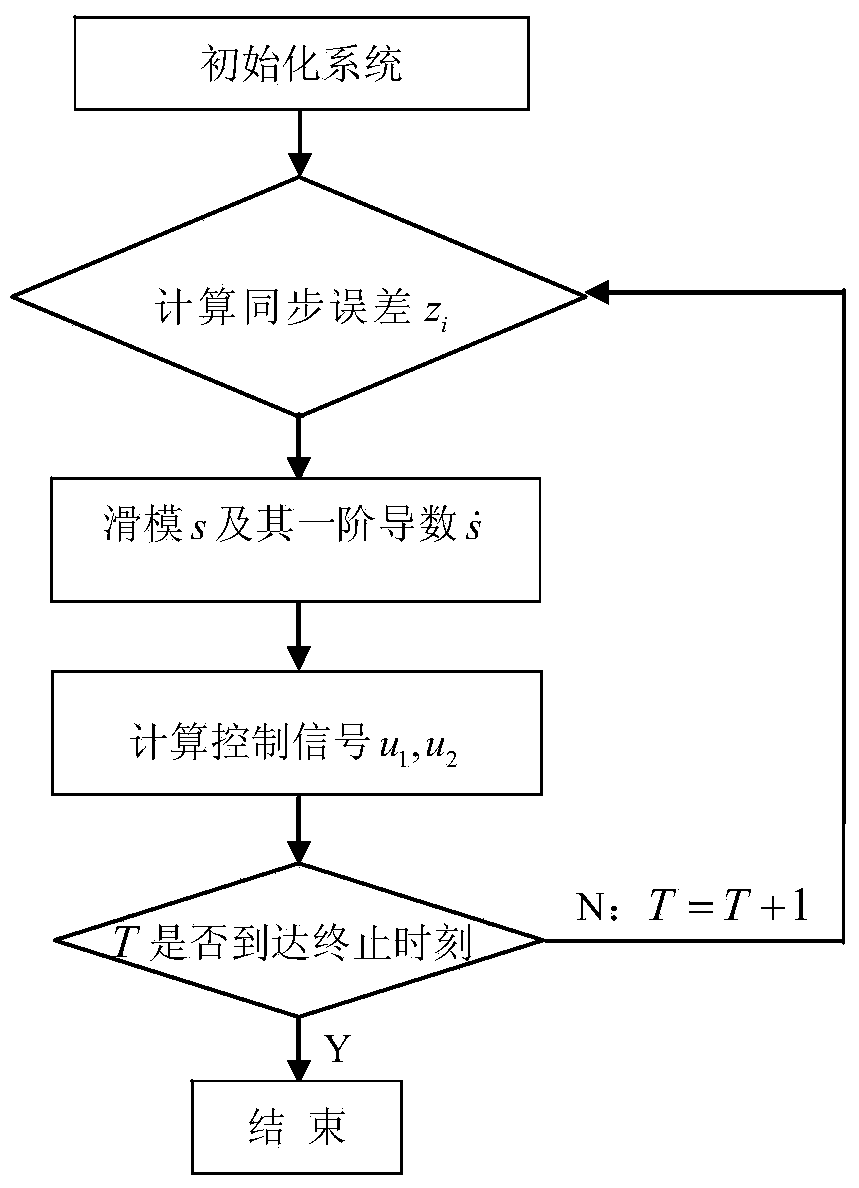
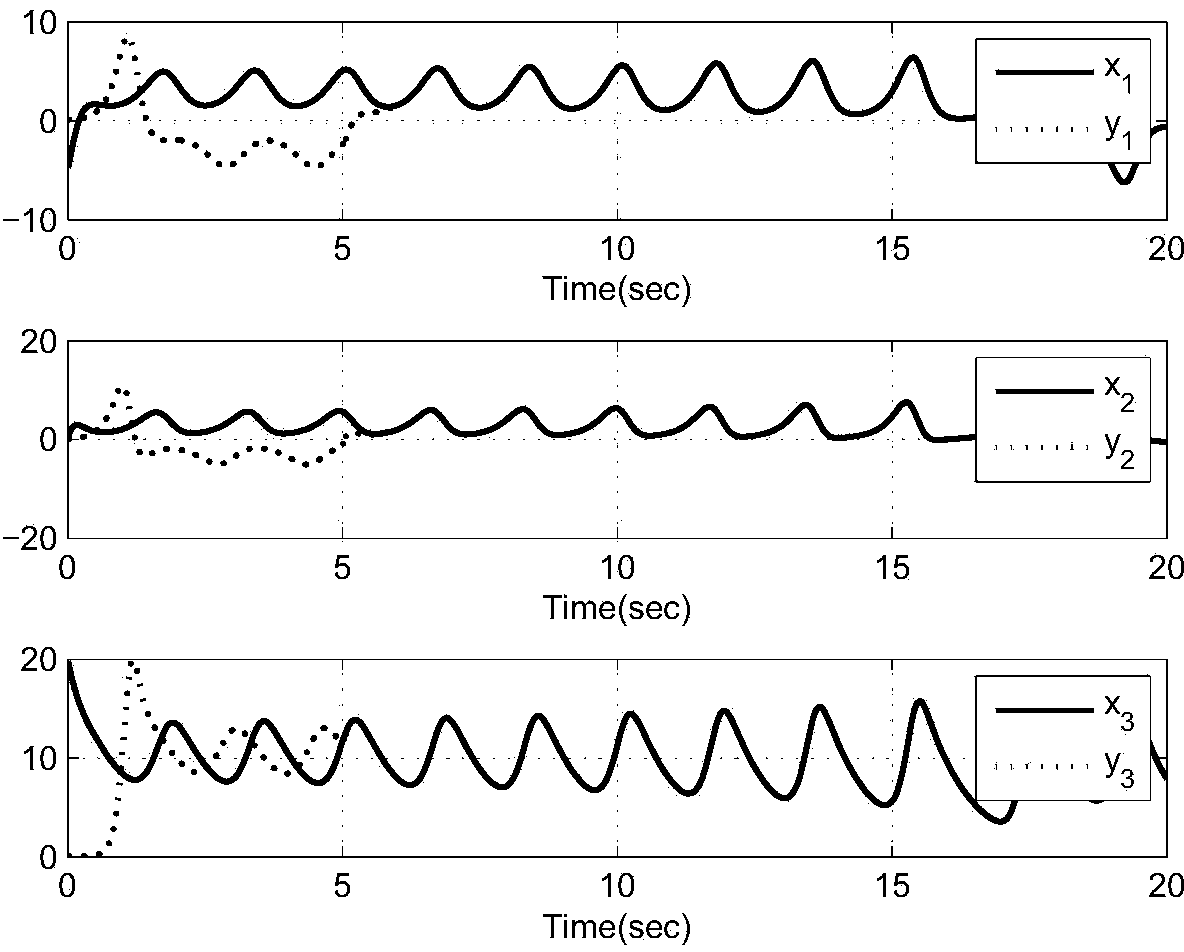
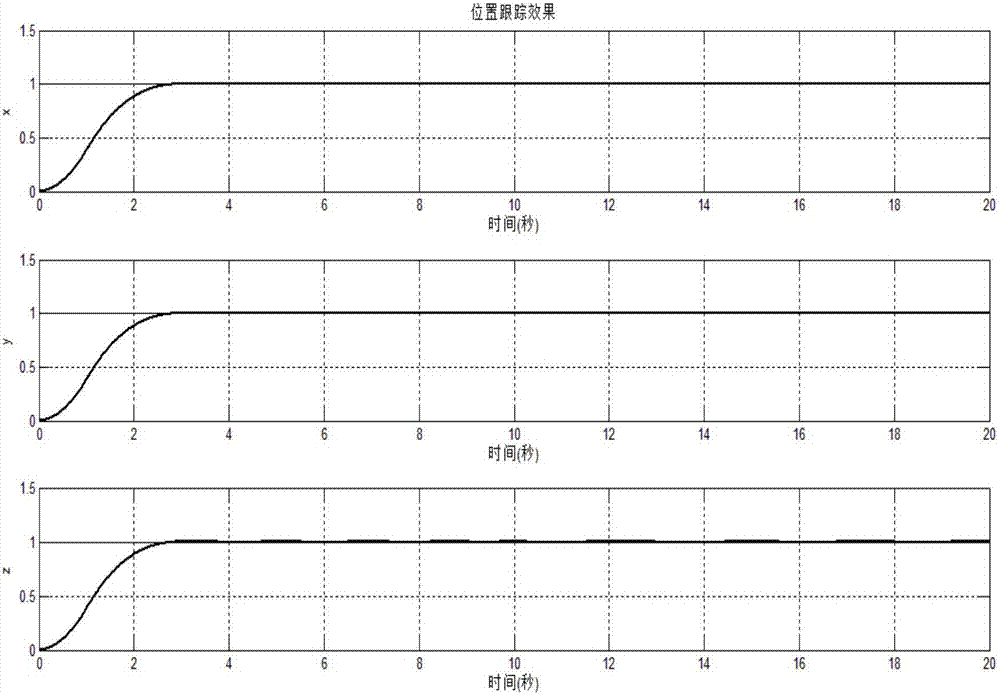
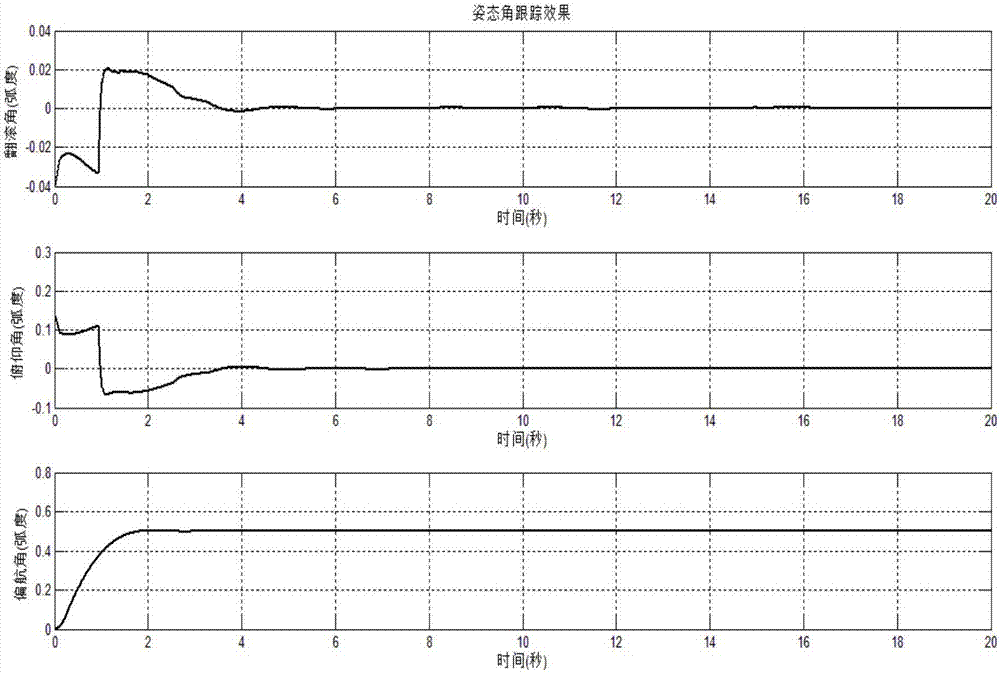
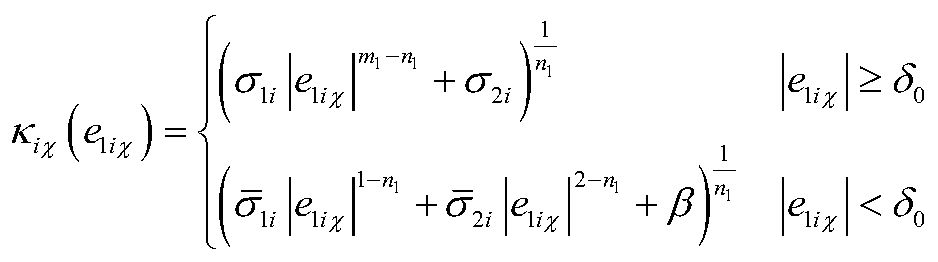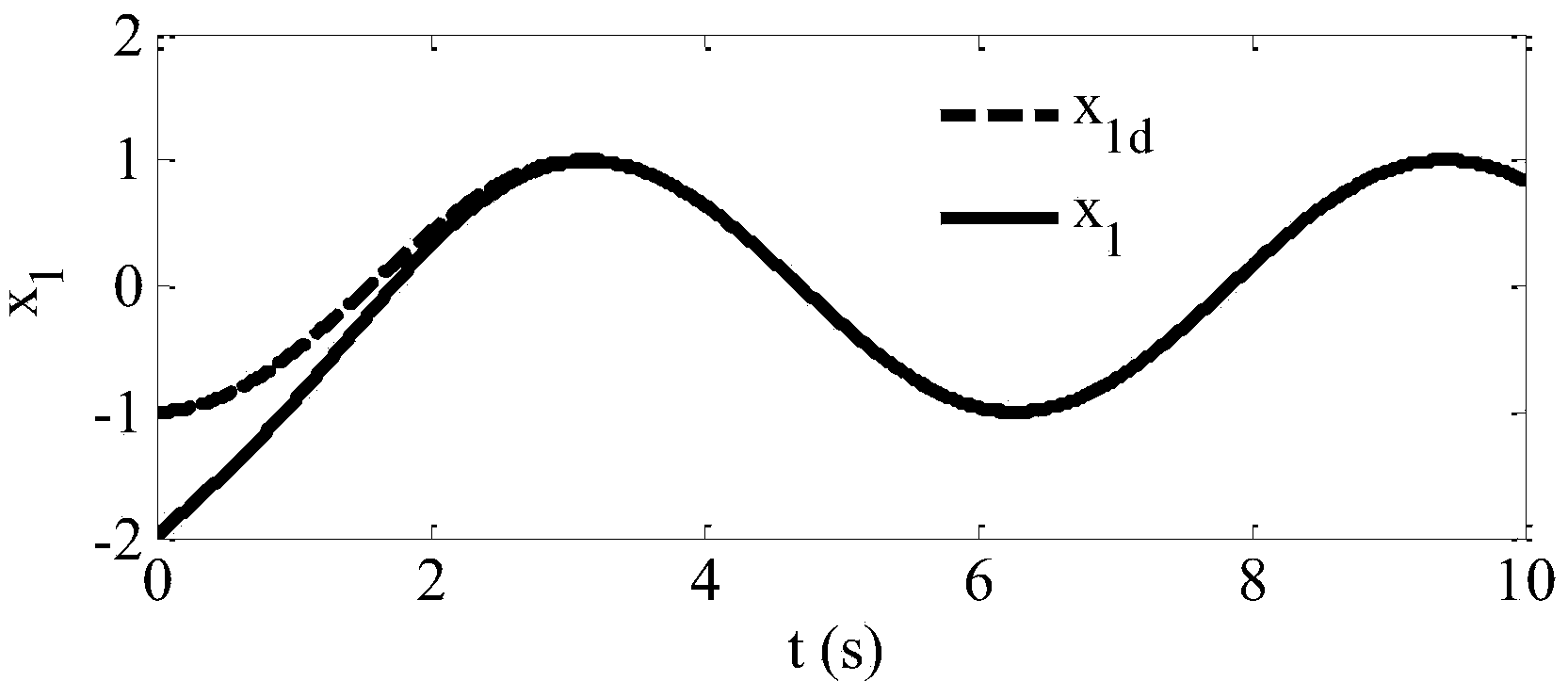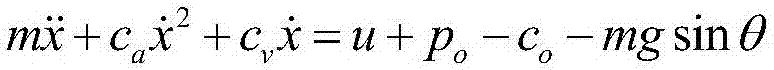Patents
Literature
74 results about "Nonsingular terminal sliding mode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
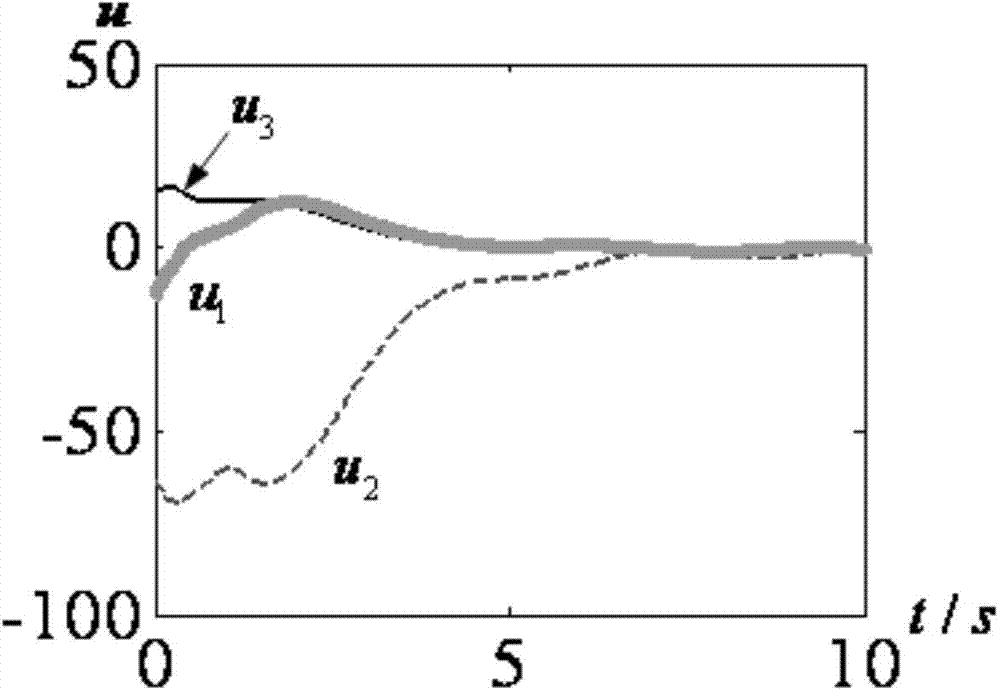
Thus, the nonsingular terminal sliding mode surface will become linear sliding mode after a period of time. By choosing a suitable , the proposed surface will have the advantage of both NTMS and linear sliding surface.
Sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method
ActiveCN104266546AReduce demand overloadDirection controllersSpecial data processing applicationsLongitudinal planeGuidance control
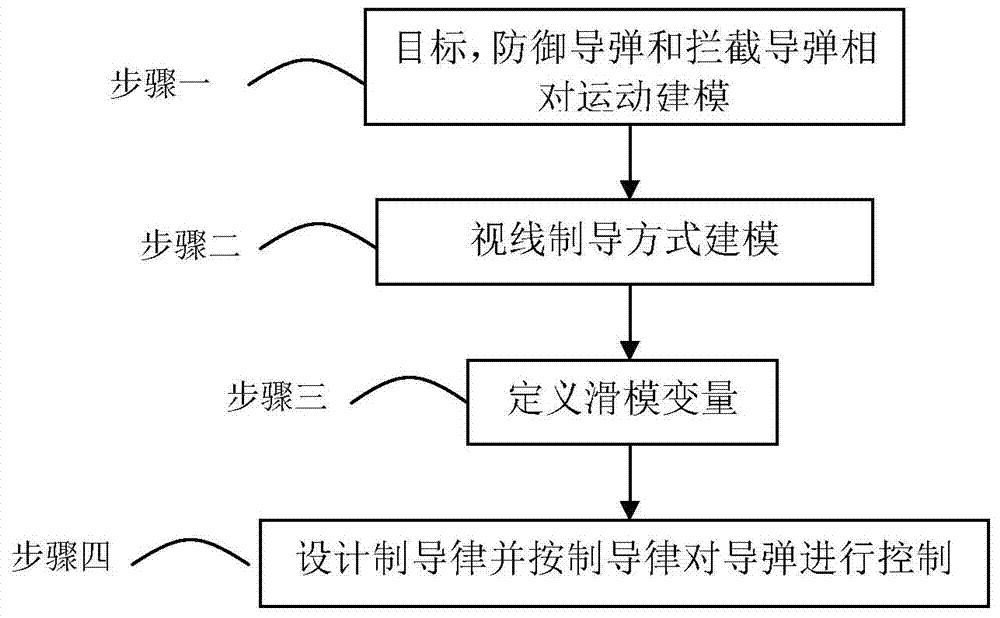
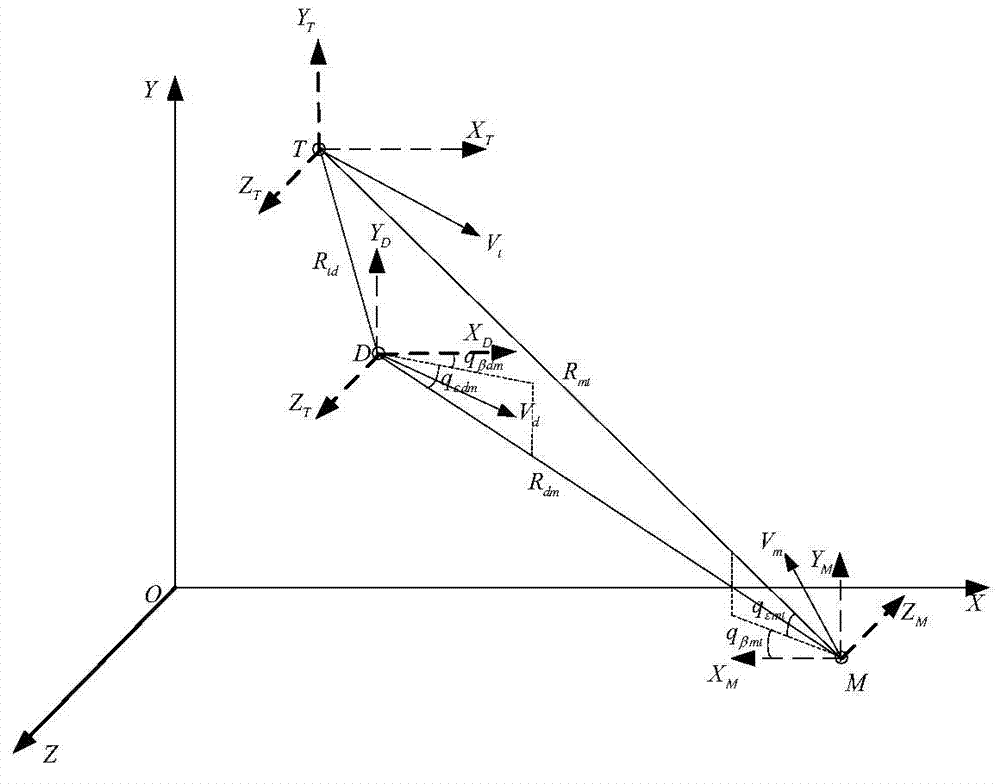
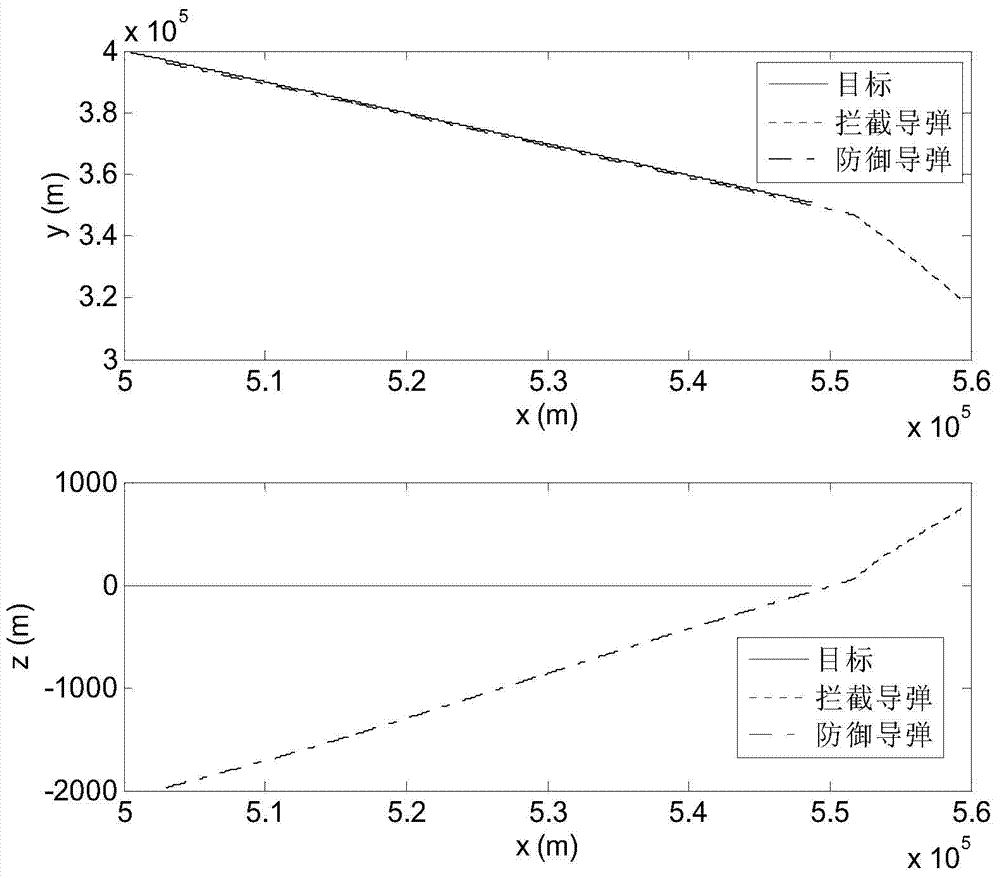
The invention provides a sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method, relates to a guidance control method, in particular to an active defense guidance control method, and aims at solving the problem that a defensive missile is limited in overload capacity. The sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method comprises the steps of firstly modeling relative motions of a target, the defensive missile and an intercept missile, adopting a sight line guidance mode to design a guidance rule for the defensive missile, then adopting a nonsingular terminal sliding mode to control the designed guidance rule, respectively defining sliding mode variables (shown in the description) of a longitudinal plane and a lateral plane, performing derivation on the sliding mode variables, substituting relative motion equations of the target, the defensive missile and the intercept missile into the variables and obtaining the guidance rule (shown in the description) of the longitudinal plane and the guidance rule (shown in the description) of the lateral plane through compilation, and controlling the missiles according to the guidance rules. By means of the sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method, overload needed by the defensive missile can be effectively reduced. The sight line based finite time convergence active defense guidance control method is suitable for active defense guidance control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
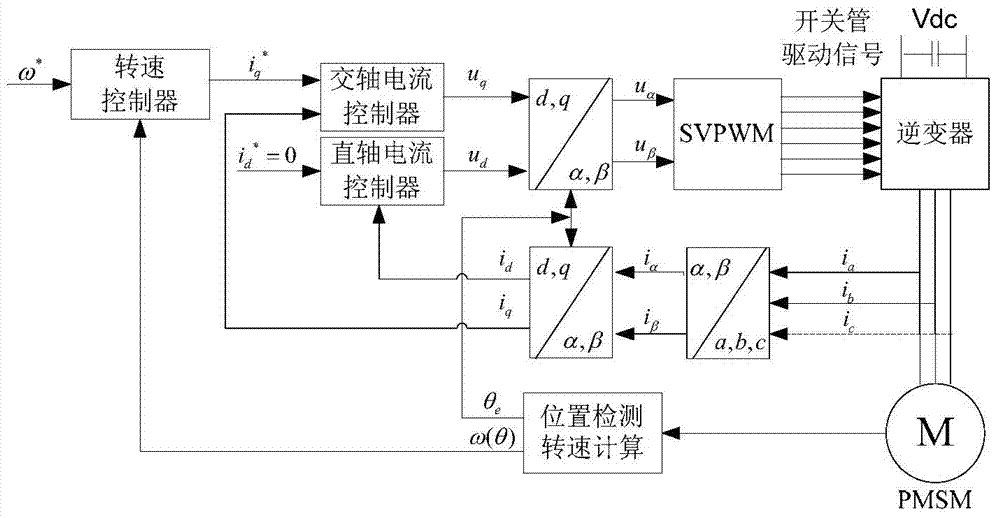
Permanent magnet synchronous motor control method
InactiveCN102969968AReduce buffetingHigh control precisionElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl systemPermanent magnet synchronous motor
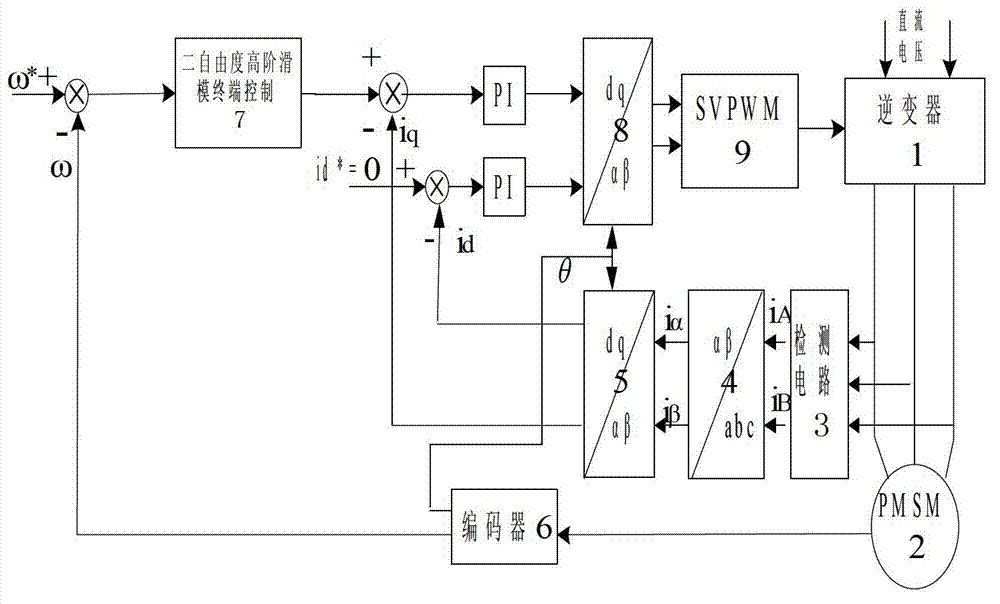
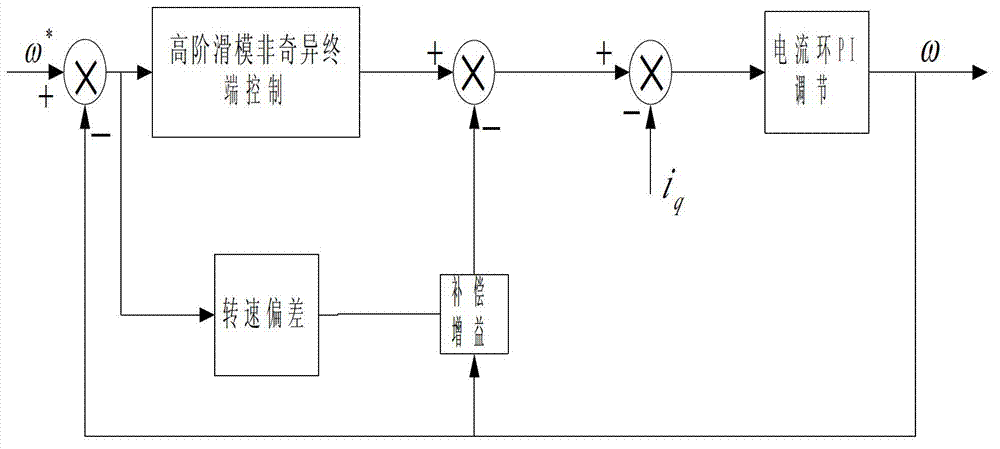
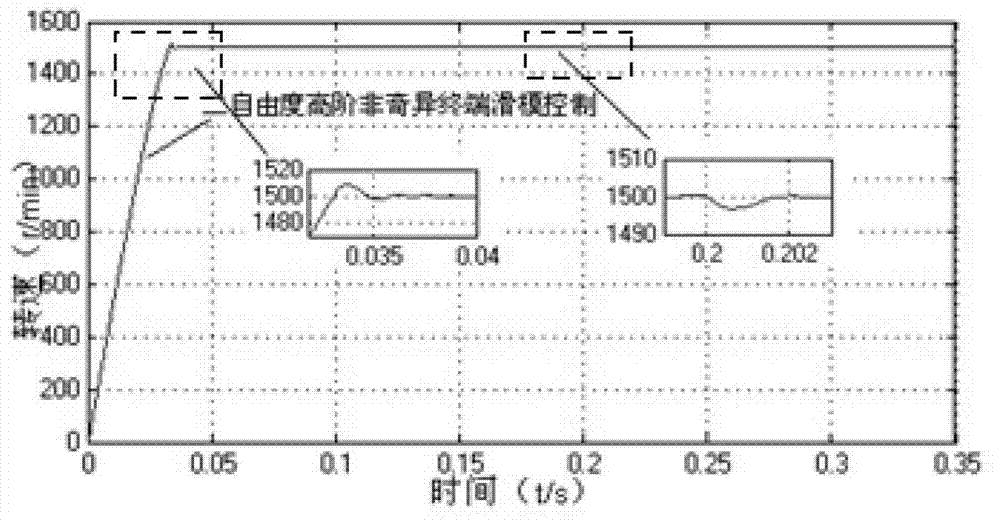
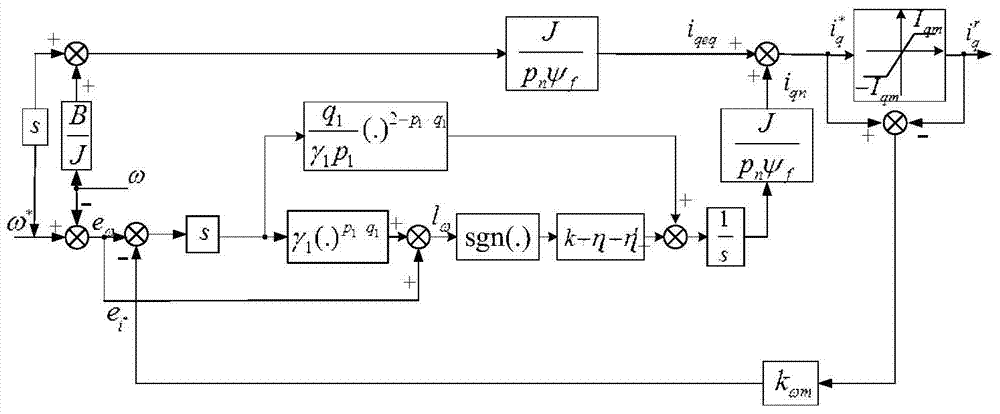
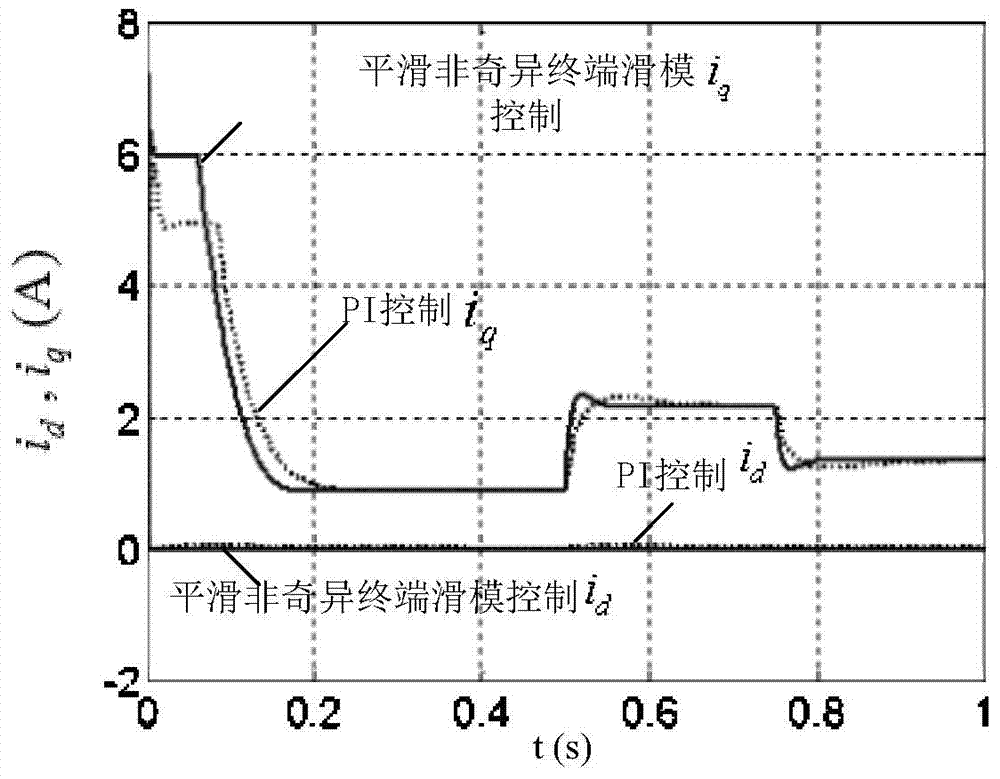
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor control method in which a vector control system is used. The vector control system comprises an outer speed ring and an inner current ring, and a PI (proportional-integral) controller of a rotating speed ring is replaced with a two-DOF (degree of freedom) higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller; the input of the two-DOF higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller is the difference between the given rotating speed w* of a motor and the actual feedback rotating speed w* of the motor; the error between the given rotating speed and the feedback rotating speed is judged, when the error of the rotating speed is less than Xi, an output exciting current iq* is calculated by a simple higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller; when the error of the rotating speed is greater than Xi, the output of the two-DOF higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller is an output iq* controlled by a higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode and the sum of the output and compensation gain of the higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode; and the size of Xi can be set according to actual situations and needs. According to the method, the system control accuracy is improved and the rapid convergence of the rotating speed of the motor is realized; and the method has strong robustness on load disturbances.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Attitude controller for quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle with dynamic characteristics being unknown and method
ActiveCN107479567AFast convergenceImprove robustnessAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsDamping factorAttitude control
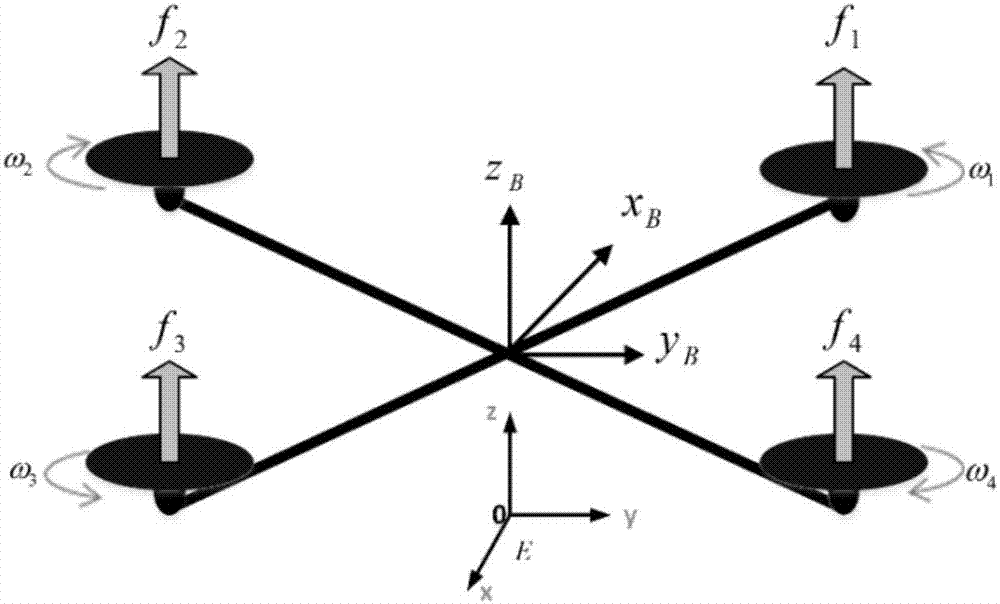
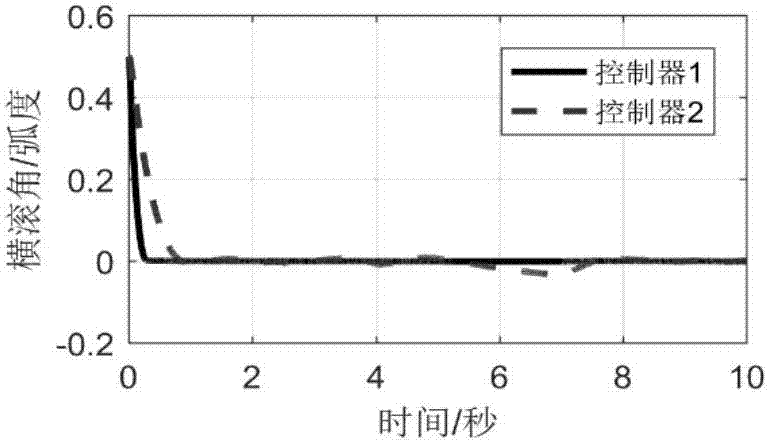
The invention discloses an attitude controller for a quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle with dynamic characteristics being unknown and a method. It is assumed that quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle model parameters such as the moment of inertia and the air damping coefficient are unknown, and bounded disturbance suffered by the system is time-varying and always exists in the system. In allusion to the unknown model parameters, the invention designs a corresponding differential estimator to perform online estimation on a position parameter. Based on a parameter estimation value, an improved adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller is designed to complete stable control for the attitude of the quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle. In addition, an adaptive disturbance compensator is further designed to perform effective compensation on the bounded disturbance. Simulation and experimental results show that the control algorithm can well accomplish stable control for the attitude of the quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle and has high robustness for the unknown dynamic characteristics and disturbance of the system.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
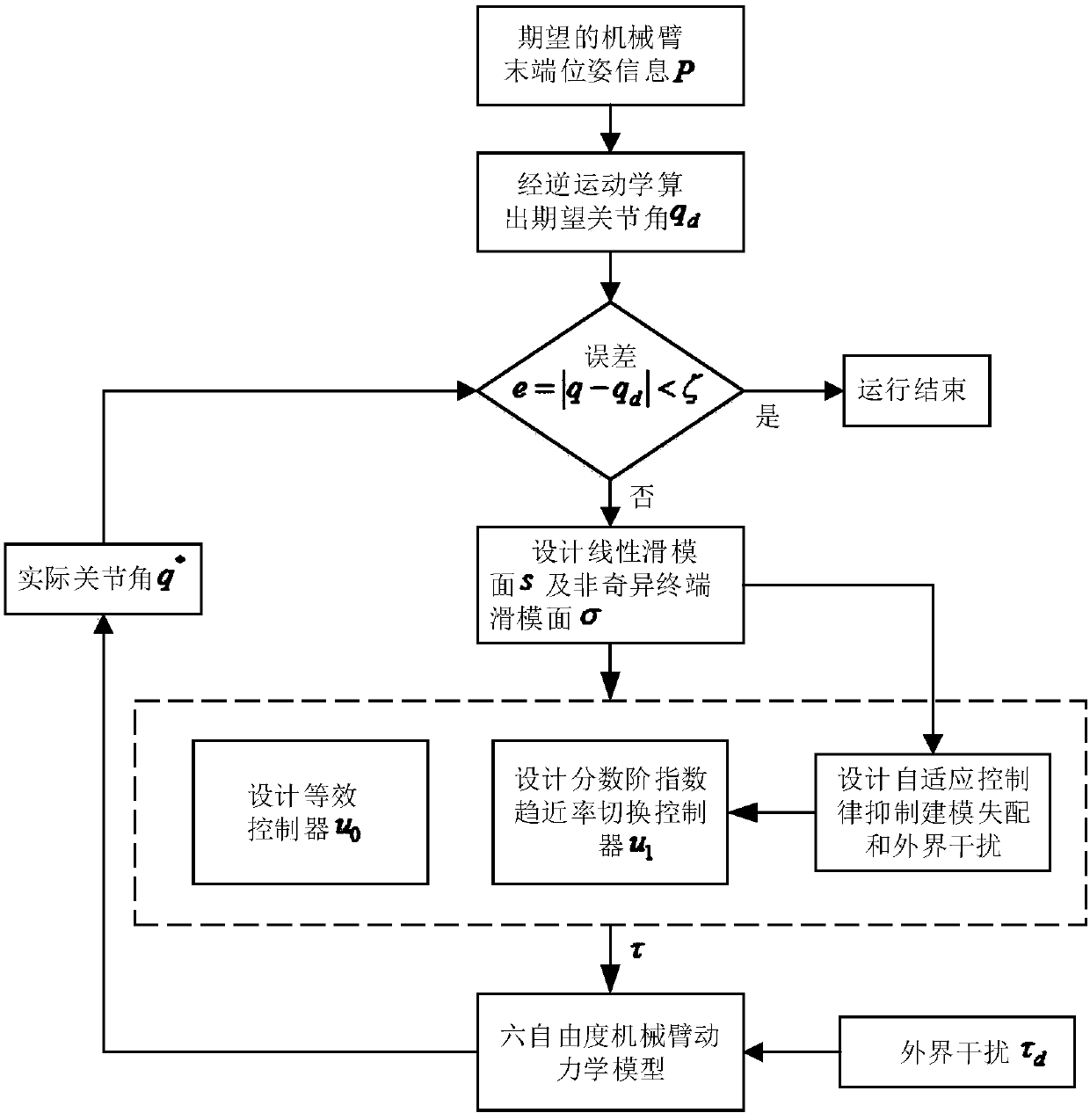
Mechanical arm trajectory tracking method based on fractional-order adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding mode
