Patents
Literature
837 results about "Pixel color" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
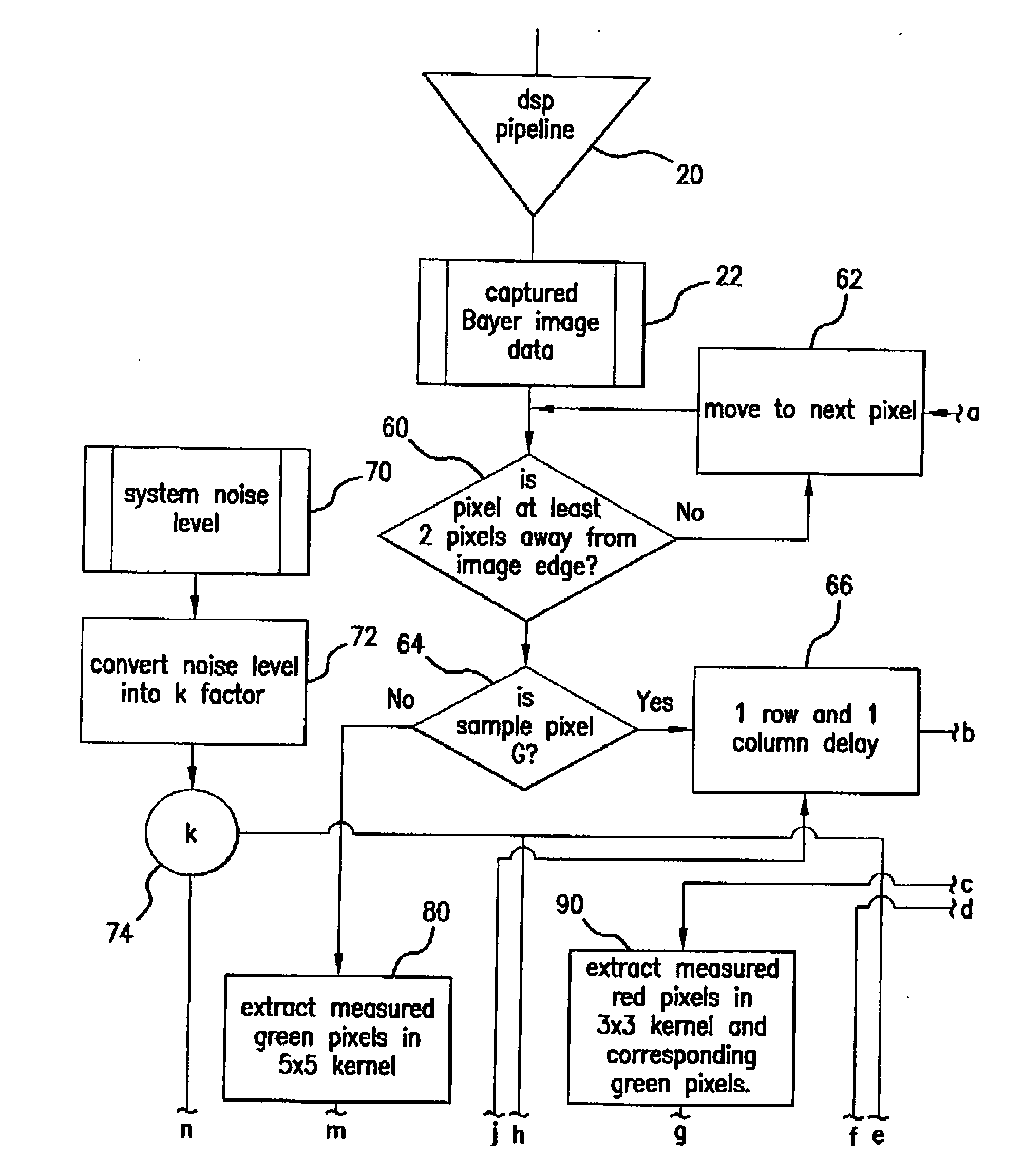
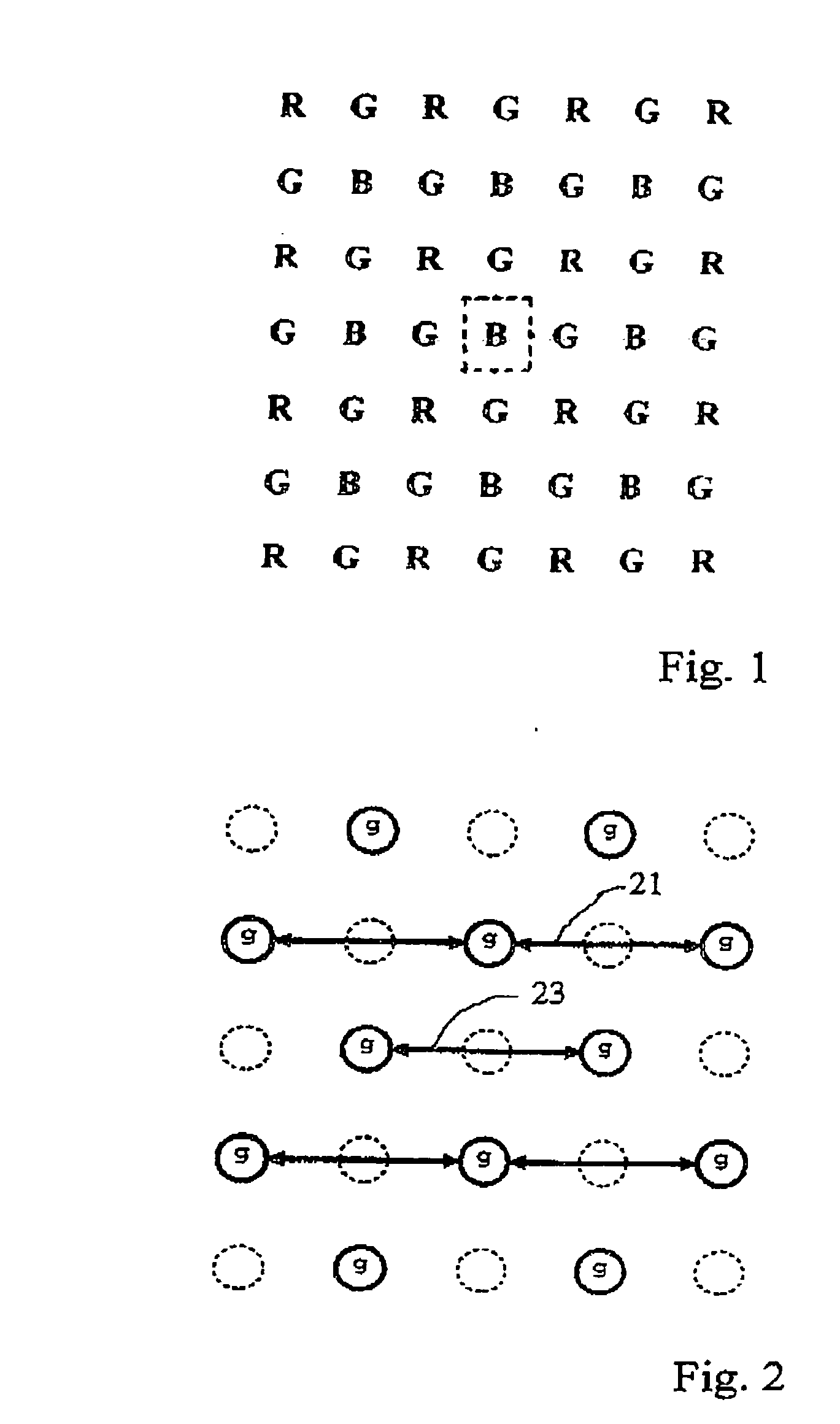
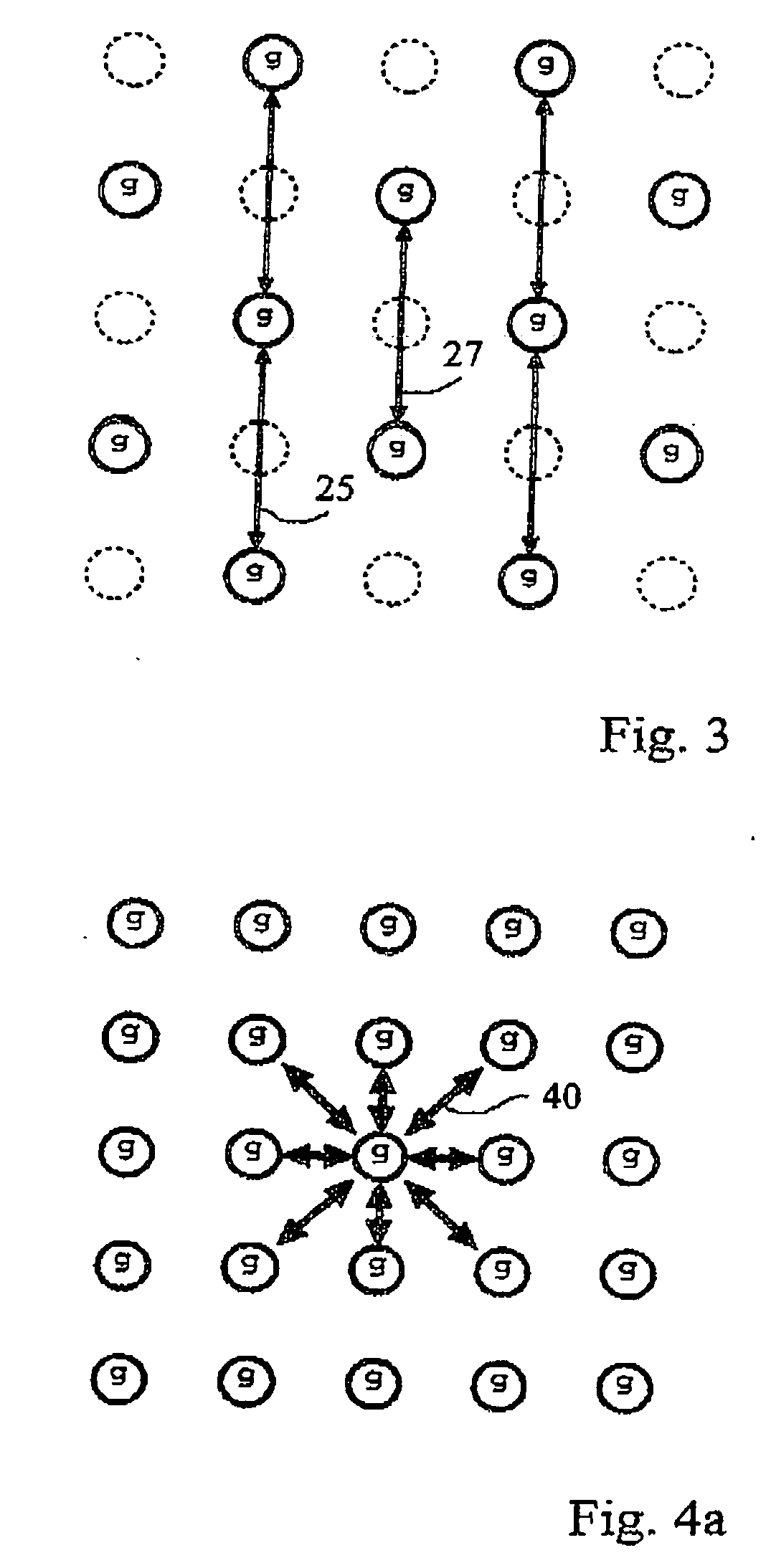
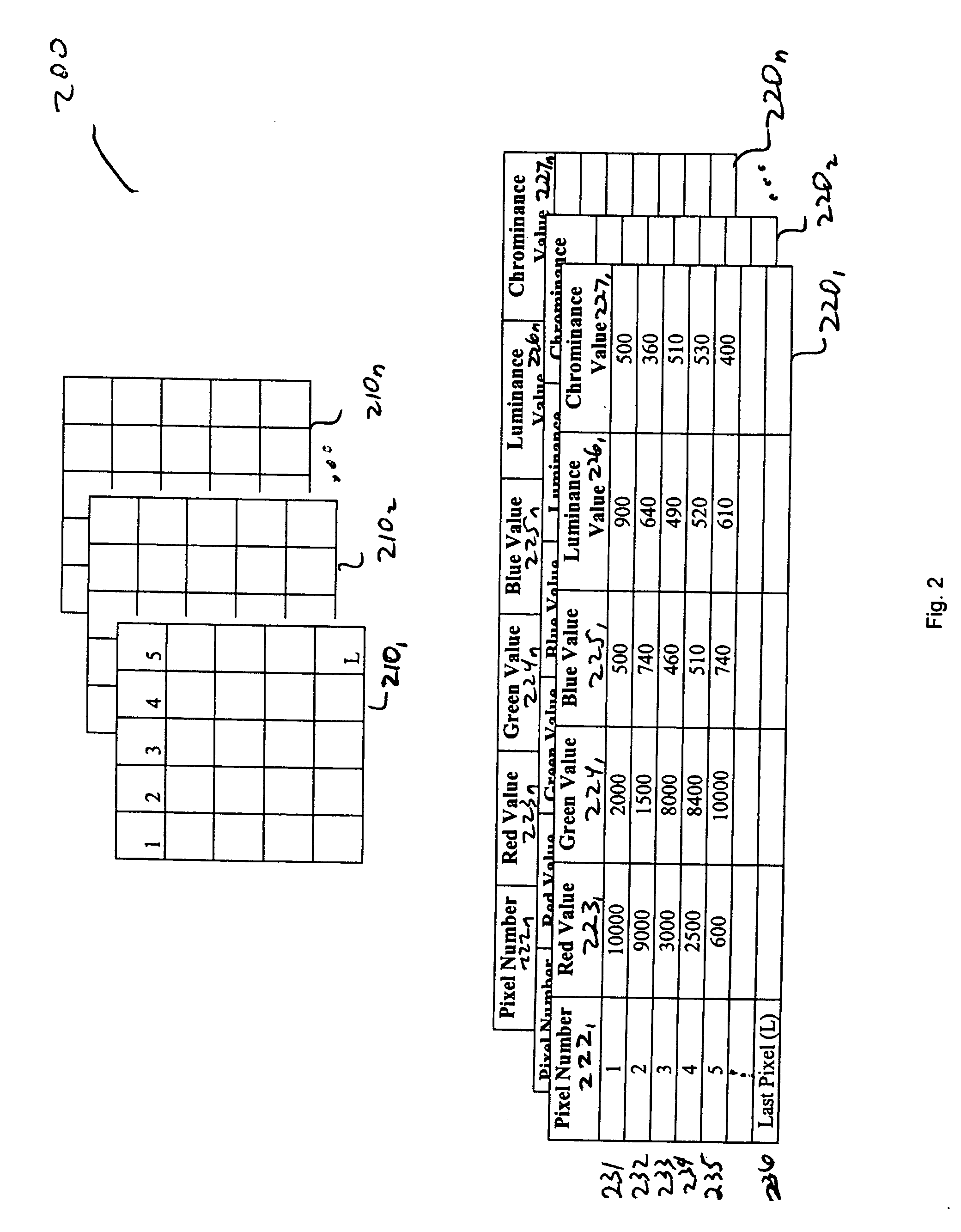
Method for reconstruction of pixel color values
InactiveUS20090263017A1Strong edge informationSuppress noise transmissionTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionPixel color
Owner:TANBAKUCHI ANTHONY AMIR
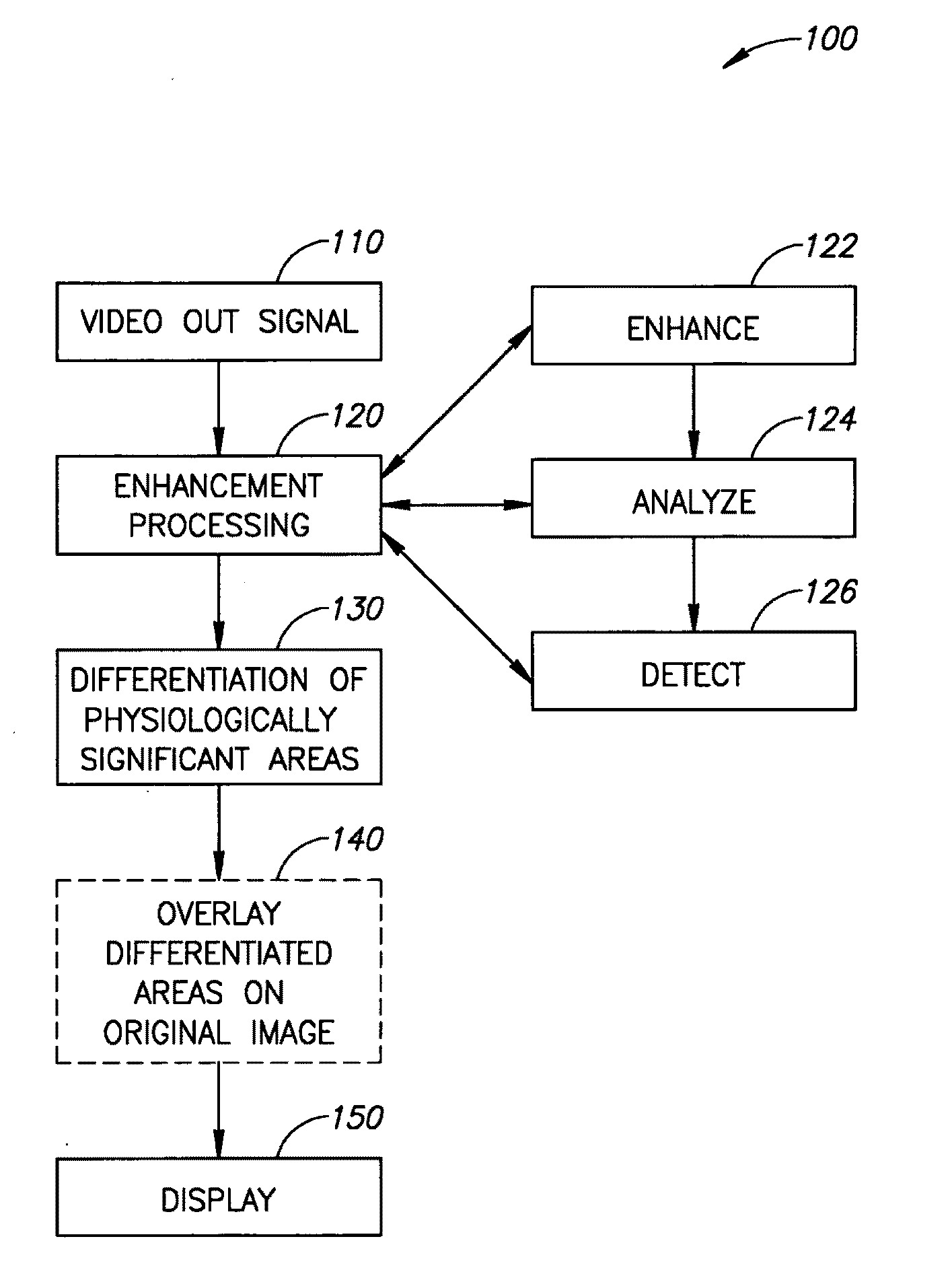
Medical Image Processing
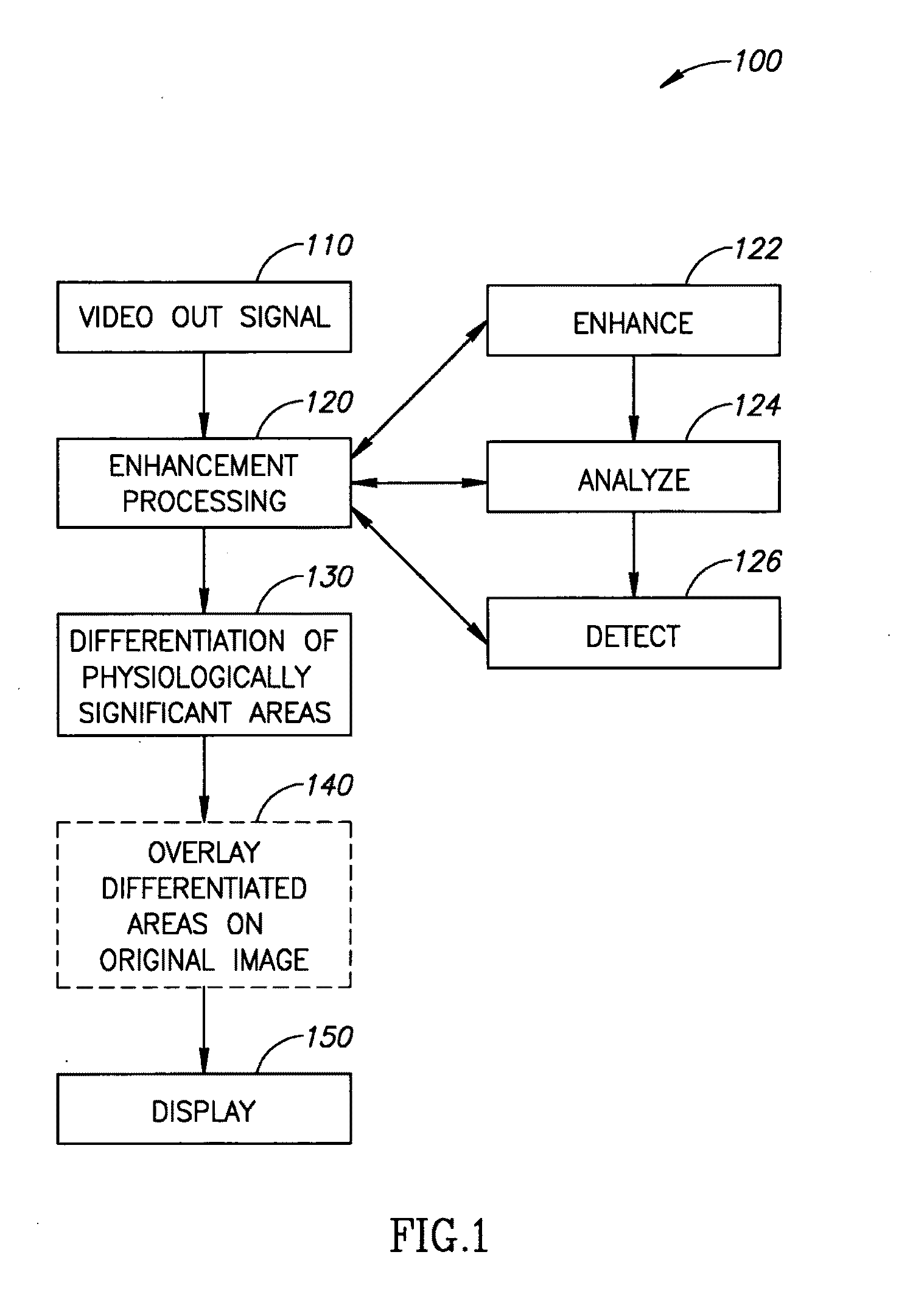
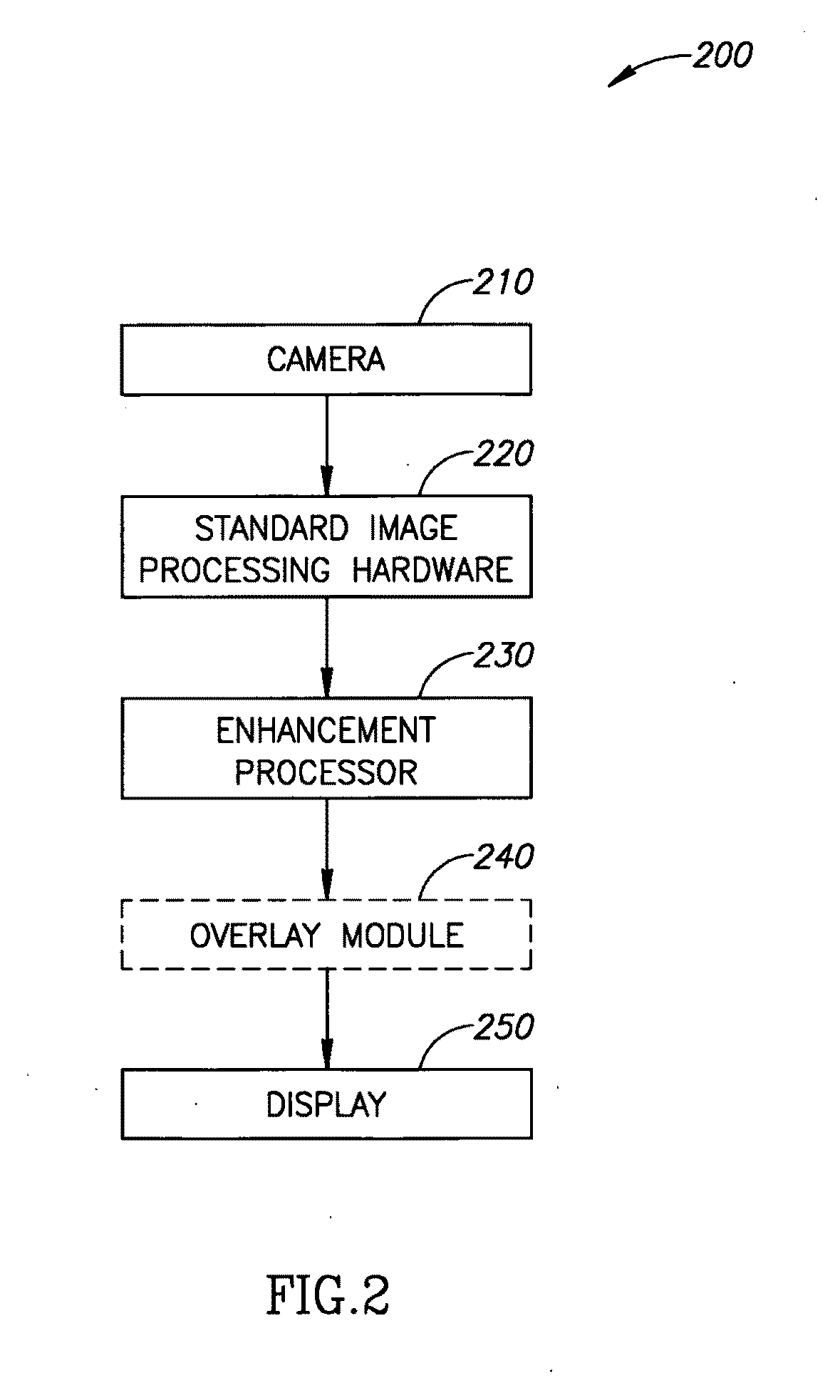
A method of image processing, including:(a) calculating at least one pixel color feature (PCF) value for each pixel in a color medical image to generate a set of PCF data; and(b) filtering the PCF data with at least one spatial adaptive bandpass filter (ABPF) to sort the pixels into physiologically significant regions;wherein the at least one PCF value for at least one pixel depends on at least 2 color components of the medical image.
