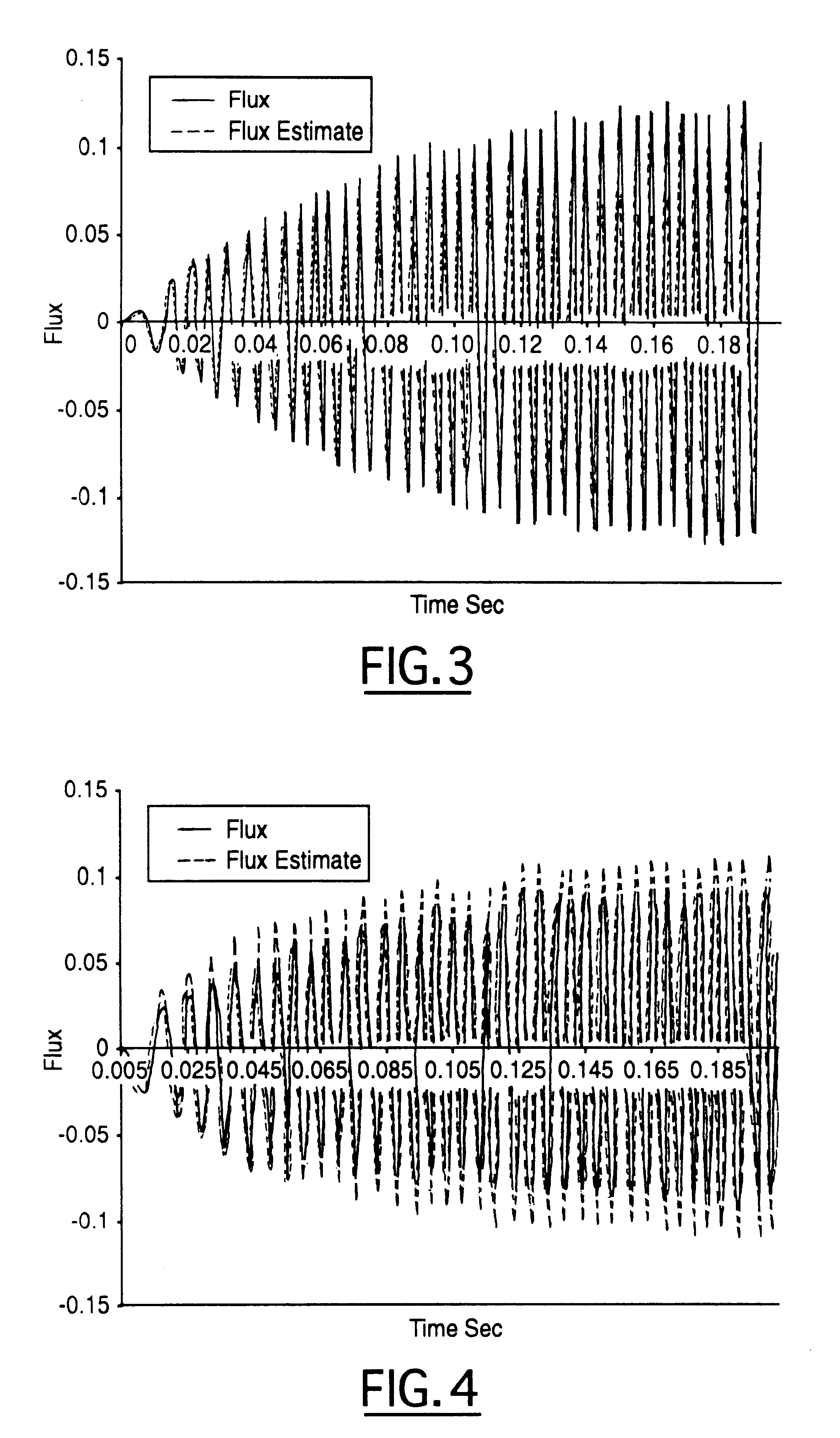
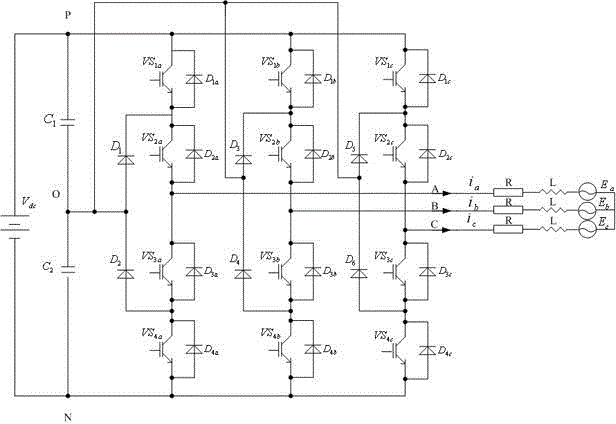
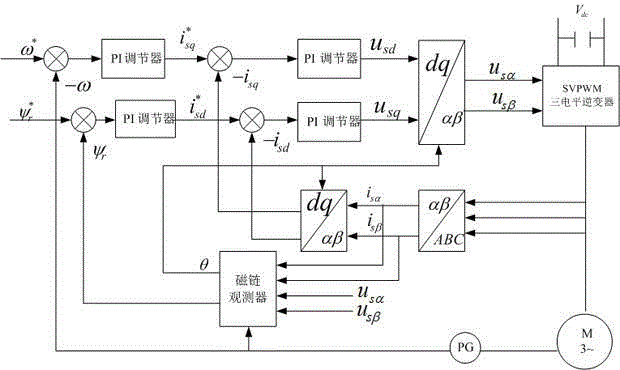
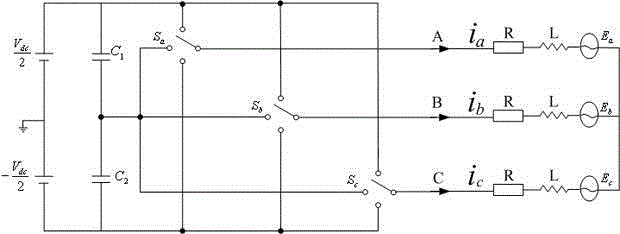
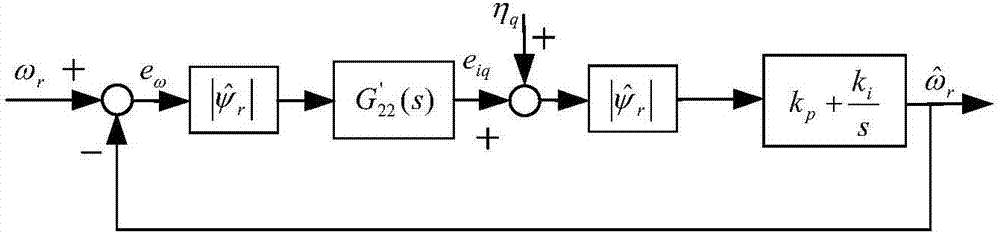
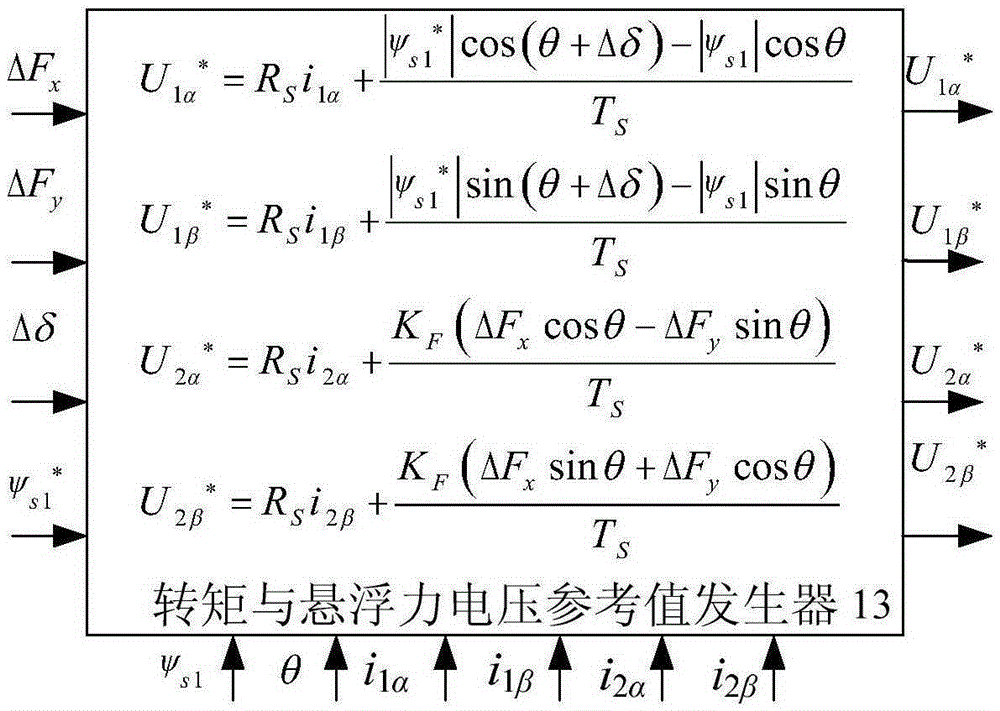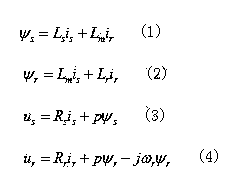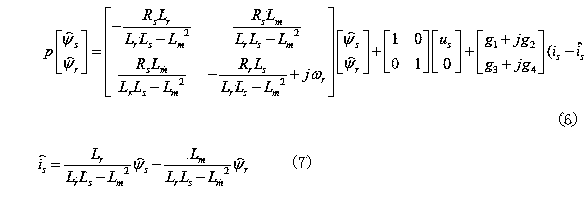Patents
Literature
66 results about "Flux observer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
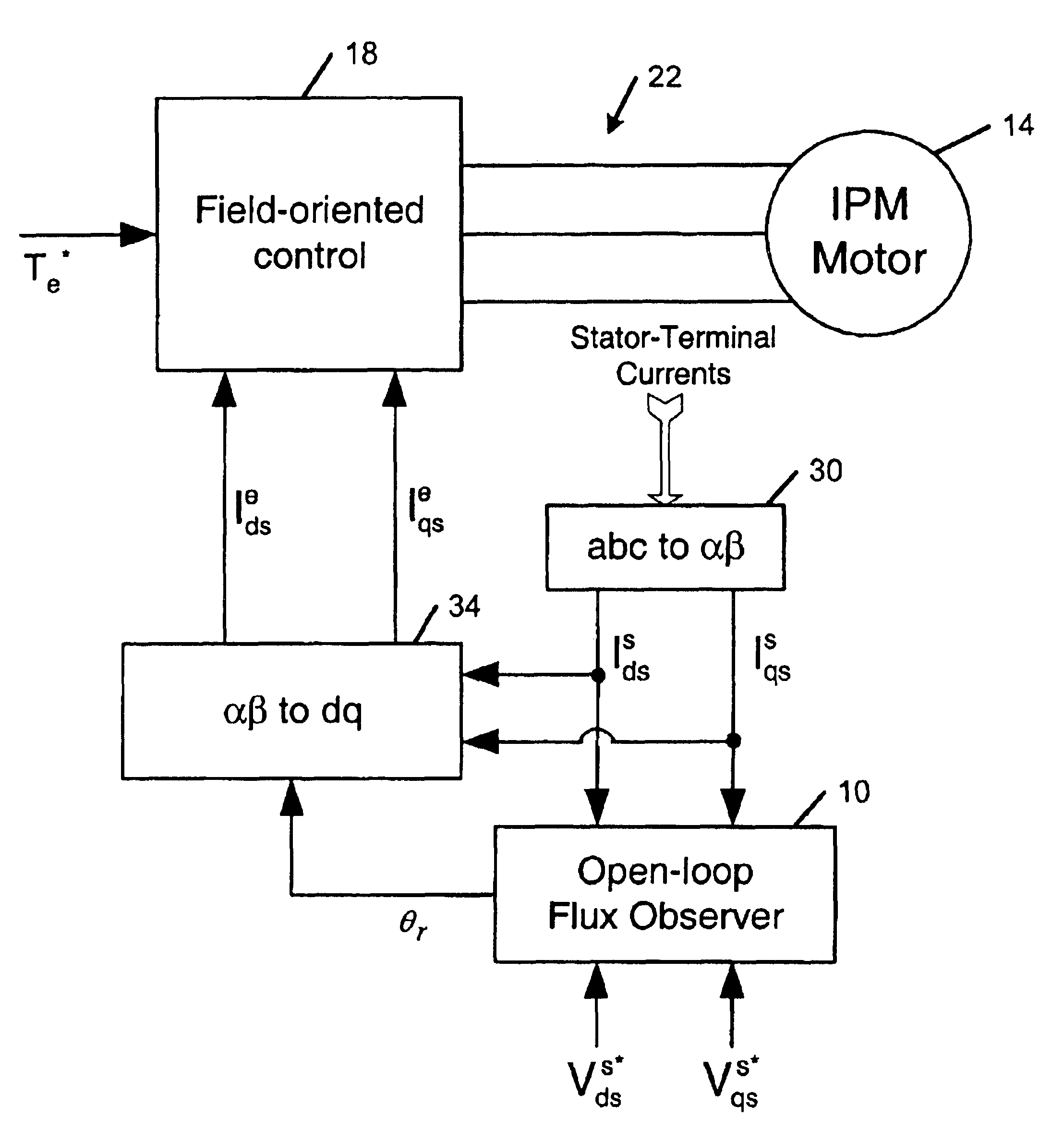
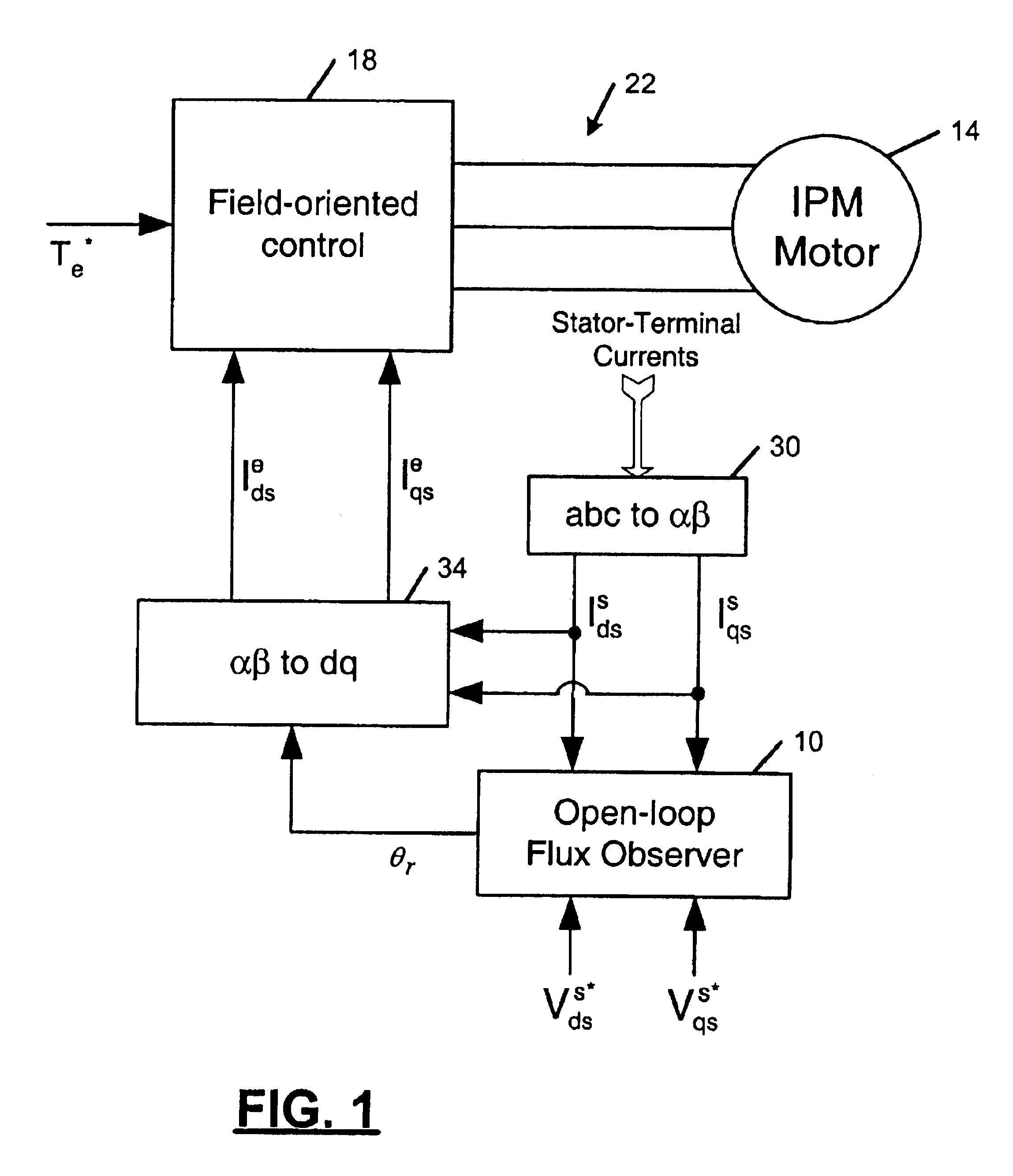
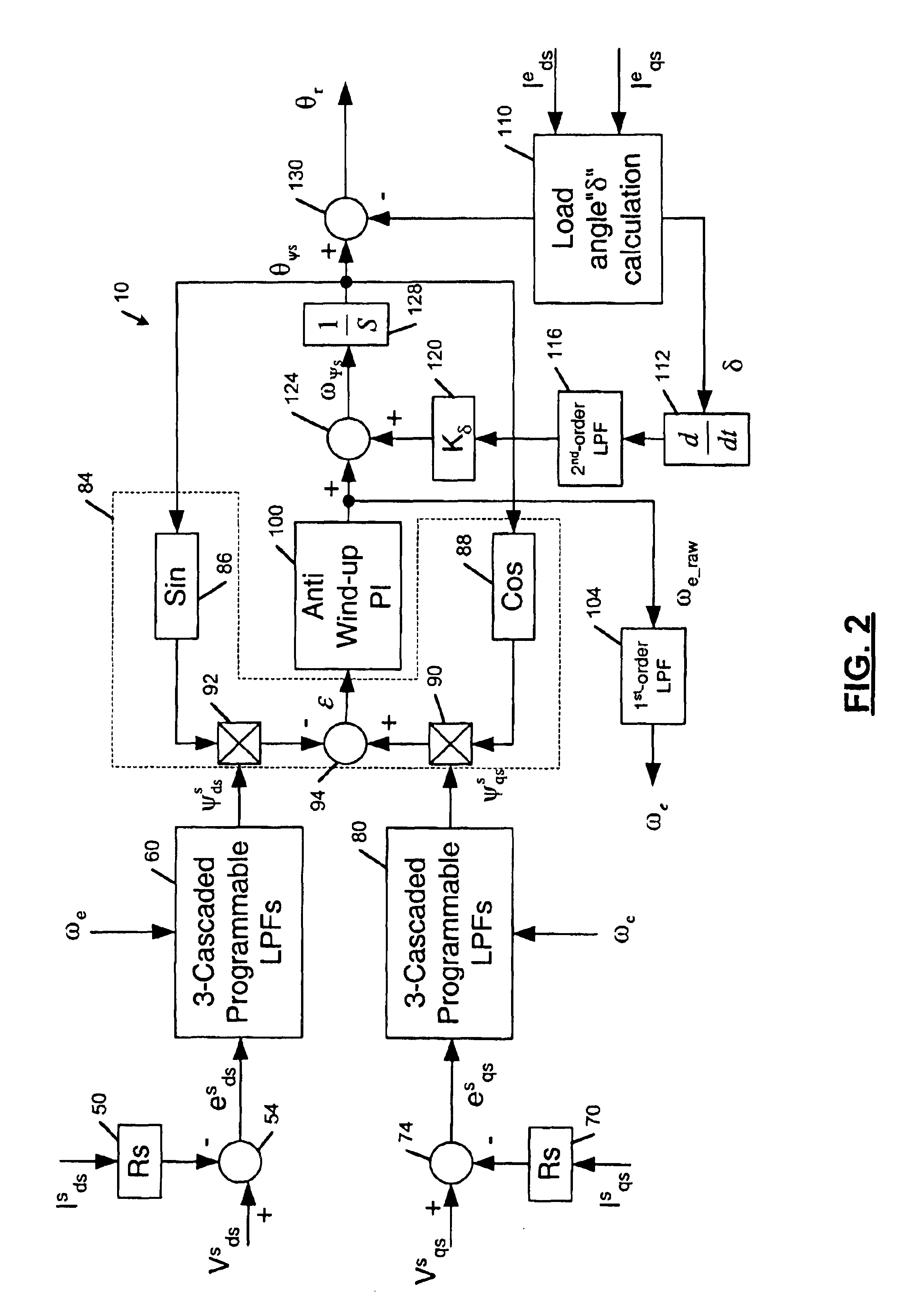
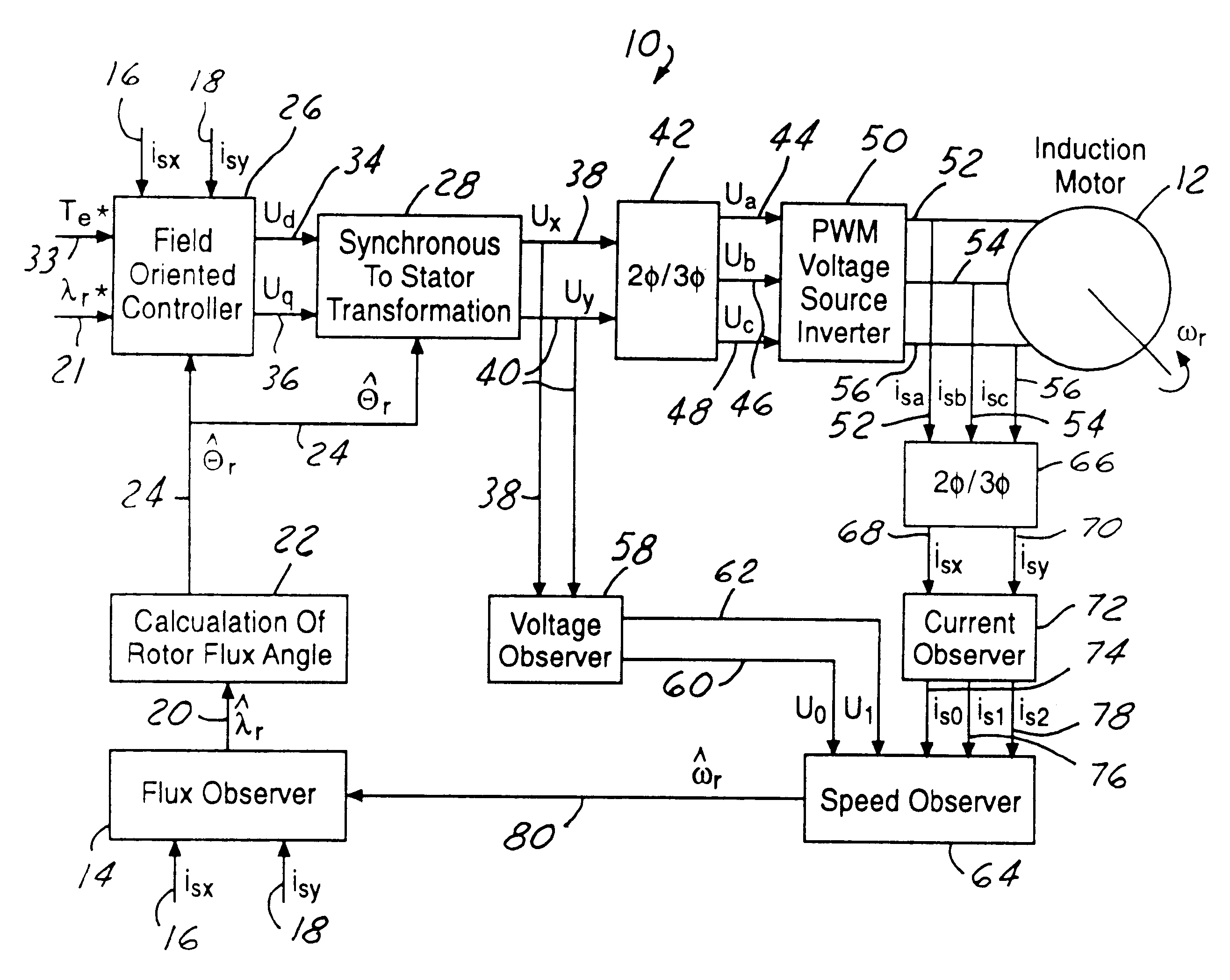
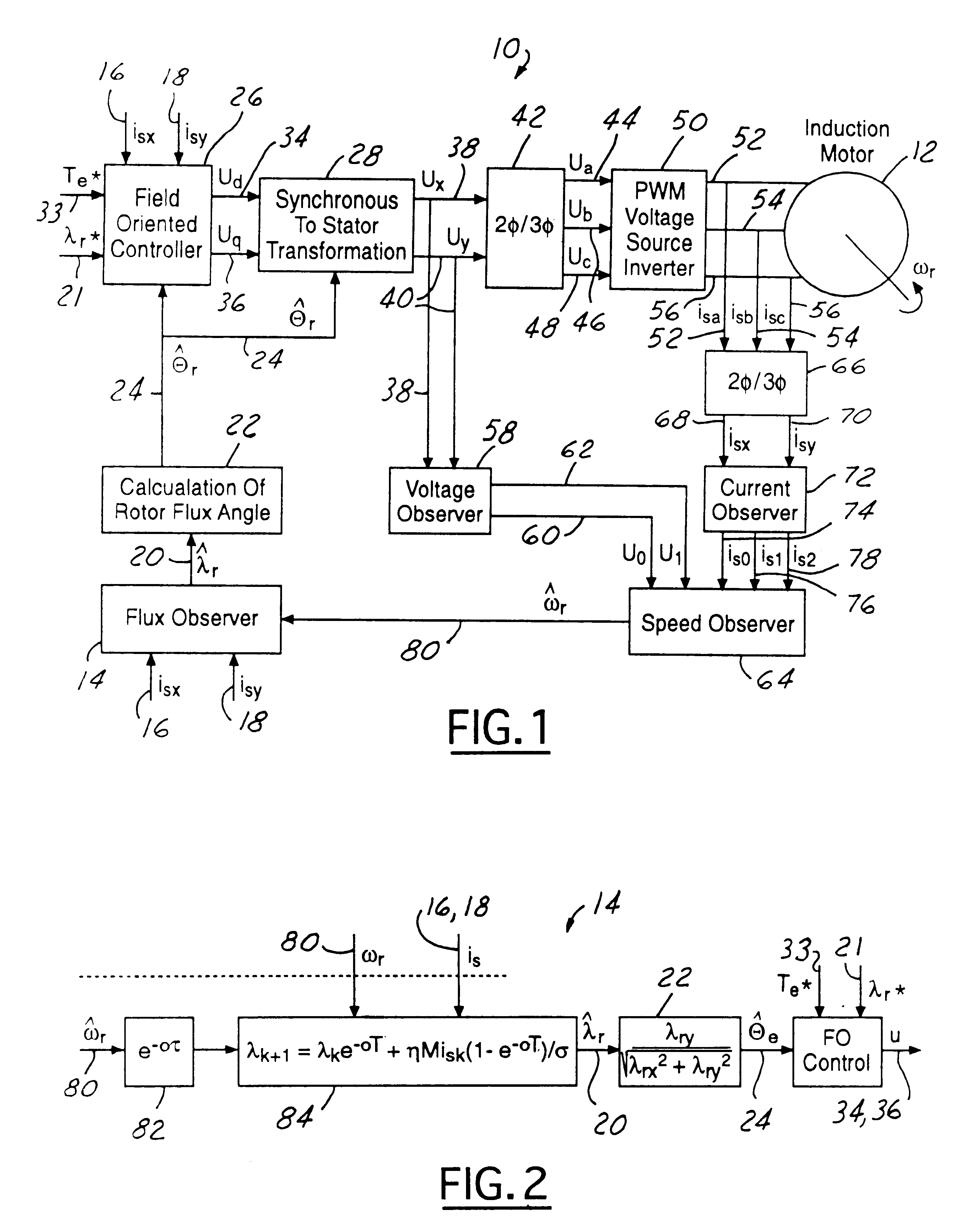
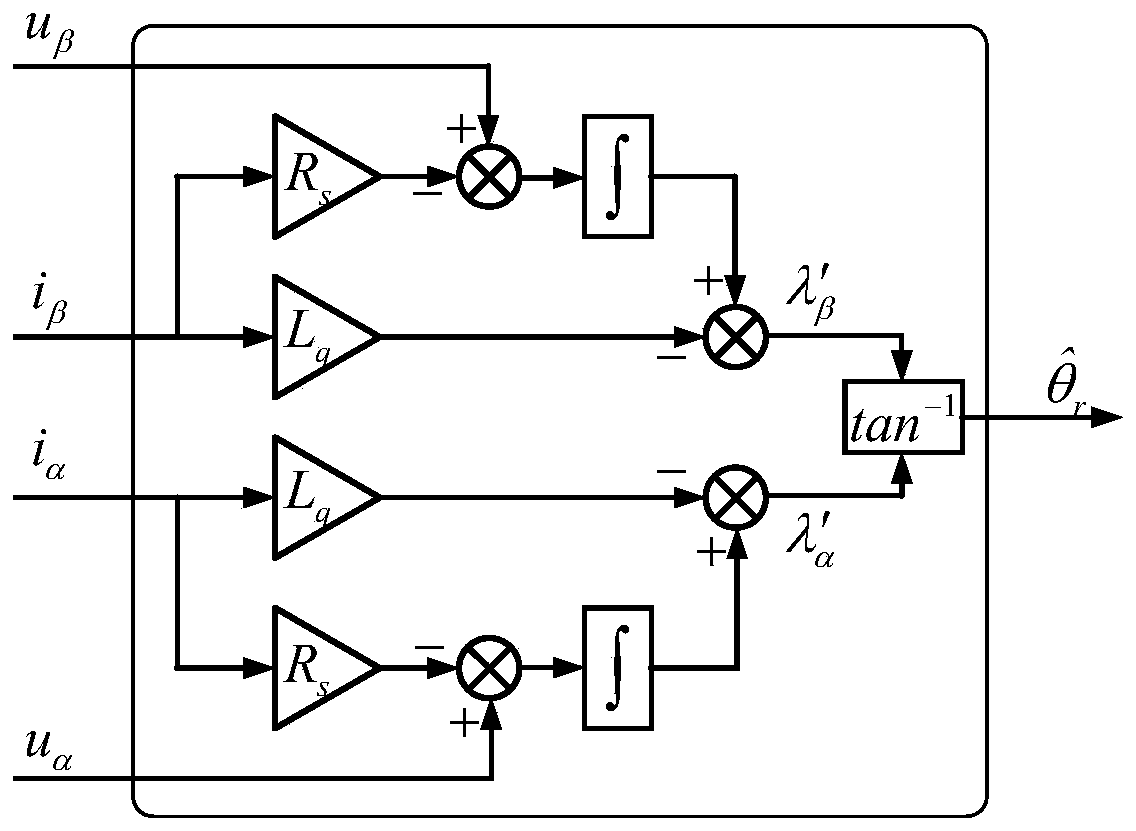
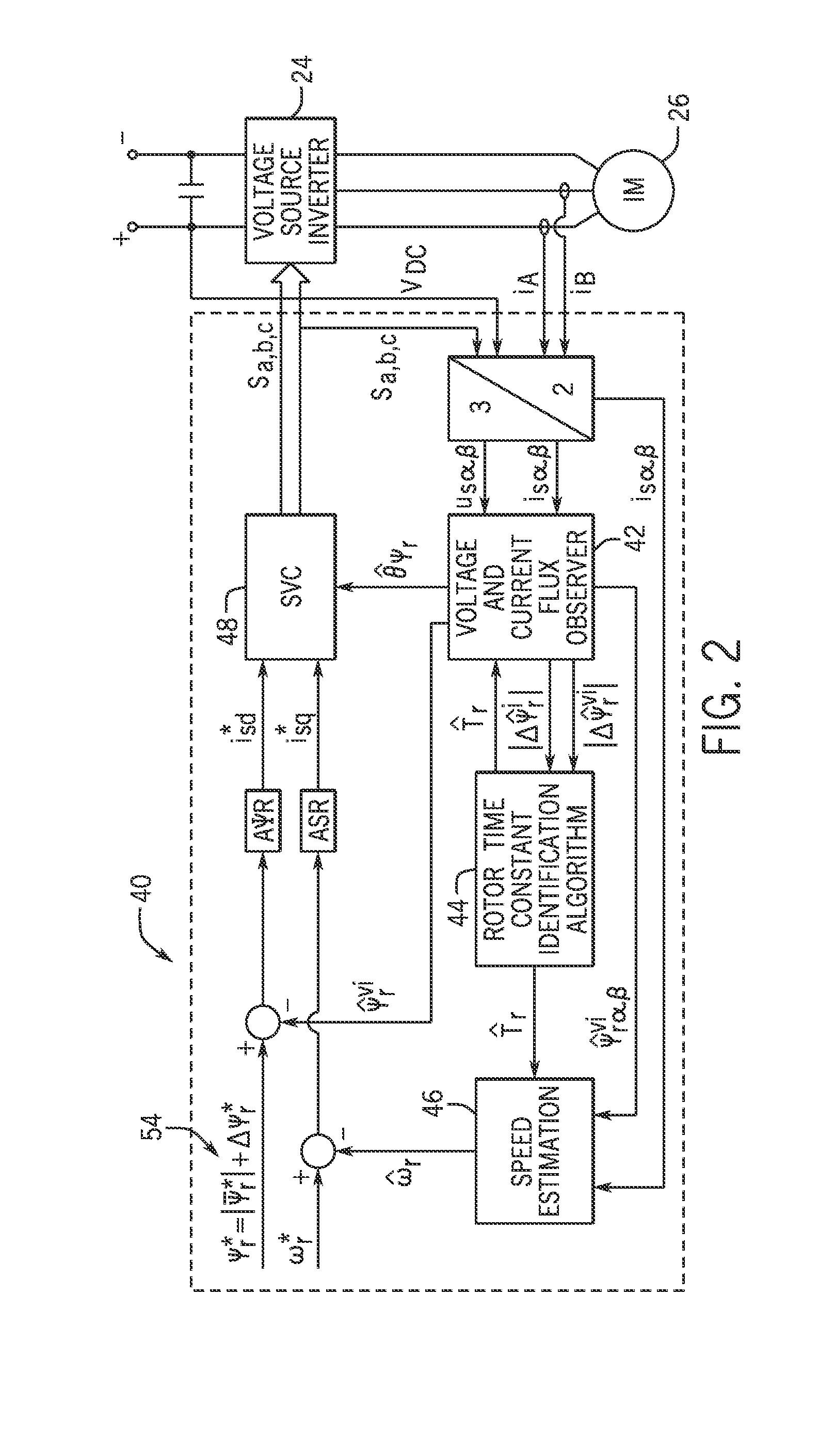
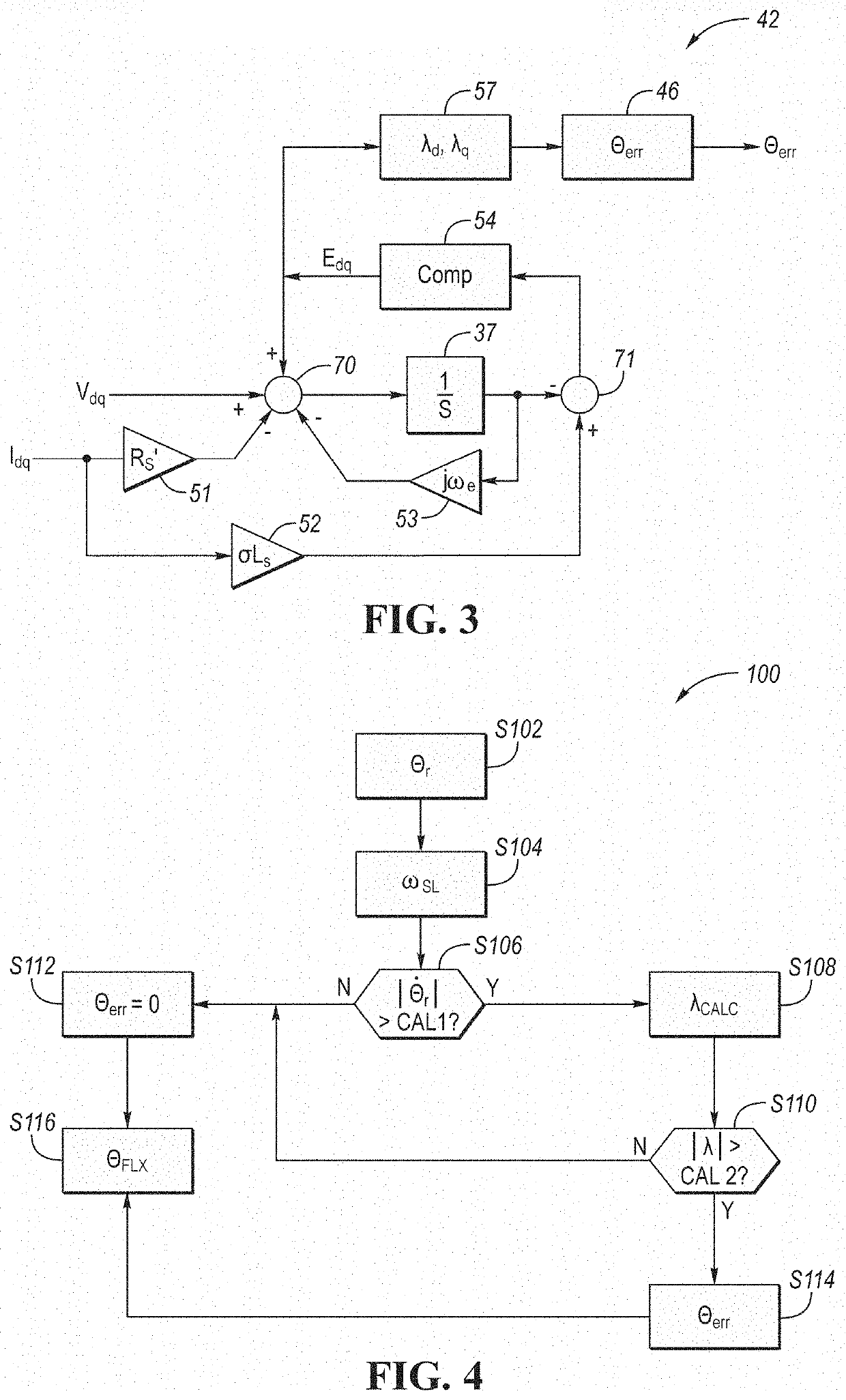
Flux observer in a sensorless controller for permanent magnet motors
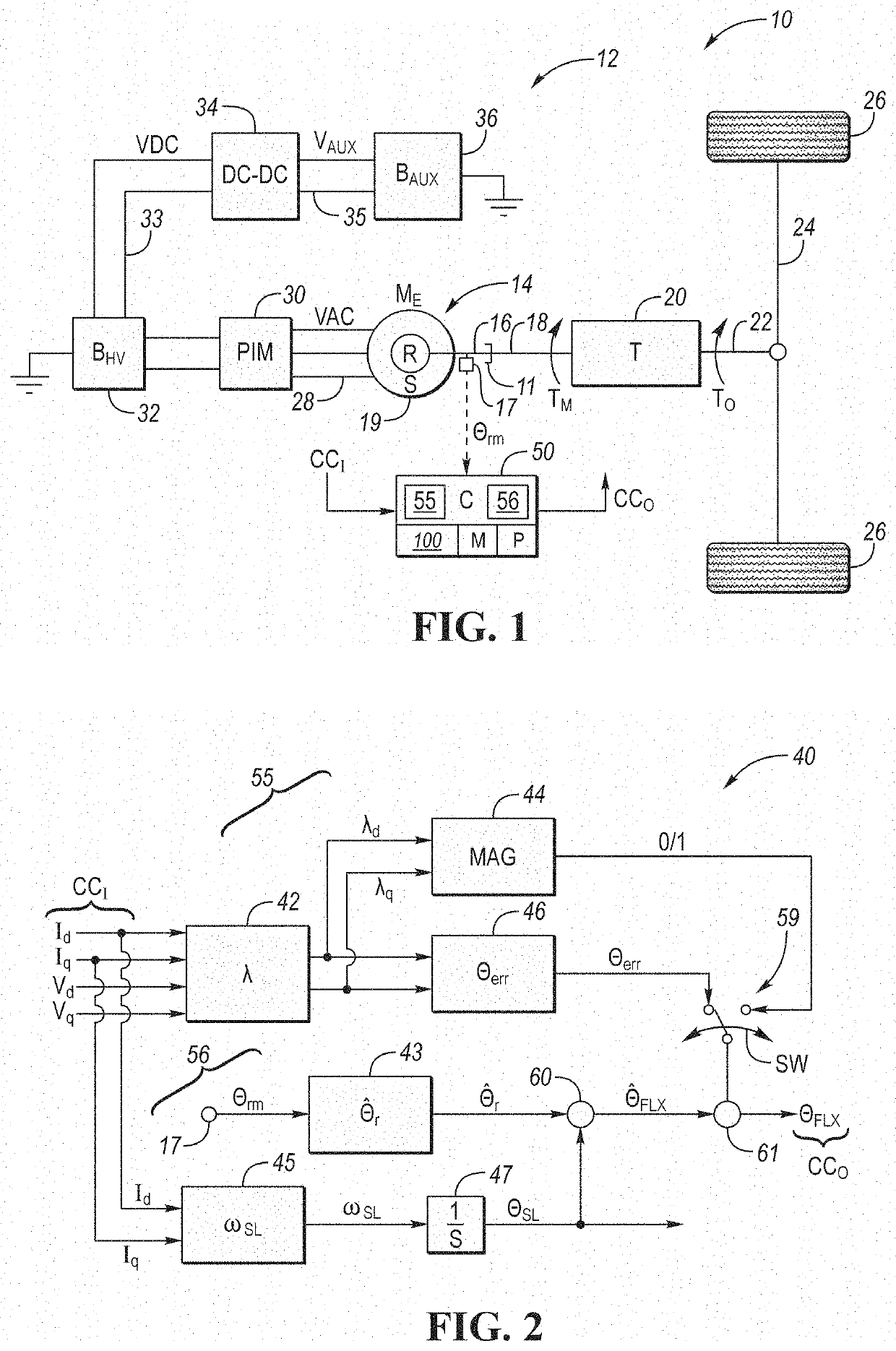
A control system includes a field oriented controller that receives a torque command and that generates phase voltages for an electric machine. A first transformation module receives stator terminal currents and generates d-axis and q-axis stationary frame currents. An open loop flux observer receives d-axis and q-axis stationary frame voltage commands and the d and q-axis stationary frame currents. The open loop flux observer includes a vector cross product calculator that generates an error signal that is proportional to an angular difference between an estimated stator flux and a computed stator flux and a proportional integral controller that generates an estimated rotor angular position based on the error signal. A second transformation module receives the d-axis and q-axis stationary frame currents and the estimated rotor angular position and generates d-axis and q-axis synchronous reference frame feedback currents that are output to the field oriented controller.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
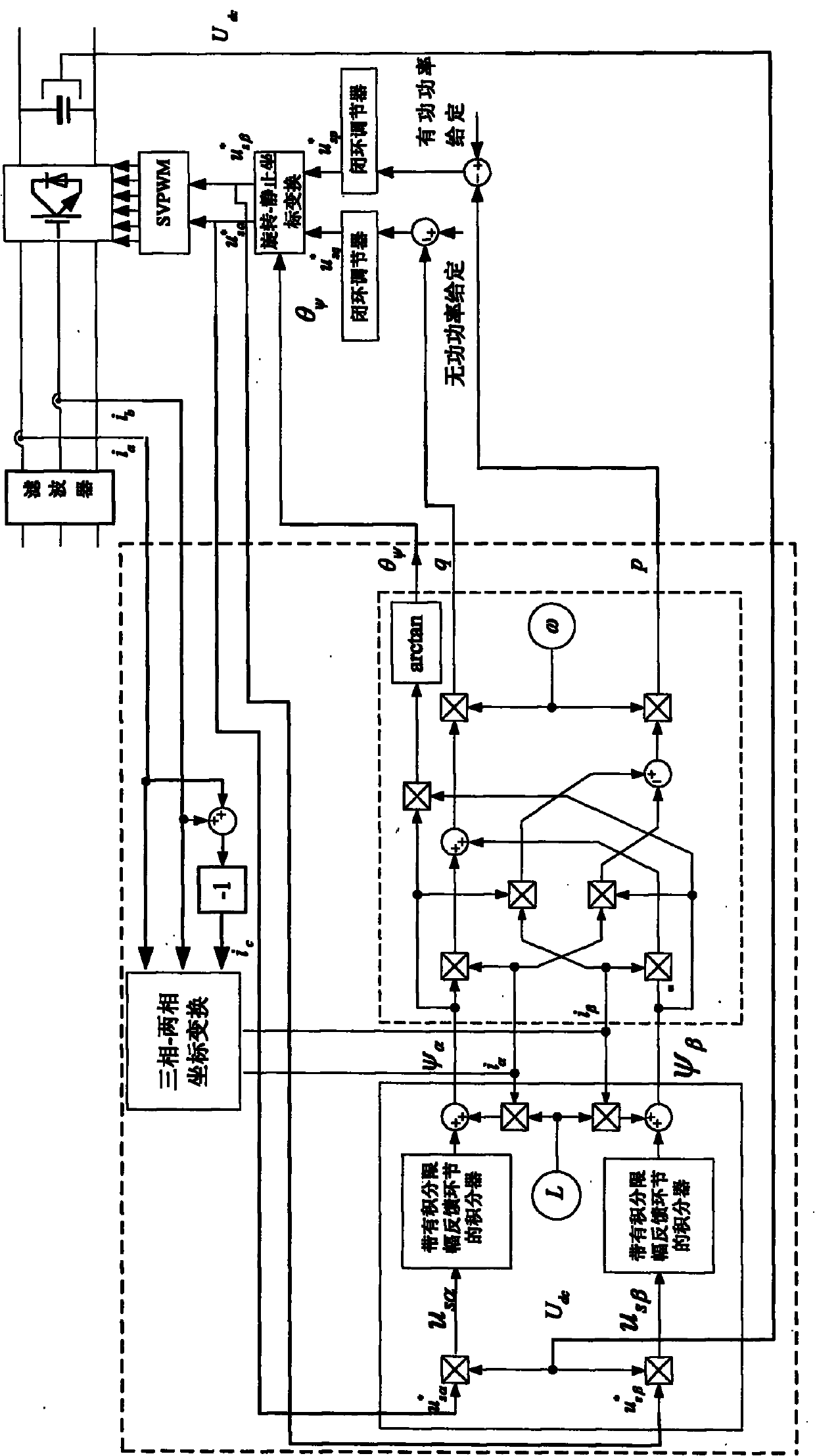
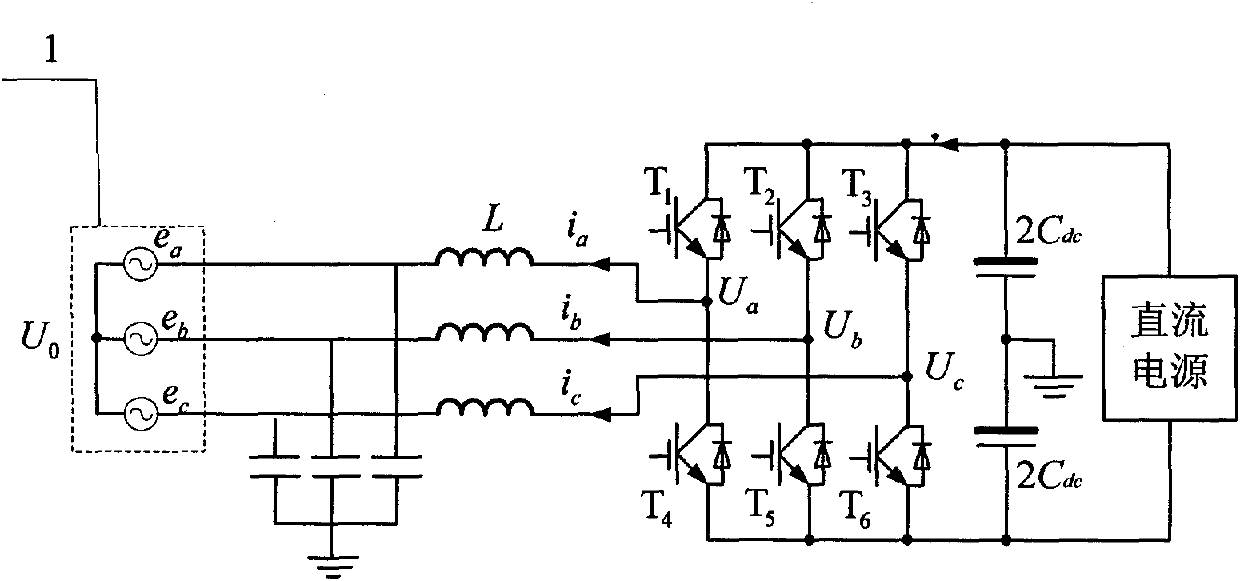
Method for controlling direct power of grid-connected inverter without non-AC voltage sensor
The invention provides a method for controlling direct power of a grid-connected inverter without any non-AC voltage sensor and belongs to the field of electric energy transformation. The invention aims to solve the problem that because an initial value of an integrator in a virtual flux observer of a voltage vector on the network side is improperly selected, the grid-connected inverter cannot normally operate. The method comprises the following steps of: by transformation, obtaining components i alpha and i beta of the three-phase current value in a two-phase stationary coordinate system; by calculation, obtaining components us alpha and us beta of the inversion voltage value of the current grid-connected inverter in the two-phase stationary coordinate system; after the integration of the integrator, calculating components psi alpha and psi beta of the magnetic flux linkage of the voltage on the network side in the two-phase stationary coordinate system; calculating the instantaneous output active power p and reactive power q of the grid-connected inverter, and obtaining components usp * and usq * of the control voltage set value of the new grid-connected inverter in a two-phase rotary coordinate system; and finally obtaining the control signal of all power devices of the grid-connected inverter. The method can be used for direct power control of the grid-connected inverter.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
