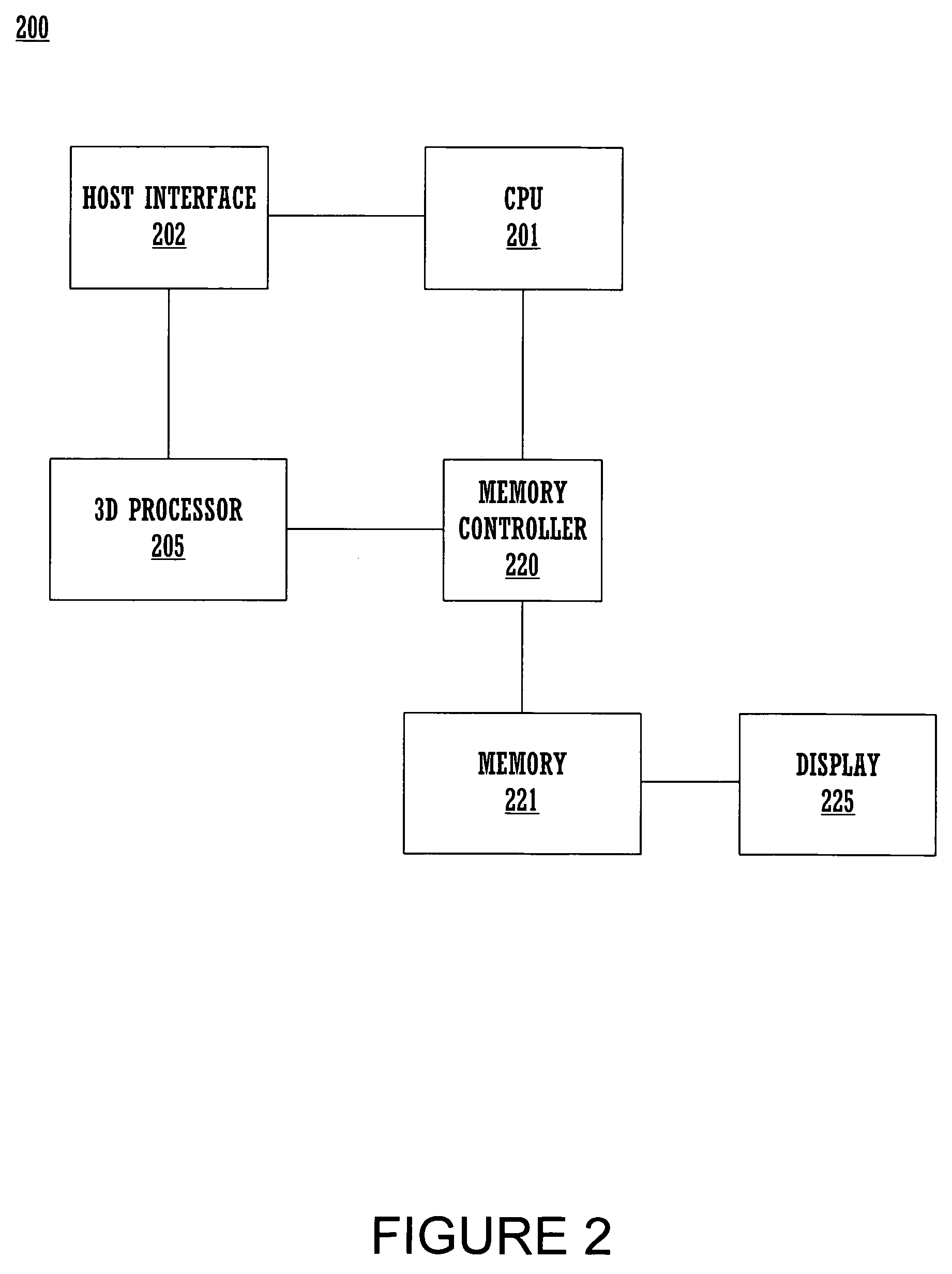
Patents
Literature
203 results about "Computational geometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
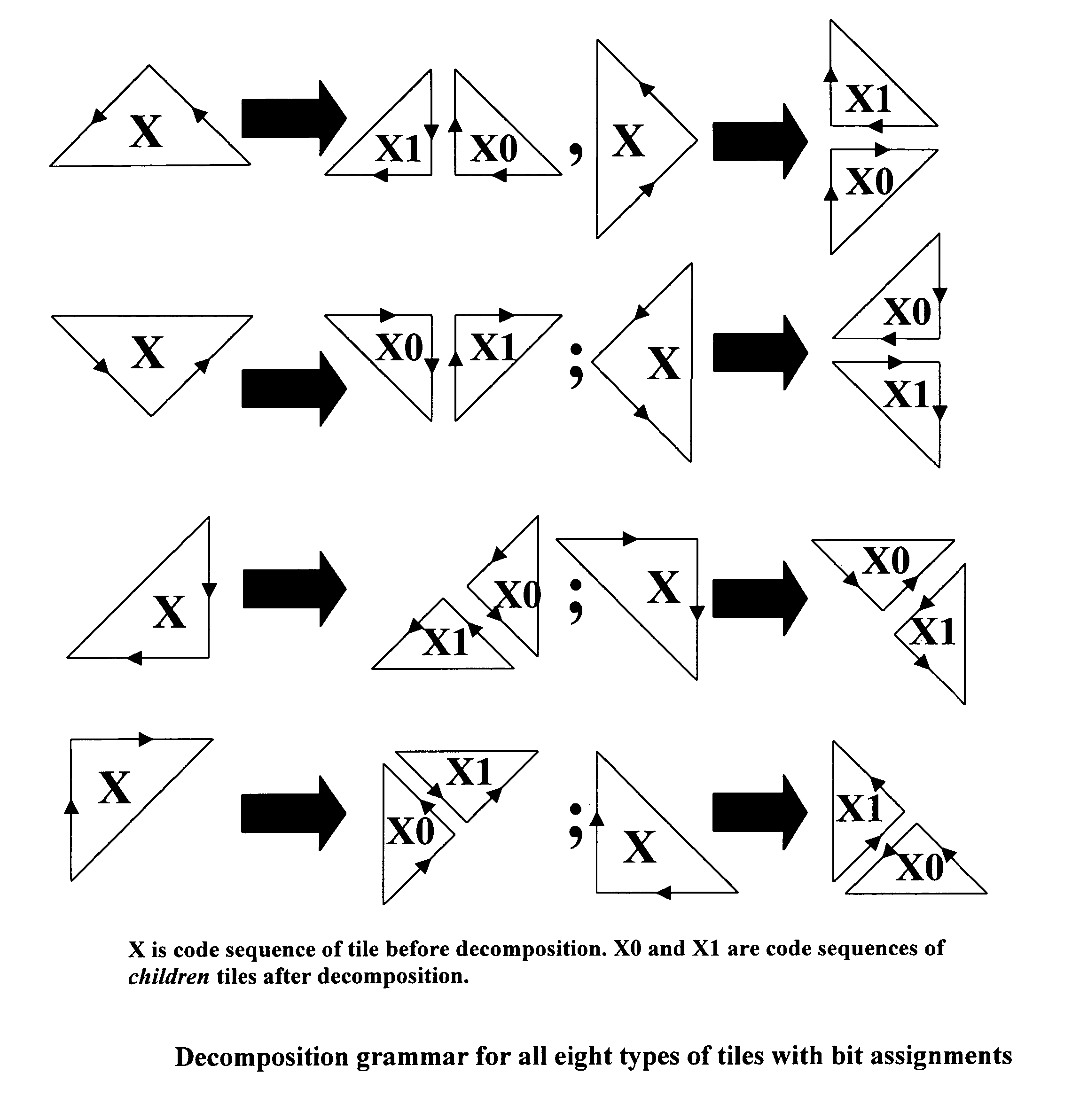
Computational geometry is a branch of computer science devoted to the study of algorithms which can be stated in terms of geometry. Some purely geometrical problems arise out of the study of computational geometric algorithms, and such problems are also considered to be part of computational geometry. While modern computational geometry is a recent development, it is one of the oldest fields of computing with history stretching back to antiquity.
Efficient large-scale access control for internet/intranet information systems
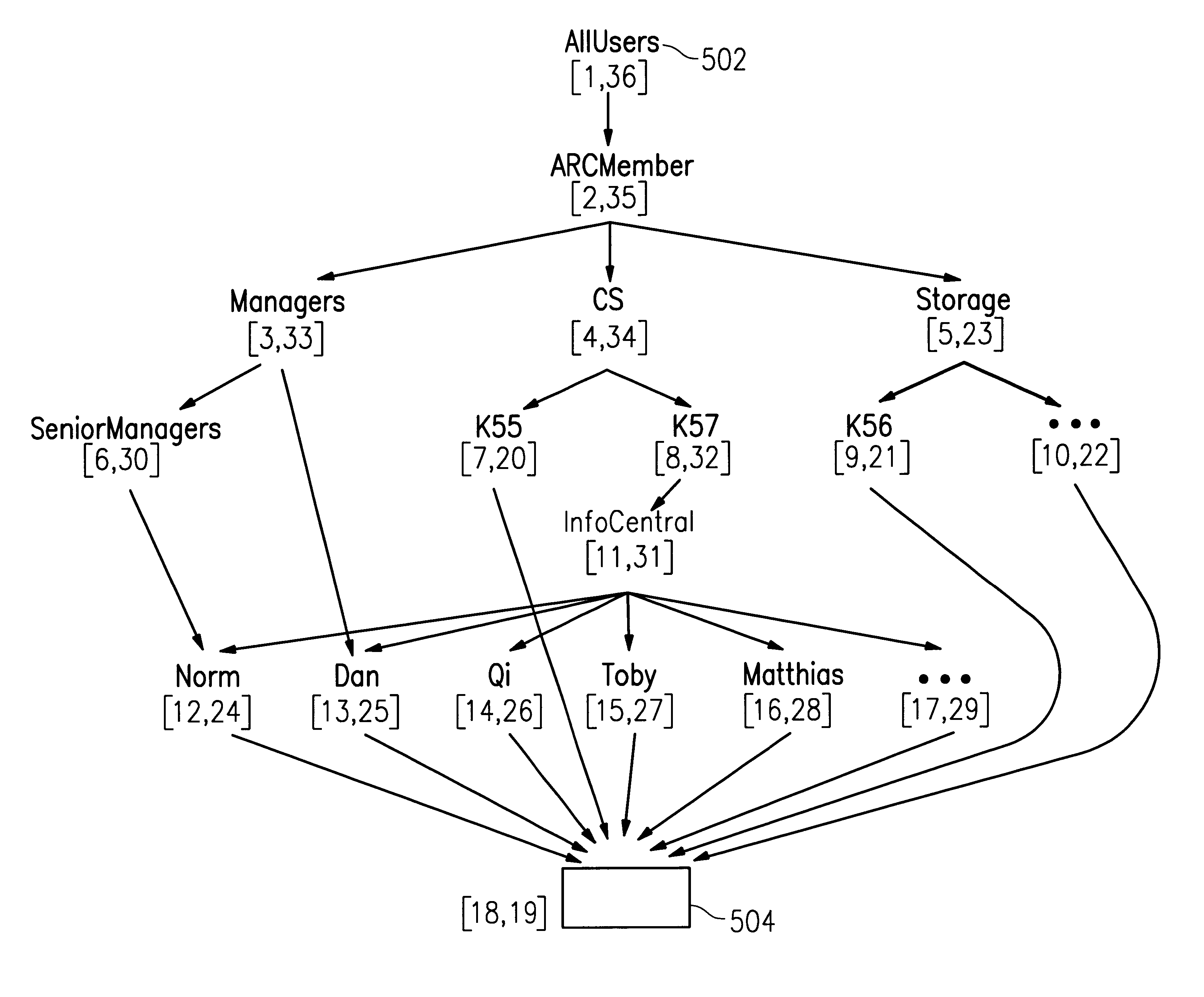
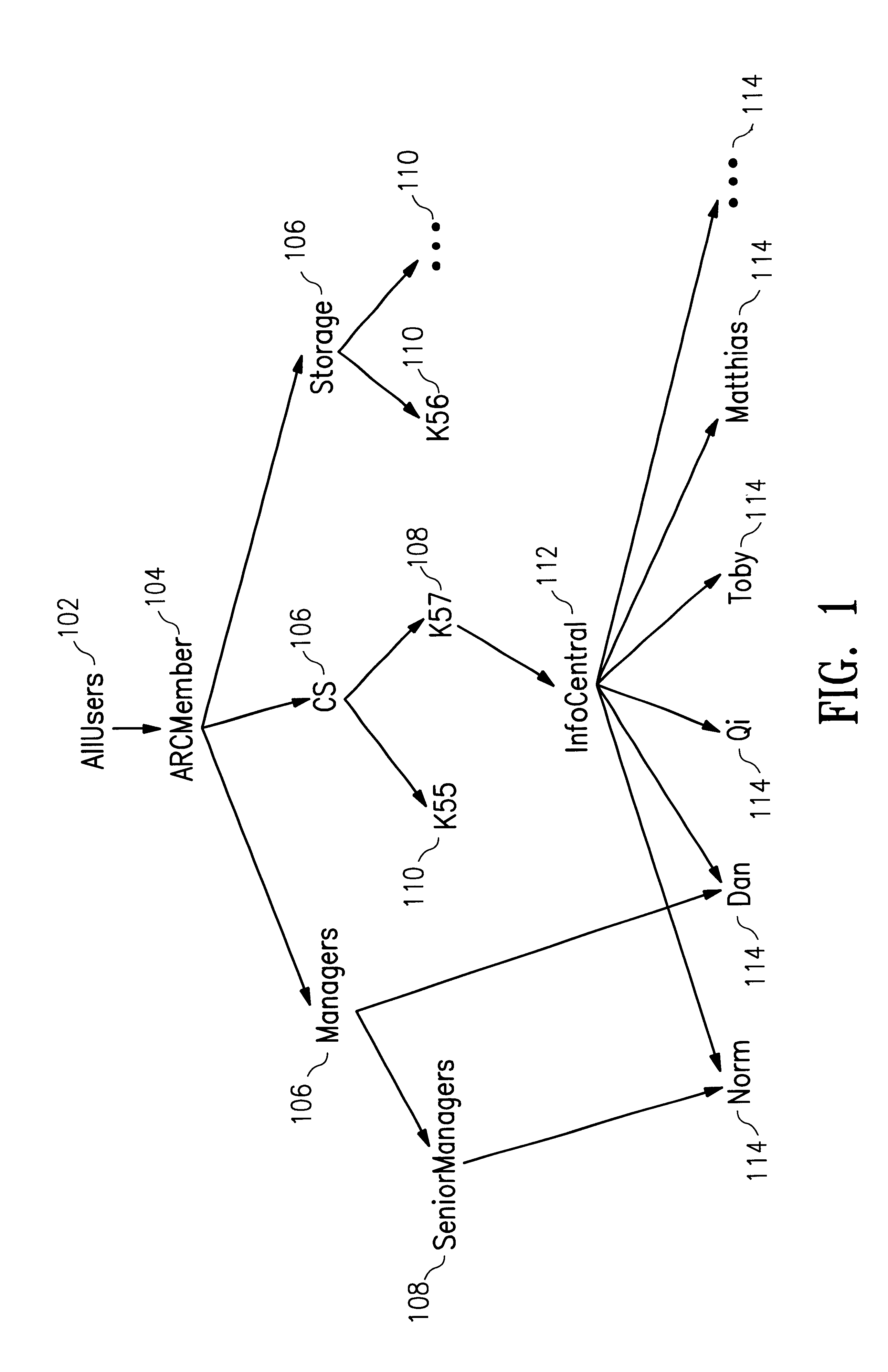
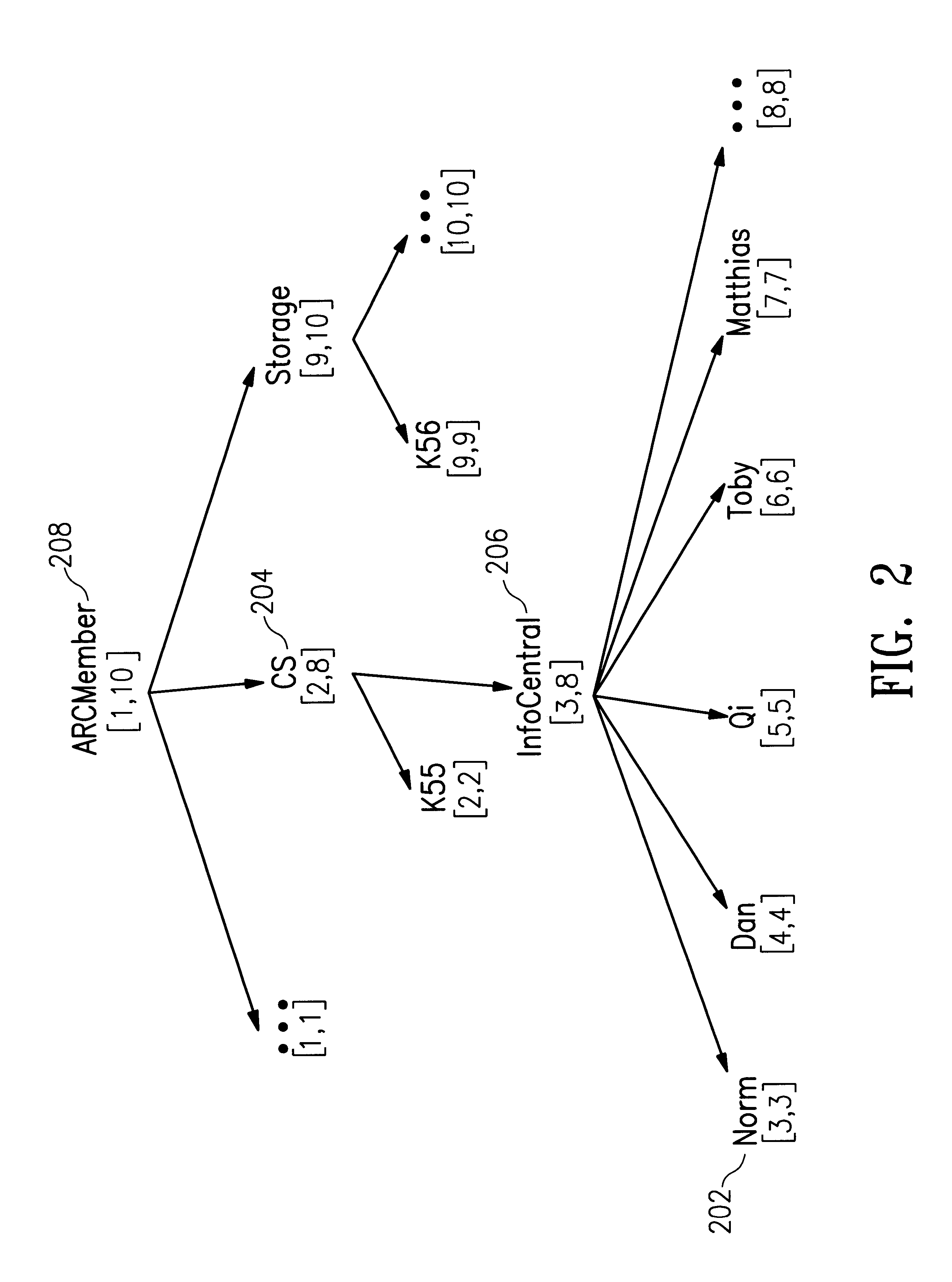
InactiveUS6219667B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDecompositionInformation object
An efficient method and apparatus for regulating access to information objects stored in a database in which there are a large number of users and access groups. The invention uses a representation of a hierarchical access group structure in terms of intervals over a set of integers and a decomposition scheme that reduces any group structure to ones that have interval representation. This representation allows the problem for checking access rights to be reduced to an interval containment problem. An interval tree, a popular data structure in computational geometry, may be implemented to efficiently execute the access-right checking method.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for content driven image compression
InactiveUS20050131660A1Small sizePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionFiltration
A method with related structures and computational components and modules for modeling data, particularly audio and video signals. The modeling method can be applied to different solutions such as 2-dimensional image / video compression, 3-dimensional image / video compression, 2-dimensional image / video understanding, knowledge discovery and mining, 3-dimensional image / video understanding, knowledge discovery and mining, pattern recognition, object meshing / tessellation, audio compression, audio understanding, etc. Data representing audio or video signals is subject to filtration and modeling by a first filter that tessellates data having a lower dynamic range. A second filter then further tessellates, if needed, and analyzes and models the remaining parts of data, not analyzable by first filter, having a higher dynamic range. A third filter collects in a generally lossless manner the overhead or residual data not modeled by the first and second filters. A variety of techniques including computational geometry, artificial intelligence, machine learning and data mining may be used to better achieve modeling in the first and second filters.
Owner:YADEGAR JOSEPH +1
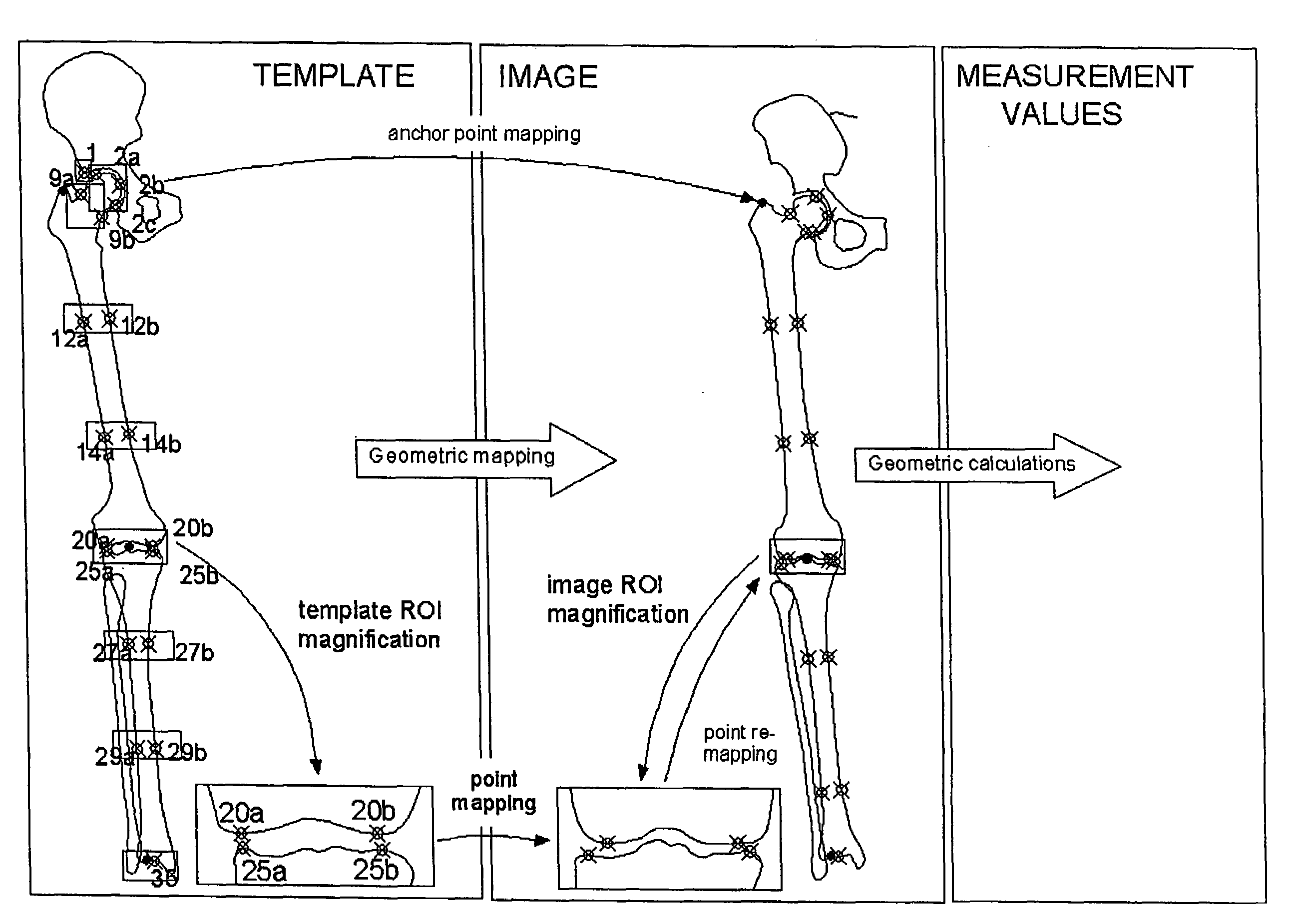
Method for automatically mapping of geometric objects in digital medical images
ActiveUS7394946B2Precise positioningReduce the numberImage enhancementImage analysisDigital imageAnchor point
A method of mapping geometrical objects to a digital image. At least one anchor point in a model is selected and mapped to the digital image. A geometric transformation is computed on the basis of at least one correspondence between an anchor object and a corresponding mapped object, and the calculated geometric transformation is applied to at least one geometric object thereby mapping it from the model image to a corresponding mapped position in the digital image.
Owner:AGFA NV
Geometric design and modeling system using control geometry
InactiveUS7196702B1Efficient regenerationComputationally efficientData processing applications3D-image renderingComputer Aided DesignAnimation
A method and system for computer aided design (CAD) is disclosed for designing geometric objects. The present invention interpolates and / or blends between such geometric objects sufficiently fast so that real time deformation of such objects occurs while deformation data is being input. Thus, a user designing with the present invention obtains immediate feedback to input modifications without separately entering a command for performing such deformations. The present invention utilizes novel computational techniques for blending between geometric objects, wherein weighted sums of points on the geometric objects are used in deriving a new blended geometric object. The present invention is particularly useful for designing the shape of surfaces. Thus, the present invention is applicable to various design domains such as the design of, e.g., bottles, vehicles, and watercraft. Additionally, the present invention provides for efficient animation via repeatedly modifying surfaces of an animated object such as a representation of a face.
