Patents
Literature
476results about How to "Reduce power supply voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
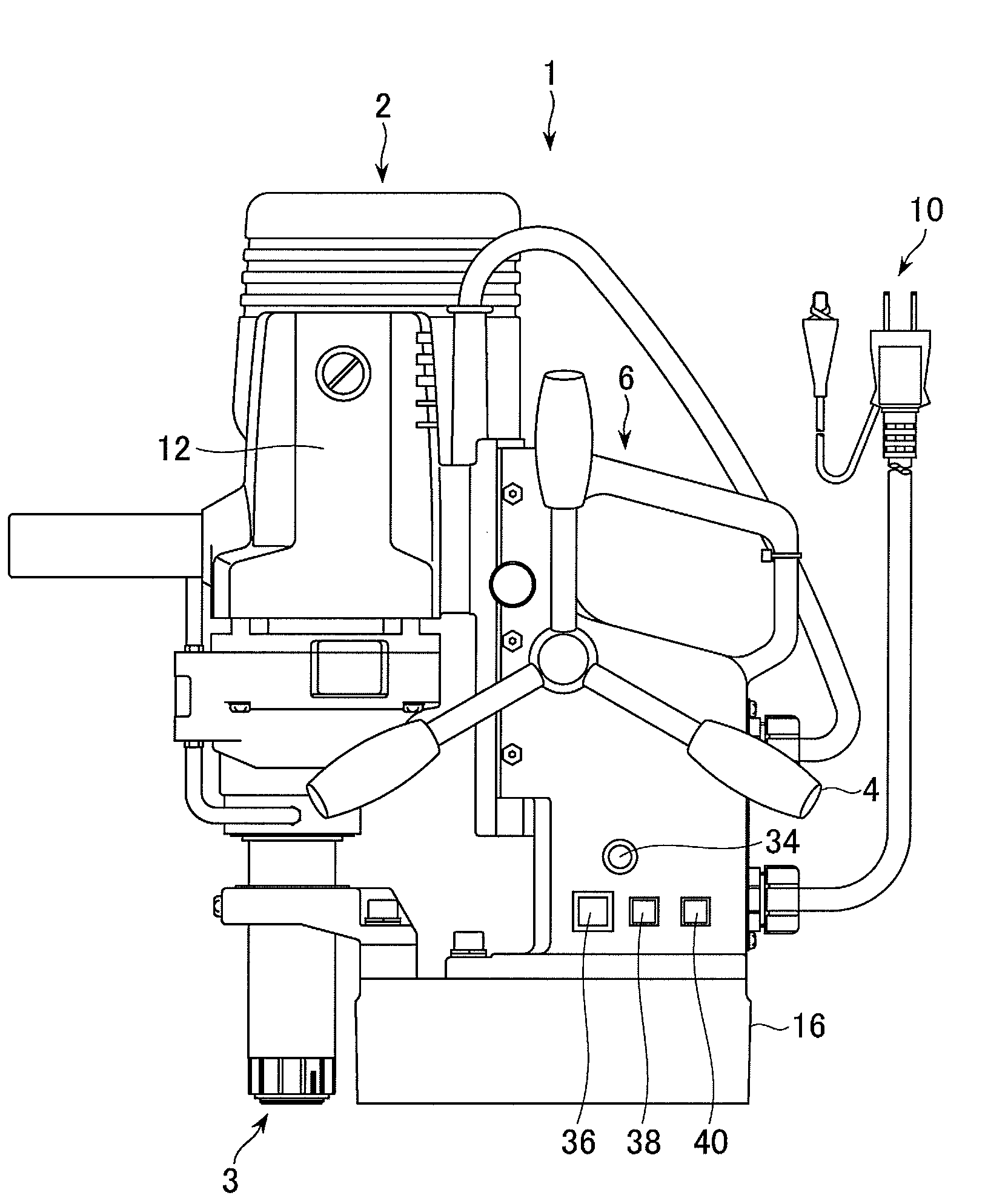
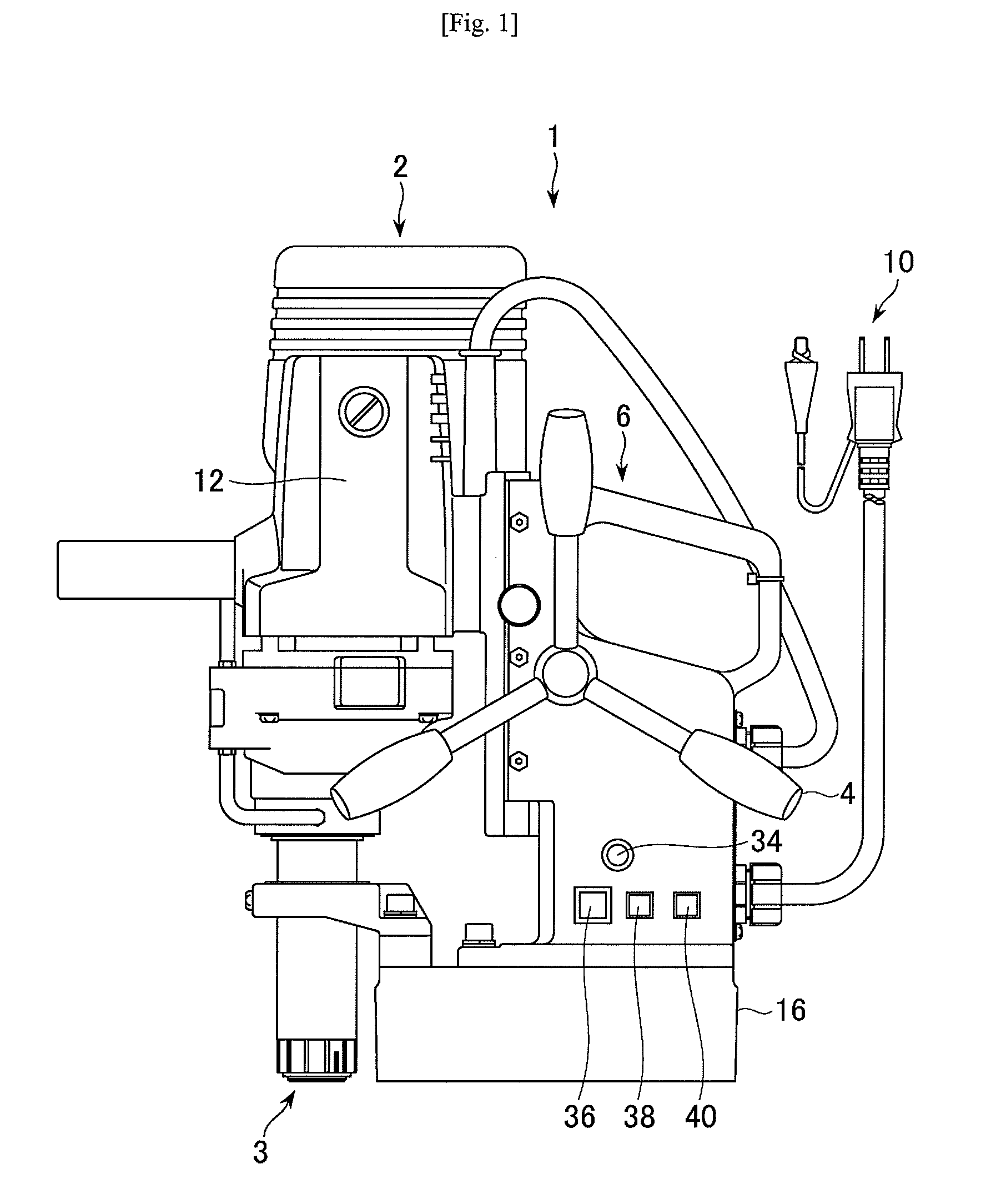
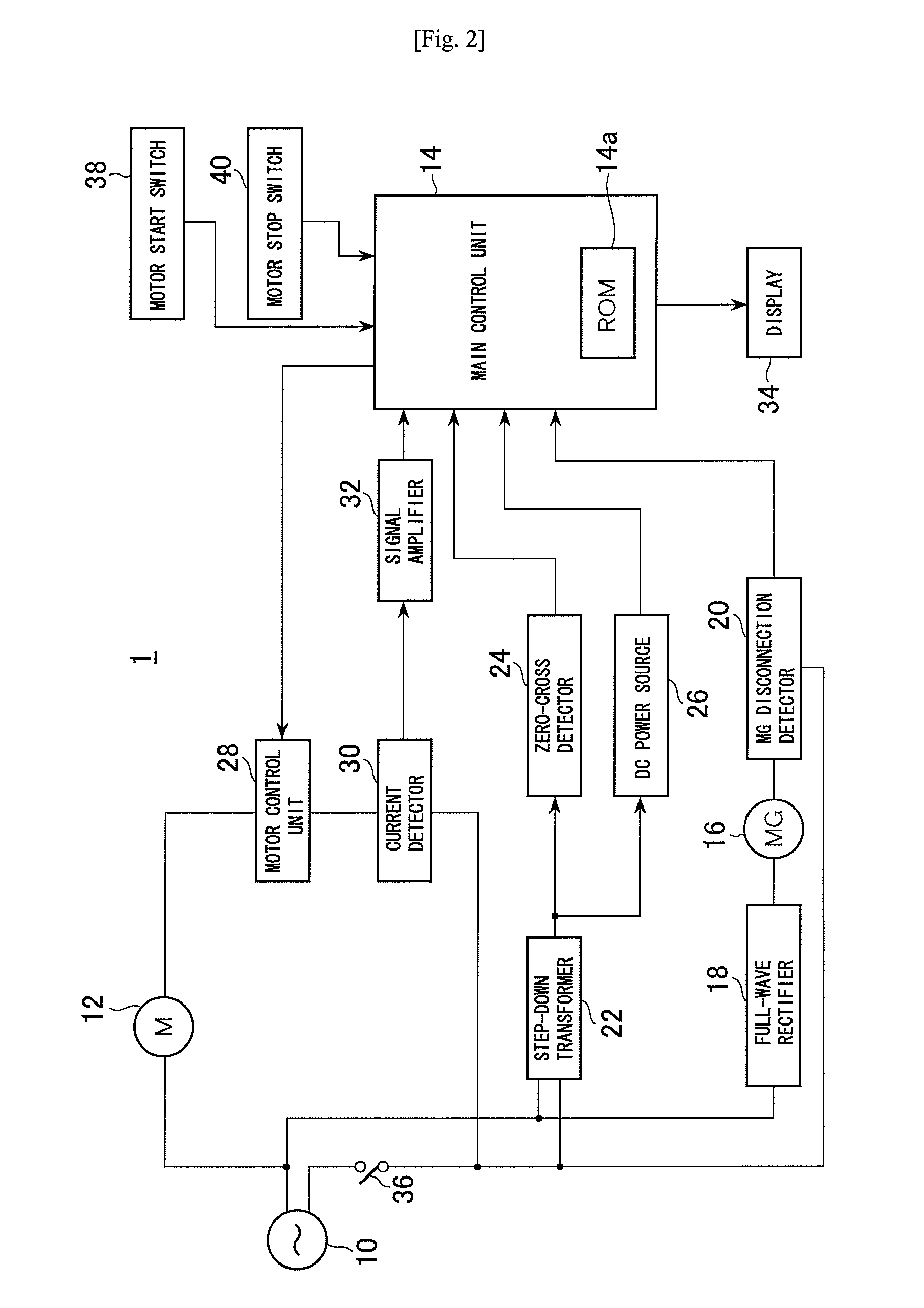
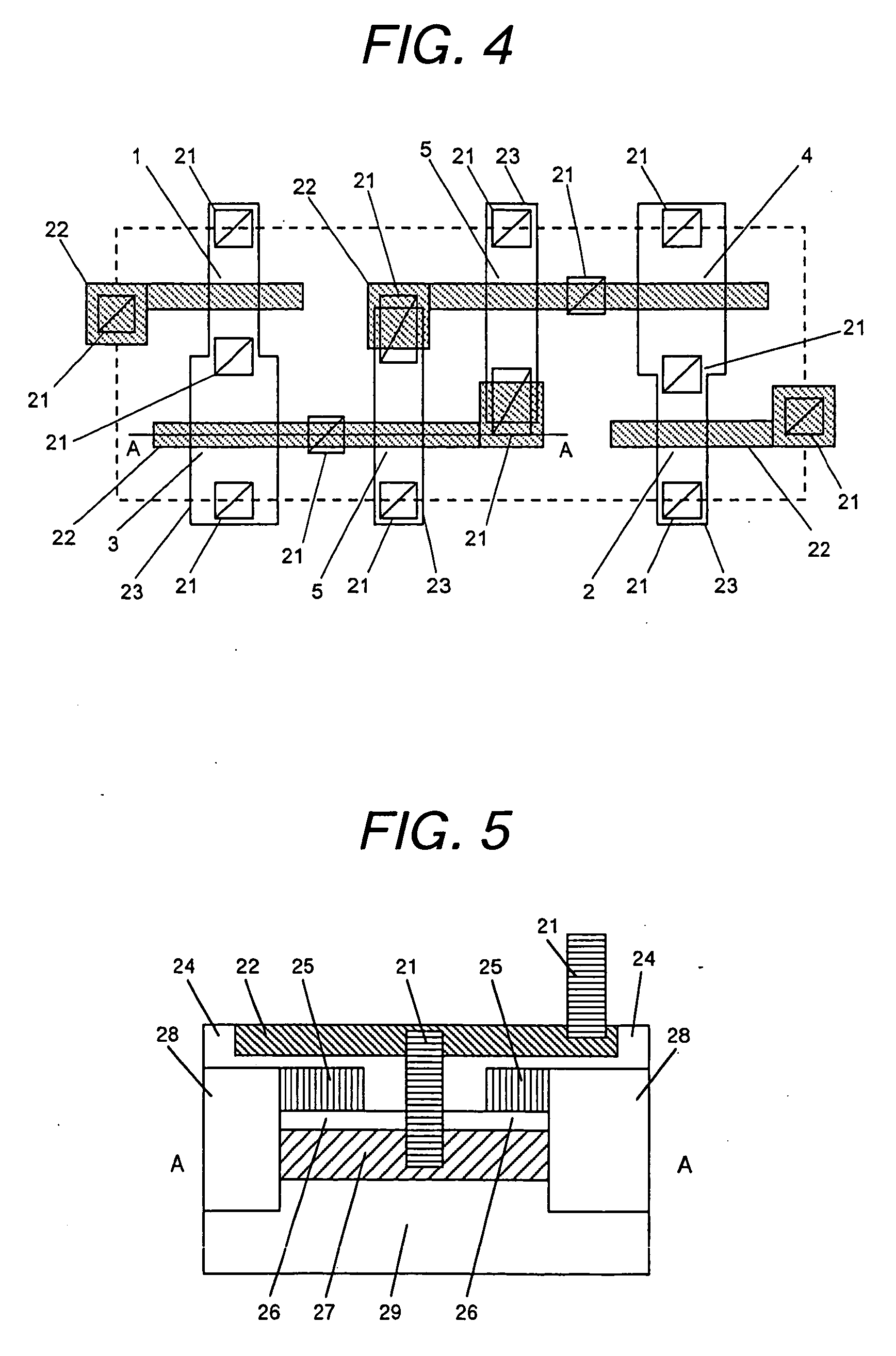
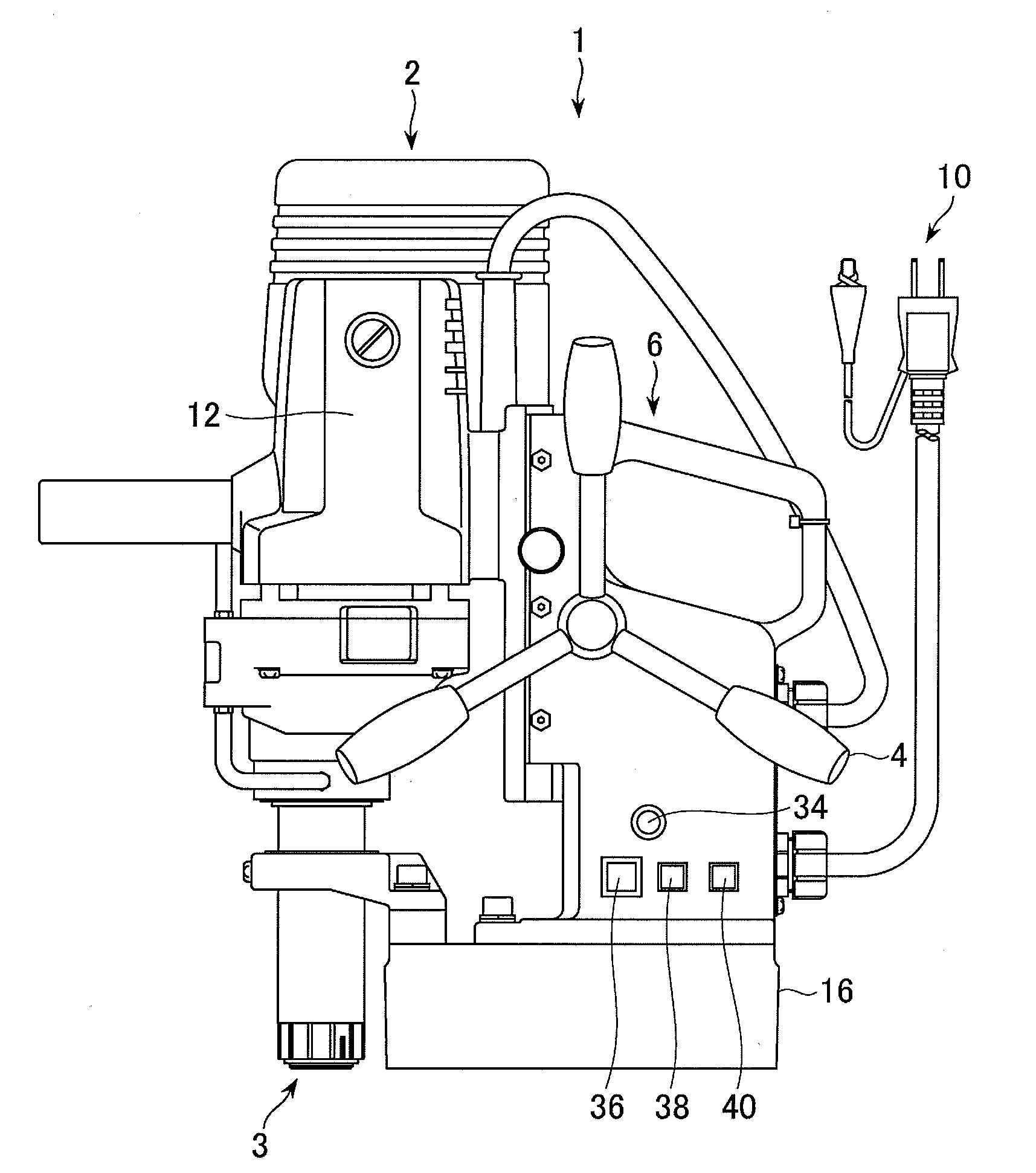
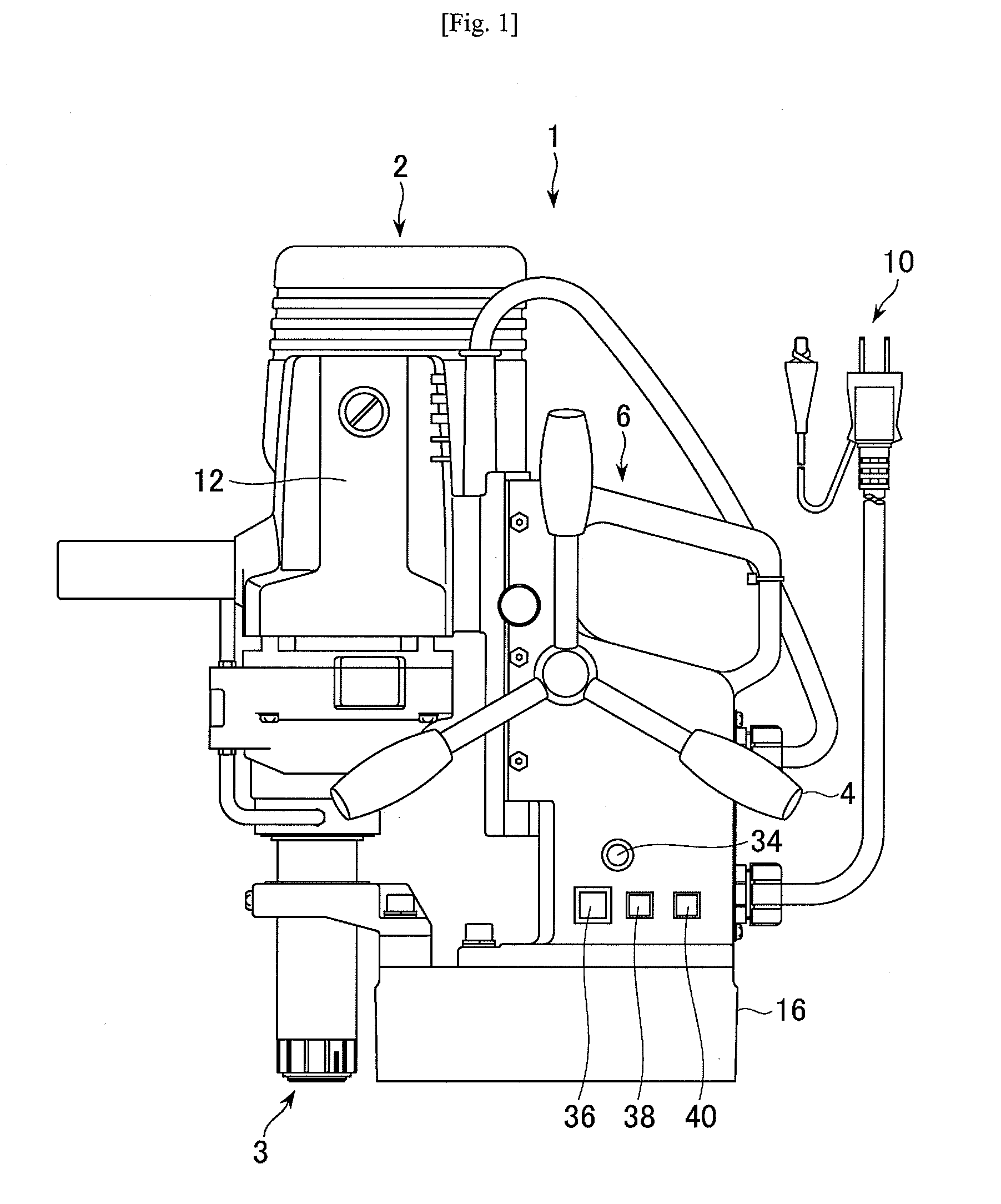
Portable drilling device
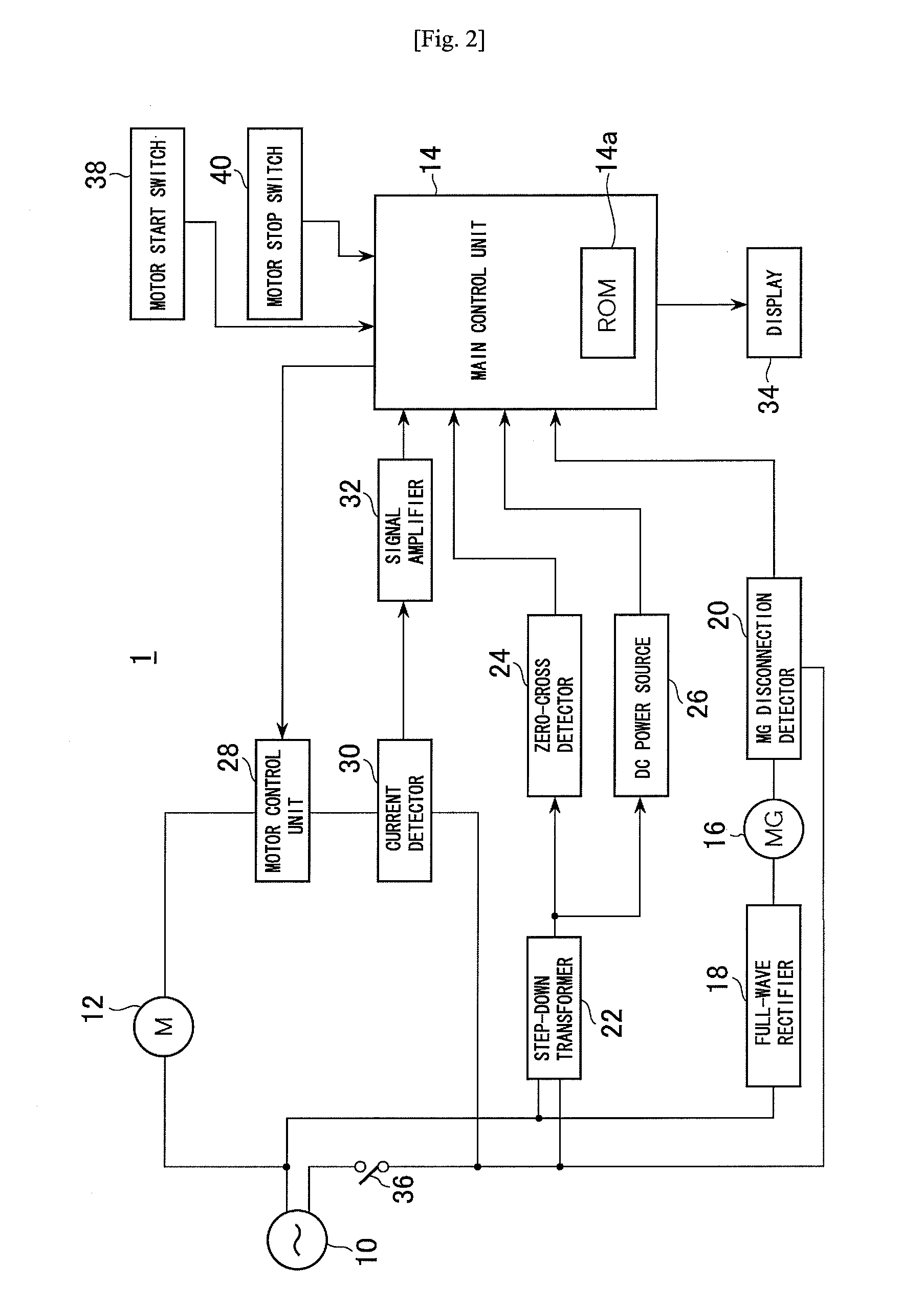
ActiveUS7936142B2Easy to operateImprove securityAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlFull waveEngineering
A drilling device prevents recurrence of an overload condition after occurrence of the overload condition, thereby improving operability and safety in the drilling device. A motor for rotating a drill is connected to an AC power source through a motor control unit, a current detector, and a power switch. A magnet is also connected to the AC power source through the power switch and a full-wave rectifier. The motor control unit rotationally drives the motor on the basis of a signal sent from a main control unit according to a state in which a motor start switch is on. The main control unit controls the motor control unit to gradually reduce a supply voltage to the motor when the motor becomes overloaded, to gradually increase the voltage to the normal power supply condition when the overload condition is vanished, and to stop power supply to the motor if the overload condition continues for a predetermined period.