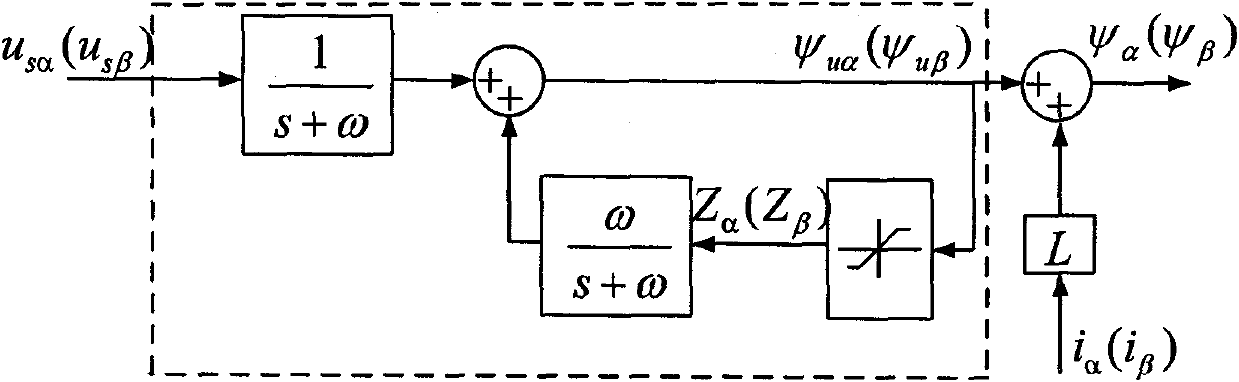
Digital rotor flux observer
InactiveUS6509711B1Improve performanceIncrease speedElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersInduction motorRotor flux
A system (10) for controlling the torque of an induction motor (12) utilizes a flux observer (14). The flux observer (14) receives stator current inputs (16, 18) and a rotor speed estimate (80) and then outputs a rotor flux estimate (20) that provides increased motor control stability at all speeds.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
NPC (neutral point clamped) three-level inverter vector control system based on novel flux observer
InactiveCN103338000AReduce complexityImprove dynamic performanceElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlThree levelVoltage vector
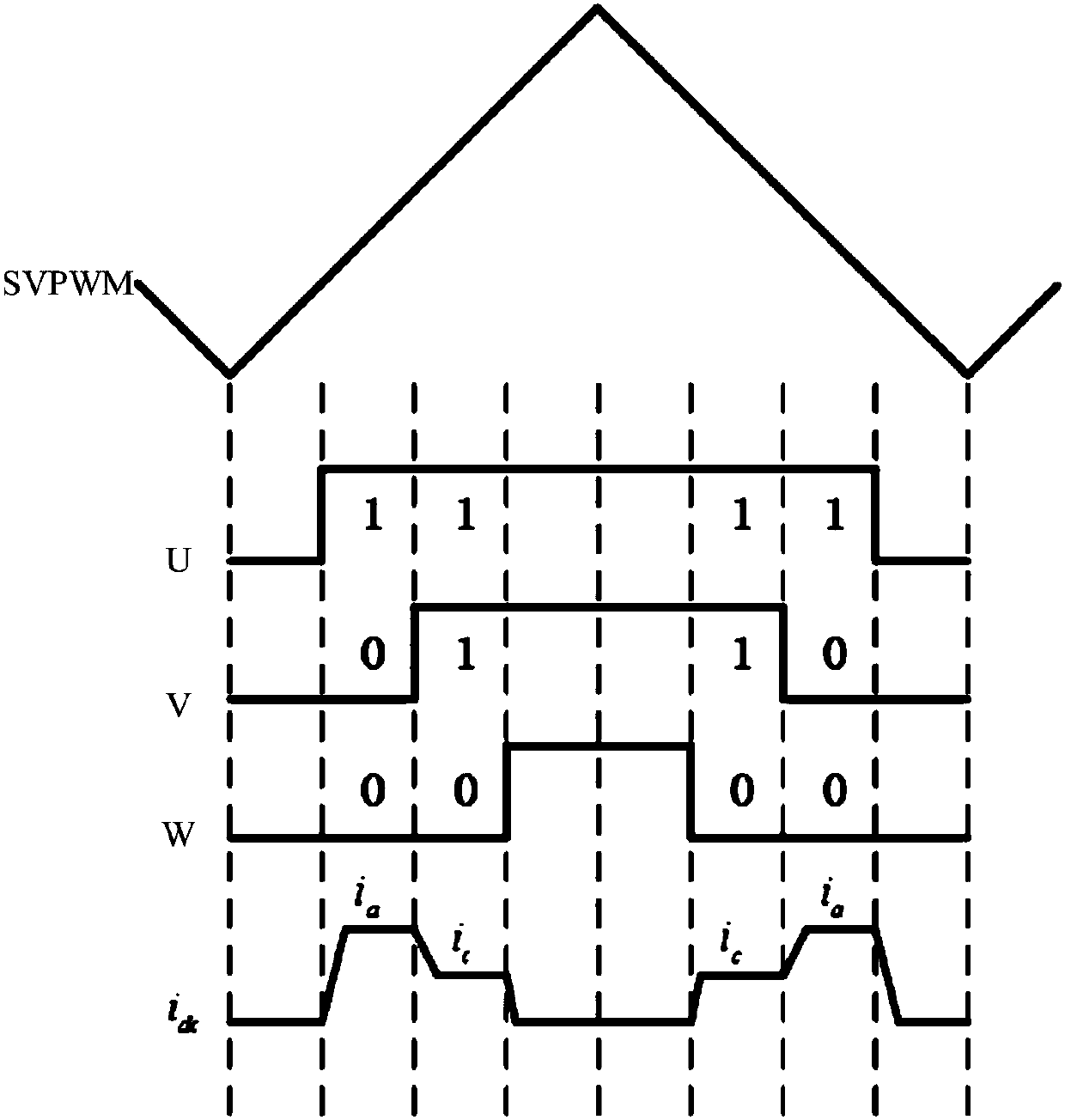
An NPC (neutral point clamped) three-level inverter vector control system based on a novel flux observer provides a simplified SVPWM (space vector pulse width modulation) algorithm. A three-level space vector is decomposed into a two-level space vector; a reference voltage vector is translated; a two-level SVPWM algorithm is used to obtain action time of each basic vector and to choose a right switching status; and the three-level inverter vector control calculation is reduced. Meanwhile, in the invention, the novel flux observer is employed to calculate the rotor flux, so that a current model and a voltage model are used respectively at a low speed and at a high speed; and when a rotation speed is between the low speed and the high speed, an invented hybrid flux observer is used to calculate the rotor flux.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Permanent magnet motor position-less direct torque control method based on novel flux observer
ActiveCN108258967AHigh precisionImprove robustnessElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPosition angleFlux linkage
The invention discloses a permanent magnet motor position-less direct torque control method based on a novel flux observer. Based on a disturbance observer, a voltage model method is improved by a current model flux calculation method, and the novel flux observer is designed. The novel flux observer inputs voltage u alpha and u beta, current i alpha and i beta, permanent magnet flux linkage psi fand an estimated position angle theta under a static coordinate system, and outputs flux estimation values psi alpha and psi beta under a static coordinate system. The novel flux observer has high anti-interference capability, and a two-phase flux linkage can be accurately estimated under the interference conditions of high frequency and part of low frequency. According to the position-less directtorque control method based on the novel flux observer, position estimation errors caused by position-less property can be resisted, the robustness of a position-less system is improved, and stable running of a permanent magnet motor position-less sensor is ensured.