Owner:CAD-SENSE LLC
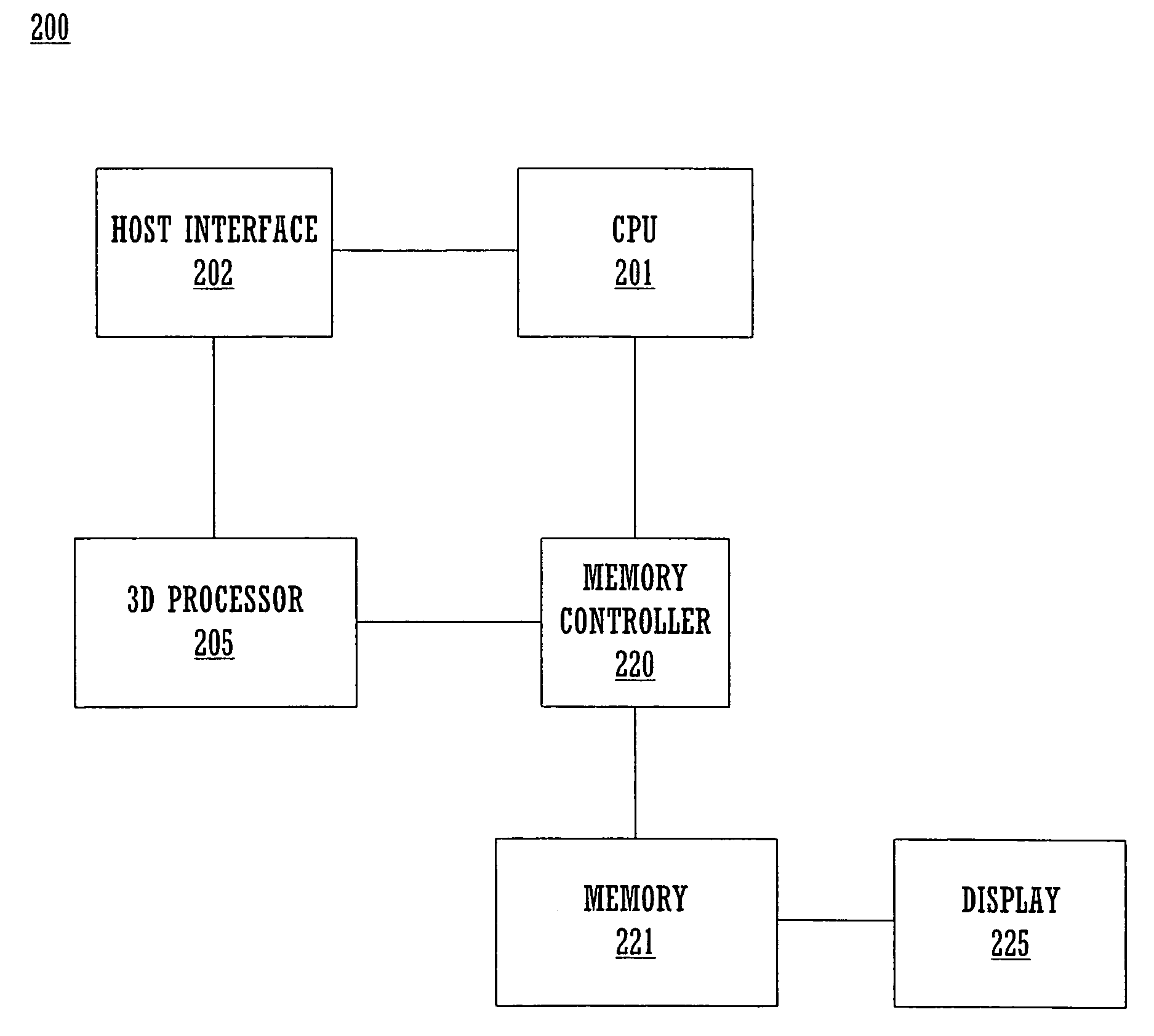
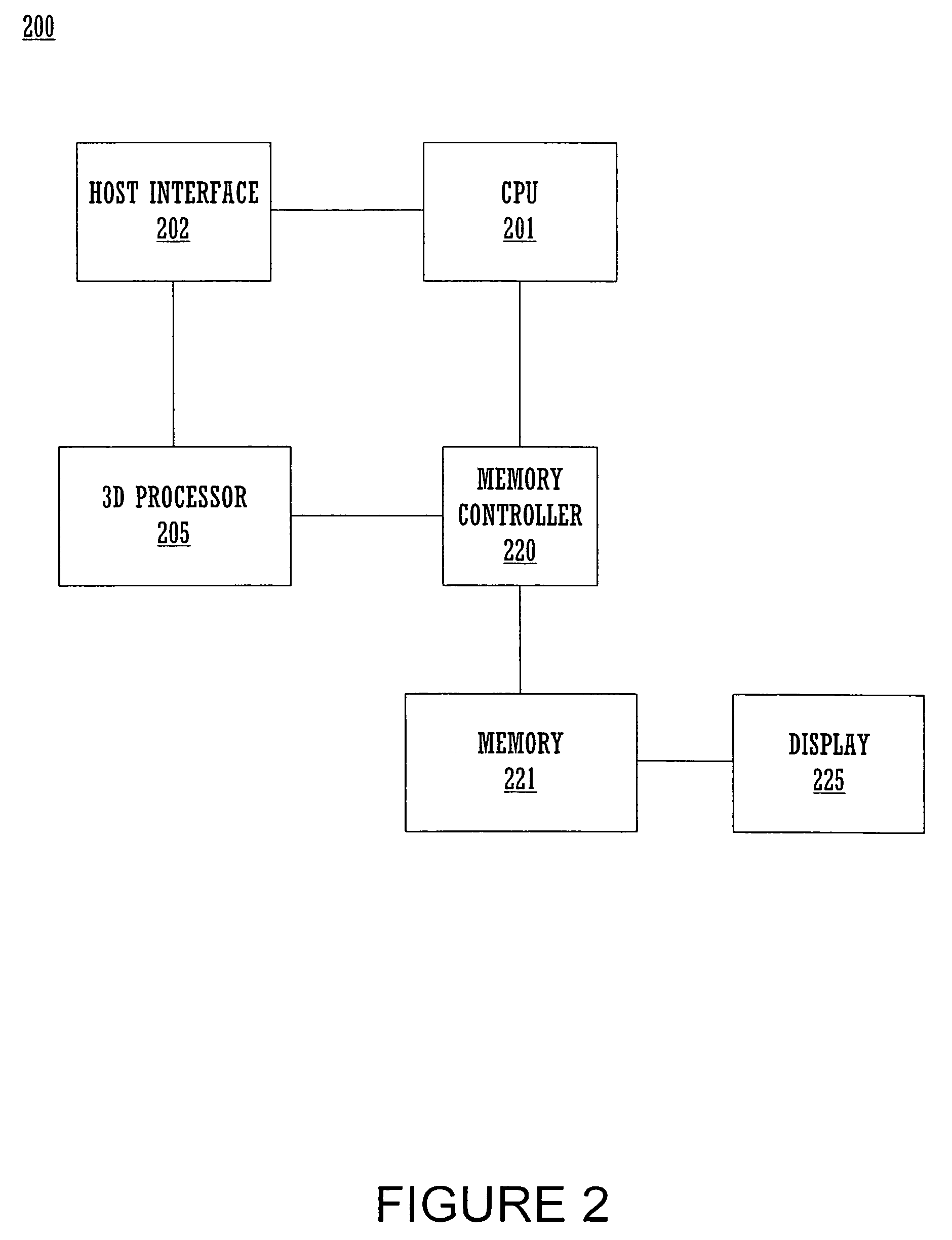
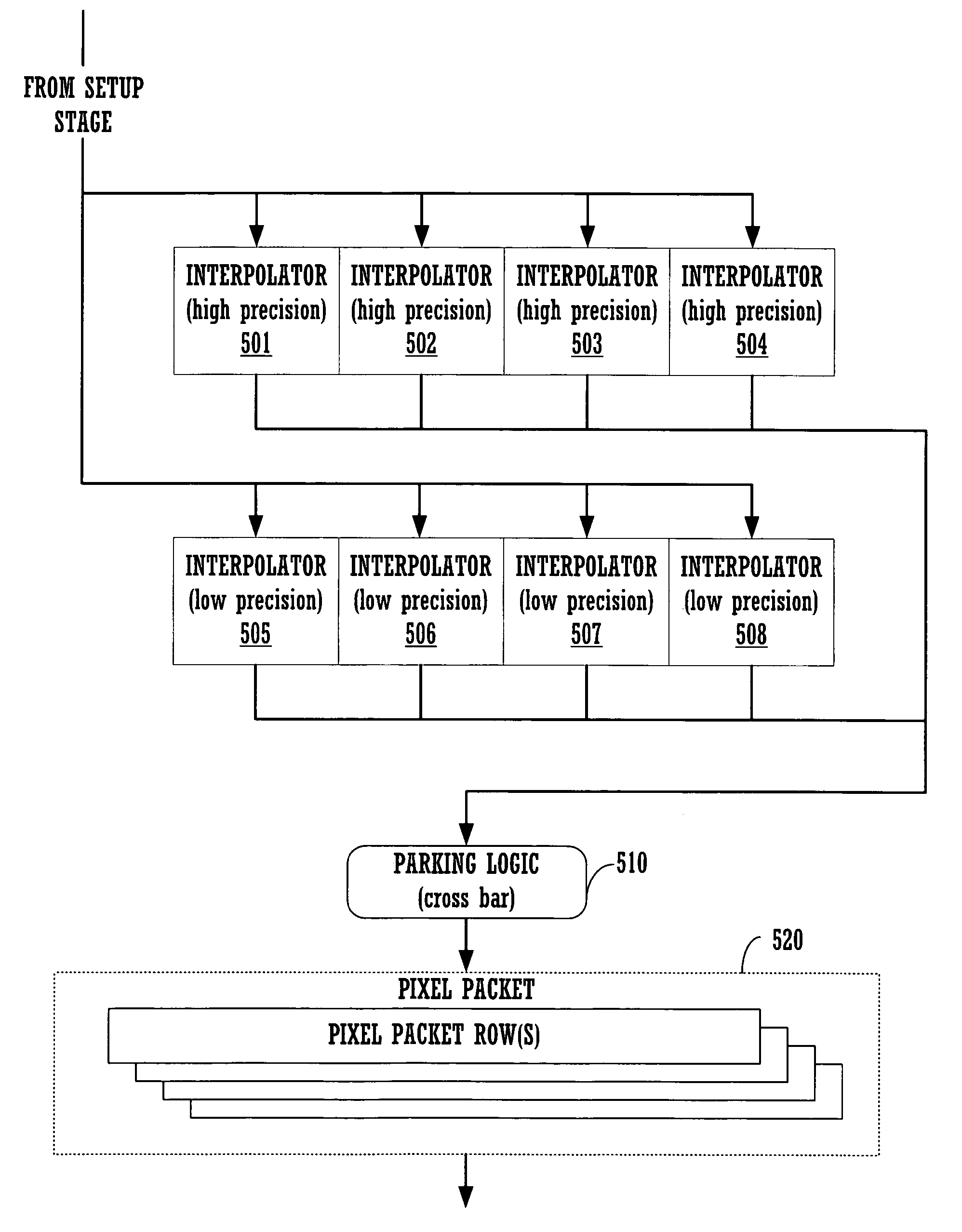
Method and system for implementing multiple high precision and low precision interpolators for a graphics pipeline
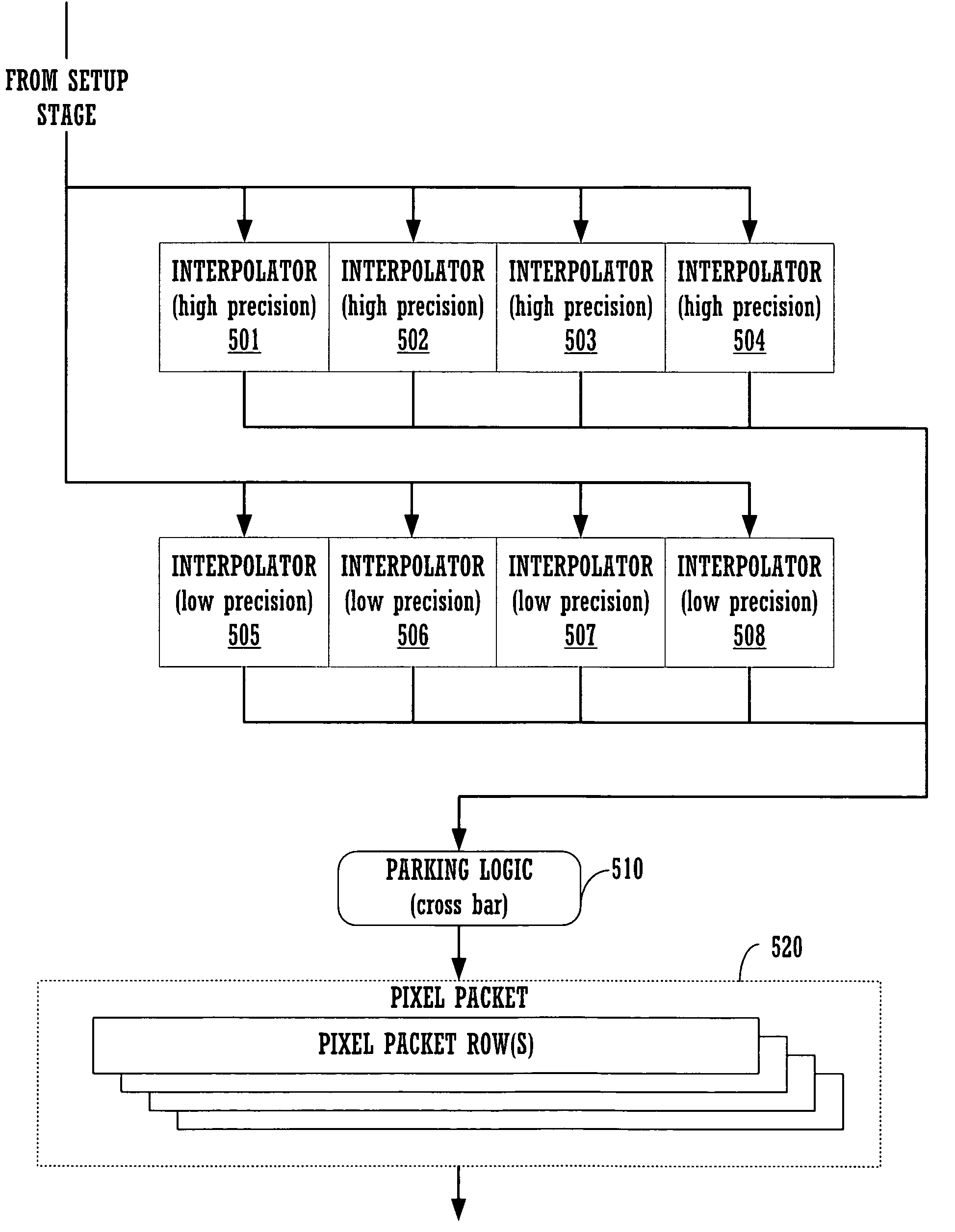
ActiveUS20060268005A1Reduce total powerMeet cutting requirementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsFilling planer surface with attributesComputational scienceGraphics
A rasterizer stage configured to implement multiple interpolators for graphics pipeline. The rasterizer stage includes a plurality of simultaneously operable low precision interpolators for computing a first set of pixel parameters for pixels of a geometric primitive and a plurality of simultaneously operable high precision interpolators for computing a second set of pixel parameters for pixels of the geometric primitive. The rasterizer stage also includes an output mechanism coupled to the interpolators for routing computed pixel parameters into a memory array. Parameters may be programmably assigned to the interpolators and the results thereof may be programmably assigned to portions of a pixel packet.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
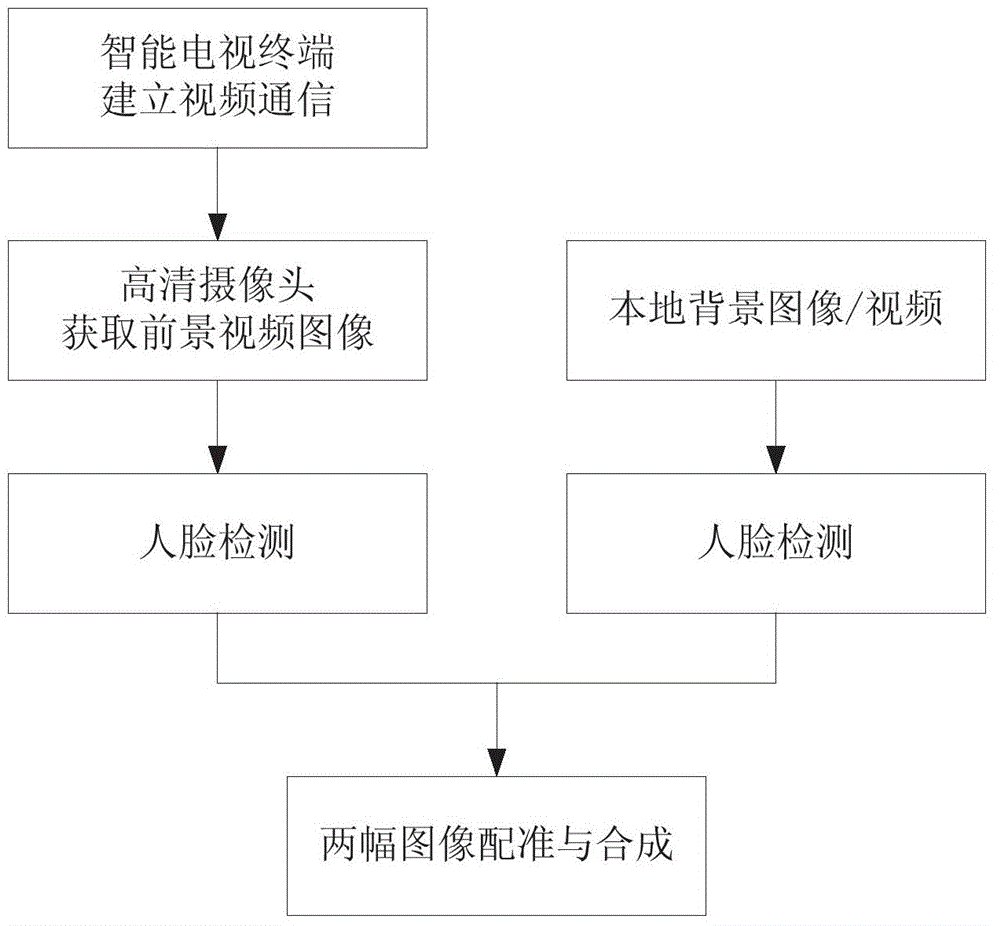
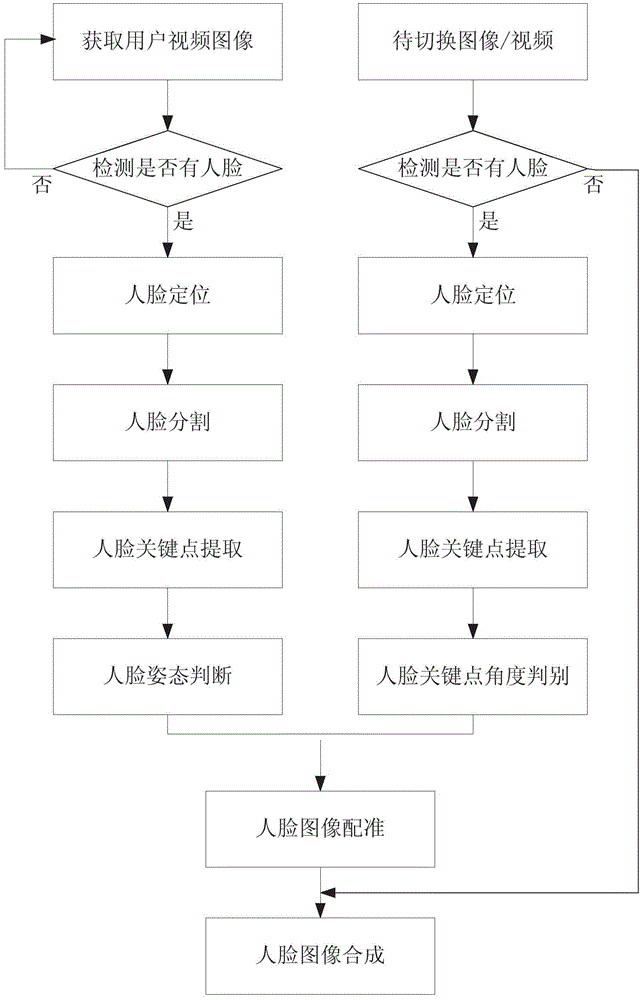
Fully-automatic face seamless synthesis-based video synthesis method
ActiveCN103607554AEasy to synthesizeSolve the lack of real-time performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionTwo-way working systemsFace detectionMinimum bounding rectangle
The invention provides a fully-automatic face seamless synthesis-based video synthesis method. With the fully-automatic face seamless synthesis-based video synthesis method adopted, insufficient real-time property in high-definition video processing of a face detection algorithm in the prior art can be solved. The fully-automatic face seamless synthesis-based video synthesis method of the invention comprises the following steps that: a video communication application provided by an intelligent television terminal is utilized to perform video connection; an image or video file which is locally arranged or arranged in a cloud server is adopted as a background (BG) to be synthesized; face detection is respectively performed on data foreground (FG) and background (BG) data which are acquired by a camera through using the face detection algorithm, and geometric transformation coefficients are calculated through face internal key point positioning and facial contour lines or a face minimum bonding rectangle frame; and accurate registration from the foreground (FG) to the background (BG), and face region data synthesis can be accomplished. With the fully-automatic face seamless synthesis-based video synthesis method of the invention adopted, the face image of a user can be conveniently synthesized into any existing images or videos in the process of video communication, and therefore, a sense of science and technology and interestingness can be added in the video communication, and fully-automatic seamless face synthesis of non-specific people can be realized.
Owner:易视星空科技无锡有限公司
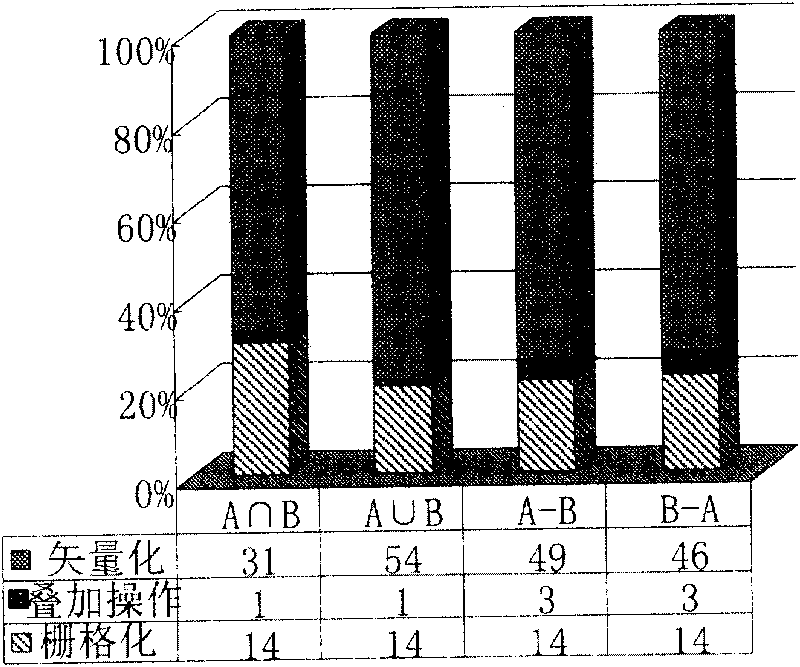
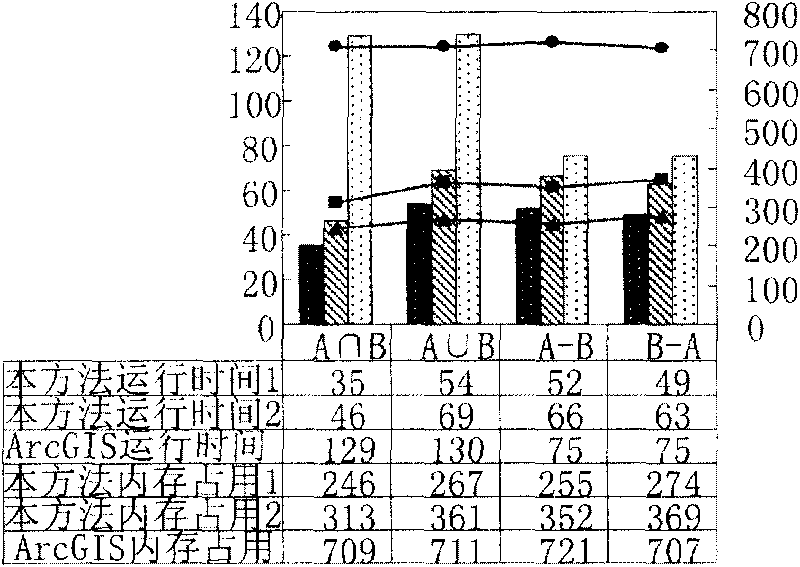
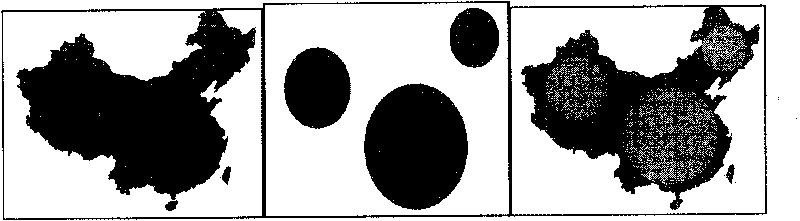
Spatial overlap analysis method and system used in geographic information system
ActiveCN101751449ABig advantageGood value for moneySpecial data processing applicationsAnalysis methodRun-length encoding
The invention discloses spatial overlap analysis method and system used in a geographic information system (GIS). The method comprises the following steps of: converting vector data input to layers in the GIS into raster data, and representing by adopting run coding; executing overlap operation on the raster data represented by adopting run coding; and converting the overlapped raster data into the vector data to obtain overlapped layers. The invention can avoid the disadvantages of computation geometric algorithms and increases the overlap efficiency by utilizing the advantages of a raster algorithm.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
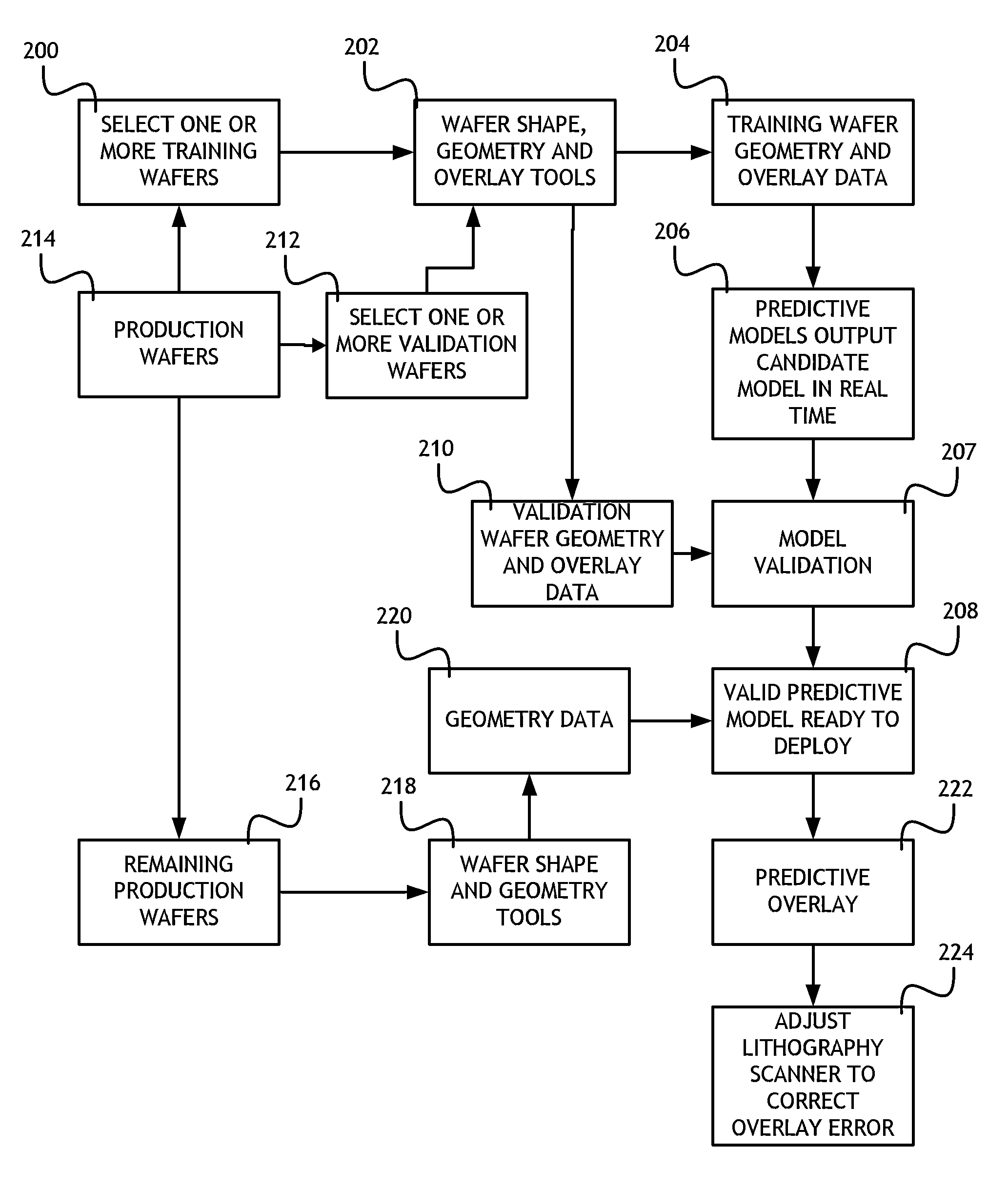
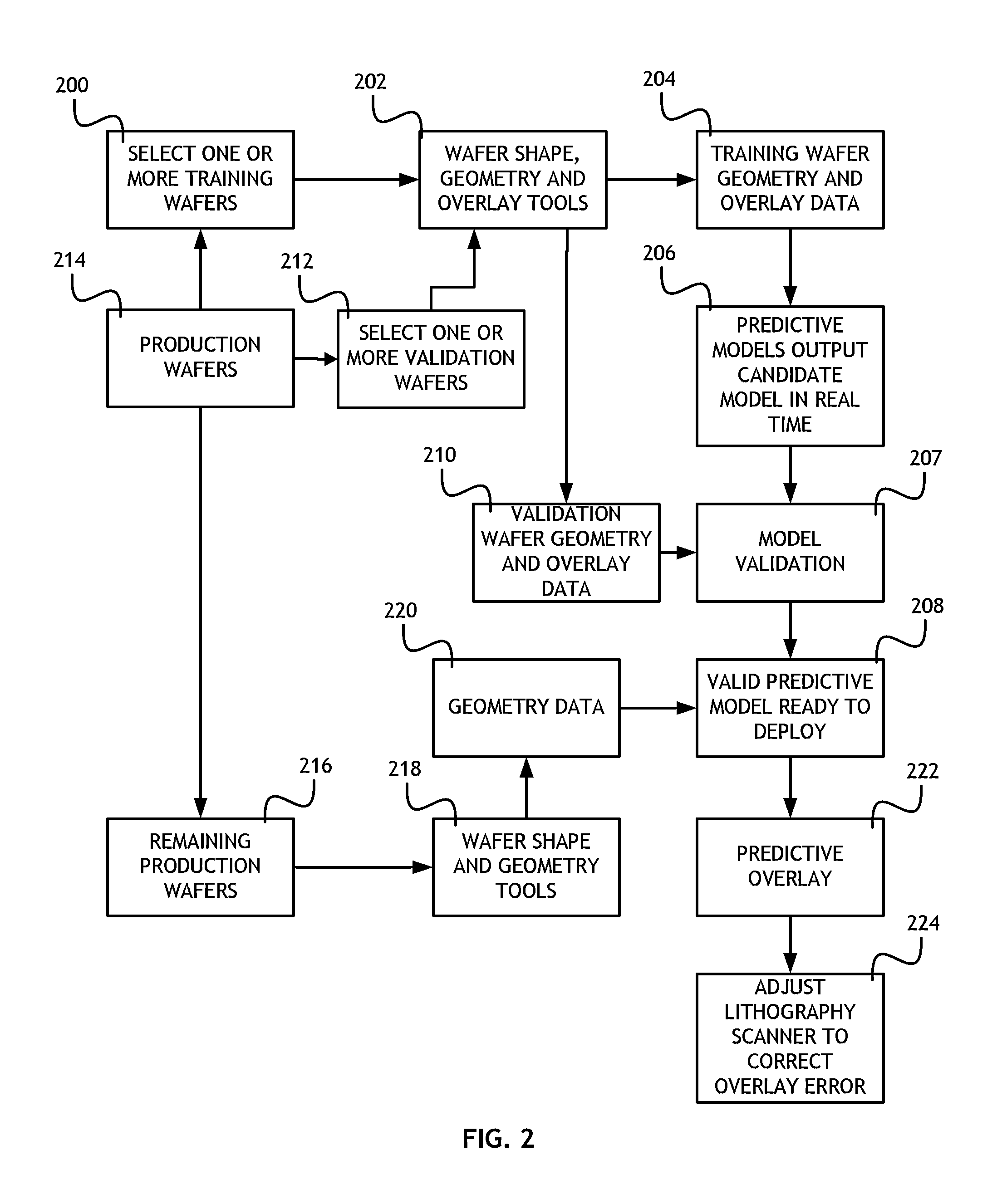
Statistical overlay error prediction for feed forward and feedback correction of overlay errors, root cause analysis and process control
ActiveUS9087176B1Accurate predictionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCAD circuit designRelevant informationLithographic artist
A method to collect data and train, validate and deploy statistical models to predict overlay errors using patterned wafer geometry data and other relevant information includes selecting a training wafer set, measuring at multiple lithography steps and calculating geometry differences, applying a plurality of predictive models to the training wafer geometry differences and comparing predicted overlay to the measured overlay on the training wafer set. The most accurate predictive model is identified and the results fed-forward to the lithography scanner tool which can correct for these effects and reduce overlay errors during the wafer scan-and-expose processes.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Computational geometry using control geometry having at least two dimensions
InactiveUS7236167B2Computationally efficientImprove computing efficiencyData processing applications3D-image renderingComputer Aided DesignAnimation
A method and system for computer aided design (CAD) is disclosed for designing geometric objects. The present invention interpolates and / or blends between such geometric objects sufficiently fast so that real time deformation of such objects occurs while deformation data is being input. Thus, a user designing with the present invention obtains immediate feedback to input modifications without separately entering a command for performing such deformations. The present invention utilizes novel computational techniques for blending between geometric objects, wherein weighted sums of points on the geometric objects are used in deriving a new blended geometric object. The present invention is particularly useful for designing the shape of surfaces. Thus, the present invention is applicable to various design domains such as the design of, e.g., bottles, vehicles, and watercraft. Additionally, the present invention provides for efficient animation via repeatedly modifying surfaces of an animated object such as a representation of a face.
