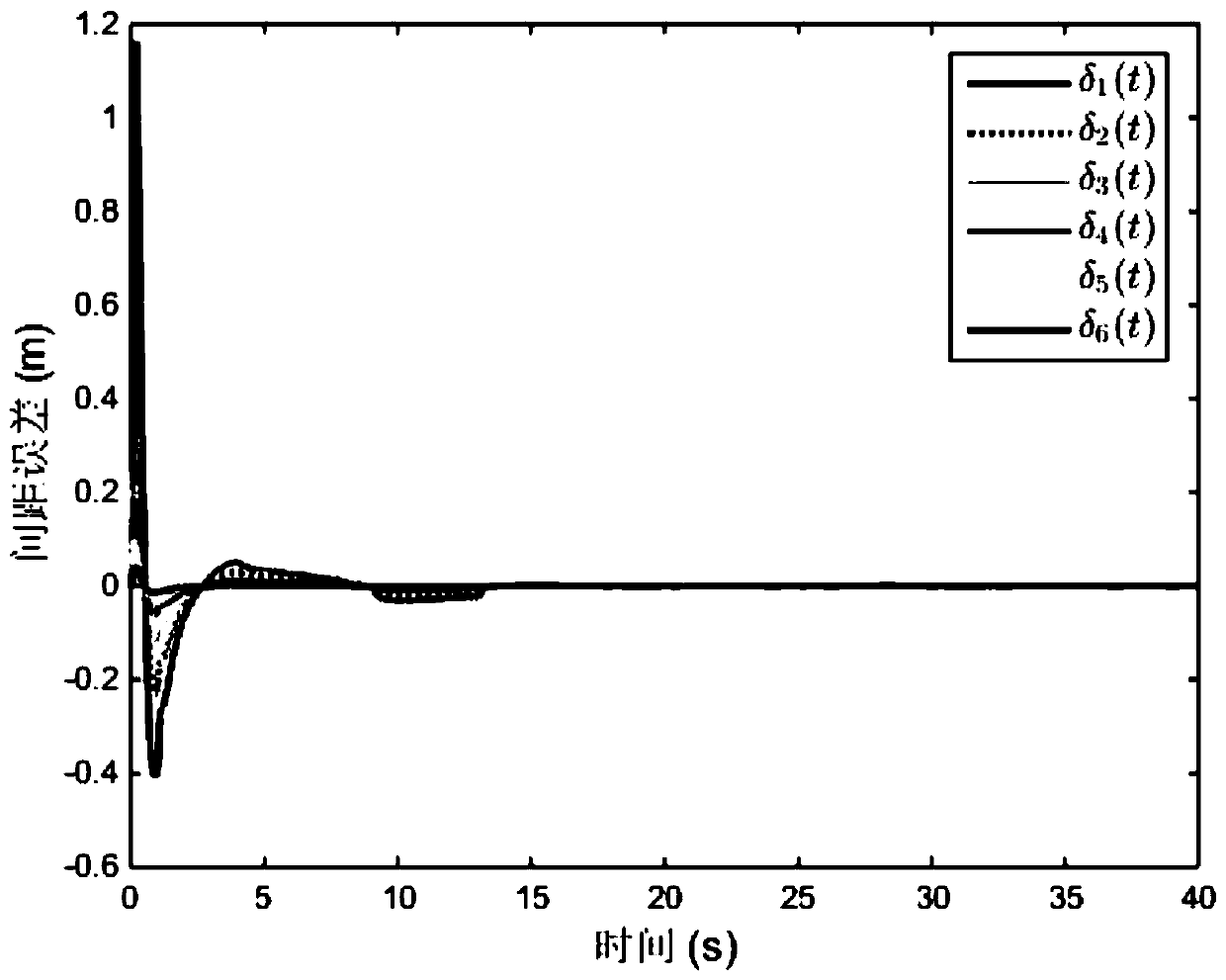
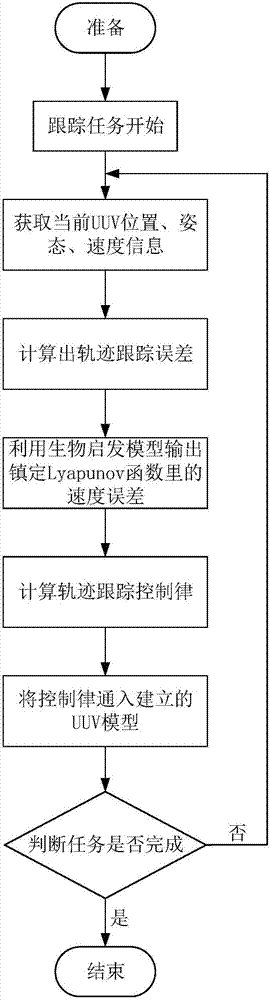
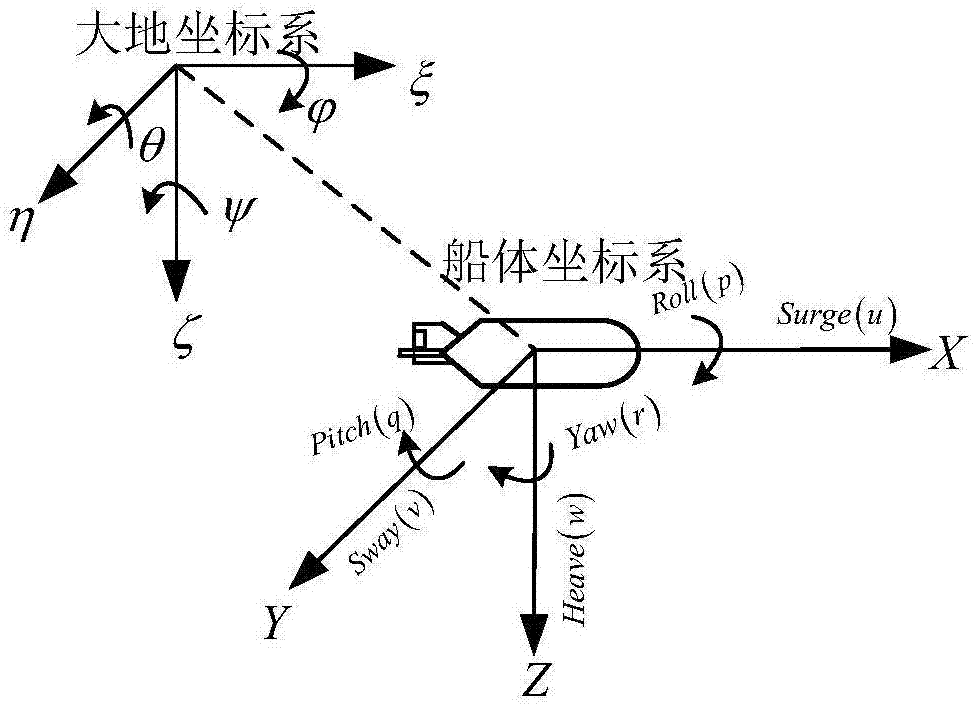
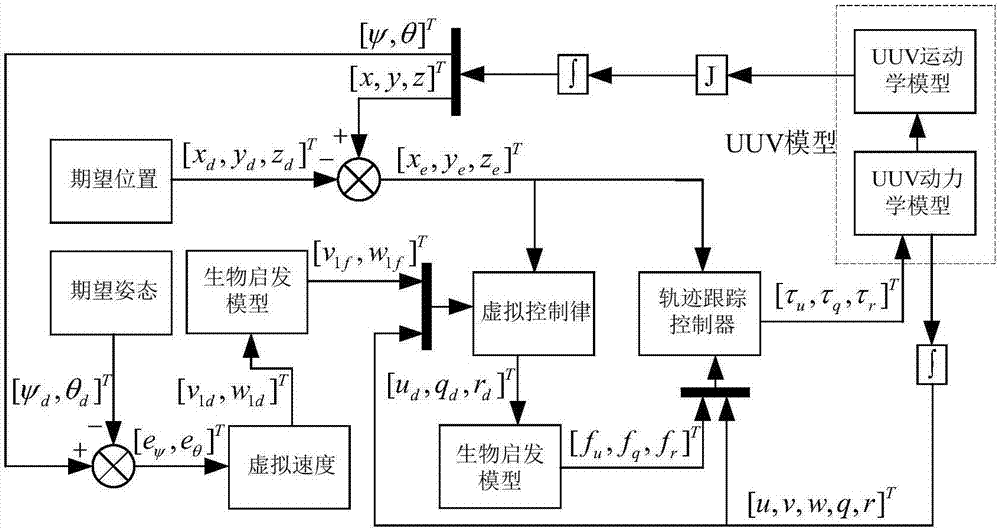
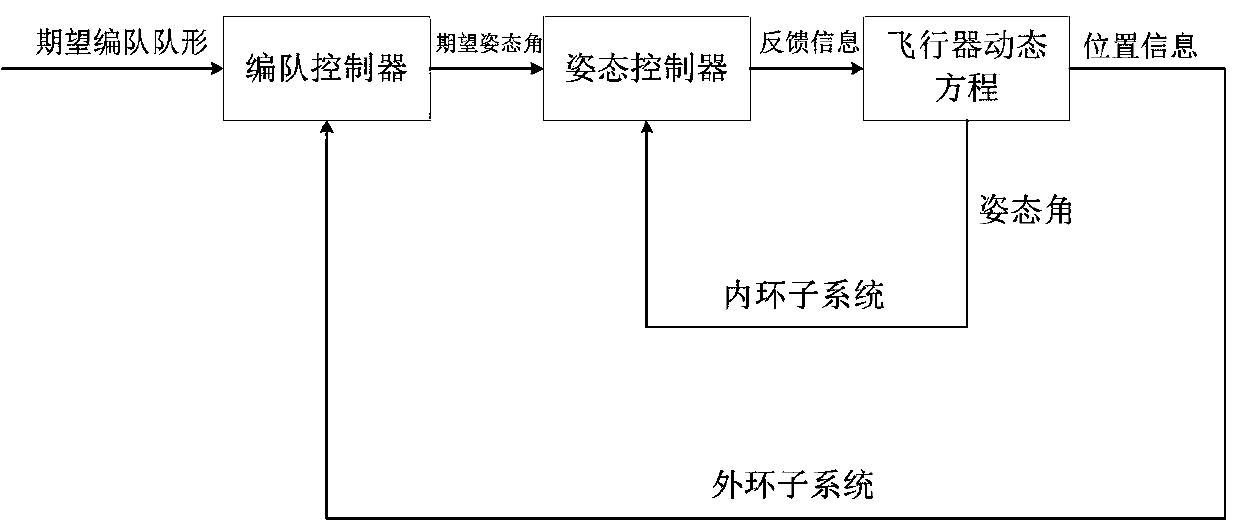
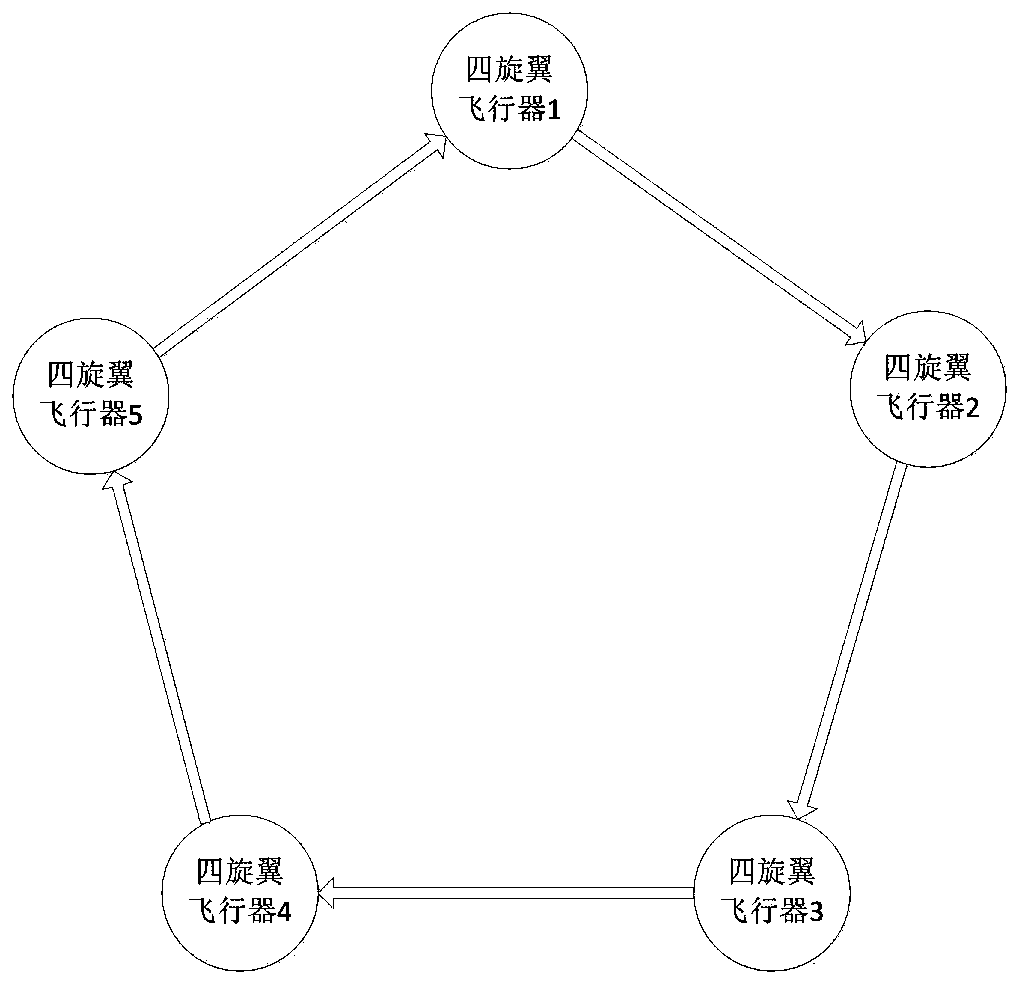
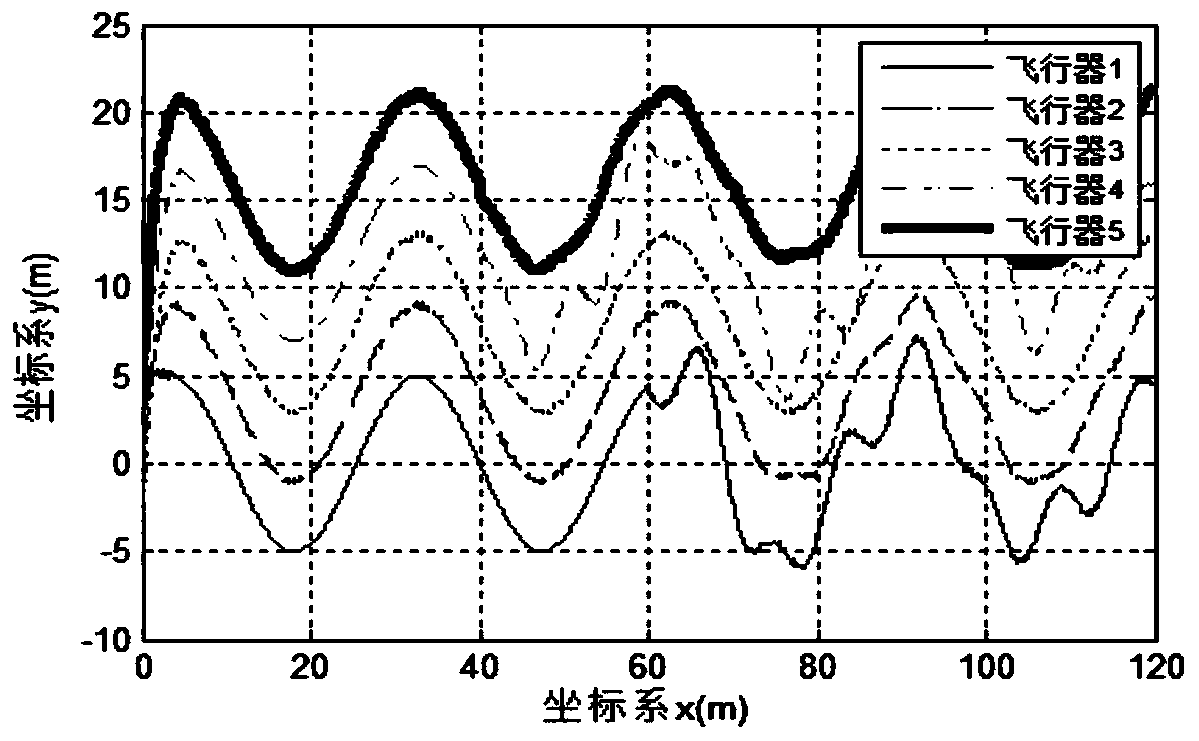
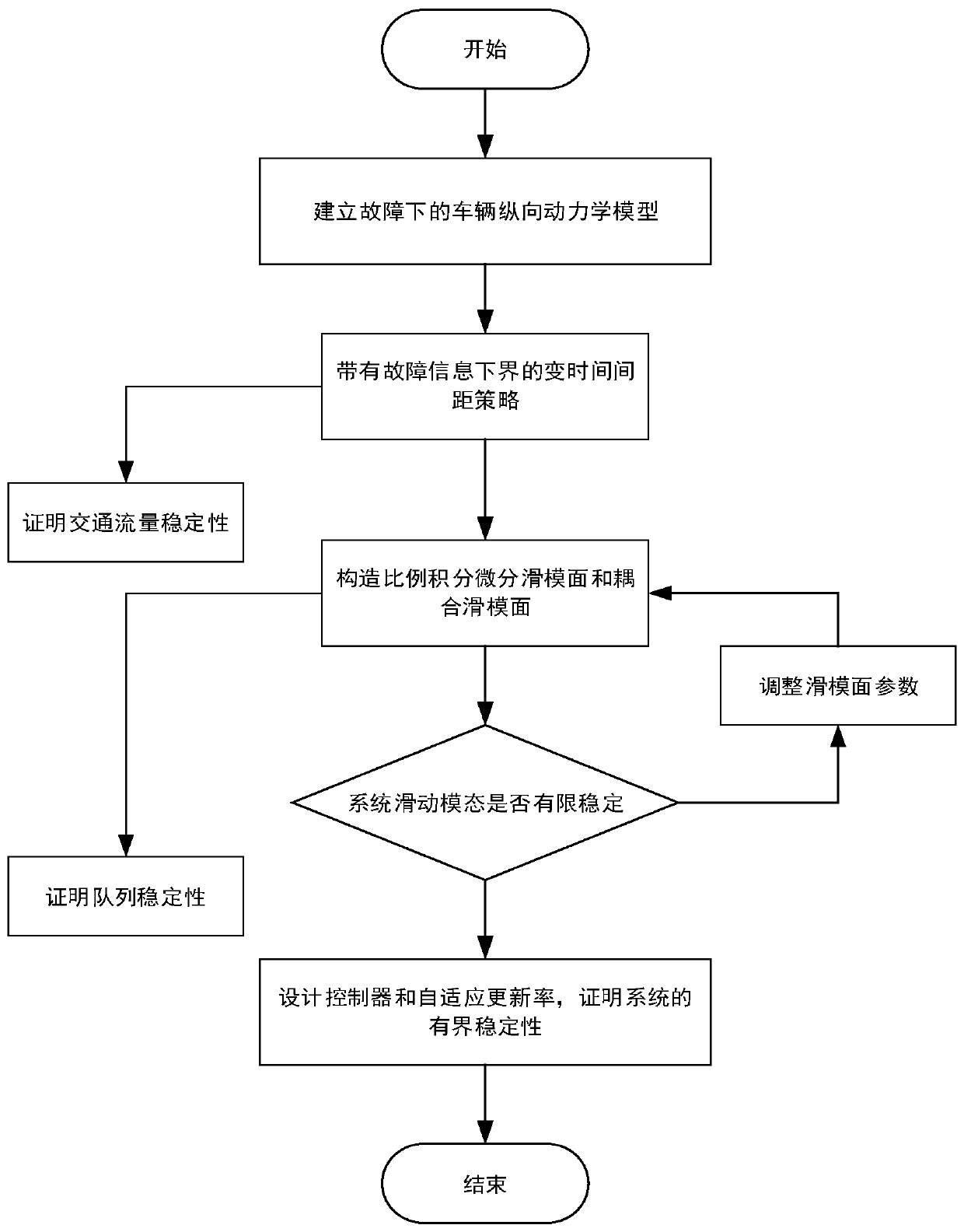
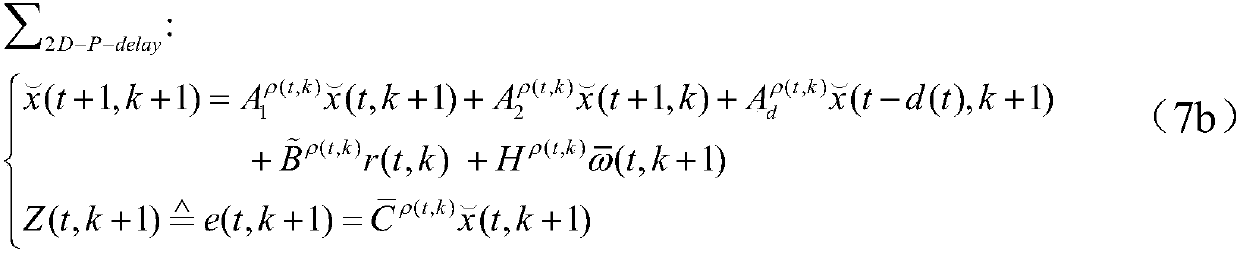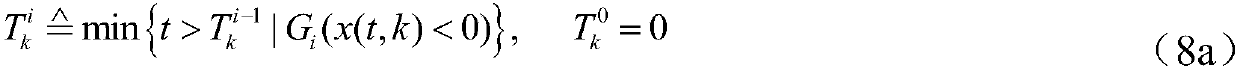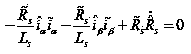Patents
Literature
666 results about "Lyapunov function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the theory of ordinary differential equations (ODEs), Lyapunov functions are scalar functions that may be used to prove the stability of an equilibrium of an ODE. Named after the Russian mathematician Aleksandr Mikhailovich Lyapunov, Lyapunov functions (also called the Lyapunov’s second method for stability) are important to stability theory of dynamical systems and control theory. A similar concept appears in the theory of general state space Markov chains, usually under the name Foster–Lyapunov functions.