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method in connection with sensorless induction motors
ActiveUS20050001583A1Fast implementationFast reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlStator voltageSystem matrix
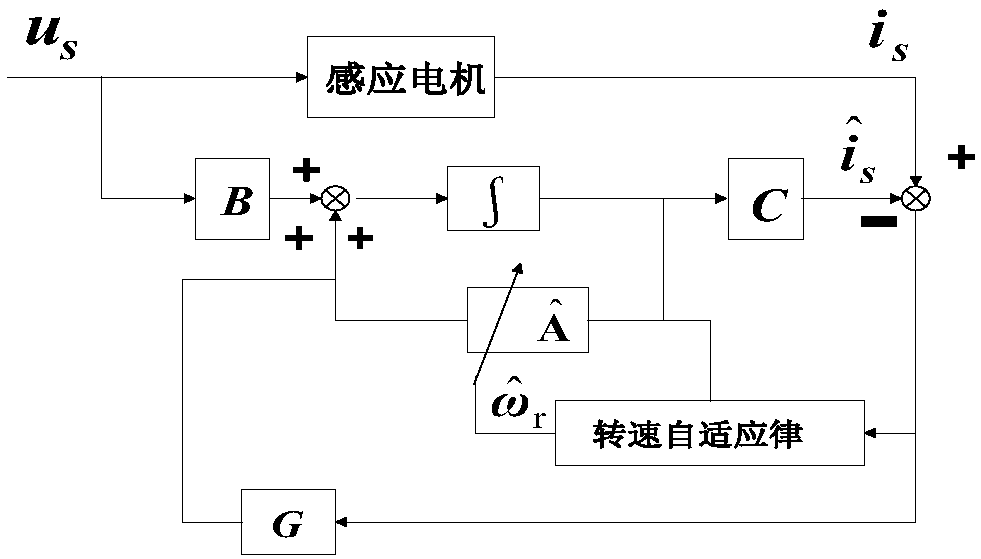
A method for the stabilization of full-order flux observers for speed-sensorless induction motors in the regenerative mode. The method comprises determining the current vector of the induction motor, determining the stator voltage vector of the induction motor, forming a full-order flux observer having a system matrix (A) and a gain matrix (L), the state-variable observer being augmented with a speed adaptation loop, and producing an estimated rotor flux linkage vector and an estimated stator current vector, determining an estimation error of the stator current vector, defining a correction angle, and forming a speed adapt-tion law based on the cross product of the estimation error of the stator current vector and the estimated rotor flux linkage vector, where the correction angle is used to turn the rotor flux linkage vector or the estimation error of the stator current vector in order to keep the observer stable.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Method in connection with sensorless induction motors
InactiveUS6940253B2Fast implementationFast reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlSystem matrixFlux linkage
A method for the stabilization of full-order flux observers for speed-sensorless induction motors in the regenerative mode. The method comprises determining the current vector of the induction motor, determining the stator voltage vector of the induction motor, forming a full-order flux observer having a system matrix (A) and a gain matrix (L), the state-variable observer being augmented with a speed adaptation loop, and producing an estimated rotor flux linkage vector and an estimated stator current vector, determining an estimation error of the stator current vector, defining a correction angle, and forming a speed adapt-tion law based on the cross product of the estimation error of the stator current vector and the estimated rotor flux linkage vector, where the correction angle is used to turn the rotor flux linkage vector or the estimation error of the stator current vector in order to keep the observer stable.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
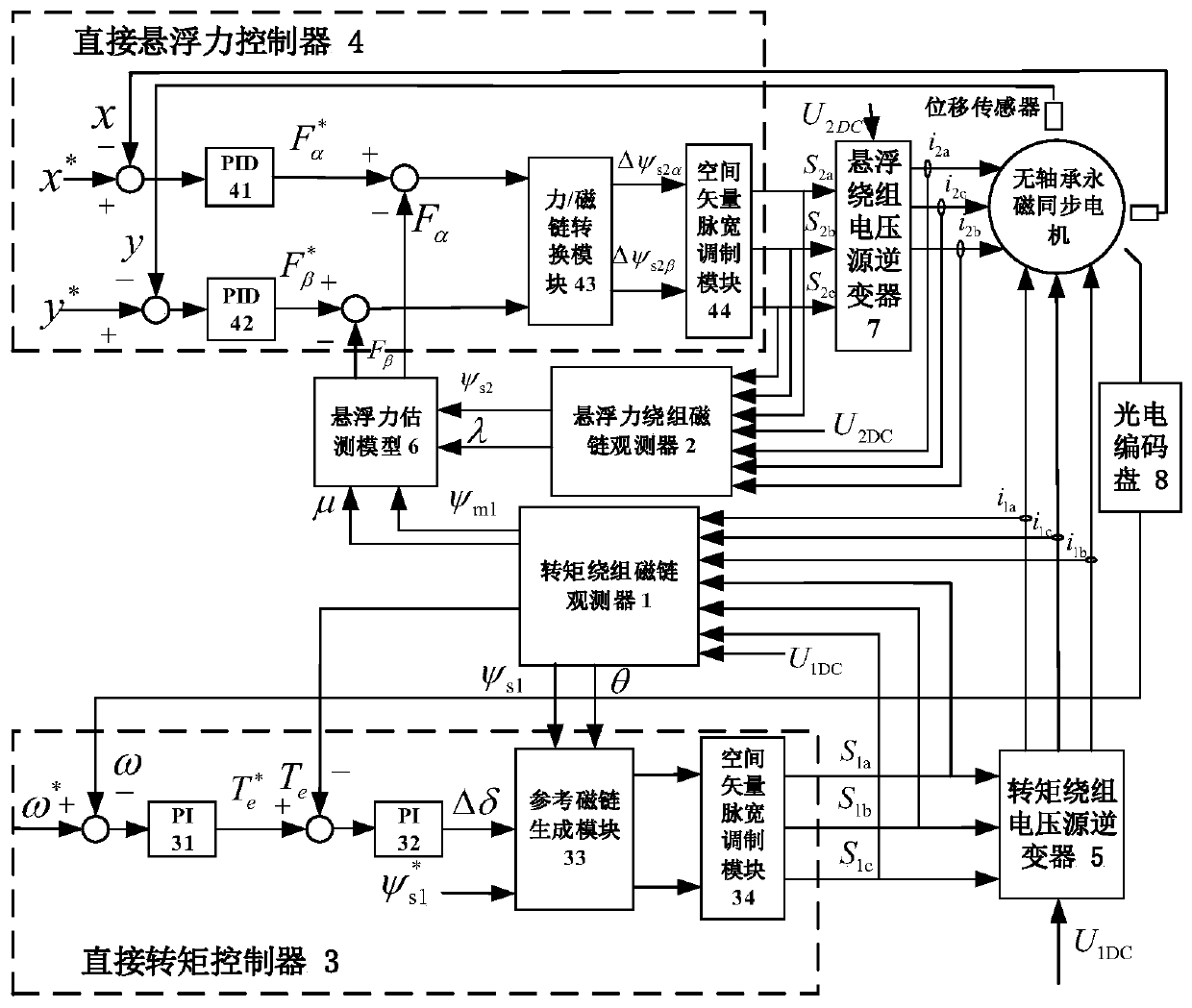
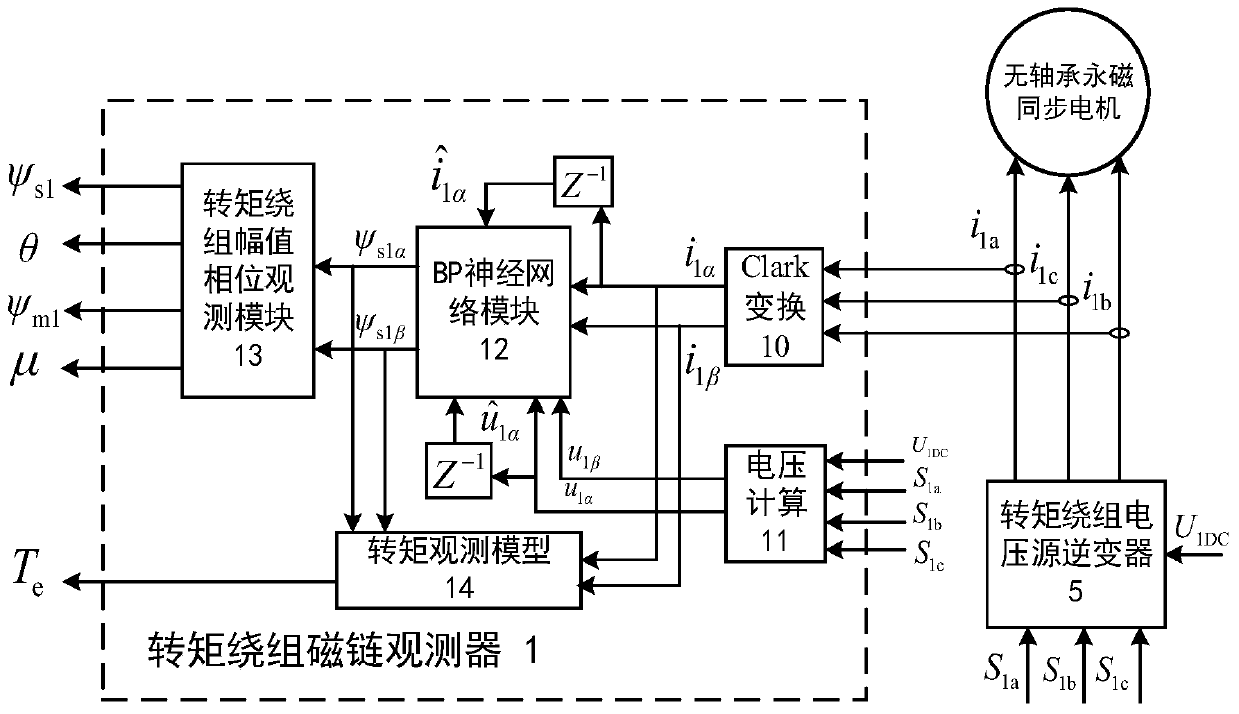
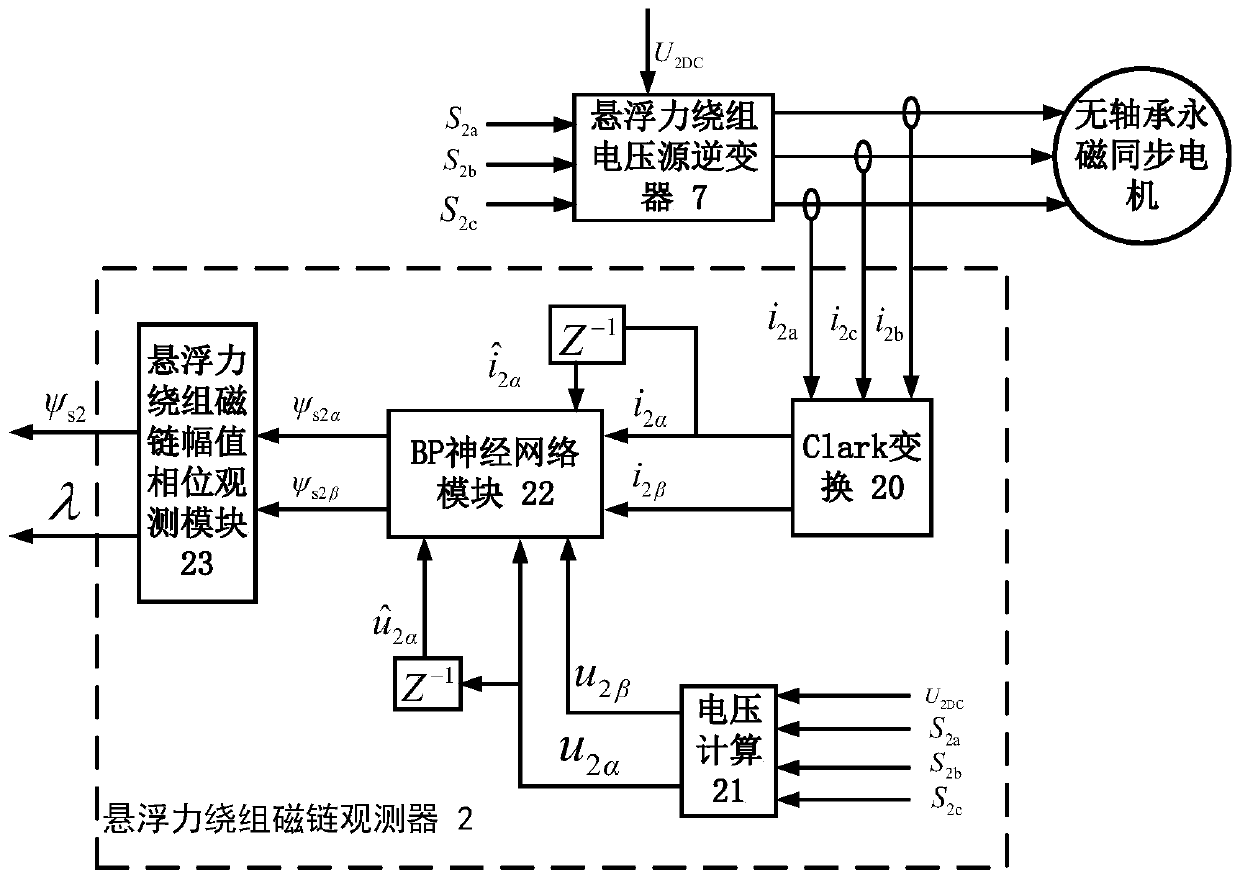
Single-winding bearingless motor torque and suspension force direct controller and construction method
