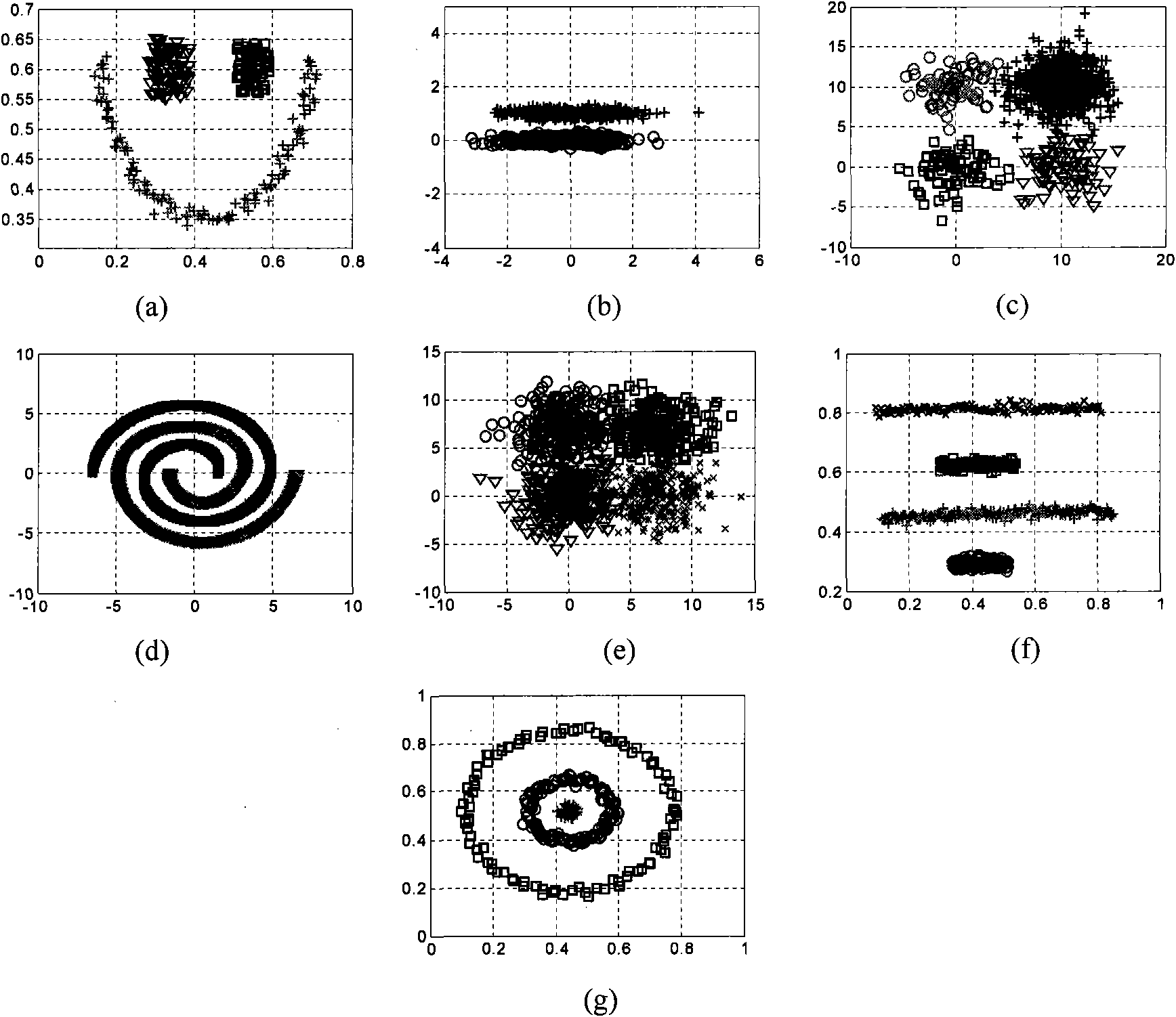
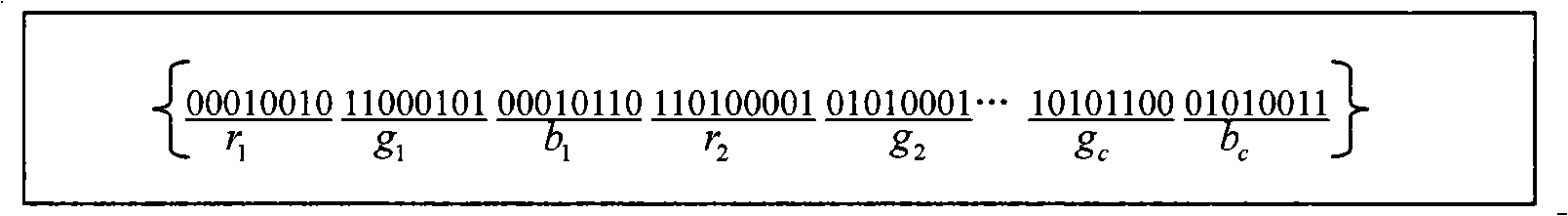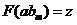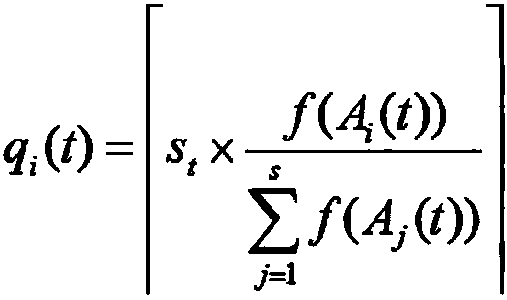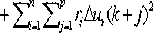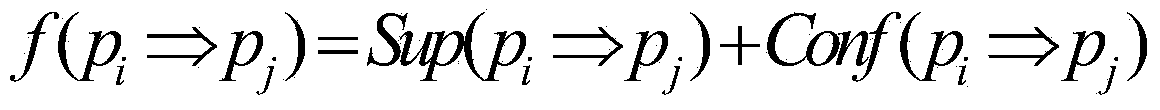Patents
Literature
67 results about "Clonal selection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
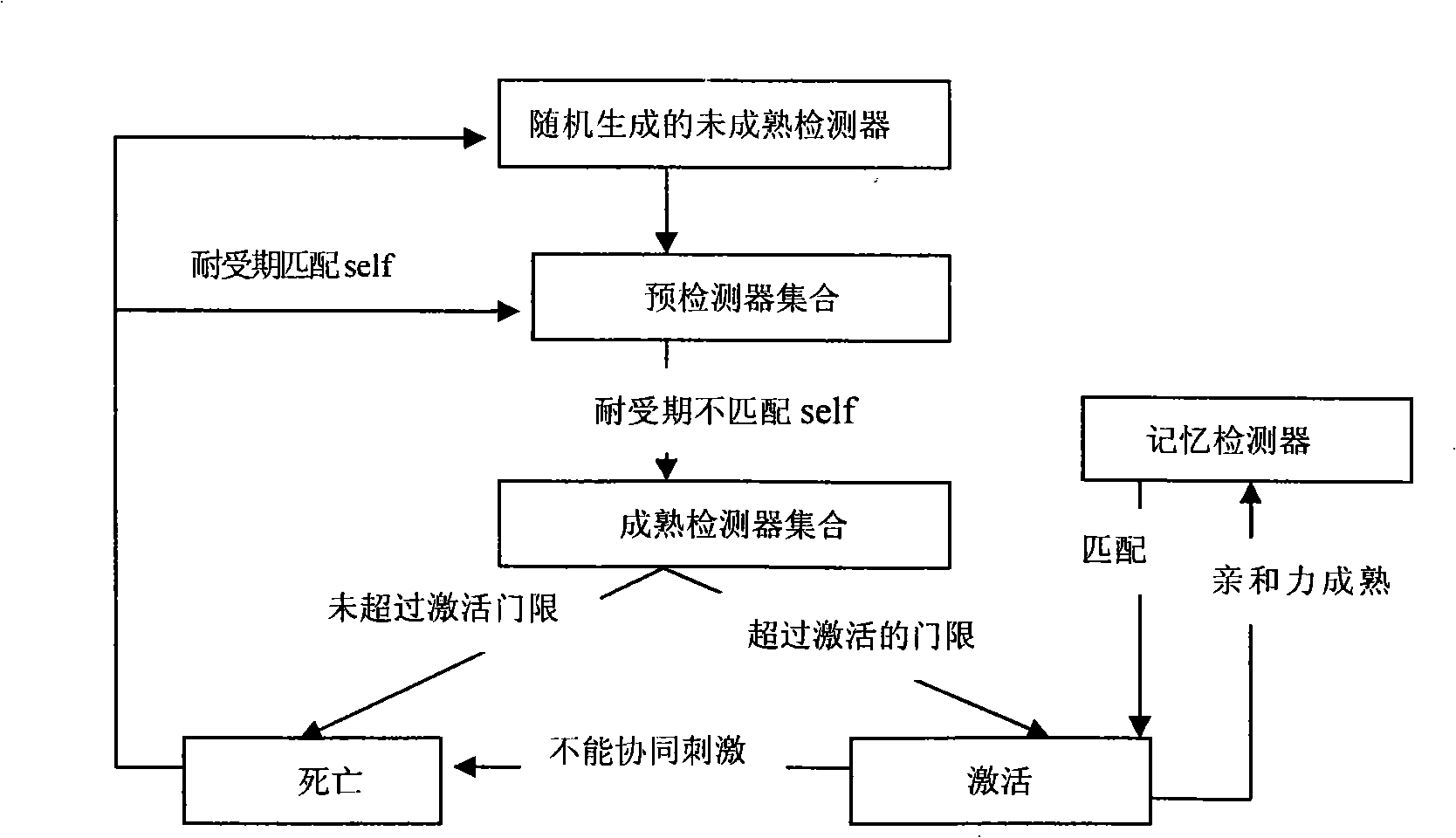
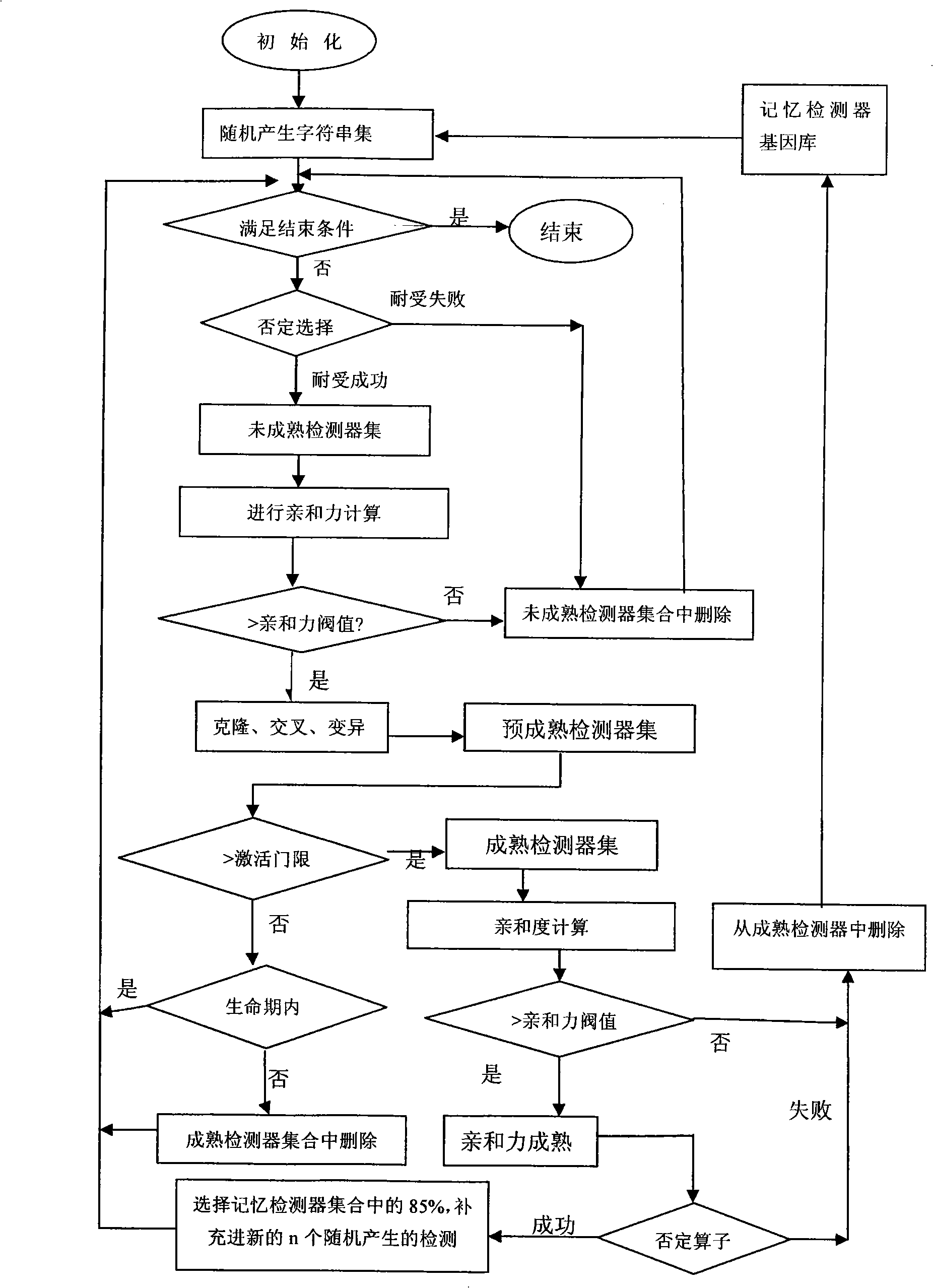
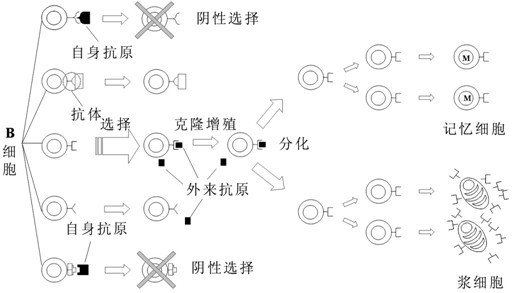
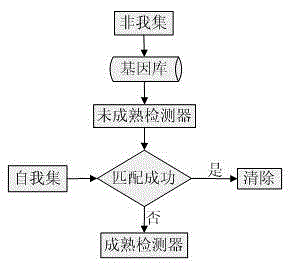
Clonal selection theory is a scientific theory in immunology that explains the functions of cells of the immune system (lymphocytes) in response to specific antigens invading the body. The concept was introduced by Australian doctor Frank Macfarlane Burnet in 1957, in an attempt to explain the great diversity of antibodies formed during initiation of the immune response. The theory has become the widely accepted model for how the human immune system responds to infection and how certain types of B and T lymphocytes are selected for destruction of specific antigens.
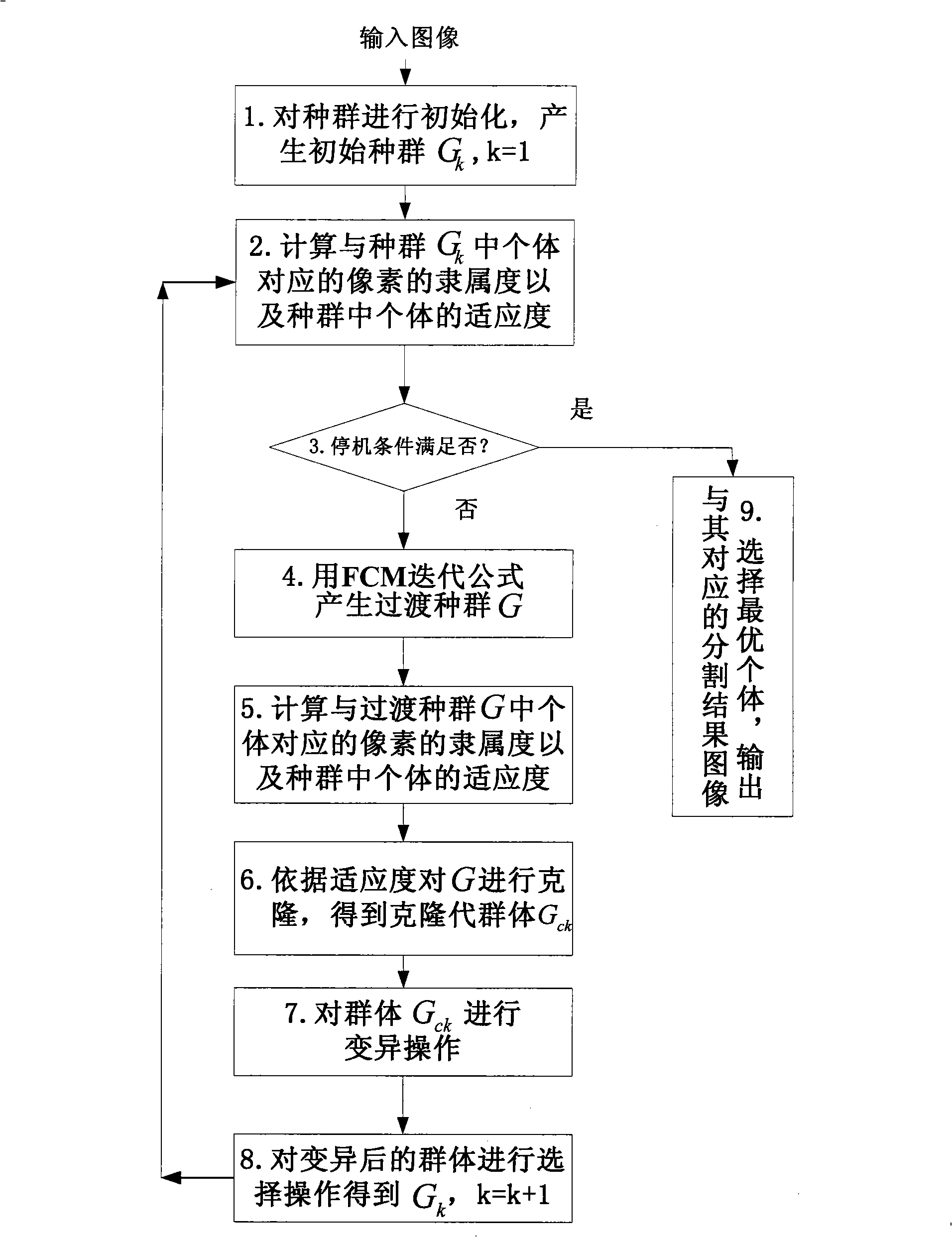
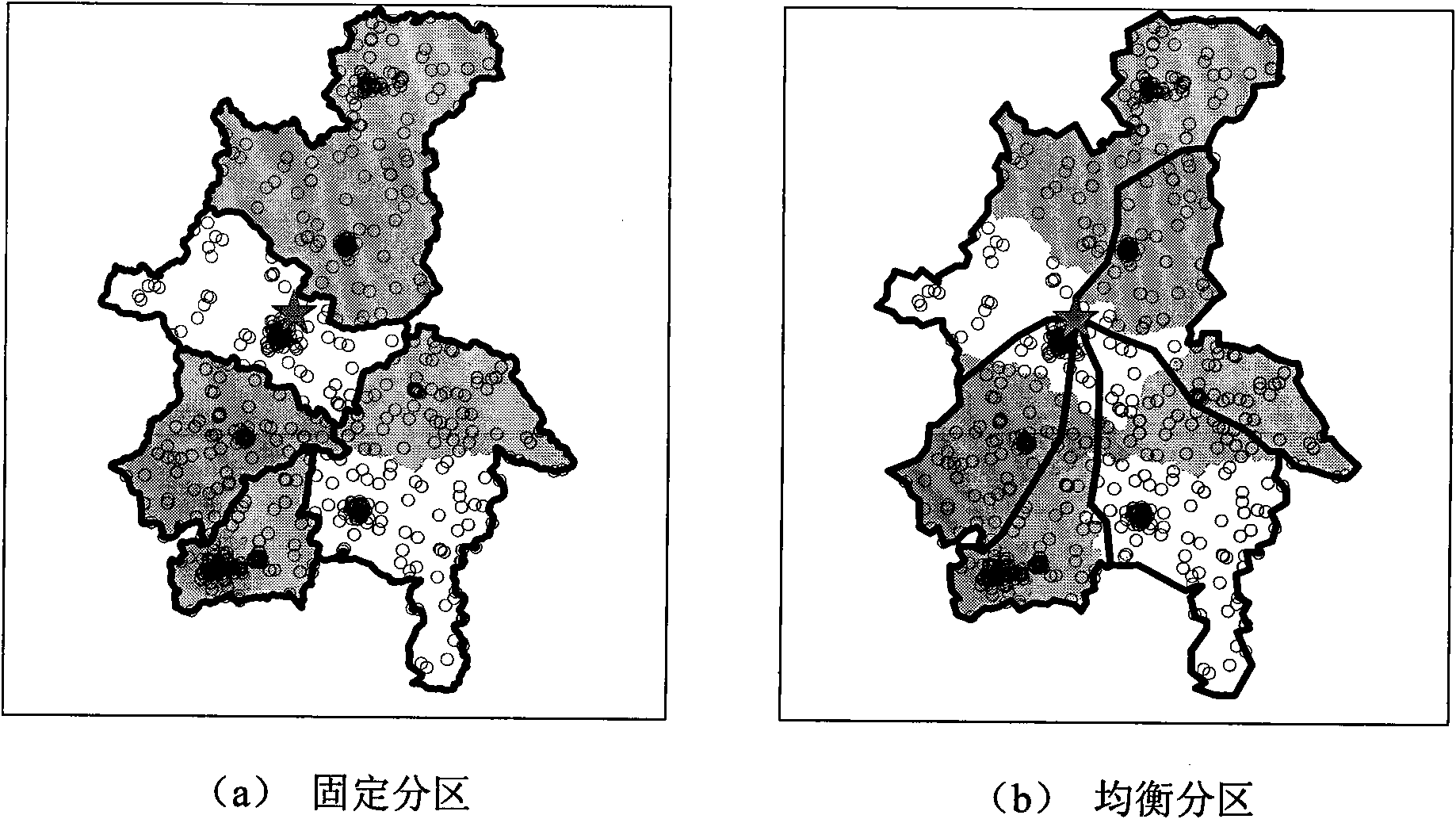
Image segmentation method based on immunity clone selection clustering
InactiveCN101271572AImage segmentation results are reasonableReduce sensitivityImage enhancementGenetic modelsClonal selectionPattern recognition
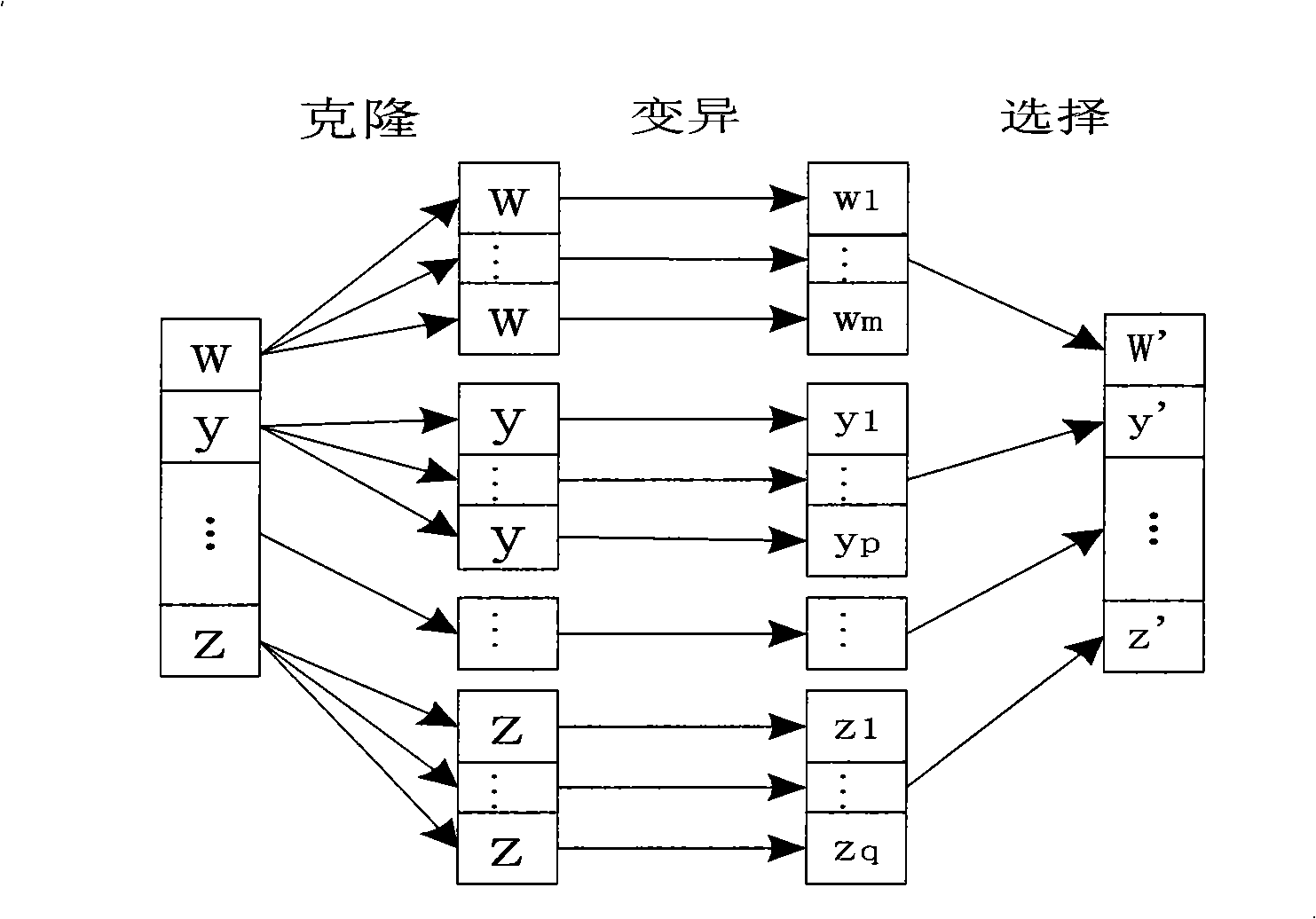
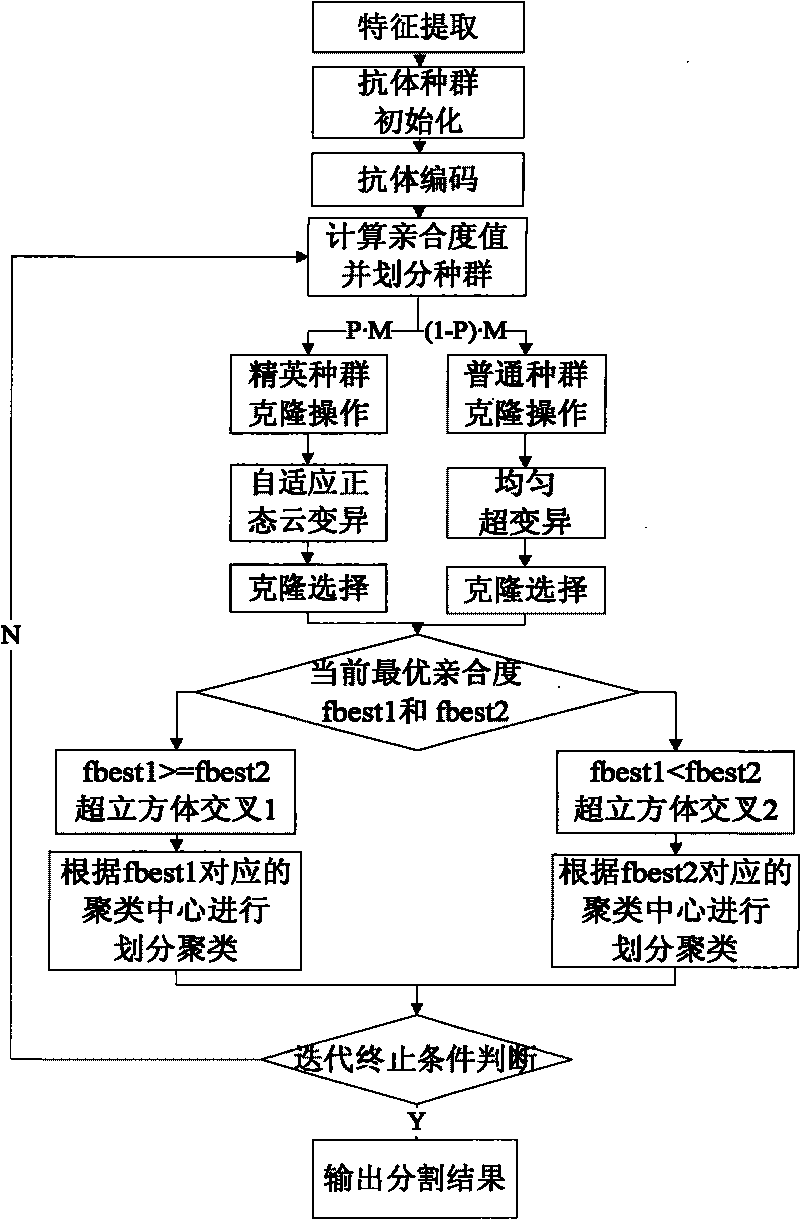
The invention discloses an image segmentation method based on an immune clonal selection cluster, and relates to the technical field of an image processing. The purpose of the invention is to solve the disadvantages that the robustness is lower due to sensitivity of a FCM cluster segmentation method to an initial clustering center and the noise; and spatial relationship between pixels of the image is not considered by the FCM cluster segmentation method. An implementation procedure of the method is as follows: an initial population is created at random according to a setup parameter; adaptation degree of each individual in the present population is calculated to judge whether a halt condition is met; a transitional population is created by a recurrence formula of the FCM; the adaptation degree of each individual in the transitional population is calculated; based on the adaptation degree, a cloning operation is made to the transitional population; a mutating operation is made to the individual in the cloned population; after the mutating operation, a roulette wheel selection is carried on to get a new population to carry out the second step; finally, an optimum individual is selected; and the image of a segmentation result corresponding to the optimum individual is output. The image segmentation method based on the immune clonal selection cluster can be used for the cluster segmentation of a pixel level of the image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
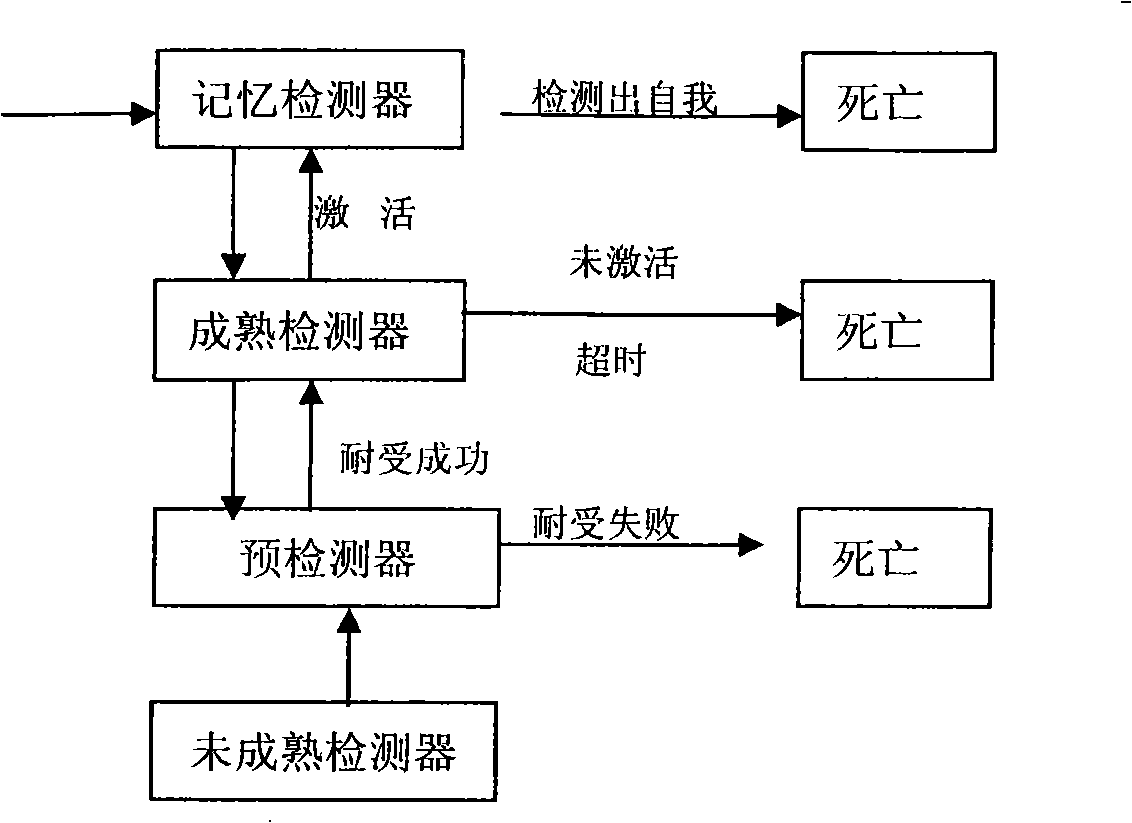
Method for detecting dynamic gridding instruction based on artificial immunity
InactiveCN101299691AEasy to coverHigh-precision detectionGenetic modelsData switching networksClonal selectionClonal selection algorithm
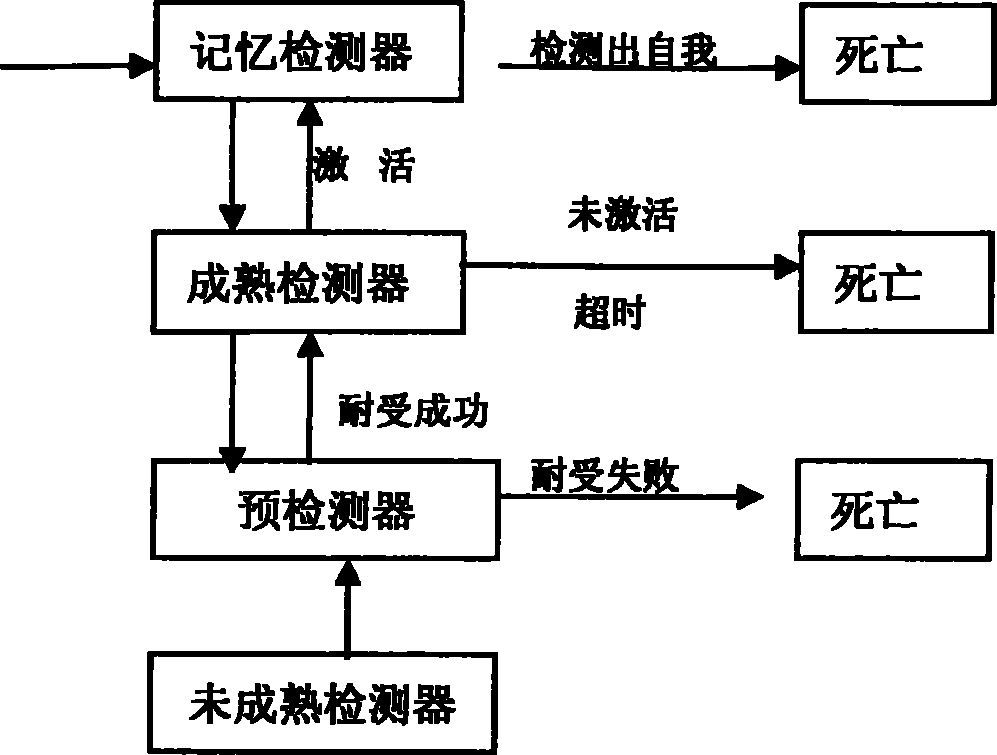
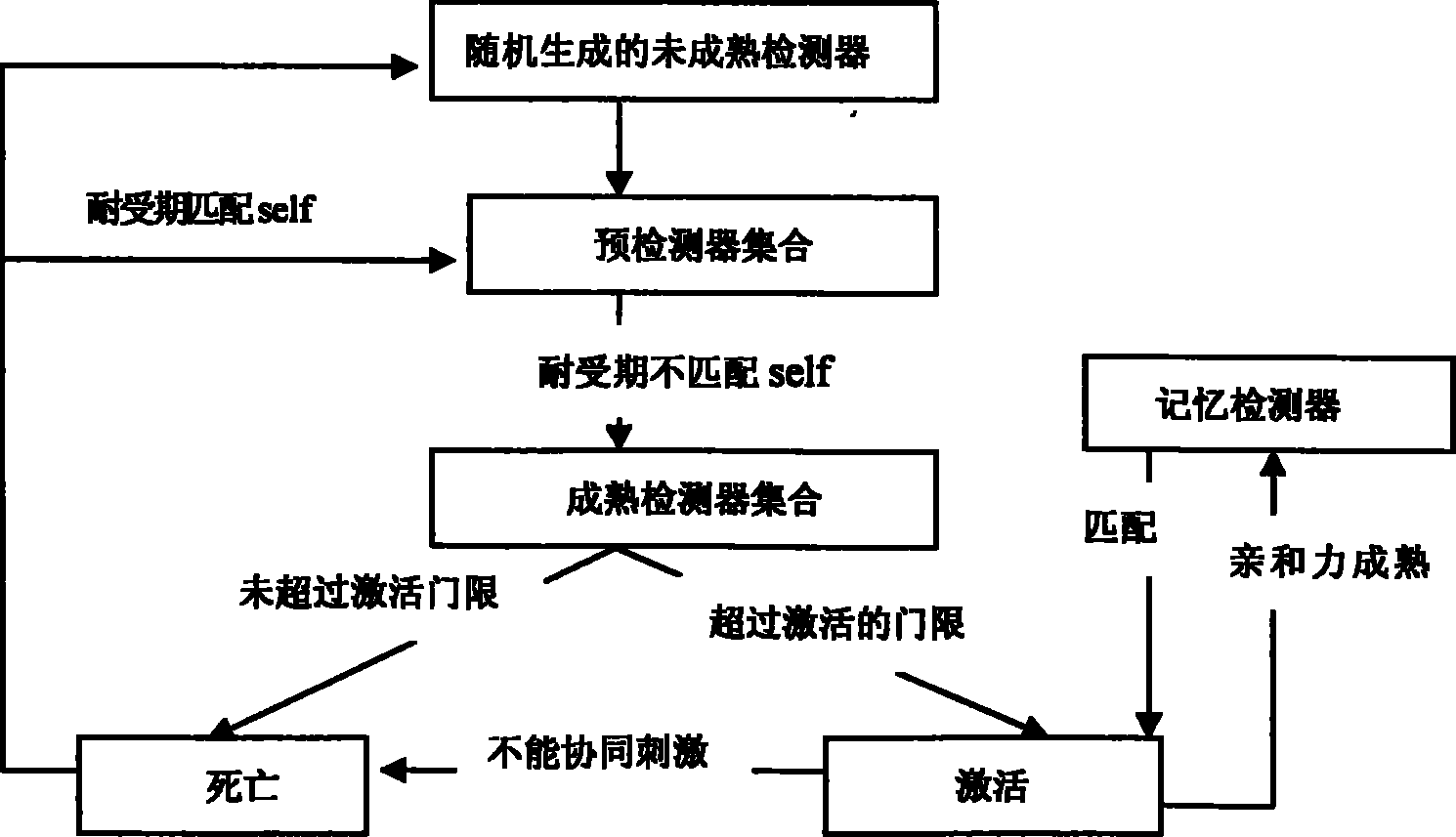
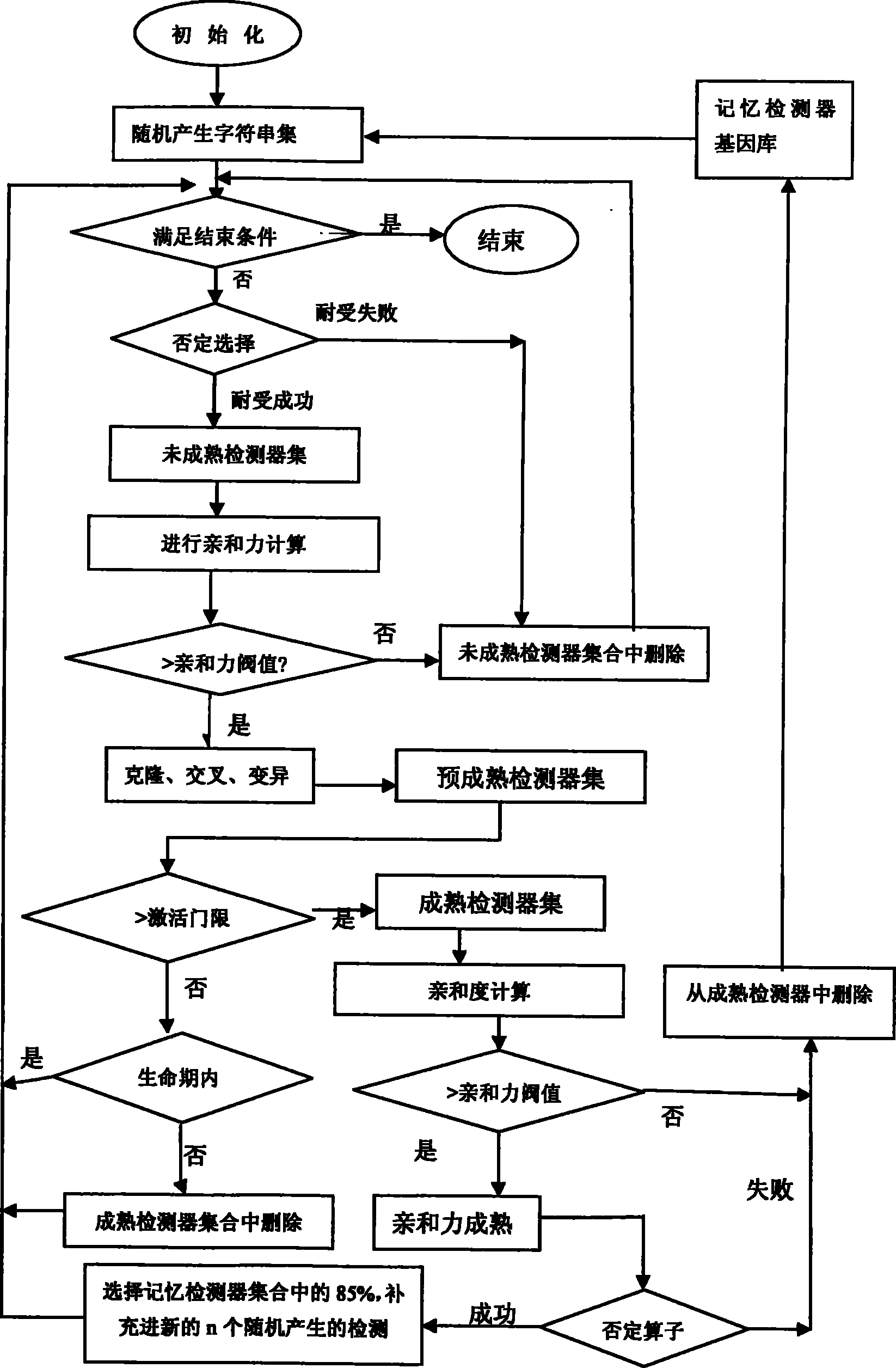
A method for detecting dynamic gridding instruction based on artificial immunity, is a method for detecting instruction facing to gridding which takes use the artificial immunity technique for reference. According to the dynamic and real time requirement of the instruction detection under gridding surroundings, the method takes the prior clonal selection algorithm as main body, combines negative selection, clonal selection, affinity maturation and memory detector gene bank method, so at to dynamic handle the instruction detection under gridding surroundings. The method includes a dynamic detector evolvement process and a gridding instruction detection process which are based on artificial immunity, which is characterized in by using the artificial immunity technique for reference, and combining the negative selection, clonal selection, affinity maturation and memory detector gene bank method; firstly obtaining an evolvement matured detector; and then dynamically handling the instruction detection problem in the gridding surroundings under the coordination of the artificial immunity mechanism, to complete the entire process of dynamic gridding instruction detection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Logistic distribution partitioning balance optimizing method based on immune algorithm
InactiveCN101782986AReduce delivery costsImprove distribution efficiencyBiological modelsLogisticsWork periodClonal selection
The invention discloses a logistic distribution partitioning balance optimizing method, which builds a logistic distribution partitioning multipurpose optimal model and designs immune algorithm solving. A model minimizes zone line number as well as the total distance and the total working time of all lines to balance the line number, the total distance, the total working time and the total demanded quantity of different zones. The model adopts VRP, TSP and a shortest path algorithm to ensure the optimization of a distribution path while balancing zones. An arithmetic operator and a mechanism aroused by designed immunity comprise clonal selection, high-frequency variation, immune clearance and immunological memory, and two stages are searched to solve by the synergy of the construction and the zone of the initial partitioning scheme. The method of the invention is suitable for the partitioning balance optimization of large-scale logistic distribution, and can lower logistic distribution cost, improve logistic distribution efficiency and improve the degree of satisfaction of customers to staff.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Immune clone quantum clustering-based SAR image segmenting method
