Method for calculating extinction coefficients of three-dimensional forest canopy by using laser-point cloud
A technology of laser point cloud and extinction coefficient, applied in the field of calculating forest canopy extinction coefficient, can solve the problem of insufficient depth of canopy extinction coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0064] The present invention is further explained by examples below:
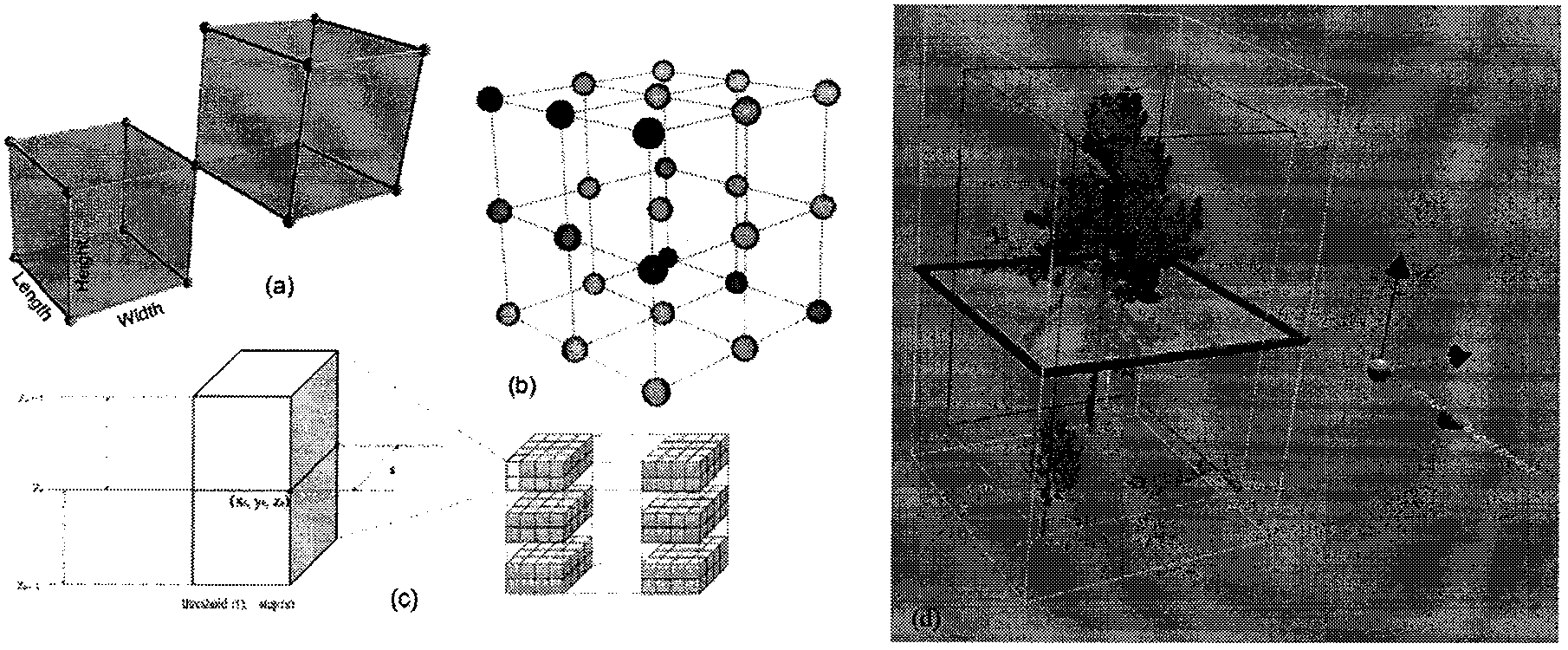
[0065] Take a Douglas-fir (Douglas-fir) as the research object (the height of the tree is about 25m), use the ground 3D laser scanner Leica ScanStation 2 (the parameters are shown in Table 1) and high-precision GPS, on one side of the tree For the collection of 3D point cloud data, the sampling interval is 2cm. Manually remove the ground point cloud and other noise point clouds to obtain the three-dimensional point cloud data of a single Douglas fir tree, as attached Figure 4 Shown.