Hypersonic flight vehicle adaptive fault-tolerant control method of considering attack angle constraint
The present invention discloses a hypersonic flight vehicle adaptive fault-tolerant control method of considering attack angle constraint which is used to solve the technical problem that a conventional hypersonic flight vehicle control method is poor in practicality. The method of the technical scheme is characterized by limiting a flight vehicle attack angle within a given range to guarantee the normal work of a scramjet engine; aiming at the fault case of an actuator, giving out a robust adaptive adjusting and controlling strategy, and utilizing a redundancy control mechanism to effectively compensate the influence brought by the failure to guarantee the safety of a system. Aiming at the model uncertainty, the method of the present invention combines the amplitude limiting design and a Barrier type lyapunov function to give out a controller, thereby being able to guarantee that the attack angle can be restrained within the given range, and guaranteeing the normal work of the scramjet engine. By using a neural network to learn and process the model uncertainty to substitute for the linear parameterization processing, the model analysis is simplified, and the actual application is convenient. Aiming at the fault case of the actuator, the redundancy control mechanism is utilized to compensate the influence brought by the faults effectively and adaptively, thereby being good in practicality.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV +1
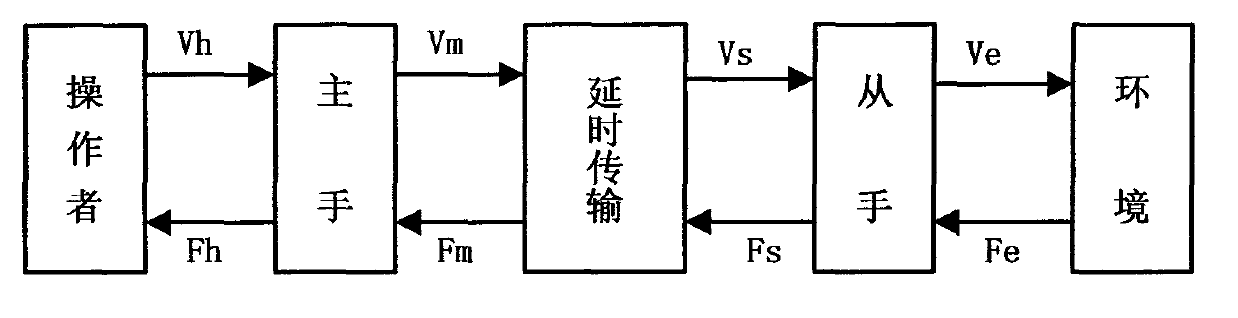
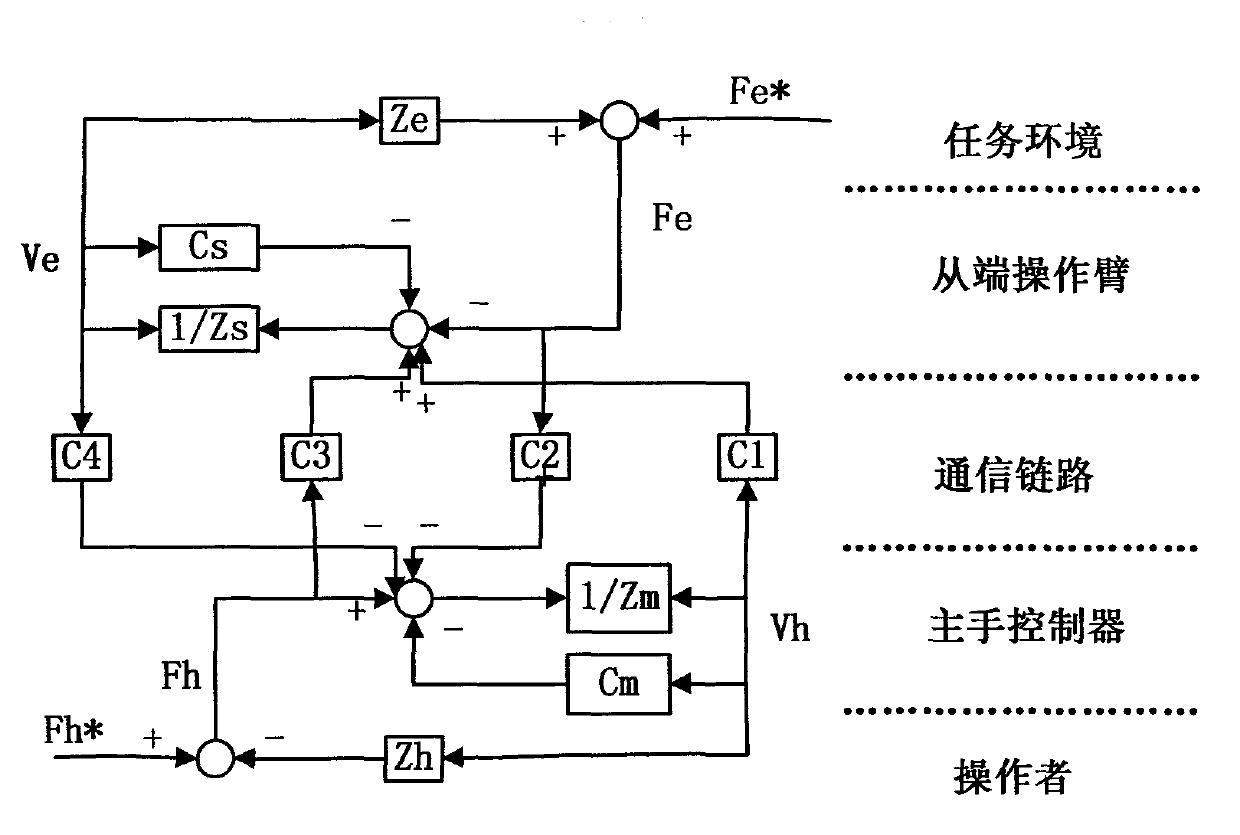
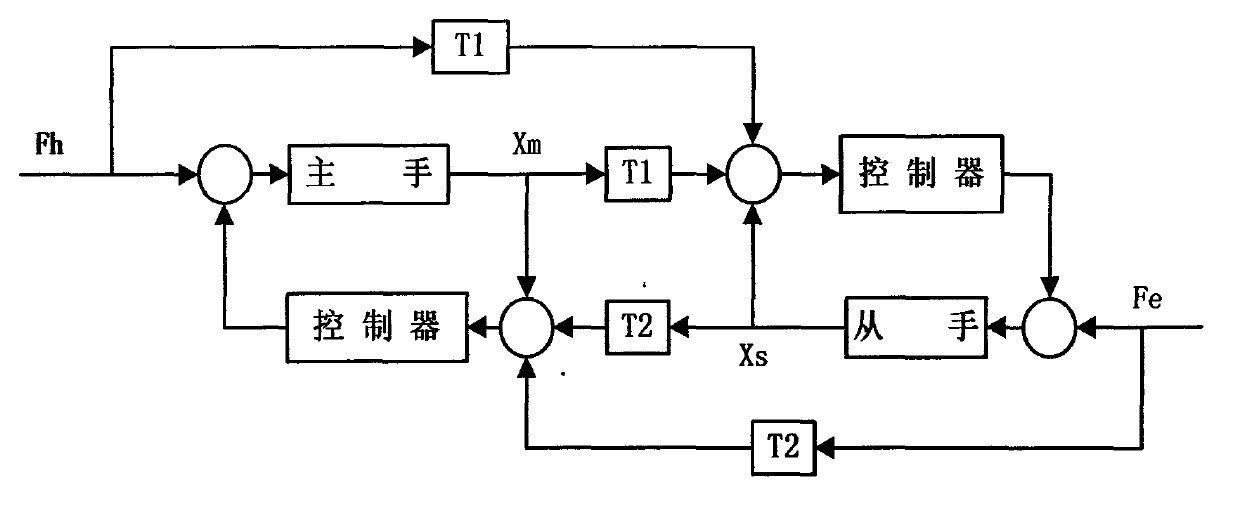
Four-channel bilateral teleoperation control system based on actual force feedback
The invention relates to a four-channel bilateral control method which is applied to a teleoperation system with an unknown slave-end environment and requirements on knowing master-slave force information, and belongs to the technical field of teleoperation control. By the system, transmission and feedback of actual force between a master end and a slave end can be realized, the force can be corrected by position errors and velocity disturbance, and accuracy of the system is improved. The invention relates to the control method for a teleoperation system with long time delay. Force applied by a master-end operator is directly transmitted to a slave-end mechanical arm, and contact force of the slave-end mechanical arm and the environment is fed back to the operator, a four-channel control structure for transmitting the actual force of the master end and the slave end in two directions is provided, and the force is corrected by the master-slave position errors. Various performance indexes in the system during free movement and contact movement are comprehensively analyzed by a Lyapunov function and a passive theory. Models are not required to be created in advance in the slave-end environment, and the four-channel bilateral control method and the system are applicable to the unknown and unstructured slave-end environment, and requirements on stability, transparency and traceability of the system can be met.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
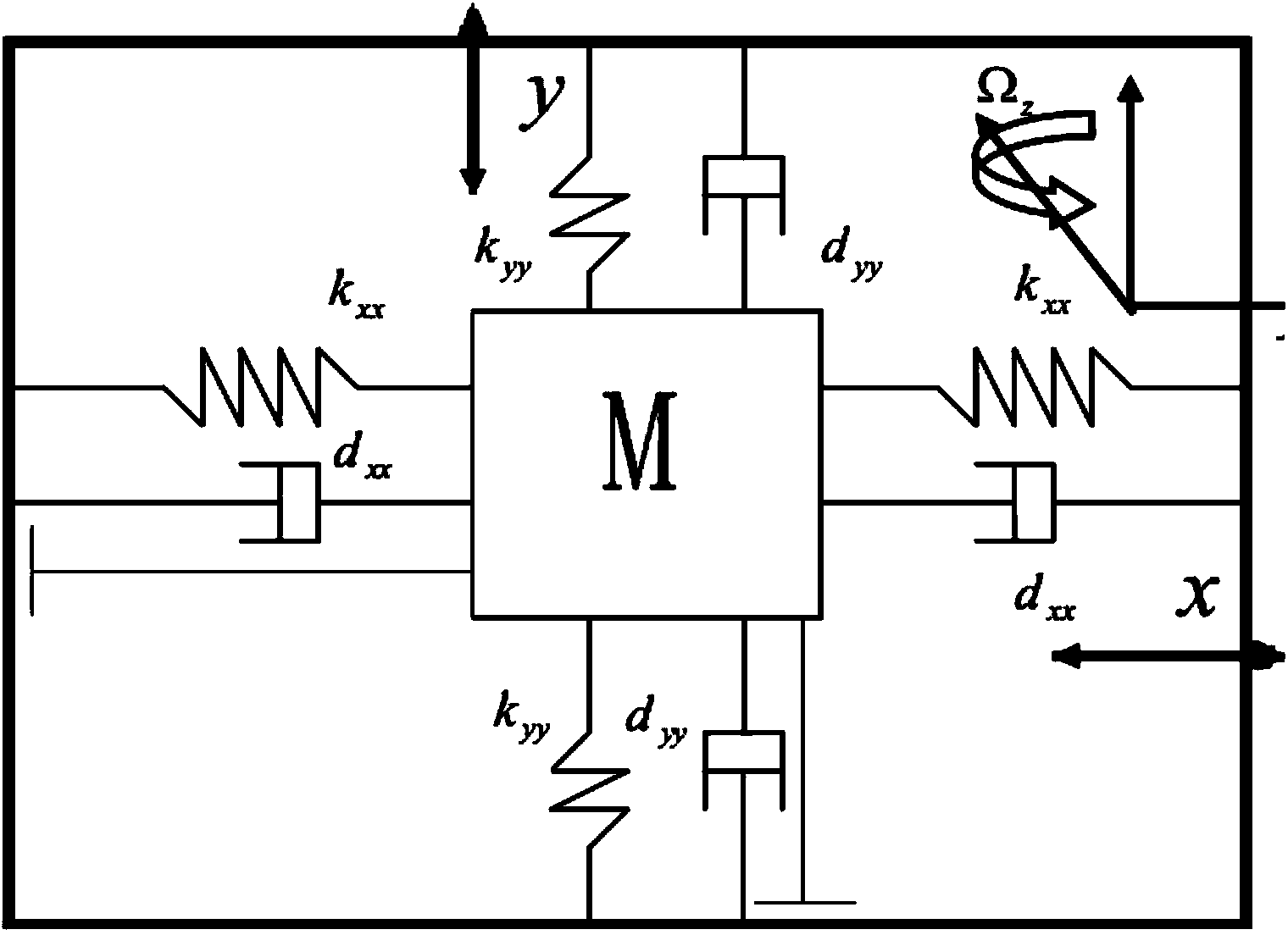
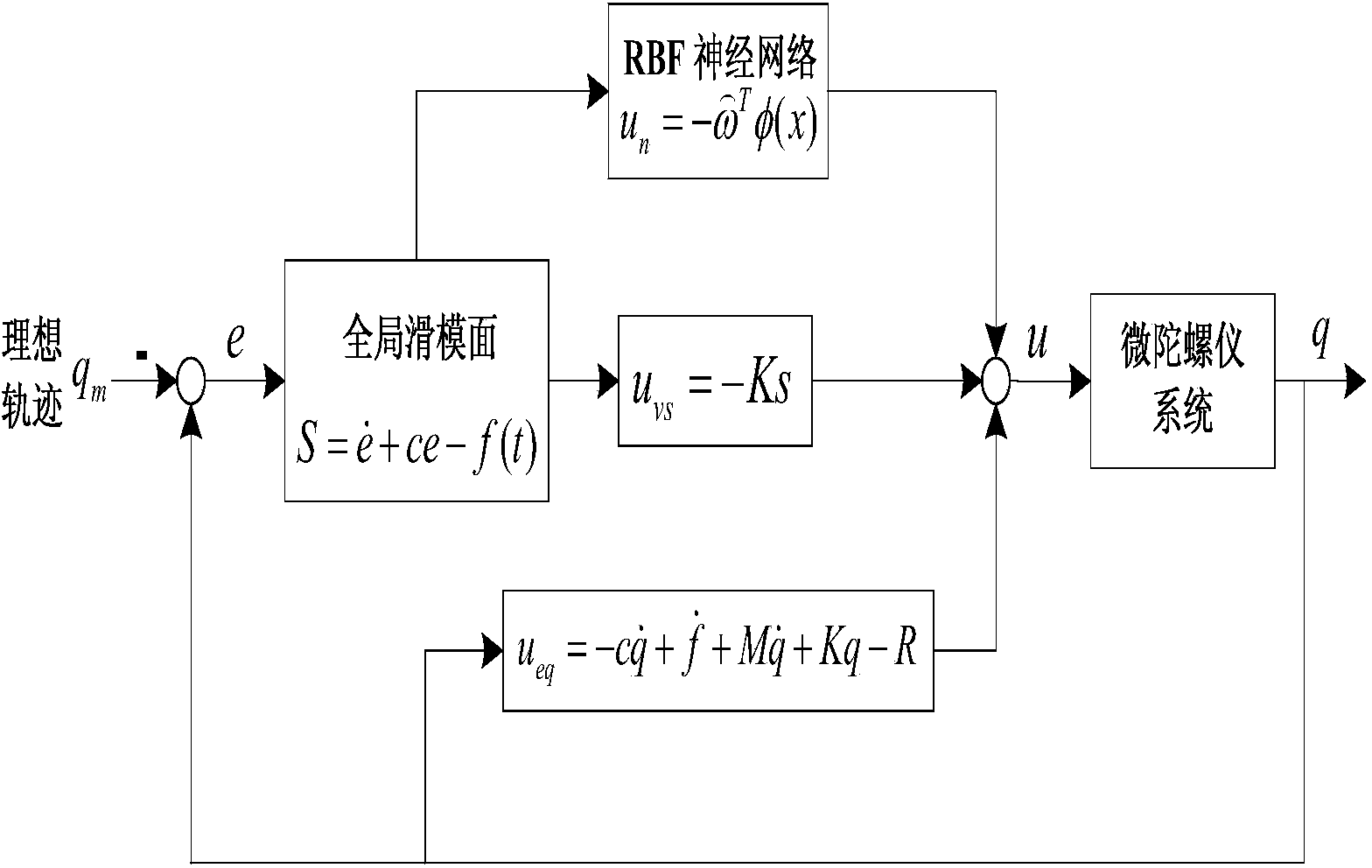
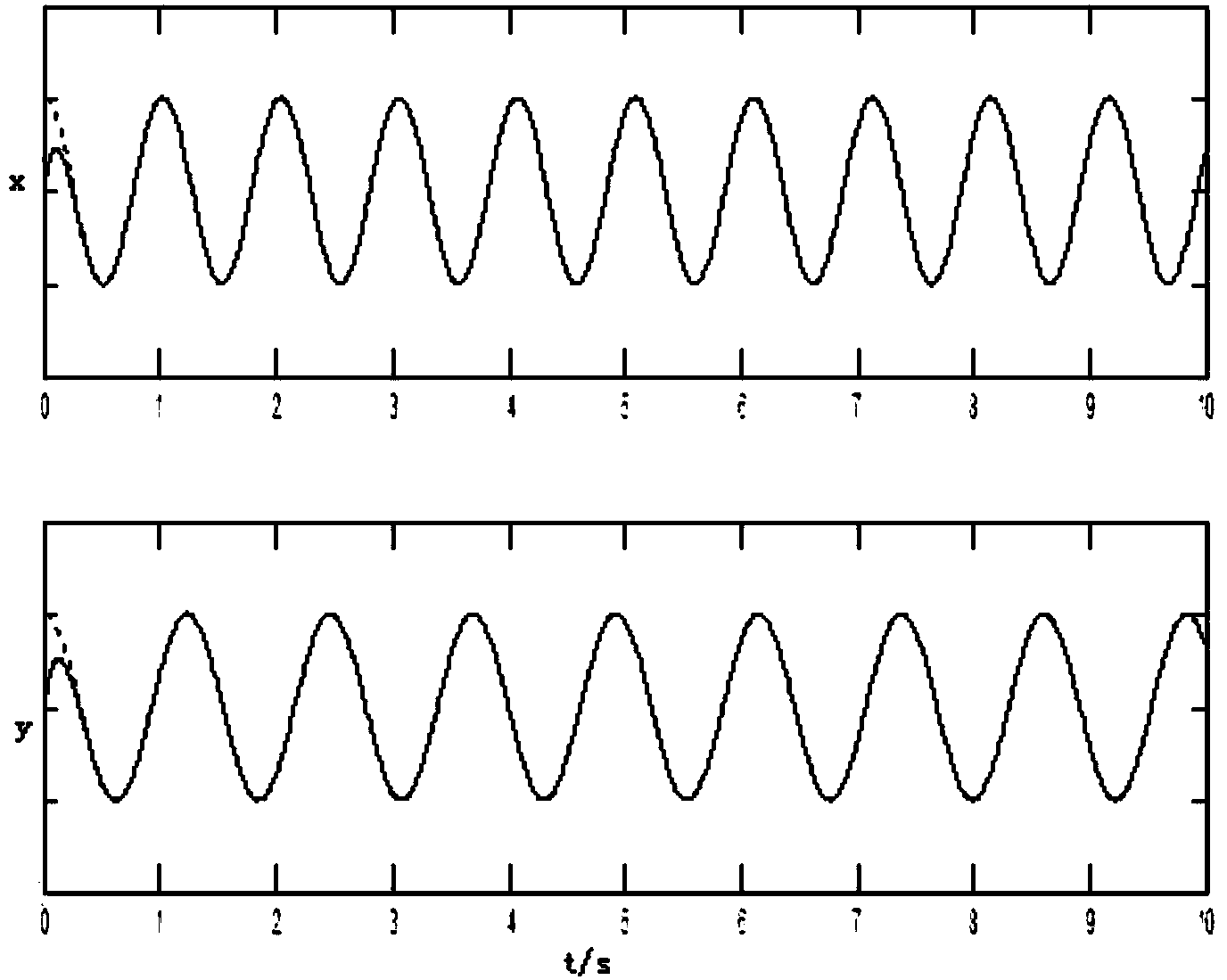
Inversing global SMFC (sliding mode fuzzy control) method for micro-gyroscope based on neural network
InactiveCN105045097AOvercome the disadvantage of not being robustQuick responseAdaptive controlProcess systemsGyroscope
The invention discloses an inversing global SMFC (sliding mode fuzzy control) method for a micro-gyroscope based on a neural network. An inversing global SMFC system based on the neural network consists of an inversing global sliding mode fuzzy controller, a neural network dynamic characteristic estimator, and a fuzzy uncertainty estimator. Global sliding-mode control can iron out a defect that an arrival mode in the conventional sliding-mode control does not have robustness, speeds up system response, and enables a system to have robustness in the whole process of response. The method enables a lyapunov function of the system and the design process of a controller to be systematic and structuralized through inverse design during the inversing control. Fuzzy control is used for approximating a switching function term, and a switching term in sliding-mode control is converted into continuous fuzzy control output, thereby weakening vibration in sliding-mode control, and achieving a stronger capability of adaptive tracking. Therefore, the method improves the transient performance and robustness of a sliding-mode control system, estimates the unknown dynamic characteristics of the micro-gyroscope, and reduces the vibration in the control of a sliding-mode control structure.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Nonlinear control method for micro-grid inverter with Anti-disturbance
ActiveUS20190288611A1Good dynamic and steady state characteristicImprove abilitiesElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsElectric power transmissionPower exchange
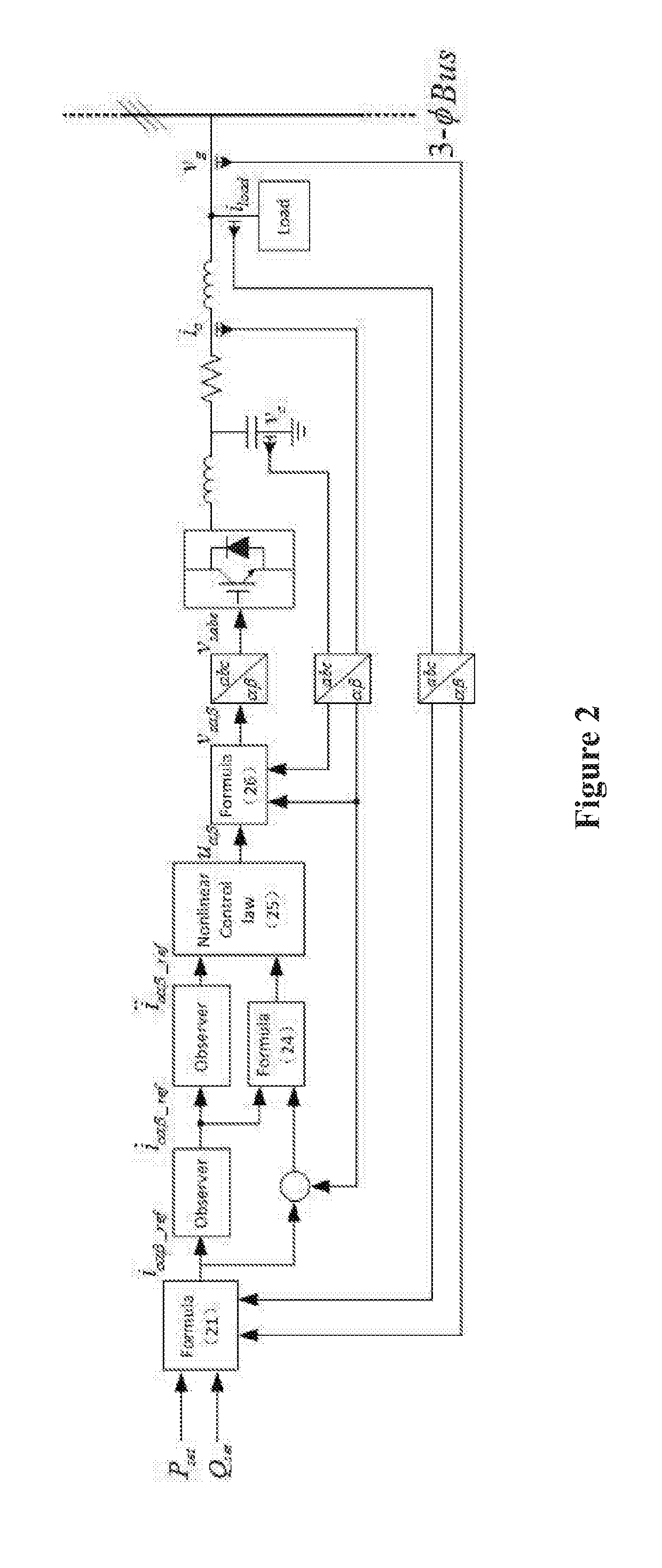
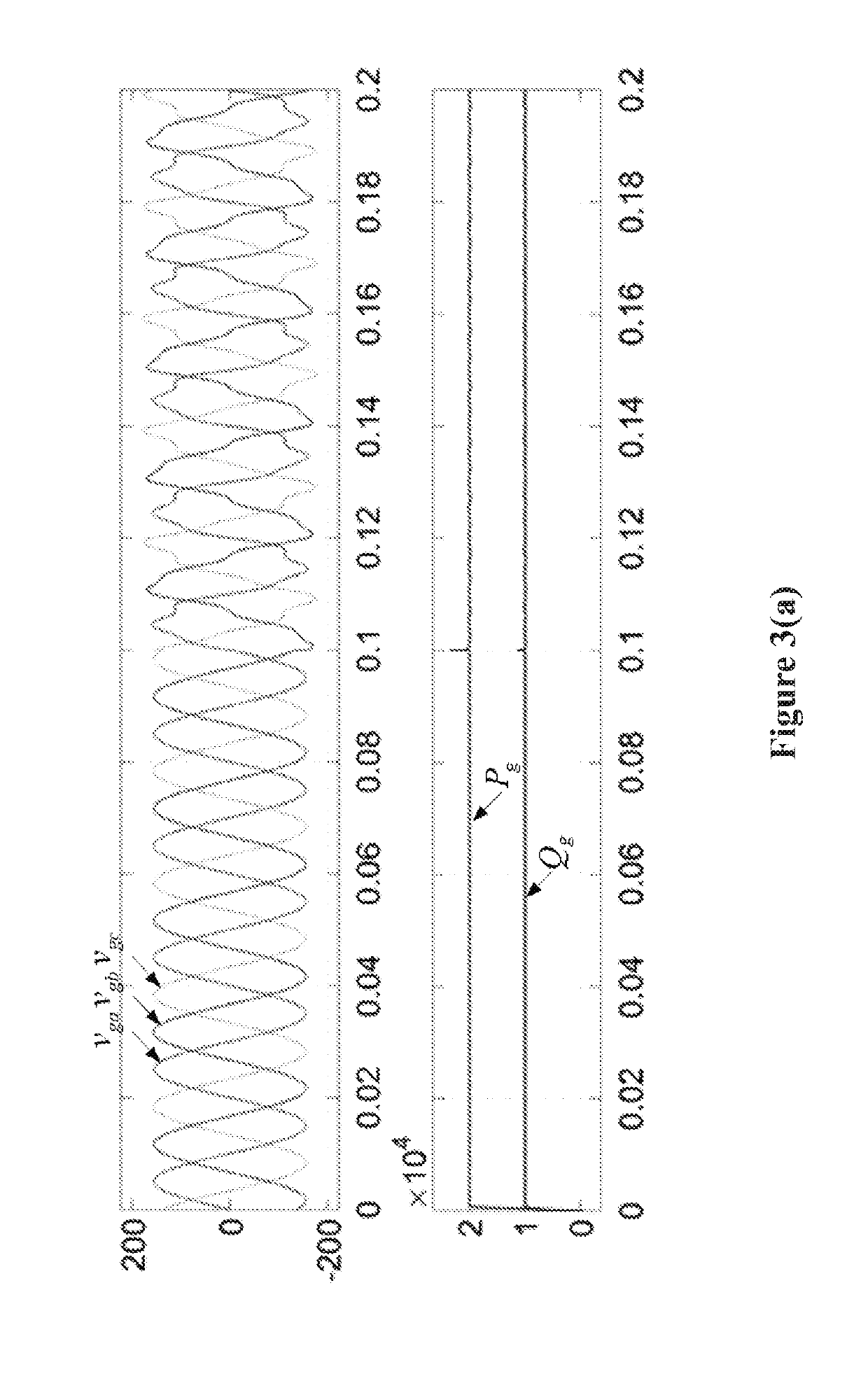
Nonlinear control method for the micro-grid inverter with anti-disturbance. By generating reference currents that satisfy specific active and reactive power command under various working conditions, and introducing a nonlinear control method based on Lyapunov function to control the inverter, fast and accurate tracking of the generated reference signals is realized. The method realizes effective decoupling control of active power and reactive power. The system has high dynamic response and good robustness. Besides, the control structure of the method is simple and easy to implement, and the synchronous control link and the additional voltage and current regulator are omitted. The method realizes fast and accurate power exchange and stable power transmission between the inverter and the grid in the micro-grid under various working conditions, and provides a guarantee for improving the energy management efficiency within the micro-grid.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
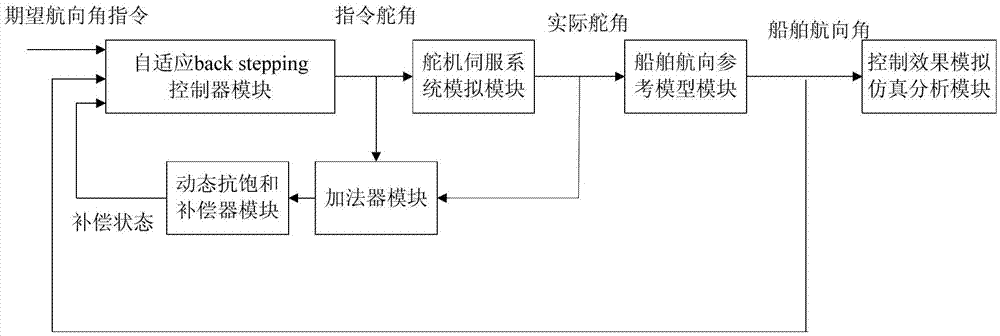
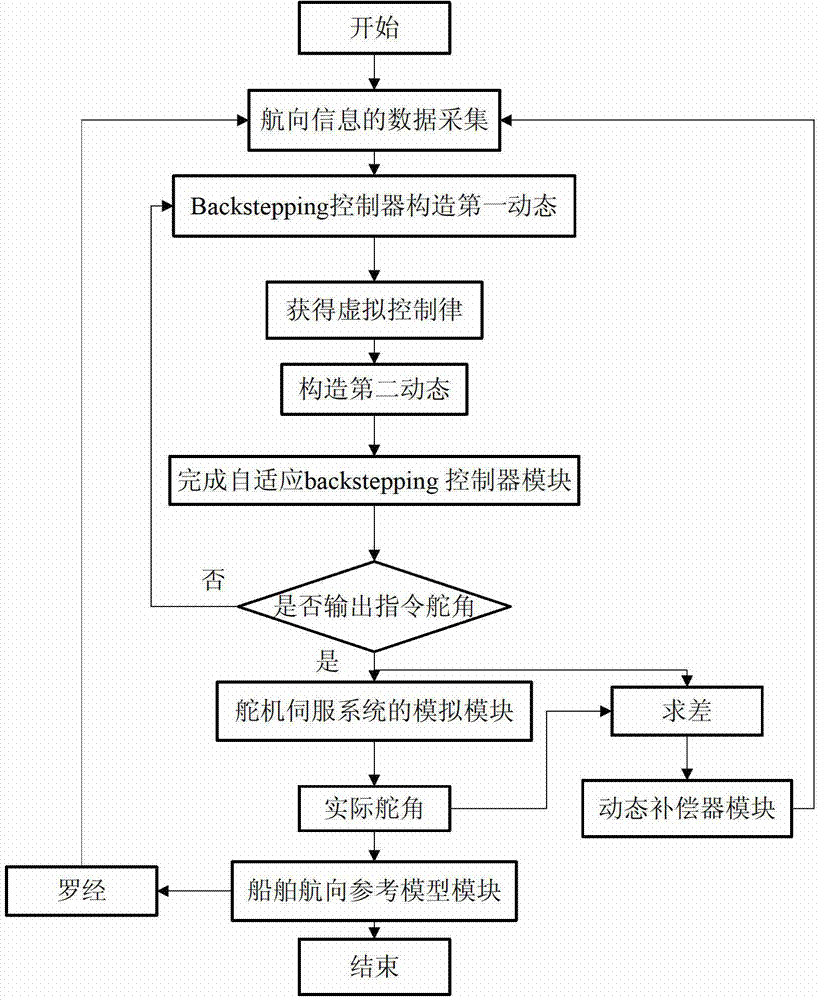
Steering engine saturation resistant self-adaptive control method for ship courses
The invention provides a steering engine saturation resistant self-adaptive control method for ship courses. The method comprises performing a mathematical description on ship course motion, and constructing a dynamic saturation-resistant compensator, a first state vector z1 of a self-adaptive backstepping controller and a Lyapunov function of the z1 to obtain virtual control; calculating a second state vector z2 of the self-adaptive backstepping controller through subtraction through combining ship course angle information, the course angular speed and the compensation state which is output by a dynamic saturation-resistant compensator module, constructing an overall Lyapunov function in the control method, and obtaining a ship course non-linear self-adaptive controller provided with the saturation-resistant compensator through combining ship course stability conditions to complete the ship course non-linear self-adaptive control method provided with the saturation-resistant compensator. The self-adaptive control method is explicit in thinking, clear and reasonable in structure and prone to engineering implementation.
