Patents
Literature
542 results about "Longitudinal plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A longitudinal plane that divides the body of a bilaterally symmetrical animal into right and left sections. the anteroposterior plane, or the section parallel to the median plane of the body. Compare frontal plane, median plane, transverse plane.
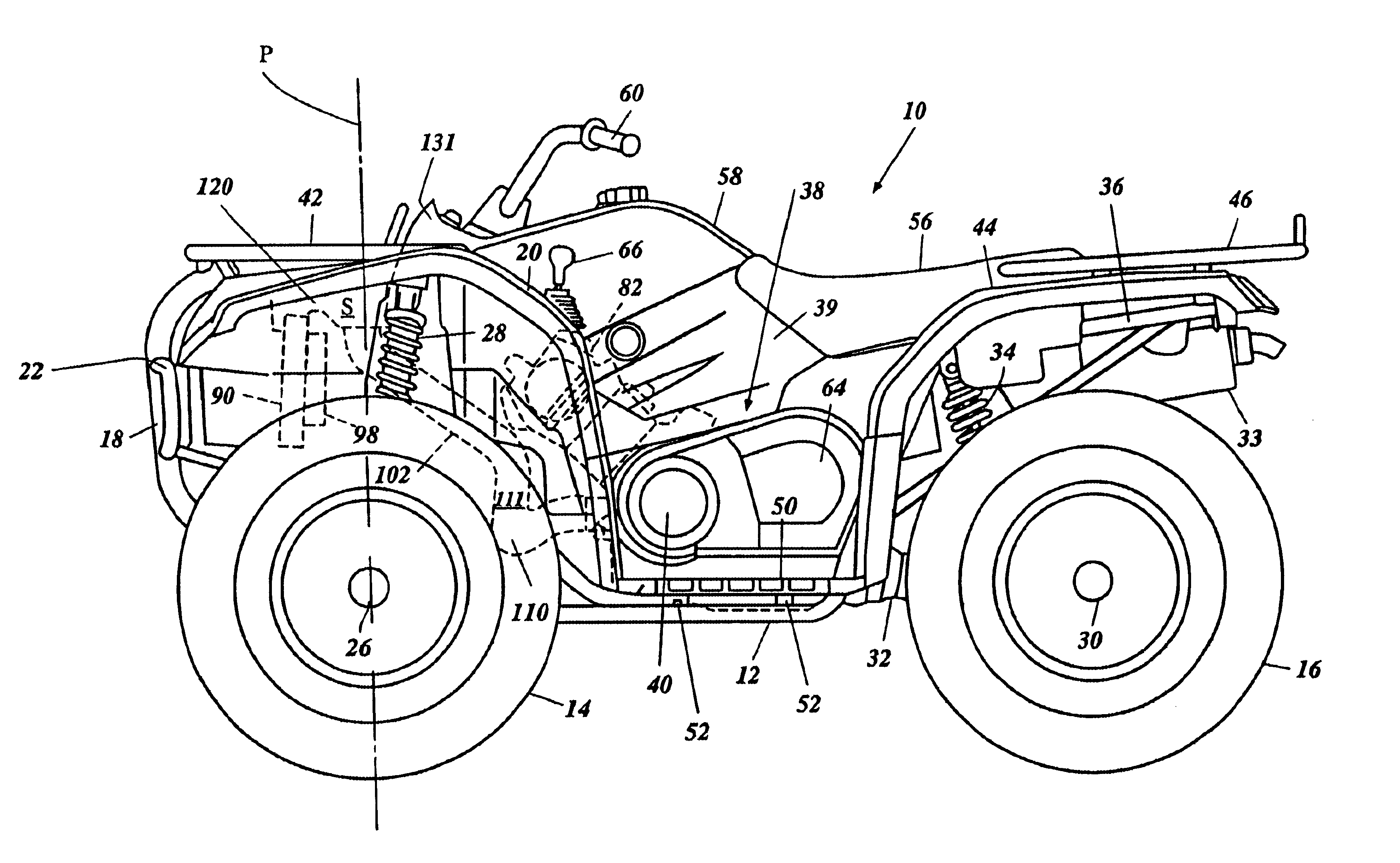
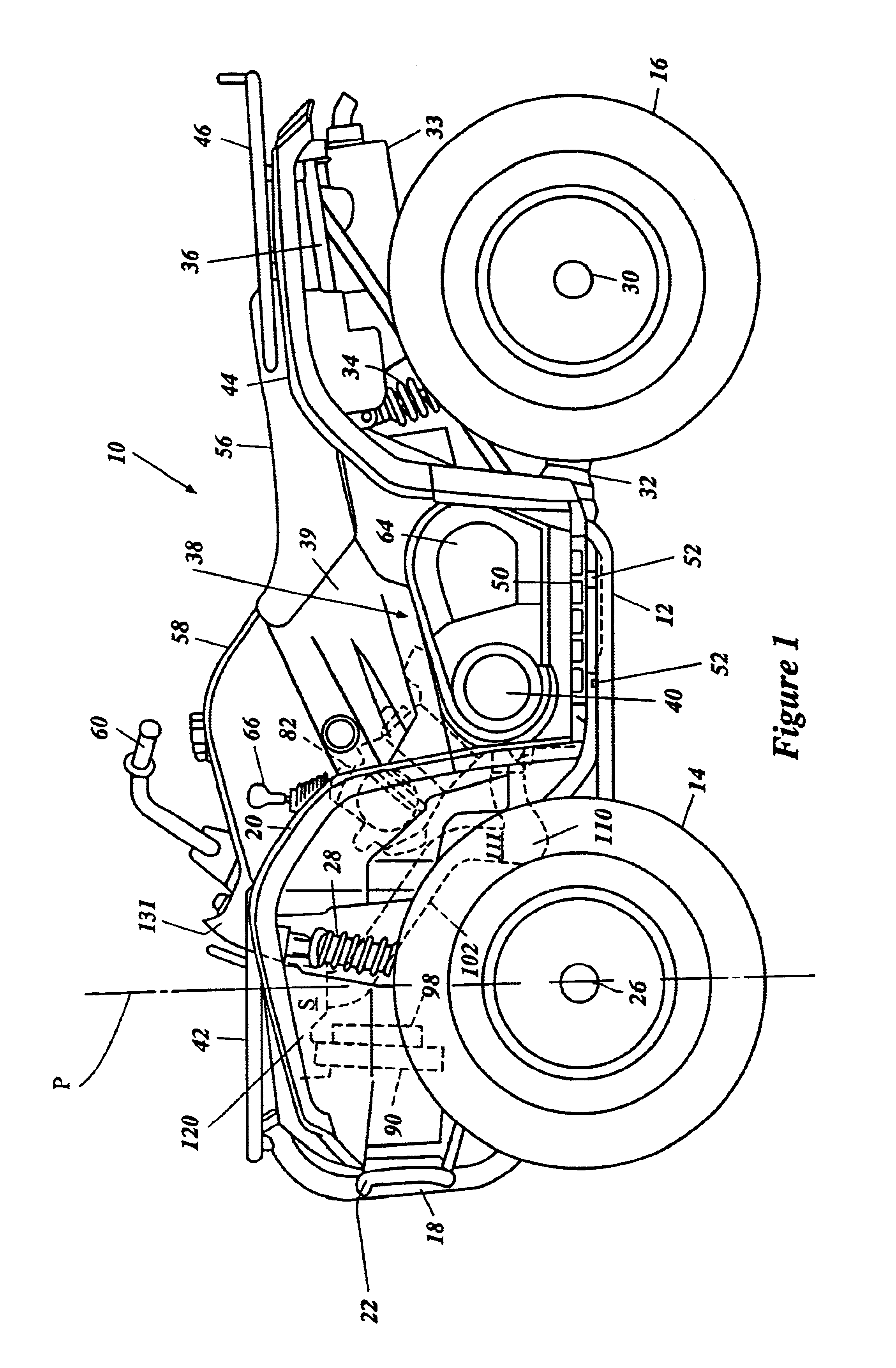
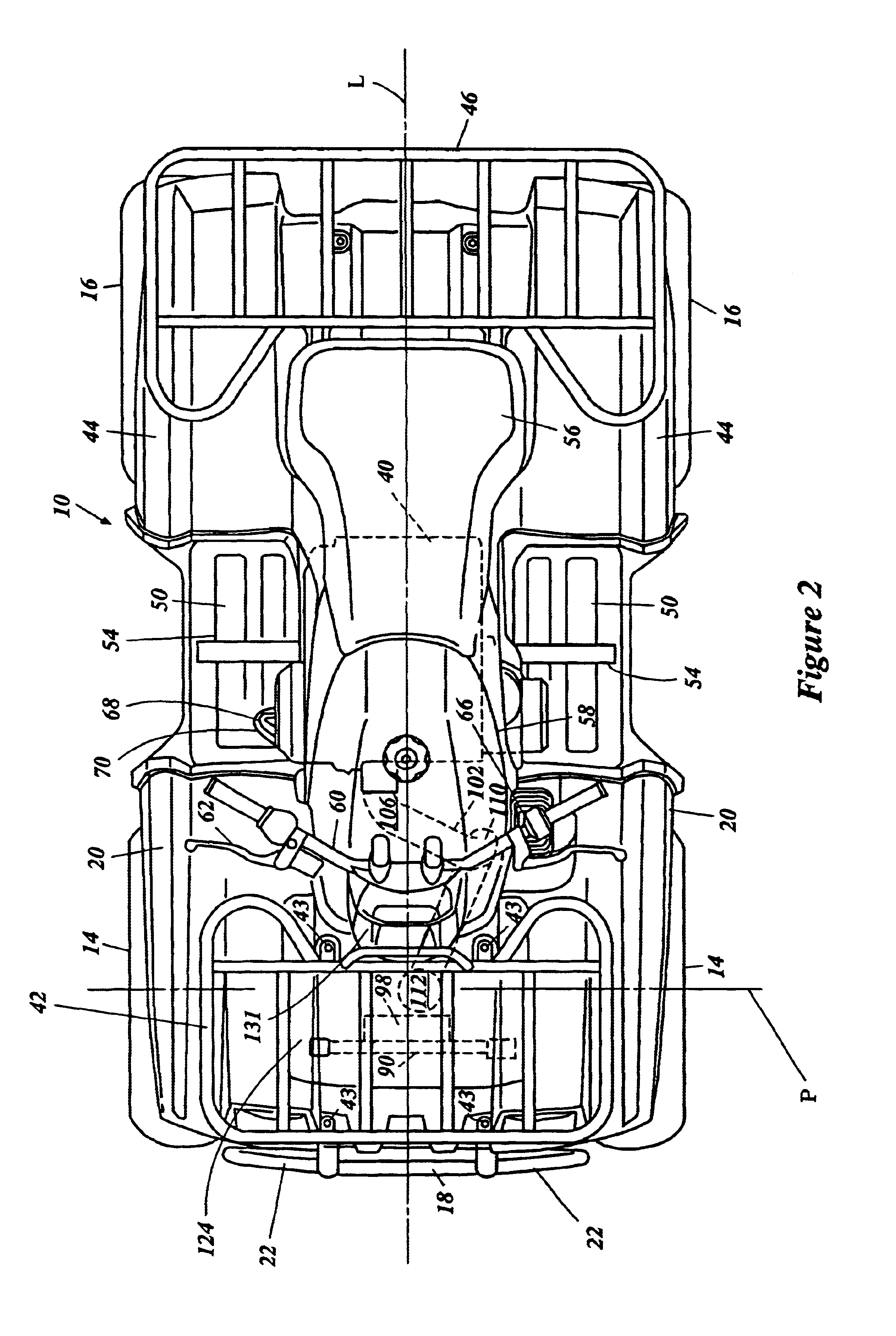
Air inlet for ATV
An all terrain vehicle has a frame assembly. A pair of front wheels and a pair of rear wheels support the frame assembly. A front fender assembly extends over at least a portion of the front wheels. An engine is disposed between the front wheels and the rear wheels. The engine is water-cooled using a radiator and fan combination that is positioned forward of the engine. A belt drive forms a portion of a transmission that transfers power from the engine to at least the rear wheels. The belt drive is air cooled with air that is pulled into the belt drive by fans positioned within a belt case. The air is drawn from an air chamber formed within the front fender assembly. The chamber is positioned vertically higher than the radiator and fan combination and rearward thereof. The air passes between the chamber and the belt case through a duct. The duct extends downward and incorporates a central trap portion. The duct is positioned to lie at least partially within an area that overlaps the fan from a front elevation view. The duct also bends across a central longitudinal plane from inlet to outlet to allow a compact configuration while positioning the duct in protected regions.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
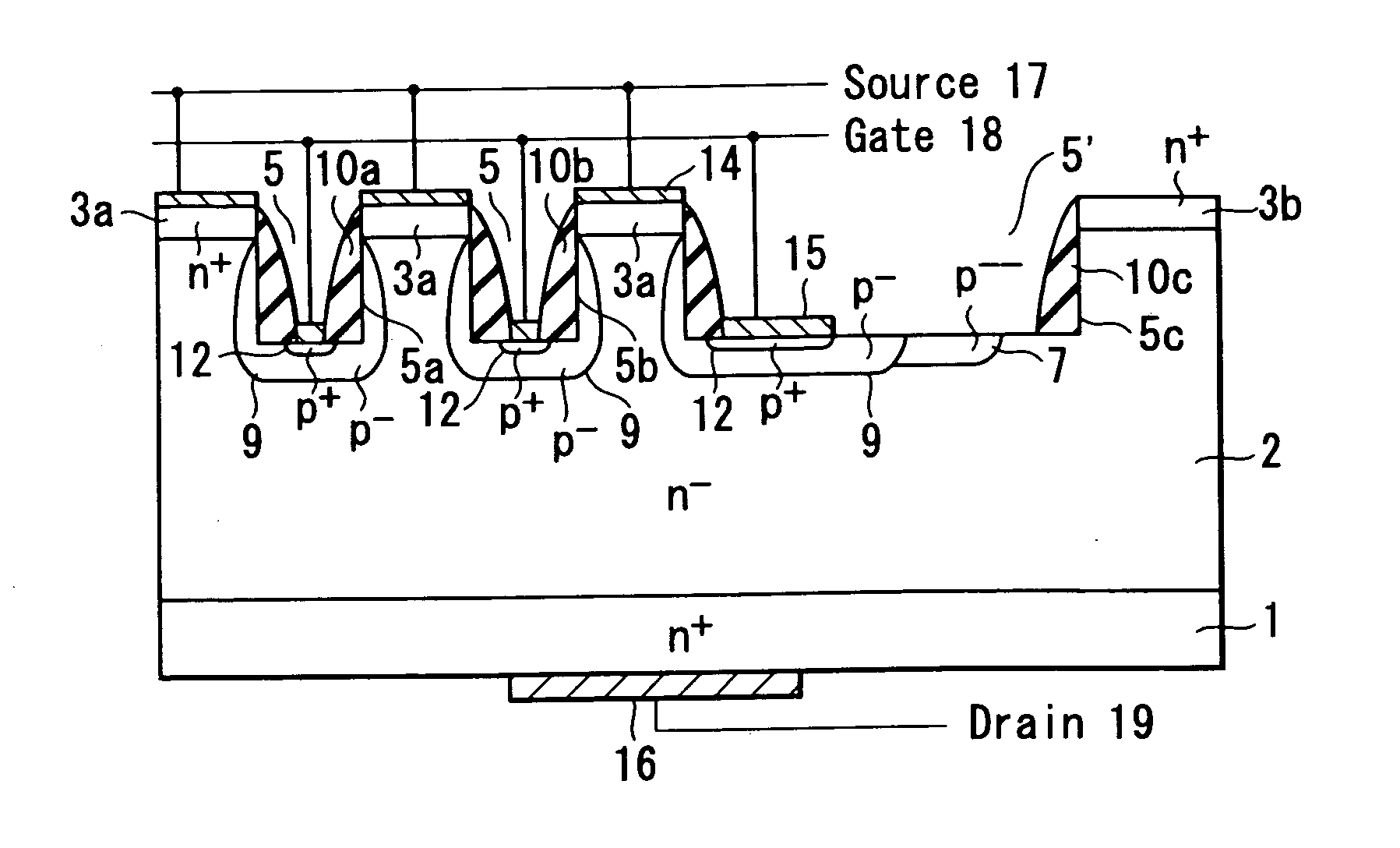
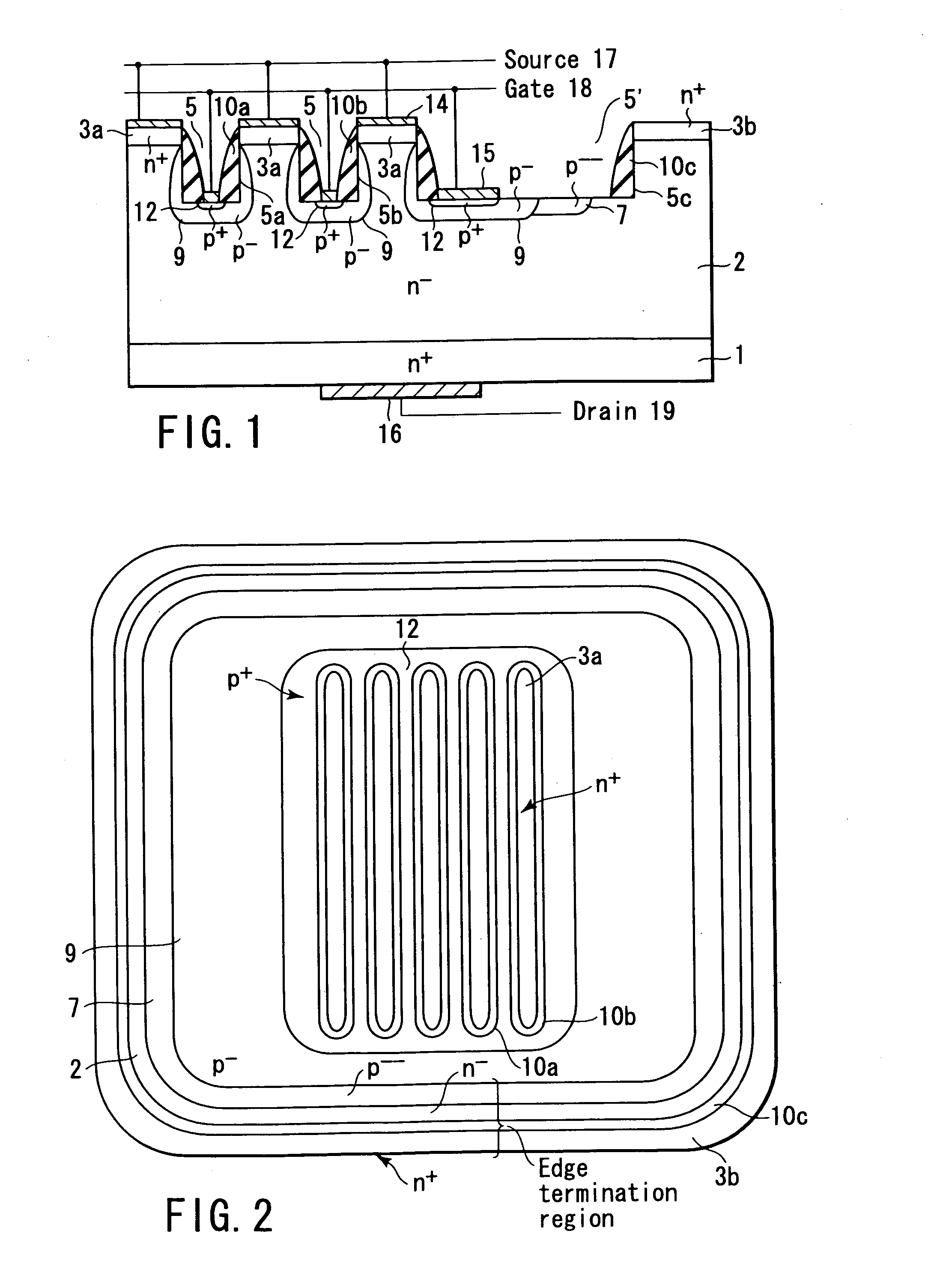
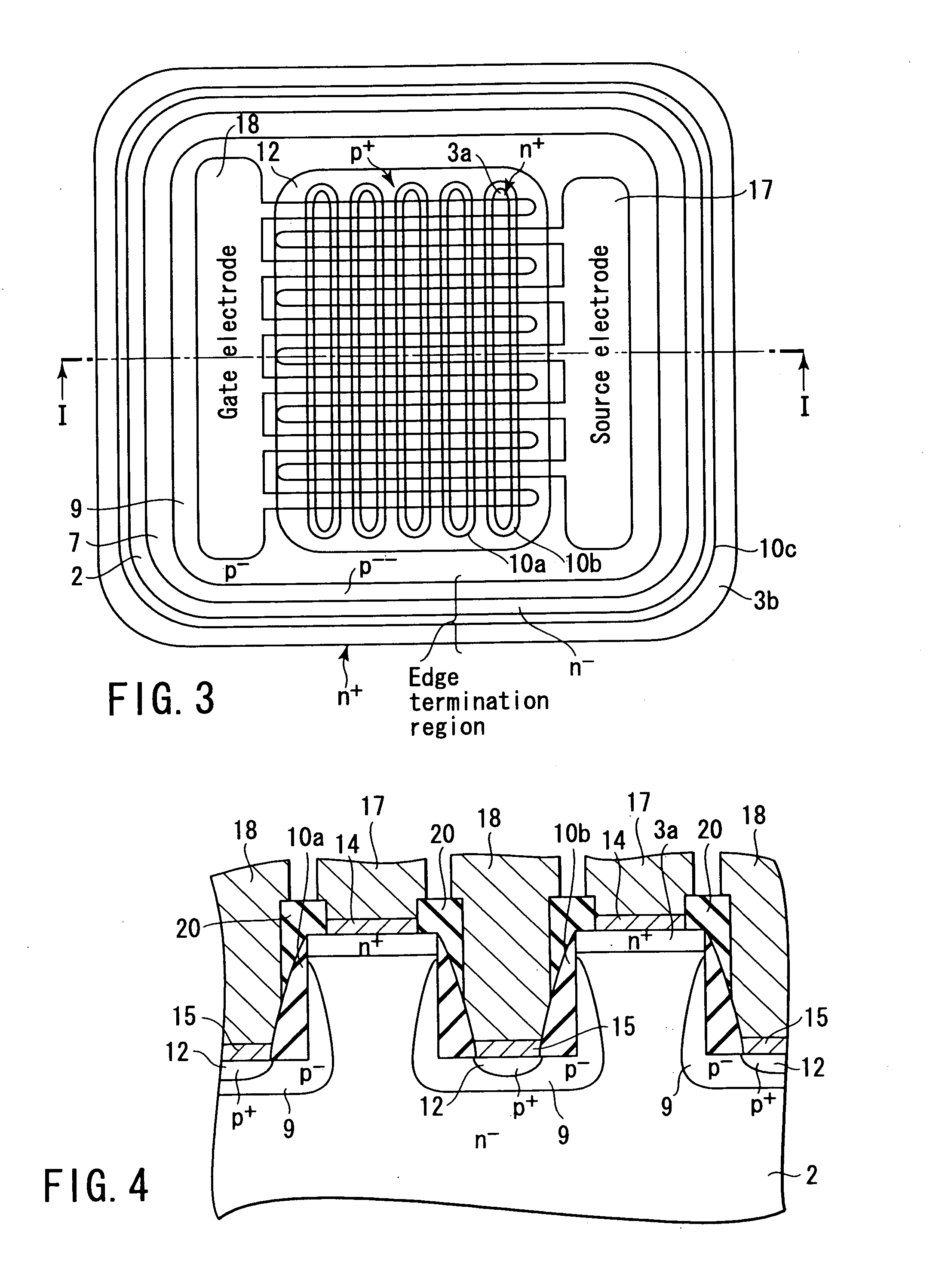
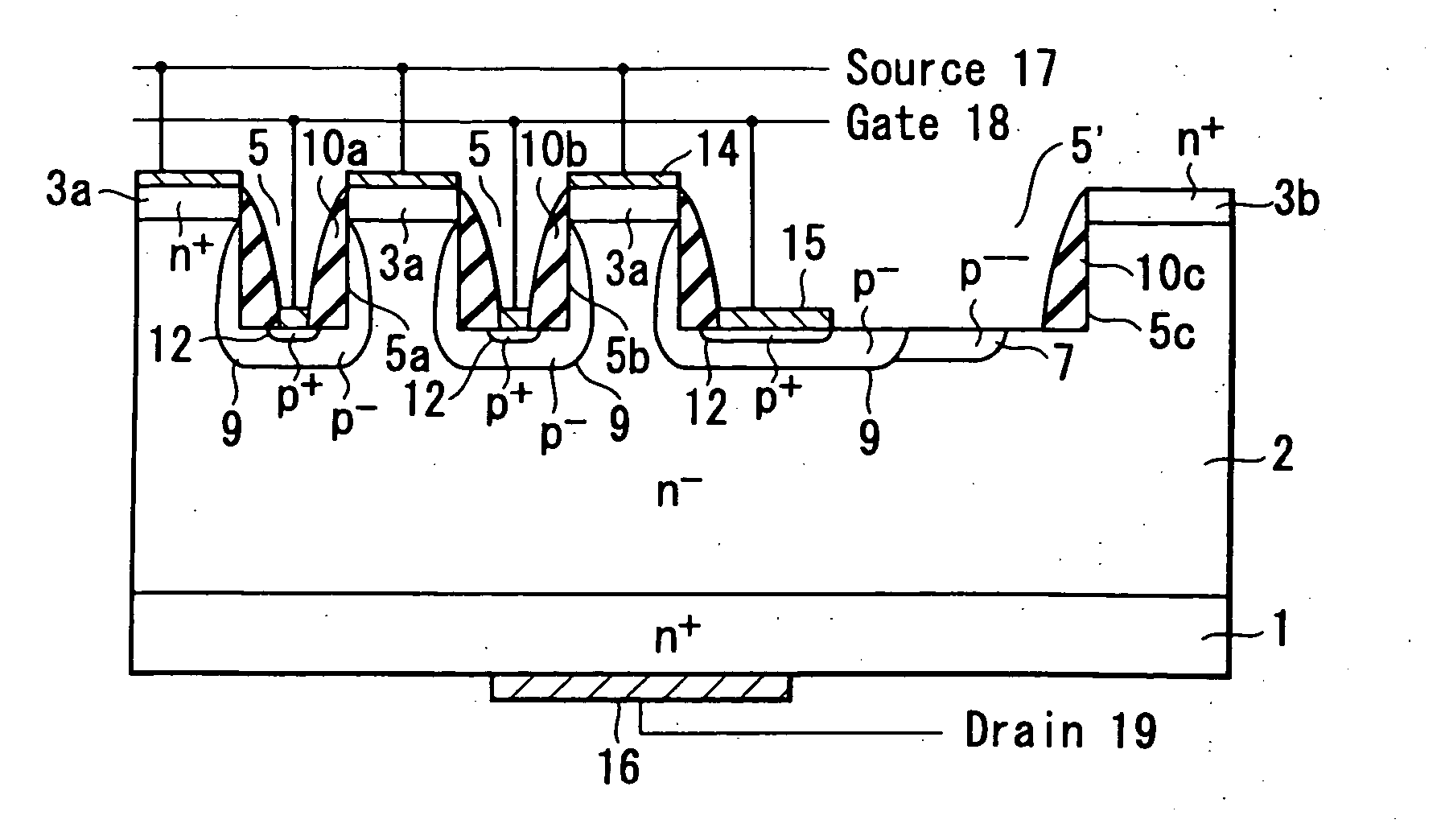
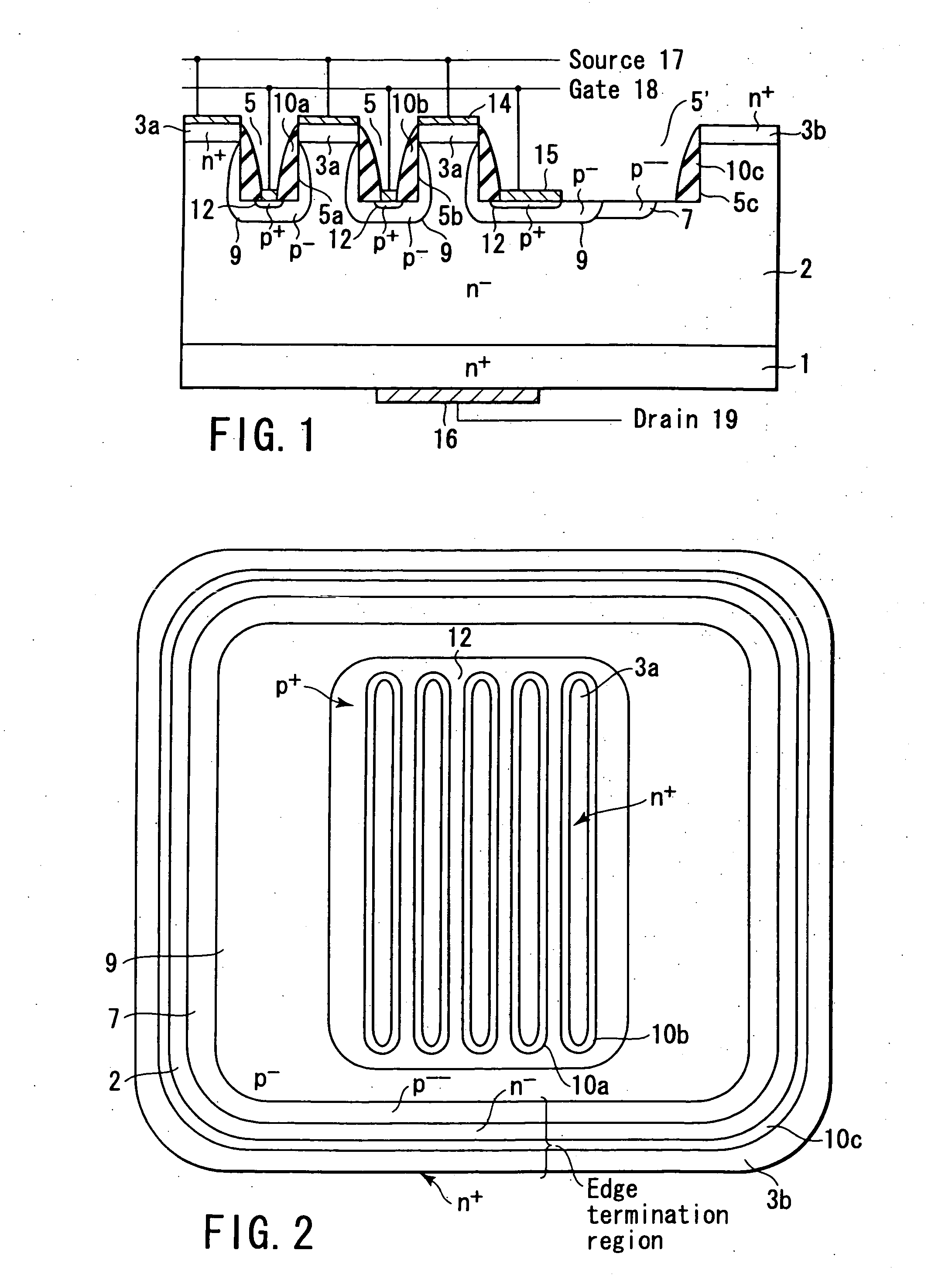
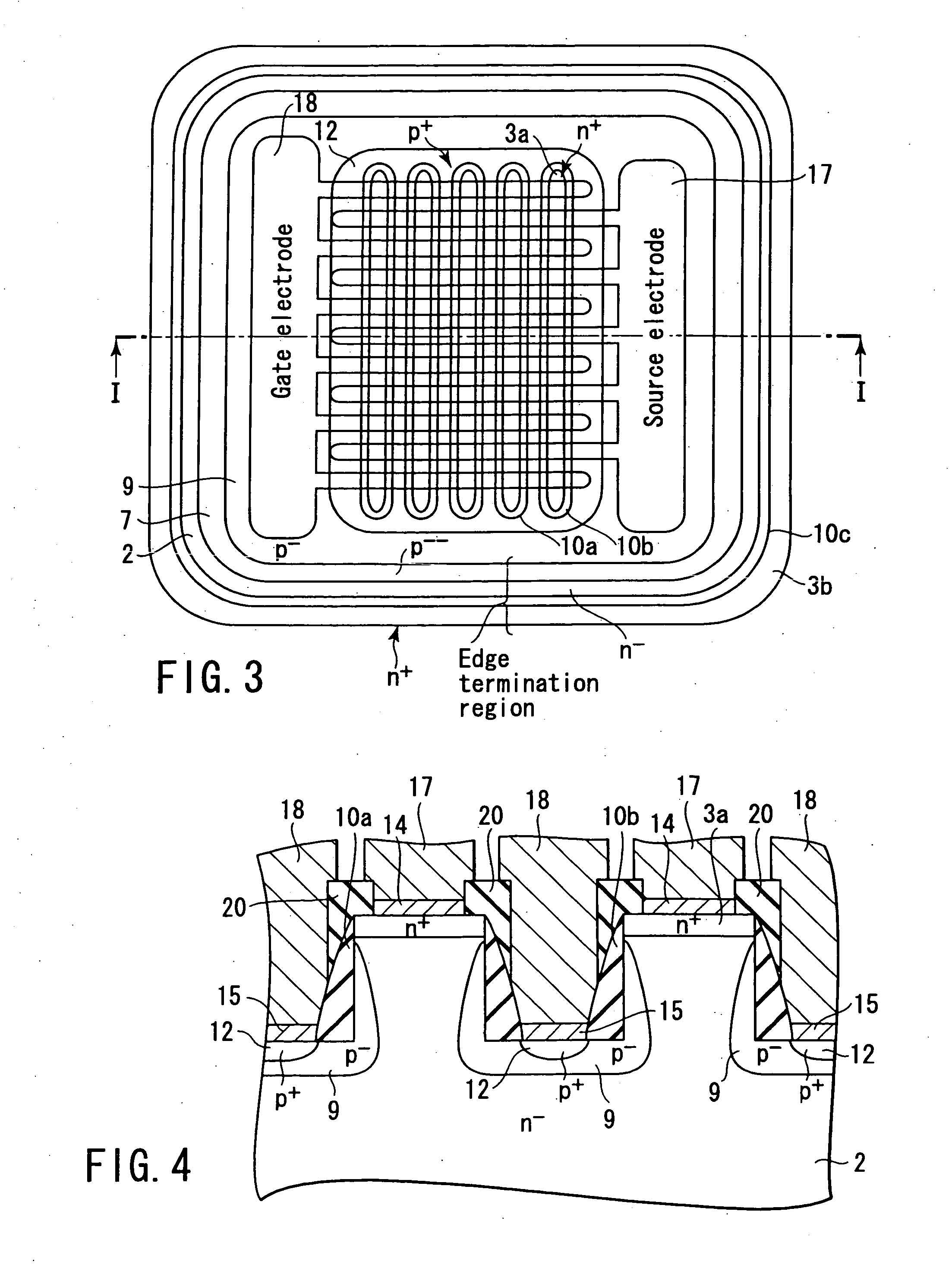
High-breakdown-voltage semiconductor device
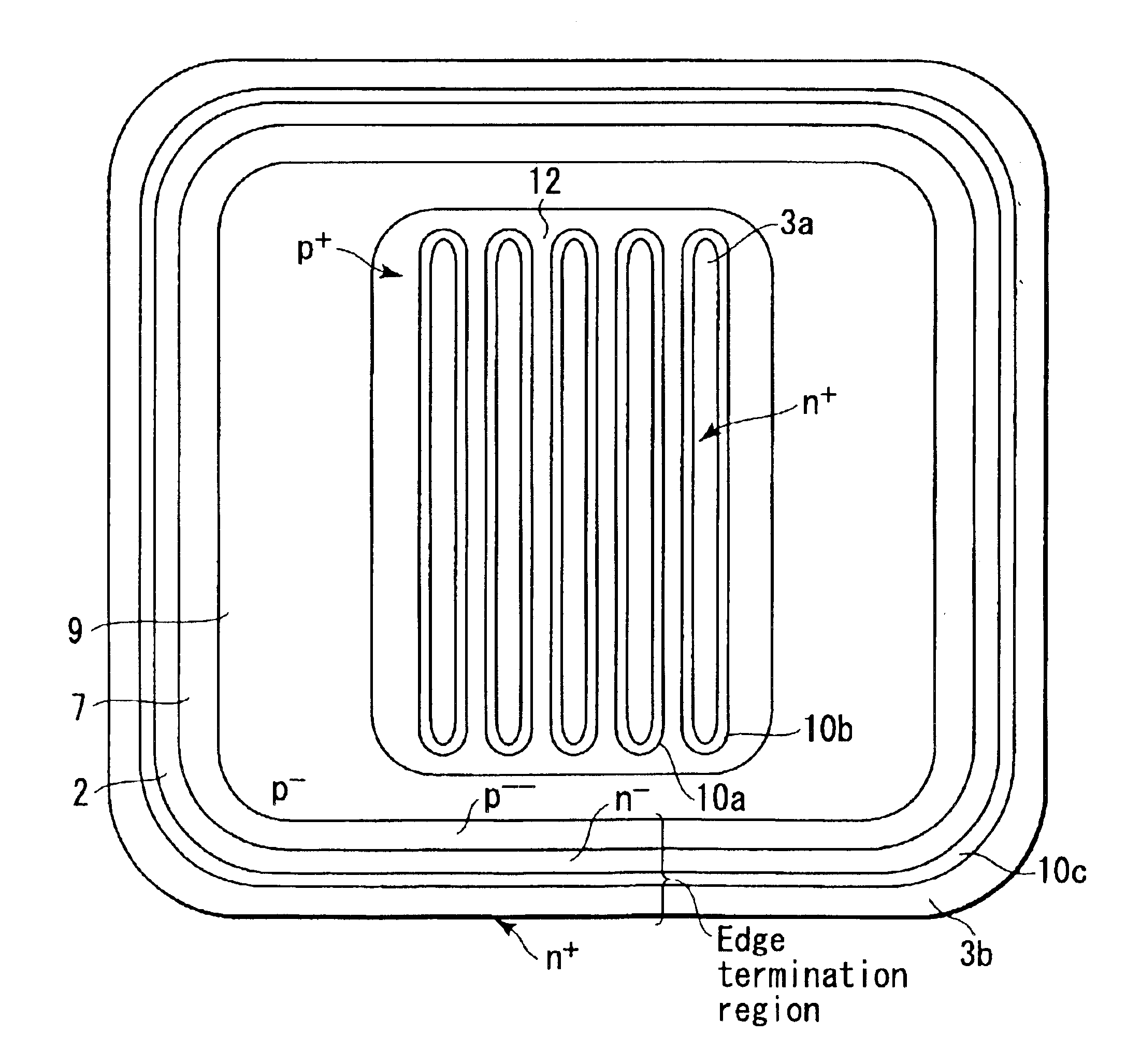
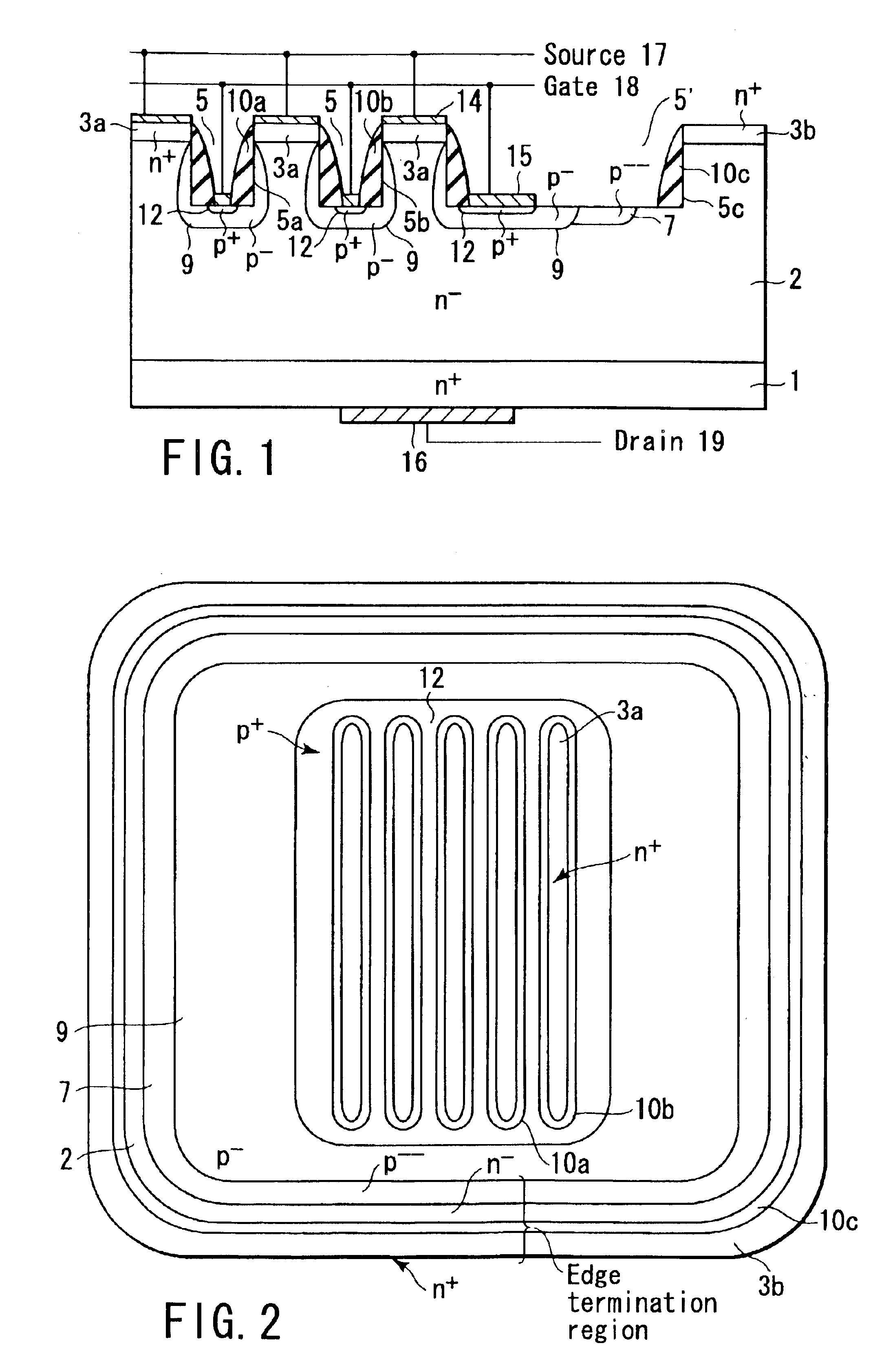
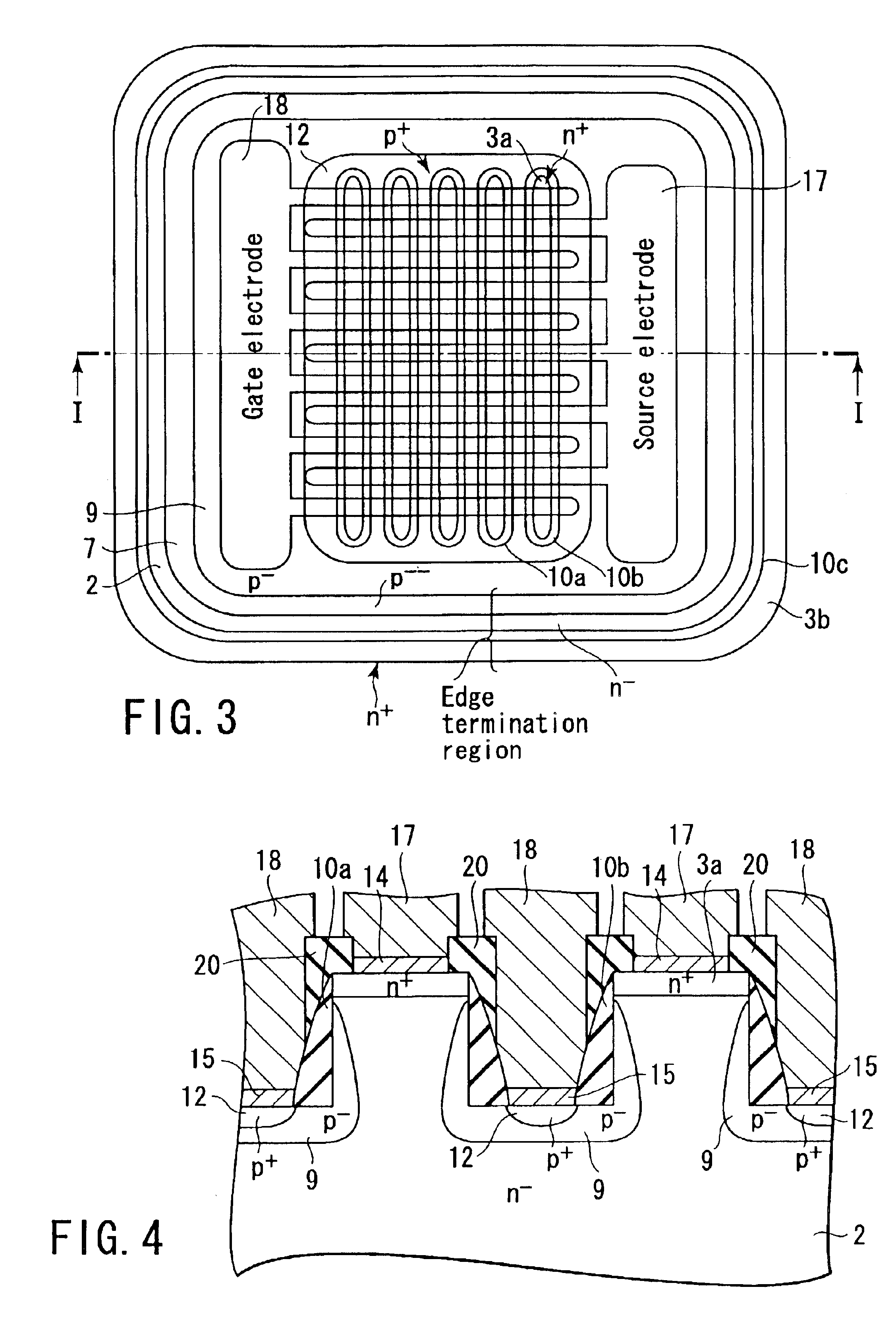
A high-breakdown-voltage semiconductor device comprises a high-resistance semiconductor layer, trenches formed on the surface thereof in a longitudinal plane shape and in parallel, first regions formed on the semiconductor layer to be sandwiched between adjacent ones of the trenches and having an impurity concentration higher than that of the semiconductor layer, a second region having opposite conductivity to the first regions and continuously disposed in a trench sidewall and bottom portion, a sidewall insulating film disposed on the second region of the trench sidewall, a third region disposed on the second region of the trench bottom portion and having the same conductivity as and the higher impurity concentration than the second region, a fourth region disposed on the back surface of the semiconductor layer, a first electrode formed on each first region, a second electrode connected to the third region, and a third electrode formed on the fourth region.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