[0066] Table 1 Three-dimensional laser scanner Leica ScanStation 2 parameters
[0067]
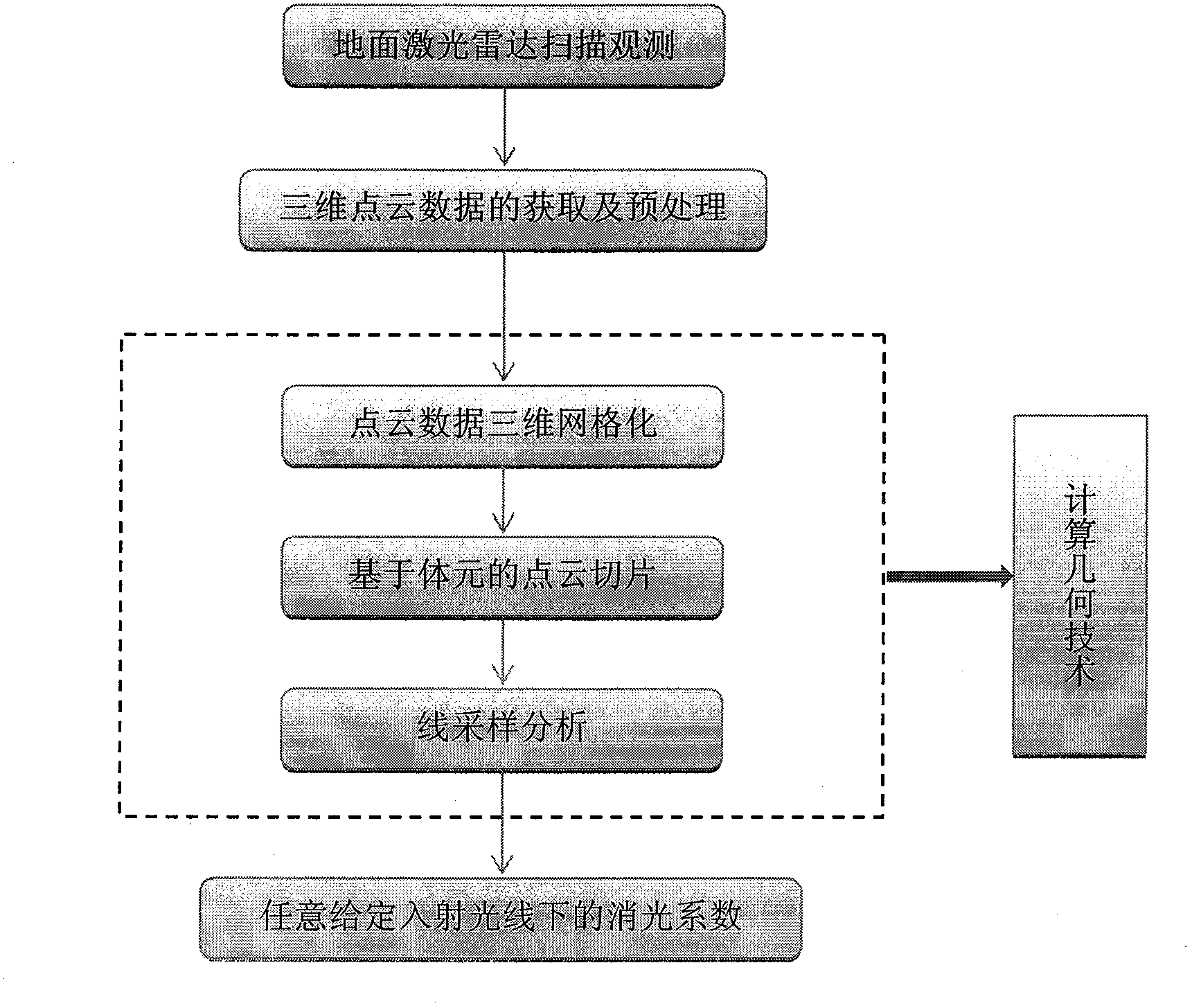
[0068] After obtaining Douglas fir point cloud data and preprocessing, as attached figure 1 As shown, computational geometry technology is used to process 3D point cloud data. The first step is 3D meshing, the second step is voxel-based point cloud slicing, and the third step is line sampling analysis.
[0069] According to the step (2) of the t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com