InactiveCN101699514AOvercome the defect that it is easy to fall into local extremumOvercome limitationsImage analysisGenetic modelsAntibody AffinitiesData set
The invention discloses an immune clone quantum clustering-based SAR image segmenting method, which relates to the technical field of image processing, and mainly solves the problem of limitation on the application of the conventional quantum clustering technology in a large-scale data set. The immune clone quantum clustering-based SAR image segmenting method is implemented by the following steps: 1) extracting features of an SAR image to be segmented; 2) initializing an antibody population and coding antibodies; 3) calculating antibody affinity according to quantum mechanical characteristics, and dividing the antibody population into an elite population and a general population; 4) designing different immune clone optimization operators for the elite population and the general population respectively, and performing a cloning operation, a normal cloud model-based adaptive mutation operation, a uniform hypermutation operation, a clonal selection operation and a hypercube interlace operation orderly; and 5) outputting an SAR image segmentation result. The immune clone quantum clustering-based SAR image segmenting method has high iteration optimization speed and high stability, can effectively segment the SAR image which contains large-scale data volume, and is suitable for object detection and identification of the SAR image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
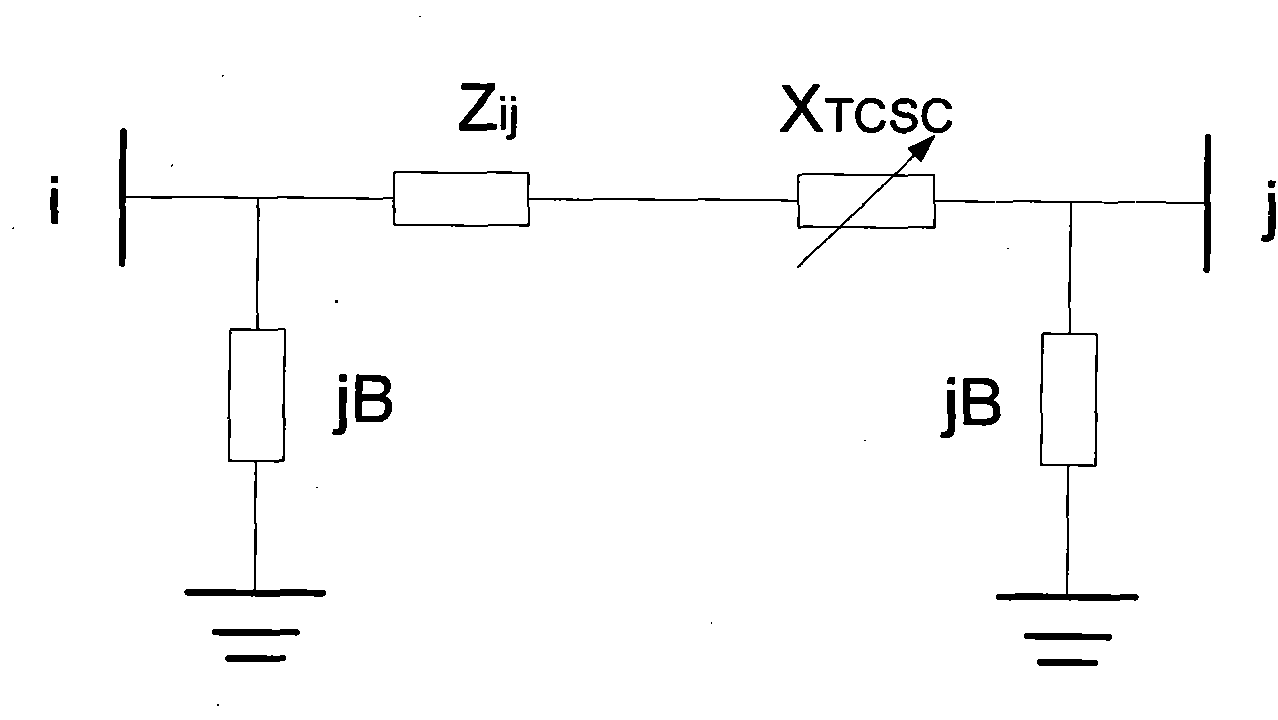
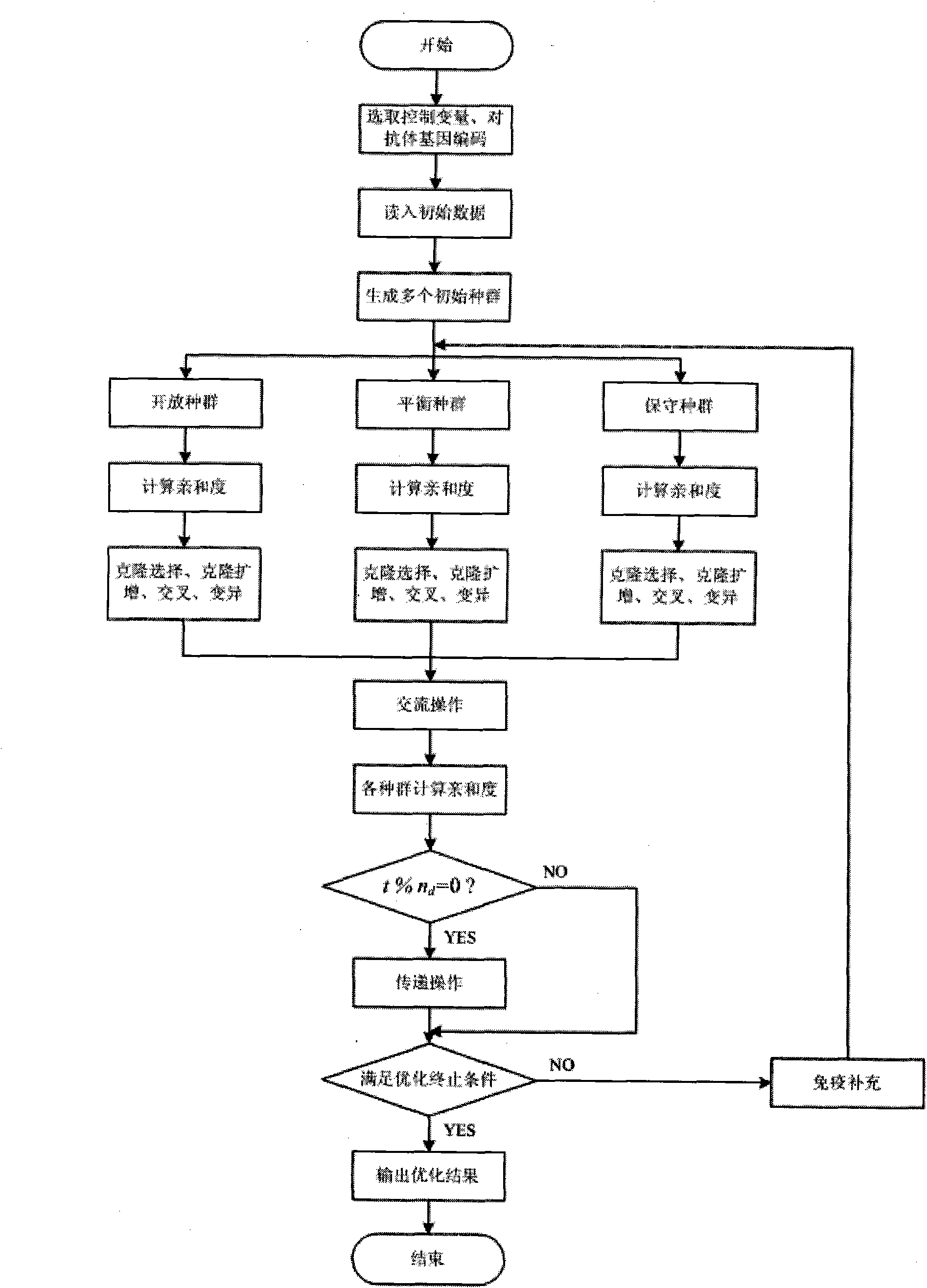
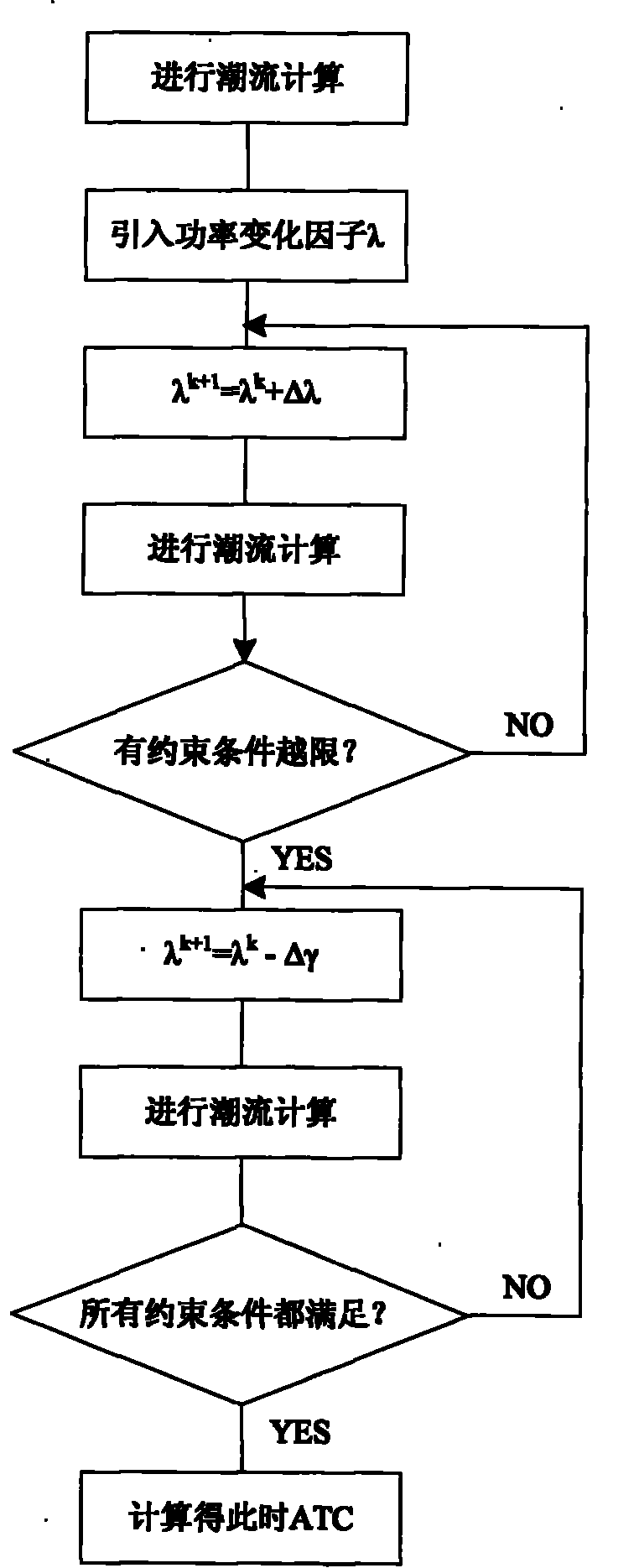
Controllable serial capacitor optimal configuration method capable of improving available transmission capacity
ActiveCN101882791ASolve the optimal configuration problemPrevent falling intoFlexible AC transmissionReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationAntigenClonal selection
The invention discloses a controllable serial capacitor optimal configuration method capable of improving available transmission capacity, which is characterized in that: the position variables and compensation degrees of TCSCs serve as antibody genes to be coded, initial data are input to generate initial populations randomly, and the initial populations are divided into an open crossover and mutation rates are set for the populations of each group, each group of populations are optimized by an immune algorithm, the affinity between each antibody and an antigen in each population in each group is calculated, and clonal selection, clonal amplification, crossover and variable immunity are performed; at the end of the evolution of each generation, a communicating operator is used to allow the populations to interexchange part of antibodies and the affinity is calculated; after the evolution of a plurality of generations, the currently optimal antibodies are distributed into all populations by a transmission operator; and after all populations evolve for one time, if an algorithm meets convergence conditions is judged, and optimal results are output if the algorithm meets the convergence conditions, or immune supplementation is performed and evolution circulation is returned to if the algorithm does not meet the convergence conditions. The method can solve the optimal configuration problem of the plurality of TCSCs.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY +2
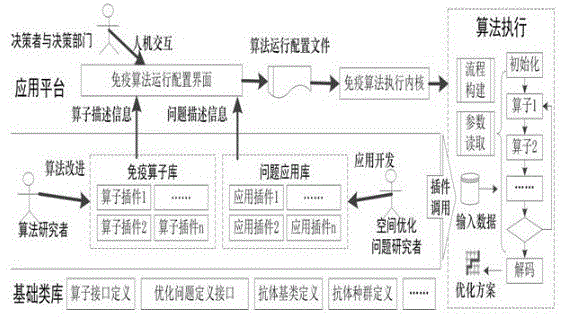
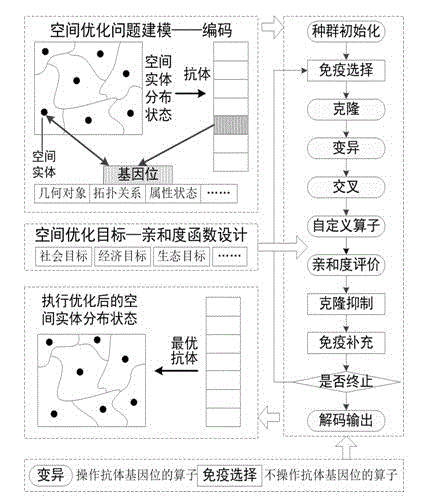
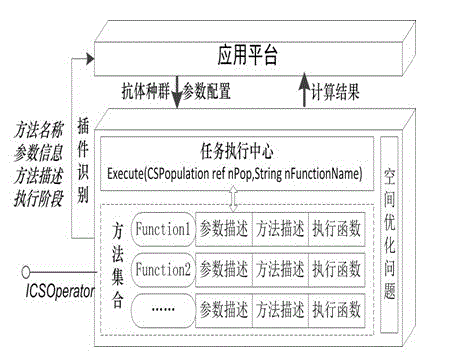
Artificial immunity intelligent optimization system facing geographical space optimization
The invention relates to an artificial immunity intelligent optimization system facing the geographical space optimization, which comprises an immune operator library, a problem application library and an application platform module. The immune operator library is used for storing immune operator plugins; the problem application library is used for storing application plugins for solving the space optimization problem; the application platform module is used for calling the corresponding immune operator plugins from the immune operator library according to the selection of a user to determine a clonal selection algorithm and calling the corresponding application plugins from the problem application library to determine an antibody code and an affinity evaluation function of the specific space optimization problem to be solved of the user; and according to the determined antibody code and affinity evaluation function, the optimal solution of the specific space optimization problem to be solved of the user is acquired by the clonal selection algorithm. The artificial immunity intelligent optimization system provided by the invention can integrate the clonal selection algorithm which is currently and most widely used in the field of geoscience, and has universality, expandability and openness.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