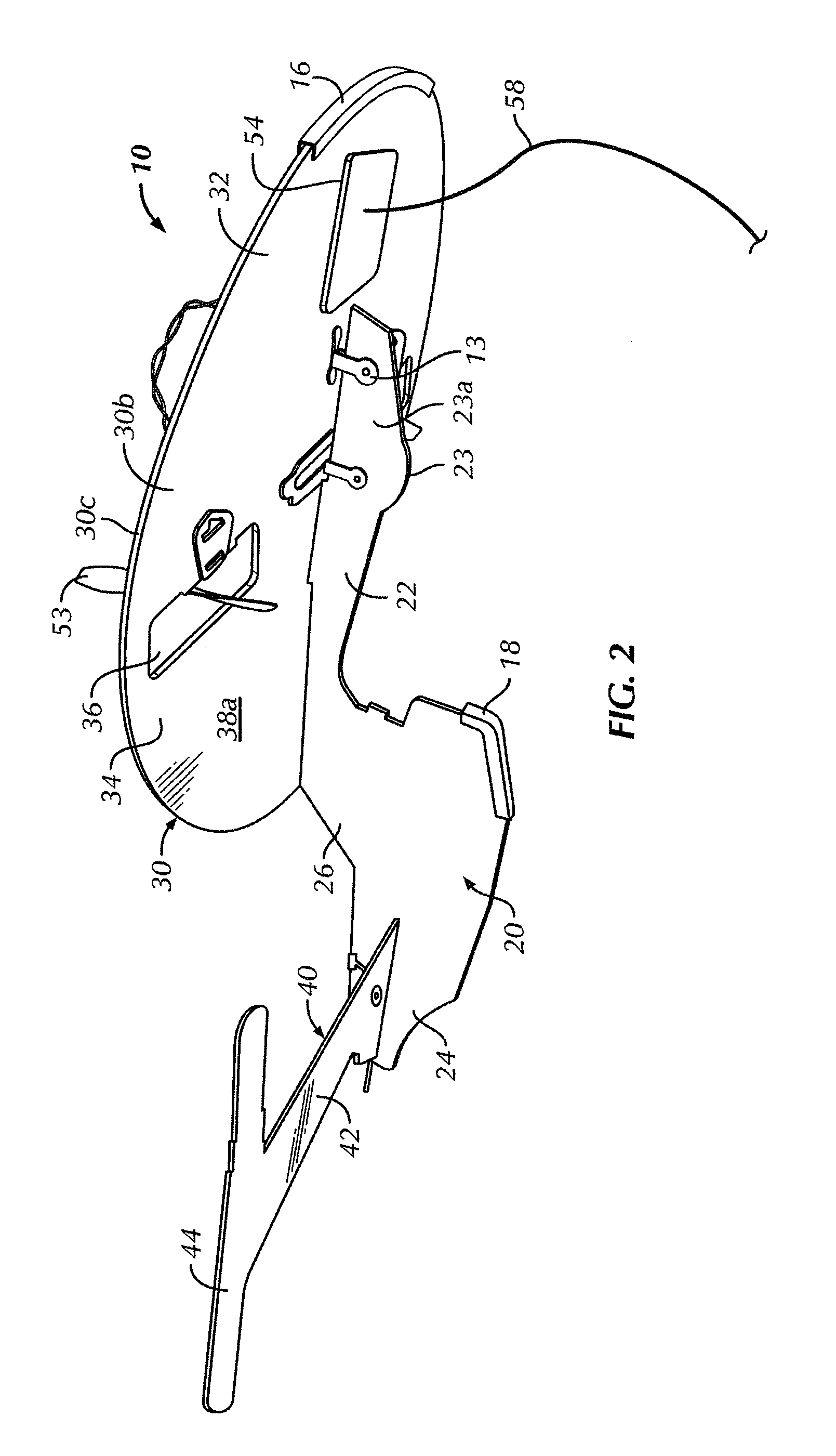
Endoscopic organ retractor and method of using the same
In an organ retractor including a shaft defining a longitudinal axis and a longitudinal plane, and at least one organ support assembly operatively coupled to the shaft. The organ support assembly includes a plurality of ribs having a first position, in which each of the plurality of ribs is parallel with one another, and a second position, in which a first rib of the plurality of ribs is transverse with respect to a second rib of the plurality of ribs. The at least one organ support assembly is pivotable from a first orientation, in which each of the plurality of ribs is disposed in the longitudinal plane of the shaft, to a second orientation, in which each of the plurality of ribs is disposed at an angle relative to the longitudinal plane of the shaft, and a support extending between and connected to each of the plurality of two ribs.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
High-breakdown-voltage semiconductor device
A high-breakdown-voltage semiconductor device comprises a high-resistance semiconductor layer, trenches formed on the surface thereof in a longitudinal plane shape and in parallel, first regions formed on the semiconductor layer to be sandwiched between adjacent ones of the trenches and having an impurity concentration higher than that of the semiconductor layer, a second region having opposite conductivity to the first regions and continuously disposed in a trench sidewall and bottom portion, a sidewall insulating film disposed on the second region of the trench sidewall, a third region disposed on the second region of the trench bottom portion and having the same conductivity as and the higher impurity concentration than the second region, a fourth region disposed on the back surface of the semiconductor layer, a first electrode formed on each first region, a second electrode connected to the third region, and a third electrode formed on the fourth region.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
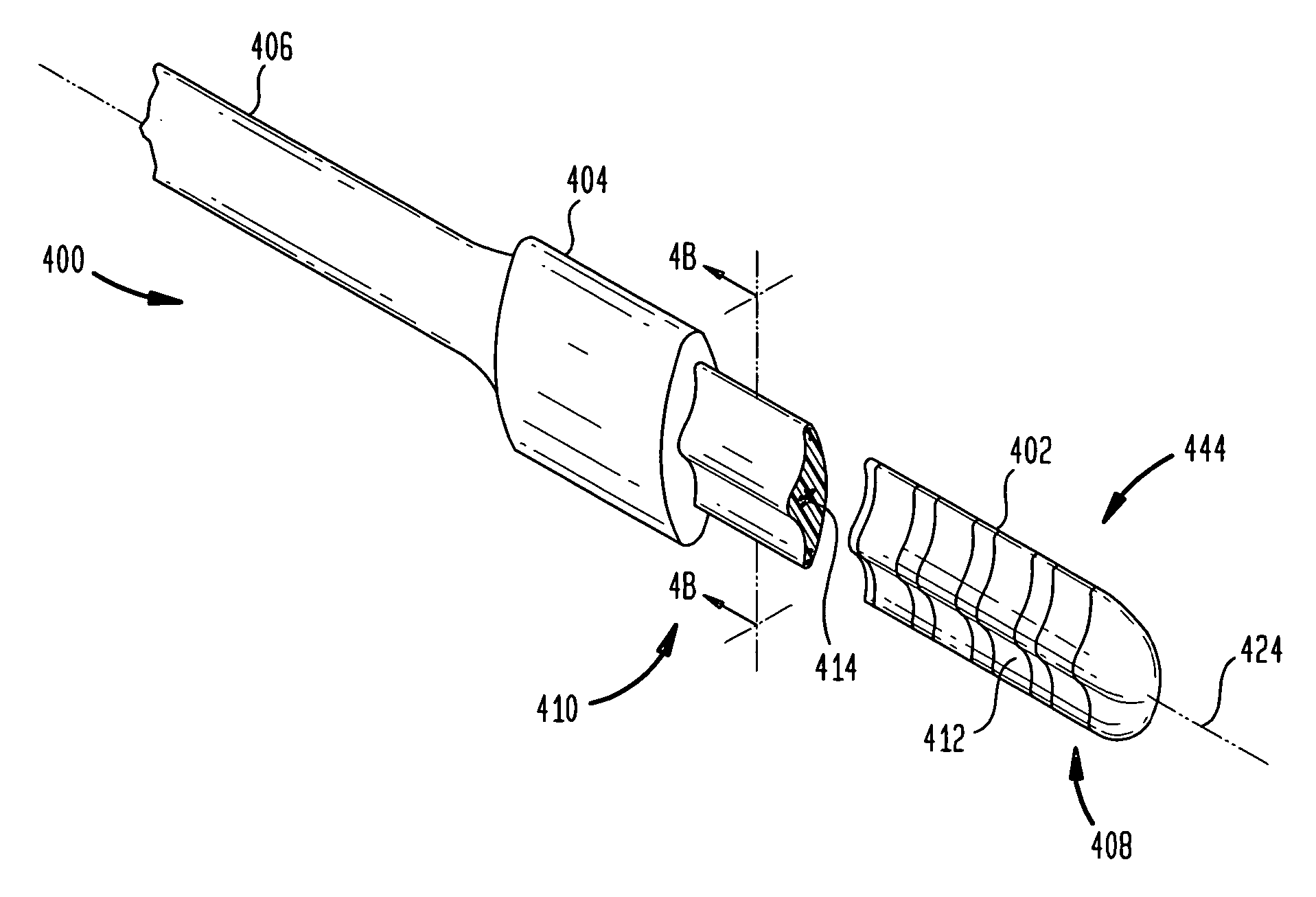
Cochlear endosteal electrode carrier member
InactiveUS20060079950A1Head electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringMedial surfaceAnatomical structures
