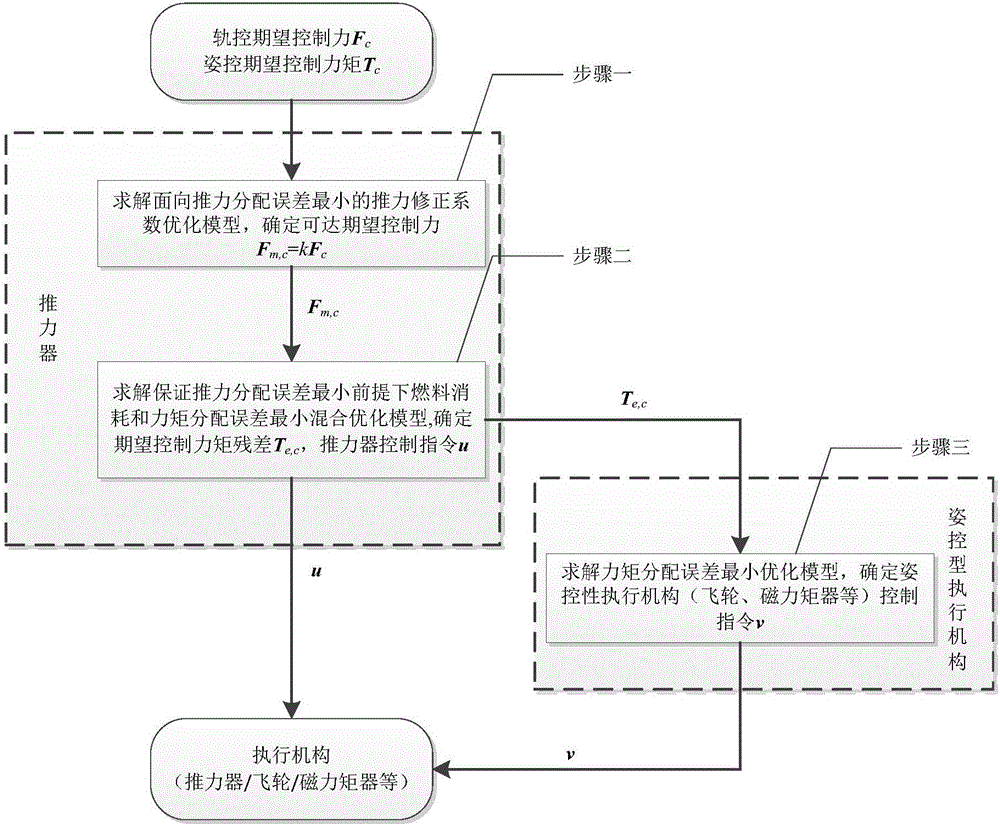
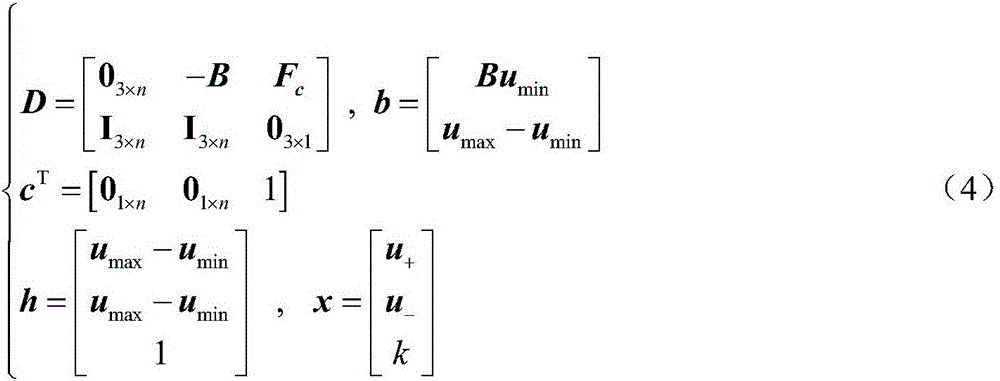
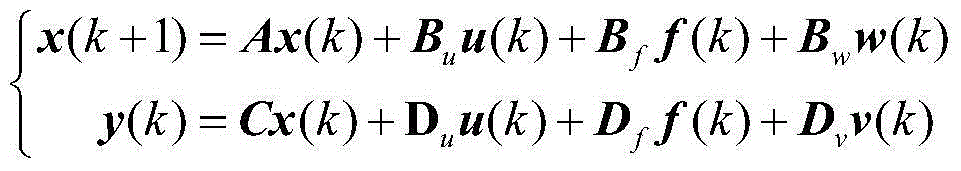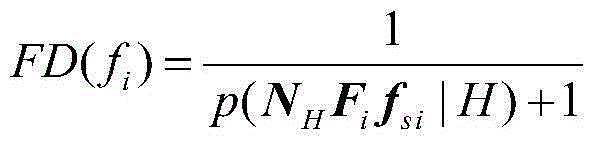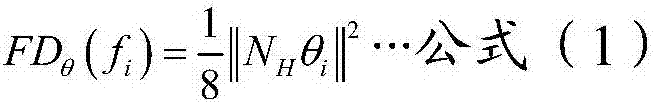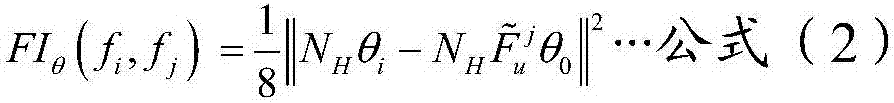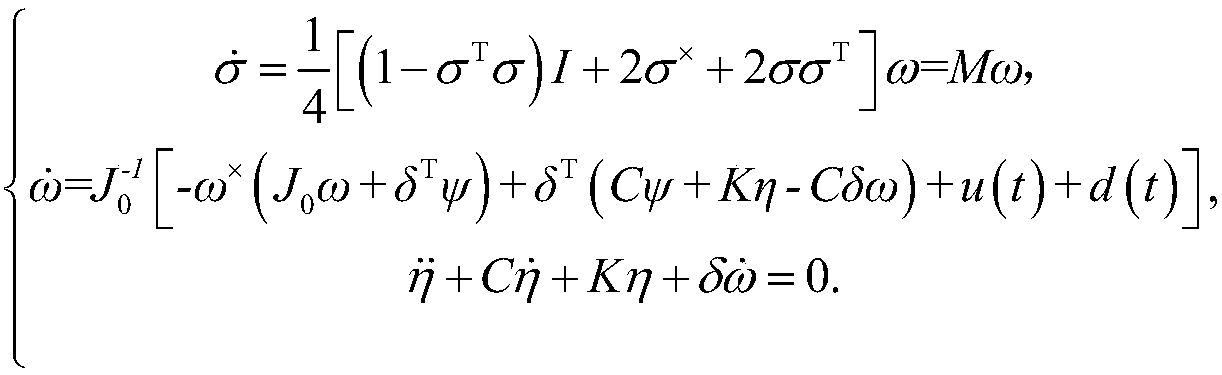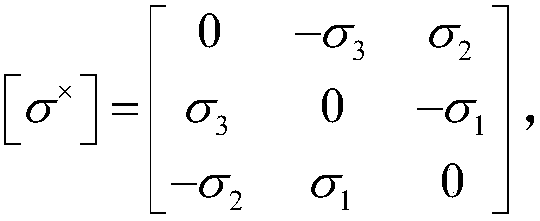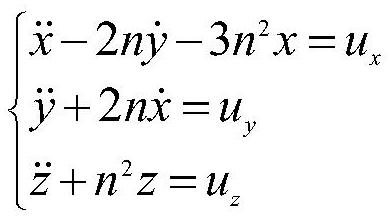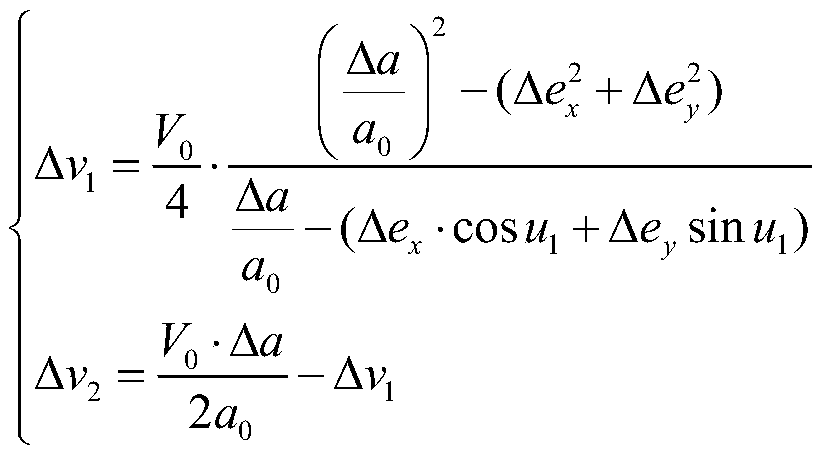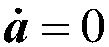Patents
Literature
127 results about "Space vehicle control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
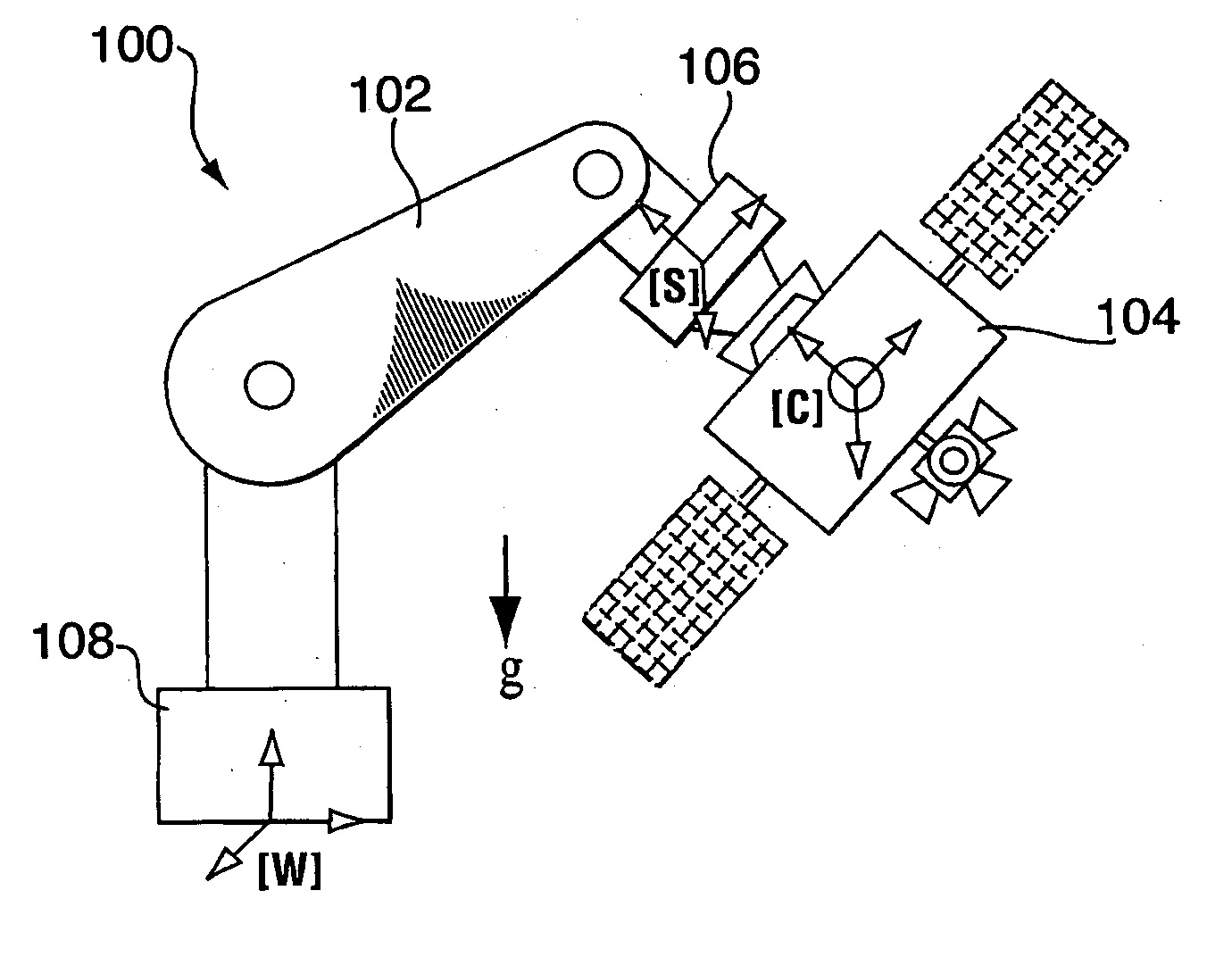
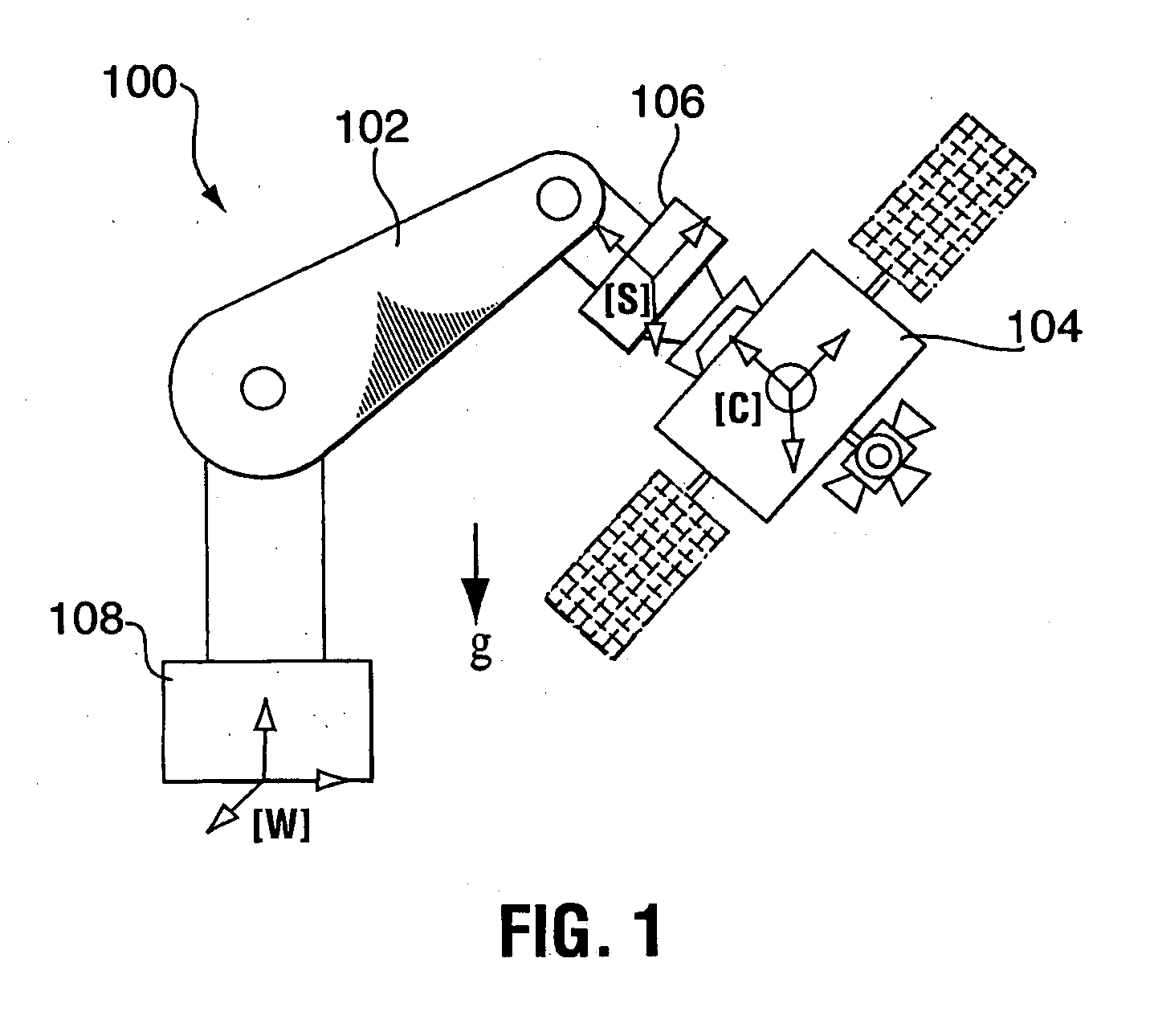
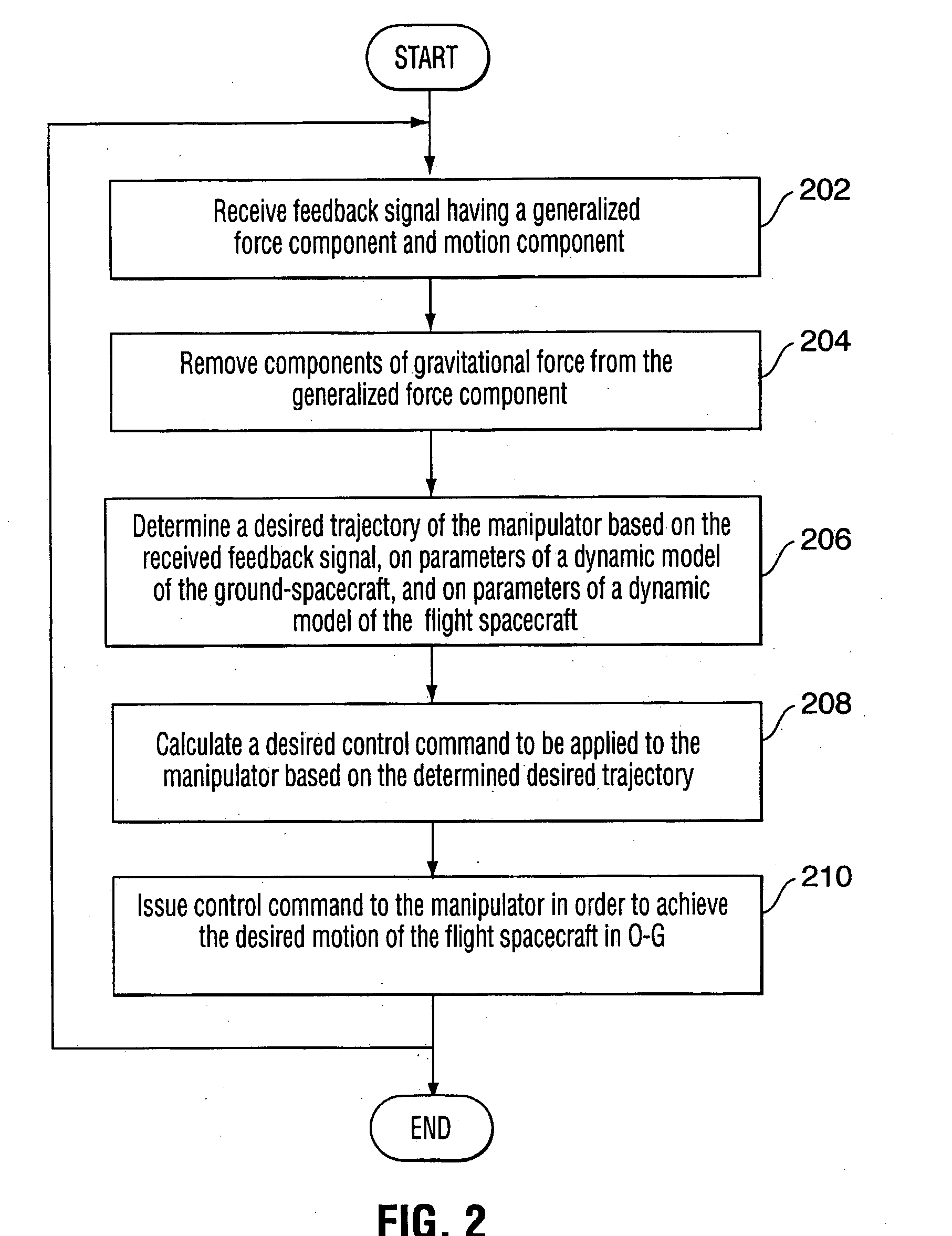
Zero-G emulating testbed for spacecraft control system
InactiveUS20050230557A1Reduces system uncertaintyReduce frictionCosmonautic condition simulationsCosmonautic ground equipmentsControl systemSpace vehicle control
The present invention provides an emulation system having a control system that allows the testing of a satellite control system with all of its hardware in place, i.e. fully integrated. The emulation methodology is applicable to the case of either a rigid spacecraft or a flexible spacecraft, provided that the spacecraft's sensors and actuators are stowed to the rigid part of spacecraft in the case of a flexible spacecraft. Practically, the latter condition is not restrictive, as the actuators and sensors are usually placed rigidly in the satellite bus, while the satellite solar panels constitute the flexible elements. The control system is used to tune the mass properties and dynamic behaviour of a rigid ground-spacecraft in a 1-G environment to those of a flight-spacecraft in 0-G. A six-axis force / moment sensor is placed at an interface of the ground-spacecraft and a manipulator. Signals received from the force / moment sensor, and in some cases signals relating to the position and velocity of manipulator joints, are received into the control system.
Owner:CANADIAN SPACE AGENCY
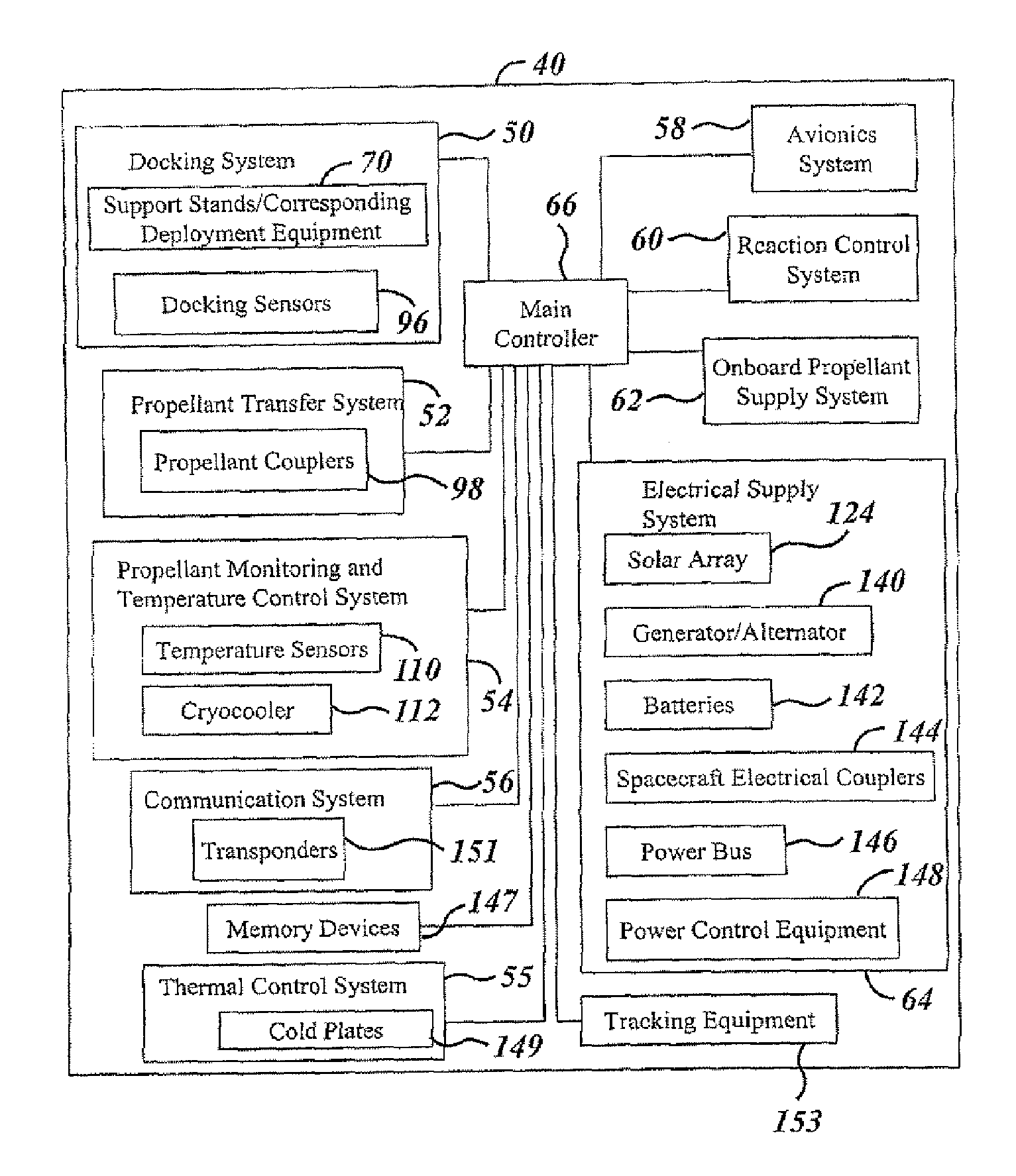
Space depot for spacecraft resupply
InactiveUS20070051854A1Efficient and inexpensive techniqueLow costCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic component separationPropellant depotSpace vehicle control
A propellant depot (40, 150) includes a utility box (42, 42′) that has space flight equipment. A propellant cartridge adaptor (95) is coupled to the utility box (42, 42′) and to an exchangeable propellant cartridge system (41). The propellant depot (40, 150) also includes a docking adaptor (44) for coupling to an approaching spacecraft (24). A controller (66) controls the transfer of propellant from within the exchangeable propellant cartridge system (41) to the spacecraft (24). A method of providing propellant to a spacecraft in space includes launching an orbital propellant depot (40, 150) into space. The spacecraft is docked to the orbital propellant depot (40, 150) in space. Propellant is transferred to the spacecraft. The spacecraft is separated from the orbital propellant depot (40, 150).
