Patents
Literature
203results about How to "Constant voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
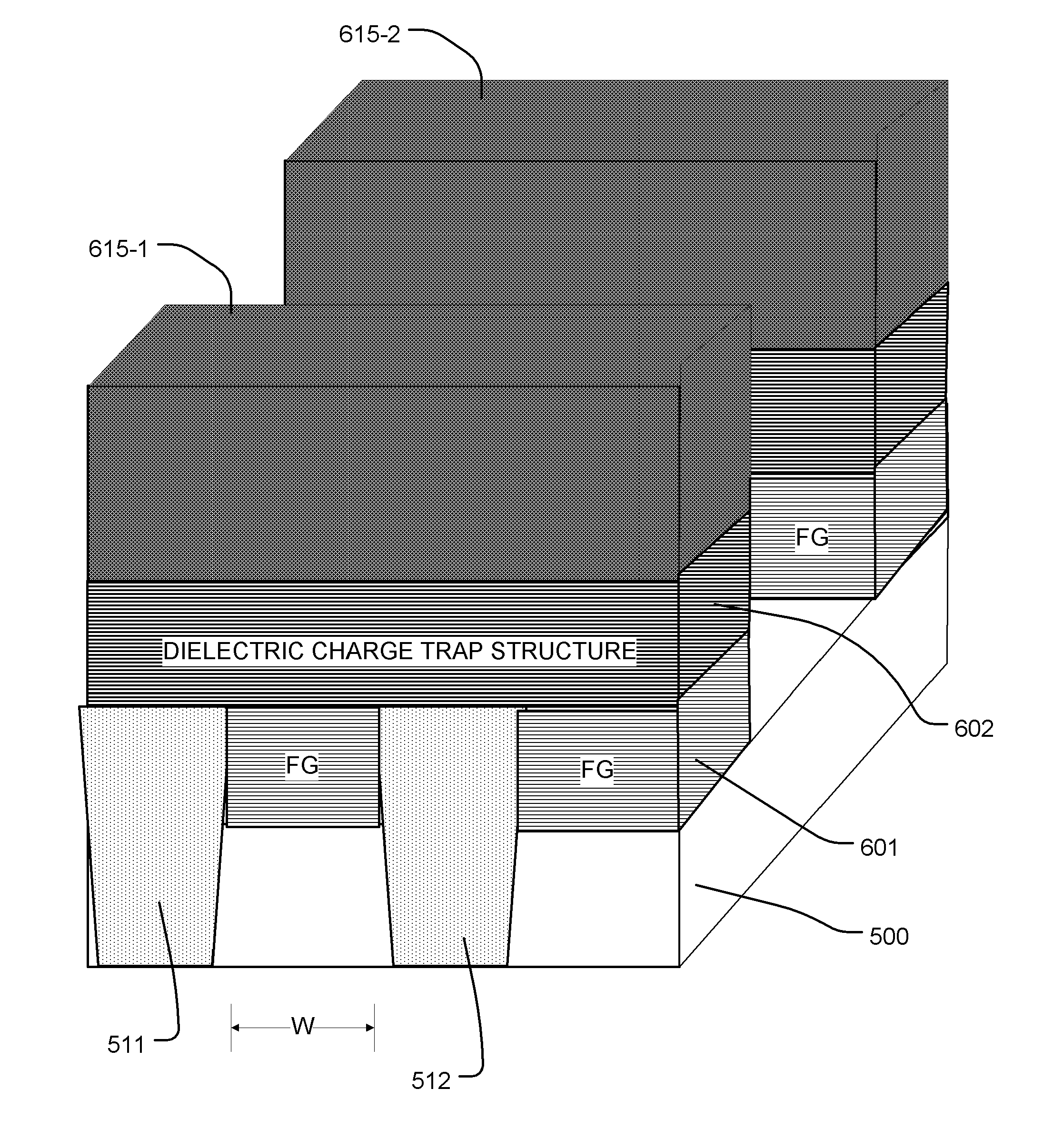
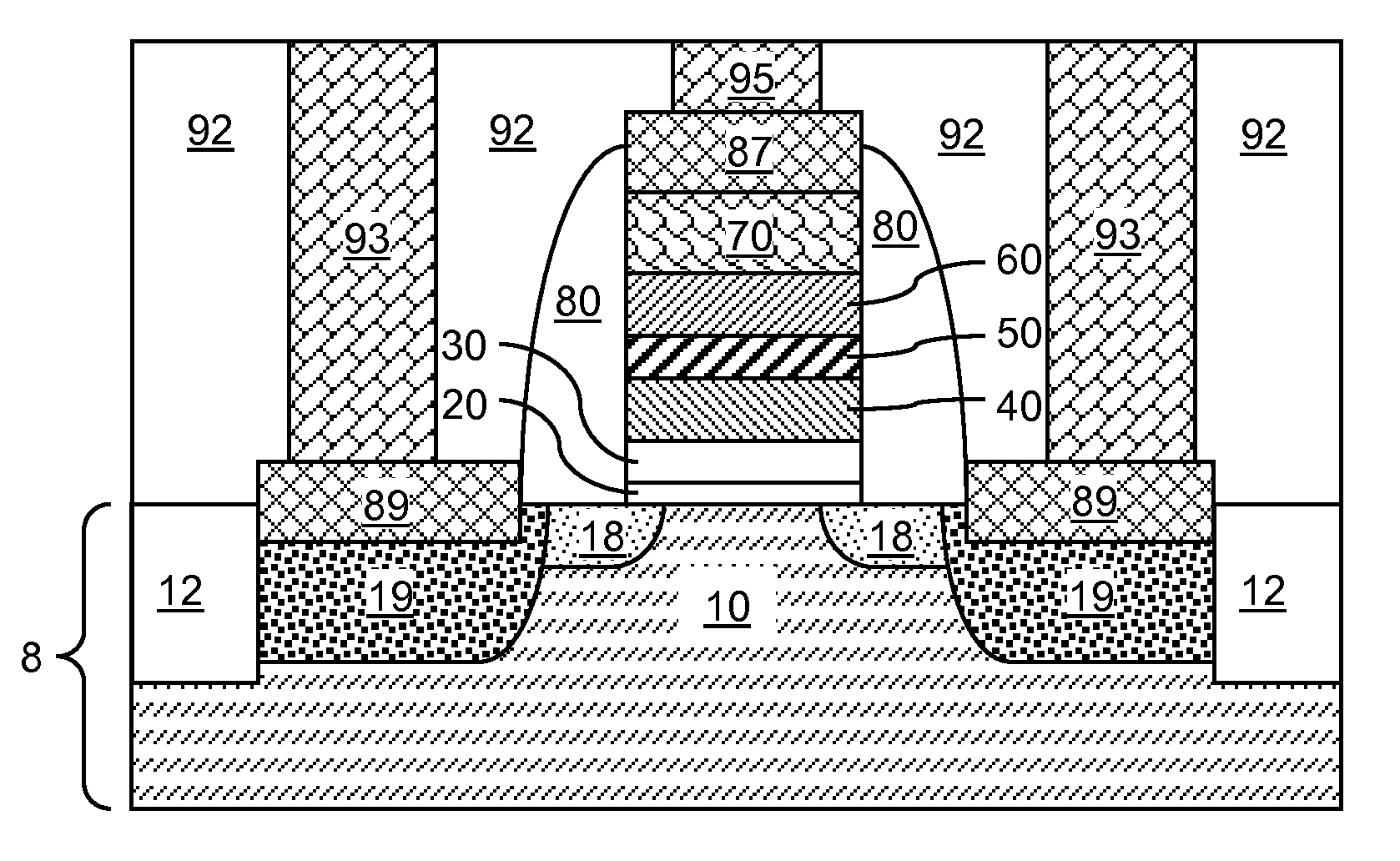
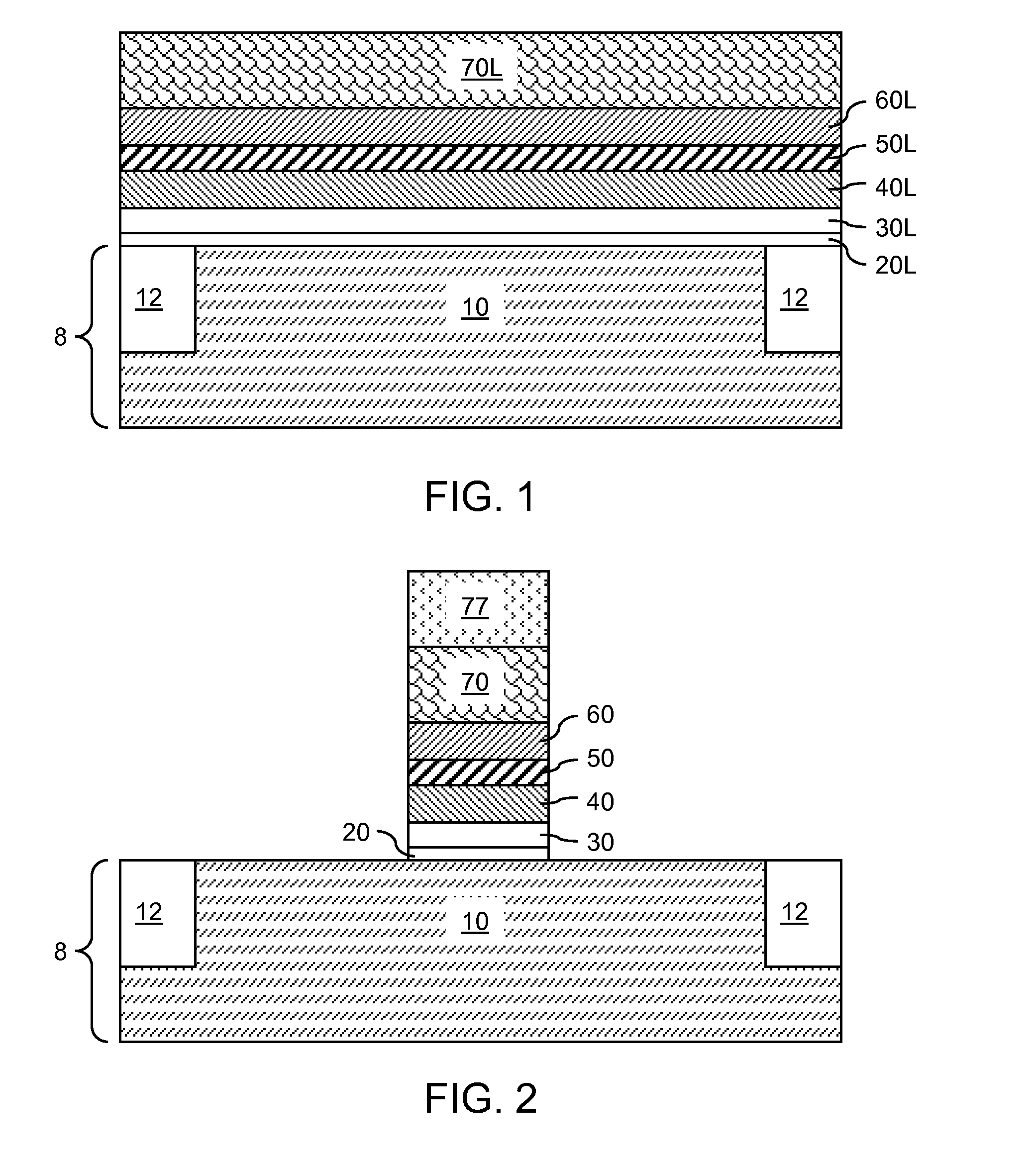
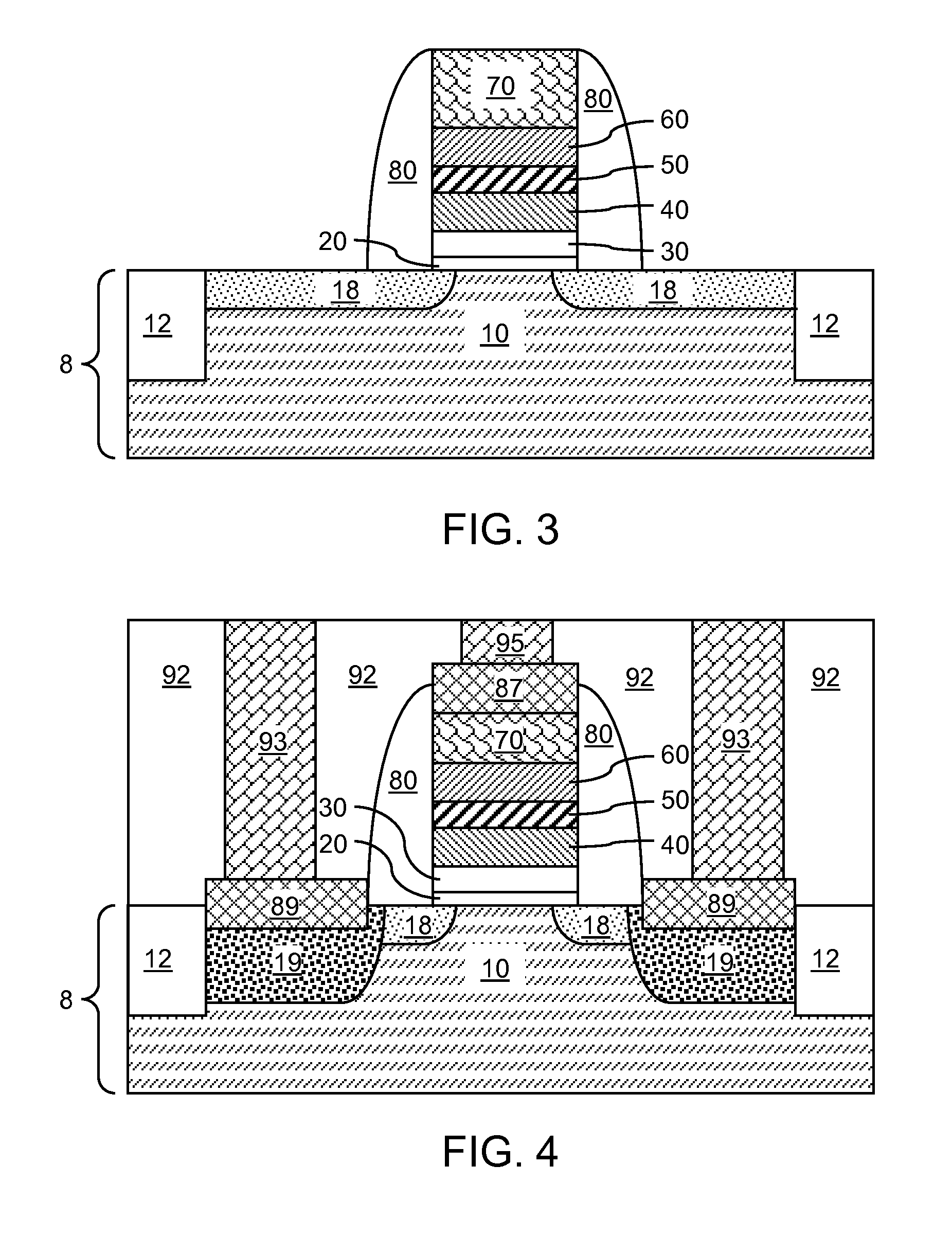
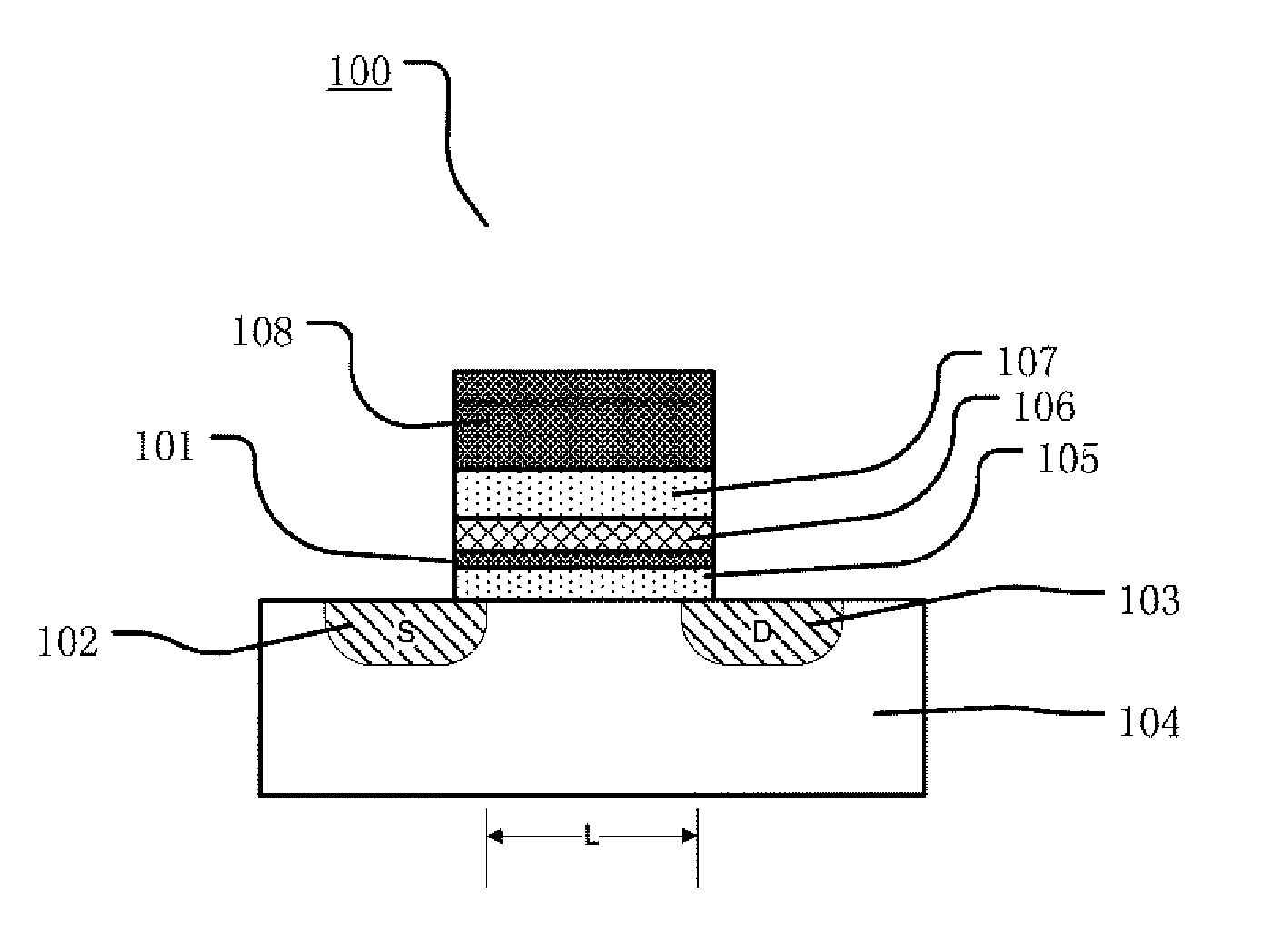
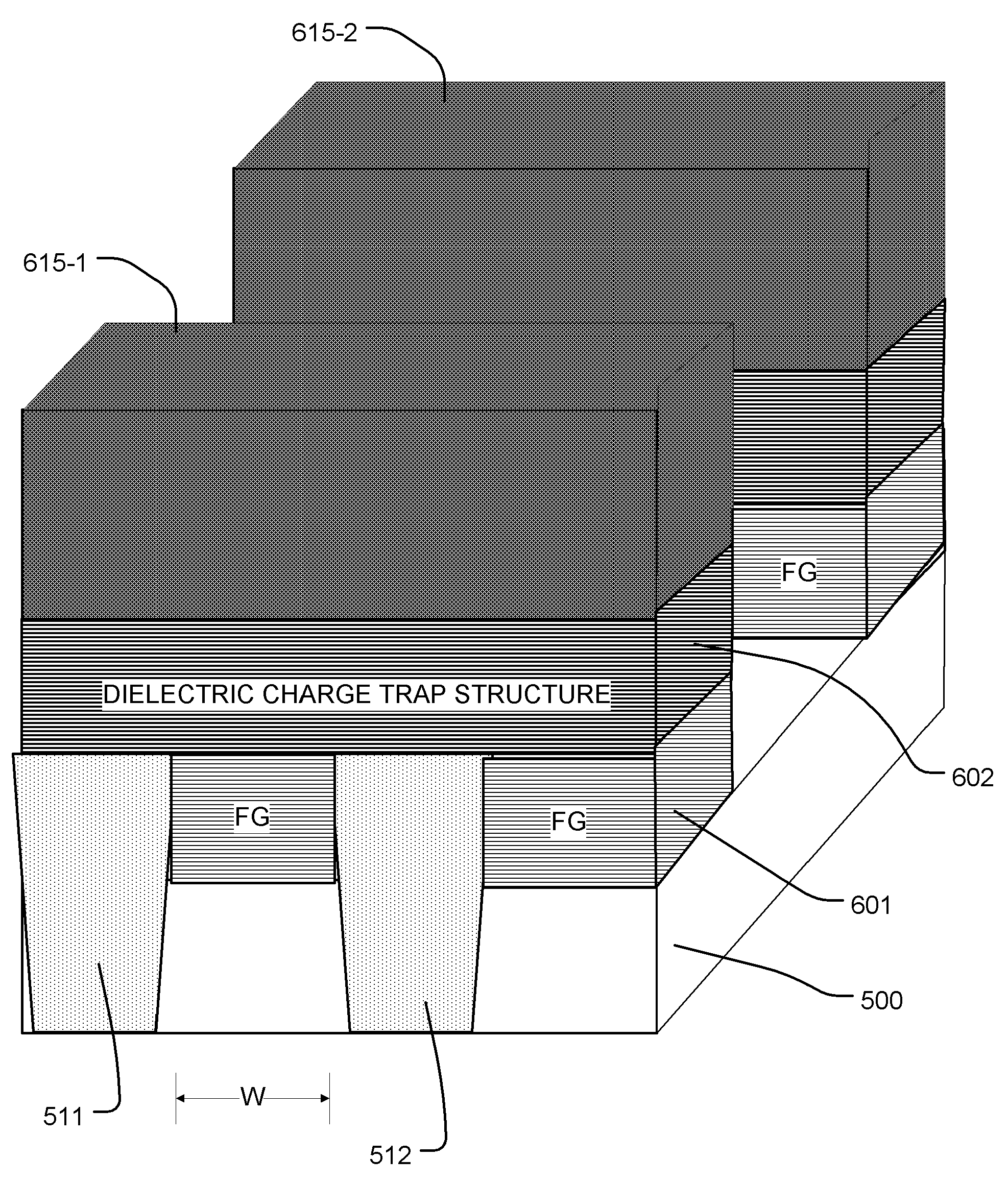
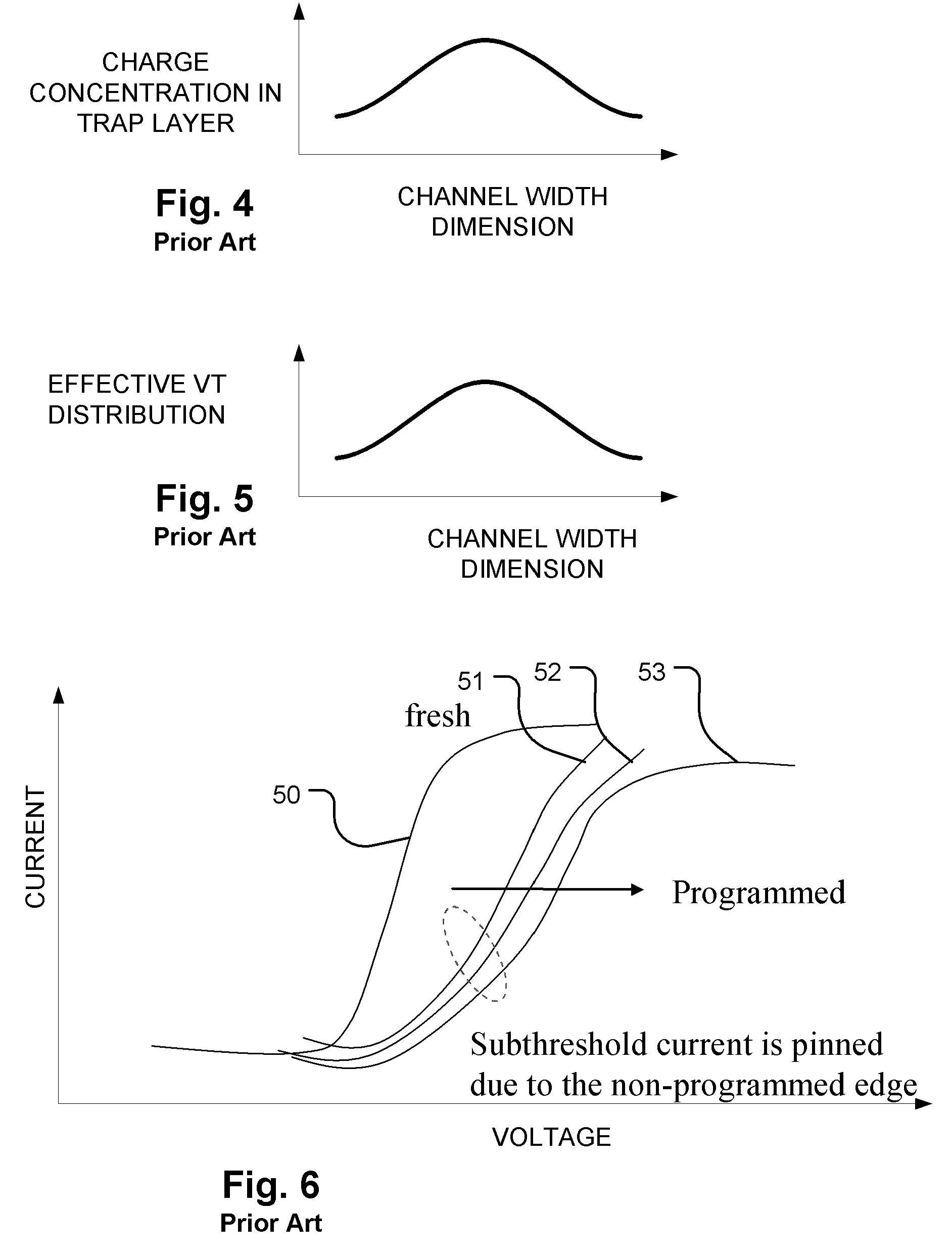
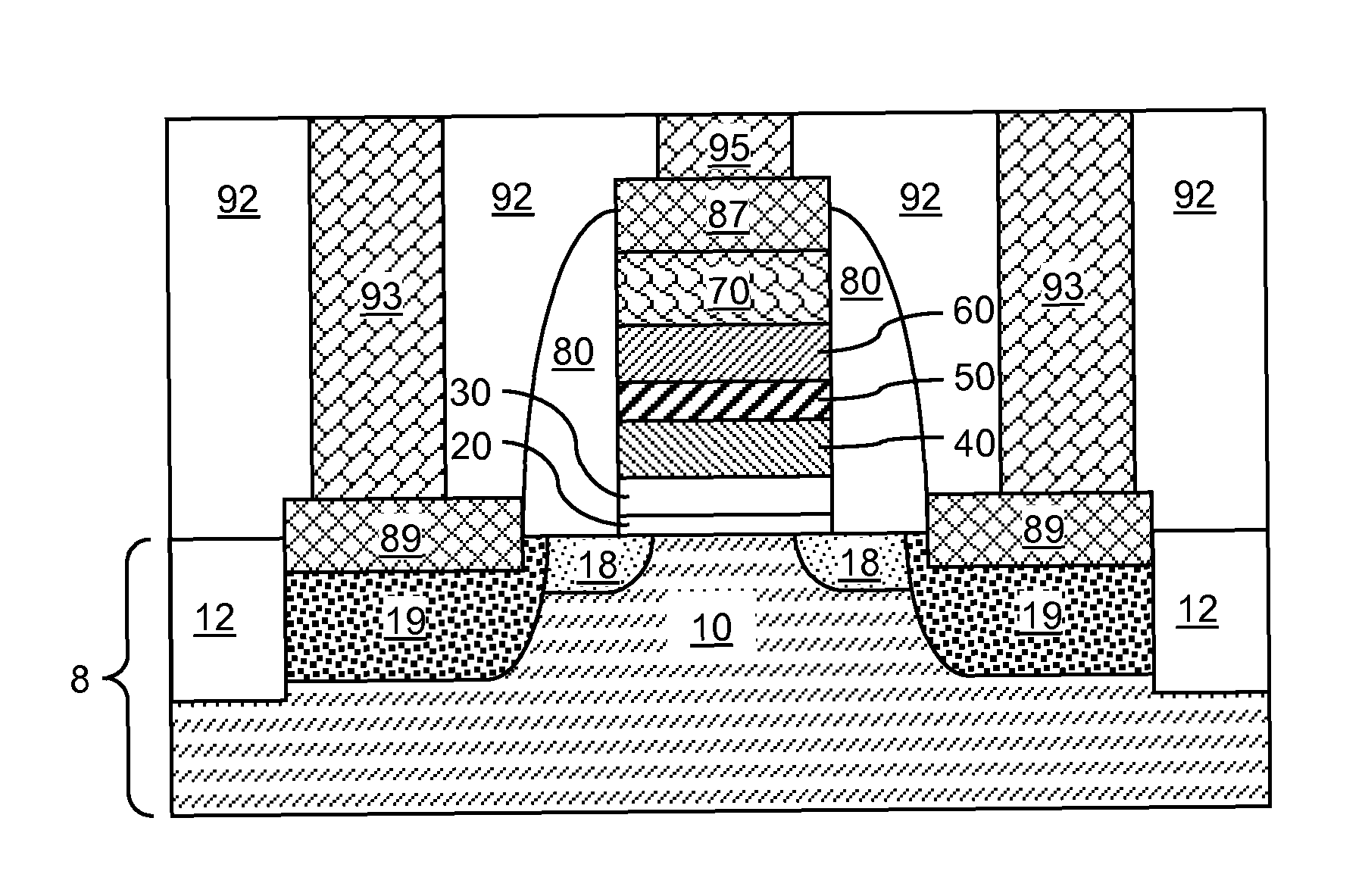
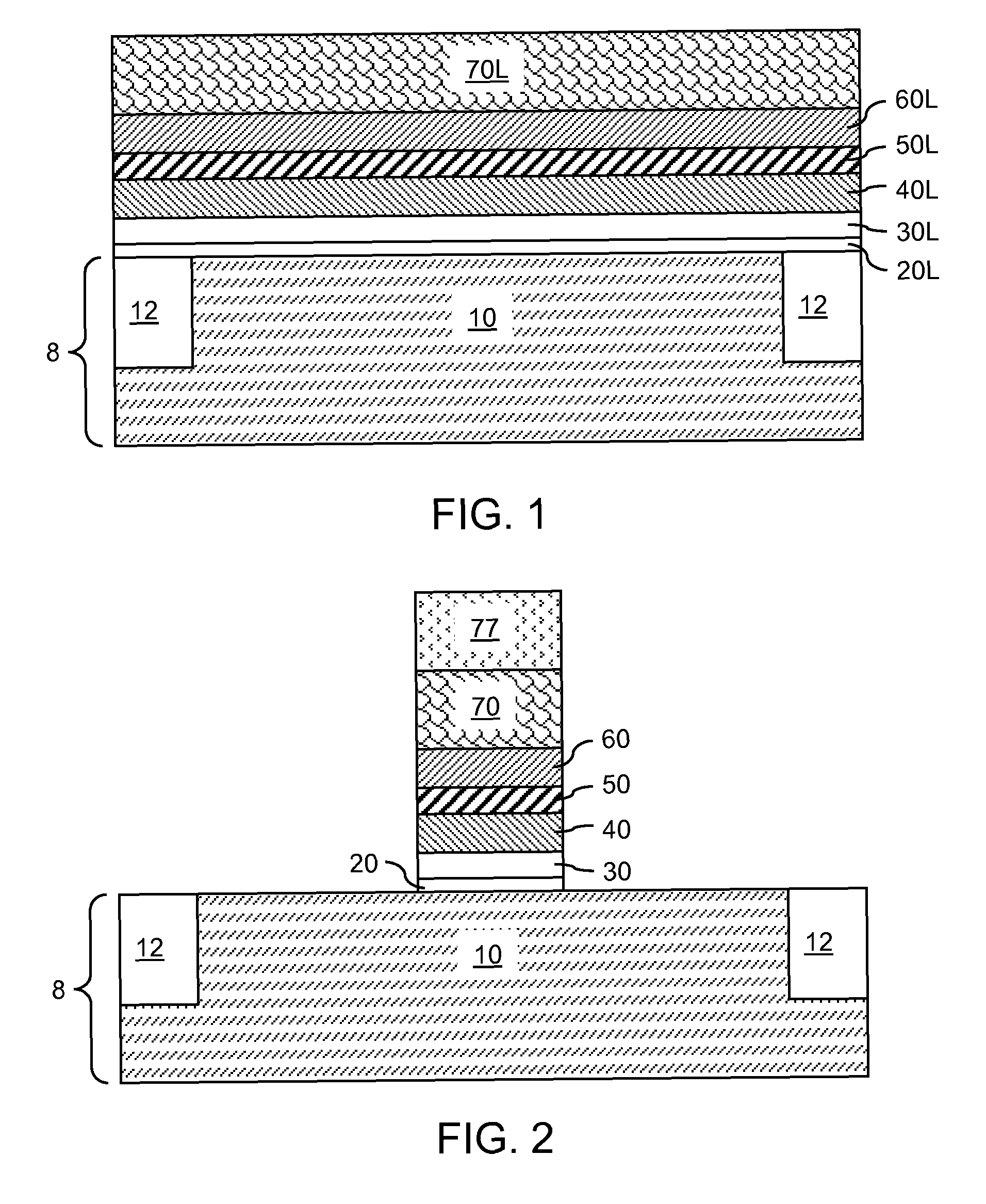
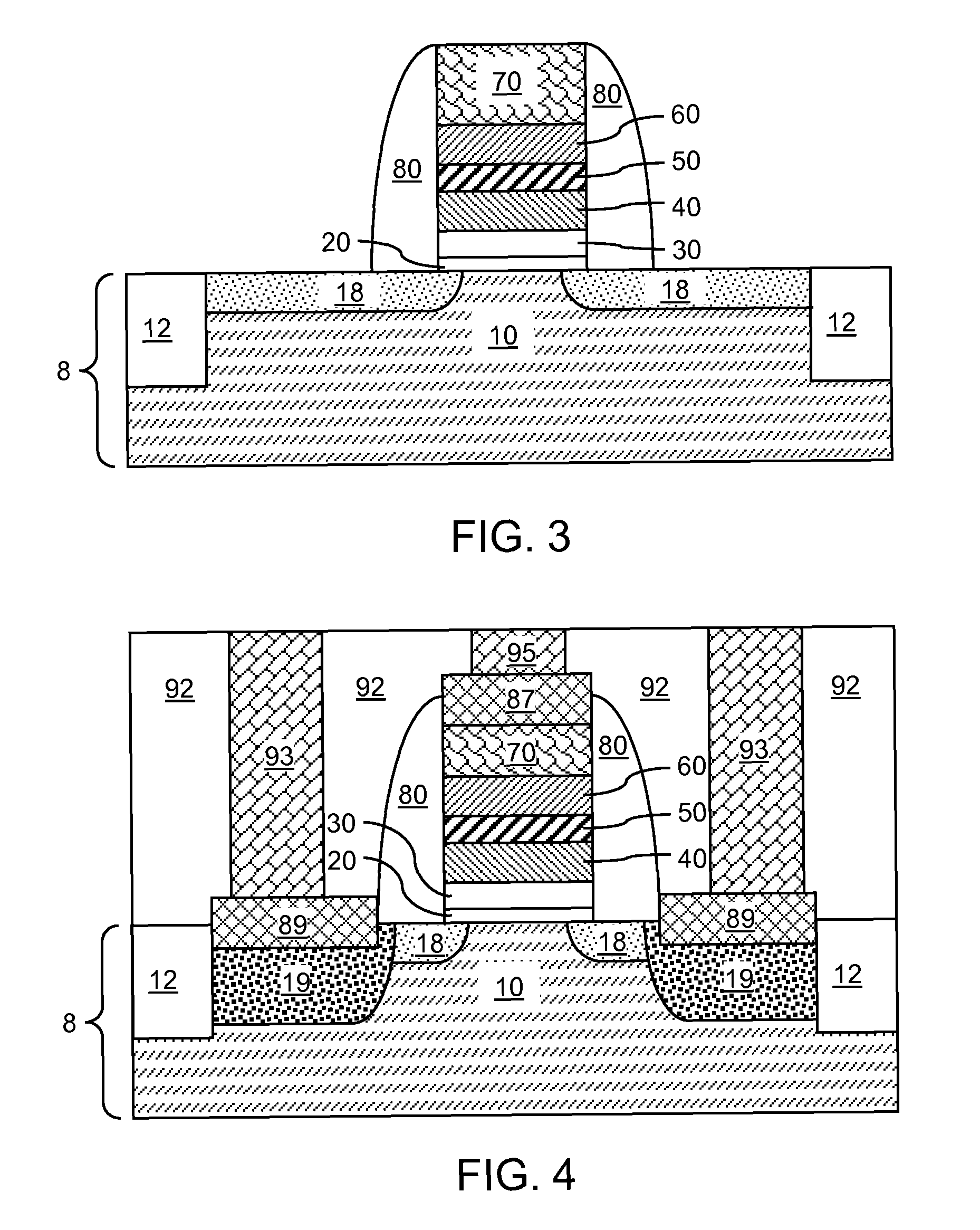
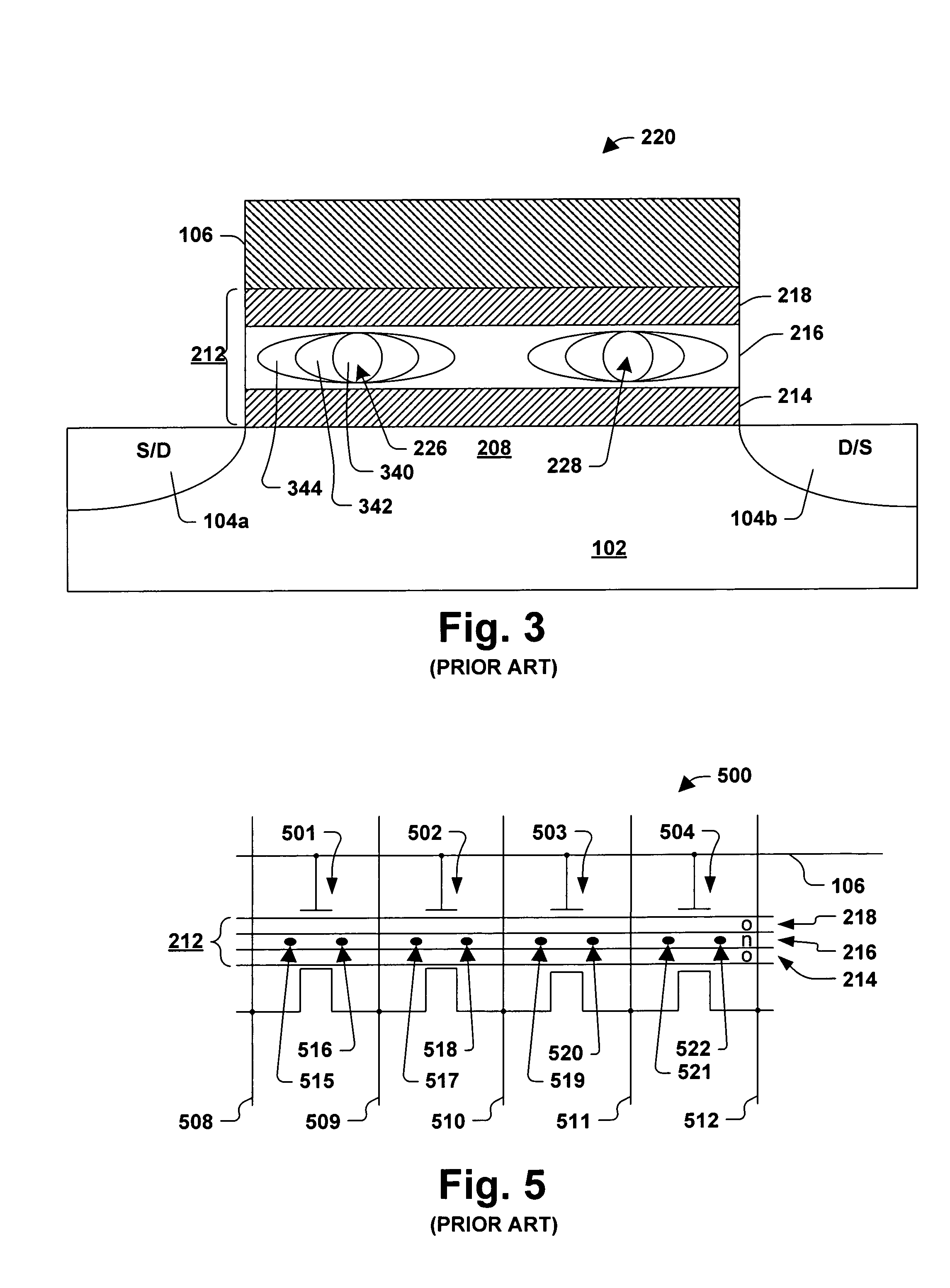
Floating gate memory device with interpoly charge trapping structure
ActiveUS20090262583A1Constant threshold voltageReduce distractionsTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorTrapping
A charge trapping floating gate is described with asymmetric tunneling barriers. The memory cell includes a source region and a drain region separated by a channel region. A first tunneling barrier structure is disposed above the channel region. A floating gate is disposed above the first tunneling barrier structure covering the channel region. A second tunneling barrier is disposed above the floating gate. A dielectric charge trapping structure disposed above the second tunneling barrier and a blocking dielectric structure is disposed above the charge trapping structure. A top conductive layer disposed above the top dielectric structure acts as a gate. The second tunneling barrier is a more efficient conductor of tunneling current, under bias conditions applied for programming and erasing the memory cell, than the first tunneling barrier structure.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
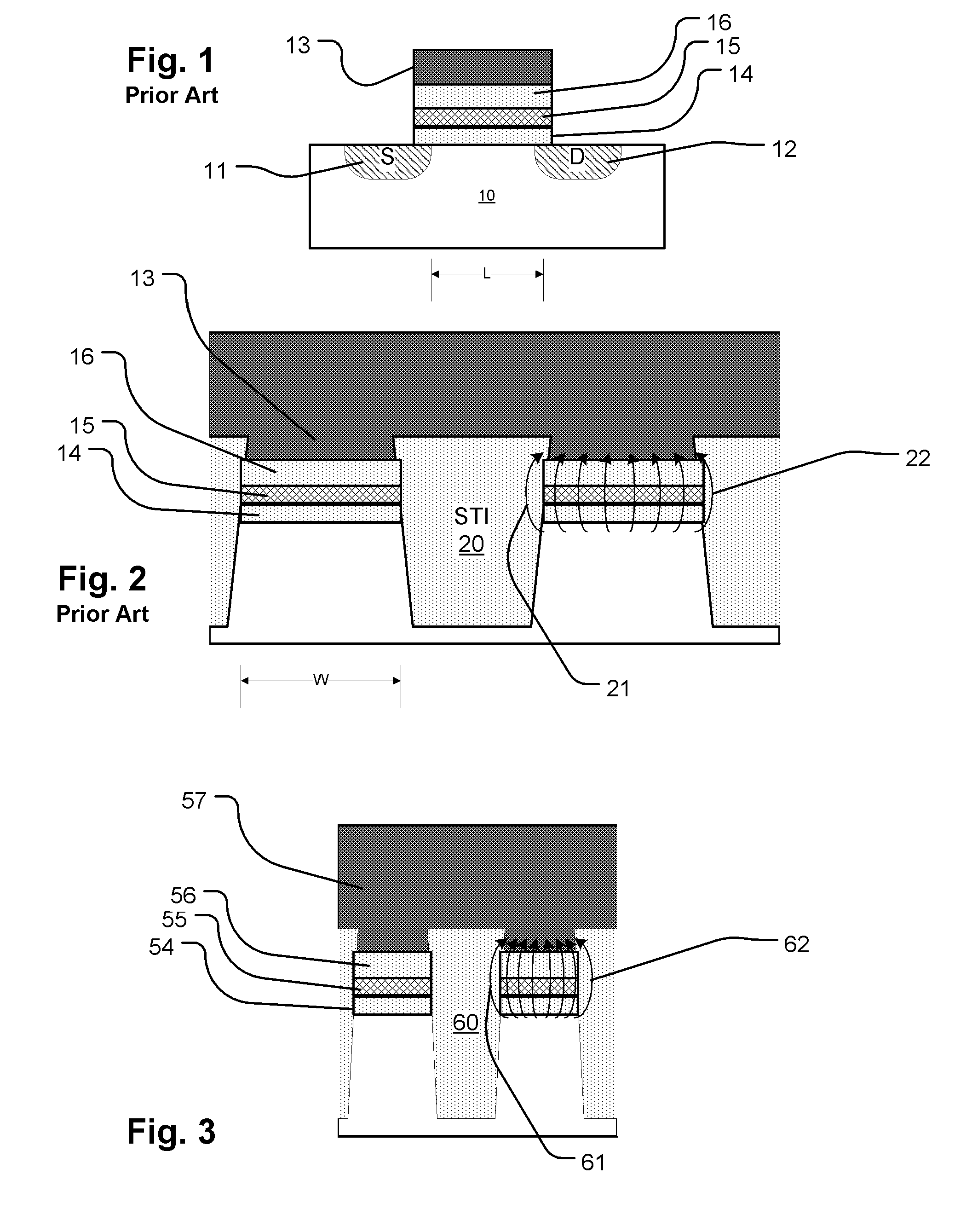
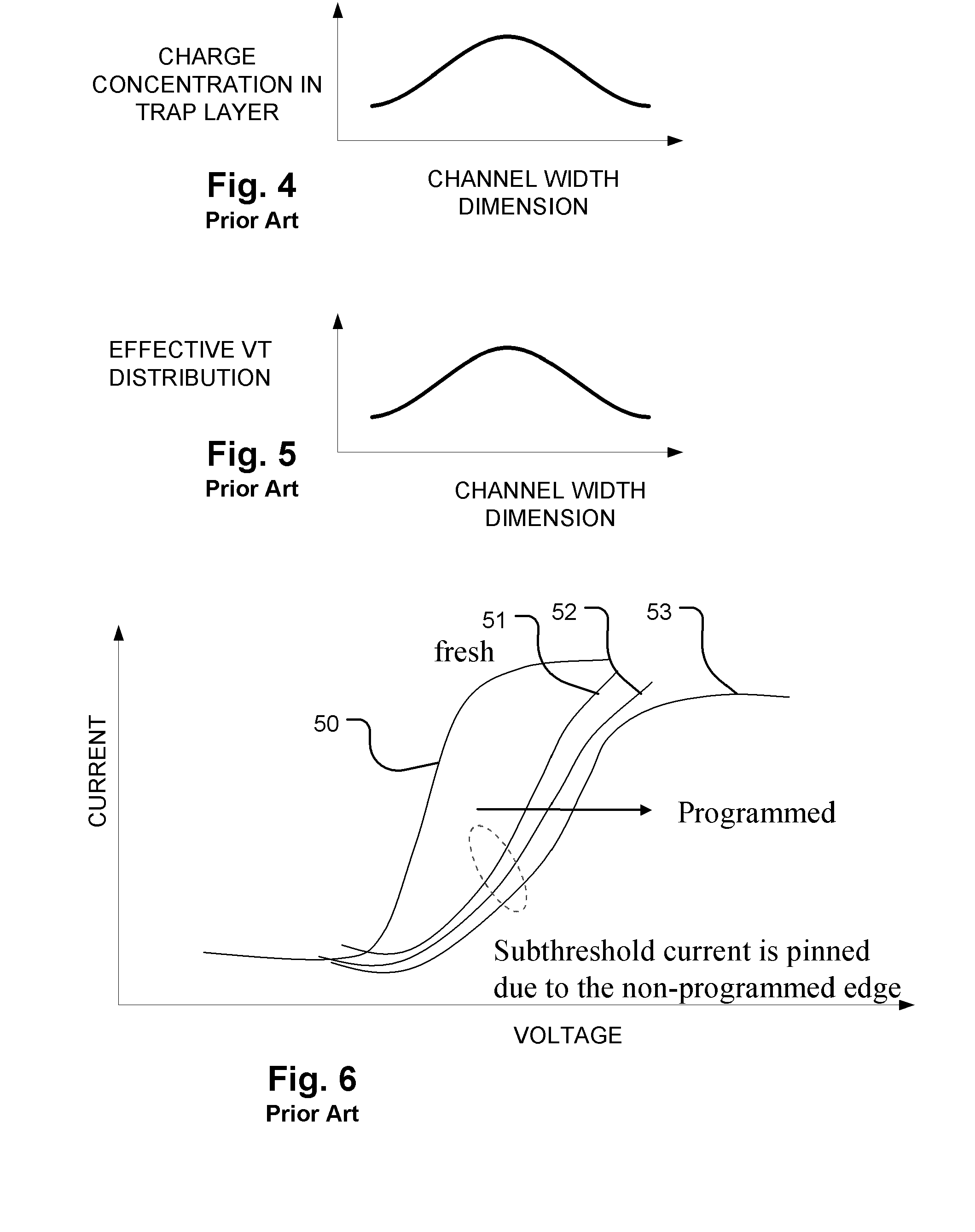
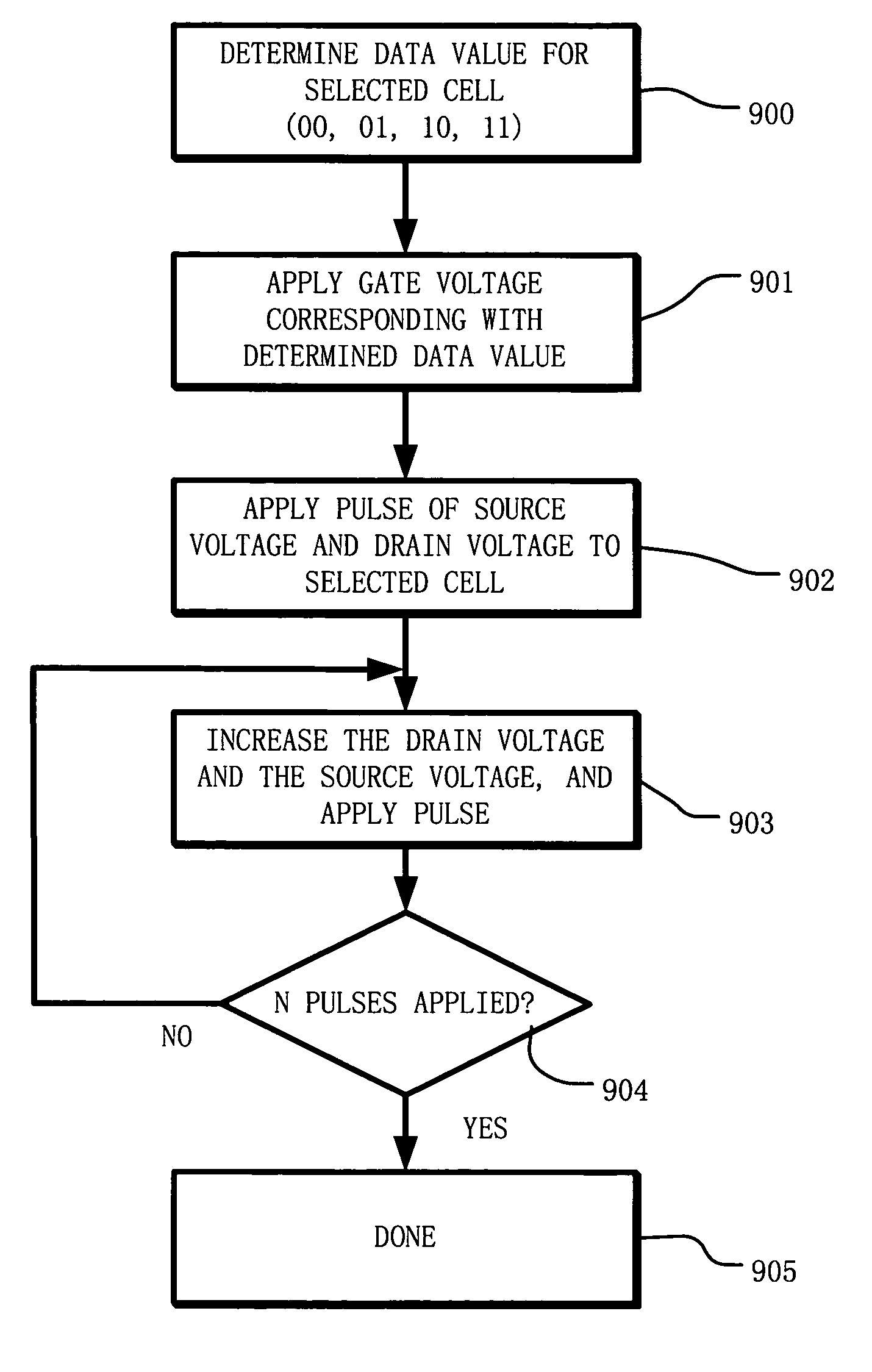
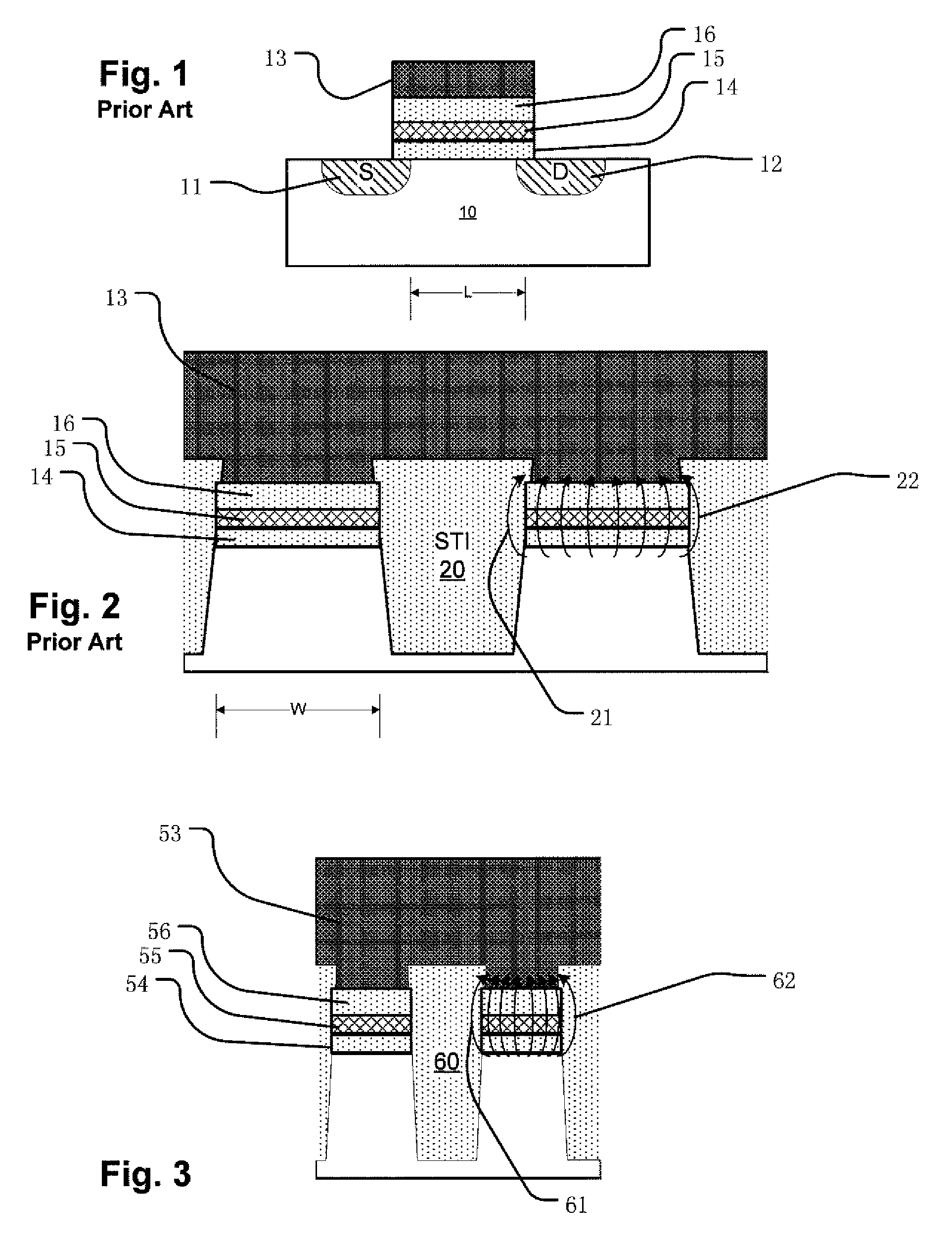
Circuit and method for programming charge storage memory cells