An elongate electrode carrier member for implantation in a location external to the cochlear canals to position at least one, and likely many, electrodes sufficiently proximate to the organ of Corti to effectively deliver stimulation signals to the auditory nerve fibers of the cochlear. Generally, the carrier member is dimensioned to be implanted in a crevice, channel or pocket formed between the spiral ligament and bony capsule of the cochlear. Embodiments of the carrier member preferably have a minimized volume to accommodate insertion into such a crevice. In addition, embodiments of the carrier member comprise an elongate bulbous central region having electrodes disposed on the medial surface thereof, and elongate tapered side regions laterally extending from the central region. The side regions have rounded edges and are preferably flexible, while the carrier is configured to coil or turn toward the medial surface. This construction facilitates implantation of the carrier member: the carrier member has sufficient longitudinal strength to maintain its form and direction while being pushed into the surgically-formed crevice, and coils in a longitudinal plane to follow the contour of the cochlear, while the side regions serve to guide the direction of travel, flexing out of the lateral plane as necessary to avoid damaging anatomical structures. Once implanted, embodiments of the carrier member are urged to remain in its implanted position due to one or more of either the side regions extending into the corners of the crevice, and / or due to the curved lateral surface of the carrier member which approximates the curvature of the endosteum along the basal turn of the cochlea.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
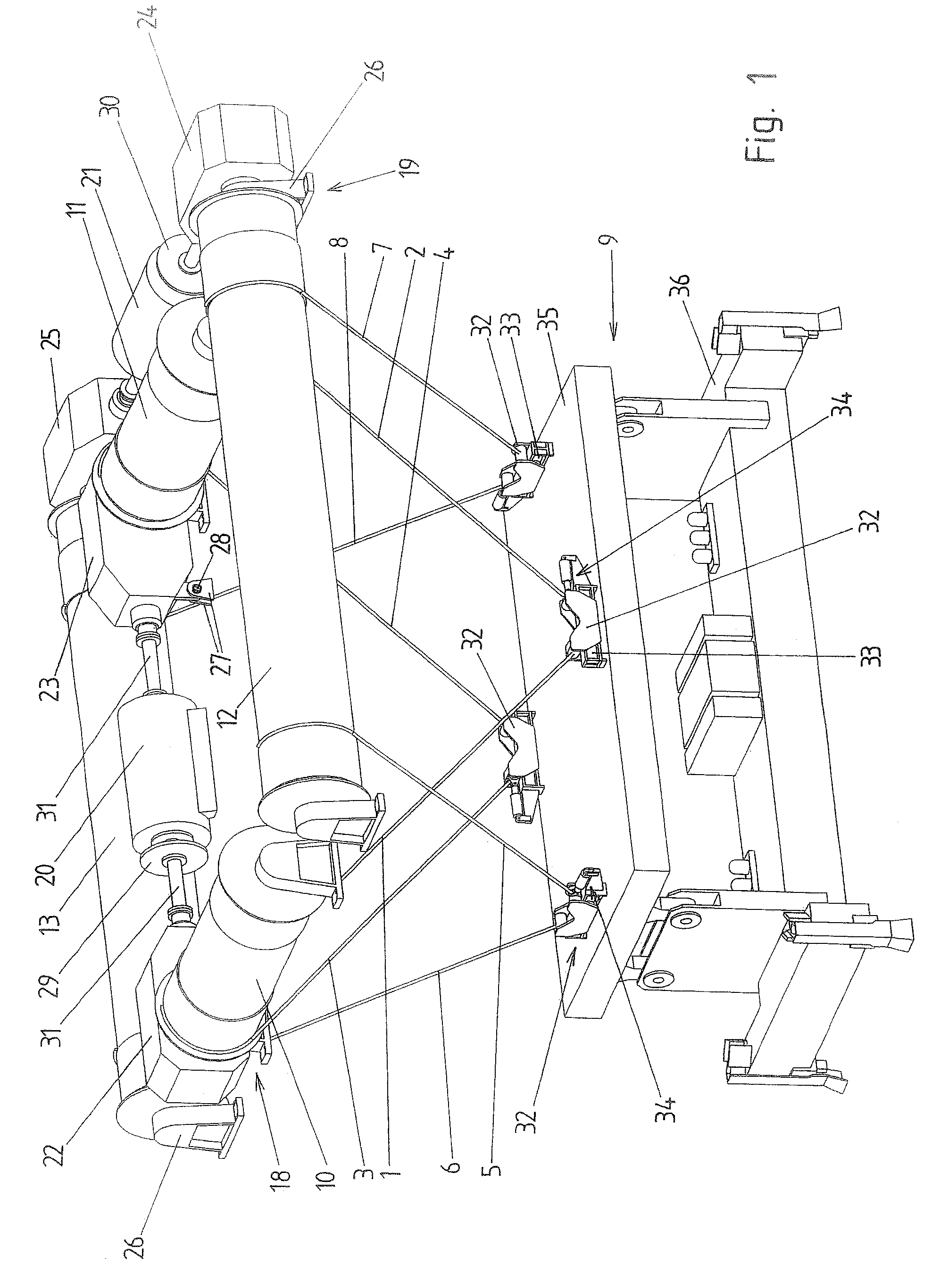
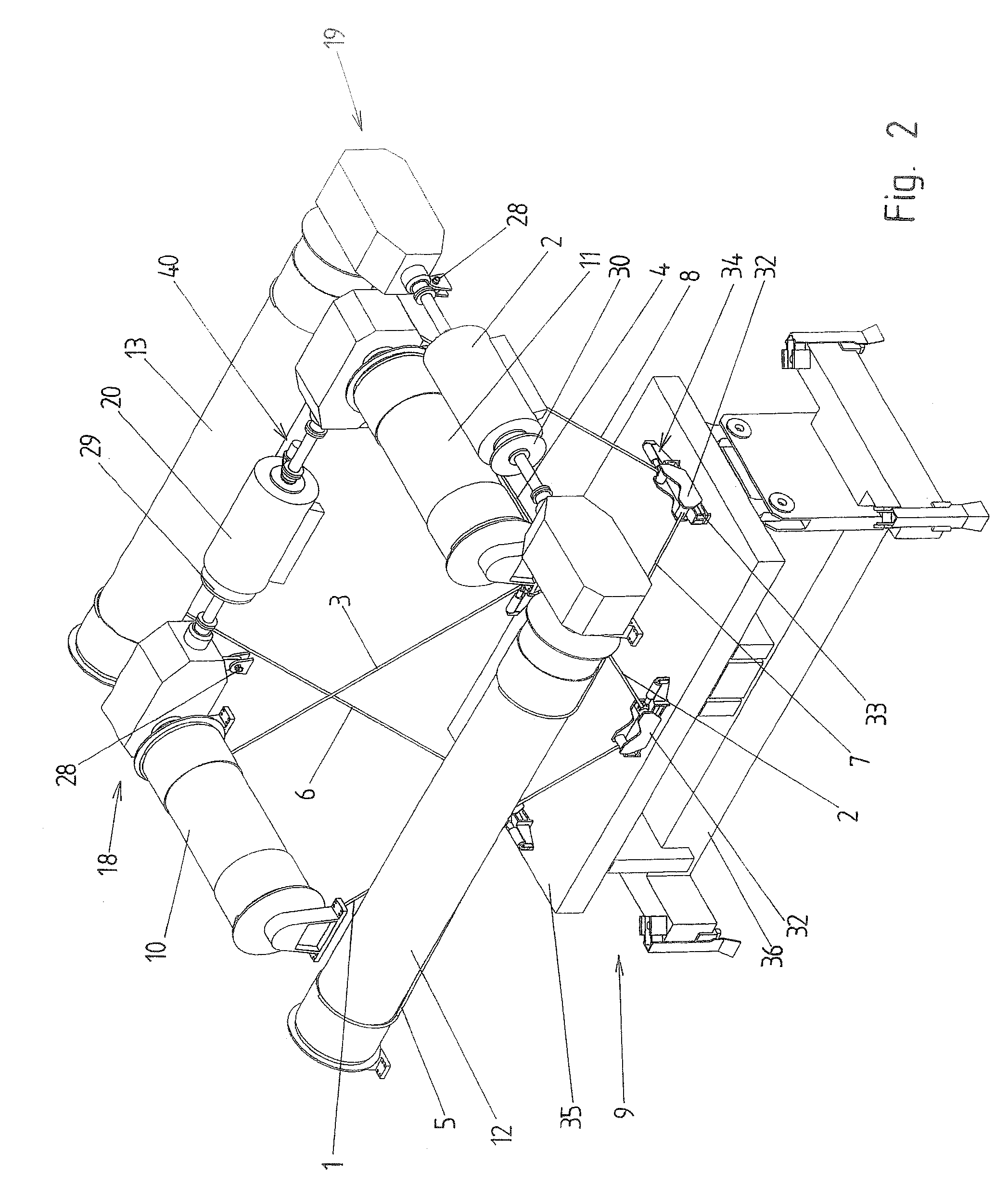
Lifting device
ActiveUS7284744B1Longer expected lifetimeWork lessWinding mechanismsLoad-engaging elementsLongitudinal planeTransverse plane
Owner:HANS KUENZ GMBH +1
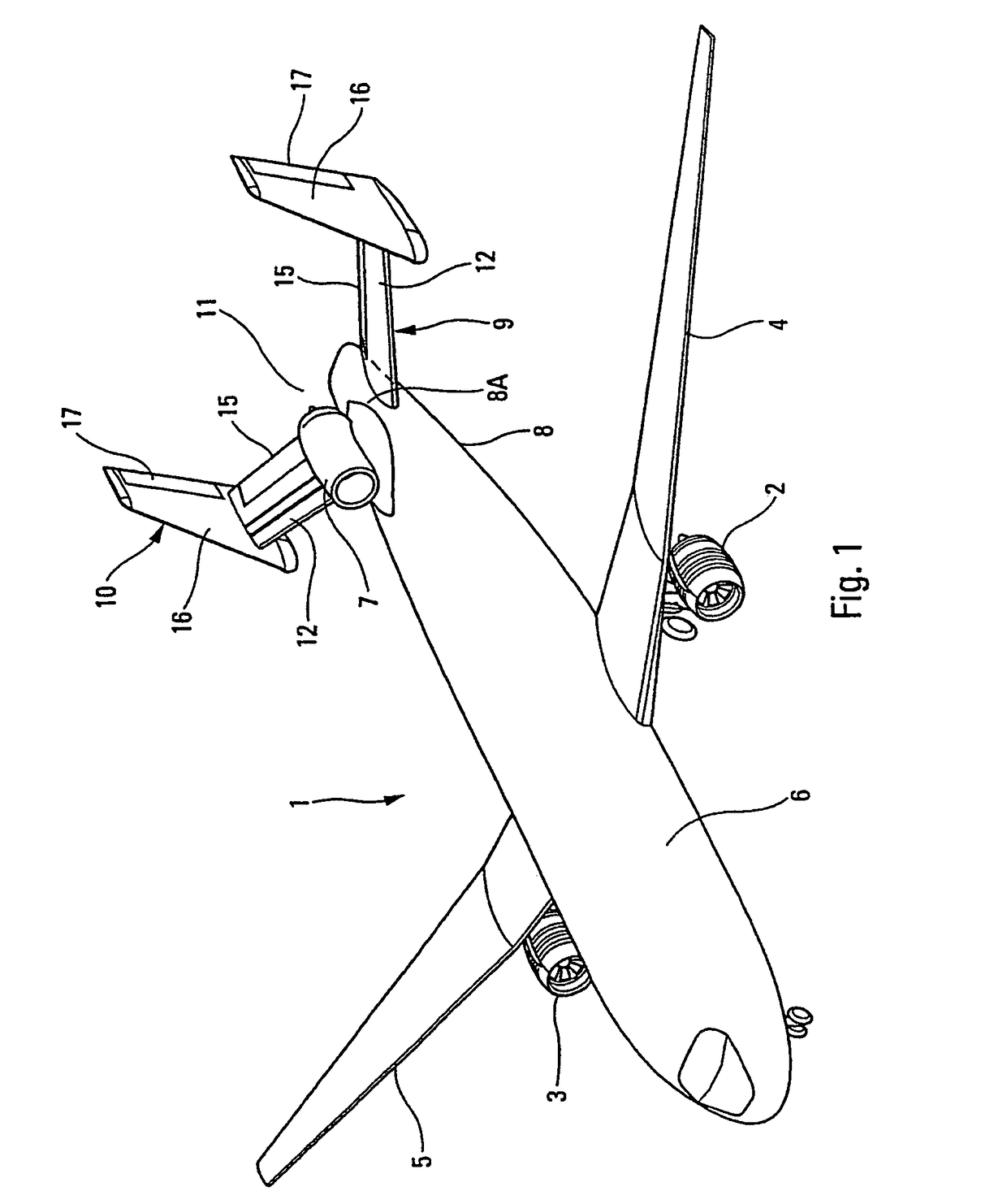
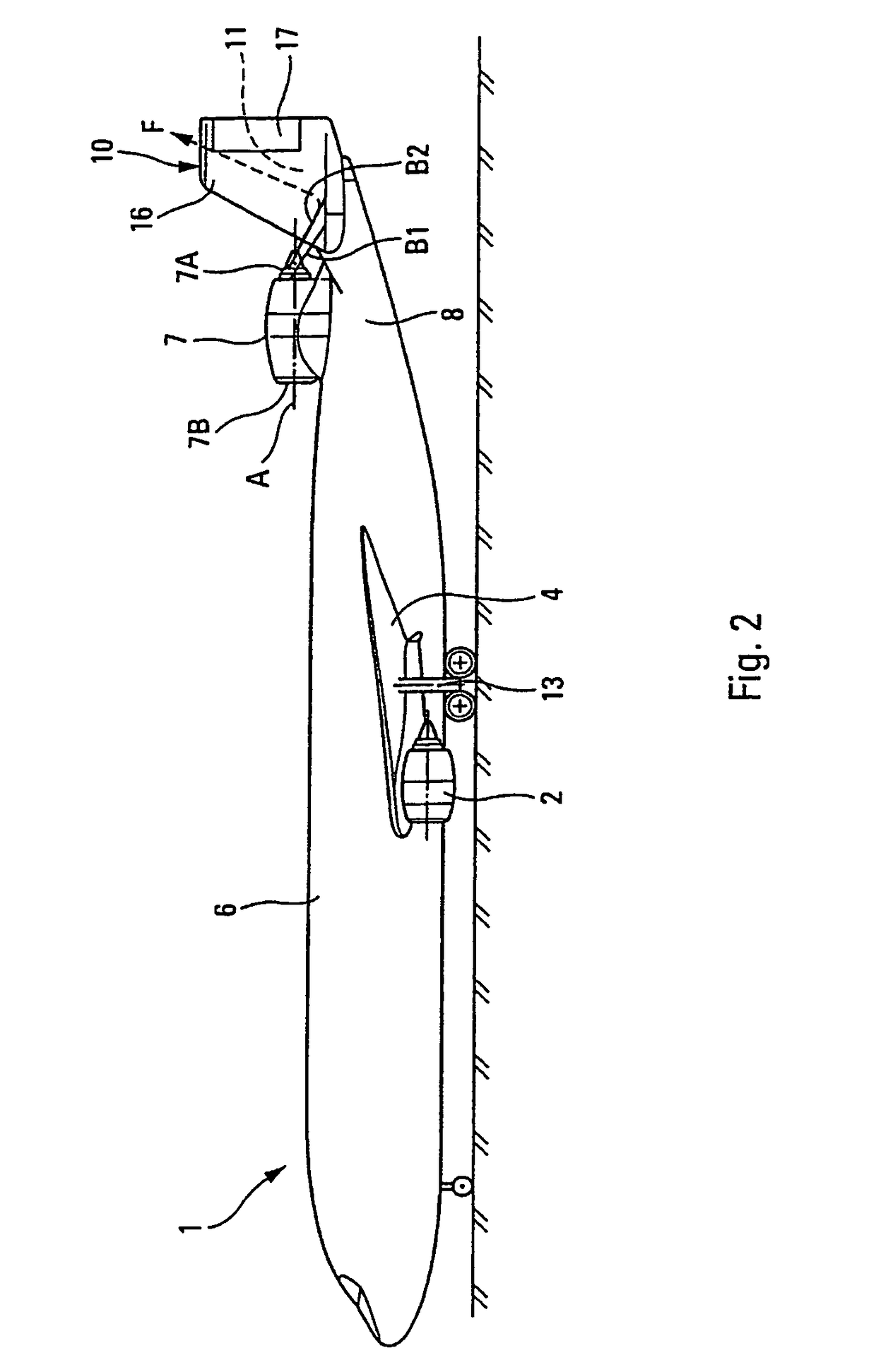
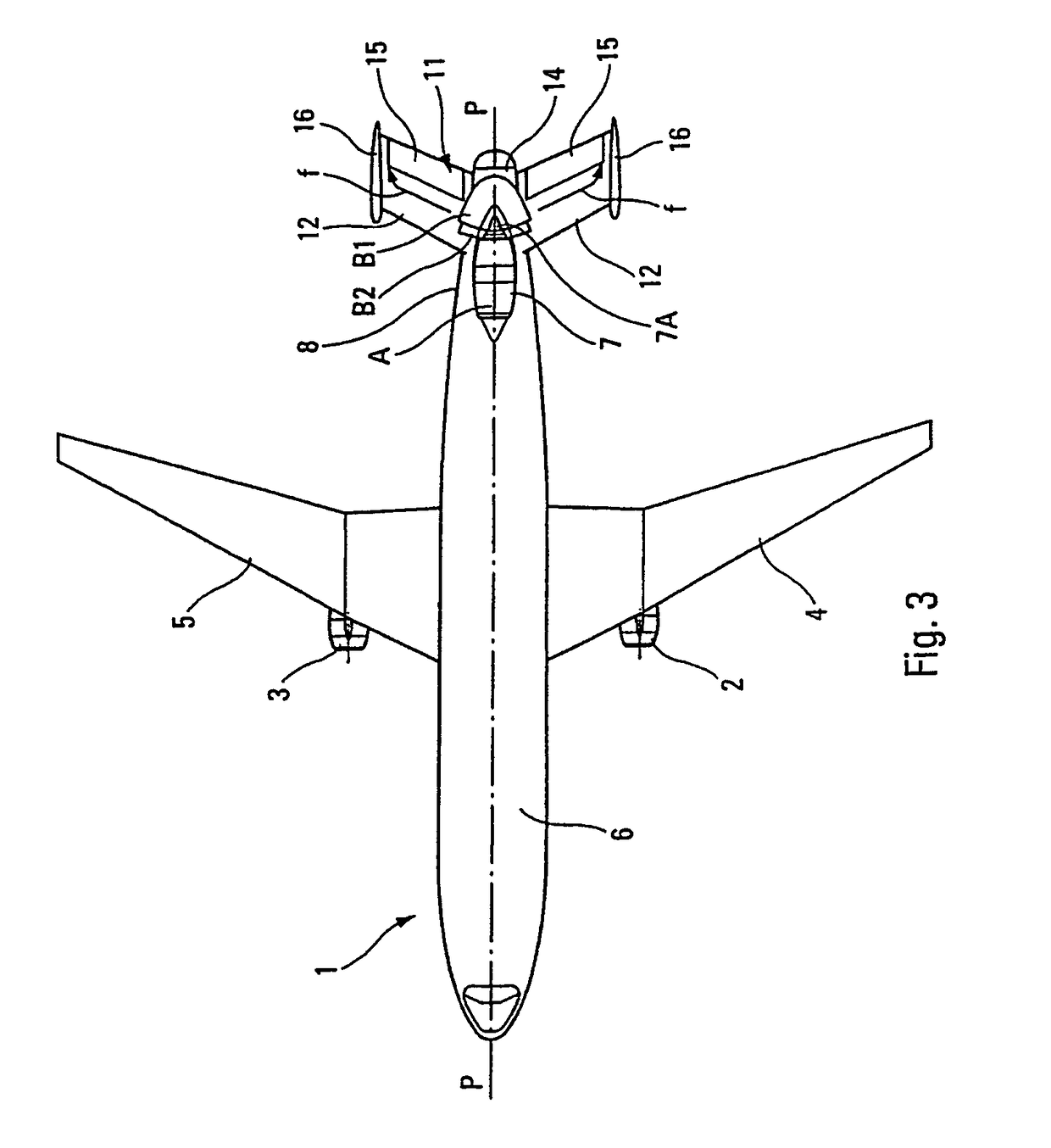
Multi-engine aircraft
InactiveUS7905449B2Reduce previous acoustic problemLess noisyPower plant exhaust arrangementsPower installationsJet aeroplaneLongitudinal plane
A multi-engine aircraft includes at least two first engines and a third engine located at a rear part of the fuselage, containing rear tail sections, along a vertical longitudinal plane of symmetry of the fuselage. The rear tail sections define a channel which is symmetrical with respect to the longitudinal plane of the fuselage. The third engine is arranged in the plane of symmetry of the channel corresponding to the longitudinal plane and is mounted on the upper part of the fuselage in a raised manner and in front of the tail sections, so that the outlet of the third engine is situated substantially at the inlet of the channel defined by the tail sections.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
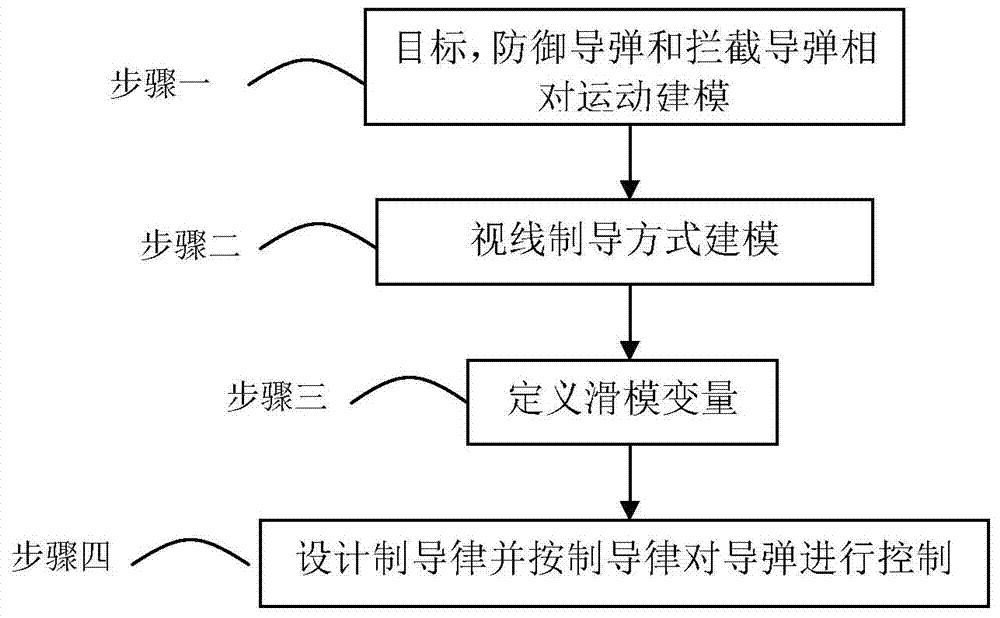