Owner:NITTO KOHKI CO LTD
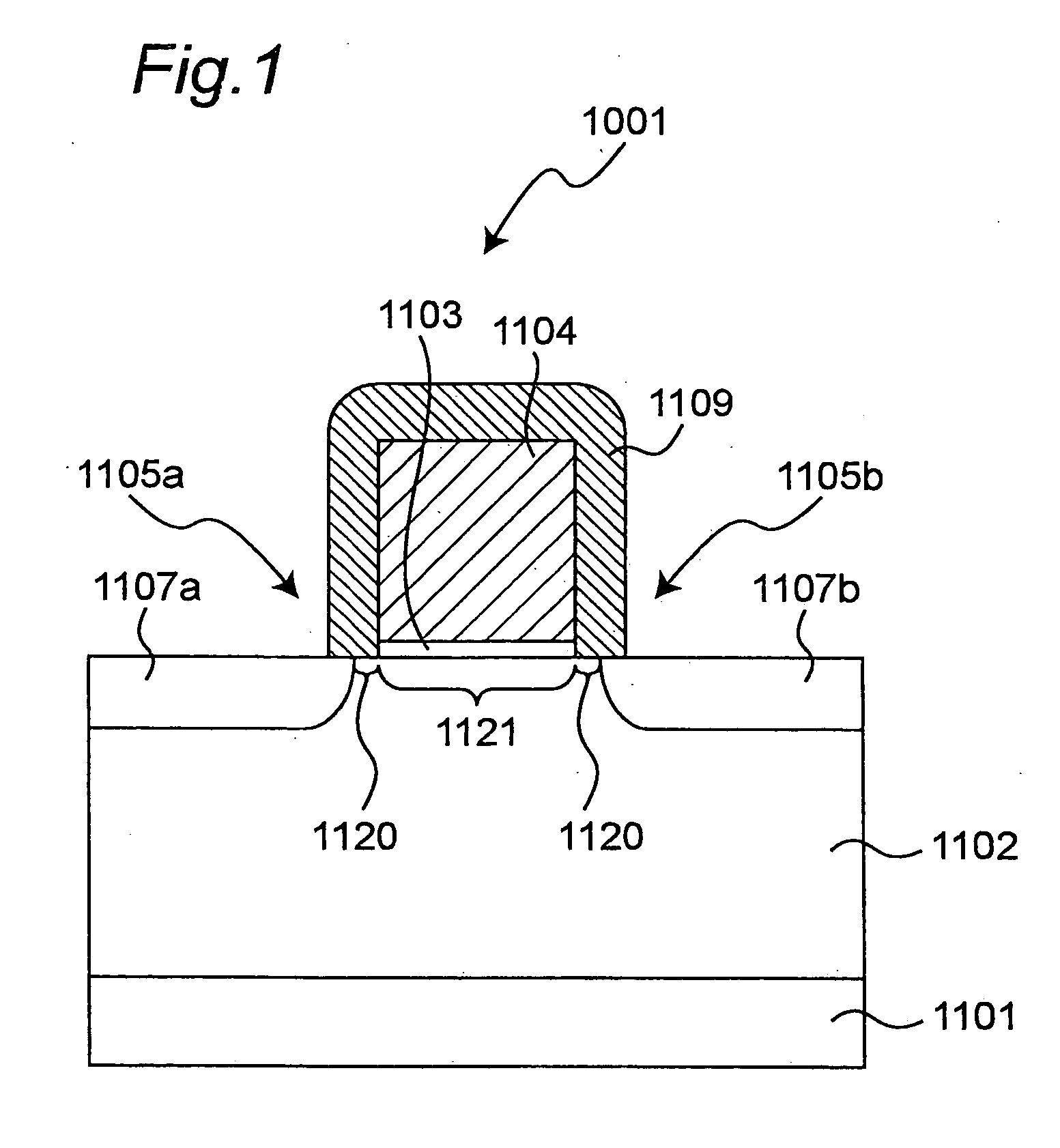
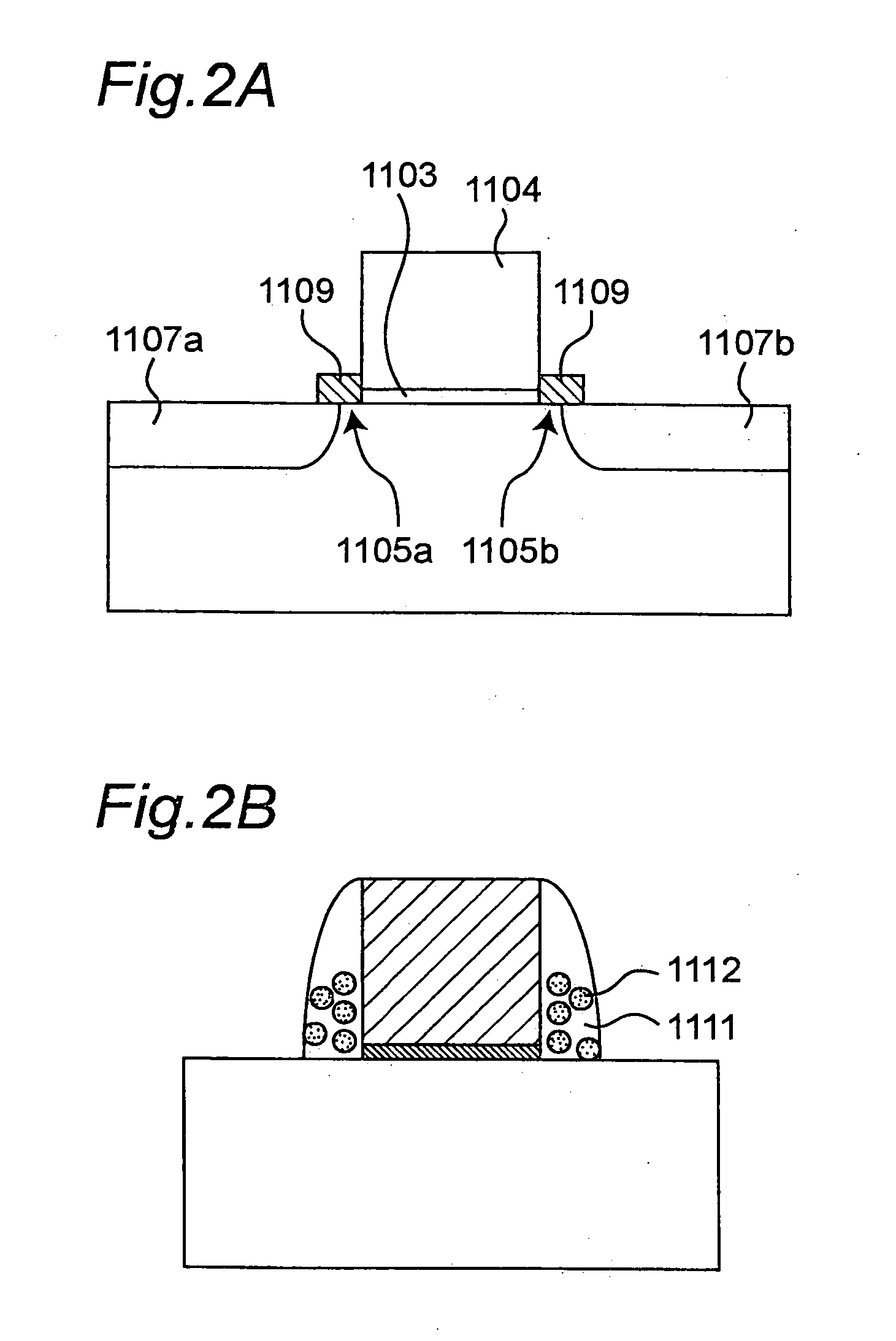
Semiconductor memory
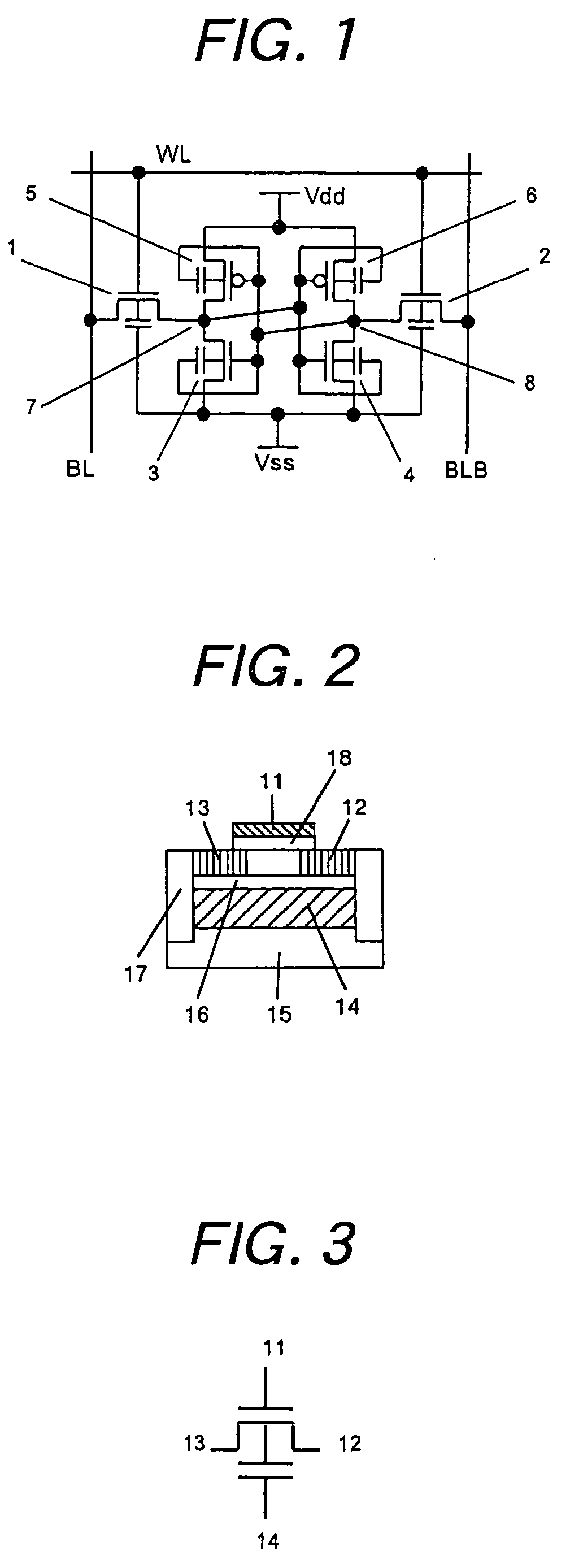
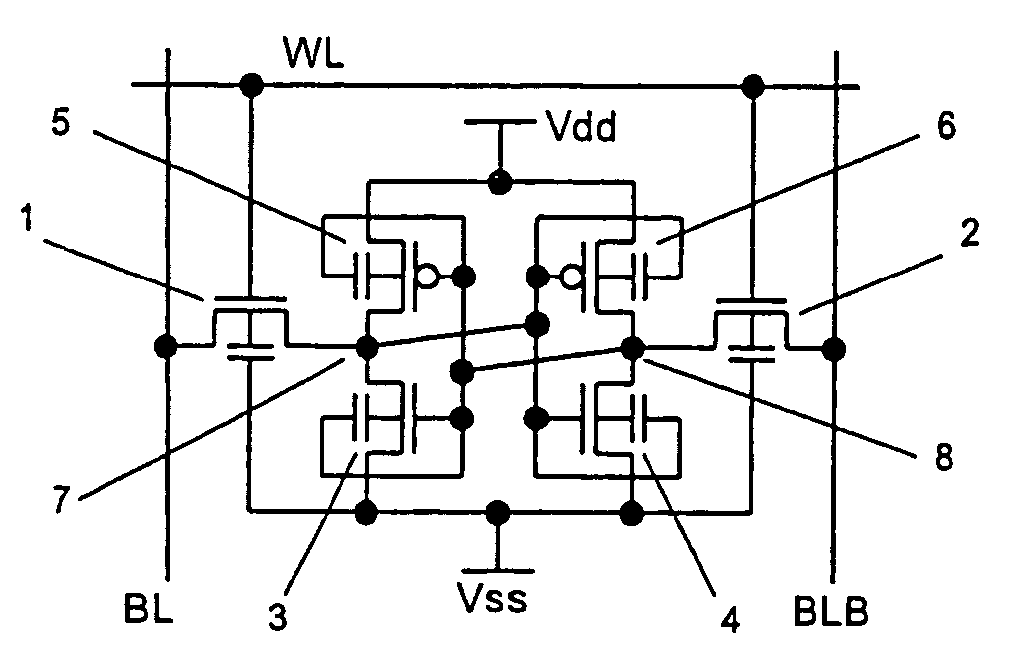
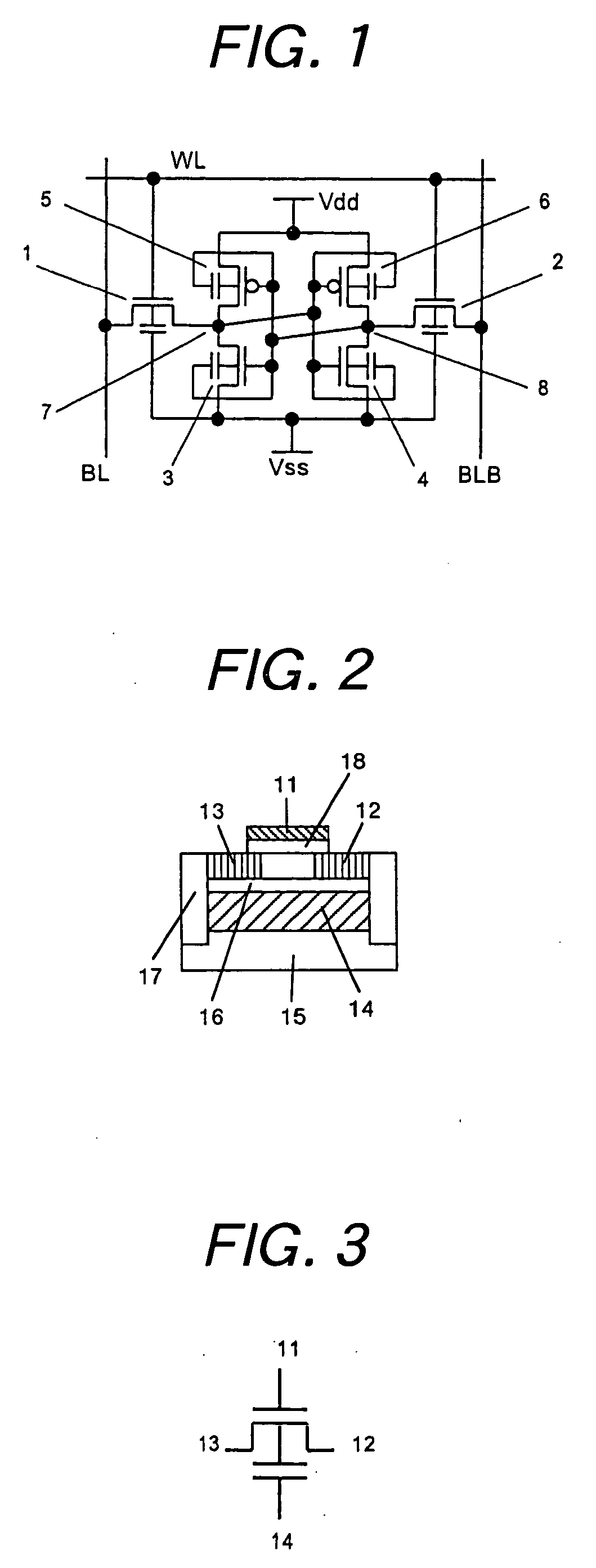
InactiveUS7498637B2Guaranteed uptimeAverage power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorThreshold voltage
A SRAM memory is composed of FD-SOI transistors, and performance of the memory cell is improved by controlling an electric potential of a layer under a buried oxide film of a SOI transistor constituting a driver transistor. Performance of the SRAM circuit in the low power voltage state is improved. In the SRAM memory cell composed of the FD-SOI transistor, an electric potential of a well under a BOX layer is controlled to control a threshold voltage Vth, thereby increasing a current. Thus, the operations of the memory cell can be stabilized.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor memory
InactiveUS20050276094A1Improve performanceIncrease in surplus leak currentTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
A SRAM memory is composed of FD-SOI transistors, and performance of the memory cell is improved by controlling an electric potential of a layer under a buried oxide film of a SOI transistor constituting a driver transistor. Performance of the SRAM circuit in the low power voltage state is improved. In the SRAM memory cell composed of the FD-SOI transistor, an electric potential of a well under a BOX layer is controlled to control a threshold voltage Vth, thereby increasing a current. Thus, the operations of the memory cell can be stabilized.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
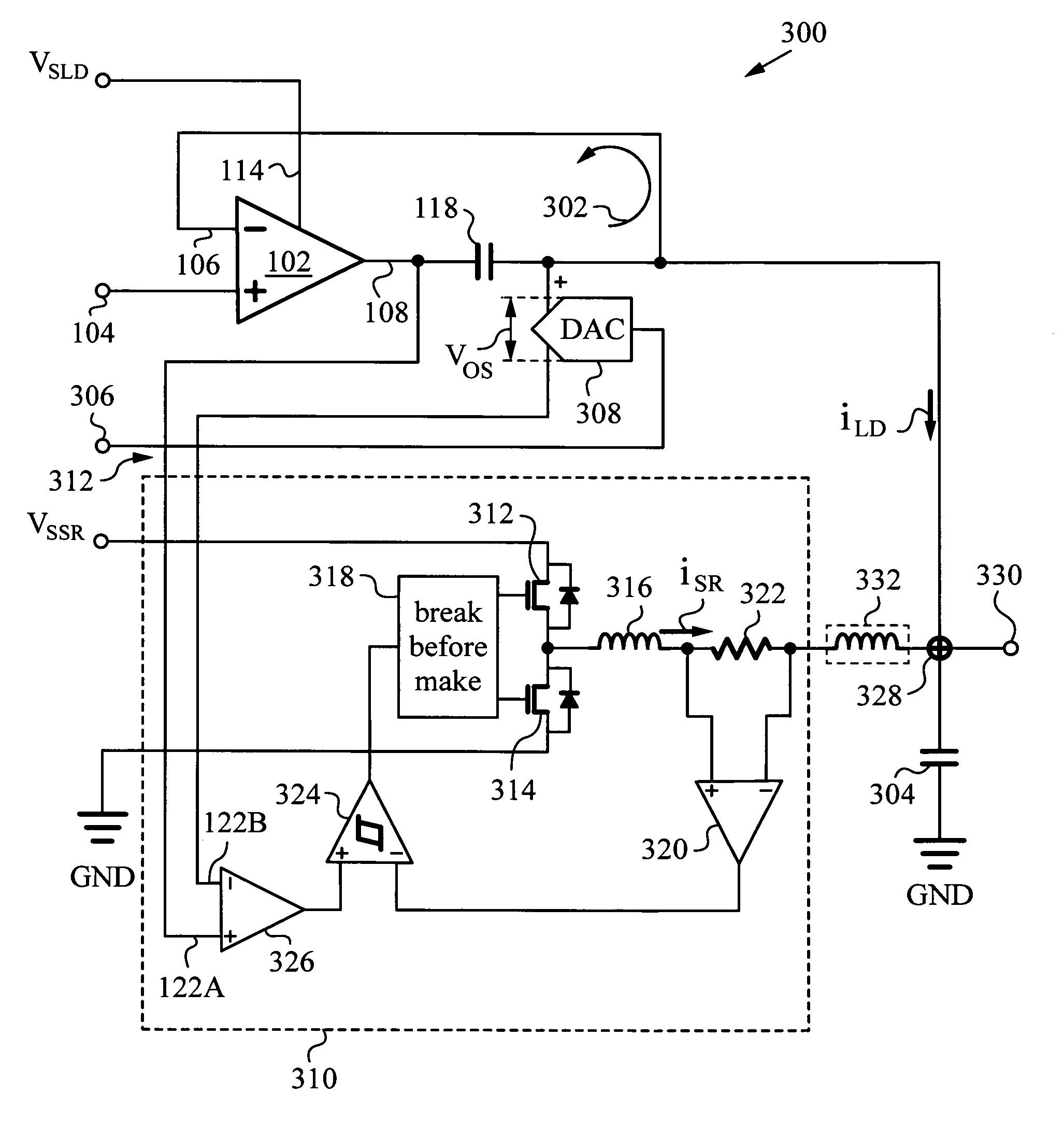
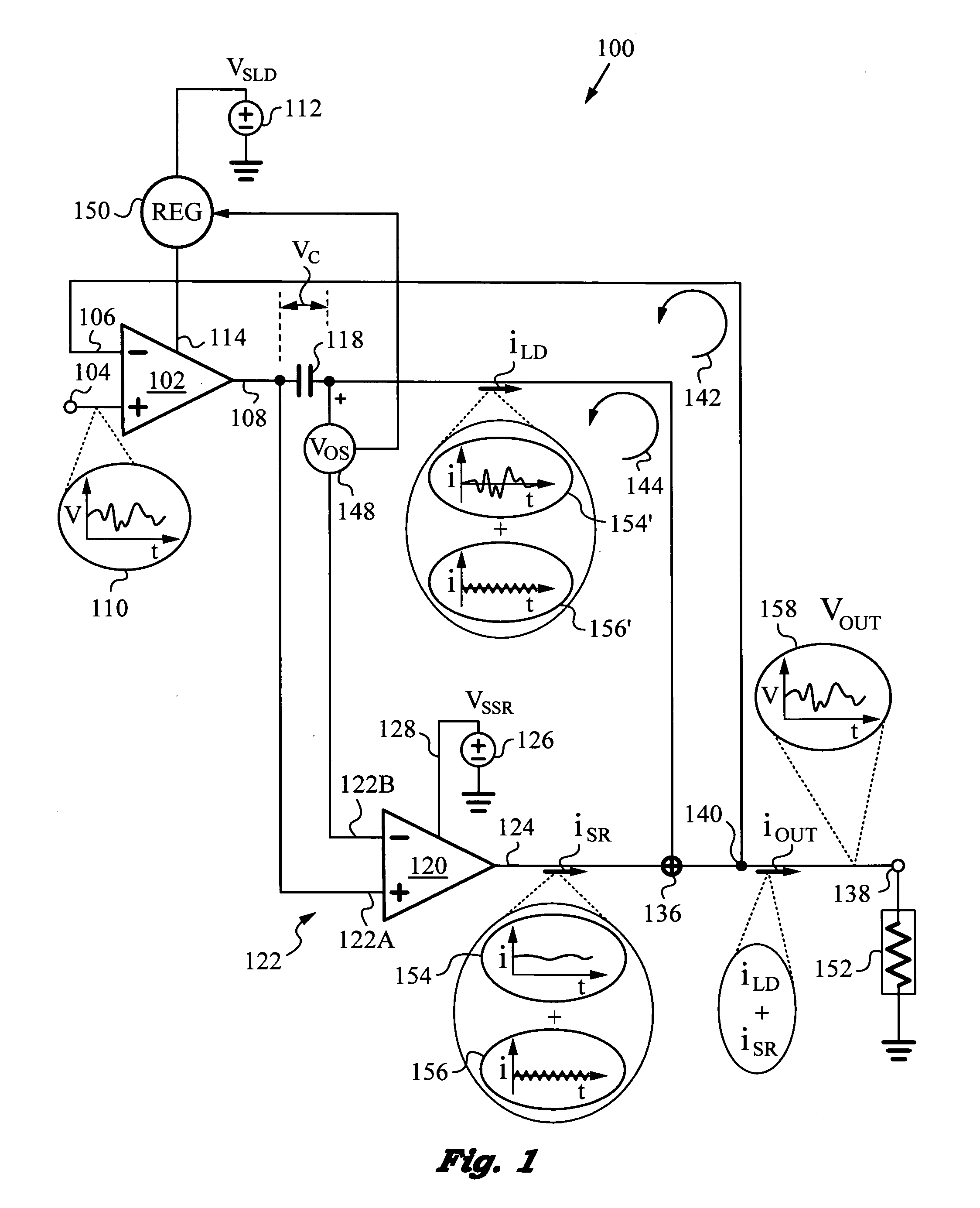
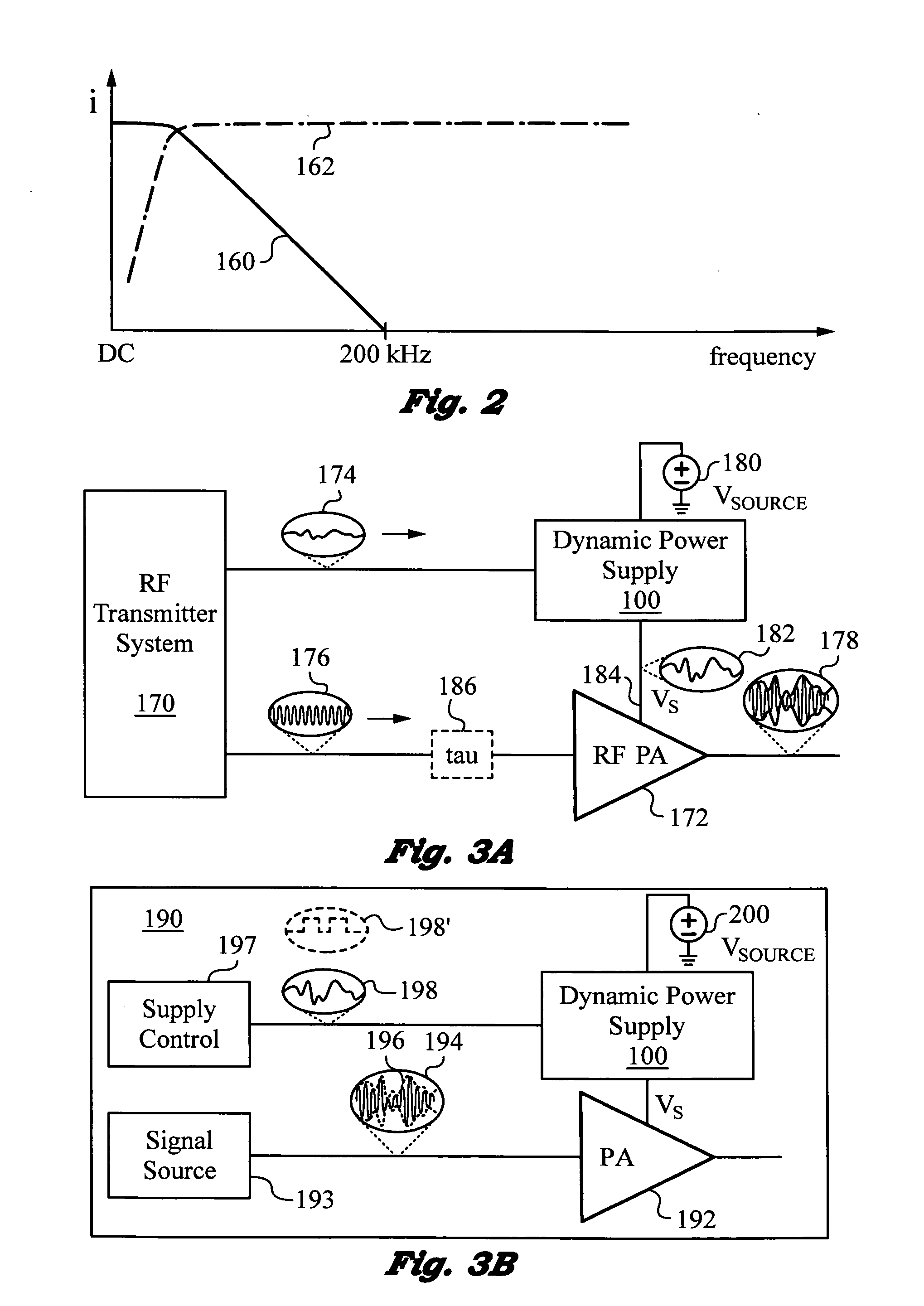
Dynamic power supply employing a linear driver and a switching regulator
ActiveUS20130214858A1Reduce power supply voltageImprove efficiencyGain controlDc-dc conversionNegative feedbackCapacitor voltage
A highly efficient, high control bandwidth and high-speed power supply with a linear driver and a switching regulator for regulating an output based on a control signal. The linear driver has a first input for receiving the control signal and a second input connected to the output for receiving negative feedback. The driver's output is controlled by its two inputs and has a capacitor connected in series with it to generate a capacitor voltage VC responsive to the DC and low frequency components in the driver's output. The switching regulator has a control input and a regulator output connected in a regulator feedback loop. The control input receives capacitor voltage VC and the regulator feedback loop minimizes capacitor voltage VC. Thus, switching regulator takes over the generation of DC and low frequency components, while the linear driver provides high frequency output current components.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Semiconductor storage device
