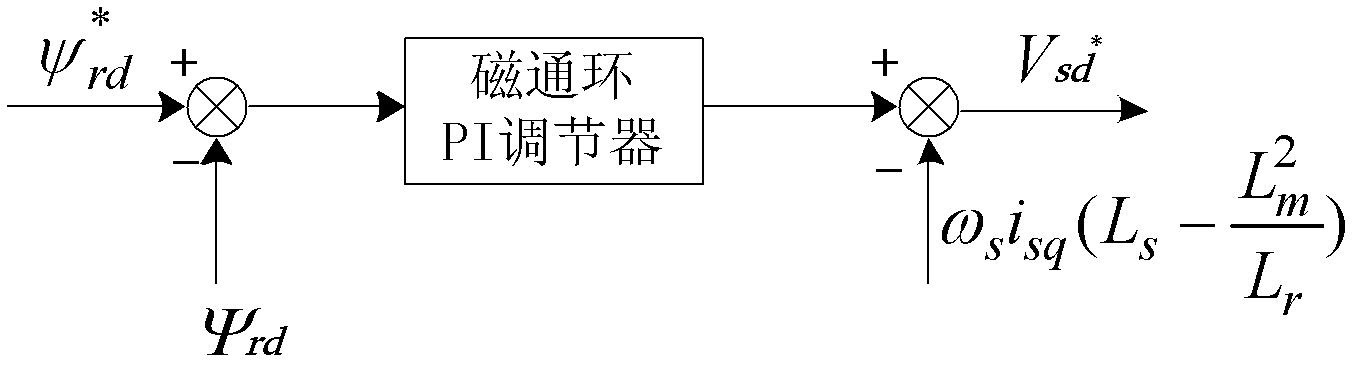
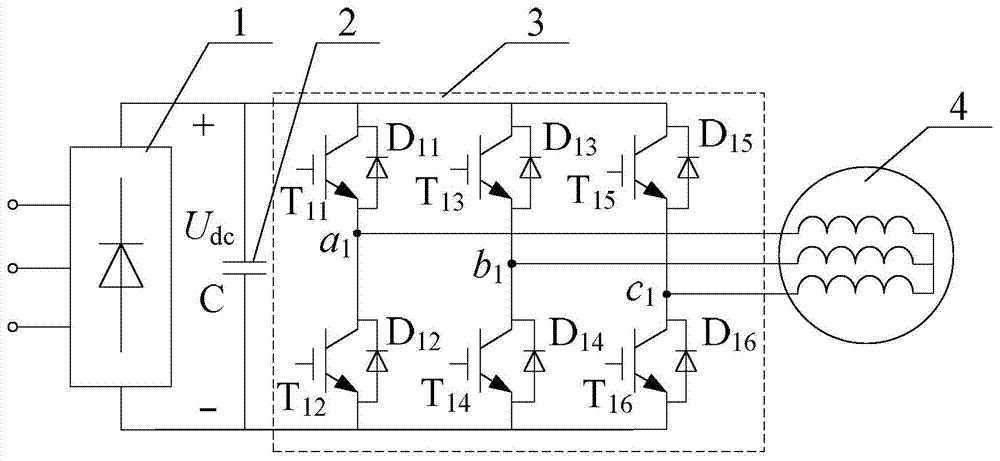
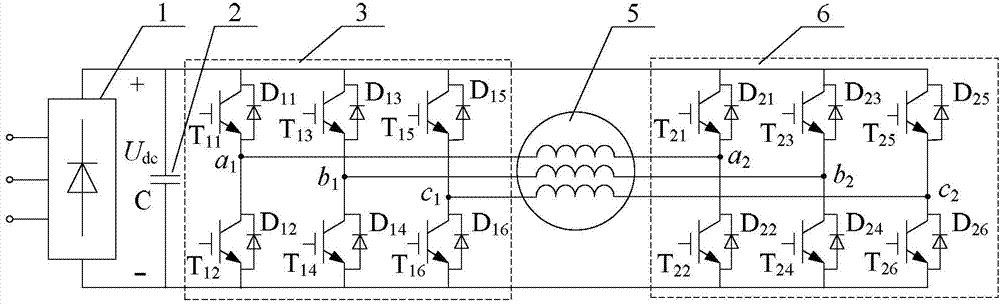
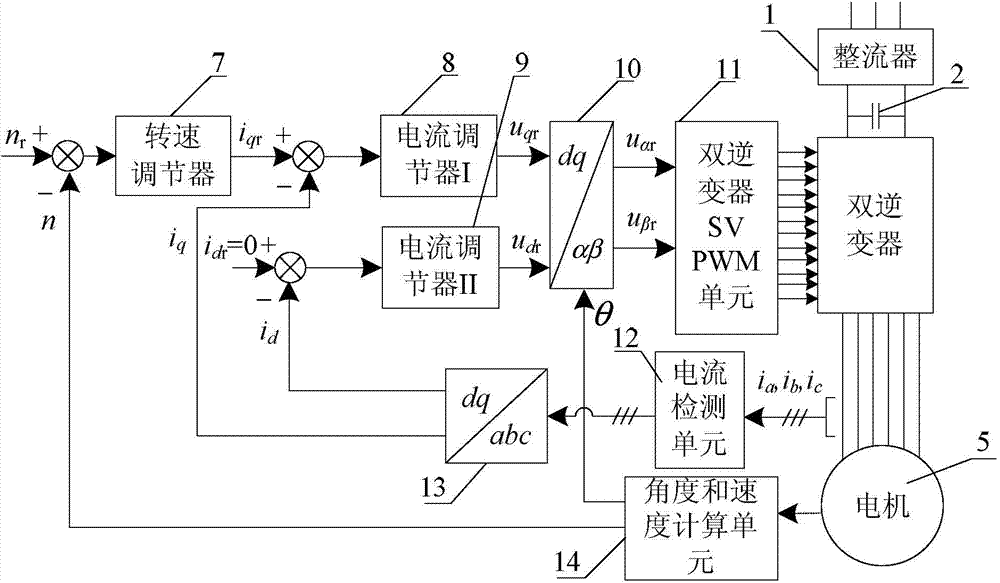
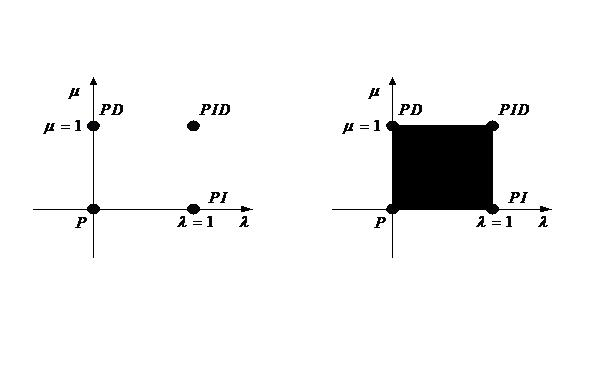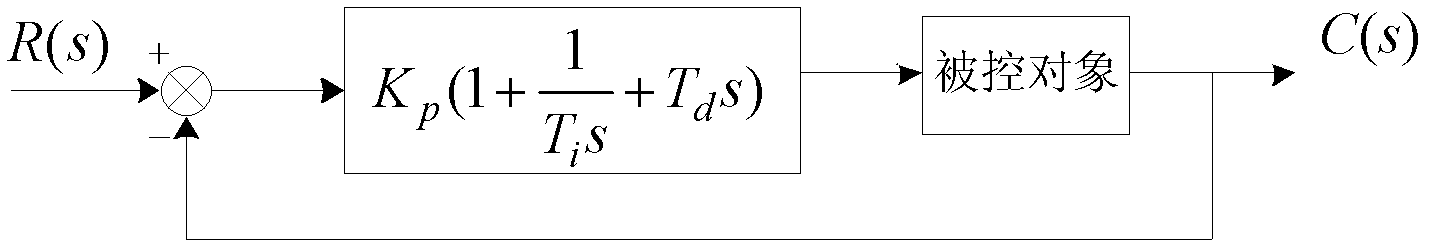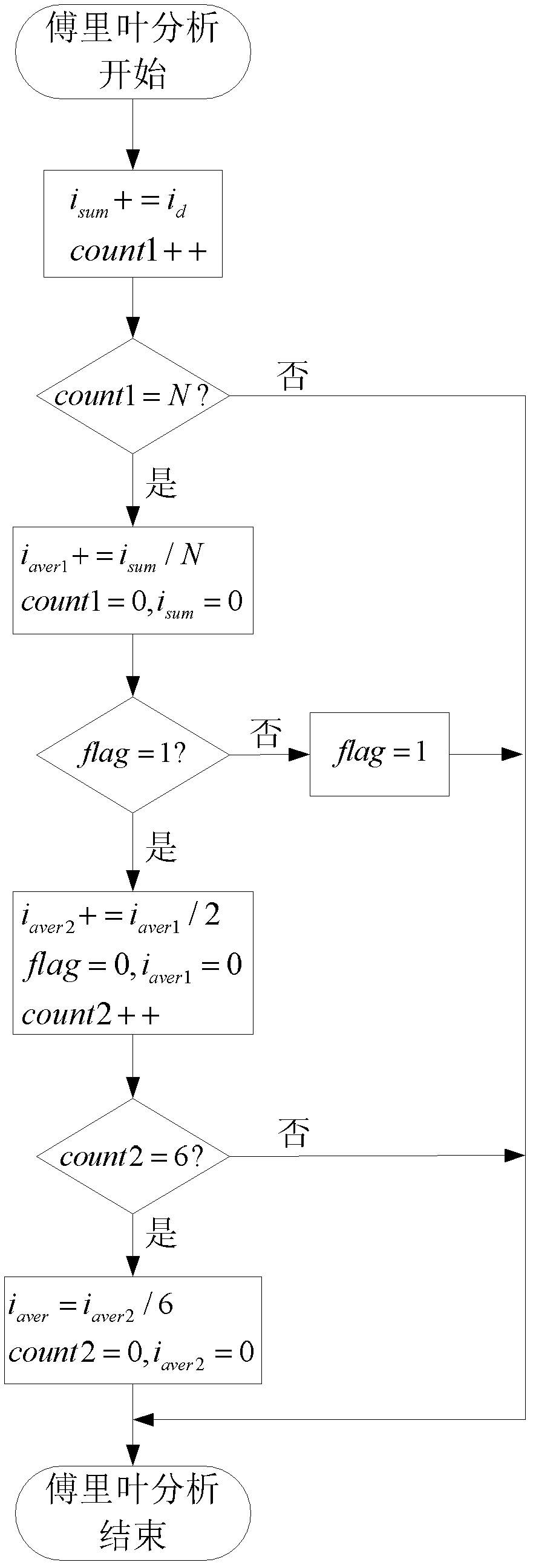Patents
Literature
344 results about "Vector control system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
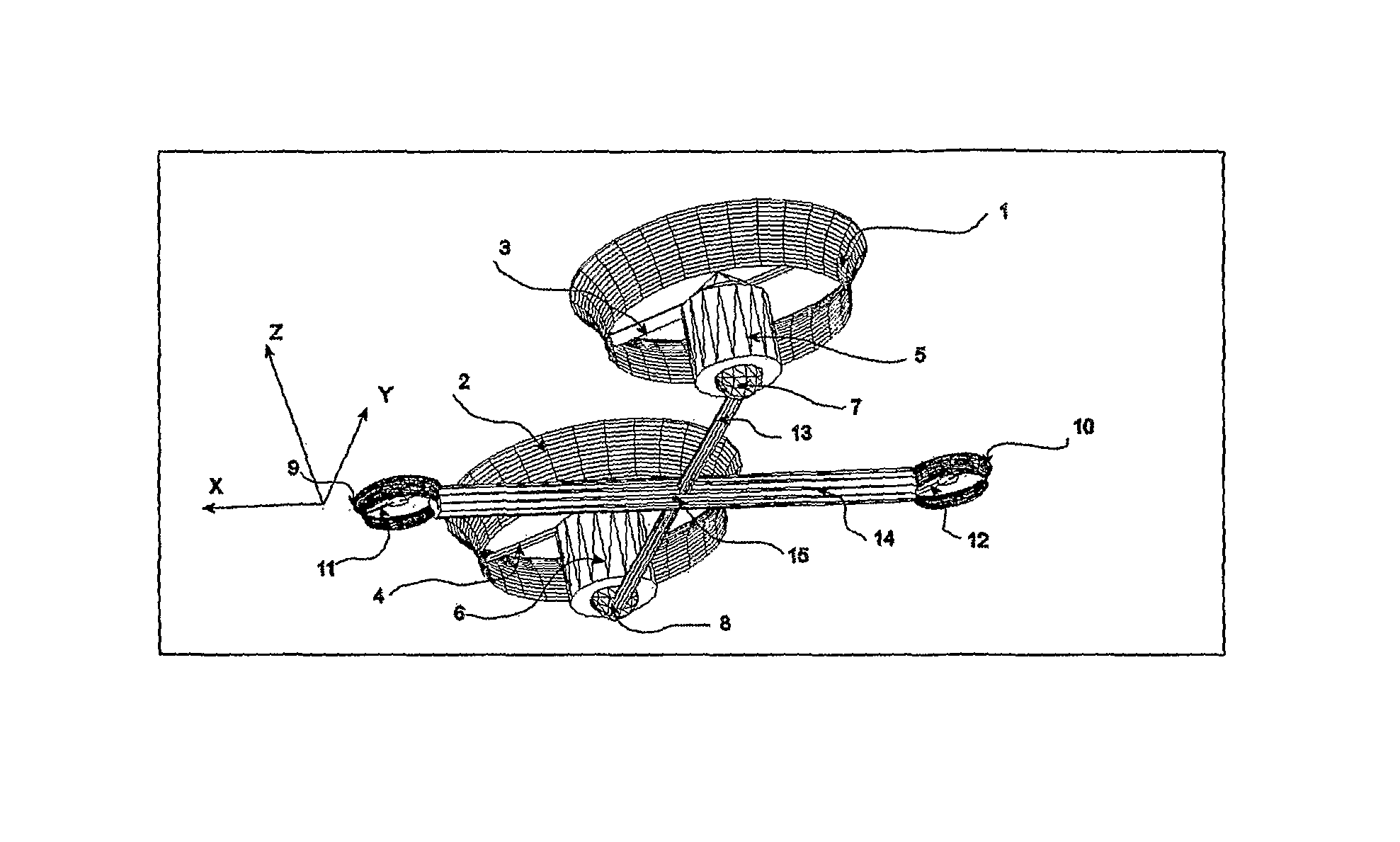
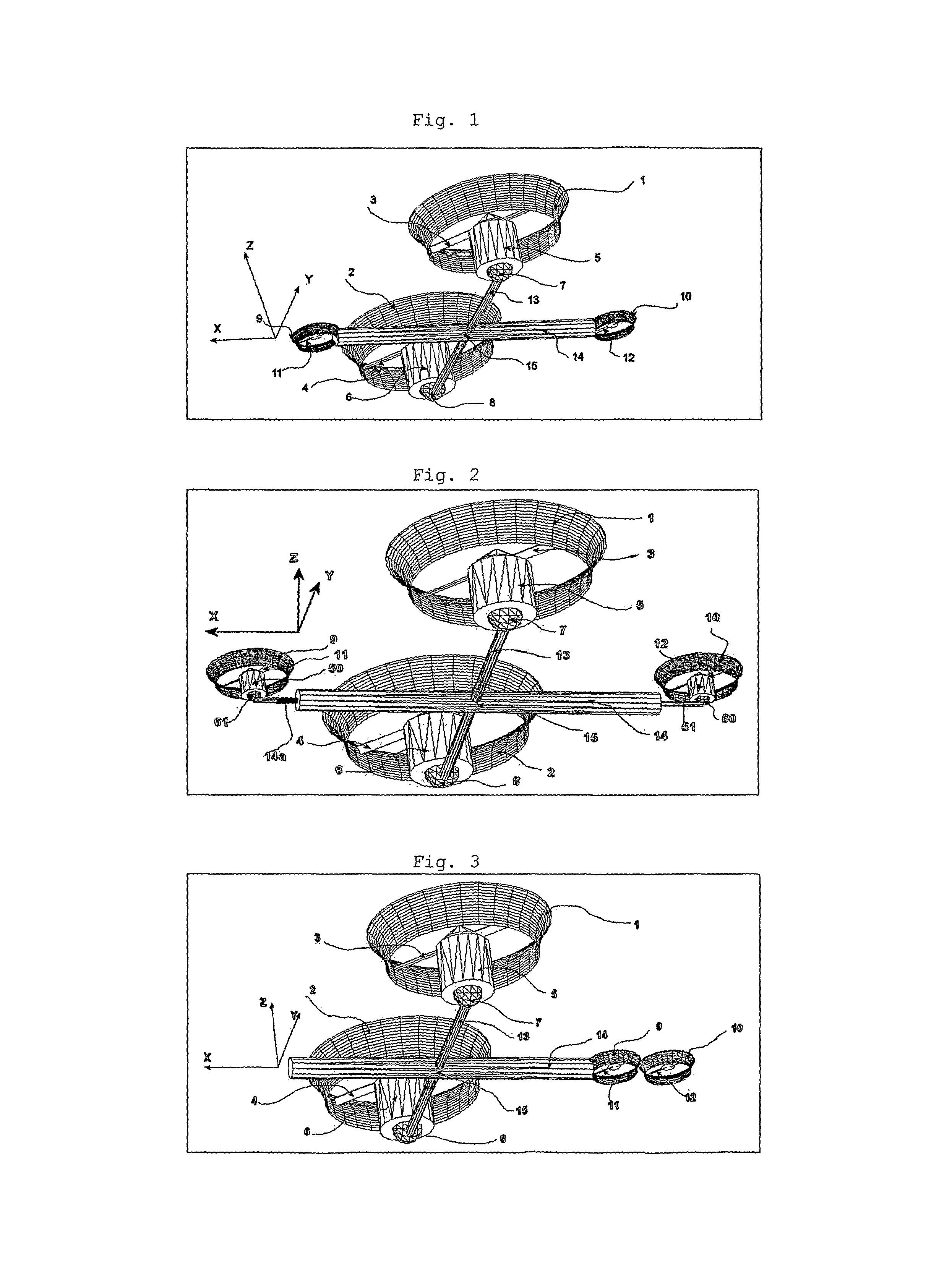
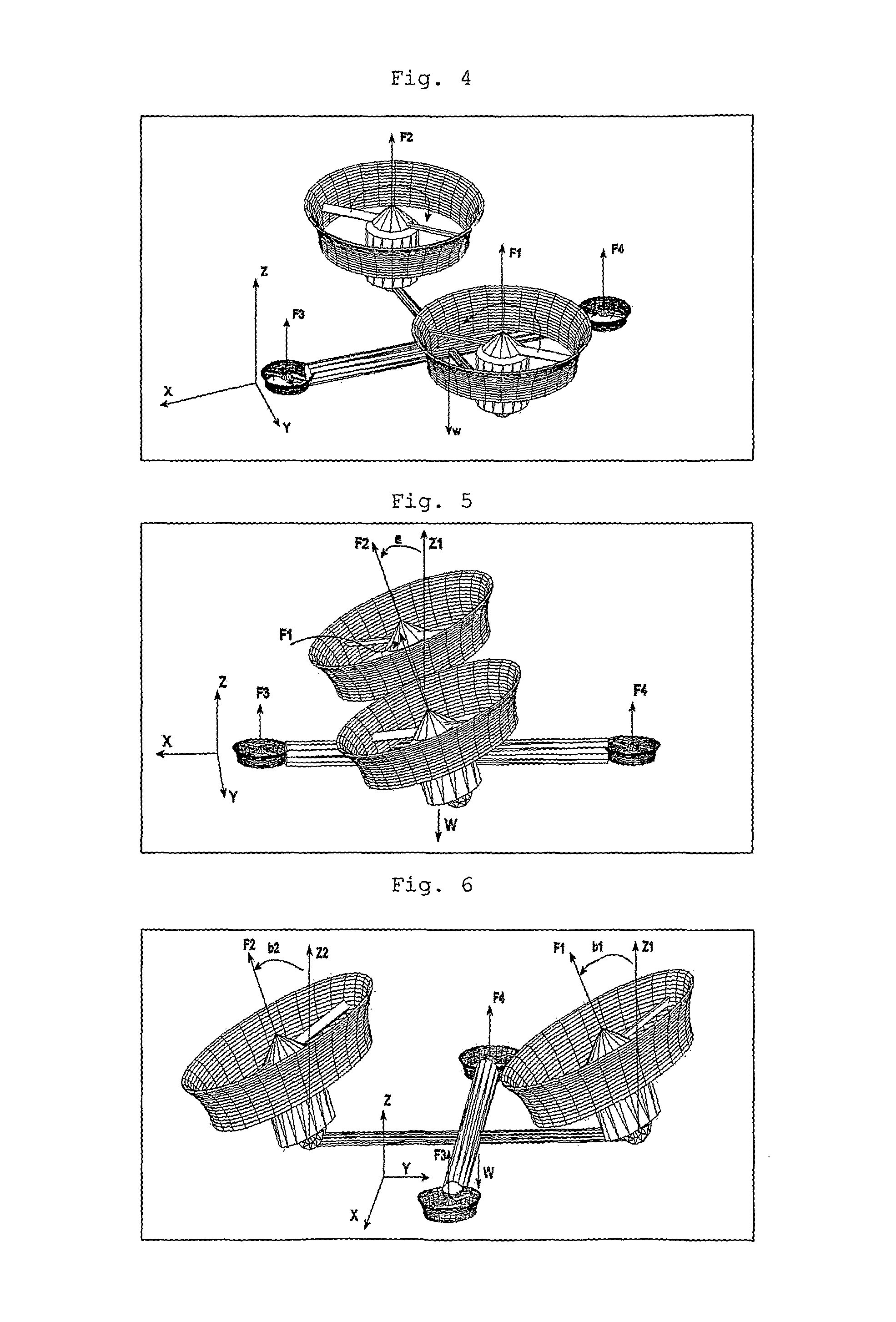
System and Process of Vector Propulsion with Independent Control of Three Translation and Three Rotation Axis
ActiveUS20100301168A1Reduces the passenger's discomfortEasy to controlCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsControl systemVector control system
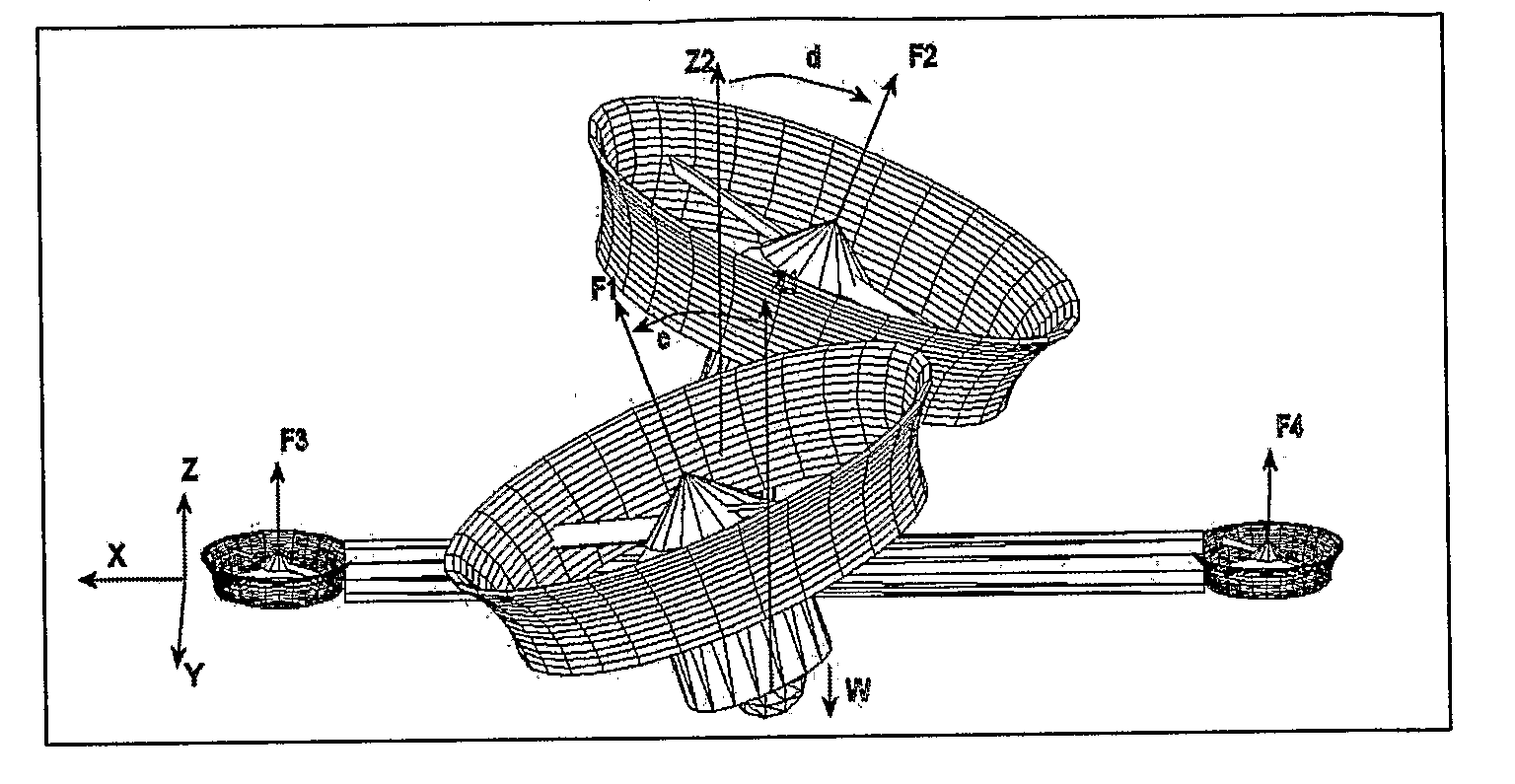
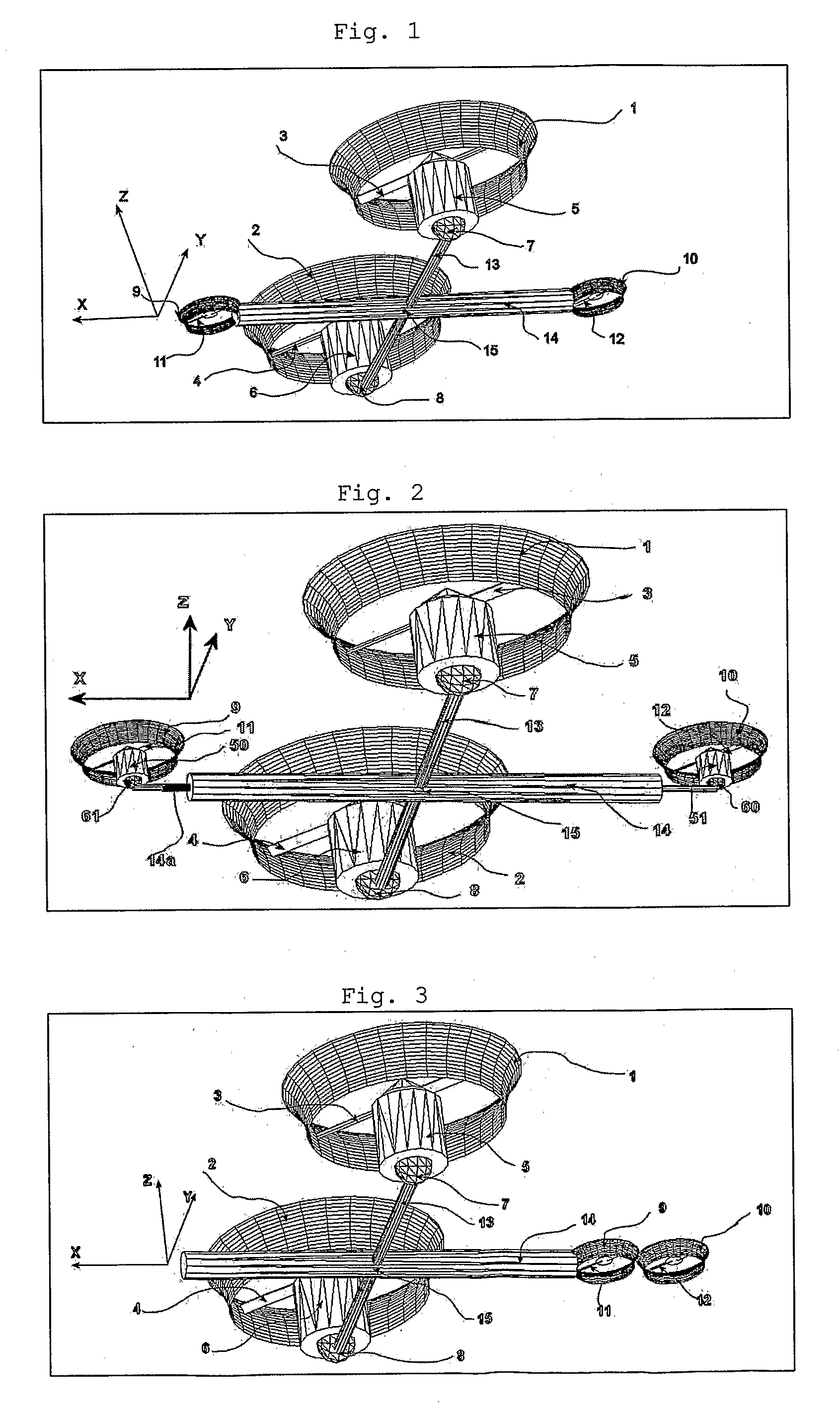
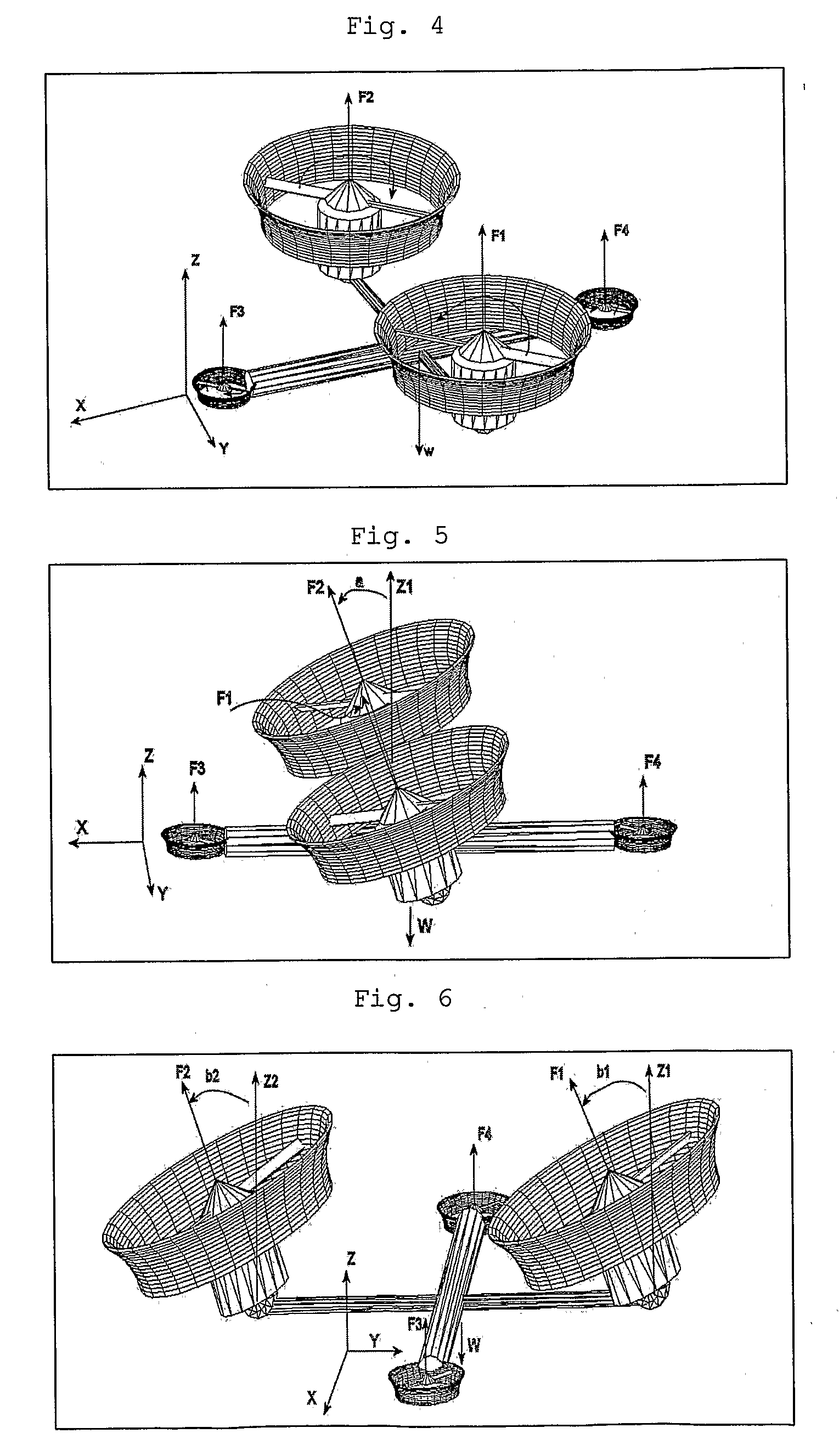
The present invention relates to a propulsion system of a vertical takeoff and landing aircraft or vehicle moving in any fluid or vacuum and more particularly to a vector control system of the vehicle propulsion thrust allowing an independent displacement with six degrees of freedom, three degrees of translation in relation to its centre of mass and three degrees of rotation in relation to its centre of mass. The aircraft displacement ability using the propulsion system of the present invention depends on two main thrusters or propellers and which can be tilted around pitch is (I) by means of tilting mechanisms and, used to perform a forward or backward movement, can be tilted around roll axis (X) by means of tilting mechanisms and, used to perform lateral movements to the right or to the left and to perform upward or downward movements (Z), the main thrusters being further used to perform rotations around the vehicle yaw axis (Z) and around the roll is (X). The locomotion function also uses one or two auxiliary thrusters or propellers and mainly used to control the rotation around the pitch axis, these thrusters or propellers and being fixed at or near the longitudinal is of the vehicle, with there thrust perpendicular or nearly perpendicular to the roll and pitch axis of the vehicle.
Owner:RAPOSO SEVERINO
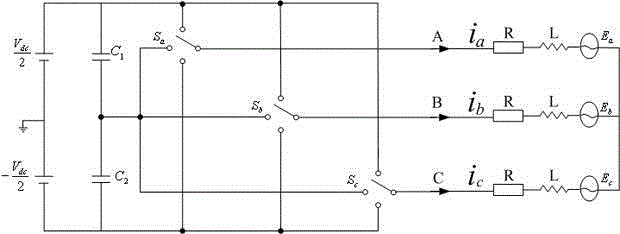
Permanent magnetism synchronous electric machine - compressor system high speed operation control method
InactiveCN101252336AImprove voltage utilizationAC motor controlVector control systemsPhase currentsSynchronous motor
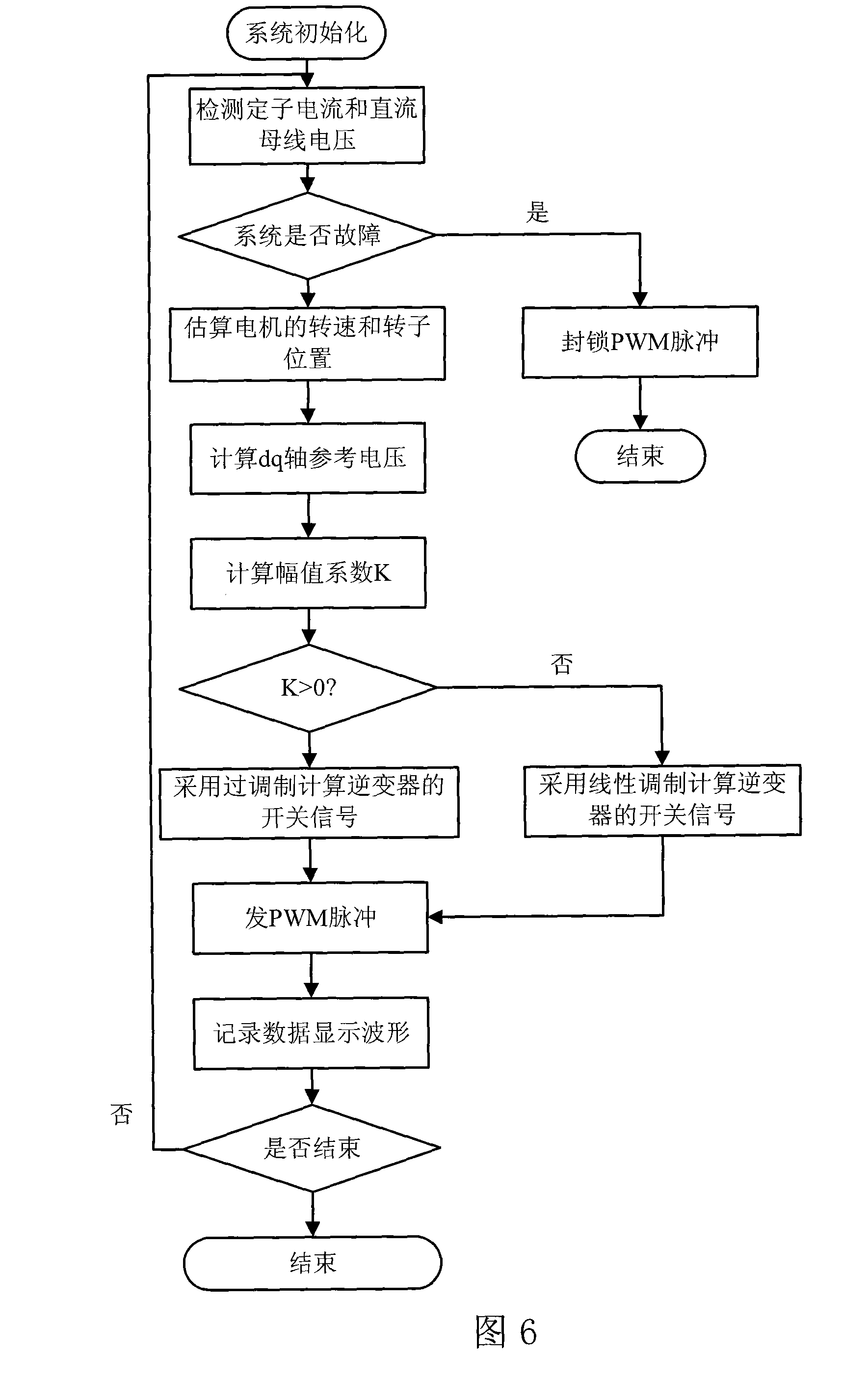
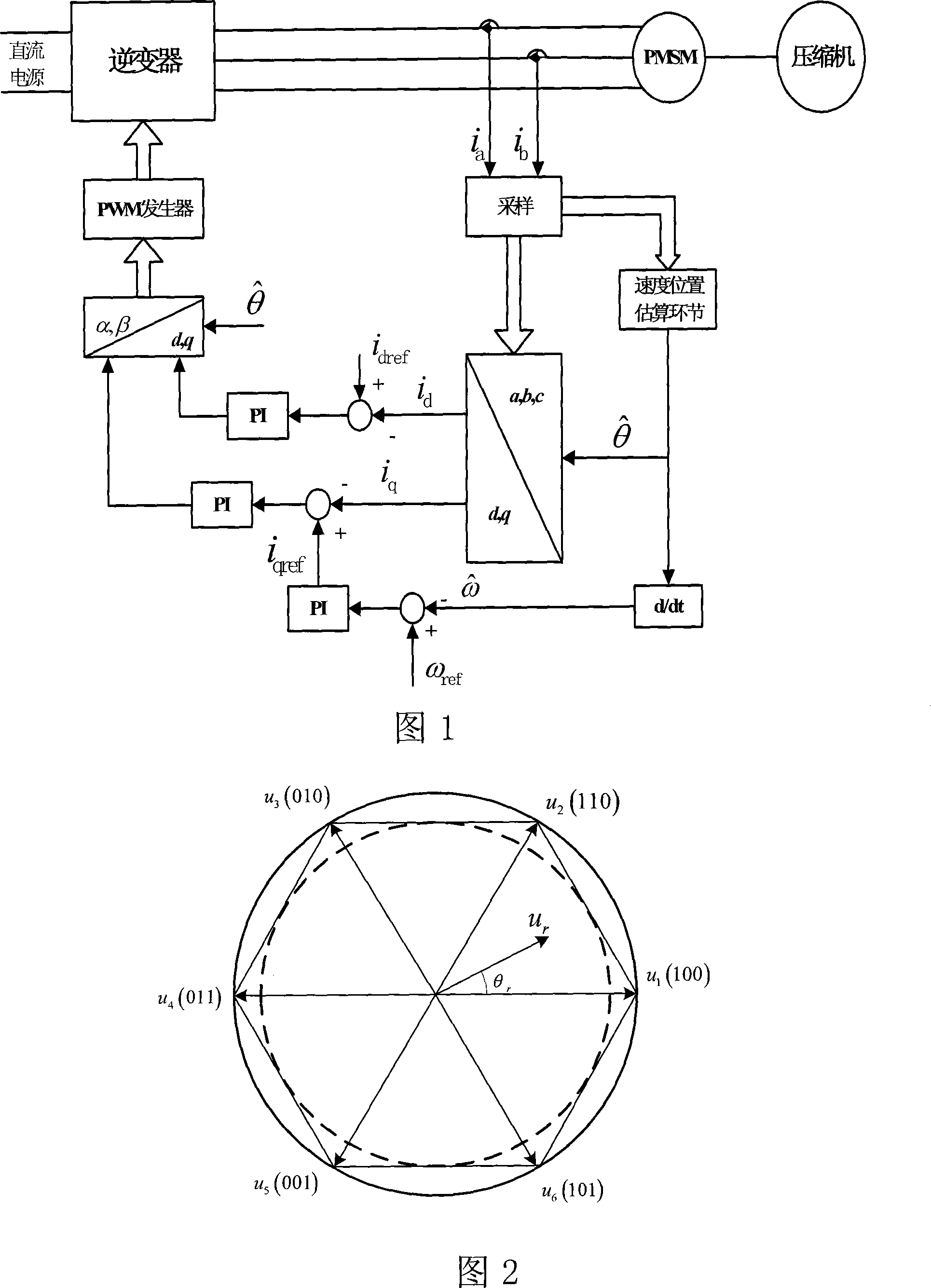
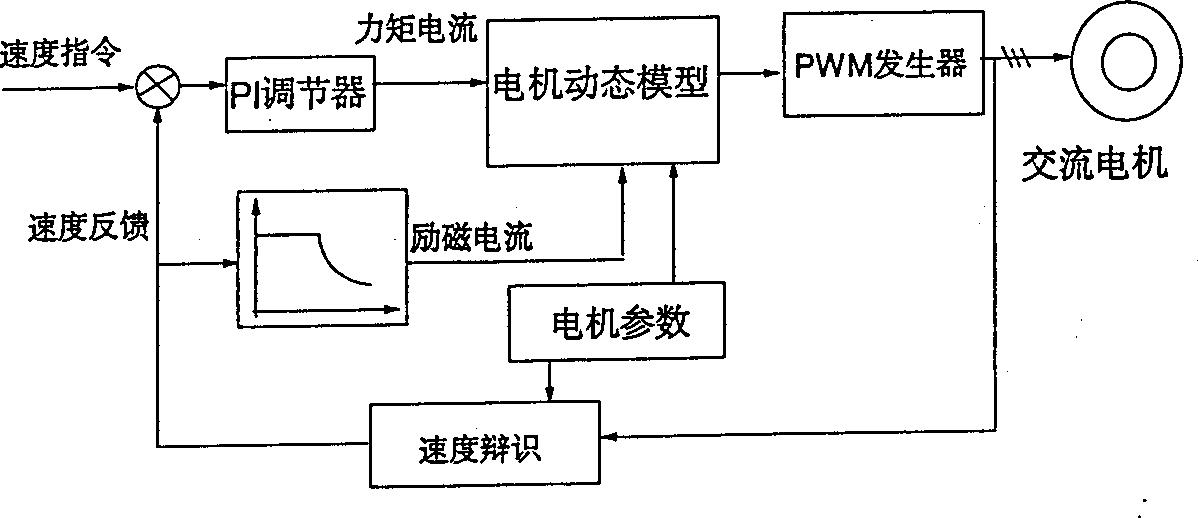
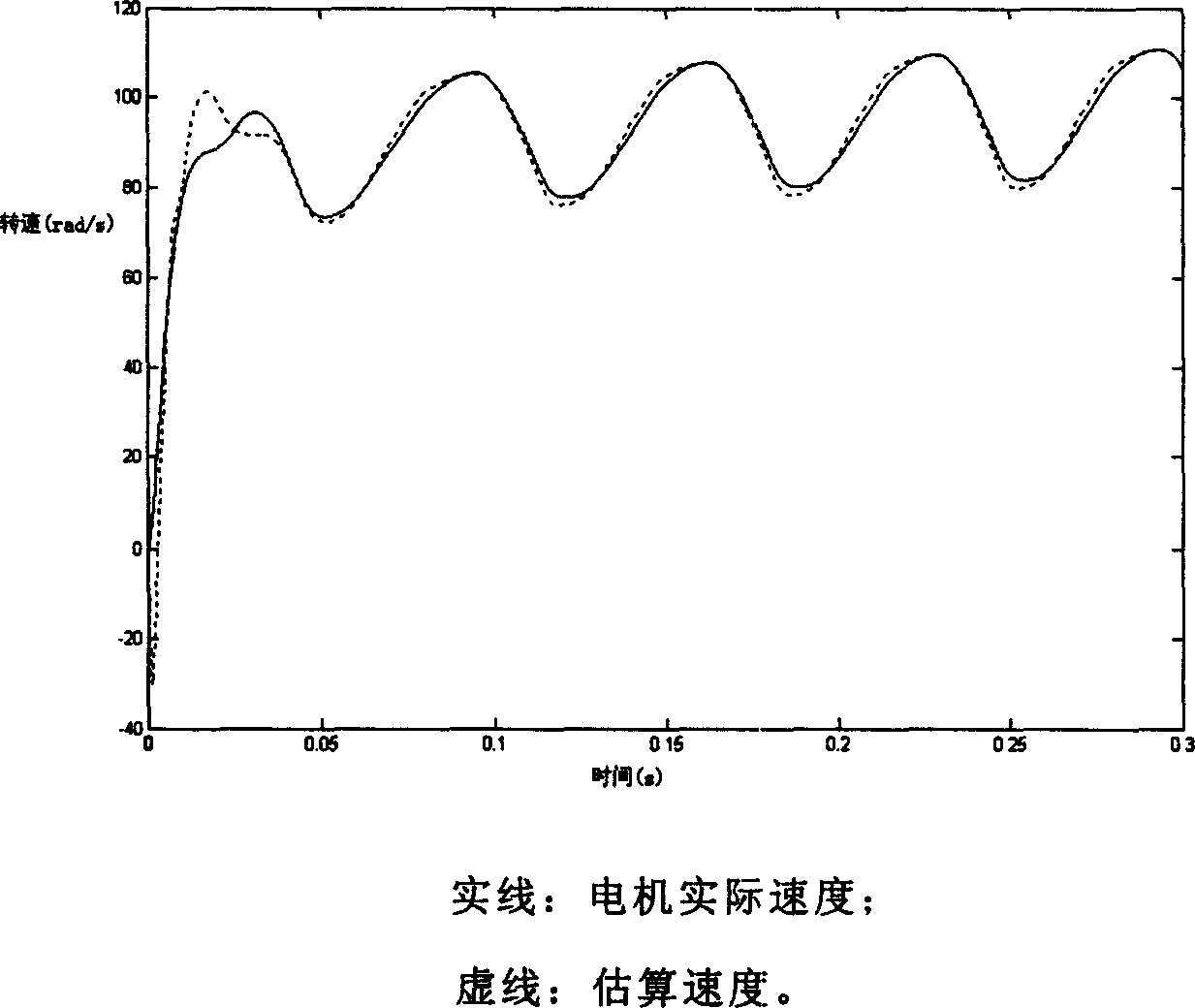
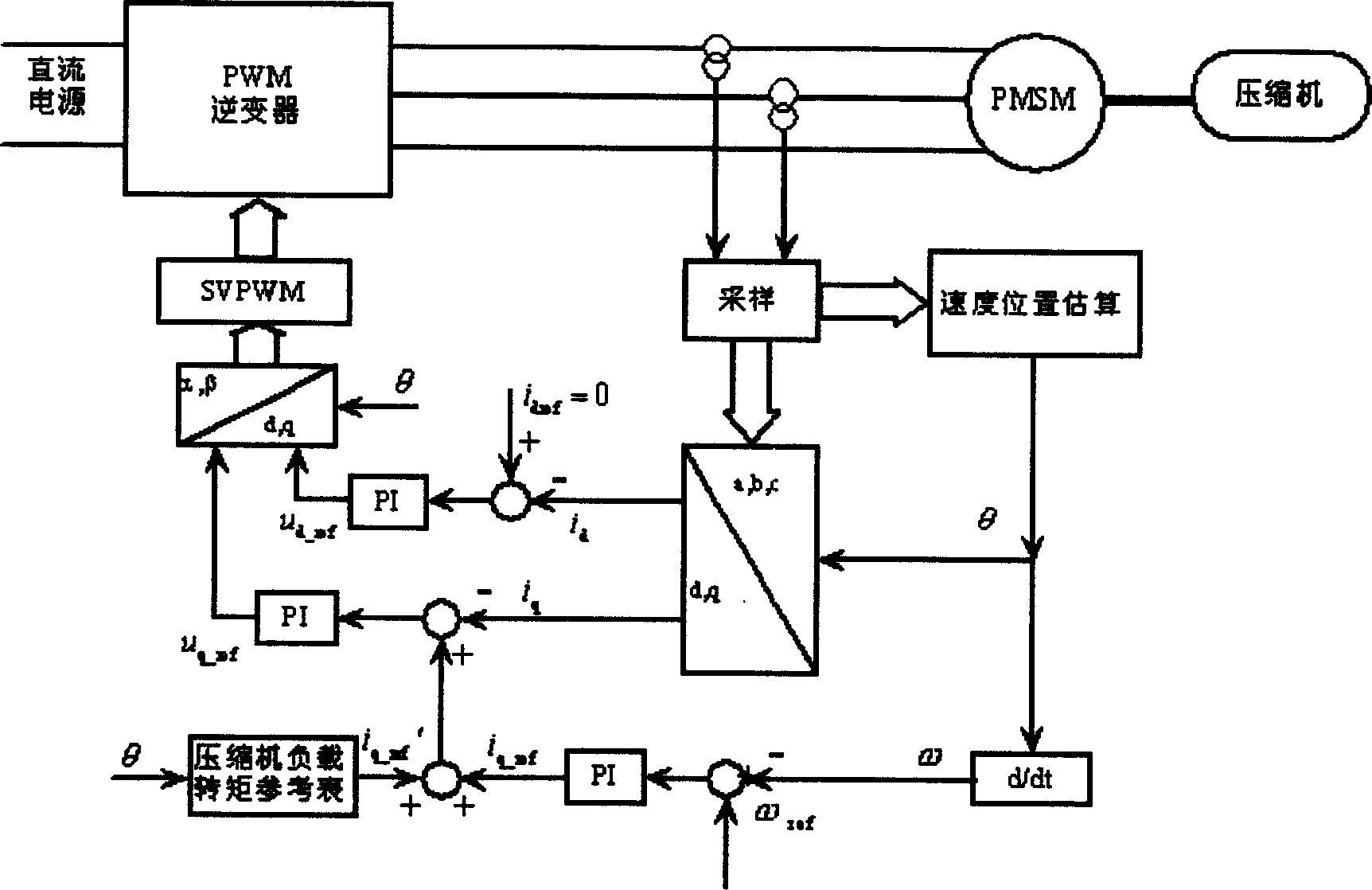
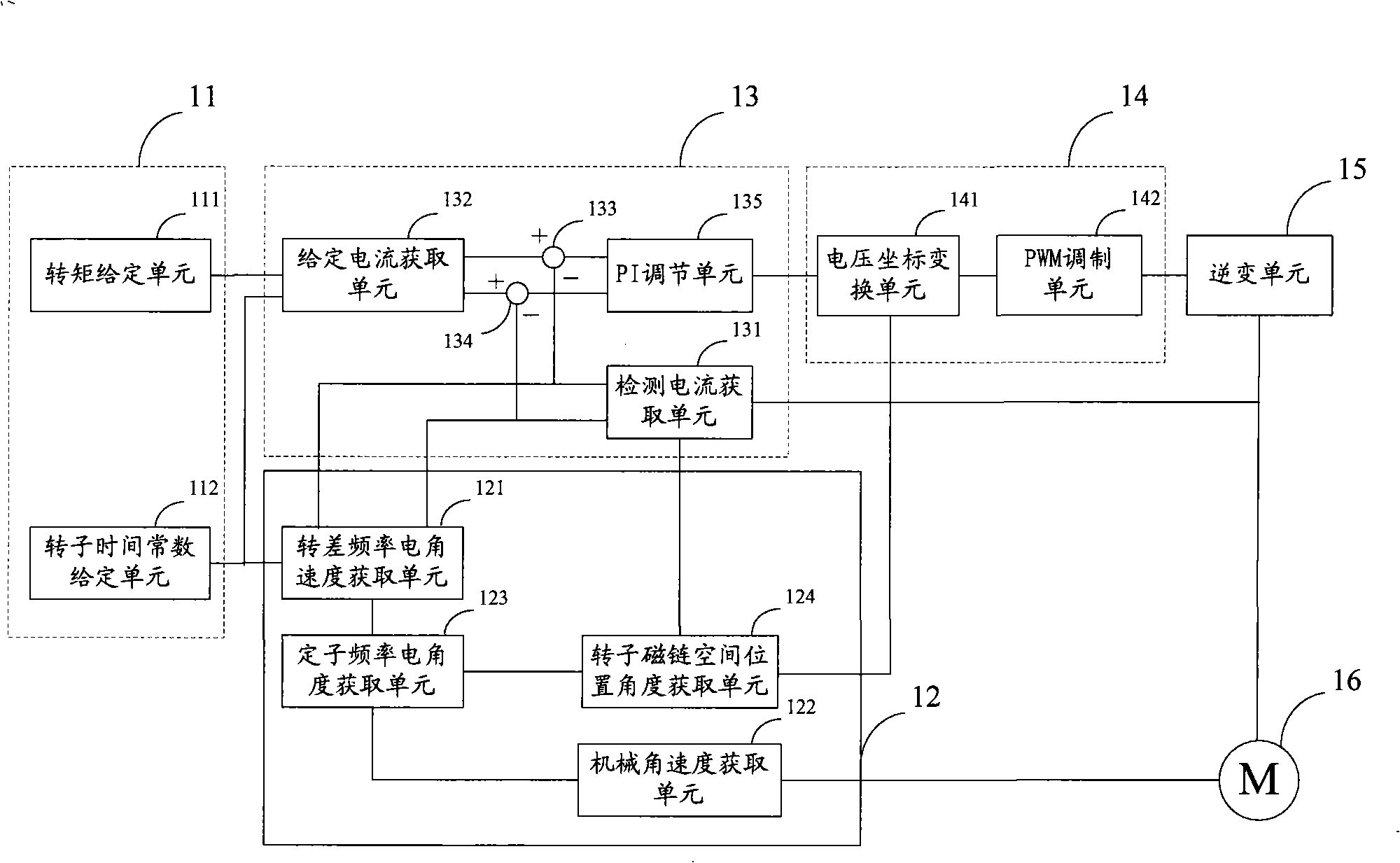
Disclosed is a high-speed control method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor-compressor system, including the following steps: initial design is carried out; a motor is detected through DSP, including detecting the two-phase current of the stator of the motor, the voltage Udc of a DC generatrix; the voltage of a d-p shaft is calculated; faults of overcurrent, overpressure and undervoltage are detected; if any fault exists, the PWM pulse signals are blocked and then the control program is paused; if no fault exists, the following steps will be carried out; the rotating speed of the motor and the position of the rotor are identified in the process of speed-position estimation; the current and the voltage of the reference d-q shaft of the motor are calculated; switching signals of an inverter are acquired through haplotype over-modulation; the data are recorded and waveforms are displayed; judgment of whether to pause the control program is carried out; if not, the second step is carried out again; if yes, the control program will be paused. The control method applies haplotype over-modulation method into the permanent magnet synchronous motor-compressor system, realizing sensorless over-modulation to the synchronous motor-compressor vector control system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Magnetic vector control system