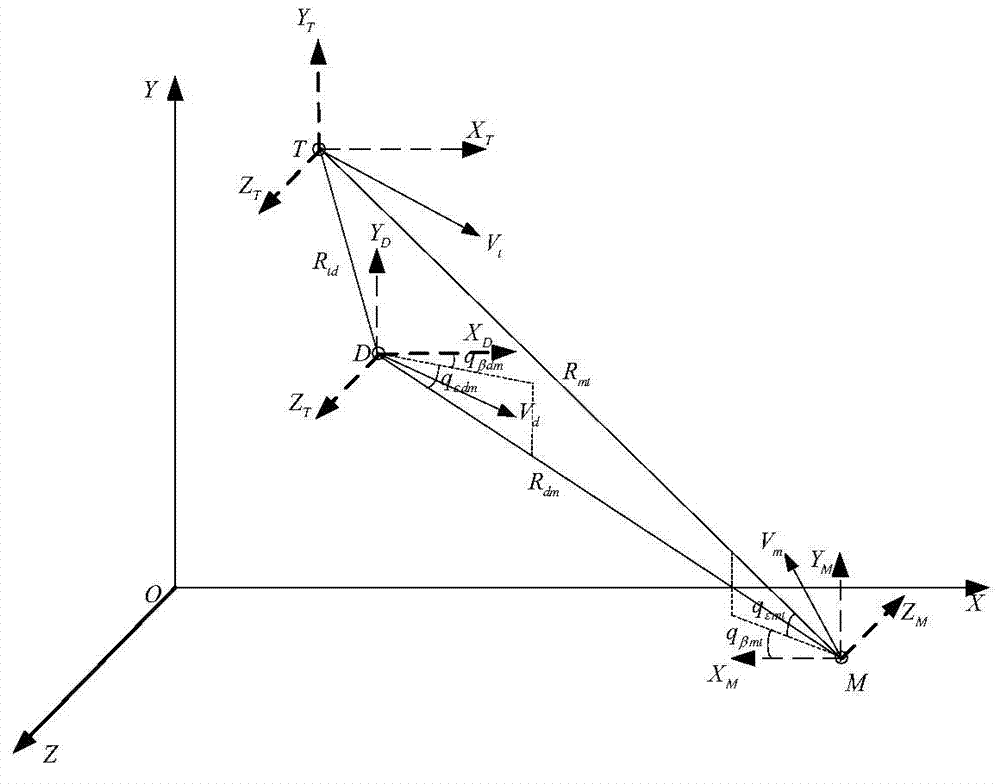
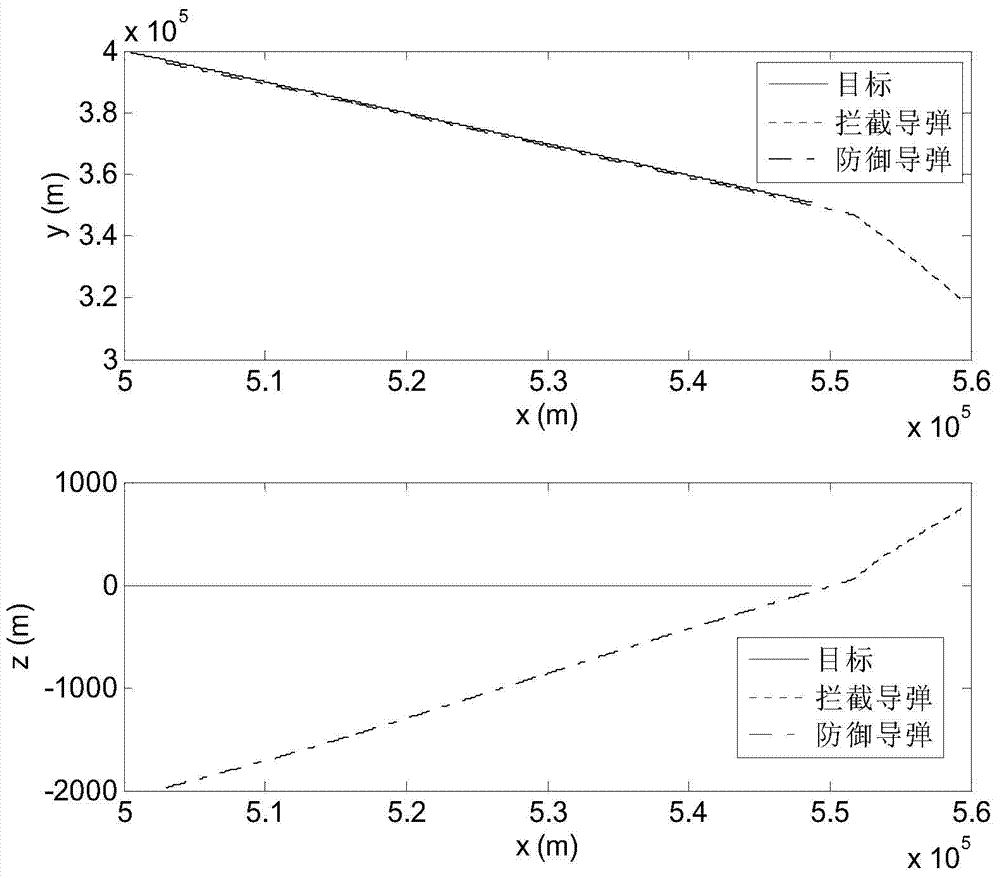
Sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method
ActiveCN104266546AReduce demand overloadDirection controllersSpecial data processing applicationsLongitudinal planeGuidance control
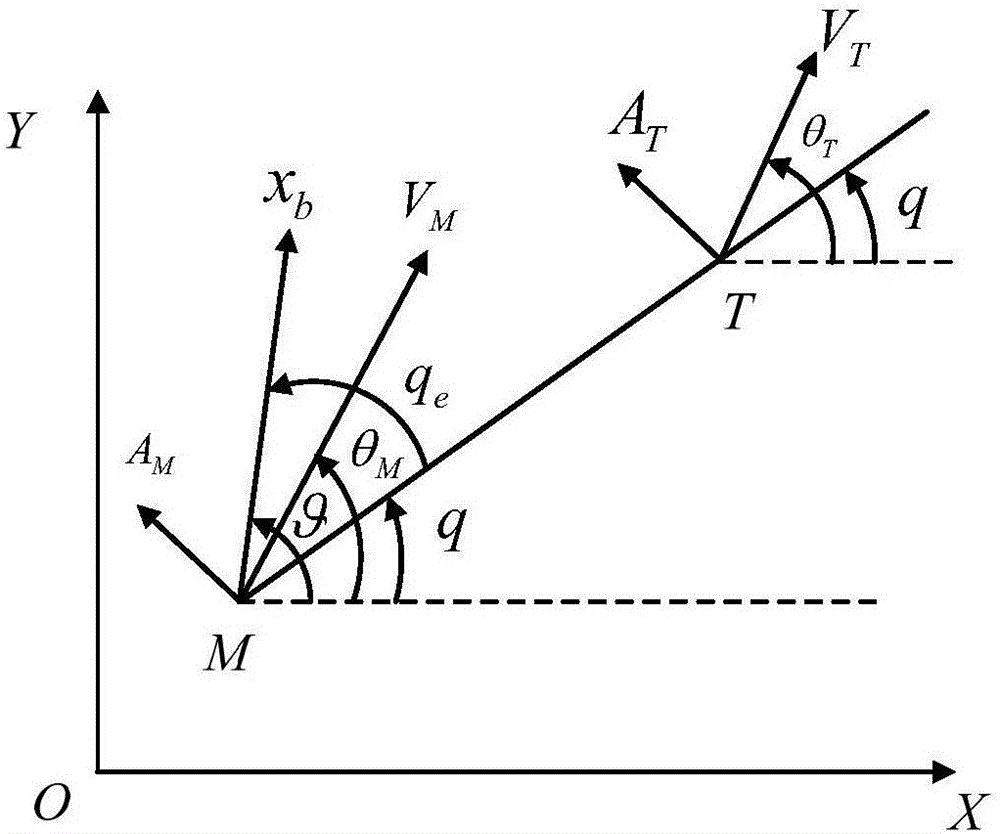
The invention provides a sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method, relates to a guidance control method, in particular to an active defense guidance control method, and aims at solving the problem that a defensive missile is limited in overload capacity. The sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method comprises the steps of firstly modeling relative motions of a target, the defensive missile and an intercept missile, adopting a sight line guidance mode to design a guidance rule for the defensive missile, then adopting a nonsingular terminal sliding mode to control the designed guidance rule, respectively defining sliding mode variables (shown in the description) of a longitudinal plane and a lateral plane, performing derivation on the sliding mode variables, substituting relative motion equations of the target, the defensive missile and the intercept missile into the variables and obtaining the guidance rule (shown in the description) of the longitudinal plane and the guidance rule (shown in the description) of the lateral plane through compilation, and controlling the missiles according to the guidance rules. By means of the sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method, overload needed by the defensive missile can be effectively reduced. The sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method is suitable for active defense guidance control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
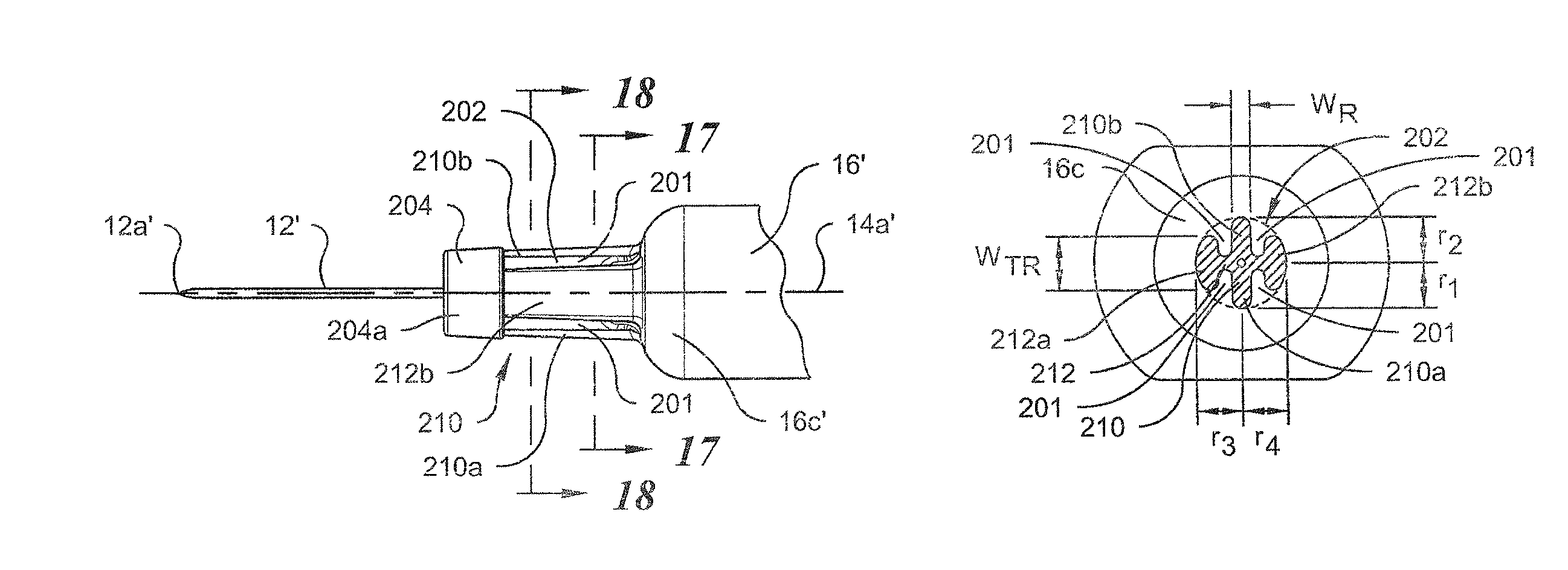
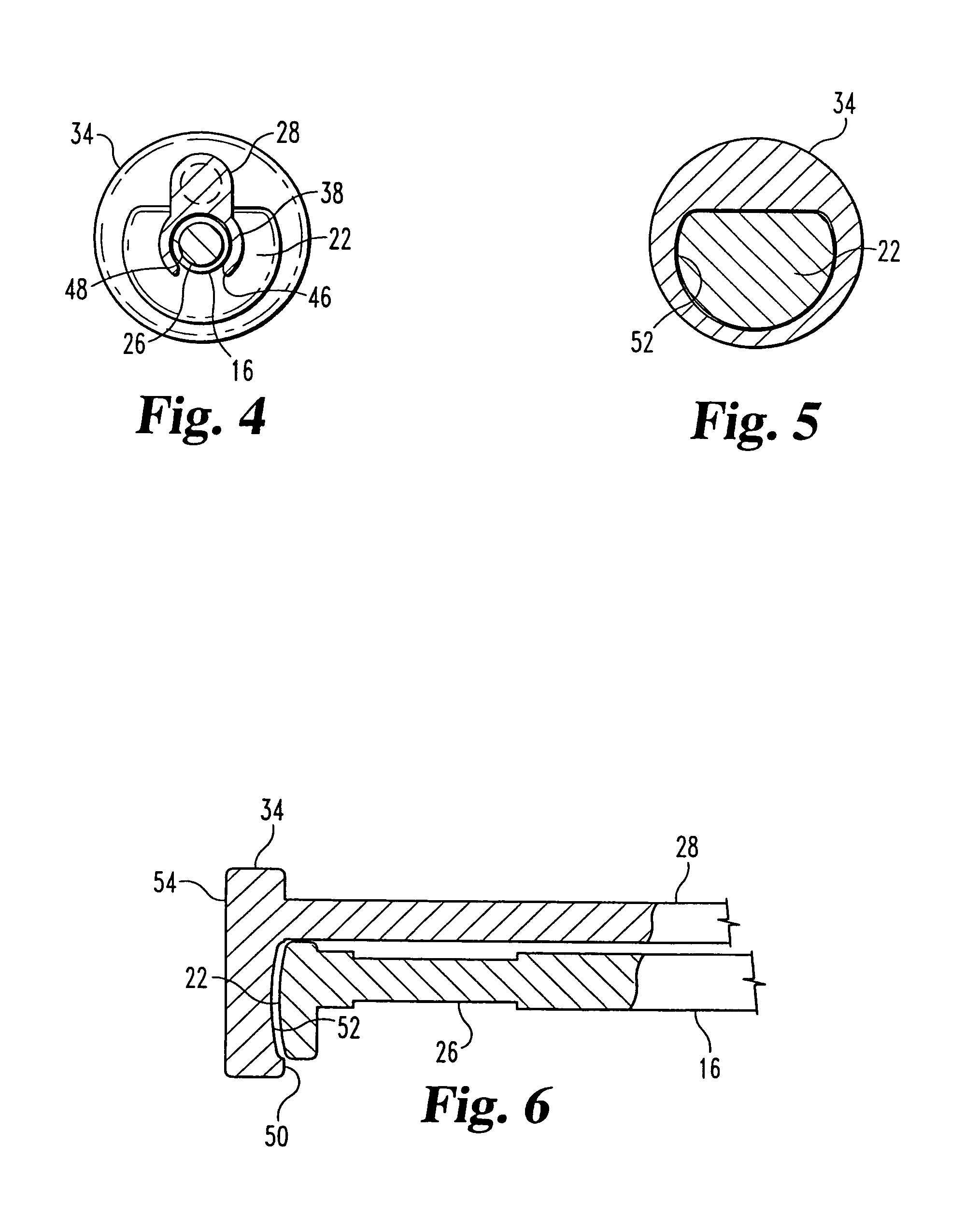
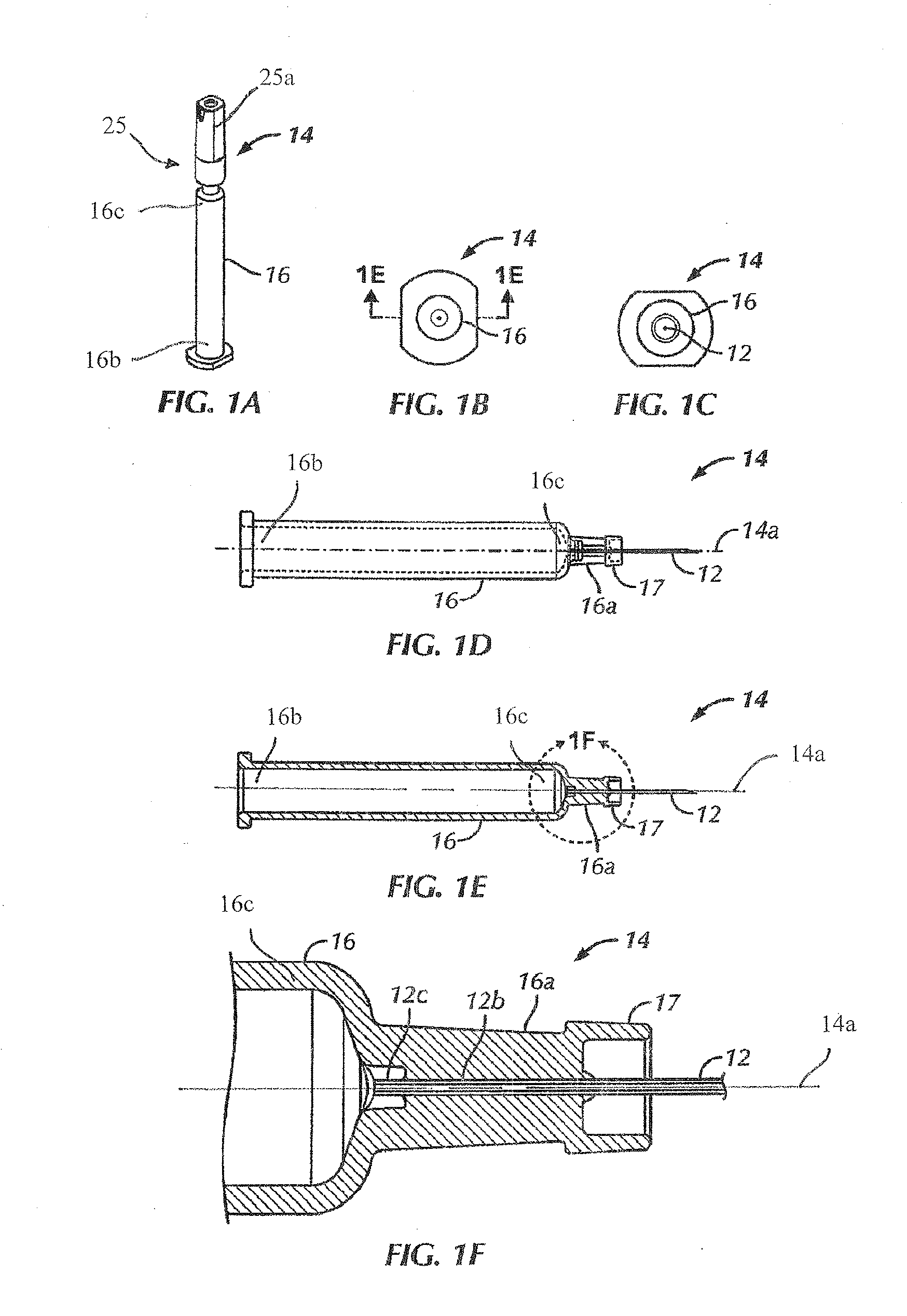
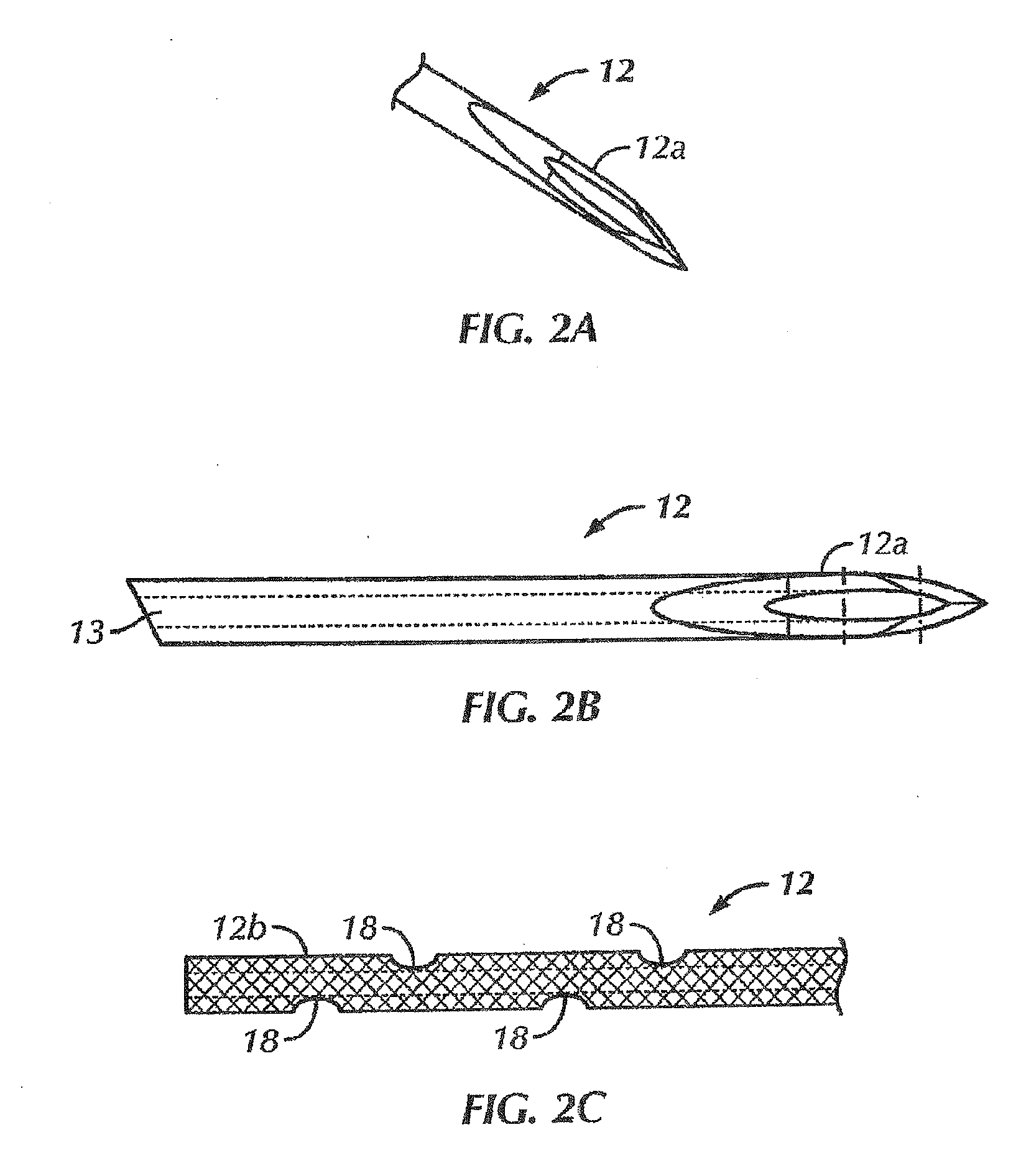
Syringe with co-molded hub and cannula
A prefilled syringe for injecting medicament into a patient includes a barrel constructed of a polymeric material, a cannula and a hub. The barrel has a diameter, a longitudinal axis, a proximal end and a distal end. The cannula has a proximal end and a tip opposite the proximal end. The proximal end of the cannula is fixed to the distal end of the barrel. The cannula is positioned generally coaxially with the longitudinal axis. The hub is integrally formed with the distal end. The hub includes a rib section and a cap. The rib section has a generally cruciform cross-section taken along a rib plane. The rib plane is generally perpendicular to the longitudinal axis. The cap has a generally U-shaped cross-section taken along a longitudinal plane. The longitudinal plane is generally parallel to the longitudinal axis.