ActiveUS6937511B2Increases the effective thresholdHot electron injection efficiencySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineeringGate voltage
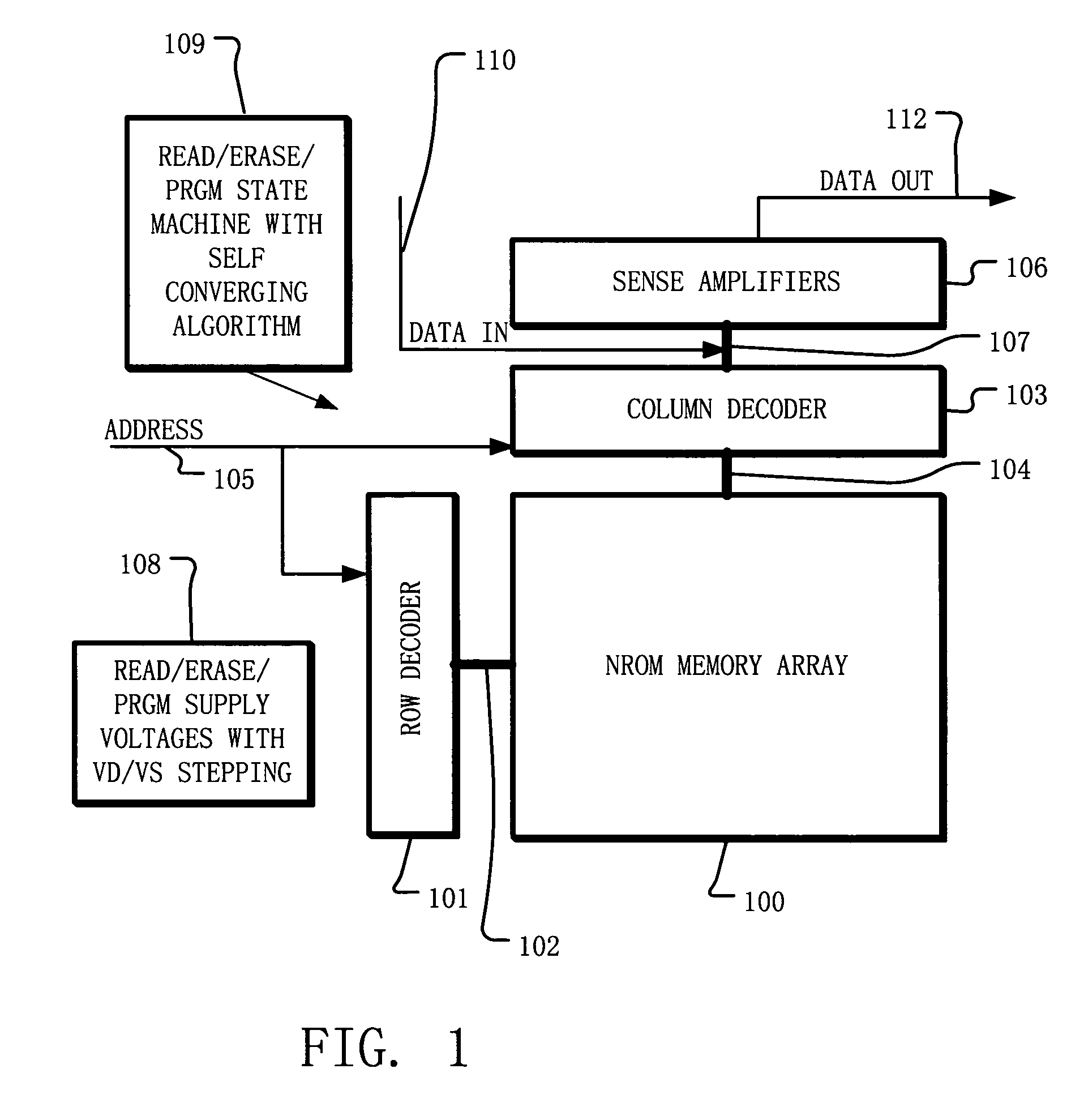
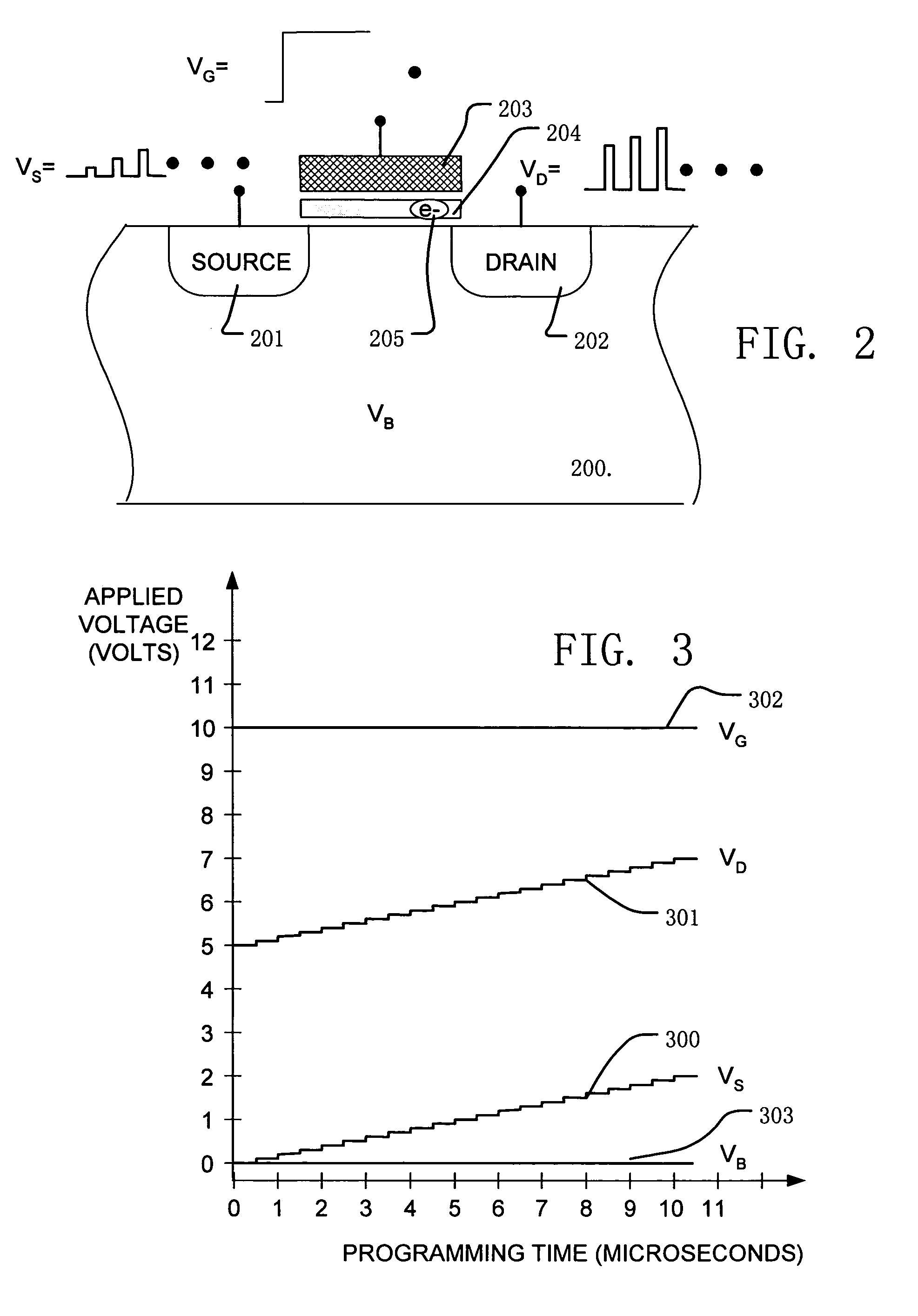
A circuit and method for self-converging programming of a charge storage memory cell, such as NROM or floating gate flash, having a source and a drain in a substrate, a charge storage element and a control gate. The method includes applying source voltage, inducing a body effect that increases the effective threshold, and increasing the source voltage along with the drain voltage to moderate hot electron injection efficiency during the program operation, at least during a portion of the program operation in which convergence on a target threshold occurs. A selected gate voltage is applied during the operation to establish the target threshold voltage. In multiple bit cells, the gate voltage is set according to the data values to be stored, enabling self-convergence at more than one target threshold.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Electro-optical device and driving device thereof
ActiveUS7274345B2Improve display qualityMore accuracyDecorative surface effectsElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentDriven element
The invention provides an electro-optical device having circuits for driving electro-optical elements, such as organic EL elements, and a driving device, which can employ driving elements having low driving ability, such as α-TFTs. By providing a charge storage capacitor between the source electrode and the gate electrode of a driving transistor which is between power sources, the electro-optical device can allow the driving transistor to control a driving current, even when an electro-optical element is connected to the source side of the driving transistor. In addition, driving data can be stored in the charge storage capacitor by applying a predetermined voltage to the source electrode of the driving transistor.
