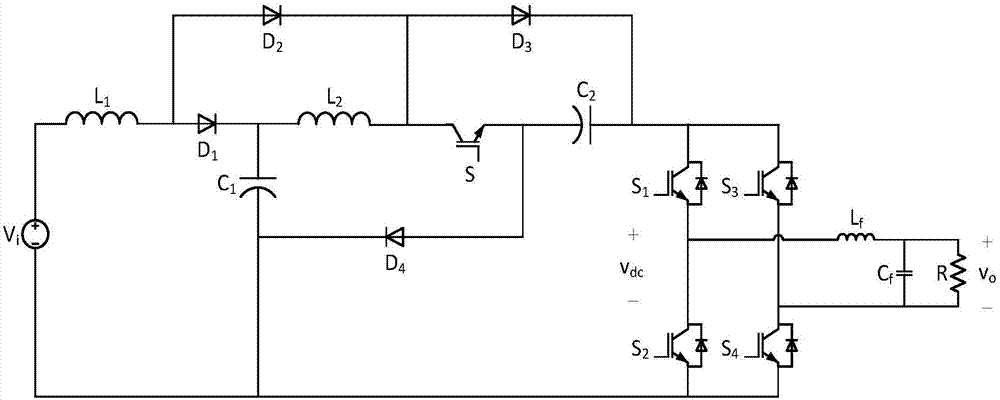
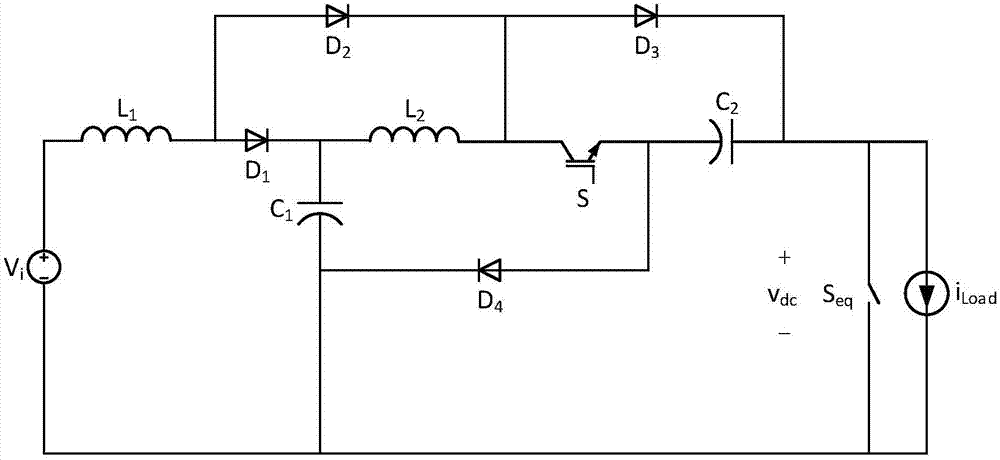
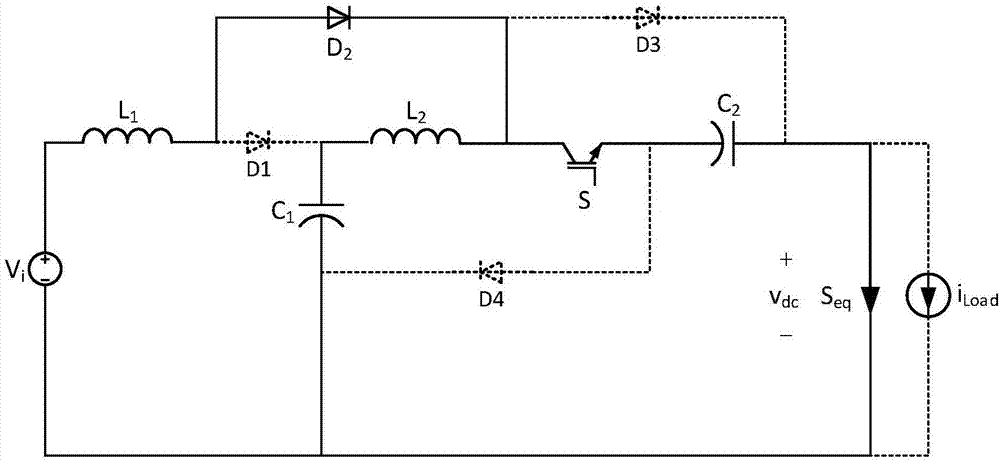
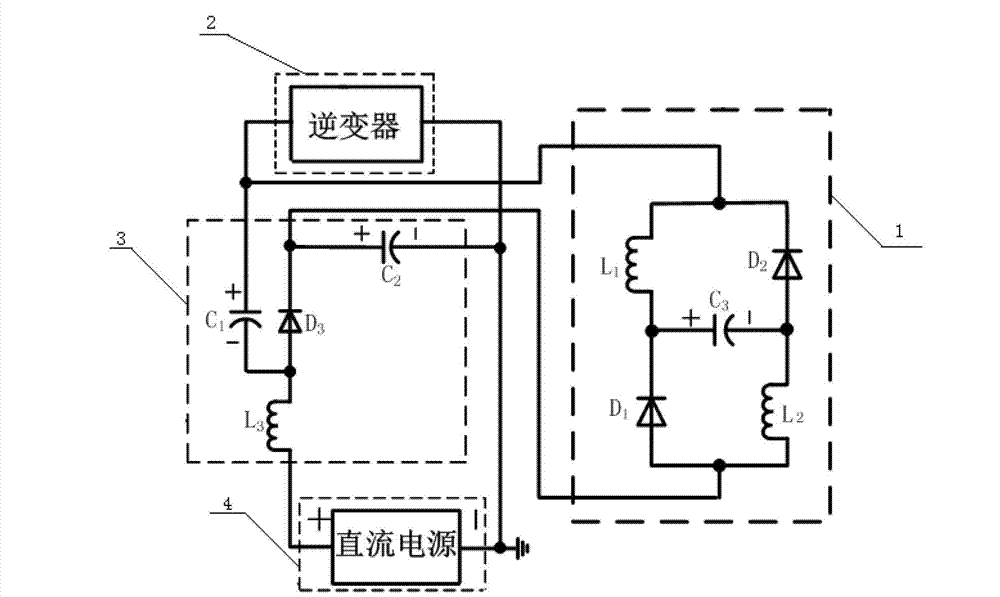
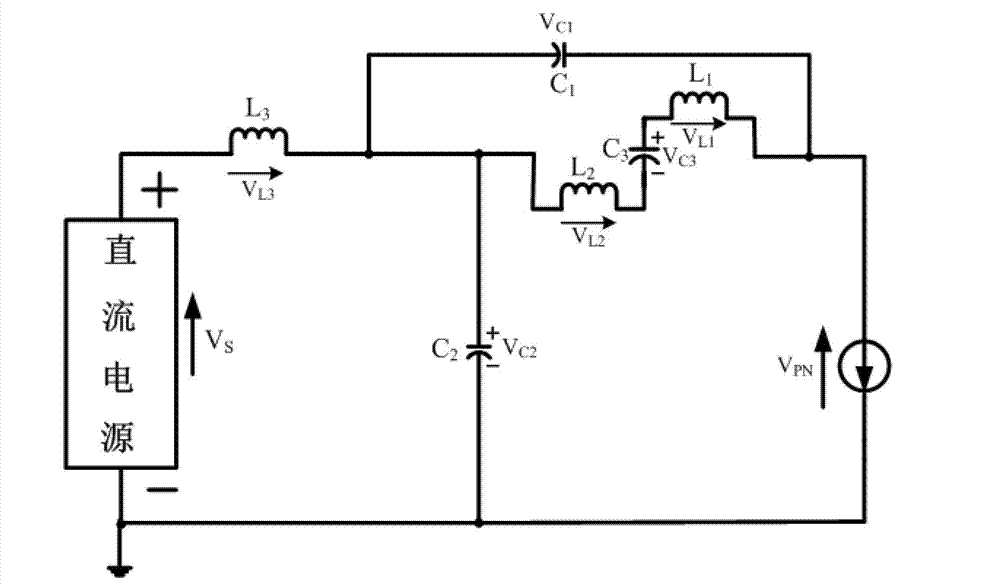
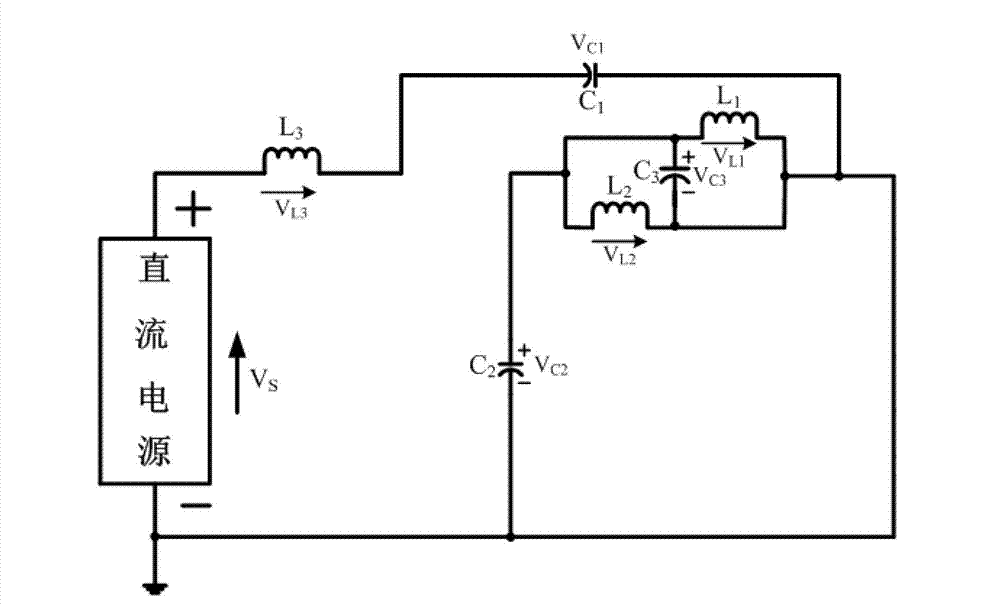
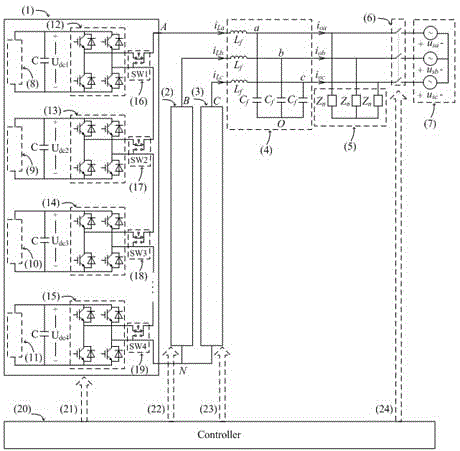
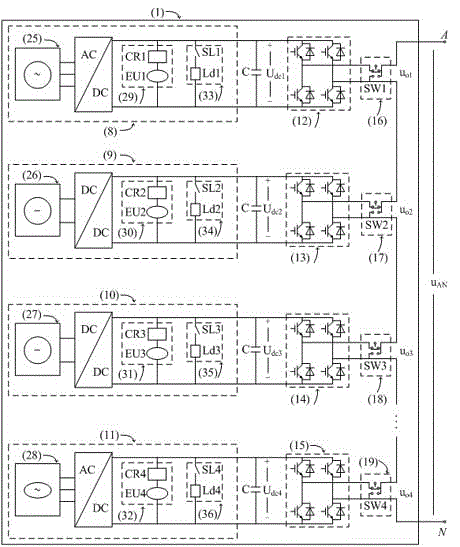
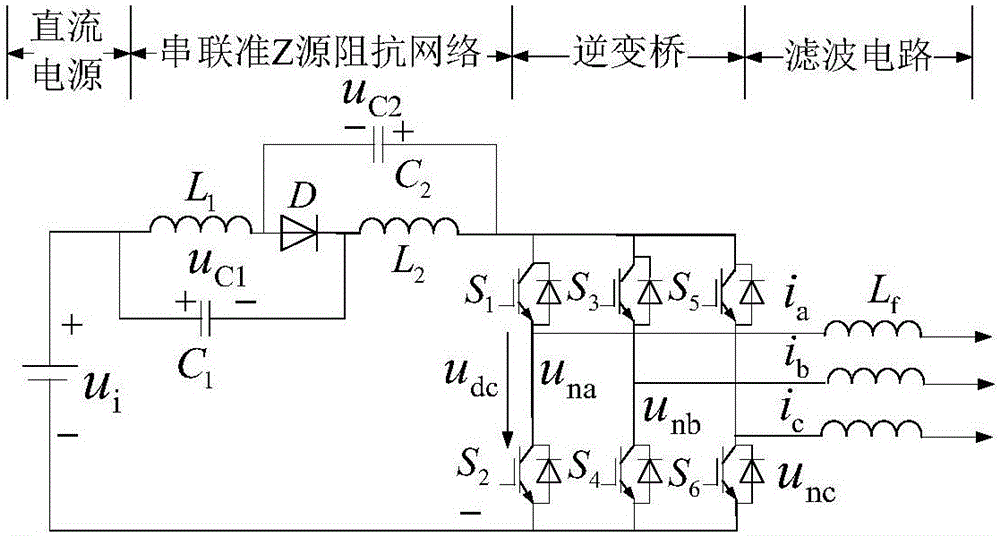
Patents
Literature
187 results about "Z-source inverter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
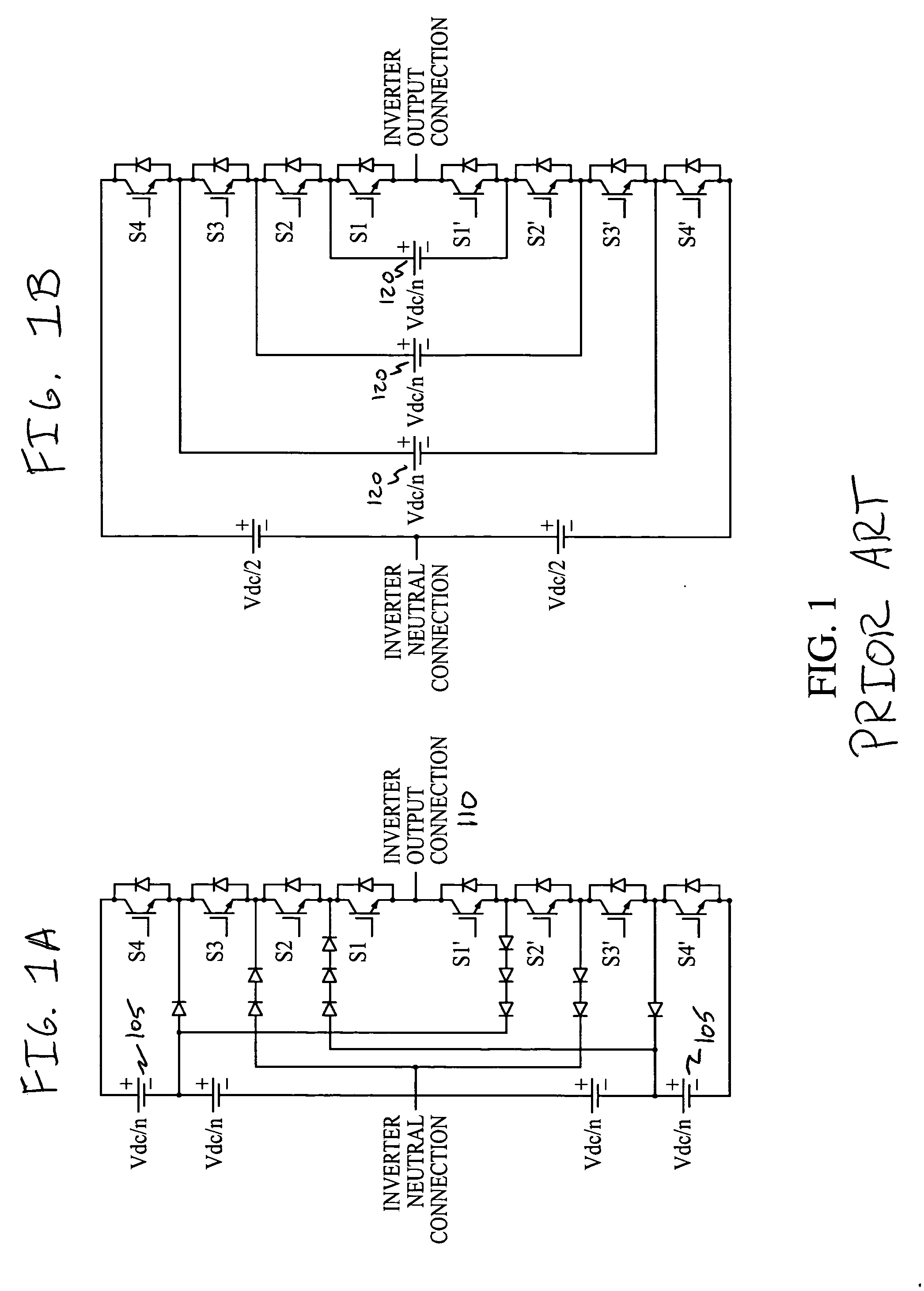
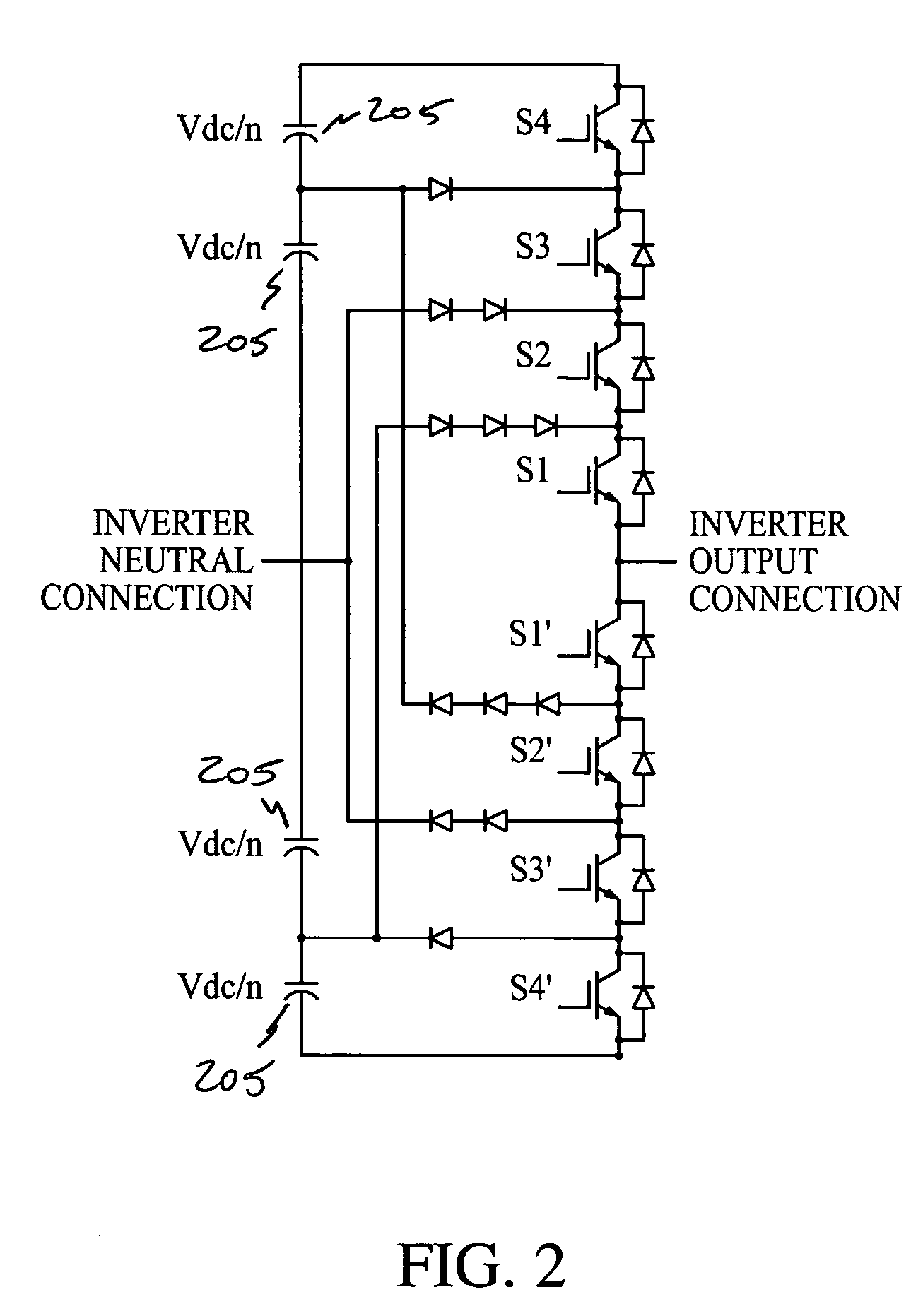
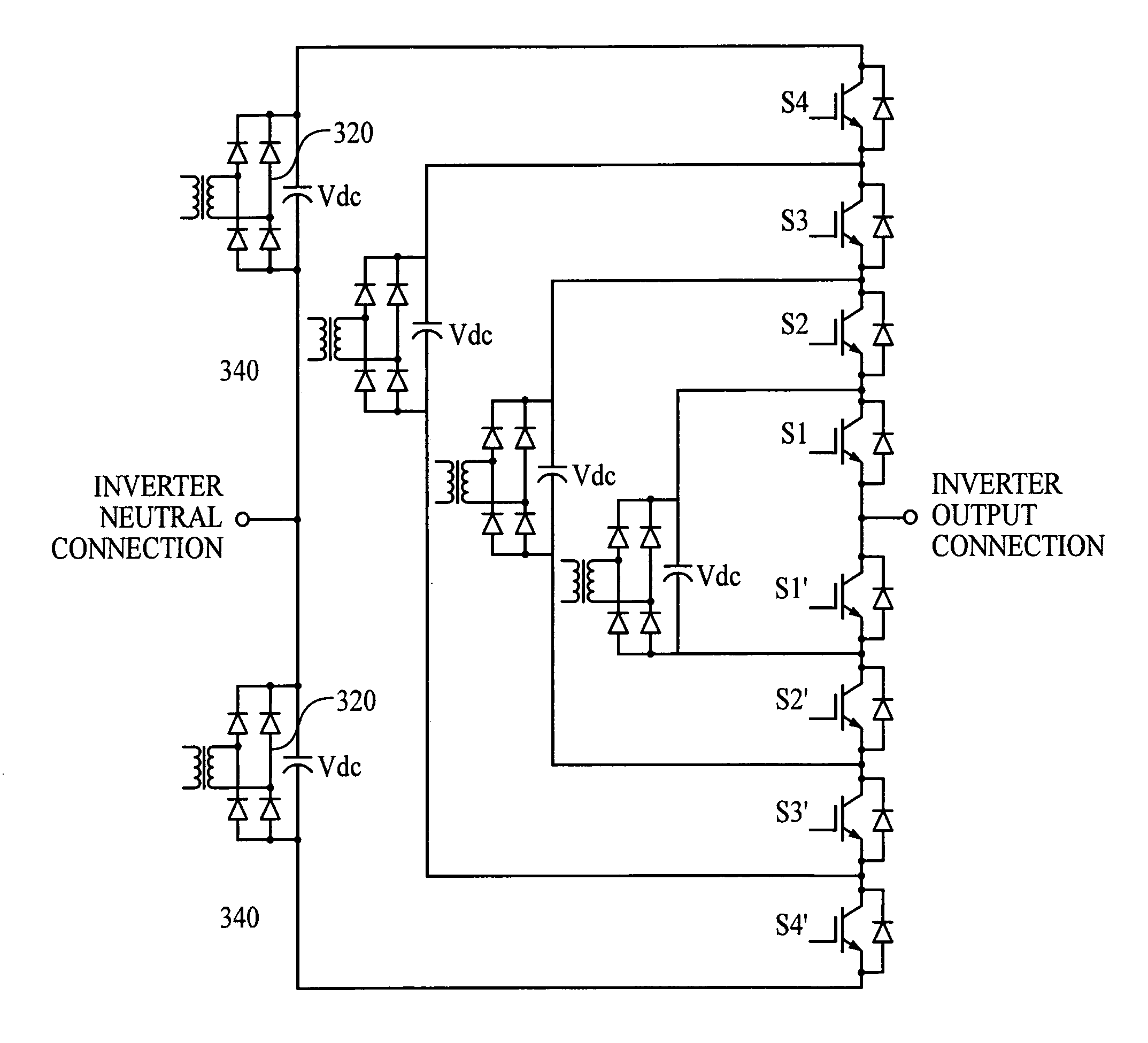
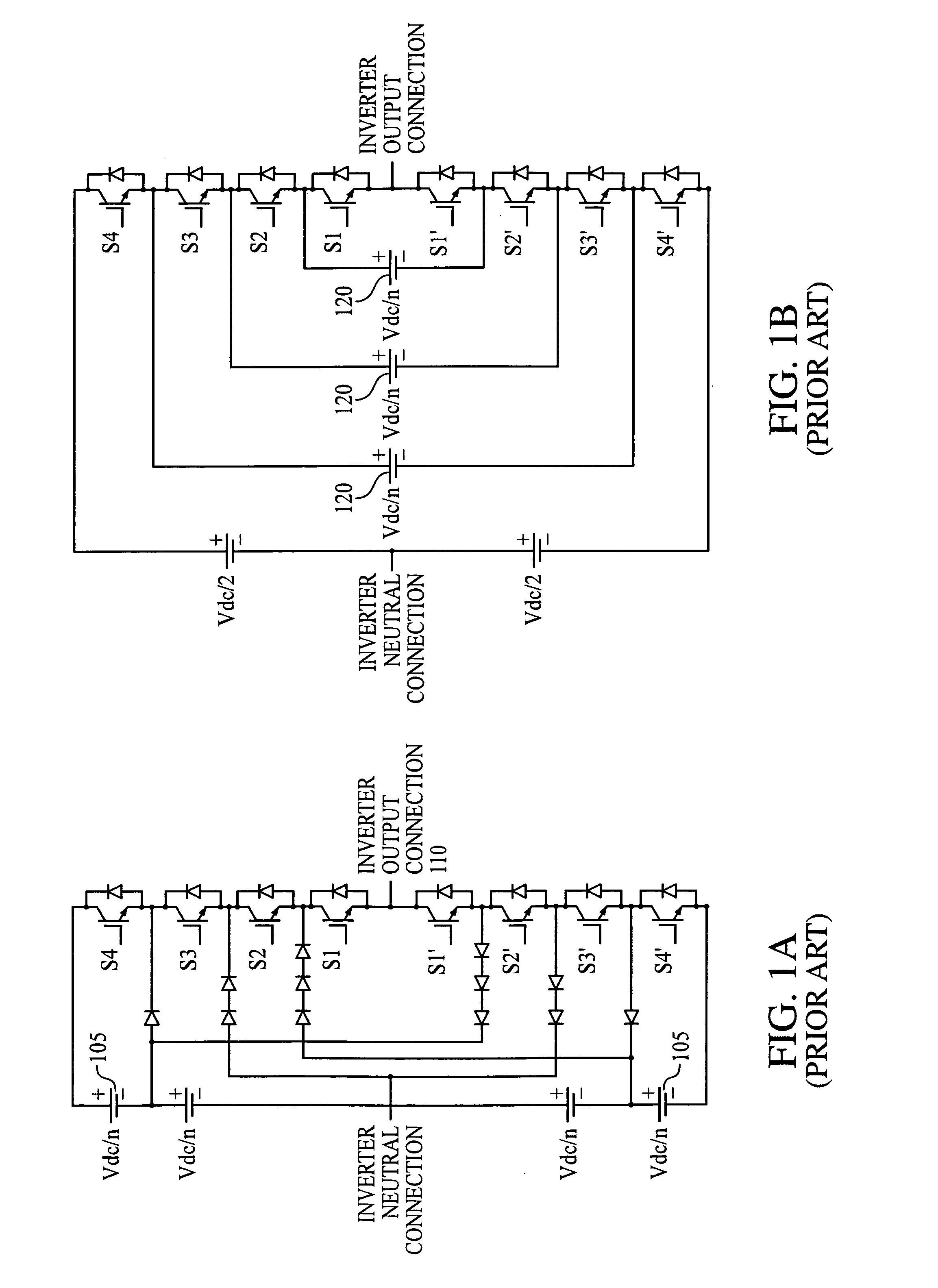
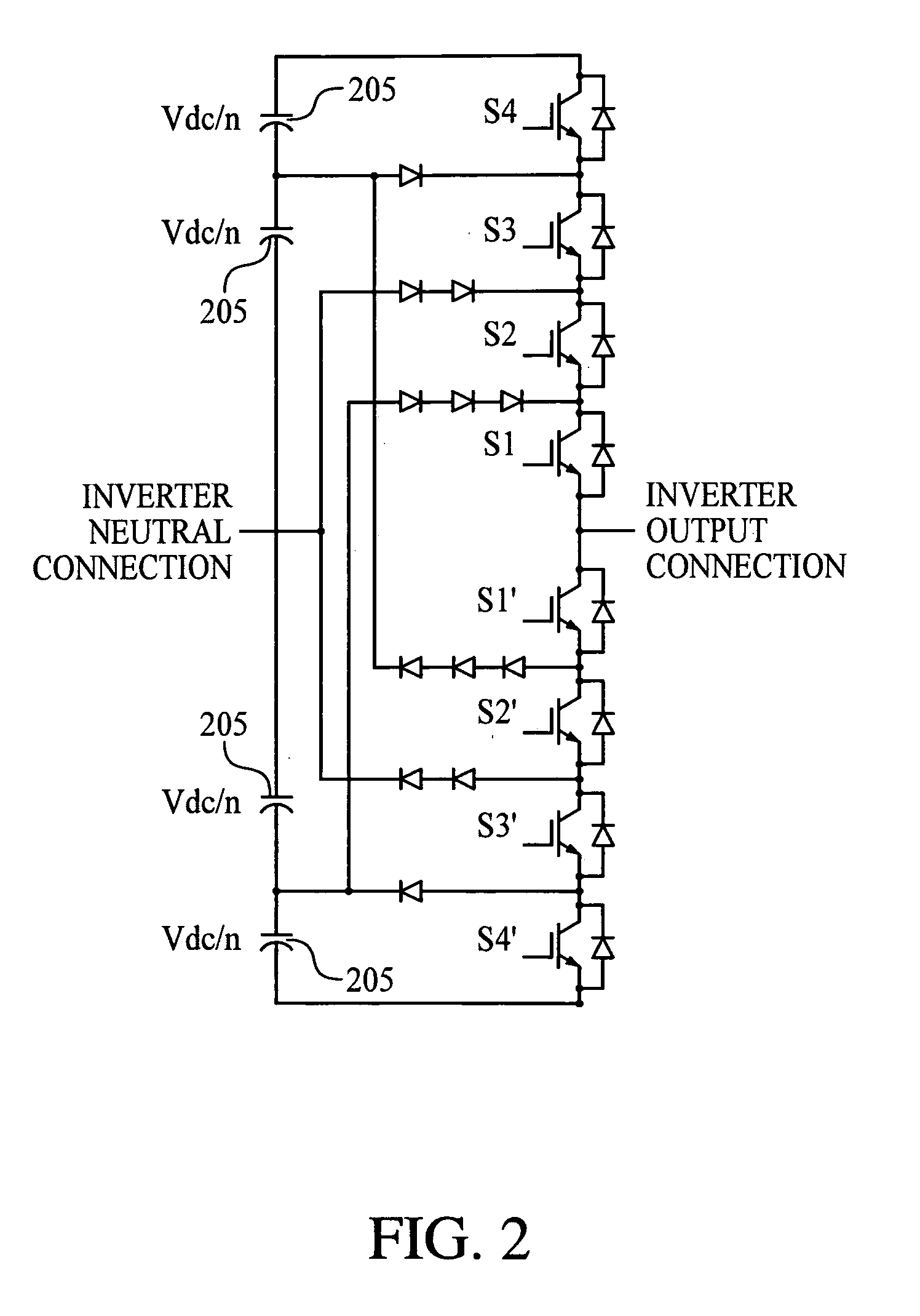
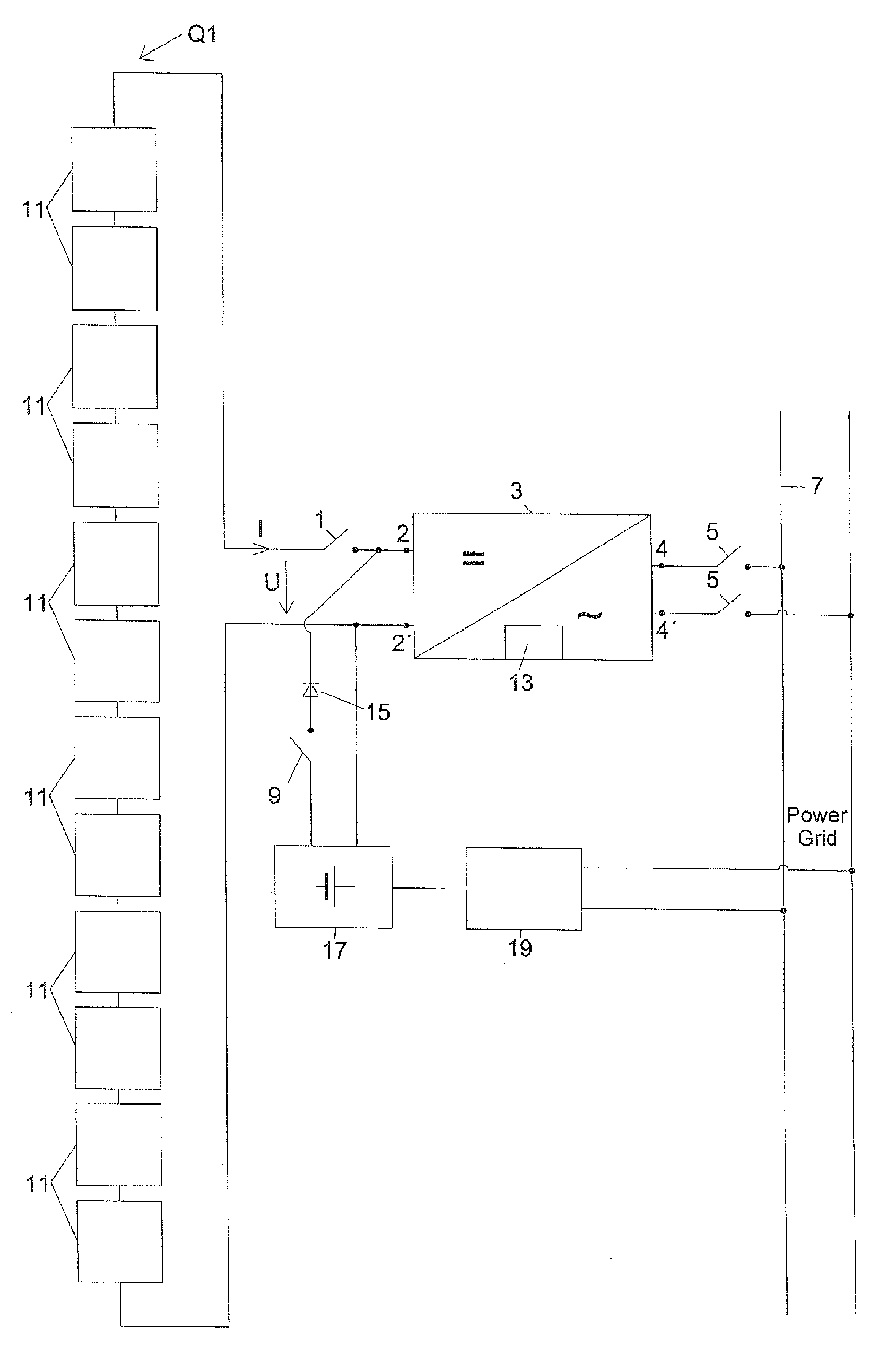
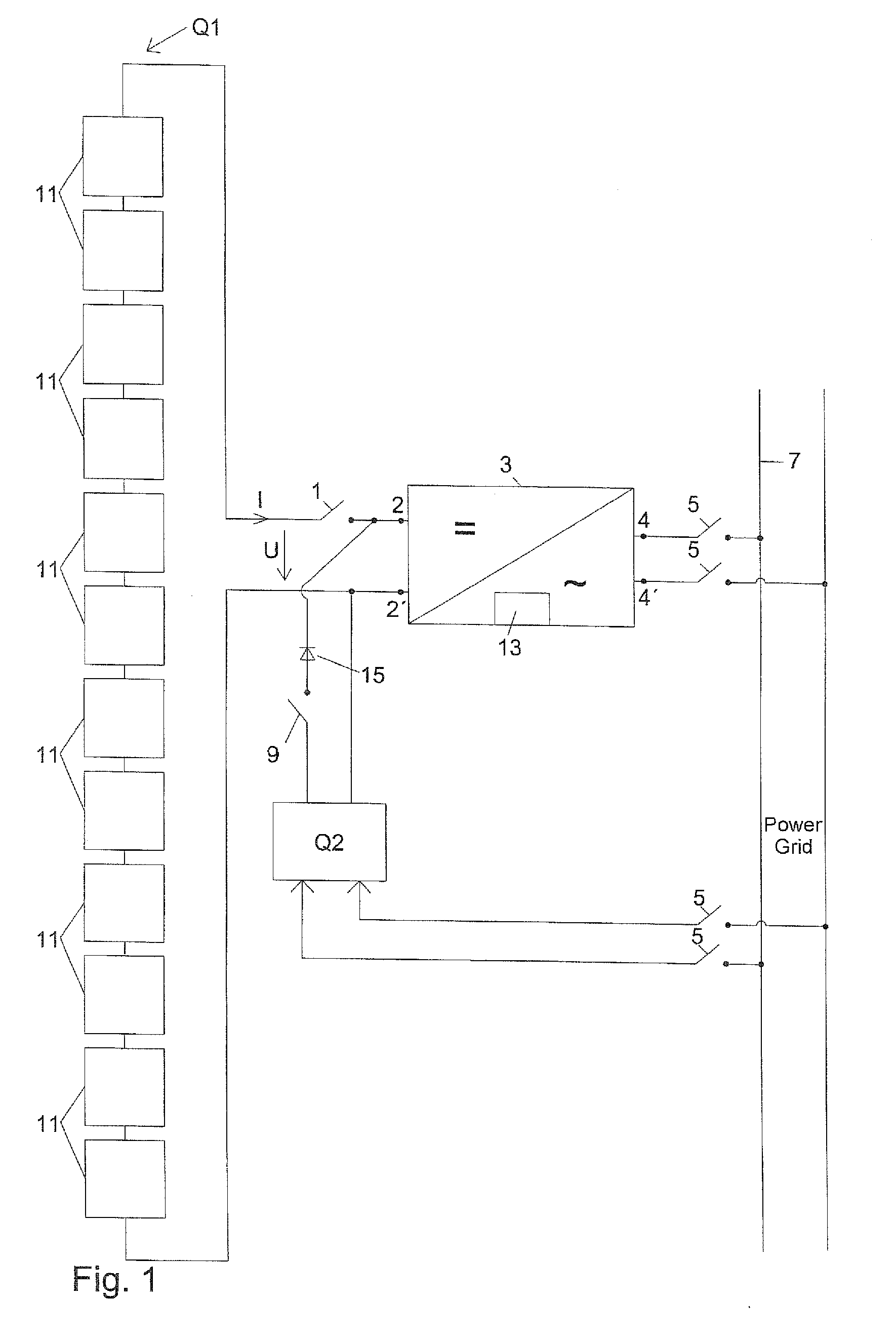
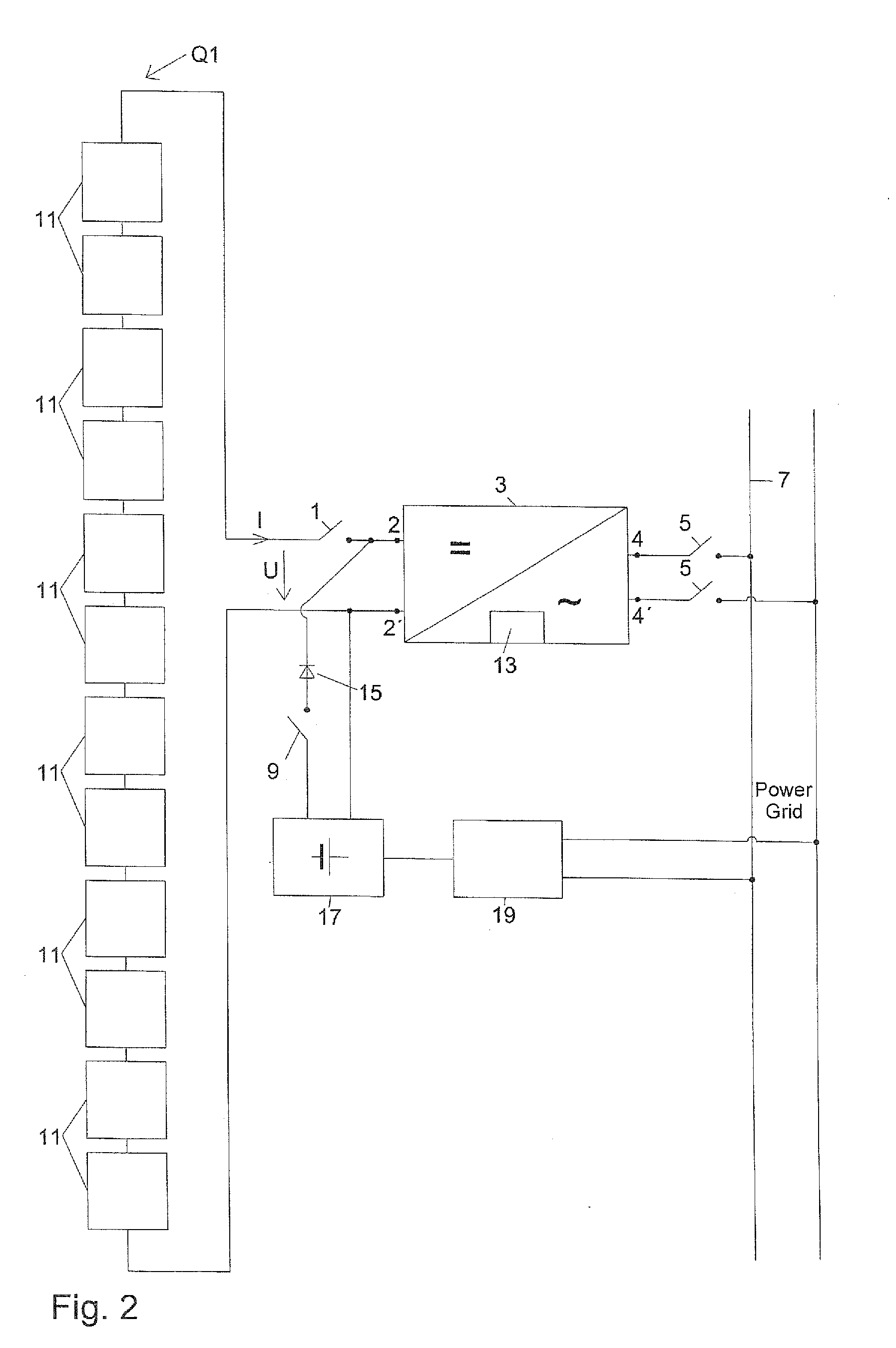
A Z-source inverter is a type of power inverter, a circuit that converts direct current to alternating current. It functions as a buck-boost inverter without making use of DC-DC converter bridge due to its unique circuit topology.
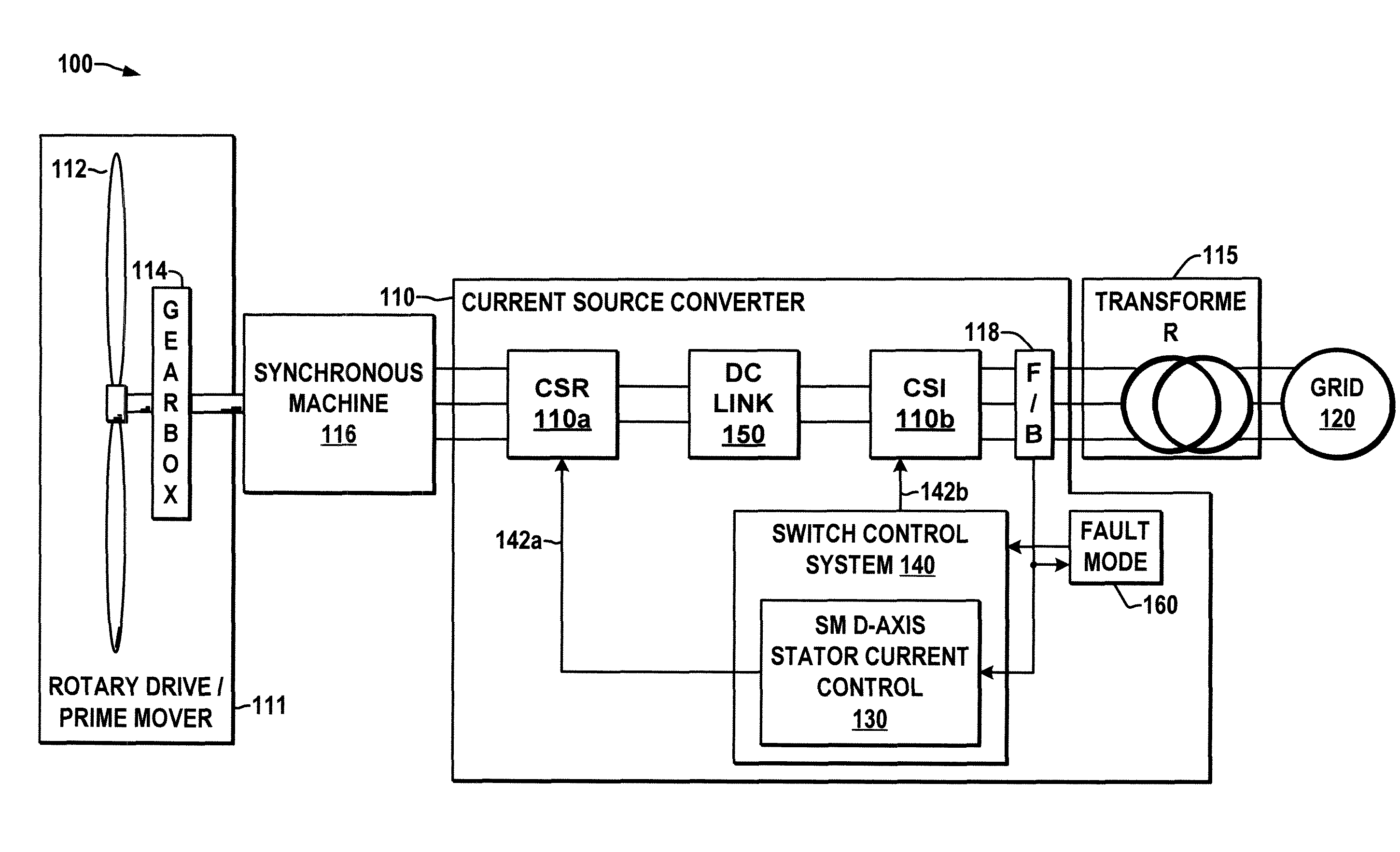
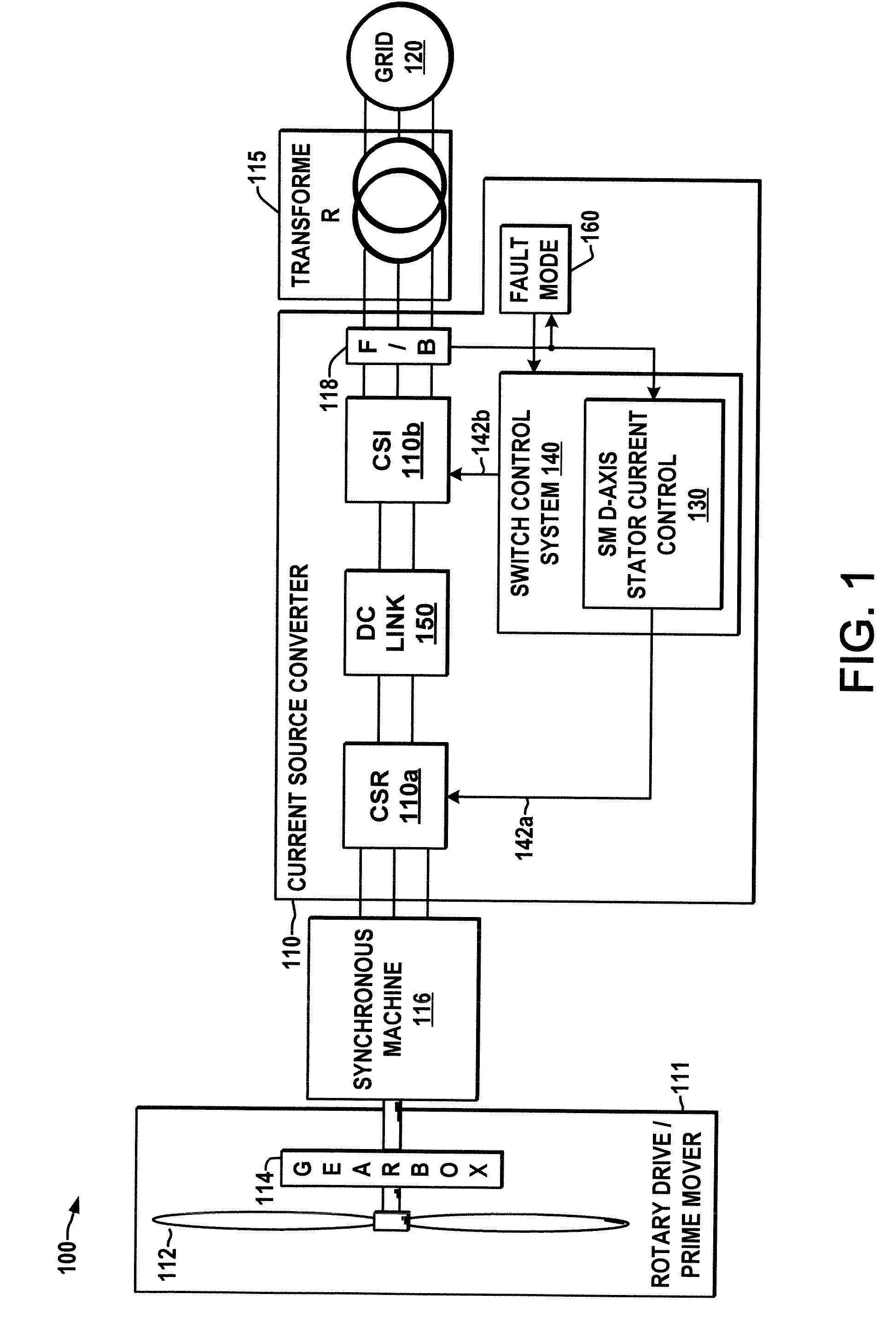
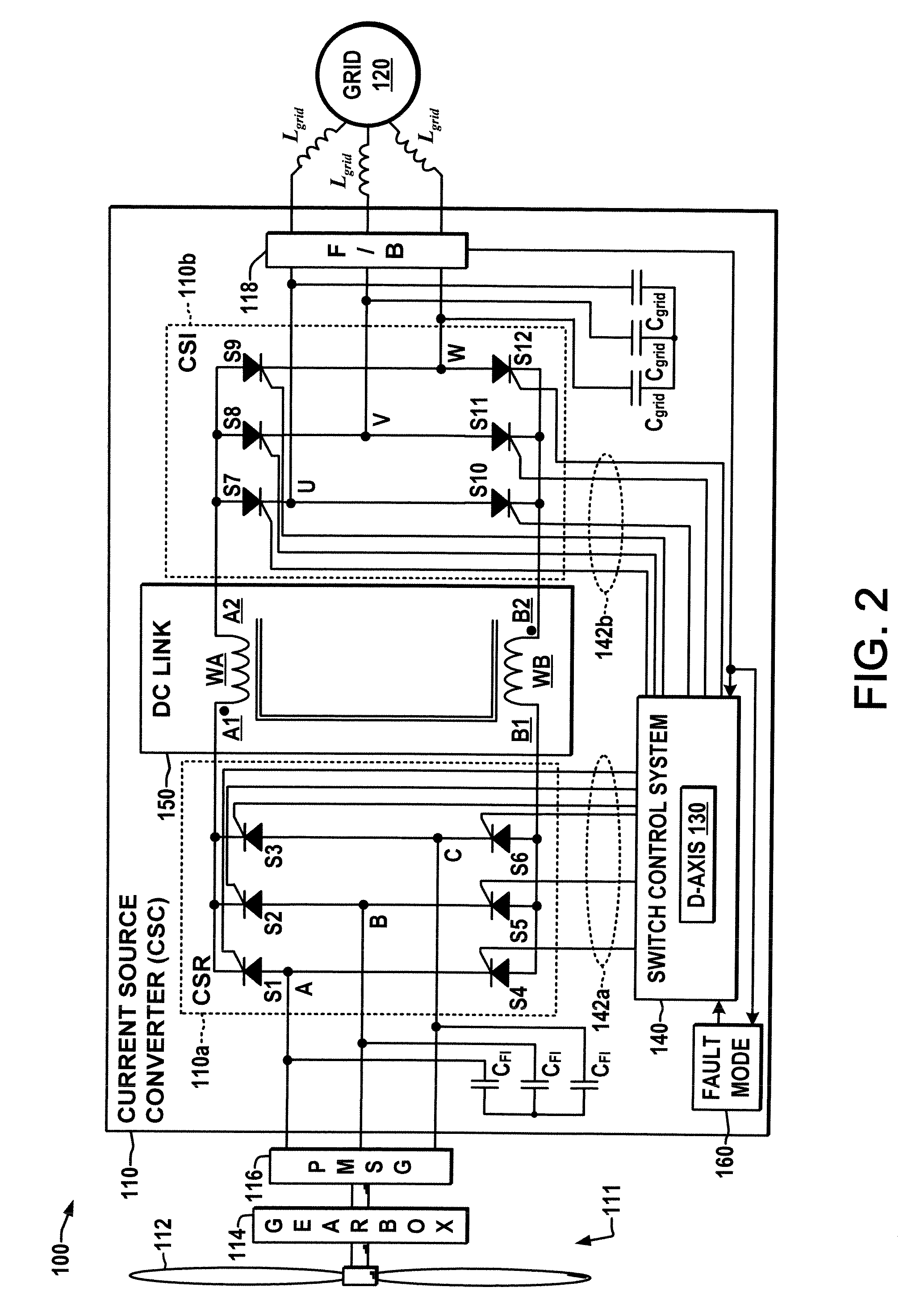
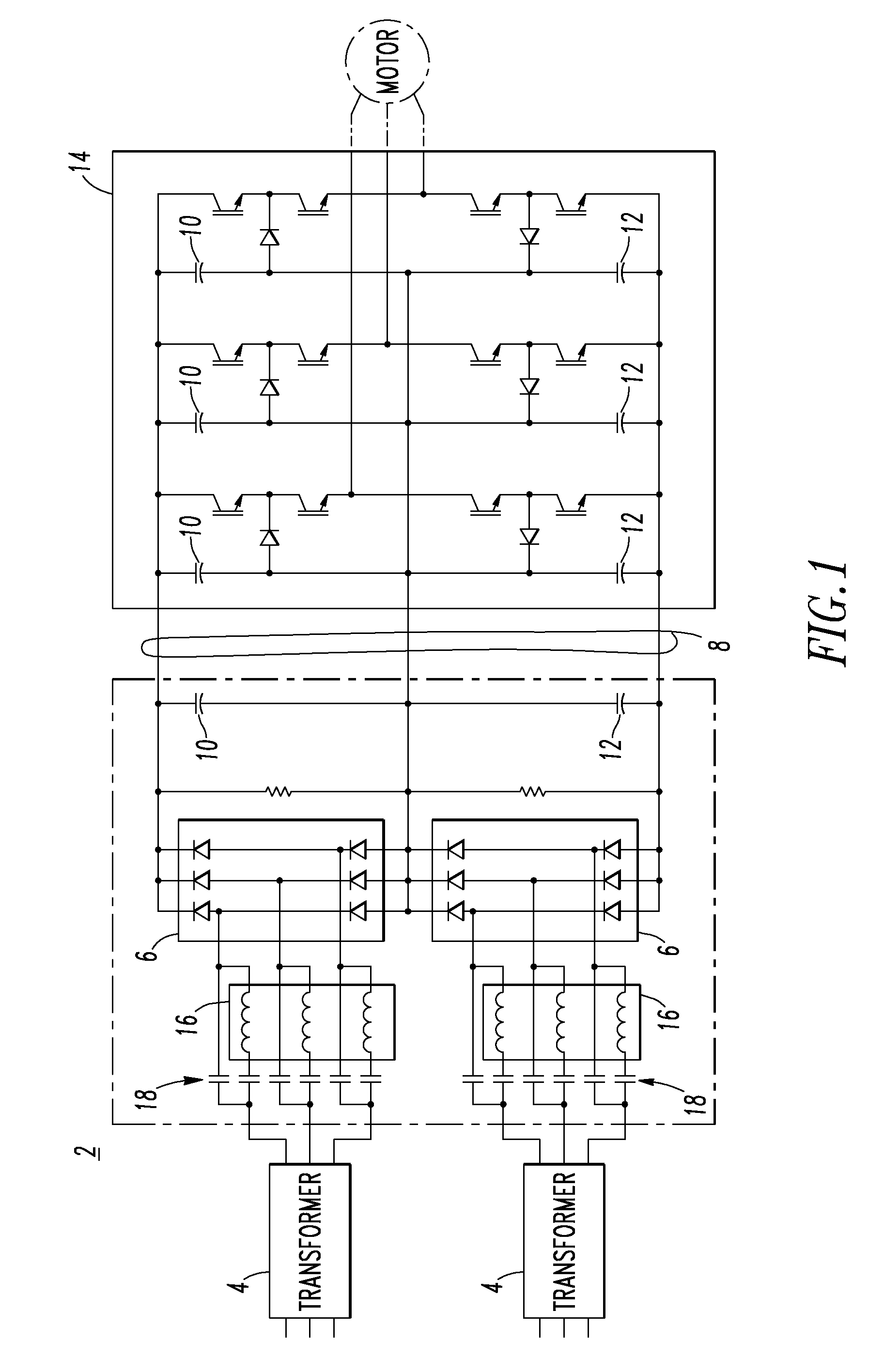
Current source converter-based wind energy system
Power conversion apparatus and methods are presented for providing electrical power to a grid or other load in which a synchronous machine is driven by a wind turbine or other prime mover to provide generator power to a switching type current source converter (CSC), with a current source rectifier (CSR) of the CSC being switched to provide d-axis control of the synchronous machine current based on grid power factor feedback, and with a current source inverter (CSI) of the CSC being switched to provide leading firing angle control and selective employment of dumping resists to dissipate excess generator energy in a fault mode when a grid voltage drops below a predetermined level.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Transformerless multi-level power converter
InactiveUS20060044857A1Need to utilize the large and complex transformers can be eliminatedEliminate needConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionZ-source inverterMotor drive
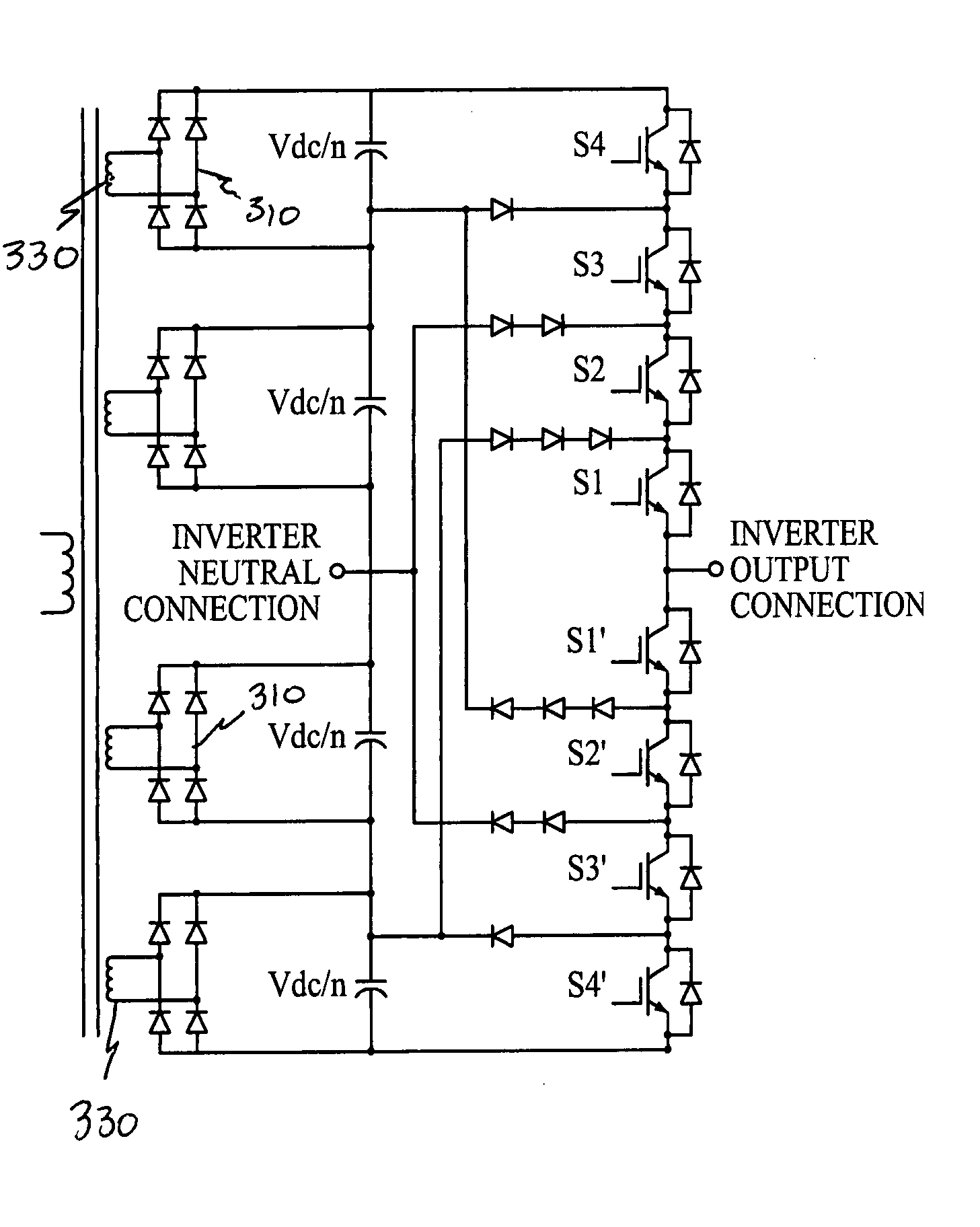
The cascaded, multi-level inverter can be found in a variety of applications and in a variety of industries. The inverter is typically used as a motor drive to provide variable voltage and variable frequency to a propulsion motor or other loads requiring variable frequency and voltage. In the present invention, the transformer is eliminated and its function included in an existing generator by adding a plurality of secondary windings to supply the isolated voltages needed by the multi-level power converter. Two specific examples of the present invention include a cascaded, multi-level inverter, or a variant referred to as the multi-source, flying source inverter, whose ac input voltage is derived from an electromagnetic generatorator.