Owner:WEST PHARM SERVICES INC
Fluidtight zip fastener
InactiveUS6343408B1Improve sealingAvoid wear and tearSnap fastenersSlide fastenersLongitudinal planeCoupling
The fluidtight zip fastener comprises a pair of fluidtight zip fastener carrying tapes carrying the zip fastener coupling member rows and which are in each case formed by a base tape with a soft, synthetic rubber or similar covering layer. They engage on one another by their edge portions. The pair of continuous coupling member rows is sewn to the zip fastener carrying tapes in a spaced offset position transversely to the longitudinal edges of said carrying tapes in such a way that the press-contact edge portions of the soft covering layers are in contact with one another along a longitudinal plane, which intersects the zip fastener at a central axis thereof and runs at right angles to the zip fastener principal plane. The press-contact edge portions project over said longitudinal plane, when the coupling member rows are disengaged. The edge portions, when the coupling member rows are engaged, are bent away from the side carrying the coupling member rows so as to extend roughly at right angles to the zip fastener principal plane. The soft covering layers of the press-contact edge portions engage on one another under pressure action when the zip fastener is closed and thus ensure the fluidtightness condition.
Owner:YKK CORP
Method and instrumentation for performing minimally invasive hip arthroplasty
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
High performance planing hull provided with a trim tab system
ActiveUS8100079B2Improve performanceIncrease awarenessVessel stability improvementMovement controllersTrim tabLongitudinal plane
Owner:FB DESIGN
Flight control method for small unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN102508493ASimple configurationImprove reliabilityPosition/course control in three dimensionsFly controlCollocation
The invention provides a flight control method for a small unmanned aerial vehicle. A homotaxial MEMS gyroscope, a barometer and a single-point GPS receiver are adopted as sensors, and the unmanned flight of the small unmanned aerial vehicle is realized through reasonable collocation and control design. In the side channel control, the homotaxial MEMS gyroscope forms a certain angle with z axis of a vehicle body coordinate system and a certain angle with x axis of the vehicle body coordinate system in the aerial vehicle longitudinal plane, so that the stability of the side channel of the small unmanned aerial vehicle is ensured, and then the small unmanned aerial vehicle can set a route and fly by utilizing GPS position information. In the longitudinal channel control, a derivative network is constructed to the barometer for damping the long period heaving vibration of the small unmanned aerial vehicle, and then the small unmanned aerial vehicle can set a height and fly by utilizing the GPS height. The method is particularly suitable for autonomous flight control of the small unmanned aerial vehicle which does not form a miniature inertial navigation system. The invention realizes the progress that the small unmanned aerial vehicle can fly autonomously according to a planned air landing site with the least sensors.
Owner:中国人民解放军92537部队
Element forming an inclined wedge used in a snowboard binding
InactiveUS6808196B2Guaranteed normal transmissionImprove distributionSki bindingsSnowboard bindingsLongitudinal planeEngineering
An element forming an inclined wedge, intended to be integrated with the front or rear end of the base plate of a snowboard binding, or directly with the upper face (5) of a snowboard, is disclosed. The element includes an upper face (9) intended to receive the bearing forces of the front or rear end of the sole of a boot, and having a mechanism for adjusting the angle of inclination, measured in a longitudinal plane, between the upper face of the element and the base plate of the binding or the upper face of the snowboard. The element may also provide a mechanism (30, 31) for adjusting the longitudinal position of the element in relation to the binding or snowboard.
Owner:SKIS ROSSIGNOL
Syringe with Co-Molded Hub and Cannula
A prefilled syringe for injecting medicament into a patient includes a barrel constructed of a polymeric material, a cannula and a hub. The barrel has a diameter, a longitudinal axis, a proximal end and a distal end. The cannula has a proximal end and a tip opposite the proximal end. The proximal end of the cannula is fixed to the distal end of the barrel. The cannula is positioned generally coaxially with the longitudinal axis. The hub is integrally formed with the distal end. The hub includes a rib section and a cap. The rib section has a generally cruciform cross-section taken along a rib plane. The rib plane is generally perpendicular to the longitudinal axis. The cap has a generally U-shaped cross-section taken along a longitudinal plane. The longitudinal plane is generally parallel to the longitudinal axis.
Owner:WEST PHARM SERVICES INC
Surgical Guide and Method for Guiding a Therapy Delivery Device into the Pterygopalatine Fossa
ActiveUS20100185258A1Facilitate delivery of therapy deliverySpinal electrodesHead electrodesPterygopalatine fossaLongitudinal plane
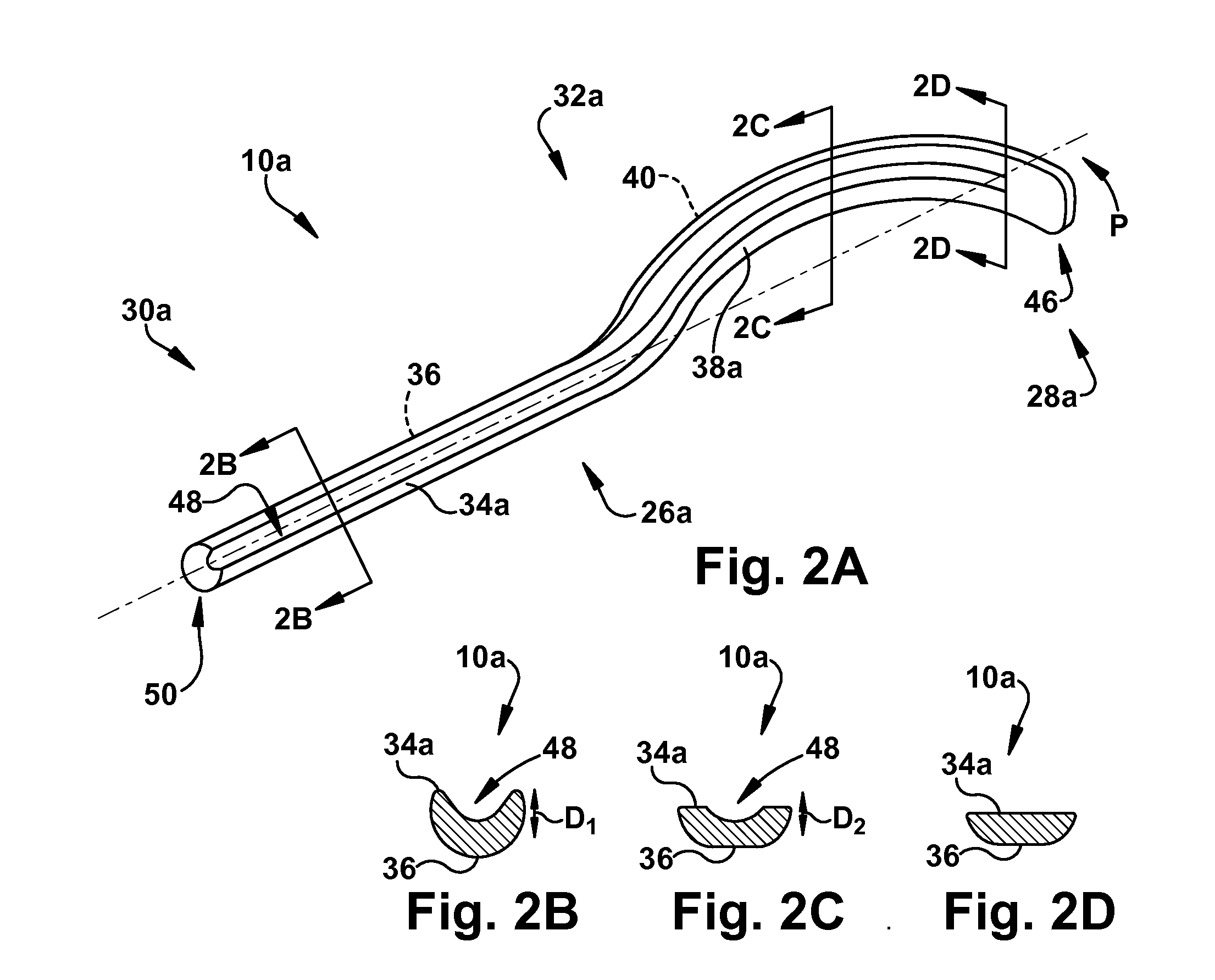
A surgical guide to facilitate delivery of a therapy delivery device into the pterygopalatine fossa of a subject includes a curvilinear body having a distal end portion, a proximal end portion, and an intermediate portion extending between the distal and proximal end portions. The proximal end portion is defined by oppositely disposed first and second surfaces. The proximal end portion and the intermediate portion define a longitudinal plane that extends between the proximal and distal end portions. The distal end portion has an arcuate configuration relative to the longitudinal plane and is defined by oppositely disposed third and fourth surfaces.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Guidance and control integrated design method considering all-strapdown seeker view field constraint
InactiveCN106681348ASatisfy test field constraintsSatisfy the field of view constraintAttitude controlLongitudinal planeMathematical model
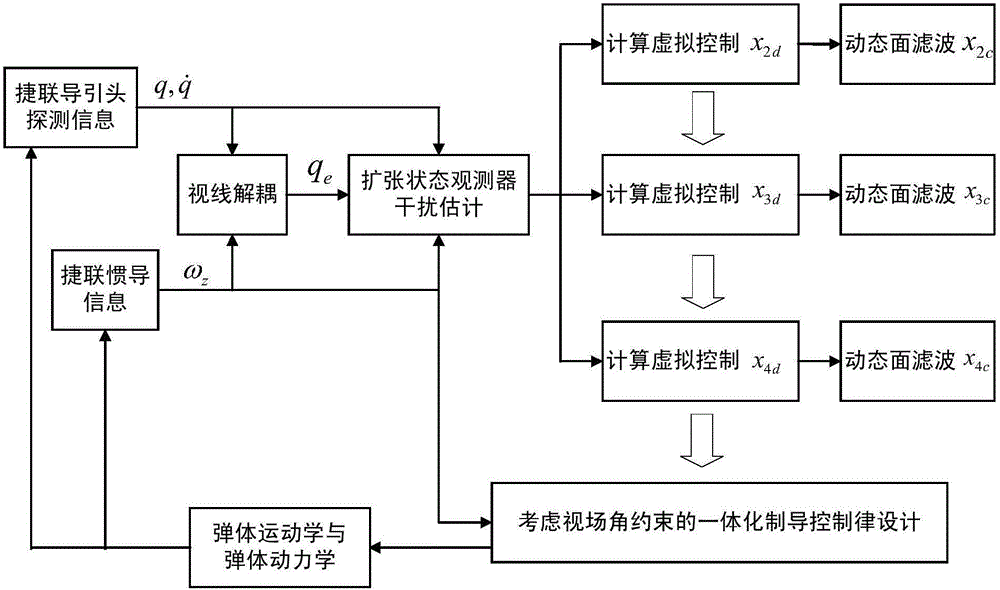
The invention discloses a guidance and control integrated design method considering all-strapdown seeker view field constraint, and aims at solving the technical problem that an existing guidance and control integrated design method is poor in practicability. According to the technical scheme, the guidance and control integrated design method comprises the steps that a missile longitudinal channel attitude control system model, a longitudinal plane missile-target relative motion model and an all-strapdown seeker longitudinal channel sight decoupling model are built; the state variable and the system output variable are selected, and a guidance and control integrated state space mathematical model considering view field angle constraint is built; a control method combining an obstacle Lyapunov function, an expansion state observer and dynamic surface control is adopted. The control method combining the obstacle Lyapunov function, the expansion state observer and dynamic surface control is adopted, and meanwhile the guidance precision and the all-strapdown seeker view field angle constraint conditions are met, so that it is guaranteed that the body sight angle detected by an all-strapdown seeker in the missile guidance and control process meets the seeker view field constraint.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Internal arrangement of the walls of the fuselage of an aircraft
InactiveUS7461816B2Lower acoustic noise levelGood lookingFuselage framesAir-treatment apparatus arrangementsLongitudinal planeCentral element
An internal arrangement of aircraft fuselage walls supports two longitudinal auxiliary passage ducts at the upper part of the fuselage and on each side of its longitudinal plane of symmetry. The arrangement includes a longitudinal central element forming a dome connecting the structural ducts, an interior ceiling panel situated under the dome and facing toward the cabin, and two lateral cover panels. A lower edge of each lateral panel is articulated with respect to the fuselage so that it may occupy a raised position in which it is connected to a respective one of the structural ducts near an upper edge of the structural duct and a lowered position in which it is distant from the structural duct. Also, the upper edge of each lateral panel is extended, in the raised position, beyond the structural duct to cover the corresponding longitudinal edges of the dome and the ceiling panel.
Owner:EADS SOGERMA SERVICES
Compliant pin for retaining and electrically connecting a shield with a connector assembly
ActiveUS7862376B2Electrically conductive connectionsCoupling contact membersLongitudinal planeBiomedical engineering
A compliant pin is configured to be press-fit into a cavity of at least one of a connector assembly and a substrate to retain the pin in the cavity. The pin includes a neck, a plurality of compliant beams, and an insertion tip. The neck interconnects the pin with the connector assembly. The beams are configured to engage an inner surface of the cavity to retain the pin in the cavity. The beams are arranged side-to-side and project along a longitudinal plane in a loading direction. The beams have arcuate portions that are arched in different directions transverse to the longitudinal plane. The arcuate portions are shaped to deflect toward the longitudinal plane without substantially engaging one another. The insertion tip interconnects the ends of the beams.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS LOGISTICS AG (CH)
Residential solar thermal power plant
InactiveUS20100326424A1Low costEstimate cost of electricitySolar heating energyStirling type enginesFollow-the-sunWorking fluid
A high-efficiency residential solar thermal power plant for economically generating power from solar-thermal energy, using a parabolic trough mirror having a longitudinal focal axis, for concentrating sunlight, a timer rotator for rotating the mirror about the focal and longitudinal rotation axis to follow the sun, and a heat collector surrounding a flow channel that preferably has an oblong cross-sectional shape with a major axis aligned with a longitudinal plane of symmetry of the parabolic trough mirror. The heat collector is coaxially positioned along the focal axis of said mirror to receive concentrated sunlight so that a working fluid is heated and provided for use through an outlet end of the heat collector.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Electro-chemical corrosion simulator with in-situ loading
InactiveCN103323387APrevent leakageReal-time adjustment of load sizeWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesLongitudinal planeAuxiliary electrode
The invention provides an electro-chemical corrosion simulator with in-situ loading and relates to the technical field of materials. The simulator consists of an electrolytic bath, an electrolytic bath upper cover, a reference electrode, an auxiliary electrode, a working electrode, a tensile testing machine fixture, a temperature gauge and an electrolyte, wherein the tensile testing machine fixture is connected with a tensile testing machine, the working electrode passes through a lower hole for mounting a sample along the electrolytic bath and is hermetically fixed; the electrolyte is filled in the electrolytic bath; an upper hole, used for mounting the sample, in the electrolytic bath upper cover and the lower hole, used for mounting the sample, in the electrolytic bath are kept in a same longitudinal plane; the reference electrode, the auxiliary electrode and the temperature gauge are respectively in a small hole, used for inserting the reference electrode, of the electrolytic bath upper cover, a small hole, used for inserting the auxiliary electrode, of the electrolytic bath upper cover and a small hole, used for inserting the temperature gauge, of the electrolytic bath upper cover. During operation, load is applied, and an electro-chemical corrosion simulation test with in-situ loading is performed. The device can be used for not only regulating the parameters such as temperature, pH value and ionic species of the electrolyte, but also regulating the load size and the load mode in real time.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
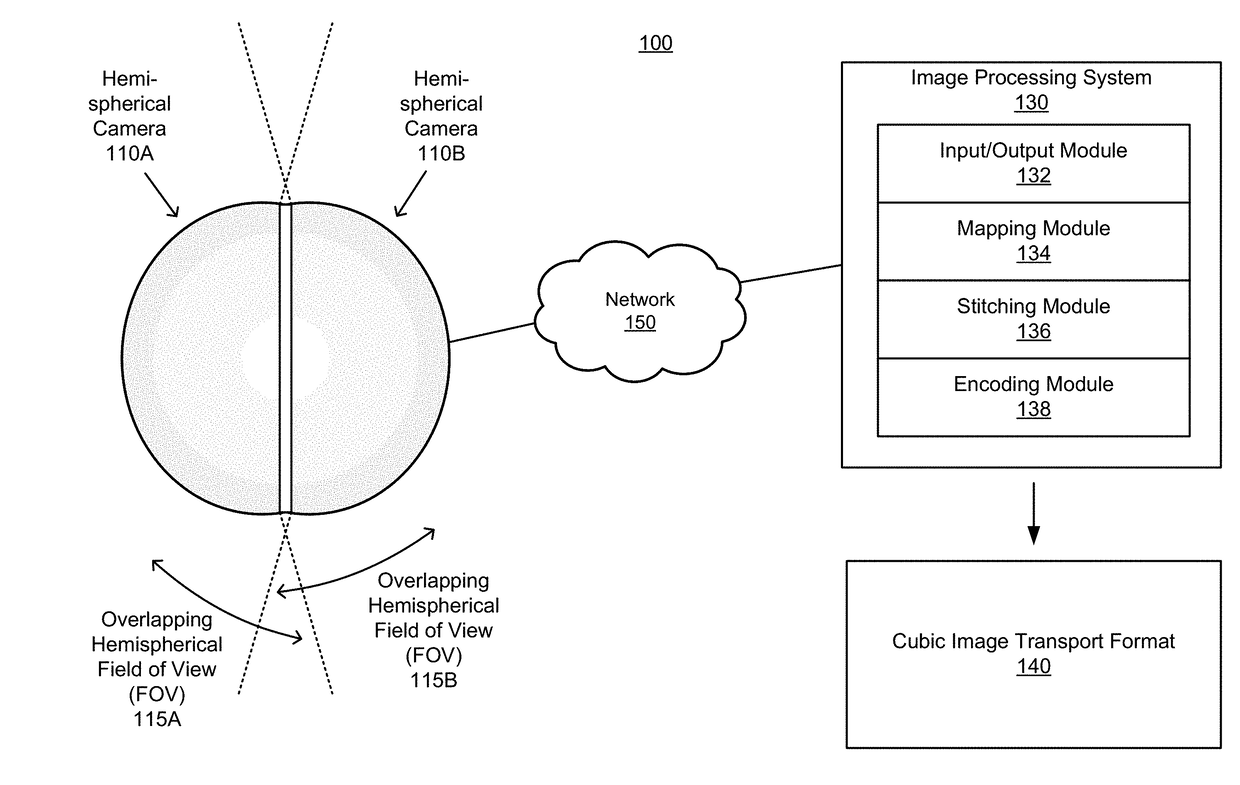
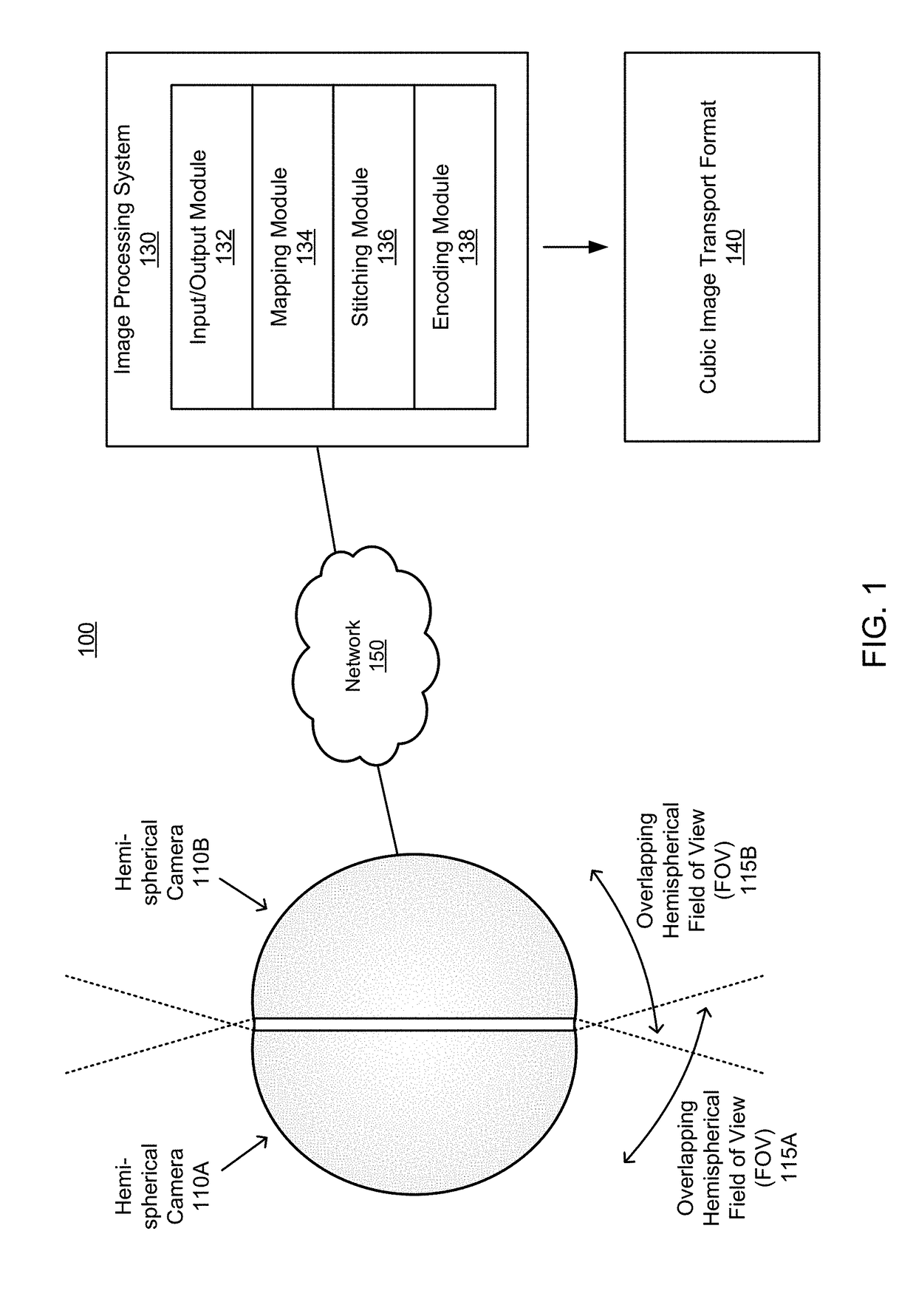
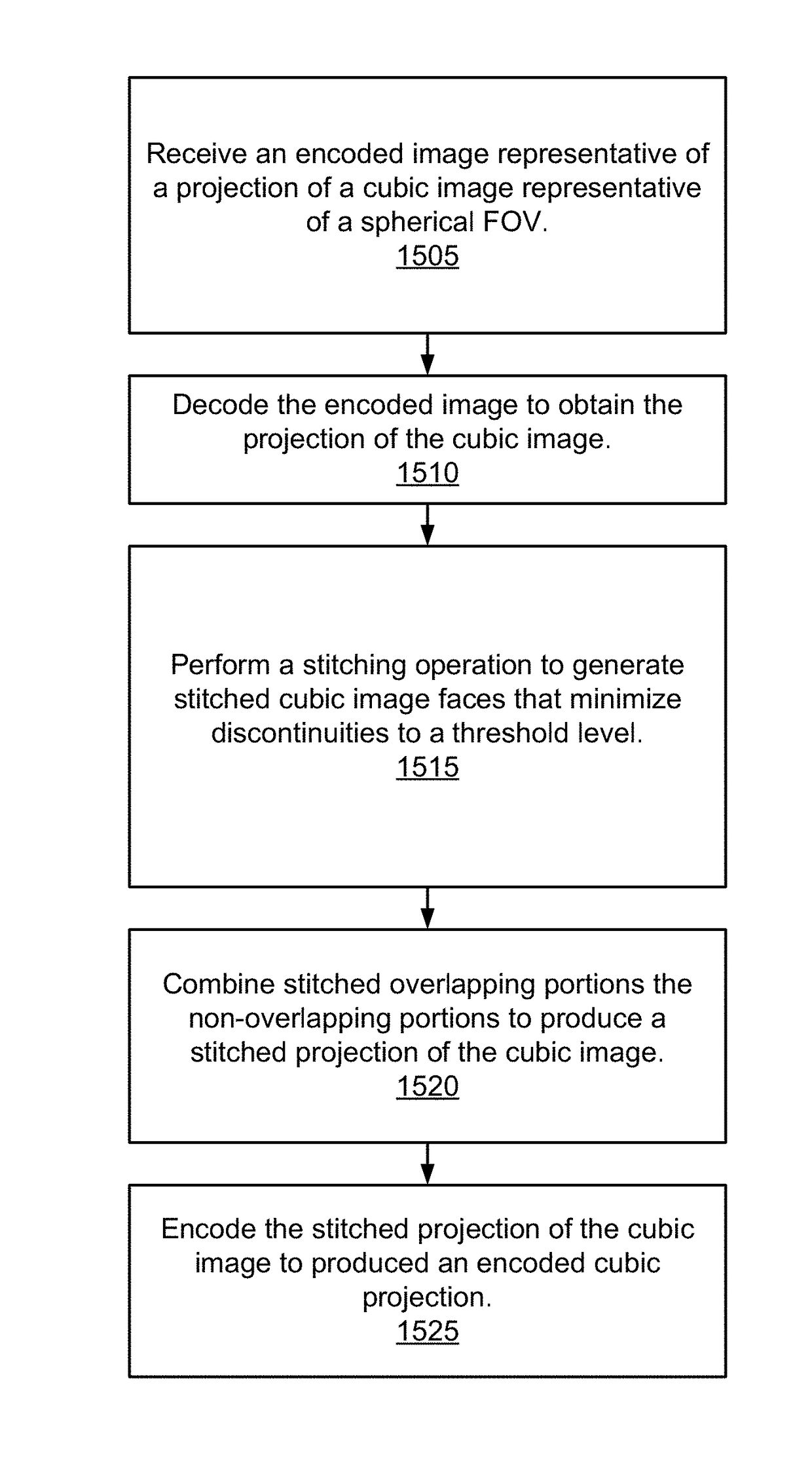
Mapping of spherical image data into rectangular faces for transport and decoding across networks
A system receives an encoded image representative of the 2D projection of a cubic image, the encoded image generated from two overlapping hemispherical images separated along a longitudinal plane of a sphere. The system decodes the encoded image to produce a decoded 2D projection of the cubic image, and perform a stitching operation to portions of the decoded 2D projection representative of overlapping portions of the hemispherical images to produce stitched overlapping portions. The system combine the stitched overlapping portions with portions of the decoded 2D projection representative of the non-overlapping portions of the hemispherical images to produce a stitched 2D projection of the cubic image, and encode the stitched 2D projection of the cubic image to produce an encoded cubic projection of the stitched hemispherical images.
