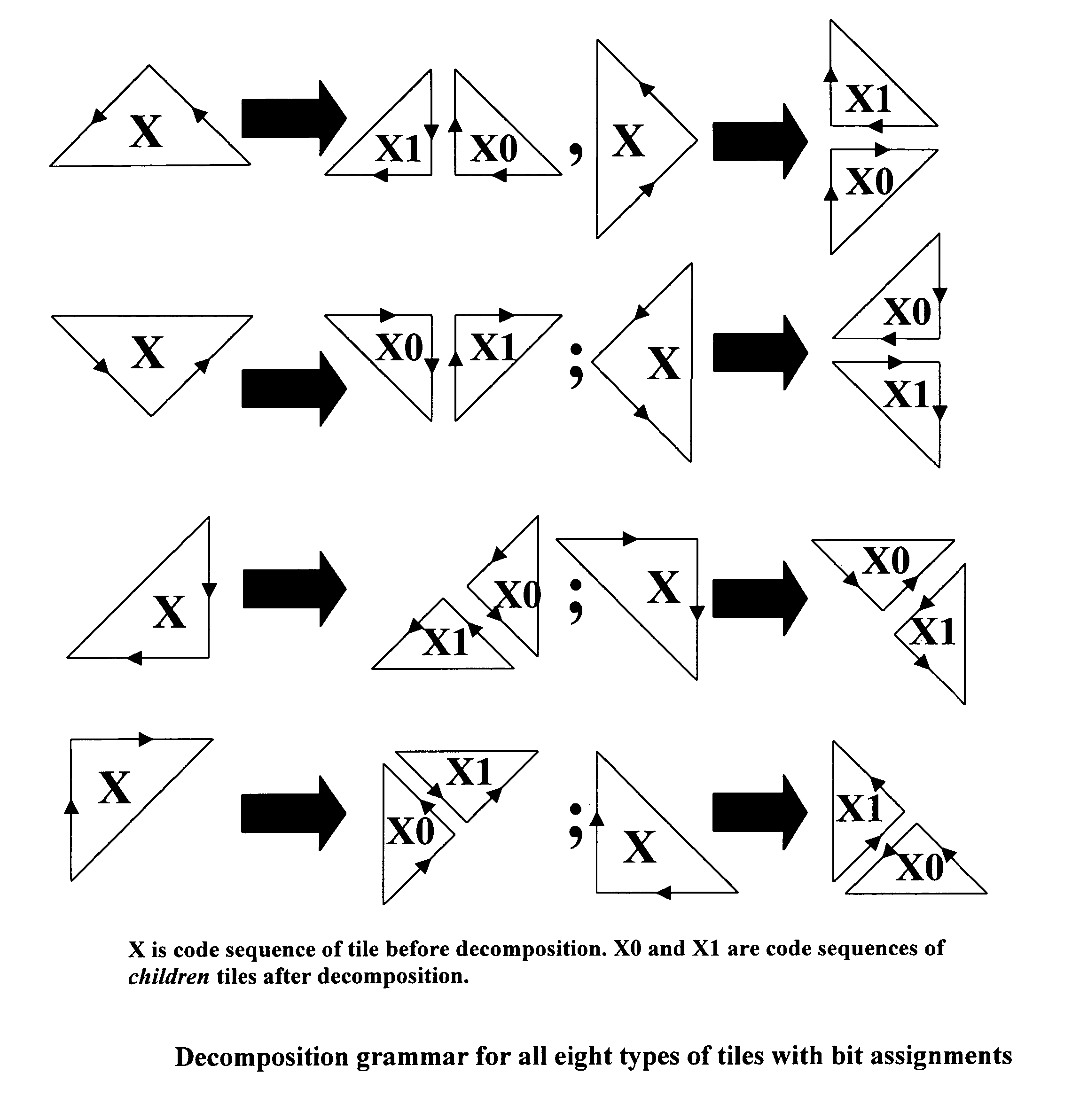
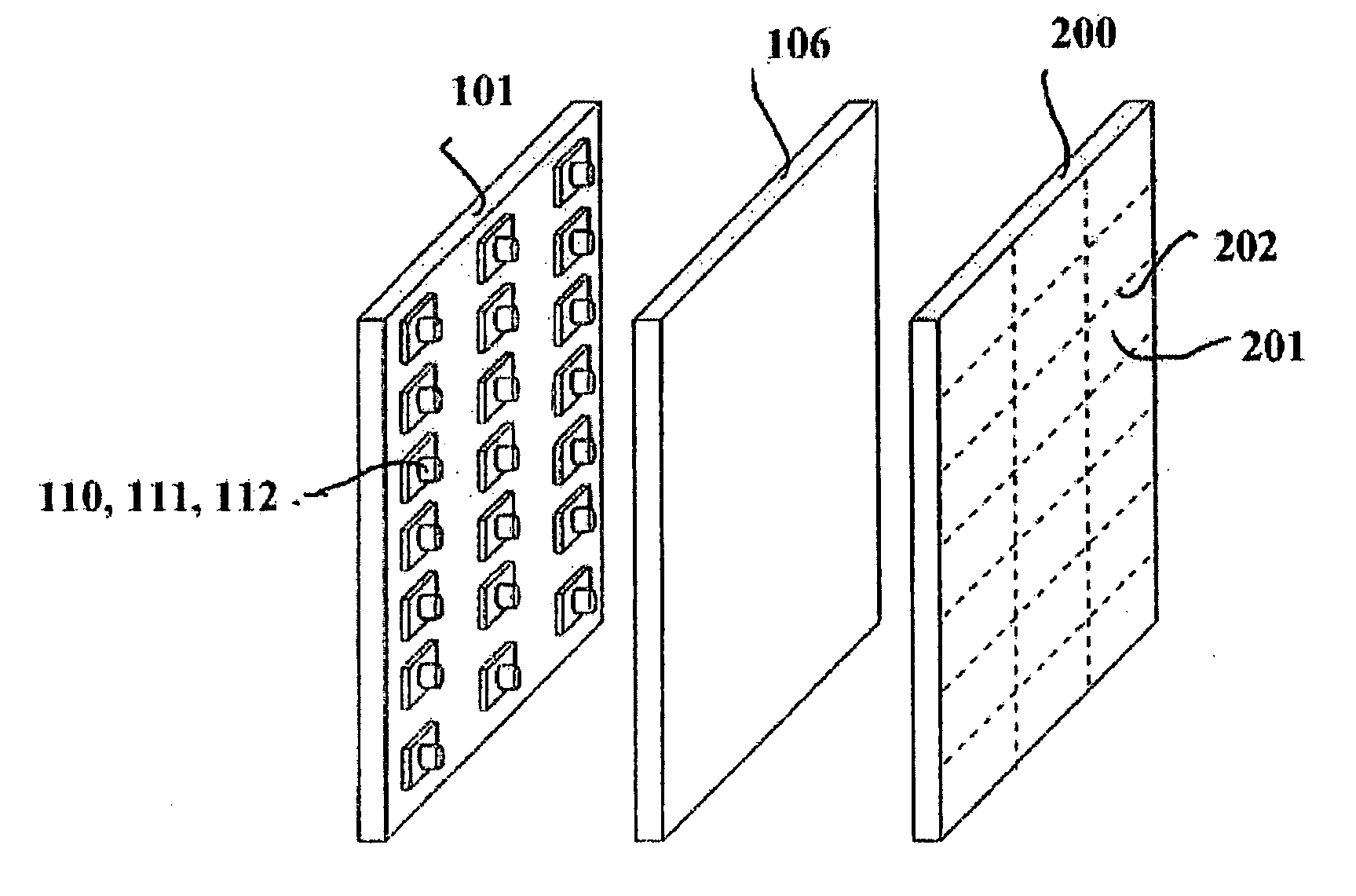
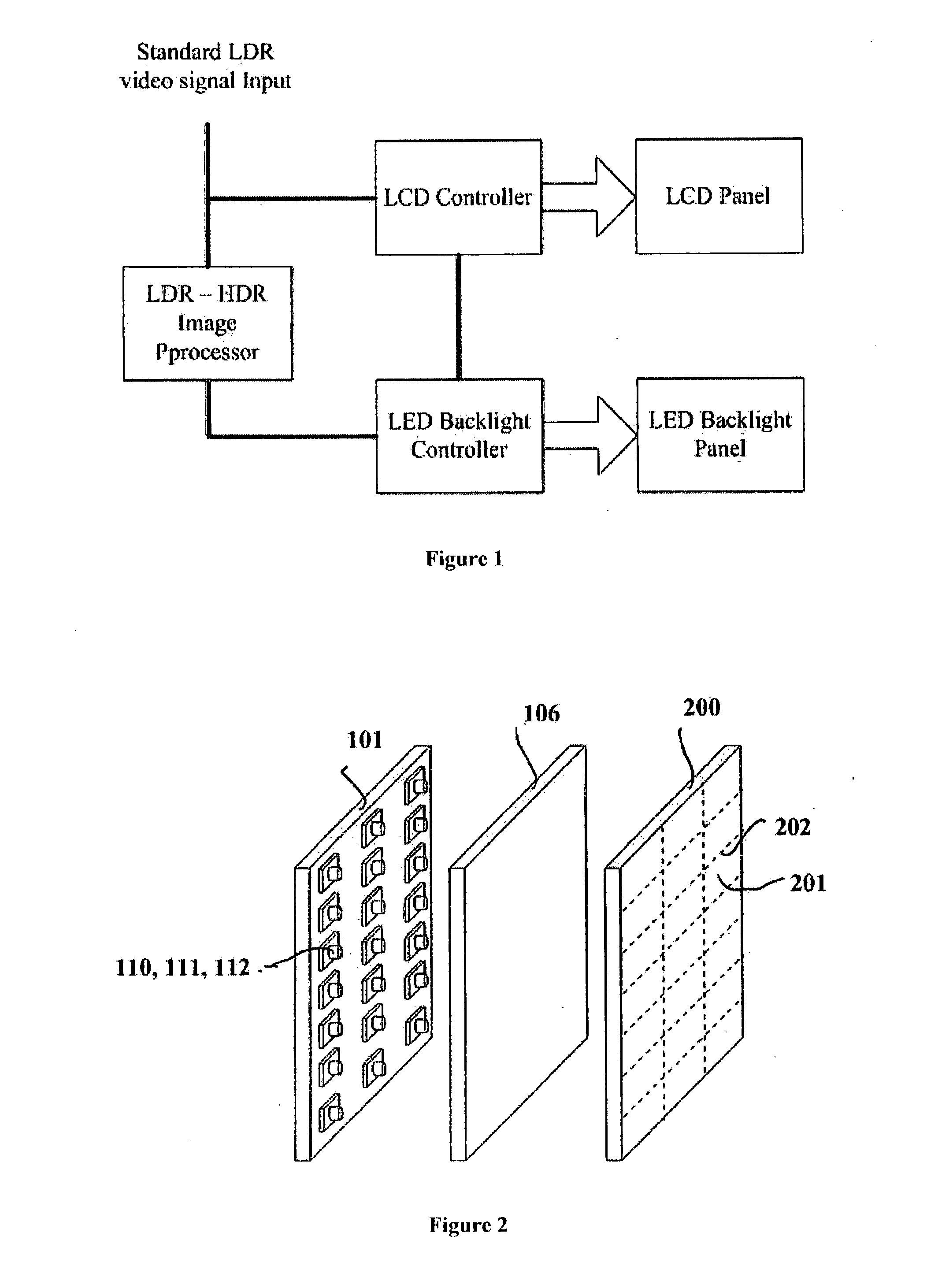
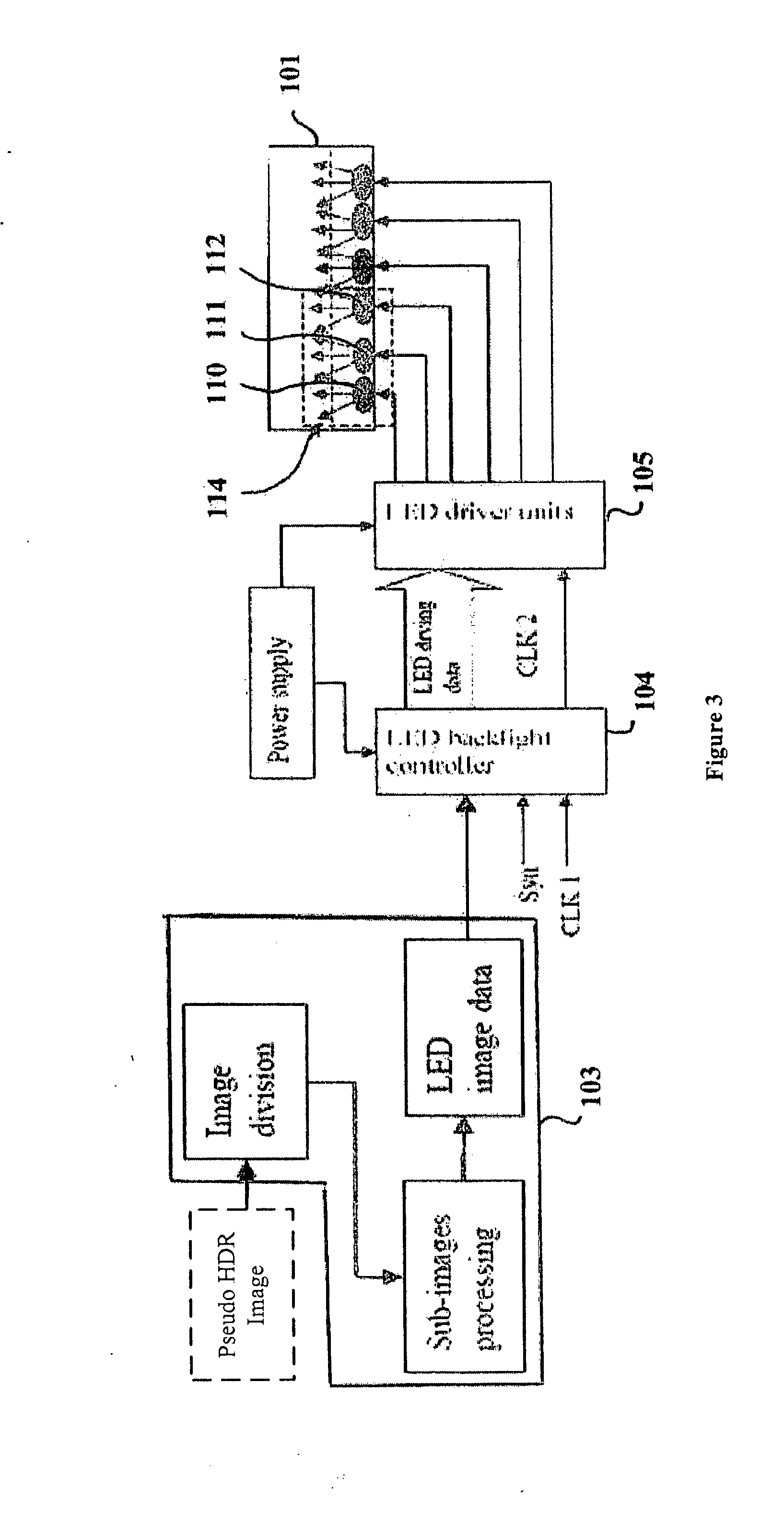
Patents
Literature
329 results about "Low dynamic range" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apparatus and method for dynamic range transforming of images
ActiveUS20140210847A1Improved dynamic range transformsImprove dynamic rangeImage enhancementRecording carrier detailsImaging processingDisplay device
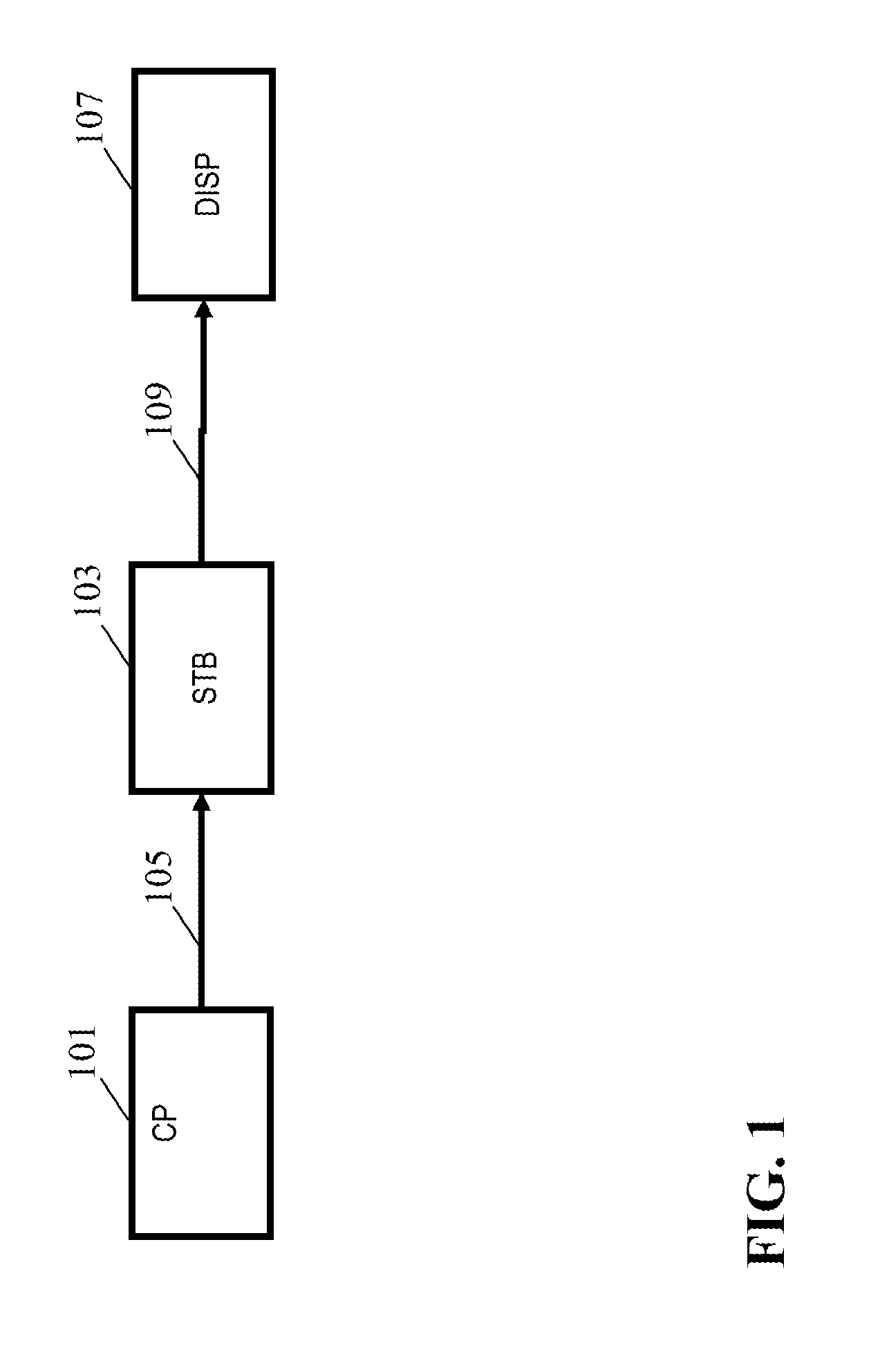
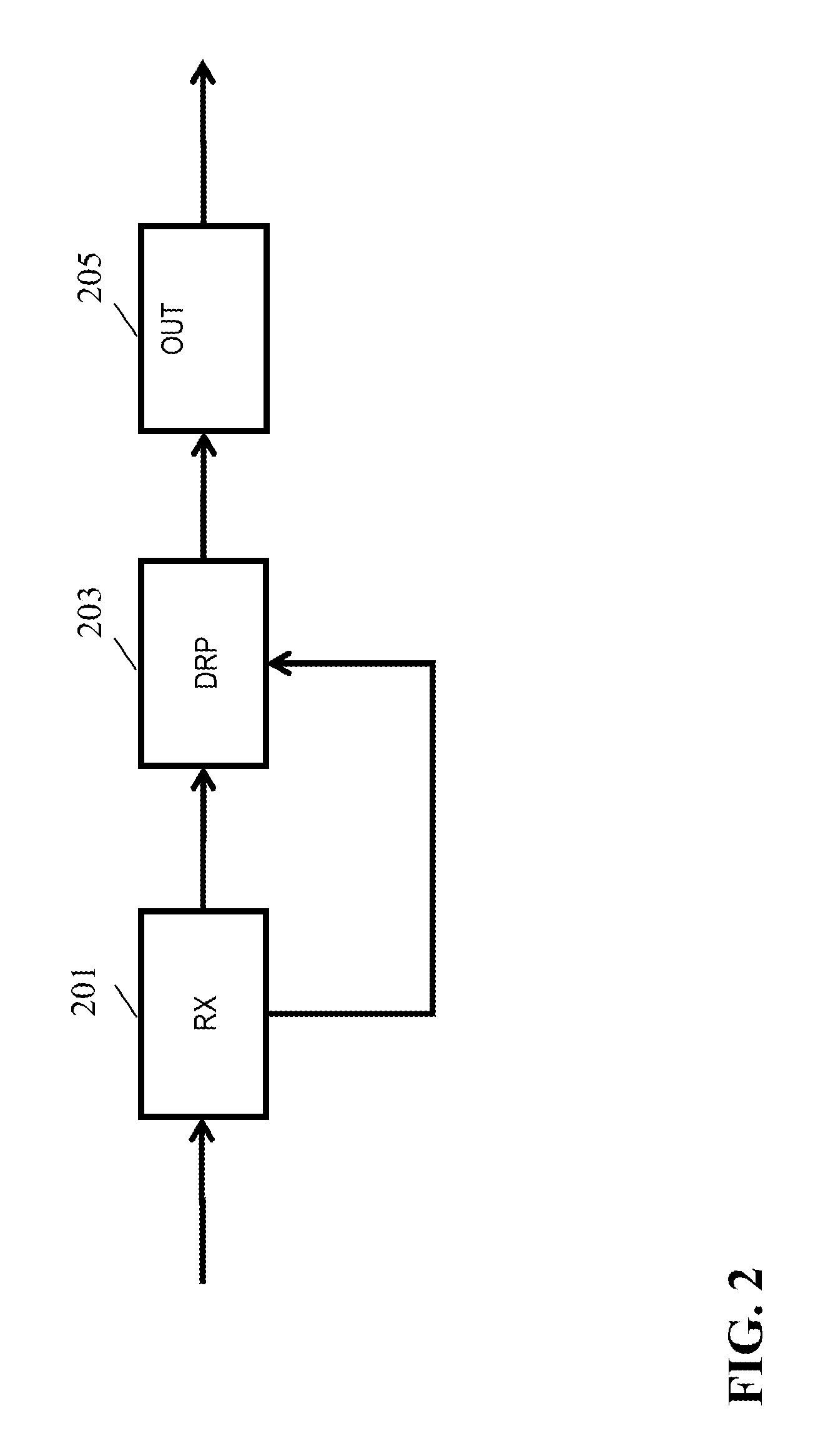
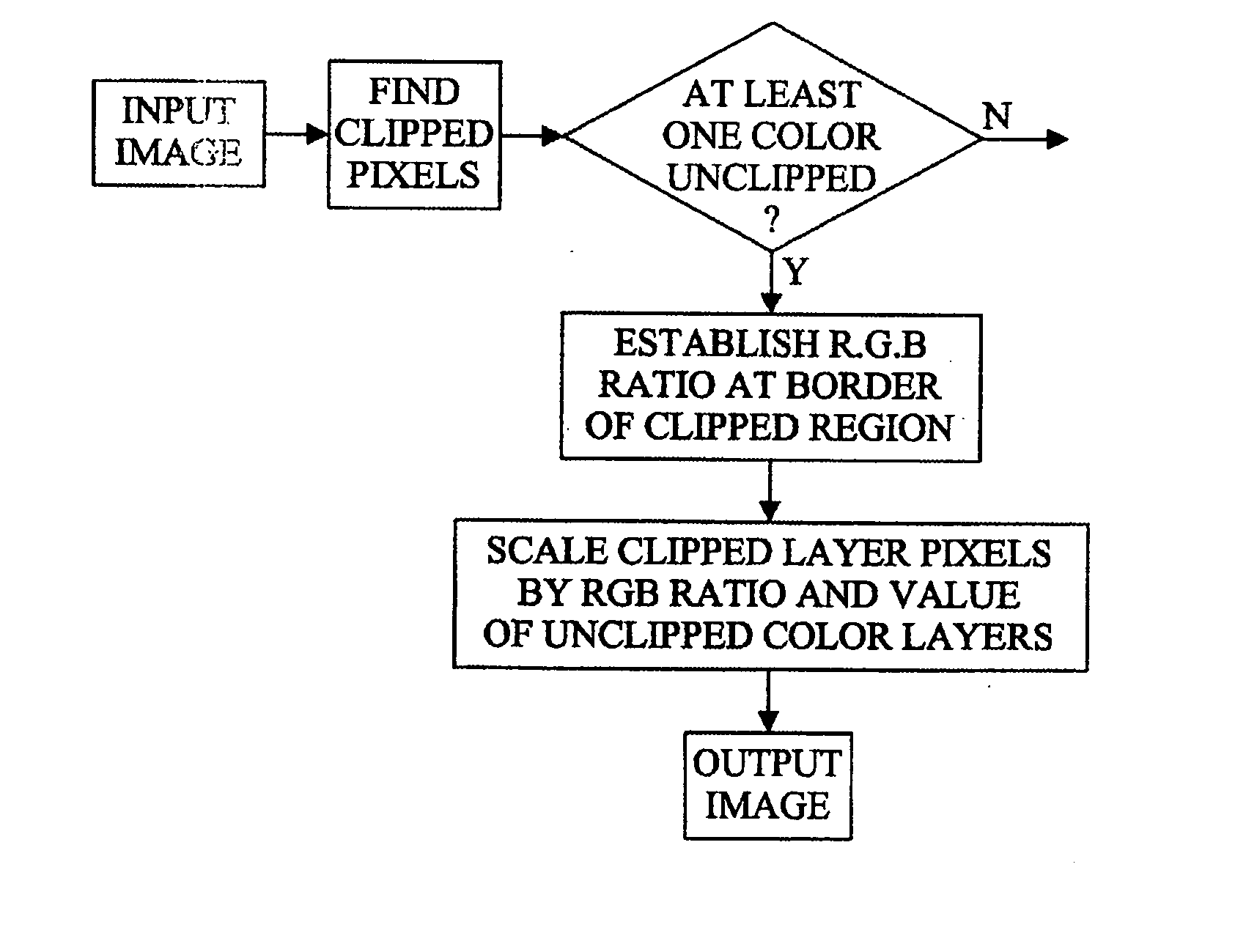
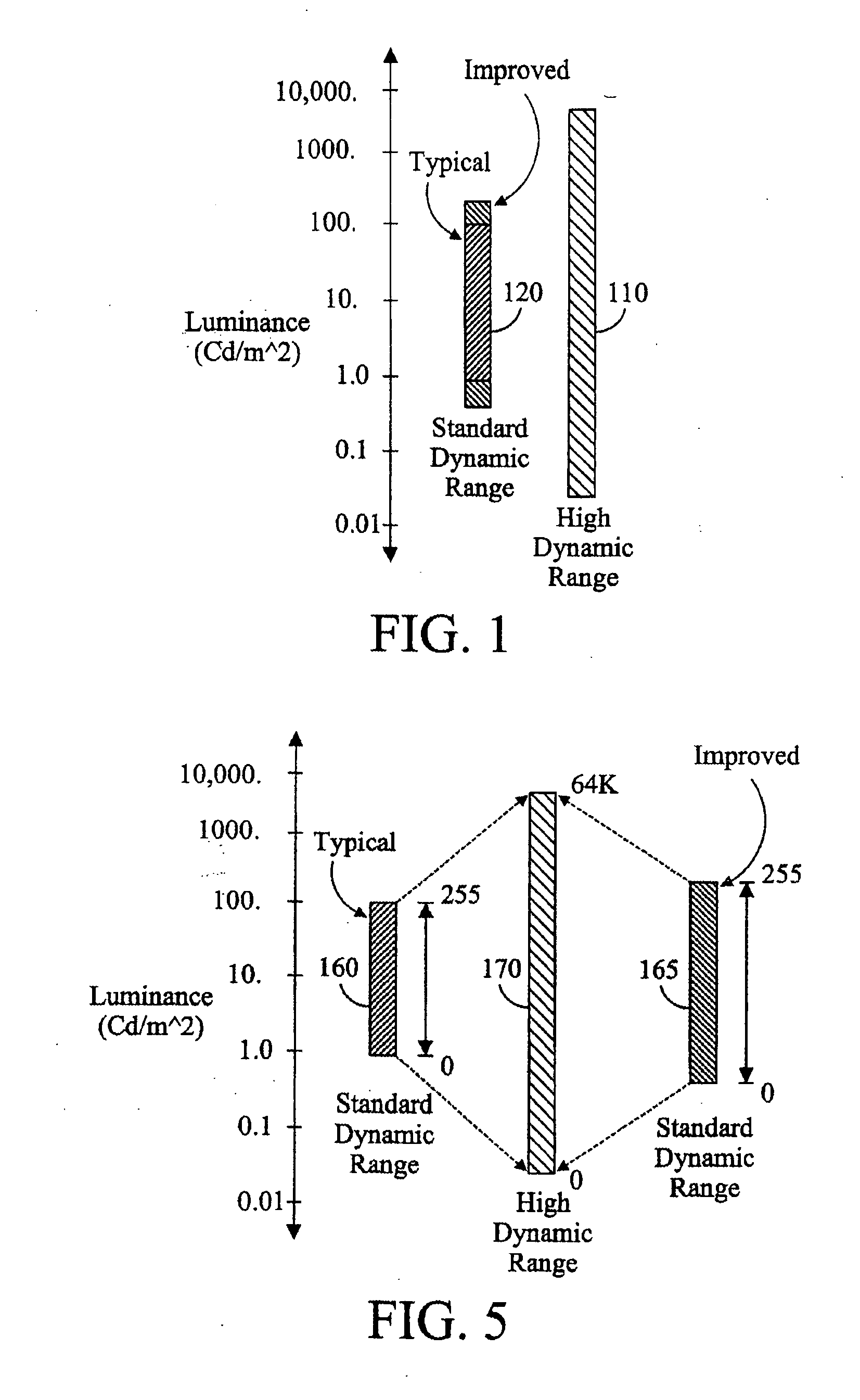
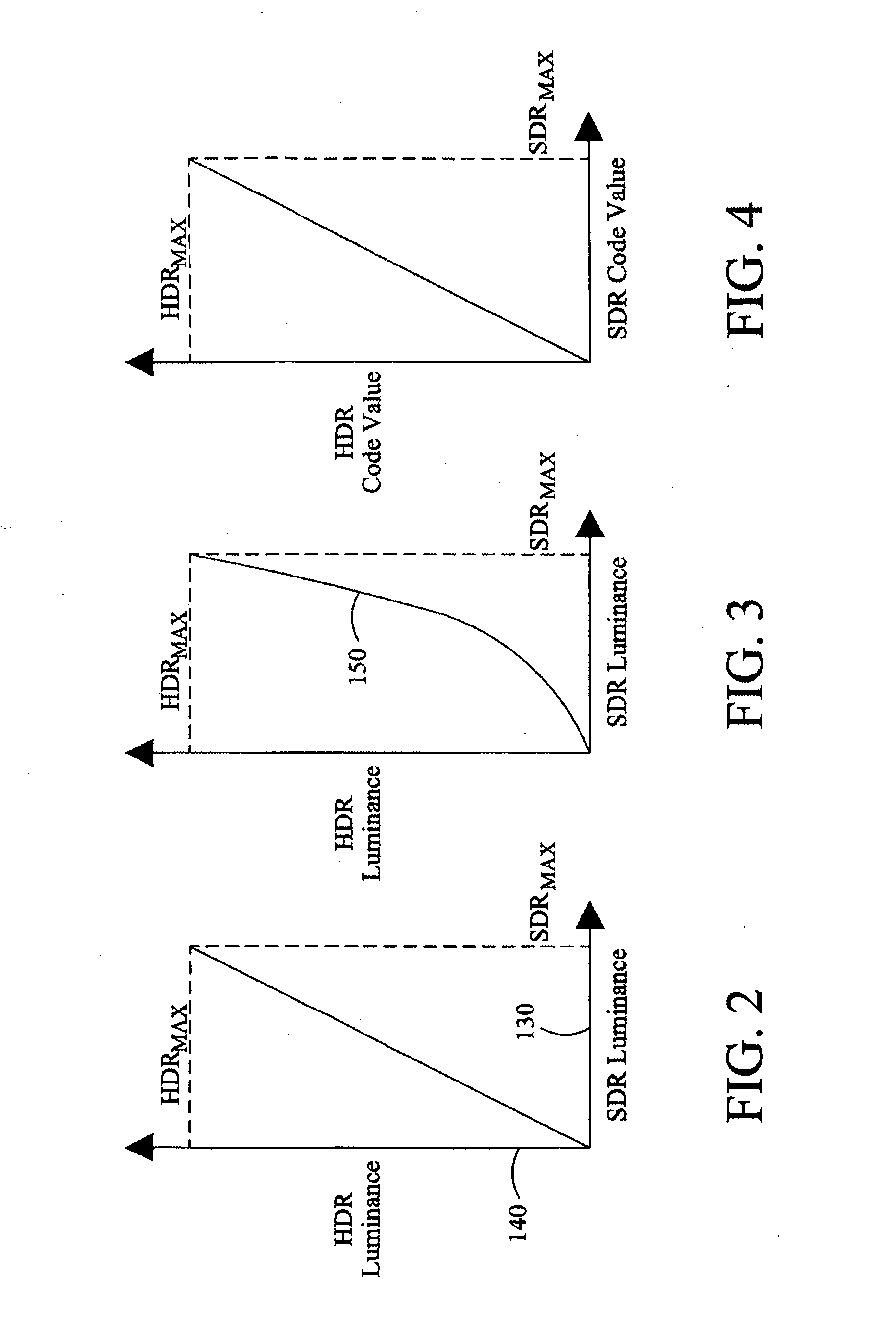
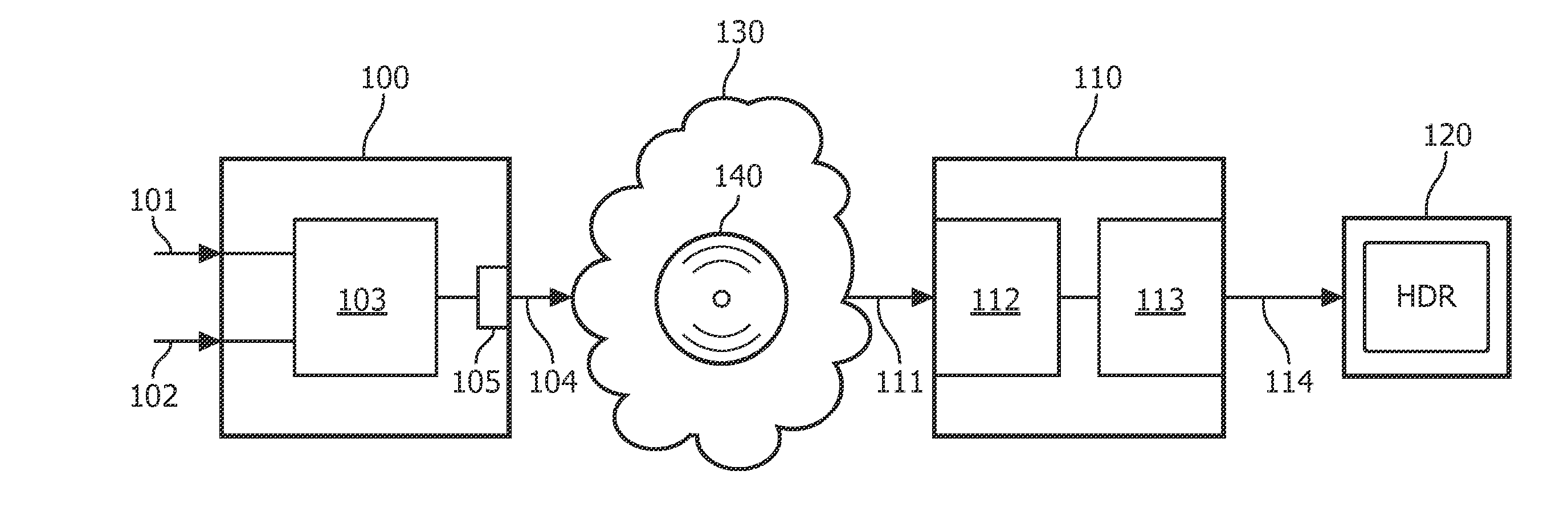
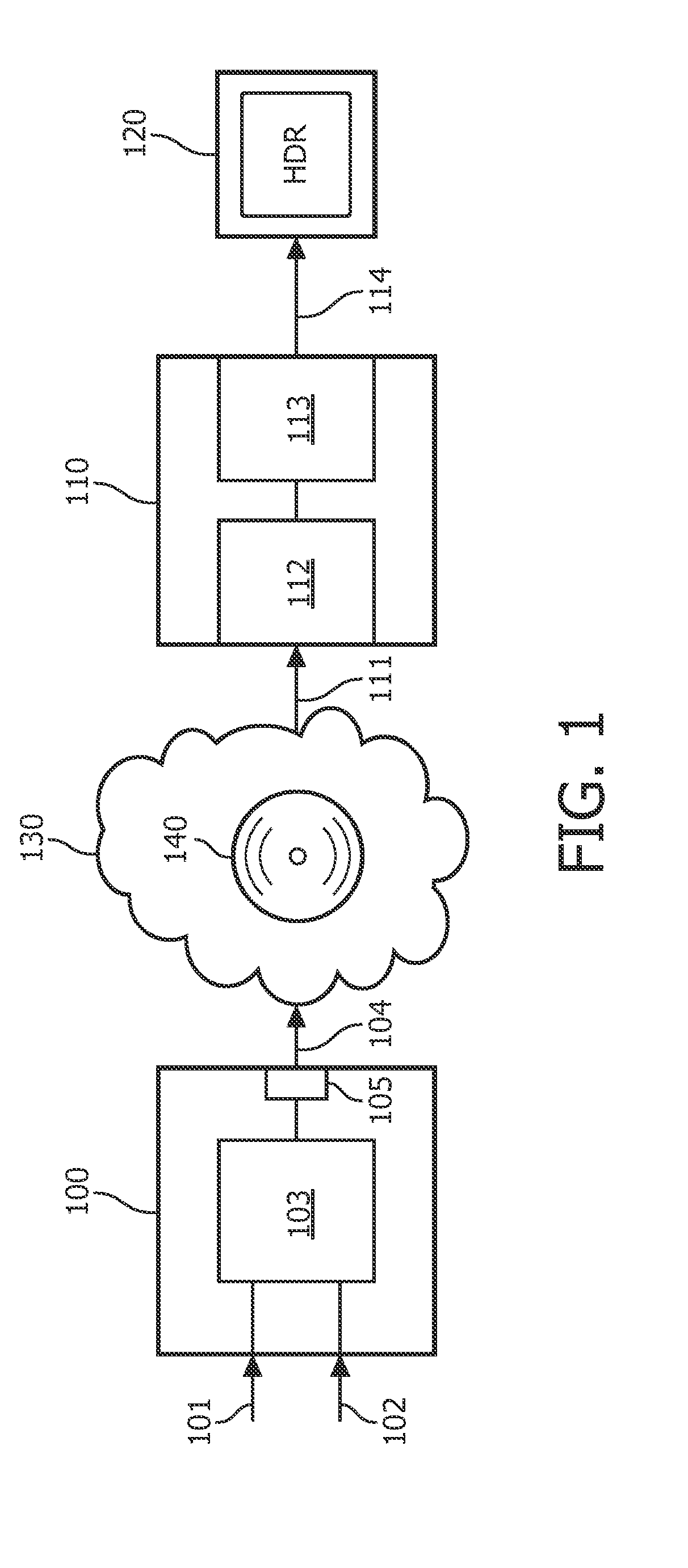
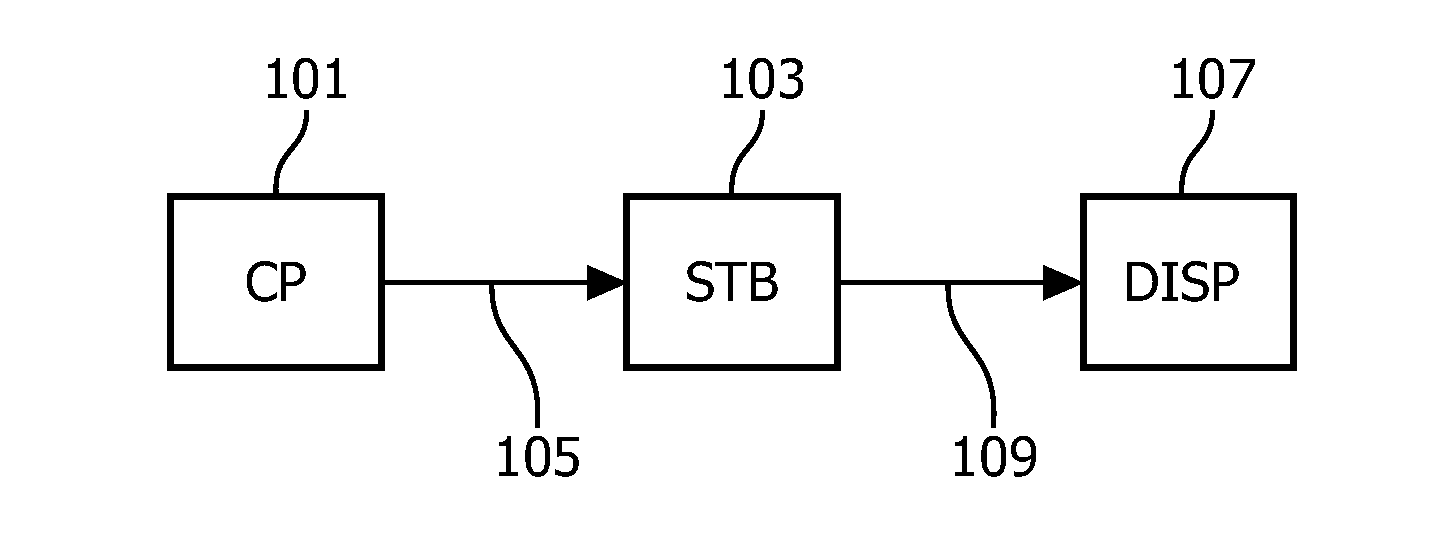
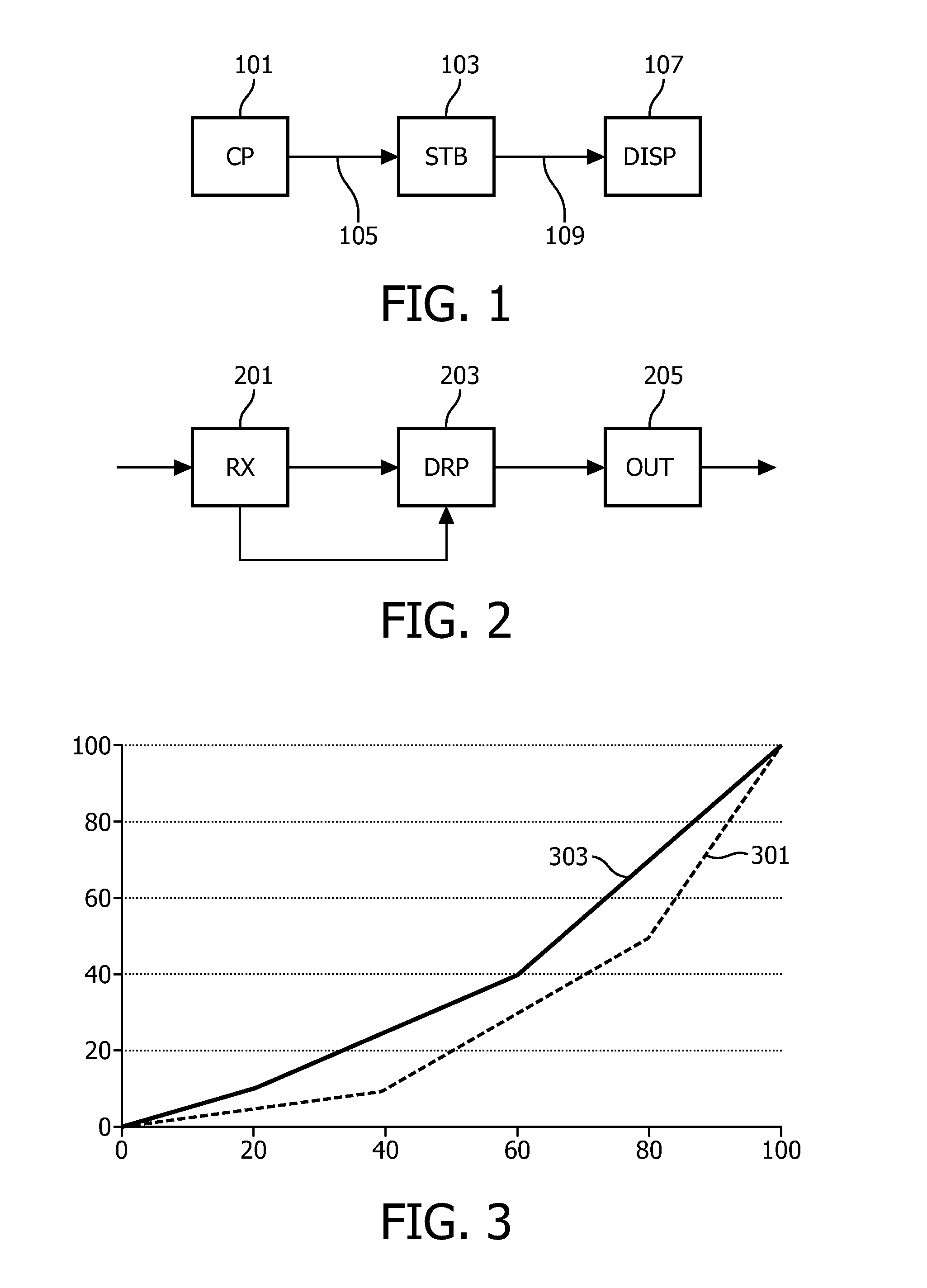
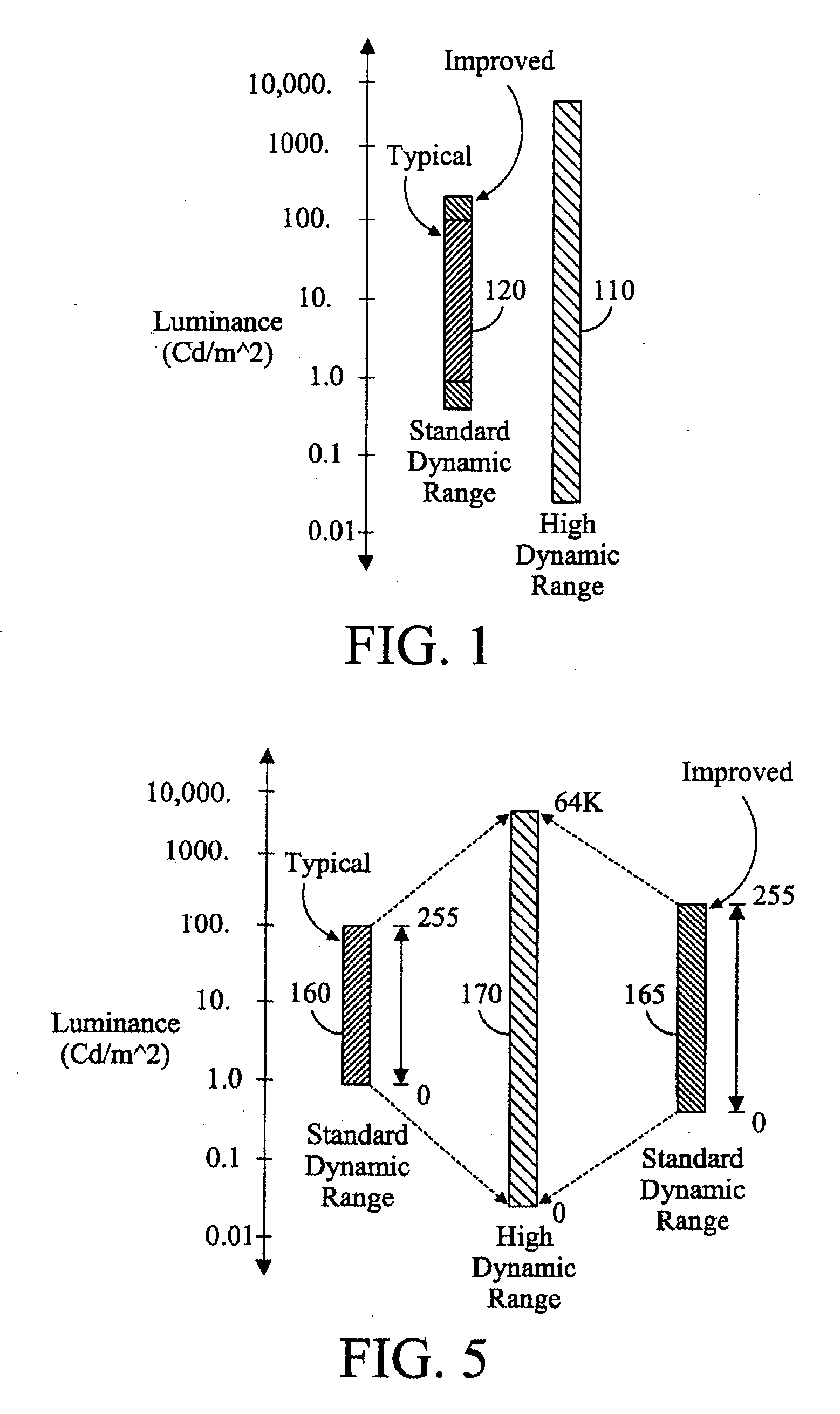
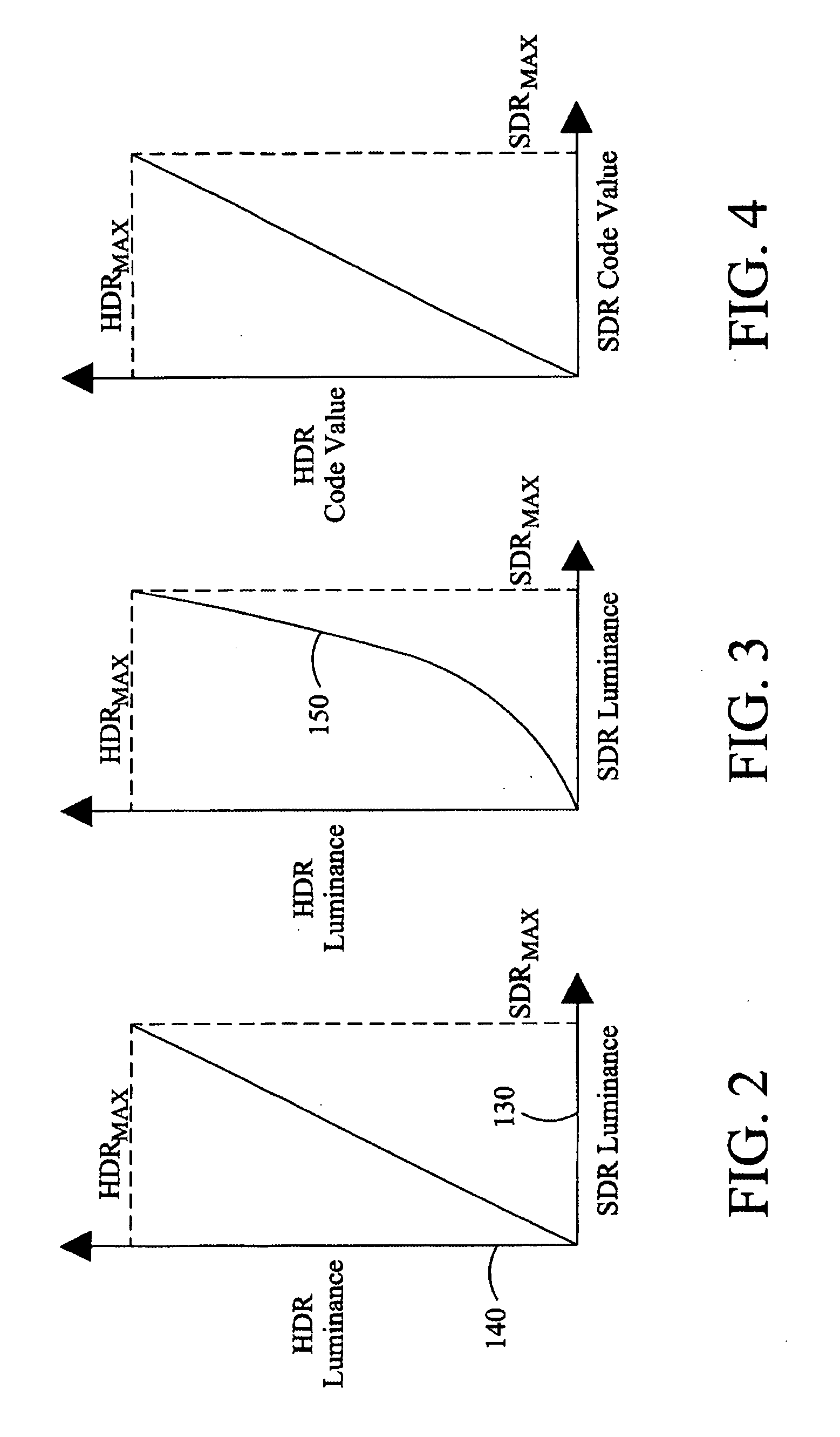
An image processing apparatus comprises a receiver (201) for receiving an image signal which comprises at least an encoded image and a target display reference. The target display reference is indicative of a dynamic range of a target display for which the encoded image is encoded. A dynamic range processor (203) generates an output image by applying a dynamic range transform to the encoded image in response to the target display reference. An output (205) then outputs an output image signal comprising the output image, e.g. to a suitable display. The dynamic range transform may furthermore be performed in response to a display dynamic range indication received from a display. The invention may be used to generate an improved High Dynamic Range (HDR) image from e.g. a Low Dynamic Range (LDR) image, or vice versa.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
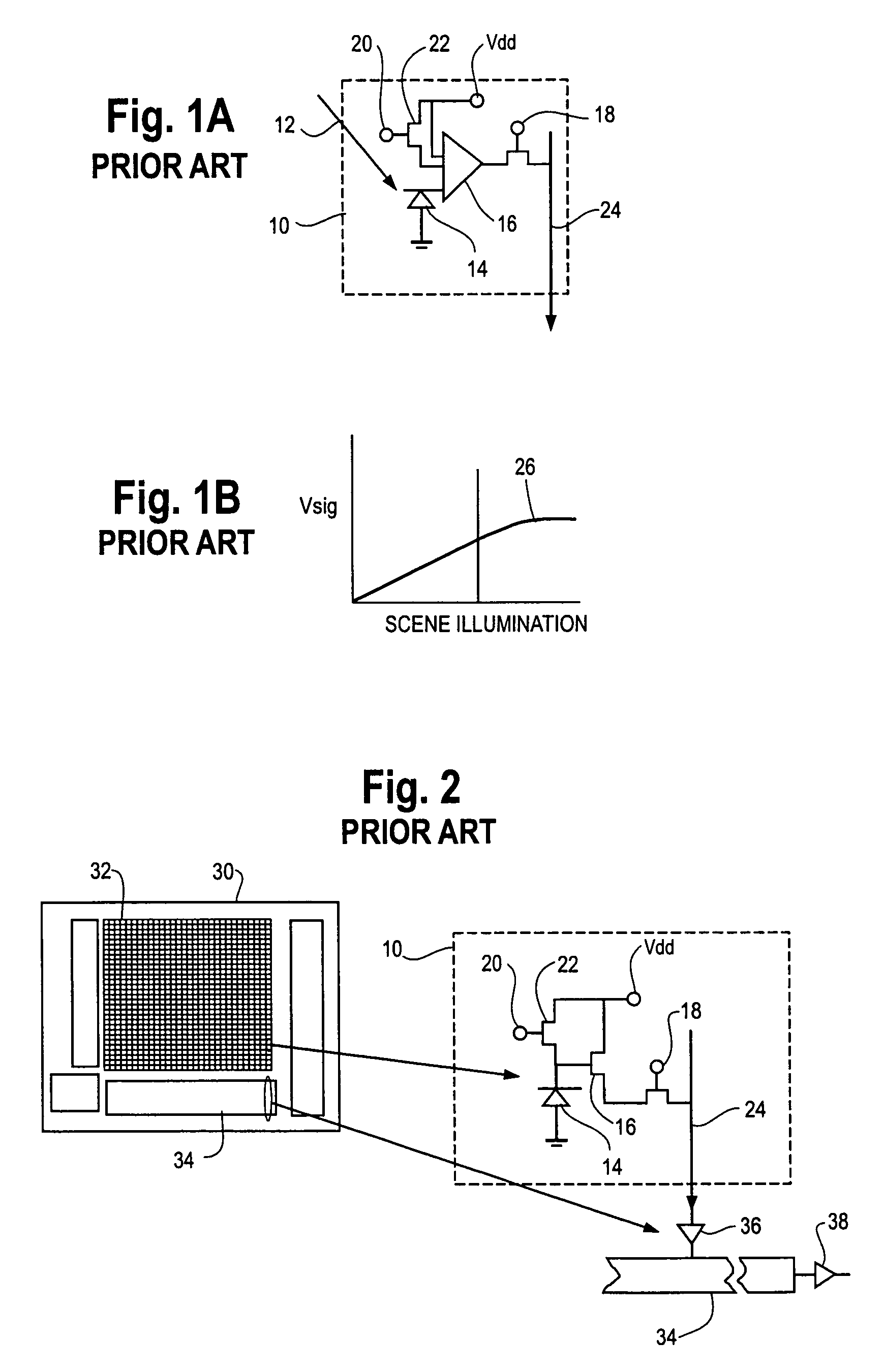
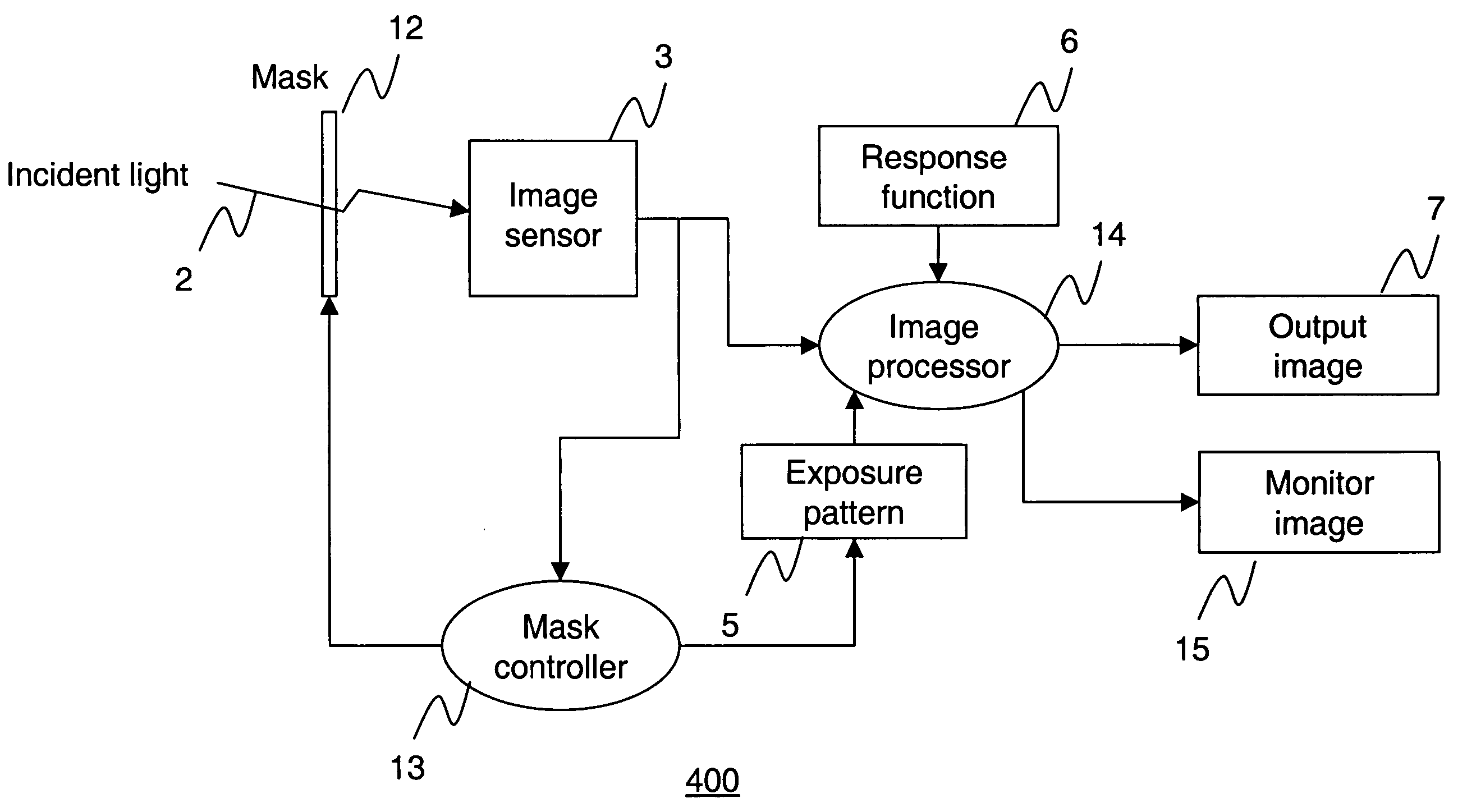
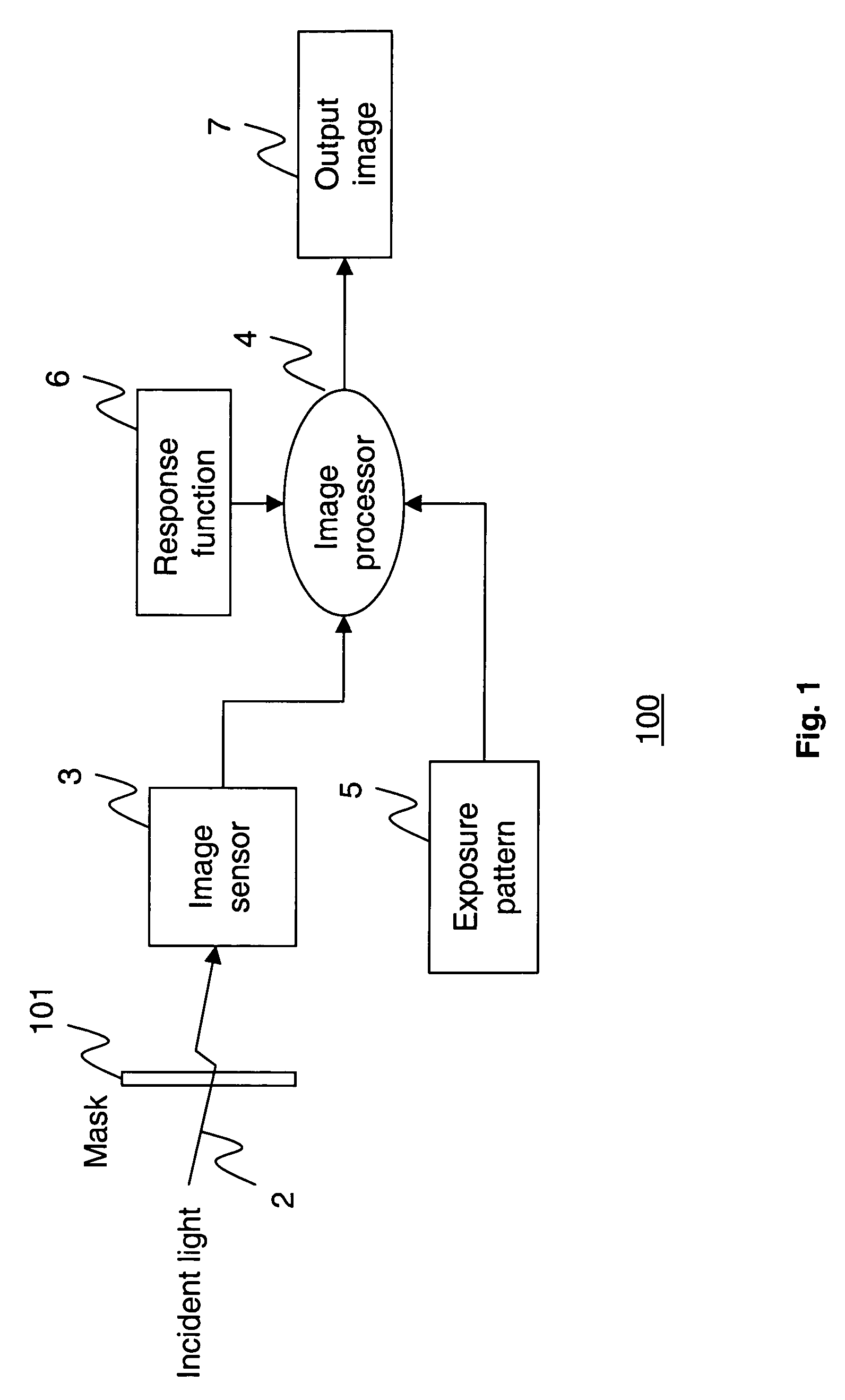
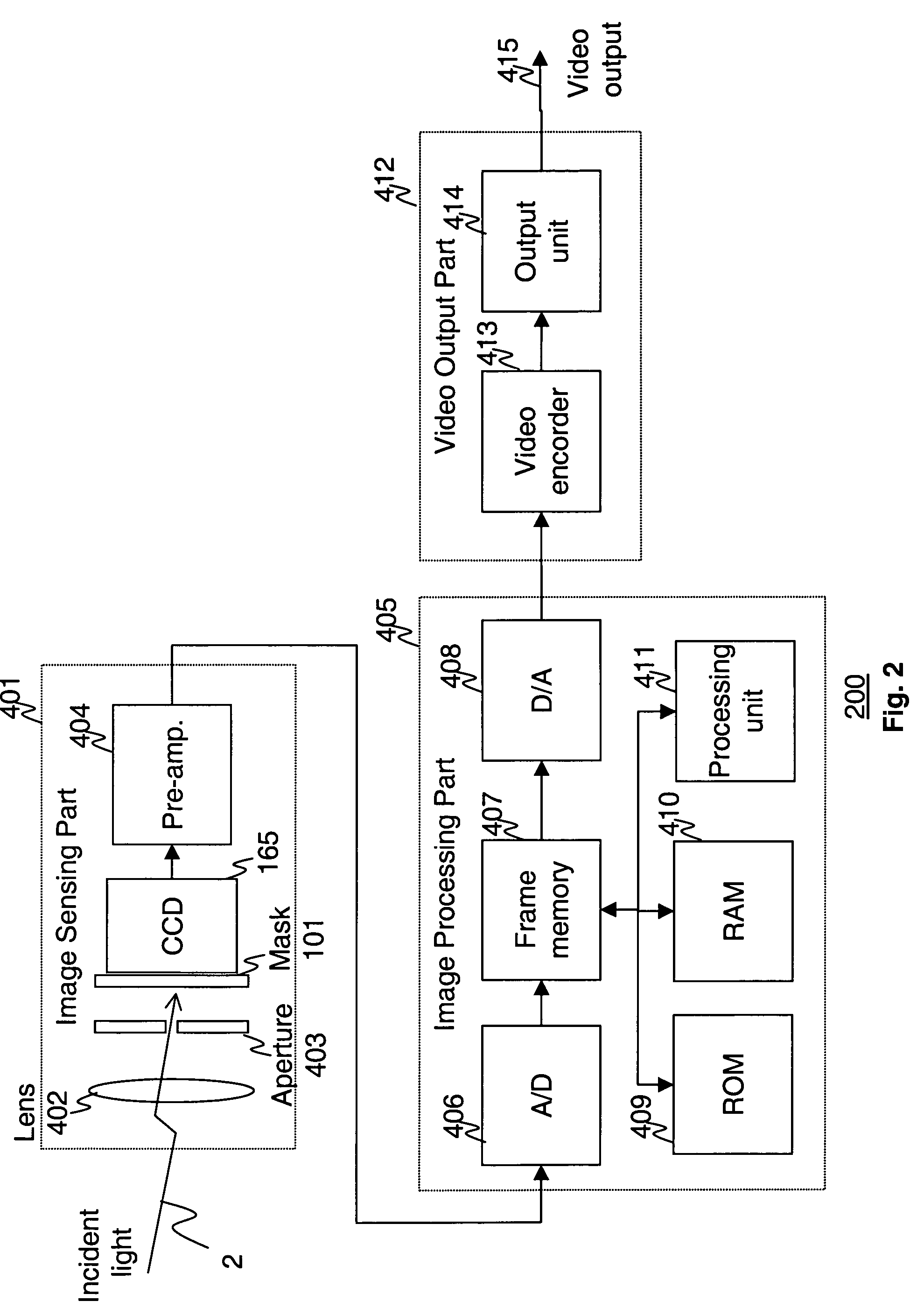
Apparatus and method for high dynamic range imaging using spatially varying exposures
InactiveUS6864916B1Minimize the numberSubstantial lossTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsHigh-dynamic-range imagingUltrasound attenuation
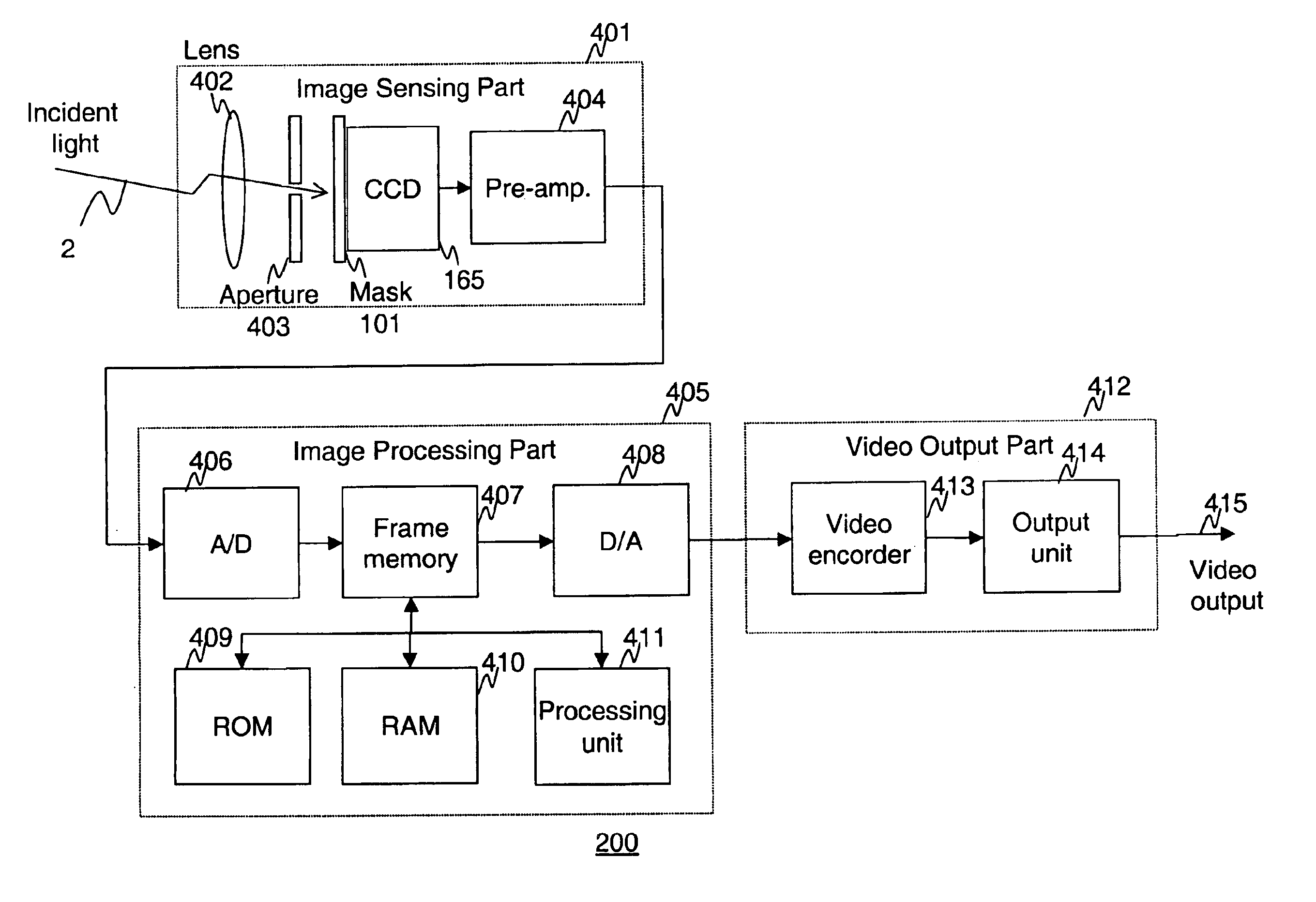
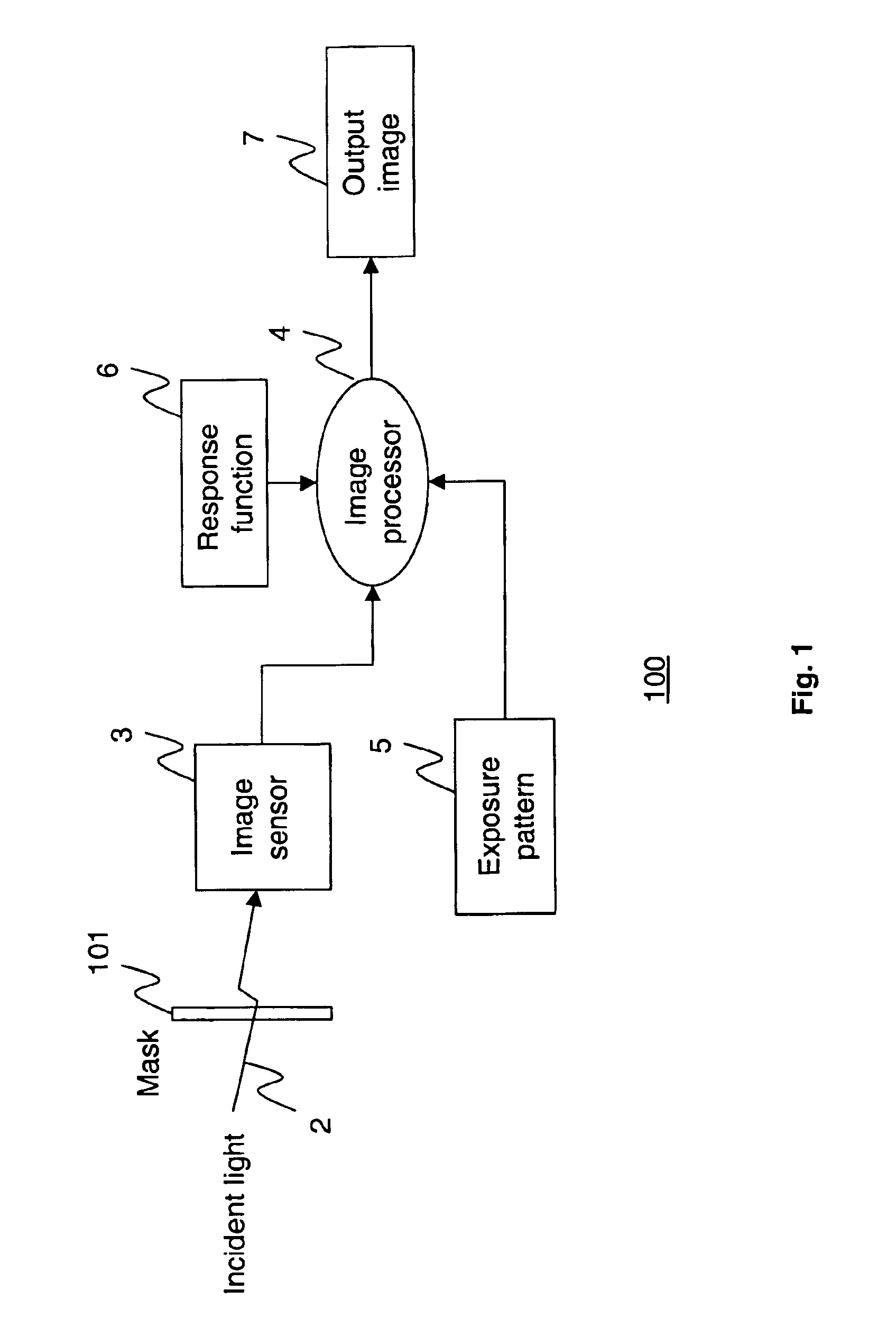
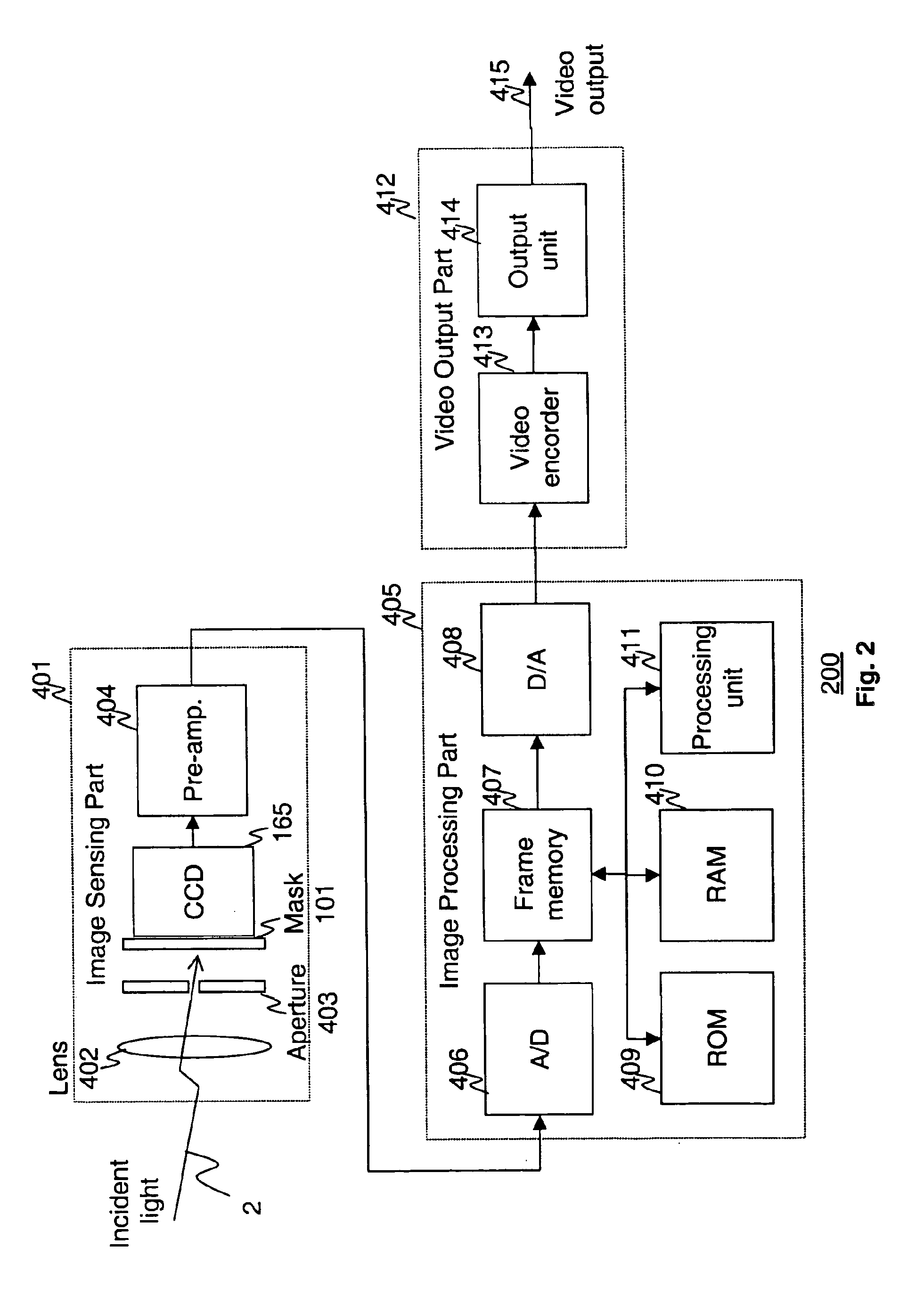
Apparatus and methods are provided for obtaining high dynamic range images using a low dynamic range image sensor. The image of a scene is captured with an image sensor using a spatially varying exposure function. The spatially varying exposure function can be implemented in a number of ways, such as by using as an optical mask with a fixed spatial attenuation pattern or by using an array of light sensing elements having spatially varying photosensitivities. The captured image is then normalized with respect to the spatially varying exposure function. The normalized image data can be interpolated to account for pixels that are either saturated or blackened to enhance the dynamic range of the image sensor.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