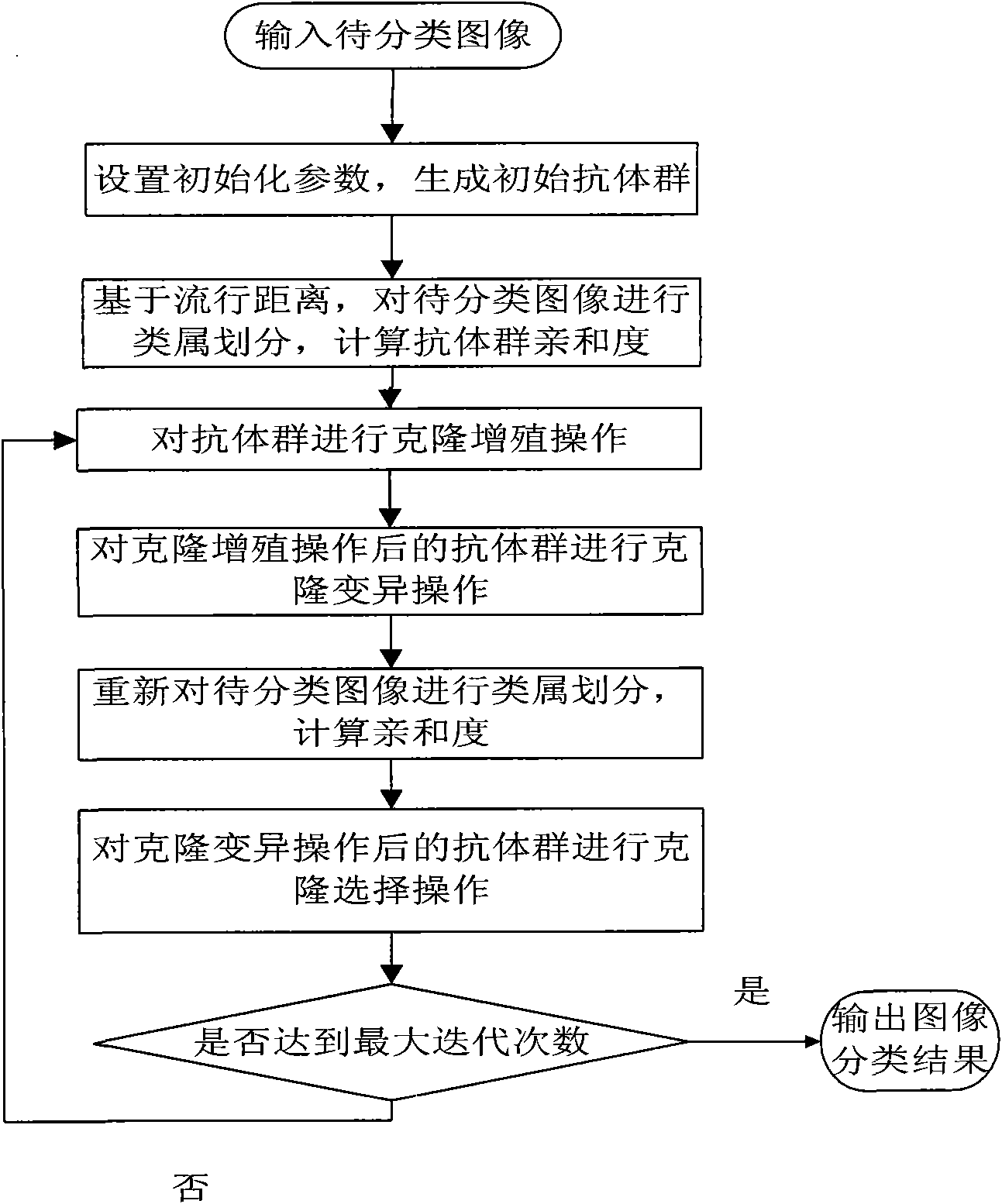
Artificial immunization non-supervision image classification method based on manifold distance
InactiveCN101625725AImage classification works wellGood edge accuracyGenetic modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionClonal selectionImaging processing
The invention discloses an artificial immunization non-supervision image classification method based on manifold distance and relates to the technical field of image processing. The specific process includes: (1) inputting an image to be classified and setting an initialization parameter to generate initialized antibody population; (2) based on the manifold distance, classifying the category of the sample point of the image to be classified and calculating the affinity of the antibody population; (3) carrying out clonal proliferation operation on the antibody population; (4) carrying out clonal variation operation on the antibody population after clonal proliferation; (5) classifying the category of the image to be classified according to a code of the antibody population after clonal variation and calculating the affinity of the antibody population; (6) carrying out clonal selection operation on the antibody population according to the antibody affinity; and (7) according to set maximum iterations, judging the stop condition of the category classification result of the image to be classified and determining the final classification result. The classification method has the advantages of low sensitivity of image data structure, non-supervision execution, good classification effect and strong robustness, and can be applied to the target identification in the field of image processing.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Clonal-selection-based method for positioning subpixel of high spectrum remote sensing image
InactiveCN102096830ASelf-learningHave self-memoryCharacter and pattern recognitionClonal selectionClonal selection algorithm
The invention provides a clonal-selection-based method for positioning a subpixel of a high spectrum remote sensing image. Subpixel positioning of the high spectrum remote sensing image is realized on the basis of a clonal theory and a subpixel positioning theory. By using a clonal selection optimizing algorithm, optimal calculation is performed on remote sensing image subpixel positioning without any future knowledge, and a result of subpixel positioning can be directly obtained according to an input image. Meanwhile, as the clonal selection algorithm has the advantages of self-learning and self-memorizing, the global optimal subpixel positioning result can be obtained.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Immune clone selection job shop scheduling method based on scheduling coding
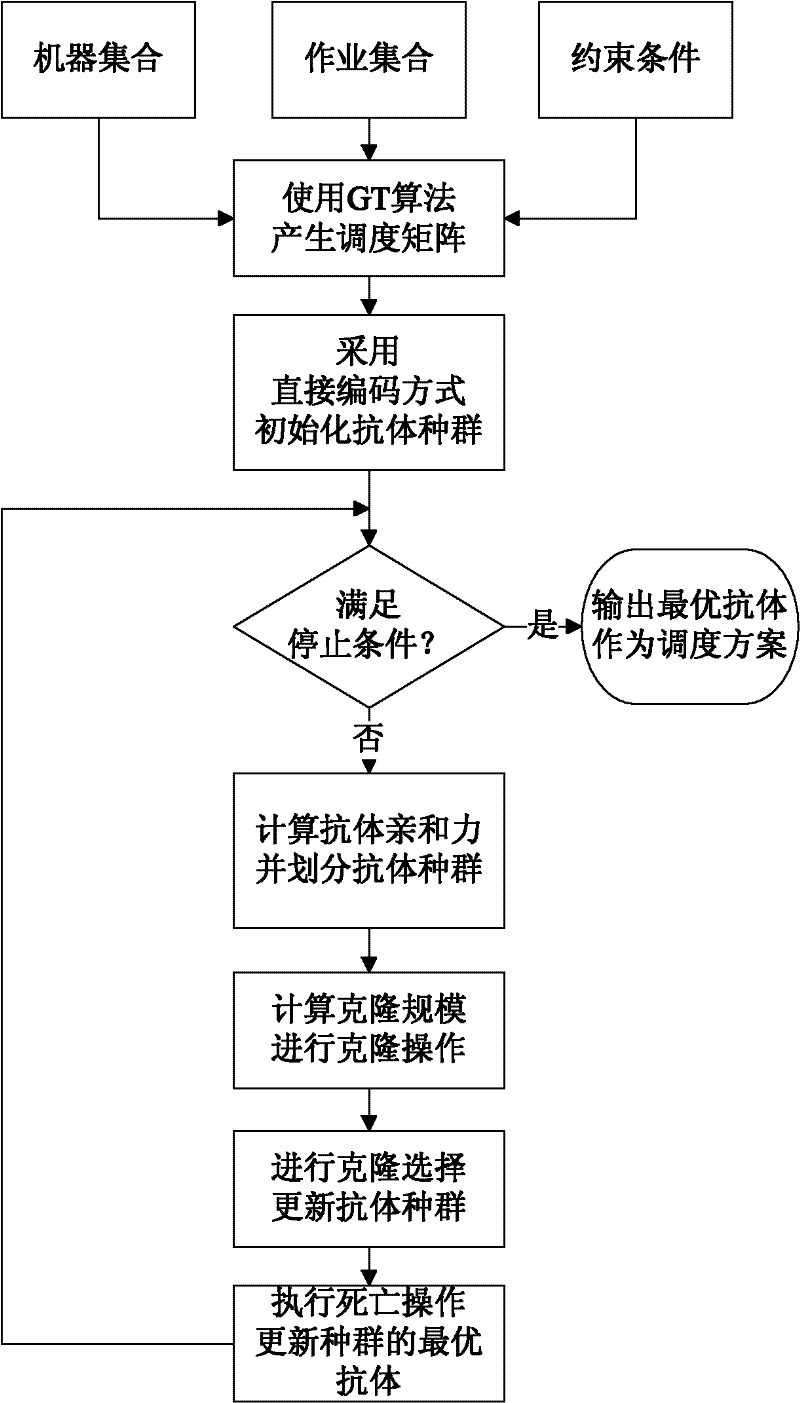
InactiveCN102222274AImprove efficiencyEliminate coding redundancyInstrumentsClonal selectionNeighborhood search
The invention discloses an immune clone selection job shop scheduling method based on scheduling coding, mainly aiming at overcoming the disadvantages that the quality is poor and the efficiency is low in the prior art when a job shop scheduling problem is solved. The method comprises the following steps: operating an input machine, operation and a constraint condition by utilizing a GT (Guo Tao) algorithm to generate a scheduling matrix; carrying out direct coding to the scheduling matrix to be used as antibody population; calculating the affinity of the antibody population and dividing the antibody population into a memory unit and a free unit; calculating the clone scale of each antibody; carrying out clone variation to the antibody population by using a clone operator based on neighborhood search according to the clone scale to obtain the clone population; carrying out clone selection to the clone population to obtain new antibody population, and carrying out updating and death to the memory unit and free unit; outputting the optimal antibody in the antibody population and mapping the optimal antibody as the scheduling sequence of the machine and the operation. The immune clone selection job shop scheduling method has the advantages of good quality and high efficiency, and can be used for solving the problem of job shop scheduling.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Immune clone intelligent multi-user detecting method
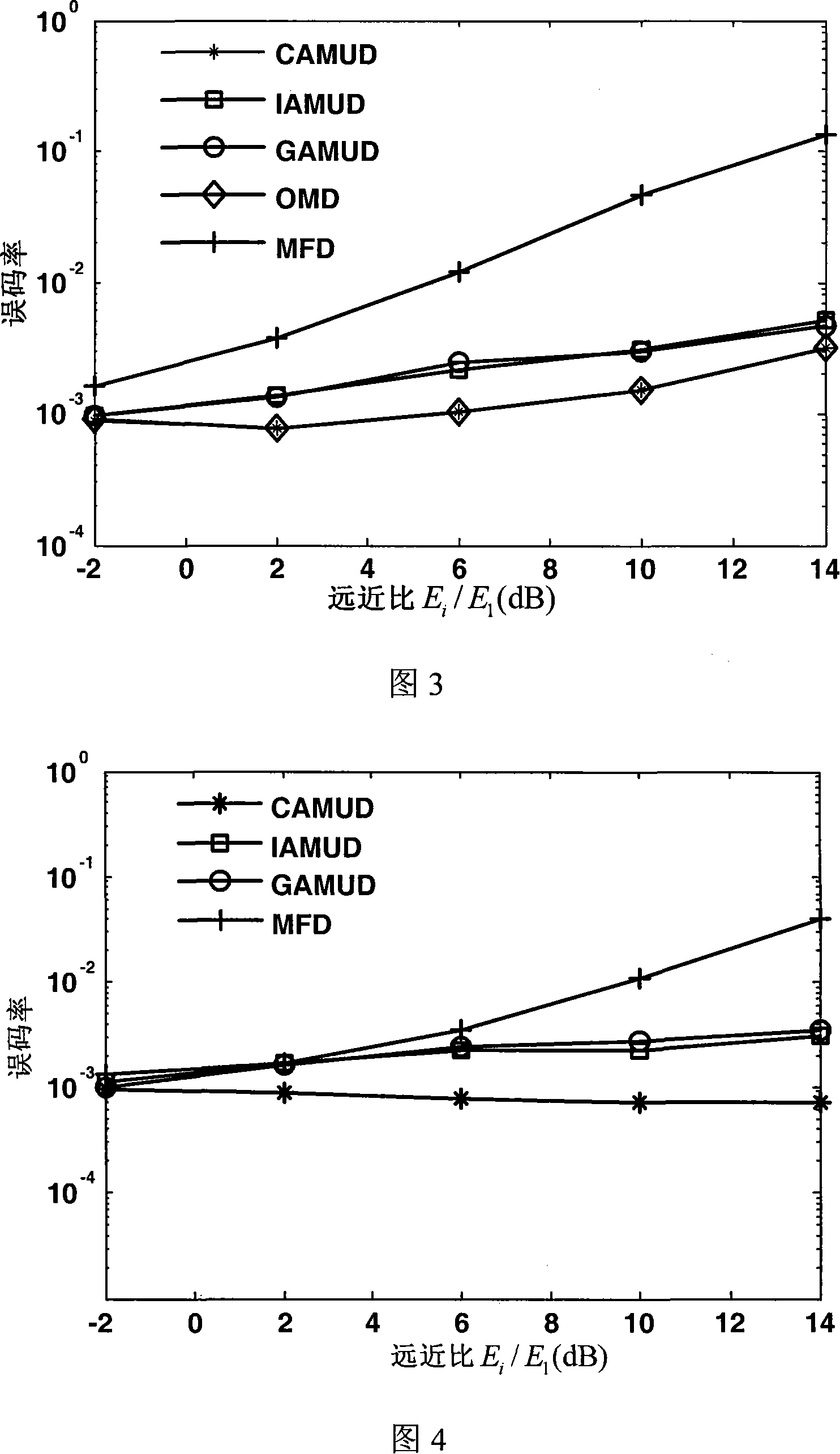
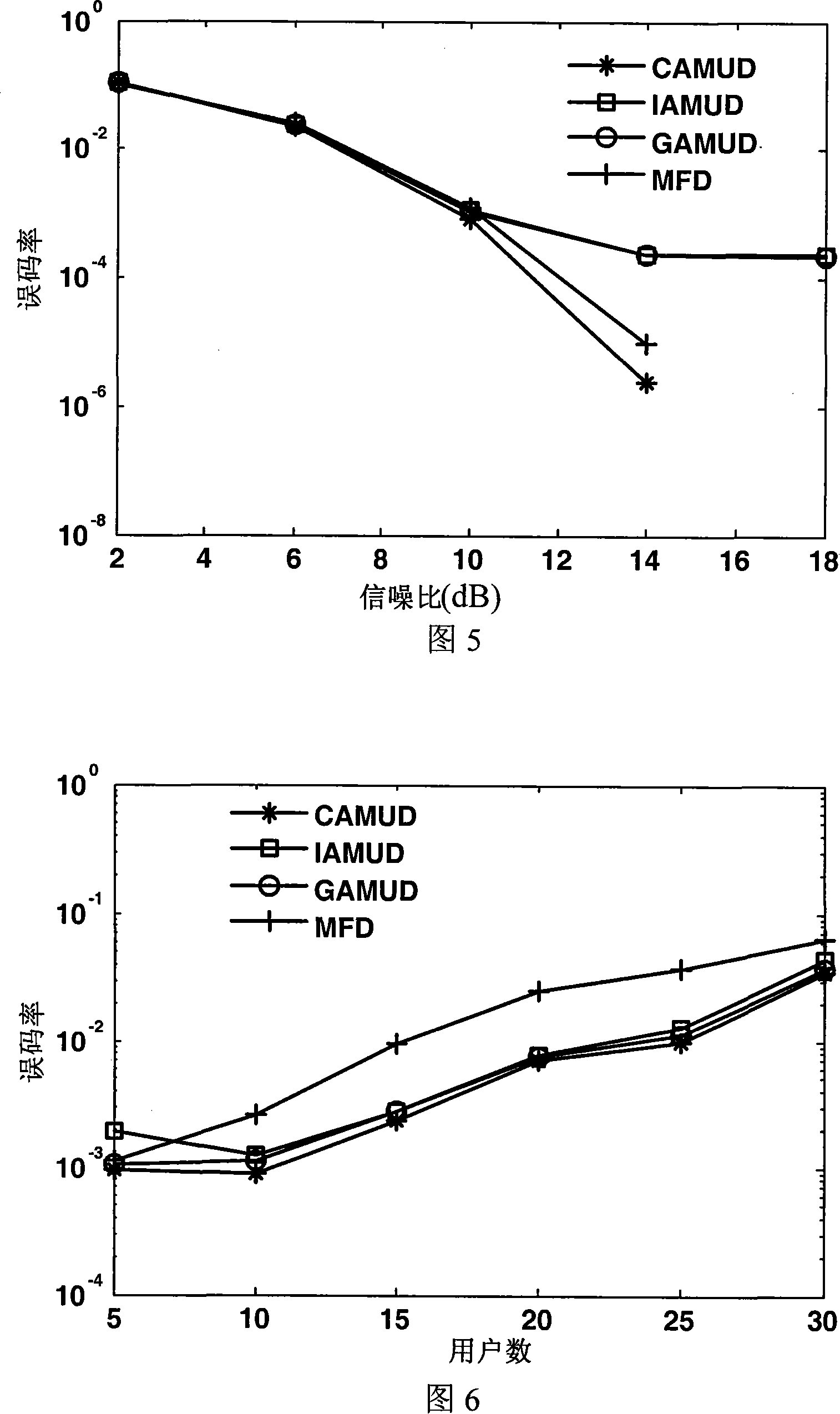
InactiveCN101141140AReduce computational complexityHeavy computationError preventionCode division multiplexClonal selectionInterference resistance
