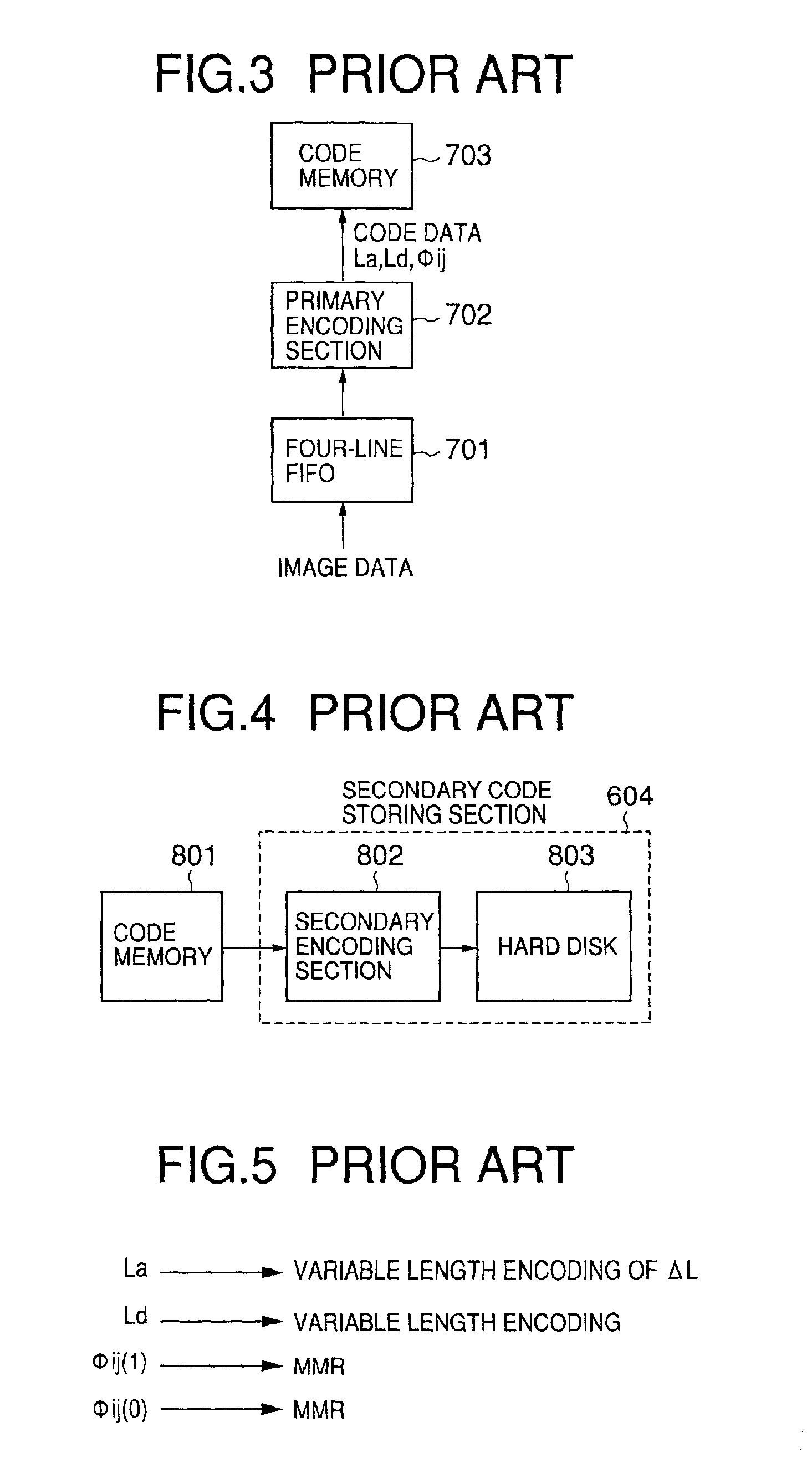
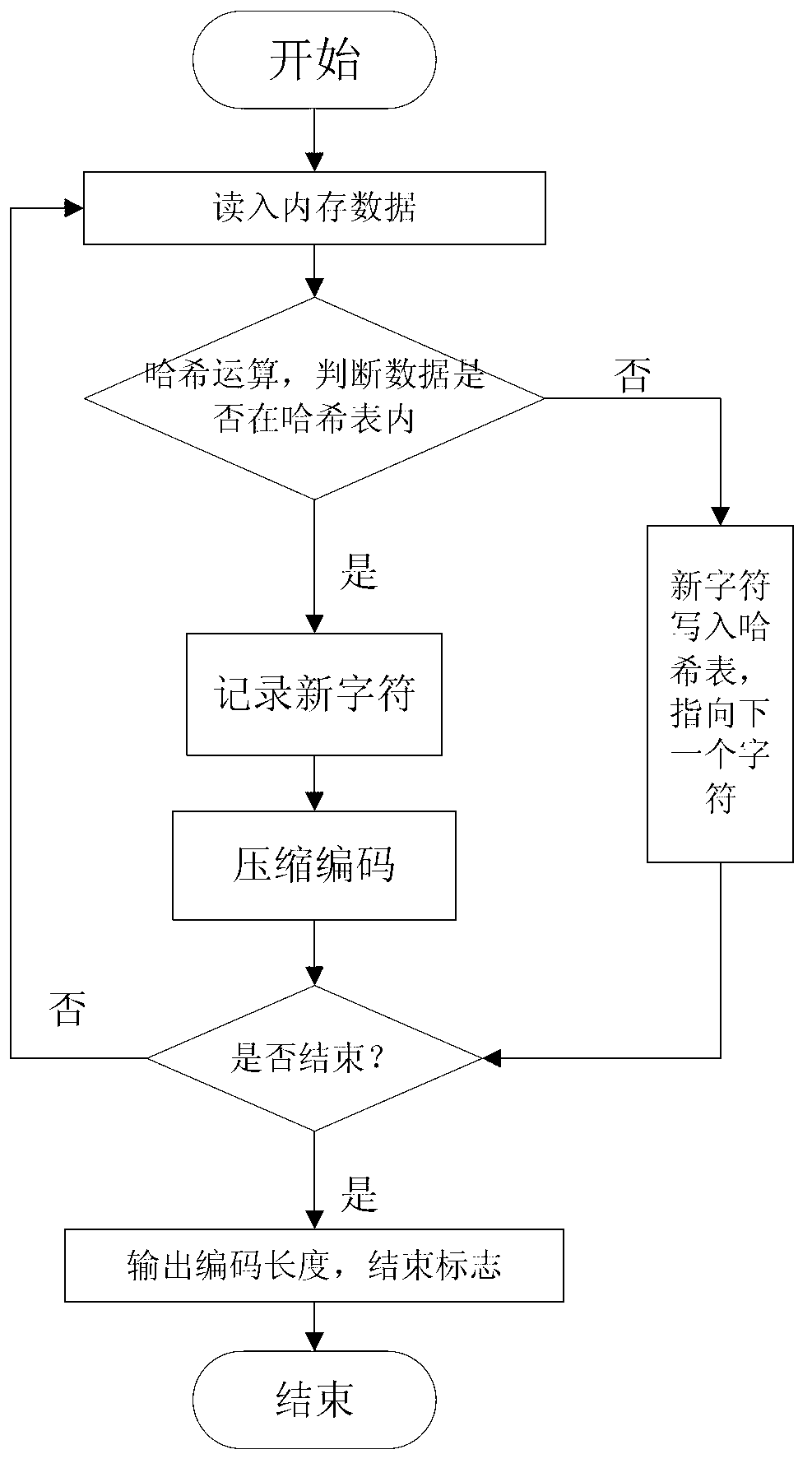
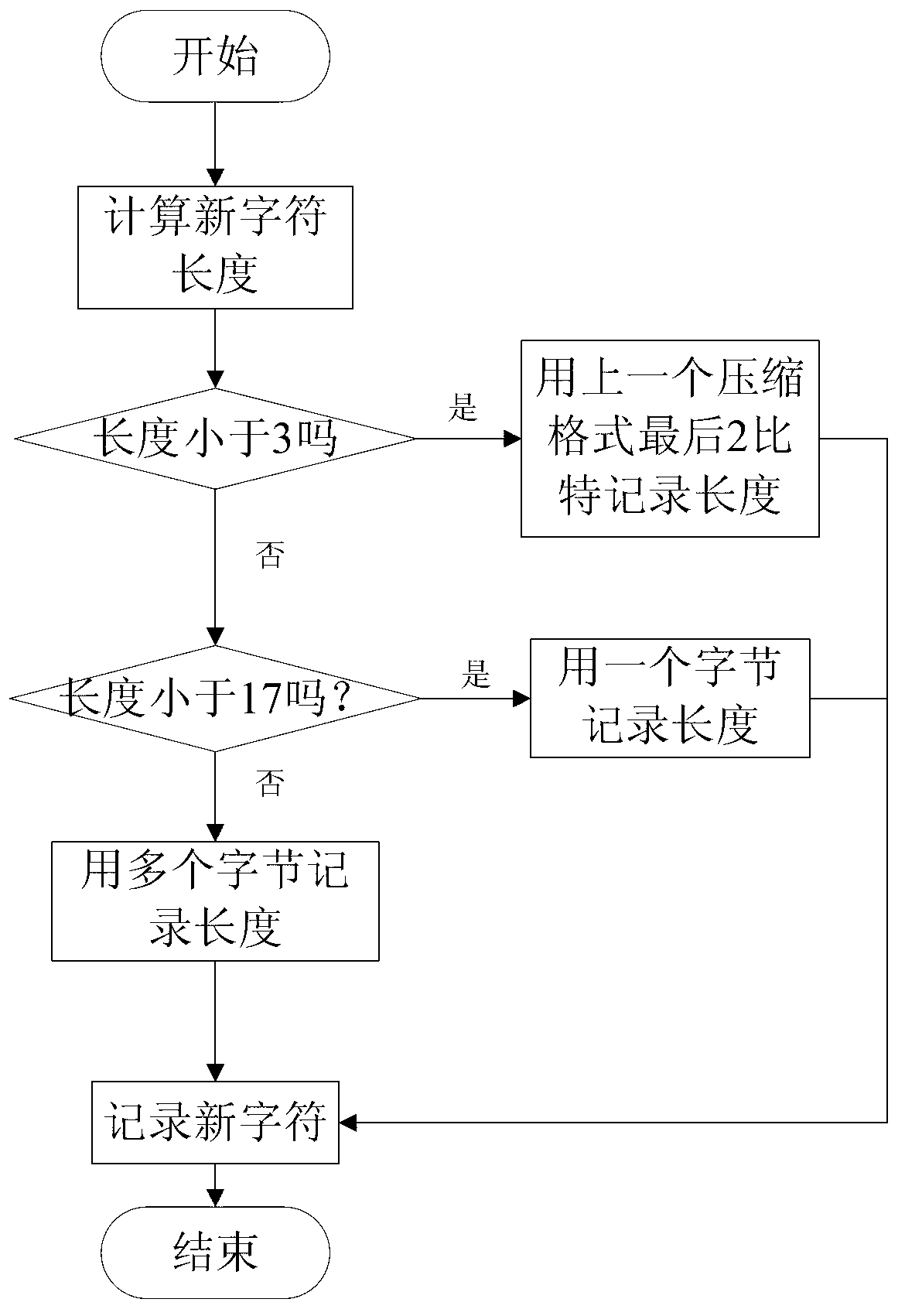
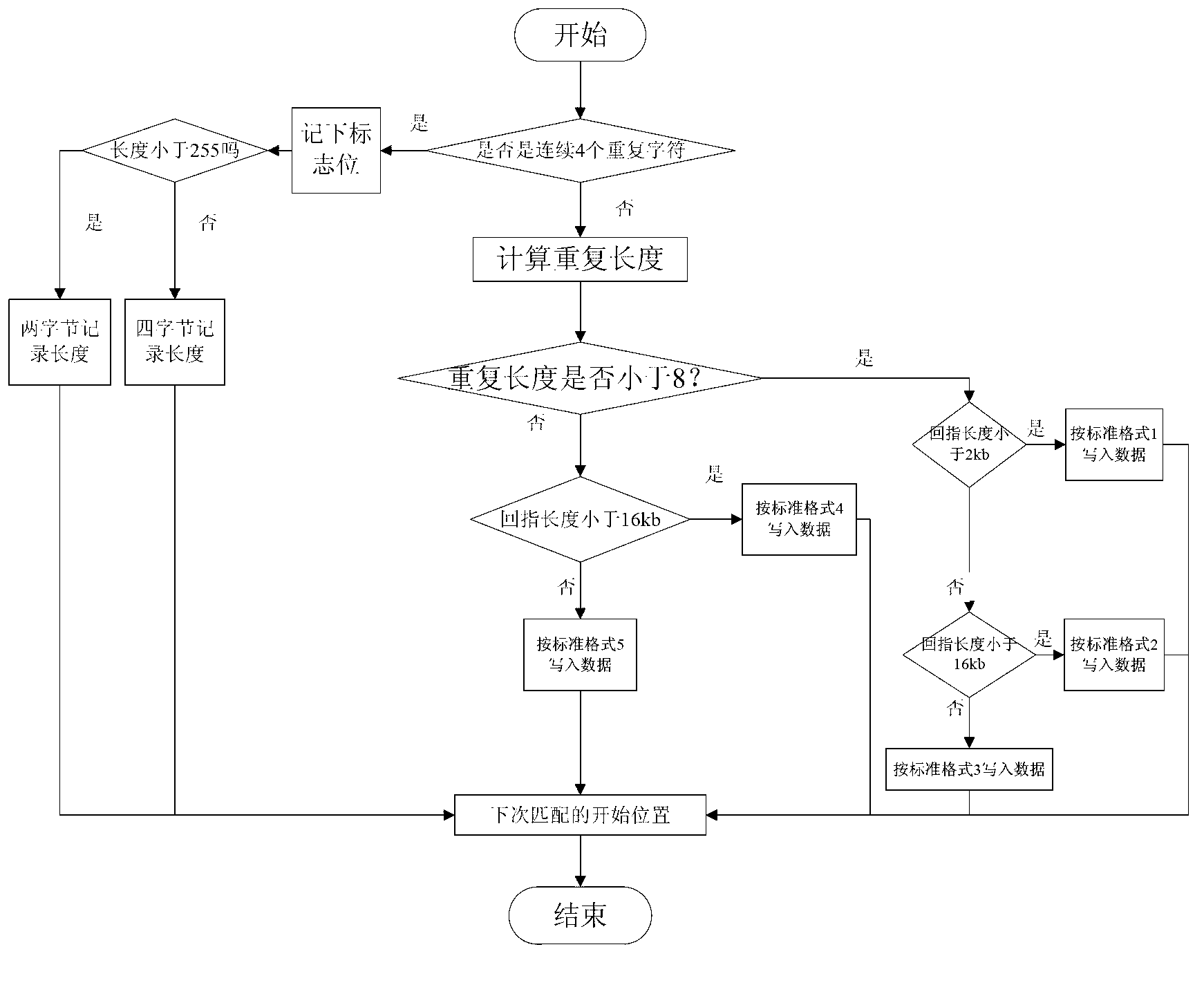
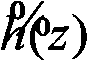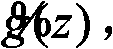Patents
Literature
249 results about "Run-length encoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Run-length encoding (RLE) is a form of lossless data compression in which runs of data (sequences in which the same data value occurs in many consecutive data elements) are stored as a single data value and count, rather than as the original run. This is most useful on data that contains many such runs. Consider, for example, simple graphic images such as icons, line drawings, Conway’s Game of Life, and animations. It is not useful with files that don't have many runs as it could greatly increase the file size.
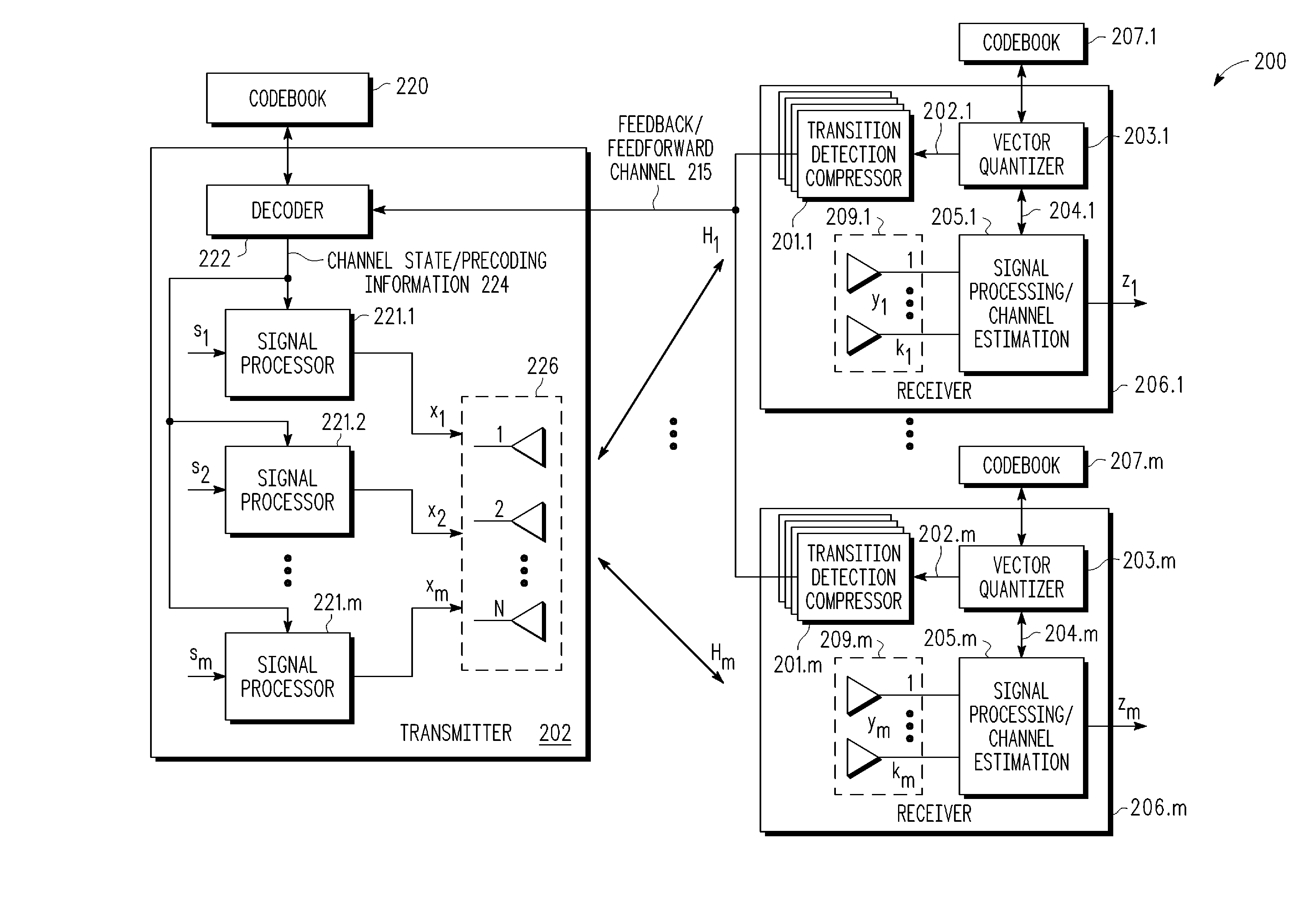
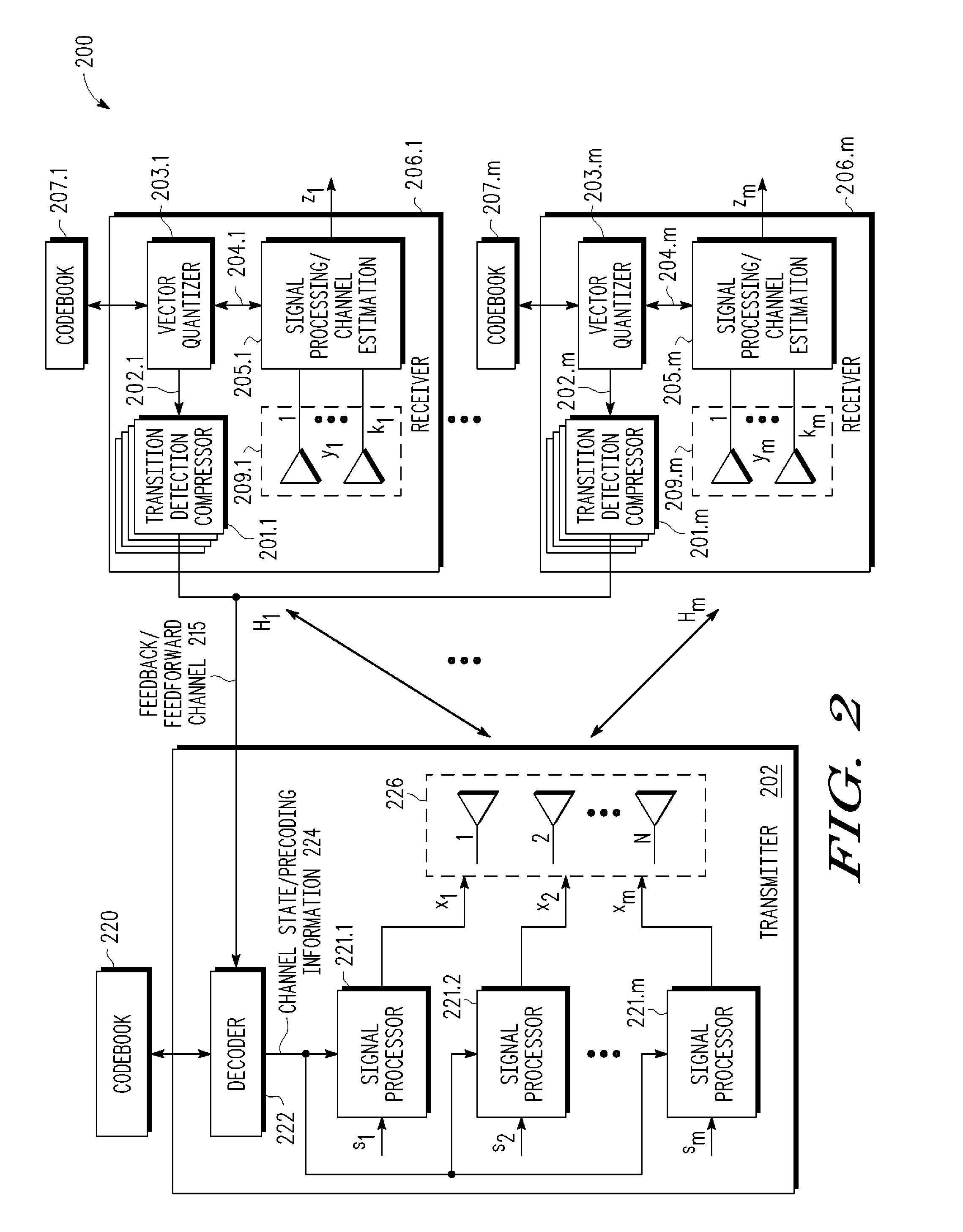
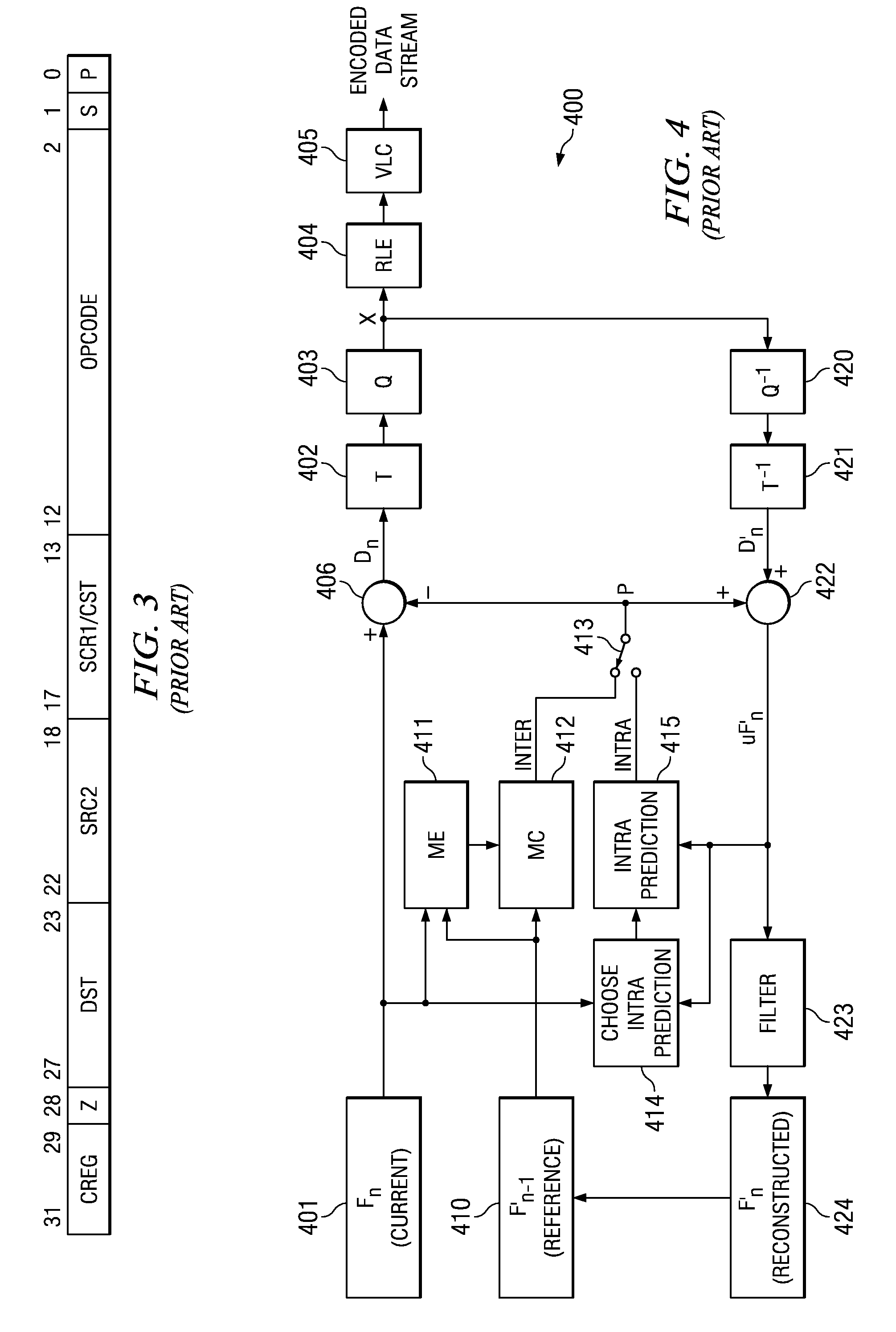
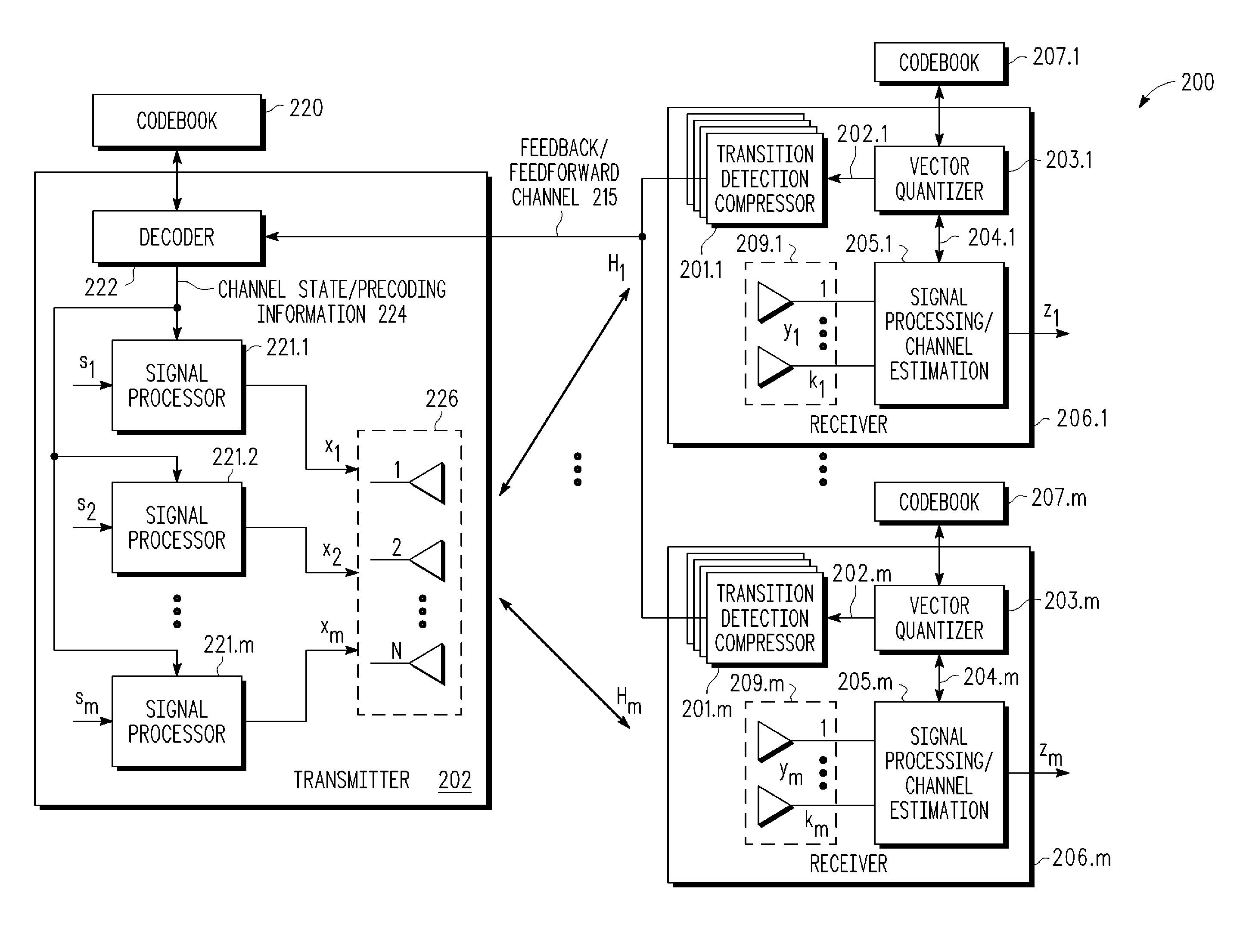
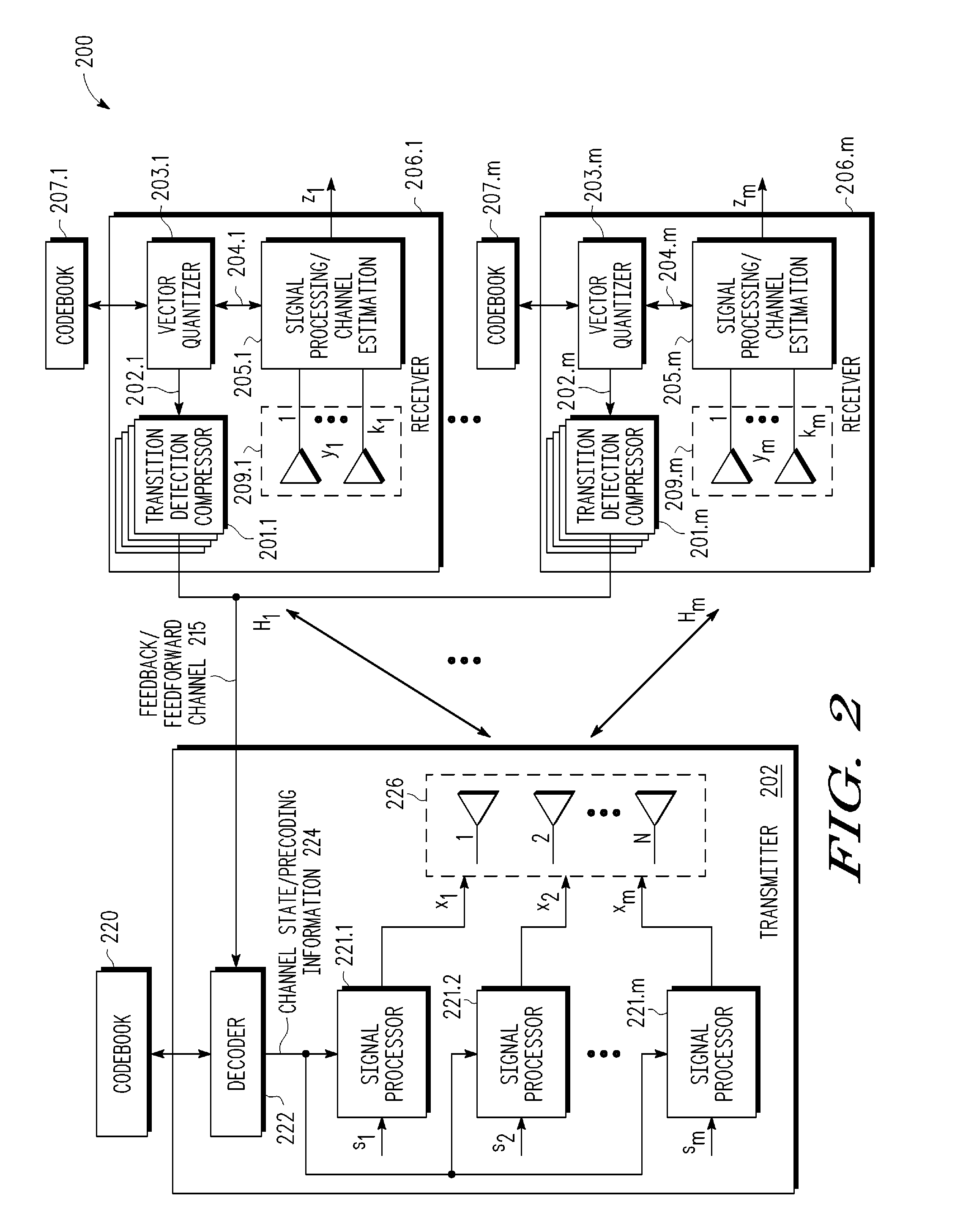
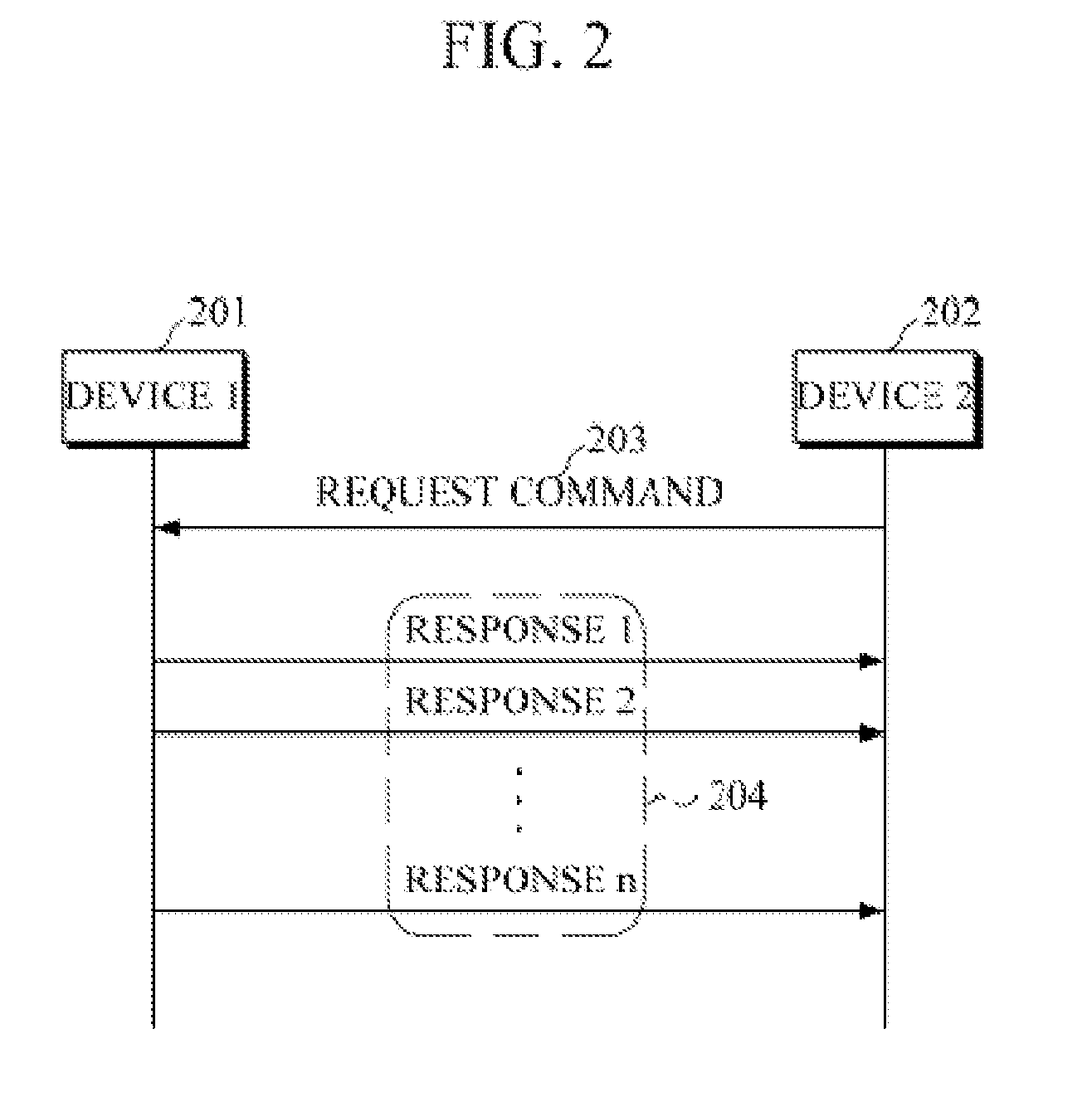
Feedback reduction for MIMO precoded system by exploiting channel correlation
ActiveUS20080080459A1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsPrecodingCommunications system
In a closed-loop wireless communication system, a codebook-based precoding feedback compression mechanism is provided to remove redundancy from the precoding feedback that is caused by channel correlation in time and frequency. Redundancy due to temporal correlation of the transmission channel is removed by sending precoding feedback only if there is a change in the precoder state for the channel to the receiver. Redundancy due to frequency correlation is removed by run length encoding the precoding feedback, thereby compressing the precoding feedback prior in the frequency domain. By compressing the precoding feedback, the average rate of precoder feedback is reduced.
Owner:NXP USA INC
