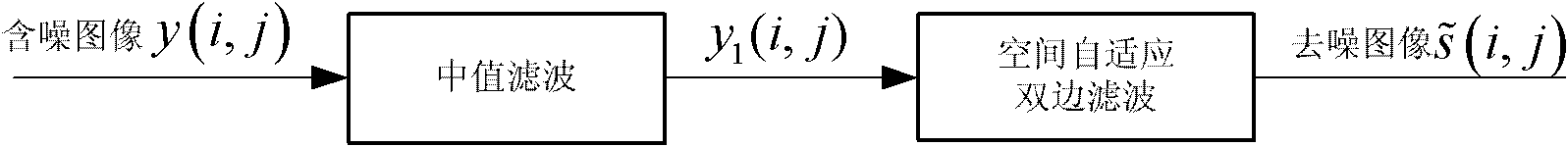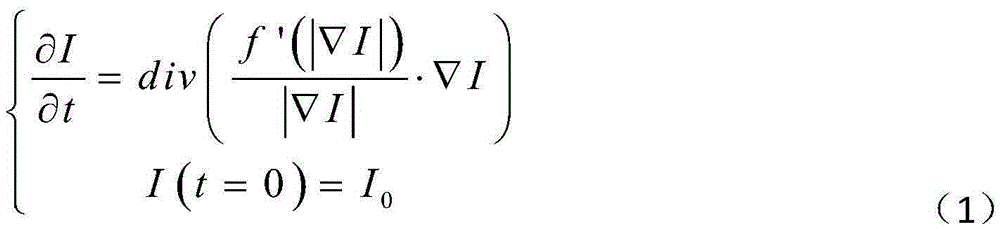Patents
Literature
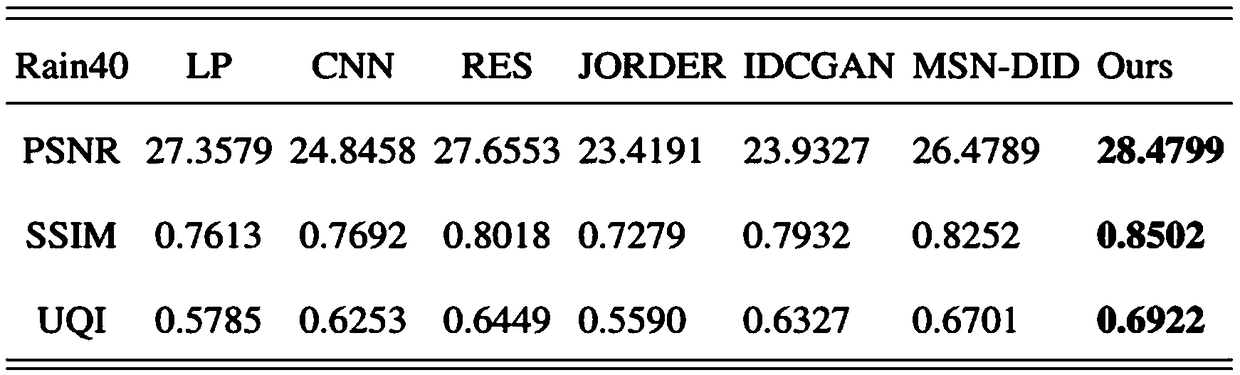
287results about How to "Improve peak signal-to-noise ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
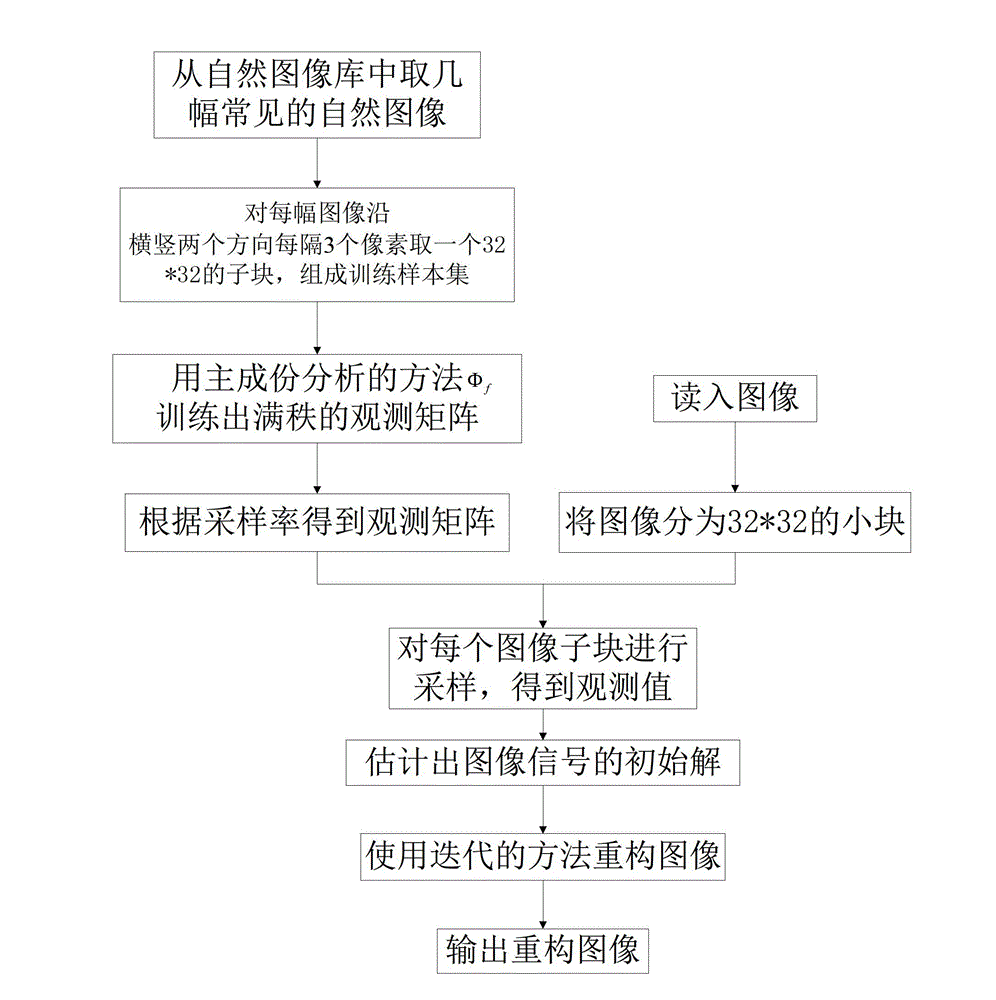
Adaptive compressed sensing-based non-local reconstruction method for natural image
InactiveCN102722896AValid reservationKeep information2D-image generationPattern recognitionAdaptive compression
The invention discloses an adaptive compressed sensing-based non-local reconstruction method for a natural image. The problems of serious reconstructed image information loss and the like in the prior art are mainly solved. The method is implemented by the steps of: (1) dividing an image into N 32*32 sub-blocks, obtaining a basic sensing matrix Phi' according to a basic sampling rate b and a sensing matrix Phi, and sampling a signal by utilizing Phi' to obtain a basic observation vector; (2) estimating a standard deviation sequence {d1, d2, ..., and dN} of the image according to the basic observation vector; (3) adaptively allocating a sampling rate ai for each sub-block according to the standard deviation sequence {d1, d2, ..., and dN}, and constructing an adaptive sensing matrix, and sampling the signal by utilizing the adaptive sensing matrix to obtain an adaptive observation vector; (4) forming an observation vector of each sub-block by using the basic observation vector and the adaptive observation vector; (5) obtaining an initial solution x0 of the image according to the observation vector; and (6) performing iteration by using x0, and reconstructing the original image until consistency with a finishing condition is achieved to obtain a reconstructed image x'. The method has the advantages of high image reconstruction quality, clear principle and operational simplicity, and is applied to the sampling and reconstruction of the natural image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Single-frame rainfall removing method based on multi-scale feature fusion
ActiveCN109360155AGood effect in removing rainUniversalImage enhancementNeural architecturesPeak valueError function
The invention provides a single frame image rain removing method based on multi-scale feature fusion, Feature extraction of rainless images with different scale receptive fields, then deconvolution operation to get the result of rainless images, using the combination of coarse-scale features and fine-scale features, to promote the rainless images generated by fine-scale to achieve the best effectof rainless. By removing rainlines on multiple scales, the algorithm can be used in a variety of rainwater situations, and the rainout algorithm is more universal. The invention cites the antagonisticerror and the perceptual error to construct a new error function, and trains the rain removing model without any prior knowledge, and does not need to preprocess and post-process the image, thus ensuring the integrity of the whole structure. The results on a plurality of test sets show that the invention can improve the peak signal-to-noise ratio on the luminance signal channel by 2-5dB.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method of quickly eliminating composite noise in images
ActiveCN101860667AImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioEasy to handleImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
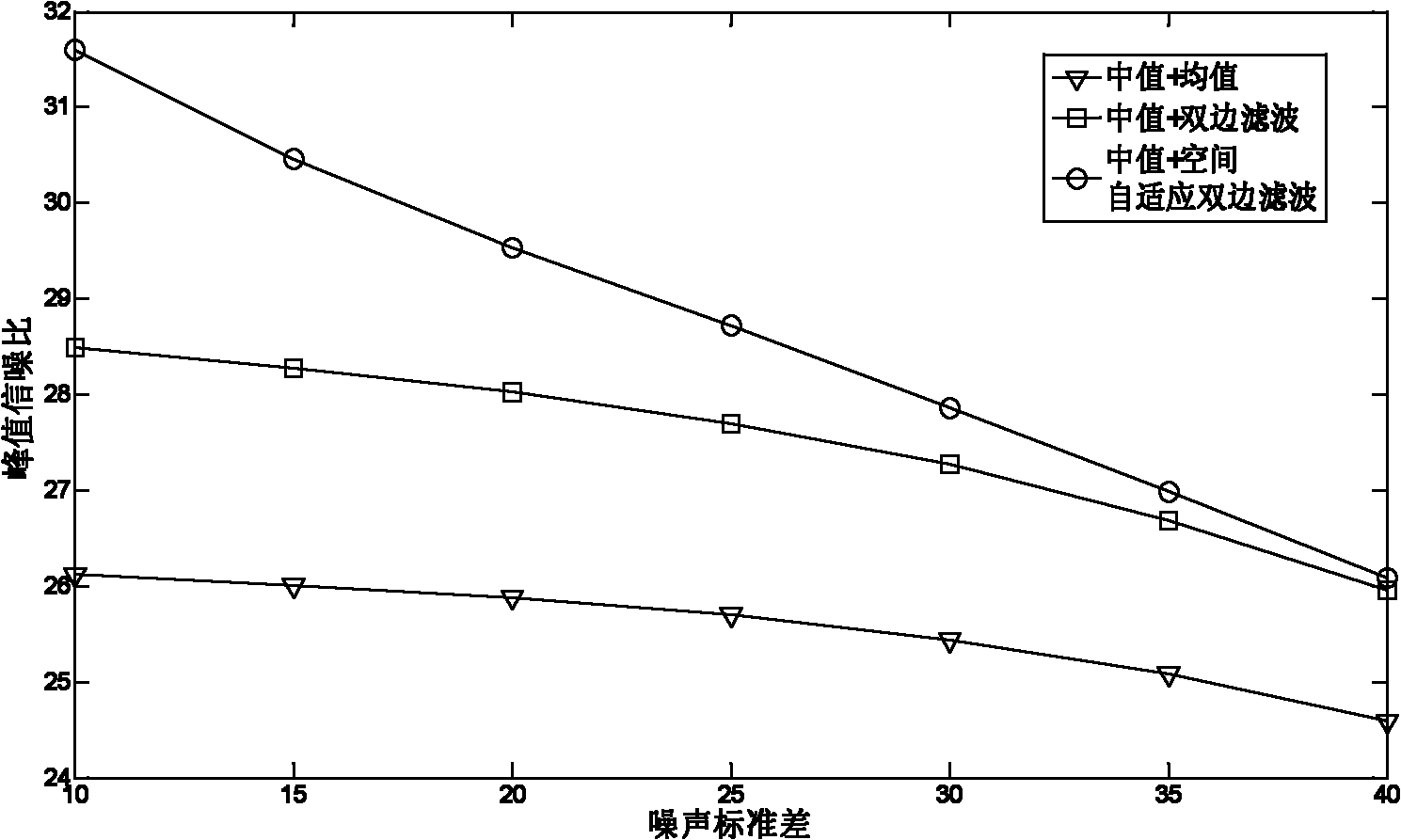
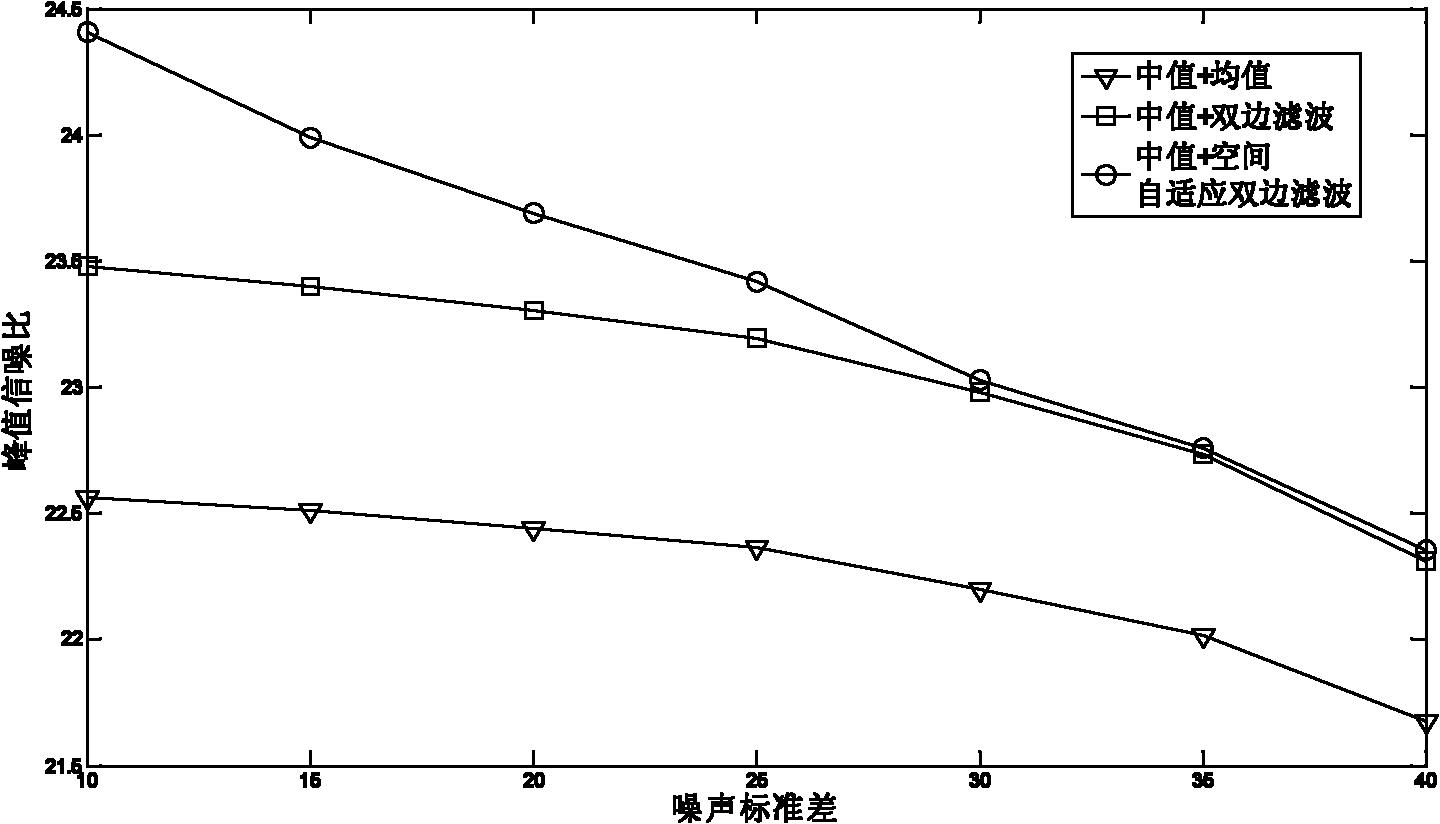
The invention discloses a method of quickly eliminating composite noise in images, which can eliminate salt and pepper noise and Gaussian noise at the same time, improve the peak signal to noise ratio(PSNR) of the images and obtain more clear images. The main technical idea comprises the following steps: the median of the images containing noise is filtered to obtain the images the salt and pepper noise of which is eliminated and space self-adaption two-sided filter is carried out on the images the salt and pepper noise of which is eliminated to obtain the images the Gaussian noise of which is eliminated, i.e. the final noise-free images. The calculation, data processing of the algorithm of the invention is definitely adapted to the real-time image quick process. The technical flow can be adjusted according to concrete application and requirement.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
