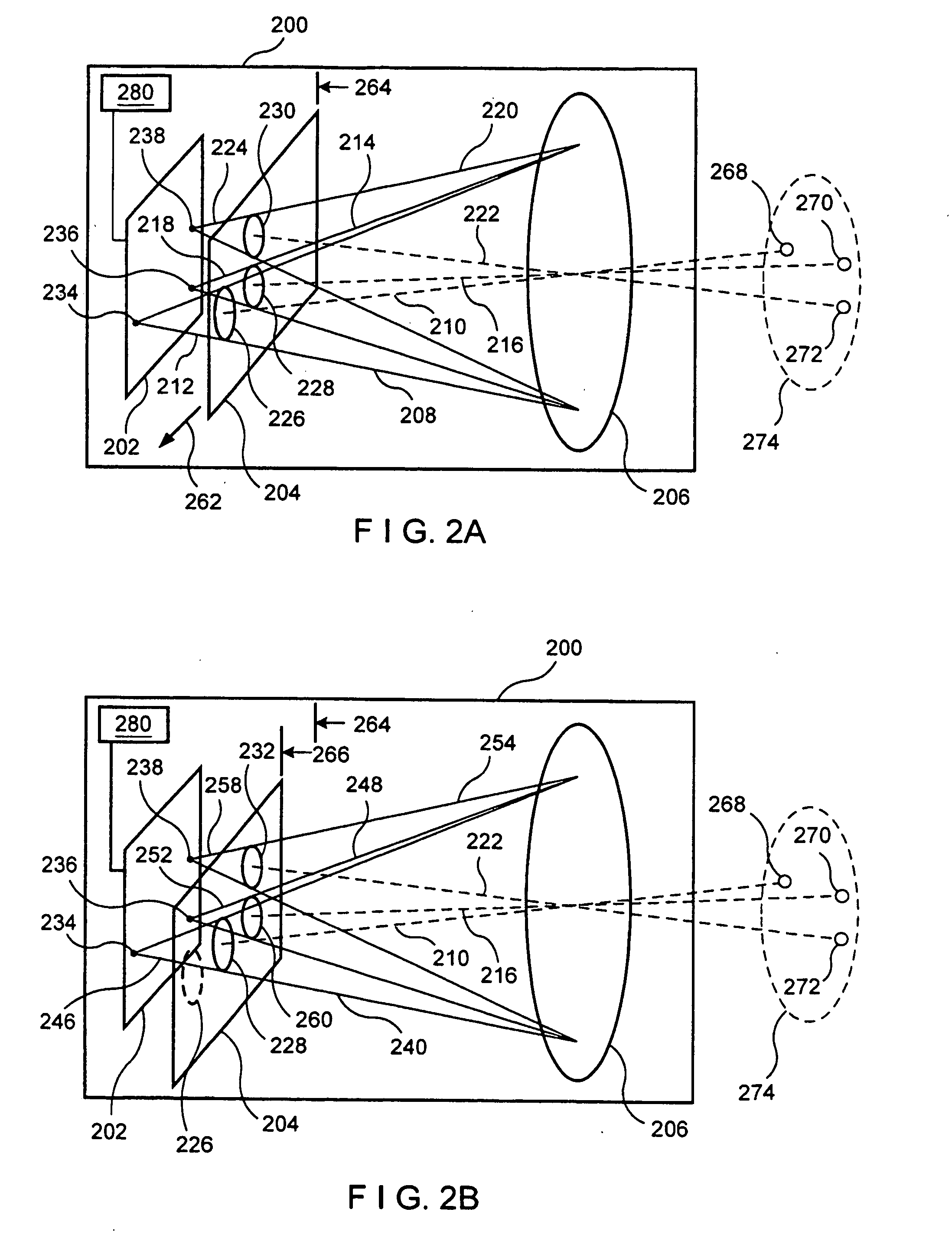
ActiveUS20050041113A1Improve spatial resolutionImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsSpectrum investigationImaging conditionImage resolution
An imager (200) including a spatially varying optical element (204) which moves while the imager records a sequence of images. The optical element (204) can be an intensity reduction filter, a spectral or polarization filter, or a refractive or reflective element. Because the optical element (204) moves between frames, each scene portion is captured under a range of imaging conditions. A spatially varying intensity reduction filter enables imaging of each scene portion using multiple, different exposure to generate a high dynamic range image. A spatially varying spectral or polarization filter enables measurement of the spectral or polarization characteristics of radiation from each scene portion. A refractive or reflective element enables imaging of scene portions under various focal characteristics, thereby providing depth information and producing an image which is focused everywhere. A refractive or reflective element is used to apply different vertical and / or horizontal shifts to the different frames, thereby generating an enhanced-resolution image.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Systems, methods and apparatus of a composite X-Ray target
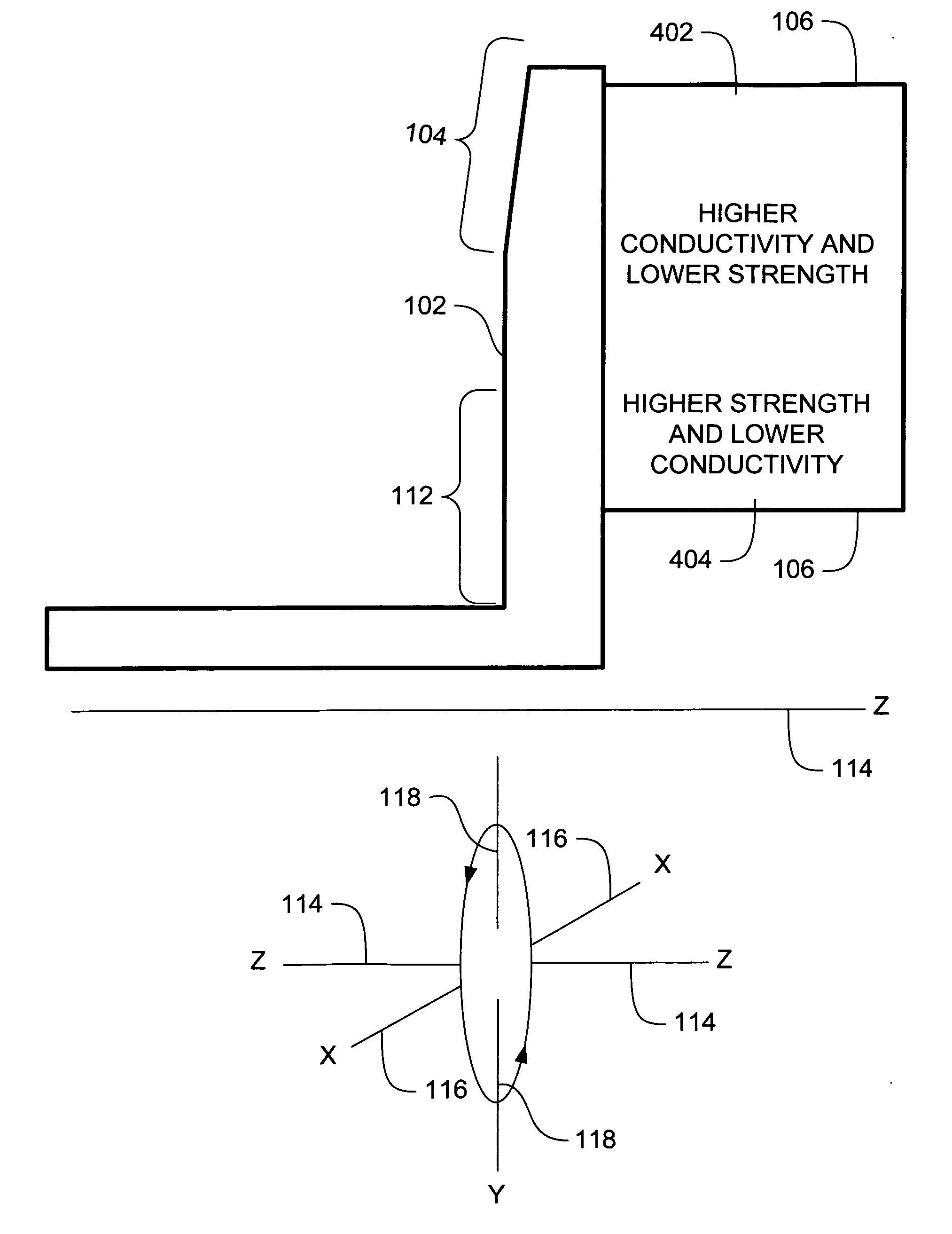
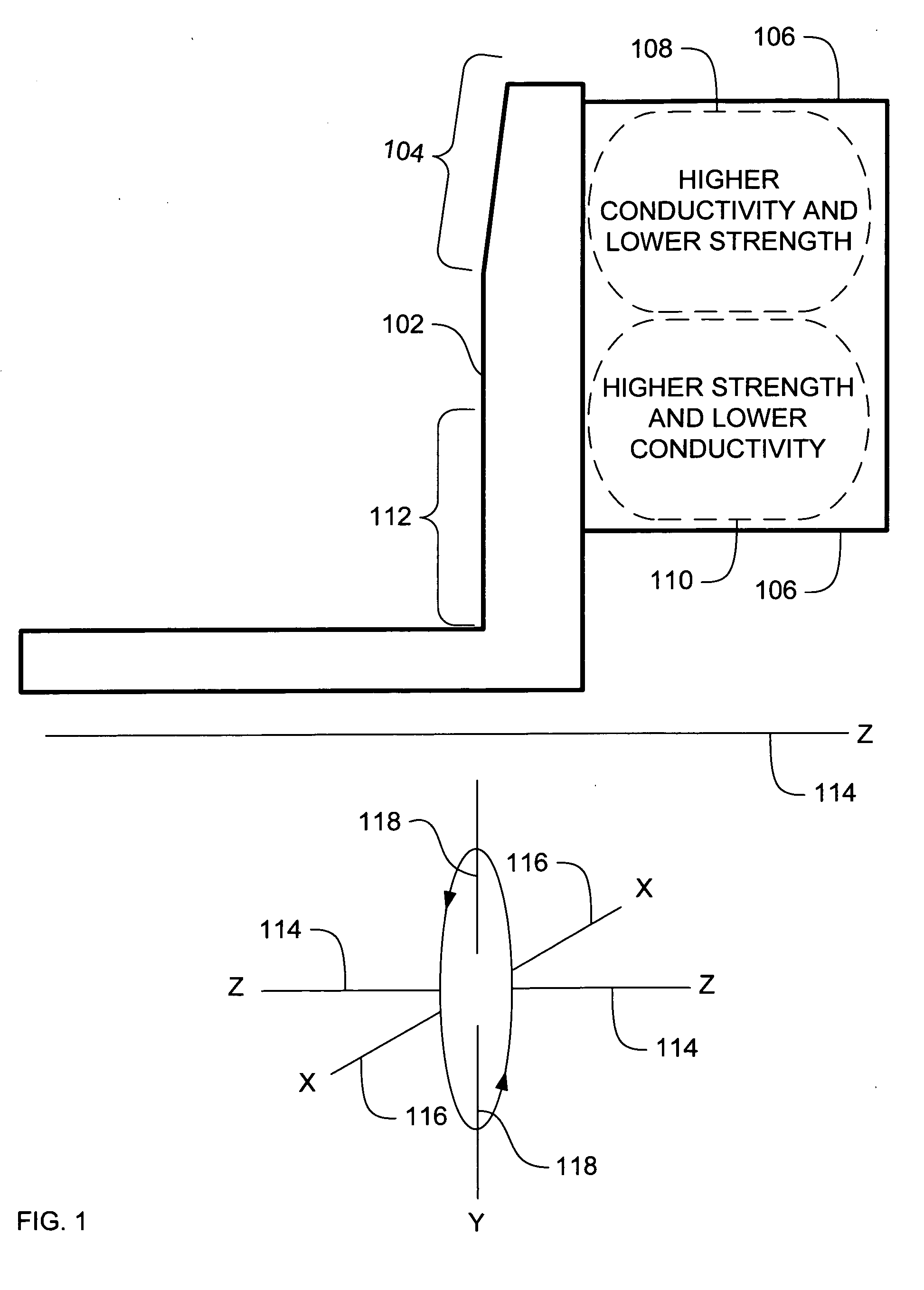
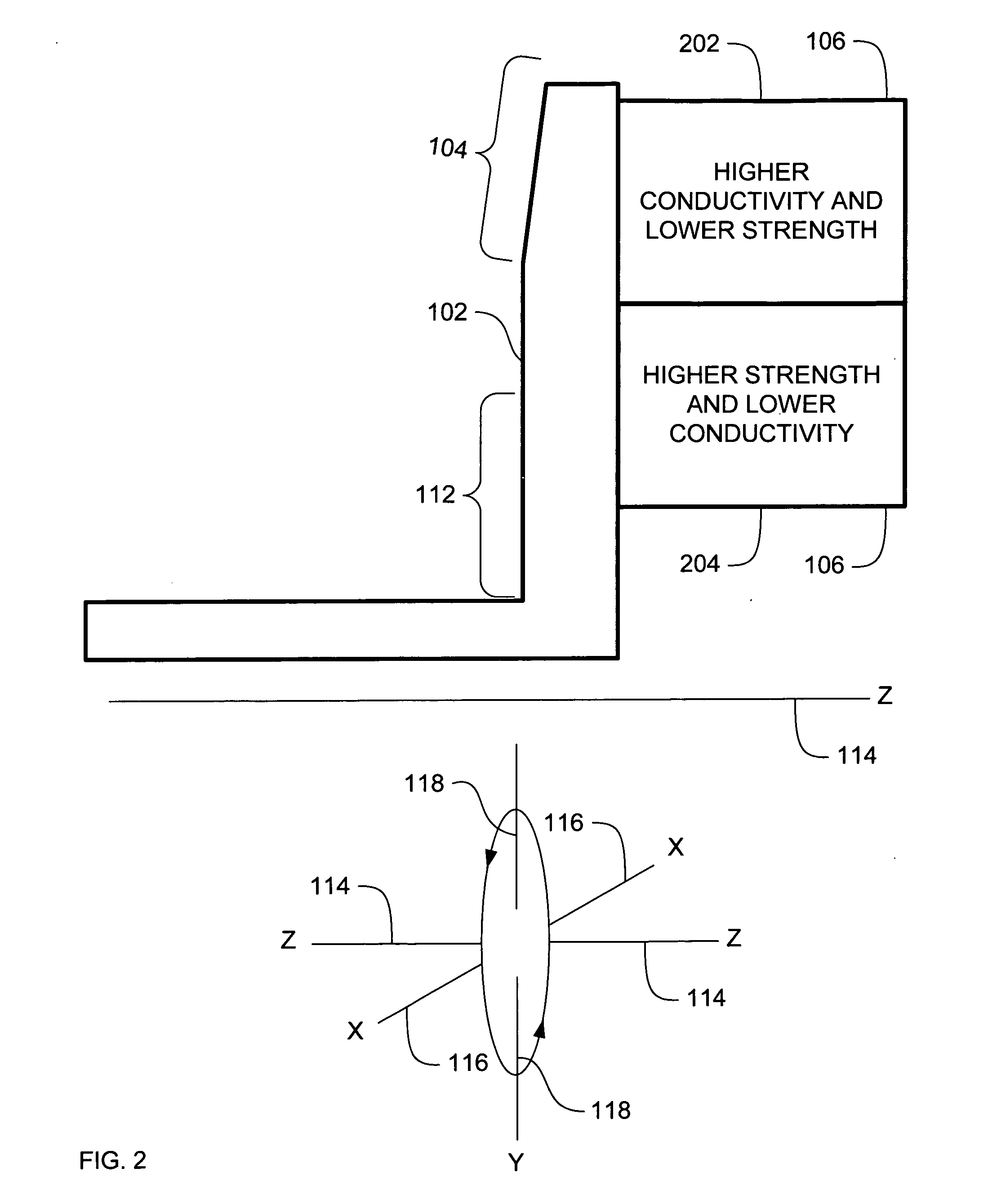
ActiveUS20070071174A1High mechanical strengthLow thermal conductivityX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesX-raySystems approaches