Owner:ELEMENT CAPITAL COMMERCIAL CO PTE LTD
Hybrid battery power source for implantable medical use
InactiveUS7136701B2Minimize impactLower internal resistanceSeveral cell simultaneous arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsInternal resistanceHigh energy
Owner:GENTCORP
Active matrix displays having high contrast values
InactiveUS6482479B1High maximum transmissionIncrease contrastLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryPyridazineActive matrix
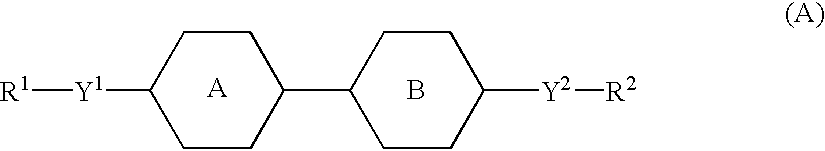
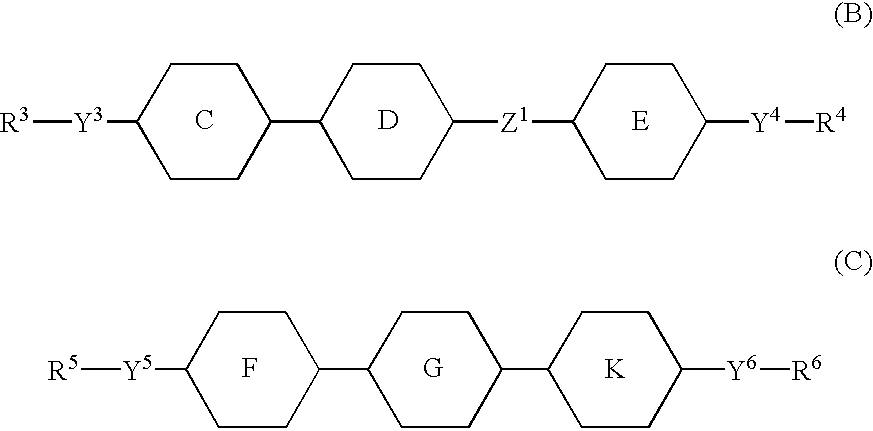
An active matrix display comprises a chiral smectic liquid crystal mixture which has the phase sequence I-N*-SmC*, a spontaneous polarization in the operating temperature range of <40 nC / cm2 and a pitch of >10 mum at at least one temperature in the nematic or cholesteric phase and comprises at least one compound each from at least two of the substance classes (A), (B) and (C) and one or more compounds from substance class (D):(A): compounds comprising two rings which are directly linked to one another and are selected from phenylene-1,4-diyl, pyrimidine-2,5-diyl, pyridine-2,5-diyl and pyridazine-2,5-diyl with the proviso that at least one of these rings is a nitrogen heterocycle;(B): compounds comprising three rings selected from phenylene-1,4-diyl, two of the rings being directly linked to one another and the third ring being linked to one of the other two rings via an -OC(=O)- or -C(=O)-group, with the proviso that at least one of the three rings is fluorophenylene-1,4-diyl or ortho-difluorophenylene-1,4-diyl;(C): compounds comprising three rings which are directly linked to one another and are selected from phenylene-1,4-diyl, pyrimidine-2,5-diyl, pyridine-2,5-diyl and pyridazine-2,5-diyl with the proviso that at least one of these rings is a nitrogen heterocycle;(D): compounds comprising mesogenic groups suitable as components of liquid crystal mixtures.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
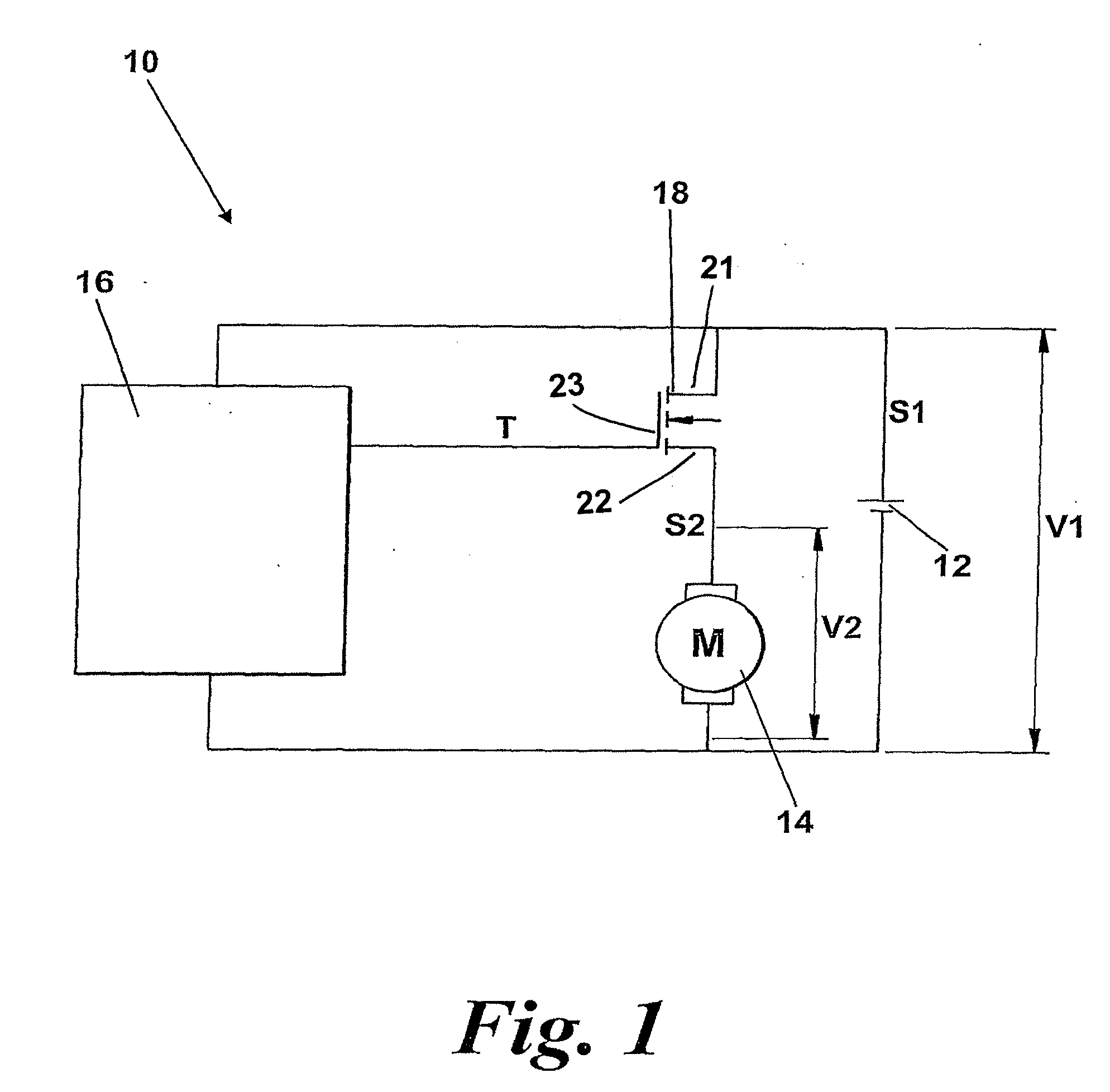
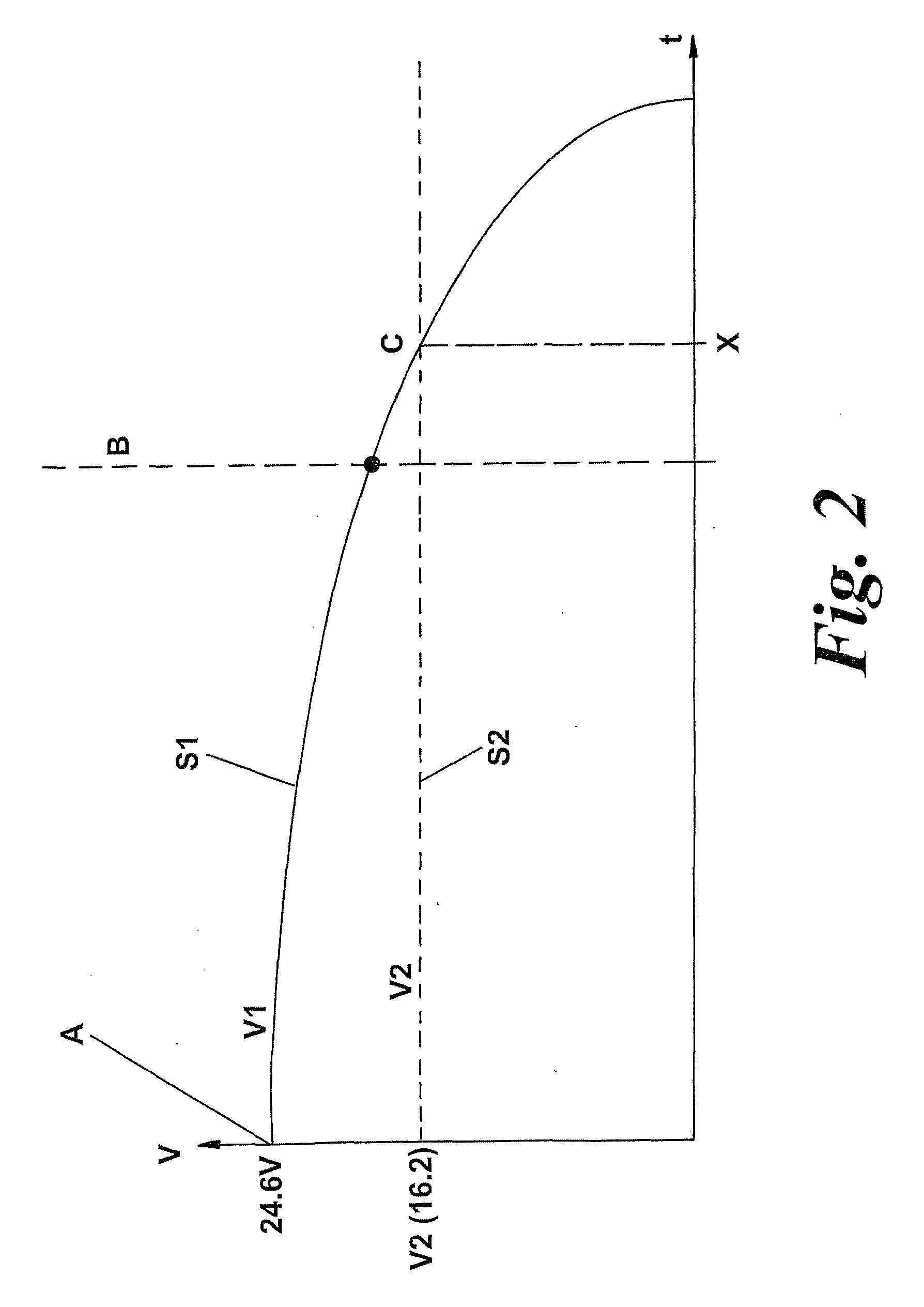
Motor driving apparatus
ActiveUS20100045215A1Eliminate needEasy to cleanBatteries circuit arrangementsSingle motor speed/torque controlPower controllerMotor drive
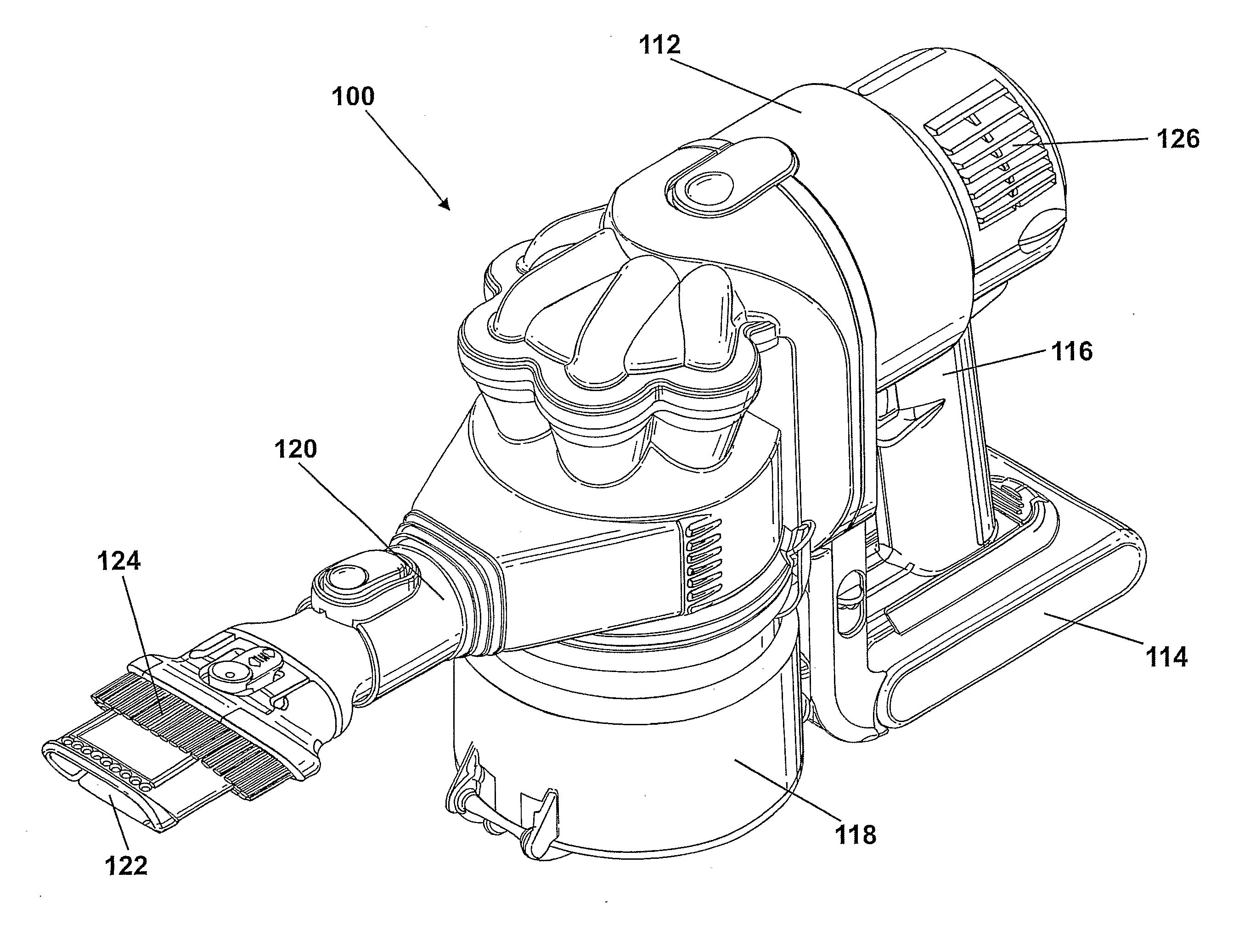
A motor driving apparatus for a cleaning appliance includes a battery source and a power controller. The battery source supplies the power controller with an output having a first voltage which decreases as the battery source is discharged. The power controller modulates the output to produce a drive signal for driving a motor that has a second voltage and a variable duty cycle. The power controller increases the duty cycle of the drive signal as the first voltage decreases in order to maintain the second voltage at a substantially constant average value per unit time. By providing the above arrangement, the motor can be supplied with a constant voltage throughout the available run time of the battery. When forming part of a cleaning appliance having a motor, the above arrangement allows the motor to operate at a substantially constant speed throughout the run time of the battery.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Scavanging metal stack for a high-k gate dielectric
ActiveUS20100320547A1Constant threshold voltageReduce equivalent oxide thicknessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricEquivalent oxide thickness
A stack of a high-k gate dielectric and a metal gate structure includes a lower metal layer, a scavenging metal layer, and an upper metal layer. The scavenging metal layer meets the following two criteria 1) a metal (M) for which the Gibbs free energy change of the reaction Si+2 / y MxOy→2x / y M+SiO2 is positive 2) a metal that has a more negative Gibbs free energy per oxygen atom for formation of oxide than the material of the lower metal layer and the material of the upper metal layer. The scavenging metal layer meeting these criteria captures oxygen atoms as the oxygen atoms diffuse through the gate electrode toward the high-k gate dielectric. In addition, the scavenging metal layer remotely reduces the thickness of a silicon oxide interfacial layer underneath the high-k dielectric. As a result, the equivalent oxide thickness (EOT) of the total gate dielectric is reduced and the field effect transistor maintains a constant threshold voltage even after high temperature processes during CMOS integration.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Modulated power supply for reduced parasitic capacitance
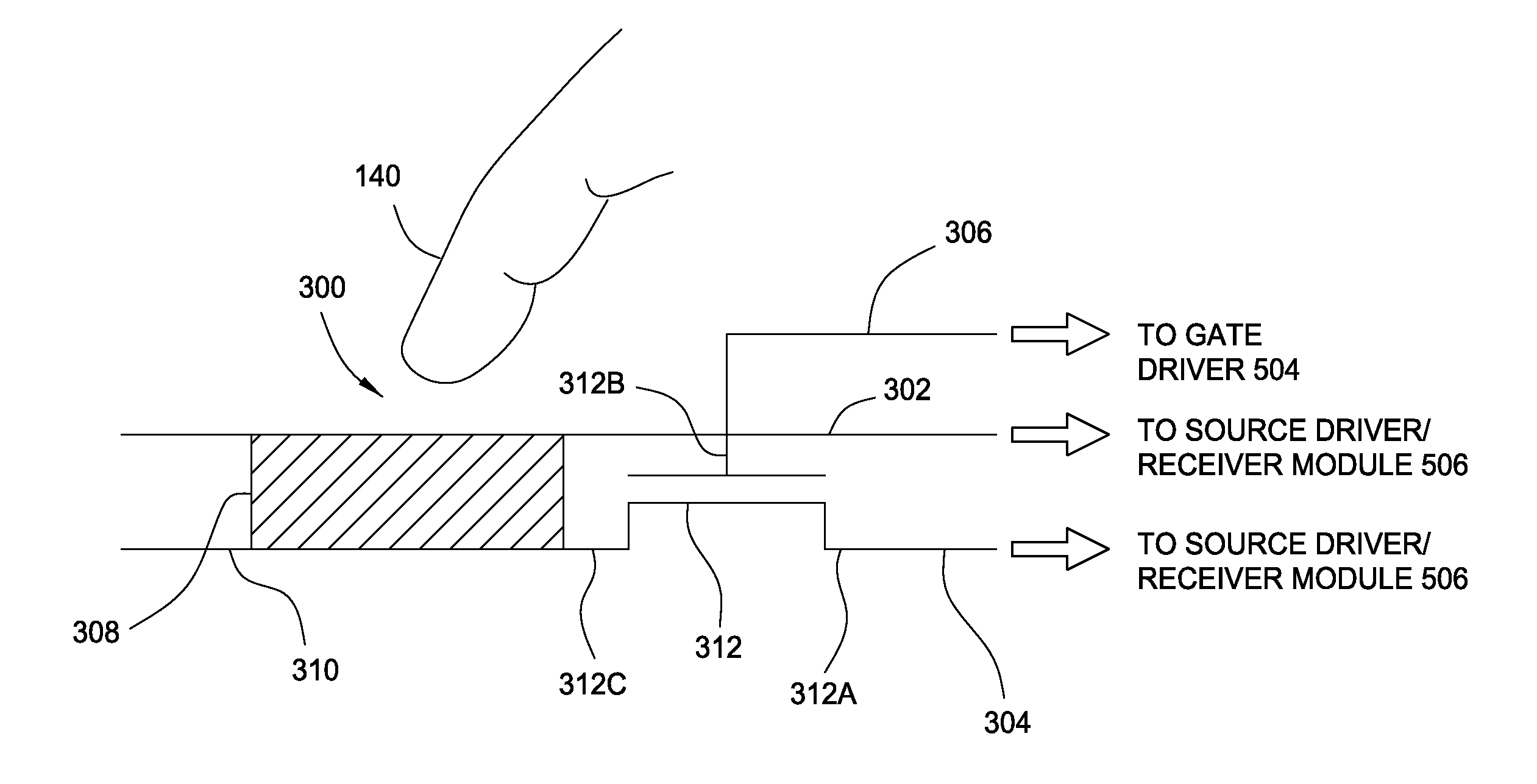
ActiveUS20150091850A1Constant voltageInput/output processes for data processingElectric variable regulationEngineeringInput device
An input device comprising a display device having an integrated capacitive sensing device. The input device includes a plurality of sensor electrodes a plurality of display electrodes, a modulated power supply configured to provide a modulated reference signal, and a processing system. The processing system includes a sensor module configured to drive a plurality of sensor electrodes with a modulated capacitive sensing signal that is based on the modulated reference signal for capacitive sensing during a first time period. The processing system also includes a display driver module configured to drive a plurality of display electrodes of a display device with modulated signals based on the modulated reference signal during the first time period. The modulated signals cause voltage between the plurality of display electrodes and the plurality of sensor electrodes to remain substantially constant.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Charge trapping devices with field distribution layer over tunneling barrier
ActiveUS20080116506A1Constant threshold voltageConstant voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesPhysicsTunnel barrier
A memory cell comprising: a semiconductor substrate with a surface with a source region and a drain region disposed below the surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunneling barrier dielectric structure with an effective oxide thickness of greater than 3 nanometers disposed above the channel region; a conductive layer disposed above the tunneling barrier dielectric structure and above the channel region; a charge trapping structure disposed above the conductive layer and above the channel region; a top dielectric structure disposed above the charge trapping structure and above the channel region; and a top conductive layer disposed above the top dielectric structure and above the channel region are described along with devices thereof and methods for manufacturing.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
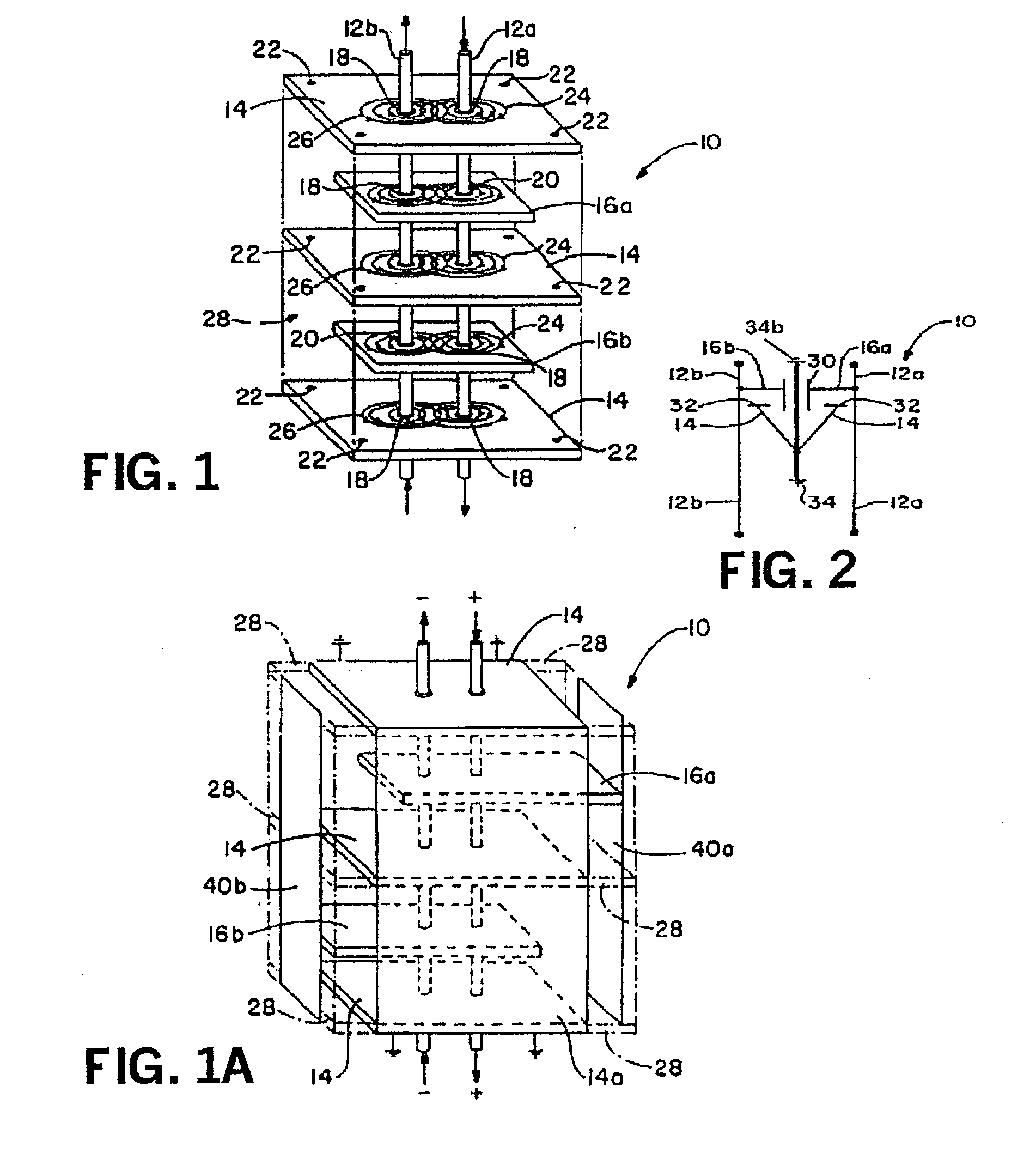
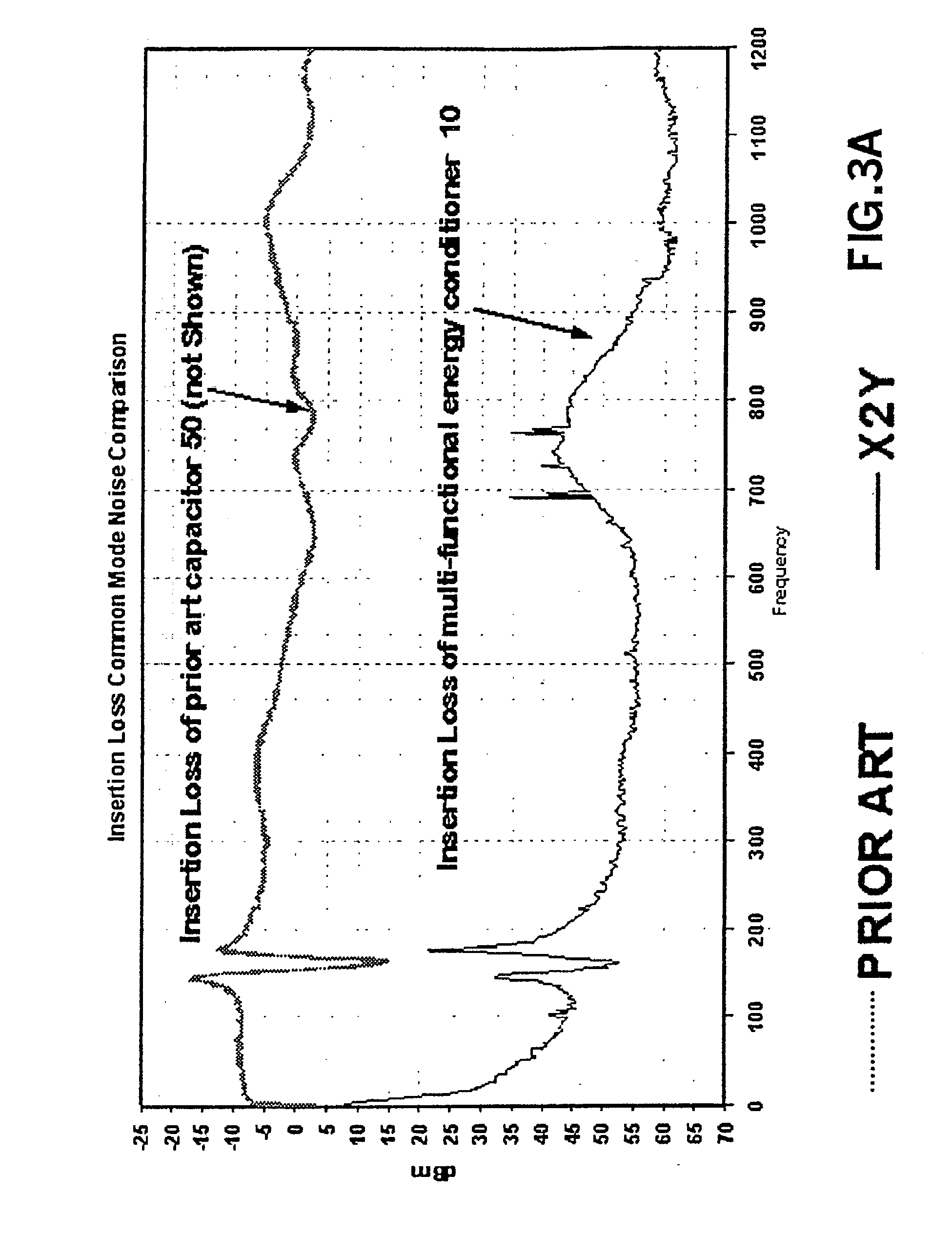
Multi-functional energy conditioner
InactiveUS20060023385A9Preventing and minimizingConstant voltageMagnetic/electric field screeningSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricCombined use
The present invention relates to a multi-functional energy conditioner having architecture employed in conjunction with various dielectric and combinations of dielectric materials to provide one or more differential and common mode filters for the suppression of electromagnetic emissions and surge protection. The architecture allows single or multiple components to be assembled within a single package such as an integrated circuit or connector. The component's architecture is dielectric independent and provides for integration of various electrical characteristics within a single component to perform the functions of filtering, decoupling, fusing and surge suppression.