Owner:THE BOEING CO
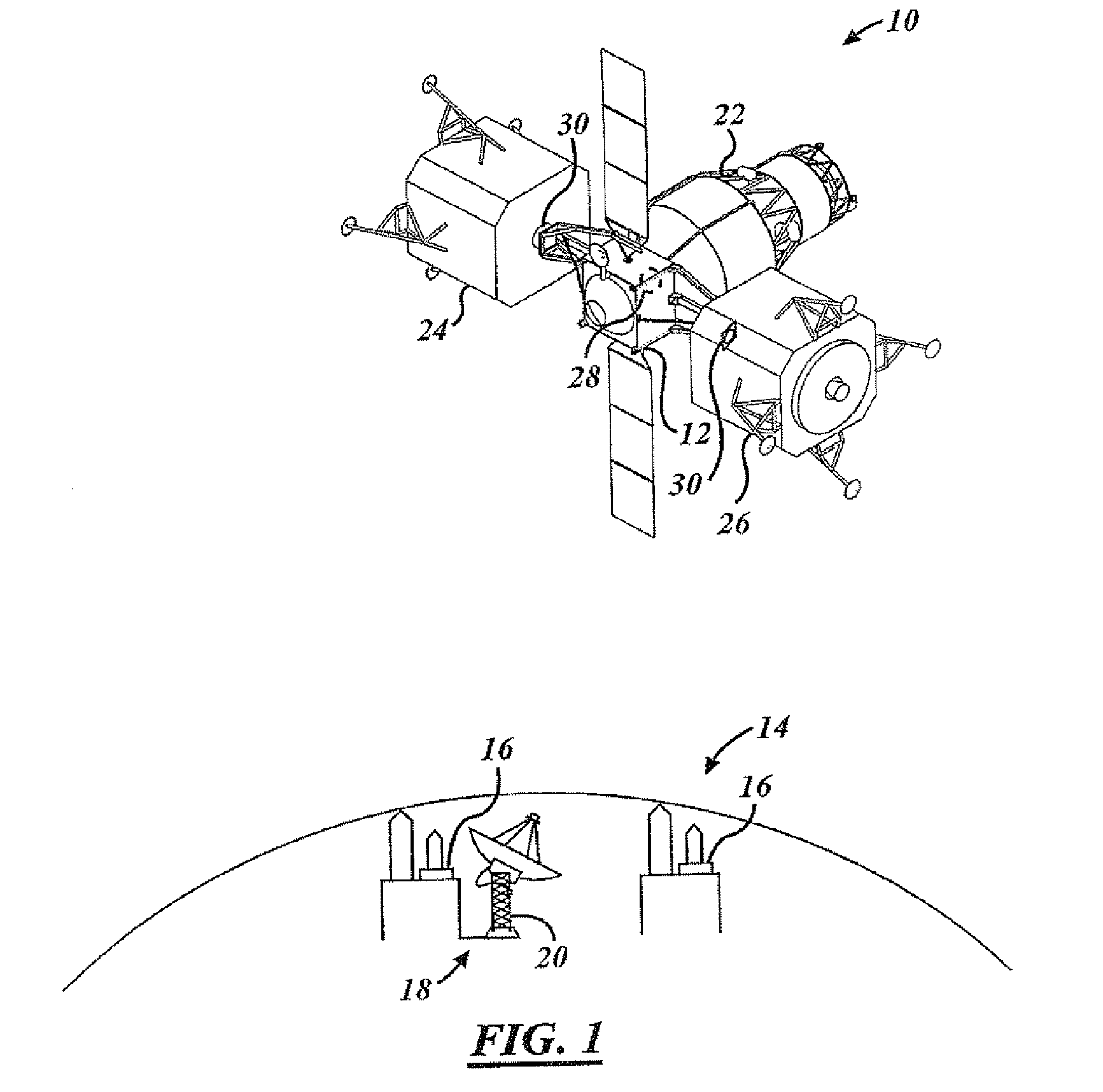
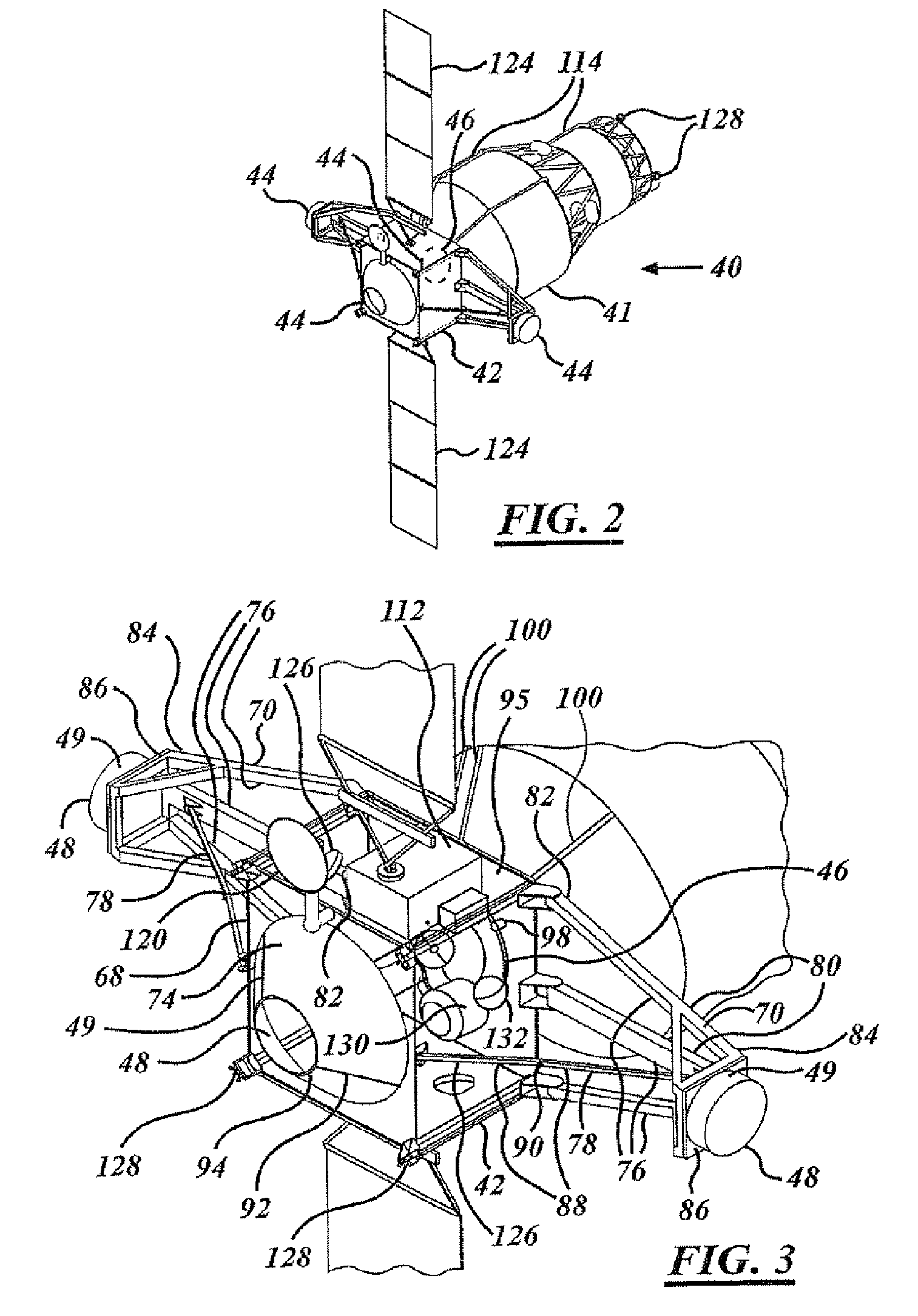
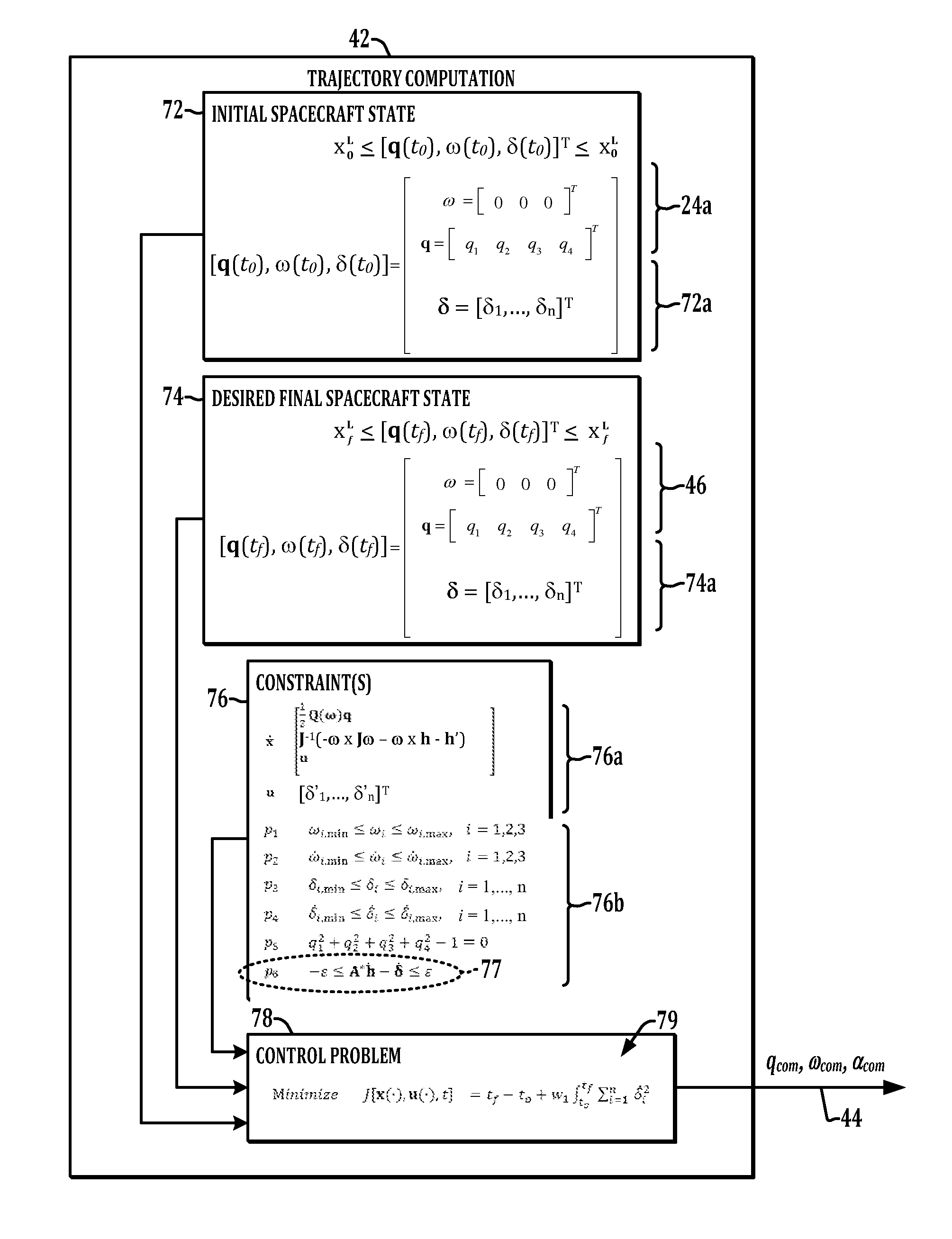
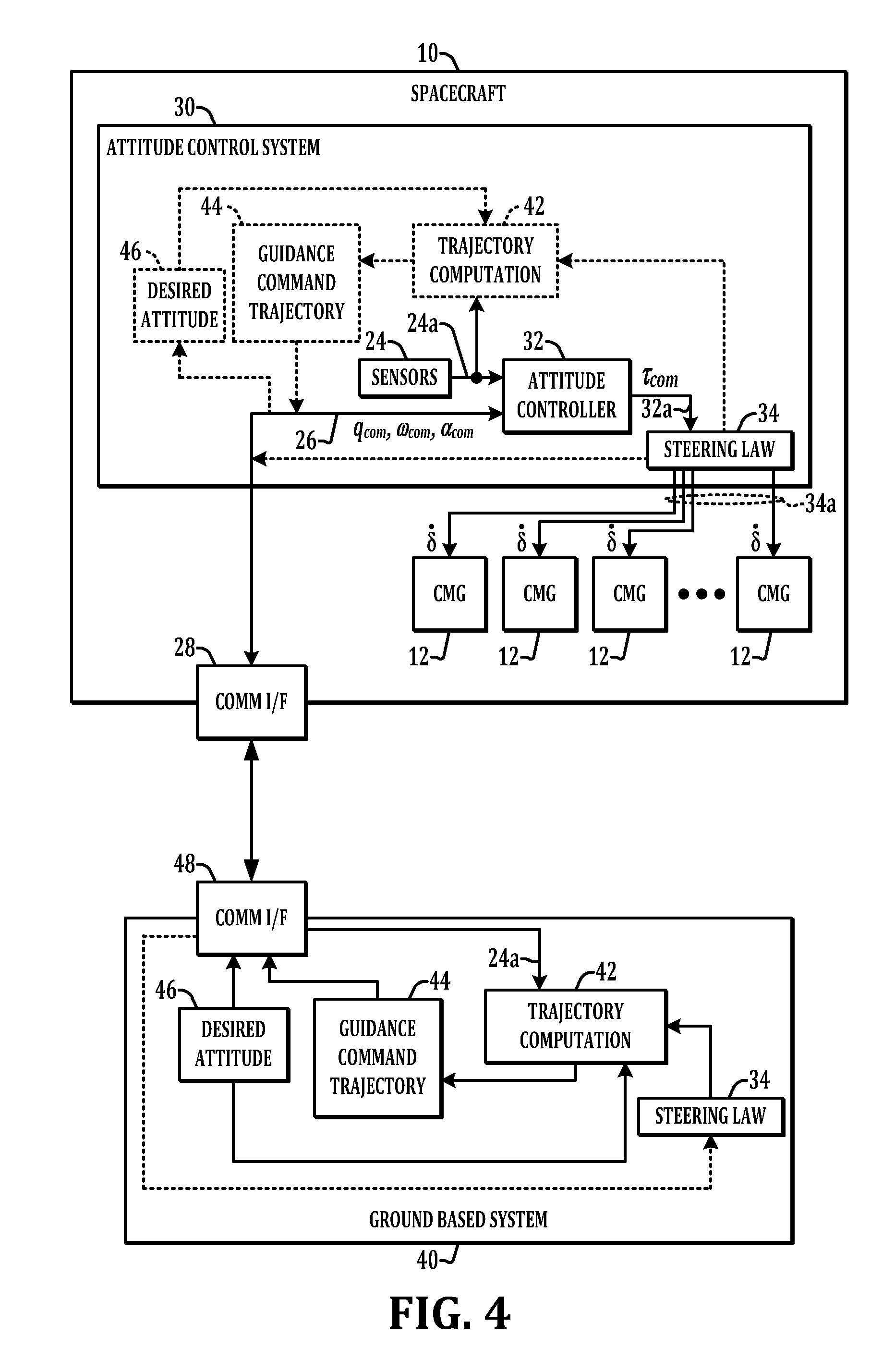
Method and apparatus for determining spacecraft maneuvers
Methods and apparatus are presented for spacecraft operation in which a control problem is formulated using a control law or steering law as a path constraint or as a dynamic constraint, and the control problem is solved to provide a guidance command trajectory for use in operating spacecraft control momentum gyroscopes to guide the spacecraft from an initial state to a desired final state.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
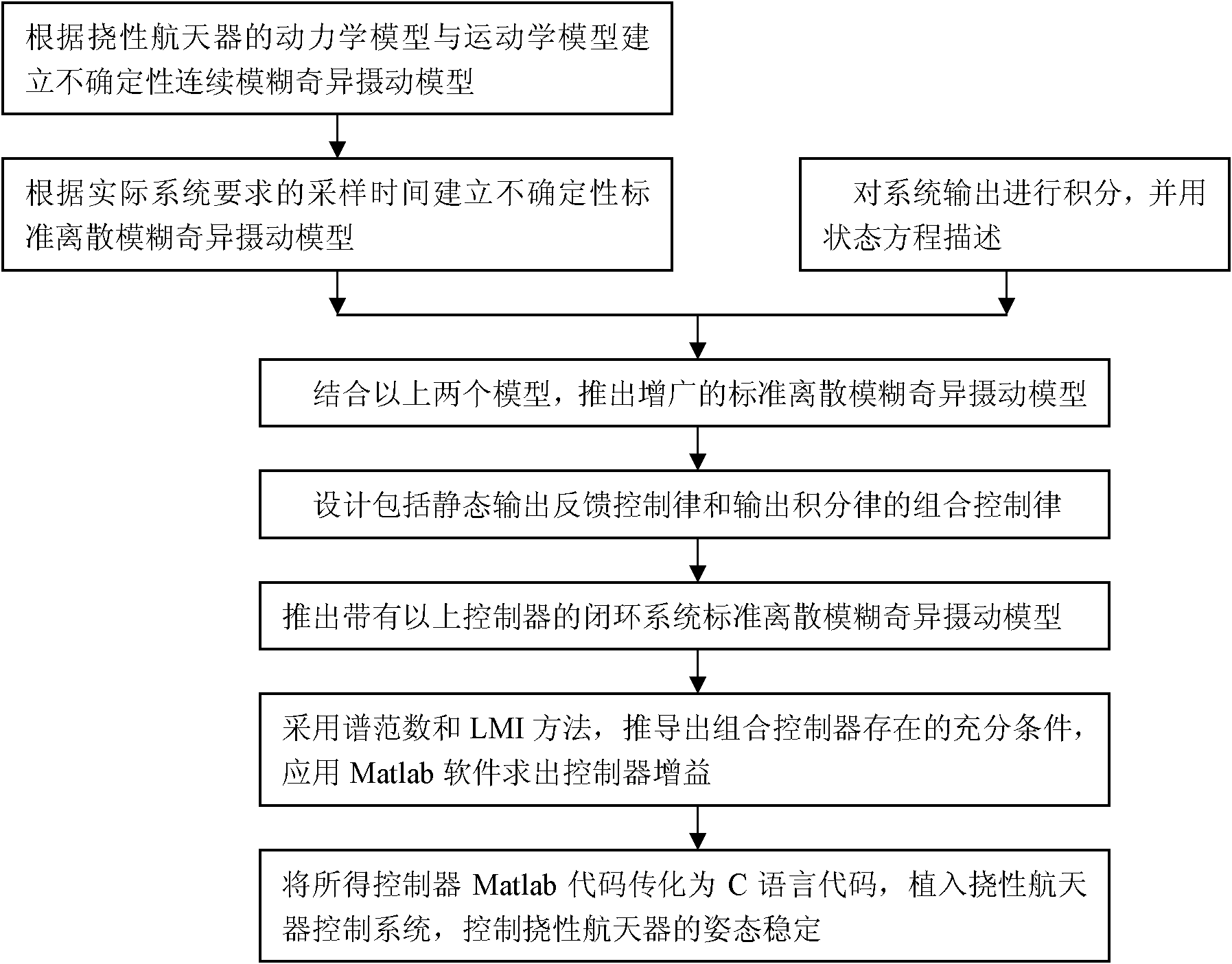
Fuzzy singular perturbation modeling and attitude control method for complex flexible spacecraft
InactiveCN102073280ASmall steady state errorAvoid inconvenienceSimulator controlIntegratorAnti jamming
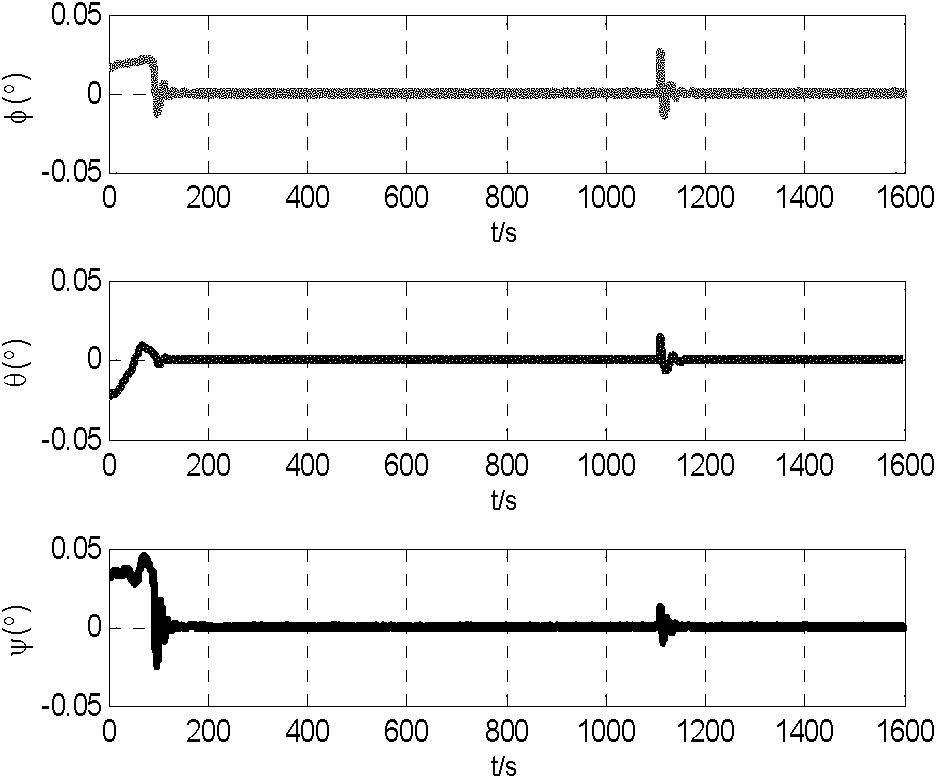
The invention belongs to the field of spacecraft control and relates to a fuzzy singular perturbation modeling and robust attitude control method for complex flexible spacecraft, namely a robust combined control method for fusing static output feedback control and output integration. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing an uncertain continuous fuzzy singular perturbation model and a standard discrete fuzzy singular perturbation model according to a dynamic model and a kinematic model of the spacecraft in combination with fuzzy logic and singular perturbation technology; and designing a robust controller combined by a static output feedback controller and an output integrator by a spectral norm and linear matrix inequality (LMI) method and resolving a group of LMIs which are unrelated to a perturbation parameter so as to obtain a controller parameter and solve an ill-conditioned problem caused by the perturbation parameter and the problem of difficulty in selection of an initial value in an LMI resolving static output feedback controller gain method. Through the method, flexible vibration and external interference can be overcome effectively, and control effects such as high response speed, high attitude control accuracy, high anti-jamming capability and high robust performance are achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for controlling index time-varying slide mode of flexible spacecraft characteristic shaft attitude maneuver
ActiveCN103412491ASuppress residual vibrationAvoid complex coupling relationshipsAdaptive controlDynamic modelsSpace vehicle control
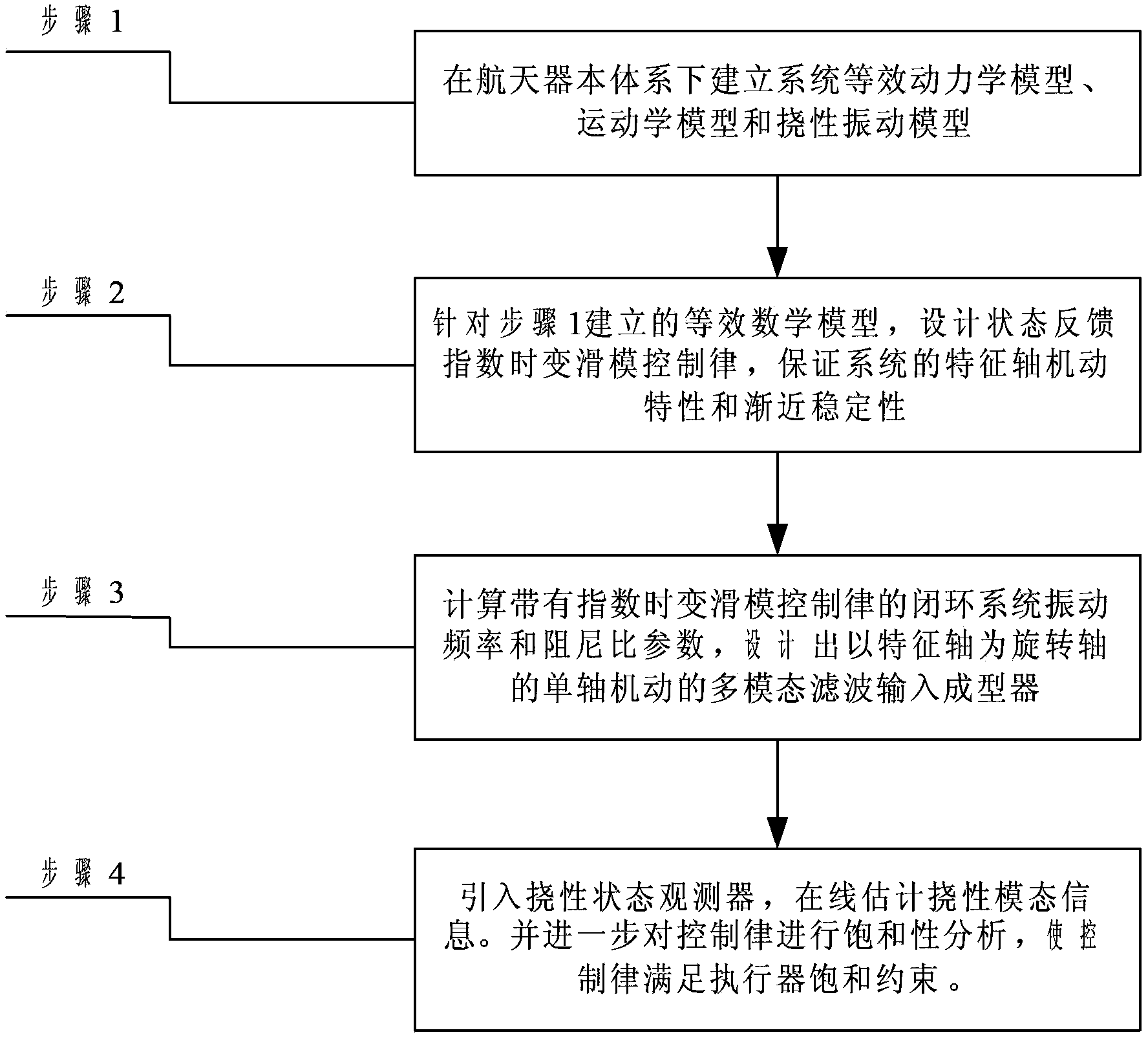
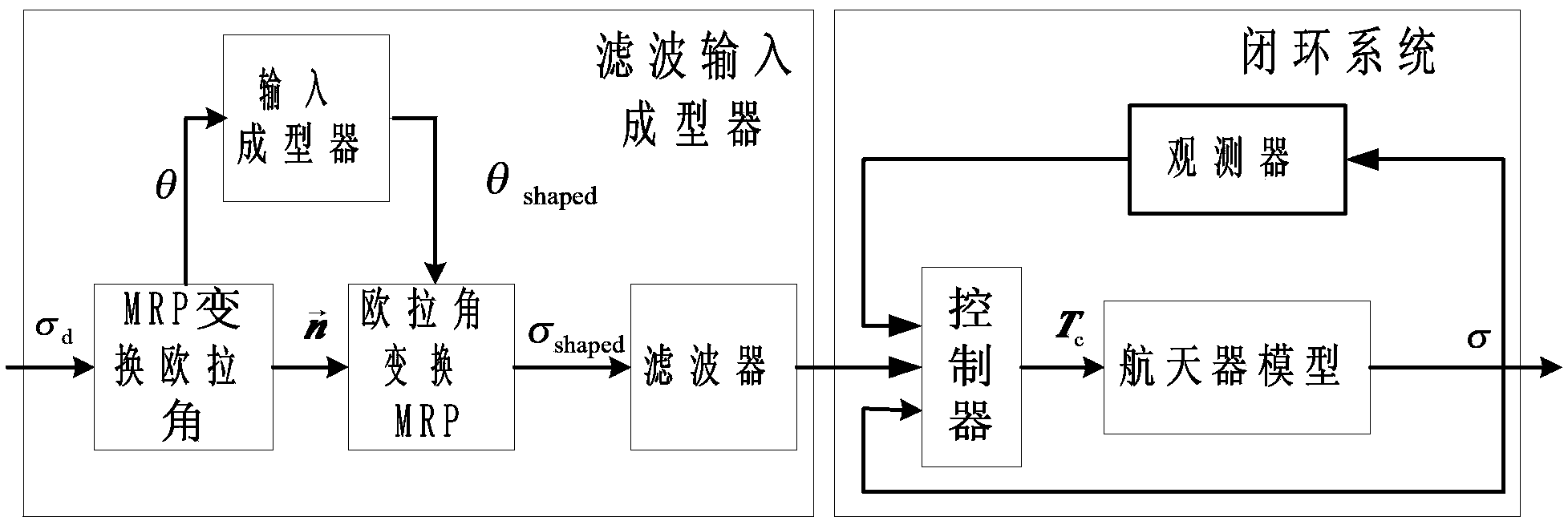
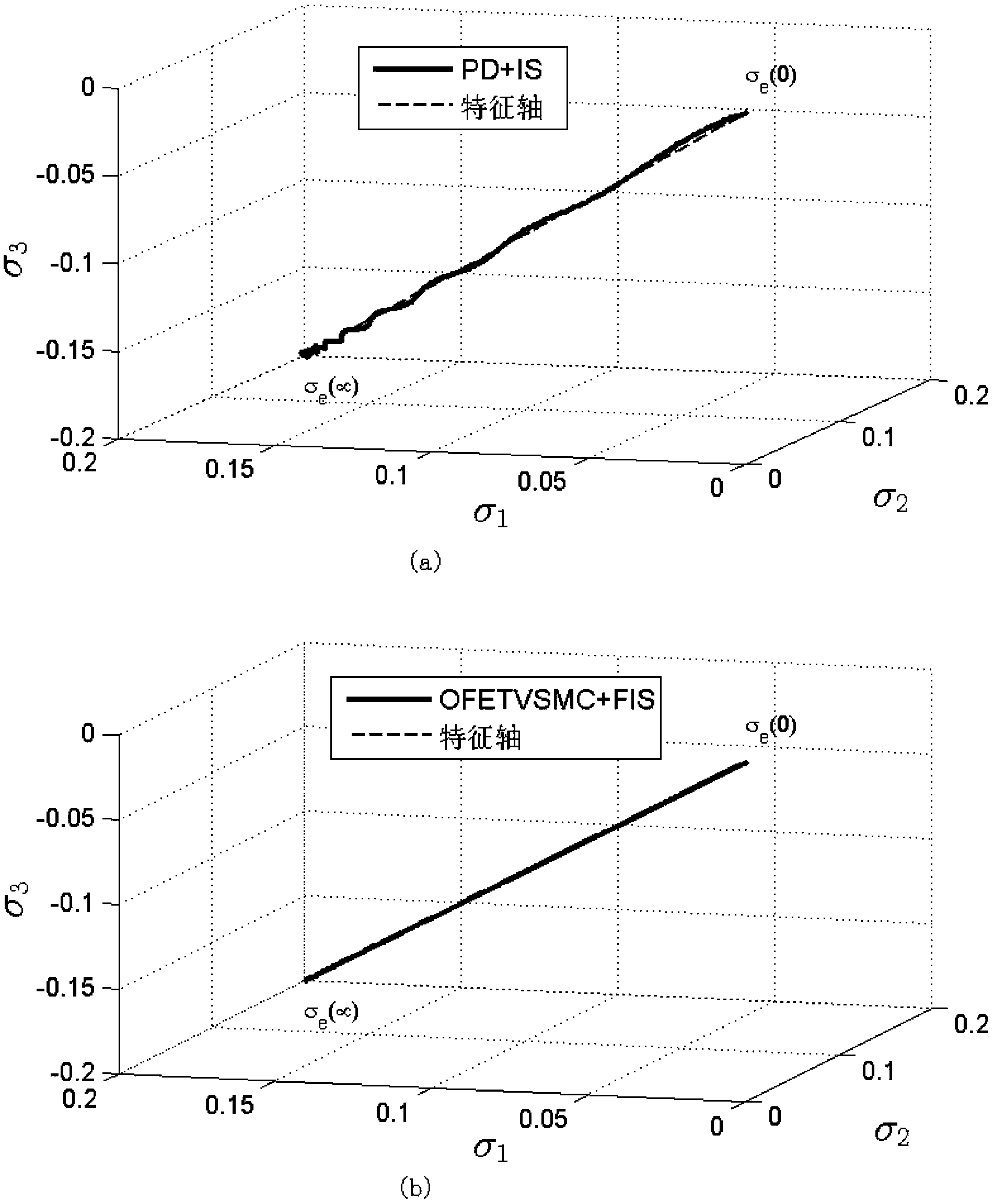
The invention relates to a method for controlling an index time-varying slide mode of flexible spacecraft characteristic shaft attitude maneuver, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft control. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a system dynamically equivalent model, a dynamic model and a flexible vibration model are established under a spacecraft system, then, the vibration frequency and the damping ratio parameter of a closed loop system with the index time-varying slide mode control law are calculated, and a single-shaft multi-modality filtering input shaping device with a characteristic shaft as a rotary shaft is designed according to the designing method of the single-shaft input shaping device to restrain flexible vibration in three-shaft motion. Meanwhile, a state observer is designed to estimate flexible modal information in real time, and the method for controlling an output feedback index time-varying slide mode is formed. At last, saturability analysis is conducted on control torque so as to satisfy the physical saturation constraint of the control torque. By means of the method, the application range of existing input shaping is expanded, the input shaping technology is expanded from single-shaft maneuver to three-shaft maneuver, the self-robustness of filter input shaping is enhanced, and the purpose that the attitude maneuver path of the spacecraft is the shortest is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Optimal control method for single frame moment gyro group for spacecraft wide angle maneuver control
The invention provides an optimal control method for single frame moment gyro group for spacecraft wide angle maneuver control characterized in that, during the process of attitude control, the gyroscope having the highest frame angular speed is selected, then a minimum frame angular speed is obtained from the gyroscope as the control frame angular speed for rapid large angle power-propelled control, when guaranteeing the gyroscope frame angular speed is lower than the given propulsion generator rotational speed limit, the lost motion frame angular speed and correction coefficient can be designed to give the gyroscope group dynamic formation a predetermined final frame angle quantity, finally the optimum control angular speed and optimum lost motion angular speed are multiplied by the correction coefficient for summing, which can obtain the optimum value of the frame angular speed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
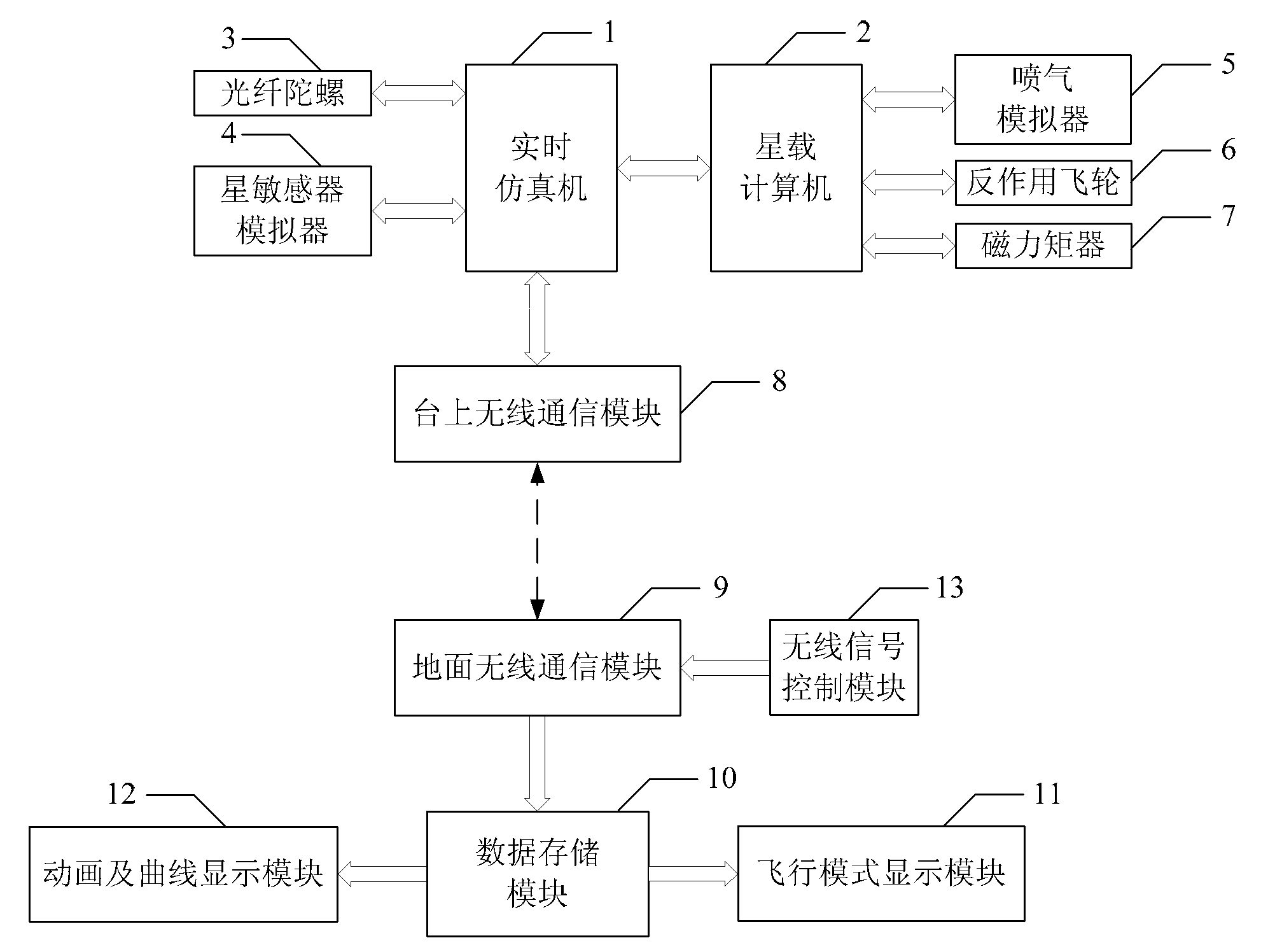
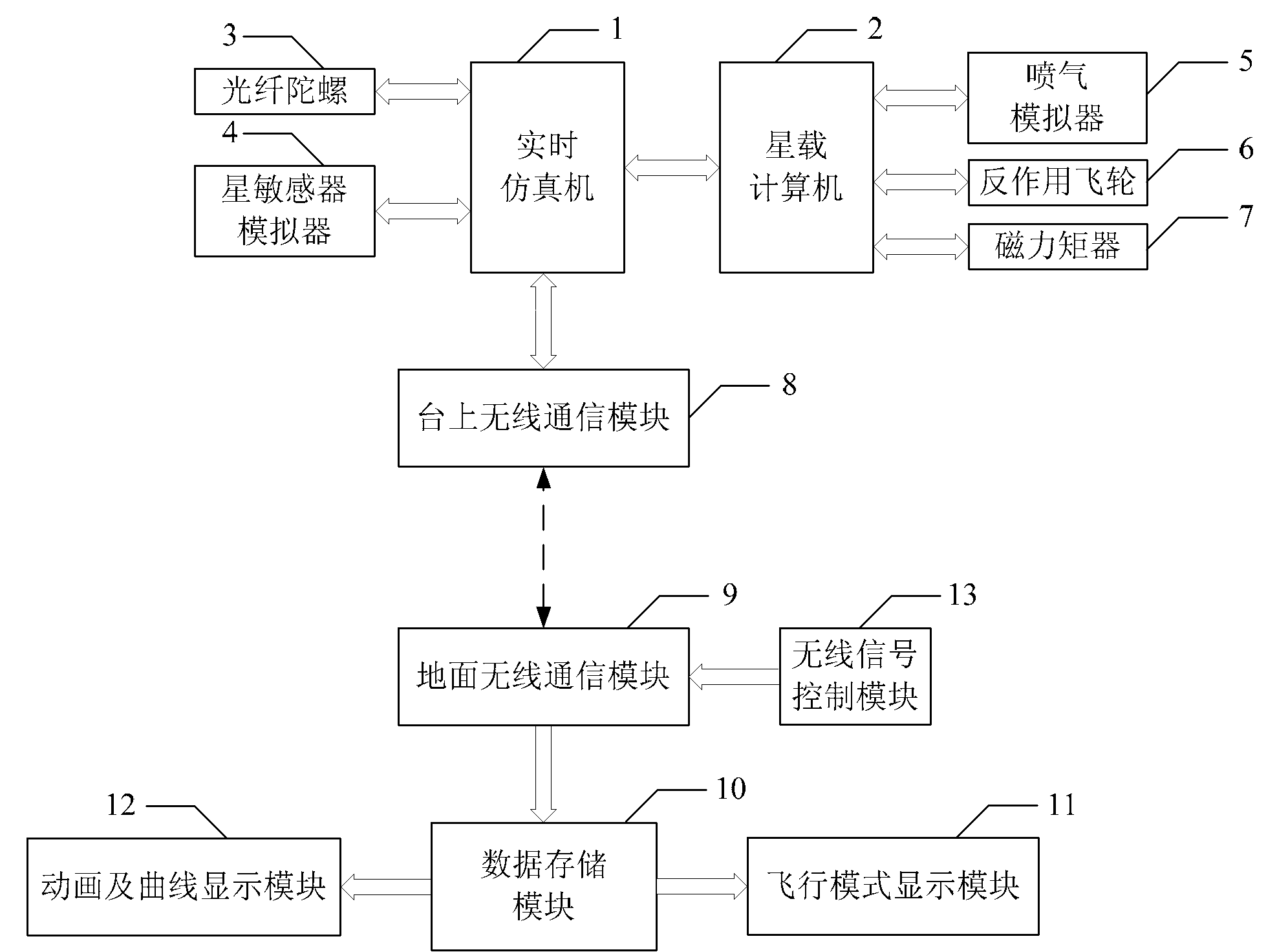
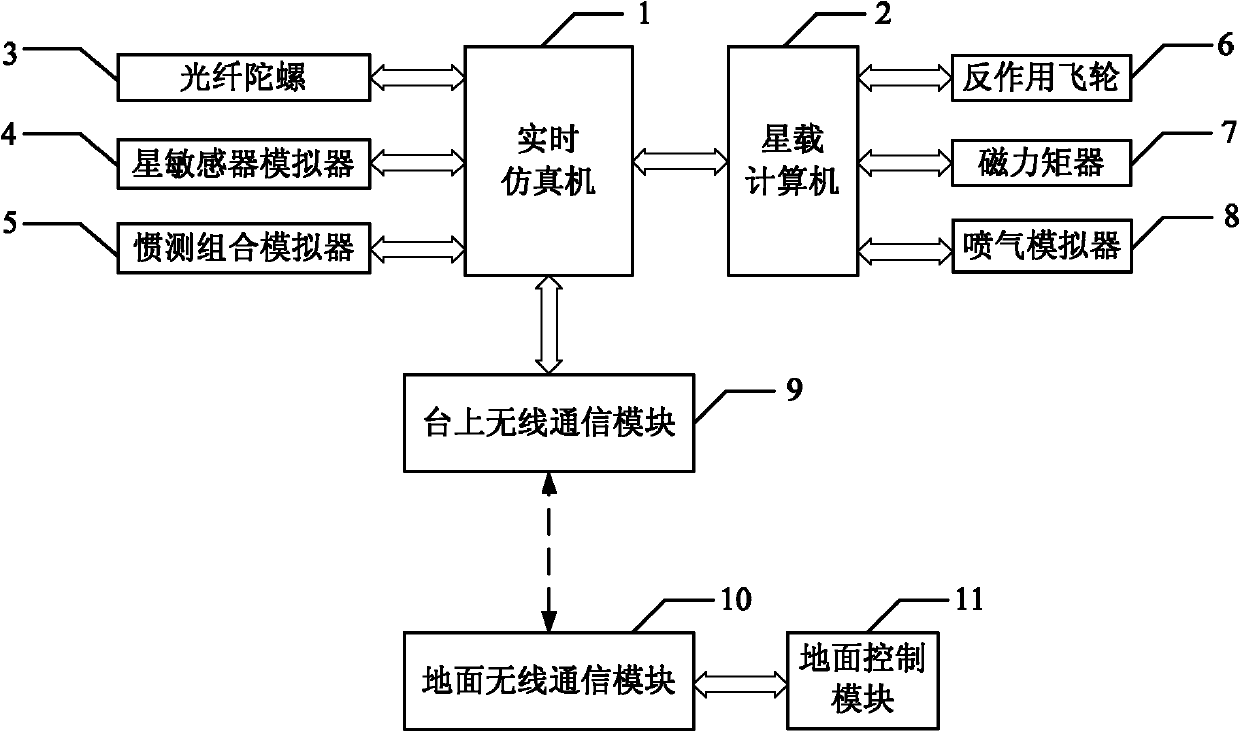
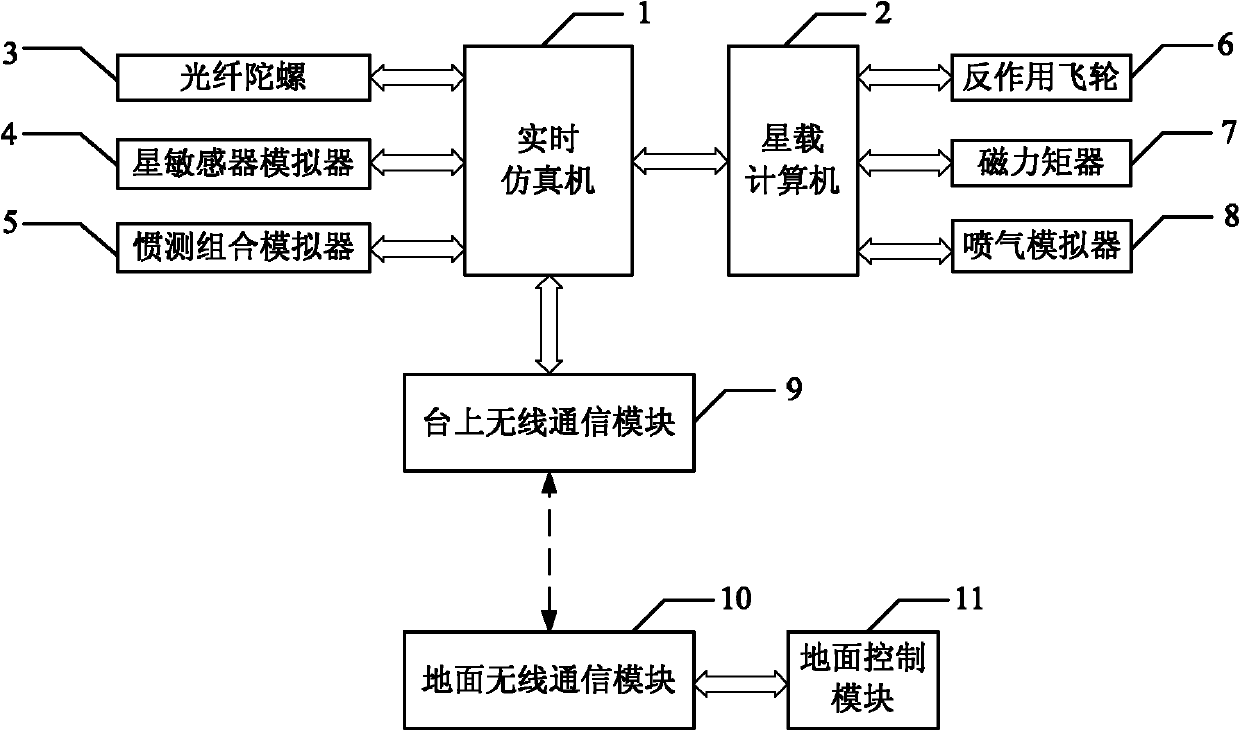
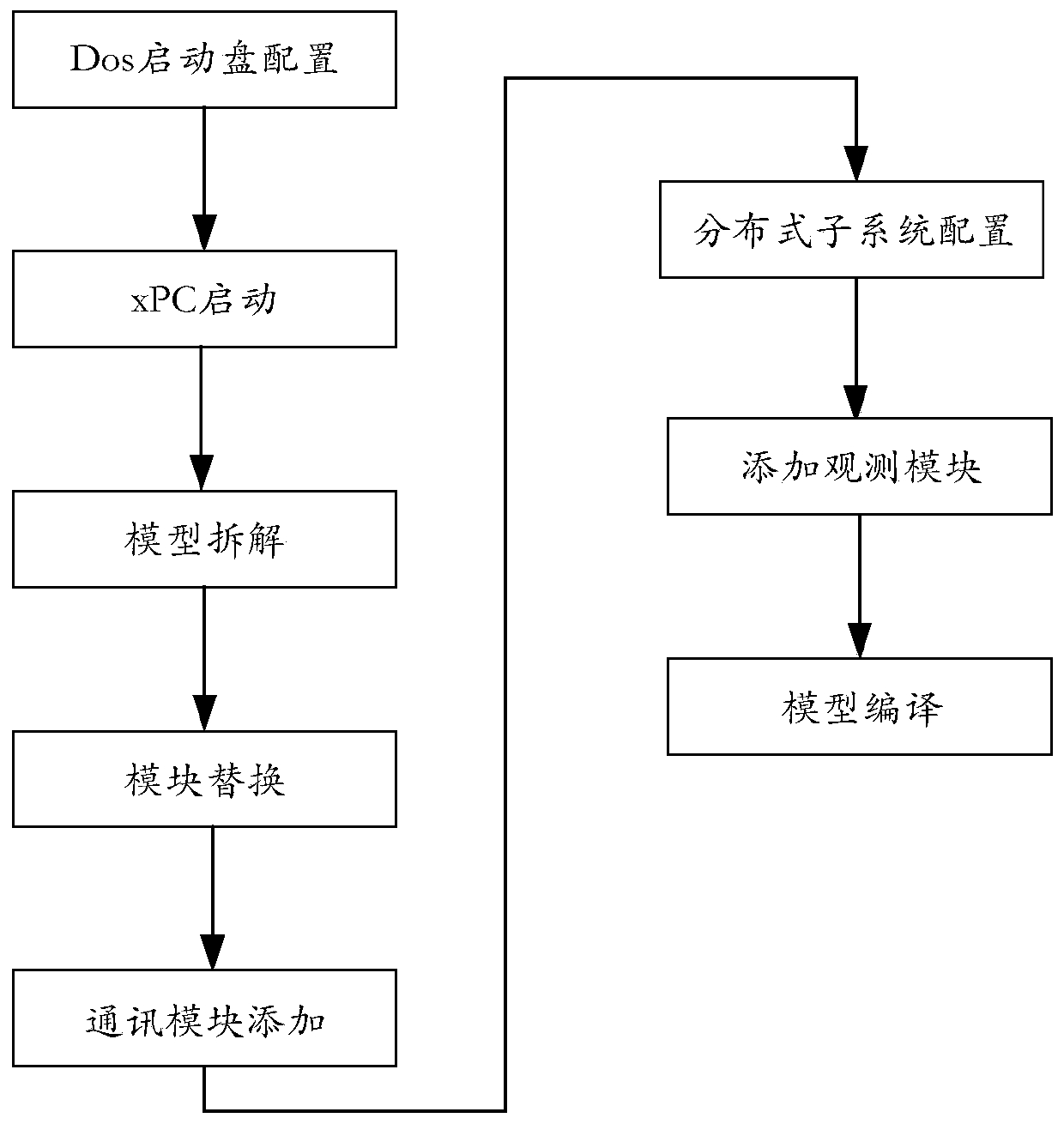
Spacecraft attitude control semi-physical simulation system
InactiveCN101937195AImprove general performanceSystematicSimulator controlAttitude controlReal-time simulationSpacecraft attitude control