Owner:D V P TECH
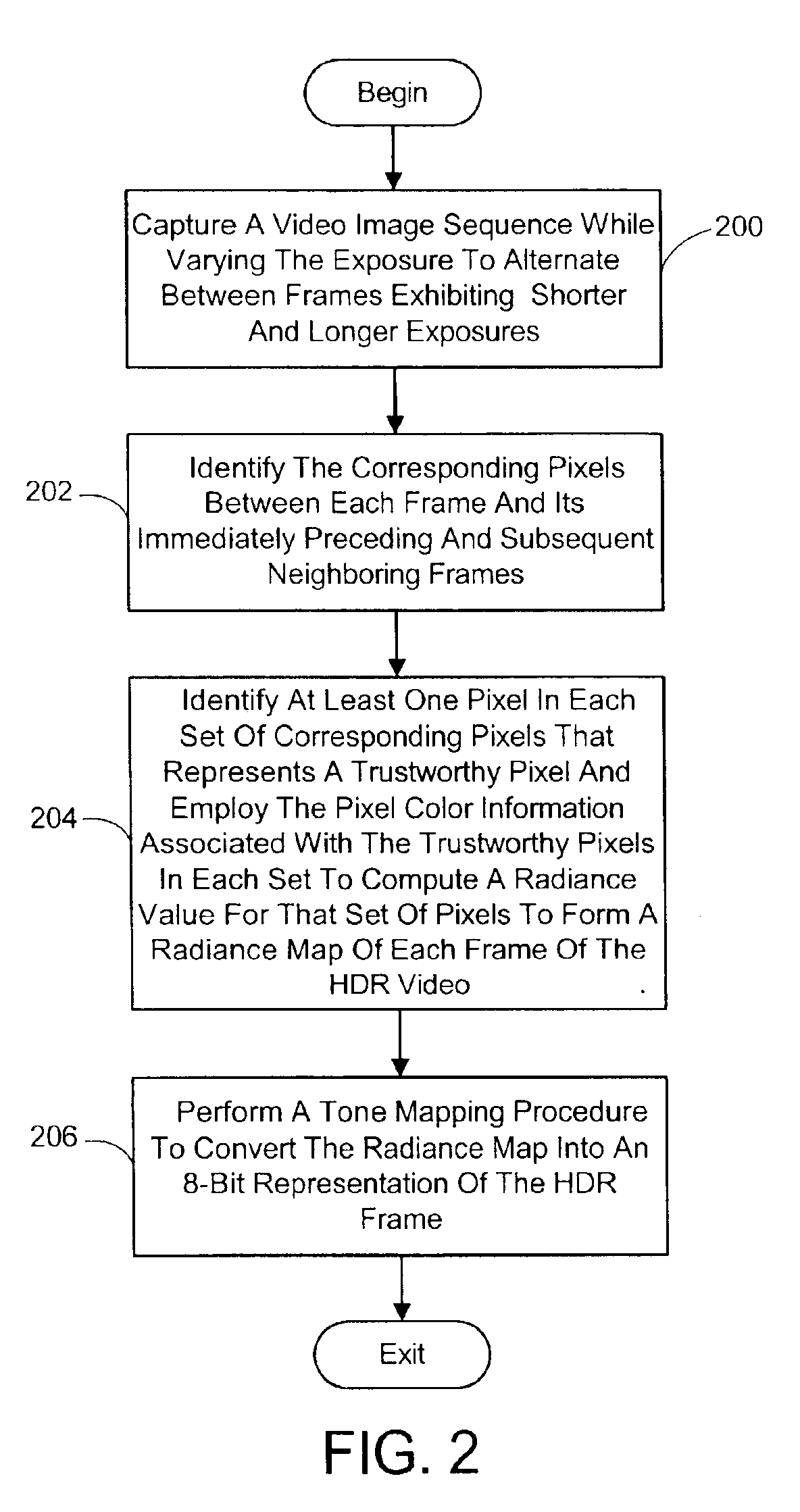
System and process for generating high dynamic range video
InactiveUS6879731B2Minimizing any discontinuityTelevision system detailsImage enhancementTone mappingRadiance
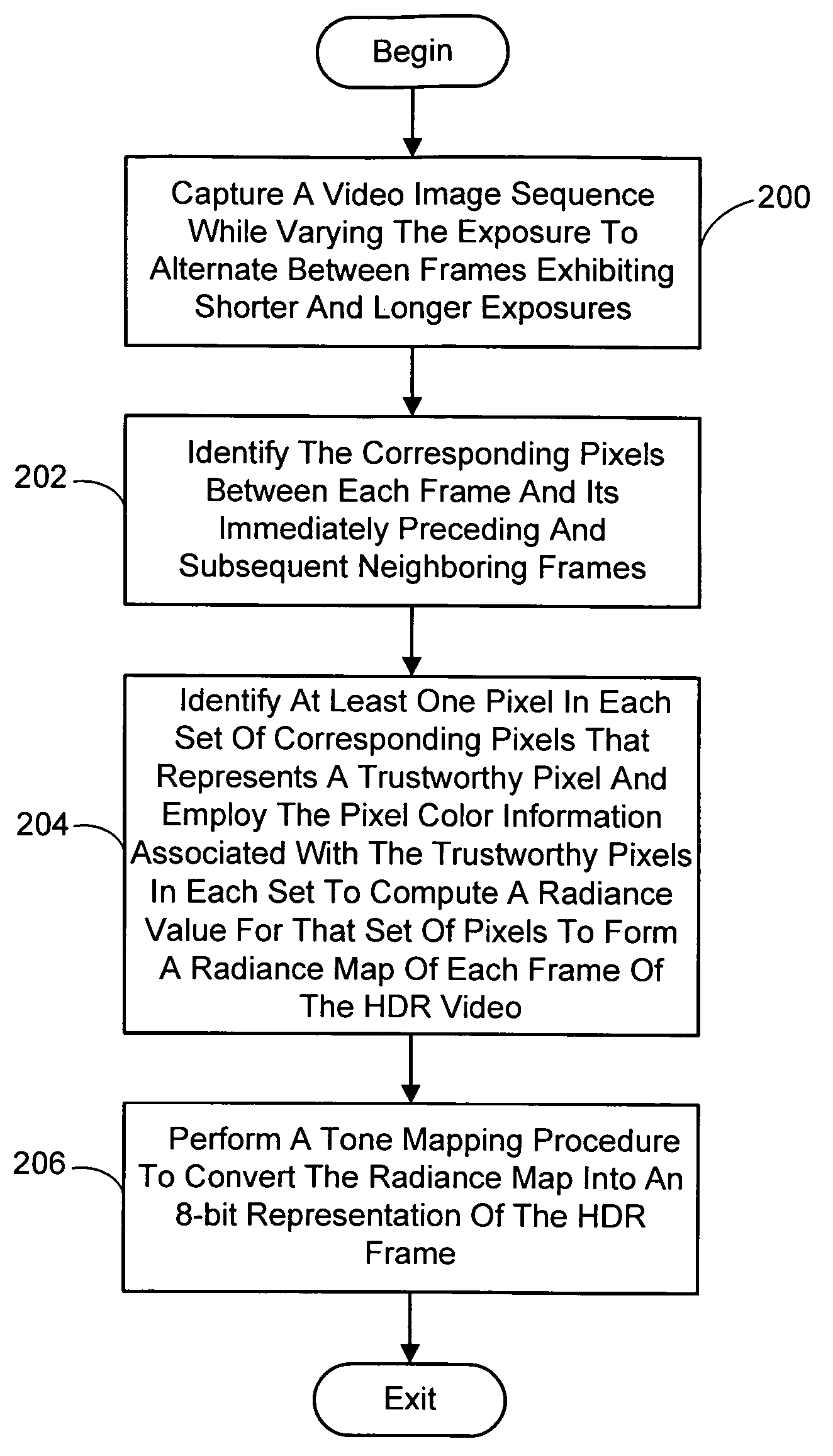
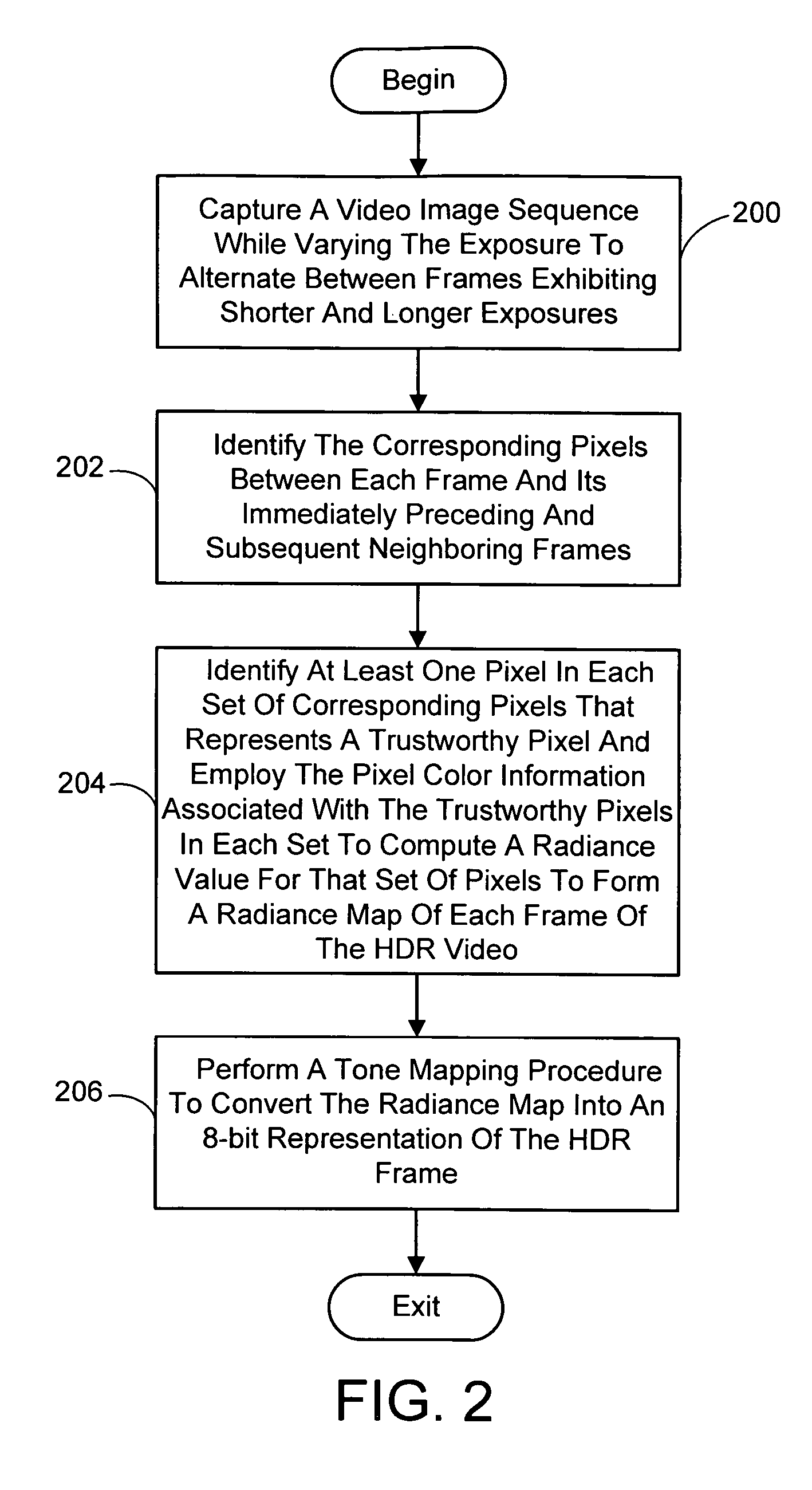
A system and process for generating High Dynamic Range (HDR) video is presented which involves first capturing a video image sequence while varying the exposure so as to alternate between frames having a shorter and longer exposure. The exposure for each frame is set prior to it being captured as a function of the pixel brightness distribution in preceding frames. Next, for each frame of the video, the corresponding pixels between the frame under consideration and both preceding and subsequent frames are identified. For each corresponding pixel set, at least one pixel is identified as representing a trustworthy pixel. The pixel color information associated with the trustworthy pixels is then employed to compute a radiance value for each pixel set to form a radiance map. A tone mapping procedure can then be performed to convert the radiance map into an 8-bit representation of the HDR frame.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Pixel image enhancement system and method
InactiveUS6038348ALow costReduce memoryCharacter and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationDisplay deviceOutput device
A pixel image enhancement system which operates on color or monochrome source images to produce output cells the same size as the source pixels but not spatially coincident or one-to-one correspondent with them. By operating upon a set of input pixels surrounding each output cell with a set of logic operations implementing unique Boolean equations, the system generates "case numbers" characterizing inferred-edge pieces within each output cell. A rendering subsystem, responsive to the case numbers and source-pixel colors, then produces signals for driving an output device (printer or display) to display the output cells, including the inferred-edge pieces, to the best of the output device's ability and at its resolution.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
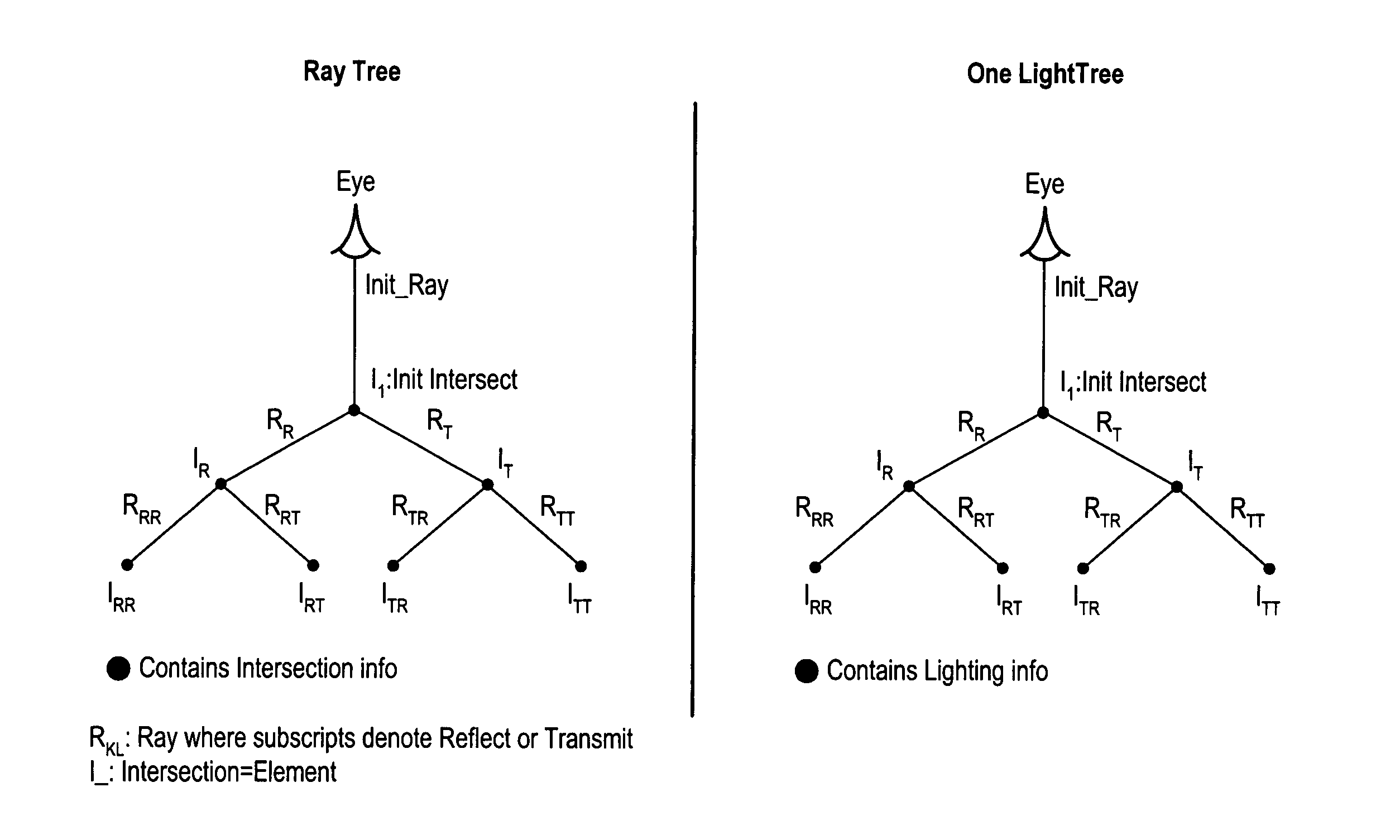
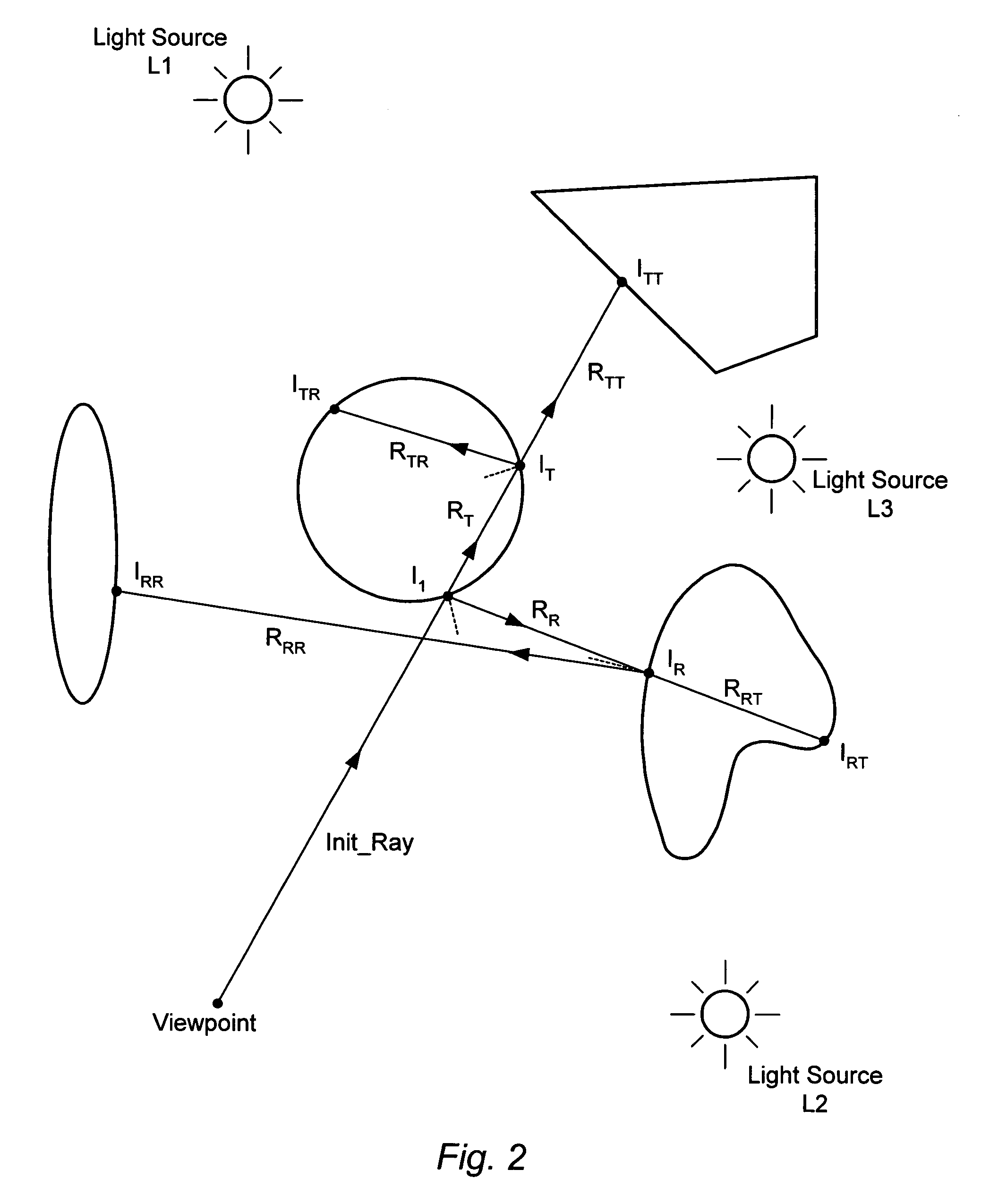
System architecture for high speed ray tracing
InactiveUS7012604B1Extension of timeImprove performance3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Light tree
A system and method for generating images of three-dimensional objects. The system includes one or more tracing processors, and one or more shading processors. Each of the tracing processors may be configured to (a) perform a first set of computations on a corresponding group of primary rays emanating from a viewpoint resulting in a ray tree and a set of one or more light trees for each primary ray of the corresponding group, (b) transfer the ray trees and associated light trees to one of the shading processors, and (c) repeat (a) and (b). Each of the shading processors may be configured to (d) receive ray trees and associated light trees from one of the tracing processors, (e) perform a second set of computations on the received ray trees and associated light trees to determine pixel color values, and (f) repeat (d) and (e) a plurality of times.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