InactiveUS6922371B2Total current dropReduce consumptionSolid-state devicesDigital storageControl signalChip select
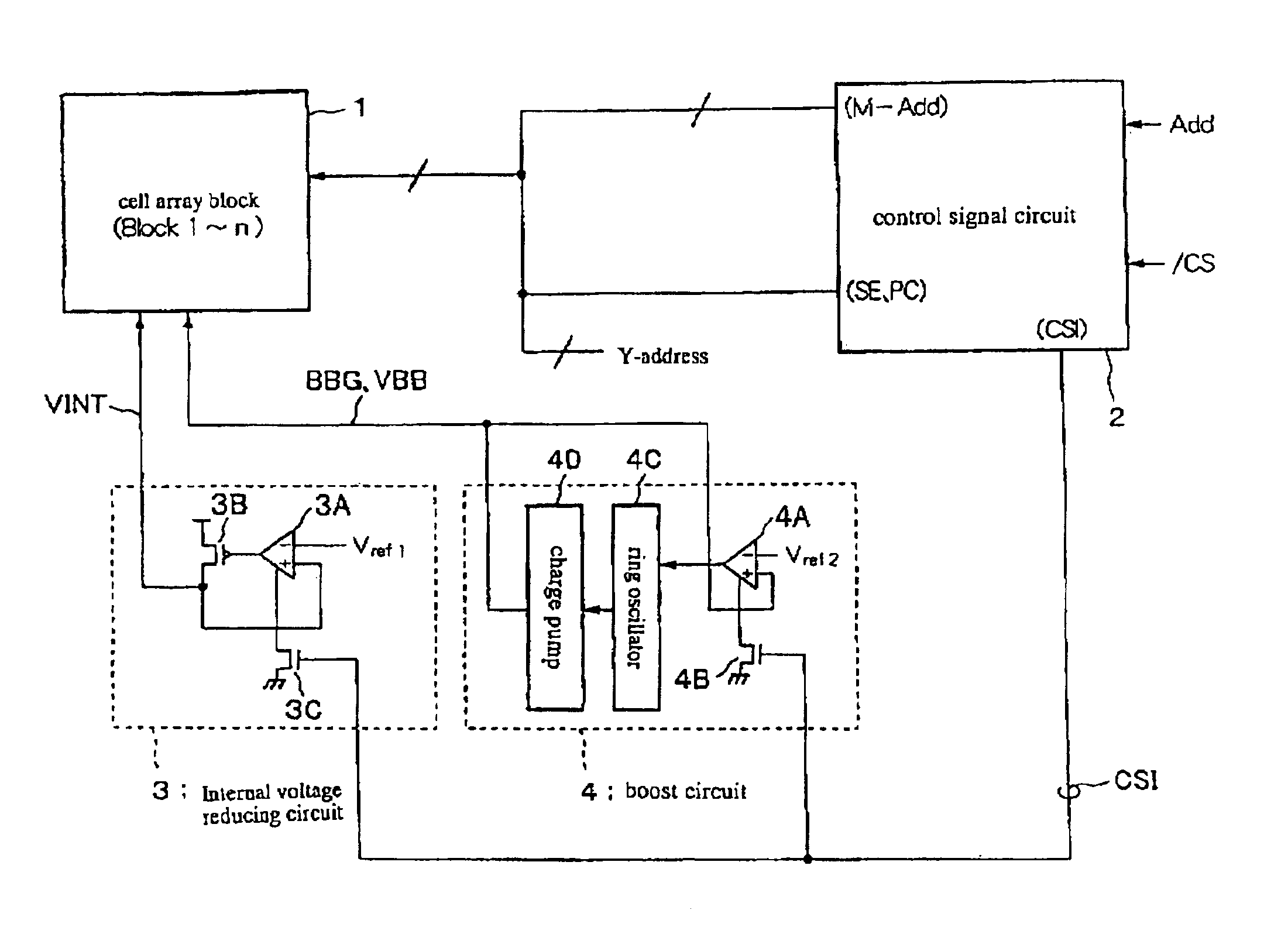
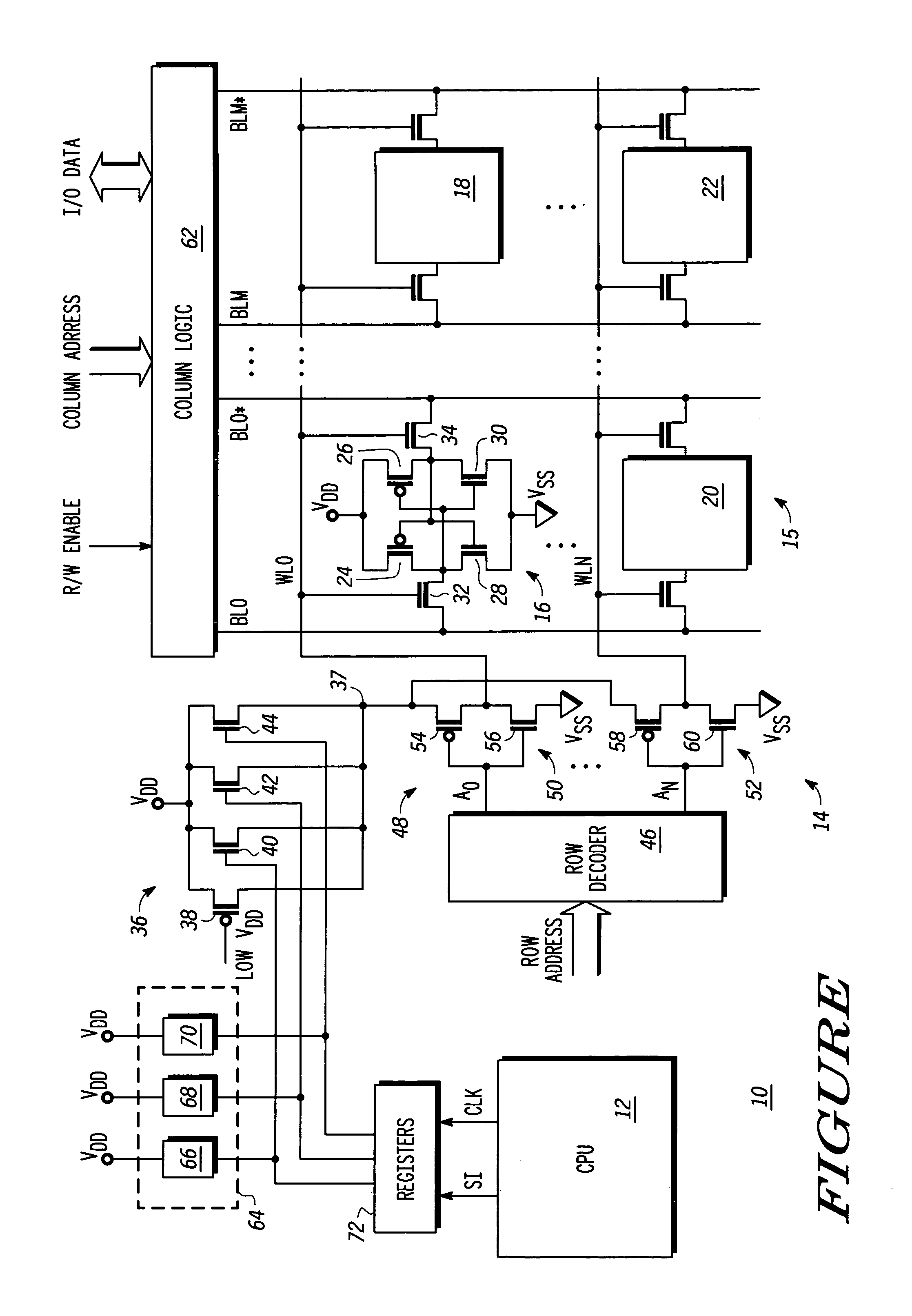
A semiconductor memory device is provided which effectively reduces a consumption of current of a system of circuits associated with refresh operations. A control signal circuit 2 controls n-channel transistors 3C, 4B to be in an OFF-state based on an internal chip select signal SCI in an interval time period between the refresh operations, wherein the n-channel transistors 3C, 4B are connected between the system of circuits associated with refresh operations (an internal voltage-down circuit 3 and a boost circuit 4) and the ground, so as to break down a leak path of the system of circuits associated with refresh operations for reducing the leakage of current. At a timing of starting the refresh operation by triggering a timer, the internal chip select signal SCI is transitioned to a high level for supplying a ground voltage to the internal voltage-down circuit 3 and the boost circuit 4.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20070076467A1Reduce consumptionSmall sizeDigital storageSubthreshold leakage currentHemt circuits
An object of the present invention is to provide a technique of reducing the power consumption of an entire low power consumption SRAM LSI circuit employing scaled-down transistors and of increasing the stability of read and write operations on the memory cells by reducing the subthreshold leakage current and the leakage current flowing from the drain electrode to the substrate electrode. Another object of the present invention is to provide a technique of preventing an increase in the number of transistors in a memory cell and thereby preventing an increase in the cell area. Still another object of the present invention is to provide a technique of ensuring stable operation of an SRAM memory cell made up of SOI or FD-SOI transistors having a BOX layer by controlling the potentials of the wells under the BOX layers of the drive transistors.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
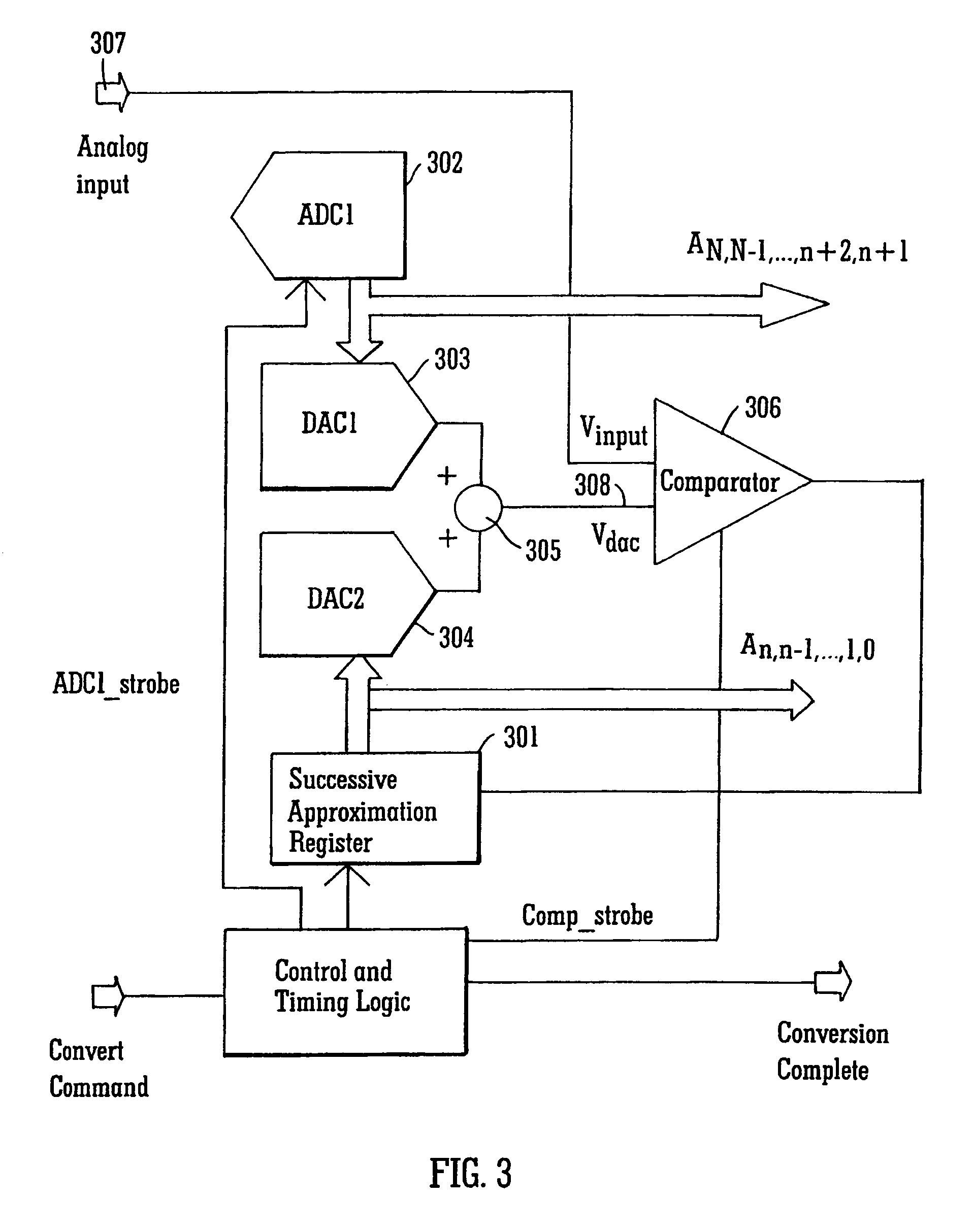
Successive approximation analog-to-digital converter with pre-loaded SAR registers
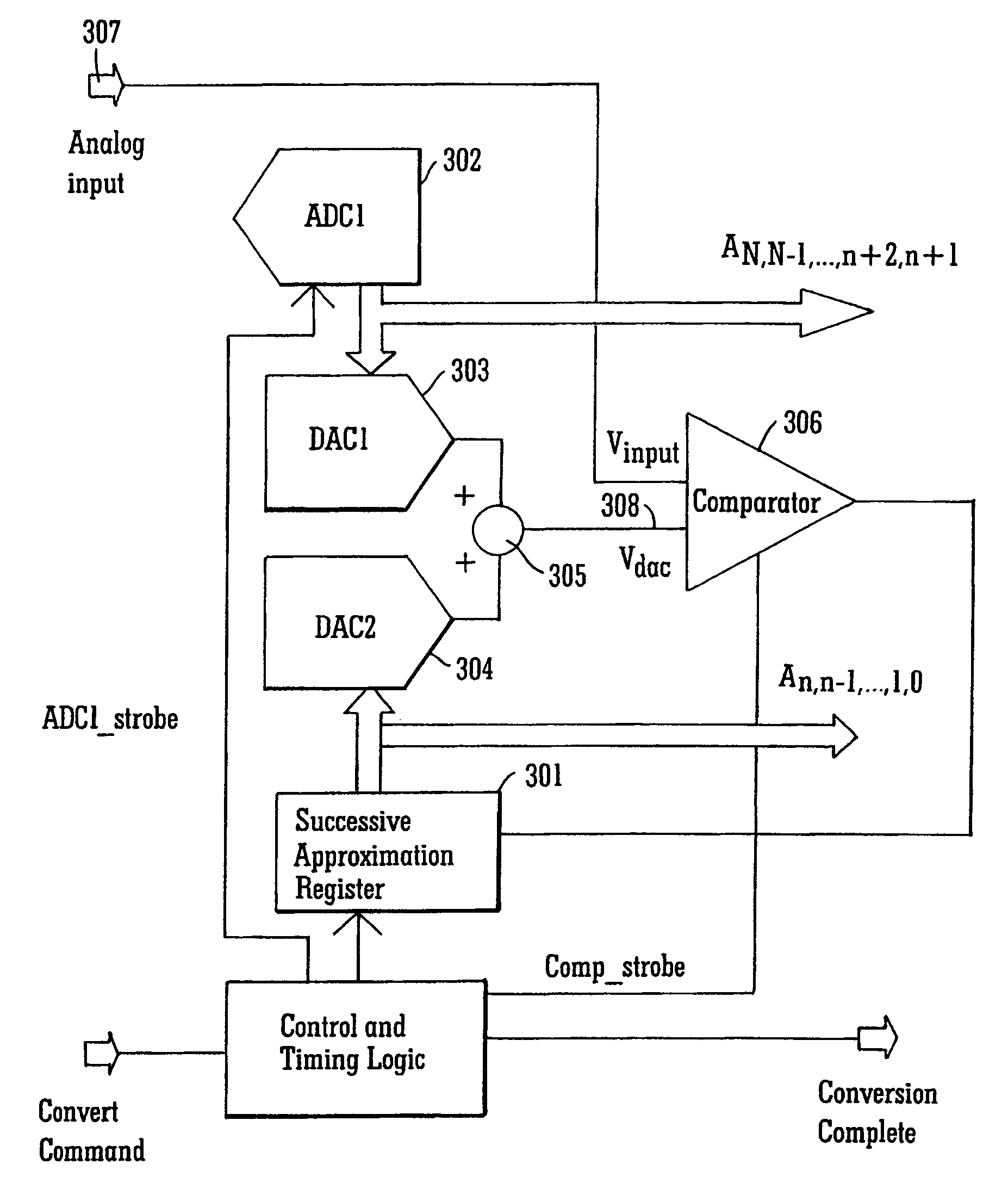
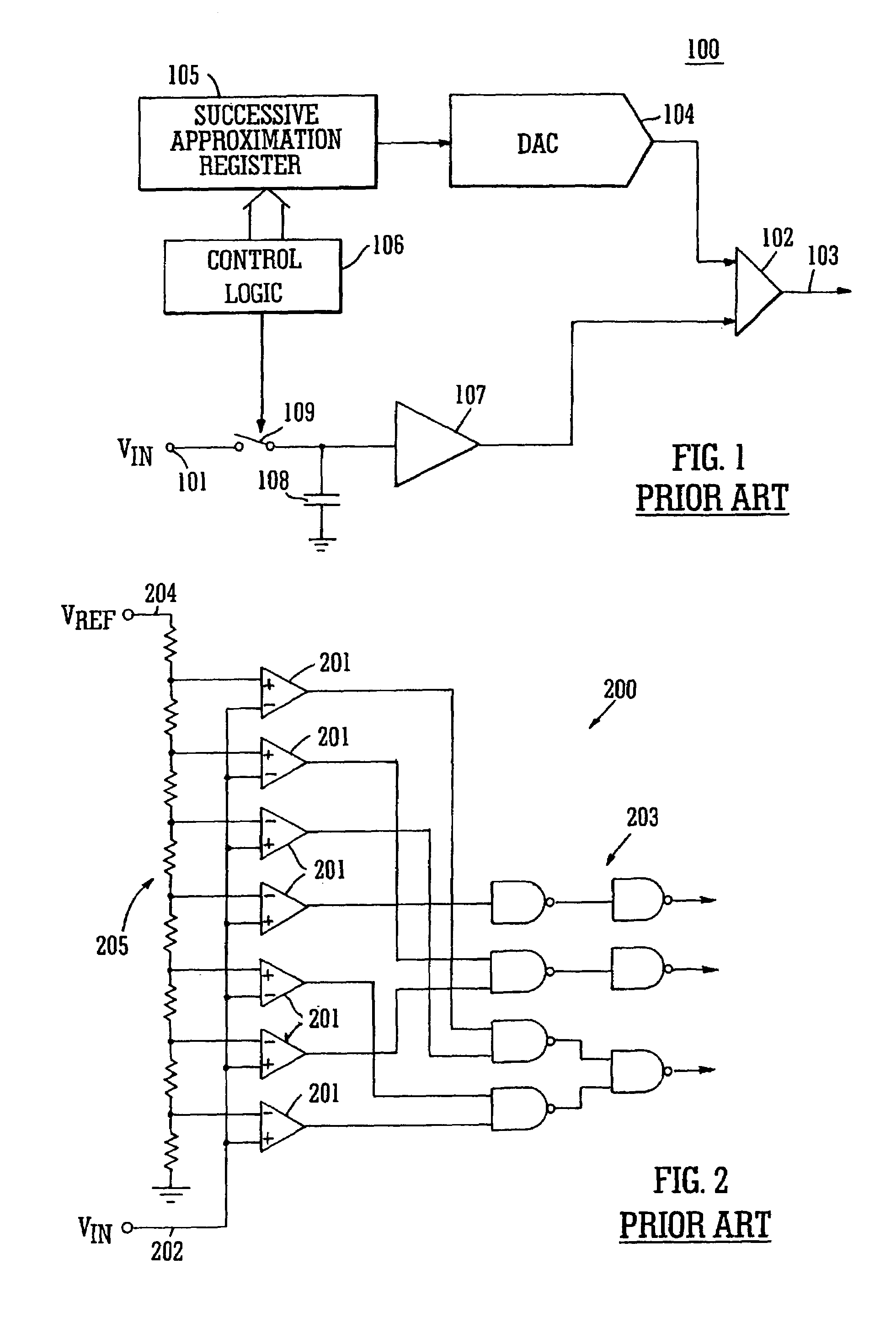
InactiveUS7038609B1Efficiently transitionEliminate effectiveElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterFlash ADC
A SAR converter having enhanced performance by virtue of effectively pre-loading the SAR's most significant bits with a value that makes the associated DAC output almost equal to the signal to be converted. A normal SAR conversion is then completed with the SAR bits that have not been pre-loaded. The value used to pre-load the most significant bits of the SAR is preferably obtained from a low-resolution, high-speed converter, such as a flash. The range of DAC bits used in the normal