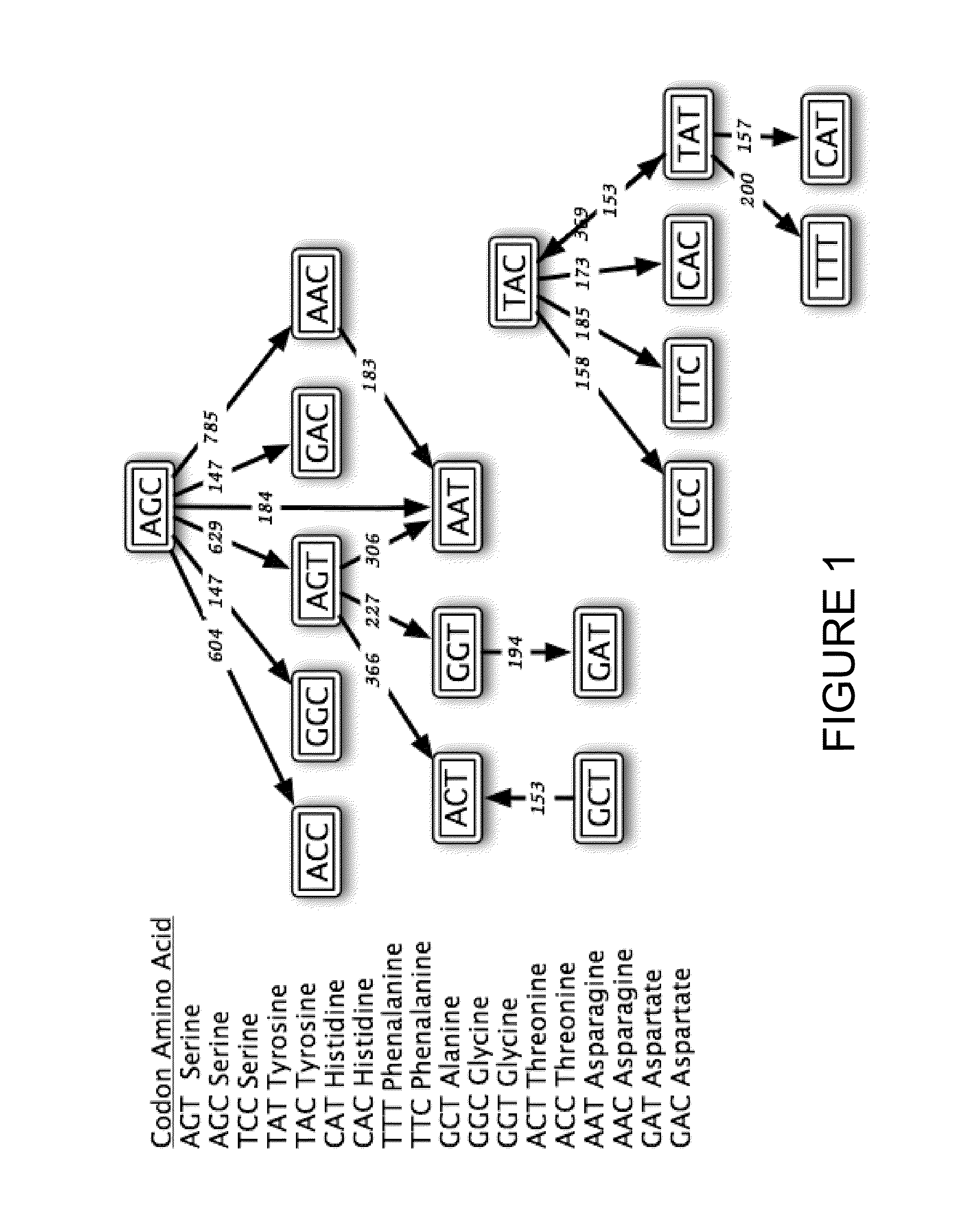
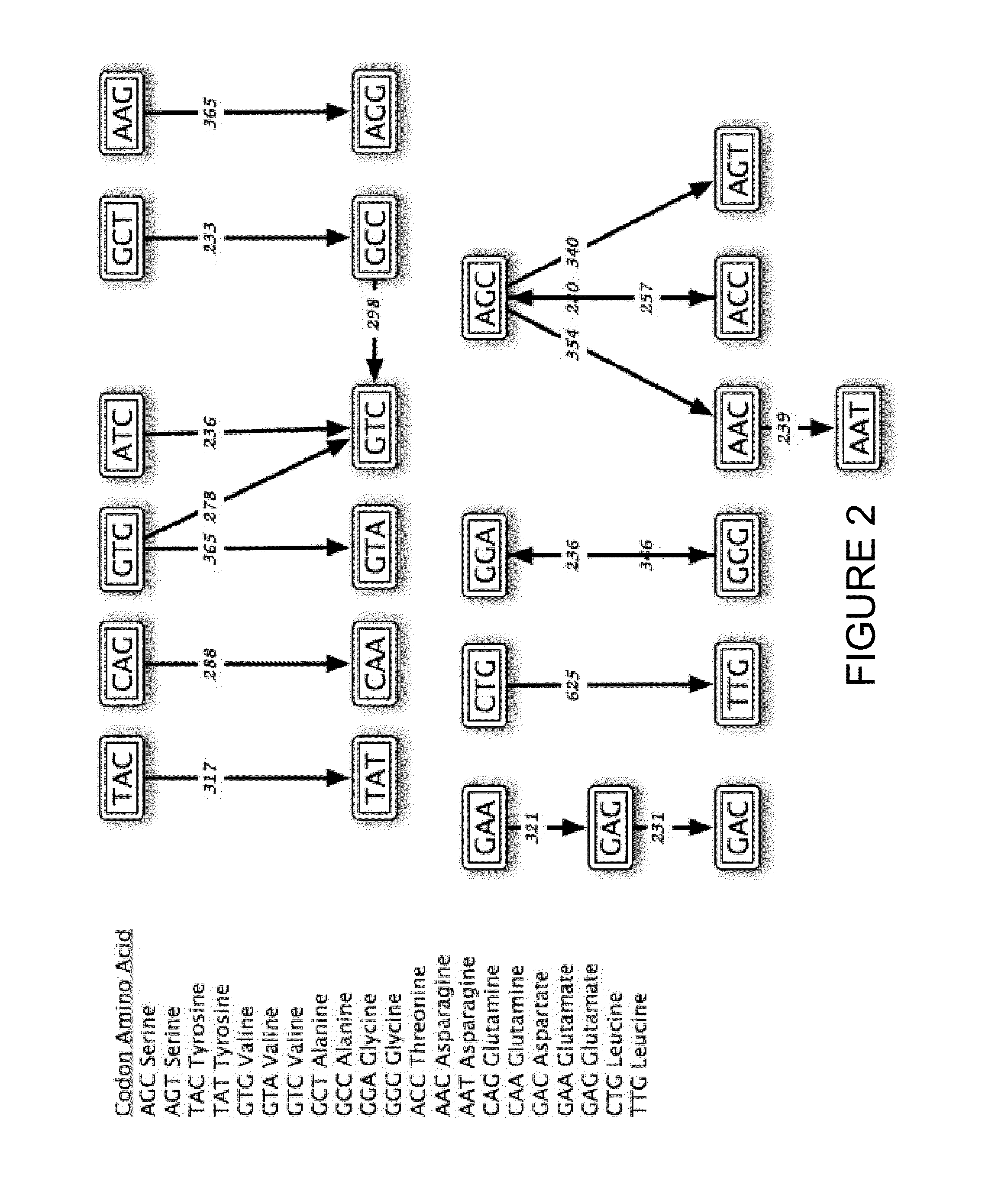
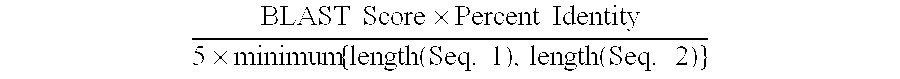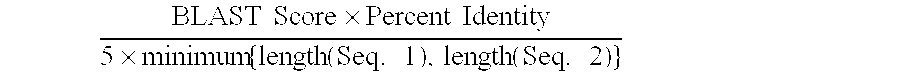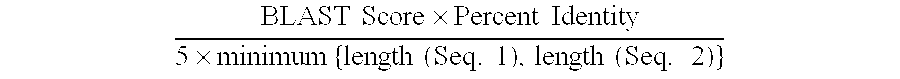Patents
Literature
62results about How to "Fast evolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Digital video decoding method based on image processor
InactiveCN101123723AFast evolutionEasy to implementPulse modulation television signal transmissionImage codingVideo decodingMap decoding
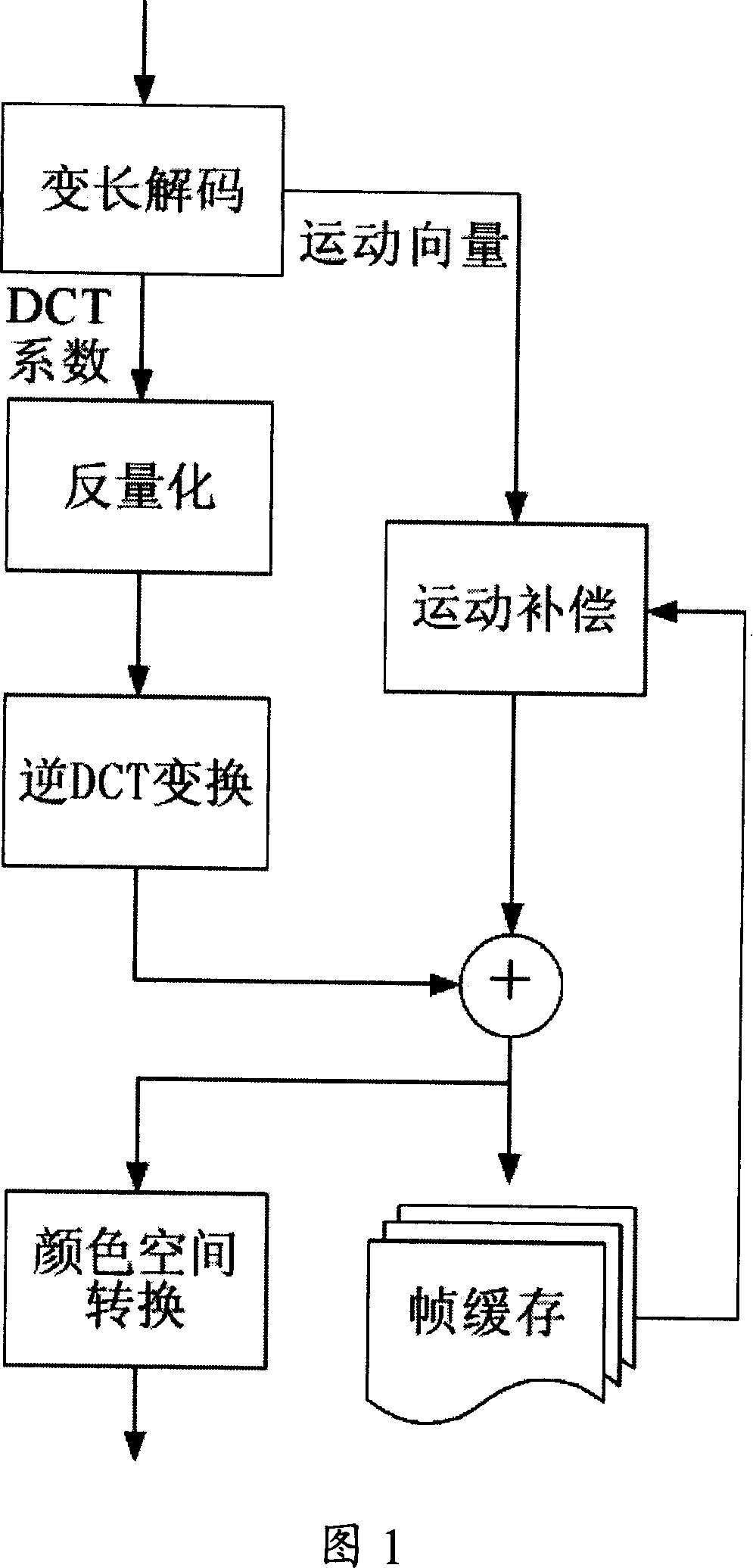
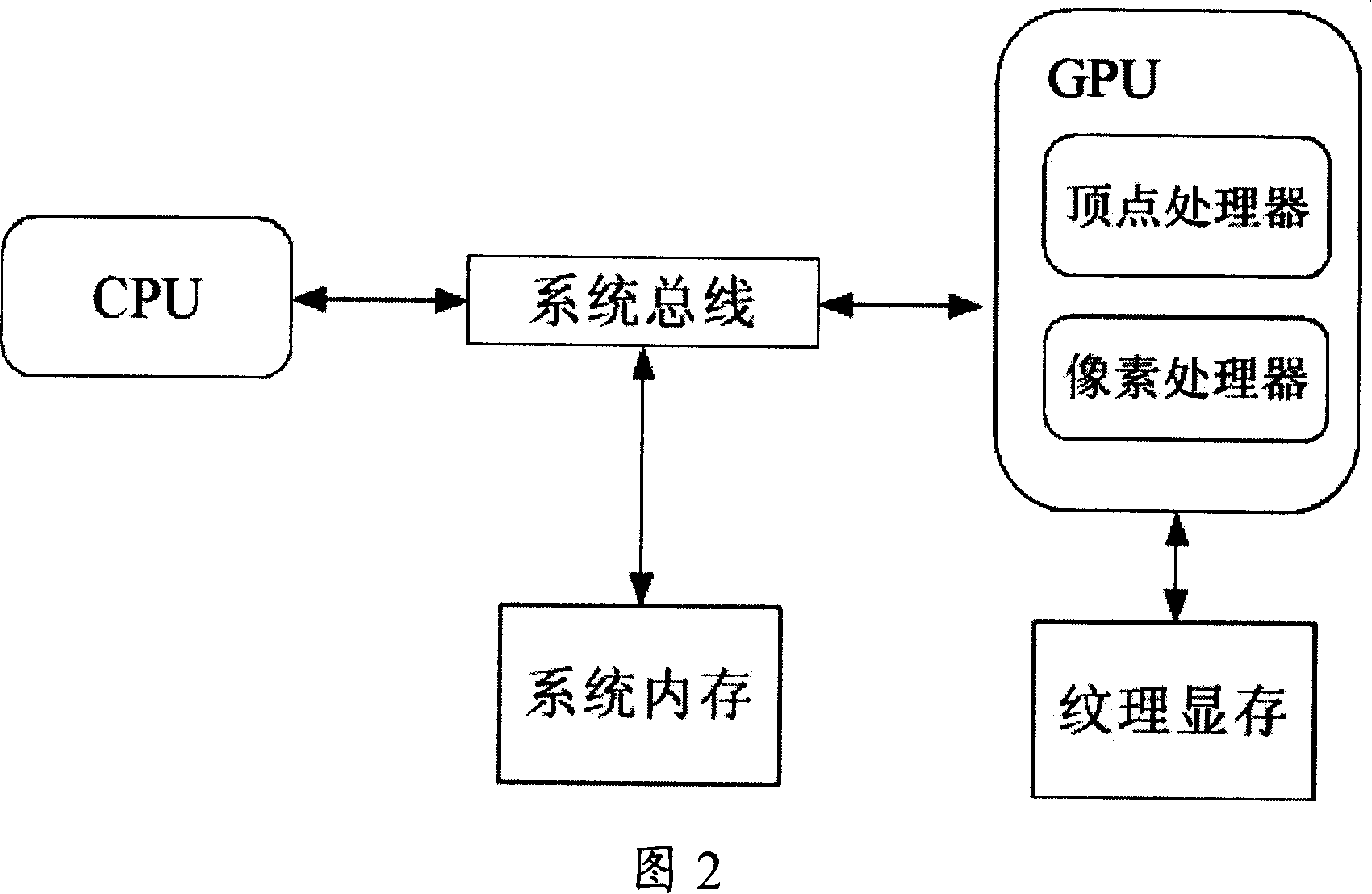
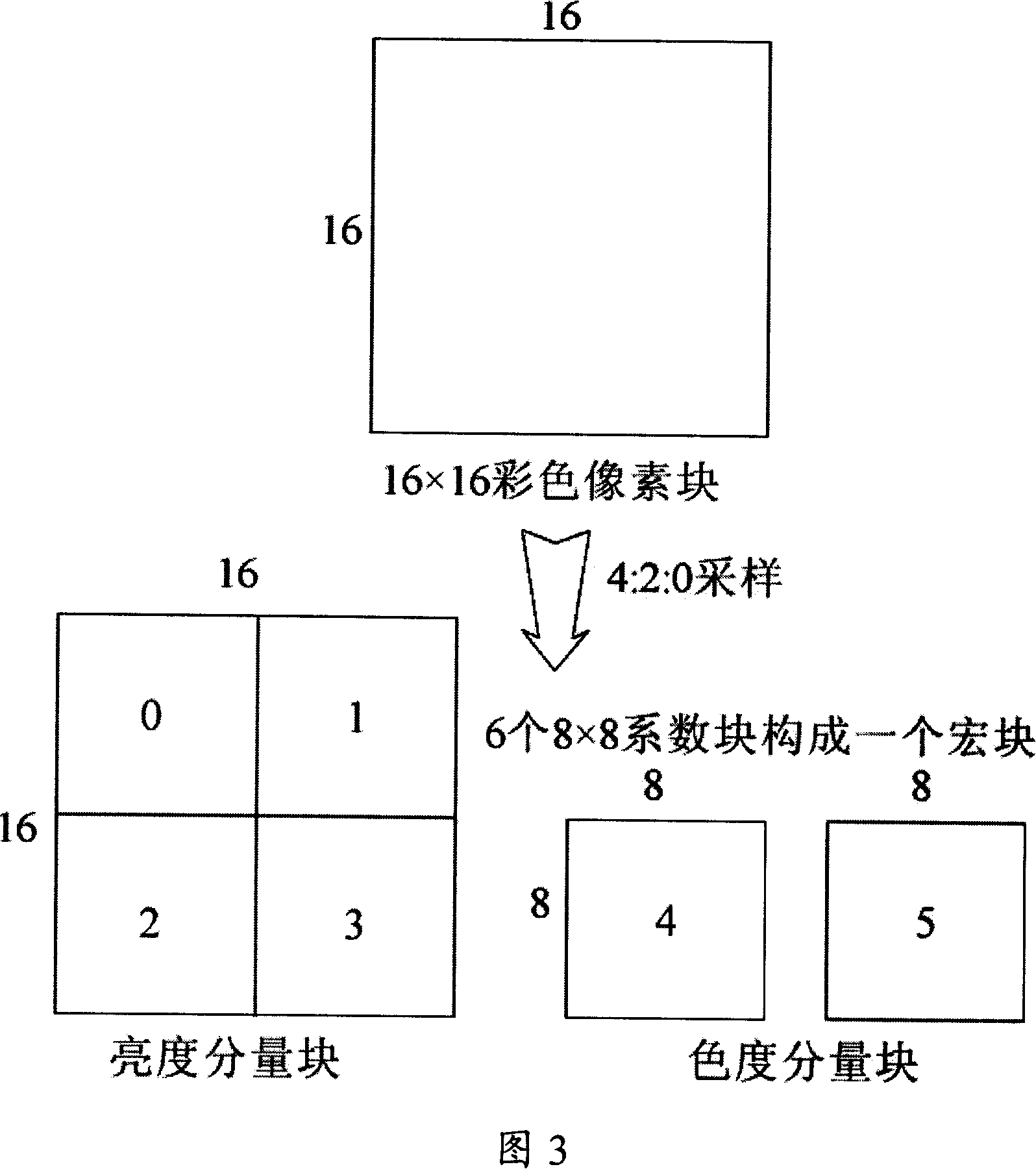
The invention provides a decoding method for compression video based on a GPU. The method utilizes point graphic element to show video block instead of square and maps decoding segments to the GPU except variable length decoding, and then the GPU organizes video data into point collection and completes decoding process by drawing point collection. The invention has the advantages of a CPU and the GPU so that the two work in parallel accelerate video decoding process; the invention has high performance of hardware decoding and flexibility of software decoding at the same time, can handle a plurality of video compression format and standard, replace a special decoding hardware of personnel computer with the GPU, a game console, a handheld mobile device, etc, and improve the utilization of hardware resources and reduce cost.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Extracellular signaling molecules
InactiveUS20020187523A1Efficiently translatedImprove expression efficiencyFungiBacteriaENCODEAntibody
The invention provides human extracellular signaling molecules (EXCS) and polynucleotides which identify and encode EXCS. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for diagnosing, treating, or preventing disorders associated with expression of EXCS.