Owner:GOPRO
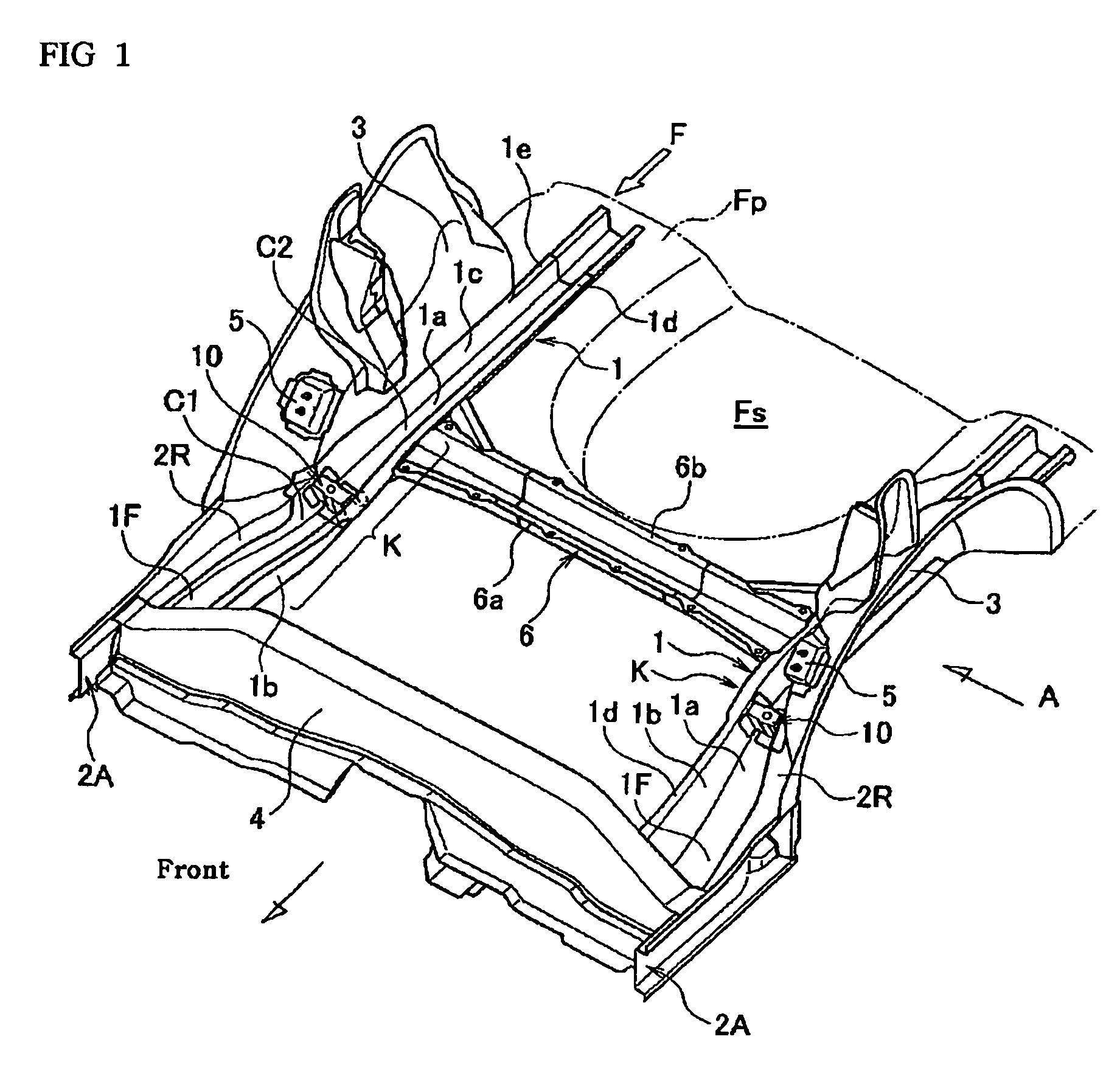
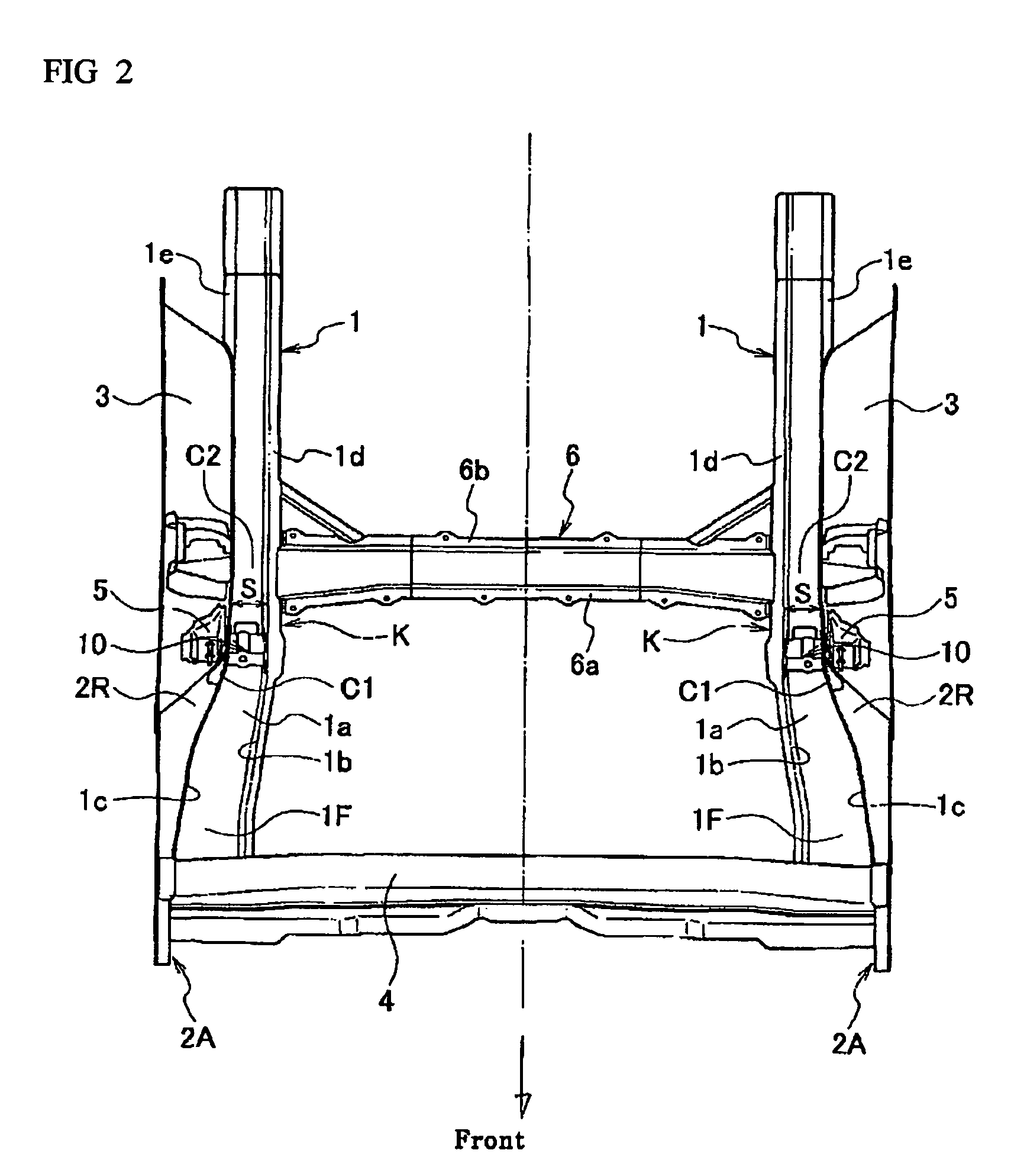
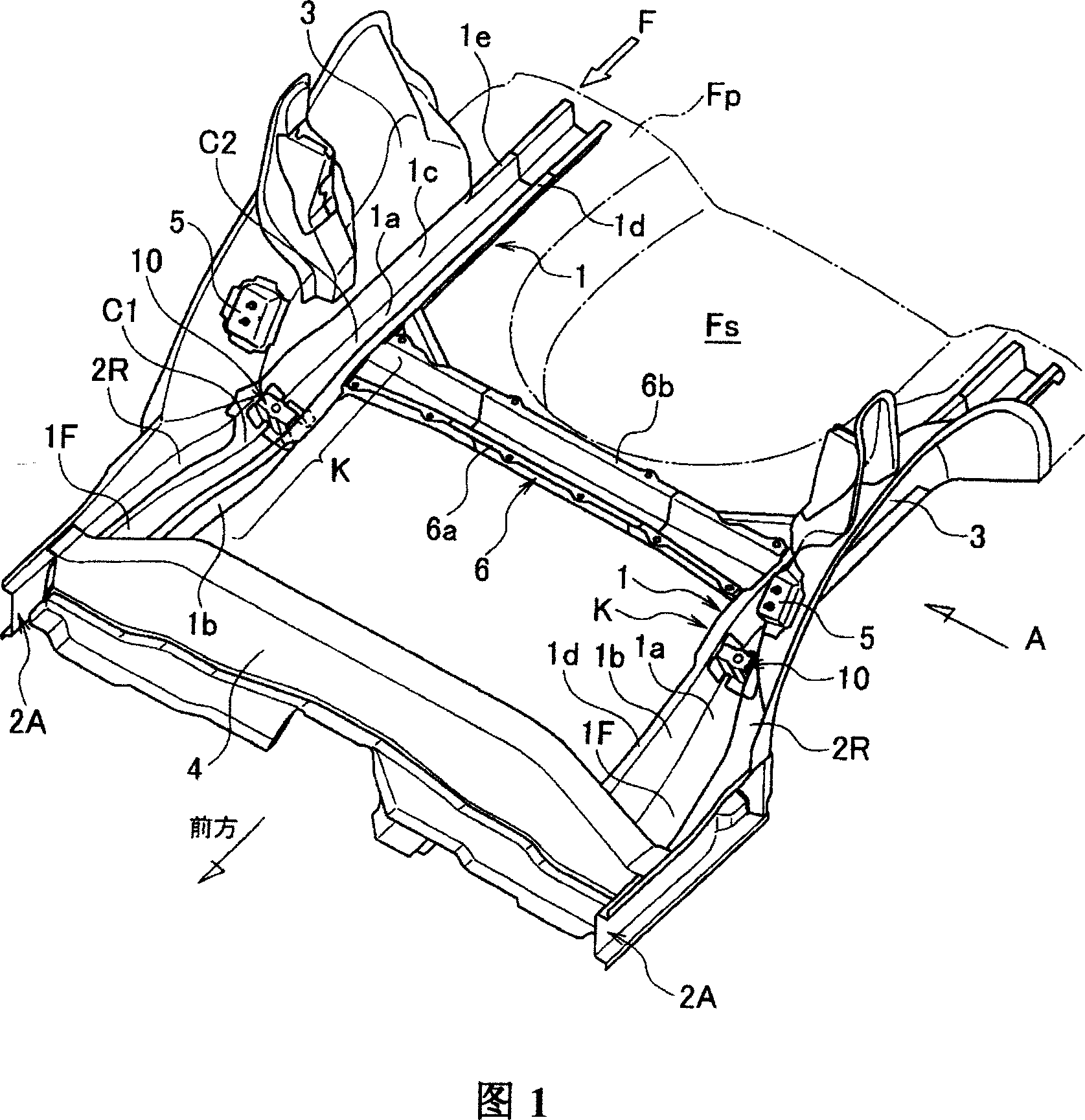
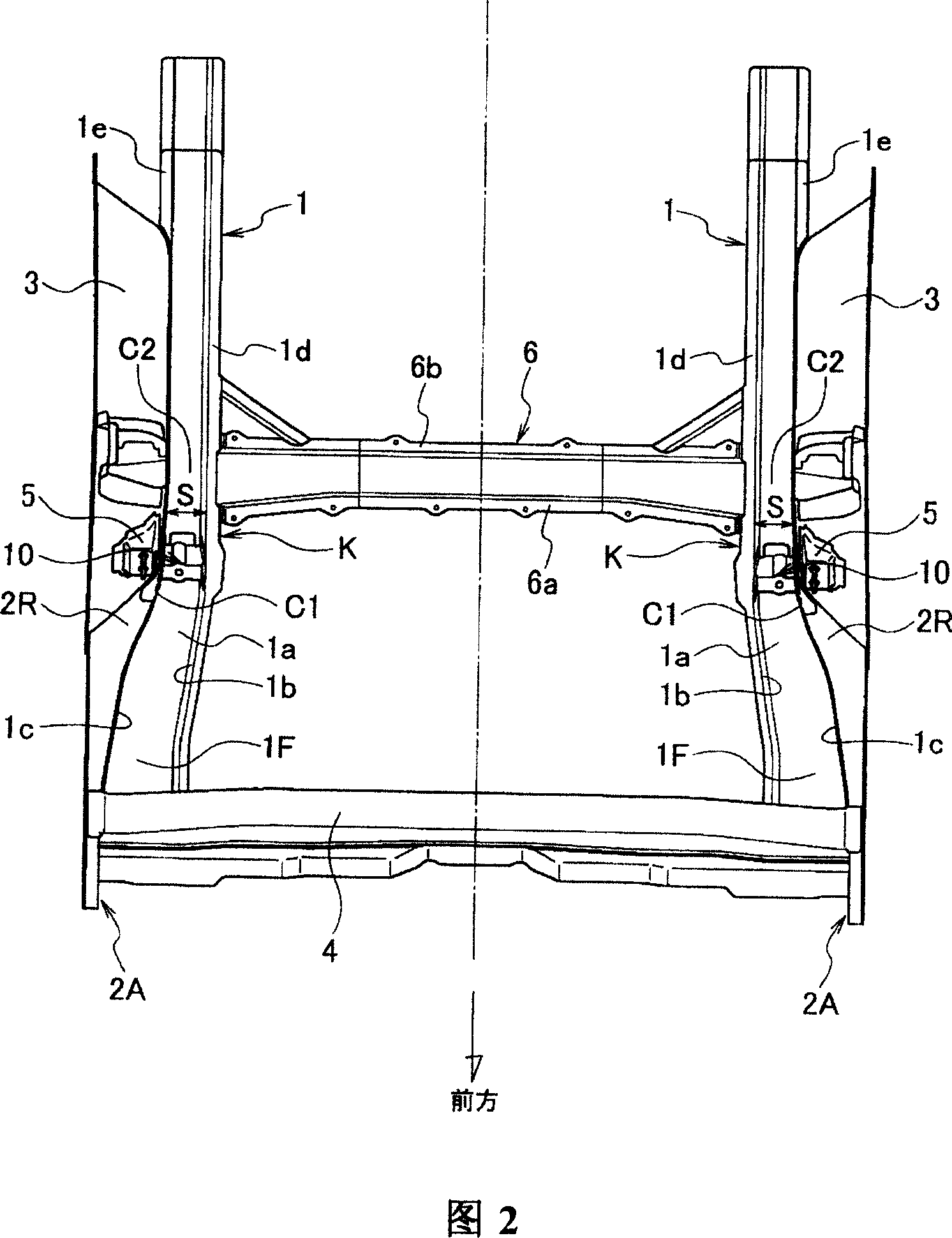
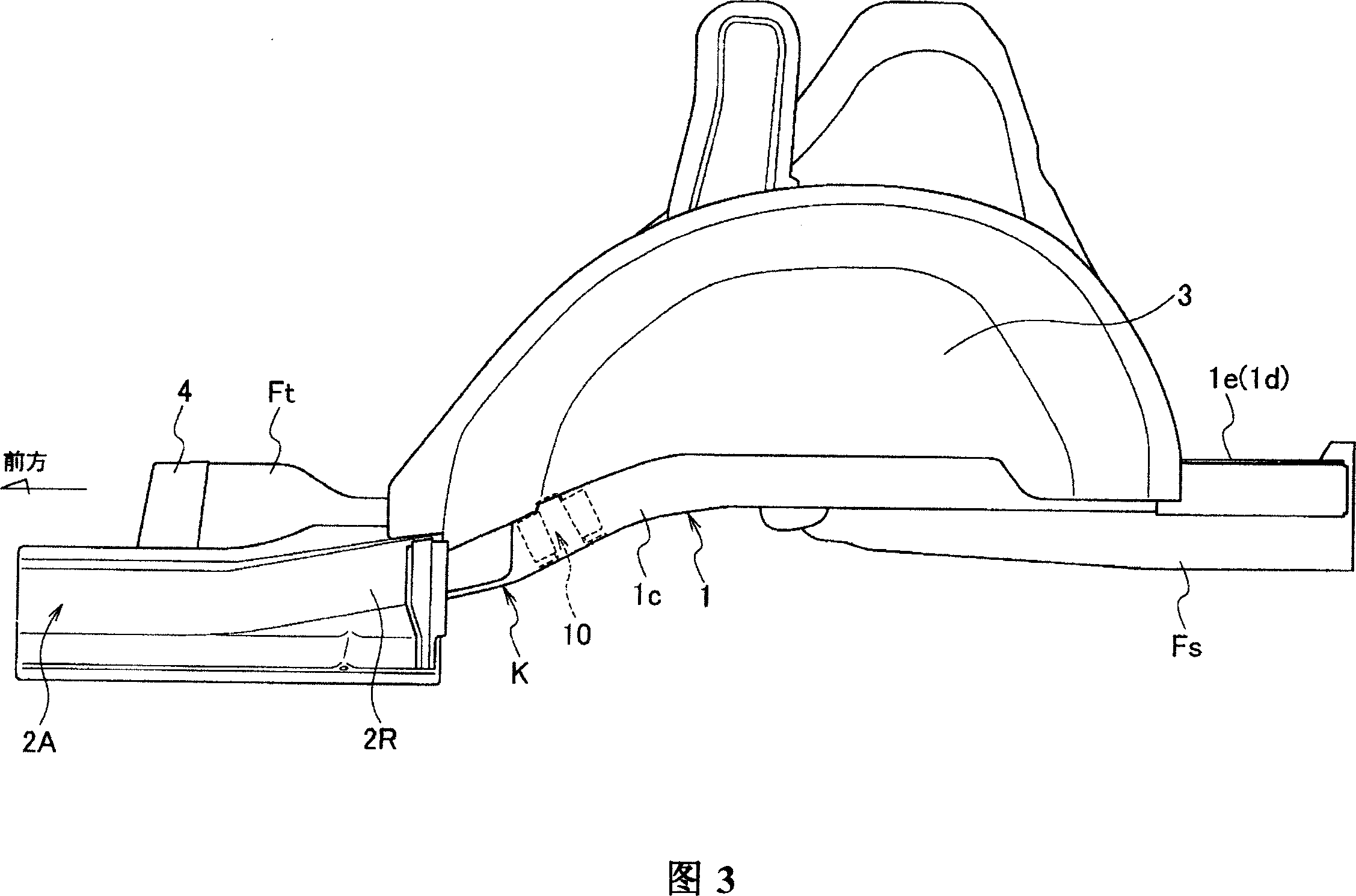
Rear structure of a vehicular body
ActiveUS7631918B2Effectively prevent an upward bending of a side rear memberMinimizing number and weightUnderstructuresSuperstructure subunitsLongitudinal planeTransverse plane
A rear structure of a vehicular body has side sills disposed at lateral ends of the vehicular body. The rear structure further has side rear members having a hat-shaped cross-section and having a kick-up portion that is upwardly inclined. The side rear members are bonded to the side sills at bonded portions, and extend toward a rear of the vehicular body. The rear structure further has a cross member connecting side sills in a lateral direction across the vehicular body. The cross member is connected to each of the side sills at connected portions at a rear of the kick-up portions. The rear structure further has reinforcements having a closed cross-section in a longitudinal plane and in a lateral plane. The reinforcements are disposed in the side rear members between the bonded portions and the connected portions.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
High-breakdown-voltage semiconductor device
A high-breakdown-voltage semiconductor device comprises a high-resistance semiconductor layer, trenches formed on the surface thereof in a longitudinal plane shape and in parallel, first regions formed on the semiconductor layer to be sandwiched between adjacent ones of the trenches and having an impurity concentration higher than that of the semiconductor layer, a second region having opposite conductivity to the first regions and continuously disposed in a trench sidewall and bottom portion, a sidewall insulating film disposed on the second region of the trench sidewall, a third region disposed on the second region of the trench bottom portion and having the same conductivity as and the higher impurity concentration than the second region, a fourth region disposed on the back surface of the semiconductor layer, a first electrode formed on each first region, a second electrode connected to the third region, and a third electrode formed on the fourth region.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Vehicle body rear part structure
InactiveCN100999232AAvoid bendingImprove rigidityUnderstructuresSuperstructure subunitsLongitudinal planeVehicle frame