Owner:CURTISS WRIGHT ELECTRO MECHANICAL
Transformerless multi-level power converter
InactiveUS7219673B2Need to utilize the large and complex transformers can be eliminatedEliminate needConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionZ-source inverterMotor drive
The cascaded, multi-level inverter can be found in a variety of applications and in a variety of industries. The inverter is typically used as a motor drive to provide variable voltage and variable frequency to a propulsion motor or other loads requiring variable frequency and voltage. In the present invention, the transformer is eliminated and its function included in an existing generator by adding a plurality of secondary windings to supply the isolated voltages needed by the multi-level power converter. Two specific examples of the present invention include a cascaded, multi-level inverter, or a variant referred to as the multi-source, flying source inverter, whose ac input voltage is derived from an electromagnetic generatorator.
Owner:CURTISS WRIGHT ELECTRO MECHANICAL
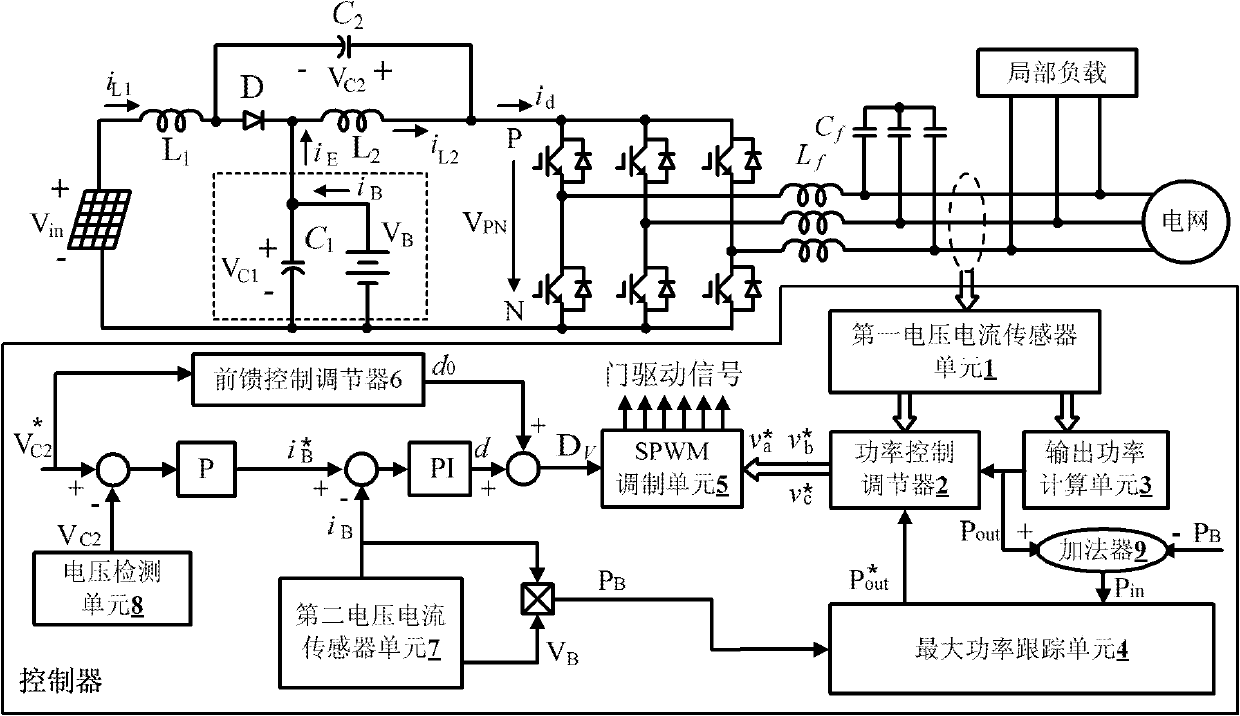
Stored energy type standard-Z source photovoltaic power generation control system and method
InactiveCN102185533AAvoid influenceConstant voltagePhotovoltaicsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsZ-source inverterCapacitor voltage
The invention discloses a stored energy type standard-Z source photovoltaic power generation control system and method. The control system comprises a controller and a stored energy type standard-Z source inverter, wherein the controller comprises a capacitor voltage outer ring and a stored energy battery current inner ring and is used for regulating the direct-connection duty ratio of the inverter, thus the voltage of a DC (direct-current) bus can be constant, although the photovoltaic cell voltage is changed in a wide range; and the output power of the inverter is controlled by a power ring, and the output power of photovoltaic cells and the inverter is controlled so as to carry out charge-discharge management on stored energy batteries, thus realizing maximum power tracking. According to the invention, single-stage power transform is used to complete boosting, reduction voltage, inversion and energy storage, so that a simpler structure is used to realize minimum inverter capacity, thus ensuring the voltage of the DC bus to be constant and a power grid to obtain stable power, thereby maximally collecting solar energy and improving generating efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Zvs voltage source inverter
ActiveUS20150194909A1Eliminate switching lossesRemoves reverse recovery lossEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionZ-source inverterFull bridge
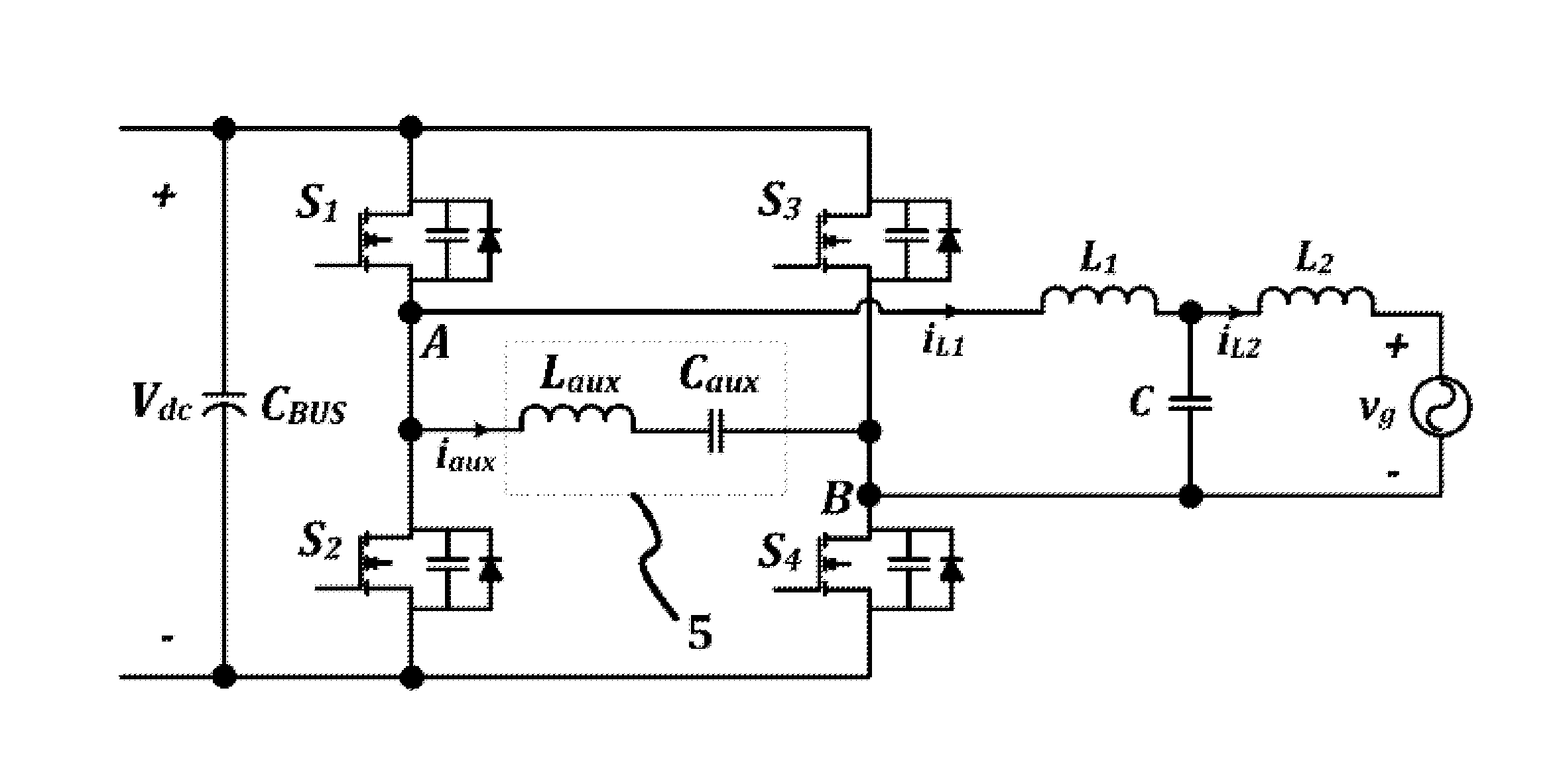
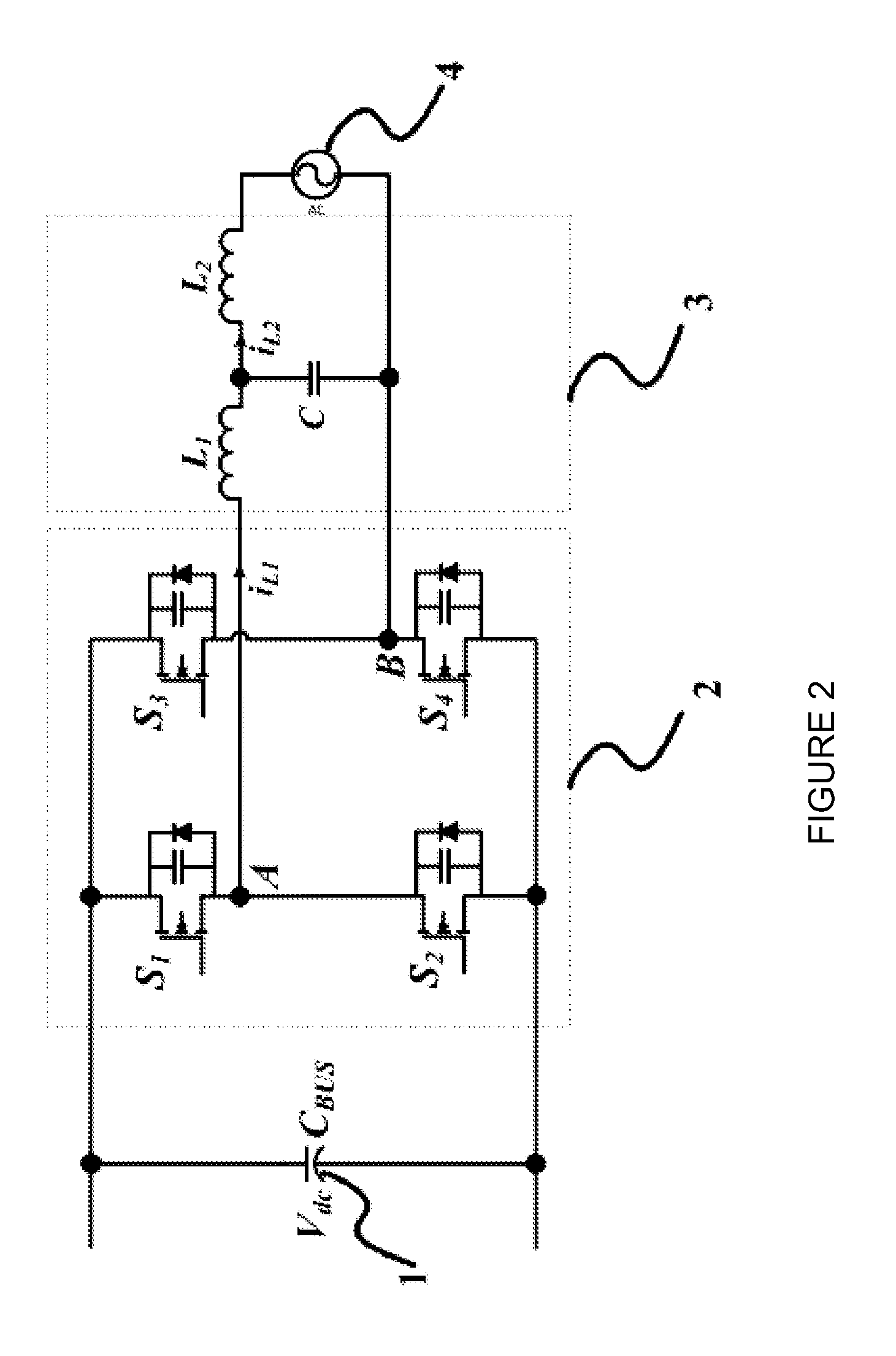
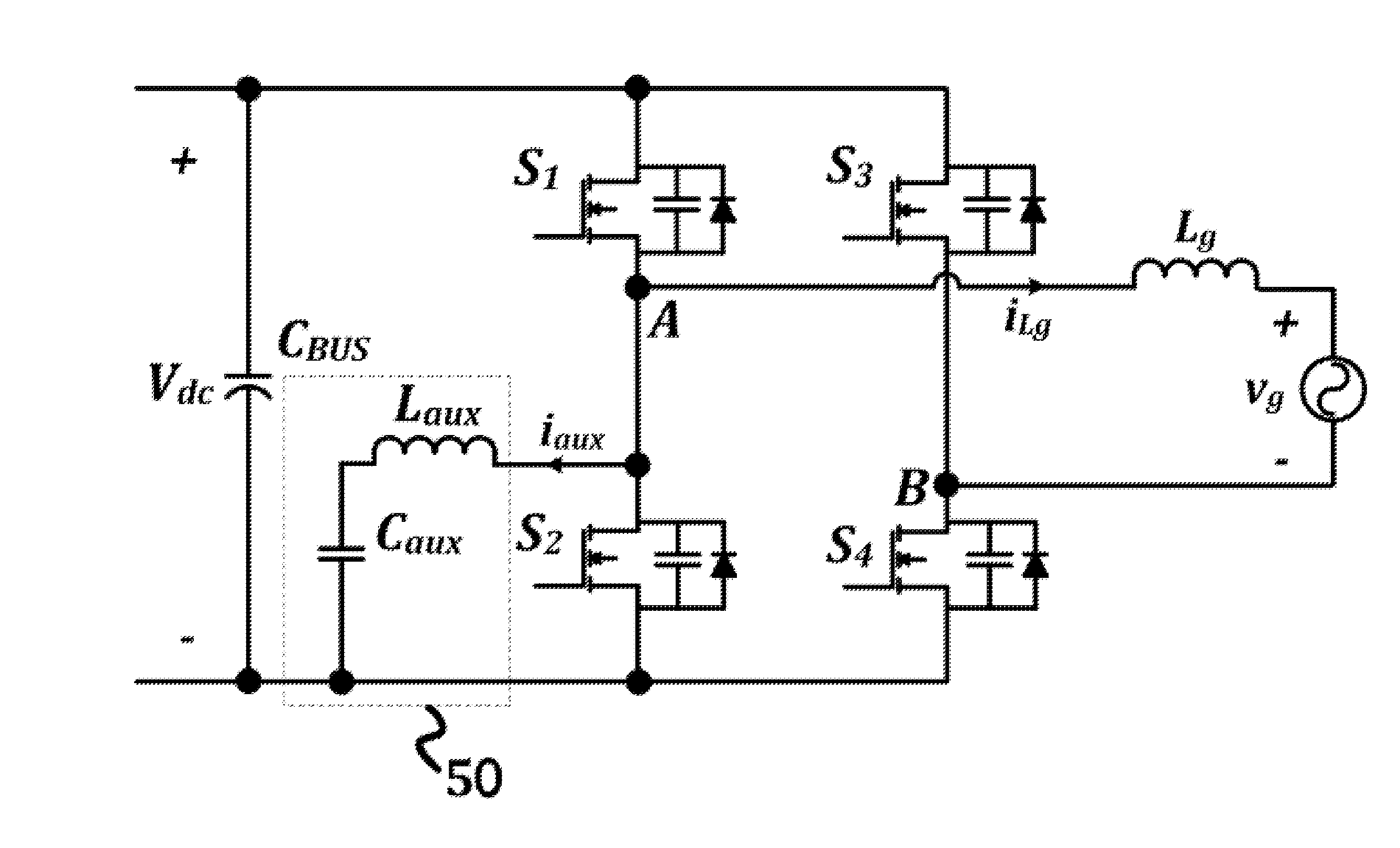
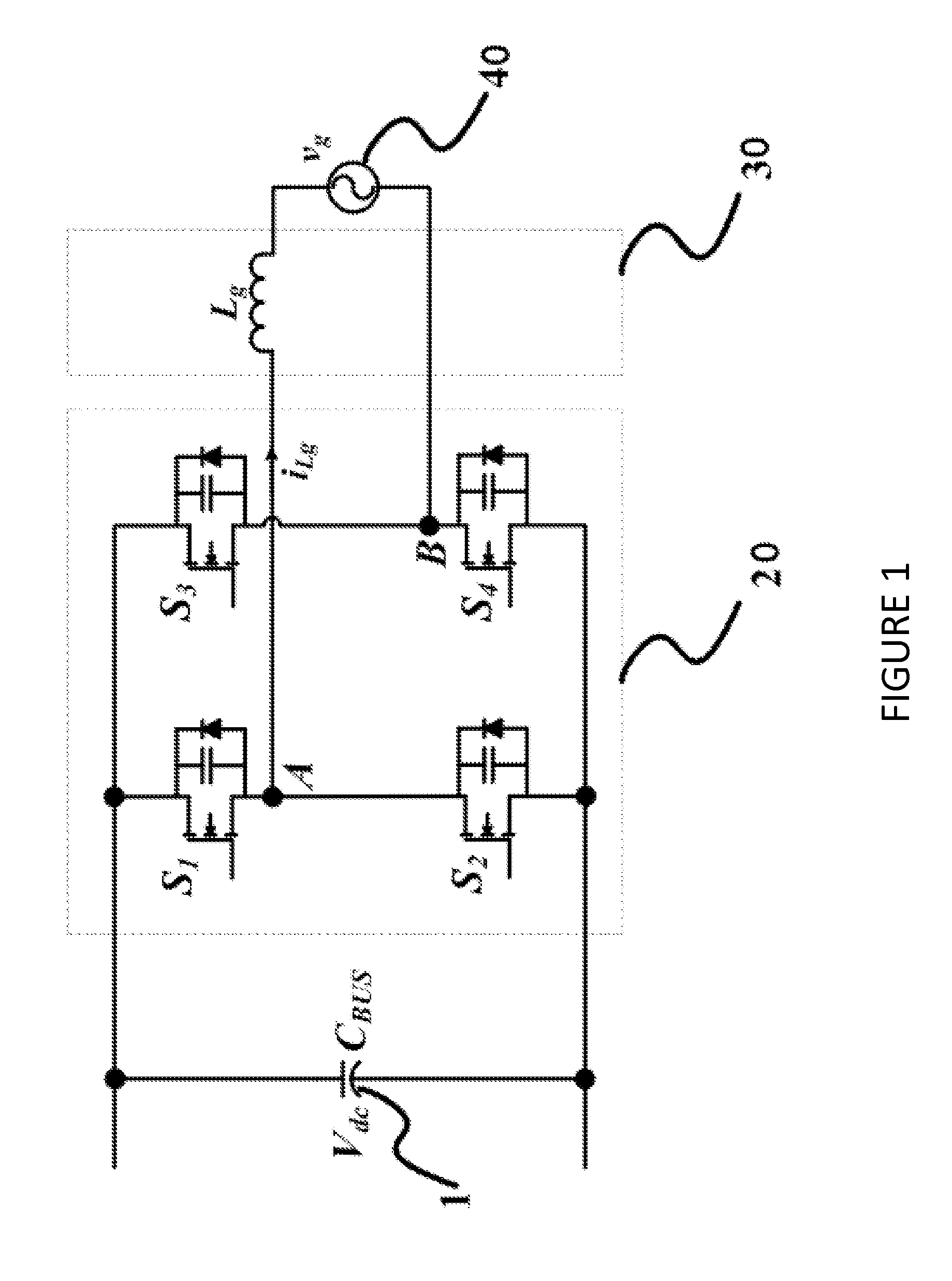
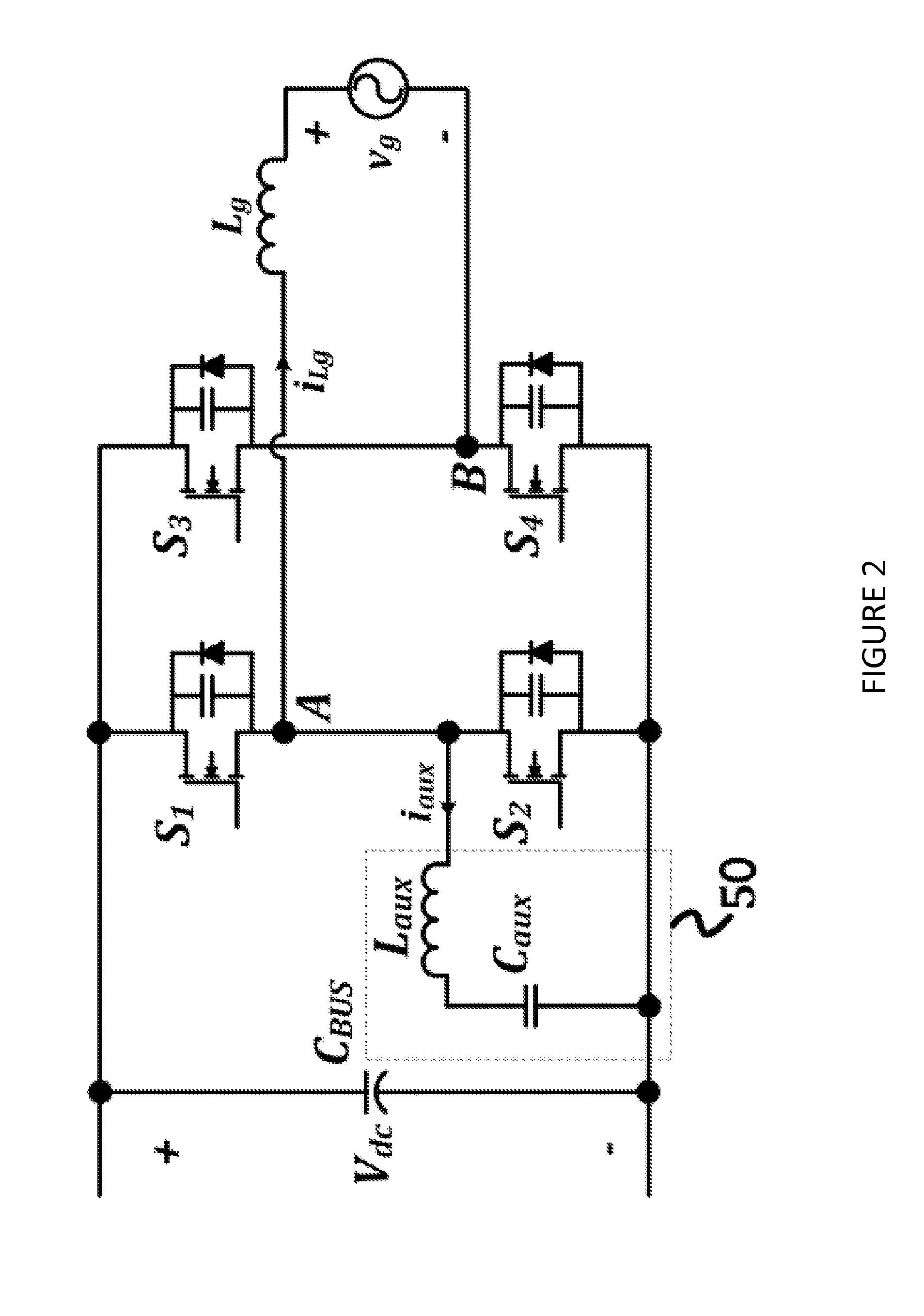
Systems and methods relating to zero voltage switching for inverters. A full bridge inverter is used in conjunction with a passive auxiliary circuit and an output filter. A control system controls the current by way of the auxiliary circuit and injects a high quality current to a power grid. The control system adjusts the duty ratio and switching frequency of the gate pulses applied to the power semiconductors in the full-bridge inverter. As well, the control system adjusts the phase shift between gate pulses for both the leading leg and lagging leg power semiconductors to control the current passing through the auxiliary circuit.