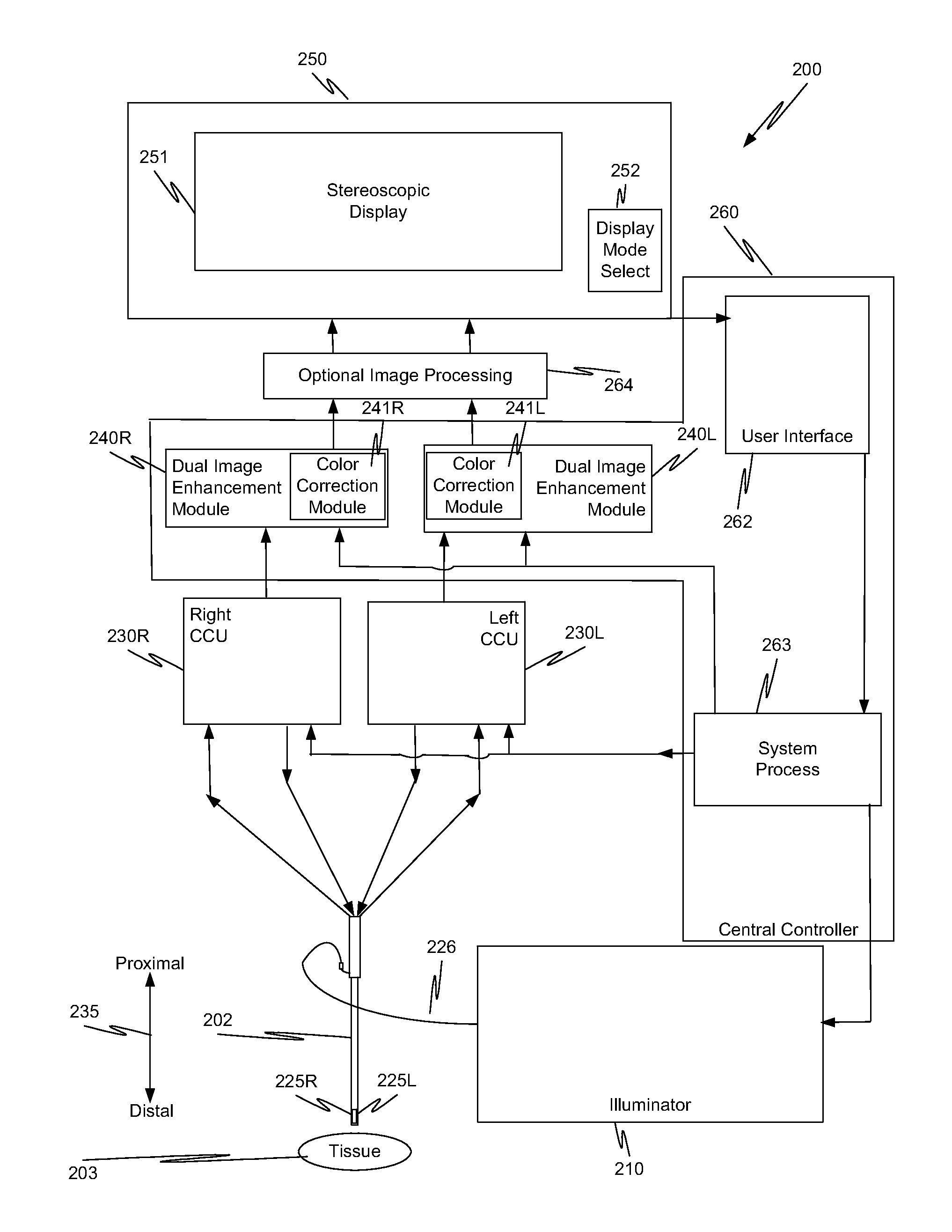
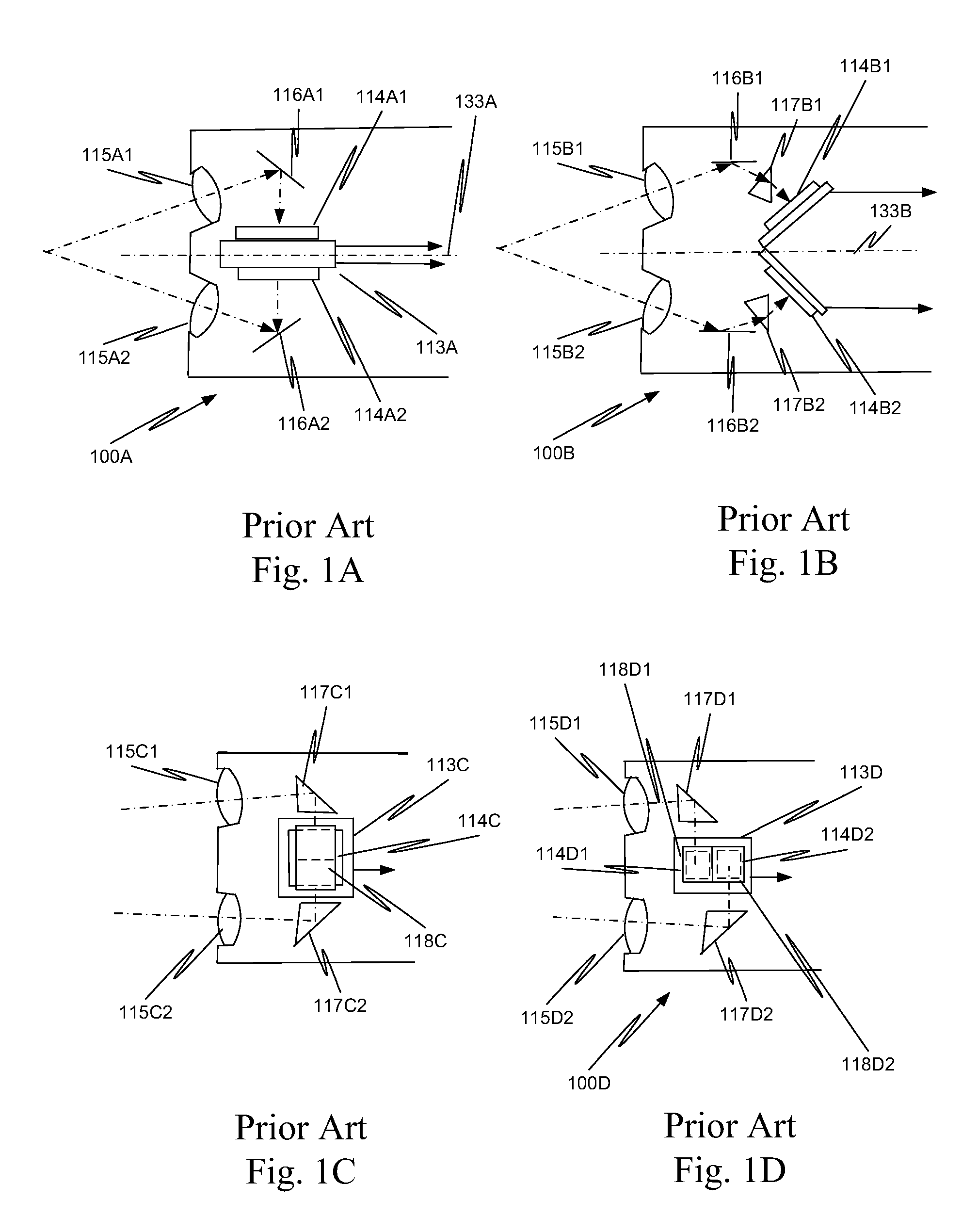
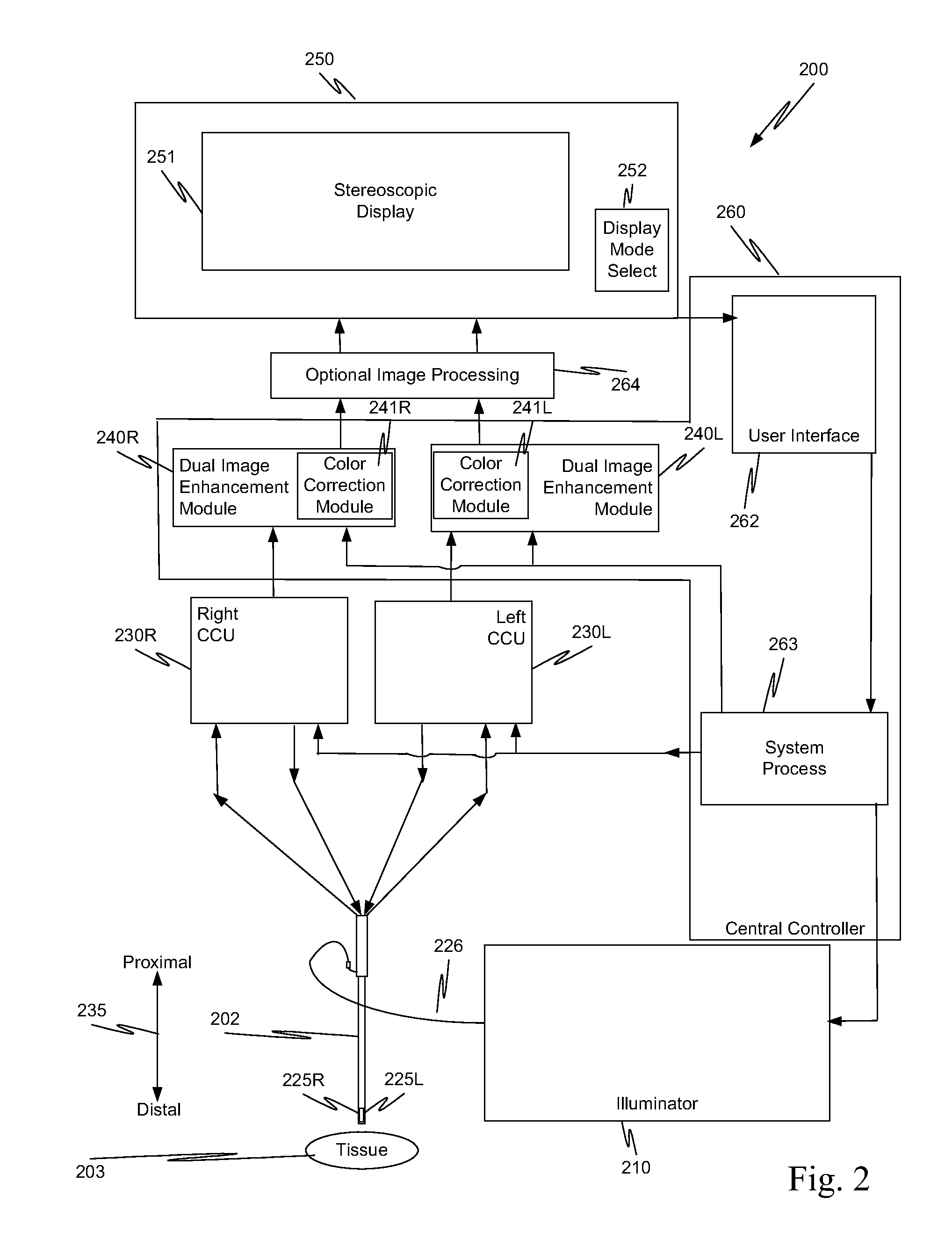
Image capture unit and method with an extended depth of field
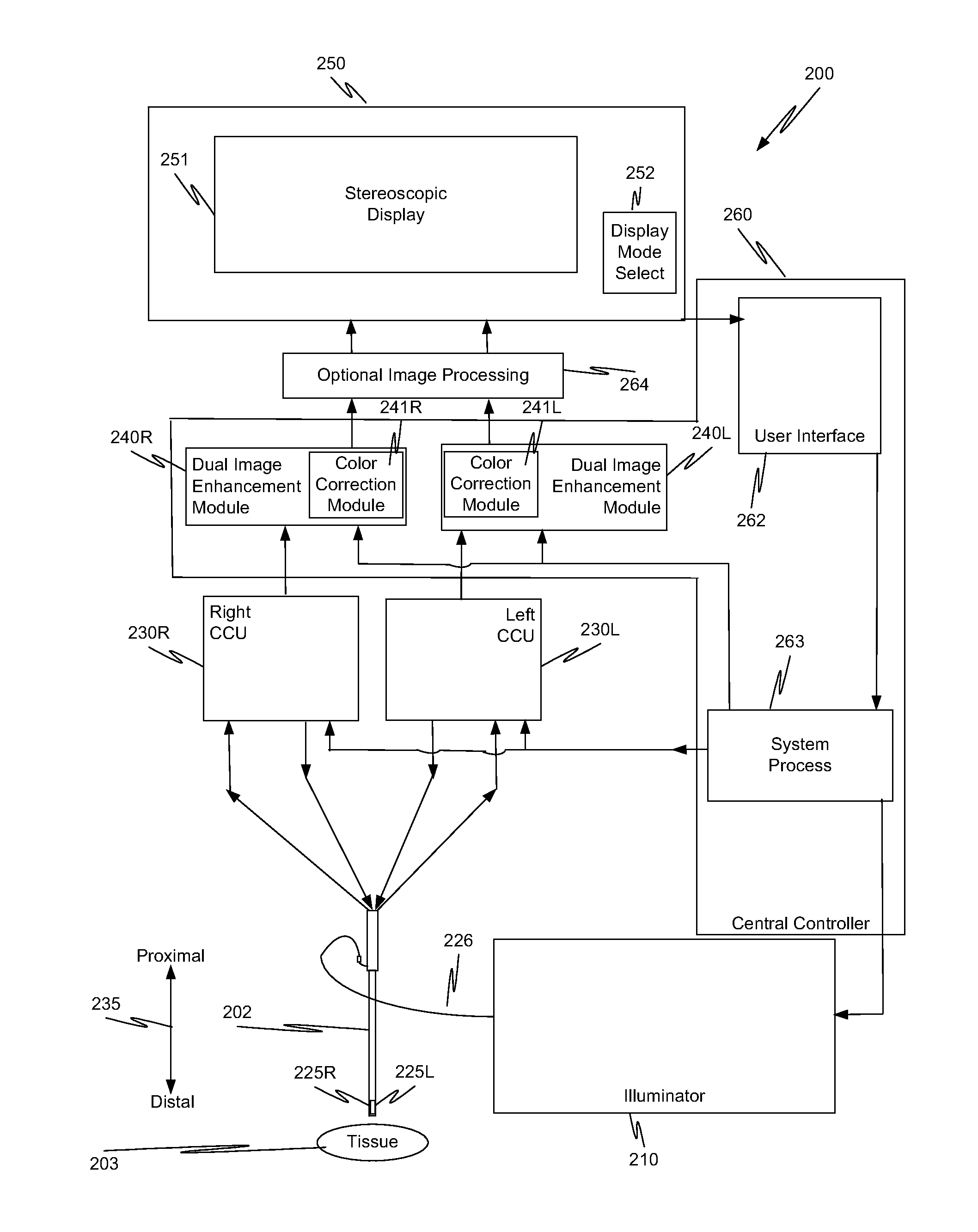
ActiveUS20130038689A1Overcomes shortcomingMore capabilityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsBeam splitterImage resolution
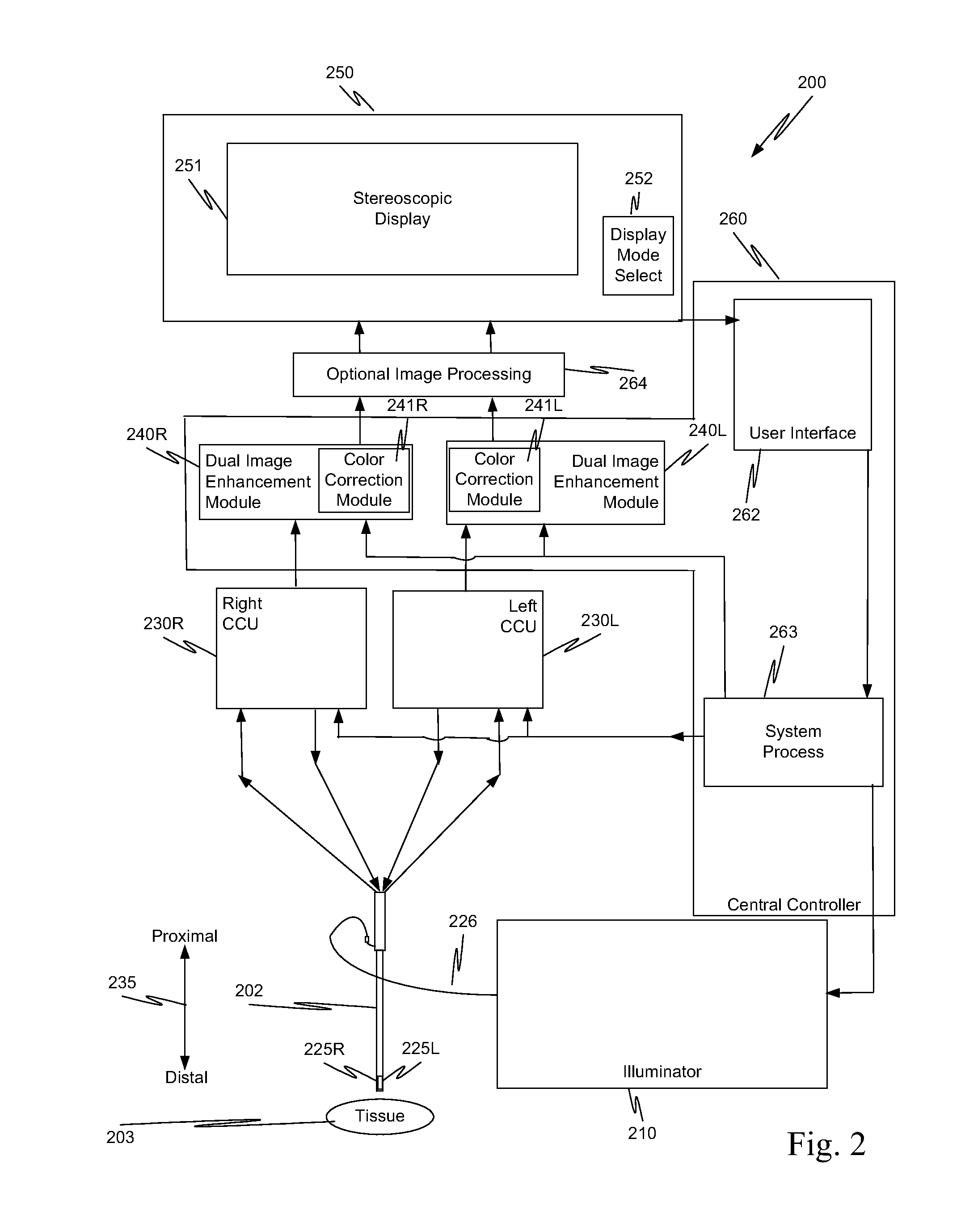
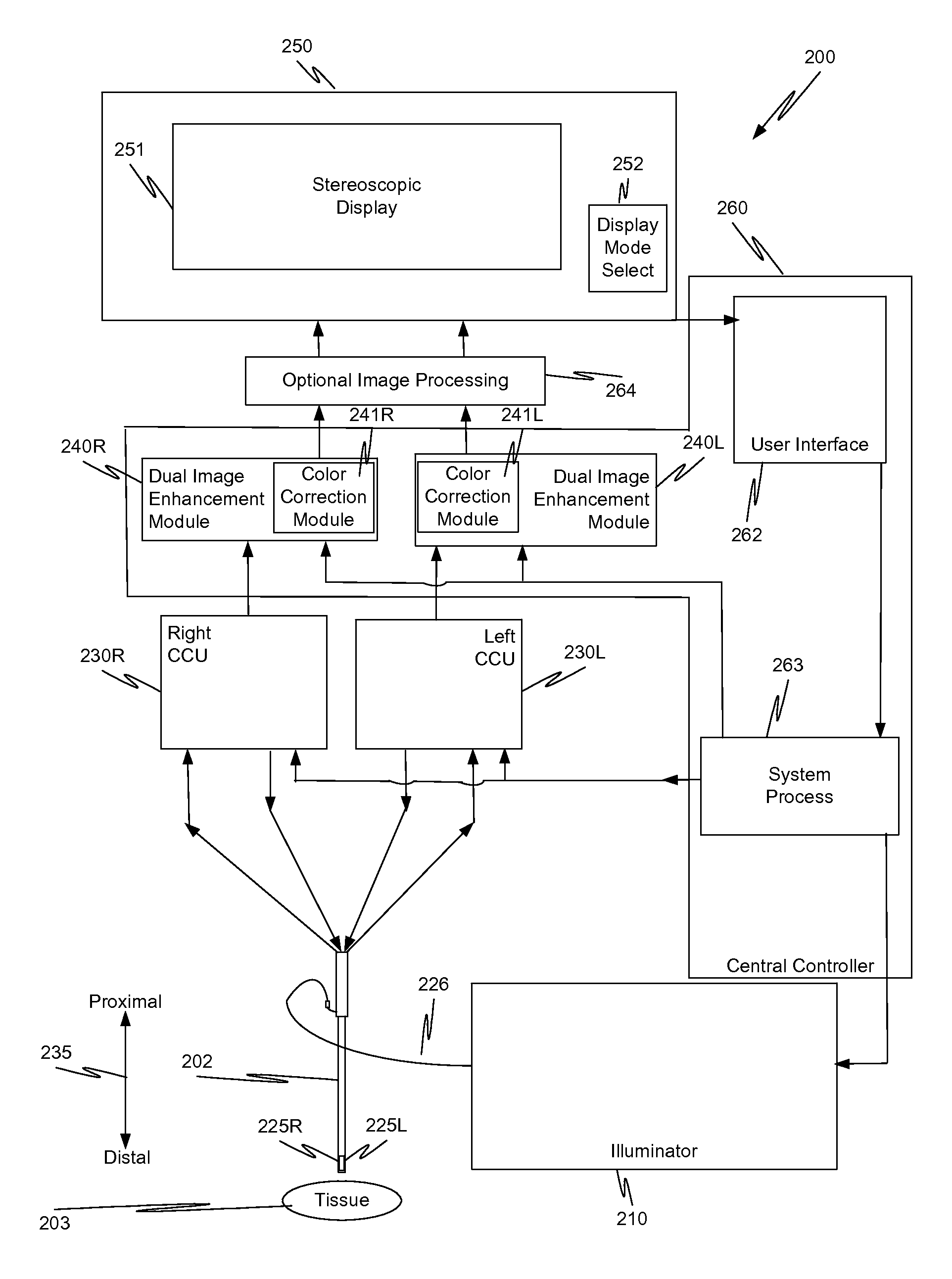
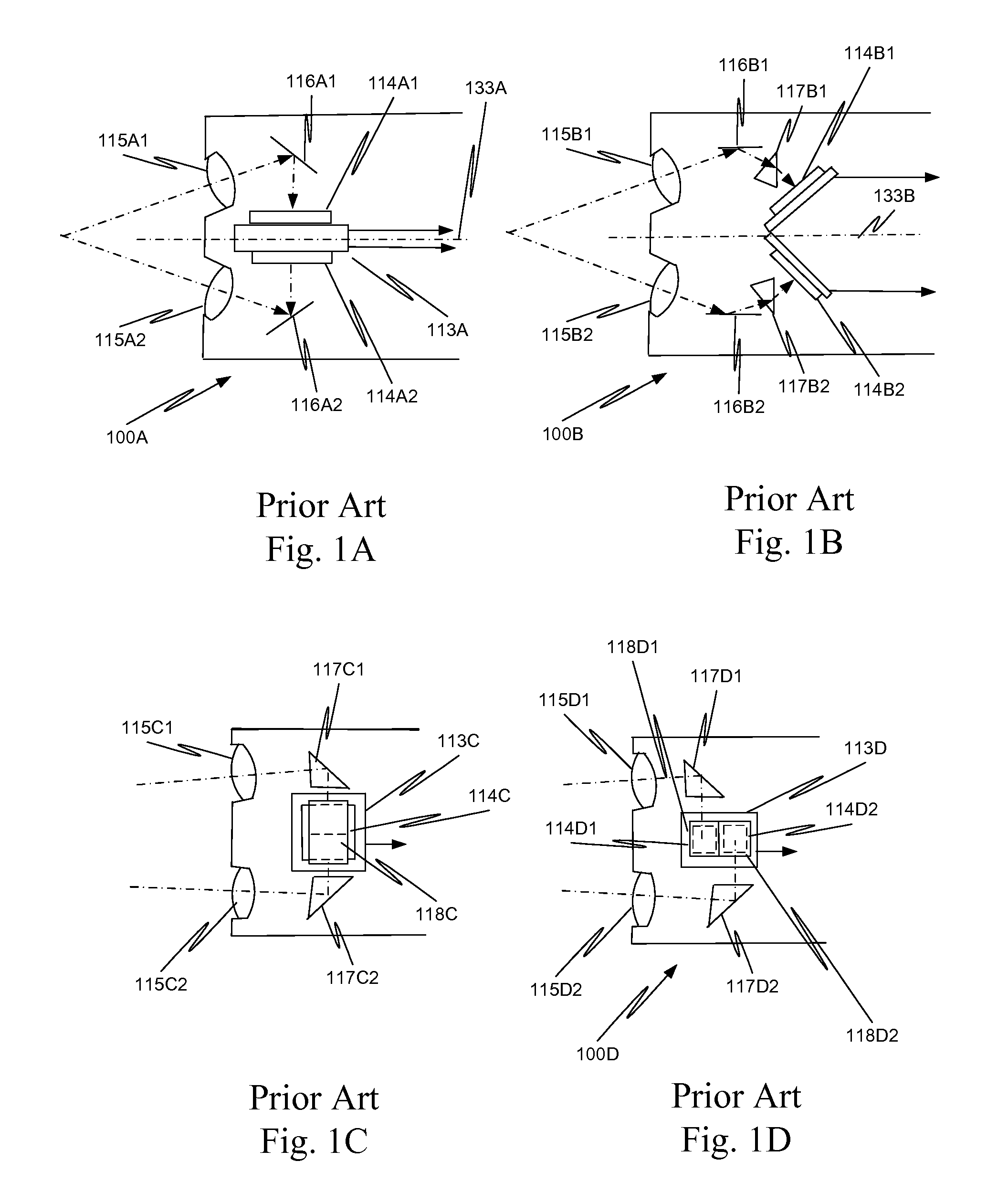
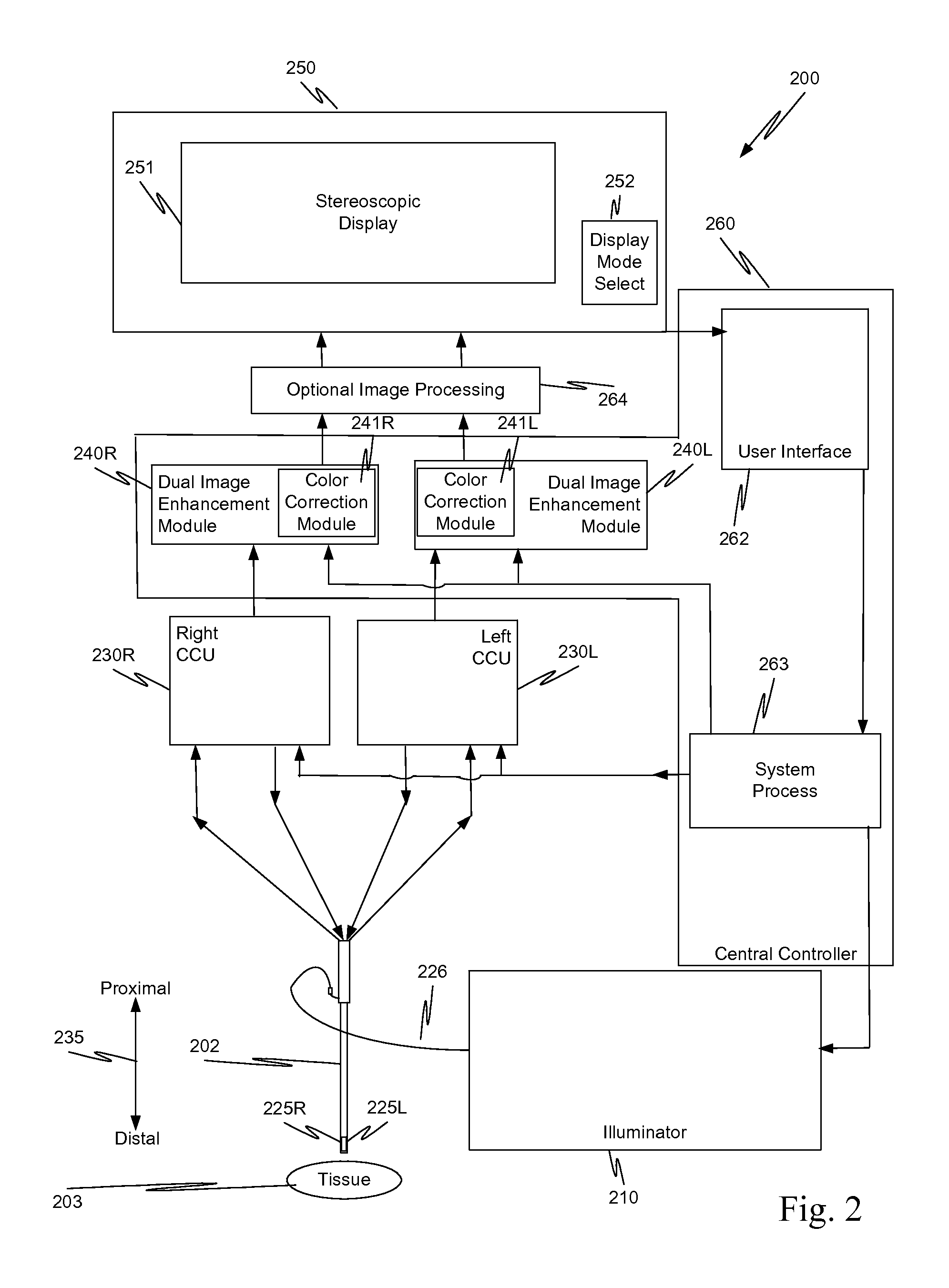
In a minimally invasive surgical system, an image capture unit includes a prism assembly and sensor assembly. The prism assembly includes a beam splitter, while the sensor assembly includes coplanar image capture sensors. Each of the coplanar image capture sensors has a common front end optical structure, e.g., the optical structure distal to the image capture unit is the same for each of the sensors. A controller enhances images acquired by the coplanar image capture sensors. The enhanced images may include (a) visible images with enhanced feature definition, in which a particular feature in the scene is emphasized to the operator of minimally invasive surgical system; (b) images having increased image apparent resolution; (c) images having increased dynamic range; (d) images displayed in a way based on a pixel color component vector having three or more color components; and (e) images having extended depth of field.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
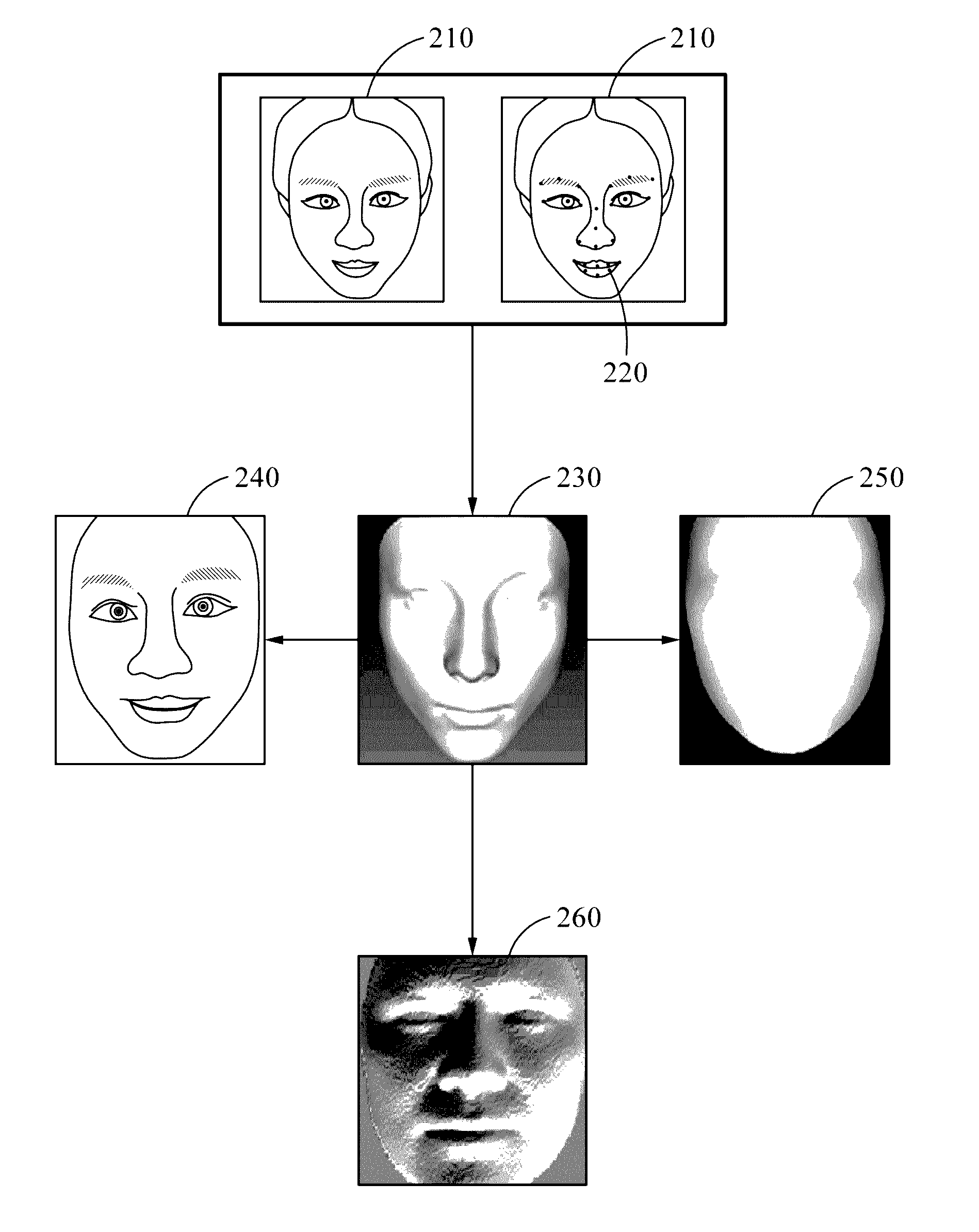
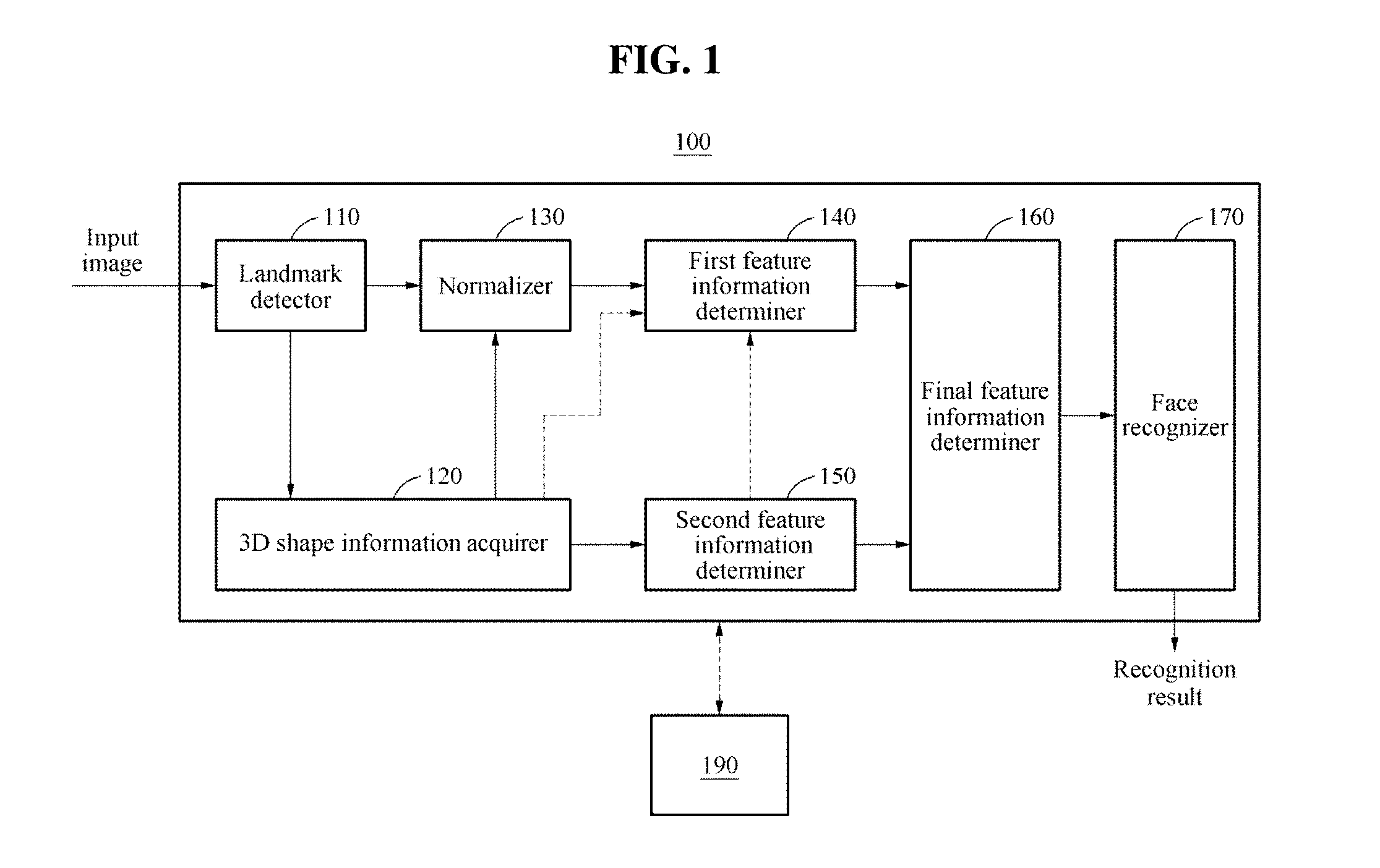
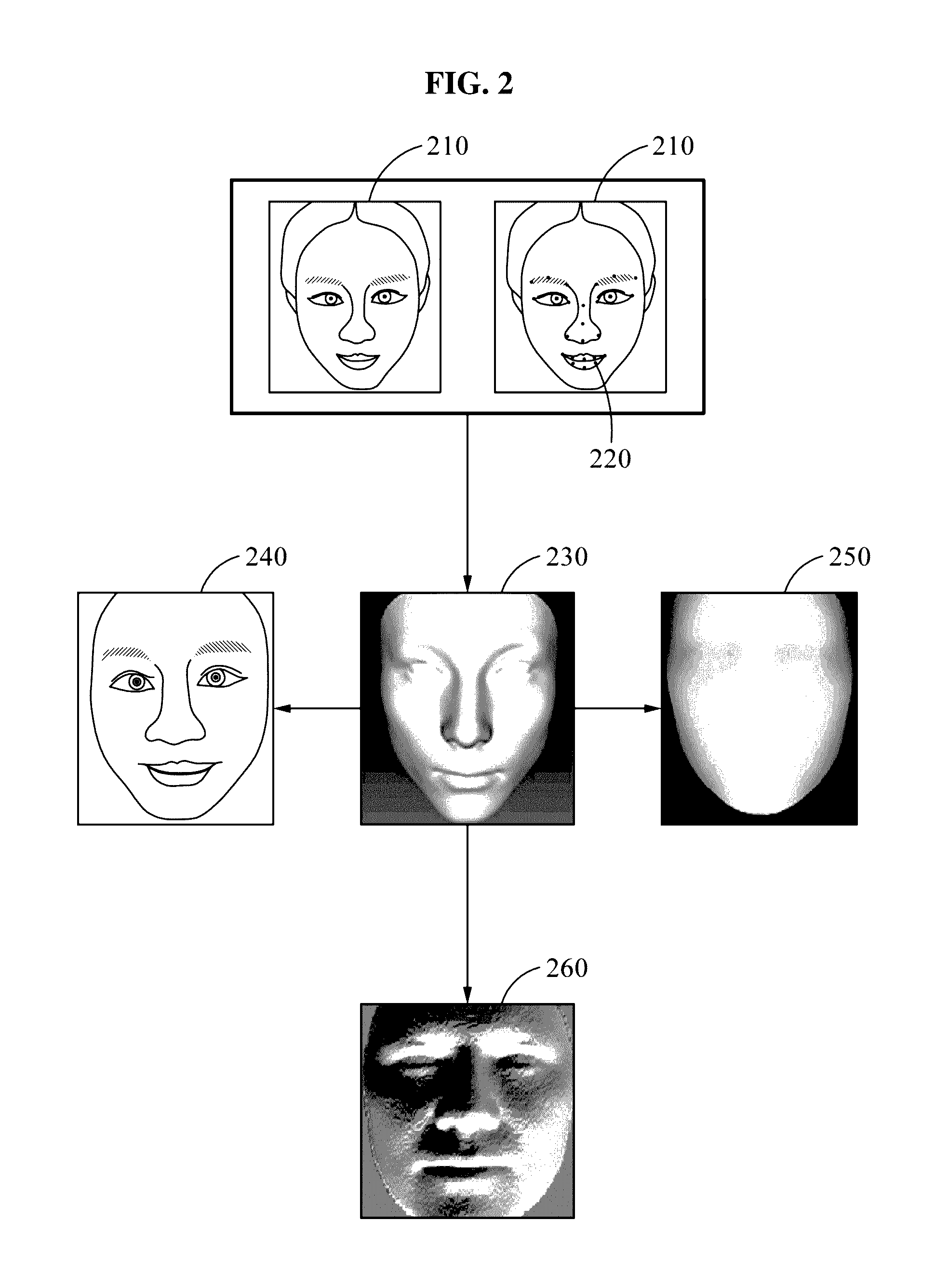
Face recognition method and apparatus
Face recognition of a face, to determine whether the face correlates with an enrolled face, may include generating a personalized three-dimensional (3D) face model based on a two-dimensional (2D) input image of the face, acquiring 3D shape information and a normalized 2D input image of the face based on the personalized 3D face model, generating feature information based on the 3D shape information and pixel color values of the normalized 2D input image, and comparing the feature information with feature information associated with the enrolled face. The feature information may include first and second feature information generated based on applying first and second deep neural network models to the pixel color values of the normalized 2D input image and the 3D shape information, respectively. The personalized 3D face model may be generated based on transforming a generic 3D face model based on landmarks detected in the 2D input image.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
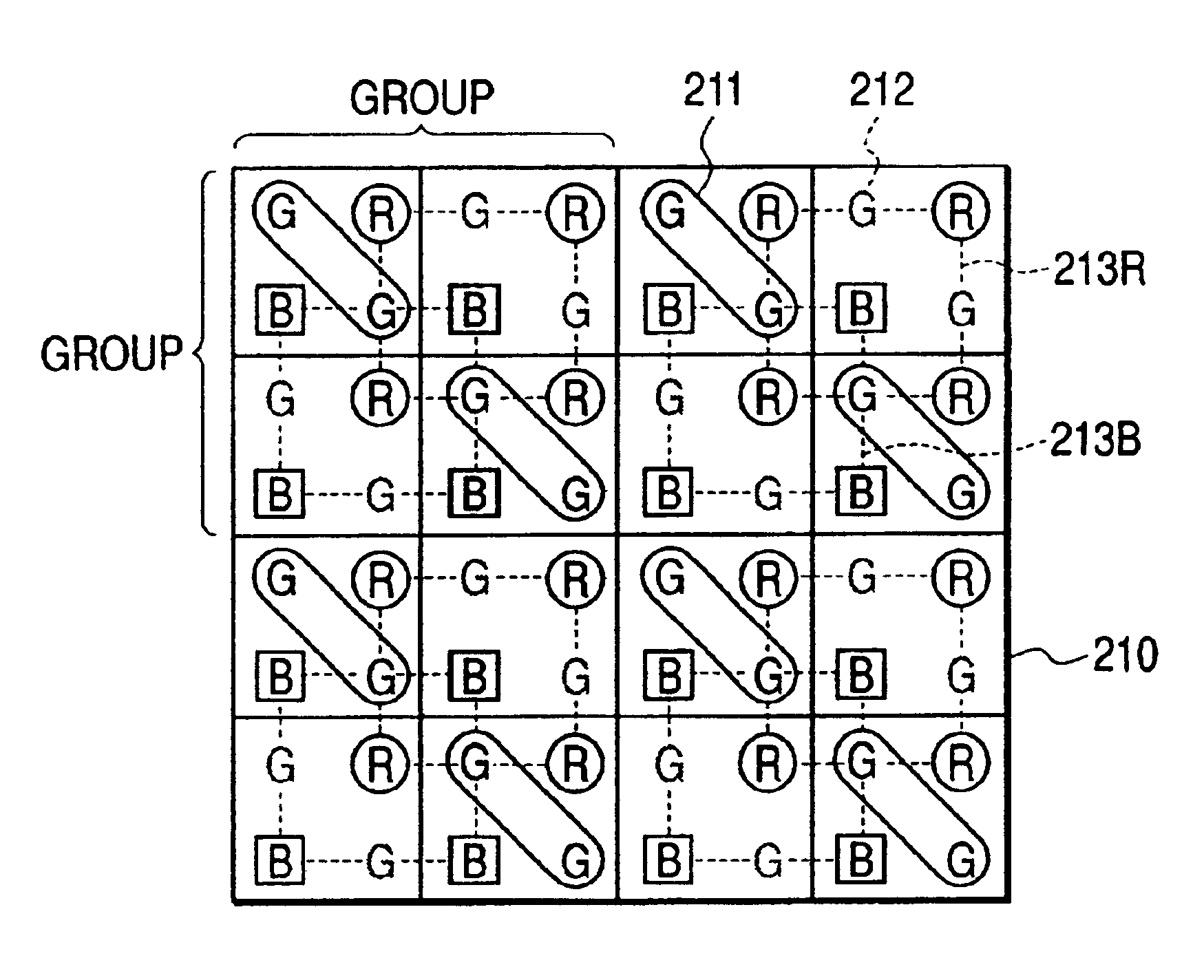
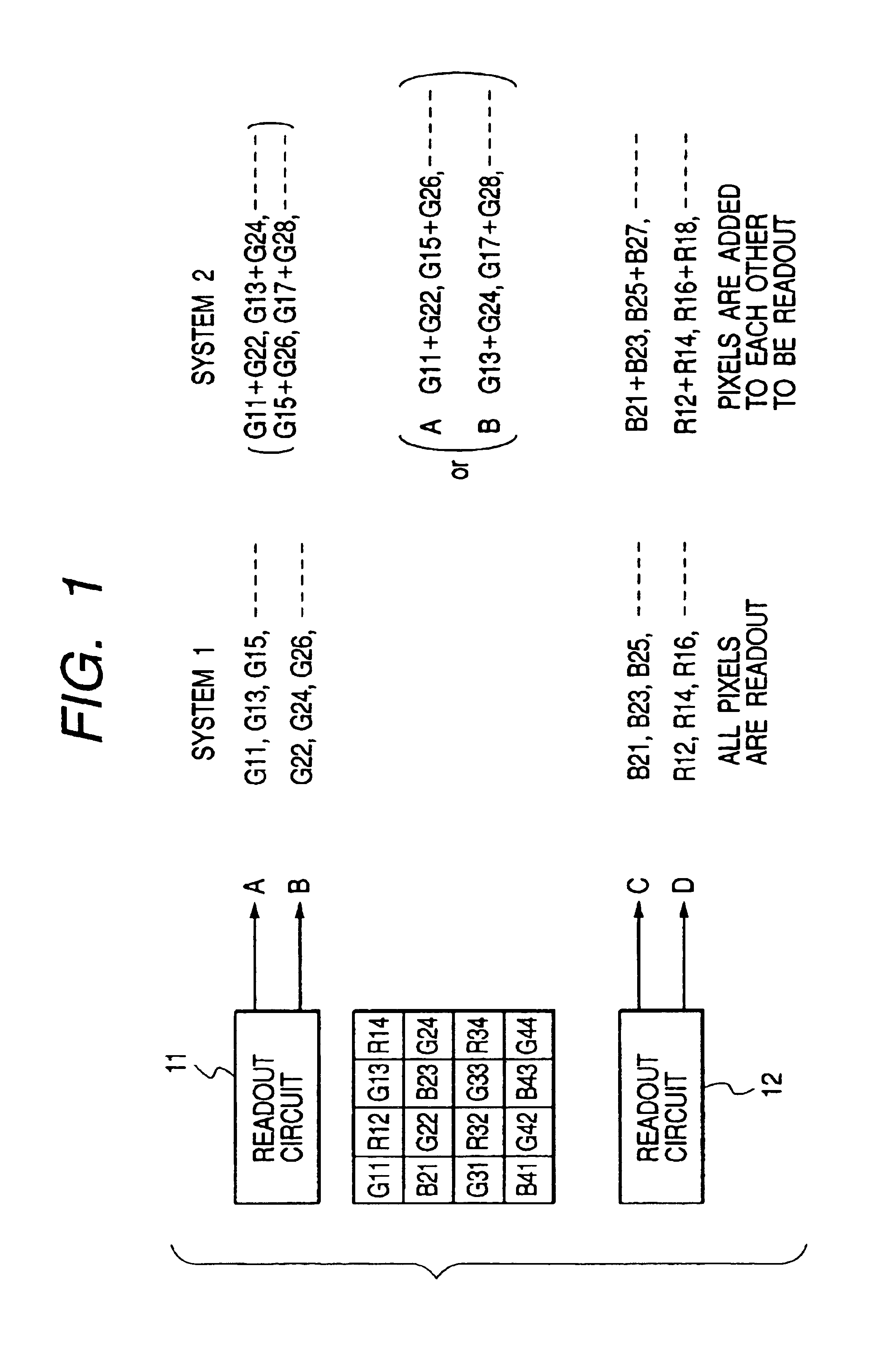
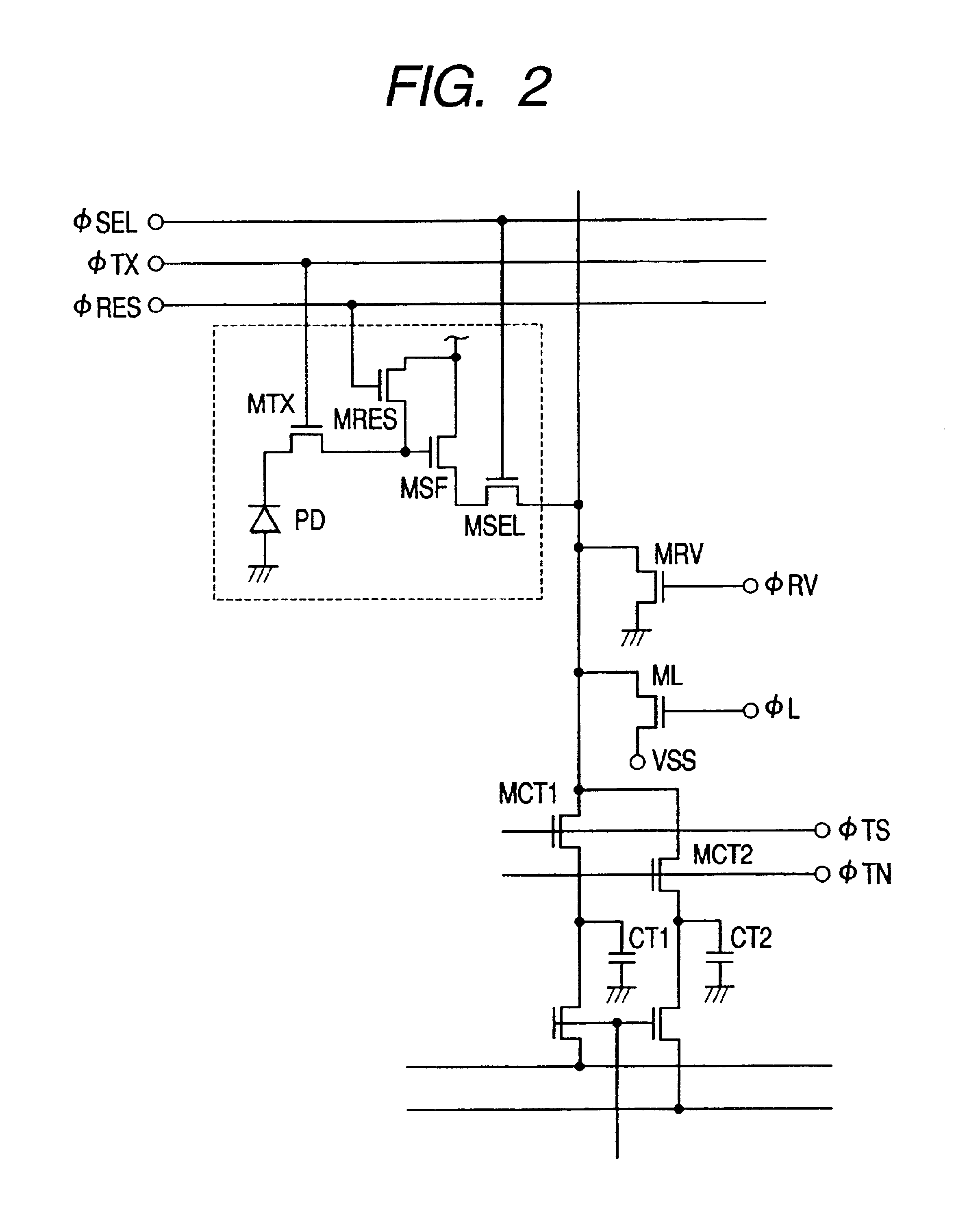
Image pickup apparatus having plural pixels arranged two-dimensionally, and selective addition of different pixel color signals to control spatial color arrangement
InactiveUS6992714B1Preferable image qualityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor filter arrayComputer science