InactiveUS20050251080A1Easy to doEasy constructionJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesBiomechanicsDisease course
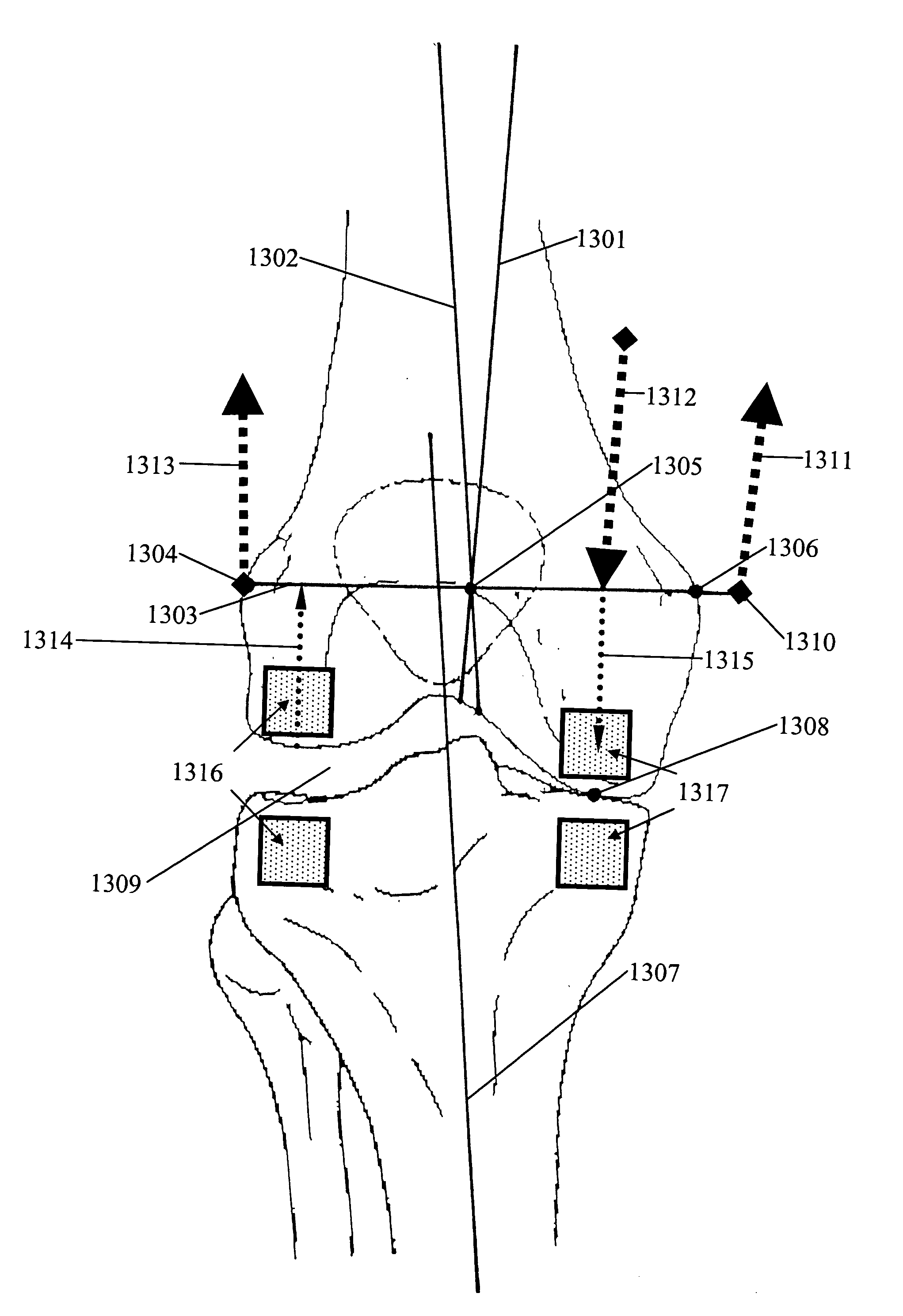
Aging, injury and / or other pathologies of joints, especially weight bearing joints, contribute to changes in natural biomechanics. Deviations from optimal biomechanics lead to acceleration of the natural history of joint pathology and ultimately osteoarthritis. A Magnetic Vector Control System made up of an assembly of magnetic field sources can be disposed at or near a joint typically on or in adjacent bones of the joint, on one side of a first mechanical axis that creates a torque or moment about a second different axis of the joint, that intersects the first mechanical axis, to decrease the joint reactive force at the joint surface or equivalently substantially shift the first mechanical axis to a new or preferred position.
Owner:HYDE EDWARD ROBERT JR
Non-synchronous motor parameter identification method
InactiveCN1354557AHigh precisionImprove stabilityElectronic commutation motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlDead timeSynchronous motor
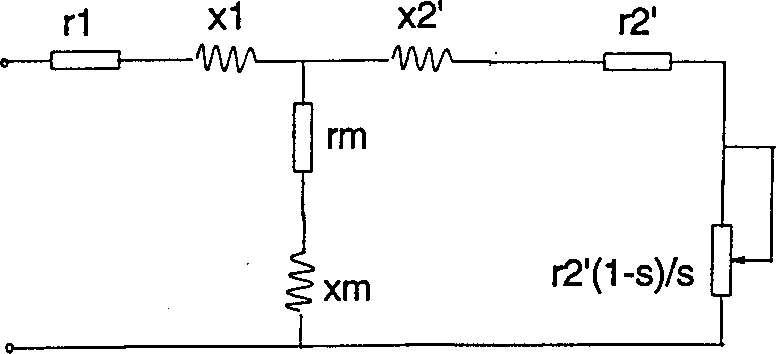
The invention relates to a method for recognizing parameters of asynchronous motor. The stator resistance of motor is measured by a method of DC volt-ampere. The rotor resistances as well as leakage inductance of stator and rotor of motor is obtained by short circuit test. Mutual inductance of stator and rotor of motor can be taken from method of no-load test. Compensating voltage drop in on state, switch time delay and dead time raises the accuracy and stability of recognized parameter. The resistance values of rotor at frequency of rating sliding difference are calculated by method of two points through test of locked rotor at two frequencies. Since skin effect is overcome, the resistance values of rotor are accurate enough so as to meet the requirement of vector control system completely.
Owner:SOMER LEROY ELECTRO TECH FUZHOU CO LTD
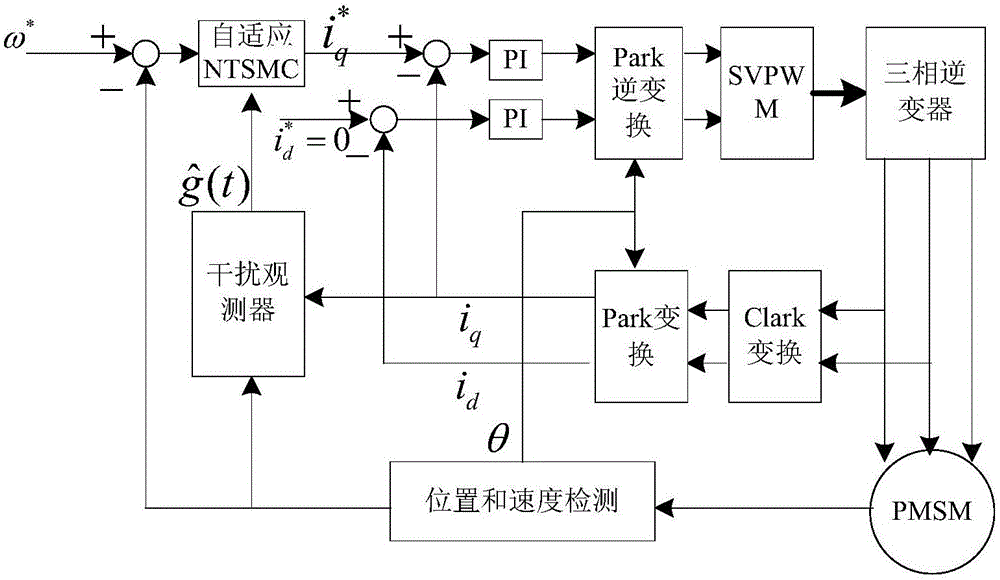
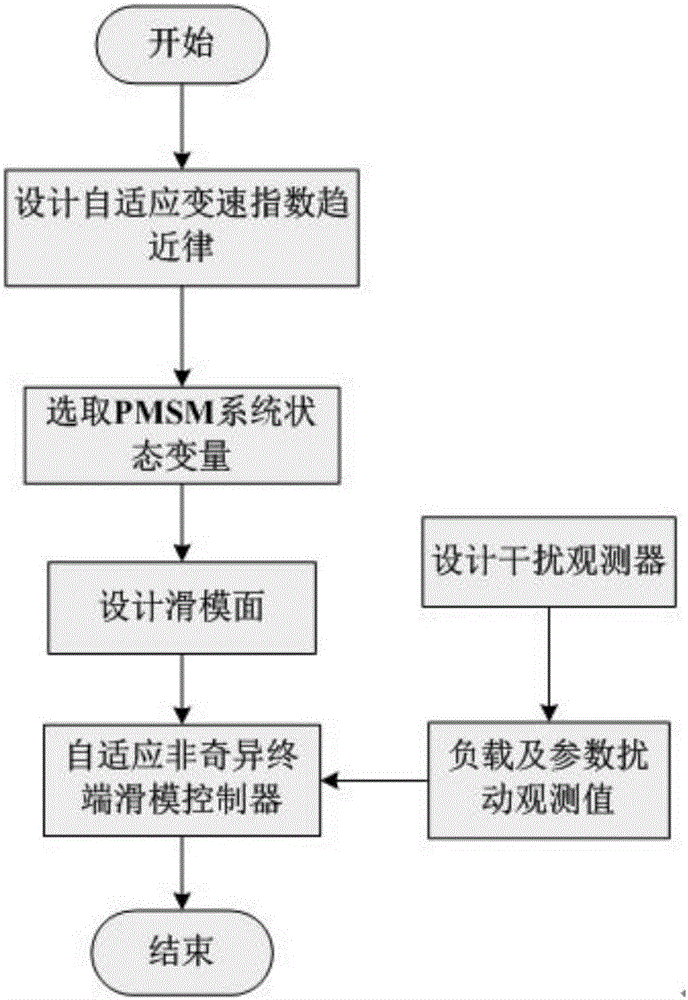
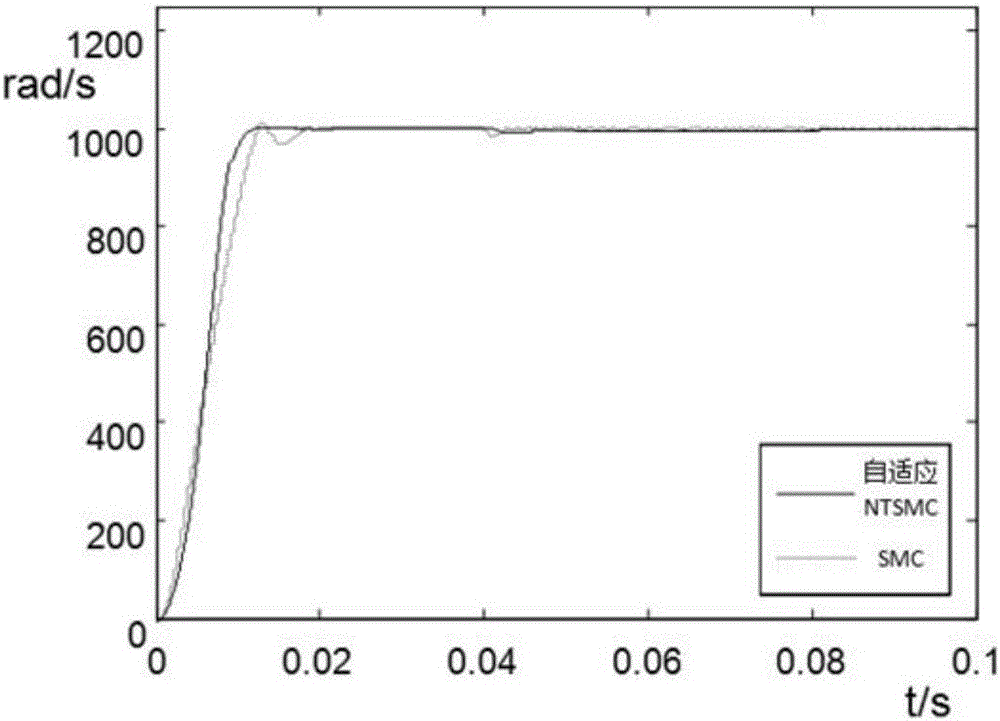
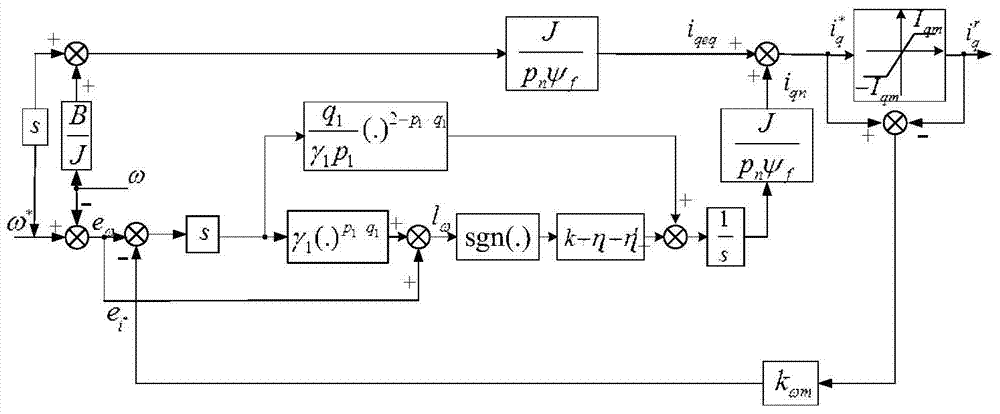
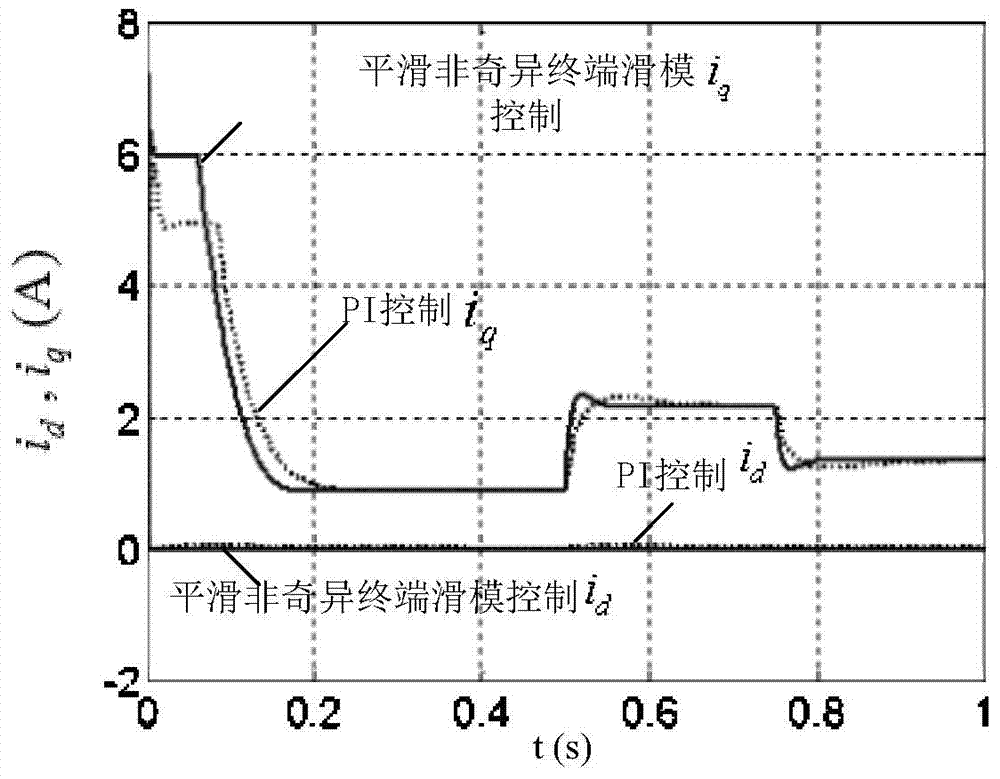
Adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding model control method for permanent magnet synchronous motors on basis of disturbance observers
InactiveCN106788044AImprove global fast convergenceShorten the timeElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl vectorControl system
The invention relates to an adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding model control method for permanent magnet synchronous motors on the basis of disturbance observers. An adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding model controller is introduced into speed loops of vector control systems for the permanent magnet synchronous motors. The adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding model control method is characterized in that an adaptive variable-speed exponential approach law is proposed, first-order norms of state variables are introduced into the approach law, index approach speeds and constant approach speeds are adaptively adjusted according to the distances from the state variables to balance points, accordingly, the approach time can be shortened, and system buffeting can be weakened; the disturbance observers are designed for solving the problems of external disturbance of existing systems and load perturbation, and observation values are fed into designs of the sliding mode controllers. Rotational speeds can be quickly tracked when the systems are disturbed or load fluctuates, accordingly, overshoot and steady-state static difference of the systems can be reduced, and the robustness of the systems can be greatly enhanced.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
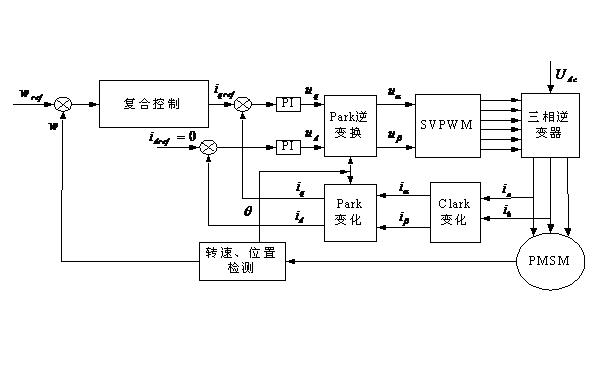
Compound control method based on vector control system of permanent magnet synchronous motor
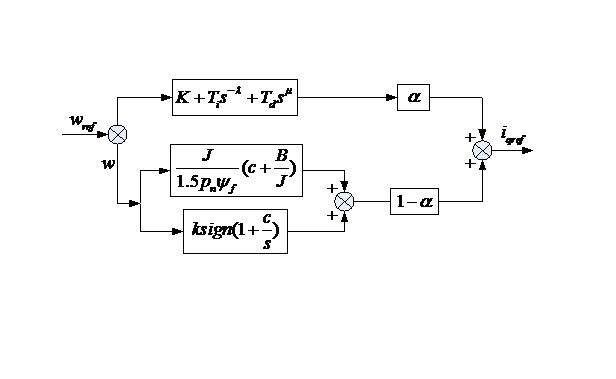
InactiveCN102122916ALarge range of controlImprove control effectElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl systemMathematical model