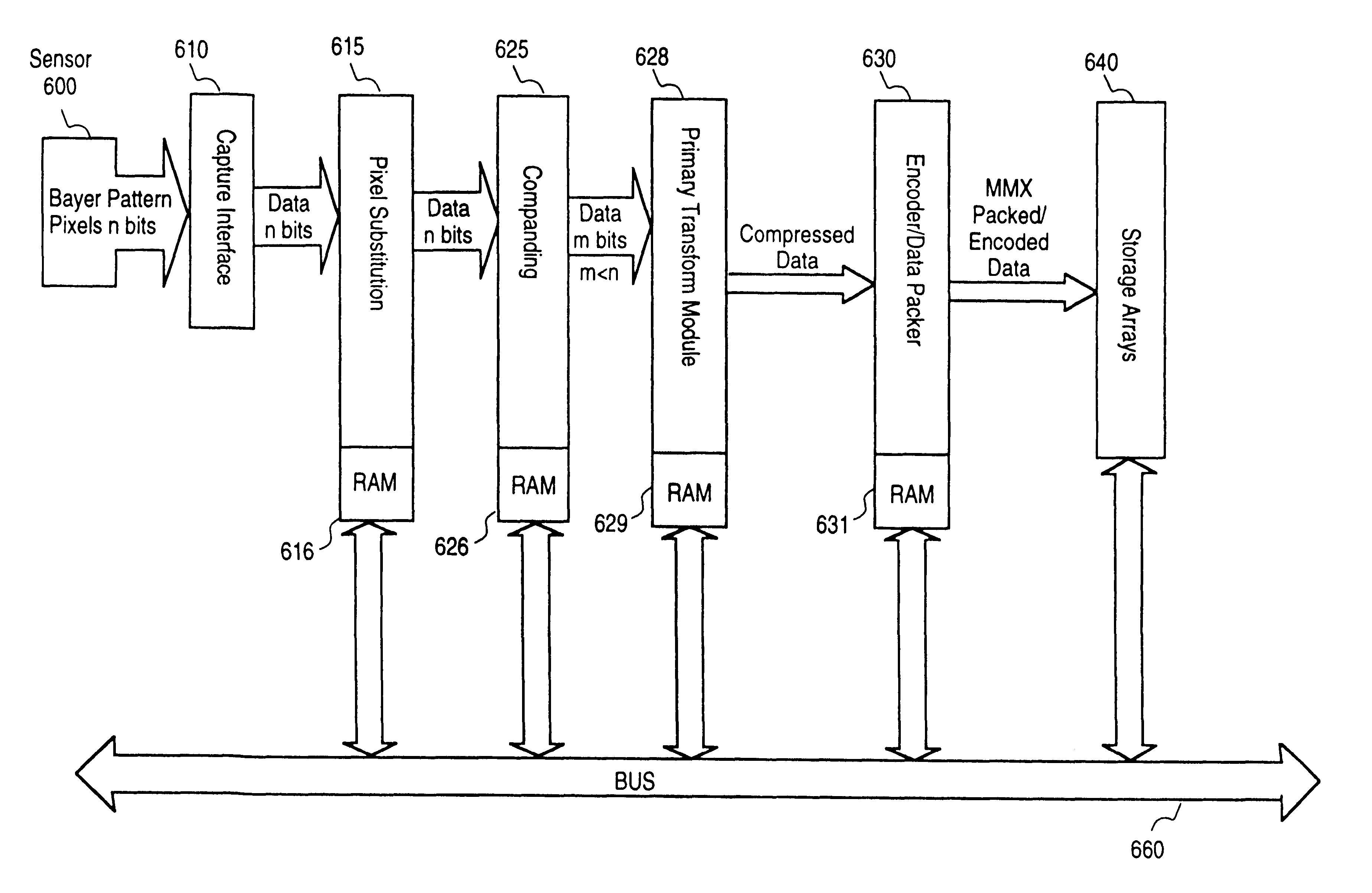
MMX optimized data packing methodology for zero run length and variable length entropy encoding
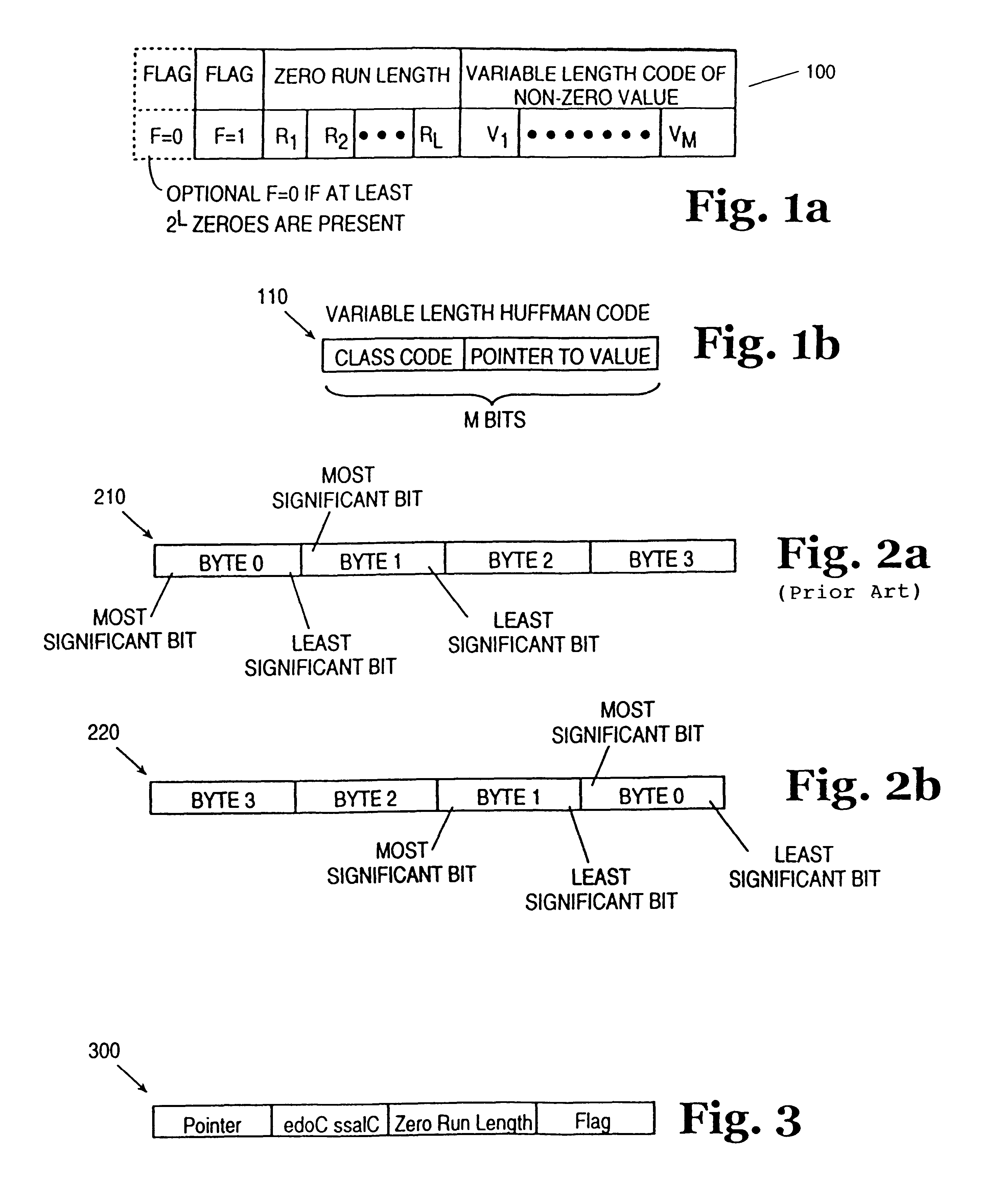
A method comprising entropy encoding into bits a set of data values, and packing into storage the entropy encoded bits by reversing the bits of words with unknown length and keeping in blocks the words with known lengths. For instance, in an entropy encoded data set that uses both Huffman coding and zero run coding, the class code may be reversed in bit order from right to left rather left to right while the words of known length such as the zero run code and Huffman pointer are stored left to right in blocks. This data arrangement is particularly useful in an MMX based machine.
Owner:INTEL CORP
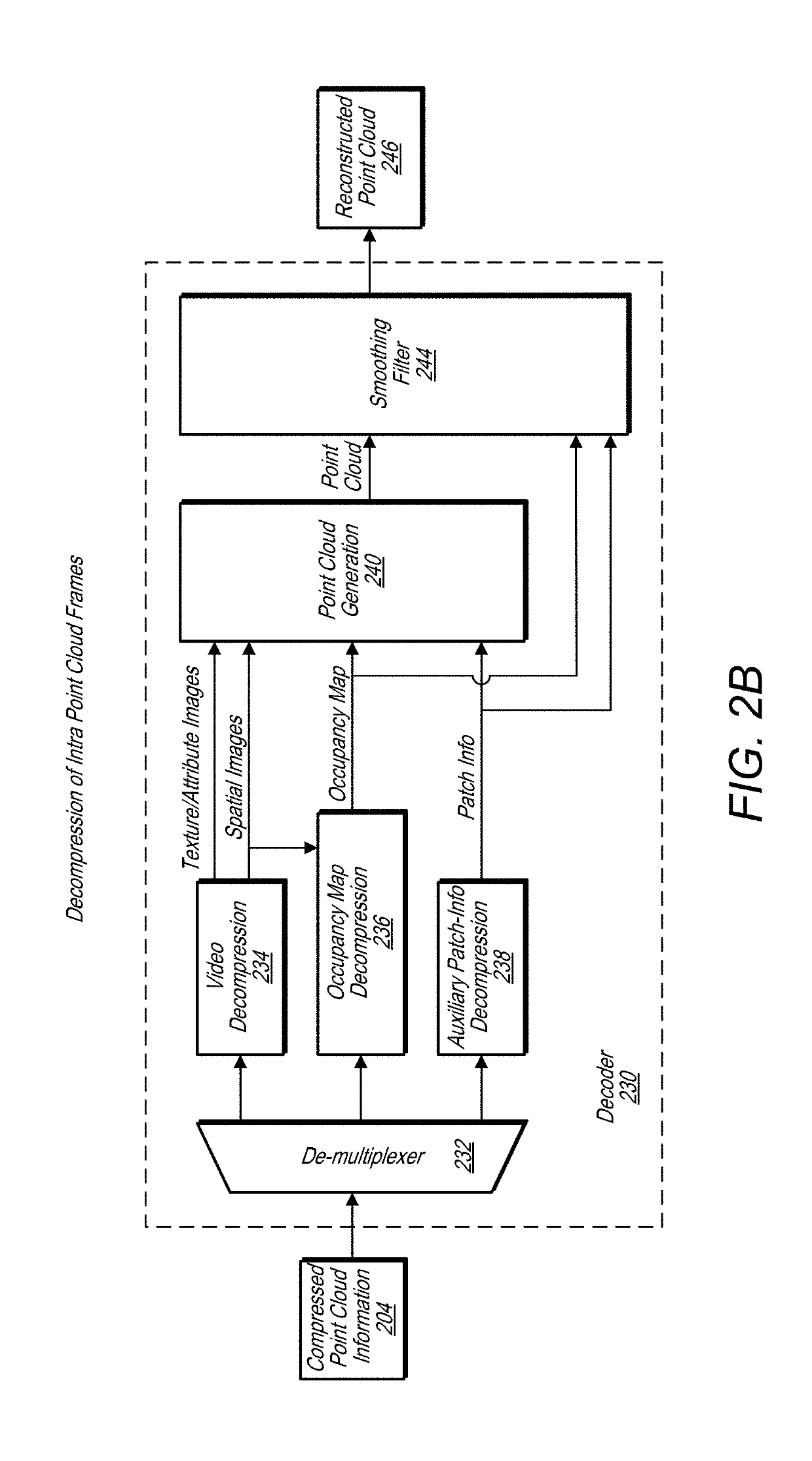
Point cloud occupancy map compression
ActiveUS20190156520A1Reduces converted sizeMinimize distortionImage enhancementImage analysisRun-length encodingImage based
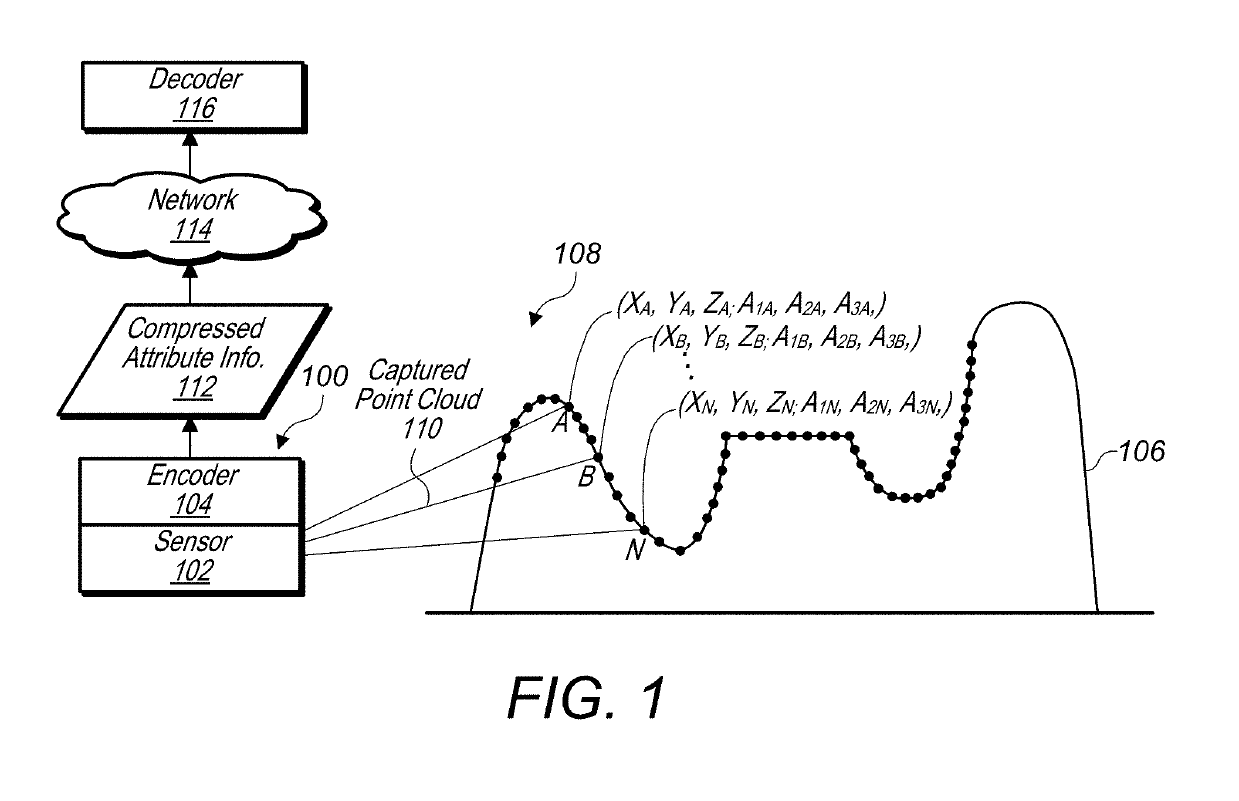
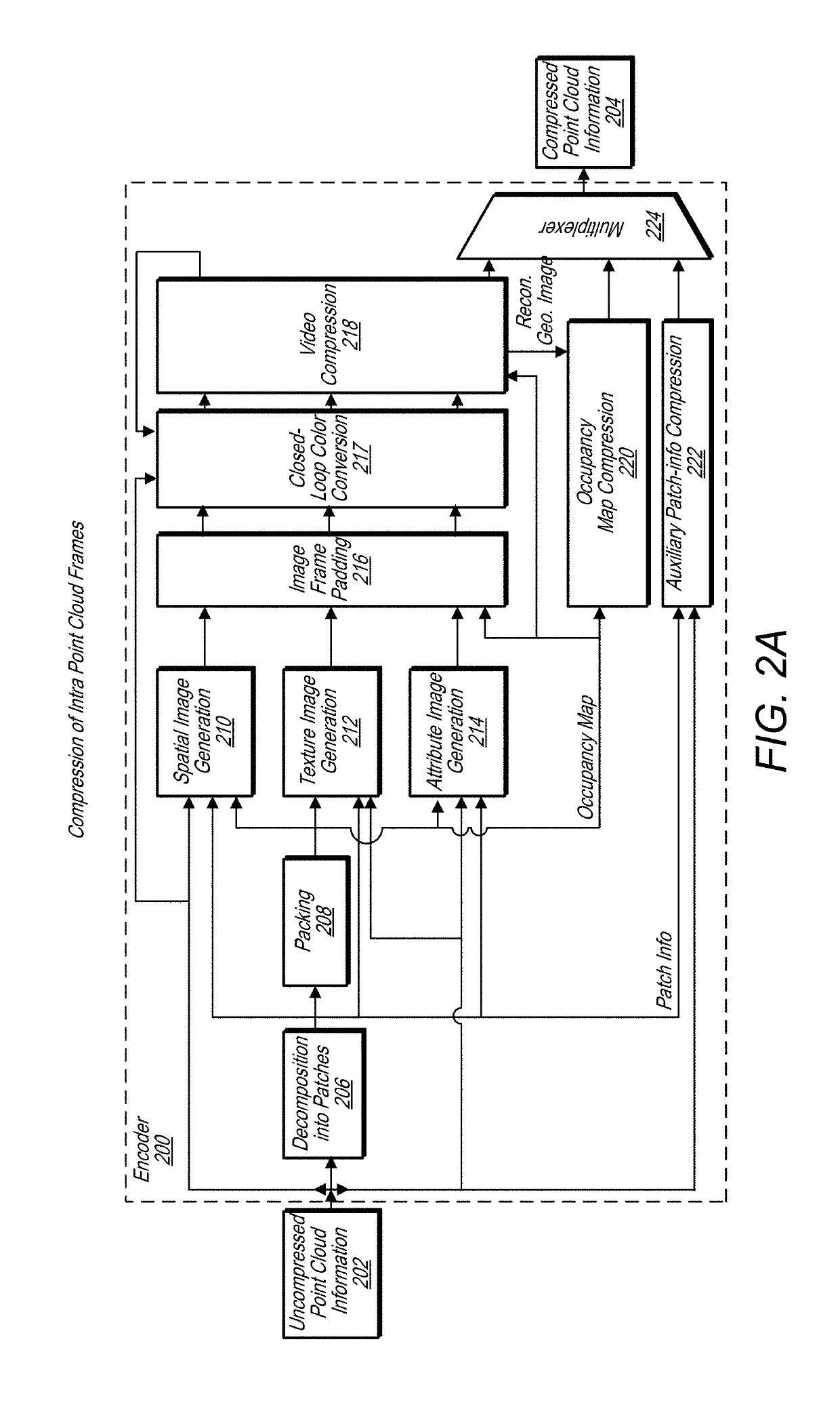
A system comprises an encoder configured to compress attribute information and / or spatial for a point cloud and / or a decoder configured to decompress compressed attribute and / or spatial information for the point cloud. To compress the attribute and / or spatial information, the encoder is configured to convert a point cloud into an image based representation. Also, the decoder is configured to generate a decompressed point cloud based on an image based representation of a point cloud. A block / sub-block organization scheme is used to encode blocks and sub-blocks of an occupancy map used in compressing the point cloud. Binary values are assigned to blocks / sub-blocks based on whether they contain patches projected on the point cloud. A traversal path is chosen that takes advantage of run-length encoding strategies to reduce a size of an encoded occupancy map. Also, auxiliary information is used to further improve occupancy map compression.