SAR part of the conversion may be increased such that errors up to a certain magnitude in the high-speed converter can be corrected. Reducing power consumption of a SAR system can be readily accomplished by reducing comparator supply voltage. For a SAR converter architecture using a CAPDAC array or CAPDAC (capacitor array DAC), fairly large variations in comparator input voltage can be expected under these circumstances. If the input voltage variation becomes too large, damage to the comparator input devices can occur, or inaccuracies may develop. In one embodiment of the invention, the most significant bits are provided by sampling the input signal through a flash ADC that does not suffer from the input voltage restriction described above.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
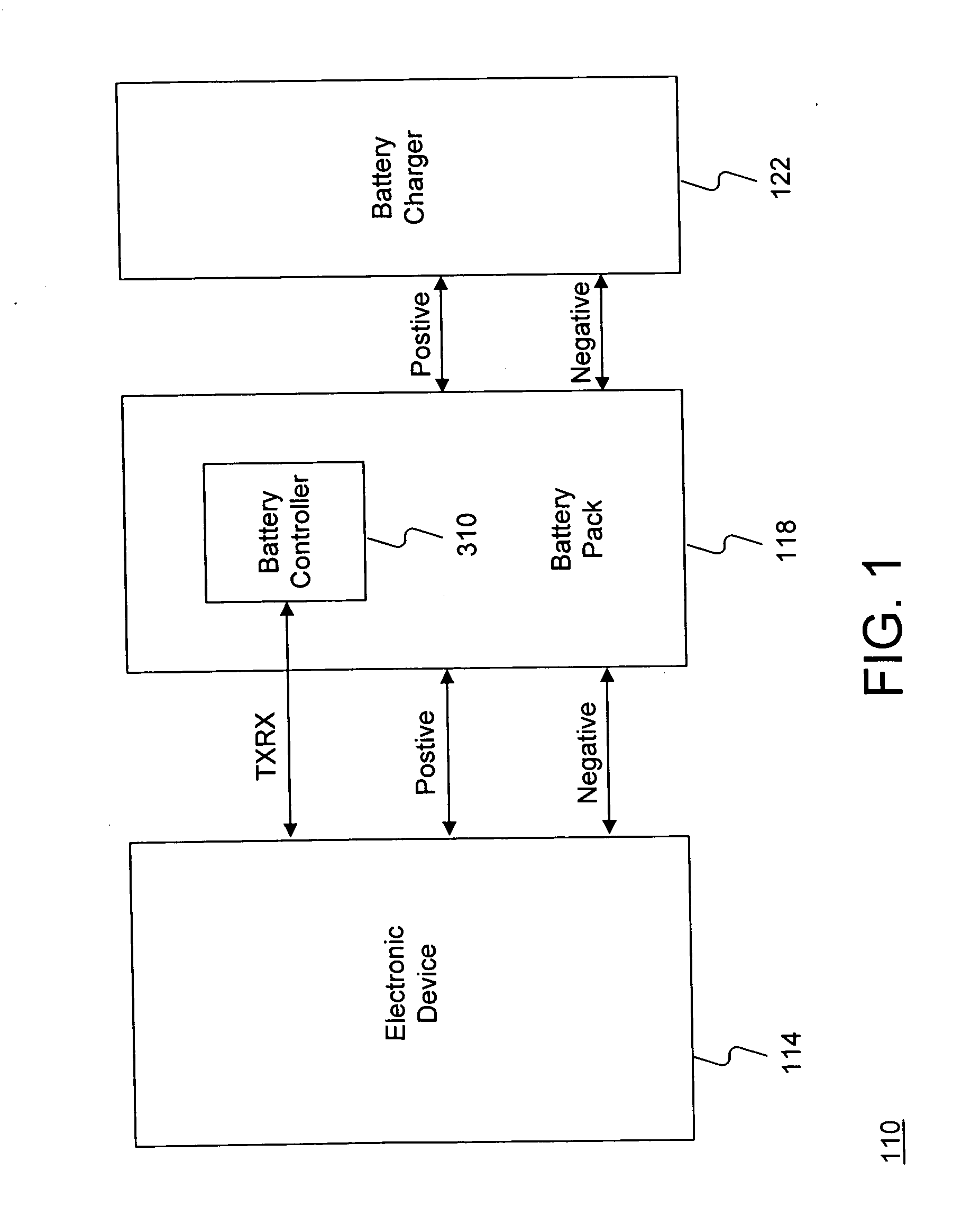
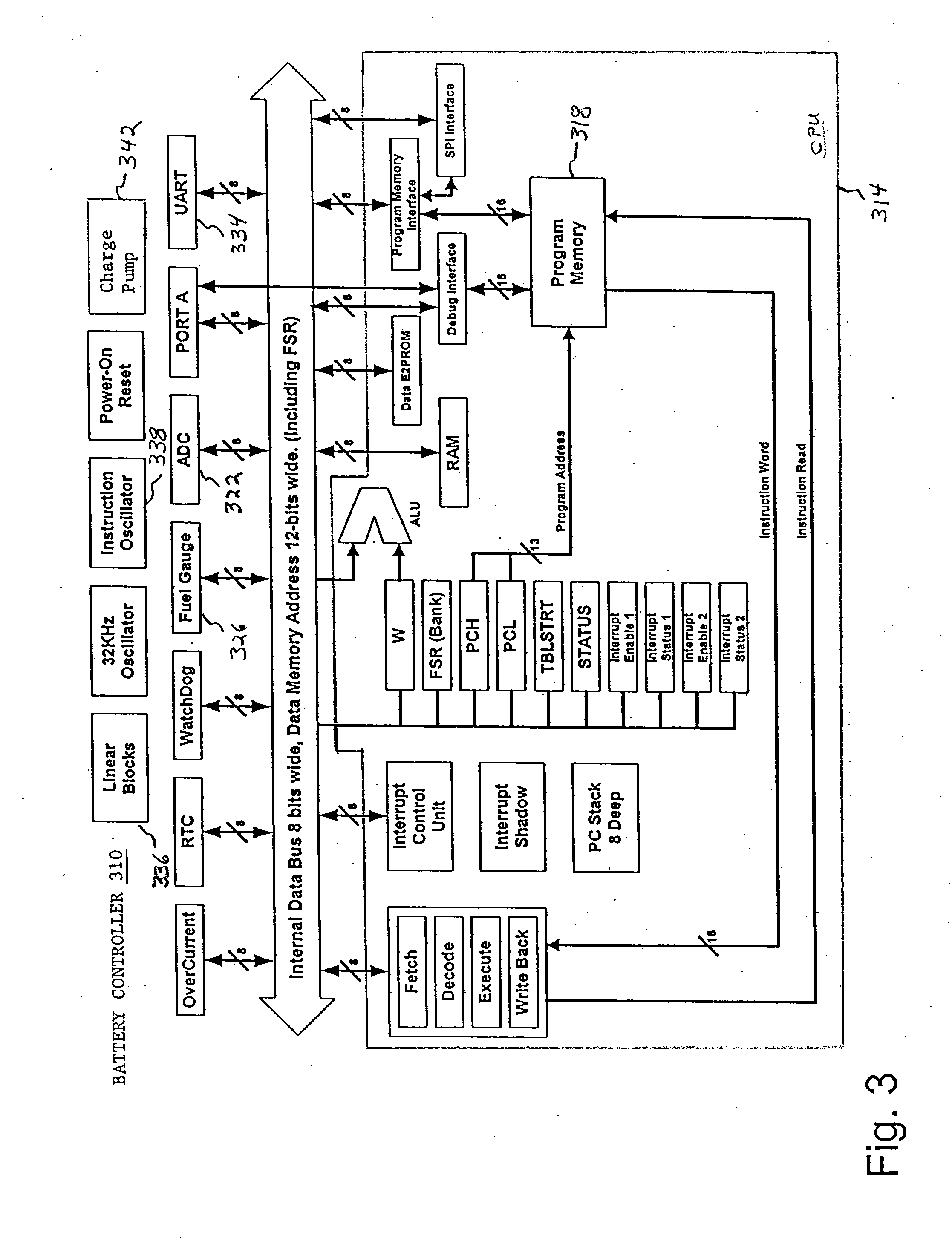
System and method for efficiently implementing a battery controller for an electronic device
ActiveUS20050093512A1Efficient implementationProviding operating powerCells structural combinationApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric forceEmbedded system
A system and method for effectively managing operating power for an electronic device may include a battery pack coupled to the electronic device for supplying operating power to the electronic device. A battery controller may be configured as a single integrated-circuit device to alternately manage the battery pack either in a single-cell implementation or in a dual-cell implementation. The battery controller may include a charge pump device to provide an internal controller power supply for operating the battery controller in the single-cell implementation.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Light source
ActiveUS20100079091A1Reduce power consumptionDecentralizing the computing capabilityElectrical apparatusElectric controllersControl systemSignal on
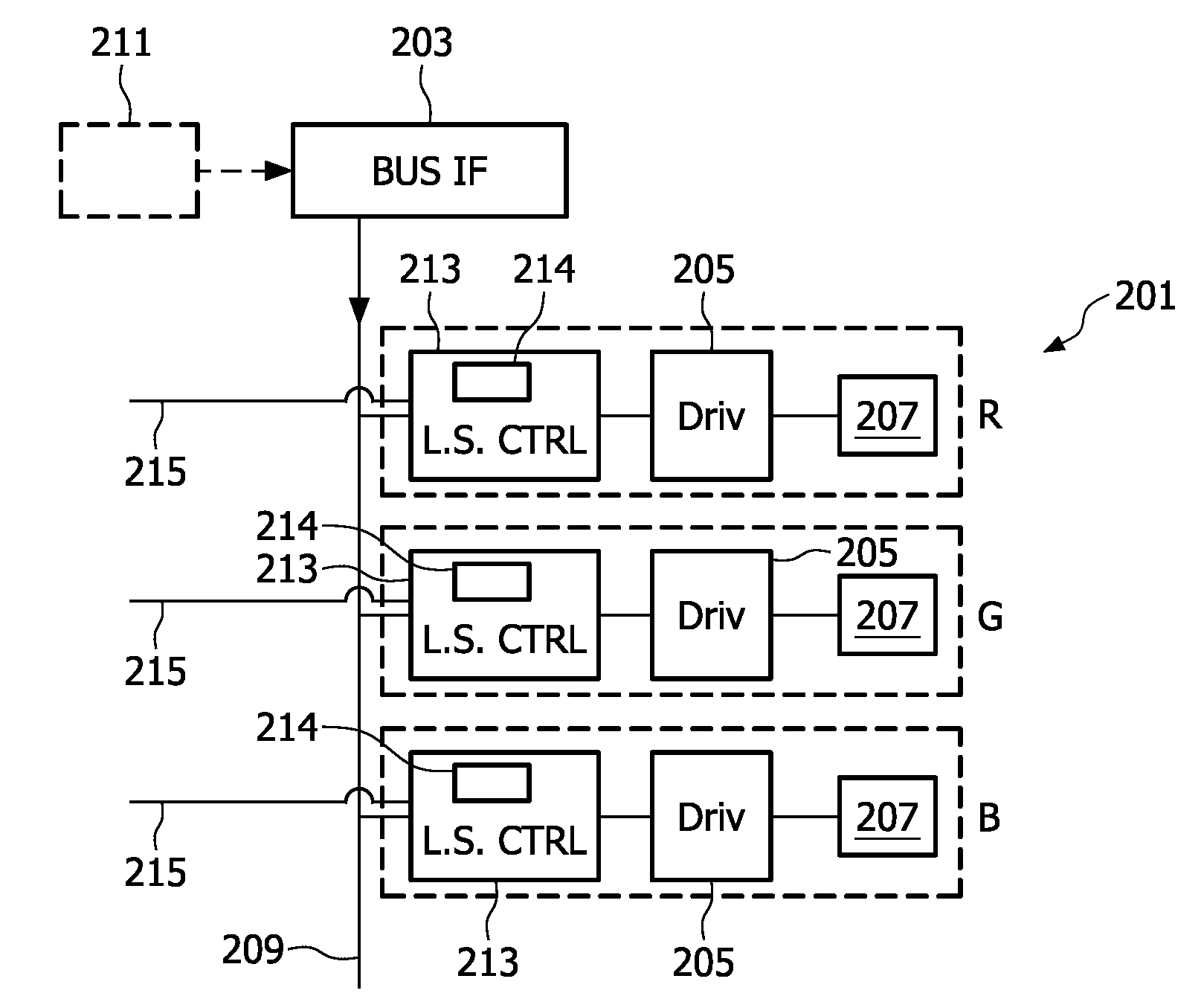
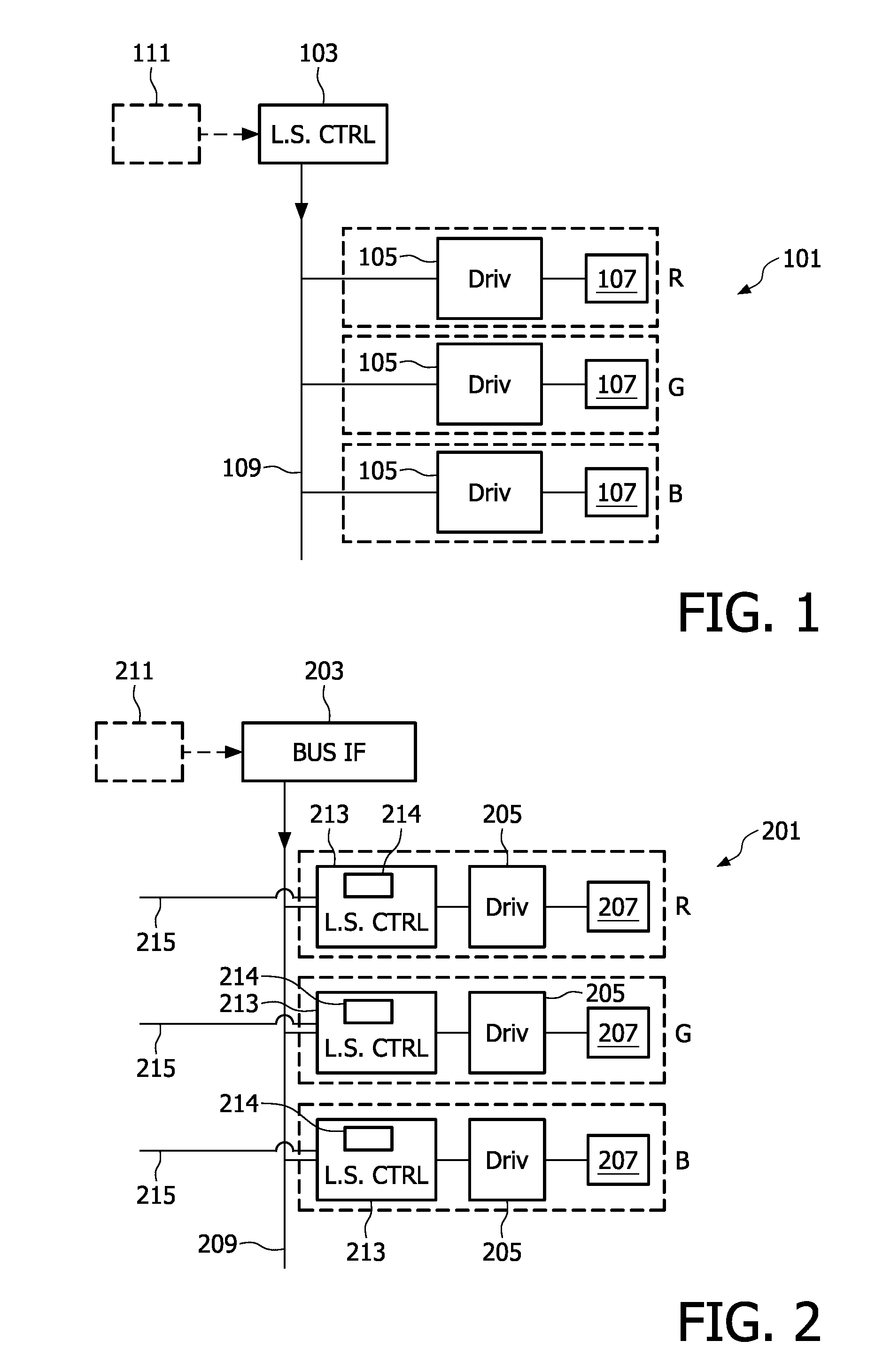
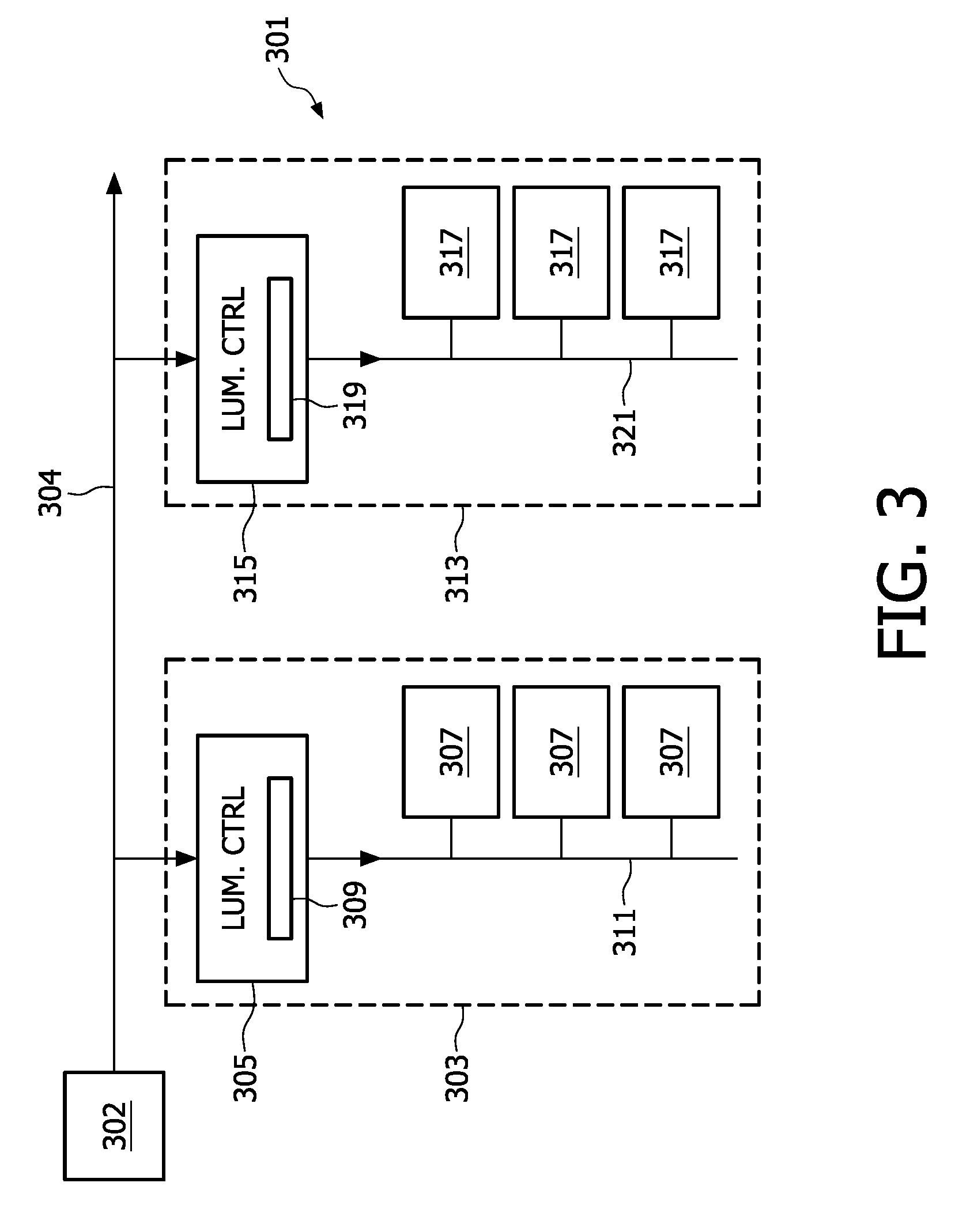
This invention relates to a light source (201) having a plurality of light elements (207) and a control system for controlling the, light elements. The control system comprises a plurality of light element controllers (213), each connected to a respective light element (207), and arranged to obtain light element data; and a bus interface (203), which is connected to the light element controllers (213) via a light source bus (209). The bus interface (203) provides the light element controllers (213) with a general command, and the light element controllers (213) generate light element drive signals on basis of the general command and the light element data.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Semiconductor memory device, method for controlling the same, and mobile electronic device
InactiveUS20060244049A1Reduce power consumptionStable operationTransistorSolid-state devicesMobile electronicsVoltage