The invention discloses a compound control method based on a vector control system of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps: converting a three-phase current of the permanent magnet synchronous motor into equivalent currents on a straight shaft and a crossed shaft by utilizing a vector conversion principle; further linearly decoupling the mathematical models of shafts d and q of the permanent magnet synchronous motor by using the method of id=0; and using fractional order PIgammaDmu control and sliding mode variable structure compound control, wherein the fractional order PIgammaDmu control and the sliding mode variable structure compound control can be used for performing joint cross-feedback control on the speed ring through a variable weighting factor alpha. The compound control method based on a vector control system of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, provided by the invention, has the advantages of both the fractional order PIgammaDmu control and the sliding mode variable structure compound control during the control of the speed ring, and the favorable factors are maximized while the unfavorable factors are minimized. Compared with the traditional PID (proportional-integral derivative) control, the fractional order PIgammaDmu control has a widened control scope, thereby more flexibly matching the sliding mode variable structure to realize the compound control to the permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Owner:SUZHOU BINGLI ELECTRIC VEHICLE TECH
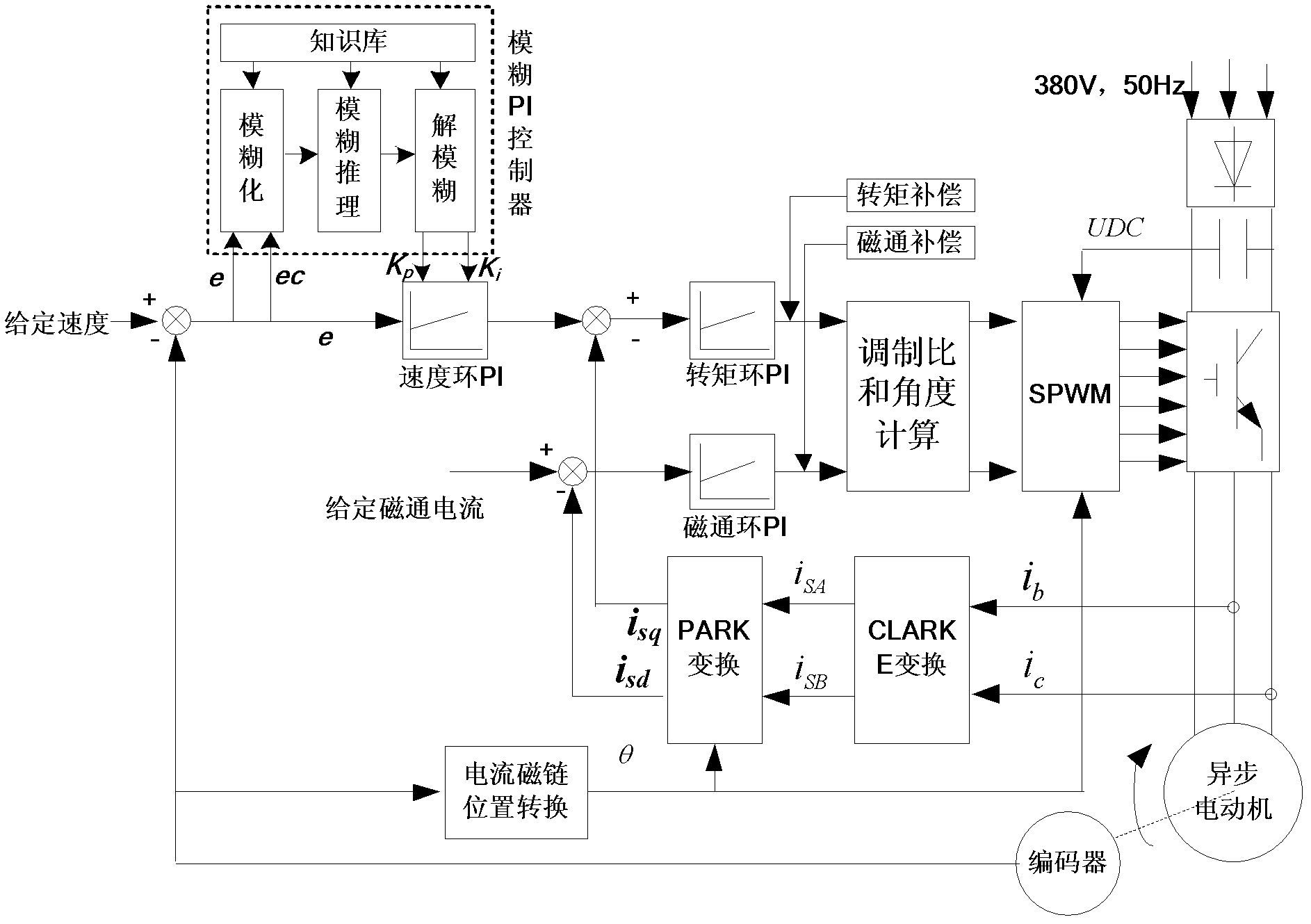
PI (Proportional Integral) parameter mixed setting method
ActiveCN102426417AVerify validityImprove dynamic performanceControllers with particular characteristicsControl vectorMathematical model
The invention relates to a PI (Proportional Integral) parameter mixed setting method, which is a model-based mixed setting method combining off-line setting and fuzzy PI on-line setting for ensuring that a closed loop vector control system works in an optimal state. The PI parameter mixed setting method comprises the following steps of: firstly deducing a mathematic model of a system according toa vector control principle, calculating rotational inertia by a method of constant torque start and machine free stop, and calculating PI parameters and inner ring compensation dosage according to the mathematic model; proposing a new PI control rule table by a fuzzy PI controller; and finally verifying the exactness of the PI parameters by a comparison test. According to the PI parameter mixed setting method disclosed by the invention, the dynamic property and the steady state precision of the system are improved and are better than those of a system utilizing a single setting method, and the validity of the method is verified.
Owner:WISDRI WUHAN AUTOMATION
Zero-sequence current suppression method of open type permanent magnet synchronous motor with double-inverter power supply
ActiveCN104242775ALow costEnhanced inhibitory effectElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlLoop controlControl system
The invention provides a zero-sequence current suppression method of open type permanent magnet synchronous motor with double-inverter power supply, belongs to the technical field of motor control, and aims at solving the problem of zero-sequence current of the open type permanent magnet synchronous motor with the double-inverter power supply. The method is characterized in that the closed loop control for zero-sequence current i0=0 is added on the basis of a vector control system, so as to realize the suppression of the zero-sequence current; the zero-sequence current is calculated by detecting the three-phase current of the motor and is treated as the feedback quantity to build the closed loop control of the zero-sequence current; the output of a zero-sequence current ring is specified by zero-sequence voltage, and the zero-sequence current is suppressed by adjusting the zero-sequence voltage produced by the double inverters. The method is applied to the suppression of the zero-sequence current in the open type permanent magnet synchronous motor with double-inverter power supply.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Sliding-mode control method of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on reaching law and disturbance observation compensation