Owner:CAD-SENSE LLC
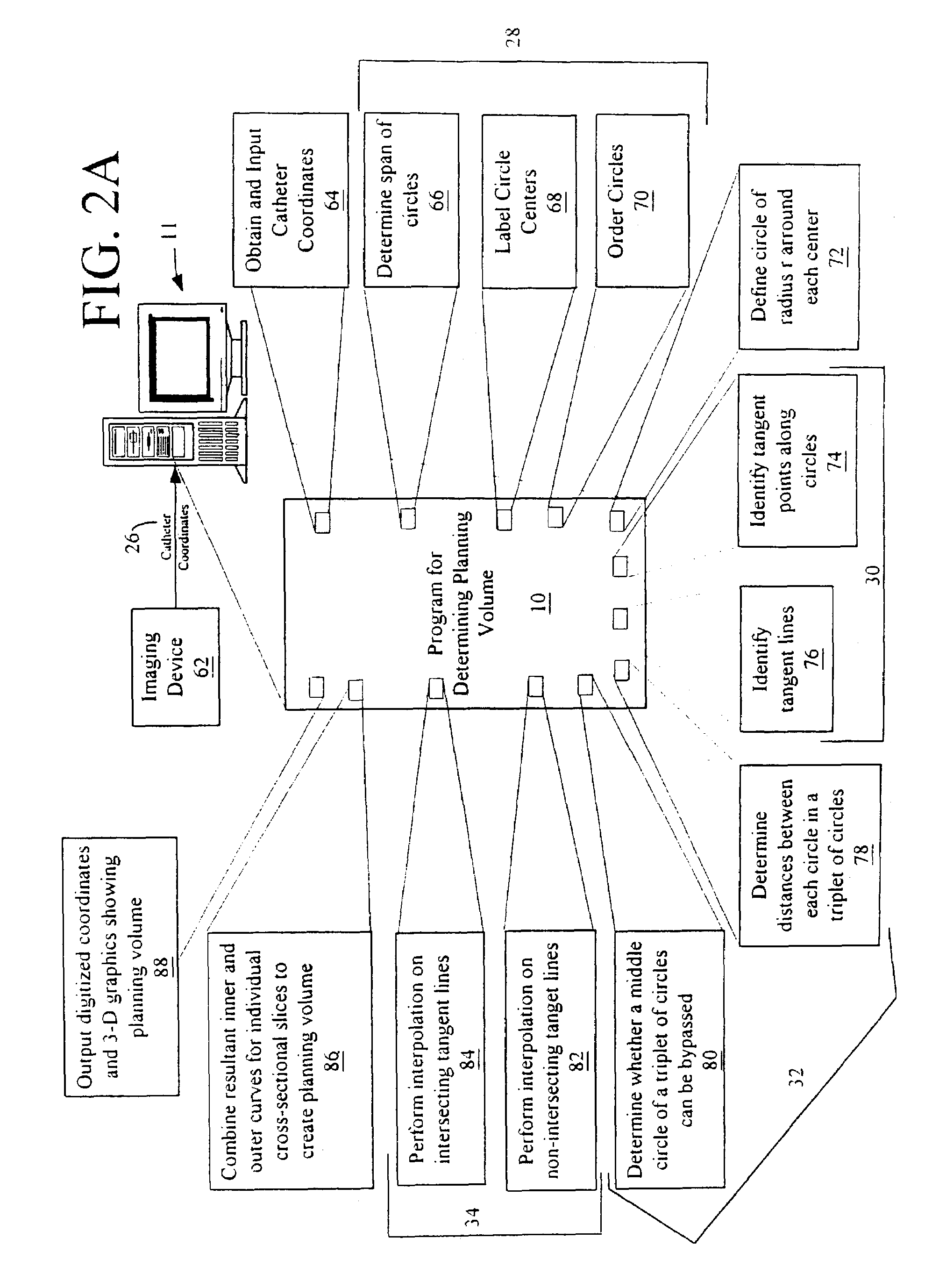
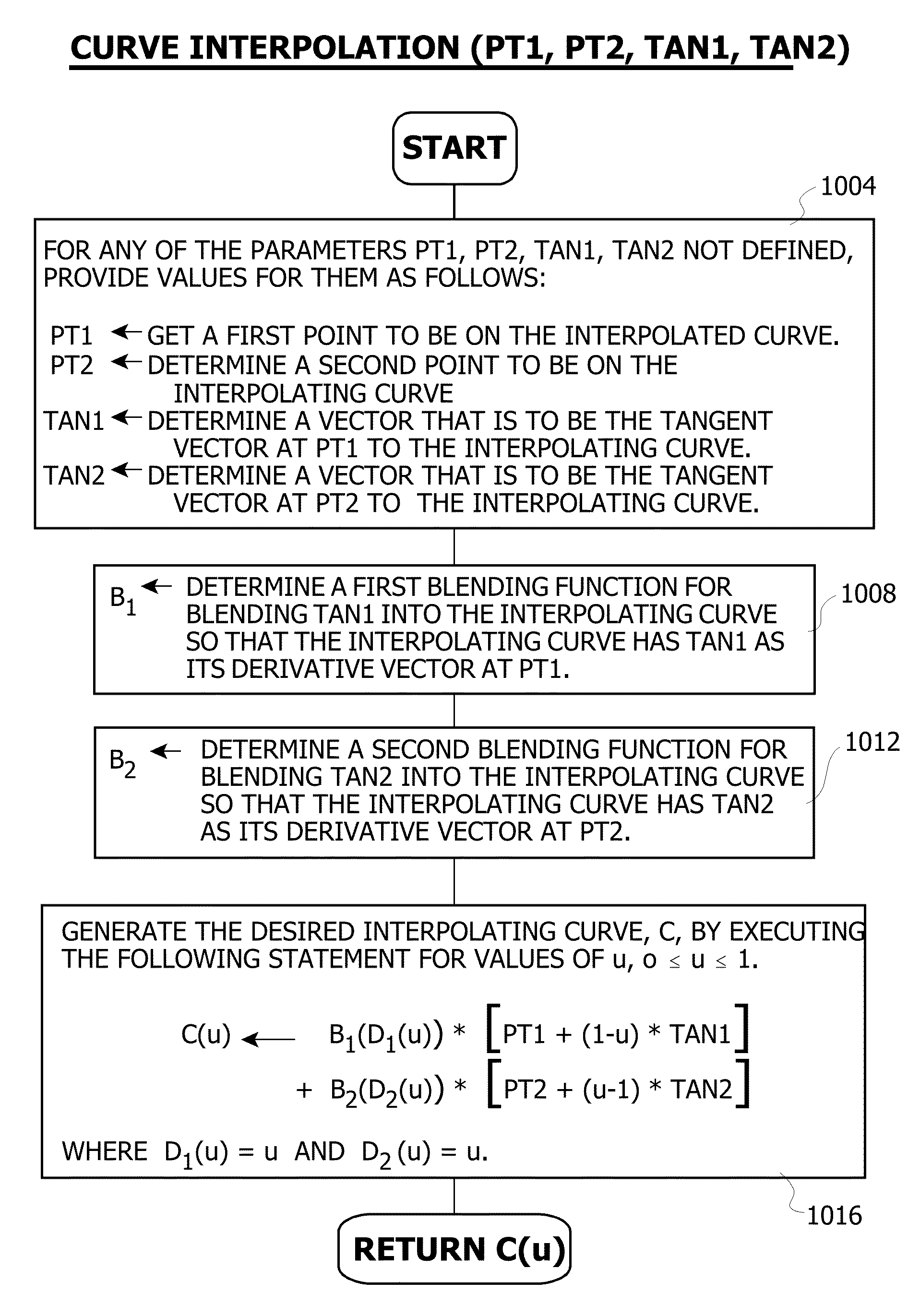
Automated planning volume contouring algorithm for adjuvant brachytherapy treatment planning in sarcoma
InactiveUS7107089B2Improve efficiencyEffective treatmentMechanical area measurementsDigital computer detailsAdjuvantBrachytherapy
A mathematical contouring algorithm that automatically determines the planning volume of a sarcoma prior to designing a brachytherapy treatment plan. The algorithm, utilizing computational geometry, numerical interpolation and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques, returns the planning volume in digitized and graphical forms in a matter of minutes. Such an automatic procedure reduces labor time and provides a consistent and objective method for determining planning volumes. In addition, a definitive representation of the planning volume allows for sophisticated brachytherapy treatment planning approaches to be applied when designing treatment plans, so as to maximize local tumor control and minimize normal tissue complications.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
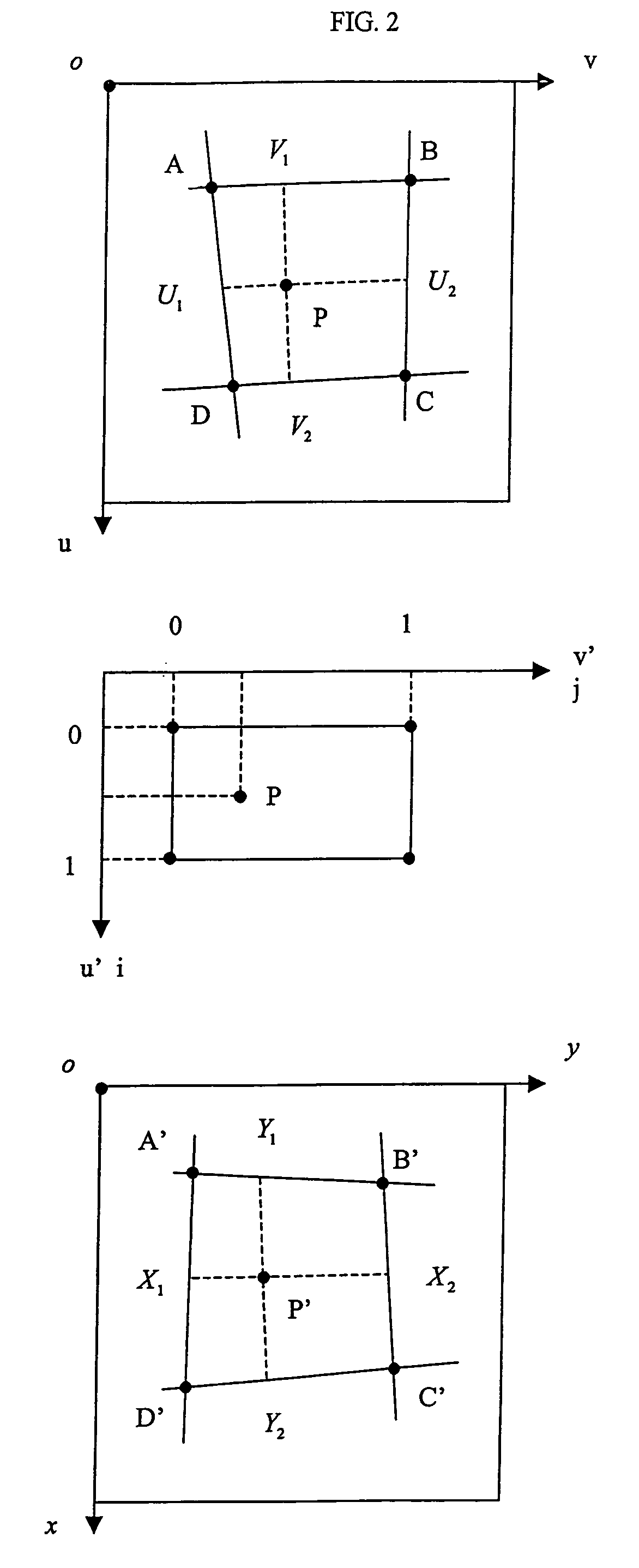
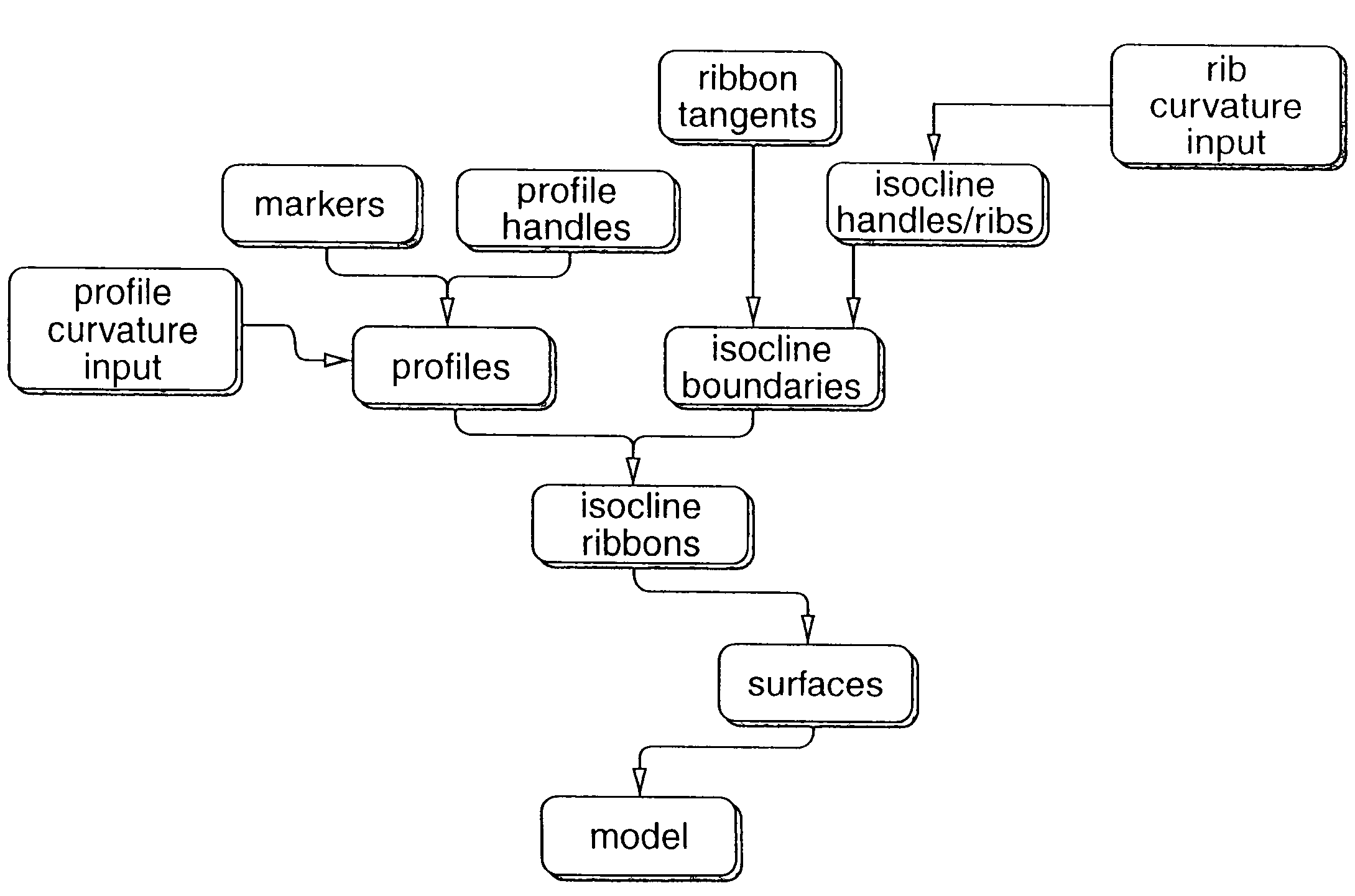
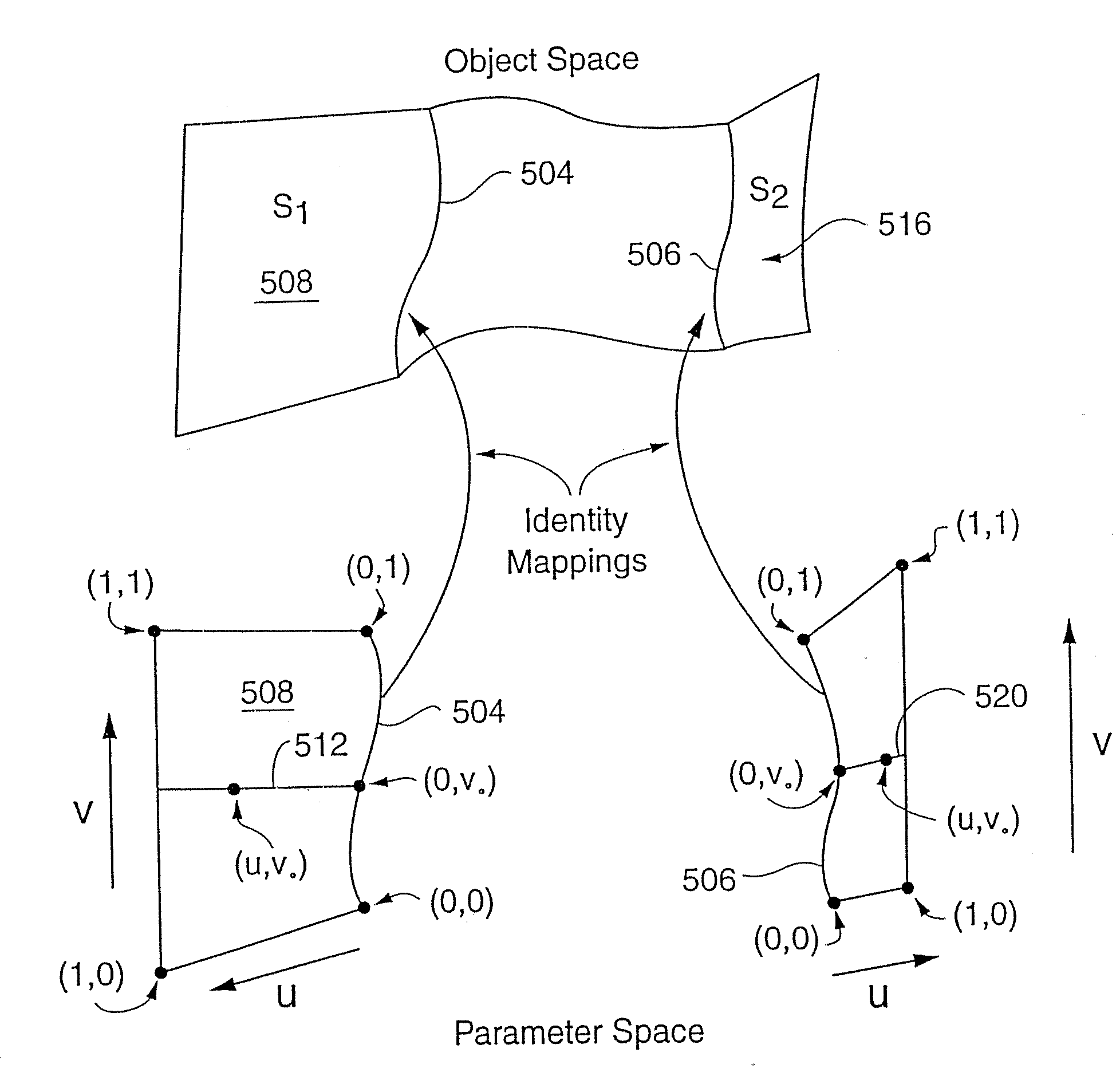
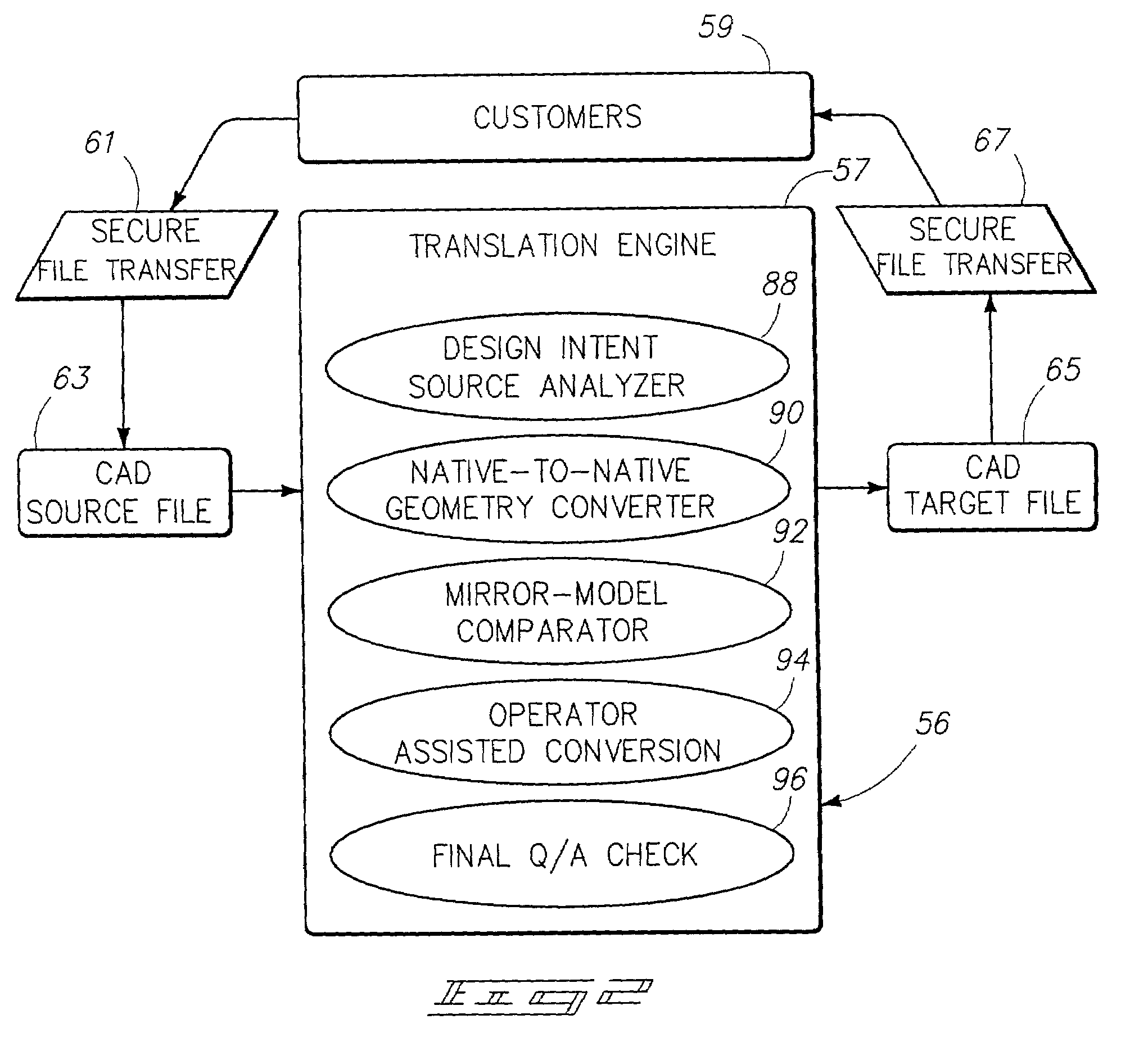
Surface patch techniques for computational geometry
InactiveUS8836701B1Fine surfaceImproved visualGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsComputer Aided DesignMorphing
A method and system for computer aided design (CAD) is disclosed for designing geometric objects, wherein interpolation and / or blending between such objects is performed while deformation data is being input. Thus, a designer obtains immediate feedback to input modifications without separately entering a command(s) for performing such deformations. A novel N-sided surface generation technique is also disclosed herein to efficiently and accurately convert surfaces of high polynomial degree into a collection of lower degree surfaces. E.g., the N-sided surface generation technique disclosed herein subdivides parameter space objects (e.g., polygons) of seven or more sides into a collection of subpolygons, wherein each subpolygon has a reduced number of sides. More particularly, each subpolygon has 3 or 4 sides. The present disclosure is particularly useful for designing the shape of surfaces. Thus, the present disclosure is applicable to various design domains such as the design of, e.g., bottles, vehicles, and watercraft. Additionally, the present disclosure provides for efficient animation via repeatedly modifying surfaces of an animated object such as a representation of a face.