The invention discloses a mechanical arm trajectory tracking method based on a fractional-order adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding mode. By designing switching control of uncertainty upper bound adaptive rate and the fractional-order adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding mode, the system state is allowed to converge to a sliding mode surface faster; and through sliding mode features of the nonsingular terminal sliding mode surface, the system state is allowed to converge to a balance point faster in a limited time, that is, tracking error is converged to 0, thereby realizing tracking of expected joint angle trajectory.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Fixed time cooperative tracking control method of second-order nonlinear multi-agent system
ActiveCN110221542AImprove robustnessAdaptableTarget-seeking controlAdaptive controlMulti-agent systemEngineering
The invention relates to a fixed time cooperative tracking control method of a second-order nonlinear multi-agent system, which comprises the steps of: designing a fixed time convergence nonsingular terminal sliding mode surface; designing an RBF neural network approximation system dynamics nonlinear term; designing a multi-agent system fixed time cooperative tracking controller; and enabling thedesigned controller to act on the system to realize the control of a multi-agent system for cooperatively tracking a target agent within fixed time. The fixed time cooperative tracking control methodhas strong robustness to external disturbance, has strong adaptability to unknown nonlinearity of a model, and can ensure the convergence of the system within fixed time, and enables the convergence time to be irrelevant to the initial state of the system. The fixed time cooperative tracking control method has wide application range and can be applied to systems with high requirement on convergence time.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Anti-rest Windup smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method for permanent magnet synchronous motor based on relative order
ActiveCN104270054ASolve chattering problemsAccurate trackingElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention relates to an Anti-rest Windup smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor based on a relative order, and aims to solve the problem that the control continuity of a system and the smoothness of an output signal are damaged by chattering of a permanent magnet synchronous motor control system due to the high-frequency control switching behavior of a conventional sliding mode control method and the problem that the permanent magnet synchronous motor control system generally has the Windup problem due to finite output capacity of an existing inverter. The anti-rest Windup smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method comprises the following steps: 1, designing a permanent magnet synchronous motor rotating speed vector control system; 2, designing an Anti-rest Windup smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode rotating speed controller; 3, designing a smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode alternating current controller; 4, designing a smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode direct current controller. The Anti-rest Windup smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method is applied to the field of robust control on the permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Owner:严格集团股份有限公司
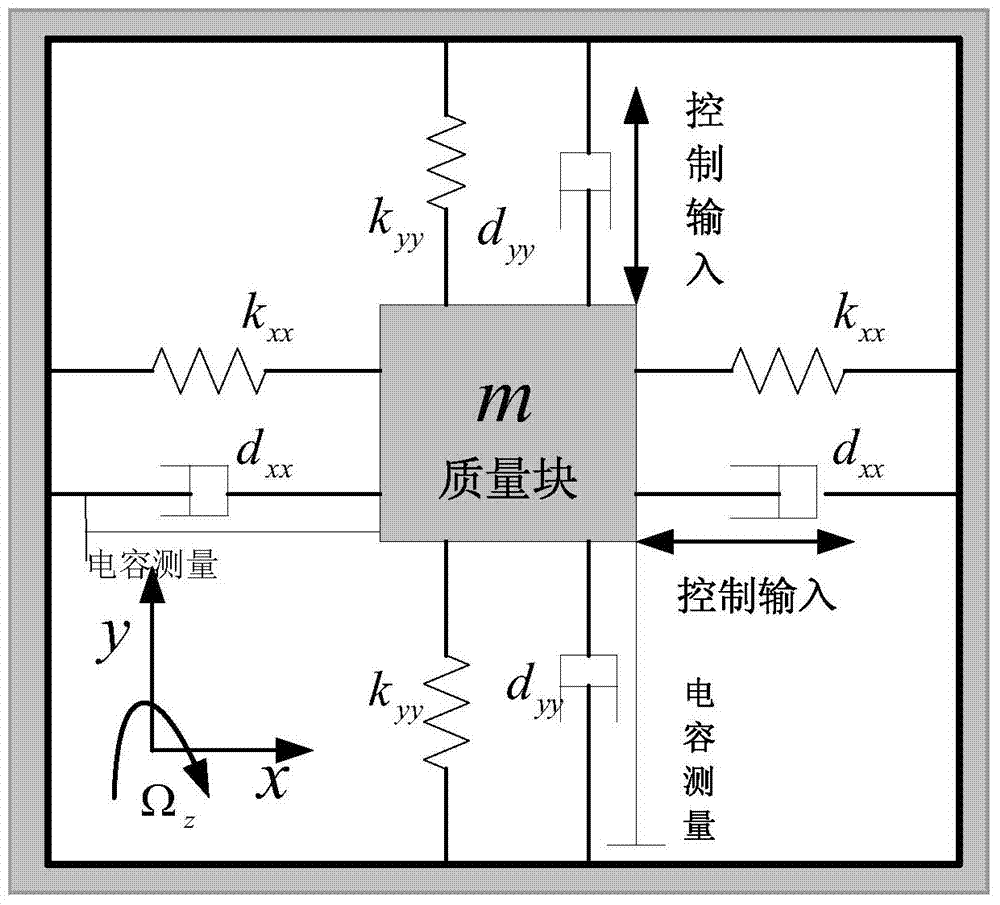
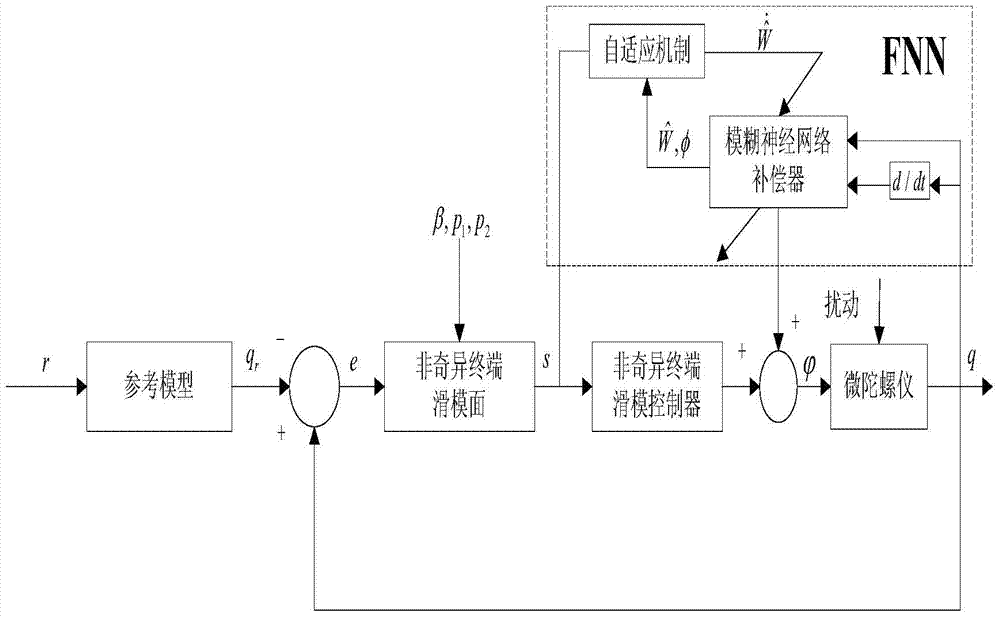
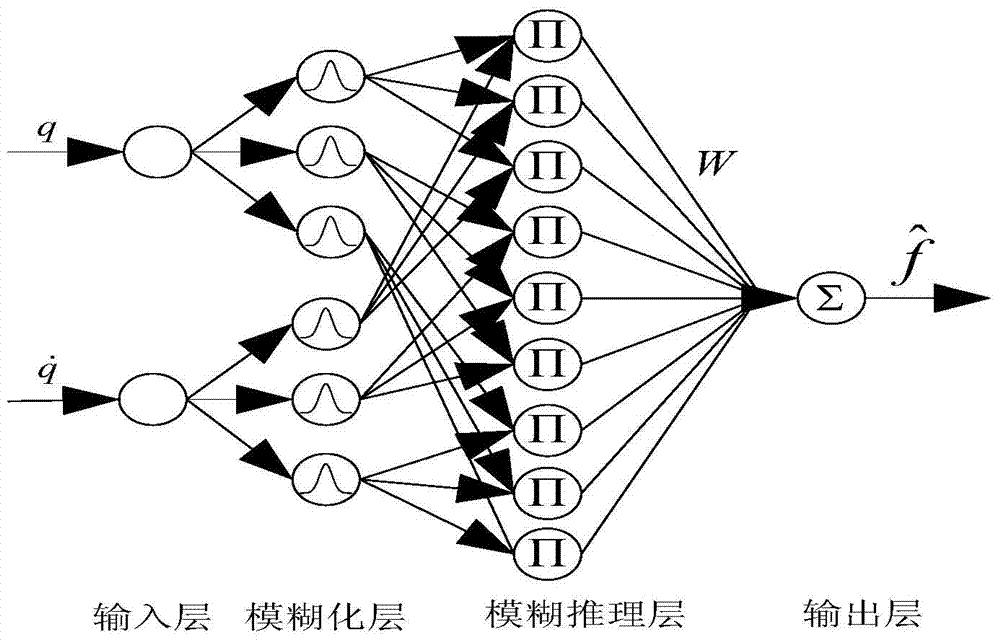
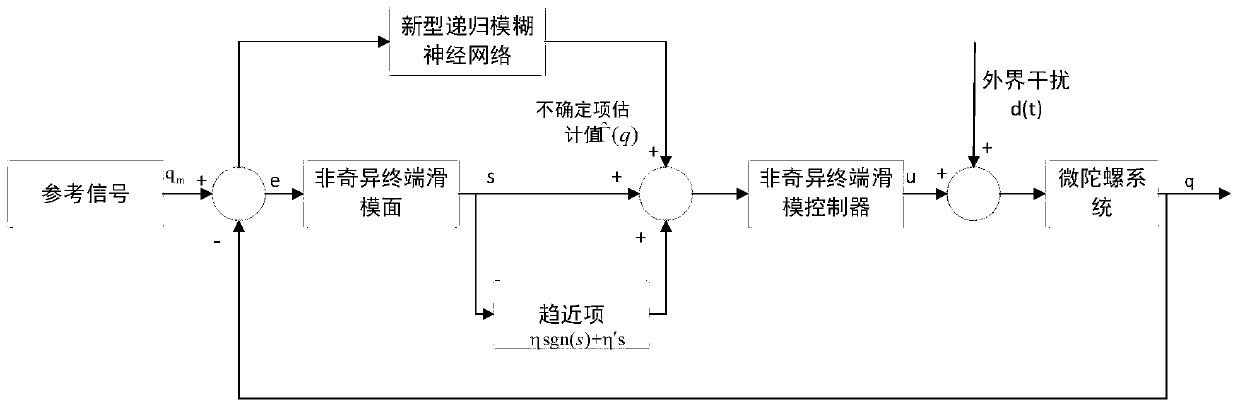
Self-adaption fuzzy neural compensating nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method of micro gyroscope
InactiveCN104122794AEnsuring Global Asymptotic StabilityImprove robustnessAdaptive controlLyapunov stabilityGyroscope
The invention discloses a self-adaption fuzzy neural compensating nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method of a micro gyroscope. The method mainly involves a nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller and a fuzzy neural network compensating controller; the designed nonsingular terminal sliding mode enables that a system can reach a sliding mode surface and a balance point within a limited time from any initial state, and therefore, the convergence rate and steady stacking precision of the system are improved; meanwhile, the fuzzy neural network compensates the parametric modeling error of the micro gyroscope and outside disturbance effect on line, in order to improve the tracking performance; the fuzzy neural network is practiced on line, the self-adaption learning algorithm of weight of the fuzzy neural is on the basis of the lyapunov stability theorem, which ensures the tracking performance and the stability of the whole control system. The simulation result shows that the method is able to improve the problem of trace tracking of the micro gyroscope and can also effectively inhibit the parameter uncertainty and the influence from the outside disturbance, and as a result, the robust tracking can be realized.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
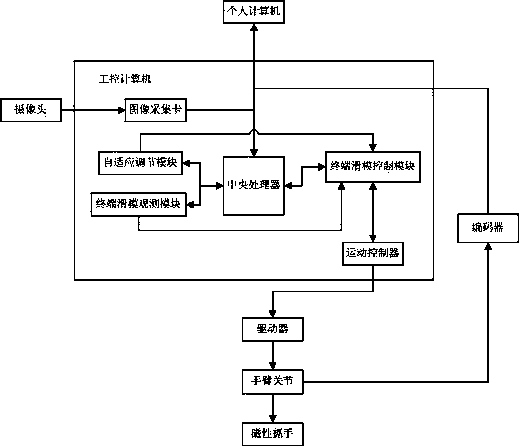
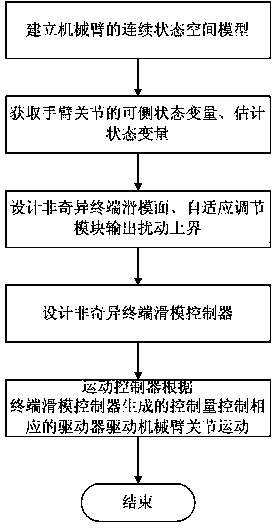
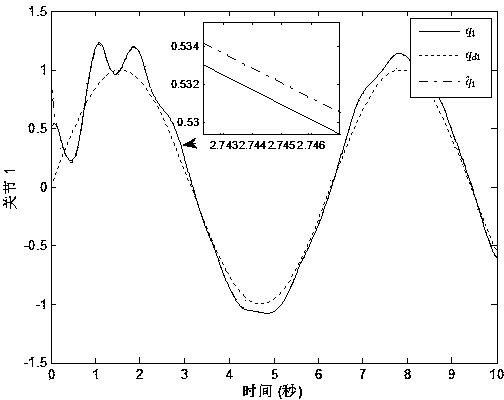
Tracking control device and method of mechanical arm system
InactiveCN103406909AReduce the impact of external disturbancesReduce chatteringManipulatorState variableControl signal
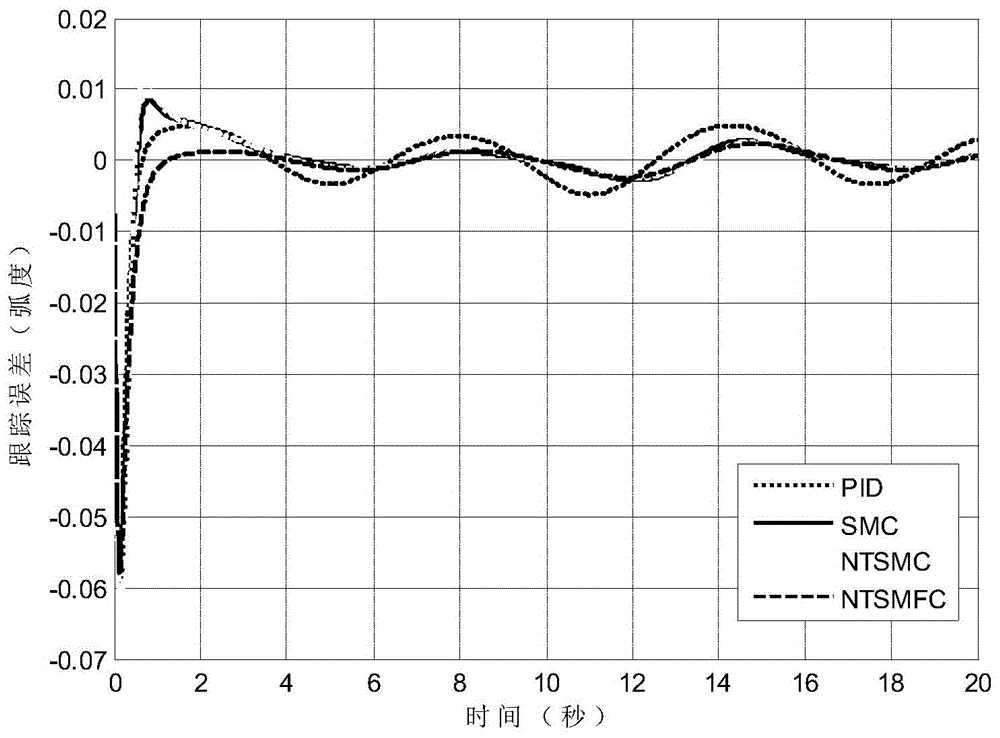
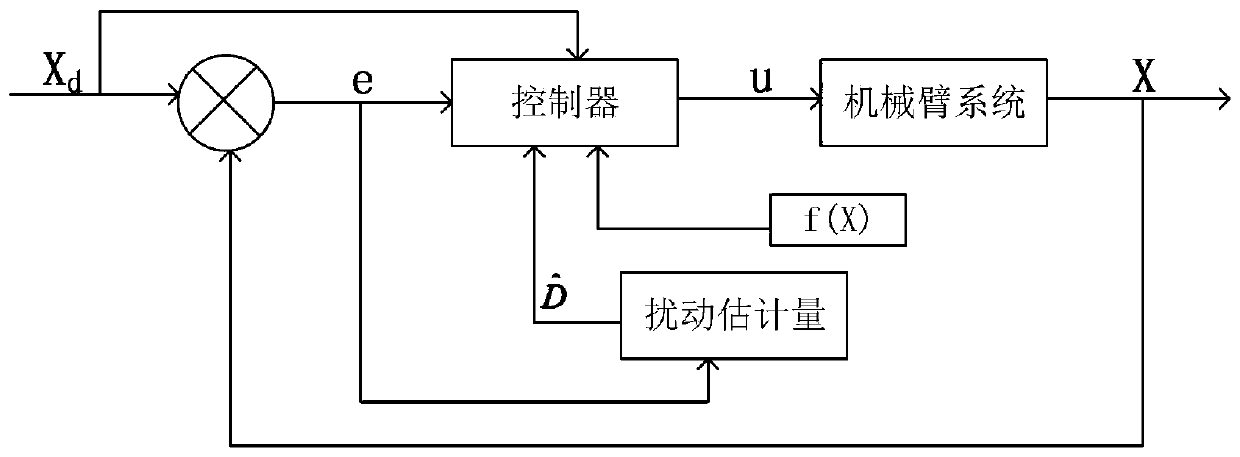
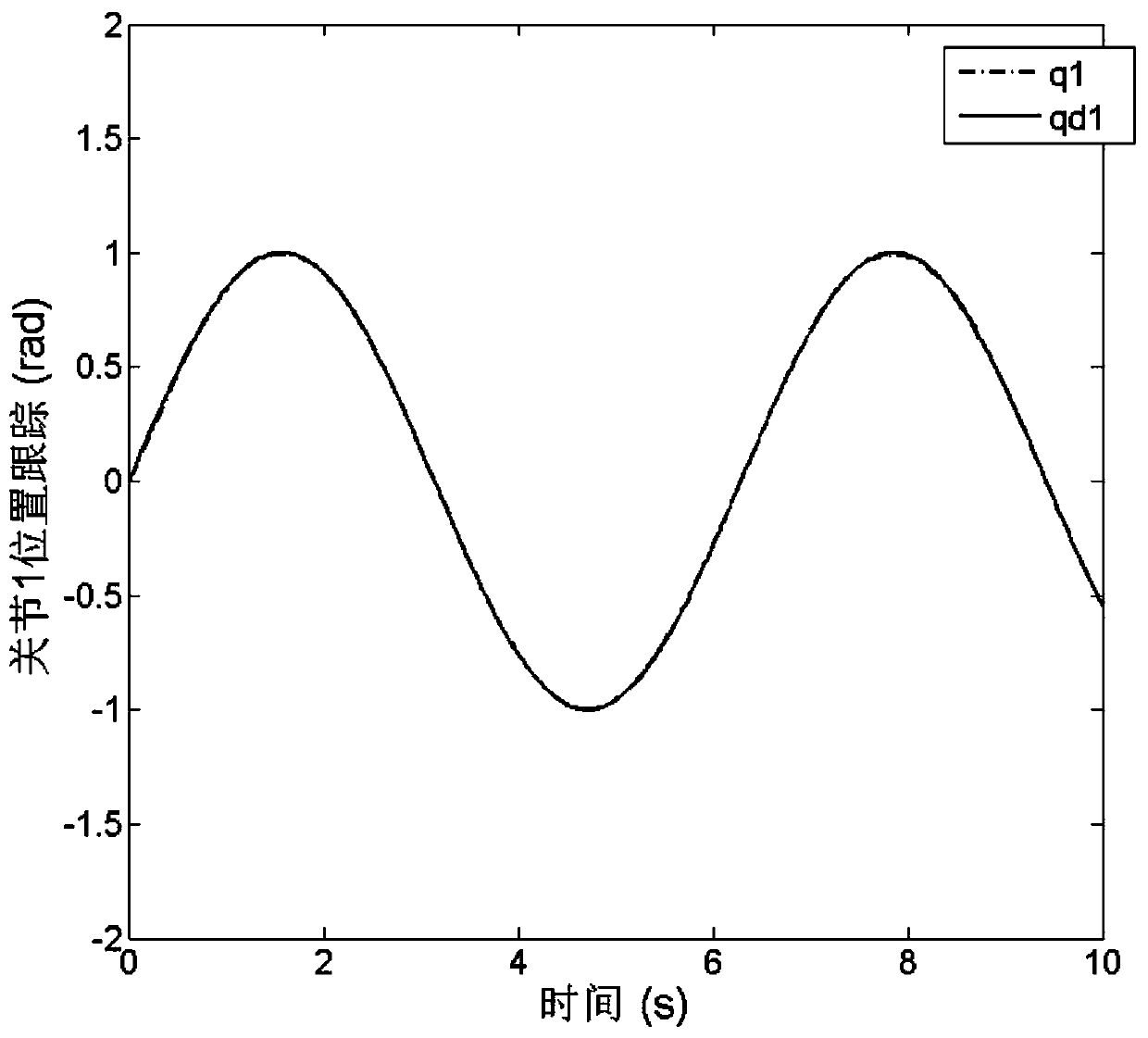
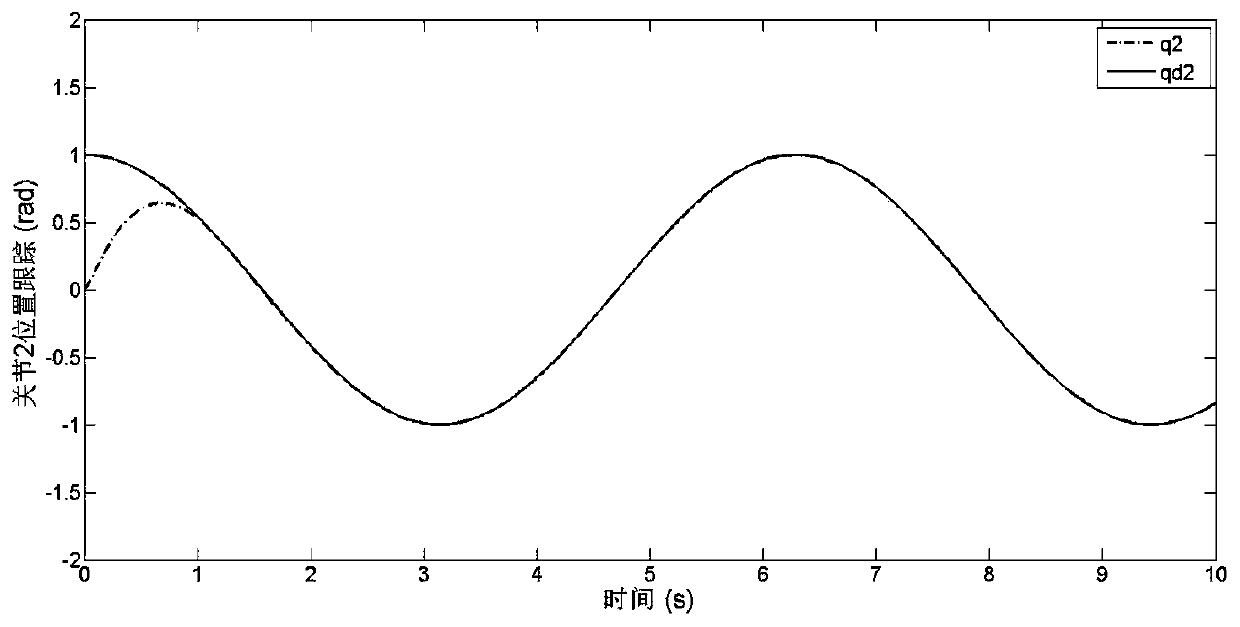