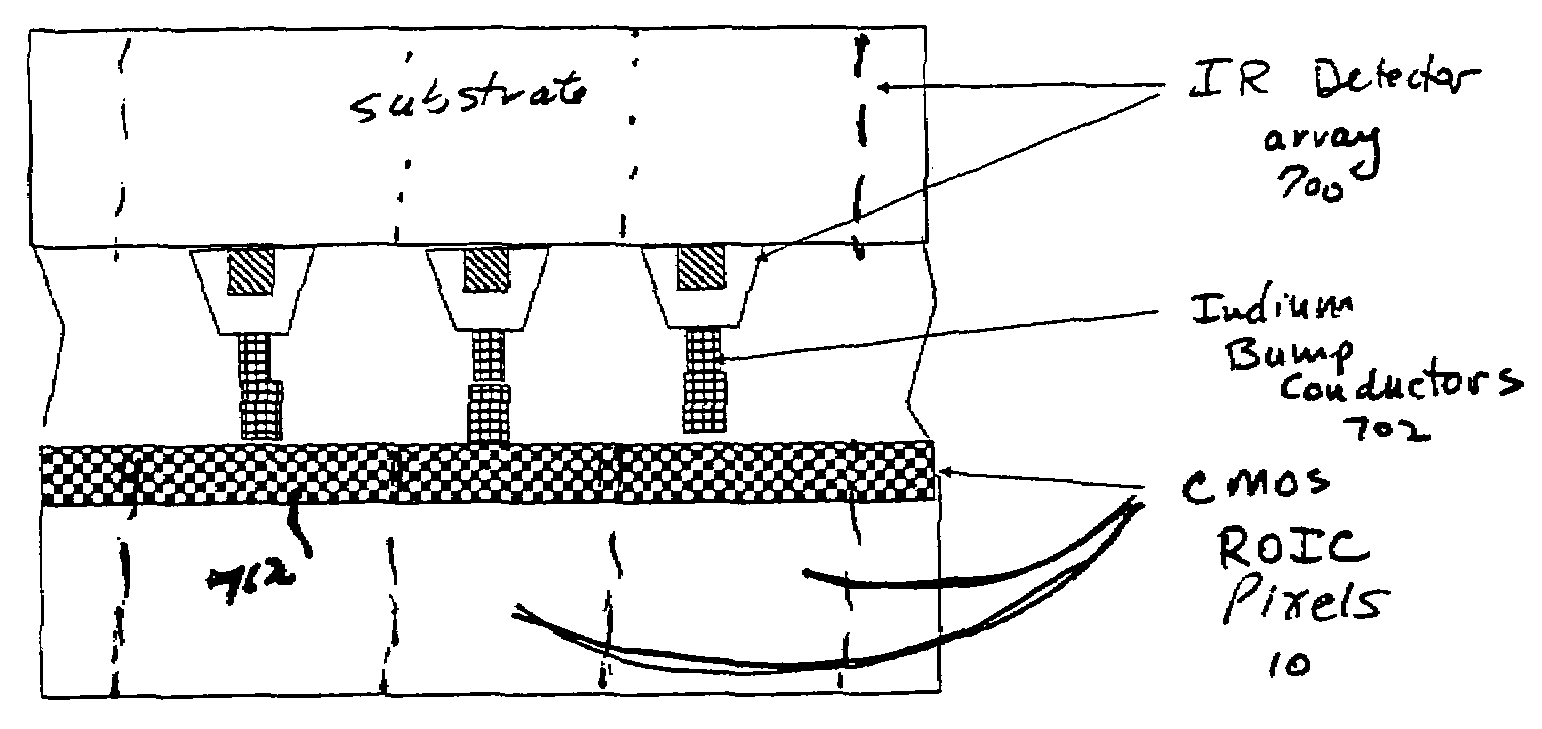
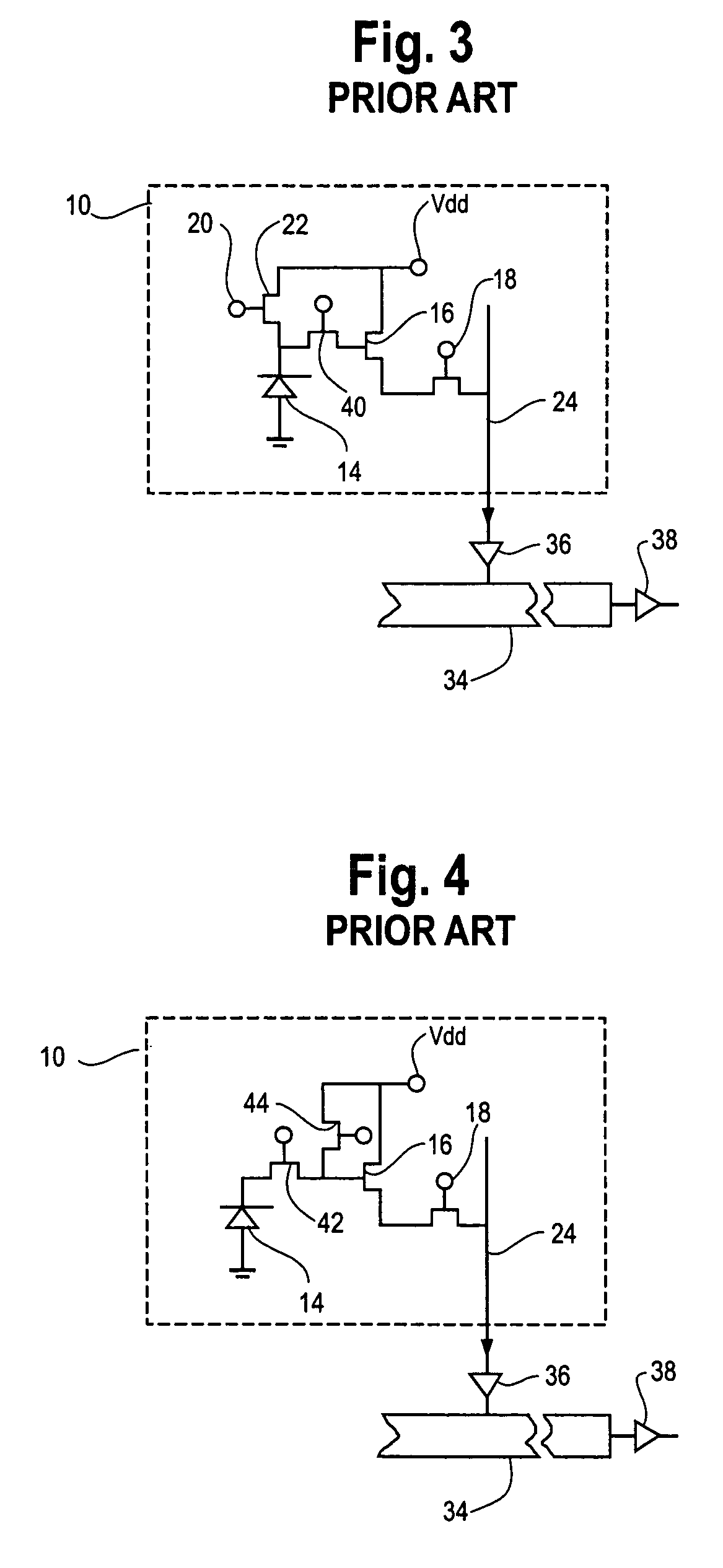
Hybrid infrared detector array and CMOS readout integrated circuit with improved dynamic range
ActiveUS20060181627A1High gainReduced dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsIndium bumpDetector array
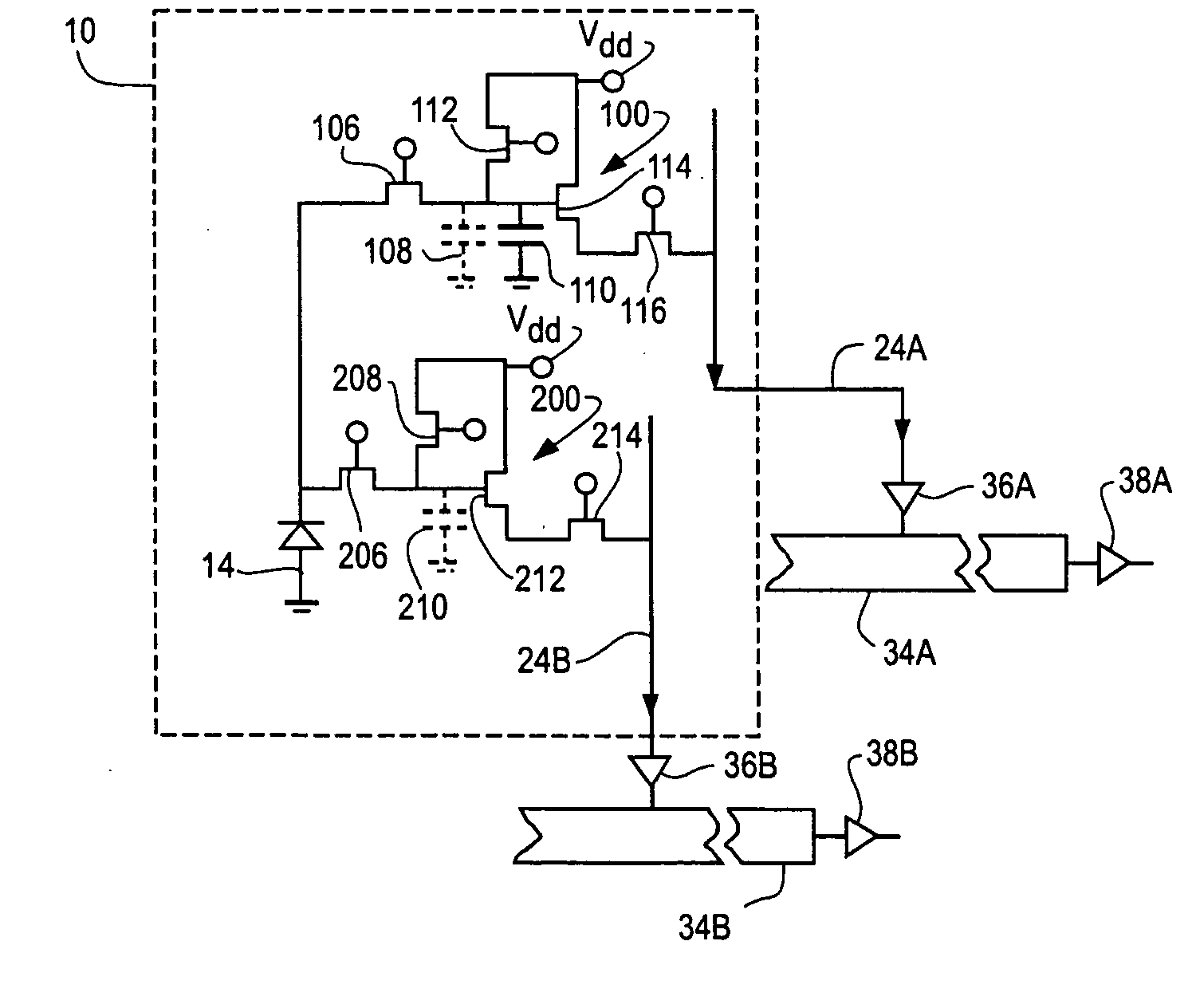
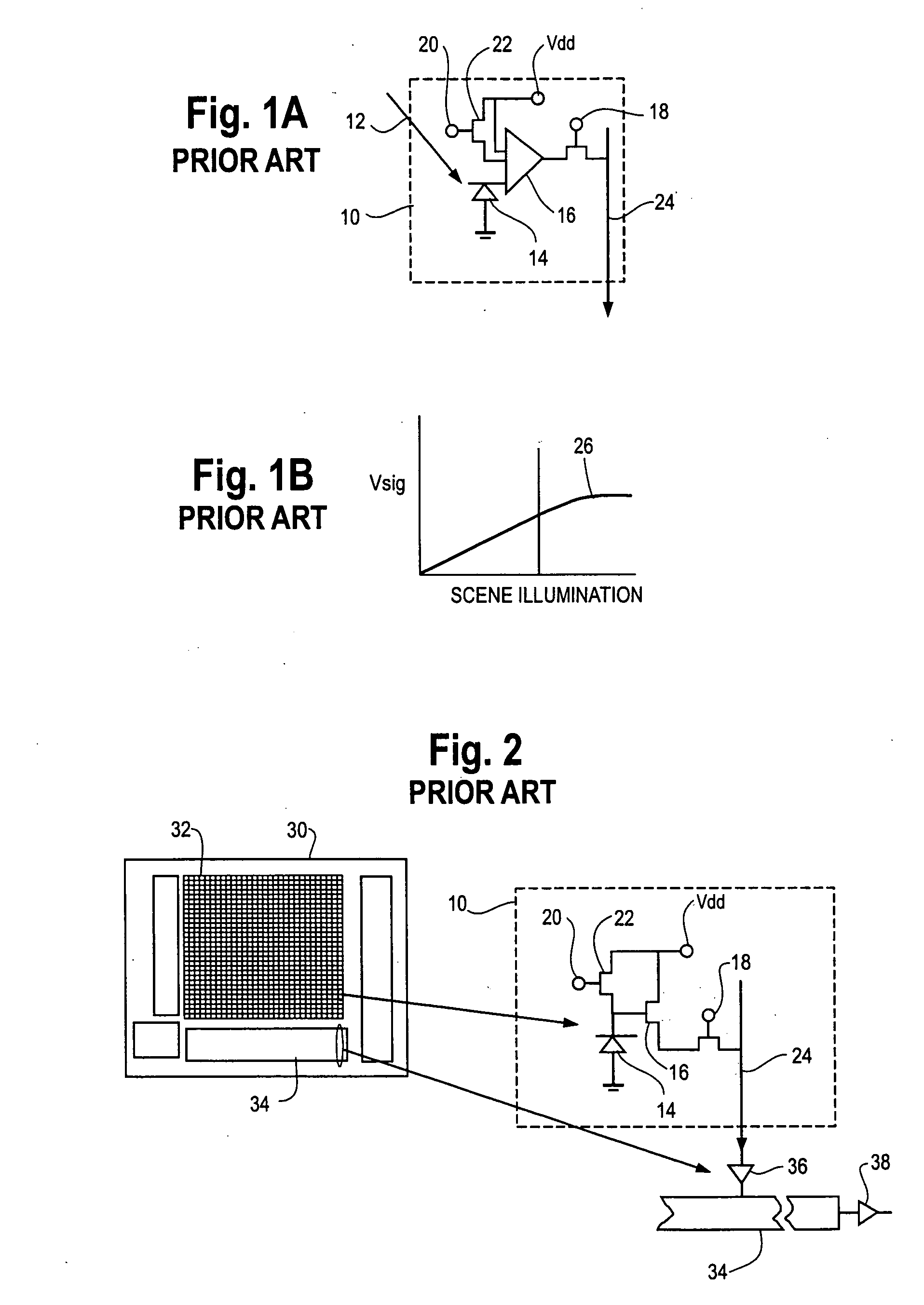
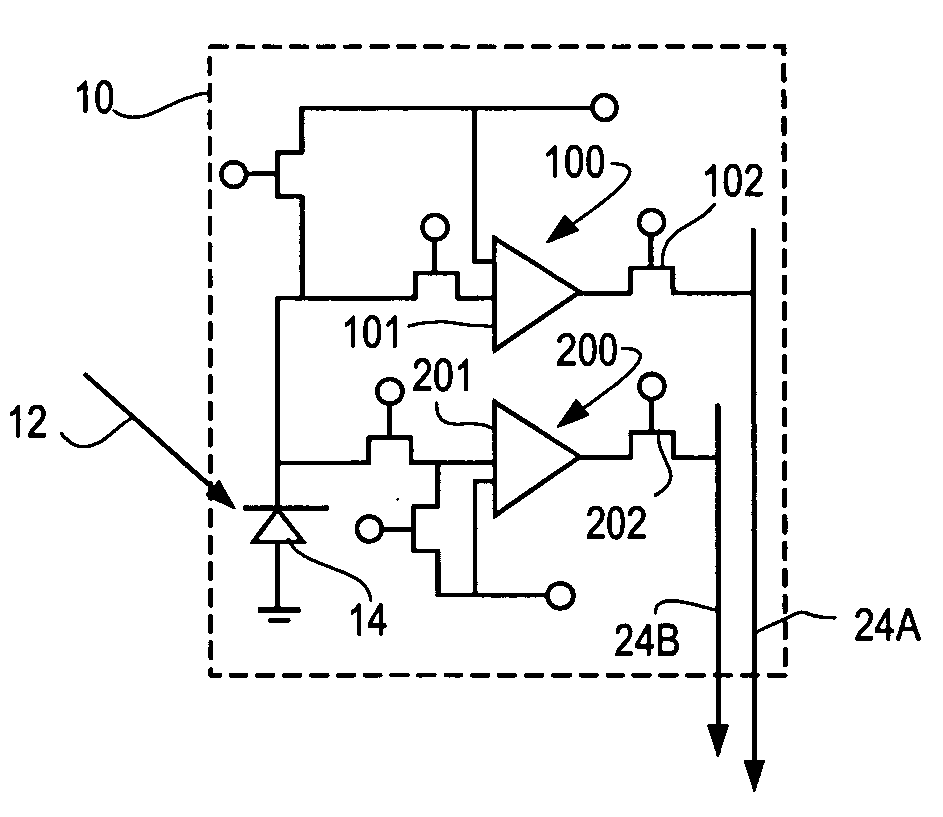
A hybrid image sensor includes an infrared detector array and a CMOS readout integrated circuit (ROIC). The CMOS ROIC is coupled to at least one detector of the IR detector array, e.g., via indium bump bonding. Each pixel of the CMOS ROIC includes a first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit which is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals from the IR detector. Each pixel also includes a second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit which is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals from the IR detector (or from a second IR detector). A first output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the first circuit to a first output multiplexer. A second output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the second circuit to a second output multiplexer. Thus, separate outputs of the first and second circuits are provided for each of the individual pixel sensors of the CMOS imaging array.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Methods and apparatuses for image processing
ActiveUS7612804B1Reduced dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImaging processingMethod of images
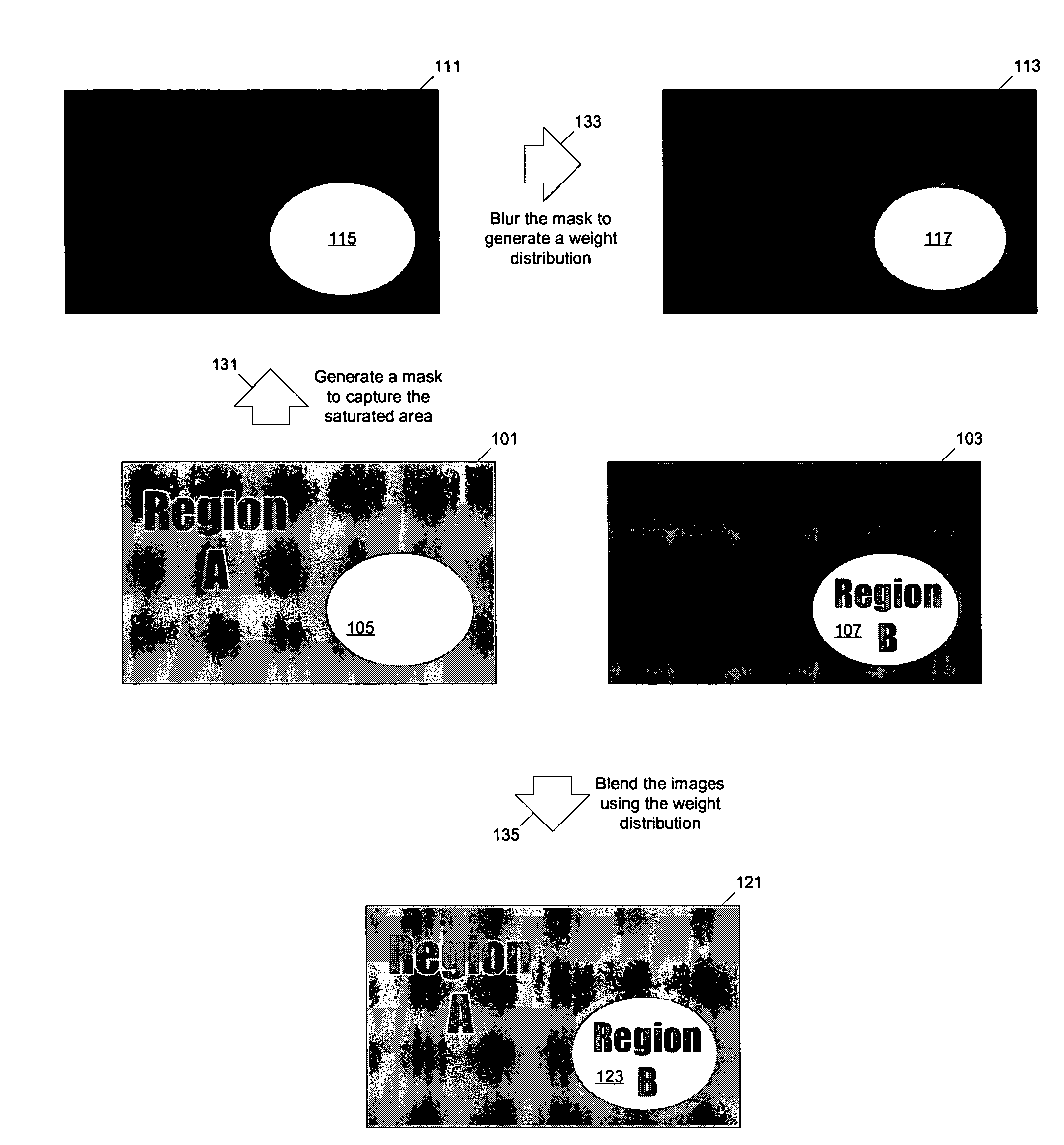
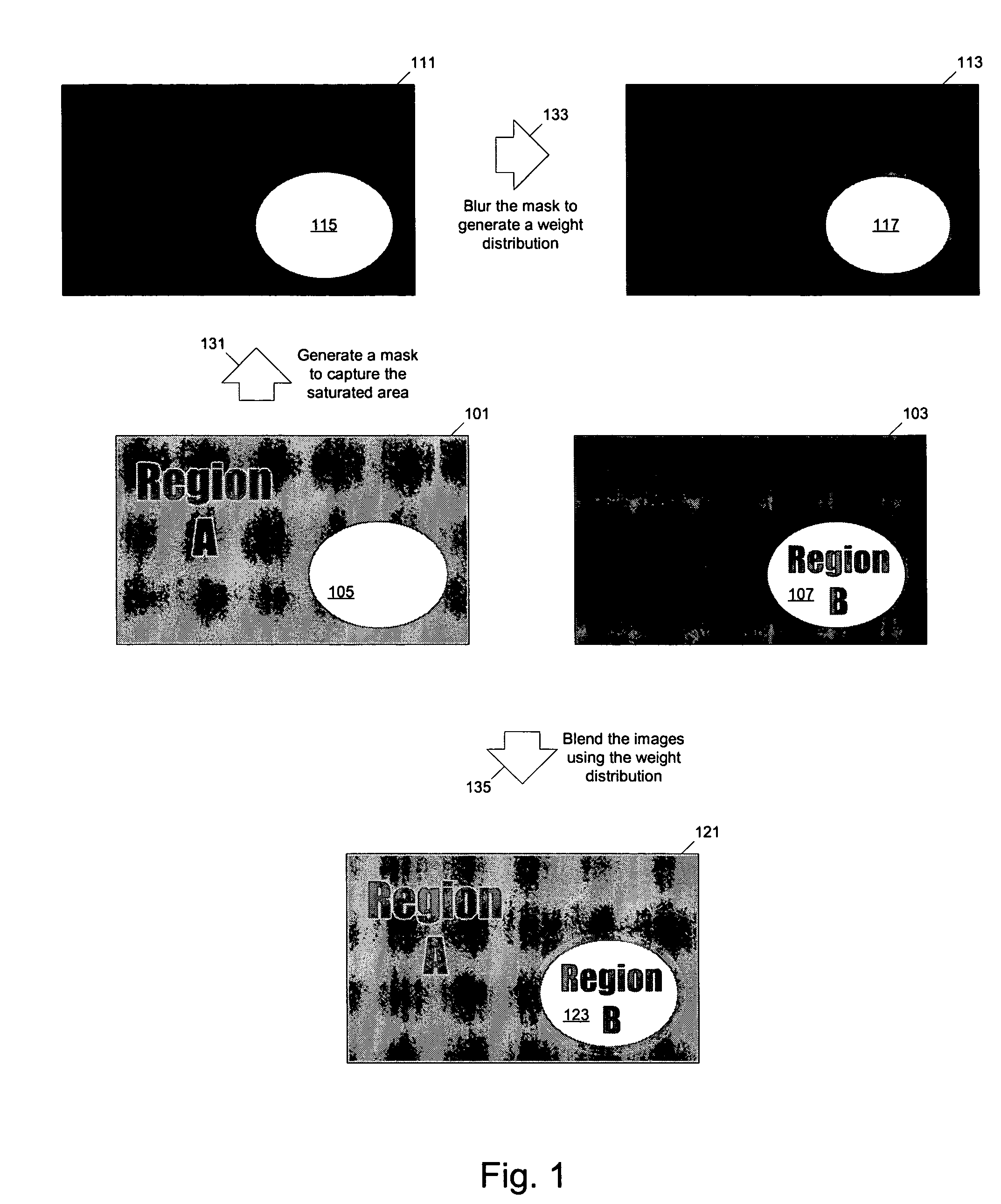
Methods and apparatuses for generating a low dynamic range image for a high dynamic range scene. In one aspect, a method to generate a low dynamic range image from a high dynamic range image, includes: determining one or more regions of the high dynamic range image containing pixels having values that are outside a first range and inside a second range; computing a weight distribution from the one or more regions; and generating the low dynamic range image from the high dynamic range image using the weight distribution. In another aspect, a method of image processing, includes: detecting one or more regions in a first image of a high dynamic range scene according to a threshold to generate a mask; and blending the first image and a second image of the scene to generate a third image using the mask.
Owner:APPLE INC
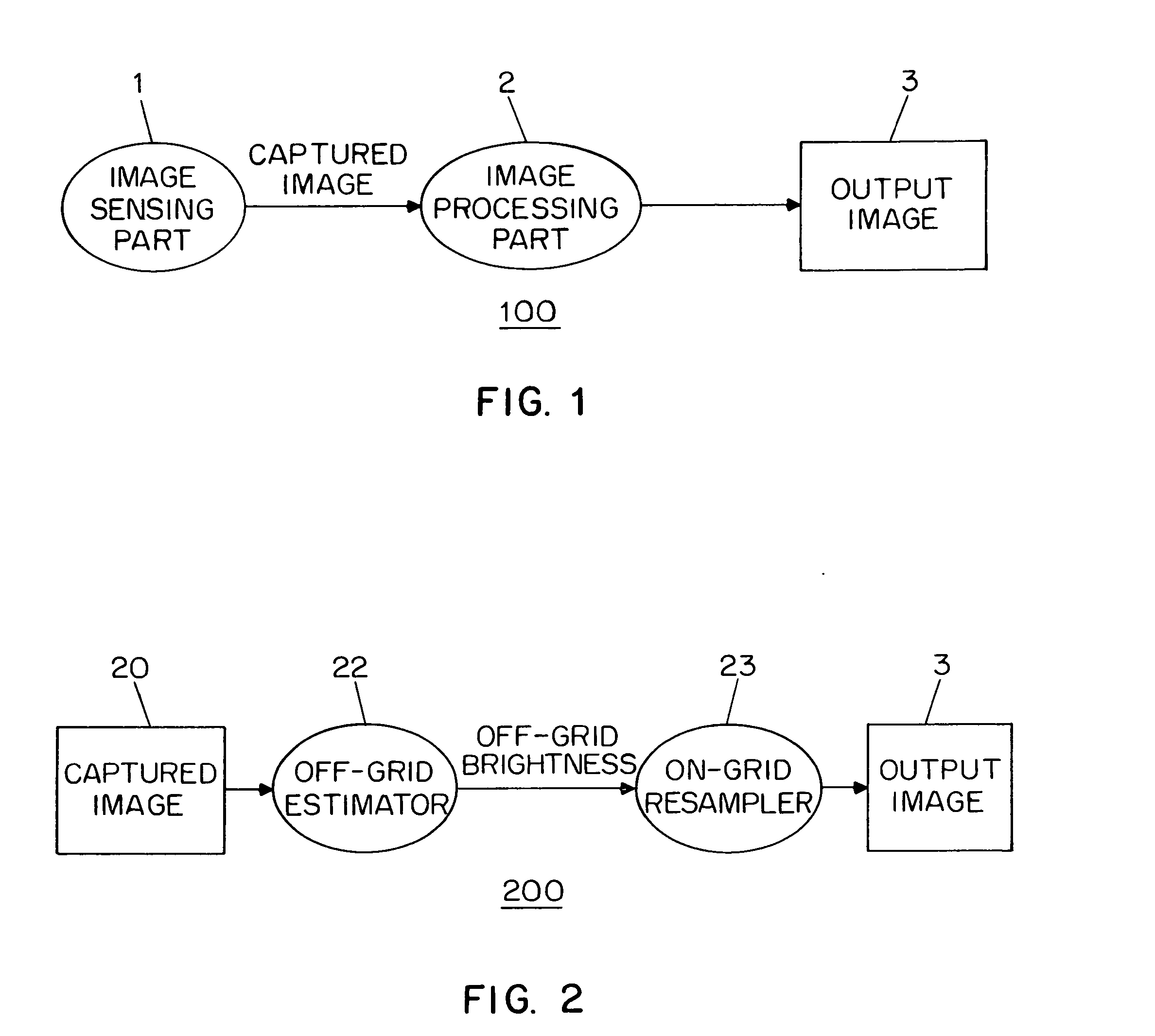
Method and apparatus for obtaining high dynamic range images
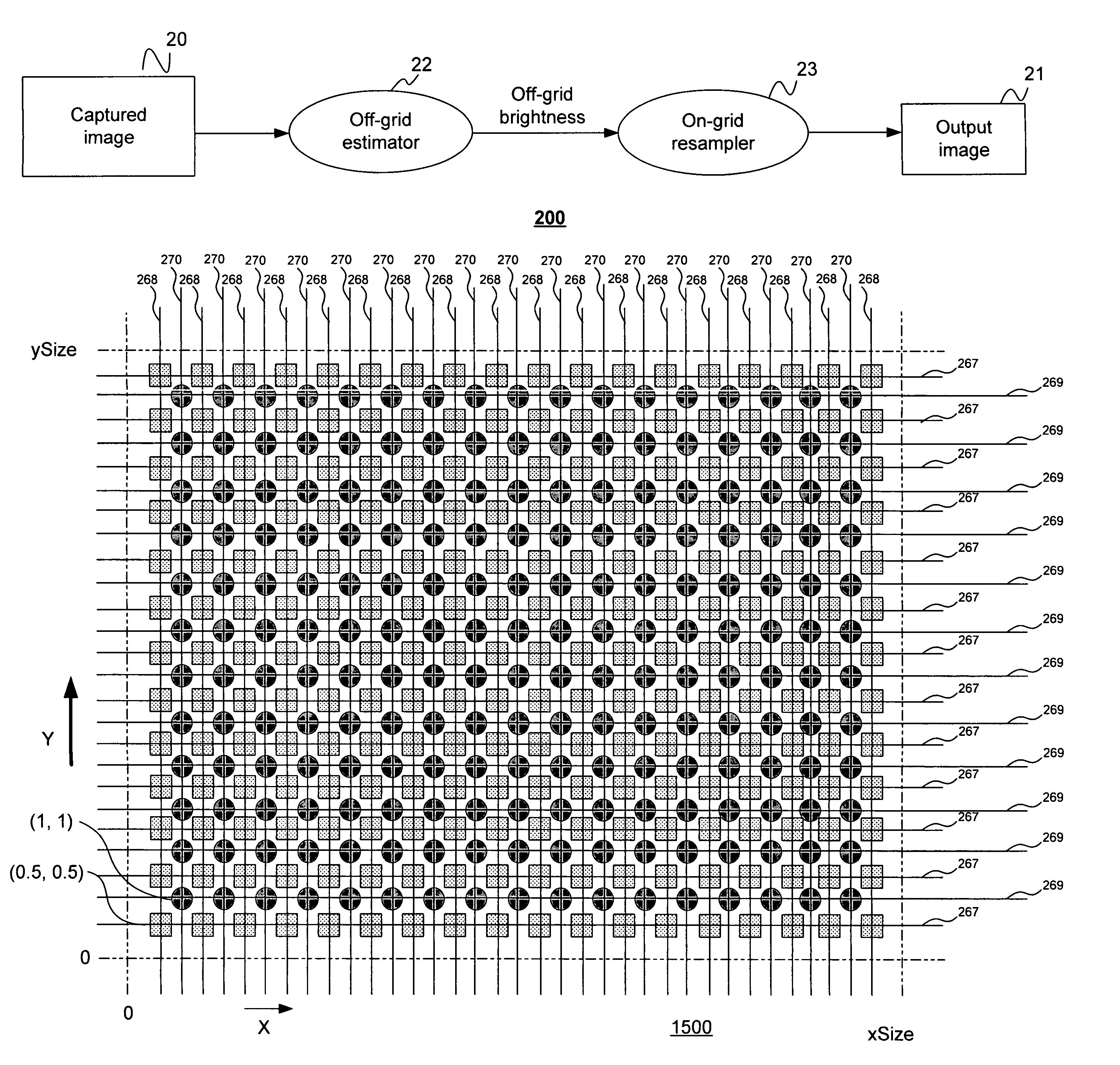
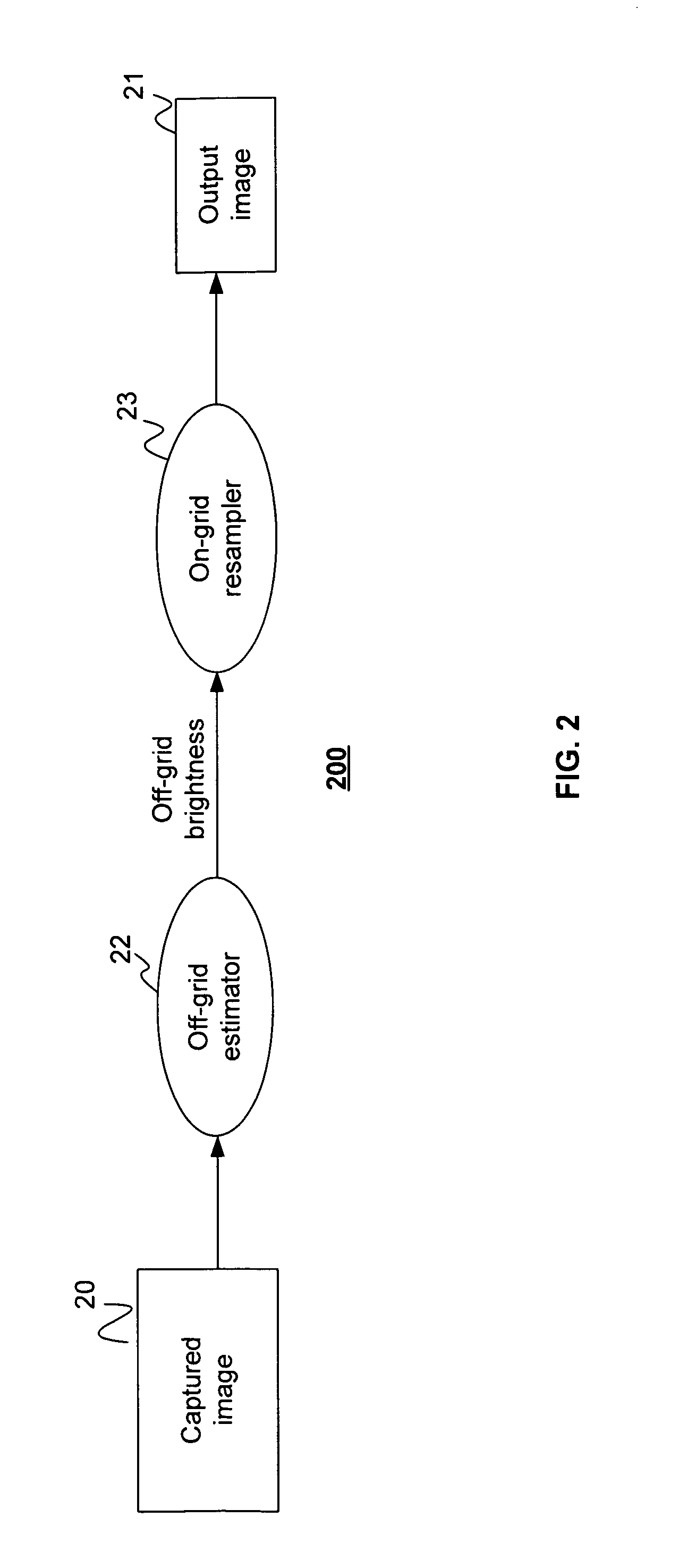
InactiveUS7084905B1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLight sensingImage resolution