An image pickup apparatus comprises a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix form, first color filters arranged in an oblique direction for the pixels, second and third color filters arranged so that a same color is arranged in a horizontal direction, a circuit for adding together signals of two or more pixels each having the first color filter, which are adjacent to each other in an oblique direction, and a circuit for adding together the signals of two or more pixels each having the second color filter, which are arranged in a horizontal direction, and for adding together the signals of two or more pixels each having the third color filter, which are arranged in the horizontal direction.
Owner:CANON KK
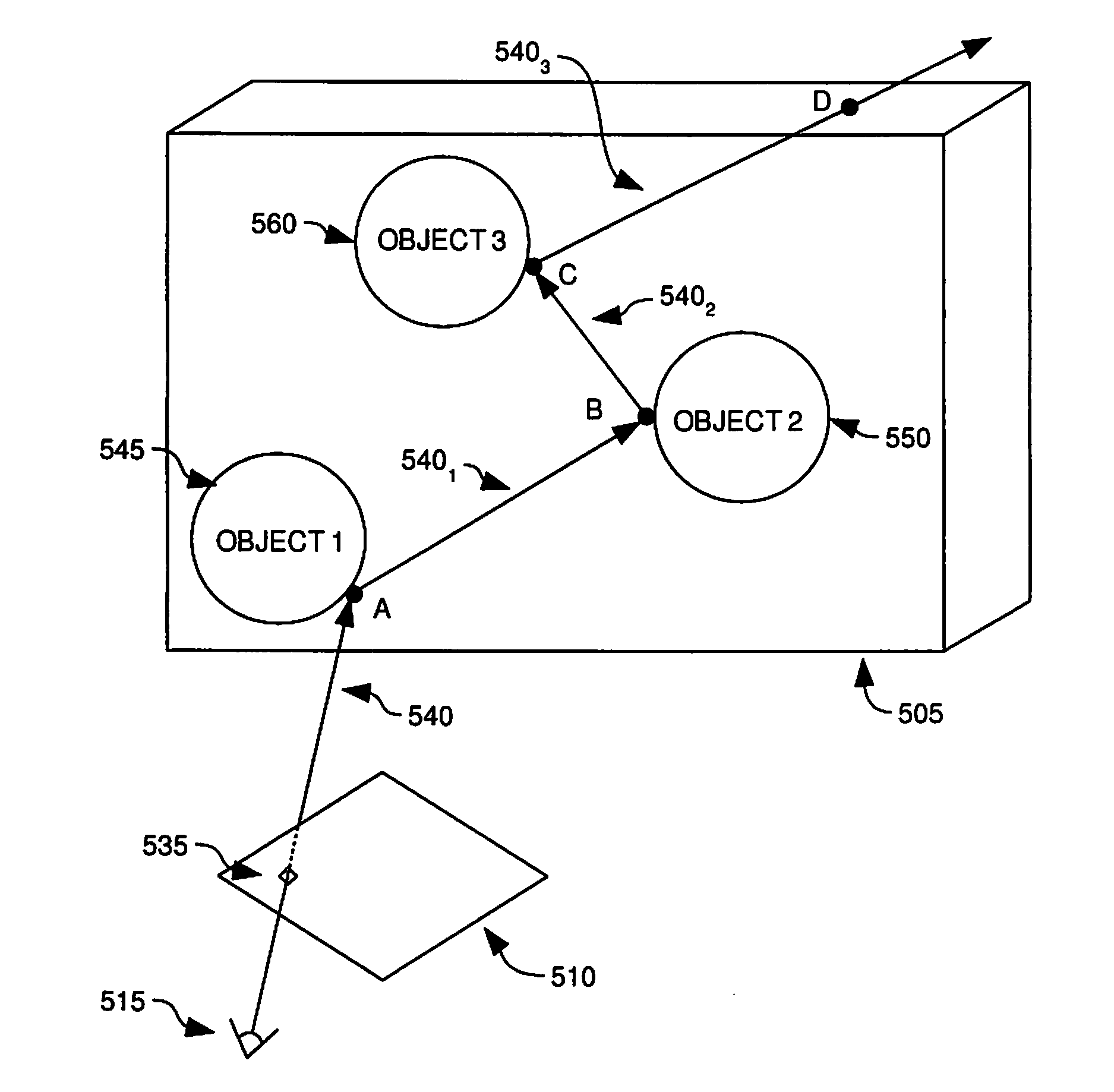
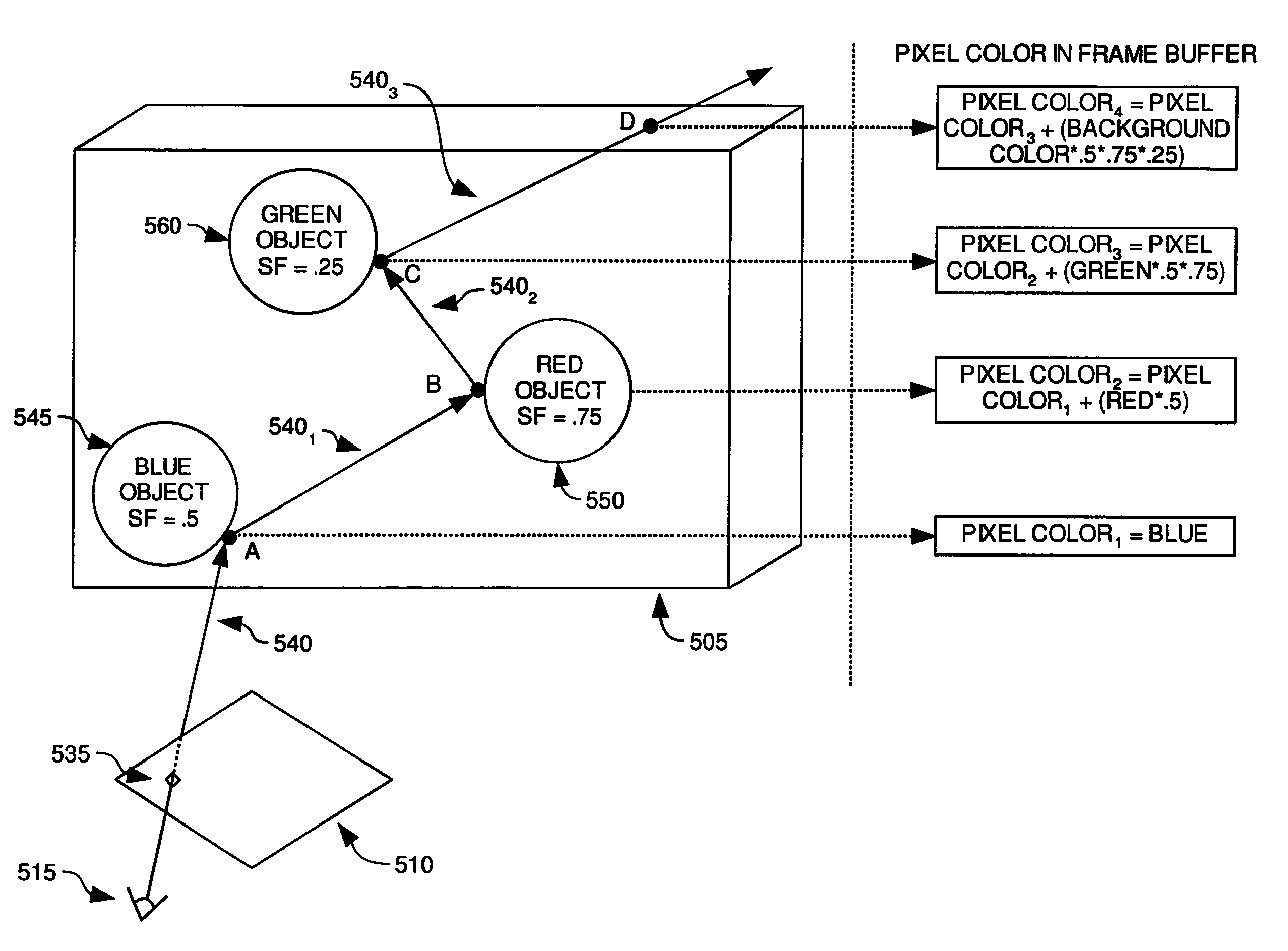
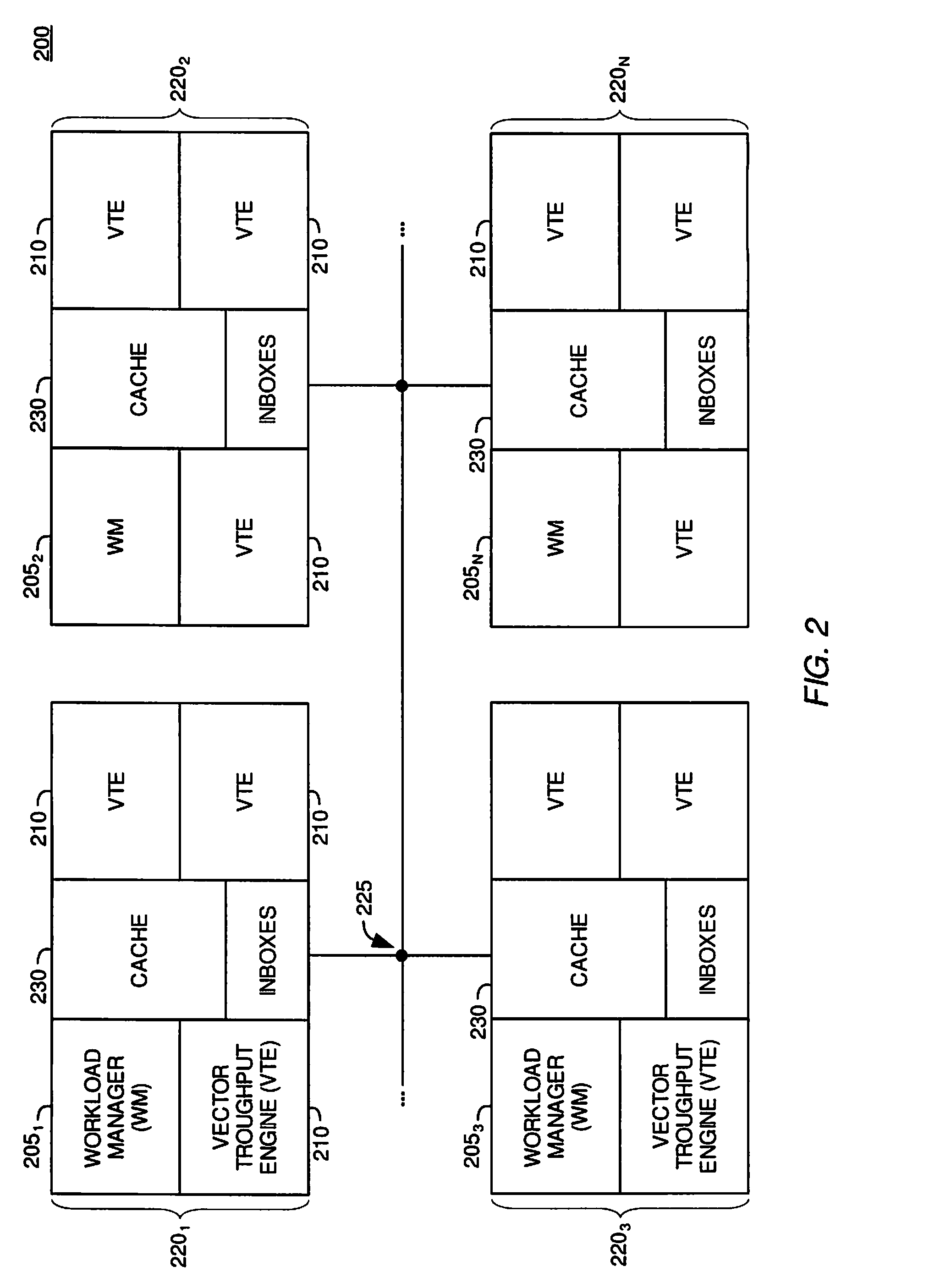
Pixel color accumulation in a ray tracing image processing system
By merging or adding the color contributions from objects intersected by secondary rays, the image processing system may accumulate color contributions to pixels from objects intersected by secondary rays as the further color contributions are determined. Furthermore, by associating a scaling factor of color contribution with objects and with secondary rays which intersect the objects, color contributions due to secondary ray / object intersections may be calculated at a later time than the color contribution to a pixel from original ray / object intersection. Consequently, it is not necessary for a vector throughput engine or a workload manager to wait for all secondary ray / object intersections to be determined before updating the color of a pixel.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
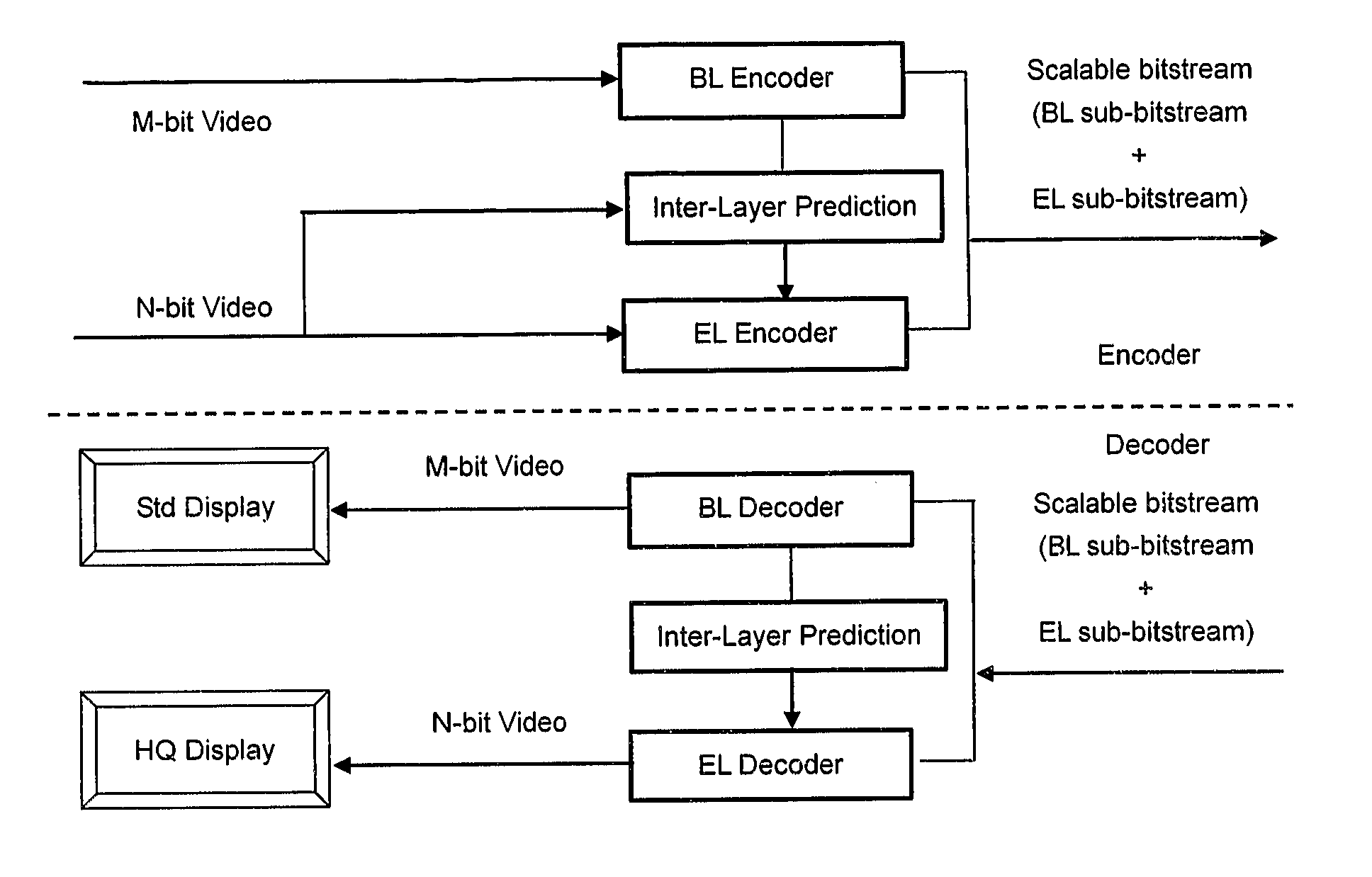
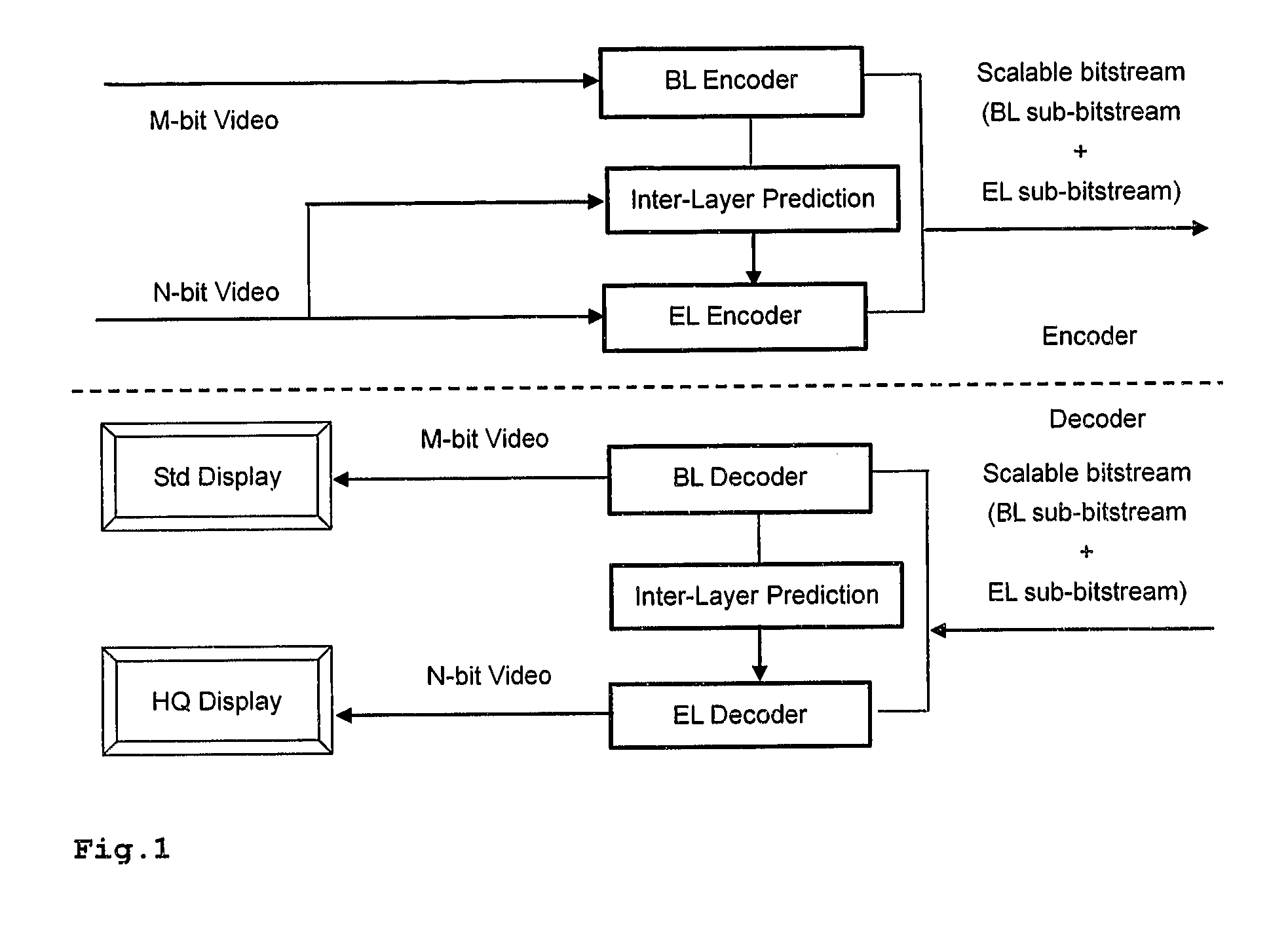
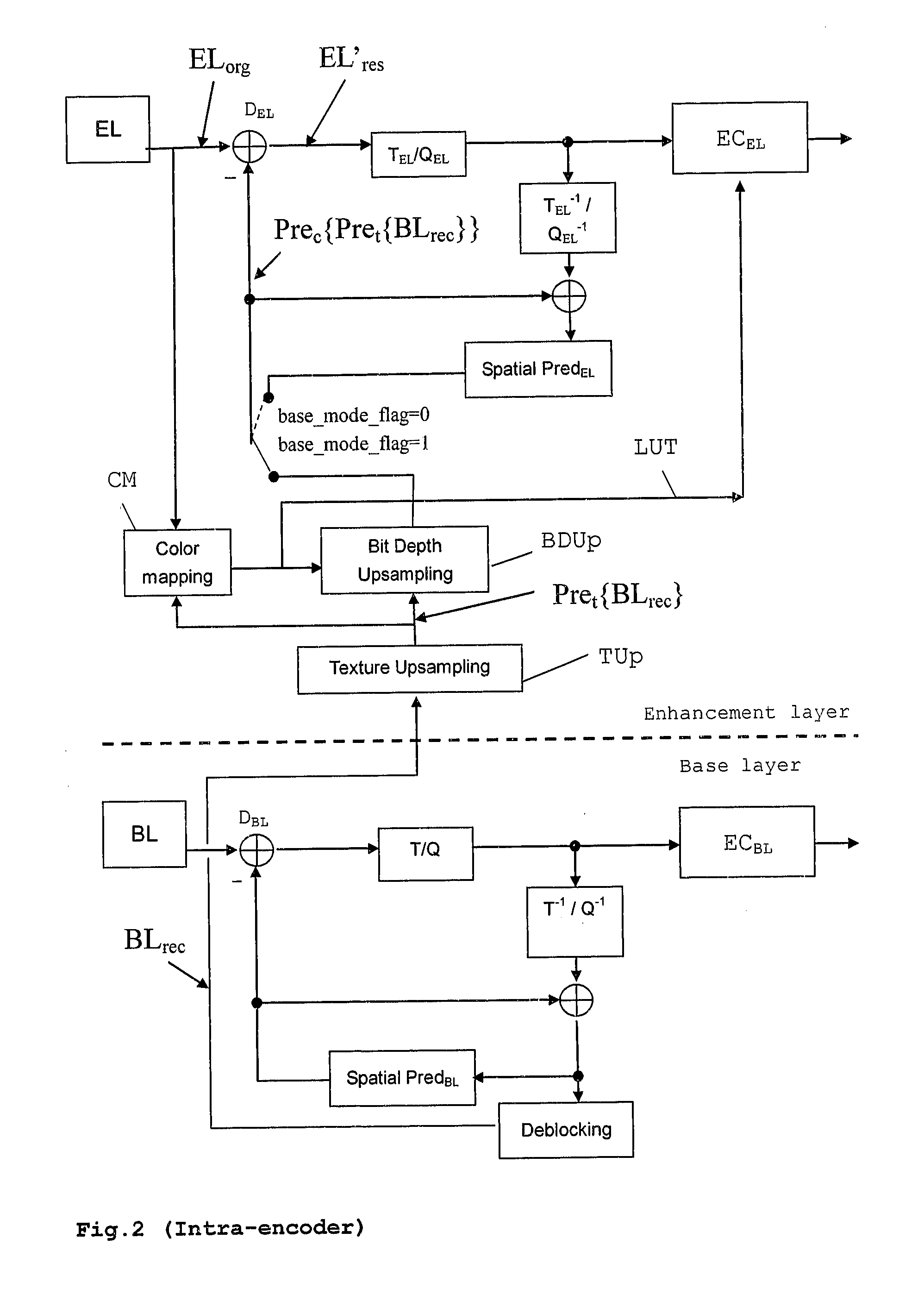
Method and apparatus for encoding and/or decoding video data using enhancement layer residual prediction for bit depth scalability
InactiveUS20100135393A1Improve coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionVideo bitstream
A scalable video bitstream may have an H.264 / AVC compatible base layer and a scalable enhancement layer, where scalability refers to color bit depth. The H.264 / AVC scalability extension SVC provides also other types of scalability, e.g. spatial scalability where the number of pixels in BL and EL are different. According to the invention, BL information is upsampled in two logical steps, one being texture upsampling and the other being bit depth upsampling. Texture upsampling is a process that increases the number of pixels, and bit depth upsampling is a process that increases the number of values that each pixel can have, corresponding to the pixels color intensity. The upsampled BL data are used to predict the collocated EL. The BL information is upsampled at the encoder side and in the same manner at the decoder side, wherein the upsampling refers to spatial and bit depth characteristics.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Image capture unit in a surgical instrument
ActiveUS20130041226A1Overcomes shortcomingMore capabilitySurgeryEndoscopesImage resolutionDepth of field