Systems, methods and apparatus are provided through which in some embodiments an X-Ray energy target includes composite material that varies spatially in thermal properties, and in some embodiments, the composite material varies spatially in strength properties. In some embodiments, the spatial variance is a continuum and in other embodiments, the spatial variance is a plurality of distinct portions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and method for projecting a variable pattern of electromagnetic energy
InactiveUS20070145136A1Reduce suddennessMore attractive or accurate rendition of the imageTelevision system scanning detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionElectronic controllerLight beam
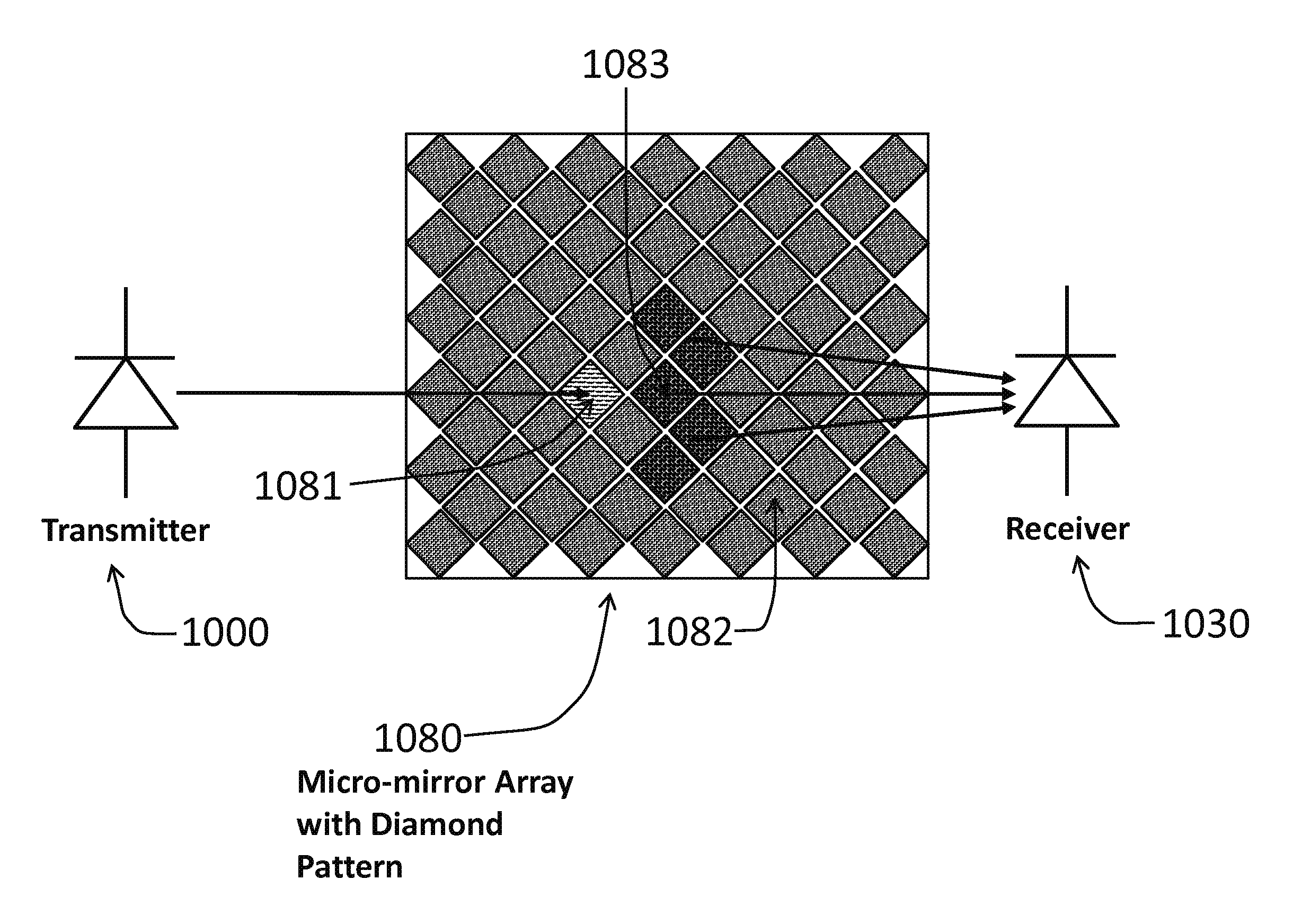
According to an embodiment, an interrogator includes a beam generator operable to scan a variable-power beam across a field of view, a detector aligned to receive an electromagnetic signal from the field of view and generate a corresponding detection signal, and a controller operatively coupled to the detector and the beam generator and operable to vary the power of the beam as it scans across the field of view responsive to the detection signal. According to an embodiment, an illumination system includes an illumination source operable to provide spatially-varying illumination, a detector configured to receive scattered energy from the spatially-varying illumination, and an electronic controller operable to vary the spatial variation of the illumination responsive to the scattered energy received by the detector. According to an embodiment, a method includes illuminating a field of view with a variable power illumination pattern, receiving scattered light from the field of view, and modifying the pattern of the variable power illumination responsive to the scattered light