Owner:X2Y ATTENUATORS L L C
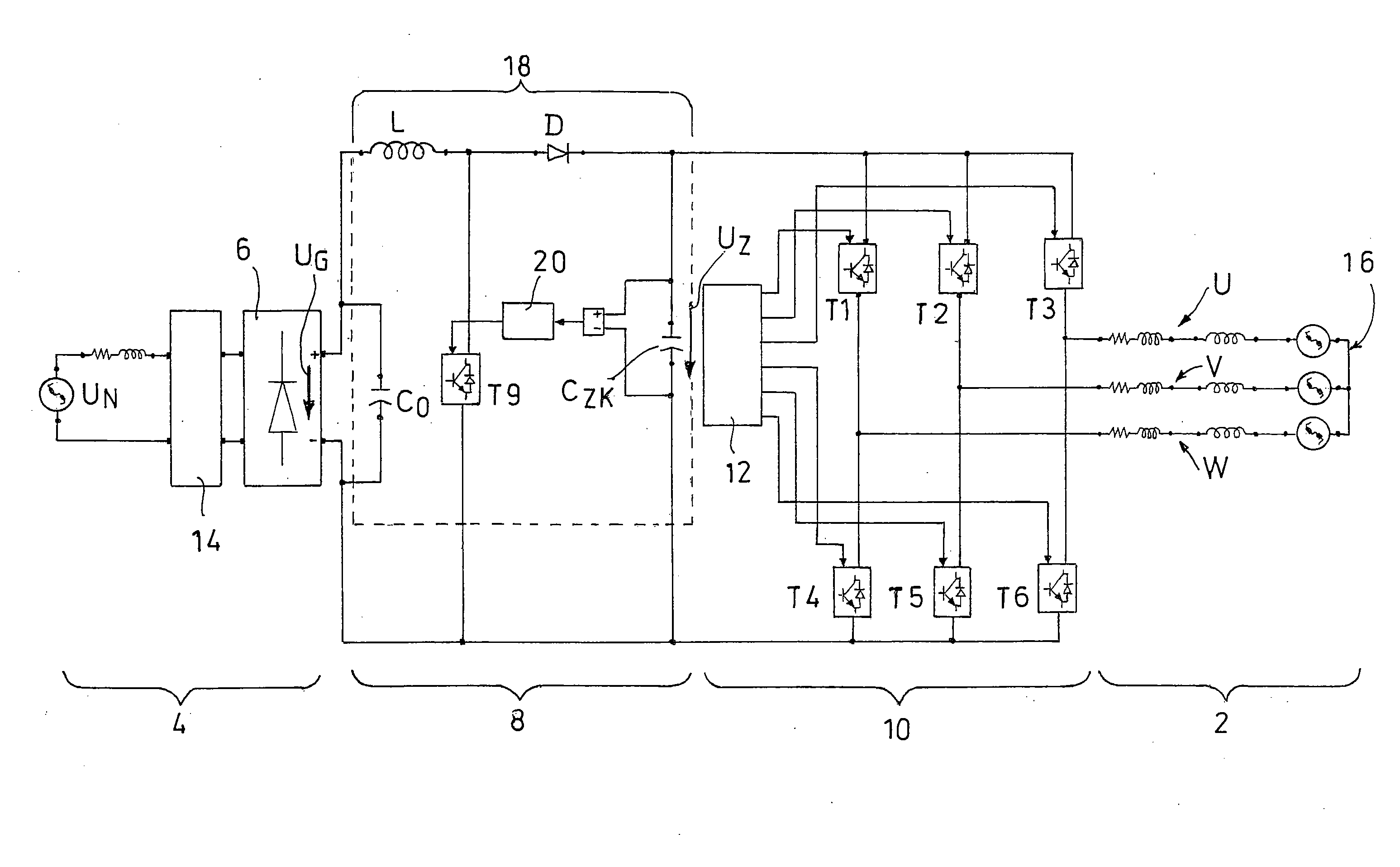
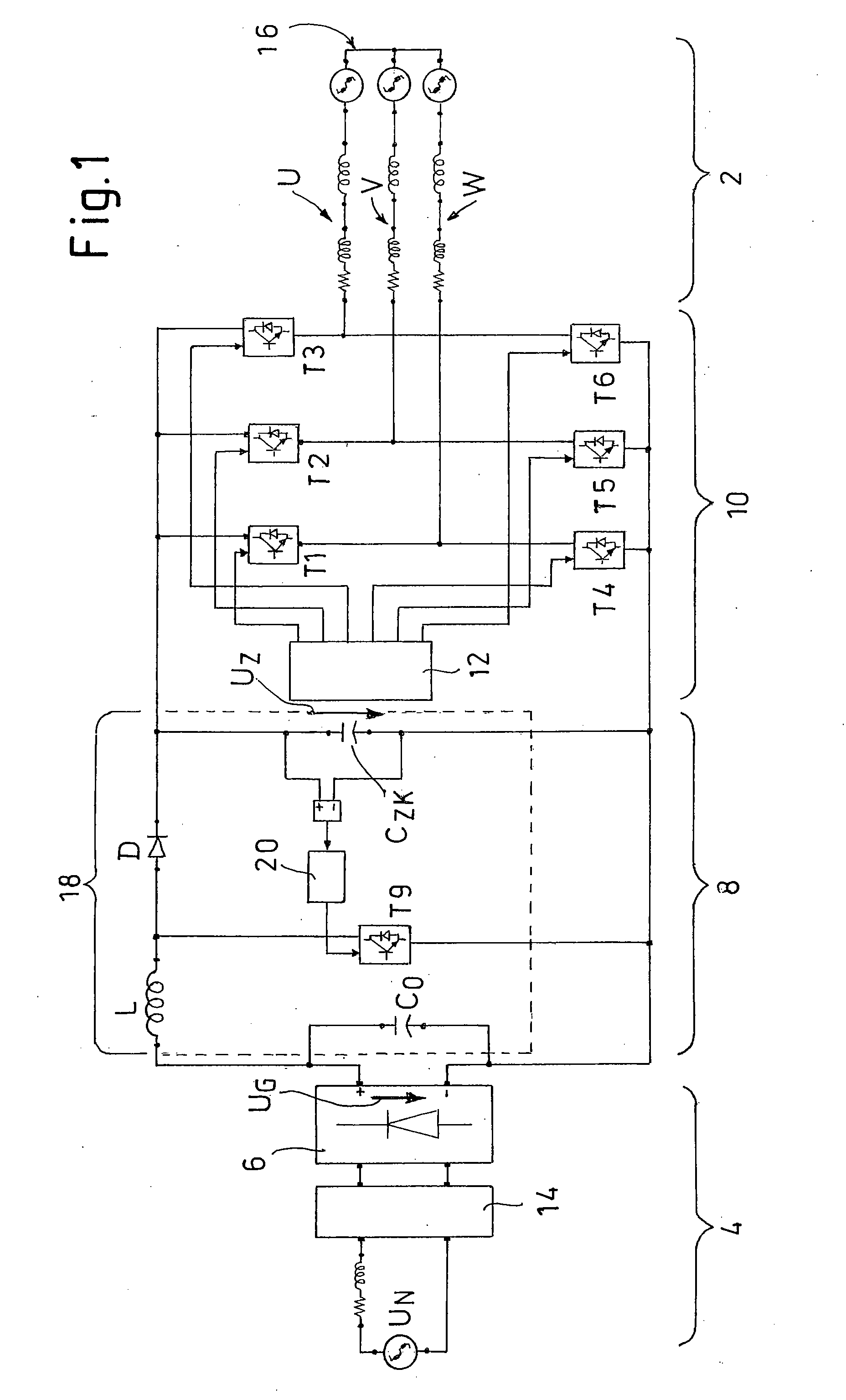
Procedures and Control System to Control a Brushless Electric Motor
ActiveUS20100315027A1Constant voltageSufficient voltageSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlBoost chopperControl system
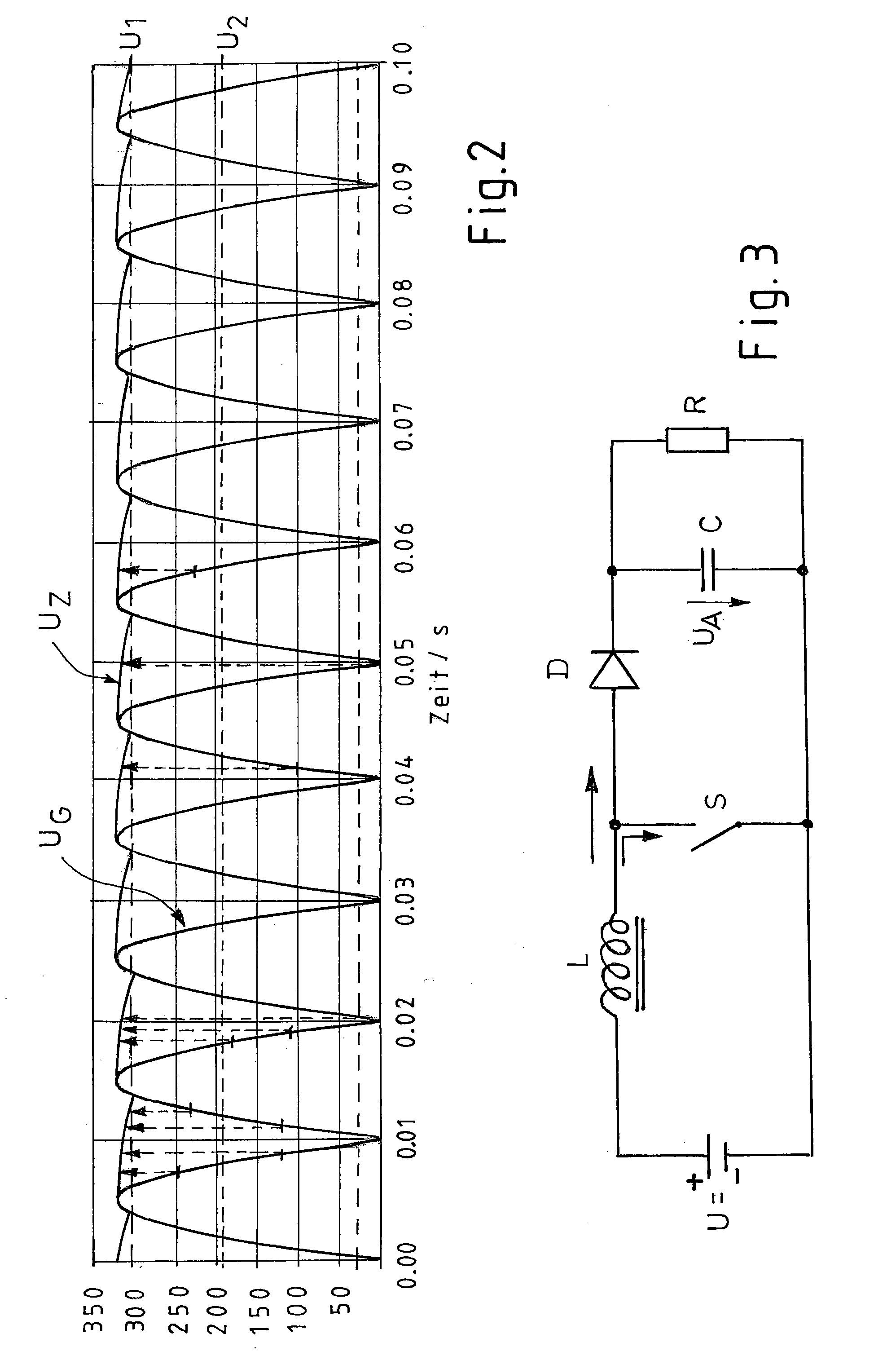
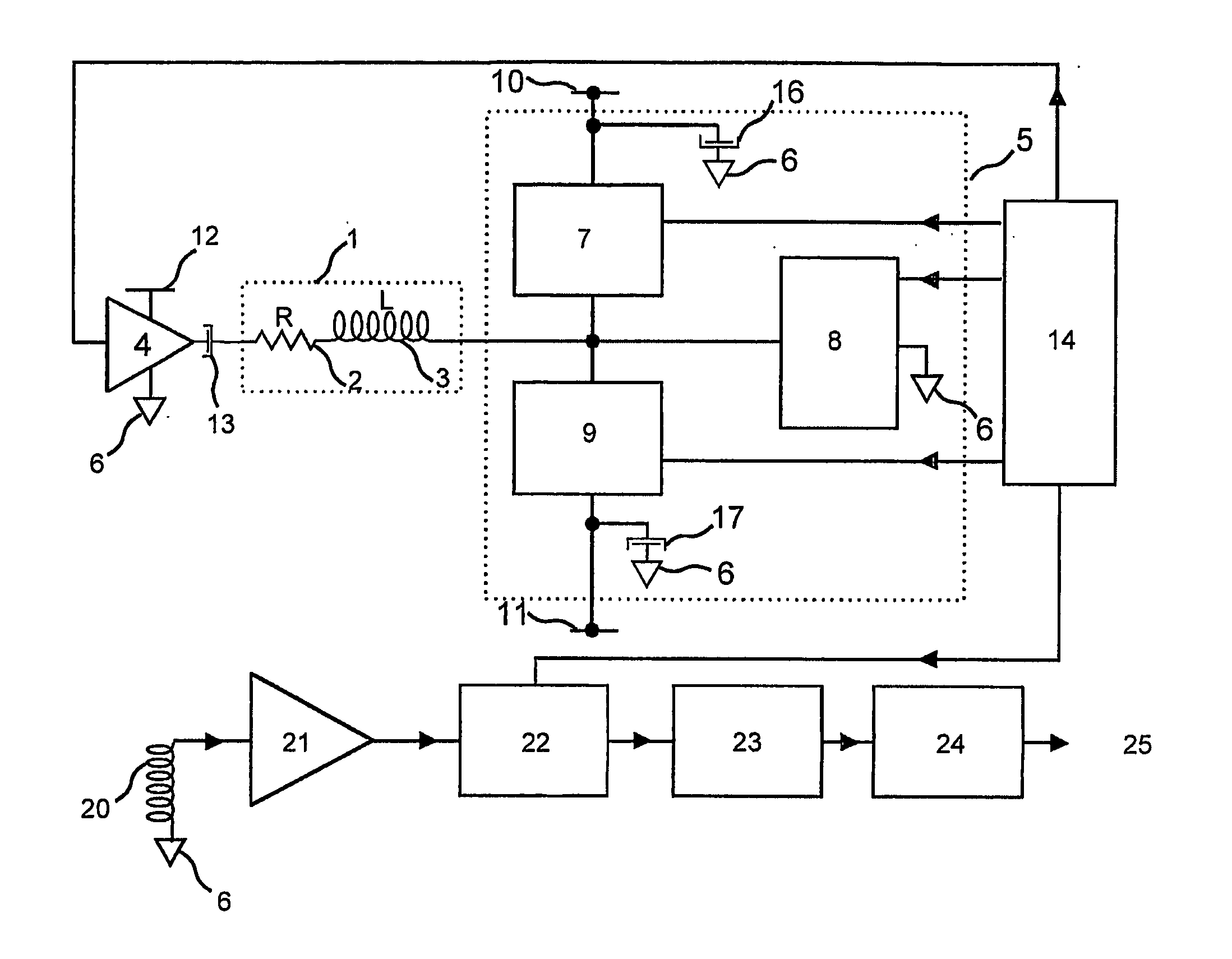
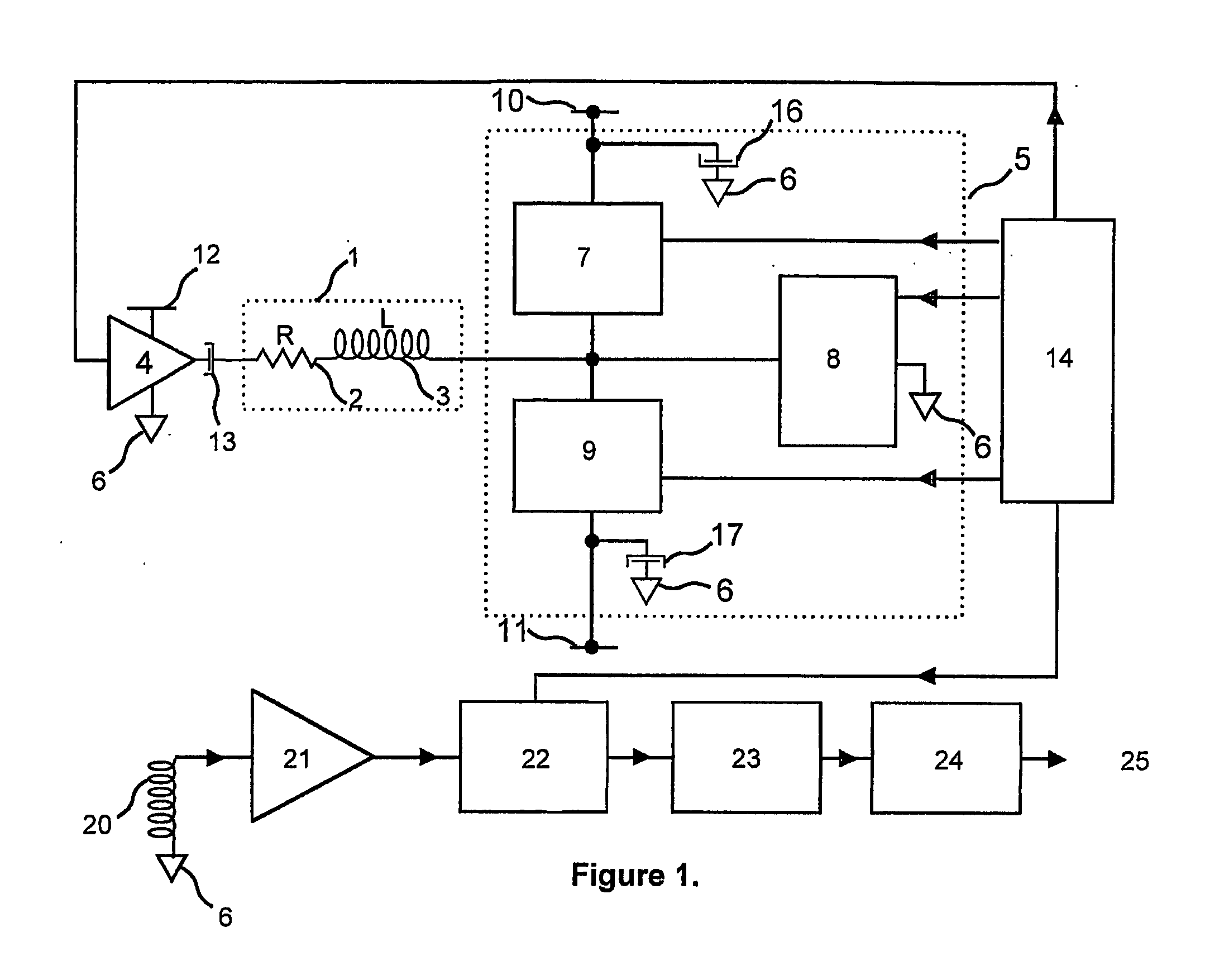
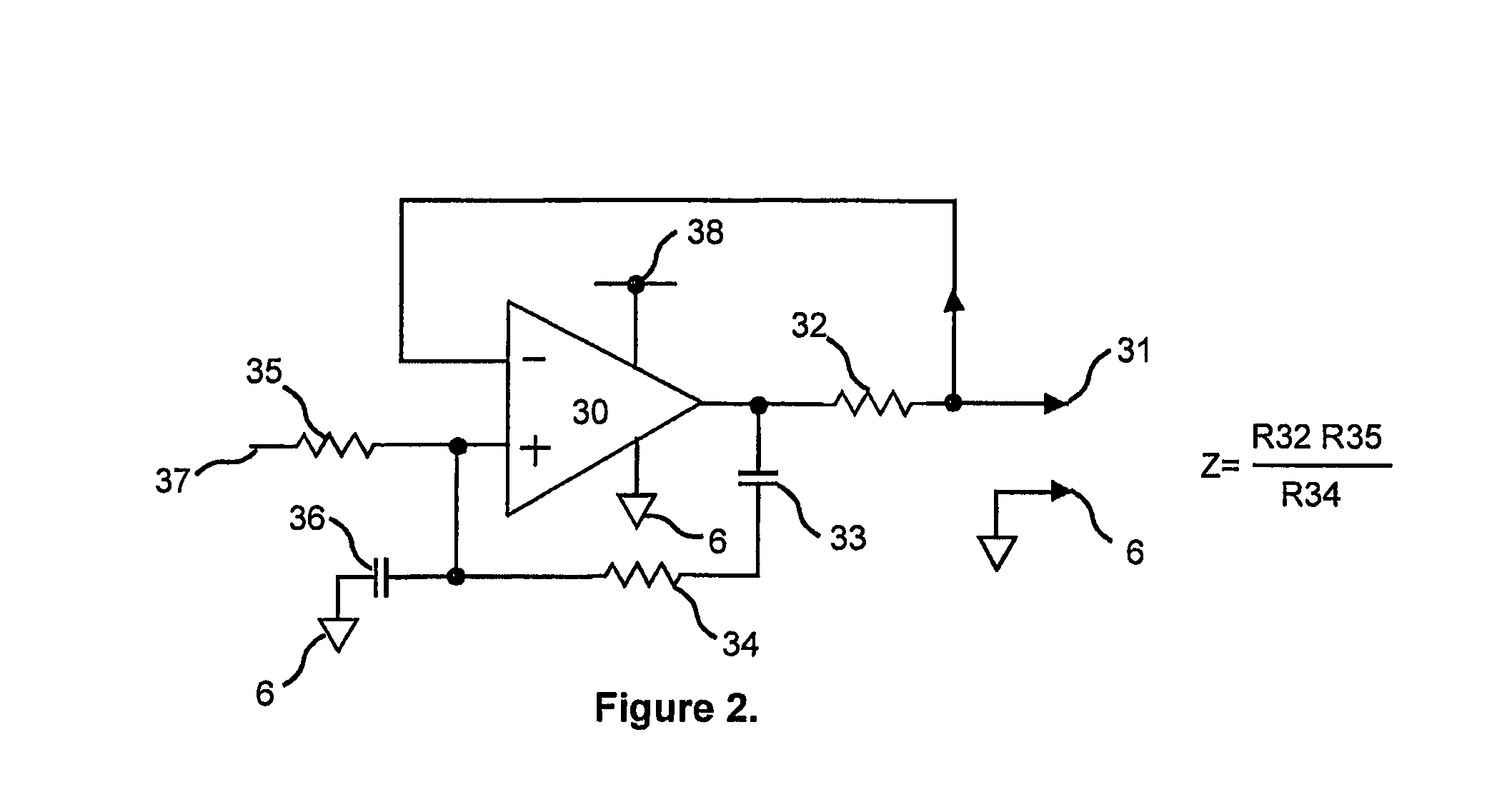
The present invention relates to a method and a control system for driving a three-strand brushless, electronically commutated electric motor (2), wherein a line AC voltage (UN) is rectified and fed via a slim DC link (8) with minimum DC link reactance as a DC link voltage (UZ) to an inverter (10) that can be driven to supply and commutate the electric motor (2). A pulsating DC voltage (UG) initially generated by rectifying the line AC voltage (UN) is dynamically increased with respect to its instantaneous values by a step-up chopper (18) in such a manner that the resulting DC link voltage (UZ) with a reduced ripple always lies above a defined limit voltage (U18 / U1) over time. The control system consists of a network rectifier (6), a downstream slim DC link (8) with minimum DC link reactance and a controllable inverter (10) that can be supplied via the DC link and driven to commutate the electric motor (2). A step-up chopper (18) is integrated therein with a controller (20) designed in such a manner that, the pulsating DC voltage (UG) rectified by the network rectifier (6) is dynamically increased with respect to its instantaneous values in such a manner that the resulting DC link voltage (UZ) with a reduced ripple always lies above a defined limit voltage (U20 / U1) over time. Stray inductances (Ls1-Ls3) of the motor winding heads present in the electric motor (2) are used as inductor (L) for the step-up chopper (18).