Owner:三亚哈尔滨工程大学南海创新发展基地
Design method of robustness fault detection filter of linear uncertain system
InactiveCN102436179ATest not conservativeExcellent RFDFTesting/monitoring control systemsAdaptive controlRobustificationUltrasound attenuation
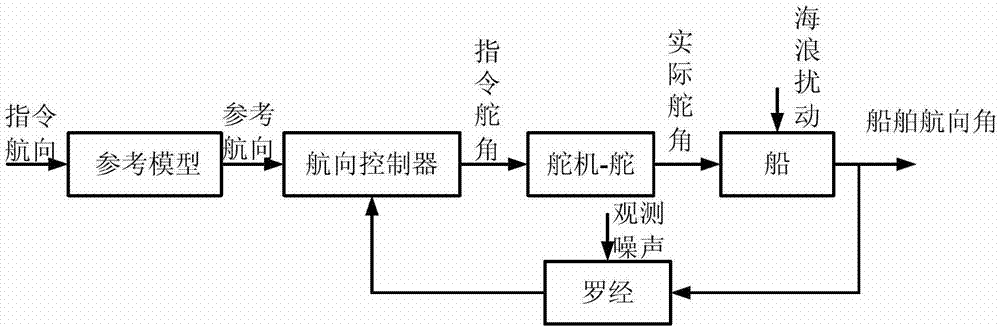
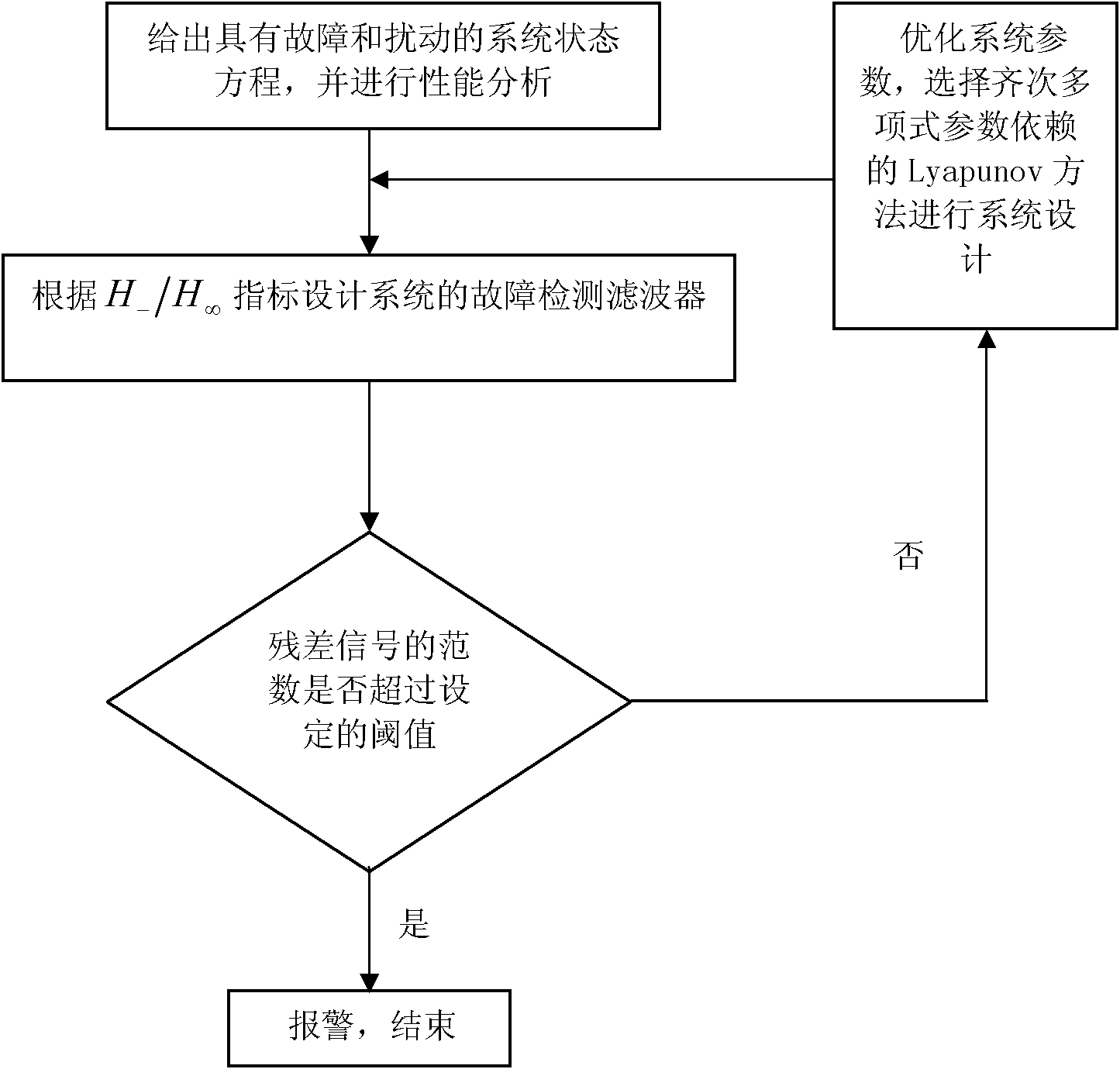
The invention belongs to the control field and provides a design method of a robustness fault detection filter of a linear uncertain system. A Lyapunov function method on which a homogeneous polynomial parameter depend is introduced into robustness fault detection of a linear time invariant system with convex polyhedron nondeterminacy. Firstly, existence of an HPPDL function used for designing an RFDF can be verified through feasibility of a linear matrix inequality; secondly, maximal fault sensitivity is obtained through solving a generalized eigenvalue problem, and an optimal RFDF is obtained. With increase of polynomial time, quantity of the linear matrix inequality and a free variable are increased, and conservation of verification is reduced substantially. The design method comprises two phases: (1) designing an optimal RFDF for a residual error generator with certain interference attenuation and largest fault sensitivity; (2) carrying out threshold design for a residual error generated by estimation. Compared with a previous analogy method, the design method in the invention has generality.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
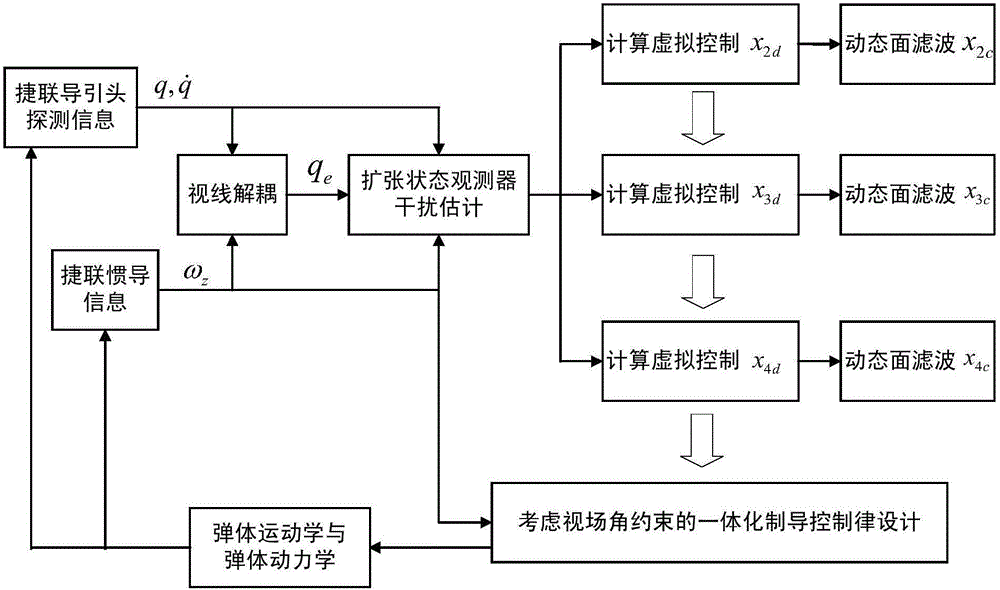
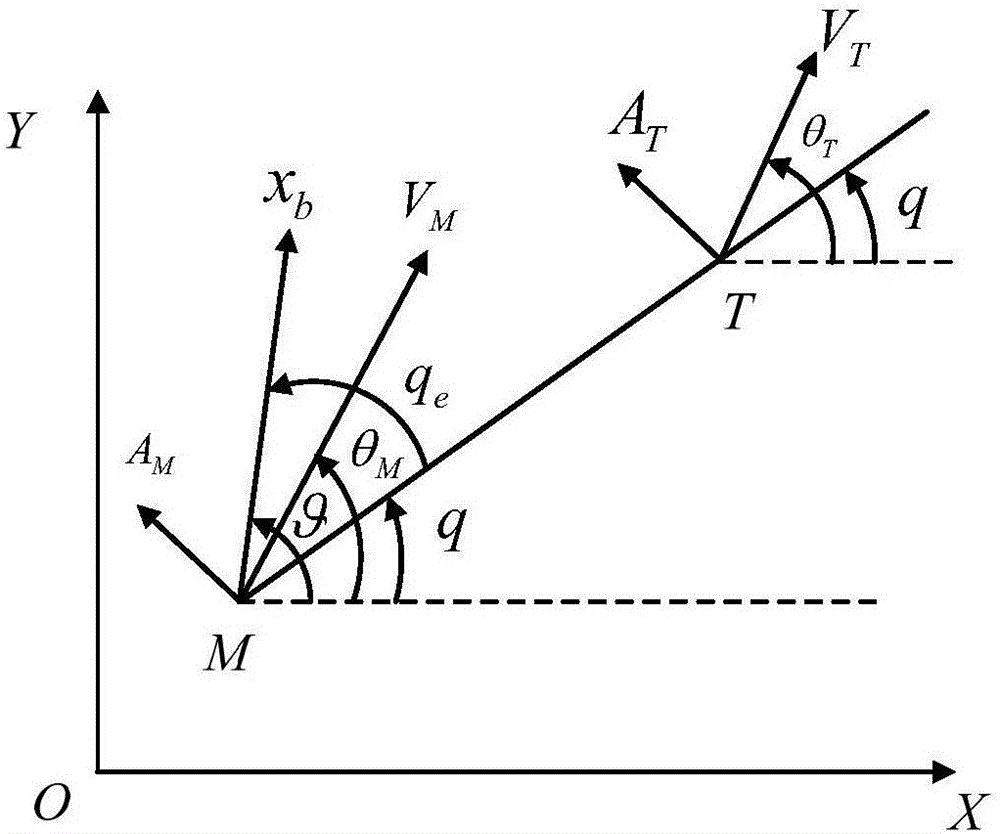
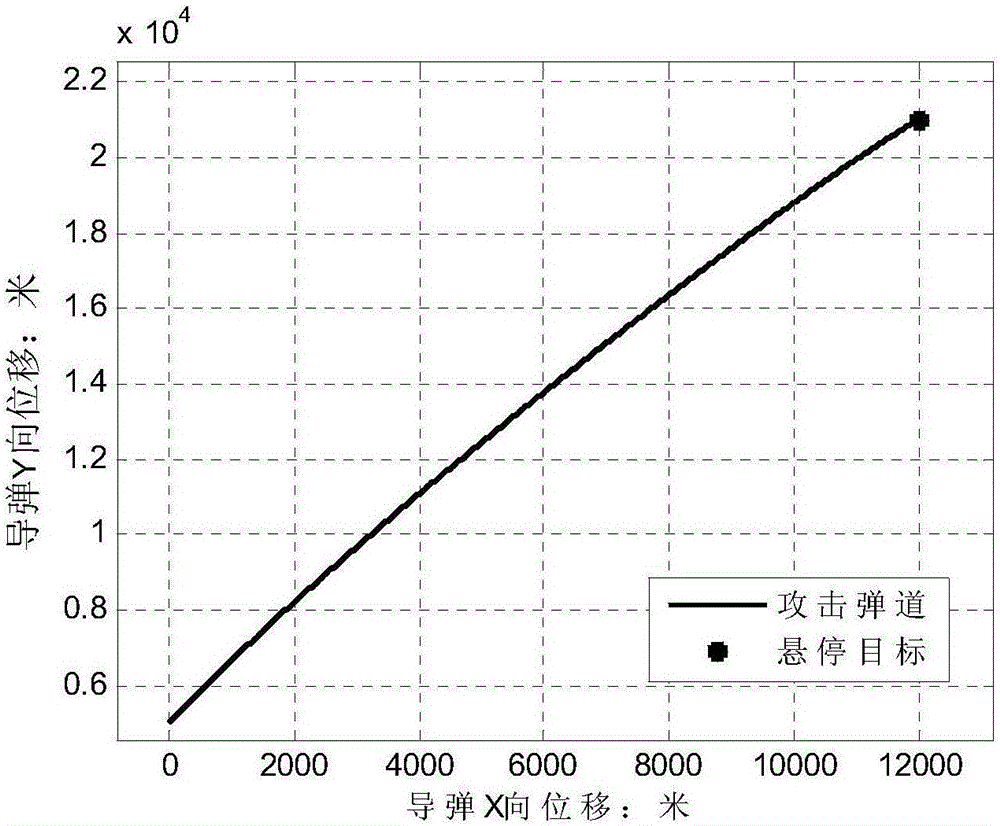
Guidance and control integrated design method considering all-strapdown seeker view field constraint
InactiveCN106681348ASatisfy test field constraintsSatisfy the field of view constraintAttitude controlLongitudinal planeMathematical model
The invention discloses a guidance and control integrated design method considering all-strapdown seeker view field constraint, and aims at solving the technical problem that an existing guidance and control integrated design method is poor in practicability. According to the technical scheme, the guidance and control integrated design method comprises the steps that a missile longitudinal channel attitude control system model, a longitudinal plane missile-target relative motion model and an all-strapdown seeker longitudinal channel sight decoupling model are built; the state variable and the system output variable are selected, and a guidance and control integrated state space mathematical model considering view field angle constraint is built; a control method combining an obstacle Lyapunov function, an expansion state observer and dynamic surface control is adopted. The control method combining the obstacle Lyapunov function, the expansion state observer and dynamic surface control is adopted, and meanwhile the guidance precision and the all-strapdown seeker view field angle constraint conditions are met, so that it is guaranteed that the body sight angle detected by an all-strapdown seeker in the missile guidance and control process meets the seeker view field constraint.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
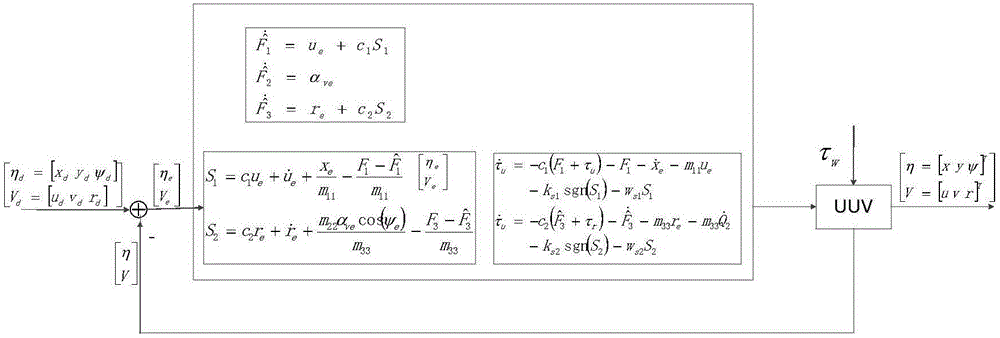
UUV (unmanned underwater vehicle) trace tracking method based on dynamic sliding mode control
InactiveCN106227223AAvoid the singular value problemResolving Modeling UncertaintyAltitude or depth controlBacksteppingSelf adaptive
The invention belongs to the technical field of trace tracking and dynamic sliding mode control of a UUV (unmanned underwater vehicle), and particularly relates to a UUV trace tracking method based on dynamic sliding mode control. The method comprises the following steps: building a UUV horizontal plane model; obtaining an error variable through coordinate transformation, and performing derivation on the error variable to obtain a derivative coefficient of the error variable; constructing a lyapunov function, and defining a virtual speed control variable to transform attitude tracking into virtual speed control; stabilizing the virtual speed control variable, adaptively estimating system parameter inaccuracy and external time-varying disturbance by a sliding mode control method, and constructing a sliding mode dynamic function; selecting a dynamic sliding mode control law to realize trace tracking of the UUV. By the combination of a backstepping method and an adaptive dynamic sliding mode control technology, the possible problems of modeling uncertainty and unknown environmental disturbance of UUV planar trace tracking and the problem of uncertain system parameters are solved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Heterogeneous vehicle team fault-tolerant control method based on actuator faults and saturation
ActiveCN110244747AGuaranteed stabilityGuaranteed uptimeAdaptive controlPosition/course control in two dimensionsProportional integral differentialTraffic capacity
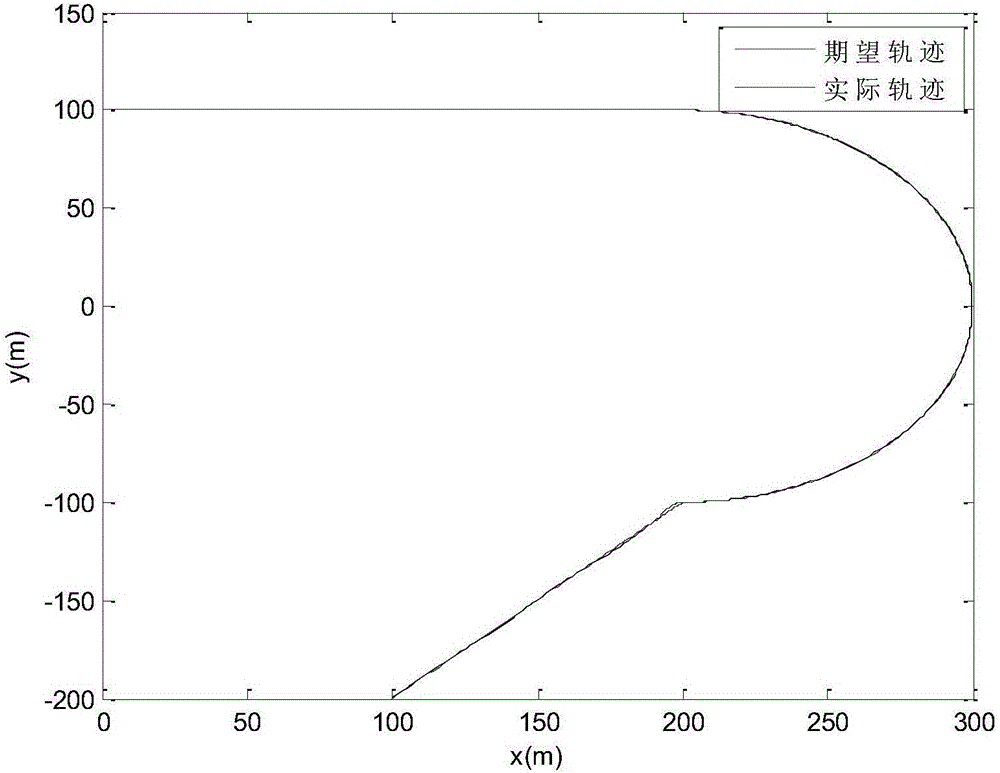
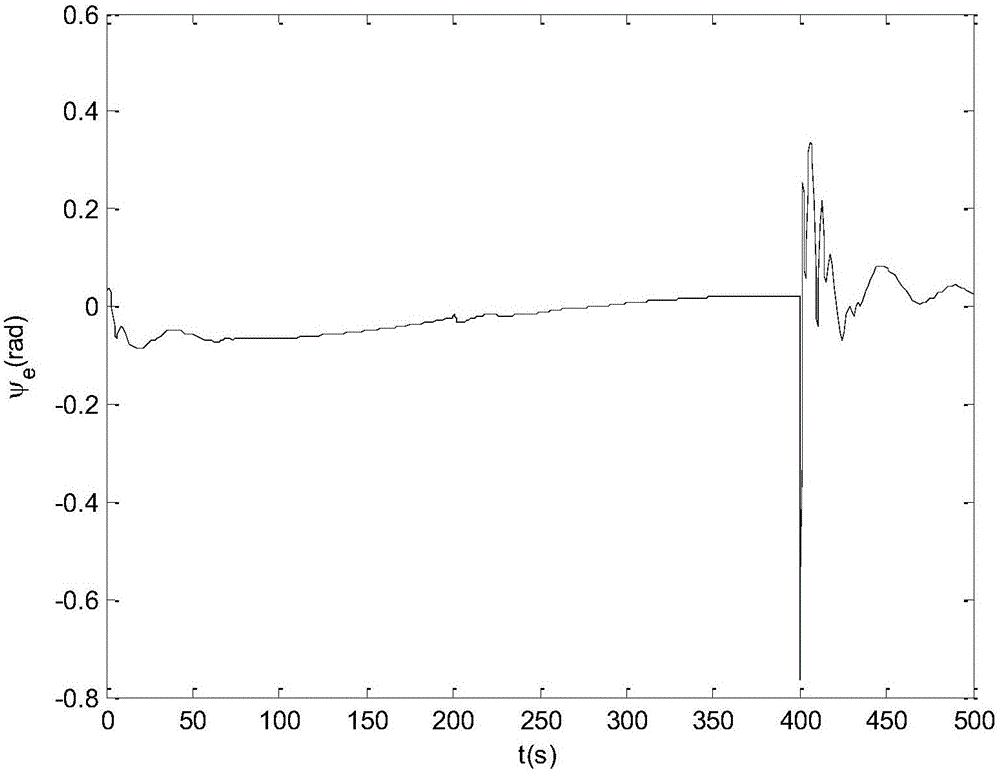
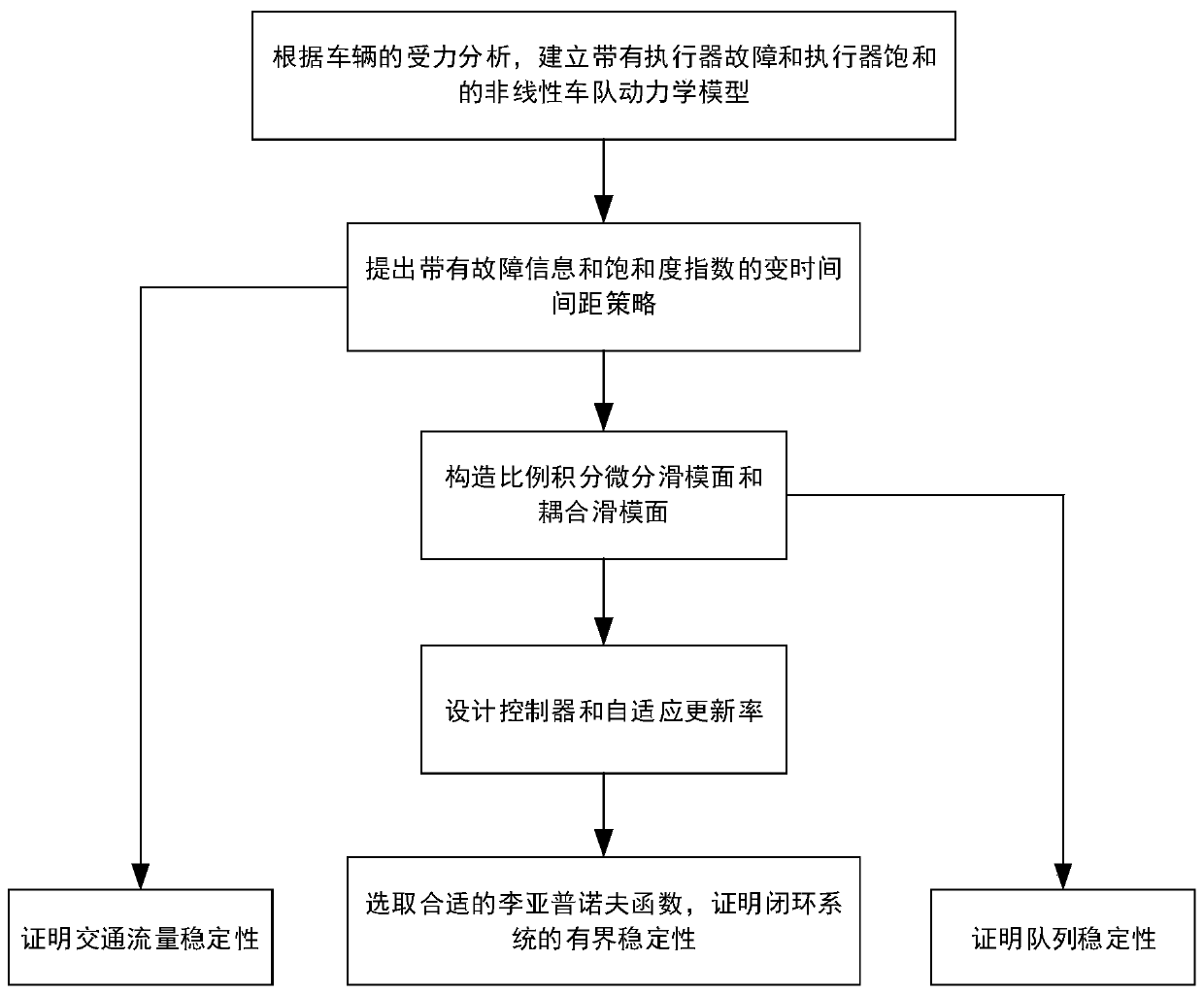
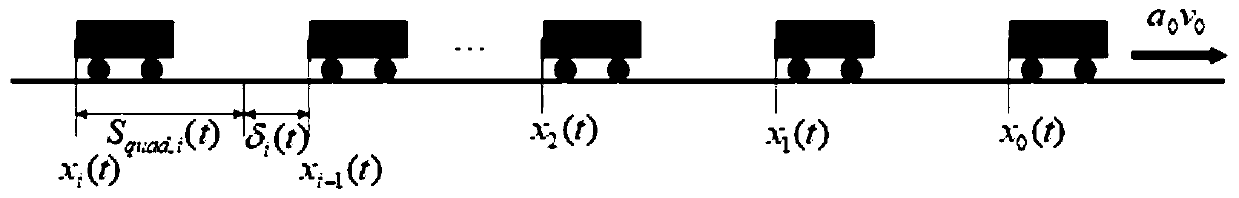
The invention provides a heterogeneous vehicle team fault-tolerant control method based on actuator fault and saturation. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out stress analysis on longitudinal movement of vehicles, and by combining actuator fault and saturation models, building a vehicle longitudinal dynamics model under the actuator fault and saturation; according to information of the vehicles, constructing a variable time interval strategy with fault information and a saturation index; and based on the constructed variable time interval strategy, establishing a proportional integral differential sliding mode surface and a coupling sliding mode surface; and selecting a proper Lyapunov function, designing a fault-tolerant controller and an adaptive updating rate, and proving the limited time stability of a system. Compared with a traditional variable time interval strategy, the variable time interval strategy with the fault information and the saturation index not only can solve the problem of non-zero initial interval error but also can expand critical traffic capacity.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
UUV trajectory tracking control method for preventing differential explosion
ActiveCN107024863ASimple calculationAvoid iterative derivationAdaptive controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsMathematical modelPropeller