Owner:SPARQ SYST INC
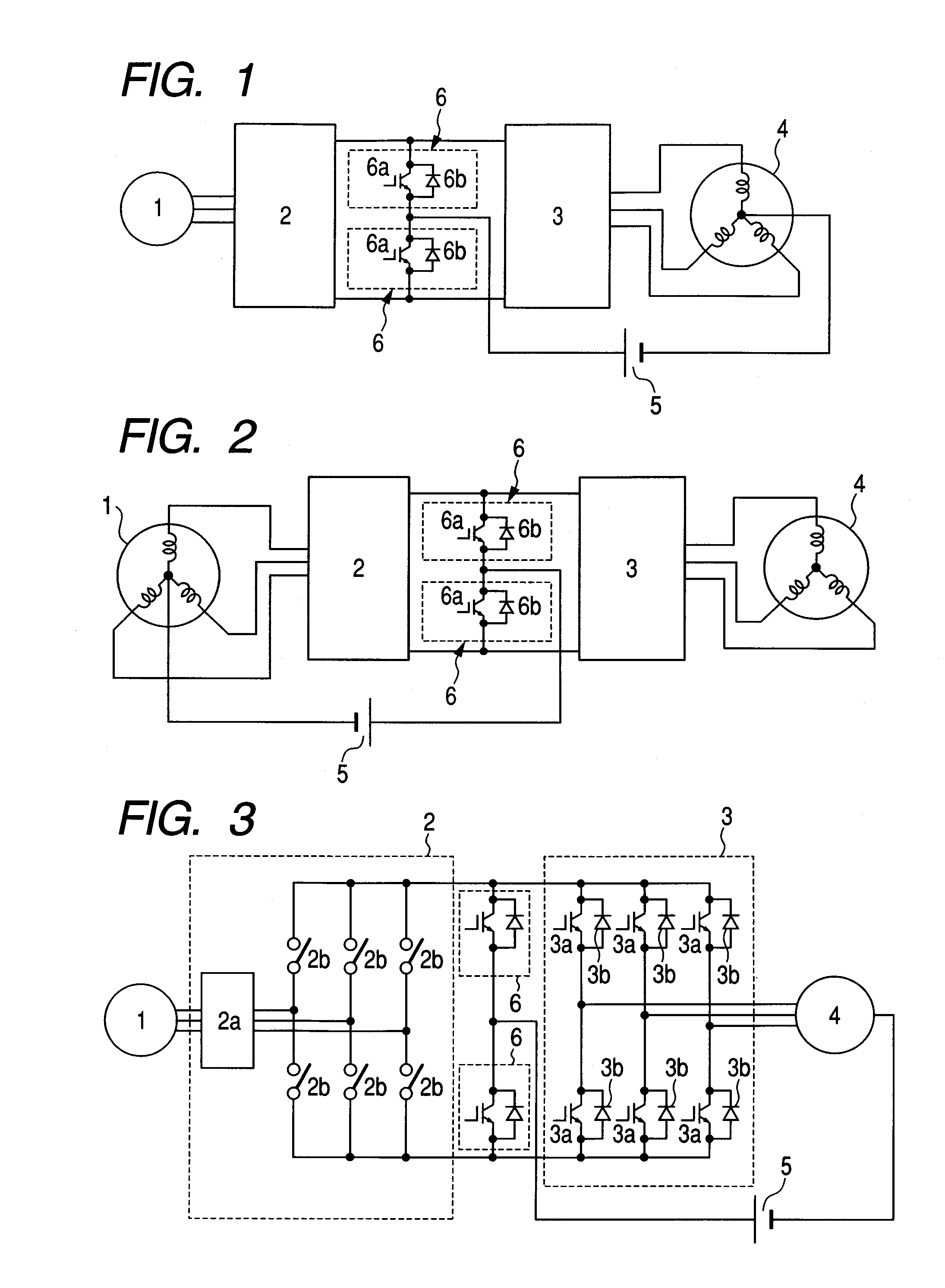
Alternating current motor drive circuit and electric vehicle drive circuit
ActiveUS20090206781A1Reduced weight and size and costSimple circuit configurationAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersZ-source inverterEngineering
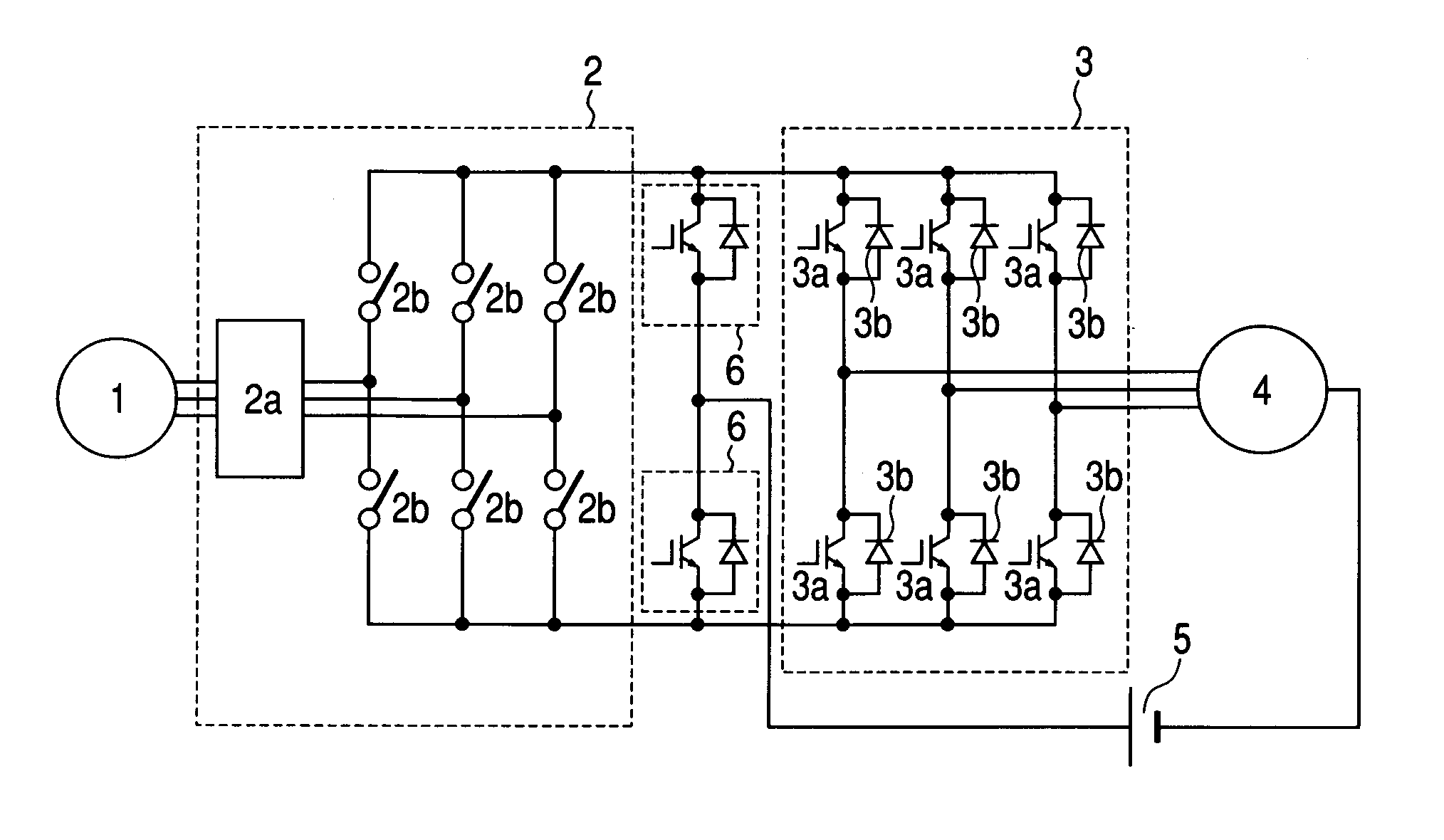
A current source rectifier is provided at an output of an alternating current generator, an alternating current motor is connected to an output of the rectifier via a voltage source inverter, furthermore, two arms having switching elements connected in inverse parallel to diodes are connected to the output of the rectifier, and one terminal of a direct current power source capable of a power supply and absorption is connected to a midpoint between the arms, while the other terminal thereof is connected to a neutral point of motor coils or generator coils, thereby eliminating a need for a large volumetric reactor in a direct current chopper, achieving a downsizing of the circuit.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP NAGAOKA UNIV TECH +1
High-gain Z-source inverter
InactiveCN102223095AImprove anti-interference abilityReduce volumeDc-ac conversion without reversalZ-source inverterCapacitance
The invention provides a high-gain Z-source inverter, comprising a three-phase inverter, which is composed of a direct-current voltage source and a three-phase inversion bridge. The high-gain Z-source inverter further comprises a Z-source network, which is composed of a power diode, a switch inductor and a capacitor. The high-gain Z-source inverter is characterized in that a single inductor is replaced by a branch circuit of the switch inductor; the head end of the Z-source network is connected with the positive electrode of a power supply; the tail end of the Z-source network is connected to the positive end of the three-phase inversion bridge; and the inversion bridge and the power supply are grounded commonly. Compared with the traditional Z-source inverter, the Z-source inverter disclosed by the invention is capable of improving the boost capacity of the inverter, realizing a high modulation factor and improving the output quality of the whole inverter; and simultaneously, the voltage stress of the Z-network capacitor can be effectively reduced so as to reduce the volume and the weight of the inverter.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
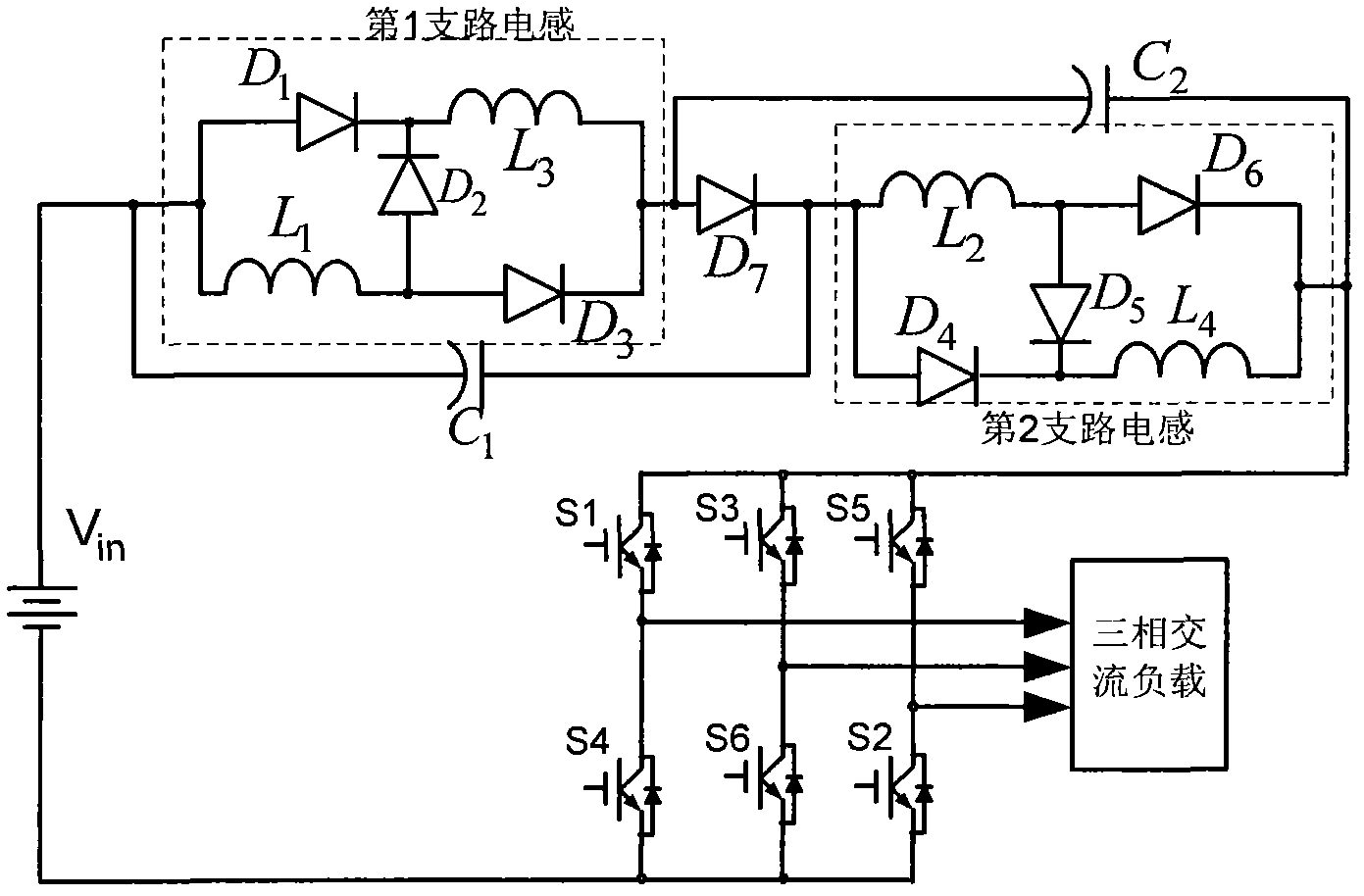
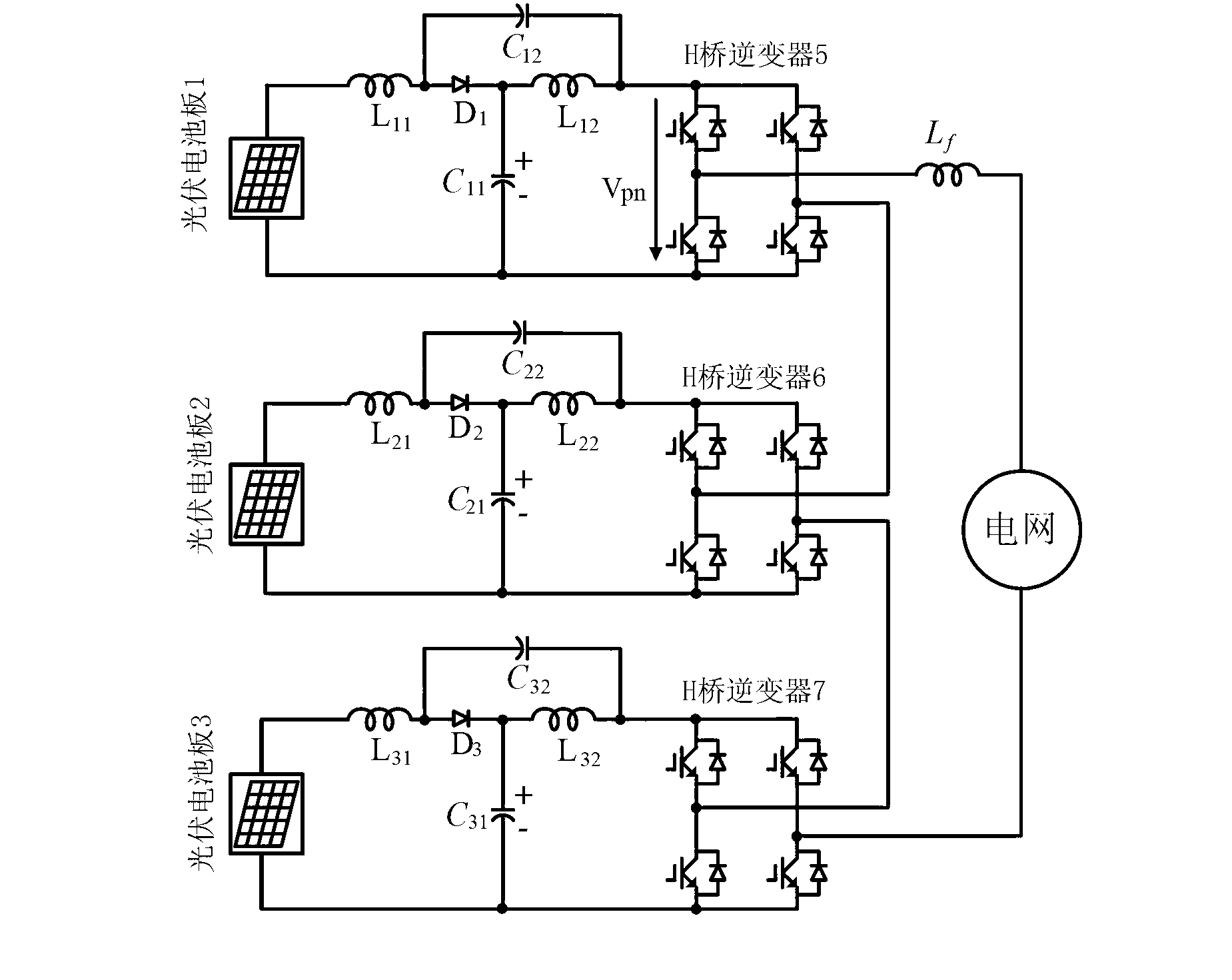
Control method of quasi-Z source cascade multi-level single-phase photovoltaic grid generation system
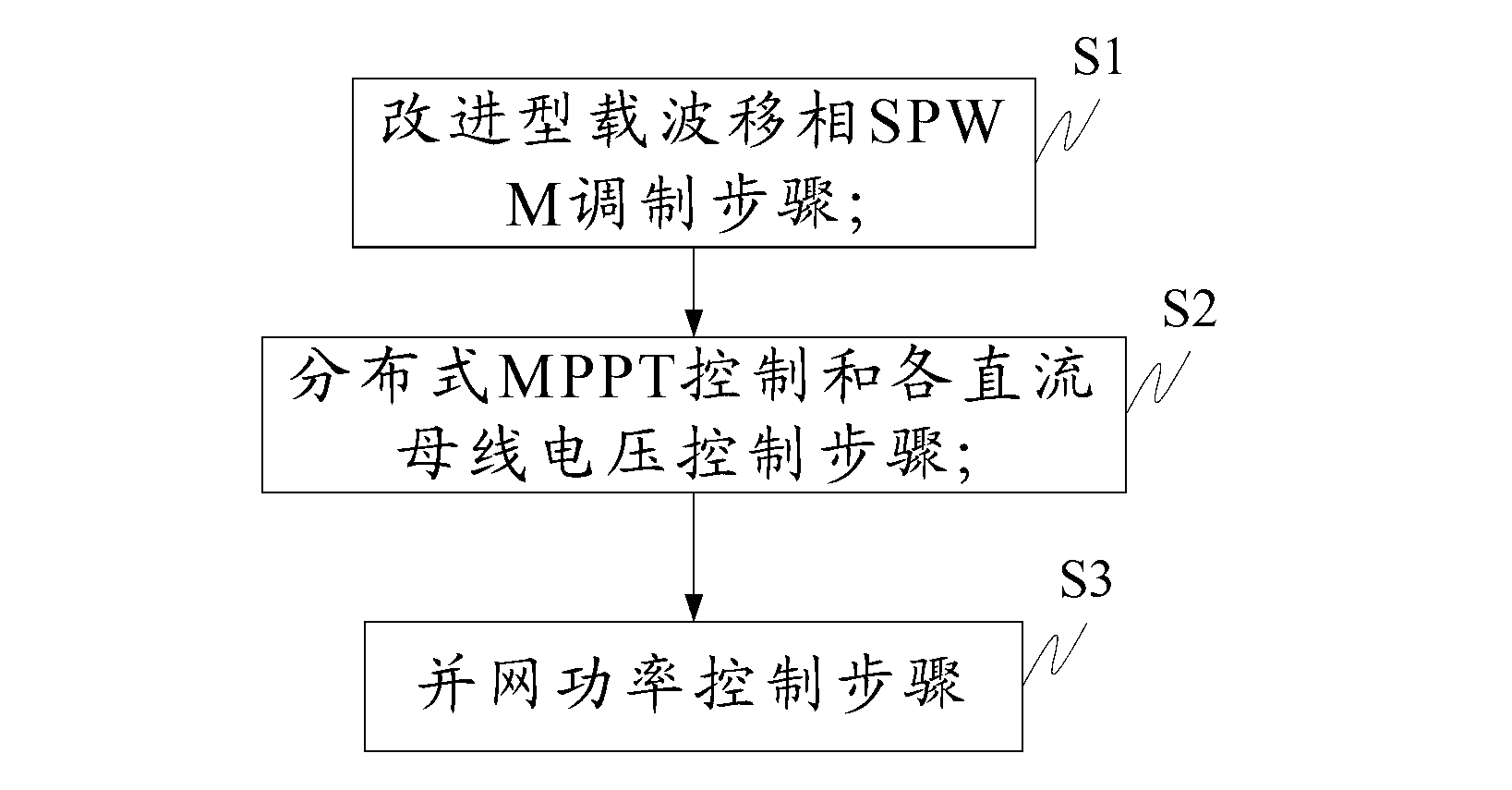
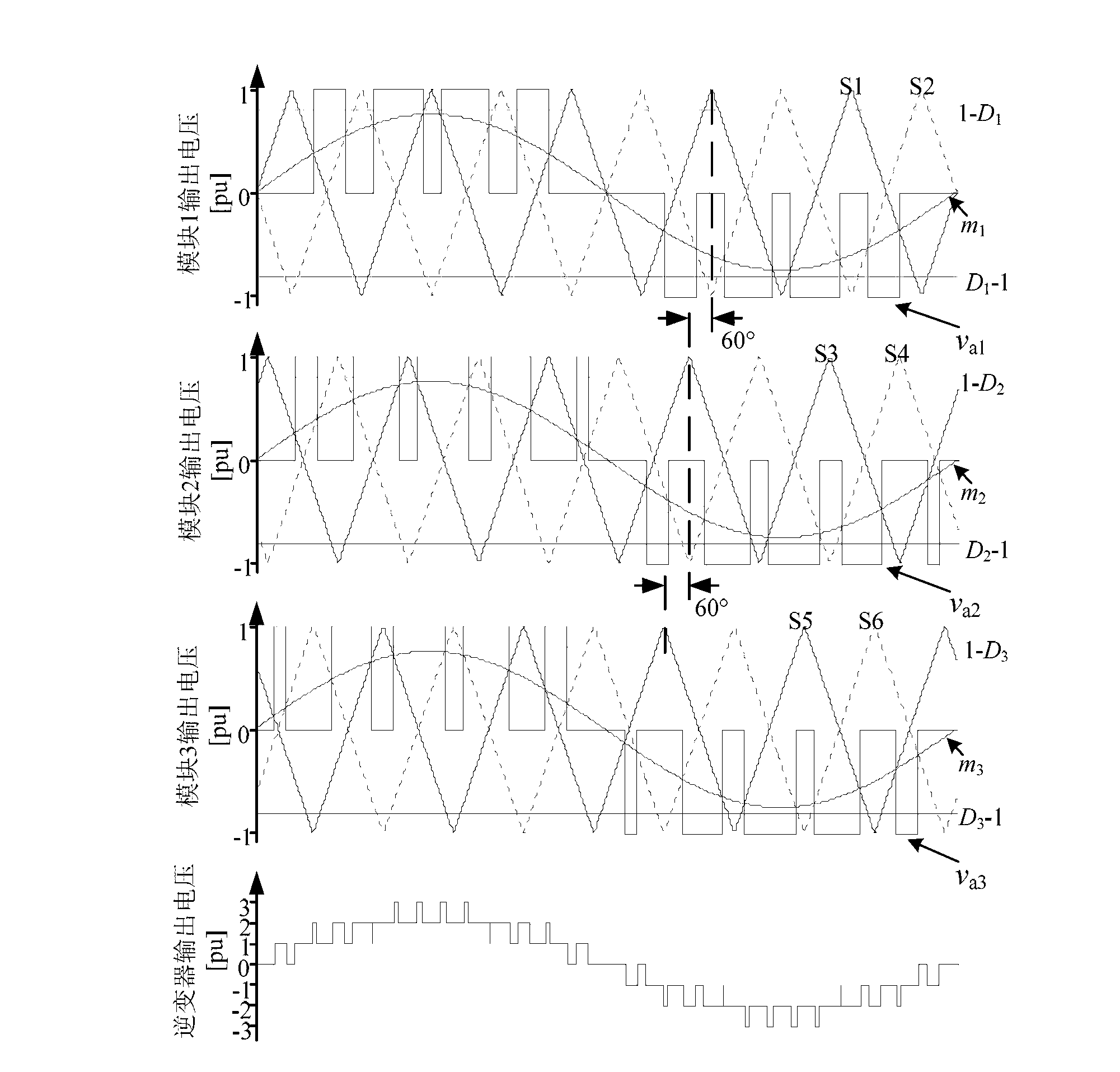
InactiveCN102709941ATo achieve separate trackingAchieve balance controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationZ-source inverterCarrier signal
The invention discloses a control method of a quasi-Z source cascade multi-level single-phase photovoltaic grid generation system, wherein a quasi-Z source inverter is provided for each photovoltaic battery as a generation module; a plurality of modules are connected in series to form a quasi-Z source cascade multi-level single-phase photovoltaic grid generation system which integrates the advantages of the quasi-Z source inverter and the cascade multi-level inverter; with the adoption of the control method, for the system, a carrier phase shift SPWM (sinusoidal pulse width modulation) modulation method, distributed MPPT (maximum power point tracking) control, direct-current bus voltage control and grid power control are improved, the quasi-Z source cascade multi-level single-phase photovoltaic power generation system can be effectively operated, solar energy is collected in a maximum manner, and multi-level output voltage and boosting control are realized. Even if the voltage wide range of the photovoltaic battery is changed, the peak voltage of the direct-current bus of each module is constant, so that the condition that the capacity of the inverter is minimum is ensured, thereby the photovoltaic generation with low expenses, high efficiency and high reliability is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
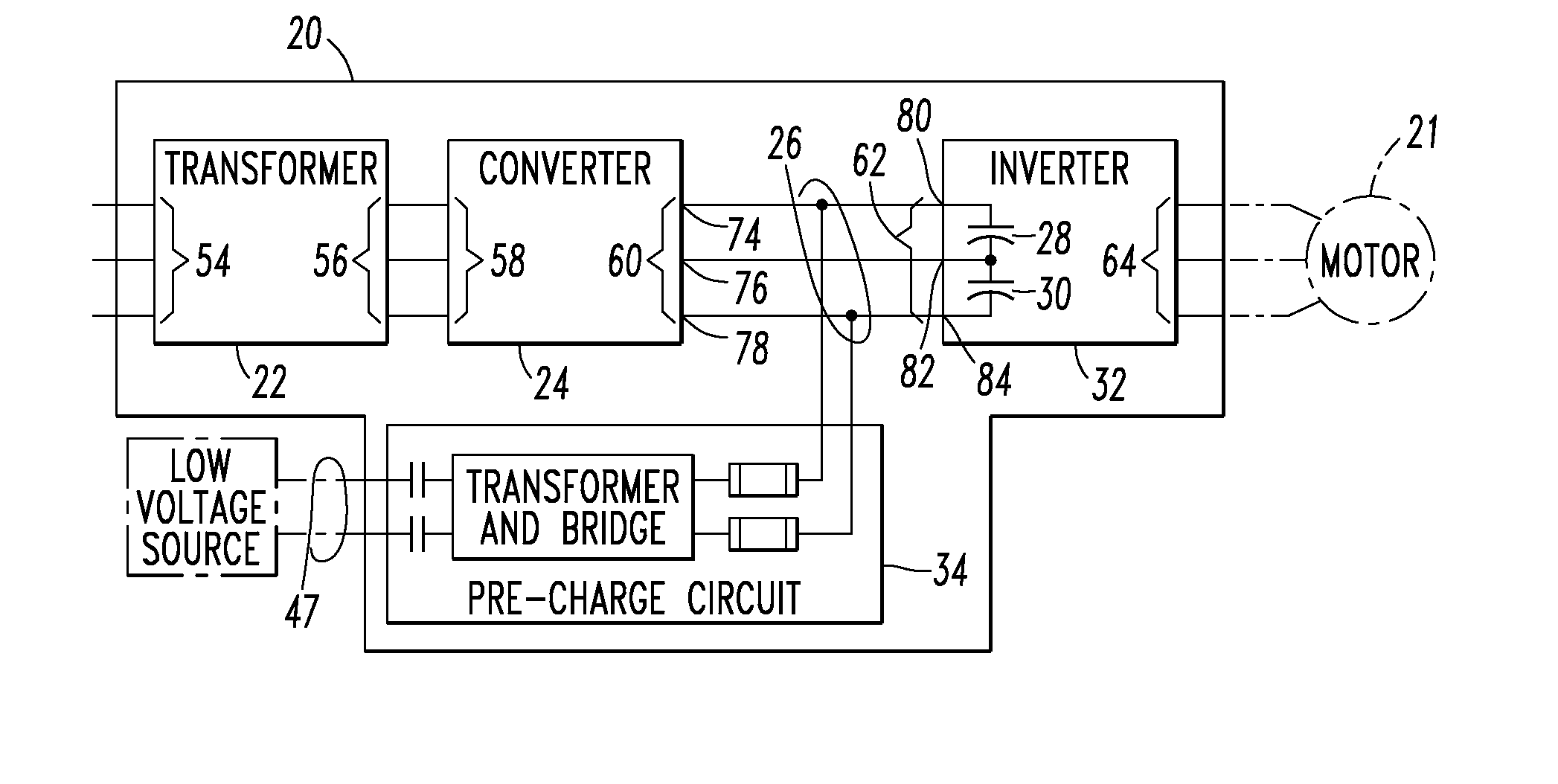
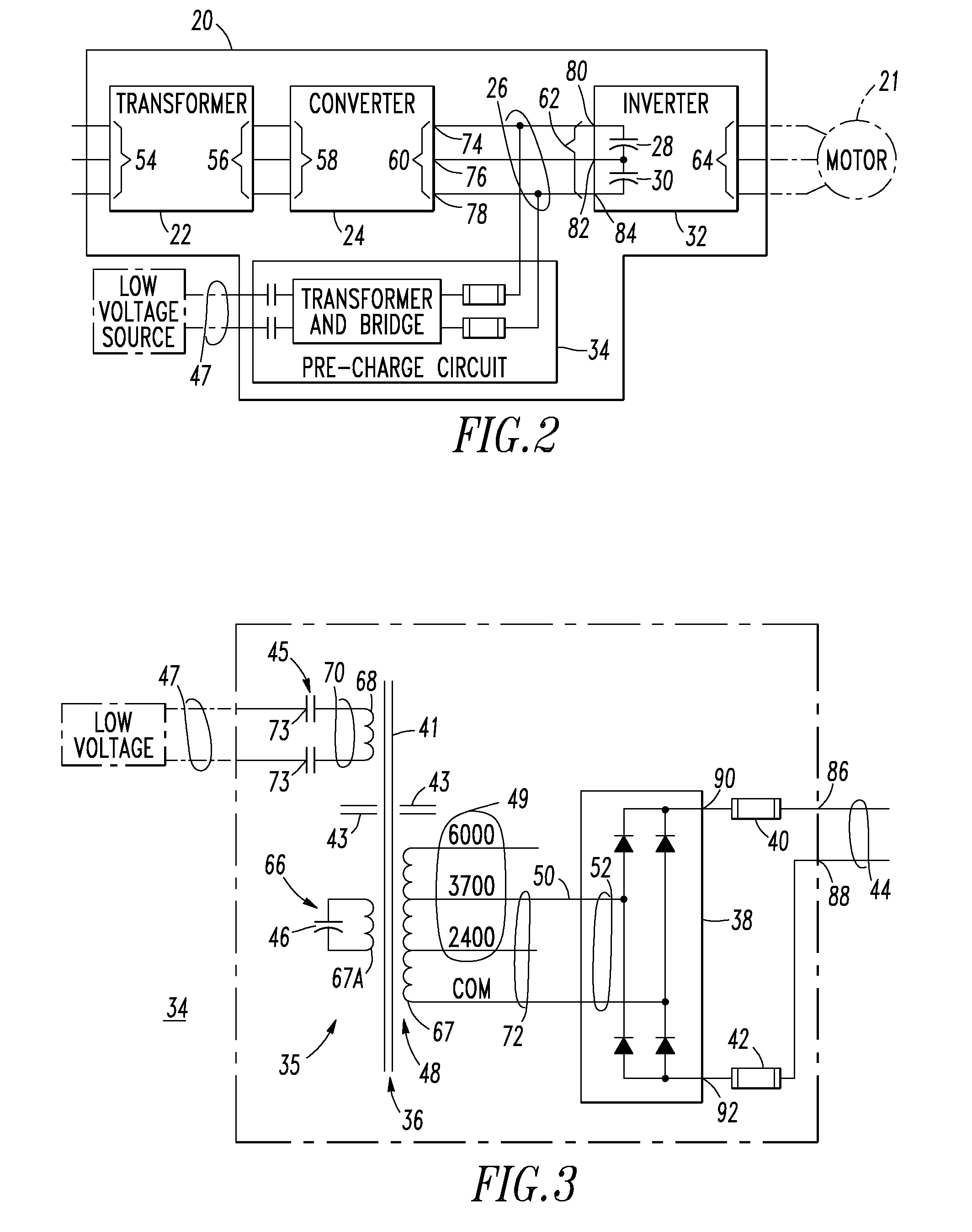
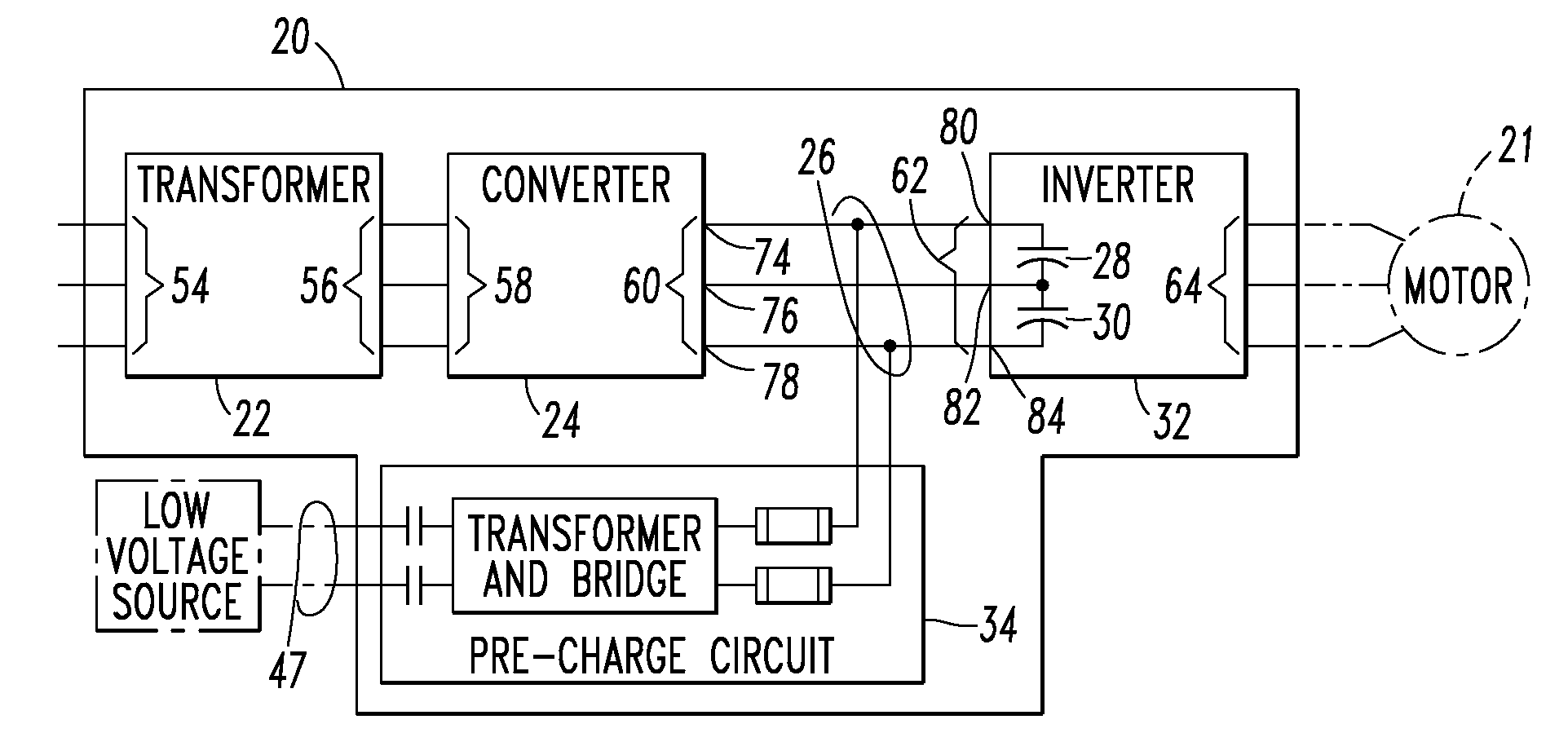
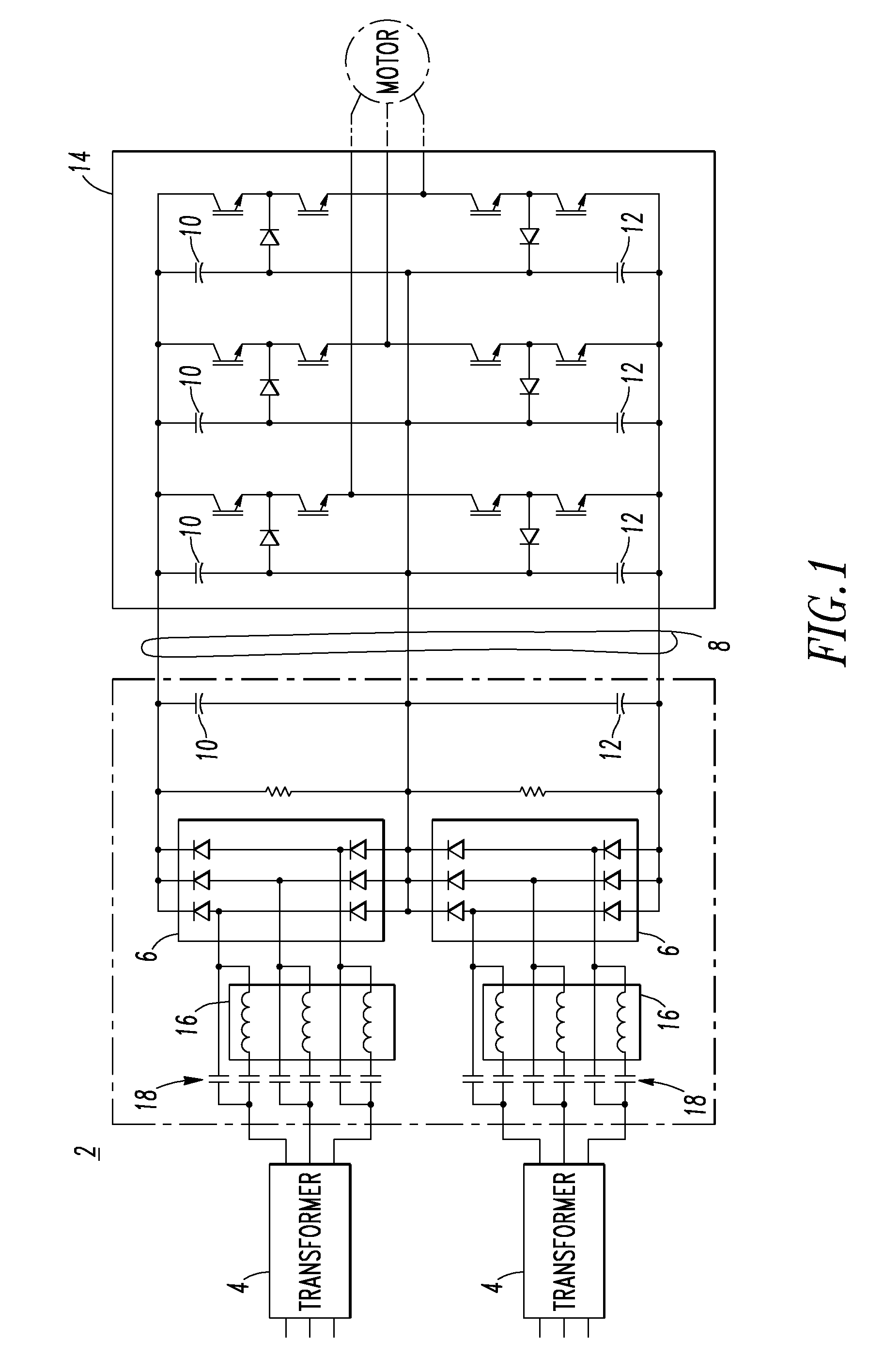
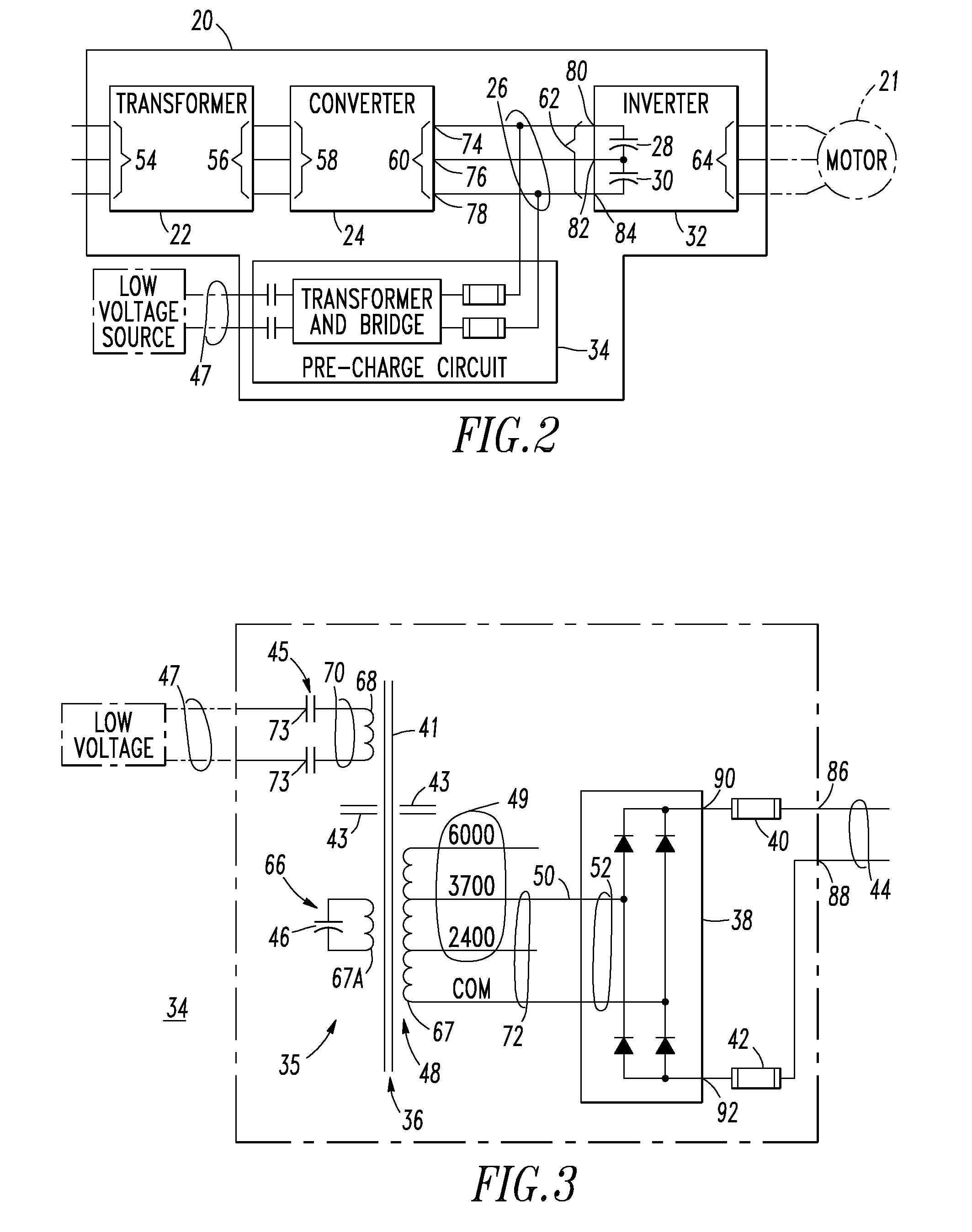
Voltage source inverter and medium voltage pre-charge circuit therefor
InactiveUS20090284999A1Ac-dc conversionElectric power transfer ac networkZ-source inverterLow voltage
A medium voltage adjustable frequency drive includes an input isolation transformer having a three-phase input and a three-phase output, a converter having a three-phase input electrically connected to the three-phase output of the input isolation transformer and an output providing a direct current bus, an inverter having an input electrically connected to the output of the converter and a three-phase output, and a pre-charge circuit. The pre-charge circuit includes a ferro-resonant transformer circuit having a primary winding structured to input a low voltage and a secondary winding structured to output a medium voltage and provide a constant current source. The pre-charge circuit also includes a medium voltage diode bridge having an input receiving the medium voltage from the secondary winding of the ferro-resonant transformer circuit and an output structured to provide the constant current source to the direct current bus.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
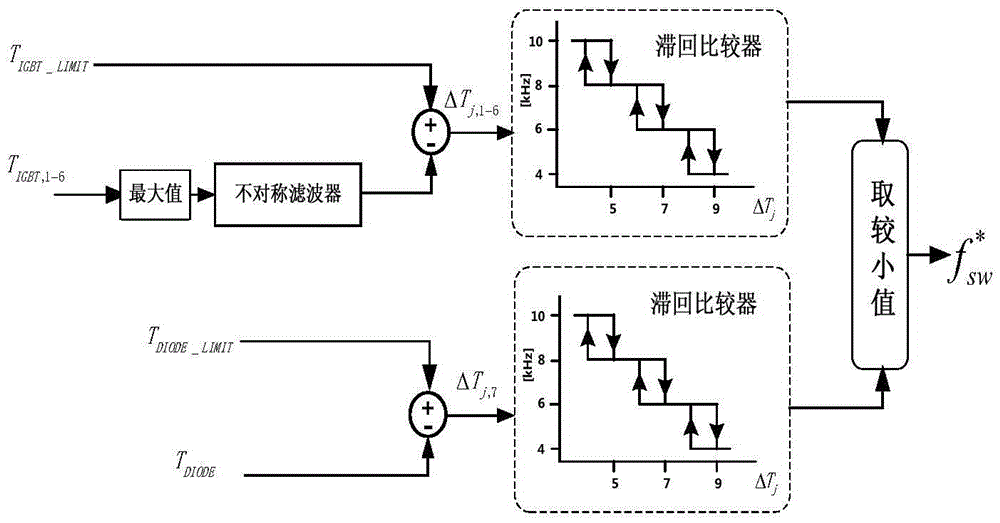
Active thermal optimization control method and device of electromobile driving system
ActiveCN105577069ASolving Control Problems for Active Thermal OptimizationImprove efficiencyAC motor controlElectric machinesZ-source inverterReal-time data
