Patents
Literature
171results about How to "High power supply voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
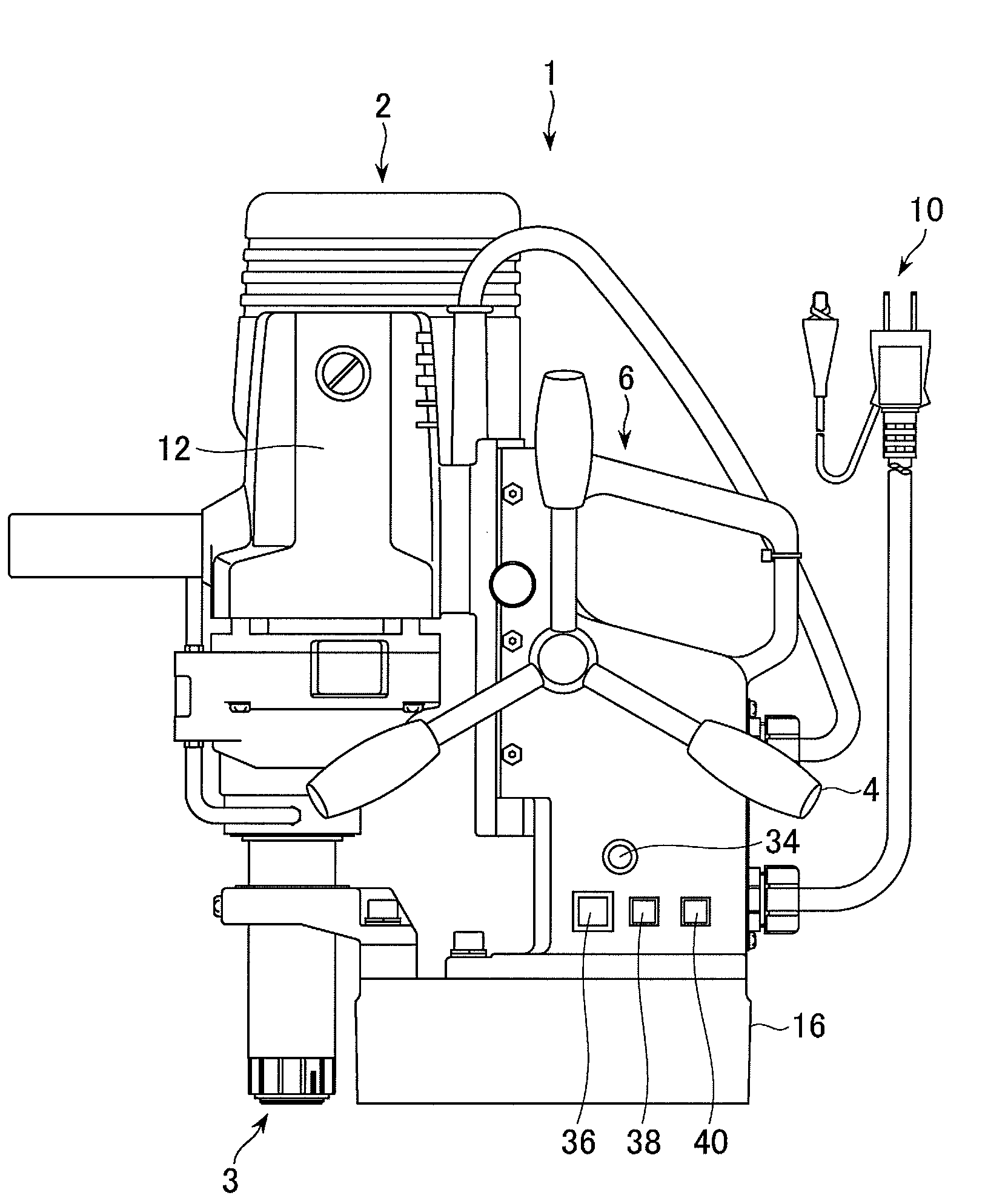
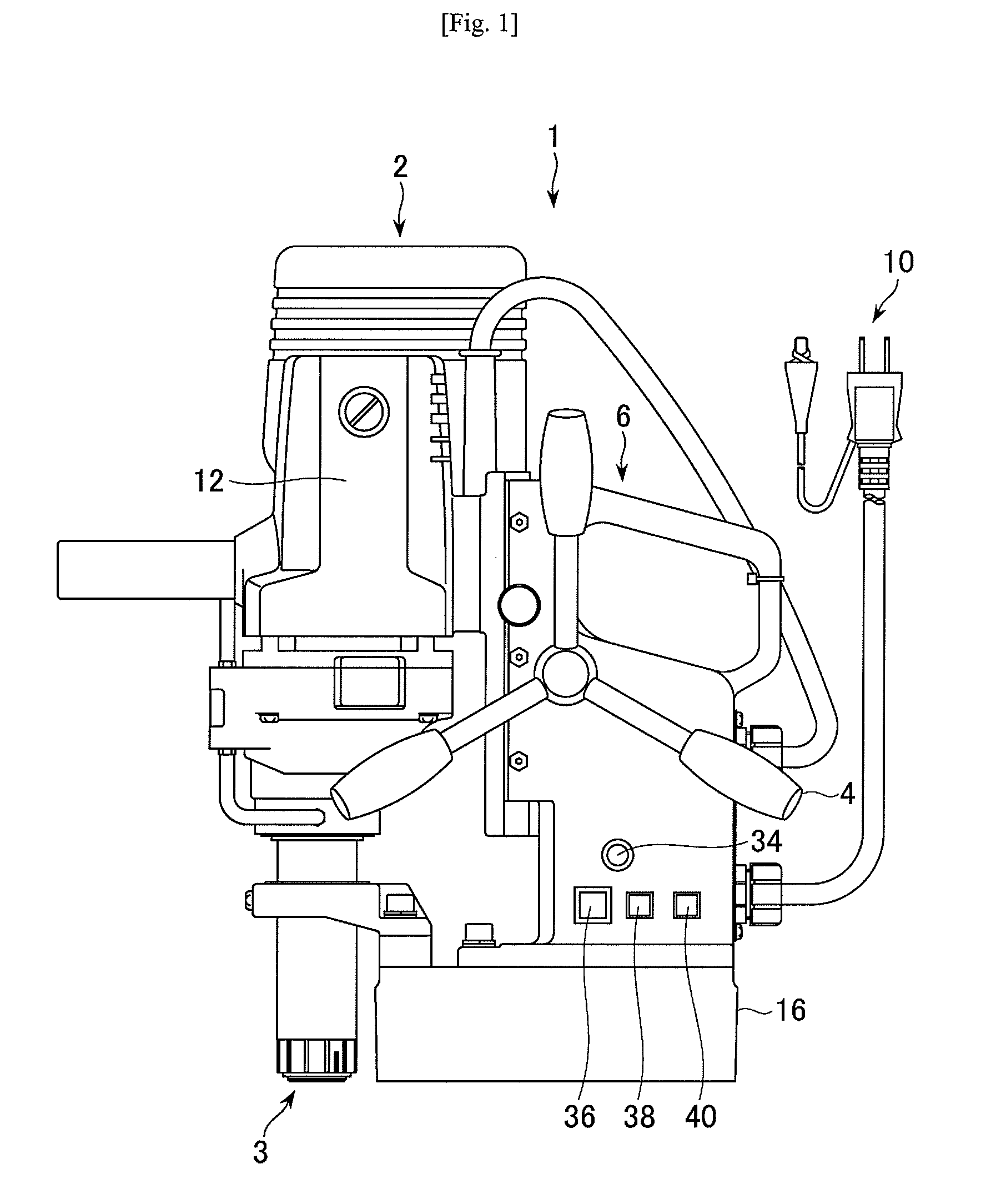
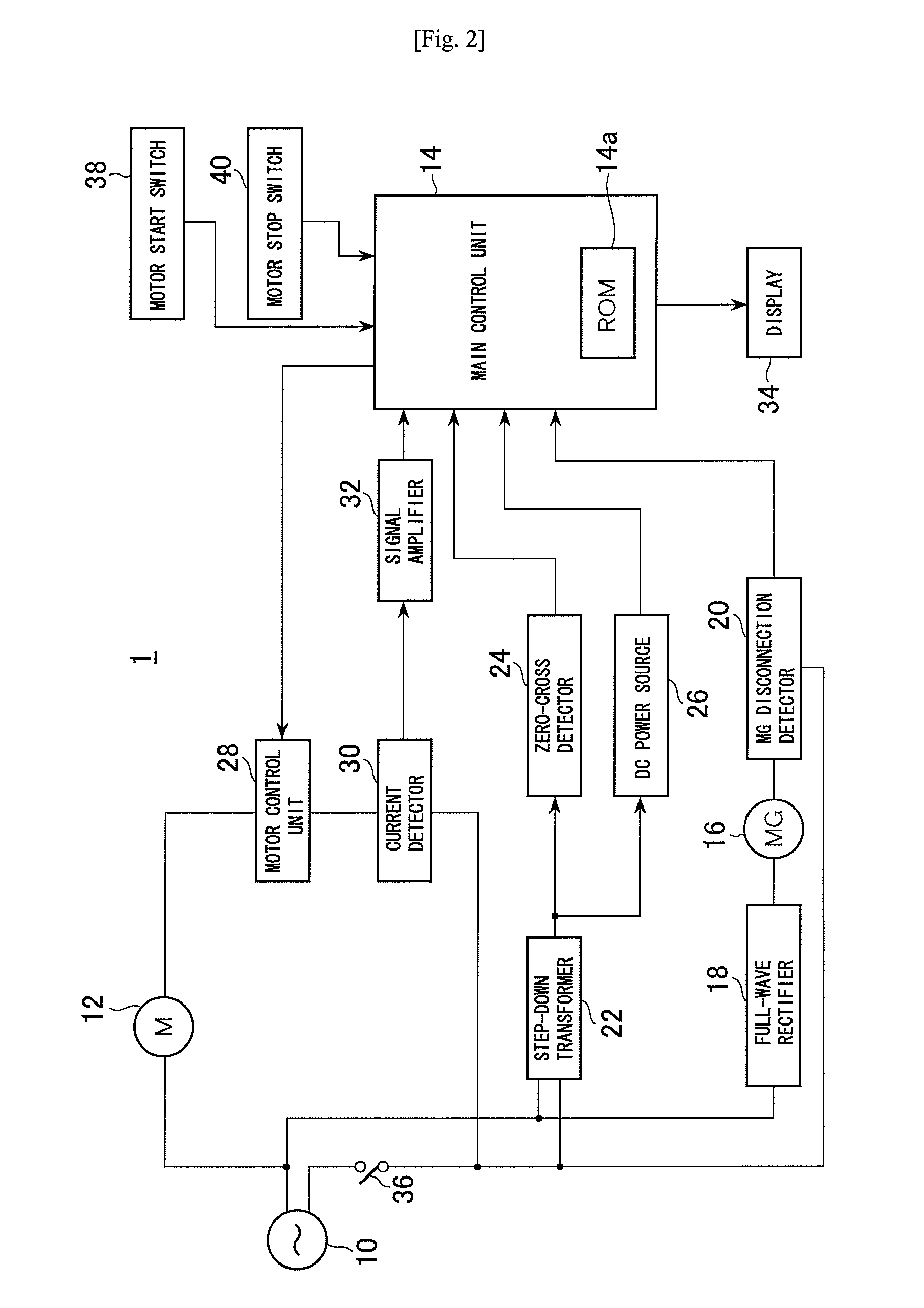
Portable drilling device
ActiveUS7936142B2Easy to operateImprove securityAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlFull waveEngineering
A drilling device prevents recurrence of an overload condition after occurrence of the overload condition, thereby improving operability and safety in the drilling device. A motor for rotating a drill is connected to an AC power source through a motor control unit, a current detector, and a power switch. A magnet is also connected to the AC power source through the power switch and a full-wave rectifier. The motor control unit rotationally drives the motor on the basis of a signal sent from a main control unit according to a state in which a motor start switch is on. The main control unit controls the motor control unit to gradually reduce a supply voltage to the motor when the motor becomes overloaded, to gradually increase the voltage to the normal power supply condition when the overload condition is vanished, and to stop power supply to the motor if the overload condition continues for a predetermined period.
Owner:NITTO KOHKI CO LTD
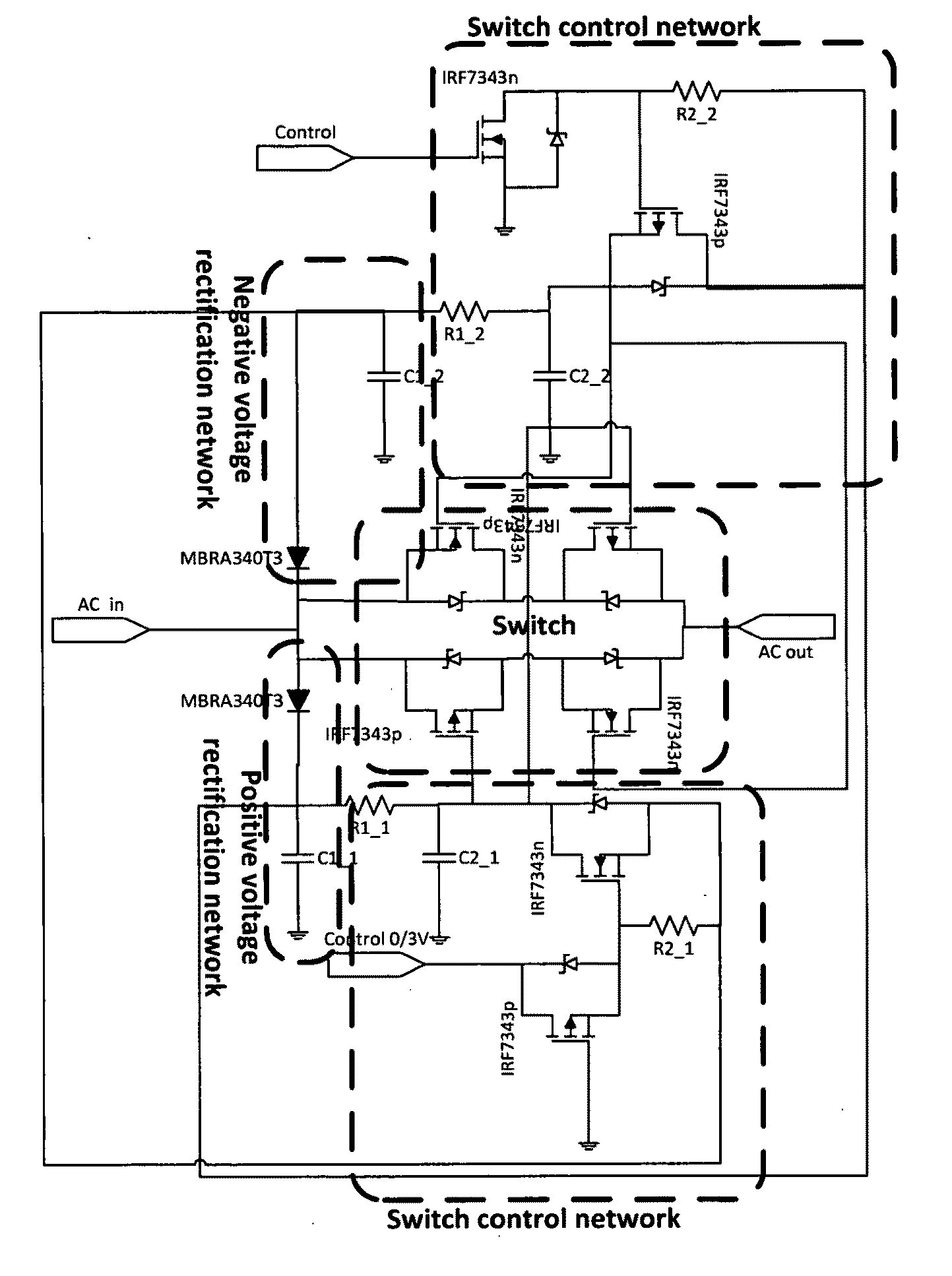
Miniature high voltage/current ac switch using low voltage single supply control
InactiveUS20100110741A1Improve efficiencyAvoid heatingAc-dc conversionSafety/protection circuitsElectric power transmissionHigh voltage igbt
Embodiments of the invention pertain to a method and apparatus for planar wireless power transfer where the receiver switches off and / or performs a duty cycle. In an embodiment, the switch can be used in a system that having a high voltage / current solid state switch, without having a high voltage control signal. An embodiment provides a switch that is capable of breaking, or greatly reducing, the connection of the receiver coil and the receiver circuitry in order to enable the receiver to decouple from the power transfer system. This embodiment can allow the transmitter to put out more power to other devices without providing power to the switched device. When the switch is used for a fully charged device, the switching can prevent or reduce damage to the fully charged device.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
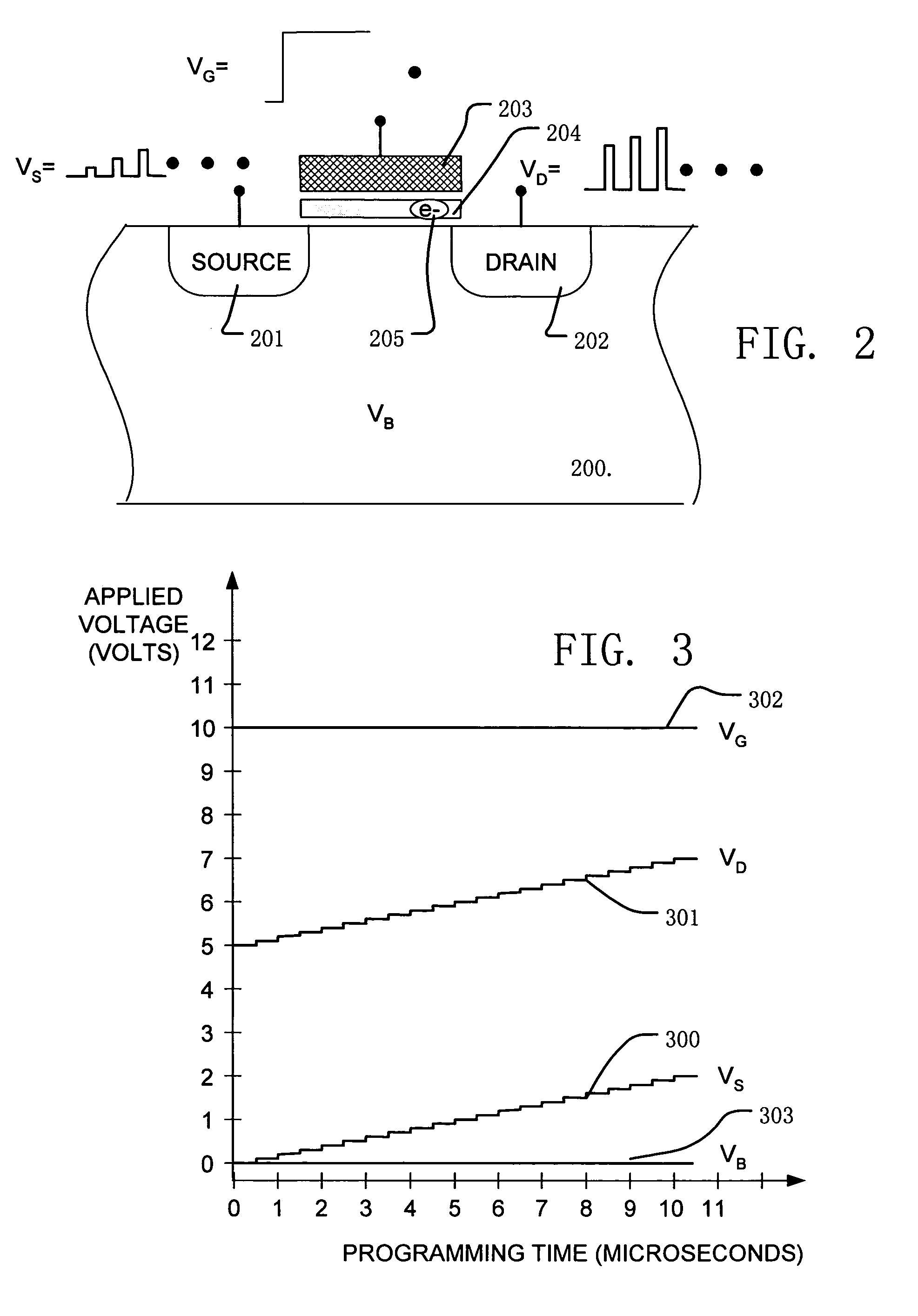
Circuit and method for programming charge storage memory cells
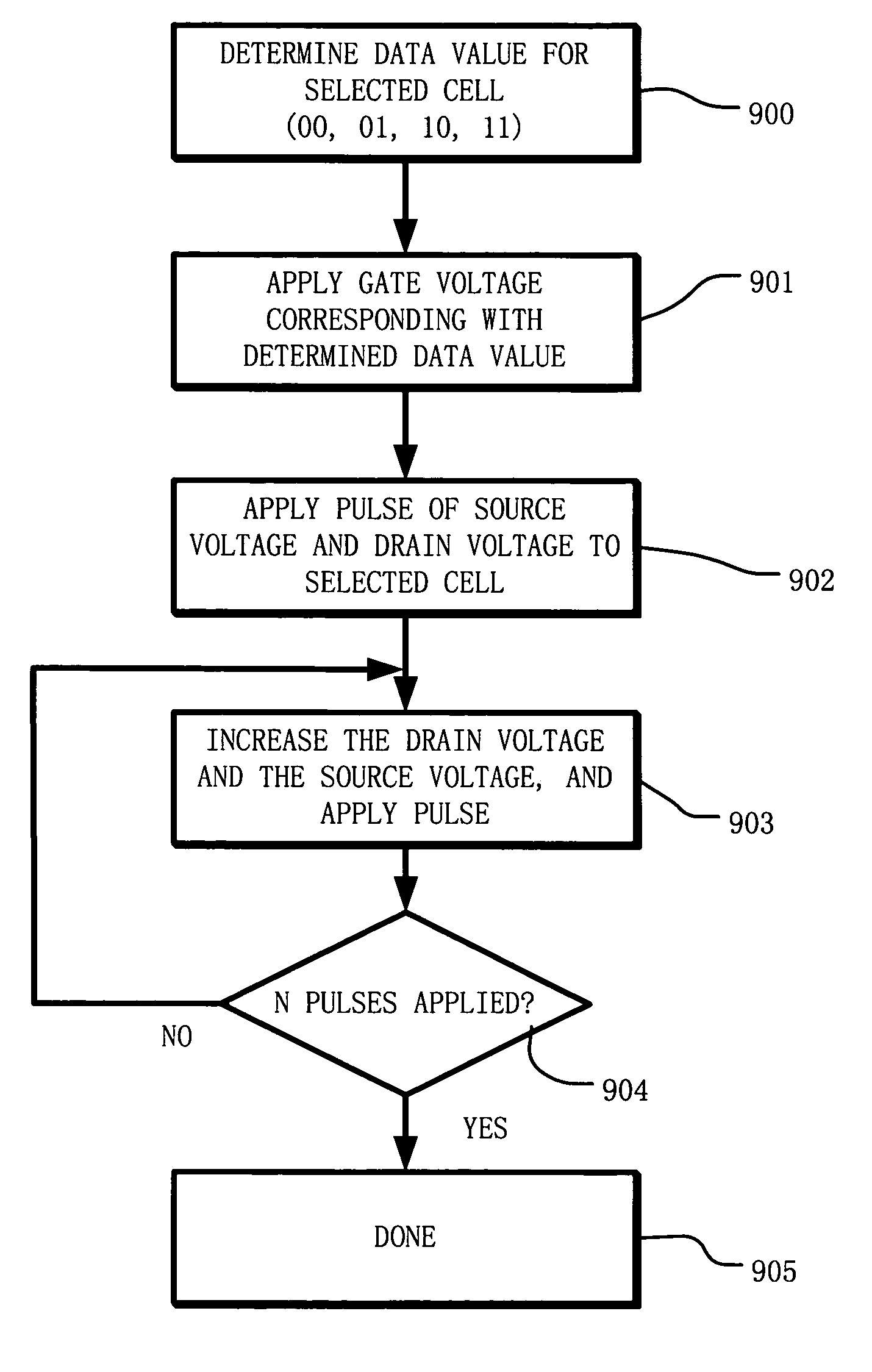
ActiveUS6937511B2Increases the effective thresholdHot electron injection efficiencySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineeringGate voltage