The invention provides a UUV trajectory tracking control method for preventing the differential explosion based on the differential output characteristics of a biological instructive model. The method comprises the following steps of 1, conducting the initialization; 2, obtaining position and attitude error variables based on an under-actuated UUV mathematical model; 3, calculating a virtual control law, and replacing a virtual expectancy control law with the output value of the biological instructive model; 4, constructing a Lyapunov function, and transferring the ballast of a position error to the ballast of a speed error, avoiding the differential explosion phenomenon through the real-time derivation of replacing a virtual control variable with the output of the biological instructive model, and realizing the ballast of the speed error; and 5, designing a trajectory tracking controller. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the differential explosion phenomenon caused by the repeated derivation of the traditional back-stepping method can be avoided, and the complexity of the controller is simplified. Meanwhile, in combination with the controller of the biological instructive model, the time constraint requirements of the thrust constraints and the under-actuated UUV trajectory tracking of a propeller on position, speed and attitude can be met.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Active formation fault-tolerant control method based on fast adaptive technology
ActiveCN110058519ACompensate for actual failureGuaranteed asymptotically stable trendsAdaptive controlDynamic equationLiapunov function
The invention discloses an active formation fault-tolerant control method based on a fast adaptive technology. The active formation fault-tolerant control method comprises the steps that a laplacian matrix and a leader-following connection matrix of distributed multi-agent systems are achieved by constructing a connection diagram of multi-agent systems; according to a four-rotor aircraft model ofan existing nonlinear term, a corresponding observer and a fast adaptive fault estimator are constructed to predict the actual size of faults;alocal augmented system error dynamic equation and a wholeaugmented system error dynamic equation are constructed; Lyapunov function is constructed, the method that parameters in a computational controller and the fault estimator are calculated is derived and achieved through corresponding theories, and the requirements of formation control are finished under the action of actuator failure of the system and external interference. According to the activeformation fault-tolerant control method, adverse influence of the external interference on fault-tolerant control is completely eliminated at the theoretical level, performance of fault estimation isimproved, and the fault-tolerant control when the actuator fault occurs at any node of four-rotor aircraft formation or when the actuator fault occurs at multiple nodes at the same time is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Heterogeneous fleet fault tolerance control method based on variable time interval strategy
ActiveCN110333728AGuaranteed stabilityIncrease critical traffic capacityPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesProportional integral differentialTraffic capacity
The invention provides a heterogeneous fleet fault tolerance control method based on a variable time interval strategy. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out force analysis on longitudinal motion of vehicles and combining an actuator fault model to establish a vehicle longitudinal dynamics model under an actuator fault; constructing the variable time interval strategy with a lower boundary of fault information according to information of the vehicles; based on the constructed variable time interval strategy, establishing a proportional integral differential sliding mode surface and a coupled sliding mode surface; and selecting an appropriate Lyapunov function to design a fault-tolerant controller and an adaptive update rate, and proving finite time stability of a system.Traffic flow stability is proved based on the variable time interval strategy with the lower boundary of the fault information. Queue stability is proved based on the proportional integral differential sliding mode surface and the coupled sliding mode surface. Compared with a traditional variable time interval strategy, by using the technical scheme of the invention, a problem of a non-zero initial spacing error can be solved, and a critical traffic capacity can be increased.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Internet of Vehicles transmission method and device based on information freshness
ActiveCN109640370ALower average age of informationReduce computational complexityParticular environment based servicesVehicle-to-vehicle communicationComputation complexityNetwork packet
The embodiment of the invention provides an Internet of Vehicles transmission method and device based on information freshness, applied to the technical field of the Internet of Vehicles. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining an update objective function according to an initial objective function and the fact that information age of the vehicle collection node is a fixed value, whenvehicle collection node does not send a data packet within a preset time period T; constraining the network by minimizing the change rate of a Lyapunov function to obtain a final objective function, calculating an upper limit of the final final objective function at T=1, determining a second-best solution of the minimum final objective function by minimizing the upper limit to obtain an update strategy function and a routing algorithm function, determining the update strategy according to the update strategy function, determining a measurement factor according to the Q-learning algorithm andthe routing algorithm function, performing, by the vehicle collection node, information update decision making according to the update strategy, and selecting a neighbor node with the maximum measurement factor to transmit the data packet. By adoption of the Internet of Vehicles transmission method and device provided by the invention, the computational complexity and the information age can be reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
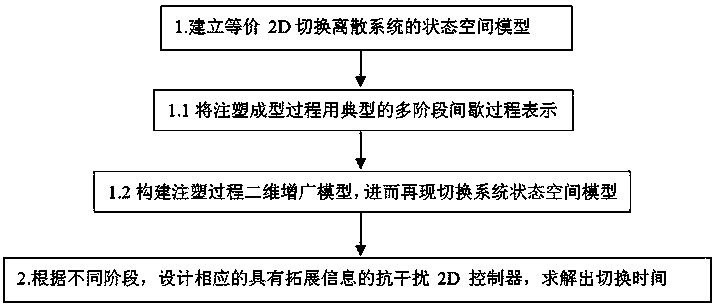
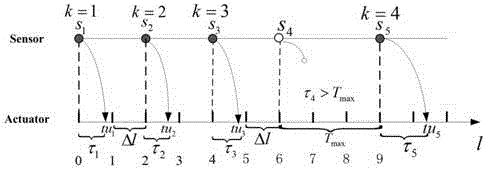
Time-varying-delay-and-interference-based hybrid 2D tracking control method of injection molding process
ActiveCN107942667AShorten the minimum run timeIncrease productivityAdaptive controlAnti jammingTime delays
The invention, which belongs to the advanced control field of the industrial process, relates to a time-varying-delay-and-interference-based hybrid 2D tracking control method of an injection molding process. An injection molding process is represented by a typical multi-stage batch process; an error is introduced and an injection molding process two-dimensional augmentation model is built to obtain a two-dimensional state space time-delay system model; a state space model of an equivalent 2D switching time-delay discrete system is established; according to different stages, a segmented Lyapunov function with time-delay information is selected; on the basis of a 2D stability theory, an anti-jamming 2D controller that has extension information and depends on the upper limit and lower limit of the time delay as well as switching time is calculated. According to the invention, a control method enabling the process to be operated stably and the control precision to be improved obviously isdeveloped, so that objectives of reducing the cost investment and improving the production efficiency are achieved; and a problem that the system performance is reduced and even is not stable becauseof the delay phenomenon is solved.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY +1