The invention discloses an active thermal optimization control method and device of an electromobile driving system. The method comprises the following steps of calculating total loss of an inverter according to real-time data of the inverter; obtaining a first junction temperature value and a second junction temperature value of an inverter equivalent thermal resistance network according to the total loss and an inverter thermal resistance model; obtaining a first switching frequency according to the first junction temperature value, a first safe temperature limit value and a hysteresis comparator; simultaneously obtaining a second switching frequency according to the second junction temperature value, a second safe temperature limit value and the hysteresis comparator; and selecting the smaller one of the first switching frequency and the second switching frequency as the switching frequency of the electromobile driving system. According to the method, a current-type quasi-Z source inverter is adopted, and the problem of active thermal optimization control of the inverter on an actual heat constraint condition is solved by adjusting the shoot-through duty ratio of the inverter, the switching frequency and a control signal output from a space vector pulse width modulator.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Loss minimized PWM for voltage source inverters taking into account inverter non-linearity
InactiveCN101047342AAC motor controlEfficient power electronics conversionZ-source inverterPower inverter
A dynamic pulse width modulation (PWM) selection device automatically switches between discontinuous PWM (DPWM) control methods. The PWM selection device comprises a PWM control module. The PWM control module determines a desired pulse width of a switching control signal according to a desired output signal. The PWM control module controls an actual pulse width of the switching control signal according to the desired pulse width and a first PWM control method. A selection module determines whether the desired pulse width exceeds a pulse width threshold. The selection module selects a second PWM control method when the desired pulse width exceeds the pulse width threshold.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECHNOLOGY OPERATIONS LLC
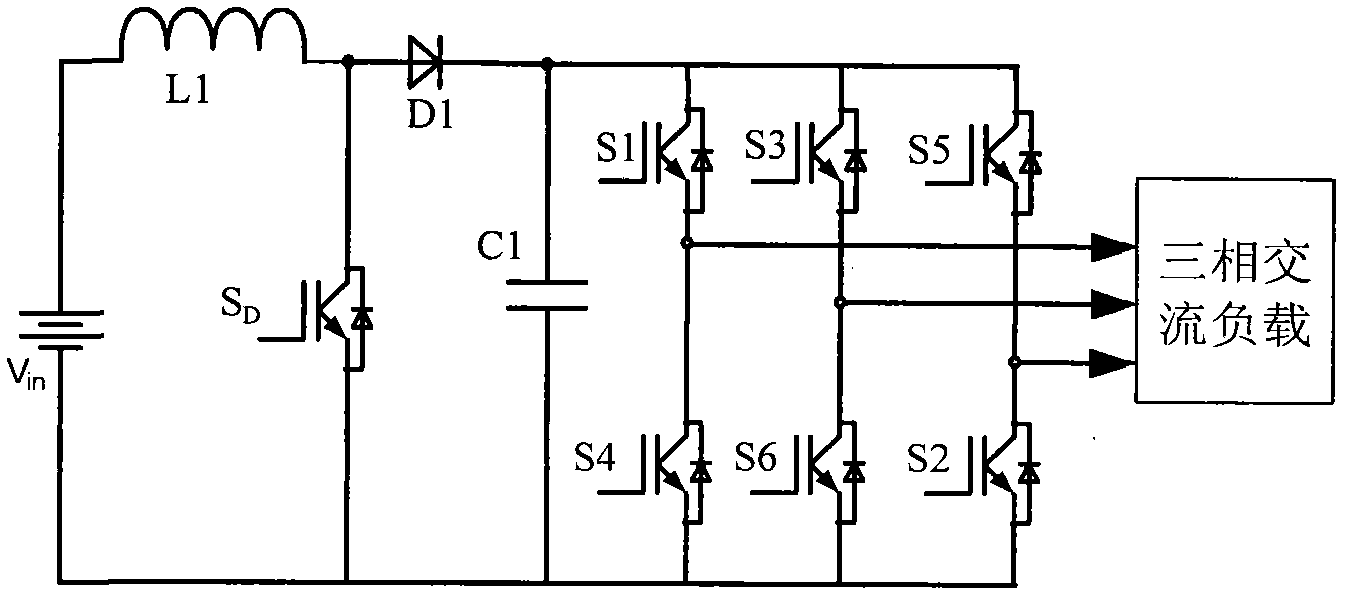
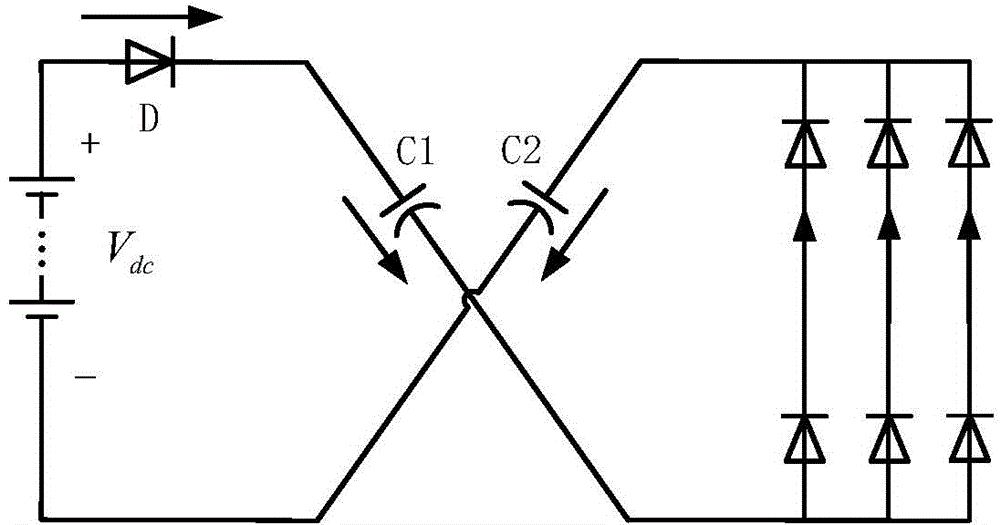
Z source reverser and soft start method
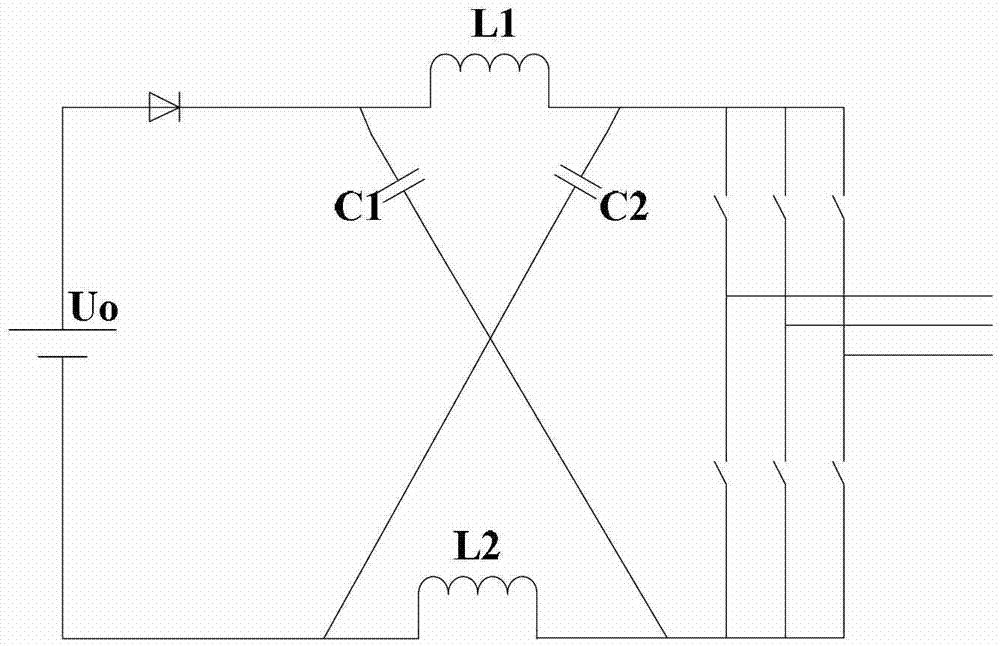
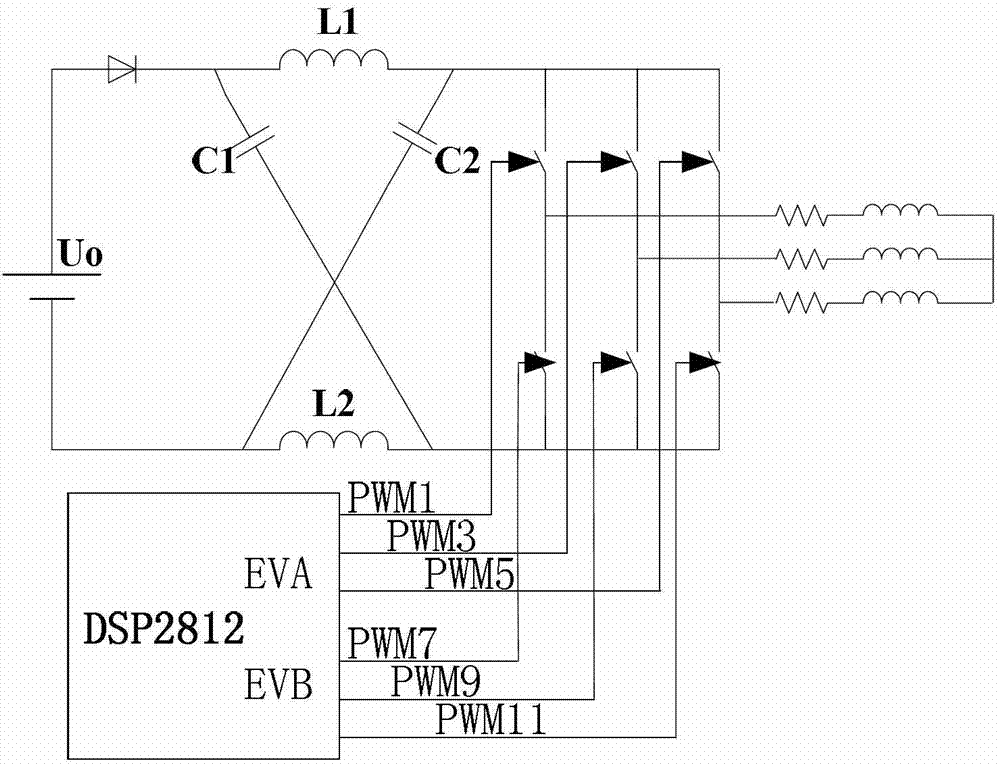
InactiveCN101267168AAchieving a soft startSimple structureAc-dc conversionZ-source inverterCapacitor voltage
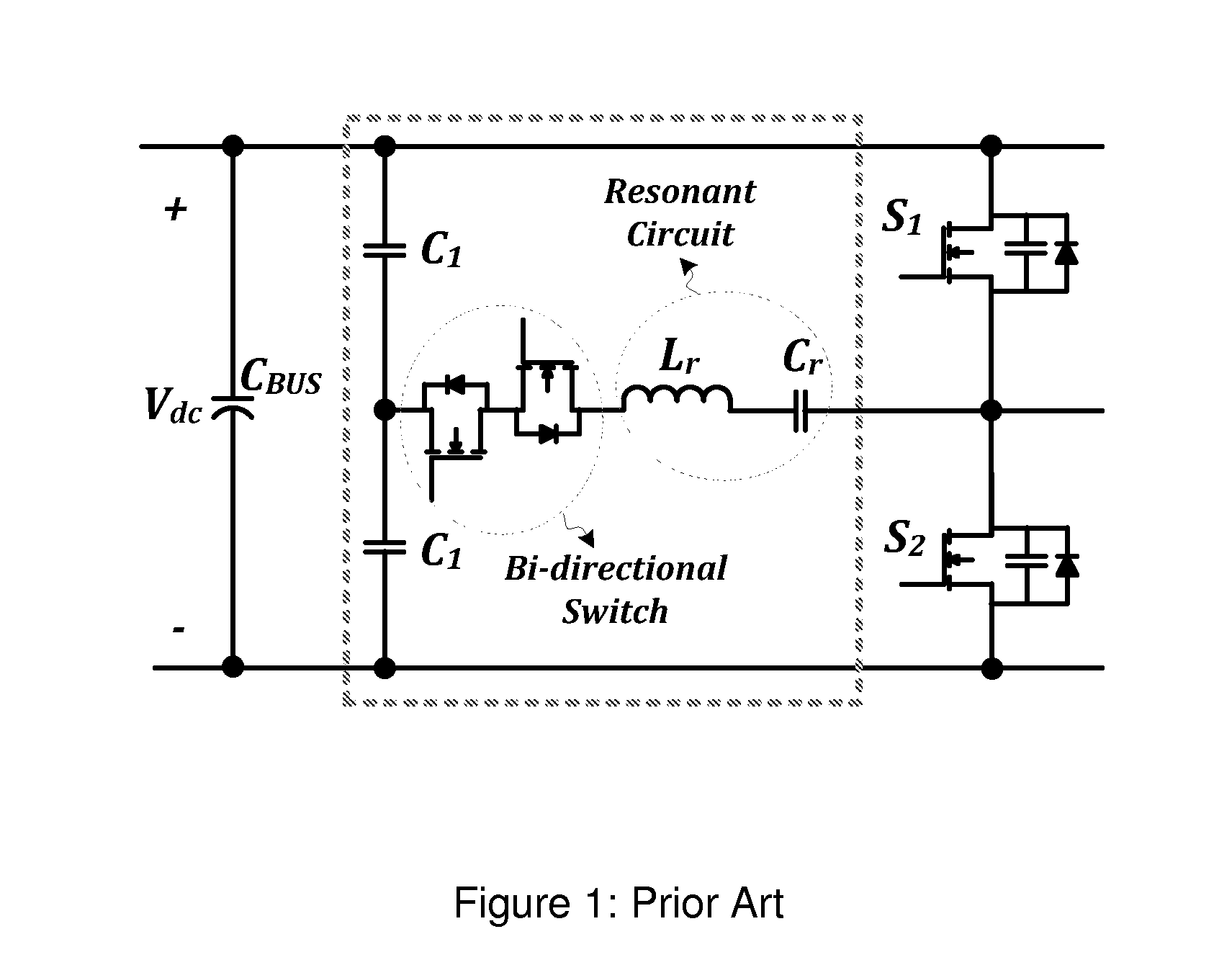
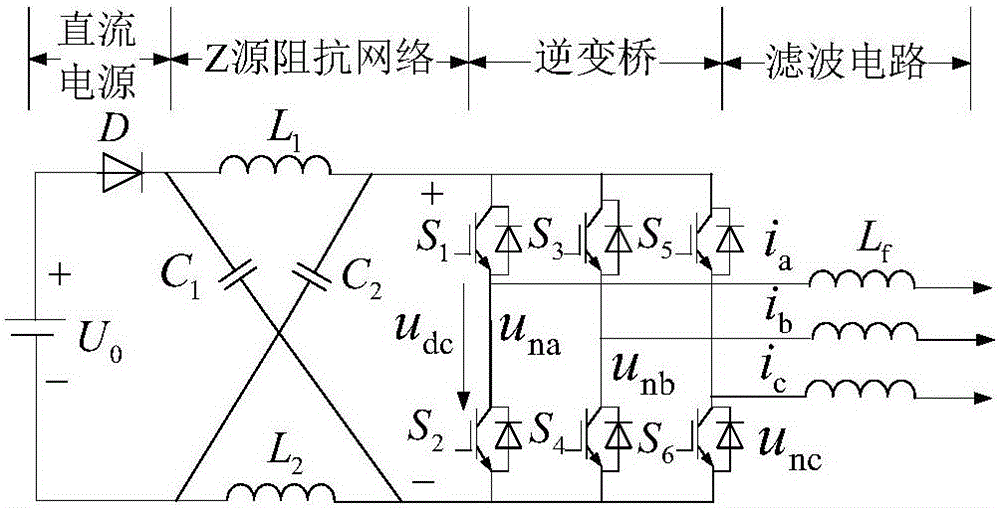
The present invention provides a z-source inverter and its soft starting method, belonging to power electronic converter. The inverter main circuit is composed of a DC voltage source, a three-phase inverter bridge, a z-source network, a power diode, characterized in that the positive end of the three-phase inverter bridge is connected to the cathode of the DC voltage source, the negative end of the three-phase inverter bridge is connected to the Z source network. Compared with the voltage source type and the current source type inverter, the Z source inverter realizes pressure raising change function, and the upper and the lower switch tubes of the same bridge arm are directly passing, so the dead zone does not need, the circuit structure is simple, having high credibility. Compared with the traditional Z source inverter, the capacitor voltage of the Z source network in the Z source inverter has small stress, and realizing the soft start of the transformer, avoiding the problems of large voltage and current when the traditional Z source inverter starts, the work of the transformer is safe and credible, and having light volume and weight.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
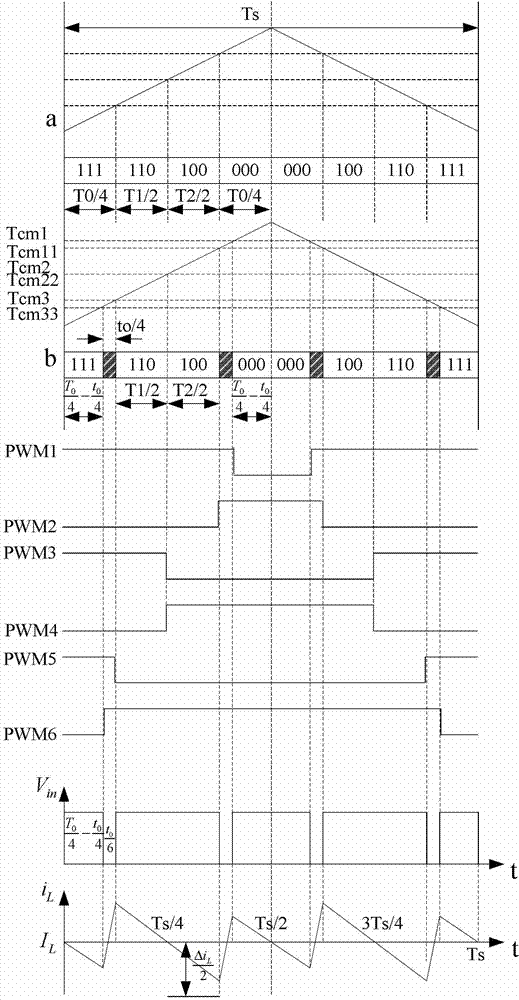
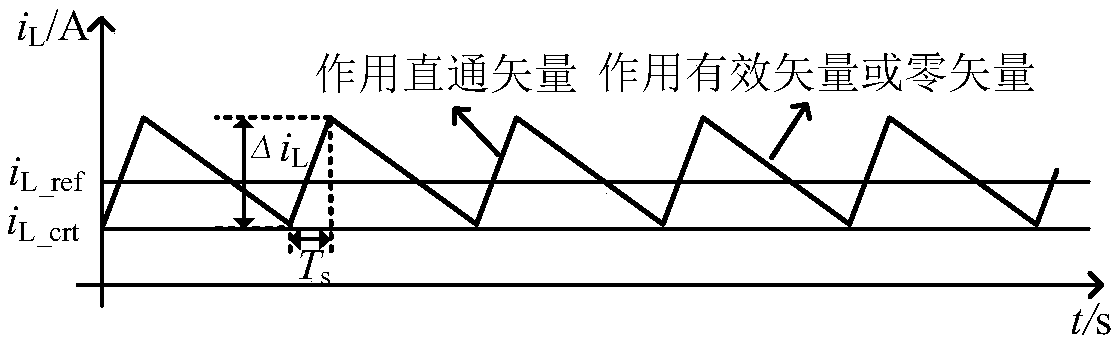
SVPWM (Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation) control method for Z-source inverter
InactiveCN102969921AReduce switching timesSmall rippleDc-ac conversion without reversalZ-source inverterEngineering
The invention relates to an SVPWM (Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation) control method for a Z-source inverter, belongs to the technical field of inverter control and solves the problem of generation of a larger inductive current ripple caused by the existing SVPWM control method for the Z-source inverter. The states of three switching tubes of an upper bridge arm are represented by eight vectors, and the eight vectors divide a control interval into six sectors. For taking the third (III) sector as an example, the vectors taking actions in Ts in each SVPWM period are allocated sequentially from left to right as 111, 110, 100, 000, 000, 100, 110 and 111, wherein the total acting time of a traditional zero vector is set as T0; the total acting time of a direct-through zero vector is set as t0 which is greater than 0 and less than or equal to T0; and the total acting time t0 of the direct-through zero vector is divided into four sections inserted between the acting times of the traditional zero vector and an adjacent effective vector, thereby realizing SVPWM control of the Z-source inverter. The SVPWM control method is suitable for the SVPWM control of the Z-source inverter.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Voltage source inverter and medium voltage pre-charge circuit therefor
A medium voltage adjustable frequency drive includes an input isolation transformer having a three-phase input and a three-phase output, a converter having a three-phase input electrically connected to the three-phase output of the input isolation transformer and an output providing a direct current bus, an inverter having an input electrically connected to the output of the converter and a three-phase output, and a pre-charge circuit. The pre-charge circuit includes a ferro-resonant transformer circuit having a primary winding structured to input a low voltage and a secondary winding structured to output a medium voltage and provide a constant current source. The pre-charge circuit also includes a medium voltage diode bridge having an input receiving the medium voltage from the secondary winding of the ferro-resonant transformer circuit and an output structured to provide the constant current source to the direct current bus.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
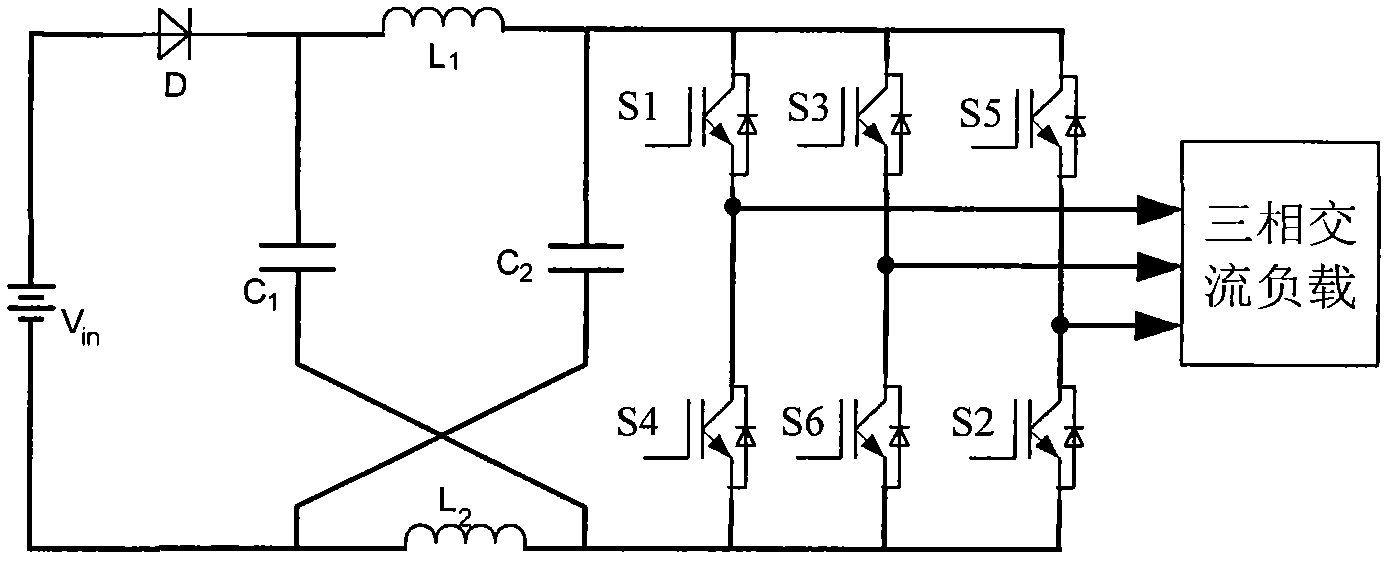
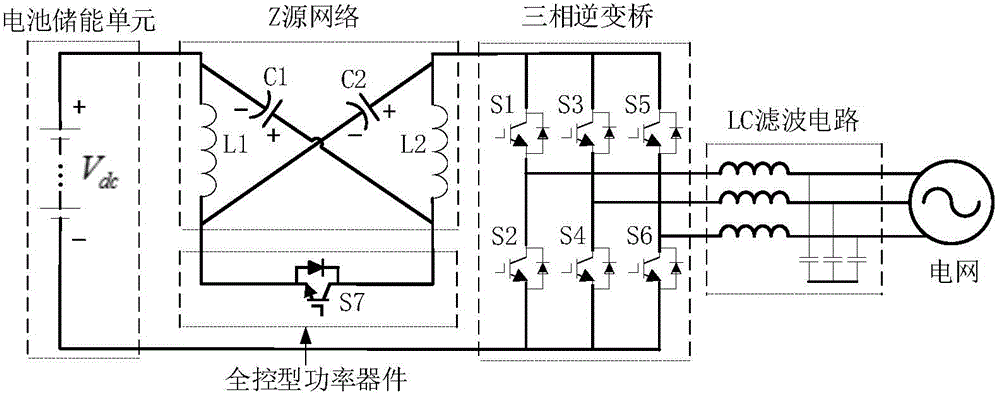
Novel Z-source grid-connected inverter
InactiveCN104578881AReduce starting inrush currentCapacitive voltage stress is smallAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsCapacitanceZ-source inverter