Disclosed are method and apparatus for obtaining relatively high dynamic range images using a relatively low dynamic range image sensor without significant loss of resolution. The image sensor has an array of light-sensing elements with different sensitivity levels in accordance with a predetermined spatially varying sensitivity pattern for the array of light-sensing elements. An image of a scene is captured with the image sensor and stored as brightness values at respective pixel positions in a linear or two-dimensional uniform grid. The brightness values of the captured image at the pixel positions are then used to estimate the brightness values at off-grid positions of a uniform off-grid array located at respective interstices of the pixel position grid. The estimated off-grid brightness values are either used directly as the pixel brightness values of a relatively high dynamic output image or interpolated to derive resampled on-grid brightness values at the pixel positions of the pixel position grid to provide a relatively high dynamic range output image. Alternatively, the brightness values of the captured image are interpolated by an on-grid interpolation filter to derive pixel brightness values of a relatively high dynamic range output image, each pixel brightness value of the output image being derived from a corresponding plurality of the captured image brightness values. In each instance, either the captured image brightness values or the pixel brightness values of the output image may be compensated for non-linearities of the radiometric response function of the light-sensing elements of the image sensor.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
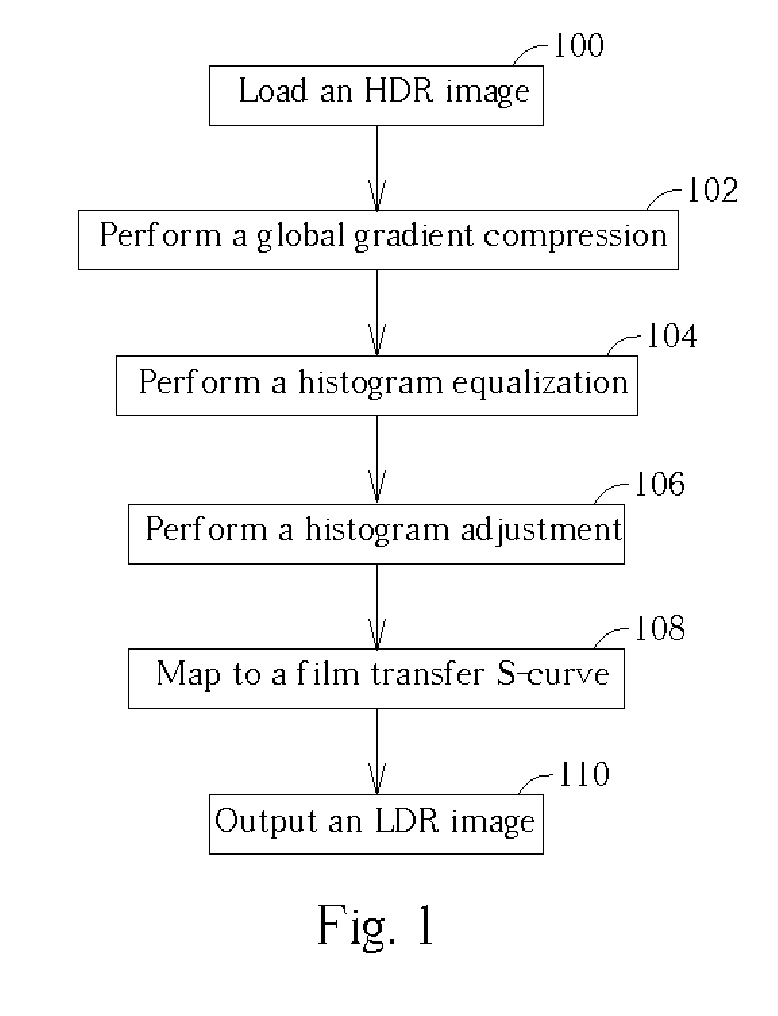
Method and apparatus for transforming a high dynamic range image into a low dynamic range image
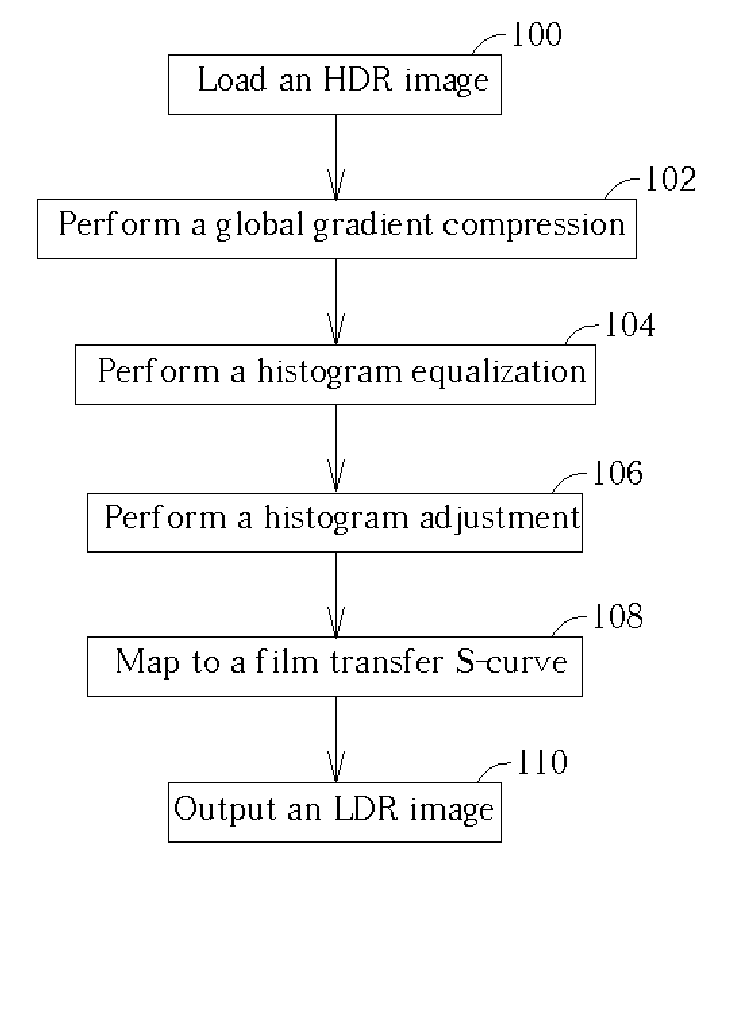
InactiveUS20050117799A1Easy to implementIncrease contrastImage enhancementImage analysisVisual artifactVisual perception
A method and an apparatus for transforming a high dynamic range image into a low dynamic range image. The method includes converting first luminance values associated with pixels into a plurality of second luminance values, and utilizing a film transfer function for mapping the second luminance values associated with the pixels into a plurality of third luminance values to generate the low dynamic range image. A second luminance range of the second luminance values is smaller than a first luminance range of the first luminance values, and the film transfer function adds no visual artifact to the low dynamic range image.
Owner:INVENTEC APPLIANCES CORP
Method and apparatus for obtaining high dynamic range images
InactiveUS20050099504A1High imagingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLight sensingBrightness perception
The application provides techniques for obtaining a relatively high dynamic range image of a scene using a relatively low dynamic range image sensor exposed to incident light from the scene for capturing an image. The image sensor has a multiplicity of light-sensing elements in an array and each light sensing element has a particular one of a plurality of sensitivity levels to incident light in accordance with a predetermined sensitivity pattern for the array of light-sensing elements and has a response function. Each light sensing element is responsive to incident light from the scene for producing a captured image brightness value at a corresponding one of a multiplicity of pixel positions of a pixel position array. Each one of the multiplicity of pixel positions corresponds to a particular one of the plurality of sensitivity levels of the light sensing elements.