The invention discloses a spacecraft attitude control semi-physical simulation system which relates to a spacecraft control semi-physical simulation system. The invention solves the problems of poor universality and systematicness in the prior spacecraft attitude control semi-physical simulation system. The simulation signal input or output end of a real-time simulation machine of the system is connected with the simulation signal output or input end of an onboard spacecraft computer; the wireless signal output or output end of a system wireless communication module is connected with the wireless signal input or output end of the real-time simulation machine; the signal output end of a ground wireless communication module is connected with the signal input end of a data storage module; the data signal output end 1 of the data storage module is connected with the data signal input end of a flight simulation display module; and the data signal output end 2 of the data storage module is connected with the data signal input end of an animation and graphic display module. The invention is suitable for simulation of spacecraft attitude control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
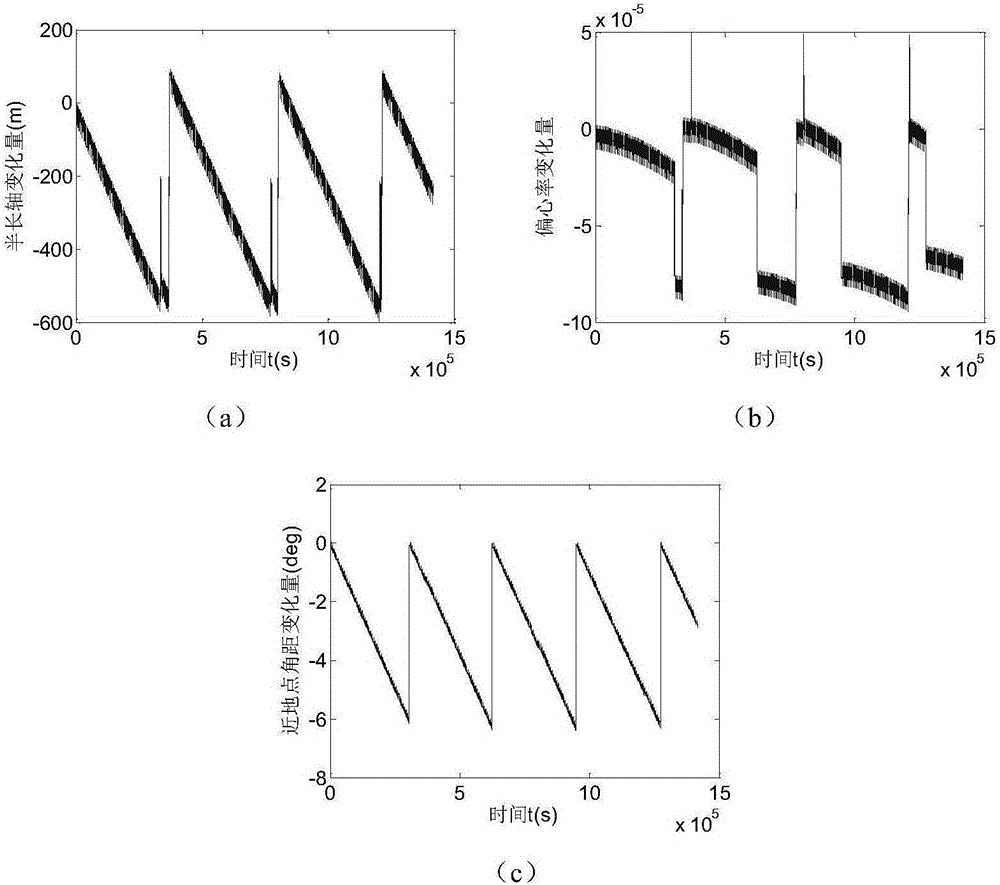
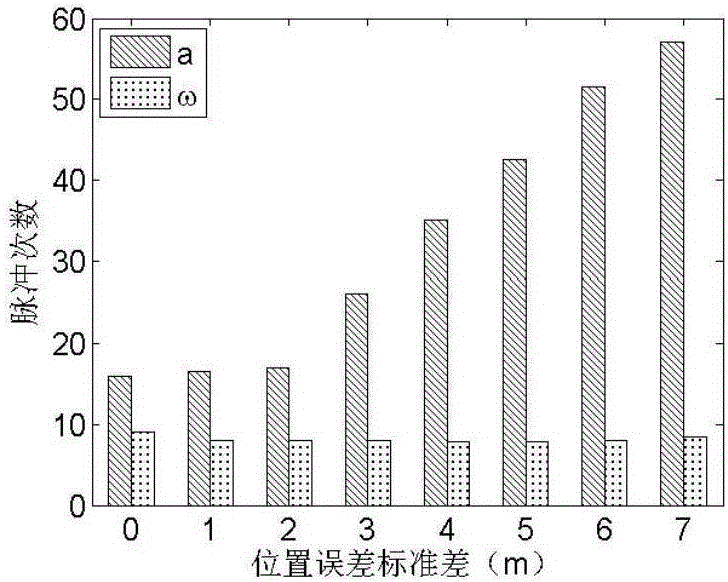
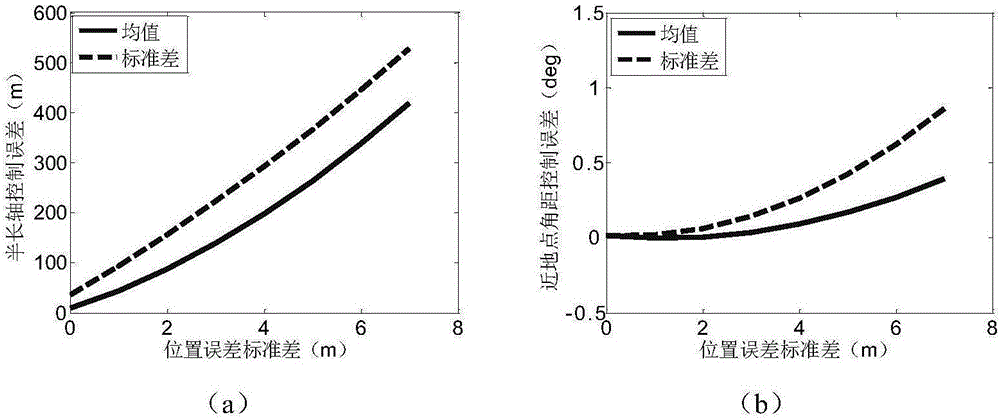
Robustness analysis method for spacecraft orbit control strategy
ActiveCN106697333ACosmonautic vehiclesSpecial data processing applicationsSpace vehicle controlComputational model
The invention relates to robustness analysis method for a spacecraft orbit control strategy, and belongs to the technical field of the spacecraft orbit dynamics and control. The robustness analysis method comprises the following steps: modeling orbital motion of the spacecraft through a Gauss orbit element perturbation equation; analyzing the non-spherical perturbation of a low-orbit satellite and the atmospheric drag perturbation; designing an orbit maintaining strategy to execute the maintaining control to the spacecraft orbit elements; using a differential correcting algorithm to improve the precision of the orbit maintaining; building a position error, velocity error and engine thrust error model in the running process of the spacecraft; designing a calculation model of spacecraft control error mean, variance and error distribution proportion; and using a Monte Carlo simulation method to execute the simulation analysis to the spacecraft orbit control strategy with the error, and building a robustness evaluation system of the orbit control strategy. In the control strategy design, the actual situation of the satellite orbit control is considered adequately, and the feasibility of the method in the actual project is guaranteed under the precondition of simpliness and convenience and according with the actual situation.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Semi-physical simulation system for attitude control of star-arrow integrated spacecraft
InactiveCN101995824ARealize simulationSimulator controlAttitude controlReal-time simulationSpacecraft attitude control
The invention discloses a semi-physical simulation system for attitude control of a star-arrow integrated spacecraft, which relates to the semi-physical simulation system for control of the star-arrow integrated spacecraft. The invention solves the problem that the conventional semi-physical simulation system for the attitude control of the spacecraft cannot simulate the spacecraft from a launching point to an active operation stage attitude control system. A simulation signal input or output end of a real-time simulator is connected with a simulation signal output or input end of an onboard computer; a wireless signal input or output end of a stage wireless communication module is connected with a wireless signal output or input end of the real-time stimulator; and a signal output or input end of a ground wireless communication module is connected with a signal input or output end of a ground control module. The system is suitable for the stimulation of the attitude control of the star-arrow integrated spacecraft.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Fault mode thrust allocation method for geostationary orbit satellite electric thruster
ActiveCN105353621AOptimal satisfactionQuick and autonomous implementationAdaptive controlElectricityMomentum
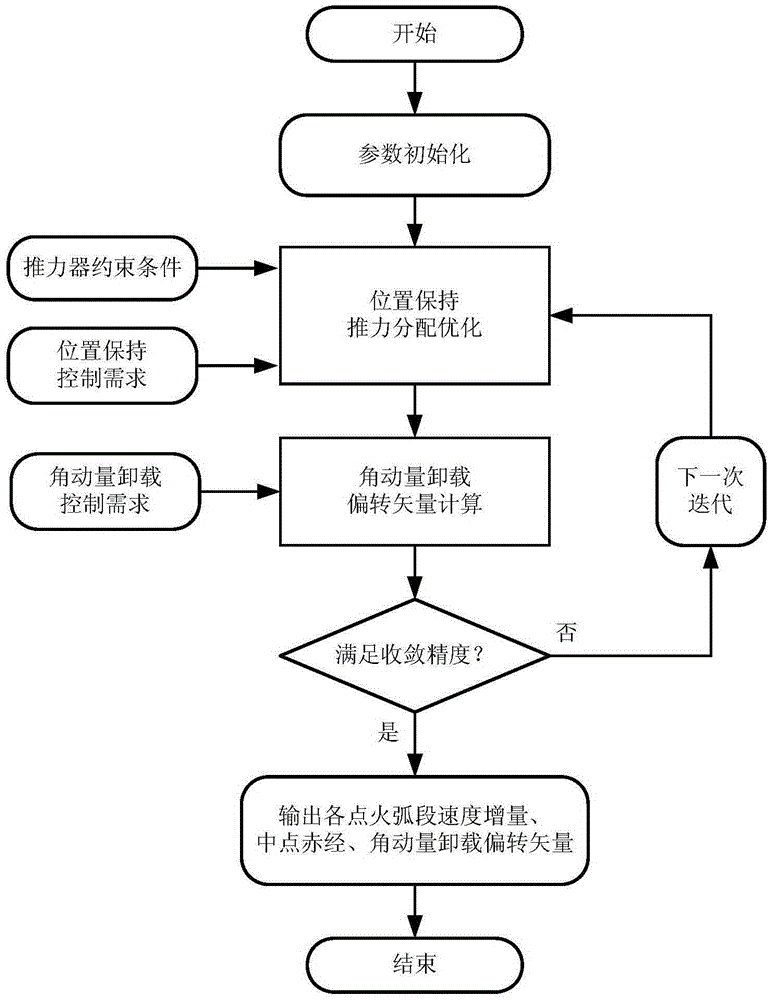
The invention belongs to the field of spacecraft control, and relates to a fault mode thrust allocation method for a geostationary orbit satellite electric thruster. The method comprises the steps of firstly, determining a thrust allocation input condition, including ignition position constraint, ignition velocity increment constraint and orbit control demand; secondly, allocating and optimizing position keeping thrust, establishing an electric thruster pointing model, selecting a thruster, defining ignition parameters, and optimizing and calculating the ignition parameters; and finally, calculating an angular momentum unloading deflecting vector. Aiming at the problem of high fuel consumption in a traditional definitive solution mode, a nonlinear hybrid constraint optimization model is established, and key parameters such as time length of each thrust ignition arc, ignition position and the like are solved by taking fuel optimization as a target, so that the method can realize fuel optimization under engineering constraints.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Method and apparatus for estimating attitude sensor bias in a satellite
InactiveUS6108593ACosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsSpace vehicle controlEngineering
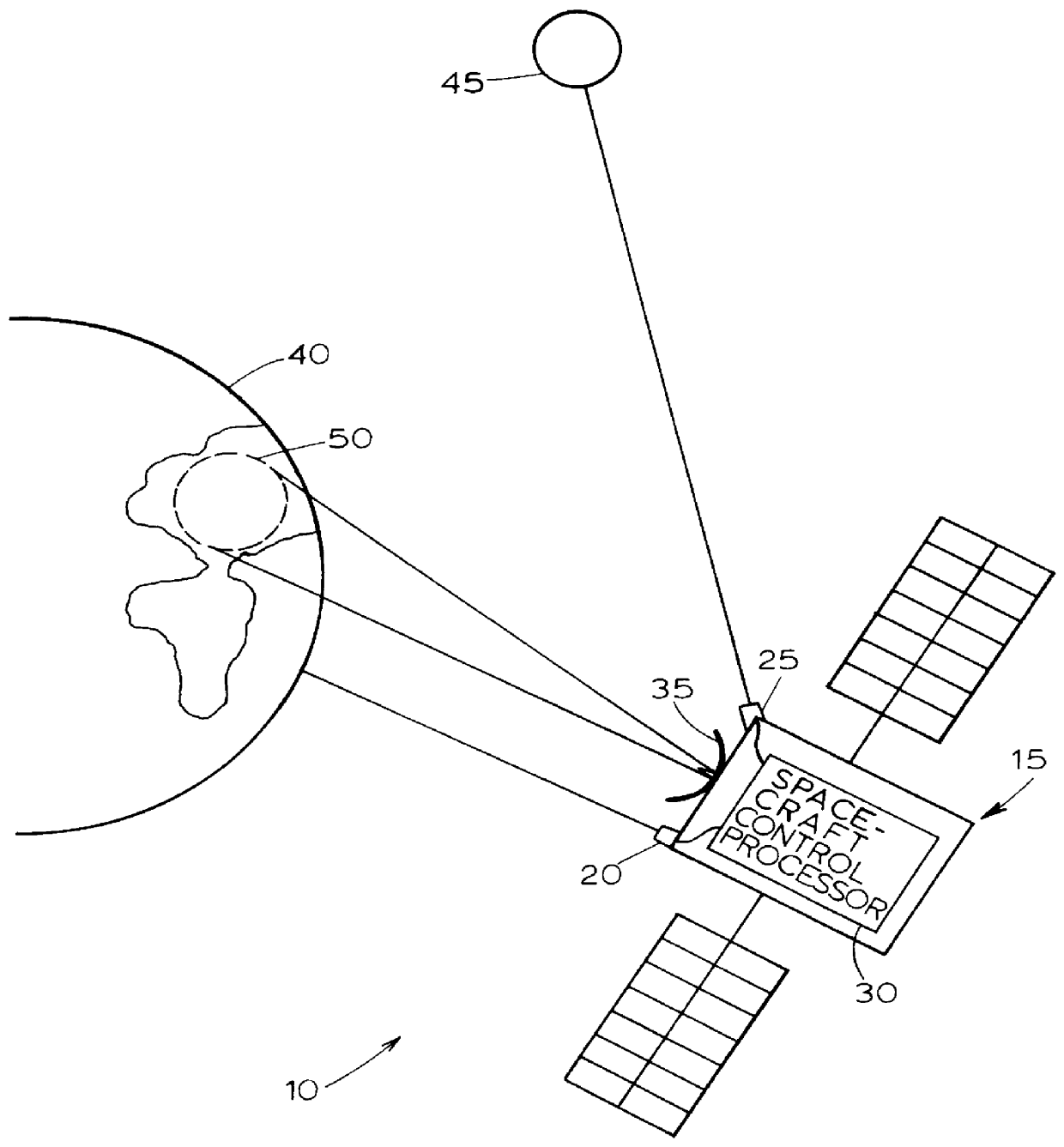
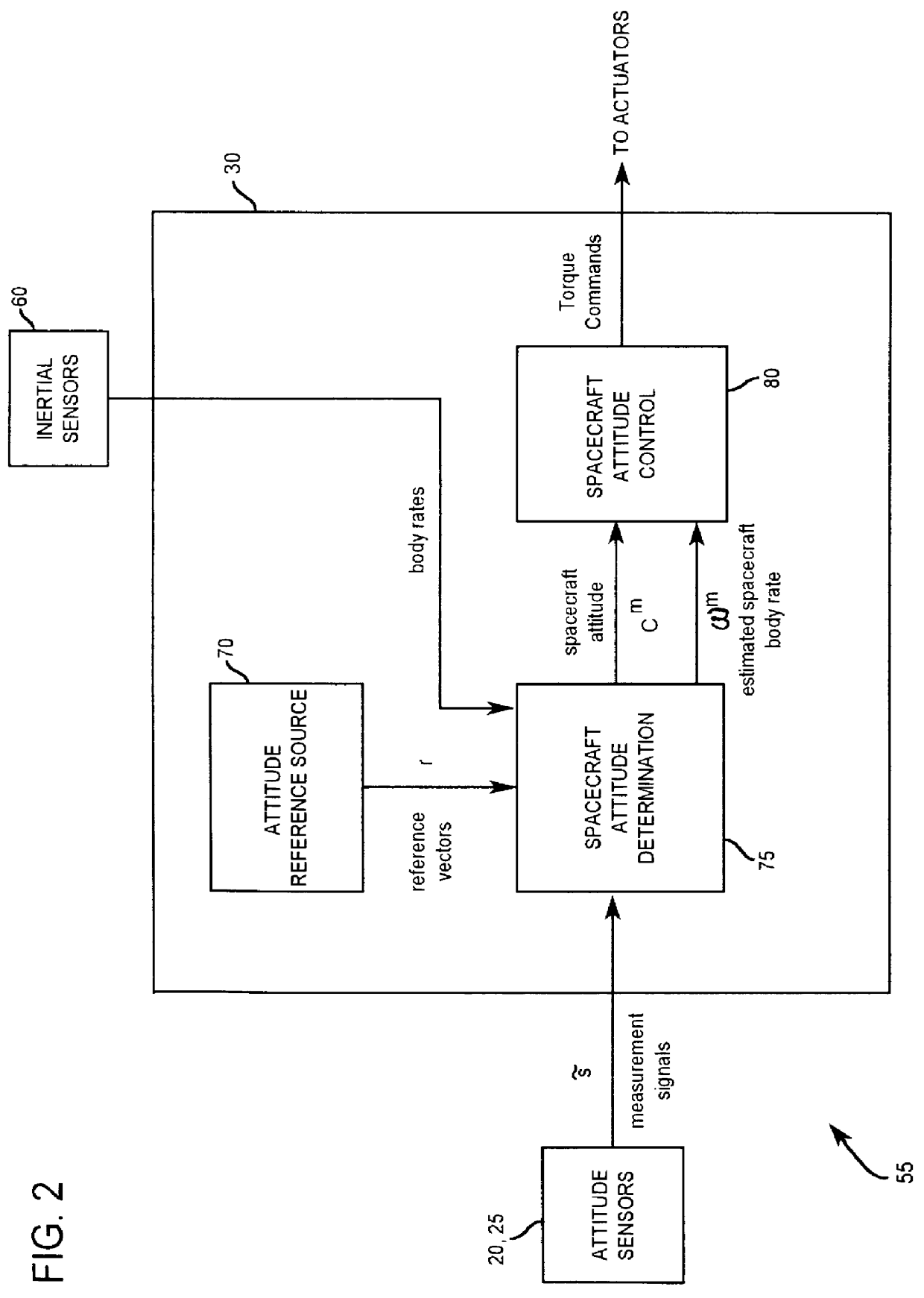
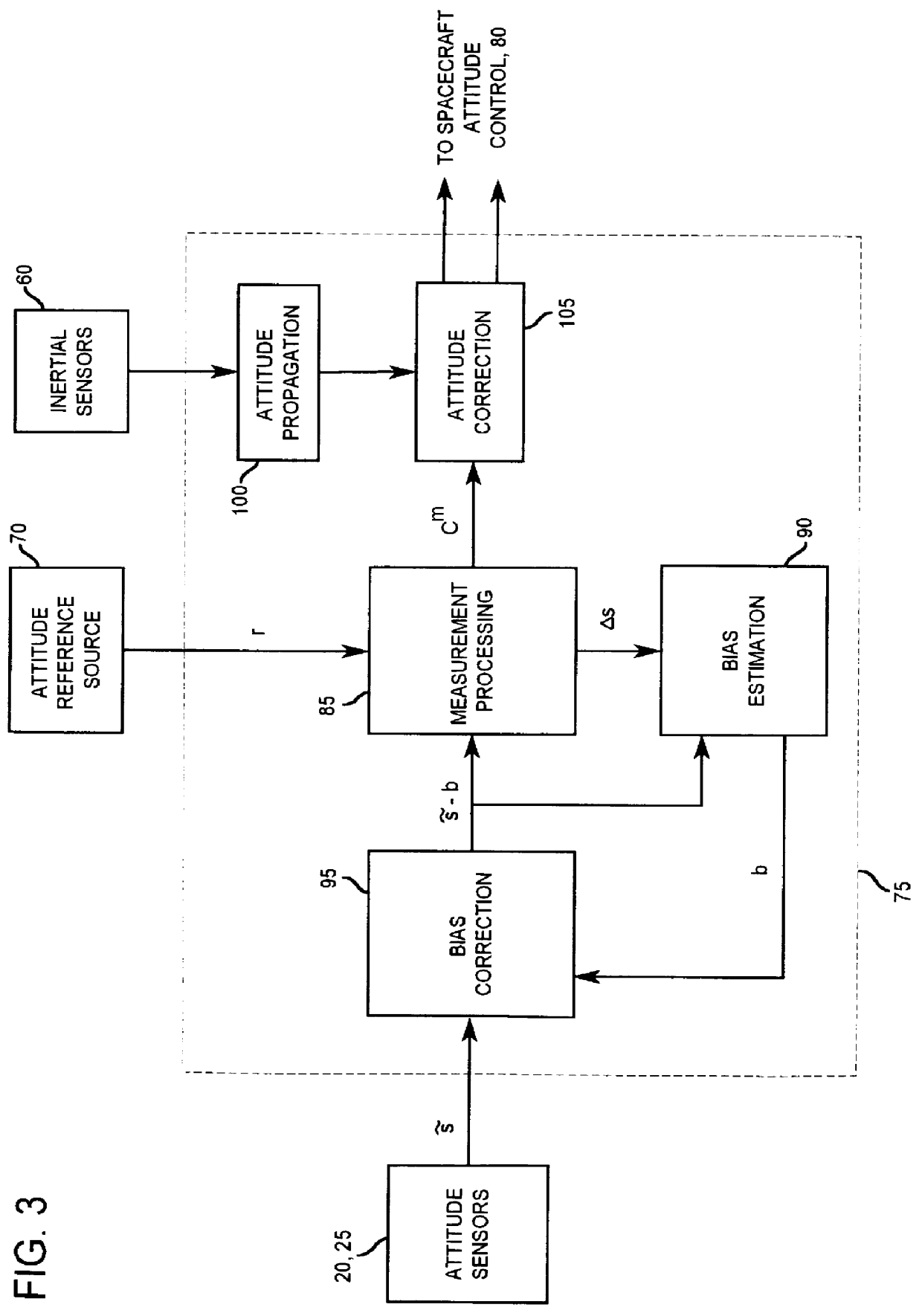
