Method for controlling direct power of grid-connected inverter without non-AC voltage sensor
An AC voltage and power control technology, which is applied in the direction of converting AC power input to DC power output, output power conversion devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of improper selection of the initial value of the integrator, failure of the grid-connected inverter, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of simple algorithm, strong anti-interference ability and fast dynamic response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
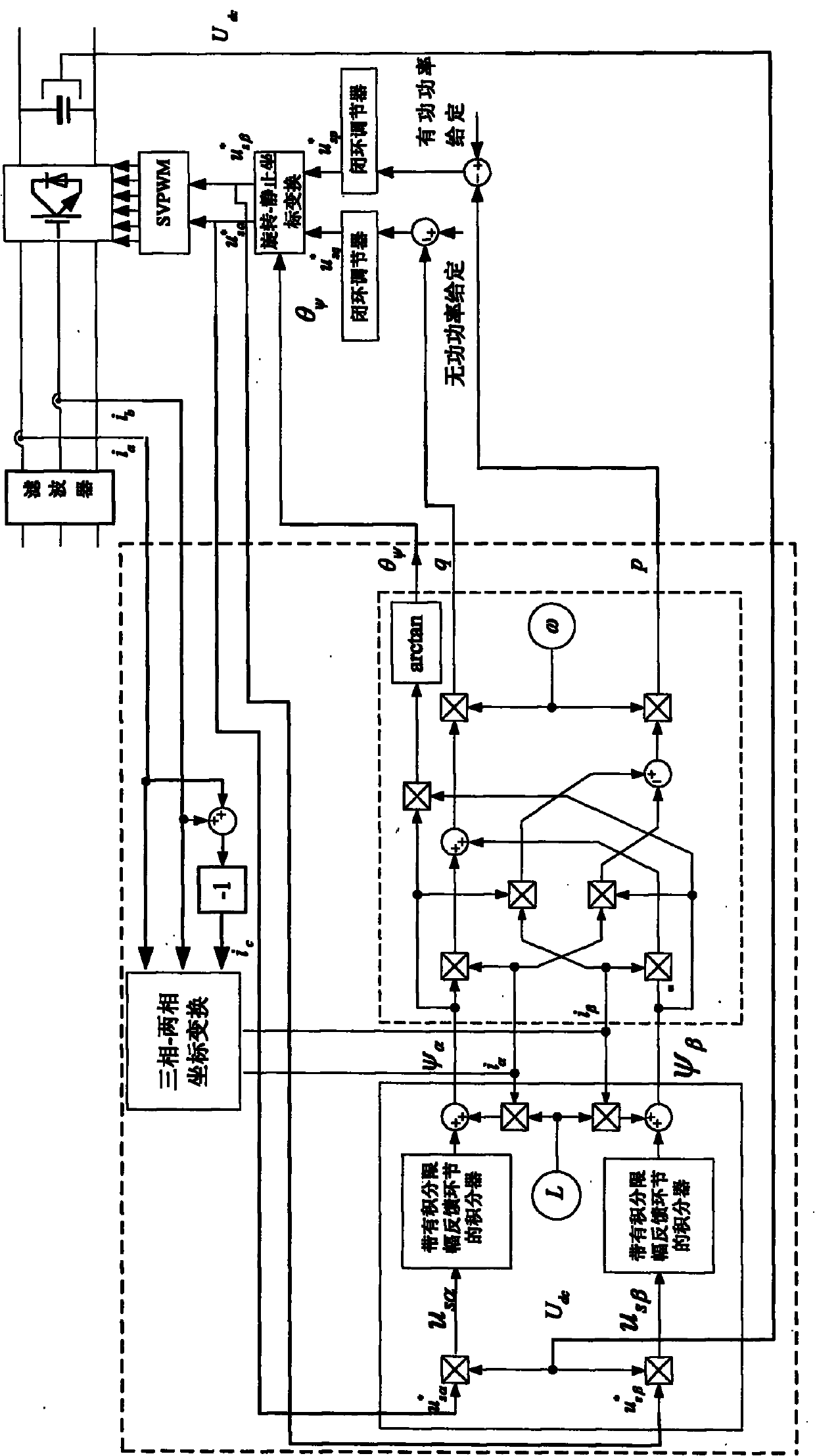
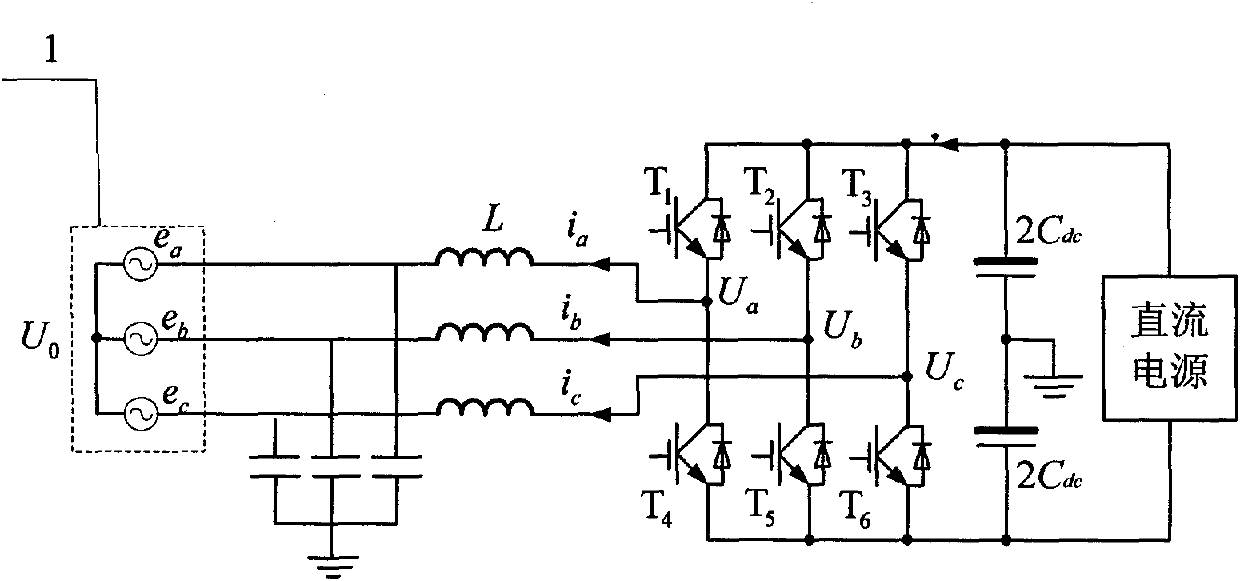
[0012] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 3 Describe this embodiment, the control method of this embodiment is:
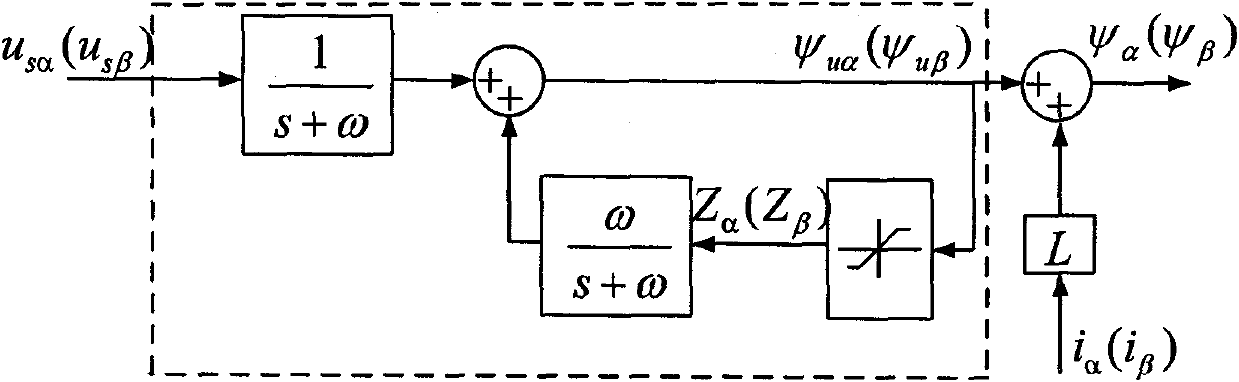
[0013] 1. Connect the filter to the output terminal of the grid-connected inverter to filter the output current, and perform a three-phase-two-phase coordinate transformation on the three-phase current value at the output terminal of the grid-connected inverter to obtain the output value of the grid-connected inverter The component i of the three-phase current value in the two-phase stationary coordinate system α and i β ; Connect the DC capacitor in parallel at the input end of the grid-connected inverter, and set the component u of the given value of the control voltage of the grid-connected inverter in the two-phase stationary coordinate system sα * and u sβ * Respectively with the voltage U across the DC capacitor dc Multiplied together to get the component u of the inverter voltage value of the current grid-co...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0034] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination Figure 4 Describe this embodiment. This embodiment is a further description of the calculation of the given values of active power and reactive power of the grid-connected inverter in the first embodiment: the given active power of the grid-connected inverter described in the third value p * It is obtained by the following method: the output voltage U of the DC capacitor dc With a given voltage of the DC capacitor U dc * comparison, and then the obtained comparison result is adjusted by the PI closed-loop regulator, and then the adjusted output value of the PI closed-loop regulator is compared with the output voltage U of the DC capacitor dc Multiply to get active power given value p * . The given value of reactive power of the grid-connected inverter mentioned in 3 is 0.
[0035] This implementation mode adopts a double-closed-loop control structure with a DC capacitor voltage outer loop and a grid-co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com