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Discrete LED backlight control for a reduced power LCD display system
ActiveUS20100045899A1Optimizes system power savingMeasurement apparatus componentsStatic indicating devicesSimulationLow dynamic range
Backlit LCD displays are becoming commonplace within many vehicle applications. The unique advantage of this invention is that it optimizes system power savings for display of low dynamic range (LDR) images by dynamically controlling spatially adjustable backlighting. This is accomplishes through use of a control technique that takes into account the sequential nature of the video display process.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
High dynamic range images from low dynamic range images
A method for displaying an image includes receiving an image having a first luminance dynamic range and modifying the image to a second luminance dynamic range free from being based upon other images, where the second dynamic range is greater than the first dynamic range. The modified image is displayed on a display.
Owner:SHARP KK
Graphics processing for high dynamic range video
ActiveUS20140125696A1Avoid effortReduced legibilityTelevision system detailsRecord information storageProcessing InstructionGraphics
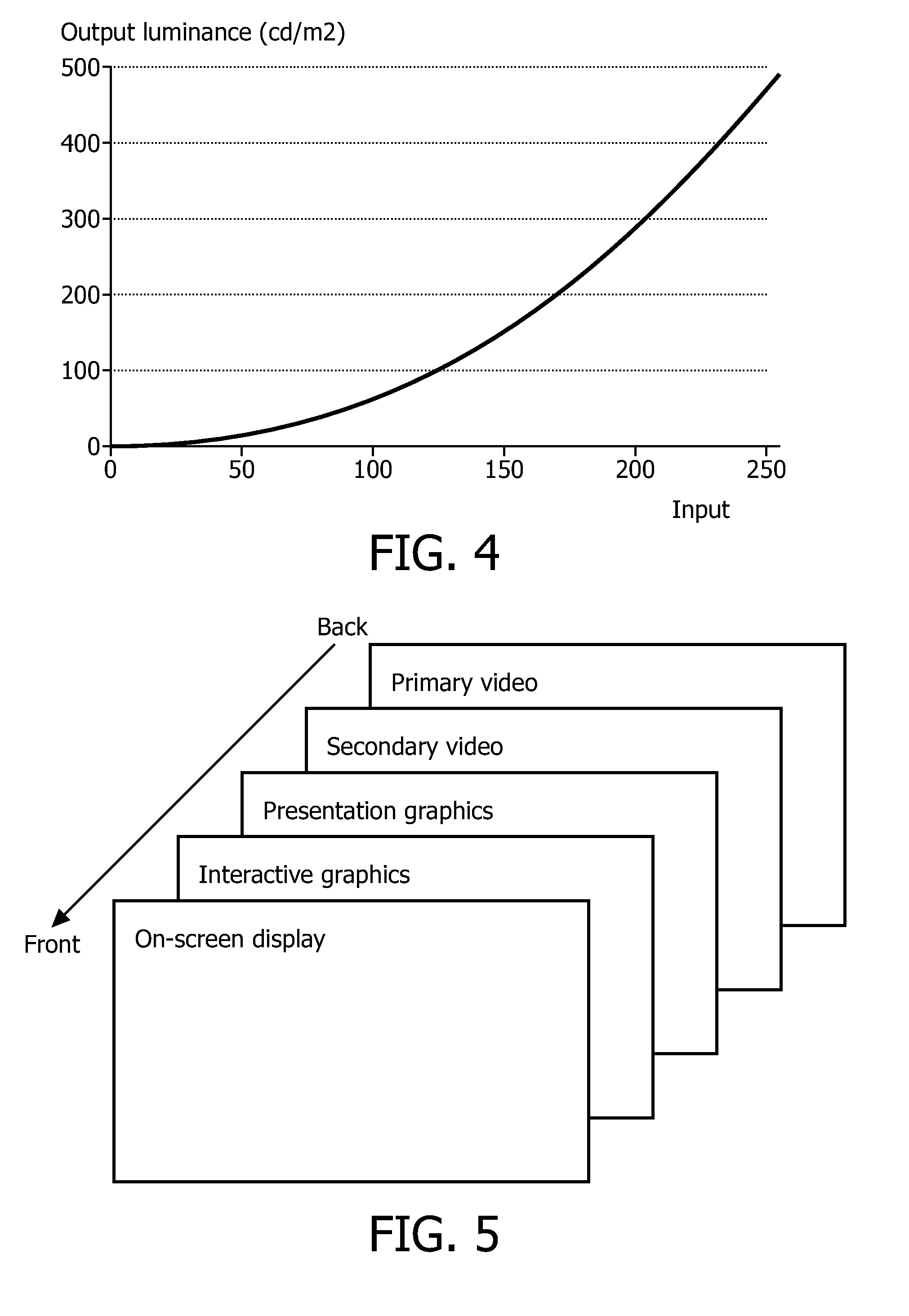
A device for processing video information has an input unit (112) for receiving the video information having low dynamic range [LDR] video data and / or high dynamic range [HDR] video data, and a video processor (113) for generating a display signal for display in a LDR display mode or HDR display mode. Graphics data is processed for generating an overlay for overlaying the video data. The input unit receives graphics processing control data comprised in the video information, the graphics processing control data including at least one HDR processing instruction for overlaying the graphics data in the HDR display mode. The video processor is constituted for adapting the processing when overlaying the graphics data in dependence on the specific display mode and the HDR processing instruction. Advantageously the source of the video information is enabled to control the processing of graphics in HDR display mode via the HDR processing instruction.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Expert system for prediction of changes to local environment
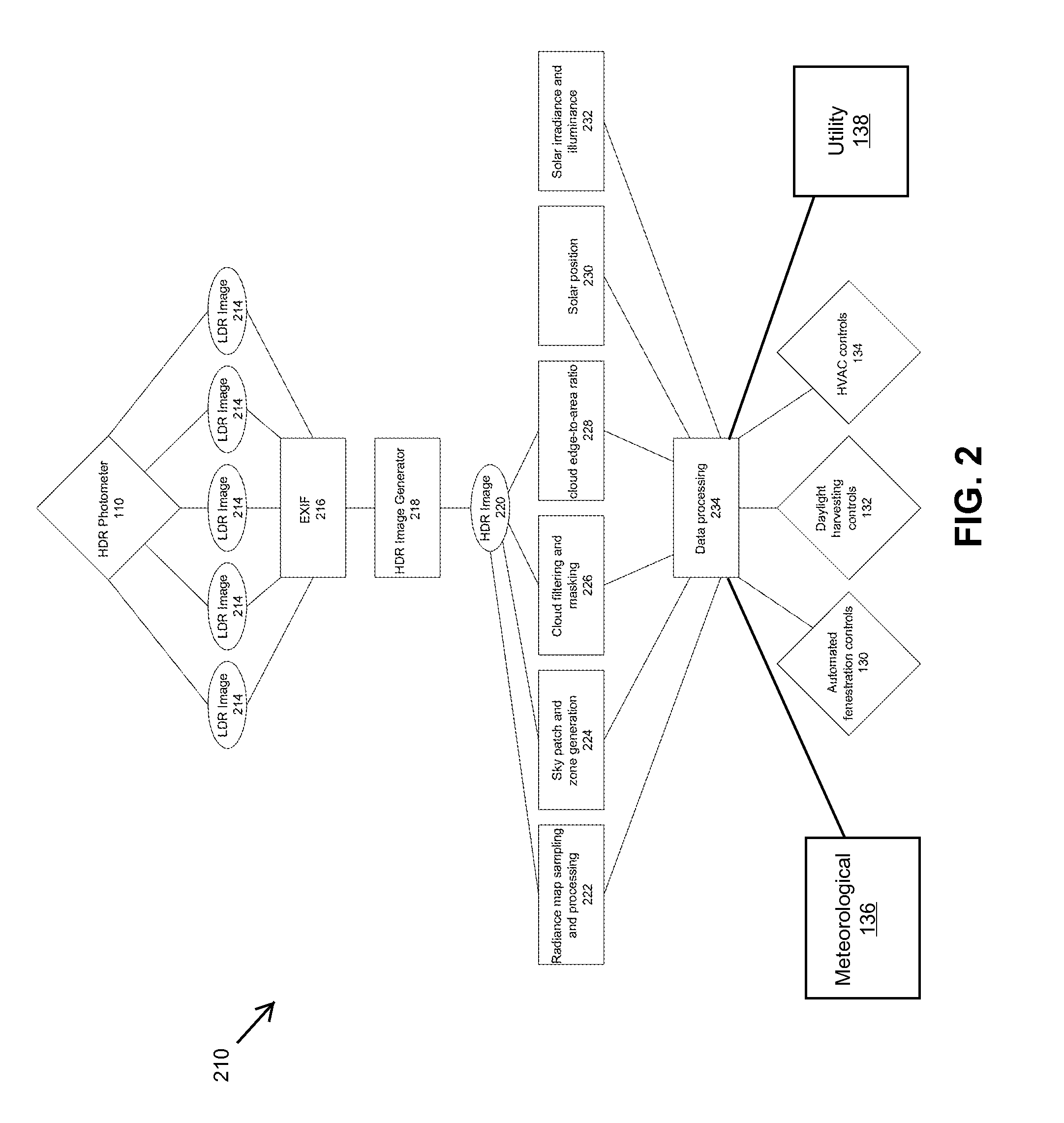
ActiveUS20140067733A1Accurate predictionMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsCamera lensColor image