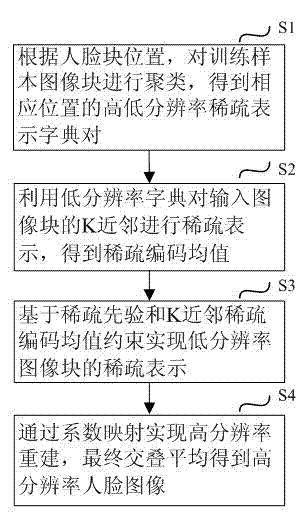
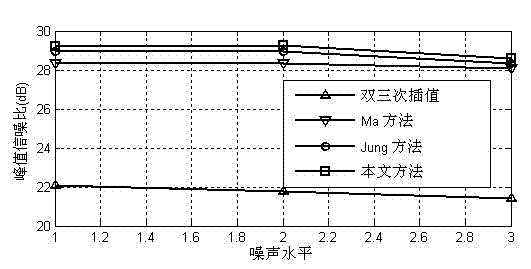
Face super-resolution processing method based on K neighbor sparse coding average value constraint
ActiveCN102902961AReduce mean square errorImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionLow resolution
The invention discloses a face super-resolution processing method based on K neighbor sparse coding average value constraint, relating to the technical field of image resolution processing, in particular to a face super-resolution processing method based on K neighbor sparse coding average value constraint. The method comprises the following steps of: according to prior information of the position of a face block, clustering image blocks of a training sample to obtain a pair of high-and-low-resolution sparse representation dictionaries in relevant positions; performing sparse representation on K neighbor of the input image block with the low-resolution dictionary, thus obtaining sparse coding average values; and realizing the sparse representation of a low-resolution image block based on sparse prior and K neighbor sparse coding average value constraint, realizing the reconstruction of a high-resolution image block through coefficient mapping, and finally overlapping and averaging to obtain a high-resolution face image. According to the method, on the basis of keeping the similarity of the reconstructed face image, the definition of the face image is improved, and the quality of the super-resolution image is enhanced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
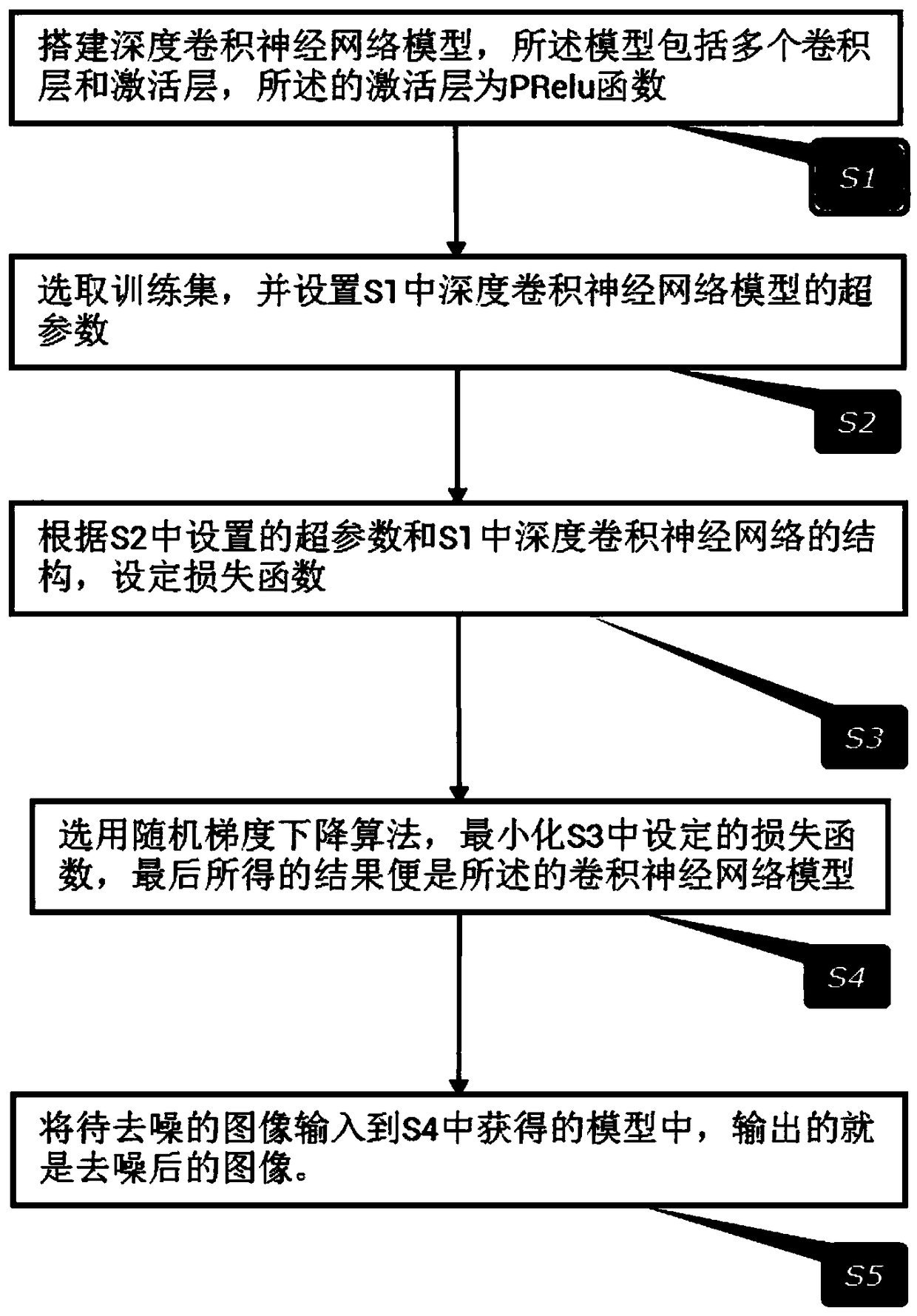
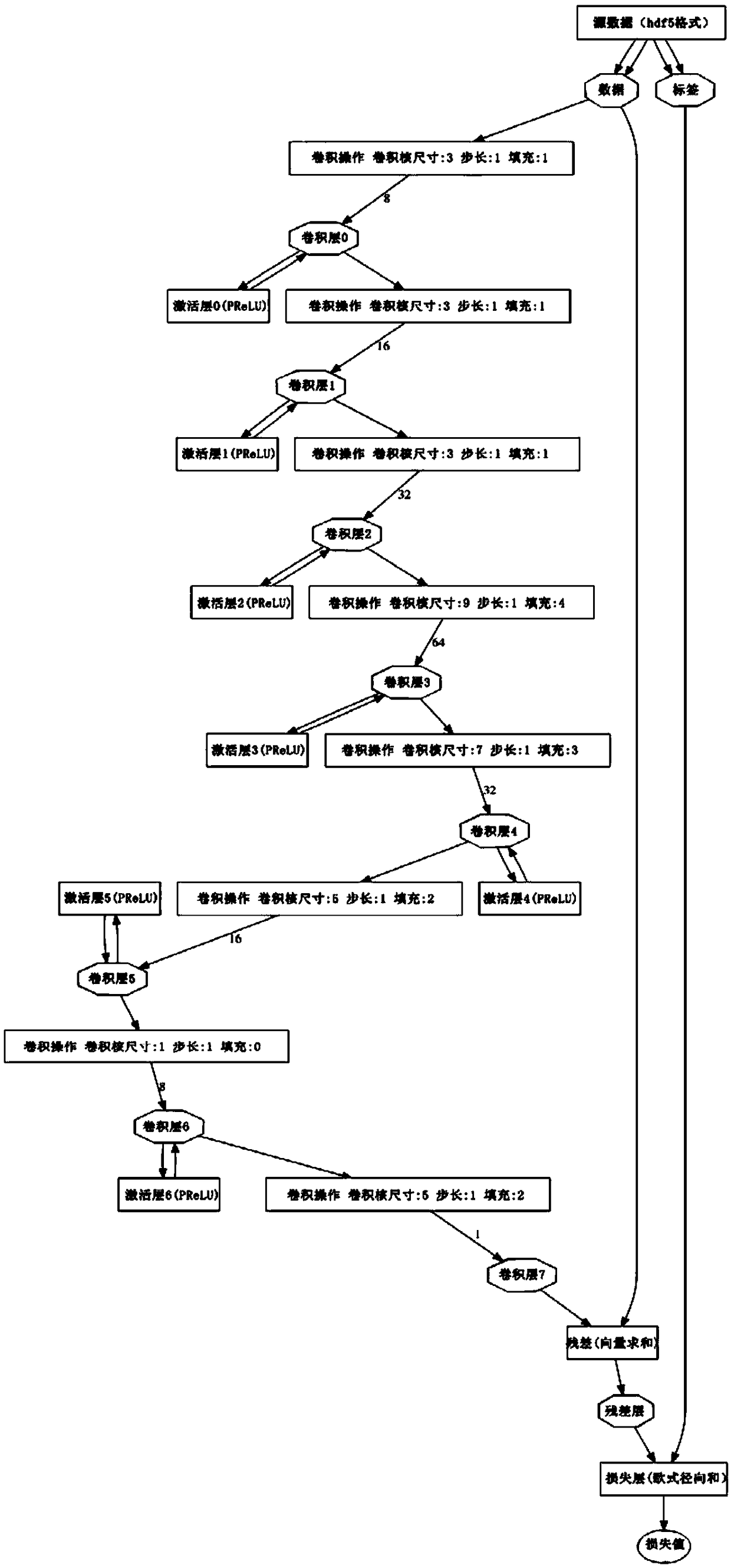
Depth residual convolution neural network image denoising method based on PReLU
InactiveCN109118435AOptimizationAvoid computational overheadImage enhancementImage analysisDenoising algorithmActivation function
The invention relates to a depth residual convolution neural network image denoising method based on PReLU, based on deep convolution neural network, combined with Gaussian noise simulating unknown real noise image denoising task, in this paper, a deep convolution neural network for image denoising is proposed, which uses PReLU activation function instead of Sigmoid and ReLU function, increases residual learning and reduces mapping complexity, and adopts optimized network training techniques and network parameter settings to improve the denoising ability of the network. Compared with other existing denoising algorithms, the present invention performs very well under various Gaussian noise environments in which the standard variance is mixed, and the detailed information in the image can bewell preserved while the noise is eliminated.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
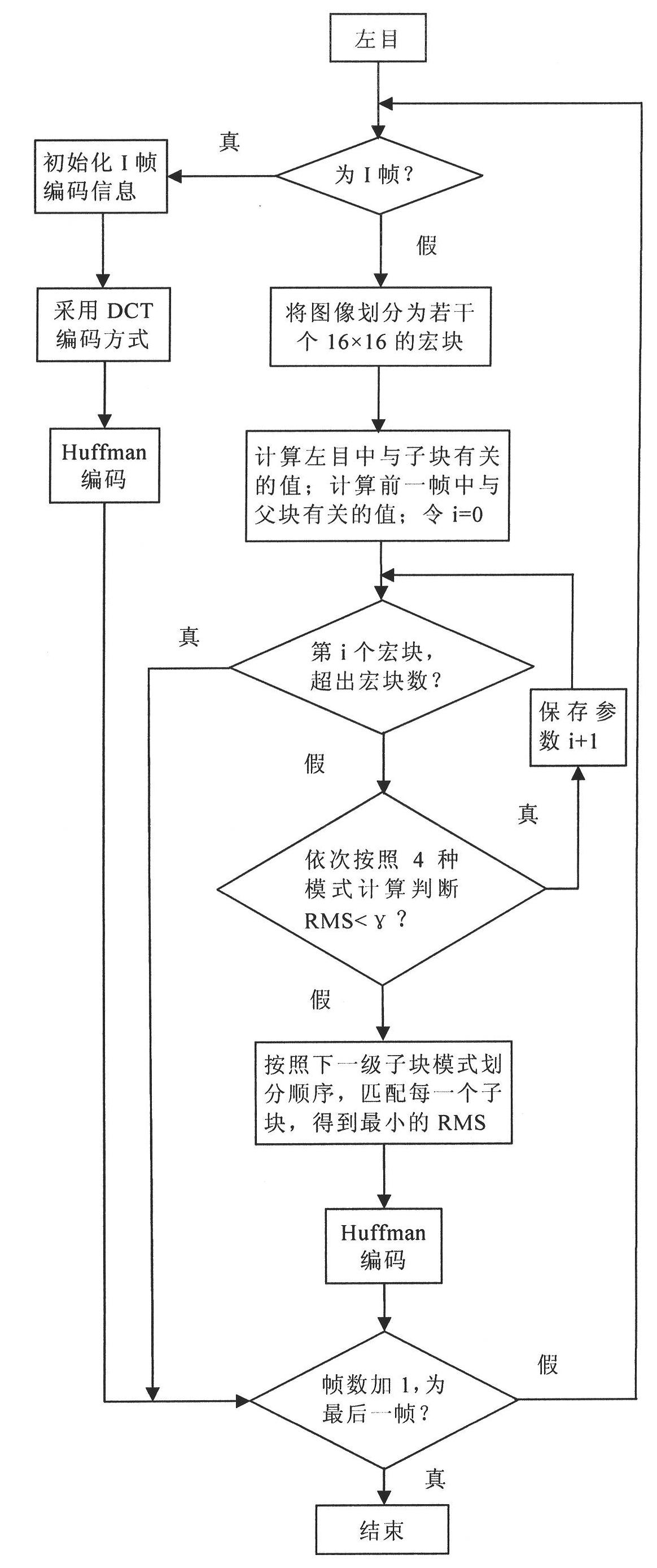
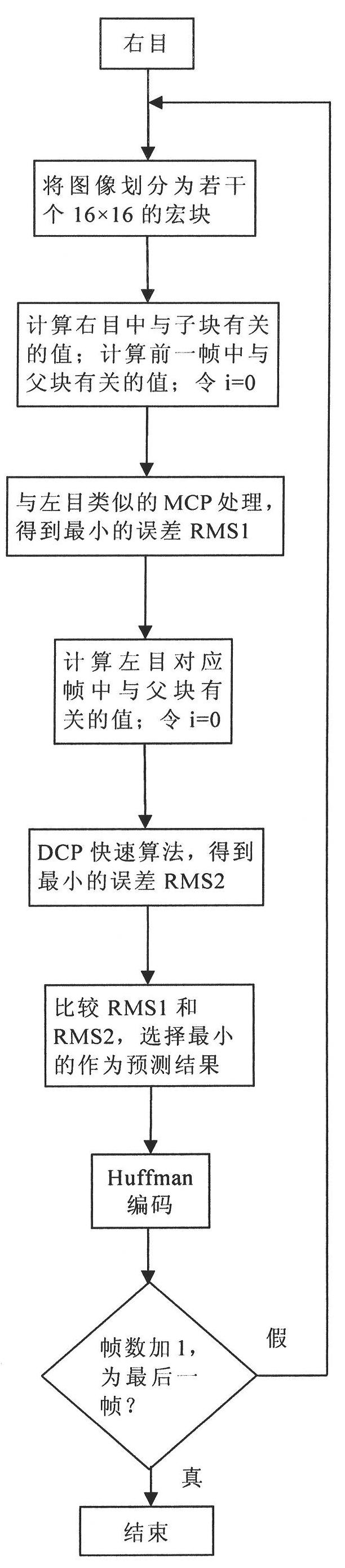
Object and fractal-based binocular three-dimensional video compression coding and decoding method
InactiveCN101980537AReduce compression timeReduce blockinessTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationIndependent motionDecoding methods
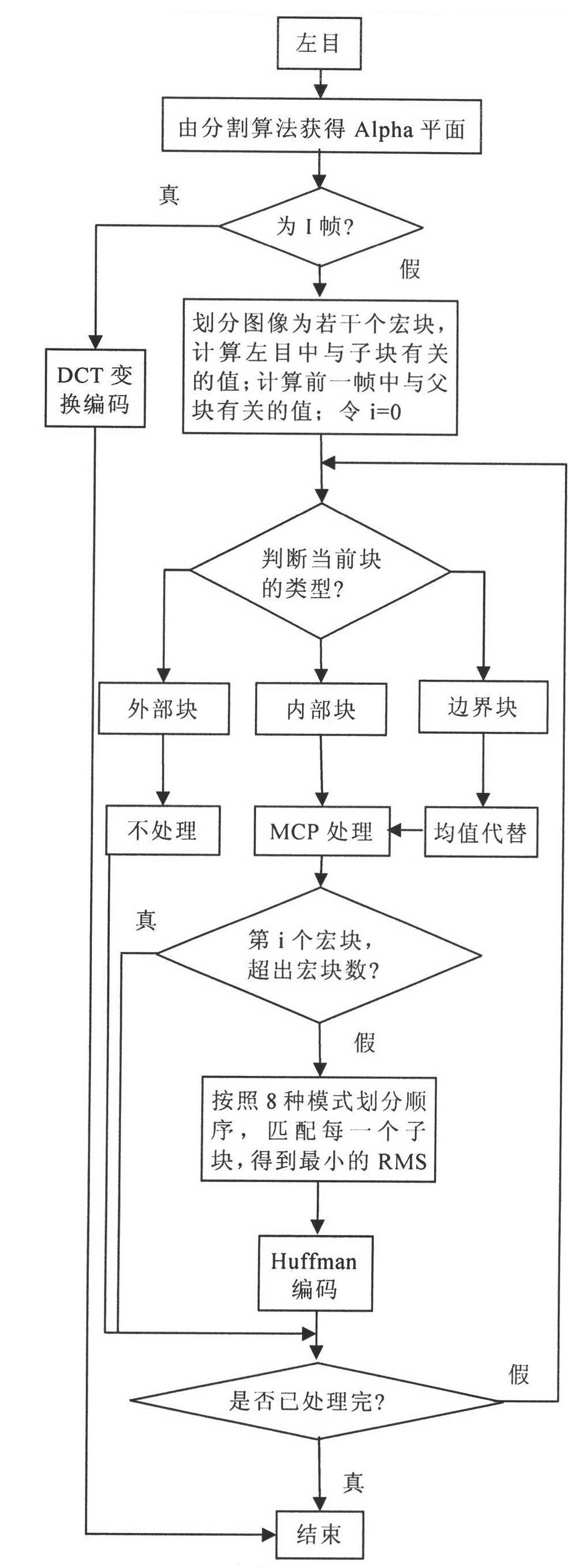
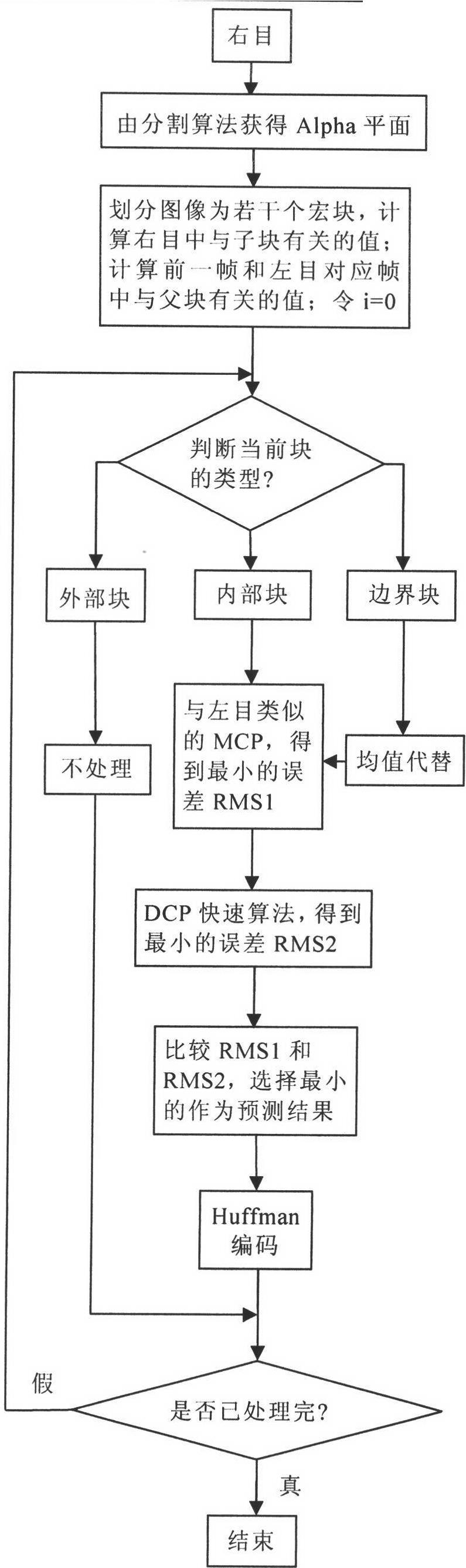
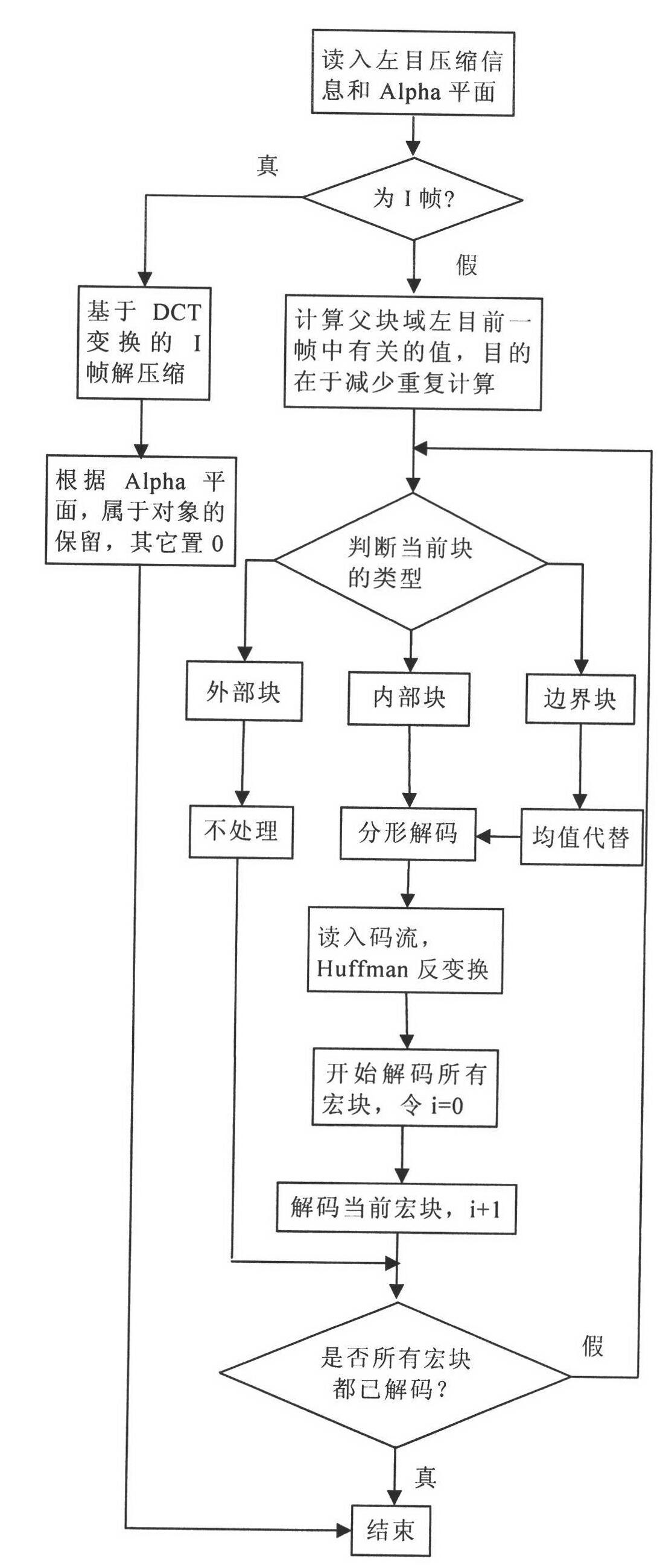
The invention provides an object and fractal-based binocular three-dimensional video compression and decompression method. In binocular three-dimensional video coding, a left channel is used as a basic layer, a right channel is used as an enhancement layer, and the left channel is encoded by an independent motion compensation prediction (MCP) mode. The object and fractal-based binocular three-dimensional video compression coding method comprises the following steps of: firstly, acquiring a video object partition plane, namely an Alpha plane by a video partition method, encoding the initial frame of a left eye through block discrete cosine transformation (DCT), and performing block motion estimation / compensation coding on a non-I frame of the left eye; secondly, determining the area attribute of an image block by utilizing the Alpha plane, and if the block is not within a video object area of the current code, not processing an external block, and if