The invention discloses a tracking control device and method of a mechanical arm system, aims to overcome defect of singularity of mechanical arm control in the terminal sliding-mode control technology adopted by a mechanical arm in the prior art, and provides a tracking control device of a mechanical arm system. According to the tracking control device, data acquired by a terminal sliding-mode observation module, a self-adaption adjusting module and an encoder are transmitted to a terminal sliding-mode control module which generates control signals for a movement controller to drive a corresponding arm joint to move. The invention further provides a tracking control method of the mechanical arm system. The method comprises steps as follows: the encoder acquires measurable state variables, the terminal sliding-mode observation module acquires estimated state variables, a nonsingular terminal sliding-mode surface is designed, uncertain external disturbance is estimated on the basis of the designed nonsingular terminal sliding-mode surface and the self-adaption adjusting module, and a nonsingular terminal sliding-mode controller is designed by utilizing a sliding mode technique and a feedback technique. According to the device and the method, final consistency and stability of the system can be guaranteed, and the device and the method are applicable to mechanical arm control.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Four-rotor unmanned plane finite time self-adaptive control method based on nonsingular terminal sliding mode
ActiveCN107479370ASuppress external interferenceAvoid singularity problemsAdaptive controlProcess systemsFinite time
A four-rotor unmanned plane finite time self-adaptive control method based on a nonsingular terminal sliding mode is provided; the method aims at a four-rotor unmanned plane system with inertia uncertainty factors and external turbulences; according to the four-rotor unmanned plane dynamic system, a nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method is employed, and self-adaptive control is combined, thus designing the four-rotor unmanned plane finite time self-adaptive control method based on the nonsingular terminal sliding mode; the nonsingular terminal sliding mode is designed so as to ensure the system finite time convergence features, thus preventing singularity problems existing in terminal sliding mode control, and effectively weakening jittering problems; in addition, the self-adaptive control is used for processing system inertia uncertainty factors and external turbulences; the method can remove the sliding mode surface singularity problems, and can effectively prevent and compensate the system inertia uncertainty factors and external turbulences, thus ensuring the system finite time convergence features.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Finite time synchronous control method of double permanent magnet synchronous motor chaotic systems
ActiveCN104201945AImprove efficiencyHigh control precisionMultiple motor speed/torque controlSampling instantSynchronous motor
Disclosed is a finite time synchronous control method of double permanent magnet synchronous motor chaotic systems. The method includes that a chaotic model of a permanent magnet synchronous motor system is established, and system state and relevant control parameters are initialized; at every sampling instant, synchronous errors, rapid nonsingular terminal sliding mode surfaces and first-order derivatives of principal and subordinate chaotic systems of a permanent magnet synchronous motor are calculated; according to the synchronous errors, the rapid nonsingular terminal sliding mode surfaces and the first-order derivatives, a synchronous controller of the double permanent magnet synchronous motor chaotic systems is designed, the problem of buffeting during sliding-mode control can be solved, and chaotic states of the principal and subordinate chaotic systems can be rapidly synchronized.
Owner:菏泽建数智能科技有限公司
Four-rotor unmanned plane finite time self-adaptive control method based on fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode
ActiveCN107479371AAvoid singularity problemsReduce buffetingAdaptive controlProcess systemsFinite time
A four-rotor unmanned plane finite time self-adaptive control method based on a fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode is provided; the method aims at a four-rotor unmanned plane system with inertia uncertainty factors and external turbulences; according to the four-rotor unmanned plane dynamic system, a fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method is employed, and self-adaptive control is combined, thus designing the four-rotor unmanned plane finite time self-adaptive control method based on the fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode; the fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode is designed so as to ensure the system finite time convergence features and fast convergence speed, thus preventing singularity problems existing in terminal sliding mode control, and effectively weakening jittering problems; in addition, the self-adaptive control is used for processing system inertia uncertainty factors and external turbulences; the method can remove the sliding mode surface singularity problems, and can effectively prevent and compensate the system inertia uncertainty factors and external turbulences, thus ensuring the system finite time convergence features.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for controlling error to be converged in fixed time
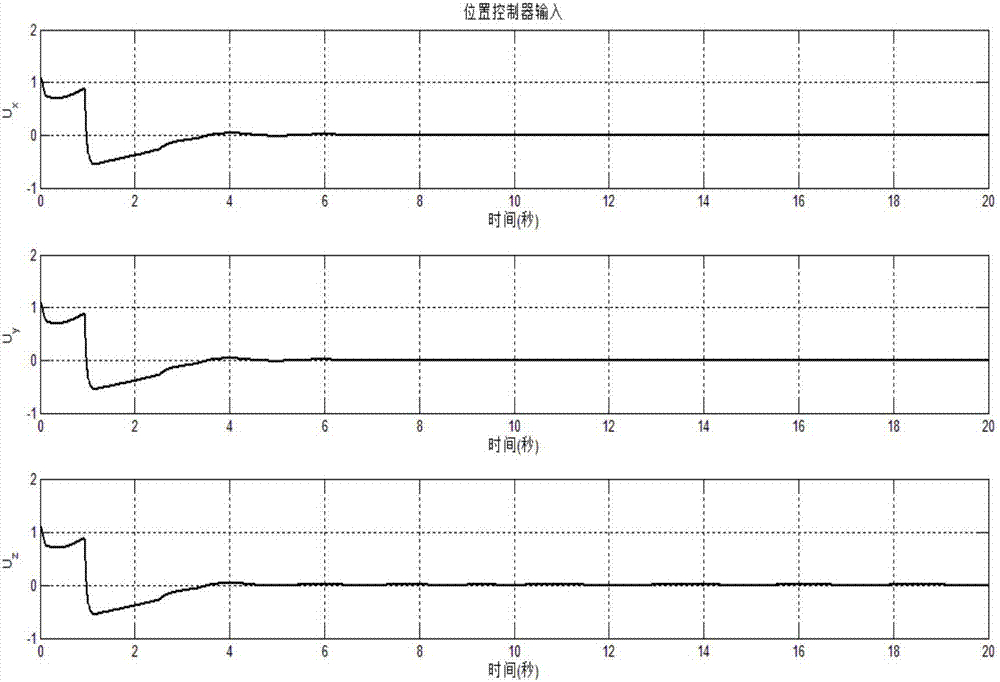
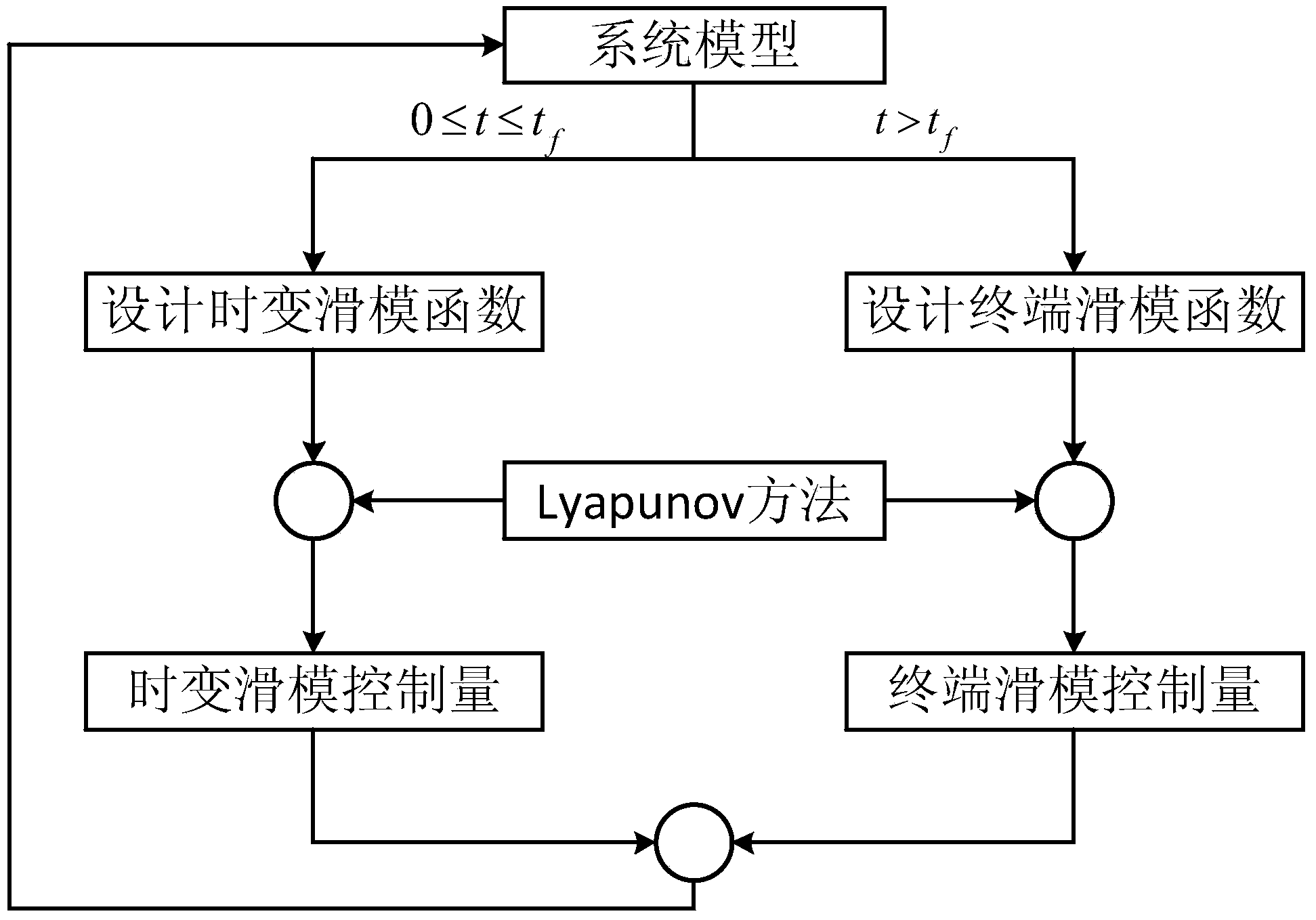
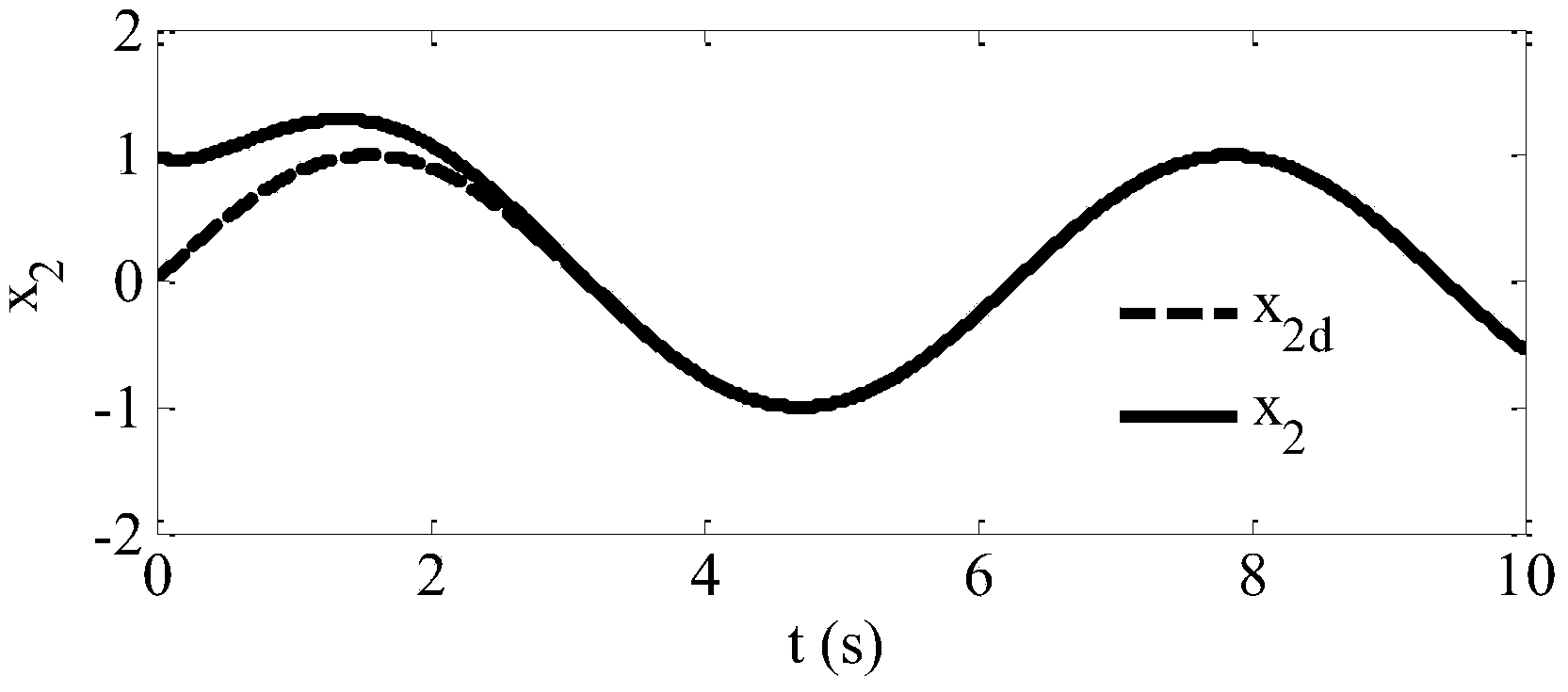
The invention relates to a method for controlling a tracking error to be converged in fixed time, and belongs to the technical field of controlling. The method comprises the steps as follows: a dynamic model of a second-order uncertain system is established; a time-varying sliding mode function and a nonsingular terminal sliding mode function are designed, and a time-varying sliding mode controlled quantity and a nonsingular terminal sliding mode controlled quantity are obtained through respective solving and input into an established system model, so that the error is converged to 0 at the expected moment; and a nonsingular terminal sliding mode control technology is combined to design the controlled quantity, thus, the error in remaining time is kept 0. With the adoption of the method, the expected error convergence time can be set in advance, the system state is always maintained in the sliding mode, and the controlled system has overall robustness on parameter uncertainty and external disturbance.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