The present invention discloses an intelligent multi-user detecting method for immune colon belonging to the technical field of artificial intelligence, which aims to remove distance effect and multiplex access interference of prior arts to enhance distance effect resistance, multiplex access interference resistance and noise interference resistance and reduce calculating complexity compared with optimal multi-user detections and includes following fulfillment steps: (1) Initializing, setting arithmetic termination terms, specifying arithmetic operating parameters and randomly creating initial antibody clusters; (2) Calculating compatibility of the antibody; (3) Judging arithmetic terminal terms; (4) Conducting colon death to antibody clusters; (5) Fulfilling colon amplification to antibody clusters after antibody death; (6) Carrying out clone variation to antibody clusters after colon amplification; (7) Calculating antibody cluster compatibility after colon variation; (8) Realizing antibody cluster colon selection after colon variation and returning step (3). The method can solve problems of multi-user detection in CDMA systems of 3G mobile communications.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
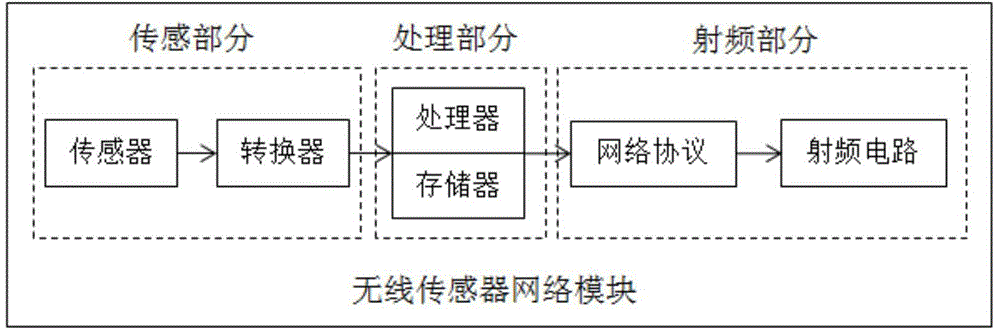
Wireless sensor network routing optimization method based on immune clonal selection
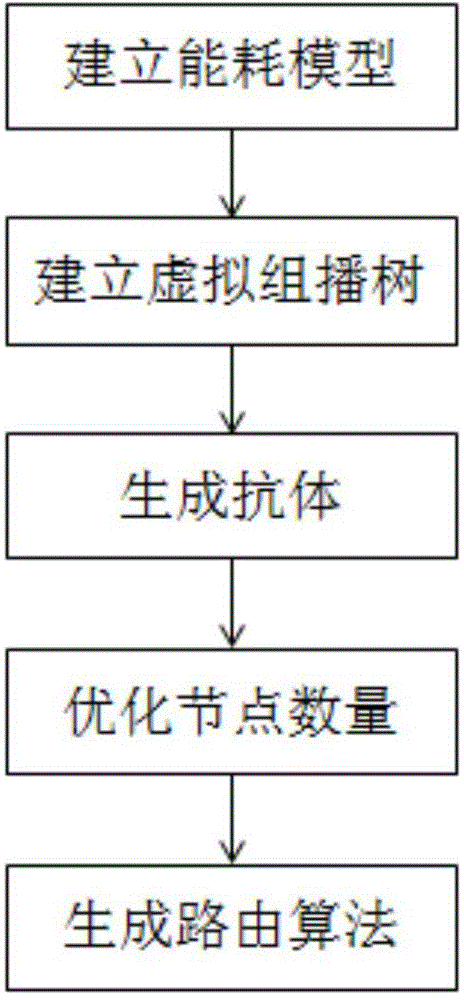
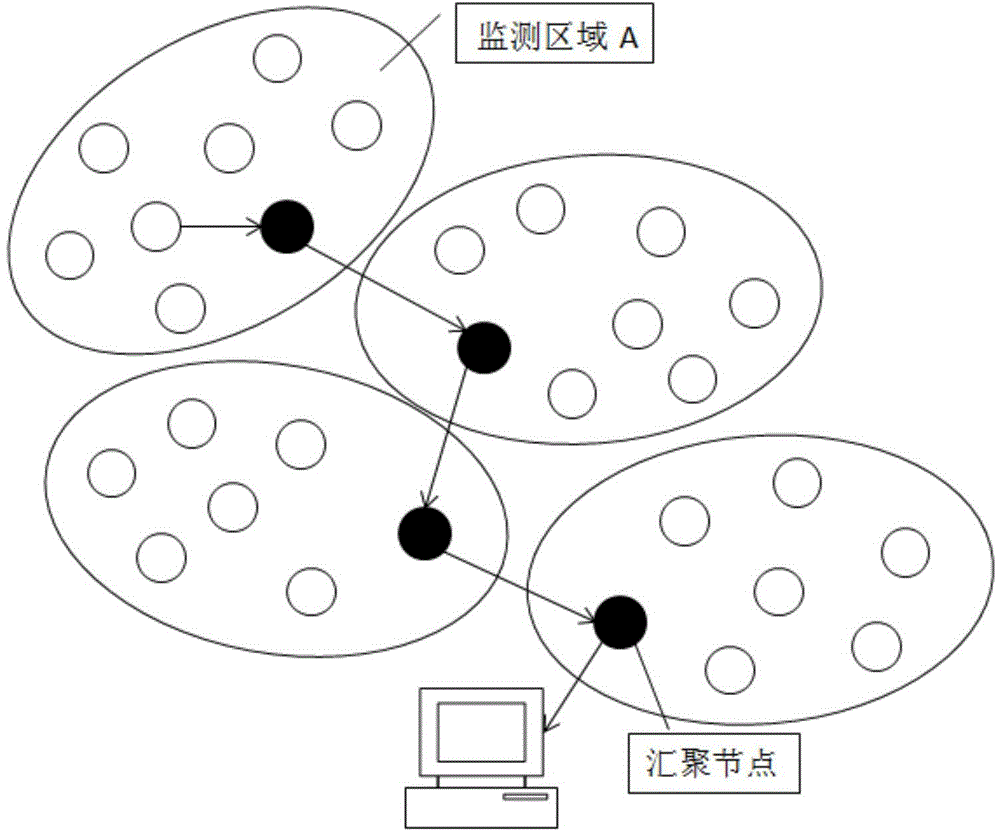
ActiveCN105764110AImprove robustnessReduce self-healing timeNetwork topologiesHigh level techniquesArtificial immune systemWireless mesh network
The present invention relates to the technical field of IOT and particularly relates to a wireless sensor network routing optimization method based on immune clonal selection. The method comprises a step of establishing an energy consumption model of multi-hop communication based on a first order RF model, a step of taking the communication routes of a source node and all multicast nodes as multicast trees, wherein a multicast tree with a smallest communication value is an optimal path in the condition of satisfying a constraint, a step of taking each multicast tree as an antibody in an immune system and taking one route from the source node in the multicast tree to the multicast nodes as a gene, a step of determining the optimal number of communication nodes, and a step of establishing the accessible routing alternative path set between the multicast source node and all multicast nodes. According to the wireless sensor network routing optimization method, a route optimization problem is established to solve the corresponding relation among an artificial immune response five-element structure according to the intrinsic link between the route optimization and an artificial immune system, the optimization speed is improved, and the recovery time of a wireless sensor network is reduced significantly.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fuzzy job-shop scheduling method based on self-adaption inheritance and clonal selection algorithm
InactiveCN104281917AReasonable distributionShorten Scheduling Fuzzy Makemaking TimeResourcesGenetic algorithmsClonal selectionCompletion time
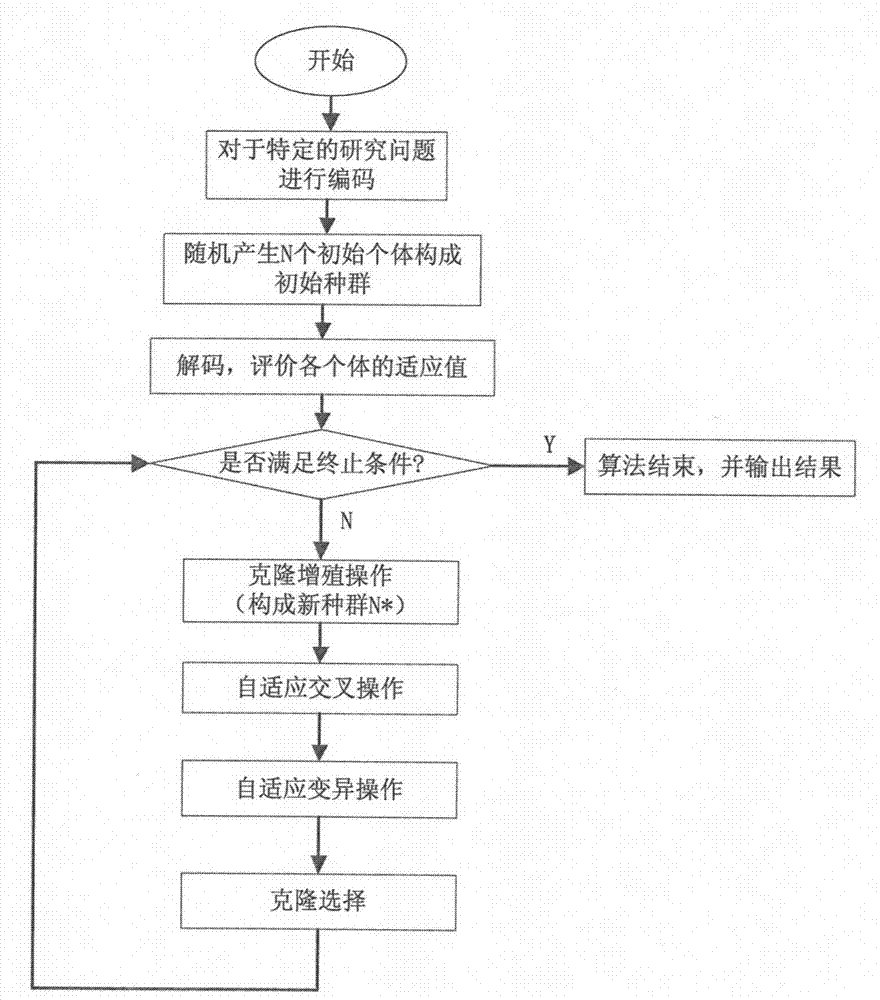
The invention relates to a fuzzy job-shop scheduling method based on self-adaption inheritance and the clonal selection algorithm. The method includes the steps of determining the coding scheme of the fuzzy job-shop scheduling problem, generating the initial population N at random, defining a solution space, defining and calculating the adaptability function of an individual, conducting clone proliferation operation on the individual according to the size of the adaptability value near each generation of optimal solution, independently conducting self-adaption cross and mutation operation on individuals obtained through reproduction, conducting clonal selection operation on the individuals obtained through cross and mutation to generate the new population N*, ending the circulation if the ending condition is met, and returning to continue the next step if the ending condition is not met. By means of the method, resources can be more reasonably distributed, the completion time of job-shop scheduling fuzziness is shortened, the efficiency of job-shop fuzzy scheduling is improved, and the requirement of actual production scheduling is better met.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Improved immune network abnormal behavior detection method
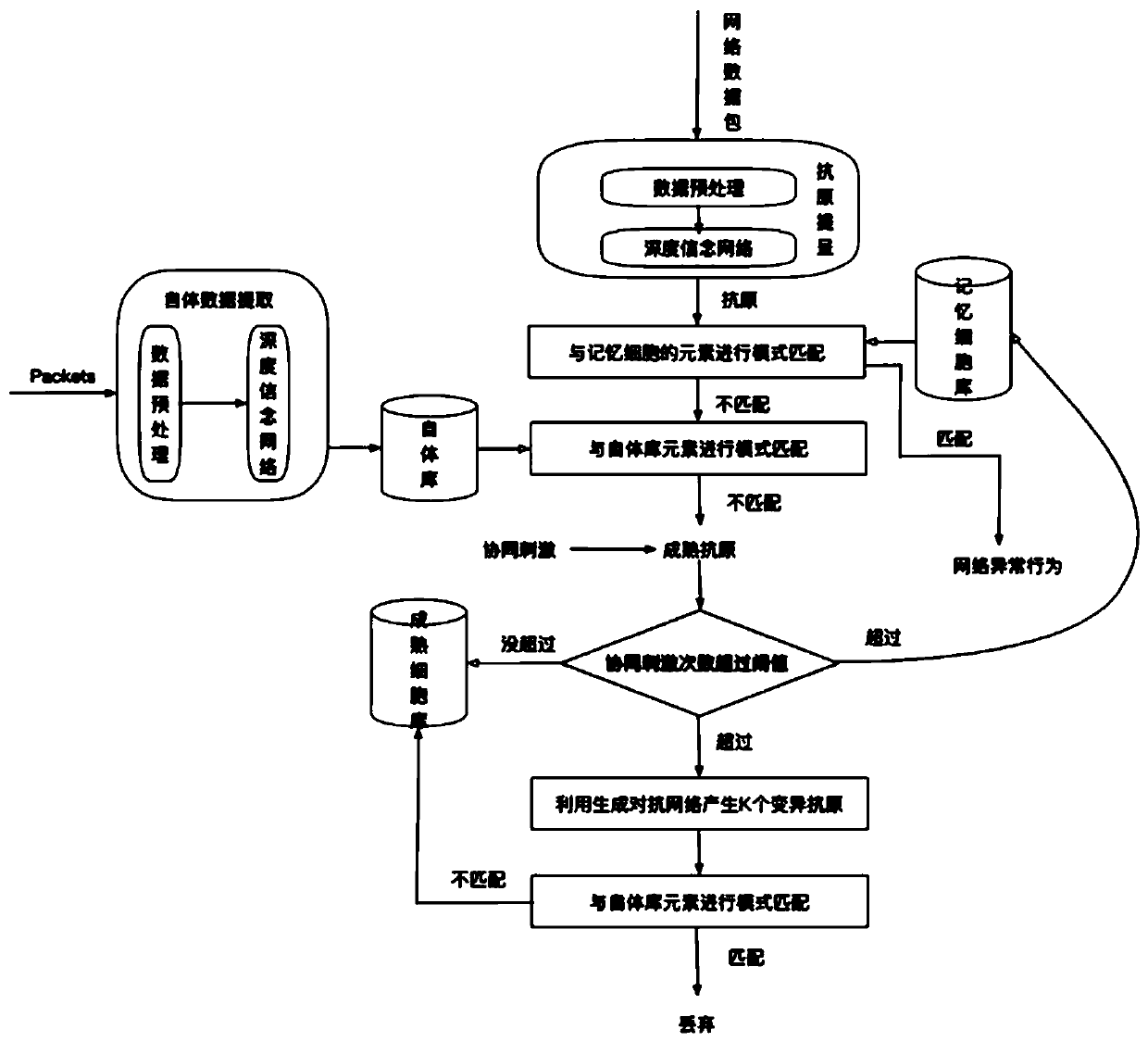
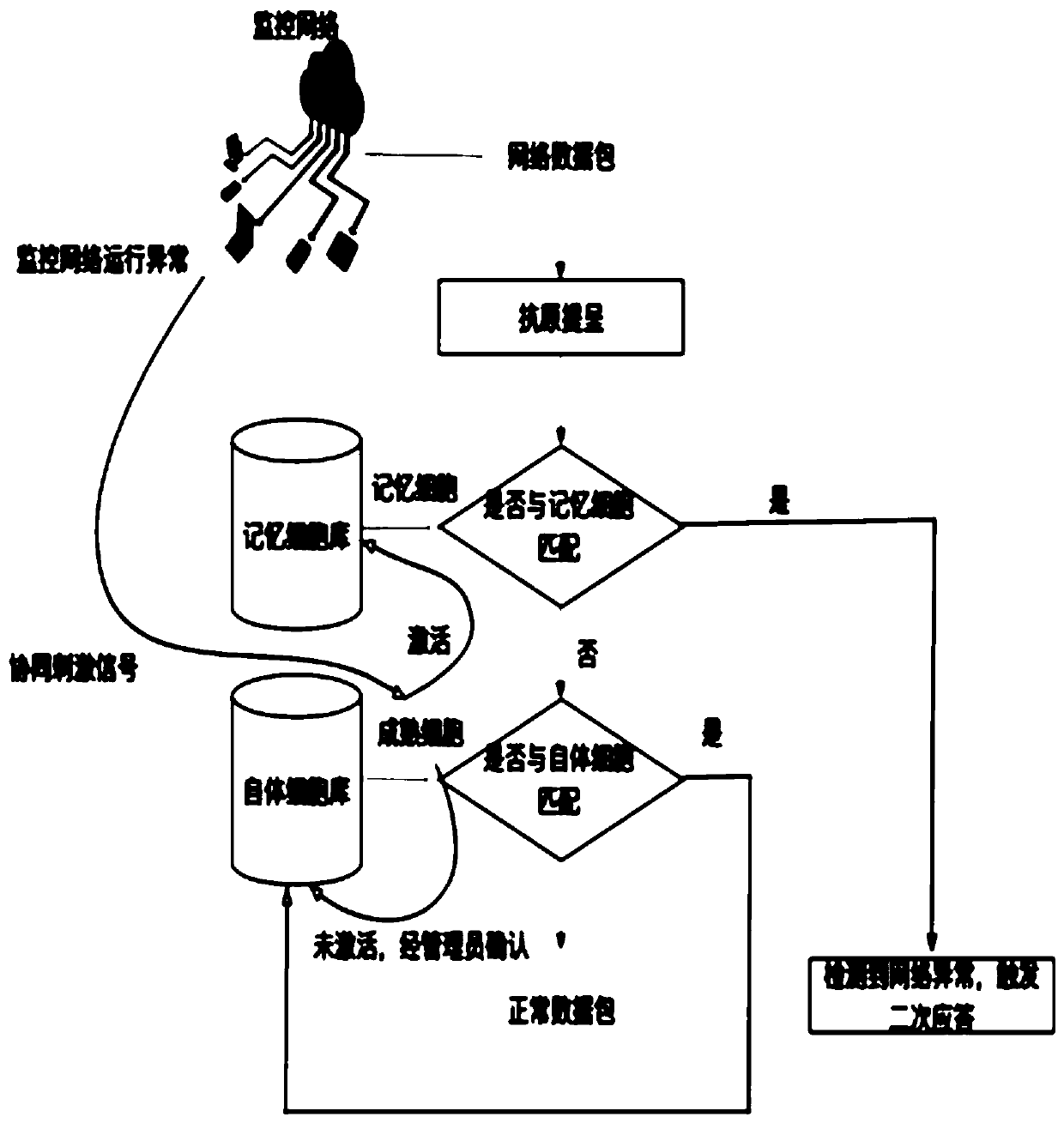
ActiveCN109347863AReduce redundancyReduce feature latitudeArtificial lifeTransmissionClonal selectionRestricted Boltzmann machine
The invention discloses an improved immune network abnormal behavior detection method. The method comprises four stages of autologous library data extraction, antigen presentation, abnormal behavior detection and clonal selection, wherein a single-category autologous data generation model based on deep belief network is adopted in the autologous library data extraction and antigen presentation; the deep belief network is formed by stacking restricted Boltzmann machines RBM; the RBM is a neural network; a method combining congenital immunity and adaptive immunity is adopted in the abnormal behavior detection; and a clonal variation method based on a generation network is adopted in the clonal selection. According to the improved immune network abnormal behavior detection method disclosed bythe invention, the deep learning model and method are introduced into a computer immune network anomaly detection model to improve the quality and efficiency of the model training, no matter the detection efficiency and the accuracy are greatly improved, and meanwhile, the defect that the traditional method is random or a large number of invalid calculations caused by cross variation are overcomeat the same time.