Owner:MICROVISION
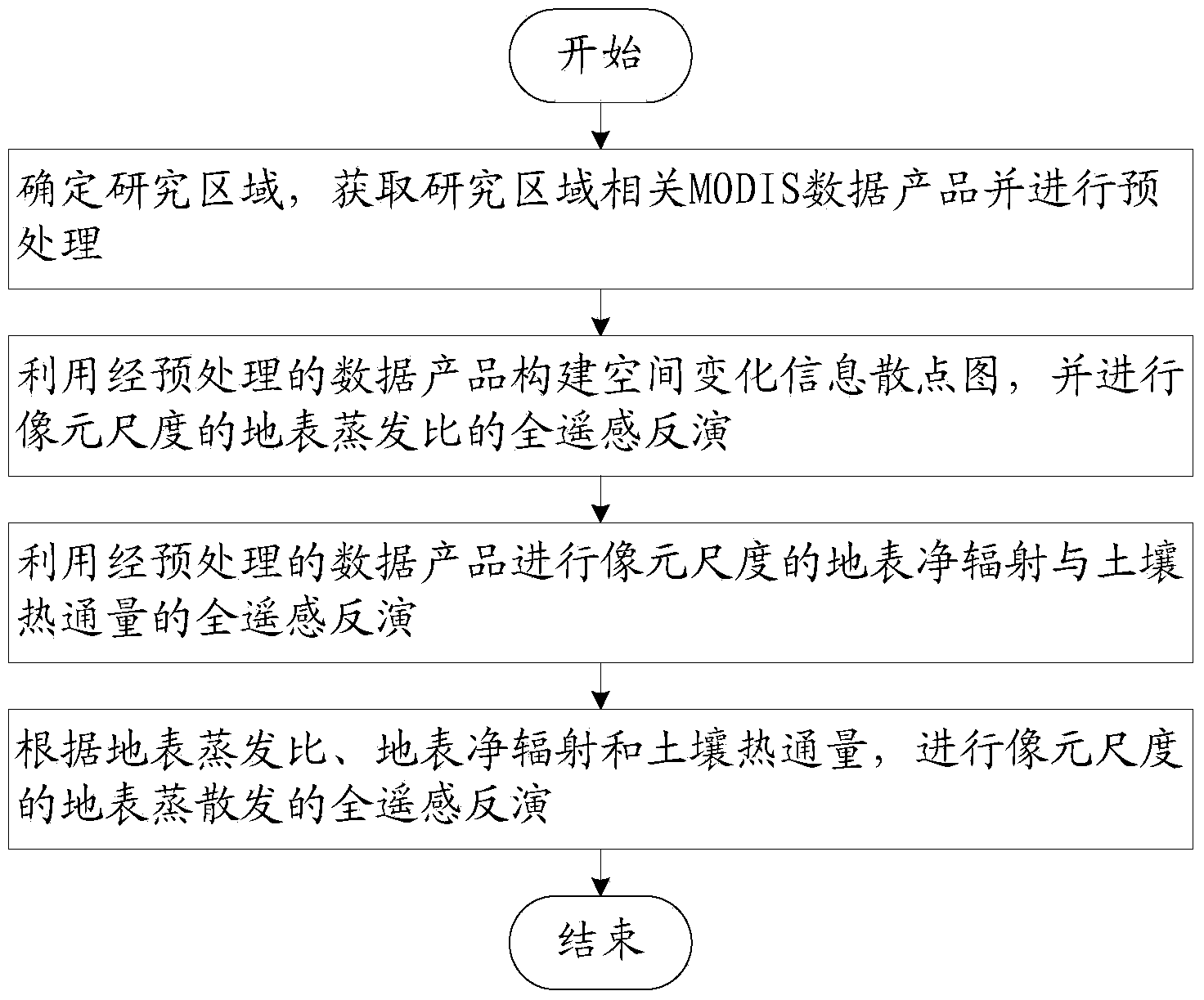
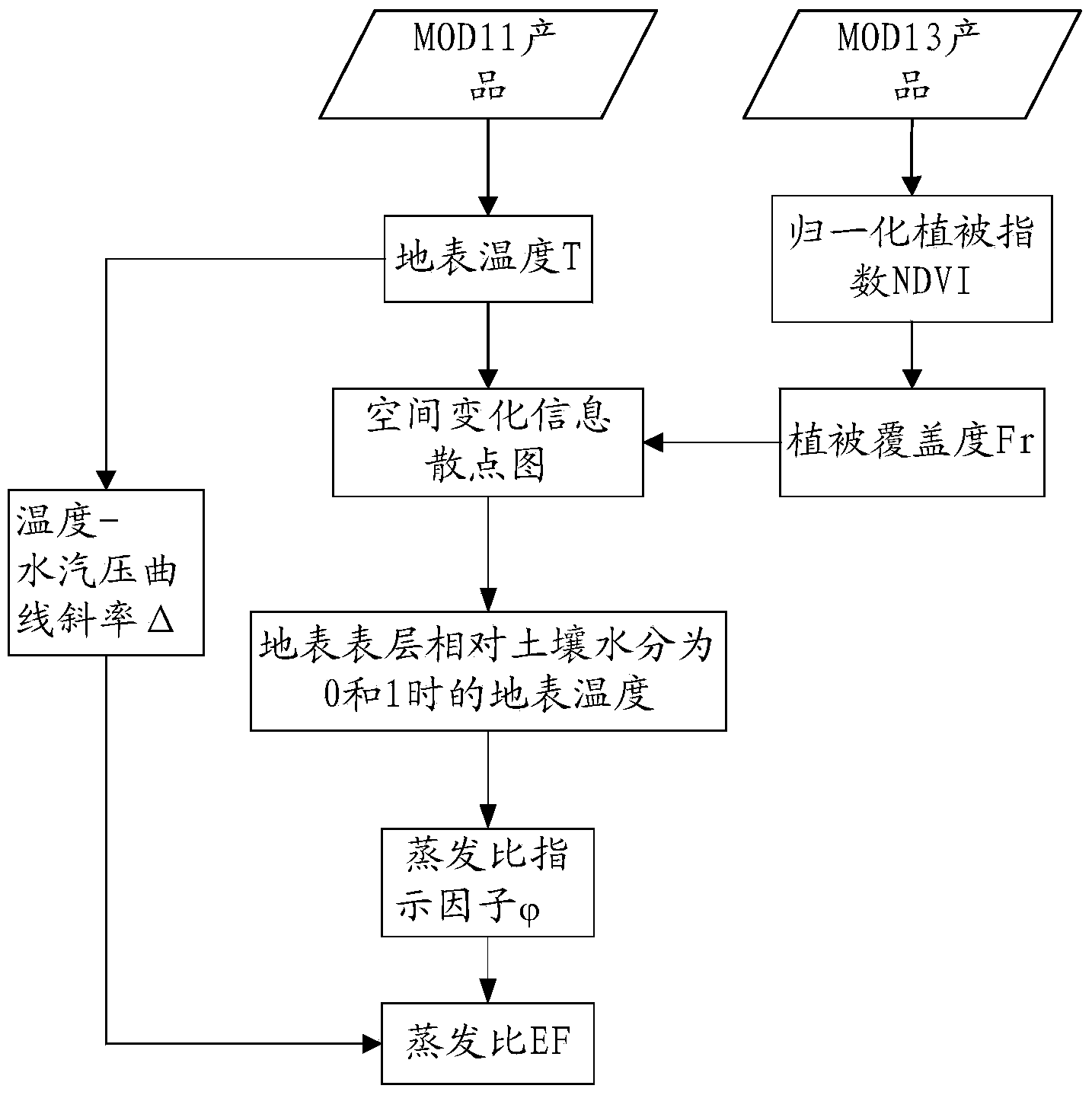
Earth face evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion method and system based on MODIS data
InactiveCN103810387AAvoid the requirement for accurate atmospheric correctionReduce uncertaintyMaterial analysis by optical meansSpecial data processing applicationsData aidedObservation data
The invention relates to an earth face evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion method and system based on MODIS data. The earth face evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion method comprises the following steps that (1), a research area is confirmed, relative MODIS data porducts in the research area are achieved and pretreated; (2), a scatter diagram of space change information is built by the utilization of the pretreated MODIS data products, a remote sensing inversion of pixel sized surface evaporation ratio EF is conducted; (3), according to the relative MODIS data products, remote sensing inversions of pixel sized surface net radiation Rn and soil heat flux G are conducted; (4), according to the surface evaporation ratio EF, the surface net radiation Rn and the soil heat flux G, a remote sensing inversion of pixel sized earth face evapotranspiration LE is conducted. The earth face evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion method only needs to input the MODIS data, the problem that the current evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion usually needs more ground observation data to assist is solved, and the earth face evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion method can be used for the evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion in the area with no data or with few data.