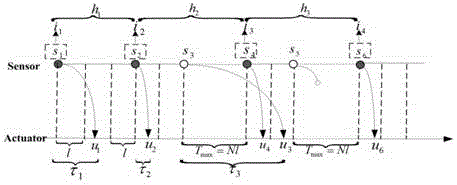
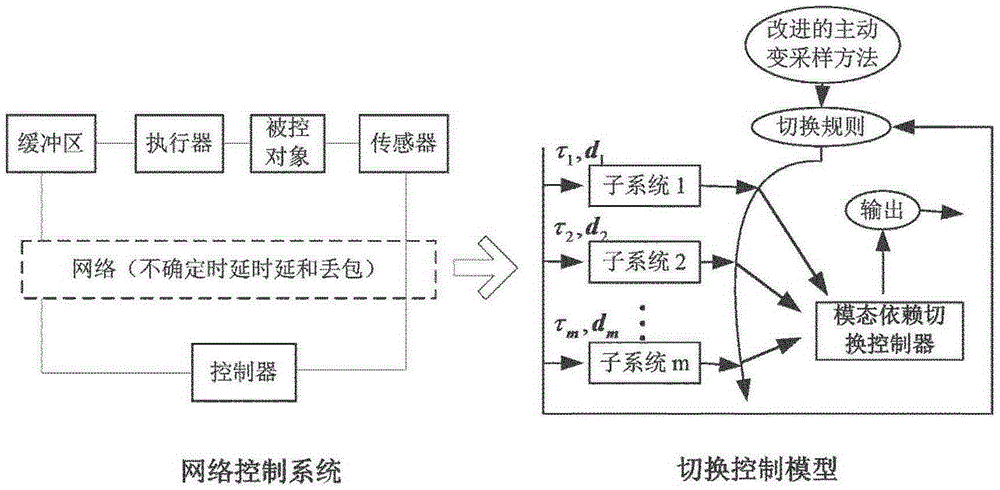
Network control system dynamic switching control method based on average residence time
Provided is a network control system dynamic switching control method based on average residence time. The method based on the average residence time is characterized by converting the influence of uncertain and randomly-changing time delay and packet loss on dynamic property of a network control system into a kind of discrete switching event, and establishing a discrete switching control model of the network control system allowing to comprise an unstable subsystem; ensuring that the network-induced time delay is always smaller than one sampling period, and meanwhile, guaranteeing that a new control variable in the current sampling period can be acted on a controlled object by utilizing an improved initiative variable sampling hybrid node driving mechanism; and providing a sufficient condition for solving the existence of a modal dependence switching controller based on a multiple-Lyapunov function method, and providing a design method of the switching controller meeting indefinite subsystem switching sequence allowing the average residence time by adopting an optimal cycle algorithm, and ensuring the stability of the network control system under the condition of limited communication and incomplete information.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
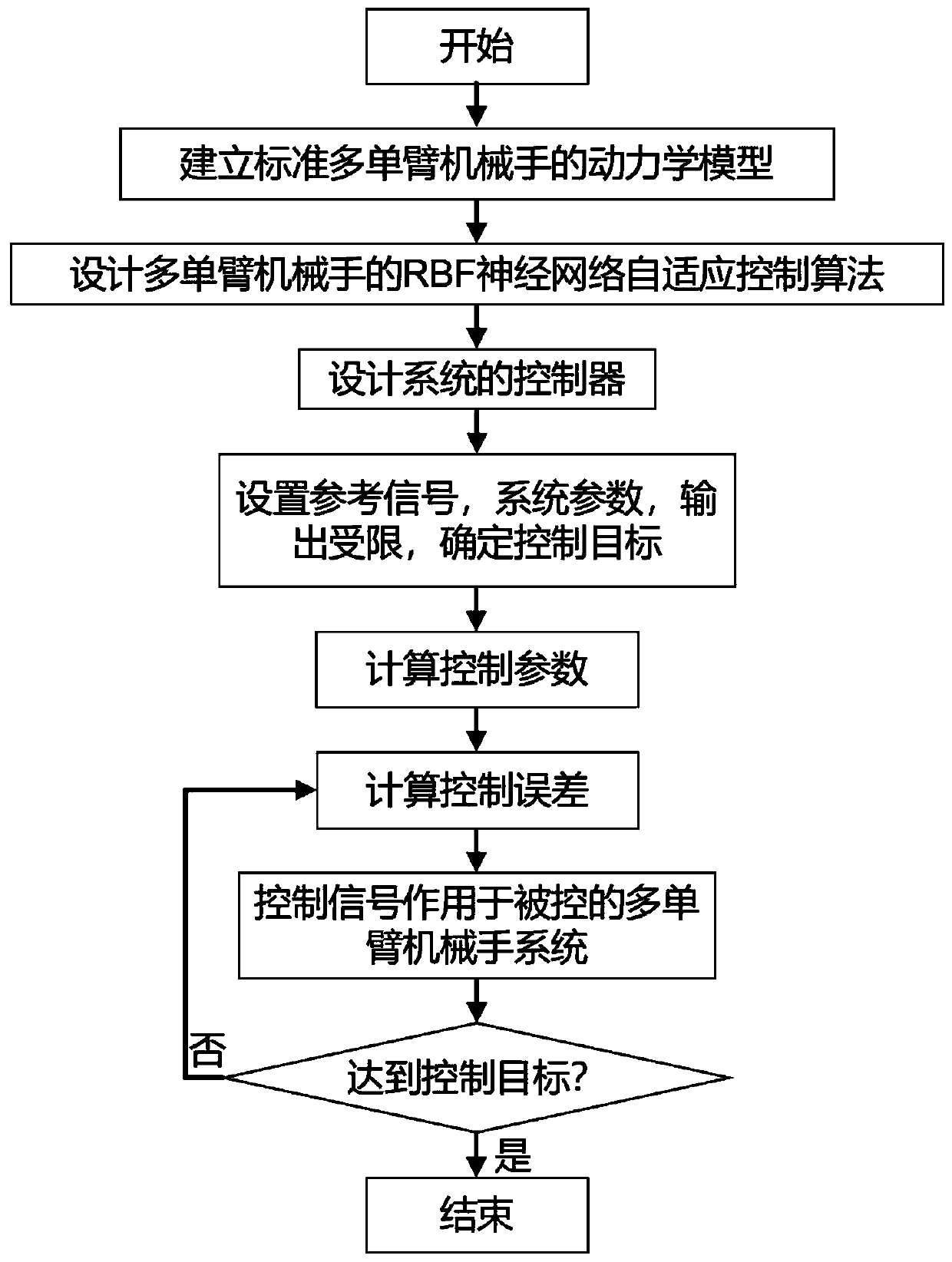
RBF neural network adaptive control method for multiple single mechanical arms
The invention discloses an RBF neural network adaptive control method for multiple single mechanical arms. The method comprises the steps of: approximating an unknown nonlinear function in a mechanical arm system by a neural network; introducing a dynamic surface technique to design a first-order filter to solve the computational explosion caused by repeated derivation on a control in a backstepping method; and processing the unknown parameters and output limitation by a Nussbaum function and an obstacle Lyapunov function. The method does not require an accurate mechanical kinetic model, can completely eliminate the output error caused by unknown kinetic parameters and random interference, solves the problem that a model-based multi-single mechanical arm control scheme depends on a precise kinetic model, and improves the dynamic performance of the mechanical arm and the trajectory tracking accuracy of a joint space. Finally, the feasibility and effectiveness of the control method are verified by simulation examples.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Inverted pendulum self-adaptive iterative learning inversion control method
An inverted pendulum self-adaptive iterative learning inversion control method is characterized in that: aiming at an inverted pendulum system containing unknown input saturation, a self-adaptive iterative learning inversion controller is designed through utilization of a neural network and an inversion control method in combination with self-adaptive iterative learning control; the construction of an integral lyapunov function solves the control problem caused by derivation of a unknown gain function; based on the median theorem, a hyperbolic tangent function is adopted to approximate an input saturation term; then, a radial basis function neural network is adopted to approximate and compensate uncertain unknown items of a system, and two combined self-adaptive laws are adopted to updatethe weight of the neural network and the bound of estimation errors. Under the condition that the system has input saturation, the invention provides the control method which can compensate the unknown uncertainty of the system, solve the control problem caused by derivation of the unknown gain function and realize two-norm convergence of a tracking error of the system to be near zero within limited iteration times.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
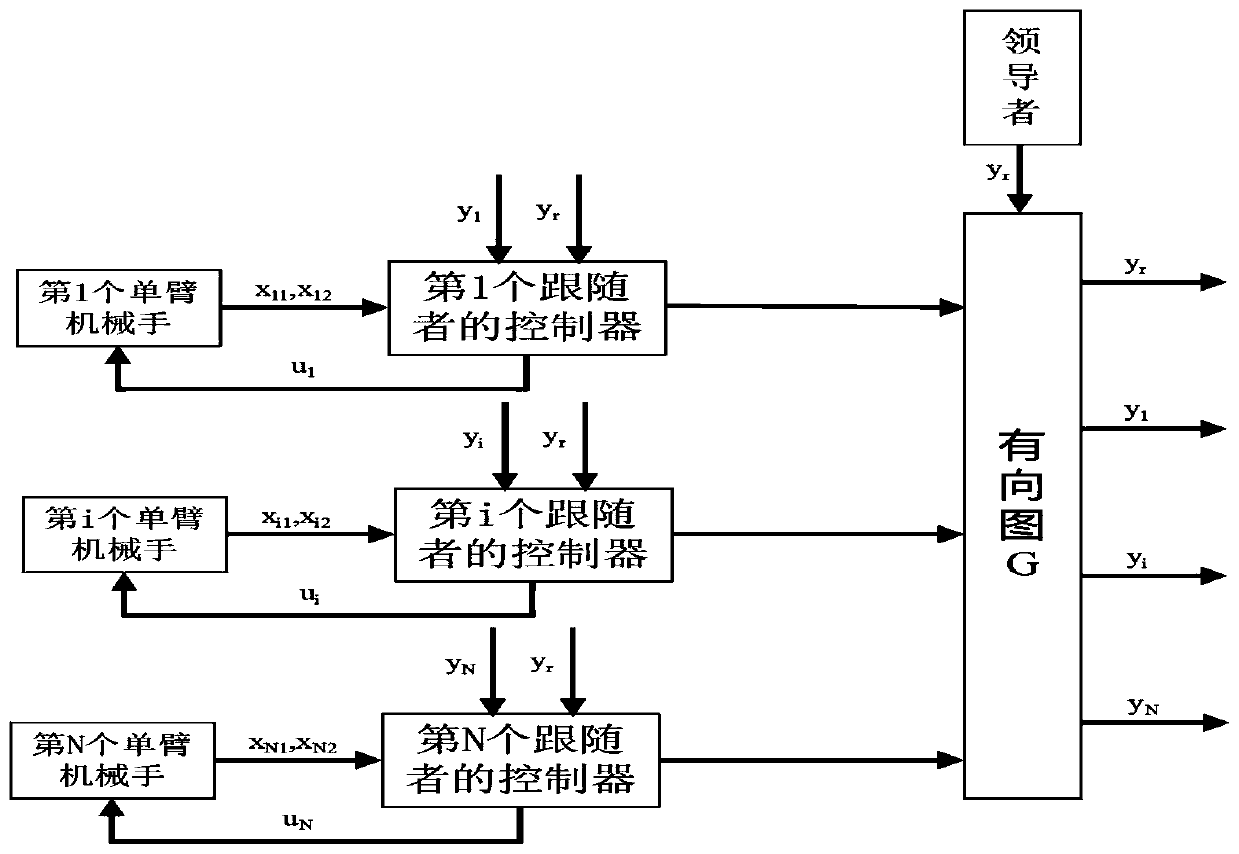
Observer-based adaptive command filter control method for output consistency of multi-single-arm manipulator
ActiveCN110275435AAvoiding the "computational explosion" problemSolve the problem of unmeasurable stateAdaptive controlDynamic modelsState observer
The invention discloses an observer-based adaptive command filter control method for output consistency of a multi-single-arm manipulator. Modeling of dynamic characteristics of a multi-single-arm manipulator is performed; and an adaptive controller is designed by combining a backstep method with a command filtering technique. During the controller design process, an unknown item of the system approximates by using a fuzzy logic system, so that the need of the precise dynamic model of the manipulator is eliminated. A state observer estimates an unmeasurable state in the system. With the command filtering technique, a complicated signal derivation calculation explosion problem is solved. Since the manipulator system output is restricted, an output restriction problem is solved by using an obstacle Lyapunov function. For a mechanical connection part of the manipulator, the driver always has a non-smooth input dead zone problem; and the influence on the system by the input dead zone is compensated by using the slope information of the input dead zone. The manipulator system output can track the reference signal effectively; and all signals are semi-globally bounded ones.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
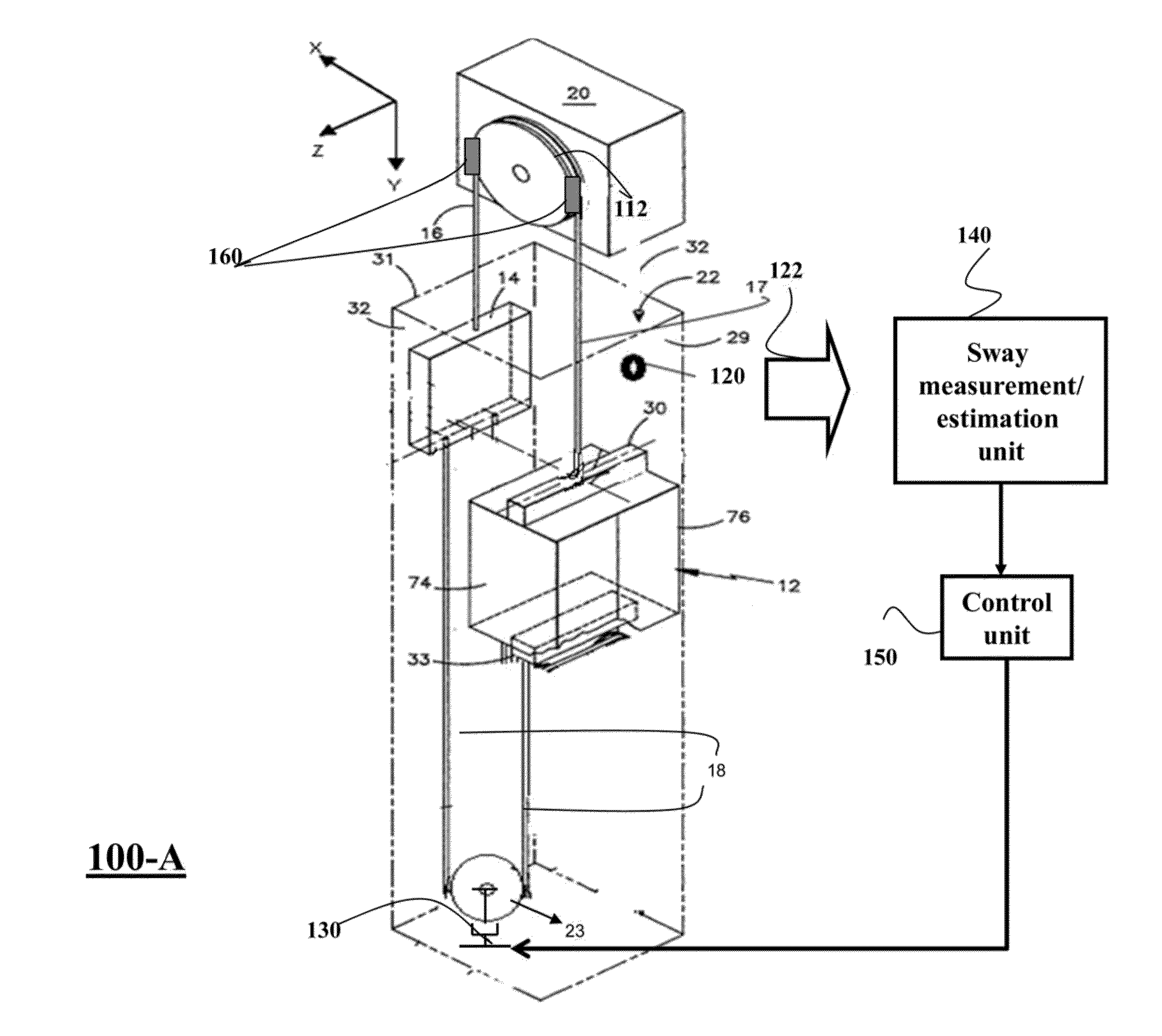
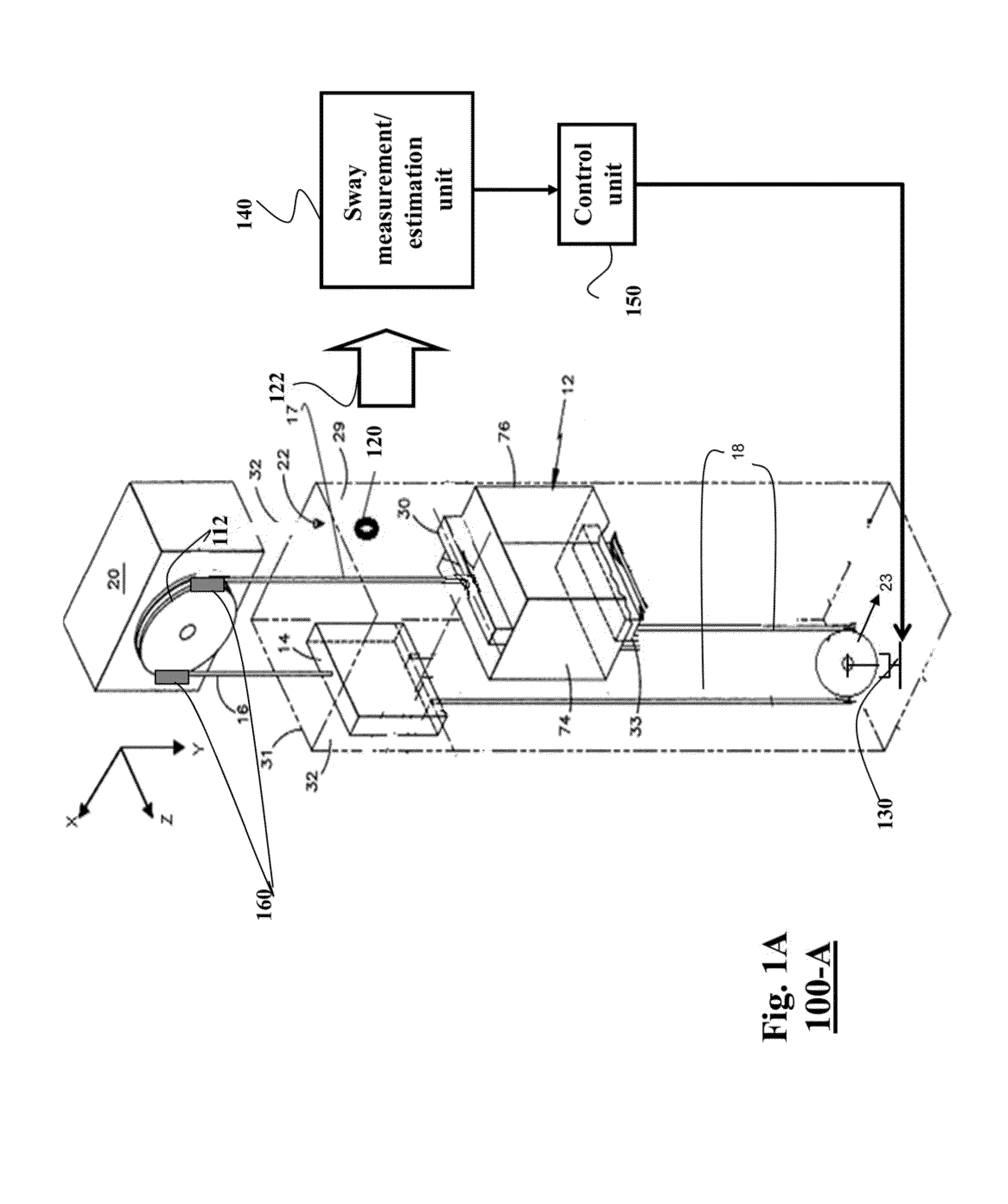
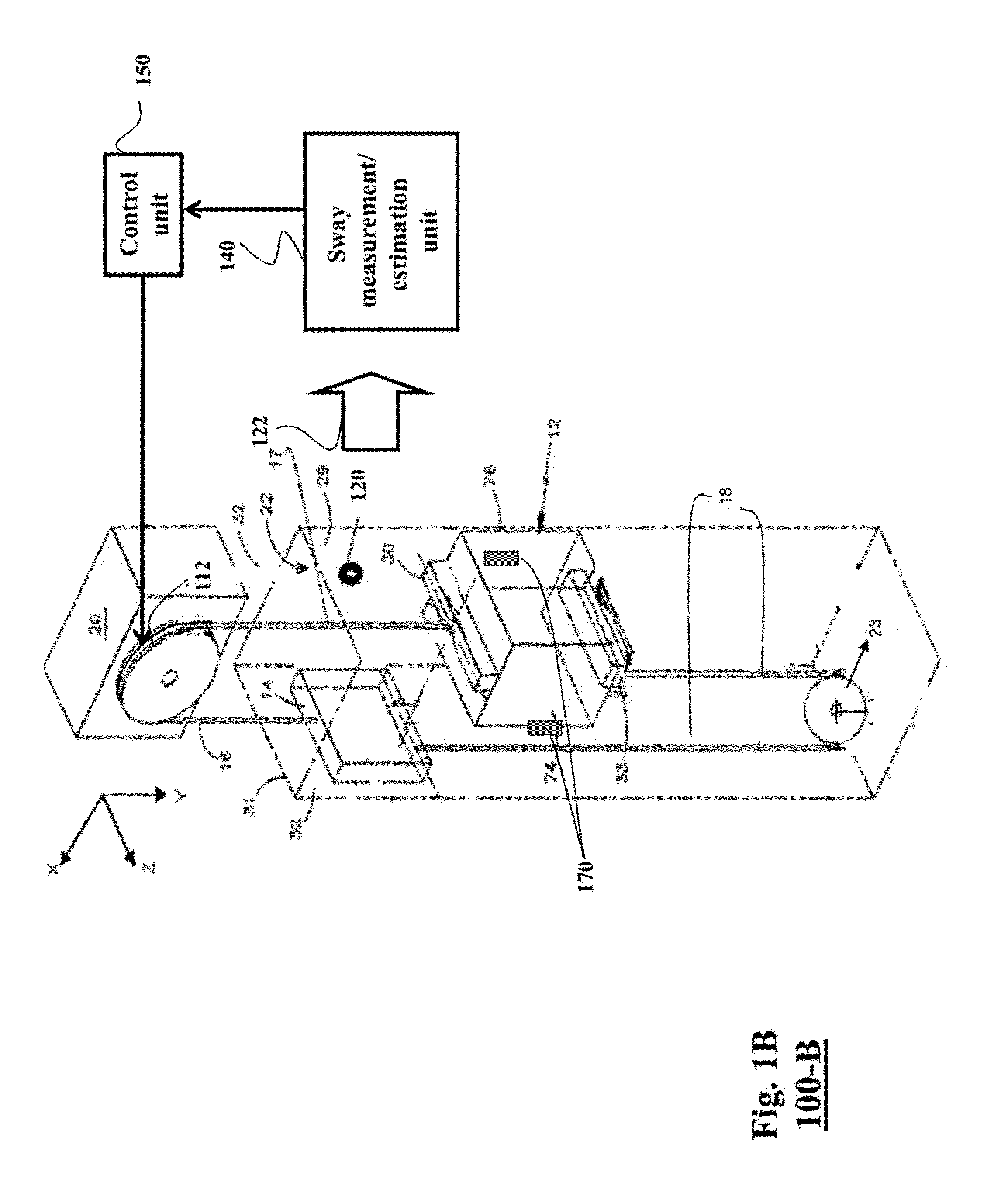
Method and System for Controlling Sway of Ropes in Elevator Systems by Modulating Tension on the Ropes
ActiveUS20140124300A1Reduce maintenance costsIncrease amplitudeComputer controlElevatorsElevator systemEngineering
A method controls an operation of an elevator system using a control law to stabilize a state of the elevator system using a tension of an elevator rope. A derivative of a Lyapunov function along dynamics of the elevator system controlled by the control law is negative definite. The control law is a function of amplitude of a sway of the elevator rope and a velocity of the sway of the elevator rope. The method determines the amplitude of the sway of the elevator rope and the velocity of the sway of the elevator rope during the operation, and determines a magnitude of the tension of the elevator rope based on the control law, and the amplitude and the velocity of the sway of the elevator rope.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
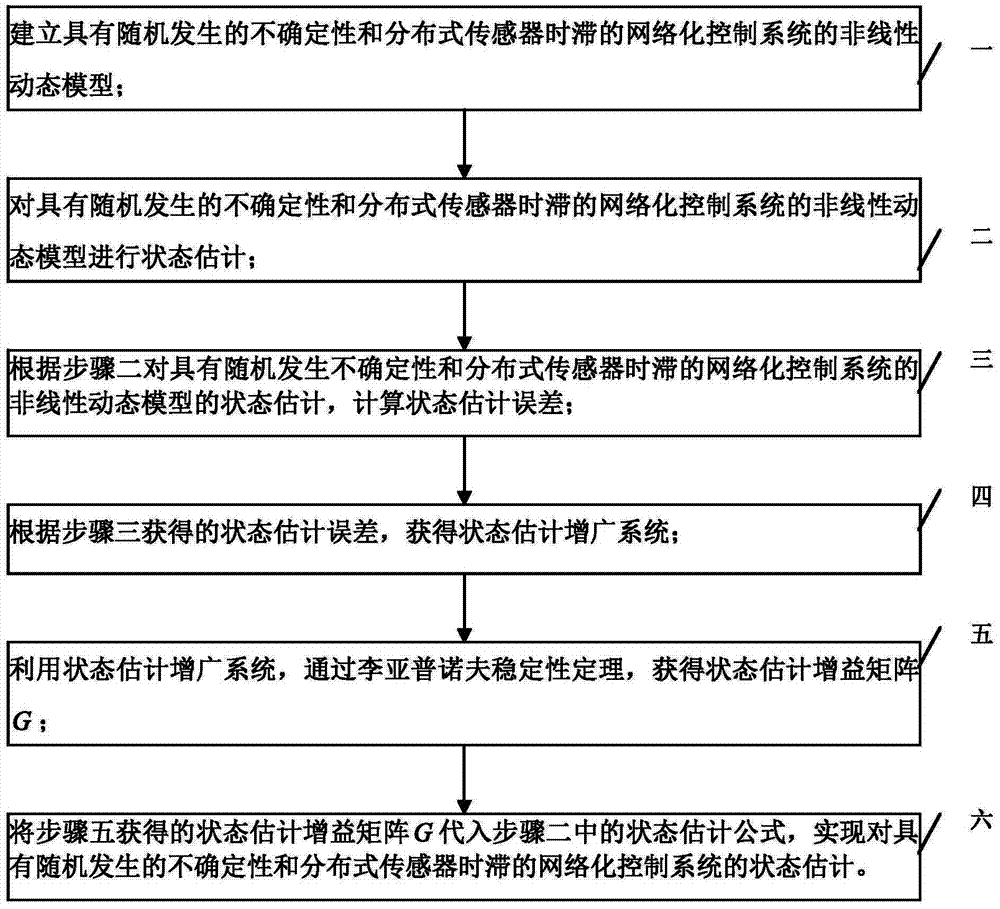
Method for estimating state of networked control system with random uncertainty and delay of distributed sensors
ActiveCN103676646ATo achieve the purpose of resisting nonlinear disturbanceEasy to solveAdaptive controlComplex dynamic systemsComputer science