A circuit and method for self-converging programming of a charge storage memory cell, such as NROM or floating gate flash, having a source and a drain in a substrate, a charge storage element and a control gate. The method includes applying source voltage, inducing a body effect that increases the effective threshold, and increasing the source voltage along with the drain voltage to moderate hot electron injection efficiency during the program operation, at least during a portion of the program operation in which convergence on a target threshold occurs. A selected gate voltage is applied during the operation to establish the target threshold voltage. In multiple bit cells, the gate voltage is set according to the data values to be stored, enabling self-convergence at more than one target threshold.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
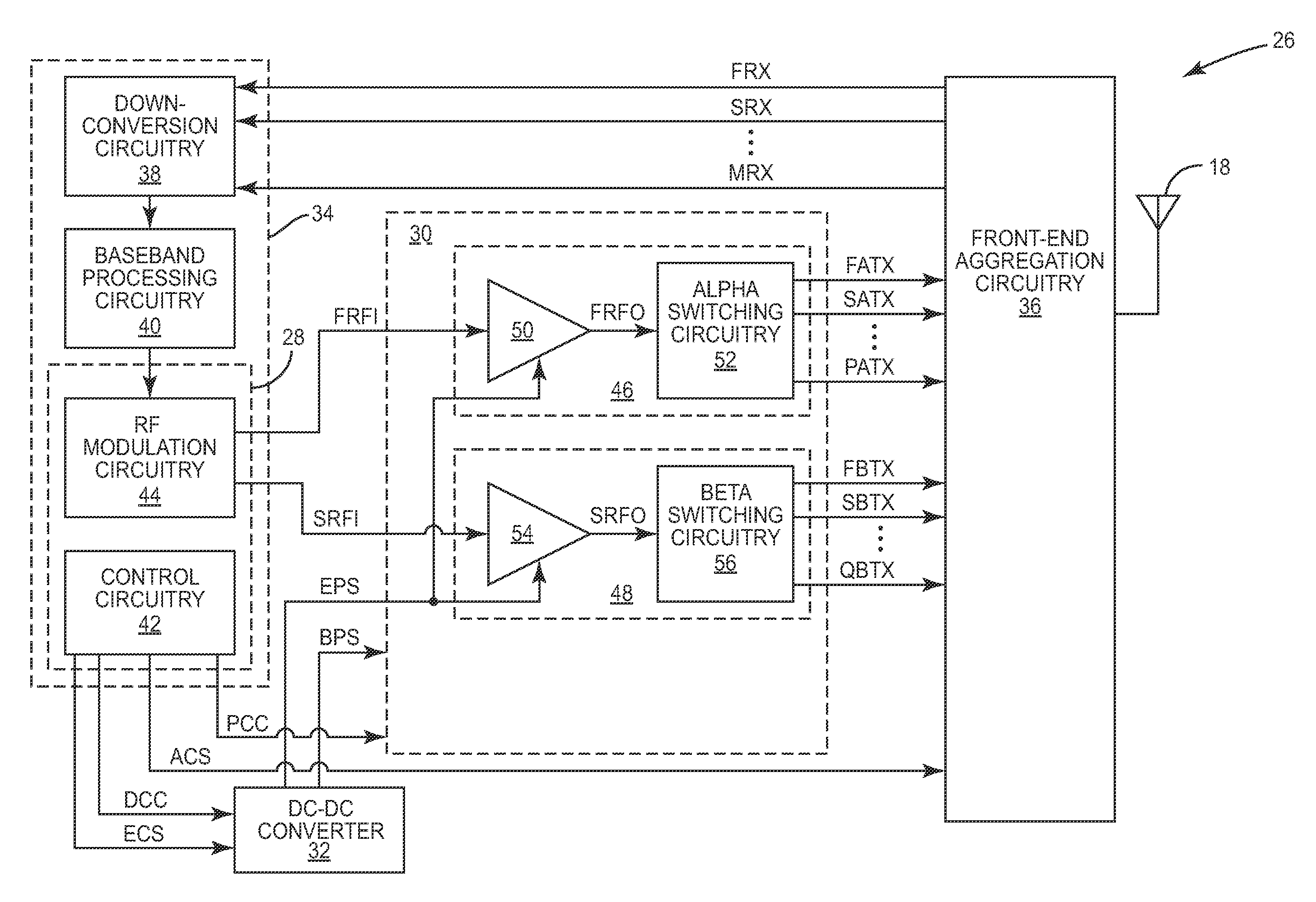
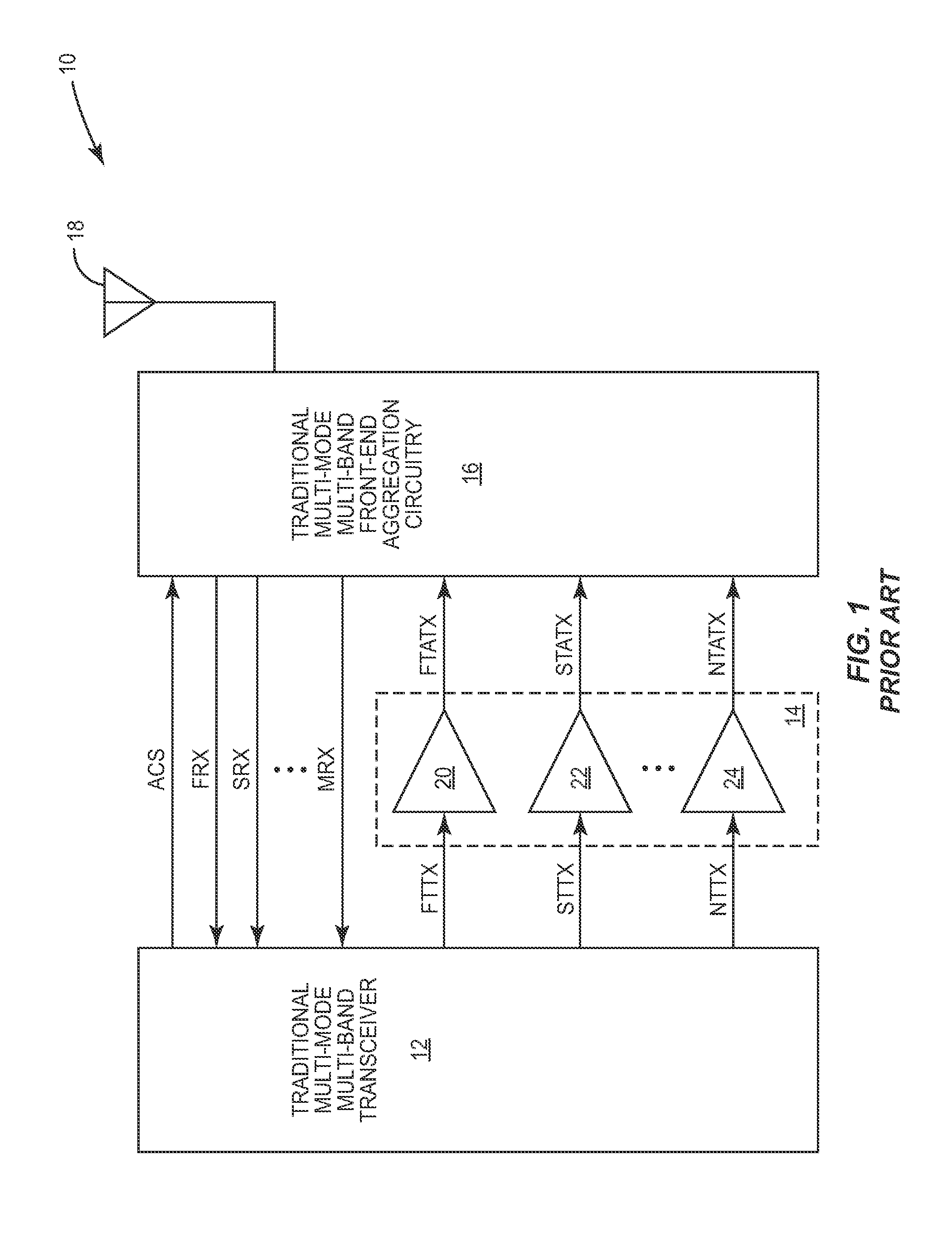
Cascaded converged power amplifier
ActiveUS8942651B2High power supply voltageSecond RF PA stage may be optimizedResonant long antennasGated amplifiersRadio frequencyAmplifier
Owner:QORVO US INC
High frequency power amplifier and transmitter
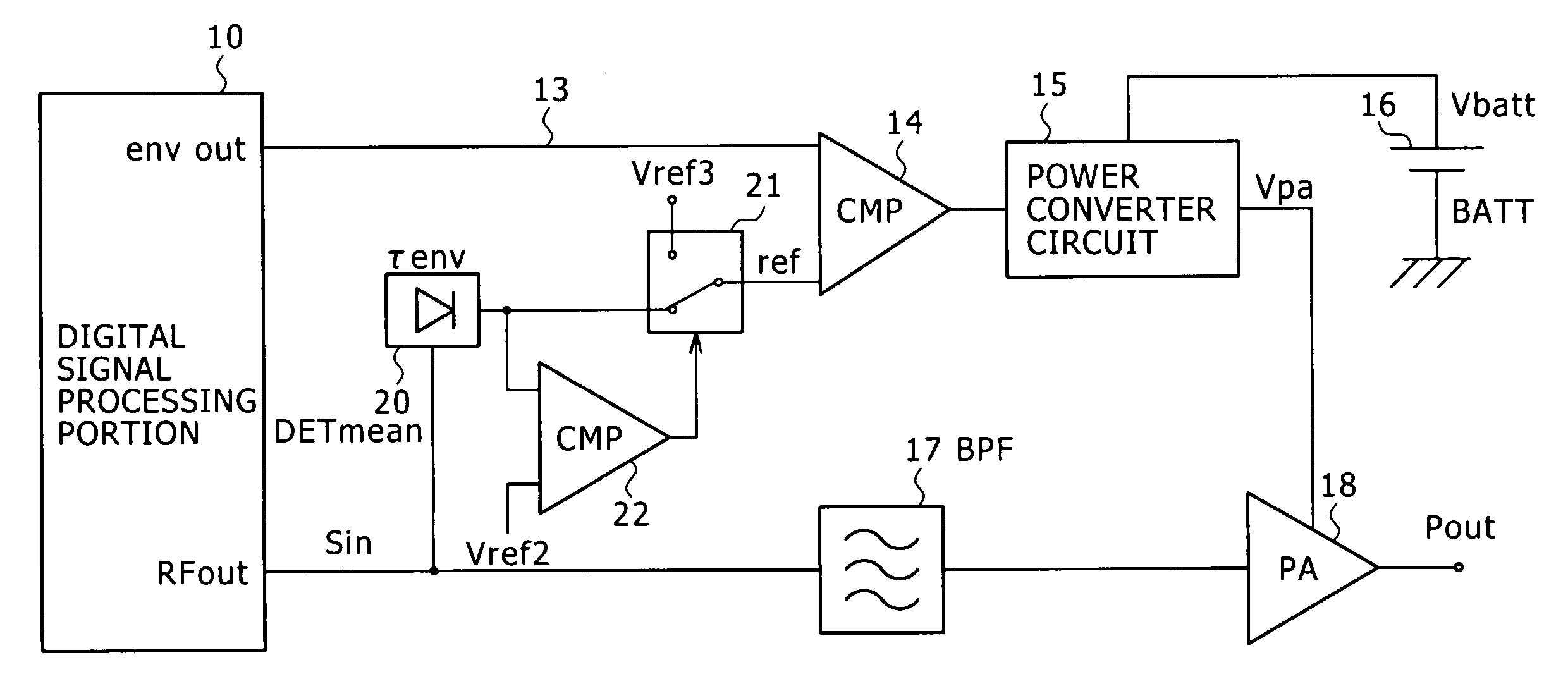
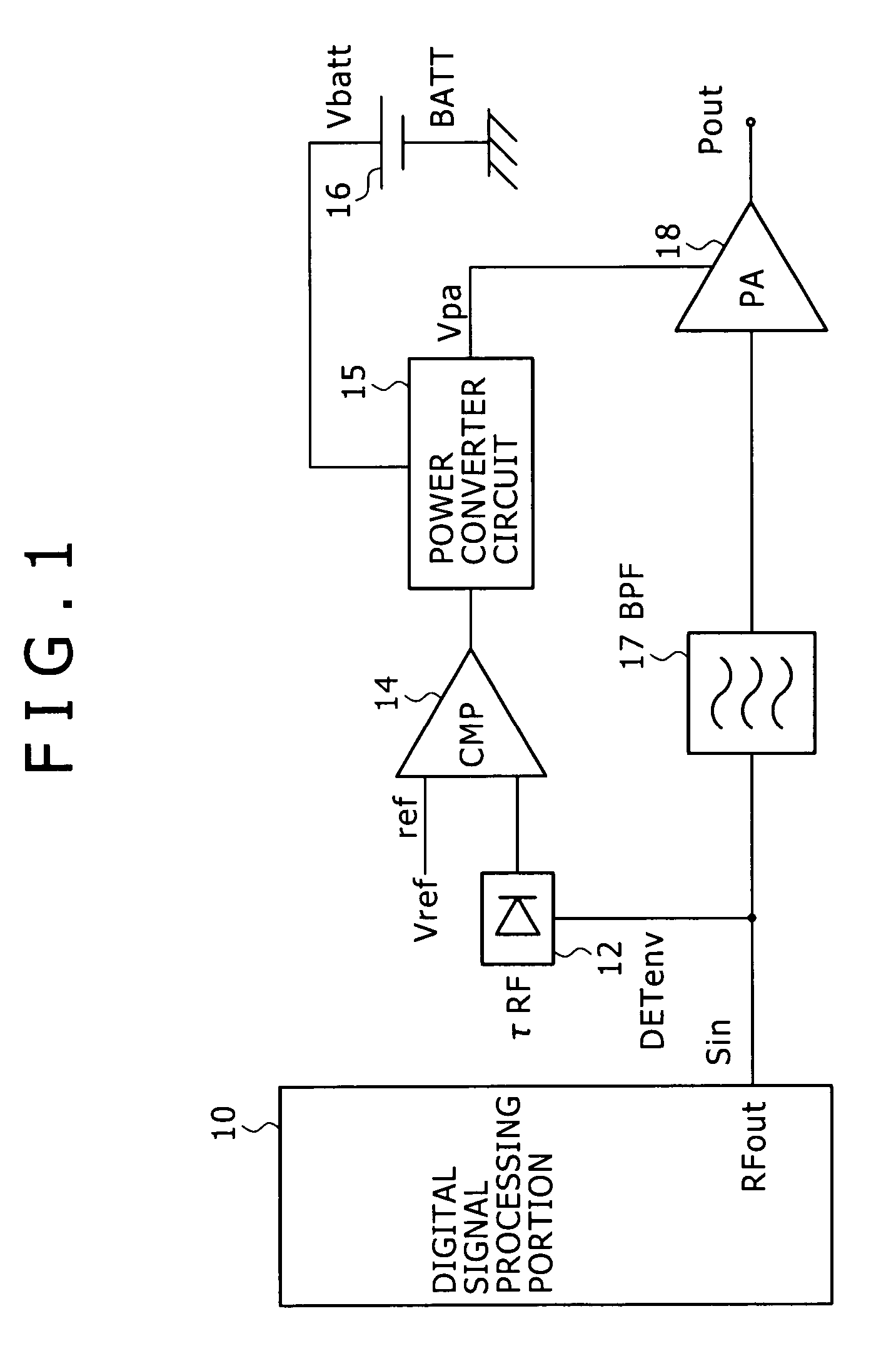
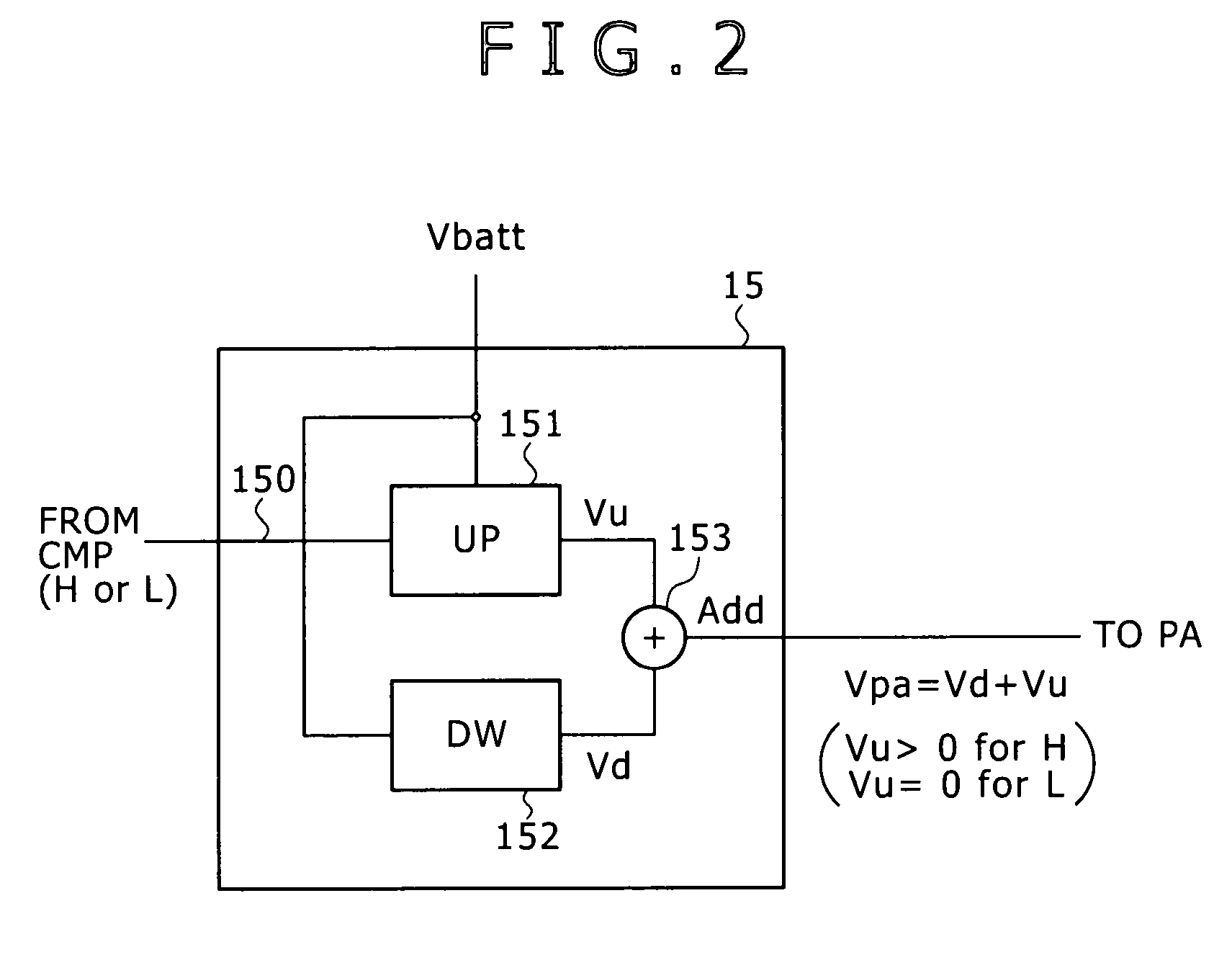
InactiveUS7368985B2Reduce distortion problemsHigh power supply voltageAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlDigital signal processingHigh frequency power
Disclosed is a digital signal processing portion that amplifies a high frequency signal resulting from digitally modulating data to be transmitted. An envelope detection portion (DETenv) generates the high frequency signal's envelope voltage. A comparator compares this envelope voltage with reference voltage Vref to generate two-state output. According to this two-state output, a power converter circuit converts power supply voltage Vbatt into power and outputs power supply voltage Vpa for a power amplifier. While the envelope voltage is larger than the reference voltage Vref, for example, the power supply voltage Vpa is changed from voltage V1 to V2 (larger than V1). In this manner, there are provided a high frequency power amplifier and a transmitter capable of decreasing distortion of transmission signals by means of a relatively simple technique.
Owner:SONY MOBILE COMM INC
Programmable Fault Protect for Processor Controlled High-Side and Low-Side Drivers
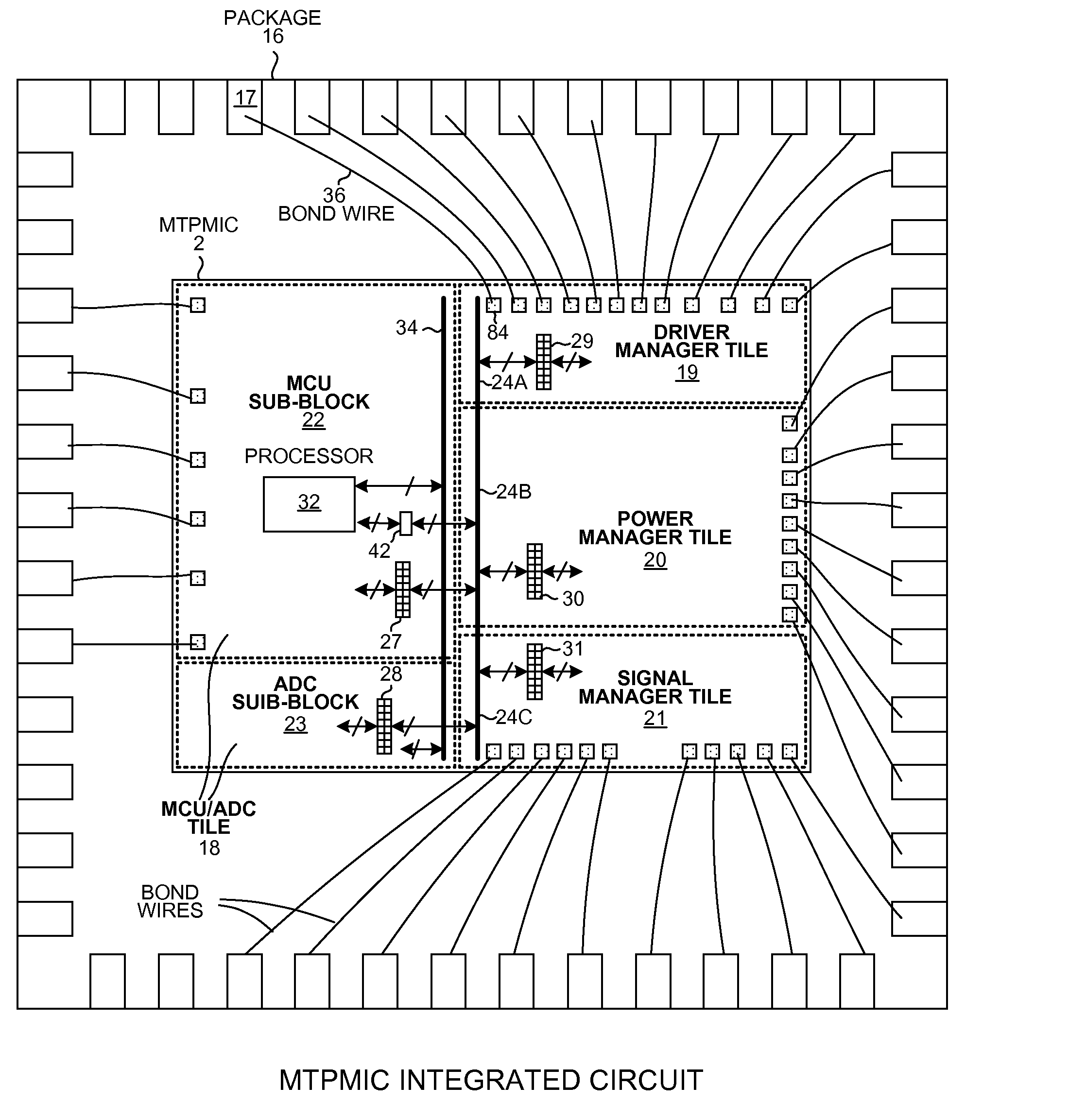
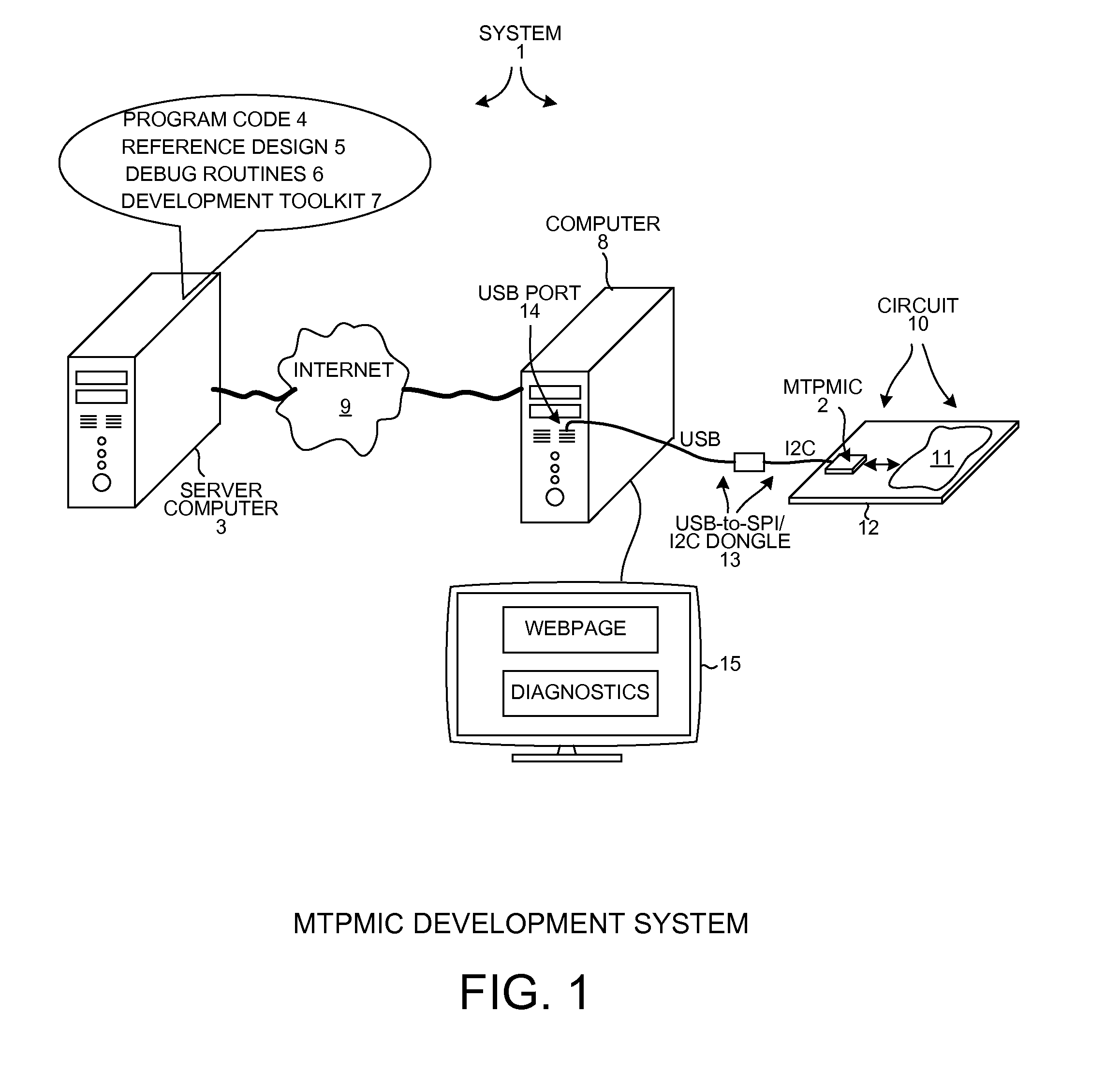
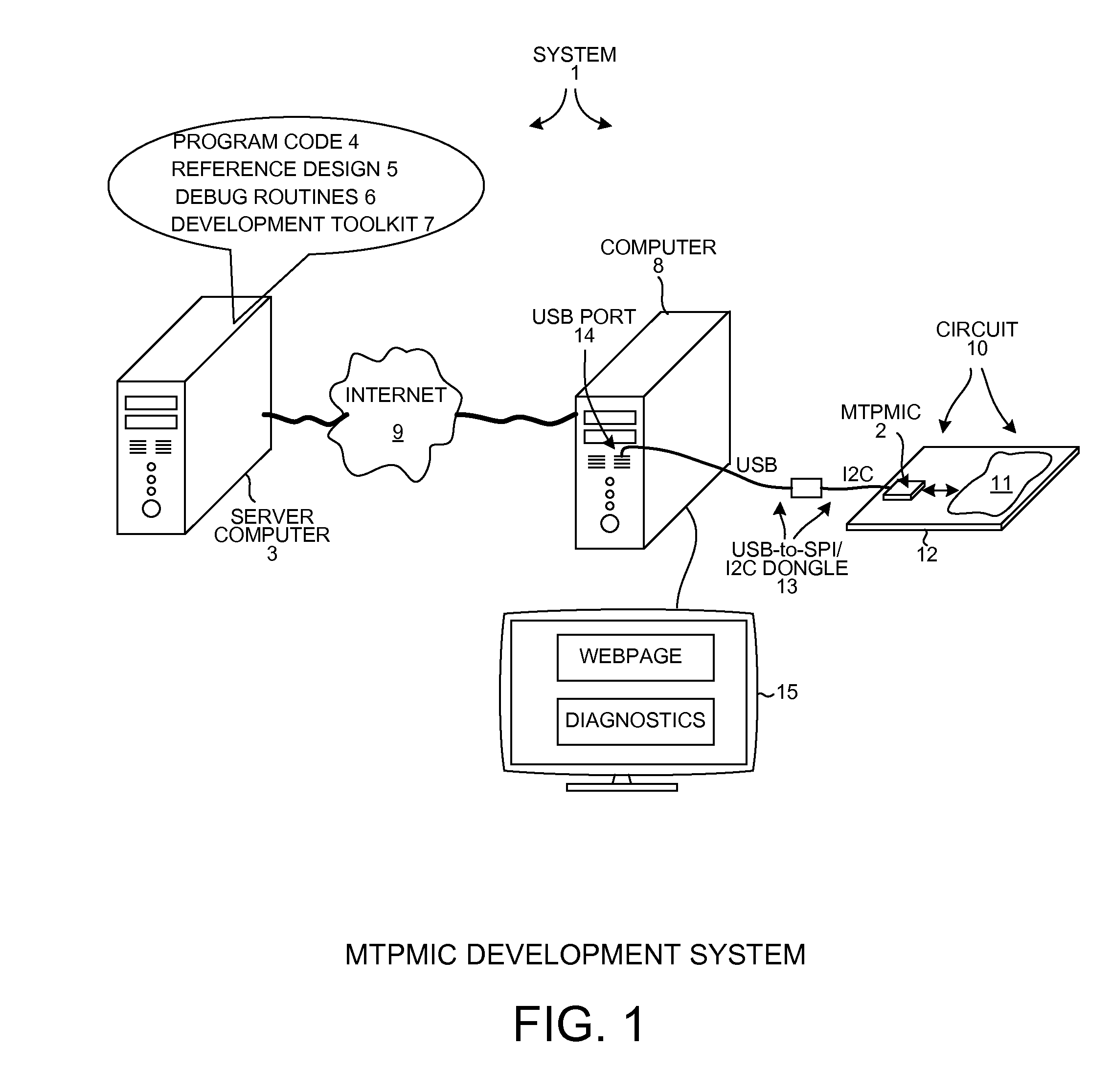
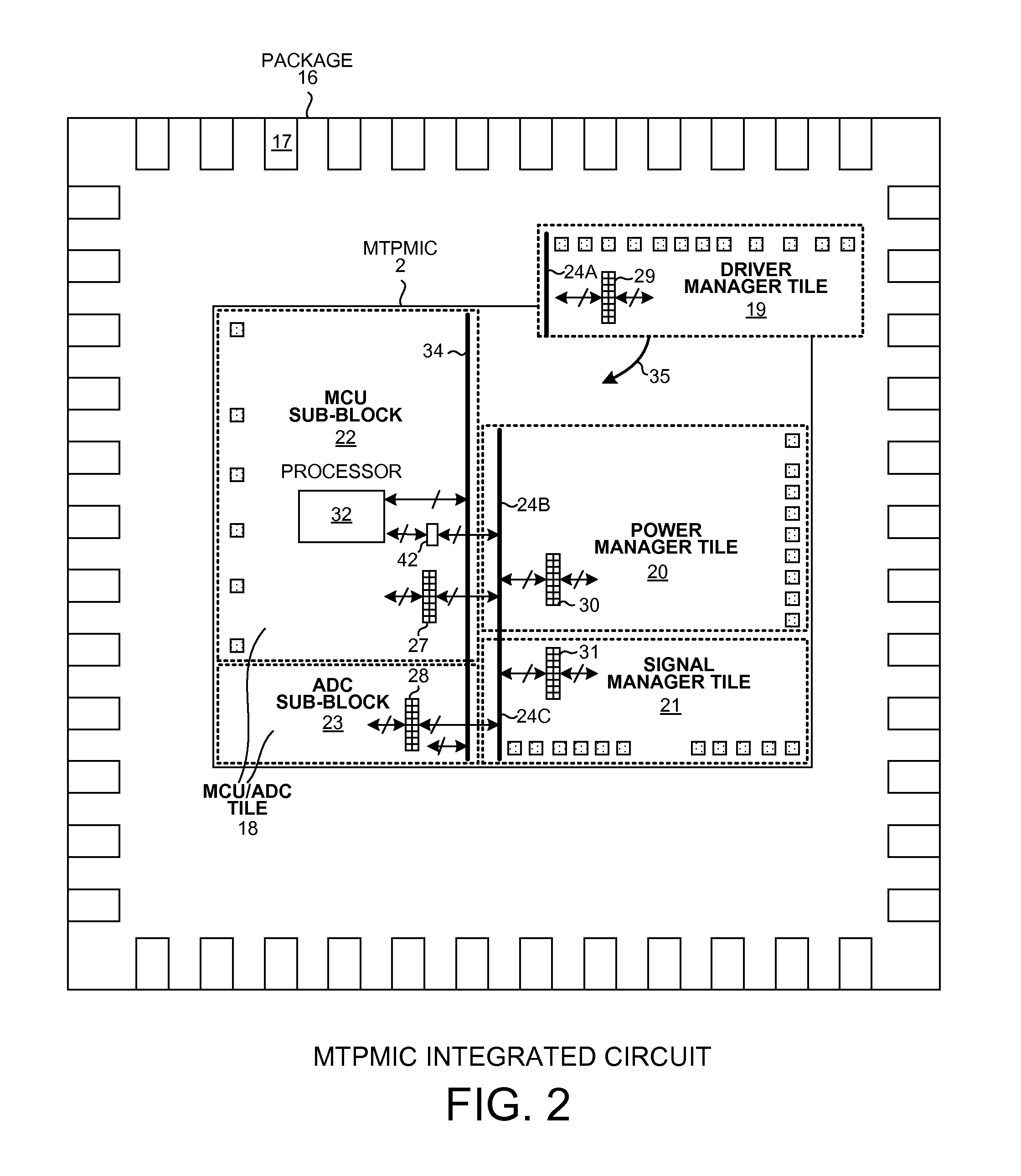
ActiveUS20130151919A1High power supply voltageError preventionTransmission systemsPower management integrated circuitEmbedded system
A Multi-Tile Power Management Integrated Circuit (MTPMIC) includes a processor, a fault protect circuit, a first terminal, a driver that drives the first terminal, a second terminal, and detection circuitry that outputs a digital detection signal indicative of whether a predetermined condition is detected on the second terminal. The processor can program the fault protect circuit so that the fault protect circuit will later disable the driver as a function of multiple signals, including the digital detection signal. The function is programmable by the processor. In one example, if the detection circuitry detects the predetermined condition on the second terminal then the fault protect circuit disables all the high-side drivers and all low-side drivers of the MTPMIC independently of and without input from the processor.