Owner:CHENGDU CHENGDIAN ELECTRIC POWER ENG DESIGN
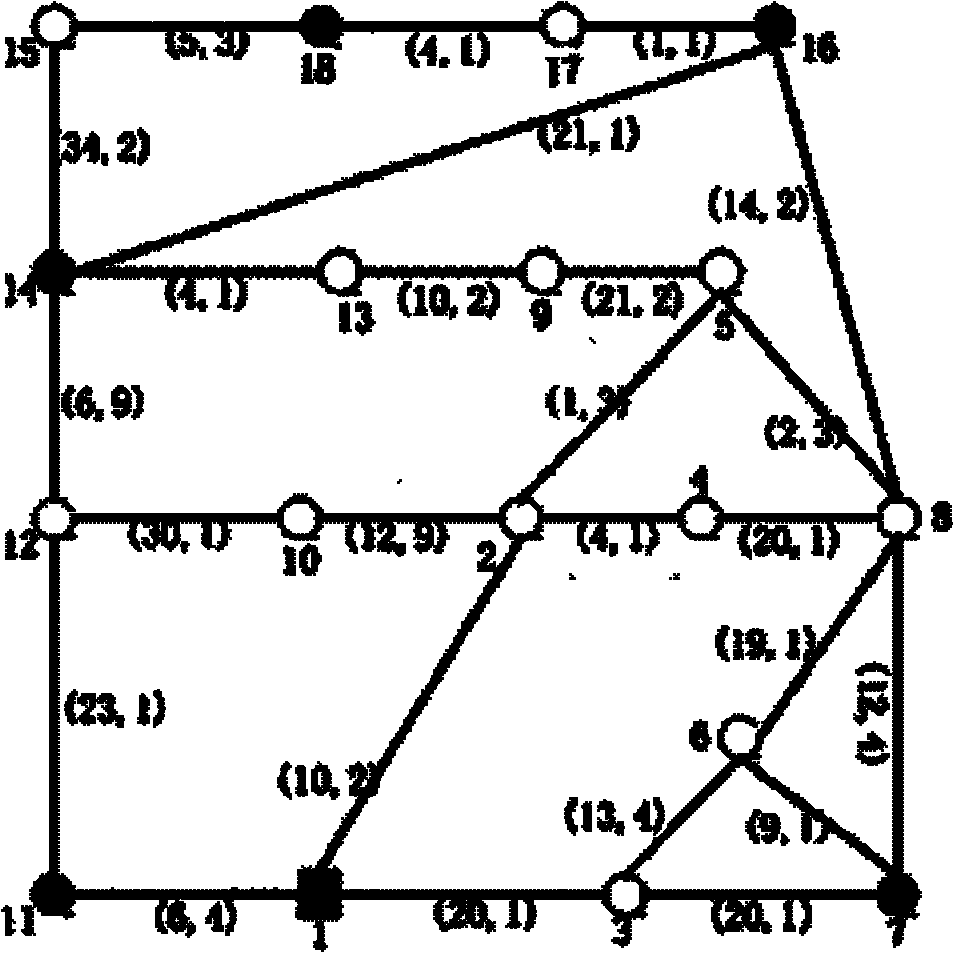
Multi-agent multicast routing method based on adjacent immune clonal selection
ActiveCN102158413ACutting costsReasonable configurationData switching networksClonal selectionNetwork model
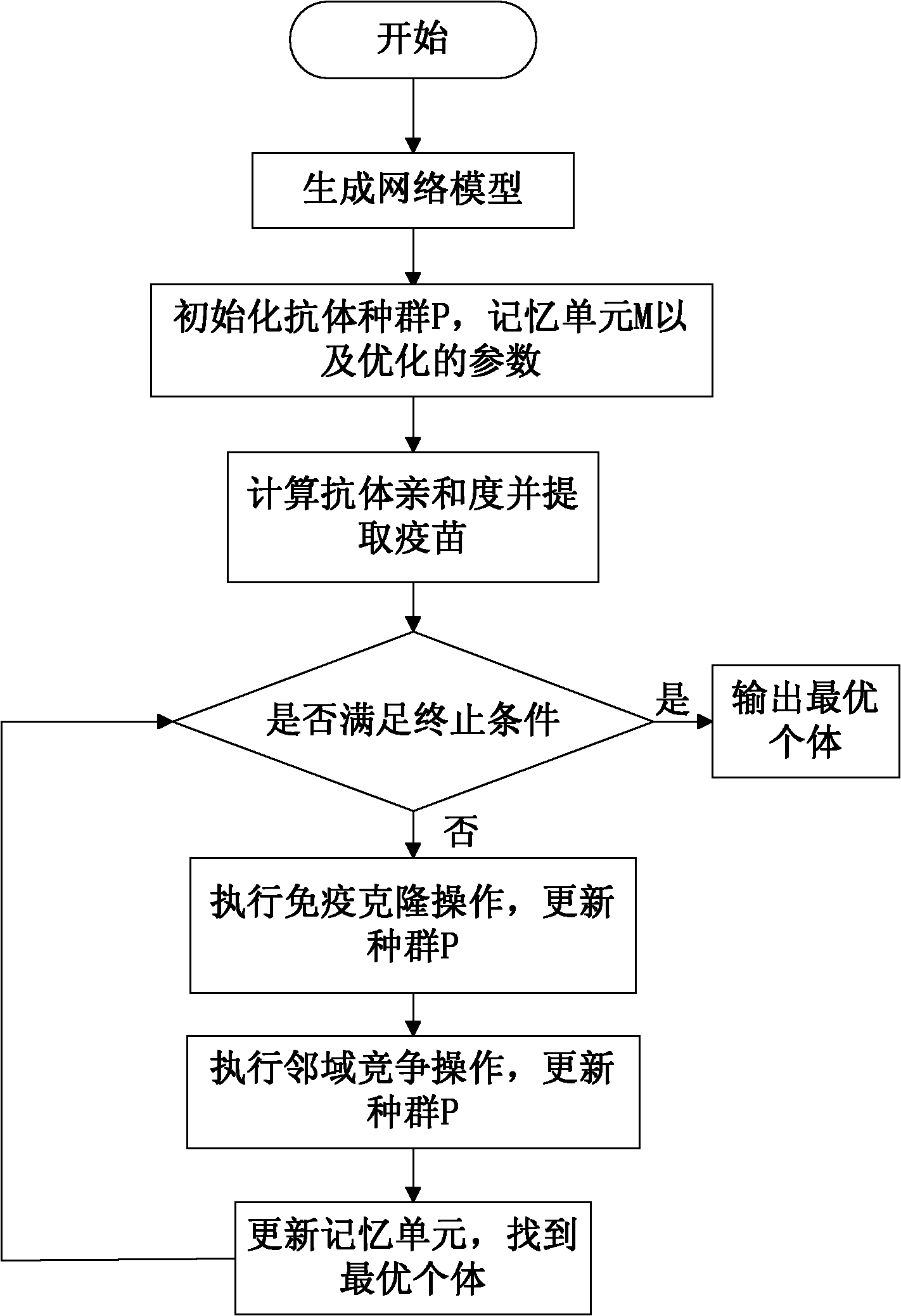
The invention discloses a multi-agent multicast routing method based on adjacent immune clonal selection, and mainly aims to overcome the shortcomings of low convergence rate and low searching capability of the conventional method when multicast routing problems are solved. The method is implemented by the following steps of: 1, generating a network model; 2, initializing antibody populations, memory unit populations and optimized running parameters; 3, calculating the affinities of all antibodies, finding an optimal antibody and extracting a vaccine; 4, judging whether termination conditionsare met or not, outputting an optimal individual if the termination conditions are met, otherwise turning to the step 5; 5, performing an immune colonization operation on all individuals in a currentpopulation; 6, performing an agent adjacent competition operation on the population obtained by the step 5, and updating the current population; and 7, extracting a better antibody updating memory unit from the antibody population obtained by the step 6, finding the optimal individual and returning to the step 4. The method has the advantages of high convergence rate and high searching capability, and can be used for solving the multicast routing problems of delay limitations.
Owner:探知图灵科技(西安)有限公司
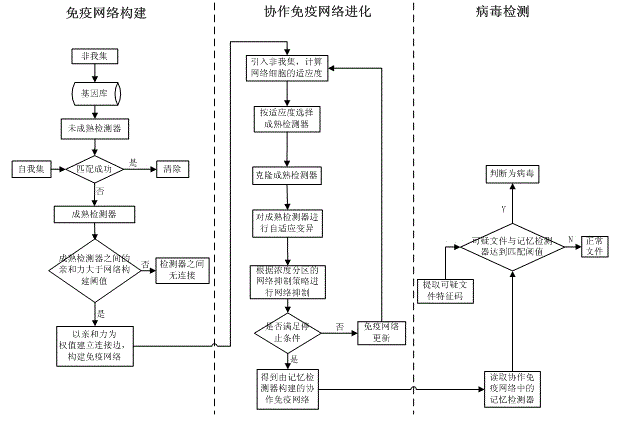
Virus detection method based on collaborative immune network evolutionary algorithm
InactiveCN102750490AFast evolutionReduce redundancyComputer security arrangementsClonal selectionEvolutionary learning
The invention discloses a virus detection method based on a collaborative immune network evolutionary algorithm, and belongs to the technical field of network security. According to the method, detectors in the immune network are optimized continually through the mutual collaboration among various immune cells. The method introducing a non-self set in the evolutionary process, and performing clonal selection on mature detectors based on the detector fitness to the non-self set; simultaneously, updating mutation methods with mutation step size self-adaptation and capable of changing mature detectors through an evolutionary algebra through the evolutionary algebra, and raising a network inhibition strategy based on concentration partition, thus, the network cell diversity is improved, and the redundancy rate of detectors is reduced simultaneously. According to the virus detection method based on the collaborative immune network evolutionary algorithm, advantages of the evolutionary algorithm and the artificial immune technology are combined and fully used, and the network virus detection efficiency is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Lung-targeting metastatic human hepatoma cell strain and establishing method thereof
InactiveCN101831405AHigh strengthDelayed quenching timeMicroorganism based processesTumor/cancer cellsEpitheliumFluorescence
The invention provides a lung-targeting metastatic human hepatoma cell strain and an establishing method thereof. The lung-targeting metastatic human hepatoma cell strain is characterized in that the mother cell is a red fluorescent protein expression hepatoma cell HCCLM3-R; the cell is named as a lung-targeting metastatic human hepatoma cell strain HCCLM3-R-LM1 by classifying, has the preservation number of 3644, and has the following biological characteristics that the cell is in polygonal epithelium shape, grows clinging to the wall, loses contact growth inhibition, has a hypo-triploid caryogram with the chromosome number of 50-58, secretes AFP protein, and has lung-targeting metastatic clonal selection advantage. The establishing method comprises the following steps of: sieving by adopting nude mouse subcutis and liver orthotopic implantation tumour model autogenetic lung metastasis, and then carrying out in-vitro cloning, purifying and propagating on the lung-targeting metastatic human hepatoma cell. The invention has wide application potential and potential societal and economic benefits in basic research of hepatoma and clinic previous research of medicines.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Current characteristic frequency extraction method of machine tool transmission system with immune random resonance
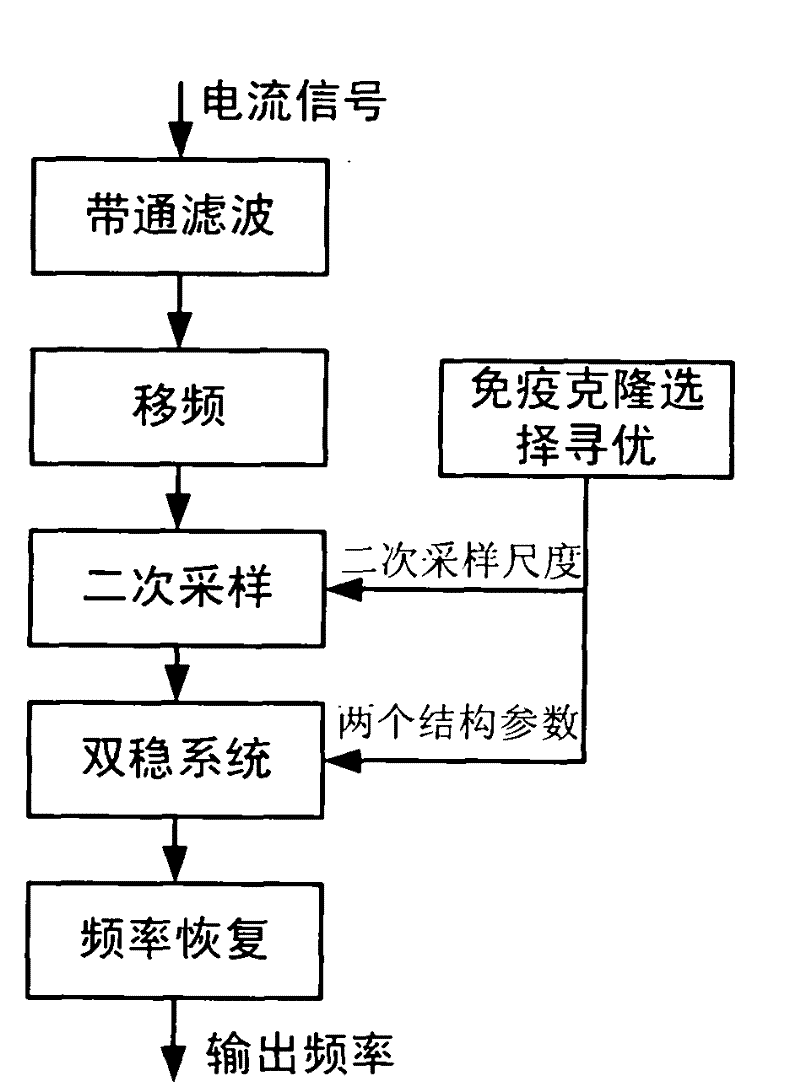
InactiveCN102175915AExtract weak eigenfrequenciesImprove optimization qualityGenetic modelsFrequency measurement arrangementBandpass filteringDiagnostic Radiology Modality
The invention relates to a current characteristic frequency extraction method of a machine tool transmission system with immune random resonance comprises the following steps: collecting a current signal of a servo driving motor of the transmission system by a current sensor; calculating the gyro frequency and the meshing frequency of each output shaft of the transmission system; processing the collected current signal by a Butterworth filter-type bandpass filter; processing the filtered current signal by frequency shift; optimizing the current signal processed by frequency shift by a multi-mode immune clonal selection method to obtain secondary sampling random resonance system parameter; selecting a parameter with the largest affinity as the optimal secondary sampling scale and structuresystem parameter; finally, achieving the compression of the input signal according to the optimal secondary sampling scale, wherein the largest peak component of the corresponding spectrum can be transformed to the characteristic frequency component of the machine tool transmission system. By using the current characteristic frequency extraction method, the optimization quality of a secondary sampling random resonance system of the current signal of the servo motor with large frequency scale can be improved, and the weak characteristic frequency of the transmission system can be effectively extracted.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Cognitive Internet of Vehicles spectrum allocation method based on immune optimization