The invention relates to a novel Z-source grid-connected inverter, and belongs to the technical field of power electronic converters. The novel Z-source grid-connected inverter comprises a battery energy storage unit, a Z-source network, a full-controlled type power device, a three-phase inverter bridge and an LC filtering circuit. The positive electrode of the battery energy storage unit is connected with the input end of the Z-source network, the output end of the Z-source network is connected with the positive end of the three-phase inverter bridge, the negative end of the three-phase inverter bridge is connected with the negative electrode of the battery energy storage unit, the Z-source network is connected between the battery energy storage unit and the three-phase inverter bridge in series, the other two ports of the Z-source network are connected with the full-controlled type power device, and the output of the three-phase inverter bridge is connected to a power grid through the LC filtering circuit. Compared with a traditional voltage source inverter of a single-stage structure, boost-buck conversion can be achieved, an upper switching tube and a lower switching tube of the same bridge arm of the inverter bridge are allowed to be directly connected, work reliability is higher, no dead zone needs to be added, and output waveform distortion is small. Compared with a traditional Z-source inverter, start impact currents are small, capacitor voltage stress is low, two-way energy flow is allowed, and the circuit structure is simple.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Quasi-Z-source inverter based single-phase photovoltaic off-grid inverter and soft switch control method thereof
InactiveCN104796030AReduce lossImprove system efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionZ-source inverterSquare waveform
The invention discloses a quasi-Z-source inverter based single-phase photovoltaic off-grid inverter and a soft switch control method thereof. A preceding quasi-Z-source inverter generates direct-current bus voltages with no-voltage slots, provides square-wave voltages with no-voltage slots for a succeeding single-phase full-bridge inversion circuit, and is synchronized with SPWM (sinusoidal pulse width modulation) signals, with low switching frequency, generated according to a rule sampling method to control on-off of a power switch of the single-phase full-bridge inversion circuit, rising edges and falling edges of the SPWM signals, acting on the single-phase full-bridge inversion circuit, of each switching cycle are within the no-voltage slot ranges of the square-wave voltages with the no-voltage slots, and no-voltage on-off of the succeeding single-phase full-bridge inversion circuit is achieved, so that switching loss is reduced and system efficiency is improved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
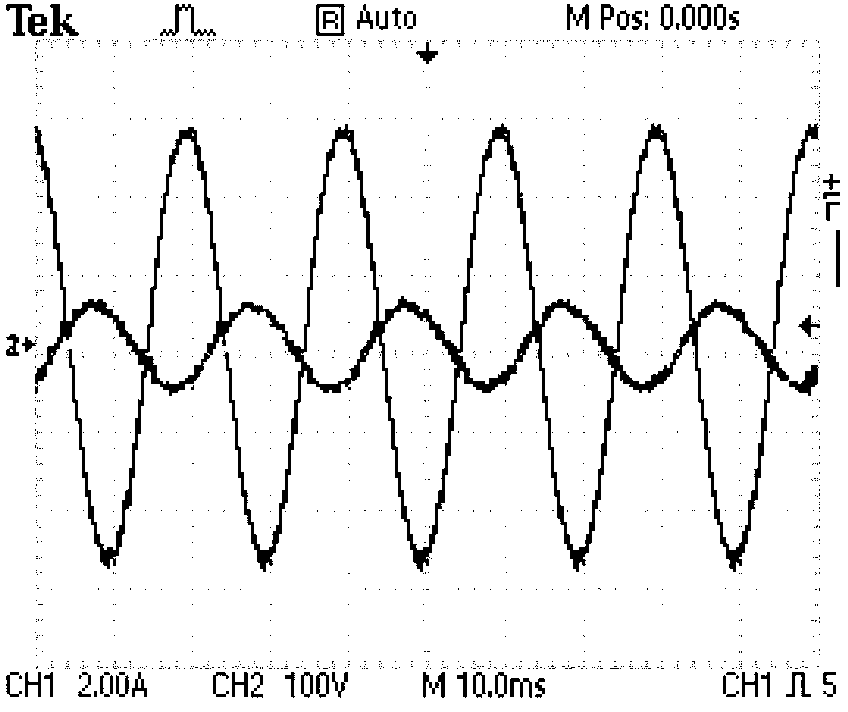
Startup source inverter
InactiveUS20100320842A1High currentNot to damageDc network circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsZ-source inverterPower grid
Owner:ADENSIS
Three-level Z source wind power generation grid-connected system
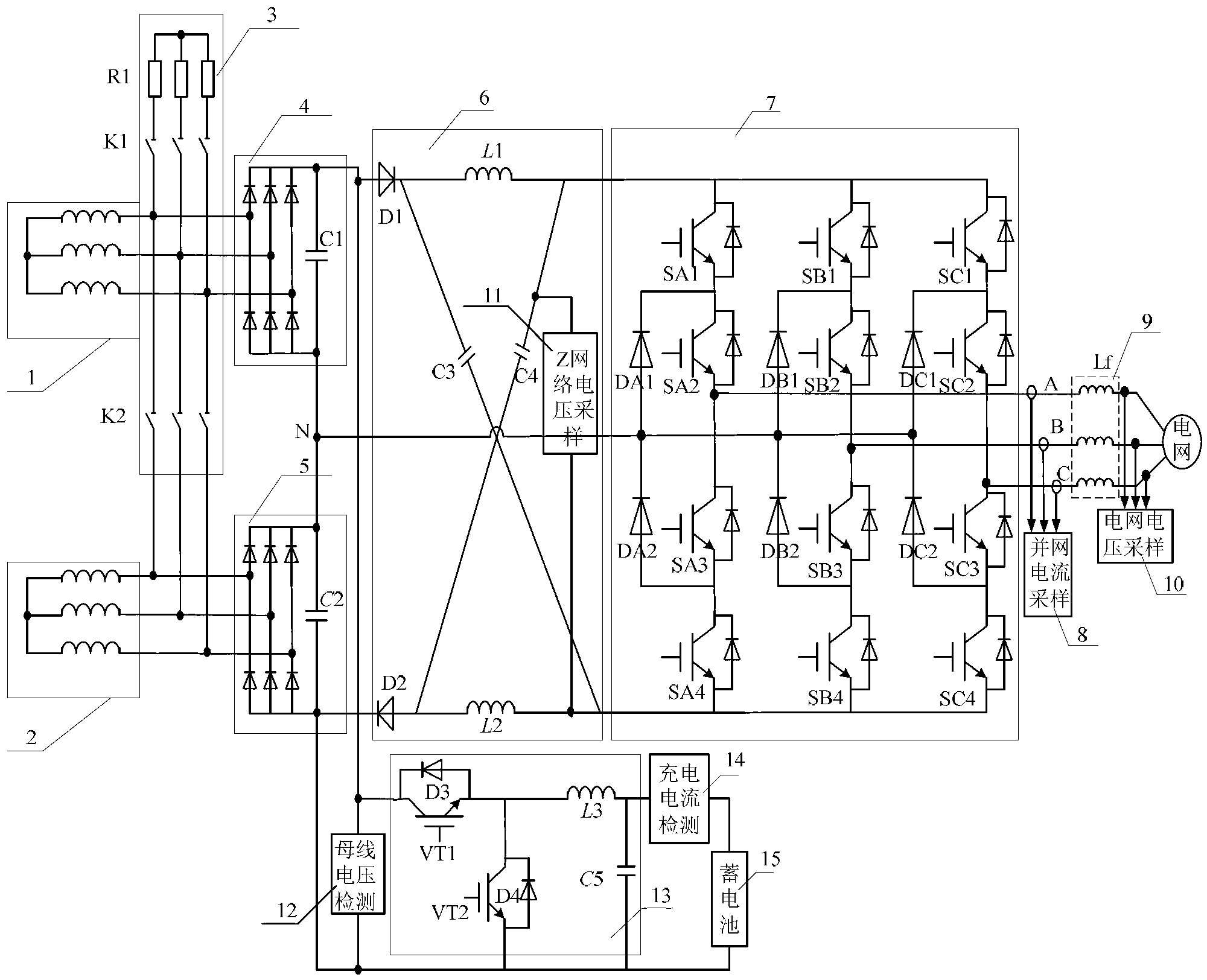
InactiveCN103259286AImprove power densityReduce volumeBatteries circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionZ-source inverterThree level
The invention provides a three-level Z source wind power generation grid-connected system, and belongs to the field of wind power generation. The three-level Z source wind power generation grid-connected system comprises a duplex winding vertical axis wind power generator, an unloading protection unit, a first uncontrolled rectification unit, a second uncontrolled rectification unit, a Z source impedance network, a midpoint clamping three-level inverter, a grid-connected current sampling unit, a filter inductor L<f>, a grid-connected voltage sampling unit, a Z network voltage sampling unit, a direct current bus voltage detecting unit, a bidirection DC / DC conversion unit, a charging current detecting unit and a storage battery pack. According to the three-level Z source wind power generation grid-connected system, wind energy is converted into power frequency alternating current through the three-level Z source inverter, the power frequency alternating current is connected into a power grid, and working modes are changed over in real time on the condition of different wind speeds. When the wind energy is abundant, the system is connected to the power grid and also charges the storage battery pack, and the energy is stored; when the wind energy is moderate, the system only conducts grid-connected operation; when the wind speed is relatively low, the system is supplied with electricity by the storage battery pack to conduct the grid-connected operation, and therefore new energy wind power generation and use thereof are realized. The three-level Z source wind power generation grid-connected system is suitable for a small and medium size duplex winding vertical axis wind power generator unit.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
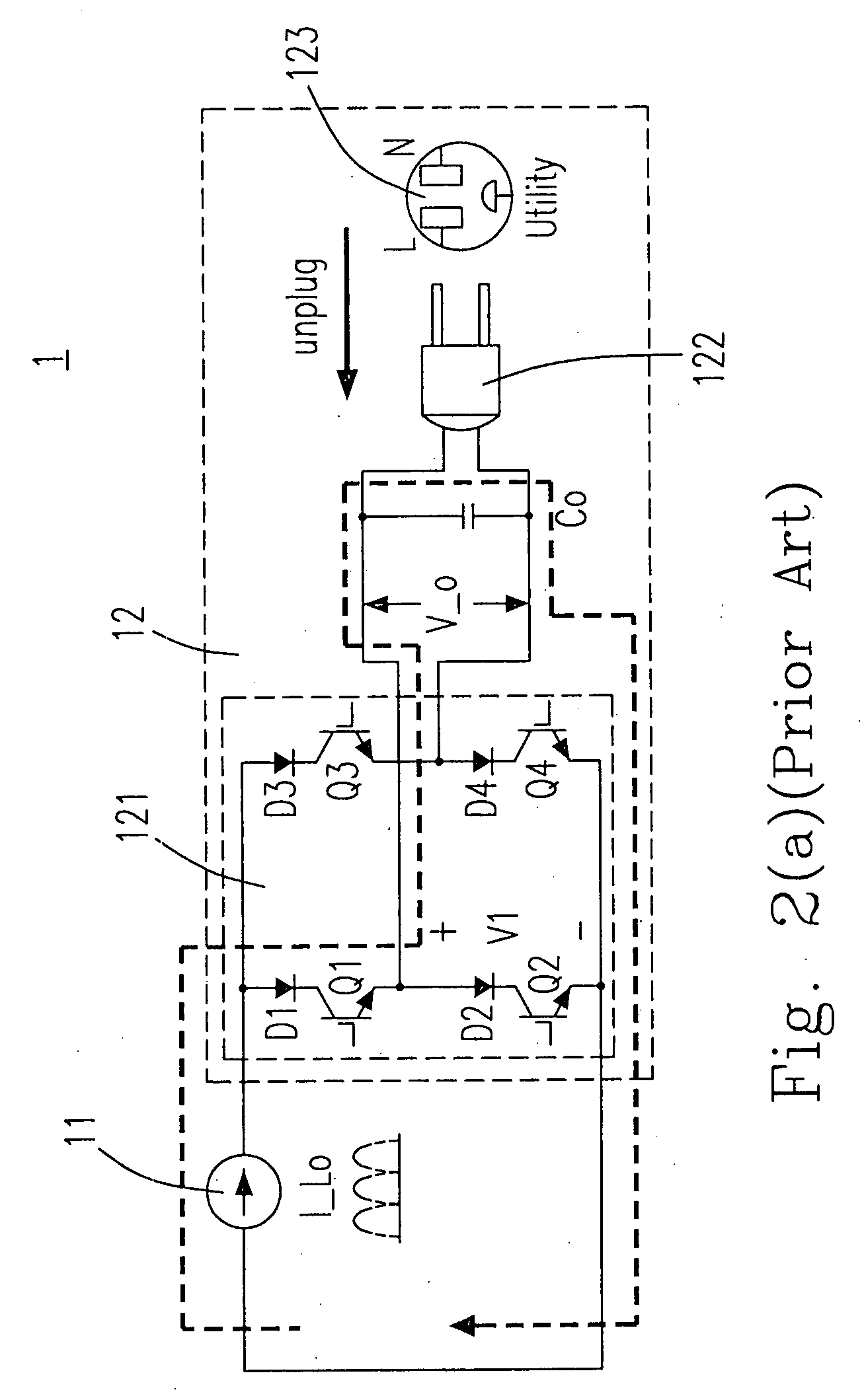
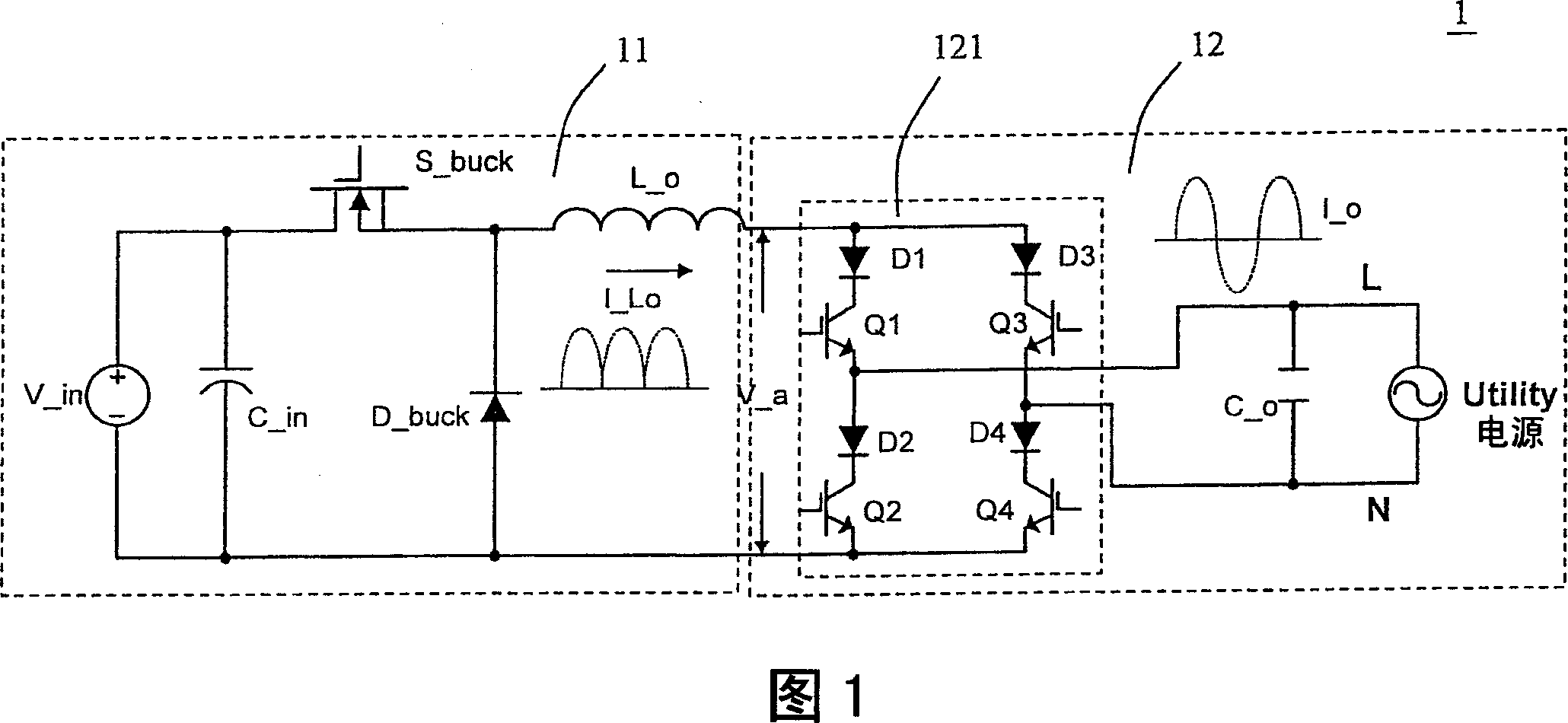
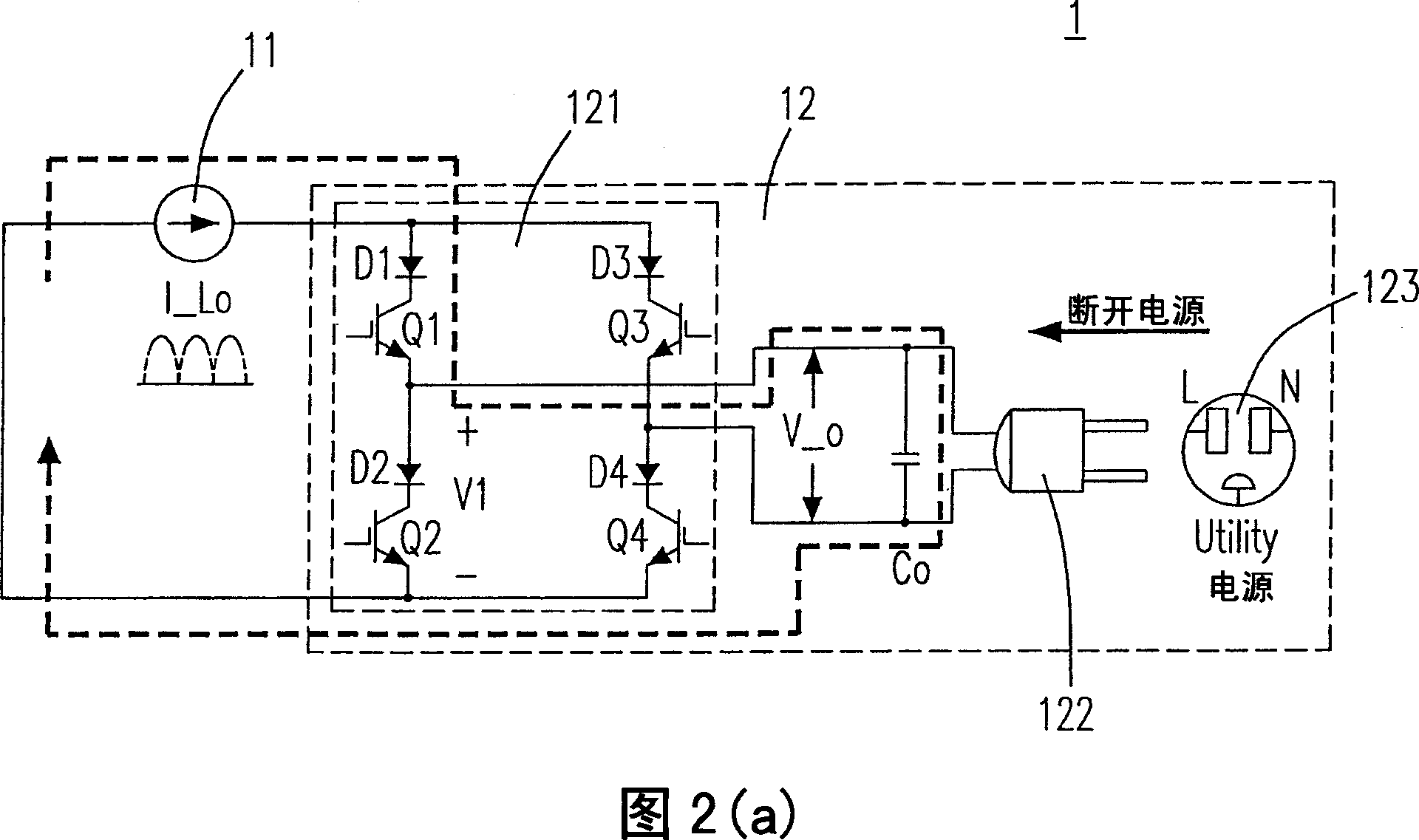
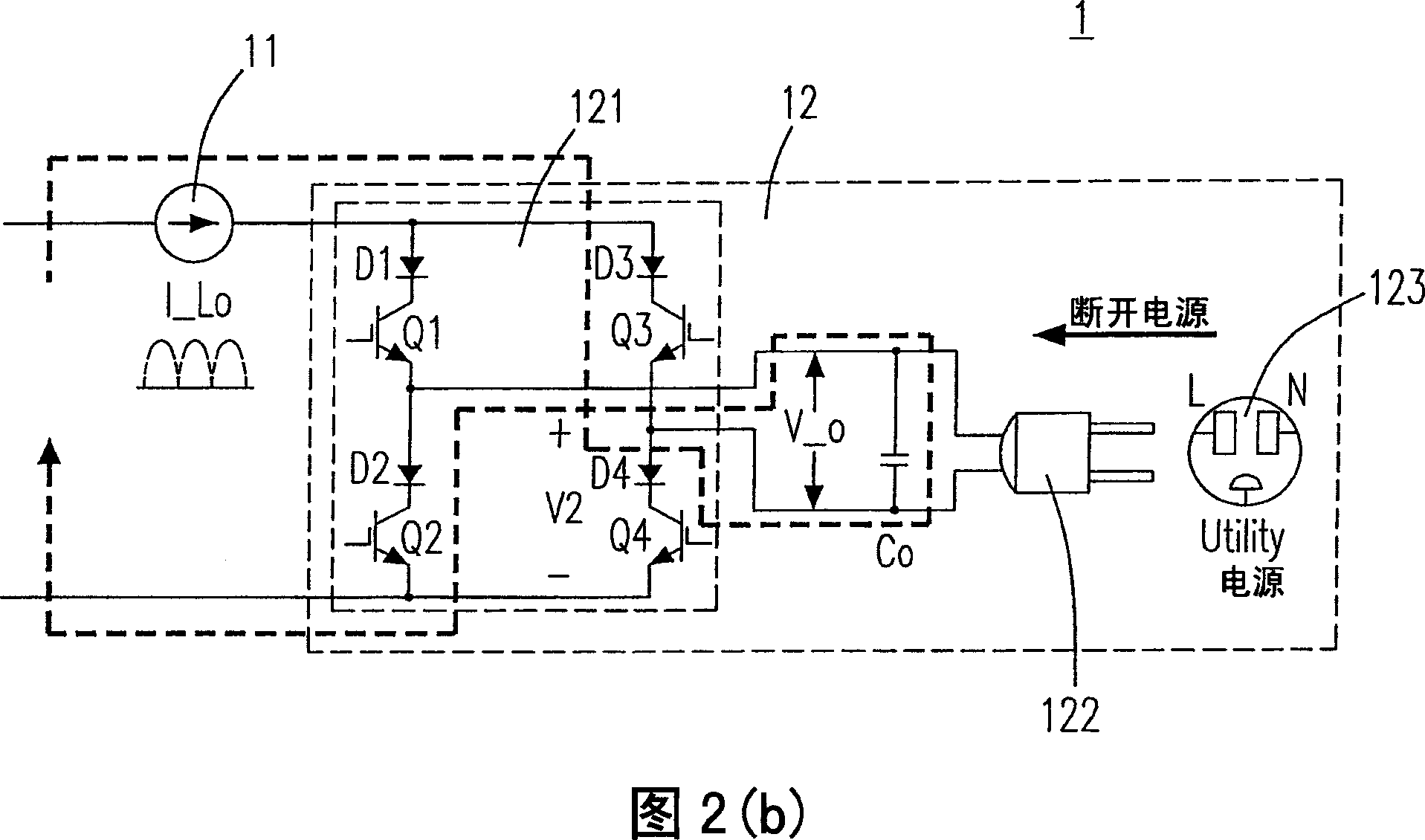
Current source inverter with energy clamp circuit and controlling method thereof having relatively better effectiveness
InactiveUS20070230220A1Reduce voltage stressImprove effectivenessAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionZ-source inverterPower flow
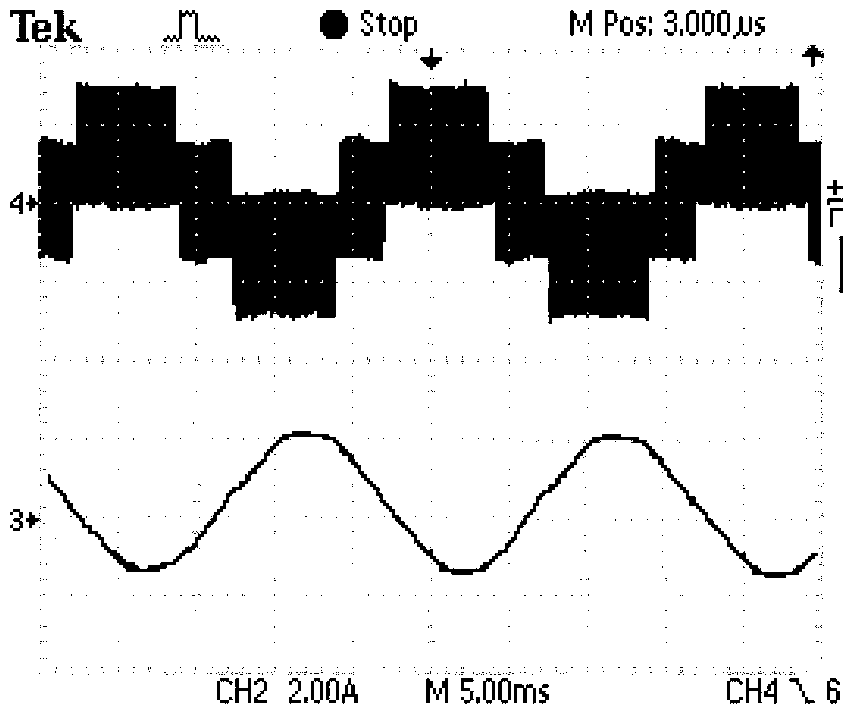
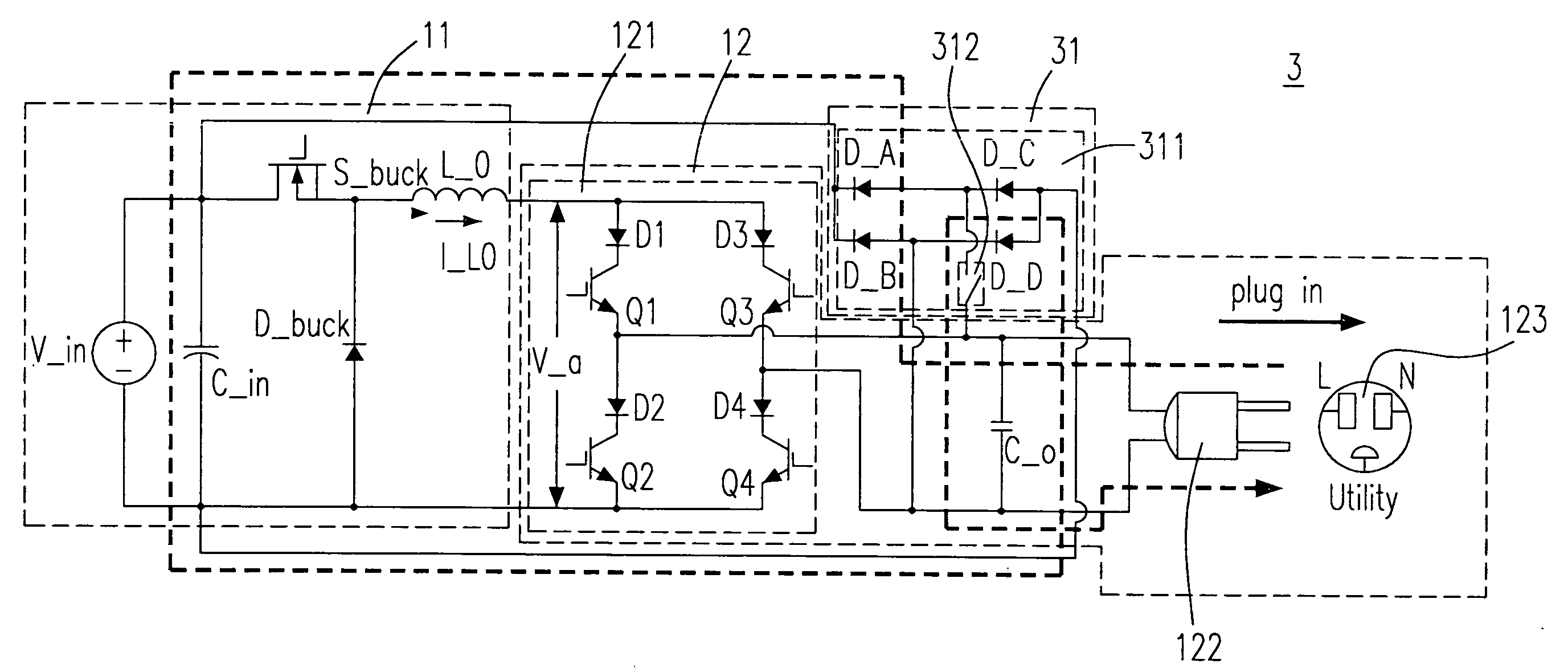
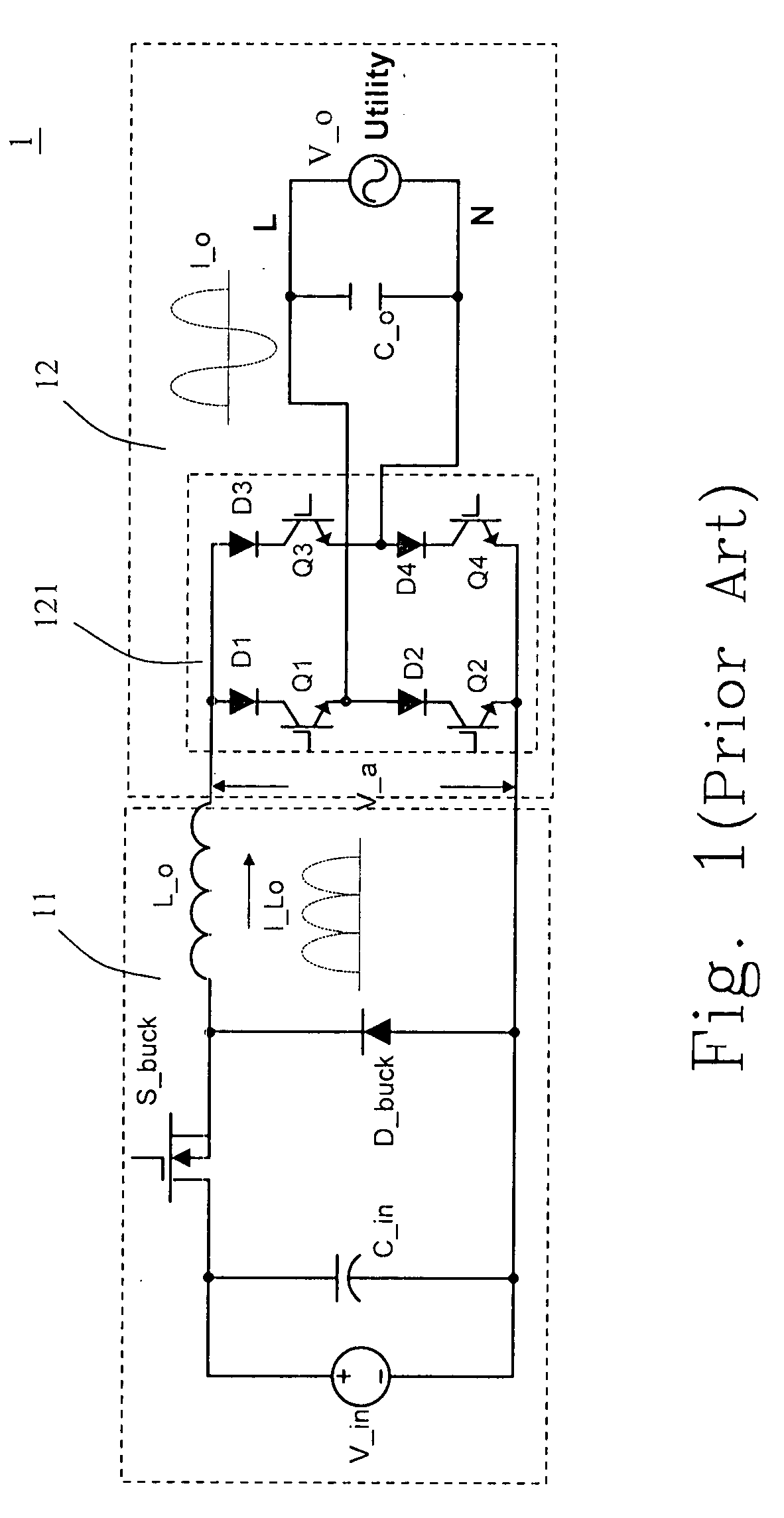
The provided current source inverter includes a buck converter having an input capacitor and an output inductor, receiving a DC input voltage, and generating an output inductor current, a DC / AC converter having an output capacitor, receiving the output inductor current and generating an AC output voltage, a load coupled to the DC / AC converter, and an energy clamp circuit coupled to the buck and the DC / AC converters. The energy clamp circuit includes a first diode and a second diode, provides a discharging route while the load is disconnected with the output capacitor such that the electrical power stored at the output inductor could be discharged to the output capacitor and the input capacitor and avoids an inrush current.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Boost unit Z-source inverter
InactiveCN104734547AWide input voltage rangeImprove conversion efficiencyDc-ac conversion without reversalZ-source inverterCapacitance