Owner:ACTIVE SEMI
Semiconductor device and display device
InactiveUS20080284710A1Reduce power consumptionLow efficiencyStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesSingle crystalShift register
A single-crystal semiconductor layer is separated from a single-crystal semiconductor substrate and is fixed to an insulating substrate to form a TFT over the insulating substrate. Then, a driver circuit is formed using the TFT. The TFT has excellent current characteristics because an active layer is almost in a single-crystal state. Accordingly, a small thin display device with low power consumption can be manufactured. Further, a controller and a shift register which is included in a source driver are operated at the same power supply voltage. Thus, power consumption can be reduced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
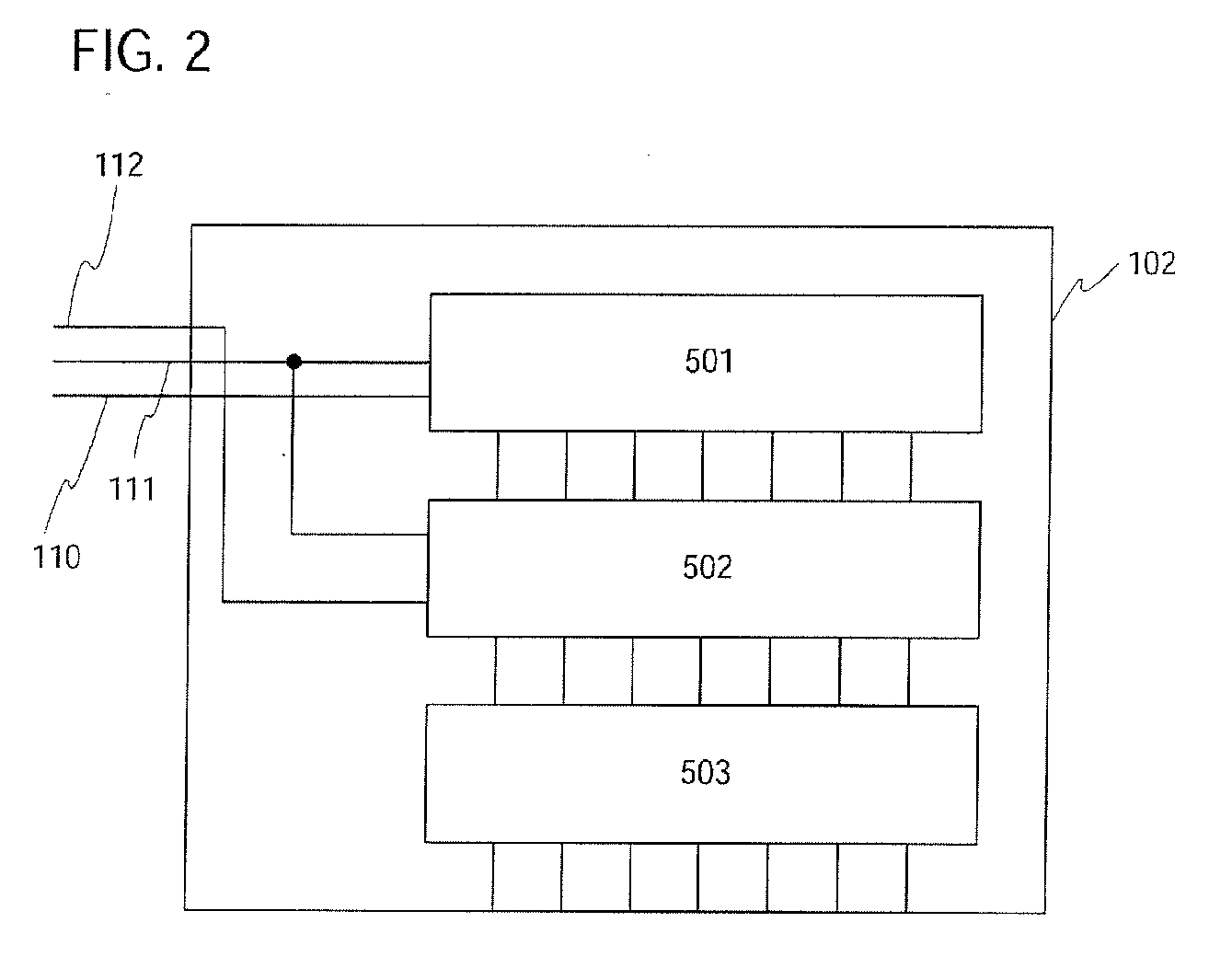
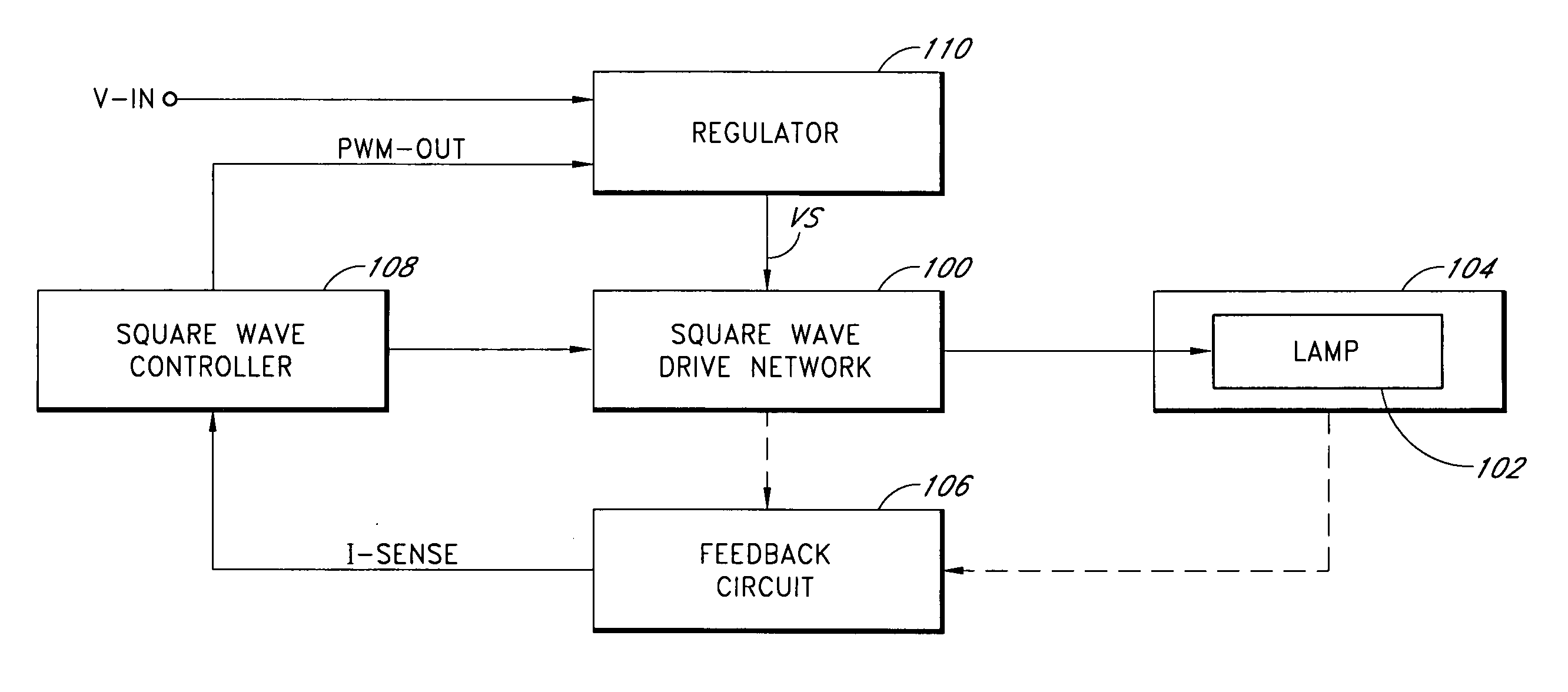
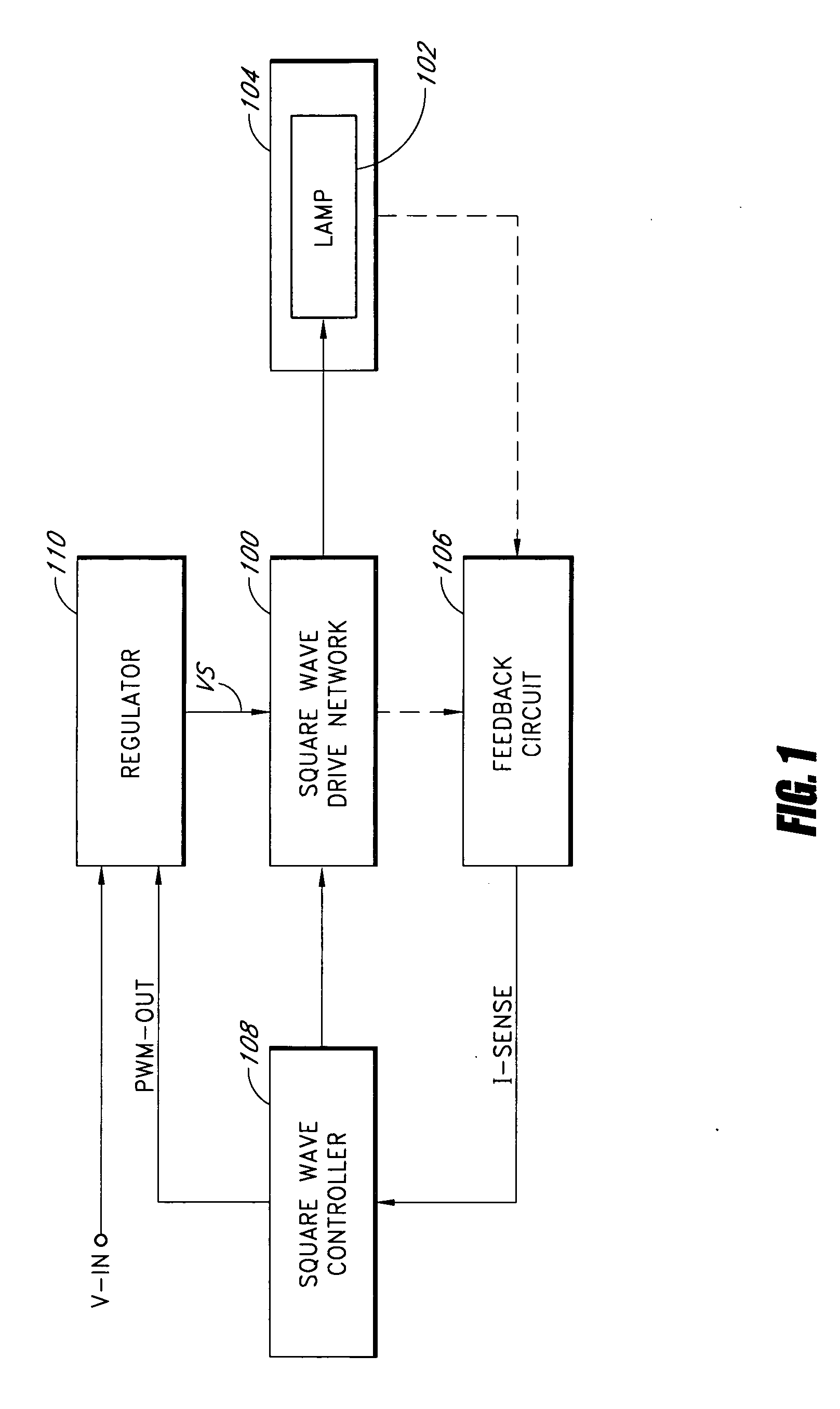
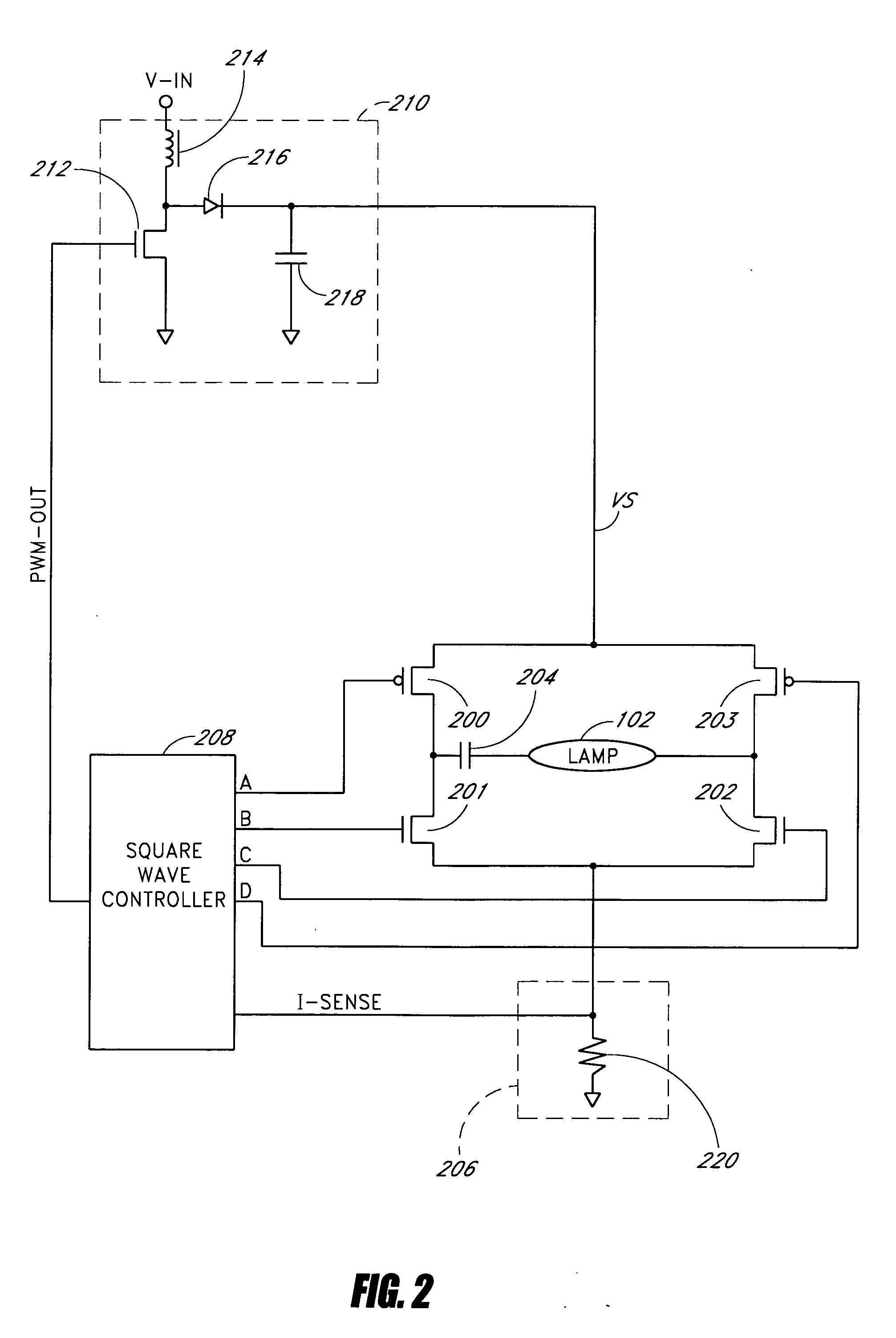
Square wave drive system
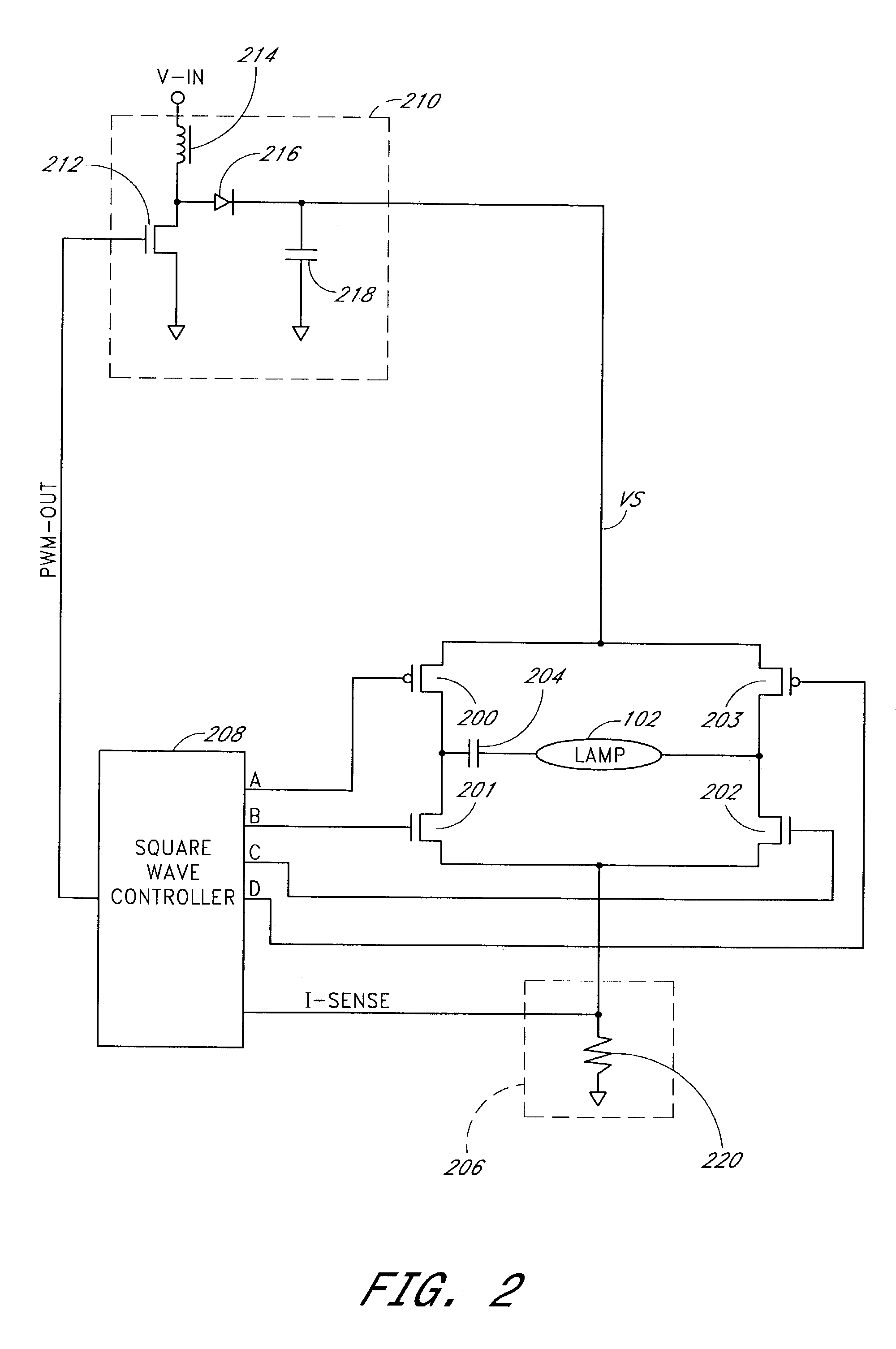
InactiveUS20060022612A1Improve efficiencyProlong lifeElectric light circuit arrangementElectric discharge lampsLamp currentPeak value
A power conversion circuit improves lamp operating life and lamp efficiency by driving a fluorescent lamp with a square wave signal. The square wave signal is an alternating current signal with relatively fast transition times. The square wave signal advantageously reduces lamp current crest factor for more efficient operation of the fluorescent lamp.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA NAT TRUST & SAVINGS ASSOC
Pixel circuit, display device, and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20080225027A1Potential differenceIncrease the differenceElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesComputer hardwareDisplay device
Owner:SONY CORP
Integrated circuits with temperature-change and threshold-voltage drift compensation
ActiveUS6933869B1Increase power supply voltageReduce eliminate negative impactElectric signal transmission systemsStatic storageOperating temperatureIntegrated circuit
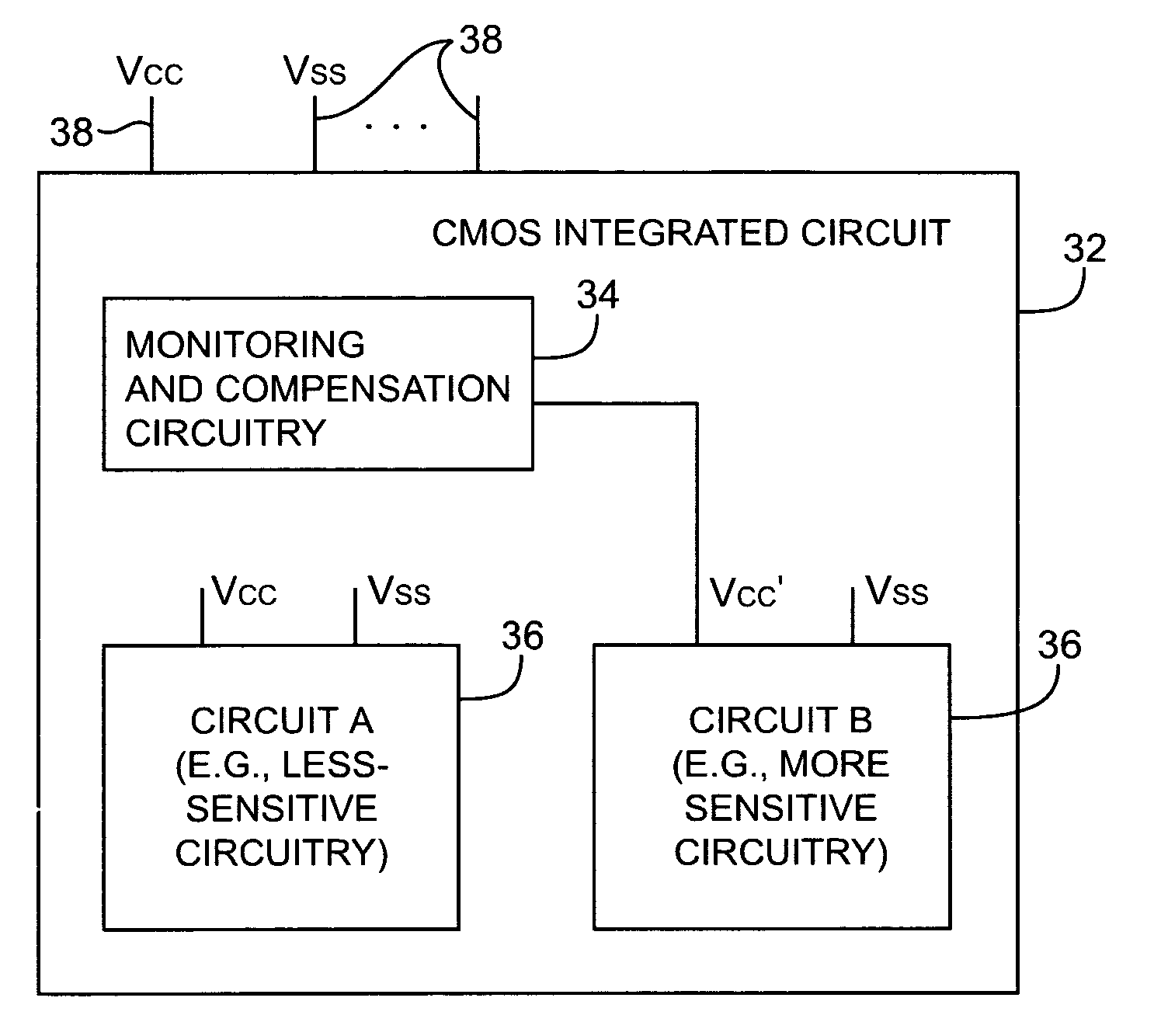
Integrated circuits are stabilized by monitoring changes that affect circuit operation and by compensating for those changes using power supply adjustments. Changes in operating temperature and threshold voltage changes may be measured. Differential measurements may be made in which threshold voltages measured in continuously-biased monitoring circuits are compared to threshold voltages measured in intermittently-biased monitoring circuits. Temperature changes may be monitored using a temperature monitoring circuit based on an adjustable current source and a diode. Monitoring and compensation circuitry on the integrated circuits may use analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog converters controlled by a control unit to make temperature and threshold voltage measurements and corresponding compensating changes in power supply voltages.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Square wave drive system
InactiveUS6969958B2Improve efficiencyProlong lifeElectric light circuit arrangementElectric discharge lampsEngineeringLamp current
A power conversion circuit improves lamp operating life and lamp efficiency by driving a fluorescent lamp with a square wave signal. The square wave signal is an alternating current signal with relatively fast transition times. The square wave signal advantageously reduces lamp current crest factor for more efficient operation of the fluorescent lamp.
