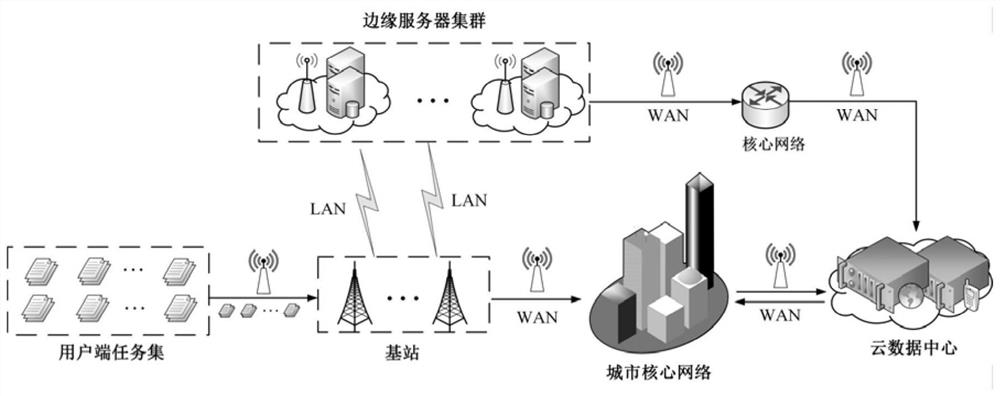
User preference-based dynamic computing migration method and device for smart city
A user and city technology, applied in the computer field, can solve problems such as not being able to meet the dynamic needs of users in smart cities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
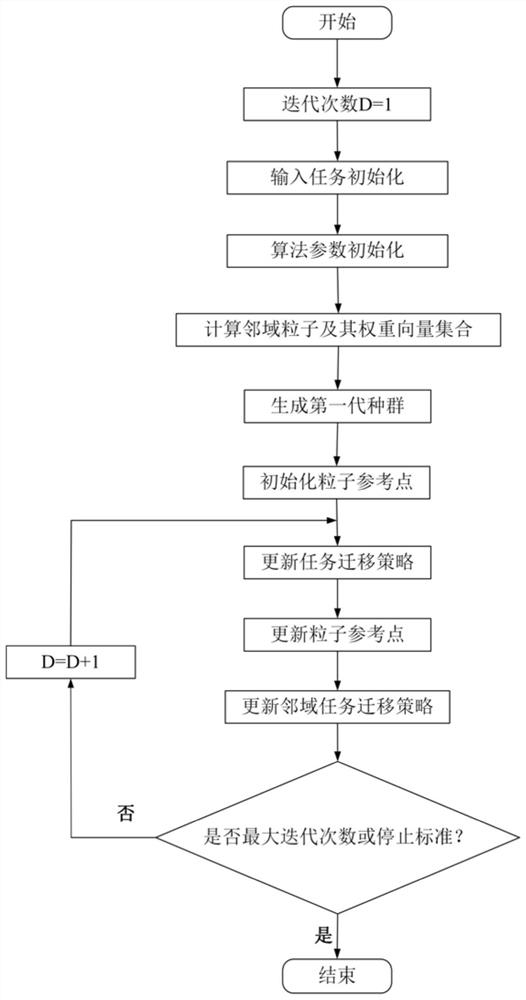
[0126] This embodiment provides a method, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
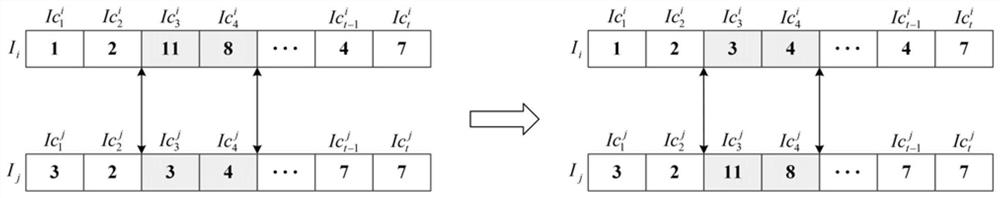
[0127] Step 1: task initialization; define task input set as It={I 1 , I 2 ,...,I N}, where each I N is defined as a group; I N Each subtask in As an individual in the population, also known as a particle, it is defined as a binary array, and has where W t N is the amount of tasks to be processed by the tth particle in the Nth population, Indicates the task amount that the tth particle in the Nth population needs to transmit to the subsequent task; the elite group Each population in the elite group Both come from the initial task group It;
[0128] Step 2: Algorithm parameter initialization; the number of sub-problems that can be decomposed into P C , Algorithm stopping criterion D off , the maximum number of iterations of the population M, a set of uniform weight vectors H={λ 1 ,λ 2 ,...,λ N}, the number T of the neighborhood vector set of each particle; the...
Embodiment 2
[0154] In this embodiment, a device is provided, such as Figure 5 As shown, the following modules are included:
[0155] The task initial module defines the task input set as It={I 1 , I 2 ,...,I N}, where each I N is defined as a group; I N Each subtask in As an individual in the population, also known as a particle, it is defined as a binary array, and has where W t N is the amount of tasks to be processed by the tth particle in the Nth population, Indicates the task amount that the tth particle in the Nth population needs to transmit to the subsequent task; the elite group Each population in the elite group Both come from the initial task group It;
[0156] Parameter initialization module, the number of sub-problems that can be decomposed into P C , Algorithm stopping criterion D off , the maximum number of iterations of the population M, a set of uniform weight vectors H={λ 1 ,λ 2 ,...,λ N}, the number T of the neighborhood vector set of each particle...
Embodiment 3
[0184] This embodiment provides an electronic device, including a memory, a processor, and a computer program stored in the memory and operable on the processor. When the processor executes the computer program, any implementation manner in Embodiment 1 can be implemented.
[0185] Since the electronic device introduced in this embodiment is the device used to implement the method in Embodiment 1 of this application, based on the method described in Embodiment 1 of this application, those skilled in the art can understand the electronic device of this embodiment. Specific implementation methods and various variations thereof, so how the electronic device implements the method in the embodiment of the present application will not be described in detail here. As long as a person skilled in the art implements the equipment used by the method in the embodiment of the present application, it all belongs to the protection scope of the present application.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com