ActiveCN109450320AEliminate chatterImprove anti-interference abilityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl systemPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention provides a sliding-mode control method of a permanent magnet synchronous motor based on reaching law and disturbance observation compensation. A new reaching law algorithm is designed, and applicable in design of a speed controller in a sliding-mode variable structure; simultaneously, a saturation function is used in a disturbance observer control law, and used for improving a disturbance observer; a value observed by the disturbance observer is compensated in the speed controller; and therefore, a new control strategy is formed. The new control method is applicable in a vector control system of the permanent magnet synchronous motor; a current-speed double-closed-ring control structure is adopted; for buffeting and anti-interference problems in the sliding-mode control, an integral sliding-mode surface and a new reaching law are added based on the conventional sliding-mode speed controller; simultaneously, the disturbance observer is added; disturbance due to load changeis effectively inhibited; the responsiveness of the system is improved; buffeting of the system is reduced; and the anti-interference performance and the robustness of the system in a complex environment are obviously improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
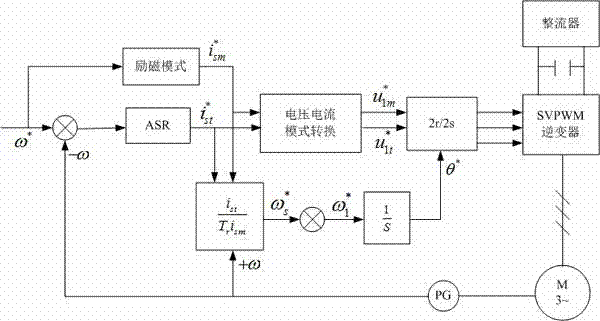
Method or controlling permanent magnet synchronous motor-air conditioner compressor system without speed sensor
InactiveCN1588793AOvercoming system stabilityOvercome system speedTorque ripple controlVector control systemsControl vectorControl system
This invention relates to nonvelocity sensor permanent-magnet synchro-motor-air conditioning compressor system. It is characterized by that nonvelocity sensor vector control is used for permanent-magnet synchromotor, so, overcoming the shortcoming of the large rotating speed pulsation. At the same time, the torque command current composite control method is used to make further lowering rotating speed pulsation of the motor. It overcomes the problem of unsatability of the system during the procedure of regulating PI regulator parameter in traditional vector control system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fuzzy fusion identification method of rotating speed of sensorless motor
InactiveCN101938246AEffective controlSmall fluctuationElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsComputer scienceVector control system
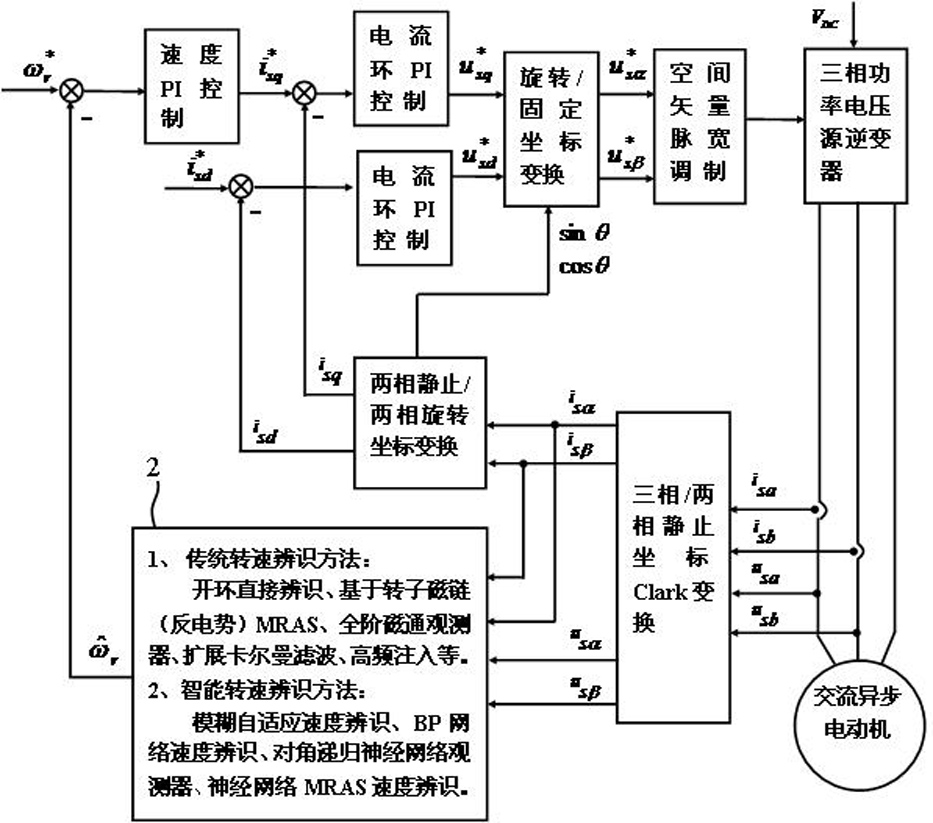
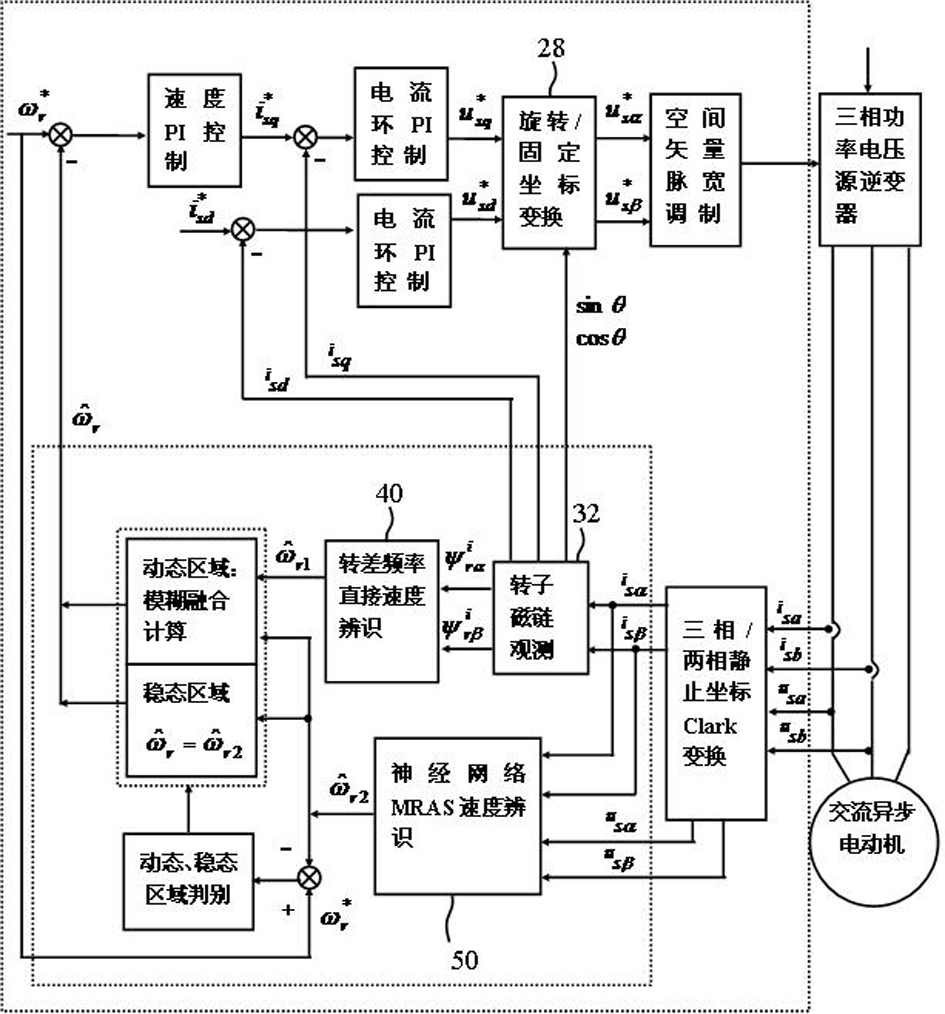
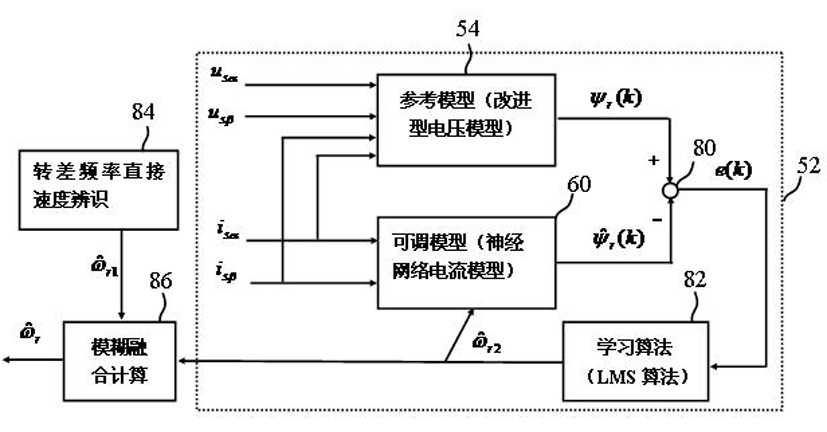
The invention discloses a fuzzy fusion identification method of rotating speed of a sensorless motor, comprising the following steps: identifying the rotating speed of the motor through neural network MRAS speed identification method and direct speed identification method of rotating difference frequency; fusing the neural network MRAS speed identification method and the direct speed identification method of rotating difference frequency through fuzzy fusion method so as to obtain the confirmation value of rotating speed of the motor. The invention has the following advantages that: the two technical indexes of dynamic and static performance of the motor are optimized; the method has quick speed identification, strong dynamic tracking performance, high speed identification precision and strong robustness during the starting and state switching processes of the motor; and the method realizes intelligent crossing comprehensive on-line speed identification of the vector control system of the sensorless motor to obtain optimal speed identification effect so as to effectively control the motor.