Disclosed is a photometer that employs high dynamic range (HDR) image processing and manipulation algorithms for capturing and measuring real-time sky conditions for processing into control input signals to a building's automated fenestration (AF) system, daylight harvesting (DH) system and HVAC system. The photometer comprises a color camera and a fitted fish-eye lens to capture 360-degree, hemispherical, low dynamic range (LDR) color images of the sky. Both camera and lens are housed in a sealed enclosure protecting them from environmental elements and conditions. In some embodiments the camera and processes are controlled and implemented by a back-end computer.
Owner:KINESTRAL TECH
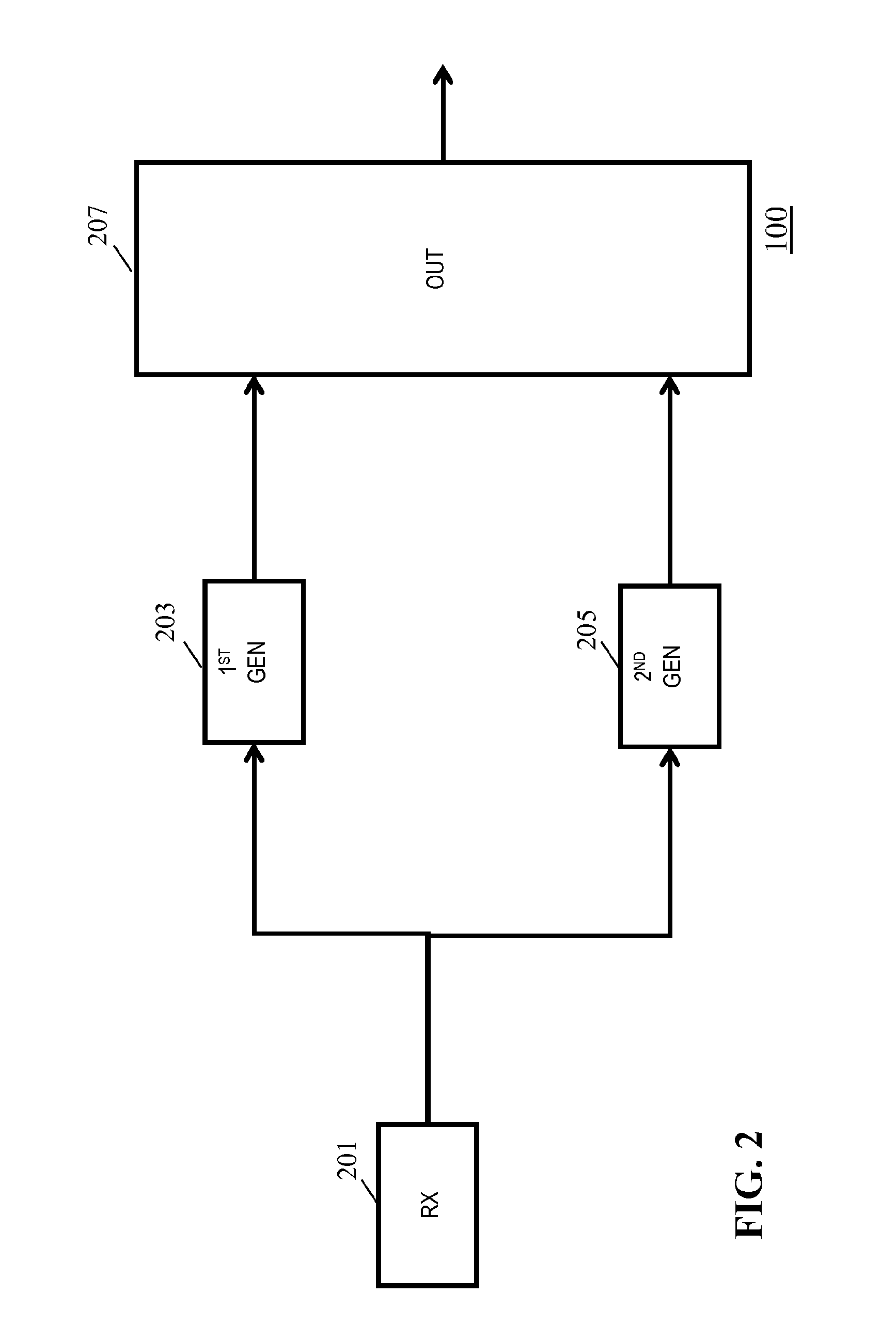
Apparatus and method for dynamic range transforming of images
ActiveUS20140225941A1Improve dynamic rangeEnhance the imageImage enhancementRecording carrier detailsImaging processingDisplay device
An image processing apparatus comprises a receiver (201) for receiving an image signal comprising an encoded image. Another receiver (1701) receives a data signal from a display (107) where the data signal comprises a data field that comprises a display dynamic range indication of the display (107). The display dynamic range indication comprises at least one luminance specification for the display. A dynamic range processor (203) is arranged to generate an output image by applying a dynamic range transform to the encoded image in response to the display dynamic range indication. An output (205) outputs an output image signal comprising the output image to the display. The transform may furthermore be performed in response to a target display reference indicative of a dynamic range of display for which the encoded image is encoded. The invention may be used to generate an improved High Dynamic Range (HDR) image from e.g. a Low Dynamic Range (LDR) image, or vice versa.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for content driven image compression
InactiveUS20050131660A1Small sizePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionFiltration
A method with related structures and computational components and modules for modeling data, particularly audio and video signals. The modeling method can be applied to different solutions such as 2-dimensional image / video compression, 3-dimensional image / video compression, 2-dimensional image / video understanding, knowledge discovery and mining, 3-dimensional image / video understanding, knowledge discovery and mining, pattern recognition, object meshing / tessellation, audio compression, audio understanding, etc. Data representing audio or video signals is subject to filtration and modeling by a first filter that tessellates data having a lower dynamic range. A second filter then further tessellates, if needed, and analyzes and models the remaining parts of data, not analyzable by first filter, having a higher dynamic range. A third filter collects in a generally lossless manner the overhead or residual data not modeled by the first and second filters. A variety of techniques including computational geometry, artificial intelligence, machine learning and data mining may be used to better achieve modeling in the first and second filters.