Owner:CAD-SENSE LLC
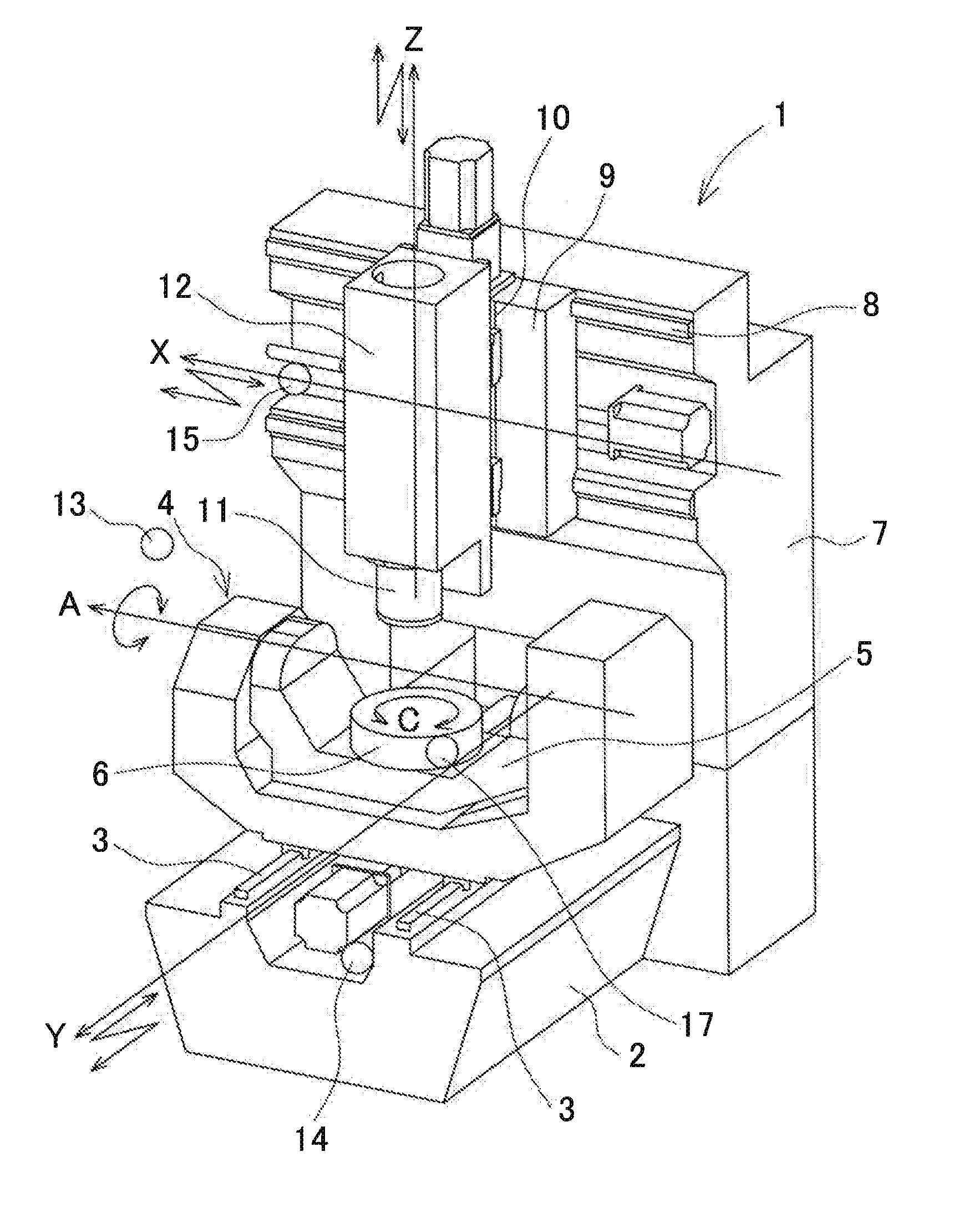
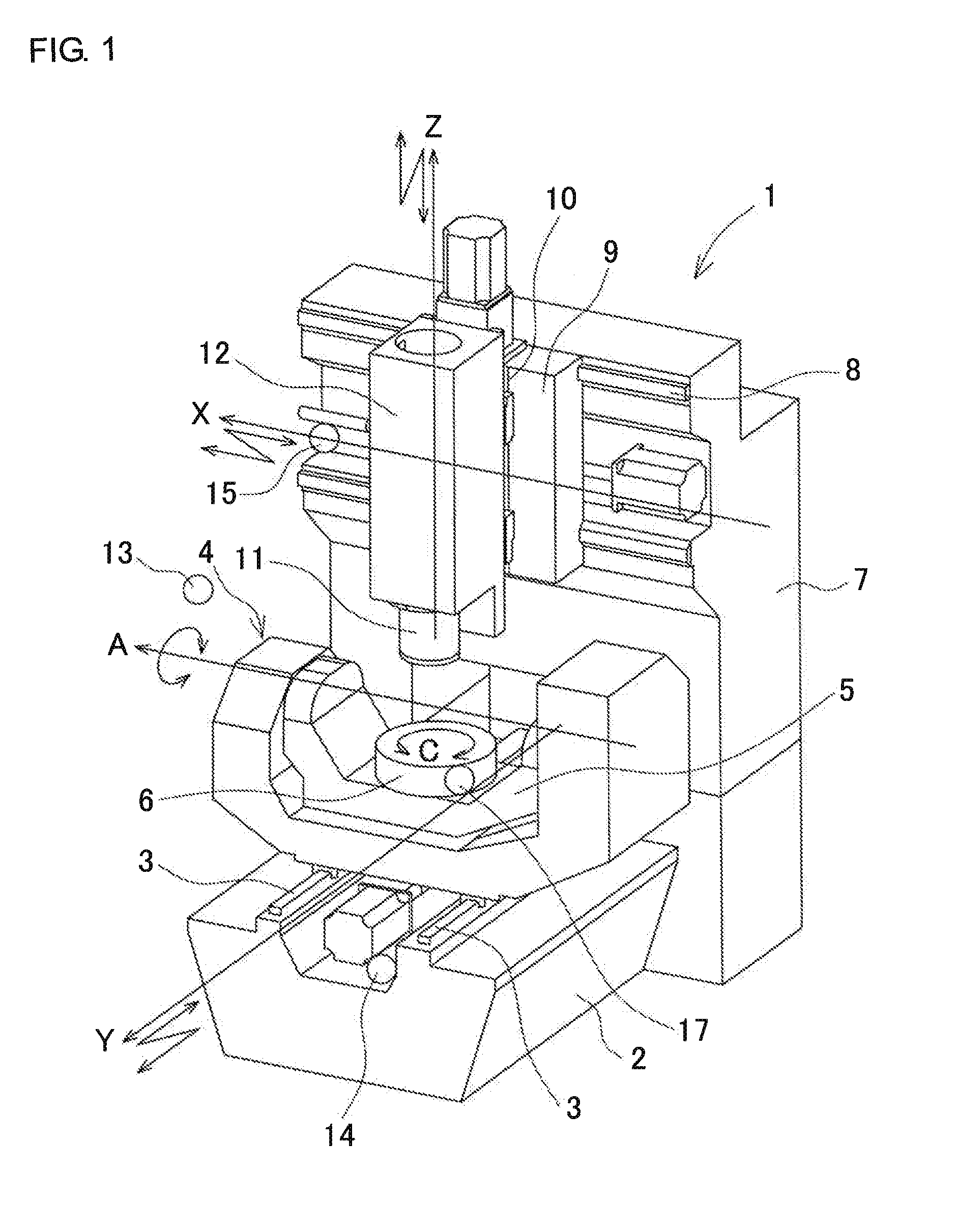
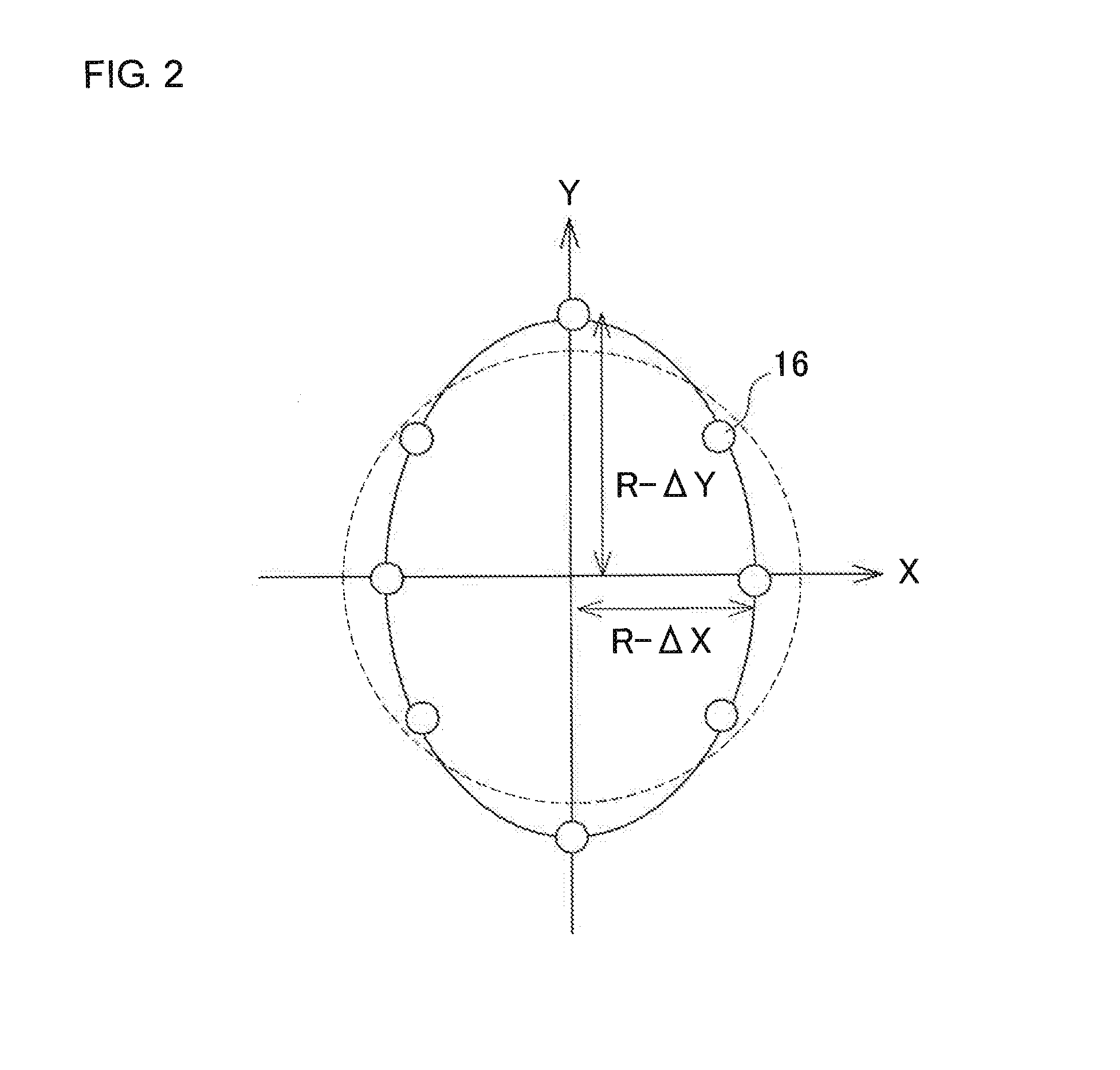
Geometric error identification method of multi-axis machine tool and multi-axis machine tool
ActiveUS20150160049A1High precision machiningHigh precisionProgramme controlMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsGeometric errorEllipse
A geometric error identification method of multi-axis machine tool includes a measuring step of indexing a position of a target ball mounted on one of a main spindle and a table into a plurality of angles around an rotation axis, and measuring the position of the target ball at respective indexed positions by using a touch probe mounted on the other one of the main spindle and the table, a geometric error calculation step of calculating a geometric error from the measured position of the target ball, an ellipse-expression calculation step of calculating an ellipse approximate expression by an arc trajectory measured by operating the rotation axis, and an error correcting step of calculating and correcting a scaling error of translation axes from the calculated ellipse approximate expression.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
Target recognition method of unmanned aerial vehicle based on minimum circle-cover matching
InactiveCN101567046ASolve the problem of object recognitionHigh speedGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionContour matchingInformation repository
The invention relates to a target recognition method of an unmanned aerial vehicle based on minimum circle-cover matching. The target recognition method comprises the following five steps of: step 1, carrying out edge detection and communicated domain calibration to a target area and dividing the target area into a plurality of areas to be matched; step 2, creating a target model shape characteristic information base; step 3, carrying out minimum circle-cover detection to all the targets to be detected in the target area, and simultaneously recording the diameter orientation of the minimum circle-cover; step 4, matching the diameters of a target template and an outline to be matched so that the subsequent step can be implemented within a certain orientation; and step 5, matching the target template with the outline to be matched, carrying out the matching orderly to a plurality of communicated domain targets of the target area, and finally comparing and obtaining a sum-of-squared difference (SSD) measure of a minimum pixel gray difference, wherein the outline matching corresponding to the sum-of-squared difference (SSD) measure is the required result. The target recognition method utilizes the computational geometry technology, the optimization theory, the computer vision technology and other technologies, realizes the multi-target recognition of the unmanned aerial vehicle, greatly improves the speed and accuracy for recognizing the targets and has great practical value and application prospect.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Computational Geometry Using Control Geometry Having At Least Two Dimensions
InactiveUS20070176923A1Computationally efficientImprove computing efficiencyData processing applicationsDrawing from basic elementsComputer Aided DesignAnimation
A method and system for computer aided design (CAD) is disclosed for designing geometric objects. The present invention interpolates and / or blends between such geometric objects sufficiently fast so that real time deformation of such objects occurs while deformation data is being input. Thus, a user designing with the present invention obtains immediate feedback to input modifications without separately entering a command for performing such deformations. The present invention utilizes novel computational techniques for blending between geometric objects, wherein weighted sums of points on the geometric objects are used in deriving a new blended geometric object. The present invention is particularly useful for designing the shape of surfaces. Thus, the present invention is applicable to various design domains such as the design of, e.g., bottles, vehicles, and watercraft. Additionally, the present invention provides for efficient animation via repeatedly modifying surfaces of an animated object such as a representation of a face.
Owner:CAD-SENSE LLC
Systems and methods for voxel warping
InactiveUS6867770B2Increase rangeEasy maintenanceCathode-ray tube indicators3D modellingDirect computationVoxel
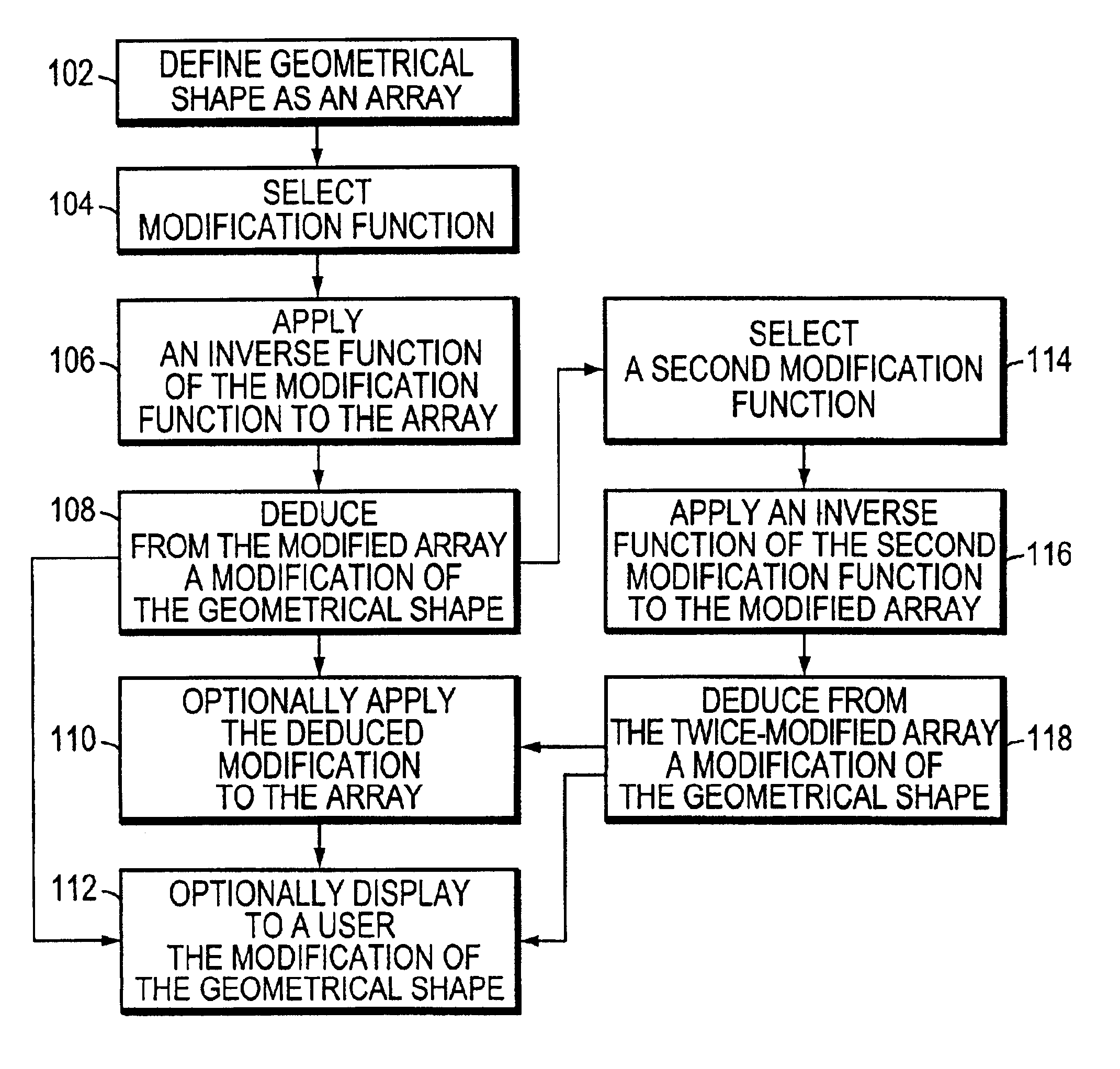
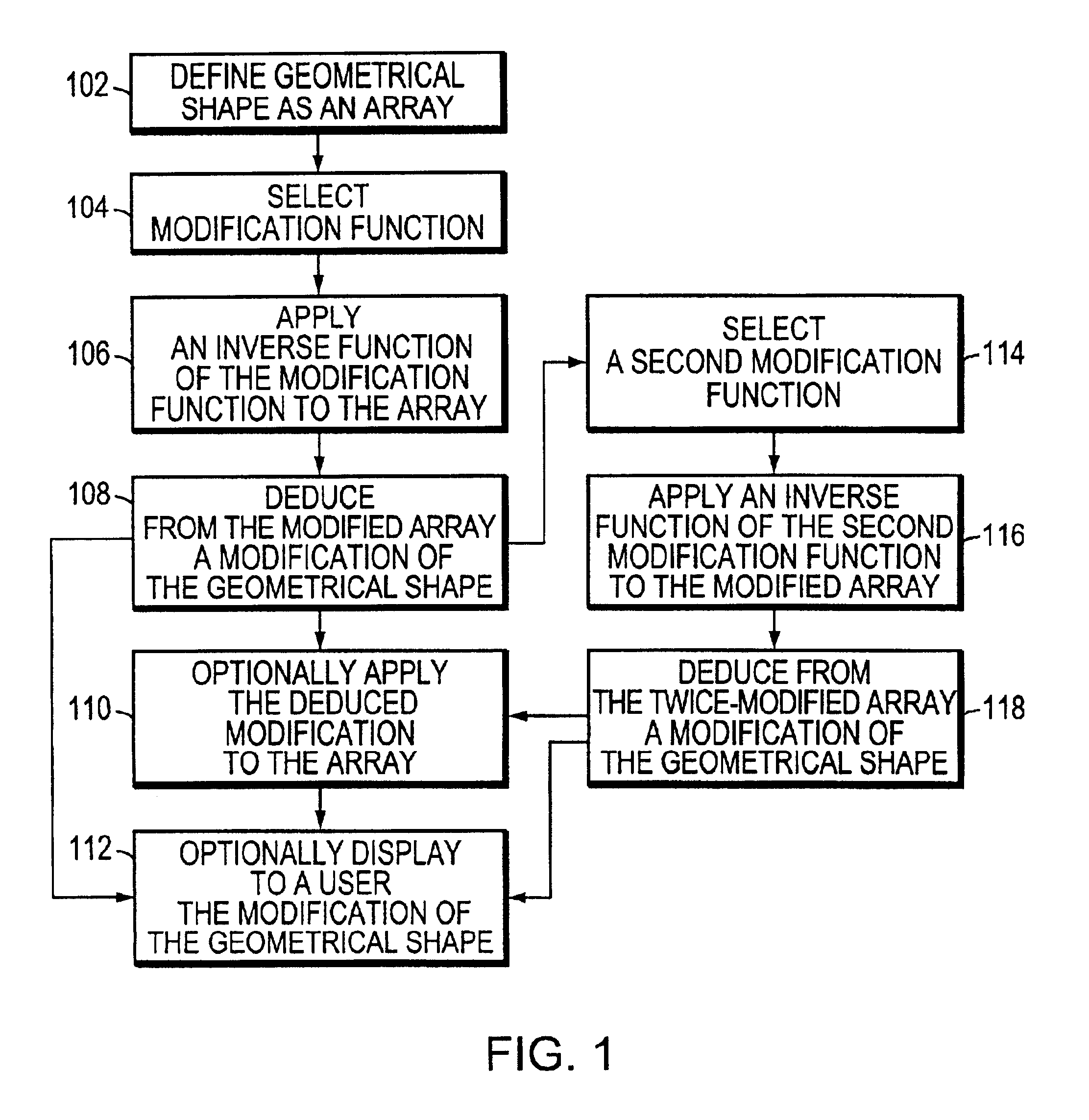
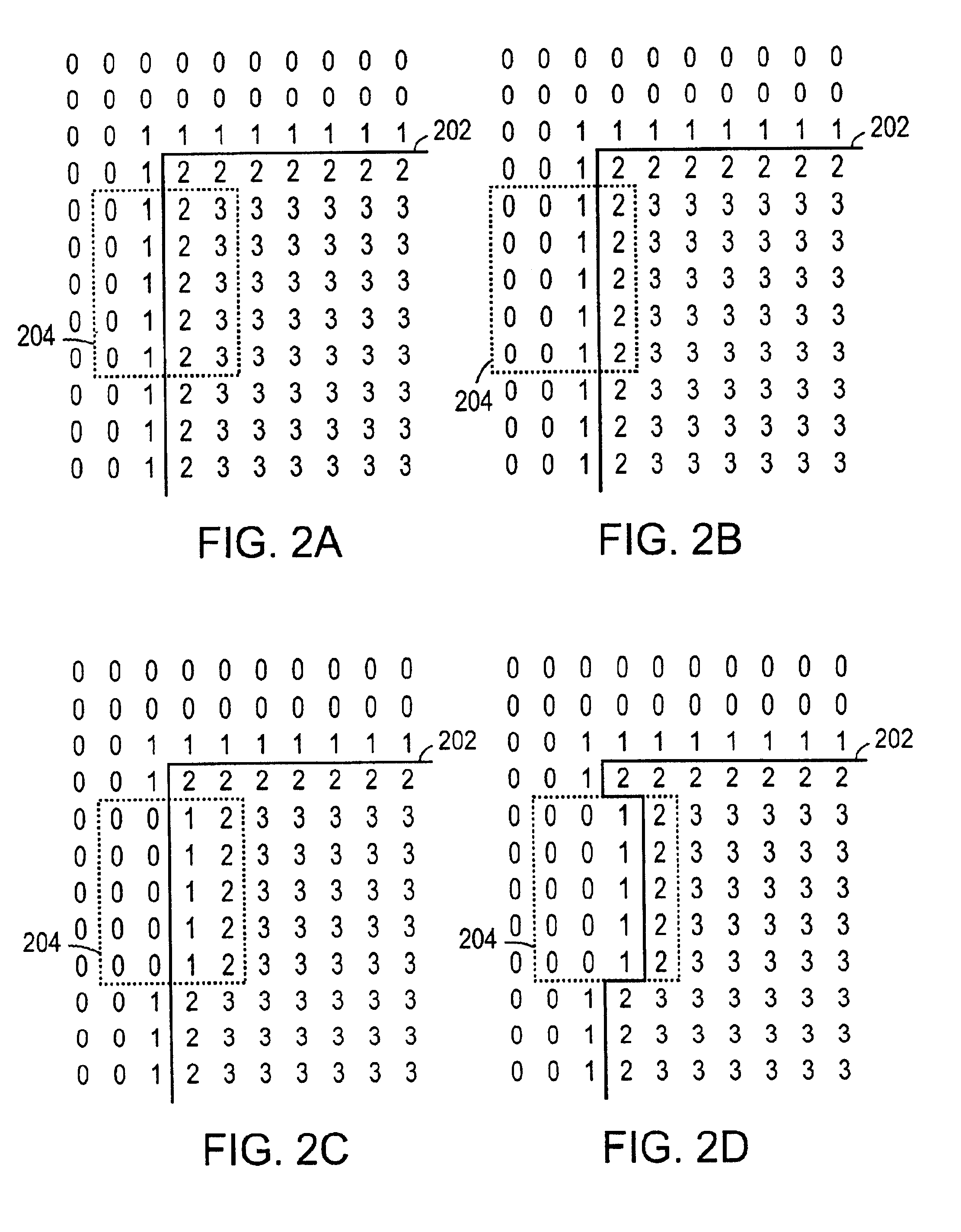
Systems and methods for calculating a modification of a geometrical shape by applying an inverse modification function to an array representing the shape. An array representing the geometrical shape is defined on a multi-dimensional space. A modification function is used to modify the geometrical shape. A user or a programmed computer can select the modification function. The computer applies an inverse of the modification function to the array. The computer deduces a change in the geometrical shape from the modified array. An advantage of the system and method is the ability to compute shape changes in certain situations where a direct computation is cumbersome or otherwise inconvenient.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Method for calculating extinction coefficients of three-dimensional forest canopy by using laser-point cloud
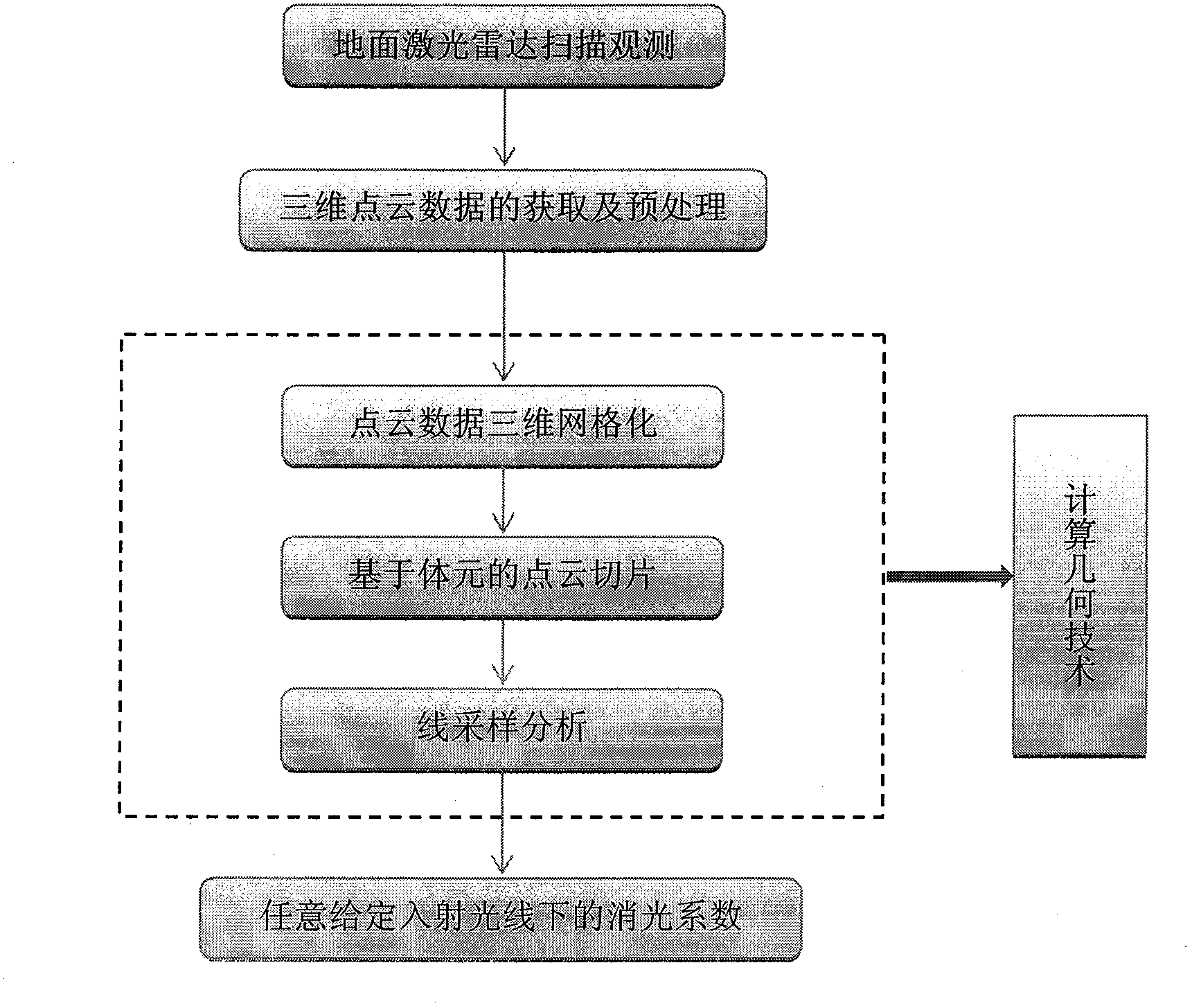
InactiveCN102914501AImprove estimation accuracyImprove estimation efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansVoxelExtinction
The invention provides a method for calculating the extinction coefficients of a three-dimensional forest canopy under any given incident ray by using a geometric algorithm, belonging to the research field of a method of acquiring the structural parameters of the forest canopy. The method for calculating the extinction coefficients of the three-dimensional forest canopy by using the geometric algorithm comprises the following steps: acquiring and preprocessing the three-dimensional laser-point cloud data of a plant canopy; carrying out three-dimensional gridding on the point cloud data; carrying out point cloud slice arithmetic based on a voxel data structure; carrying out linear sampling analysis on the point cloud slices; calculating an average projection coefficient of a kth layer of slices; and calculating the extinction coefficient of any given incident ray in each layer of slices and the extinction coefficient of whole canopy. Compared with the traditional observing way, the invention has the characteristics of being small in working amount, and free from the contact observation and the damage of the canopy structure and radiation, and has objectiveness, high efficiency and precision; a method of extracting the three-dimensional structures and biological and physical diversity information from the laser radar data is developed to characterize the horizontal and vertical distribution change rules of the leaves.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
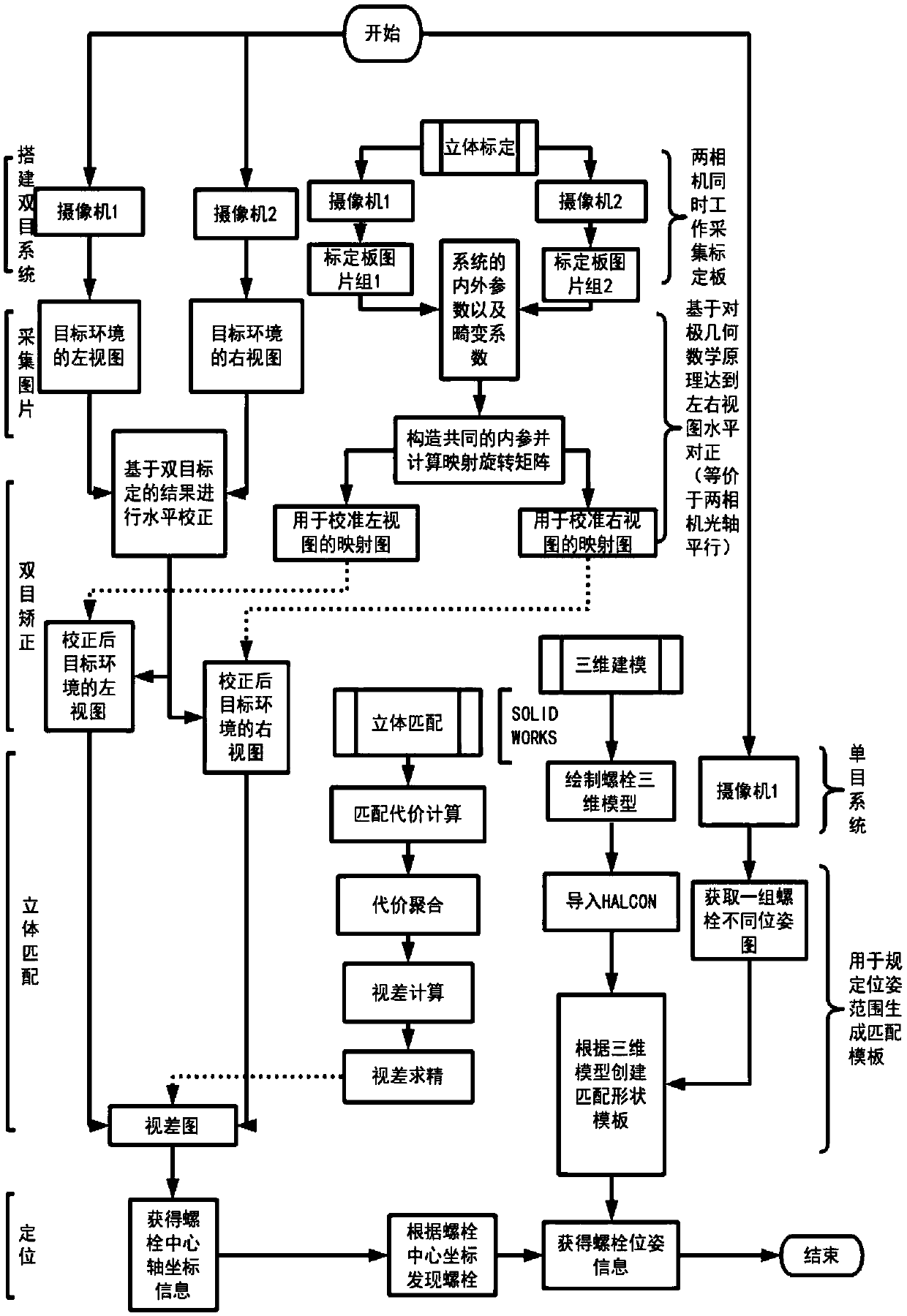
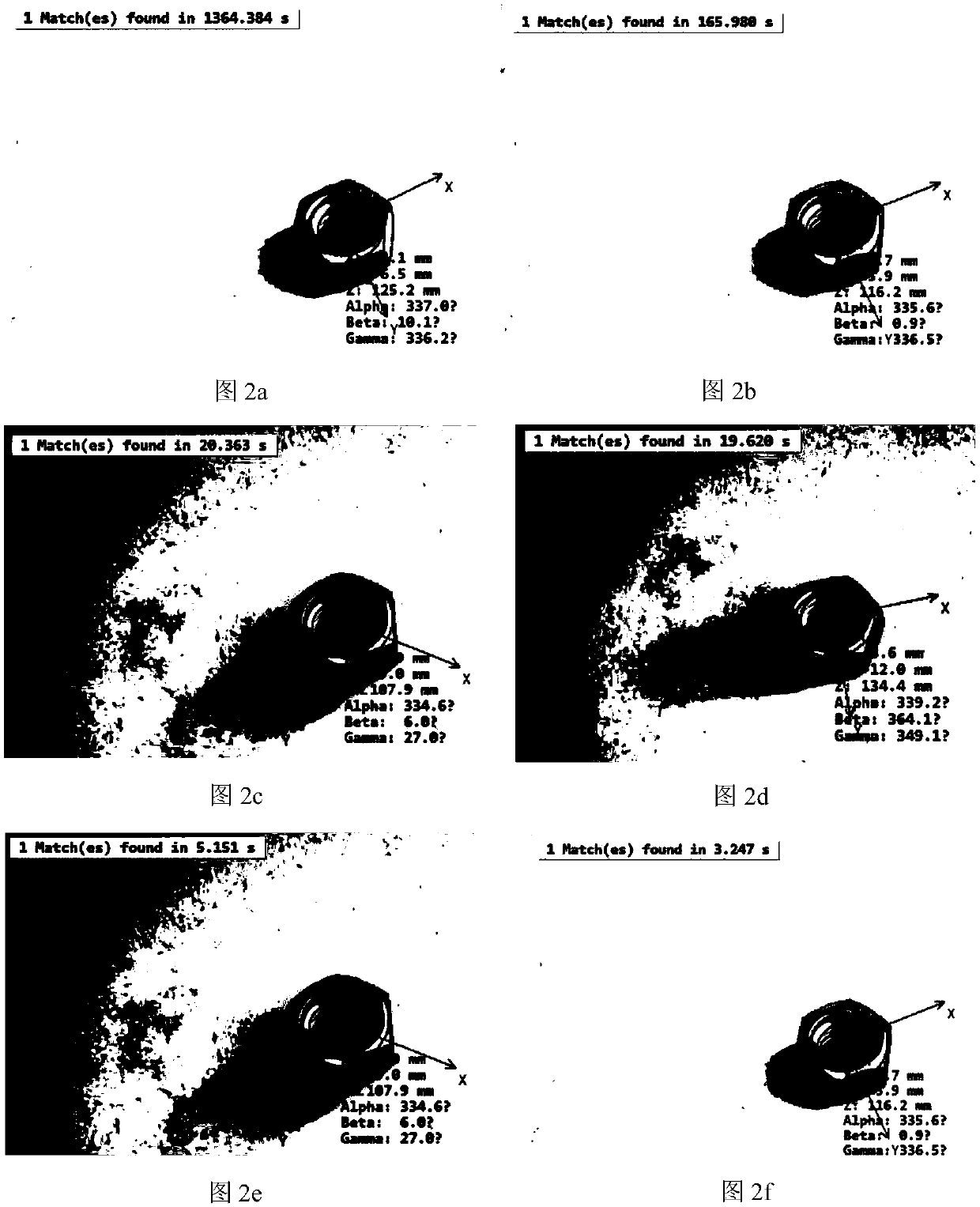
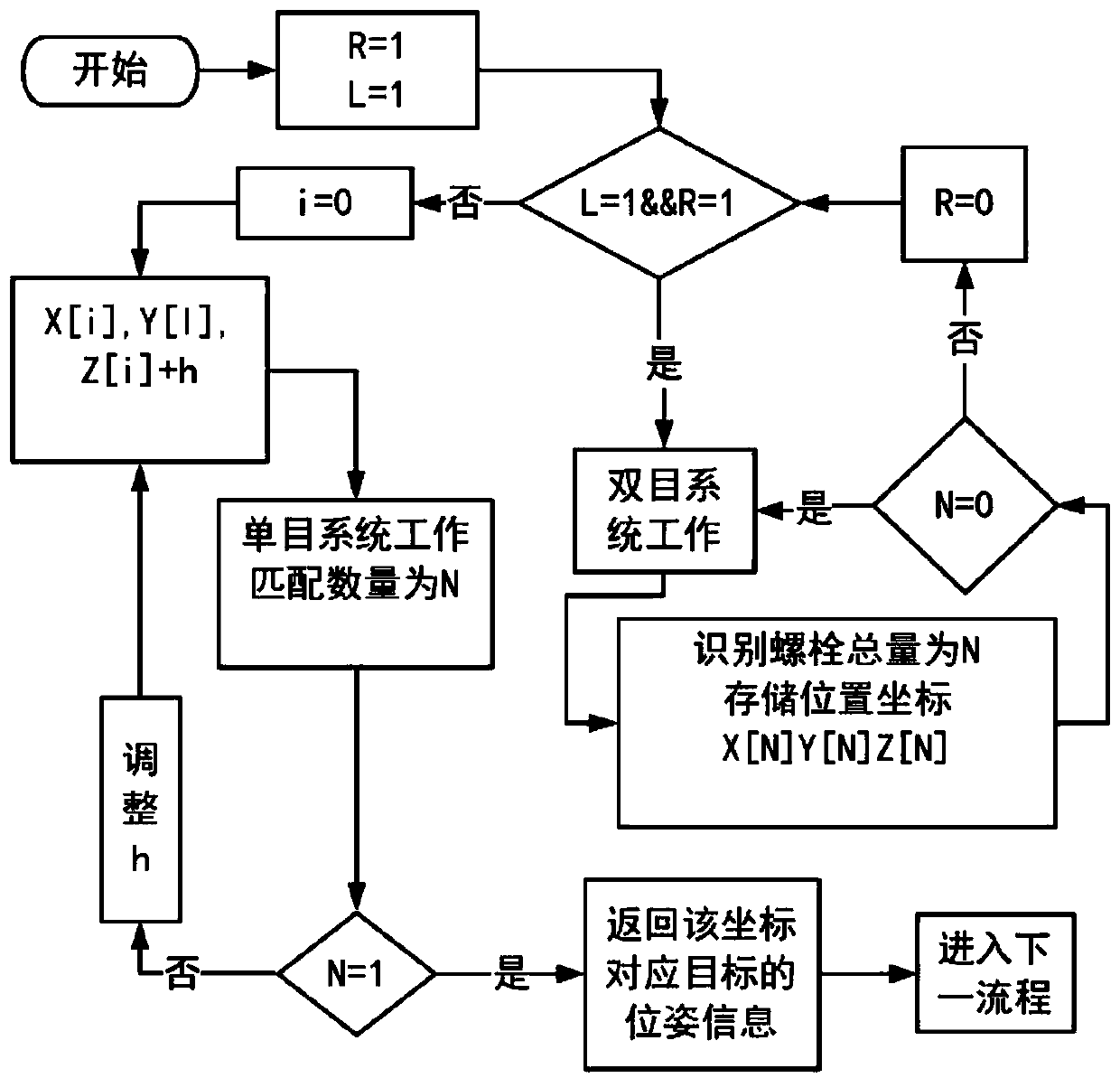
A bolt positioning and posture detection method based on monocular and binocular vision cooperation
ActiveCN109035200AAchieving identifiabilityEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisFixed positionVisual perception
The invention discloses a bolt positioning and posture detection method based on monocular and binocular vision cooperation. Firstly, a bolt image collected and processed by a binocular vision systemunder a fixed position is used to obtain an edge contour of the bolt image, and the geometrical centroid is calculated to obtain the position coordinates of the feature points in the bolt image. Wheninstalling the two industrial cameras in the binocular system, the left camera is mounted on the left robot arm which can control the movement trajectory, and the right camera is mounted on the properheight of the fixed support of the inspection robot. The left and right camera optical axes are set to be parallel and perpendicular to the baseline, and the right camera interface is closed by the control system after work, and the end of the left manipulator is controlled to move above the acquired coordinate point, at this time, the monocular vision system is operated. The invention combines the function of positioning by using depth information of the binocular system and the flexible 3d posture matching function of the monocular system, and realizes the identification and posture detection of the bolt to be detected in the obstacle environment.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Fast lighting processors
InactiveUS7075530B2Effective calculationConvenient lightingElectrical apparatusCathode-ray tube indicatorsDiffuse illuminationEffect light
The present invention provides methods, apparatus and systems for enabling real-time lighting of 3D geometric models. While these are well-suited for all processors, these are particularly useful on low power processors typically found in PDAs, cell phones, and embedded display systems. Methods+presented utilize a preprocessing scale factor and real-time shift factor to efficiently calculate diffuse lighting intensities for the bound vertices of the geometric model. An example embodiment includes scaling first digitized data of a 3D model in a floating point datatype by a scaling factor to form scaled digitized data. The scaling factor being a proper power of two. Converting said scaled digitized data into an integer datatype forming second digitized data. Enabling a transfer of said second digitized data to a display system, and facilitating lighting and shading said second format of digitized data.
Owner:IBM CORP
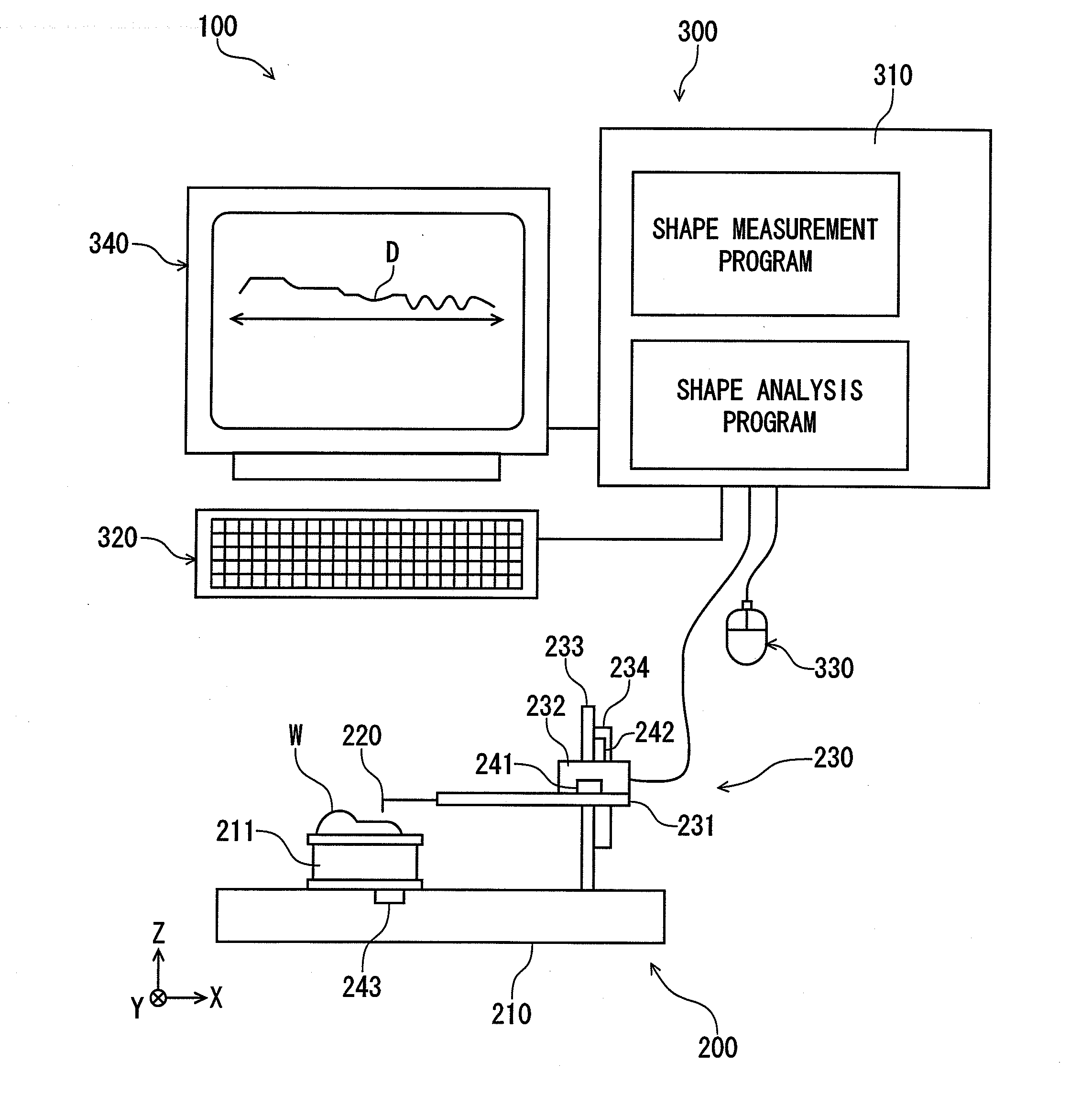
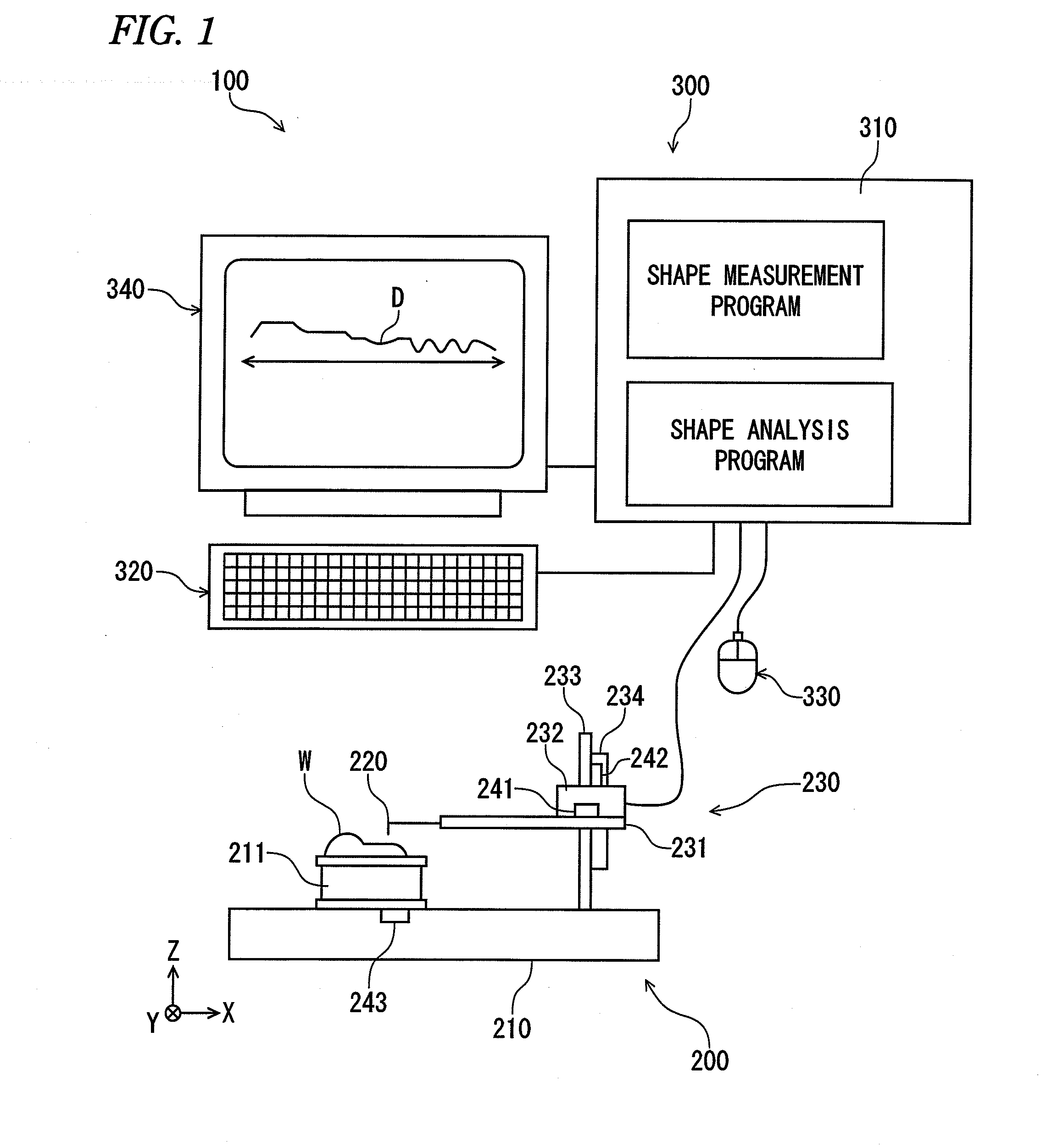
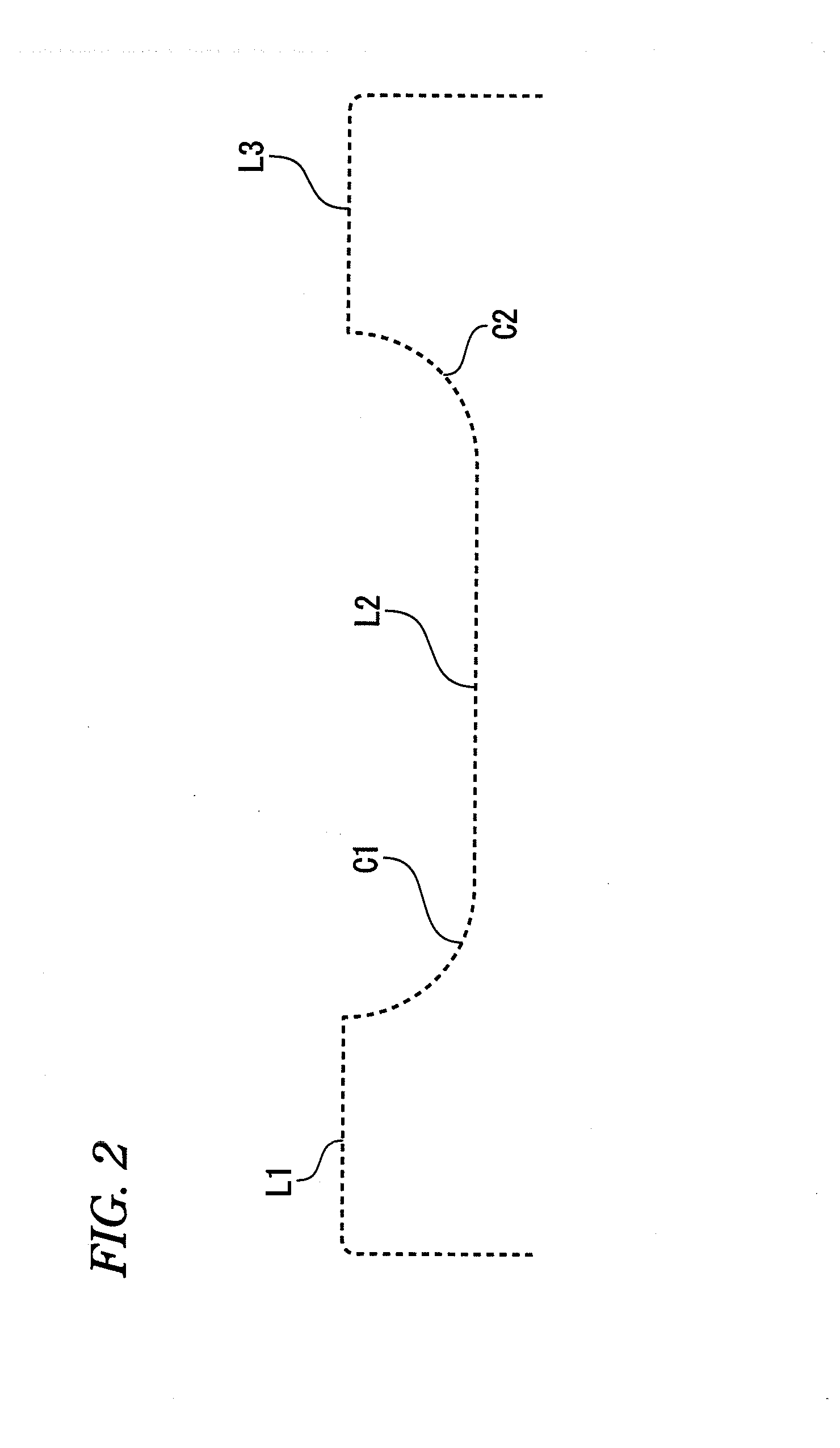
Shape analysis method and shape analysis program
ActiveUS20140005978A1Easy to operateImproving stabilizing evaluationAngles/taper measurementsFeeler-pin gaugesGeometric propertyData mining
A shape analysis method for analyzing shape data acquired by measuring a contour shape of a workpiece to be measured, includes: deciding a geometric element used in shape analysis; deciding one data point to be included in an evaluation range; applying the geometric element to an interval including the one data point; searching the widest interval for satisfying a threshold condition of a preset shape tolerance while changing a width of the interval; pinpointing two boundary points between which the interval found by the search is sandwiched; obtaining two edge points at which the two boundary points are respectively shifted by preset shift amounts; setting a range sandwiched between the edge points in the evaluation range; and targeting the shape data within the evaluation range for calculation of geometric properties.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
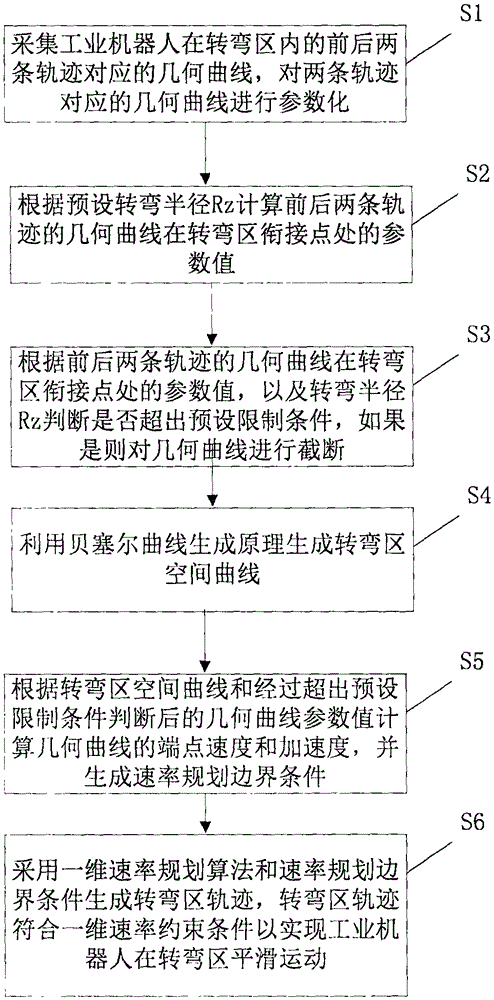
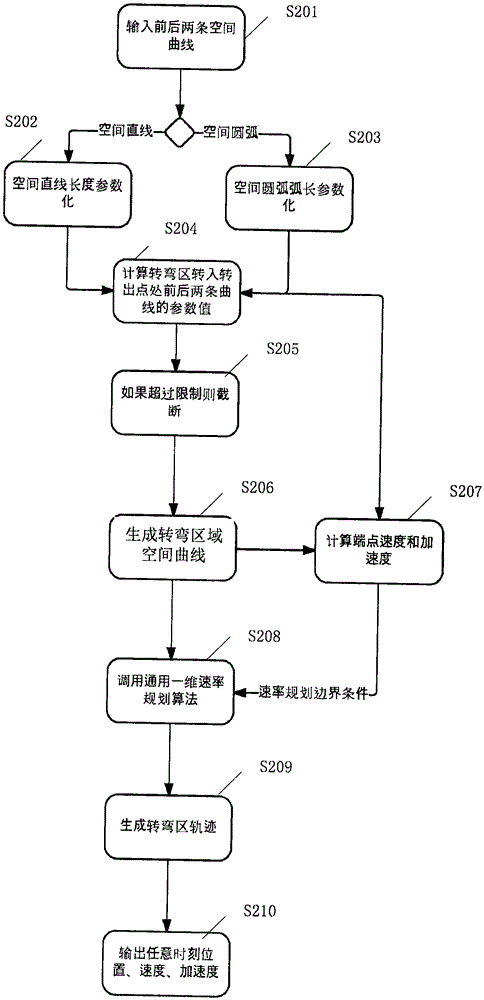
Industrial robot Cartesian space trajectory geometric smoothing method
ActiveCN105573315AGuaranteed continuous curvatureGuaranteed accuracyPosition/course control in two dimensionsThermal velocityComputer science
The invention provides an industrial robot Cartesian space trajectory geometric smoothing method. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out parameterization on geometrical curves corresponding to front and back two trajectories in a turning area; calculating parameter values of the geometrical curves of the front and back two trajectories in a turning area connecting point; judging whether the geometrical curves surpass preset limit conditions according to the parameter values of the geometrical curves of the front and back two trajectories in the turning area connecting point and turning radius, and if so, cutting off the geometrical curves; generating a turning area space curve by utilizing the Bezier curve generation principle; calculating terminal velocity and acceleration velocity of the geometrical curves; and generating a turning area trajectory by utilizing a one-dimensional velocity planning algorithm and velocity planning boundary conditions. The method enables the front and back two trajectories of an industrial robot in the turning area to realize geometric superposition smoothing to ensure curvature continuity of the geometrical curves corresponding to the trajectories; and velocity planning is carried out on the smoothed geometrical curves to achieve the purpose of speed control of the turning area.