A method and apparatus for estimating attitude sensor bias in a satellite system uses attitude sensors and a spacecraft control processor. Attitude sensors provide output signals, which may contain bias. The present invention interprets the signals, determines the bias present in the signals, and generates an output signal to offset the bias in the signals from the attitude sensors, thereby leading to more accurate positioning of the satellite employing the present invention.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
Flight Gear general three-dimensional scene data displaying method based on field programmable gate array (FPGA)
InactiveCN103235852ARealize the designRealize simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAviationSpace vehicle control
Provided is a Flight Gear general three-dimensional scene data displaying method based on a field programmable gate array (FPGA). The method includes that an FPGA chip is adopted, coding of Verilog hardware description language (HDL) language is conducted on the FPGA chip, and a data transmission protocol 1 is self-defined so as to enable the FPGA chip to finish receiving of serial data of specific frame format and with the baud rate of 115200 bps, analysis of data of a self-definition communication protocol 1 is finished in the FPGA, and the data is processed through corresponding algorithms. Then, the processed data is coded and packaged through another self-definition communication protocol 2 and transmitted to a Simulink project operated on a personal computer (PC) with the baud rate as 115200 bps, a series of data processing is conducted in the Simulink. Finally, corresponding gesture data is transmitted to Flight Gear software through a user datagram protocol (UDP) network transmission module to be displayed in real time in a three-dimensional (3D) mode. The Flight Gear general three-dimensional scene data displaying method has the advantage that design and simulation of an aerospace vehicle controller, simulation of an unmanned aerial vehicle controller, simulation of guided missile control, simulation of vehicle and ship controllers and 3D visual reproduction of actual aircraft test flight data and the like can be well achieved, and a use range is wide.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
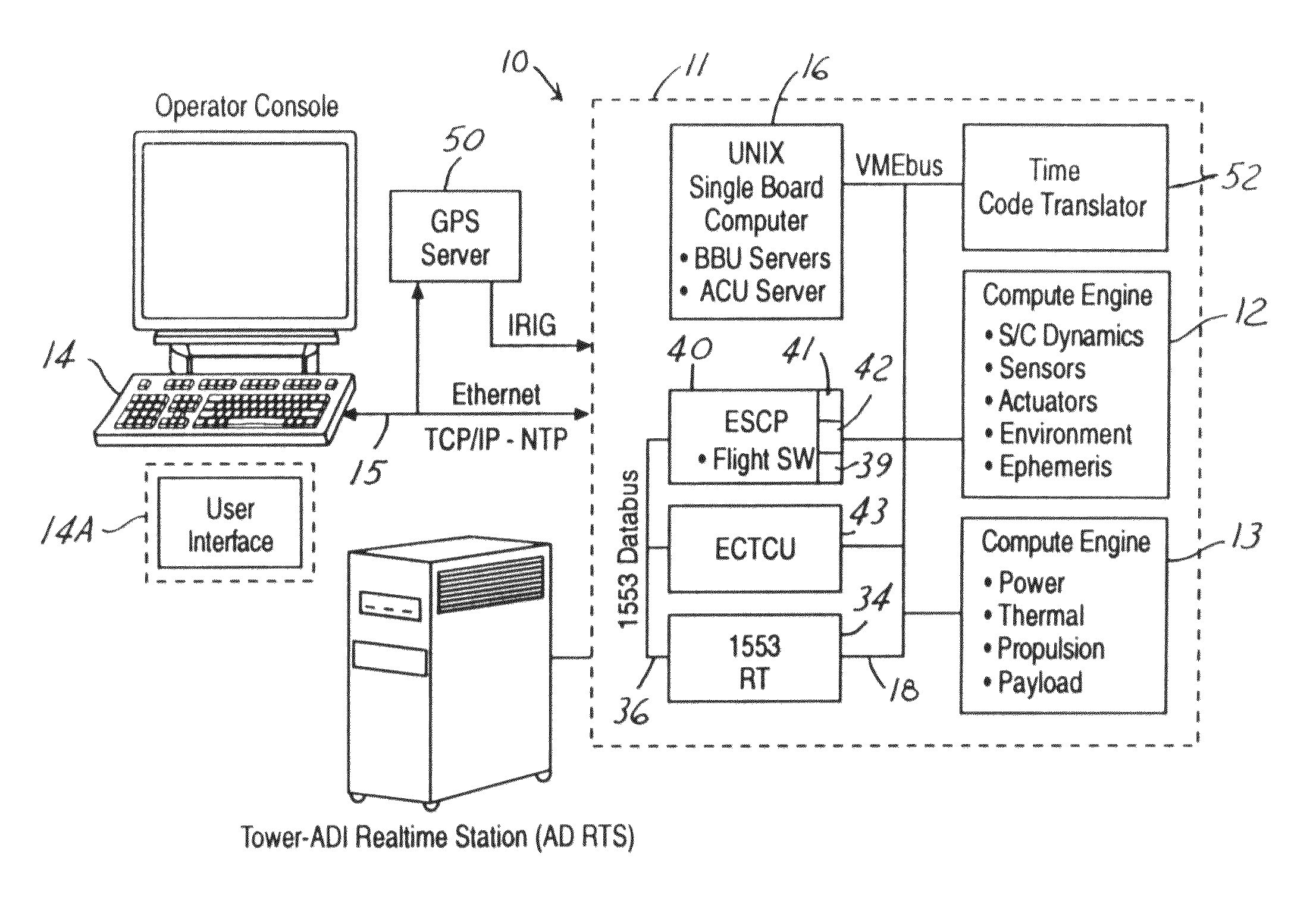
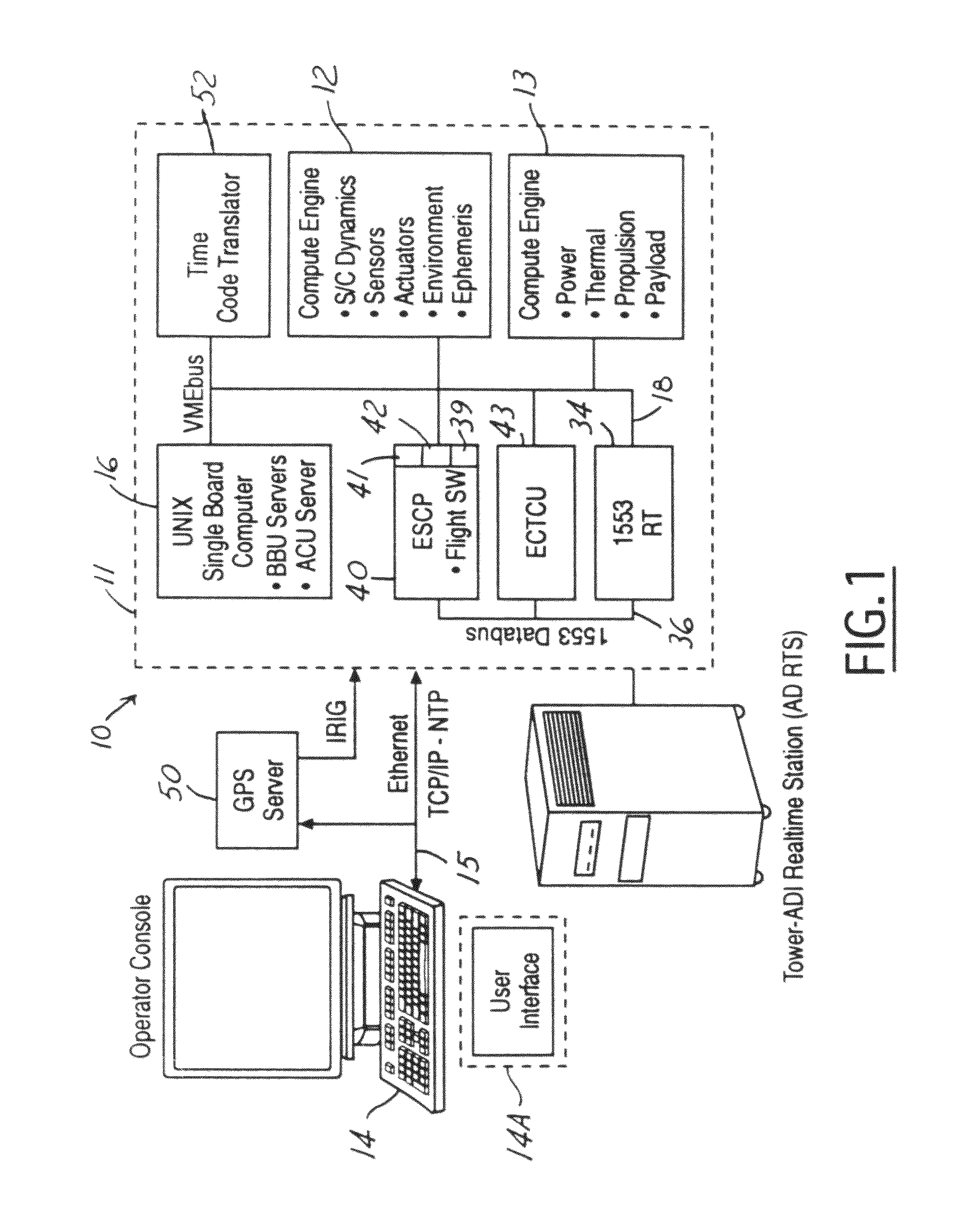
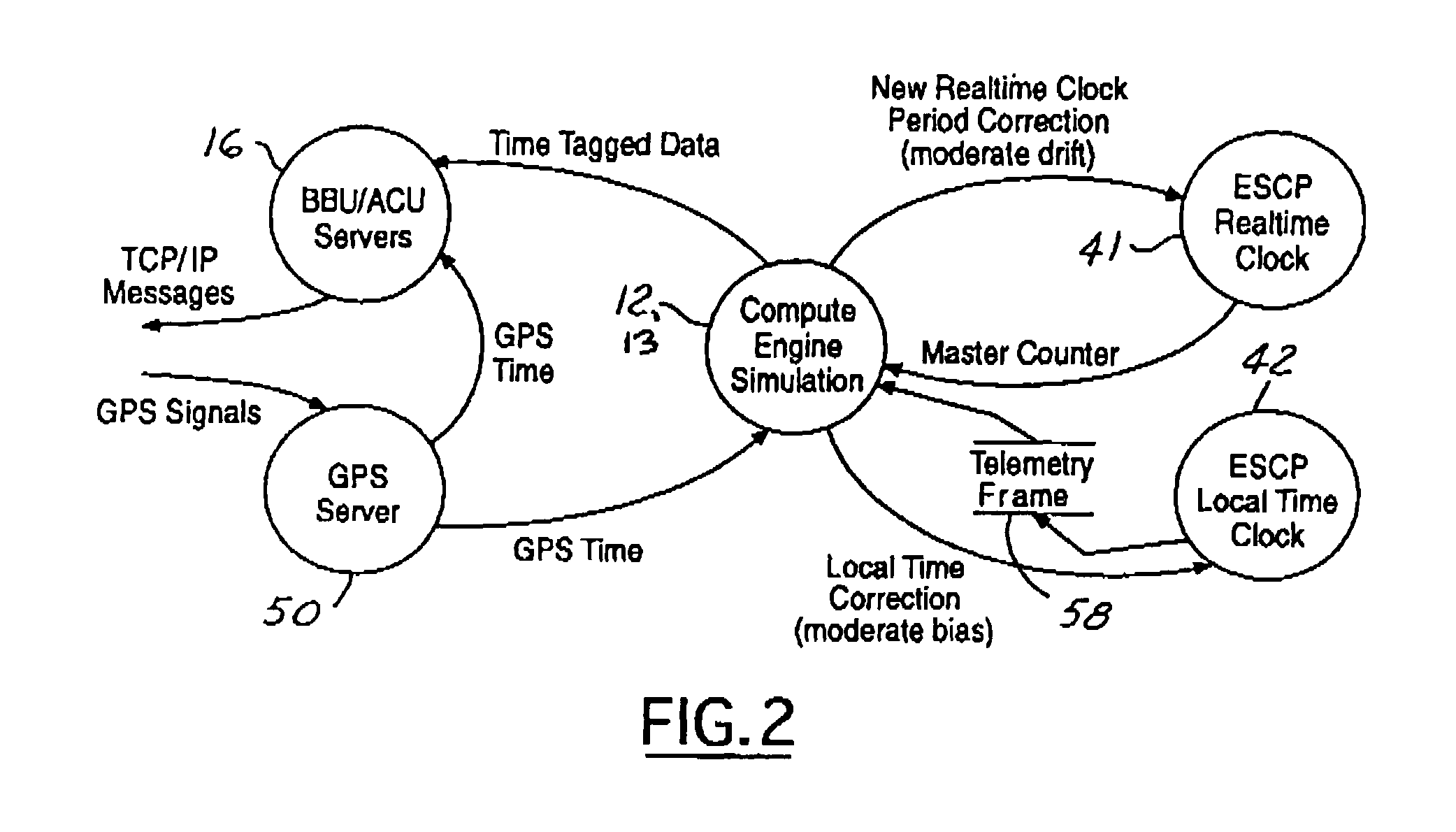
High fidelity time domain for spacecraft emulation systems
InactiveUS8370124B1Improve fidelityDuplicate precise behaviorDigital data processing detailsFluid pressure measurementSpace vehicle controlSystem dynamics
An emulation system includes a central time source generating a time reference and an emulated spacecraft control processor which contains an embedded processor that provides an emulated input / output interface to communicate simulated spacecraft data. The embedded processor processes the simulated spacecraft data and contains a real time clock engine having a real-time clock period. The system further has a first simulation that processes attitude control system data from the emulated spacecraft control processor to simulate an attitude control system of the spacecraft in real-time. The first simulation engine operative to produce sensor data for input to the emulated spacecraft control processor based on the simulated system dynamics and adjusts the real time clock period in response to the time reference.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
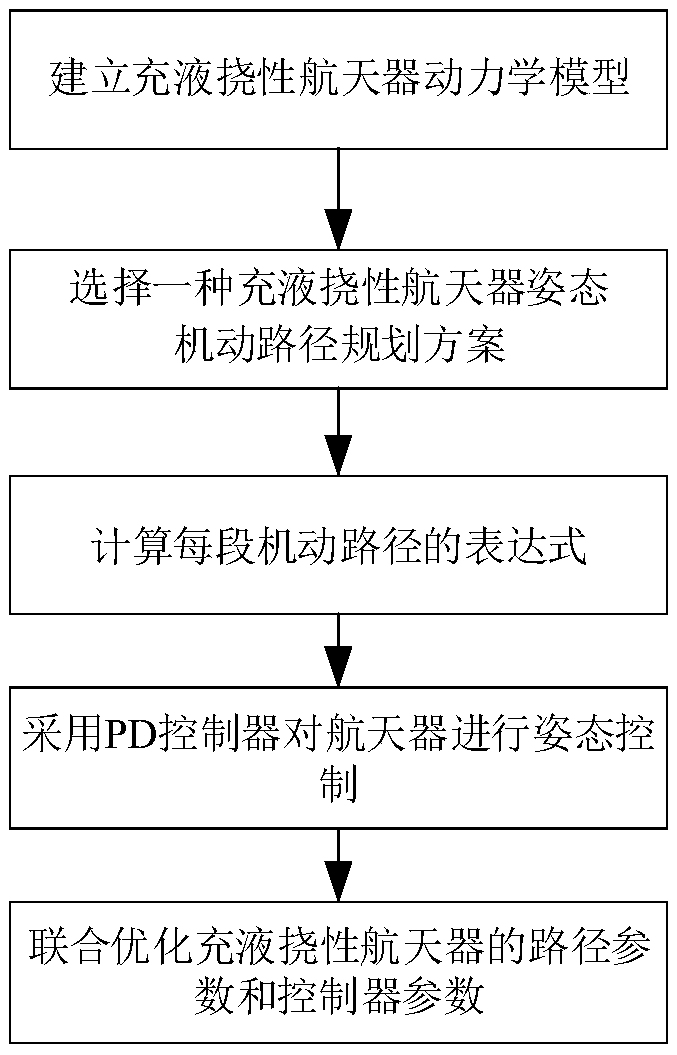
Rigid-flexible liquid coupling system attitude controller and maneuvering path combination optimization method
PendingCN108958275AFast maneuveringReduce the impact of attitude controlCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsSpace vehicle controlFlexible spacecraft
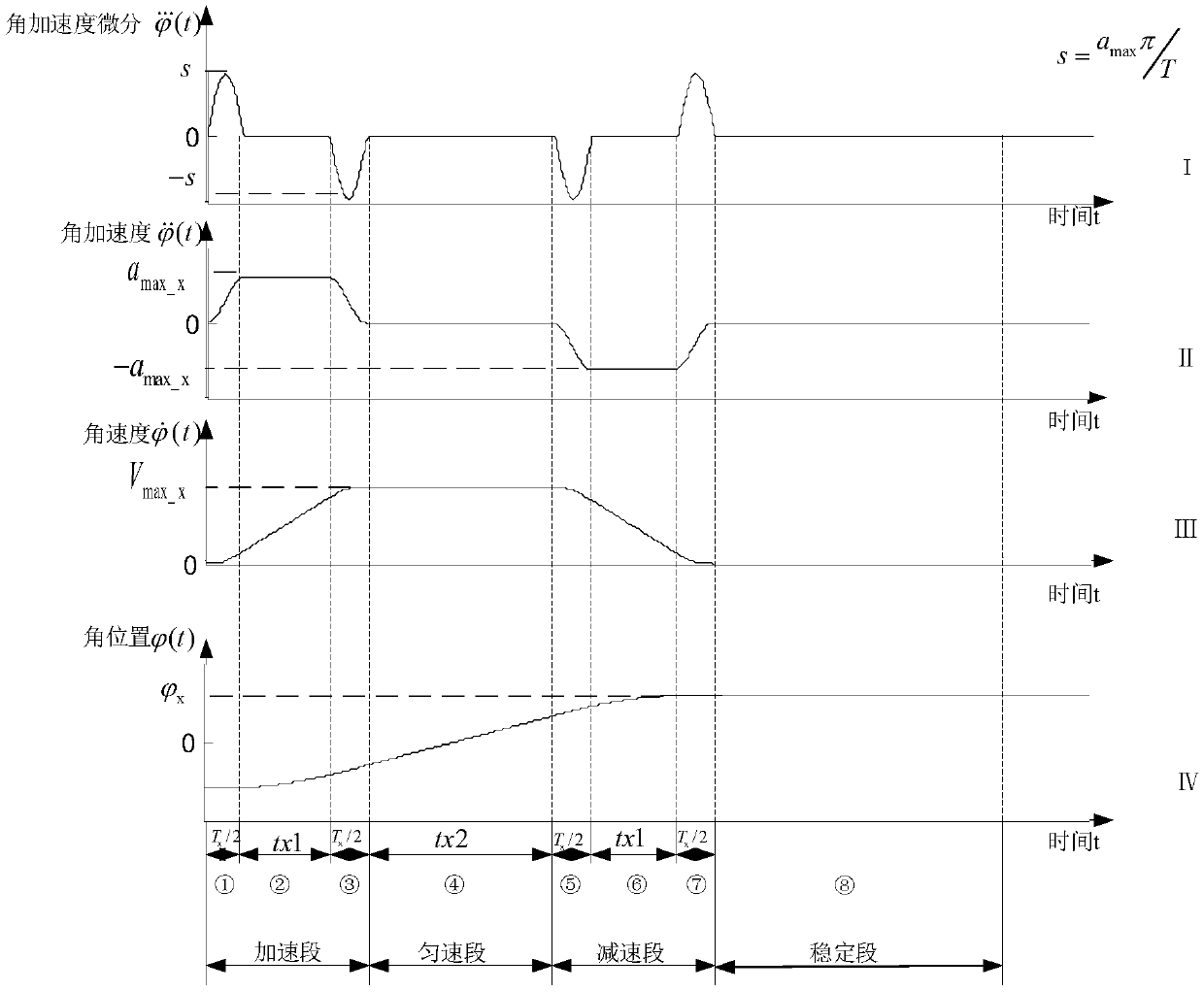
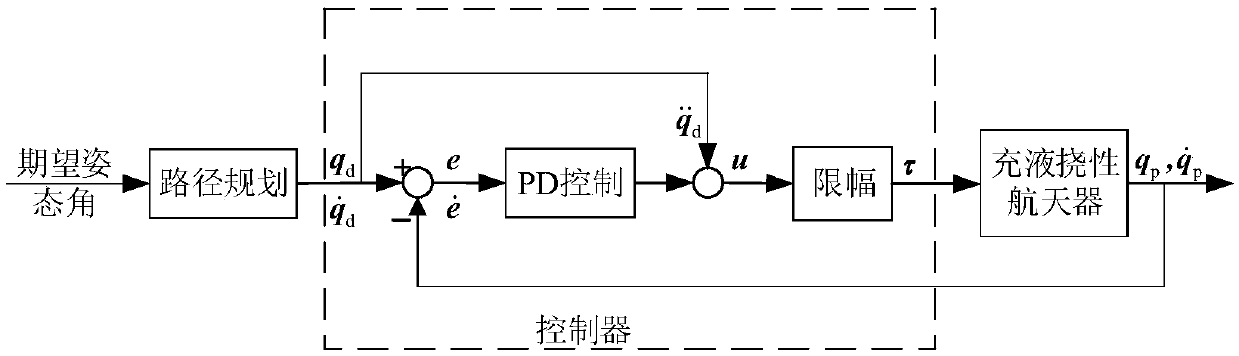
The present invention provides a rigid-flexible liquid coupling system attitude controller and maneuvering path combination optimization method. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a dynamical model of a liquid-filled flexible spacecraft; obtaining an angular acceleration curve, an angular speed curve and obtained multi-section angular position curve of the liquid-filled flexible spacecraft, and planning the attitude maneuvering path of the liquid-filled flexible spacecraft; calculating the expression of each section of the curve in the multi-section curve; employing a PDcontrol system to perform attitude control of the liquid-filled flexible spacecraft; and performing combined optimization of the parameters of the liquid-filled flexible spacecraft controller and themaneuvering path. The method reduces the motivation of the attitude maneuvering for the flexible accessory vibration and liquid shaking so as to achieve large-angle rapid maneuvering and rapid and stable control for the liquid-filled flexible spacecraft.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Vibration and loading combined device of steering engine room
ActiveCN108168812AVersatileLow costMachine part testingCosmonautic condition simulationsSpace vehicle controlEngineering
The invention relates to a vibration and loading combined device of a steering engine room, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft controllers. The combined device is capable of control surface loading and vibration clamping of a spacecraft. The device is composed of a vibration tool and a torsional moment loading tool. The vibration tool as a clamp can fix the steering engine room to avibration table by switching. Four elastic rod assemblies are mounted on the vibration tool, and elastic torsional moment loads are applied to four steering engines in a stern room simultaneously viatorsinoal deformation of elastic rods. The vibration and loading combined device is characterized by being multifunctional, low in cost, easy to dismount, simple in structure, smooth in load output, consistent in elastic coefficients, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING AUTOMATION CONTROL EQUIP INST