The invention relates to a method for estimating the state of a networked control system with random uncertainty and delay of distributed sensors, particularly to a method for estimating the state of random uncertainty and delay of distributed sensors. The method solves the problem that the existing method for state estimation can not treat the random uncertainty and the delay of distributed sensors at the same time, so the performance of state estimation is influenced. According to the method of the invention, the influence of random uncertainty and delay of distributed sensors on the performance of state estimation is considered at the same time, and a Lyapunov function is used to fully consider the effective information of the delay. Compared with the existing method for estimating the state of a nonlinear complex dynamic system, the method for state estimation of the invention can be used to treat random uncertainty, delay of distributed sensors and bounded time-varying delay at the same time so as to obtain a method for state estimation on the basis of the solution of a linear matrix inequality; therefore, the purpose of resisting nonlinear perturbation can be achieved. The method is suitable for estimating the state of the nonlinear complex dynamic system.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Four-rotor aircraft output-limited backstepping control method based on integral sliding mode obstacle Lyapunov function
ActiveCN108037662AImprove dynamic response performancePrevent overshootAdaptive controlResponse processFlight vehicle
Provided is a four-rotor aircraft output-limited backstepping control method based on an integral sliding mode obstacle Lyapunov function. For the dynamic system of a four-rotor aircraft, an integralsliding mode obstacle Lyapunov function is selected, and a four-rotor aircraft output-limited backstepping control method based on the integral sliding mode obstacle Lyapunov function is designed. Theintegral sliding mode obstacle Lyapunov function is designed in order to ensure that the output of the system is limited within a certain range, avoid too large overshoot and reduce the time of arrival. Therefore, the dynamic response performance of the four-rotor aircraft system is improved. The invention provides a four-rotor aircraft output-limited backstepping control method based on an integral sliding mode obstacle Lyapunov function, which enables the system to have a good dynamic response process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
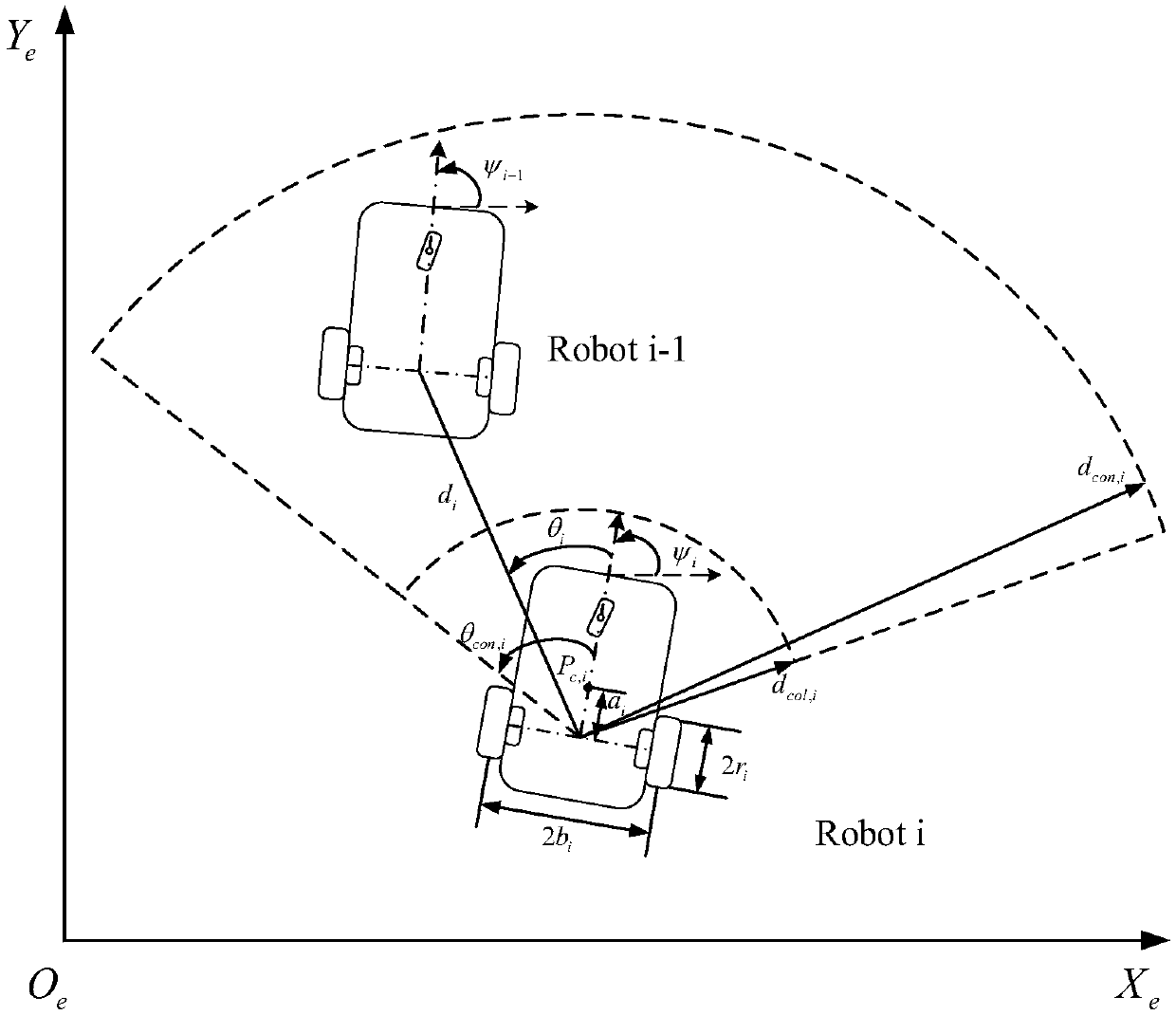
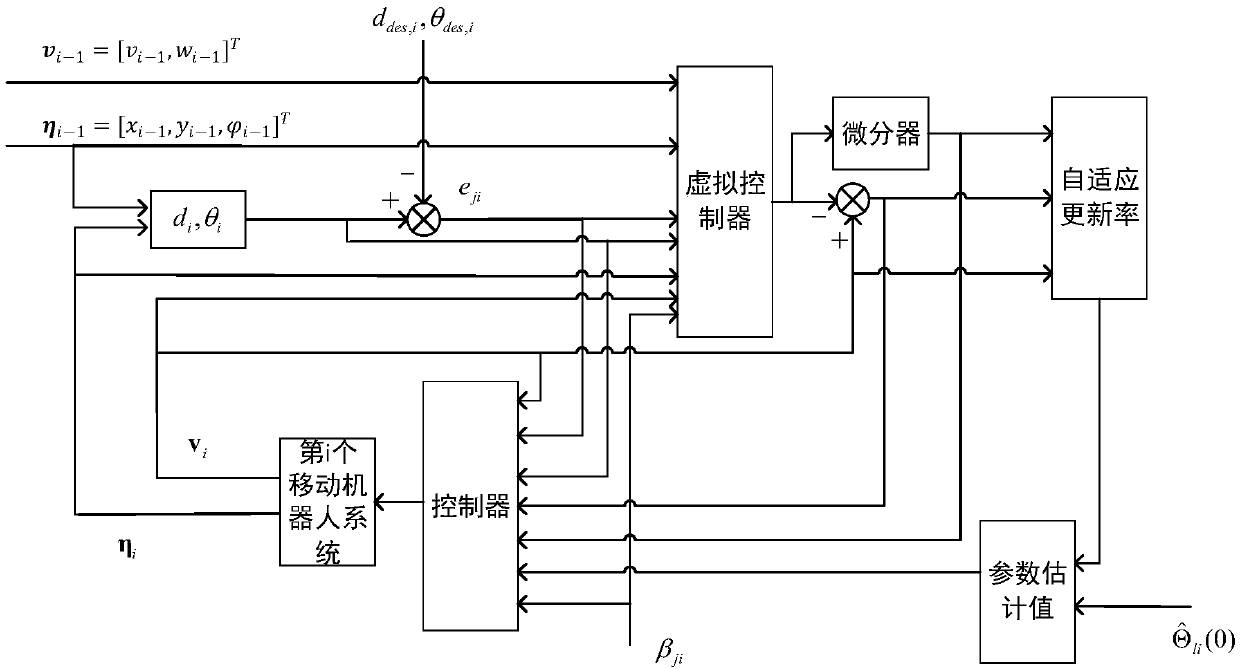
Formation control method of mobile robots under constraint of communication range
InactiveCN108983786AGuaranteed Transient PerformanceAvoid collisionPosition/course control in two dimensionsPerformance functionBackstepping
The invention discloses a formation control method of mobile robots under constraint of a communication range. The formation control method of mobile robots under constraint of a communication range designs a formation controller for uncertainty of models for mobile robots and guarantees that the formation error eventually converges to zero point. The formation control method of mobile robots under constraint of a communication range includes the steps: constructing dynamic models for mobile robots; defining a distance variable and an azimuth variable between the i-th mobile robot and the leader of the i-th mobile robot in a leader-follower formation structure; designing a performance function for the formation distance error and the azimuth error; combining the performance function with the tan-type obstacle Lyapunov function and a backstepping design method, designing a formation controller; and using an adaptive control technology to solve the uncertainty problem of models in the controller design. The formation controller designed by the formation control method of mobile robots under constraint of a communication range enables each mobile robot in the leader-follower formationstructure to measure both the information of the leader of the each mobile robot and avoid collision with the leader, and the formation error satisfies the preset transient performance, and eventually can converge to the zero point.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
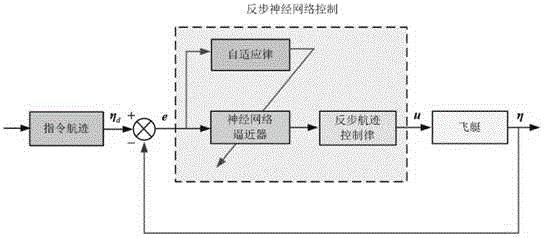
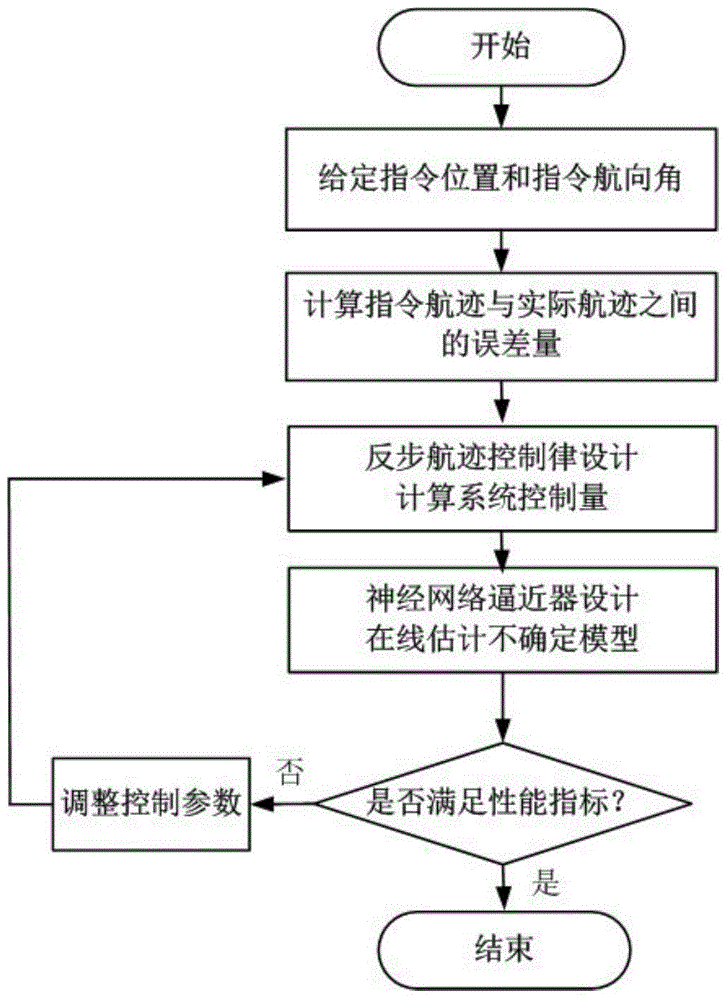
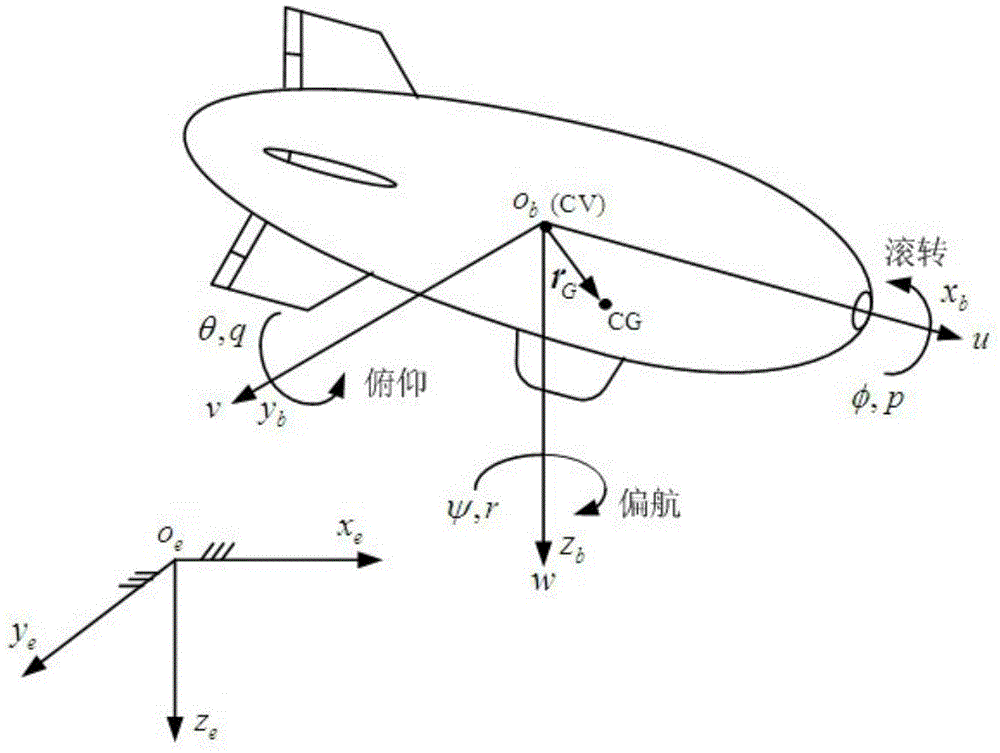
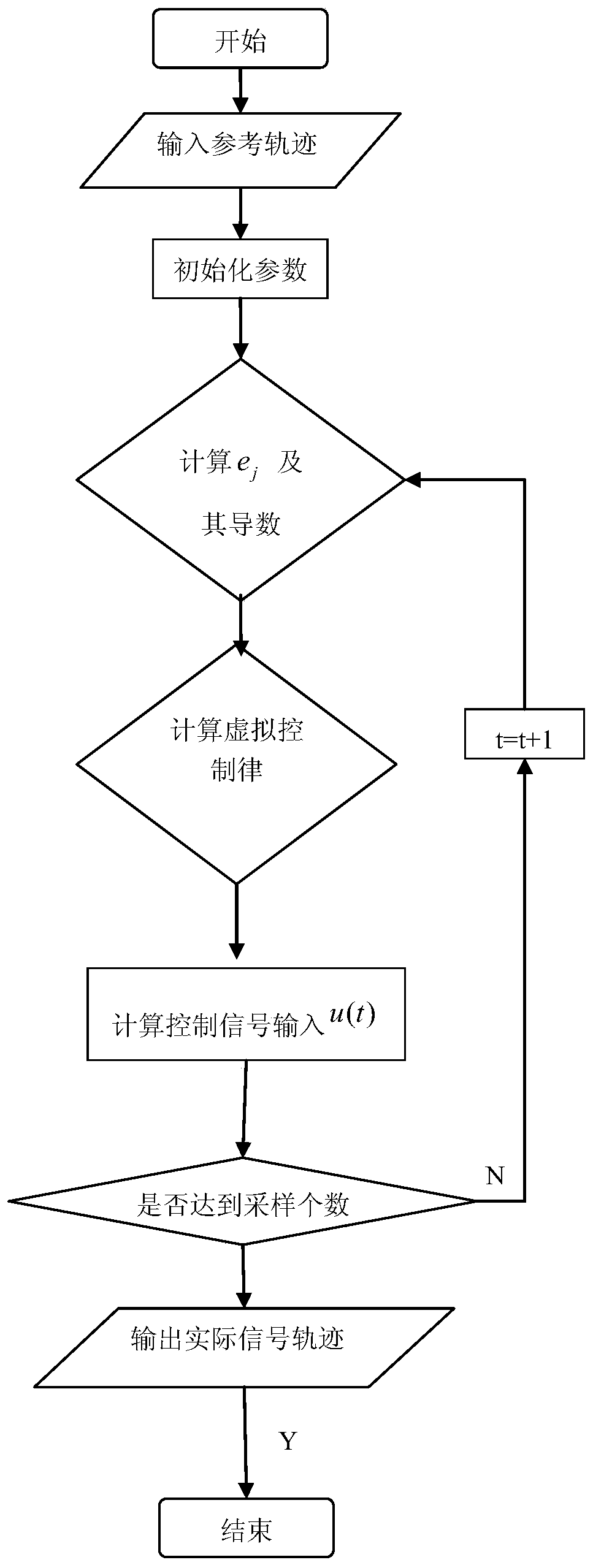
Method for controlling backstepping neural network for tracking three-dimensional flight path of airship
ActiveCN104793629AAdaptableImprove robustnessAdaptive controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsBacksteppingSimulation
The invention relates to a method for controlling a backstepping neural network for tracking a three-dimensional flight path of an airship. In order to control tracking of the flight path of the airship, a nonlinear kinetic model of the airship is established; the nonlinear kinetic model of the airship serves as a controlled object and is divided into two subsystems, a Lyapunov function and a middle virtual controlled quantity are designed for each subsystem by using a backstepping method, proper virtual feedback is determined, and the previous state of a system is gradually stable until the whole system is gradually stable in an inverse deducing mode; and in order to solve the problem that the kinetic model of the airship is uncertain, an unknown kinetic model of the airship is estimated accurately by a neural network approximator, and the control precision and the system performance are improved. A closed-loop system controlled by the method can track an optional parameterized command flight path precisely and has high stability, adaptability, robustness and dynamic performance, and an effective scheme is provided for an airship flight path control project.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Adaptive control method for robotic arm system based on time-varying asymmetric obstacle Lyapunov function
ActiveCN110687787AAchieve precise tracking controlSimple designAdaptive controlRobotic armMathematical model
An adaptive control method for a robotic arm servo system based on a time-varying asymmetric obstacle Lyapunov function comprises the following steps of step 1, establishing a mathematical model of the robotic arm servo system, and designing the time-varying asymmetric obstacle Lyapunov function; step 2, designing an adaptive controller by using the time-varying asymmetric obstacle Lyapunov function and combining an inversion method; and step 3, analyzing stability. By setting the parameter value of a constraint boundary function, the adaptive control method provided by the invention can effectively solve the system output constraint problem and ensure the steady-state performance and transient performance of the system. In addition, the uncertain part of a neural network approximation model and the derivative of the virtual control quantity are used to effectively simplify the design of the controller, improve the robustness of the system to a certain extent, and enable the robotic arm servo system to achieve accurate and fast tracking control.