InactiveCN105406784AGuaranteed uptimeEasy to implement direct controlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsComputer moduleVoltage reference
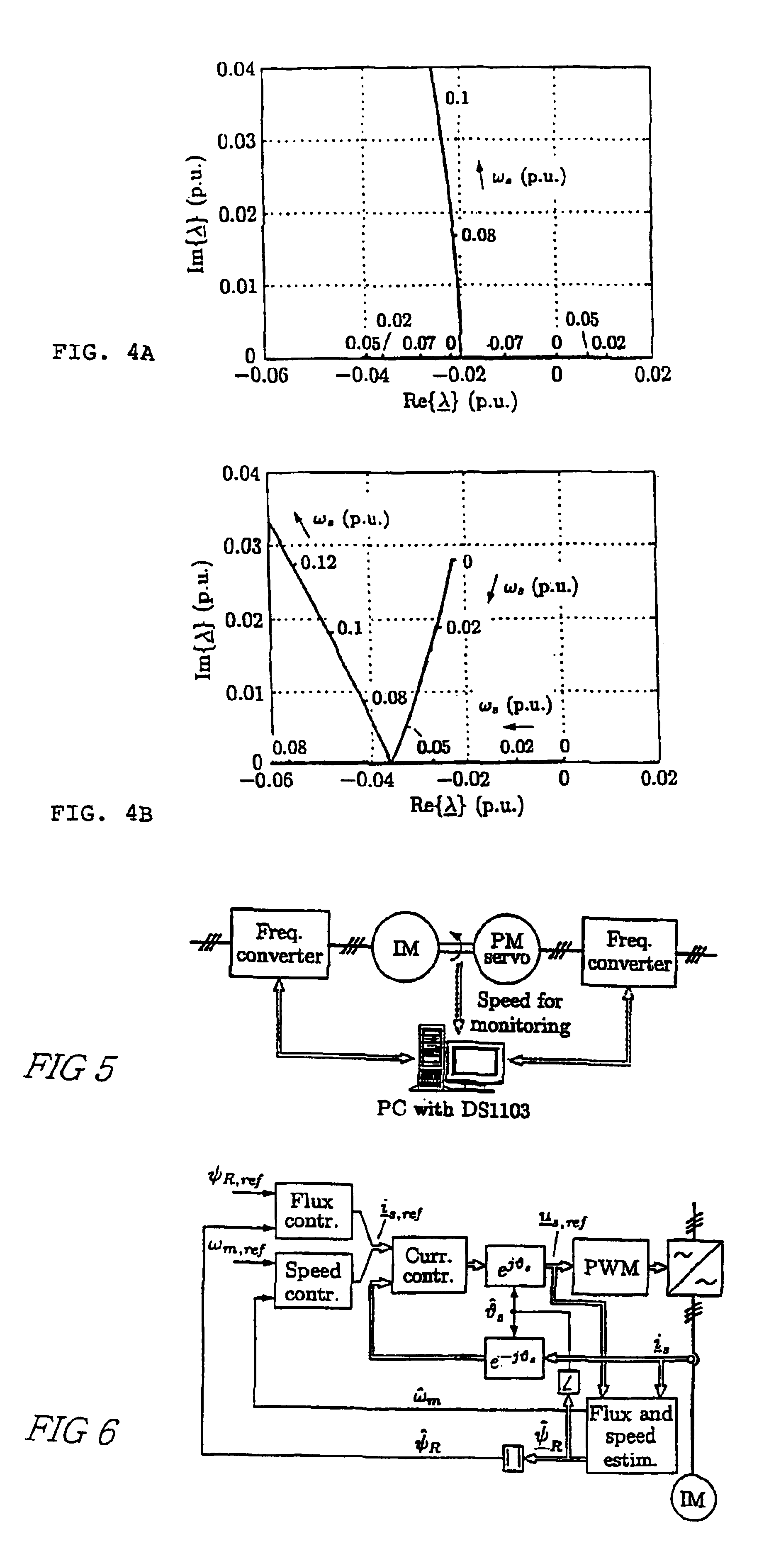
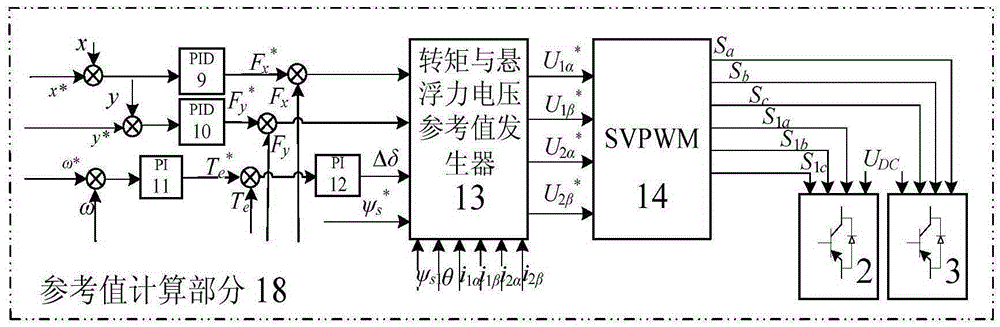
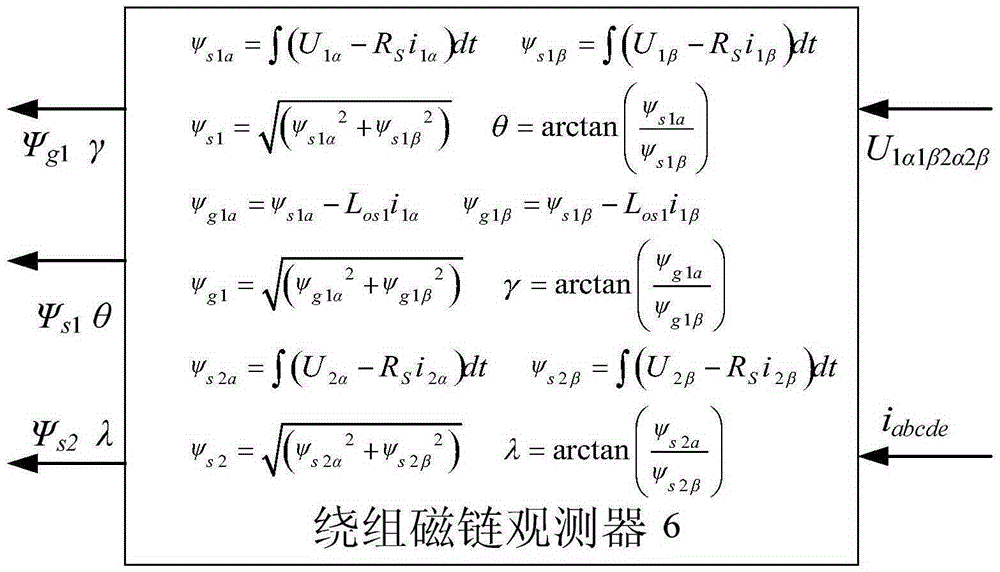
The invention discloses a single-winding bearingless motor torque and suspension force direct controller and a construction method. The controller comprises a reference value calculation part and an observation value calculation part, wherein the observation value calculation part comprises a winding flux observer, a suspension force observer, a torque observer and two matrix transform modules; output of the first matrix transform module is connected with input of the winding flux observer; the output of the winding flux observer is connected with the suspension force observer and the torque observer respectively; the output of the second matrix transform module is connected with the winding flux observer and the torque observer respectively; a observed winding real-time flux is applied to the torque observer, the suspension force observer and a torque and suspension force voltage reference value generator; a voltage static coordinate instruction value is generated in the torque and suspension force voltage reference value generator according to a flux amplitude instruction value, real-time winding torque component flux amplitude and phase and an actual feedback current; and the torque and rotor radial suspension force are directly controlled.
Owner:江苏科海生物工程设备有限公司
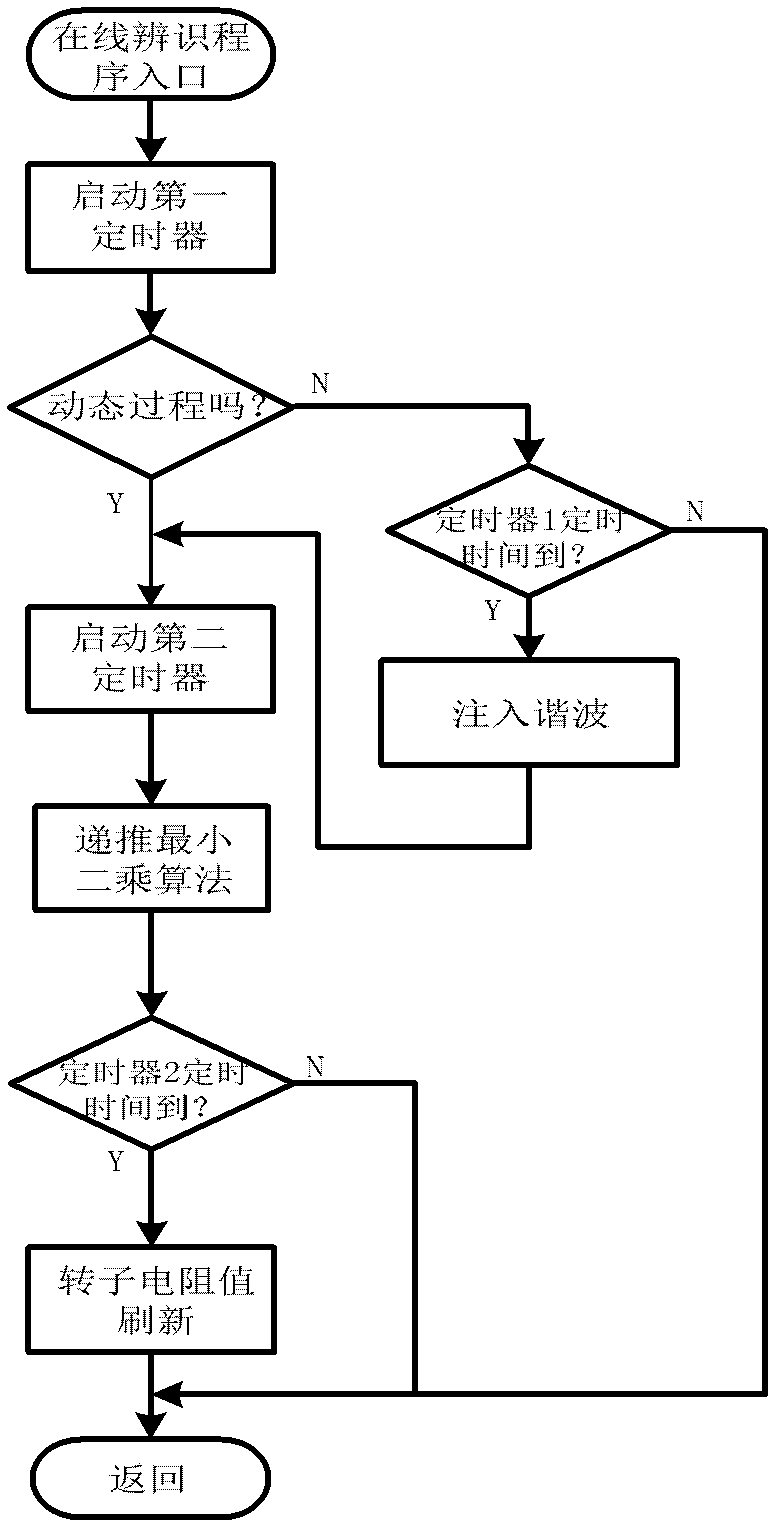
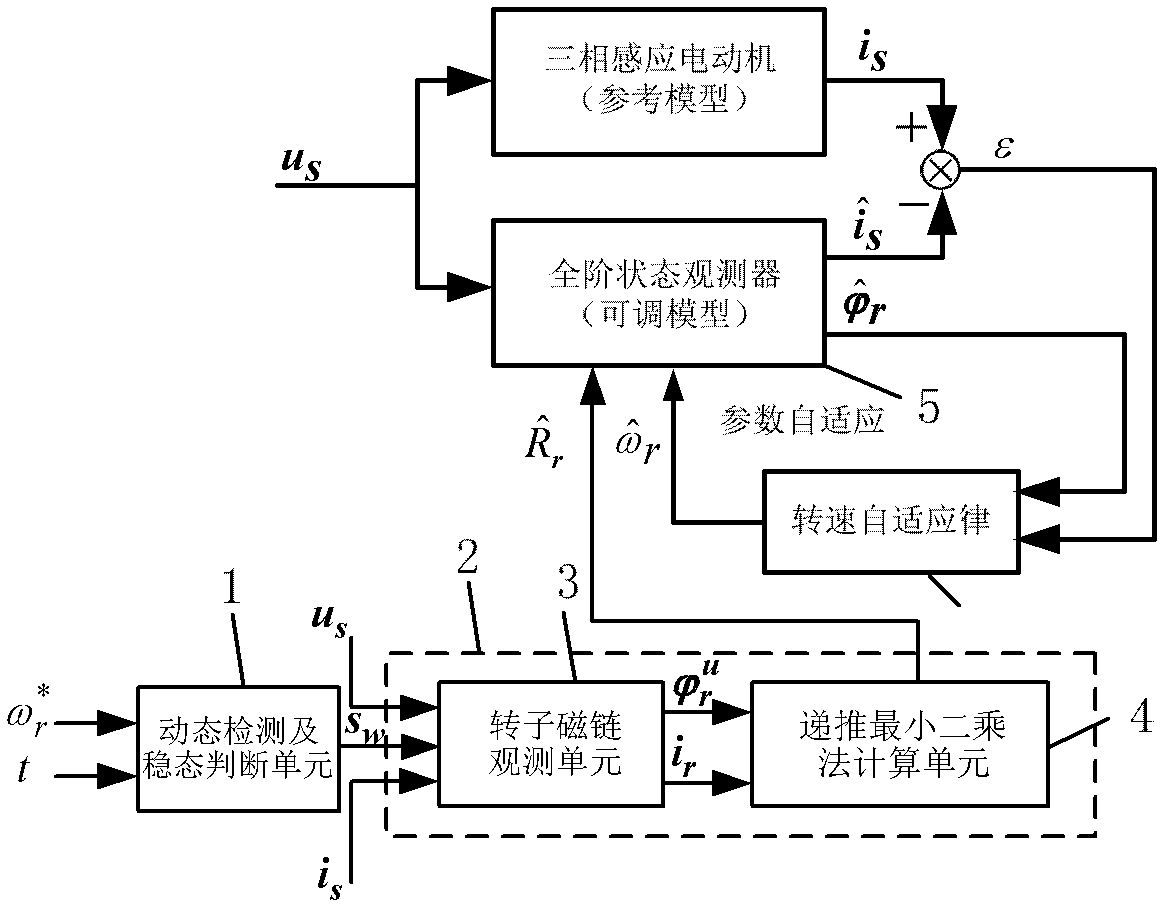
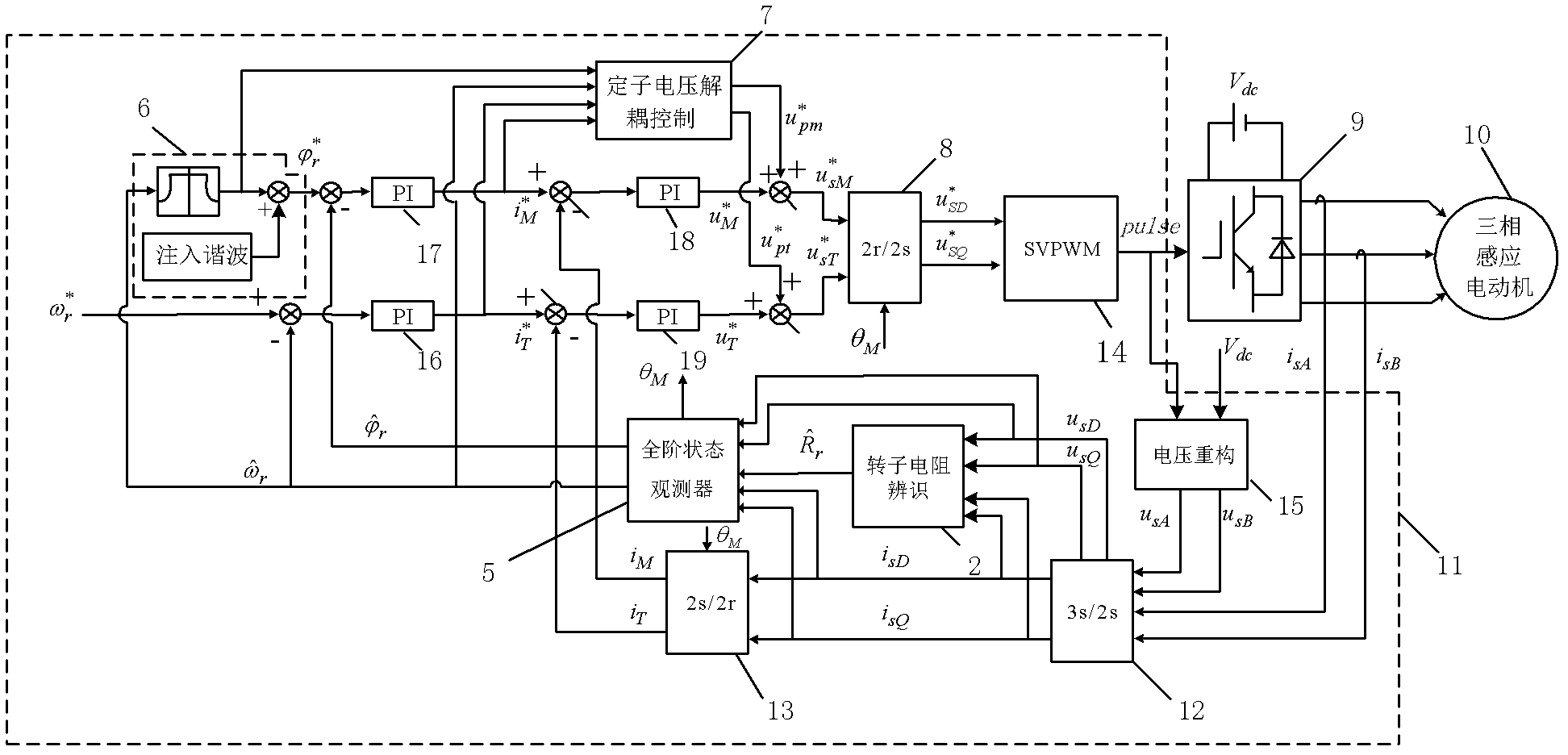
Online rotor resistance identification method of asynchronous motor
ActiveCN102611382AEasy to driveImprove robustnessElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsForgetting factorEngineering
The invention relates to an online motor parameter identification method, in particular to an online rotor resistance identification method of a non-speed sensor vector control system. The method is characterized in that, during dynamic adjustment of a system, the online rotor resistance identification can be realized by using transient flux change process and by adopting an adaptive forgetting factor recursive least square algorithm in combination with an integral-improved voltage model flux observer independent from a full-order adaptive state observer; during stable operation of the system, the rotor flux is subjected to a specific harmonic transiently at a certain time interval to generate dynamic flux change, and the rotor resistance can be identified by adopting the adaptive forgetting factor recursive least square algorithm in combination with the integral-improved voltage model flux observer so as to online refresh the rotor resistance in the full-order adaptive state observer. The online motor rotor resistance identification method provided by the invention can calculate the motor parameter change so as to regulate a motor controller, thereby improving the performance of the motor controller.