Owner:YADEGAR JOSEPH +1
Hybrid infrared detector array and CMOS readout integrated circuit with improved dynamic range
ActiveUS7551059B2High gainReduced dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsIndium bumpDetector array
A hybrid image sensor includes an infrared detector array and a CMOS readout integrated circuit (ROIC). The CMOS ROIC is coupled to at least one detector of the IR detector array, e.g., via indium bump bonding. Each pixel of the CMOS ROIC includes a first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit which is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals from the IR detector. Each pixel also includes a second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit which is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals from the IR detector (or from a second IR detector). A first output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the first circuit to a first output multiplexer. A second output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the second circuit to a second output multiplexer. Thus, separate outputs of the first and second circuits are provided for each of the individual pixel sensors of the CMOS imaging array.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
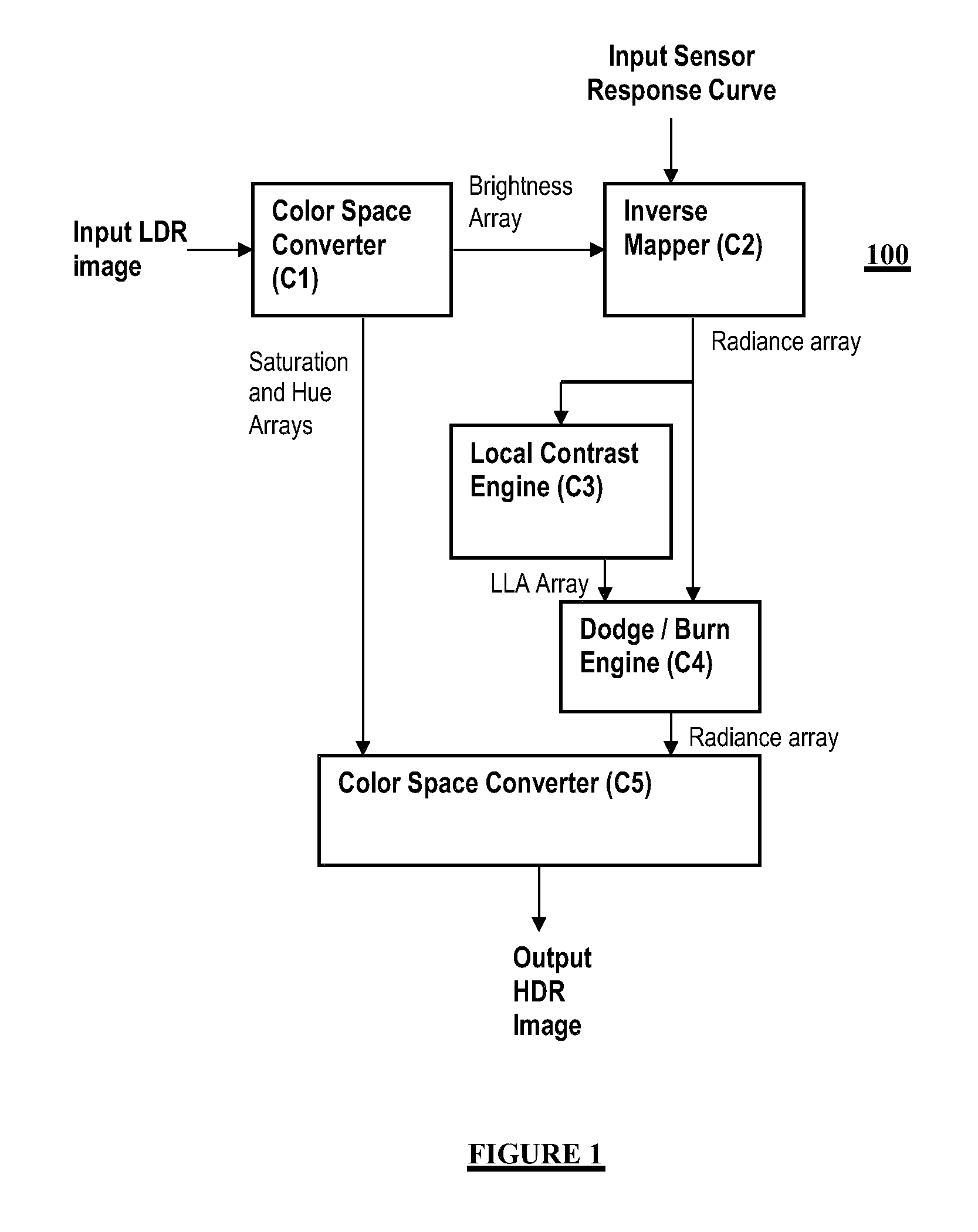
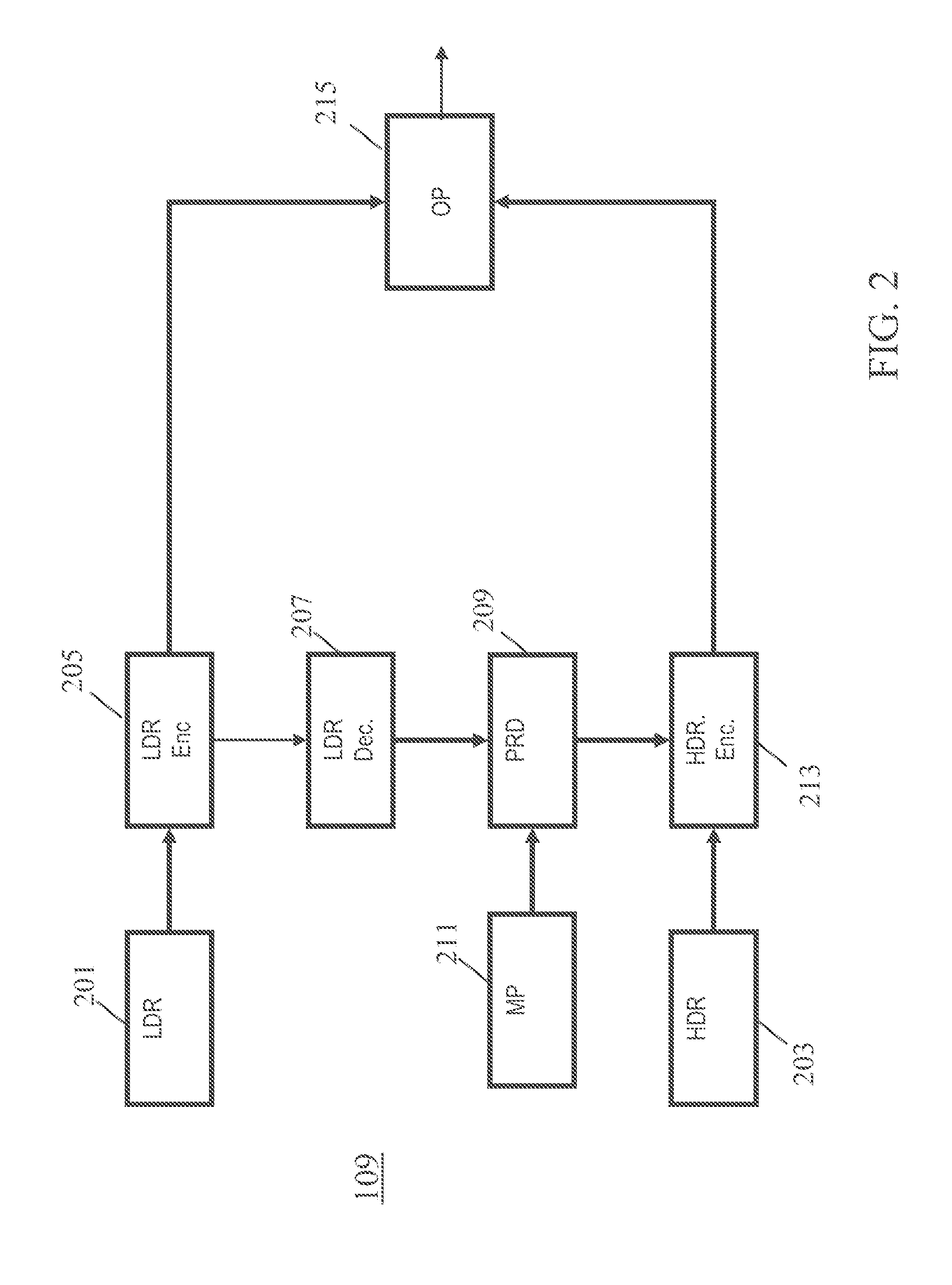
Transforming a digital image from a low dynamic range (LDR) image to a high dynamic range (HDR) image
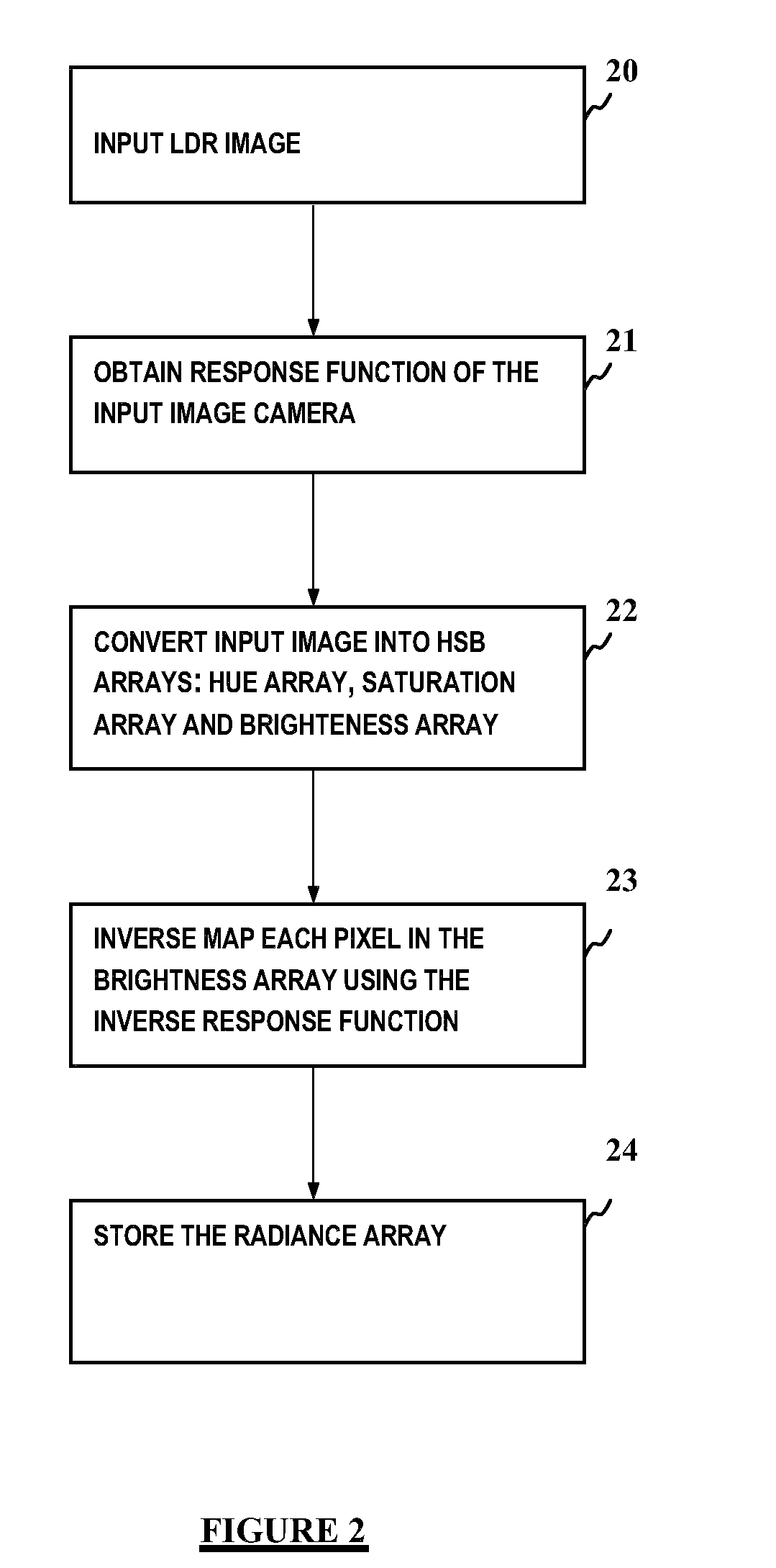
The invention provides a method for transforming an image from a Low Dynamic Range (LDR) image obtained with a given camera to a High Dynamic Range (HDR) image, the method comprising:obtaining the exposure-pixel response curve (21) for said given cameraconverting the LDR image to HSB color space arrays (22), said HSB color space arrays including a Hue array, a Saturation array and a Brigthness array; anddetermining a Radiance array (23, 24) by inverse mapping each pixel in said Brightness array using the inverse of the exposure-pixel response curve (f-1).
Owner:IBM CORP
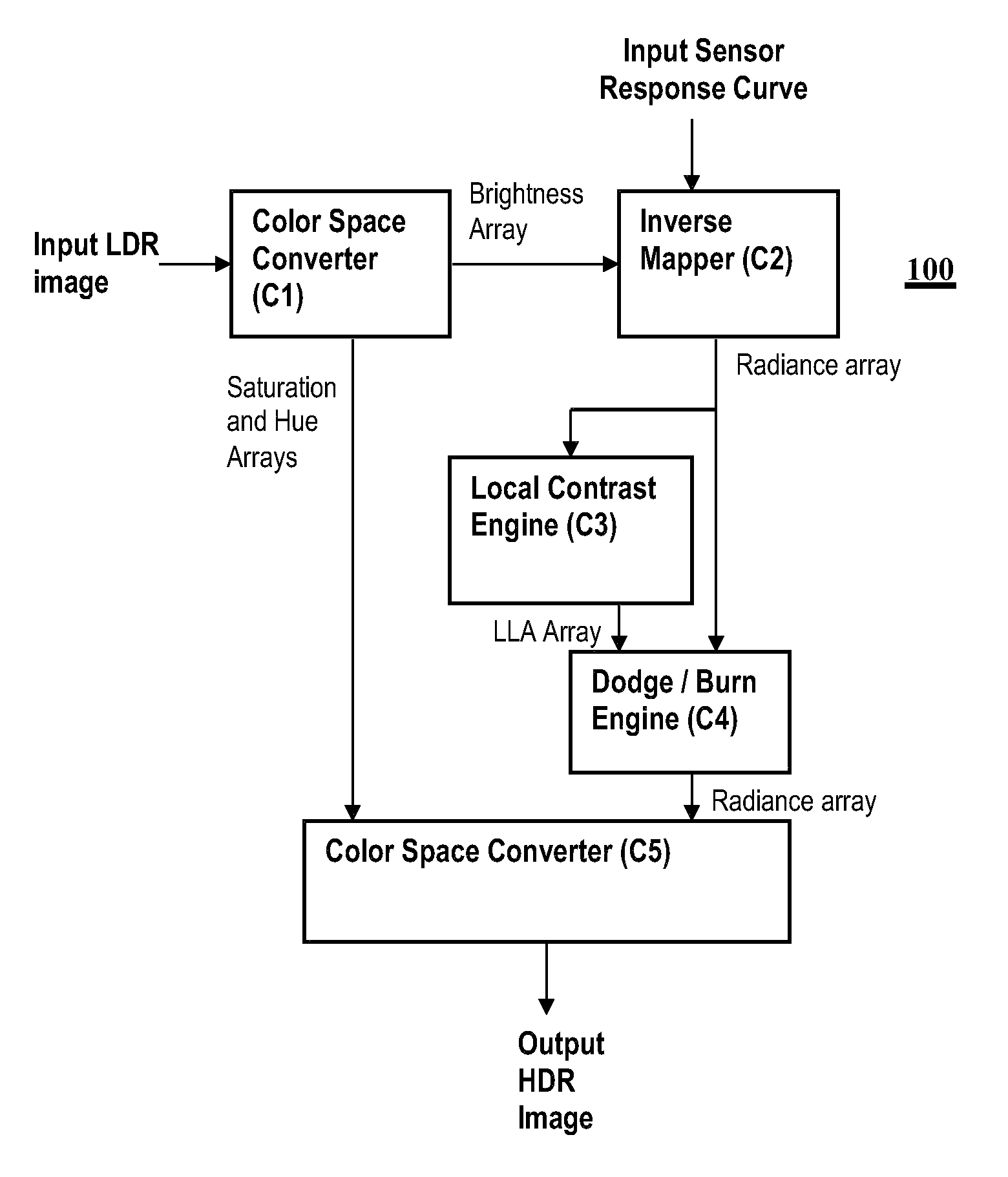
CMOS active pixel sensor with improved dynamic range and method of operation
ActiveUS20060146159A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotodetectorLinearity
A CMOS imaging array includes a plurality of individual pixels arranged in rows and columns. Each pixel is constructed the same and includes a photodetector (e.g., photodiode) receiving incident light and generating an output. A first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit is provided responsive to the output of the photodetector. The first circuit is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals. A second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit is also provided which is responsive to the output of the photodetector. The second circuit is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals. A first output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the first circuit to a first output multiplexer. A second output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the second circuit to a second output multiplexer. Thus, separate outputs of the first and second circuits are provided for each of the individual pixel sensors of the CMOS imaging array. Alternative embodiments incorporate two ore more photodetectors and two or more amplifier circuits and output select circuits. Three photodetectors and three amplifier circuits are useful for an embodiment where the sensor includes a three-color filter matrix.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Apparatus and method for high dynamic range imaging using spatially varying exposures
InactiveUS7924321B2Minimize the numberSubstantial lossTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsHigh-dynamic-range imagingUltrasound attenuation
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
High dynamic range images from low dynamic range images
A method for displaying an image includes receiving an image having a first luminance dynamic range and modifying the image to a second luminance dynamic range free from being based upon other images, where the second dynamic range is greater than the first dynamic range. The modified image is displayed on a display.
Owner:SHARP KK
High dynamic range image signal generation and processing
ActiveUS20140079113A1Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one orPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningColor representationImage signal
An apparatus generates an image signal in which pixels are encoded in N-bit words which encode at least a luma per pixel. A receiver (201) obtains high dynamic range pixel values in accordance with a first color representation in M-bitwords. A first generator (203) includes the high dynamic range pixel values in the image signal in the N-bit words according to a second color representation. A second generator (205) includes in the image signal an indicator that high dynamic range pixel values are encoded. In some examples, the high dynamic range pixel values may be provided in a segment that can alternatively contain high or low dynamic range pixel values, and the indicator may indicate which type of data is included. The approach may e.g. facilitate introduction of high dynamic range capability into e.g. HDMI systems.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Generation of high dynamic range images from low dynamic range images in multiview video coding
ActiveUS20130108183A1Easy to identifyEasy to codeImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionStructure analysis3d image
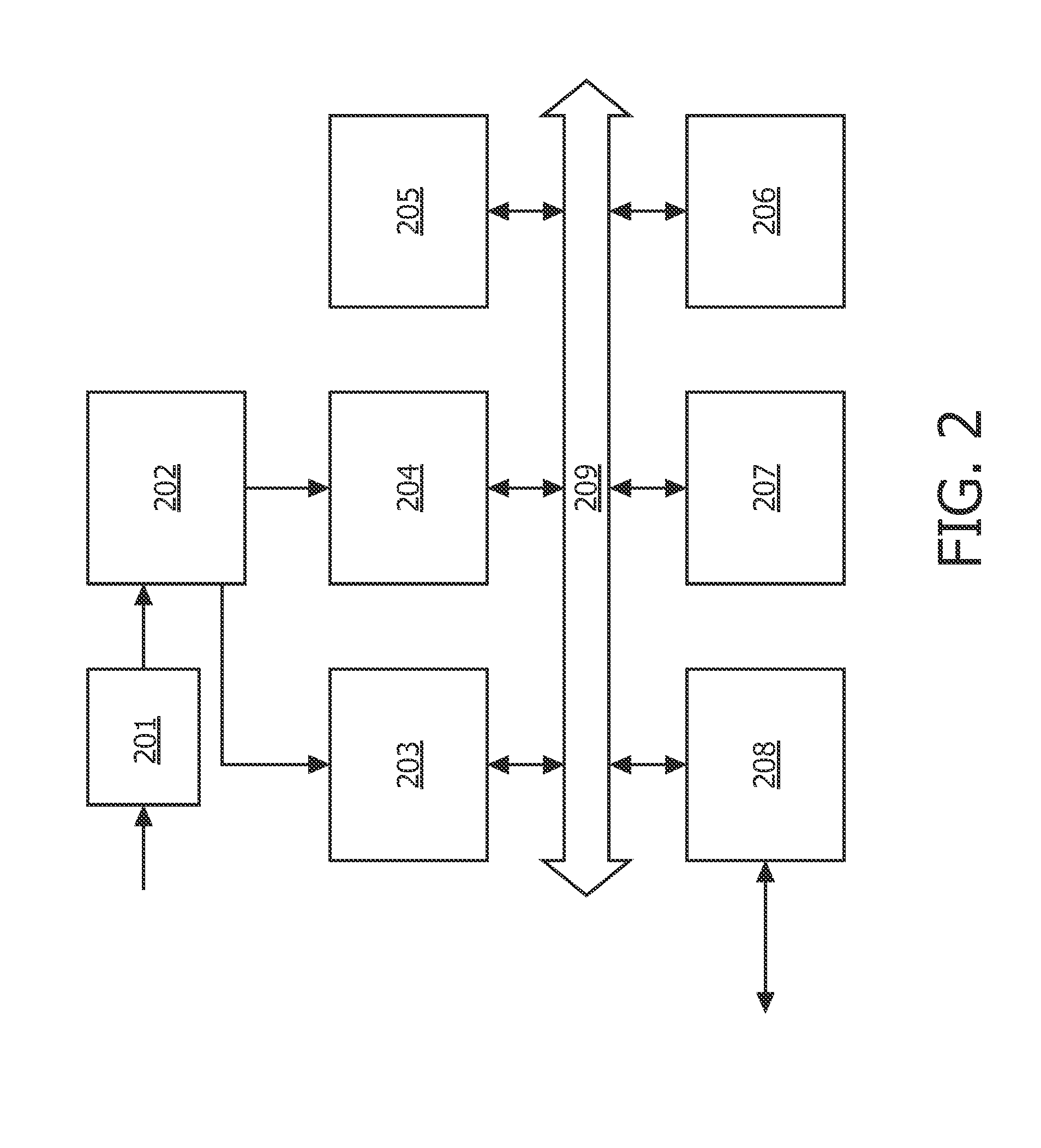