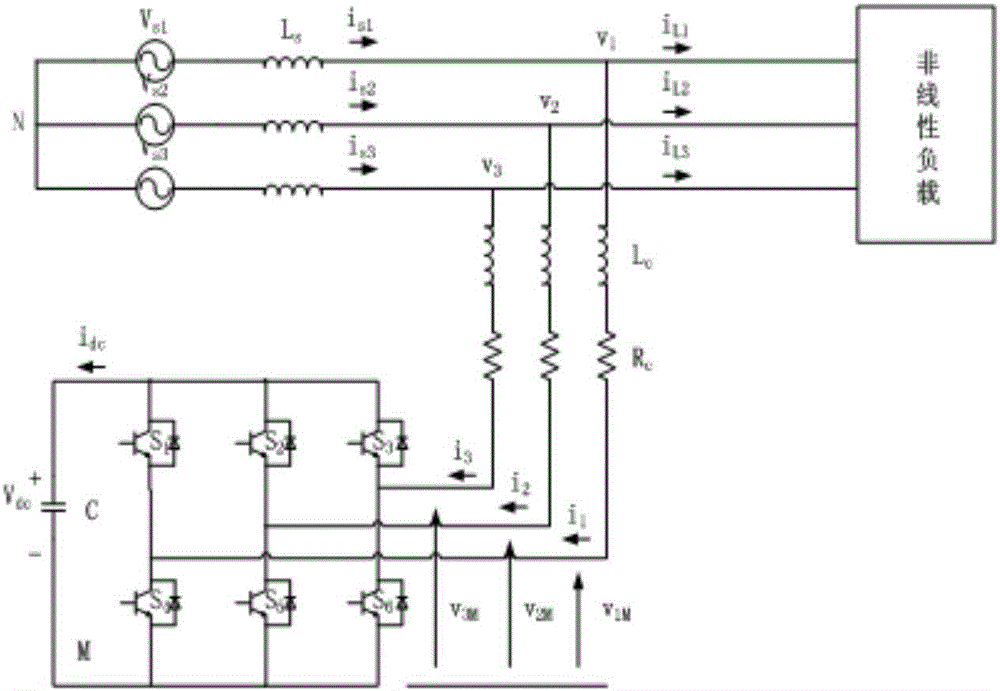
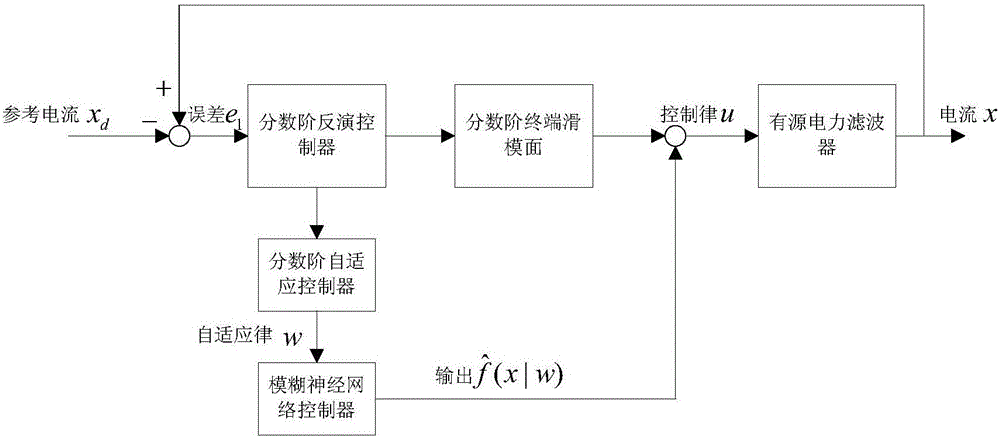
Fractional order terminal sliding mode-based AFNN control method of active power filter
InactiveCN106374488AEnsure real-time trackingAvoid uncertaintyActive power filteringAc network to reduce harmonics/ripplesNeural network controllerMathematical model
The invention discloses a fractional order terminal sliding mode-based AFNN control method of an active power filter. The method comprises the steps of designing a mathematical model of an active filter, a fractional order-based nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller and a fractional order-based adaptive fuzzy neural network controller; and controlling the active power filter by using output of a fractional order-based nonsingular terminal sliding mode adaptive fuzzy neural network controller. According to the AFNN control method, the disadvantage that a nonsingular inversion terminal sliding mode control strategy needs accurate system information is overcome and the robustness is improved; good performance can still be kept when an external load changes; operation of the active power filter along a sliding mode track is ensured through designing the sliding mode controller; for the disadvantages of an inversion control law, an AFNN controller is adopted to approach a nonlinear part in the active power filter. A fractional order module is introduced into the sliding mode controller and the adaptive controller, so that an adjustable item is added by a fractional order in comparison with an integer order, and the overall performance of a system is improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
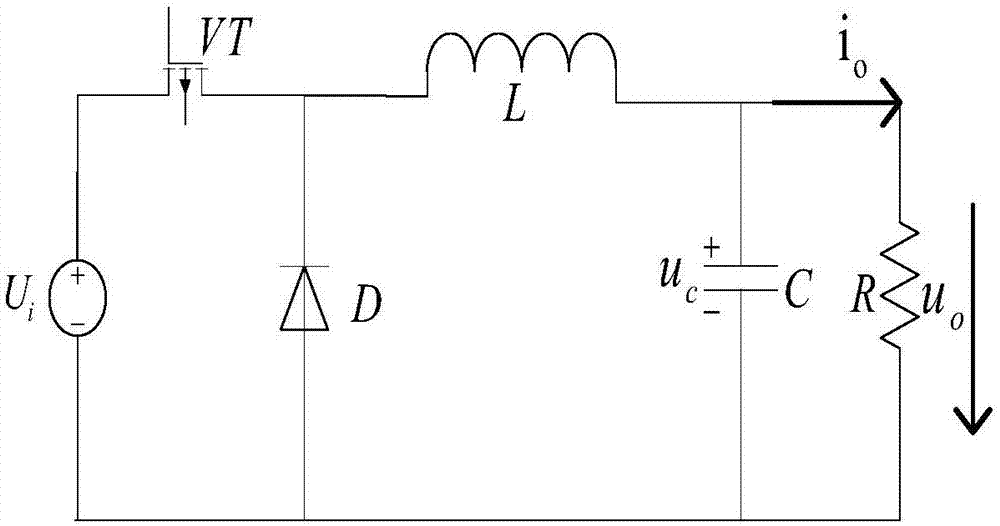
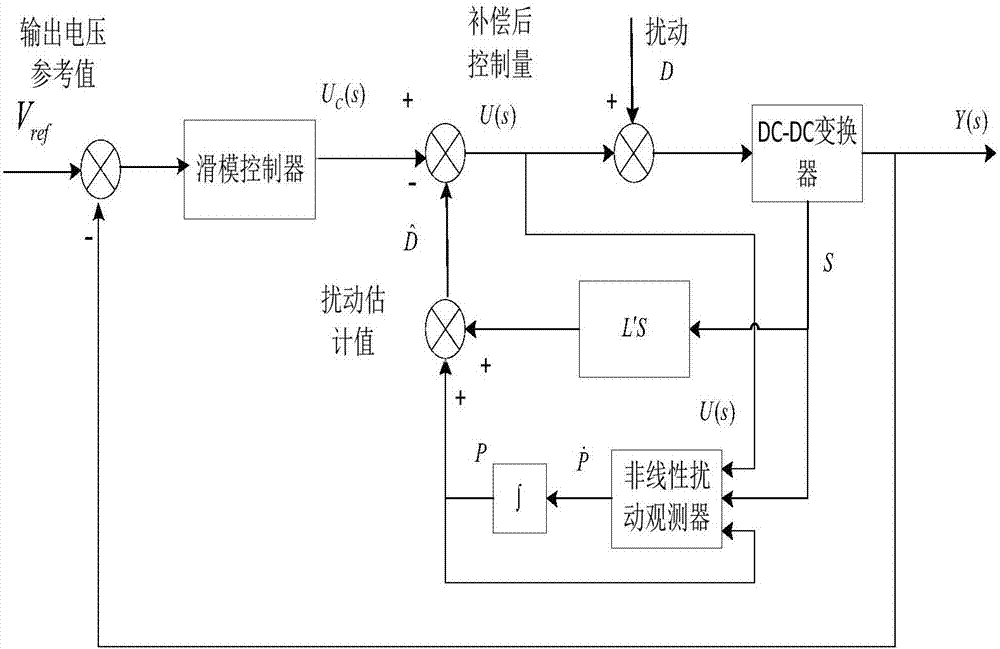
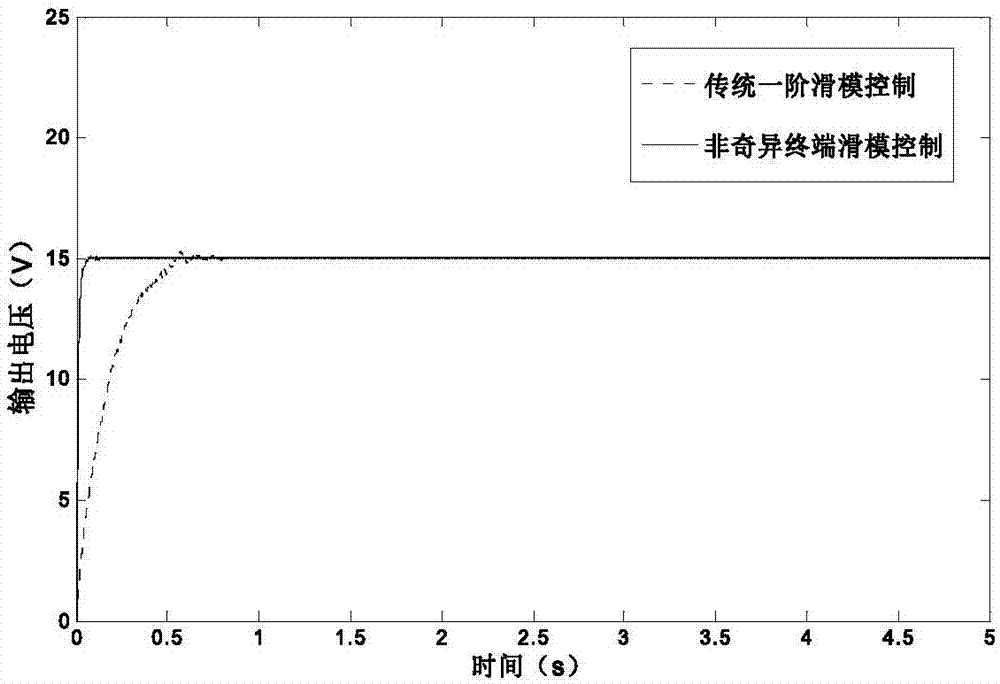
Combined nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method of power converter
ActiveCN106877658AFast convergenceImprove robustnessDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationState modelControl system
The invention discloses a combined nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method of a power converter, and relates to a control scheme of combining a sliding mode control method and a disturbance observation technology of a buck converter. According to the invention, first-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode control is enabled to be combined with a nonlinear disturbance observation technology based on an average state model of the buck converter, on-off is controlled by changing the duty ratio of a switching device through adopting a fixed-frequency PWM mode, and thus target voltage output of the buck converter is realized. Provided by the invention is a power converter control method based on combination of a nonsingular terminal sliding mode and the disturbance observation technology so as to solve a problem that traditional sliding mode / PID control is slow in response speed, low in voltage output quality, poor in disturbance resistance and the like. In the control method, the nonsingular terminal sliding mode has the advantages of fast global convergence and high accuracy, and the disturbance observation technology can perform equivalent compensation on the disturbance, so that influences imposed on output voltage by high-frequency vibration are eliminated to a great extent, and thus the anti-disturbance performance of the power converter control system is improved.
Owner:张家港市华天电子科技有限公司
Adaptive neural network nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method for micro gyroscope
InactiveCN105929694ACompensate for manufacturing errorsCompensate for interferenceAdaptive controlGyroscopeNegative exponential
The invention discloses an adaptive neural network nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method for a micro gyroscope. The method includes the steps of the establishing a mathematical model of the micro gyroscope, approximating the sum of the dynamic characteristics and external disturbance of the micro gyroscope by using a neural network control method, designing an adaptive neural network nonsingular terminal sliding mode device based on a dynamic surface; and controlling the micro gyroscope by using the adaptive neural network nonsingular terminal sliding mode device based on the dynamic surface. Through the method, a micro gyroscope system can rapidly reach a stable state, and manufacturing error and environment interference can be compensated. The algorithm designed based on dynamic surface method reduces parameters introduced, simplifies calculation and minimizes buffeting. Meanwhile, a nonsingular terminal sliding mode is introduced in the method to ensure that the system state converges in the sliding phase for a finite time and the control rules have no negative exponential terms, so that the effectiveness of the system can be improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
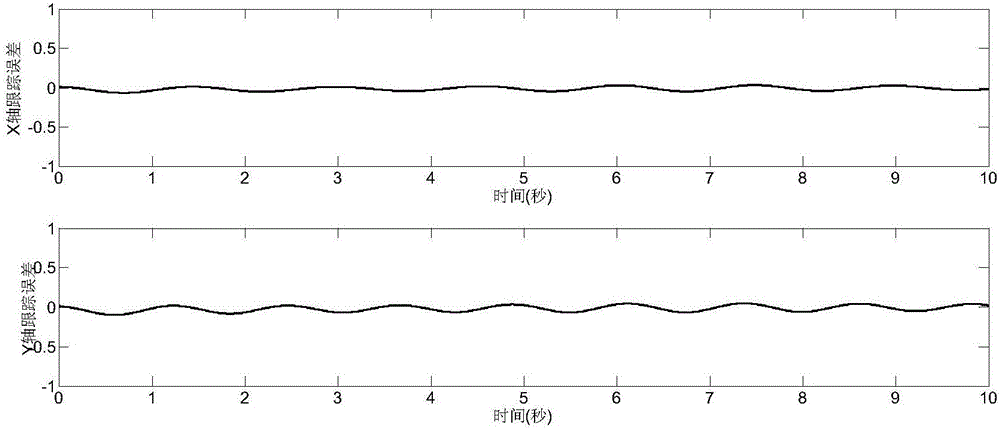
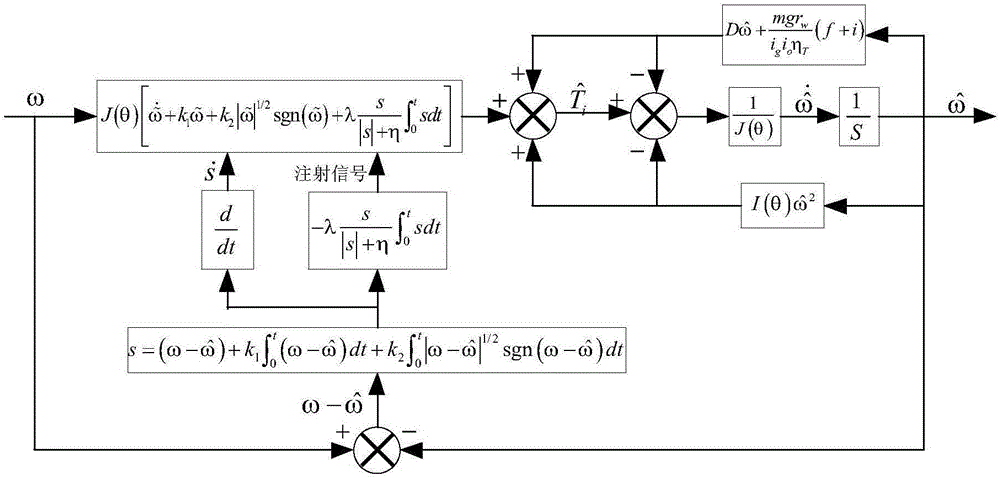
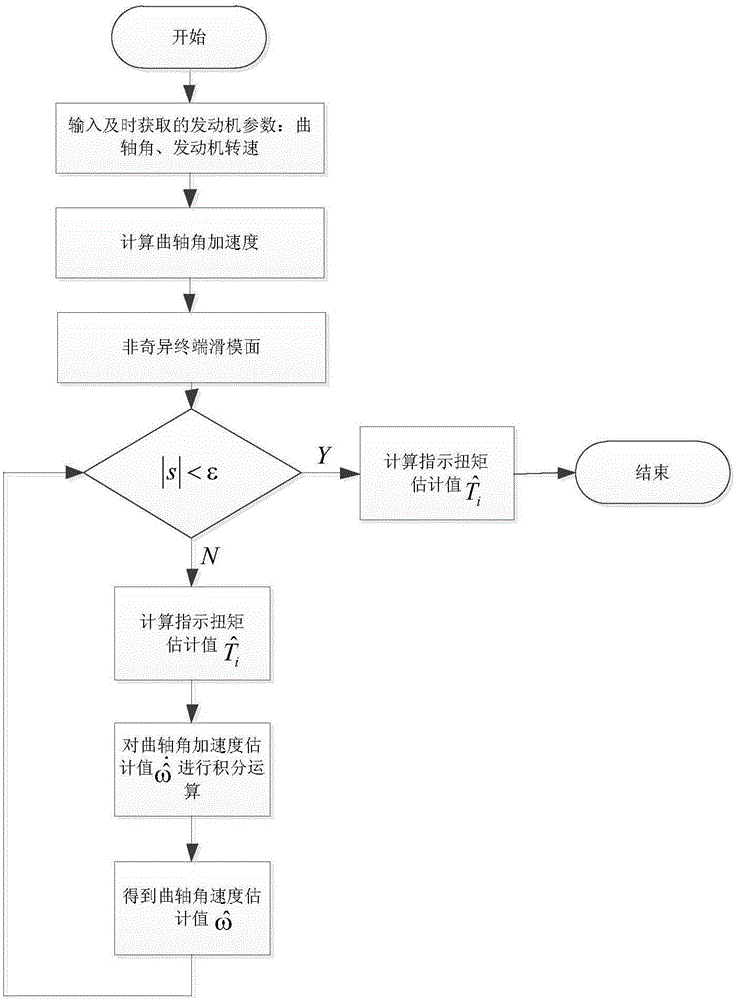
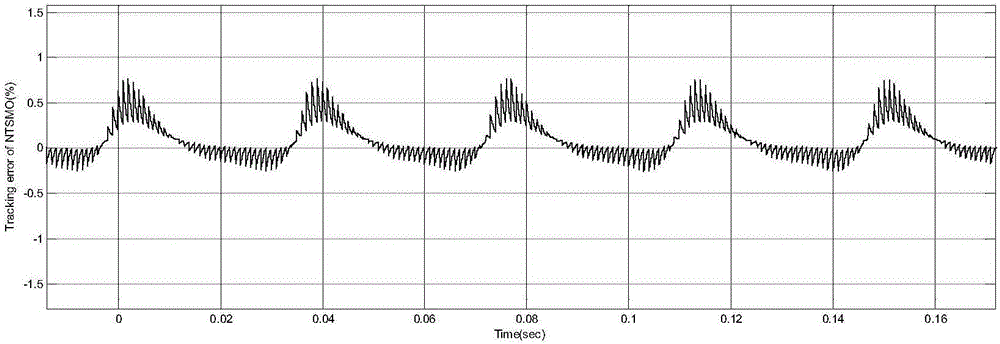
Method for estimating indicating torque of engine based on nonsingular terminal sliding mode observer
ActiveCN106647288AGood for online estimationHigh precisionAdaptive controlAngular velocityCrankshaft