Owner:CHANGZHOU LIANLI AUTOMATION TECH +1
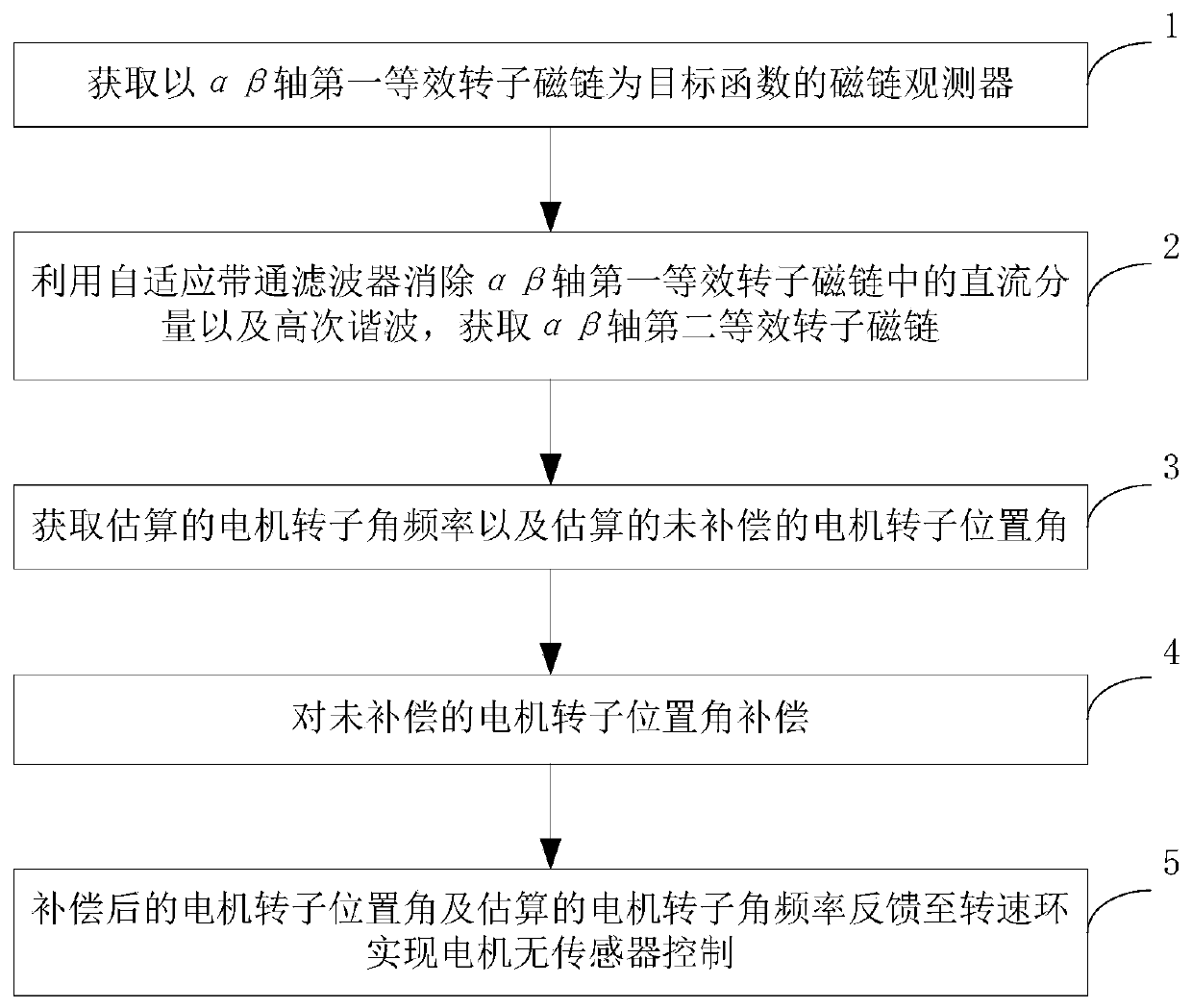
Sensorless control method and system for permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN110492820AAccurate observationElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlPosition anglePermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a sensorless control method and a sensorless control system for a permanent magnet synchronous motor, which belong to the field of sensorless control of the permanent magnet synchronous motor and comprise the following steps of: acquiring a flux observer taking an alpha-beta axis first equivalent rotor flux as a target function; eliminating direct-current components and higher harmonics in the alpha-beta axis first equivalent rotor flux linkage by using an adaptive band-pass filter; acquiring the estimated motor rotor angular frequency and the estimated uncompensated motor rotor position angle through a phase-locked loop by means of the per-unit alpha-beta axis second equivalent rotor flux linkage; and compensating the estimated uncompensated motor rotor position angle by using a transfer function of an adaptive band-pass filter. According to the invention, the self-adaptive band-pass filter is adopted to filter direct current components introduced by current sampling and higher harmonics introduced by inverter nonlinearity, compensate the position angle of the motor rotor and estimate the angular frequency of the motor rotor, so that the rotating speed of the motor and the position information of the rotor can be accurately observed.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and method of rotor time constant online identification in an ac induction machine
ActiveUS20150002071A1Electronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlRotor fluxRotor time constant
A system and method for determining a rotor time constant of an AC induction machine is disclosed. During operation of the induction motor, a flux signal is injected into a rotor flux command so as to generate a time-variant rotor flux. A voltage-current flux observer determines amplitudes of rotor flux variations resulting from the time-variant rotor flux, with the amplitudes of the rotor flux variations comprising an amplitude of a rotor flux variation based on a current model of the voltage-current flux observer and an amplitude of a rotor flux variation based on a combined voltage-current model of the voltage-current flux observer. A rotor time constant of the induction motor is then estimated based on the determined amplitudes of the rotor flux variations.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Squirrel cage asynchronous motor equivalent circuit parameter identification method based on measurable electrical capacity
InactiveCN103281031AEasy to implementMany identifiable parametersElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsStator voltageInduction motor
The invention discloses a squirrel cage asynchronous motor equivalent circuit parameter identification method based on measurable electrical capacity and belongs to the field of on-line identification of squirrel cage asynchronous motor parameters. The squirrel cage asynchronous motor equivalent circuit parameter identification method based on measurable electrical capacity does not depend on a velocity sensor and a motor flux observer does not need to be designed. The voltage data and the current data of a stator of a motor are measured directly, a motor parameter identification model based on a least square method under a dq0 coordinate system is adopted, parameters of the stator and a rotor of an asynchronous motor equivalent circuit can be identified on line through a recursion augmentation least squares algorithm on the basis that the factors which influence identification precision are fully considered. The squirrel cage asynchronous motor equivalent circuit parameter identification method based on measurable electrical capacity is simple in algorithm, small in calculated amount and suitable for on-line identification of the motor parameters. Therefore, the purpose that the real-time parameters of the motor are accurately obtained is achieved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Speed sensorless starting method for synchronization motor
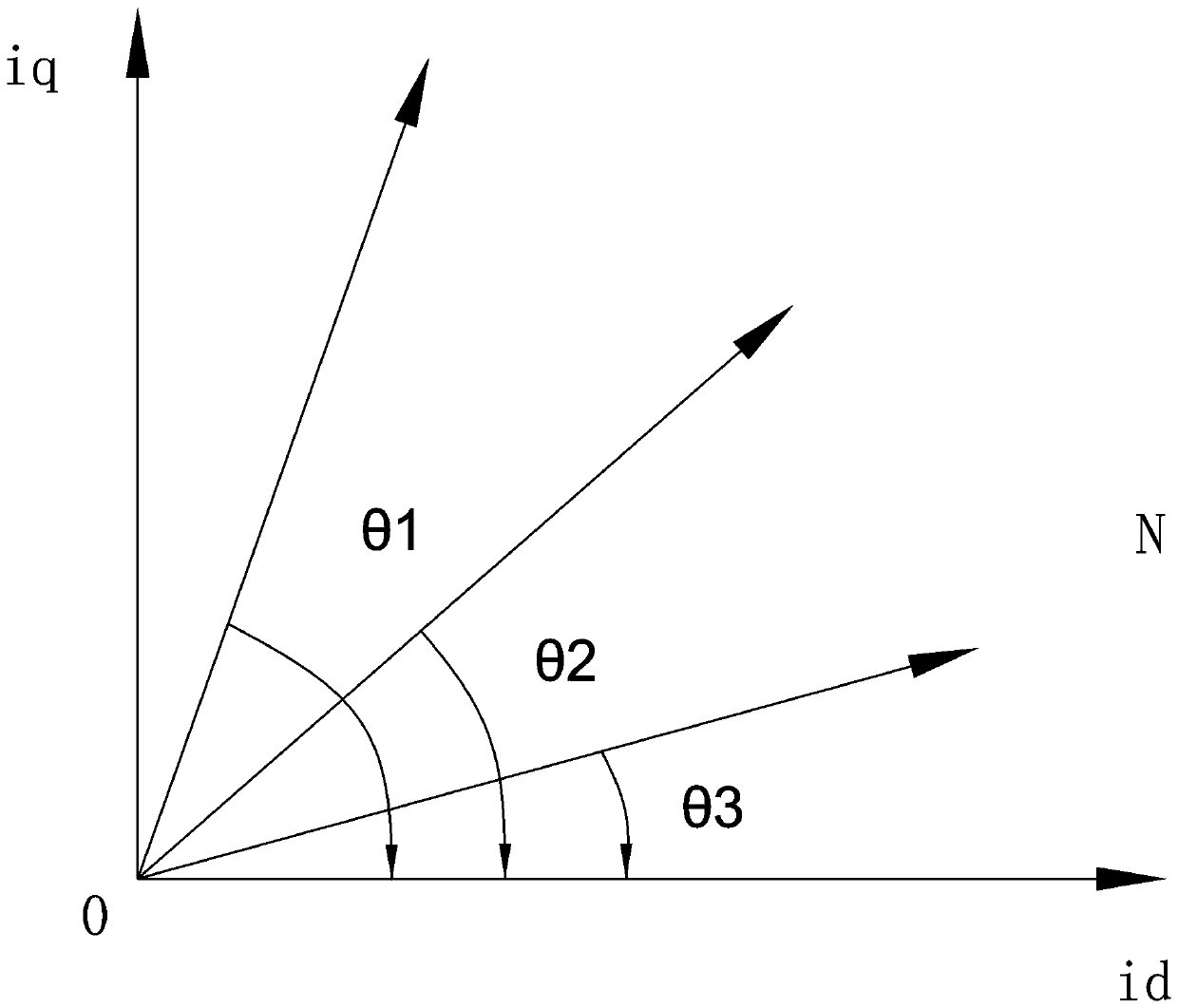
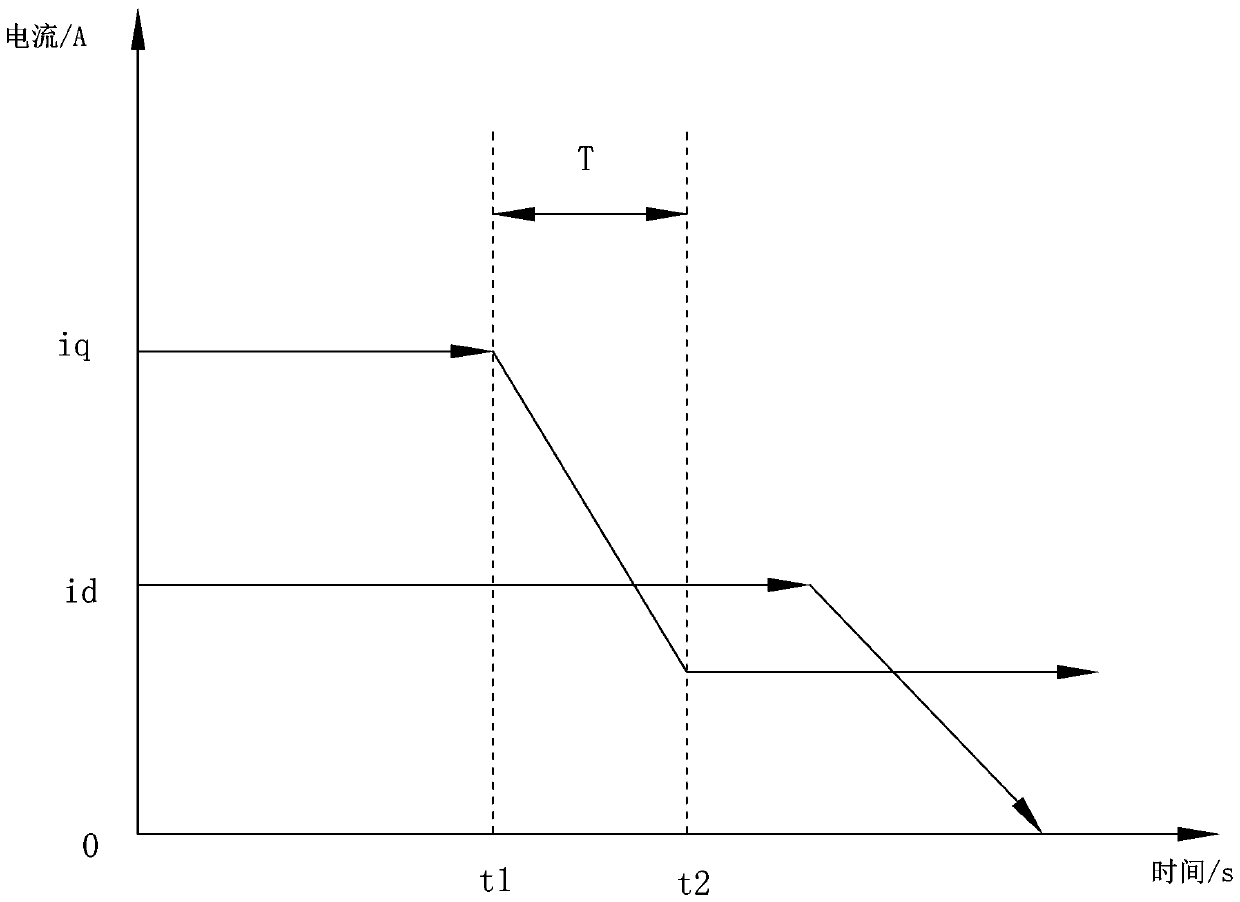
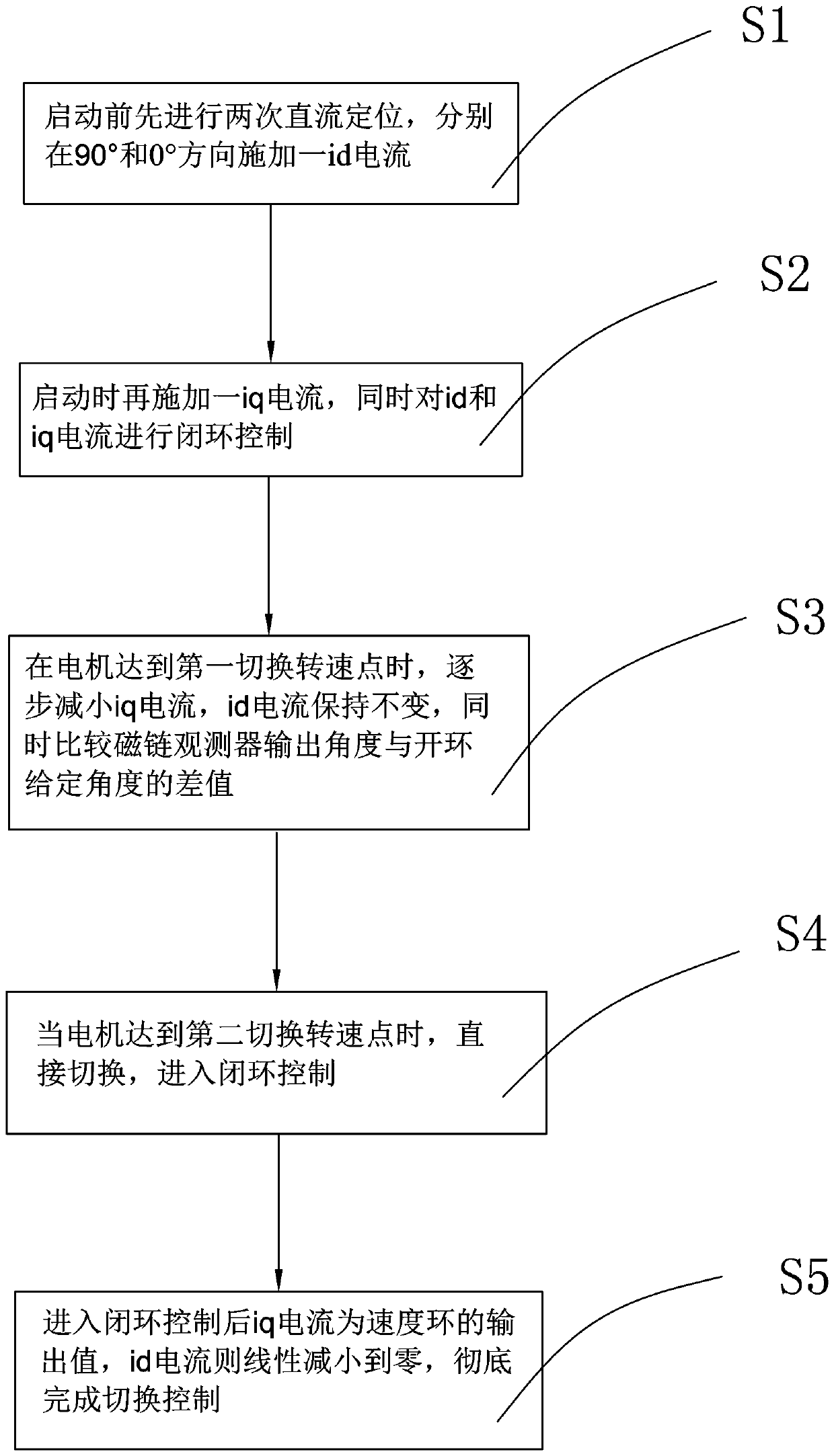
ActiveCN107623467APlay a positioning roleWon't get out of stepStarter arrangementsPower flowElectric machine
The invention relates to a speed sensorless starting method for a synchronization motor. The method includes performing two processes of DC positioning before starting, applying id current in a 90-degree direction and a 0-degree direction separately, and applying iq current when starting, and performing closed-loop control on id and iq current at the same time; when the motor reaches a first switch rotation speed point, reducing the iq current gradually, keeping the id current unchanged, and comparing to obtain a difference value between an output angle and an open loop given angle of a flux observer; when the motor reaches a second switch rotation speed point, switching directly and entering into closed-loop control. According to the invention, new id axial current is introduced and a positioning effect is achieved for the motor. Smooth switching can be realized during the switching process of the motor. Besides, even a load has comparatively large fluctuation during the switching process, motor out-of-step can also be prevented. The method has excellent stability and switching quickness.
Owner:厦门金龙汽车新能源科技有限公司
Method for detecting sensor board of linear motor traction system
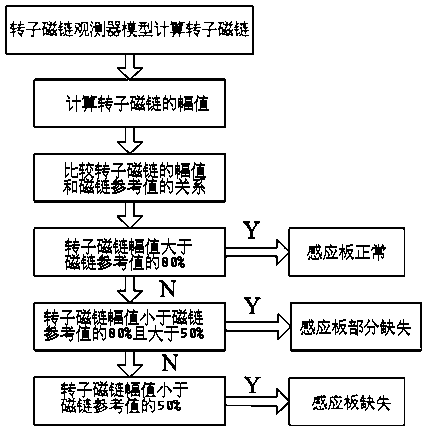
ActiveCN103901483AAccurate detectionImprove real-time performanceElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationElectric machineControl system
The invention discloses a method for detecting a sensor board of a linear motor traction system. A flux observer model for observing a linear motor rotor is set up, a flux reference value is set, and if a sensor board area exists is judged and detected by observing changes of a flux of the linear motor rotor and comparing the relationship between the amplitude of the flux of the linear motor rotor and the flux reference value. The rotor flux observer and a control system are integrated. If the amplitude of the flux of the rotor is larger than 80% of the flux reference value, the sensor board is normal; if the amplitude of the flux of the rotor is smaller than 80% and larger than 50% of the flux reference value, the sensor board is partially lost; if the amplitude of the flux of the rotor is smaller than 50% of the flux reference value, the sensor board is lost. The condition of the sensor board is judged by observing the flux of the rotor, any hardware is not needed, a non-sensor-board area can be accurately detected, the real-time performance of results is good, observation of the flux of the rotor is accurate, and the condition of the sensor board can be accurately reflected.