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Spatially Multiplexed Dielectric Metasurface Optical Elements
ActiveUS20170219739A1Improve performanceEasy to createNon-linear opticsOptical elementsDielectricPhase response
A multifunctional dielectric gradient metasurface optical device has a layer of nanoscale dielectric gradient metasurface optical antenna elements deposited on a substrate layer, arranged with spatially varying orientations, shapes, or sizes in the plane of the device such that the optical device has a spatially varying optical phase response capable of optical wavefront shaping. The spatially varying optical phase response is a spatial interleaving of multiple distinct phase profiles corresponding to multiple optical sub-elements, thereby providing multifunctional wavefront shaping in the single optical element.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
Spectrometric systems and methods for improved focus localization of time- and space-varying measurements
ActiveUS20150109617A1Radiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPath lengthTissue sample
A system and method of dynamically localizing a measurement of parameter characterizing tissue sample with waves produced by spectrometric system at multiple wavelengths and detected at a fixed location of the detector of the system. The parameter is calculated based on impulse response of the sample, reference data representing characteristics of material components of the sample, and path lengths through the sample corresponding to different wavelengths. Dynamic localization is effectuated by considering different portions of a curve representing the determined parameter, and provides for the formation of a spatial map of distribution of the parameter across the sample. Additional measurement of impulse response at multiple detectors facilitates determination of change of the measured parameter across the sample as a function of time.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
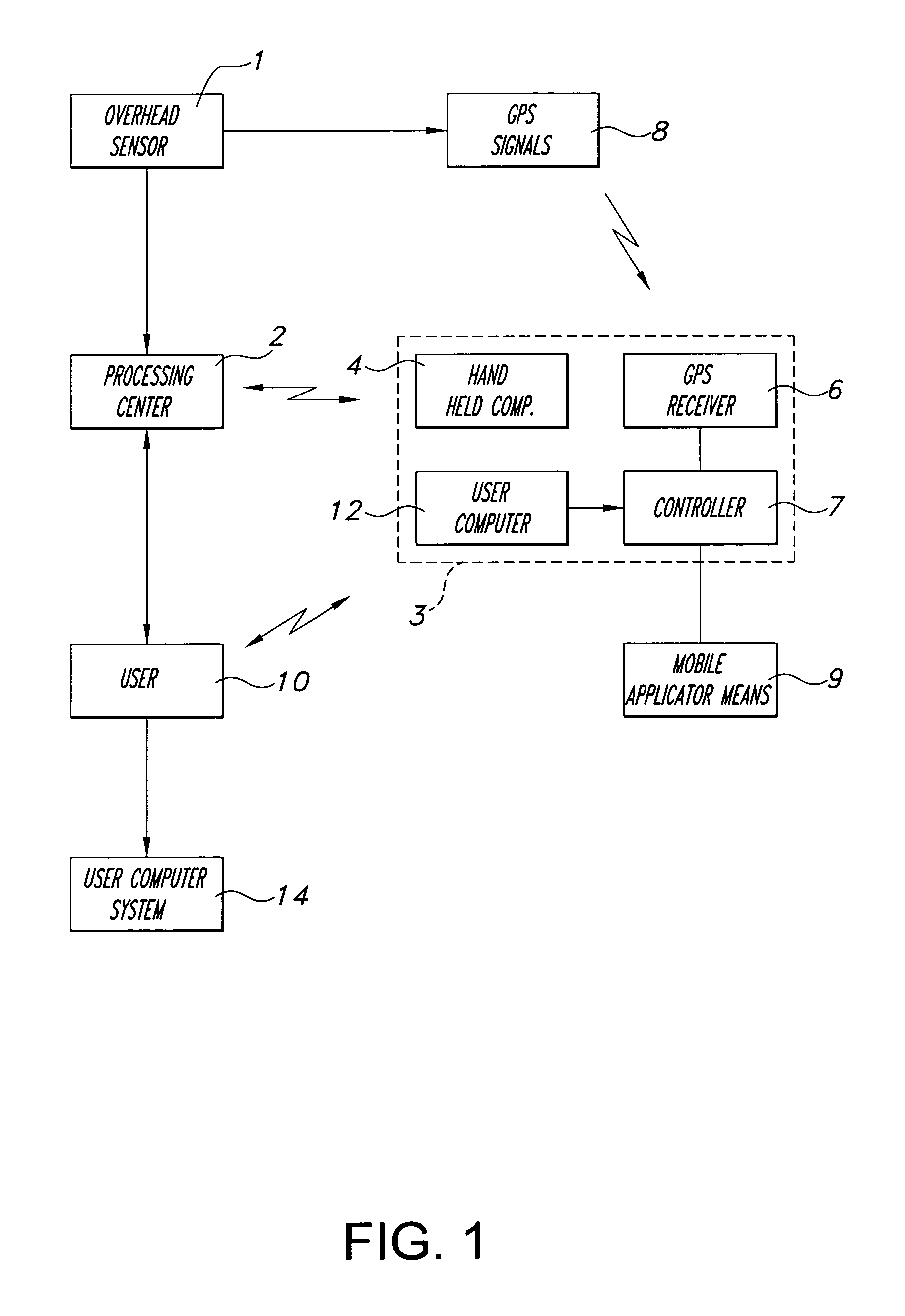
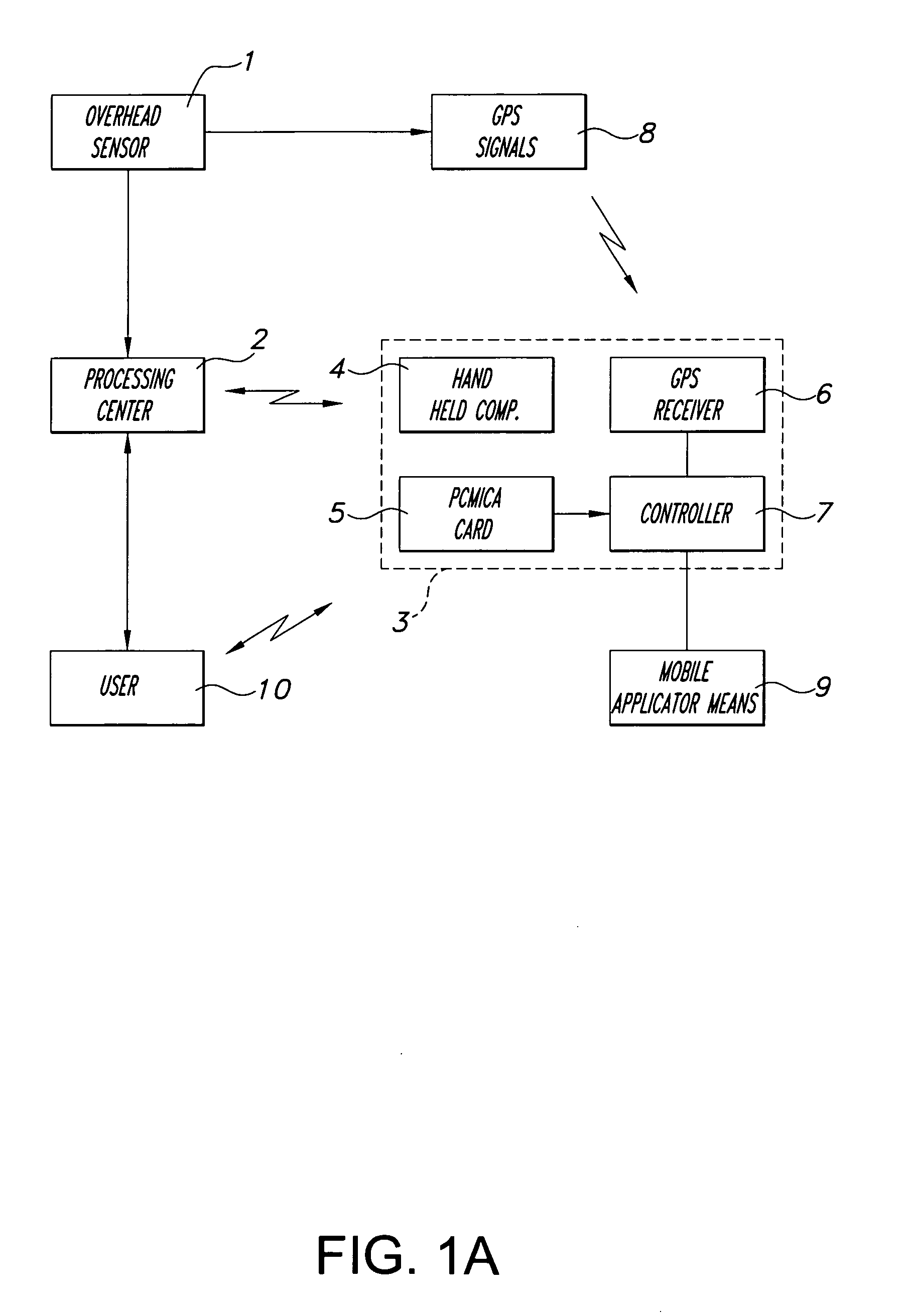
Method and system for spatially variable rate application of agricultural chemicals based on remotely sensed vegetation data
InactiveUS7103451B2Controlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsCharacter and pattern recognitionVariable Rate ApplicationVegetation
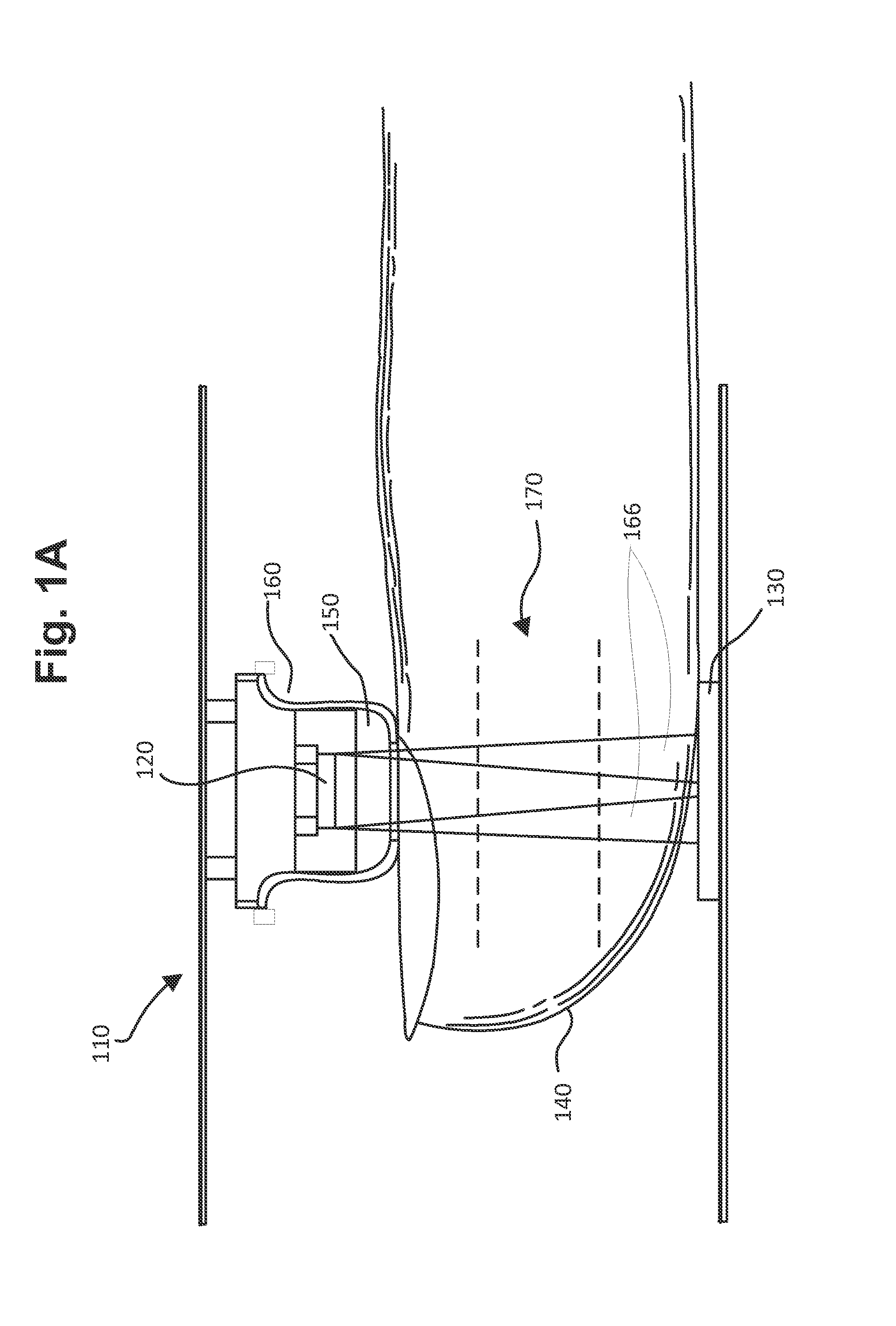
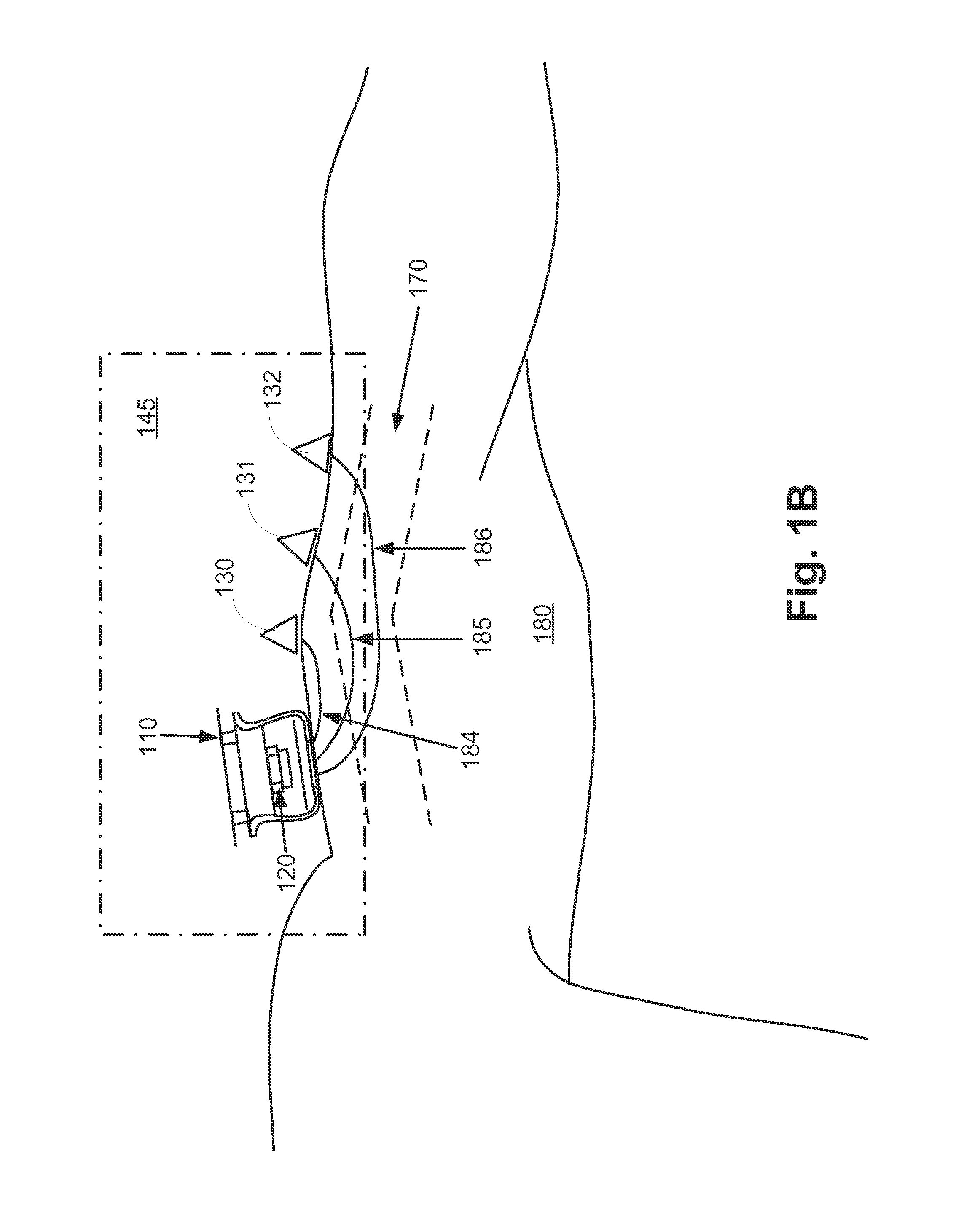
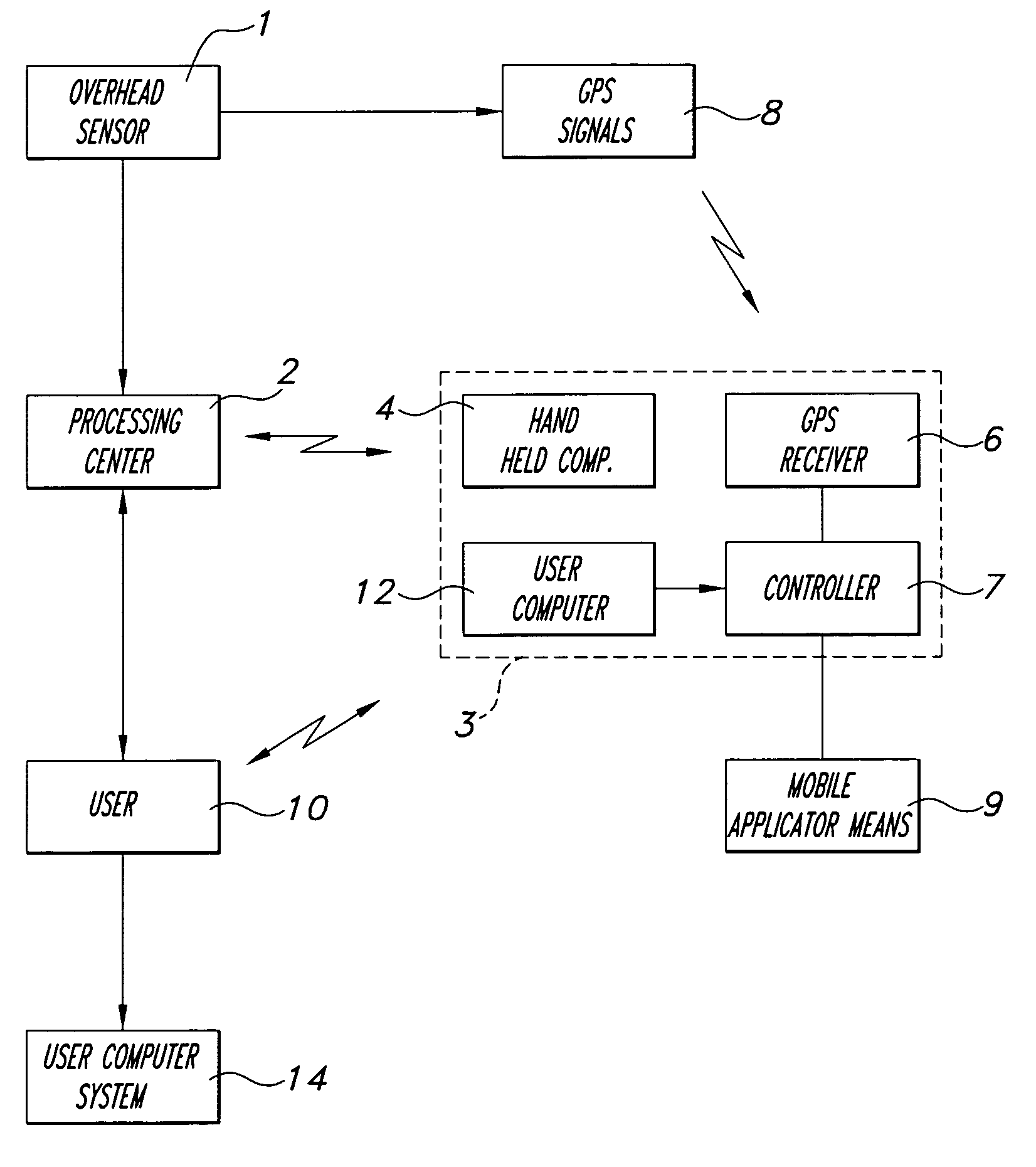
Remotely sensed spectral image data are used to develop a Vegetation Index file which represents spatial variations of actual crop vigor throughout an area that is under cultivation. The latter information is processed to place it in a format that can be used by personnel to correlate and calibrate it with actually observed crop conditions existing at control points within the area. Based on the results, personnel formulate a prescription request, which is forwarded to a central processing site, where the prescription is prepared. The latter is returned to a mobile application means that directly applies inputs to the field at a spatially variable rate.