InactiveCN108551676AGuaranteed search abilityHigh throughput of cognitive nodesNetwork planningNODALClonal selection
The invention discloses a cognitive Internet of Vehicles spectrum allocation method based on immune optimization. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, group initialization; step 2, affinity function evaluation; step 3, termination condition judgment; step 4, proportional cloning; step 5, clonal variation Tm; and step 6, clonal selection Ts. For cognitive Internet of Vehicles spectrumallocation, based on a graph theory model, an optimization problem to maximize the cognitive node throughput is modeled and thus a solving algorithm based on the immune optimization is proposed; and amatrix coding mode, an antibody correction mode and proportional cloning and other strategies suitable for spectrum allocation problems are designed to ensure the optimizing ability of the algorithm.A simulation experiment shows that the method provided by the invention can obtain higher cognitive node throughput and is suitable for the spectrum allocation of the cognitive Internet of Vehicles.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
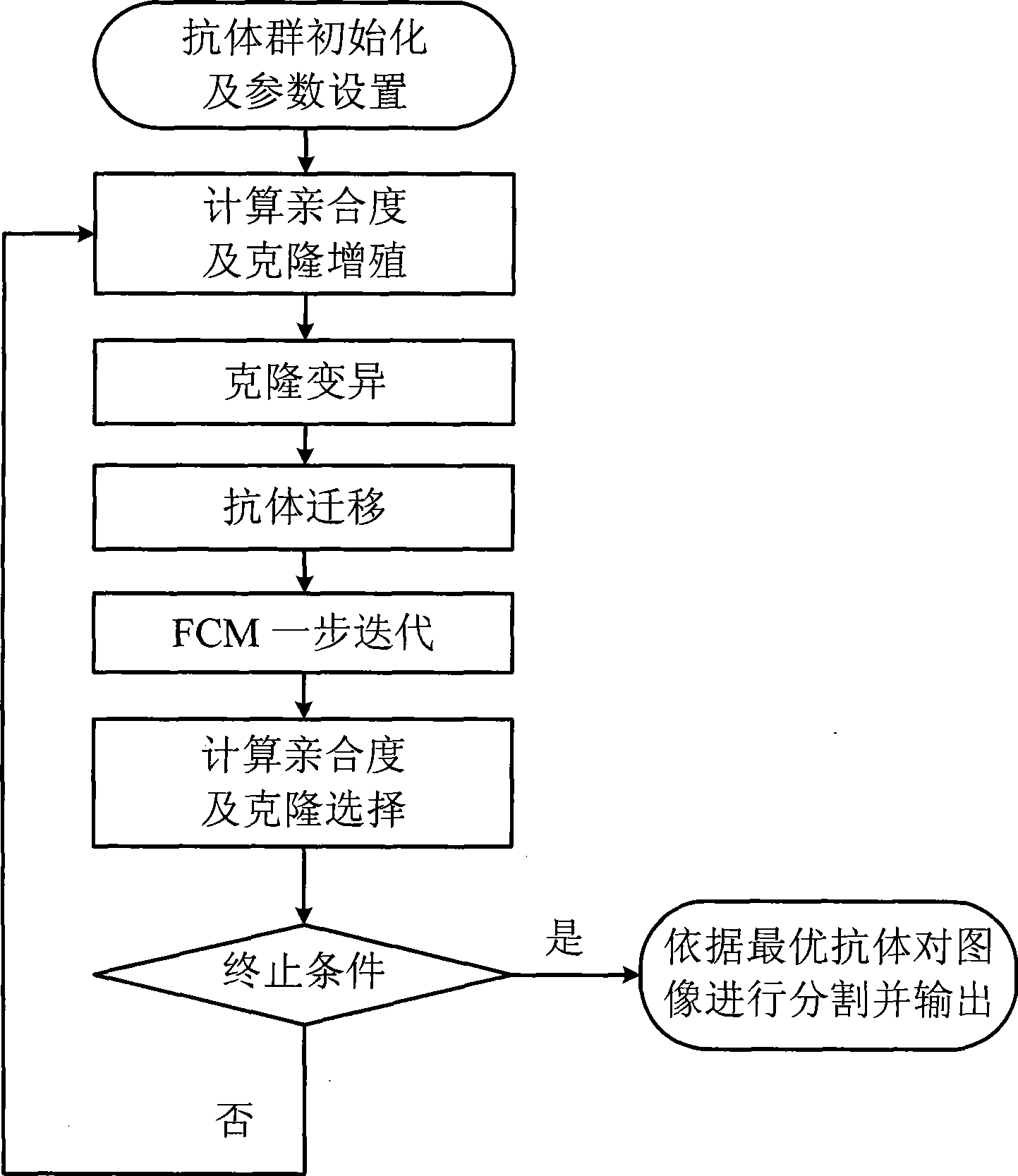
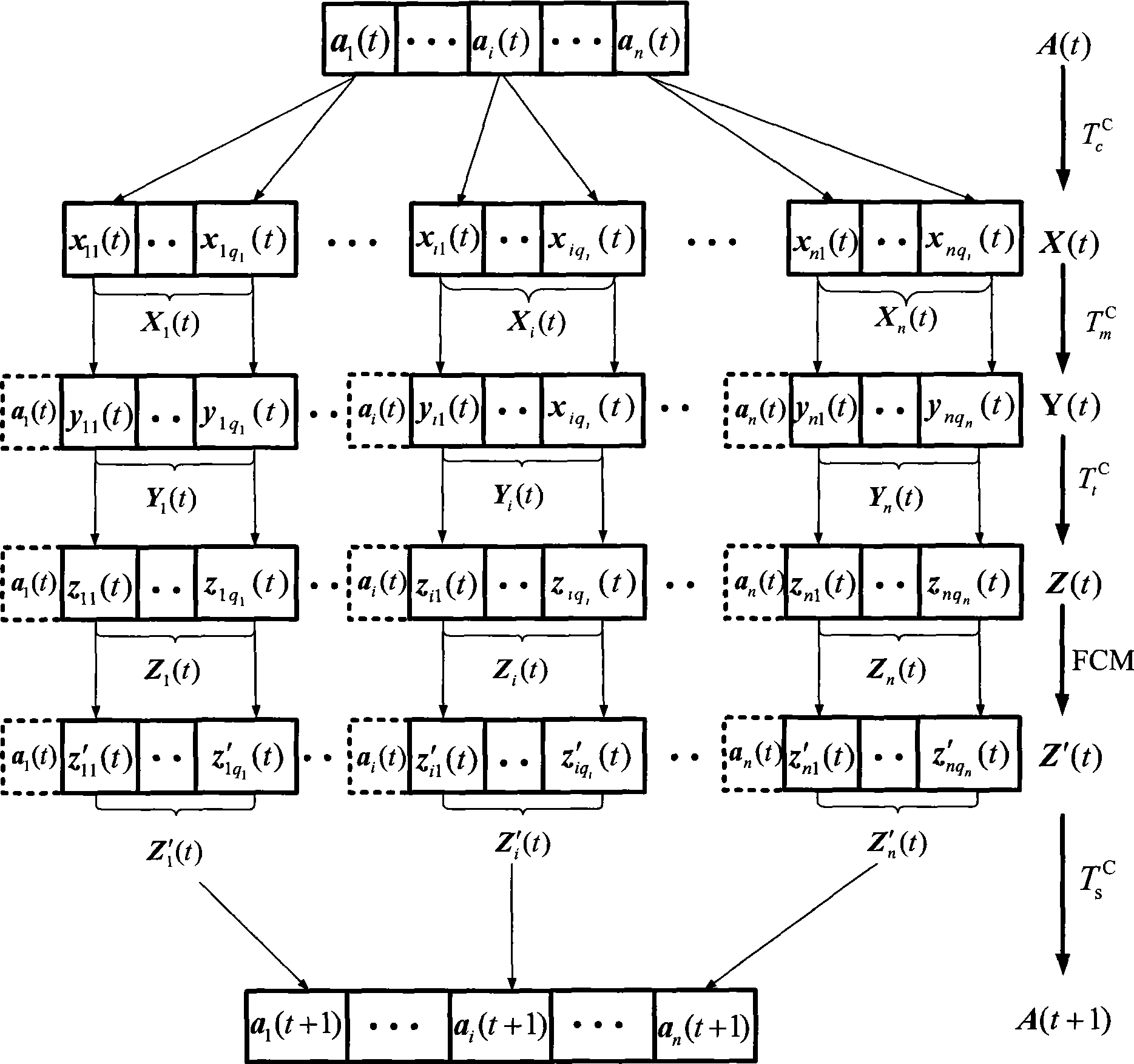
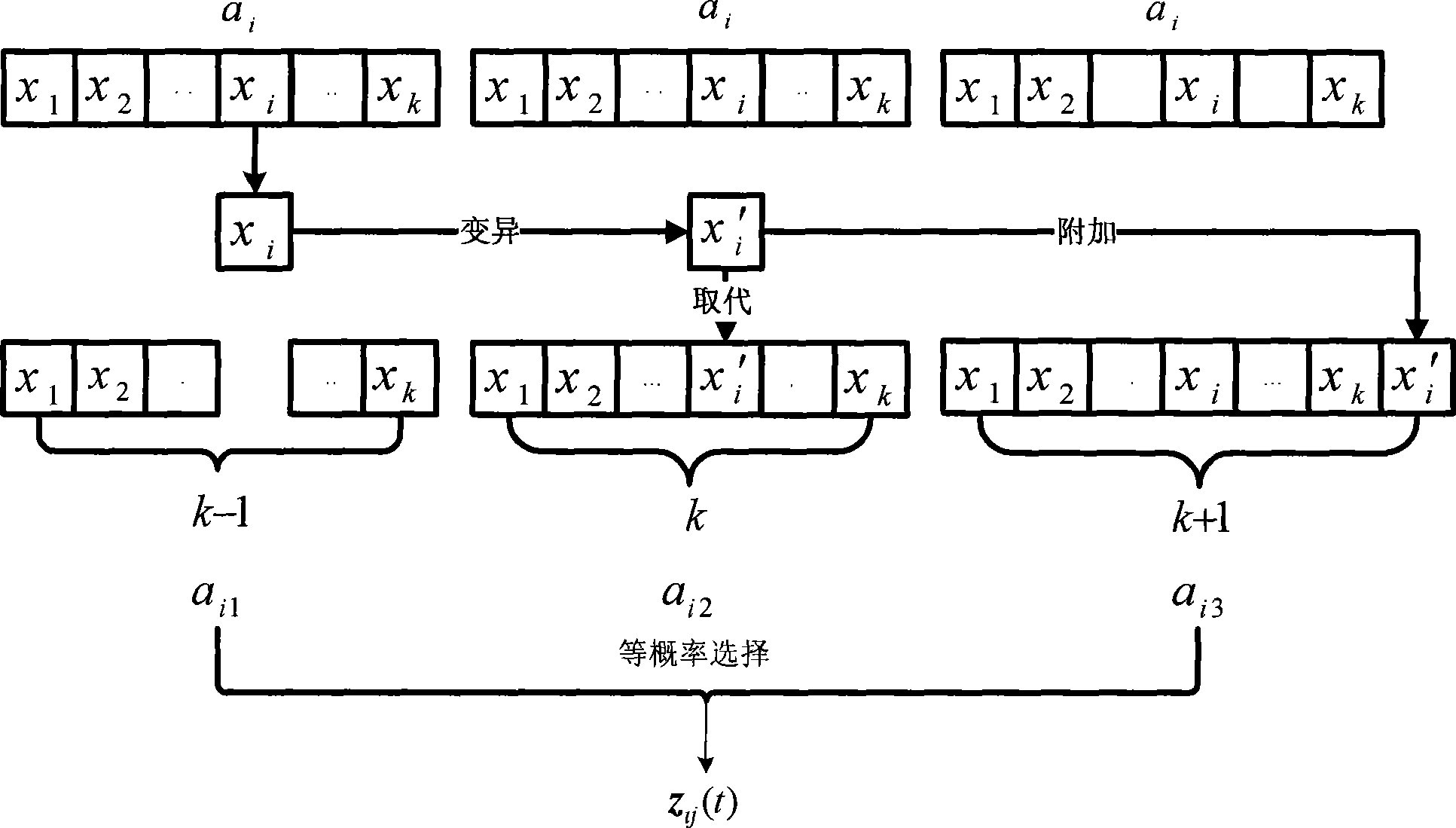
Nonsupervision image segmentation process based on clone selection
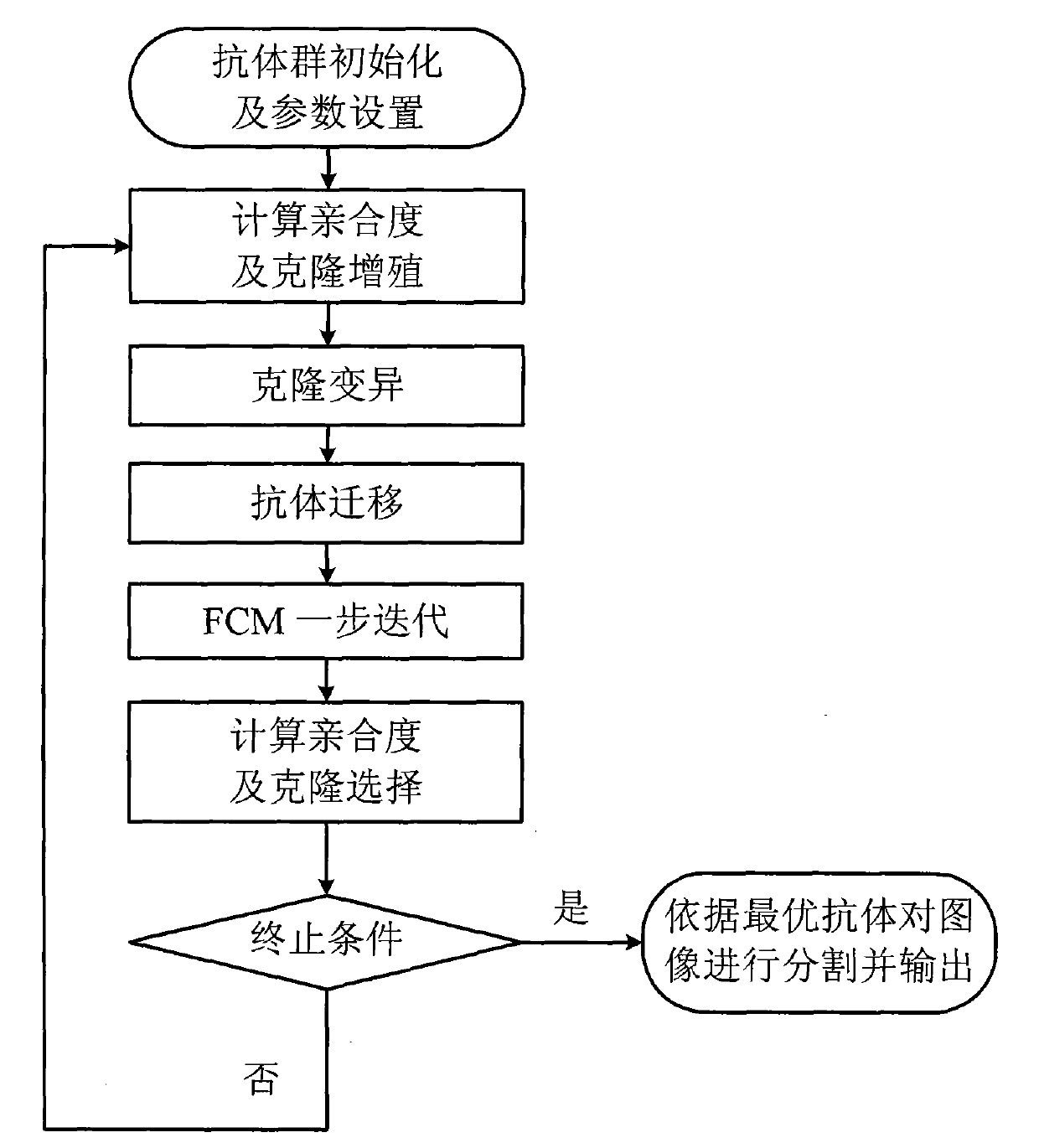
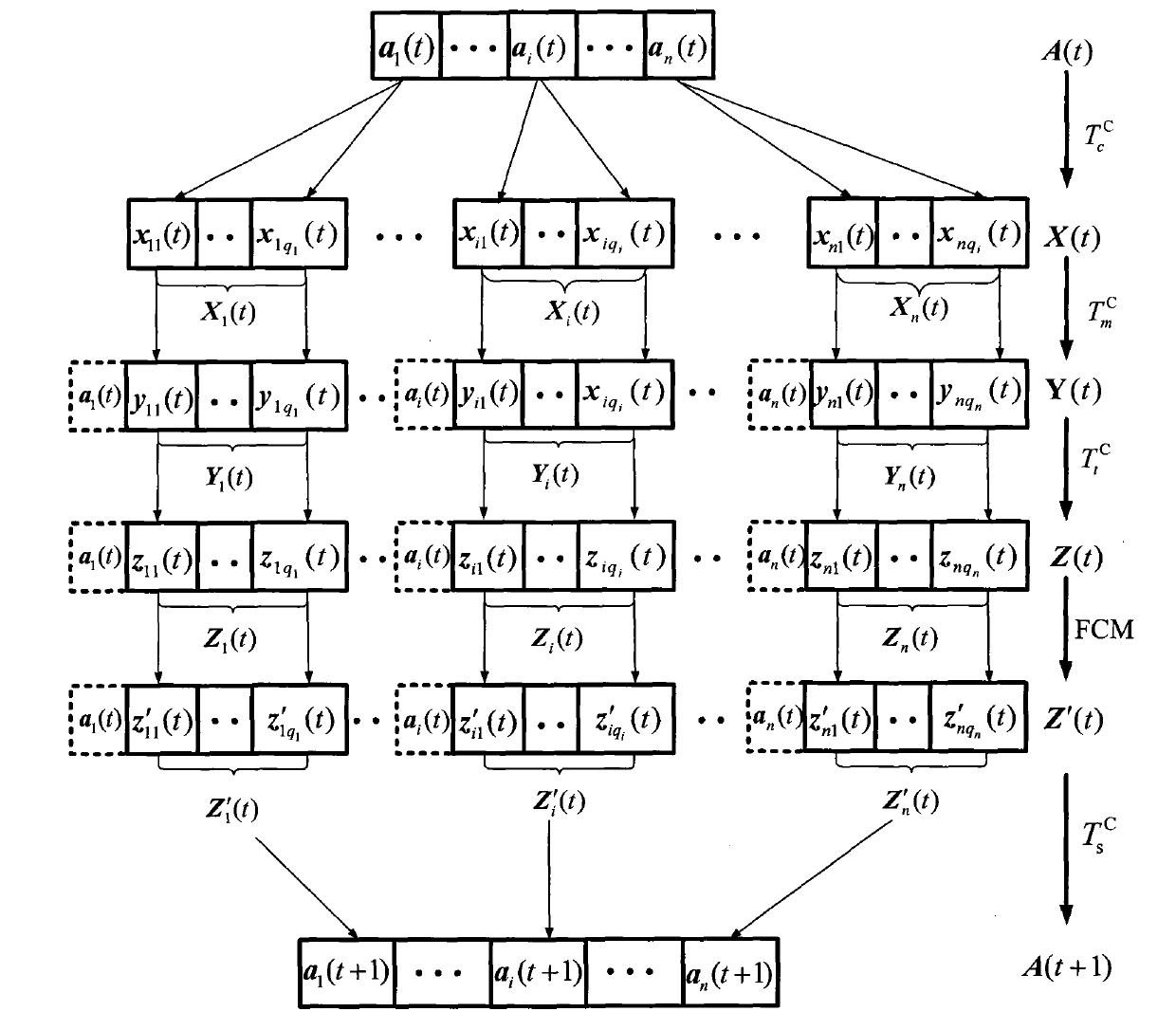
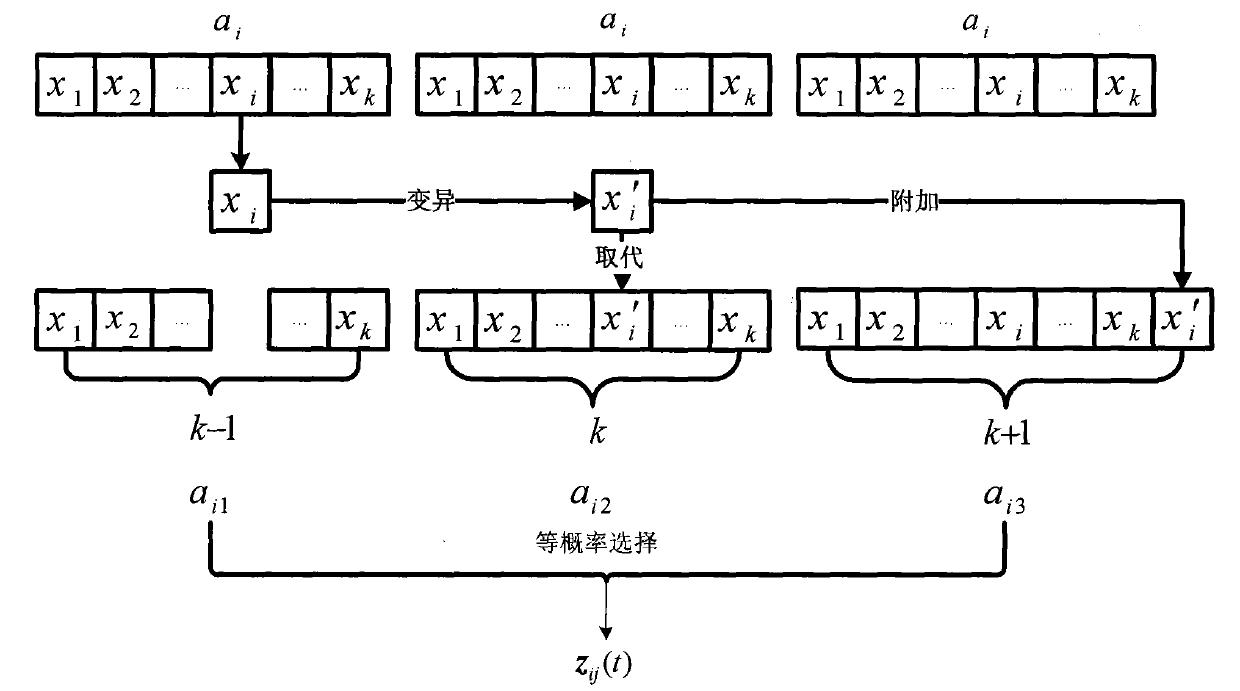
The invention discloses an unsupervised image segmentation method, which belongs to the technical field of image processing, and aims to reduce the dependence on user apriori knowledge as well as ensure segmentation precision. The method comprises the following steps: (1) initializing an antibody population and setting up parameters; (2) calculating an affinity degree and operating clonal reproduction; (3) carrying out a clonal variation operation on the clonal reproduced antibody population; (4) carrying out a migration operation on the clonal variated antibody population; (5) carrying out an iterative operation on the FCM; (6) calculating the affinity degree of the antibody population and carrying out clonal selection operation; (7) repeating the steps and ending the iterative operation according to iterative conditions; and (8) dividing an image according to the antibody optimal and outputting the segmentation result. The method has the advantage that the image can be automatically segmented effectively under the circumstance that the amount of the segmentation regions is unspecified.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Nonsupervision image segmentation process based on clone selection
The invention discloses an unsupervised image segmentation method, which belongs to the technical field of image processing, and aims to reduce the dependence on user apriori knowledge as well as ensure segmentation precision. The method comprises the following steps: (1) initializing an antibody population and setting up parameters; (2) calculating an affinity degree and operating clonal reproduction; (3) carrying out a clonal variation operation on the clonal reproduced antibody population; (4) carrying out a migration operation on the clonal variated antibody population; (5) carrying out an iterative operation on the FCM; (6) calculating the affinity degree of the antibody population and carrying out clonal selection operation; (7) repeating the steps and ending the iterative operationaccording to iterative conditions; and (8) dividing an image according to the antibody optimal and outputting the segmentation result. The method has the advantage that the image can be automaticallysegmented effectively under the circumstance that the amount of the segmentation regions is unspecified.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
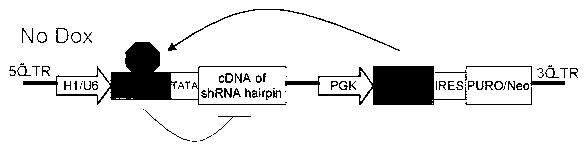
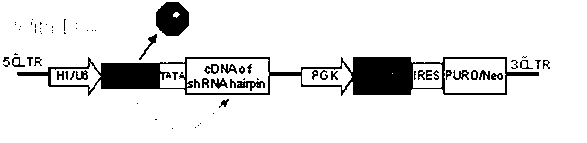
Inducible shRNA (short hairpin ribonucleic acid) lentiviral expression vector and construction method and application thereof
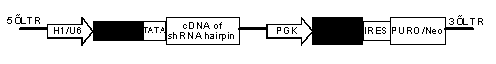
The invention provides an inducible shRNA (short hairpin ribonucleic acid) lentiviral expression vector and a construction method and application thereof. The inducible shRNA lentiviral expression vector comprises an shRNA expression frame and a tetracycline repressor protein expression frame, wherein the shRNA expression frame comprises a first promoter, a tetracycline response element being combined with tetracycline repressor protein, a TATA box and an shRNA coding sequence, and the tetracycline repressor protein expression frame comprises a second promoter, a tetracycline repressor protein expression gene, an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence and a marker gene. Compared with an existing inducible shRNA expression vector, the inducible shRNA lentiviral expression vector has the advantages of being capable of rapidly establishing inducible shRNA expressing a silent gene in various cell strains by using a single vector, having no need of clone selection of cells, and being applicable to in vitro culture and in vivo study of cells.