Owner:INCYTE
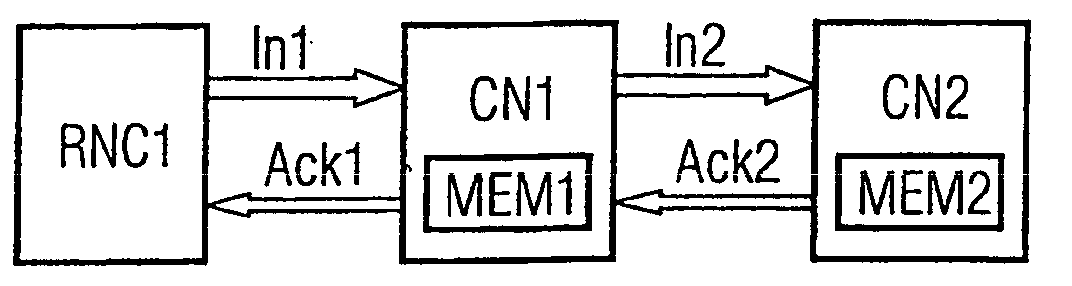
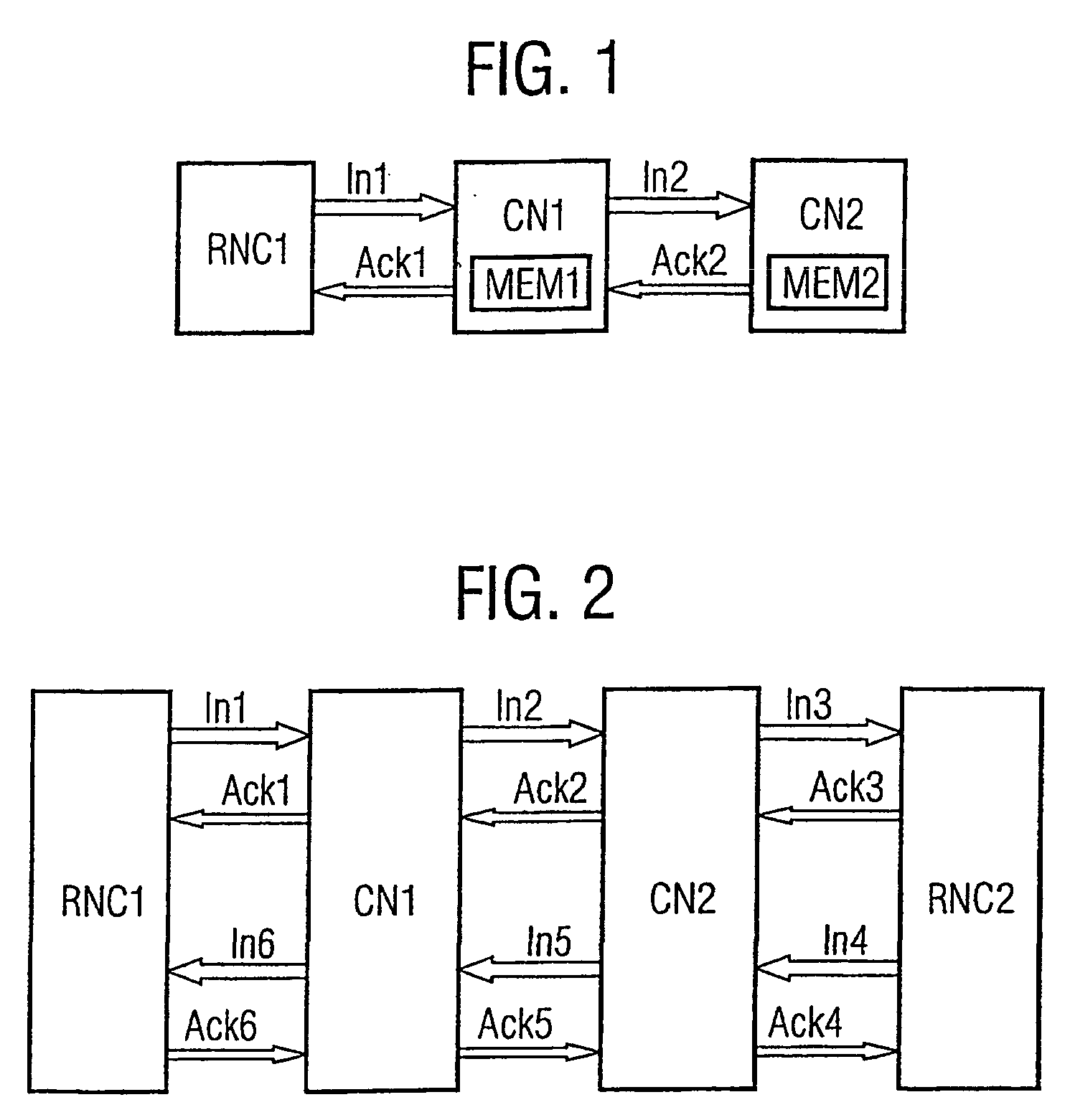
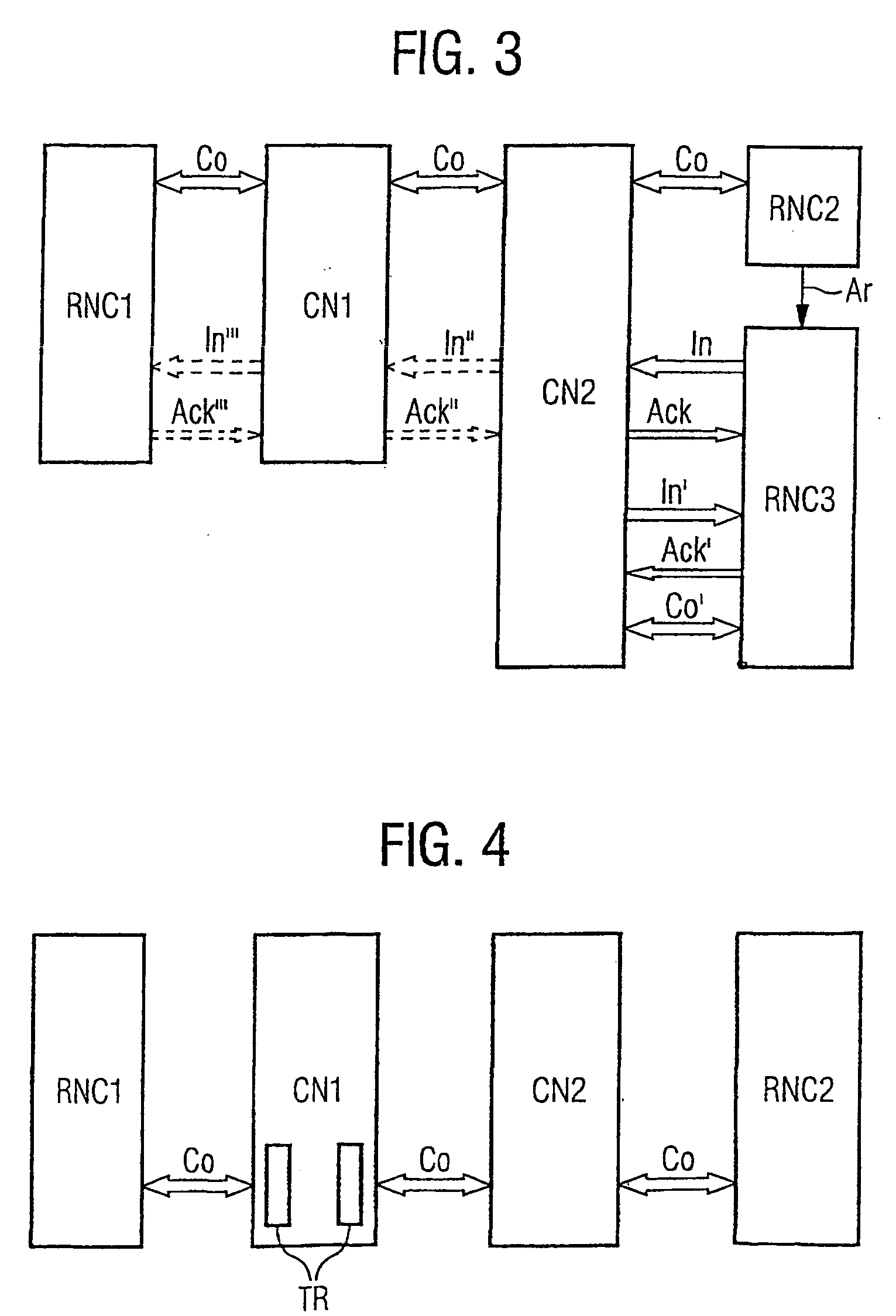
Method for a connection through a core network
InactiveUS20040100914A1Simple methodActive connectionConnection managementStore-and-forward switching systemsEngineeringProgram unit
In a method for the establishment of a connection between a first node (RNC1) and a second node (RNC2), both are connectable to a core network which comprises interconnected core network nodes (CN1, CN2). The first node (RNC1) signals a call request to a first core network node (CN1). If the first node is an access node, it sends an initialization according to a framing protocol, wherein a set of parameters for the framing of information sent over the interface between the first access node (RNC1) and the first core network node (CN1). If the first node is no access node, a first control server (MSC1) defines said set of parameters. The set of parameters is transmitted to the first core network node (CN1) and the first core network node (CN1) stores the parameter set. The first core network node (CN1) initializes the connection (Co) to a further core network node according to said protocol and the further core network node stores the parameter set. The initialization of the connection (Co) to and the storing of parameters in further core network nodes is performed stepwise until a final core network node (CN2) is reached which is connectable to the second access node (RNC2). The final core network node (CN2) initializes the connection (Co) to the second access node (RNC2) according to said protocol and the second access node (RNC2) stores the parameter set. A core network node and a program unit embodying the invention are also described.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Receptors and membrane-associated proteins
InactiveUS20040166501A1Maximizing genetic diversityGood biological propertiesNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsENCODEAgonist
The invention provides human receptors and membrane-associated proteins (REMAP) and polynucleotides which identify and encode REMAP. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for diagnosing, treating, or preventing disorders associated with aberrant expression of REMAP.
