Patents
Literature
129 results about "Run length coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
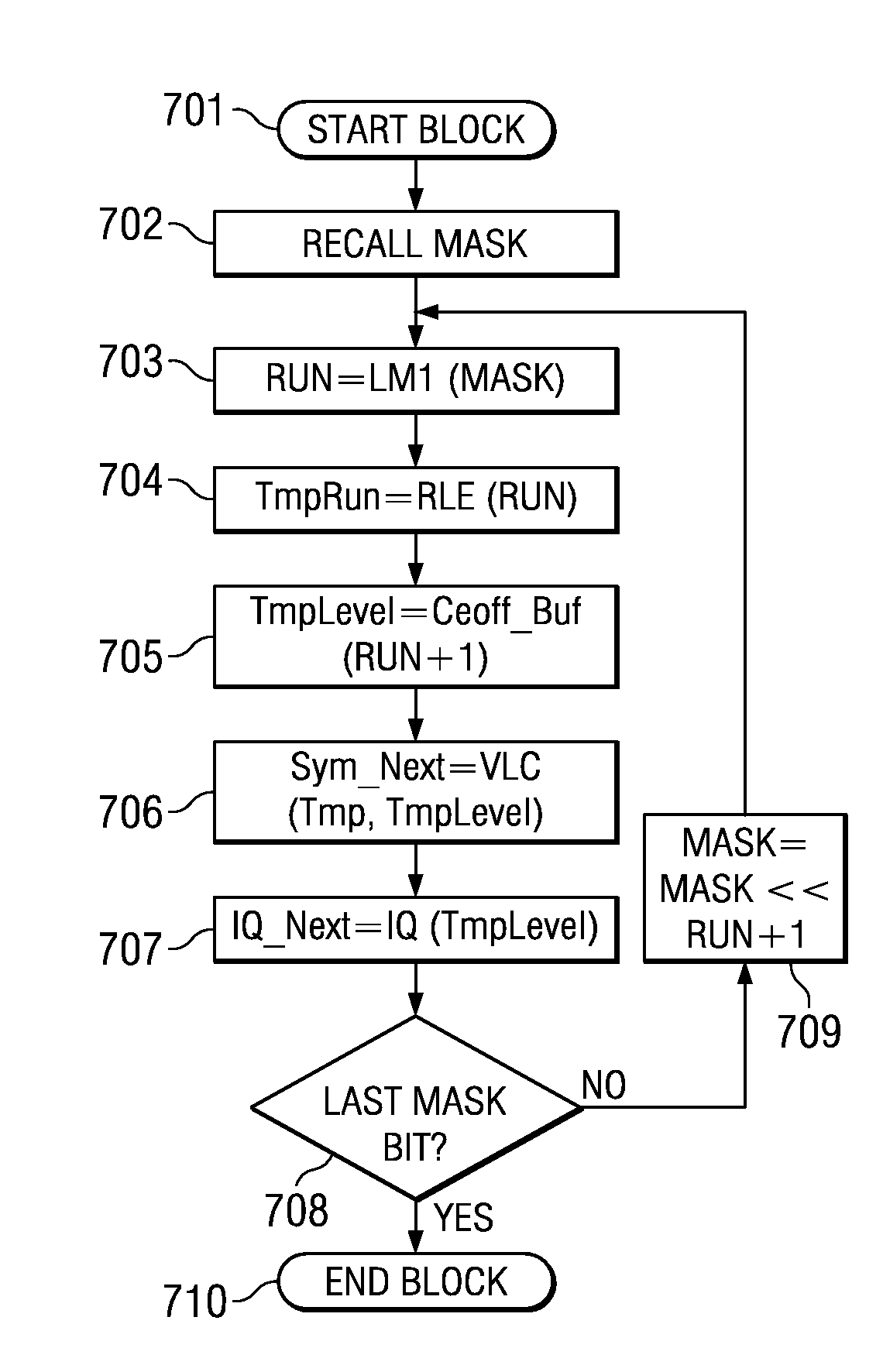
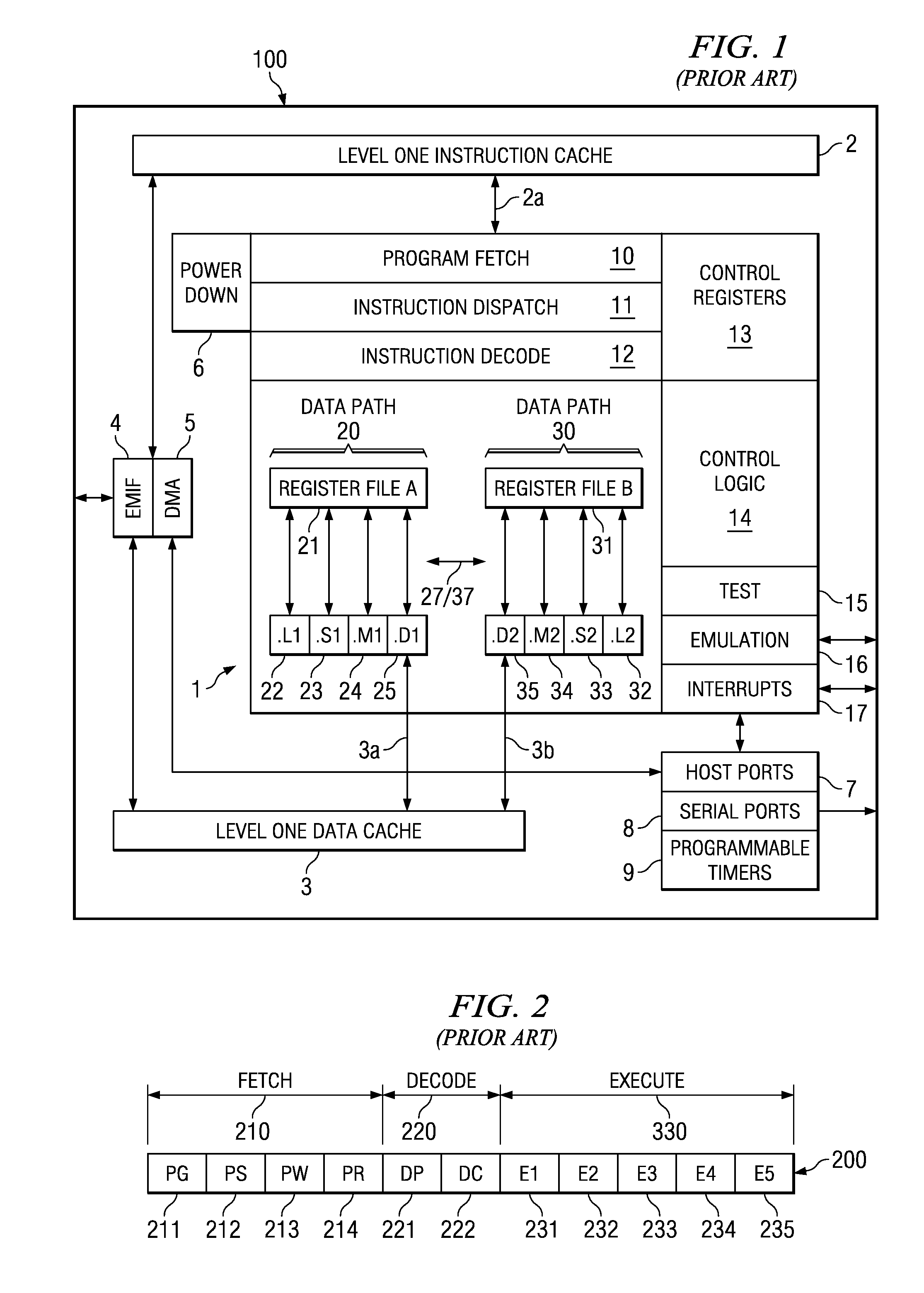
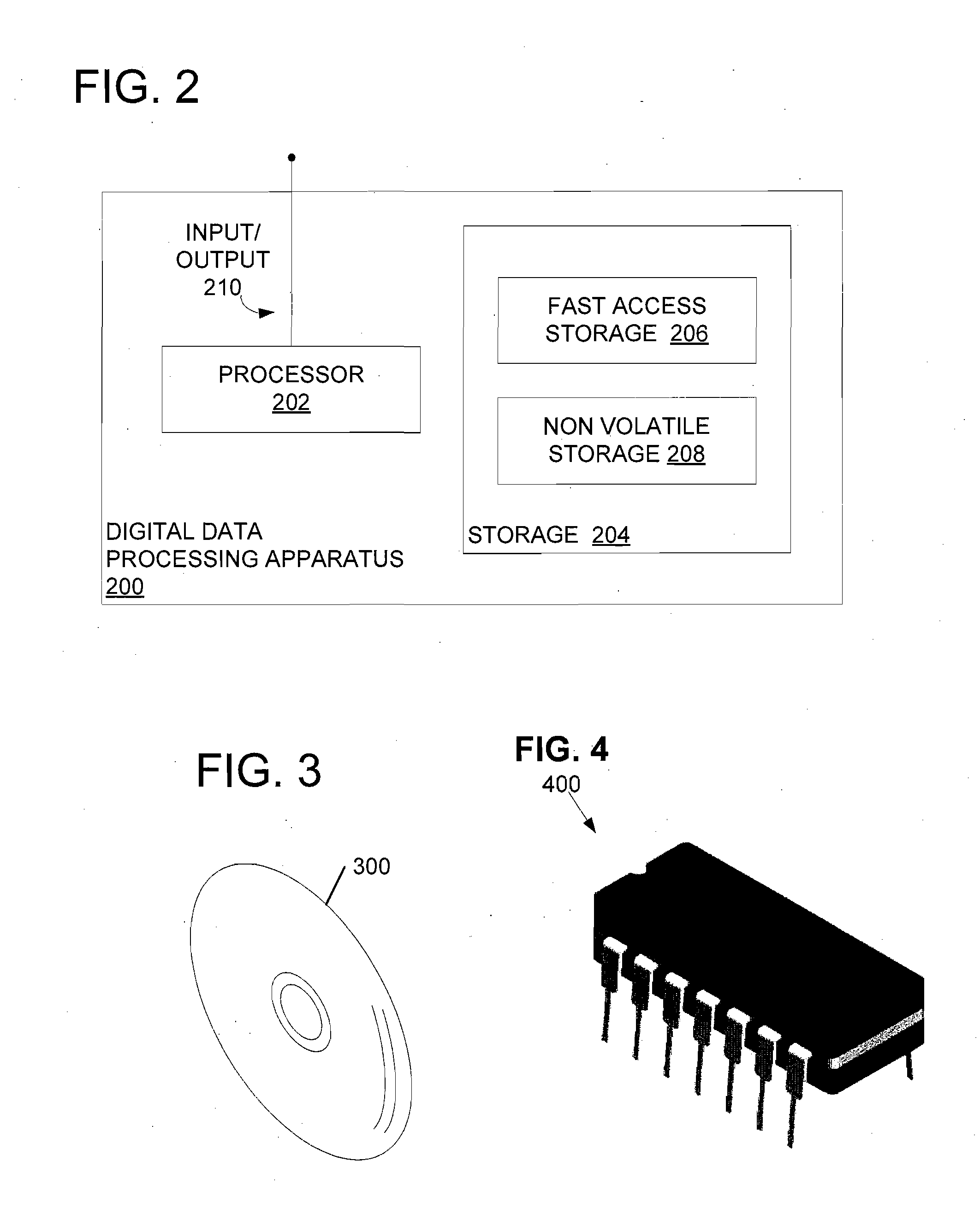
Run Length Encoding in VLIW Architecture
ActiveUS20080046698A1Reduce bitrateEasy to harvestPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningVariable-length codeGlyph
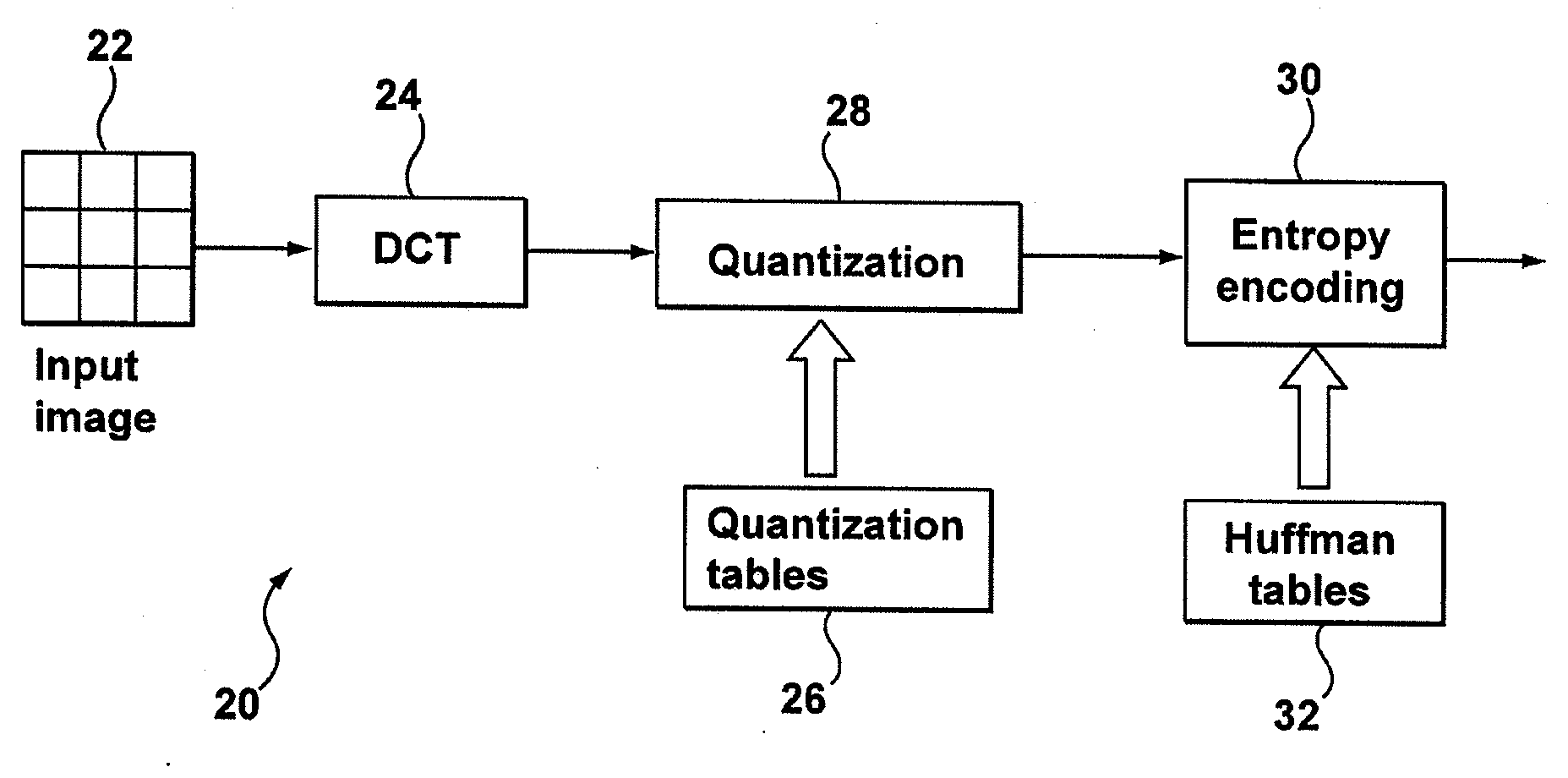
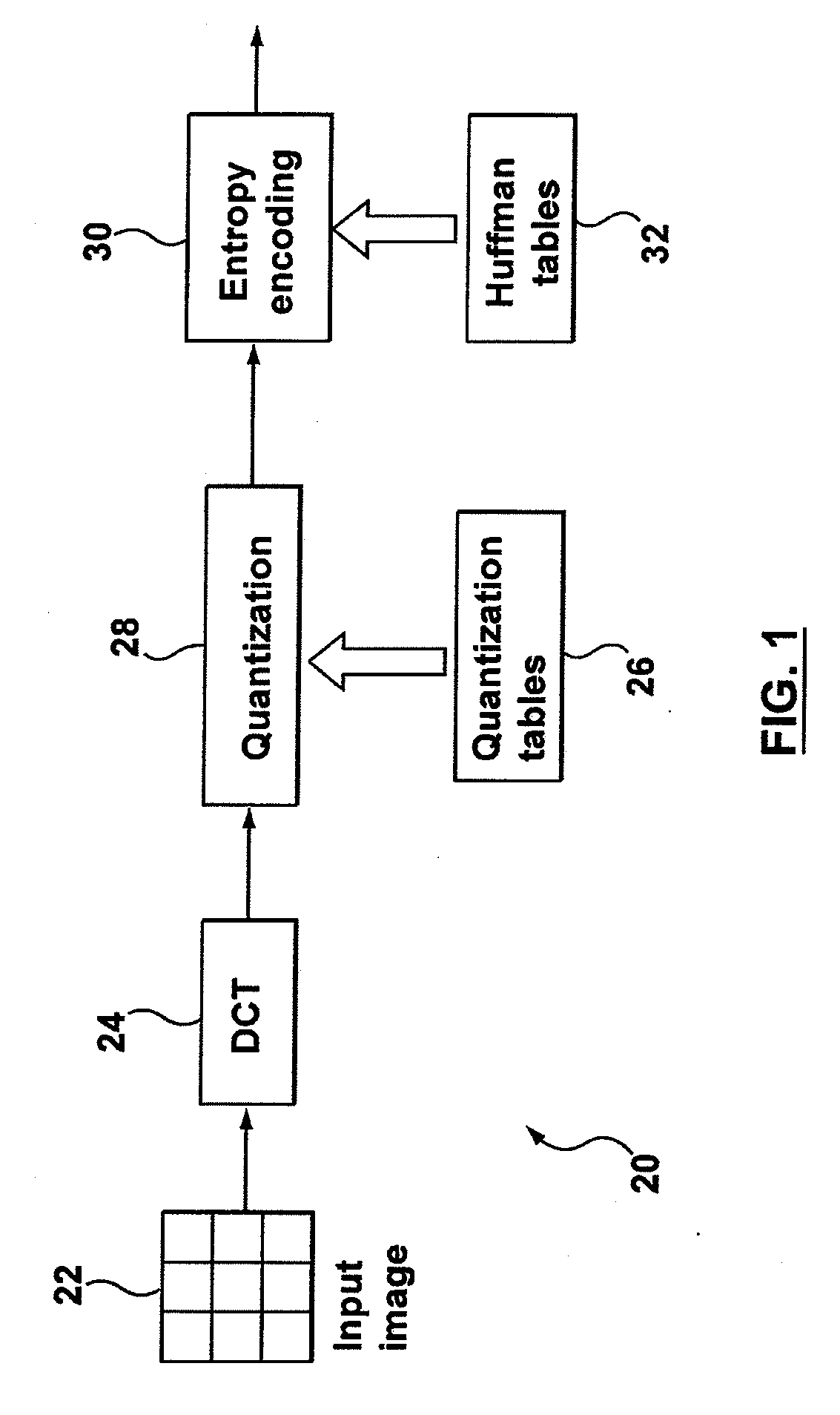
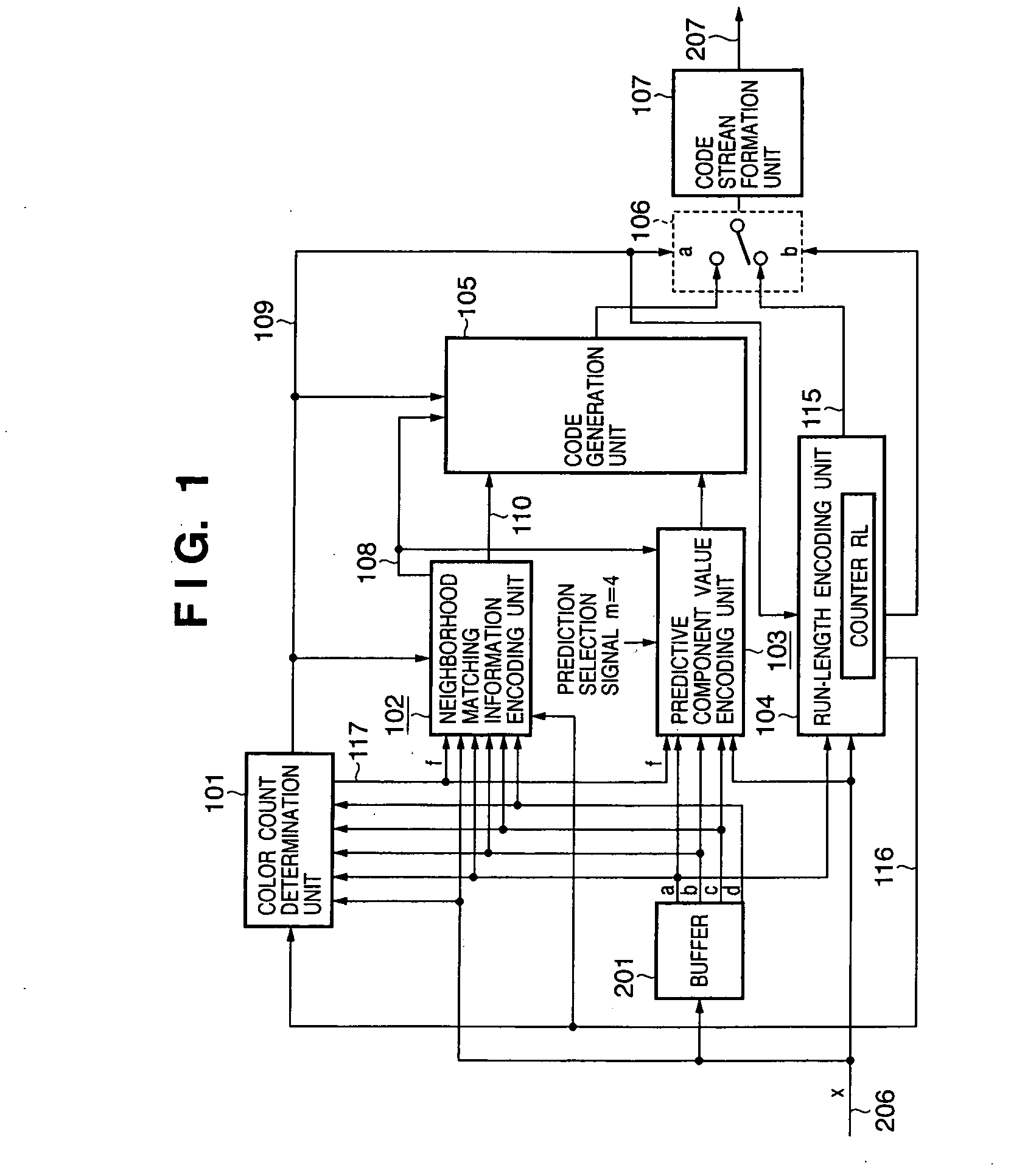
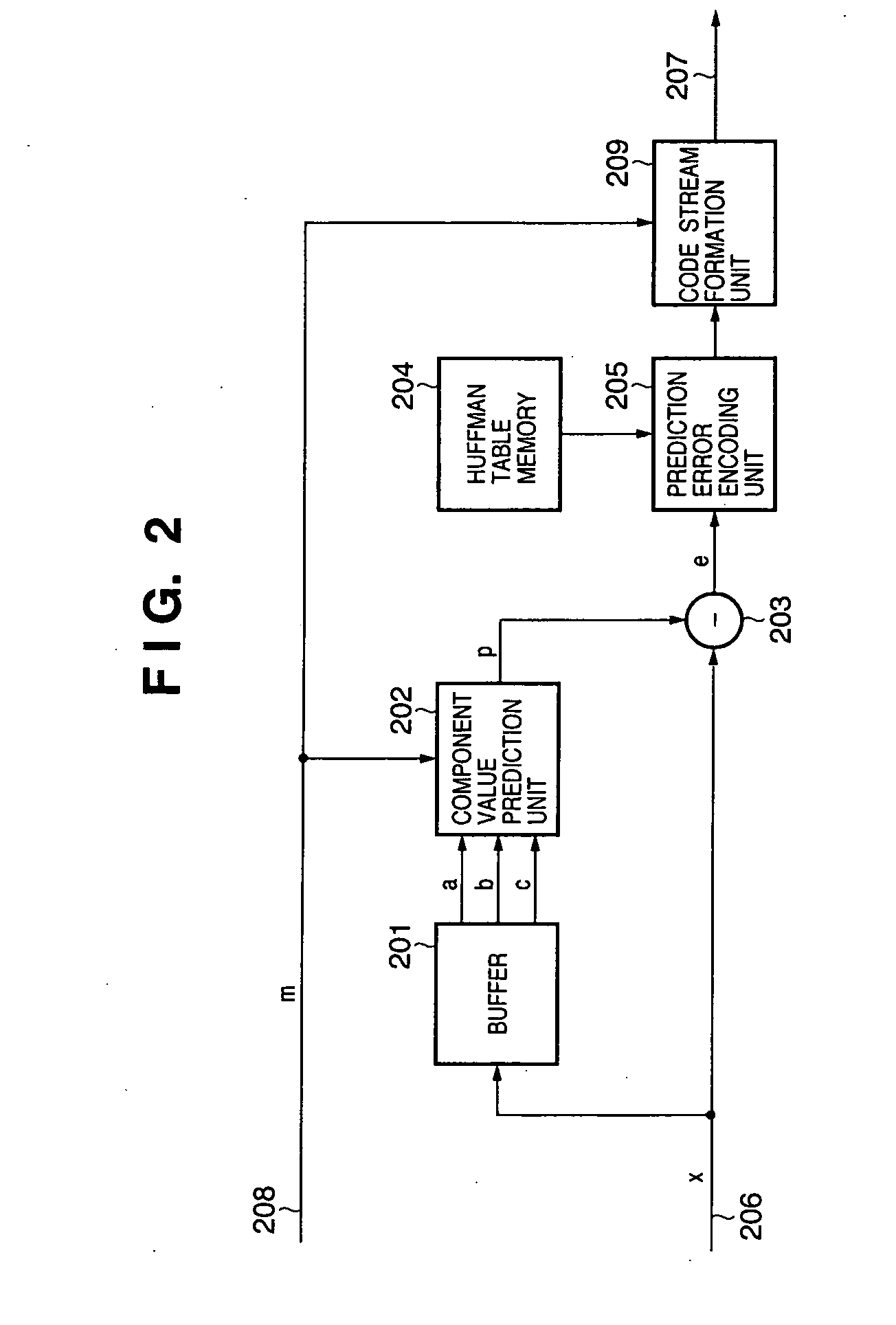
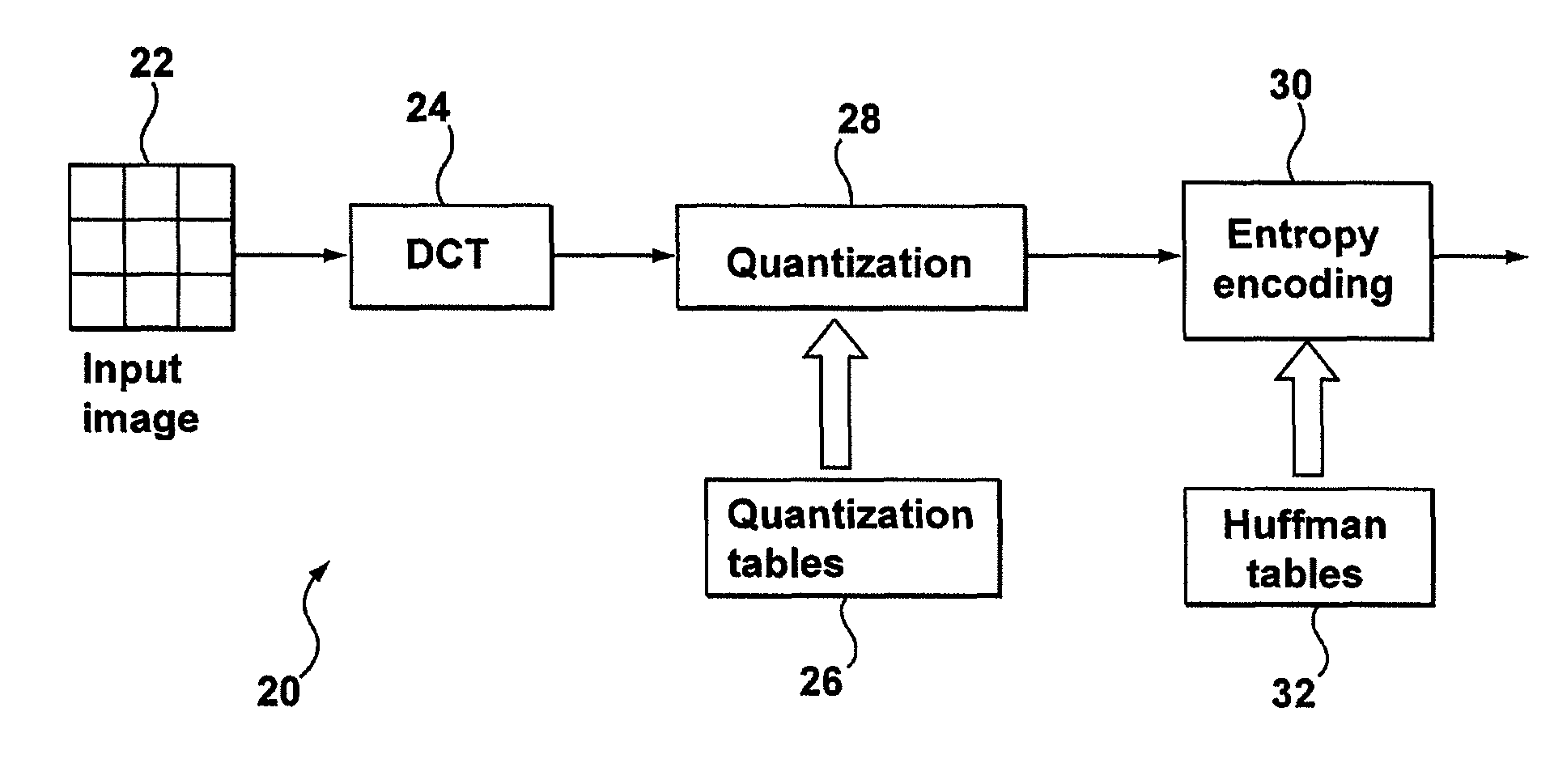
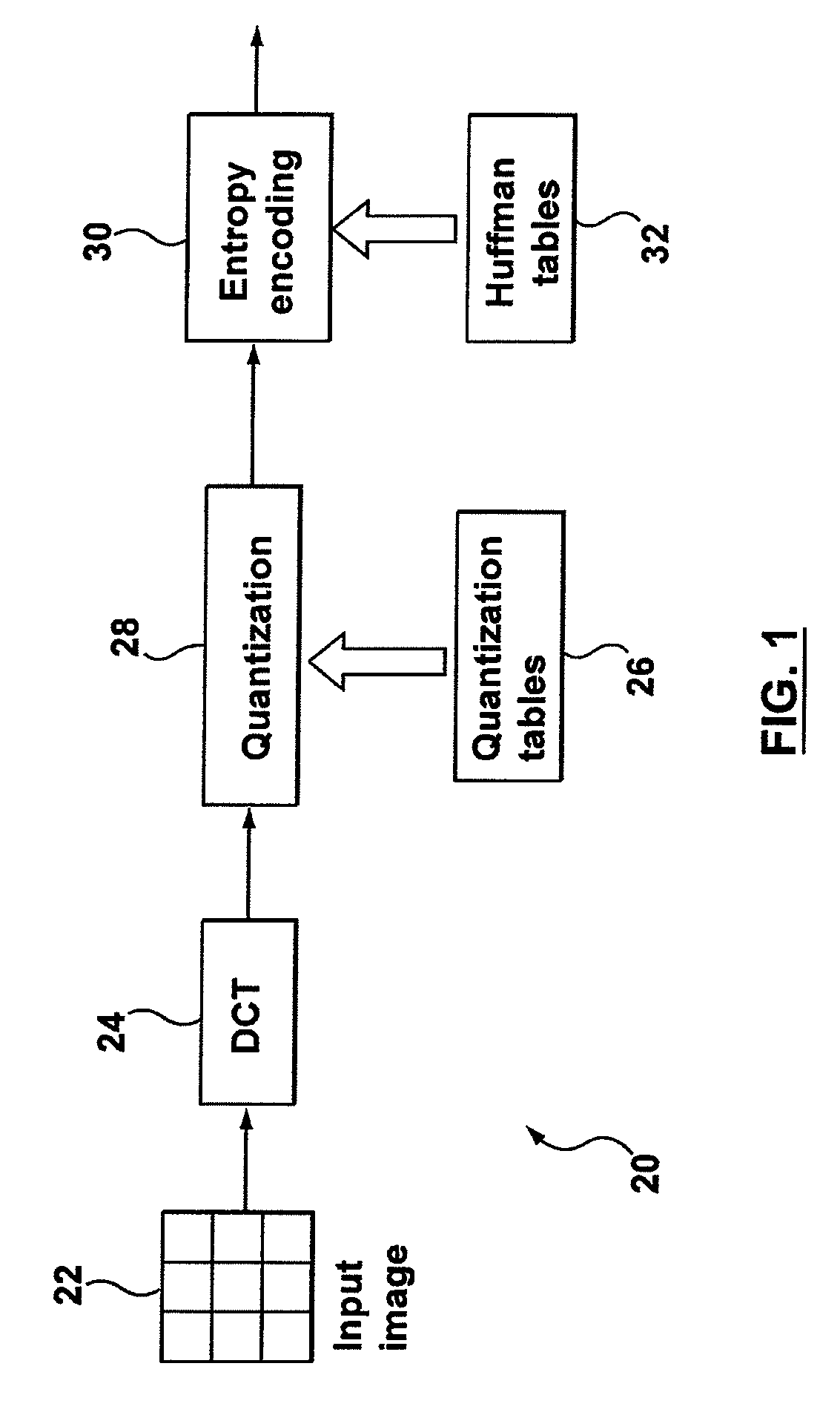
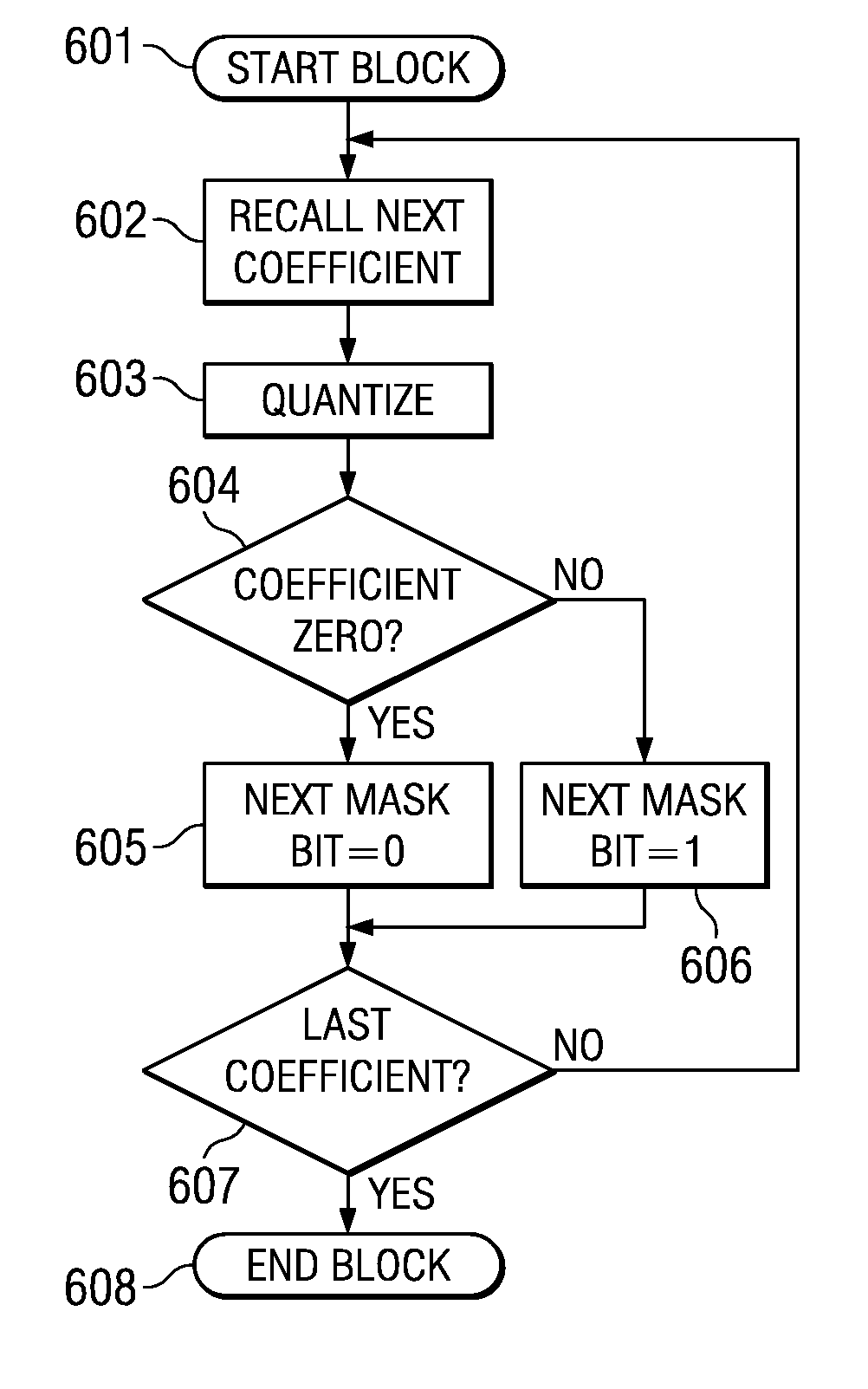
A computer implemented method of video date encoding generates a mask having one bit corresponding each spatial frequency coefficient of a block during quantization. The bit state of the mask depends upon whether the corresponding quantized spatial frequency coefficient is zero or non-zero. The runs of zero quantized spatial frequency coefficients determined by a left most bit detect instruction are determined from the mask and run length encoded. The mask is generated using a look up table to map the scan order of quantization to the zig-zag order of run length encoding. Variable length coding and inverse quantization optionally take place within the run length encoding loop.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Fisheye image correction method based on distorted straight slope calculation
InactiveCN102156970AReduce operational complexityImage enhancementComputation complexityComputer graphics (images)
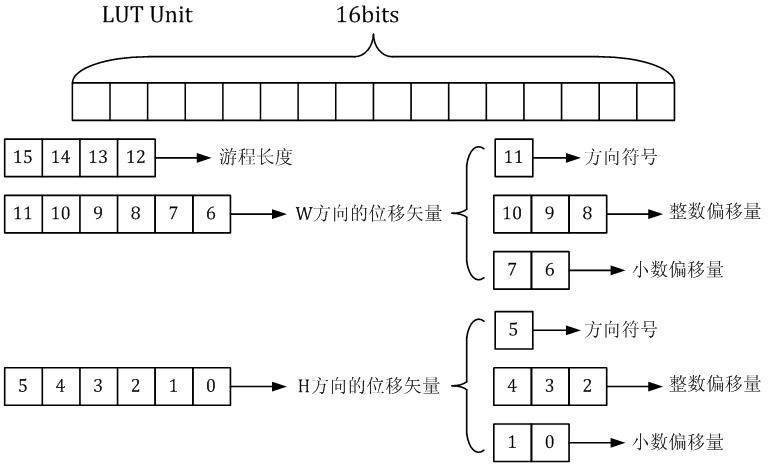
The invention relates to a fisheye image correction method based on distorted straight slope calculation, belonging to the field of digital image processing. According to the fisheye image correction method, the actual slope of a distorted straight line is calculated according to a projective invariance principle by utilizing the specific geometric characteristics of radial distortion and parameter values of a polynomial correction model are obtained by solving