Several approaches are disclosed for combining HDR and 3D image structure analysis and coding, in particular an encoding apparatus for encoding a first view high dynamic range image and a second view high dynamic range image comprising: first and second HDR image receivers (203, 1201) arranged to receive the first view high dynamic range image and a second view high dynamic range image; a predictor (209) arranged to predict the first view high dynamic range image from a low dynamic range representation of the first view high dynamic range image; and a view predictor (1203) to predict the second view high dynamic range image from at least one of the first view high dynamic range image, a low dynamic range representation of the second view high dynamic range image, or a low dynamic range representation of the first view high dynamic range image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method of displaying a low dynamic range image in a high dynamic range
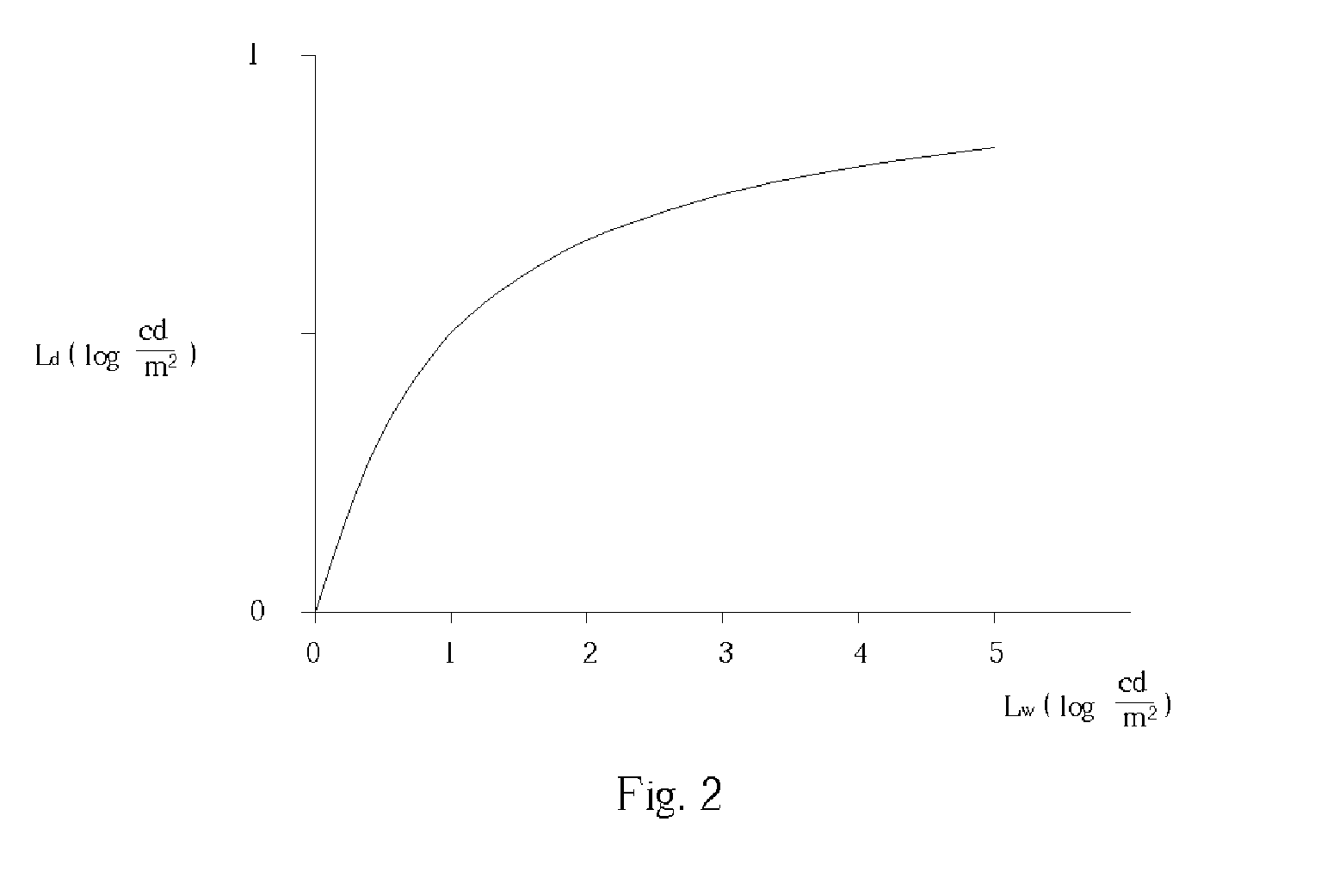
ActiveUS20080297460A1Extended imaging rangeImprove viewable contest and detailCathode-ray tube indicatorsConversion factorLightness
A method of increasing the dynamic range of an image comprising a plurality of pixels each having a luminance value within a first luminance dynamic range. The method includes determining a background luminance value for each pixel of the image and determining a minimum and a maximum of the background luminance values. A conversion factor is then determined for each pixel of the image based on the minimum and maximum of the background luminance values. The image id converted from the first luminance dynamic range to a second luminance dynamic range by multiplying the luminance value of each pixel of the image by its conversion factor.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
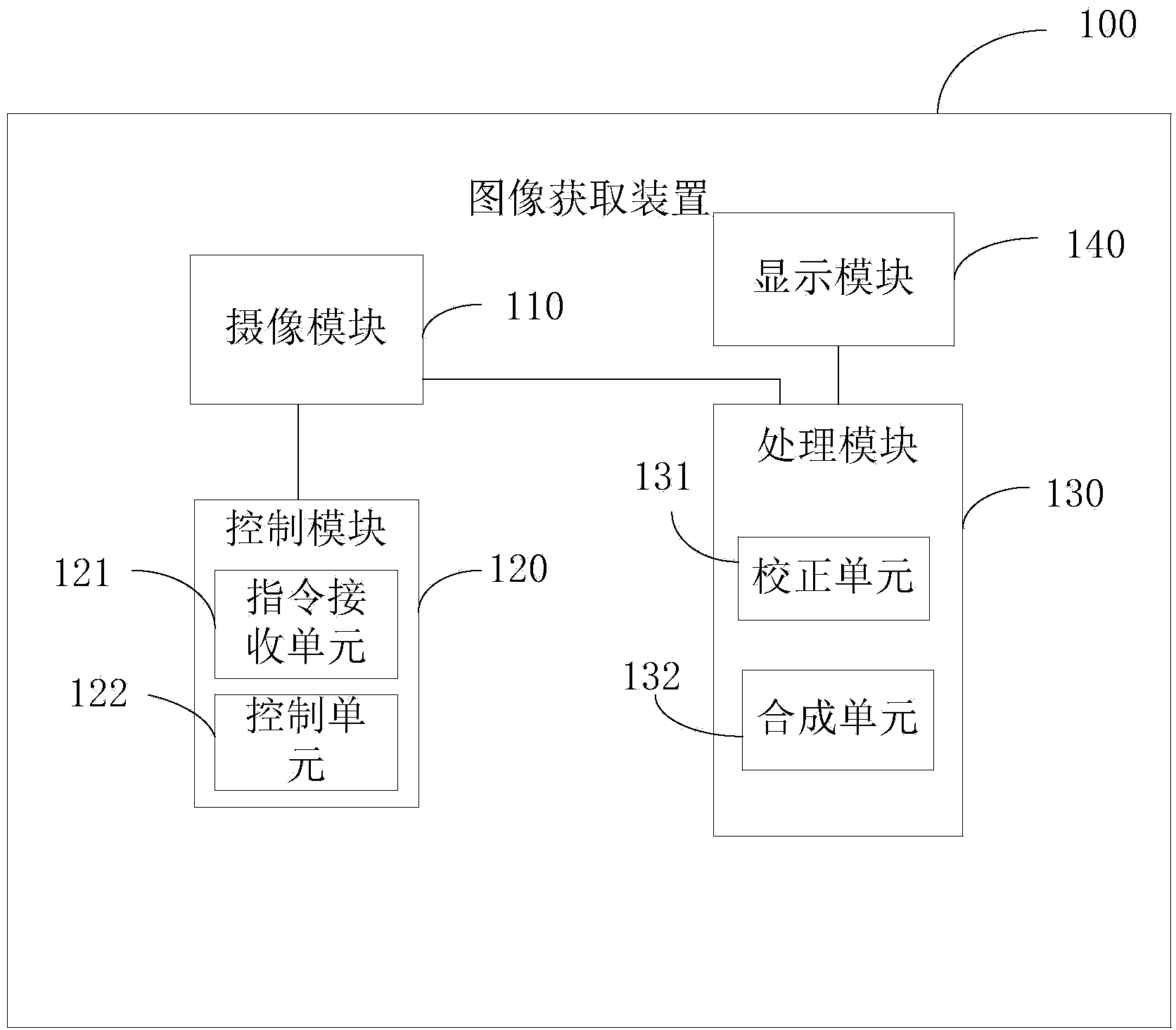
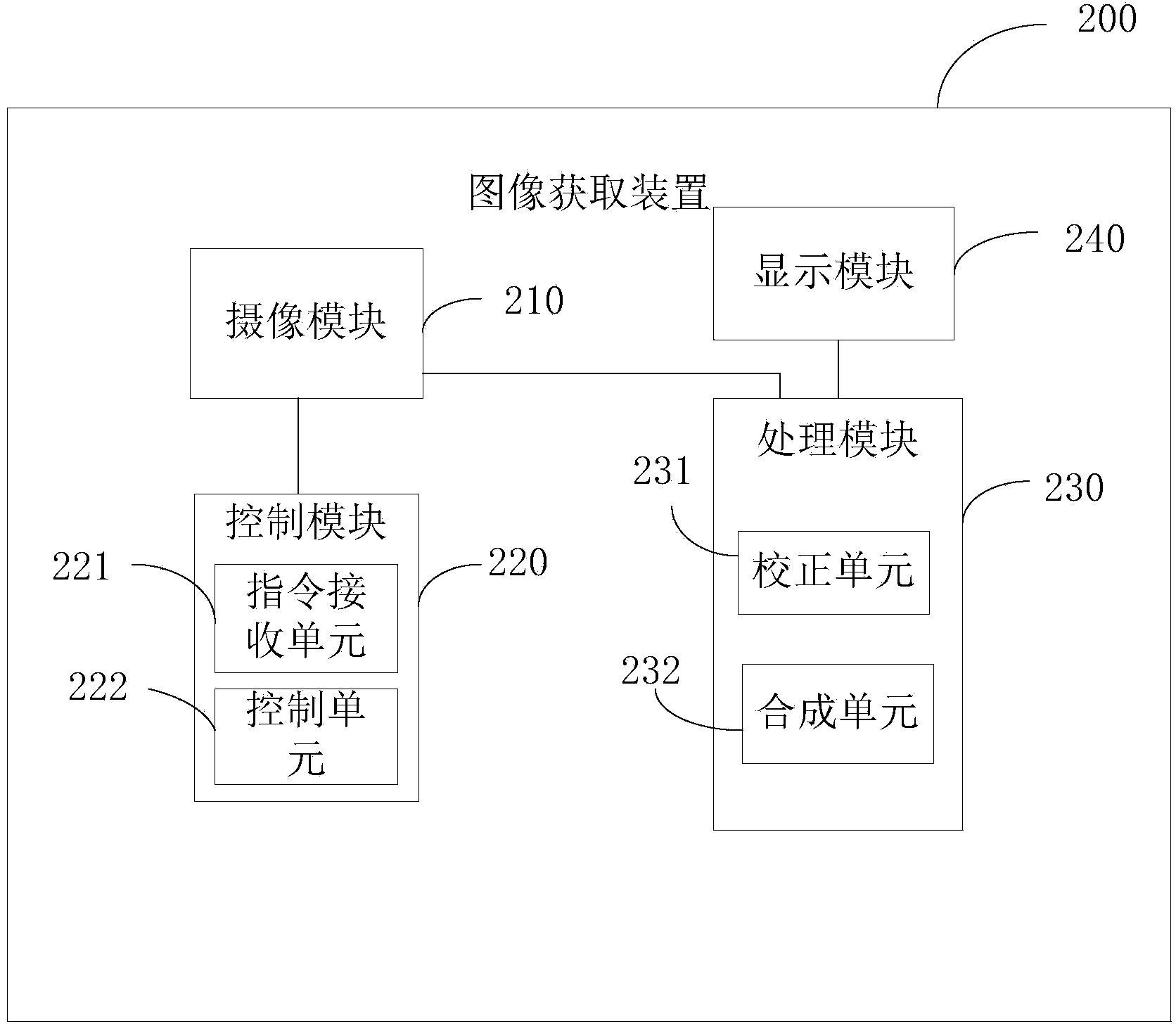
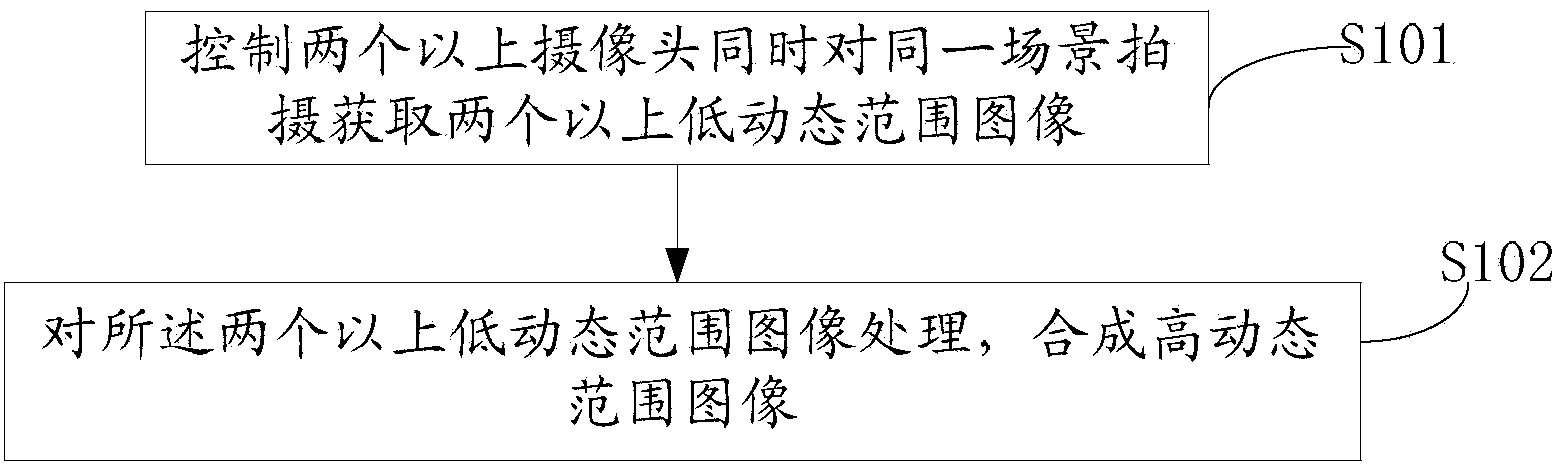
Image acquiring device, method and terminal and video acquiring method
InactiveCN103986875AFix low resolutionEasy to solveTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage resolutionLow dynamic range
The invention provides an image acquiring device. The image acquiring device comprises a camera shooting module, a control module and a processing module, wherein the camera shooting module comprises at least two cameras, the control module is used for controlling the two cameras of the camera shooting module to shoot the same scene to output two or more low-dynamic range images, and the processing module is used for processing and combining the two or more low-dynamic range images into a high-dynamic range image. The invention further provides an image acquiring method and terminal and a video acquiring method. The image acquiring device, method and terminal and the video acquiring method can achieve the high-dynamic range image with the good combining effect and a high-dynamic video with the high resolution ratio.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
CMOS active pixel sensor with improved dynamic range and method of operation
ActiveUS7518645B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotodetectorEngineering
A CMOS imaging array includes a plurality of individual pixels arranged in rows and columns. Each pixel is constructed the same and includes a photodetector (e.g., photodiode) receiving incident light and generating an output. A first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit is provided responsive to the output of the photodetector. The first circuit is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals. A second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit is also provided which is responsive to the output of the photodetector. The second circuit is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals. A first output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the first circuit to a first output multiplexer. A second output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the second circuit to a second output multiplexer. Thus, separate outputs of the first and second circuits are provided for each of the individual pixel sensors of the CMOS imaging array. Alternative embodiments incorporate two ore more photodetectors and two or more amplifier circuits and output select circuits. Three photodetectors and three amplifier circuits are useful for an embodiment where the sensor includes a three-color filter matrix.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
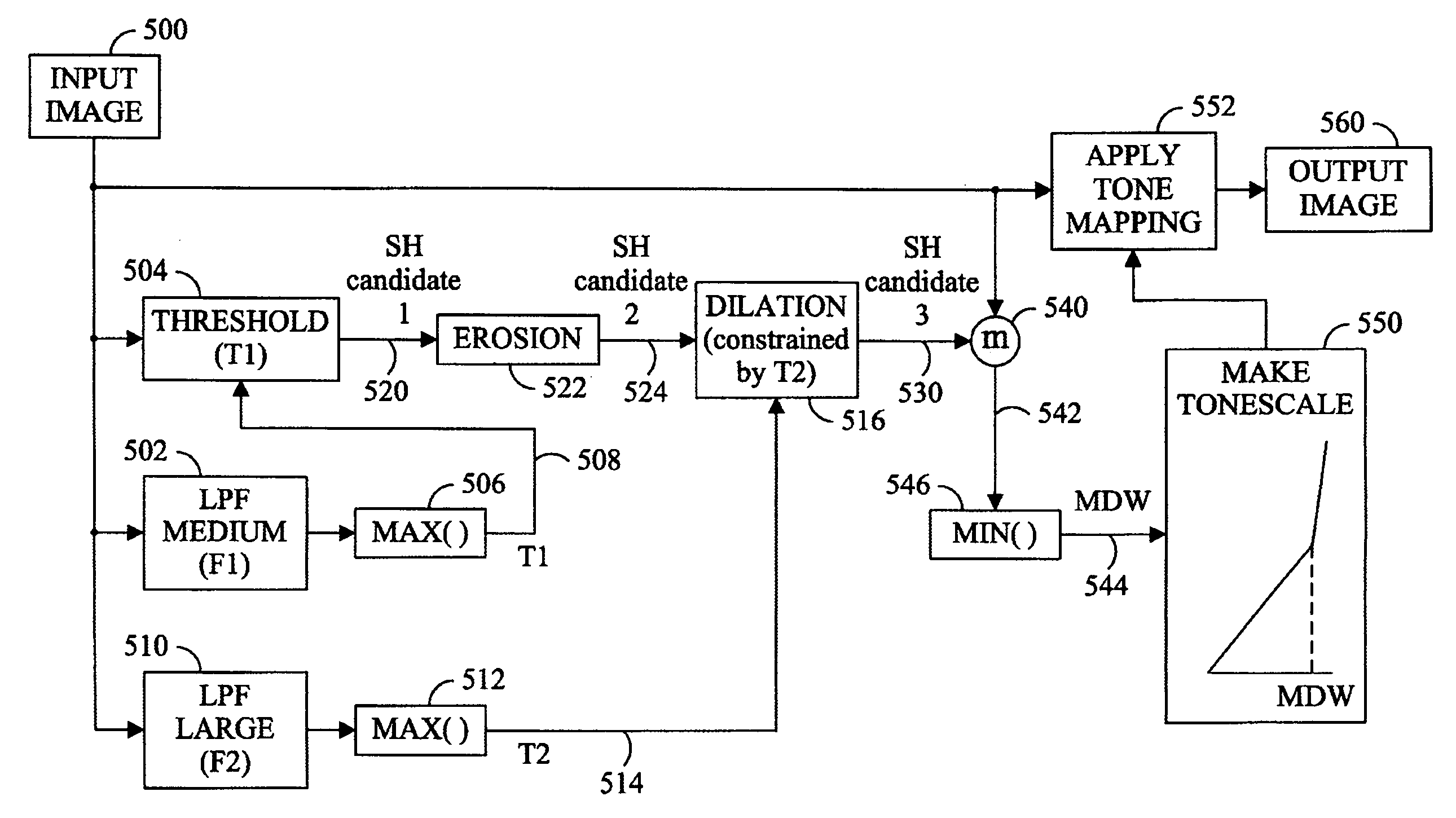
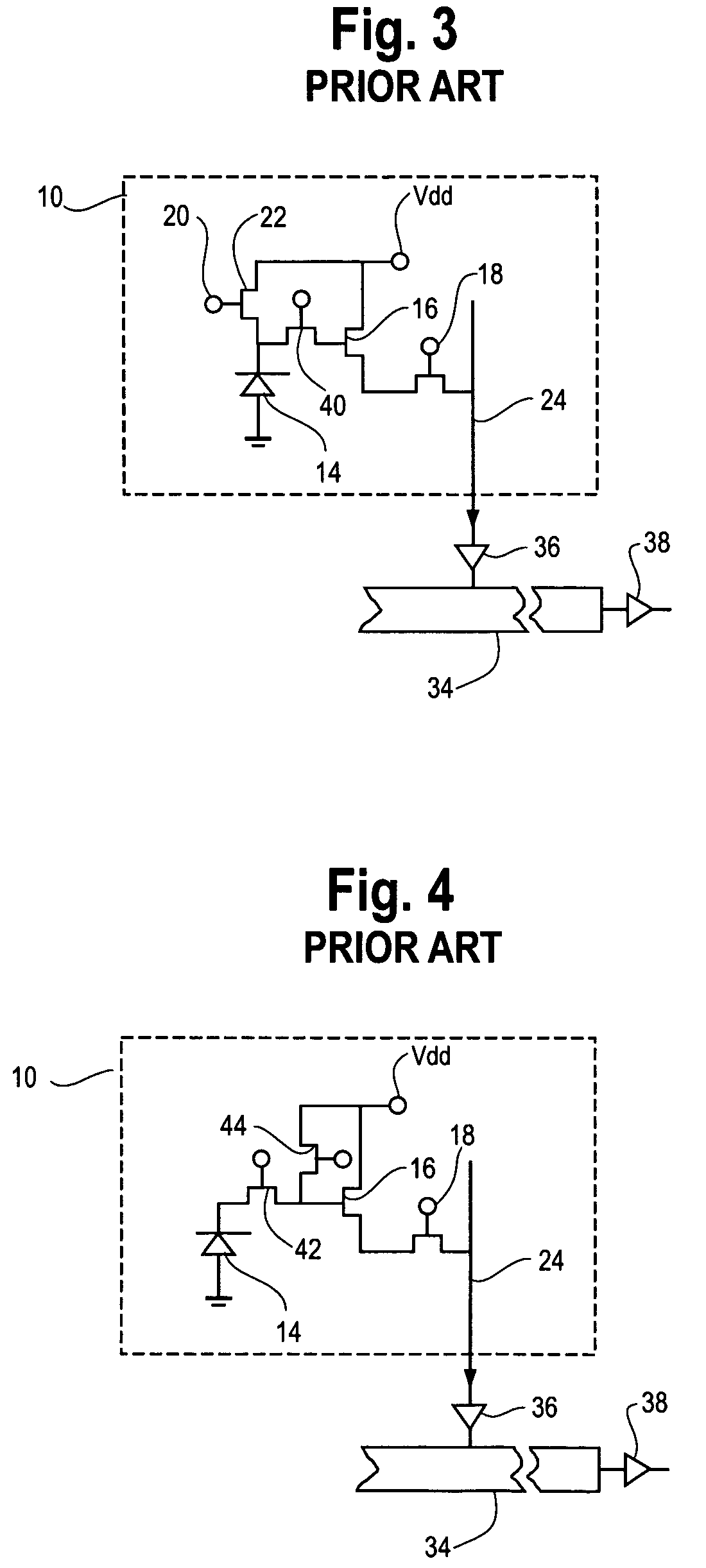
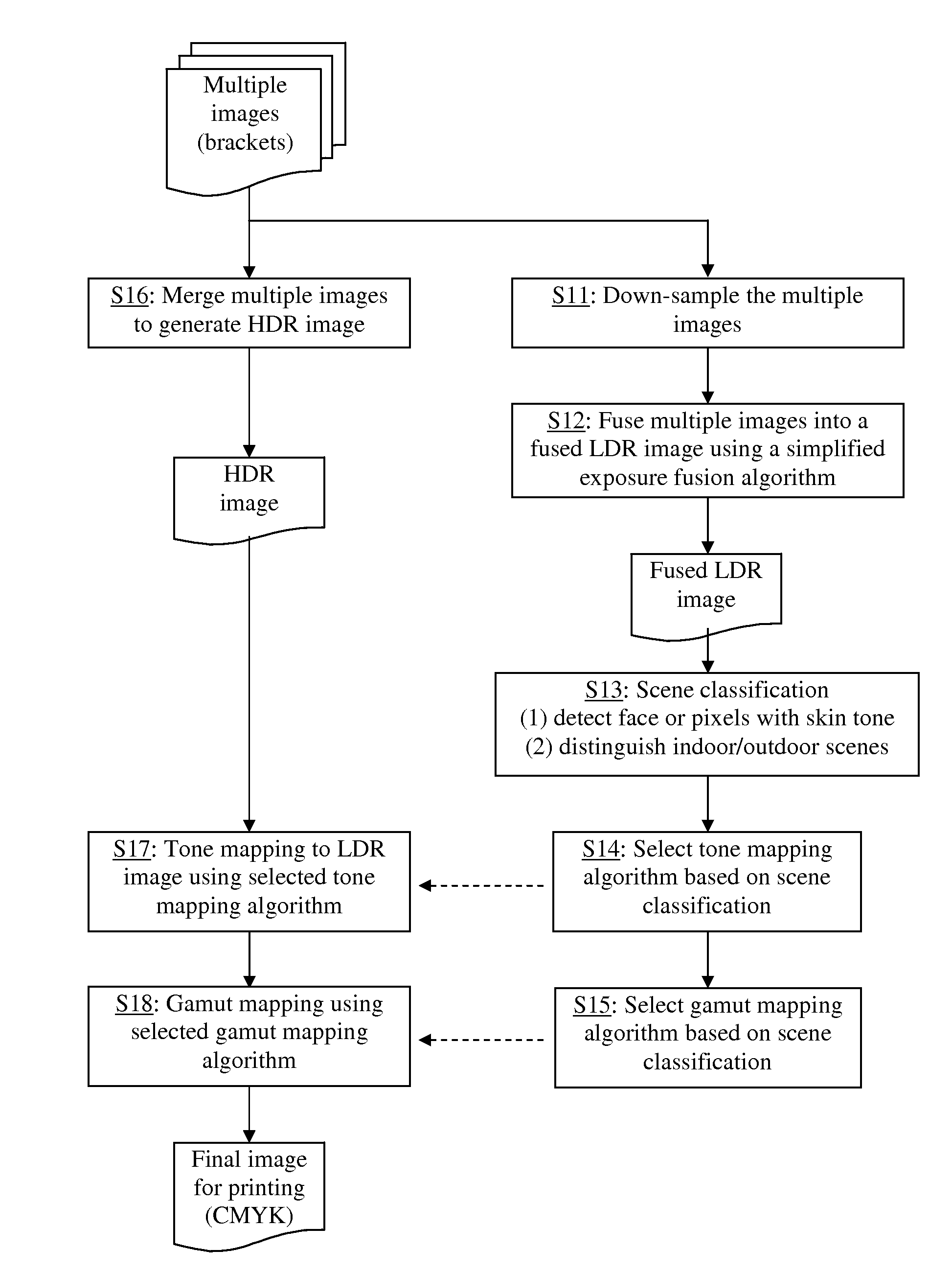
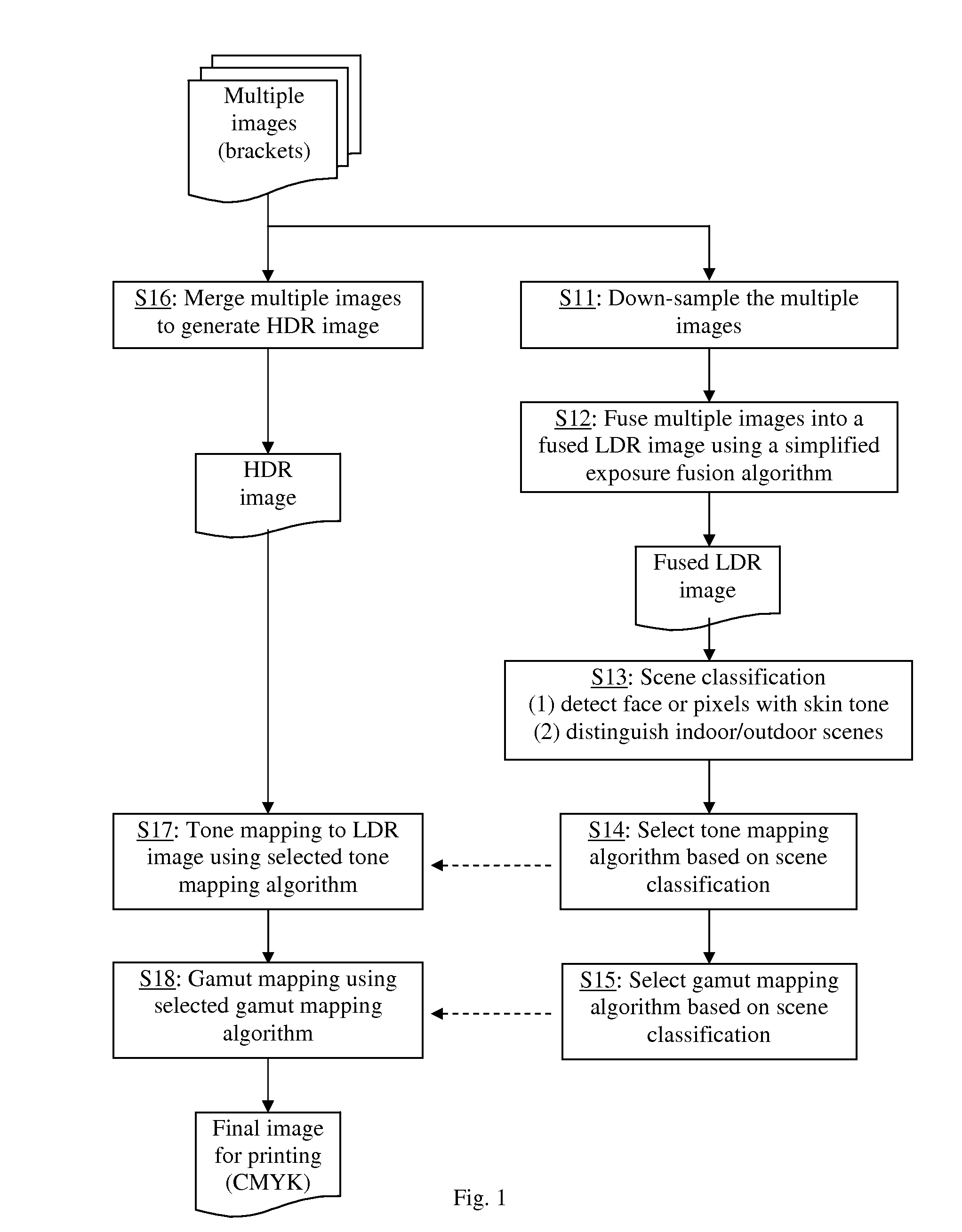
Automatic selection of optimum algorithms for high dynamic range image processing based on scene classification
InactiveUS20150170389A1Enhance HDR image processingImprove image processing capabilitiesImage enhancementImage analysisHigh-dynamic-range imagingTone mapping
A method for processing high dynamic range (HDR) images by selecting preferred tone mapping operators and gamut mapping algorithms based on scene classification. Scenes are classified into indoor scenes, outdoor scenes, and scenes with people, and tone mapping operators and gamut mapping algorithms are selected on that basis. Prior to scene classification, the multiple images taken at various exposure values are fused into a low dynamic range (LDR) image using an exposure fusing algorithm, and scene classification is performed using the fused LDR image. Then, the HDR image generated from the multiple images are tone mapped into a LDR image using the selected tone mapping operator and then gamut mapped to the color space of the output device such as printer.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA LAB U S A INC
Automatic exposure estimation for HDR images based on image statistics
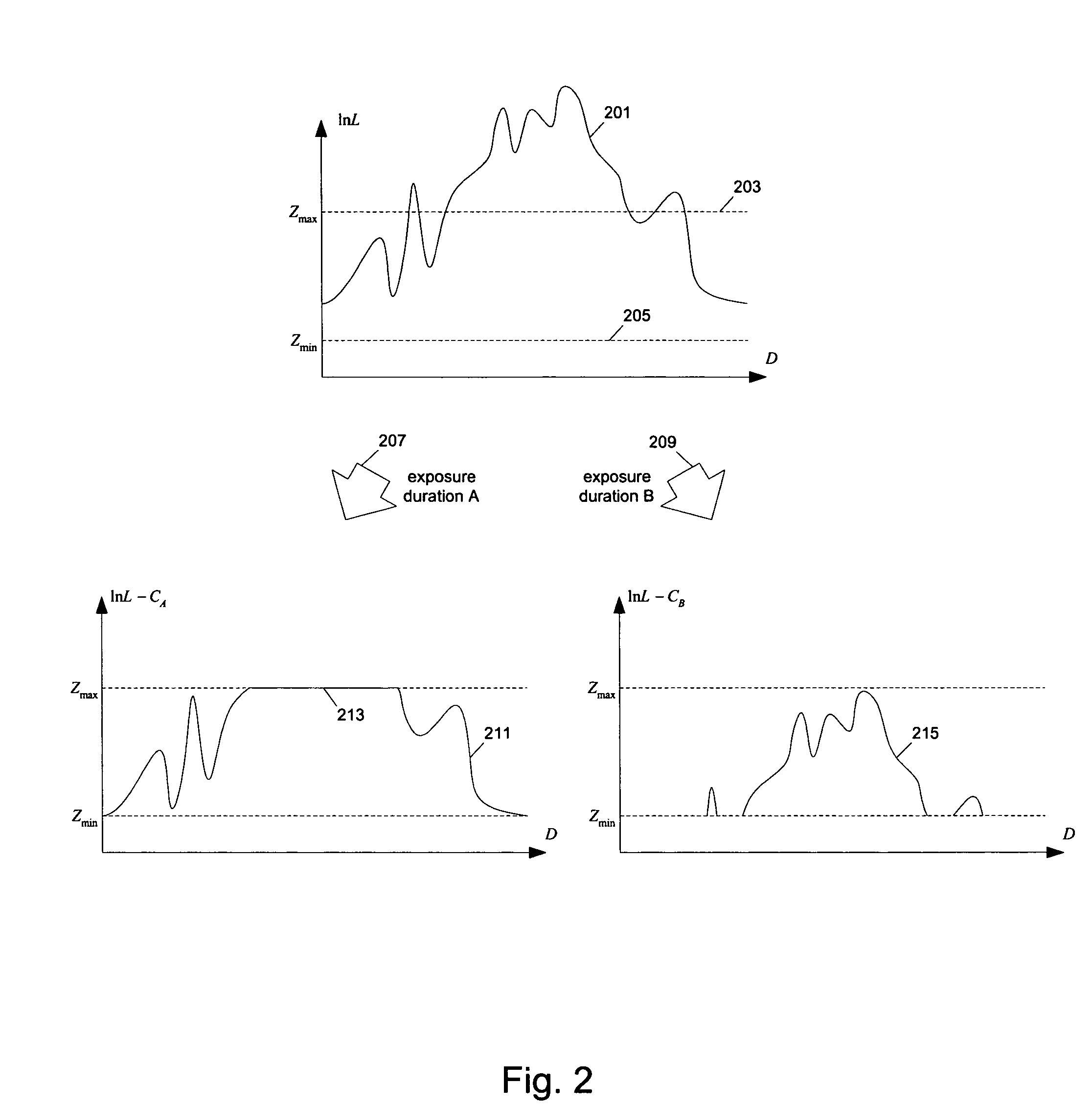