The invention discloses a method for estimating an indicating torque of an engine based on a nonsingular terminal sliding mode observer. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing an accurate nonlinear engine crankshaft dynamical model; performing real-time measurement on crankshaft angle and engine speed, taking as an observer input and performing differential operation; and utilizing the nonsingular terminal sliding mode observer to change an estimating value of the indicating torque, thereby causing the estimating value of the crankshaft angular velocity gradually approach to the constantly changing practical measurement value. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the nonsingular terminal sliding mode observer is utilized to online estimate the indicating torque of the engine, has excellent robustness to the modeling error and the parameter perturbation, is short in convergence time and is high in estimating precision. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the estimating precision of the indicating torque is guaranteed.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
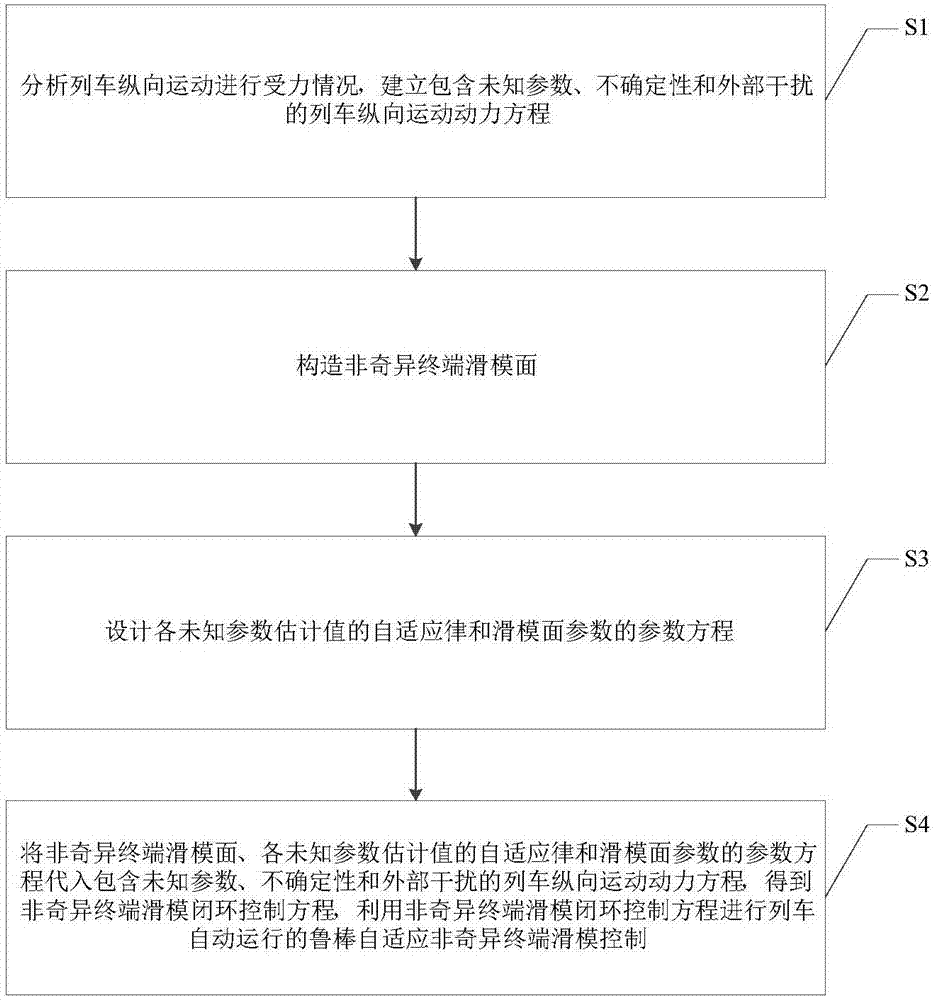
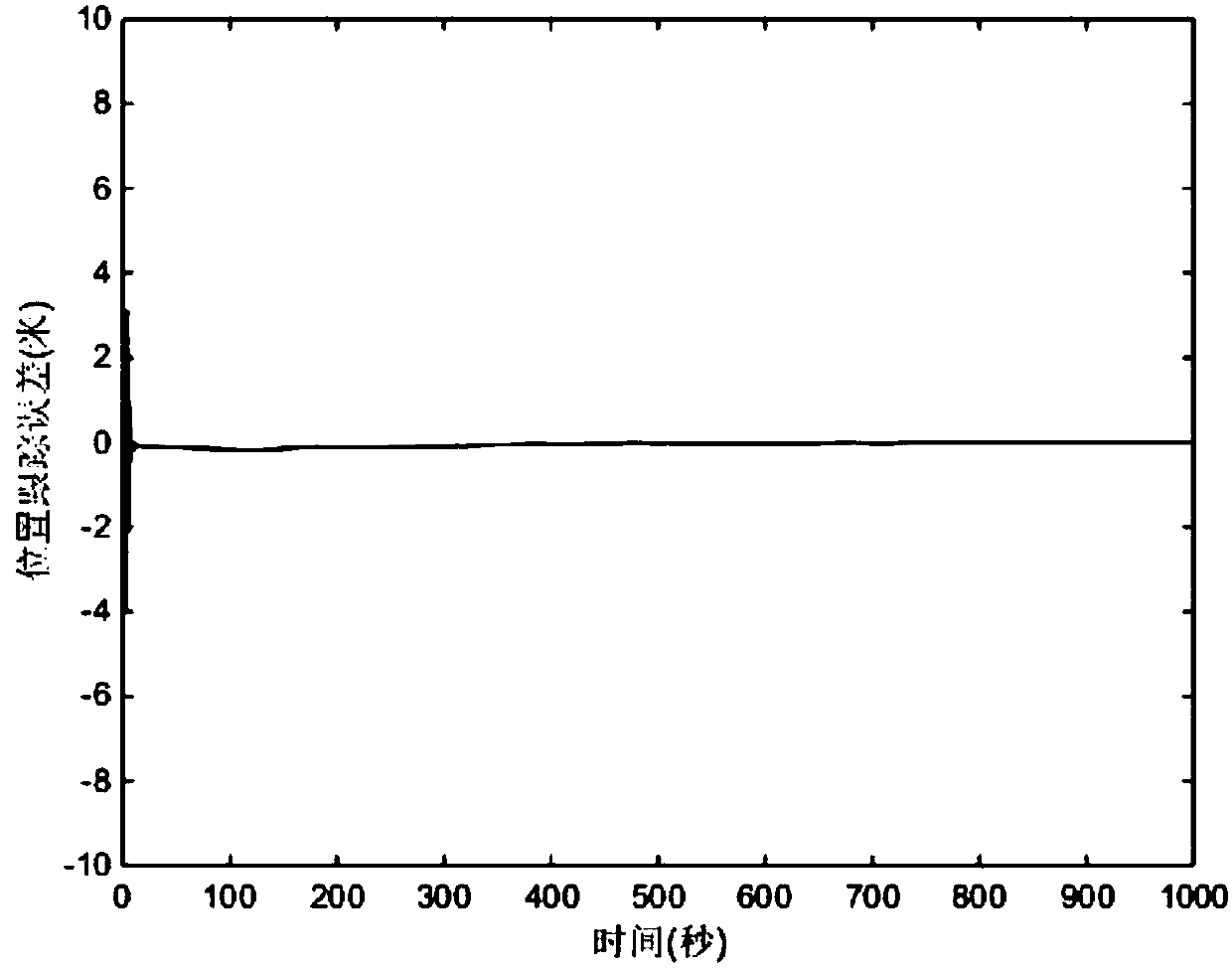
Robust adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control method of automatic train operation
InactiveCN107102542AReduce singularityCompensation uncertaintyAdaptive controlLoop controlClosed loop
The invention discloses a robust adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control method of automatic train operation. The method comprises that S1) the bearing condition of vertical movement of a train is analyzed, and a train vertical movement power equation including unknown parameters, uncertainty and external interference is established; S2) a nonsingular terminal sliding-mode surface is constructed; S3) an adaptive law of estimated values of the unknown parameters and a parameter equation of parameters of the sliding mode surface are designed; and S4) the nonsingular terminal sliding-mode surface, the adaptive law of estimated values of the unknown parameters and the parameter equation of parameters of the sliding mode surface are substituted into the train vertical movement power equation including the unknown parameters, uncertainty and external interference, a nonsingular terminal sliding-mode closed-loop control equation is obtained, and the nonsingular terminal sliding-mode closed-loop control equation is used to implement robust adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control of automatic train operation. Thus, position and speed tracking errors of an ATO system can reach the sliding surface within limited time and converged to 0 within limited time.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
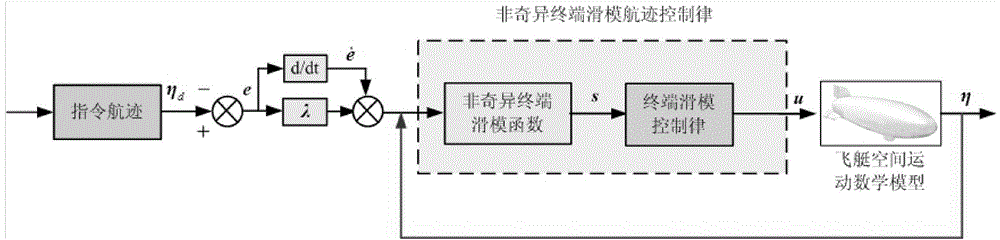
Nonsingular terminal sliding mode flight path control method for airships
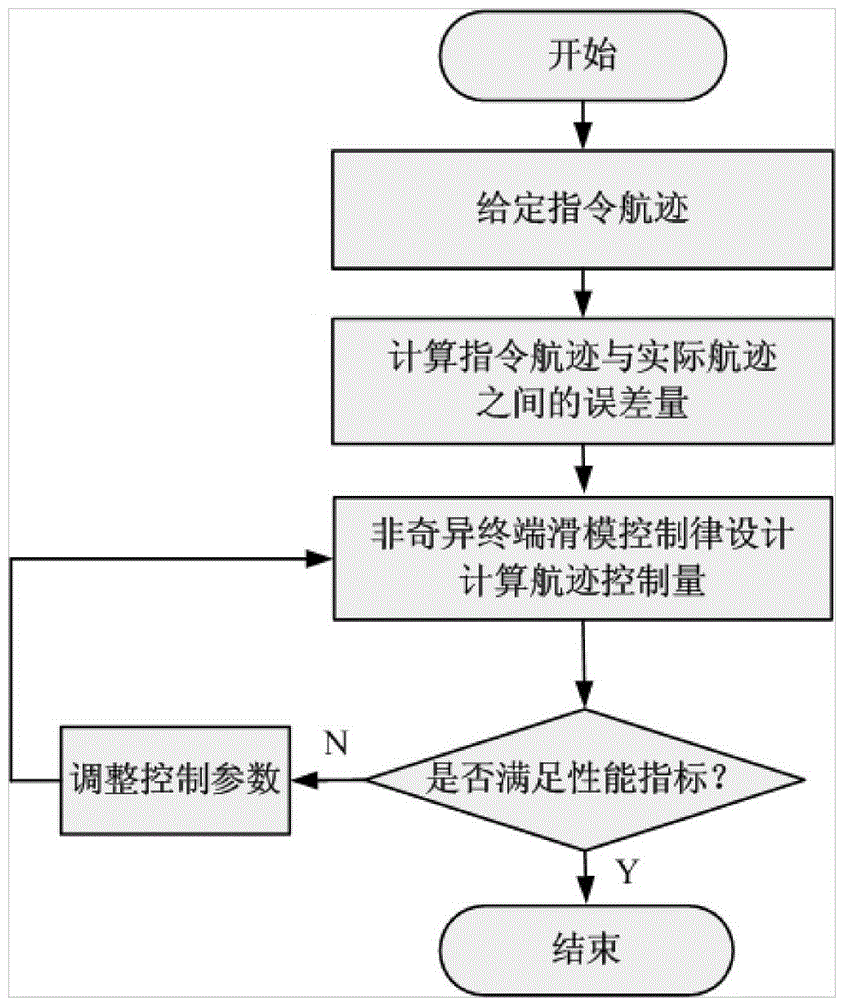
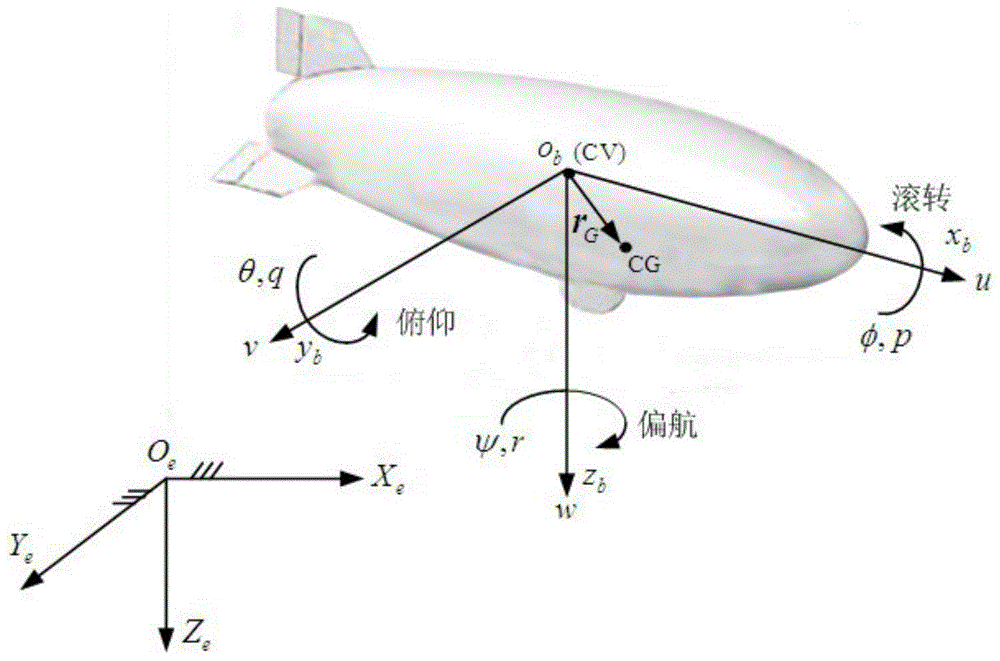
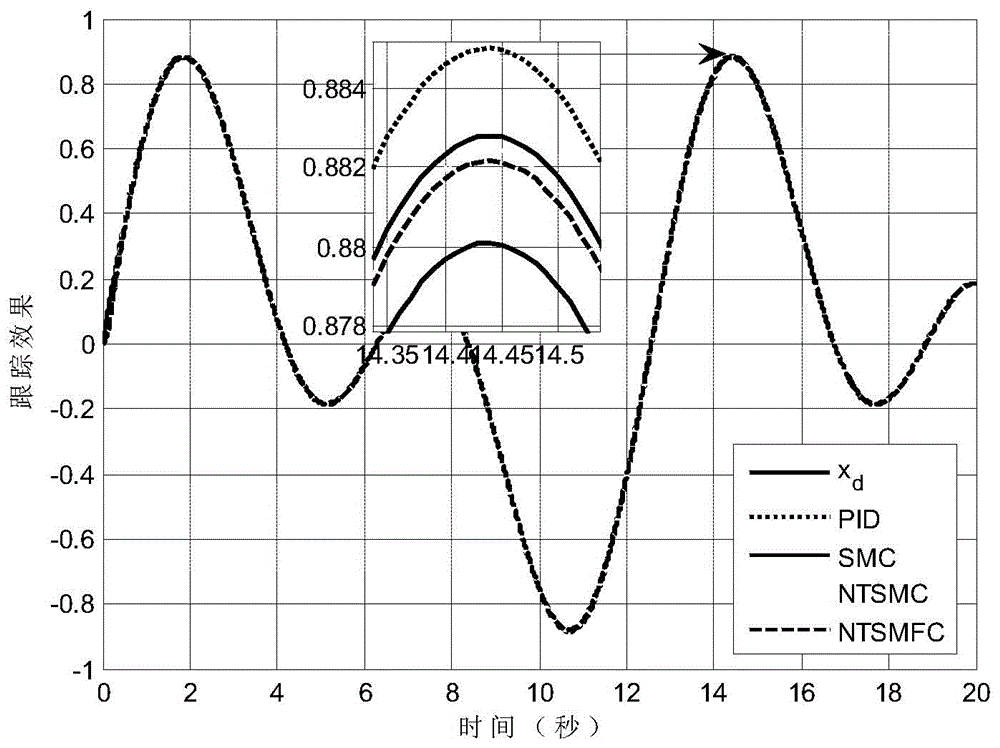
ActiveCN104360686AOvercome limitationsWiden the operating point variation rangePosition/course control in two dimensionsLyapunov stabilityAttitude control
A nonsingular terminal sliding mode flight path control method for airships includes: calculating error amount according to a given command flight path and an actual flight path, selecting a terminal sliding mode function to design a flight path control law according to a nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method, and applying the Lyapunov stability theory to prove stability of a control system. In practical application, an airship flight path is measured by a combined navigation system, and a flight path control function can be realized by transmitting control quantity obtained by calculation according to the method to an execution mechanism. A mathematical model of spatial motion of unmanned airships is built aiming at the problem of tracking flight paths of the unmanned airships; the flight path control law is designed according to the nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method by taking the model as a controlled object, attitude control errors are converged to zero in finite time by selection of the terminal sliding mode function, and system response speed and control precision are improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Nonsingular terminal sliding mode (NTSM) designated performance control method of turntable servo system
ActiveCN104698847AAvoid dead zone with additional compensationImplement specified performance controlsAdaptive controlDifferential coefficientDynamic models
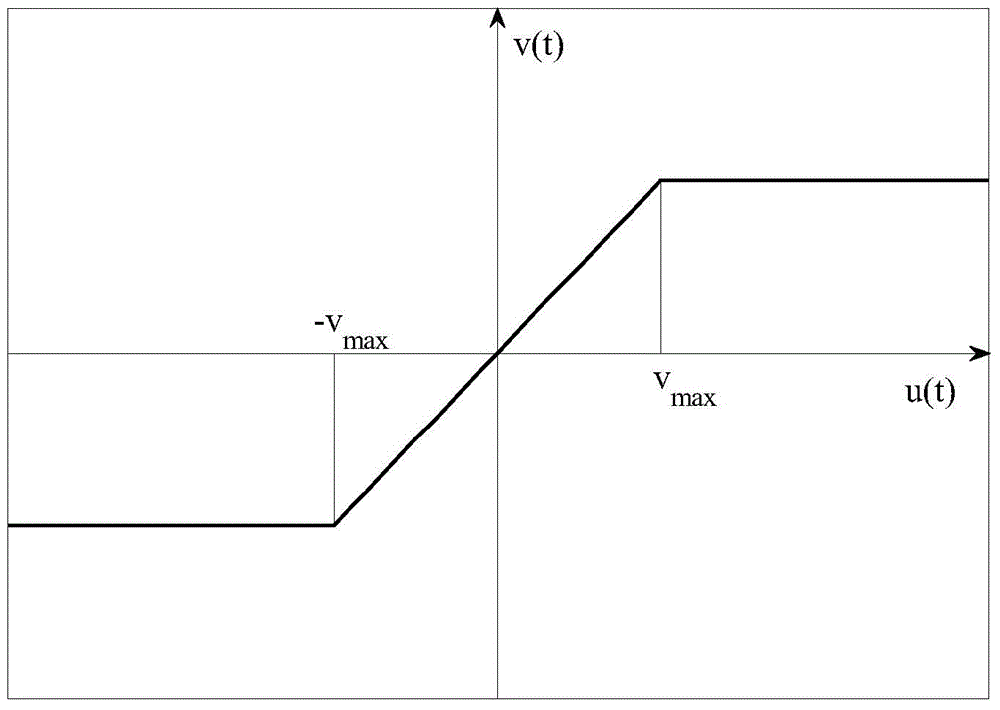
Disclosed is a nonsingular terminal sliding mode (NTSM) designated performance control method of a turntable servo system. The NTSM designated performance control method of the turntable servo system includes: building a dynamic model of the turntable servo system, and initializing status, sampling time and related control parameters of the turntable servo system; using a smooth affine function to approximate an input saturation function in the turntable servo system, and deriving a turntable servo system model with a saturation function; calculating tracking error of a control system, an FC (funnel control) error variable, and a first order differential coefficient and a second order differential coefficient of the control system; selecting a neural network to approximate an unknown dynamic condition according to an NTSM theory based on the turntable servo system model with the saturation function, designing an NTSM designated performance controller, and updating a weight matrix of the neural network. The NTSM designated performance control method of the turntable servo system can effectively prevent input of the saturation function from influencing the turntable servo system, and achieves control effects of designated performance.