linear equations on the basis of the actual slope of the distorted straight line. The fisheye image correction method outstandingly reduces the calculation complexity under the condition of having ideal correction accuracy and completes the position mapping codes between a distorted image and a corrected image according to the solved polynomial correction model by utilizing a run length coding LUT (Look Up Table), thereby realizing the weighting bilinear interpolation of the corrected image; and in addition, the fisheye image correction method has convenient hardware implementation and efficient real-time processing capacity.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Optimization of image encoding using perceptual weighting
ActiveUS20100220937A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationRate distortionPerceptual weighting
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method for improving the performance of embedded graphics coding
ActiveUS20110033126A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationGraphicsLeast significant bit
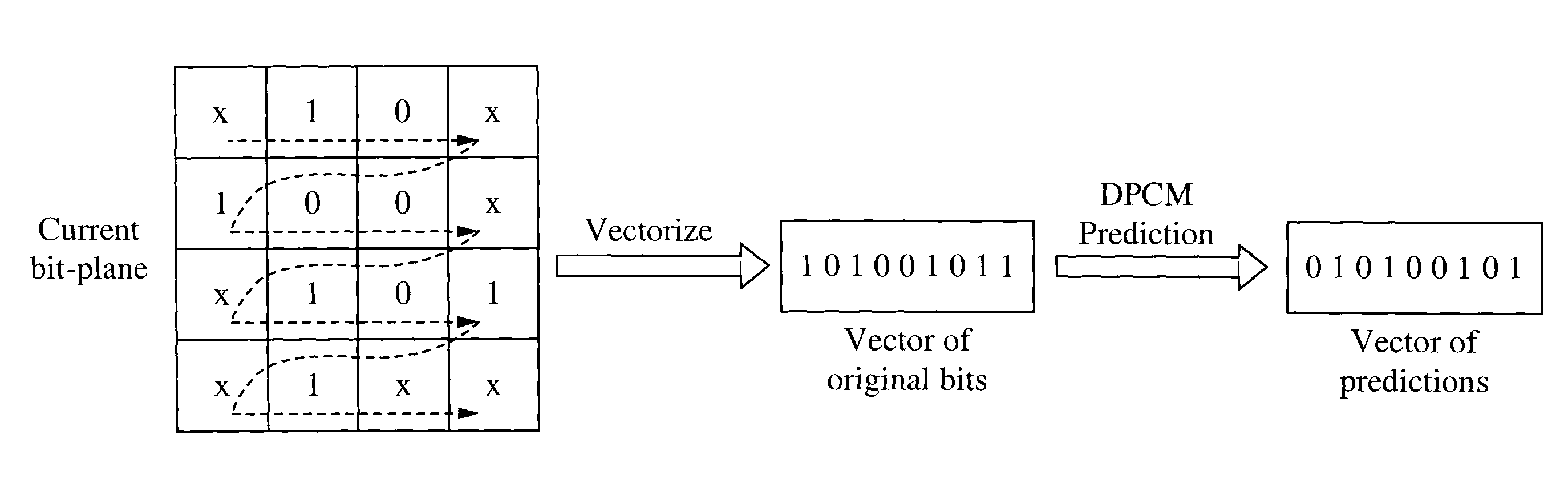
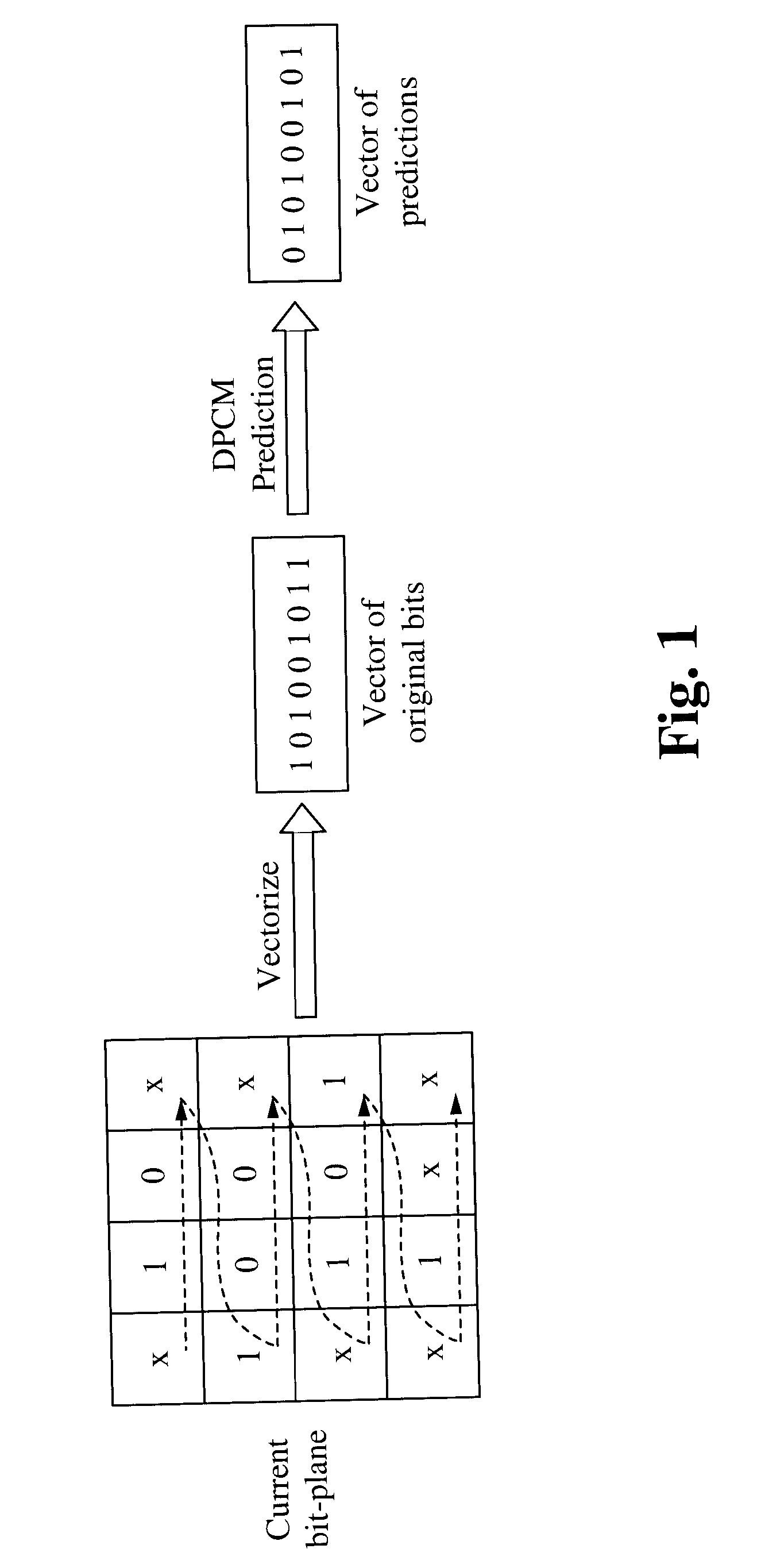
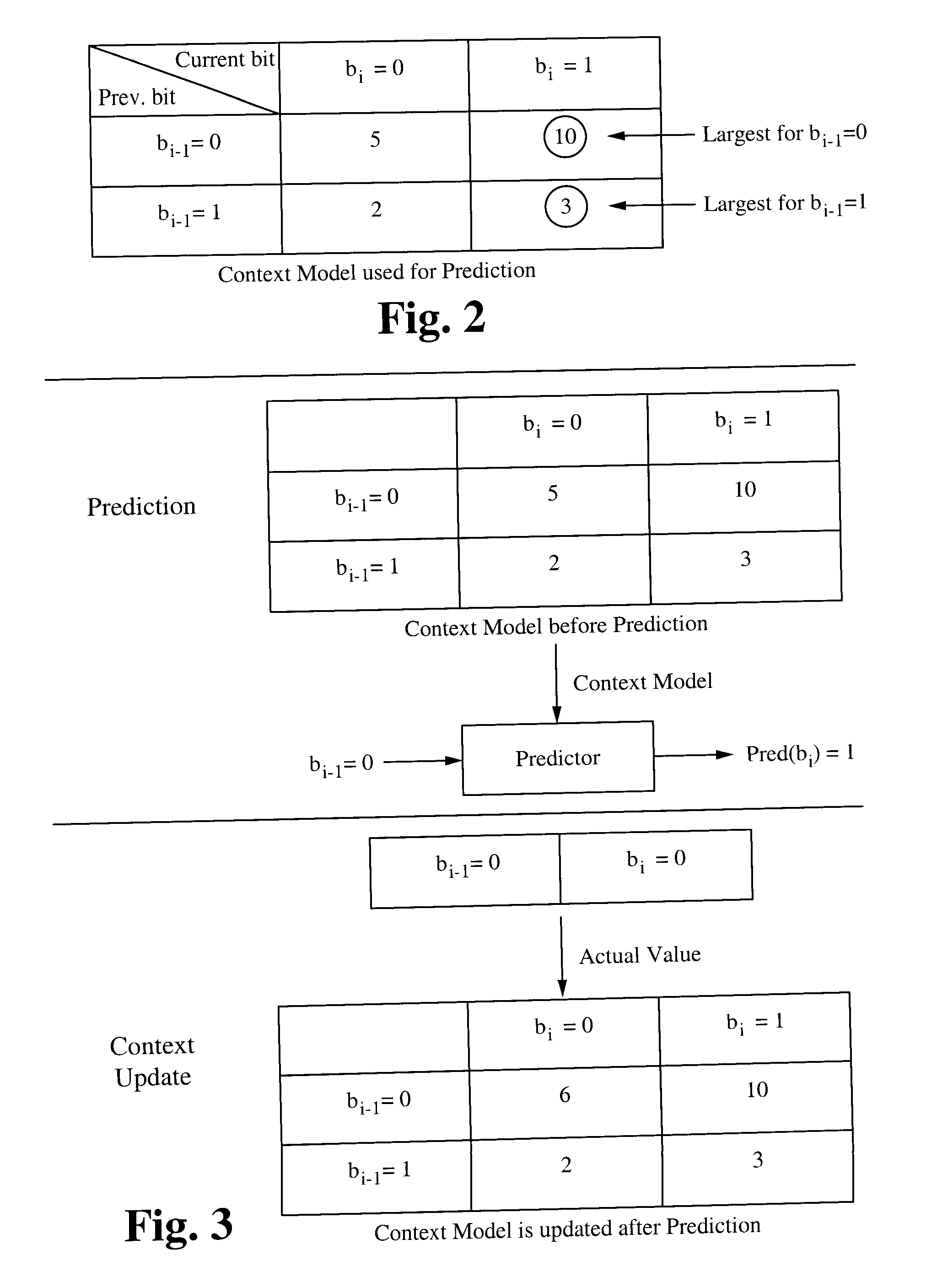
Embedded Graphics Coding (EGC) is used to encode images with sparse histograms. In EGC, an image is divided into blocks of pixels. For each block, the pixels are converted into binary representations. For each block, the pixels are scanned and encoded bit-plane by bit-plane from the most significant bit-plane (MSB) to the least significant bit-plane (LSB). The pixels in the block are partitioned into groups. Each group contains pixels with the same value. From the MSB to the LSB, the groups in the current bit plane are processed. During the processing, a group is split into two, if pixels in the group have different bit values in the bit-plane being encoded. Then, the encoder sends the refinement bit for each pixel in the group and the encoder splits the original group into two. A method is described herein to compress the refinement bits which employs context-adaptive prediction and binary run-length coding.