Owner:NINGBO YAOHUA ELECTRIC TECH
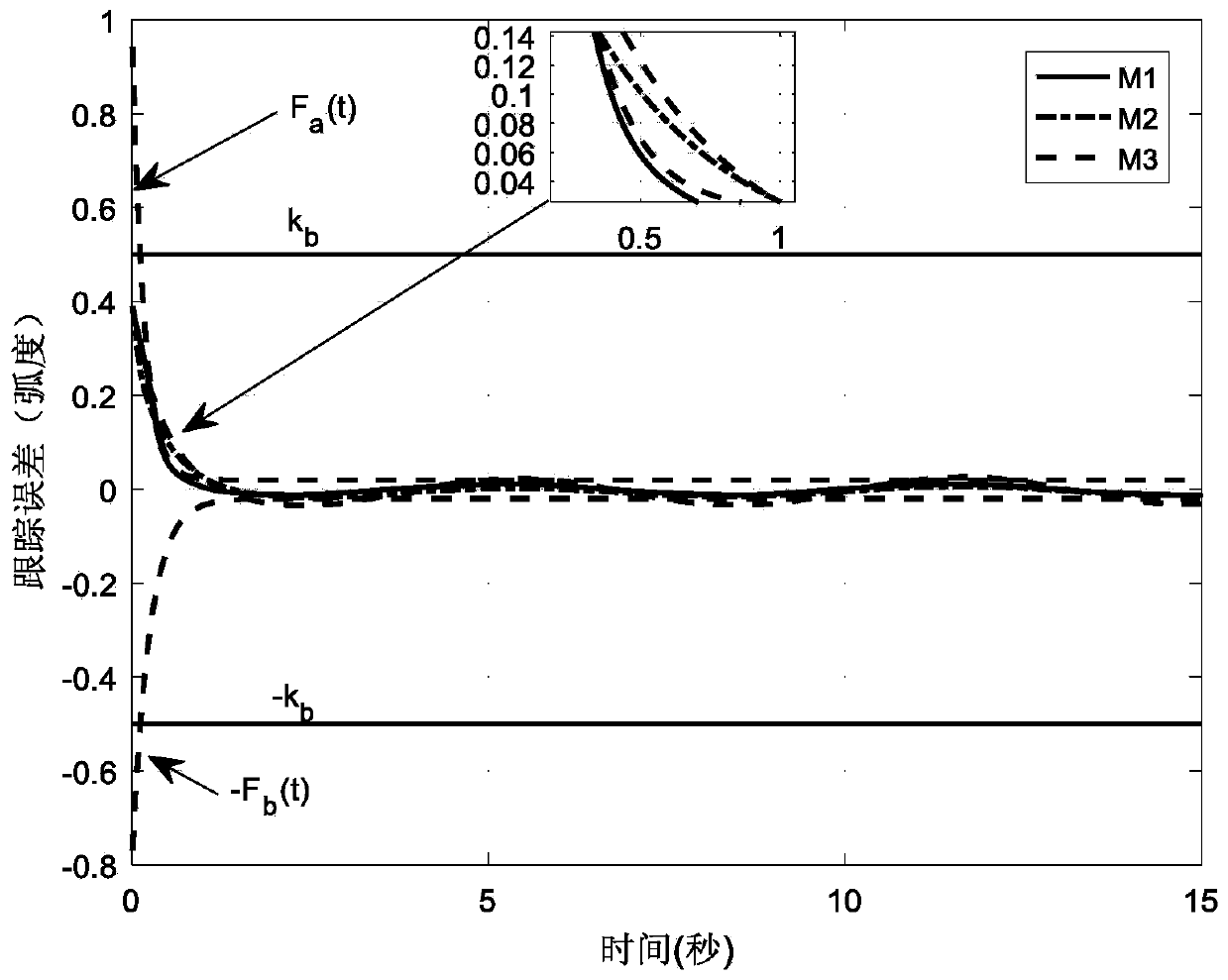
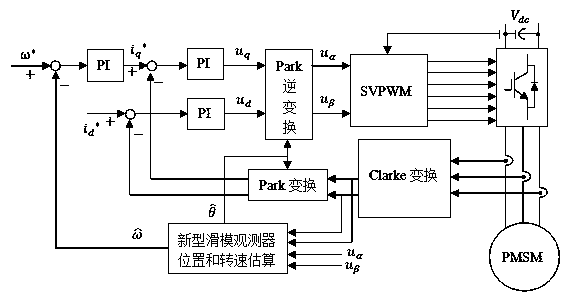
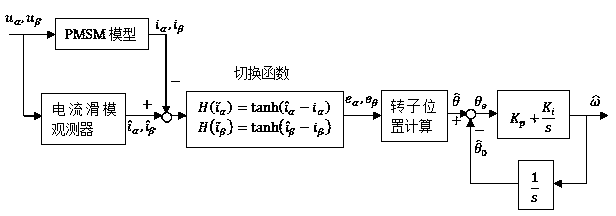
Speed regulating control strategy for sensorless permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN104135197AReduce precisionSingle motor speed/torque controlElectronic commutatorsMathematical modelPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention belongs to the field of control over a permanent magnet synchronous motor, and relates to a speed regulating control strategy for a sensorless permanent magnet synchronous motor. The speed regulating control strategy is characterized in that a three-phase current of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is detected, the current under an alpha and beta coordinate system is obtained through Clarke conversion, and the current under the dq coordinate system is obtained through Park conversion; a sliding-mode observer is designed according to a mathematic model of the permanent magnet synchronous motor under the alpha and beta two-phase static coordinate system; a hyperbolic tangent function is used as a switching function; a sliding-mode face is selected; the estimation value of the rotor position is obtained through counter electromotive force; a speed estimator is adopted for estimating the speed; a Lyapunov function is selected, and an adaptive law is obtained through the stability condition; According to the speed regulating control strategy, the structural switching discontinuity is relieved, the buffeting is obviously weakened, the rapidness, the robustness and the dynamic performance are improved, when an error exists in the estimation value of the rotor position, the speed estimation error is made to be within the controllable range, and the rotating speed estimation precision is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
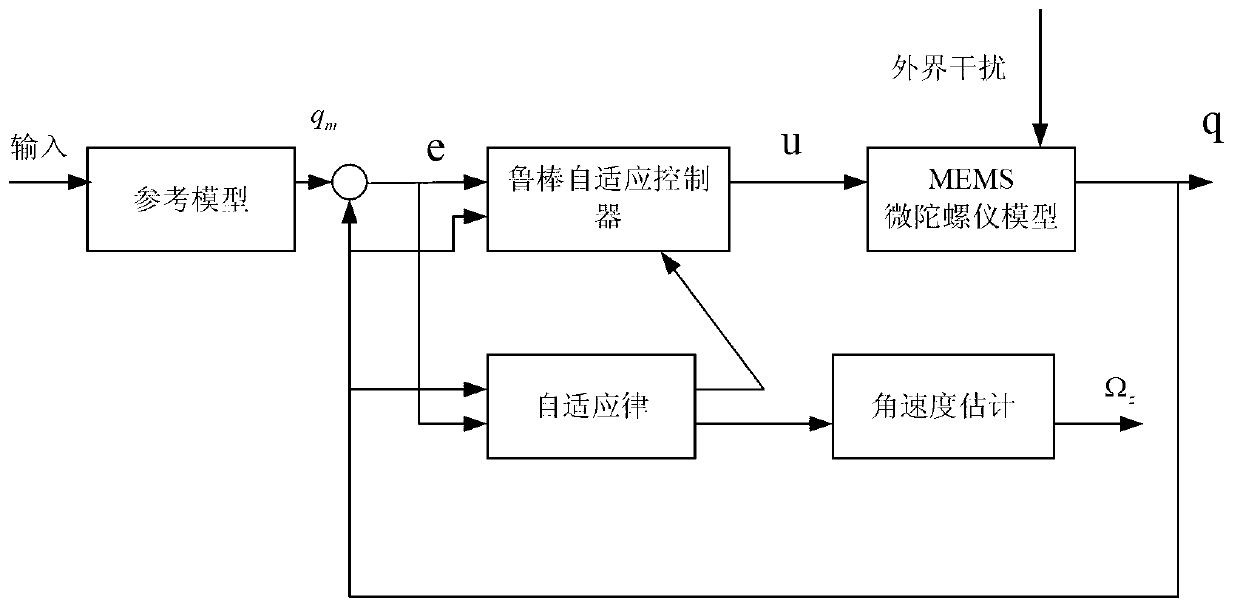
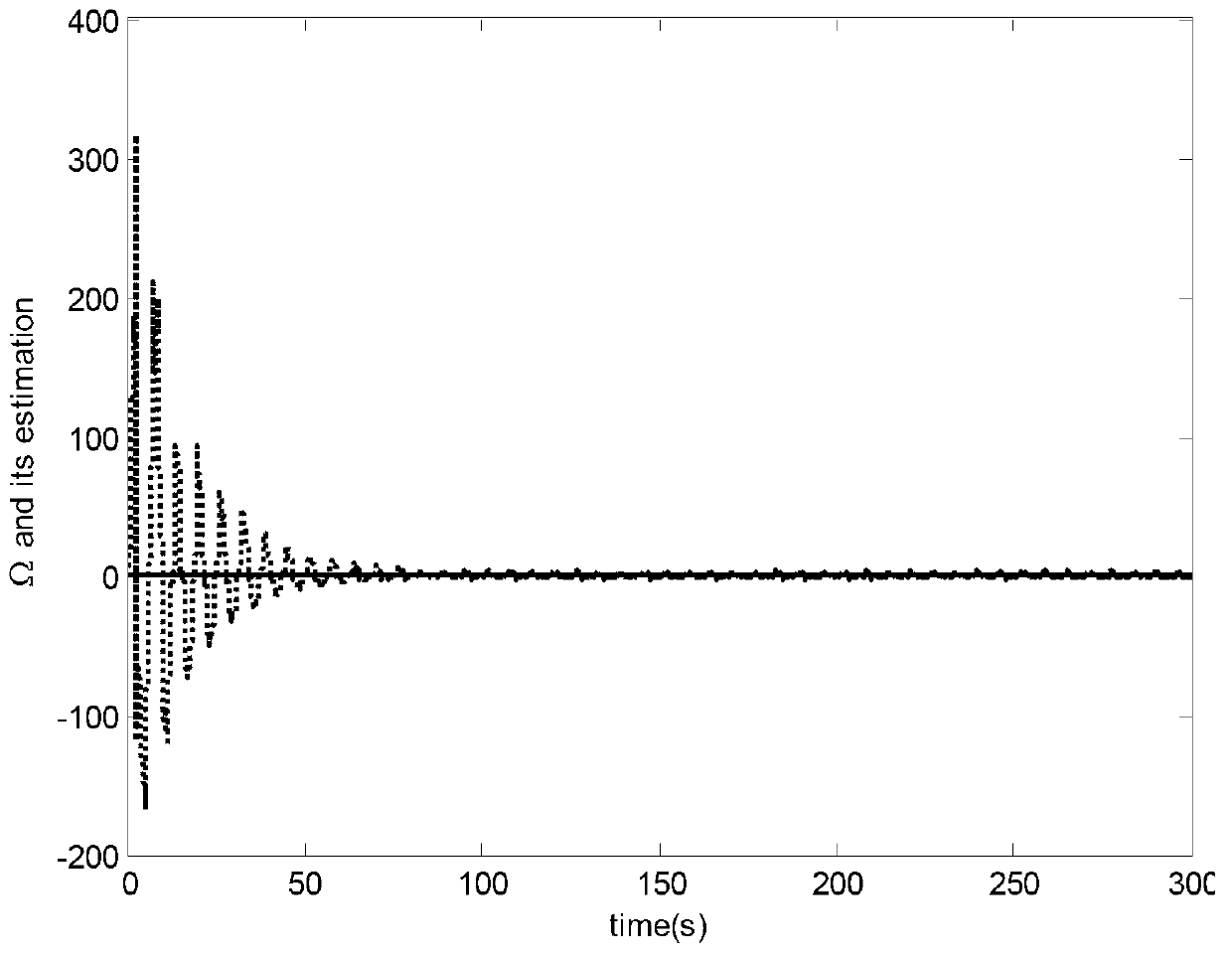
Micro gyroscope robust self-adaptive control method
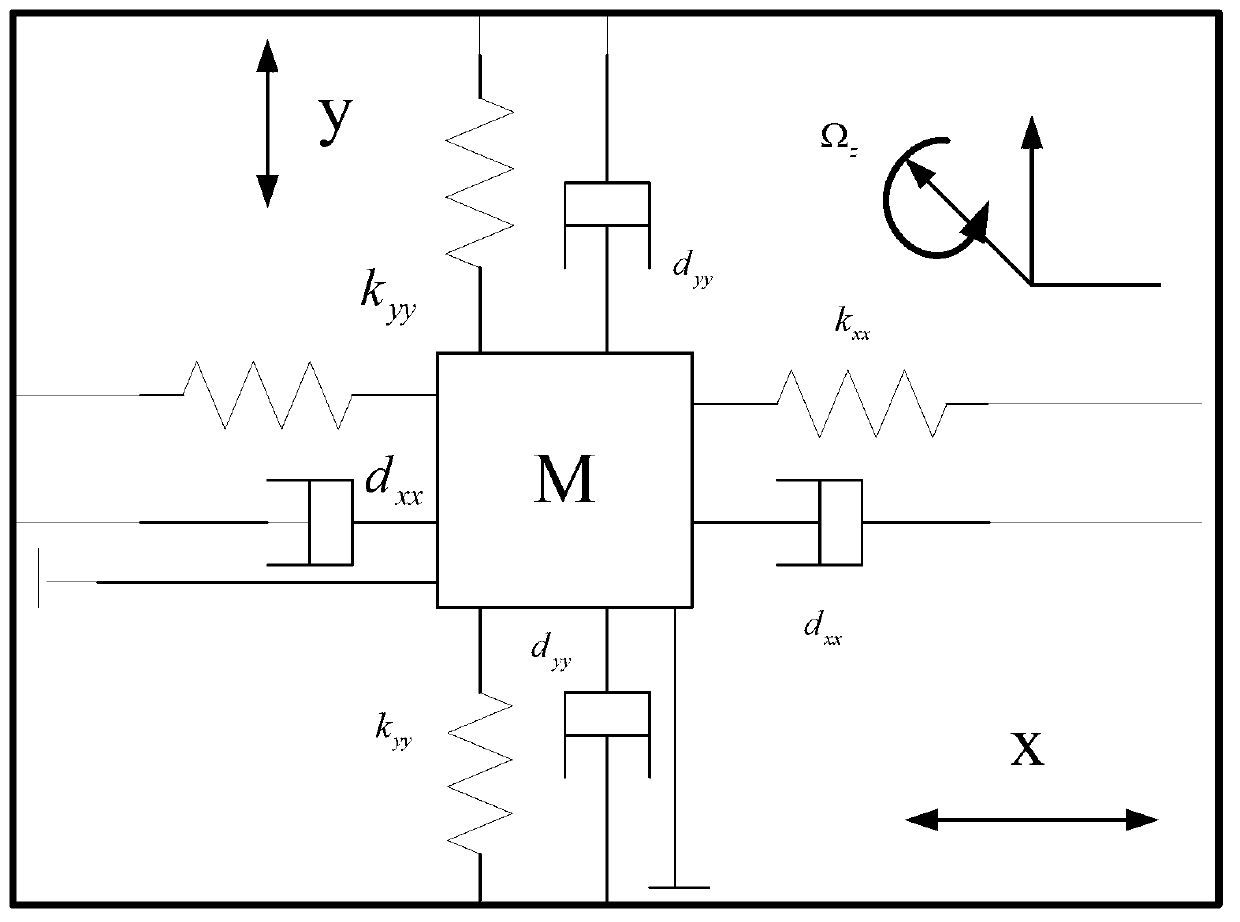
InactiveCN103345148AGuaranteed global stabilityCompensate for manufacturing errorsAdaptive controlVibration amplitudeGyroscope
The invention discloses a micro gyroscope robust self-adaptive control method, and the method is applied to a controller comprising a micro gyroscope. The method includes the following steps of establishing an ideal dynamics model, establishing a dimensionless dynamics model of the micro gyroscope, designing a sliding mode function and making the derivative of the sliding mode function to time be zero to acquire a control law, adding a feedback item and a robust item to the control law, wherein the control law with feedback item and the robust item is used as a robust self-adaptive control law, controlling the micro gyroscope based on the Lyapunov function method, and designing an self-adaptive law. According to the micro gyroscope robust self-adaptive control method, the feedback item is added to the control law, so that micro gyroscope two axle vibration trajectory tracking and parameter estimation speed is greatly improved, and vibration amplitude is reduced; the robust item is added to the control law, so that external interference and parameter uncertainty are removed, and robustness and dynamic characteristics of a system are improved; the self-adaptive law is designed based on the Lyapunov function method, so that globally asymptotic stability of the whole system is guaranteed, and reliability of the system and robustness to parameter change are improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
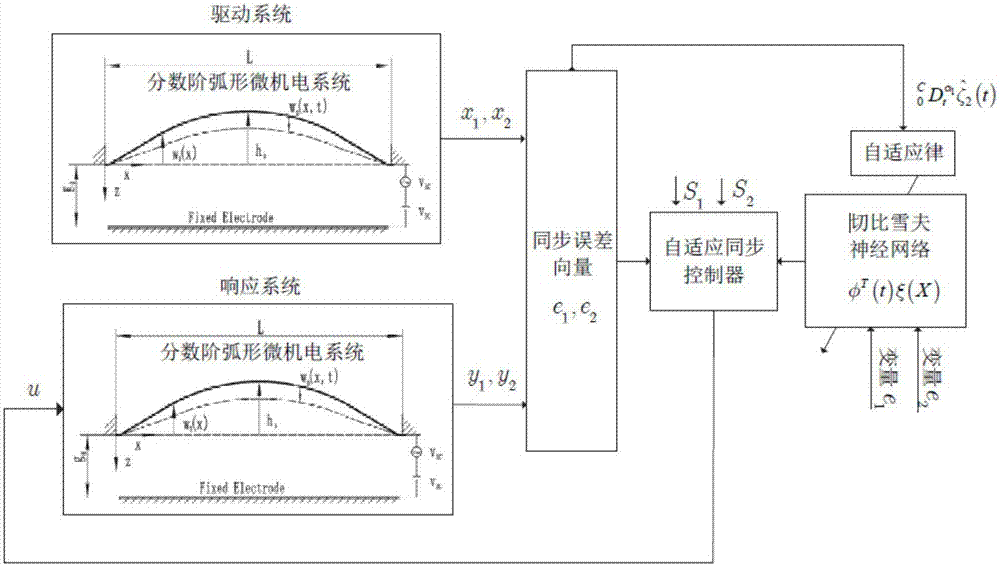
Adaptive synchronous control method of fractional arc micro-electromechanical system
ActiveCN107479377ASynchronous Control GuaranteeReduced impact on synchronous control performanceAdaptive controlVirtual controlSystems modeling
The invention discloses an adaptive synchronous control method of a fractional arc micro-electromechanical system, which comprises the following steps: 1)establishing a driving system and a responding system model of a fractional arc micro-electromechanical system based on Euler-Bernoulli beams to obtain the synchronous error vector; 2)constructing the Chebyshev neural network with adaptive control law according to the error vector; using the fractional Lyapunov function to construct the virtual control input; using the Chebyshev neural network to estimate the unknown nonlinearity function for the system; in combination with fractional adaptive law, constituting the actual control input; in the back stepping framework, constructing an adaptive synchronization controller; and inputting the controller's output signal to the responding system in the fractional arc micro-electromechanical system. The method of the invention realizes the synchronous control between the driving system and the responding system which ensure the transient and steady performance of the system and reduces the influence of the uncertain factors in the fractional arc micro-electromechanical system on the synchronous control performance.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