Owner:苏州科诺机器人有限责任公司
Method and system for implementing multiple high precision and low precision interpolators for a graphics pipeline
ActiveUS7079156B1Reduce countReduce power consumptionCathode-ray tube indicatorsFilling planer surface with attributesComputational geometryGeometric primitive
A rasterizer stage configured to implement multiple interpolators for graphics pipeline. The rasterizer stage includes a plurality of simultaneously operable low precision interpolators for computing a first set of pixel parameters for pixels of a geometric primitive and a plurality of simultaneously operable high precision interpolators for computing a second set of pixel parameters for pixels of the geometric primitive. The rasterizer stage also includes an output mechanism coupled to the interpolators for routing computed pixel parameters into a memory array. Parameters may be programmably assigned to the interpolators and the results thereof may be programmably assigned to portions of a pixel packet.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
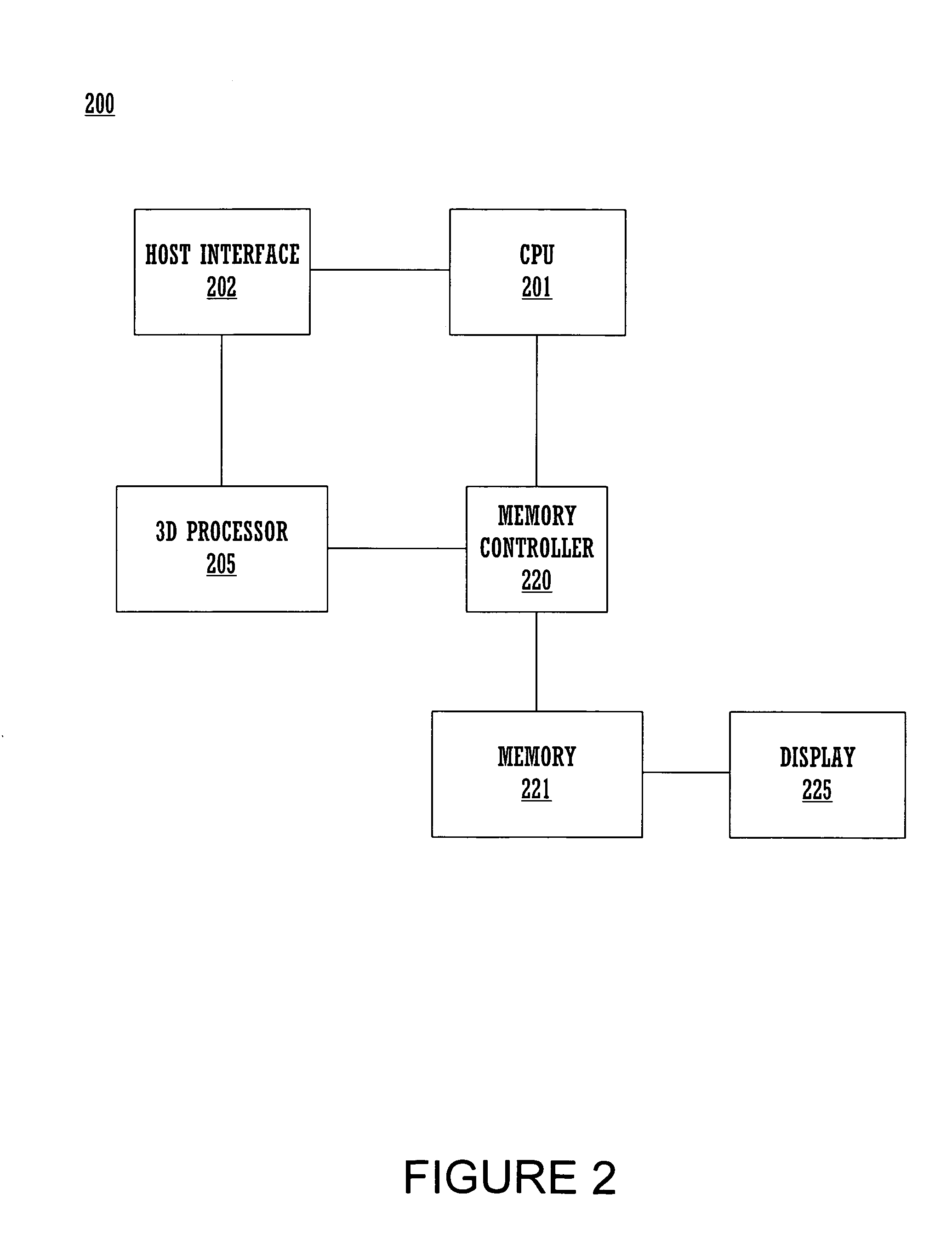
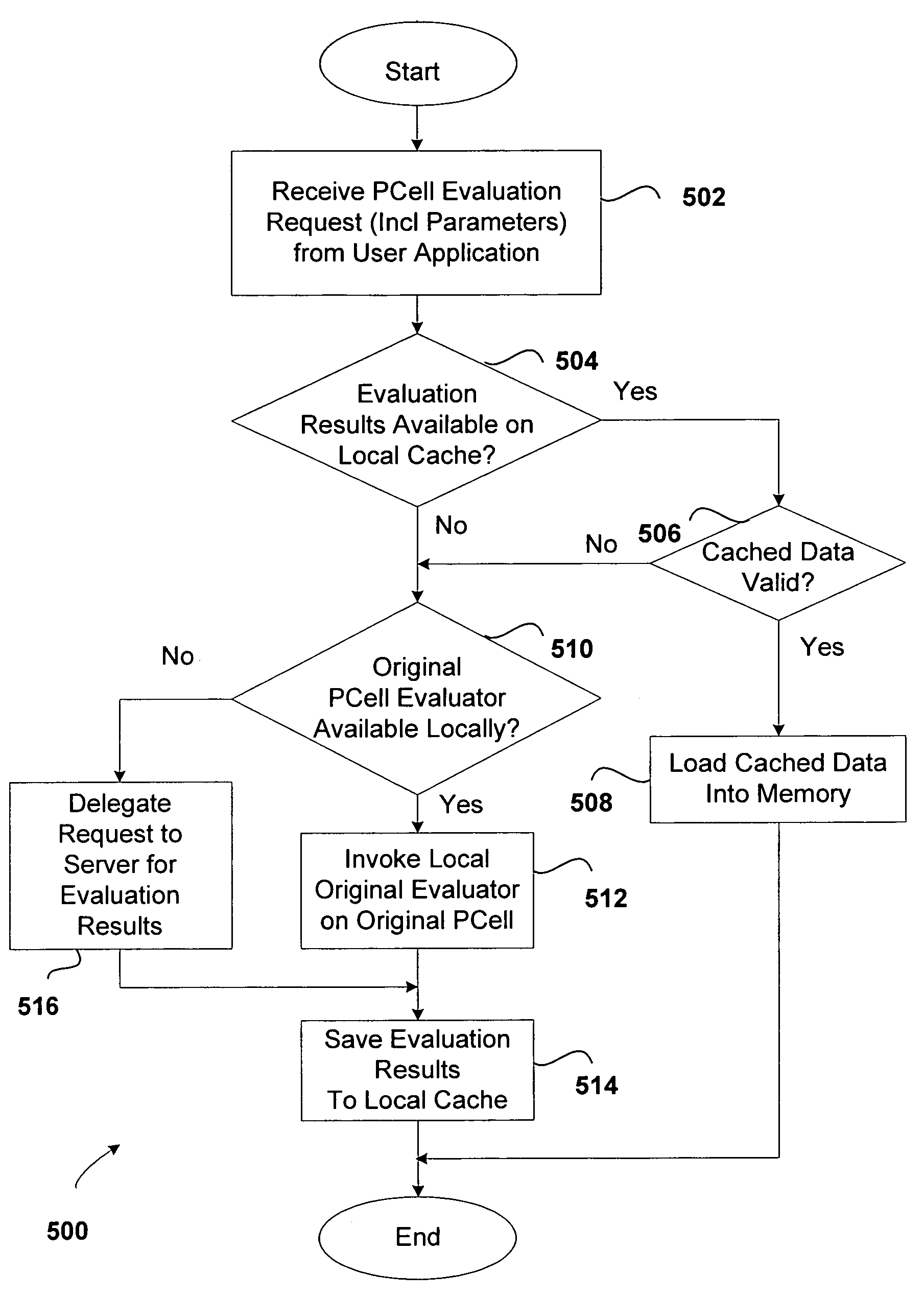
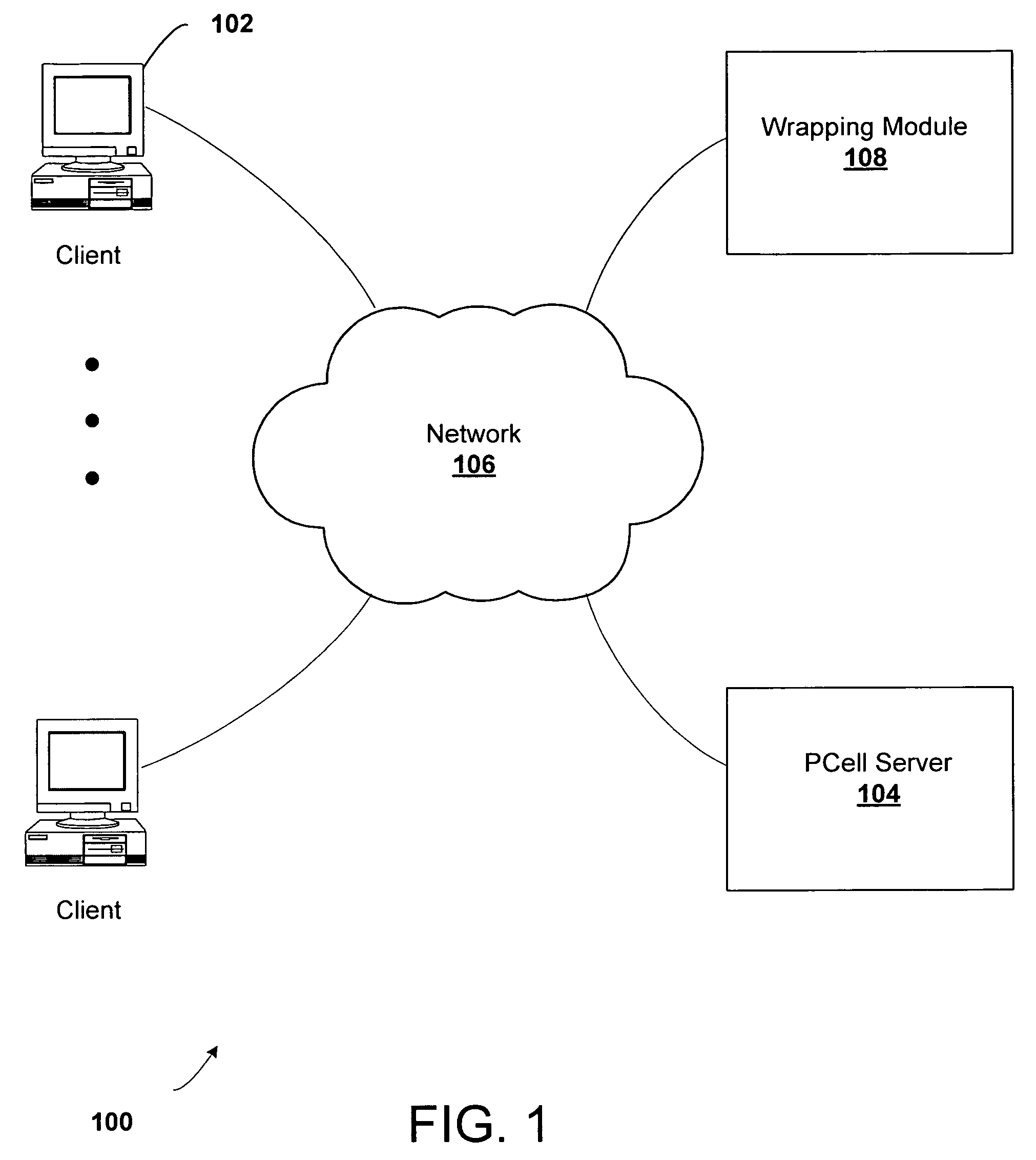
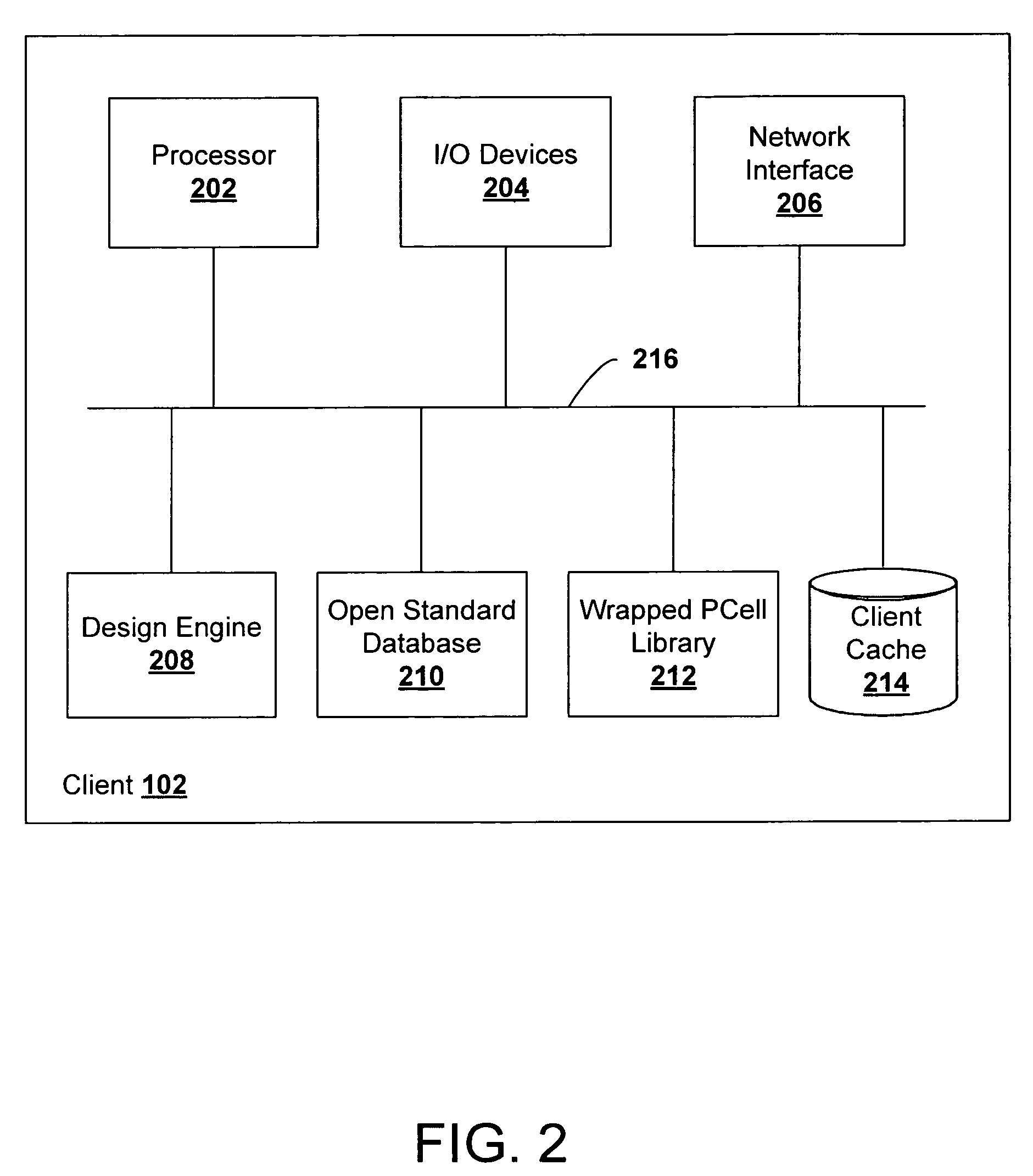
System and method for proxied evaluation of PCells
Systems and methods of laying out integrated circuits are disclosed. During the layout stage of an integrated circuit device, a fixed, physical geometry is created of the parameterized cells (PCells) included in the integrated circuit schematic. The systems include a proxy engine configured to save to cache the geometries created during the layout stage such that the geometries need not be recomputed when the design is opened after a save to disk operation, during which geometries may otherwise be destroyed. The proxy engine may further be configured to delegate requests for the creation of geometries to other components of the integrated circuit design system. In addition, the proxy engine may be configured to perform customized evaluations of PCells, other than or in addition to caching and delegation.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method and apparatus for generating graphic hair motion
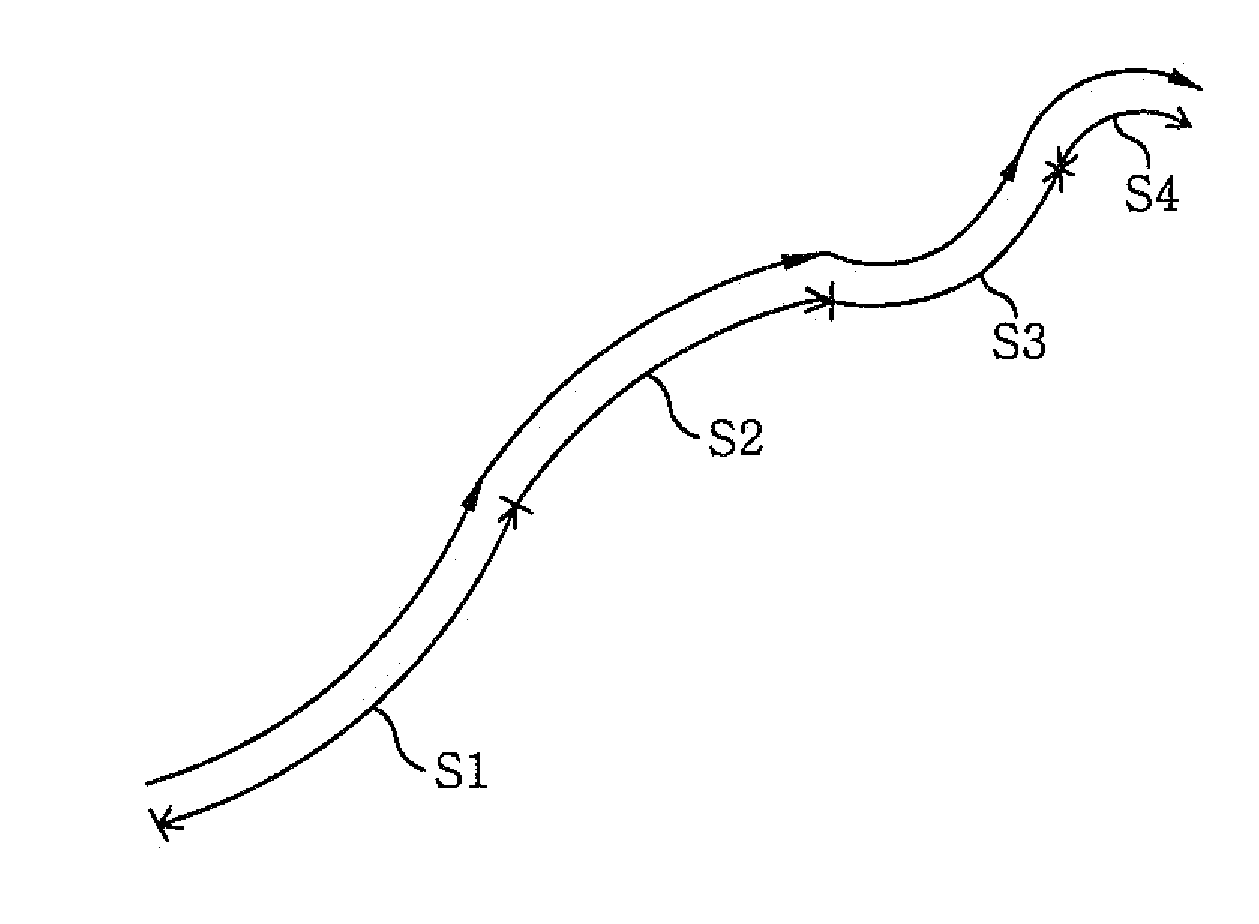
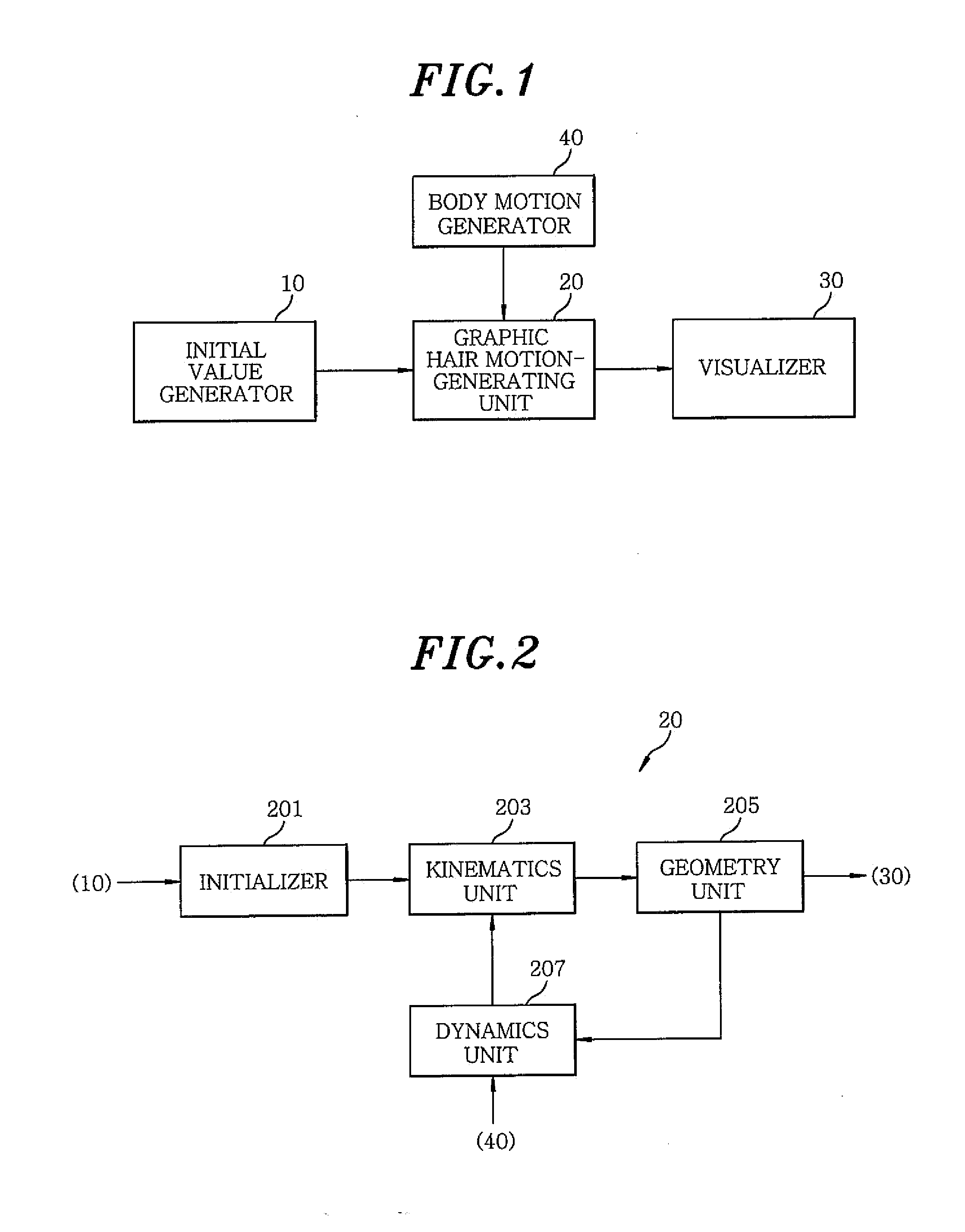
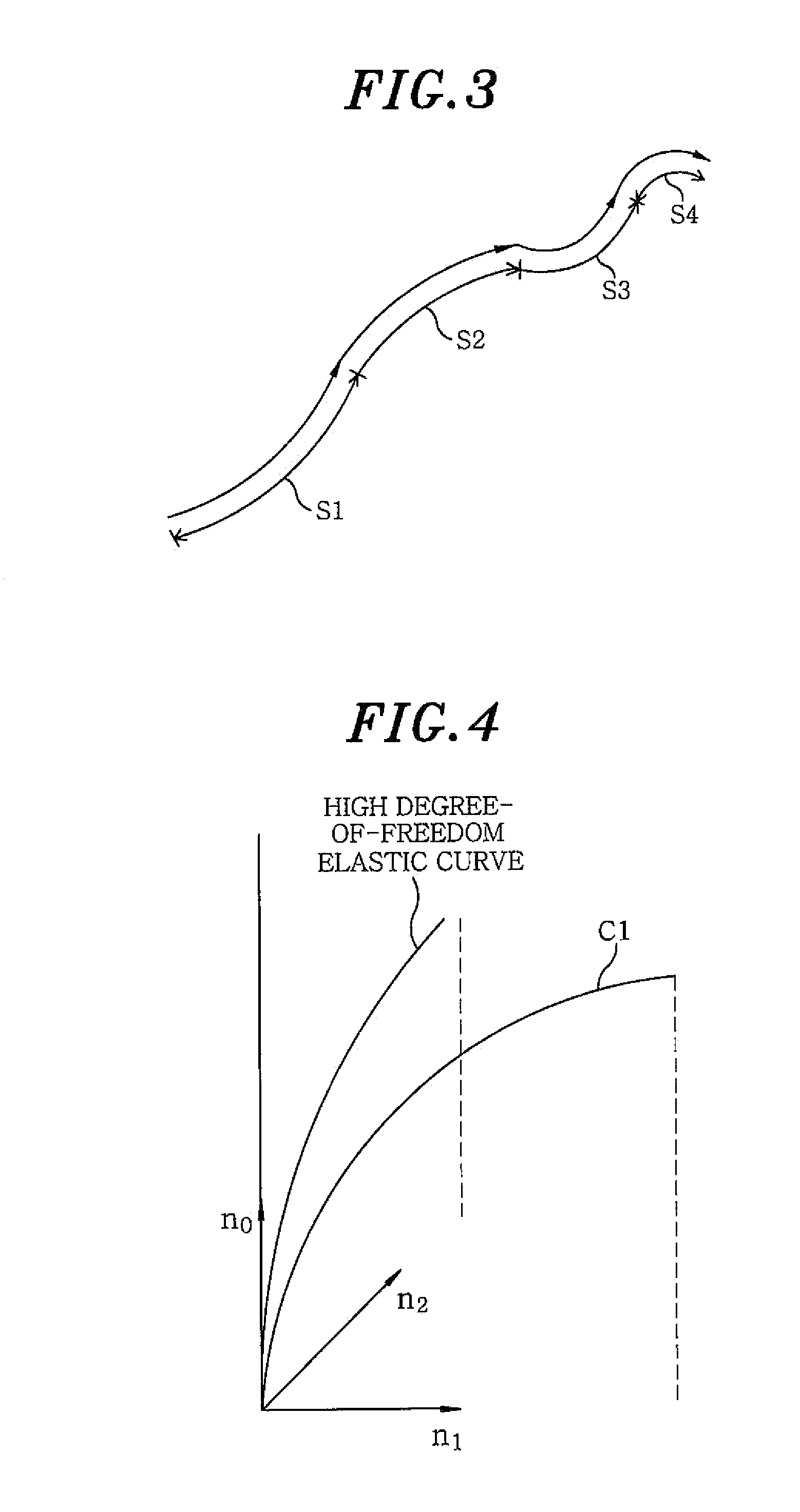
InactiveUS20100156902A1Remove the burdenShorten the timeAnimation3D-image renderingGraphicsElastic curve
The present invention provides a graphic motion generating method and apparatus for modeling hair into elastic curves that are inextensible while twisting and curling of hair can be expressed, for applying an adaptive different subdividing method to subdivide a single strand of hair into several segments such that detailed bending and curling of the strands of hair can be expressed in the vicinities of roots and ends of the strands of hair, for modeling the respective segments of respective strands of hair into low degree-of-freedom elastic curves with degrees of freedom less than two such that geometric and dynamic physical quantities can be calculated in a short time, and for automatically generating a curvature vector of the elastic curve model from an initial hair curve by using a minimizing technique.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Data retrieval method and system
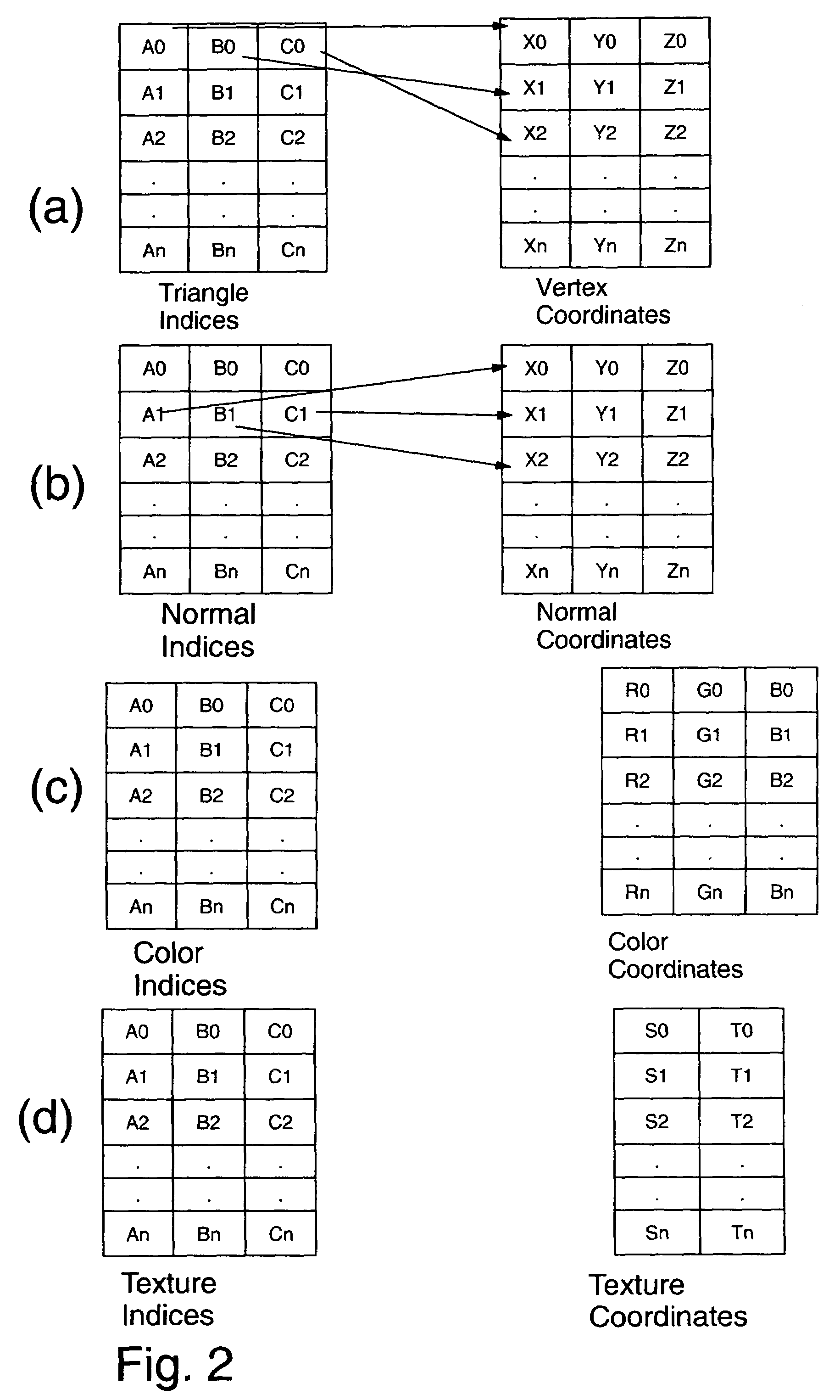
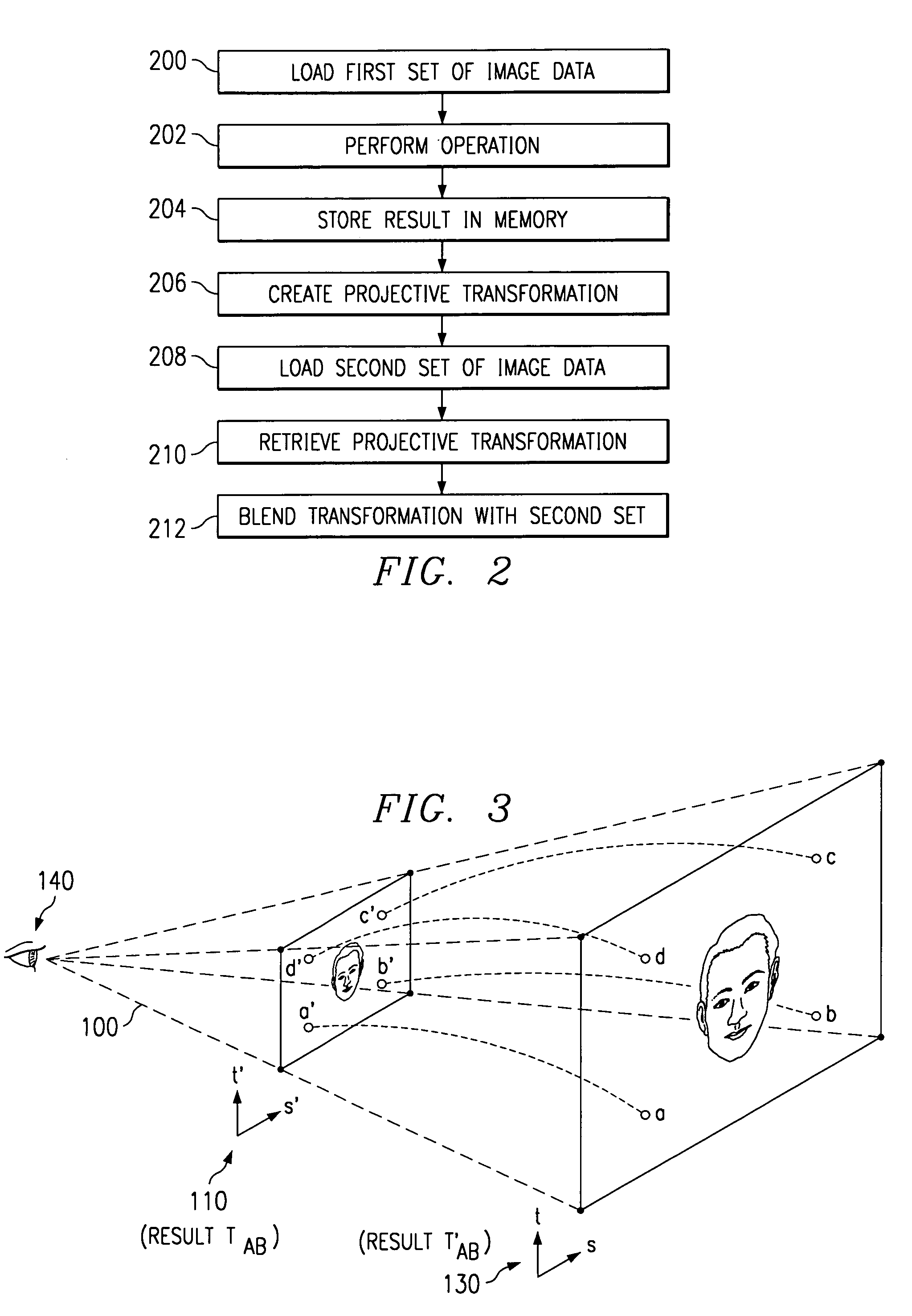
InactiveUS7116333B1Effective expansionDrawing from basic elementsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Data retrieval
One aspect of the invention is a method for data retrieval. The method includes the step of rendering geometry from a selected perspective (140) to produce a plurality of data values (130, T′AB). The method also includes the steps of storing at least a subset of the plurality of data values (130, T′AB) in a memory (40, 80) and computing a plurality of texture coordinates (a′–d′) of the geometry from a projective transformation corresponding to the selected perspective (140). The method also includes the step of retrieving at least one of the stored data values (TAB) that correspond to the texture coordinates (a′–d′) from the memory (40, 80).