Owner:SONY CORP
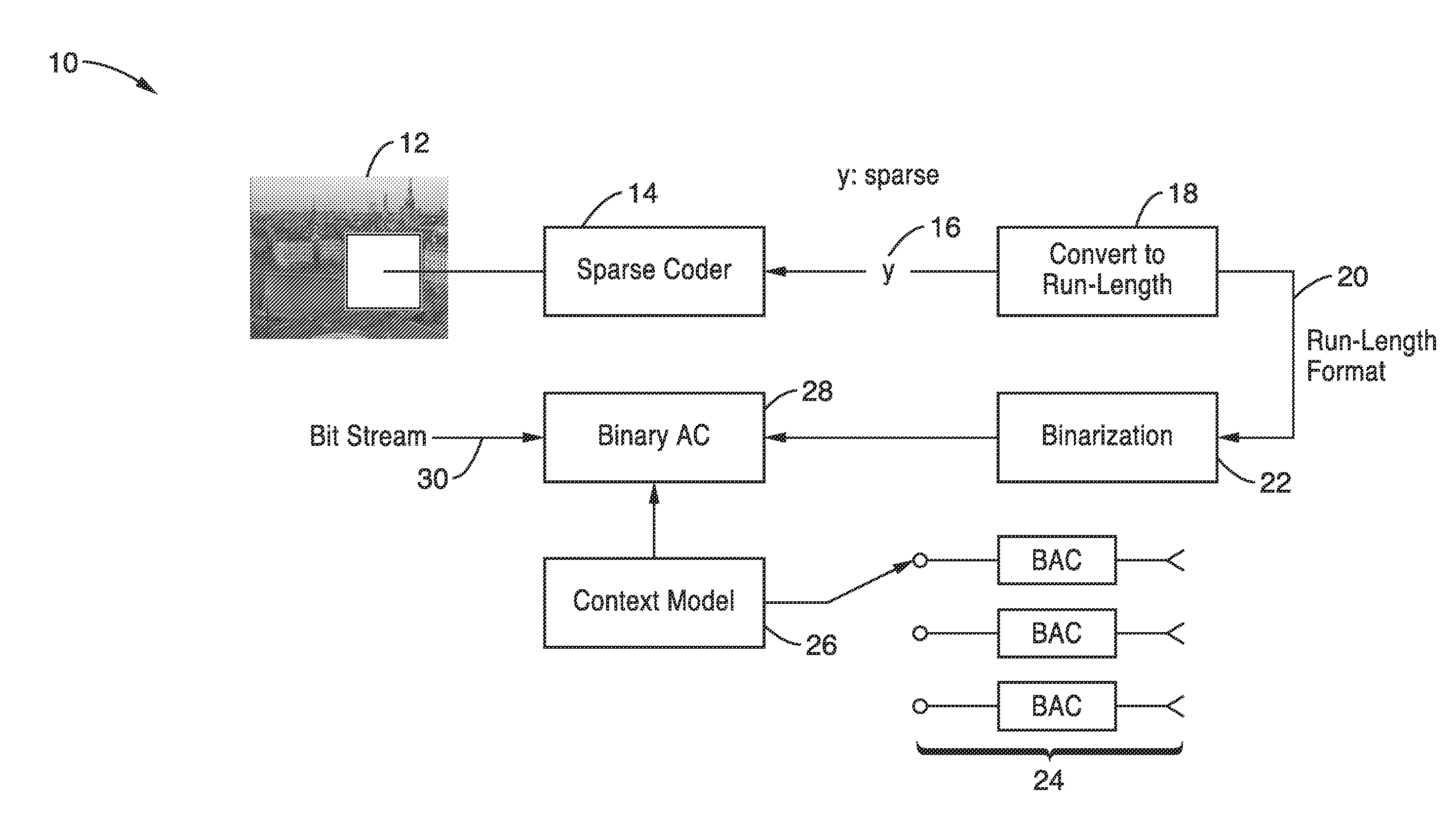
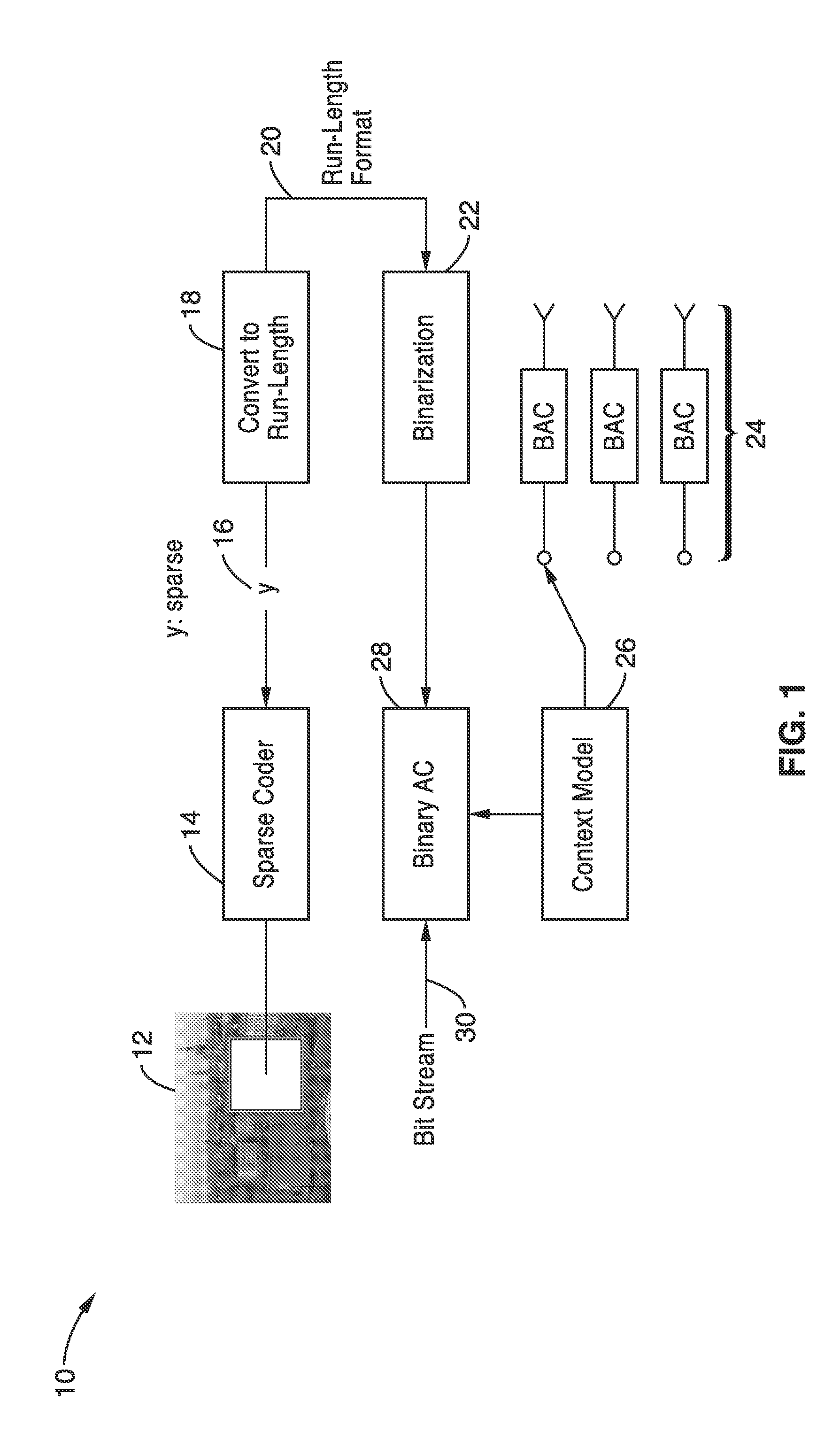
Run length coding with context model for image compression using sparse dictionaries
InactiveUS20120057799A1Reduce impactIncrease productionCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionContext modelAlgorithm
Apparatus and methods for coding images geometric vector quantization (GVQ) having an over-complete dictionary which produces a sparse vector of coefficients as it contains large runs of zeros. The sparse encoding is particularly well suited for use with run-length entropy coding techniques. Image blocks are sparse coded using GVQ, with the vector of coefficients converted to RUN-LENGTH symbols, and binarized into a set of binary symbols. At least a portion of the binary symbols are used as contexts which can be selected when performing binary arithmetic coding of the binary coded RUN and LENGTH data to generate a bit stream containing the encoded image that provides enhanced compression.
Owner:SONY CORP
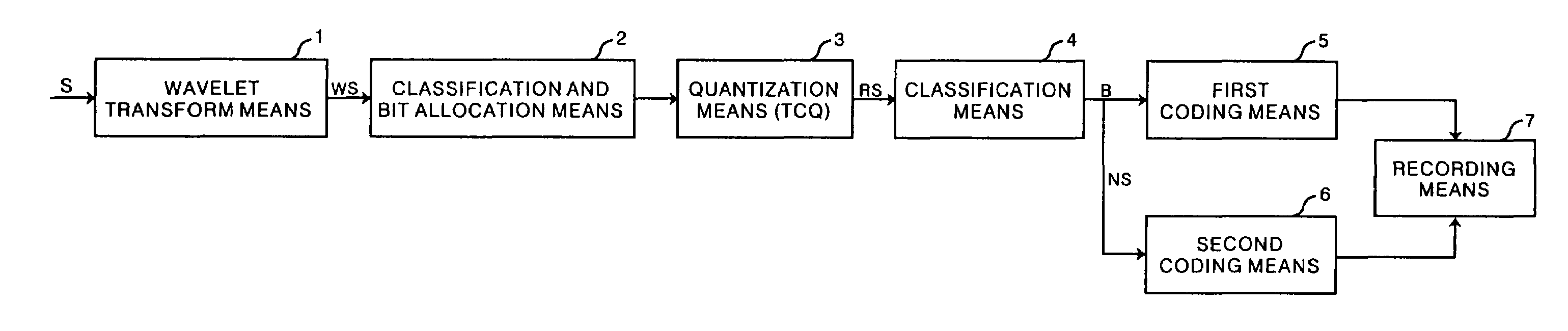
Method, apparatus and recording medium for data compression
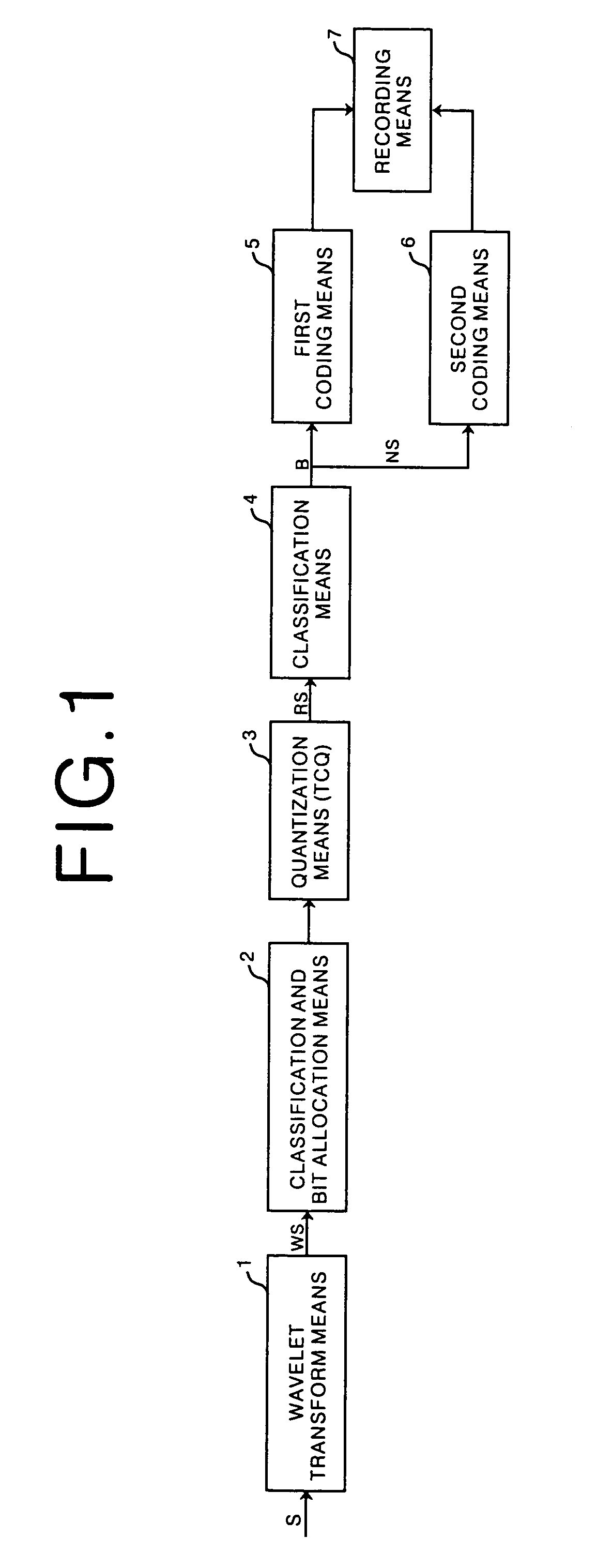
InactiveUS7003171B1Fast and efficient data compressionComputational loadCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationBit allocationBinary classification
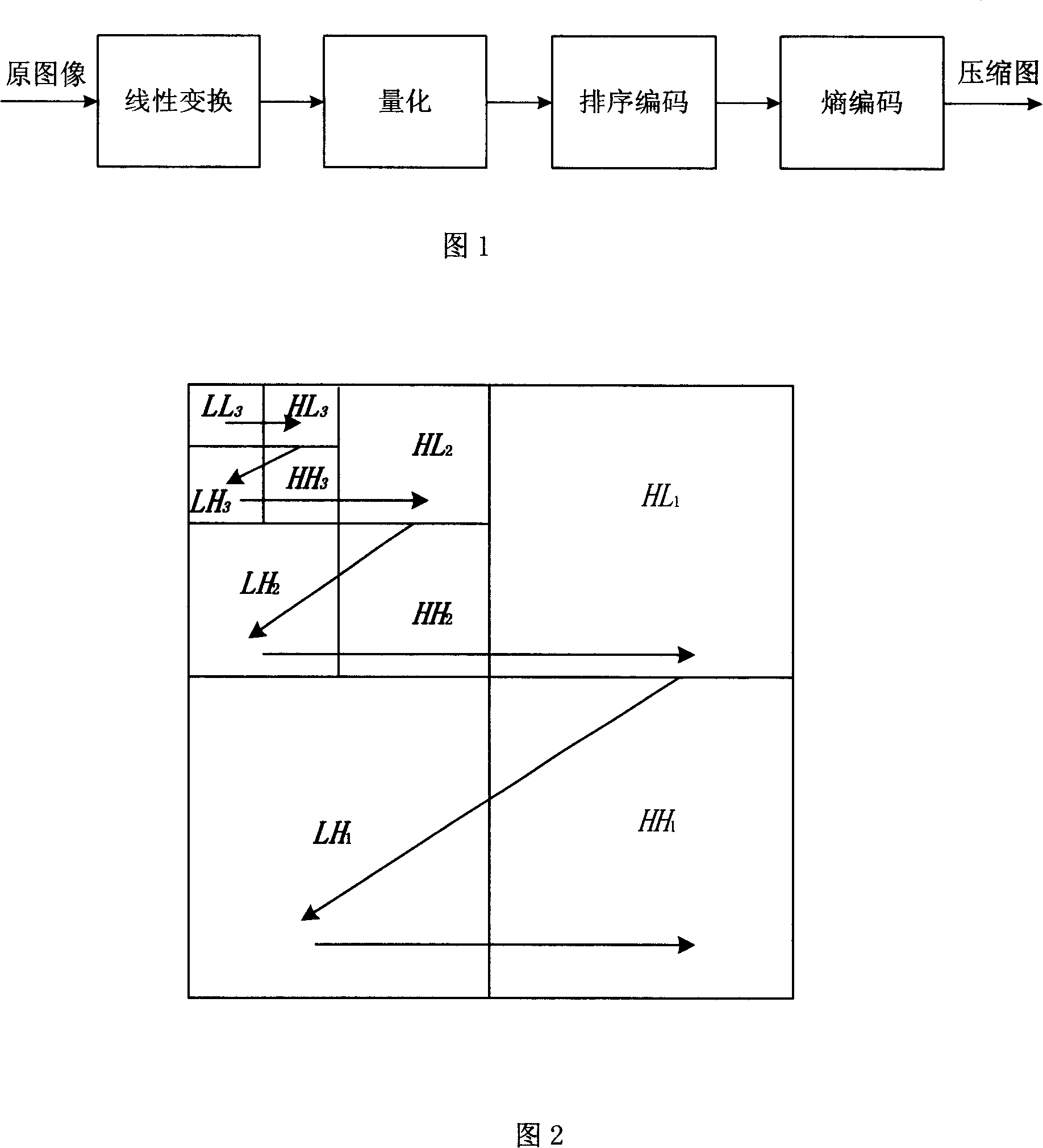
Fast and efficient data compression can be carried out. Original image data are subjected to wavelet transform. The obtained wavelet-transformed data are classified and bit allocation is determined. Based on the determined bit allocation, the wavelet-transformed data are quantized and quantized data are obtained. The quantized data are classified into 0 data and non-zero data. Binary classification information data indicating this classification are also obtained. The classification information data are coded according to a coding method having a comparatively simple operation, such as Huffman coding and run length coding. The multi-valued, non-zero data are coded according to a coding method having a high compression efficiency although having a comparatively complex operation, such as universal coding and Golomb-Rice coding.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
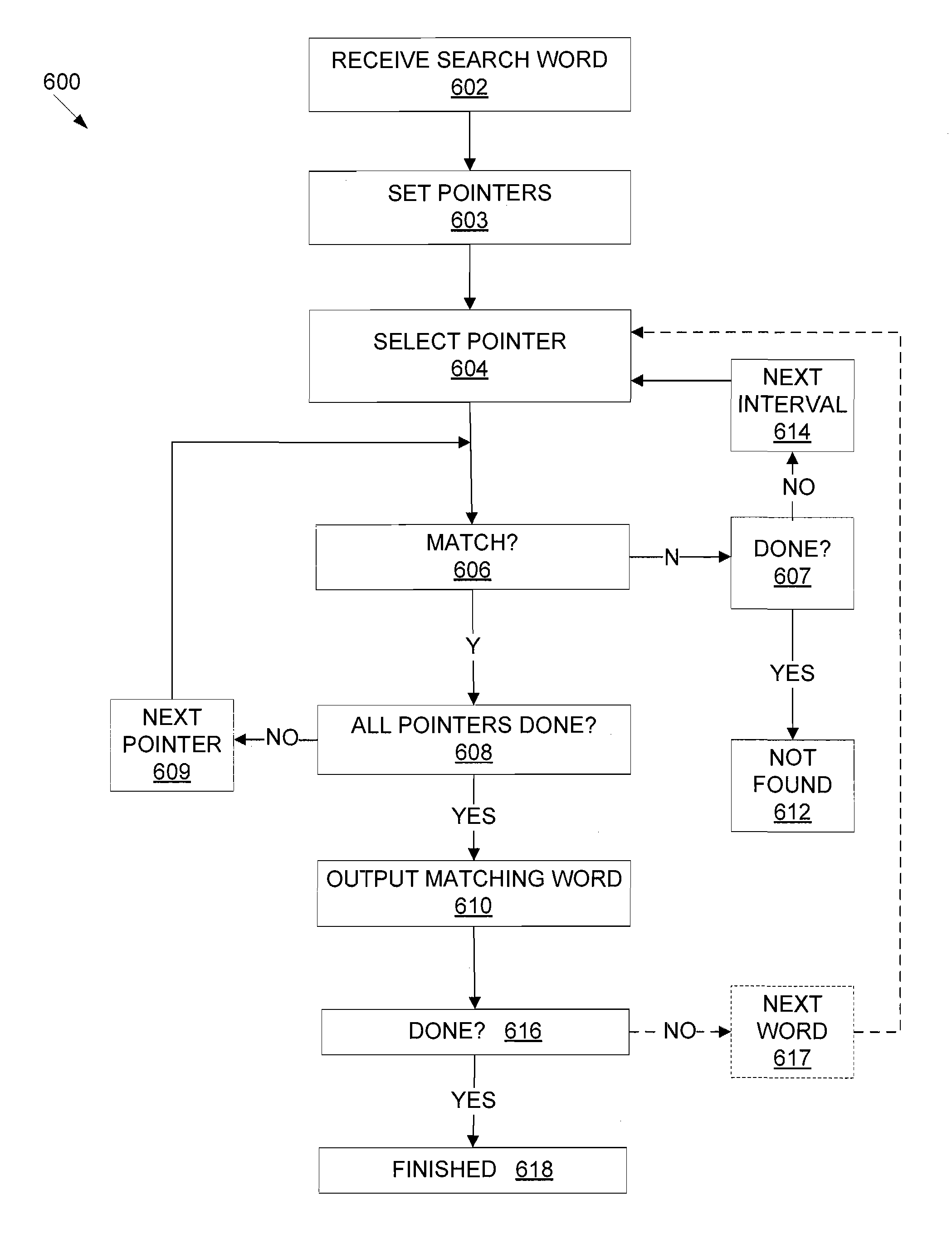
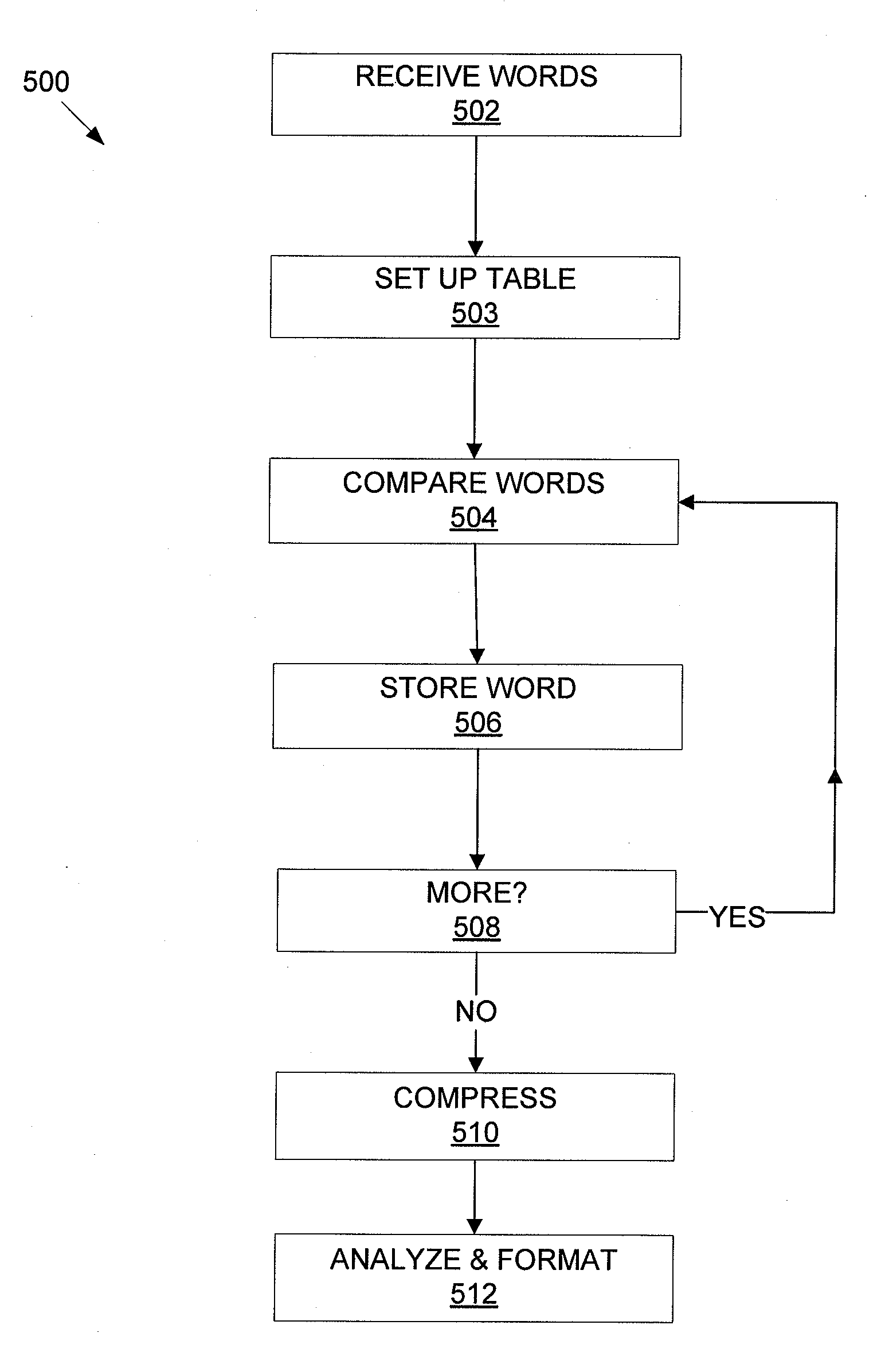
Efficient storage and search of word lists and other text
ActiveUS7580925B2Maximize lengthImprove compression efficiencyDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsDigital dataWord list
A computer readable storage medium tangibly embodying machine-readable digital data arranged to facilitate expedited searching. The data includes a plurality of words residing in a table having rows and columns, each word residing in a different row and each letter of the word occupying a different column in that row. Each continuous run of same letters in a column forms an interval. The words are positioned relative to each other to maximize lengths of the intervals, and / or optimize efficiency of compression of the columns by run length encoding.