Owner:INCYTE
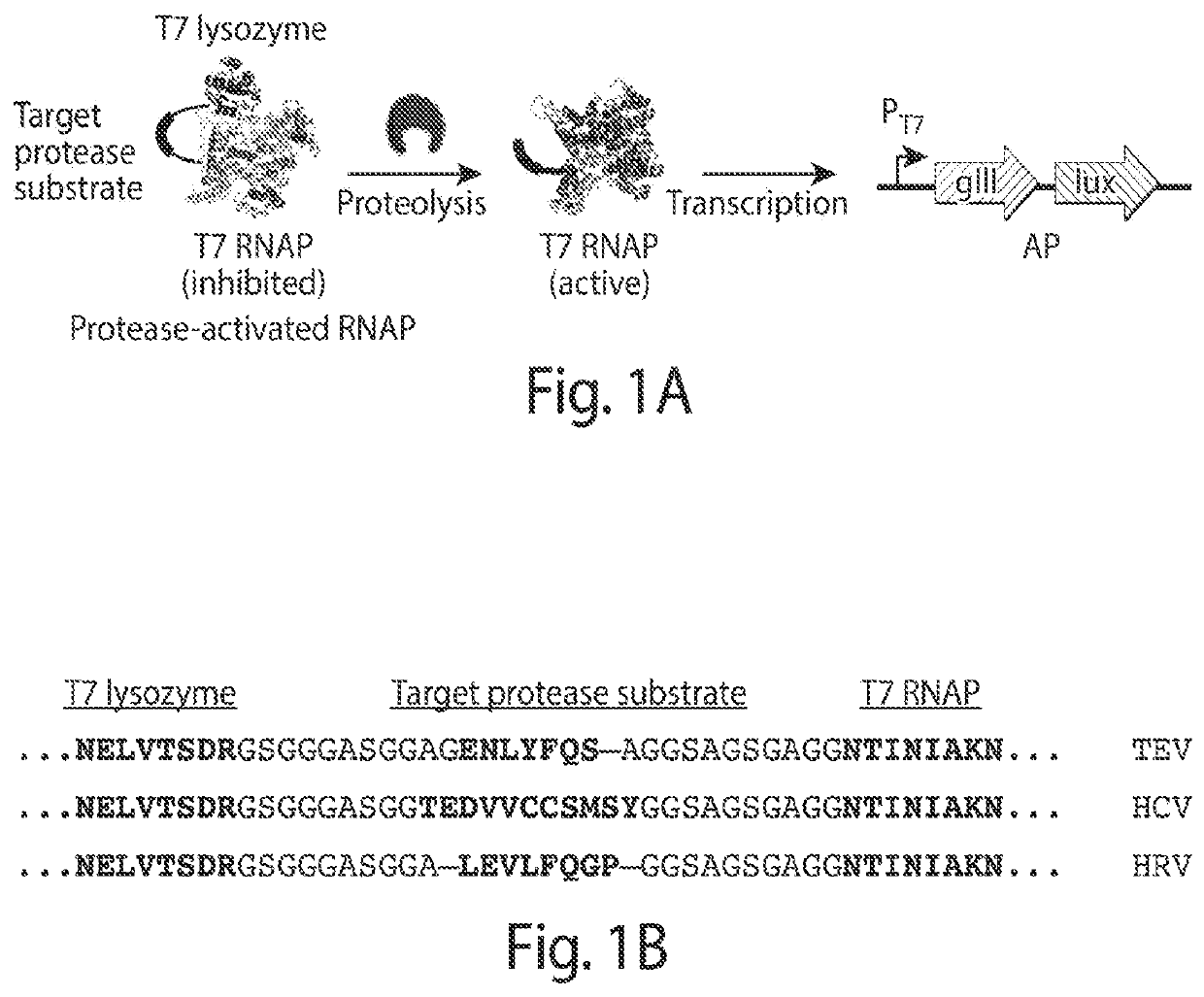
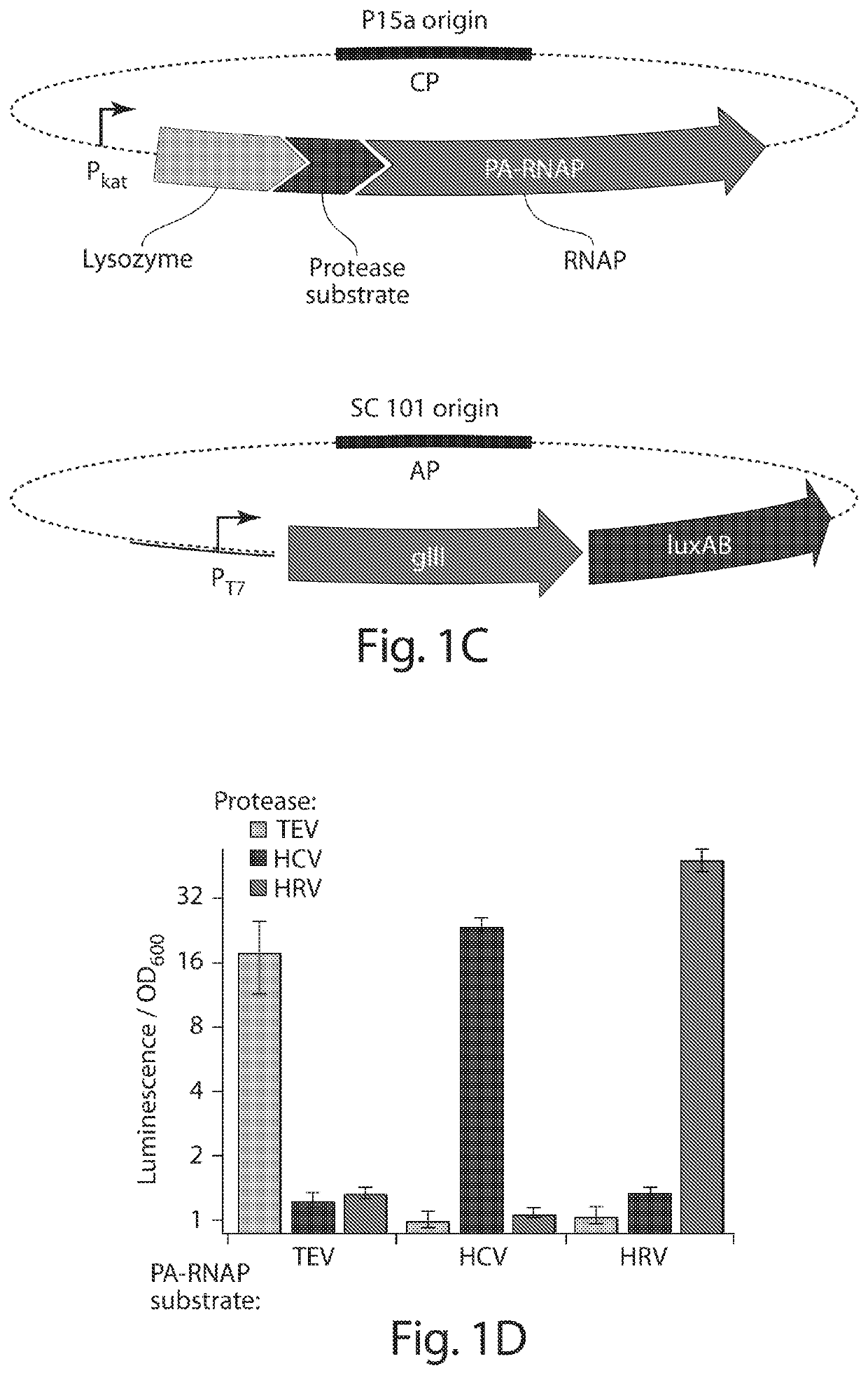
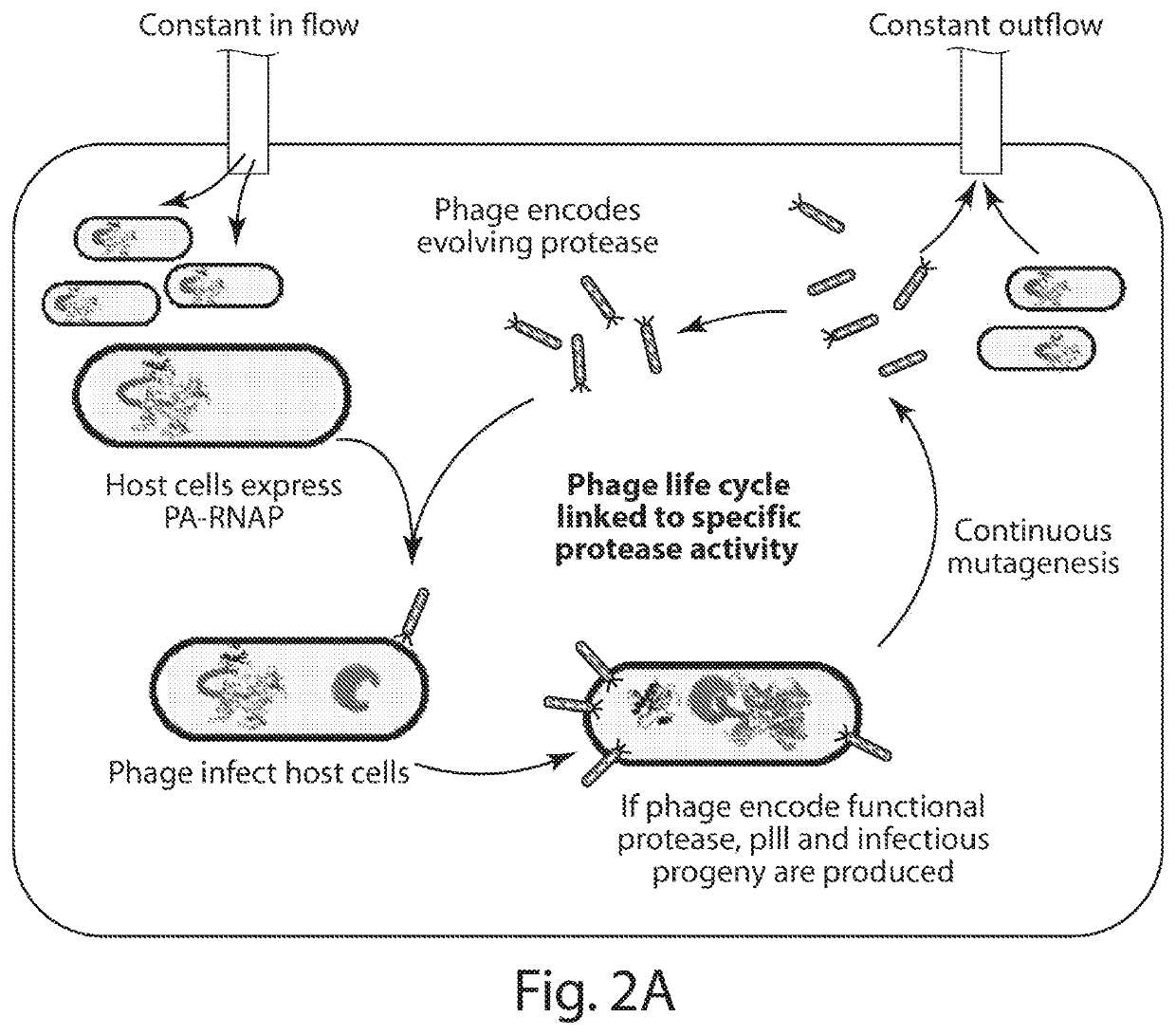
Evolution of proteases
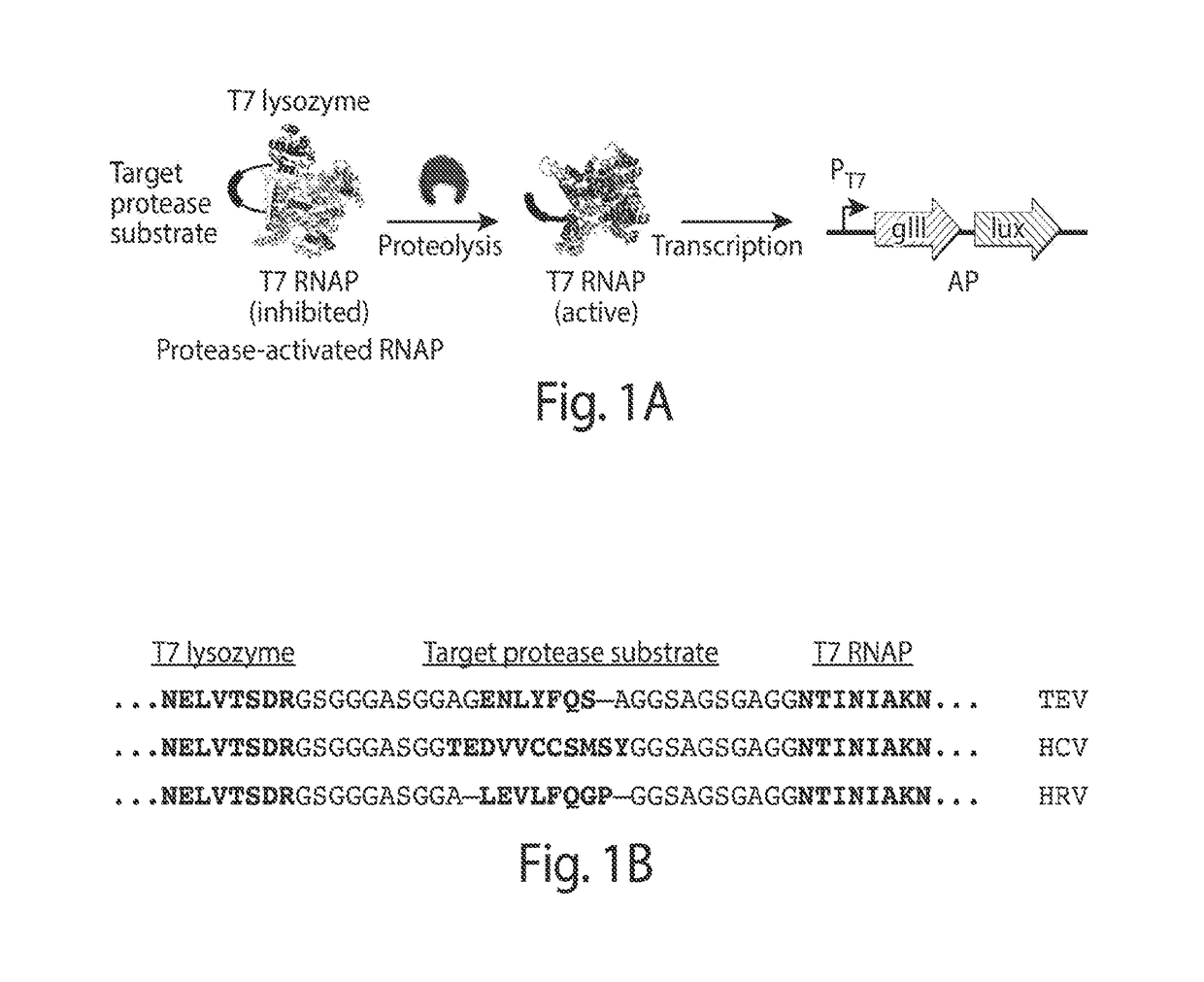
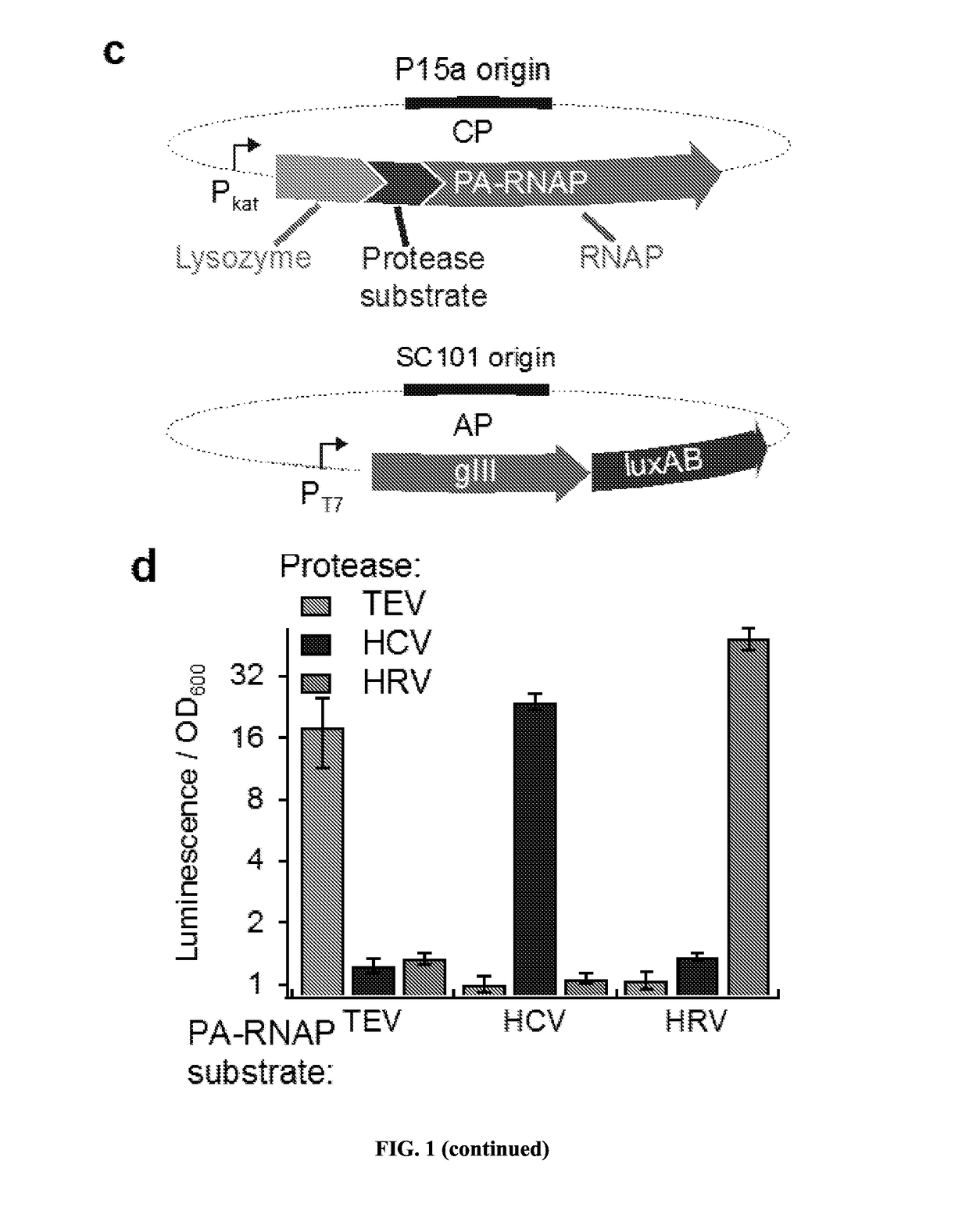
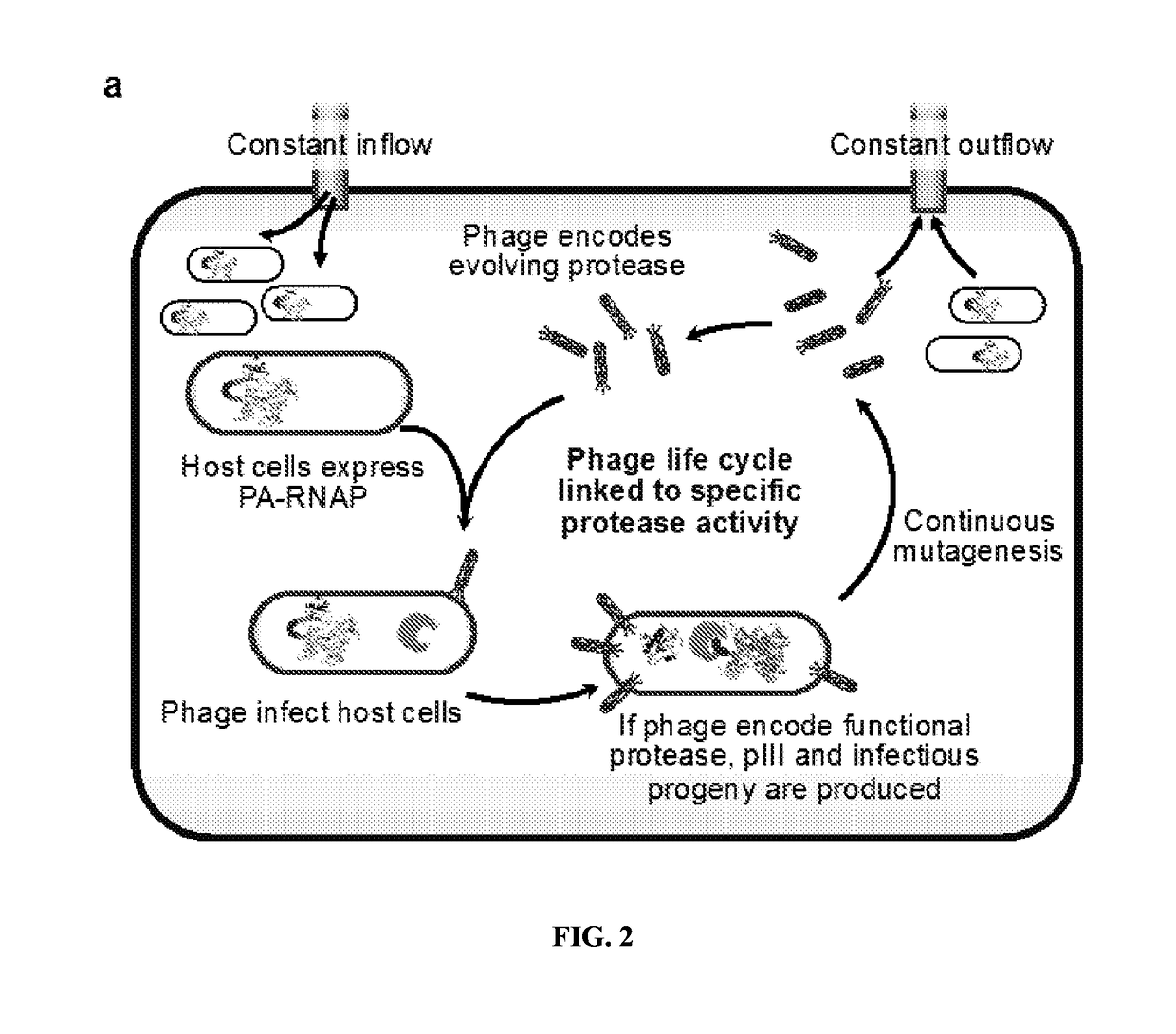
ActiveUS20170233708A1Speed and efficiencyRapid identificationTransferasesFusion with protease siteBiologyContinuous evolution
Some aspects of this disclosure provide methods for phage-assisted continuous evolution (PACE) of proteases. Some aspects of this invention provide methods for evaluating and selecting protease inhibitors based on the likelihood of the emergence of resistant proteases as determined by the protease PACE methods provided herein. Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, methods, and reagents for protease PACE, including fusion proteins for translating a desired protease activity into a selective advantage for phage particles encoding a protease exhibiting such an activity and improved mutagenesis-promoting expression constructs. Evolved proteases that recognize target cleavage sites which differ from their canonical cleavage site are also provided herein.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
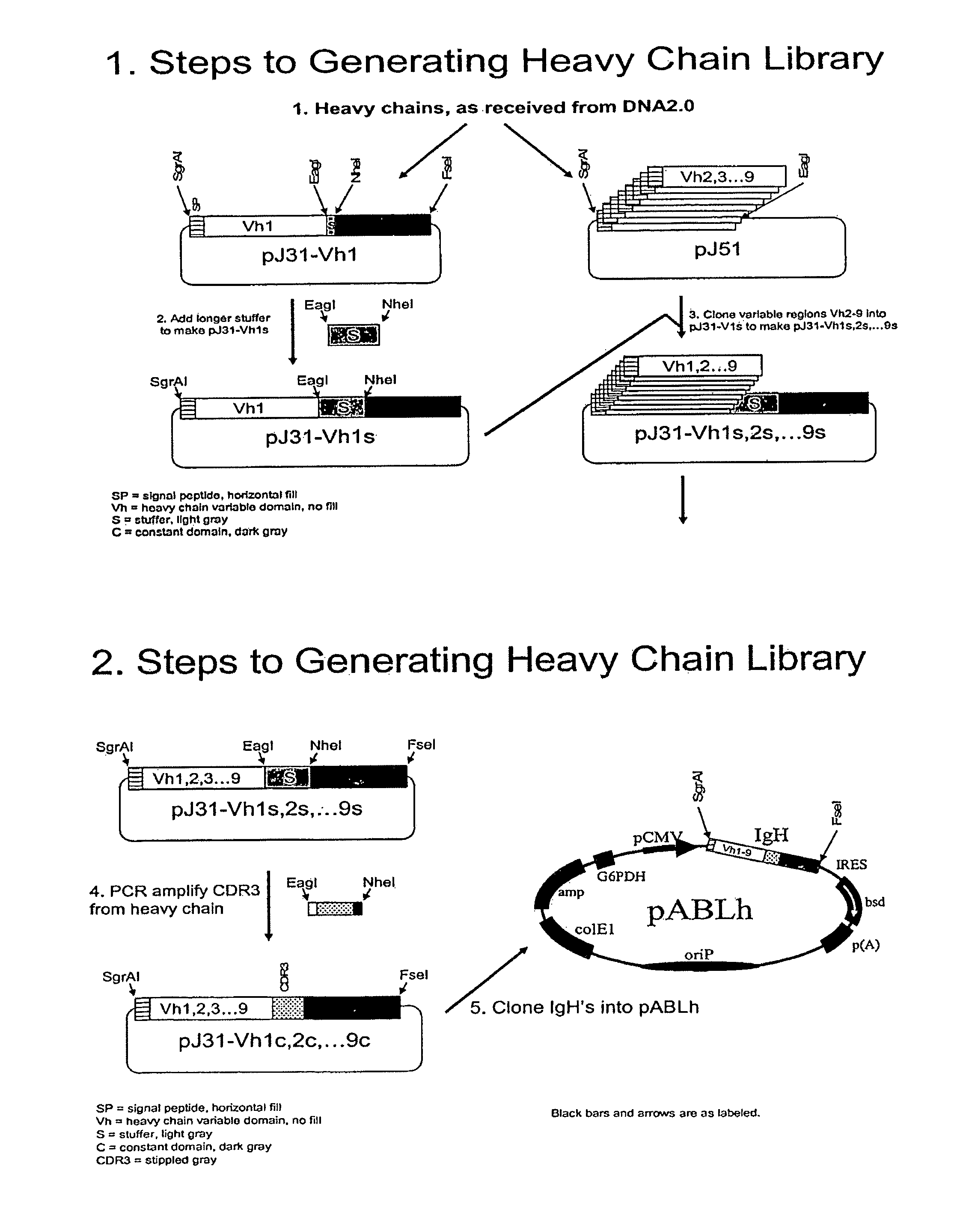
Methods of generating libraries and uses thereof
ActiveUS8685897B2High affinityHigh reactivityImmunoglobulins against growth factorsFermentationHeavy chainActivation-induced (cytidine) deaminase
This invention relates to methods for the generation of humanized antibodies, particularly a humanized antibody heavy chain protein and a humanized antibody light chain protein. The method comprises using cells that express or can be induced to express Activation Induced Cytidine Deaminase (AID).