the block is within the video object area of the current code completely, searching the most similar matching block by a full-searching method in a previous frame of an internal block, namely a reference frame searching window of a left eye video; and finally, compressing coefficients of an iterated function system by a Huffman coding method, and if part of pixels of the block are within the video object area of the current code, and the other part of pixels are not within the video object area of the current code, processing a boundary block independently. The right channel is encoded by a MCP mode and a disparity compensation prediction (DCP) mode, the MCP is similar to the processing of the left eye, and the block with the minimum error is used as a prediction result. When the DCP coding mode is performed, the polarization and directionality in a three-dimensional parallel camera structure are utilized fully.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
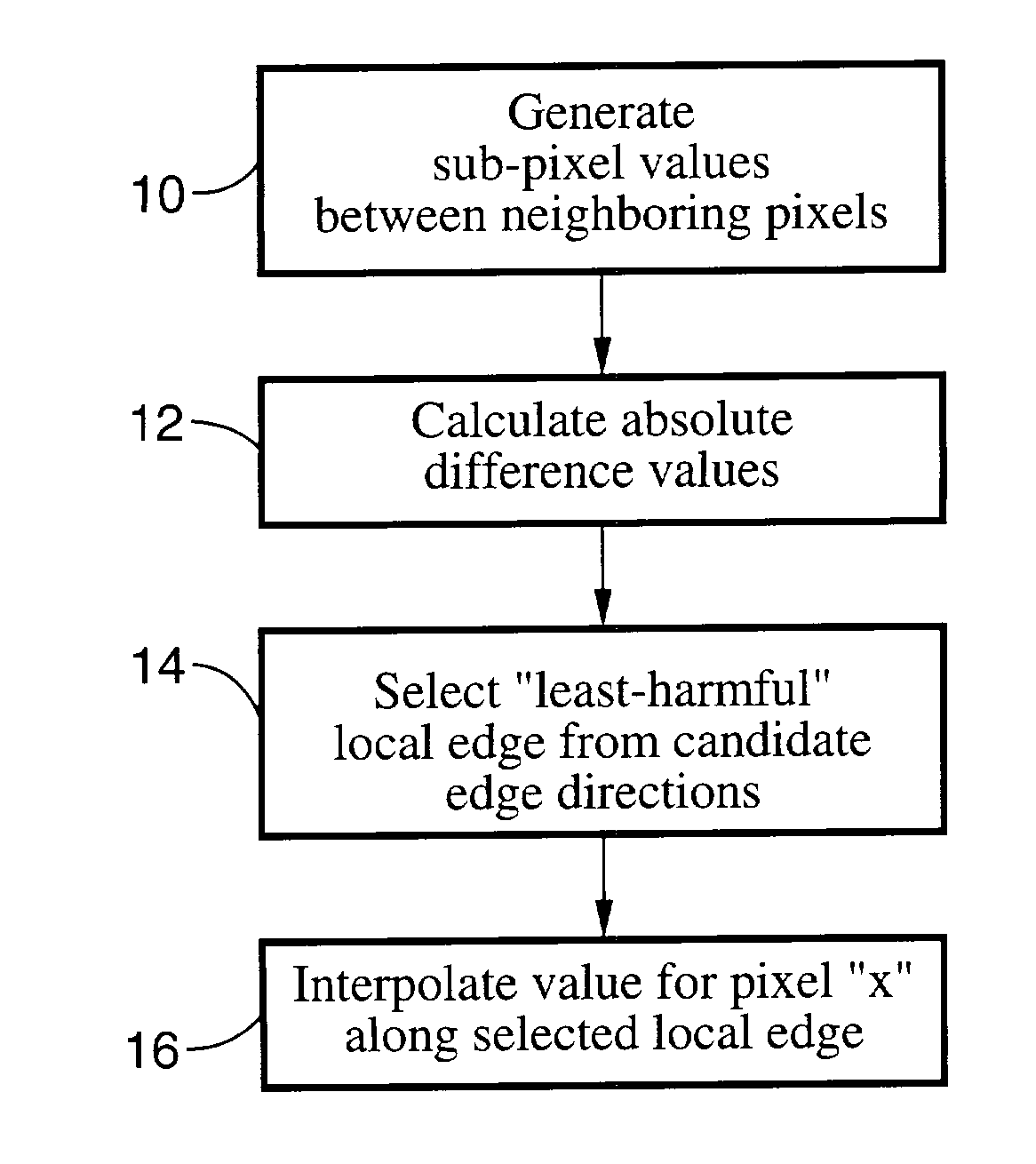
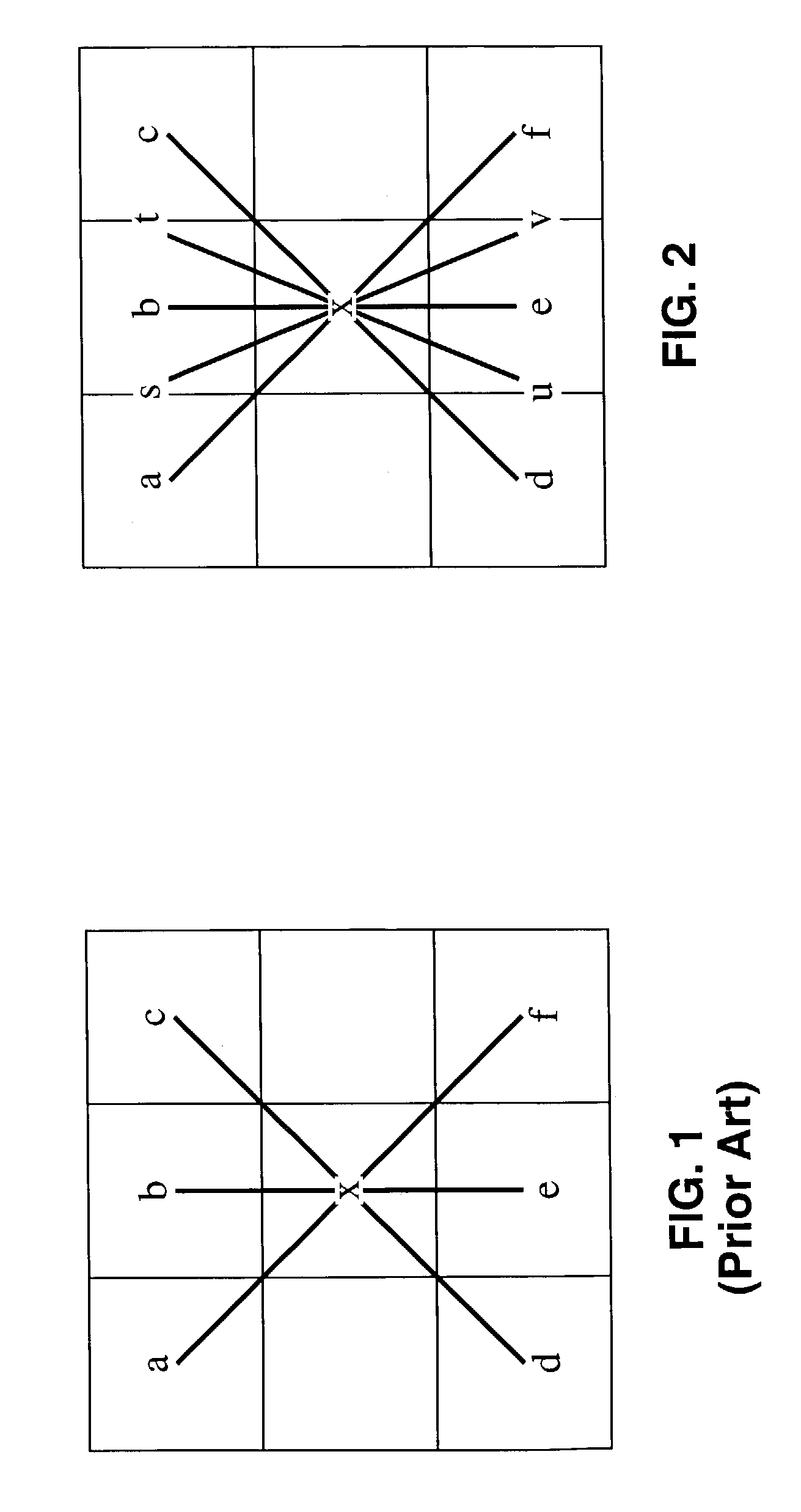
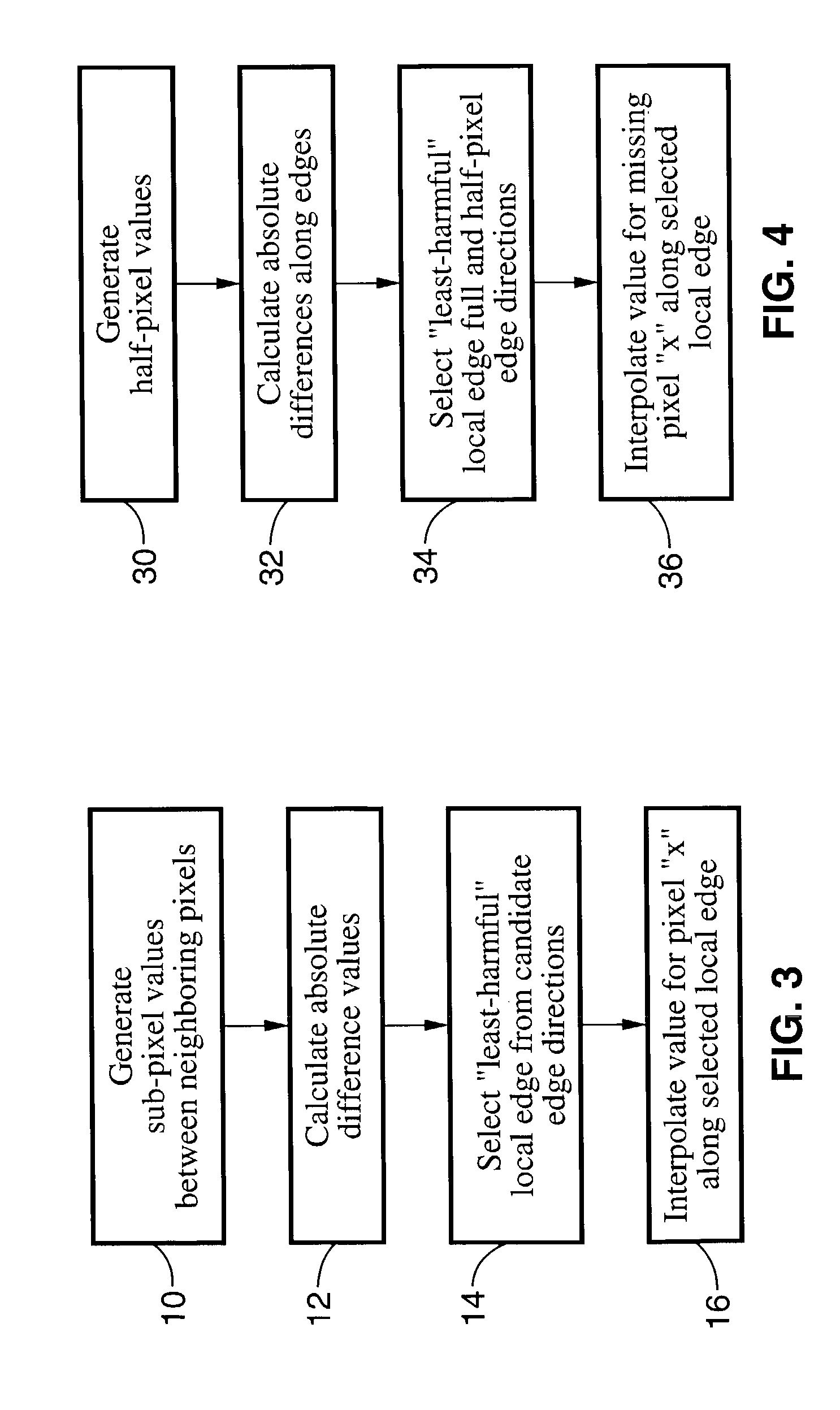
Method of performing sub-pixel based edge-directed image interpolation
InactiveUS7136541B2Improve accuracyHigh computational complexityImage enhancementGeometric image transformationAbsolute differencePixel based
A method of generating a value for a missing pixel “x” by determining a “least harmful” local edge direction between pixels, or sub-pixels, on substantially opposing sides of the missing pixel, and interpolating the difference to arrive at a value for pixel “x”. The method involves generating sub-pixel values for locations within neighboring pixels, the sub-pixels may comprise half-pixels, quarter-pixels, three-quarter pixels, and so forth, wherein any fractional pixel quantity may be created. Absolute difference values are calculated between neighboring pixels, or sub-pixel values, to determine a least harmful local edge direction along which a value is generated for pixel “x” by interpolation.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
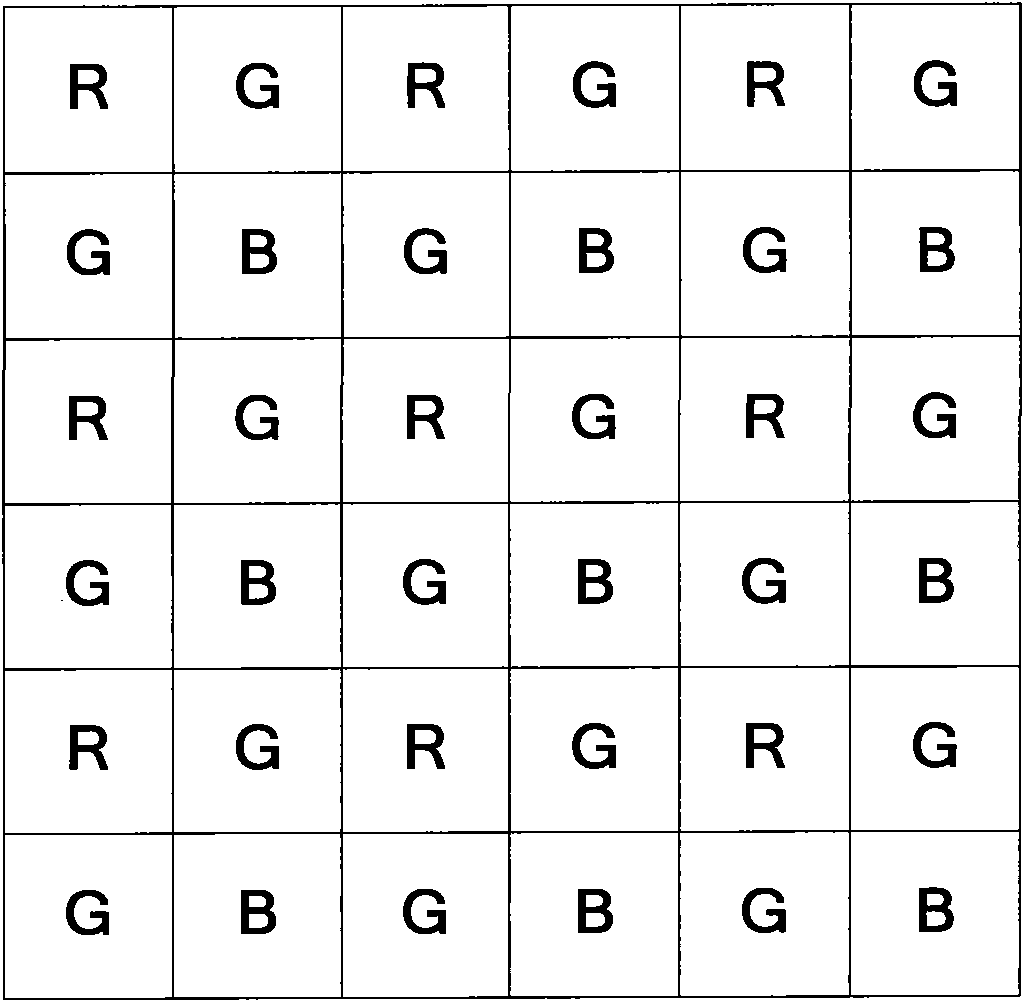
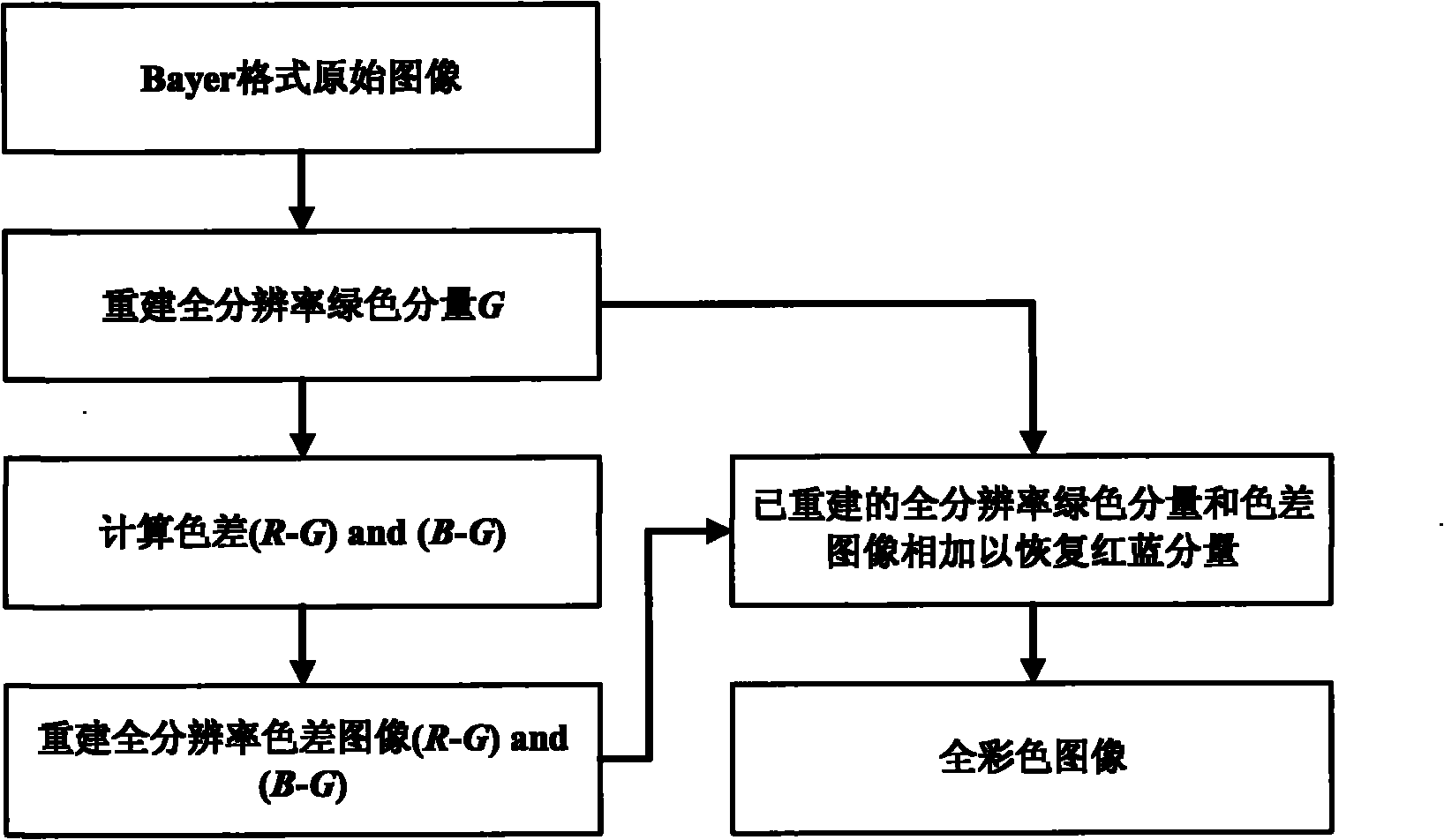
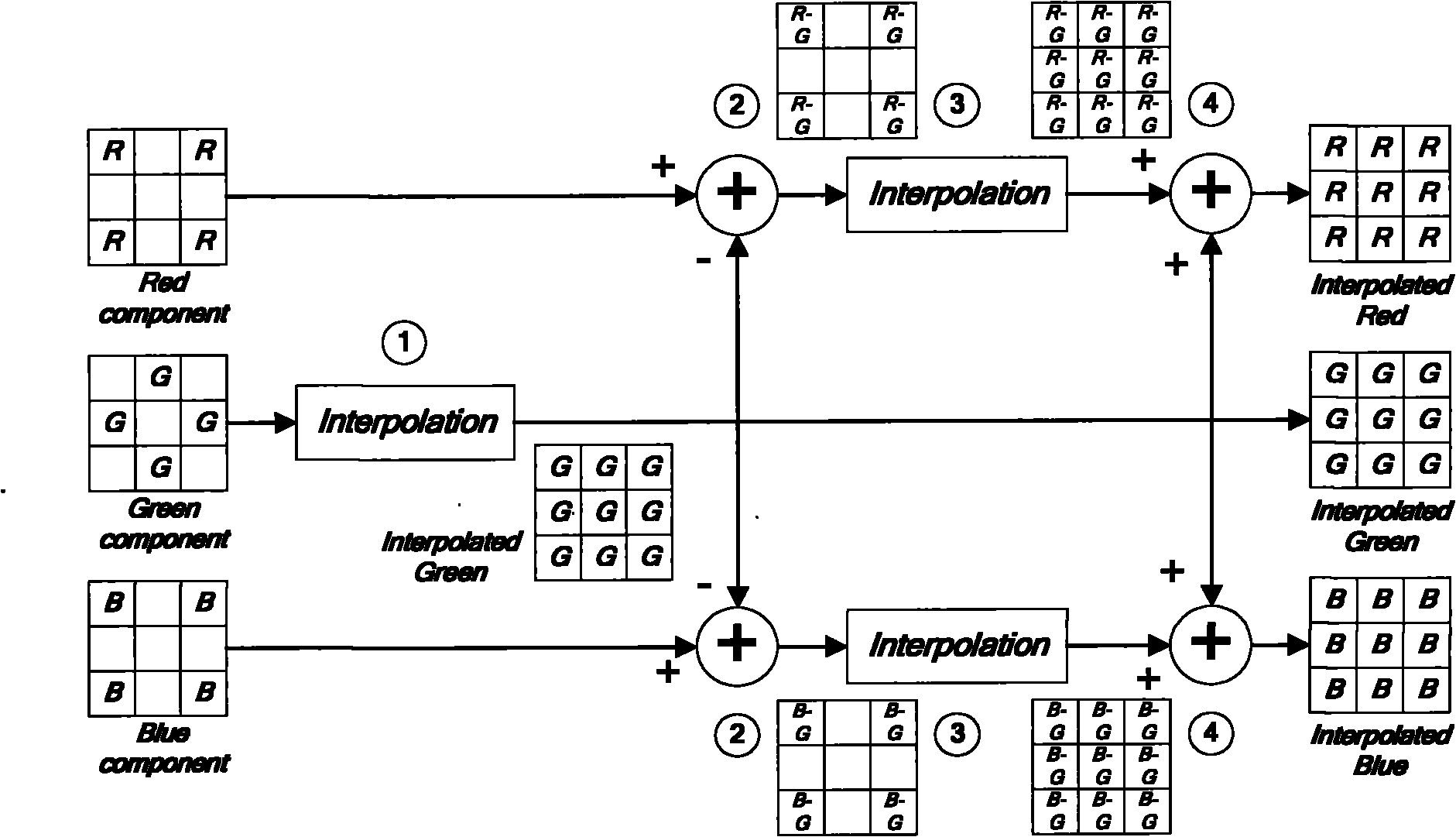
Green component and color difference space-based Bayer format color interpolation method
InactiveCN101917629AReduce operational complexityImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioBrightness and chrominance signal processing circuitsPicture signal generatorsJaggiesImage resolution
The invention relates to a green component and color difference space-based Bayer format color interpolation method. Two main errors which are jaggies and pseudo colors respectively exist in the conventional color interpolation methods. In the method, in a full-color image recovery process, color recovery is realized by adopting a combined way of interpolating green components, red components and blue components in steps; and the method comprises the reconstruction of the full-resolution green components G, the calculation of pixel point color differences R-G or B-G comprising the red or blue components, the reconstruction of full-resolution color difference images R-G and B-G, and the recovery of the red components R and the blue components B by the addition of the reconstructed full-resolution green components and the reconstructed color difference images. The method of the invention has the advantages of effectively solving the problem that the images have blurry edges and unsharp detail textures, reducing the color distortion of the images, preventing color mutation and improving color smoothness.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and apparatus for removing block effect
InactiveCN101321277AImprove subjective qualityImplement deblocking operationPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationLoop filterSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A block reducing method and device, mainly including the steps of: firstly, calculating flatness of pixel in both sides of edge in pane corresponding to row of part of lines in current block, calculating flatness of region of the pane obtained; then, determining edge intensity in the pane according to the flatness of region of the pane and filtering the edge in the pane according to the edge intensity; or, firstly regulating the edge intensity according to a comparing result of a motion vector of blocks on both sides of the edge and the predetermined threshold value to obtain edge intensity value regulated; then filtering the current block by regulated edge intensity. Thereof, the implement solution of loop filter provided by the embodiment of the invention can implement block reducing process effectively in the image decoding process, which enables the subject quality of the image decoded to be high and peak value Signal-to-Noise to be improved objectively.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