A memory cell array employs a memory element as a memory cell. The memory element is constructed of a gate electrode formed via a gate insulation film on a semiconductor layer, a channel region arranged under the gate electrode, diffusion regions that are arranged on both sides of the channel region and have a conductive type opposite to that of the channel region, and memory function bodies that are arranged on both sides of the gate electrode and have a function to retain electric charges. When first and second power voltages VCC1 and VCC2 supplied from the outside are lower than a prescribed voltage, a rewrite command to a memory circuit 34 that includes the memory cell array is inhibited by a lockout circuit 33a. With this arrangement, there are provided a semiconductor storage device capable of achieving storage retainment of two bits or more per memory element and stable operation even if the device is miniaturized and preventing the occurrence of a malfunction of rewrite error and so on attributed to a reduction in the power voltage supplied from the outside and a control method therefor.
Owner:SHARP KK
Portable drilling device
ActiveUS20090196696A1Reduce power supply voltageEasy to operateDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlFull waveEngineering
It is an object of the present invention to prevent recurrence of an overload condition after occurrence of the overload condition, thereby improving operability and safety in a drilling device. A motor 12 for rotating a drill is connected to an AC power source 10 through a motor control unit 28, a current detector 30, and a power switch 36. A magnet 16 is also connected to the AC power source 10 through the power switch 36 and a full-wave rectifier 18. The motor control unit 28 rotationally drives the motor on the basis of a signal sent from a main control unit according to a state in which a motor start switch 38 is on. The main control unit 14 controls the motor control unit 28 to gradually reduce a supply voltage to the motor 12 when the motor 12 becomes overloaded, to gradually increase the voltage to the normal power supply condition when the overload condition is vanished, and to stop power supply to the motor 12 if the overload condition continues for a predetermined period.
Owner:NITTO KOHKI CO LTD
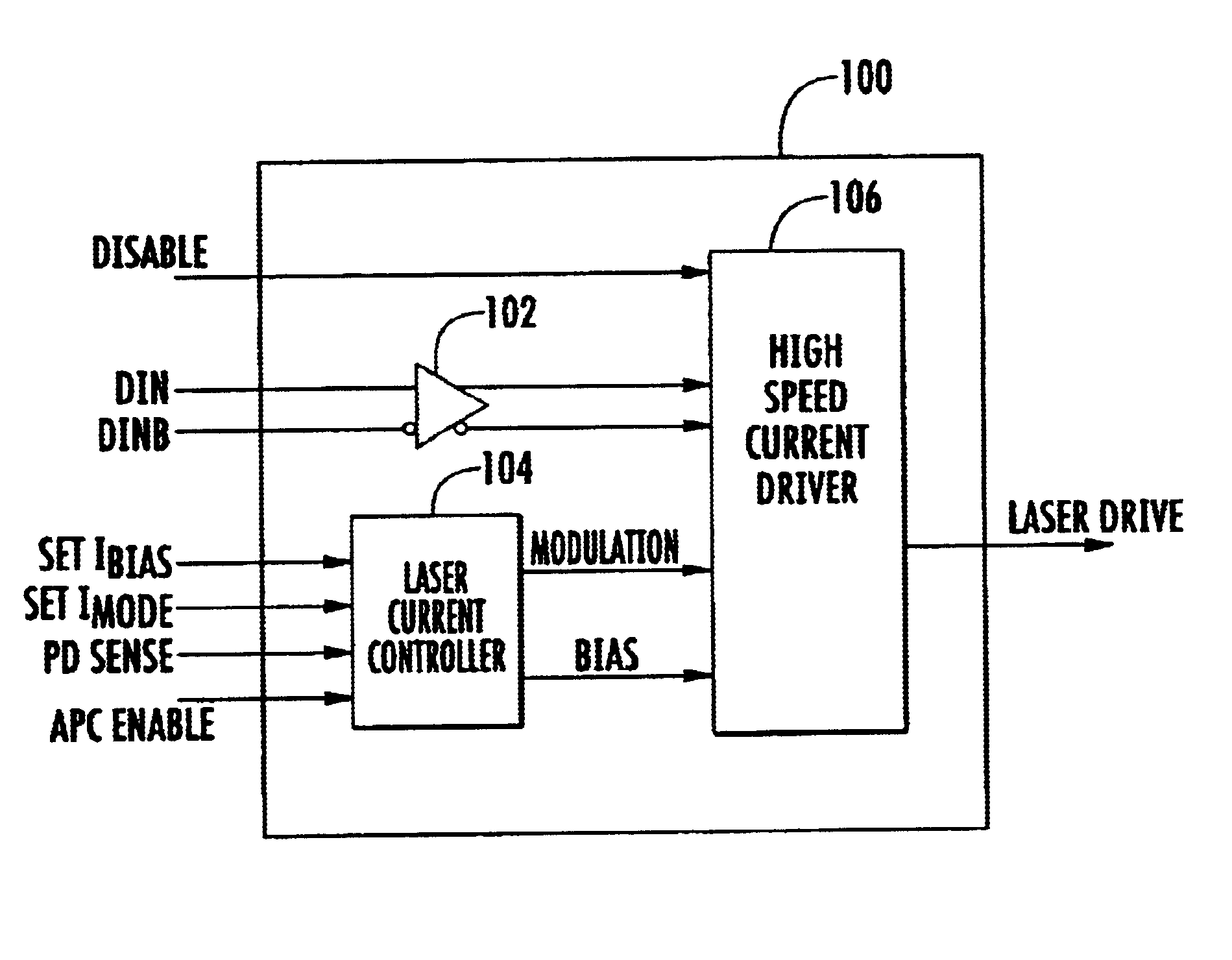
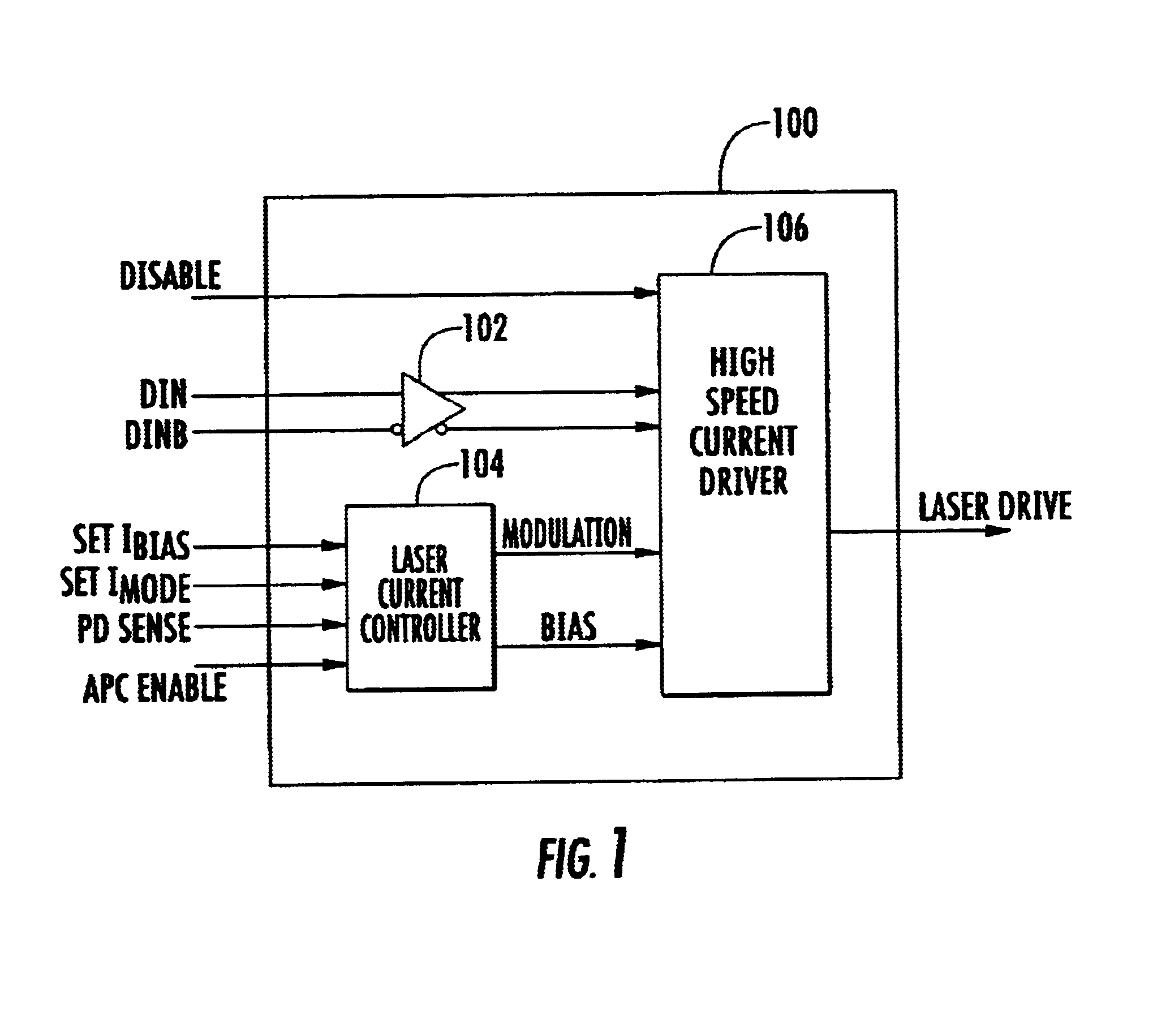
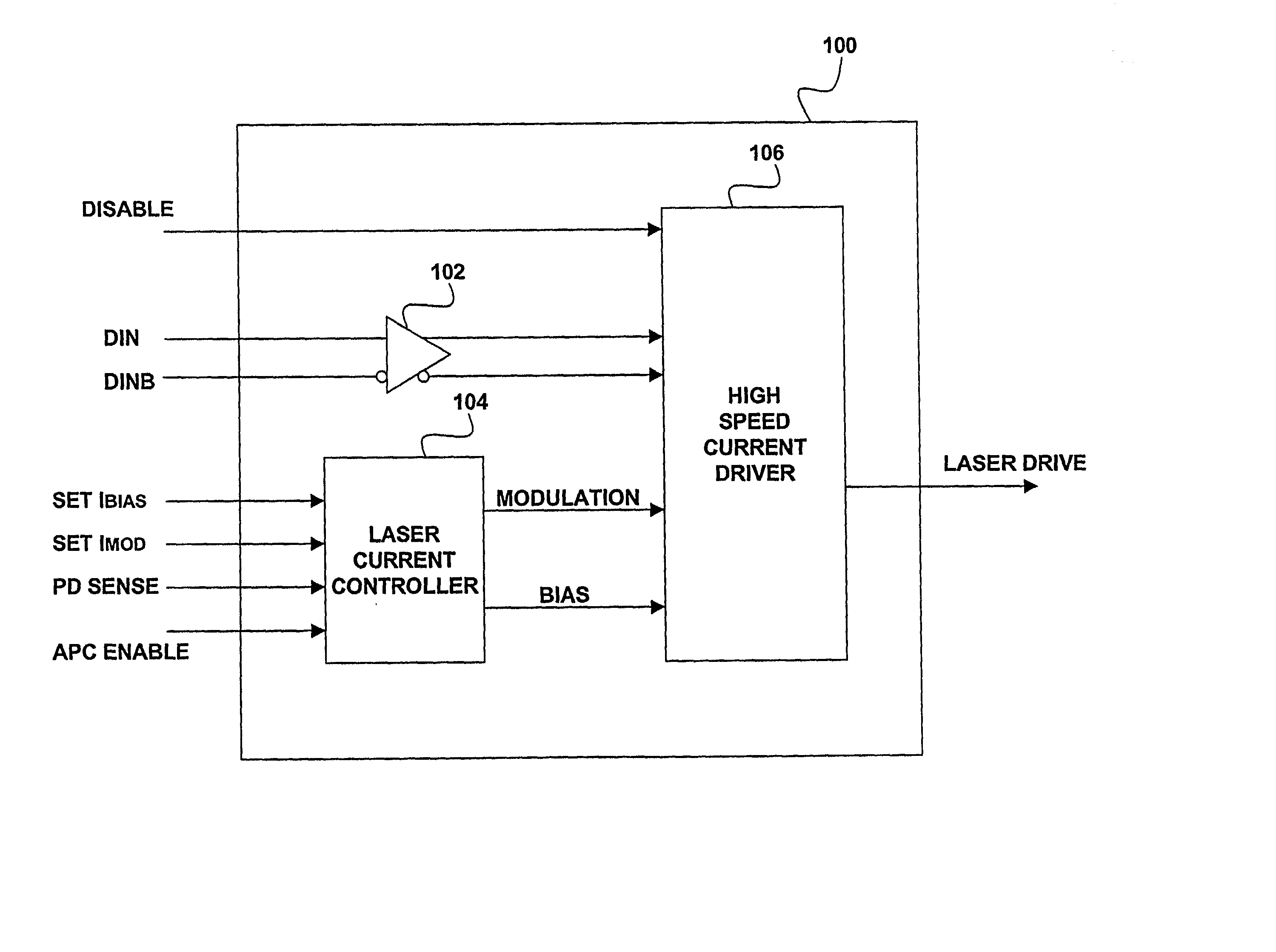
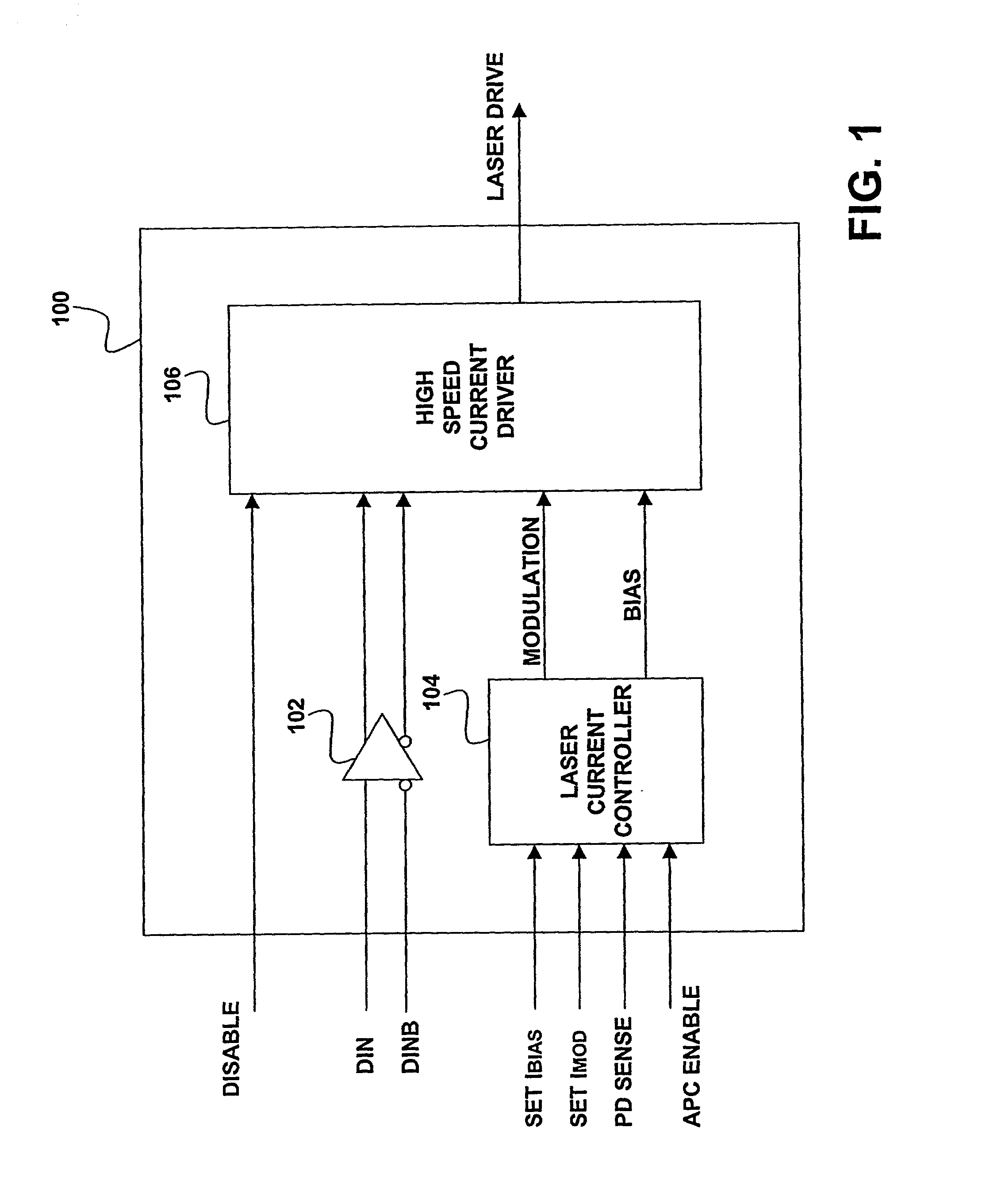
High-speed laser array driver
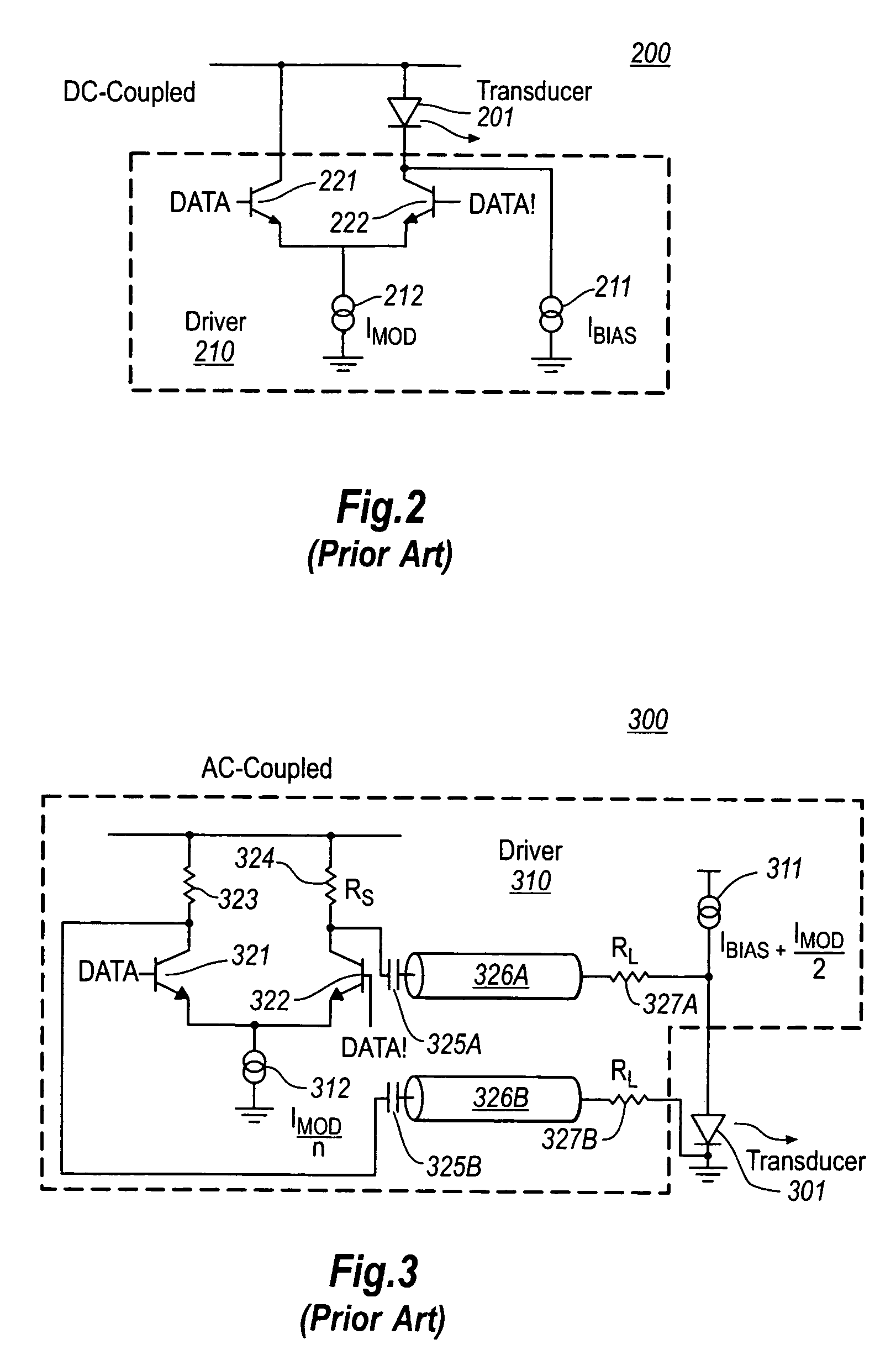
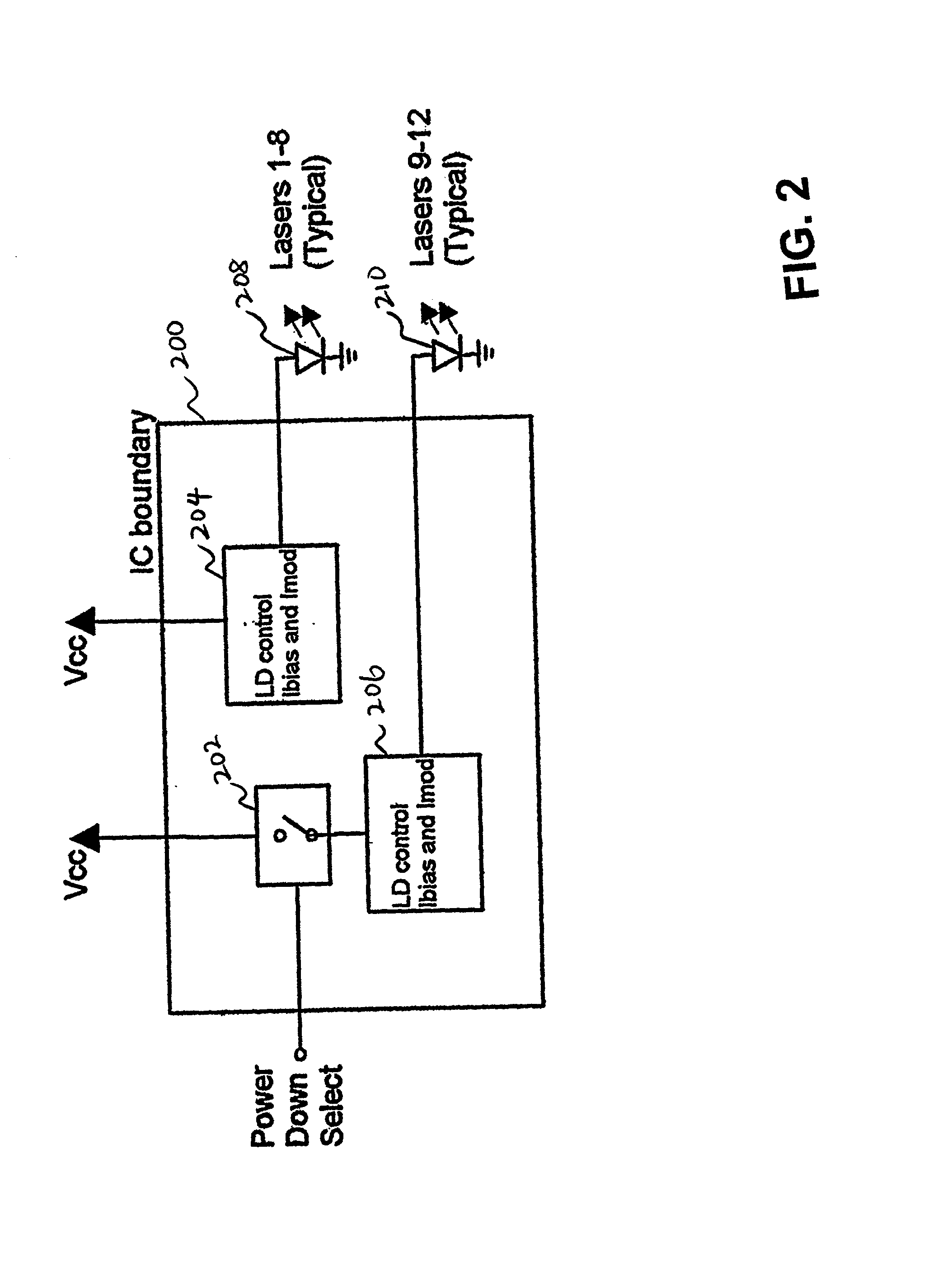
InactiveUS6822987B2Reduce power consumptionReduce power supply voltageSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsCapacitanceLaser array