Owner:CHONGQING JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Permanent magnet synchronous motor control method
InactiveCN102969968AReduce buffetingHigh control precisionElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl systemPermanent magnet synchronous motor
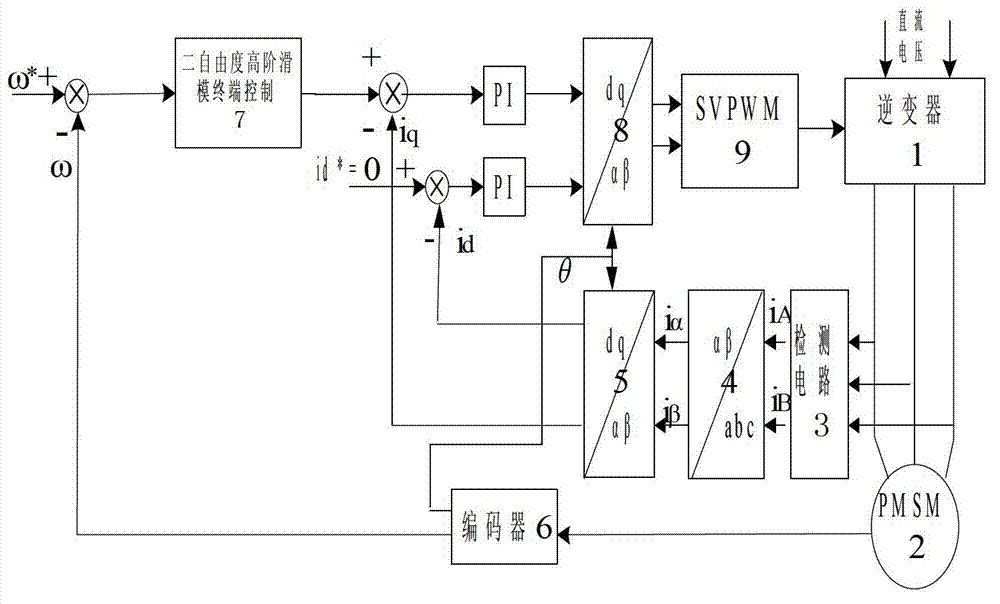
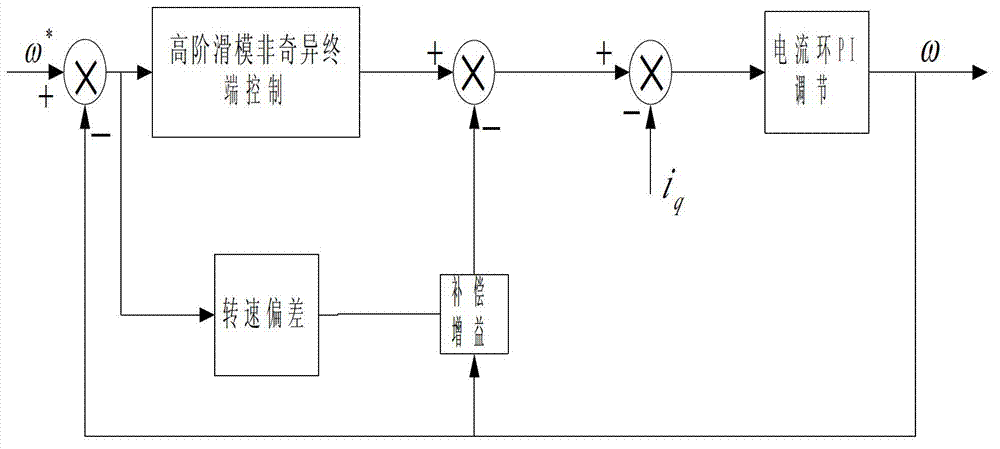
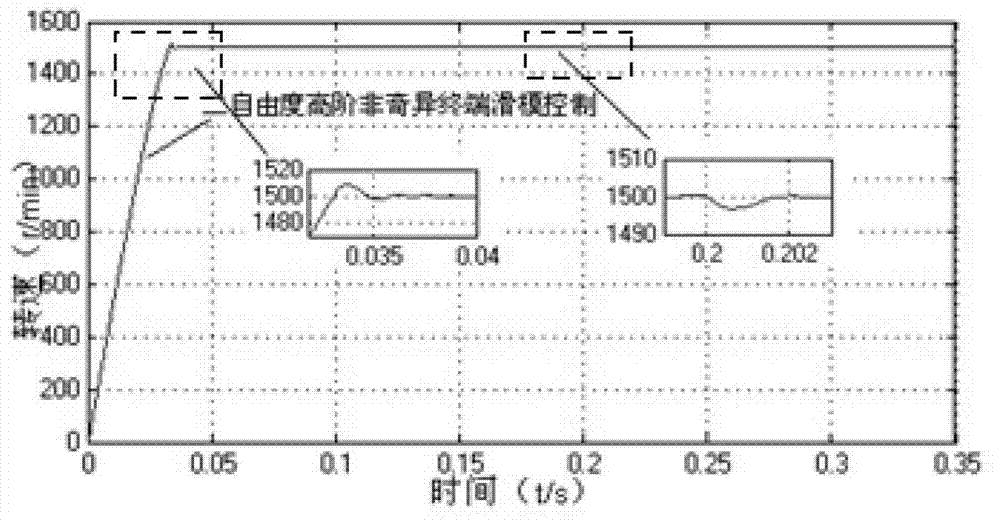
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor control method in which a vector control system is used. The vector control system comprises an outer speed ring and an inner current ring, and a PI (proportional-integral) controller of a rotating speed ring is replaced with a two-DOF (degree of freedom) higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller; the input of the two-DOF higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller is the difference between the given rotating speed w* of a motor and the actual feedback rotating speed w* of the motor; the error between the given rotating speed and the feedback rotating speed is judged, when the error of the rotating speed is less than Xi, an output exciting current iq* is calculated by a simple higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller; when the error of the rotating speed is greater than Xi, the output of the two-DOF higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller is an output iq* controlled by a higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode and the sum of the output and compensation gain of the higher-order nonsingular terminal sliding mode; and the size of Xi can be set according to actual situations and needs. According to the method, the system control accuracy is improved and the rapid convergence of the rotating speed of the motor is realized; and the method has strong robustness on load disturbances.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
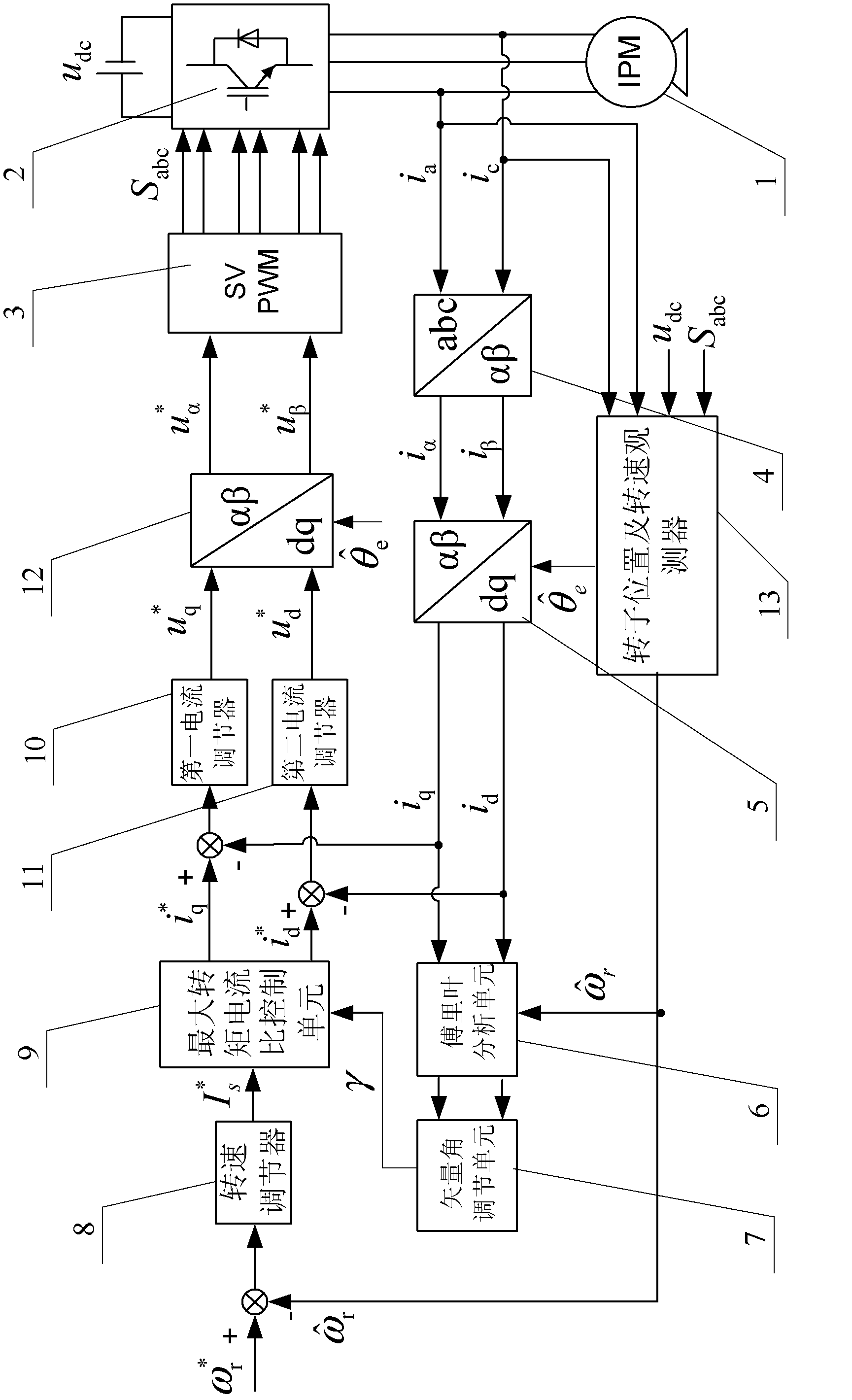
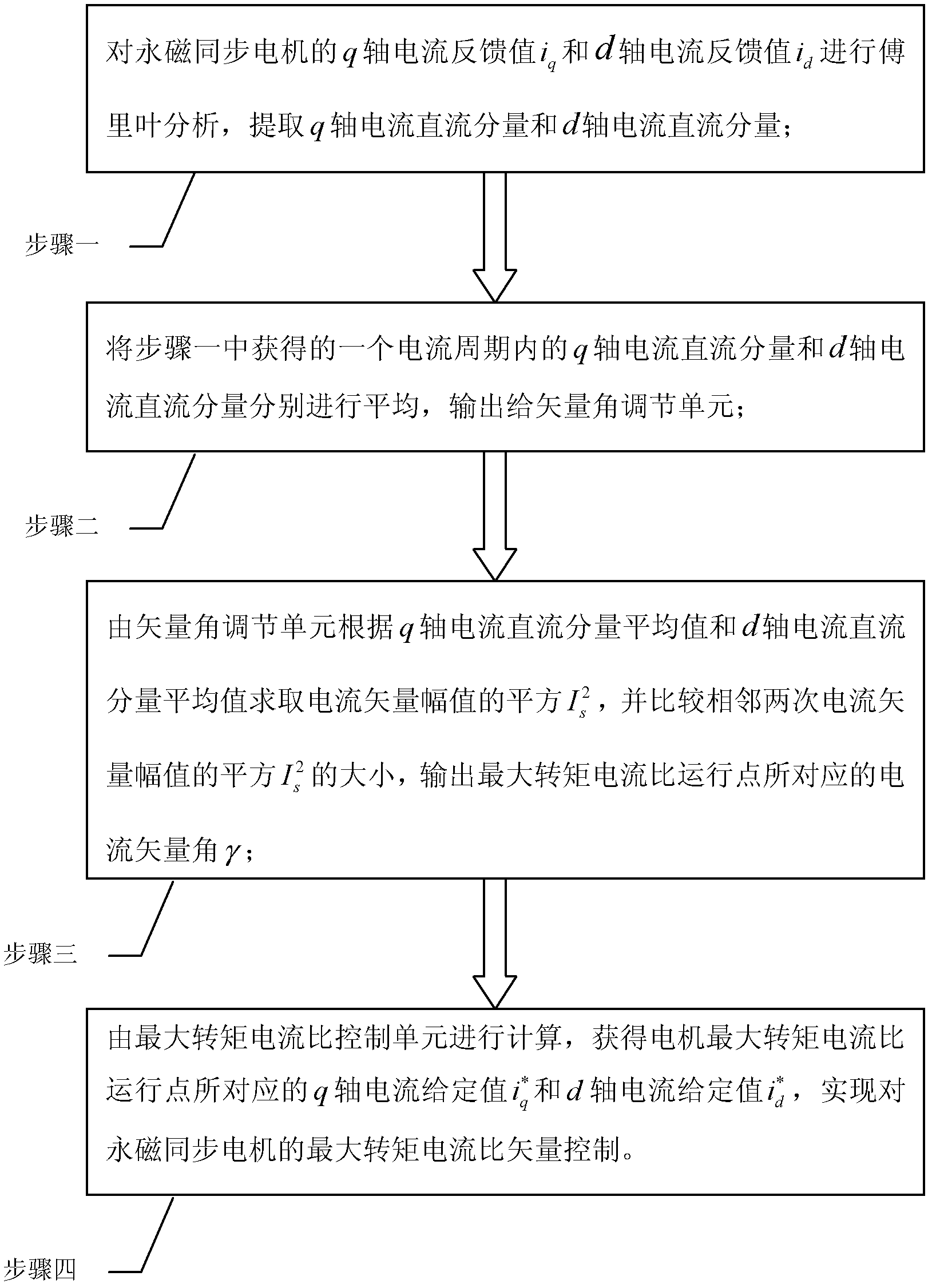
Maximum torque per ampere vector control system and control method for position sensor-free internal permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN102594250AImprove overload capacityImprove power densityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsOperating pointAmpere
The invention discloses a control method of a maximum torque per ampere vector control system for a position sensor-free internal permanent magnet synchronous motor, and belongs to the field of motor control. The problems of complexity of a computing method and low accuracy of an obtained current set value in the conventional maximum torque per ampere control strategy are solved. The control system comprises a permanent magnet synchronous motor, an inverter, a space vector pulse width modulation unit, a three-phase-two-phase coordinate conversion unit, a static-rotational coordinate conversion unit, a Fourier analysis unit, a vector angle regulation unit, a rotating speed regulator, a maximum torque per ampere control unit, a first current regulator, a second current regulator, a rotational-static coordinate conversion unit and a rotor position and rotating speed observer. According to the control method, the magnitude of current amplitude is automatically regulated and compared on the basis of a current vector angle gamma, and an operating point with maximum torque per ampere is automatically searched. The system and the method are applied to maximum torque per ampere vector control over the motor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
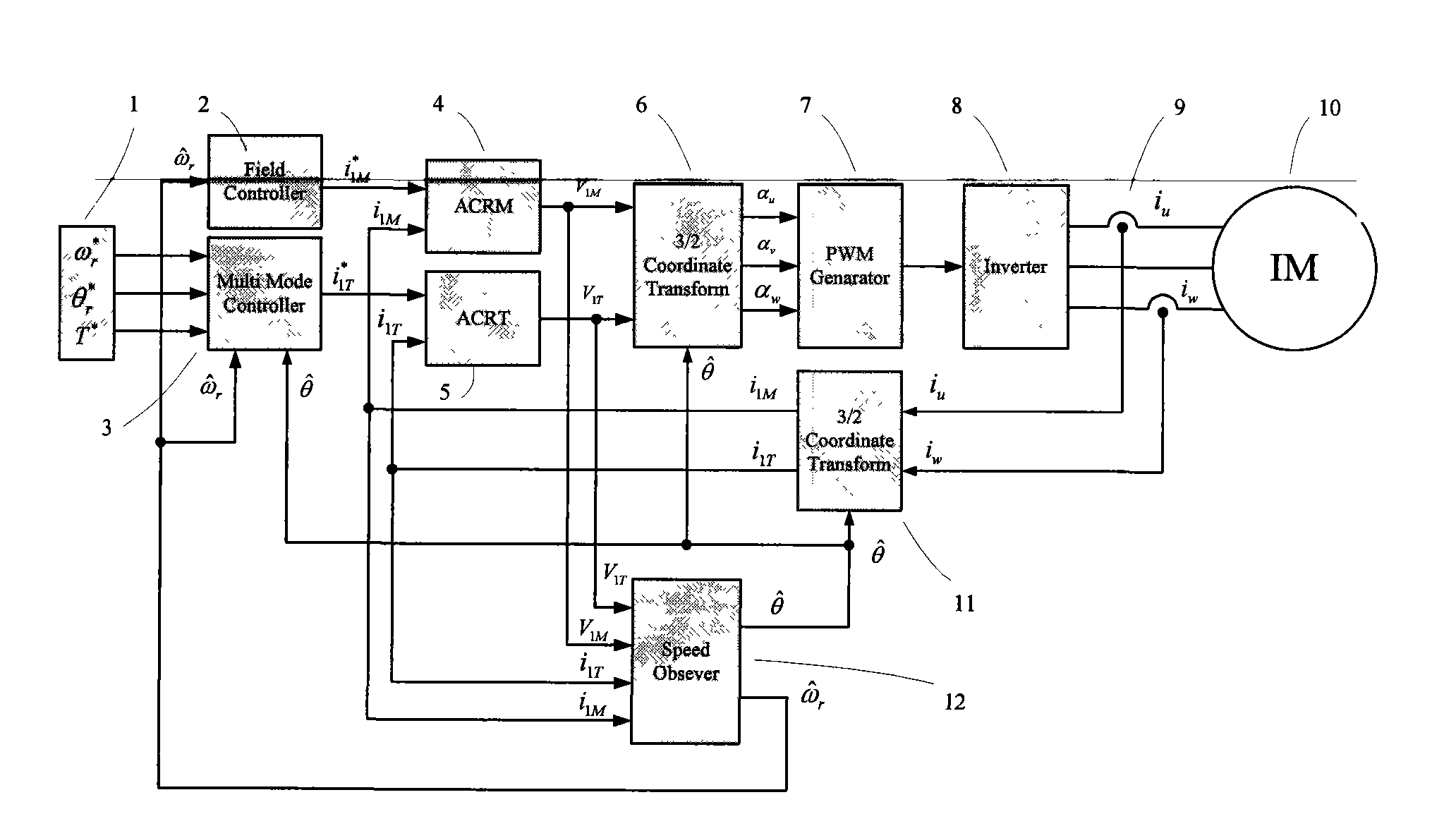
Conjecture method of stator magnetic linkage oriented AC motor rotation velocity and rotor position
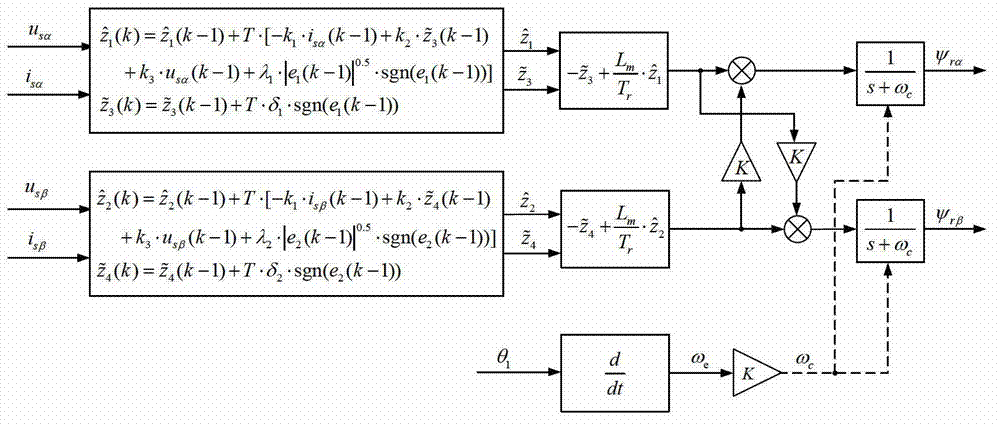
ActiveCN101247104ARealize vector controlChange insensitiveElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsAngular velocityVoltage reference
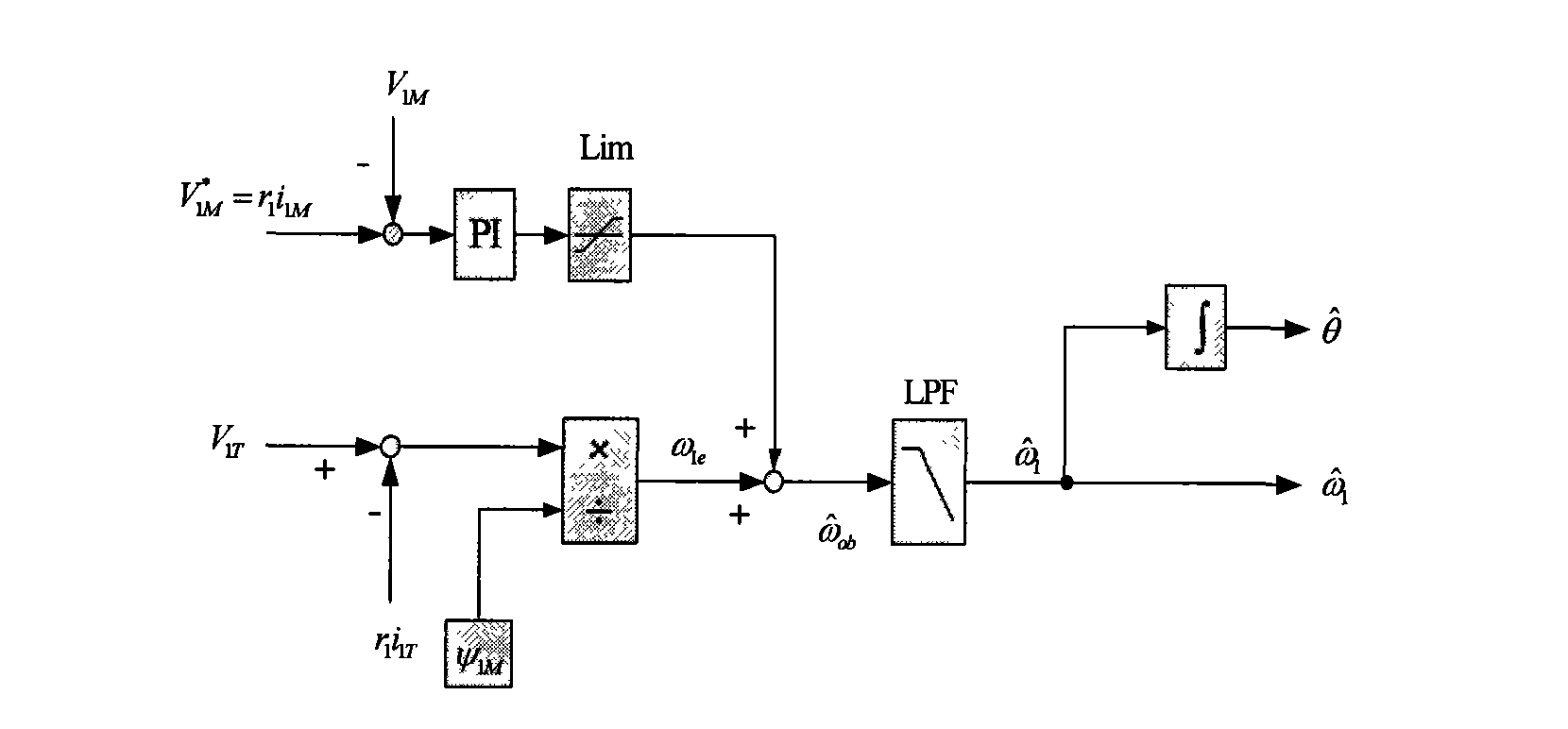
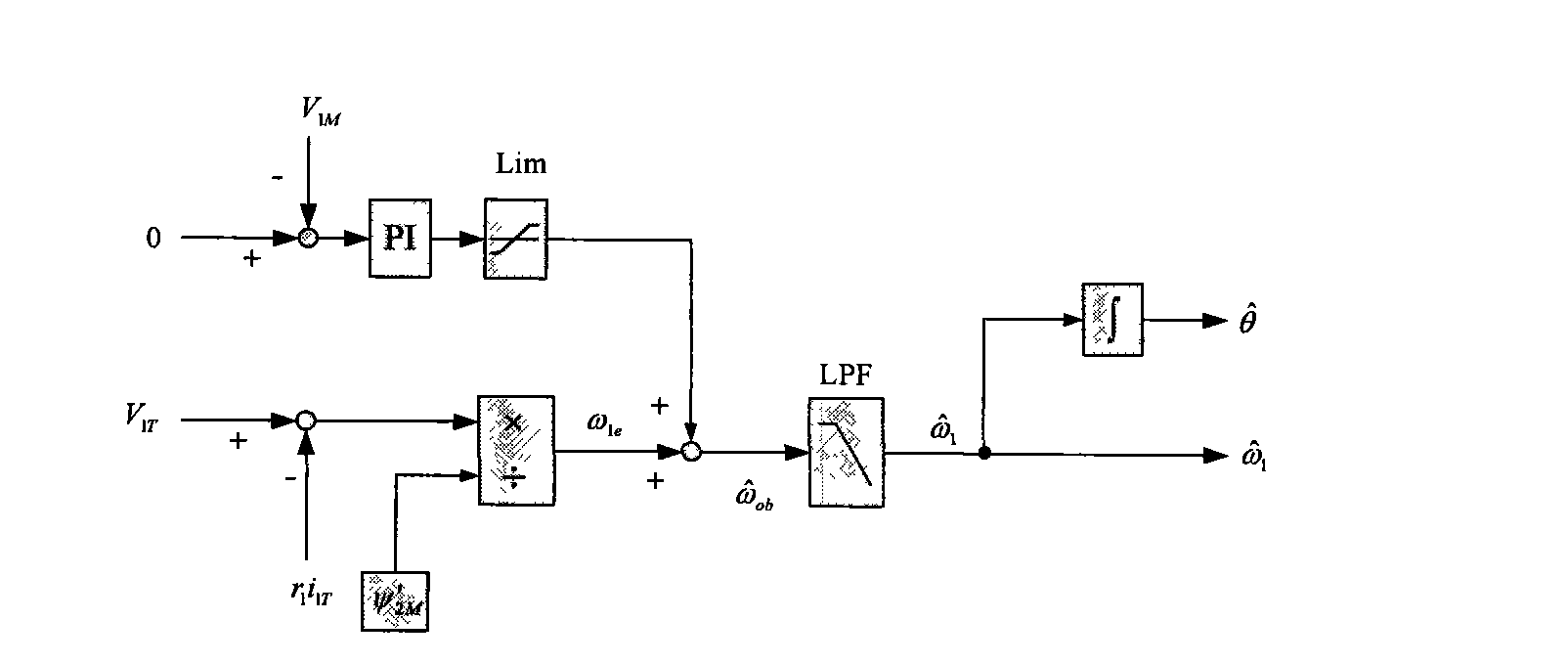
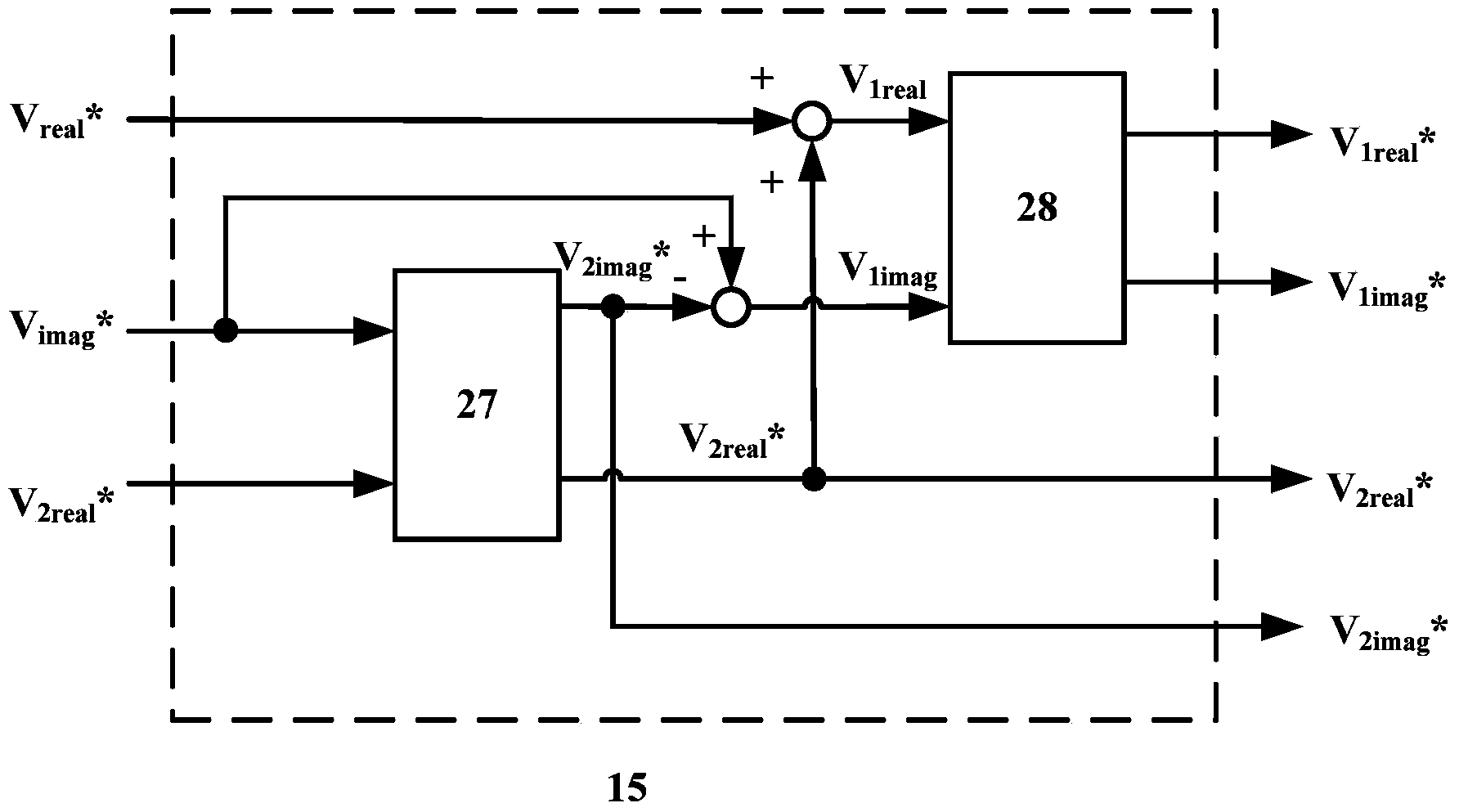
The target of the invention is an asynchronous machine stator magnetic linkage flux-oriented vector control system. The torque voltage V1T outputted by the torque current control loop is used for calculating out the basic estimated value omega1e of the rotating angular velocity of the stator magnetic linkage. At the same time when the excitation voltage reference value V1M<*> is calculated out the adjusting angular velocity delta omega is obtained by calculating the comparison of proportional integral of the error between V1M<*> and the output excitation voltage V1M. The estimated value omega1 of the rotating angular velocity of the stator magnetic linkage can be obtained by adding the delta omega with the omega1e, and at the same time the estimated value theta of the phase angle of the rotational coordinate system of the electric motor MT can be obtained after executing integral operation to the omega1. Finally by real-time dynamically calculating and adjusting the magnitude of the angular velocity delta omega with a high speed the control system obtains the purpose that the MT rotational coordinate system is kept with a synchronous state to the actual rotary speed of the controlled objective magnetic linkage of the alternating current rotating electric machine and the phases are always kept consistent, thereby realizing the vector controlling of the no-velocity position sensor of the asynchronous machine.