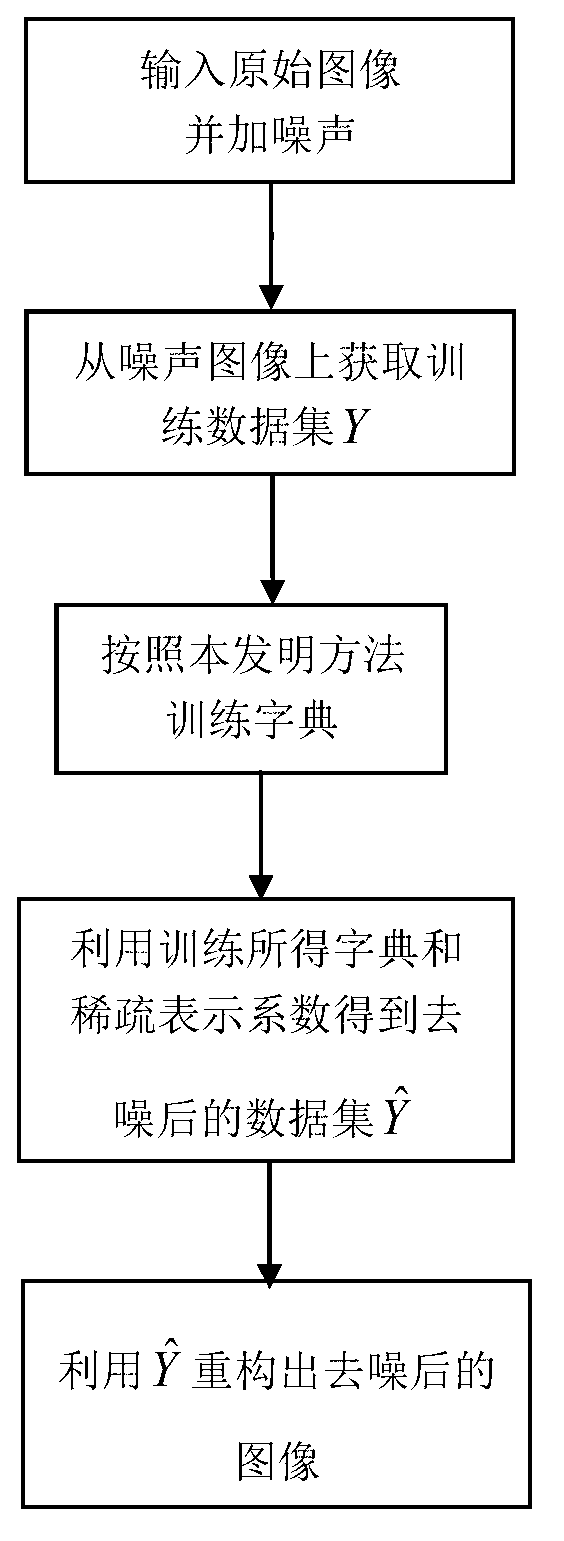
Image de-noising method based on sparse self-adapted dictionary
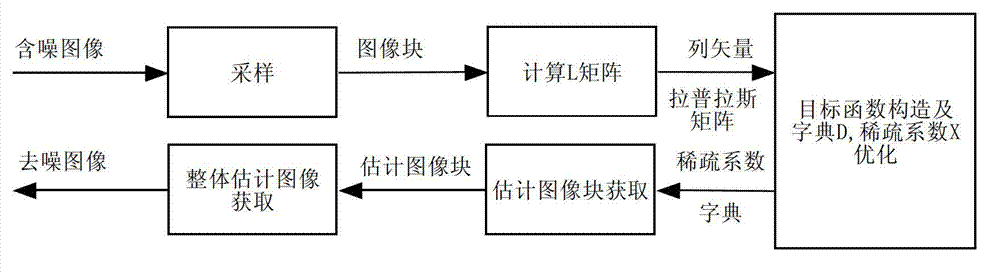
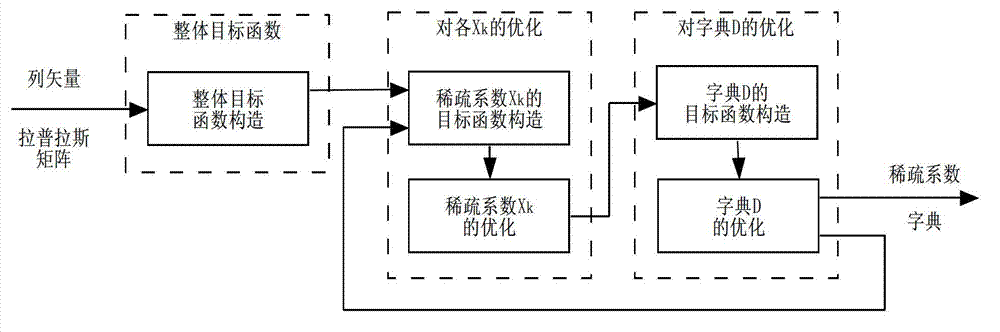
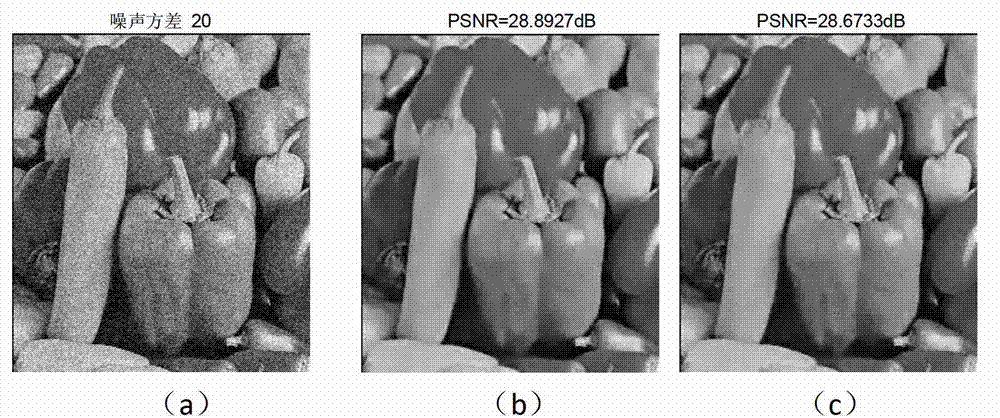
InactiveCN103218791AReduce noiseDisadvantages of preventing fitting noiseImage enhancementPattern recognitionComputed tomography
The invention discloses an image de-noising method based on a sparse self-adapted dictionary, and the method is mainly used for overcoming the defects that over-fitting exists when an existing method is used for training the dictionary, and the self-adaption is insufficient. The realization process comprises the following steps of: (1) obtaining image blocks from images with noises and paralleling the image blocks into vectors to form a training data set; (2) utilizing the training data set to iteratively train the dictionary; in an iteration process, taking the dictionary obtained by iteration as a basic dictionary of the iteration, and after the iteration is finished, obtaining a final dictionary and an encoding coefficient matrix of the training data set on the dictionary; (3) utilizing the dictionary and the encoding coefficient matrix obtained by training to obtain a de-noised data set; and (4) utilizing the de-noised data set to reconstruct a de-noised image. The dictionary trained by the method disclosed by the invention has sparseness and better self-adaptation; the effect of de-noising the image is improved; and the method can be used for de-noising a natural image and a medical CT (Computed Tomography) image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
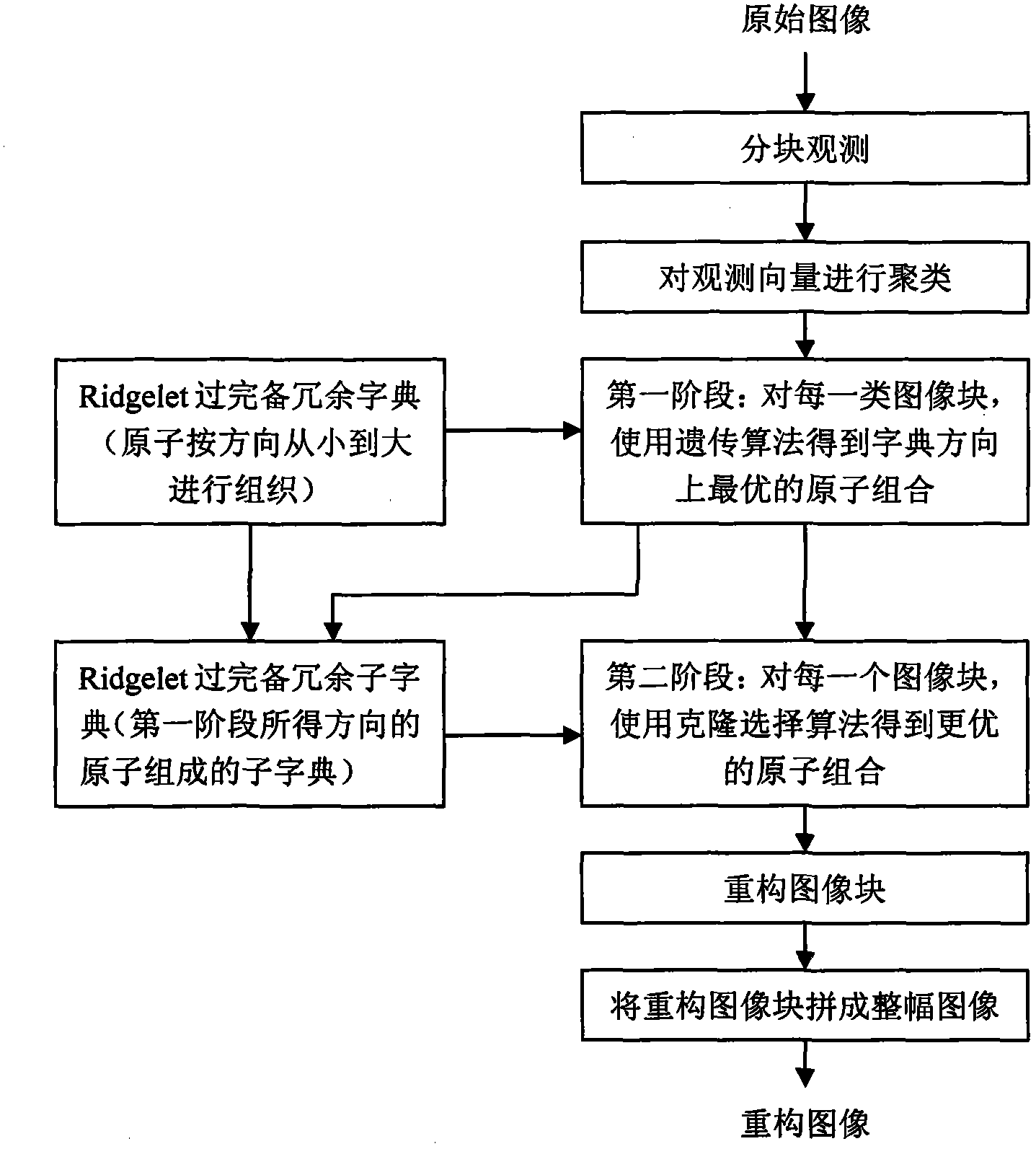
Non-convex compressed sensing image reconstruction method based on redundant dictionary and structure sparsity
InactiveCN103295198AImprove visual effectsImprove refactoring qualityImage enhancementClonal selection algorithmReconstruction method
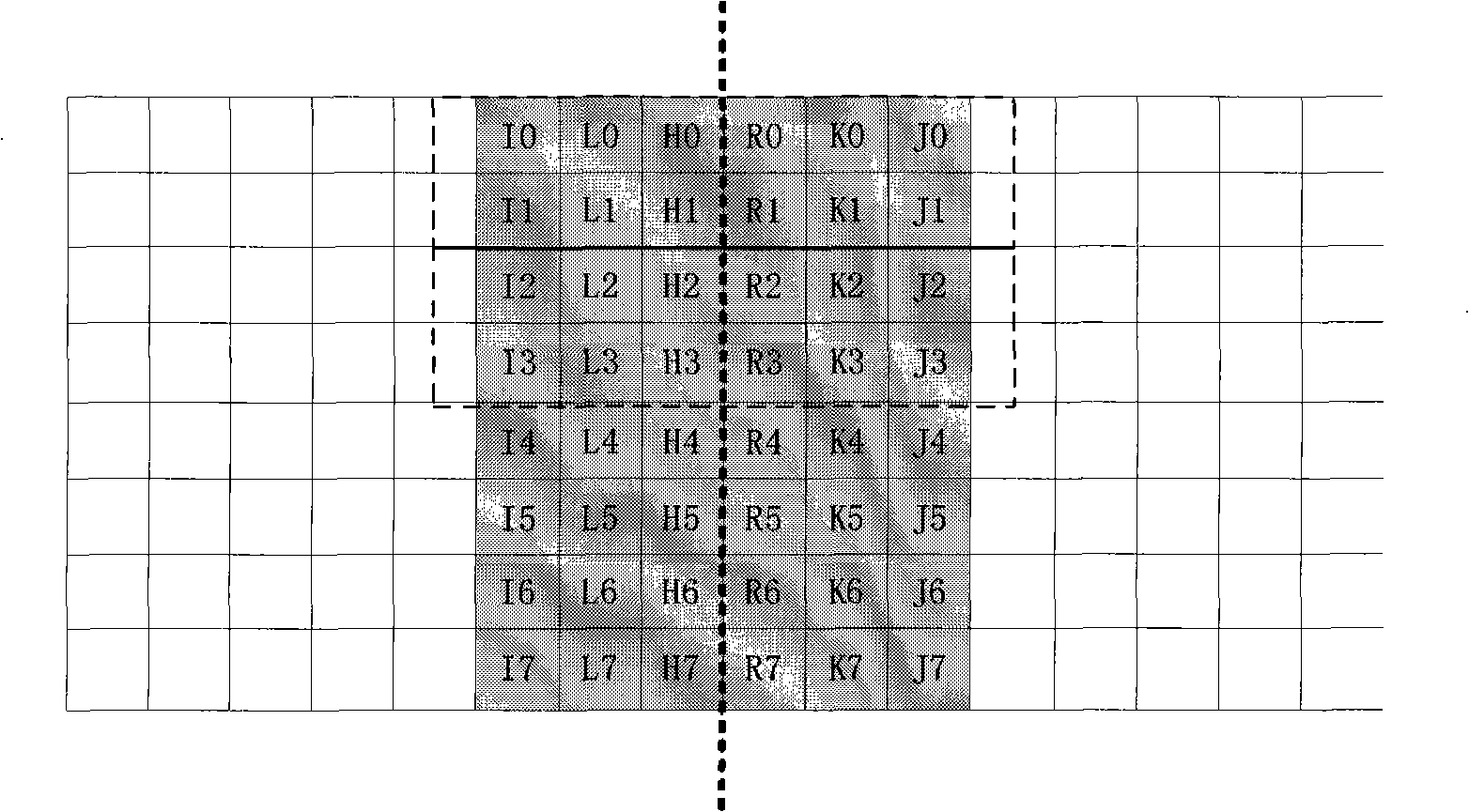
The invention discloses a non-convex compressed sensing image reconstruction method based on a redundant dictionary and structure sparsity. A reconstruction process of the method includes: observing original image blocks; using a mutual neighboring technology for clustering observation vectors; using a genetic algorithm for finding optimal atom combinations in a dictionary direction for each class of observation vectors, and preserving species; after species expansion operation is executed on each image block, using a clonal selection algorithm for finding an optimal atom combination on scale and displacement in a determined direction for each image block; reconstructing each image block by the optimal atom combination; and piecing all the constructed image blocks in sequence to form an entire constructed image. Image structure sparsity prior and redundant dictionary direction features are fully utilized, the genetic algorithm is combined with the clonal selection algorithm, and the method is used as a nonlinear optimization reconstruction method to realize image reconstruction. The reconstructed image is good in visual effect, high in peak signal noise ratio and structural similarity, and the method can be used for non-convex compressed sensing reconstruction of image signals.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for distributing information based on increment fountain
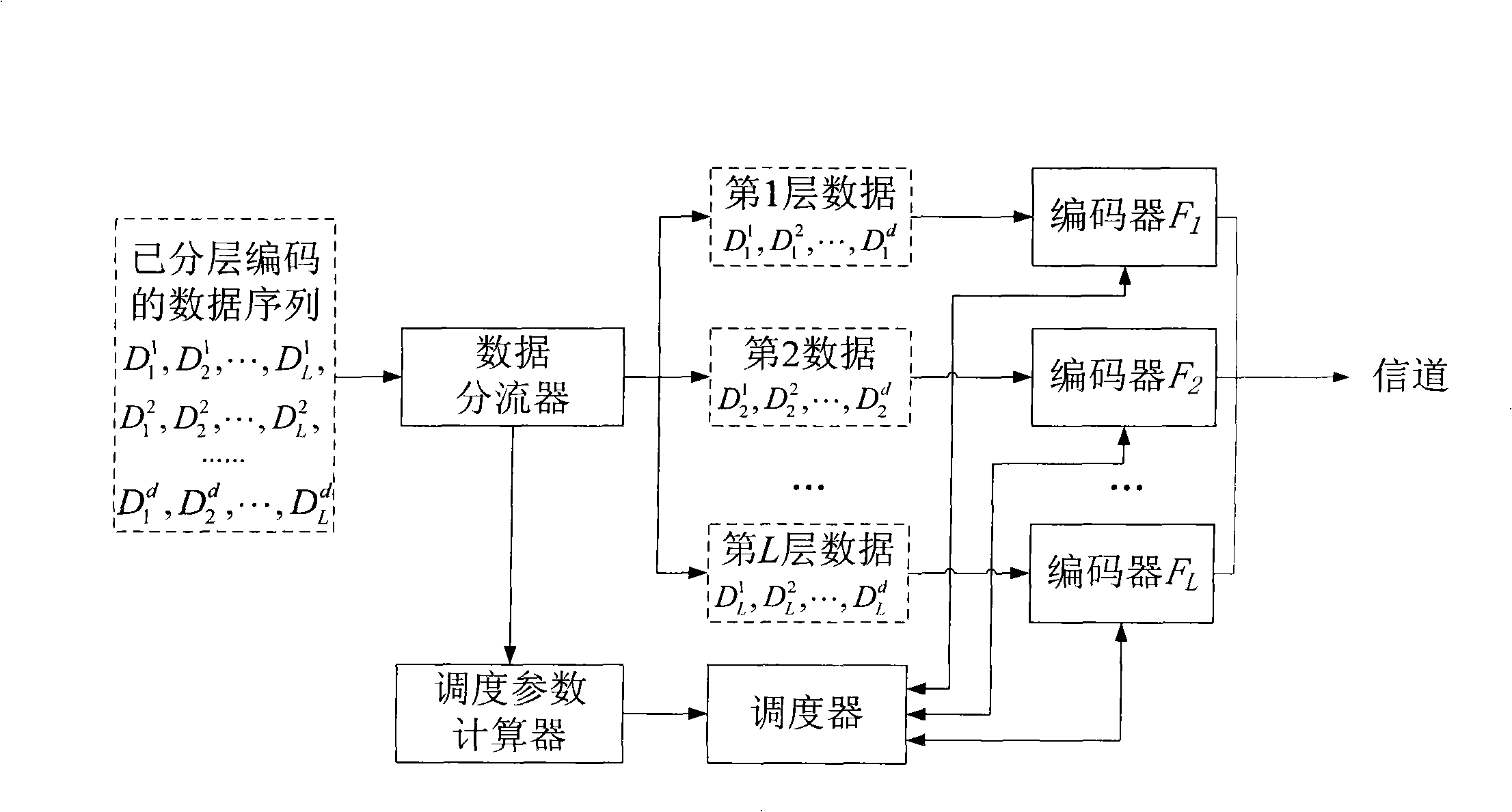
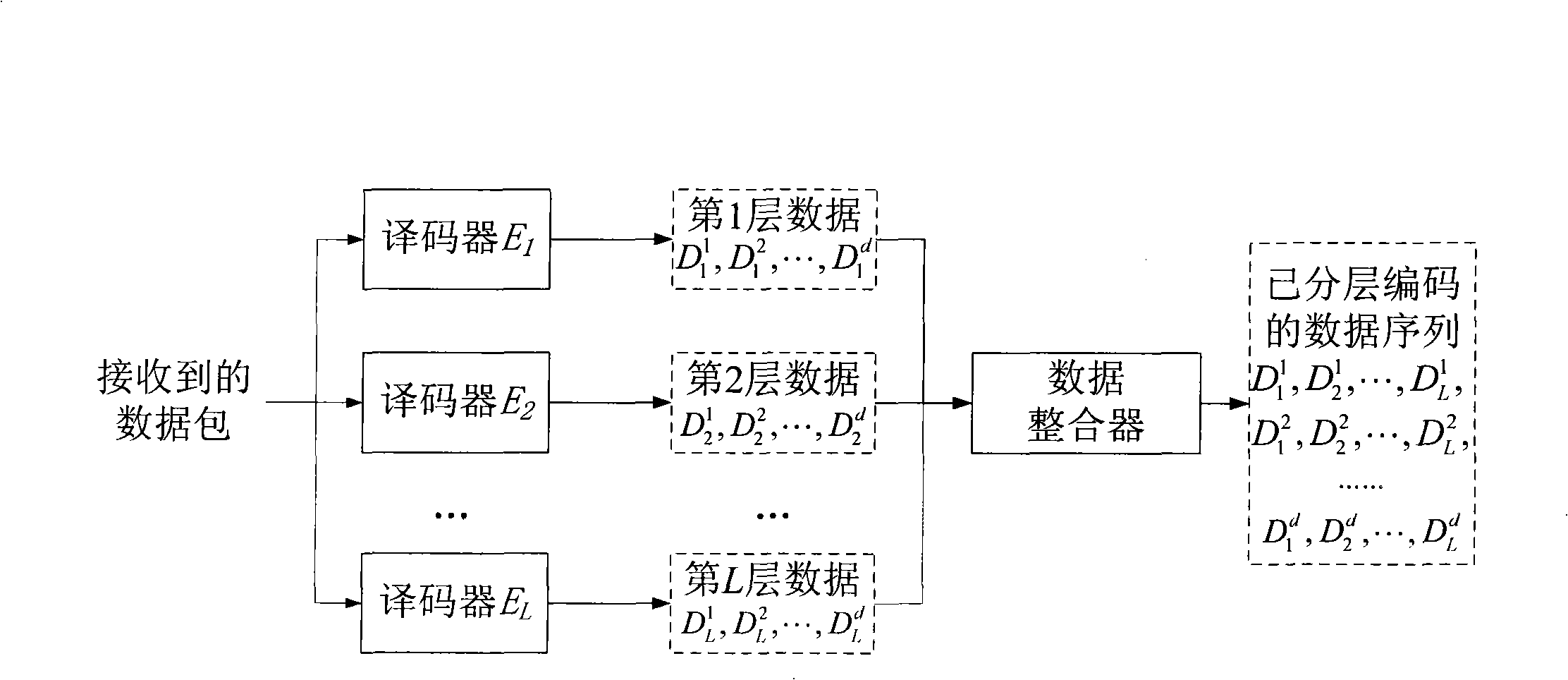
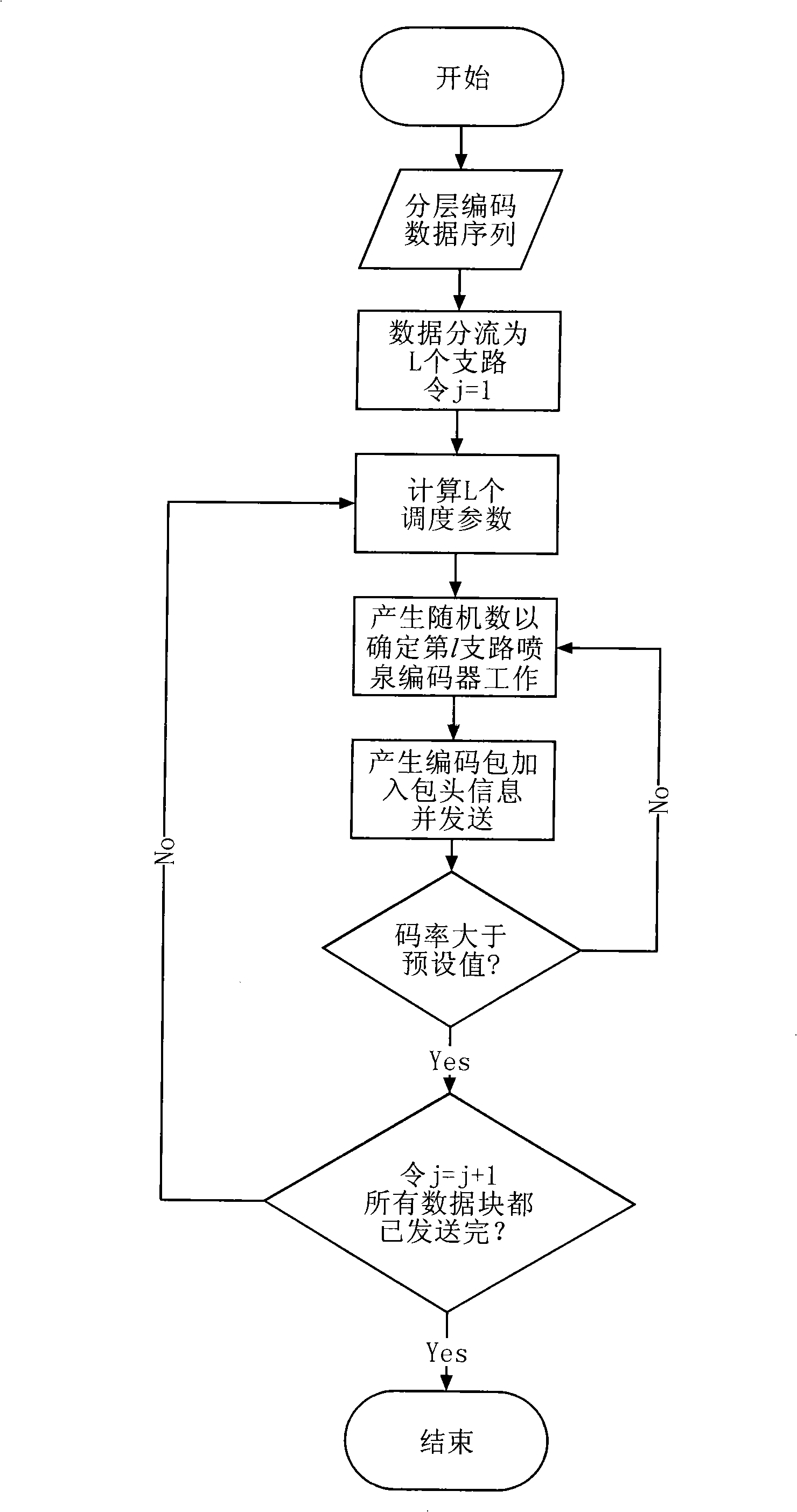
InactiveCN101350699AGood data recoveryMuch useful informationSpecial service provision for substationError preventionDistribution methodOriginal data