In a minimally invasive surgical system, an image capture unit includes a prism assembly and sensor assembly. The prism assembly includes a beam splitter, while the sensor assembly includes coplanar image capture sensors. Each of the coplanar image capture sensors has a common front end optical structure, e.g., the optical structure distal to the image capture unit is the same for each of the sensors. A controller enhances images acquired by the coplanar image capture sensors. The enhanced images may include (a) visible images with enhanced feature definition, in which a particular feature in the scene is emphasized to the operator of minimally invasive surgical system; (b) images having increased image apparent resolution; (c) images having increased dynamic range; (d) images displayed in a way based on a pixel color component vector having three or more color components; and (e) images having extended depth of field.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
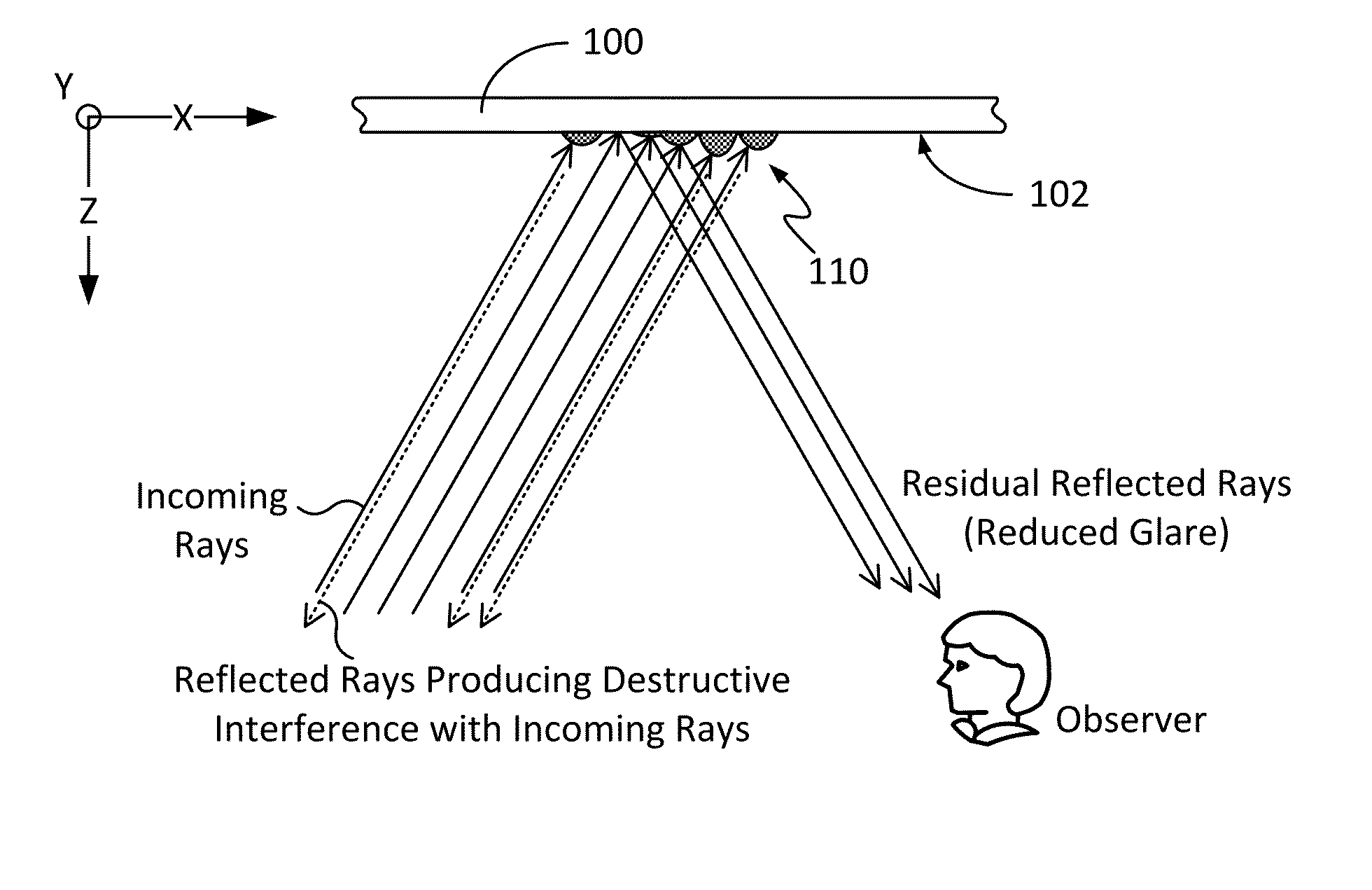
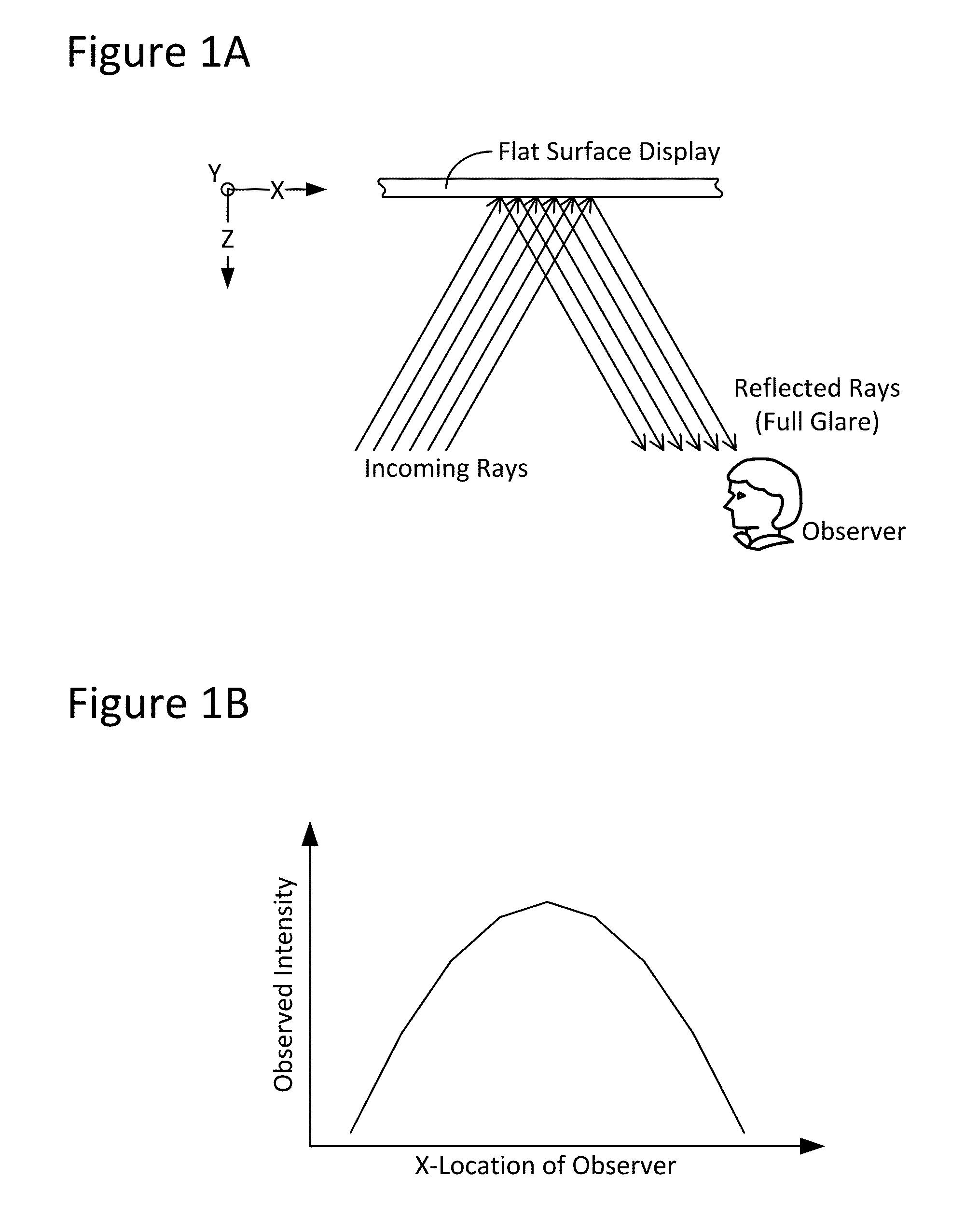
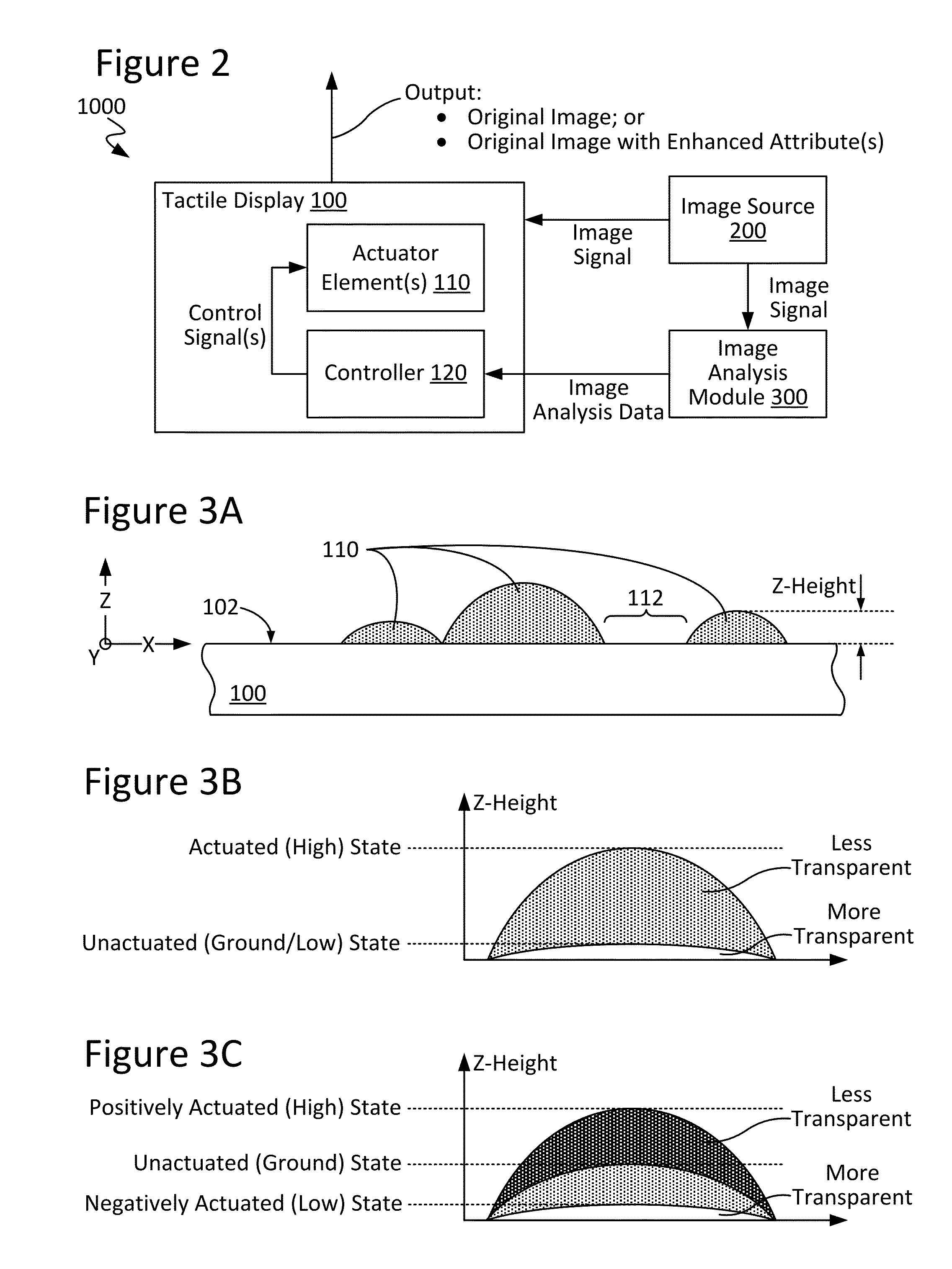
Techniques for image enhancement using a tactile display
Techniques are disclosed for enhancing the quality of a displayed image using a tactile or other texture display. In particular, the disclosed techniques leverage active-texture display technology to enhance the quality of graphics by providing, for example, outlining and / or shading when presenting a given image, so as to create the effect of increased contrast and image quality and / or to reduce observable glare. These effects can be present even at high viewing angles and in environments of high light reflection. To these ends, one or more graphics processes, such as edge-detection and / or shading, may be applied to an image to be displayed. In turn, an actuator element (e.g., microelectromechanical systems, or MEMS, devices) of the tactile display may be manipulated (e.g., in Z-height) to provide fine-grain adjustment of image attributes such as: pixel brightness / intensity; pixel color; edge highlighting; object outlining; effective shading; image contrast; and / or viewing angle.
Owner:INTEL CORP
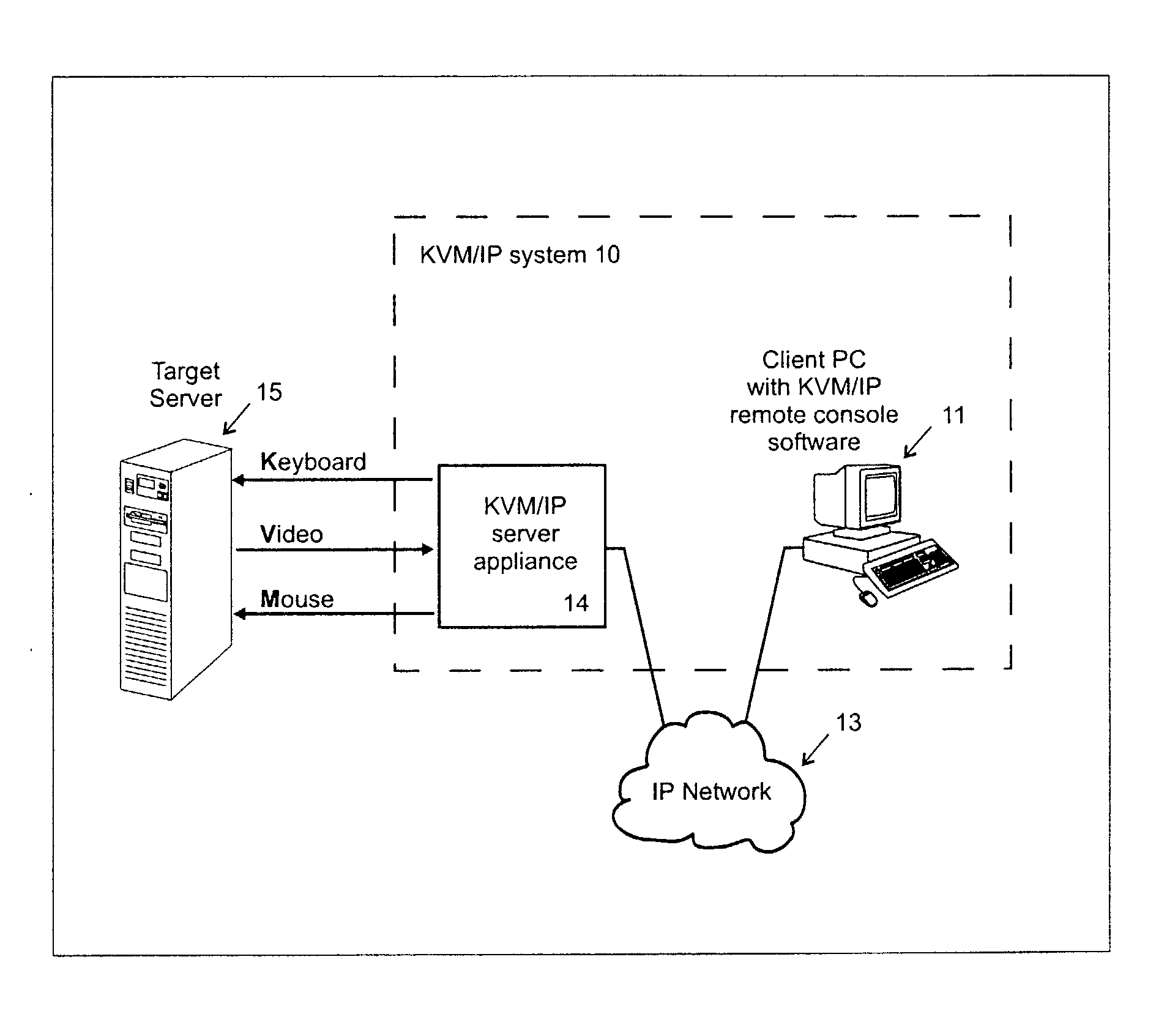
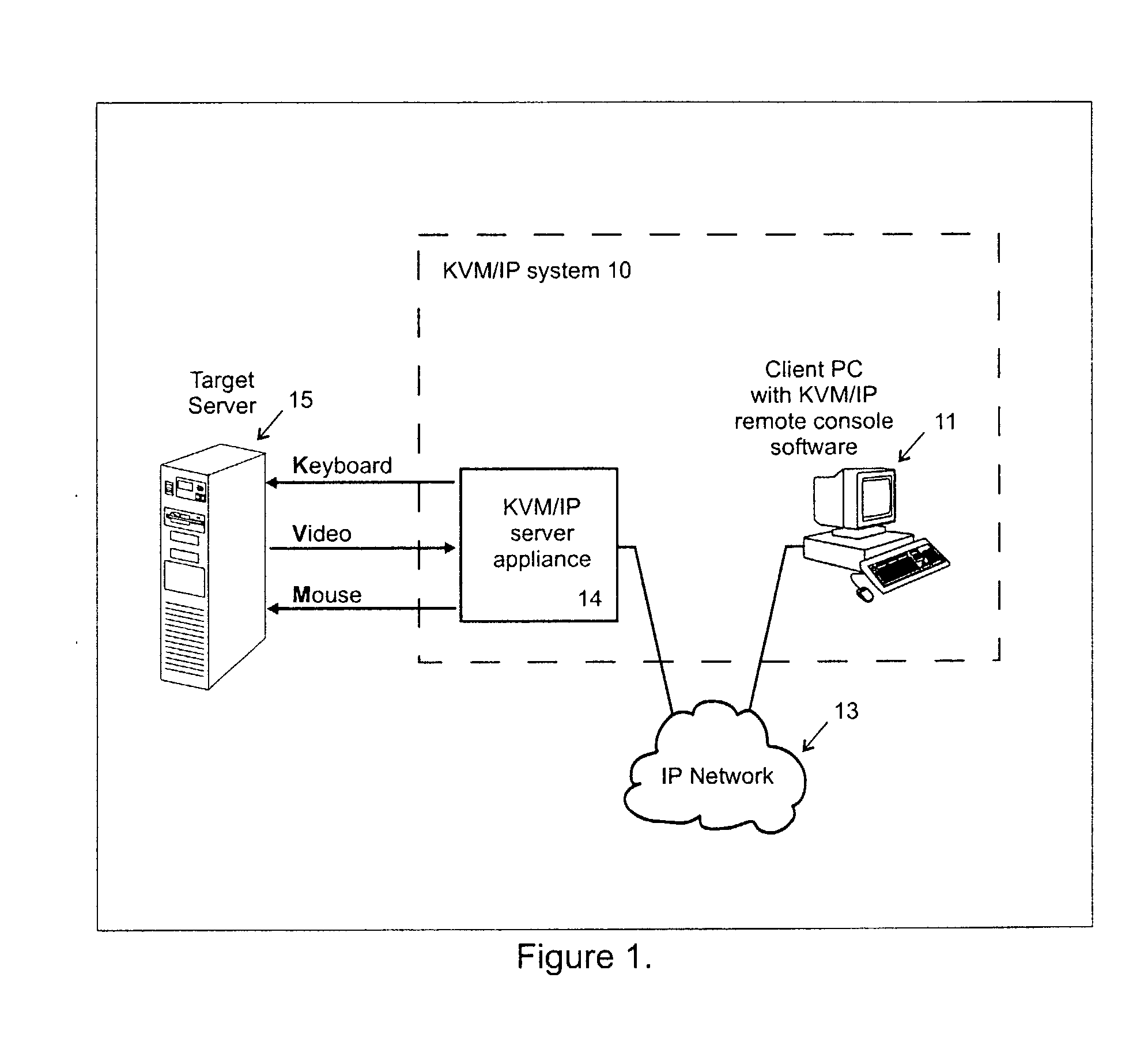
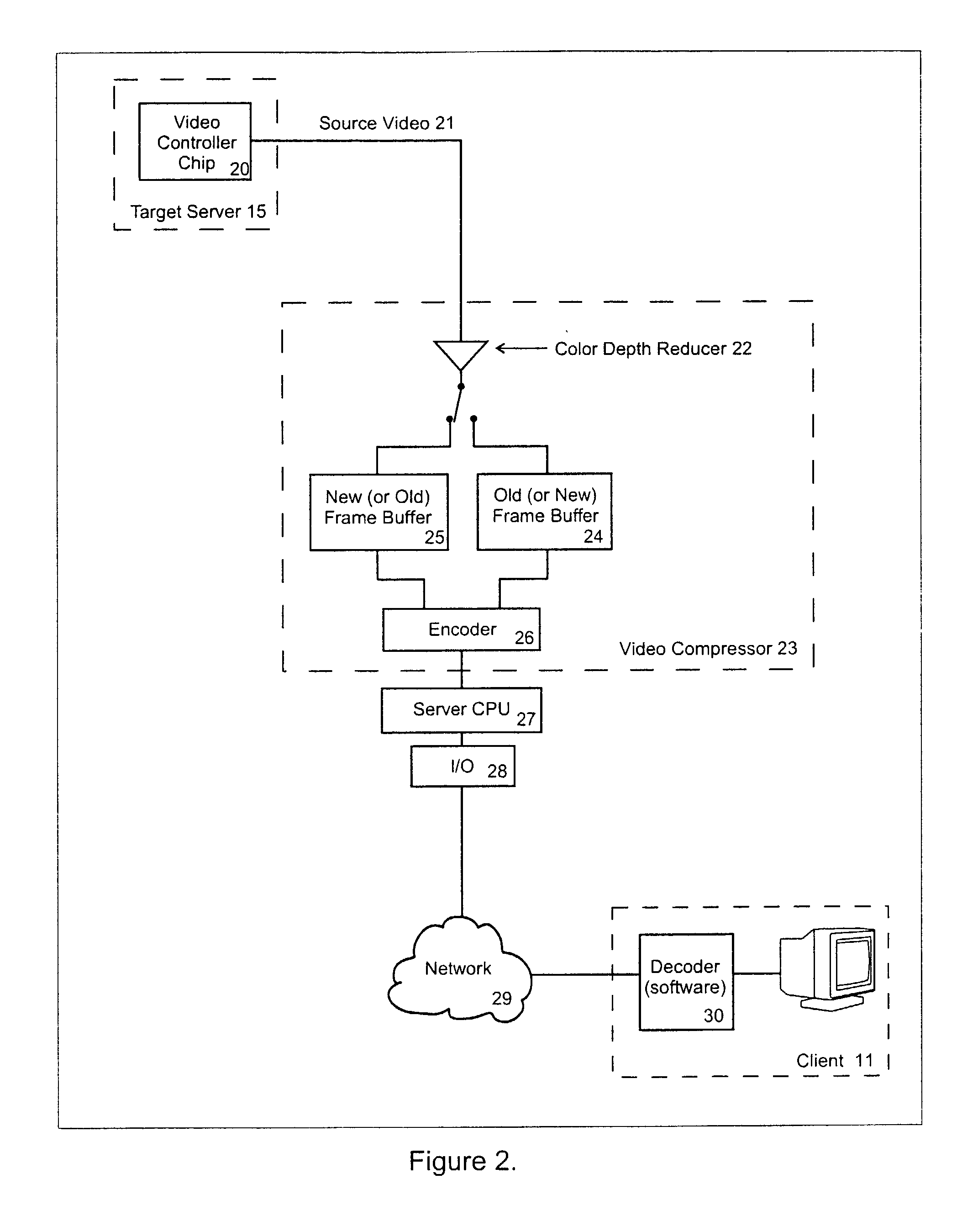
Video compression system
ActiveUS20050069034A1Efficient captureMinimum delayStatic indicating devicesPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer usersComputer graphics (images)
A video compression system is disclosed that is optimized to take advantage of the types of redundancies typically occurring on computer screens and the types of video loss acceptable to real time interactive computer users. It automatically adapts to a wide variety of changing network bandwidth conditions and can accommodate any video resolution and an unlimited number of colors. The disclosed video compression encoder can be implemented with either hardware or software and it compresses the source video into a series of data packets that are a fixed length of 8 bits or more. Sequences of one or more of these packets create unique encoding “commands” that can be sent over any network and easily decoded (decompressed) with either software or hardware. The commands include 3 dimensional copying (horizontal, vertical and time) and unique efficiencies for screen segments that are comprised of only two colors (such as text). Embodiments are also disclosed that improve the video compression depending on the popularity of pixel colors.