Owner:JIANGSU REYA ELECTRIC
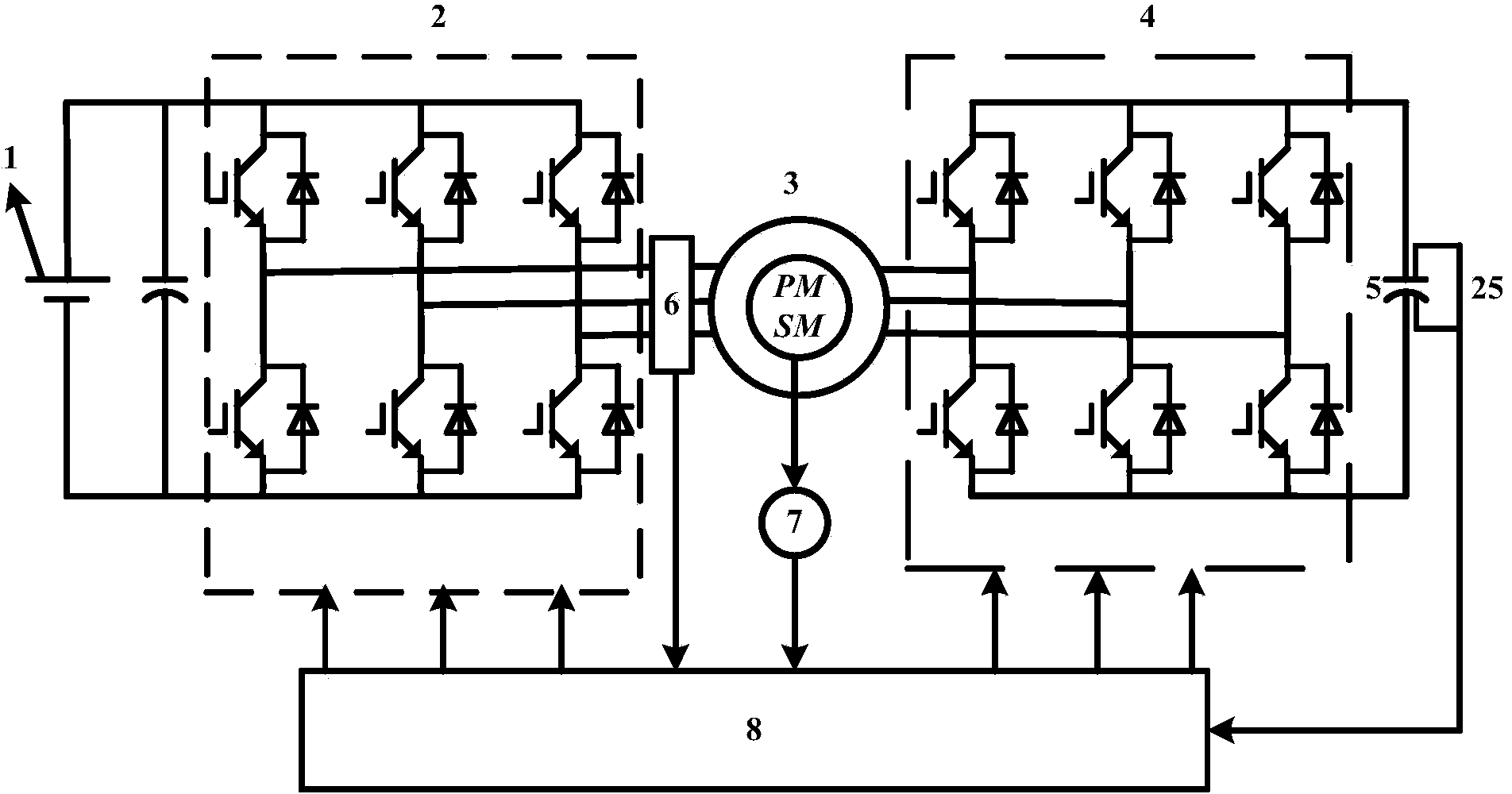
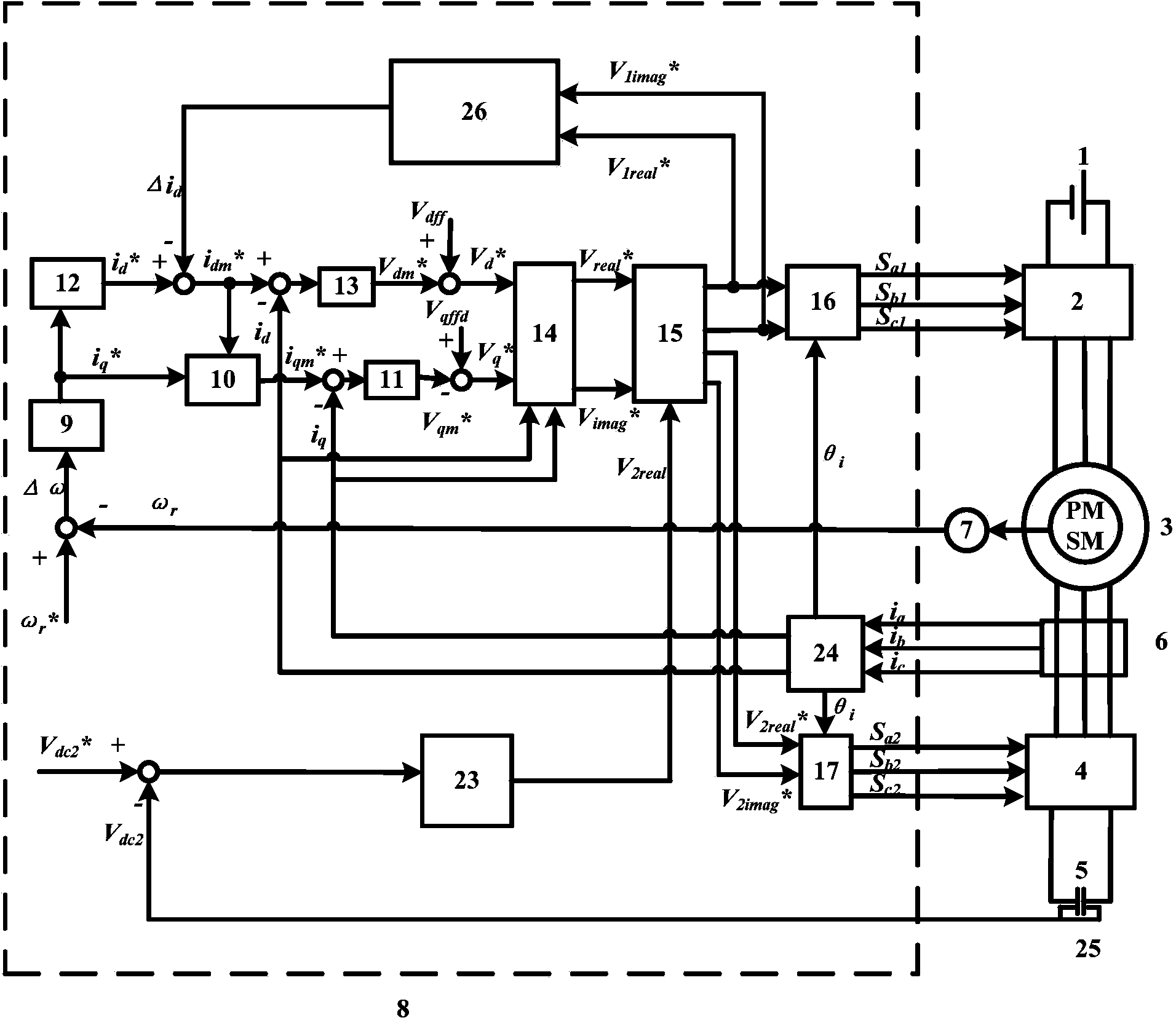
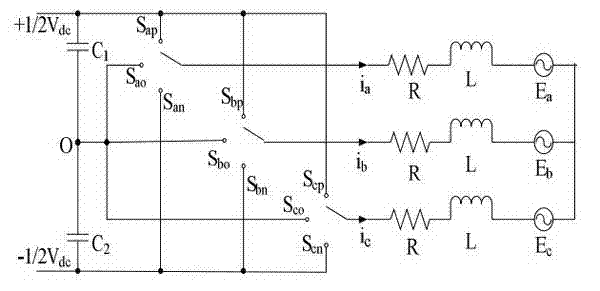
Open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor series compensation vector control system and control method
ActiveCN103780191AExtended Field Weakening Control AreaImprove performanceElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsCapacitancePower factor
The invention discloses an open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor series compensation vector control system which is composed of a direct-current power source, a main converter powered by the direct-current power source, an open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor, a compensation converter powered by a power supply capacitor, voltage sensors arranged at the two ends of the power supply capacitor, a current sensor arranged on the stator side of the open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor, a speed sensor arranged on a rotation shaft of the open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor, and a controller controlling the main converter and the compensation converter. According to the open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor series compensation vector control system, the compensation converter which is arranged at the stator tail end of the open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor and powered by the power supply capacitor is controlled to equivalently change stator winding impedance, so that the power factor of the main converter approaches to or reaches 1; through cooperation control over the main converter and the compensation converter, distribution of active power and reactive power is changed, performance of the motor is improved, a flux weakening control area of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is expanded, and the operation range is widened.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
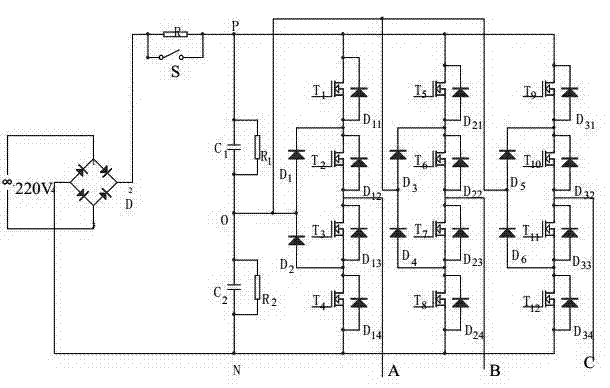
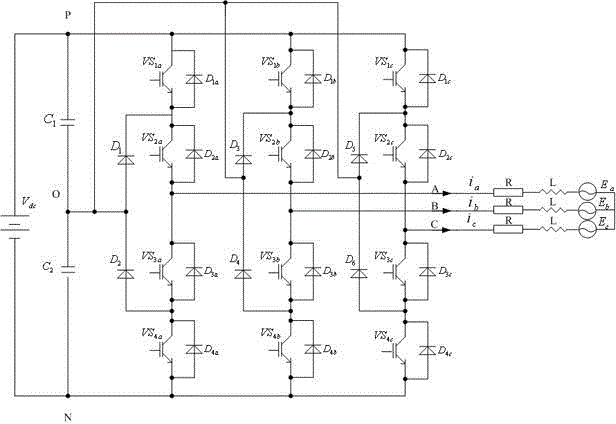
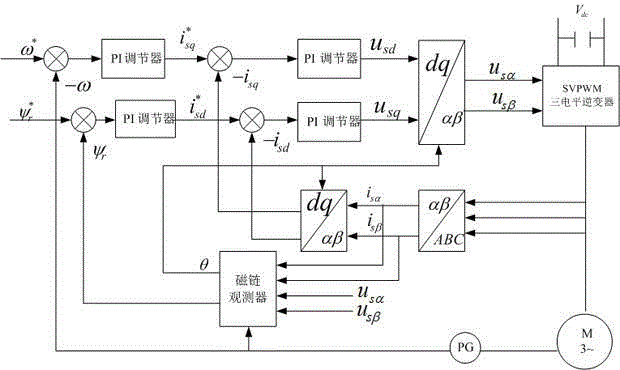
Tri-level inversion indirect vector control system based on simplified SVPWM (space vector pulse width modulation)
InactiveCN103248304ARealize real-time controlReduce pulsationElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlVoltage vectorIndirect vector control
The invention relates to a tri-level inversion indirect vector control system based on simplified SVPWM (space vector pulse width modulation). On bases of the SVPWM simplification algorithm under a 60-degree coordinate system, an asynchronous motor dynamic mathematical model, a vector control fundamental principle and a main circuit in the step A, the tri-level inverter vector control system based on network parameter control (NPC) is established. The method dispenses with judgment that a reference voltage vector is in a large section or a small section, as well as a great deal of trigonometric functional operation, and only requires simple logical judgment, so that nearest three vectors for synthesizing the reference voltage vector can be obtained; and meanwhile, an output switch state equation is introduced in the algorithm, so that midpoint electric potential balance on the direct current side can be effectively controlled, and the method can be easily popularized to inverters with higher level.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Thrust vector control
InactiveUS20060150612A1Cosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusControl vectorControl system
A thrust vector control system for a flight vehicle comprises a fixed nozzle defining a first thrust vector direction and at least one exhaust deflector moveable to a location downstream of said fixed nozzle to provide a second thrust vector direction. Movement of the at least one exhaust deflector may allow for simultaneous control of both thrust vector direction and nozzle throat area. Translational motion of each exhaust deflector may be independently controlled. A flight vehicle incorporating a thrust vector control apparatus, and a method for thrust vector control are also disclosed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Constant slip frequency vector control method and system for linear induction motor
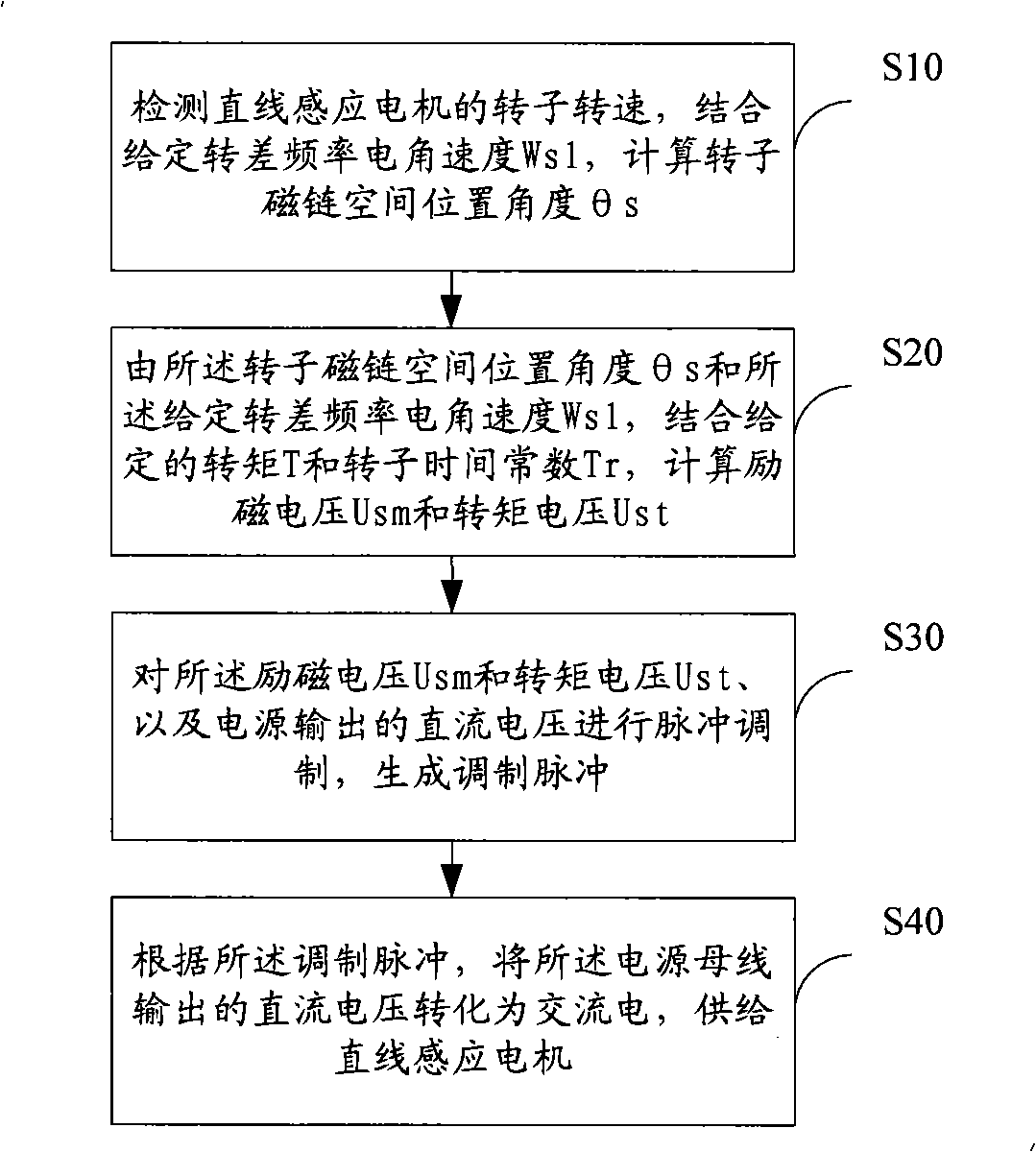
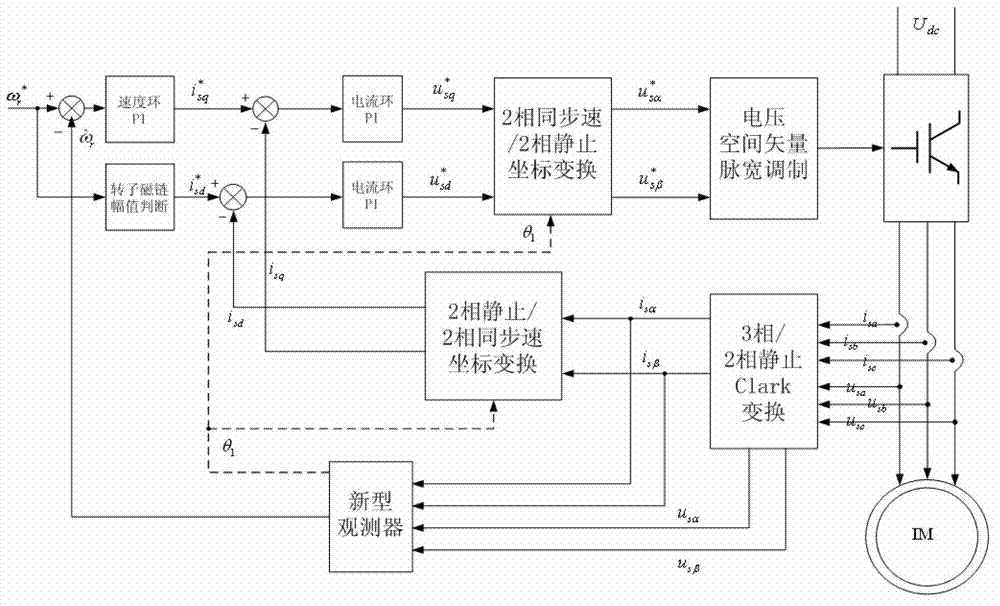
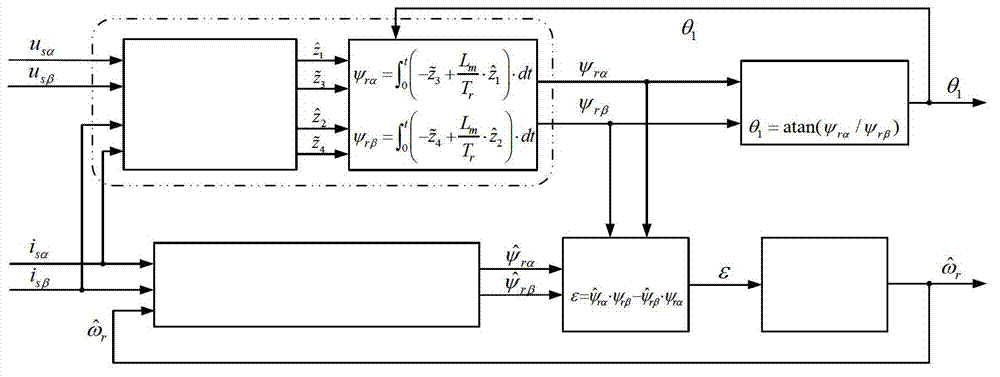
ActiveCN101316093AExcellent slip frequency electrical angular velocitySmooth orientation angleElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPosition angleAngular velocity
The invention discloses a linear induction motor constant slip frequency vector control method. The method comprises the steps as follows: detecting the rotation speed of a rotor of a linear induction motor, calculating the magnetic chain space position angle Theta<s> of the rotor according to the given slip frequency electric angular velocity Wsl; calculating the excitation voltage Usm and torque voltage Ust according to the magnetic chain space position angle Theta<s> and the given slip frequency electric angular velocity Wsl and combining a given torque T and a rotor time constant Tr; generating modulation pulses by pulse-modulating the excitation voltage Usm and the torque voltage Ust and the DC voltage output by the power supply; converting the DC voltage output by the power supply into the AC electricity so as to be supplied to the linear induction motor according to the modulation pulse. The invention also discloses a linear induction motor constant slip frequency vector control system. The linear induction motor constant slip frequency vector control method and system of the invention can realize the constant slip frequency vector control of the linear induction motor.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CSR TIMES ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for asynchronous motor rotor flux linkage observation and rotation speed identification
InactiveCN102931906AGuaranteed observation accuracyImprove recognition accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsVector control systemFlux linkage
The invention discloses a method for asynchronous motor rotor flux linkage observation and rotation speed identification, which comprises the following steps of: according to stator voltage and current signals measured in real time, observing to obtain a rotor flux linkage through a sliding mode observer based on a super-twisting theory and using the rotor flux linkage as a reference value; using a rotor flux linkage calculated according to a rotor flux linkage current model as an adjustable value; constructing a model reference self-adaptive system (MRAS) based on the rotor flux linkages; and identifying the asynchronous motor rotation speed through the self-adaptive law. The rotation speed identification method provided by the invention has high robustness for the variation of stator resistance, and can provide accurate rotor flux linkages and rotation speed values, thereby being especially suitable for an asynchronous motor vector control system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Control system and method for electric drives with a.c. motors
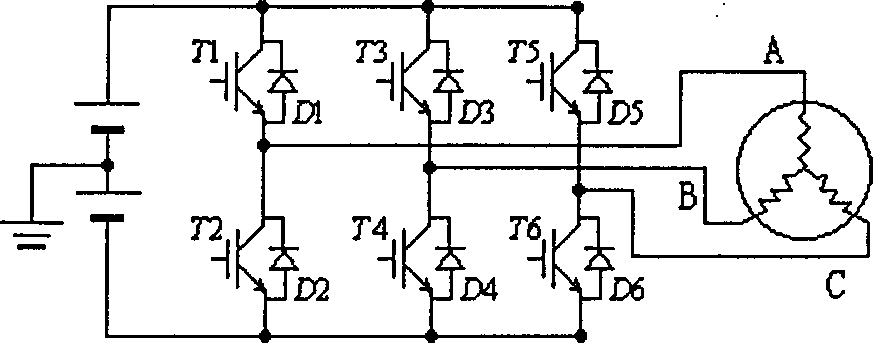
InactiveUS7180262B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersControl systemElectric drive
A vector-control system and method of a “sensorless” type for electric drives with a.c. motors is based upon generation of an oscillating magnetic field and upon measurement of the deviation, with respect to said oscillating field, of the flux generated thereby on account of anisotropy, whether natural or induced, of the magnetic structure of the machine.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CATANIA