Owner:EBM PAPST MULFINGEN GMBH & CO KG
Hybrid battery power source for implantable medical use
InactiveUS7079893B2Increase energy densityInternal resistance is relatively low and stable over timeSeveral cell simultaneous arrangementsElectrotherapyInternal resistanceHigh energy
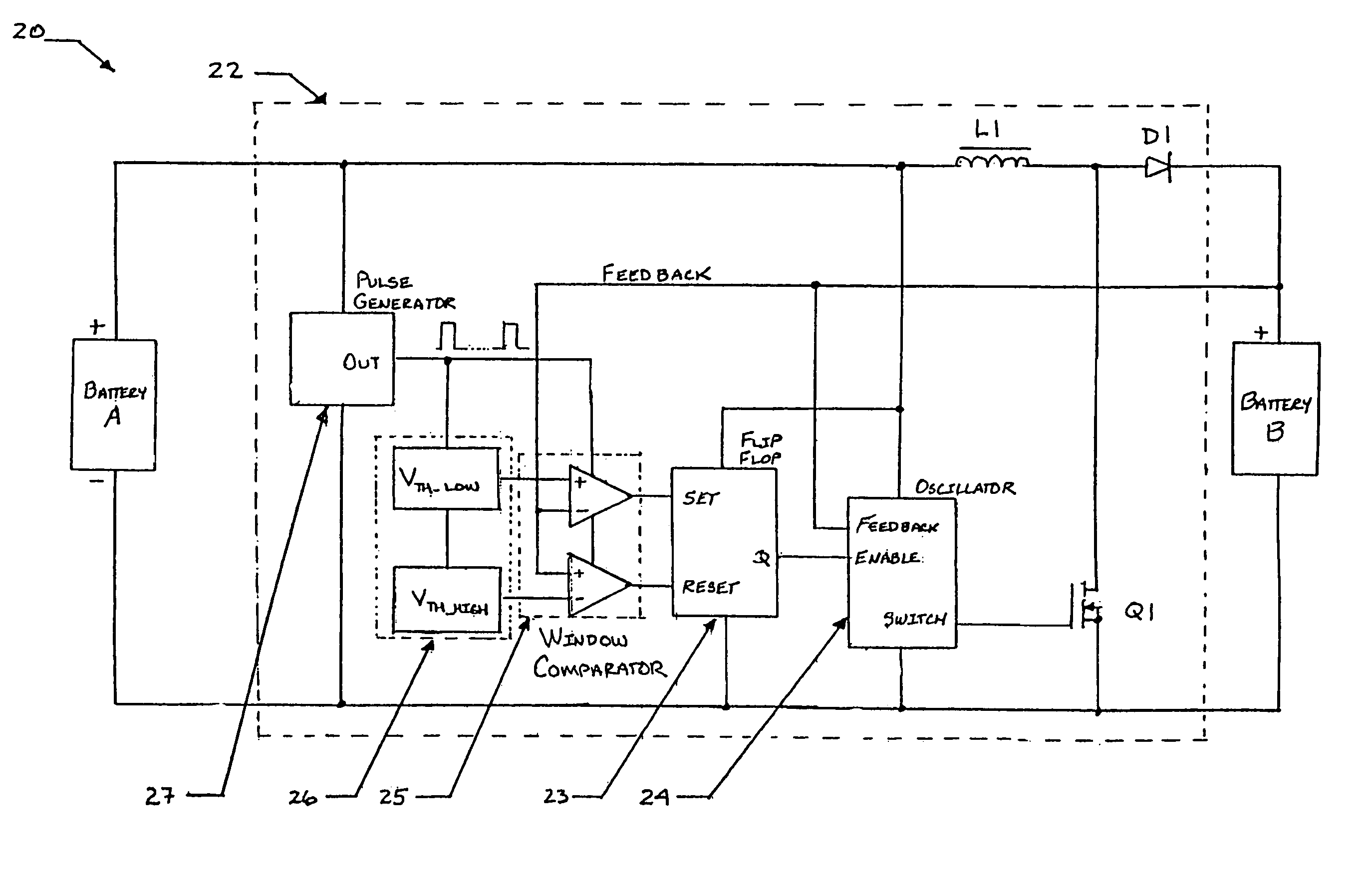
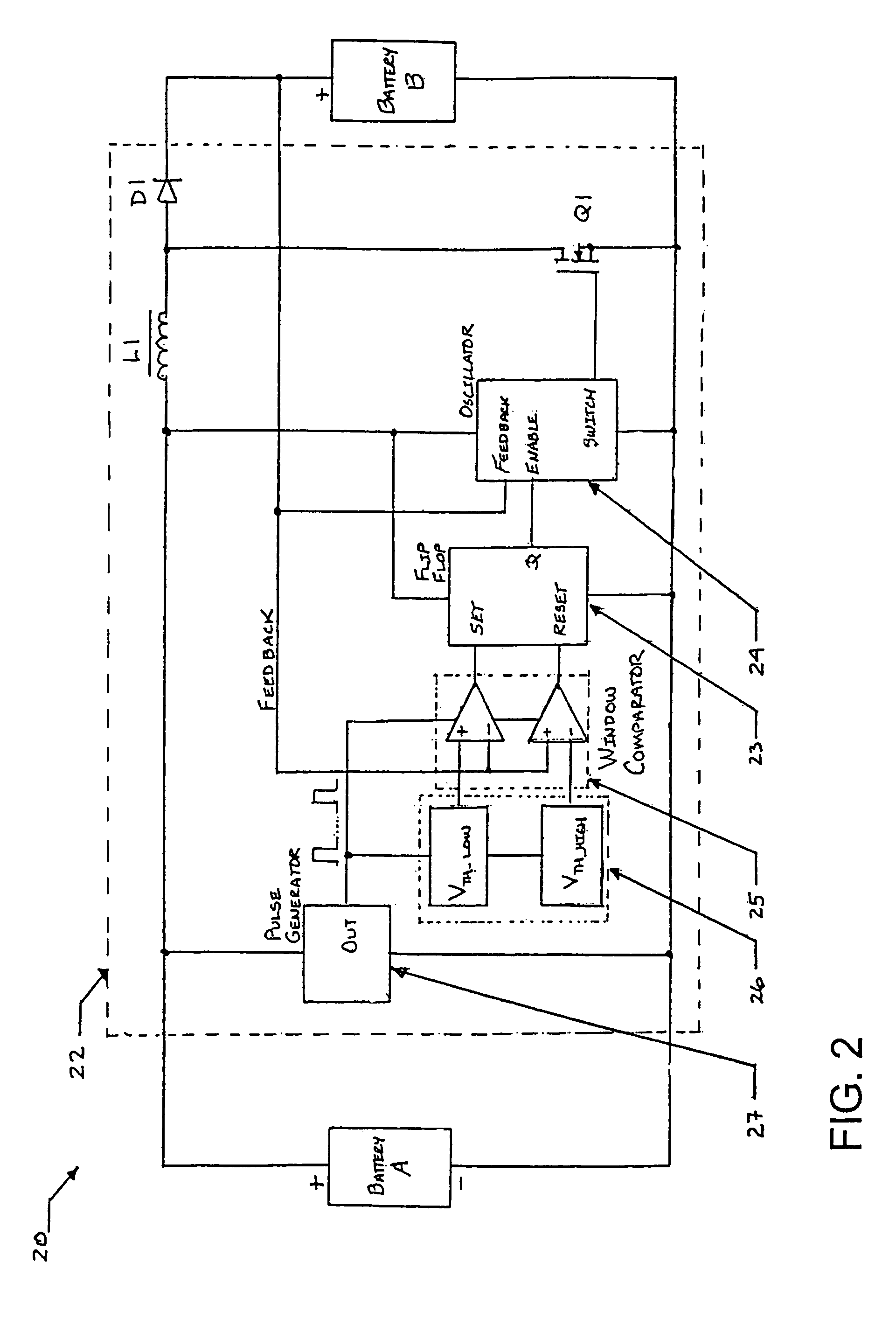
A hybrid battery power source for implantable medical use provides a generally constant low internal resistance during discharge and avoids voltage delays of the type that develop as a result of run down-induced resistance increase in Li / SVO cells. The hybrid battery power source utilizes two batteries or cells, one being a primary cell of relatively high energy density and the other being a secondary cell of relatively low internal resistance that is rechargeable. The primary and secondary cells are connected in a parallel arrangement via a voltage boost / charge control circuit that is powered by the primary cell and adapted to charge the secondary cell while limiting charge / discharge excursions thereof in a manner that optimizes its output for high energy medical device use. The energy storage capacitors of the medical device in which the hybrid battery power source is situated are driven by the secondary cell. The primary cell is used to as an energy source for recharging the secondary cell.
Owner:GENTCORP
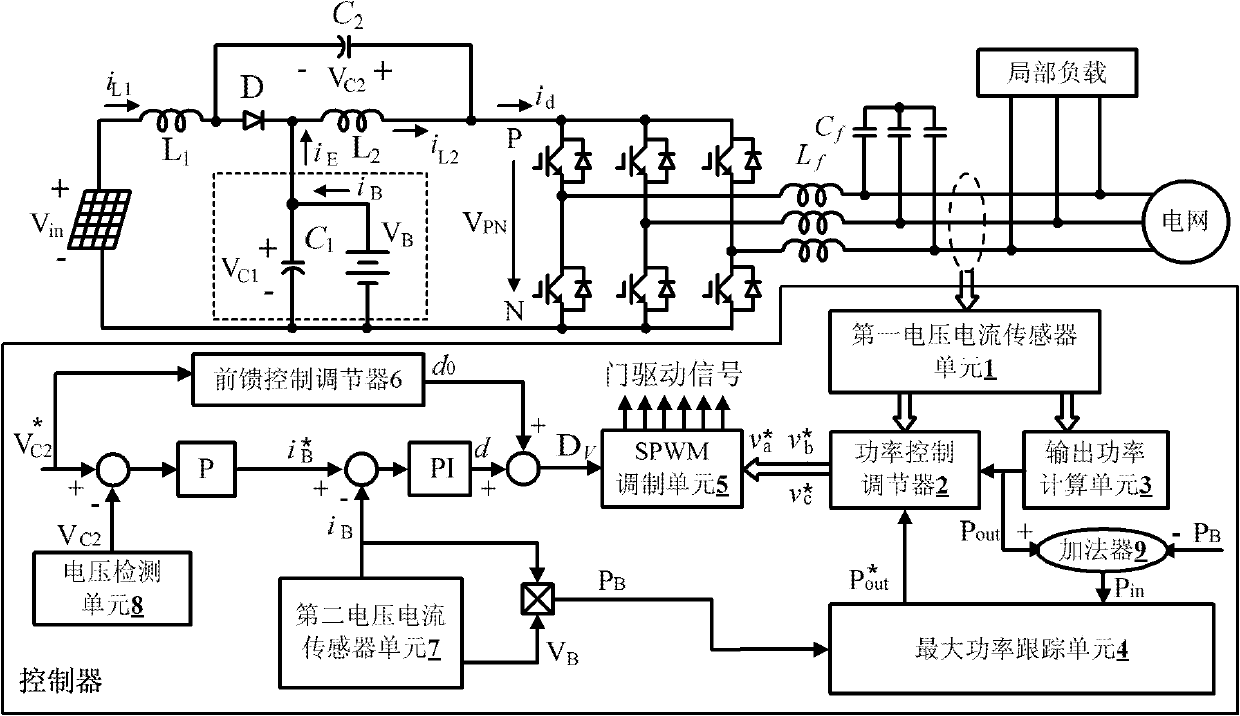
Stored energy type standard-Z source photovoltaic power generation control system and method
InactiveCN102185533AAvoid influenceConstant voltagePhotovoltaicsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsZ-source inverterCapacitor voltage
The invention discloses a stored energy type standard-Z source photovoltaic power generation control system and method. The control system comprises a controller and a stored energy type standard-Z source inverter, wherein the controller comprises a capacitor voltage outer ring and a stored energy battery current inner ring and is used for regulating the direct-connection duty ratio of the inverter, thus the voltage of a DC (direct-current) bus can be constant, although the photovoltaic cell voltage is changed in a wide range; and the output power of the inverter is controlled by a power ring, and the output power of photovoltaic cells and the inverter is controlled so as to carry out charge-discharge