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
Plane target drone characteristic point automatic matching method for demarcating video camera
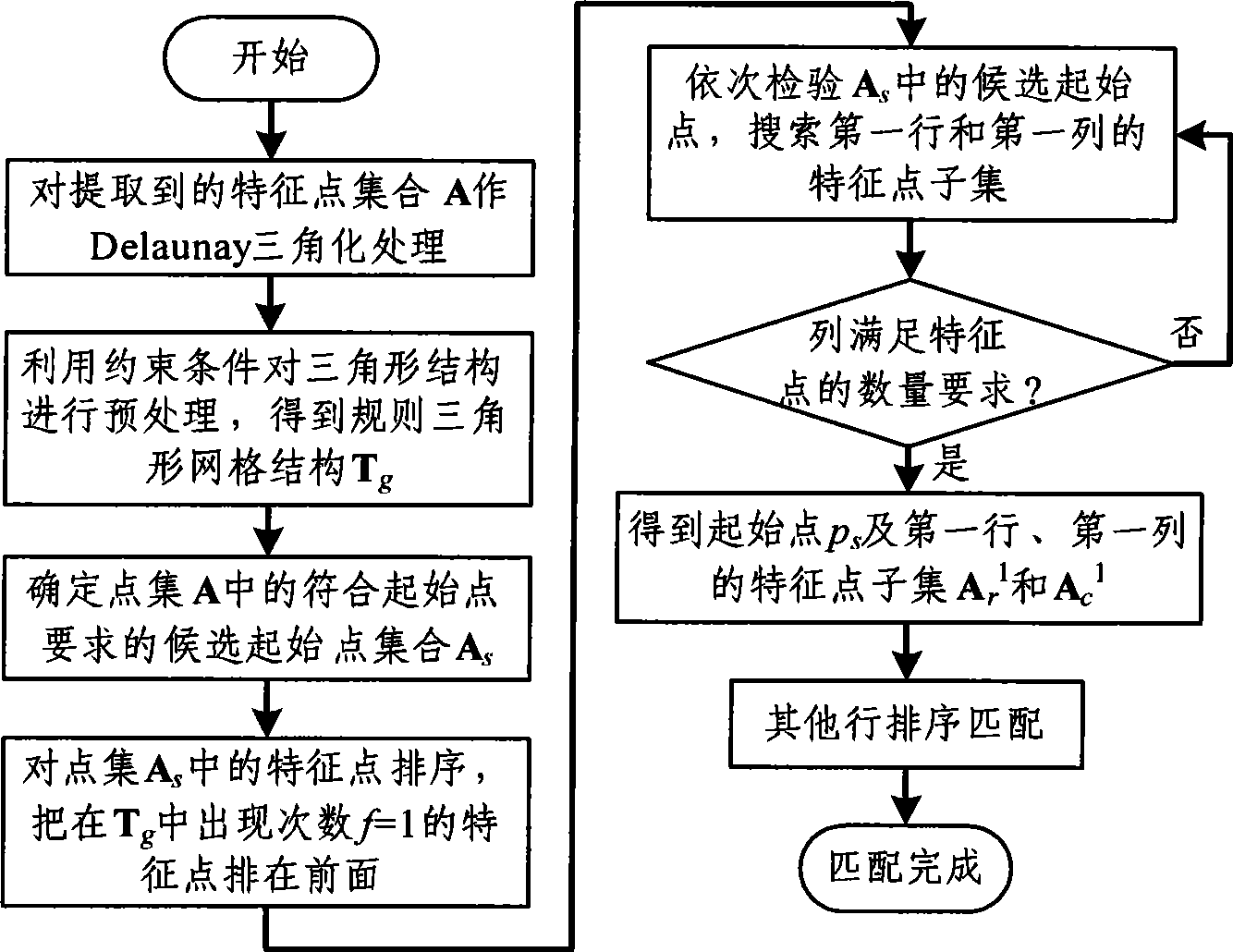
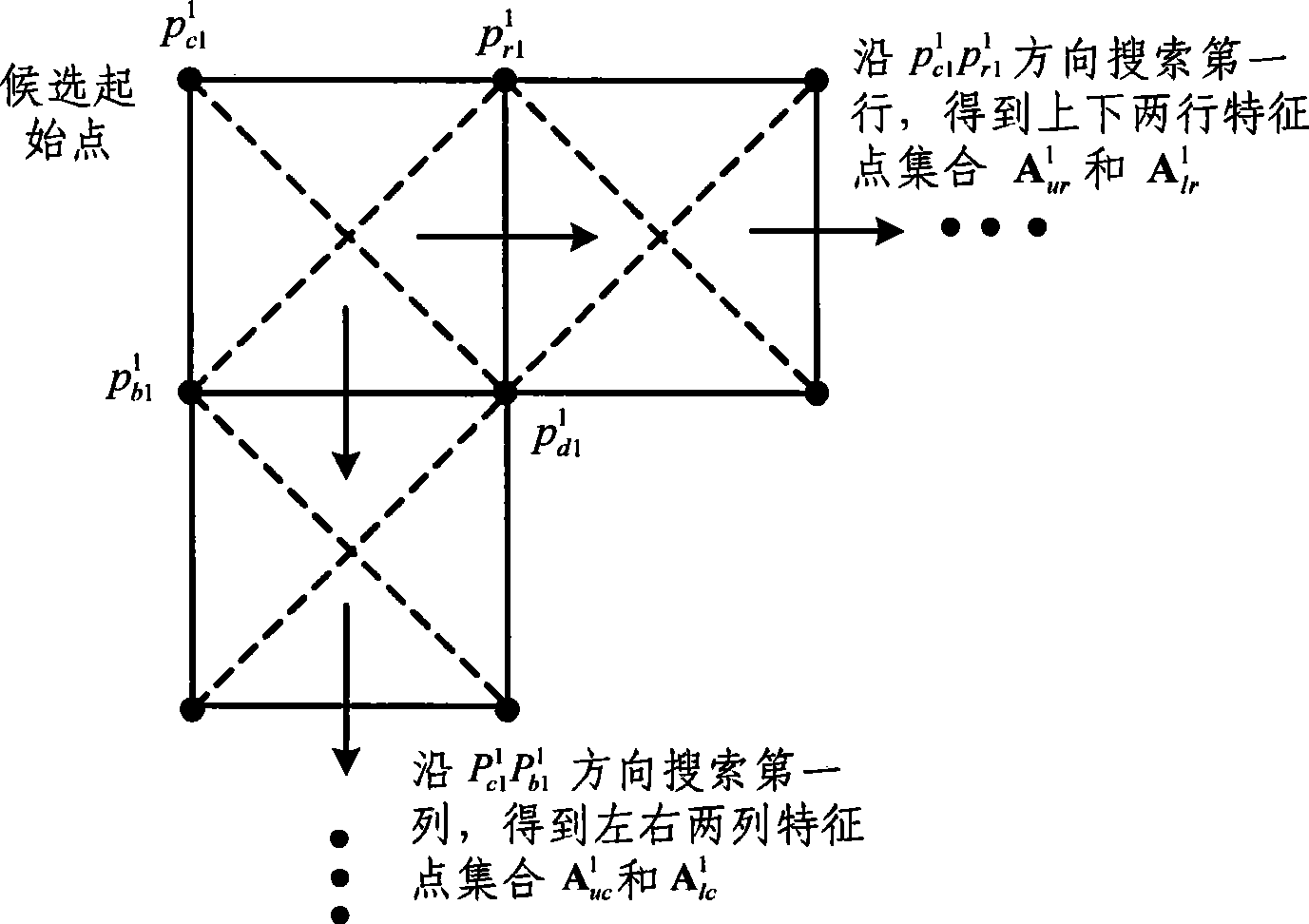
InactiveCN101419709AHigh degree of automationSimplify the calibration processImage analysisCamera lensMachine vision
The invention belongs to the technical field of machine vision, and provides an automatic matching method of planar target characteristic points for camera calibration. The method comprises the following steps: performing Delaunay triangularization and necessary preprocessing in a computational geometry theory on the obtained calibration characteristic point set to obtain a geometrical connection relation between adjacent characteristic points; then searching the point set for an initial point, a characteristic point of a first line and a characteristic point of a first row which are used for determining the search direction; and finally, completing the matching of the rest lines according to the geometrical connection relation between the adjacent characteristic points, and realizing the matching between image coordinates of the planar target characteristic points in checkered array distribution and the world coordinates. The matching method of the characteristic points has simple realization and strong robustness, is insensitive to lens distortion, and is suitable for the matching of the characteristic points matching under the condition that the shooting inclination angle is large and the target is partially blocked, and is particularly suitable for online automatic calibration of cameras.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
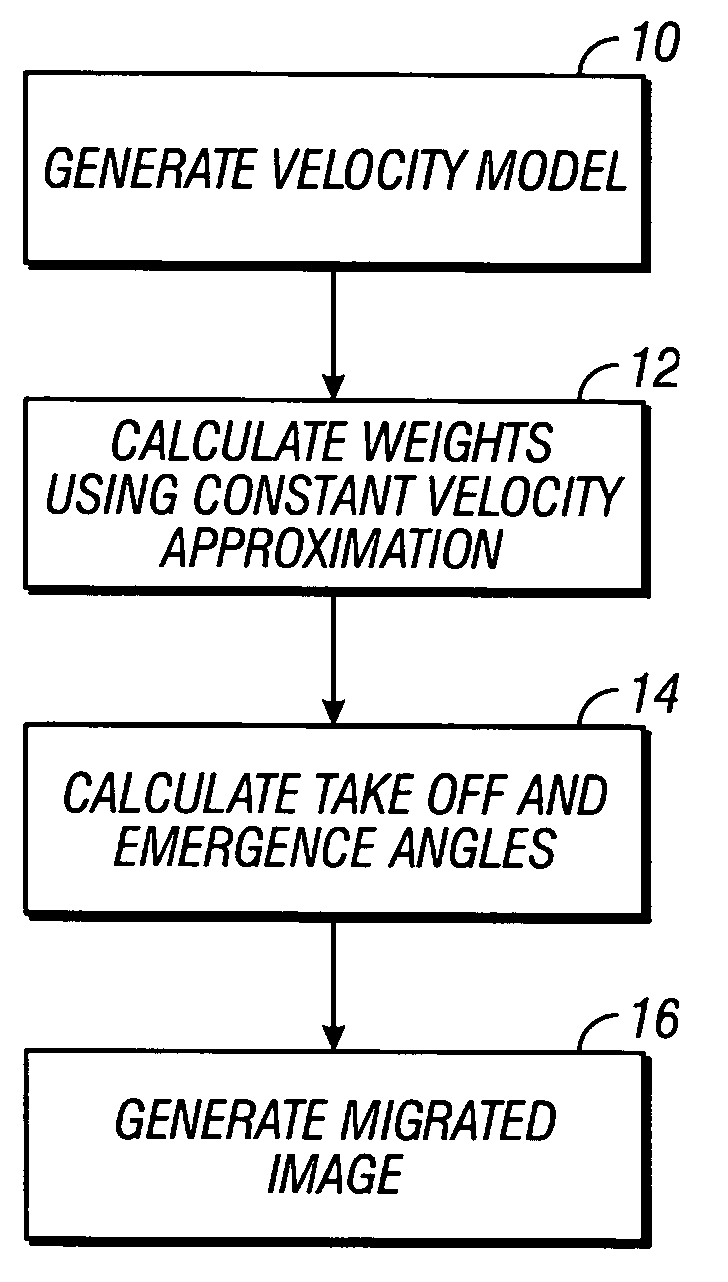
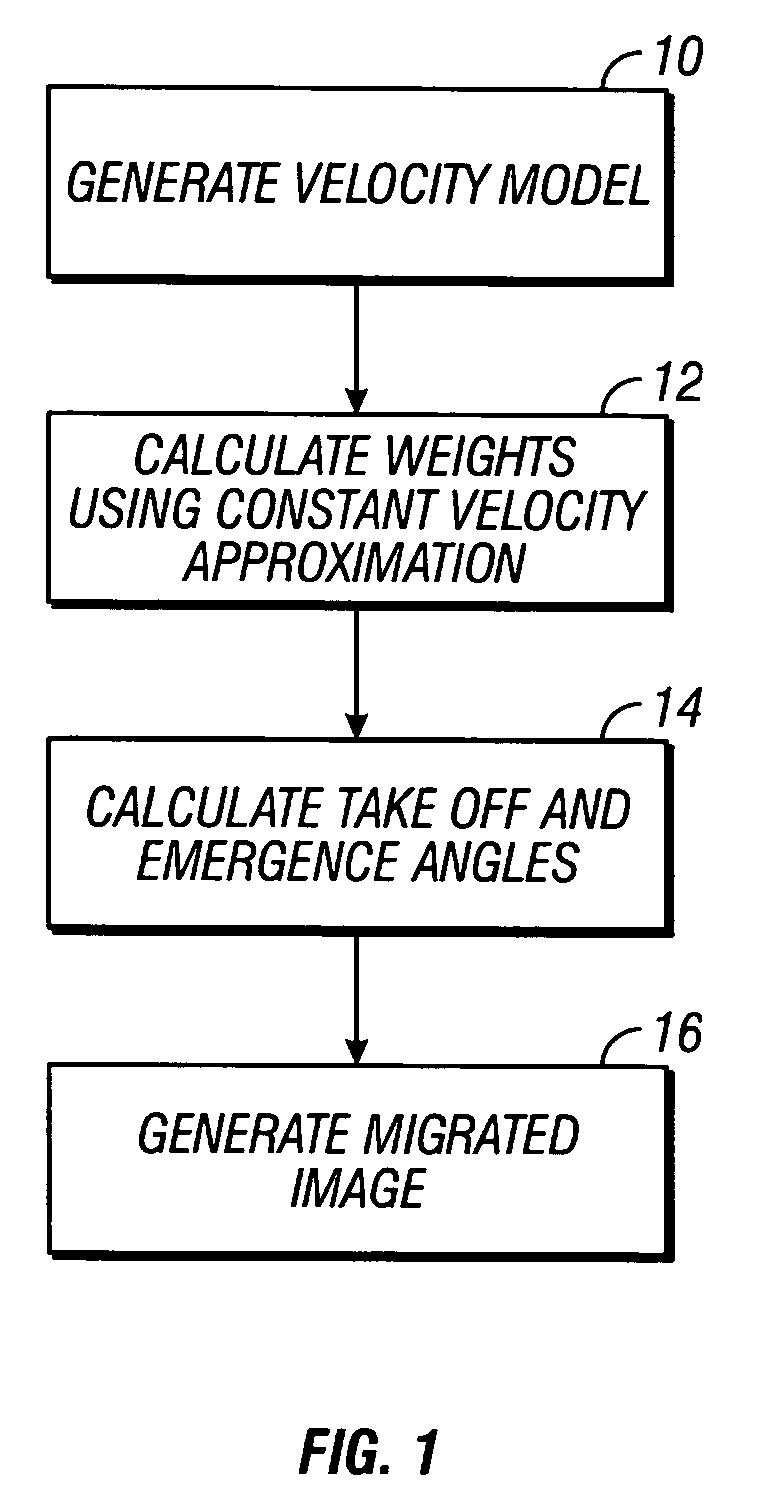
Amplitude preserving prestack migration method
A method is disclosed for amplitude preserving Kirchhoff time migration. The method includes calculating estimates of the geometrical spreading terms using a constant velocity approximation. Takeoff and emergence angles are accurately calculated based on a model of velocity which varies with respect to travel time. An image can be calculated at at least one travel time using the estimated weights and calculated takeoff and emergence angles.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
Method and system for a general instruction raster stage that generates programmable pixel packets
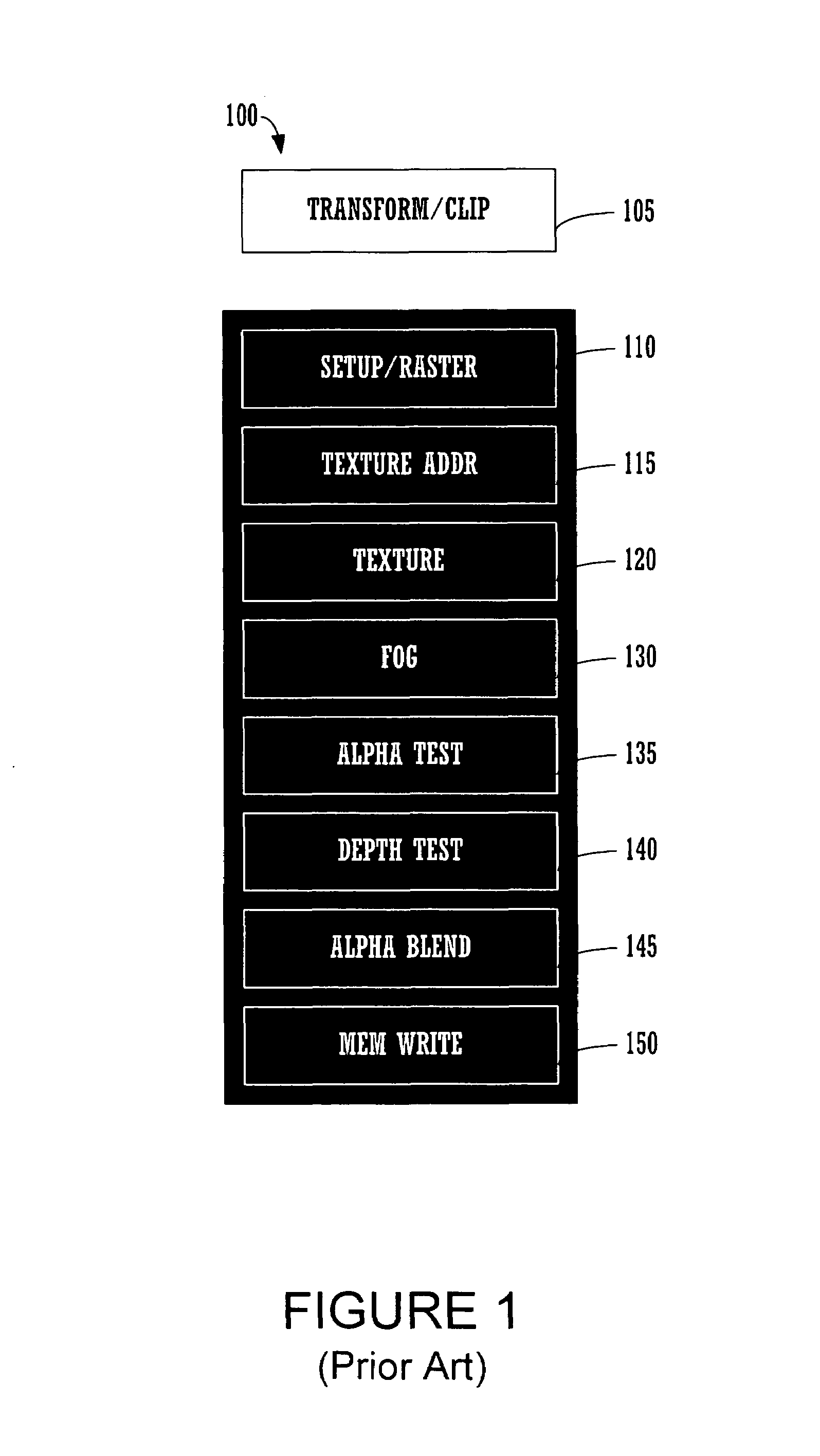
ActiveUS20050275657A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsReduce power consumptionProcessor architectures/configurationElectric digital data processingComputational scienceGraphics
A method and system for a general instruction capable raster stage that generates flexible pixel packets is disclosed. In one embodiment, the rasterizing of a geometric primitive comprising a plurality of vertices wherein each vertex comprises a respective color value, is performed by a rasterization module of a graphics pipeline. The rasterizing includes a plurality of programmable interpolators for computing pixel parameters for pixels of a geometric primitive. The rasterizing module further includes a memory for storing a first instruction associated with a first programmable interpolator for indicating a first parameter on which said first programmable interpolator is to operate and for indicating a first portion of a pixel packet in which to store its results. The rasterizing module additionally includes a memory for storing a second instruction associated with a second programmable interpolator for indicating a second parameter on which said second programmable interpolator is to operate and also for indicating a second portion of said pixel packet in which to store its results.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