Owner:VERTIV IT SYST INC
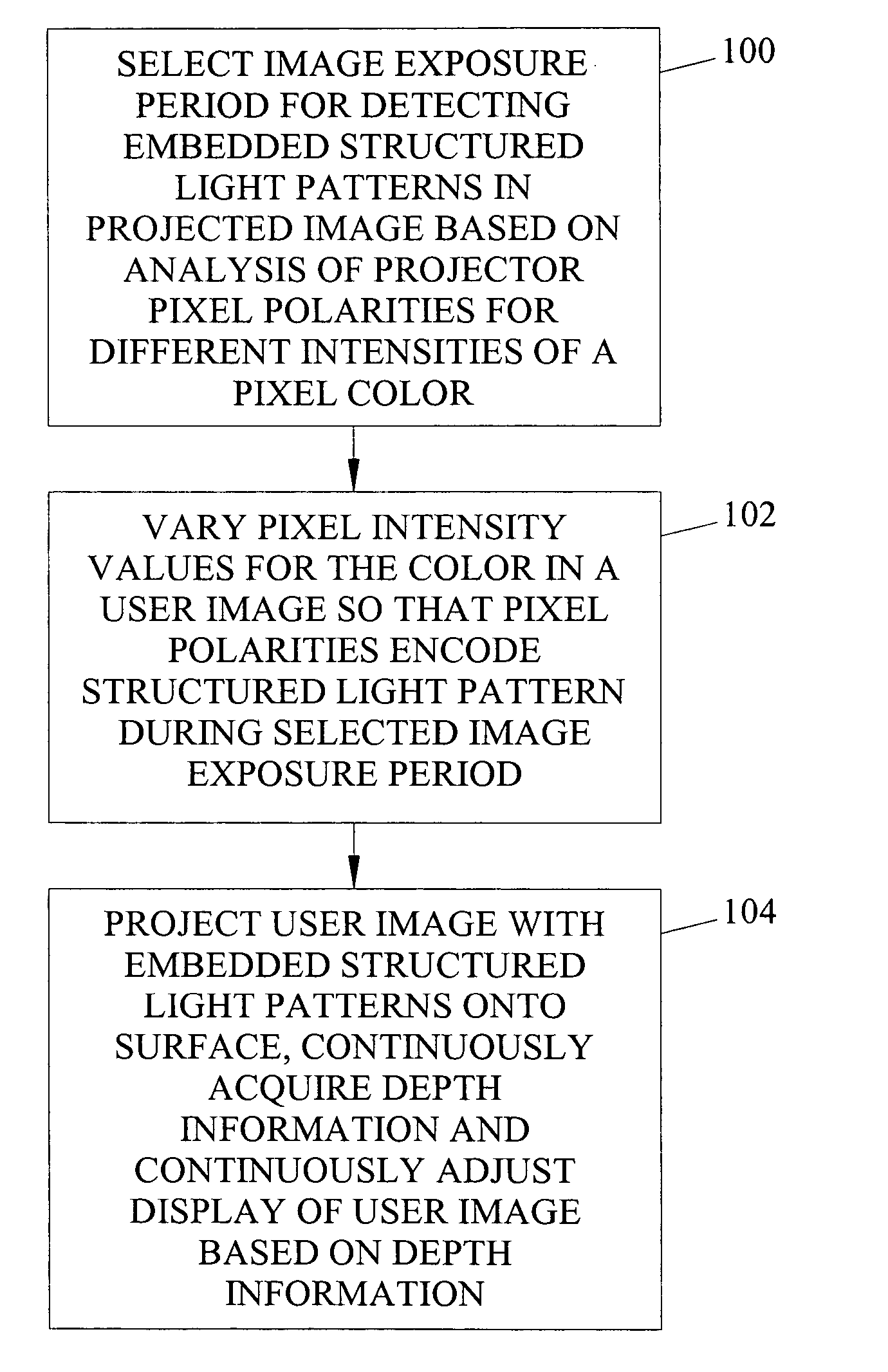
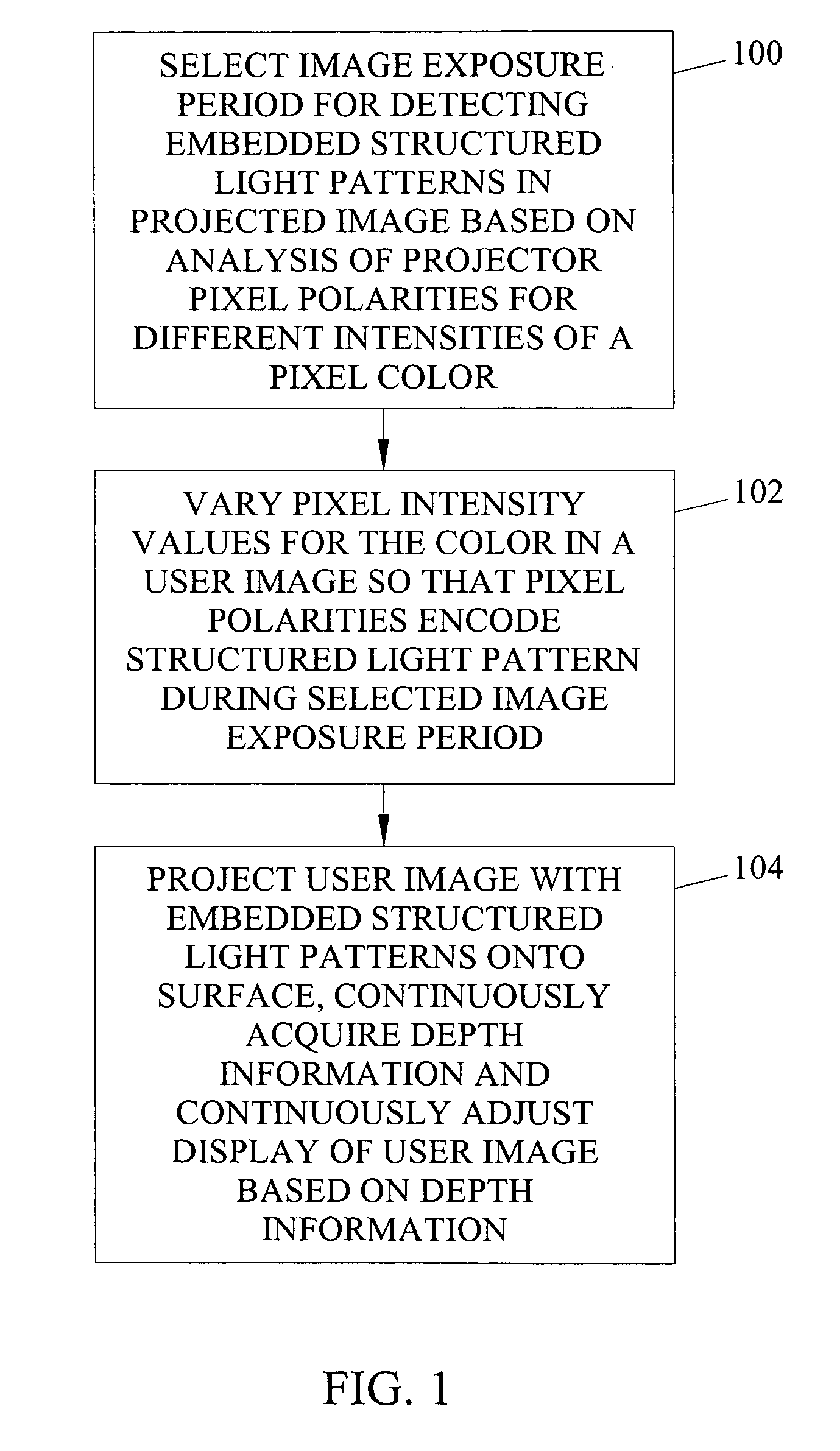
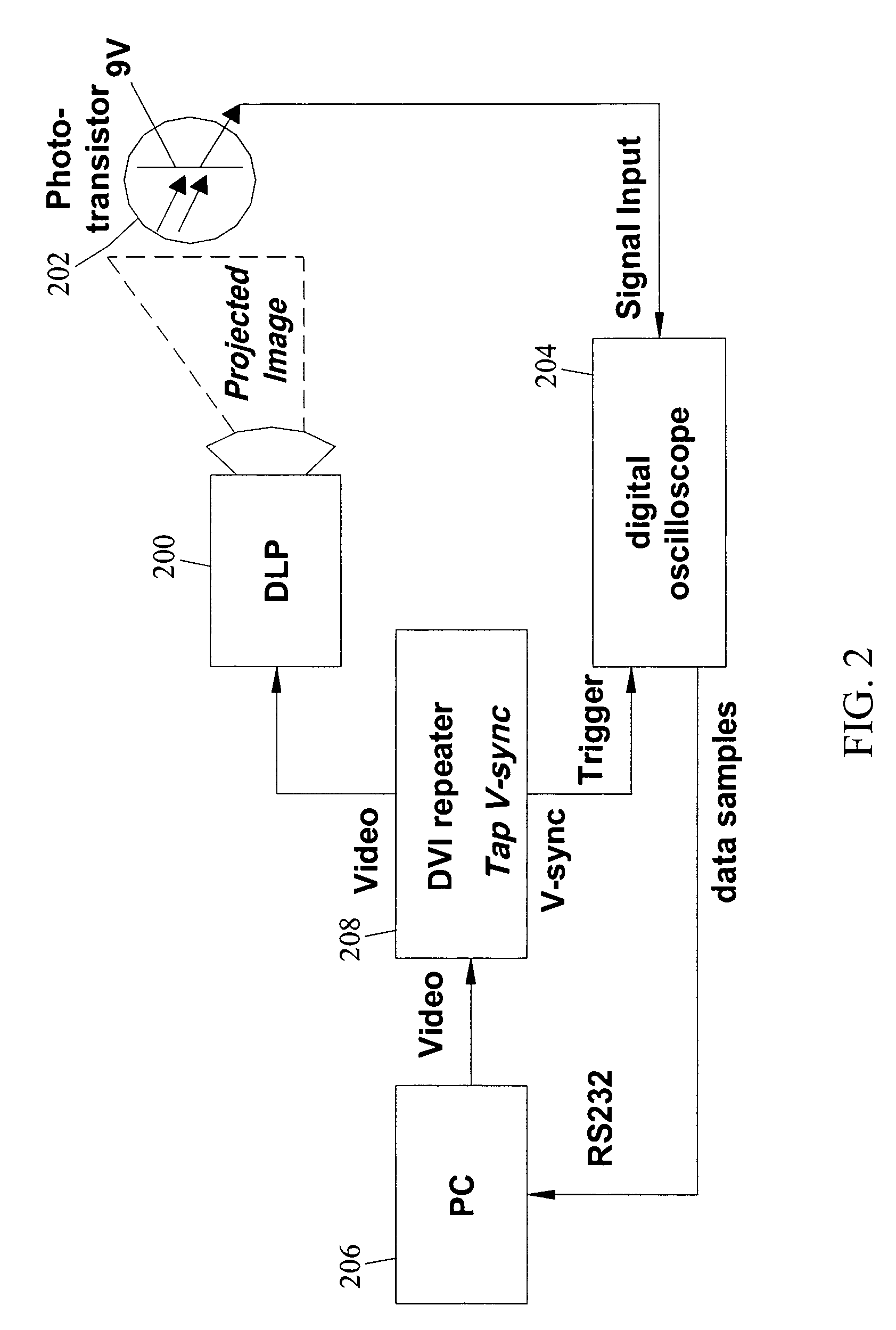
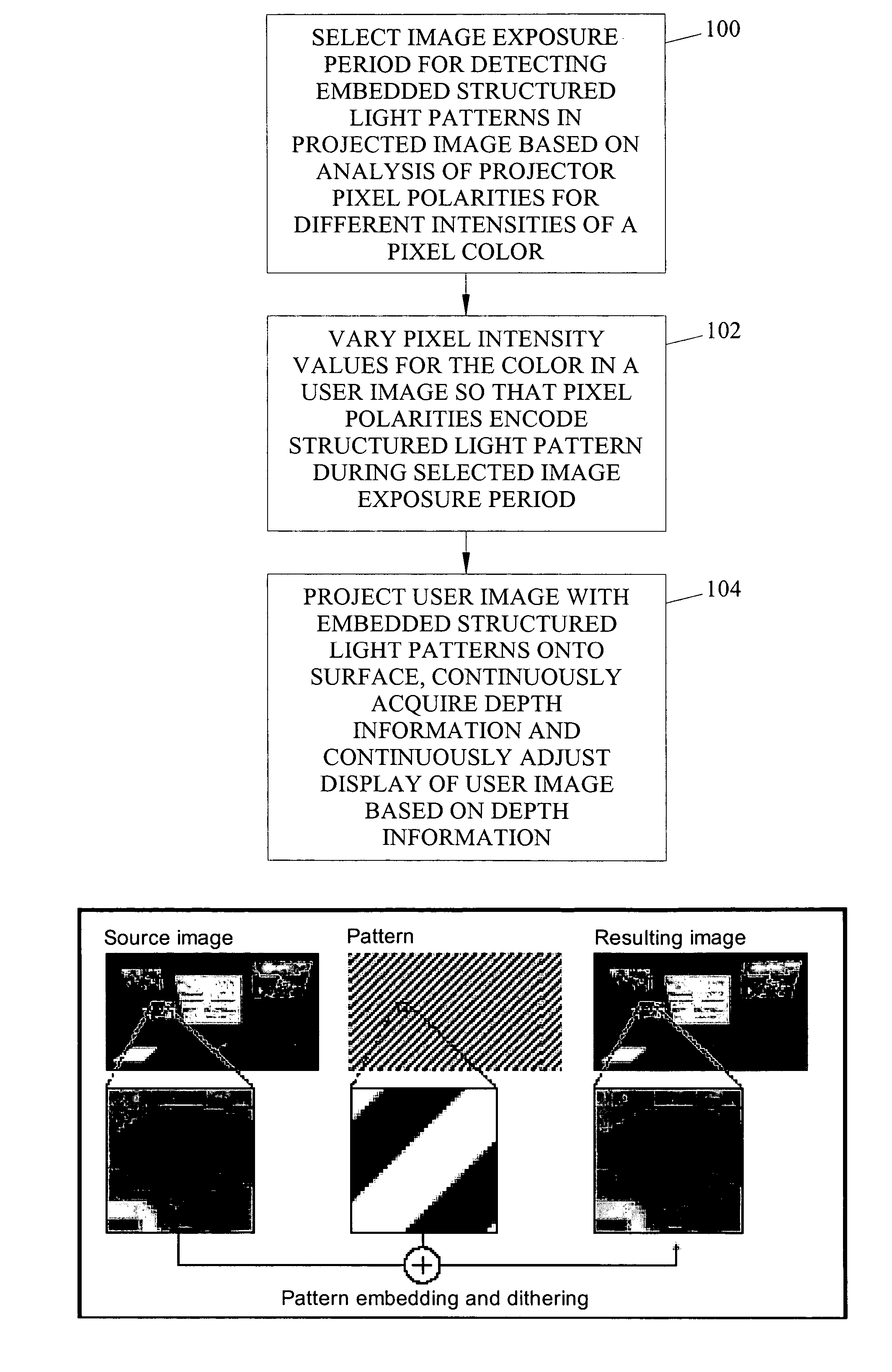
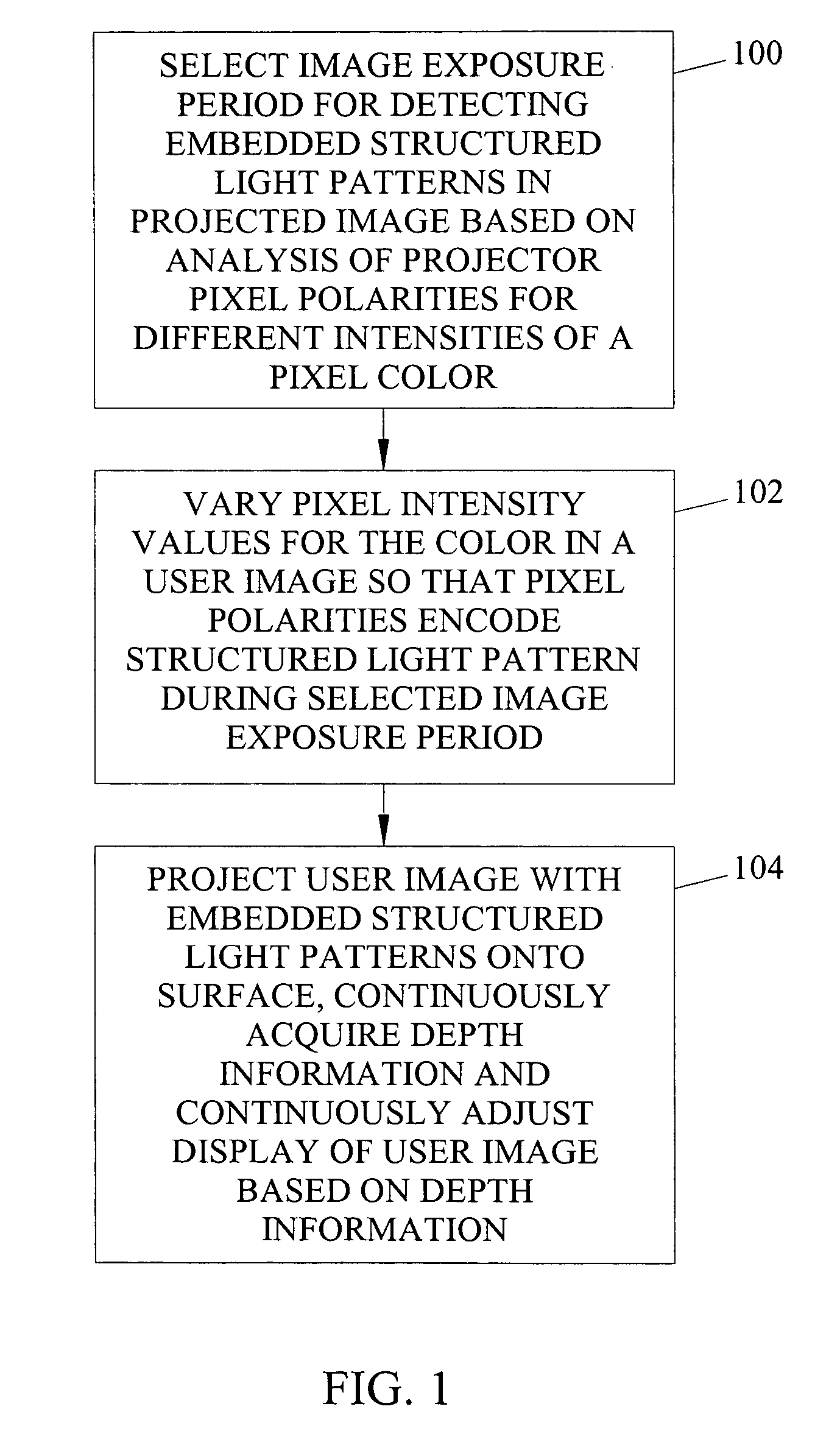
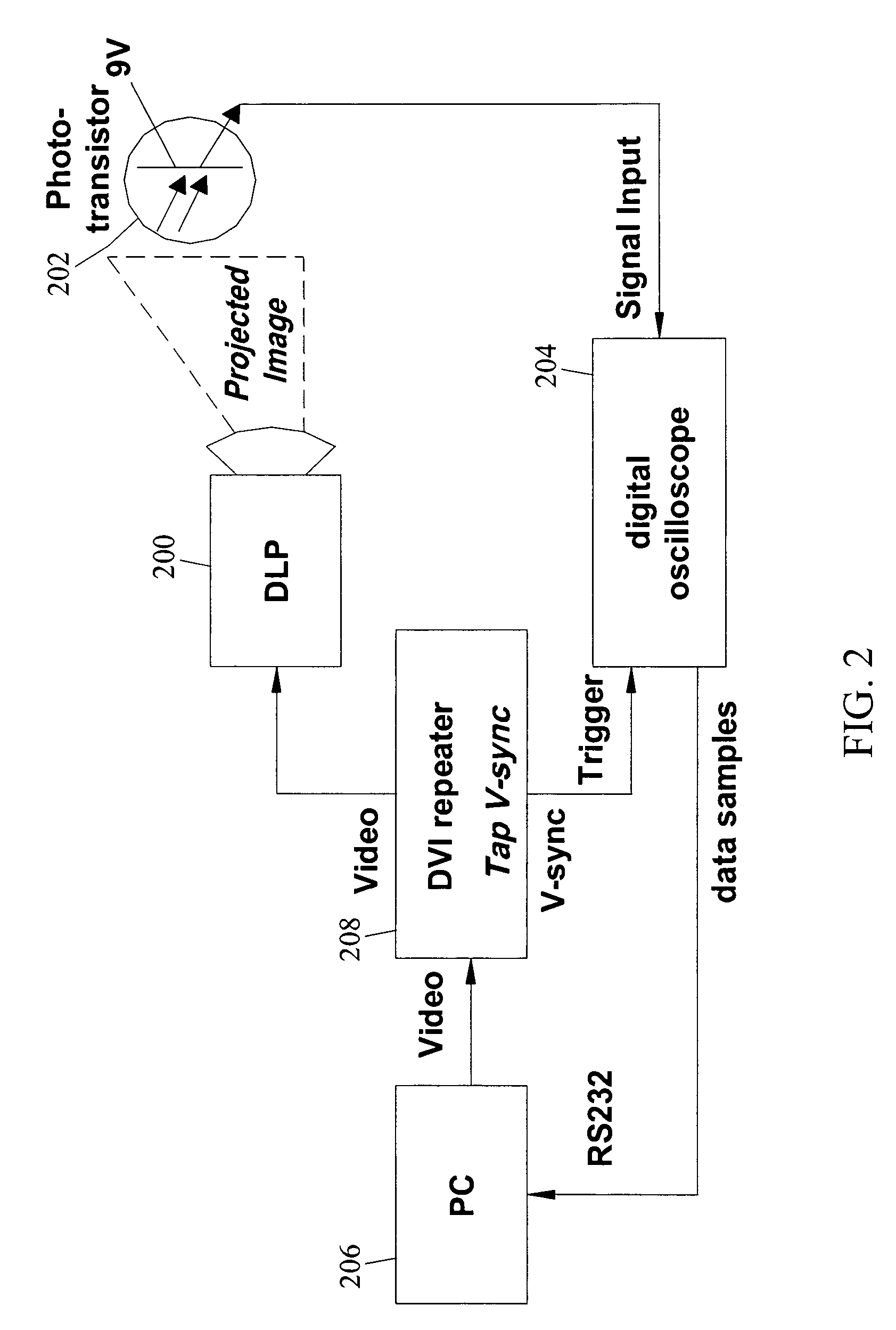
Methods, systems, and computer program products for imperceptibly embedding structured light patterns in projected color images for display on planar and non-planar surfaces
Methods, systems, and computer program products for imperceptibly embedding structured light patterns in projected color images for display on planar and non-planar surfaces are disclosed. According to one method, an image exposure period for detecting an embedded structured light patterns in a projected image is selected based on analysis of pixel polarities for different pixel intensities of a pixel color. Pixel intensities for the color are varied in the user image so that pixel polarities encode the structured light patterns during image exposure period. The user image is projected with the structured light patterns onto the surface. Depth information is continuously acquired and used to adjust display of the user image.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
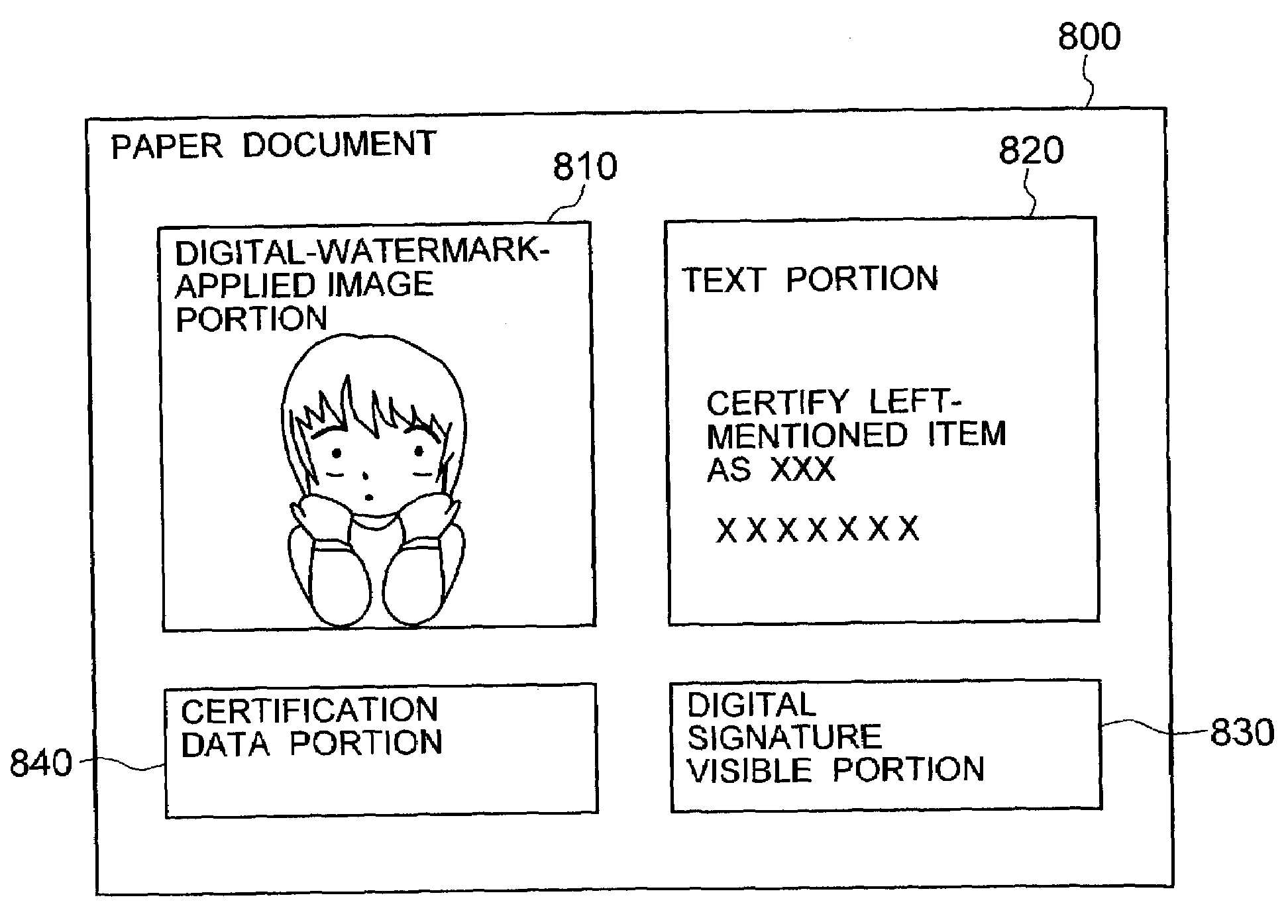
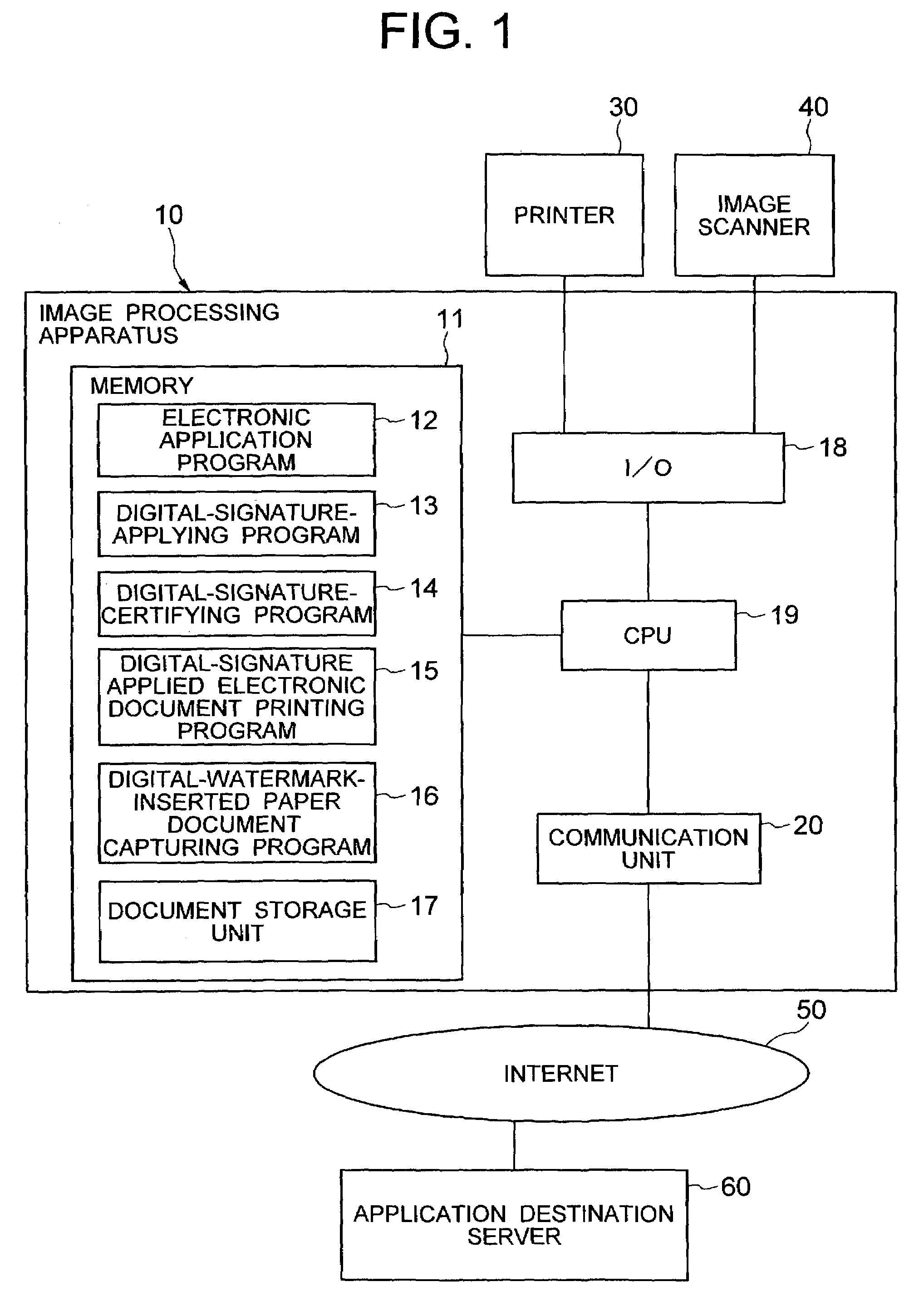
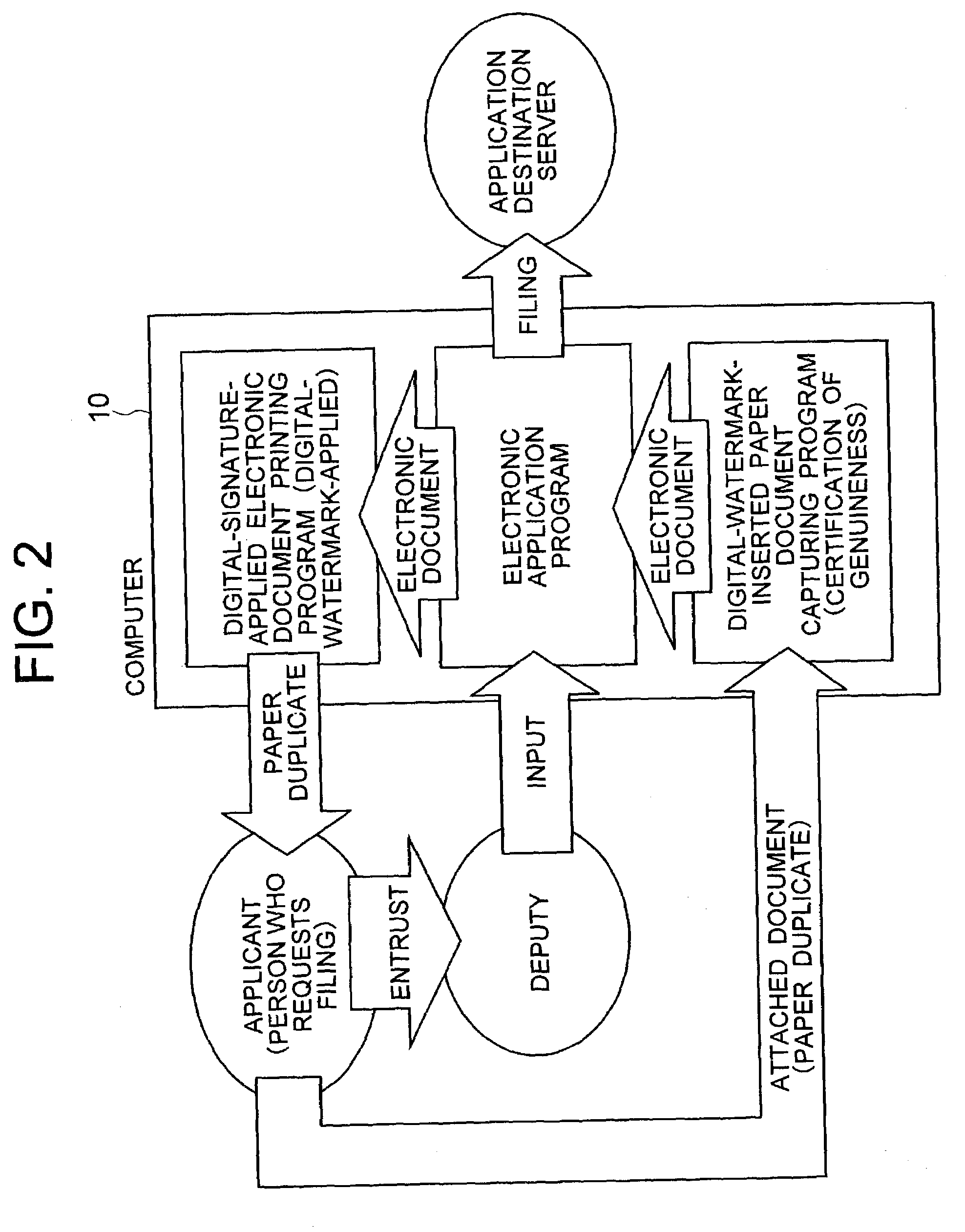
Electronic document, genuineness management method for print medium thereof, genuineness management system, program, and program recording medium
InactiveUS7224820B2User identity/authority verificationCharacter and pattern recognitionElectronic documentComputer graphics (images)
A method for managing genuine characteristics of both an electronic document and a print medium comprising: a step for recognizing image data contained in the electronic document; a step for applying an extraction condition of an image feature previously determined and must be considered to the recognized image data to calculate a coordinate set corresponding to a pixel or a set of pixels, constituting the image feature; a step for recognizing at least a coordinate value among coordinate values and pixel color values, corresponding to each of coordinates constituting the coordinate set, and for embedding the recognized coordinate value as a code of a digital watermark into the pixel or the pixel set, constituting the image feature, or into an area in the vicinity; and a step for outputting the electronic document where the digital watermark embedding process operation has been carried out to the print medium.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Methods, systems, and computer program products for imperceptibly embedding structured light patterns in projected color images for display on planar and non-planar surfaces
Methods, systems, and computer program products for imperceptibly embedding structured light patterns in projected color images for display on planar and non-planar surfaces are disclosed. According to one method, an image exposure period for detecting an embedded structured light patterns in a projected image is selected based on analysis of pixel polarities for different pixel intensities of a pixel color. Pixel intensities for the color are varied in the user image so that pixel polarities encode the structured light patterns during image exposure period. The user image is projected with the structured light patterns onto the surface. Depth information is continuously acquired and used to adjust display of the user image.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Efficient color display using low-absorption in-pixel color filters
InactiveUS6097456AImprove efficiencyTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesSurface plasmonLight beam
A display system having a non-absorbing and reflective color filtering array and a reflector to improve light utilization efficiency. One implementation of the color filtering array uses a surface plasmon filter having two symmetric metal-dielectric interfaces coupled with each other to produce a transmission optical wave at a surface plasmon resonance wavelength at one interface from a p-polarized input beam on the other interface. Another implementation of the color filtering array uses a metal-film interference filter having two dielectric layers and three metallic films.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
System and method for transmitting live audio/video information
InactiveUS20050180641A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningComputer visionAudio frequency
A method and apparatus for encoding, segment by segment, frames of audio / video data, including pixels each having a plurality of pixel color components by creating a frame group table of encoded pixel values in which each pixel entry includes a dominant pixel color component of the plurality of pixel color components, determining a set of segment reference pixels for each encoded segment, wherein each one of the segment reference pixels is comprised of segment reference pixel parameter values and is a pixel within each one of the encoded segments having a most intense dominant pixel color value, communicating the frame group table and the segment reference pixels over a network to a receiver, and at the receiver, decoding the frame group table on a pixel-by-pixel basis by scaling the segment reference pixel parameter values according to each entry in the frame group table of encoded pixel parameter.