Owner:CSR ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE RES INST
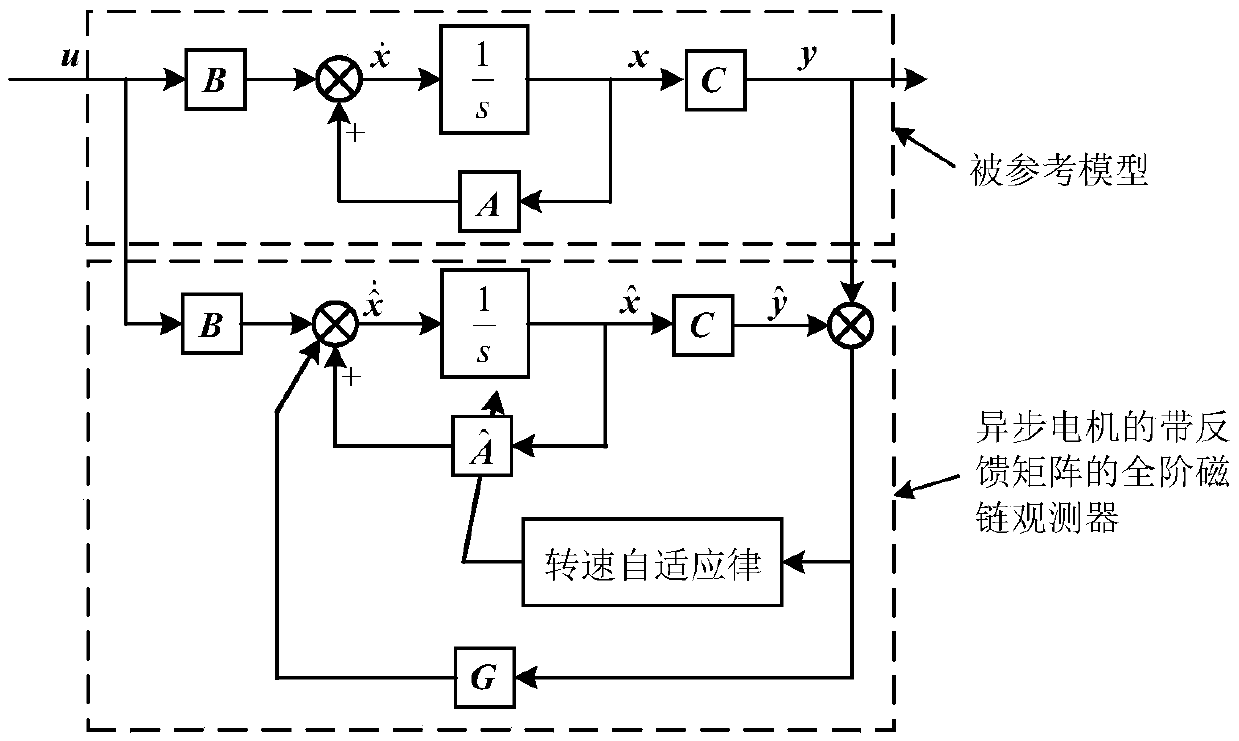
Full-order flux observer feedback matrix acquisition method and non-speed sensor
ActiveCN109104130AImprove instabilityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMotor speedElectric machine
A full-order flux observer feedback matrix acquisition method and a non-speed sensor belong to the technical field of motors. The method obtains a feedback matrix G under the condition of state stability requirement of full-order flux linkage observer and stability constraint of speed estimation of asynchronous motor. The obtained feedback matrix is applied to non-speed sensor control of asynchronous motors to improve the instability region of asynchronous motors in the low-speed power generation region. By selecting the designed feedback gain matrix, the invention can improve the instabilityproblem when the asynchronous motor is in the low-speed power generation region. By selecting the parameters of the configuration feedback gain matrix, the critical frequency can be reduced and the unstable region can be reduced.
Owner:BEIJING MECHANICAL EQUIP INST
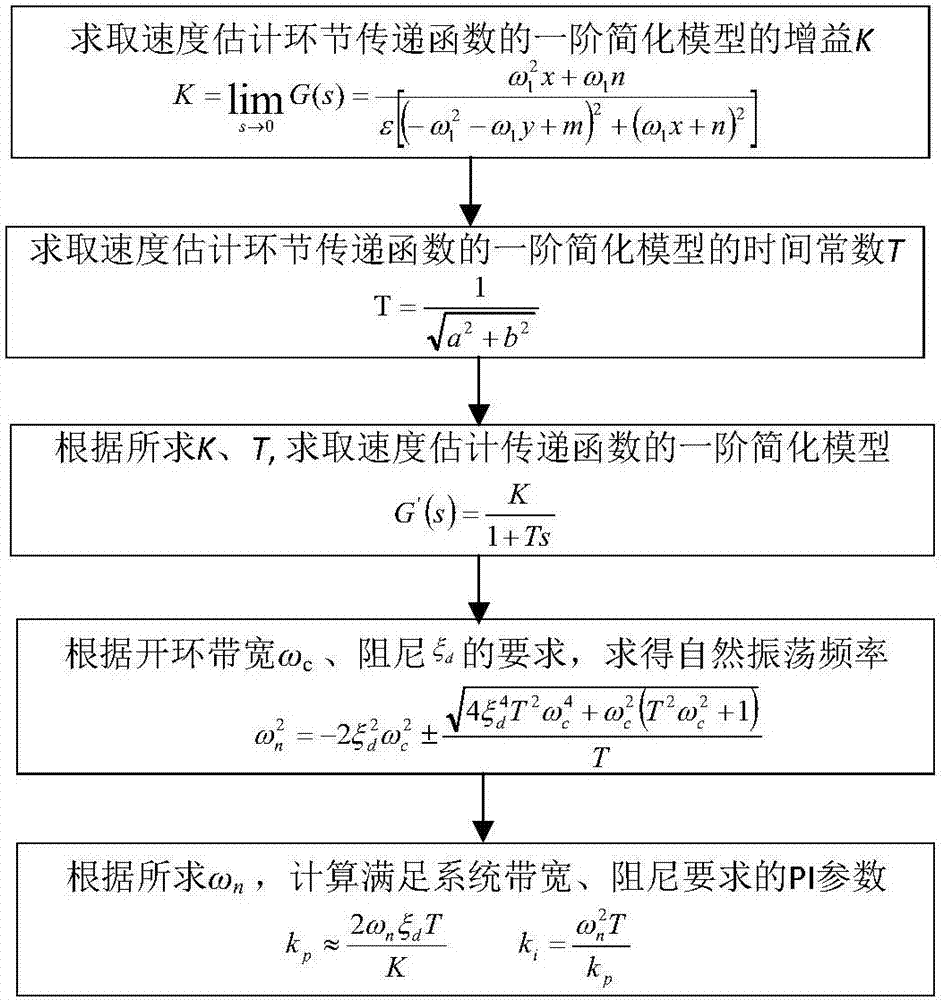
DSP-based rotation speed estimation link PI parameter quantitative setting method
ActiveCN107196569AAvoid blindnessReduce computationElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlReduced modelLoop bandwidth
The invention relates to the technical field of asynchronous motors, and particularly relates to a DSP-based rotation speed estimation link PI parameter quantitative setting method. Firstly, parameters of a control object motor, the synchronization frequency and controller parameters are acquired; according to the original transfer function in the speed estimation link, the gain K of a first-order simplified model is calculated; according to the complex vector model of an asynchronous motor full-order flux observer, the time constant T of the first-order simplified model is calculated; according to the acquired gain K and the constant T, the first-order simplified model for a speed estimation link transfer function is obtained; and according to requirements of an open-loop bandwidth omega<c><*> and damping xi<d><*>, after the natural oscillation frequency omega<n><2> meeting the requirements is acquired, and the final PI parameter for speed estimation link is solved. Thus, the DSP-based rotation speed estimation link PI parameter quantitative setting method solves fuzziness and blindness during the traditional speed adaptive PI parameter configuration process.
Owner:CHANGZHOU LIANLI AUTOMATION TECH
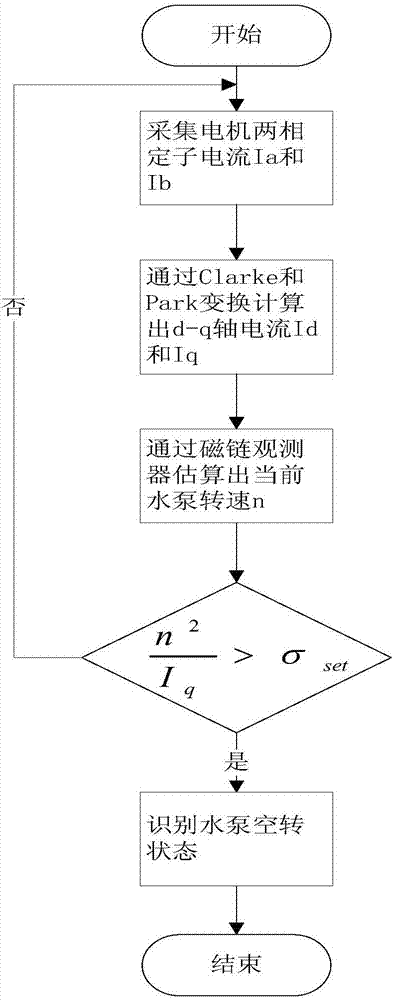
Method for detecting running state of direct current water pump
ActiveCN107448398AJudging the idling running stateStop in timePump controlNon-positive displacement fluid enginesPower flowEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection, in particular to a method for detecting the running state of a direct current water pump. The method for detecting the running state of the direct current water pump includes the steps that (1) a motor of the water pump starts to run, a system collects two-phase stator currents Ia and Ib of the motor, and the Ia and Ib are processed by Clarke conversion to obtain components I alpha and I beta in an alpha-beta axis system; (2) an alpha-beta two-phase static coordinate system is processed by Park conversion to obtain a d-q axis rotating coordinate system and corresponding components Id and Iq under the coordinate system; (3) after estimation is conducted by a flux observer, the current motor rotation speed n of the water pump is obtained; (4) a specific parameter showed in the description is compared with a set tolerance value sigma, and when it is recognized that the water pump is in an idling condition, the motor stops running. The method for detecting the running state of the direct current water pump has the advantages that through a relationship between the motor rotation speed n and the q axis current Iq, the idling running condition of the direct current water pump can be precisely judged, and the water pump can be switched off timely.
Owner:东莞市深鹏电子有限公司
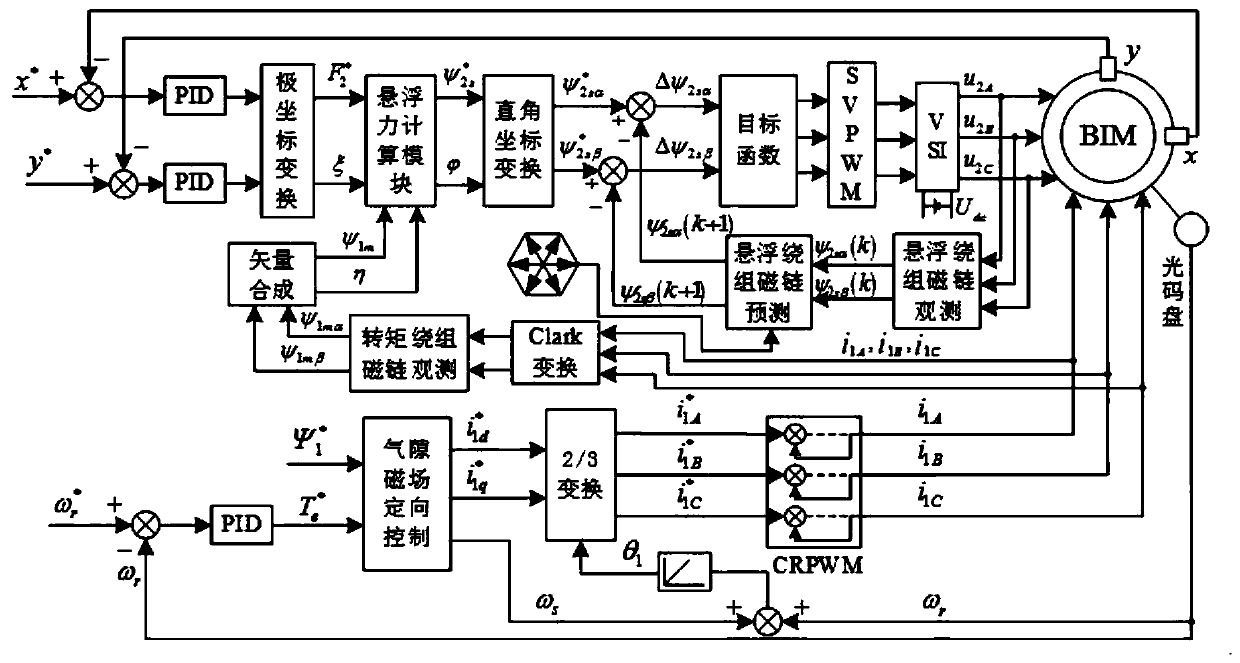
Bearingless asynchronous motor direct suspension force control method based on model prediction
InactiveCN110266231ALoad torque constantSolve the accuracy problemElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlRectangular coordinatesElectric machine
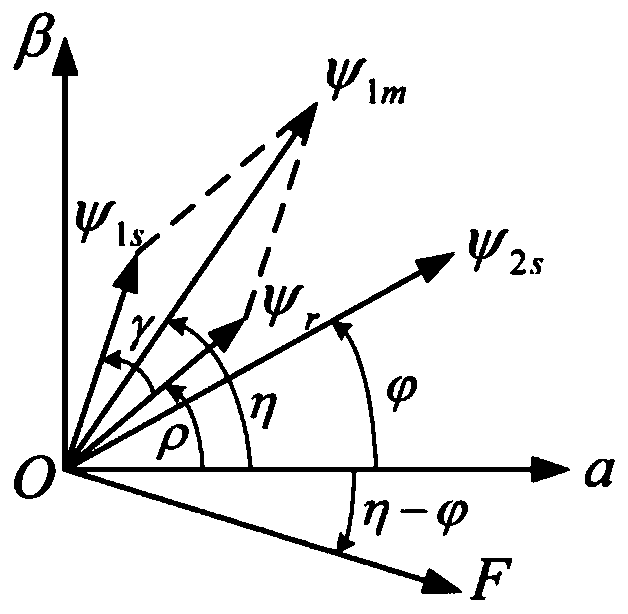
The invention discloses a bearingless asynchronous motor direct suspension force control method based on model prediction. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining radial suspension force amplitude and phase xi after PID adjustment and polar coordinate conversion of difference values of displacement signals x and y and given displacement signals x* and y* through suspension control; calculating synthesis air gap flux linkage psi 1m and phase eta through torque winding flux observer and vectorial resultant of three-phase current; inputting radical suspension force amplitude and phase xi, air gap flux linkage psi and phase eta into a suspension force calculating module, carrying out rectangular coordinate conversion treatment to obtain a suspension winding flux linkage reference value, screening a difference value with a suspension winding flux linkage reference value at the next moment through a target function to obtain a flux linkage in an optimal switch state, obtaining the voltage signal of a drive inverter after SVPWM modulation of the flux linkage, and finally obtaining three-phase voltage required for a control motor so as to realize bearingless asynchronous motor direct suspension force control. The method can solve the problem that precision is insufficient and is greatly influenced by motor parameters caused by traditional suspension force indirect control.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
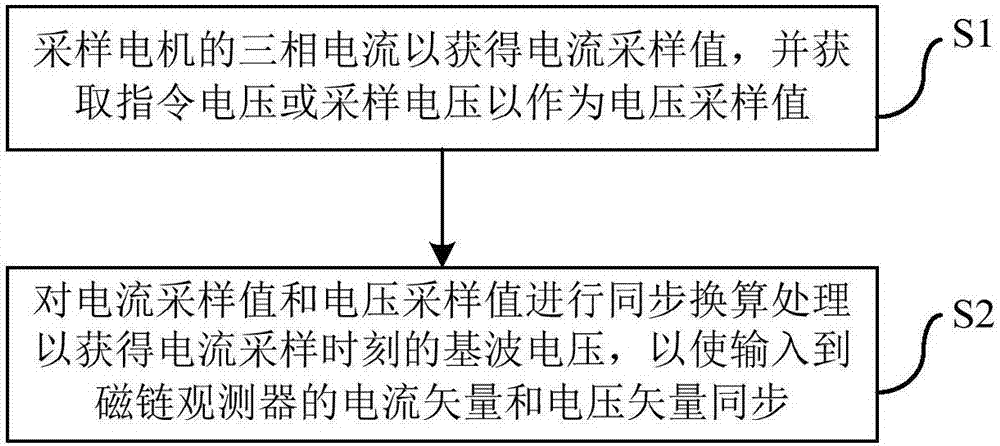
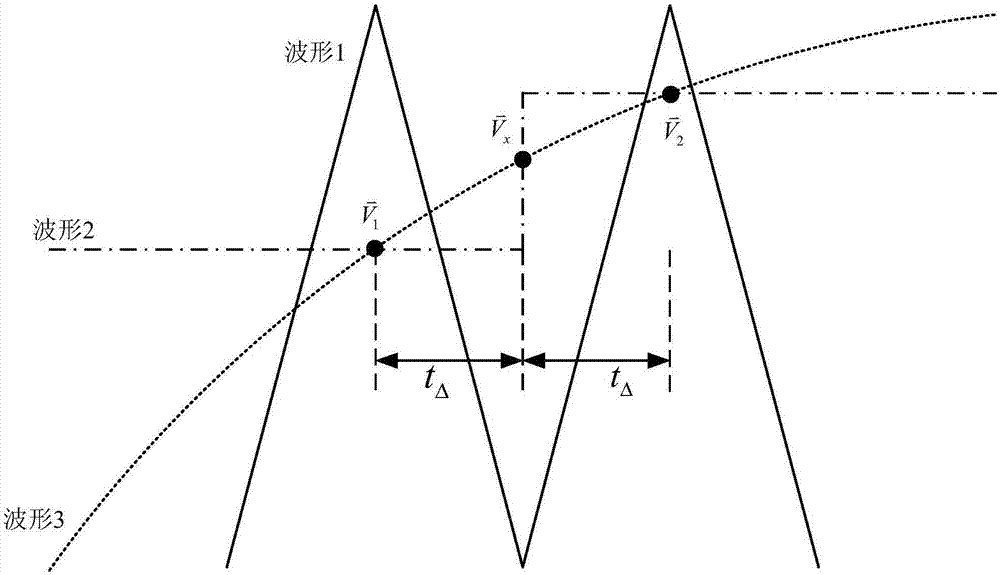
Motor driving system, and method and device for synchronous computation through reconstructing phase current and phase voltage by employing motor driving system
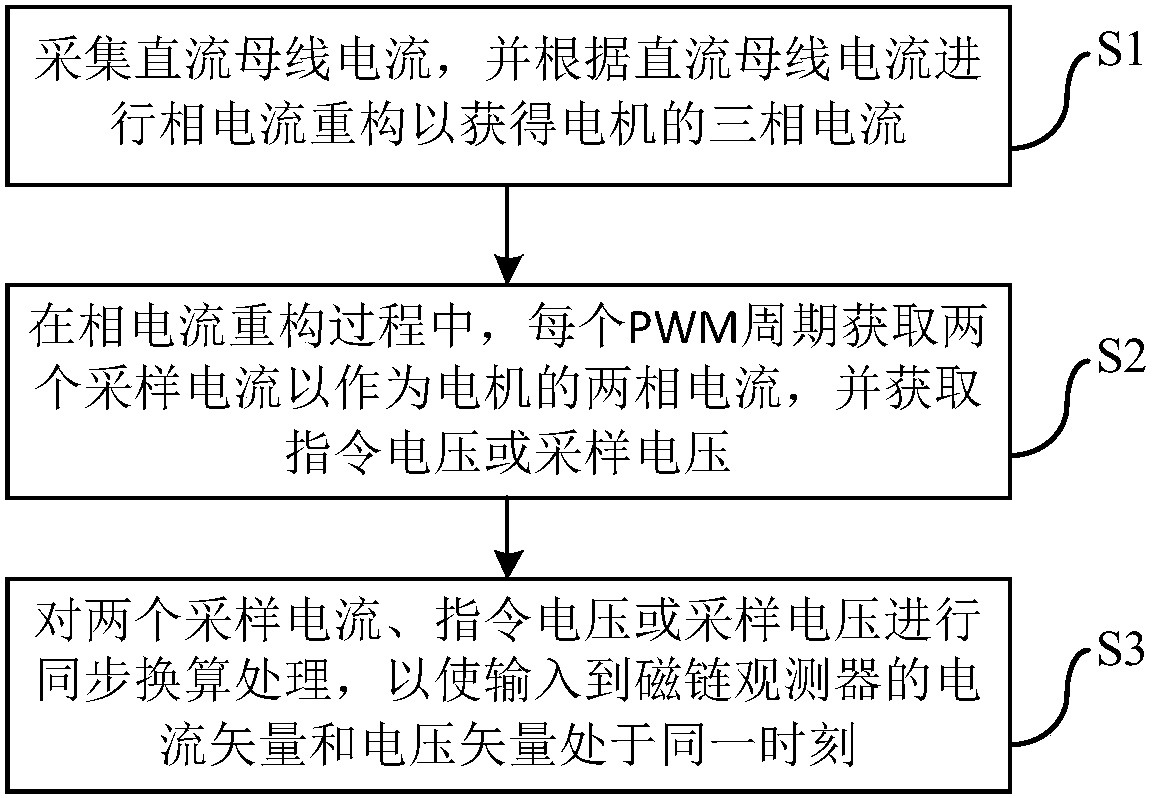
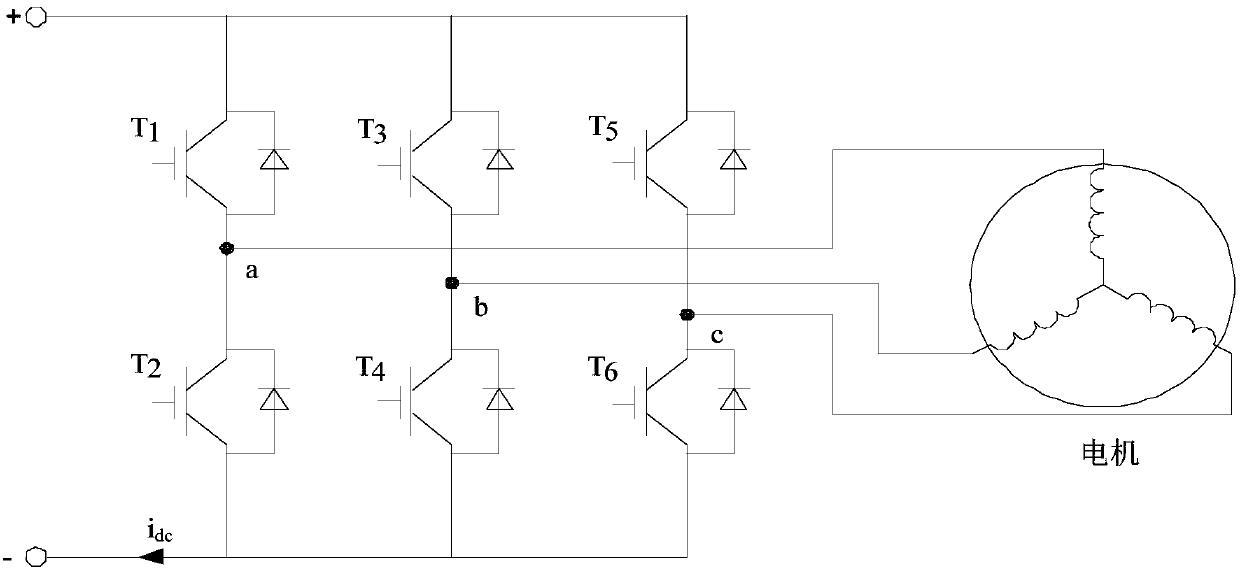
ActiveCN107834927AGuaranteed uptimeSmall amount of calculationElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPhase currentsVoltage vector
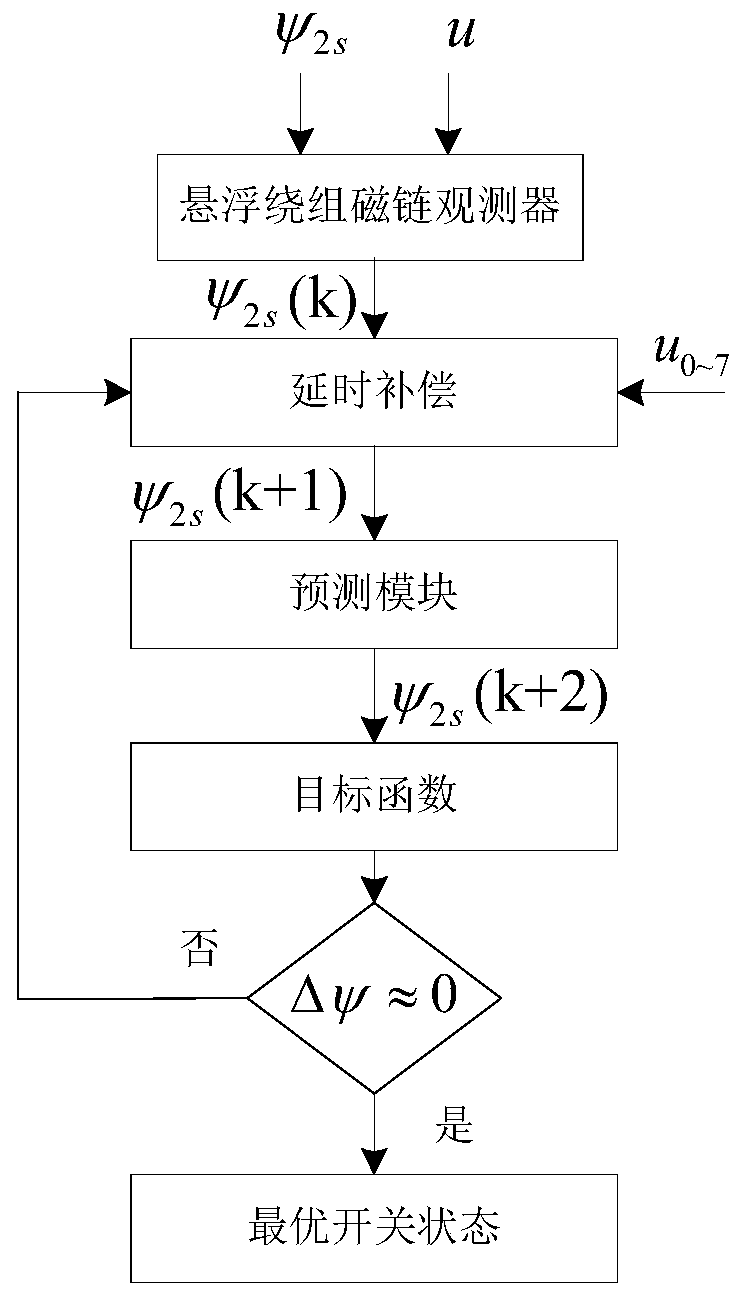
The present invention discloses a motor driving system, and a method and a device for synchronous computation through reconstructing a phase current and a phase voltage by employing a motor driving system. The method comprises the following steps of: performing sampling of a direct current bus current, and performing reconstruction of a phase current according to the direct current bus current toobtain a three-phase current of a motor; in a reconstruction process of the three-phase current, obtaining two sampling currents in each PWM period to take as a two-phase current of the motor, and obtaining an instruction voltage or a sampling voltage; and performing synchronous conversion processing of the two sampling currents, the instruction voltage or the sampling voltage to allow a current vector and a voltage vector input to a flux observer to be in the same moment. According to the invention, the accuracy of an output angle of the flux observer can be ensured, the normal operation of the motor can be guaranteed, the calculated amount of the calculation method is small, and the calculation method is easy to implement.