Owner:TEGIC COMM +1
Image lossless compression and image decompressing method
ActiveCN101039374AEasy to handleIncrease the compression ratioTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsRound complexity
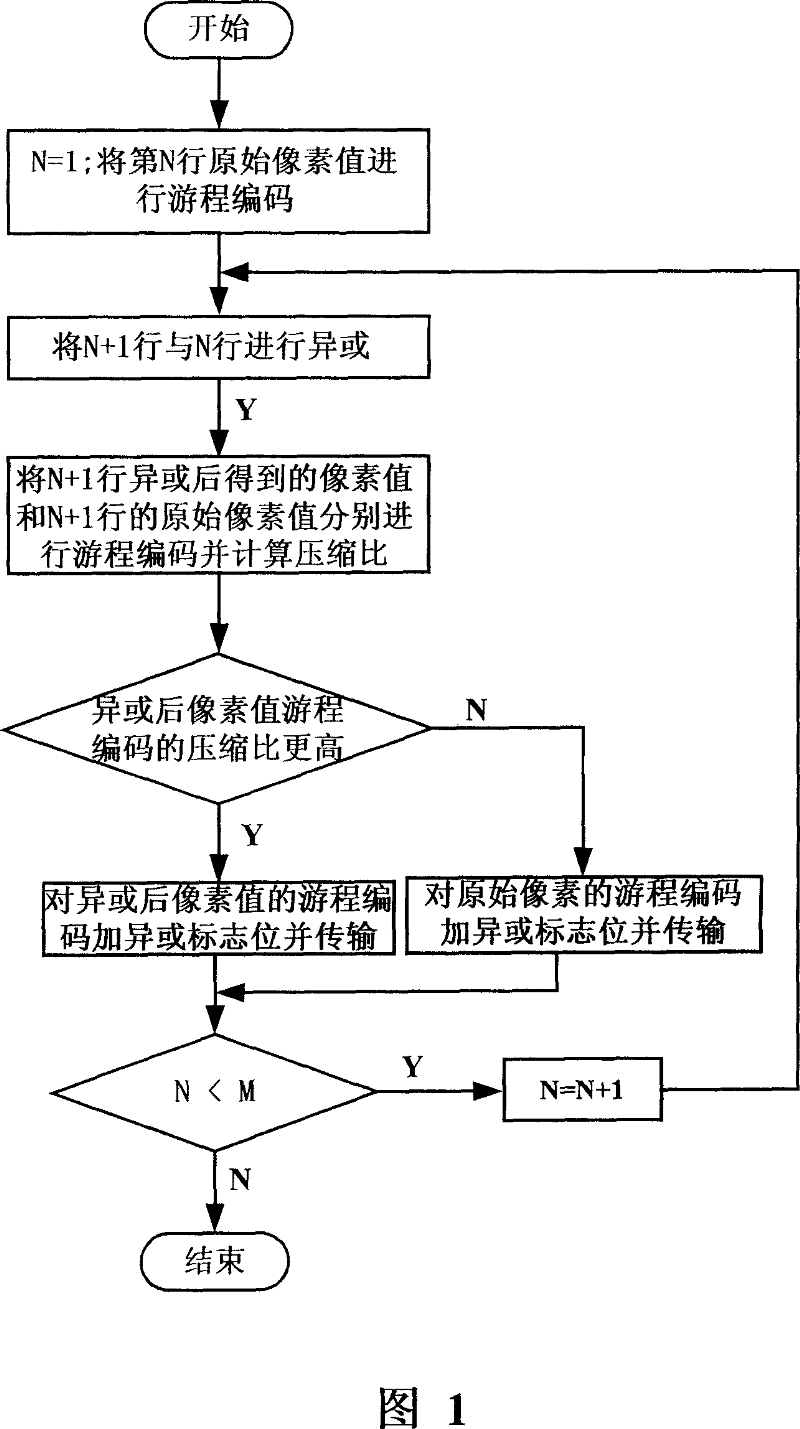
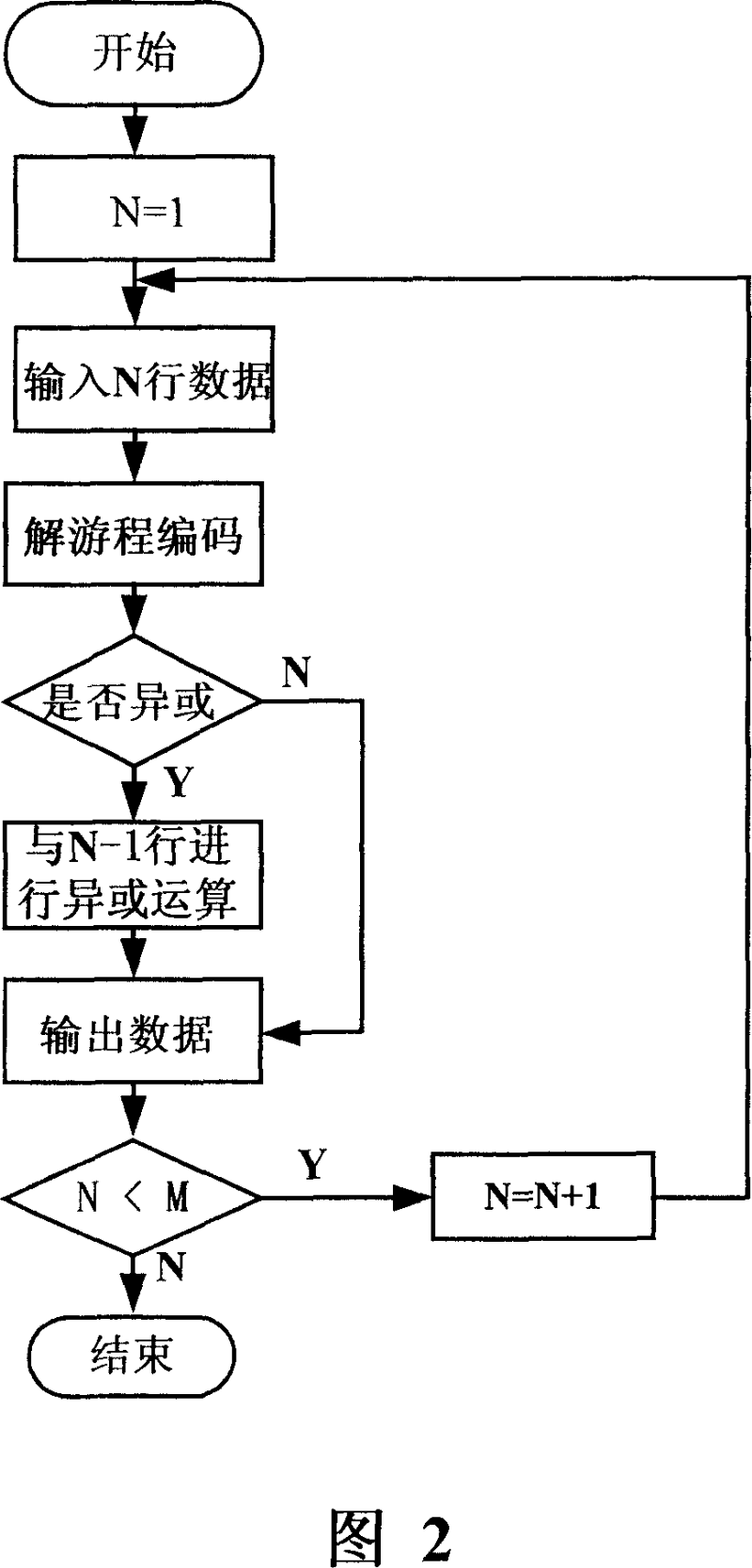
The present invention discloses an image nondestructive compressing method including following steps: starting from a first row and rank of the original image data, original pels values of this row and rank and those of the adjacent ones are logically xor to obtain the next row and rank xor pels; a selection between the original pels and the xor pels is made and the selected one is executed the run length coding, and xor mark are added to the head coating and the head coating is output. The invention also discloses an image decoding method including following steps: the run length coding of the row and rank are decoded; the xor pels are also decoded and output. The invention improves the compressing ratio as far as possible, at the same time, the realizing complexity is also reduced, the coding arithmetic is simple and the computing amount is little; the method does not need the special compressing / decompressing chip, so the realizing cost is low.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) LTD
Image encoding apparatus and method, computer program, and computer-readable storage medium
InactiveUS20060262982A1Valid encodingCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingAlgorithmRun length coding
Owner:CANON KK
Compensation table compression method and decompression method for OLED display device
ActiveCN107294538AReduce data volumeCompress the amount of data, and adjust the size of the preset number thresholdCode conversionProduction lineDisplay device
The invention provides a compensation table compression method and a decompression method for an OLED display device. The compensation table compression method for an OLED display device compresses data size of compensation tables through run-length coding of data which is arranged continuously and equal in values in the compensation tables, and through adjusting the size of a preset number threshold value, condition of the run-length coding to start is controlled, to prevent to increase redundancy and expand data size caused by coding. The method can compress size of the compensation tables, reduce system storage space occupied by the compensation tables, and shorten time for transmitting and burning data on a production line.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
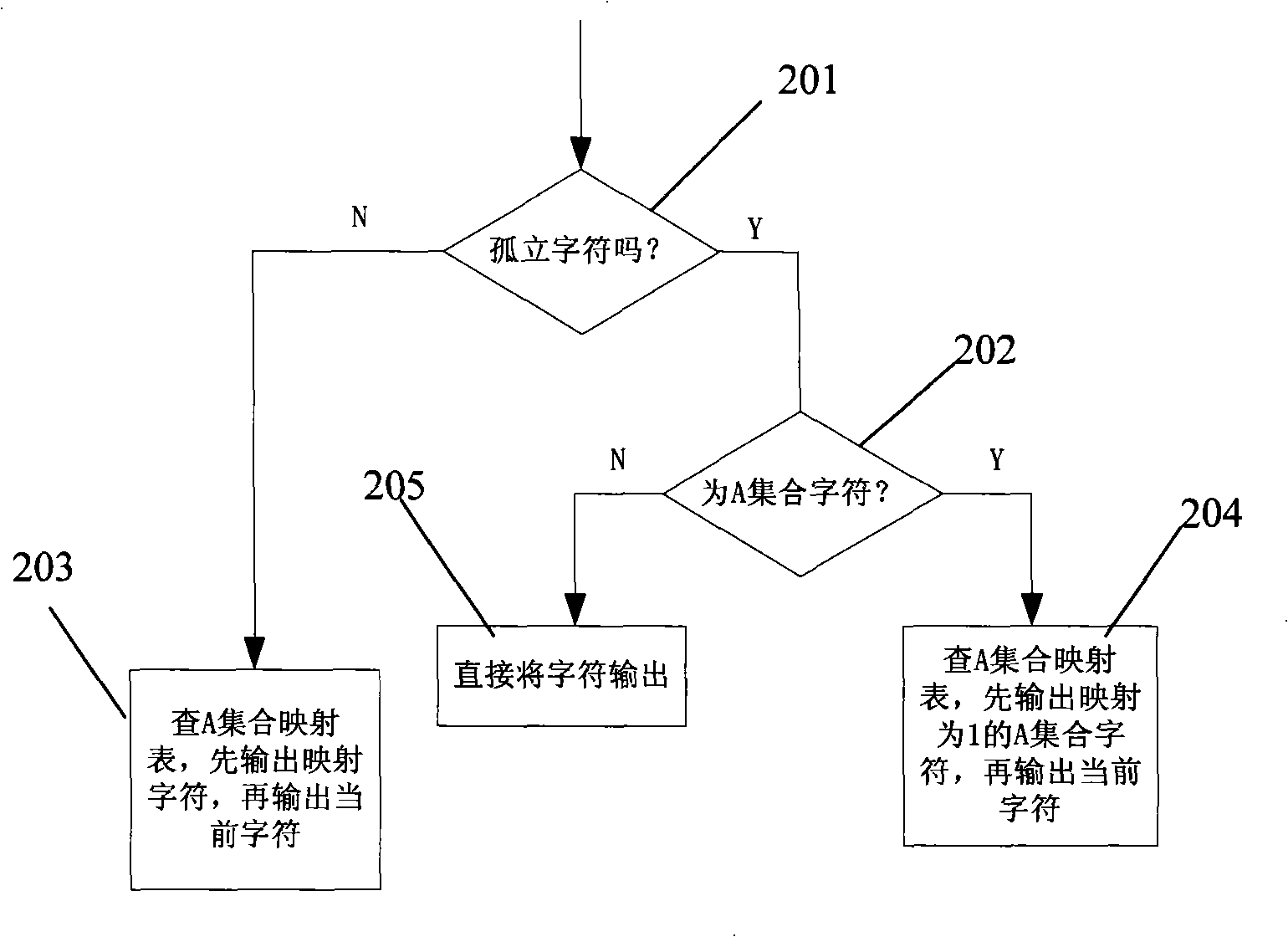
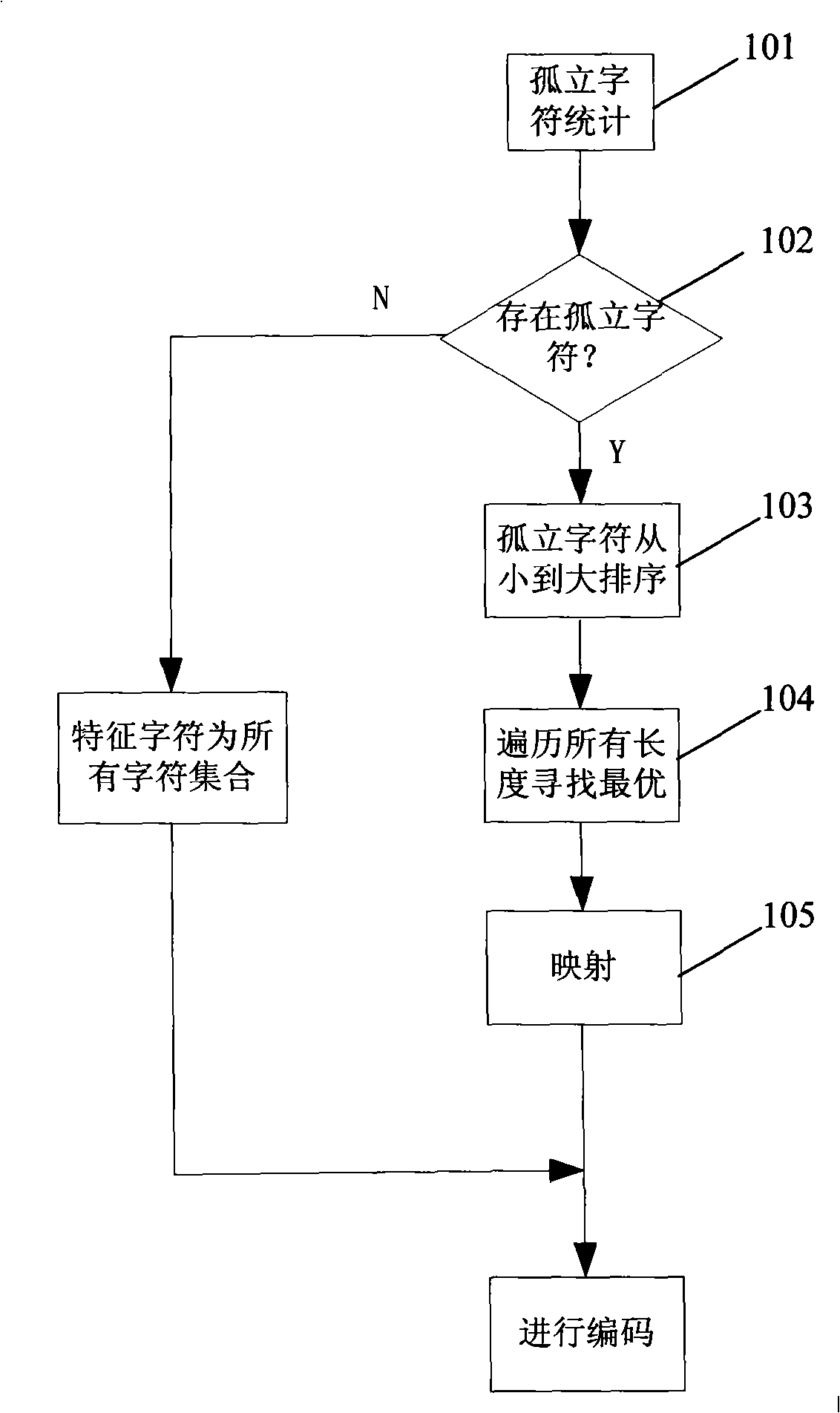
Data compression method based on set run
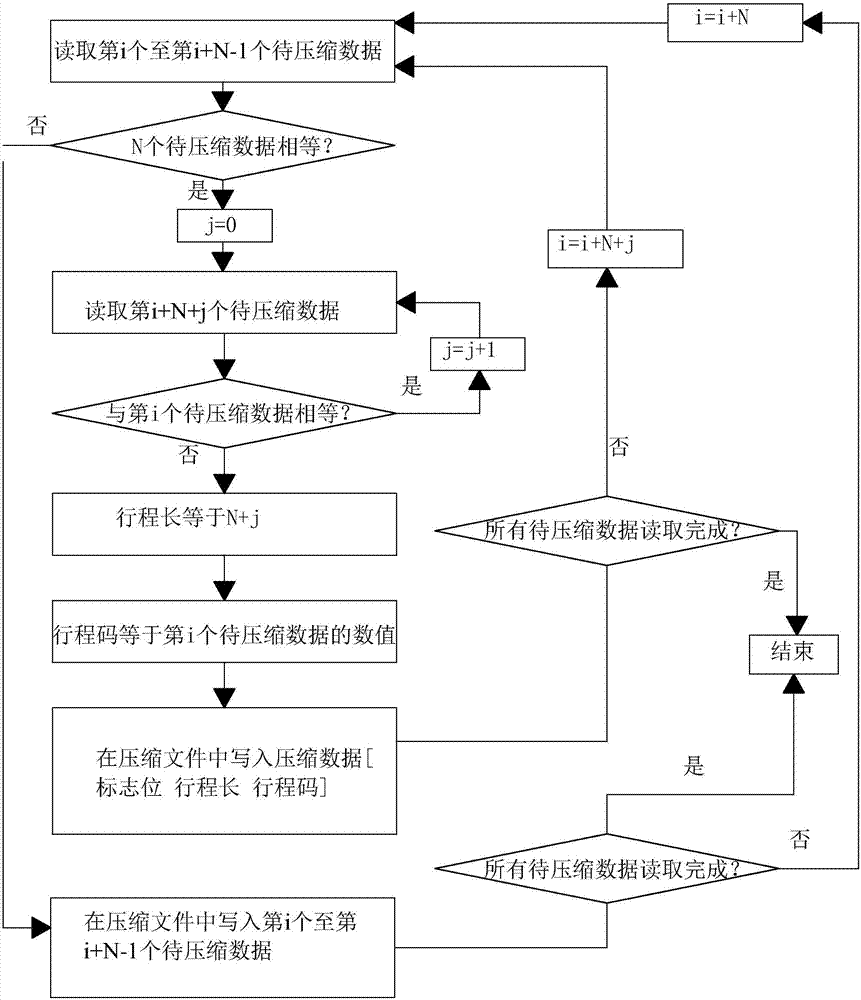
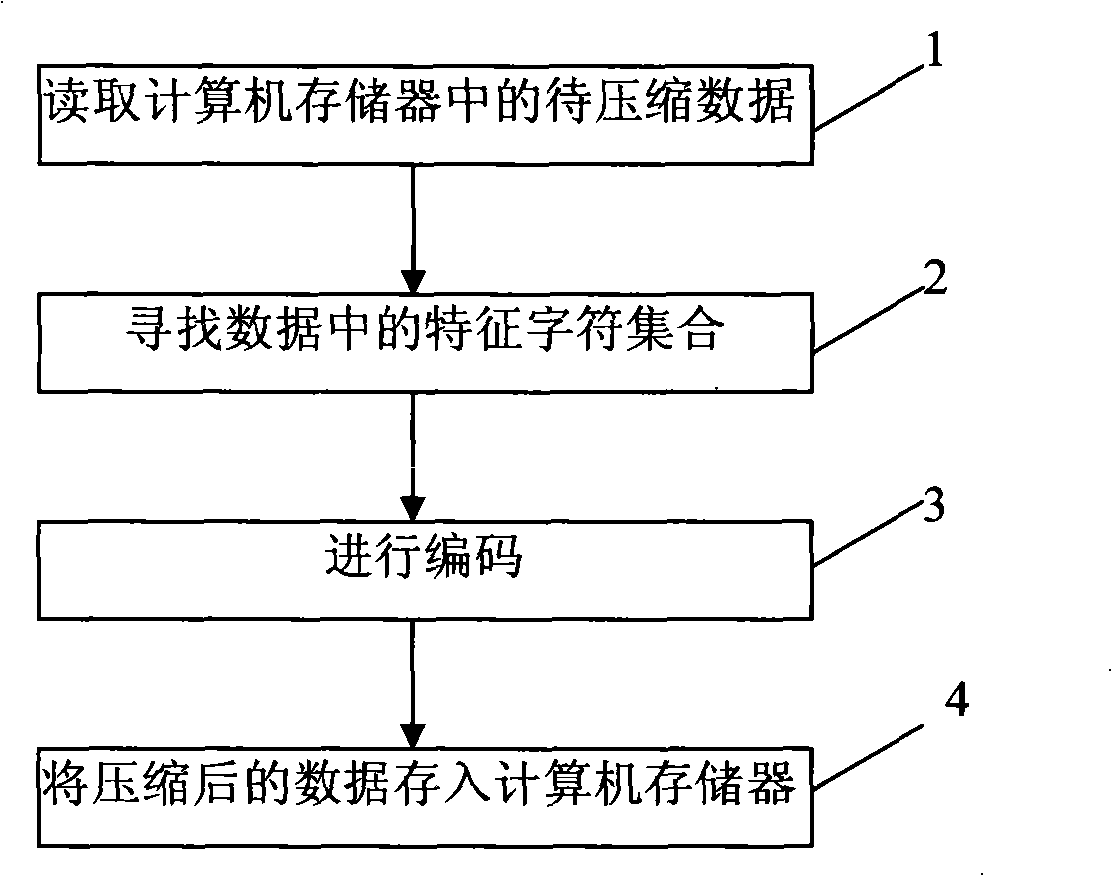
InactiveCN101299611AIncrease the compression ratioOvercome the problem of low coding efficiencyCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceComputer memory
The invention discloses a data compression method based on the set run, including reading the data to be compressed in the memorizer of the computer; looking for the characteristic character set in the data; coding; storing the compressed data into the memorizer of the computer. Looking for the characteristic character set in the data includes the following steps: counting the isolated character; judging whether presenting the isolated character, if true, executing the next step, else converting all the characters into the characteristic characters, wherein the continuous occurrence number mapped by each character is the numerical value, and converting to the coding step; sorting the isolated character; traversing the number of each element that may occur of all the characteristic character set, selecting the number of the characteristic character set when the compression ratio reach the minimum; mapping each element in the characteristic character set till the element appears continuously. The invention advances the efficiency of the run length coding, and obtains better data compression effect in the computer data compression process.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
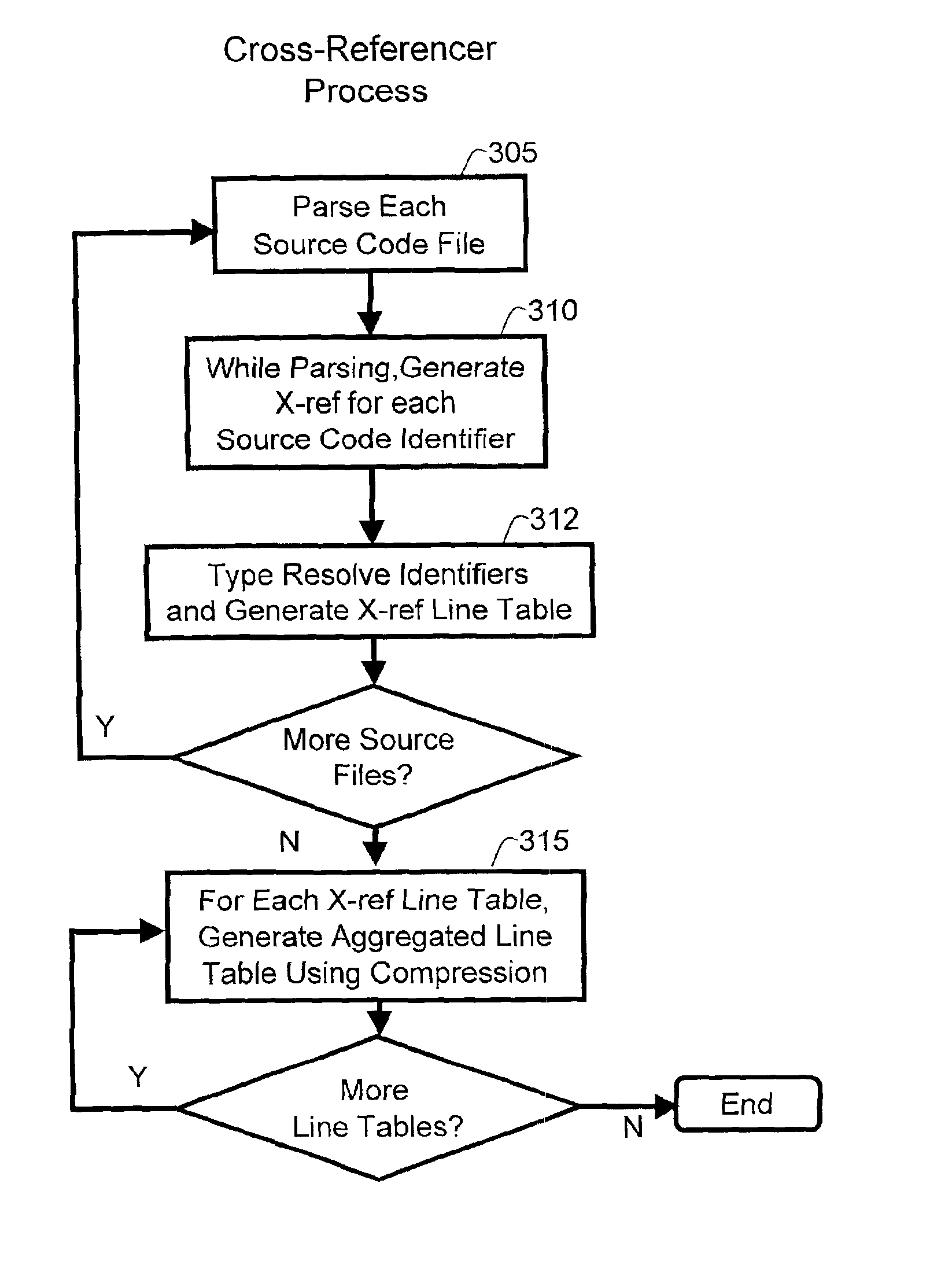
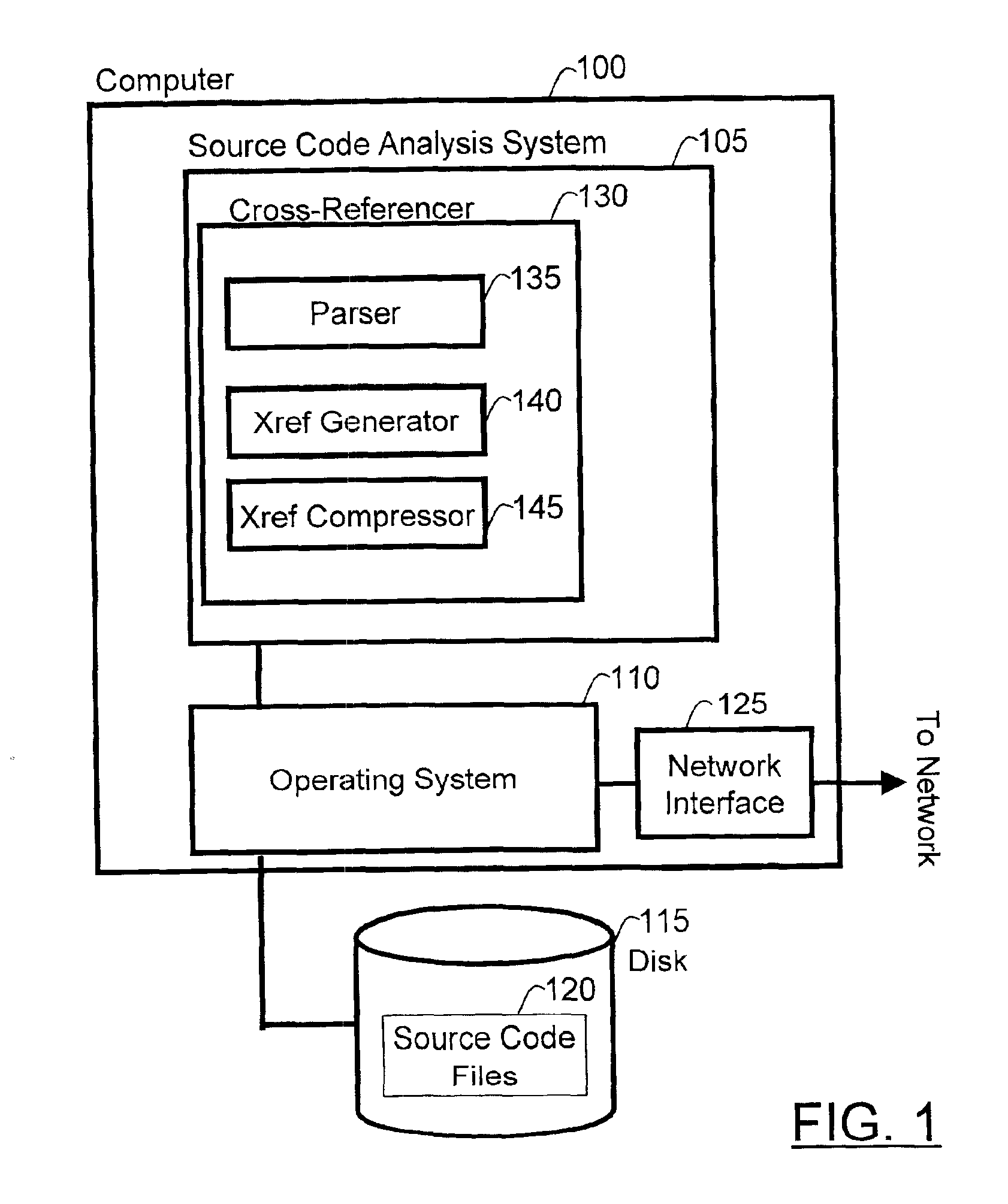
Method and data structure for compressing file-reference information
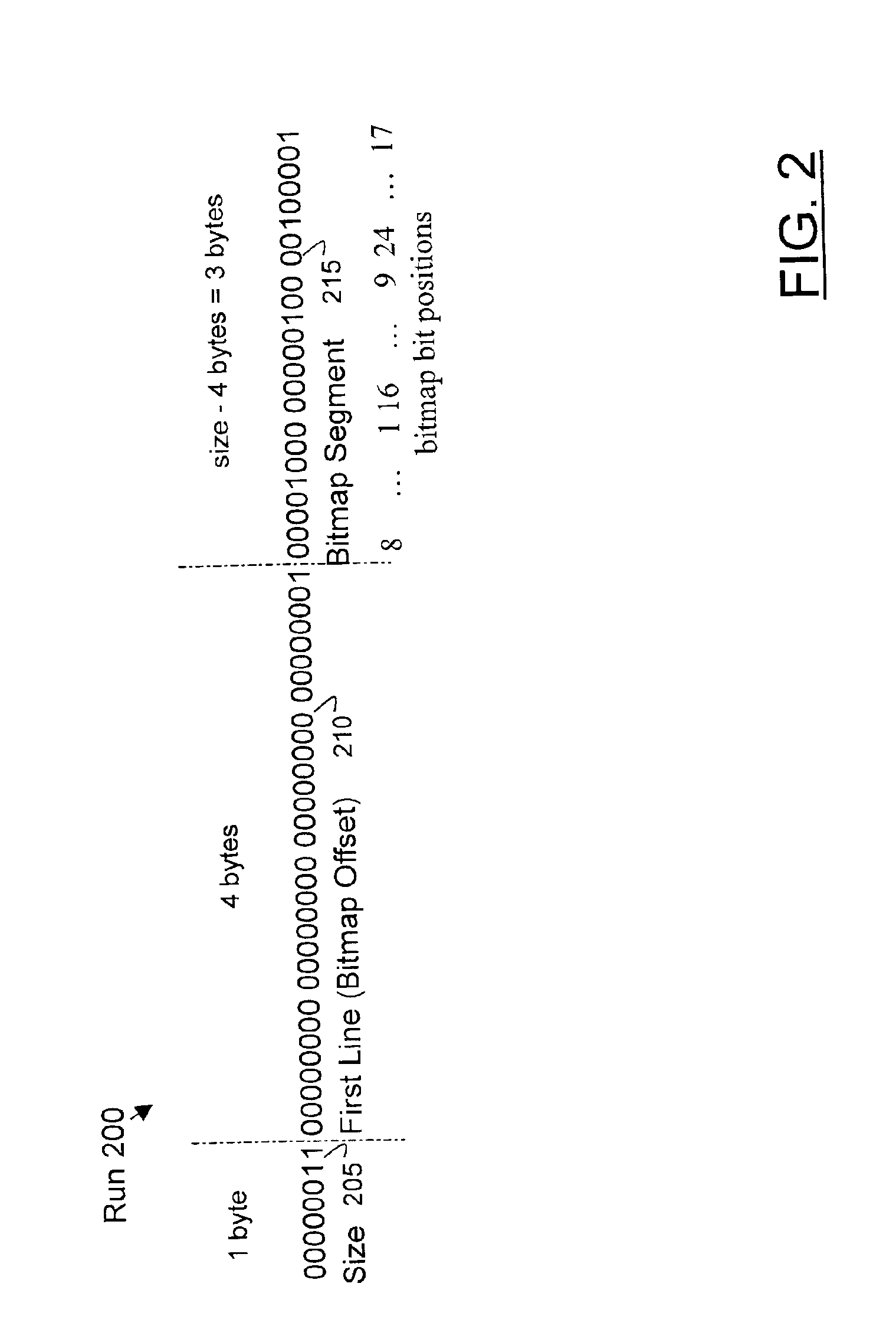
InactiveUS6886161B1Quick decompressionMinimizing delay of responseSoftware maintainance/managementProgram loading/initiatingSource code fileBitmap