Owner:南京申威光电技术研究院有限公司
Inversion sliding mode mechanical arm controller design method based on finite time disturbance observer
ActiveCN110421569ASimple structureShorten convergence timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorAdaptive controlDynamic modelsComputer terminal
The invention provides an inversion sliding mode mechanical arm controller design method based on a finite time disturbance observer. According to the method, a dynamic model of a mechanical arm is established at first, then a finite-time disturbance observer for external disturbance is designed and stability analysis is carried out, real-time detection and online estimation on unknown disturbancequantity are carried out, a controller of a nonsingular terminal sliding mode is designed by using the obtained disturbance estimation information, in combination with an inversion and sliding mode control method, the control law of a system is solved by designing an intermediate virtual quantity, moreover, a reaching law control method is added, then the asymptotic stability of the system is proved by a lyapunov function theory, and finally, the asymptotic stability of the system is verified through simulation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
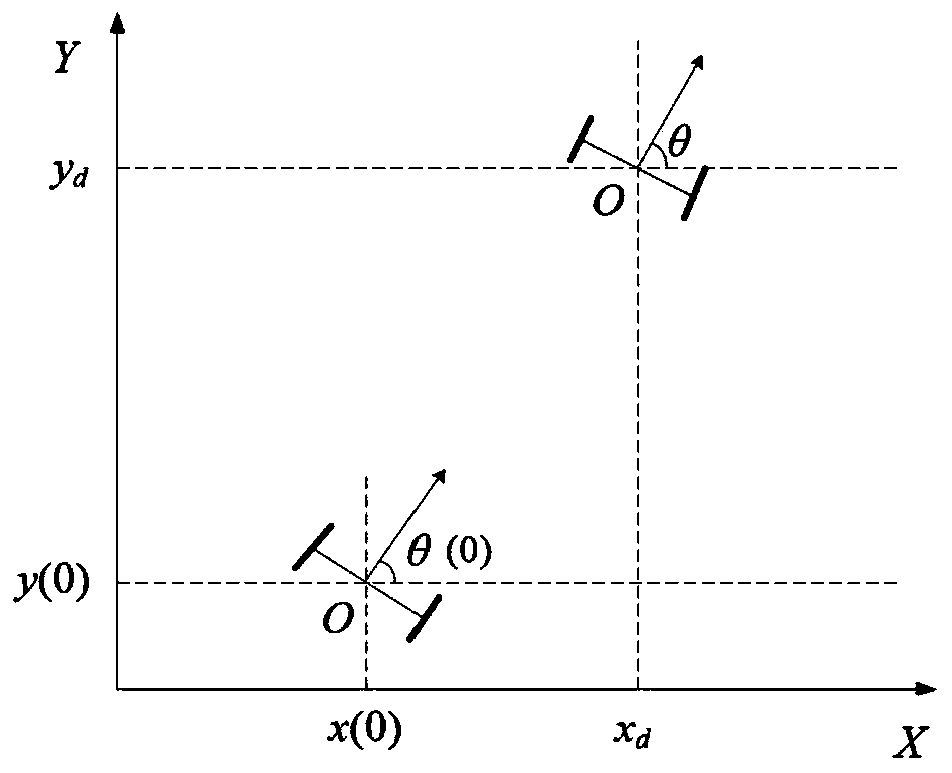
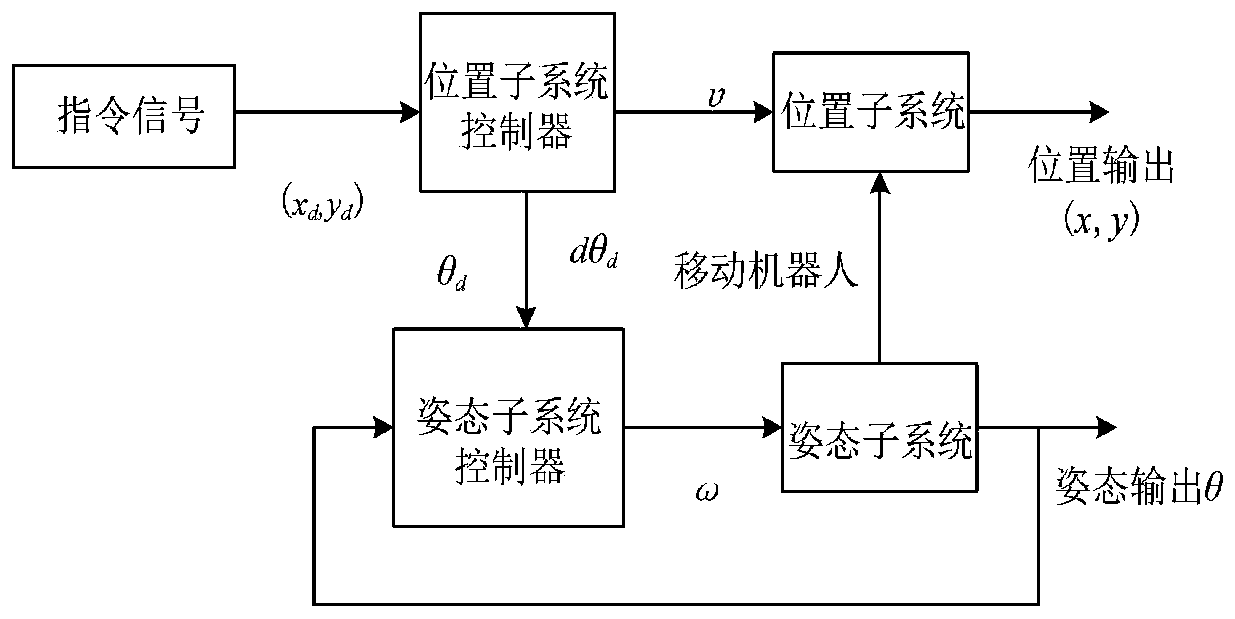
Wheeled mobile robot control method
ActiveCN110083061AGood anti-interference performanceImprove stabilityAdaptive controlClosed loopCombined method
The invention relates to a wheeled mobile robot control method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of 1, establishing a kinematic model of a wheeled mobile robot; and 2, establishing a double closed-loop system and tracking the position track and angle of the mobile robot through a nonsingular terminal sliding mode and generalized type-2 fuzzy combined method, specifically, tracking the position track of the mobile robot by the outer loop of the double closed-loop system, tracking the angle of the mobile robot by the inner loop of the double closed-loop system, taking a sliding mode surface as control input of a fuzzy system by both the outer loop and the inner loop, taking the output of the fuzzy system as a sliding mode reaching law parameter, and designing theconvergence speed of the inner loop to be higher than the convergence speed of the outer loop. The invention discloses the wheeled mobile robot control method, particularly relates to a double closed-loop control system; and through a generalized type-2 fuzzy control and sliding mode control combined method, the external interference resistance is improved and the systems stability is enhanced.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID NINGXIA ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
Finite-time decoupling control method of cart inverted pendulum system
ActiveCN104267596AReduce complexityAvoid Saturation EffectsAdaptive controlDynamic modelsEngineering
A finite-time decoupling control method of a cart inverted pendulum system includes the steps that a fourth-order dynamic model of the cart inverted pendulum system is set up, and the system state and sampling time first-order related control parameters are initialized; a saturation function in the system is approximated to be a simple time-varying system, and a system model with the saturation function is deduced; the cart inverted pendulum system is divided into two second-order subsystems, and the tracking error, the nonsingular terminal sliding mode surface and the first-order derivative of a control system are calculated; aiming at the cart inverted pendulum system, a neural network is selected to approximate an unknown function, a finite-time decoupling controller of the neural network is designed according to the tracking error and the nonsingular terminal sliding mode surface of the system, and a weight matrix of the neural network is updated. The influence of the saturation function can be avoided, the complex degree of the controller is reduced, and the cart inverted pendulum system can be fast stabilized within finite time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Smooth nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control method suitable for control system with relative degree of 1
ActiveCN104267605AEliminate chatterEliminate time-varying uncertaintyAdaptive controlReference modelMulti input
The invention discloses a smooth nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control method suitable for a control system with a relative degree of 1, relates to a nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control method, and solves the problems that the existing nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control method exists buffeting to cause a controller not to output continuous smooth control signals and not be applied to the control system with the relative degree of 1. The smooth nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control method comprises the following steps: if the controlled system serves as a single-input single-output control system with the relative degree of 1, then acquiring the system state differential in real time, designing a nonsingular terminal sliding mode, introducing a virtual controlled quantity and utilizing an integral action to enable the actual output controlled quantity to be smooth and continuous; if the controlled system serves as a matched multi-input multi-output control system, then converting a scalar realization form of the control system to a matrix vector realization form; if the controlled system serves as a non-matching indeterminate multi-input multi-output control system, then conducting nonsingular state change for two times according to the controllability index r to resolve the system into r subsystems, introducing a reference model to eliminate time-varying uncertainty of input channels of the subsystems, and further designing a control law and a minor control law. The smooth nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control method disclosed by the invention can be applied to smooth nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control of the control system with the relative degree of 1.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Robustness self-adaption nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control method for train ATO system
InactiveCN107390517AReduce singularityCompensate for interferenceAdaptive controlStress conditionsLoop control
The present invention discloses a robustness self-adaption nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control method for a train ATO system. The method comprises: S1, analyzing stress condition of vertical motion of a train, and establishing a train vertical motion power equation comprising unknown parameters, nondeterminacy and external interference; S2, defining position tracking errors, speed tracking errors and acceleration tracking errors, and constructing a nonsingular terminal sliding-mode surface; S3, design self-adaption rules of each unknown parameter estimation value and the control strategy of the nonsingular terminal sliding-mode surface; and S4, putting the nonsingular terminal sliding-mode surface, the self-adaption rules of each unknown parameter estimation value and the control strategy of the nonsingular terminal sliding-mode surface into the train vertical motion power equation, obtaining a nonsingular terminal sliding-mode closed-loop control equation, and performing control through adoption of the nonsingular terminal sliding-mode closed-loop control equation. The tracking errors of the position speed of the train ATO system can arrive the slide surface in a limited time and can be converged to zero in the limited time.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
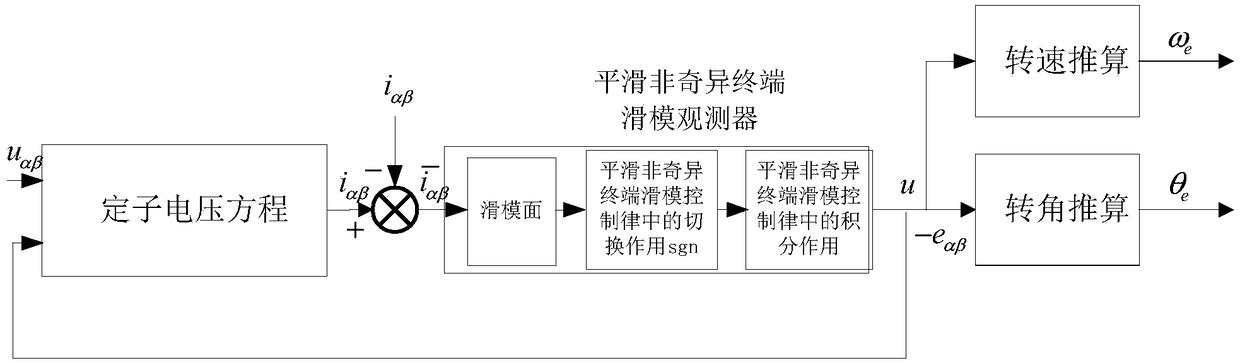
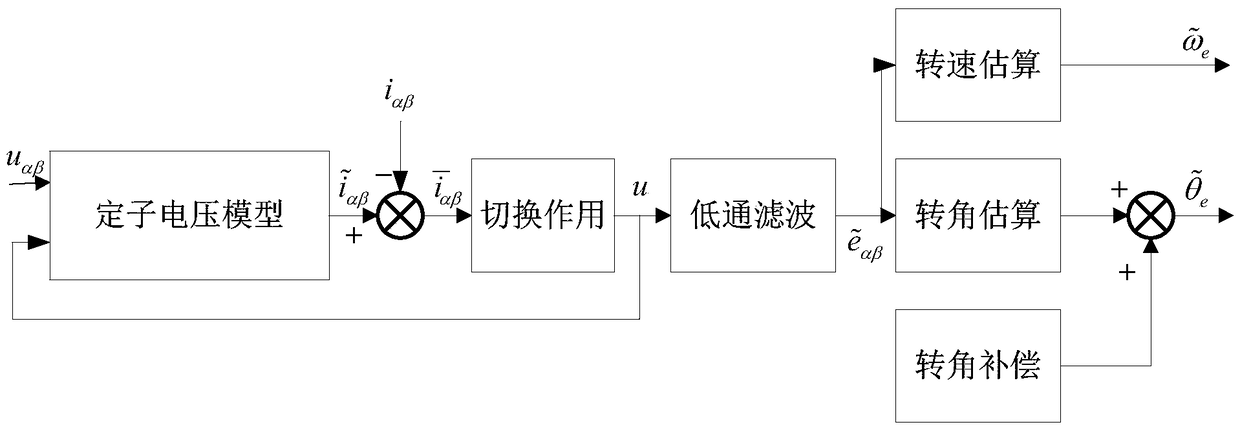
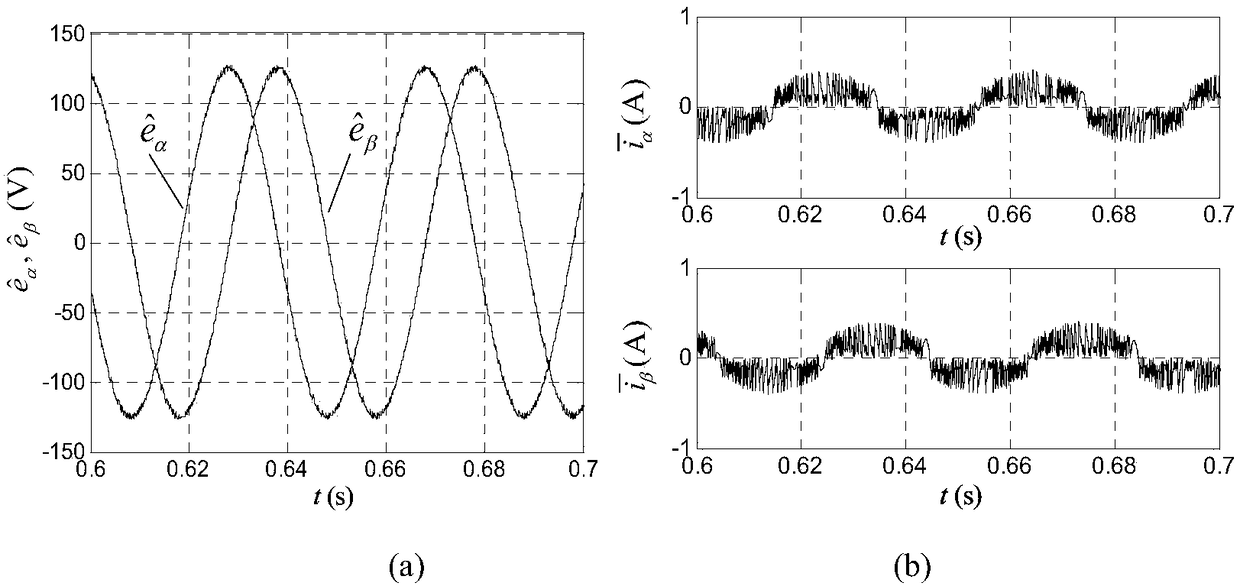
Position Sensorless Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Smooth Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Observer