Owner:GUANGDONG MIDEA WHITE HOME APPLIANCE TECH INNOVATION CENT CO LTD +1
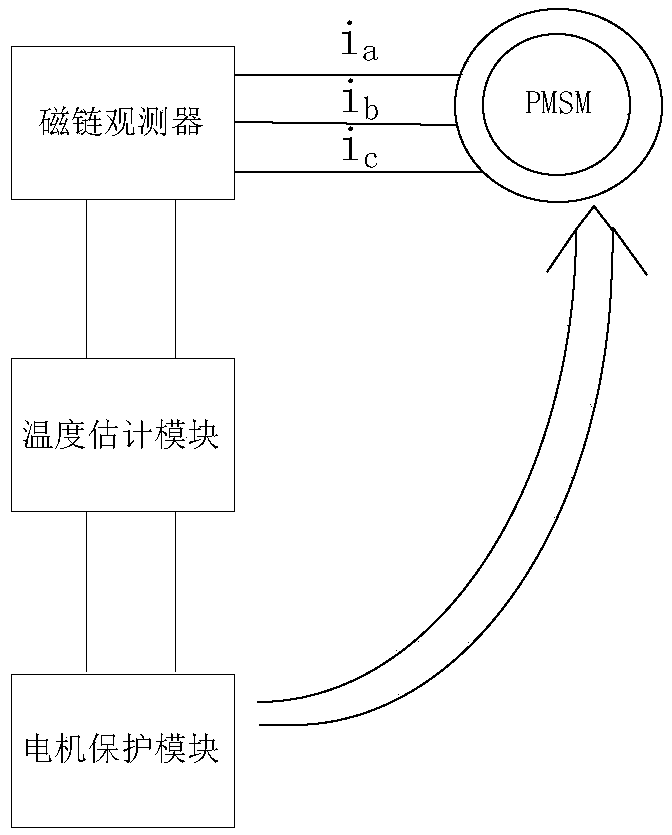
A motor protection method for automobile based on rotor magnet steel temperature
InactiveCN109039219AImprove estimation accuracyImprove accuracyAC motor controlElectric motor controlStator voltagePower flow
A motor protection method for an automobile based on rotor magnetic steel temperature includes adopting a rotor magnetic steel temperature on-line estimation system to realize rotor magnetic steel temperature monitoring, and protecting the automobile motor according to current rotor magnetic steel temperature. The rotor magnetic steel temperature online estimation system comprises a flux observer,a temperature estimation module and a motor protection module. The input signal of the flux linkage observer is stator voltage and current, the output signal is rotor magnetic steel flux linkage signal, the rotor magnetic steel flux linkage signal is calculated according to the stator voltage and current, and the rotor magnetic steel flux linkage signal is output to the temperature estimation module; the temperature estimation module receives the output signal of the flux linkage observer, calculates the rotor magnetic steel temperature, and transmits the calculated rotor magnetic steel temperature to the motor protection module; and the motor protection module receives the rotor magnet steel temperature and takes protective measures for the automobile motor according to the rotor magnetsteel temperature.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LEAPMOTOR TECH CO LTD
Asynchronous motor low-speed performance improving method and system
InactiveCN108233808AGuaranteed uptimeElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlLyapunov stabilityLow speed
The invention provides an asynchronous motor low-speed performance improving method and system. A stator flux linkage psi s and stator current is of a motor are adopted as state variables, an asynchronous motor state equation is constructed, state estimation and state feedback in the modern control theory are utilized, the state equation of the asynchronous motor is used for constructing a rotating speed self-adaption flux observer, and according to the Lyapunov stability law, the rotating speed self-adaption law is derived. Due to the fact that a true value of the motor rotor flux linkage cannot be obtained, a traditional rotating speed self-adaption law ignores the rotor flux linkage value, when the motor is operated at low speed, a big error can be made, and the system is not stable. Inorder to solve the problem, the rotating speed self-adaption law needs to be improved, one compensation dosage is introduced, and the self-adaption flux observer can be stably operated when the motorrotates at low speed.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Flux observer-based control strategy for an induction motor
ActiveUS20200119680A1Increasing torque linearityImprove accuracyElectric motor controlVector control systemsElectric machineClassical mechanics
A method for regulating operation of an induction motor having a rotor includes calculating a rotor flux angle error value, via a flux observer of a controller, using estimated d-axis and q-axis flux values of the rotor, estimating rotor position using a position observer of the controller, and calculating slip position of the rotor using d-axis and q-axis stator currents. The method also includes estimating a rotor flux angle as a function of slip position and estimated rotor position, calculating a corrected rotor flux angle by selectively adding the rotor flux angle error value to the estimated rotor flux angle, and controlling output torque of the motor using the corrected rotor flux angle. A logic switch may be used to selectively add the rotor flux angle.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
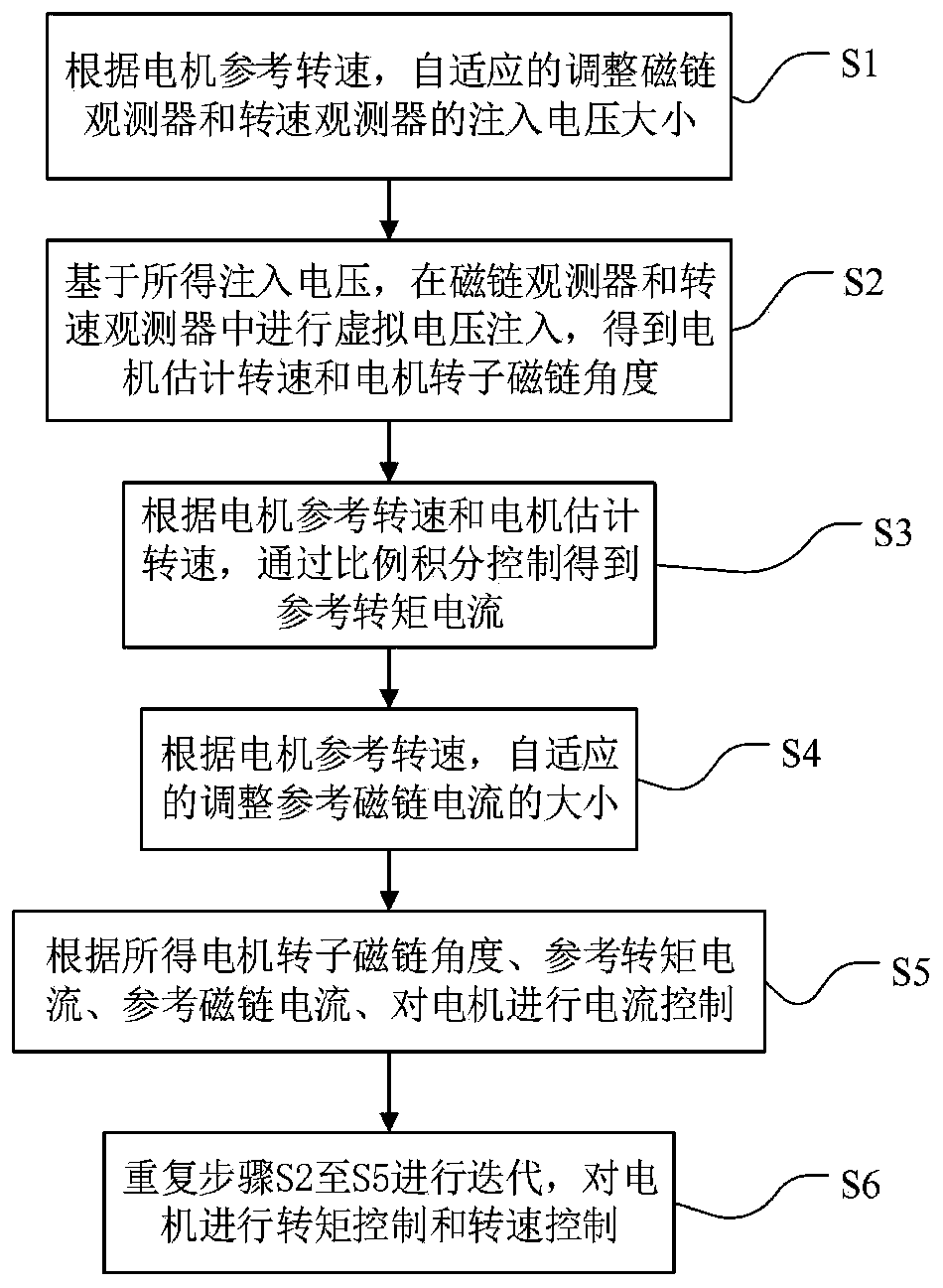
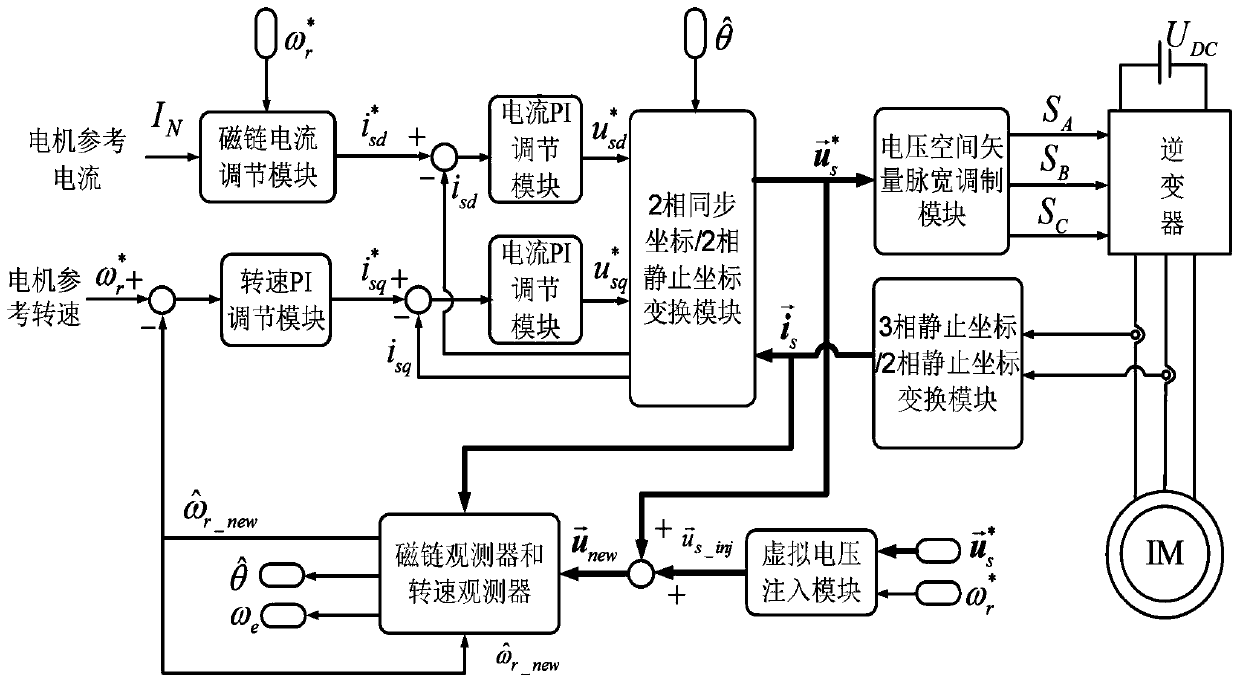
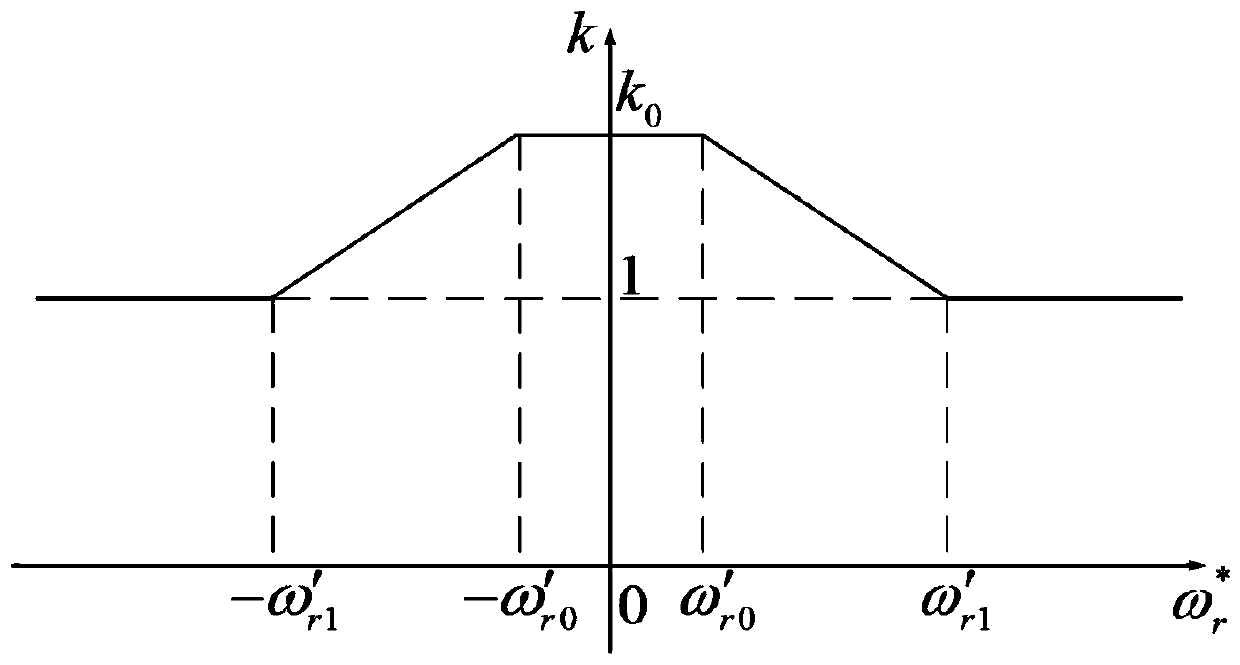
Asynchronous motor control method without speed sensor driving
ActiveCN111342719AAccurate speedGuaranteed speed control accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlControl systemClassical mechanics
The invention discloses an asynchronous motor control method without speed sensor driving. The method comprises the steps: according to the reference rotating speed of a motor, adaptively and smoothlyadjusting the reference flux linkage current and the injection voltage of a flux linkage observer and a rotating speed observer; performing virtual voltage injection on the flux linkage observer andthe rotating speed observer; therefore, according to the method provided by the invention, the rotating speed control precision of the asynchronous motor driven by the speed sensorless control systemduring medium-high rotating speed operation is ensured; when the motor operates at a low synchronous rotating speed or even a zero synchronous rotating speed, 200% of rated torque can be stably outputfor a long time, and smooth switching can be realized, so that the rotating speed of the motor can be accurately controlled within a full-speed rotating speed range, and the motor can stably operate.Moreover, the method provided by the invention can be operated on the basis of any one of the motor flux observer and the rotating speed observer constructed based on the motor model, and is wide inapplication range.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bearingless permanent magnet synchronous motor controller based on flux observer
ActiveCN110061676ASimple working principleAchieve approximation fitElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlControl systemPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a bearingless permanent magnet synchronous motor controller based on a flux observer, which is used for direct torque and direct suspension force control of a bearingless permanent magnet synchronous motor. Through a torque winding flux observer, a direct torque controller and a torque winding voltage source inverter, the torque of the bearingless permanent magnet synchronous motor is directly controlled; through a suspension force winding flux observer, a direct suspension force controller, a suspension force estimation model and a suspension force winding voltage source inverter, a suspension force of the bearingless permanent magnet synchronous motor is directly controlled; and first-order delays of part of input signals are used as inputs of a neural network, and novel flux observers of a torque winding and a suspension force winding are designed by adopting the improved BP neural network, so that the flux size, the phase and the torque of the torque windingand the flux size and the phase of the suspension winding can be accurately estimated, and the stability of a control system is improved.