Owner:ANAPTYSBIO INC
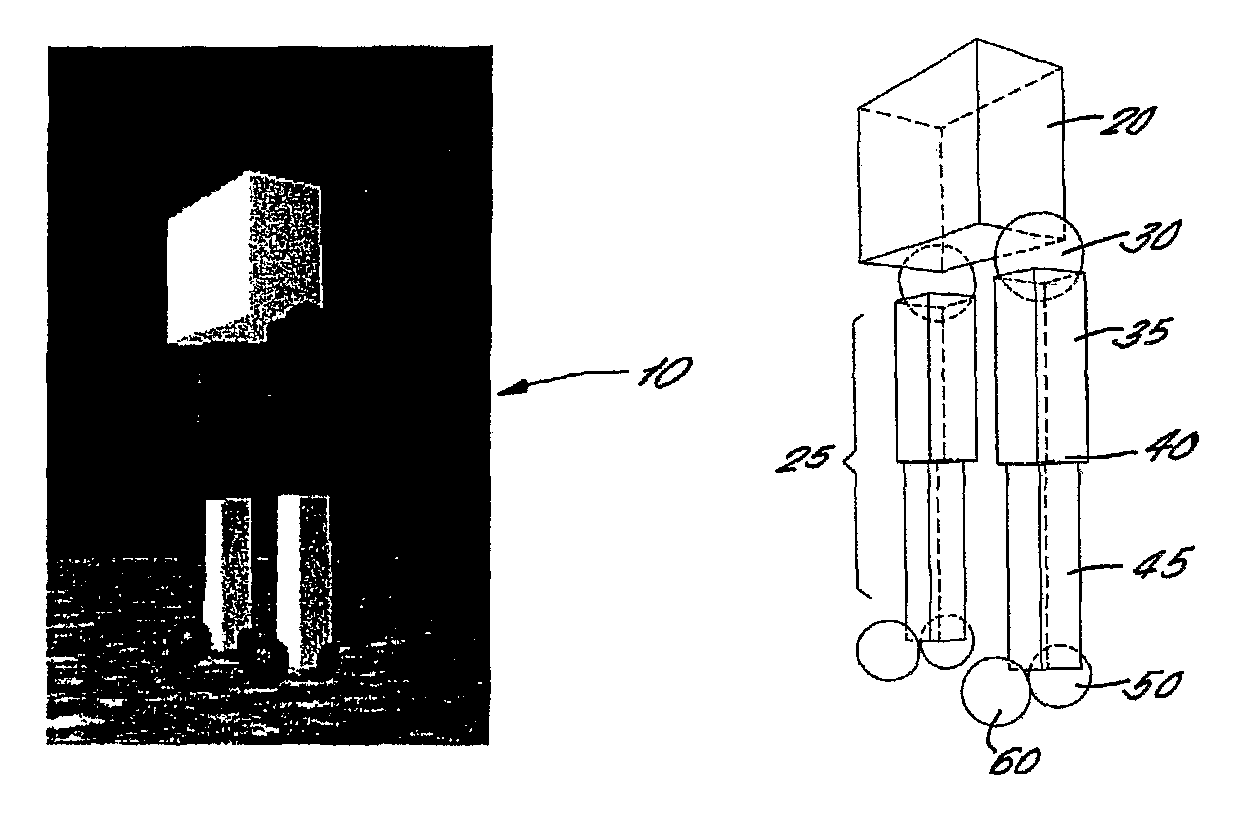
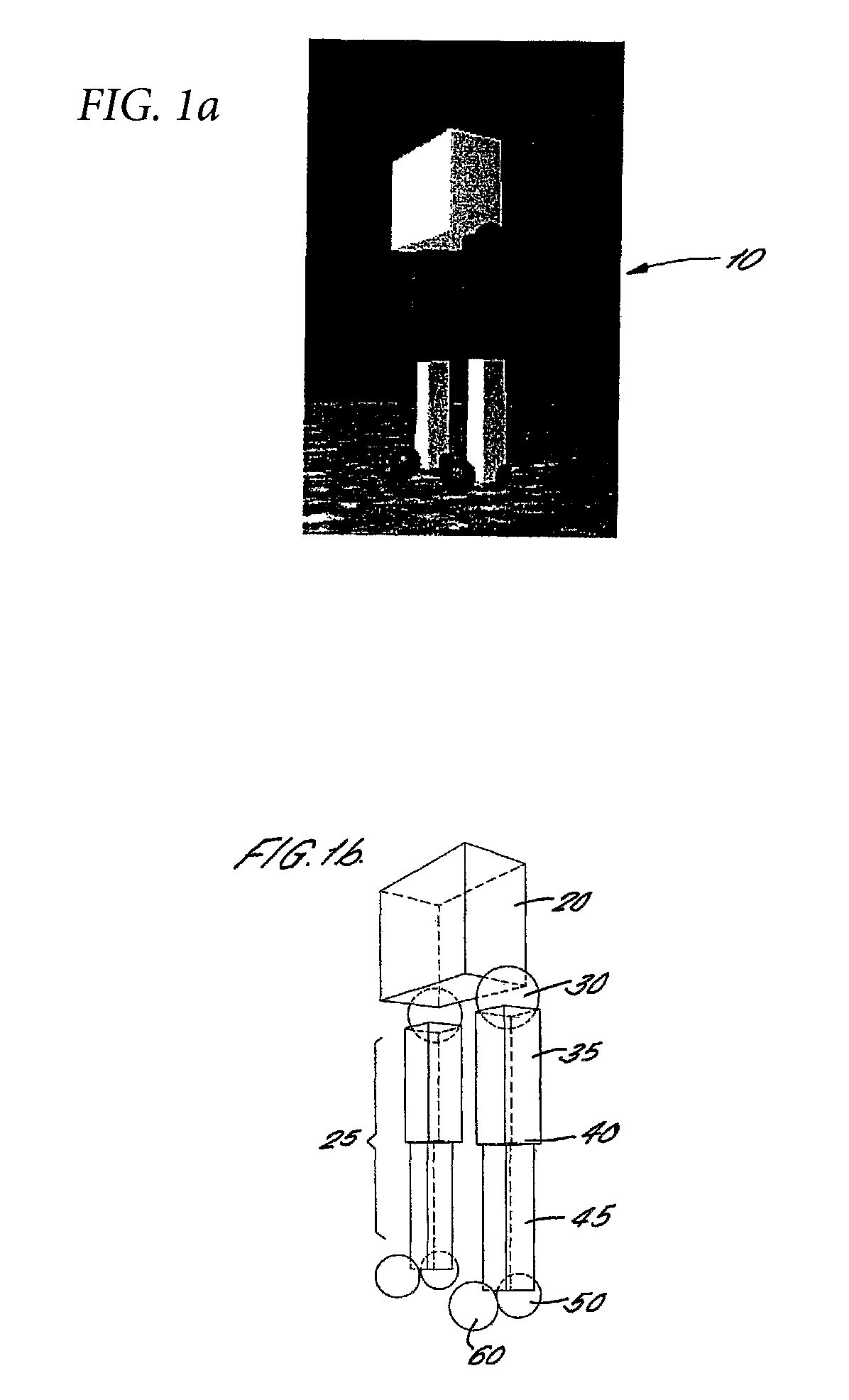
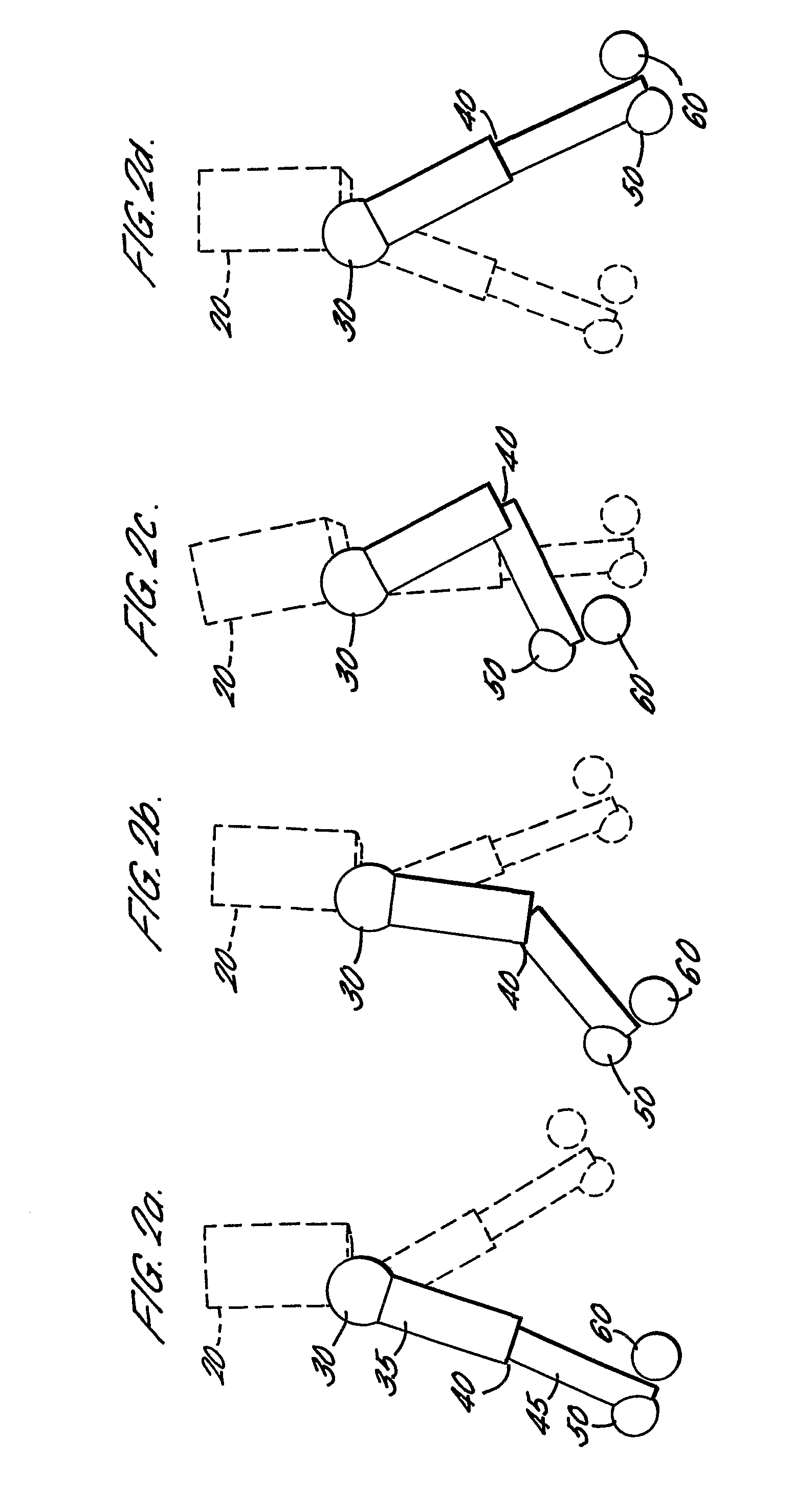
Bipedal Walking Simulation
InactiveUS20080275831A1Shorten the lengthGood mannersProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSagittal planeNeural network controller
An artificial multiped is constructed (either in simulation or embodied) in such a way that its natural body dynamics allow the lower part of each leg to swing naturally under the influence of gravity. The upper part of each leg is actively actuated in the sagittal plane. The necessary input to drive the above-mentioned actuators is derived from a neural network controller. The latter is arranged as two bi-directionally coupled chains of neural oscillators, the number of which equals twice that of the legs to be actuated. Parameter optimisation of the controllers is achieved by evolutionary computation in the form of a genetic algorithm.