The invention discloses a boost unit Z-source inverter. A boost unit is arranged in a Z-source structure and comprises a coupling inductor, a third capacitor and a second power diode, the coupling inductor comprises a first winding and a second winding which are connected in series in the forward direction, the unlike end of the first winding is connected with one end of the third capacitor and the positive pole of the second power diode, the dotted terminal of the second winding is connected with the other end of the third capacitor, and the unlike end of the second winding is connected with the negative pole of the second power diode. Compared with a traditional quasi-Z-source inverter, the input voltage range is wider, conversion efficiency is higher, and higher boost characteristic is achieved during low-voltage input.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method and arrangement for measuring output phase currents of a voltage source inverter under a load
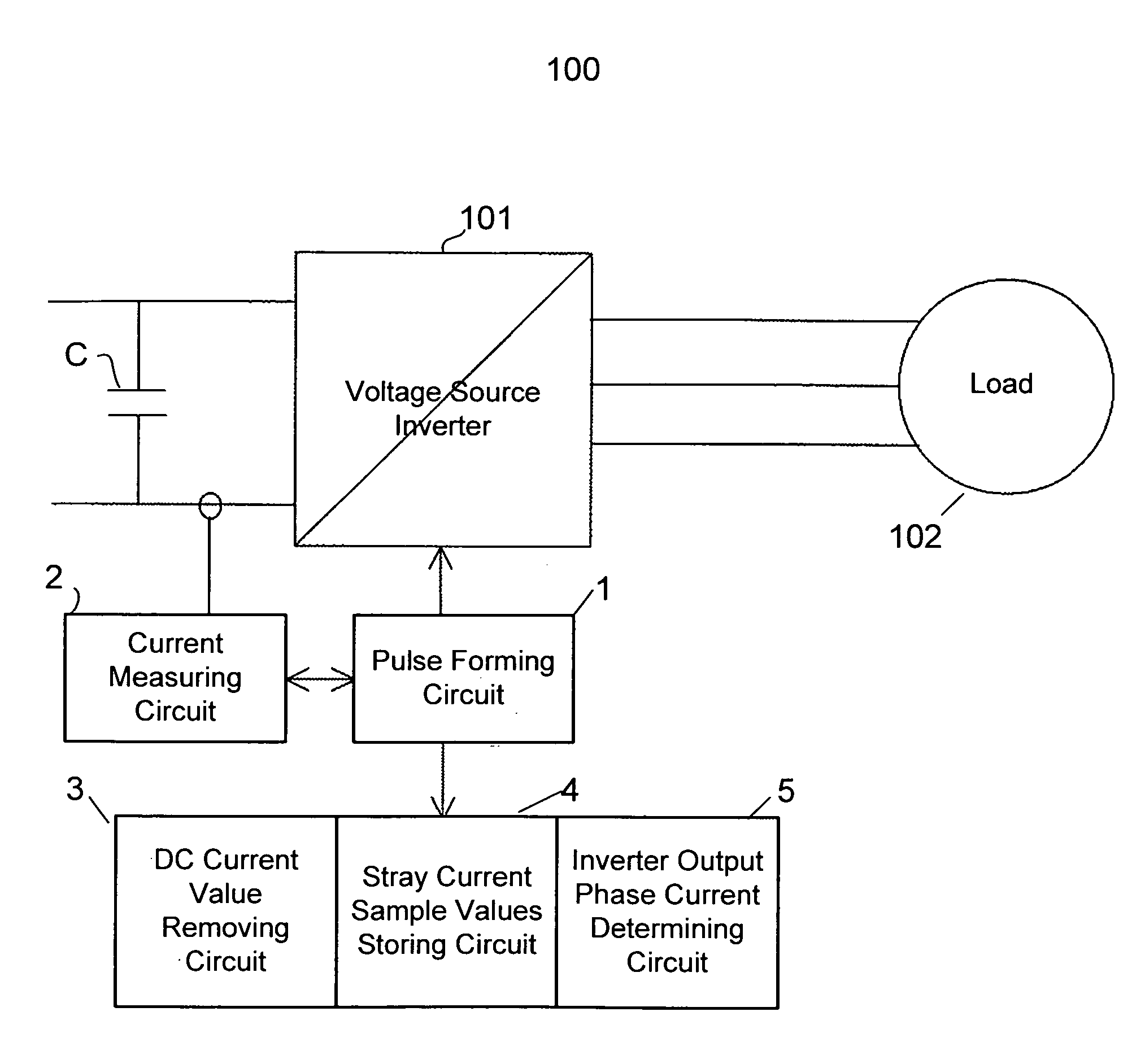
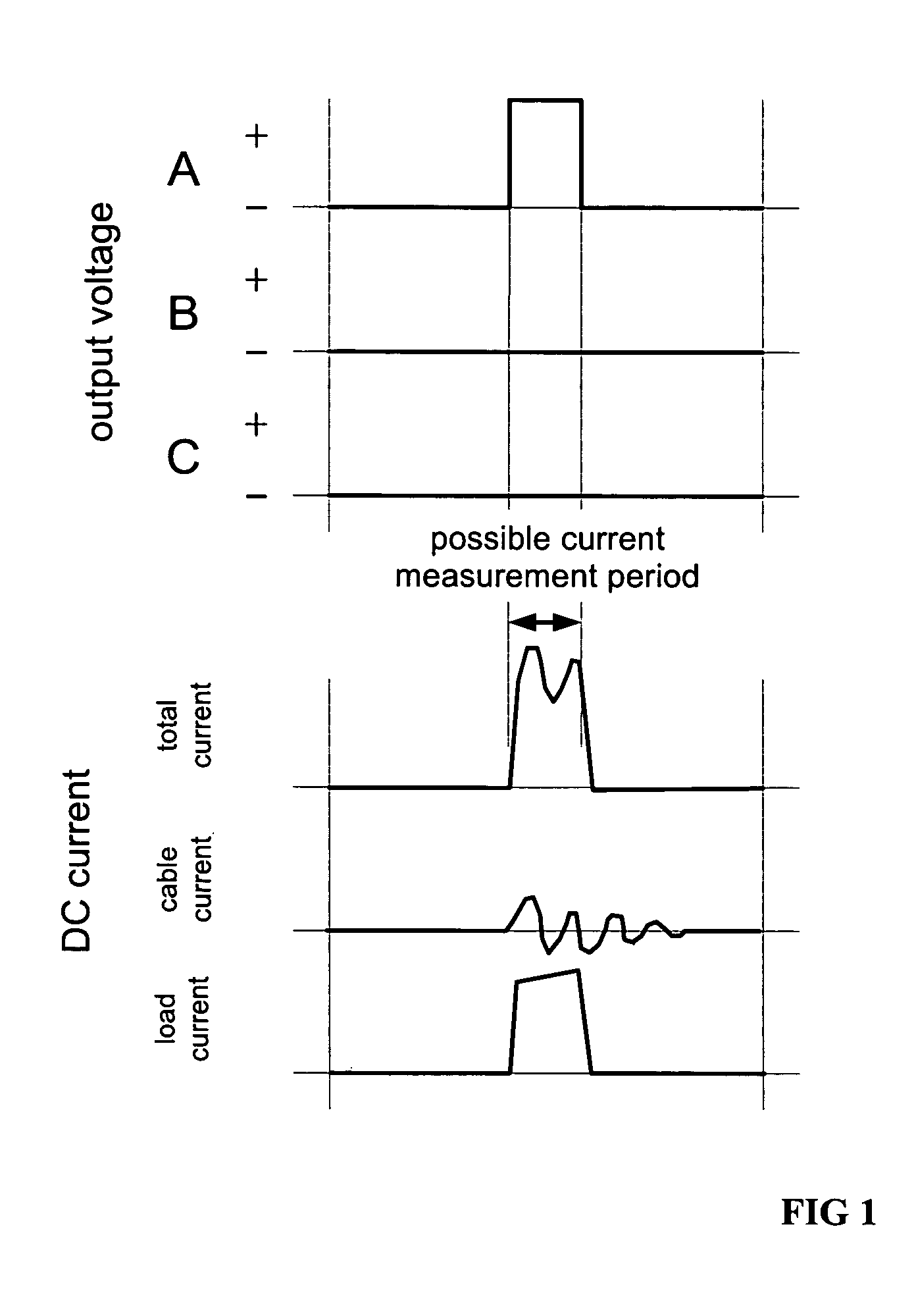
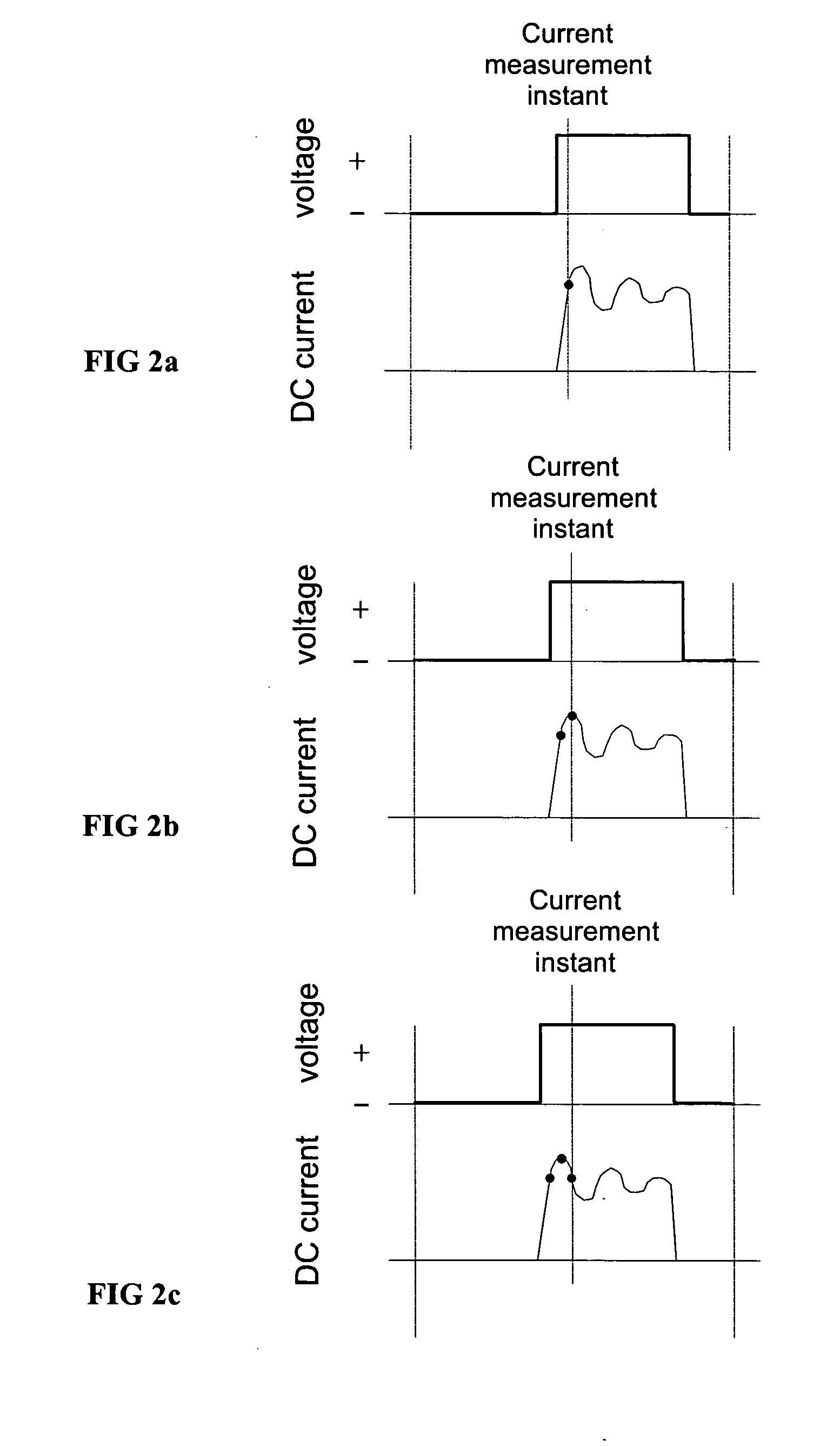
ActiveUS7508688B2Accurately determineCurrent/voltage measurementConversion with intermediate conversion to dcZ-source inverterPhase currents
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
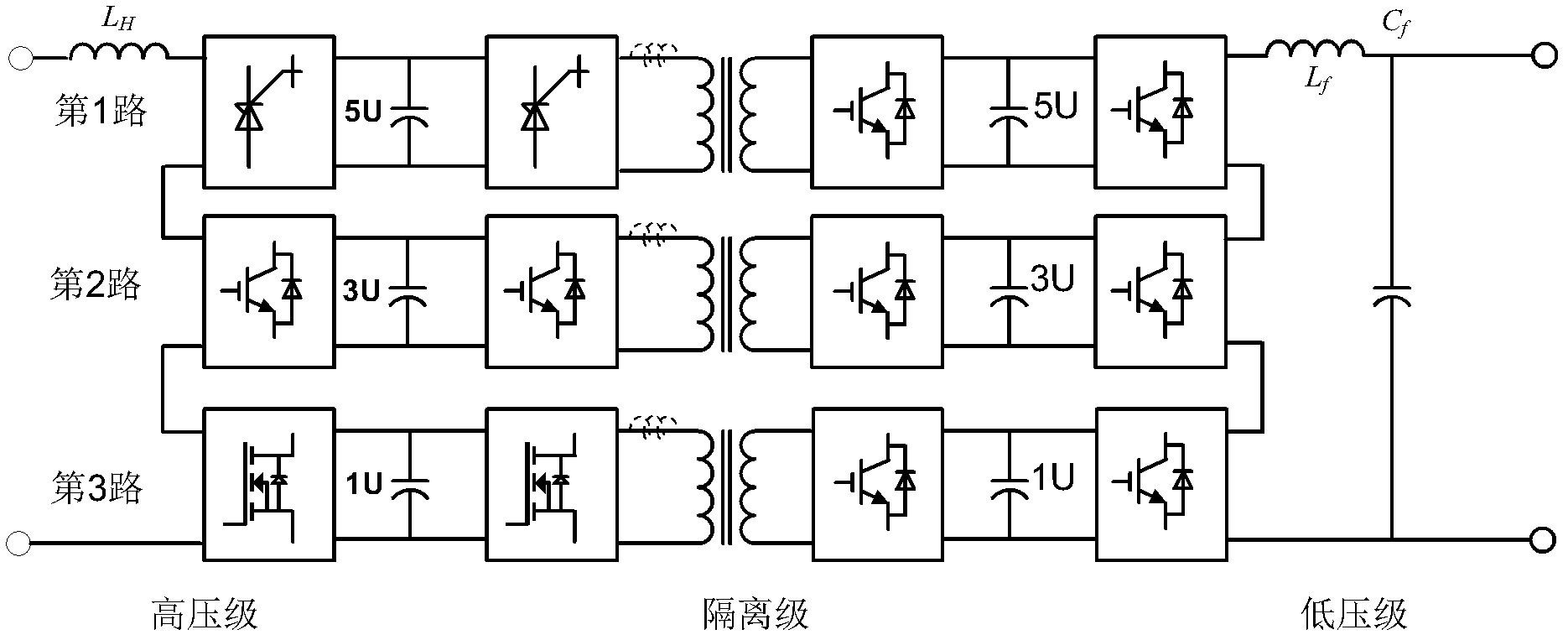
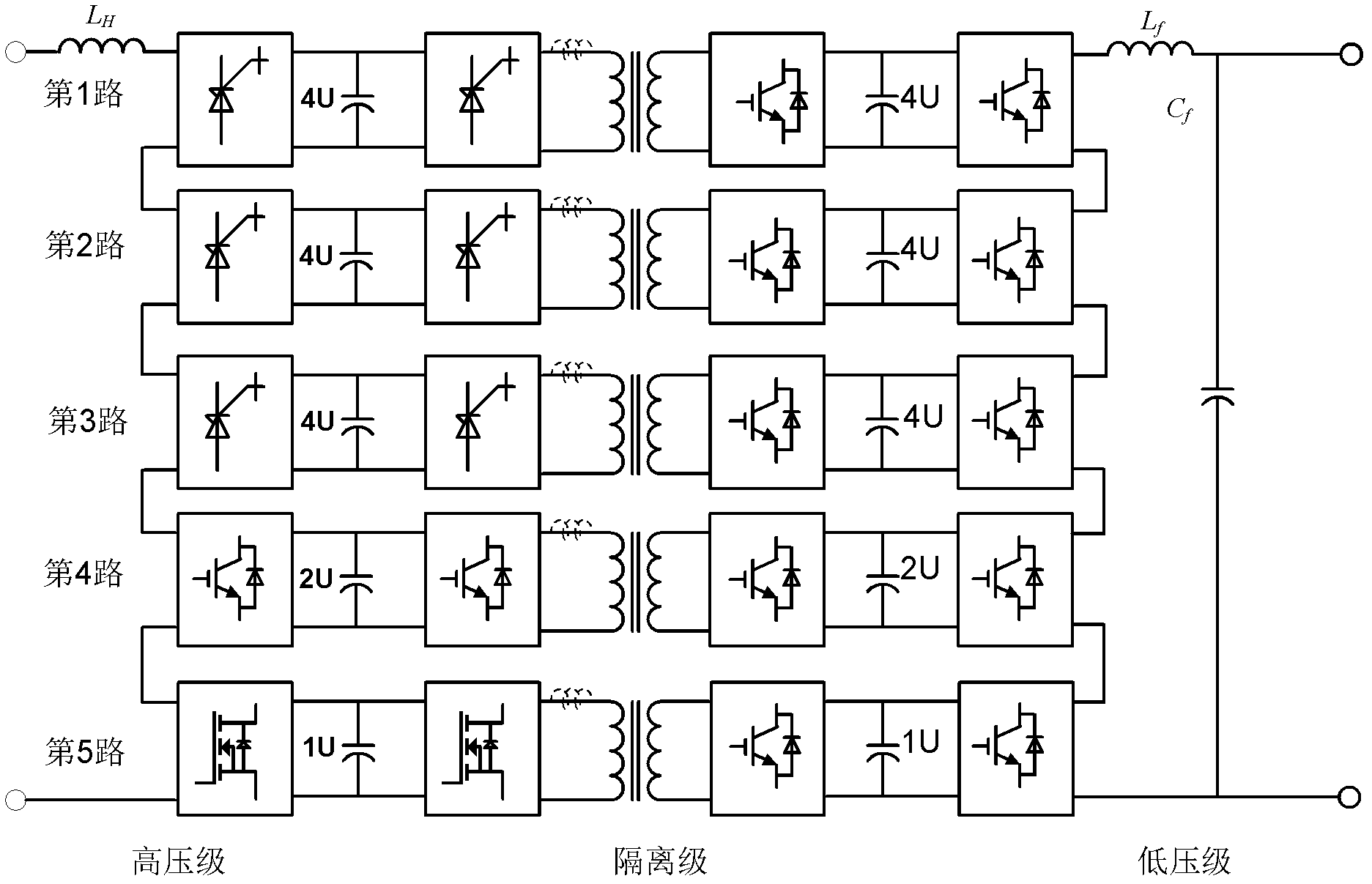
Hybrid cascade multilevel electronic power transformer
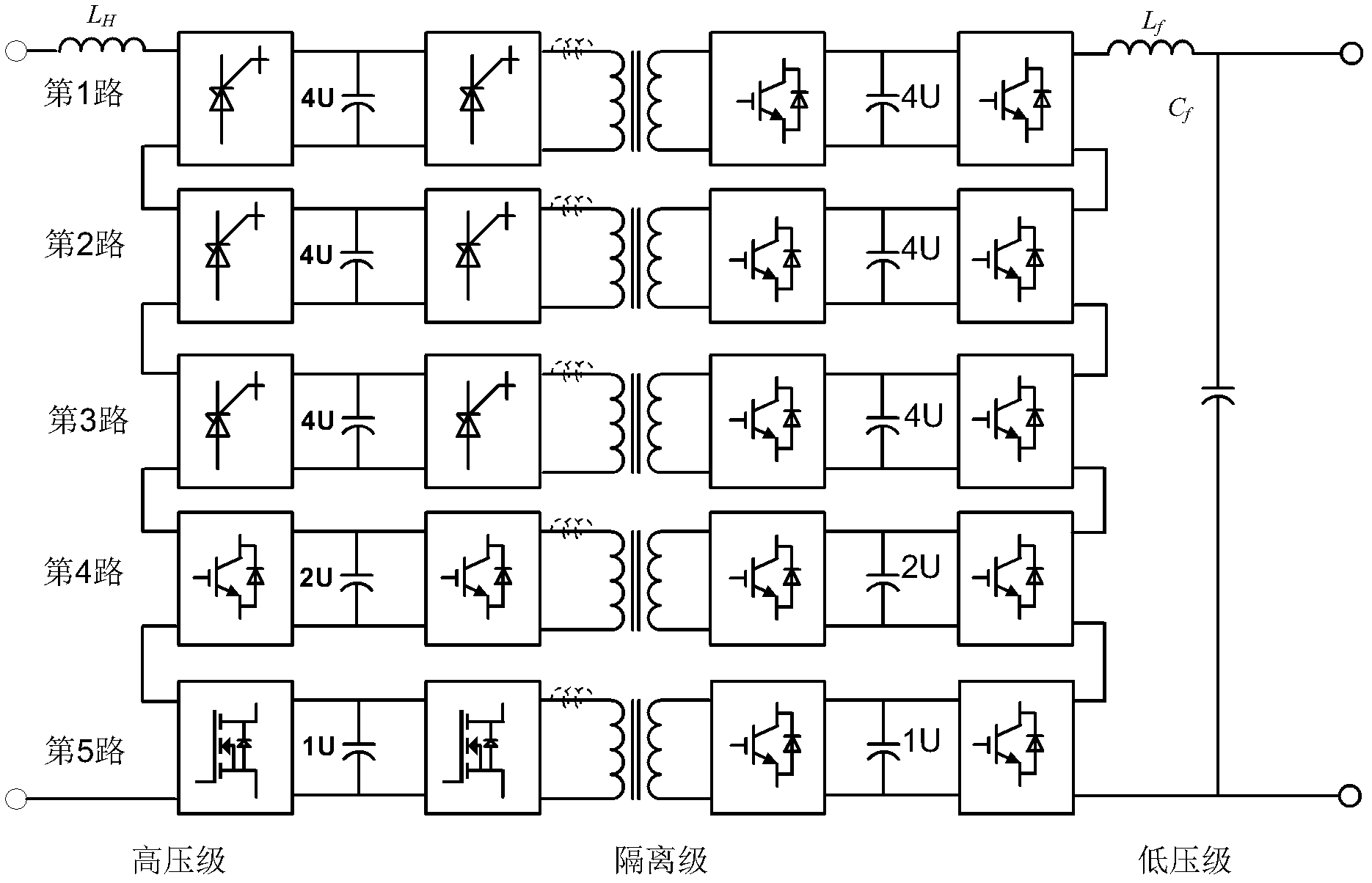
InactiveCN102638176AHigh quality powerReduce switching lossesDc-dc conversionAc-ac conversionZ-source inverterPower quality
The invention discloses a hybrid cascade multilevel electronic power transformer. The hybrid cascade multilevel electronic power transformer comprises A, B and C-phase electric energy transformation units with the same structure, wherein each phase electric energy transformation unit is formed by concatenation of M sub-units of the electronic power transformer, and M is not less than 2; each sub-unit of the electronic power transformer comprises a three-stage structure formed by series connection of a high-voltage stage, an isolation stage and a low-voltage stage; each high-voltage stage comprises a PWM (pulse width modulation) rectifier, each PWM rectifier is in concatenation with the PWM rectifiers of other sub-units in the same phase, each isolation stage comprises an isolation type DC-DC (direct current-direct current) converter, each low-voltage stage is of a voltage source inverter, and each voltage source inverter is in concatenation with the voltage source inverters of other sub-units in the same phase; and the alternating current input ends of the PWM rectifiers and the direct current output ends of the voltage source inverters are respectively connected with reactors in series. The hybrid cascade multilevel electronic power transformer disclosed by the invention can be used for improving the quality of electric energy by expanding the level number of output voltage; and furthermore, a used switching device does not need to be limited by the same frequency, thereby reducing the loss of a switch and a filter.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
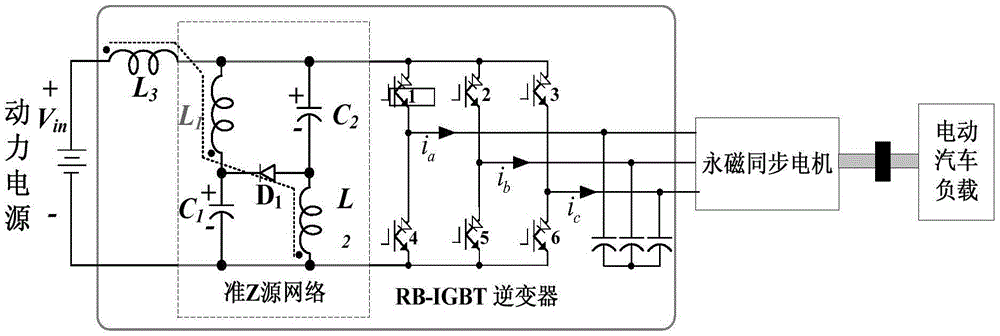
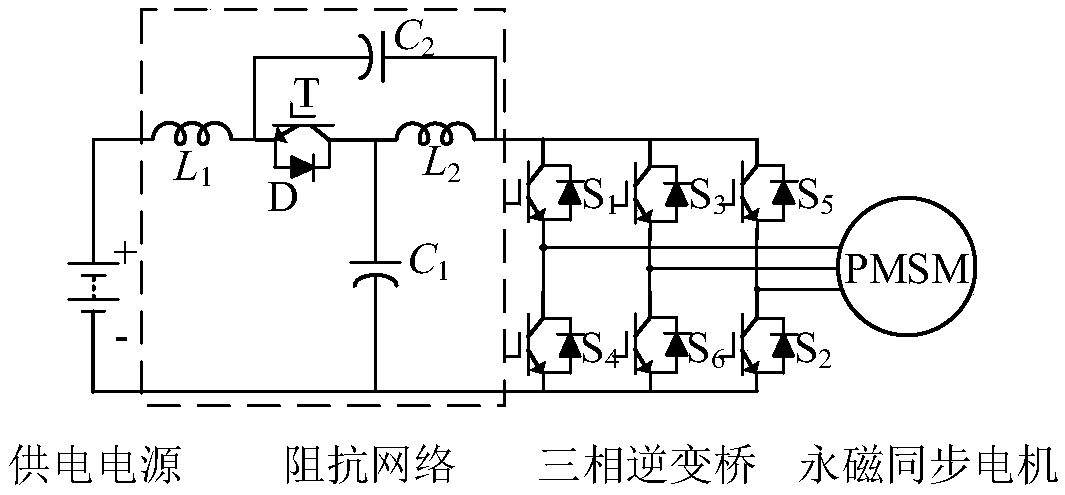
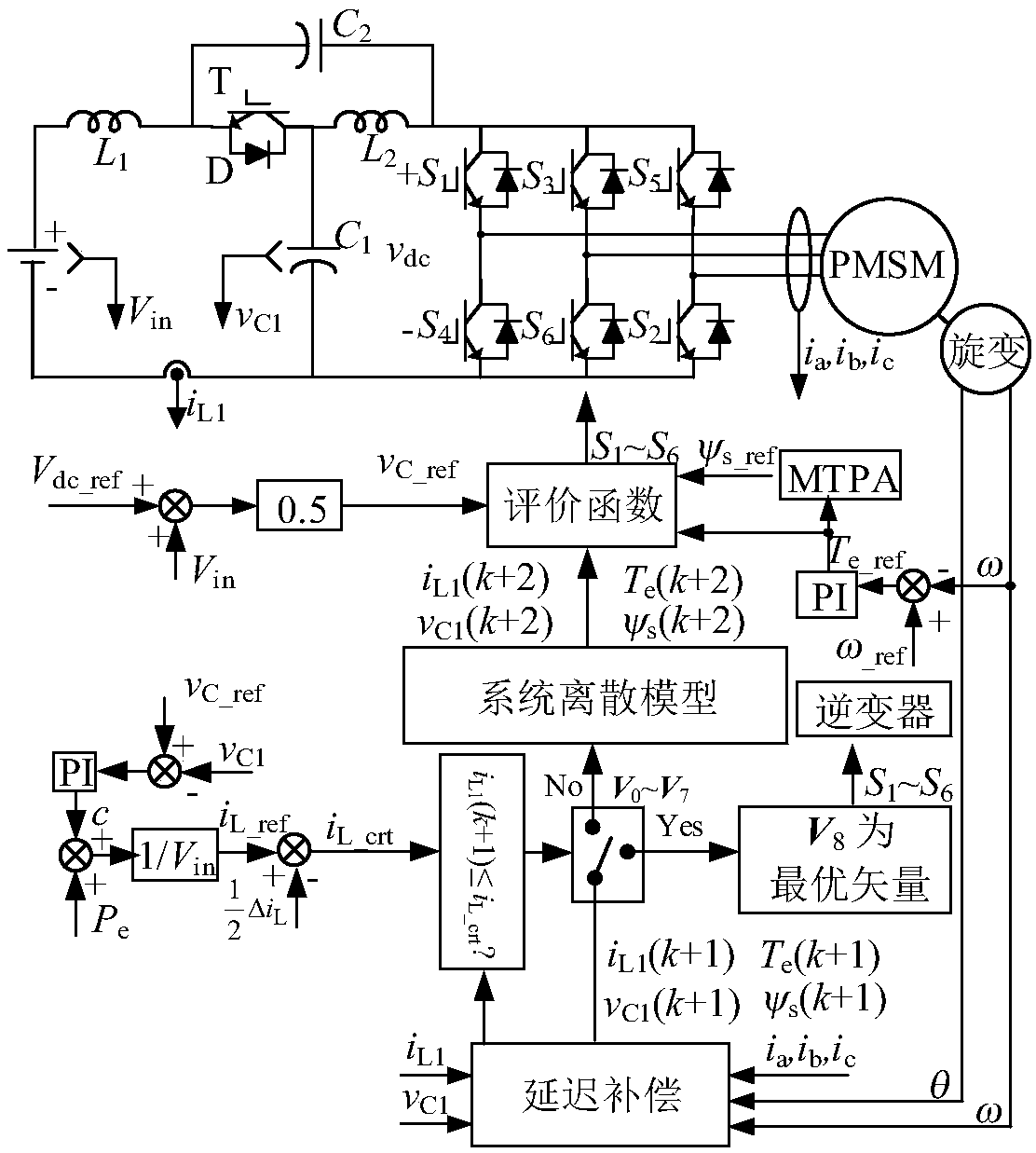
Uniform prediction control method for quasi-Z source inverter-permanent magnet synchronous motor systems
ActiveCN109412482AAchieving Unified Predictive ControlResolving Control ConflictsElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlZ-source inverterPower compensation
The invention discloses a uniform prediction control method for quasi-Z source inverter-permanent magnet synchronous motor systems. According to the method, stator current d and q axis components areobtained through coordinate transformation, each control variable is obtained through a delay compensation link, a torque given value is obtained through a rotation speed closed loop, and d and q axiscurrent given values are obtained to calculate a stator flux linkage given value; an inductive current given value is calculated through a power compensation manner so as to obtain an inductive current critical value; and an optimum vector is judged according to a relationship between inductive current and the inductive current given value so as to obtain each control variable at the next moment,the control variables at the next moment are substituted in an evaluation function to obtain an optimum vector, and a switch state corresponding to the optimum vector is output to an inverter. The uniform prediction control method is capable of decreasing the operand of controllers, avoiding the influences, on prediction control of quasi-Z source inverter-permanent magnet synchronous motor systems, of quasi-Z source inverter negative modulation, realizing the uniform prediction control of quasi-Z source inverter-permanent magnet synchronous motor systems, and solving the control conflict problems in two-stage control.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Current source inverter with energy clamping circuit and its control method
InactiveCN101060290AReduce voltage stressEliminate inrush currentAc-dc conversionZ-source inverterCapacitance
The disclosed current source inverter with energy clamp circuit comprises: a voltage-reduced translator with input capacitor and output inductor to receive the dc input voltage and output induction current, a dc / ac converter with output capacitor to receive the last current and generate ac current, a load coupling with the dc / ac converter to provide discharge path and avoid impulse current, and an energy clamp circuit including two diodes. This invention reduces the voltage stress on transistors greatly, and avoids the generation of impulse current.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Quasi Z-source inverter of active switched capacitor
The invention discloses a quasi Z-source inverter of an active switched capacitor. The quasi Z-source inverter of the active switched capacitor comprises a voltage source, a quasi Z-source unit, an active switched capacitor unit, a single-phase bridge inverter, an output filtering inductor, an output filtering capacitor and a load, wherein the quasi Z-source unit is composed of a first inductor, a second inductor, a first capacitor, a first diode and a second diode, and the active switched capacitor unit is composed of an MOS tube S, a second capacitor, a third diode and a fourth diode. According to the quasi Z-source inverter of the active switched capacitor, the high-gain property of the quasi Z-source and the property of charging in parallel and discharging in series of the active switched capacitor are combined; compared with traditional Z-source inverters, the number of inductors and capacitors used is the same, but the voltage gain is obviously improved; compared with an enhanced boost quasi Z-source inverter with a switched impedance network, the voltage gains are the same, but the number of inductors and capacitors decreases by two respectively, so that the number of passive components is greatly reduced, a higher output voltage gain is achieved with a lower duty ratio, and the power density of the system is improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Quasi Z source inverter