A method and apparatus for driving lasers. An example laser driving system includes a laser current controller for providing a modulation signal and a bias signal. The modulation signal and bias signal is used by a plurality of high-speed current drivers that accept the modulation signal and the bias signal and produce a plurality of laser drive signals. The example system also has a disable input that disconnects power from a high-speed current driver when the high-speed current driver is not in use. The exemplary system develops the modulation and bias signals by feeding back a signal developed from detection of laser light from one of the lasers driven by the system. The laser may be a data laser or a control laser that is modulated by a signal having a lower frequency than the data lasers. If a control laser is used then the photodetector circuit used for feedback can have a lower frequency response because of the lower frequency of the control laser signal. The photodetector system may also employ a peak detector capacitor discharge circuit where a large capacitance is simulated by having the capacitor discharge through the base of a transistor have a current source in the emitter circuit.
Owner:OPTICAL COMM PRODS
High efficiency active matching electro-optic transducer driver circuit operable with low supply voltages
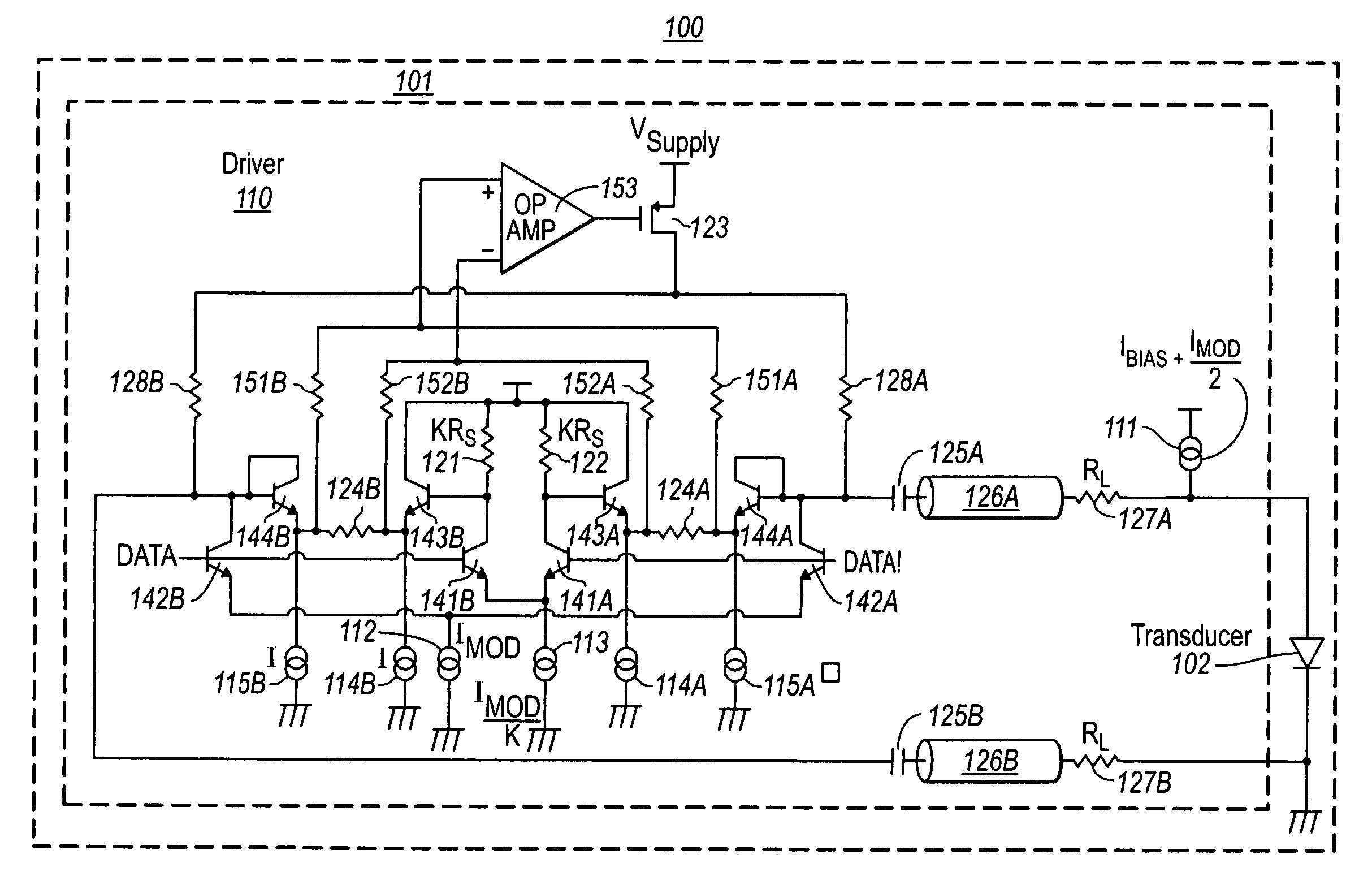
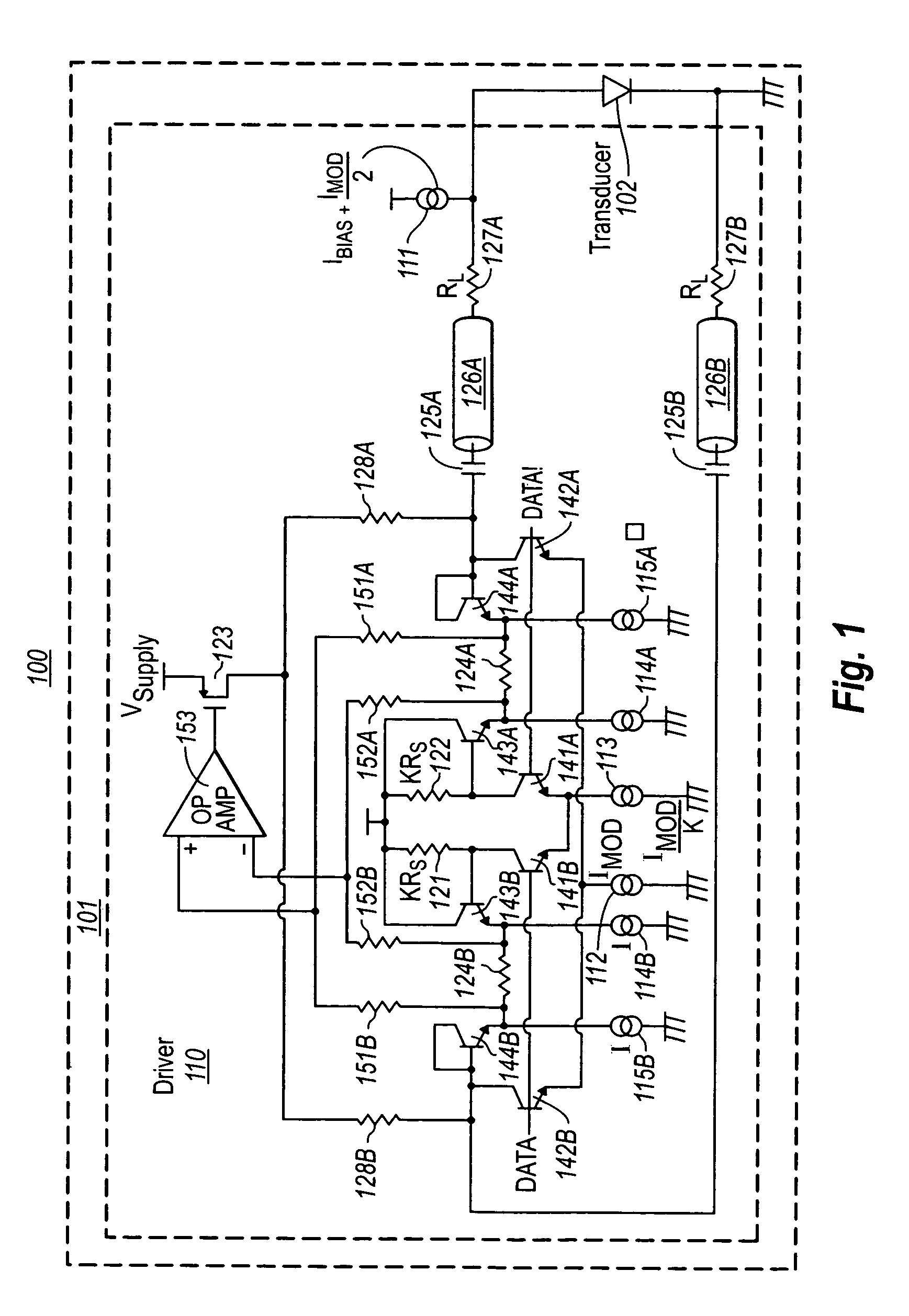
ActiveUS6965722B1Improve efficiencyImproving Impedance MatchingLaser detailsAmplifier combinationsEngineeringTransistor
An optical transmitter and / or a constituent electro-optic transducer driver that performs active matching. The transducer driver performs active matching using a voltage step down through one base-emitter bipolar transistor, followed by a step up approach through the base-emitter of another bipolar transistor, thereby allowing for lower supply voltages. Furthermore, the voltage drop across the source resistor is minimal by using an operation amplifier in a feedback configuration, thereby further encouraging operability with low supply voltages. The electro-optic transducer driver is also beneficial in that it has high AC-coupling efficiency of the modulation current to the electro-optic transducer, may operate at high speeds with reduced jitter.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Word line driver circuit for a static random access memory and method therefor
ActiveUS7085175B2Improve static noise marginReduce decreaseRead-only memoriesDigital storageStatic random-access memoryLow voltage
A static random access memory (14) has a normal mode of operation and a low voltage mode of operation. A memory array (15) includes memory cells (16) coupled to a first power supply node (VDD) for receiving a power supply voltage. A plurality of word line drivers is coupled to word lines of the memory array (15) and to a second power supply node (37). A word line driver voltage reduction circuit (36) has an input coupled to the first power supply node (VDD) and an output coupled to the second power supply node (37) for reducing a voltage on the output in relation to a voltage on the input in response to a low power supply voltage signal, and thus improving a static noise margin of the memory cells (16).