Owner:NATURALMOTION
Adaptive genetic algorithm based on population evolution process
InactiveCN106934459AIncrease diversityFast global search capabilityGenetic algorithmsAlgorithmSelection operator
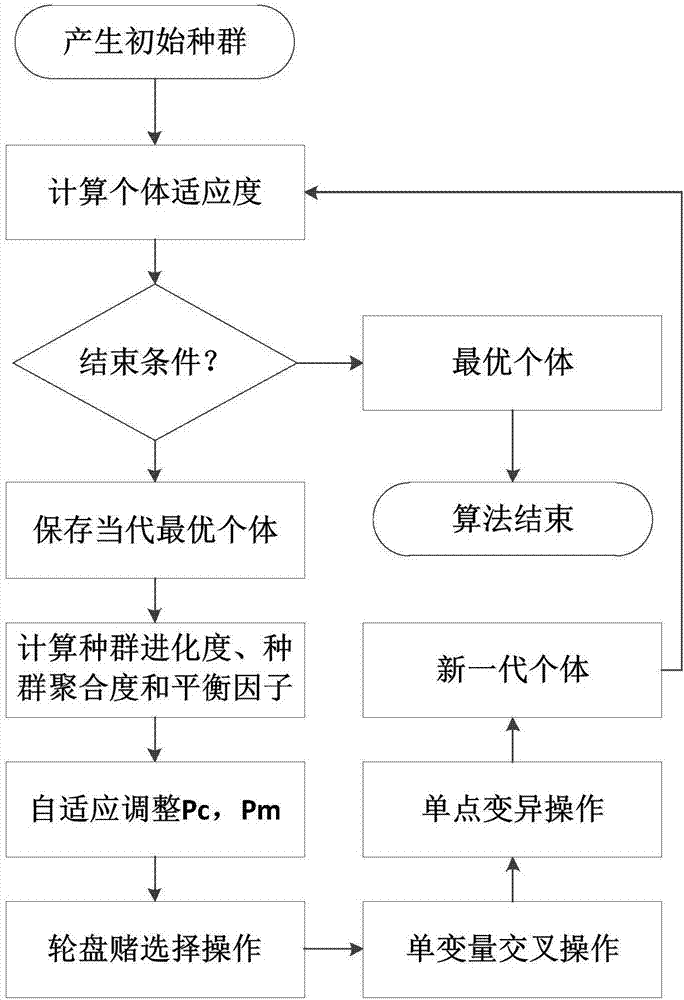
The invention discloses a self-adaptive genetic algorithm based on the population evolution process, including the first step, setting the parameters of the BAGA algorithm, setting the number of iterations of the algorithm, the number of populations in each generation, the discrete precision of the independent variable, and the total number of shooting times , a constant; the second step is to use binary code to generate the initial population; the third step is to judge whether the maximum number of iterations is satisfied, and if so, output the optimal individual of the last generation, which is the optimal value found, otherwise turn to the fourth step; The fourth step is to establish the relationship between the objective function and the fitness function, and then calculate the fitness of each individual and the average fitness of contemporary individuals, save the individual with the largest contemporary fitness, and calculate the evolutionary degree of the contemporary population, the degree of population aggregation, and Balance factor, crossover probability and mutation probability; the fifth step, selection, crossover and mutation operations to generate new populations, the selection operator uses roulette technology, the crossover operation uses univariate crossover, and the mutation operation uses basic bit mutation; the sixth step, Find the best individual in the contemporary population, keep it, and then go to the second step.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Specific primer pair for identification of spermatophyte species and applications of specific primer pair
InactiveCN102978208AEfficient identificationImprove developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentation3-deoxyriboseDNA barcoding
The invention discloses a specific primer pair for identification of spermatophyte species and applications of the specific primer pair. The invention provides a pair of specific primers consisting of a single stranded DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) A and a single stranded DNA B. The single stranded DNA A is 15-40bp and has a DNA fragment same as the DNA fragment shown as a sequence I in a sequence table. The single stranded DNA B is 15-40bp and has a DNA fragment same as the DNA fragment shown as a sequence II of the sequence table. In the invention, with the ycflb gene of a plant to be tested as a template, the DNA fragment obtained by PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification with the specific primer pair is also protected. The DNA fragment can be used for assisting identification of the spermatophyte species. The specific primer pair can be used for developing general kits, effectively identifying land plant species, and promoting the development of plant DNA bar codes, contributing to social progress.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
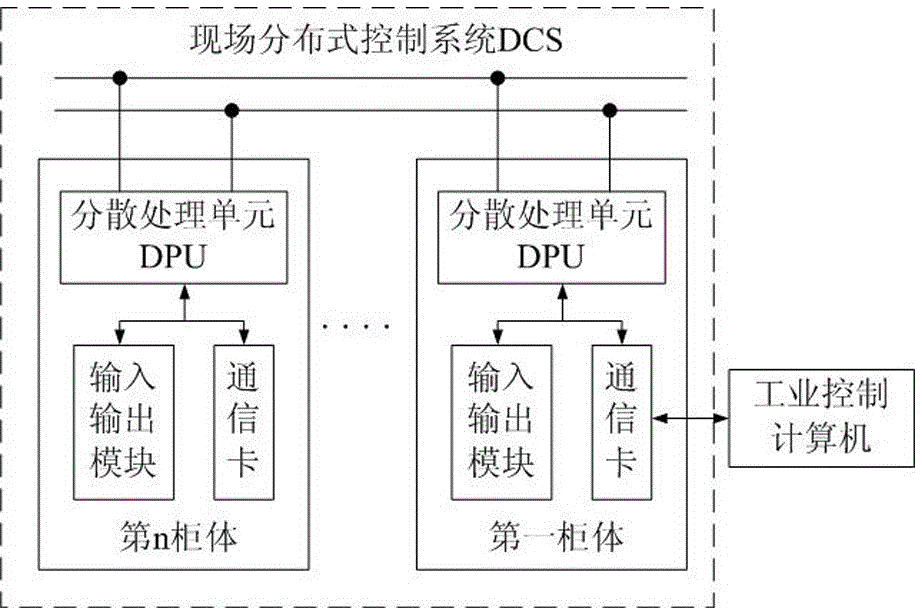
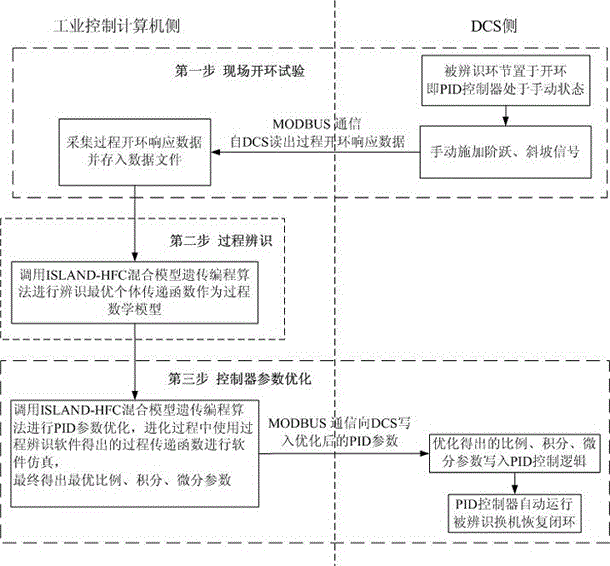
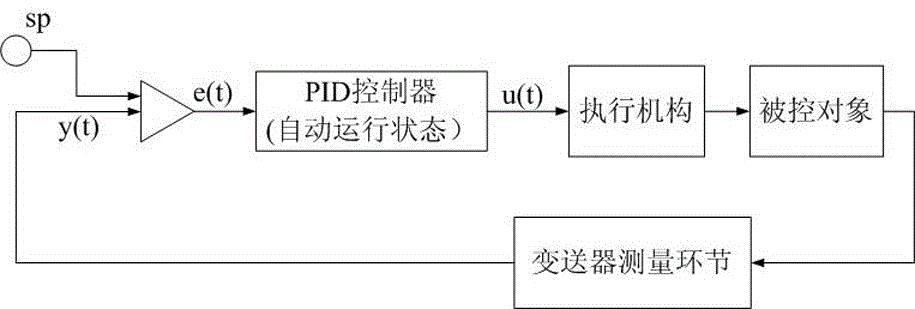
Optimization method for heat-engine plant thermal on-line process identification and control algorithm based on dual-objective parallel ISLAND-HFC mixed model genetic programming algorithm
ActiveCN105487496AStrong anti-premature astringencyFast evolutionEnergy industryTotal factory controlField testsPID controller
The invention discloses an optimization method for a heat-engine plant thermal on-line process identification and control algorithm based on a dual-objective parallel ISLAND-HFC mixed model genetic programming algorithm. The steps comprise: 1, establishing a hardware platform; 2, the optimization method being completed by executing foreground interface software and background software by the hardware platform, the background software being formed by field test and data acquisition software, process identification software, and PID controller parameter optimization software. The method makes an ISLAND model and a HFC model organically combine together, anti-prematurity convergence property is good, multi-core CPU resources of an industrial control computer are fully used, multithreading run concurrently, evolution speed is fast, and the method is suitable to solve comprehensive problems. On one hand, dual-objective evolution controls errors between an evolution model and an ideal model, and on the other hand, the structure of an evolution individual is controlled, and finally, optimal individual structure and parameters satisfy requirements. For process identification, a field process model is accurately matched, and for parameter optimization of a PID controller, optimal proportion, integral, and differential parameters are obtained.
Owner:STATE GRID HEBEI ENERGY TECH SERVICE CO LTD +2
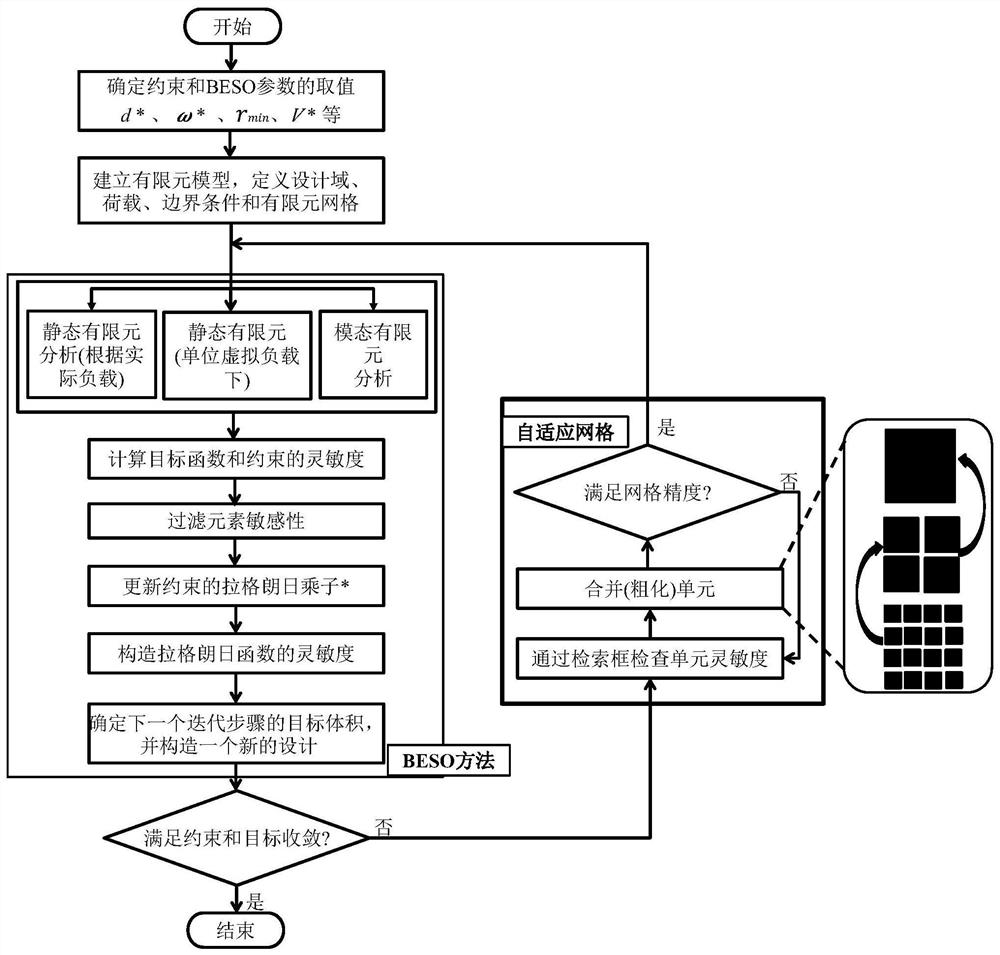
BESO topological optimization method based on dynamic evolution rate and adaptive grid and application of BESO topological optimization method
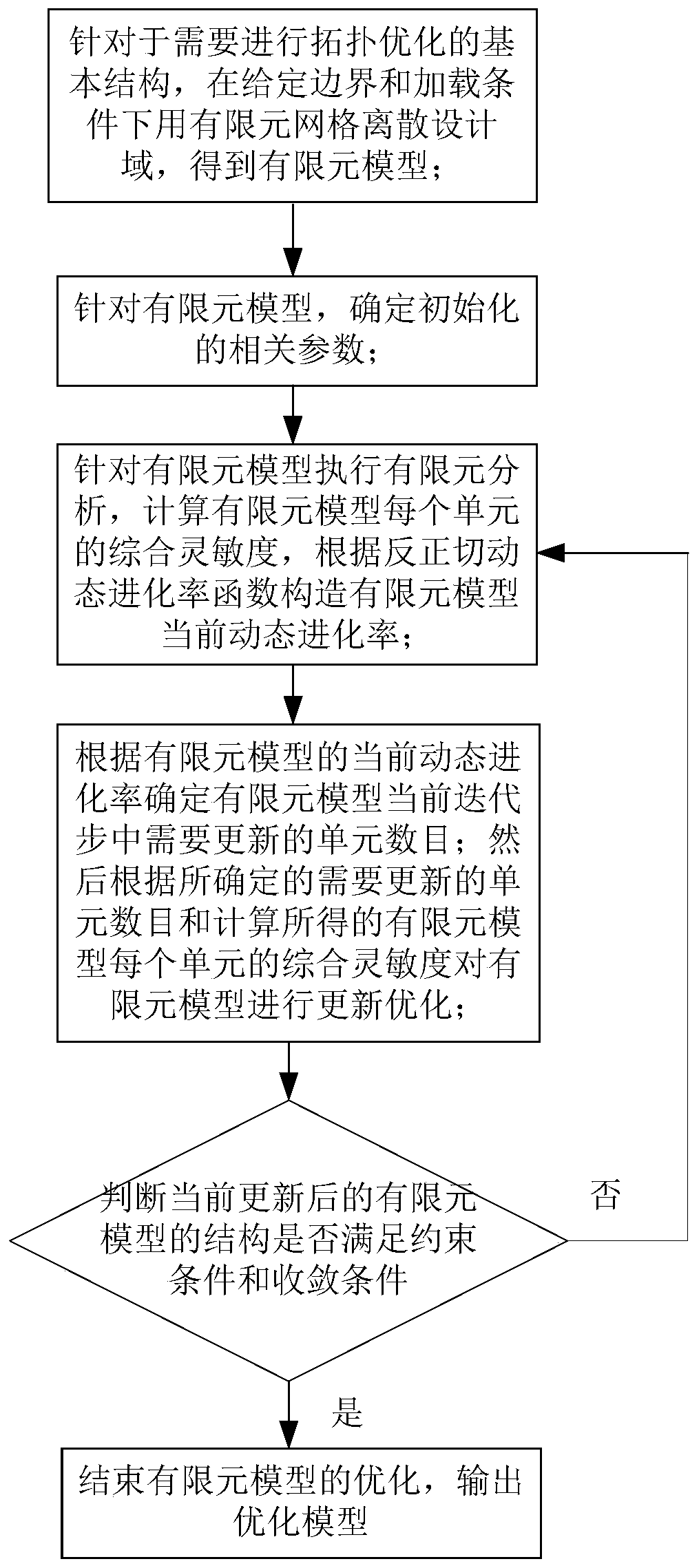
ActiveCN111737839ASmall amount of calculationImprove calculation accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelElement analysis
The invention discloses a BESO topological optimization method based on a dynamic evolution rate and an adaptive grid and application thereof, and the method comprises the steps: building a finite element model for a to-be-topologically optimized basic structure, and defining a design domain, a load, a boundary condition and a grid size; determining a constraint value and BESO necessary parameters; performing finite element analysis on the structure after mesh division, and calculating unit sensitivity under a target function and a constraint condition; filtering the unit sensitivity and updating the constrained Lagrange multiplier, and constructing the sensitivity of a Lagrange function; determining an evolution rate of the current iterative step based on a dynamic evolution rate functionof a Logistic function according to the volume rate of the current iterative step; and updating a design variable according to a set constraint function, judging whether constraint conditions and convergence conditions are met or not, if not, performing grid adaptive updating, then performing unit updating, and stopping iteration until the constraint conditions and the convergence conditions aremet. According to the invention, the calculation amount of single finite element analysis and the number of iterations required by topological optimization are effectively reduced while high calculation precision is ensured, so that the total calculation time consumption of topological optimization is greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Protein modification and maintenance molecules
InactiveUS20050069877A1Maximizing genetic diversityGood biological propertiesFungiBacteriaDiseaseAbnormal expression
Various embodiments of the invention provide human proteinmodification and maintenance molecules (PMOD) and polynucleotides which identify and encode PMOD. Embodiments of the invention also provide expression vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, andantagonists. Other embodiments provide methods for diagnosing, eating, or preventing disorders associated with aberrant expression of PMOD.
Owner:INCYTE
Secreted proteins
InactiveUS20040198651A1Maximizing genetic diversityGood biological propertiesAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsENCODEAgonist
The invention provides human secreted proteins (SECP) and polynucleotides which identify and encode SECP. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for diagnosing, treating, or preventing disorders associated with aberrant expression of SECP.