Owner:APPLE INC
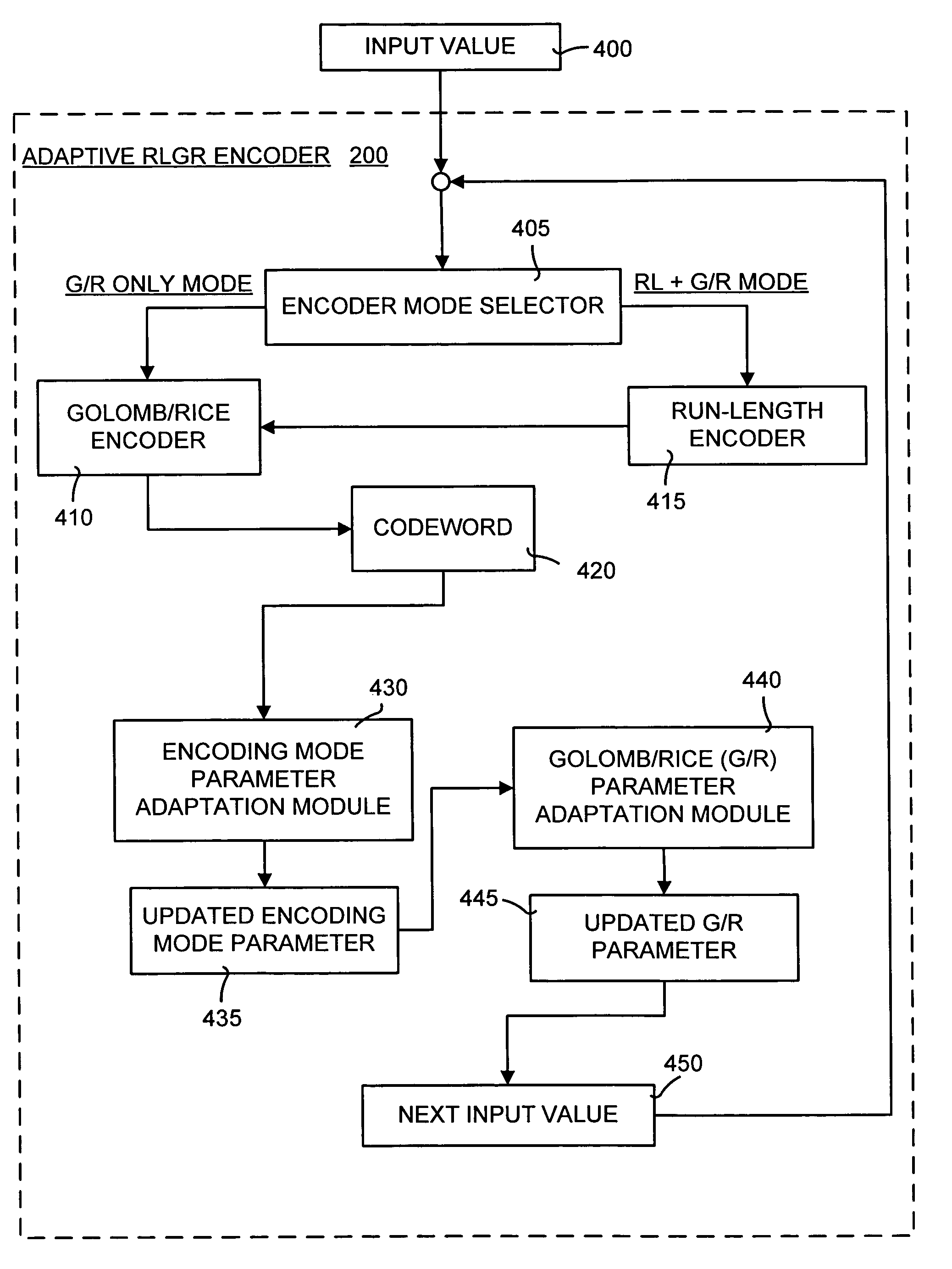
Lossless adaptive encoding and decoding of integer data
ActiveUS6987468B1Lossless encodingFast trackCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive encodingLossless compression
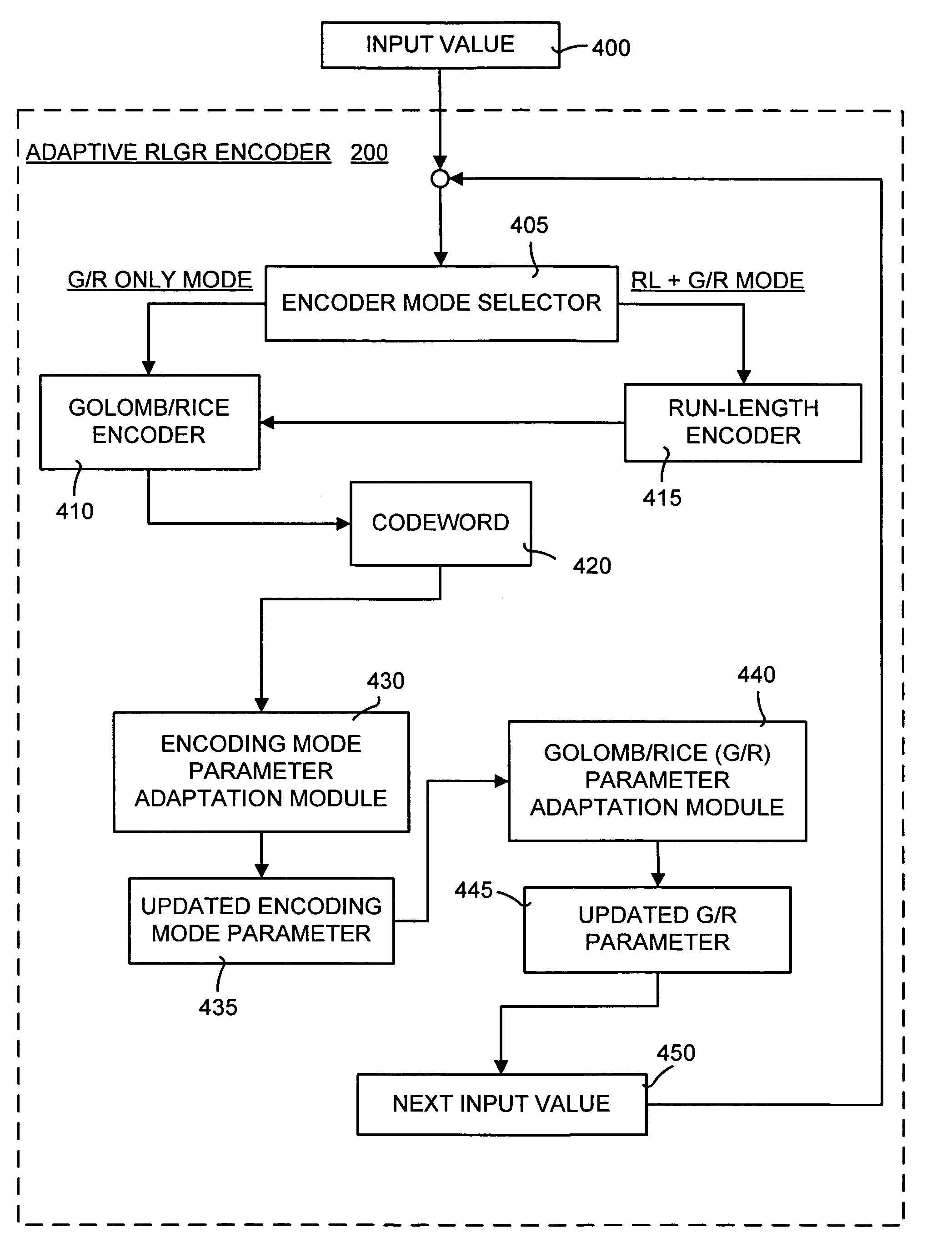
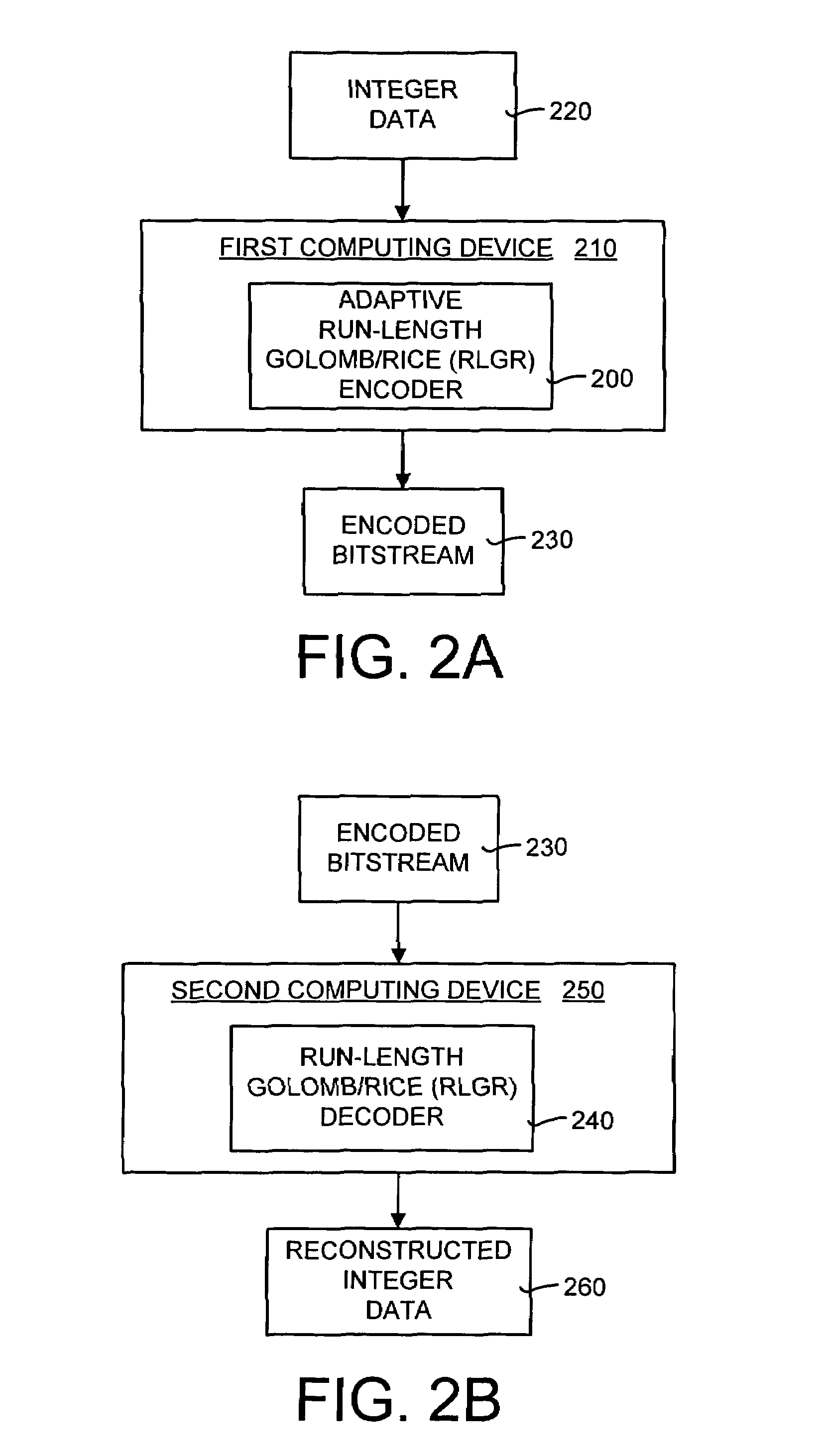
A method and system of lossless compression of integer data using a novel backward-adaptive technique. The adaptive Run-Length and Golomb / Rice (RLGR) encoder and decoder (codec) and method switches between a Golomb / Rice (G / R) encoder mode only and using the G / R encoder combined with a Run-Length encoder. The backward-adaptive technique includes novel adaptation rules that adjust the encoder parameters after each encoded symbol. An encoder mode parameter and a G / R parameter are adapted. The encoding mode parameter controls whether the adaptive RLGR encoder and method uses Run-Length encoding and, if so, it is used. The G / R parameter is used in both modes to encode every input value (in the G / R only mode) or to encode the number or value after an incomplete run of zeros (in the RLGR mode). The adaptive RLGR codec and method also includes a decoder that can be precisely implemented based on the inverse of the encoder rules.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
Lossless adaptive encoding and decoding of integer data
A method and system of lossless compression of integer data using a novel backward-adaptive technique. The adaptive Run-Length and Golomb / Rice (RLGR) encoder and decoder (codec) and method switches between a Golomb / Rice (G / R) encoder mode only and using the G / R encoder combined with a Run-Length encoder. The backward-adaptive technique includes novel adaptation rules that adjust the encoder parameters after each encoded symbol. An encoder mode parameter and a G / R parameter are adapted. The encoding mode parameter controls whether the adaptive RLGR encoder and method uses Run-Length encoding and, if so, it is used. The G / R parameter is used in both modes to encode every input value (in the G / R only mode) or to encode the number or value after an incomplete run of zeros (in the RLGR mode). The adaptive RLGR codec and method also includes a decoder that can be precisely implemented based on the inverse of the encoder rules.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
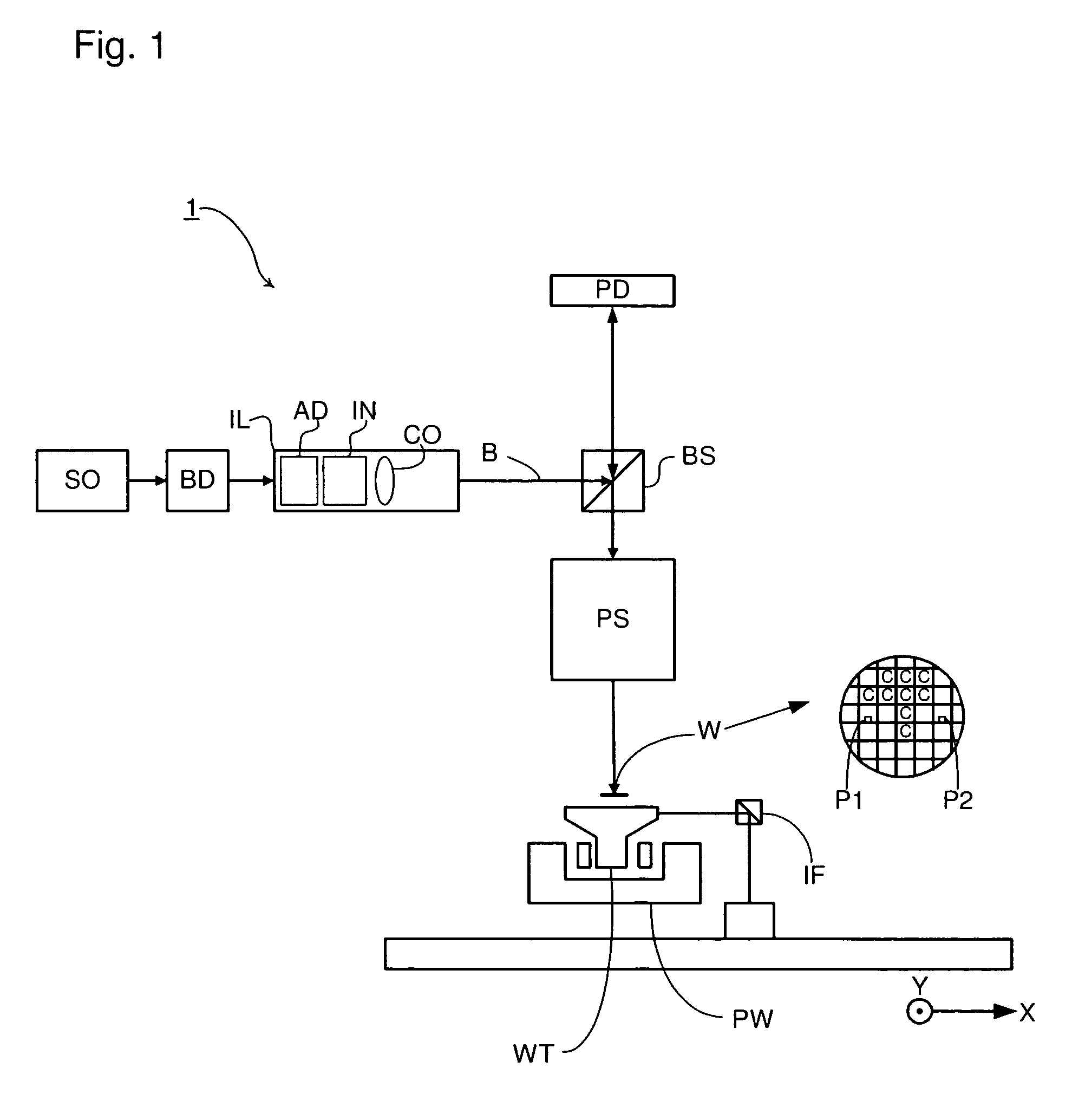
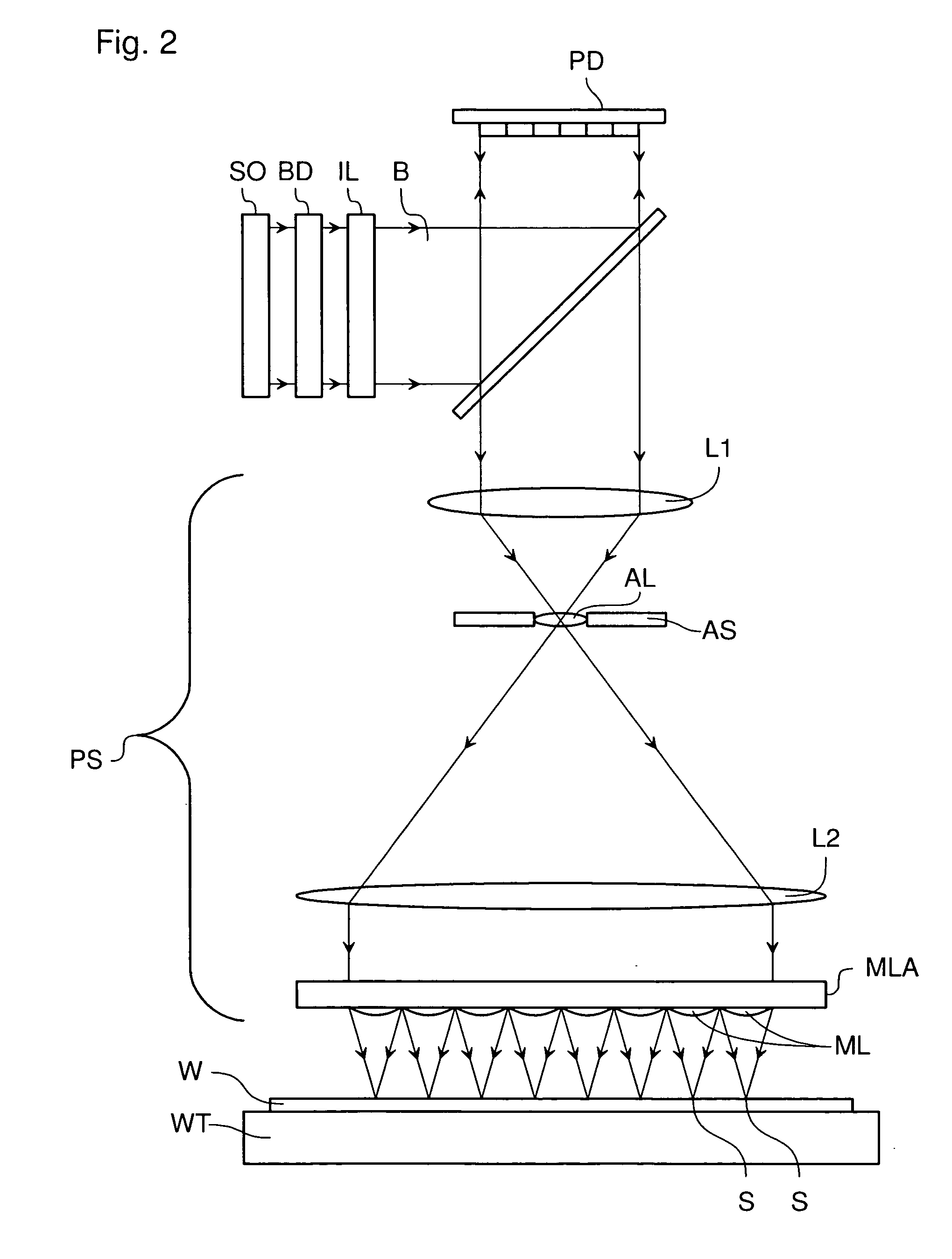
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method utilizing 2D run length encoding for image data compression
A lithographic apparatus comprises an array of individually controllable elements and a data processing pipeline. The array of individually controllable elements modulates a beam of radiation. The data processing pipeline converts a first representation of a requested dose pattern to a sequence of control data suitable for controlling the array of individually controllable elements in order substantially to form the requested dose pattern on a substrate. The data processing pipeline comprises an offline pre-processing device and an online rasterizer. The offline pre-processing device converts the first representation of the requested dose pattern to an intermediate representation, which can be rasterized in a fewer number of operations than the first representation. The storage device stores the intermediate representation. The online rasterizer accesses the stored intermediate representation and produces therefrom a stream of bitmap data to be used to generate the sequence of control data substantially in real time.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
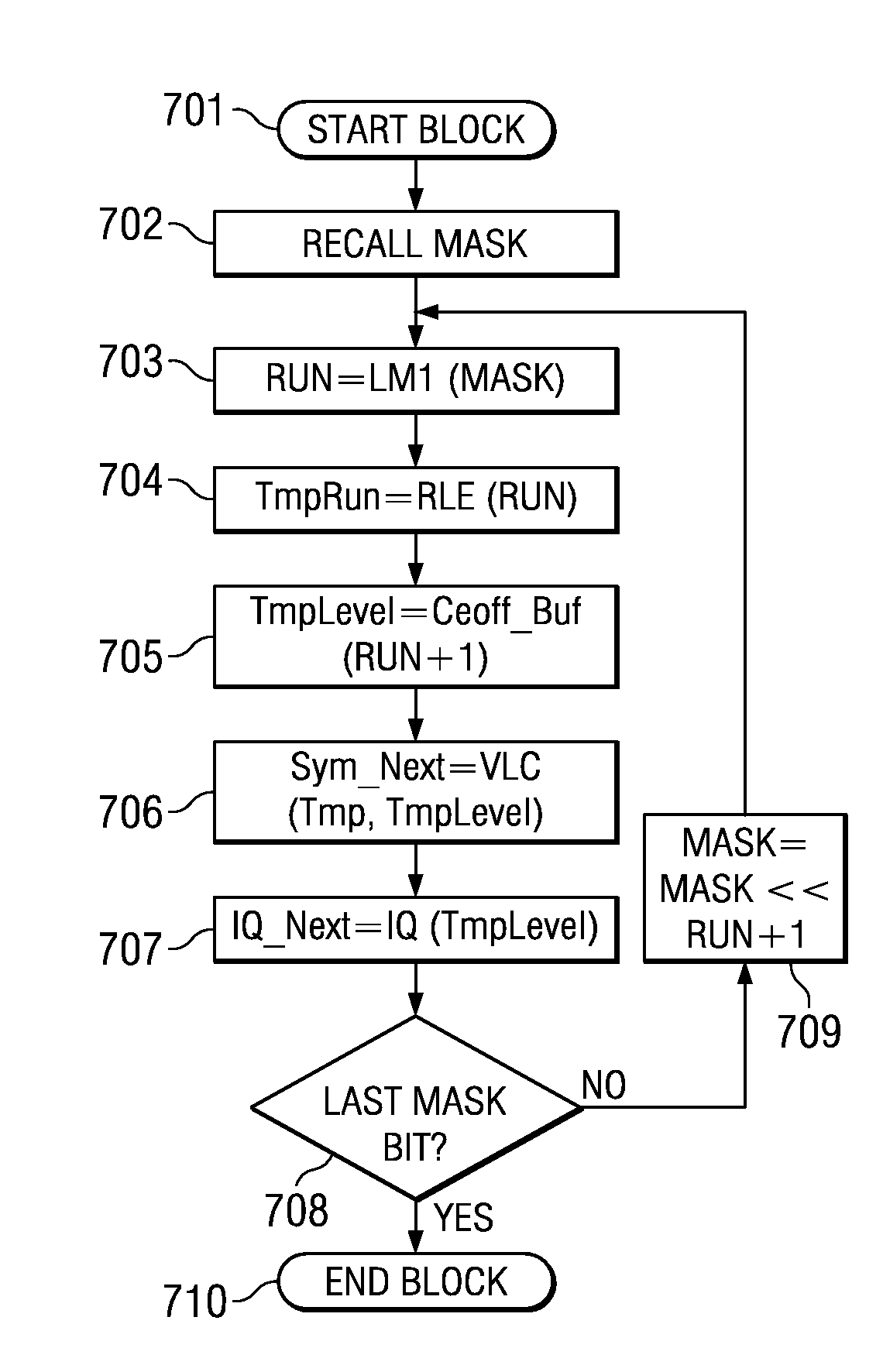
Run Length Encoding in VLIW Architecture
ActiveUS20080046698A1Reduce bitrateEasy to harvestPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningVariable-length codeGlyph
A computer implemented method of video date encoding generates a mask having one bit corresponding each spatial frequency coefficient of a block during quantization. The bit state of the mask depends upon whether the corresponding quantized spatial frequency coefficient is zero or non-zero. The runs of zero quantized spatial frequency coefficients determined by a left most bit detect instruction are determined from the mask and run length encoded. The mask is generated using a look up table to map the scan order of quantization to the zig-zag order of run length encoding. Variable length coding and inverse quantization optionally take place within the run length encoding loop.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Feedback reduction for MIMO precoded system by exploiting channel correlation
ActiveUS8023457B2Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsPrecodingCommunications system
In a closed-loop wireless communication system, a codebook-based precoding feedback compression mechanism is provided to remove redundancy from the precoding feedback that is caused by channel correlation in time and frequency. Redundancy due to temporal correlation of the transmission channel is removed by sending precoding feedback only if there is a change in the precoder state for the channel to the receiver. Redundancy due to frequency correlation is removed by run length encoding the precoding feedback, thereby compressing the precoding feedback prior in the frequency domain. By compressing the precoding feedback, the average rate of precoder feedback is reduced.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Spatial overlap analysis method and system used in geographic information system