Owner:傅开屏 +1
Steel production energy consumption immune prediction control model
InactiveCN103135444ASolve the blockageThe impact of weakening controlsAdaptive controlSimulationPredictive controller
The invention discloses a steel production energy consumption immune prediction control model. The energy consumption immune prediction control model basing on rough set-immune prediction control is built, a rolling optimal method is achieved by utilizing a clonal selection algorithm, and an equation and an inverse matrix for solving Diophantine are avoided. A nonlinear autoregressive moving average model is adopted directly in a prediction model. The nonlinear autoregressive moving average model is adopted according to controlled members by basing on an immune feedback adjustment principle, feedback errors are controlled to be optimal performance indicators, the rolling optimal method is achieved by utilizing evolutionary computation based on immune clone, a prediction controller based on immune parameter identification is designed, the equation and the inverse matrix for solving the Diophantine are avoided, relative gain parameters and lag time parameters are optimized on line, and the influences of model errors to system control are reduced.
Owner:徐雪松
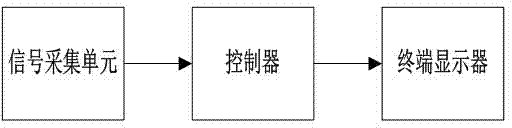
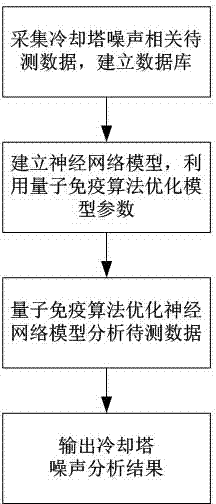
Cooling tower noise monitoring system and method
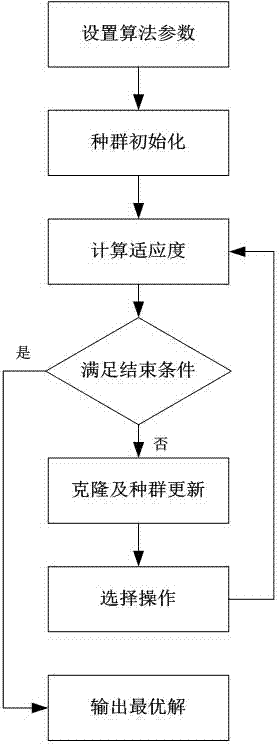
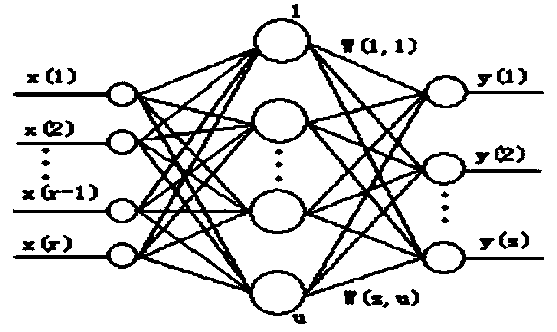
InactiveCN104713408AThe analysis result is accurateImprove classification rateHeat exchange apparatusNoise monitoringCooling tower
The invention relates to a cooling tower noise monitoring system and method, and belongs to the field of cooling tower systems. The system comprises a signal acquisition unit, a controller and a terminal display, wherein the controller is connected with the signal acquisition unit and receives the signal parameters of the signal acquisition unit; the terminal display is connected with the controller and receives and displays signals of the controller. By means of the cooling tower noise monitoring system and method, components related to cooling tower noise can be monitored in real time, a quantum immune optimization neural network model is utilized to analyze and process the detected data related to the cooling tower noise, a quantum searching mechanism and an immune algorithm clonal selection principle are combined, a primitive population and a cloning subgroup are generated through cloning operation of the neural network algorithm to achieve population expansion, the local searching ability is improved, the optimal model parameter is obtained through good processing and analysis, the parameter data classification probability is increased, the false alarm rate is lowered, and the problem that in the prior art, the root cause of the cooling tower noise is neglected is solved.
Owner:WUHU KAIBOER HI TECH IND
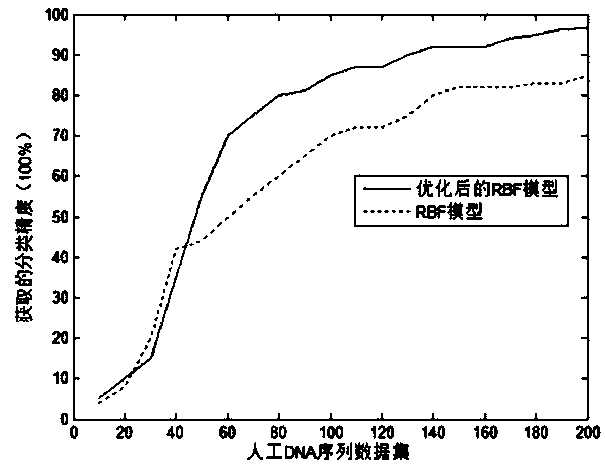
RBF network modeling method based on immune polyclonal optimization in DNA sequence classification
InactiveCN103745090AImprove classification efficiencyImprove classification accuracyNeural learning methodsSpecial data processing applicationsClonal selectionNew population
The invention discloses an RBF (Radial Basis Function) network modeling method based on immune polyclonal optimization in DNA (Desoxvribose Nucleic Acid) sequence classification. The RBF network modeling method comprises the following steps of randomly generating an initial antibody population A={a1, a2,..., an}, calculating the affinity function f(x) of the antibodies in the antibody population, putting the antibodies in the antibody population in a descending order according to the values of f(x) to obtain A'={a'1, a'2,..., a'N}, selecting m antibodies, each of which the affinity function f(x) has a greater value, from A', and performing cloning operation on the m antibodies to obtain a new antibody population A', performing clonal variation and clonal crossover operations on the current population A'', respectively, to obtain a new population FORMULA, performing clonal selection operation FORMULA on the population FORMULA, outputting the antibody which simultaneously satisfies the conditions of the minimum support and the minimum confidence, and in the meantime, reducing the antibody into the primitive attribute value and remaining the antibody in the population, and when k is greater than or equal to Genmax, finishing the algorithm and completing molding, otherwise, determining that k is equal to k+1, taking the present population as the initial antibody population for the calculation of next generation and turning to the step 2. As a result, the purposes of improving the DNA sequence classification efficiency and improving the reserve ratio are achieved.
Owner:LIUZHOU VOCATIONAL & TECHN COLLEGE
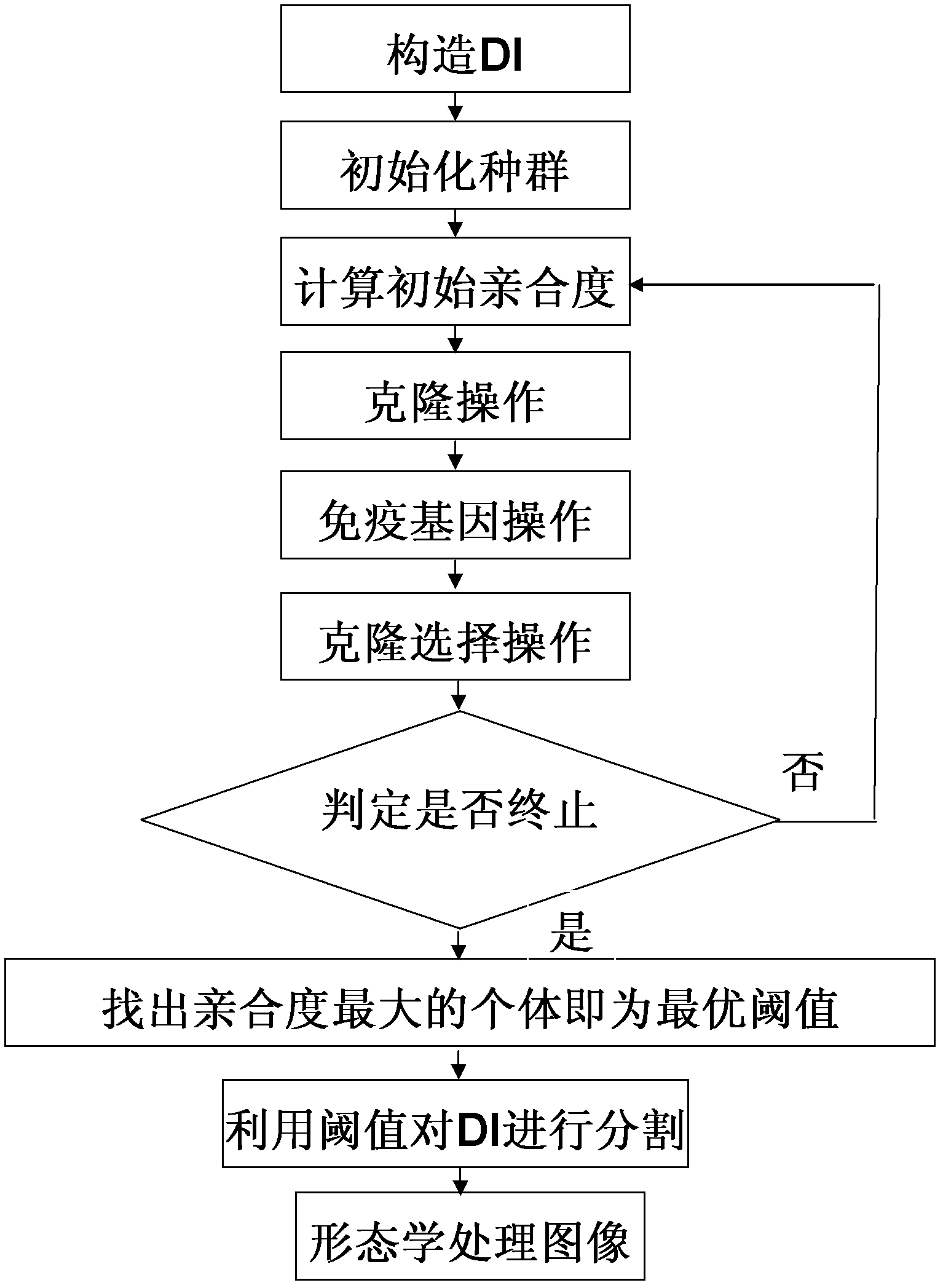
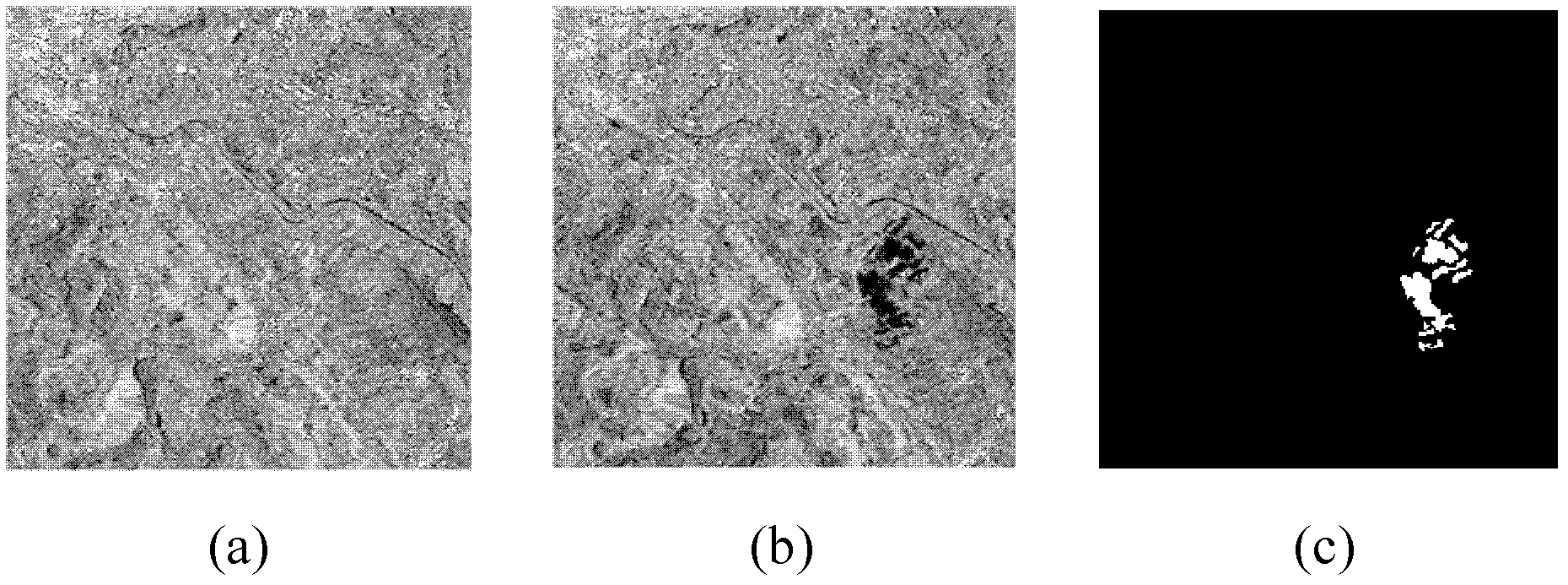
Clonal selection-based method for detecting change of remote sensing image with optimal entropy threshold
InactiveCN102509297AReduce noiseLow total bugchecksImage analysisBiological modelsClonal selectionClonal selection algorithm
The invention discloses a clonal selection-based method for detecting change of a remote sensing image with an optimal entropy threshold. The method comprises the following implementation steps of: (1) constructing difference imagemaps of dual-time phase remote sensing images by logarithmic ratio operators; (2) initializing a population and setting parameters; (3) calculating affinities of the population by an optimal threshold algorithm, and descending the sort of the affinities; (4) performing clonal selection operation on each individual according to a clonal selection algorithm, generating a new population, and storing the individual with the maximal affinity in the population; (5) judging whether termination conditions are reached, retuning to the step (3) if the termination conditions are not reached, otherwise sorting the affinities of all the individuals in a storage result, and taking the individual corresponding to the maximum value of the affinities as an optimal threshold; (6) segmenting the threshold of the difference imagemaps by the optimal threshold to obtain an initial change detection result; and (7) processing an initial change detection result map by morphology to obtain a final change detection result. The clonal selection-based method has the advantages of stable and effective operation and fewer total detection errors.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
High spectral waveband selection method based on entropy redundancy and clonal selection
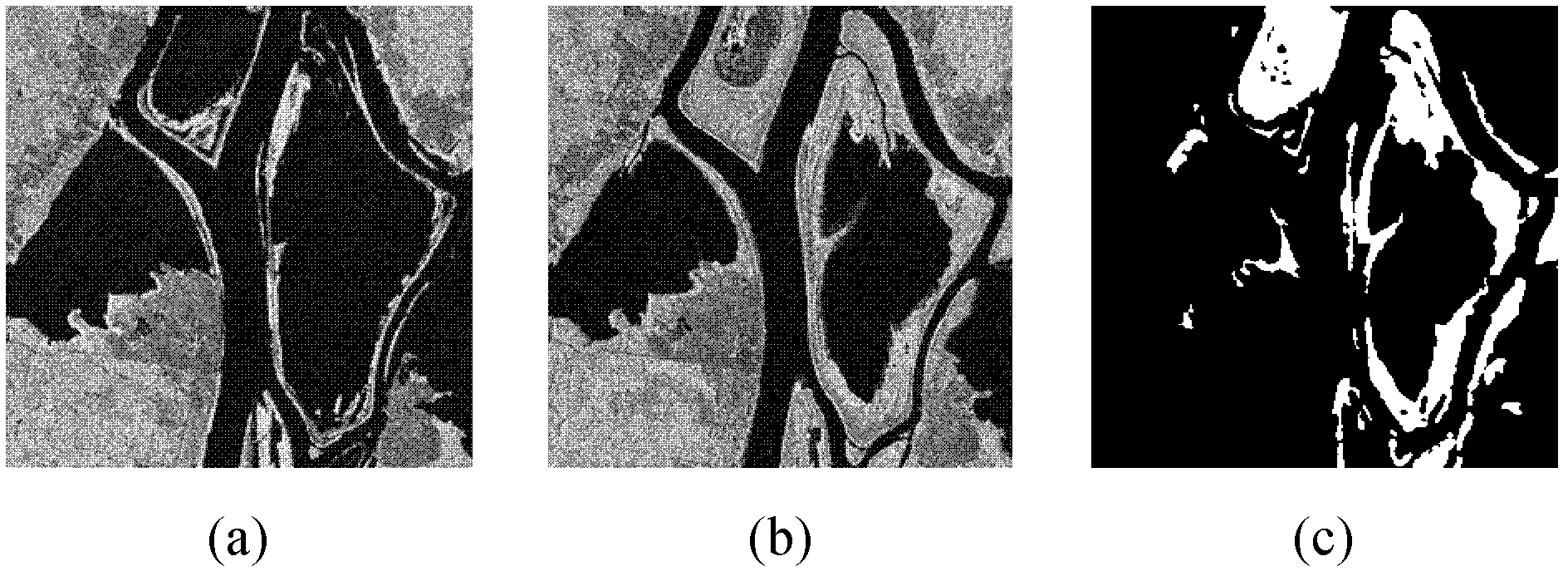
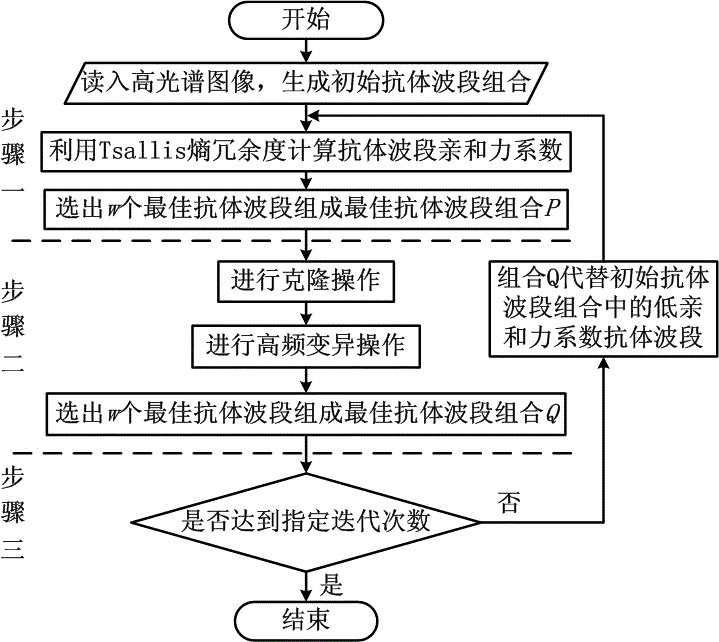
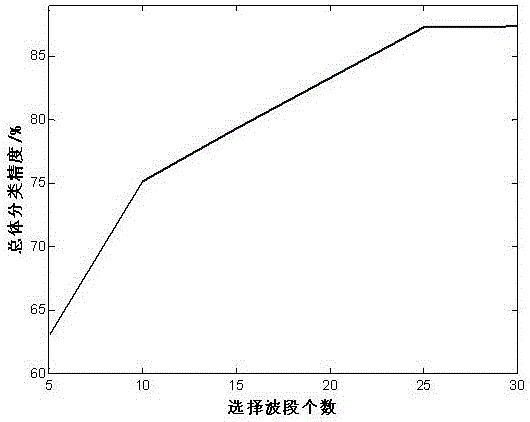
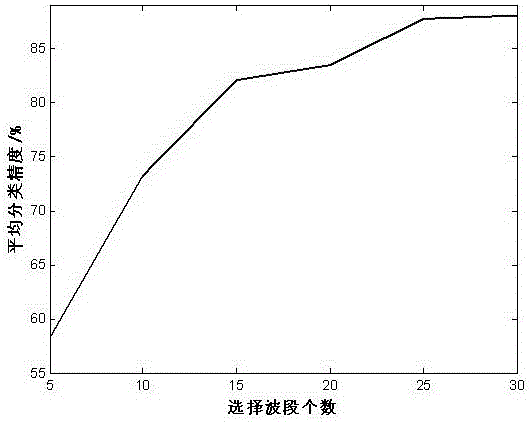
InactiveCN106485709AImprove classification accuracyReflect the size of redundancyImage enhancementImage analysisClonal selectionData compression