Owner:INCYTE
Evolution of proteases
ActiveUS10920208B2Reduce effortReduced likelihoodTransferasesFusion with protease siteEnzyme Inhibitor AgentProteinase activity
Some aspects of this disclosure provide methods for phage-assisted continuous evolution (PACE) of proteases. Some aspects of this invention provide methods for evaluating and selecting protease inhibitors based on the likelihood of the emergence of resistant proteases as determined by the protease PACE methods provided herein. Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, methods, and reagents for protease PACE, including fusion proteins for translating a desired protease activity into a selective advantage for phage particles encoding a protease exhibiting such an activity and improved mutagenesis-promoting expression constructs. Evolved proteases that recognize target cleavage sites which differ from their canonical cleavage site are also provided herein.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Preparation method of kit for fast detecting fox ingredients in food and feed and detection method of fox ingredients in food and feed
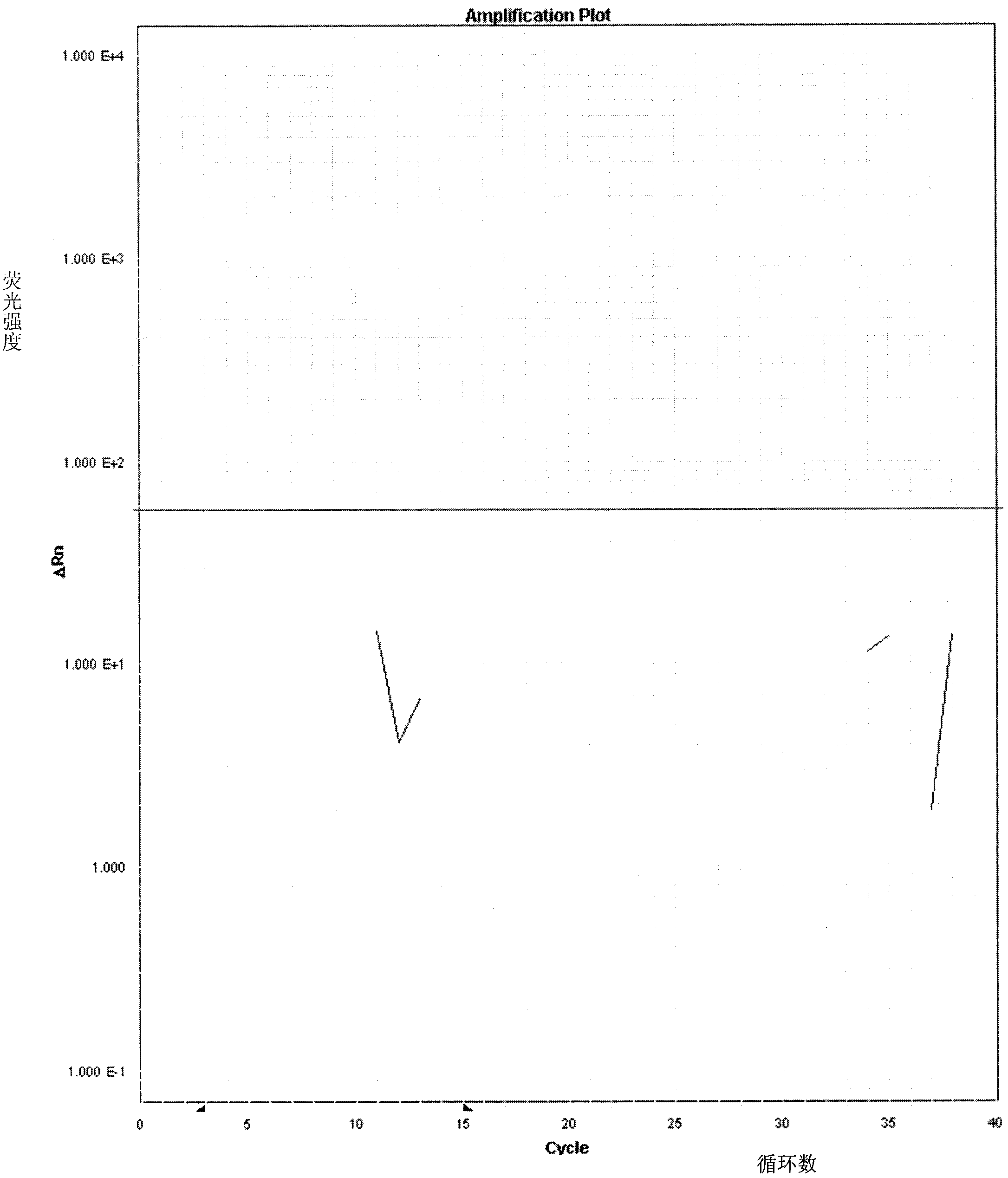
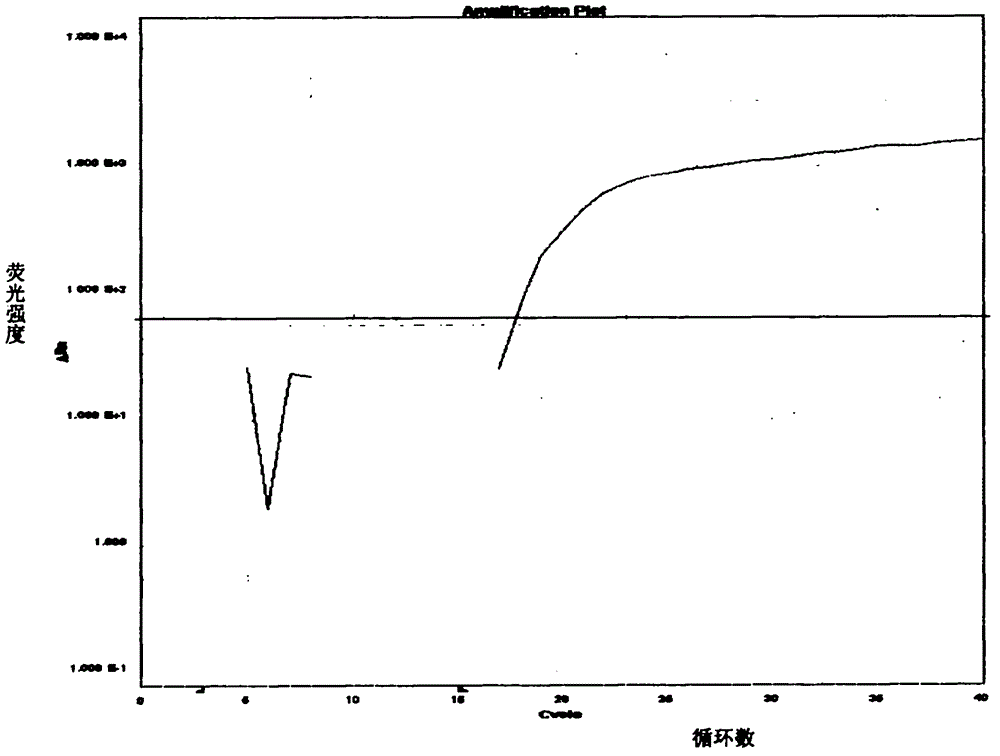
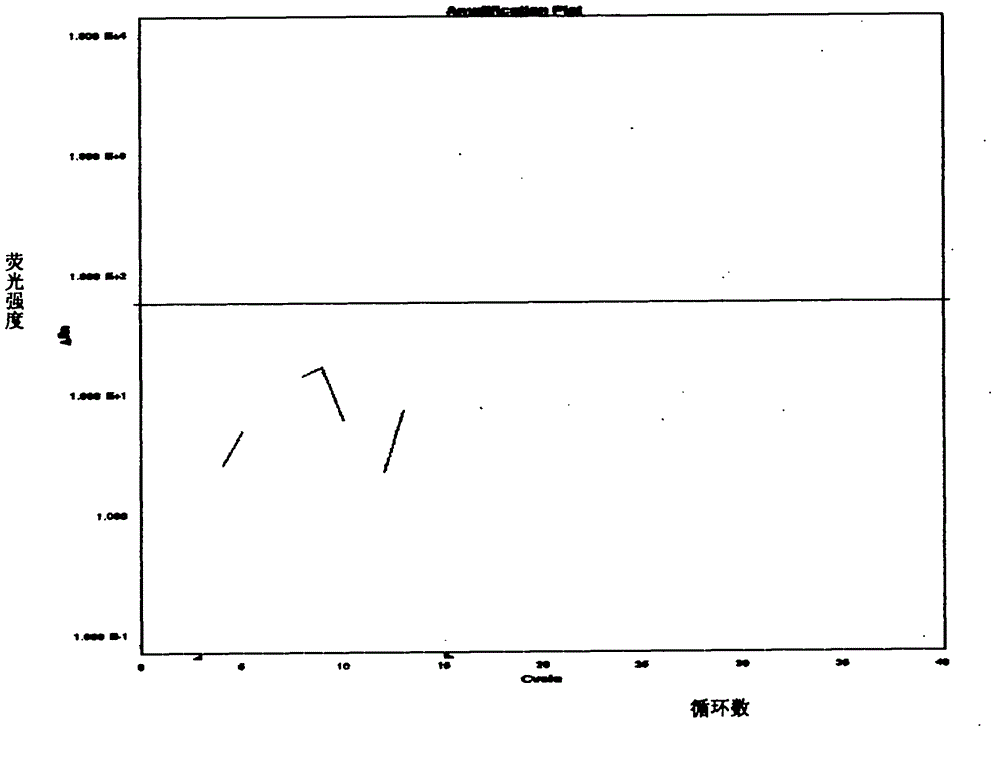
ActiveCN103088116AHigh copy numberCheckout GuaranteeMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceAdditive ingredientFluorescence
The invention belongs to a qualitative detection technology of animal origin ingredients in food and feed, and in particular relates to a kit and a method for detecting the fox ingredients in the food and the feed by using the real-time PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology. The kit comprises 2*PCRMaster Mix, an upstream primer, a downstream primer and a Taqman probe, wherein 2*PCRMaster Mix contains Taq DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase, a reaction buffer, a magnesium chloride and dNTP (diethyl-nitrophenyl thiophosphate), an upstream primer sequence is 5'-TGGAGCATCAGTAGACCTTACAATTT-3 ', a downstream primer sequence is 5'-GGCGGGAGGTTTTATATTGATAATAG-3 ', and a TaqMan probe sequence is 5'-FAM-CCCTGCACCTGGCCGGAGTC-TRAMA-3 '. The method for fast detecting the fox ingredients comprises DNA extraction of the food and the feed, a real-time PCR amplification and a result determination of the fox ingredients. The detection method is fast, strong in specificity, high in sensitivity, easy in operation and good in repeatability.
Owner:山东众合天成检验有限公司
Dynamic evolution rate BESO topological optimization method based on arc tangent and application thereof
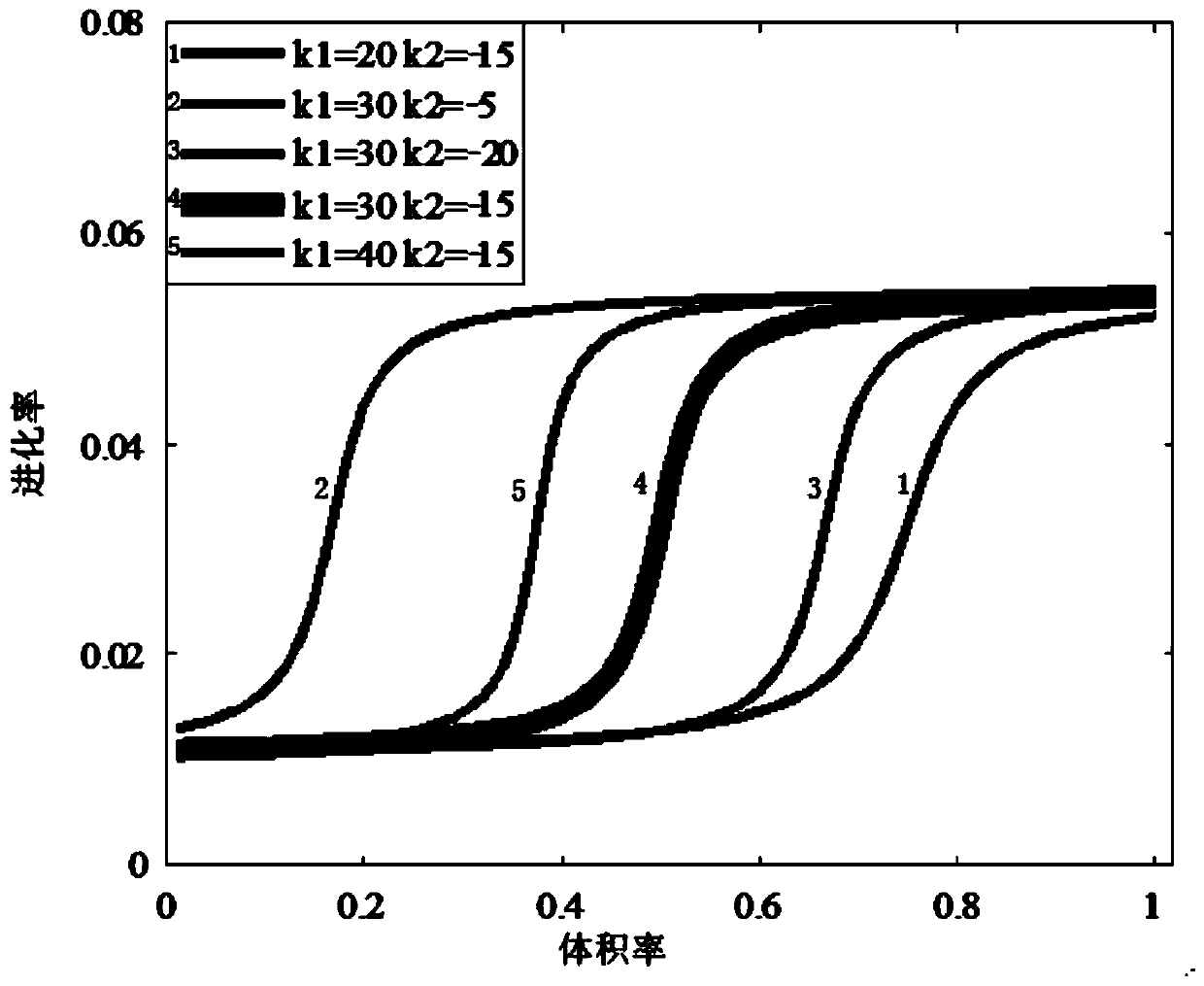
ActiveCN110348102AGuaranteed stabilityFast evolutionDesign optimisation/simulationConstraint-based CADElement modelElement analysis
The invention discloses a dynamic evolution rate BESO topological optimization method on arc tangent and an application thereof. The dynamic evolution rate BESO topological optimization method comprises the steps: firstly, for a basic structure needing topological optimization, carrying out the discrete design of a domain through a finite element grid under a given boundary and loading condition,and obtaining a finite element model; determining initialized related parameters; executing finite element analysis for the finite element model, calculating the comprehensive sensitivity of each unitof the finite element model, and constructing the current dynamic evolution rate of the finite element model according to an arc tangent dynamic evolution rate function; determining the number of units needing to be updated in the current iterative step of the finite element model according to the current dynamic evolution rate of the finite element model; updating and optimizing the finite element model according to the number of units to be updated and the comprehensive sensitivity; and if the structure of the currently updated finite element model meets a constraint condition or a convergence condition, ending the optimization, and outputting an optimization model. According to the invention, the topology optimization of the basic structure can be accelerated by using the dynamic evolution rate, and the efficiency and flexibility of topology optimization are improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Primers and probes for detecting fox component in food and feed
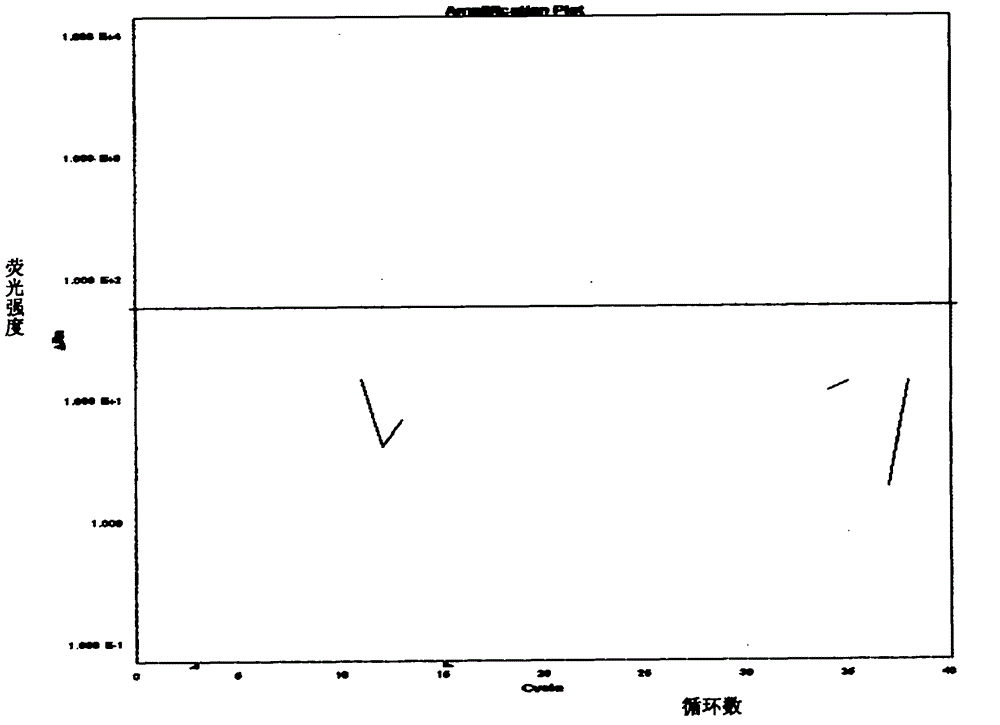
ActiveCN103060435AFast evolutionGuaranteed check outMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceRedox enzymesMicrobiology
The invention belongs to technology of qualitative detection of animal-derived components in food and feed, and particularly relates to a primer / probe group for detecting fox component in food and feed. The invention selects mitochondrion cytochrome C redox enzyme I subunit gene sequence of fox, and designs a group of specific primers and probes. After using the primers and probes, the real-time fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology can be adopted to quickly, sensitively and specifically detect the fox component in food and feed. The primers and probes can also be provided together with other reagents in the form of a kit, and is used for nucleic acid amplification reaction. The method is simple to operate and has favorable repetitiveness.