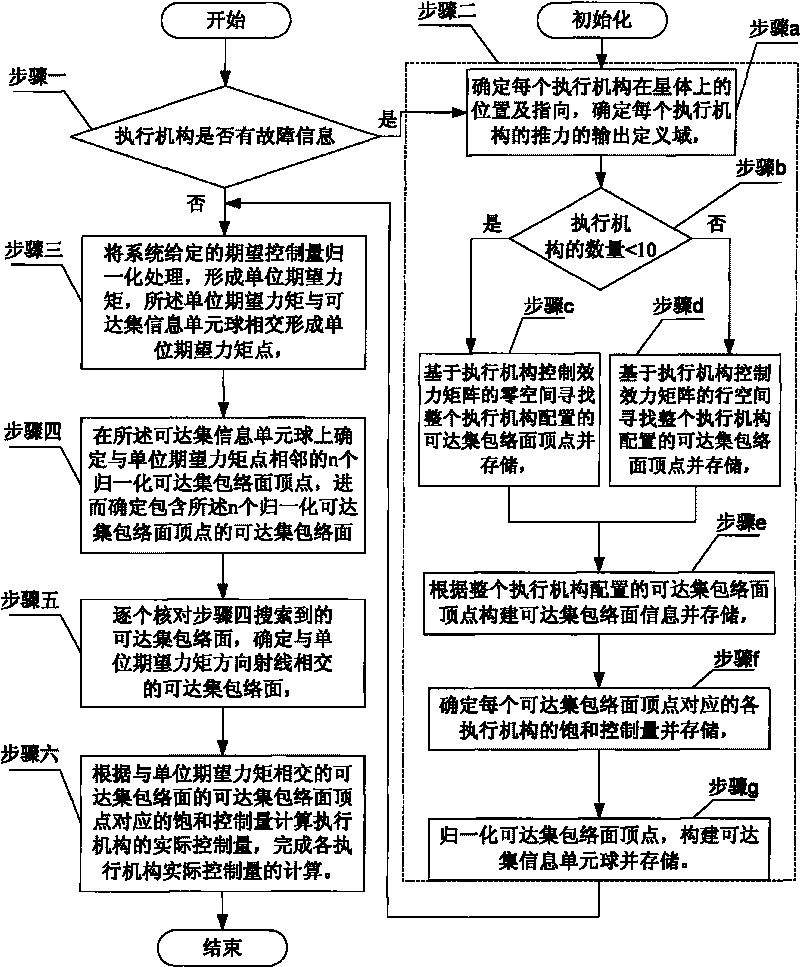
Executing agency normalized reachable set peak -based control allocation method
InactiveCN101695961AReduce computing timeNarrow searchSpacecraft guiding apparatusSpace vehicle controlComputer science
The invention discloses an executing agency normalized reachable set peak-based control allocation method, which belongs to the field of spacecraft control, and aims at solving the problem that the allocation control method of the traditional redundancy executing agency configuration scheme cannot achieve large allocating space, strong real-time calculating capability and small memory space occupation at the same time. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: 1, judging whether an executing agency has fault information, wherein if an executing agency has fault information, a step 2 is performed, or a step 3 is performed; 2, calculating and updating the reachable information of the executing agent offline; 3, normalizing an expected control quantity given by a system, and forming an expected unit torque point by intersecting with a reachable information unit ball; 4, determining n peaks of a normalized reachable enveloping surface adjacent to the expected unit torque point on said reachable information unit ball; 5, checking one by one to determine a reachable enveloping surface intersected with a ray in the direction of the expected unit torque; and 6, finishing calculating the control quantity of each executing agency according to the control quantity corresponding to the peaks of the reachable enveloping surface.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
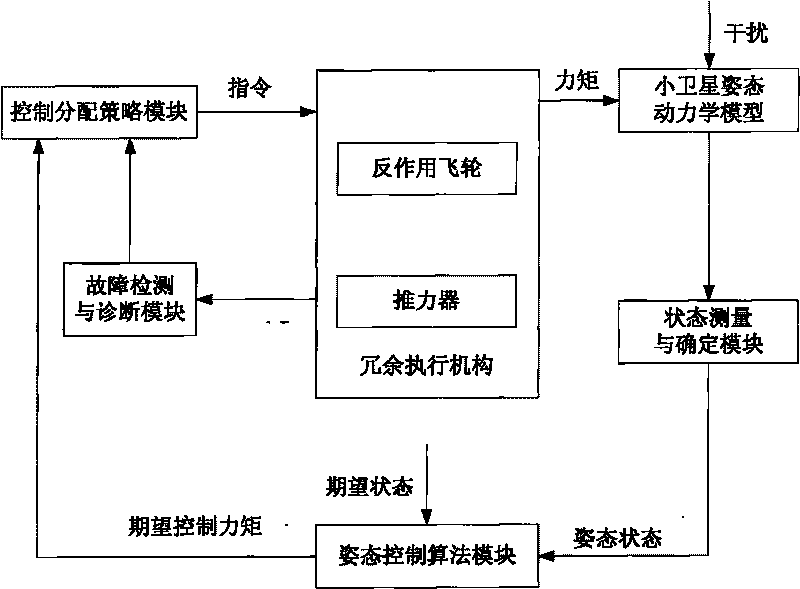
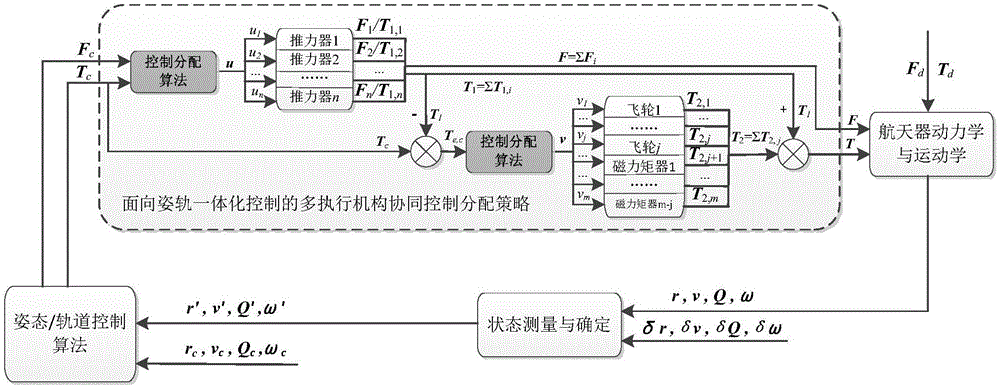
Attitude-orbit integrated control oriented multi-execution mechanism cooperative control distribution method
ActiveCN105892478AEffectively completedImprove efficiencyAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsControl orientedSpace vehicle control
The invention discloses an attitude-orbit integrated control oriented multi-execution mechanism cooperative control distribution method and relates to a multi-execution mechanism cooperative control distribution method. The invention is aimed at solving the problems of low utilization rate of thruster fuel and little mutual cooperation among execution mechanisms of existing attitude-orbit integrated control oriented distribution strategy. In the invention, the orbit control expectation control force and the attitude control expectation control torque are distributed among the thrusters enabling both orbit control and attitude control; in the distribution process, the needs of track control are met first, and a thruster control distribution scheme proximal to the attitude control expectation control moment is optimally solved without additionally consuming redundant fuel; and after that, the remaining expectation control moment only can be distributed among the attitude-control execution mechanisms. While the attitude-orbit integrated control task is finished, the fuel consumption of the thruster is reduced, the burden on the attitude-control execution mechanisms such as flywheels and magnetic moments is alleviated, and the in-orbit life of spacecraft is prolonged. The method disclosed by the invention is applied to the field of spacecraft control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
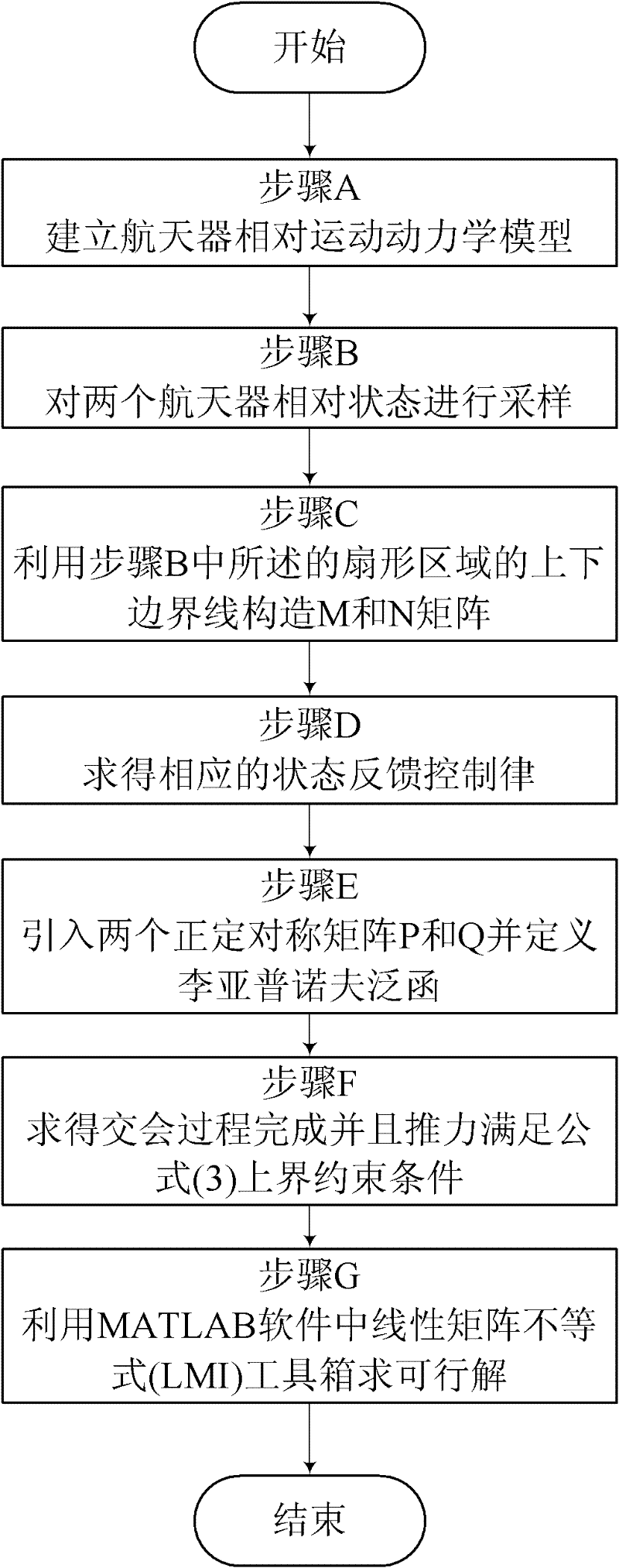
Sampling control method for relative motion of spacecrafts
InactiveCN102354218AHigh precisionImprove securityPosition/course control in three dimensionsSpace vehicle controlPositive definite symmetric matrix
The invention relates to a sampling control method for a spacecraft, more particularly to a sampling control method for relative motion of spacecrafts. According to the current sampling control method for a spacecraft relative motion, a processing period and a deviation of a digital controller are neglected, so that an accuracy and security of a spacecraft track are influenced; however, the above-mentioned problems can be solved with utilization of the sampling control method provided in the invention. The method comprises the following steps that: step A, a dynamical model on a spacecraft relative motion is established; step B, sampling is carried out on relative states of two spacecrafts; step C, an M matrix and an N matrix are constructed by utilizing an upper boundary line and a lowerboundary line of a sector area described in the step B; step D, a corresponded state feedback control law is obtained; step E, two positive definite symmetric matrixes P and Q are introduced and a following lyapunov function is defined; step F, an intersection process is obtained and is completed, wherein a trust satisfies a formula upper boundary constraint condition (3); and step G, a feasible solution is obtained by utilizing an LMT of MATLAB software. According to the invention, the sampling control method can be applied in design of a spacecraft controller.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
System for counteracting a disturbance in a spacecraft
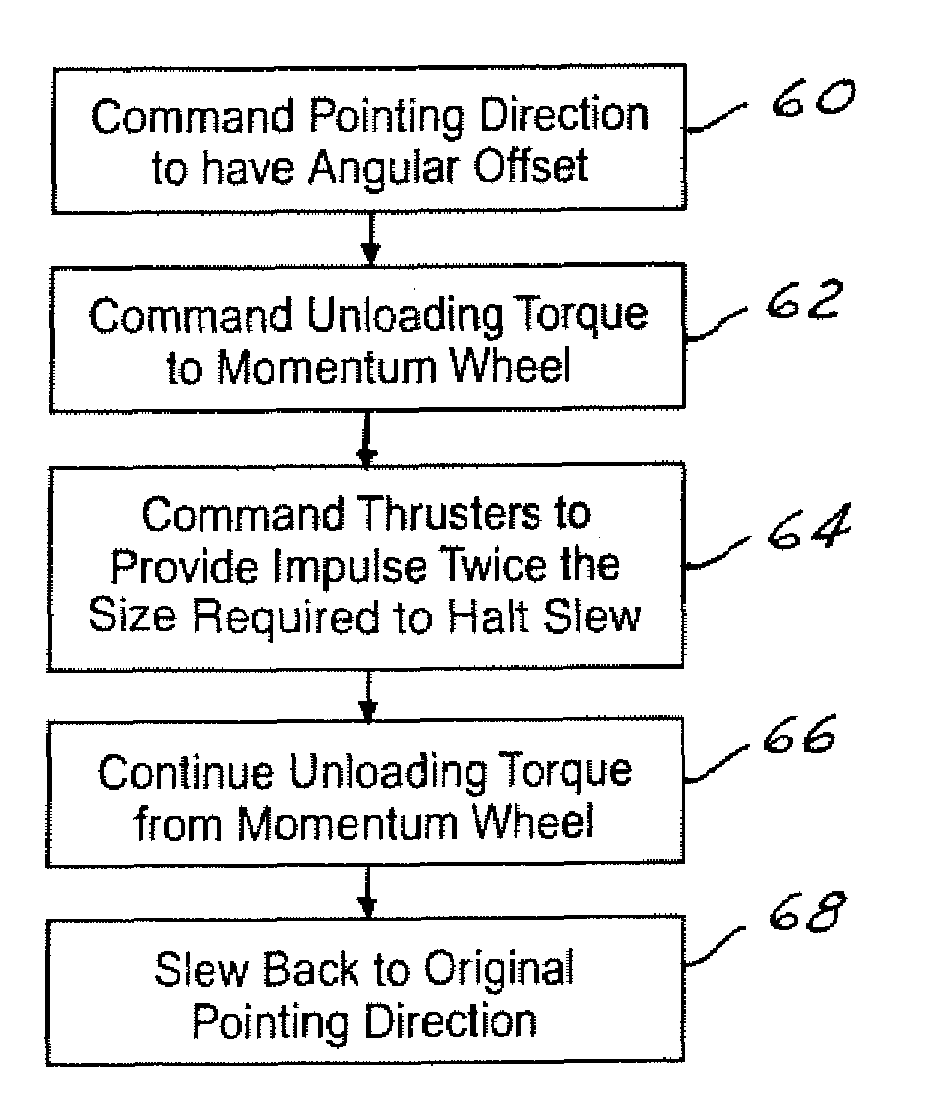
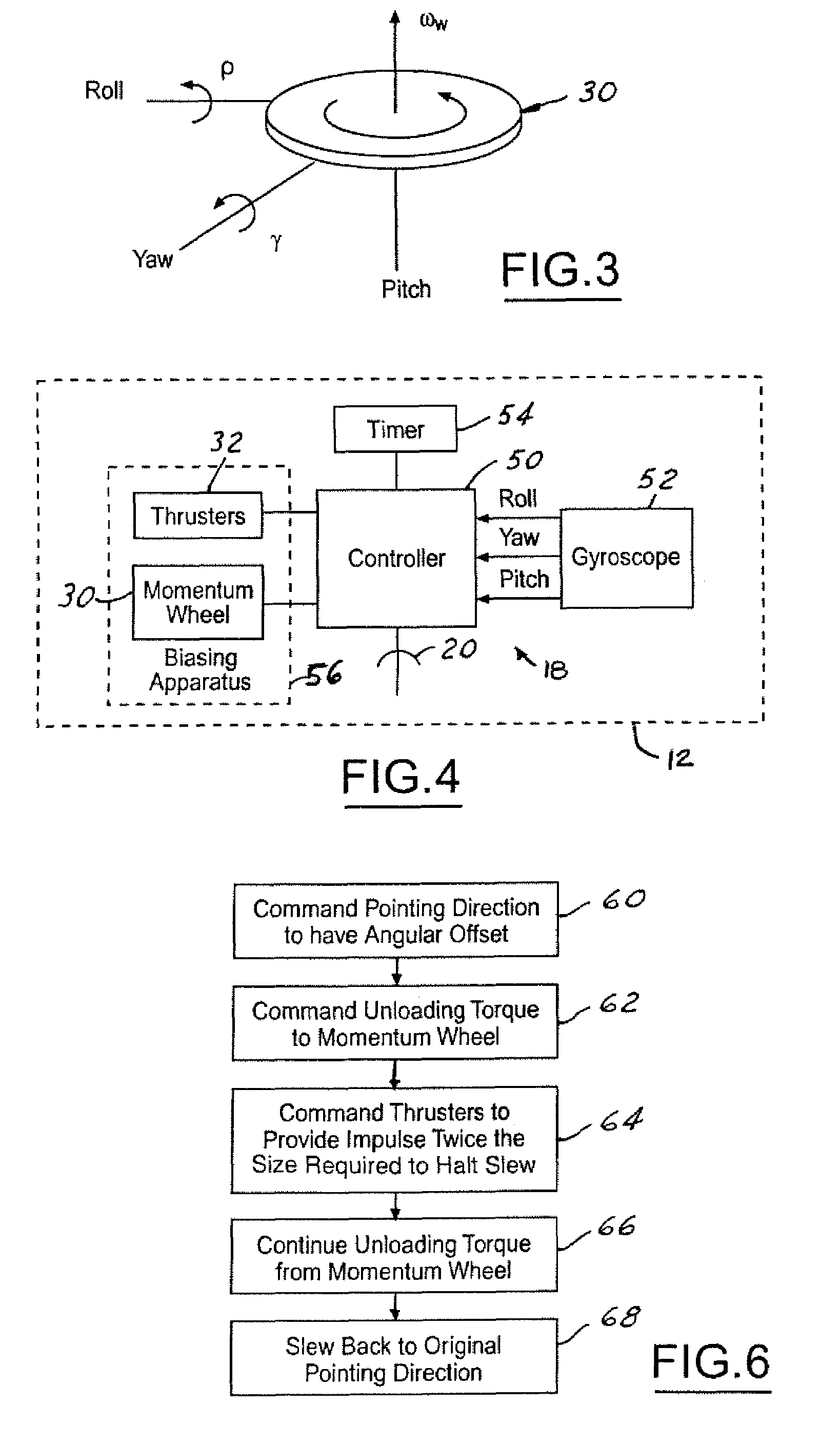
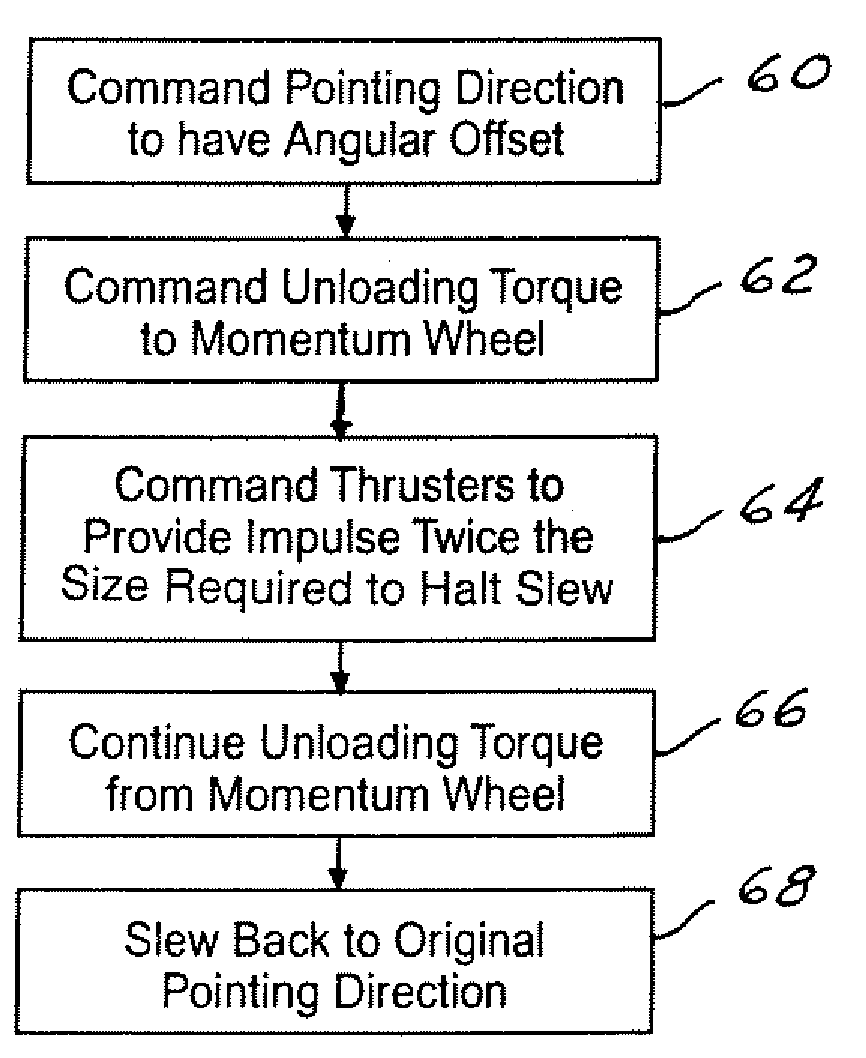
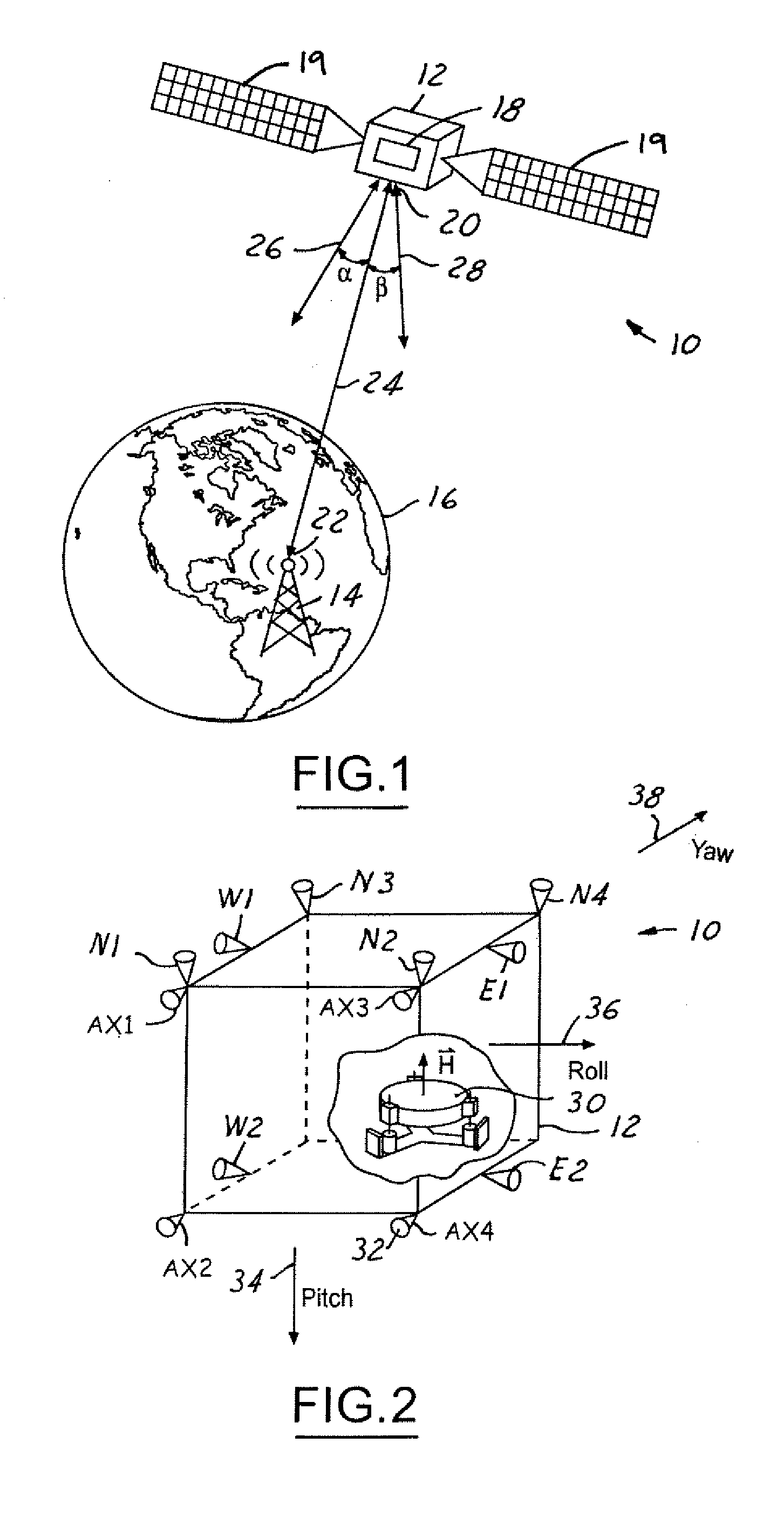
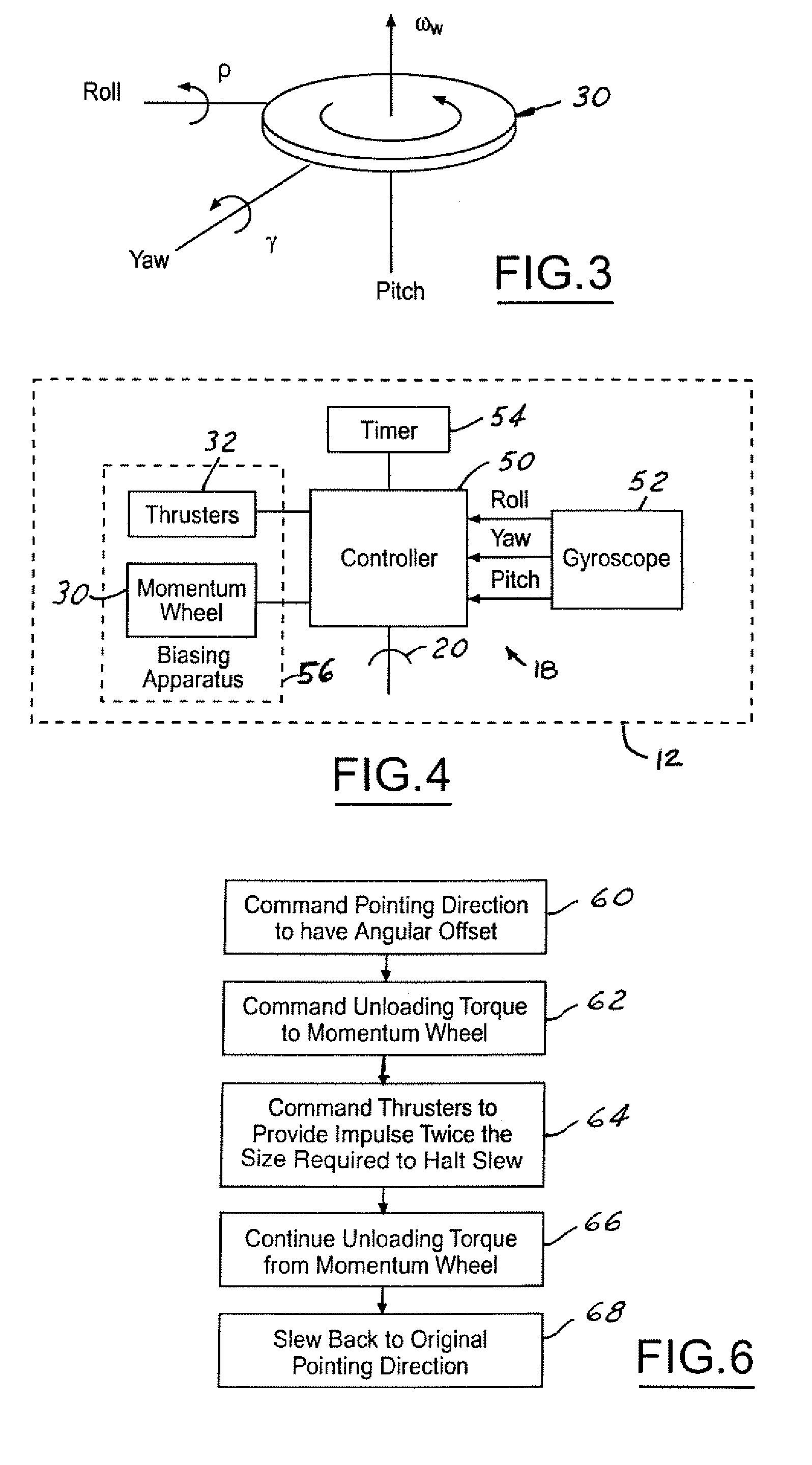
ActiveUS6921049B2Extended burn timeReduce the number of timesCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsMomentumSpace vehicle control