Owner:ADAMS PLATFORM PTY LTD ACN 104 372 287 +2
Pixel color accumulation in a ray tracing image processing system
ActiveUS20080074420A12D-image generation3D-image renderingImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
By merging or adding the color contributions from objects intersected by secondary rays, the image processing system may accumulate color contributions to pixels from objects intersected by secondary rays as the further color contributions are determined. Furthermore, by associating a scaling factor of color contribution with objects and with secondary rays which intersect the objects, color contributions due to secondary ray / object intersections may be calculated at a later time than the color contribution to a pixel from original ray / object intersection. Consequently, it is not necessary for a vector throughput engine or a workload manager to wait for all secondary ray / object intersections to be determined before updating the color of a pixel.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
System and process for generating high dynamic range video
InactiveUS20050047676A1Minimizing any discontinuityTelevision system detailsImage enhancementTone mappingRadiance
A system and process for generating High Dynamic Range (HDR) video is presented which involves first capturing a video image sequence while varying the exposure so as to alternate between frames having a shorter and longer exposure. The exposure for each frame is set prior to it being captured as a function of the pixel brightness distribution in preceding frames. Next, for each frame of the video, the corresponding pixels between the frame under consideration and both preceding and subsequent frames are identified. For each corresponding pixel set, at least one pixel is identified as representing a trustworthy pixel. The pixel color information associated with the trustworthy pixels is then employed to compute a radiance value for each pixel set to form a radiance map. A tone mapping procedure can then be performed to convert the radiance map into an 8-bit representation of the HDR frame.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Deghosting mosaics using multiperspective plane sweep
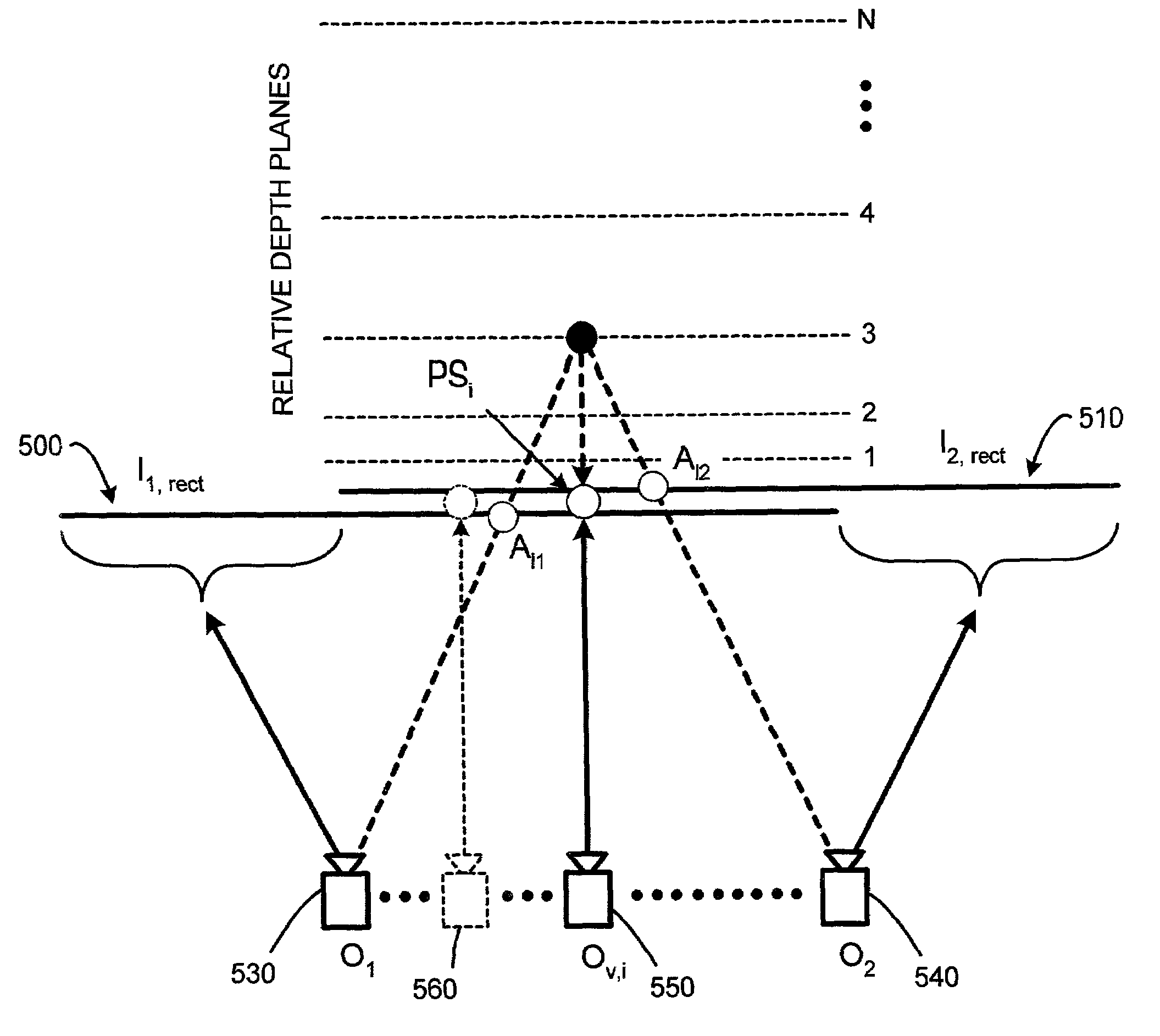
InactiveUS20060072851A1Computationally efficientMinimize distortionImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxVirtual camera
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Automatic and semi-automatic generation of image features suggestive of motion for computer-generated images and video
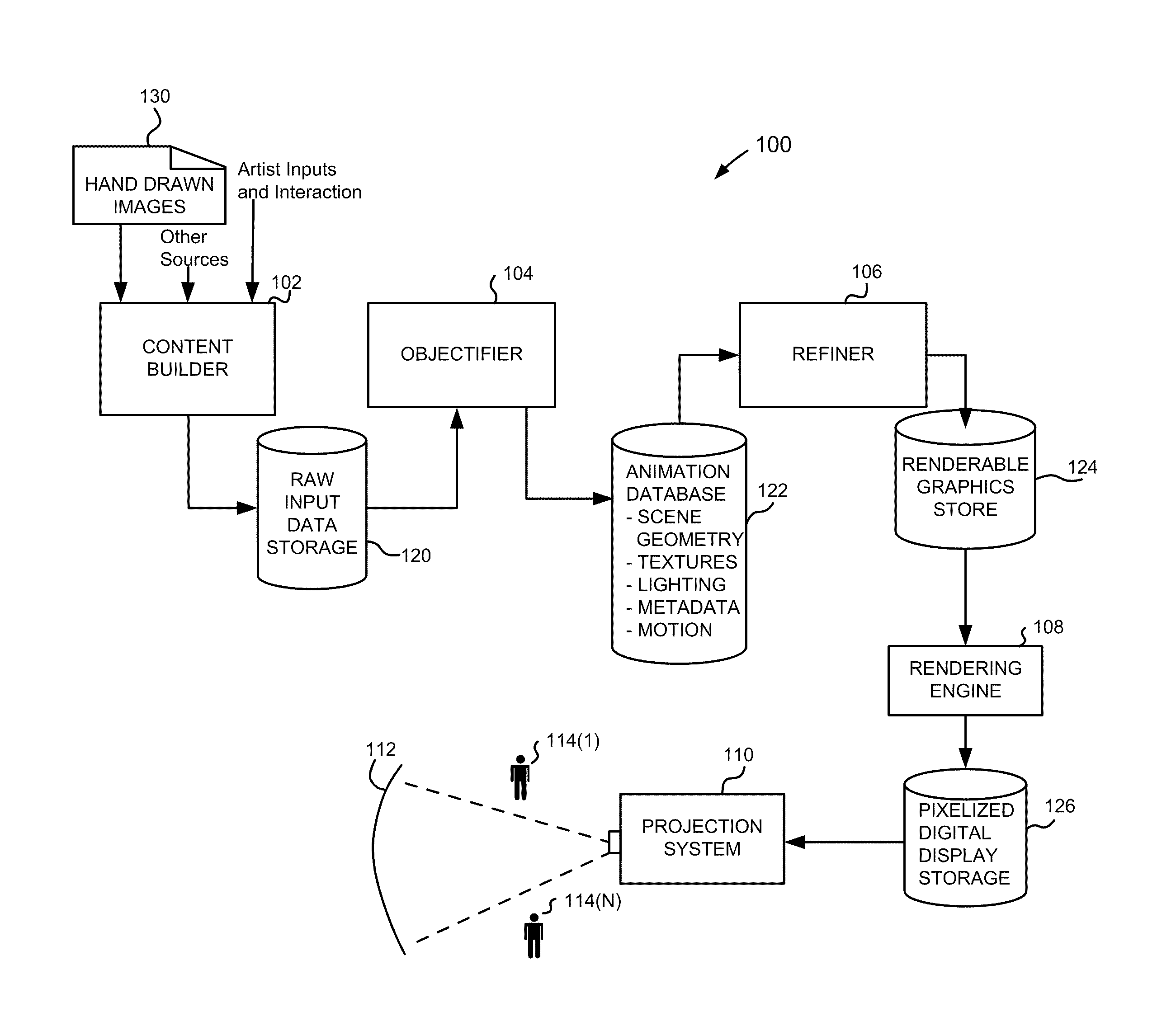
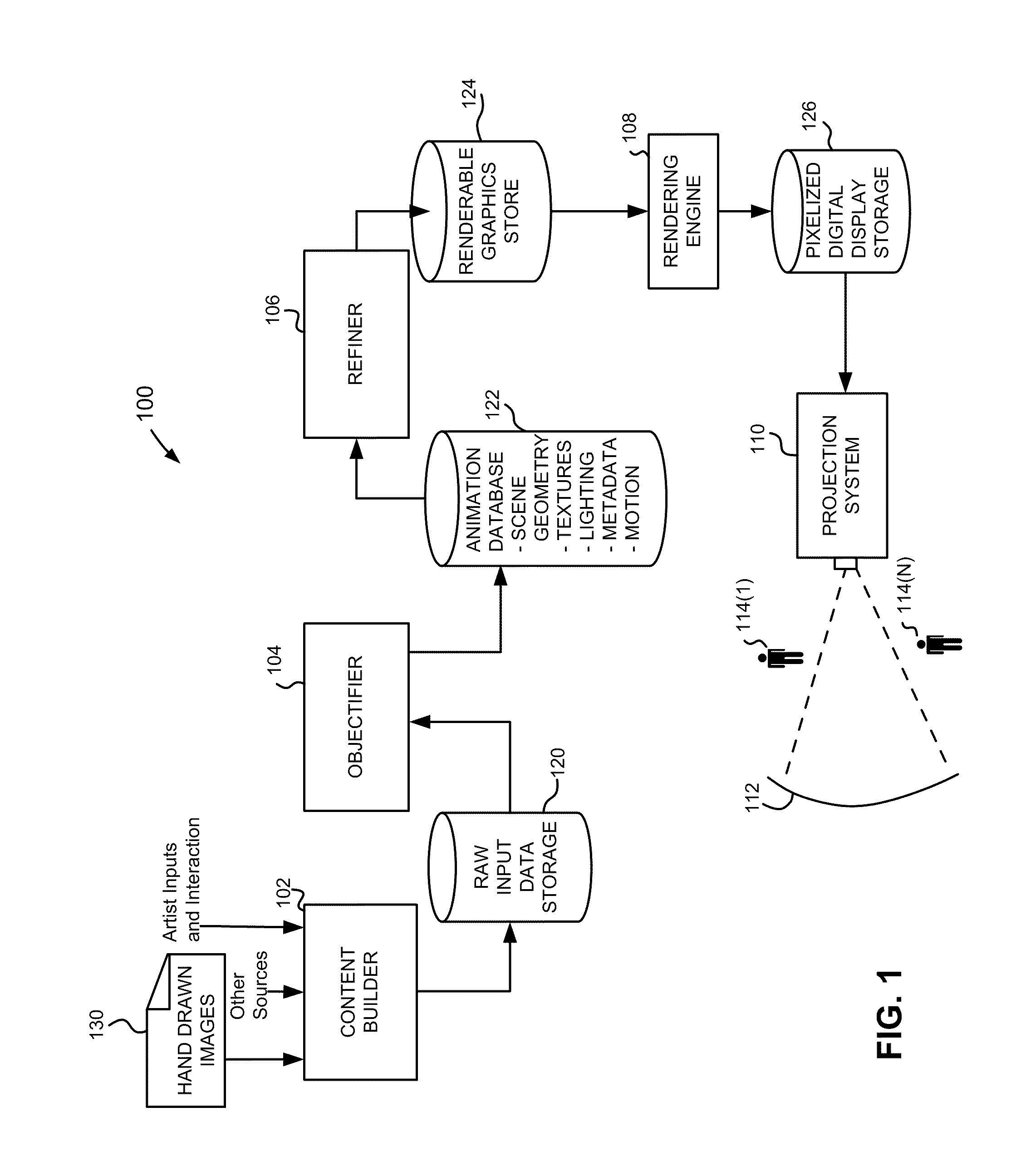
In an animation processing system, generating images to be viewable on a display using a computer that are generated based on scene geometry obtained from computer readable storage and animation data representing changes over time of scene geometry elements, but also images can be modified to include shading that is a function of positions of objects at other than the current instantaneous time for a frame render such that the motion effect shading would suggest motion of at least one of the elements to a viewer of the generated images. Motion effects provide, based on depiction parameters and / or artist inputs, shading that varies for at least some received animation data, received motion depiction parameters, for at least one pixel, a pixel color is rendered based on motion effect program output and at least some received scene geometry, such that the output contributes to features that would suggest the motion.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC +1
System and method deghosting mosaics using multiperspective plane sweep
InactiveUS7006709B2Computationally efficientMinimize distortionImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxVirtual camera
A system and method for deghosting mosaics provides a novel multiperspective plane sweep approach for generating an image mosaic from a sequence of still images, video images, scanned photographic images, computer generated images, etc. This multiperspective plane sweep approach uses virtual camera positions to compute depth maps for columns of overlapping pixels in adjacent images. Object distortions and ghosting caused by image parallax when generating the image mosaics are then minimized by blending pixel colors, or grey values, for each computed depth to create a common composite area for each of the overlapping images. Further, the multiperspective plane sweep approach described herein is both computationally efficient, and applicable to both the case of limited overlap between the images used for creating the image mosaics, and to the case of extensive or increased image overlap.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
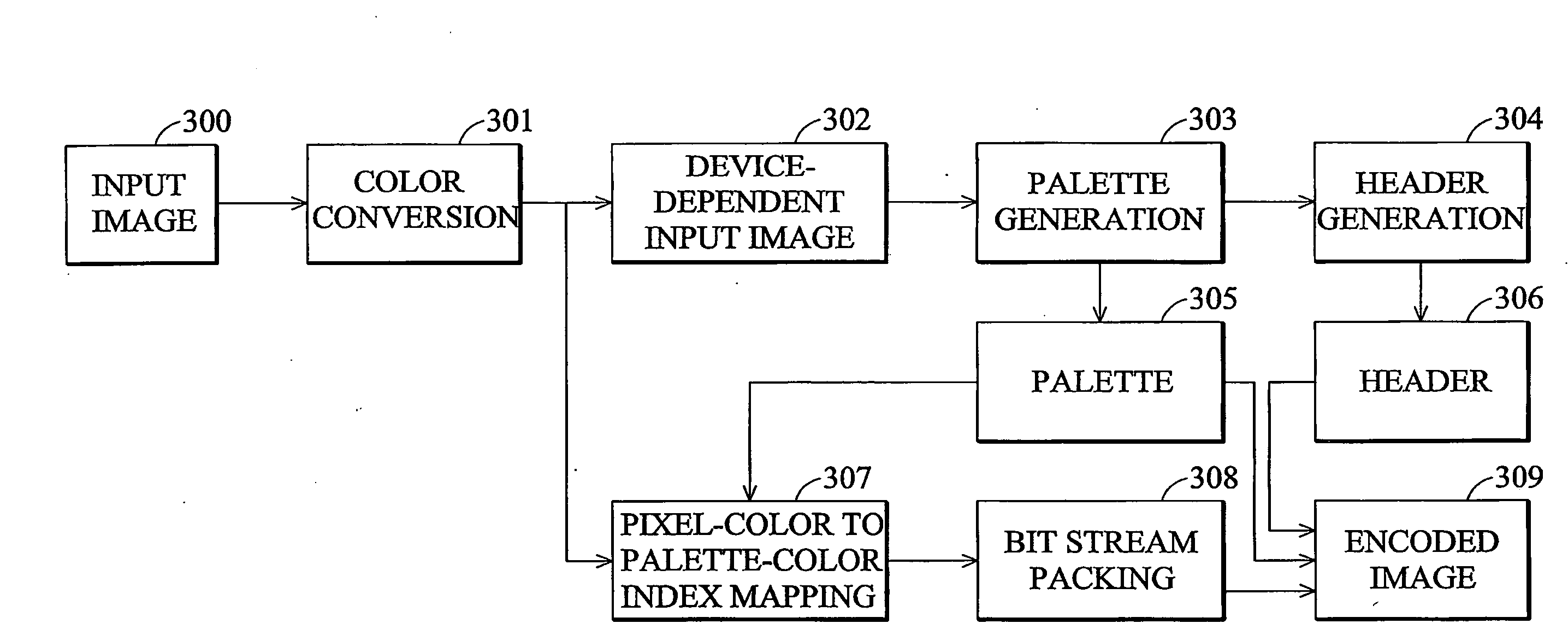
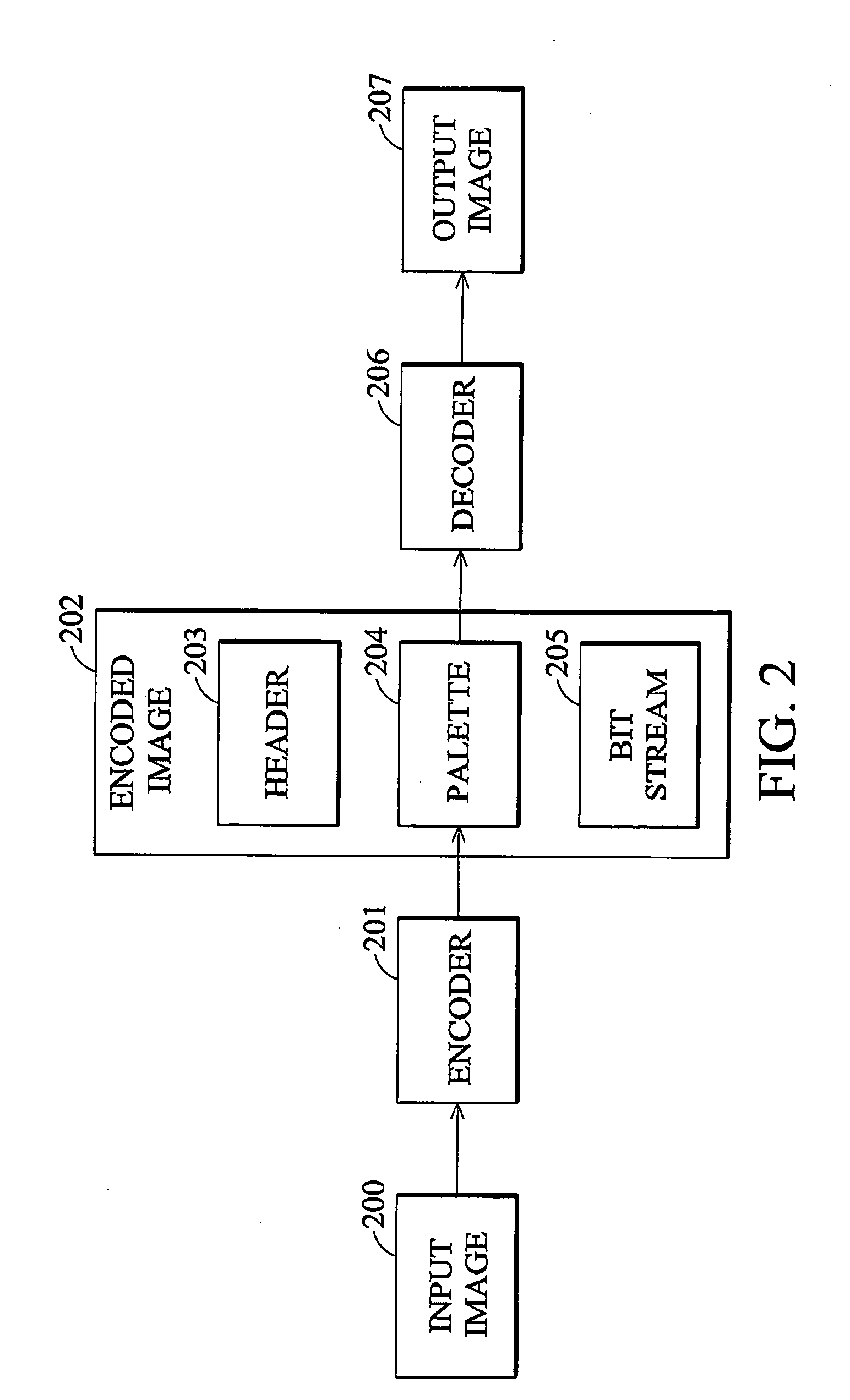
Method for encoding input image, method and apparatus for displaying an encoded image
InactiveCN101340587AShorten playback timeEfficient encoding and decodingColor television with pulse code modulationTelevision systemsDisplay deviceComputer vision
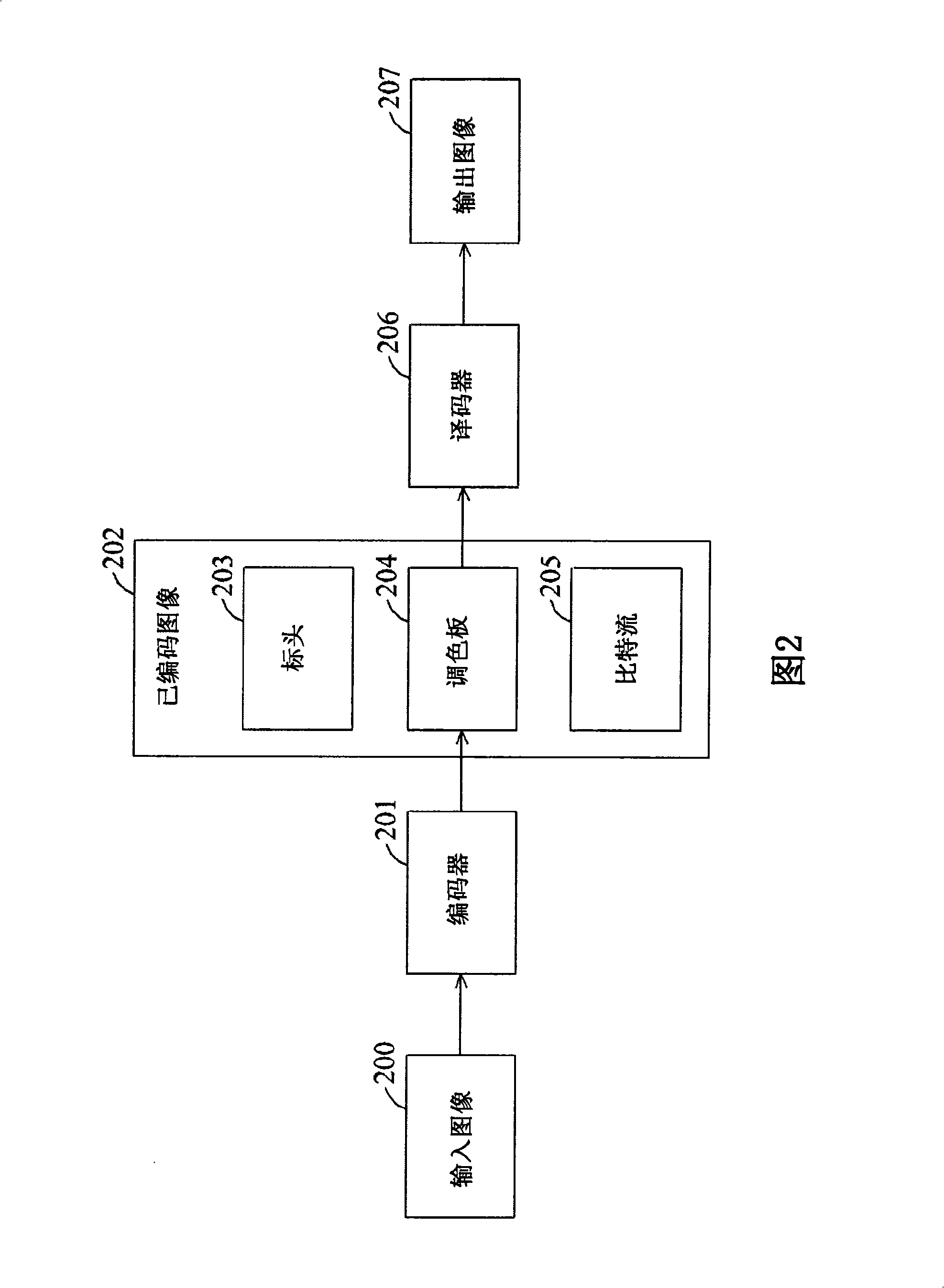
This invention provides a method for displaying encoded images, method and apparatus for playing the encoded images. The apparatus comprises a display device and a decoding unit. The decoding unit acquires a Bit-Per-Pixel (BPP) value from an encoded image, acquires a first bit stream from a first encoded image, acquires multiple first pixel data indices by segmenting the first bit stream every lengths of the BPP value, acquires a first pixel color value of each pixel data index by retrieving a palette comprising multiple unique pixel color values respectively labeled by multiple first pixel data indices, and outputs the acquired first pixel color values so as to play the first encoded image. The method and apparatus for playing the encoded images provided this invention play the encoded images through acquiring the pixel color values of the pixel data indices and outputting the acquired pixel color values to the player, so that coding and decoding can be effectively executed and the image playing time can be reduced.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Method and apparatus for displaying an encoded image
InactiveUS20090010533A1Reduce image imageShorten the timeCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingDisplay deviceComputer vision