The present invention relates to an information distribution method based on the incremental fountain, and belongs to the technical field of wireless data transmission. The information distribution method has the following characteristics: a data splitter is used at the transmitting end for arranging the data of the same layer number in the layered and encoded data sequence, so as to form a branch; the sum of the branches is the sum of the layers; a weighting sequence is designed according to the principle of smaller layer number and higher degree of importance; a scheduling parameter calculator is used for calculating the scheduling parameters of each layer in each original data block; the scheduling parameters are transmitted to a scheduling device, which is used for controlling the work of the fountain encoder of different layers according to different probabilities, so as to complete different types of redundancy protection of different layers, thus the system has the capacity of adapting to complex and changeable states of the channel. The method can be used for effective data distribution of no feedback and low redundancy in the poor channel.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TUGUIYAO INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Wavelet image denoising process based on sliding window adjacent region data selection
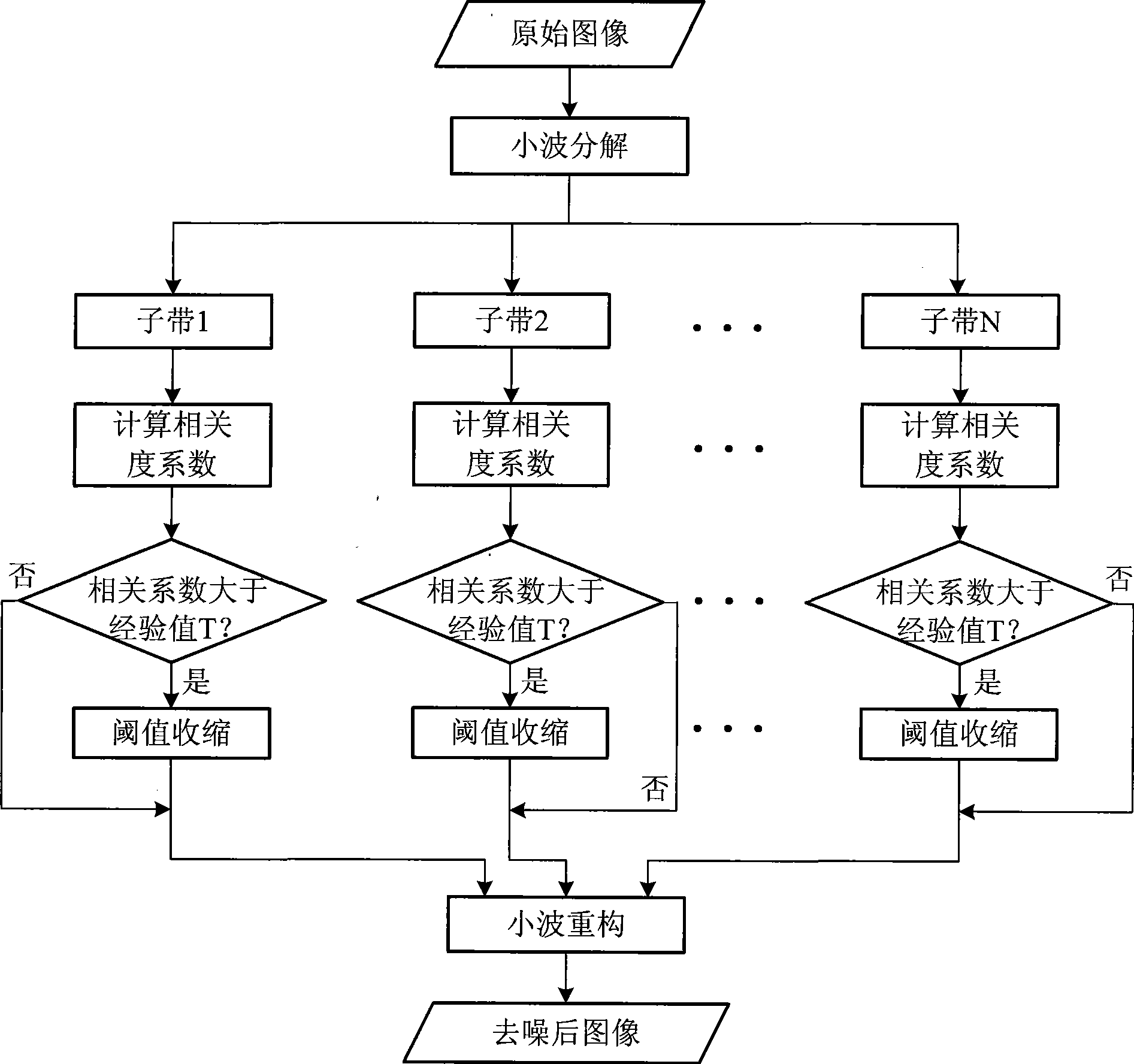
InactiveCN101477680AImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioGood image edge protectionImage enhancementImage denoisingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention relates to a method for denoising wavelet images chosen on the basis of the neighbor data of a sliding window. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, decomposing a noisy image into sub-bands by wavelet transformation processing; step 2, processing the wavelet coefficient of each sub-band according to the following steps: 1), carrying out threshold judgment of the center wavelet coefficient of each neighbor centering on each wavelet coefficient in each sub-band, comparing the correlativity coefficient Theta of each neighbor of the coefficient, and carrying out 2) if the maximal correlativity coefficient Theta is higher than an empirical value, or carrying out step 3 directly if the maximal correlativity coefficient Theta is lower than the empirical value; 2), calculating the Bayes adaptive threshold value of the threshold processing window chosen in 1) so as to obtain a scaling factor; and 3), scaling the wavelet coefficient in the center of the window according to the scaling factor; and step 3, reconstructing the wavelet coefficient so as to obtain the filtered image after processing each sub-band of the wavelet with adaptive sliding window neighbor wavelet process. The method has the advantages of higher peak value signal-to-noise ratio and better protection effect for image edges.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Region of interest-based H. 265 video quality improvement method
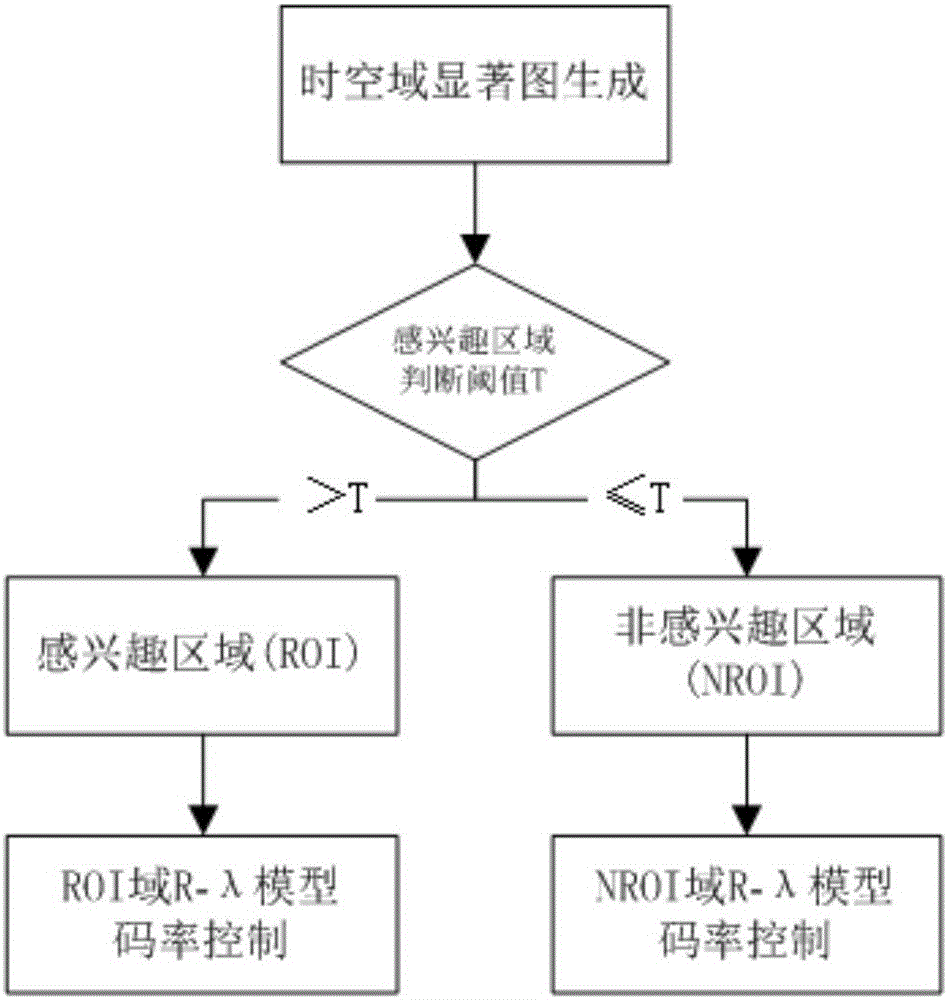
InactiveCN106604031AImprove subjective qualityImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionBit allocation
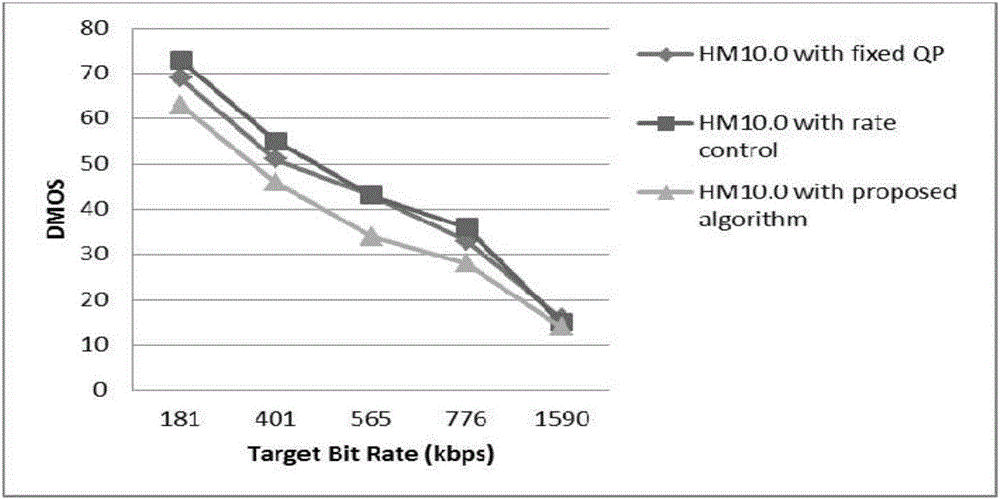
The present invention discloses a region of interest-based H. 265 video quality improvement method. The objective of the invention is to improve subjective visual quality and maintain bit rate control accuracy. According to the method of the invention, a new graph-based saliency model is put forward; the region of interest of a current frame is estimated through a time-space domain saliency graph, so that the region of interest (ROI) can be determined, and frame-level and largest coded macroblock (LCU)-level bit allocation are guided; and for the problem of video quality smoothing, the adjustment of lambda values and QP values in the space domain and the time domain is restricted respectively. As indicated by experimental results, the algorithm can make an output bit rate reach a target value, and improve the peak area signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) of the region of interest (ROI) of a video frame, and therefore, the overall subjective visual quality of a coded sequence is greatly increased compared with that obtained by using a bit rate control algorithm in the HM10.0 standards.