Compression of local data uses various methods to encode location data (e.g. line numbers and, optionally, column numbers) representing references to a source code information symbol in a source code file. Run length encoding and other run encoding methods are used. A preferred run encoding method encodes a run-encoded bitmap comprising a set of runs, in which each run has a first run field that provides a starting line for the run, and a second run field that encodes as a bitmap the remaining lines in the run in which the reference appears. A run length field may be used to indicate the length of the second run field. Another run field may be used to encode the length of the first run field, to permit further compression.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Reversible image watermark method based on quantized DCT coefficient zero values index
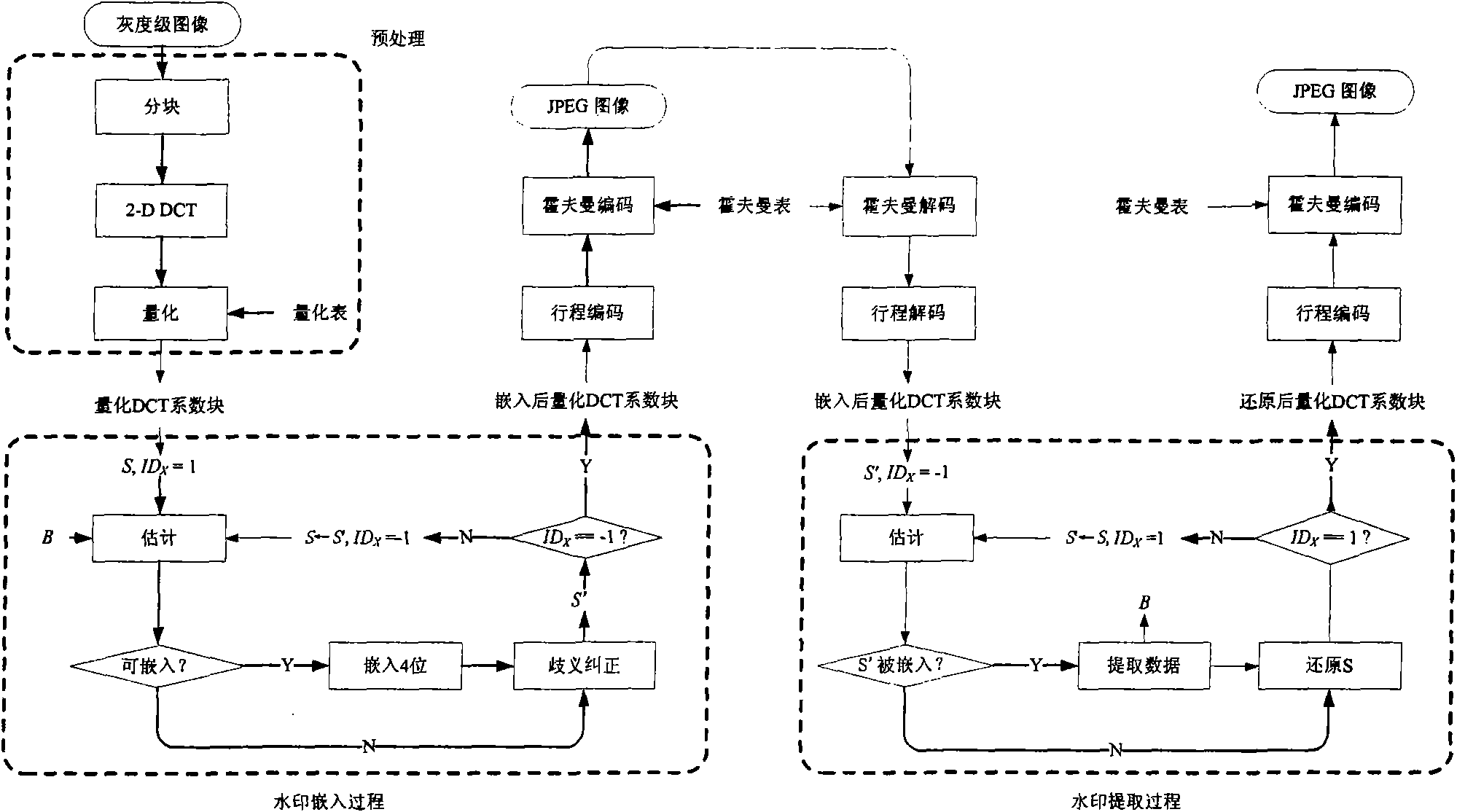
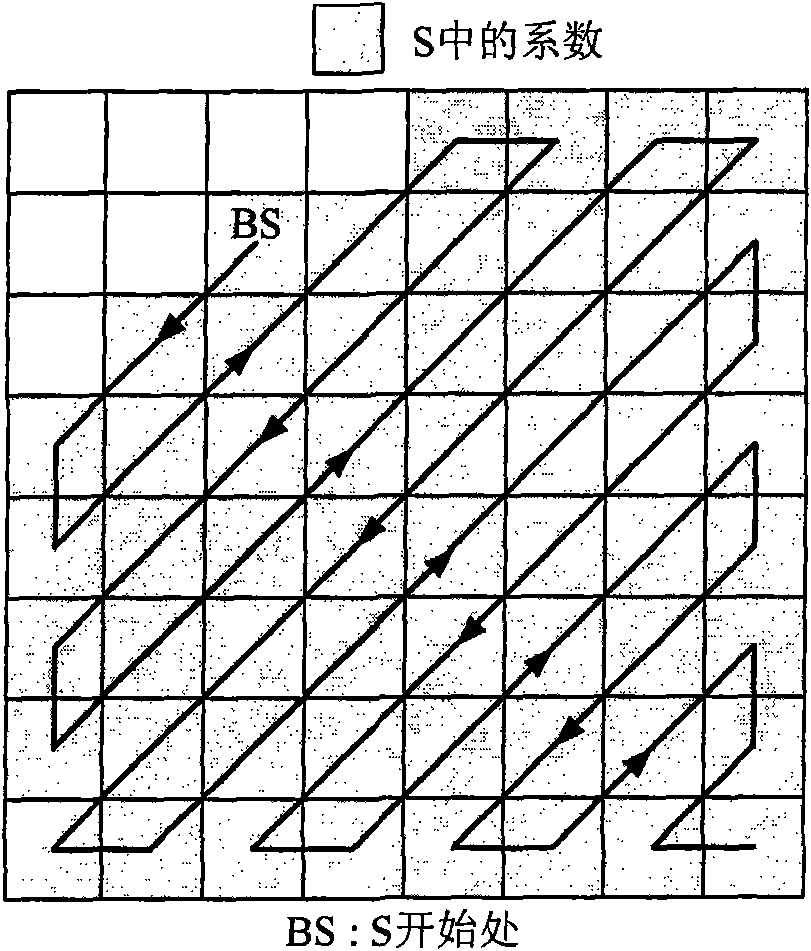
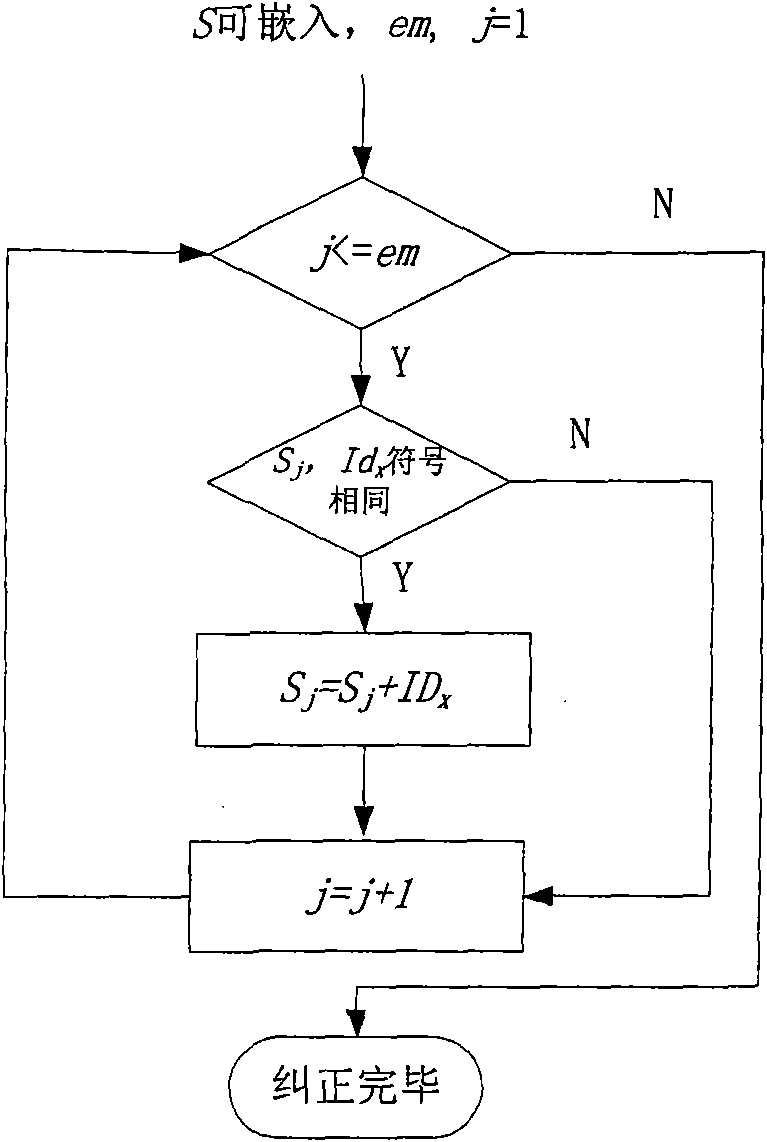
InactiveCN101572819AImprove visual qualityIncrease embedding capacityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationWatermark methodJPEG
A reversible image watermark method based on quantized DCT coefficient zero values index includes a watermark embedding process, a watermark extraction process and an image recovery process; wherein the watermark embedding can be applied in two modes: embedding is carried out during the process in which pixel image is compressed into JPEG image, or embedding is carried out in coded JPEG image. Specific embedding process aiming at mode I includes: (1) the original image is preprocessed, namely blocking (the size of block is generally 8*8), DCT transforming (discrete cosine transform) and quantization, thus obtaining quantized DCT block; (2) index value of medium-high frequency zero coefficient of the quantized DCT block is used for watermark embedding, and non zero coefficient probably generating ambiguity at extraction end is modified; (3) losses coding, such as run length coding and entropy coding, is carried out on the quantized DCT block embedded with watermark to obtain JPEG image; in the extraction process, the medium-high frequency coefficient index value of the quantized DCT block is utilized to extract watermark and recover the original image without loss by inverse operation of embedding method; the embedding and extraction process of mode II is similar. The invention has reversibility, reduces the ratio of the modified coefficient and embedded watermark digit, and can embed massive watermarks while causing less distortion.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
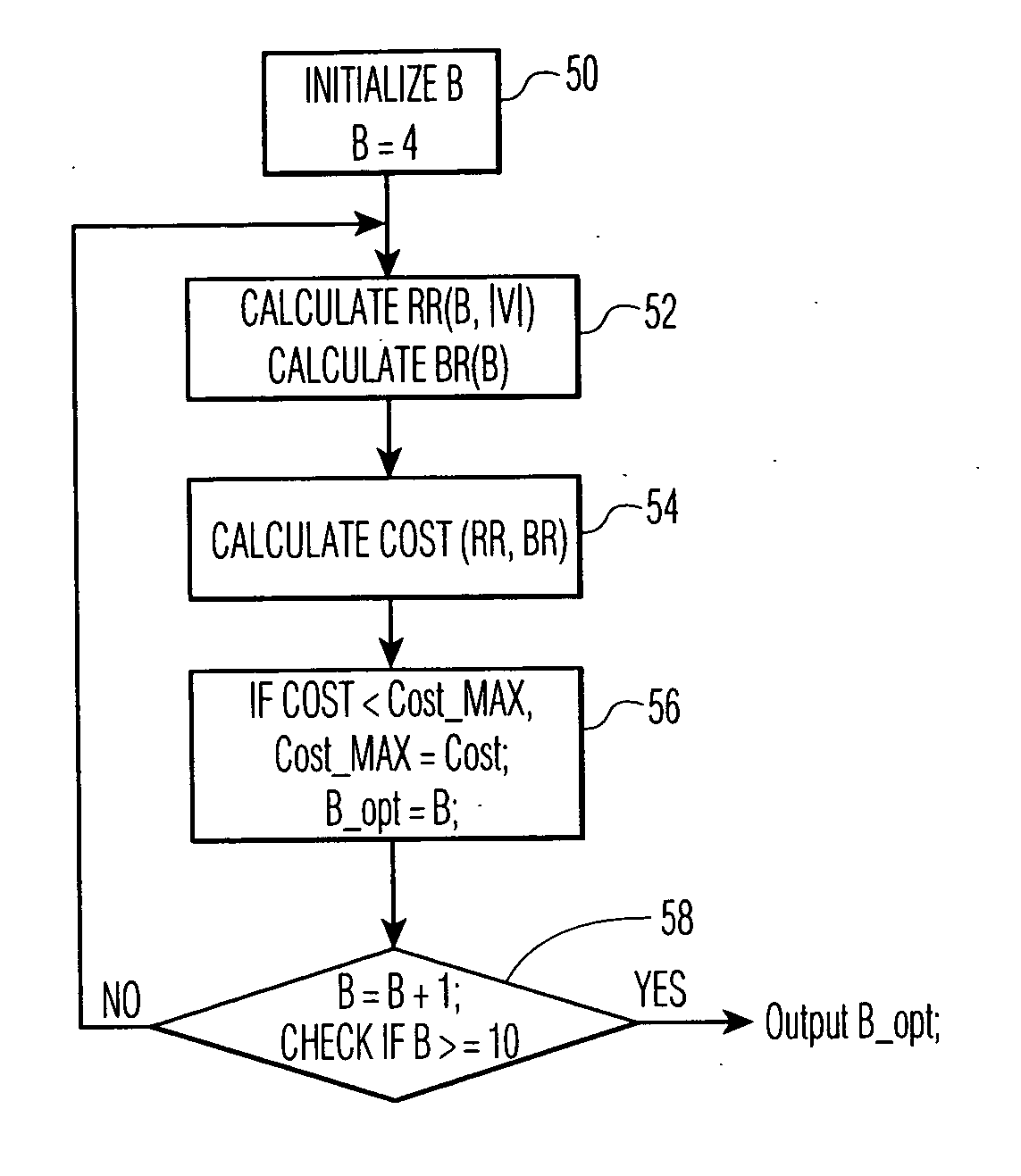
Distributed speech recognition using dynamically determined feature vector codebook size
InactiveUS20050267753A1Reduce capacityReduced ability to recognizeSpeech recognitionProximal pointSpeech identification
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
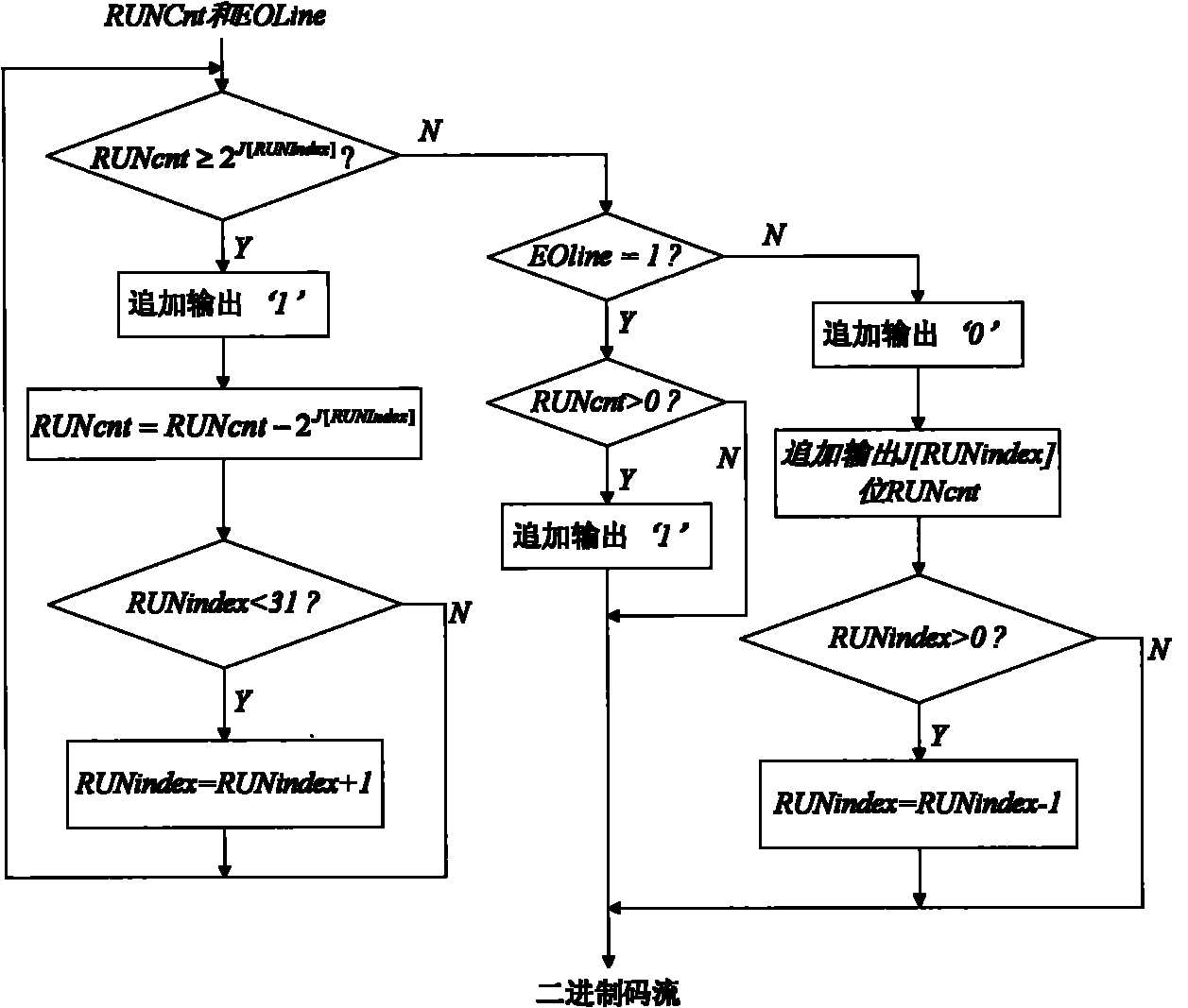
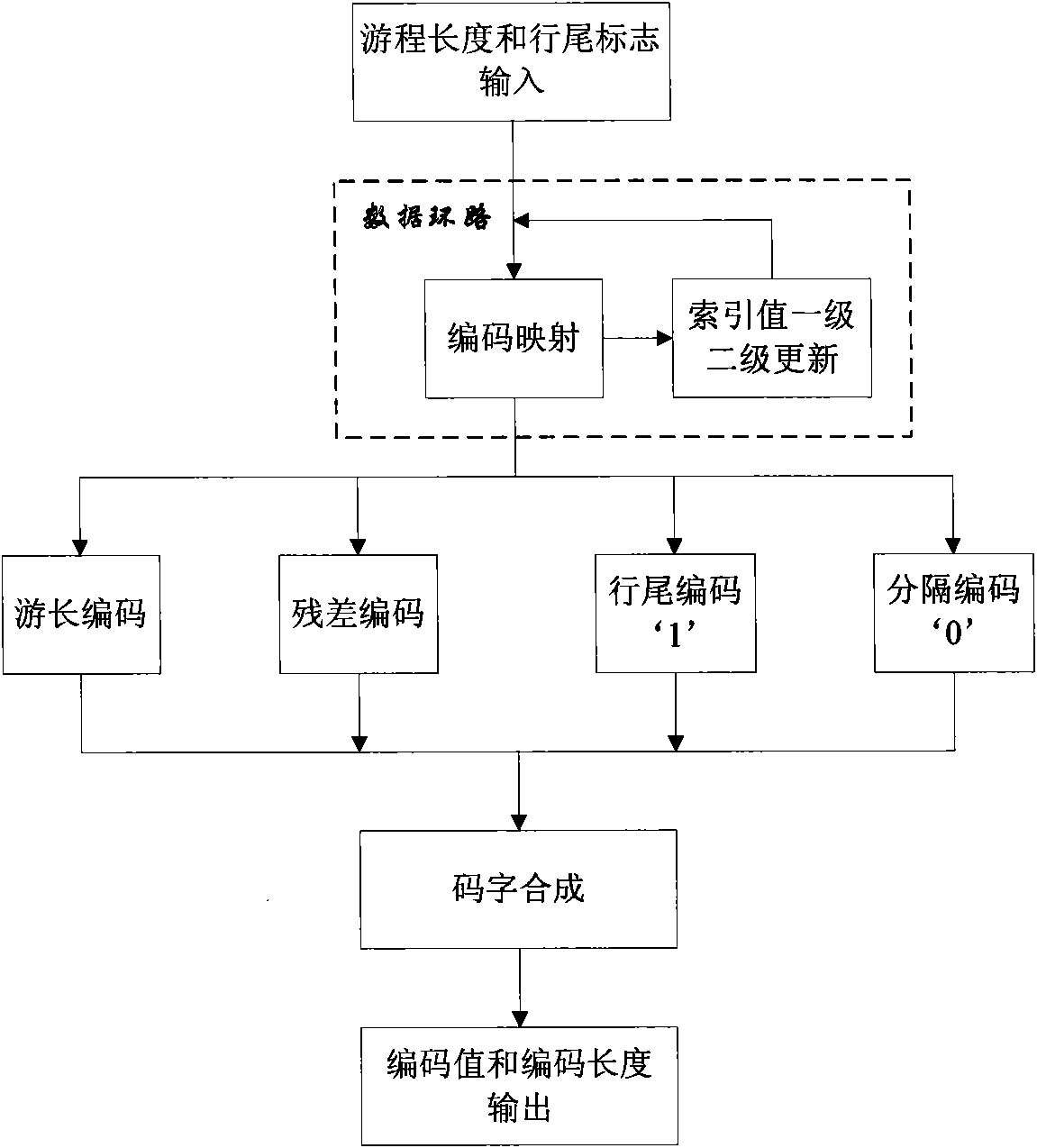
JPEG-LS run length coding hardware implementation method
InactiveCN101783953AWith full pipelineImprove real-time performanceTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationComputer architectureFpga implementations
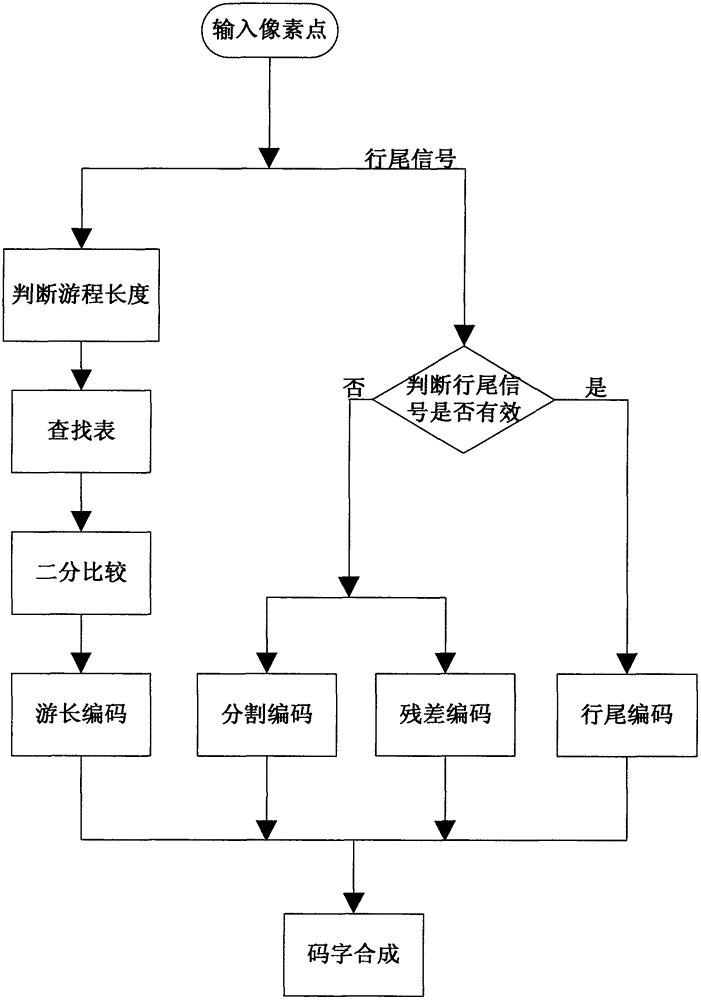
The invention discloses a JPEG-LS run length coding hardware implementation method which improves and optimizes the standard procedure of JPEG-LS run length coding, introduces coding mapping operation, implements coding by comparing a table look-up operation pipeline, and solves cycle coding in multiple clock cycles in an original algorithm; in addition, since only residual coding adopts index value RUN index single-cycle update operation and tour length coding and residual coding adopt index value RUNindex two-cycle update operation, coding speed is improved. The method is completely implemented by FPGA, has the advantages of full pipeline and good real time property, and can be applied to hardware algorithm of JPEG-LS lossless and near lossless compression.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
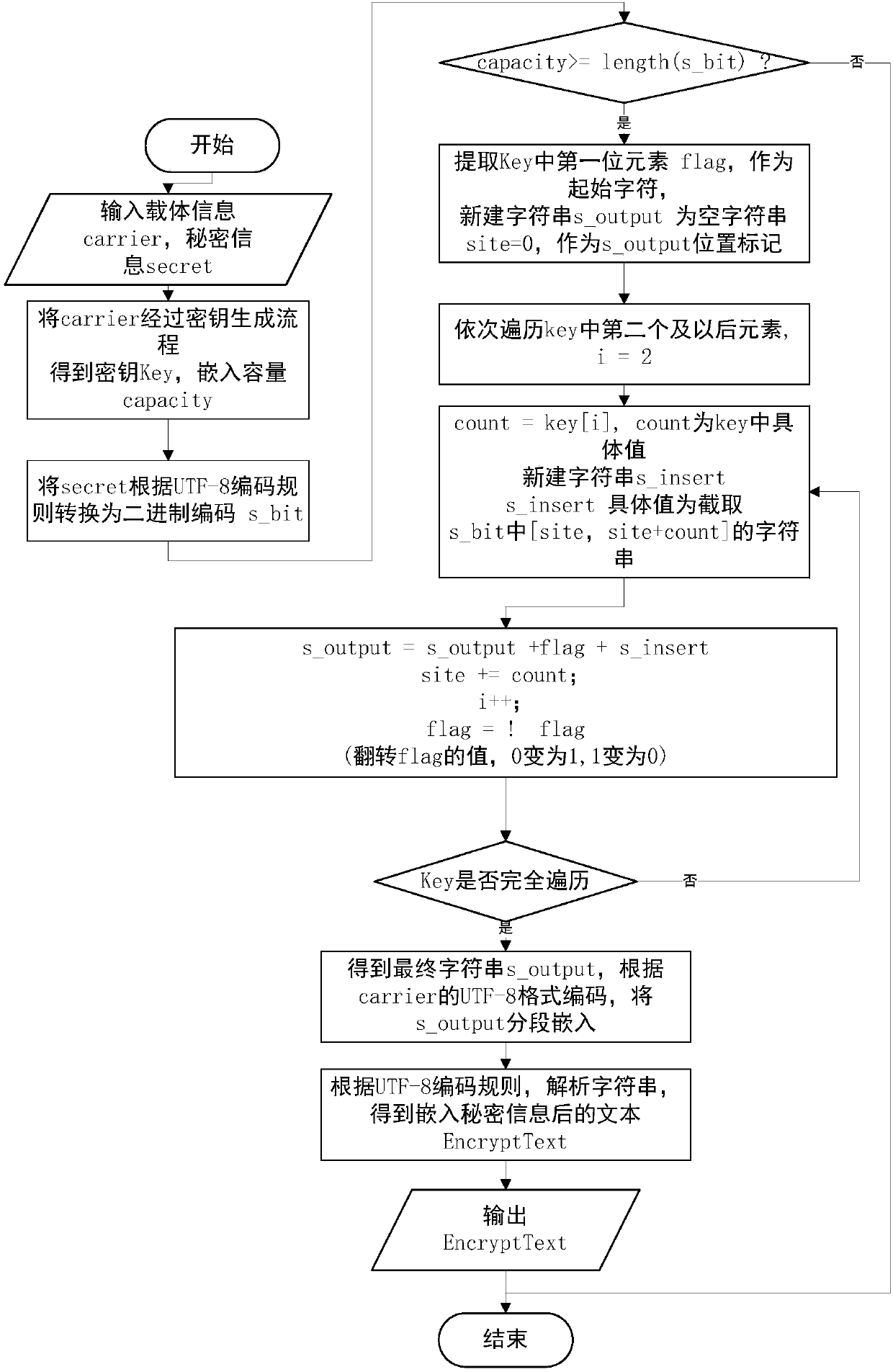
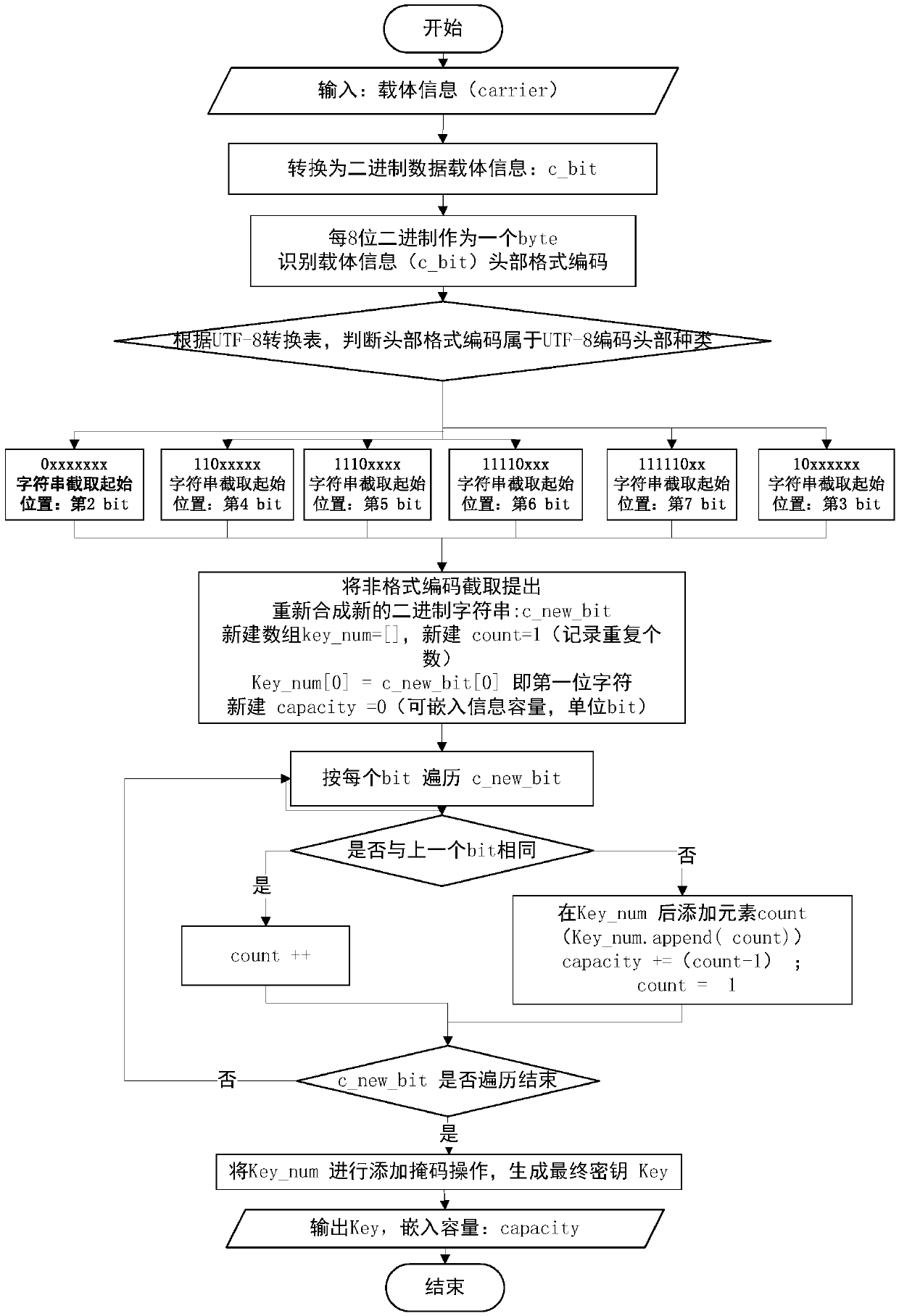
Two-dimensional code information hiding method based on run-length coding
ActiveCN109657769AAvoid the possibility of exposureImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationRecord carriers used with machinesInformation CardEncoding algorithm