Owner:MICROSEMI
Current-controlled CMOS circuit using higher voltage supply in low voltage CMOS process
InactiveUS6911855B2Speed maximizationDissipates static currentElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorTransceiverEngineering
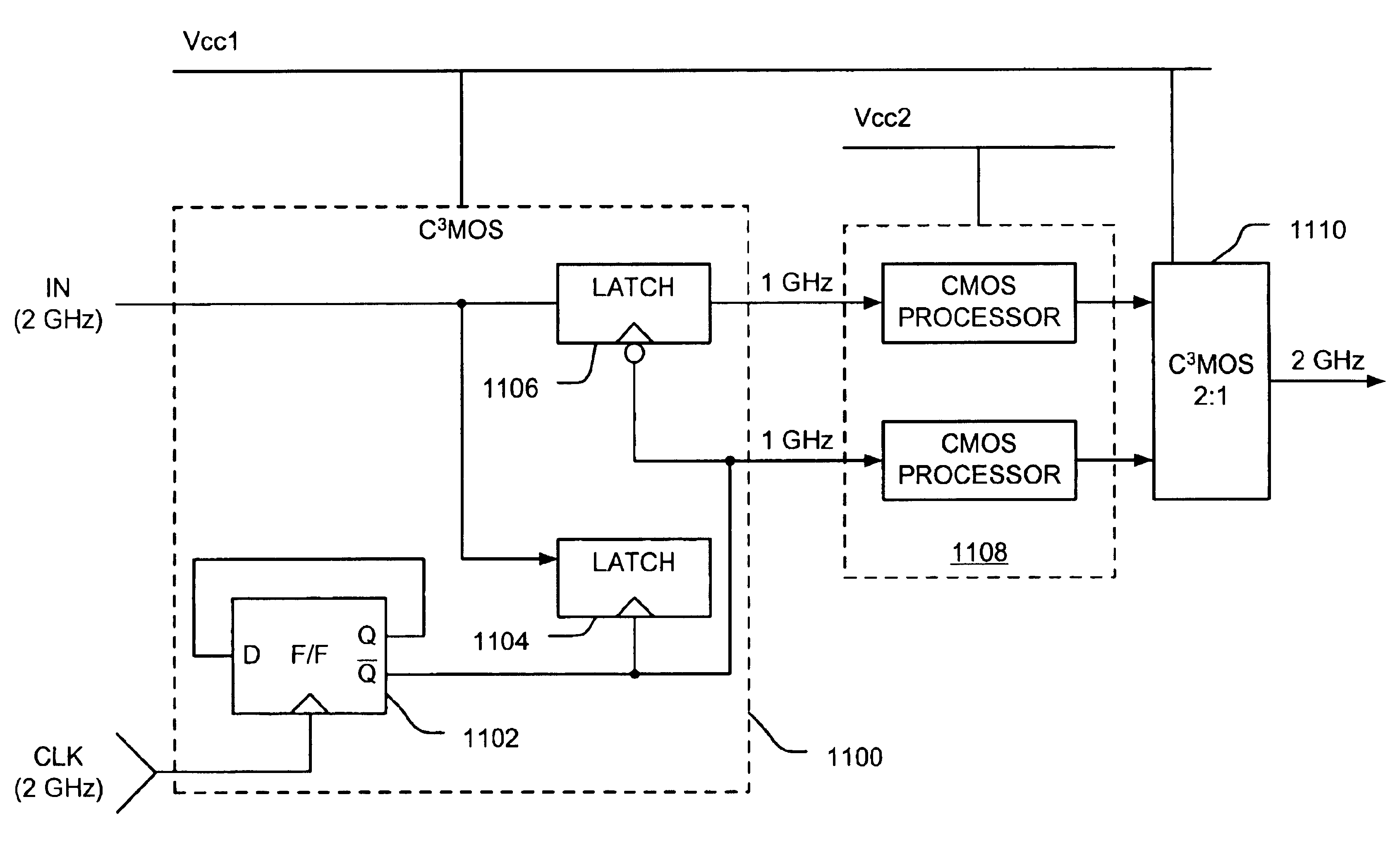
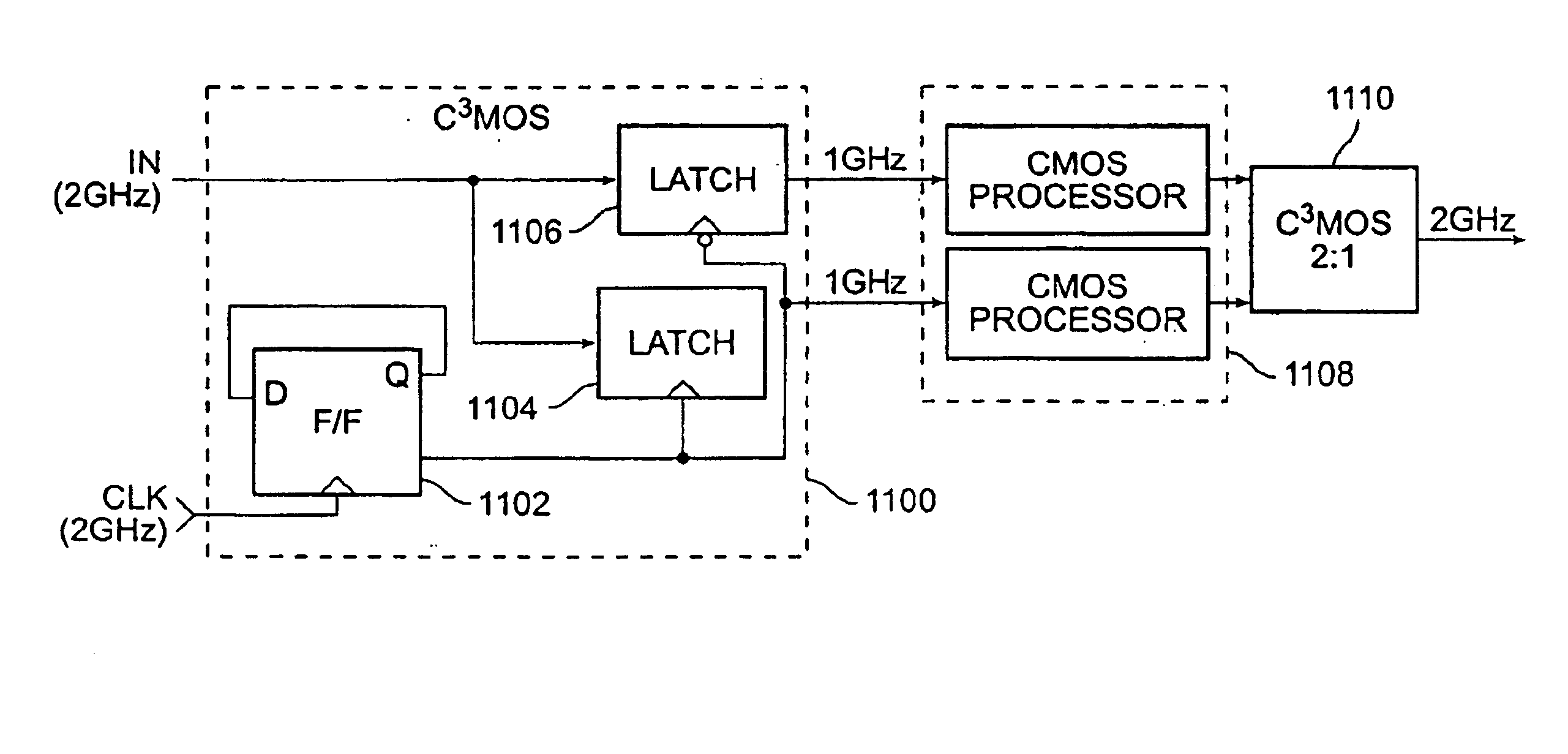
Various circuit techniques for implementing ultra high speed circuits use current-controlled CMOS (C3MOS) logic fabricated in conventional CMOS process technology. An entire family of logic elements including inverter / buffers, level shifters, NAND, NOR, XOR gates, latches, flip-flops and the like are implemented using C3MOS techniques. Optimum balance between power consumption and speed for each circuit application is achieve by combining high speed C3MOS logic with low power conventional CMOS logic. The combined C3MOS / CMOS logic allows greater integration of circuits such as high speed transceivers used in fiber optic communication systems. The C3MOS structure enables the use of a power supply voltage that may be larger than the voltage required by the CMOS fabrication process, further enhancing the performance of the circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Circuits and design structures for monitoring nbti (negative bias temperature instability) effect and/or pbti (positive bias temperature instability) effect
ActiveUS20090189703A1High power supply voltageResistance/reactance/impedencePulse generation by logic circuitsNOR gateNAND gate
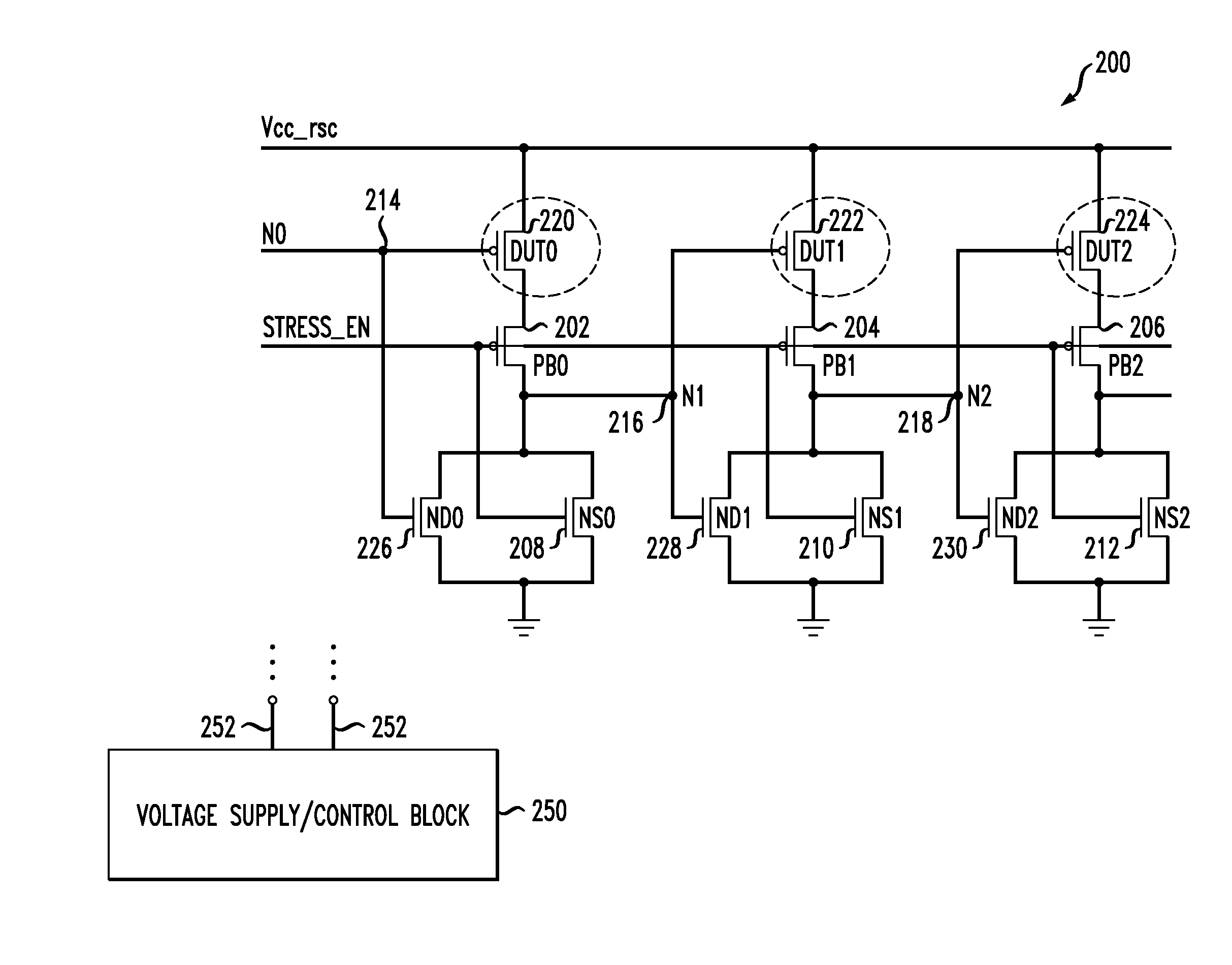
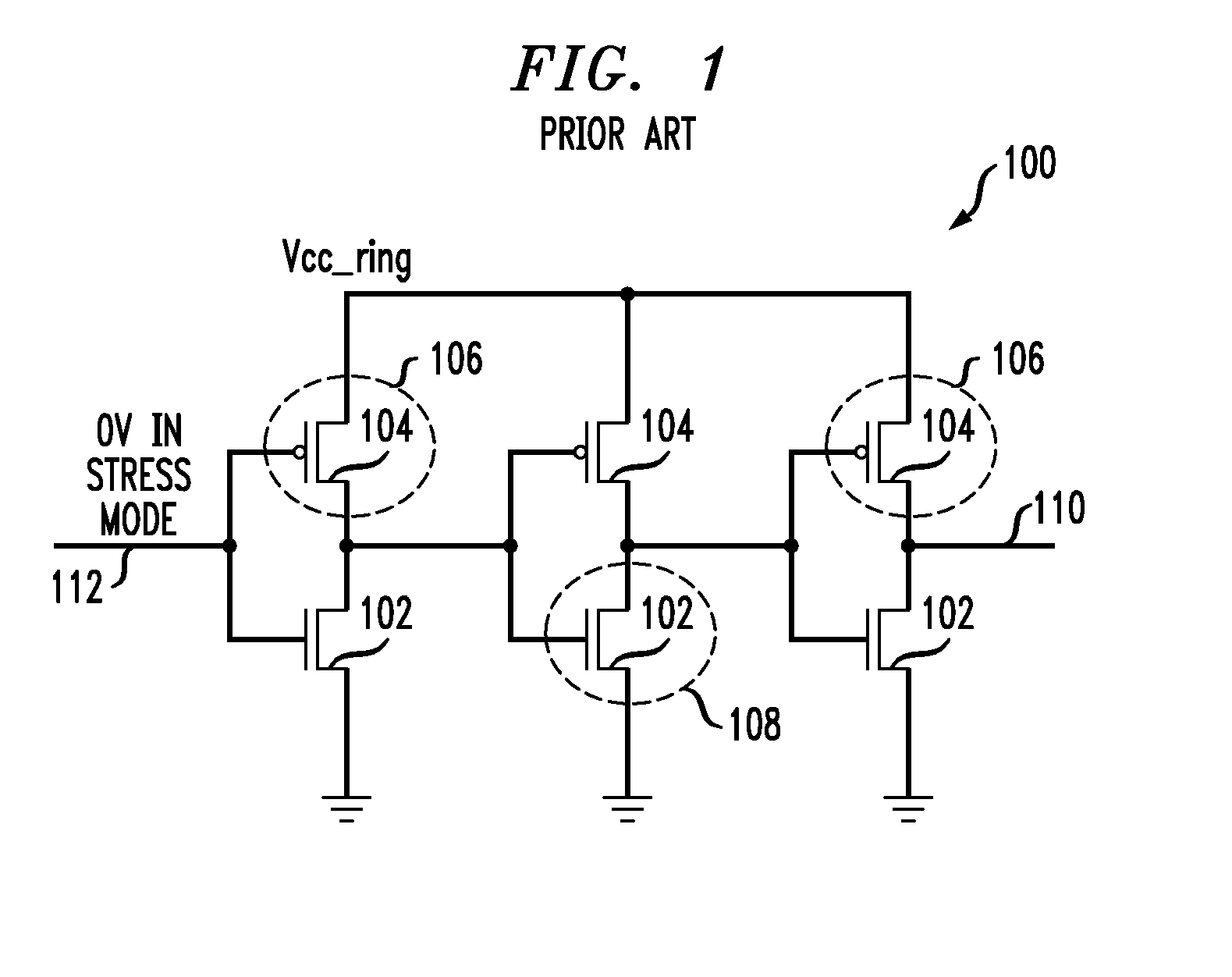
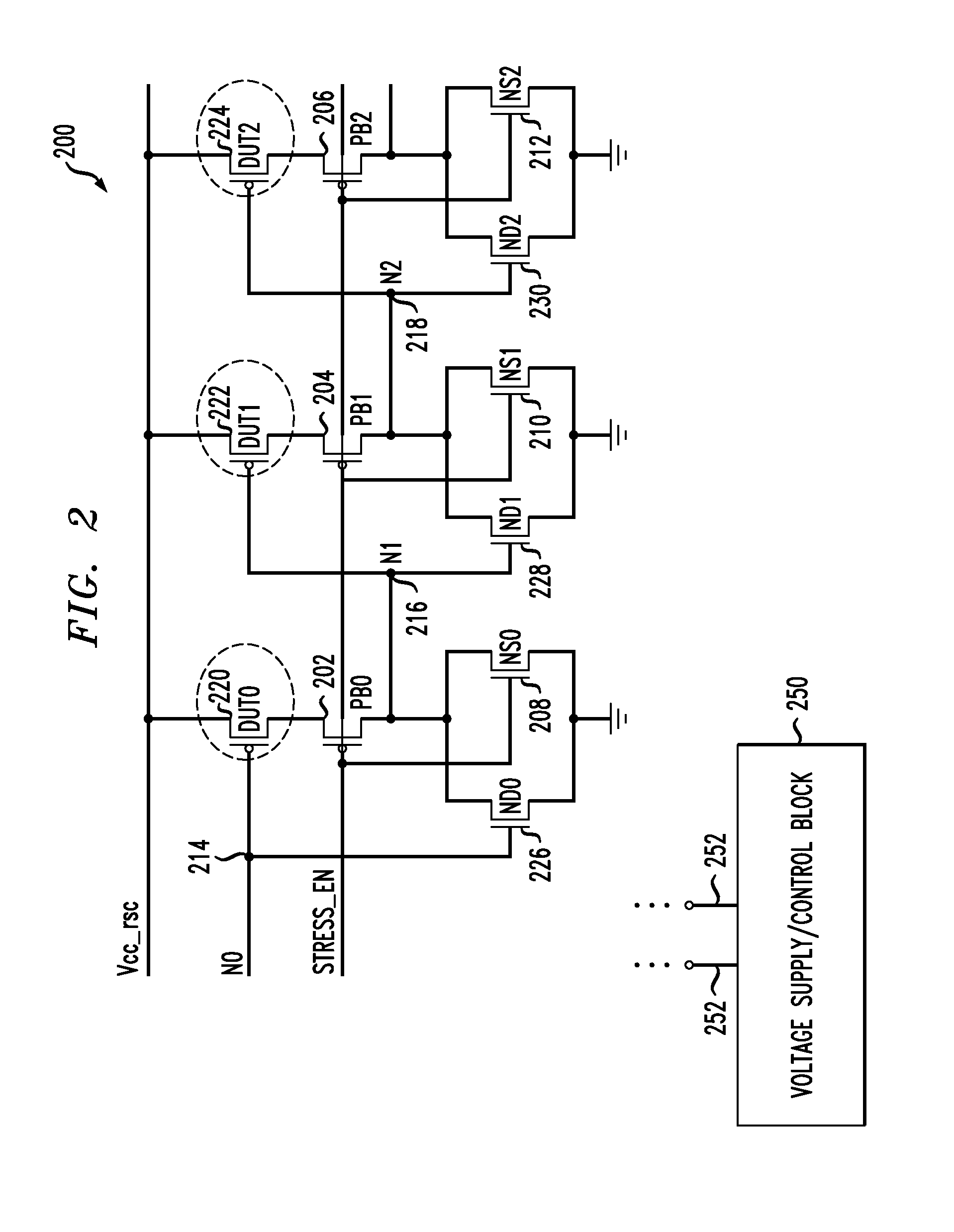
A ring oscillator has an odd number of NOR-gates greater than or equal to three, each with first and second input terminals, a voltage supply terminal, and an output terminal. The first input terminals of all the NOR-gates are interconnected, and each of the NOR-gates has its output terminal connected to the second input terminal of an immediately adjacent one of the NOR-gates. During a stress mode, a voltage supply and control block applies a stress enable signal to the interconnected first input terminals, and an increased supply voltage to the voltage supply terminals. During a measurement mode, this block grounds the interconnected first input terminals, and applies a normal supply voltage to the voltage supply terminals. Also included are an analogous NAND-gate based circuit, a circuit combining the NAND- and NOR-aspects, a circuit with a ring oscillator where the inverters may be coupled directly or through inverting paths, and circuits for measuring the bias temperature instability effect in pass gates.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Current-controlled CMOS circuit using higher voltage supply in low voltage CMOS process
InactiveUS6897697B2Speed maximizationDissipates static currentExclusive-OR circuitsElectronic switchingTransceiverEngineering
Various circuit techniques for implementing ultra high speed circuits use current-controlled CMOS (C3MOS) logic fabricated in conventional CMOS process technology. An entire family of logic elements including inverter / buffers, level shifters, NAND, NOR, XOR gates, latches, flip-flops and the like are implemented using C3MOS techniques. Optimum balance between power consumption and speed for each circuit application is achieve by combining high speed C3MOS logic with low power conventional CMOS logic. The combined C3MOS / CMOS logic allows greater integration of circuits such as high speed transceivers used in fiber optic communication systems. The C3MOS structure enables the use of a power supply voltage that may be larger than the voltage required by the CMOS fabrication process, further enhancing the performance of the circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
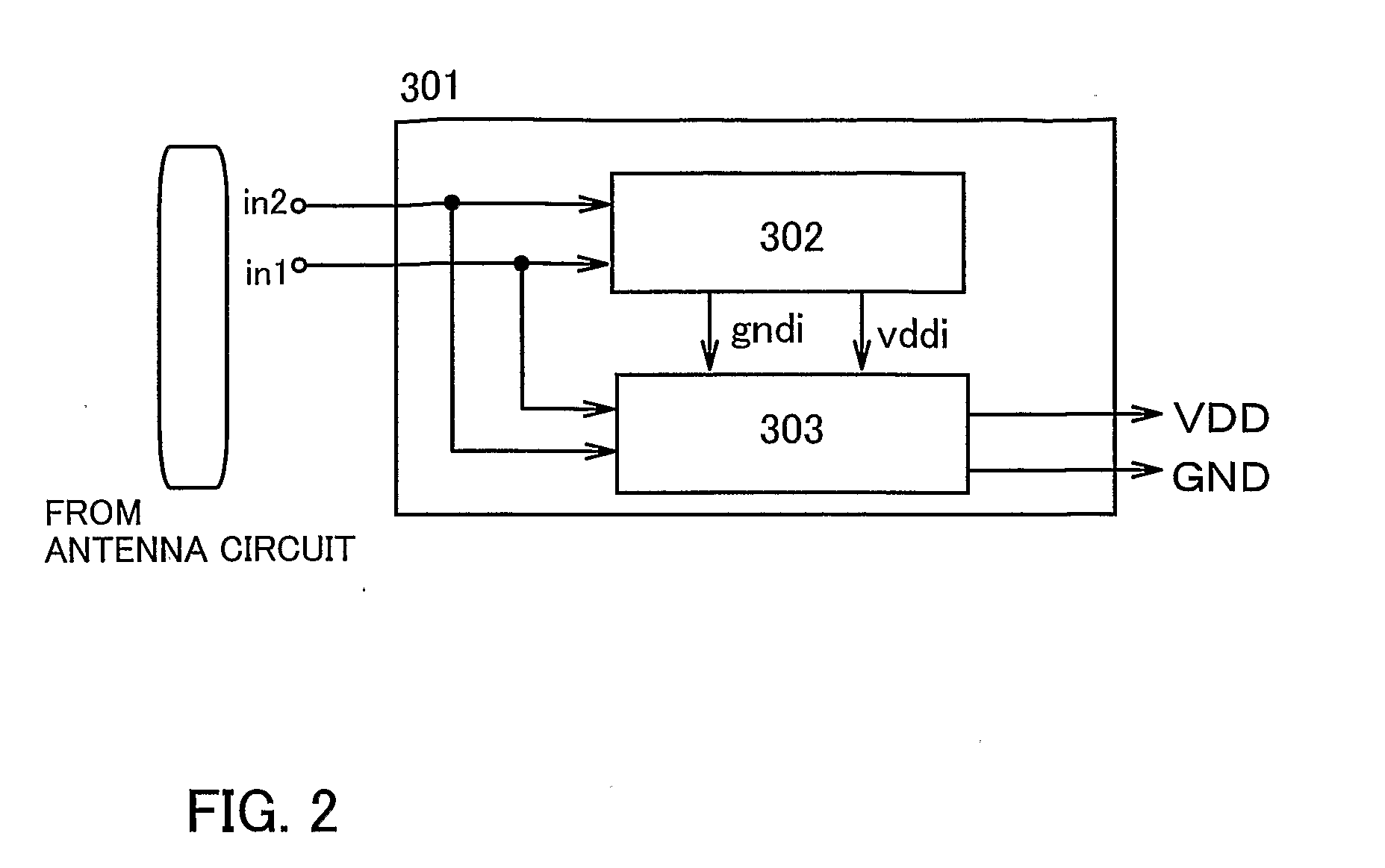
Wireless Chip
InactiveUS20080093934A1High power supply voltageImprove communication distanceElectromagnetic wave systemSolid-state devicesEngineeringPower circuits
The size of a wireless chip is often determined according to an antenna circuit thereof. Power source voltage or power supplied to the wireless chip can be more easily received with a larger antenna. On the other hand, there has been an increasing demand for a compact wireless chip, and it is thus necessary to downsize an antenna. In view of this, the invention provides a wireless chip capable of data communication with a small antenna, namely a compact wireless chip having an improved communicable distance. A power source circuit of an ID chip of the invention generates a higher power source voltage than a power source voltage generated in a conventional ID chip, by using a boosting power source circuit having a boosting circuit and a rectifier circuit.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light-emitting element having at least one light-emitting chip crystal
InactiveUS20070090391A1Remove heatPremature overheating is also preventedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsEngineeringLight-emitting diode
A light-emitting element, in particular a light-emitting diode, having at least one light-emitting chip crystal, in particular a semiconductor crystal, is described. At least free surfaces of the light-emitting chip crystal are covered with an inert material—liquid fluid—which is in direct contact with the light-emitting chip crystal.