Speed and current double closed-loop control system and method for permanent magnet synchronous linear motor
ActiveCN110138297AHigh precisionGood precisionElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsReference currentPermanent magnet synchronous motor
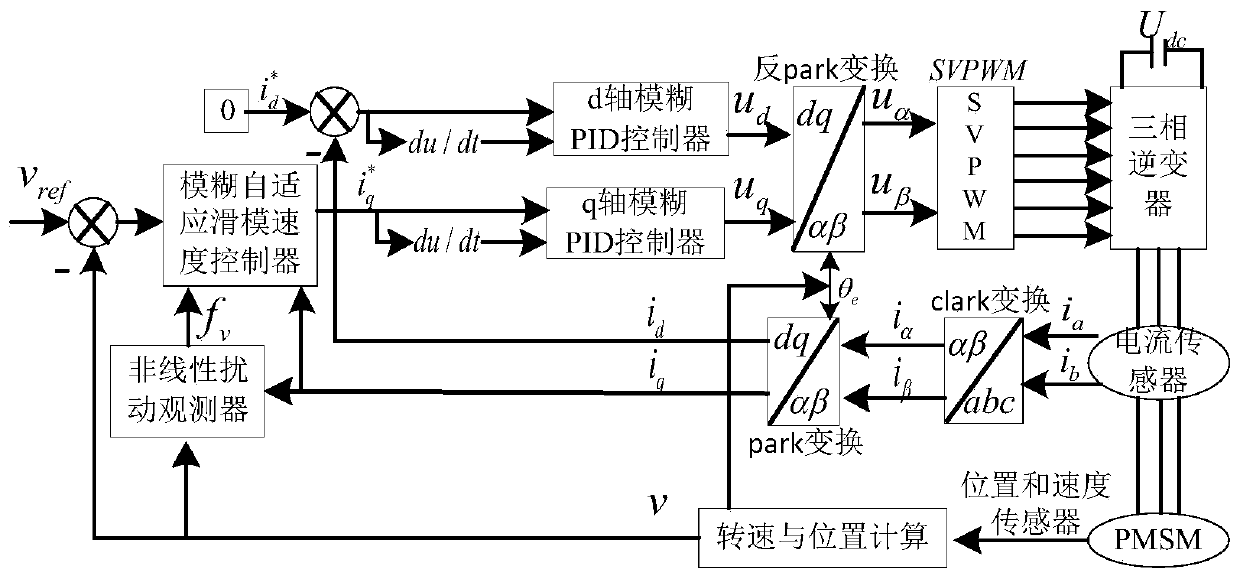
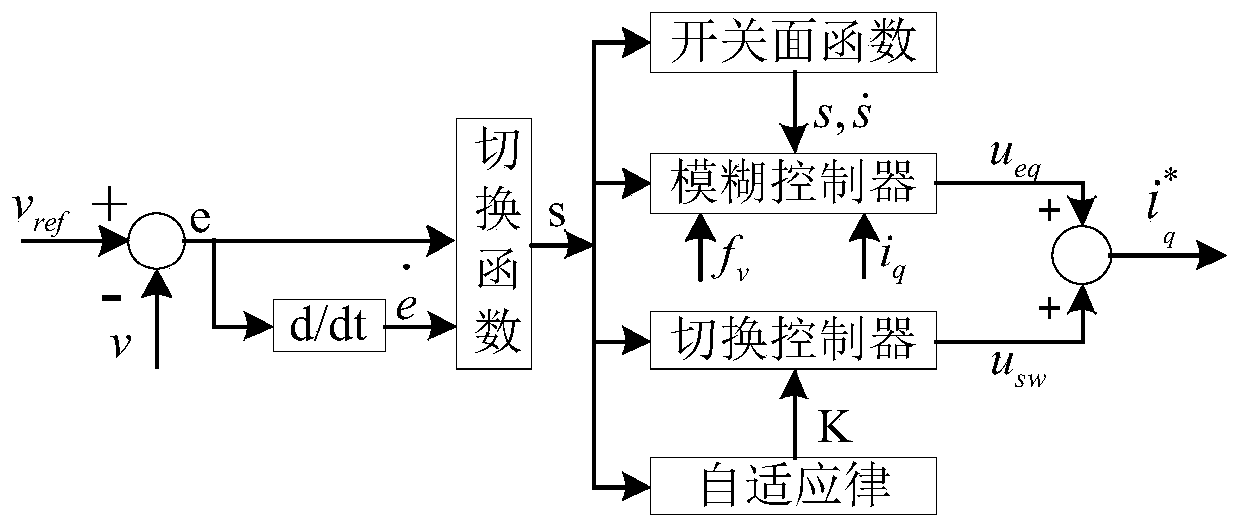
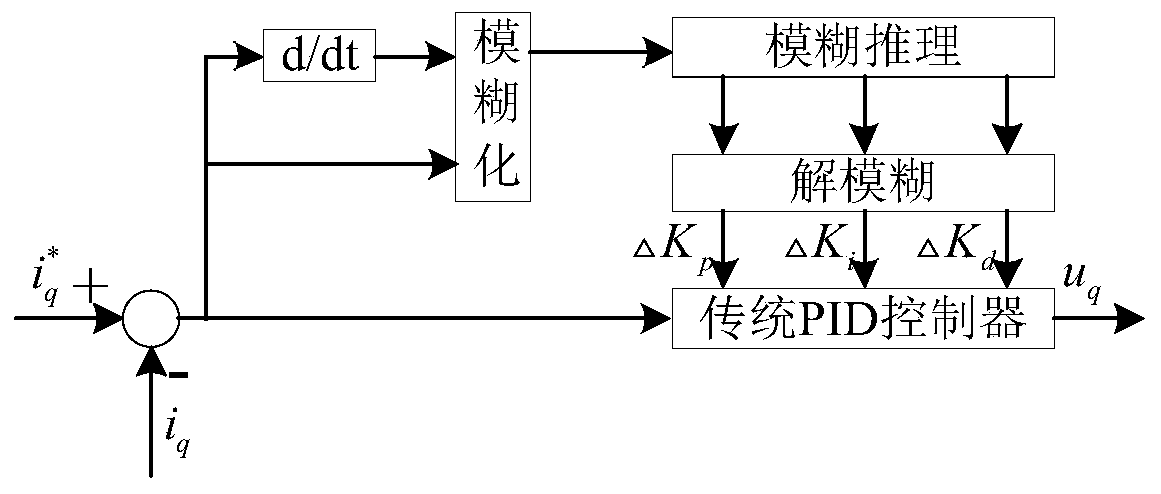
The invention discloses a speed and current double closed-loop control system and method for a permanent magnet synchronous linear motor. The method comprises the steps of: designing a permanent magnet synchronous linear motor vector control system; designing a fuzzy adaptive sliding-mode speed controller; designing a nonlinear disturbance observation; designing a d-axis fuzzy PID controller; designing a q-axis fuzzy PID controller; obtaining a desired q-axis current reference value as an input of the q-axis fuzzy PID controller according to the designed nonlinear disturbance observer and thedesigned fuzzy adaptive sliding-mode speed controller; setting a d-axis reference current value as 0, and using the id obtained by subtracting park transform from 0 as the input of the d-axis fuzzy PID controller; after the processing by the d-axis fuzzy PID controller and the q-axis fuzzy PID controller, obtaining the ud, uq of the vector control system, and finally outputting the current operating driving voltage of the permanent magnet synchronous linear motor by the anti-park transformation and SVPWM modulation through the vector control and an inverter. The method enhances the robustnessof the system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Aircraft fluidic thrust vector control system
InactiveCN102991669AHigh positioning accuracyPrecise adjustment of secondary flow air flowAircraft navigation controlControl systemAttitude control
The invention discloses an aircraft fluidic thrust vector control system. With the control system, 306-degree flying attitudes of the aircraft can be controlled; response time of the control system is shortened; control precision of the control system is increased; a structure of the control system is simplified; and the weight of the aircraft is reduced. The aircraft fluidic thrust vector control system comprises a fuel gas turbine engine, a main airflow channel, a secondary flow nozzle, a secondary flow channel assembly and a Coanda effect surface. A small part of the gas is introduced out from an engine compression chamber to be used as a secondary flow gas source of the vector thrust control system in the same direction, and is injected into the secondary flow channel by using a Coanda effect. A wall attachment effect is produced after the secondary flow in the same direction with the main airflow flows through the Coanda effect surface, and Coanda effect is further generated by guiding the main airflow along the wall attachment direction, so that a deflection torque is obtained. Precision control for pitching, being off-course and rolling of the aircraft can be realized by controlling the outflow direction and the flow rate of the secondary flow.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
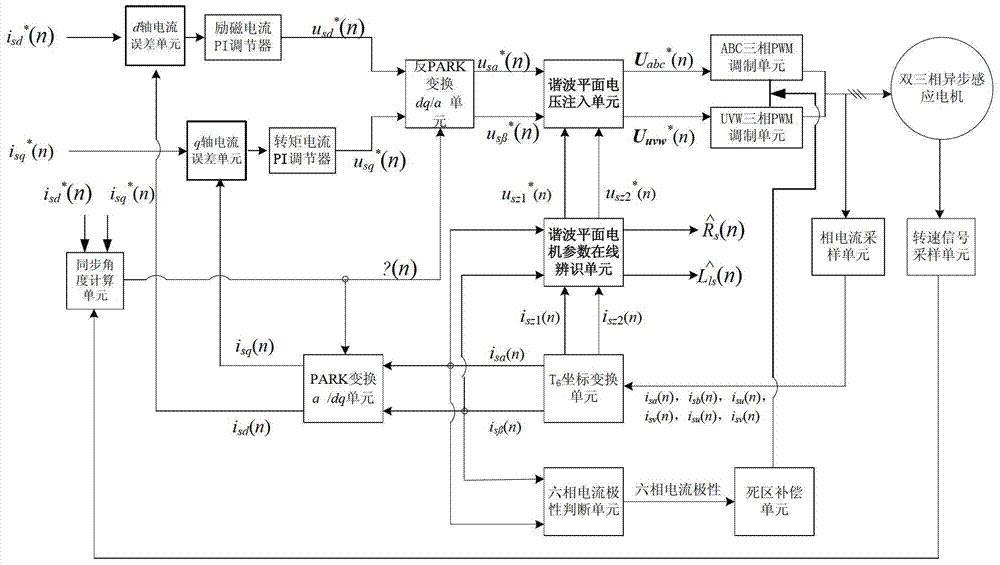
Method and device for distinguishing double-three-phase motor parameter on line on harmonic plane
ActiveCN103401503AFast convergenceDoes not affect controlElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPhase currentsReference current
The invention specifically relates to a method and a device for distinguishing a double-three-phase motor parameter on line on a harmonic plane, and belongs to the field of mechanical and electrical technology. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of carrying out coordinate transformation on collected phase current in a motor vector control system to obtain the feedback current of a fundamental wave plane and a harmonic plane; according to the feedback current of the fundamental wave plane, calculating the reference voltage of the fundamental wave plane and the reference current of the harmonic plane; according to the error of the reference current and the feedback current of the harmonic plane, calculating stator resistance, stator leakage inductance and the reference voltage of the harmonic plane; according to the reference voltage of the fundamental wave plane and the harmonic plane, calculating the reference voltage of two sets of windings, i.e. ABC and UVW; and finally, according to a three-phase PWM (pulse-width modulation) strategy, calculating the conduction state and time of an inverter switching tube, and driving the motor to operate. The invention has the advantages of high distinguishing accuracy, quickness in convergence, simple algorithm and device and easiness in realizing, and a distinguishing result does not depend on other motor parameters.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
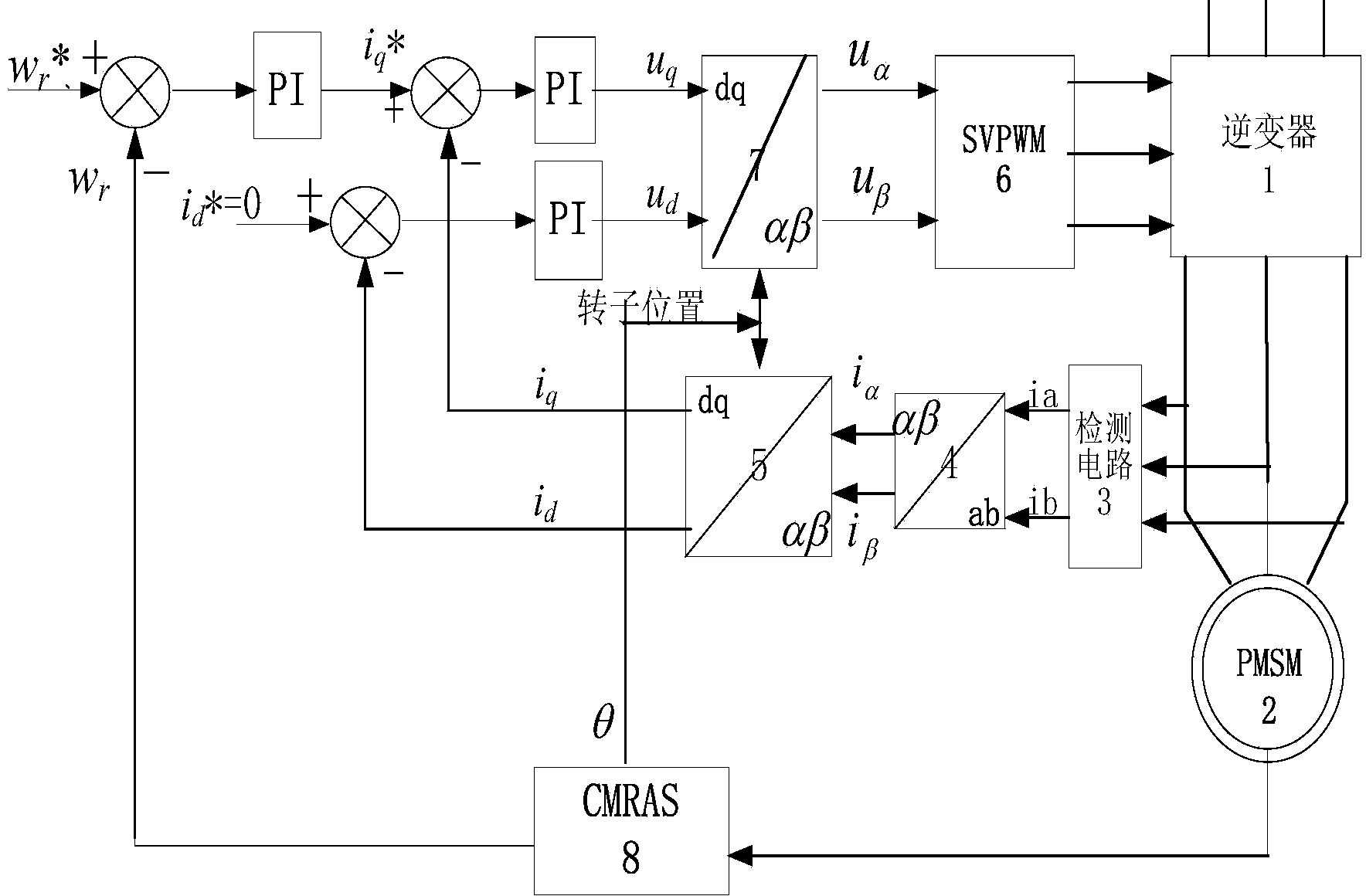
Parameter identification method of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN103684182AImproved low-speed control performanceGood low speed control performanceElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlElectrical resistance and conductanceLow speed
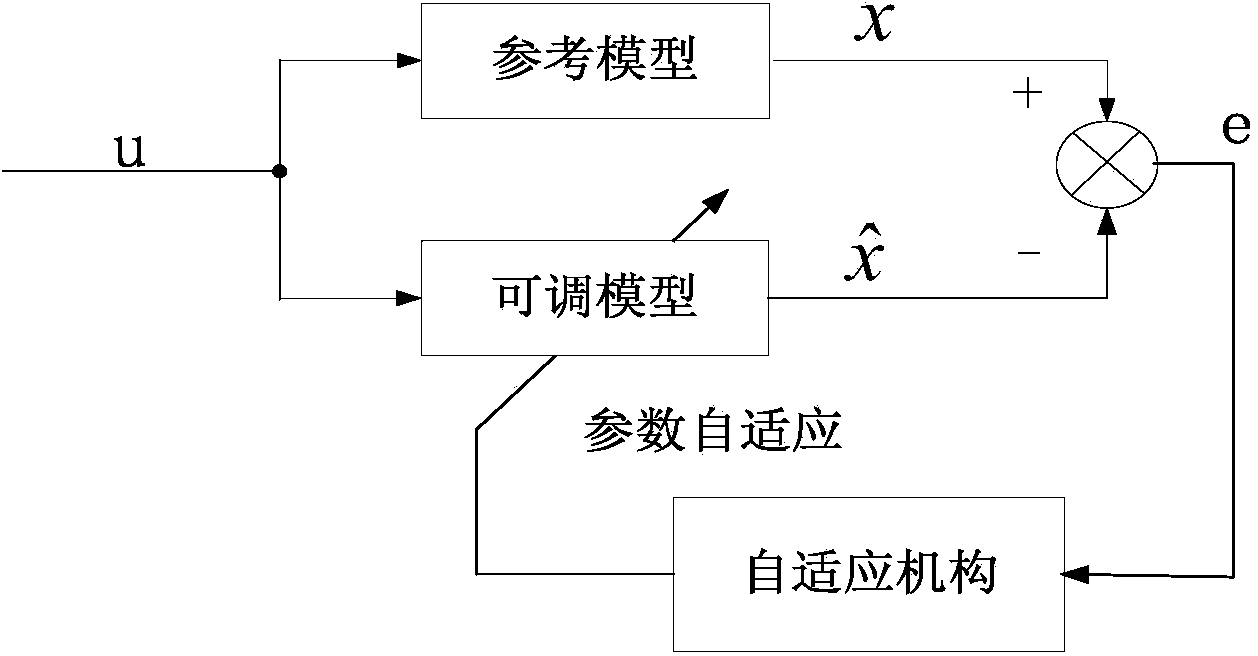
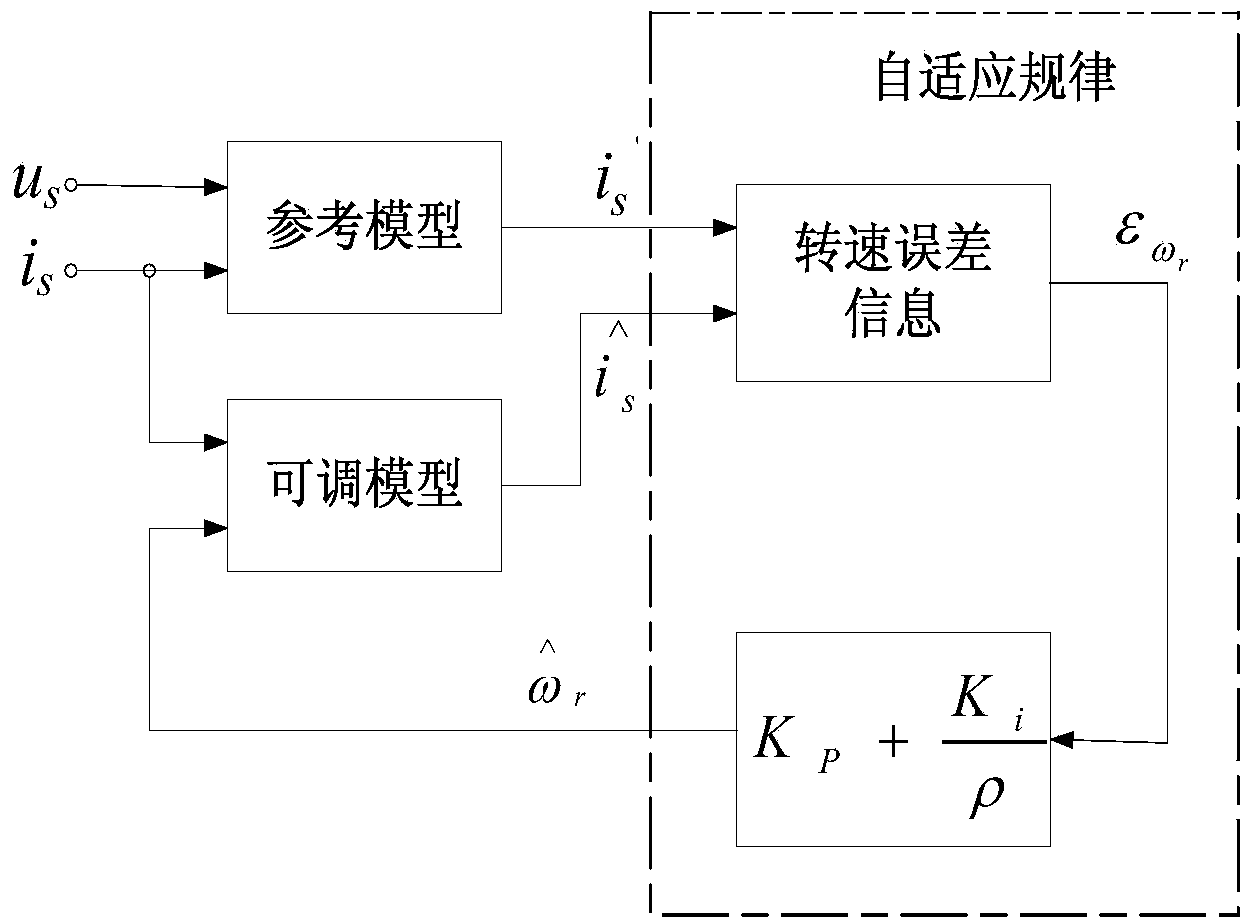
A parameter identification method of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. A conventional model is improved with reference to an adaptive structure, i.e., based on an original MRAS1 module, a new MRAS2 module is constructed, so that a cascade model reference adaptive control (CMRAS) module is constructed; the MRAS1 is used for identification of a rotor speed; and the MRAS2 is used for identification of a stator resistance and rotor flux. In the invention, while the rotor speed is fed back in the real time manner, the stator resistance and rotor flux identification value is fed back to a vector control system, so that an influence of motor parameters on the system can be effectively lessened; and since the stator resistance identification value is updated in the real time manner at the low speed, the low speed control performance of the system can be effectively improved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Flux linkage error observation-based acquisition method of full-order flux linkage observer of asynchronous motor without speed sensor
ActiveCN103701386AGuaranteed uptimeImprove accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsLow speedLow - observation
The invention discloses a flux linkage error observation-based acquisition method of a full-order flux linkage observer of an asynchronous motor without a speed sensor and belongs to the field of a speed sensorless vector control full-order flux linkage observer. The problem that the existing speed sensorless vector control system causes low observation accuracy of the full-order flux linkage observer due to larger errors of motor parameters when a motor runs at low speed, and finally, the running stability of the system is poor is solved. A full-order flux linkage observer error feedback matrix coefficient is obtained according to the following rules, namely, the pole real part of the observer is smaller than the pole real part of an asynchronous motor, the real parts are both negative numbers, the zero pole real parts of an estimation rotation speed and a transfer function are both negative numbers, the error between an estimation flux linkage and a real flux linkage is utilized, when the motor runs at low speed, the equivalence of the system is a current model, and when the motor runs at high speed, the equivalence of the system is a voltage model. The rotor flux linkage phase position error coefficient ilambda is utilized and the rotor flux linkage amplitude error coefficient k is introduced, so that the estimation rotating speed precision is increased. The flux linkage error observation-based acquisition method of the full-order flux linkage observer of the asynchronous motor without the speed sensor is particularly used in the field of speed sensorless vector control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Anti-rest Windup smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method for permanent magnet synchronous motor based on relative order