Owner:金华就约我吧网络科技有限公司
Black-and-white image colorizing method based on two-sided filter
InactiveCN101860655AOvercome the problem of not being able to colorAchieve fixColor signal processing circuitsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Peak value
The invention relates to a black-and-white image colorizing method based on a two-sided filter in the field of image processing, comprising the following steps of: labeling a black-and-white image; carrying out distance conversion on the black-and-white image to obtain the processing priority of an image block; calculating a geometrical distance weight and an average gray gradient value between the current block and an adjacent block under the frame of the two-sided filter, wherein if the average gray gradient value is greater than a threshold value, the similarity of the adjacent block and the current block is insufficient, and therefore, the average gray gradient value can not be used for forecasting the current block; conversely, if the average gray gradient value is less than the threshold value, calculating gray value variable weights of the current and the adjacent blocks; and finally obtaining the recovery value of the current block by the current block, the geometrical distance weight and the gray change weight. The invention overcomes the defect of the dependence assumption of brightness and chromaticity in the colorizing process, effectively colorizes the damaged black-and-white image, and has short used time and high signal to noise ratio of an obtained peak value.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Bridge crack image barrier detection and removal method based on generative adversarial network
InactiveCN108492281AReduce training difficultyAccurate detection and removalImage enhancementImage analysisSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Generative adversarial network
The invention relates to a bridge crack image barrier detection and removal method based on a generative adversarial network. The method comprises the steps that first, multiple barrier pictures are collected, then tags are added, and the pictures with the tags are input into a Faster-RCNN for training; multiple barrier-containing crack pictures are collected, and barrier position calibration is performed through the Faster-RCNN; second, multiple barrier-free crack pictures are collected, and the pictures are turned over to amplify a dataset; third, the amplified dataset is input into the generative adversarial network to train a crack generation model; fourth, information erasure is performed on the positions of barriers in the barrier-containing crack pictures to obtain damaged images; and fifth, the damaged images are input into a cyclic discrimination restoration model for iteration, and then restored crack images are obtained. Through the method, barrier information in the crack pictures can be accurately detected and removed, the peak signal-to-noise ratio of the restored crack images is increased by 0.6-0.9dB compared with before, and therefore a large quantity of crack images with a high restoration degree are generated under a finite crack dataset condition.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
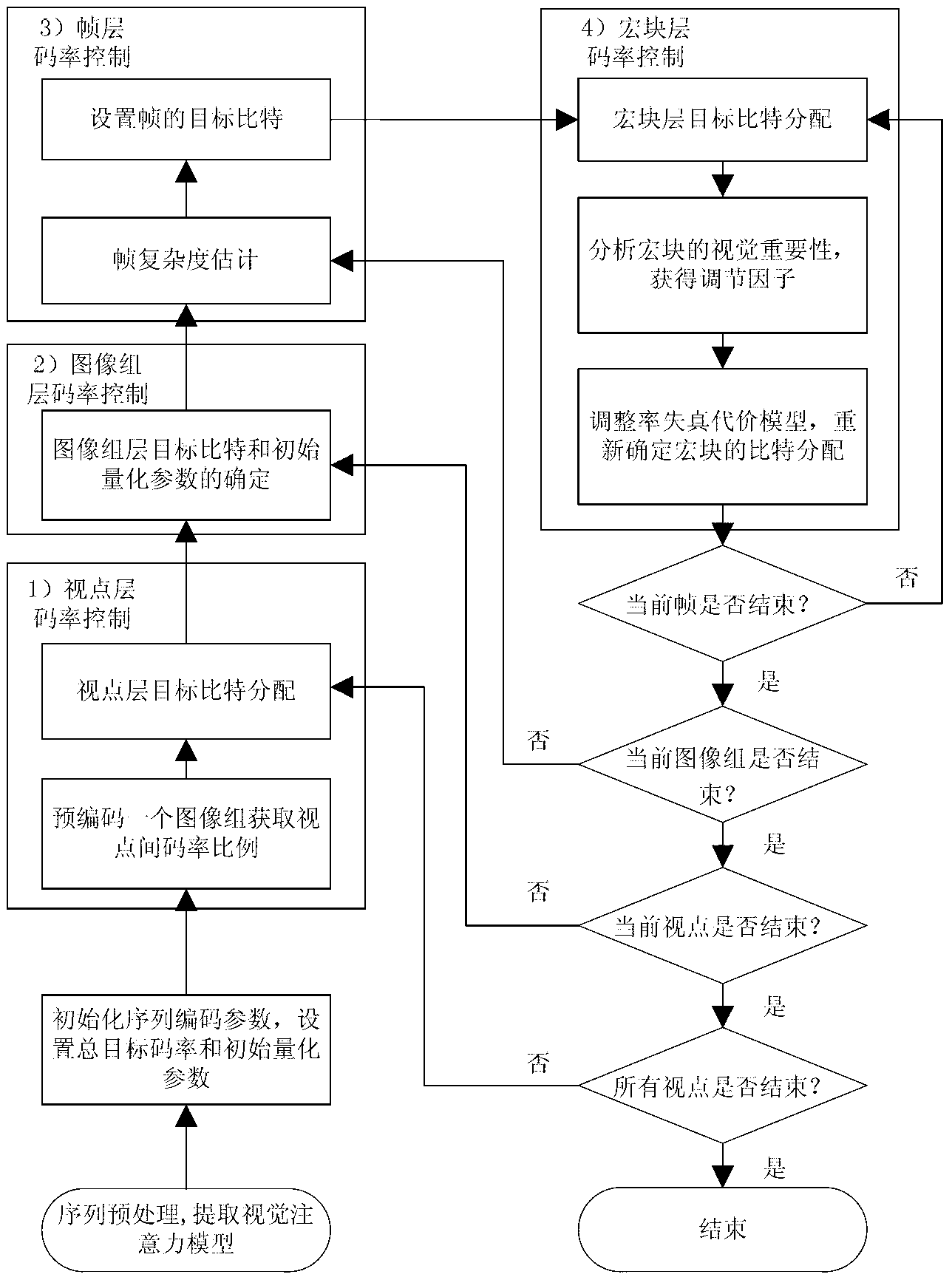
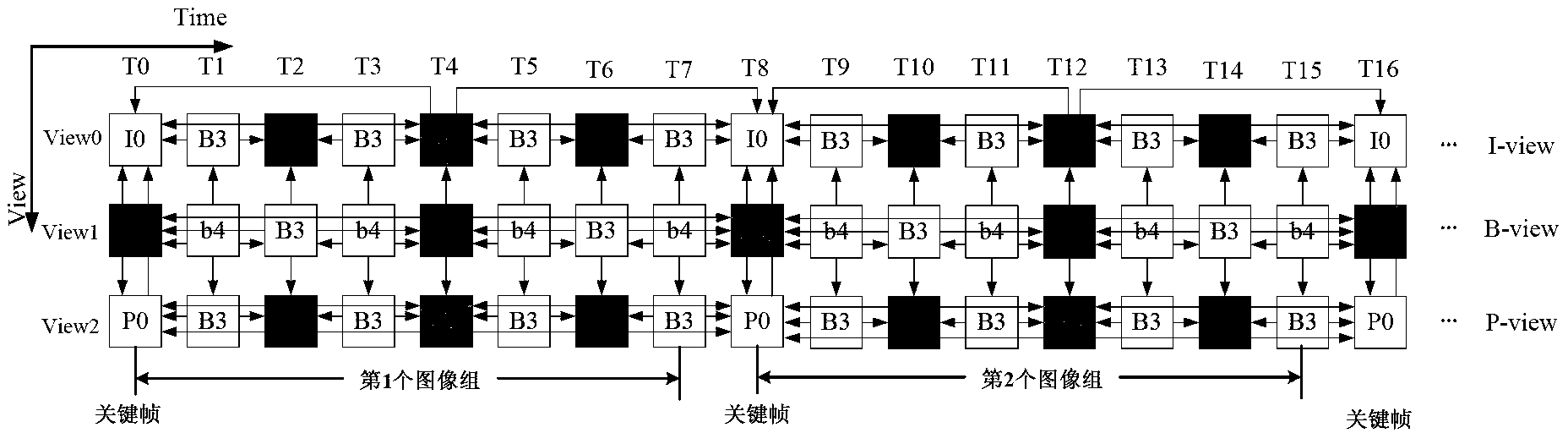
Multi-view video bit rate control method based on sensing
InactiveCN103024387AImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioVideo quality is stableTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Bit allocation
The invention discloses a multi-view video bit rate control method based on sensing. The method is characterized in that bit rates of a view layer, an image group layer, a frame layer and a macro-block layer are respectively controlled, bit allocation of views is determined by pre-encoding an image group in the view layer, target bits and initial quantization parameters of the image group are calculated according to structural characteristics of layered frames B in the image group layer, target bits of each frame are determined according to predicted complexity in the frame layer, and bit allocation of macro-blocks is determined according to a visual perception characteristic modification rate distortion model in the macro-block layer. The method has the advantages that the stability of video quality and the quality of a visual sensitive area are effectively improved by the bit rate control method, the peak signal-to-noise ratio of the most visually sensitive area is increased by 0.18-0.54dB, and subjective effects are obviously improved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
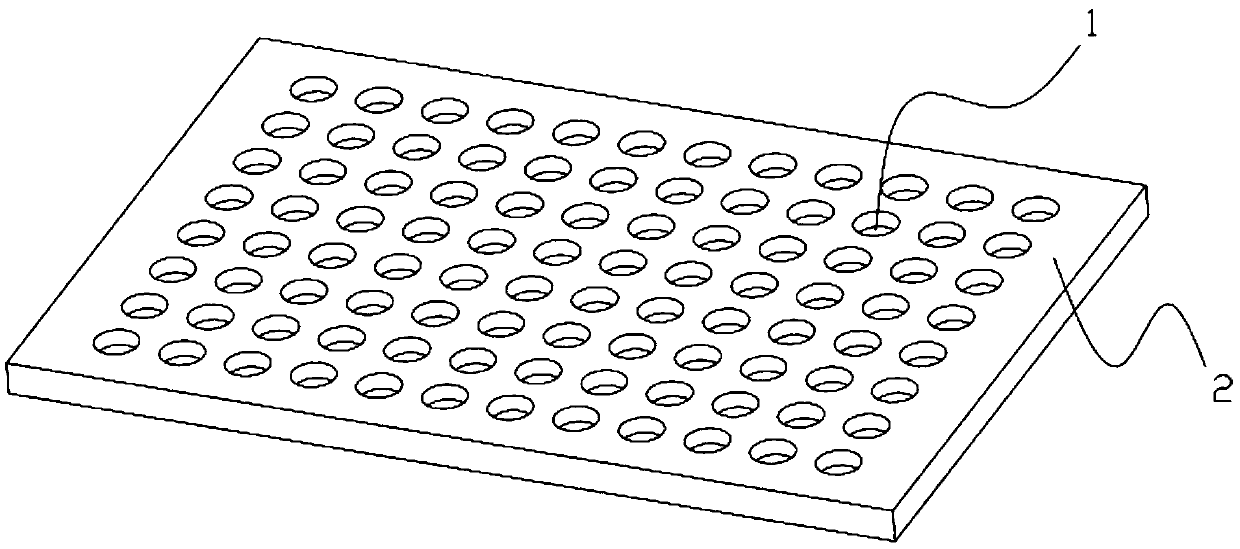
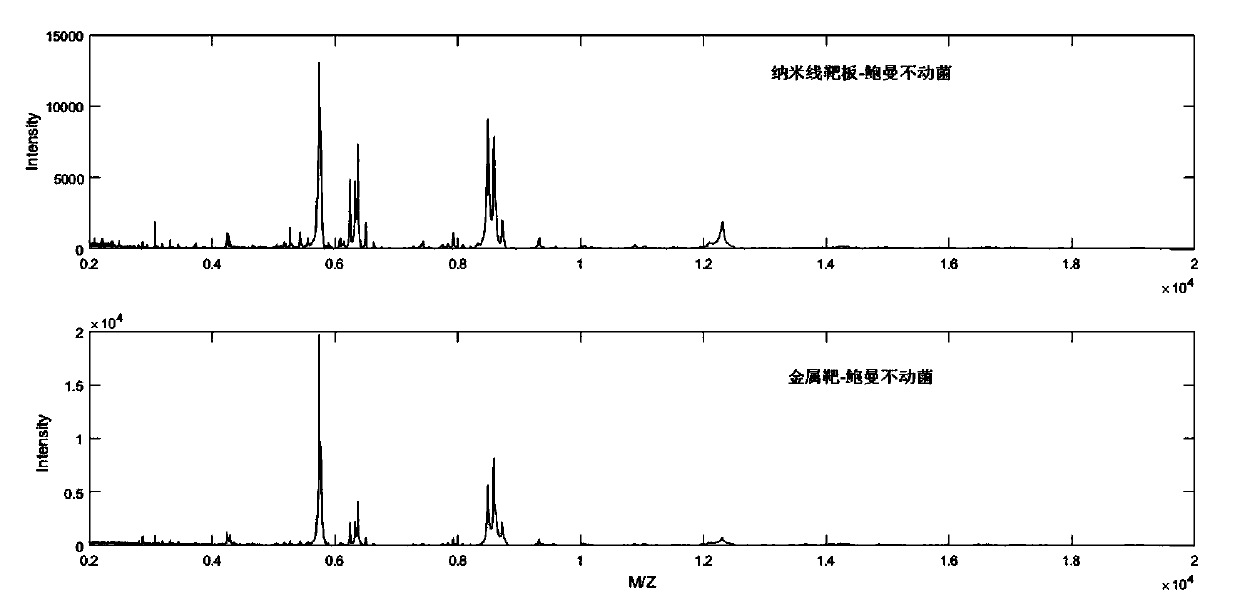
General-purpose nanochip for mass spectrometry and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109541012APossess apical enhancement effectFacilitated ionizationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNanosensorsSemiconductor materialsEnergy absorption
The invention discloses a general-purpose nanochip for mass spectrometry, and relates to the technical field of mass spectrometry. The host material of the nanochip is silicon-based semiconductor material, array spotted holes are distributed at the surface of the host material, the inner surfaces of the spotted holes are nanostructures; the surface of the host material has regional hydrophobic modification, the internal portions of the array spotted holes are hydrophilic zones, and the outer portions of the array spotted holes are hydrophobic zones; or the internal portions of the array spotted holes are hydrophobic zones, and the outer portions of the array spotted holes are hydrophilic zones. The present invention further discloses a preparation method and a clinical application of the nanochip. The nanostructures can be used to extract the molecules at the surface of the sample of the biological tissue sample to be tested to improve the laser energy absorption and utilization so asto improve the ionization efficiency and enhance the mass spectrometry signals. The general-purpose nanochip can be widely applied to the field of clinical testing.