Owner:INTIME
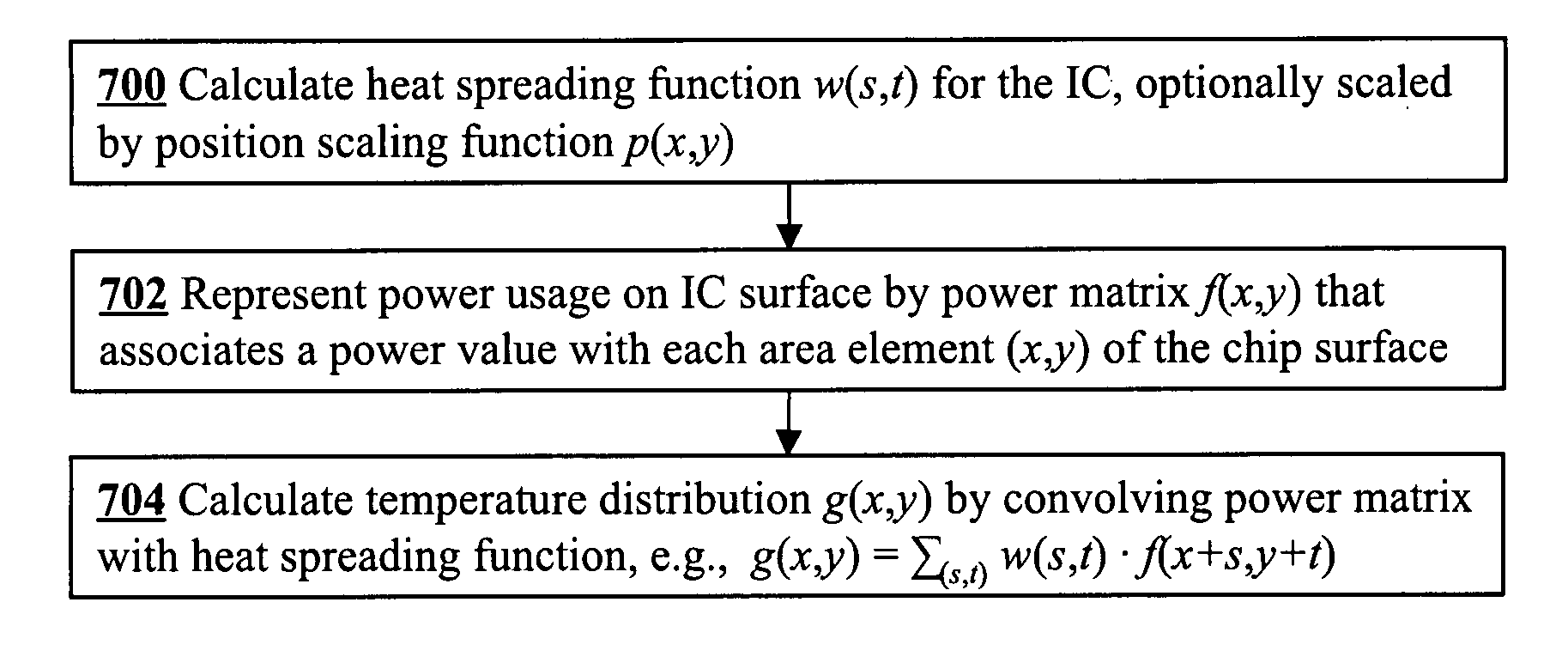
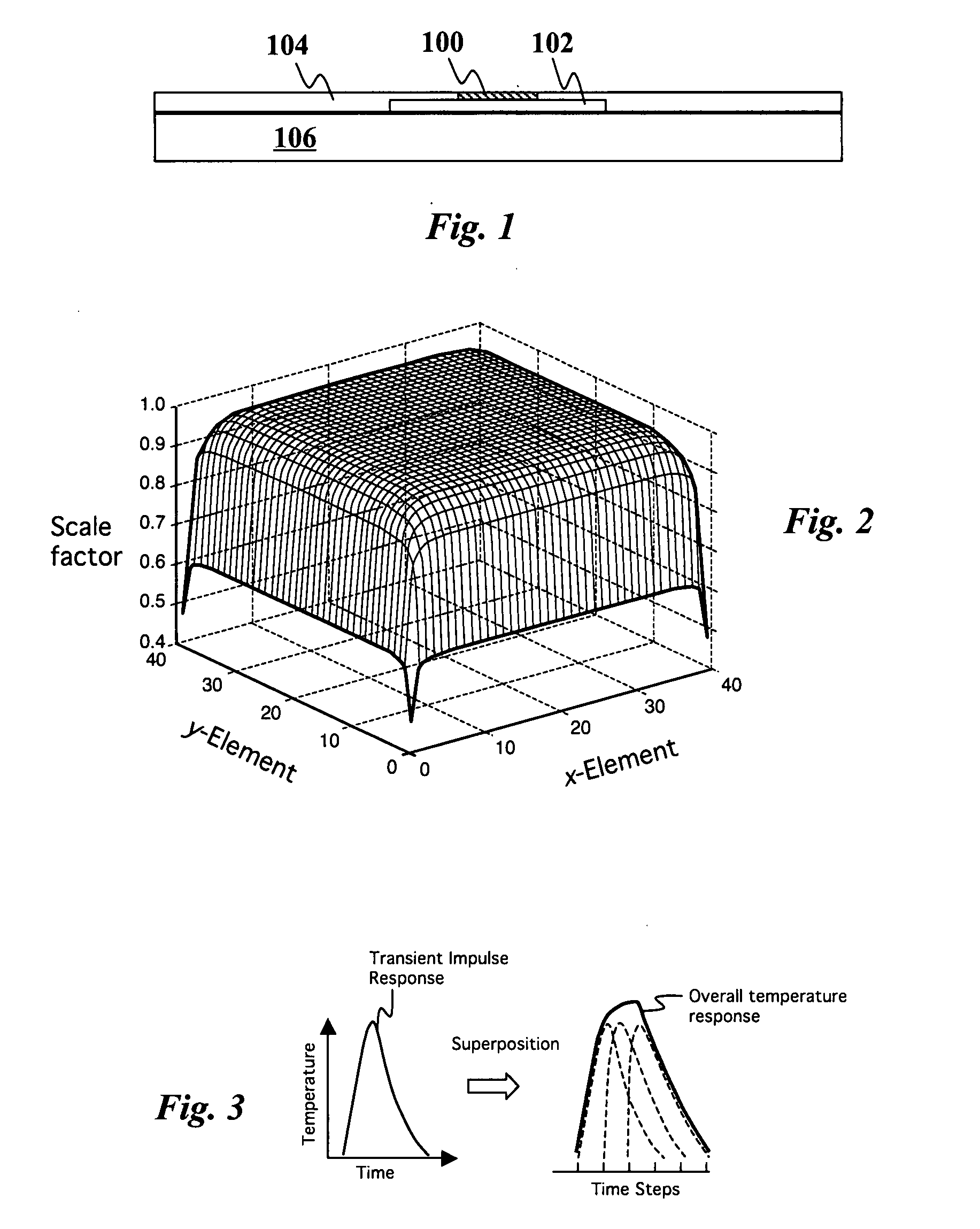
Efficient method to predict integrated circuit temperature and power maps
InactiveUS20080026493A1Fast and accurate methodMinimizes localized heatingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDetecting faulty computer hardwareElement analysisDiffusion function
The temperature distribution associated with a design of an integrated circuit is calculated by convoluting a surface power usage represented by a power matrix with a heat spreading function. The heat spreading function may be calculated from a simulation of a point source on the integrated circuit using a finite element analysis model of the integrated