The invention discloses a run length coding-based two-dimensional code information hiding method. The method comprises the following steps of: simultaneously processing carrier information carrier andsecret information set; Before a two-dimensional code is generated, embedding secret information secret to be encrypted into carrier information card through an encryption algorithm, then generatingencrypted information into a two-dimensional code image QR, and genertaing a key Key; enabling The sender to send the two-dimensional code image QR to a receiver; And after receiving the QR of the two-dimensional code image, enabling the receiver to decrypt the QR through a decryption algorithm to obtain carrier information carrier and secret information set. And compressing the text information by adopting a run-length coding algorithm to obtain bits in which information can be embedded, thereby achieving the encryption purpose of the invention. The two-dimensional code information hiding method based on run-length coding has the advantages of being large in transmitted information amount, good in information concealment, high in robustness and compression resistance, high in safety and the like.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Optimization of image encoding using perceptual weighting
ActiveUS8326067B2Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationRate distortionPerceptual weighting
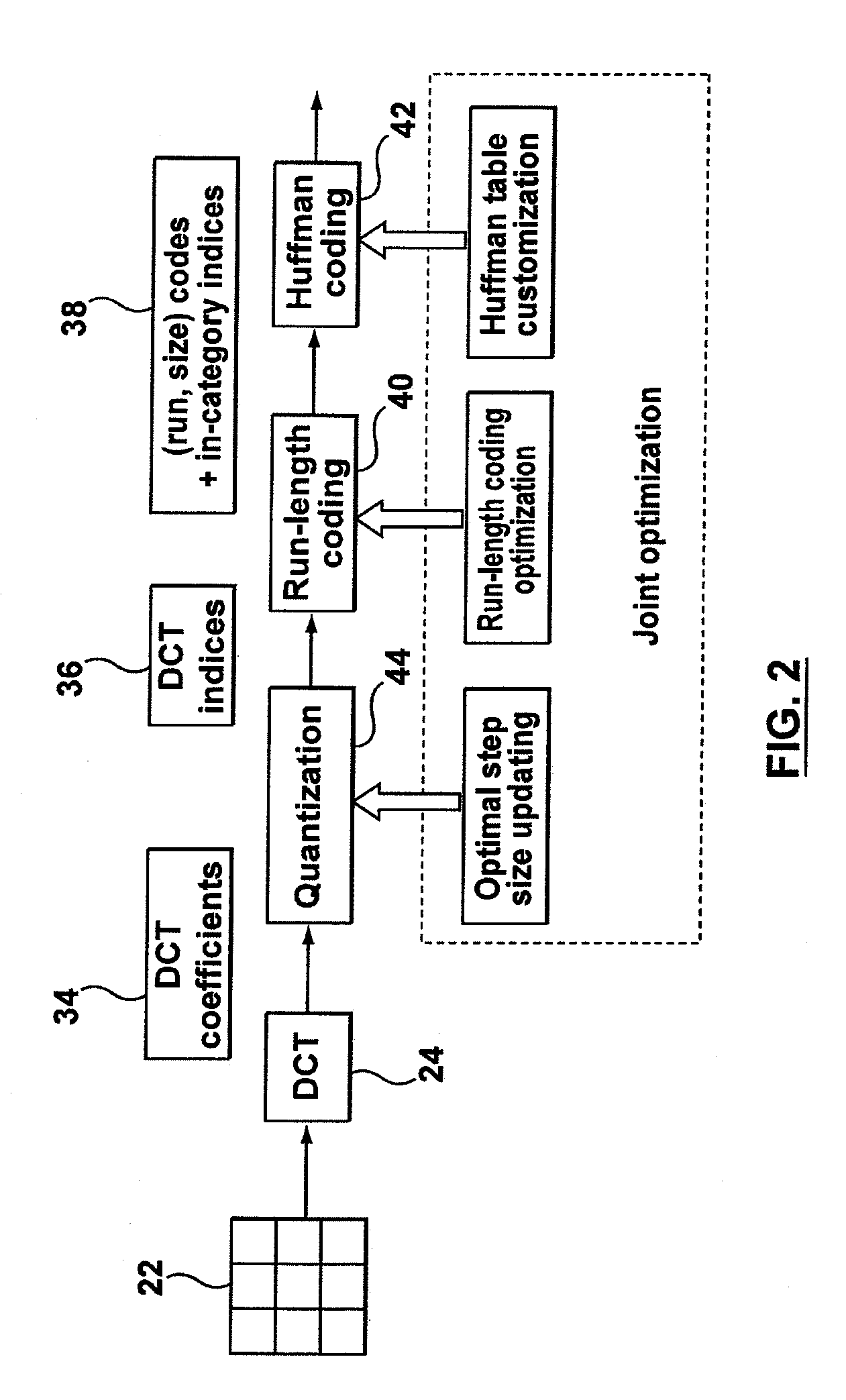
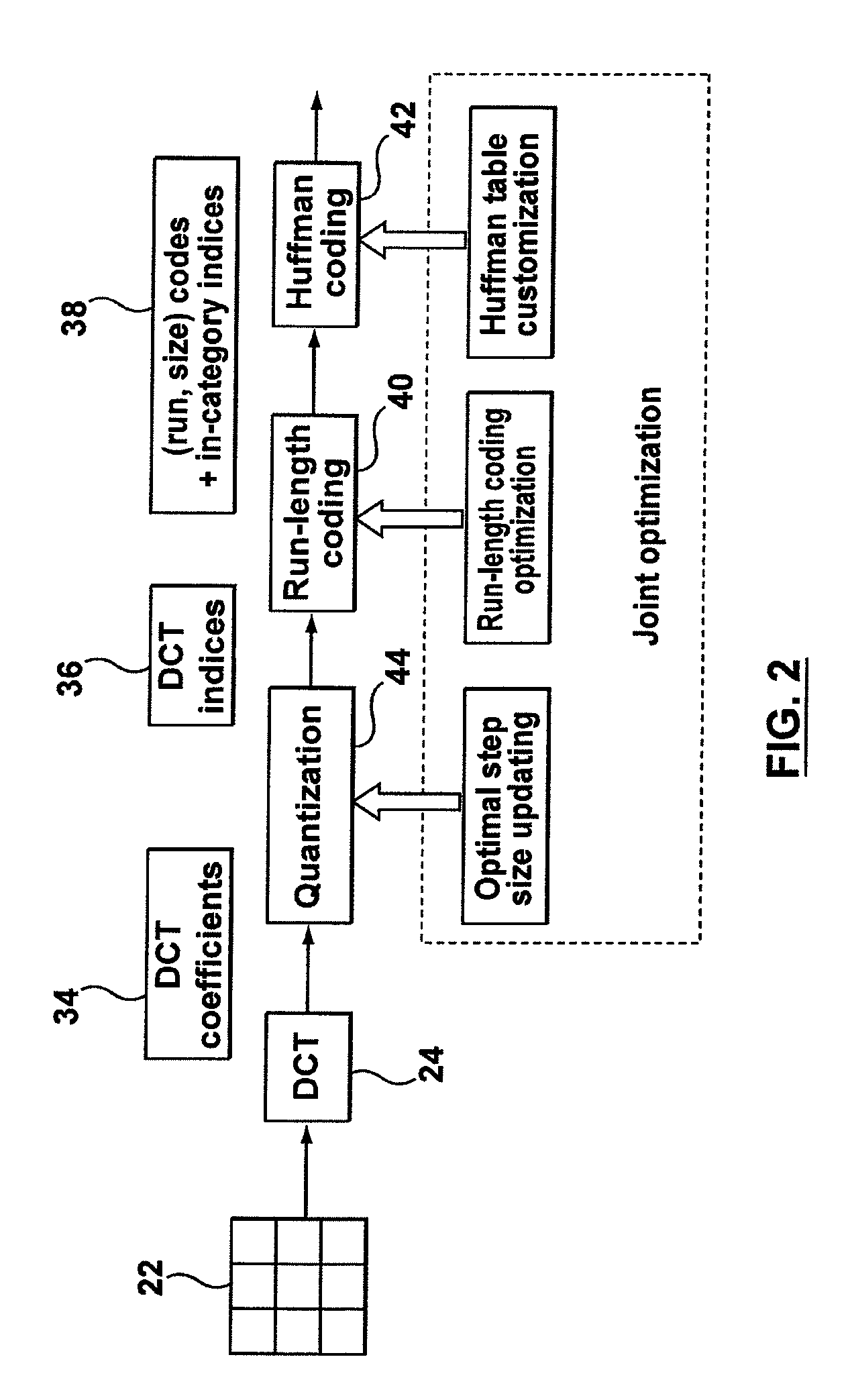
A method, system and computer program product for optimal encoding for an image defined by image data. The quantization table, run-length coding and Huffman codebook are selected to minimize a Lagrangian cost function, wherein the minimization includes iteratively determining the optimal run-size pairs and in-category indices for minimizing a rate-distortion cost function, and wherein the rate-distortion cost function includes a perceptual weighting factor applied to a quantization error. The perceptual weighting factor adjusts the rate-distortion cost function to apply greater weight to lower frequency quantization error than to higher frequency quantization error.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Run length encoding in VLIW architecture
ActiveUS8233545B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVariable-length codeVariable length
A computer implemented method of video data encoding generates a mask having one bit corresponding each spatial frequency coefficient of a block during quantization. The bit state of the mask depends upon whether the corresponding quantized spatial frequency coefficient is zero or non-zero. The runs of zero quantized spatial frequency coefficients determined by a left most bit detect instruction are determined from the mask and run length encoded. The mask is generated using a look up table to map the scan order of quantization to the zig-zag order of run length encoding. Variable length coding and inverse quantization optionally take place within the run length encoding loop.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
High-speed image compression method and device based on optimally quantized wavelet sub-band interlacing
InactiveCN102833546AReduce resource usageHigh speedTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationData streamField programmable logic devices
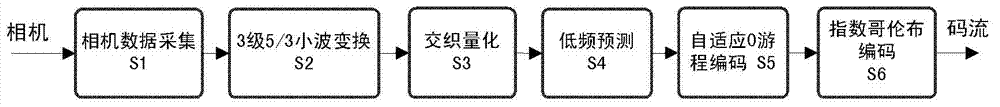
The invention relates to a high-speed image compression method based on optimal wavelet sub-band interlacing, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera data and carrying out 3-level wavelet transform on the CCD camera data; converting parallel sub-band data subjected to the wavelet transform into a sub-band interlaced serial data stream and carrying out optimal quantization; predicating quantized lowest frequency wavelet sub-band data by using a JPEG-LS (Joint Photographic Experts Group-Lossless Standard) algorithm; and carrying out run-length coding and exponential-Golomb coding on the quantized and predicated data to obtain a final code stream of an acquired image. The invention also provides a compression device. According to the image compression method and device, the whole process of image data acquisition, coding and transmission can be achieved by only using a single-chip field programmable logic device, the compression ratio can be adjusted by a quantization step and the throughput of single-channel data can reach 350 MSPS (Million Samples Per Second).
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
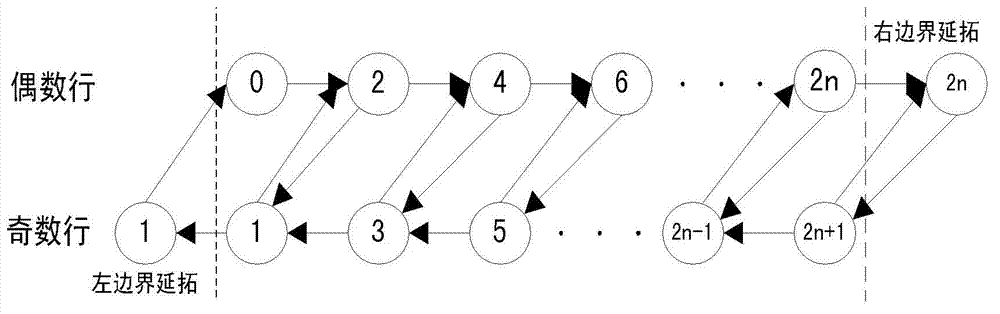
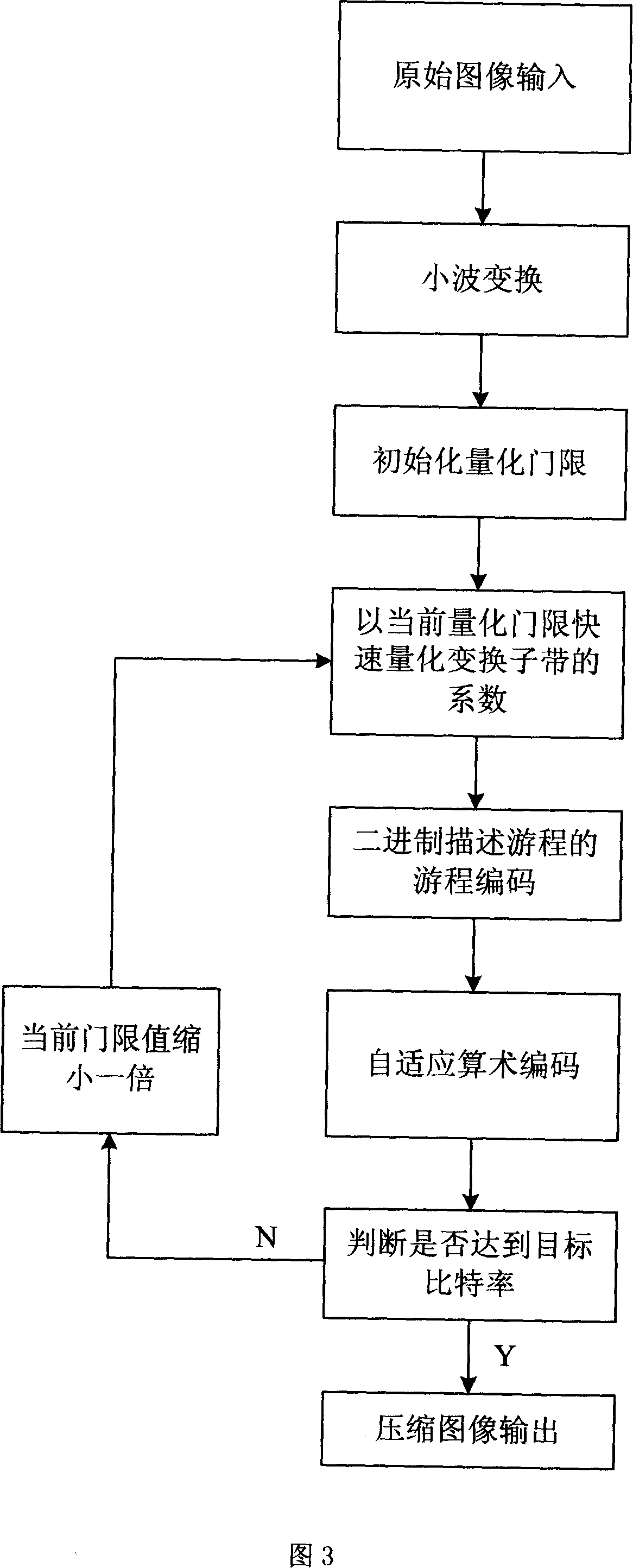