Owner:HANGZHOU WELL HEALTHCARE TECH CO LTD
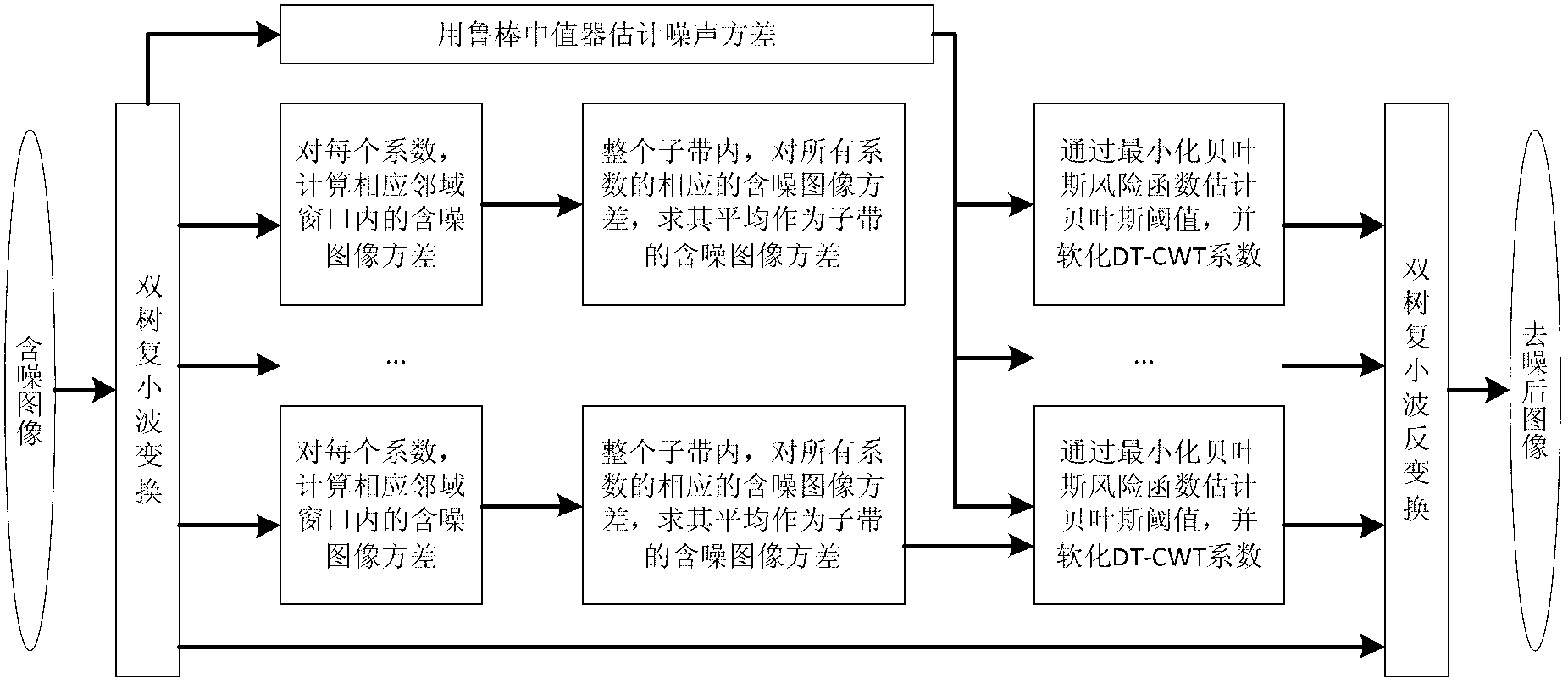
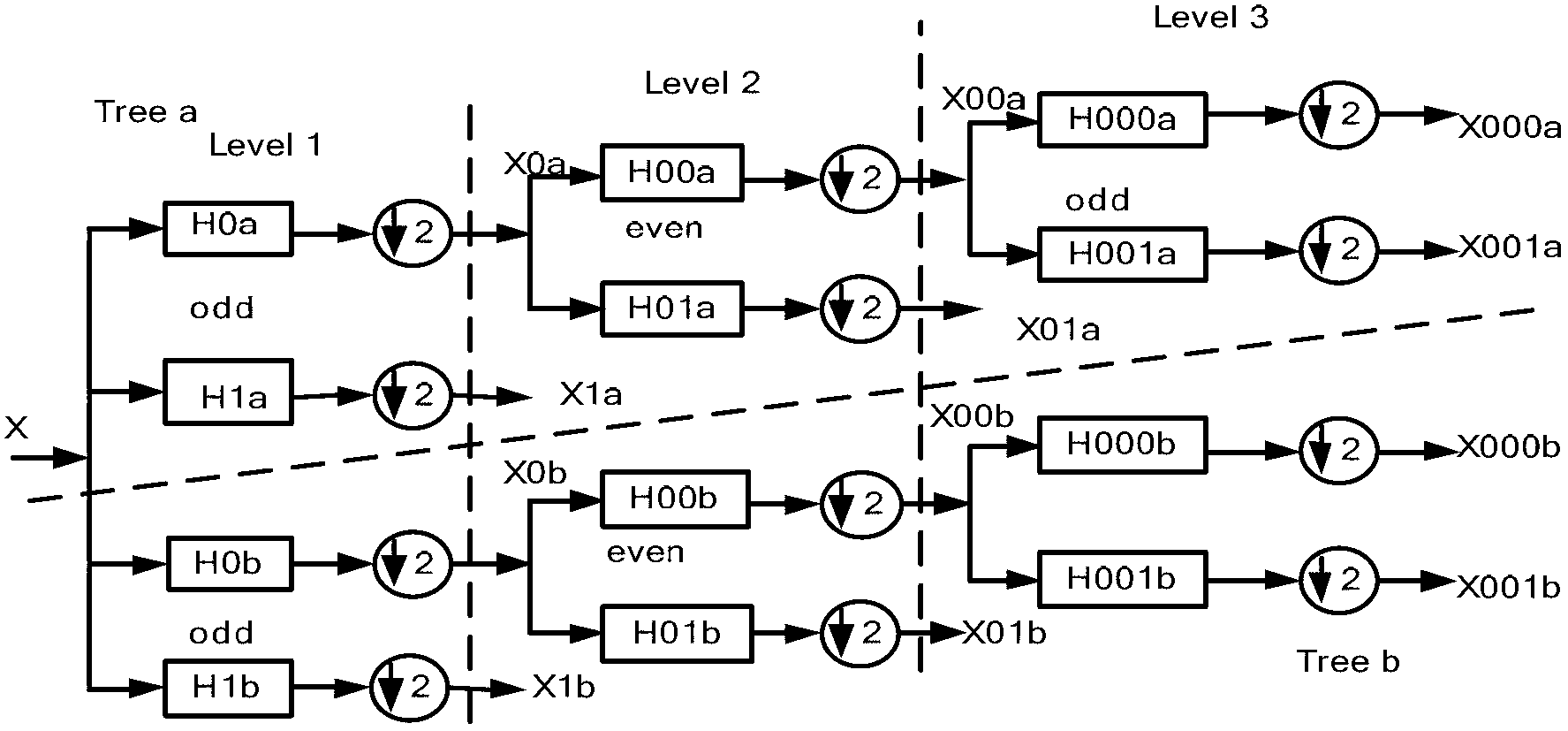
Neighborhood adaptive Bayes shrinkage image denoising method based on dual-tree complex wavelet domain
InactiveCN102800056AEfficient denoisingImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementThree levelImage denoising
The invention discloses a neighborhood adaptive Bayes shrinkage image denoising method based on a dual-tree complex wavelet domain. The method comprises the following steps: 1) performing dual-tree complex wavelet transform on a noisy image, and performing three-level decomposition to obtain multiple sub-band coefficients; 2) estimating the noise variance by use of a robust median device; 3) processing each sub-band coefficient except the low-pass sub-band coefficient in the following steps: a) calculating the variance of the noisy image in corresponding neighborhood window for each DT-CWT (dual-tree complex wavelet transform) coefficient; b) averaging the variances of the noisy image corresponding to all the coefficients to estimate the neighborhood variance of the noisy image of the sub-band; and c) assuming that a statistical model of the DT-CWT coefficients of the image obeys a GGD (general Gaussian distribution) model, estimating the optimal threshold through a minimal Bayes risk function, and softening the wavelet coefficient in the sub-band; and 4) performing dual-tree complex wavelet inverse transform reconstruction on the wavelet coefficient to obtain the denoised image. The method disclosed by the invention has perfect denoising performance and good adaptivity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Earthquake data compression method based on tensor adaptive rank truncation
ActiveCN106646595ASimplify compression workGuaranteed compressionSeismic signal processingData compressionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses an earthquake data compression method based on tensor adaptive rank truncation. According to the method, based on given compression conditions and a different-dimension singular value setting truncation rank acquired through instant higher-order singular value decomposition, tensor decomposition is carried out further according to singular value distribution determination truncation rank magnitude; on the condition that a compression rate is guaranteed, a compression peak value signal to noise ratio is improved, and the compression effect is improved; through designing the tensor decomposition flow based on adaptive rank truncation, manual parameter regulation and control in the compression process can be reduced, and data compression work is simplified. On the basis of the singular value distribution setting truncation rank magnitude, data anisotropy characteristics are utilized, a singular value standard deviation is introduced to calculate weight of a truncation rank corresponding to different dimensions, the compression peak value signal to noise ratio is improved, and the data compression effect is further improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
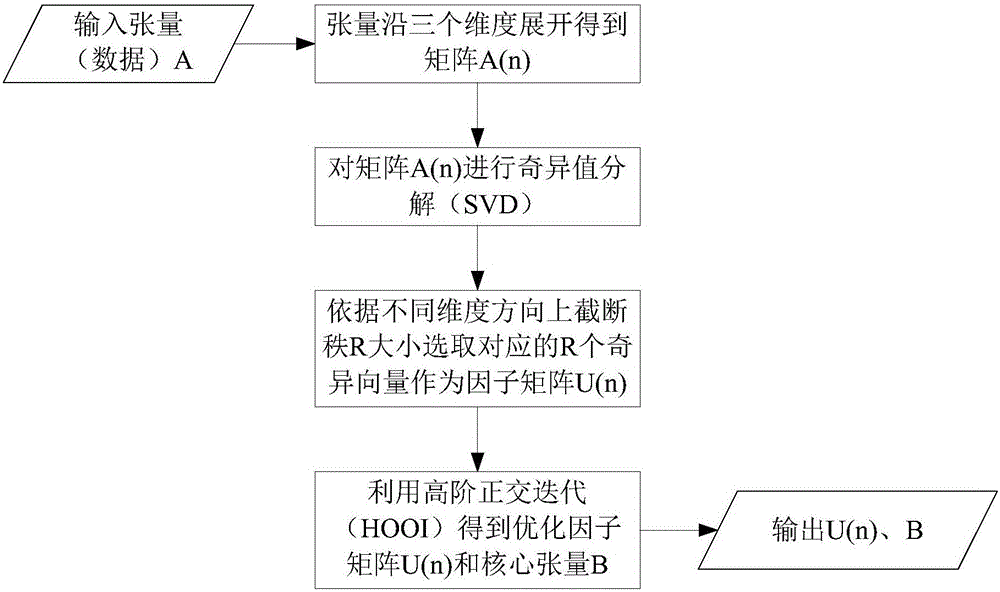
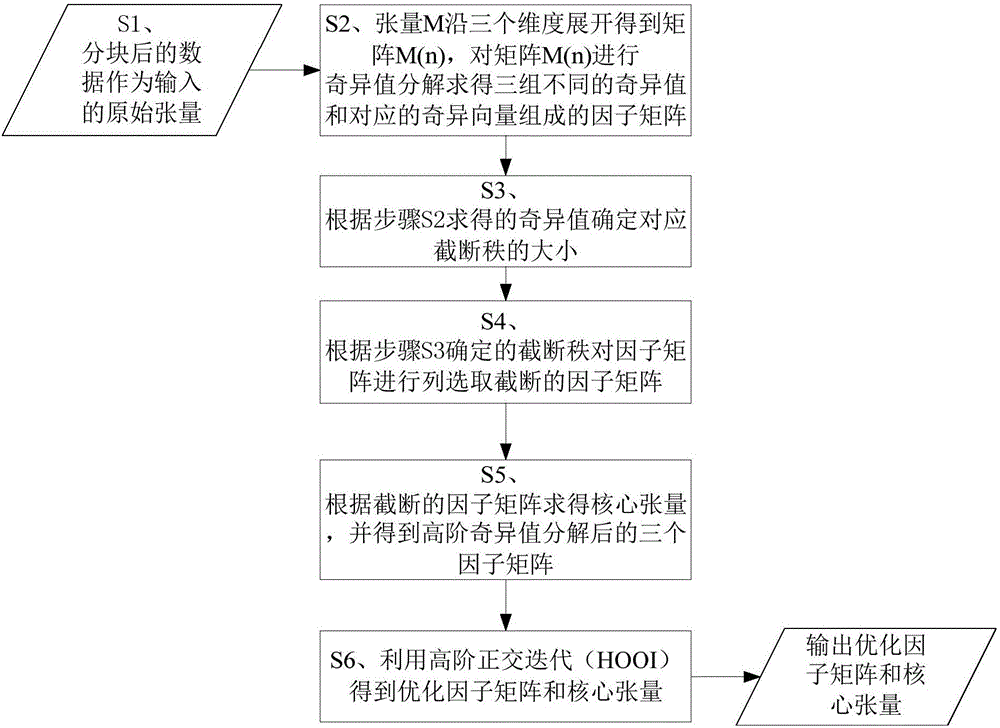
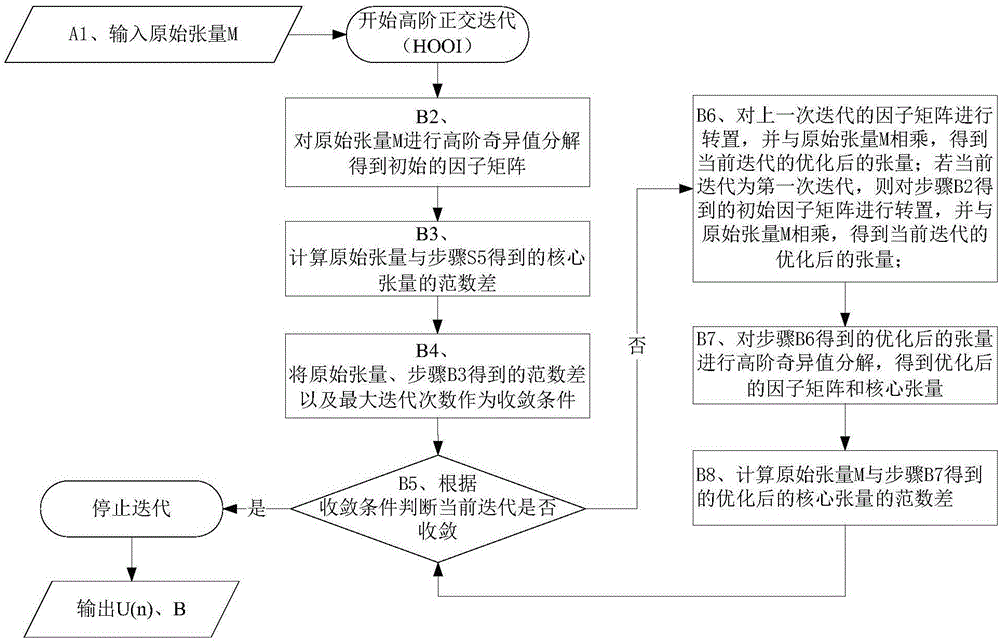
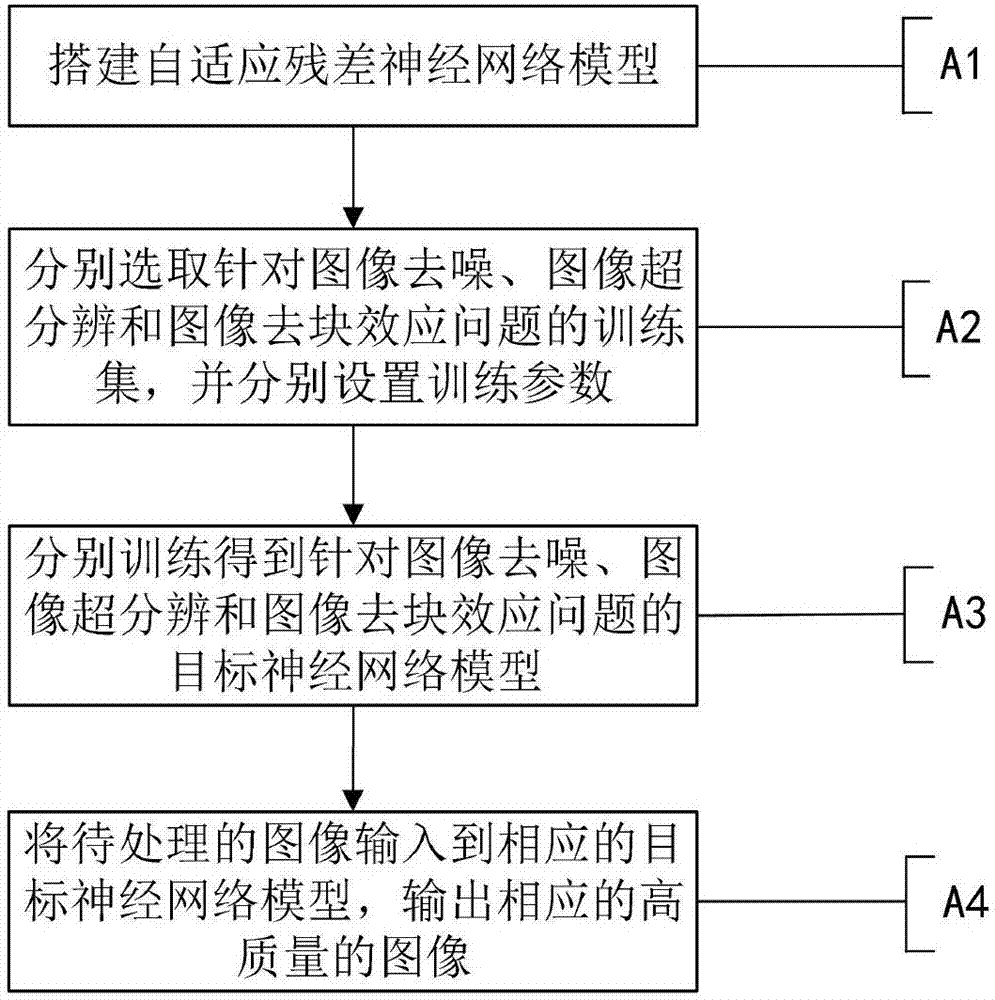
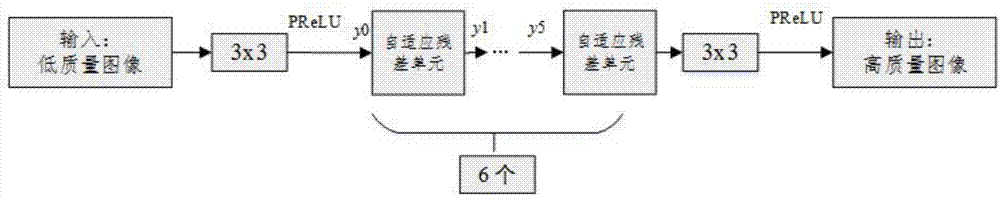
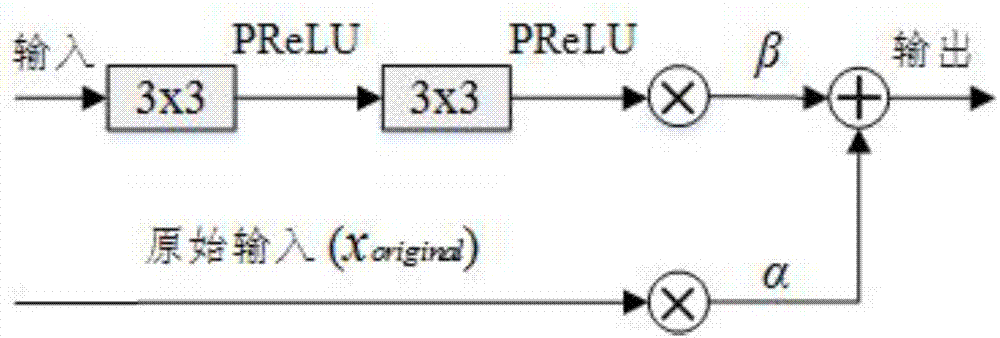
Image restoration method based on adaptive residual neural network
InactiveCN107507141AImprove learning effectQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisImage denoisingNerve network
The invention discloses an image restoration method based on an adaptive residual neural network. The method comprises the steps that an adaptive residual neural network model is built, wherein the adaptive residual neural network comprises a number of adaptive residual units connected in series; training sets for image denoising, image super-resolution and image deblocking effects are respectively selected, and corresponding training parameters are respectively set; according to the adaptive residual neural network model and the training parameters for image denoising, image super-resolution and image deblocking effects, the corresponding target neural network model is trained respectively with the goal of minimizing a loss function; and according to the trained target neural network model for the problem of image denoising, image super-resolution and image deblocking effects, an image to be processed is input to the corresponding target neural network model, and a corresponding high-quality image is output. According to the invention, the PSNR, SSIM and visual effect of the image can be remarkably improved, and the method has the advantages of good recovery effect, high speed and strong robustness.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
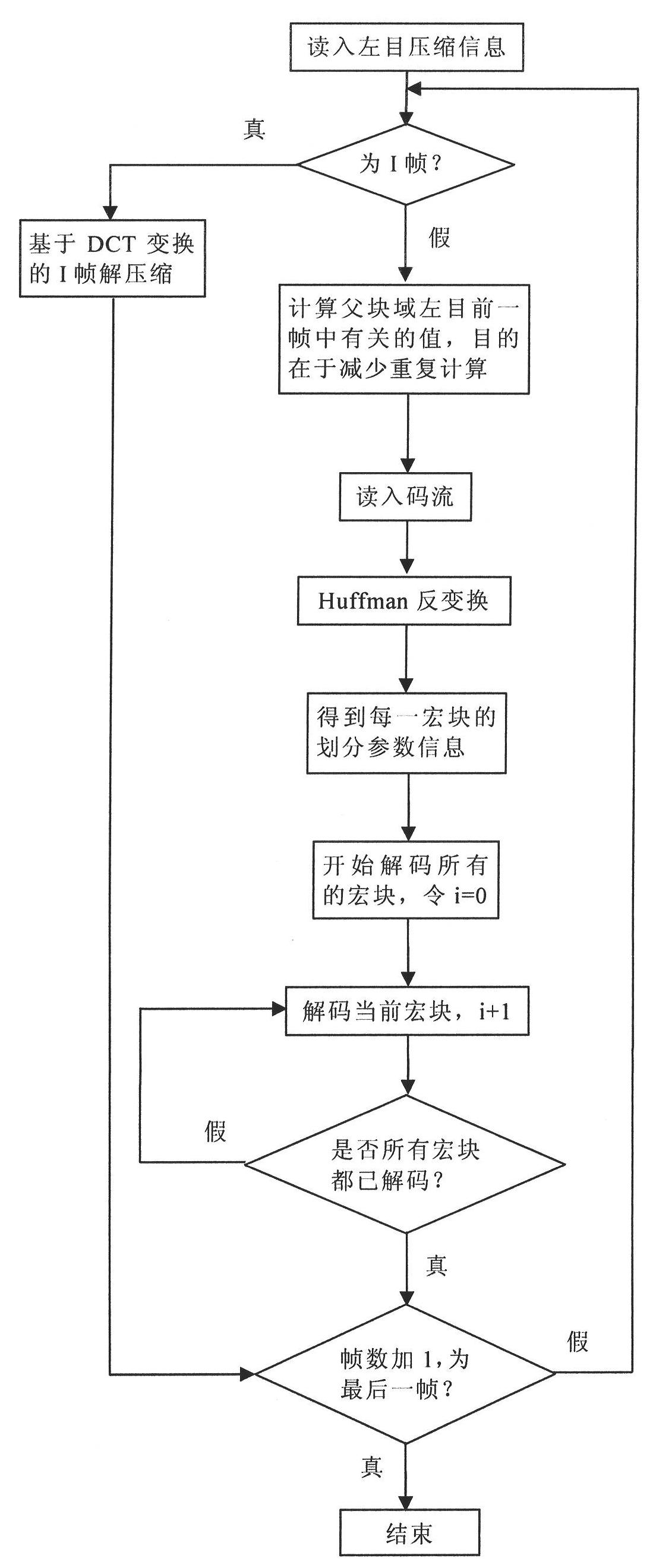
Fractal-based binocular stereoscopic video compression coding/decoding method
InactiveCN101980538AReduce compression timeReduce blockinessTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationStereoscopic videoDecoding methods
The invention provides a fractal-based binocular stereoscopic video compression and decompression method. In binocular stereoscopic video coding, a left channel is taken as a basic layer, a single motion compensation predictive mode (MCP) is adopted for coding, and the method comprises the following steps of: performing block DCT transformation coding on a left-eye start frame, performing motion estimation / compensation coding on a left-eye non-I frame, and calculating the pixel sum and the sum of squares of pixels of subblock domain and father block domain-related subblocks; searching the most similar matching block by using a full search method in a previous frame, namely a reference frame searching window of left-eye video; and finally compressing the coefficient of an iterated function system by using a Huffman coding method. A right channel is taken as an enhancement layer, the MCP and a parallax compensation predictive mode (DCP) are adopted for coding, and the lowest error is selected as a predicted result. During the DCP coding mode, the polalization and directionality in a stereoscopic parallel shooting structure are fully utilized; and the corresponding decompression process comprises the following steps of: for the left eye, decoding the start frame I by adopting a reverse DCT transformation mode, and performing Huffman decoding on the non-I frame so as to acquire the coefficient of the iterated function system; performing macrolbock-based decoding, calculating the pixel sum and the sum of squares of pixels of father block domain-related subblocks in the previous frame; and for a right eye, calculating the pixel sum and the sum of squares of pixels of the father block domain-related subblocks in the right-eye previous frame and a left-eye corresponding frame.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Video sequence reconstruction method based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN107360426AQuality improvementReduce data volumeDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a video sequence reconstruction method based on compressed sensing. An encoding end separates an original video sequence into two types of frames, i.e., key frames and non-key frames, and measurement is performed respectively by use of different sampling rates. At a decoding end, different video sequences are subjected to performance judgement of two different algorithms, i.e., motion estimation / compensation prediction and optical flow method prediction, and then through combination with a comparison result, all the non-key frames are subjected to good-performance algorithm reconstruction by use of inter-frame correlation . When a video is processed, the amount of data needing to be sampled is small and the quality of the recovered video is good. Compared with a traditional algorithm of video independent reconstruction, the peak signal-to-noise ratio at a low sampling rate is improved and the reconstruction time is shortened.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
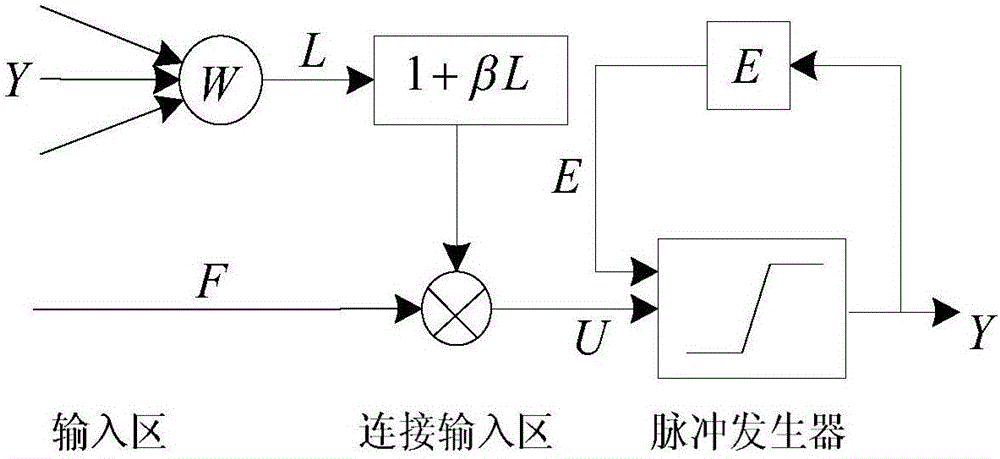
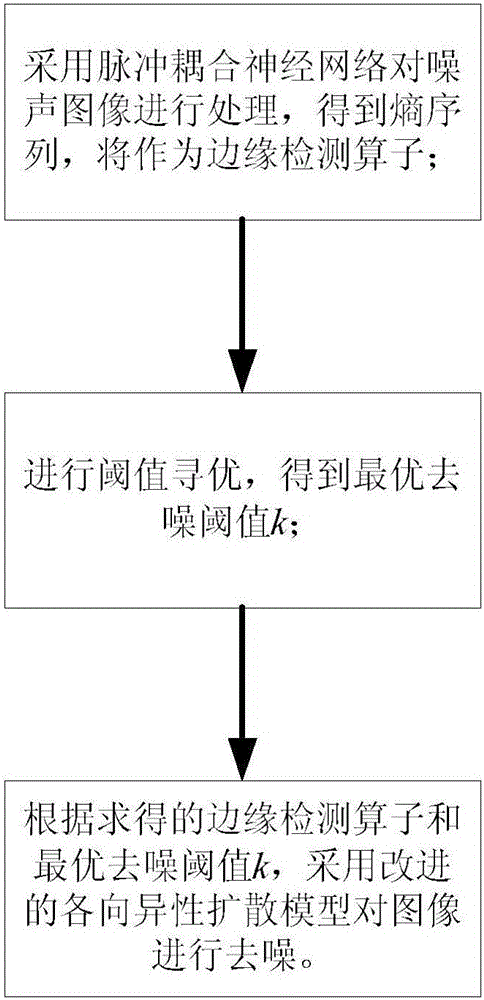
Image de-noising method based on anisotropic diffusion of image entropy and PCNN
ActiveCN105005975AAvoid errorsImprove edge detection capabilitiesImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDe noise