ActiveCN104270054ASolve chattering problemsAccurate trackingElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention relates to an Anti-rest Windup smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor based on a relative order, and aims to solve the problem that the control continuity of a system and the smoothness of an output signal are damaged by chattering of a permanent magnet synchronous motor control system due to the high-frequency control switching behavior of a conventional sliding mode control method and the problem that the permanent magnet synchronous motor control system generally has the Windup problem due to finite output capacity of an existing inverter. The anti-rest Windup smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method comprises the following steps: 1, designing a permanent magnet synchronous motor rotating speed vector control system; 2, designing an Anti-rest Windup smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode rotating speed controller; 3, designing a smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode alternating current controller; 4, designing a smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode direct current controller. The Anti-rest Windup smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method is applied to the field of robust control on the permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Owner:严格集团股份有限公司
NPC (neutral point clamped) three-level inverter vector control system based on novel flux observer
InactiveCN103338000AReduce complexityImprove dynamic performanceElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlThree levelVoltage vector
An NPC (neutral point clamped) three-level inverter vector control system based on a novel flux observer provides a simplified SVPWM (space vector pulse width modulation) algorithm. A three-level space vector is decomposed into a two-level space vector; a reference voltage vector is translated; a two-level SVPWM algorithm is used to obtain action time of each basic vector and to choose a right switching status; and the three-level inverter vector control calculation is reduced. Meanwhile, in the invention, the novel flux observer is employed to calculate the rotor flux, so that a current model and a voltage model are used respectively at a low speed and at a high speed; and when a rotation speed is between the low speed and the high speed, an invented hybrid flux observer is used to calculate the rotor flux.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and process of vector propulsion with independent control of three translation and three rotation axis
ActiveUS8128033B2Reduces the passenger's discomfortEasy to controlCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusControl systemVector control system
The present invention relates to a propulsion system of a vertical takeoff and landing aircraft or vehicle moving in any fluid or vacuum and more particularly to a vector control system of the vehicle propulsion thrust allowing an independent displacement with six degrees of freedom, three degrees of translation in relation to its centre of mass and three degrees of rotation in relation to its centre of mass. The aircraft displacement ability using the propulsion system of the present invention depends on two main thrusters or propellers and which can be tilted around pitch is (I) by means of tilting mechanisms and, used to perform a forward or backward movement, can be tilted around roll axis (X) by means of tilting mechanisms and, used to perform lateral movements to the right or to the left and to perform upward or downward movements (Z), the main thrusters being further used to perform rotations around the vehicle yaw axis (Z) and around the roll is (X). The locomotion function also uses one or two auxiliary thrusters or propellers and mainly used to control the rotation around the pitch axis, these thrusters or propellers and being fixed at or near the longitudinal is of the vehicle, with there thrust perpendicular or nearly perpendicular to the roll and pitch axis of the vehicle.
Owner:RAPOSO SEVERINO
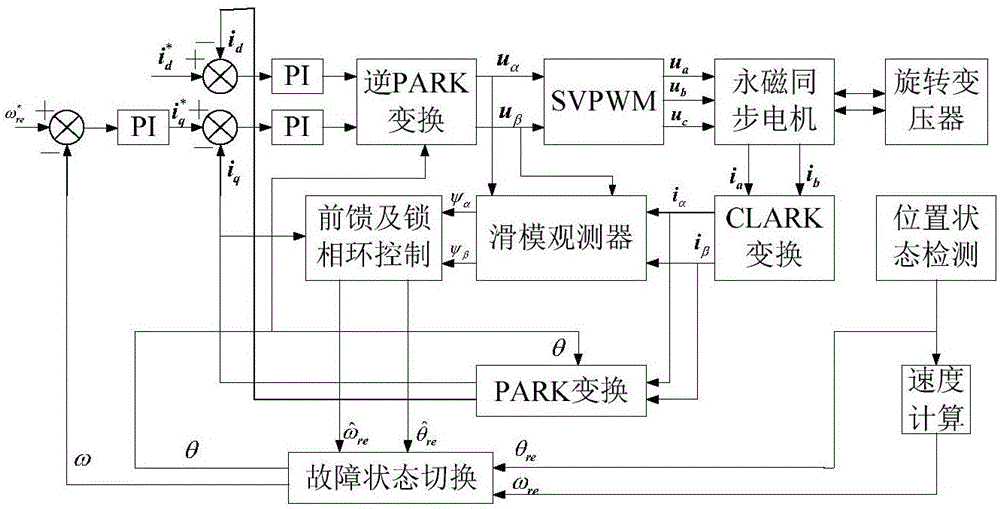
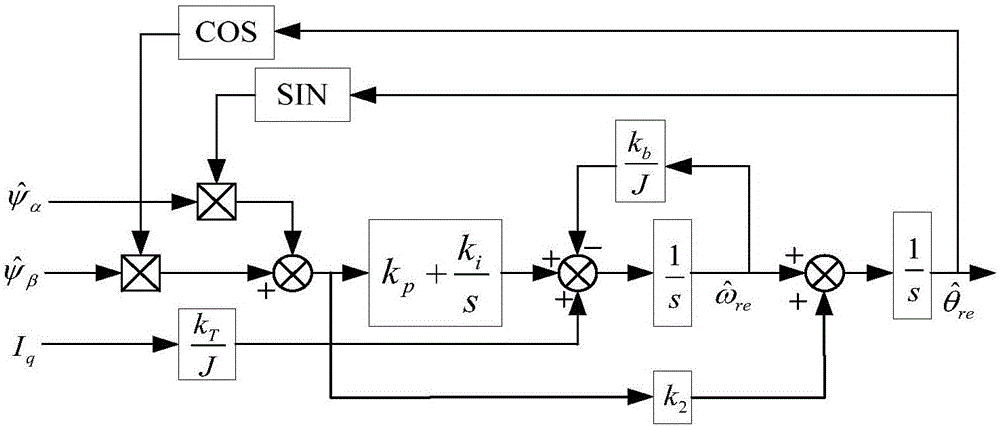
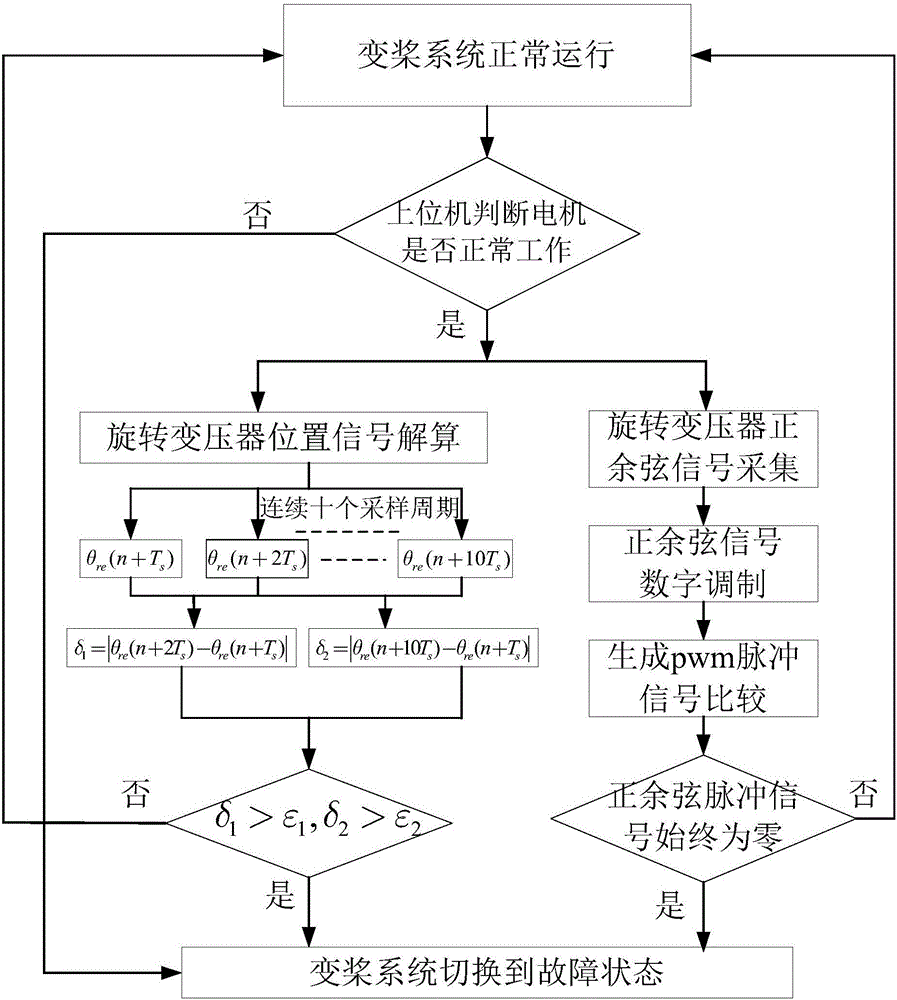
Position failure fault-tolerant driving control method for wind power generation pitch system
ActiveCN106685291ARealize seamless dockingElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlControl vectorControl system
The invention discloses a position failure fault-tolerant driving control method for a wind power generation pitch system. During the operation of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, the electromagnetic parameters of the motor are detected; when the permanent magnet synchronous motor normally operates on the condition that a position sensor exists, the motor status information is calculated in real time; the position working status of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is judged, smooth switching between sensor control and sensor-less control of a driving control system is flexibly conducted according to the working status; under the sensor-less vector control double closed loop condition, the permanent magnet synchronous motor driving control method is set up; after the position sensor output signal breaks down during the normal operation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, the permanent magnet synchronous motor is switched from a vector control system with actual position and rotation speed feedback into a sensor-less vector control mode using an estimated position and a speed signal. After the breakdown signal is removed, the system is switched from a sensor-less vector control mode into a position vector control mode in real time.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
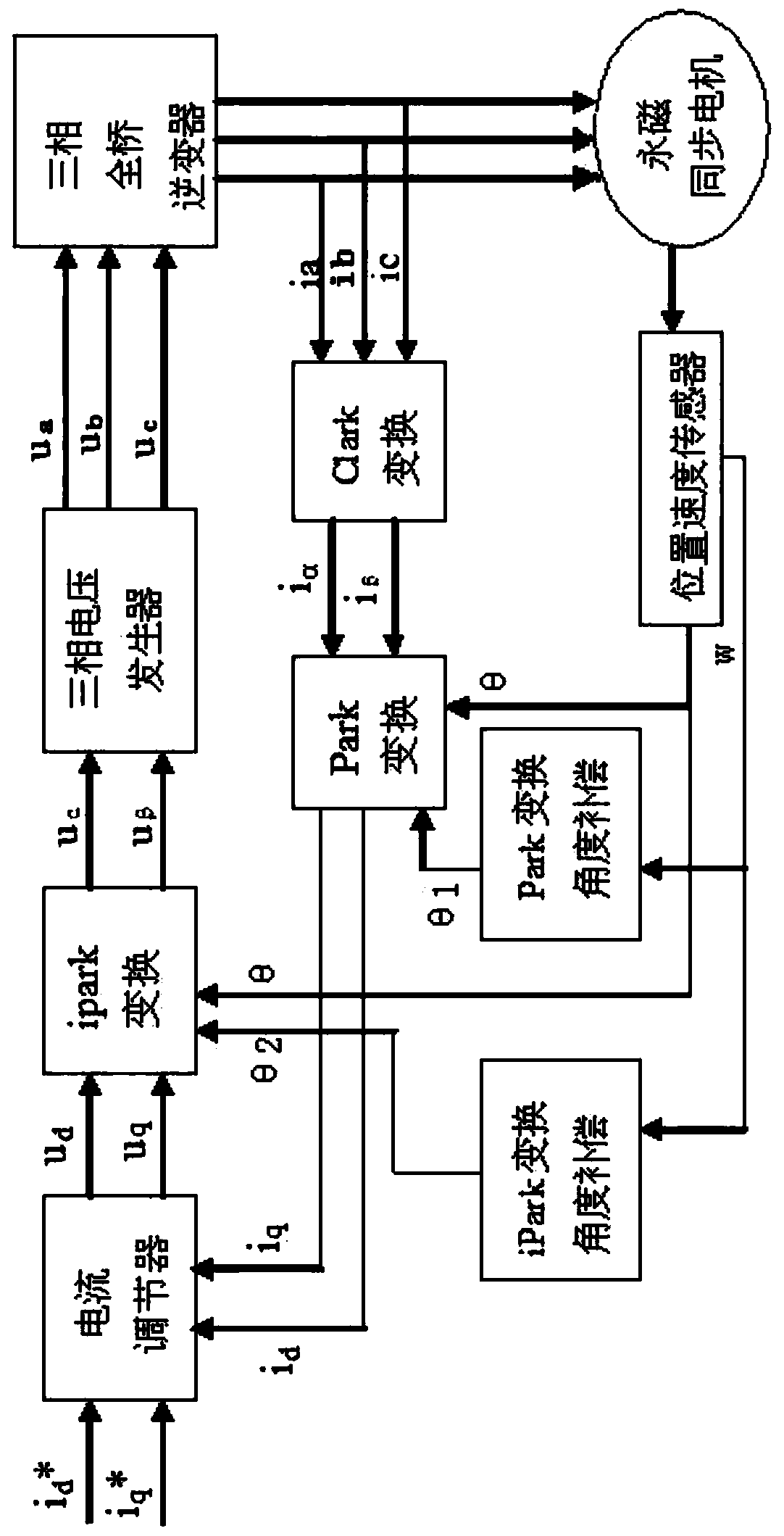
Rotor position angle compensation method of motor vector control
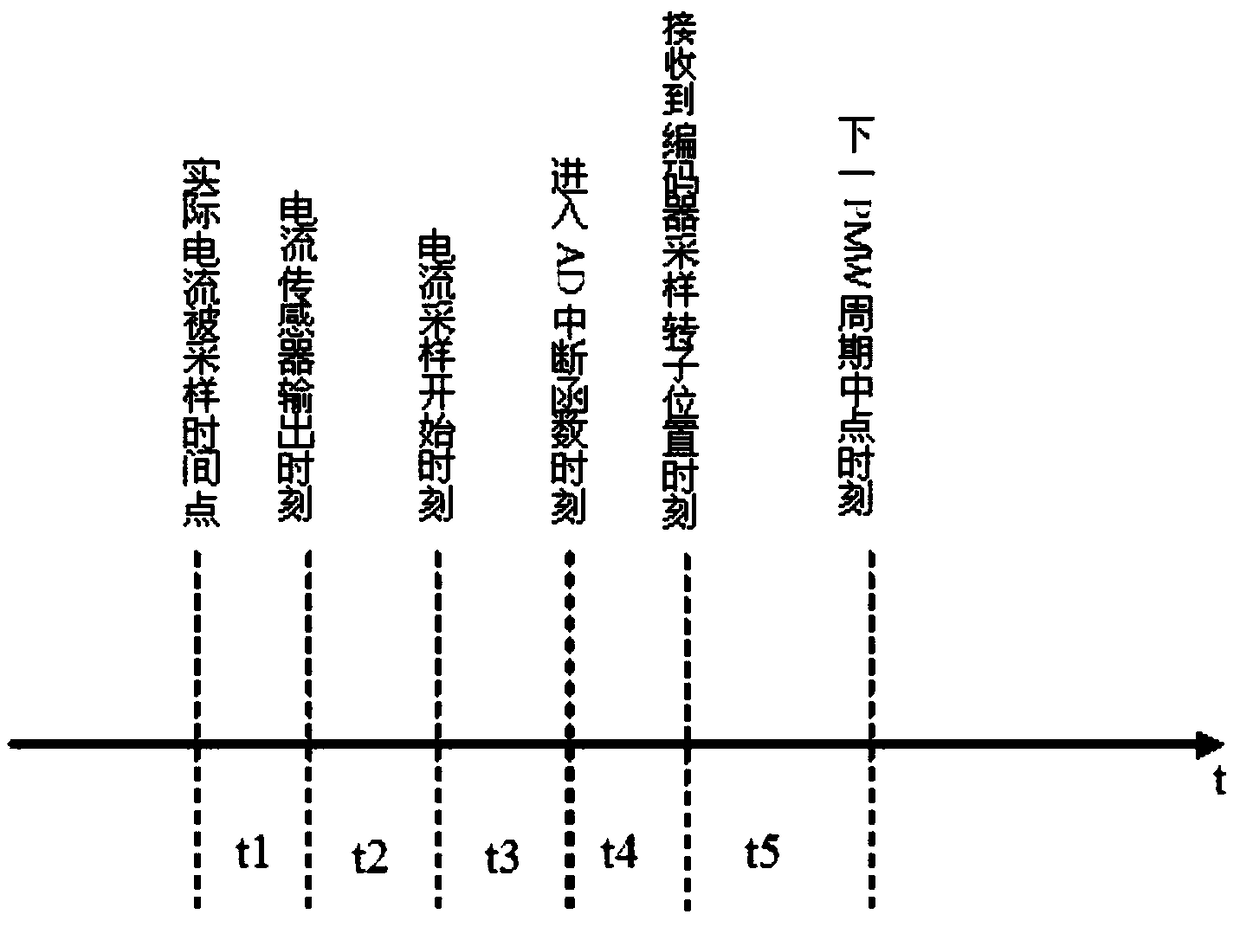
ActiveCN108282124AImprove current control accuracyImprove dynamic performanceElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl vectorPosition angle
The invention relates to a rotor position angle compensation method of motor vector control. A rotor position angle Theta obtained by sampling is compensated by a controller, Park conversion is performed on the compensated rotor position angle Theta', Theta'=Theta-Theta1, Theta1=w*(t1+t2+t3+t4), Theta1 is a Park conversion compensation angle, w is a running frequency of the motor, t1 is delay timeof a current sensor for sampling a stator current, t2 is delay time of a filtering circuit for filtering an output signal of the current sensor, t3 is time from an initial sampling moment of an AD external sampling module of the controller on the stator current to AD interrupt function moment, and t4 is time from the AD interrupt function moment to a moment when the rotor position angle Theta sampled by a rotor position detection device is received by the controller. By the rotor position angle compensation method, the current control accuracy of a vector control system under a high-speed working condition can be improved, and the dynamic performance of a motor control system is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIGRINER STEP ELECTRIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com