Owner:NOCTRON
Near field communication device, electronic system having the same and method of controlling power in near field communication device
ActiveUS20150079903A1Reduce power consumptionReduced magnitudePower managementNear-field systems using receiversPhysicsVoltage
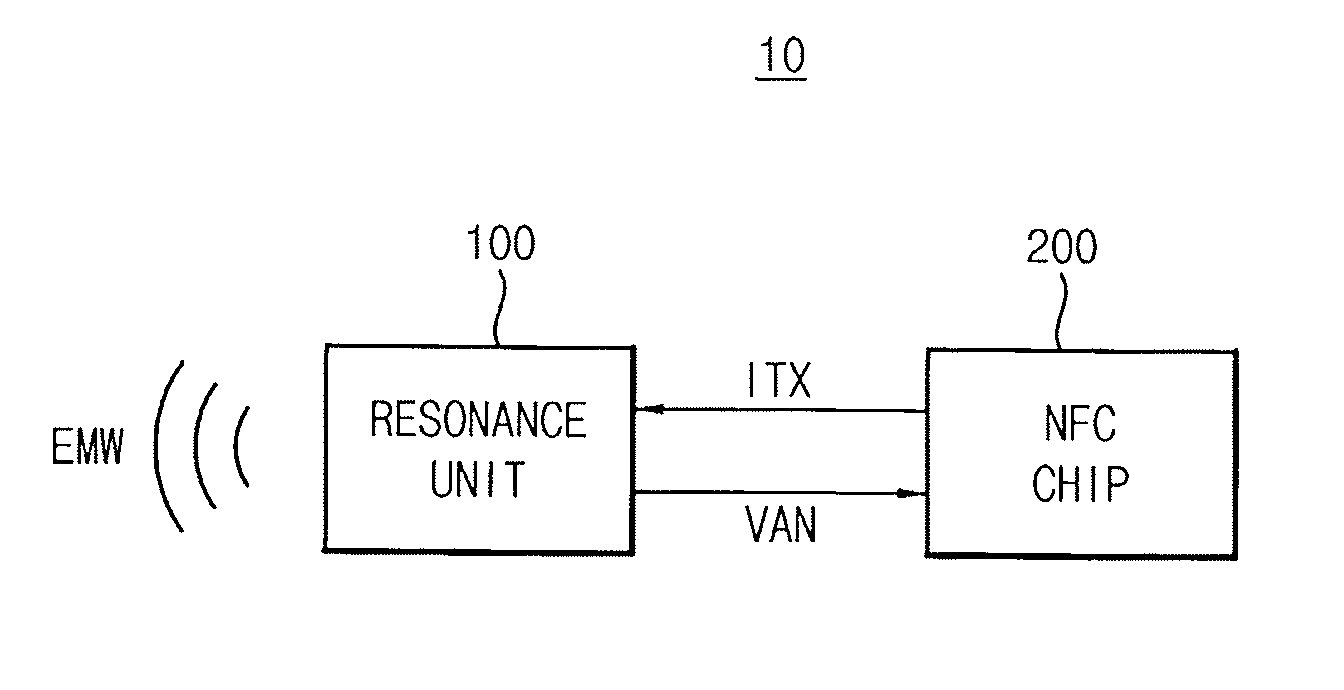
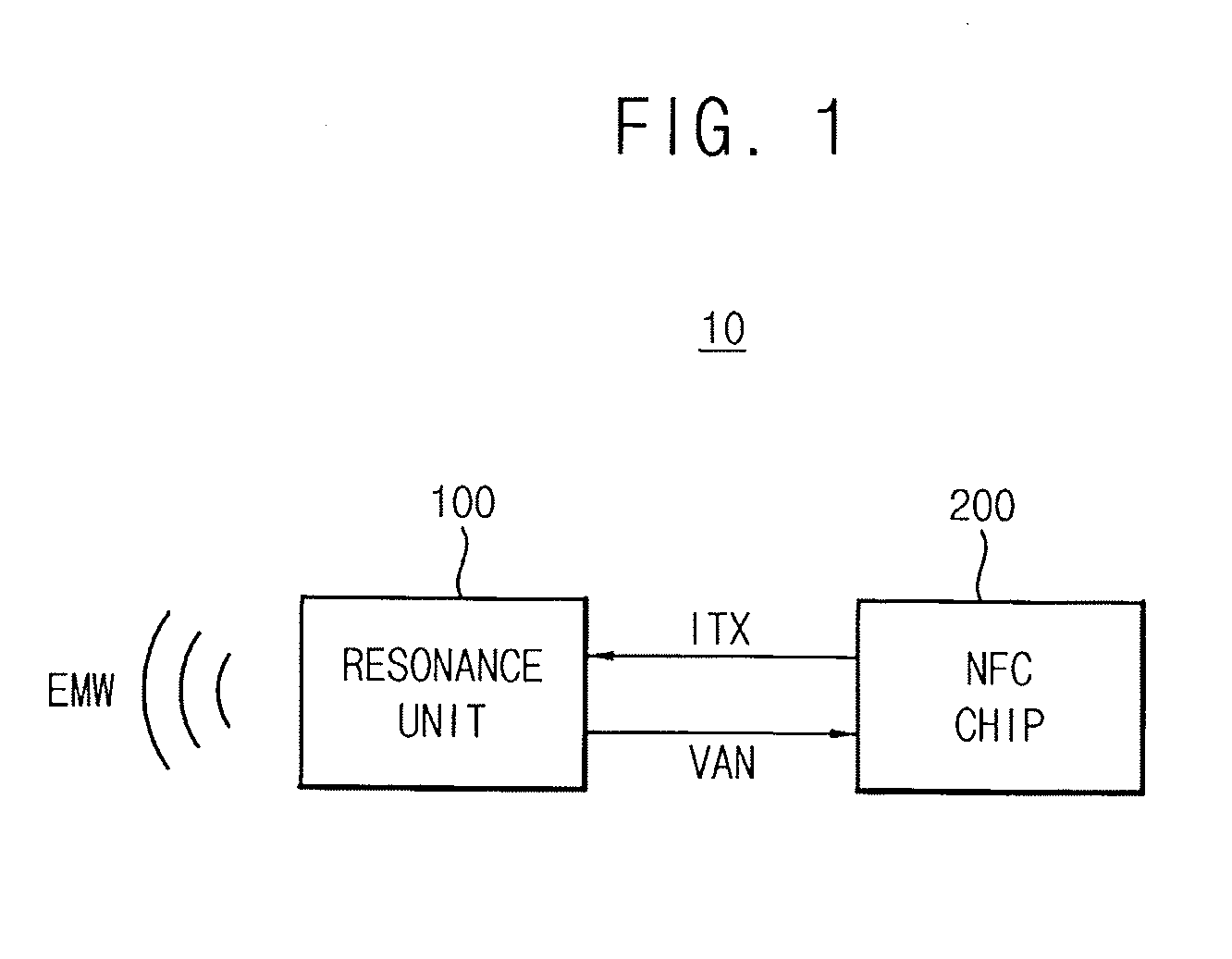
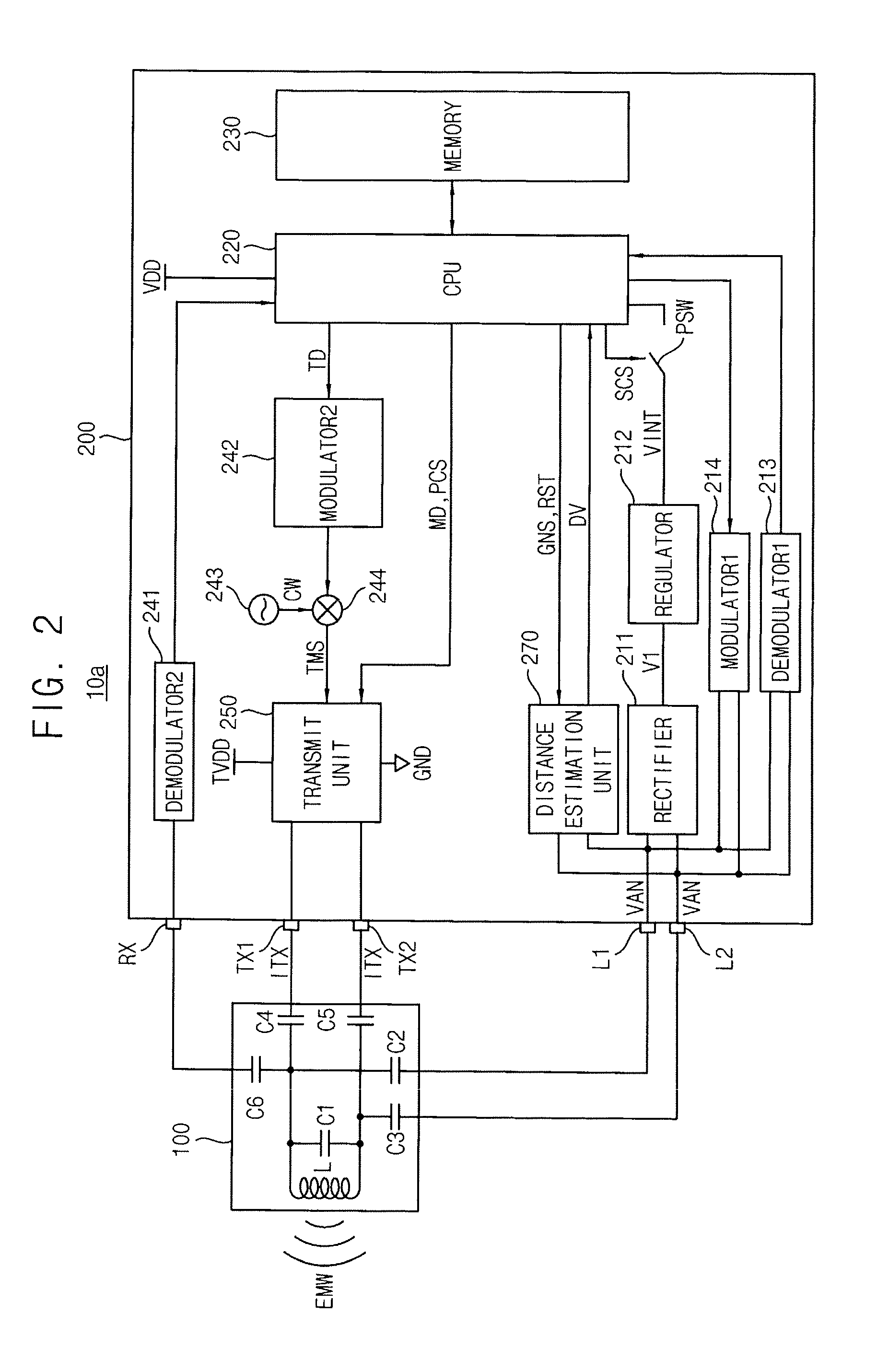
A near field communication (NFC) device includes a resonance unit and an NFC chip. The resonance unit emits an electromagnetic wave to communicate data with an external NFC card in a reader mode. The NFC chip estimates a distance between the resonance unit and the external NFC card based on an antenna voltage generated by the resonance unit while the resonance unit emits the electromagnetic wave, and adjusts a magnitude of the electromagnetic wave based on the estimated distance.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
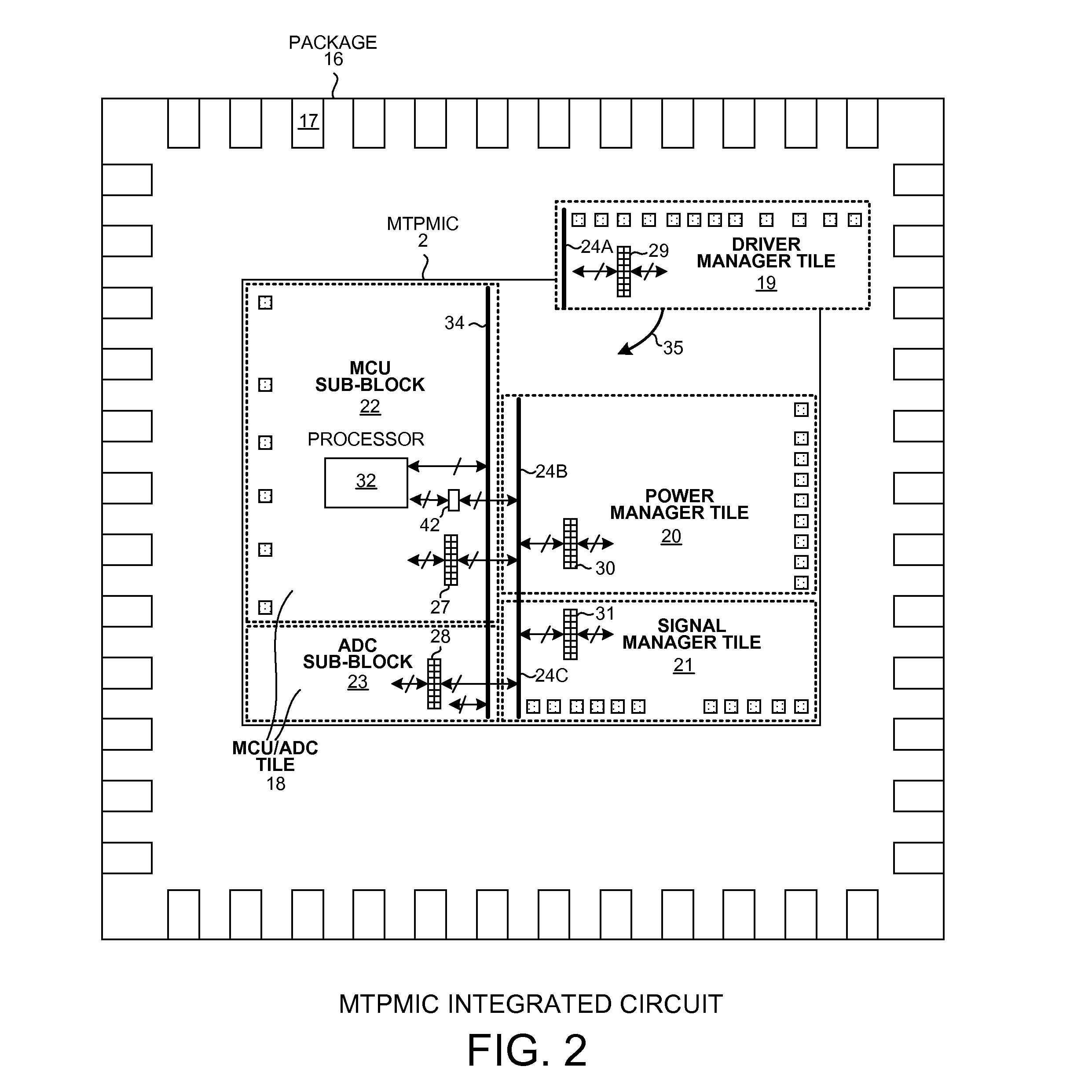
Multi-Mode Power Manager For Power Management Integrated Circuit
ActiveUS20130151825A1High power supply voltageEfficient power electronics conversionVolume/mass flow measurementElectrical conductorEngineering
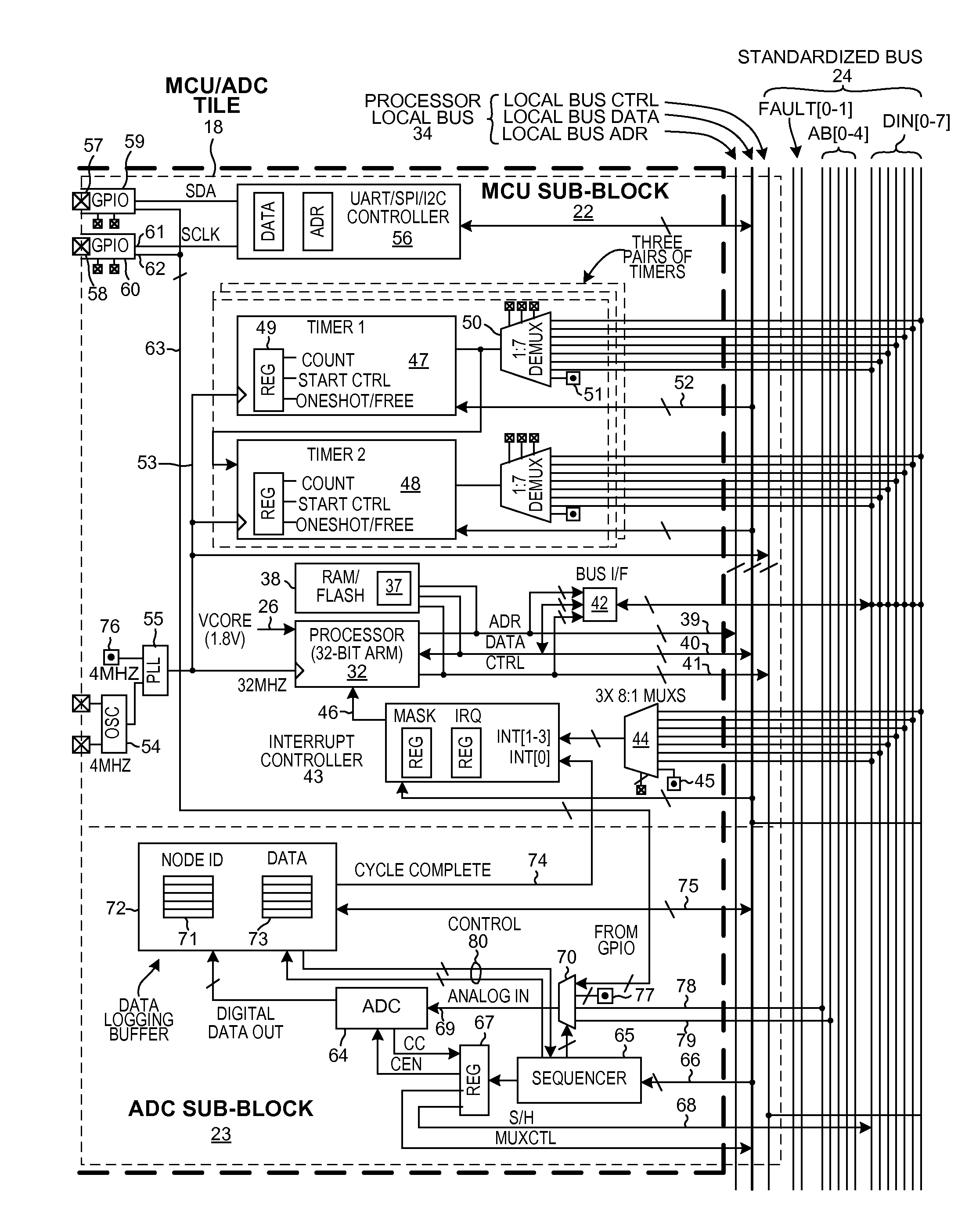
A Multi-Tile Power Management Integrated Circuit (MTPMIC) includes tiles including an MCU / ADC tile and a power manager tile. The power manager tile includes a set of Configurable Switching Power Supply Pulse Width Modulator (CSPSPWM) components. These components, in combination with other circuitry external to the integrated circuit, are configurable to form a selected one of a number of different switching power supply circuits. Upon power up, an internal regulator supplies power to the CSPSPWM. The CSPSPWM then controls the power supply to begin switching in a low frequency start-up mode. The CSPSPWM determines during start-up the current sensing method based on circuitry external to the integrated circuit. A supply voltage generated is then supplied via a conductor of a standardized bus to a processor in the MCU / ADC tile. The processor begins executing instructions, and as a result writes across the standardized bus to configure the various tiles of the MTPMIC.
Owner:ACTIVE SEMI
Secondary-battery monitoring device and battery pack
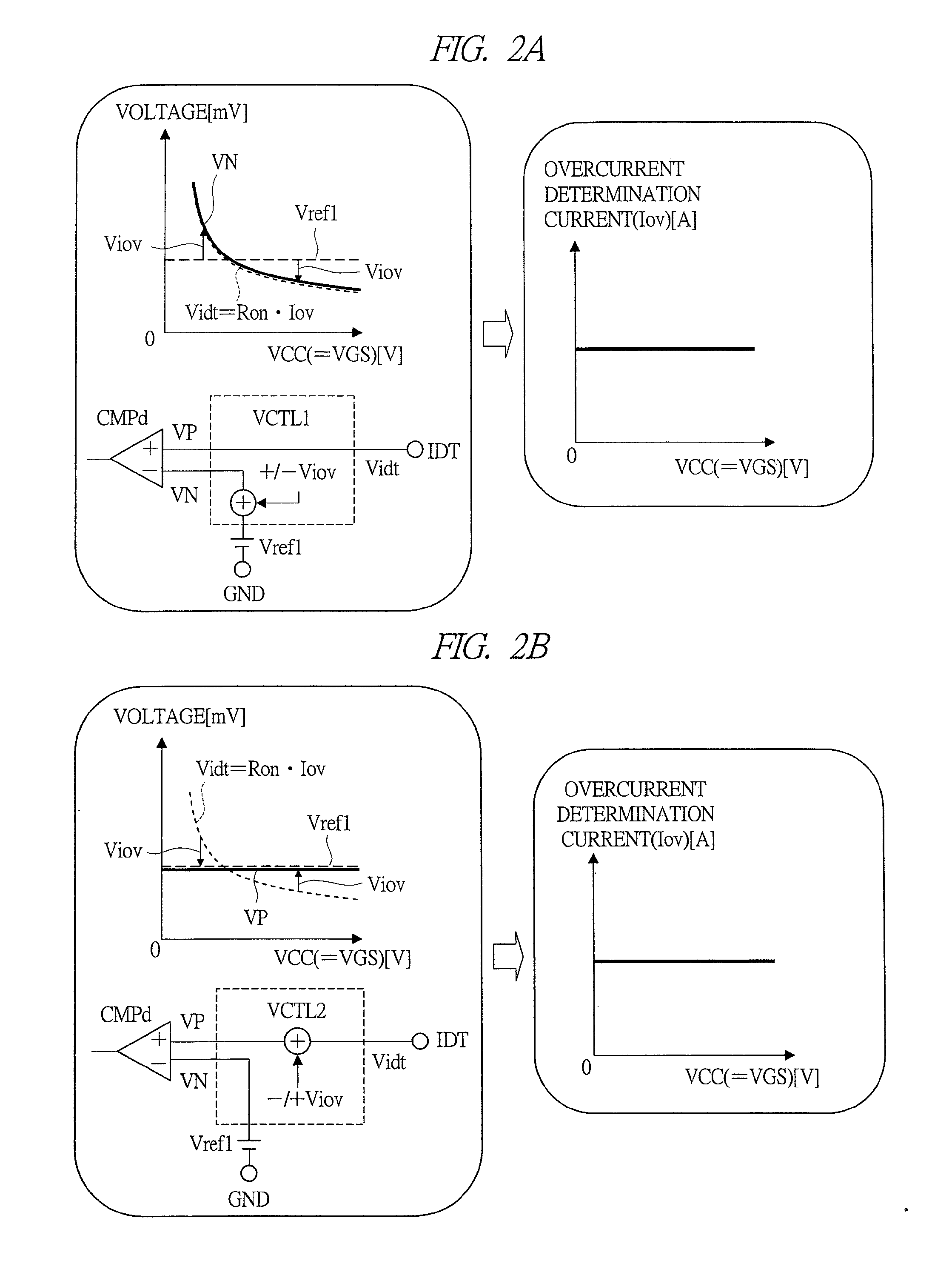
ActiveUS20130229144A1Reduce variationVoltage is accurateEmergency protective circuit arrangementsRate of change measurementOvercurrentElectrical polarity
A secondary-battery monitoring device capable of realizing highly reliable overcurrent detection and a battery pack having it are provided. When an overcurrent flowing to a secondary battery is to be detected by utilizing a current detection voltage generated via on-resistance of a discharge-control switch and a charge-control switch, a voltage correction circuit that generates a correction voltage having a characteristic varied by positive slope or negative slope along with increase in a power supply voltage is provided, and the correction voltage is added to the detection voltage or a reference power supply voltage with the polarity that cancels out the slope of voltage variation caused in the detection voltage, and then the voltage is input to a comparator circuit. In this manner, variation in the overcurrent determination current is reduced.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Low power static random access memory