A system for counteracting a disturbance in a spacecraft includes a biasing apparatus that is coupled to the spacecraft and a spacecraft controller within the spacecraft. The disturbance has a known sign, magnitude and time. The biasing apparatus controls the biasing apparatus to place the spacecraft in a first dynamic state or position as a function of the sign, magnitude, and time of the disturbance. The controller also controls the spacecraft to a second dynamic state as a function of the known sign, magnitude, and time so that the spacecraft is oriented in a position other than the desired orientation so that after the disturbance the spacecraft is oriented in the desired orientation in response to the disturbance. The biasing apparatus may comprise a momentum wheel and the disturbance may comprise thrusting firing used for controlling momentum dumping.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
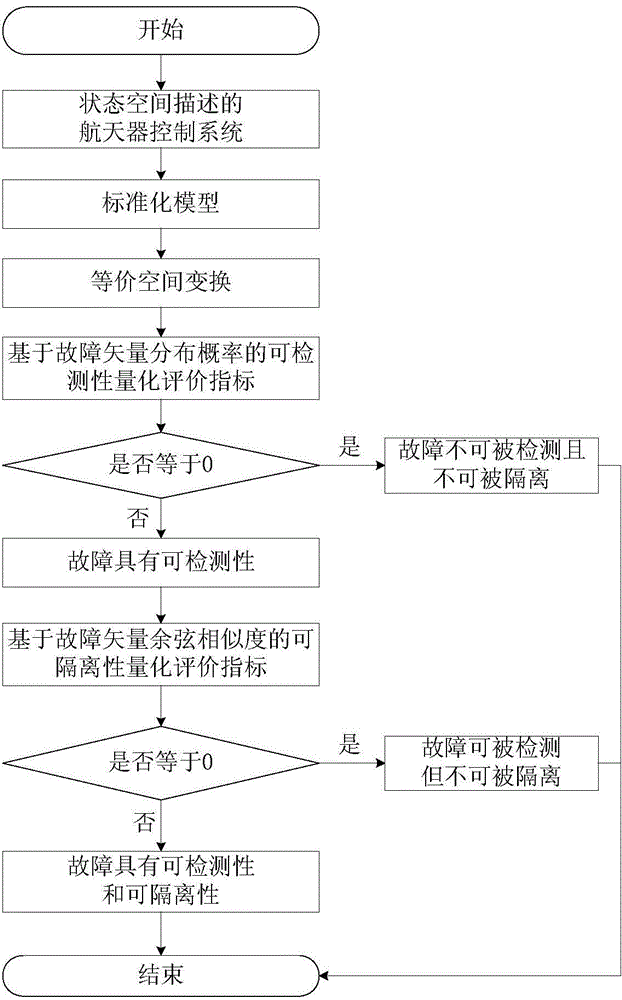
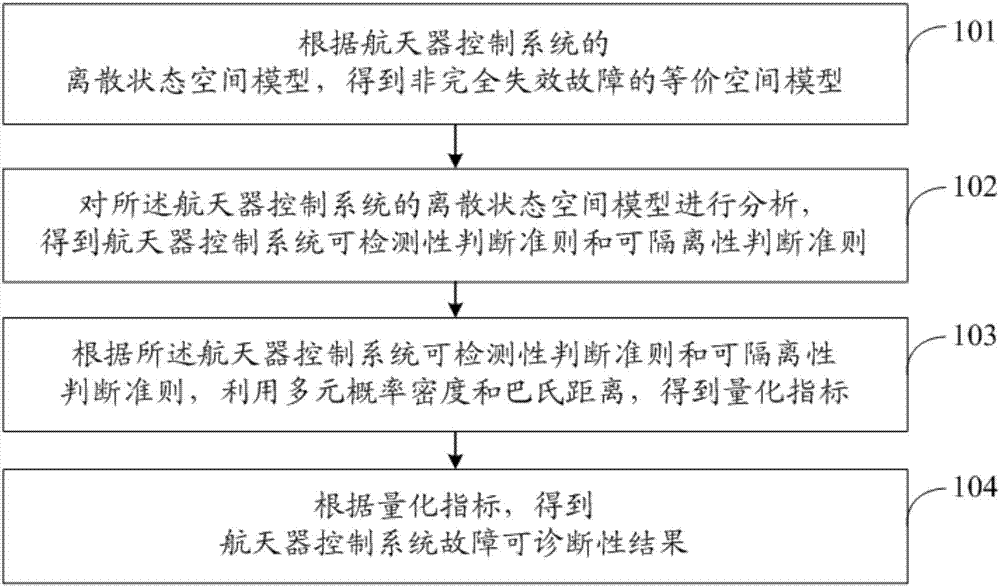
Diagnostic determination method for spacecraft control system under influence of noise
ActiveCN104571087AAccurately describe fault diagnosability performanceImprove accuracyElectric testing/monitoringSpecial data processing applicationsSpace vehicle controlInterference factor
The invention provides a diagnostic determination method for a spacecraft control system under influence of noise. First, a multivariate probability distribution statistic model of the spacecraft control system is built through a standard model and an equivalent space method; then a detectability index is obtained; and fault detectability is determined; finally, an isolability index is obtained, and the fault isolability is determined. According to the diagnostic determination method, influence of process noise, observation noise and other interference factors on diagnostic performance are fully taken into consideration, fault diagnosis algorithms are not required to be designed, and the fault detectability and the isolability can be determined according to system information including kinetics, kinematics, a controller model and the like of the spacecraft control system and the configuration and installation condition of a sensor and an actuator, the fault diagnosis process of the spacecraft control system is simplified, meanwhile, a theoretical basis can be provided for design of a diagnosis algorithm, the design method of the spacecraft control system is optimized, and the controllability of the spacecraft control system is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
System for counteracting a disturbance in a spacecraft
ActiveUS20050116111A1Extended burn timeReduce the number of timesCosmonautic vehiclesRocket engine plantsMomentumSpace vehicle control
A system for counteracting a disturbance in a spacecraft includes a biasing apparatus that is coupled to the spacecraft and a spacecraft controller within the spacecraft. The disturbance has a known sign, magnitude and time. The biasing apparatus controls the biasing apparatus to place the spacecraft in a first dynamic state or position as a function of the sign, magnitude, and time of the disturbance. The controller also controls the spacecraft to a second dynamic state as a function of the known sign, magnitude, and time so that the spacecraft is oriented in a position other than the desired orientation so that after the disturbance the spacecraft is oriented in the desired orientation in response to the disturbance. The biasing apparatus may comprise a momentum wheel and the disturbance may comprise thrusting firing used for controlling momentum dumping.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Magnetic propelling device for spacecraft
InactiveCN104554825ASimple structural designMaximum total coil currentCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusPower flowSpace vehicle control
The invention discloses a magnetic propelling device for a spacecraft. The structural design is simple, the propelling device adopts a strip-shaped coil structure, and a higher total coil current can be generated through multi-circle wire-wrap connection of a low current wire; the direction and size of pushing force can be adjusted along with the direction of the coil and the size of the coil current, the direction of the pushing force is vertical to the direction of the coil current, and the spacecraft adopting the magnetic propelling device disclosed by the invention is simpler to control. Compared with a magnetic moment propelling method, the pushing force in a propelling method of the magnetic propelling device for the spacecraft is higher under the environments of equal current intensity and earth magnetic field; moreover, a plurality of propelling devices can be arranged in an overlapped mode for combined use, so that high pushing force propelling of the spacecraft is realized; when the propelling device works, a magnetic field is generated around, space charged particles are deflected under the effect of the magnetic field when getting close to the spacecraft, and the device has certain shielding and protecting effects on the space charged particles for the spacecraft; moreover, the magnetic moment sizes of the propelling devices counteract with each other, and no extract magnetic moment effect is generated for the spacecraft.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Diagnostic quantification method with consideration of incomplete failure of spacecraft control system
ActiveCN107544460AImprove fault diagnosis abilitySimple designElectric testing/monitoringSpace vehicle controlSystem configuration