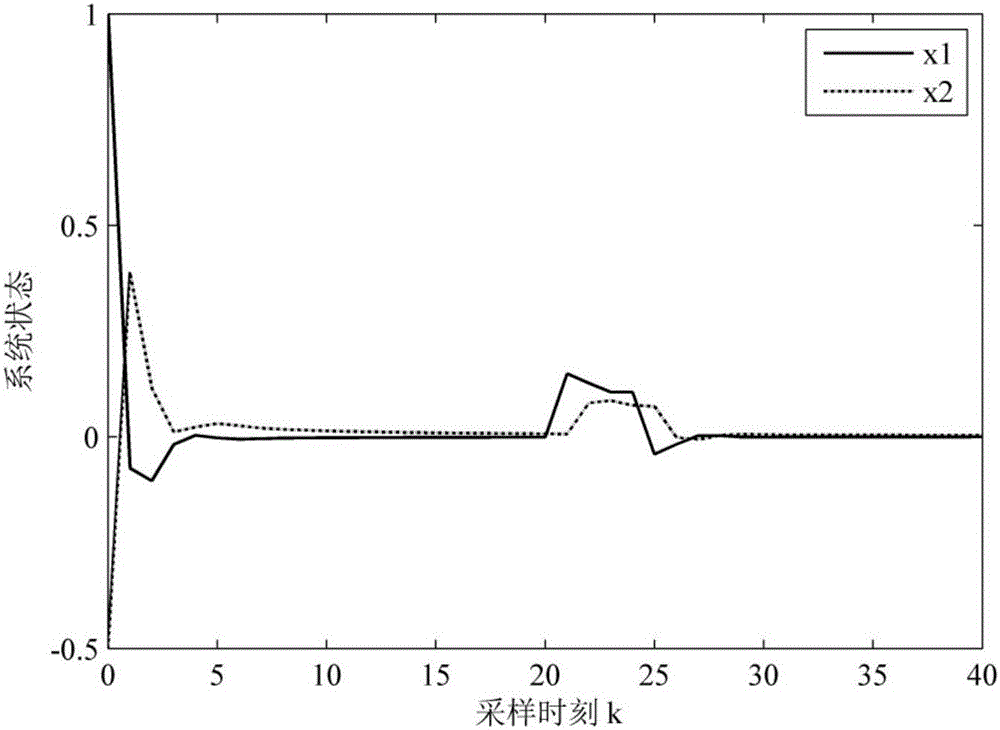
Nonlinear networked control system non-fragile H-infinity fault tolerance control method
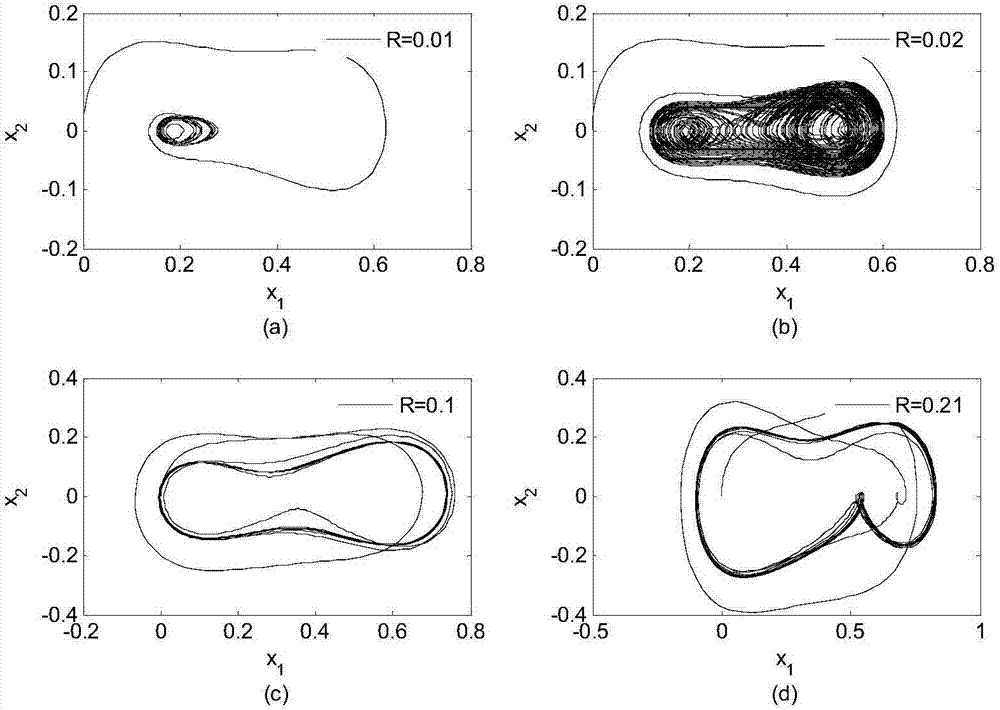
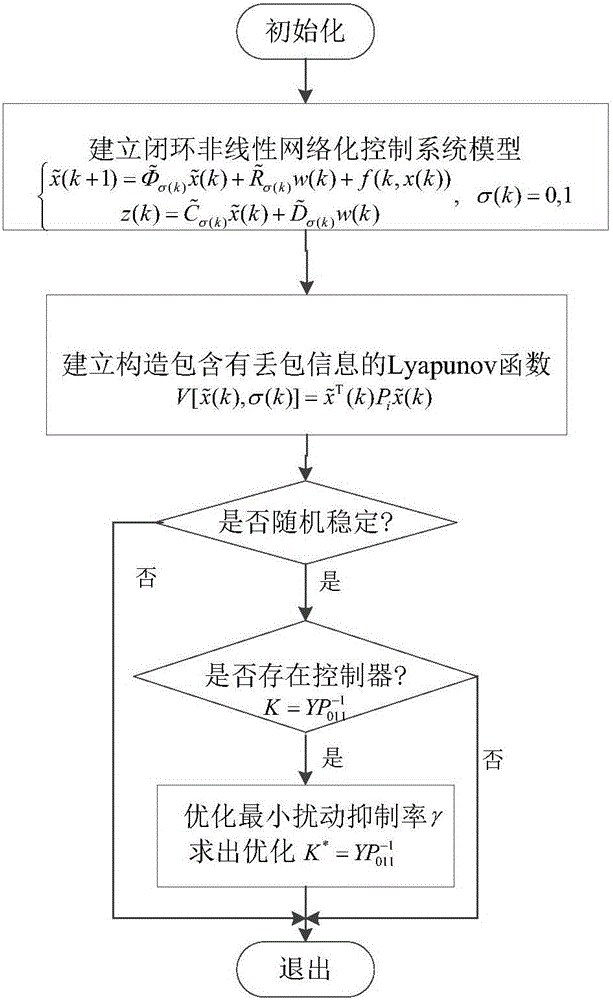
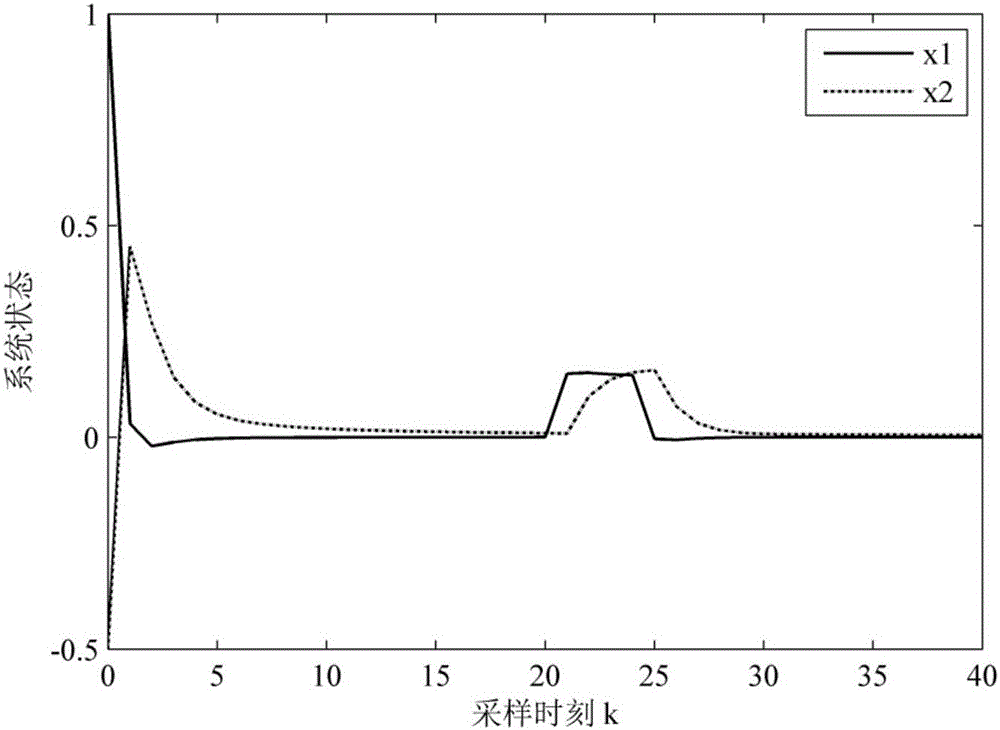
ActiveCN106257873AImprove anti-interference abilityData switching networksLyapunov stabilityPacket loss
The invention discloses a nonlinear networked control system non-fragile H-infinity fault tolerance control method. Firstly a closed-loop nonlinear networked control system model is established for considering the situation of parameter perturbation, time delay and packet loss of the nonlinear networked control system and random fault of an actuator, and then a Lyapunov function including packet loss information is constructed. The sufficient conditions of nonlinear networked control system stochastic stability and existence of an H-infinity fault tolerance controller are obtained by using the theory of Lyapunov stability and a linear matrix inequality analysis method. Solving is performed by using a Matlab LMI tool box, a non-fragile fault tolerance controller gain matrix K=YP<-1><011> is given, the conditions for optimization of the minimum disturbance suppression ratio gamma are given, and the optimized controller gain matrix K* under the minimum disturbance suppression ratio gamma<min> (the square root of e) is acquired. The situation of the random fault of the actuator is considered, and the probability of the random fault meets BerRoulli distribution so as to have more practical meaning.
Owner:北京新桥信通科技股份有限公司
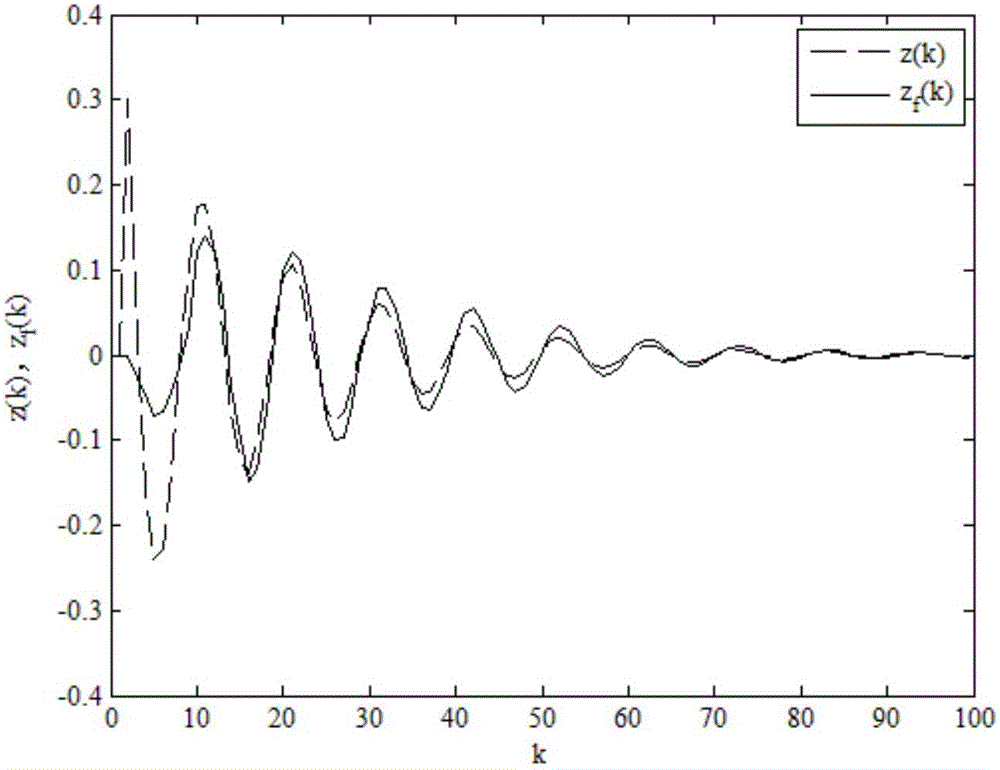
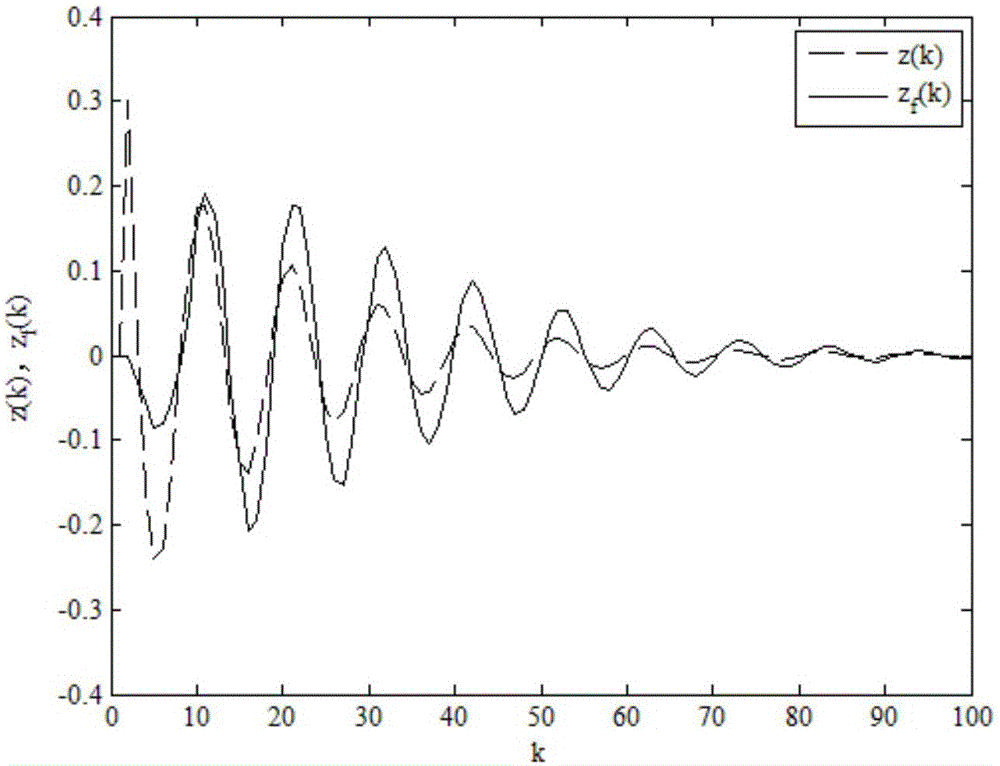
Non-fragile dissipative filtering method of nonlinear networked control system
ActiveCN106529479AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove performance indicatorsCharacter and pattern recognitionLyapunov stabilityPacket loss
The present invention discloses a non-fragile dissipative filtering method of a nonlinear networked control system. The method comprises the steps of firstly establishing a nonlinear networked filtering error system model on the conditions of considering the time delay and the packet loss of the nonlinear networked control system and the perturbation of the filter parameters, then constructing a Lyapunov function, and then utilizing a Lyapunov stability theory and a linear matrix inequality analysis method to obtain the sufficient conditions of the mean square exponential stability of a nonlinear networked filtering error system and the existence of a non-fragile dissipative filter, utilizing a Matlab LMI tool kit to solve, and definding a non-fragile dissipative filter parameter matrix. The method of the present invention considers the random time delay and the pocket loss situations between the sensors and the filters, is suitable for the general dissipative filtering including the H-infinite filtering, and enables the conservatism of the non-fragile dissipative filter design to be reduced. Moreover, a non-modeling state of the system is considered when a full-order filter is designed, thereby being able to reduce the calculation burdens and the design cost.
Owner:毛国全
Method of global sliding mode control of neural network of micro-gyroscope
InactiveCN103529701ARealize online updateEliminate online updatesAdaptive controlRobustificationGyroscope
The invention discloses a method of a global sliding mode control of a neural network of a micro-gyroscope, which comprises the following steps of establishing a global sliding mode control system of the neural network, designing a control law and taking as a control input of the micro-gyroscope, designing a self-adaptive law based on an Lyapunov function theory, and verifying the stability of a closed-loop system. The global sliding mode control is realized by designing a dynamic nonlinear sliding mode surface, the defect of no robustness in a reach movement stage of the sliding mode control is eliminated, the system has robustness in the whole process of response, and the respective defects of the global sliding mode control and the neural network are reduced by utilizing the intelligent control function of global sliding mode and the neural network. According to the method, the selection of sliding mode coefficients is simplified, the transient performance and the robustness of the sliding mode control system are improved, so that the closed-loop control system has global robustness, buffeting in the sliding mode control is eliminated, and thus a powerful foundation is provided for expansion of an application range of the micro-gyroscope.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com