management on stored energy batteries, thus realizing maximum power tracking. According to the invention, single-stage power transform is used to complete boosting, reduction voltage, inversion and energy storage, so that a simpler structure is used to realize minimum inverter capacity, thus ensuring the voltage of the DC bus to be constant and a power grid to obtain stable power, thereby maximally collecting solar energy and improving generating efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
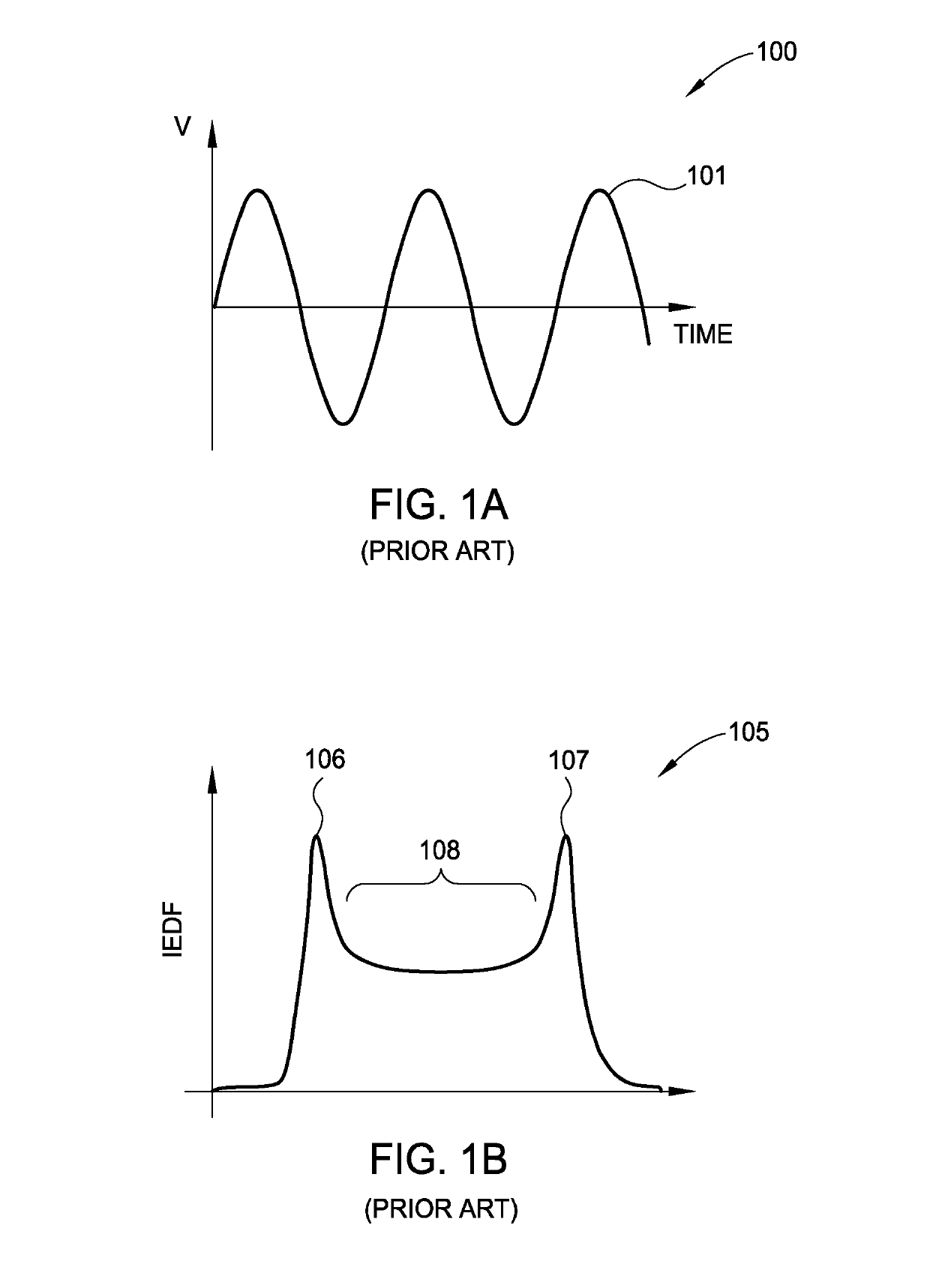
Method of controlling ion energy distribution using a pulse generator with a current-return output stage
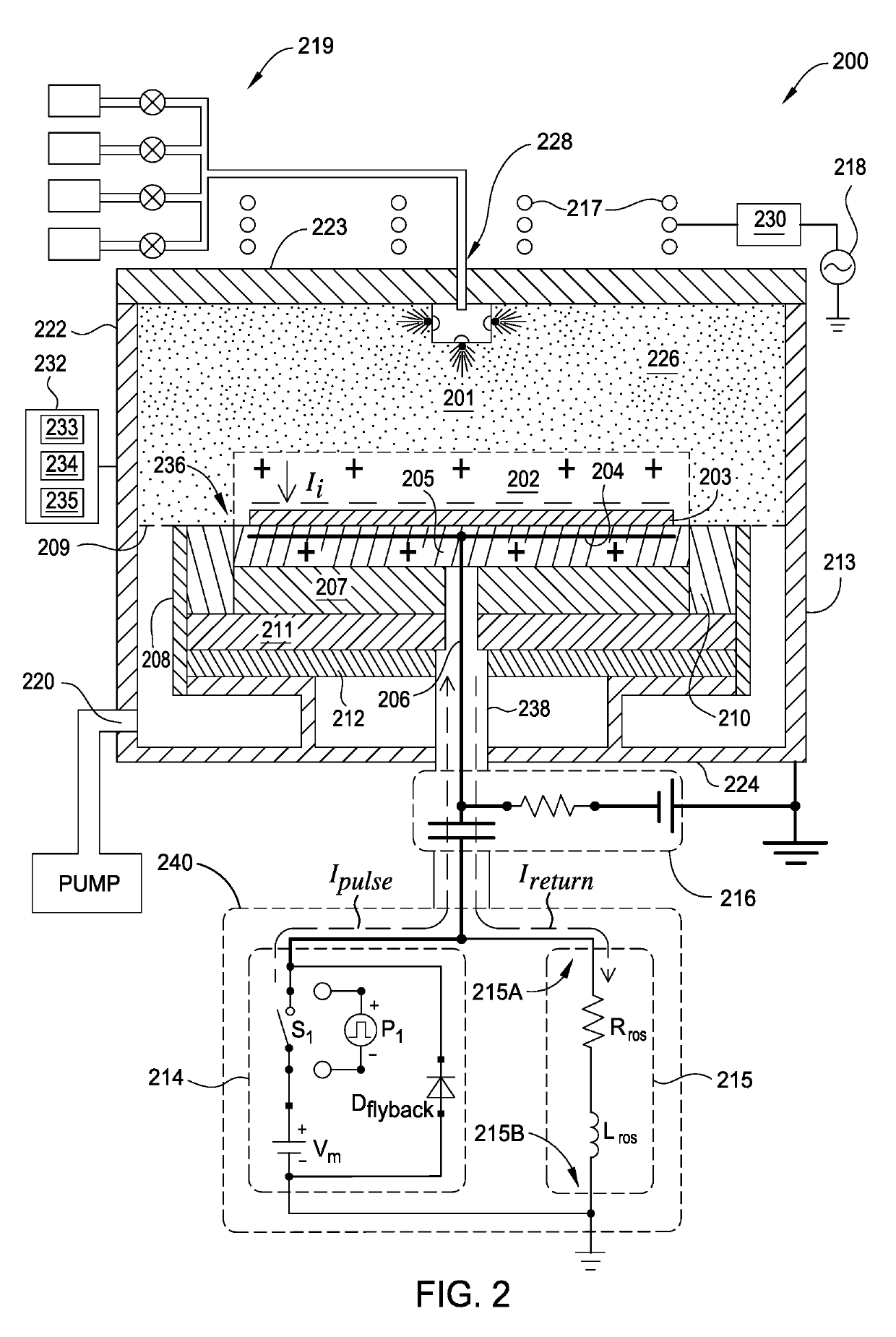
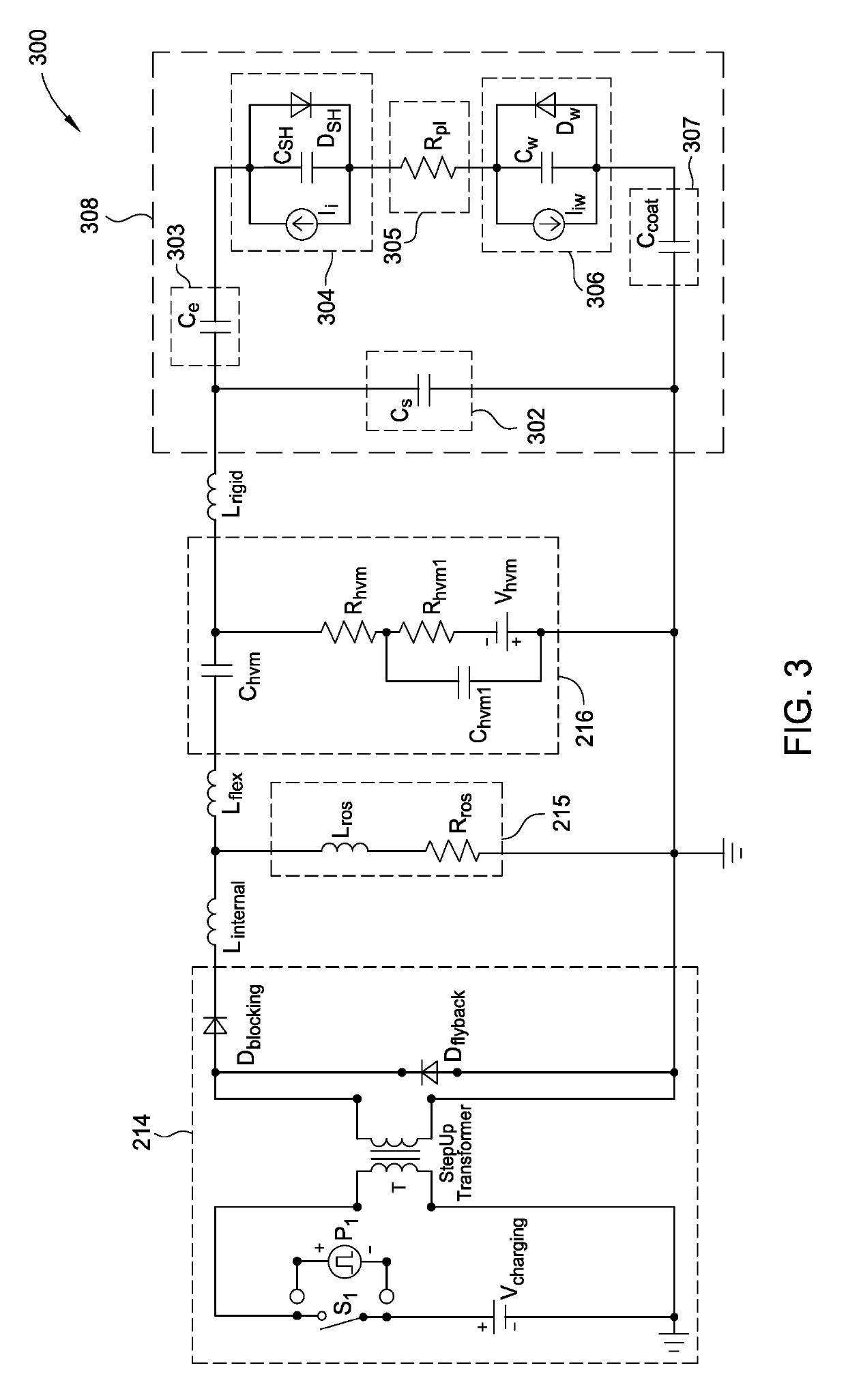
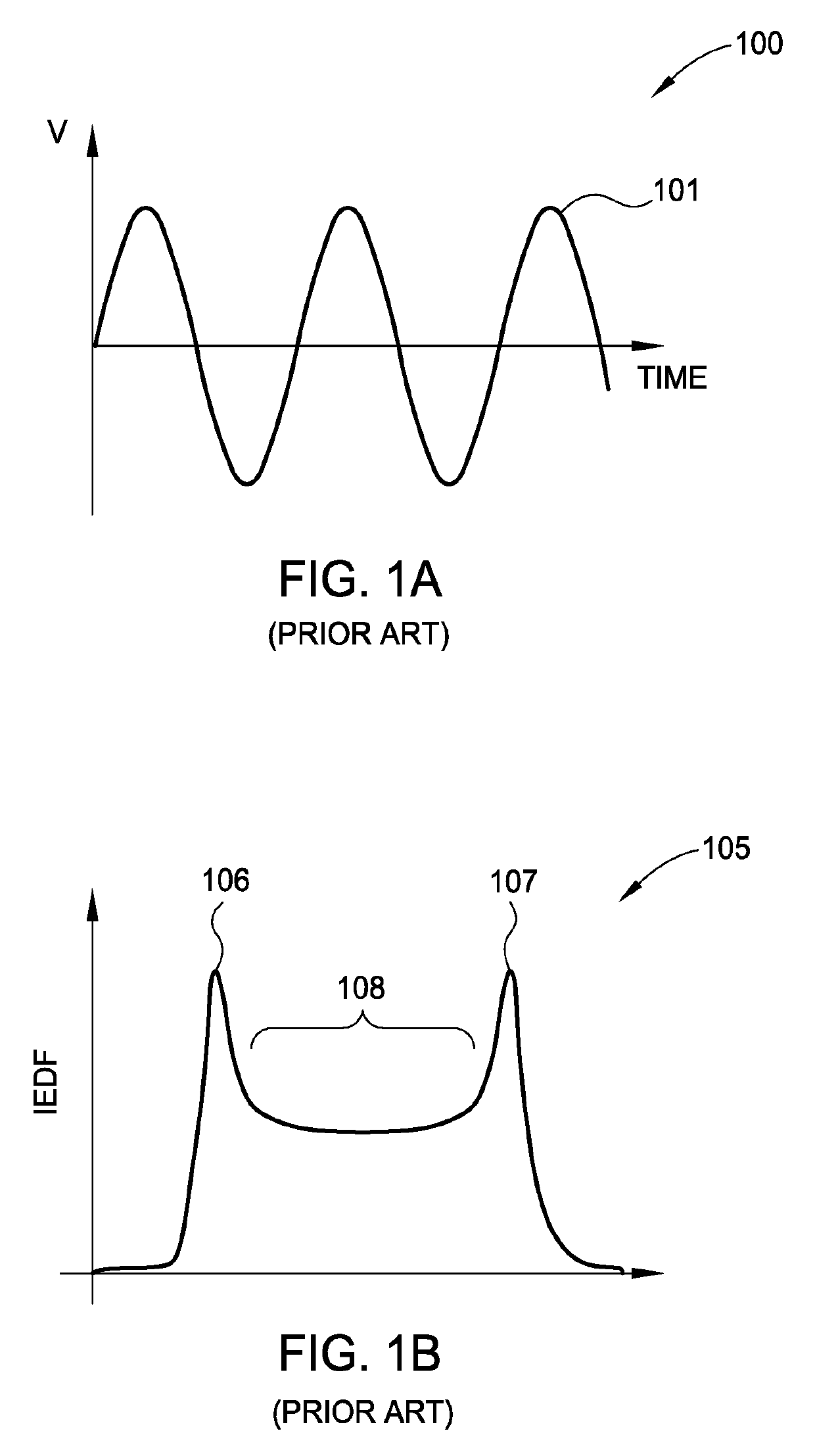
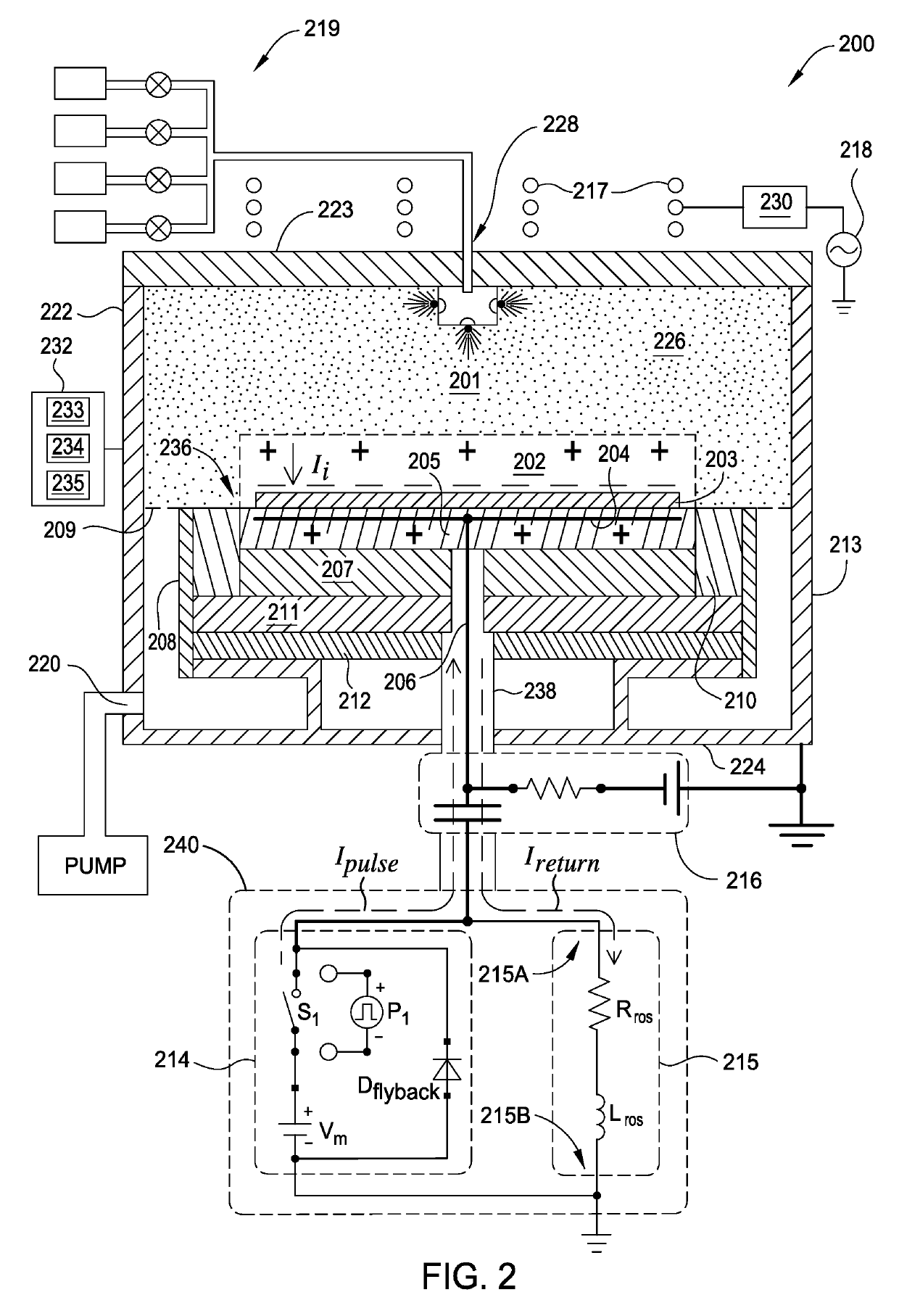
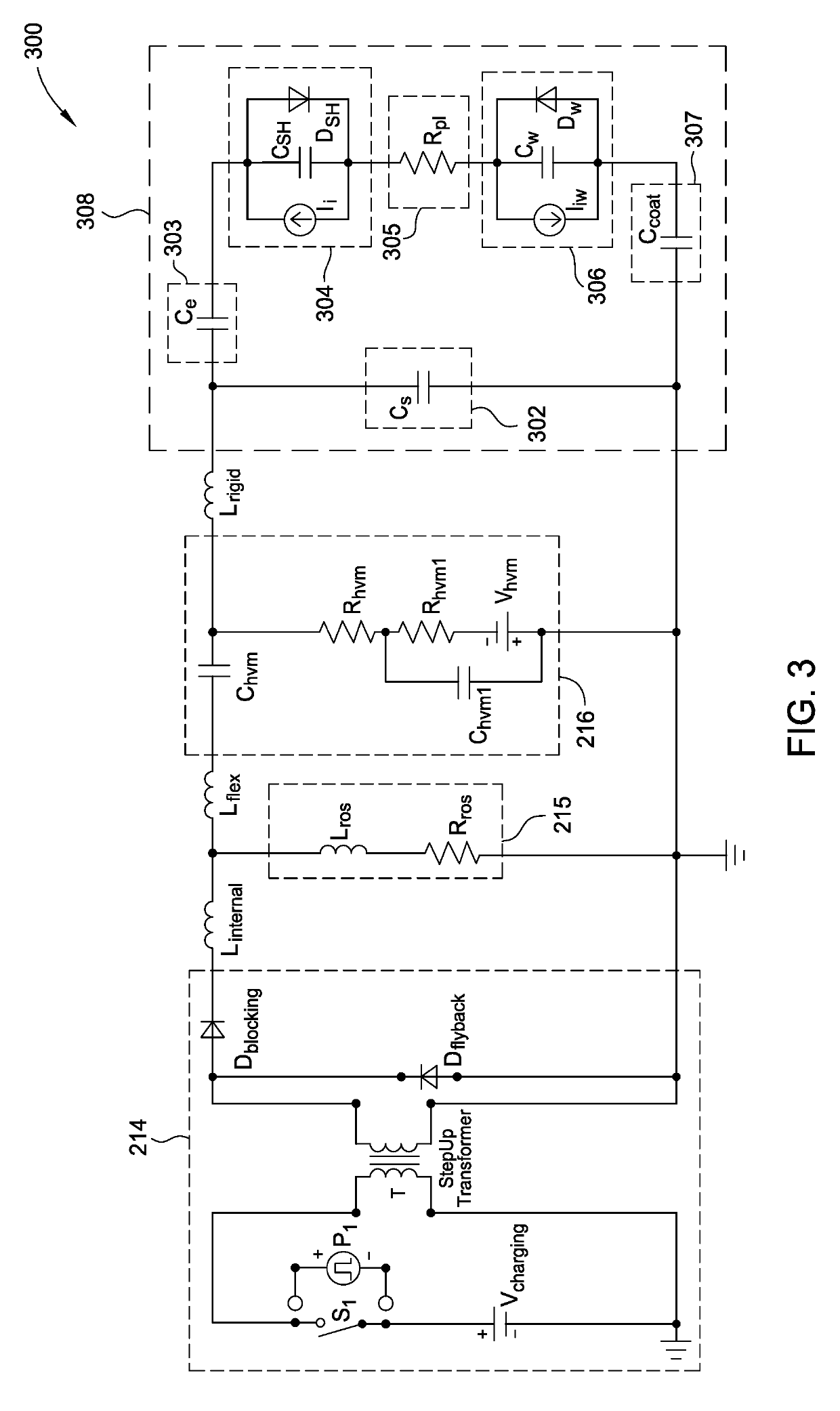
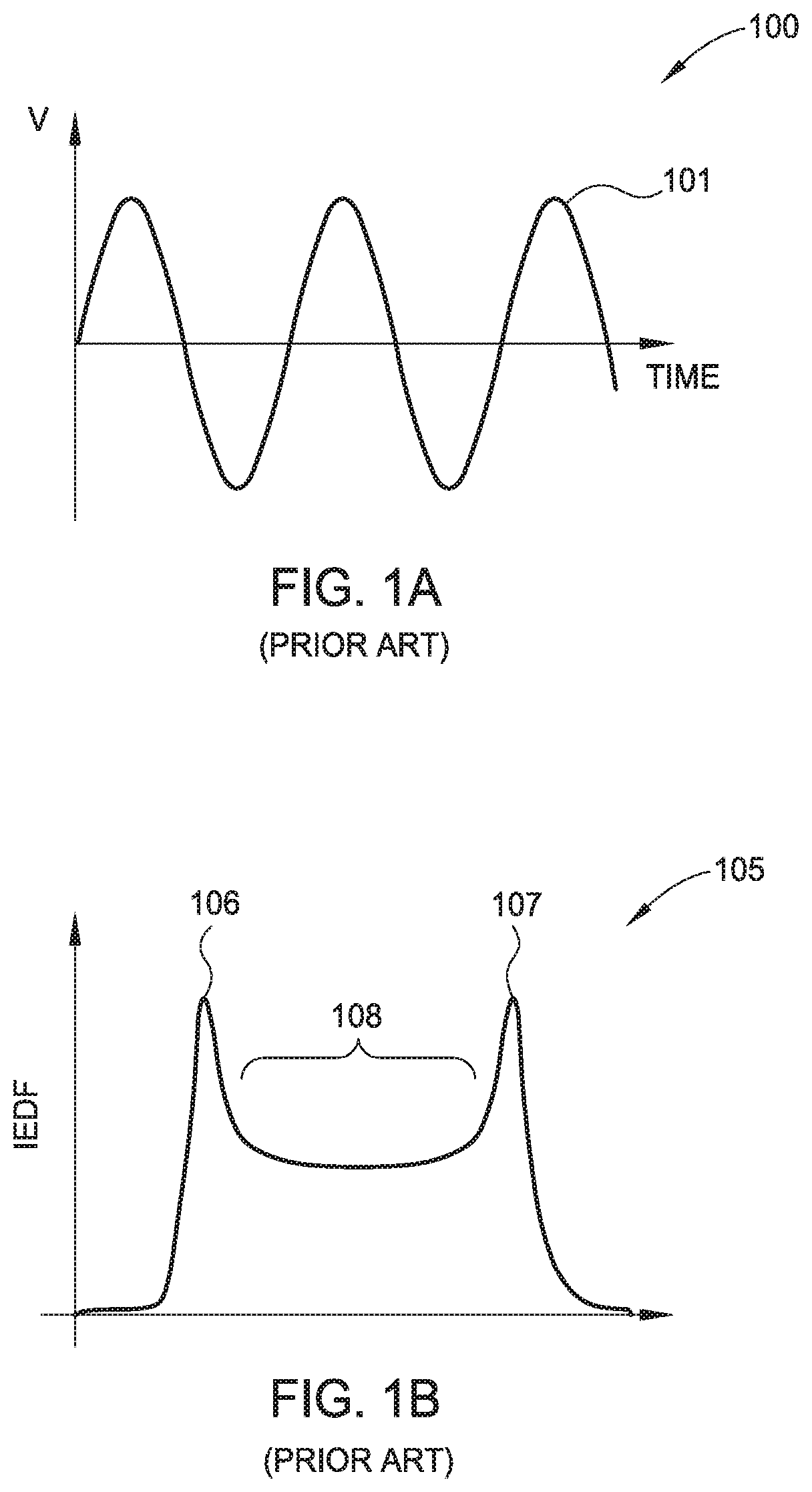
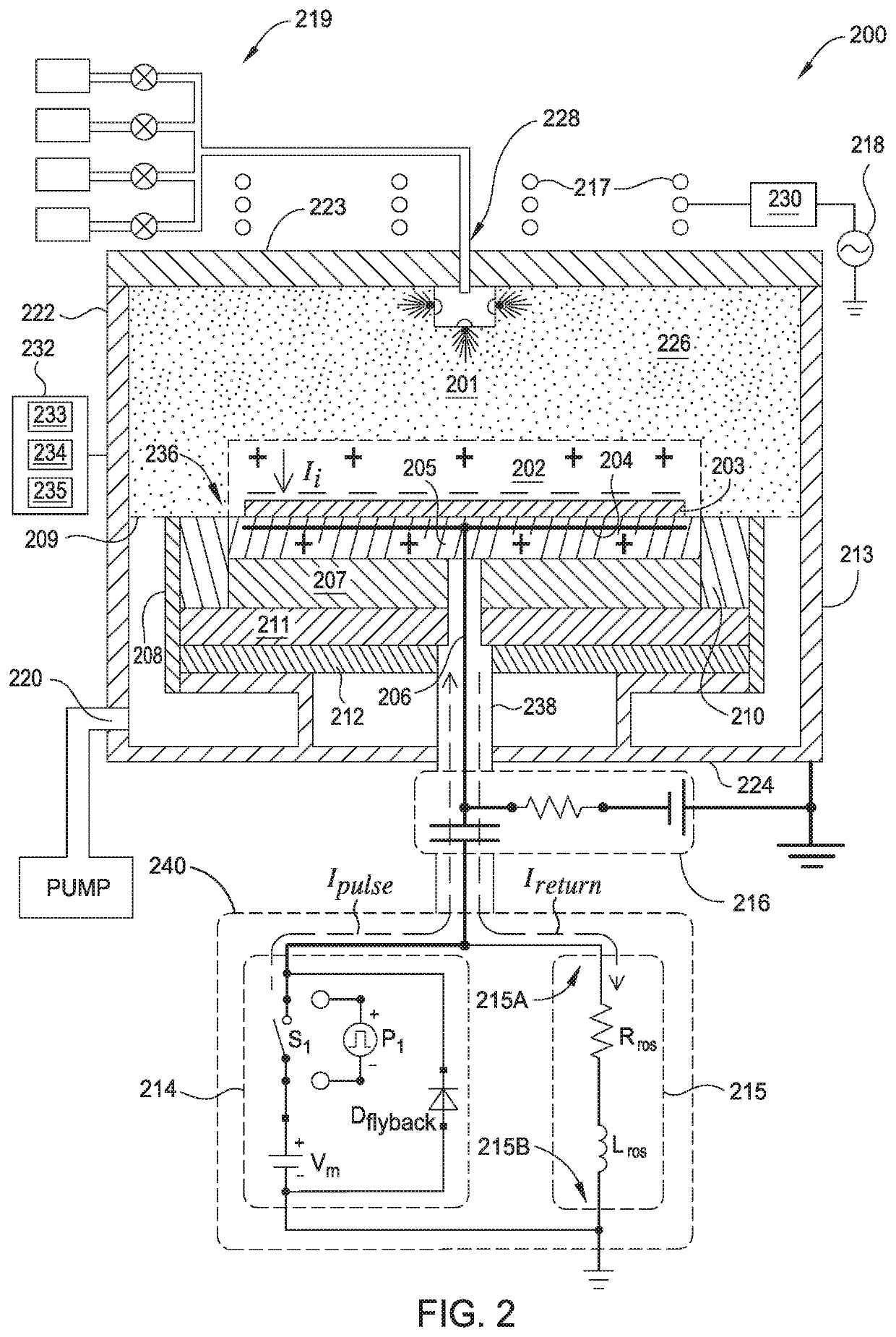
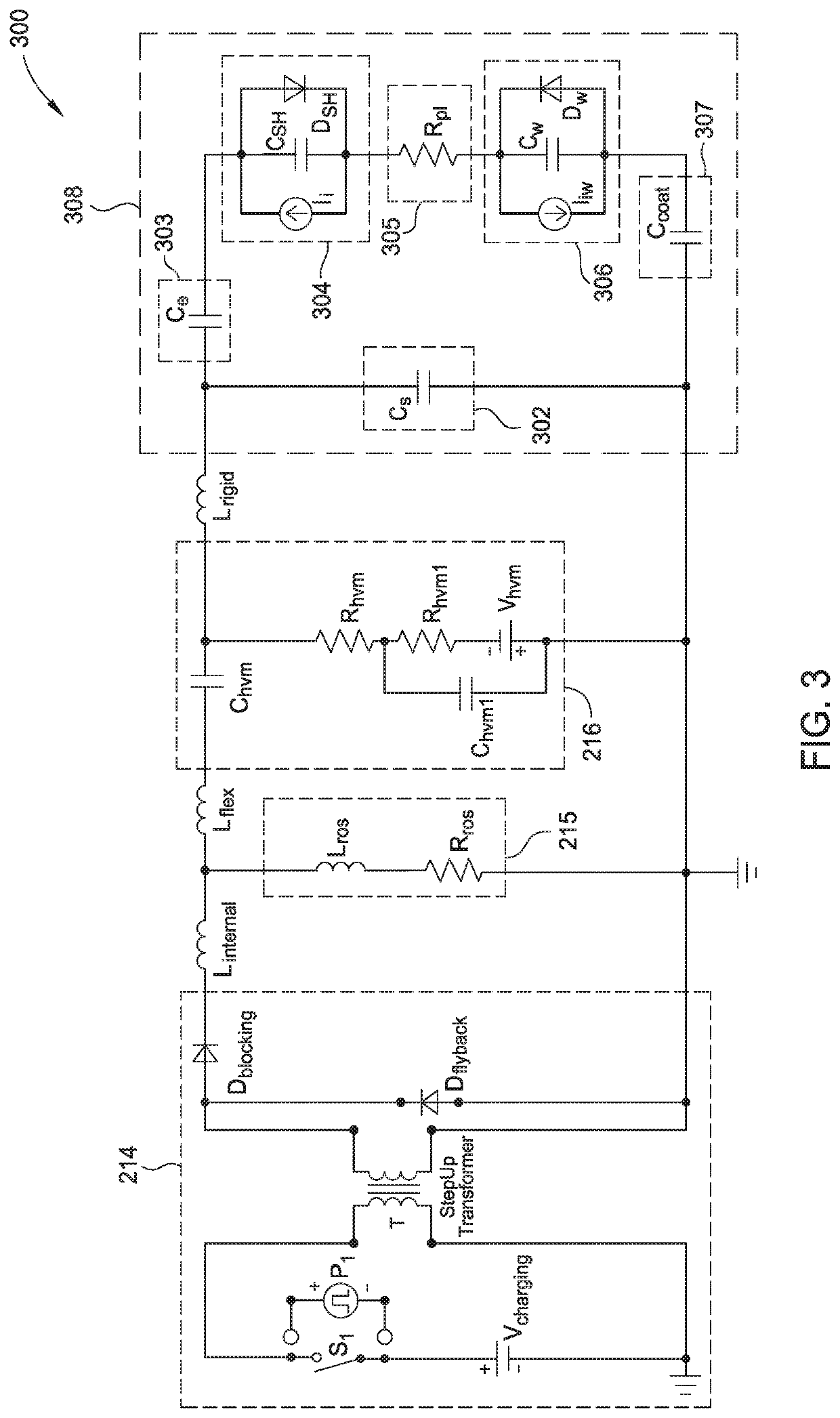
ActiveUS10448494B1Constant voltageElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingPower flowEngineering
Embodiments of this disclosure describe an electrode biasing scheme that enables maintaining a nearly constant sheath voltage and thus creating a mono-energetic IEDF at the surface of the substrate that consequently enables a precise control over the shape of IEDF and the profile of the features formed in the surface of the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Solid-state image capturing apparatus and electronic information equipment
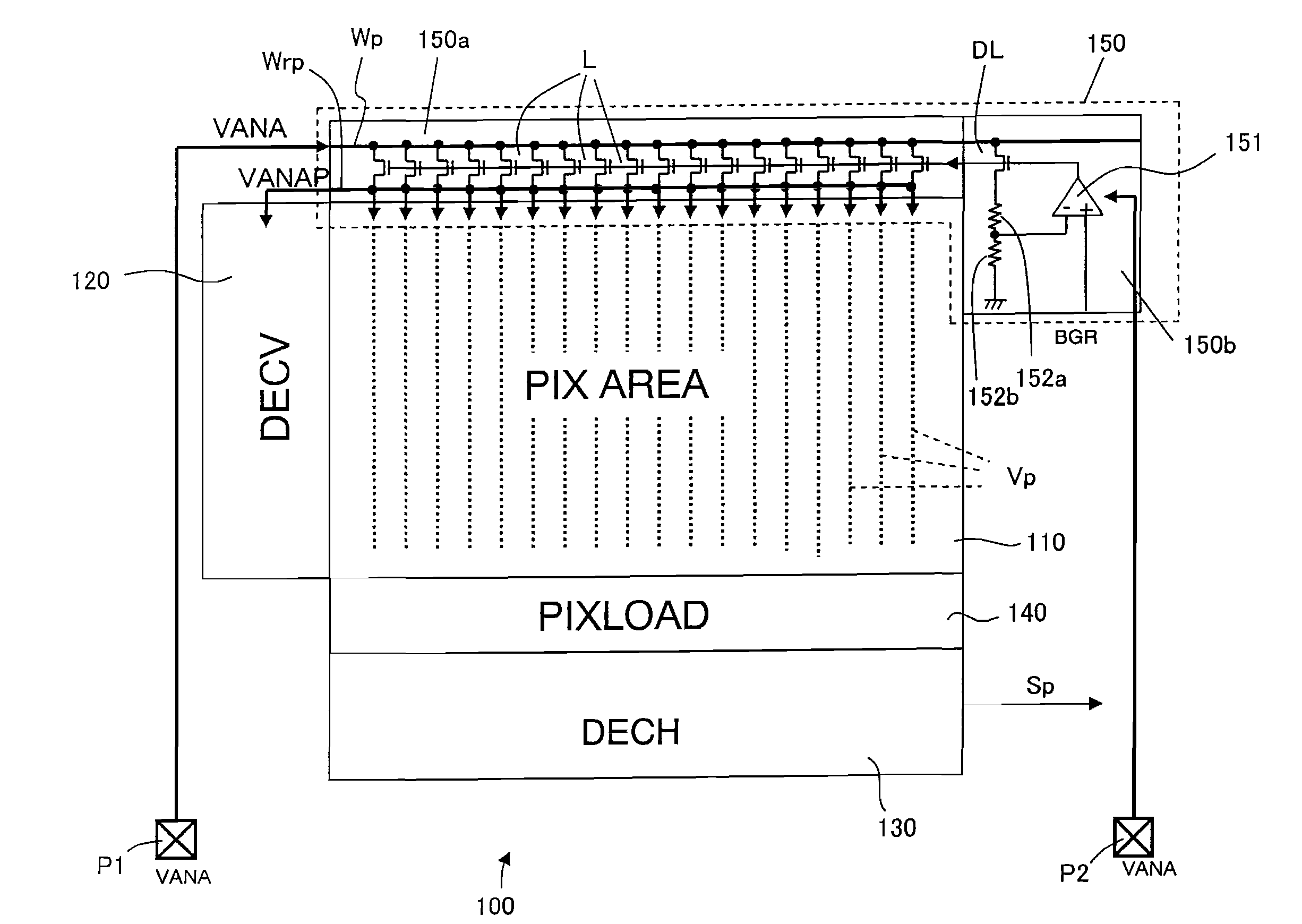
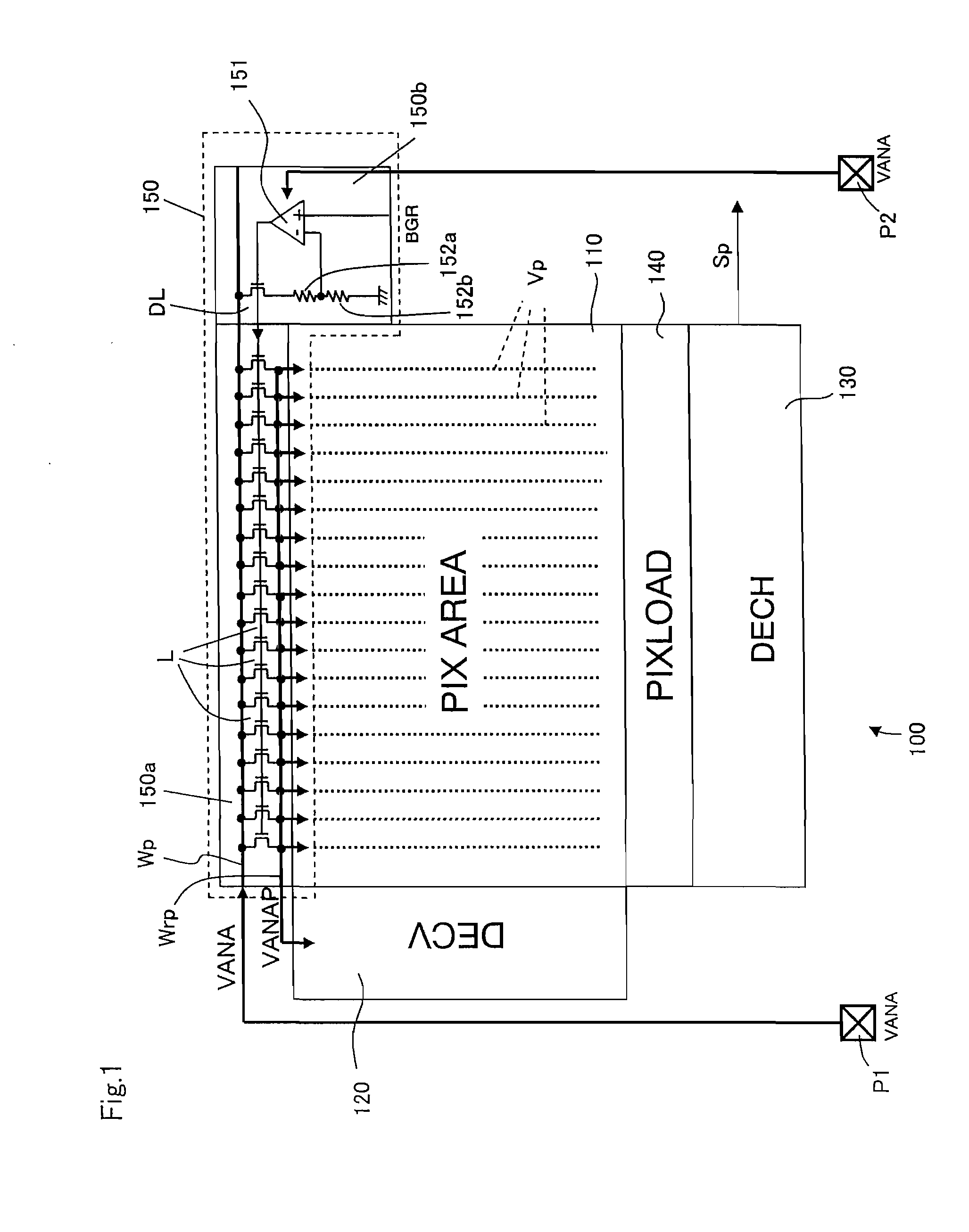
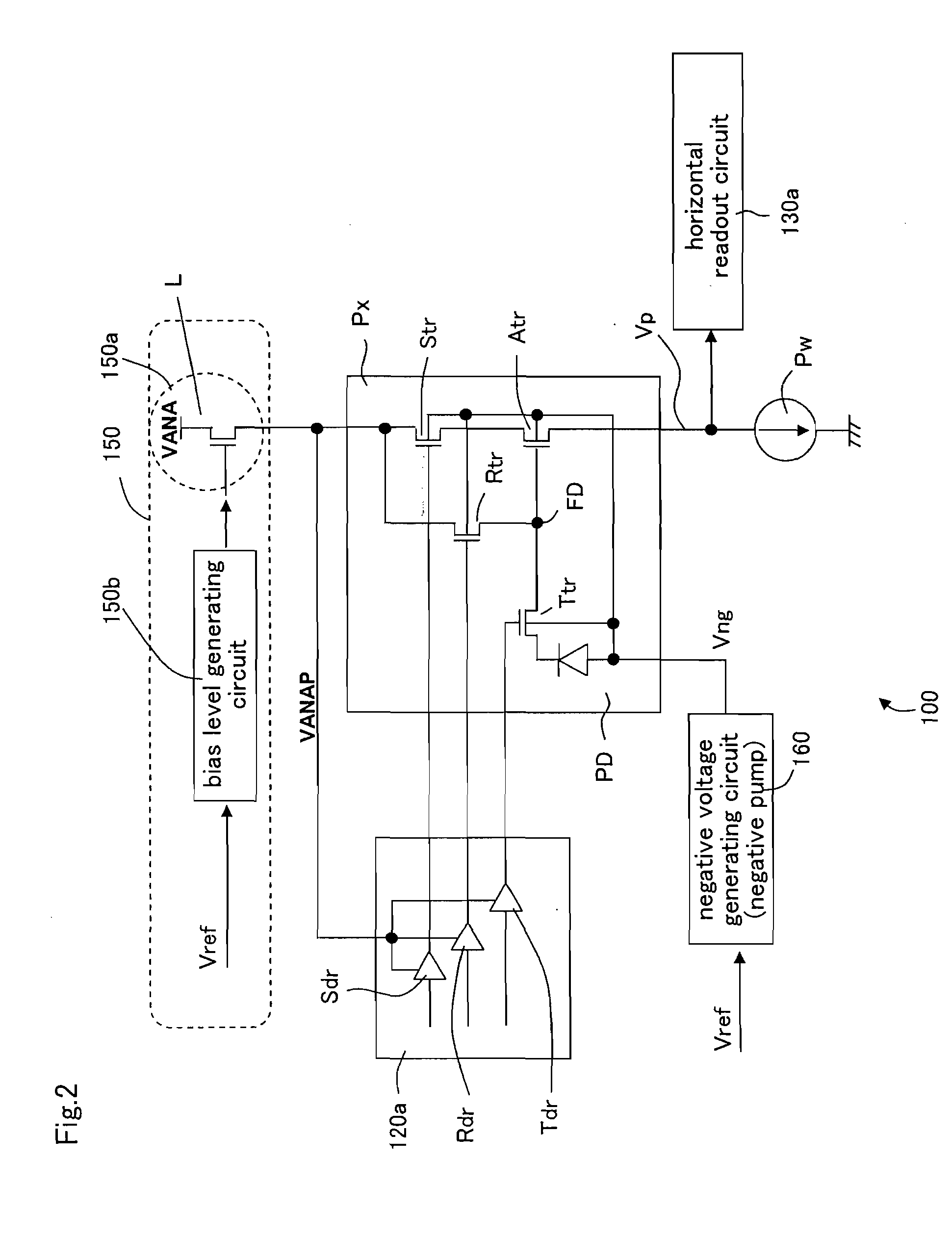
ActiveUS20090251576A1Avoid noise impactConstant voltageTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringElectronic information
A solid-state image capturing apparatus according to the present invention includes: a pixel array in which a plurality of pixels are arranged; a driving circuit for driving each pixel of the pixel array; and a power supply circuit for stepping down an external source voltage supplied from an external power source to generate a pixel source voltage to be supplied to each pixel of the pixel array, where the power supply circuit includes a driver transistor for generating a pixel source voltage from the external source voltage and the driver transistor is operative in a saturated state.