circuit or other techniques. To account for spatial variations on the chip, the heat spreading function may be made dependent on position using a position scaling function. Steady-state or transient temperature distributions may be computed by using a steady-state or transient heat spreading function. A single heat spreading function may be convolved with various alternative power maps to efficiently calculate temperature distributions for different designs. In an inverse problem, one can calculate the power map from an empirically measured temperature distribution and a heat spreading function using various de-convolution techniques. While the forward problem is analogous to image blurring, the inverse problem is analogous to image restoration.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
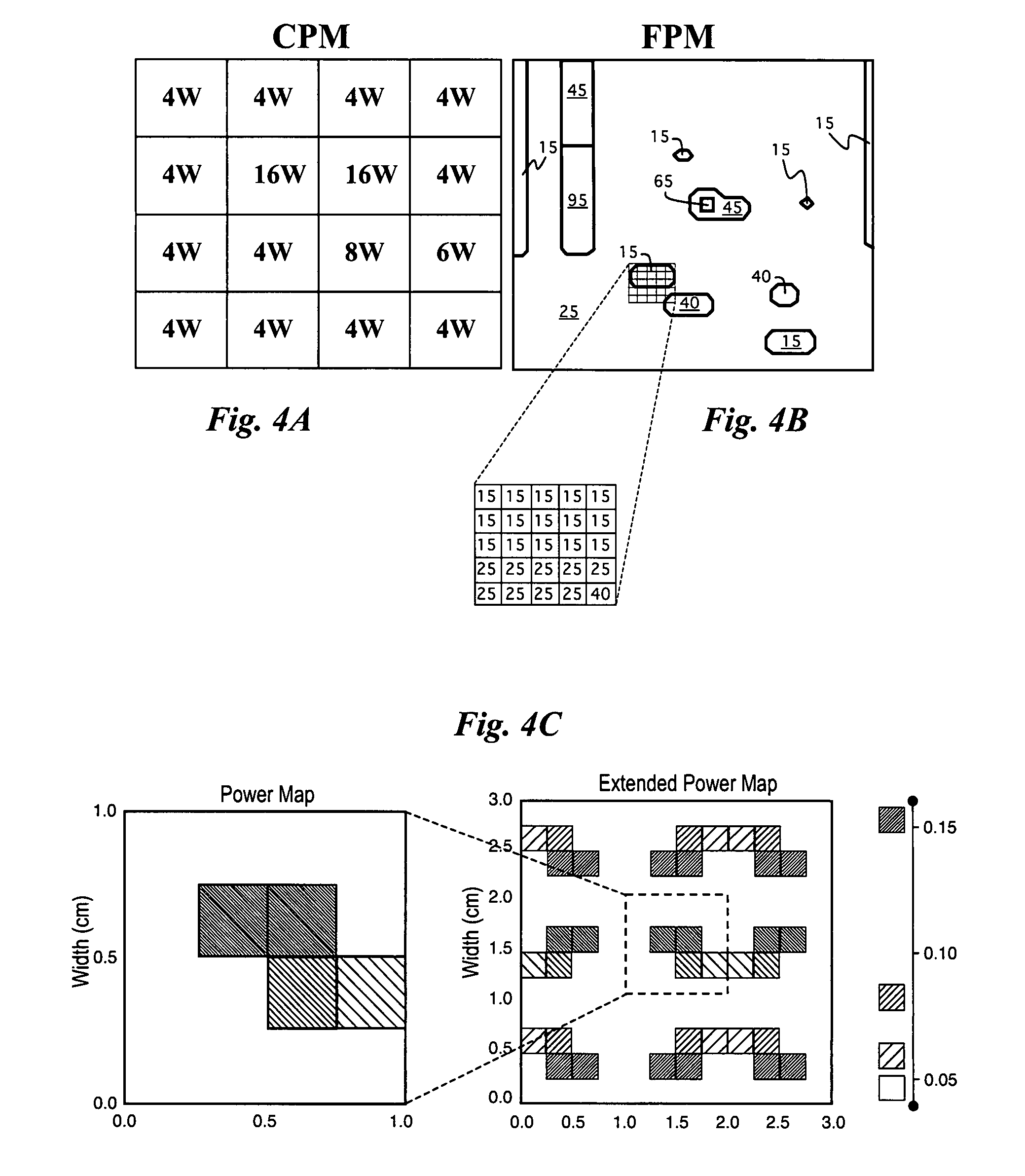
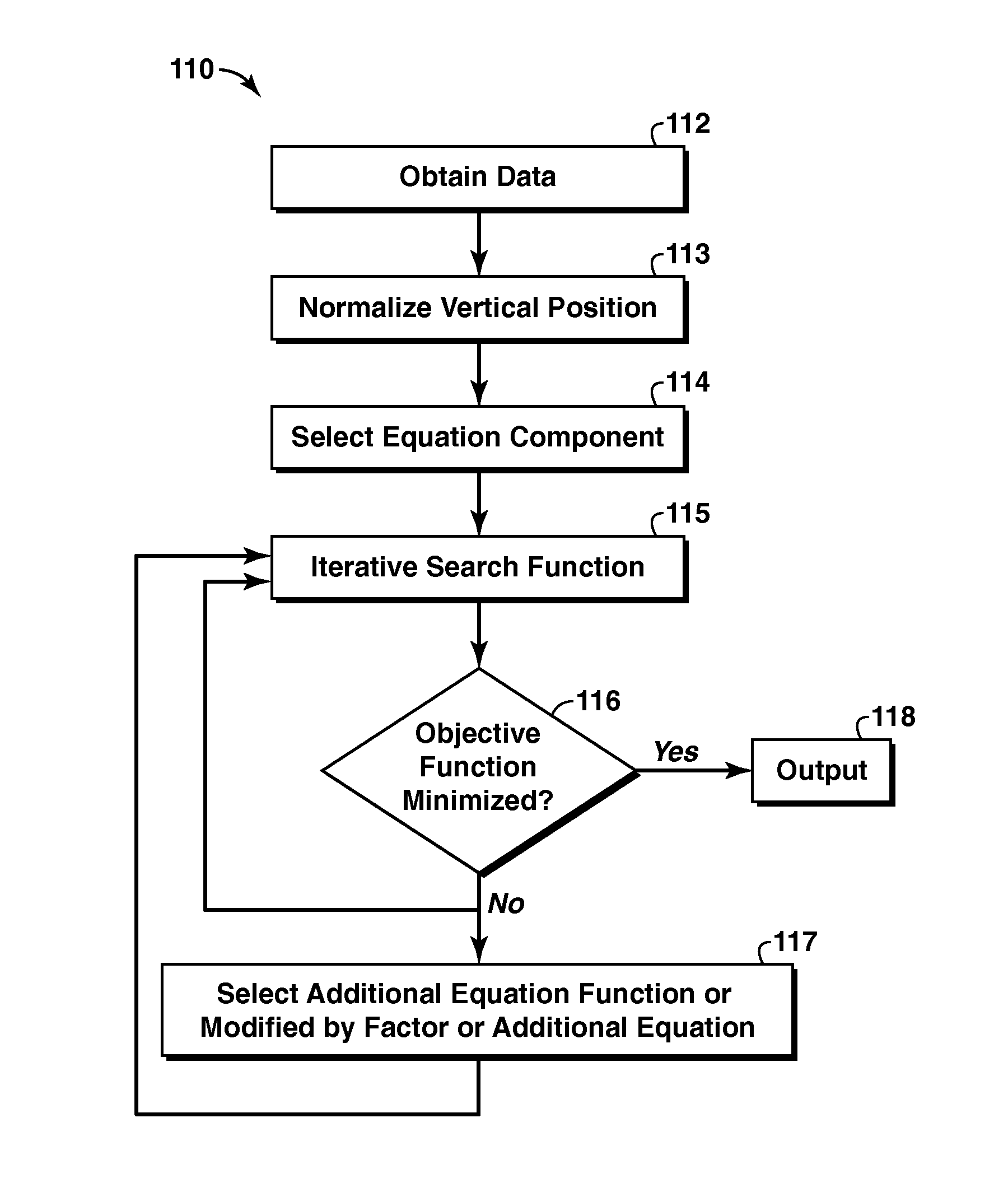
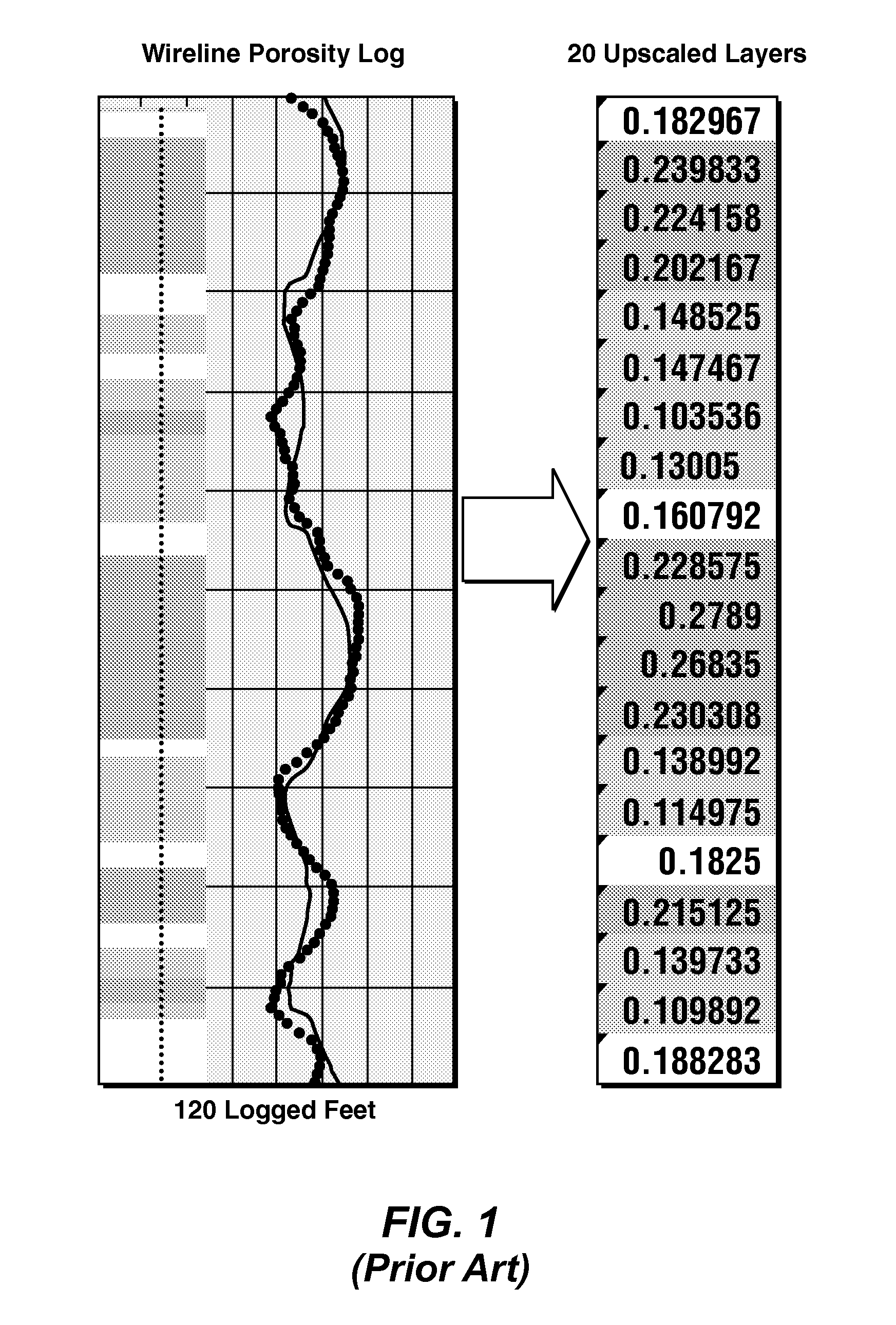
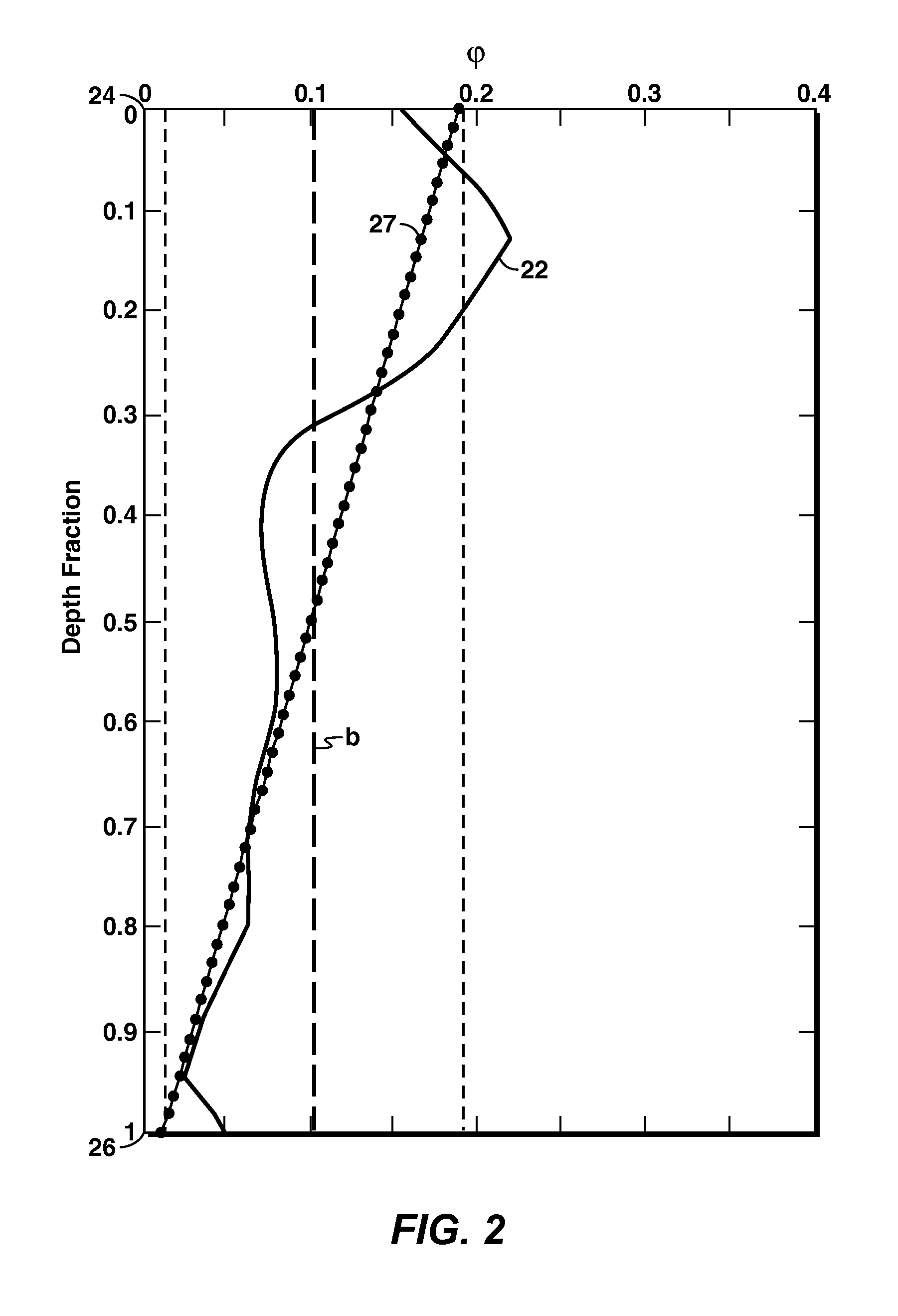
Reservoir Quality Characterization Using Heterogeneity Equations With Spatially-Varying Parameters
InactiveUS20120010865A1Geological measurementsAnalogue processes for specific applicationsSpatial changeObject function
Owner:BENSON GREGORY S
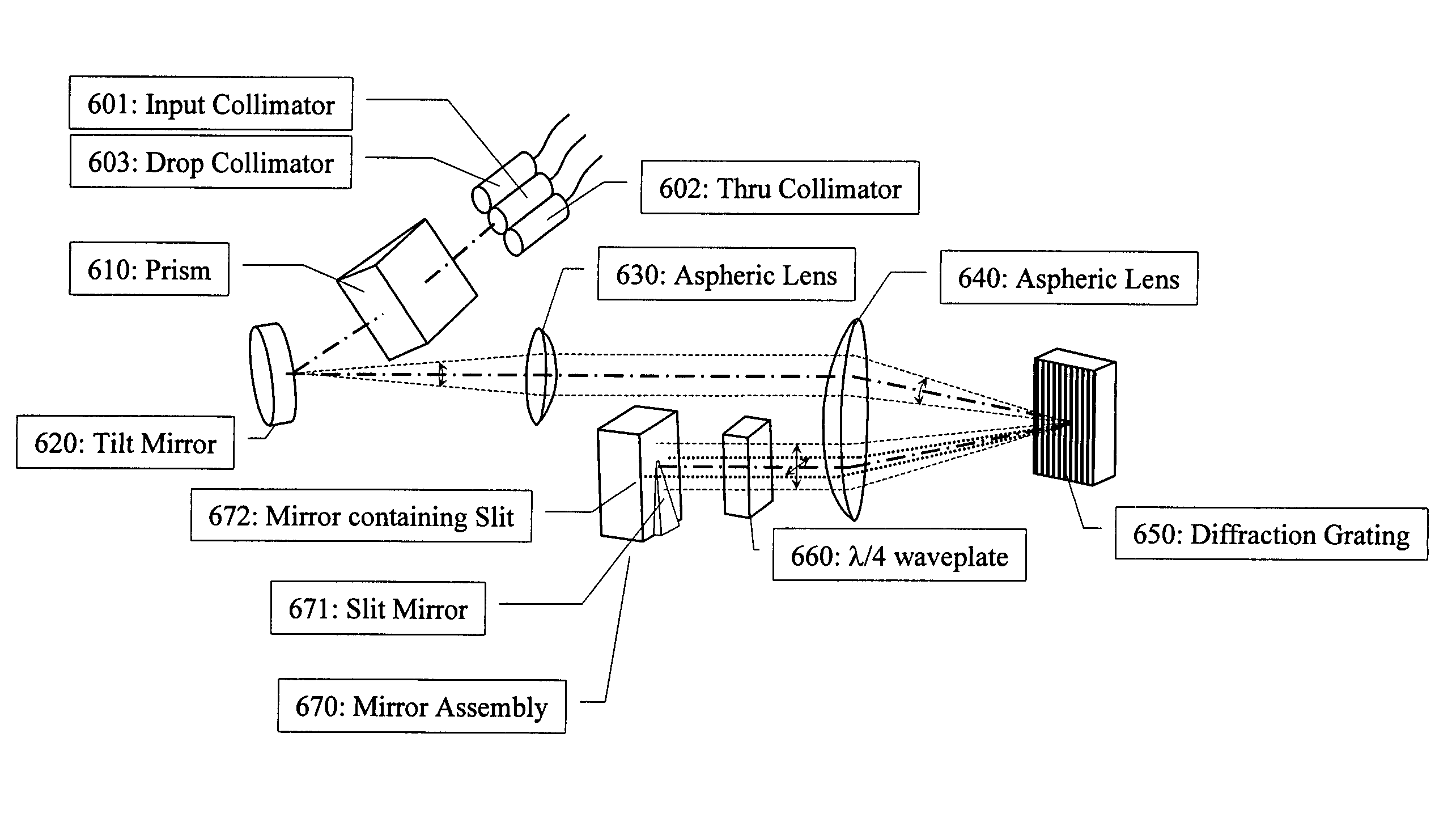
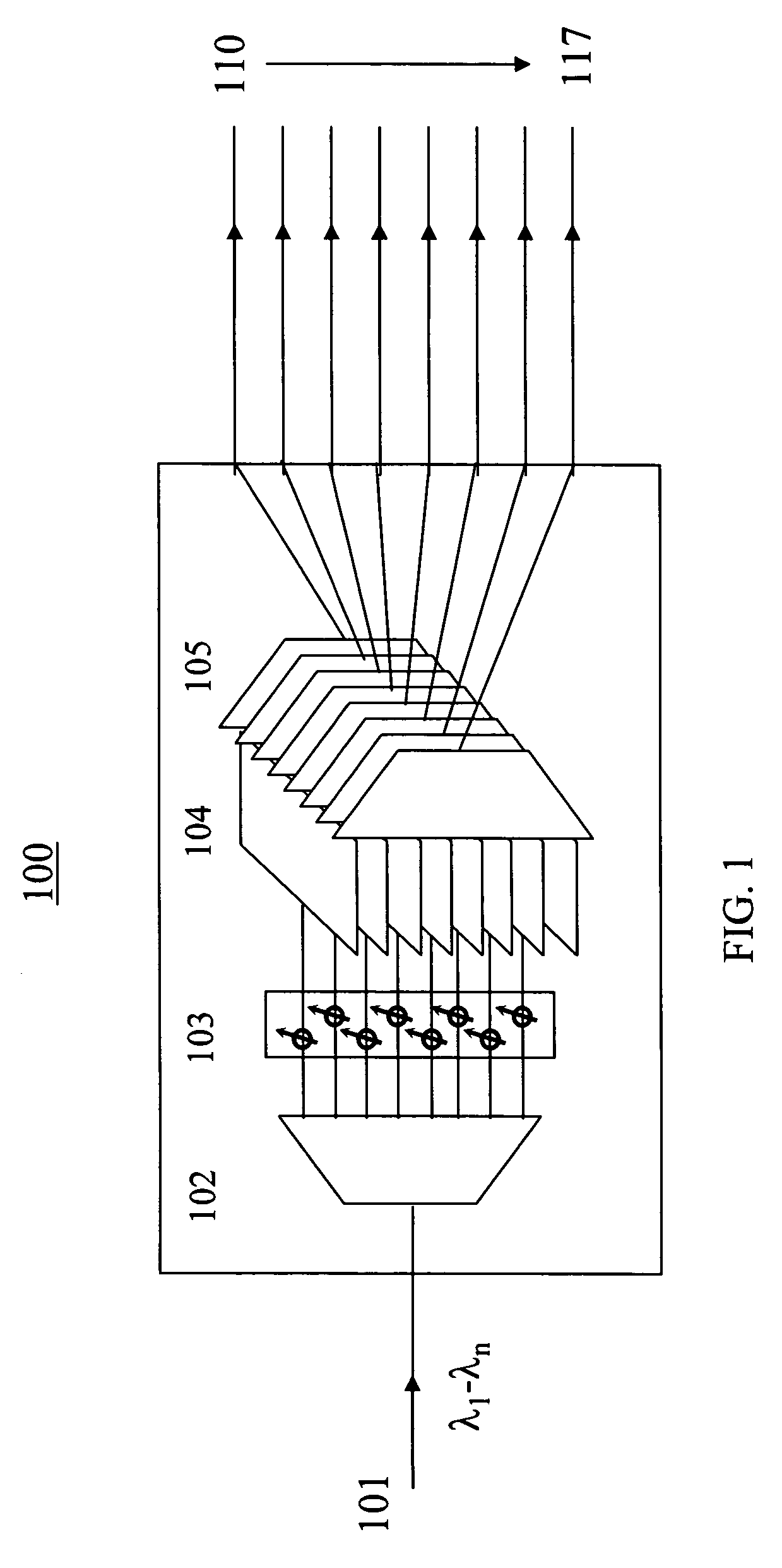
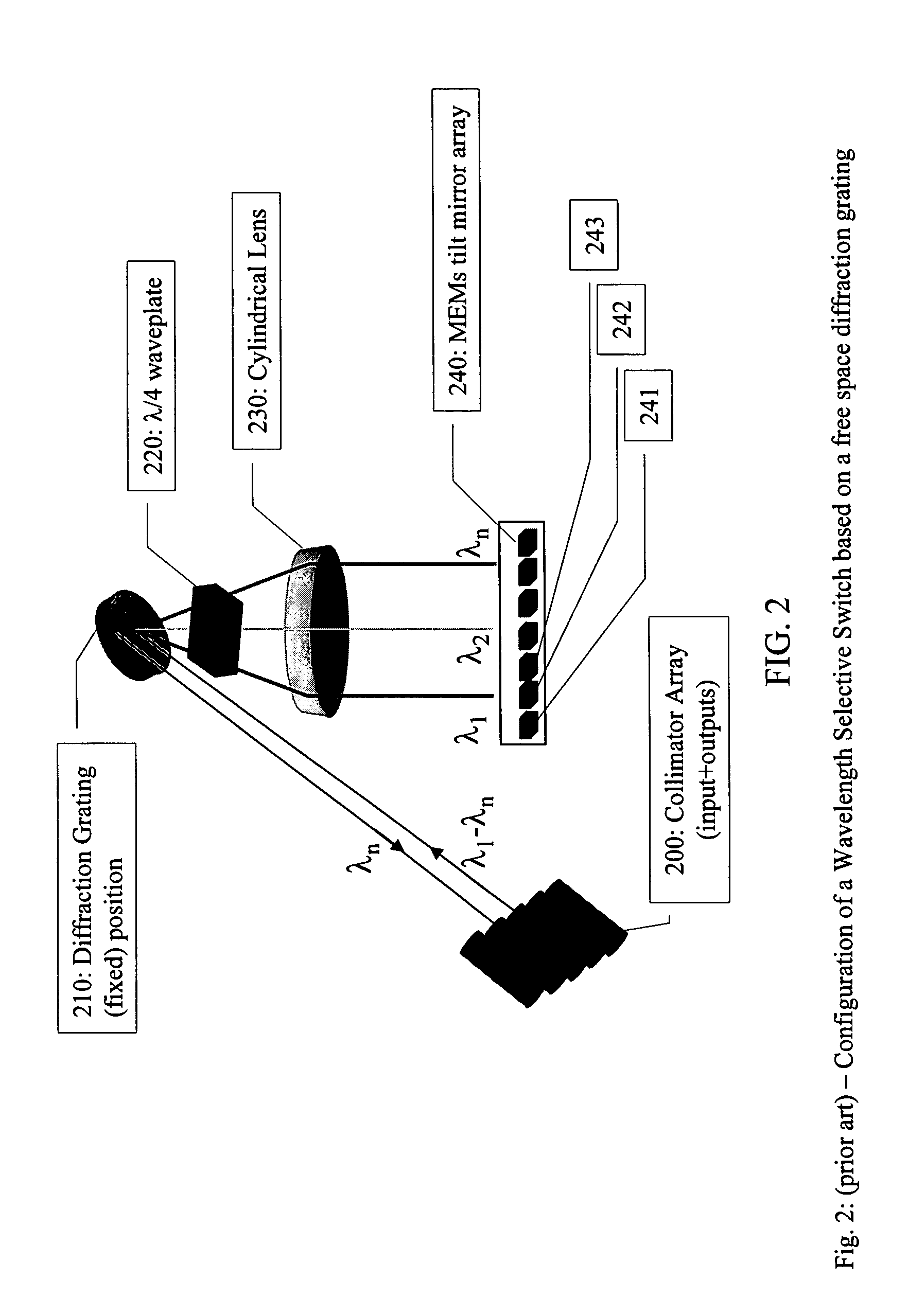
Tunable optical routing systems
Owner:MOLEX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com