An apparatus for displaying an encoded image is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a display device and a decoding unit. The decoding unit acquires a Bit-Per-Pixel (BPP) value from an encoded image, acquires a bit stream from the encoded image, acquires multiple pixel data indices by segmenting the bit stream every lengths of the BPP value, acquires a pixel color value of each pixel data index by retrieving a palette comprising multiple unique pixel color values respectively labeled by the pixel data indices, and outputs the acquired pixel color values to the display device for display of the encoded image.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
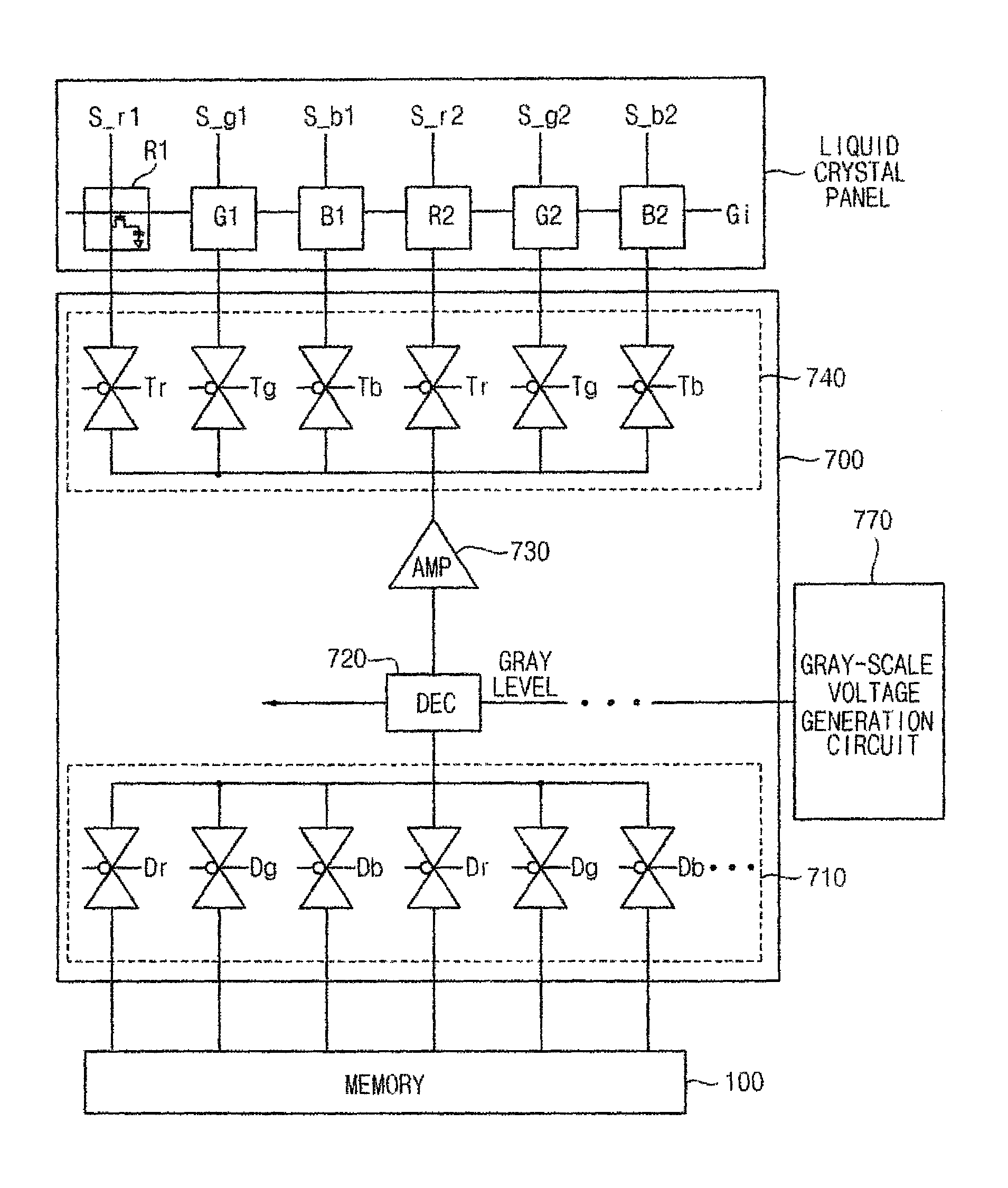
Method and circuit of selectively generating gray-scale voltage
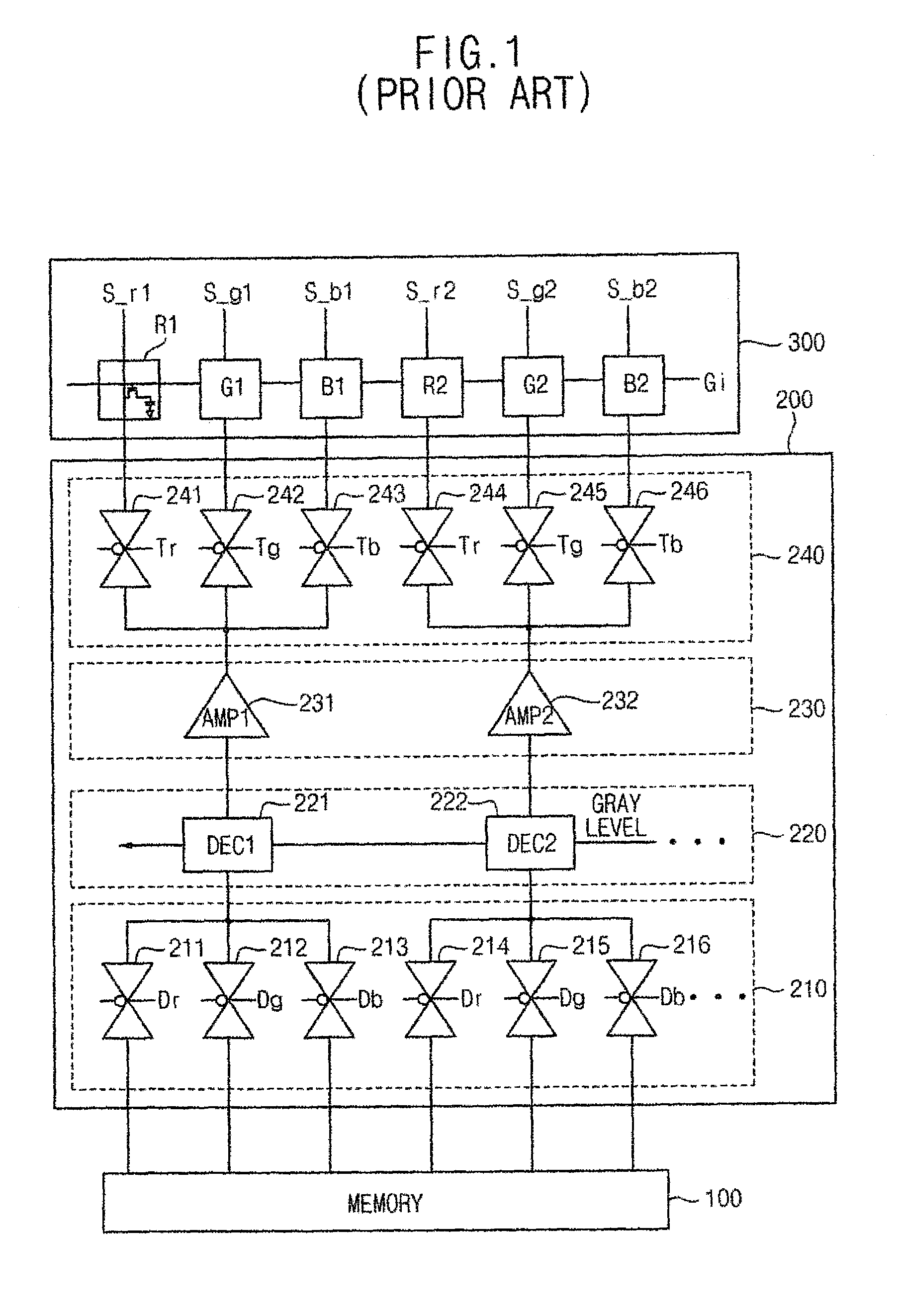
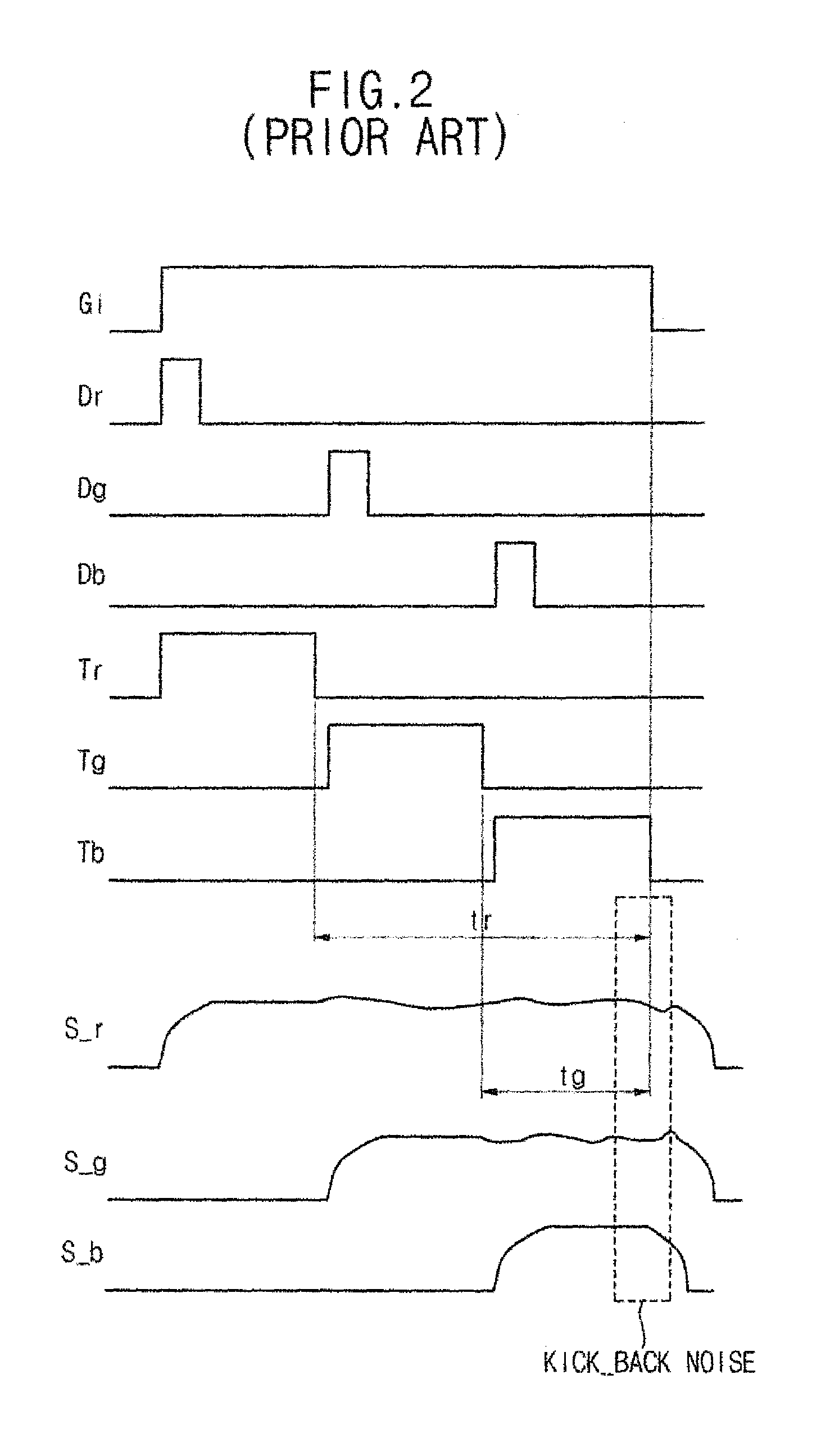
InactiveUS7920116B2Reduce couplingEliminate artifactsCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDynamic range
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method for driving a liquid crystal display (LCD) device using gray-scale voltages whose dynamic ranges are different from each other depending on pixel color. The gray-scale voltages are output to a source line driver. Embodiments of the invention also provide a gray-scale voltage generation circuit coupled to a LCD source line driver. The disclosed method and circuit reduce coupling phenomena in source lines to substantially remove artifacts such as stripes or flicker in an LCD device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Video manipulation of red, green, blue, distance (RGB-Z) data including segmentation, up-sampling, and background substitution techniques
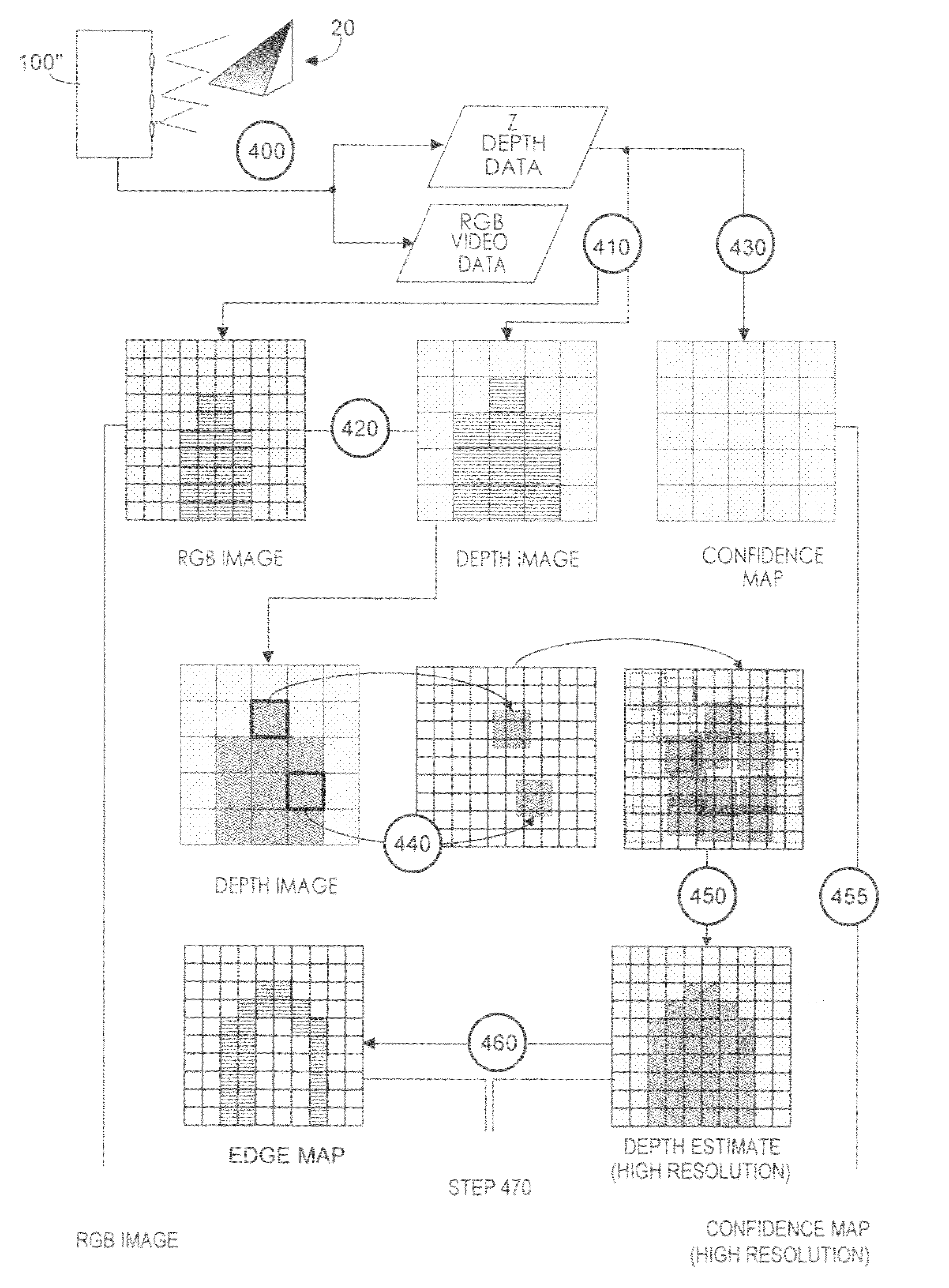
ActiveUS8139142B2Easy to processRobust substitutionTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersImage resolutionVideo processing
RGB-Z imaging systems acquire RGB data typically with a high X-Y resolution RGB pixel array, and acquire Z-depth data with an array of physically larger Z pixels having additive signal properties. In each acquired frame, RGB pixels are mapped to a corresponding Z pixel. Z image resolution is enhanced by identifying Z discontinuities and identifying corresponding RGB pixels where the Z discontinuities occur. Thus segmented data enables RGB background substitution, which preferably blends foreground pixel color and substitute background color. The segmented data also enables up-sampling in which a higher XY resolution Z image with accurate Z values is obtained. Up-sampling uses an equation set enabling assignment of accurate Z values to RGB pixels. Fixed acquisition frame rates are enabled by carefully culling bad Z data. Segmenting and up-sampling enhanced video effects and enable low cost, low Z resolution arrays to function comparably to higher quality, higher resolution Z arrays.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Image processing device and method, and program
InactiveUS20110176614A1Deterioration in compression can be suppressedColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImaging processingMotion vector
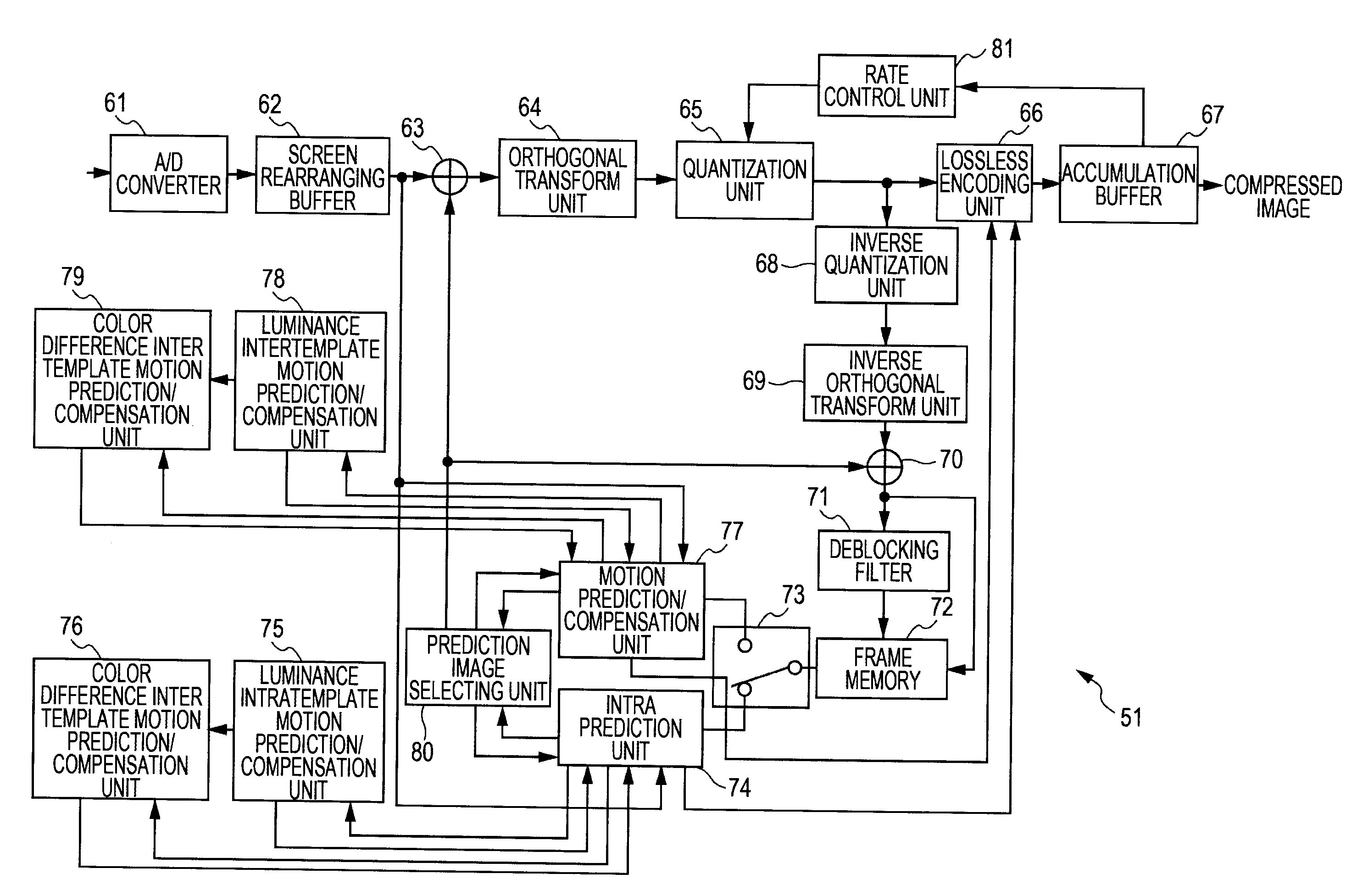
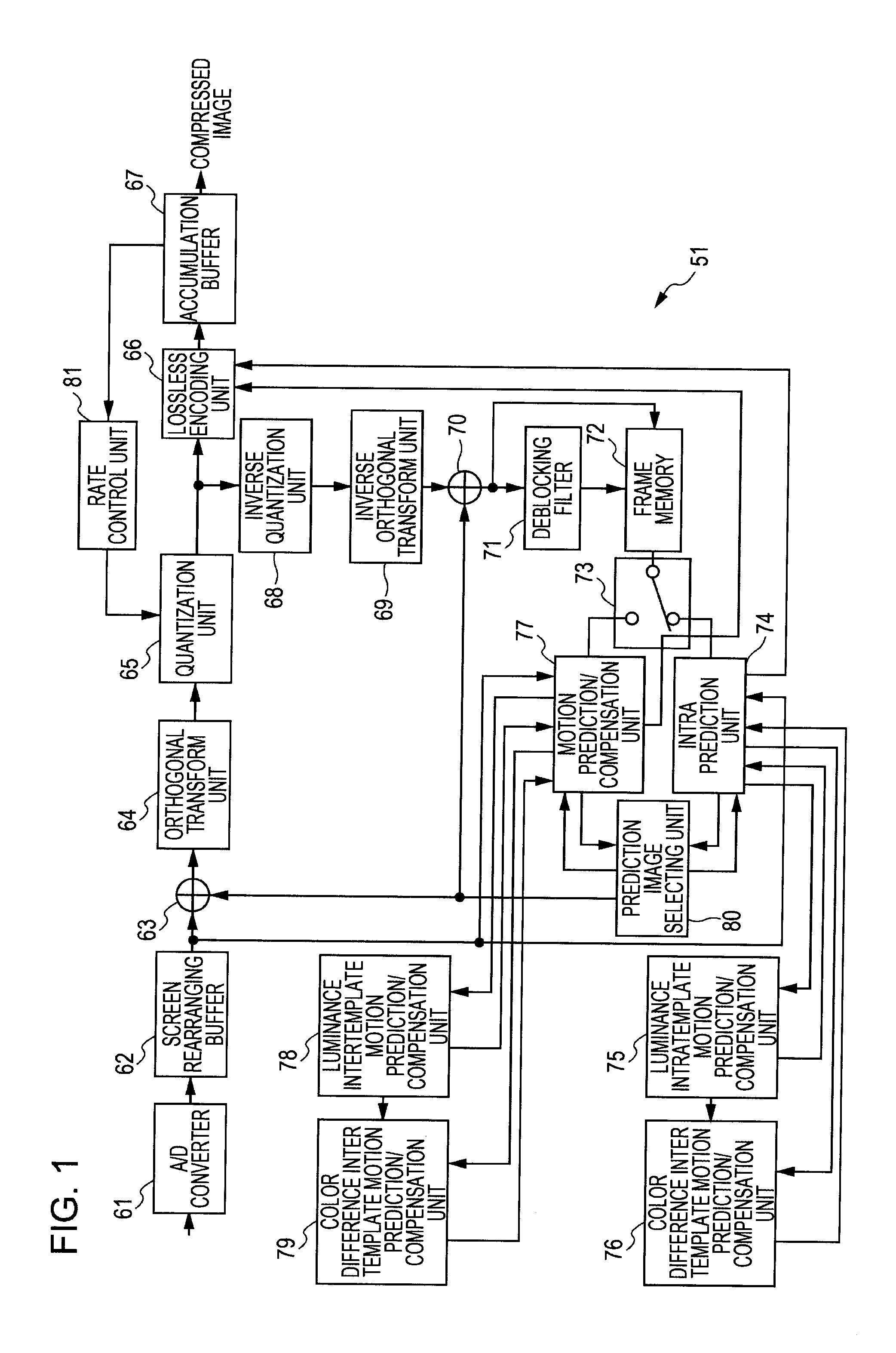
The present invention relates to an image processing device and method, and program, wherein compression efficiency can be improved.With regard to a luminance block AY of 4×4 pixels, motion prediction and compensation processing is performed on the luminance signals using a template region BY which is configured of decoded pixels and is adjacent to the block AY, thereby obtaining motion vector information VY. a color difference TP motion prediction / compensation unit performs motion prediction on a 2×2 pixel color difference block AC regarding color difference signals Cb and Cr, using a template region BC which is configured of decoded pixels and is adjacent to a luminance block AC, with a range E, centered on motion vector information VY′ obtained by scaling the motion vector information VY, as the range of searching. The present invention can be applied to an image encoding device which performs encoding with the H.264 / AVC format, for example.
Owner:SONY CORP
Indicating light status real time monitor and identification method for power equipment fault indicator
InactiveCN101419663AReduce error rateEnsure safetyCharacter and pattern recognitionFault indicatorDigital video
The invention relates to the power distribution net monitoring field and provides a real-time state monitoring recognition method for indicator lights of a power device fault indicator. In the method, digital video signals collected by image collecting equipment of a camera, and the like are processed; video frames are extracted from the video signals; monitoring targets are determined, that is the target region of each indicator light in the video frames, and corresponding numbers are distributed; the pixel color change and the intensity roughness of each indicator light in the target regions of two adjacent frames are used for identifying the flash alarming of the fault indicator; specific conditions of faults are determined according to the identified target numbers of the flash alarming and the combinations thereof; the result is real-timely transmitted to a backstage by a distribution communication network to remind working personnel of the fault happening. The real-time state monitoring recognition method realizes the real-time monitoring recognition alarming for the light state of the fault indicator of the power equipment, ensures the reliability of a system, facilitates the installation and the modification of the system and guarantees the safety of installing and maintaining personnel.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Image capture unit and an imaging pipeline with enhanced color performance in a surgical instrument and method
ActiveUS20130041221A1Overcomes shortcomingMore capabilityTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsBeam splitterImage resolution
In a minimally invasive surgical system, an image capture unit includes a prism assembly and sensor assembly. The prism assembly includes a beam splitter, while the sensor assembly includes coplanar image capture sensors. Each of the coplanar image capture sensors has a common front end optical structure, e.g., the optical structure distal to the image capture unit is the same for each of the sensors. A controller enhances images acquired by the coplanar image capture sensors. The enhanced images may include (a) visible images with enhanced feature definition, in which a particular feature in the scene is emphasized to the operator of minimally invasive surgical system; (b) images having increased image apparent resolution; (c) images having increased dynamic range; (d) images displayed in a way based on a pixel color component vector having three or more color components; and (e) images having extended depth of field.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com