InactiveCN103117650AWon't impactImplementing the Soft-Start FeatureDc-ac conversion without reversalZ-source inverterCapacitance
The invention discloses a quasi Z source inverter which comprises a direct-current power source, an inverter, a switch inductance set and an auxiliary circuit in mutual connection. The quasi Z source inverter can realize boost-buck of any proportion of voltage on a direct-current side without a DC-DC (direct current) booster circuit before inversion, has good effects in terms of reliability and efficiency, has higher boost-buck times than common impedance network type inverters, is free of impact to an electrolytic capacitor when a system is started, can realize soft start characteristics and has the advantages of high step-up, stability, small size, high efficiency and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Combined three-phase microgrid system with serially-connected microsource inverters
InactiveCN104953589AReduce harmonic contentReduce construction costsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network load balancingZ-source inverterMicrogrid
Disclosed is a combined three-phase microgrid system with serially-connected microsource inverters. The combined three-phase microgrid system is formed by combining three symmetric subsystems including a phase-A subsystem, a phase-B subsystem and a phase-C subsystem. H-bridge microsource inverters in the three symmetric subsystems inside the combined three-phase microgrid system are serially connected together. Different main microsource direct-current chains are configured with energy storing systems so as to suppress fluctuation of voltage of direct-current chains. Additionally, microsource disconnection / recovery operation can be achieved through corresponding switching operation. By the aid of the structure, the combined three-phase microgrid system is low in output voltage harmonic content and good in sine degree; a rated operational voltage grade of each microsource is low, and accordingly, system construction cost is low; the microsource inverters are the same in output frequency and current, so that system output frequency is stable and power coordinated control is simple. By the aid of the networking mode, the combined three-phase microgrid system is capable of structurally solving the problems of harmonic waves, circular current, control complexity and the like in common alternating-current , direct-current and alternating-current and direct-current hybrid microgrids.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Quasi Z-source inverter with high boost gain
The invention relates to a quasi Z-source inverter with high boost gain. The quasi Z-source inverter comprises a DC power supply Vin, a quasi Z-source boost network, and a three-phase inverter. The quasi Z-source boost network comprises a tap inductor, a first diode D1, a first capacitor C1, a second capacitor C2, and a switched inductor group. When the three-phase inverter is in a non shoot-through state, the tap inductor charges the first capacitor C1 and the switched inductor group charges the second capacitor C2 in order to improve the boost capability of the Z-source inverter and reduce the voltage stress of the first capacitor C1, the second capacitor C2, and the switched inductor group. Compared with a product in the prior art, the quasi Z-source inverter uses single-stage structure and reduces circuit size and cost. A shoot-through zero vector enables the top bridge arm and the bottom bridge arm of an inverter bridge to be simultaneously switched on, thereby improving circuit security. The quasi Z-source inverter reduces voltage stress of devices while achieving high boost gain.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Zvs voltage source inverter with reduced output current ripple
ActiveUS20150236617A1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionZ-source inverterPower inverter
Systems, methods, and devices relating to DC / AC converters. A circuit including a full bridge inverter is provided. One leg of power semiconductor subcircuits of the inverter is switched at line frequency while the other leg is soft switched at a higher frequency using an auxiliary circuit. A control system is used to calculate this higher optimal frequency. To minimize the output current ripple in the output filter, the output inductor is coupled to the auxiliary inductor in the auxiliary circuit.
Owner:SPARQ SYST INC
Series quasi Z source inverter based grid-tied PV control method
InactiveCN105932713AReduce voltage stressImprove power qualitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationVirtual synchronous generatorZ-source inverter
The present invention discloses a series quasi Z source inverter based grid-tied PV control method. A PV battery inverter system is seen as a virtual synchronous generator, and an integral of an output voltage of a series quasi Z source inverter is taken as a virtual motor magnetic chain. An outer ring is controlled by using a power ring, so that active power transmission and reactive power compensation are realized. An inner ring is a current ring, so that current rapid tracking is realized. PI modulation is performed on the current inner ring, so as to generate a modulated wave signal. Three times of harmonic wave modulation is performed on a modulated signal obtained at a PV side and the modulated wave signal. On and off of an inverter bridge are controlled, so as to realize power adjustment of the grid-tied PV system. According to the method, a virtual synchronous generator quasi direct power control policy is adopted for controlling the system, the virtual magnetic chain directly orients, an alternating current voltage sensor is omitted, system reliability is improved, device cost is saved, quasi direct power control can directly control active power and reactive power of the grid-tied inverter, and the system has the advantages of simple structure and good dynamic response performance.
Owner:CHANGZHOU POWER SUPPLY OF JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com