Owner:NXP USA INC
Switching power supply device, semiconductor integrated circuit device and power supply device
InactiveUS20070103005A1Guaranteed uptimeRapid responseBatteries circuit arrangementsBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsInductorPower MOSFET
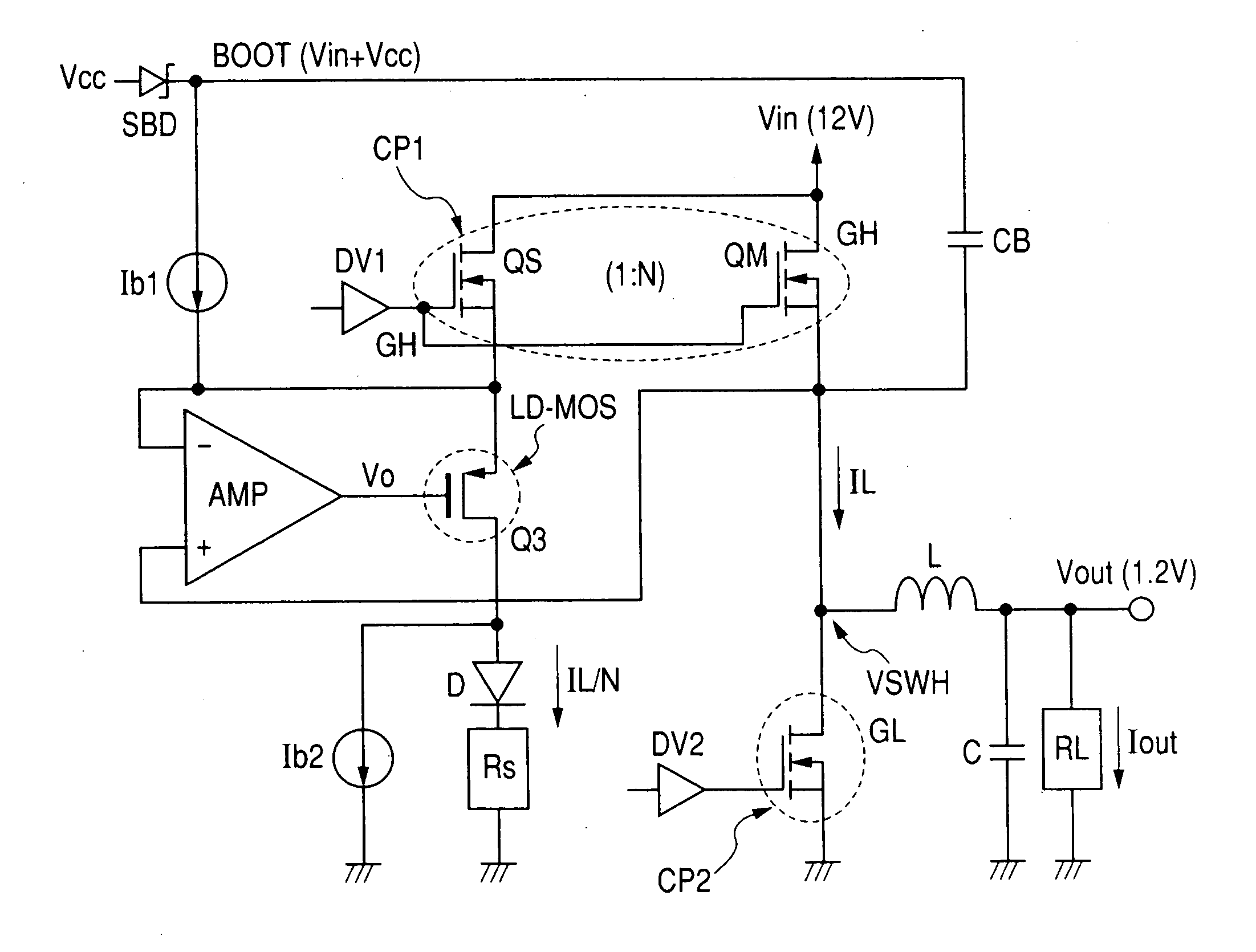
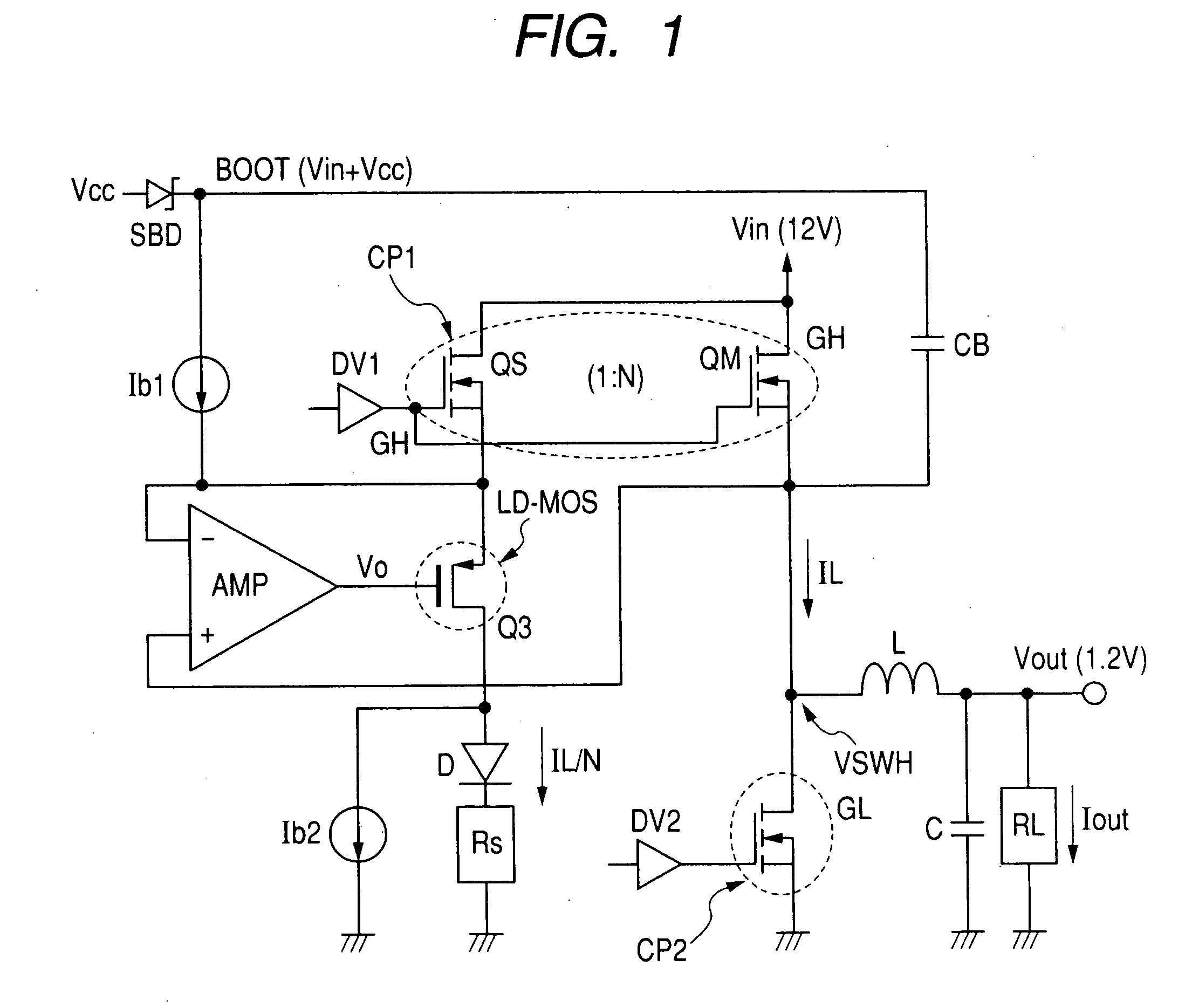
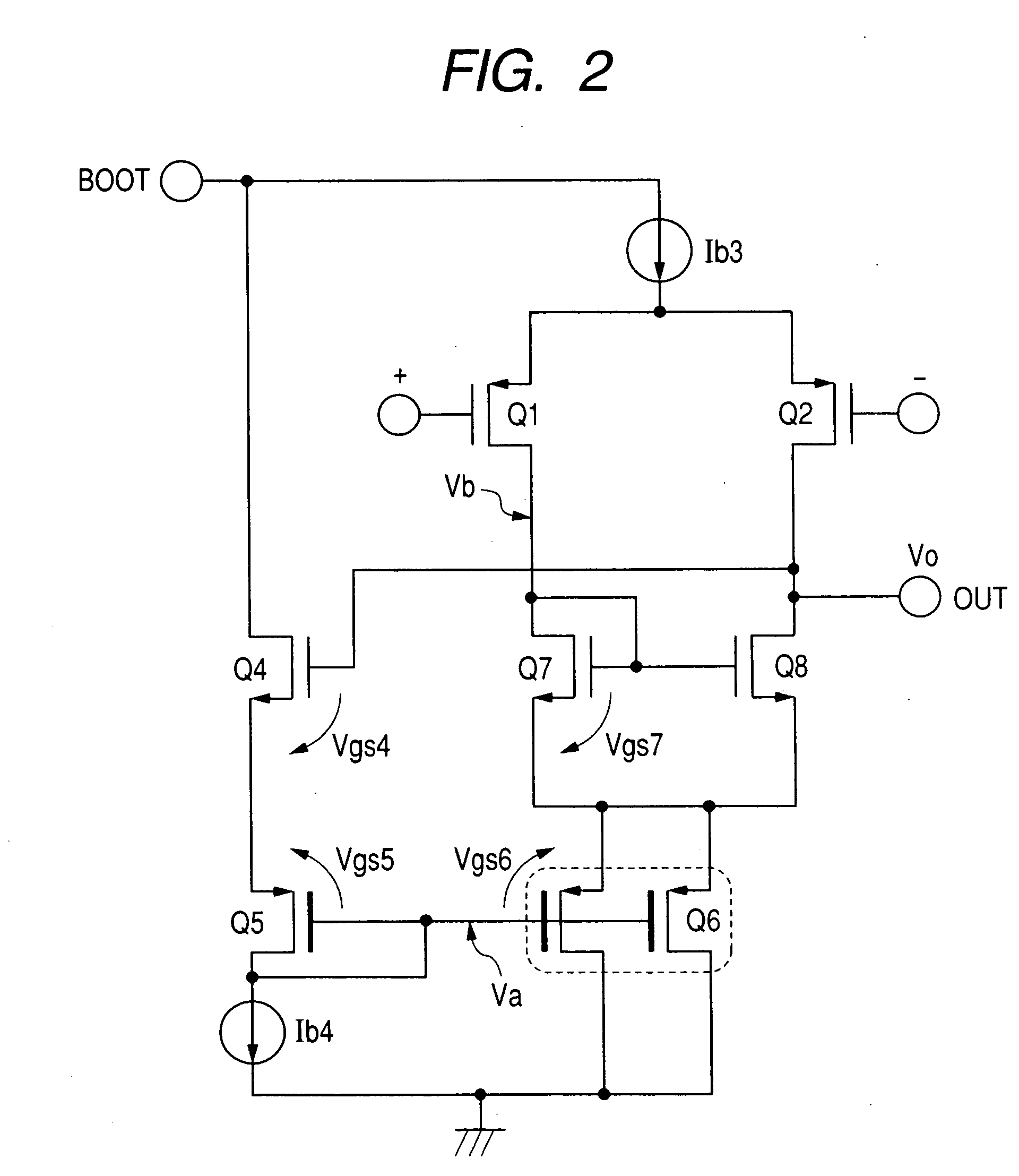
There are provided a switching power supply device performing a stable operation with fast response, a semiconductor integrated circuit device, and a power supply device. A capacitor is provided between the output side of an inductor and a ground potential. A first power MOSFET supplies an electric current from an input voltage to the input side of the inductor. A second power MOSFET turned on when the first power MOSFET is off allows the input side of the inductor to be of a predetermined potential. A first feedback signal corresponding to an output voltage obtained from the output side of the inductor and a second feedback signal corresponding to an electric current flowed to the first power MOSFET are used to form a PWM signal. The first power MOSFET has plural cells of a vertical type MOS-construction. The number of cells is 1 / N. A detection MOSFET in which the gains and the drains are shared over the same semiconductor substrate with the first power MOSFET is provided to form a second feedback signal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Bias Control for Stacked Transistor Configuration
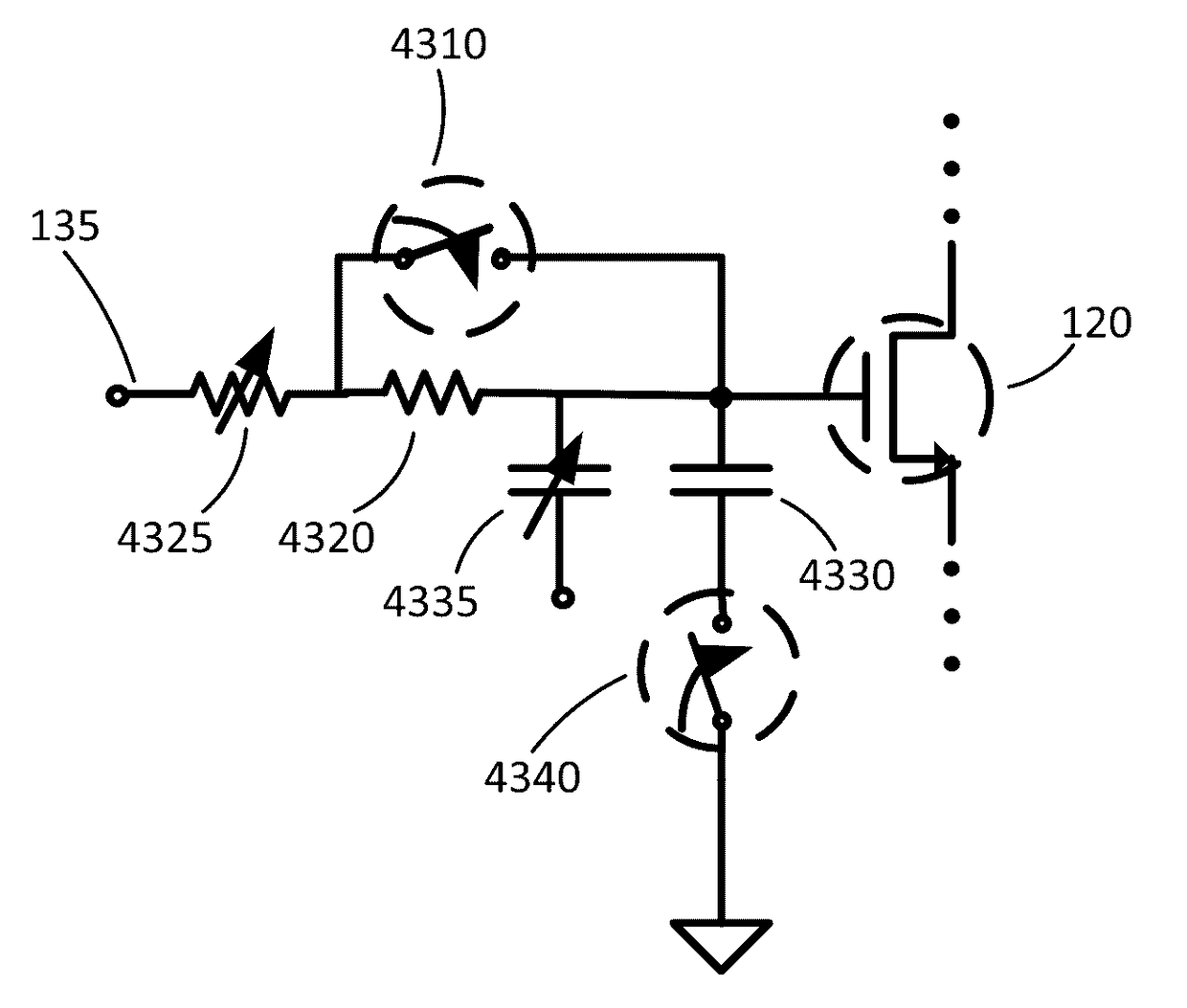
ActiveUS20170133989A1Reduce the voltage levelImprove power linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier details to increase power/efficiencyAudio power amplifierEngineering
Various methods and circuital arrangements for biasing one or more gates of stacked transistors of an amplifier are presented, where the amplifier can have a varying supply voltage that varies according to a control voltage. The control voltage can be related to a desired output power of the amplifier and / or to an envelope signal of an input signal to the amplifier. Particular biasing for selectively controlling the stacked transistors to operate in either a saturation region or a triode region is also presented. Benefits of such controlling, including increased linear response of an output power of the amplifier, are also discussed.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
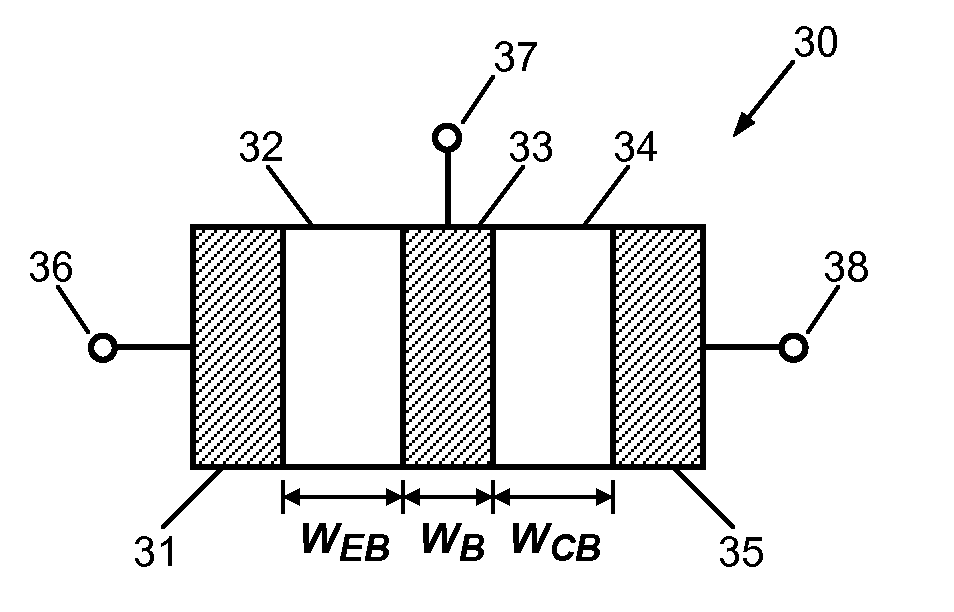
Schottky barrier quantum well resonant tunneling transistor
InactiveUS20100102298A1High speedReduce series resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesQuantum wellSchottky barrier
A semiconductor transistor device includes one or more conductive base regions, a first semiconductor barrier region, a second semiconductor barrier region, a conductive emitter region, and a conductive collector region. The first semiconductor barrier region or the second semiconductor barrier region has a dimension smaller than 100 Å. A first Schottky barrier junction is formed at the interface of the first semiconductor barrier region and the one or more conductive base regions. A second Schottky barrier junction is formed at the interface of the second semiconductor barrier region and the one or more conductive base regions. A third Schottky barrier junction is formed at the interface of the conductive emitter region and the first semiconductor barrier region. A fourth Schottky barrier junction is formed at the interface of the conductive collector region and the second semiconductor barrier region.