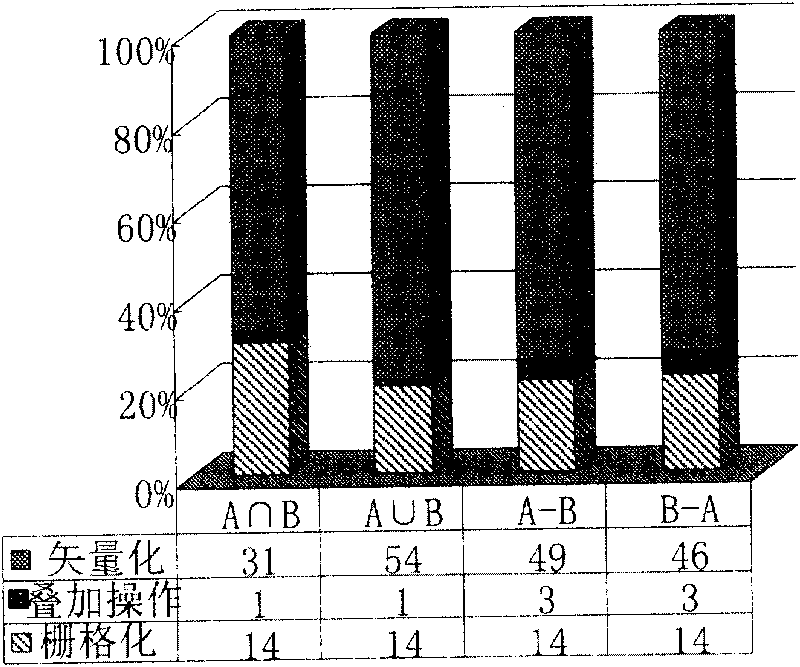
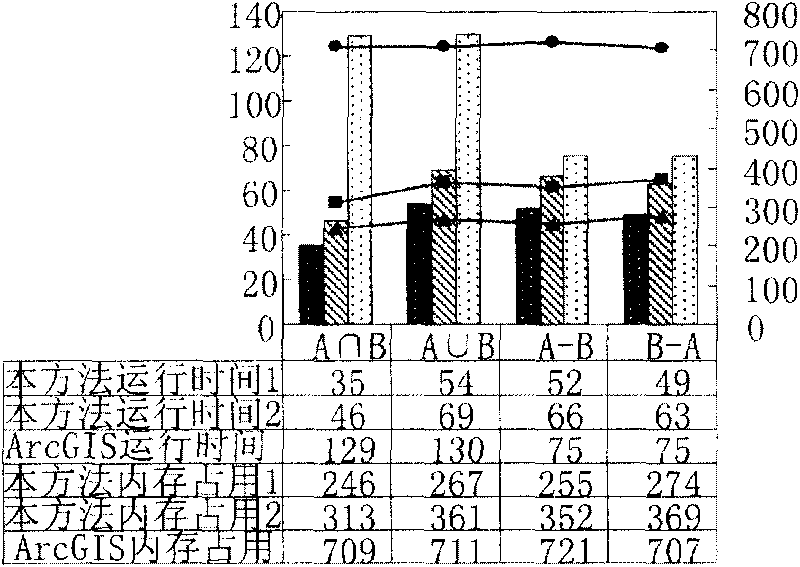
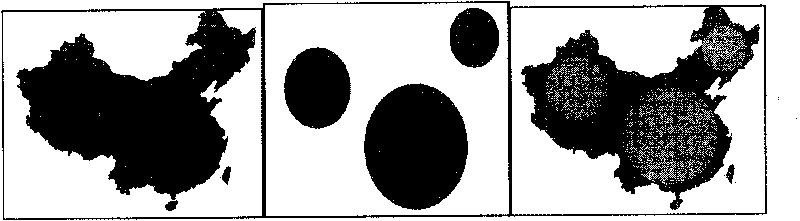
ActiveCN101751449ABig advantageGood value for moneySpecial data processing applicationsAnalysis methodRun-length encoding
The invention discloses spatial overlap analysis method and system used in a geographic information system (GIS). The method comprises the following steps of: converting vector data input to layers in the GIS into raster data, and representing by adopting run coding; executing overlap operation on the raster data represented by adopting run coding; and converting the overlapped raster data into the vector data to obtain overlapped layers. The invention can avoid the disadvantages of computation geometric algorithms and increases the overlap efficiency by utilizing the advantages of a raster algorithm.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
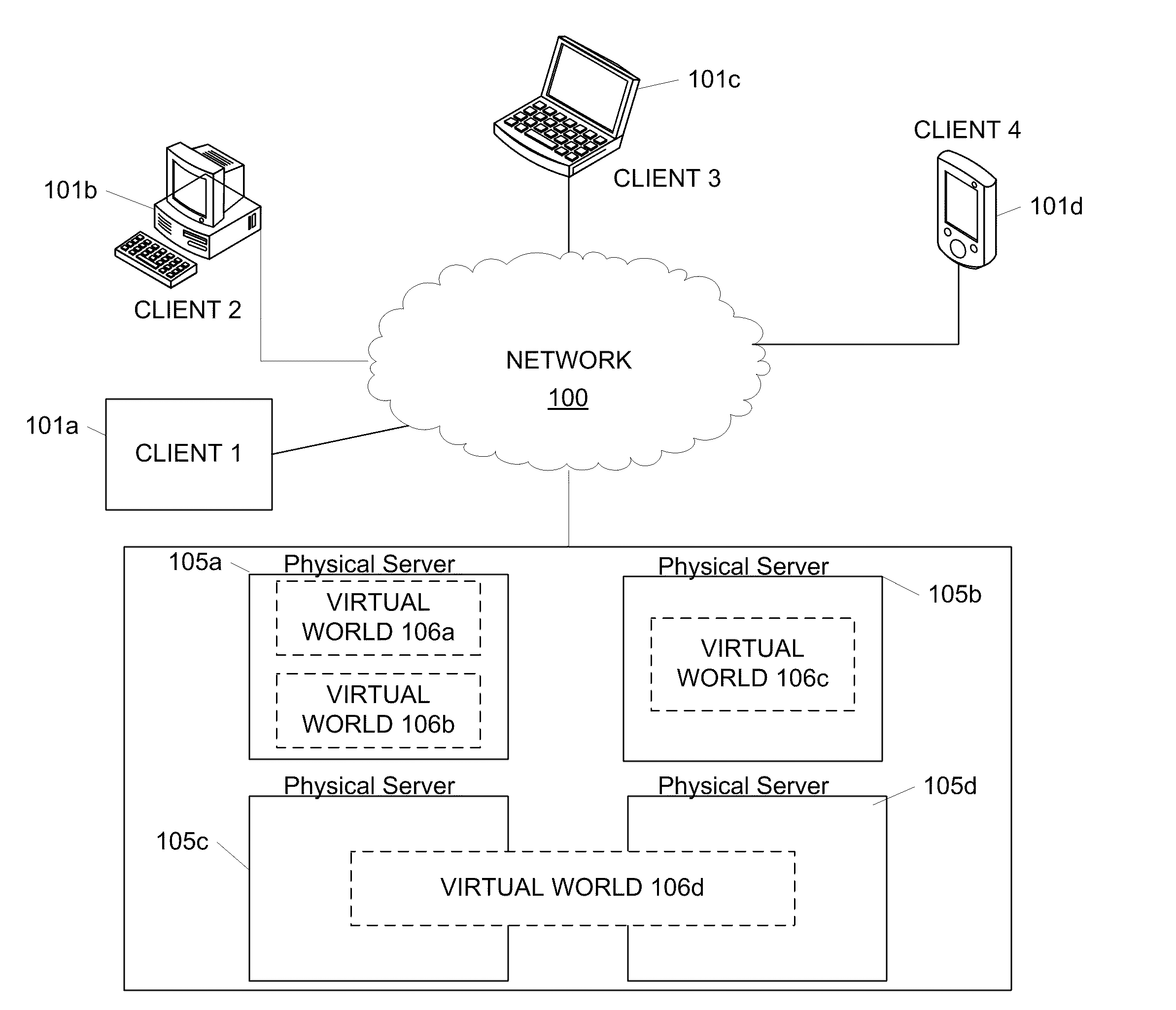
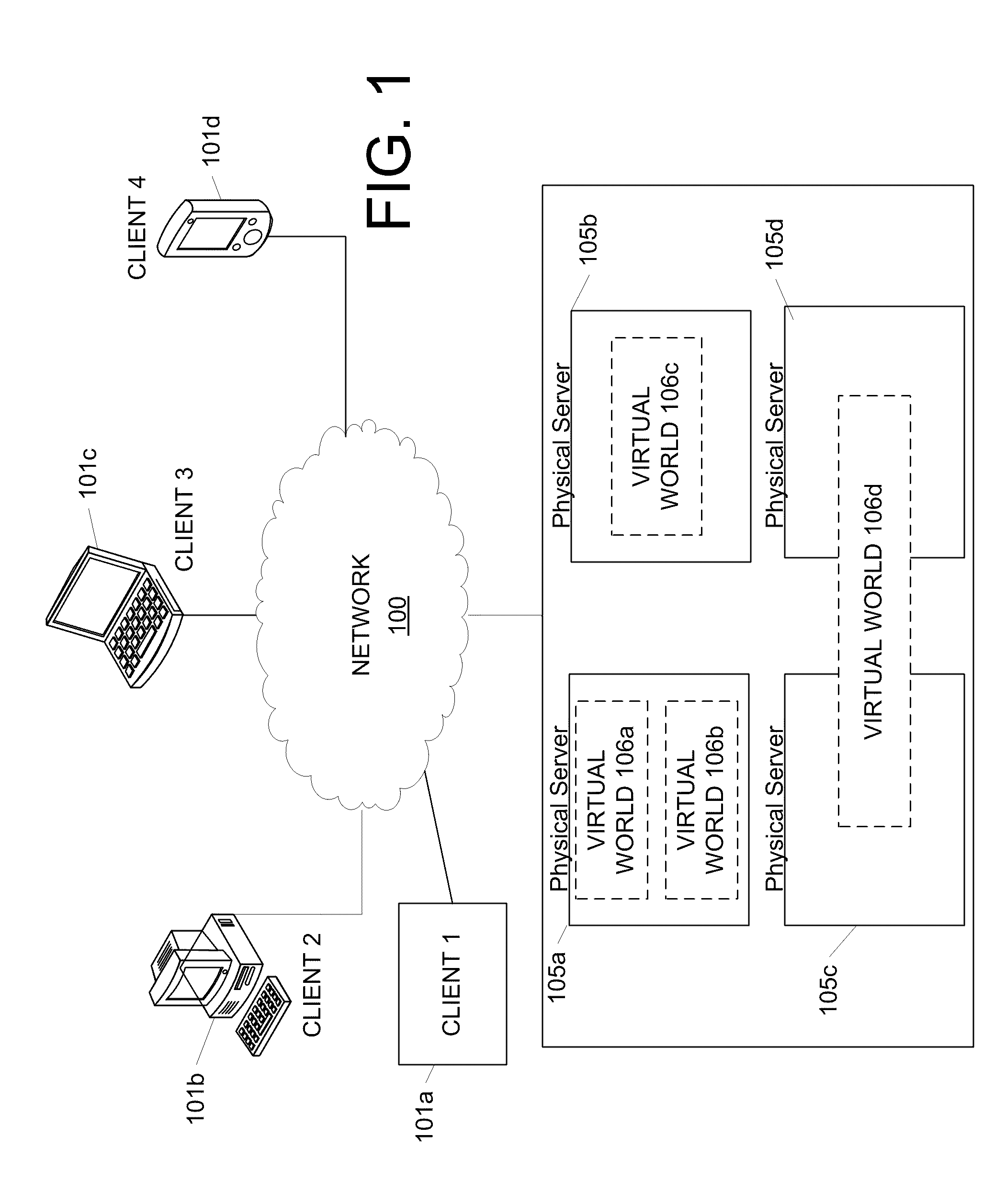
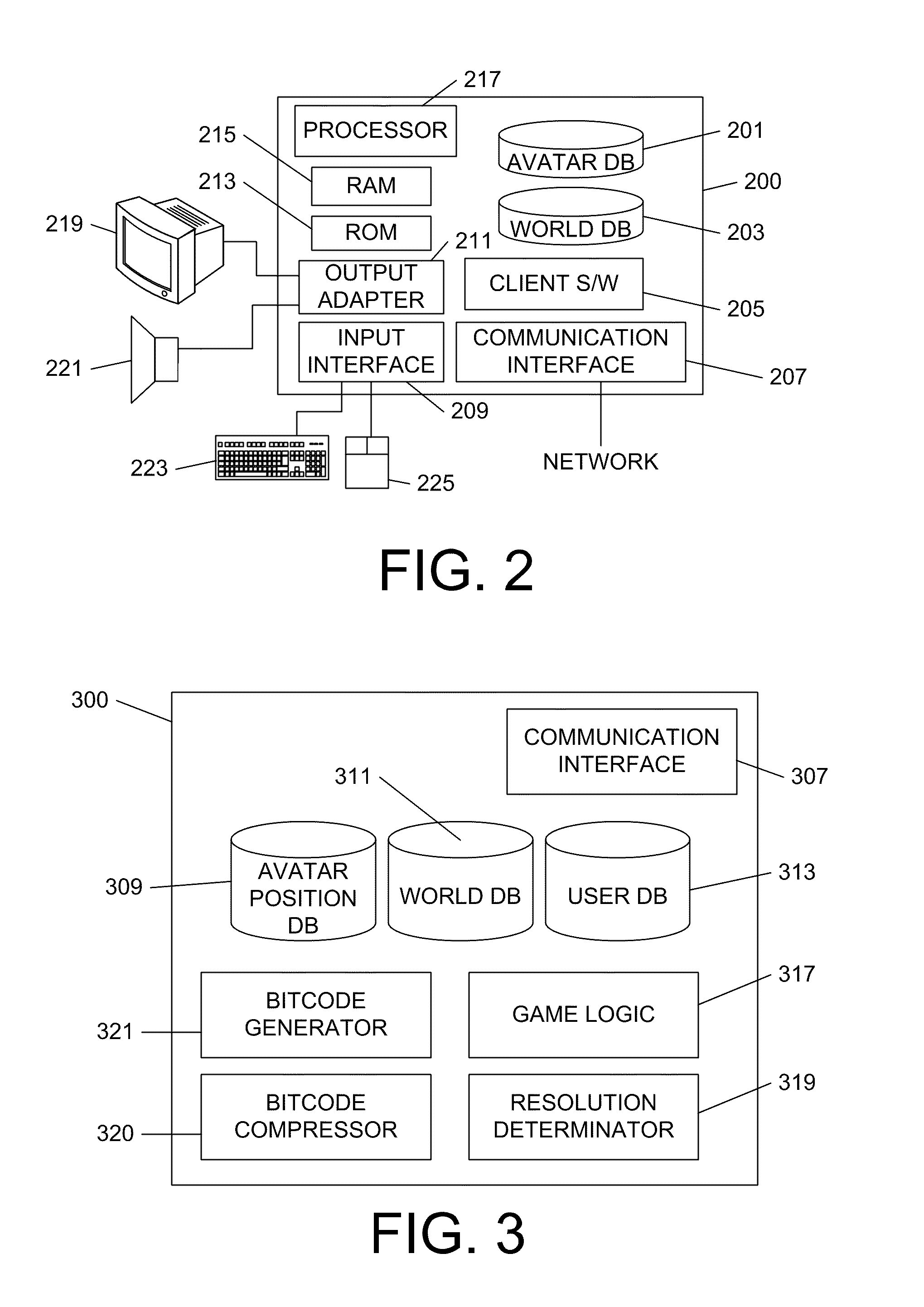
Position tracking in a virtual world
ActiveUS20100275136A1Reduce processing timeMultiple digital computer combinationsAnimationTemporal resolutionImage resolution
Positions of avatars in a virtual world may be communicated to clients using multiple bitcode resolutions to minimize required communication bandwidth between a virtual world server and virtual world clients, thereby allowing transmission of all avatars' positions to every other player. Lower resolution bitcodes may be based on a lower resolution grid overlaid on the virtual world, whereas higher resolution bitcodes may be based on a higher resolution grid overlaid on the virtual world. In one example, a virtual world server may determine the bitcode resolution to use based on a distance between an avatar to which the position information is to be sent and other avatars in the virtual world. Resolution may include spatial resolution, where nearer avatars' locations are provided with higher resolution bitcodes, or temporal resolution, where the transmission frequency of position information is greater for nearer avatars. Position information in a transmission stream may further be condensed by using run length encoding.
Owner:JAGEX
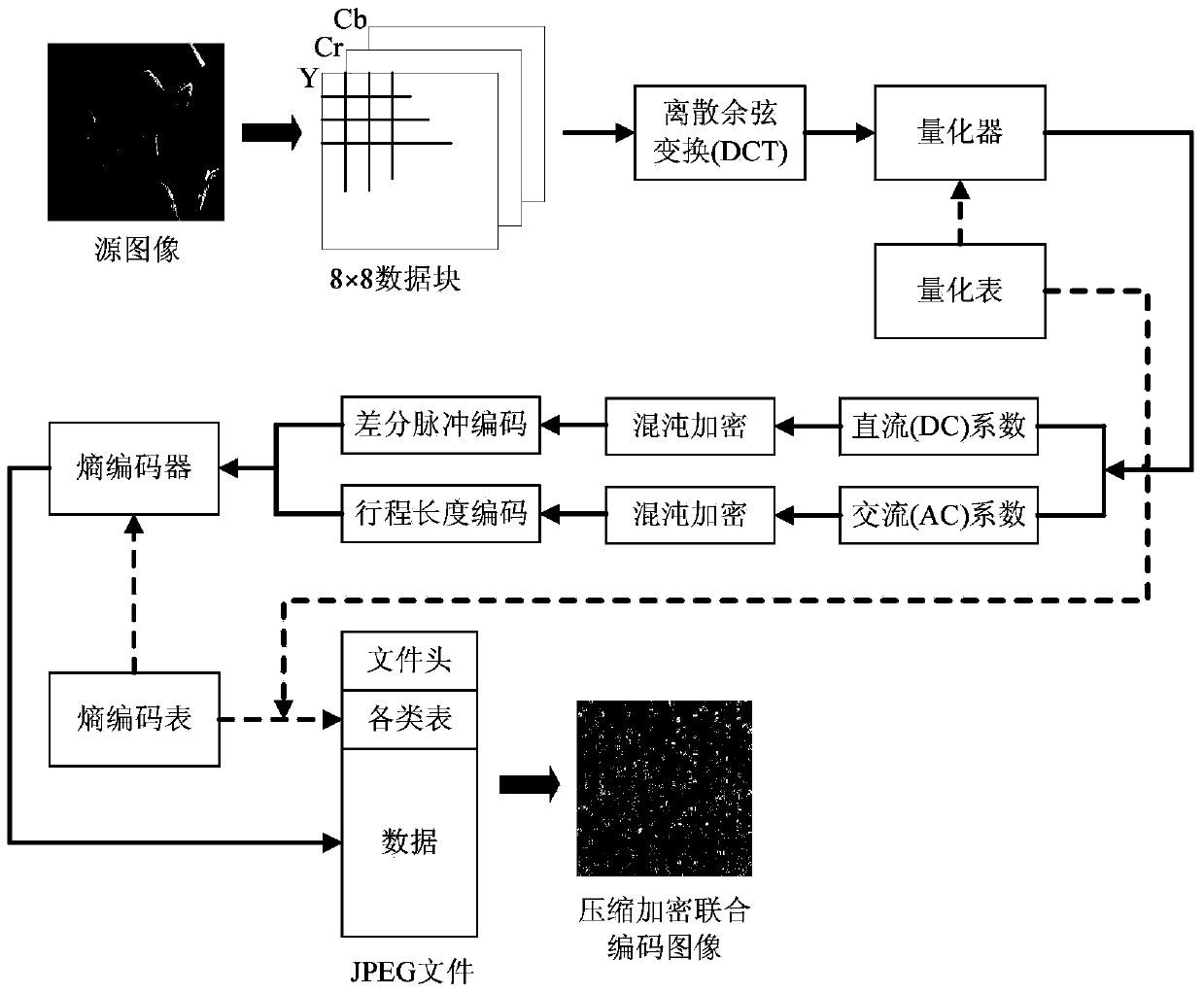
Digital image compressing, encrypting and encoding combined method
ActiveCN104144343ASolve the problem that effective compression cannot be performedEffective security protectionDigital video signal modificationAc coefficientJPEG
The invention discloses a digital image compressing, encrypting and encoding combined method, and belongs to the technical field of image encrypting. The method is achieved on the basis of the JPEG compressing and encoding standard which is most widely applied at present, and the encrypting algorithm based on chaos is integrated with the encoding process; according to the characteristic that DC coefficients and AC coefficients are separately encoded on the basis of the JPEG standard, the DC coefficients and the AC coefficients of an image are separately encrypted; in order to give consideration to both security and compressing efficiency, all the DC coefficients and part of the AC coefficients are encrypted through the method, coefficients at the same positions in all DCT blocks are divided into different groups and are scrambled and diffused within the groups, and damage to differential encoding and run length encoding in the encrypting process is reduced as much as possible; scrambling and diffusing are achieved on the basis of logistic chaotic mapping and Chebyshev chaotic mapping respectively. The experiments prove that the method has high data compressing capacity while providing effective image data security protection.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Image compression using variable bit size run length encoding
ActiveUS7483585B2Increase the lengthVariable sizeCharacter and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationAlgorithmImage compression
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Remote sensing image near-lossless compression hardware realization method based on improved JPEG-LS algorithm
InactiveCN101534373ABreaking the Loop Feedback ModelLower latencyTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDirect computationAlgorithm
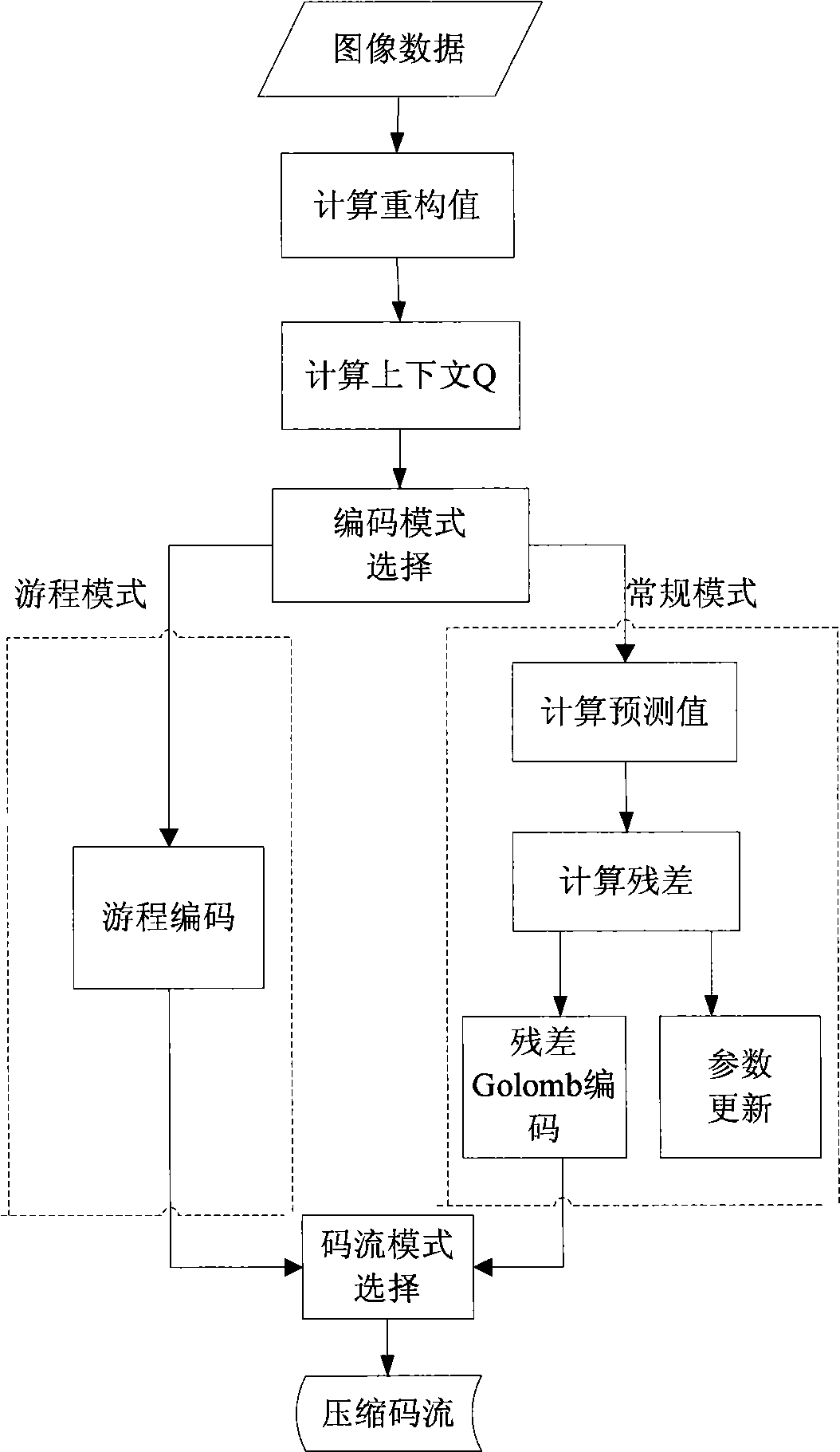
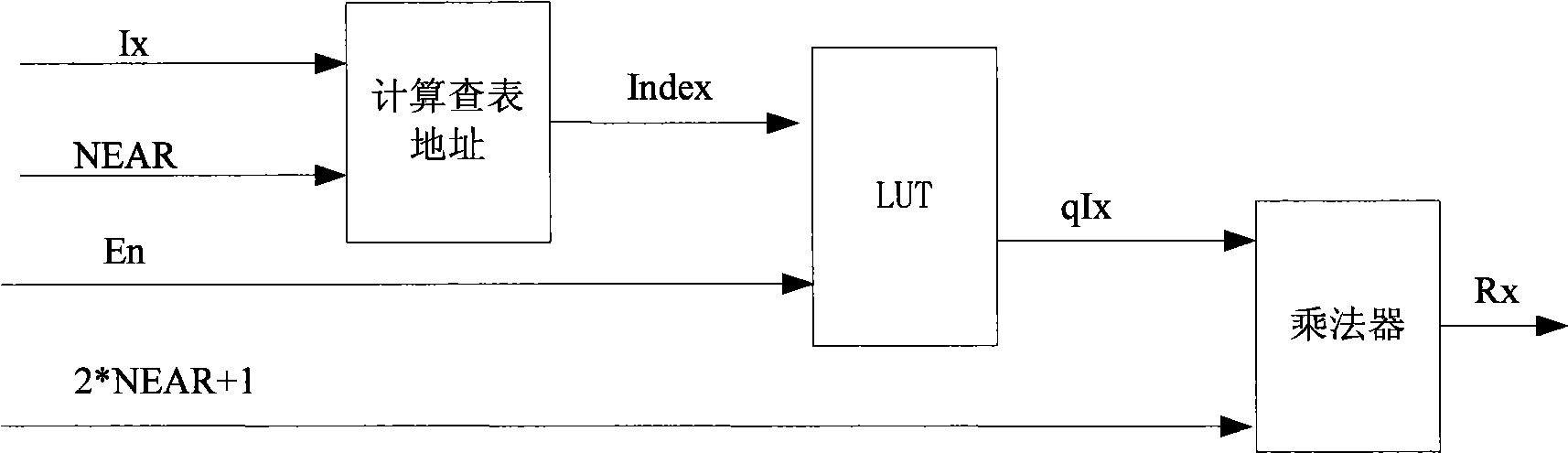
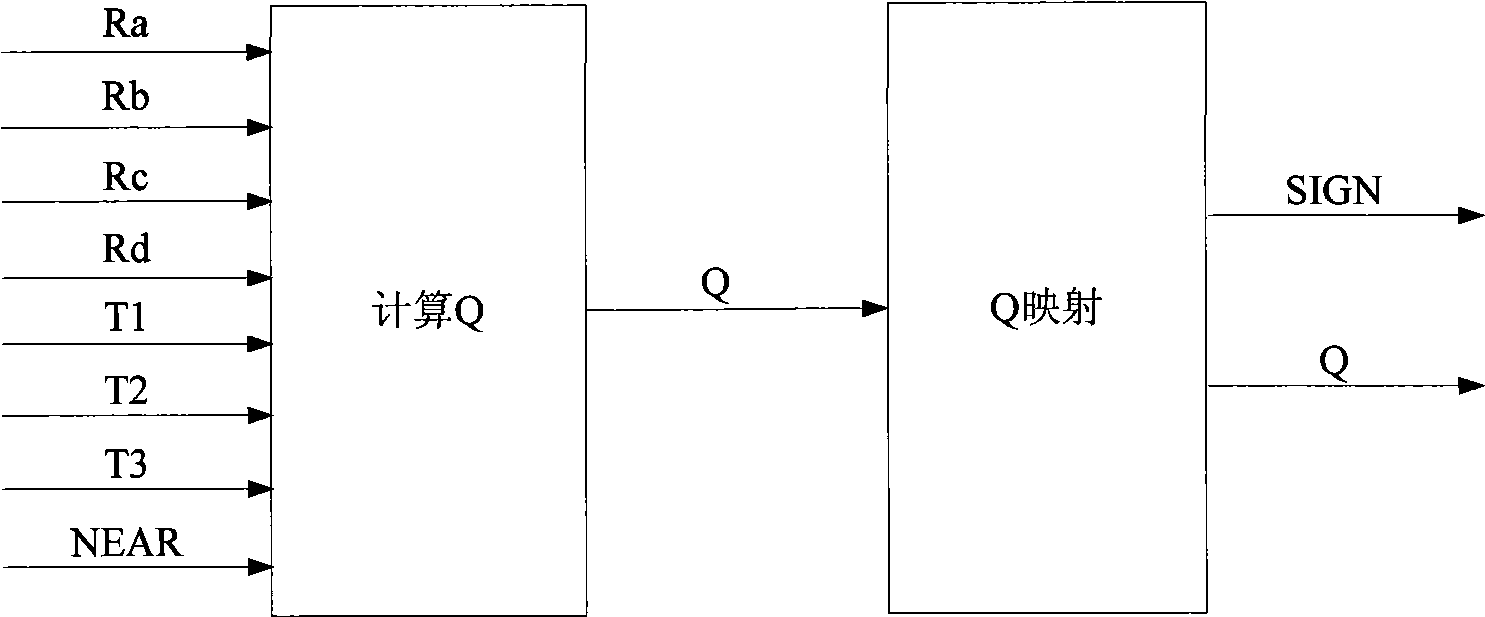
A remote sensing image near-lossless compression hardware realization method based on improved JPEG-LS algorithm comprises the steps (1) directly calculating to obtain a pixel reconstruction value by the pixel actual value of an input image and accomplishing the calculation in a single clock period by using a formula Rx=int[Ix / (2Near+1)]*(2Near+1), in the formula, the Rx and the Ix are respectively the pixel reconstruction value and actual value, the int is rounding operation, and the Near is a compression ratio control factor; (2) calculating a context environmental variable Q according to the obtained pixel reconstruction value, if Q is equal to 0, performing run coding, otherwise, going to a step (3) of performing conventional coding; (3) calculating the predictive value of the current pixel by the pixel reconstruction value according to the geometric position relation between the current pixel and the adjacent pixel; (4) calculating the residual value between the predictive value and actual value of the current pixel; and (5) performing Golomb coding after quantising the obtained residual value, and synchronously updating the parameter variable corresponding to the context environmental variable Q using the quantisation result.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Method and apparatus for data management in advanced metering infrastructure network