A method for tone mapping high dynamic range images for display on low dynamic range displays wherein high dynamic range images are first accessed. The high dynamic range images are divided the into different regions such that each region is represented by a matrix, where each element of the matrix is a weight or probability of a pixel value. An exposure of each region is determined or calculated by estimating an anchor point in each region such that most pixels in each region are mapped to mid grey and the anchor points are adjusted to a key of the images to preserve overall brightness. The regions are then placed or mapped to zones and exposure values are applied to the regions responsive to the weight or probability. The regions are fused together to obtain a final tone mapped image.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Image processing method and mobile terminal
ActiveCN105227858AAvoid distortionReal-time adjustment of high dynamic exposure timeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHigh-dynamic-range imagingImaging processing
Embodiments of the invention provide an image processing method and a mobile terminal, and belong to the technical field of communication. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining image data of collected frames in a high dynamic range image shooting process; analyzing the brightness of the image data, determining ambient brightness, and adjusting a high dynamic exposure time based on the determined ambient brightness; shooting according to the adjusted high dynamic exposure time to generate low dynamic range image data; and calculating the low dynamic range image data according to a preset synthesis algorithm to generate a high dynamic range image. The image processing method provided by the embodiments of the invention can be used for avoiding a high dynamic range image distortion problem caused by a fixedly set high dynamic exposure time and enabling the high dynamic range image to reflect the true environments of all scenes, namely, true details of a picture can be restored.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
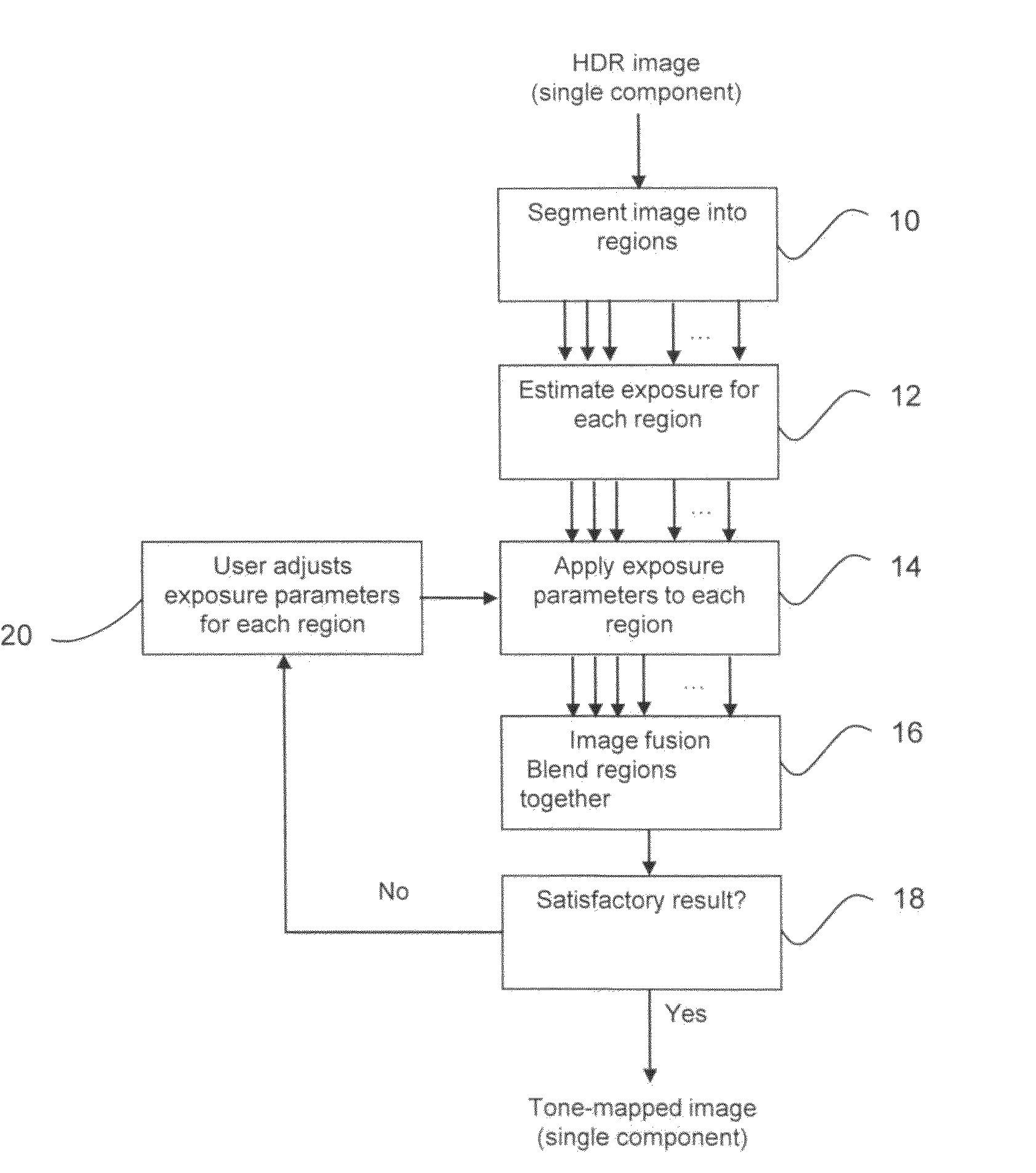
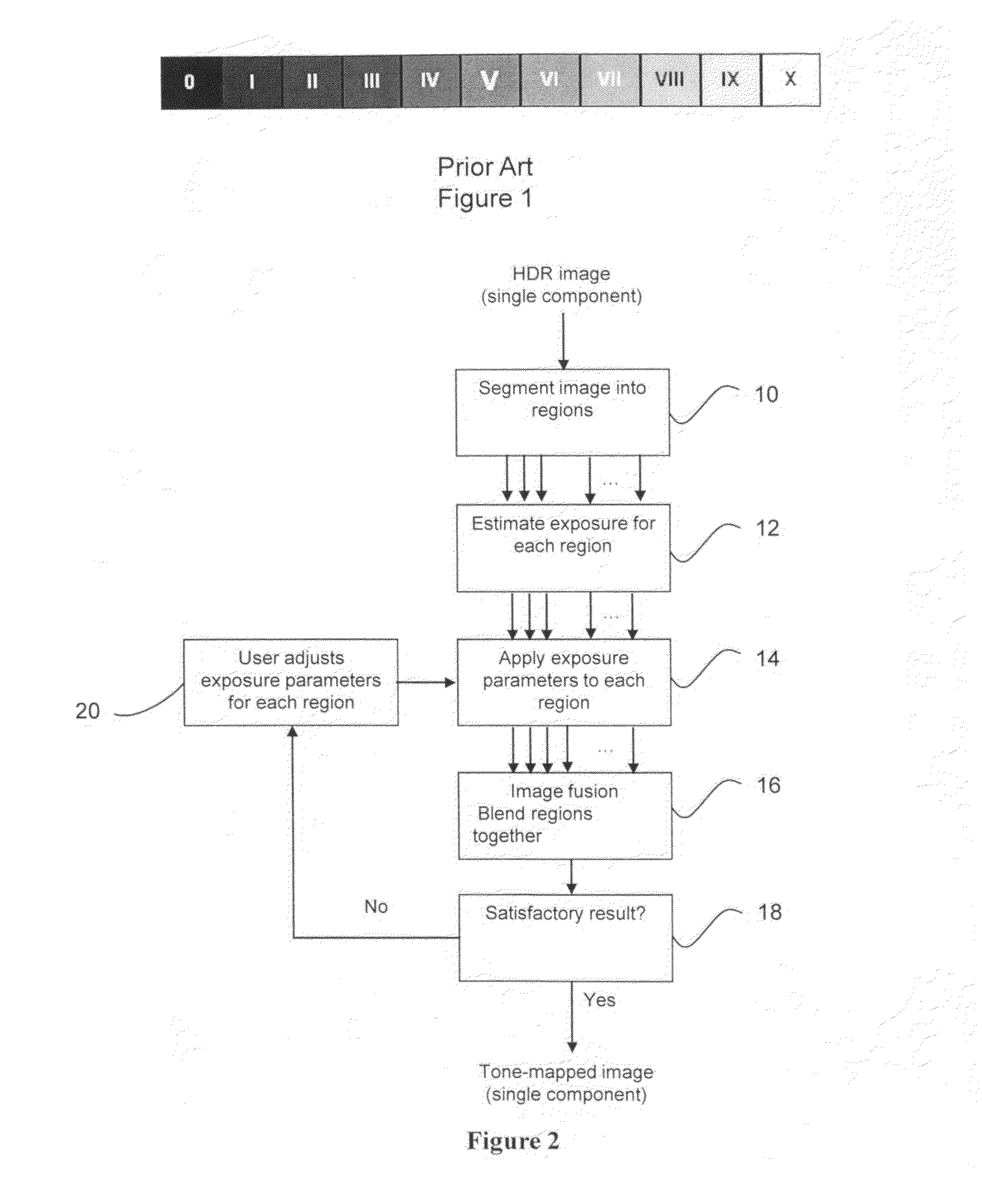
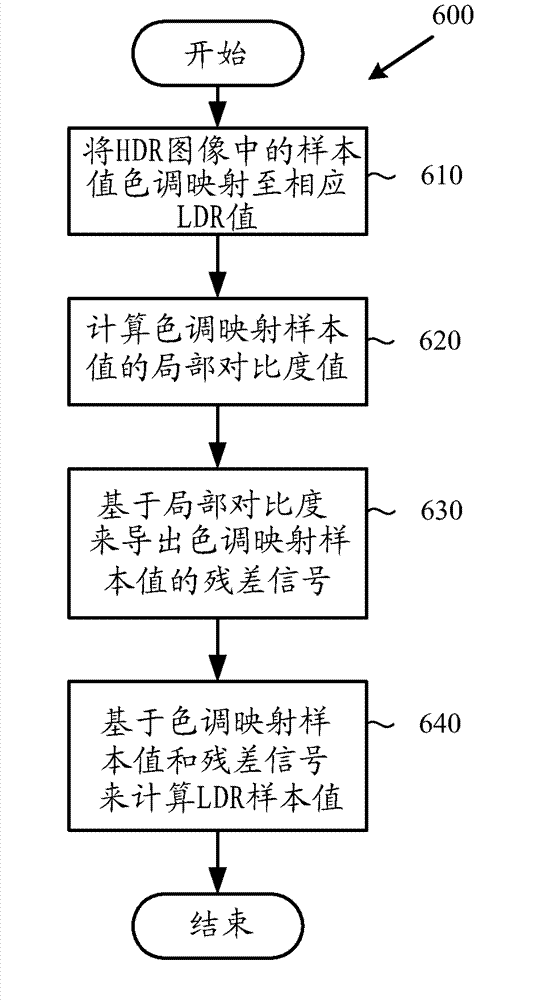
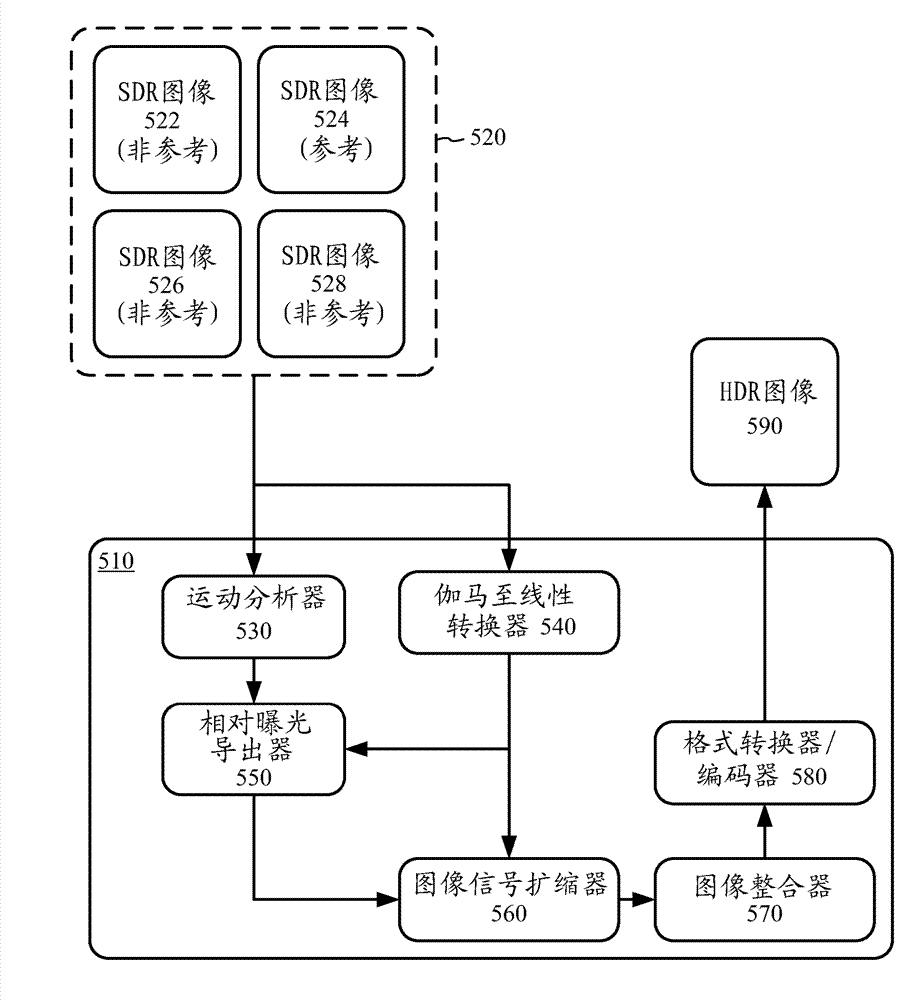
High dynamic range image generation and rendering
Techniques and tools for high dynamic range (HDR) image rendering and generation. An HDR image generating system performs motion analysis on a set of lower dynamic range (LDR) images and derives relative exposure levels for the images based on information obtained in the motion analysis. These relative exposure levels are used when integrating the LDR images to form an HDR image. An HDR image rendering system tone maps sample values in an HDR image to a respective lower dynamic range value, and calculates local contrast values. Residual signals are derived based on local contrast, and sample values for an LDR image are calculated based on the tone-mapped sample values and the residual signals. User preference information can be used during various stages of HDR image generation or rendering.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and device for generating images with high dynamic ranges
ActiveCN104349066AQuality improvementImage enhancementTelevision system detailsReference imageLow dynamic range
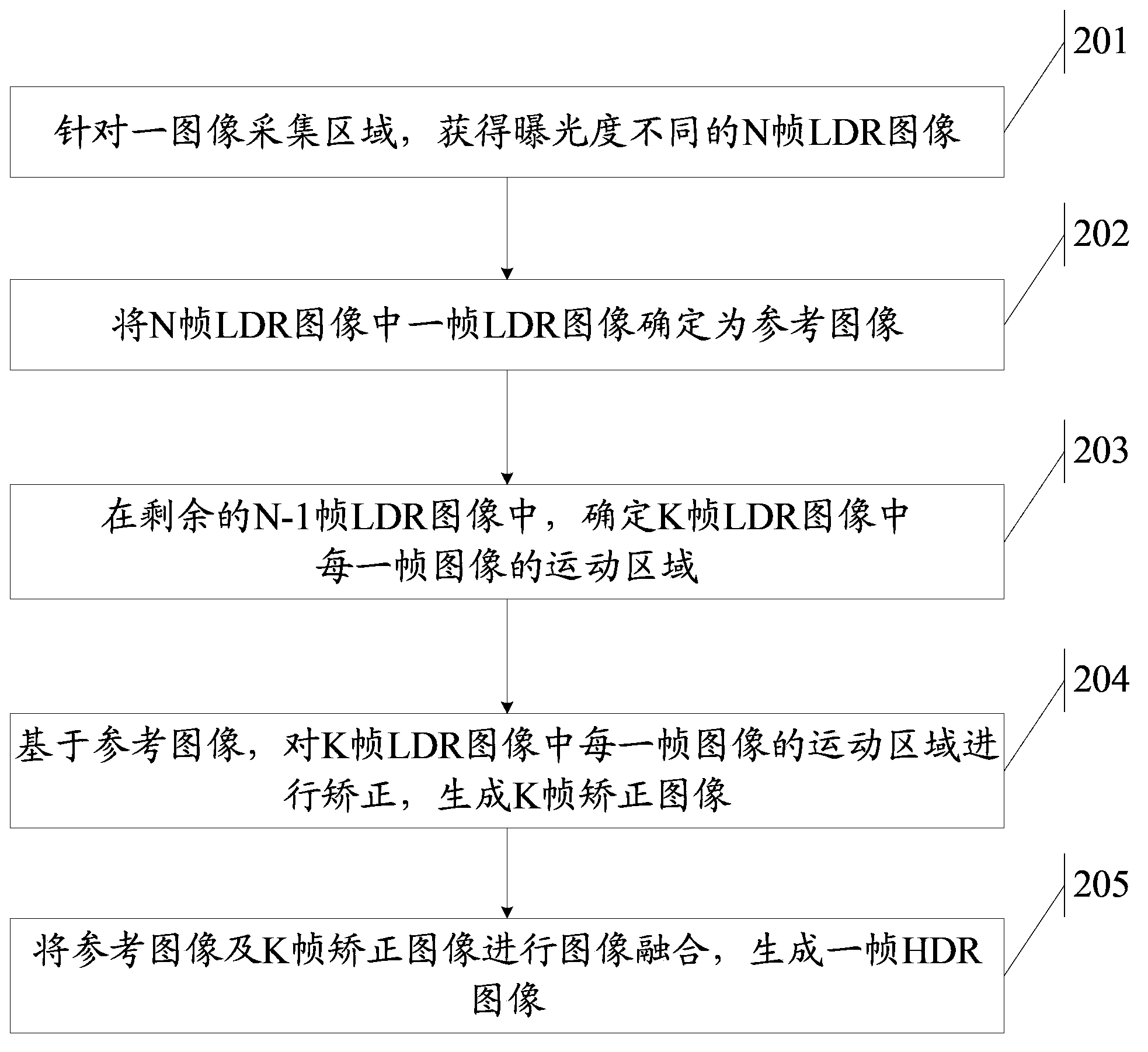
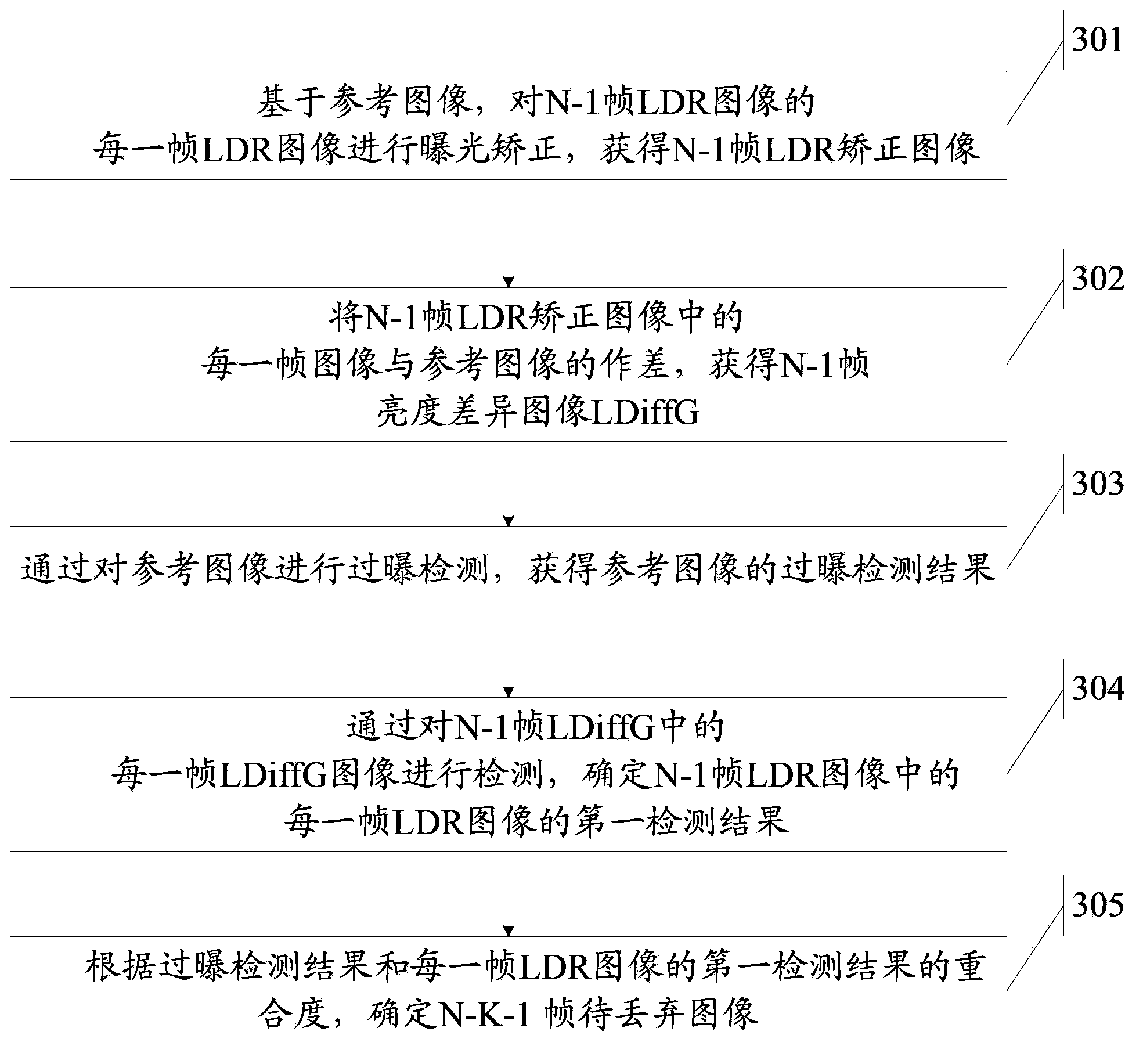
A method and apparatus for generating a high dynamic range image are disclosed by the present invention, which is used to remove "ghost" in the high dynamic range image. The method includes: for an image collecting area, obtaining N-frame low dynamic range images which have different exposure, wherein, N is an integer greater than or equal to 2; determining one frame low dynamic range image of the N-frame low dynamic range images as a reference image; in remaining N-1 frame low dynamic range images , determining a motion area of each frame image of K-frame low dynamic range images, wherein, K is an integer greater than 0 and less than or equal to N-1; based on the reference image, correcting the motion area of each frame image of the K-frame low dynamic range images, and generating K-frame corrected images; fusing the reference image and the K-frame corrected images, then generating one frame high dynamic range image.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
Adjusting method and device with high dynamic range
InactiveCN101707666AReasonable high dynamic range adjustment technologyImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHigh-dynamic-range imagingImaging quality
Owner:VIMICRO CORP
Device and method for high dynamic range image display
ActiveCN103024300AImprove the display effectGenerate efficientlyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingImage segmentation algorithm
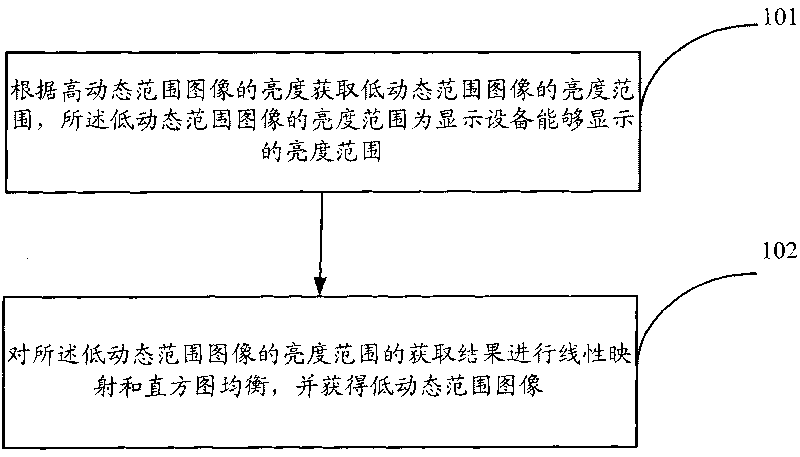
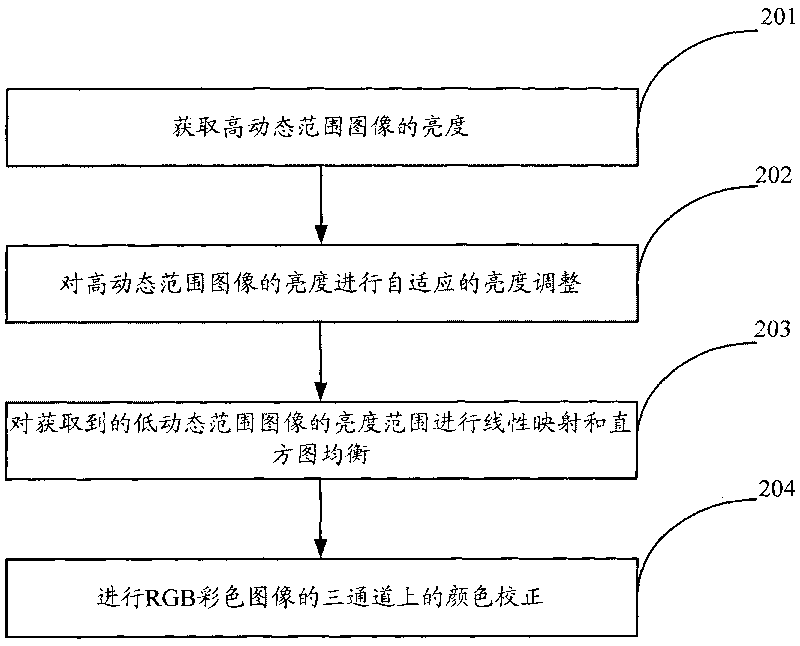
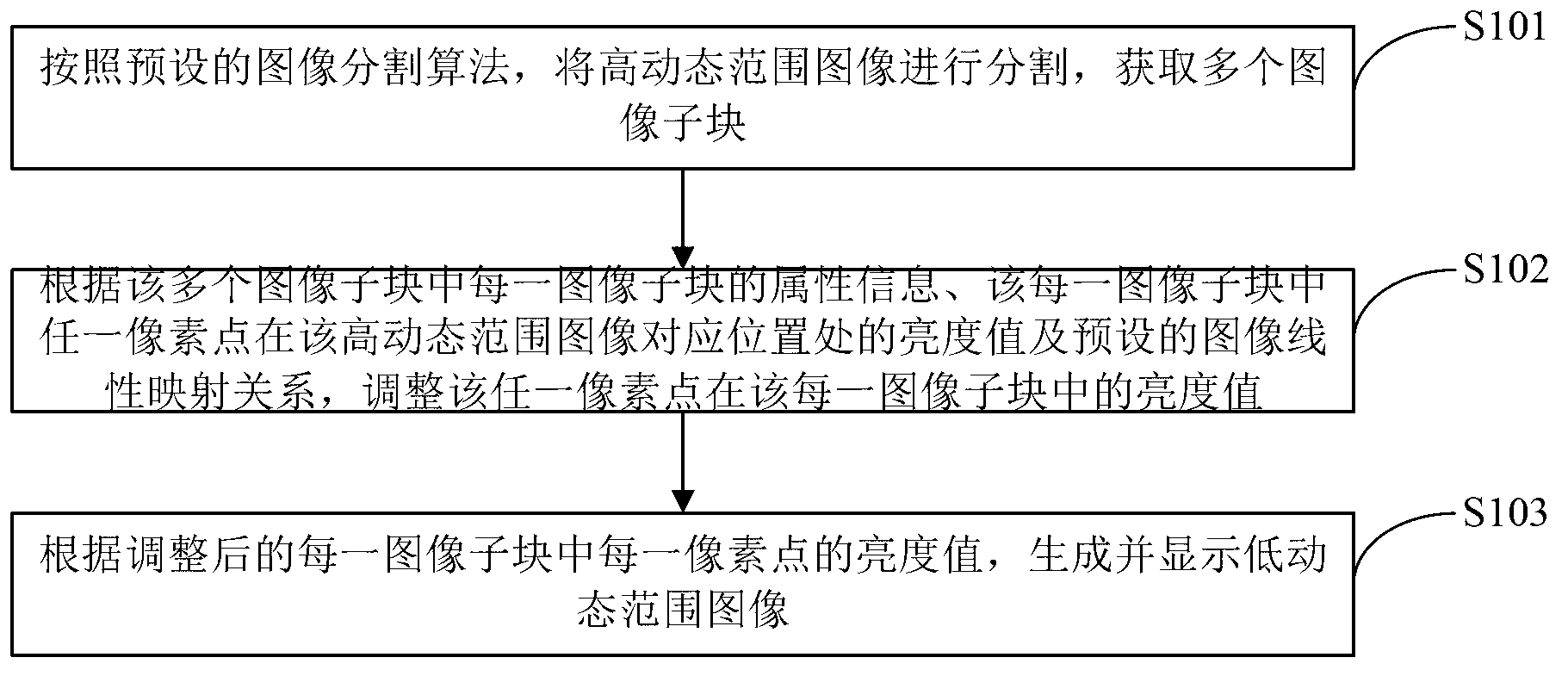
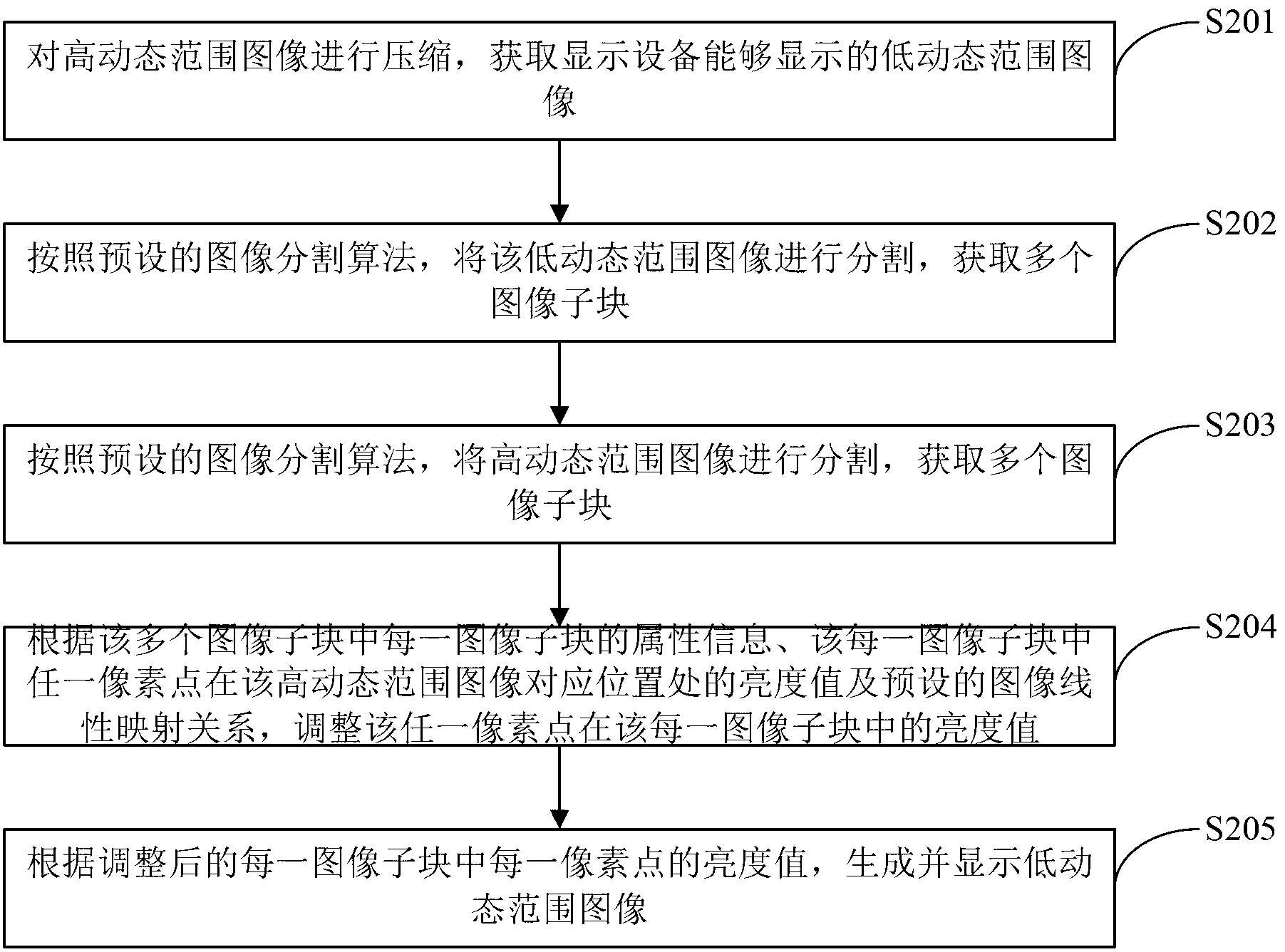
The invention is applicable to the technical field of image processing and provides a device and a method for high dynamic range image display. The method includes: segmenting a high dynamic range image according to preset image segmentation algorithm to acquire a plurality of image subblocks; adjusting the brightness value of any pixel point in each image subblock according to attribute information of each image subblock, the brightness value of the pixel point at the corresponding position of each image subblock and the preset image linear mapping relation; and generating and displaying a low dynamic range image according to the adjusted brightness value of each pixel point in each image subblock. Displaying effects of the generated low dynamic range image are greatly improved by adjusting the brightness value of any pixel point in each image subblock according to attribute information of each image subblock, the brightness value of the pixel point at the corresponding position of the high dynamic range image and the preset image linear mapping relation.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com