Method for implementing built-in image compression based on run-length coding
InactiveCN101132530AImprove performanceShorten the timeImage codingTelevision systemsPeak valueCompression method
This invention discloses a method for realizing inserted image compression based on travel coding including: inputting images, carrying out wavelet transformation, approaching to quantization quickly step by step and travel coding based on a binary system description and entropy coding and outputting compressed images, in which, the image coefficient after wavelet transformation is quickly quantized by setting up sub-band peak value to reduce the time necessary for approaching to quantization and increase the performance of the compression method and reduce the complexity of the method compared with many wavelet image compression methods with a zero-tree structure as the character.
Owner:ZTE CORP
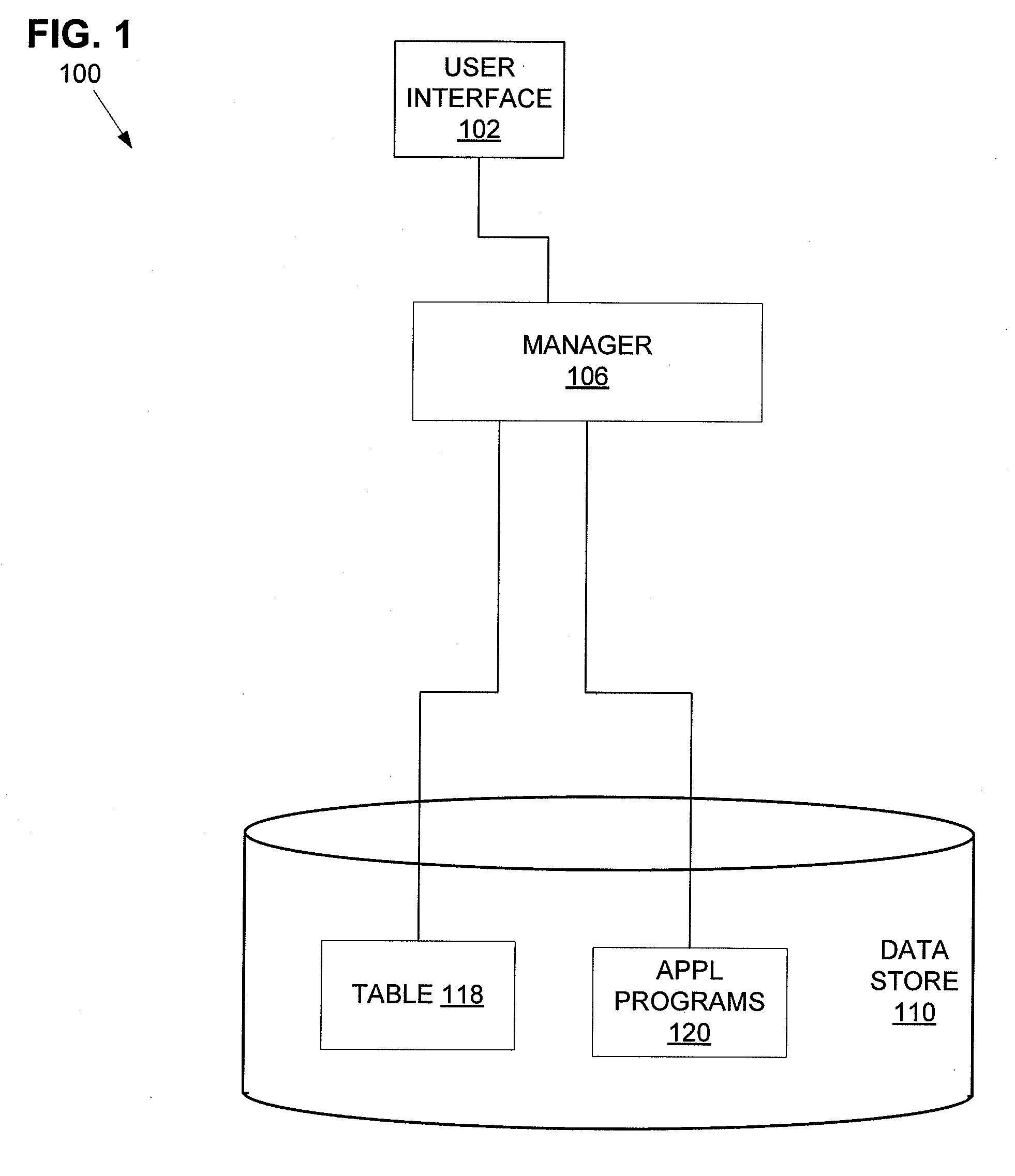
Method and System for Database Storage Management
ActiveUS20130097127A1Digital data processing detailsOther databases indexingStorage managementBitmap
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
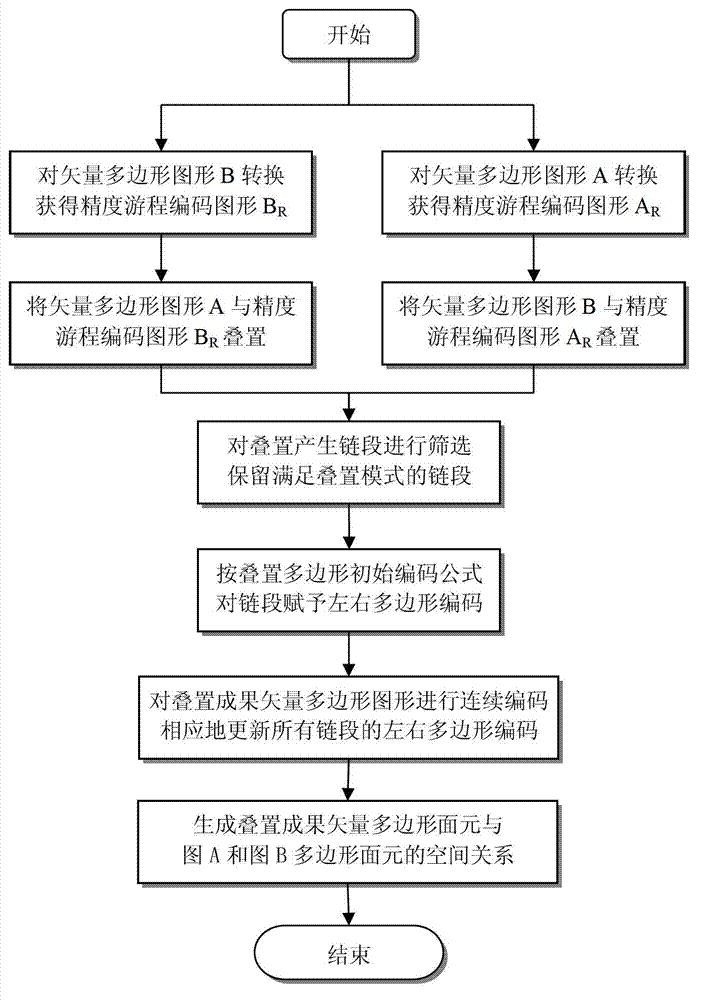
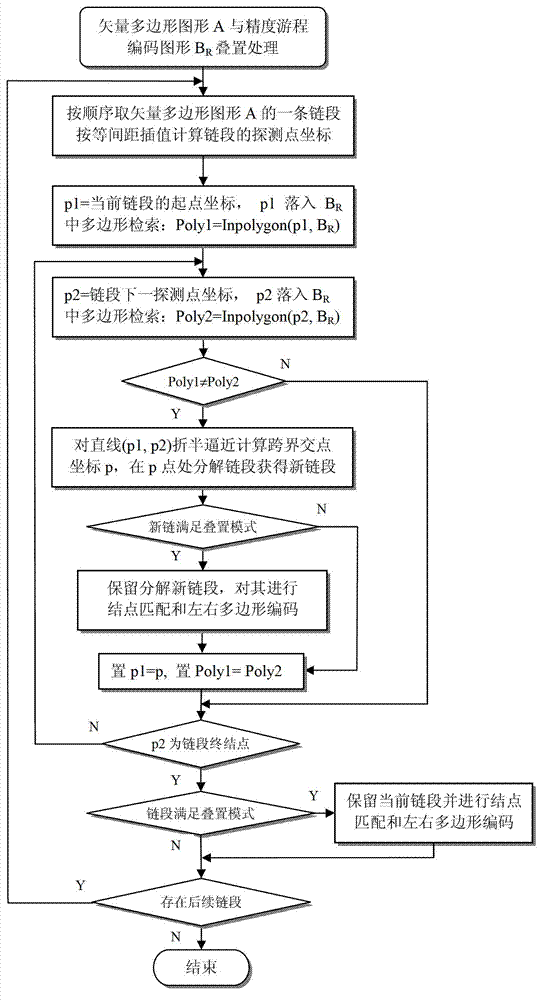
Graphic space superposition analysis drafting method of complex vector polygon
InactiveCN102902837AEasy to operateImprove robustnessSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsAlgorithm
The invention relates to a graphic space superposition analysis drafting method of a complex vector polygon, belonging to the technical field of spatial analysis drafting and spatial data mining techniques in a geographic information system. The method comprises the steps of: converting two vector polygon graphs into precision run length coding graphs; carrying out overlying transverse superposition, polygon spanning detection and decomposition on another vector polygon graphic chain segment in an interleaved mode and a mode that one of the precision run length coding graphs is used as a background base graph, so as to obtain resolved and unresolved chain segments; screening a qualified chain segment which conforms to the superposition mode to be used as a constituting chain segment of a superposition achievement vector polygon graph; and constructing the superposition achievement vector polygon graph containing a definite spatial relationship. According to the graphic space superposition analysis drafting method, the intersecting judgment of a great number of chain segments and possible misjudgment and omission which are caused by the direct superposition of vector polygon graphs are avoided, the condition for effectively establishing a new topology relationship is created, the operability, the robustness and the practicability of a vector polygon graphic spatial superposition analysis drafting technique are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Multidimensional characteristic extraction method and device based on connected domain analysis
ActiveCN106529550AHigh precisionMeet processing needsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionDomain analysis
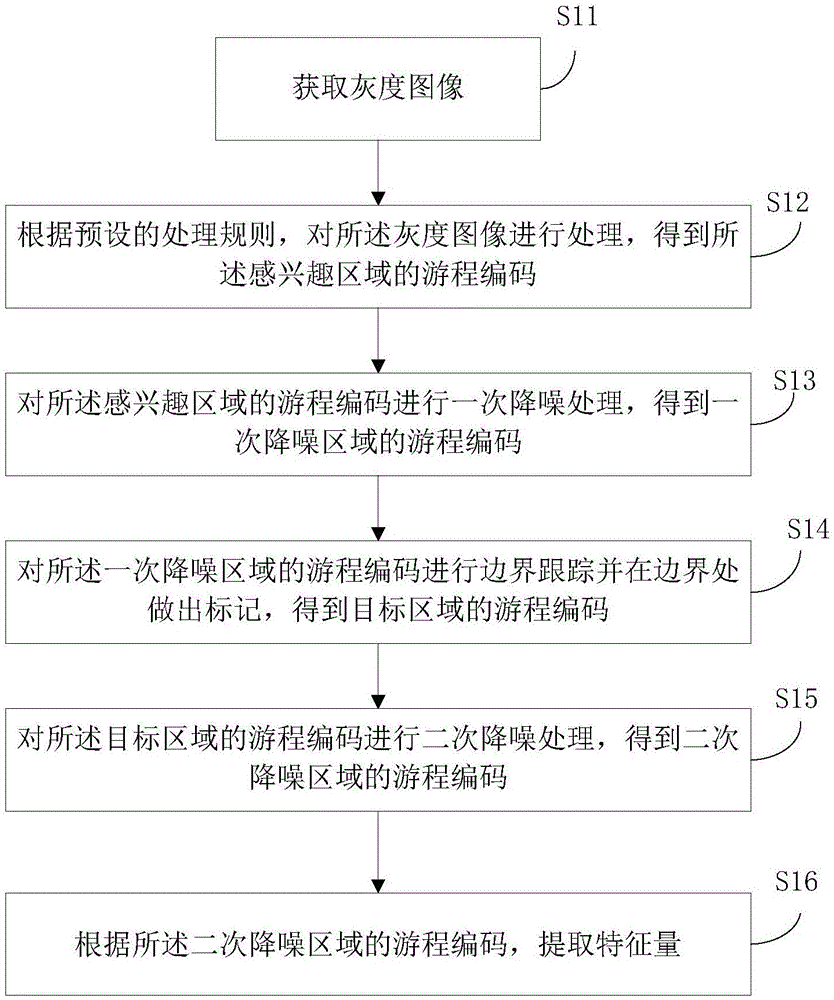
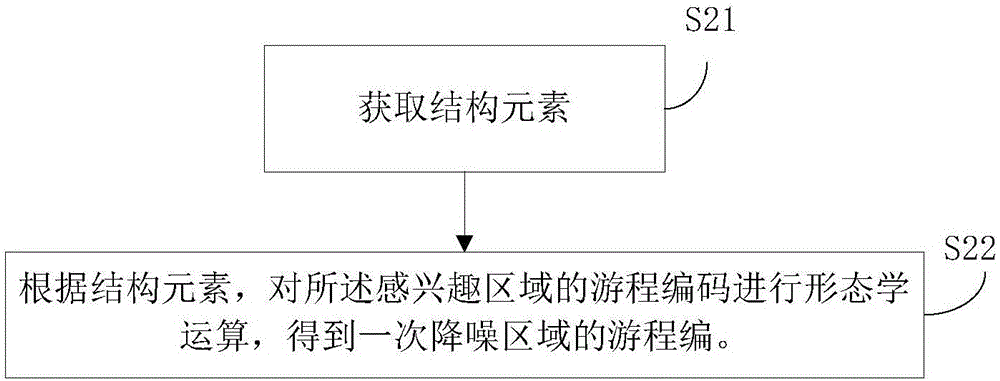
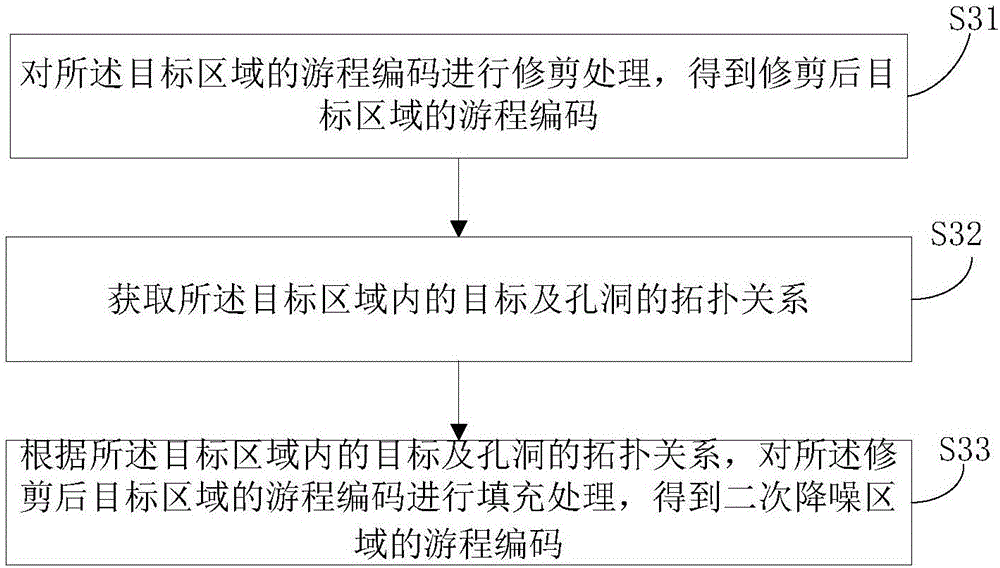
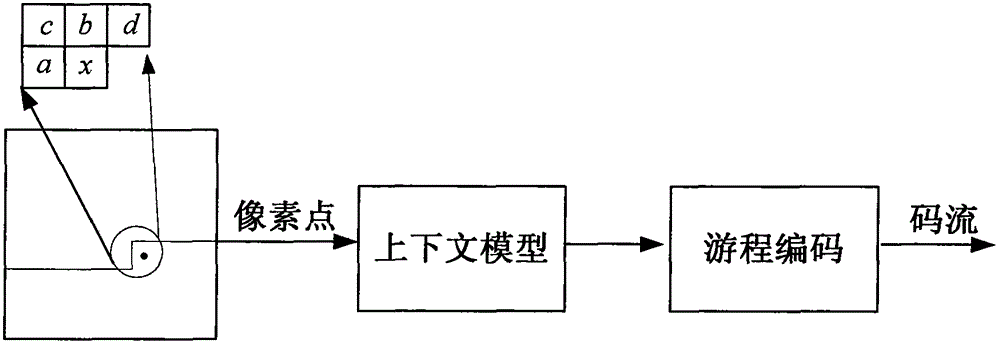
The invention discloses a multidimensional characteristic extraction method and device based on connected domain analysis. An obtained gray scale image is preprocessed to obtain a region of interest, the region of interest is subjected to first noise reduction to remove noise points, then the region of interest after the first noise reduction is subjected to boundary tracking and marking to obtain a target region, the target region is subjected to second noise reduction to remove noise blocks in the target region, and finally characteristic extraction is carried out. The accuracy of the image is improved by two times of noise reduction processing before extracting the characteristics, and the extracted characteristics are enabled to be more accurate; the gray scale image is compressed by run-length coding, and the run-length coding of the gray scale image conversion is operated in the preprocessing, two times of noise reduction and boundary tracking and connected characteristic marking of the gray scale image, so that the operation speed is improved, and processing demands of real-time images are met; and 20 characteristics can be extracted, and industrial field detection demands can be basically met.