ActiveUS20130285835A1Guaranteed normal transmissionEfficient storageElectric signal transmission systemsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsSequential dataData management
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
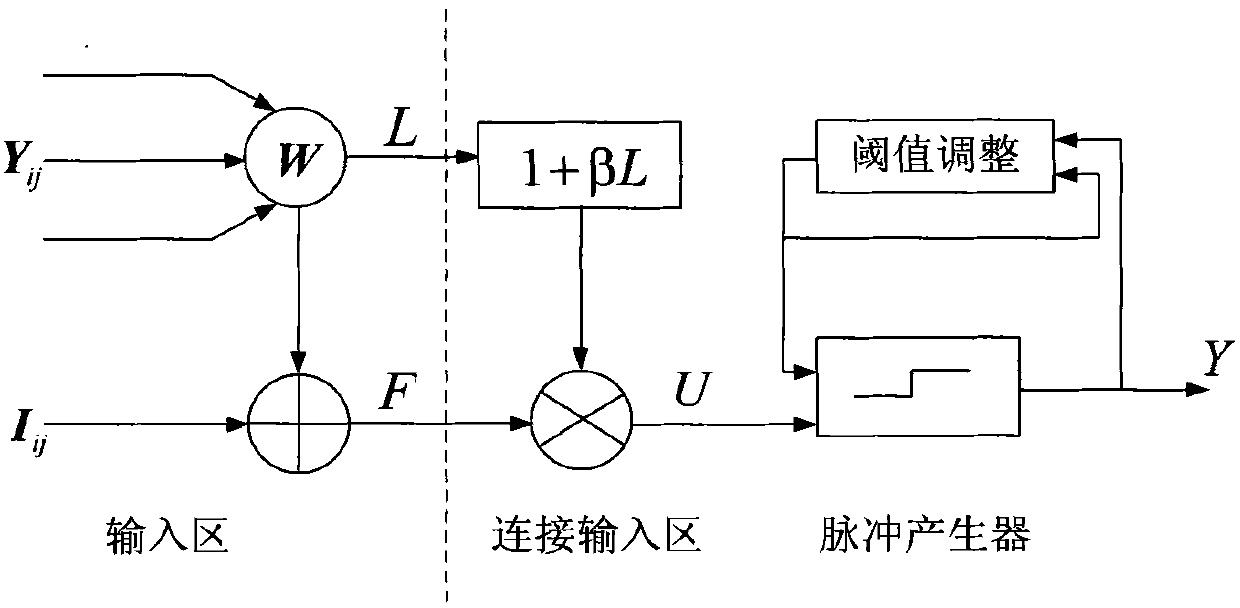
Medical image ROI (Region of Interest) compression method based on lifting wavelet and PCNN (Pulse Coupled Neural Network)
InactiveCN101908891AEfficient storagePromote recoveryCode conversionImage codingBiorthogonal wavelet transformImaging processing
The invention publishes a medical image ROI compression method based on a lifting wavelet and a PCNN, which comprises the following steps of: circling a region of interest by a doctor, and separating the region of interest from a region of no interest by a difference image method; adopting lossless compression in the region of interest, constructing compactly supported biorthogonal wavelet transformation through a lifting scheme, and then carrying out Huffman encoding; adopting lossy compression in the region of no interest, segmenting gray-value pixel approximate points through the PCNN, carrying out ignition operation, and then carrying out run-length encoding; and finally carrying out inverse transformation restoration, merging the region of interest and the region of no interest, and eliminating a boundary discontinuity problem through linear interpolation. Experimental results prove that the region of interest can be flexibly selected and controlled by the compression method, the used information for doctor diagnosis can be completely reserved, and the compression ratio is higher. Meanwhile, the computation for an ROI mask and the computation and the encoding for a wavelet coefficient difference value are omitted, the compression and decompression time and the algorithm complexity are reduced, and the image processing and transmitting efficiency is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Multilayer Hash structure and run coding-based lossless compression method for data
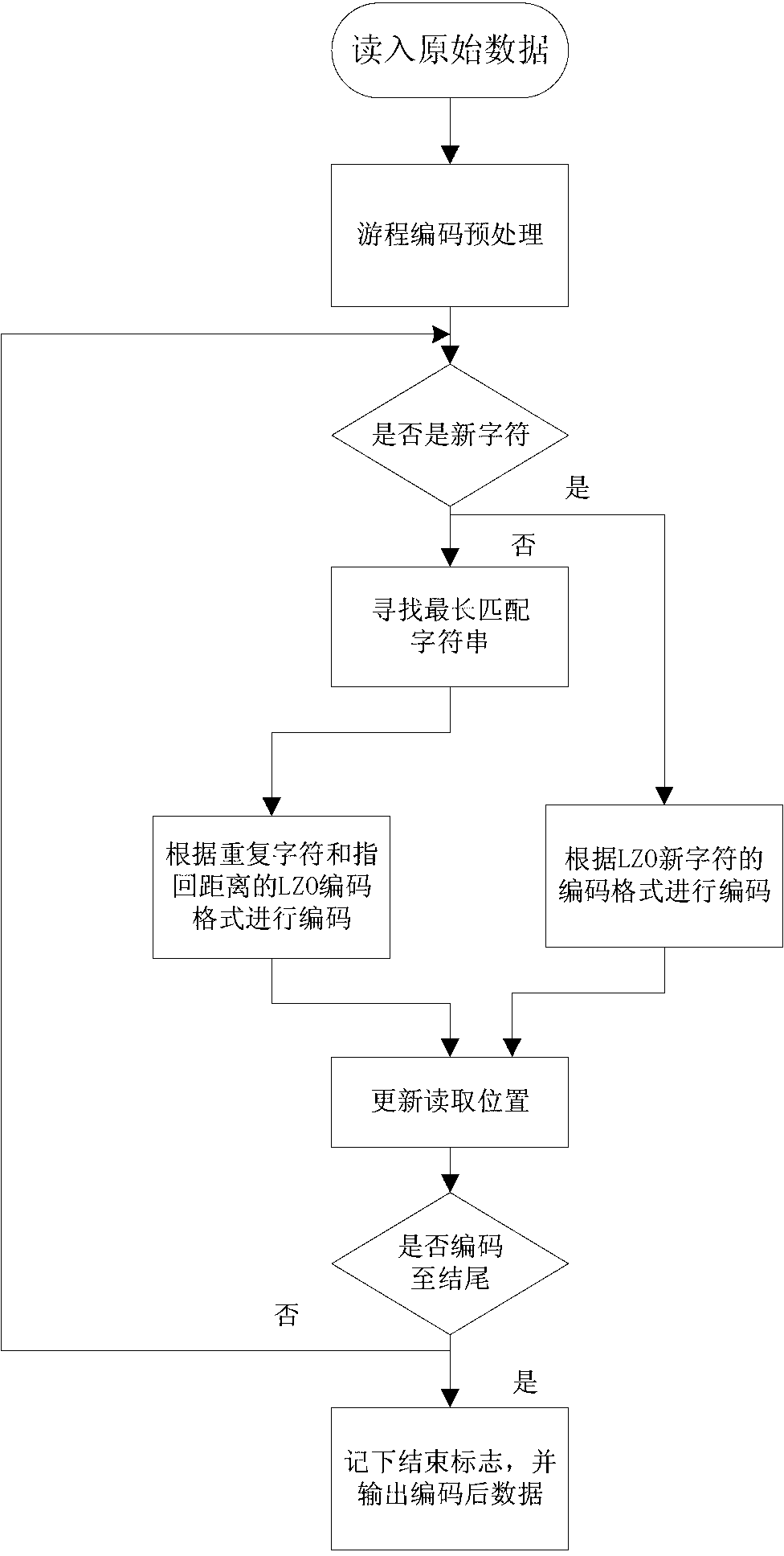
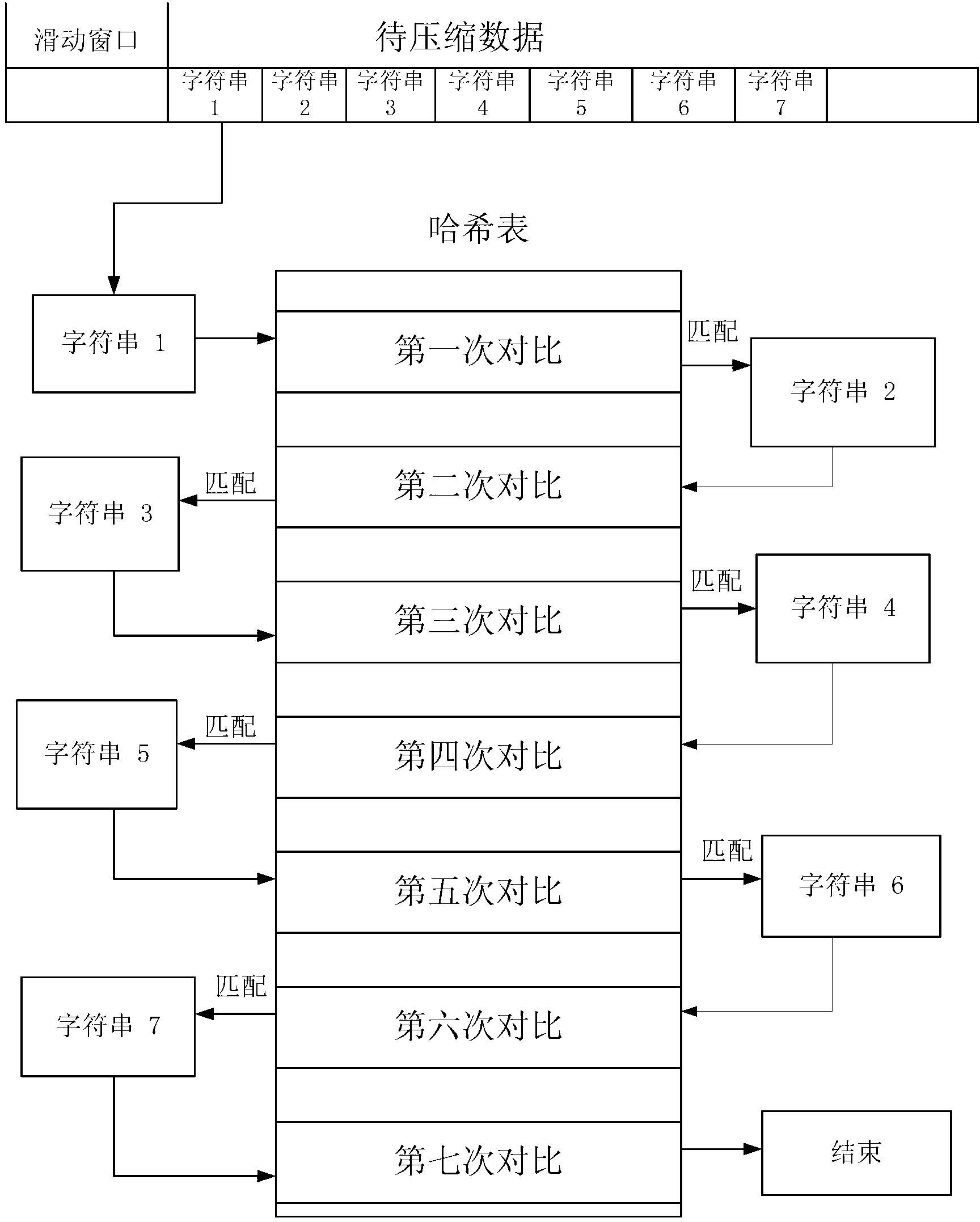
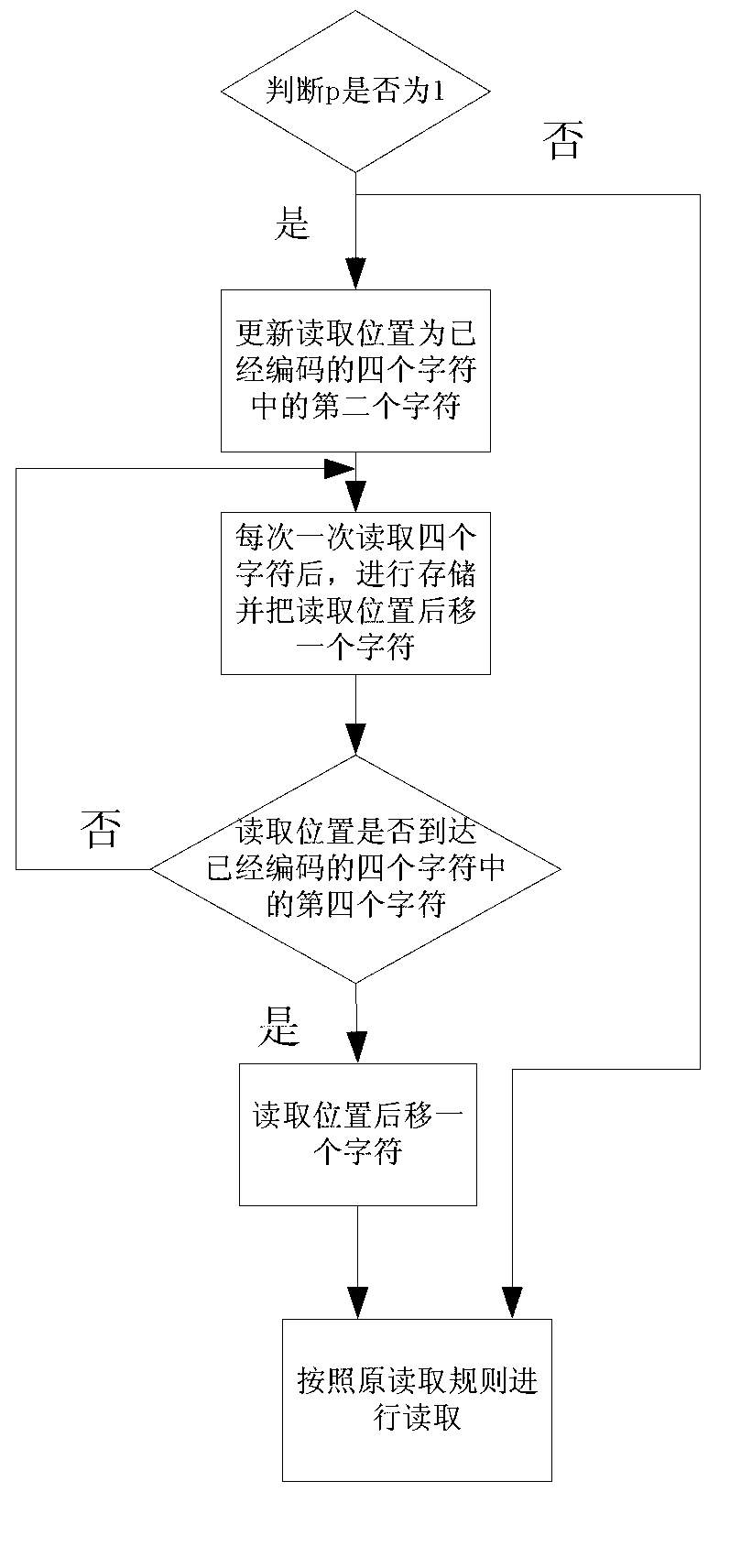
ActiveCN103236847AFast codec speedEliminates the disadvantage of poor compressionCode conversionSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmOriginal data
The invention discloses a multilayer Hash structure and run coding-based lossless compression method for data and mainly aims to solve the problems that a compression effect on repeating data is poor and the longest matching character string is hard to find out when matching character strings are searched by adopting a Lempel-Ziv-Oberhumer (LZO) compression method. The multilayer Hash structure and run coding-based lossless compression method for the data comprises the following implementation steps of: (1) reading in original data, and preprocessing the original data by using run coding to obtain to-be-compressed data; (2) judging the read data is a new character or not; searching the longest matching character string if the read data is not the new character, and coding according to the repeated length and the anaphora distance of the character, and coding according to a coding method for the new character if the read data is the new character; and (3) updating a reading position according to the coded character, and judging whether the end of the to-be-compressed data is coded or not, ending if the end of the to-be-compressed data is coded, and continuously reading in the to-be-compressed data if the end of the to-be-compressed data is not coded, and returning to the step (2). Compared with other traditional lossless compression methods, the multilayer Hash structure and run coding-based lossless compression method for the data is higher in compression efficiency, and can be used in storage devices with requirements on the compression speed and the compression efficiency of the data.
Owner:中裕广恒科技股份有限公司
Method and device for compressing film thumbnails
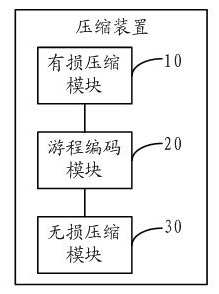
ActiveCN102088604AReduce digitsSmooth displayTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationThumbnailLossless compression
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for compressing film thumbnails, comprising the following steps: carrying out loss compression on the film thumbnails to acquire film thumbnails with specific digits; carrying out run coding on the film thumbnails with the specific digits; and carrying out lossless compression on the film thumbnails which are subjected to the run coding to acquire compressed pictures. The embodiment of the invention also provides a device for compressing film thumbnails. In the invention, the loss compression, the run coding and the lossless compression are combined effectively to compress the film thumbnails, thus having the advantages of higher compression ratio, high compression efficiency, low degree of distortion and fast decoding speed.