Owner:山东众合天成检验有限公司
Separation/purification and pathogenicity identification method for pathogenic bacteria of fusarium root rot of Medicago sativa
InactiveCN106350453AIdentification operation is simpleImprove accuracyFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenicityCladosporium herbarum
The invention discloses a separation / purification and pathogenicity identification method for pathogenic bacteria of fusarium root rot of Medicago sativa. The method comprises the specific steps of collecting and preparing diseased Medicago sativa plants, carrying out separation and purification on the pathogenic bacteria, carrying out morphological observation on the pathogenic bacteria, carrying out molecular biology identification, constructing an evolutionary tree and carrying out pathogenicity identification. According to the method, the identification on pathogens of root rot of the Medicago sativa is simple in operation and high in accuracy and is simple, convenient and rapid; the separation and purification purity is high, the identification result is reliable, and the strength of pathogenicity of each strain is determined through pathogenicity identification.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Flexible workshop personnel configuring and work sorting method
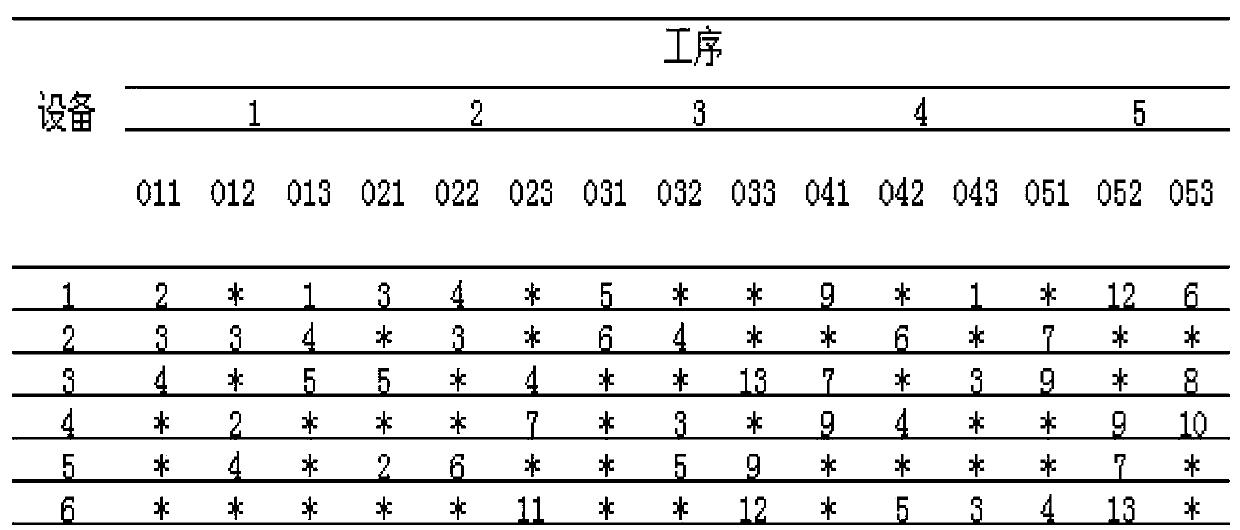
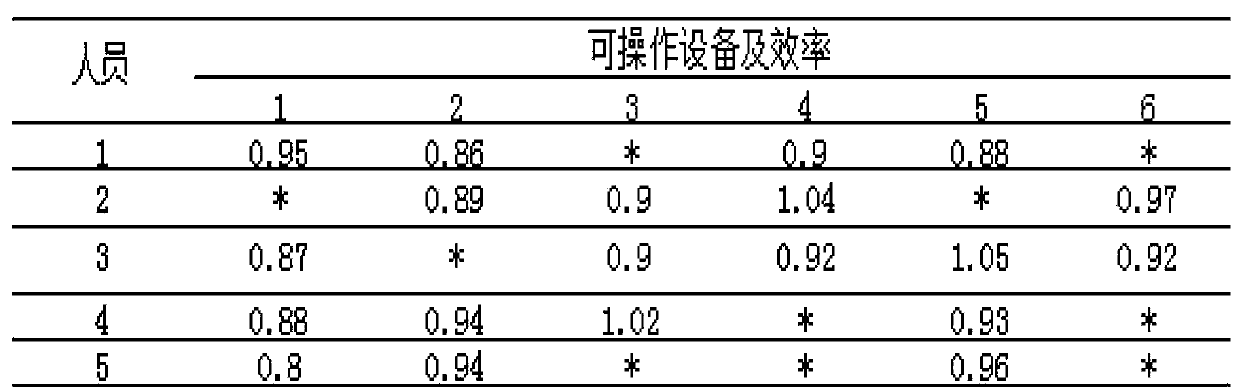
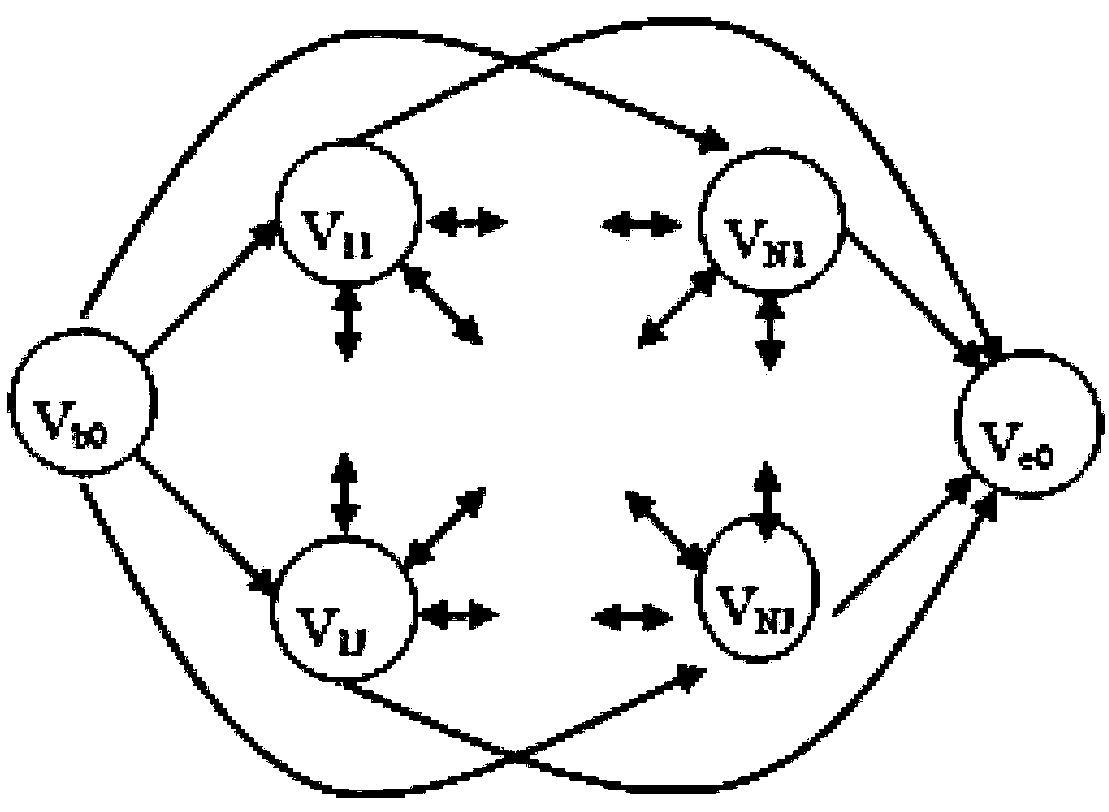
InactiveCN107944748AReduce randomnessSimplify the coding processArtificial lifeResourcesAlgorithmSorting problem
The invention relates to a flexible workshop personnel configuring and work sorting method. An upper-layer ant colony algorithm is used for solving a resource configuration problem. A lower-layer antcolony algorithm is used for solving a work sorting problem on the condition of a fixed resource configuration solution. In the upper-layer ant colony algorithm, for facilitating configuring machiningequipment and operators of the step in an ant traversal process, a new ant traversal map and an ant traversal mode are designed, and furthermore local inspiration regulation information is designed.In the lower-layer ant colony algorithm, a process-based coding and real-number decoding mode utilized; a parent-child ranking elitist preservation strategy which promotes algorithm convergence is performed; and furthermore a calculated adaption value is fed back to the upper-layer ant colony algorithm, thereby guiding a subsequent ant traversal process.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Wireless network evolution method and data center
The invention relates to the field of communications, in particular to a wireless network evolution method. The method comprises the steps in which, a data center determines a pre-cooperative communication region; the data center divides the region into grids and determines the grid points on the grids; the data center determines whether the grid points satisfying the signal coverage requirement reach a preset ratio; and if not, the data center executes a preset processing scheme based on positions of the grid points not satisfying the signal coverage requirement, so as to enable the grid points satisfying the signal coverage requirement to reach the preset ratio. The invention determines whether wireless network evolution is required by determining whether the grid points satisfying the signal coverage requirement reach the preset ratio, and executes the preset processing scheme according to the positions of the grid points not satisfying the signal coverage requirement if the wireless network evolution is required, thereby promoting rapid evolution of a wireless network and reducing the cost of layout.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
User preference-based dynamic computing migration method and device for smart city
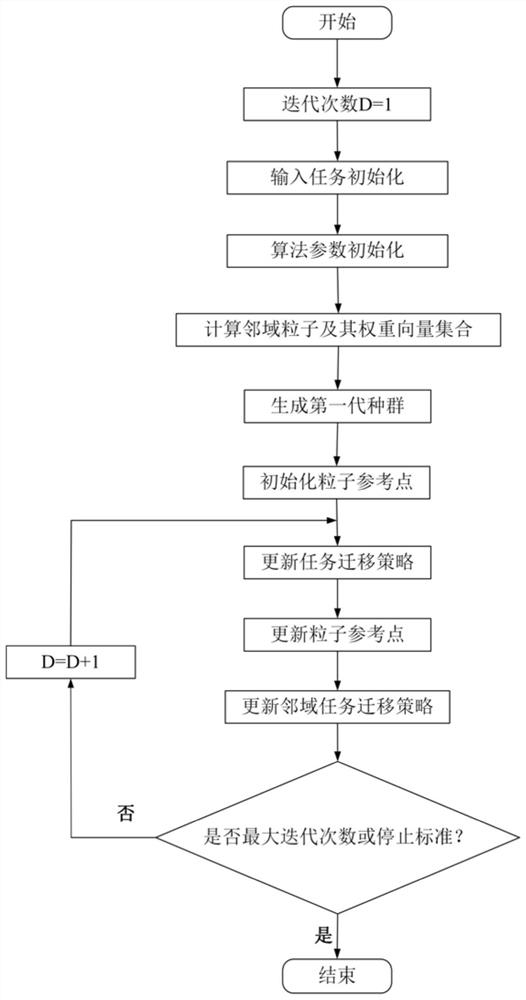
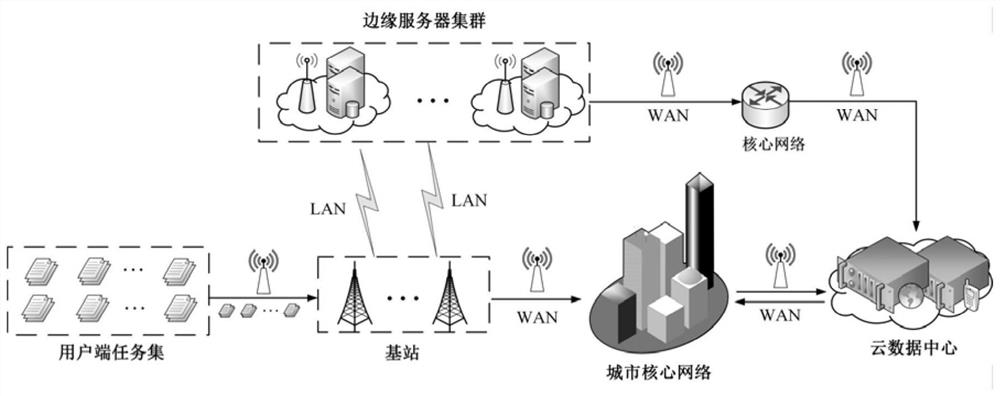
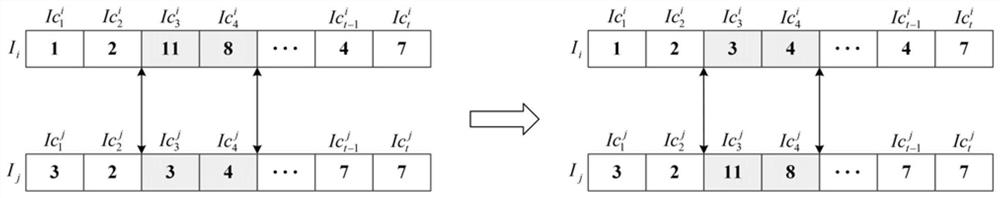
ActiveCN112214301ATo achieve the purpose of multi-objective optimizationFast convergenceProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationIntelligent citySimulation
The invention provides a user preference-based dynamic computing migration method and device for a smart city, and the method comprises the steps of initializing a set of input tasks; stipulating an algorithm stop standard, a population maximum iteration frequency, the number of neighborhood vector sets of each particle and a population initial migration strategy, and defining a group of weight vector sets required to be used in the algorithm; then, on the basis of an MOEA / D algorithm, continuously updating a migration strategy of the task by taking optimization of total energy consumption andtotal time delay of the mobile equipment task of the user side from generation to completion as a target; meanwhile, in order to meet the requirements of the user, adding an elitist strategy which can be changed in a directed mode according to the requirements and preferences of the user; according to the invention, an elitist strategy is adopted, energy consumption and time delay generated by task processing are comprehensively considered while user preferences are met, an appropriate calculation migration strategy is formulated for user tasks in an MEC environment, and the purpose of multi-objective optimization is achieved.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Molecules for disease detection and treatment
InactiveUS20040053396A1Confer resistanceMaximizing genetic diversityBacteriaAnimals/human peptidesDiseaseENCODE
The invention provides full-length human molecules for disease detection and treatment (MDDT) and polynucleotides which identify and encode MDDT. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for diagnosing, treating, or preventing disorders associated with aberrant expression of MDDT.
Owner:INCYTE
Bipedal walking simulation
InactiveUS7685081B2Fast evolutionReduce decreaseProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSagittal planeNeural network controller
An artificial multiped is constructed (either in simulation or embodied) in such a way that its natural body dynamics allow the lower part of each leg to swing naturally under the influence of gravity. The upper part of each leg is actively actuated in the sagittal plane. The necessary input to drive the above-mentioned actuators is derived from a neural network controller. The latter is arranged as two bi-directionally coupled chains of neural oscillators, the number of which equals twice that of the legs to be actuated. Parameter optimisation of the controllers is achieved by evolutionary computation in the form of a genetic algorithm.
Owner:NATURALMOTION
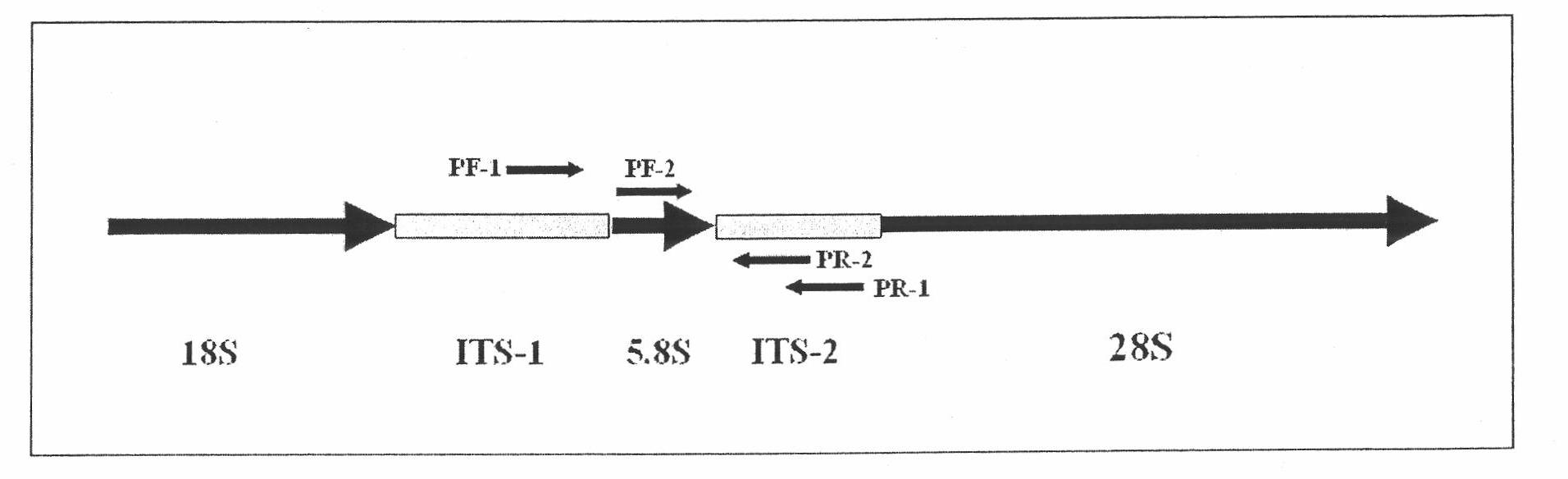
Method for amplifying ITS break sequence in Bactrocera dorsalis rDNA by nesting PCR
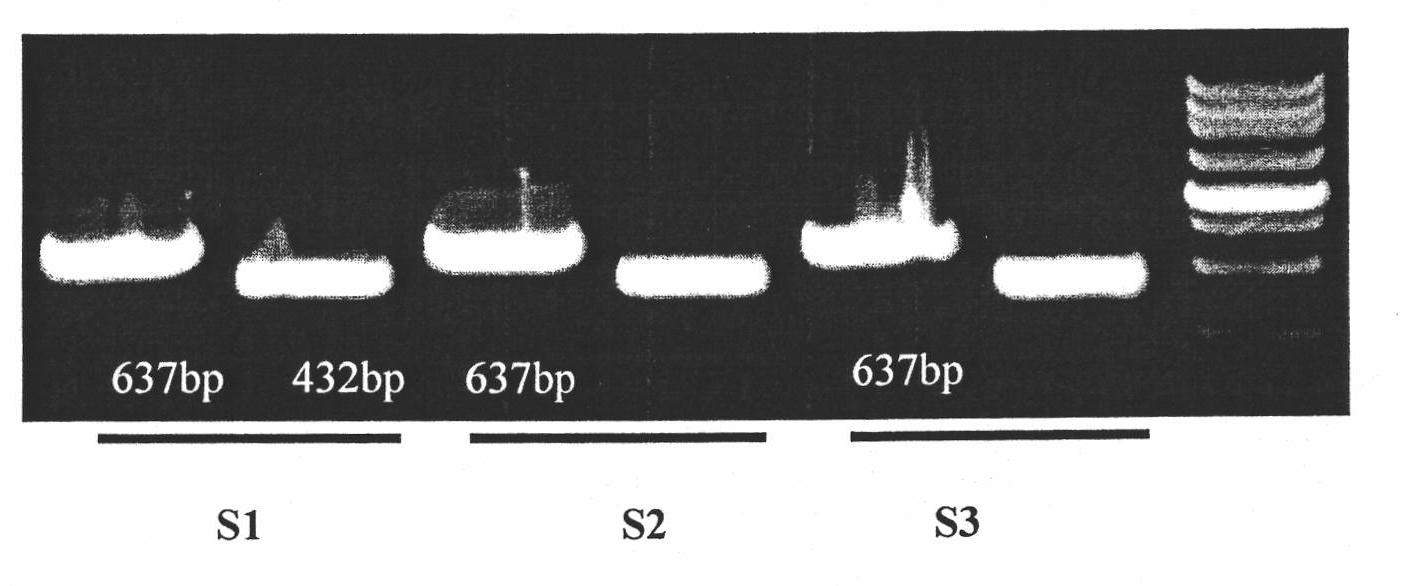
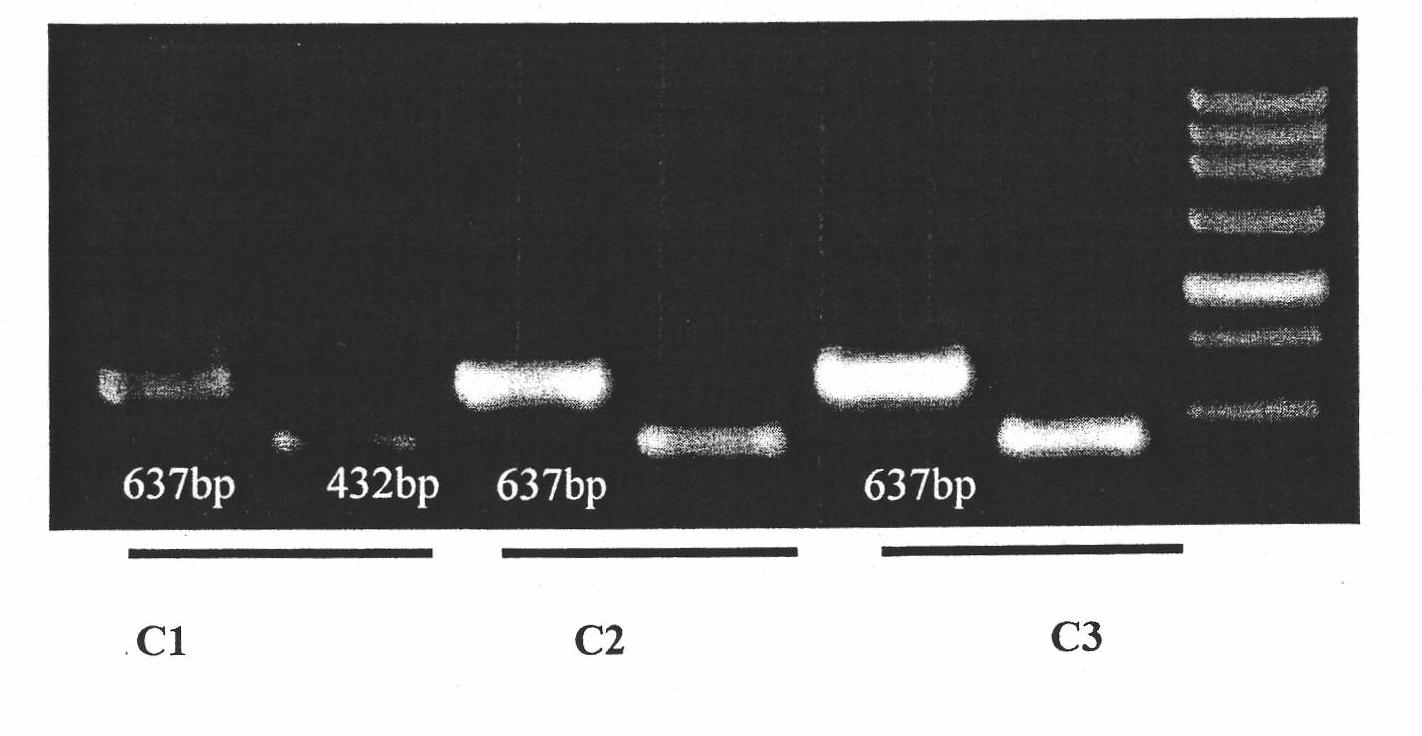
InactiveCN101824469AQuick checkReliable resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisBactrocera dorsalis
The invention discloses the amplification of ITS break sequence in Bactrocera dorsalis rDNA by nesting PCR, comprising the following steps: amplifying the specific ITS fragment of the Bactrocera dorsalis rDNA by designing a nesting specific primer; using the specific ITS fragment of the amplified Bactrocera dorsalis rDNA to accurately and quickly identify actrocera dorsalis flyblow in fruit, and determining the difference of the amplification Bactrocera dorsalis flyblow and relative species by sequences. The method has reliable result, can quickly detect the existence of Bactrocera dorsalis flyblow in fruit and determines the species evolutionary relationship through sequence analysis.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Human kinases
InactiveUS20030207299A1Maximizing genetic diversityGood biological propertiesFungiBacteriaAgonistKinase
The invention provides human human kinases (PKIN) and polynucleotides which identify and encode PKIN. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for diagnosing, treating, or preventing disorders associated with aberrant expression of PKIN.