The invention relates to a high spectral waveband selection method based on entropy redundancy and clonal selection, belongs to a dimension reduction method of a high spectral image, and solves the problem that a waveband image cannot be evaluated reasonably in the waveband selection process of the high-spectral image. The method comprises the steps that 1) the high spectral image is read in, an initial antibody waveband is generated, an antibody waveband affinity coefficient is calculated by utilizing the Tsallis entropy redundancy, and an optimal antibody waveband is selected according to the affinity coefficient; 2) the optimal antibody waveband is cloned to generate a temporary antibody waveband, a high-frequency variation operation is carried out, and an optimal antibody waveband is selected again; and 3) antibody wavebands of relatively low affinity coefficient are replaced, and iterative computation is carried out, and is not stopped till the specific iteration frequency is reached. The Tsallis entropy redundancy serves as a criterion function for waveband selection, the waveband of the high spectral image can be selected in high efficiency, and the method is suitable for fields including dimension reduction and data compression of the high spectral image.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for detecting dynamic gridding instruction based on artificial immunity
InactiveCN101299691BDetection speedQuality improvementGenetic modelsData switching networksClonal selectionClonal selection algorithm
A method for detecting dynamic gridding instruction based on artificial immunity, is a method for detecting instruction facing to gridding which takes use the artificial immunity technique for reference. According to the dynamic and real time requirement of the instruction detection under gridding surroundings, the method takes the prior clonal selection algorithm as main body, combines negative selection, clonal selection, affinity maturation and memory detector gene bank method, so at to dynamic handle the instruction detection under gridding surroundings. The method includes a dynamic detector evolvement process and a gridding instruction detection process which are based on artificial immunity, which is characterized in by using the artificial immunity technique for reference, and combining the negative selection, clonal selection, affinity maturation and memory detector gene bank method; firstly obtaining an evolvement matured detector; and then dynamically handling the instruction detection problem in the gridding surroundings under the coordination of the artificial immunity mechanism, to complete the entire process of dynamic gridding instruction detection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Social network false information control method based on clonal selection algorithm
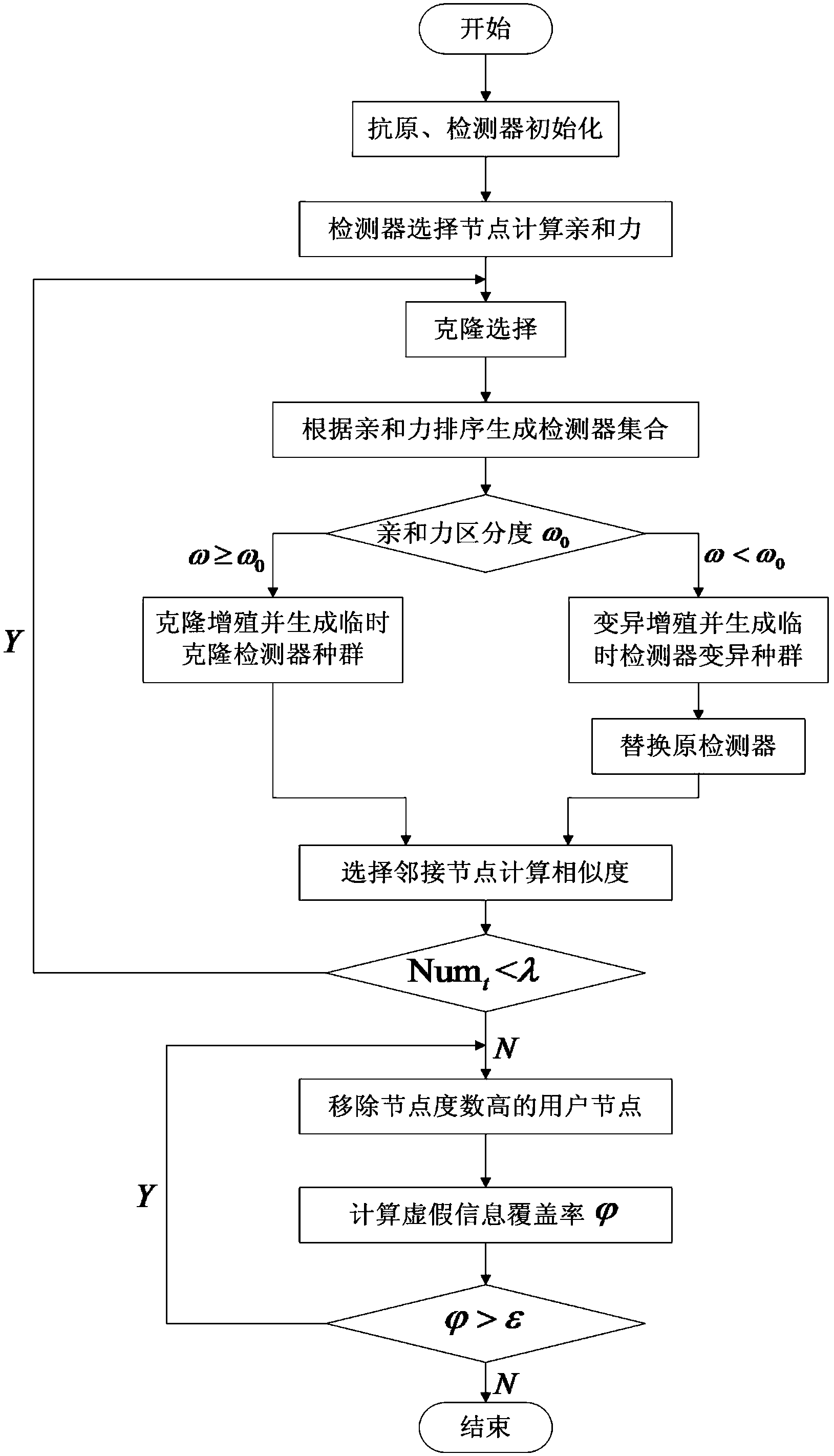
InactiveCN104281972AReduce coverageEasy to controlData processing applicationsGenetic algorithmsInformation controlNODAL
The invention discloses a social network false information control method based on a clonal selection algorithm. The method comprises the following steps that antigen and detectors are initialized; the detector selects nodes and calculates affinity; clonal selection is conducted; the detector is subjected to clonal proliferation; the detector is subjected to variation proliferation; the affinity of the detector subjected to variation proliferation is calculated again, and another detector is selected again; user nodes are selected again, and information similarity is calculated; assuming that Numt=Numc+Numv, when Numt>Lambada, the next step is carried out; the information coverage rate is calculated, and then the social network false information control process is completed. By means of the clonal selection information control method, varied network information can be effectively controlled; compared with a traditional social network false information control method, the efficiency and the accuracy of the method are both improved remarkably.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
Image retrieval method based on memetic algorithm
InactiveCN102591987AFast convergenceFinish quicklyImage analysisSpecial data processing applicationsMemetic algorithmAntibody Affinities
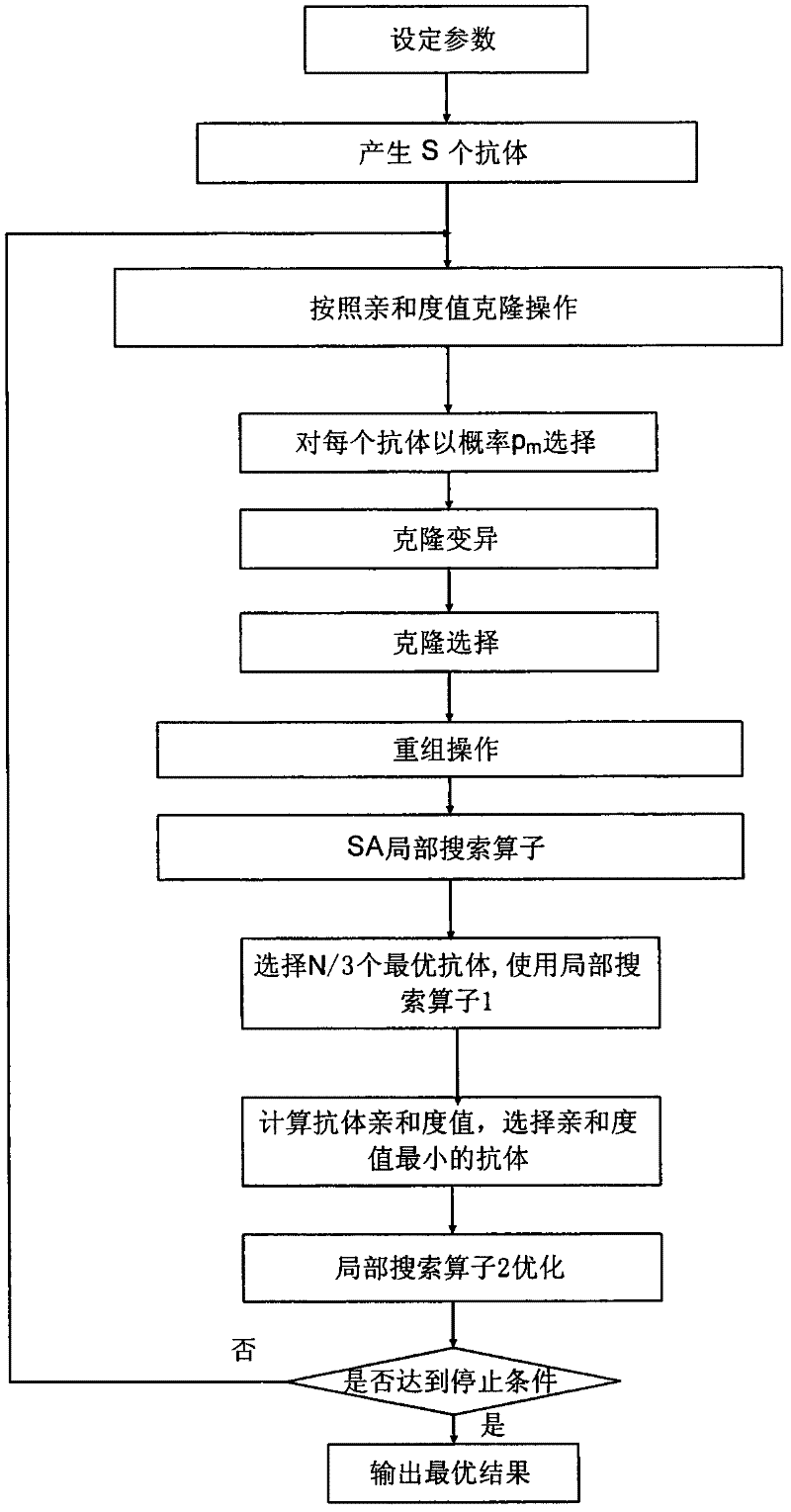
The invention discloses an image retrieval method based on memetic algorithm, and relates to shape-based image retrieval. The image retrieval method comprises setting parameters; generating an initial population; calculating antibody affinity; cloning; executing clonal variation based on probability; performing clonal selection; recombining; subjecting the antibody to local search operator optimization based on simulated annealing algorithm; optimizing superior antibodies by using a local search operator (1) and a local search operator (2); and repeating the operations to realize rapid and effective image retrieval. By combining the clonal selection algorithm with the local search operators, the image retrieval method provided by the invention has high global search capacity, high convergence rate and high image retrieval efficiency. The local search operators with high local search capacity can further improve the retrieval result of the clonal selection algorithm so as to improve the accuracy of the image retrieval results. In addition, the method can overcome the difficulty in determining the number of classes by using a coding method based on class marks. Based on the advantages of high efficiency and high accuracy, the image retrieval method provided by the invention can be used for retrieving and classifying network pictures.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
A Rechargeable Wireless Sensor Network Immune Routing Restoration Method
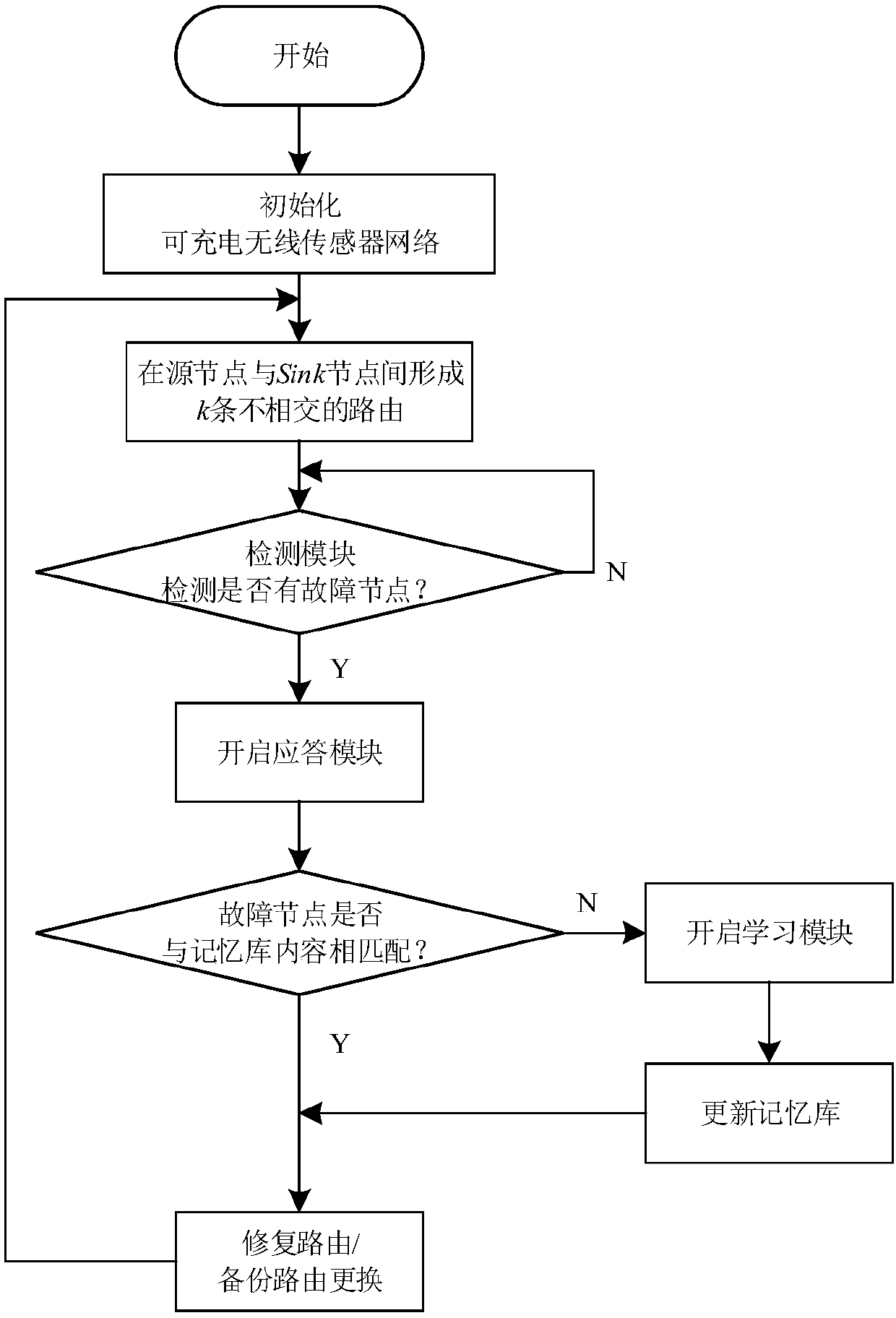
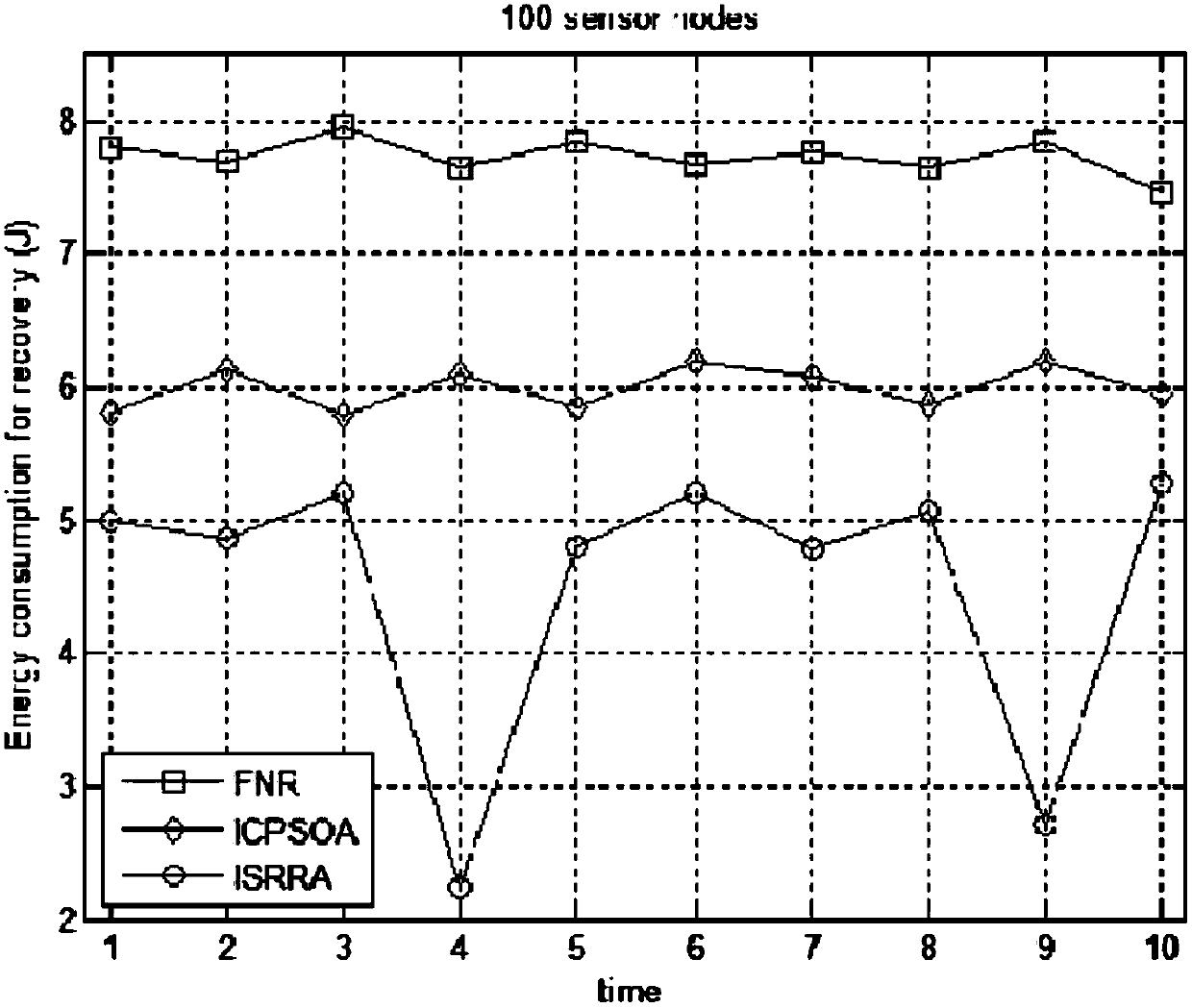
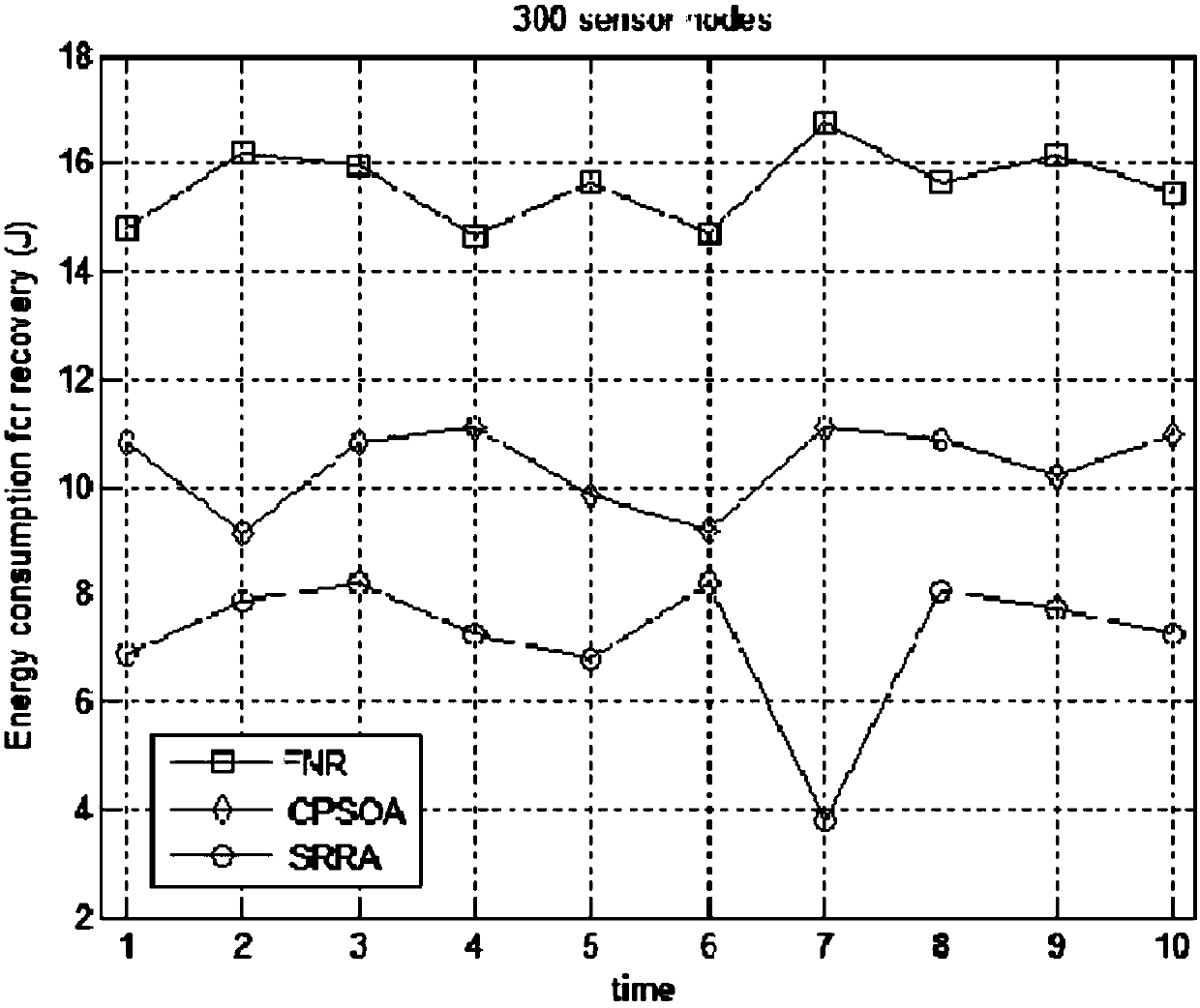
InactiveCN105897577BBest disjoint routingBest disjoint pathsNetwork topologiesData switching networksAntigenEngineering
The invention relates to a rechargeable wireless sensor network immune routing repair method, k disjoint routes are established between the source node and the sink node, one of the routes is used by the network, and the other k-1 are backup routes, which will be used by the nodes The routing failure caused by the energy-depleted node is used as an antigen, and the corresponding repair routing is used as an antibody; the corresponding detection module, response and learning module, and memory module are used to simulate the working mechanism of the immune system to eliminate antigens. In the learning module, a clonal selection algorithm is used. The cloning and mutation mechanism has been improved based on the hormone regulation mechanism of the endocrine system. By simulating the cooperative work of various modules of the immune system, ISRRA can effectively provide a repair strategy for faulty routes, especially suitable for the situation where the same faulty route occurs multiple times in EH‑WSNs. In addition, in the process of repairing the faulty route, ISRRA also evaluates the quality of the backup route and judges whether to replace the backup route, so as to ensure the quality of the route.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com