Owner:SHENZHEN SKYWORTH DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
Signal compressing system
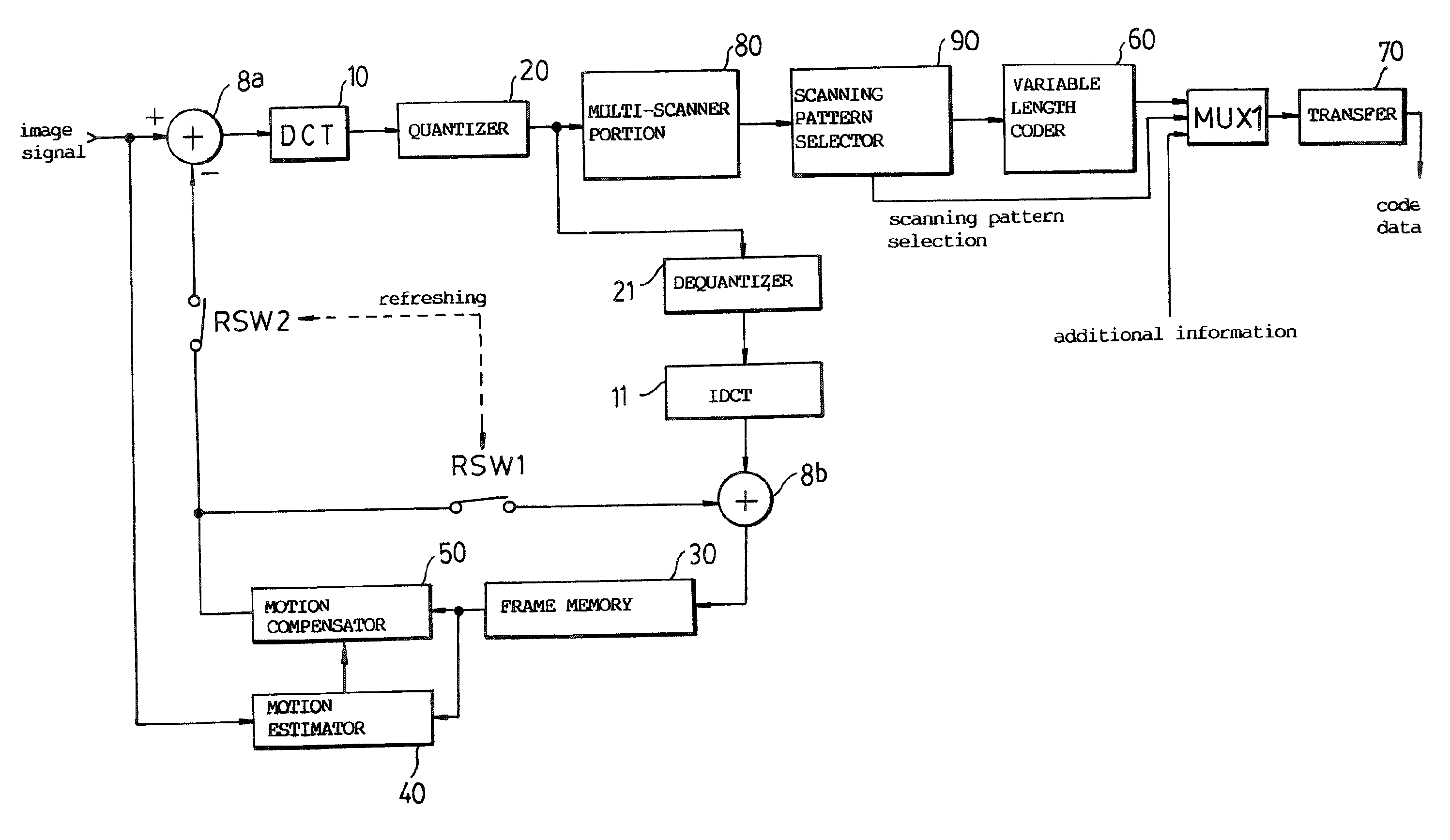
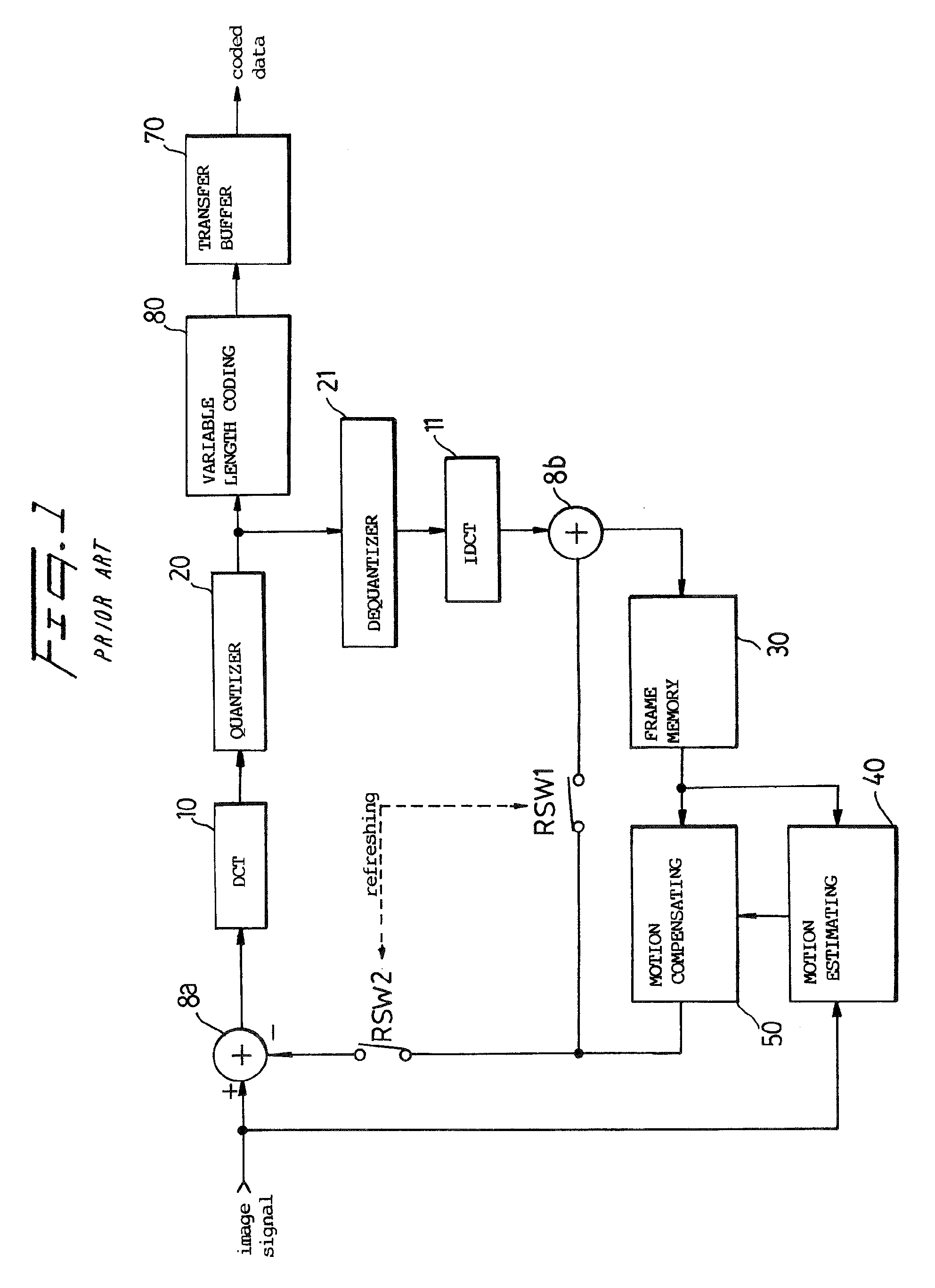
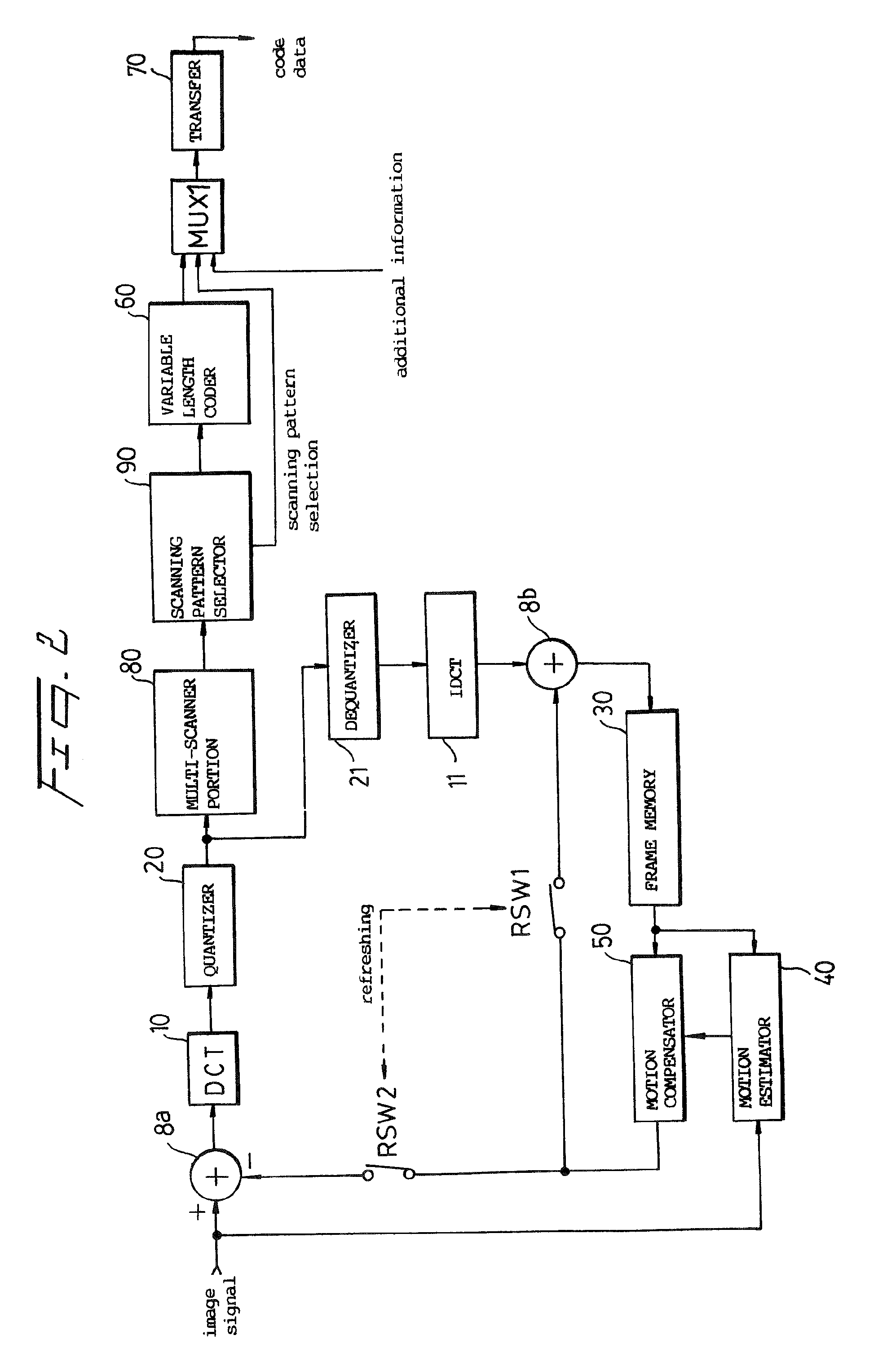
InactiveUS20090097569A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionRun-length encodingMode selection
A multi-scanner scans a signal according to several different patterns. A scanning pattern selector determines which scanning pattern produced the most efficient coding result, for example, for runlength coding, and outputs a coded signal, coded most efficiently, and a selection signal which identifies the scanning pattern found to be most efficient.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Using run length encoding to detect target images
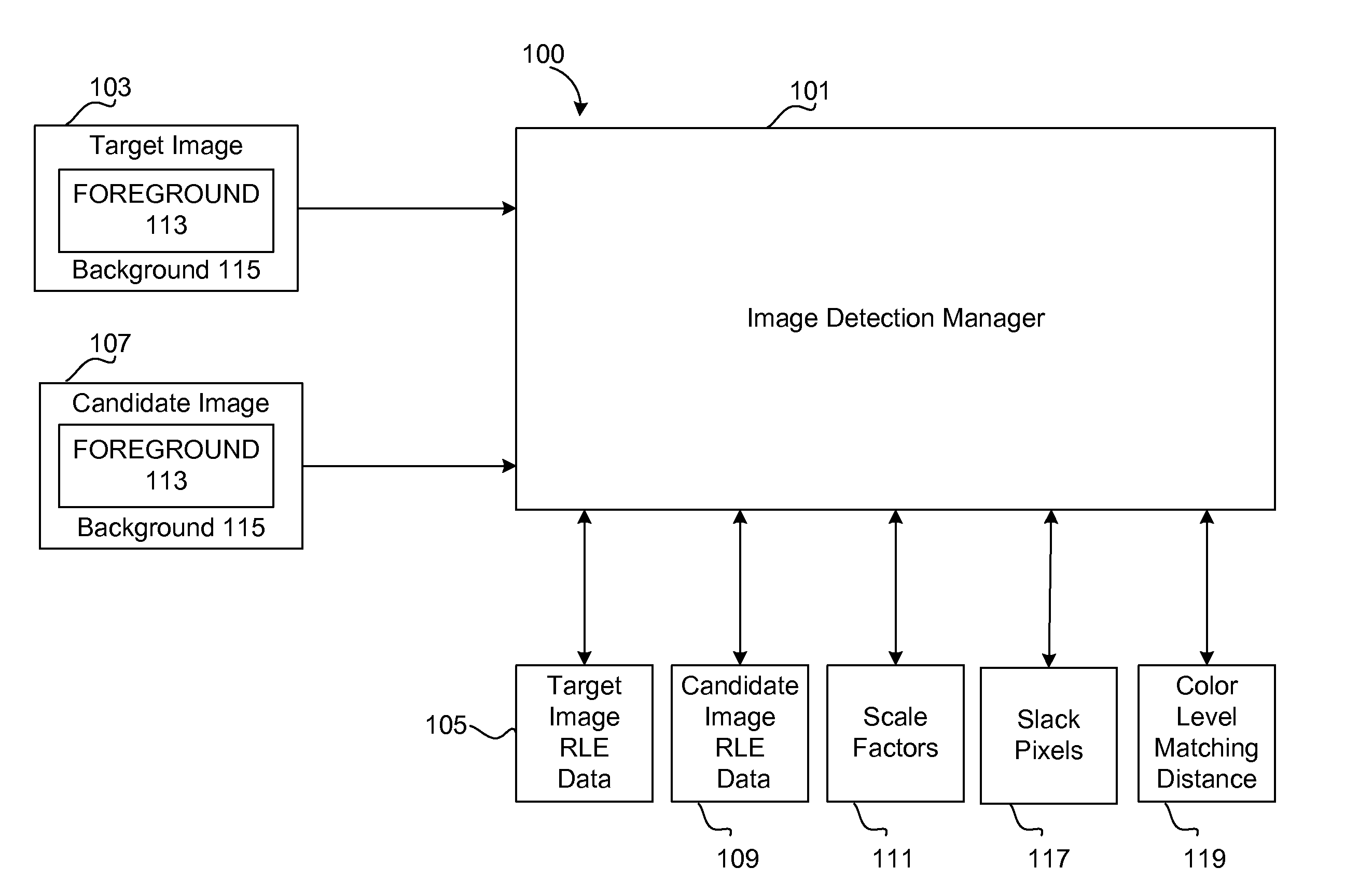
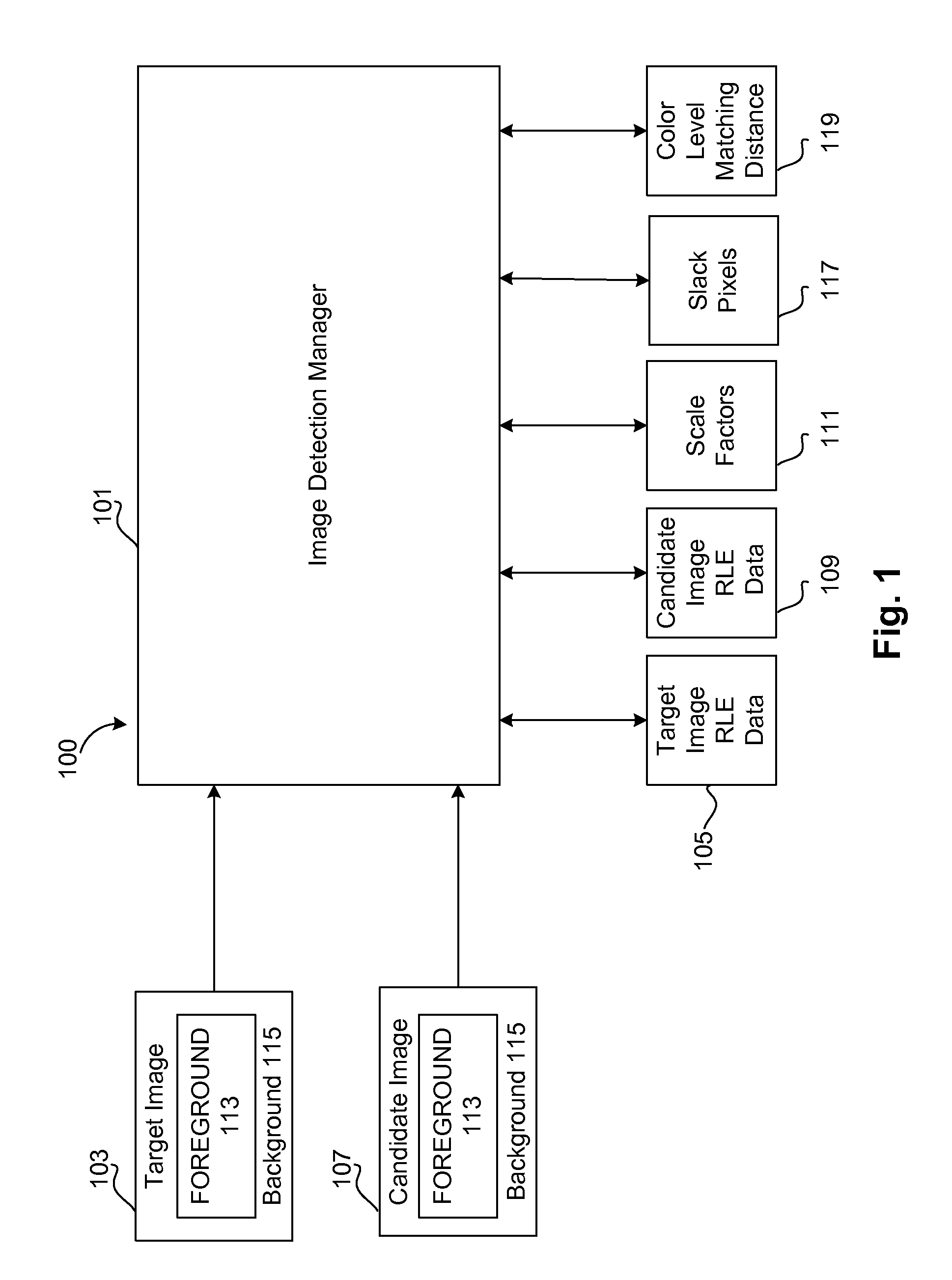
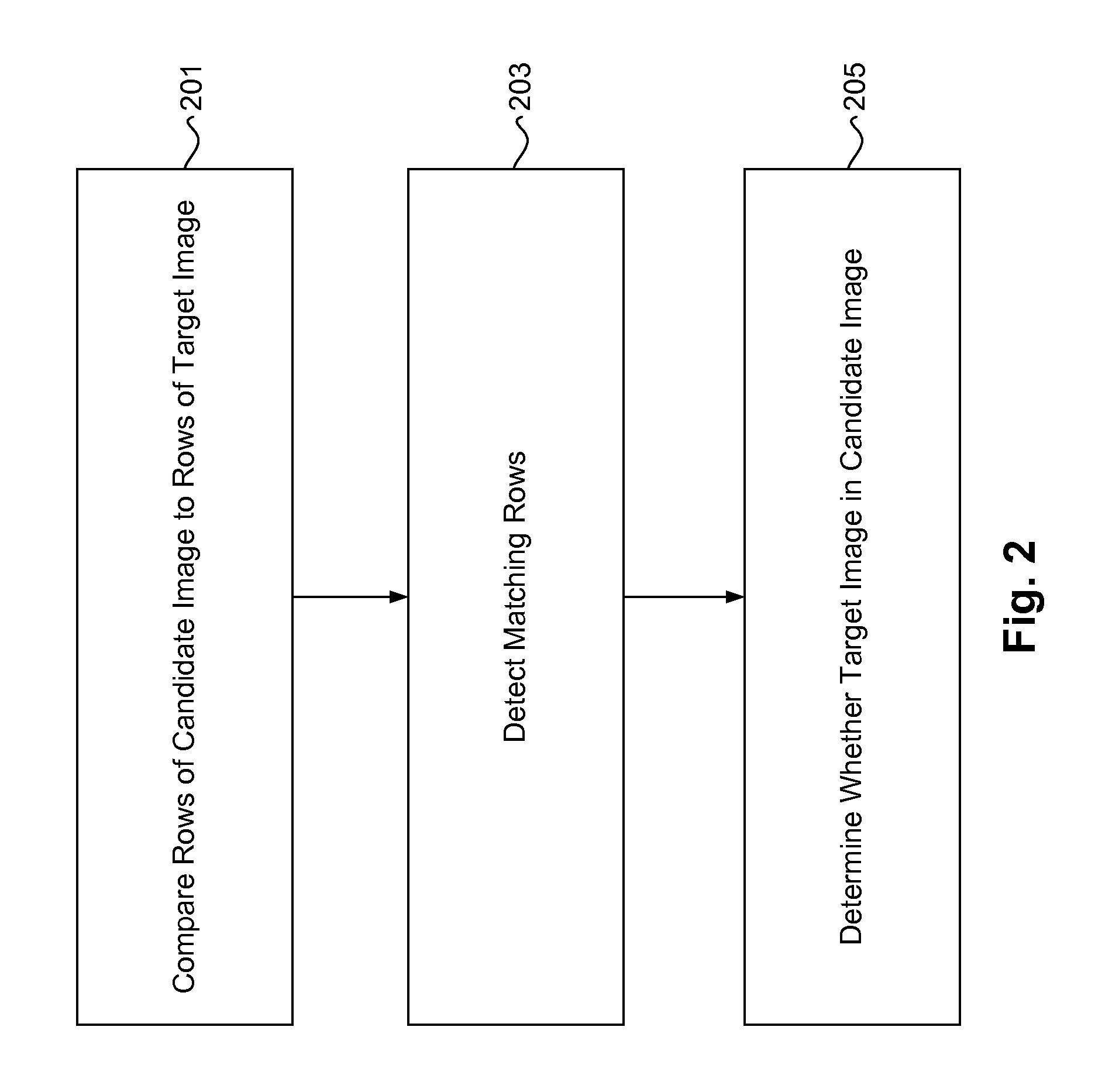
InactiveUS7492957B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage detectionRun-length encoding
An image detection manager uses run length encoding to detect a target image in a candidate image. The image detection manager extracts run length encoding data from the candidate image. The image detection manager distinguishes between a foreground and background of the candidate image and target image, and takes into account an interval of scale factors for matching color runs in the foreground and length runs in the background. The image detection manager treats background pixels as wildcards, and utilizes fuzzy color matching in which color levels of adjacent pixels in the foreground are allowed a specified variation. Using such functionality, the image detection manager compares rows of the run length encoding data from the candidate image to rows of run length encoding data from the target image, and determines whether the target image is present in the candidate image.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Image processing apparatus and method for image processing
InactiveUS20110033125A1Solve problemsImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingImage resolution
While a natural image having a resolution of 600 dpi is enlarged at a predetermined magnification ratio and is printed at a resolution of 1200 dpi, if the magnification ratio is equal to or more than two, the natural image is enlarged by using a nearest neighbor method. If the magnification ratio is less than two, a reduction image is generated by reducing an enlargement image obtained by enlarging an object image based on a magnification ratio to 1 / 2, and the reduction image is enlarged to twice the size by using the nearest neighbor method. The natural image obtained by enlarging in this manner is compressed and encoded by using prediction encoding and run-length encoding with which a run-length value having a prediction error of 0 is calculated.
Owner:RICOH KK
Time-of-flight measuring device
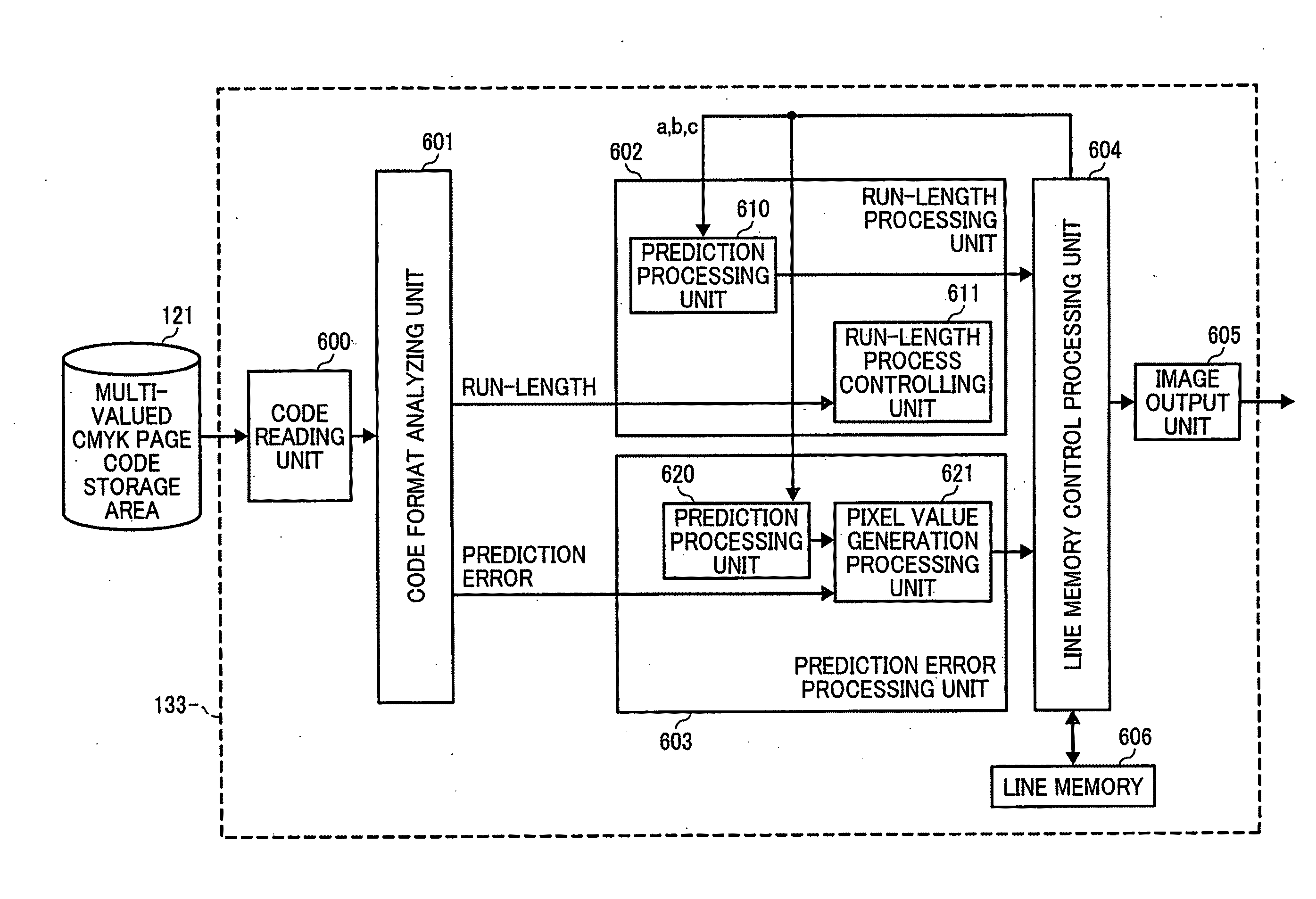
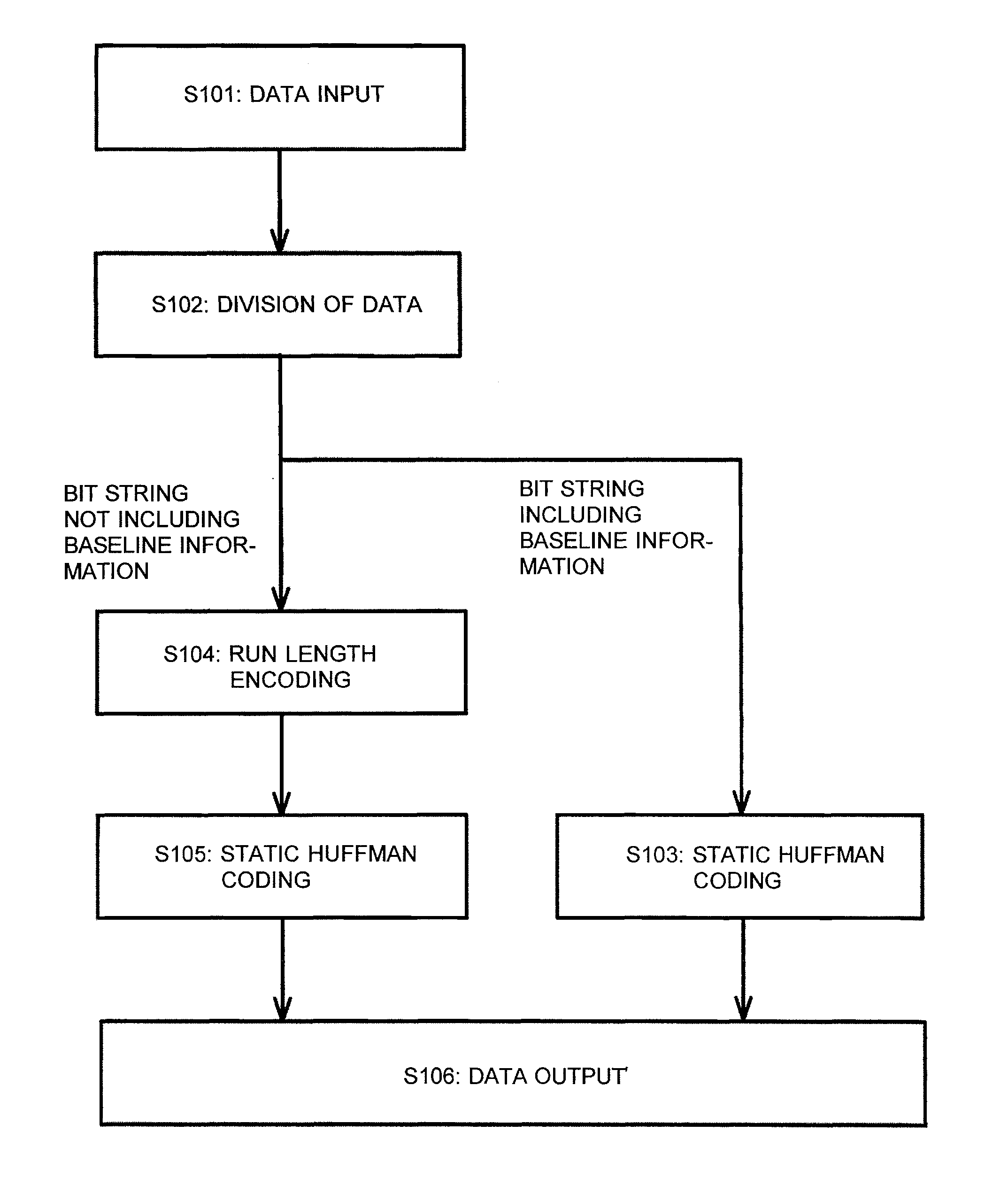
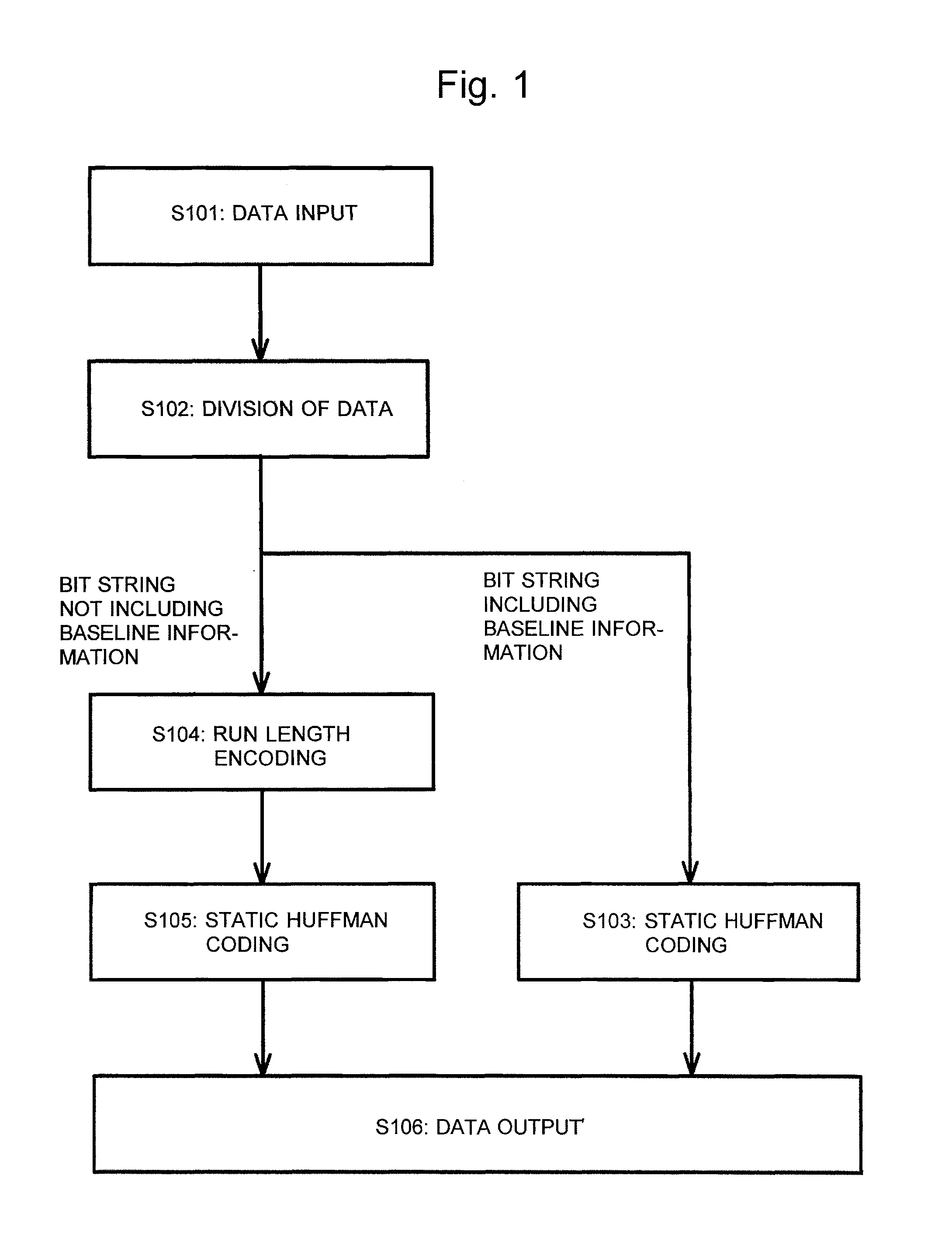
InactiveUS8004432B2Shorten the time periodEasy to processTime-of-flight spectrometersCode conversionComputer hardwareData treatment
A time-of-flight measuring device for performing a hardware-based high-speed data compression process before transferring the data from a signal recorder to a data processor is provided. A time-series digital signal recorded by a signal recorder is converted to a plurality of time-series digital signals by being divided into a bit string including baseline information and a bit string not including the baseline information. Then, the time-series digital signal consisting of a bit string not including the baseline information is compressed by run-length encoding, such as zero length encoding or switched run-length encoding. Subsequently, static Huffman coding is performed on each of the time-series digital signals to reduce the data amount.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Drawing processing apparatus and method for compressing drawing data
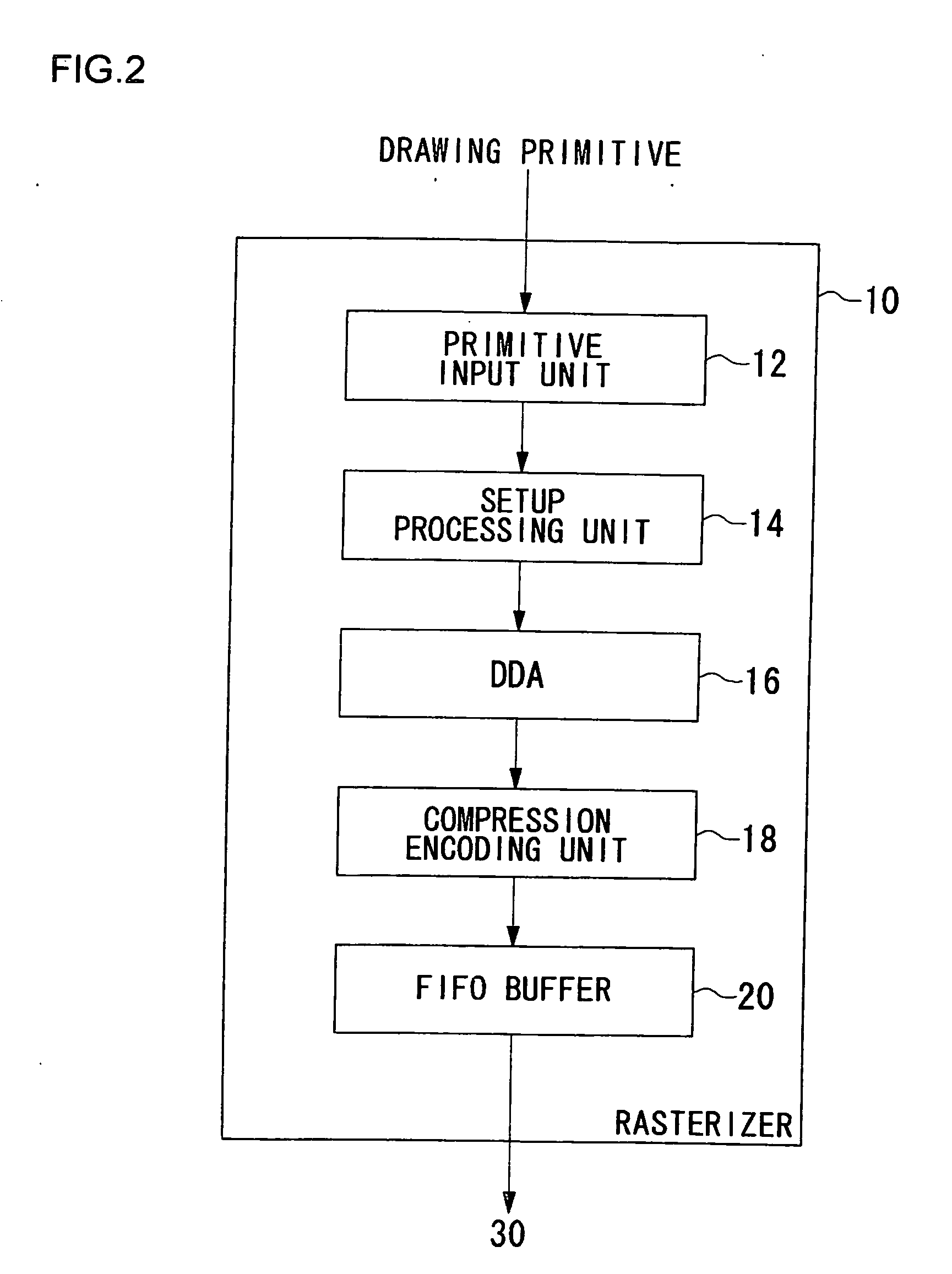
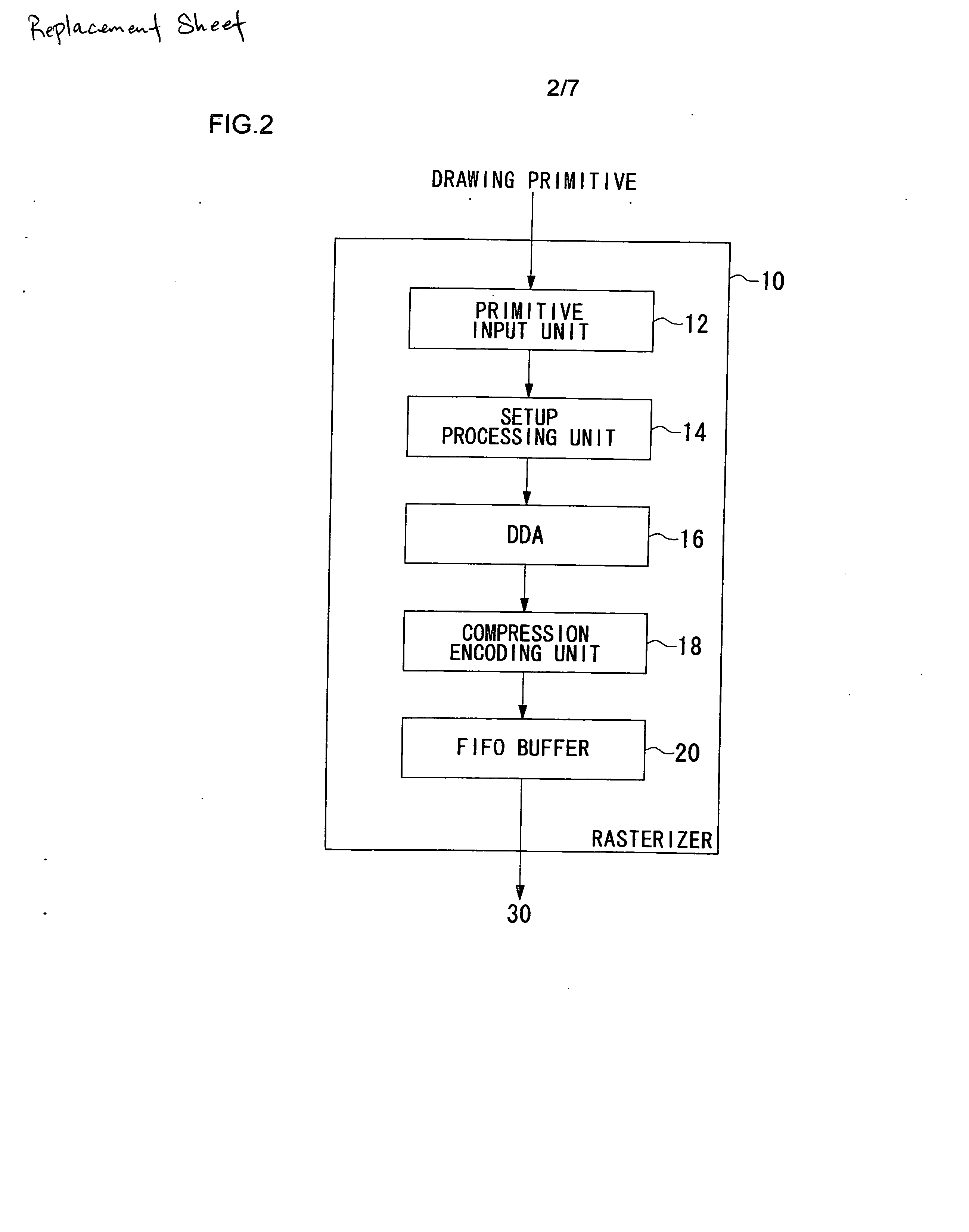
InactiveUS20060176316A1High-quality drawingEffective amountImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionComputational scienceScan line
A drawing processing apparatus is provided to solve the problems in which pixels of a drawing primitive with sub-pixel information may have an increased amount of data causing a burden on implementation. A setup processing unit sets up various parameters to allow a digital differential analyzer (DDA) to process the stream of a drawing primitive supplied from a primitive input unit. The DDA performs DDA processing on the drawing primitive supplied from the setup processing unit for conversion into pixel data. The DDA performs the DDA processing on a per rectangular pixel set basis along a scan line to output the pixel data of the drawing primitive on a per rectangular pixel set basis. A compression encoding unit encodes the sub-pixel information of each pixel contained in the rectangular pixel set by run length encoding for output to a FIFO buffer.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC +1