Owner:INCYTEC
Vesicle trafficking proteins
InactiveUS20030220240A1Efficiently translatedImprove expression efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention provides human vesicle trafficking proteins (VETRP) and polynucleotides which identify and encode VETRP. The invention also provides expession vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for diagnosing, treating or preventing disorders associated with expession of VETRP.
Owner:INCYTE
Proteases
InactiveUS20040029249A1Maximizing genetic diversityGood biological propertiesSugar derivativesHydrolasesDiseaseAbnormal expression
The invention provides human proteases (PRTS) and polynucleotides which identify and encode PRTS. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for diagnosing, treating, or preventing disorders associated with aberrant expression of PRTS.
Owner:INCYTE
Receptors and membrane-associated proteins
InactiveUS20040097707A1Maximizing genetic diversityGood biological propertiesCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesAbnormal expressionMedicine
The invention provides human receptors and membrane-associated proteins (REMAP) and polynucleotides which identify and encode REMAP. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for diagnosing, treating, or preventing disorders associated with aberrant expression of REMAP.
Owner:INCYTE CORP
Transmembrane proteins
InactiveUS20040049010A1Maximizing genetic diversityGood biological propertiesCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesENCODEAntibody
The invention provides human transmembrane proteins (TMP) and polynucleotides which identify and encode TMP. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for diagnosing, treating, or preventing disorders associated with aberrant expression of TMP.
Owner:INCYTE
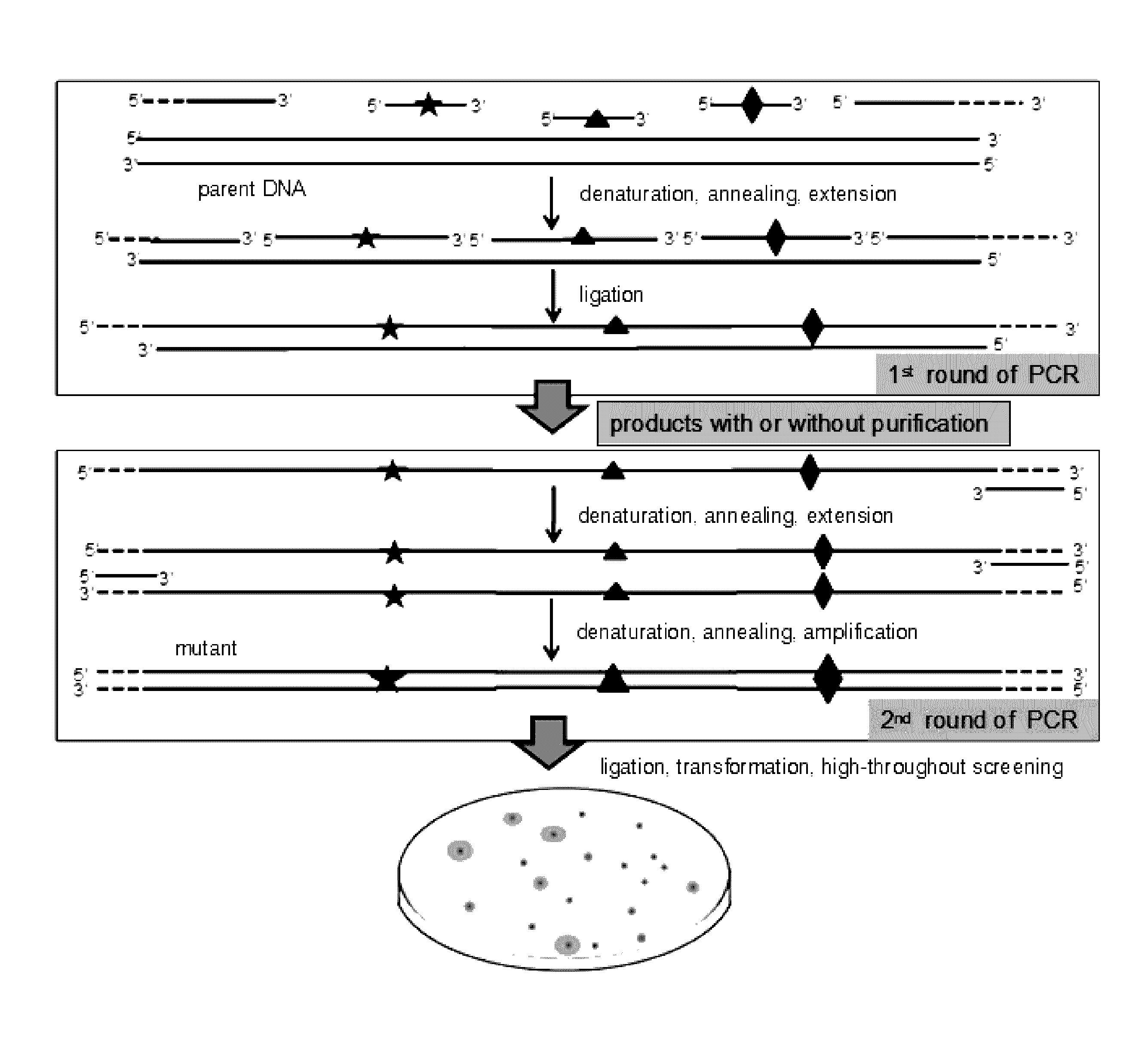
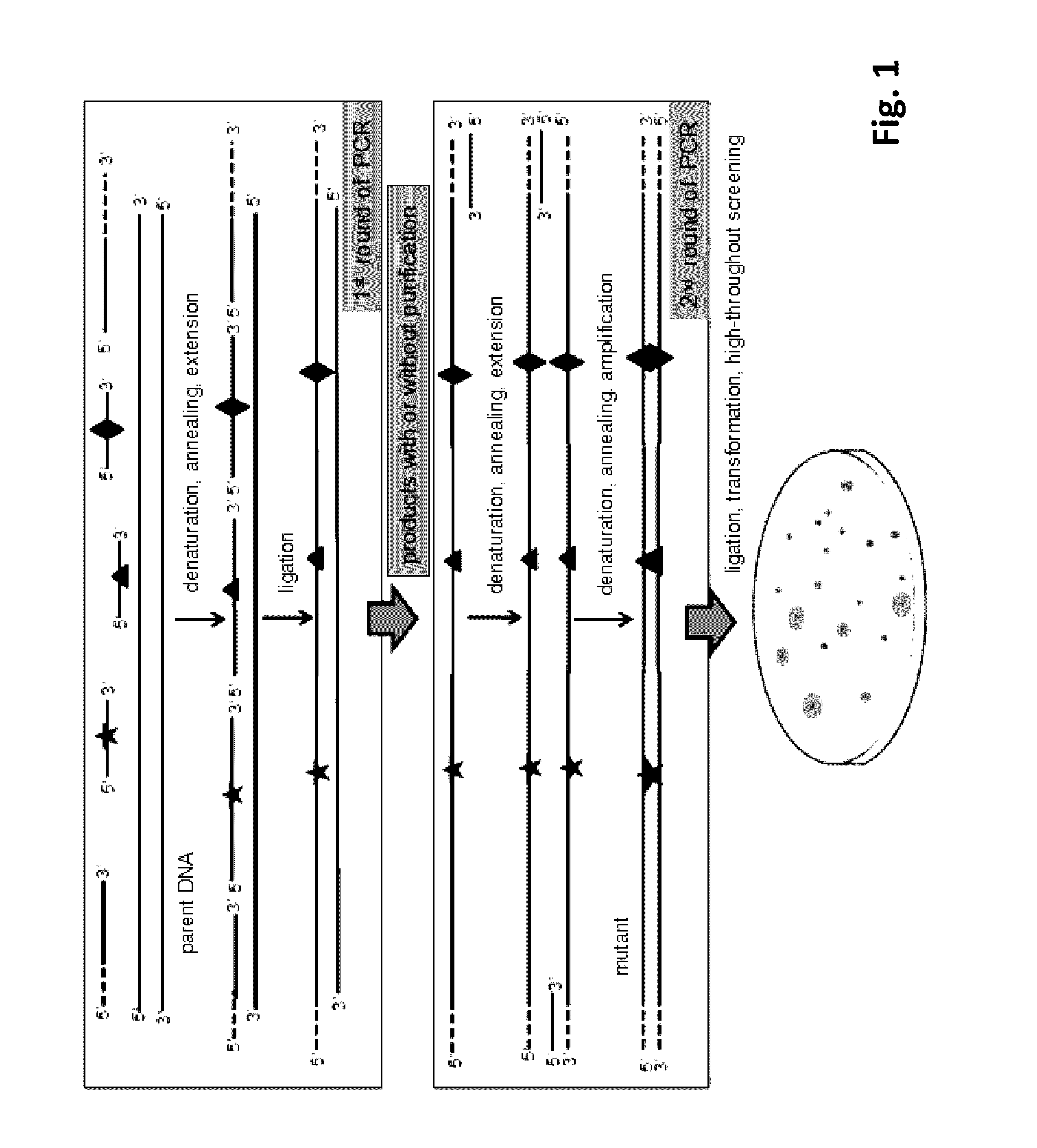
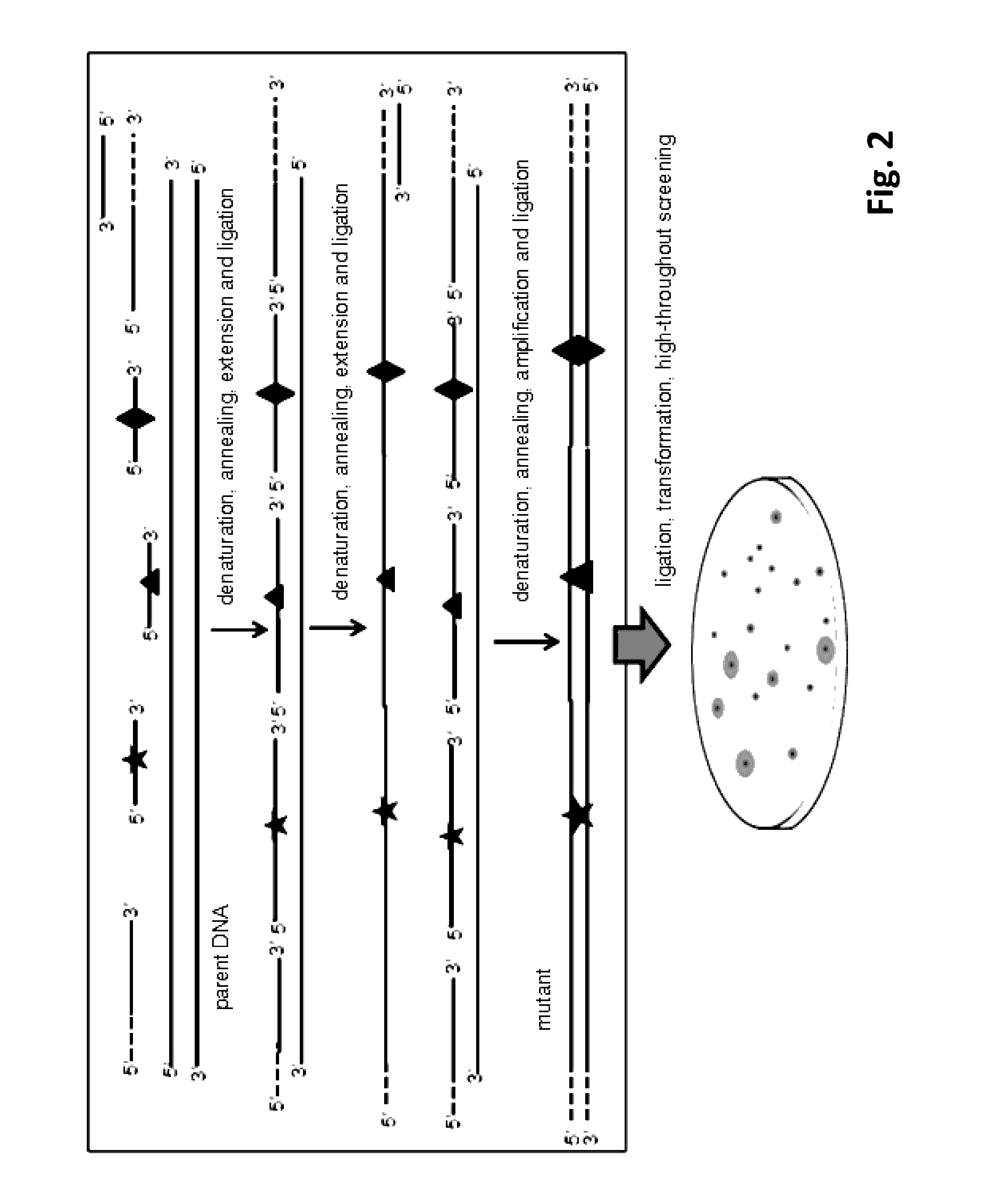
Method for Directed DNA Evolution using Combinatorial DNA Libraries
InactiveUS20160319272A1Highly degenerateReduce probabilityDNA preparationMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsNucleotide
The present invention provides a method of rapid directed DNA evolution based on single-stranded combinatorial DNA mutant library. The single- and double-stranded mutant library are constructed either separately or simultaneously using editing primers that contain mutated nucleotides and are targeted to different regions of the parent DNA sequence. The mutant library is then inserted into expression vectors and mutants with desired property are obtained by high throughput screening. Evolution of promoters, enzymes and metabolic pathways were successfully achieved using this method and mutants with excellent properties were obtained. The method of the present invention is simple, rapid, and efficient. It can be used for directed evolution of regulatory sequence such as promoters and ribosome binding sites, and is especially suitable for introducing diverse mutations into protein encoding genes, leading to rapid directed evolution of gene of interest.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com