Owner:合肥九川智能装备有限公司
Realization of rapid coding-decoding circuit with run-length
InactiveCN1779716AProcessing speedReduce the size of the implementationImage codingGraphicsComputer architecture
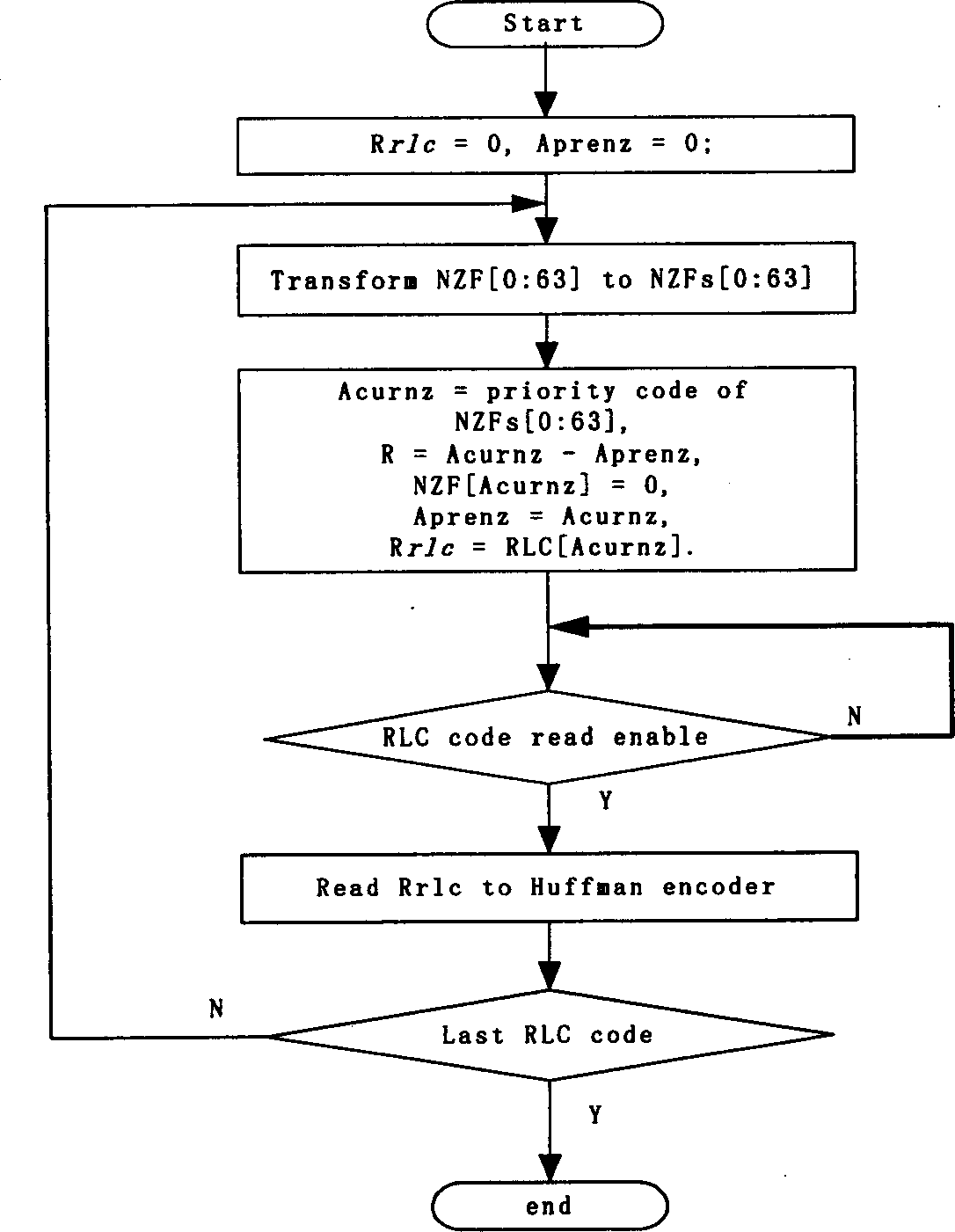
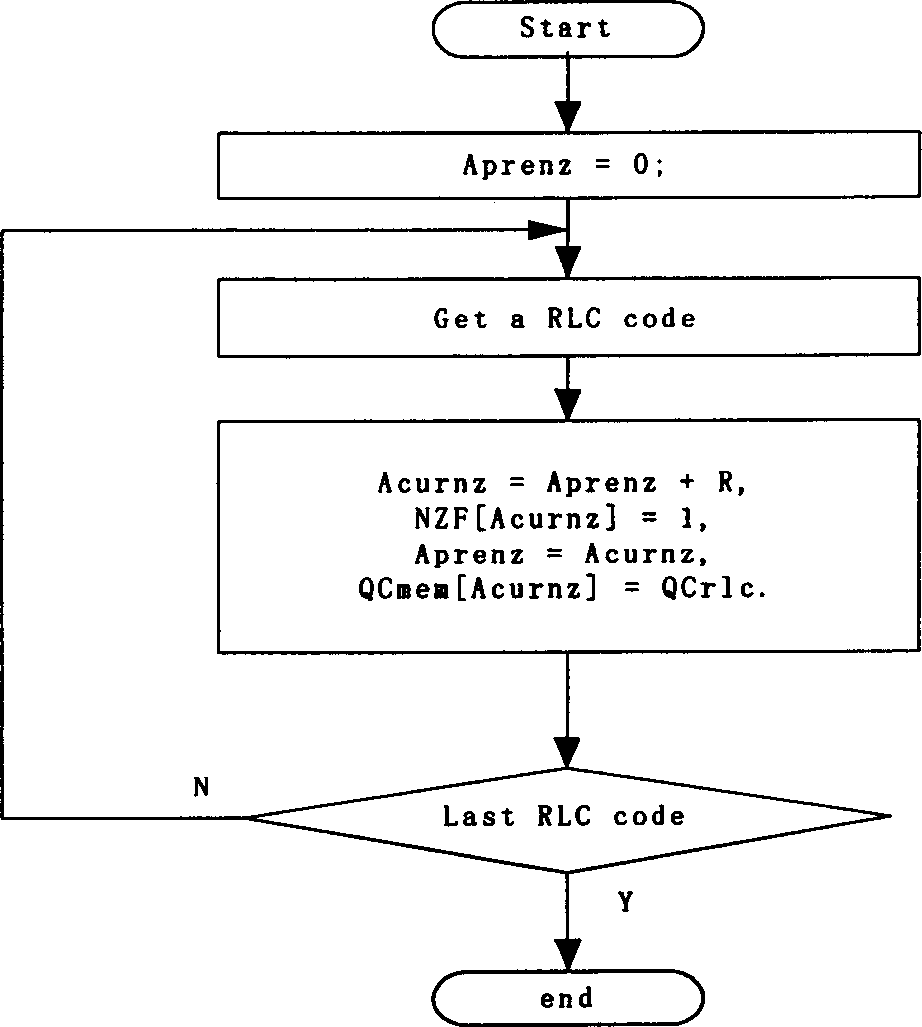
A method for realizing quick run length coding / decoding circuit includes marking nonzero coefficient while quantizing when run length is coded and finalizing real time RLC coding when Hoffman coding is carried on in system, obtaining RLC coding while finalizing counter ¿C scanning when run length is decoded and finalizing recovery of quantization coefficient when counter ¿C quantizing is carried on.
Owner:CHIPNUTS TECH INC
Efficient storage and search of word lists and other text
ActiveUS20090037371A1Maximize lengthImprove compression efficiencyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDigital dataWord list
A computer readable storage medium tangibly embodying machine-readable digital data arranged to facilitate expedited searching. The data includes a plurality of words residing in a table having rows and columns, each word residing in a different row and each letter of the word occupying a different column in that row. Each continuous run of same letters in a column forms an interval. The words are positioned relative to each other to maximize lengths of the intervals, and / or optimize efficiency of compression of the columns by run length encoding.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods and systems for rate control in image compression
ActiveUS20060078211A1Efficient compressionReduce the amount requiredCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
High-resolution video image compression transmission method and system based on FPGA
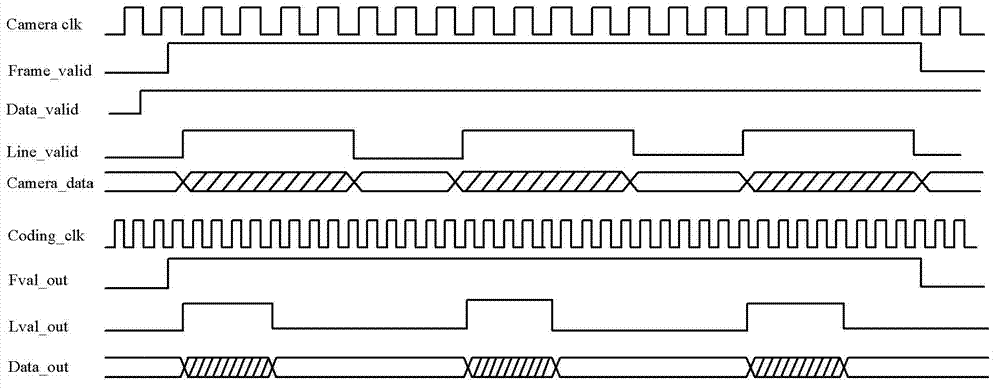
ActiveCN111726634ASave construction resourcesMeet different needsDigital video signal modificationComputer hardwareData stream
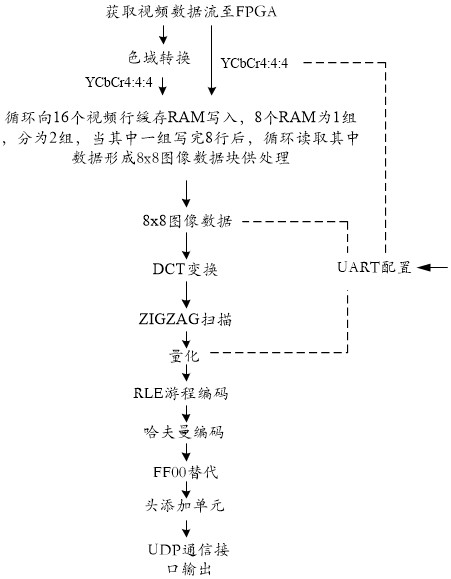
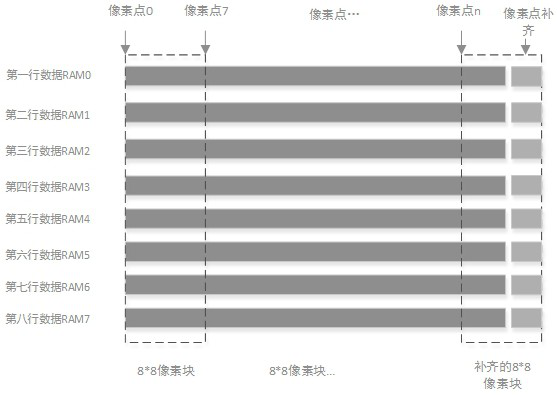
The invention discloses a high-resolution video image compression transmission method and system based on an FPGA. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a video data stream and sending the video data stream to the FPGA; obtaining a YCbCr4:4:4 format through color gamut conversion, circularly writing into 16 video row cache RAMs, dividing eight RAMs into one group and two groups, andafter each group of RAMs is written, sequentially reading data from left to right and reading eight columns each time to form an 8X8 image data block until the whole group of data is completely read;performing DCT transform, ZIGZAG scanning, quantification, RLE run length coding and Huffman coding sequentially on the 8*8 image data blocks until all the 8 rows of data are processed according to the 8*8 image data blocks, and if the number of points of the last block is smaller than 8 pixels, performing corresponding complementation; and completing compression until the processing of the wholeframe of image is finished. The system comprises an FPGA, and the FPGA comprises video data stream input, write RAM control, a video cache RAM, 8*8 block generation, DCT, ZIGZAG scanning, quantification, RLE run length coding, Huffman coding and the like. The high-resolution video image compression is realized by only using the single FPGA, so that the data volume is greatly reduced.
Owner:CHENGDU FOURIER ELECTRONICS TECH +1
Variable length encoding method and device
InactiveCN101198056AReduce the compression rateImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioCode conversionTelevision systemsVariable-length codeSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
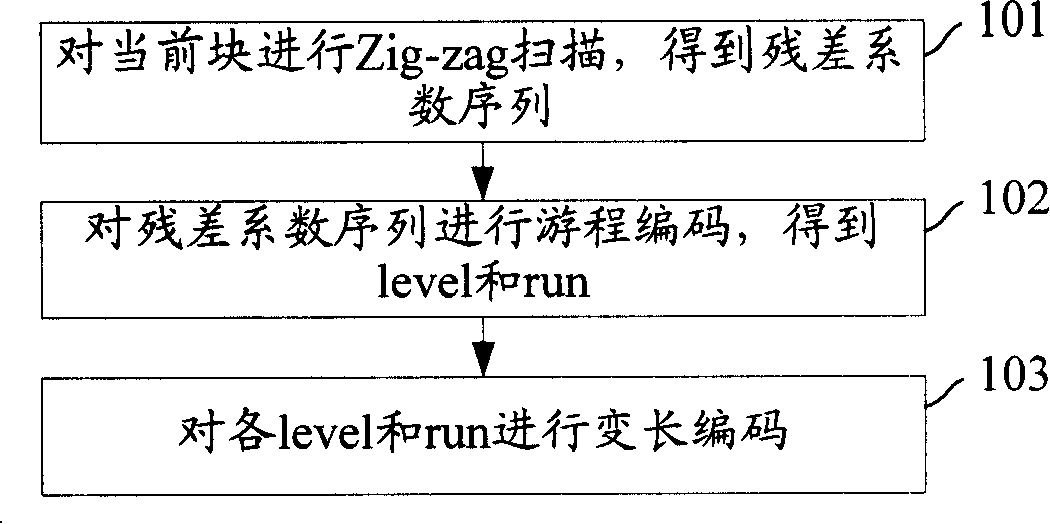
The invention discloses a variable length coding method which comprises the following steps: residual coefficient sequences of input data blocks are obtained; run length coding of the residual coefficient sequences is performed; after a level sequence and a run sequence are obtained, run length coding of the level sequence and the run sequence is performed, and then variable length coding of two run length code word pairs obtained is respectively performed. The invention simultaneously discloses a variable length coding device which comprises a pretreatment module and a variable length coding module. The invention further utilizes characteristic information of levels which are 1 in the level sequence and characteristic information of runs which are 0 in the run sequence and has the advantages of reduction of compressed code rate and improvement of peak signal-to-noise ratio. The invention can be applied in various coders and simultaneously also can be completely compatible with prior international H.264 standard and domestic AVS standard.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
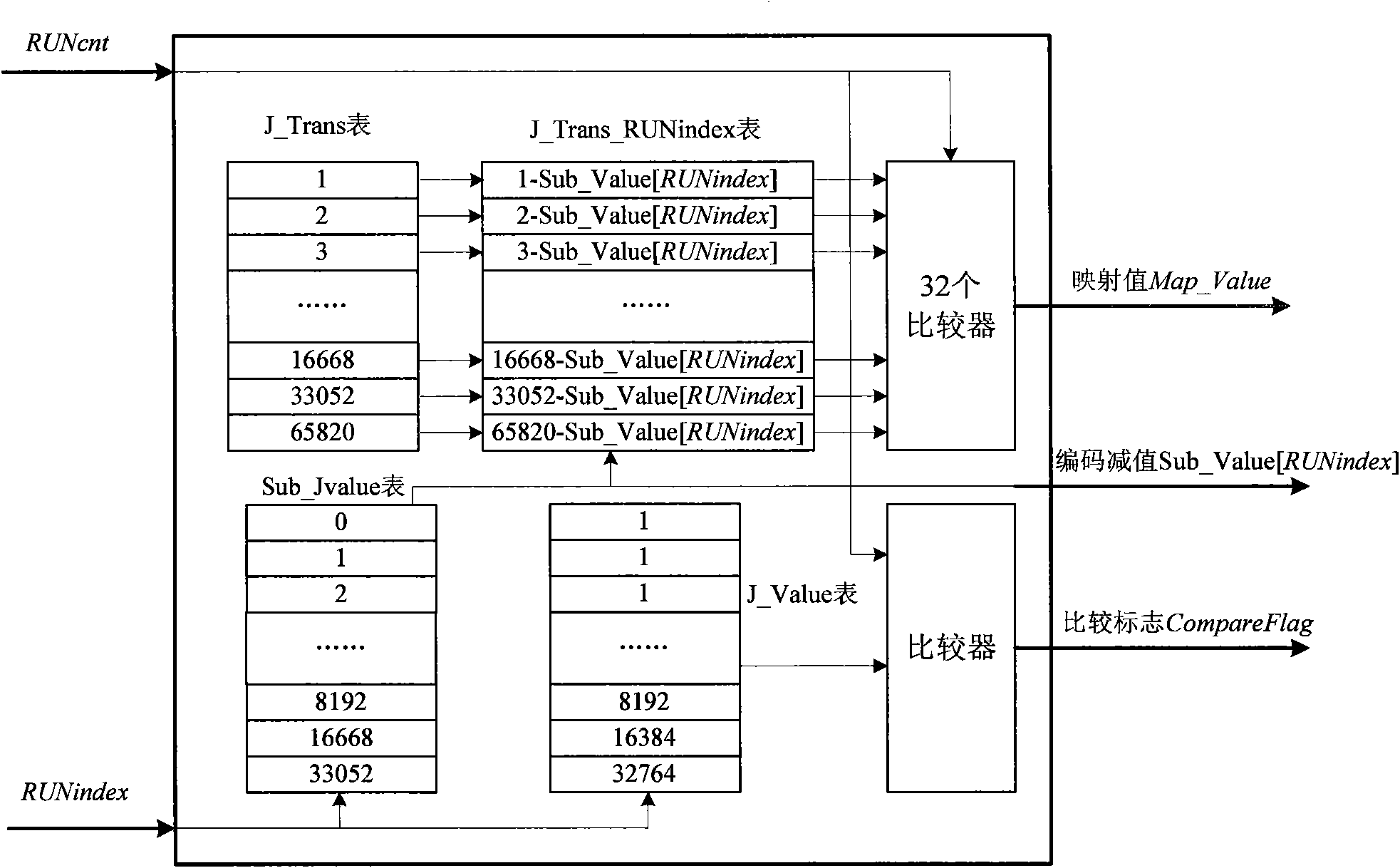
Run-length coding FPGA (field programmable gate array) implementing method in JPEG-LS (joint photographic experts group-lossless standard)
InactiveCN102724505ASpeed up the compression processThe loop structure is simpleTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationArray data structureFpga implementations
The invention discloses a run-length coding FPGA (field programmable gate array) implementing method in a JPEG-LS (joint photographic experts group-lossless standard). The method includes: on the basis of a JPEG-LS implementing method, setting up, storing and looking up a mapping table according to index values so as to obtain an accumulated sum array, comparing run lengths with values in the accumulated sum array for five times according to a binary comparison method so as to obtain cycle indexes to achieve run-length coding, and simply and effectively achieving index value updating in two steps. By the method, the problem of complex updating structures of the index values is solved, run-length coding is achieved in short period, a mapping table structure is simplified by accumulated operations, and hardware resources are saved. Besides, a fully-pipelined structure is adopted, hardware resource consumption is less, and the method is real-time and easy to implement a field programmable gate array.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Efficient storage and search of word lists and other text
ActiveUS20070250469A1Facilitate expedited searchingMaximize lengthData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDigital dataWord list
A computer readable storage medium tangibly embodying machine-readable digital data arranged to facilitate expedited searching. The data includes a plurality of words residing in a table having rows and columns, each word residing in a different row and each letter of the word occupying a different column in that row. Each continuous run of same letters in a column forms an interval. The words are positioned relative to each other to maximize lengths of the intervals, and / or optimize efficiency of compression of the columns by run length encoding.
Owner:TEGIC COMM +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com