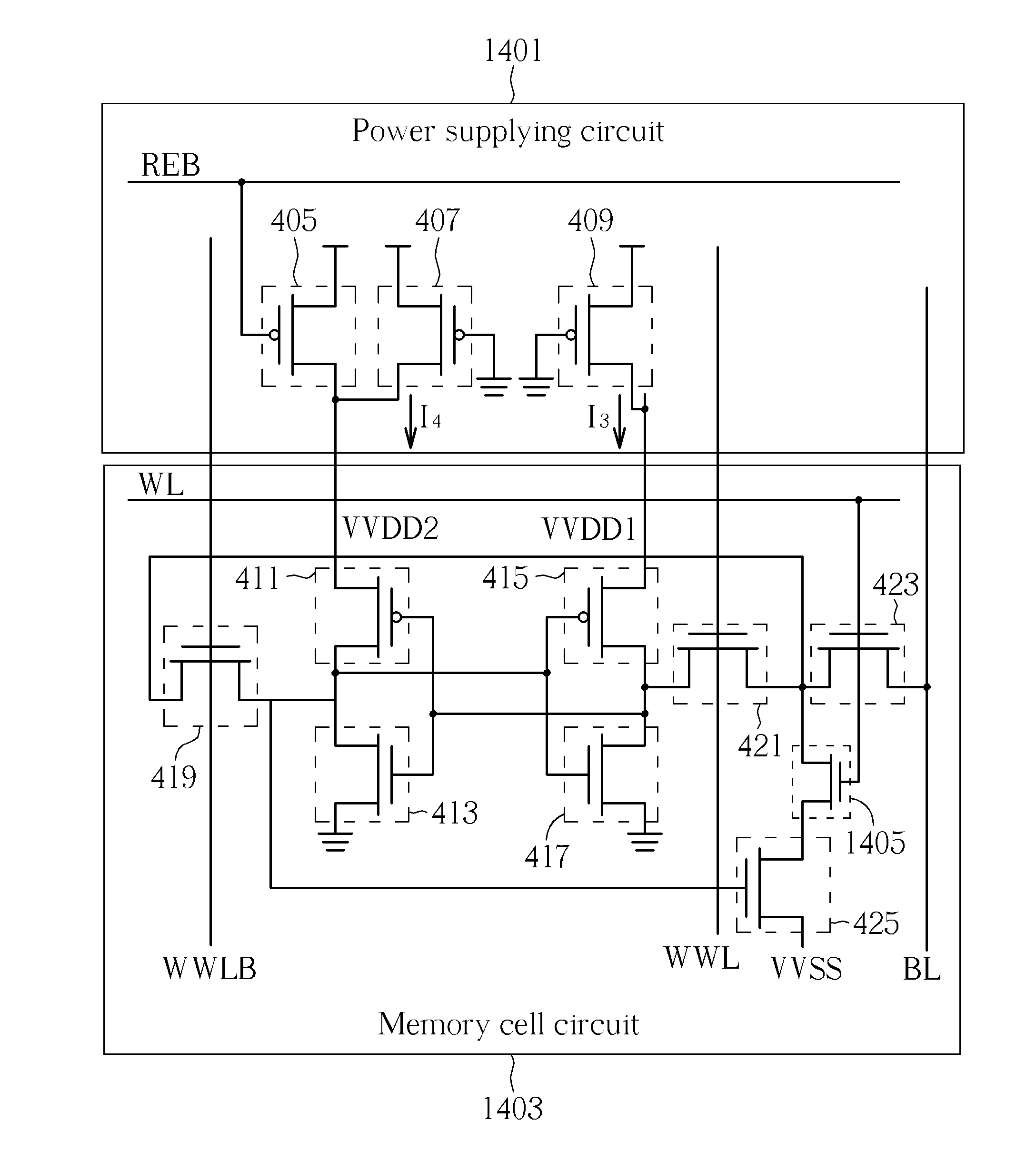
ActiveUS20120008449A1Reduce voltageFacilitate writing of data into the memory cellDigital storageStatic random-access memoryLow voltage
A SRAM that keeps the memory cell array under a low voltage in the Standby mode and Write mode, and raises the memory cell array supply voltage to a high voltage in the Read mode. A SRAM comprising: at least one memory cell circuit, comprising a latch circuit with at least two inverters, and comprising two power receiving terminals for receiving power; and a power supplying circuit, for providing the power to the memory cell circuit, such that the voltages at the power receiving terminals of the latch circuit is below a predetermined voltage level when data is written to the latch circuit. In one embodiment, the memory cell circuit includes a plurality of data accessing terminals and the data accessing terminals are respectively controlled by at least two pass-transistor switch devices.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP +1
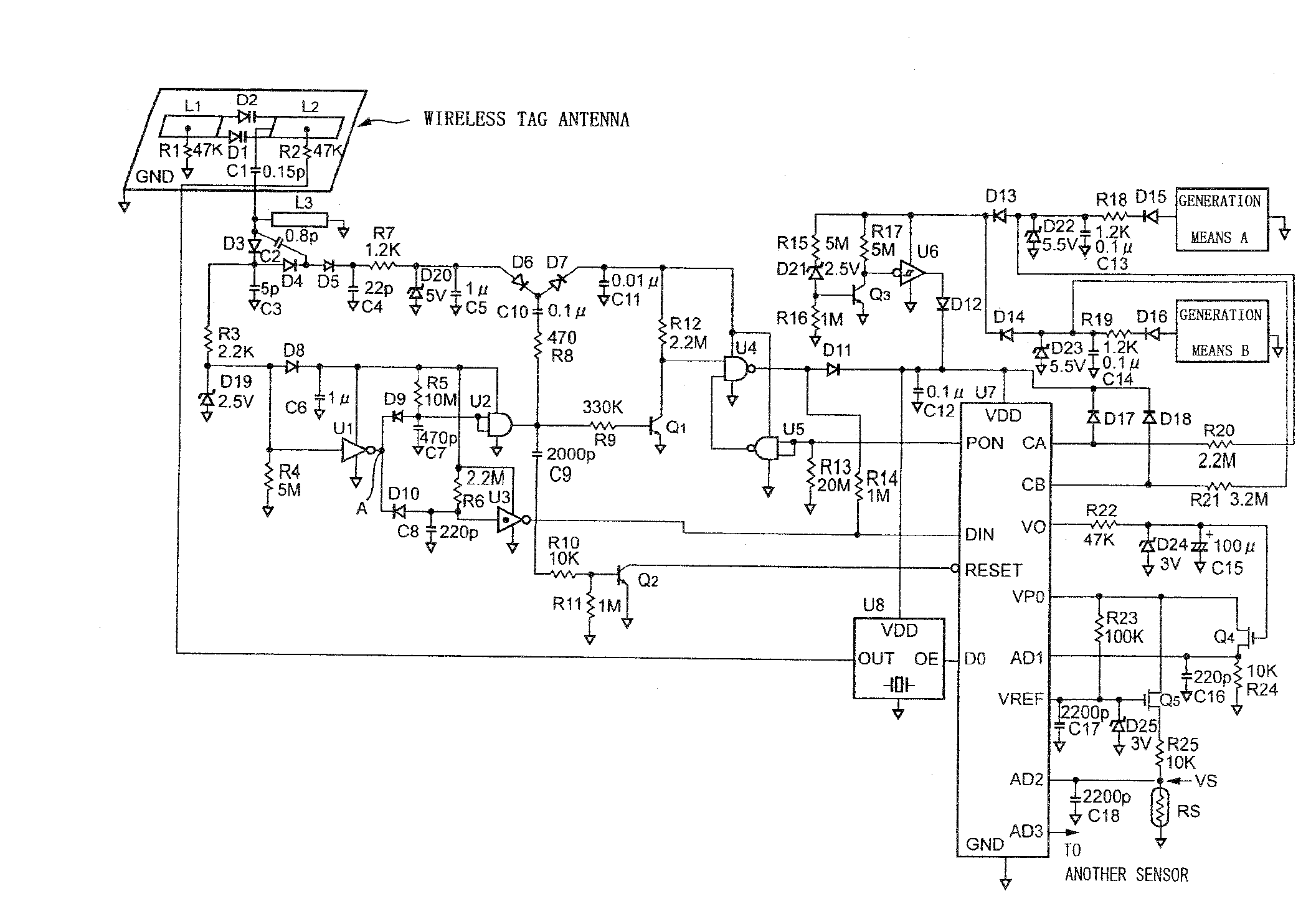
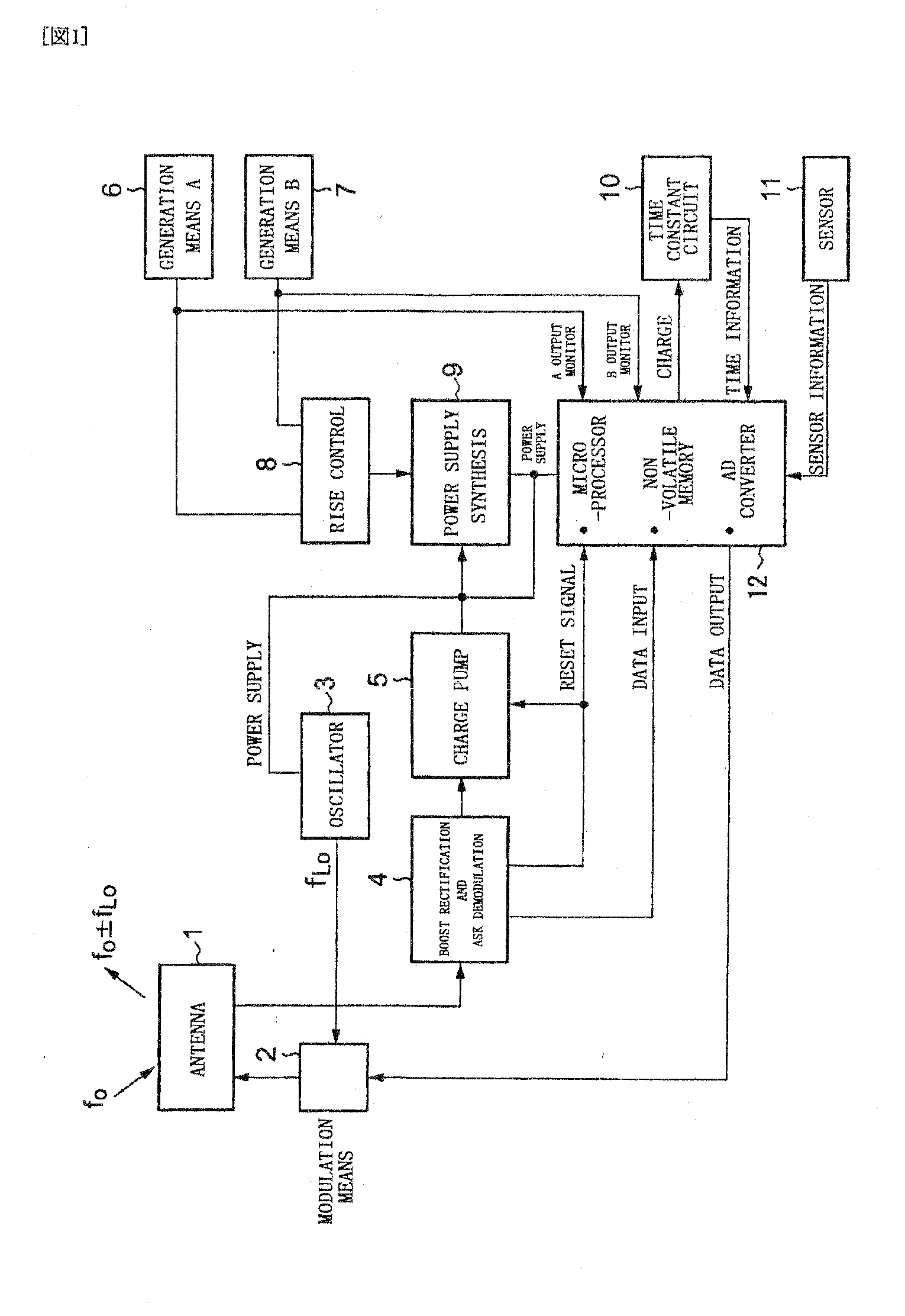
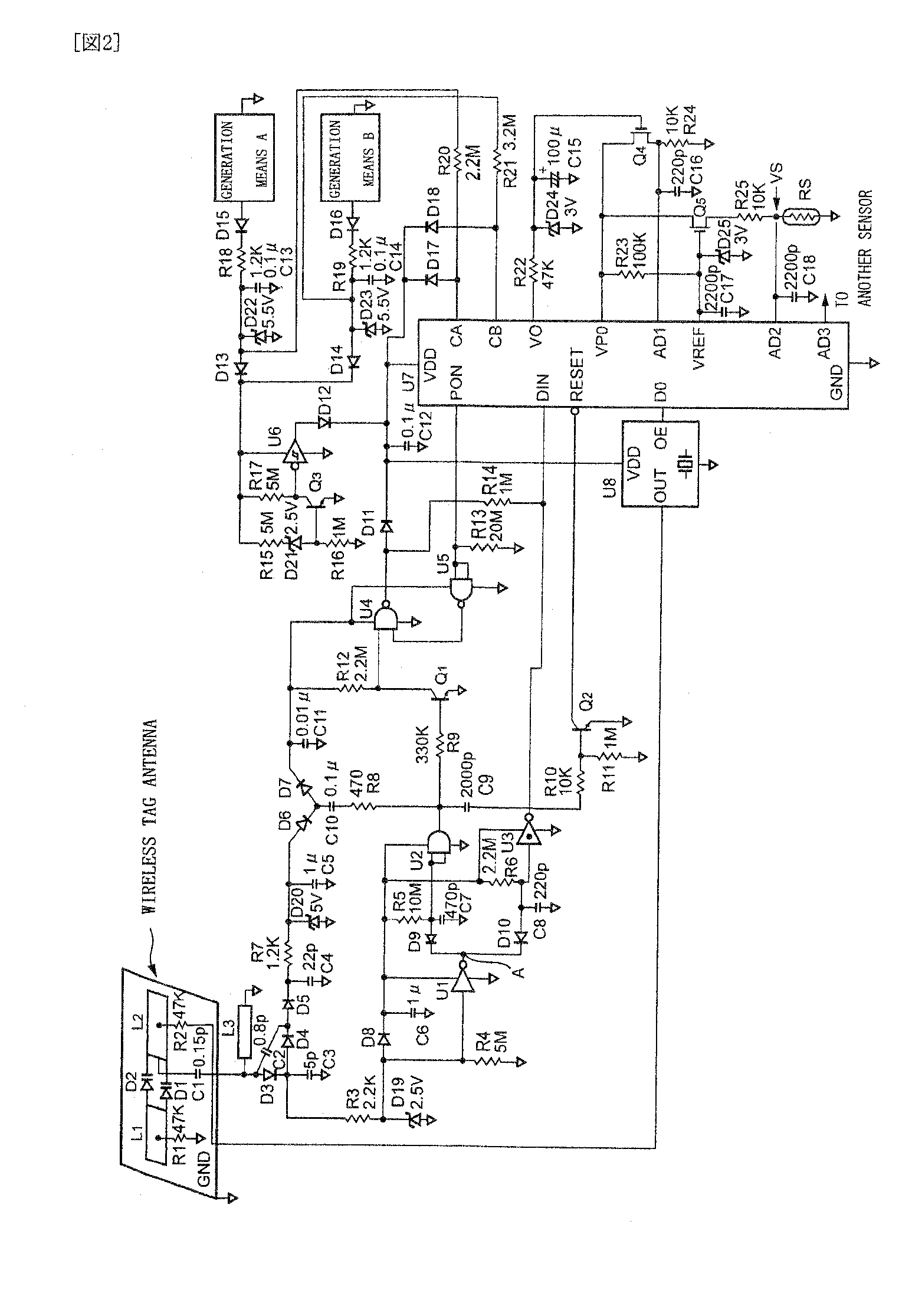
Sensor tag, sensor tag device, power receiving circuit, and sensor tag device power supply method
InactiveUS20090121837A1Long wireless communication distanceImprove receiving efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTTicket-issuing apparatusResonanceEvent data
There is provided a sensor tag device capable of detecting event data by a sensor tag all the time even when no radio wave is received, saving power supply for a microprocessor, and enlarging the radio communication distance. The sensor tag device includes generation means 6 and 7 using one or more environmental changes, power supply voltage rise control means 8, and power supply synthesis means 9, and power is supplied to a microprocessor 12 and event data is stored in the microprocessor 12 when an event, i.e., an environmental change has occurred. A power receiving circuit having a transmission / reception antenna, a built-in power receiving circuit, and the microprocessor and capable of bi-directional communication by radio waves is combined with a stab resonance RF boost circuit and a ladder boost rectification circuit.
Owner:KITAYOSHI HITOSHI +1
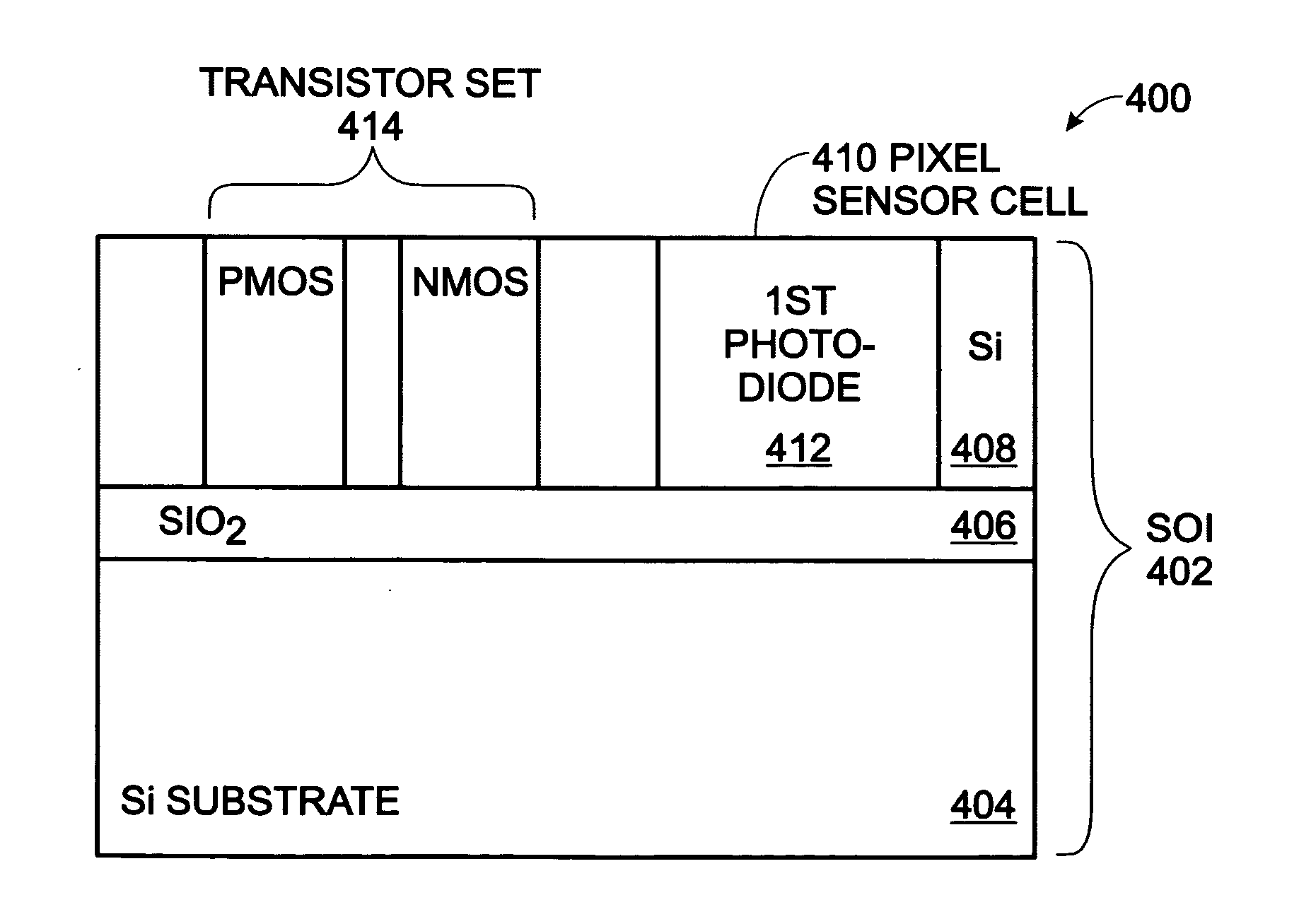
Wide output swing CMOS imager
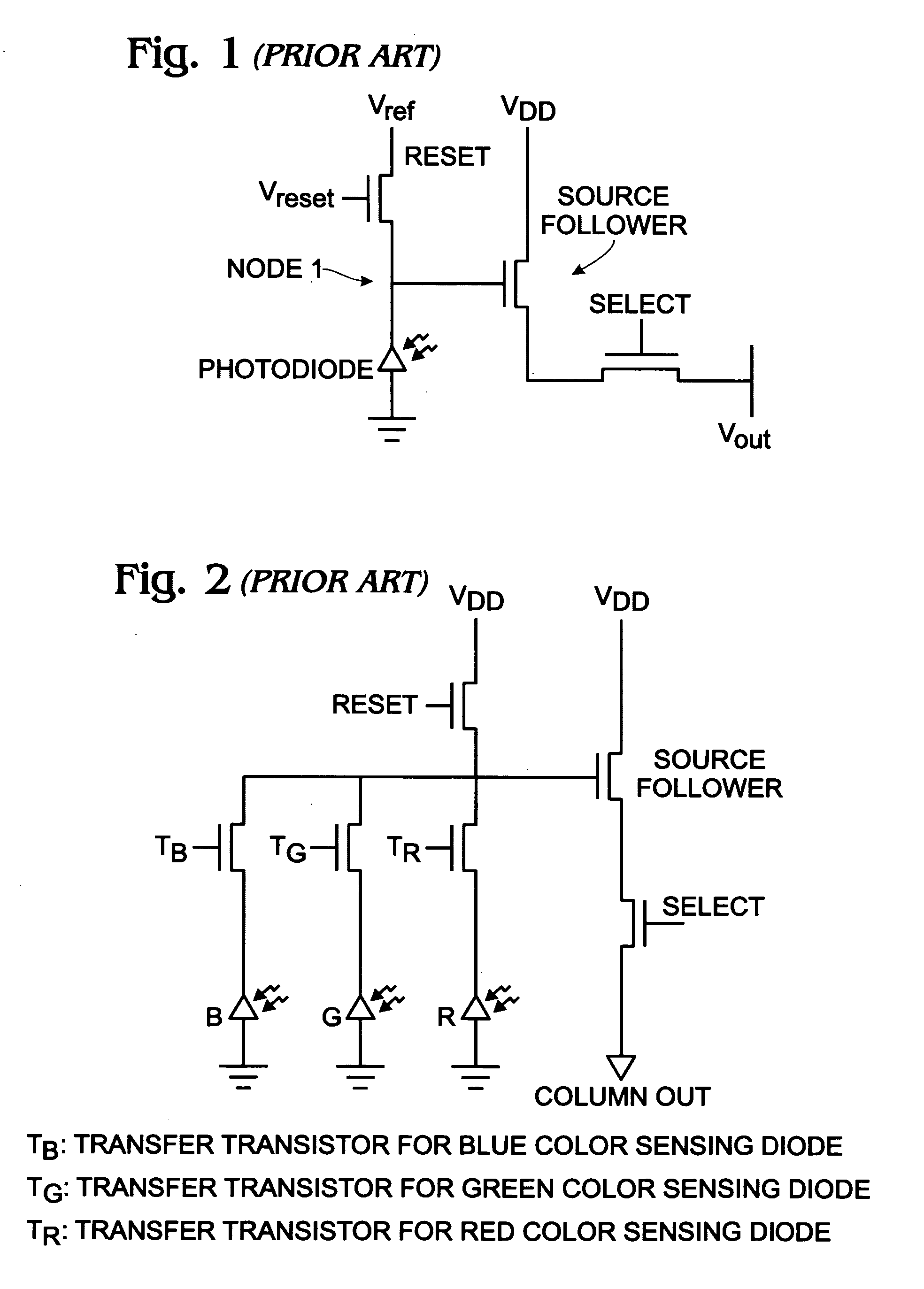
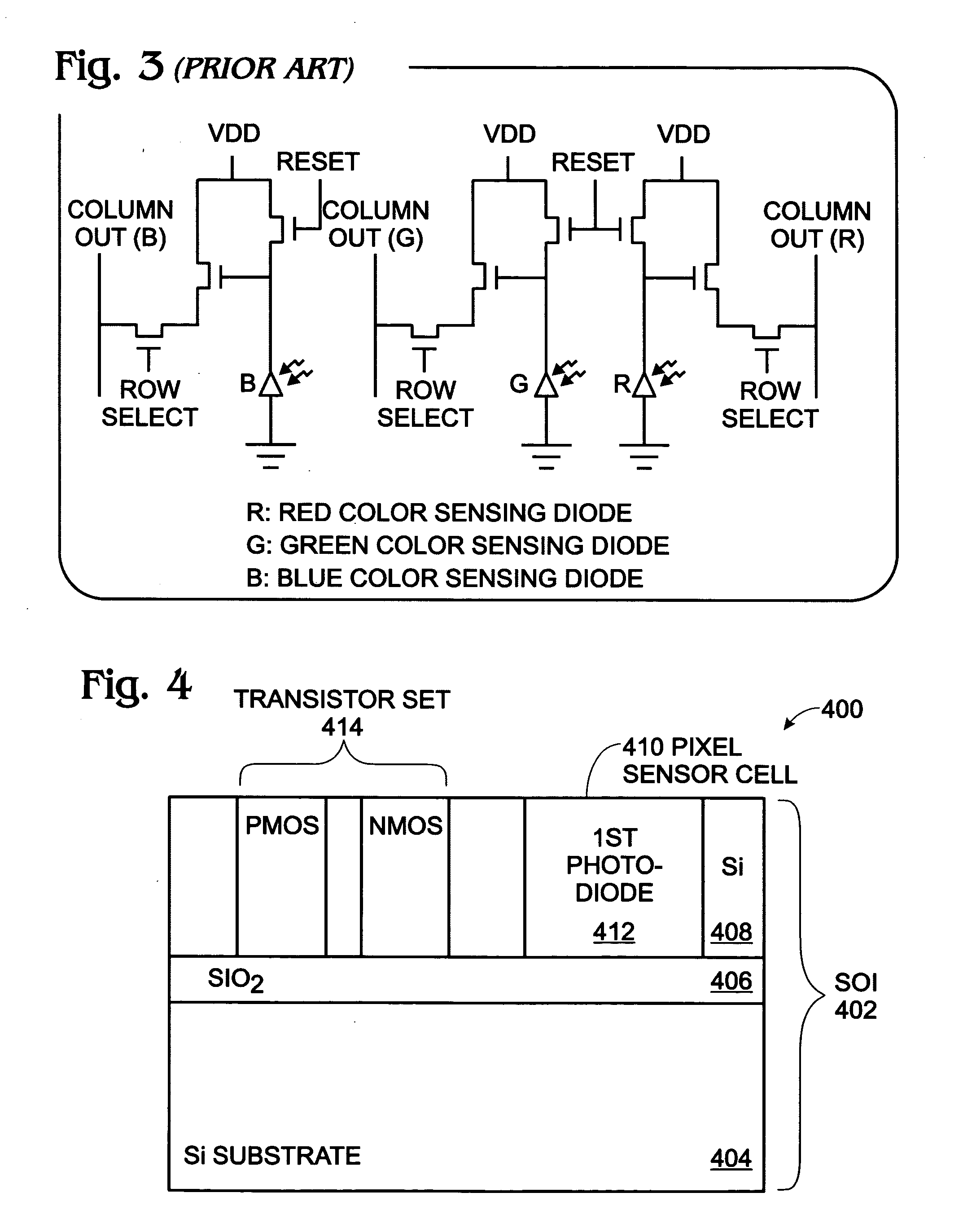
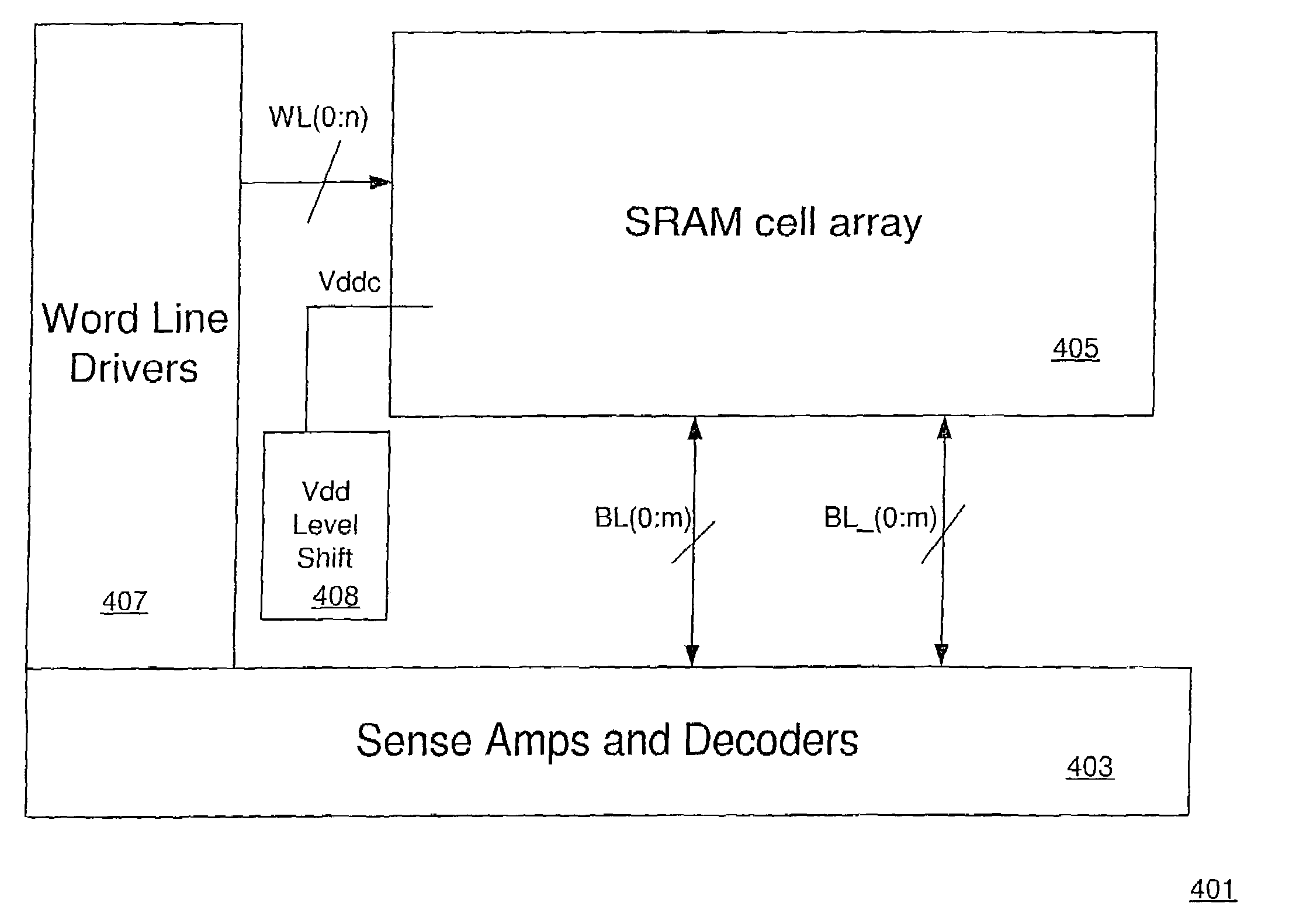
InactiveUS20070218579A1Increase output swingIncrease supply voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSN channel
A CMOS active pixel sensor (APS) imager cell is provided on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) substrate. The APS imager cell is made from a SOI substrate including a silicon (Si) substrate, a silicon dioxide insulator overlying the substrate, and a Si top layer overlying the insulator. A pixel sensor cell including a photodiode is formed in the Si top layer of the SOI substrate. A pixel transistor set is formed in the SOI top Si layer and connected to the pixel sensor cell. The pixel transistor set includes at least one p-channel MOS (PMOS) transistor and at least one n-channel MOS (NMOS) transistor. In the case of a three-transistor (3T) pixel transistor set, the selected transistor is NMOS, the reset transistor is PMOS, and the source follower may be either NMOS or PMOS.