The invention discloses an image de-noising method based on anisotropic diffusion of image entropy and PCNN. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, processing a noise image with a pulse coupling neural network to obtain a entropy sequence En; using the En as an edge detection operator; then searching an optimal threshold to obtain an optimal de-noising threshold value k; finally de-noising the image by using an improved anisotropic diffusion model according to the obtained edge detection operator En and the optimal de-noising threshold value k. The method of the invention not only could effectively remove the image noise, but also could completely hold the area information of the image simultaneously.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Compressive sensing method based on principal component analysis
InactiveCN102722866AEfficient use ofKeep informationImage enhancementKernel principal component analysisPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a compressive sensing method based on principal component analysis and mainly solves the problem of low sampling efficiency in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) taking z images from a gray natural image library, taking a 32*32 sub-block from each image which is taken at intervals of three pixels along the horizontal and vertical directions to form a training sample set x1, x2, ..., and xm, and training a full-rank observation matrix Phi(f) for the training sample set x1, x2, ..., and xm by using a principal component analysis method, wherein z is not less than 15 and not more than 25, and m is the quantity of training samples; (2) dividing an image which is required to be sampled into n 32*32 sub-blocks x1, x2, ..., and xn, acquiring an observation matrix Phi according to sampling rate s and the full-rank observation matrix Phi(f), sampling each image sub-block by using the observation matrix Phi, and thus obtaining an observation vector y; (3) acquiring an initial solution x0 of the image according to the observation vector y; and (4) iterating according to the initial solution x0 until iteration is in accordance with end conditions, and thus obtaining a reconstructed image x'. The compressive sensing method has the advantages of high sampling efficiency, high image reconstruction quality and clear principle, and is easy to operate and applicable to sampling and reconstruction of a natural image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
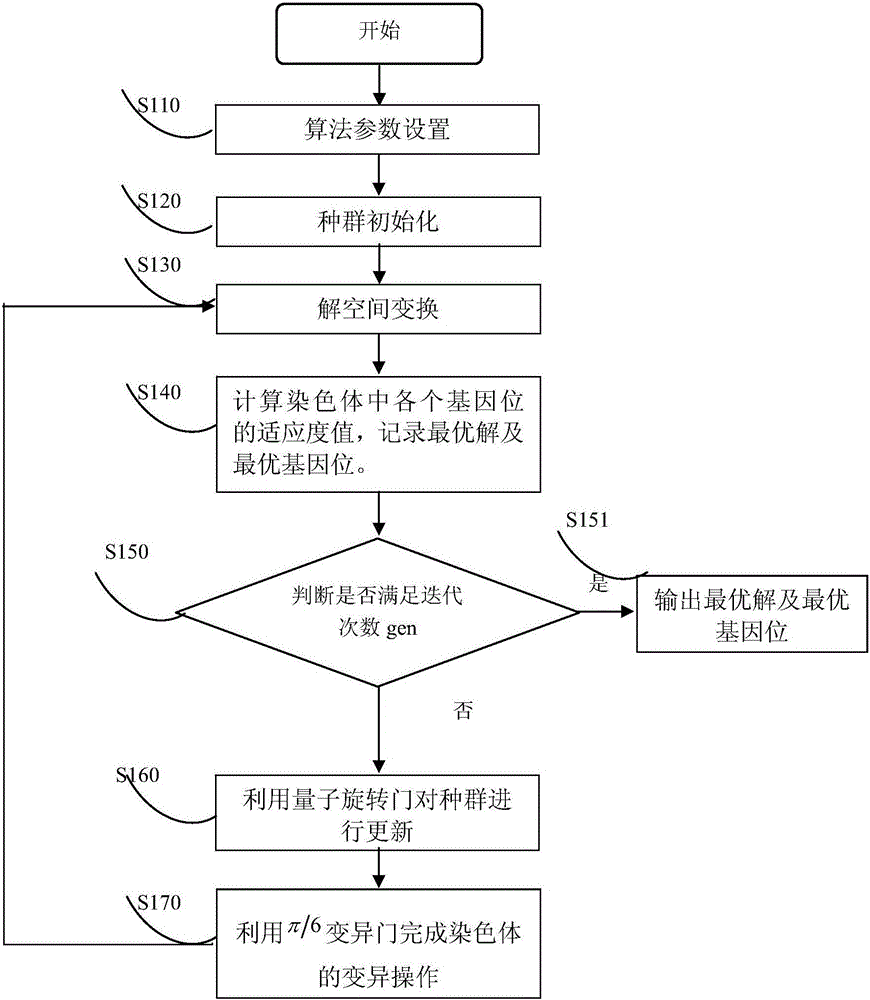
Wavelet threshold image denoising method based on F-type double-chain quantum genetic algorithm
The invention discloses a wavelet threshold image denoising method based on an F-type double-chain quantum genetic algorithm. First of all, single-value mapping processing is performed on a coding space, the search space of the algorithm is reduced, and search density is increased; secondly, a self-adaptive step length factor is introduced during quantum updating to enable a step length to change along with the gradient change of a target function at a search point so that the problem of global optimal solution search difficulty caused by an "oscillation" phenomenon generally existing in a conventional searching optimization algorithm at present is effectively solved; and finally, a pi / 6 gate is brought forward during chromosome variation updating so that the disadvantage is improved that conventional NOT gate variation cannot update quantum bit probability amplitude. According to the invention, an F_DCQGA optimization algorithm is also applied to a threshold selection mechanism of wavelet threshold de noising, at the same time, a self-adaptive threshold function is brought forward, and accordingly, a conventional wavelet threshold denoising method is improved. The method provided by the invention improves the convergence speed and the search precision of a wavelet threshold function.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Image noise reduction system and method based on K-SVD (Singular Value Decomposition) and locally linear embedding
InactiveCN102789633AHighlight the internal information structureImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementSingular value decompositionImage denoising
The invention discloses an image noise reduction system and method based on K-SVD (Singular Value Decomposition) and locally linear embedding, and particularly relates to a signal sparse representation and reconstruction technique based on dictionary learning and an image noise reduction technique based on manifoid learning. A K-SVD method is adopted to be a frame as the signal sparse representation and reconstruction technique based on the dictionary learning, the locally linear embedding used as a constrain condition is added into a target function while the signal sparse representation is solved, so that the relation of the decomposed sparse coefficients is strengthened, the influence of the random noise on the sparse coefficients is overcome, and the image noise reduction effect better than that of the original K-SVD method is obtained.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Image de-noising method based on bidirectional enhanced diffusion filtering
InactiveCN105427262AImprove contourWeaken texture detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionAutomatic control
The invention discloses an image de-noising method based on bidirectional enhanced diffusion filtering, which simplifies a diffusion equation. The method comprises the steps of establishing a bidirectional diffusion coefficient so that a model can implement a bidirectional process of smoothing and sharpening in the diffusion process, enhancing an image in order to further improve the smoothing and sharpening strength, performing wavelet transform to enhance the overall outline of the image and weaken texture details of the image, then adaptively designing and improving a gradient threshold to automatically control the gradient threshold according to the maximum gray value and the iterative times of the image and further retain edge and detail features of the image, finally, simulating the purposed model, and performing simulation verification on the method by using MATLAB software. The method can be used for removing image noise and protecting detail information of edge, texture and the like, greatly improves the peak signal to noise ratio, has more excellent de-noising performance, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Image noise detection and denoising method based on Hessian matrix
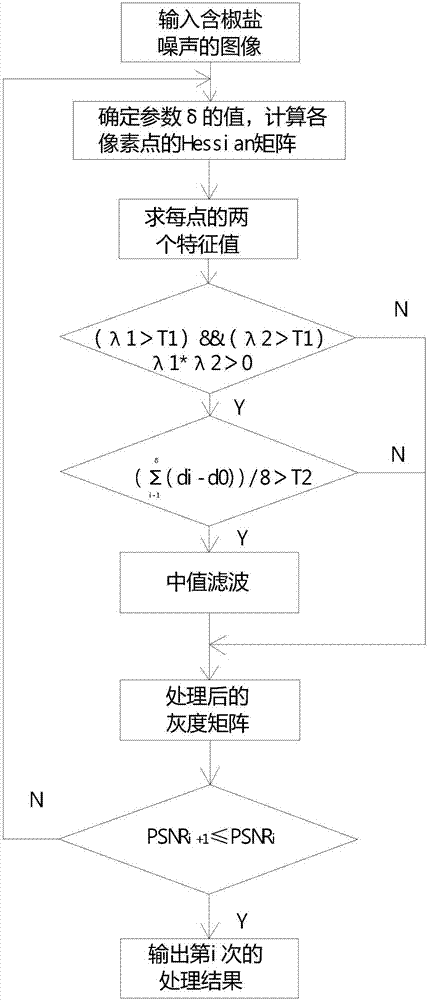
PendingCN107038688AProtection detailsProtection edgeImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage edge
The invention discloses an image noise detection and denoising method based on a Hessian matrix, and the method comprises the steps: detecting a noise point through different characteristics of the feature value of the Hessian matrix of the noise point, an edge point and a smooth region point for impulse noise, employing the median filtering idea in a 3*3 window which takes the detected point as the center, employing the central value of the window to replace the noise point, and carrying out no processing for other points; proposing the concept of a noise point detection rate for the algorithm evaluation. Because the smooth region point or the edge point can be taken as the noise point during the detection of the noise point, a third discrimination condition is set for further improving the detection accuracy and denoising effect. For an image with the large noise density, the method also can obtain a better effect through multi-iteration. The method is better in denoising effect, and keeps more image edge and detail information. Compared with the median filtering, the method is better in effect under the condition of large noise density.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
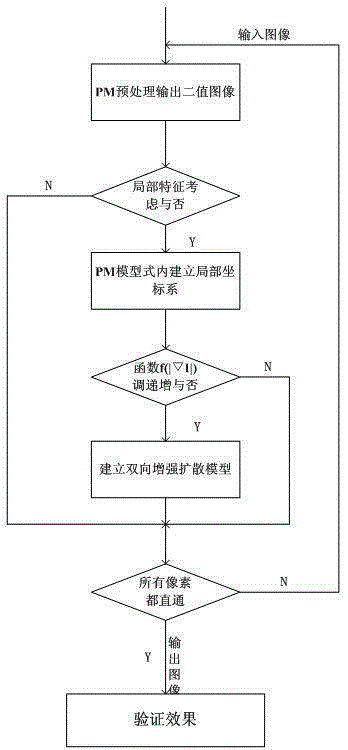
Image smoothing method with combination of gradient and curvature
ActiveCN104331869AEasy to handleImprove clarityImage enhancementPattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
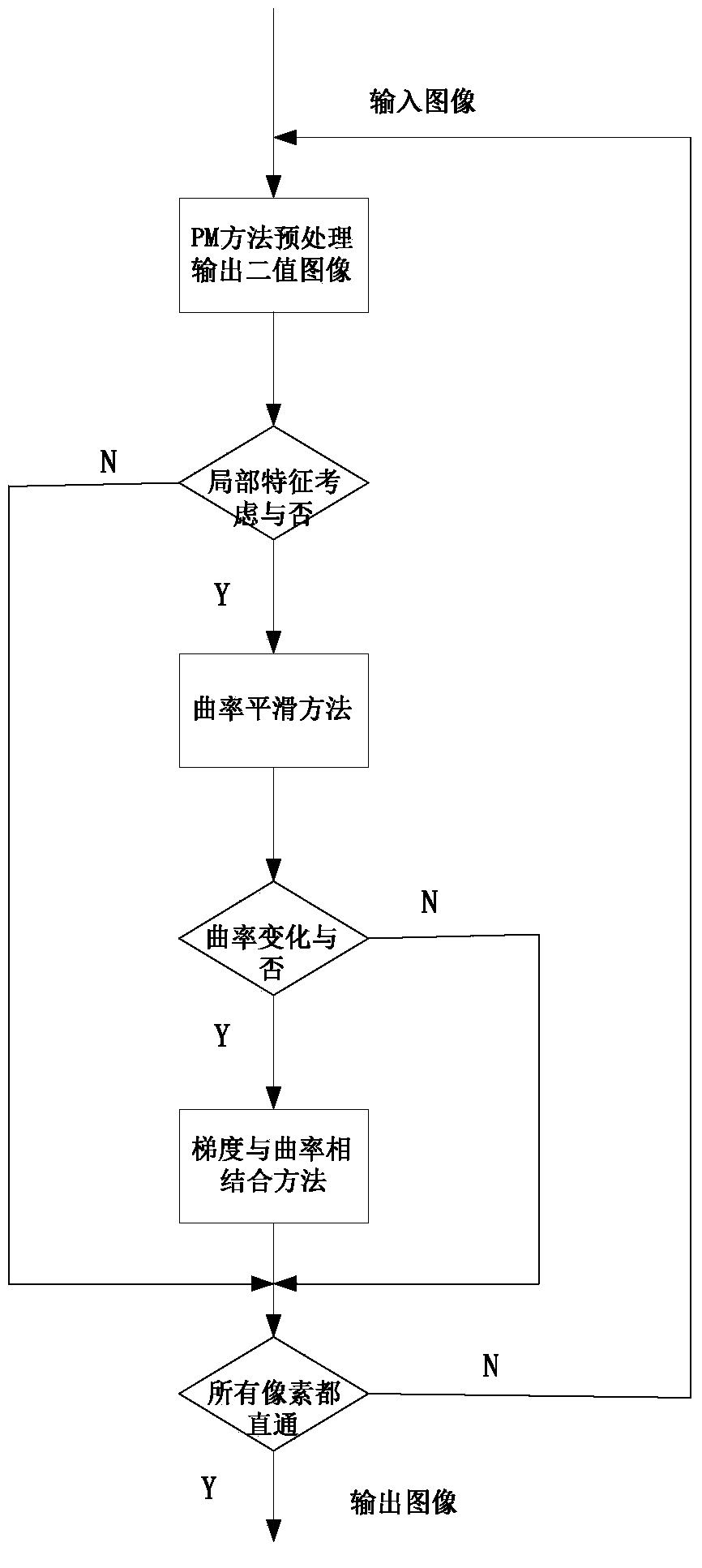
The invention firstly provides an image curvature smoothing method, and the method takes the image level set curvature as the second order micro component for describing the image morphological feature and improving the image processing effect. The curvature obviously changes while the image is polluted by the noise, the method further takes the image level set curvature as the detection factor to be applied to the PM method, the image smoothing method with combination of gradient and curvature is provided, and the method can keep the feature of the image, the peak value signal to noise ratio is greatly improved compared with the previous anisotropy method, the complexity is low, the timeliness is high, the image resolution is improved, the method has more effectiveness and veracity compared with the previous image smoothing method, and the image processing effect is better.
Owner:上海芯辉电子股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com