A rear structure of a vehicular body has side sills disposed at lateral ends of the vehicular body. The rear structure further has side rear members having a hat-shaped cross-section and having a kick-up portion that is upwardly inclined. The side rear members are bonded to the side sills at bonded portions, and extend toward a rear of the vehicular body. The rear structure further has a cross member connecting side sills in a lateral direction across the vehicular body. The cross member is connected to each of the side sills at connected portions at a rear of the kick-up portions. The rear structure further has reinforcements having a closed cross-section in a longitudinal plane and in a lateral plane. The reinforcements are disposed in the side rear members between the bonded portions and the connected portions.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
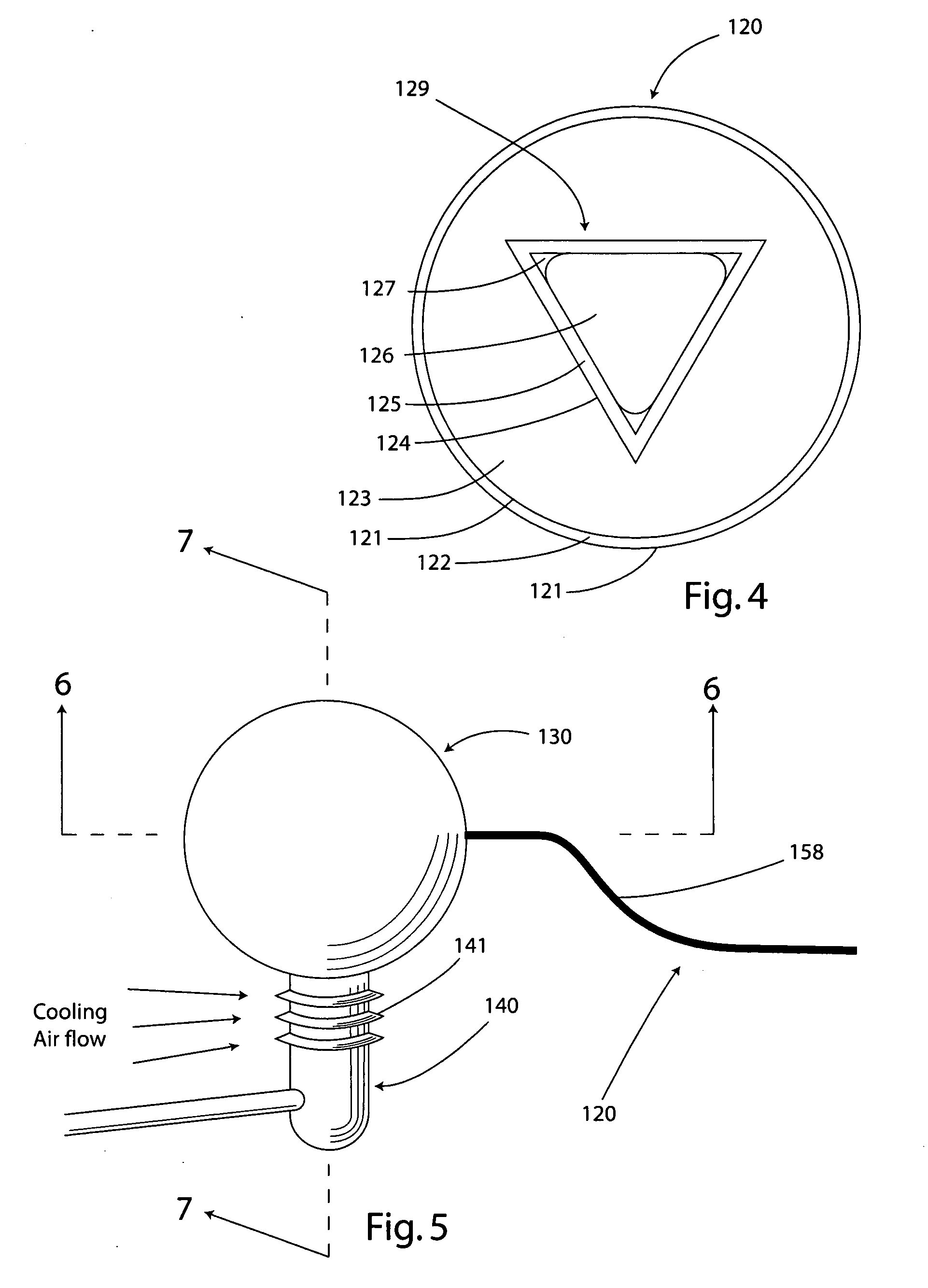
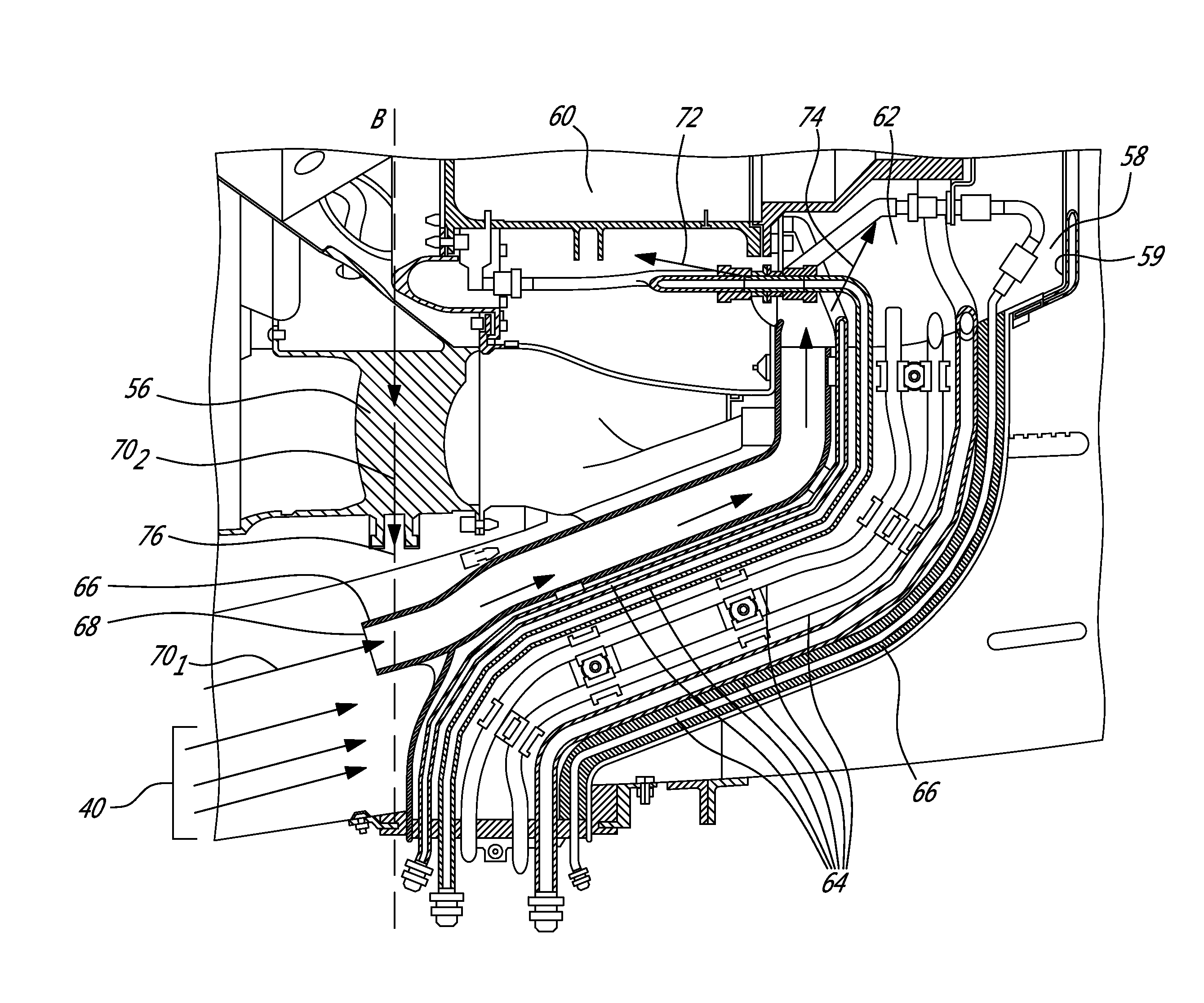
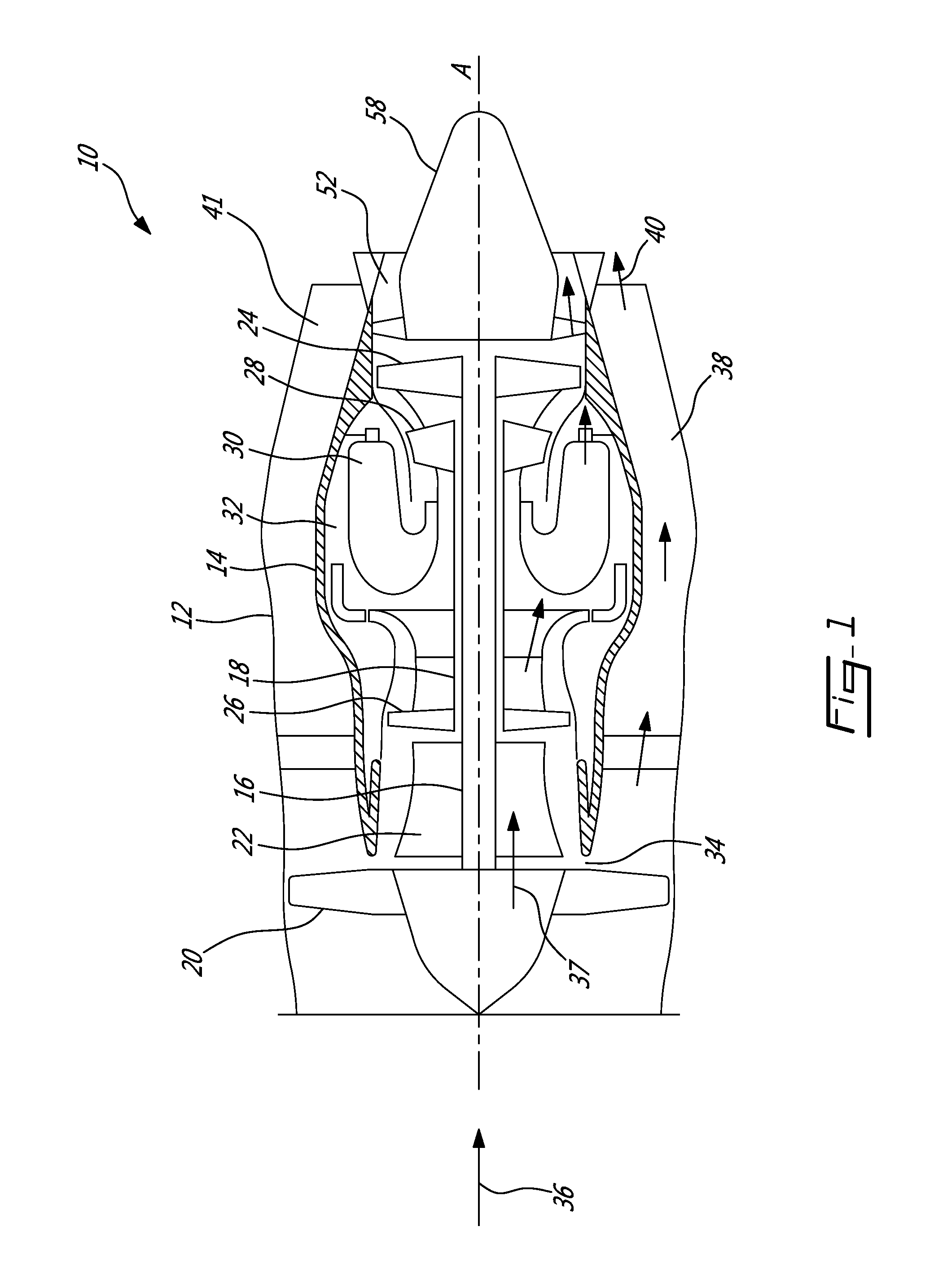
Air cooling design for tail-cone generator installation
ActiveUS9097134B2Turbine/propulsion engine coolingEfficient propulsion technologiesLongitudinal planeElectric generator
A system for cooling a generator mounted in the tail-cone of an engine. The system comprises a fairing, which receives through an inlet thereof air from a bypass duct and directs the bypass air towards a cavity of the tail-cone for cooling the generator. The bypass air is then expelled through an outlet of a support strut positioned in fluid communication with the tail-cone cavity. The fairing inlet and the strut outlet are both positioned in a plane substantially perpendicular to a longitudinal plane of the engine. In this manner, circulation of the bypass air through the fairing, the tail-cone cavity, and the strut may be achieved. The bypass air directed through the fairing further enables cooling of service lines accommodated in the fairing. A lobe mixer is further used to direct the fairing and shield the latter from core exhaust.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
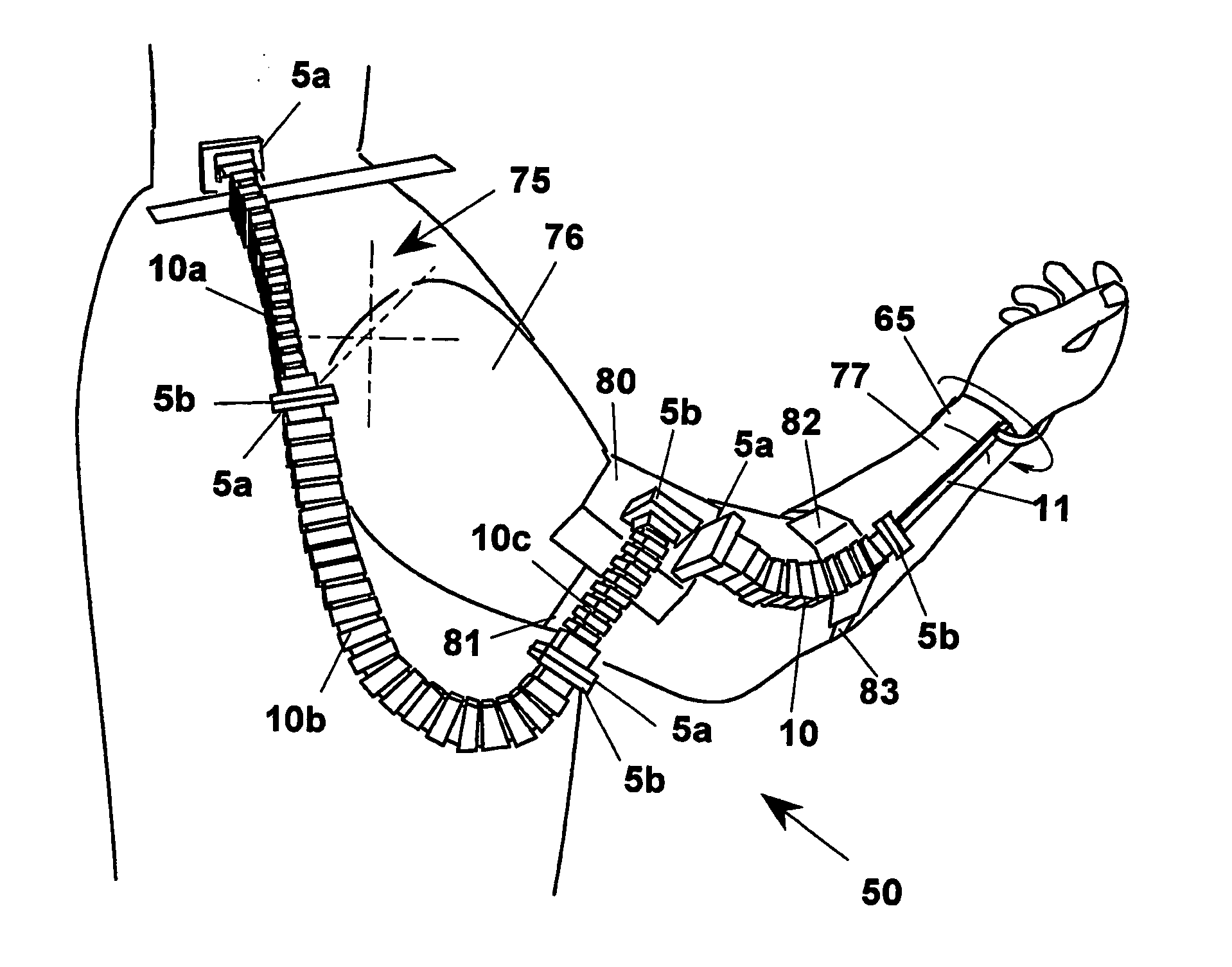
Device for gioniometric measurements
InactiveUS20060130347A1Not expensive to makeReduce the burden onMeasurement devicesSurgeryLongitudinal planeEngineering
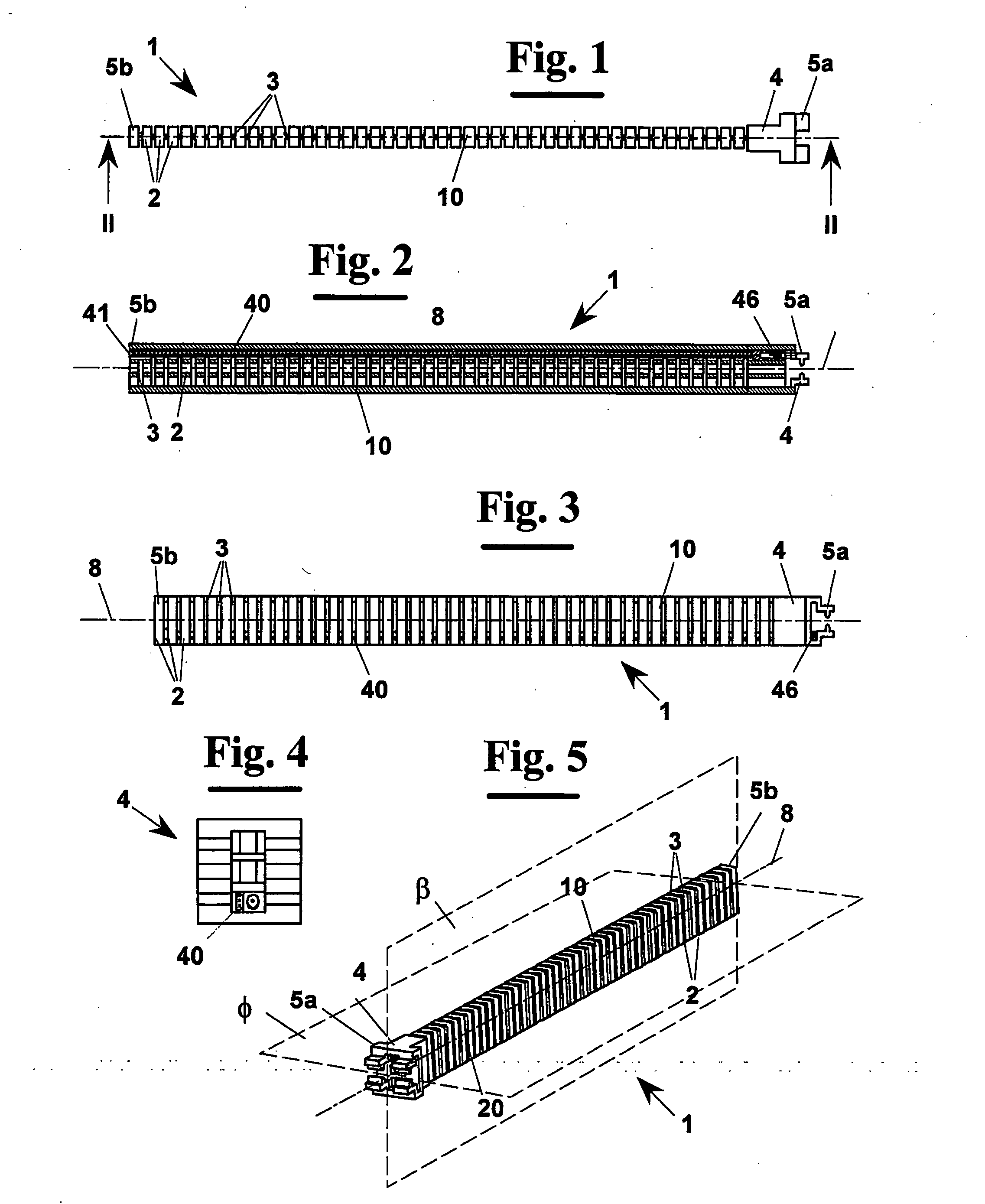
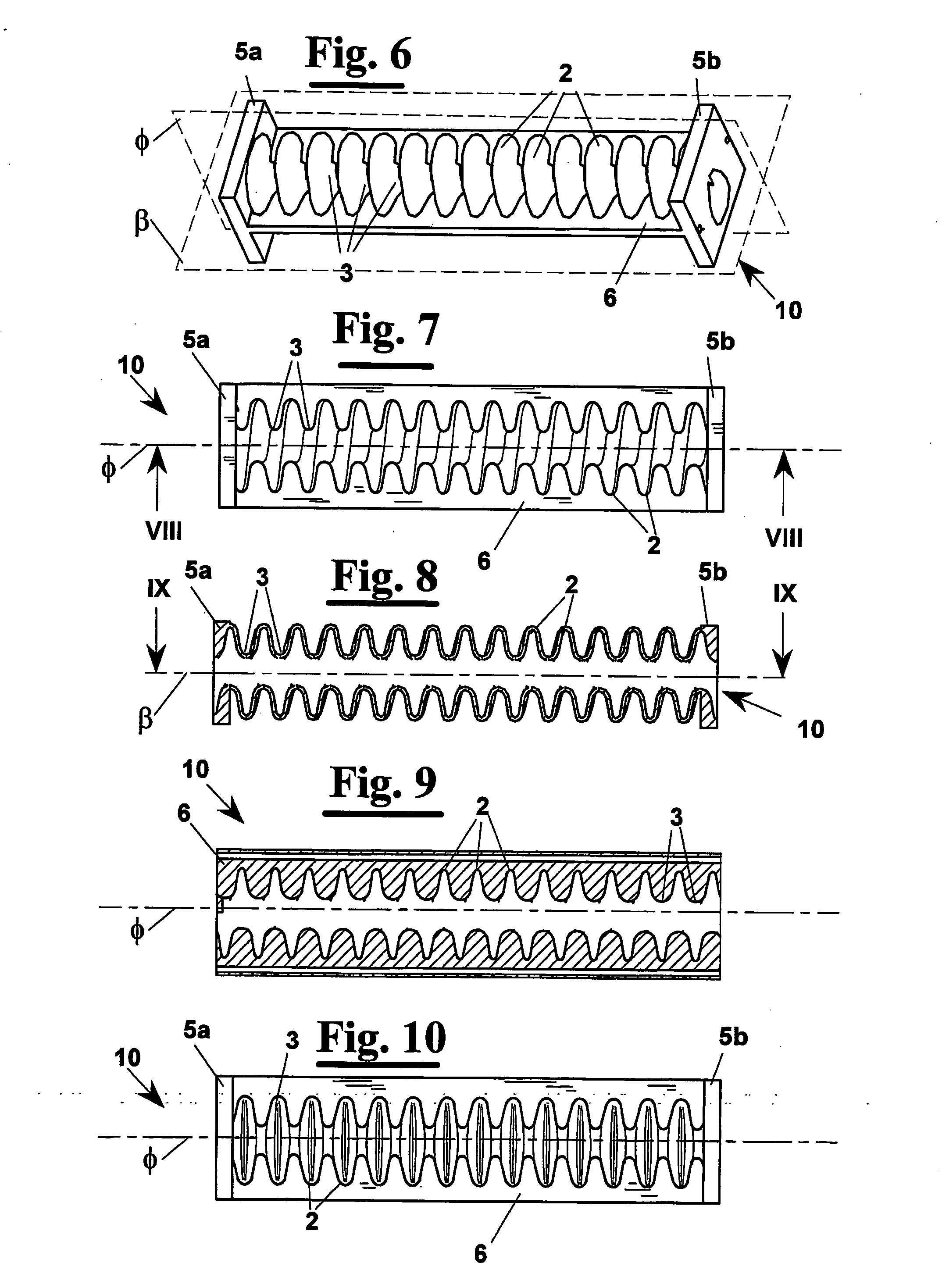
A device (1) for measuring the relative orientation according to at least one degree of freedom for two objects, including a constraint generator (10) suitable for causing a goniometric sensor (40) to move in a plane, having the function of measuring the variation of relative orientation of the two objects in this plane. The goniometric sensor (40) is arranged in a housing (41) that crosses longitudinally the constraint generator (10), which has high flexional stiffness in a first longitudinal plane (β) and a low flexional stiffness in a second longitudinal plane (φ) orthogonal to the first (β) . The sensor measures rotations in a plane and the constraint generator induces a rotation in that plane. With the device (1) a data suit (50) can be made for measuring the movement of limbs of an individual. For example, arranging three devices (10a, 10b, 10c) in series, but capable of measuring angles in orthogonal planes, the rotation can be measured of the arm (76) with respect to a shoulder (75) of an individual.