Owner:SHARP LAB OF AMERICA
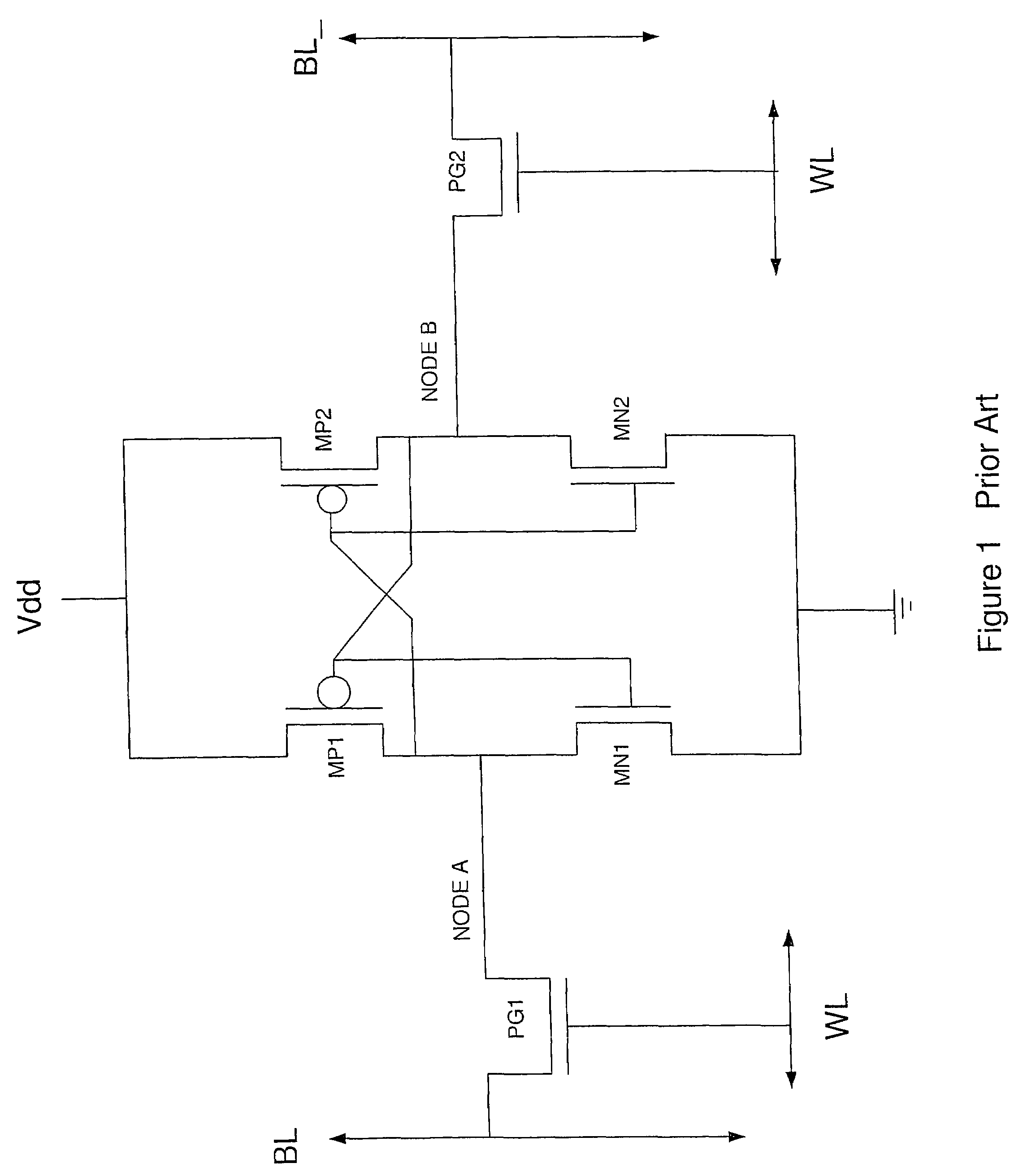
Circuit and method for an SRAM with reduced power consumption
A circuit and method for providing an SRAM memory with reduced power consumption, the SRAM memory particularly useful for embedding SRAM memory with other logic and memory functions in an integrated circuit. A lower supply voltage is provided to the peripheral circuitry for the SRAM memory. A level shifter circuit is provided coupled to the lower power supply and outputting a higher supply voltage. An array of SRAM memory cells that may comprise 4T, 6T or 8T static RAM memory cells are coupled to the higher supply voltage during read and write operations. Operating the peripheral circuitry of the SRAM memory at the lower supply voltage achieves reduced power consumption for the SRAM memory and the integrated circuit.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor device including a current mirror circuit
InactiveUS7667272B2Stable supplyHigh power supply voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductorSemiconductor device
In a semiconductor device, where, with respect to a parasitic resistor in a current mirror circuit, a compensation resistor for compensating the parasitic resistor is provided in the current mirror circuit, the current mirror circuit includes at least two thin film transistors. The thin film transistors each have an island-shaped semiconductor film having a channel formation region and source or drain regions, a gate insulating film, a gate electrode, and source or drain electrodes, and the compensation resistor compensates the parasitic resistor of any one of the gate electrode, the source electrode, and the drain electrode. In addition, each compensation resistor has a conductive layer containing the same material as the gate electrode, the source or drain electrodes, or the source or drain regions.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Apparatus and method used in disk drive for driving spindle motor
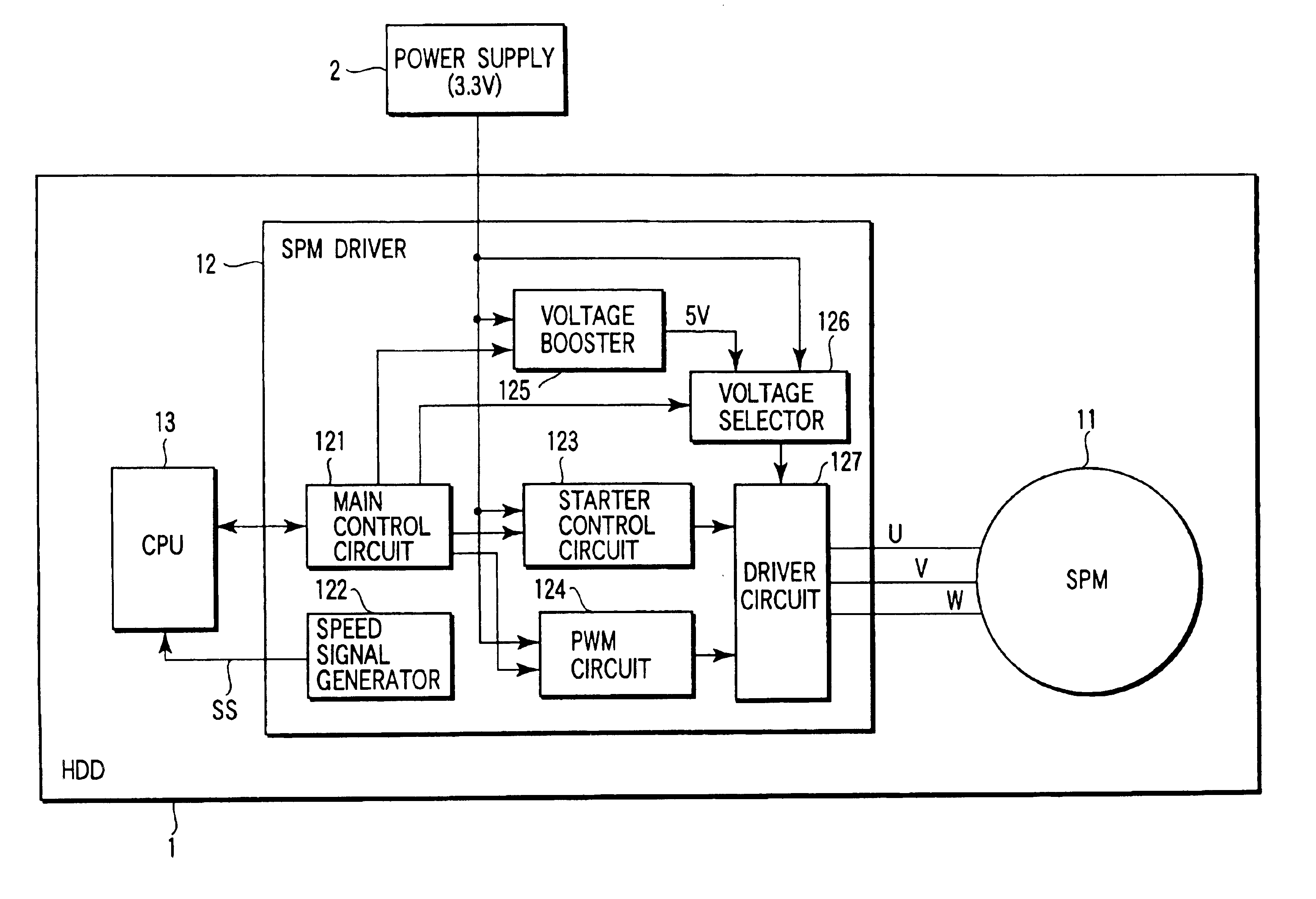
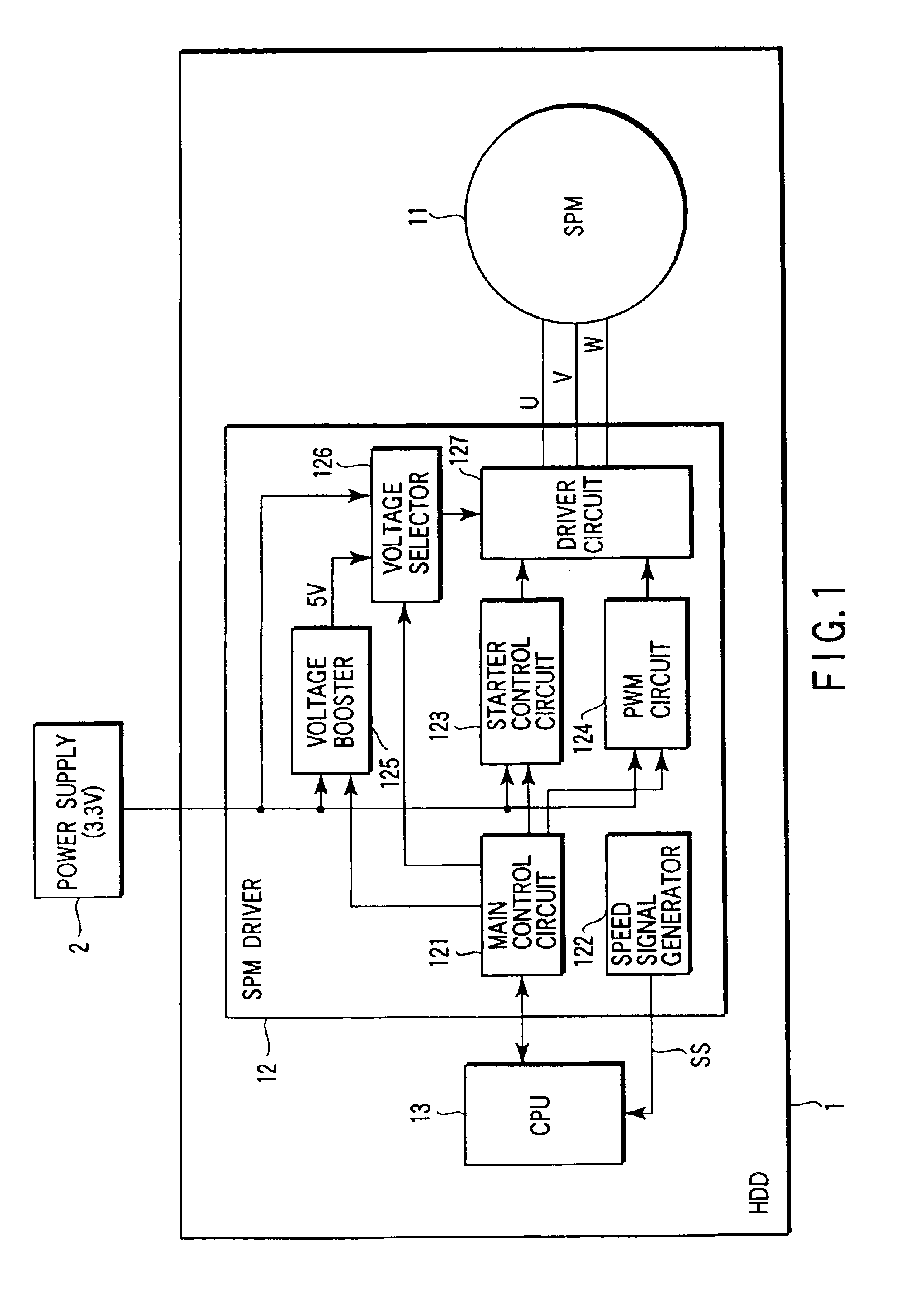
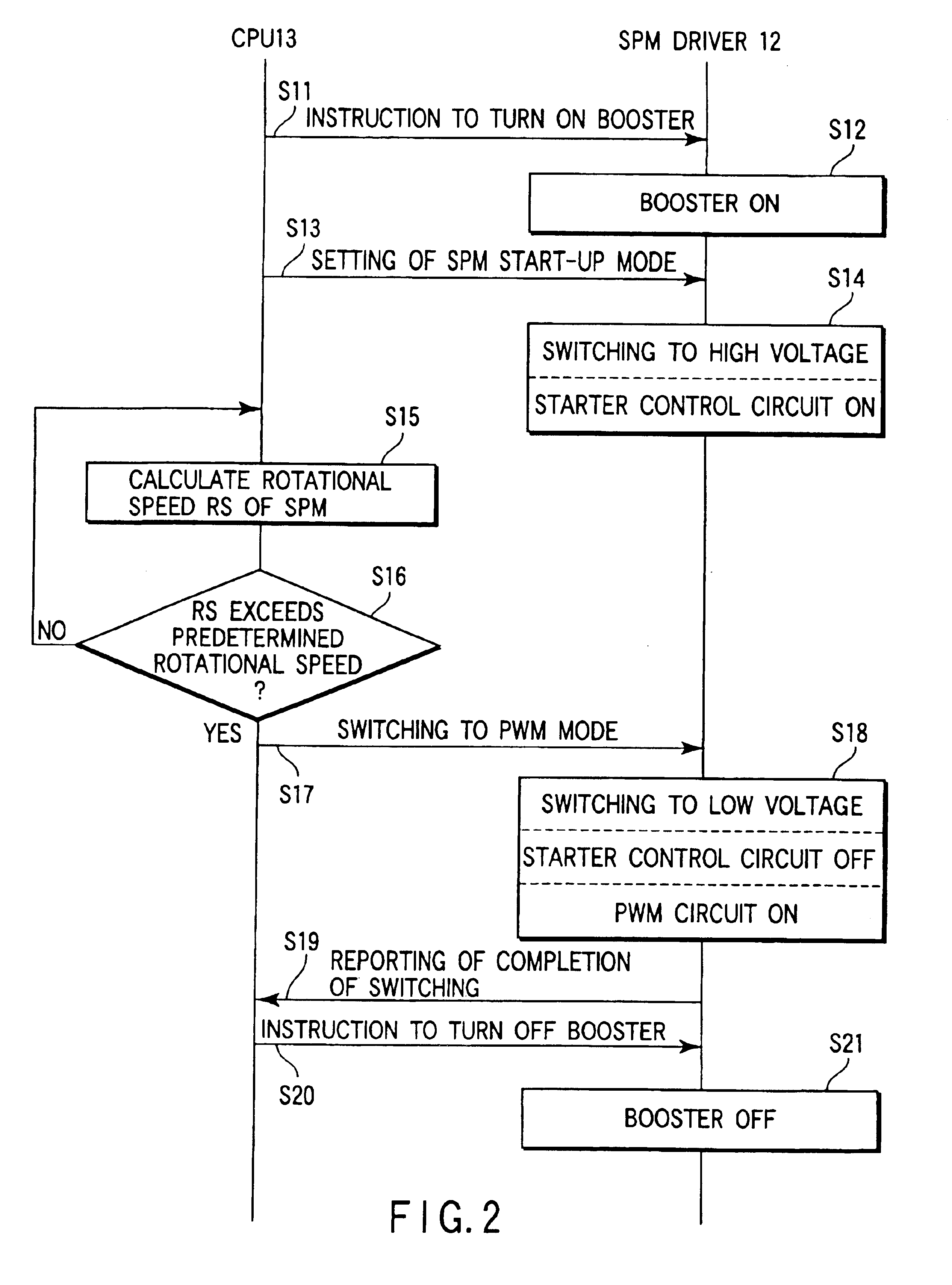
InactiveUS6841954B2High power supply voltageReduce power consumptionDC motor speed/torque controlMultiple dynamo-motor startersDriver circuitLow voltage
A CPU sets an SPM driver in SPM start-up mode when a SPM is started up. At this time, a voltage selector applies, to a driver circuit, a voltage (high voltage) boosted by a voltage booster. A starter control circuit controls, during the period of an SPM start-up mode, the driver circuit with the high voltage applied thereto, thereby starting up the SPM. After the SPM has been started up, the CPU sets the SPM driver in PWM mode. At this time, the voltage selector switches the voltage applied to the driver circuit, from the boosted voltage to the voltage (low voltage) of a power supply. During the period of the PWM mode, a PWM circuit controls the driver circuit with the low voltage applied thereto, so as to rotate the SPM at a rated speed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Charging Control Apparatus and Charging Apparatus
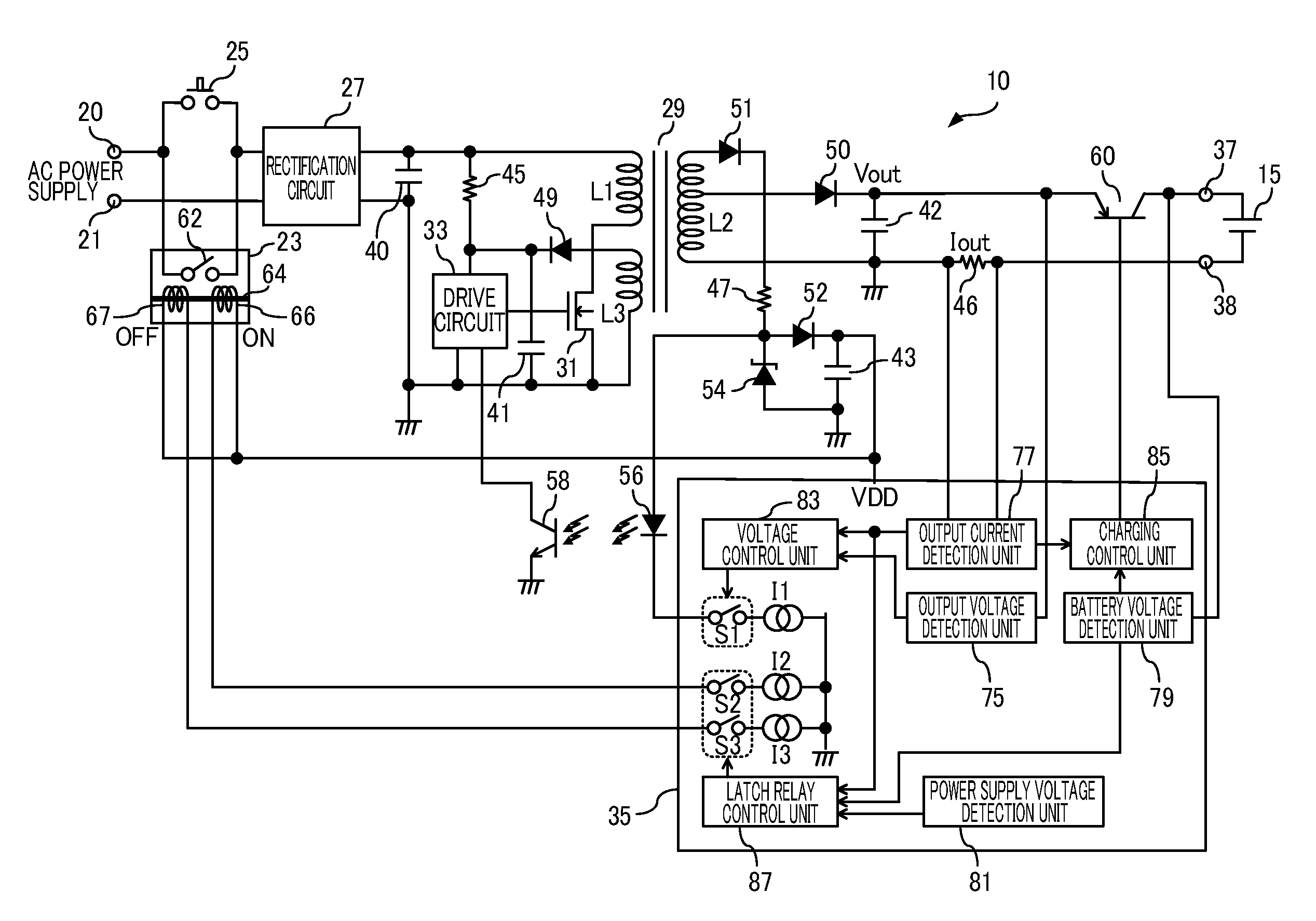
ActiveUS20100001695A1High power supply voltageBatteries circuit arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsCharge controlVoltage control
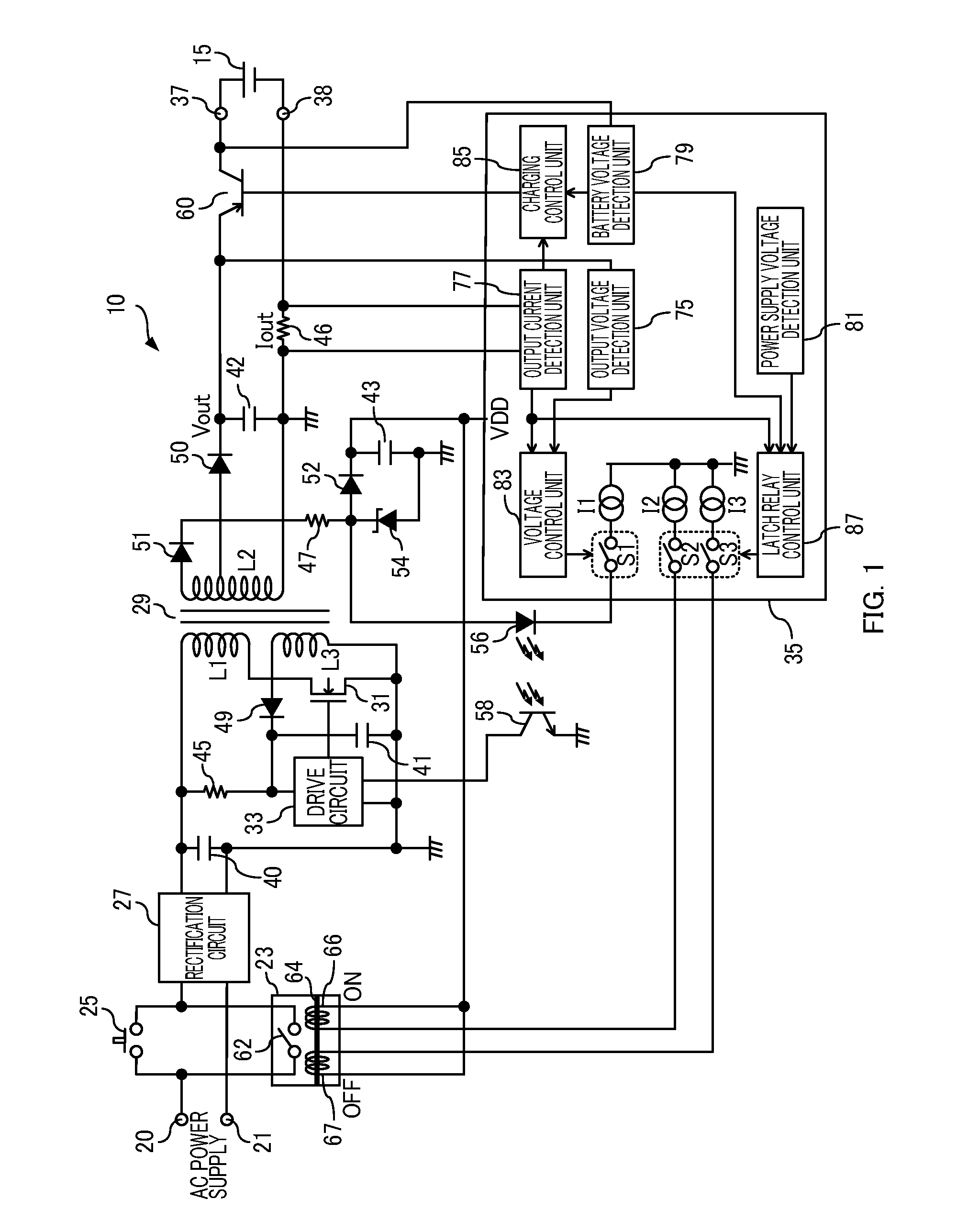
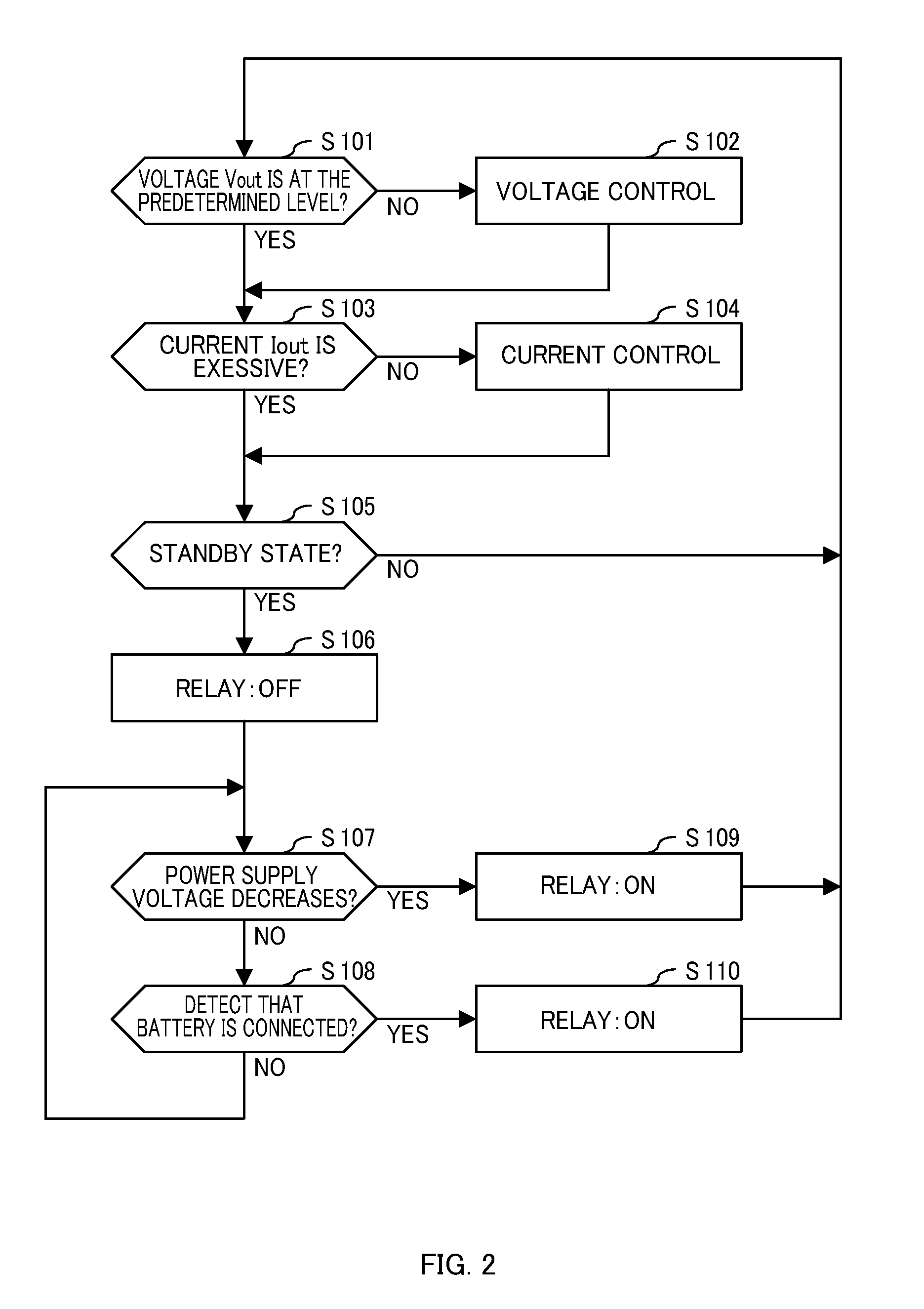
A charging control apparatus comprising: a voltage control unit in a charging apparatus configured to control generation of an output voltage and a power supply voltage, the charging apparatus being an apparatus configured to generate, from a voltage of an input power supply applied through a relay, the output voltage for charging a battery and the power supply voltage for control; and a relay control unit operated by the power supply voltage, the relay control unit configured to drive the relay so as to stop applying the voltage of the input power supply to the charging apparatus, when detecting a standby state in which the battery is not being charged, and drive the relay so as to increase the power supply voltage by applying the voltage of the input power supply to the charging apparatus, when the power supply voltage decreases below a predetermined level.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Semiconductor device and display device