The present invention discloses a diagnostic quantification method with the consideration of a incomplete failure of a spacecraft control system. A diagnostic quantification problem is transformed into a multivariate distribution similarity judgment problem in mathematical statistics, and an equivalent space model of the incomplete failure is obtained. Then concrete judgment criteria of the detectability and isolability of the incomplete failure are given. Finally, according to the judgment criteria, a diagnostic quantification index of the incomplete failure is proposed by using a Bhattacharyya distance, and an analysis result is obtained based on the diagnostic quantification index. The influence of system uncertainty in spacecraft control system on-orbit actual work is considered, according to the obtained result, a designer can conveniently understand weak links of the system, the guide of the design of a diagnosis algorithm and system configuration is facilitated, thus the fault diagnosis ability of the spacecraft control system can be improved to the maximum at a ground design stage, and finally a target of improving the system overall comprehensive design ability is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
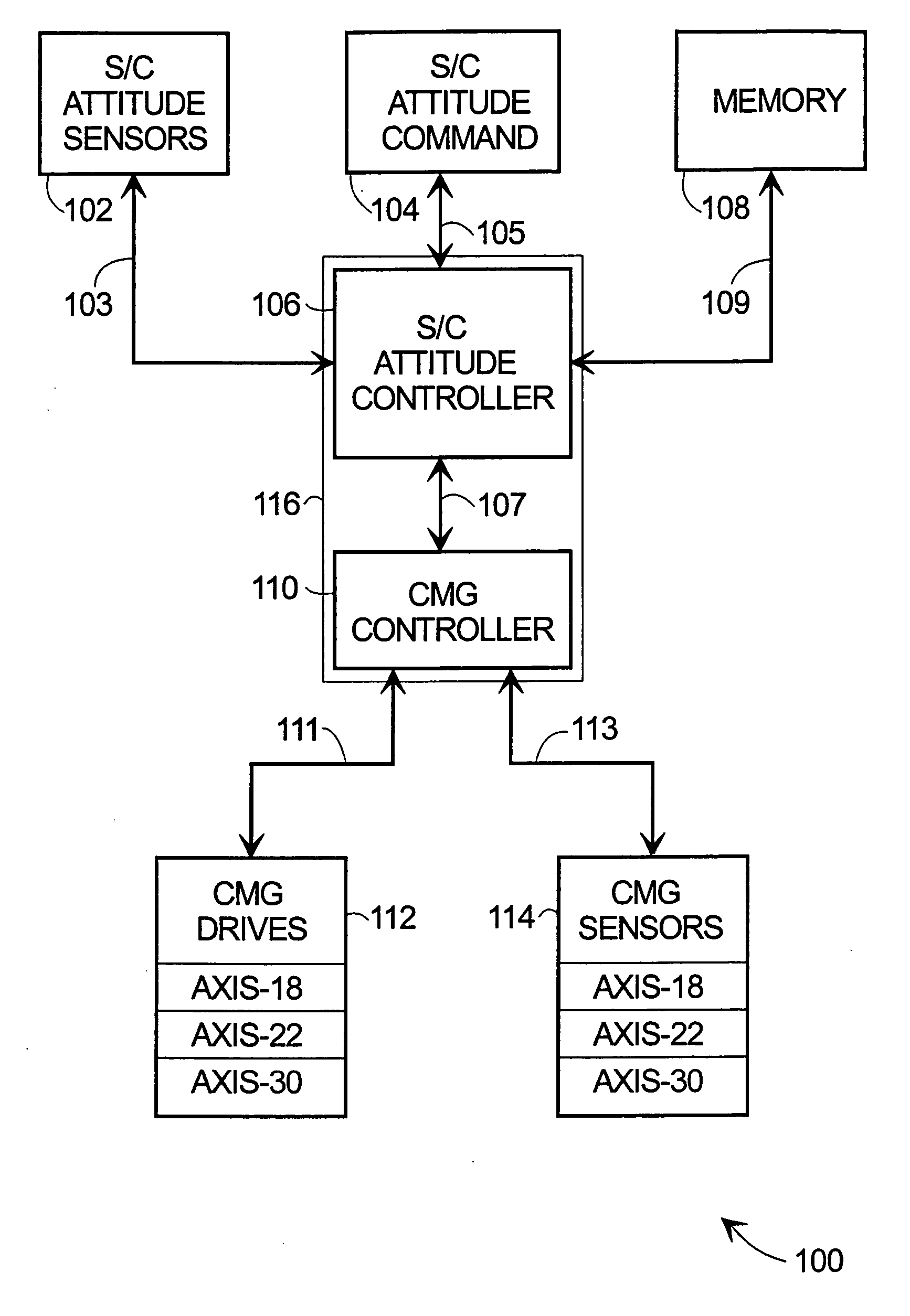
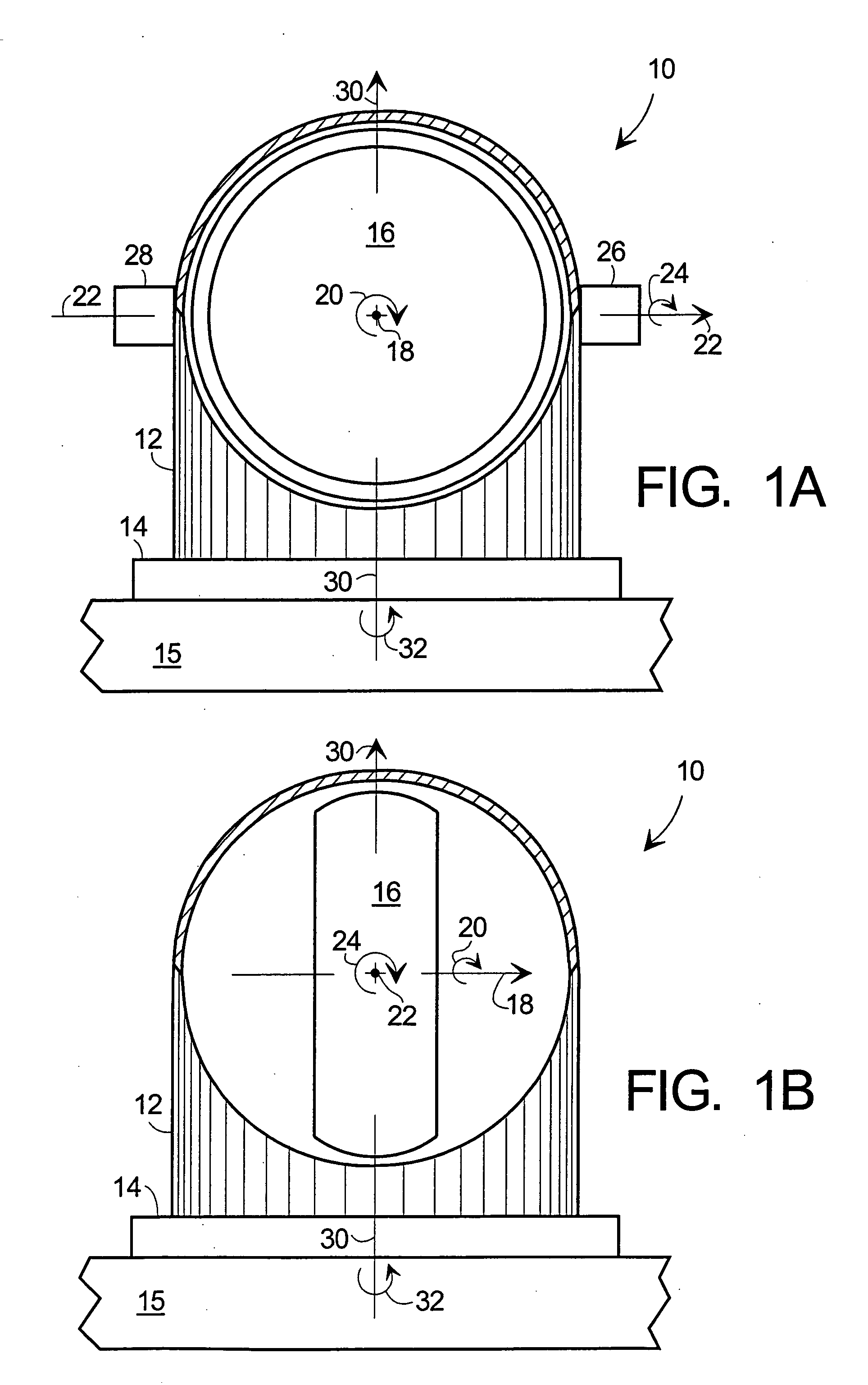
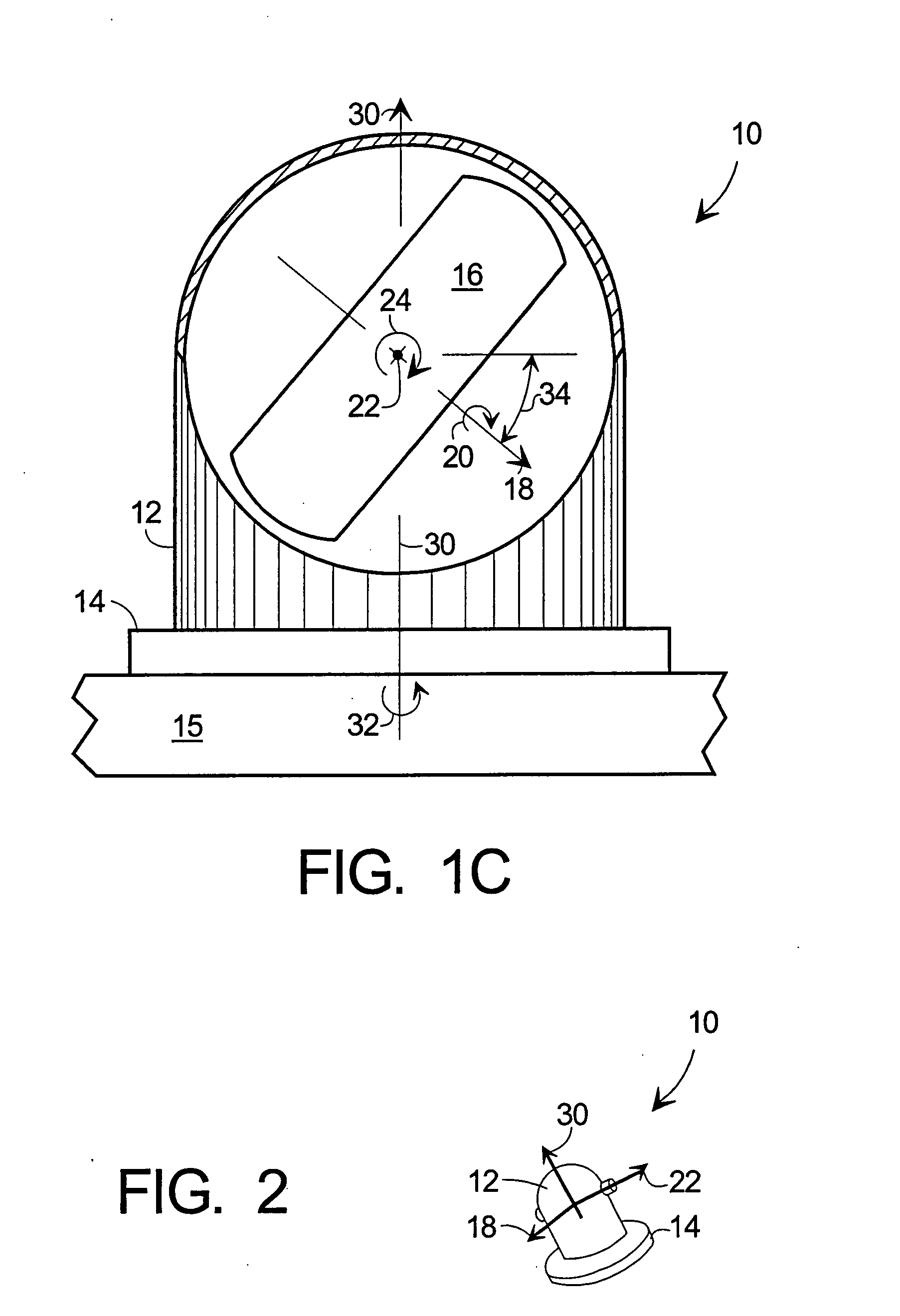
Dynamic CMG array and method
ActiveUS20050125111A1Cosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsSpace vehicle controlEngineering
Methods and apparatus are provided for reorienting control moment gyros (CMGs) to compensate for CMG failure or change in spacecraft (S / C) mass properties or mission. An improved CMG comprises a drive means for rotating the CMG around an axis not parallel to the CMG gimbal axis. Releasable clamps lock the CMG to the spacecraft except during CMG array reorientation. CMGs arrays are combined with attitude sensors, a command module, memory for storing data and programs, CMG drivers and sensors (preferably for each CMG axis), and a controller coupling these elements. The method comprises determining whether a CMG has failed or the S / C properties or mission changed, identifying the working CMGs of the array, determining a new array reorientation for improved spacecraft control, unlocking, reorienting and relocking the CMGs in the array and updating the S / C control parameters for the new array orientation.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Flexible spacecraft adaptive attitude control law based on modified Rodrigo parameters
InactiveCN107678281AResolve inhibitionImprove real-time performanceCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsKinematics equationsKinematics
The invention provides a flexible spacecraft adaptive attitude control law based on modified Rodrigo parameters, which includes the following steps: S1, establishing a kinematics equation and a dynamics equation of a flexible spacecraft based on modified Rodrigo parameters; and S2, using an adaptive back-stepping method to design an adaptive attitude controller based on a modal observer. The beneficial effects of the invention are as follows: the problem that a flexible spacecraft is suppressed by interference signals is solved, and attitude control is realized; and through computation using modified Rodrigo parameters (MRPs), the amount of computation can be reduced by 20-40% compared with computation using quarternions, and the real-time performance of control on a flexible spacecraft can be better enhanced.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
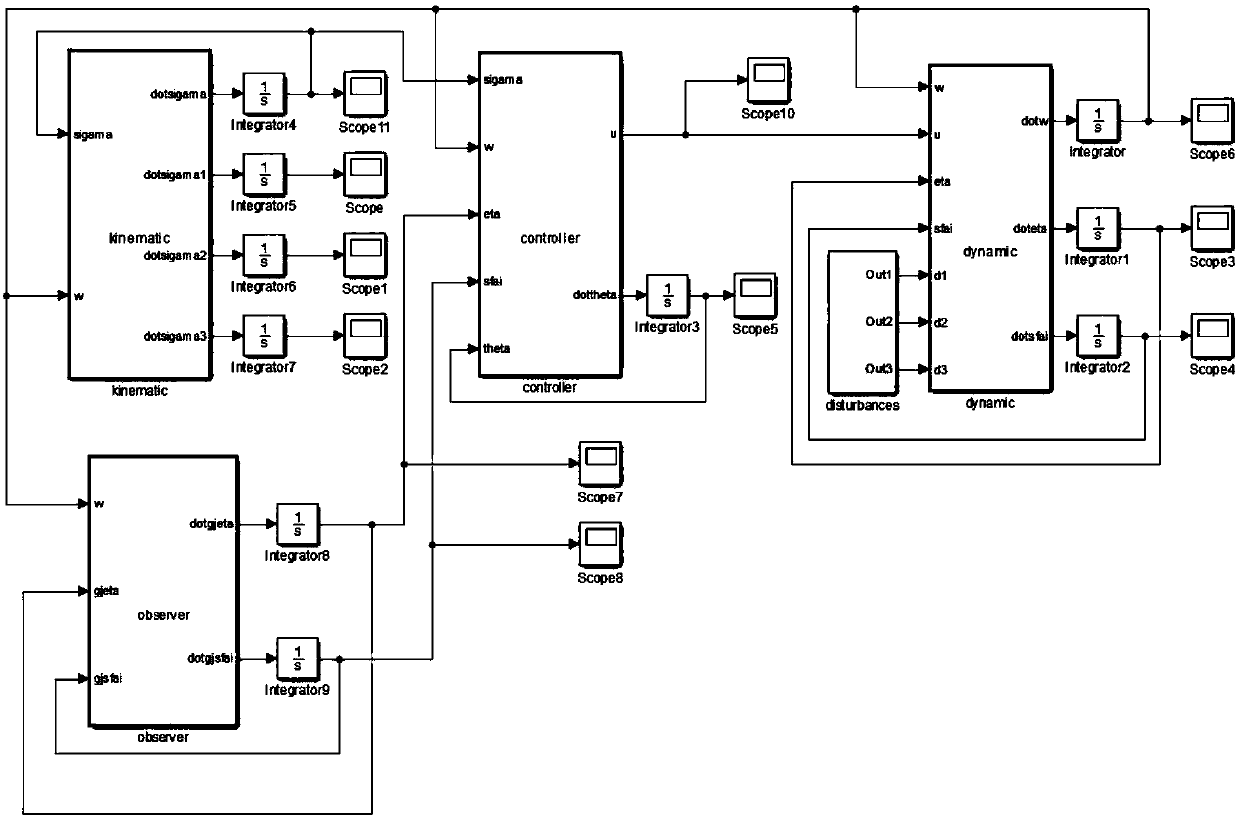
Spacecraft attitude stability control real-time simulation verification and three-dimensional demonstration method
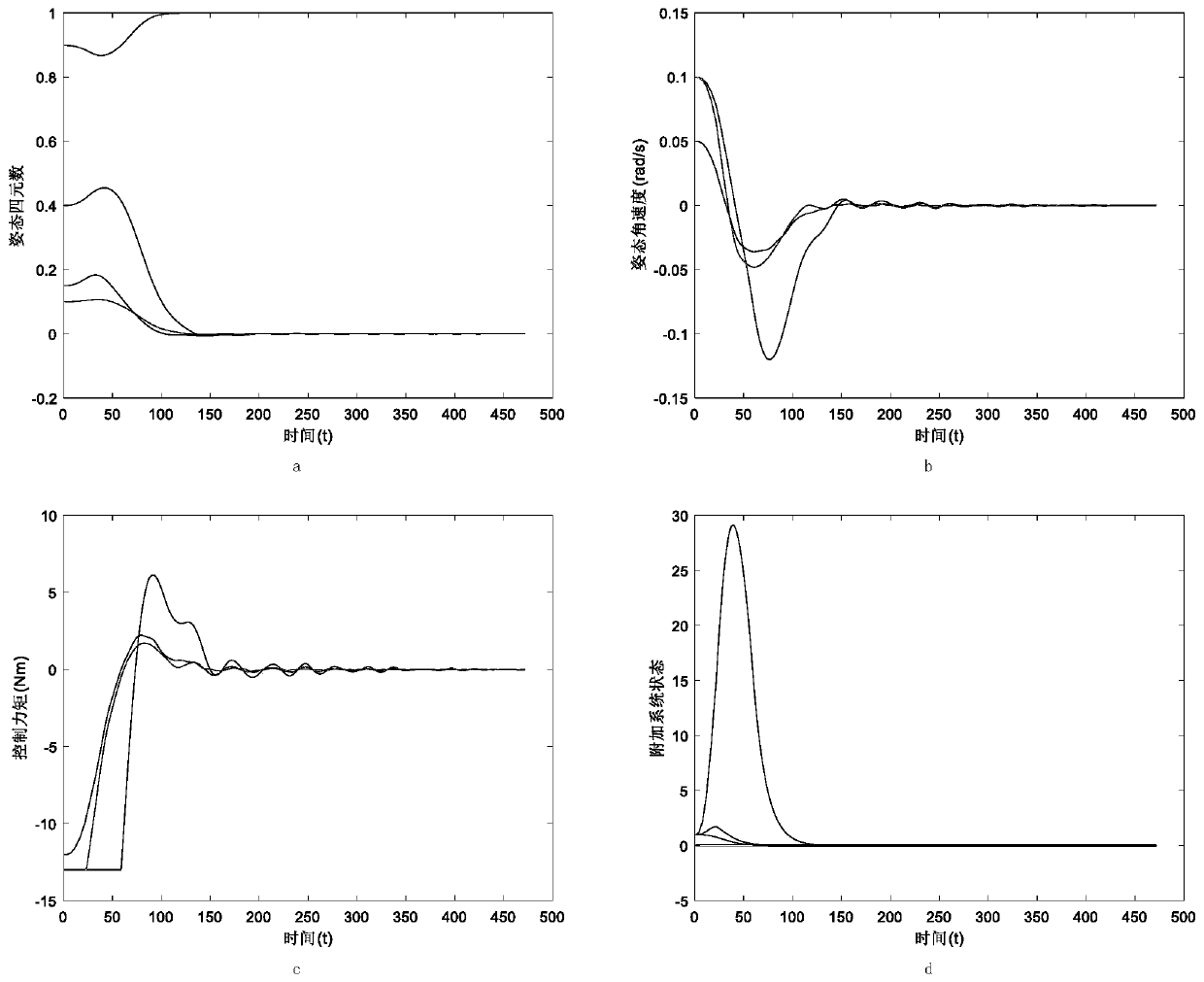
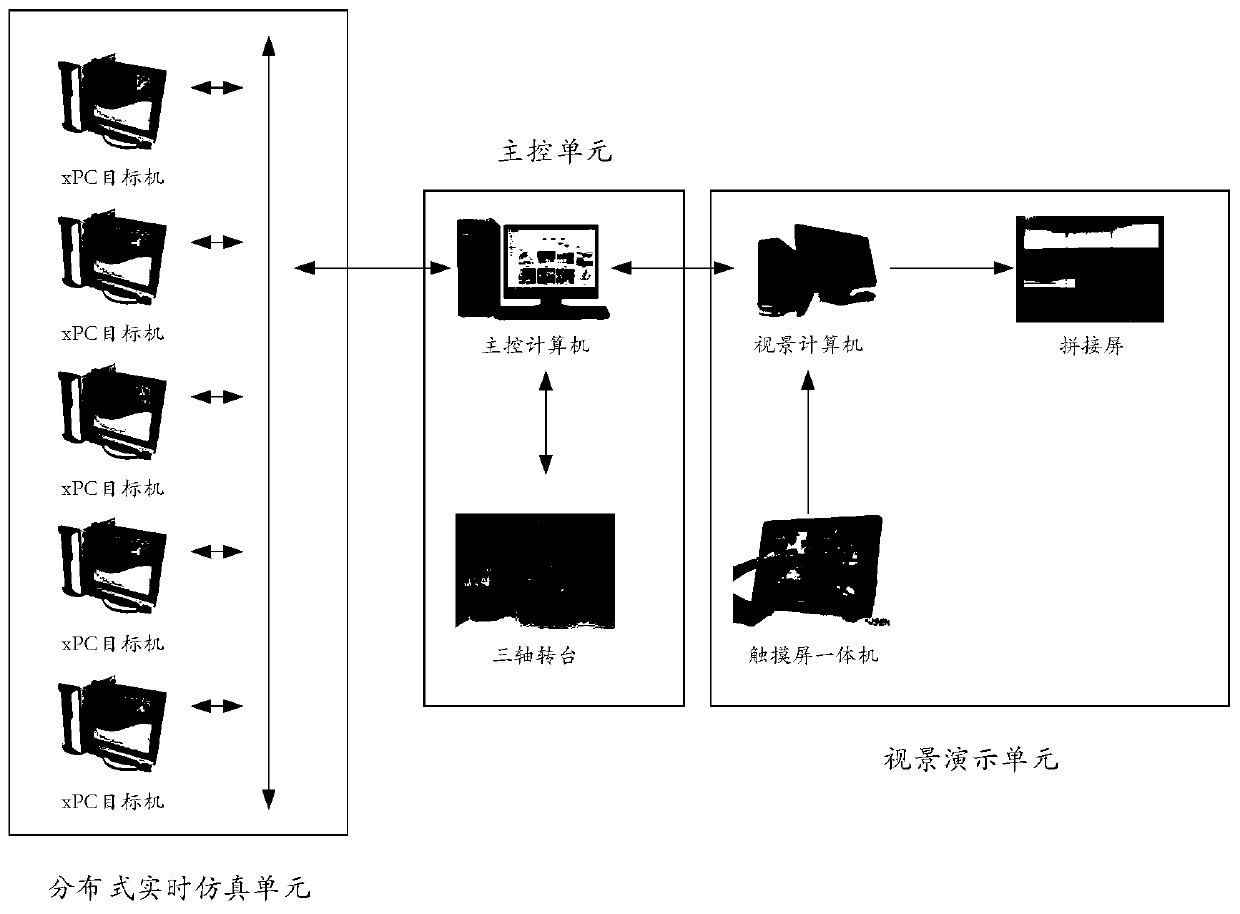
ActiveCN111191374AGet simulation dataGuaranteed reliabilityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationReal-time simulationSpace vehicle control
The invention relates to the field of complex spacecraft control technologies and simulation verification, and aims to perform real-time simulation verification and achieve the purpose of verifying the real-time performance, safety and reliability of a designed control algorithm. Therefore, the technical scheme adopted by the invention is a spacecraft attitude stability control real-time simulation verification and three-dimensional demonstration method, which comprises the following steps: 1, finite time control algorithm design under input constraints: designing a finite time additional system dynamic state, and designing a controller by combining backstepping control on the basis to realize finite time attitude stability control of a spacecraft; 2, structural design and construction ofa spacecraft real-time simulation platform: performing structural design and construction work of the spacecraft real-time simulation platform according to the control algorithm verification requirement and the spacecraft control structure proposed in the step 1; and 3, design and realization of spacecraft master control software. The method is mainly applied to complex spacecraft control design occasions.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
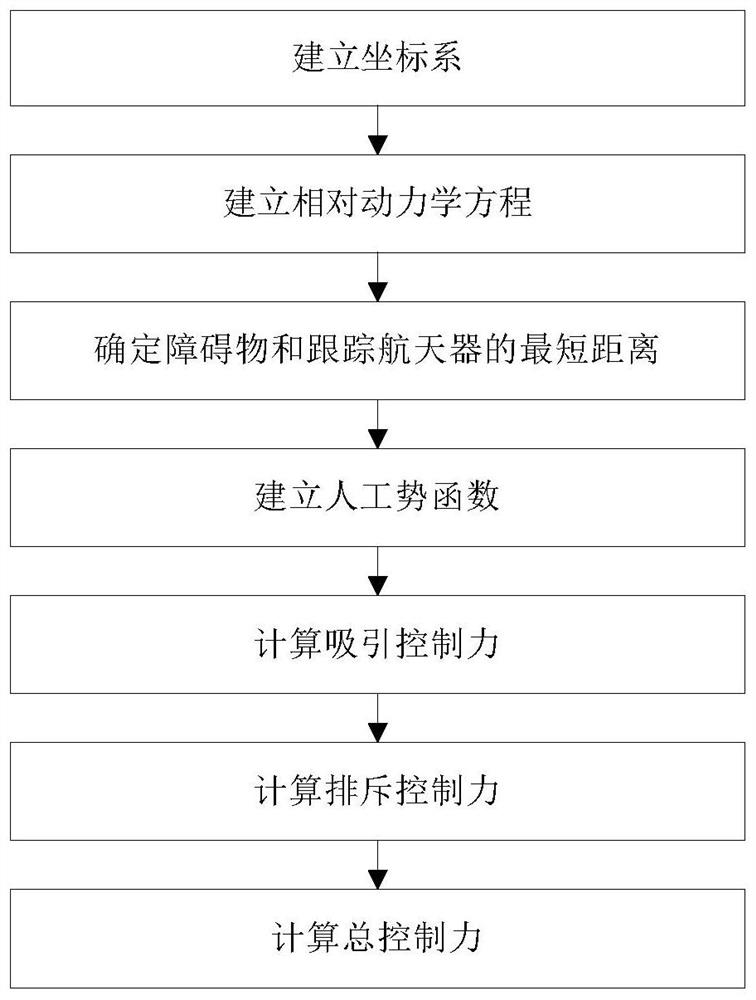
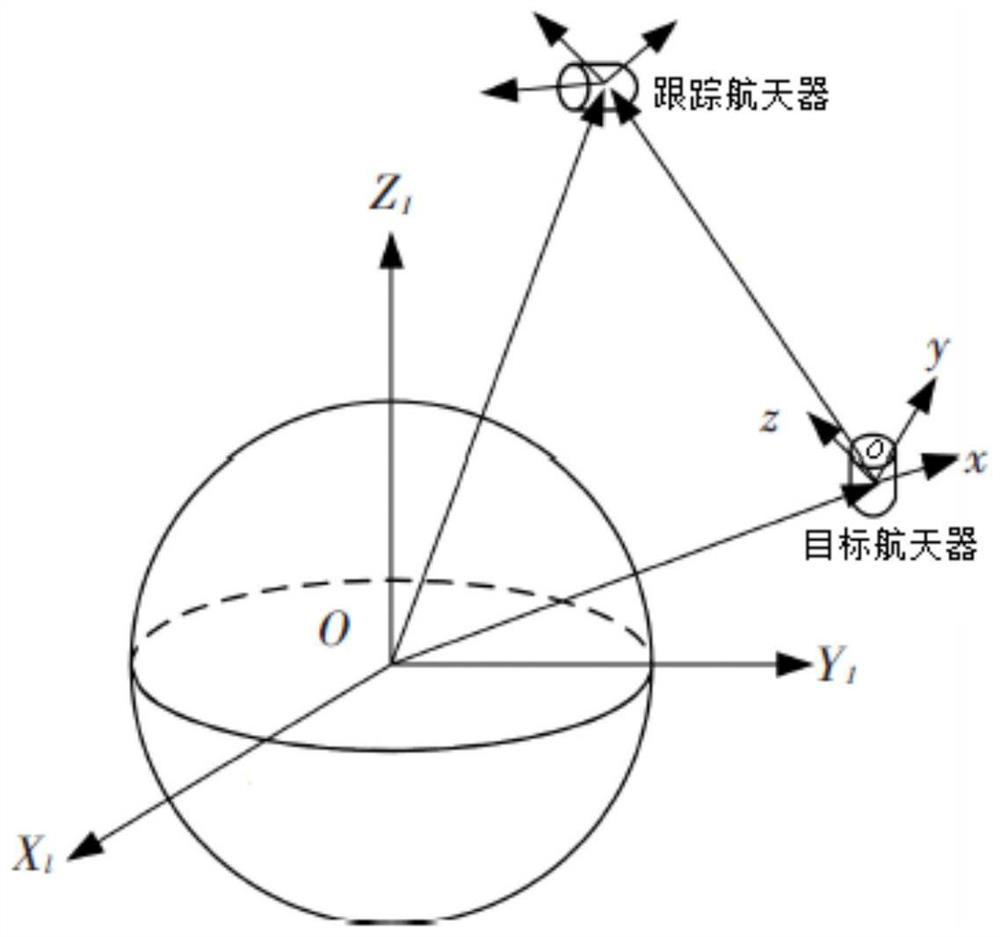
Spacecraft obstacle avoidance control method based on ellipsoid description
InactiveCN112000132AHigh control precisionReduce consumption rateCosmonautic vehiclesTarget-seeking controlSpace vehicle controlKinetics equation