Owner:BERGAMASCO MASSIMO +3
Toy flying aircraft
A toy flying aircraft has a fuselage defining a central vertical longitudinal plane, with an upper front portion and a lower rear portion. The upper front and lower rear portions are coupled by a vertical support angling forward and upward from a front upper side of the rear portion to a lower rear side of the front portion. The aircraft has an at least generally circular and horizontally planar wing intersecting the front portion of the fuselage. A forward half of the wing defines an upper horizontal plane generally perpendicular to the central vertical longitudinal plane, and a rear half of the wing is downwardly offset from the upper horizontal plane to define a lift surface. A generally V-shaped planar rear stabilizer is bisected and supported by the rear portion of the fuselage so as to be located vertically entirely below the wing.
Owner:MATTEL INC
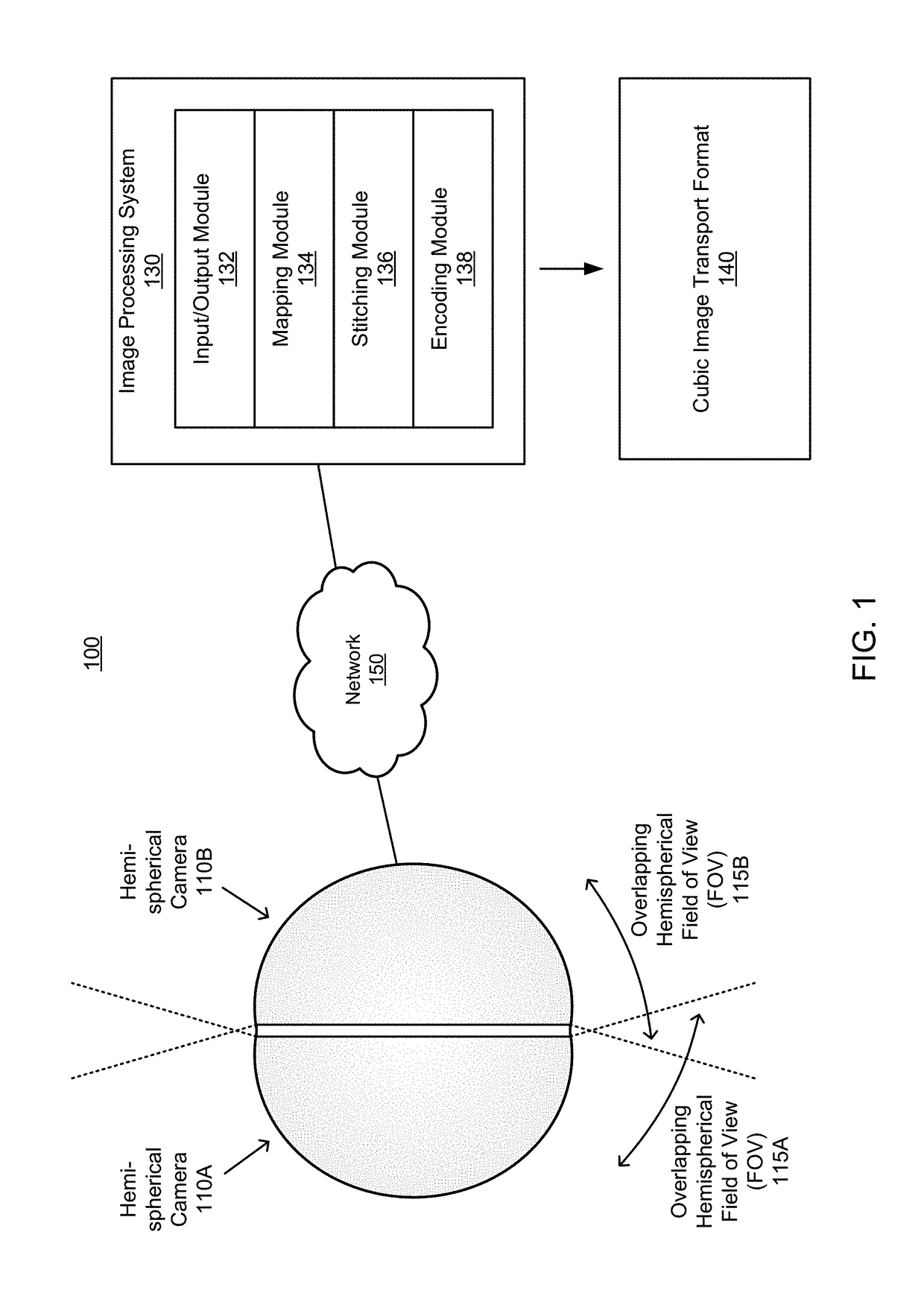
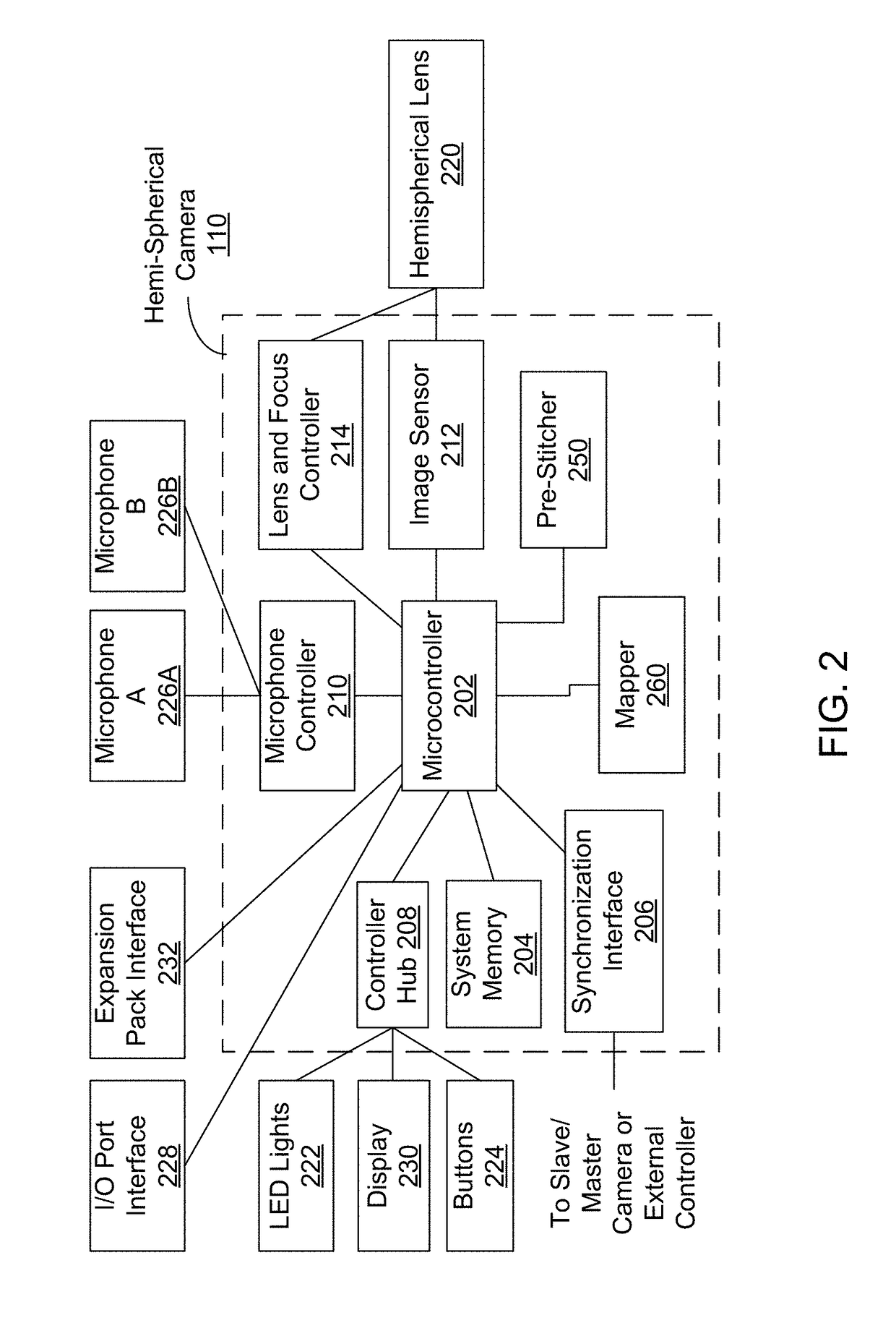
Mapping of spherical image data into rectangular faces for transport and decoding across networks
A system captures a first hemispherical image and a second hemispherical image, each hemispherical image including an overlap portion, the overlap potions capturing a same field of view, the two hemispherical images collectively comprising a spherical FOV and separated along a longitudinal plane. The system maps a modified first hemispherical image to a first portion of the 2D projection of a cubic image, the modified first hemispherical image including a non-overlap portion of the first hemispherical image, and maps a modified second hemispherical image to a second portion of the 2D projection of the cubic image, the modified second hemispherical image also including a non-overlap portion. The system maps the overlap portions of the first hemispherical image and the second hemispherical image to the 2D projection of the cubic image, and encodes the 2D projection of the cubic image to generate an encoded image representative of the spherical FOV.
Owner:GOPRO
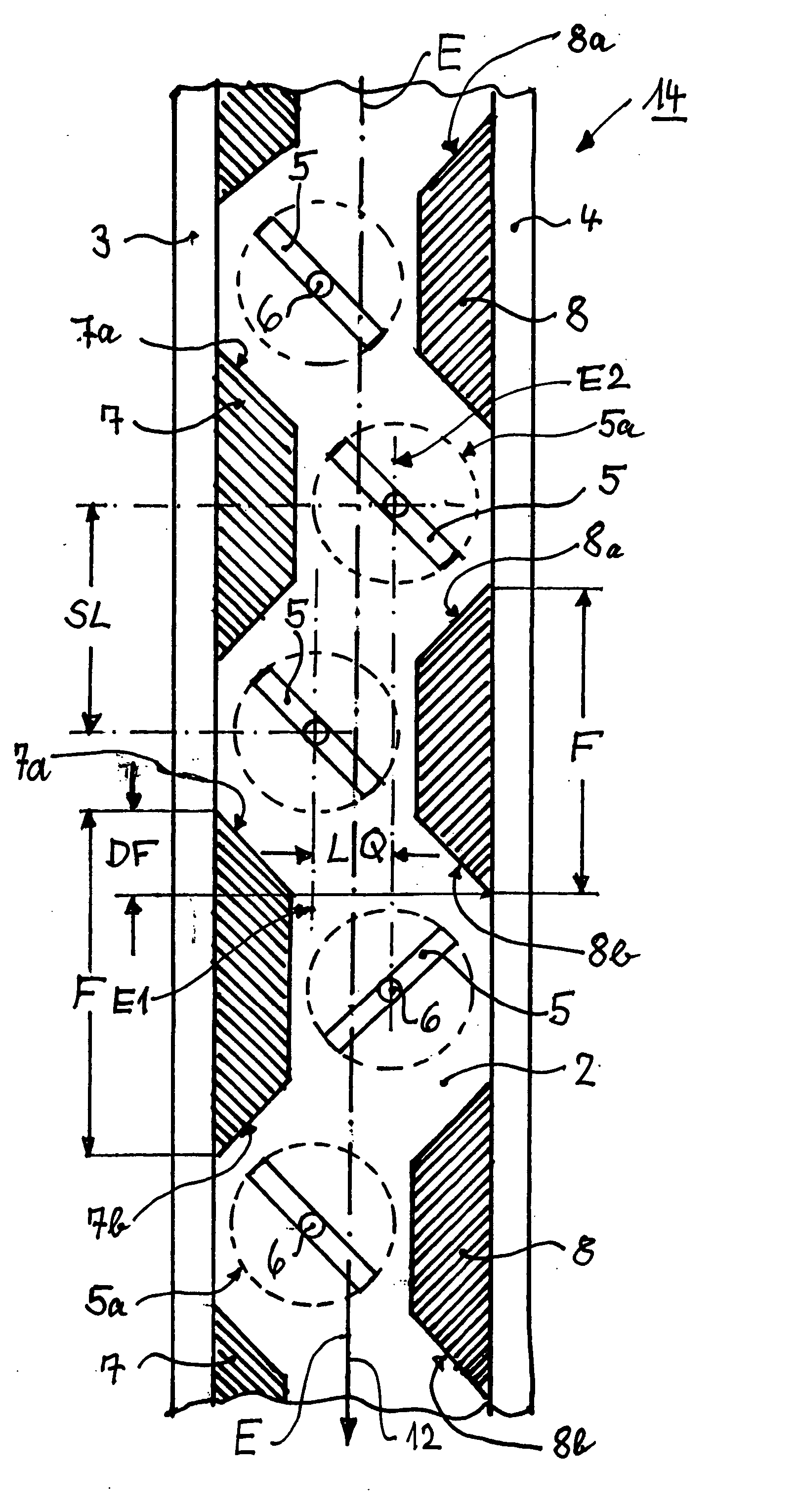
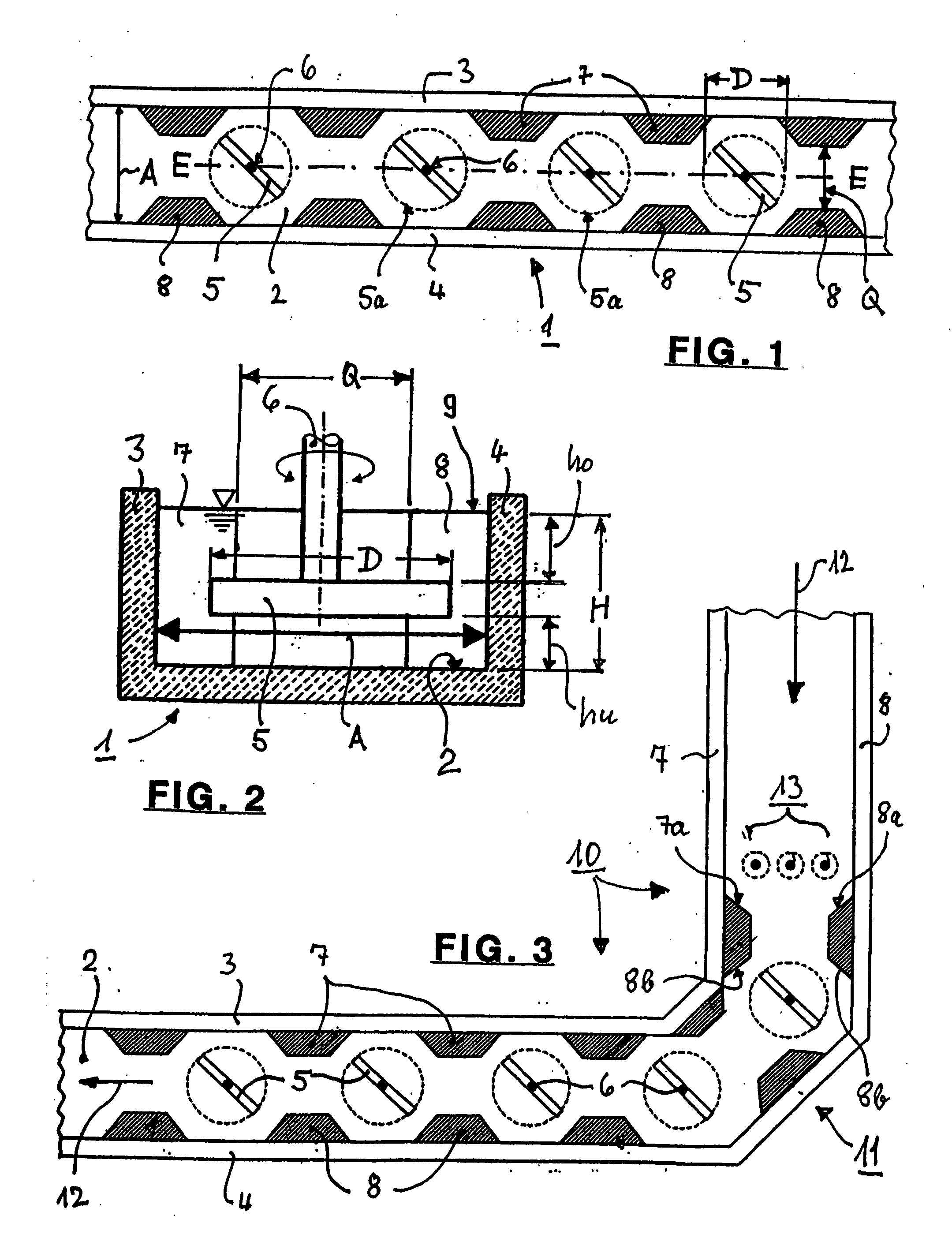
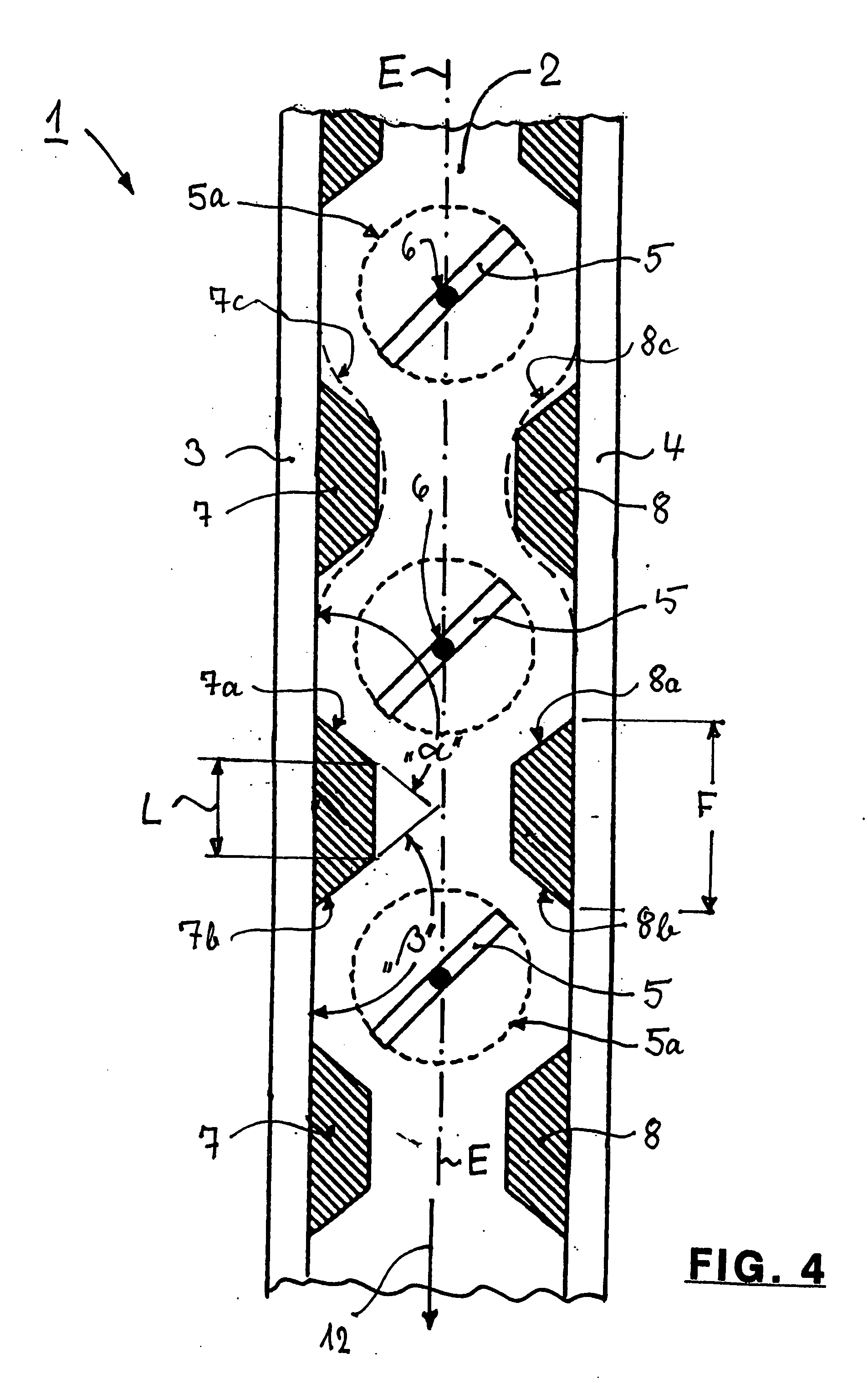
Method and apparatus for the conditioning and homogenization of glass melts
InactiveUS20070089460A1Efficient HomogenizationIncrease flexibilityForehearthsFlow mixersLongitudinal planeEngineering
A method and apparatus for the conditioning and homogenization of glass melts that are transported in flow channels with a vertical central longitudinal plane and side walls, by using the effect of alternating cross-section changes in the flow direction and stirrers with vertical stirrer shafts installed in the flow direction. The glass melt is transported through at least one flow channel, in which cross-section changes on both sides are created by several consecutive protrusions installed in the flow direction. The protrusions are directed towards the central longitudinal plane and on their upstream sides and downstream sides have wall areas that are arranged at such an angle to the central longitudinal plane, that no right-angled or acute-angled corners are created in the flow channel. The stirrers are installed between consecutive downstream sides and the upstream sides of the protrusions.
Owner:BETEILIGUNGEN SORG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com