Device and method for encoding image data
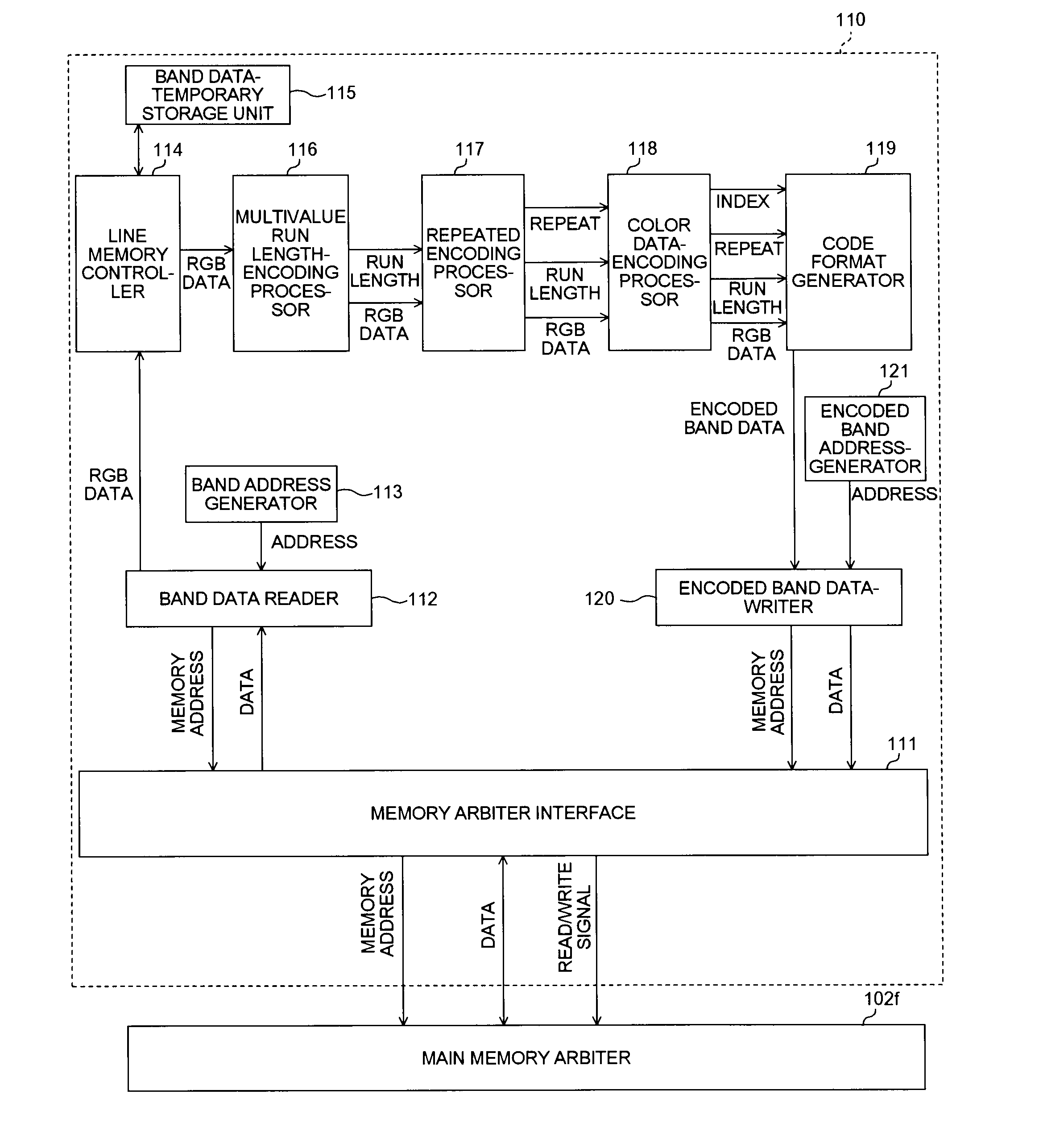
InactiveUS20090060325A1Solve problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationData encodingRun-length encoding
A reading unit reads image data. A re-reading unit that re-reads the image data read by the reading unit by performing, in a pixel matrix consisting of a plurality of pixels of the image data read by the reading unit, a process of scanning pixels in a partition in which at least two pixels are respectively aligned in a column direction and in a row direction in a predetermined order in a predetermined alignment sequence of partitions. A multivalue run length-encoding unit encodes the image data re-read by the re-reading unit to multivalue run length data indicating at least color data and run lengths of the color data.
Owner:RICOH KK
Video image color encoding
InactiveUS6301389B1Significant overheadLow efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationCode conversionDigital videoVideo image
A method is described of encoding pixel color values for a digital video image frame in which each different color within the image is assigned a color value. A predominant color is identified for the image frame and, in a first embodiment (FIG. 5), each pixel having a color other than the predominant color is separately coded as its respective color value (0010 to 1111), with runs of three or more successive pixels of the predominant color being run-length encoded. A further code (0000 0011 cccc), similar in arrangement to that indicating a run, is provided to allow a change in the specified predominant color during the course of a frame. In a further embodiment, runs of all colors are run-length encoded but with a shorter coding scheme for runs of the predominant color or, in a still further embodiment, a small range of predominant colors. A principle use for these coding schemes is to improve efficiency of coding for certain classes of image material.
Owner:U S PHILIPS CORP
Efficient storage and search of word lists and other text
ActiveUS7580925B2Maximize lengthImprove compression efficiencyDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsDigital dataWord list
A computer readable storage medium tangibly embodying machine-readable digital data arranged to facilitate expedited searching. The data includes a plurality of words residing in a table having rows and columns, each word residing in a different row and each letter of the word occupying a different column in that row. Each continuous run of same letters in a column forms an interval. The words are positioned relative to each other to maximize lengths of the intervals, and / or optimize efficiency of compression of the columns by run length encoding.
Owner:TEGIC COMM +1
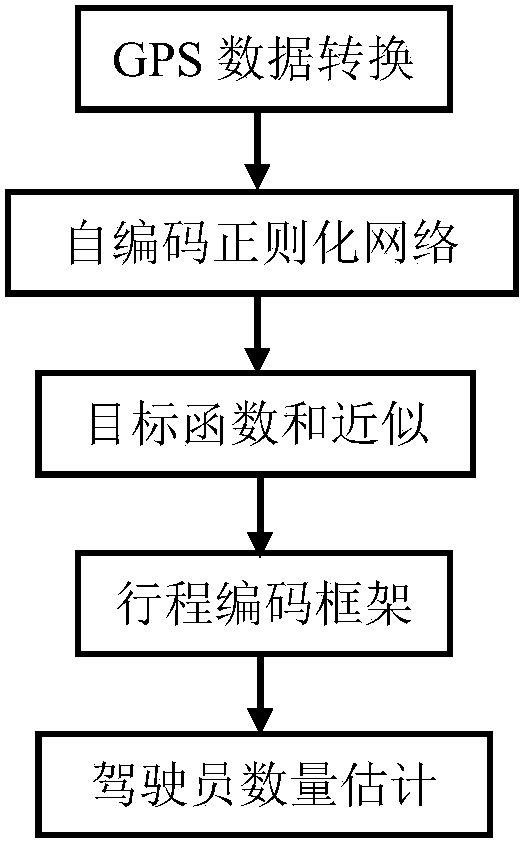
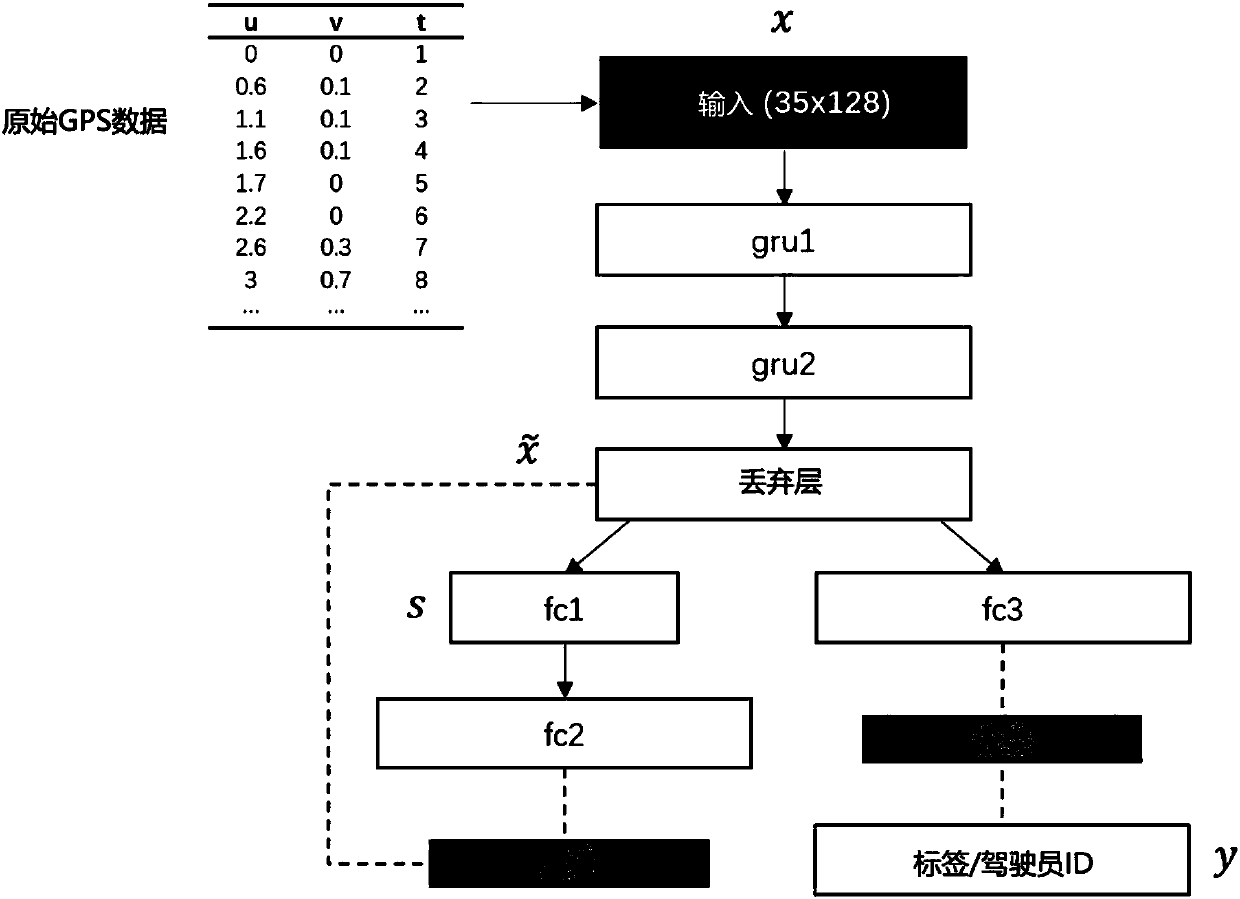
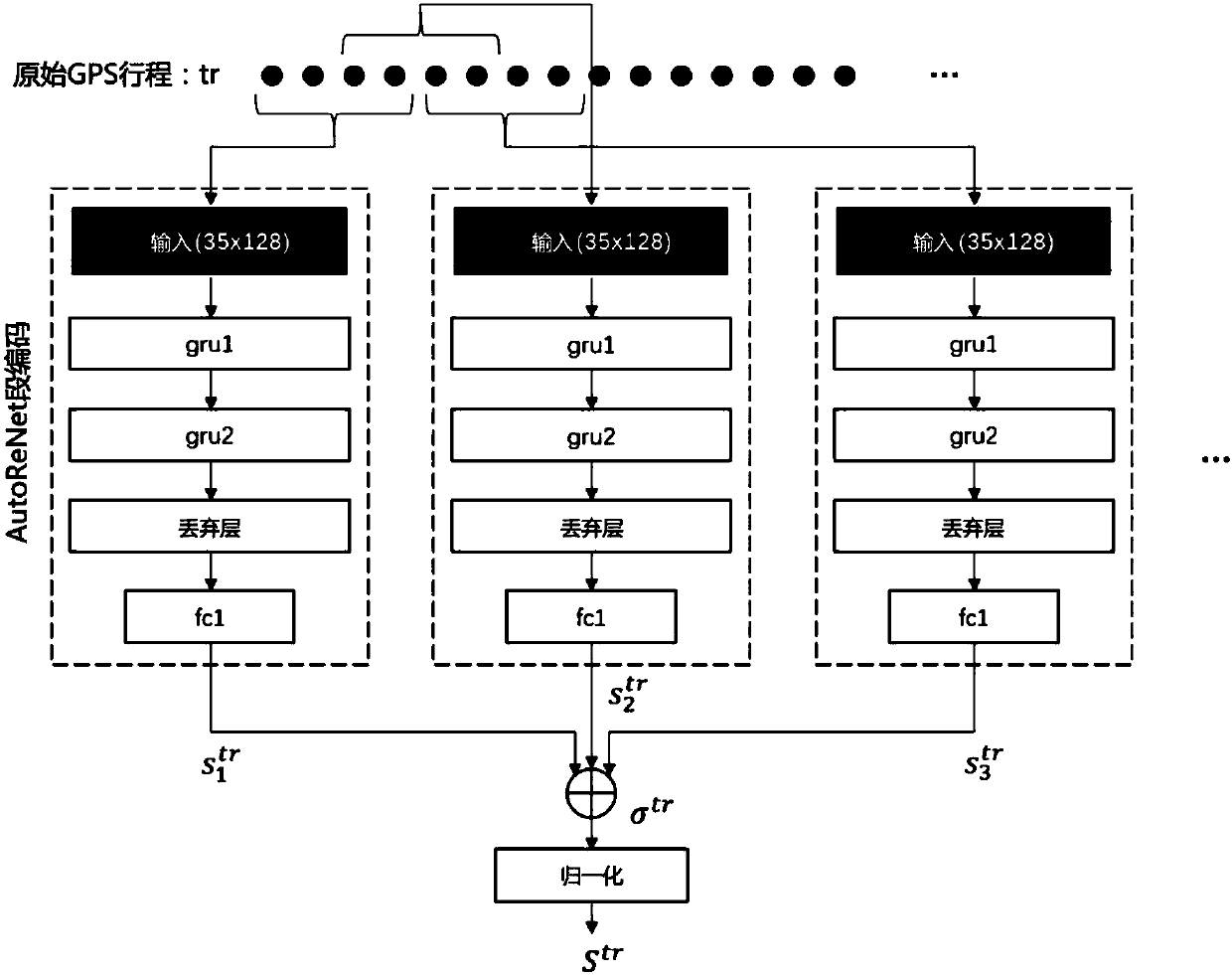
Method for learning driving style based on self-coded regularization network
InactiveCN106875511ARegistering/indicating working of vehiclesCharacter and pattern recognitionDriver/operatorSimulation
The invention discloses a method for learning driving styles based on a self-coded regularization network. The method mainly comprises the following steps: performing GPS (Global Positioning System) data conversion, performing regularization network self coding, performing target function sum approximation, establishing a run length encoding frame, and establishing the number of drivers, namely, in a group of unknown driving, inputting GPS data of vehicles establishing a statistic characteristic matrix as network input, introducing a marker of a limited training set as a prior into an unsupervised automatic encoder, reconstructing hidden layer RNN (Recurrent Neural Network) characteristics, extracting a neck layer of a regularization self-coding structure as a final driving style characteristic representation layer, and estimating the number of drivers in the driving process. By adopting the method, the limit that the driving style of an unknown driver is hard to describe can be solved, a self-coded regularization network is designed to directly learn driving habits of the driver from the GPS data, then recognition and classification precision of different drivers can be improved, and a relatively safe and accurate method can be provided for design of assistant and automatic driving systems.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
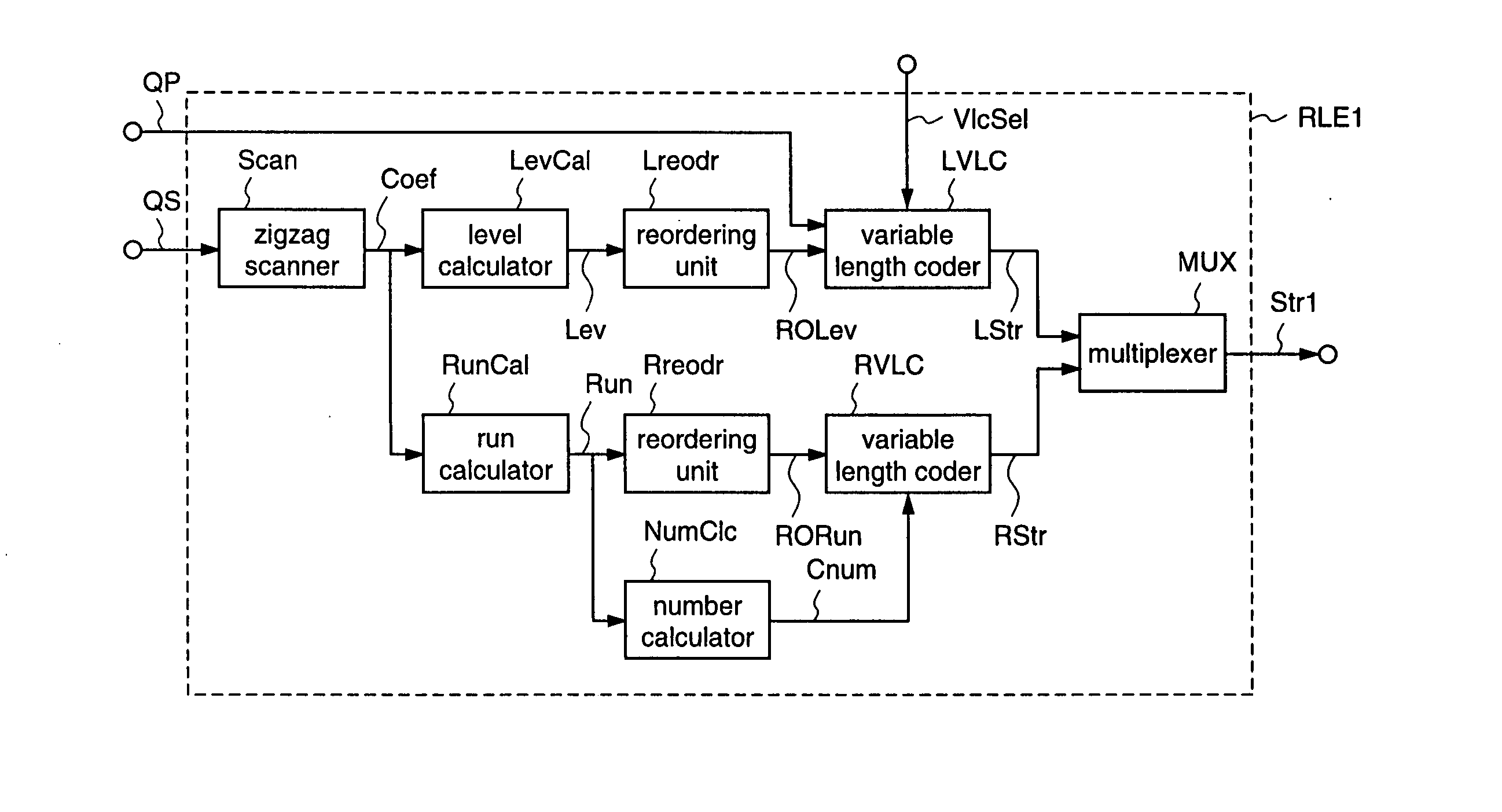
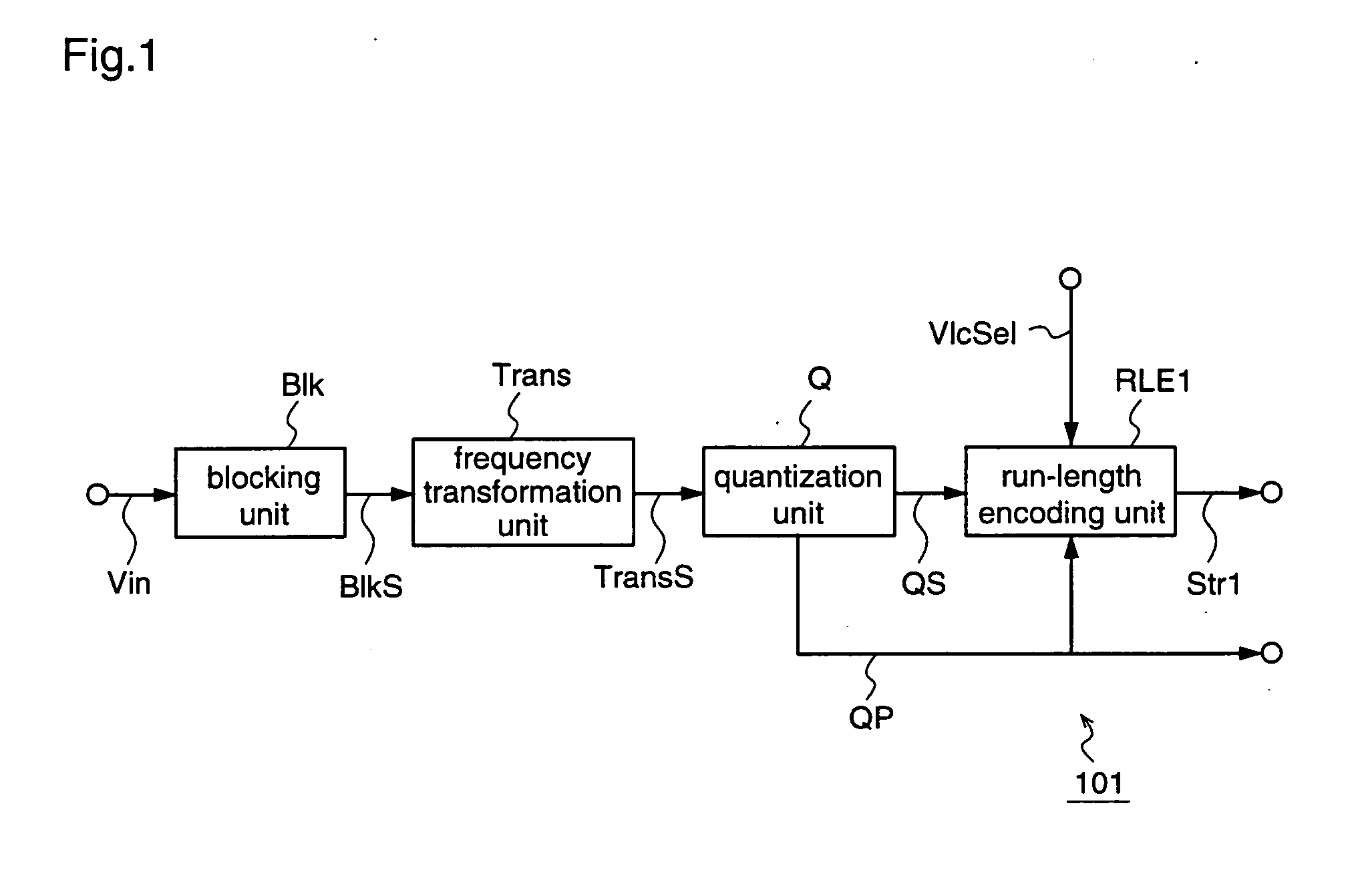
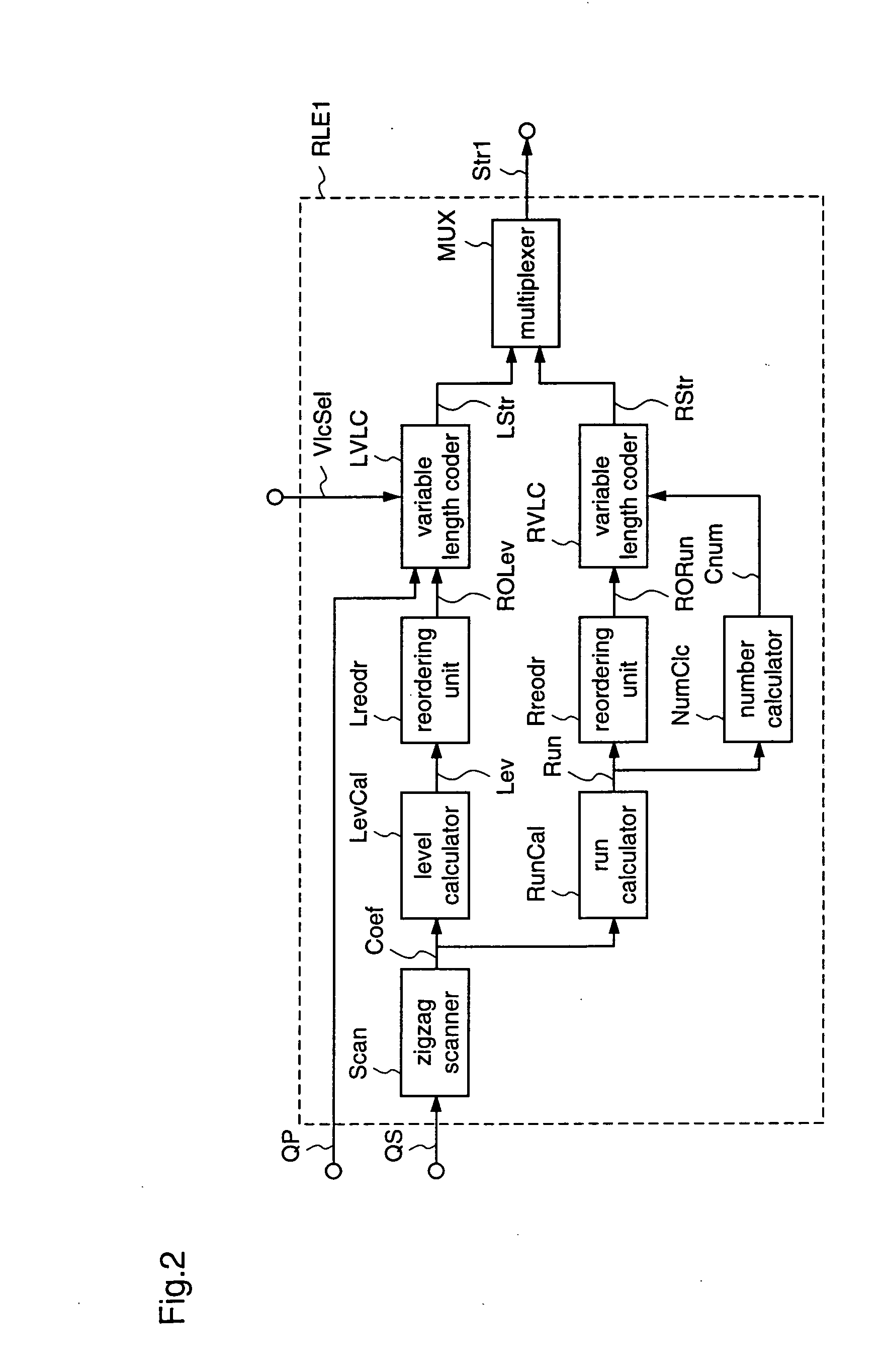
Variable length coding method and variable length decoding method
InactiveUS20050015248A1Increasing variable length efficiencyImprove coding efficiencySpeech analysisRecord information storageProgramming languageVariable-length code