The invention discloses a spacecraft obstacle avoidance control method based on ellipsoid description. The method is used for achieving autonomous obstacle avoidance of a target spacecraft and a tracking spacecraft and comprises the steps: establishing a coordinate system; establishing a relative kinetic equation; determining the shortest distance between an obstacle and the tracking spacecraft; establishing an artificial potential function; calculating an attraction control force; calculating a repulsion control force and calculating a total control force. According to the spacecraft obstacleavoidance control method based on ellipsoid description, the ellipsoid is adopted to describe the appearances of the spacecraft and the obstacle, and the modeling precision can be improved so as to improve the spacecraft control precision; meanwhile, a repulsion potential function is designed by applying a Sigmoid function to generate an obstacle avoidance control force; the attraction potentialfunction is designed by using the state-dependent Riccati equation to generate the attraction control force, and the integrated design of the corresponding controller is completed by using the terminal sliding mode control theory, so that the rapid obstacle avoidance control of the spacecraft can be realized; the control precision is high, the fuel consumption rate is low, and the method can be suitable for the on-orbit real-time operation of the spacecraft.
Owner:NAT INNOVATION INST OF DEFENSE TECH PLA ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
Method for constructing belt-shaped tethered satellite release kinetic model
ActiveCN110210047AConfiguration changes accurately reflectDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic equationSpace vehicle control
The invention discloses a method for constructing a belt-shaped tethered satellite release kinetic model, relates to the field of spacecraft control, can accurately describe complex configuration changes of the space band-shaped tether in the release process, effectively reveals the influence of the band-shaped tether with different bending stiffness on system dynamics, and accurately reflects theconfiguration changes of the band-shaped tether in the release process. The present invention comprises: a constraint equation used for uniformly dispersing the space band-shaped tether into a plurality of rigid body units, establishing a kinetic equation of a single rigid body unit and a constraint equation between the rigid body units, wherein the release length of the tether is continuously changed according to the release stage; constraint equations among rigid body units are divided into three classes of constraints between units which are not released in the main satellite, constraintsbetween rigid body units which are released and previous units, and constraints between released units, and then according to a constraint equation between the rigid body units in the releasing process, a dynamic equation of the releasing process of the belt-shaped tethered satellite system is obtained through final derivation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Eccentricity ratio freezing common-rail double-pulse control intermediate rail determination method
ActiveCN111338367AIncrease available working arcsImprove reliabilityAttitude controlPulse controlSpace vehicle control
The invention discloses an eccentricity ratio freezing common-rail double-pulse control intermediate orbit determination method. The method is specifically implemented according to the following steps: 1, determining a pre-control satellite orbit at an intermediate moment of first orbital transfer; 2, calculating the position and speed of a satellite when the orbit is not changed at the intermediate moment of the first orbit change; 3, determining a satellite orbit after secondary orbit transfer intermediate time control; 4, confirming the control type, the control quantity and the control phase of a double-pulse track; 5, respectively calculating a track eccentricity ratio variable quantity, a track flat semi-major axis variable quantity, a first track control actual speed increment and asecond track control actual speed increment; 6, calculating a satellite speed vector after the first orbital transfer intermediate time control; 7, determining a double-pulse control middle arc section track. By means of the method, the available working arc section of the orbit in the spacecraft control period can be improved, and certain economic benefits are achieved for on-orbit operation ofthe spacecraft.
Owner:CHINA XIAN SATELLITE CONTROL CENT
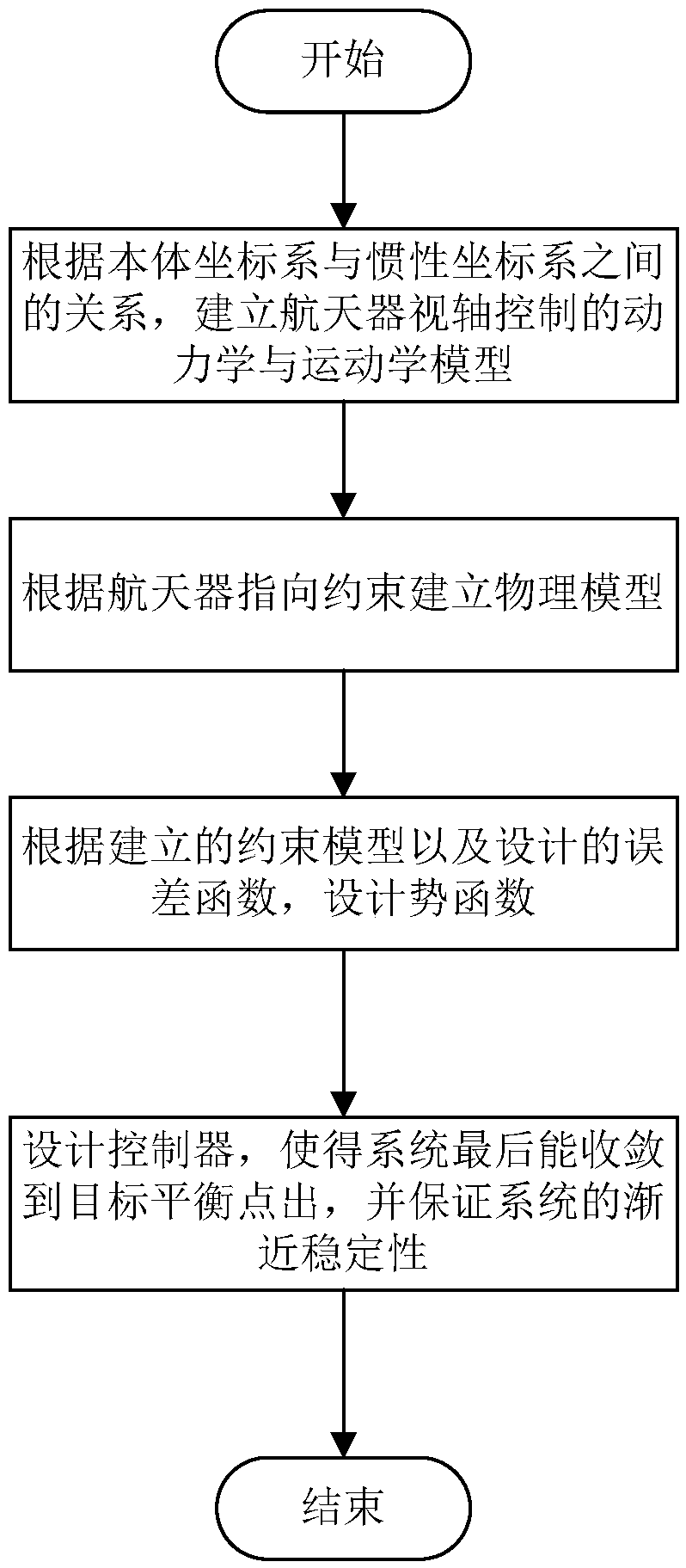
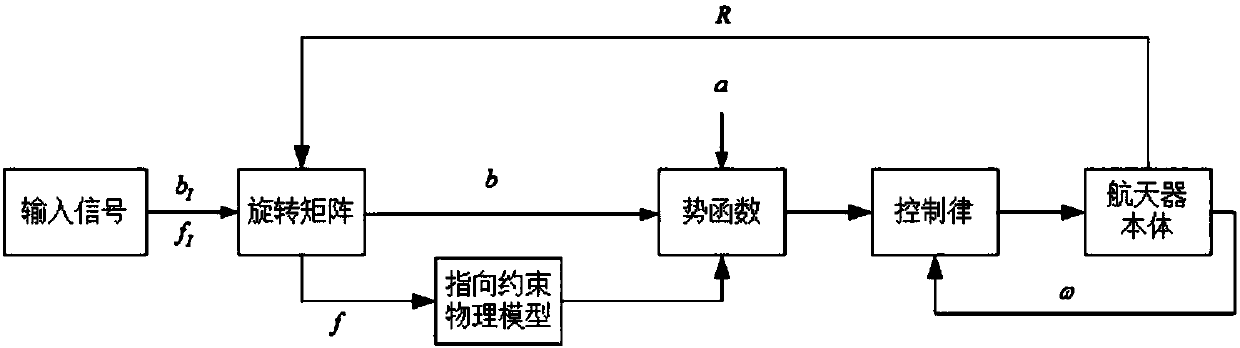
Spacecraft visual axis maneuvering control device considering dynamic pointing constraint
ActiveCN108427429AReduce the amount of informationImprove on-orbit autonomous operation capabilityCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsSpacecraft attitude controlSpace vehicle control
The invention provides a spacecraft visual axis maneuvering control device considering a dynamic pointing constraint. The method includes the steps that a spacecraft visual axis control system model is established, a mathematic model of the dynamic constraint is provided, and a potential function and a control rule of a design system are established. Aiming at the spacecraft visual axis maneuvering control problem, the practical problem that the dynamic pointing constraint exists in spacecraft rotating space is considered, the spacecraft control rule combined with a potential function method is provided, and a spacecraft can complete control tasks and autonomously achieve the dynamic constraint. By means of the method, the stability of a spacecraft attitude control system is guaranteed when the dynamic pointing constraint exists in the space, the constraint can be autonomously avoided, the requirements of the spacecraft on ground communication are reduced, and the autonomous control capacity of the spacecraft is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com