Variable length coding method and variable length decoding method
a variable length and coding technology, applied in the field of variable length coding methods and variable length decoding methods, can solve the problems of inability to transmit an output image of a television camera having a large quantity of data as it is by the isdn, inability to handle such massive data, and inability to improve compression rate, so as to increase the variable length coding efficiency, increase the coding efficiency, and maximize the coding efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
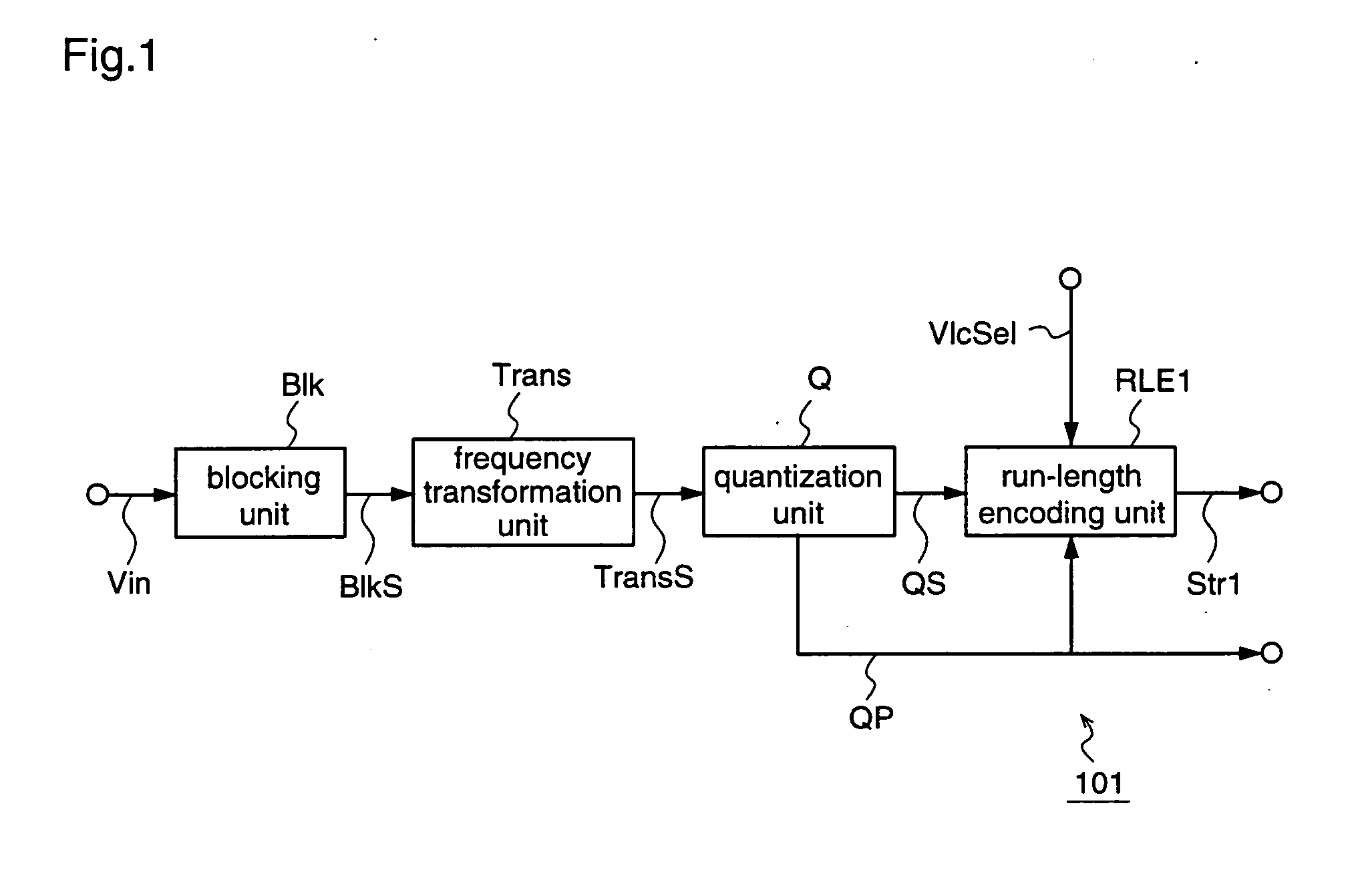
[0252]FIG. 1 is a block diagram for explaining an image coding apparatus according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
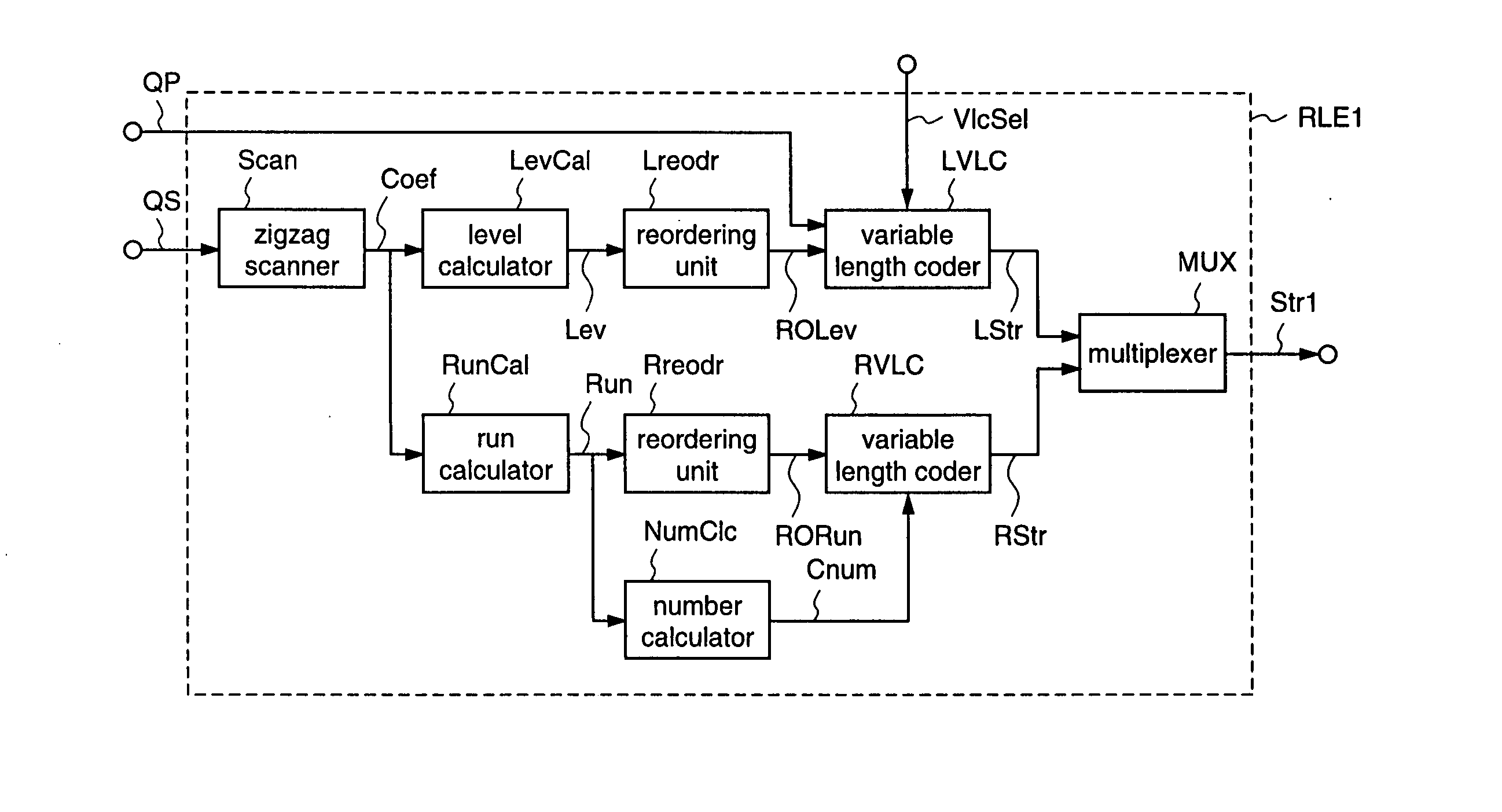
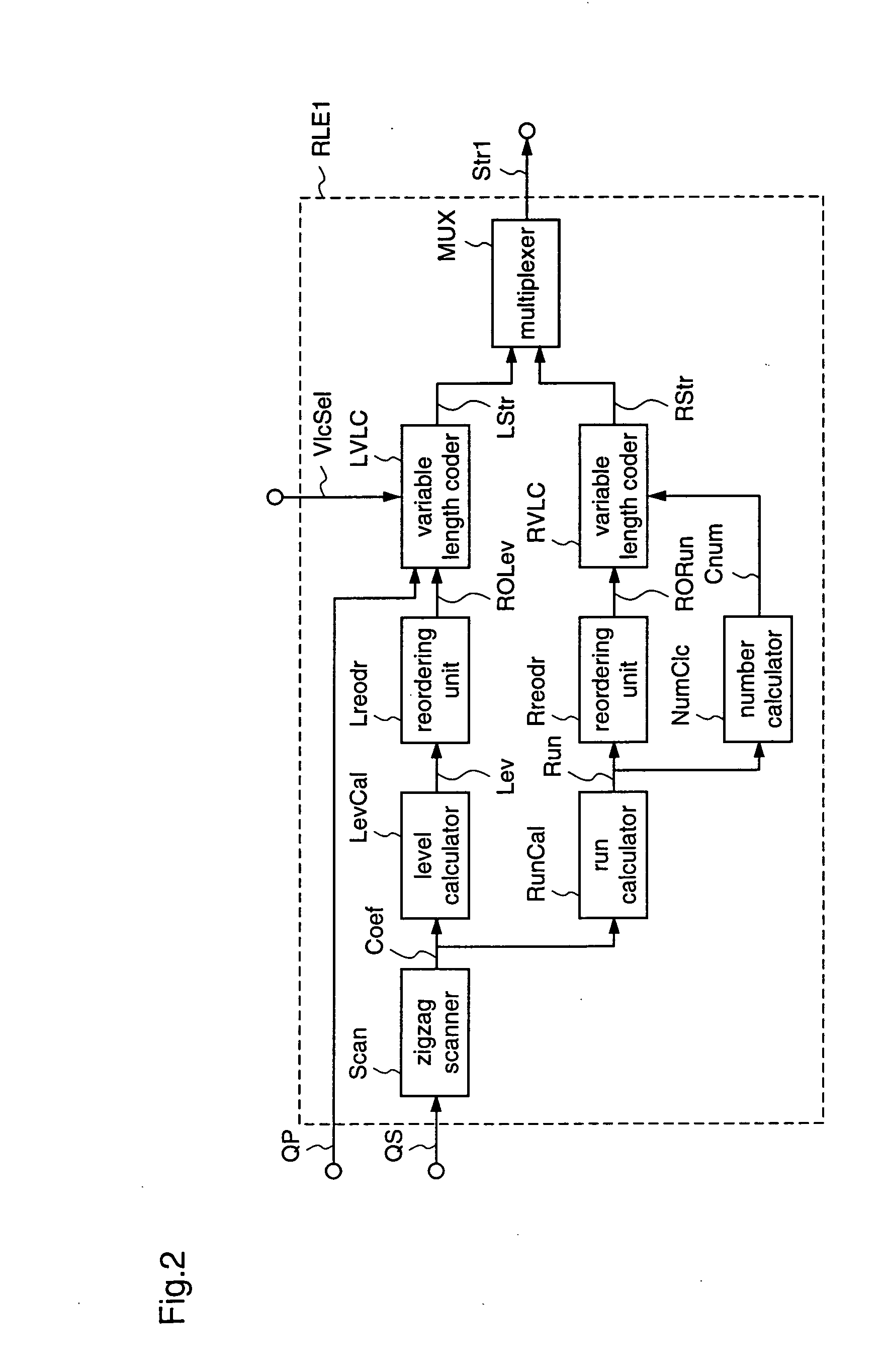
[0253] This image coding apparatus 101 according to the first embodiment has, in place of the run-length encoding unit RLEOb in the conventional image coding apparatus 201b shown in FIG. 34, which subjects outputs (quantized components) QS from the quantization unit Q to a variable length coding process and outputs a coded stream Str0b, a run-length encoding unit RLE1 for subjecting the output QS from the quantization unit Q to a variable length coding process on the basis of a quantization parameter QP and a VLC selection signal VlcSel, and outputs a coded stream Str1.