Owner:SHARP KK
Pixel of an organic light emitting diode display device and organic light emitting diode display device
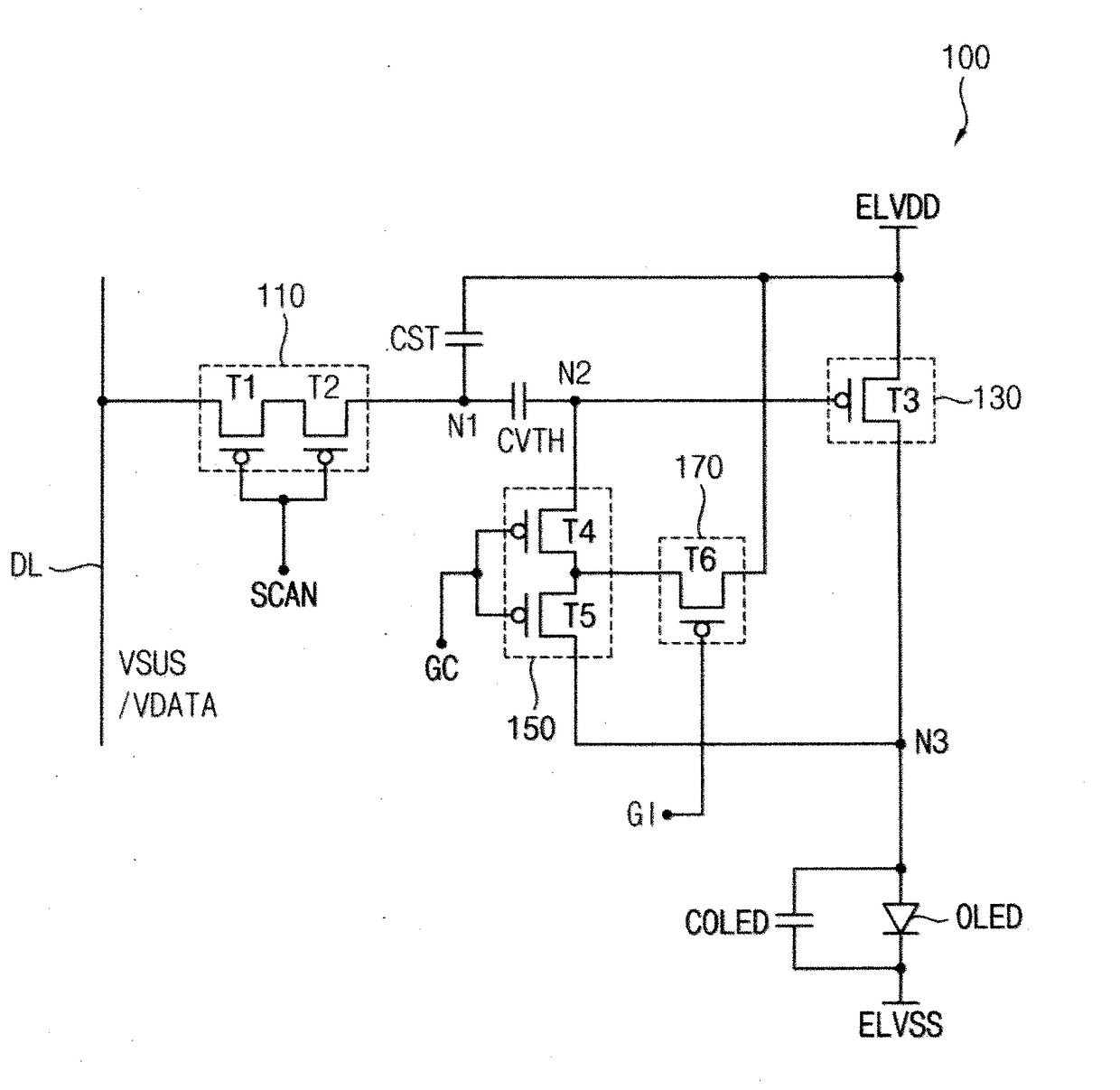
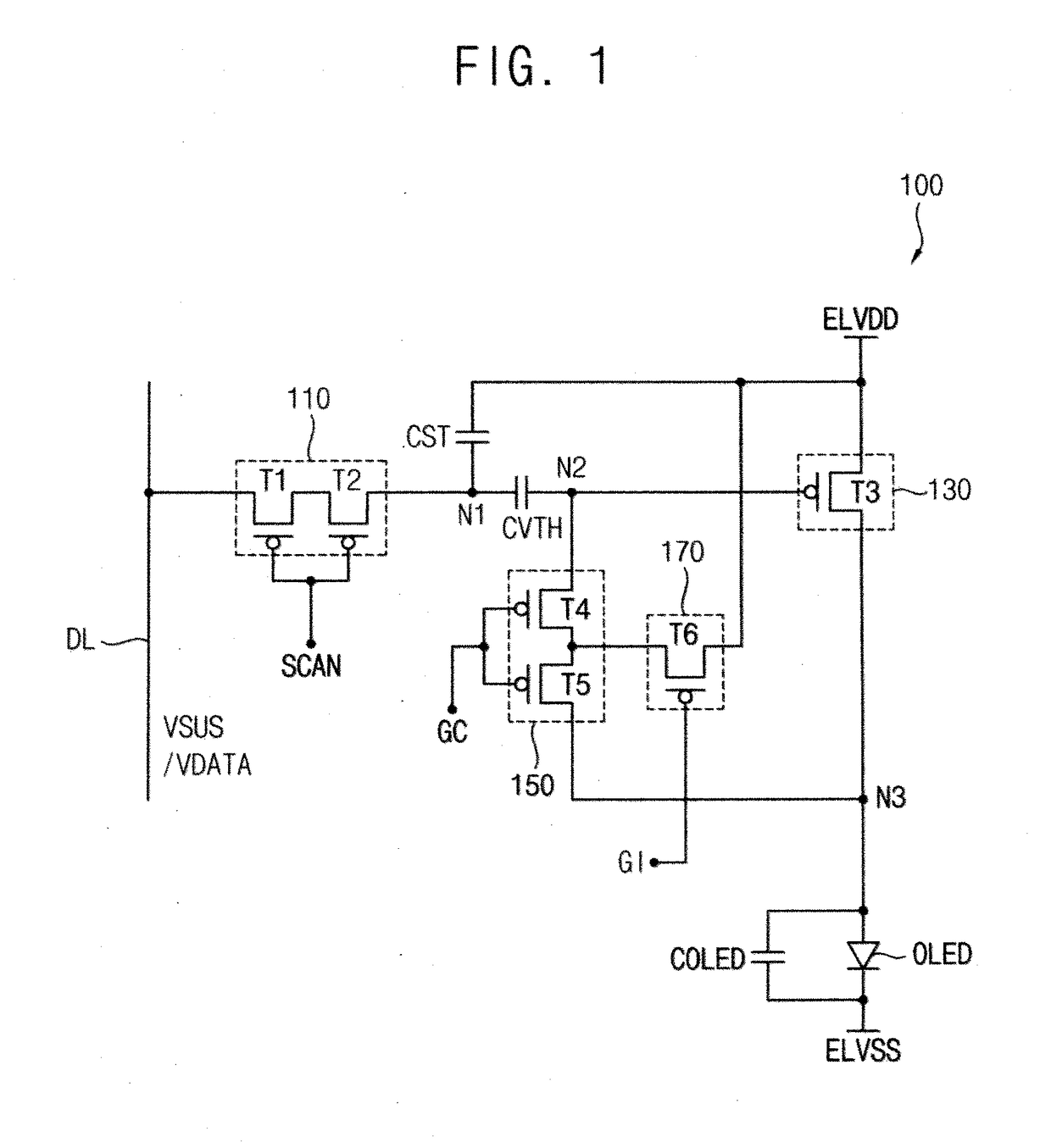
ActiveUS20170124954A1Relieve pressureAccurate compensationStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesControl signalDisplay device
A pixel of an organic light emitting diode display device includes a scan transistor configured to connect a data line to a first node in response to a scan signal, a storage capacitor connected between the first node and a first power supply voltage, a compensation capacitor connected between the first node and a second node, a driving transistor having a gate connected to the second node, a source connected to the first power supply voltage, and a drain connected to a third node, a compensation transistor configured to connect the second node to the third node in response to a compensation control signal, an organic light emitting diode connected between the third node and a second power supply voltage, and an initialization transistor configured to transfer an initialization voltage in response to an initialization control signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
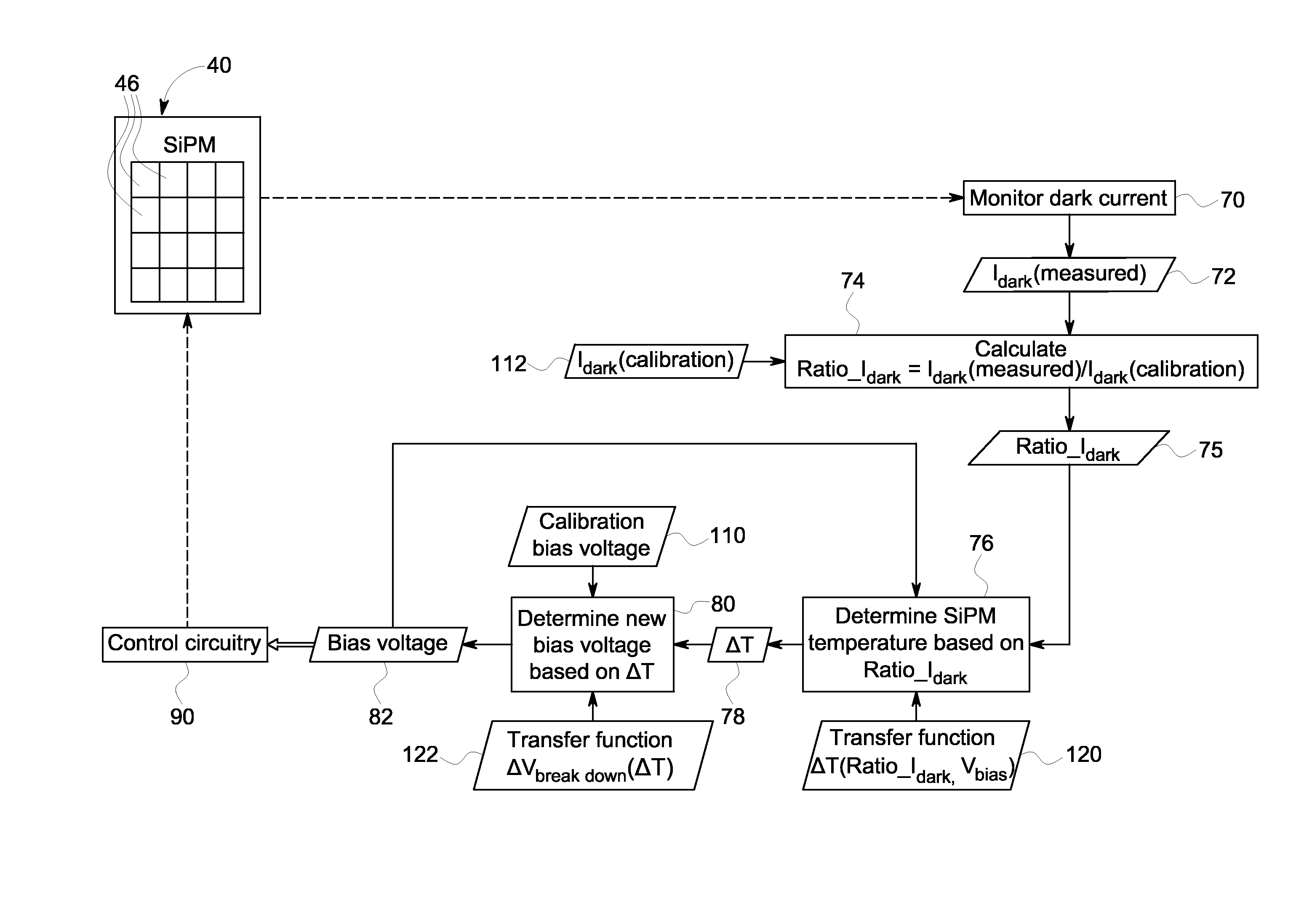
System and method for compensating temperature gain variation in radiation detectors
InactiveUS20150177394A1Constant voltageVoltage be maintainSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhysicsRadiation
In accordance with the present approach, a dark current is measured for one or more detector elements and used to determine a gain or gain compensation for the respective detector elements. In certain embodiments, the dark current is used to determine a temperature for the respective detector element and the temperature is used to determine the gain or gain compensation. In other embodiments, the dark current is used to calculate the gain or gain compensation for the respective detector element without calculating an intermediate temperature value, such as via the use of a transfer function.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
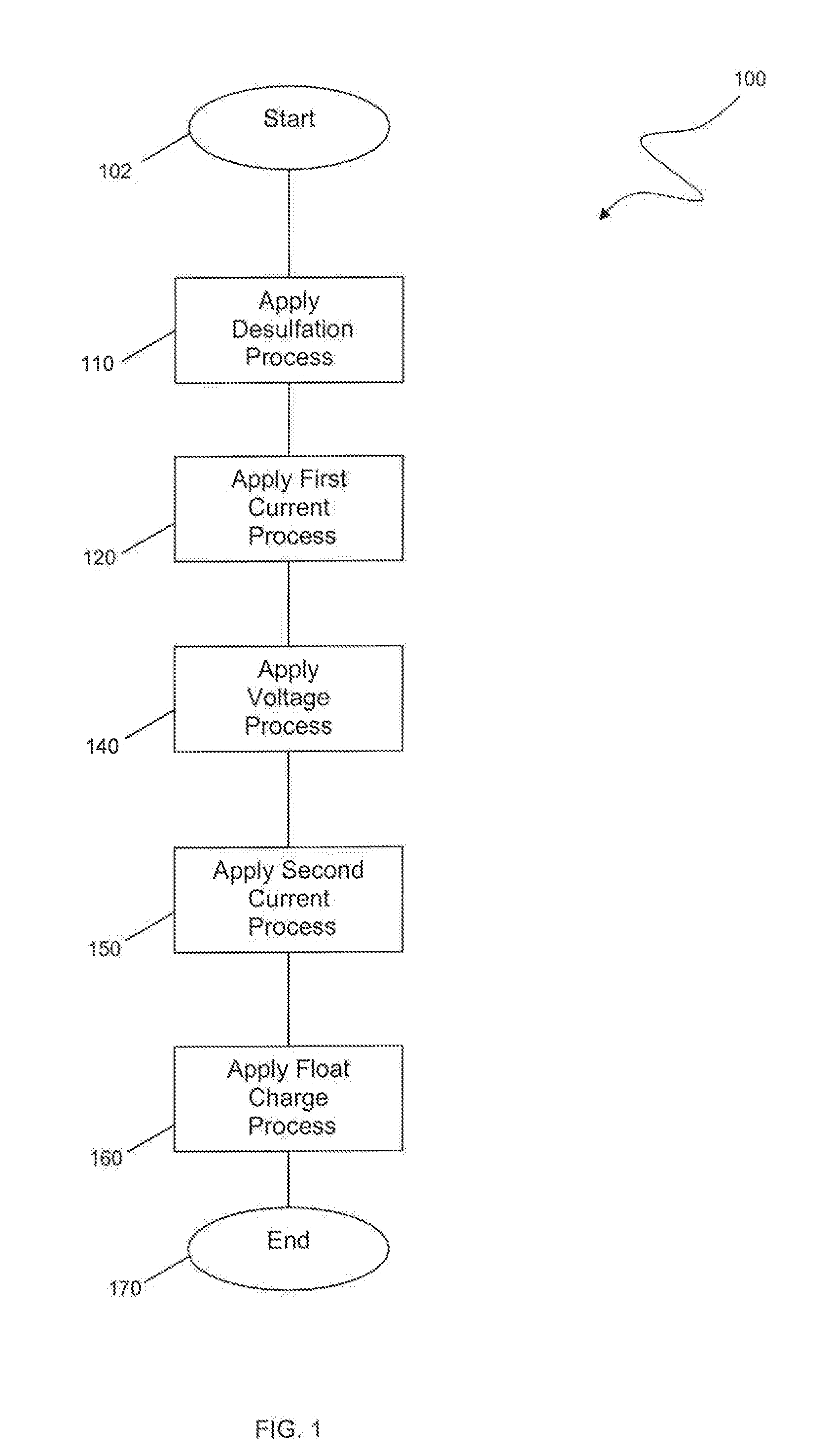
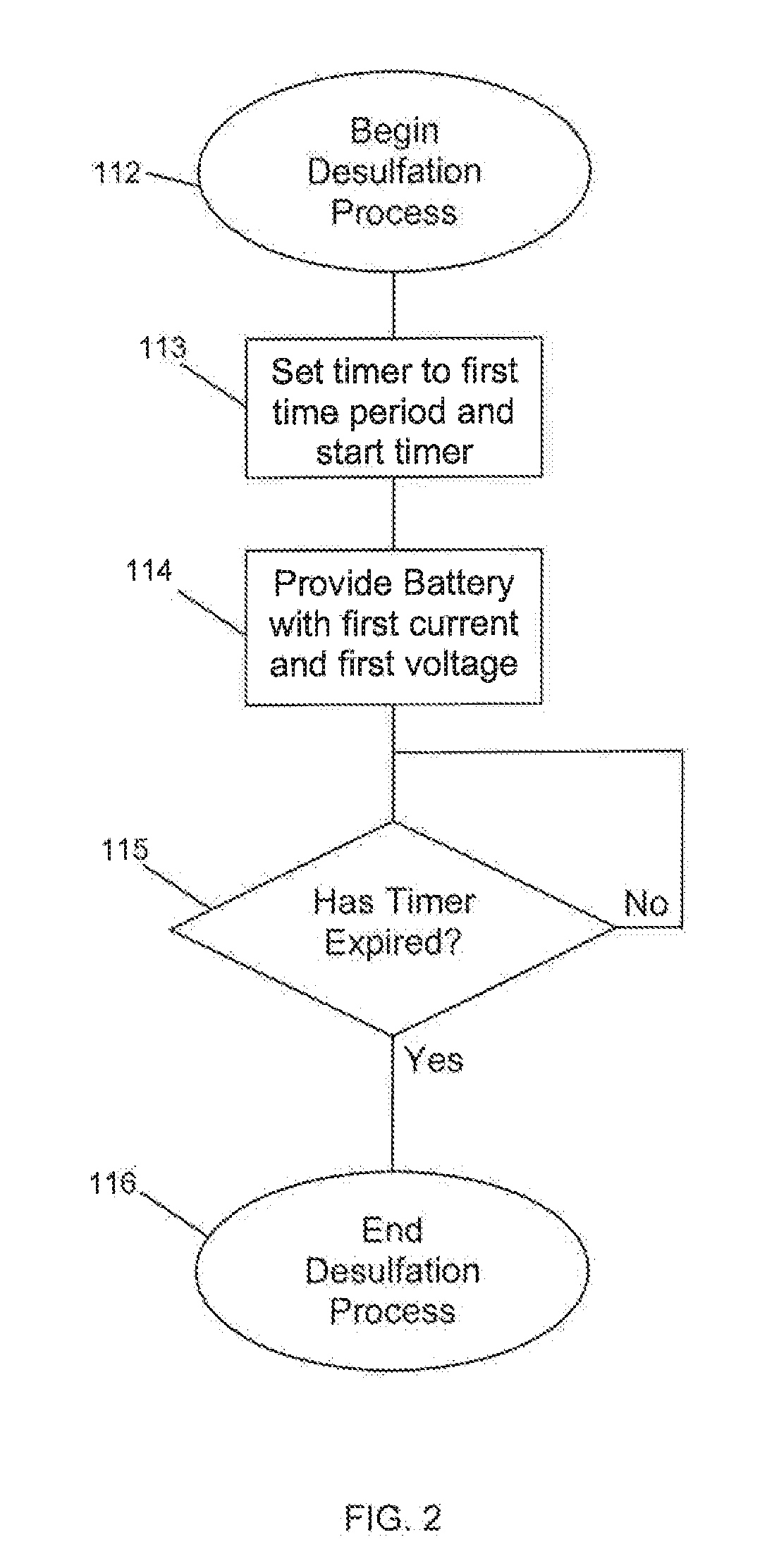
Battery charging device and method
ActiveUS20110057624A1Constant voltageElectric powerCharge maintainance charging/dischargingFloating chargeBattery charge
An improved battery charging method is usable by a battery charger to charge a battery. The charging method may include an optional desulfation process, a first constant current process, a constant voltage process, a second constant current process and a float charge process. The charging method preferably improves various charge and usage characteristics of the battery through a single or continued use of the battery charger utilizing the charging method.
Owner:CPS TECH HLDG LLC
Floating gate memory device with interpoly charge trapping structure
ActiveUS8068370B2Reduce distractionsImprove data retentionTransistorSolid-state devicesPower flowElectrical conductor
A charge trapping floating gate is described with asymmetric tunneling barriers. The memory cell includes a source region and a drain region separated by a channel region. A first tunneling barrier structure is disposed above the channel region. A floating gate is disposed above the first tunneling barrier structure covering the channel region. A second tunneling barrier is disposed above the floating gate. A dielectric charge trapping structure disposed above the second tunneling barrier and a blocking dielectric structure is disposed above the charge trapping structure. A top conductive layer disposed above the top dielectric structure acts as a gate. The second tunneling barrier is a more efficient conductor of tunneling current, under bias conditions applied for programming and erasing the memory cell, than the first tunneling barrier structure.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
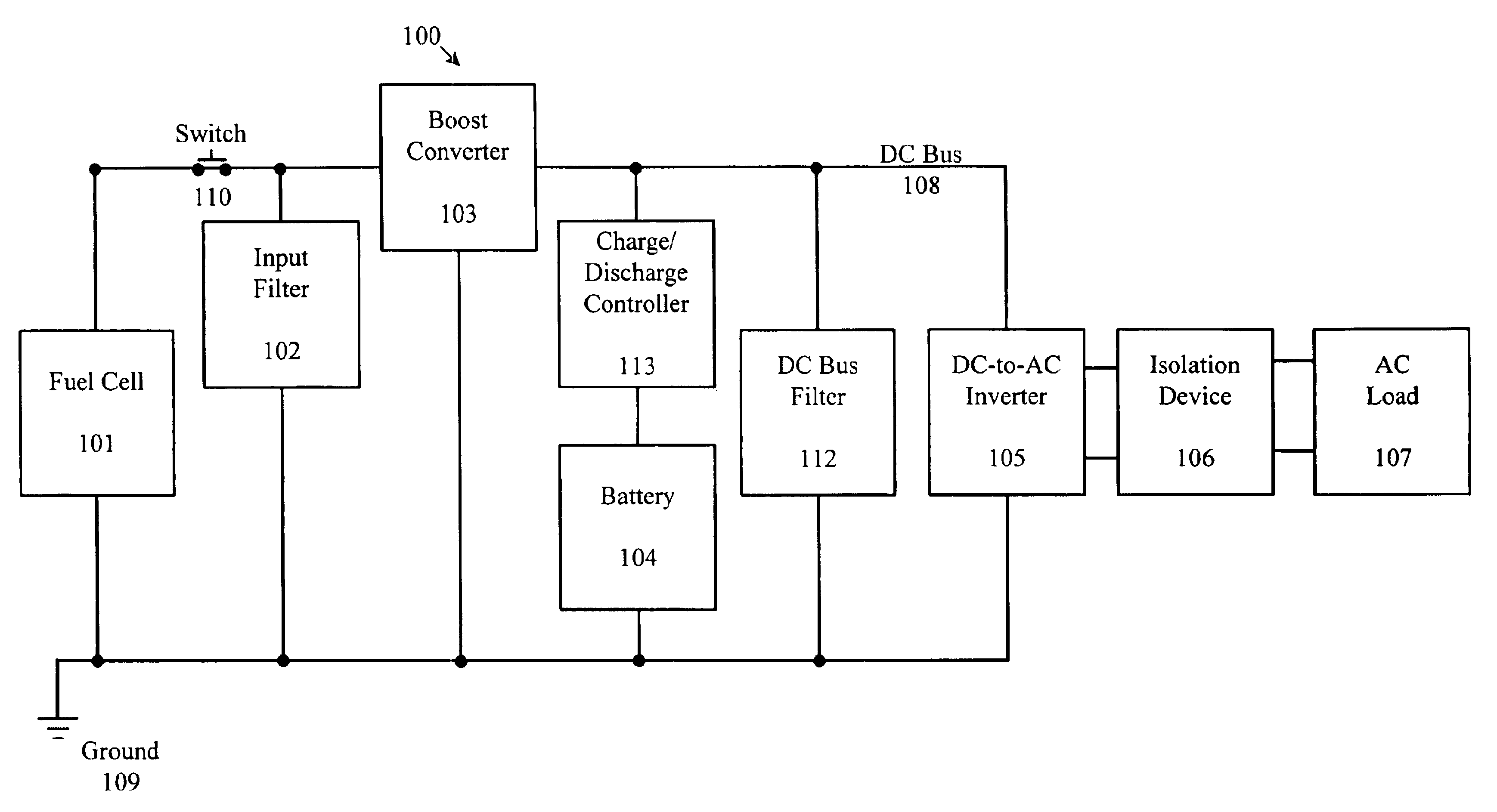
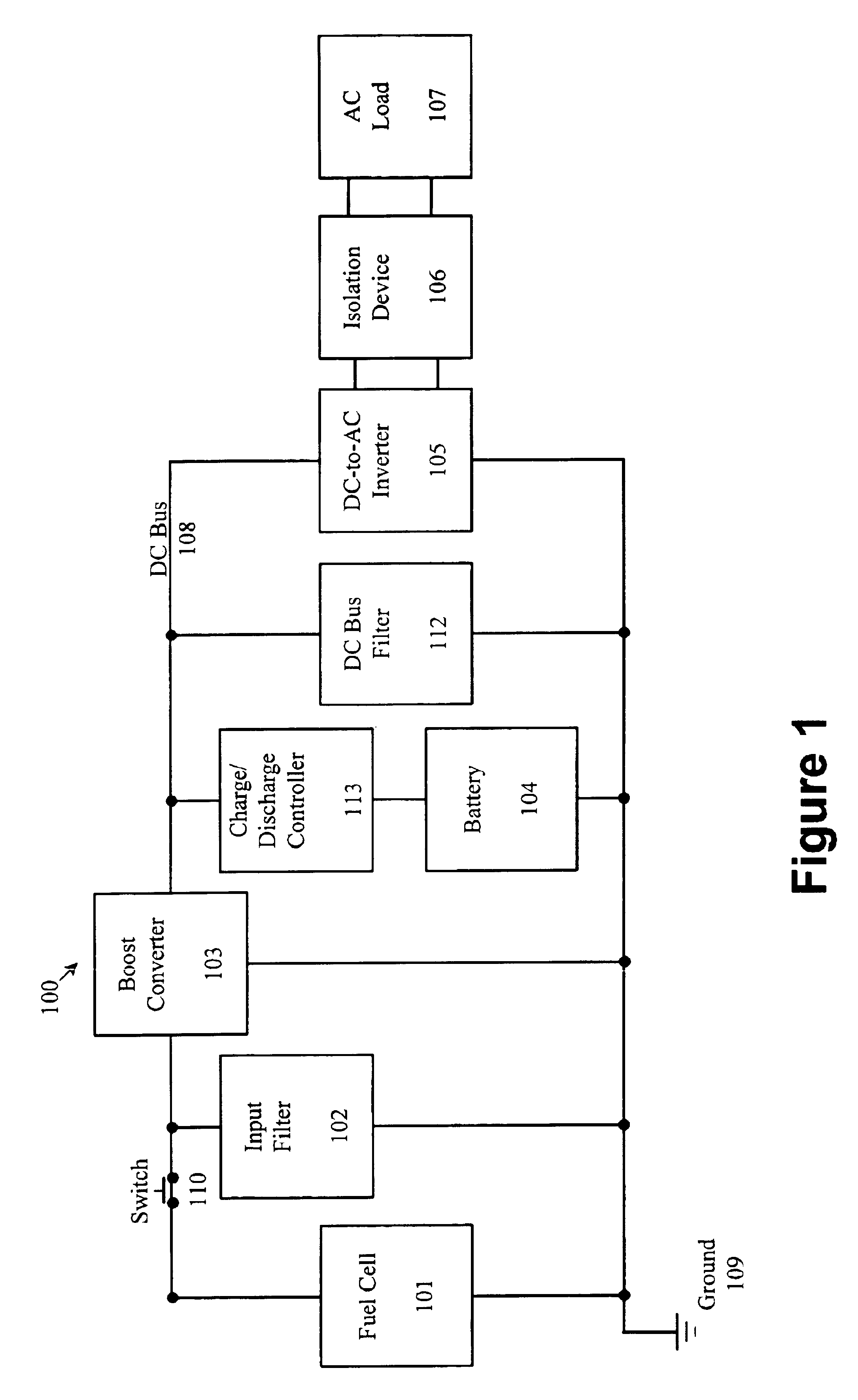
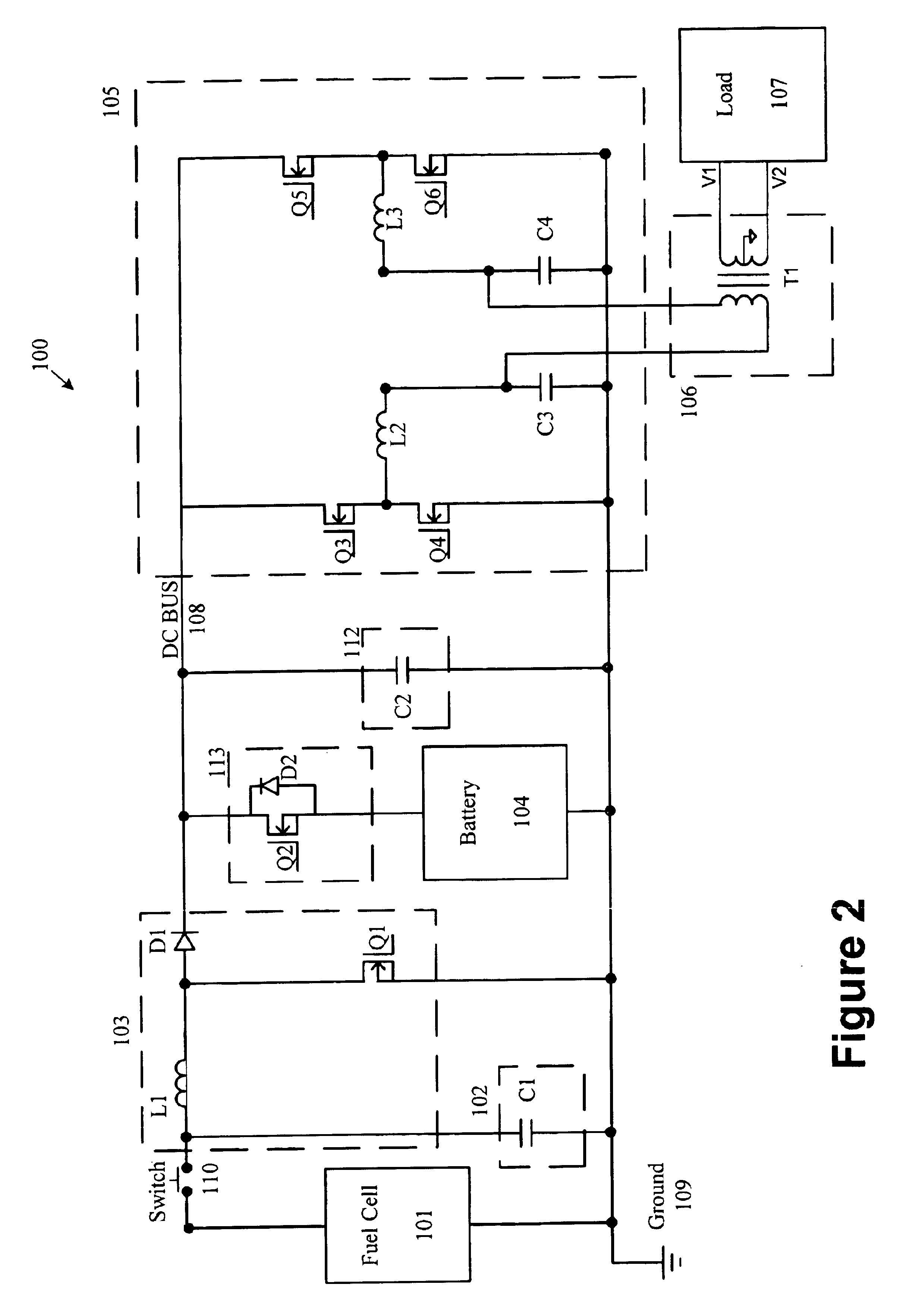
Fuel cell inverter
InactiveUS6930897B2Constant DC voltageAvoid flowDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsDC-BUSElectricity
The invention is directed to a method, system and device for converting direct current (DC) electrical voltage from a fuel cell to an alternating current (AC) voltage. The inventive method regulates power drawn from the fuel cell and from a battery to maintain a substantially constant DC voltage across a DC bus, and inverts the DC voltage from the DC bus to the AC voltage. The method may further electrically isolate the fuel cell from the load. Also, the inventive method may prevent current from flowing to the fuel cell. The inventive method may also provide a charging current to the battery.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Scavenging metal stack for a high-k gate dielectric
ActiveUS7989902B2Constant voltageReduce thicknessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricEquivalent oxide thickness
A stack of a high-k gate dielectric and a metal gate structure includes a lower metal layer, a scavenging metal layer, and an upper metal layer. The scavenging metal layer meets the following two criteria 1) a metal (M) for which the Gibbs free energy change of the reaction Si+2 / y MxOy→2x / y M+SiO2 is positive 2) a metal that has a more negative Gibbs free energy per oxygen atom for formation of oxide than the material of the lower metal layer and the material of the upper metal layer. The scavenging metal layer meeting these criteria captures oxygen atoms as the oxygen atoms diffuse through the gate electrode toward the high-k gate dielectric. In addition, the scavenging metal layer remotely reduces the thickness of a silicon oxide interfacial layer underneath the high-k dielectric. As a result, the equivalent oxide thickness (EOT) of the total gate dielectric is reduced and the field effect transistor maintains a constant threshold voltage even after high temperature processes during CMOS integration.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
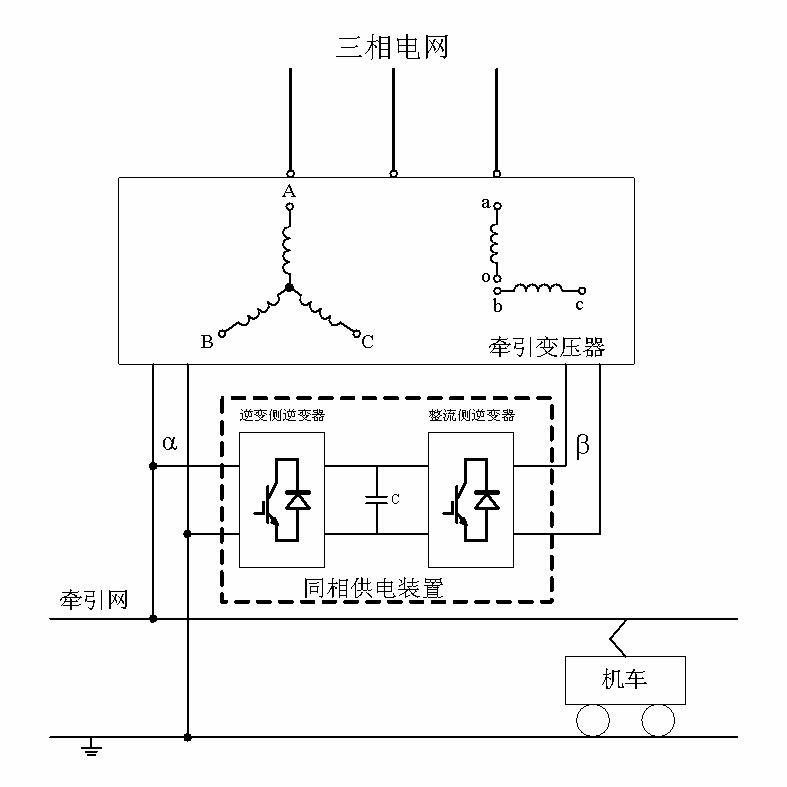
Electrified railway in-phase power supply device and multi-target coordinated instantaneous current control method
InactiveCN102166969AExtend power supply distanceImprove power qualityConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPower supply linesPower qualityElectric network
The invention relates to an electrified railway in-phase power supply device and a multi-target coordinated instantaneous current control method adopted by the device. After the in-phase power supply device is used, the electrified railway whole-line in-phase power supply can be realized, the output power of two power supply arms of a traction transformer can be balanced, and the negative sequence problem can be thoroughly solved; the load reactive power and the harmonic current can be compensated, and the electric energy quality of a traction power supply system can be comprehensively improved; the voltage of a traction electric network can be stabilized, the transient state stability of the voltage can be improved, the power supply distance of the power supply arms can be increased, and the amount of power substations can be reduced; the electrified railway in-phase power supply device and the multi-target coordinated instantaneous current control method are multiple in targets, the multi-target can be simultaneously controlled, the control harmony at two sides can be guaranteed, the dynamic response capability is stronger; a rectification side inverter takes the active power transfer and the stable direct voltage as a control target, and participates the reactive power control; and an inversion side inverter performs active power, reactive power and harmonic wave control, and participates the stable control of the direct voltage.