According to the present invention, an image coding apparatus (103) that encodes quantized coefficients corresponding to an image signal as target data to be processed is provided with a run-length encoding unit (RLE2) that assigns variable length codes to the quantized coefficients using code tables. The run-length encoding unit (RLE2) forms a second code table by optimizing a first code table to the target data to be processed, and selects one of the first and the second code tables as a code table that is to be employed for the assignment of the variable length codes in accordance with a quantization parameter (QP) or a variable length coding selection signal (VlcSel), whereby redundancy of information included in the target data to be processed can be effectively eliminated, and the compression ratio for the image signal or the like can be further increased.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Image lossless compression and image decompressing method
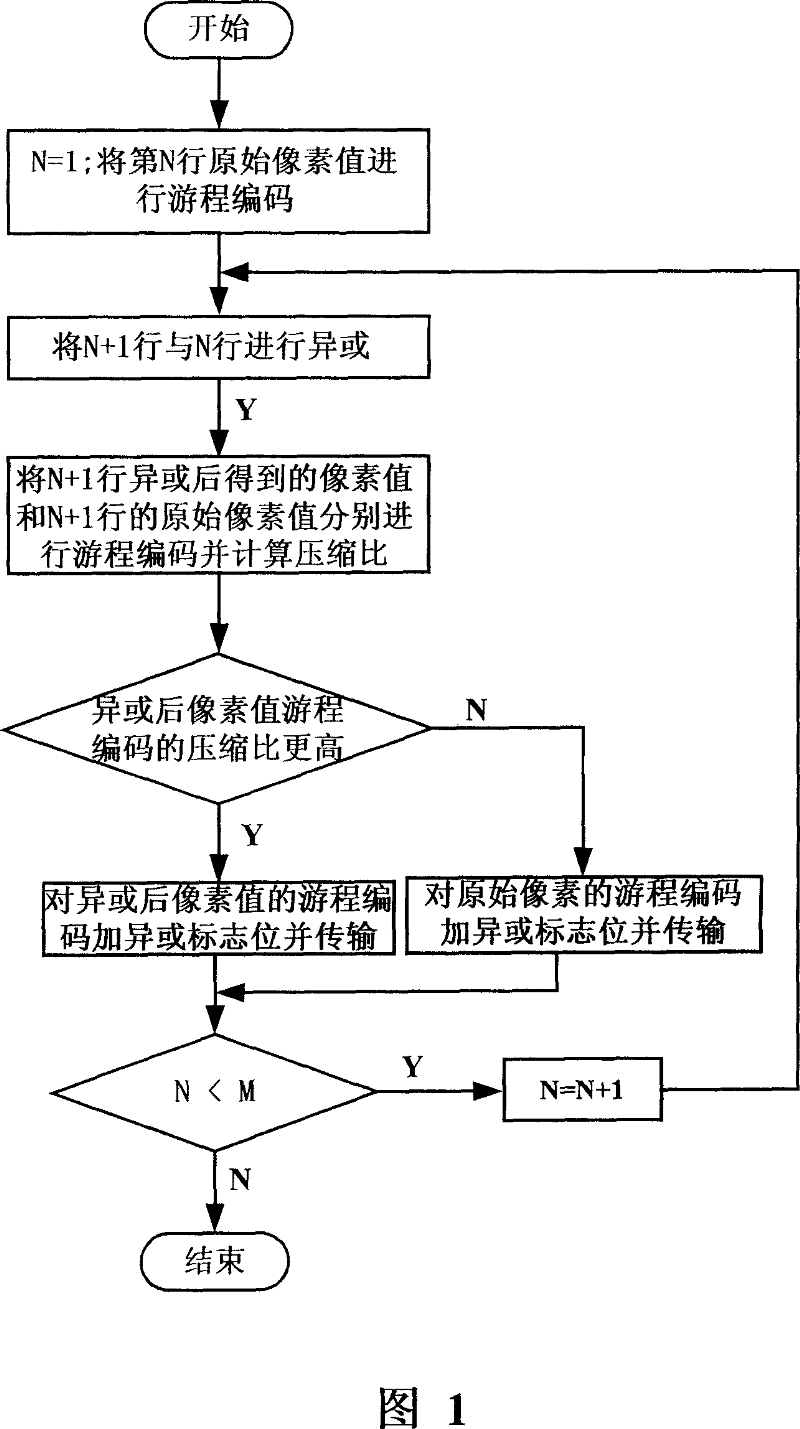
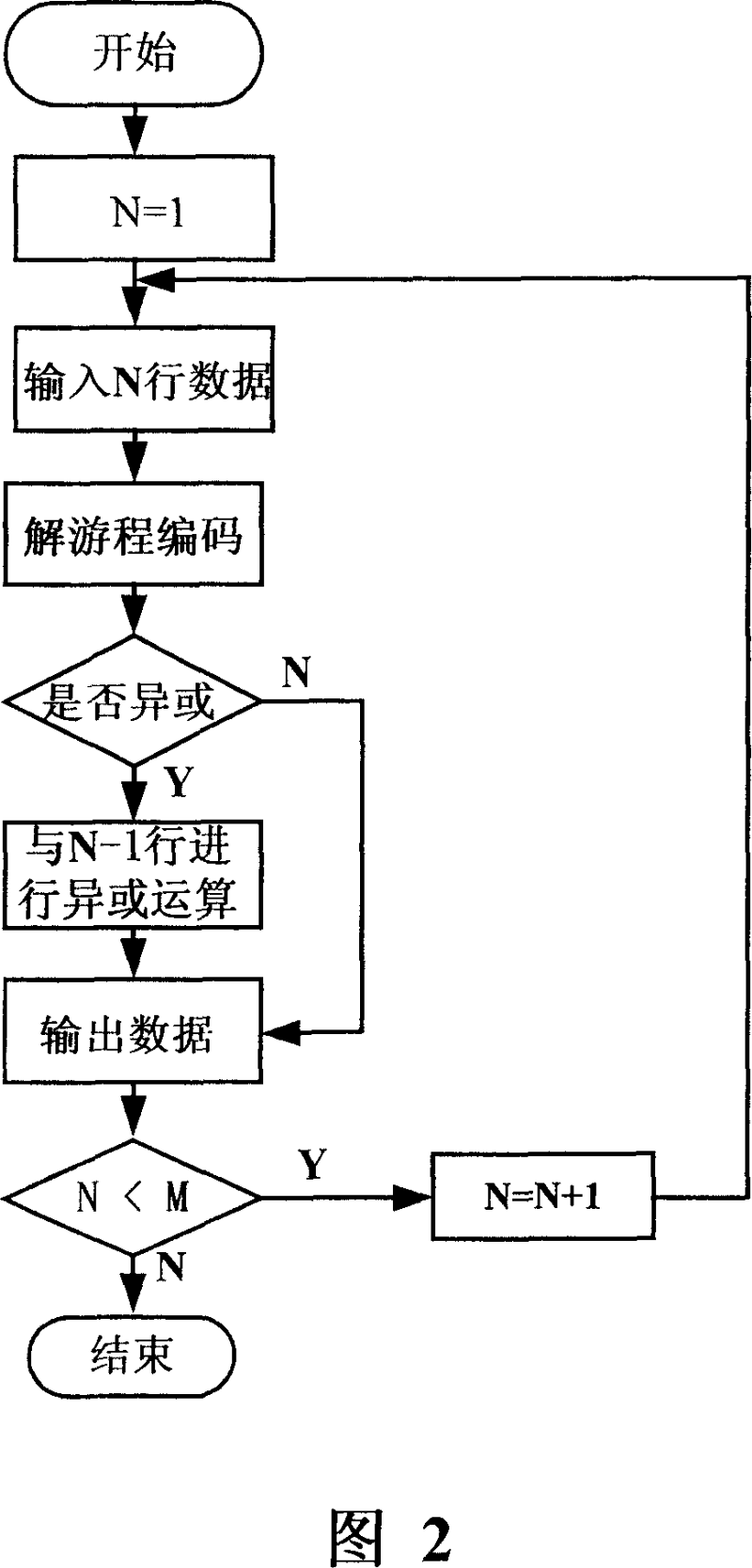
ActiveCN101039374AEasy to handleIncrease the compression ratioTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsRound complexity
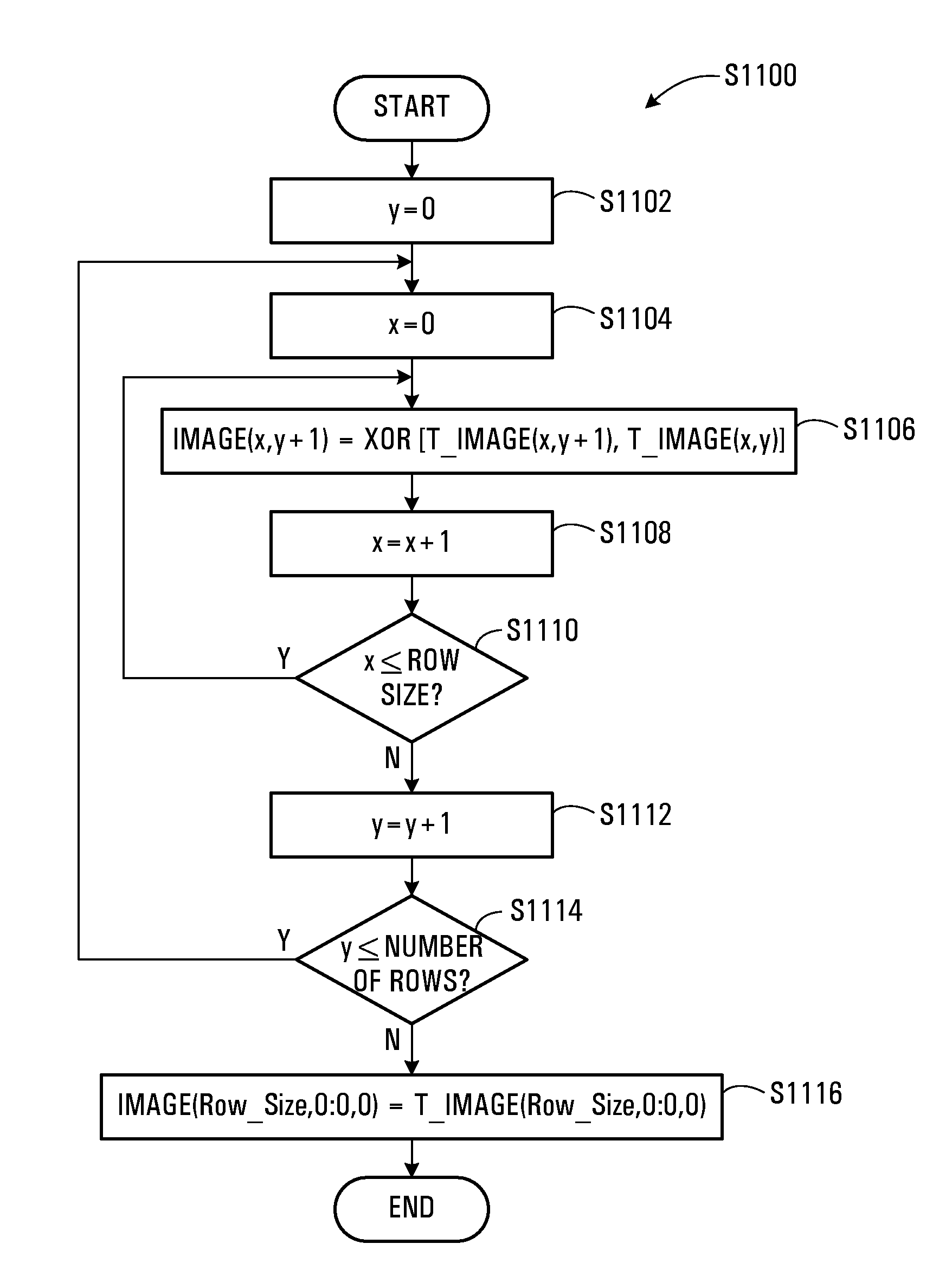
The present invention discloses an image nondestructive compressing method including following steps: starting from a first row and rank of the original image data, original pels values of this row and rank and those of the adjacent ones are logically xor to obtain the next row and rank xor pels; a selection between the original pels and the xor pels is made and the selected one is executed the run length coding, and xor mark are added to the head coating and the head coating is output. The invention also discloses an image decoding method including following steps: the run length coding of the row and rank are decoded; the xor pels are also decoded and output. The invention improves the compressing ratio as far as possible, at the same time, the realizing complexity is also reduced, the coding arithmetic is simple and the computing amount is little; the method does not need the special compressing / decompressing chip, so the realizing cost is low.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) LTD
Image data compression apparatus for compressing both binary image data and multiple value image data
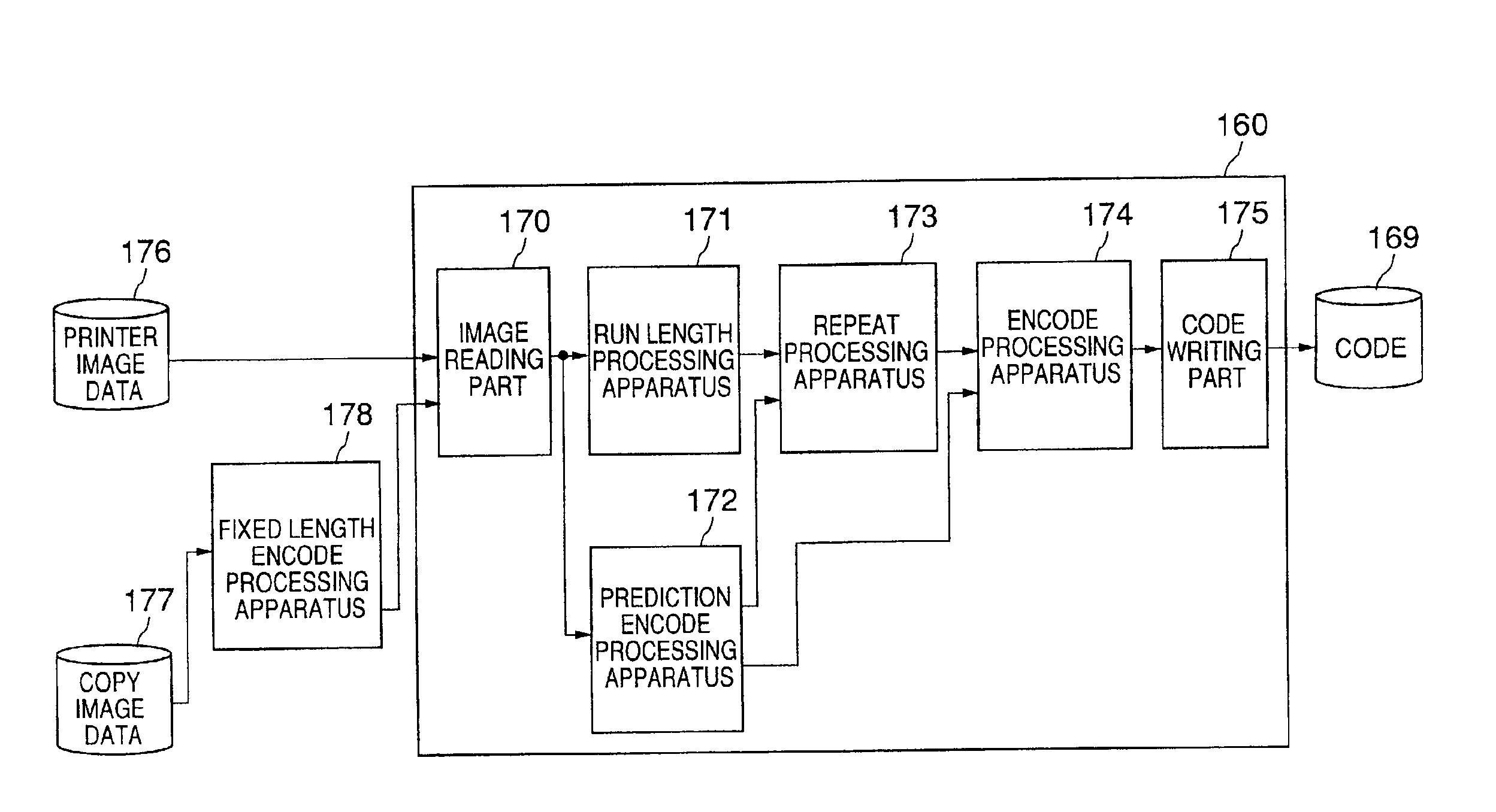
ActiveUS6941023B2Eliminate the problemReduce development costsCode conversionImage codingPattern recognitionImage compression
An image data compression apparatus which compresses code data obtained by compressing image data by a fixed length encoding method so as to reduce a scale of hardware and reduce a development cost of software for an image data compression a binary image data processing part processes binary image data in accordance with a run length encoding method, the binary image data processing part including an encoding part which encodes run lengths of the binary image data by an encoding part. A multiple value image data processing part processes multiple value image data in accordance with a prediction encoding method. The encoding part of the binary image data processing part is commonly used by the multiple image data processing part so that the encoding part compresses both the binary image data and the multiple value image data.
Owner:RICOH KK
Mobile device memory compression method based on dictionary encoding and run-length encoding
InactiveCN103258030AImprove operational efficiencyIncrease the compression ratioCode conversionSpecial data processing applicationsImage compressionCompression method
The invention discloses a mobile device memory compression method based on dictionary encoding and run-length encoding. The mobile device memory compression method based on the dictionary encoding and the run-length encoding mainly solves the problem that an existing dictionary encoding compression method and an existing run-length encoding compression method are low in compression ratio of memory data. The mobile device memory compression method based on the dictionary encoding and the run-length encoding mainly comprises the following steps of (1) reading in the memory data and the lengths of the storage data, (2) judging whether the memory data are compressible data, directly recording the lengths of the data and the data when the data are not compressible data, and using a run-length encoding compressed format to compress continuous identical character strings when the data are compressible data, (3) using a dictionary compressed format to compress other ordinary memory data, (4) judging whether compression is carried out on the tail of the memory data, stopping compressing when the compression is carried out on the tail of the memory data, and continuing reading in the memory data when the compression is not carried out on the tail of the memory data. Compared with existing other storage compression methods, the mobile device memory compression method based on the dictionary encoding and the run-length encoding is higher in compression ratio, thus more residual space can be released for an internal storage of a mobile device, operating efficiency of the mobile device can be improved, and the mobile device memory compression method based on the dictionary encoding and the run-length encoding can be used in mobile devices which need memory compression.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com