[0254] Here, the quantization parameter QP is a parameter that indicates a value of a quantization step, and the quantization step is approximately proportional to the quantization parameter QP. To be more specific, when the quantization parameter QP is larger, quantized components have s...
embodiment 2
[0302]FIG. 9 is a block diagram for explaining an image decoding apparatus according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
[0303] This image decoding apparatus 102 according to the second embodiment decodes, for example, the coded stream Str1 that is outputted from the image coding apparatus 101 of the first embodiment.
[0304] The image decoding apparatus 102 has, in place of the run-length decoding unit RLD0b in the conventional image decoding apparatus 202b shown in FIG. 36 which subjects an inputted coded stream Str0b to a variable length decoding process, a run-length decoding unit RLD1 that subjects the inputted coded stream Str1 to a variable length decoding process on the basis of the quantization parameter QP and a VLD selection signal VldSel, to reconstitute quantized coefficients. The construction except for the run-length decoding unit RLD1 is the same as that of the image decoding apparatus 202b as shown in FIG. 36.
[0305]FIG. 10 is a block diagram for explain...
embodiment 3
[0334]FIG. 13 is a block diagram for explaining an image coding apparatus according to a third embodiment of the present invention.
[0335] This image coding apparatus 103 according to the third embodiment has, in place of the run-length encoding unit RLE0c in the image coding apparatus 201c shown in FIG. 38 which subjects outputs (quantized components) QS from the quantization unit Q to a variable length coding process and outputs a coded stream Str0c, a run-length encoding unit RLE2 that subjects the outputs QS from the quantization unit Q to a variable length coding process on the basis of a quantization parameter QP or a VLC selection signal VlcSel and outputs a coded stream Str2. Other components of the image coding apparatus 103 of the third embodiment are the same as those in the conventional image coding apparatus 201c.
[0336] To be more specific, the run-length encoding unit RLE2 has, like the conventional run-length encoding unit RLE0c, the first code table T1 (see FIG. 42)...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| variable length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length coding method | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com