InactiveUS8803781B2Low efficiencyIncrease power consumptionStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesShift registerDriver circuit
A single-crystal semiconductor layer is separated from a single-crystal semiconductor substrate and is fixed to an insulating substrate to form a TFT over the insulating substrate. Then, a driver circuit is formed using the TFT. The TFT has excellent current characteristics because an active layer is almost in a single-crystal state. Accordingly, a small thin display device with low power consumption can be manufactured. Further, a controller and a shift register which is included in a source driver are operated at the same power supply voltage. Thus, power consumption can be reduced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
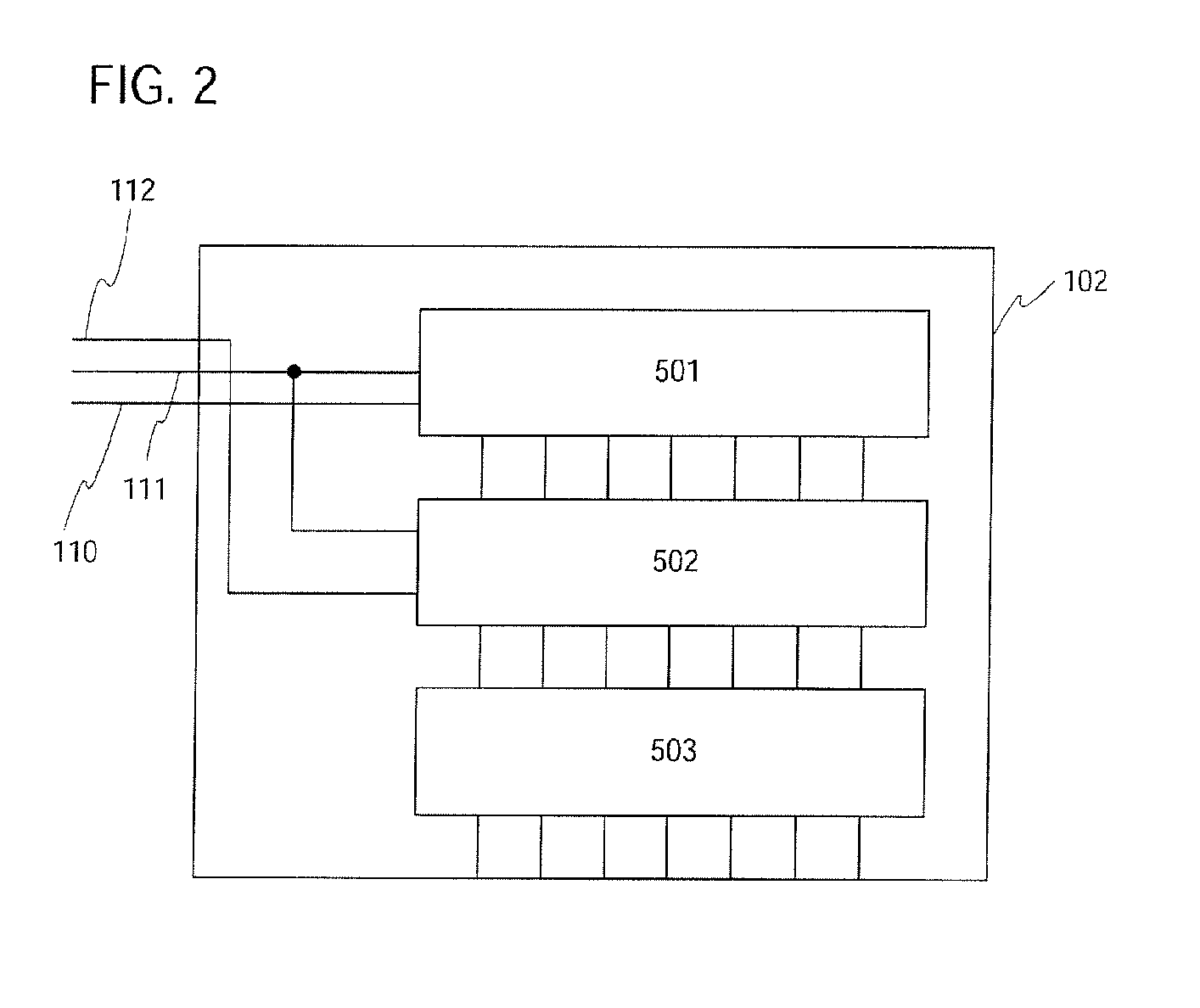
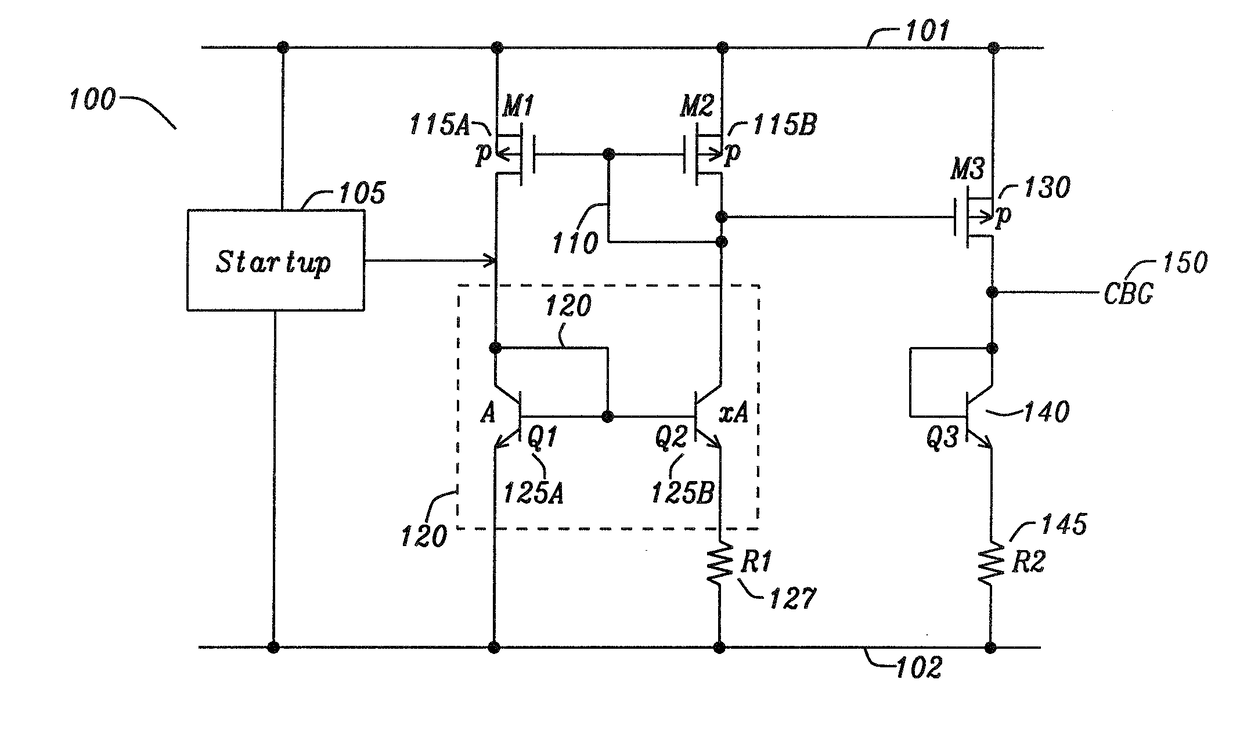
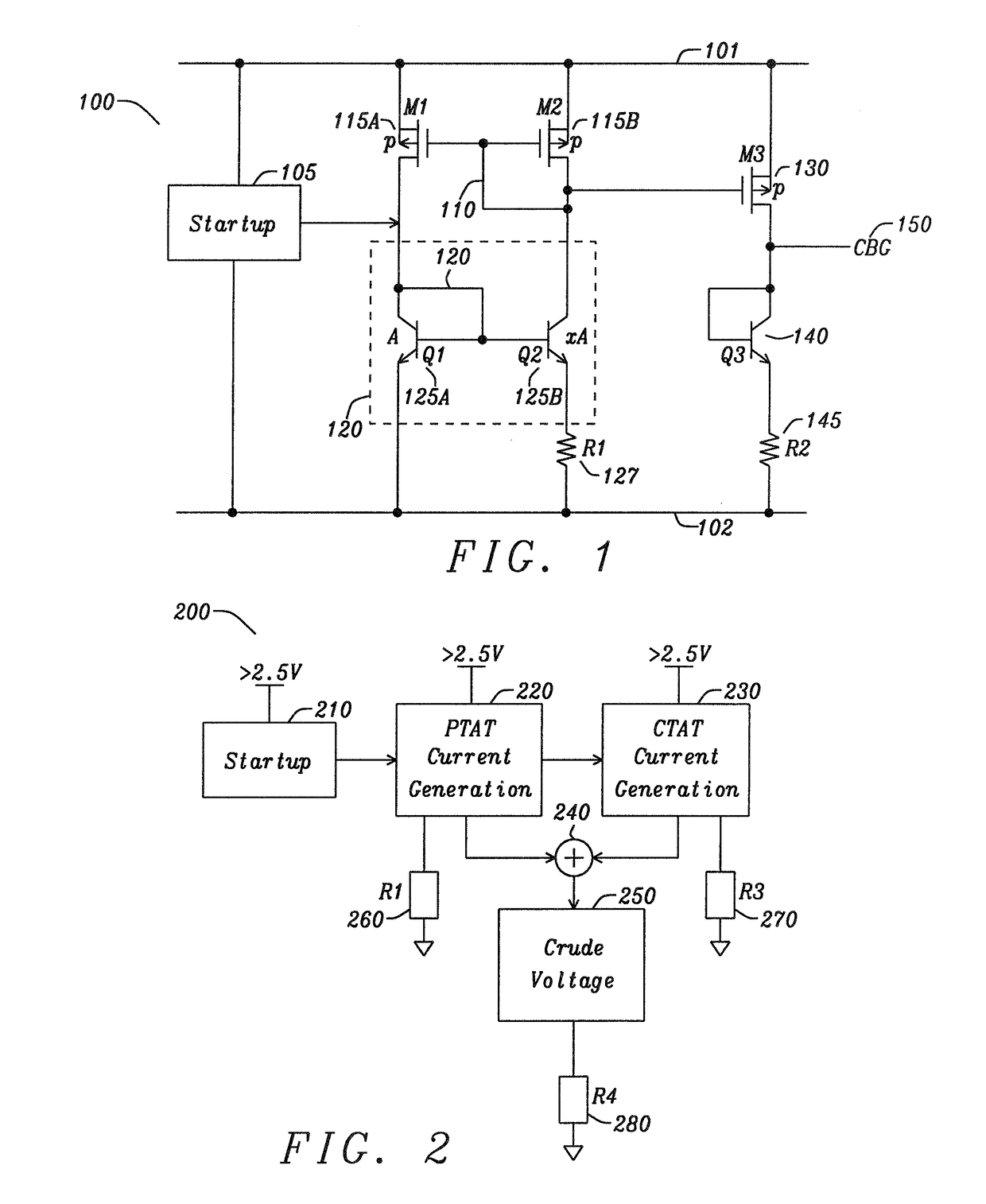
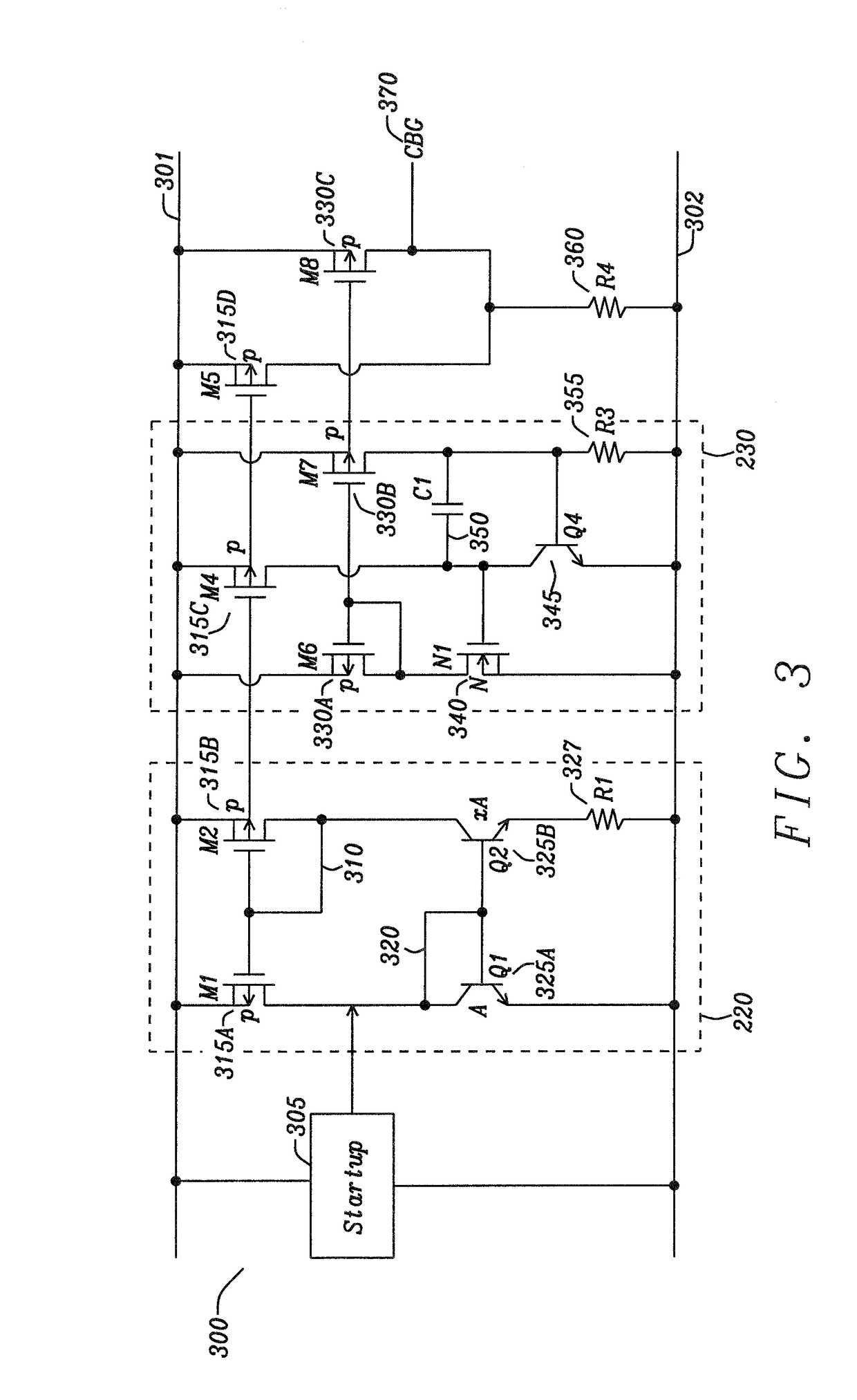
Apparatus and Method for High Voltage Bandgap Type Reference Circuit with Flexible Output Setting
ActiveUS20170131736A1Avoid startingAvoid noiseElectric variable regulationPower conversion systemsEngineeringHigh pressure
An apparatus and method for a voltage reference circuit with flexible and adjustable voltage settings. A voltage reference circuit, comprising a PTAT Current Generator configured to provide current through a first resistor, a CTAT Current Generator configured to provide a CTAT current through a second resistor, a PTAT-CTAT Adder circuit configured to sum the PTAT current, and the CTAT current, wherein said sum of the PTAT and CTAT current through a third resistor is configured to provide an output voltage greater than a silicon bandgap voltage.
Owner:APPLE INC
Motor drive device and drive method
InactiveUS20070126384A1High power supply voltageLow costSingle-phase induction motor startersCommutation monitoringMotor speedControl signal
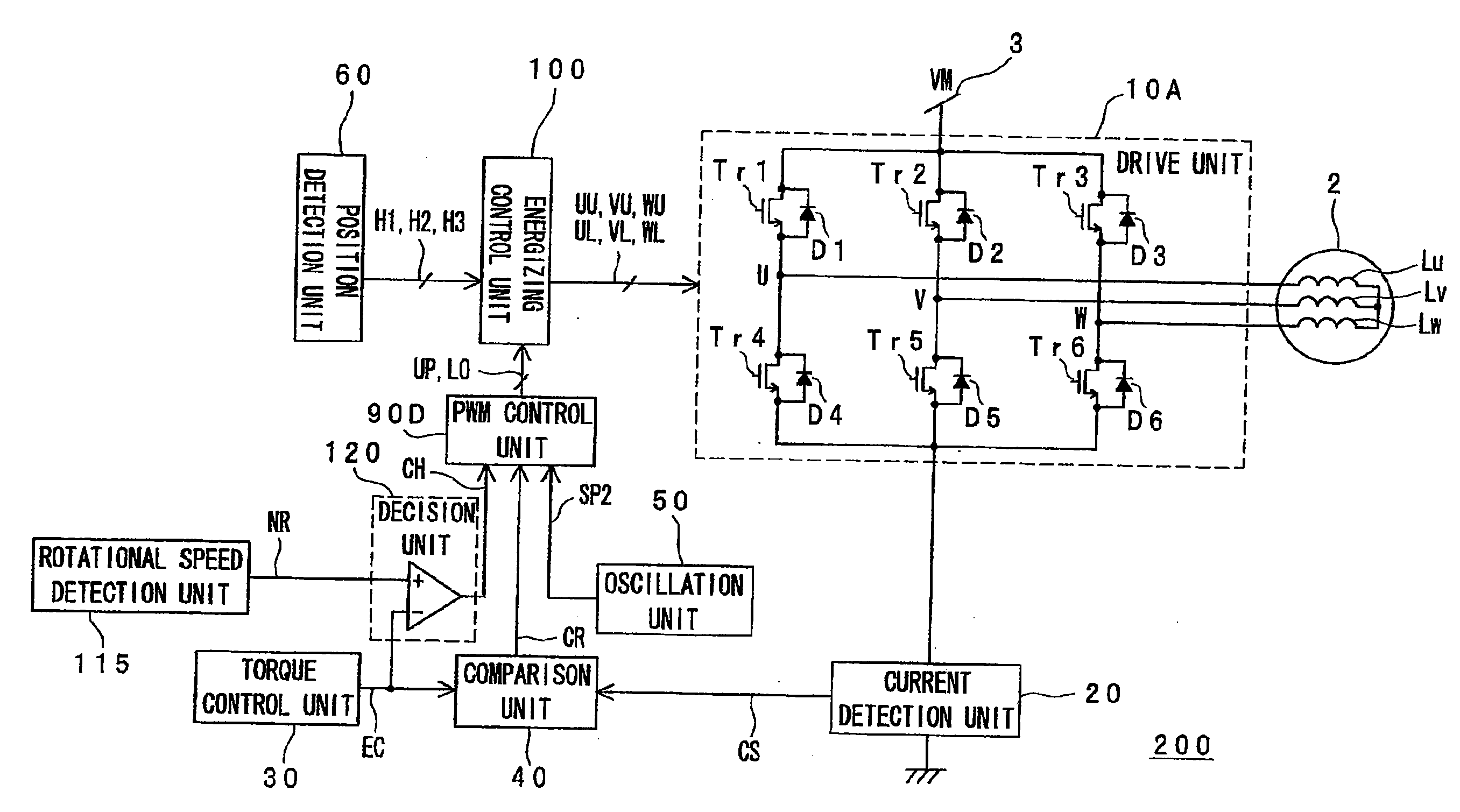
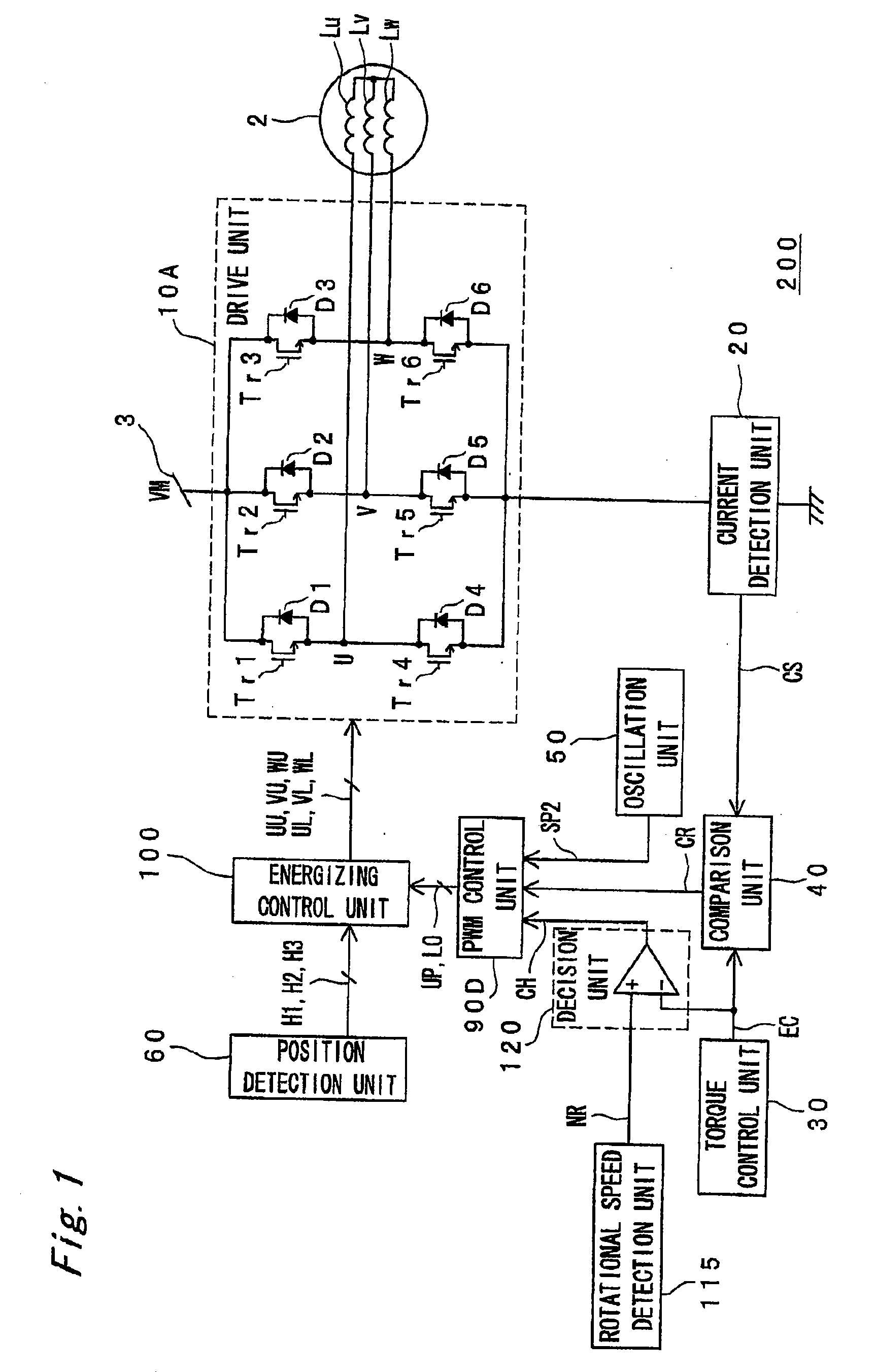
A rise in the power supply voltage as a result of a sudden speed reducing command causing the motor current to flow to the power supply is prevented. The motor drive device has a drive signal generating unit for generating a drive signal by an energizing control unit, PWM control unit, and oscillation unit; a drive unit for producing drive power to drive the motor based on the drive signal; a torque control signal generating unit for generating a torque control signal specifying the motor torque; a speed detection unit for detecting the rotational speed of the motor and generating a rotational speed signal denoting motor speed information; and a decision unit for generating a speed difference detection signal denoting the difference between the torque control signal and the rotational speed signal. The drive signal generating unit is controlled based on the speed difference detection signal.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
Source follower circuit or bootstrap circuit, driver circuit comprising such circuit, and display device comprising such driver circuit
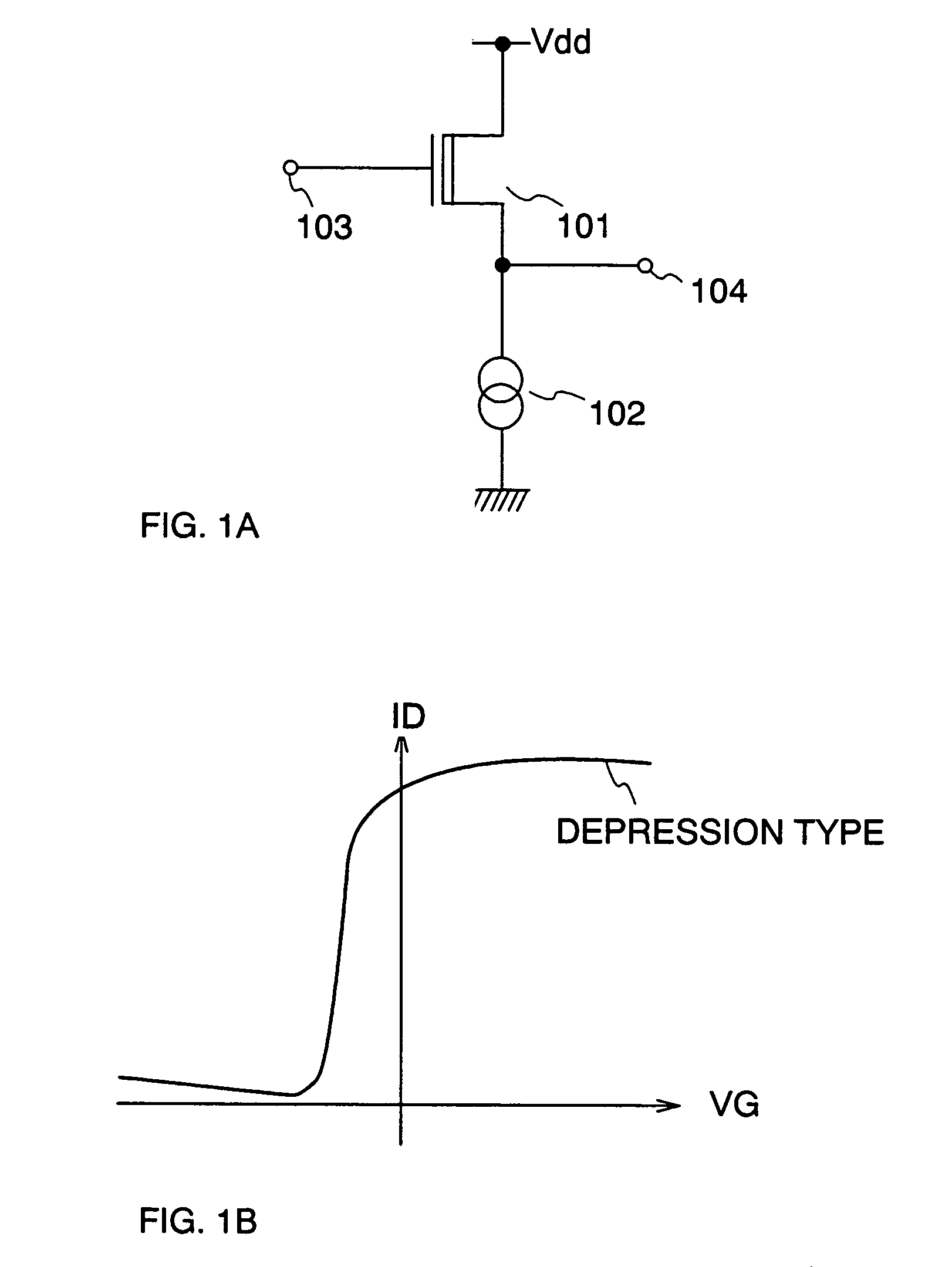
ActiveUS7205610B2Reduce power consumptionHigh power supply voltageTransistorStatic indicating devicesDriver circuitLiquid-crystal display
In the case of using an analog buffer circuit, an input voltage is required to be added a voltage equal to a voltage between the gate and source of a polycrystalline silicon TFT; therefore, a power supply voltage is increased, thus a power consumption is increased with heat. In view of the foregoing problem, the invention provides a depletion mode polycrystalline silicon TFT as a polycrystalline silicon TFT used in an analog buffer circuit such as a source follower circuit. The depletion mode polycrystalline silicon TFT has a threshold voltage on its negative voltage side; therefore, an input voltage does not have to be increased as described above. As a result, a power supply voltage requires no increase, thus a low power consumption of a liquid crystal display device in particular can be realized.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com