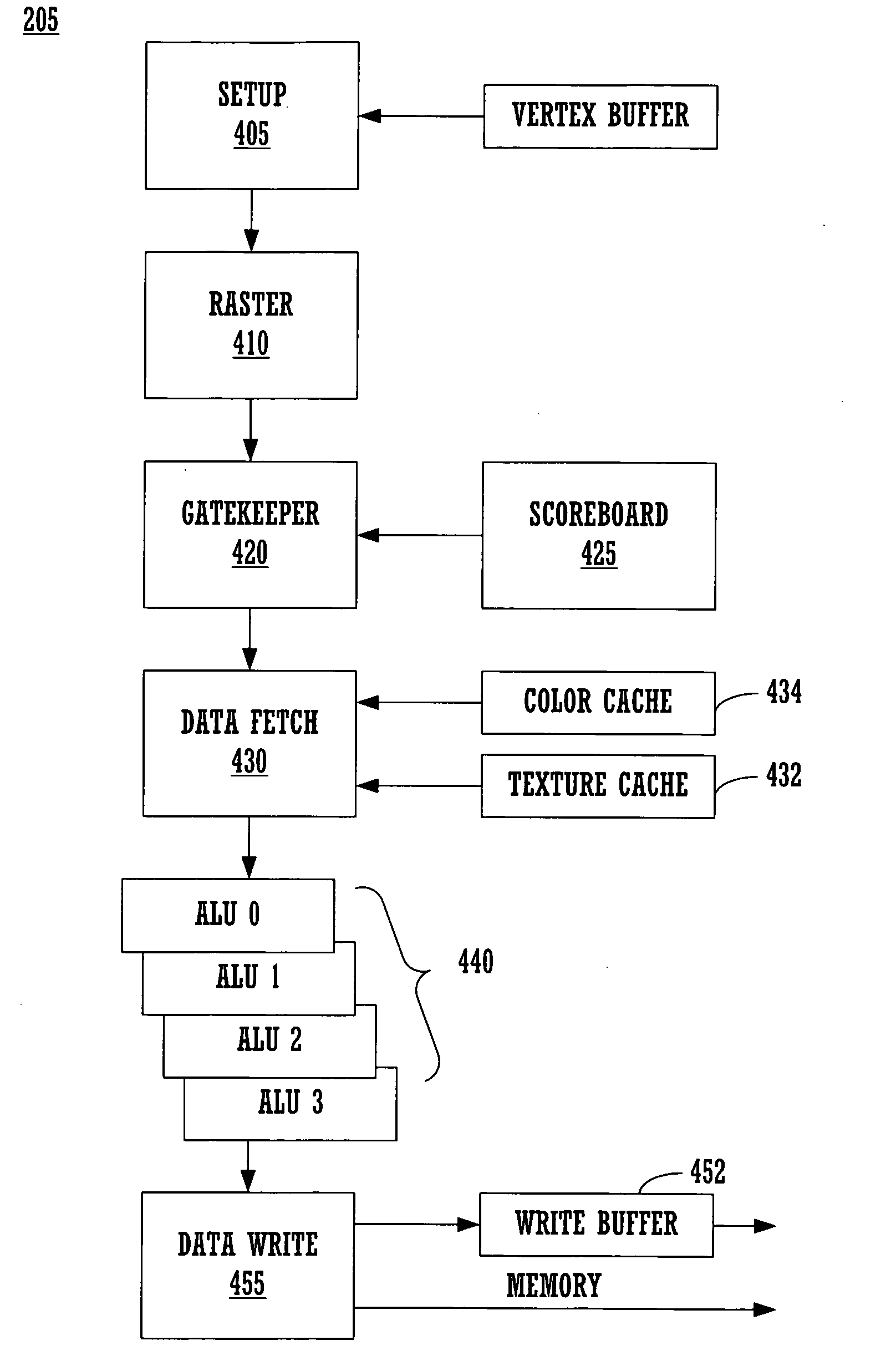
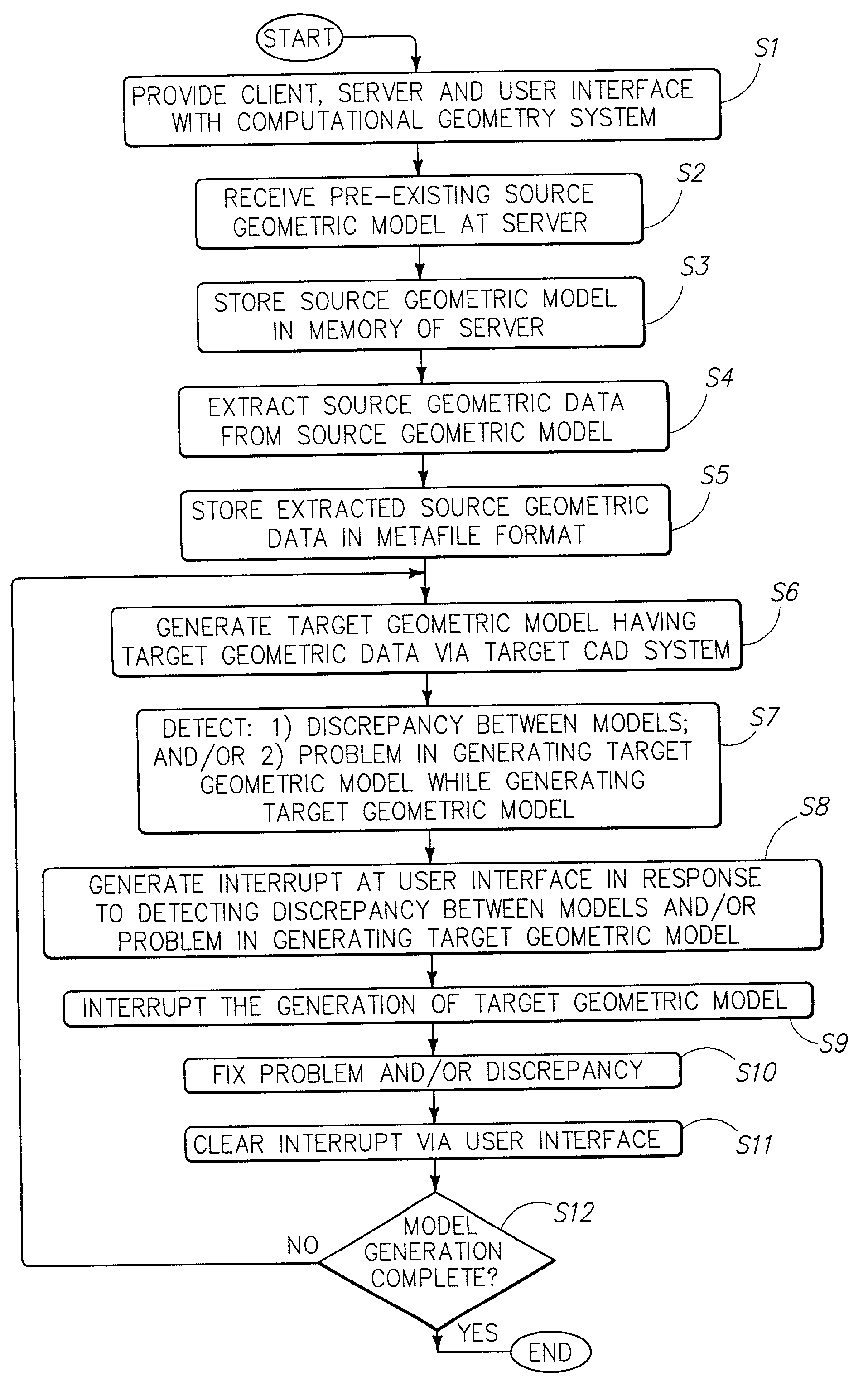
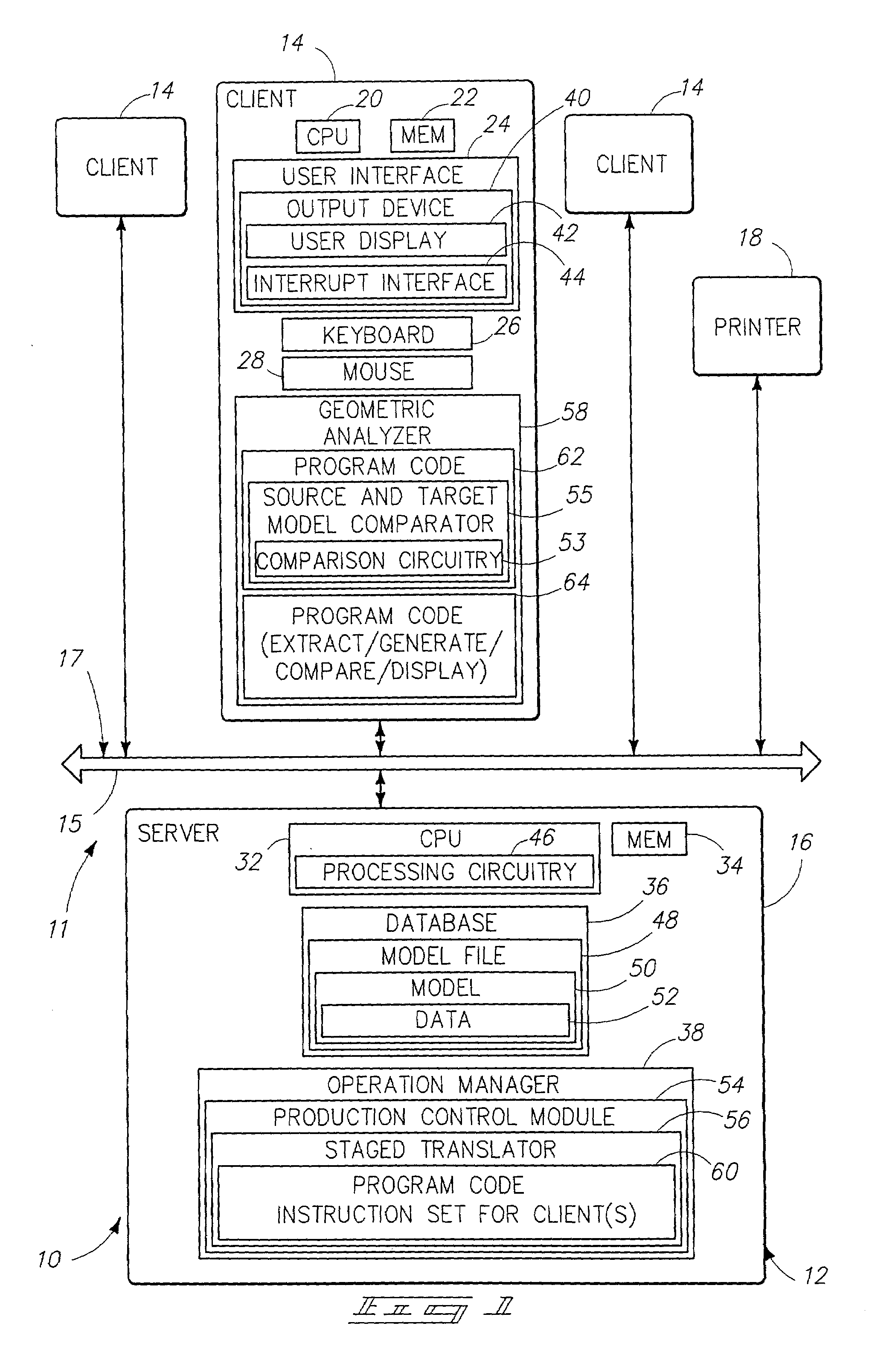
Computational geometry system, interrupt interface, and method
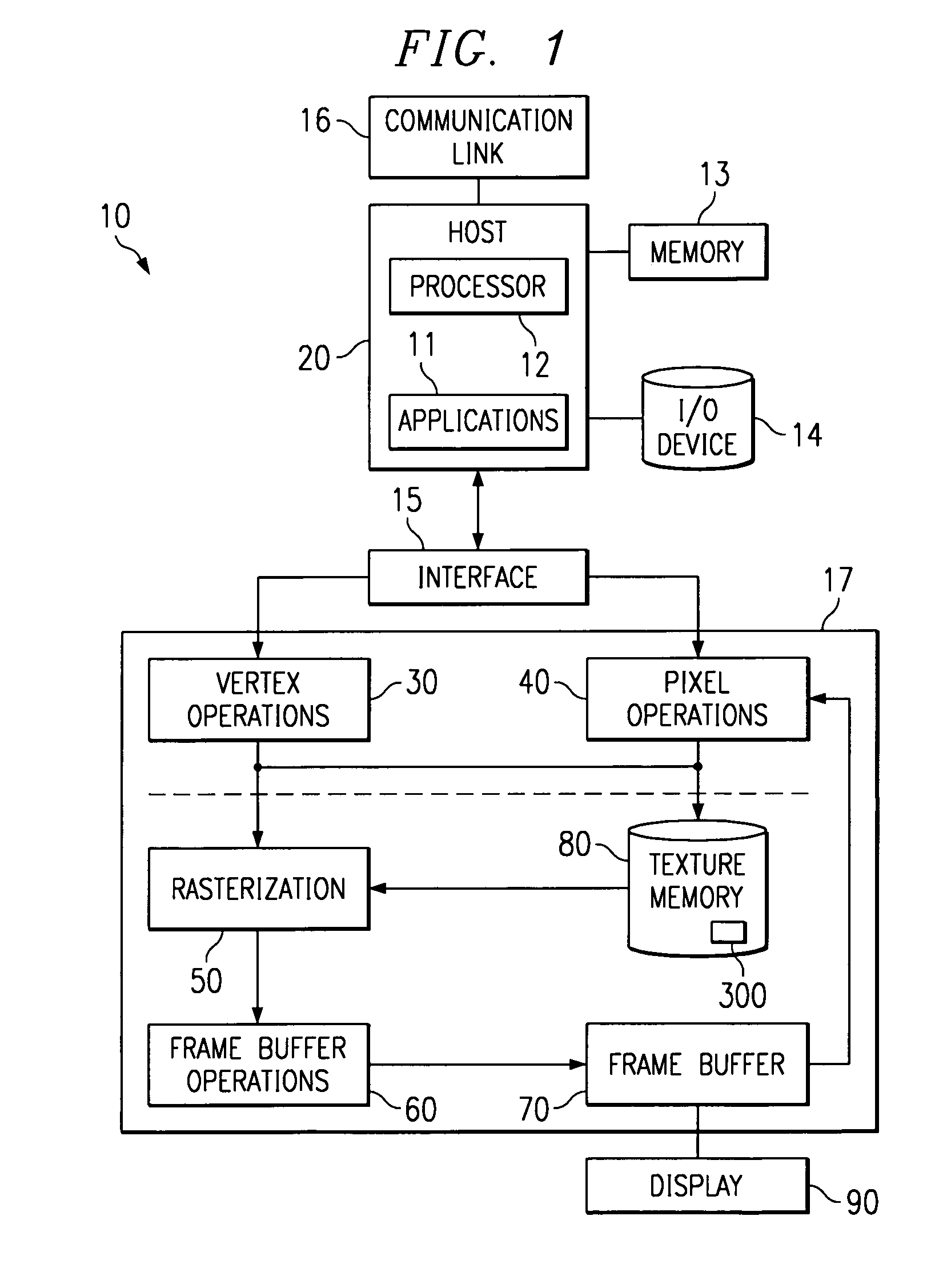
InactiveUS7203634B2Increase speedCAD network environmentImage data processing detailsTheoretical computer scienceGeometric modeling
A computational geometry server is provided that includes a server, a communication link, at least one client, and an interrupt interface. The server has processing circuitry and an operation manager. The operation manager is configured to compare source geometric data in a source geometric model with target geometric data in a target geometric model. Furthermore, the operation manager is operative to identify discrepancies in the geometric data between the source geometric data and the target geometric data. The at least one client communicates with the server over the communication link. The interrupt interface is operative to notify a user of the presence of an inability to automatically generate an accurate representation of the source geometric model in the target geometric model. A method is also provided.
Owner:TTI ACQUISITION CORP
Method and system for a general instruction raster stage that generates programmable pixel packets
ActiveUS7190366B2Consumes less powerReduce widthProcessor architectures/configurationElectric digital data processingComputational scienceGraphics
A method and system for a general instruction capable raster stage that generates flexible pixel packets is disclosed. In one embodiment, the rasterizing of a geometric primitive comprising a plurality of vertices wherein each vertex comprises a respective color value, is performed by a rasterization module of a graphics pipeline. The rasterizing includes a plurality of programmable interpolators for computing pixel parameters for pixels of a geometric primitive. The rasterizing module further includes a memory for storing a first instruction associated with a first programmable interpolator for indicating a first parameter on which said first programmable interpolator is to operate and for indicating a first portion of a pixel packet in which to store its results. The rasterizing module additionally includes a memory for storing a second instruction associated with a second programmable interpolator for indicating a second parameter on which said second programmable interpolator is to operate and also for indicating a second portion of said pixel packet in which to store its results.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
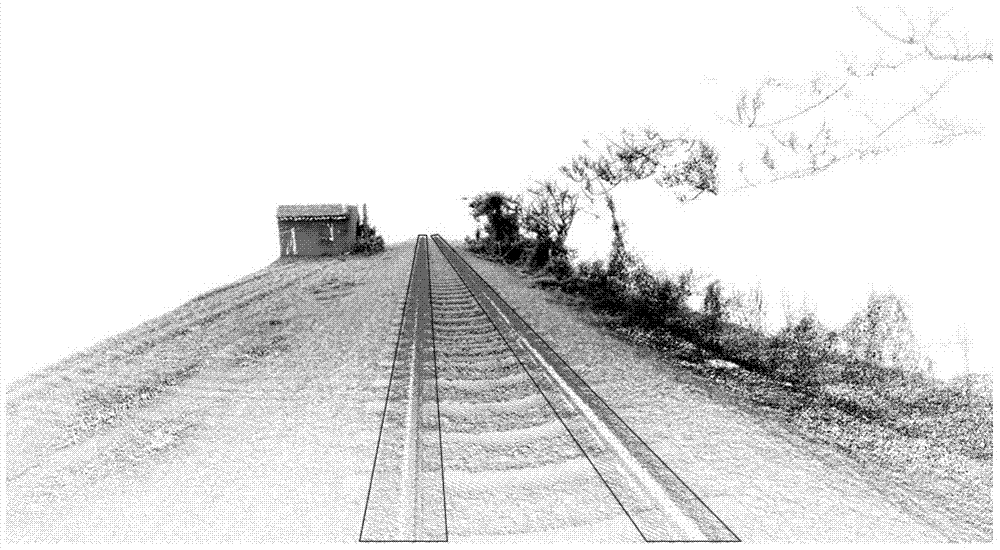
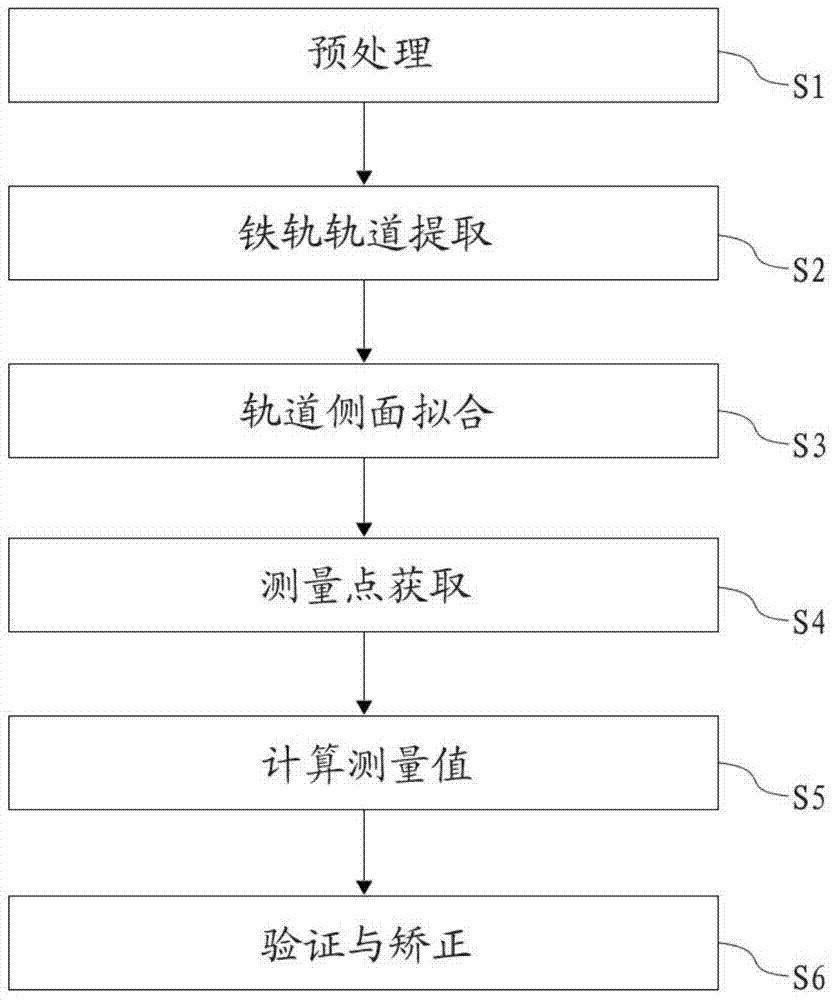
Automatic measurement method for railway on basis of point cloud data
ActiveCN104236499AGet goodHigh degree of automationImage analysisMeasurement devicesComputational geometryWorkload
The invention discloses an automatic measurement method for a railway on the basis of point cloud data. The automatic measurement method comprises the following steps of: S1, pre-treating; S2, extracting a rail track; S3, fitting the side surface of the track; S4, acquiring a measurement point; S5, calculating a measurement value; S6, verifying and correcting. According to the automatic measurement method disclosed by the invention, the measurement working for the railway is automatic and accurate by adopting a computation geometry fitting method and combining with laser point cloud data, thus avoiding the high workload needed by field surveying and mapping.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com