ActiveCN109150029AAccurate estimateSolving Phase Lag IssuesElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlControl systemPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention relates to a position sensorless control method of a permanent magnet synchronous motor based on a smooth non-singular terminal sliding mode observer, which relates to the position sensorless technology field. The present invention solves the problem of phase lag caused by external filter in the position sensorless control system of the permanent magnet synchronous motor of the priorsliding mode observer, and needs to compensate the rotation angle estimation, so that the rotor position and the rotational speed of the motor can not be accurately obtained. In the alpha beta axis coordinate system, the stator current of PMSM is tracked by a smooth non singular terminal sliding mode observer, and the stator current deviation is obtained. When the stator current deviation is in continuous sliding mode motion state, the stator current deviation is processed by the sliding mode surface, and then the output vector u without high frequency switching is obtained by the switching function and integral function in the smooth non-singular terminal sliding mode control law, so that the back electromotive force is obtained. The speed and rotor position of permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) are obtained according to back electromotive force (BEMF). It is used to obtain the rotor position and rotational speed accurately.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
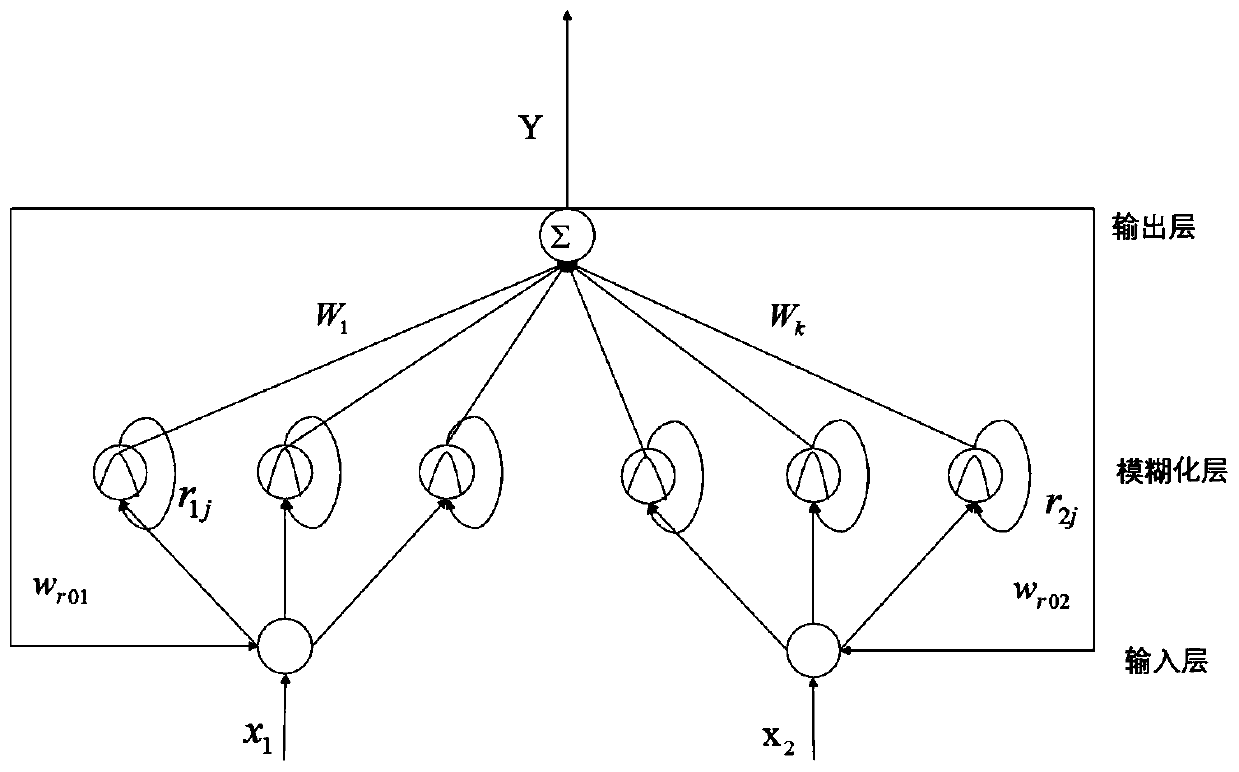
Recursive fuzzy neural network nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method of micro gyroscope
ActiveCN110703610AAdjust output in real timeGuaranteed drive frequencyAdaptive controlLyapunov stabilityNetwork structure
The invention discloses a novel recursive fuzzy neural network nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method of a micro gyroscope system. The recursive fuzzy neural network nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method comprises the steps of: designing a nonsingular terminal sliding mode surface function of the micro gyroscope system; determining a nonsingular terminal sliding mode control rate added into the nonsingular terminal sliding mode surface function based on a first Lyapunov stability criterion function; and replacing an uncertain item in the nonsingular terminal sliding mode control rate with output of a constructed recursive fuzzy neural network, and constructing a final control rate according to a result output by means of the constructed recursive fuzzy neural network and the nonsingular terminal sliding mode control rate based on a second Lyapunov stability criterion function, so as to realize tracking control over the micro gyroscope system. The nonsingular terminal sliding mode control adopted by recursive fuzzy neural network nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method has the advantages of high control precision and high robustness, and the singular problem existing in terminal sliding mode control is avoided; and parameters of the novel recurrent fuzzy neural network can be automatically stabilized to the optimal value according to a designed adaptive algorithm, so that the parameter training time is shortened, and the universality of the network structure is enhanced.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
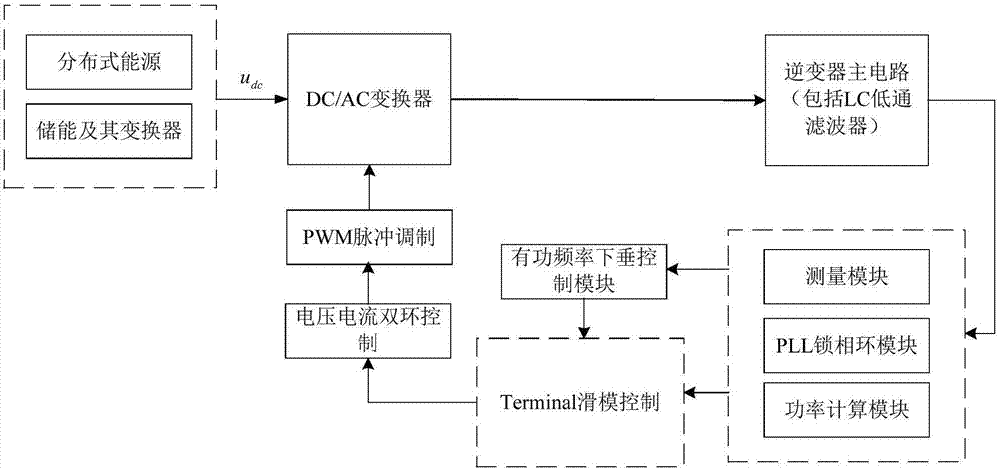
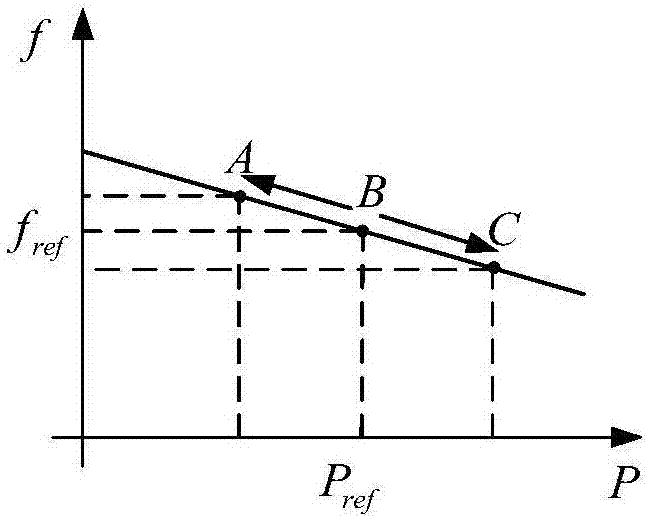
VSG control method based on adaptive Terminal robust sliding mode
InactiveCN107394821AImprove stabilityGood dynamic effectSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionVirtual synchronous generatorElectric power system
The invention discloses a VSG (virtual synchronous generator) control method based on adaptive Terminal robust sliding mode. The VSG control method based on adaptive Terminal robust sliding mode includes the steps: enabling a distributed power supply with energy storage to be equivalent to a direct current voltage source so as to be taken as the prime mover portion of a virtual synchronous generator for supplying electric energy for the whole system; establishing the corresponding relationship between the inverter filtering parameters, the output voltage, the voltage and current of the point of common coupling and each parameter of the synchronous generator; considering a synchronous generator four-order model with an excitation system and valve adjustment to simulate the characteristics of the synchronous generator, and establishing a system mathematic model; according to the characteristics of two input variables of the system, determining two nonsingular Terminal sliding mode surfaces to realize decoupling control, and obtaining the control rule of the inverter based on Terminal robust sliding mode control; and after the control rule of the inverter is controlled through voltage and current double loop control, obtaining a driving signal of pulse width modulation (PWM) to control a DC / AC converter. The VSG control method based on adaptive Terminal robust sliding mode can significantly inhibit system oscillation, can improve stability of electric power system, and has good engineering application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
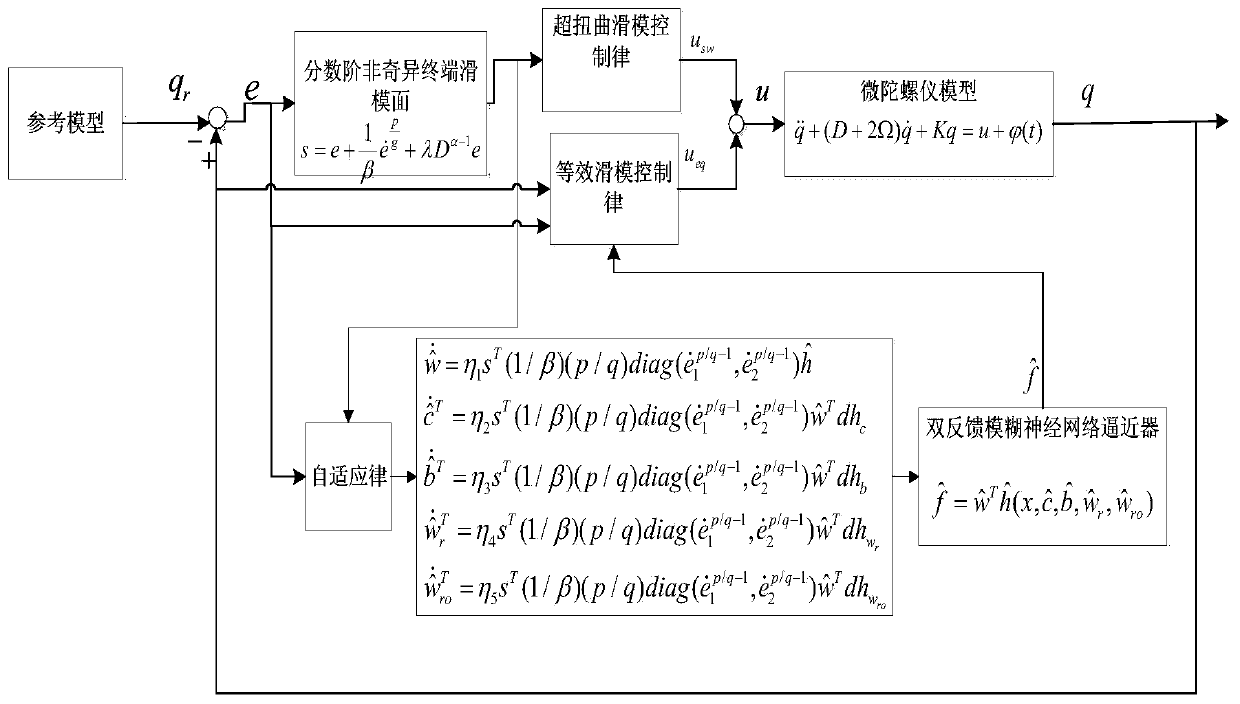
Micro gyroscope super-distortion sliding mode control method based on double-feedback fuzzy neural network
ActiveCN110262237AIncrease flexibilityAchieve an exact approximationAdaptive controlReference modelGyroscope
The invention discloses a micro gyroscope super-distortion sliding mode control method based on a double-feedback fuzzy neural network, wherein a sliding mode surface is formed by fractional order nonsingular terminal sliding mode control, and a control system structure comprises a reference model, fractional order nonsingular terminal sliding mode surface design, self-adaptive law design and double-feedback fuzzy neural network approximator design. The control method is simple and easy in design and convenient to apply, further expands the application range of the micro gyroscope, can effectively control the controlled system, and enables the track tracking of the micro gyroscope system to have strong robustness, high convergence rate and high accuracy.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Grid-connection control method of grid-side converter of small permanent magnet direct-driven wind power system
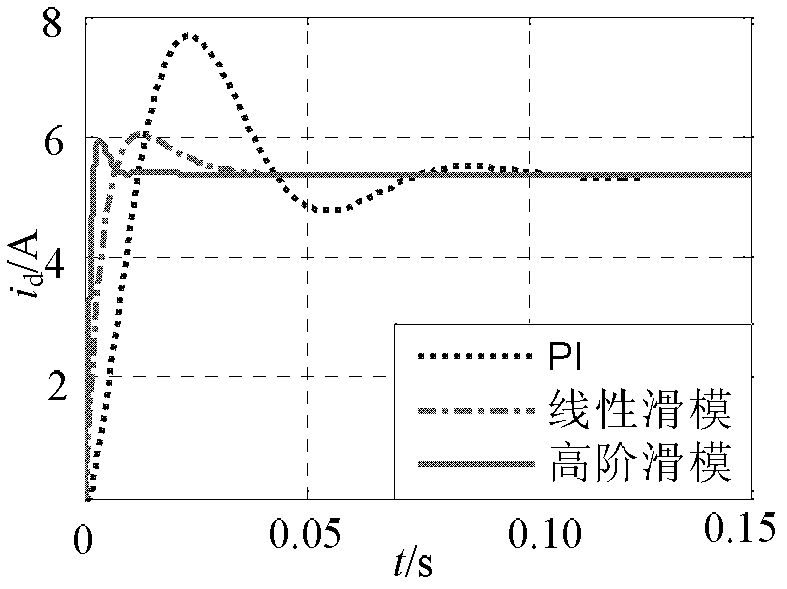
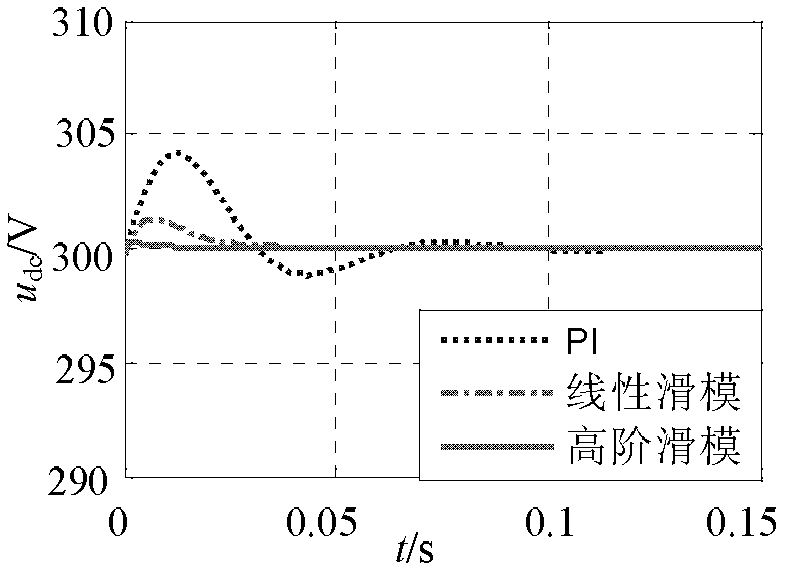
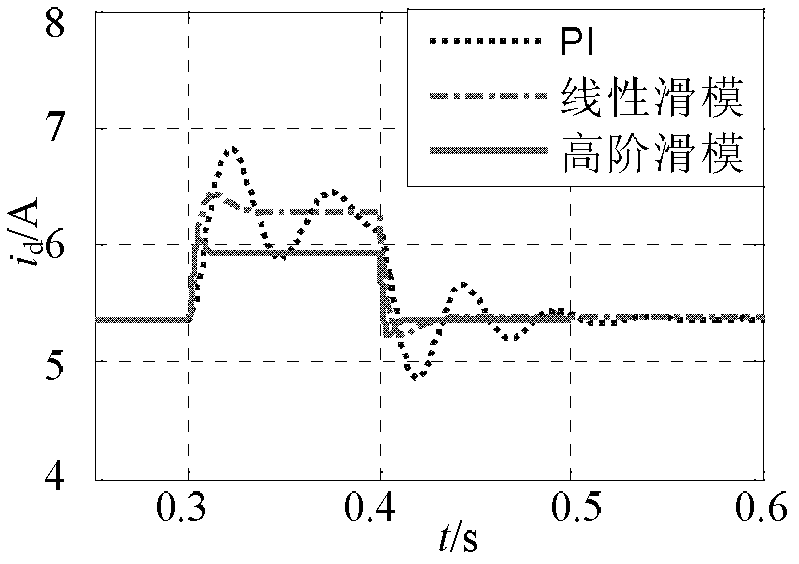
InactiveCN102347622AAvoid damageShort response timeSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAlternate currentNonsingular terminal sliding mode
The invention discloses a grid-connection control method of a grid-side converter of a small permanent magnet direct-driven wind power system, which relates to a grid-connection control method of a grid-side converter of a wind power system. The invention aims to solve the problems of large overshoot and long system response time of the traditional PI (Proportional Integral) control and a buffeting phenomenon existing in the linear sliding mode control. The concrete method comprises the following steps of: collecting a three-phase voltage signal and a three-phase current signal of a power grid and converting the three-phase voltage signal and the three-phase current signal into a two-phase rotating voltage signal and a two-phase rotating current signal; obtaining a d-axis given current, ad-axis high-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode surface s1 and a q-axis high-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode surface s2; obtaining a q-axis control law uq and a d-axis control law ud; andobtaining a drive signal of a grid-side converter, inputting the drive signal into the grid-side converter and converting the direct current generated by a permanent magnet direct-driven wind power system into alternating current for being input into the power grid by utilizing the grid-side converter. The method is used for the control of the grid-connection process of a wind power generator.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
ASR adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method based on multiple agents
ActiveCN111665726AEliminate calculationsGuaranteed smoothAdaptive controlGraph theoreticControl engineering
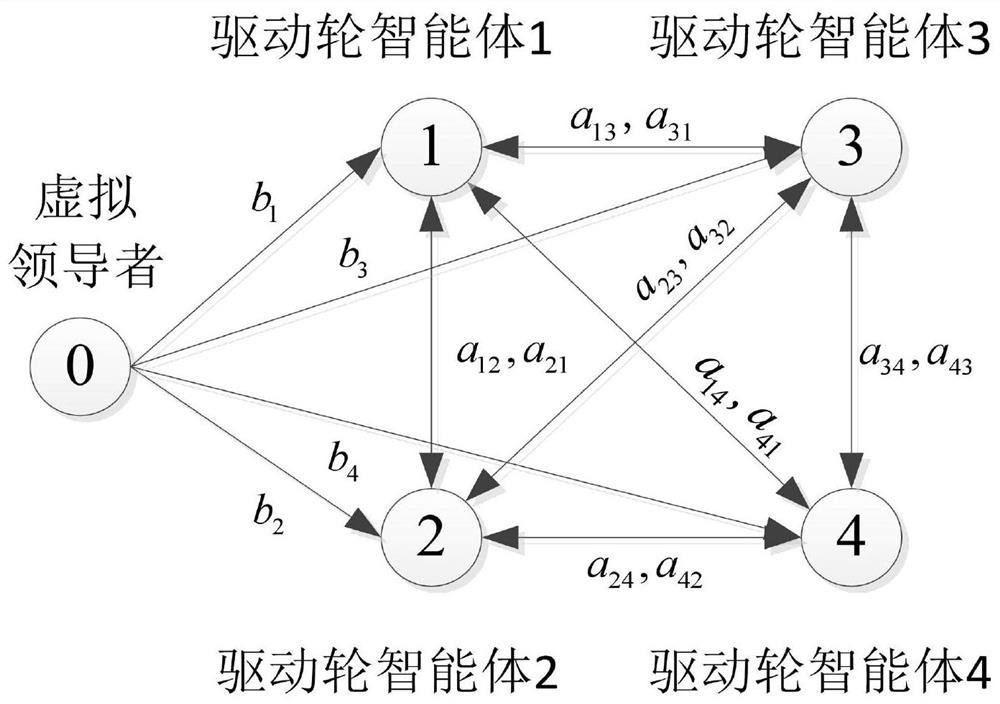
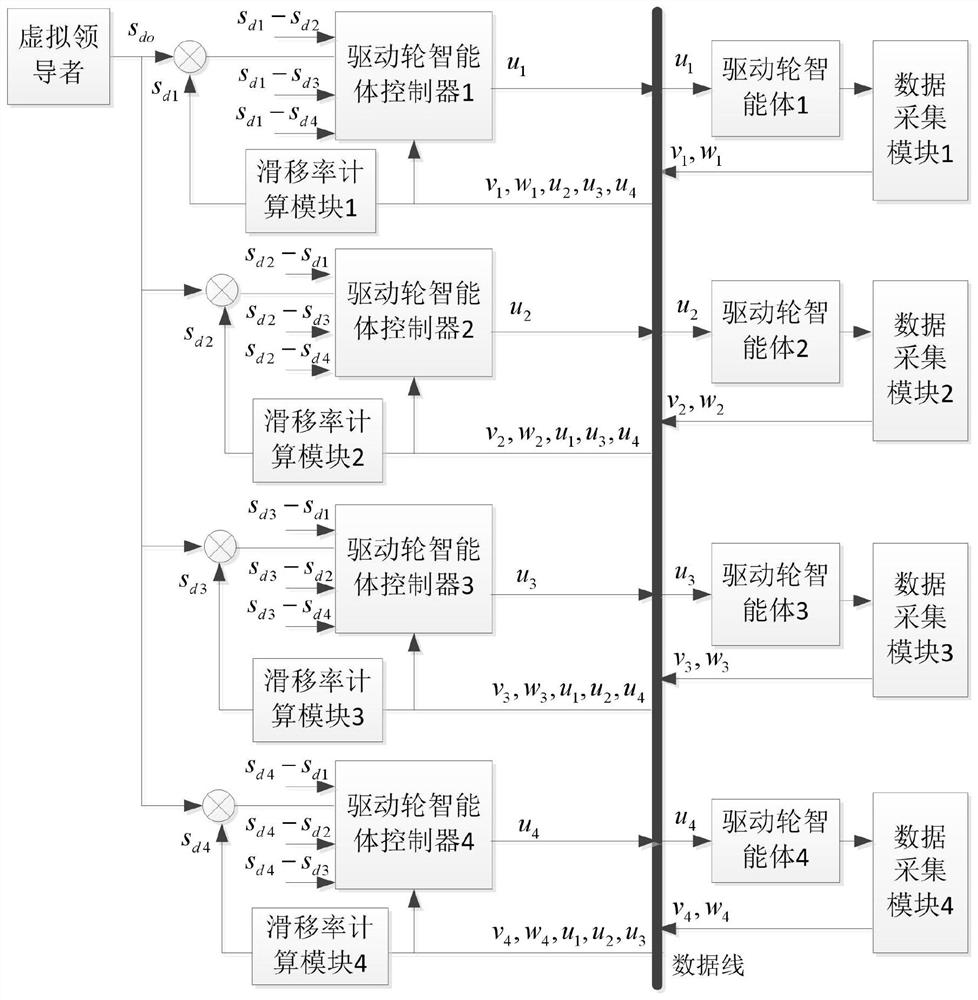
The invention discloses an ASR adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method based on multiple agents, and relates to the field of ASR control. According to the method, ASR is decomposed into four single-wheel intelligent agent subsystems based on a graph theory so as to reduce the model dimension; the design of an ASR controller is converted into the design of a single-wheel intelligent agent subsystem controller, a single-wheel agent self-adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller is provided, a self-adaptive estimation mechanism is adopted to select controller switching item gains, and the time for the actual slip rate to reach an ideal slip rate value can be adjusted through selection of control parameters. According to the invention, under different road adhesion conditions, the actual slip rate of the wheel reaches an ideal slip rate value within limited time, so that the problem of wheel slip is effectively solved, and the safety and the driving capabilityof the system are improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com