Owner:江苏大也环境有限公司
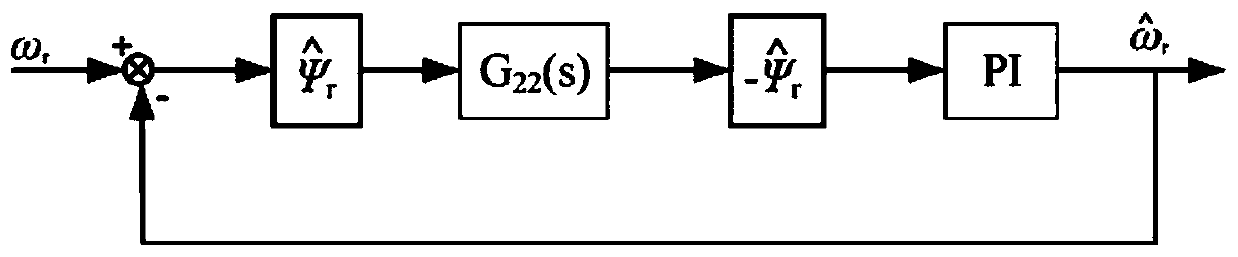
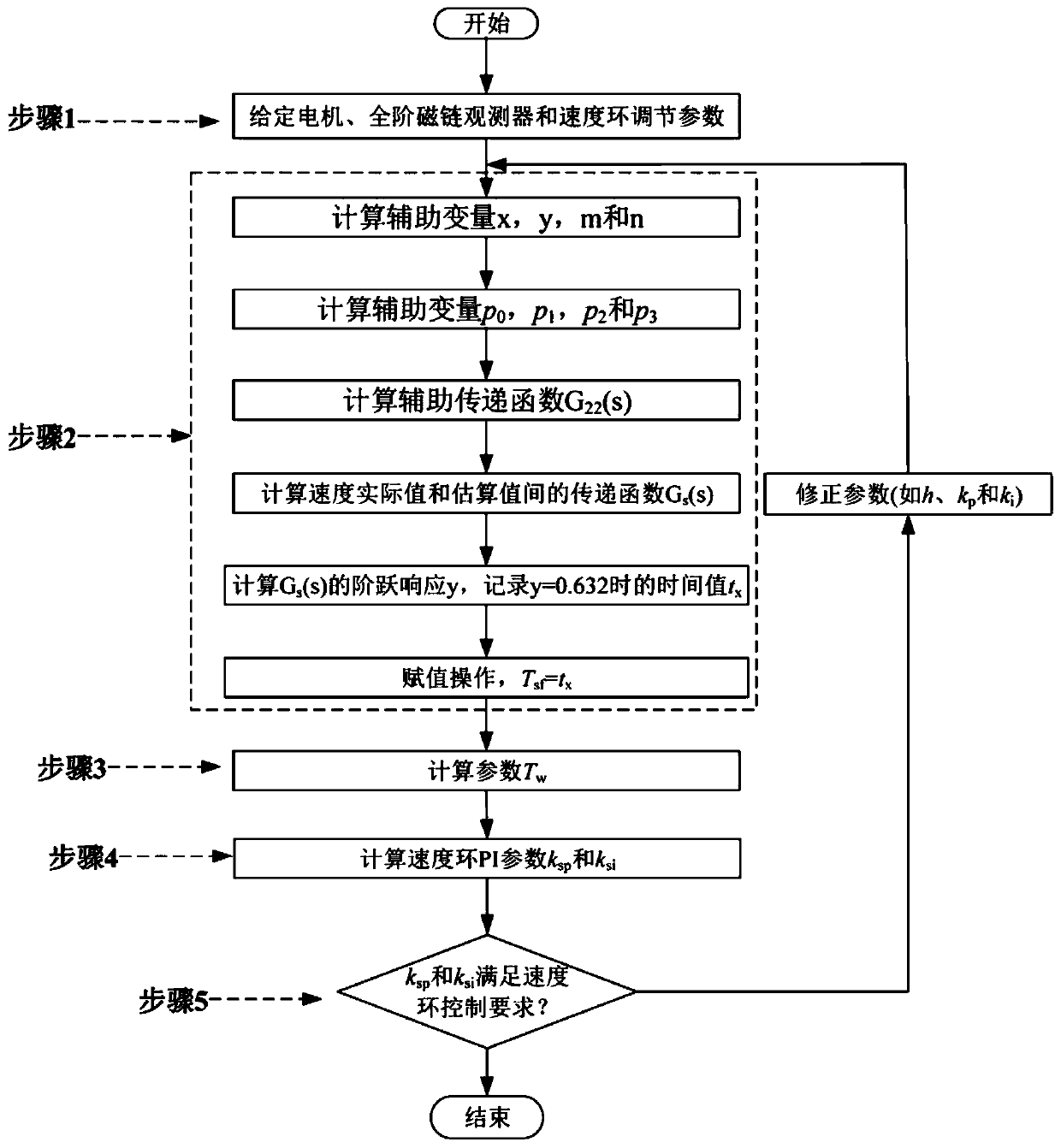
PI parameter setting method for asynchronous motor speed-sensorless speed adjustment system
InactiveCN109802609AImprove practicalityImprove accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMotor speedTotal delay
The invention discloses a PI parameter setting method. The PI parameter setting method is suitable for a full-order flux observer-based asynchronous motor speed-sensorless speed adjustment system. Themethod includes the following steps that: step 1, motor parameters, full-order flux observer parameters and speed loop adjustment parameters are given; step 2, time Tsf of the conversion of a speed actual speed value into a speed estimated value is determined; step 3, the total delay time of a speed loop is determined, wherein the total delay time is represented by an equation that Tomega=Tsf+pic; step 4, the proportional coefficient ksp and integral coefficient ksi of a speed loop PI controller are calculated; and step 5, the feasibility of the parameter ksp and parameter ksi are verified, if the parameter ksp and parameter ksi do not satisfy a speed loop control requirement, the proportional coefficient kp and integral coefficient ki of a rotational speed adaptive law, and a speed loopbandwidth coefficient h are adjusted, the step 2 3, and 4 are repeated again until the parameter ksp and parameter ksi meet the requirement. According to the method of the invention, the transfer function of the speed actual speed value and the speed estimated value is established; and the delay time Tsf between the actual speed value and the estimated value is obtained through a numerical value calculation method; and the PI parameters of the system speed loop are calculated on the basis of an engineering setting method.
Owner:WUHAN MARINE ELECTRIC PROPULSION RES INST CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP NO 712 INST
Systems and methods for interior permanent magnet synchronous motor control
ActiveUS11239772B1Reduce and minimize and eliminate amount of timeImprove efficiencyAssociation with control/drive circuitsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineClassical mechanics
Systems and methods for robust control of a sensorless interior permanent magnet synchronous motor during severe operating conditions that causes motor parameter variation. A multi-model flux observer and a dynamic direct flux motor controller act in concert to generate driving commands. The flux observer transitions between providing flux-based rotor characteristic estimates based on different motor models. DHFI filtered currents can be utilized to obtain flux-based characteristic estimates using a motor magnetic model that are unaffected by motor parameter variations. The multi-model flux observer can be configured to transition between suitable estimation methods to reduce, minimize, or eliminate the effects of motor parameter variations.
Owner:WOLONG ELECTRIC GRP CO LTD
Motor drive system, and synchronous calculation method and device capable of sampling phase currents and phase voltages
ActiveCN107994827AGuaranteed uptimeGuaranteed accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPhase currentsMotor drive
The present invention discloses a motor drive system, and a synchronous calculation method and a device capable of sampling phase currents and phase voltages. The method comprises the following steps:sampling three-phase current(s) of a motor to acquire current sampling value(s), and acquiring instruction voltage(s) or sampling voltage(s) as voltage sampling value(s); and performing synchronous conversion processing on the current sampling value(s) and the voltage sampling value(s), and acquiring fundamental wave voltage(s) at current sampling time to allow current vector(s) and voltage vector(s) input into a flux observer to keep synchronous. The method can ensure accuracy of output angle(s) of the flux observer and the normal operation of the motor.
Owner:GUANGDONG MIDEA WHITE HOME APPLIANCE TECH INNOVATION CENT CO LTD +1
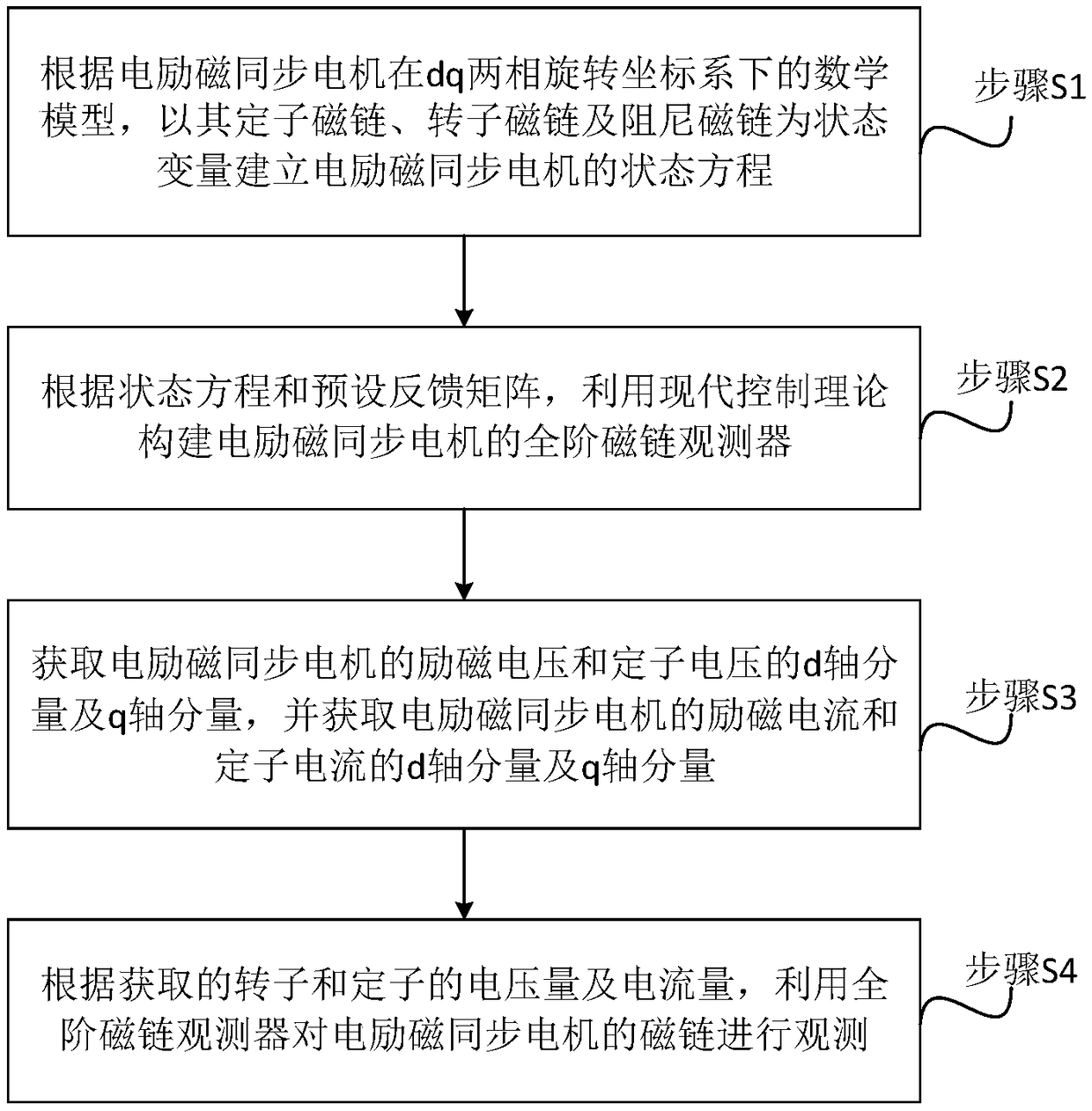
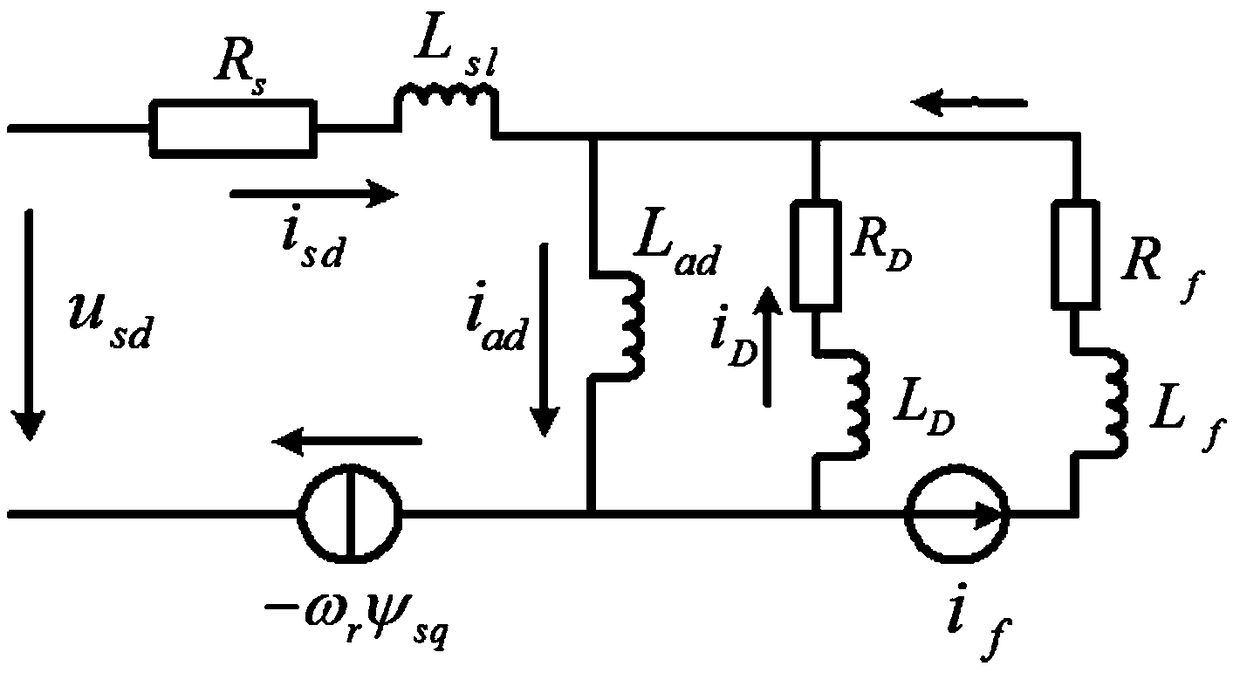
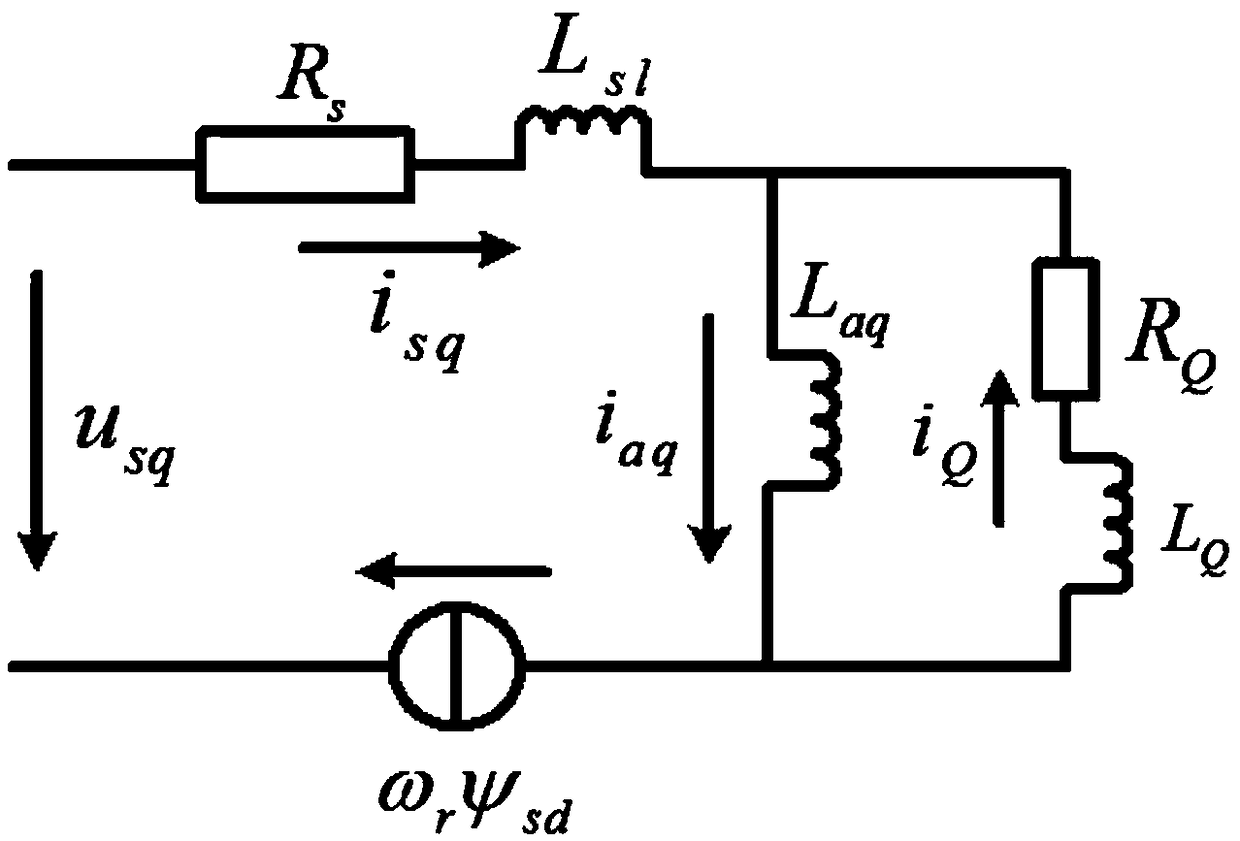
A flux linkage observation method and system for an electrically excited synchronous machine
ActiveCN109150051AElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMathematical modelEquation of state
The invention discloses a flux linkage observation method and a system of an electrically excited synchronous machine. The method comprises the following steps: according to a mathematical model of the electrically excited synchronous machine in a dq two-phase rotating coordinate system, a state equation of the electrically excited synchronous machine is established with a stator flux linkage, a rotor flux linkage and a damping flux linkage thereof as state variables. According to the state equation and the preset feedback matrix, the full-order flux observer of the electrically excited synchronous machine is constructed by using the modern control theory. Acquiring d-axis and q-axis components of excitation voltage and stator voltage of an electrically excited synchronous machine, and acquiring d-axis and q-axis components of excitation current and stator current of the electrically excited synchronous machine; According to the obtained voltage and current of rotor and stator, the flux linkage of electrically excited synchronous machine is observed by full-order flux observer. As can be seen, the present application establishes a full-order flux linkage model to observe the flux linkage of an electrically excited synchronous machine, and the steady-state accuracy and the dynamic performance are excellent, thereby ensuring the high-performance control of the motor control system.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CSR TIMES ELECTRIC CO LTD
System and method of rotor time constant online identification in an AC induction machine
ActiveUS9024569B2Single-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlRotor fluxRotor time constant
A system and method for determining a rotor time constant of an AC induction machine is disclosed. During operation of the induction motor, a flux signal is injected into a rotor flux command so as to generate a time-variant rotor flux. A voltage-current flux observer determines amplitudes of rotor flux variations resulting from the time-variant rotor flux, with the amplitudes of the rotor flux variations comprising an amplitude of a rotor flux variation based on a current model of the voltage-current flux observer and an amplitude of a rotor flux variation based on a combined voltage-current model of the voltage-current flux observer. A rotor time constant of the induction motor is then estimated based on the determined amplitudes of the rotor flux variations.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Device and method for identifying stator resistance of motor
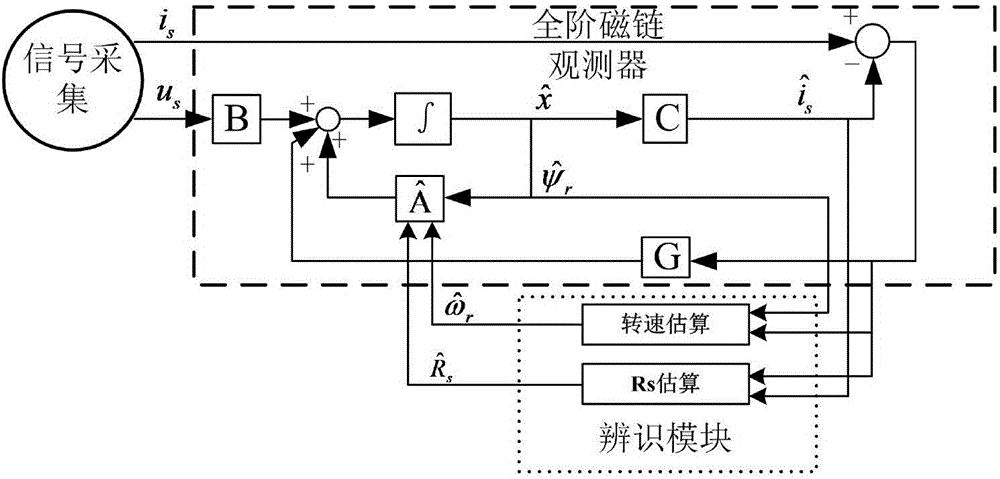
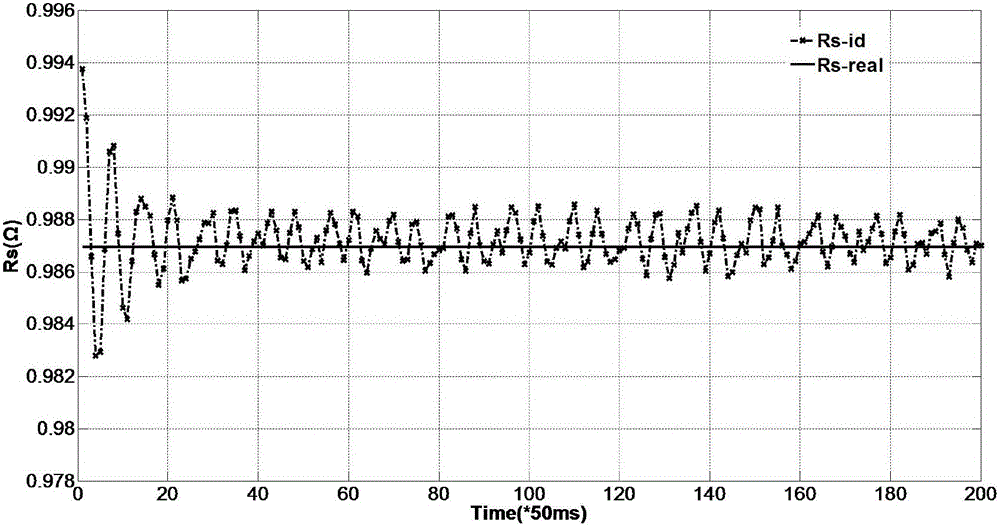
ActiveCN106712621AReduce mistakesMeet the needs of high-precision controlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsStator voltageRotor flux
The invention discloses a device used for identifying stator resistance of an induction motor and a device for implementing the method. For an induction motor in operation, estimated values of stator current and rotor flux of the induction motor are calculated by adopting a full-order flux observer of the induction motor according to stator voltage and stator current of the induction motor; and the rotor speed and the stator resistance of the induction motor are accurately calculated according to a stator current actual value, the stator current estimated value and the rotor flux estimated value of the induction motor.
Owner:WISDRI WUHAN AUTOMATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com