Owner:XUJI GRP +2
Hybrid battery power source for implantable medical use
InactiveUS7020519B2Minimize effectLow internal resistanceSeveral cell simultaneous arrangementsElectrotherapyEnergy sourceMedical device
A hybrid battery power source for implantable medical use provides a generally constant low internal resistance during discharge and avoids voltage delays of the type that develop as a result of run down-induced resistance increase in Li / SVO cells. The hybrid battery power source utilizes two batteries or cells, one being a primary cell of relatively high energy density and the other being a secondary cell of relatively low internal resistance that is rechargeable. The primary and secondary cells are connected in a parallel arrangement via a voltage boost / charge control circuit that is powered by the primary cell and adapted to charge the secondary cell while limiting charge / discharge excursions thereof in a manner that optimizes its output for high energy medical device use. The energy storage capacitors of the medical device in which the hybrid battery power source is situated are driven by the secondary cell. The primary cell is used to as an energy source for recharging the secondary cell.
Owner:GENTCORP
Collectorless direct current motor, driver circuit for a drive and method of operating a collectorless direct current motor
InactiveUSRE37589E1Constant operation voltageReduce power consumptionTemperature control using analogue comparing deviceMotor/generator/converter stoppersDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
Owner:PAPST MOTOREN GMBH & CO KG
Method of controlling ion energy distribution using a pulse generator with a current-return output stage
ActiveUS10448495B1Constant voltageElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingEngineeringVoltage
Embodiments of this disclosure describe an electrode biasing scheme that enables maintaining a nearly constant sheath voltage and thus creating a mono-energetic IEDF at the surface of the substrate that consequently enables a precise control over the shape of IEDF and the profile of the features formed in the surface of the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of controlling ion energy distribution using a pulse generator with a current-return output stage
ActiveUS20190350072A1Constant voltageElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingEngineeringIon energy
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Current sensing circuit with a current-compensated drain voltage regulation
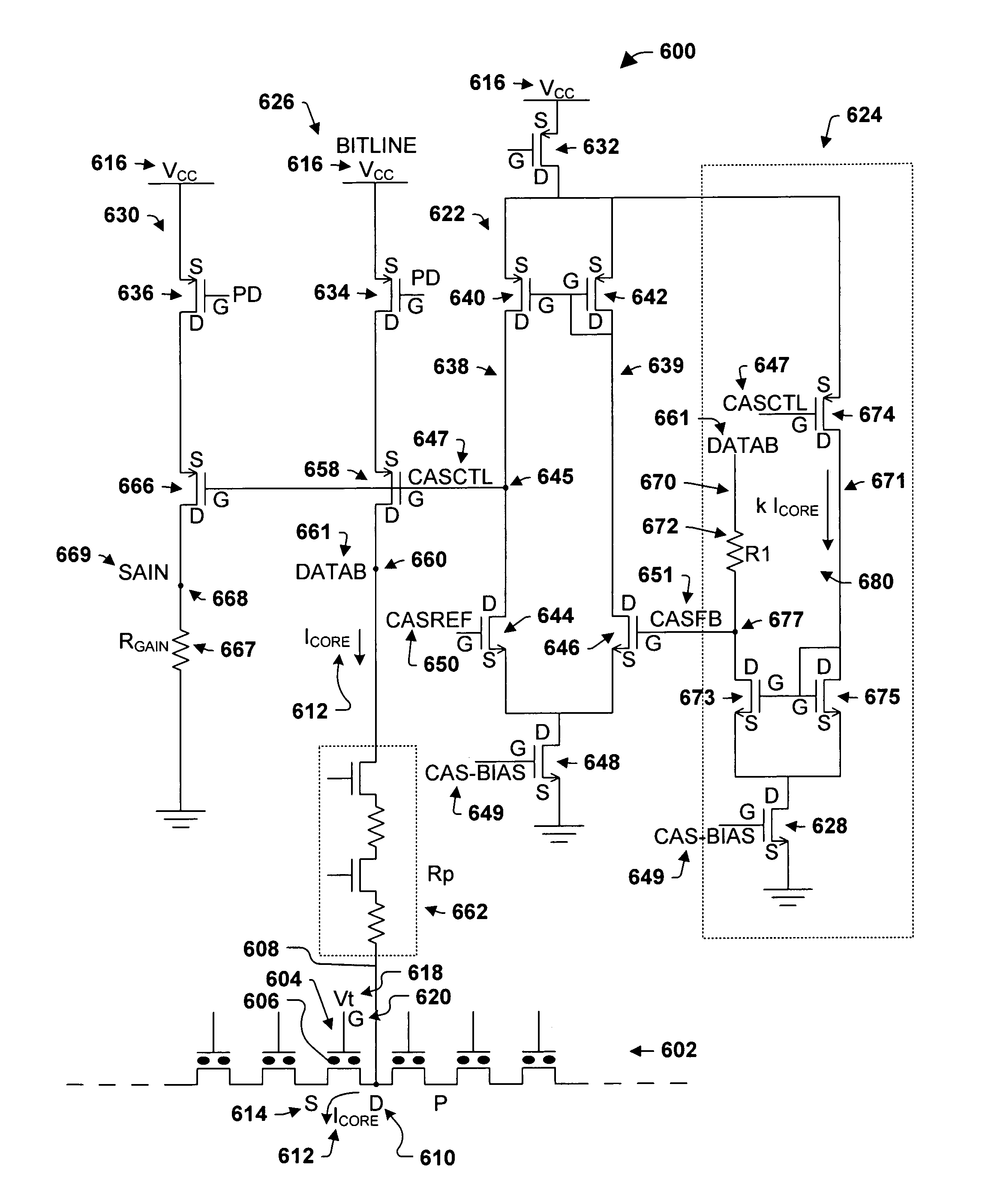
ActiveUS7099204B1Constant voltageReliable dataRead-only memoriesDigital storageVoltage regulationVirtual ground
The present invention facilitates more accurate data reads by compensating for parasitic behavior—thus regulating the voltage at the drain of a core memory cell rather than at the output of a sensing circuit. More particularly, respective voltages at one or more nodes, such as the start of a bitline at a sensing circuit, for example, are adjusted to compensate for voltage drops that may occur due to parasitic behavior. Maintaining the substantially constant voltage levels at core memory cells allows comparisons to be made under ideal conditions while reducing the side leakages in virtual ground schemes. This mitigates margin loss and facilitates more reliable data sensing.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
Multi-Frequency Metal Detector Having Constant Reactive Transmit Voltage Applied To A Transmit Coil
ActiveUS20080074114A1Lower implementationSimple circuitElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationMetal detectorsVoltage
An electronic metal detector having a transmit coil (1) adapted to transmit an alternating magnetic field associated with a reactive transmit voltage, wherein the transmit voltage signal is selected such that the reactive transmit voltage is approximately constant for at least a time period during which a magnetic field signal to be processed is received by the detector for processing.
Owner:MINELAB ELECTRONICS
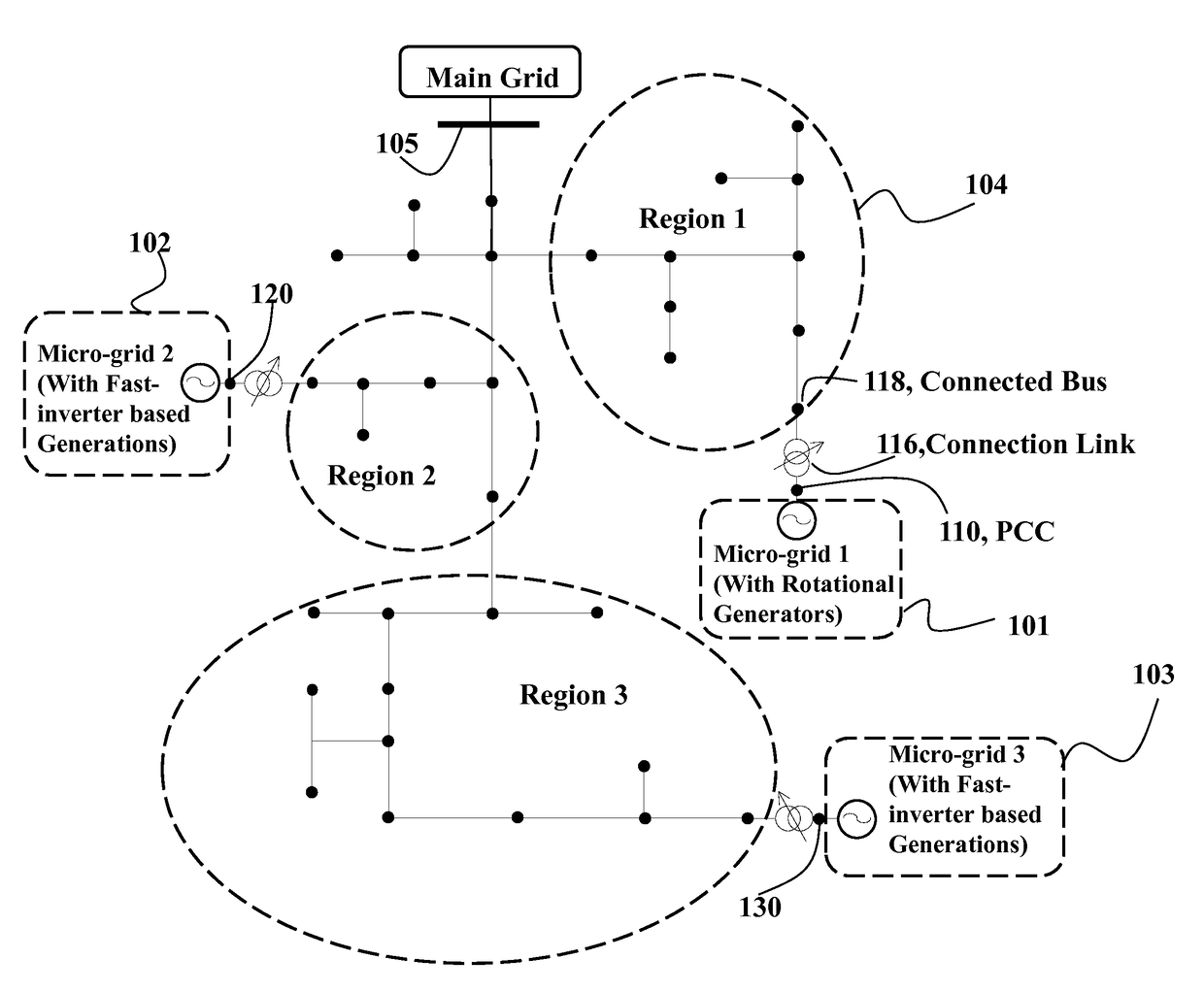
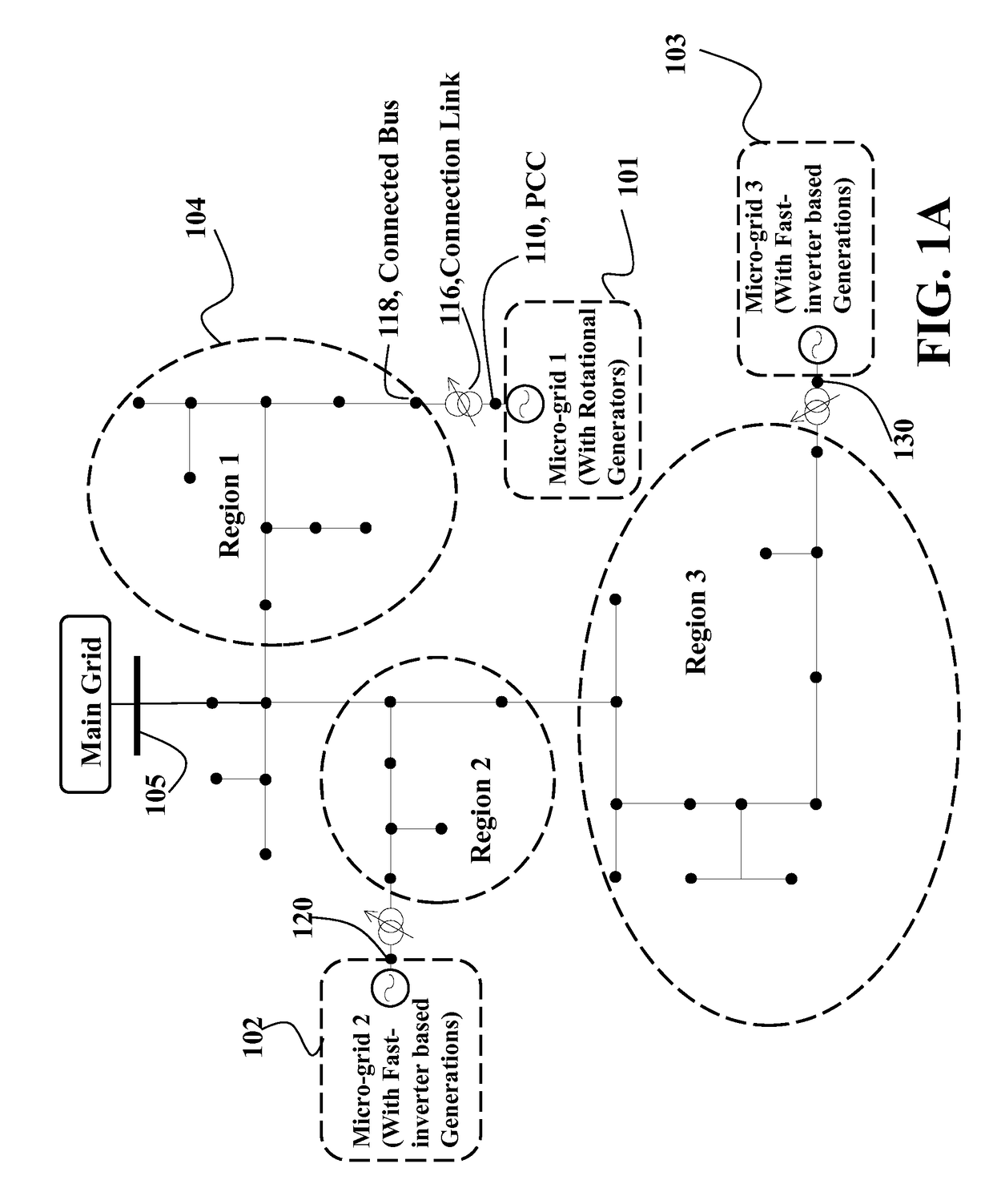
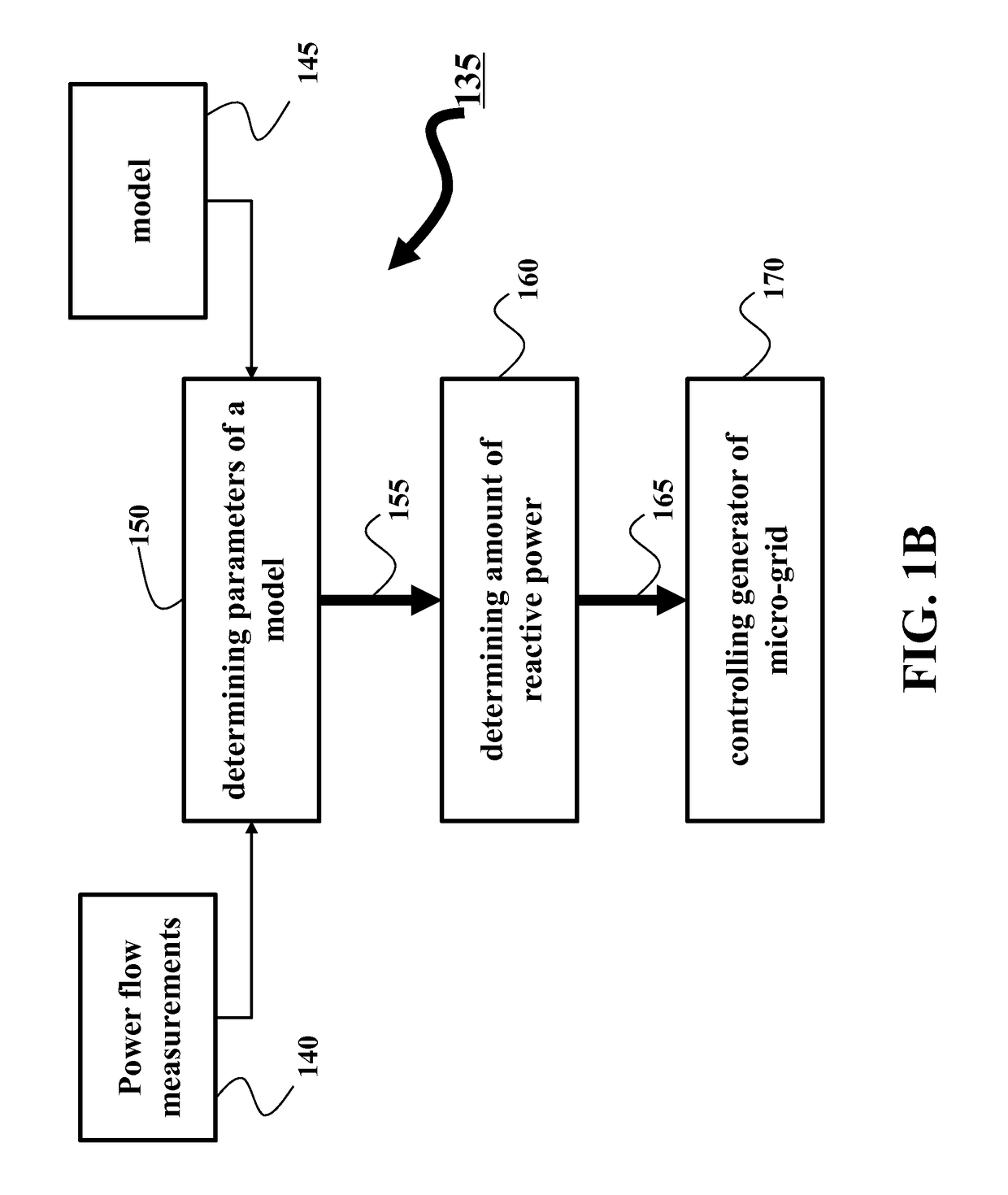
Automatic Power Generation Control in Micro-Grids
ActiveUS20170077700A1Constant voltageImprove power qualitySimulator controlEnergy industryAutomatic Generation ControlPower flow
A method controls a micro-grid connected to a power distribution system. The method determines parameters of a model of dynamics of the micro-grid using measurements of power flow at a point of common coupling (PCC) of the micro-grid with the power distribution system. The model is exponentially stable on a voltage set-point at the PCC and the method determines, using the parameters of the model, an amount of reactive power required to maintain the voltage at the PCC asymptotically stable on the voltage set-point. Next, the method controls a generator of the micro-grid to produce the amount of reactive power.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Charger with over-voltage and over-current protection and method for using the same
InactiveUS20150043117A1Constant working voltageEliminate hidden dangersDc-dc conversionElectric powerEngineeringCharge current
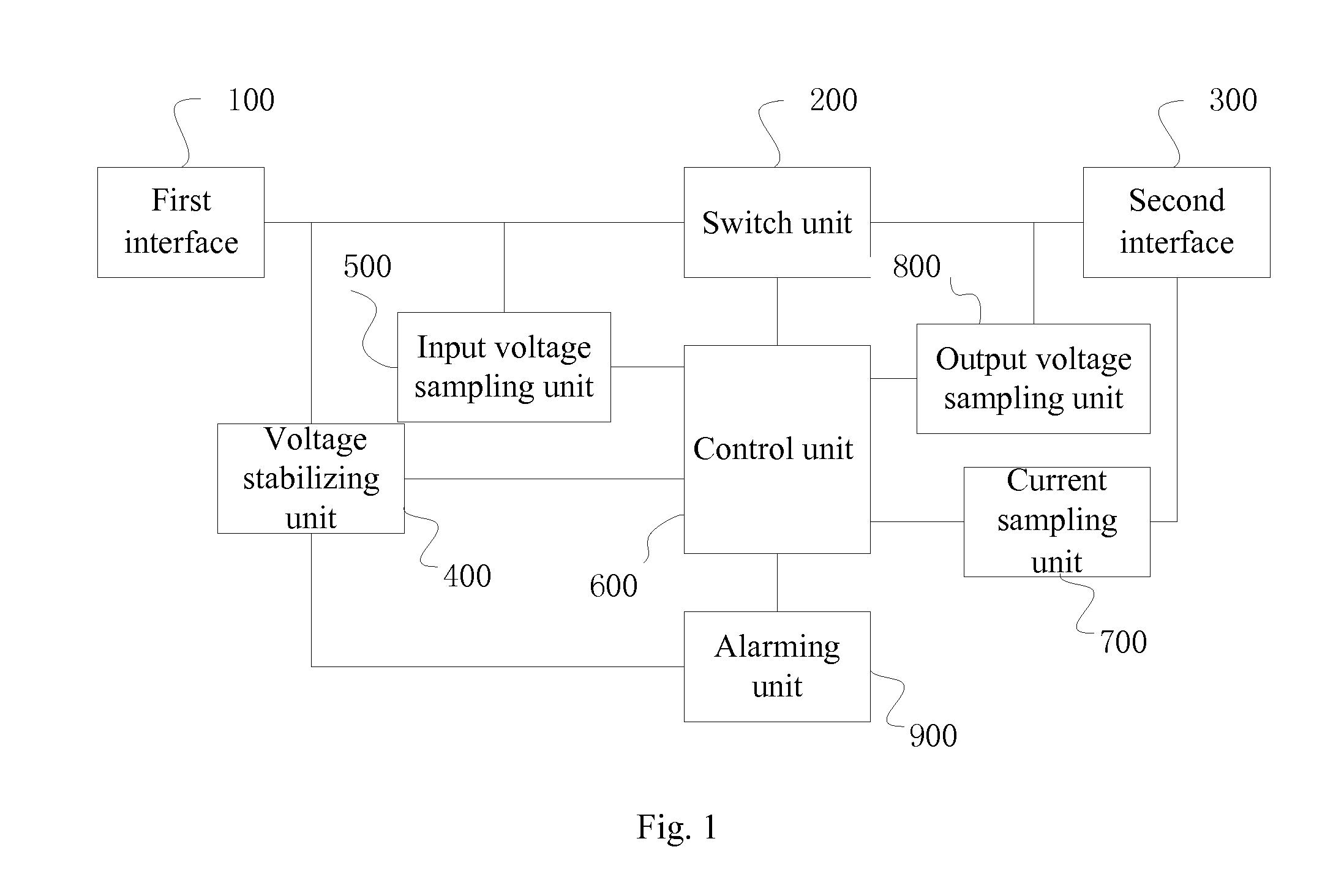
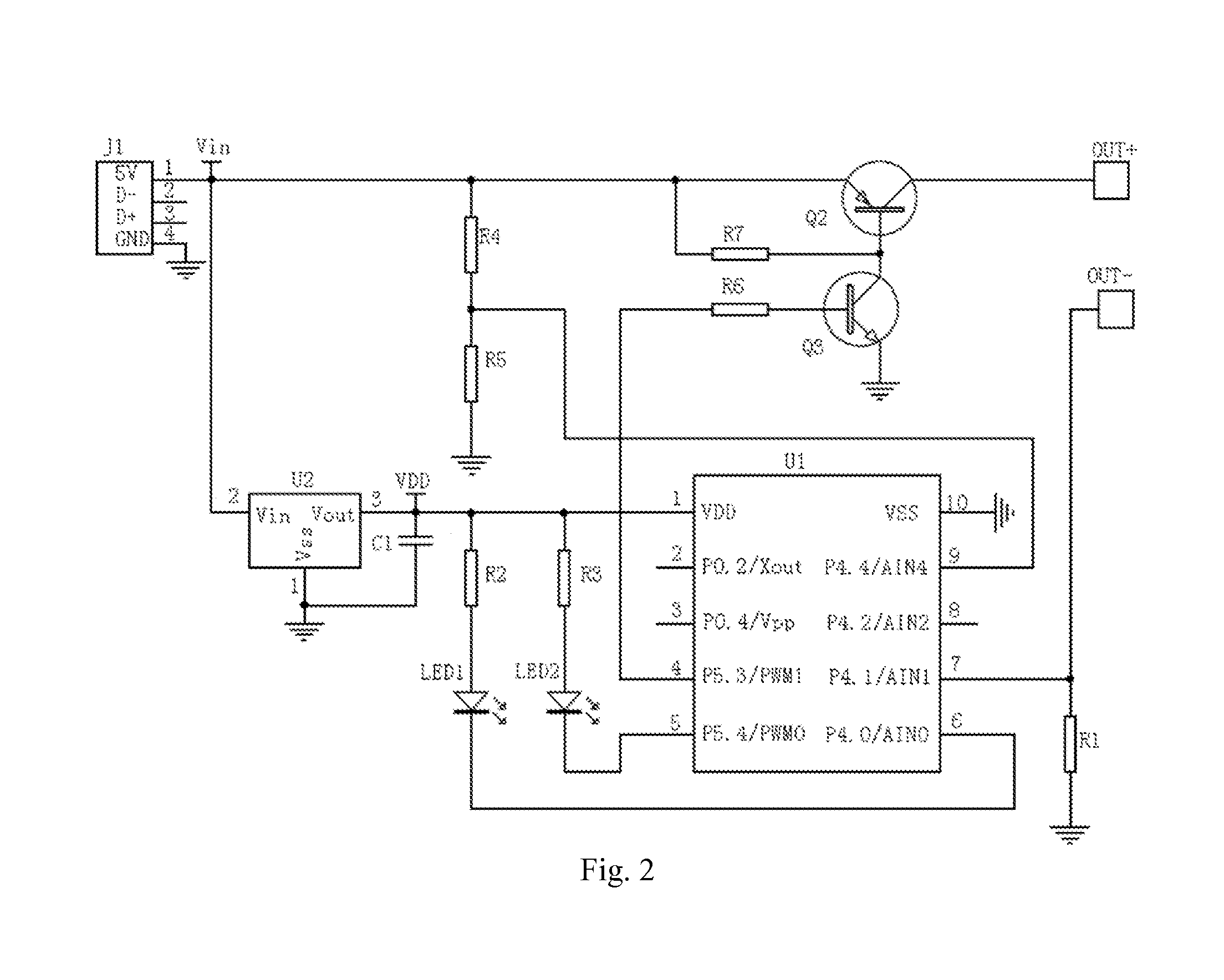
A charger with over-voltage and over-current protection and a method for using the same are provided. The charger comprises a first interface, a second interface, a voltage stabilizing unit, a control unit, an input voltage sampling unit, a switch unit, and a current sampling unit. The voltage stabilizing unit receives an input voltage of an external power supply and provides a constant working voltage to the control unit. The input voltage sampling unit detects the input voltage real-timely. The current sampling unit detects charging current of the battery rod real-timely. The control unit determines whether the input voltage detected by the input voltage sampling unit generates over-voltage or not, or determines whether the charging current detected by the current sampling unit generates over-current or not, and controls the switch unit to turn on or turn off according to the determination results.
Owner:HUIZHOU KIMREE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com