Owner:WU KOUCHENG
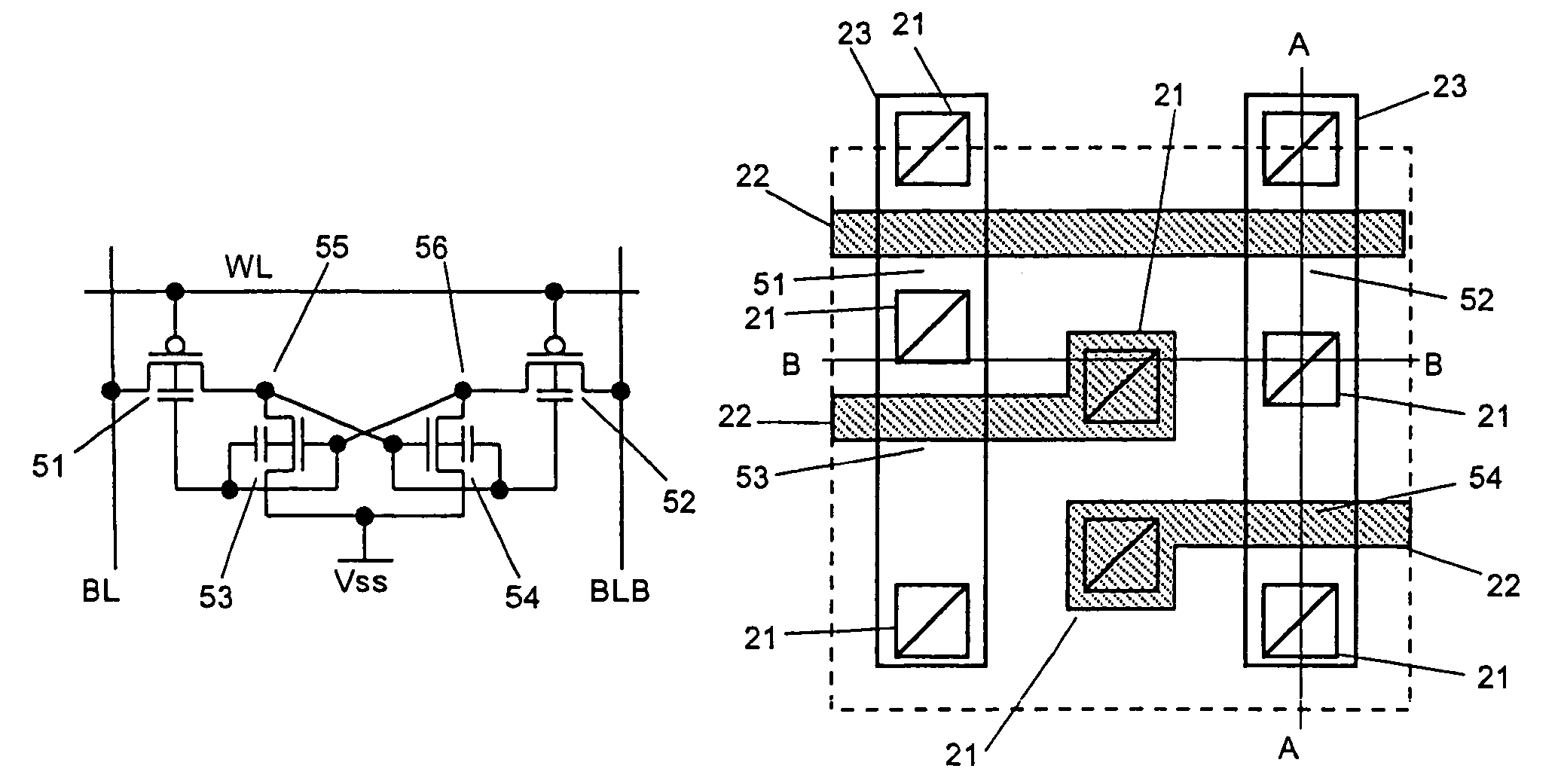
Memory elements with increased write margin and soft error upset immunity
Memory elements are provided that exhibit immunity to soft error upset events when subjected to radiation strikes such as high-energy atomic particle strikes. The memory elements may each have four inverter-like transistor pairs that form a bistable element and a pair of address transistors. There may be four nodes in the transistor each of which is associated with a respective one of the four inverter-like transistor pairs. There may be two control transistors each of which is coupled between the transistors in a respective one of the inverter-like transistor pairs. During data writing operations, the two control transistors may be turned off to temporarily decouple the transistors in two of the four inverter-like transistor pairs.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
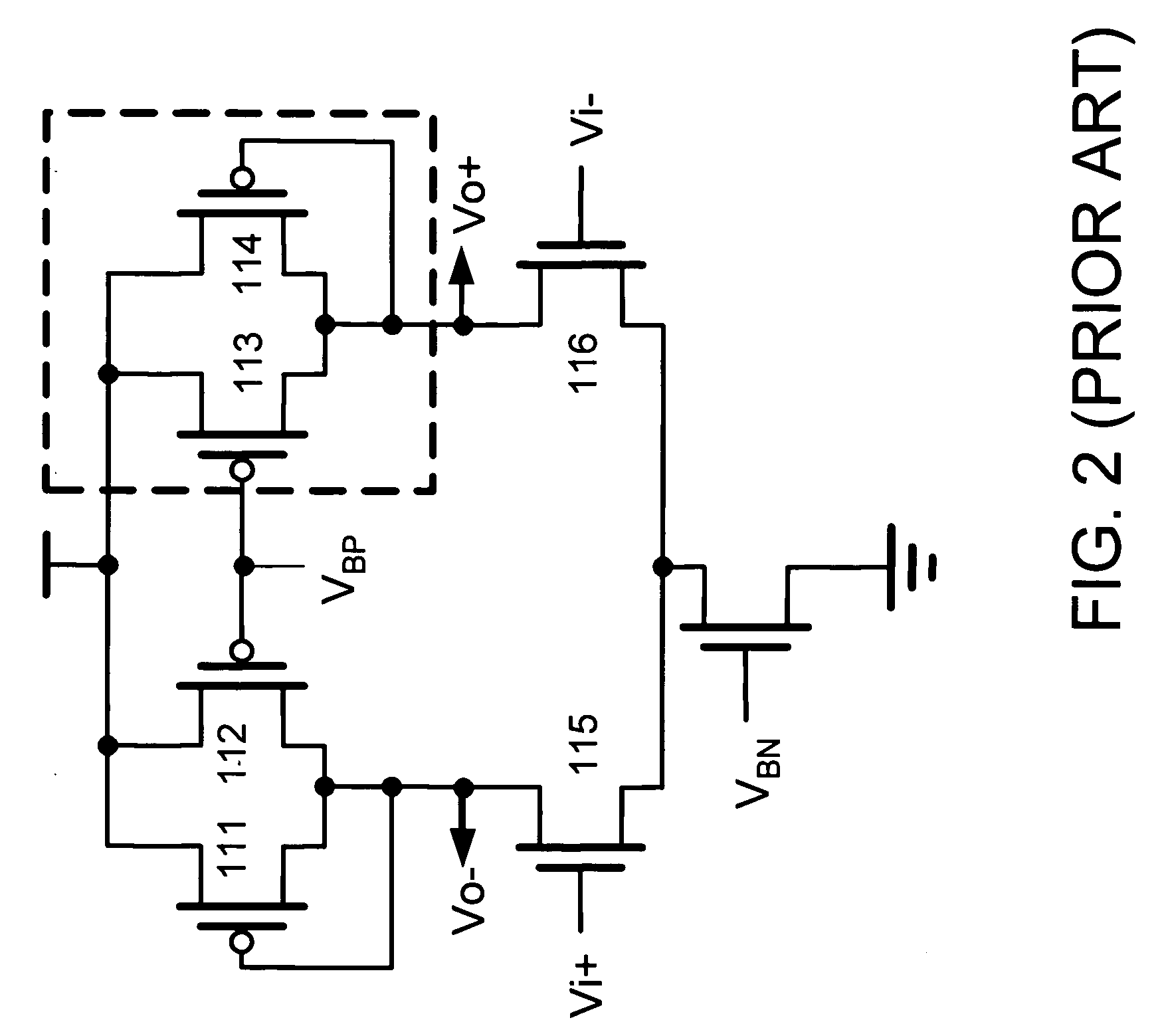
Active mixer circuit and a receiver circuit or a millimeter-wave communication unit using it
ActiveUS20090221259A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce deteriorationTransmissionMulti-frequency-changing modulation transferenceLow noiseCommunication unit
The present invention provides a semiconductor integrated circuit including an active mixer circuit that is operated at low voltage, low noise, and low power consumption. It includes a transconductance amplifier, a transformer, and a multiplier, connects a transformer between the transconductance amplifier and the multiplier, and separates between the transconductance amplifier and the multiplier with respect to direct current inside the transformer. Further, each of the tranconductance amplifier and the multiplier is configured of transistors that are single-stacked between the supply voltage terminal and ground terminal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Photodetector with hetero-structure using lateral growth
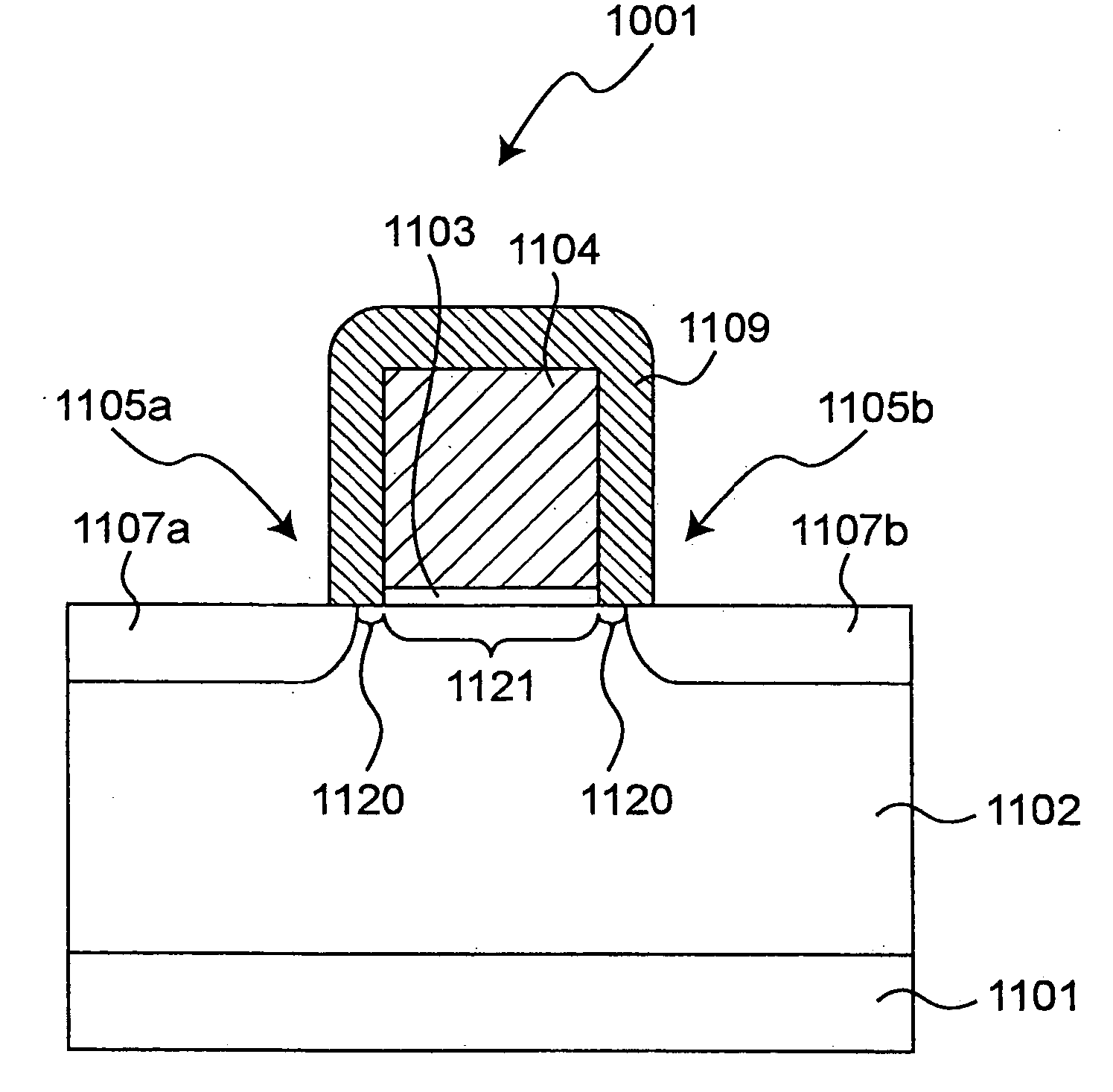
InactiveUS20050127275A1Increase speedRapid responseFinal product manufactureMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A structure and method of fabrication for a Si based material p-i-n photodetector is disclosed. The light is absorbed in an undoped layer containing SiGe or Ge in such a manner that the absorption length is not limited by a critical thickness of the SiGe or Ge layer. The result is achieved by growing the SiGe or Ge layer from the walls of a trench in monocrystalline Si using lateral epitaxial. A second, doped material is disposed over the undoped layer for biasing and photocarrier collection in the p-i-n diode.
Owner:IBM CORP
Switching power supply apparatus and semiconductor device
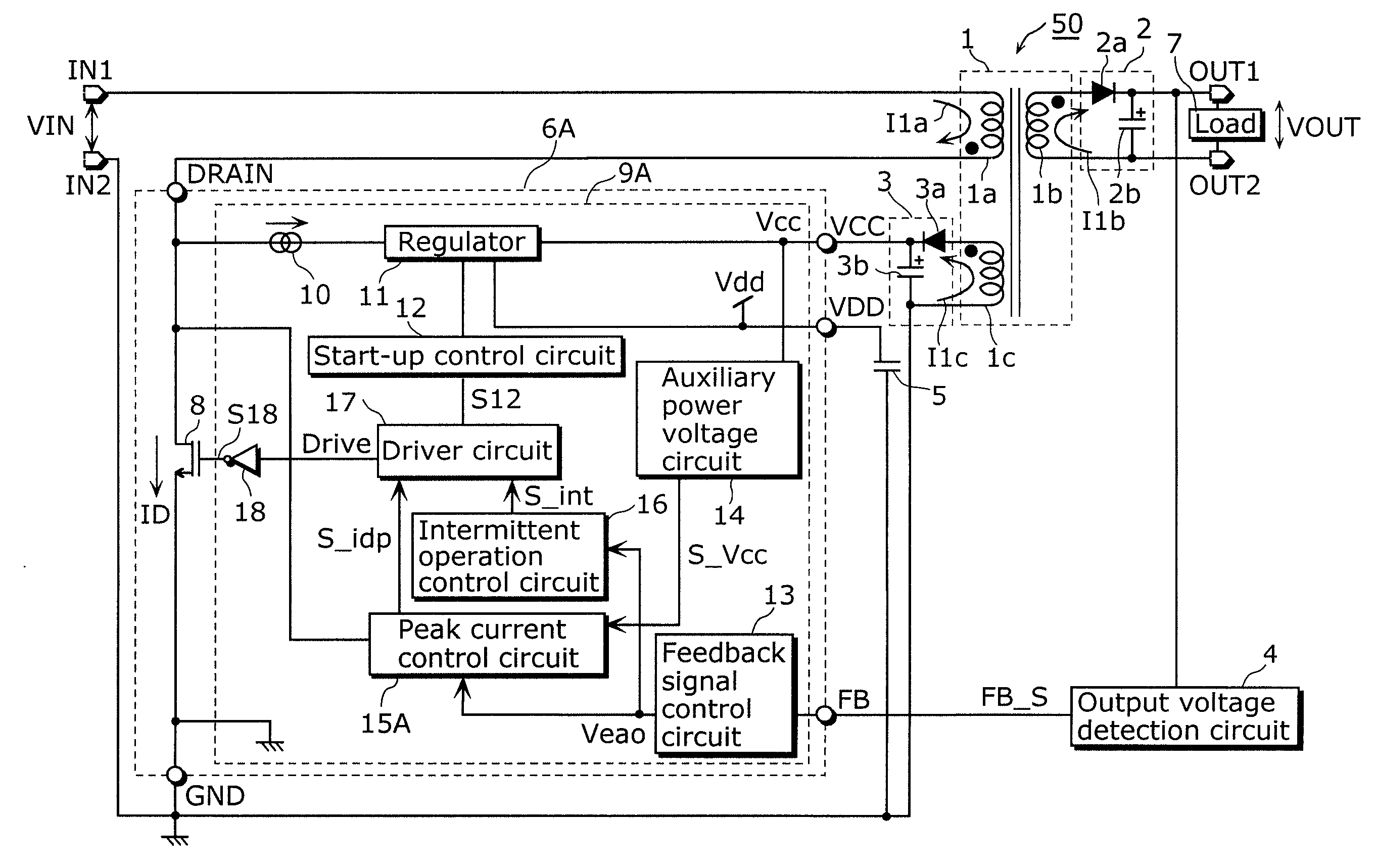
ActiveUS20100309690A1Shortening suspension periodIncreased power consumptionDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationNormal modePeak value
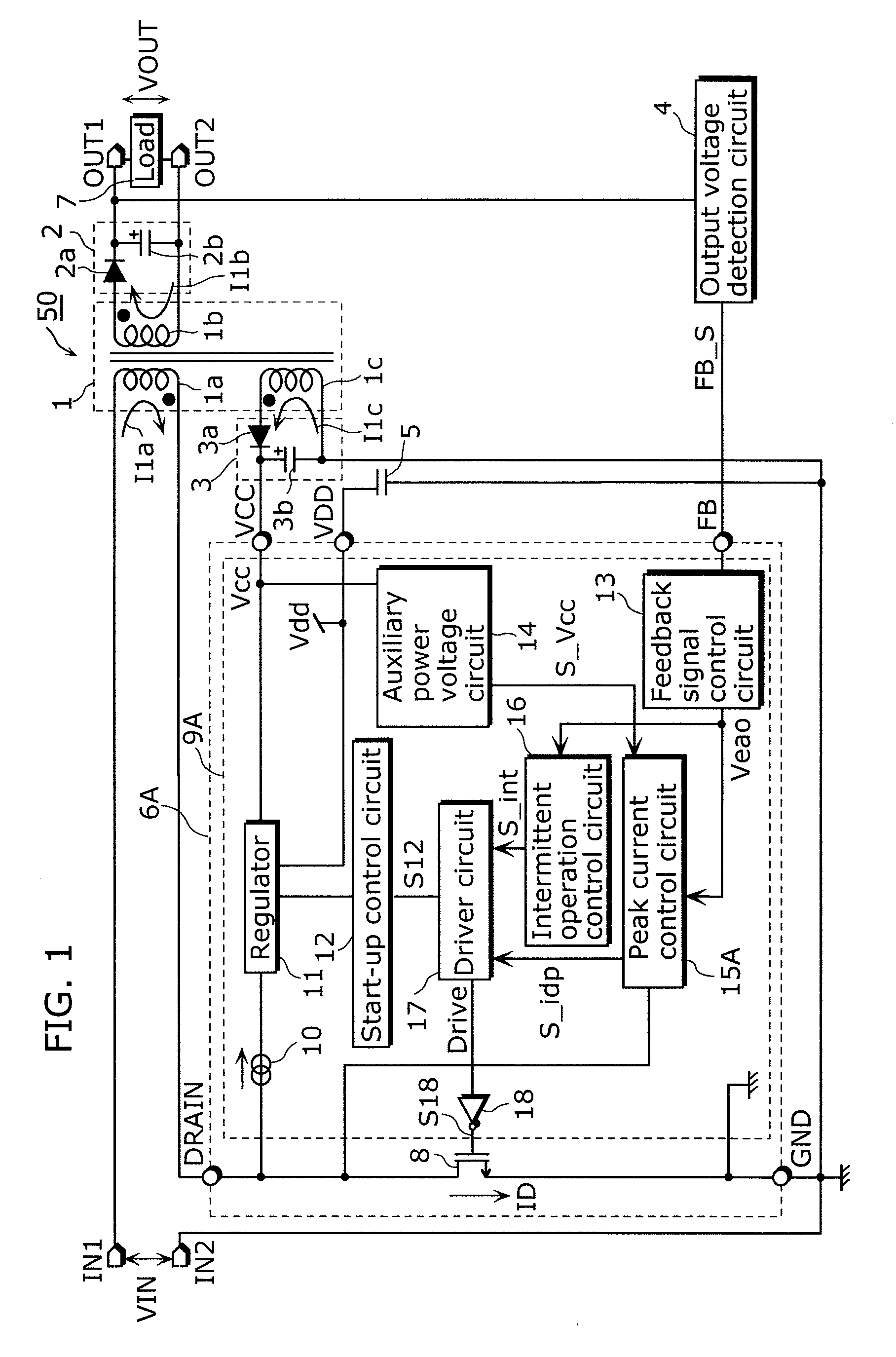
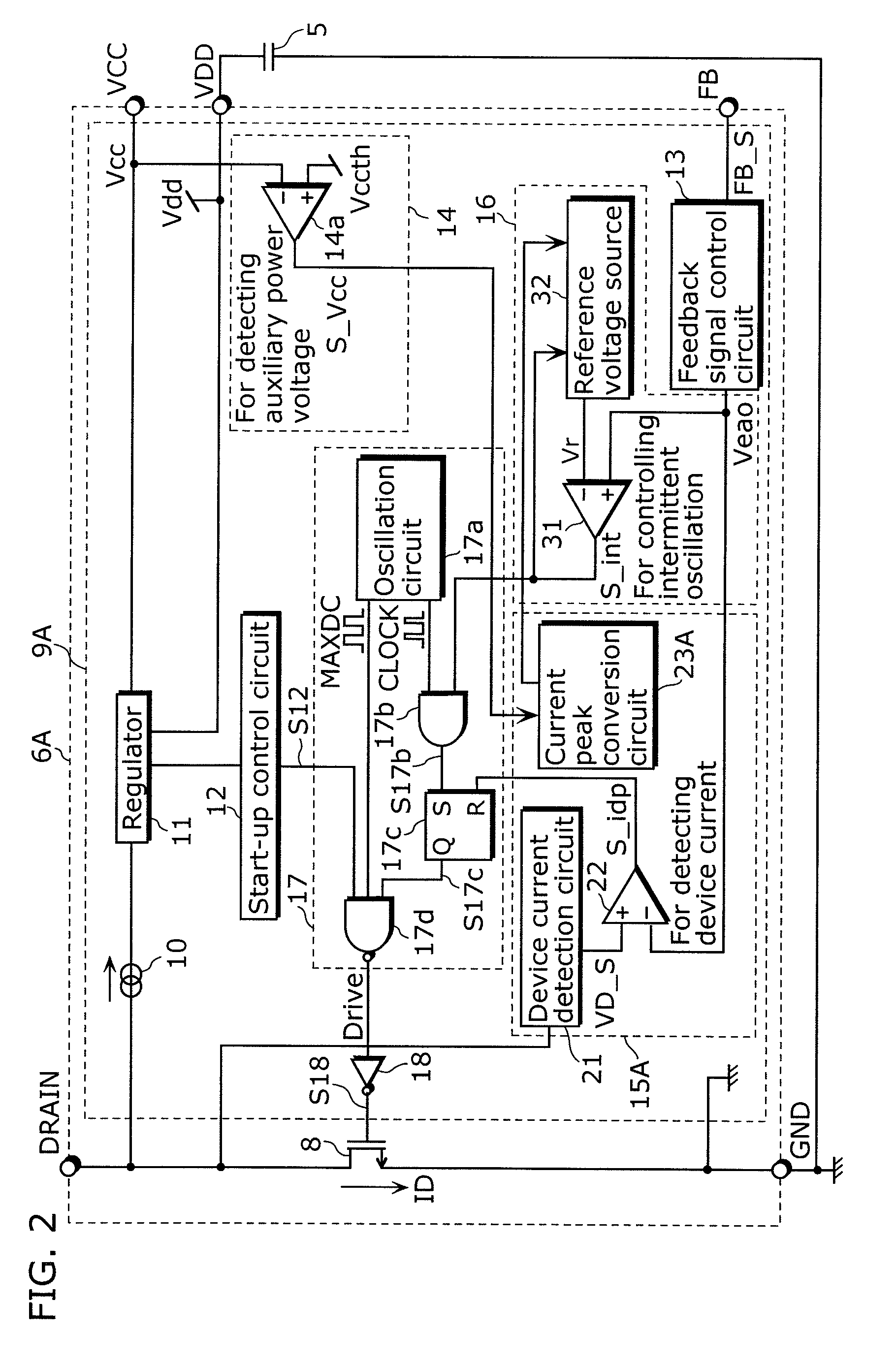
The switching power supply apparatus according to the present invention includes: a transformer including a primary winding, a secondary winding, and an auxiliary winding; a switching device connected to the primary winding; an output voltage generation circuit which is connected to the secondary winding and generates an output voltage; an auxiliary power voltage generation circuit which is connected to the auxiliary winding and generates an auxiliary power voltage; and a control circuit which operates using the auxiliary power voltage and controls a driver circuit so that an intermittent oscillation is performed when the output voltage is higher than a first output voltage and controls a peak of a current flowing through a switching device is lower than a peak in a normal mode, when the auxiliary power voltage is lower than a first auxiliary power voltage in the intermittent oscillation.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Adc-based mixed-mode digital phase-locked loop
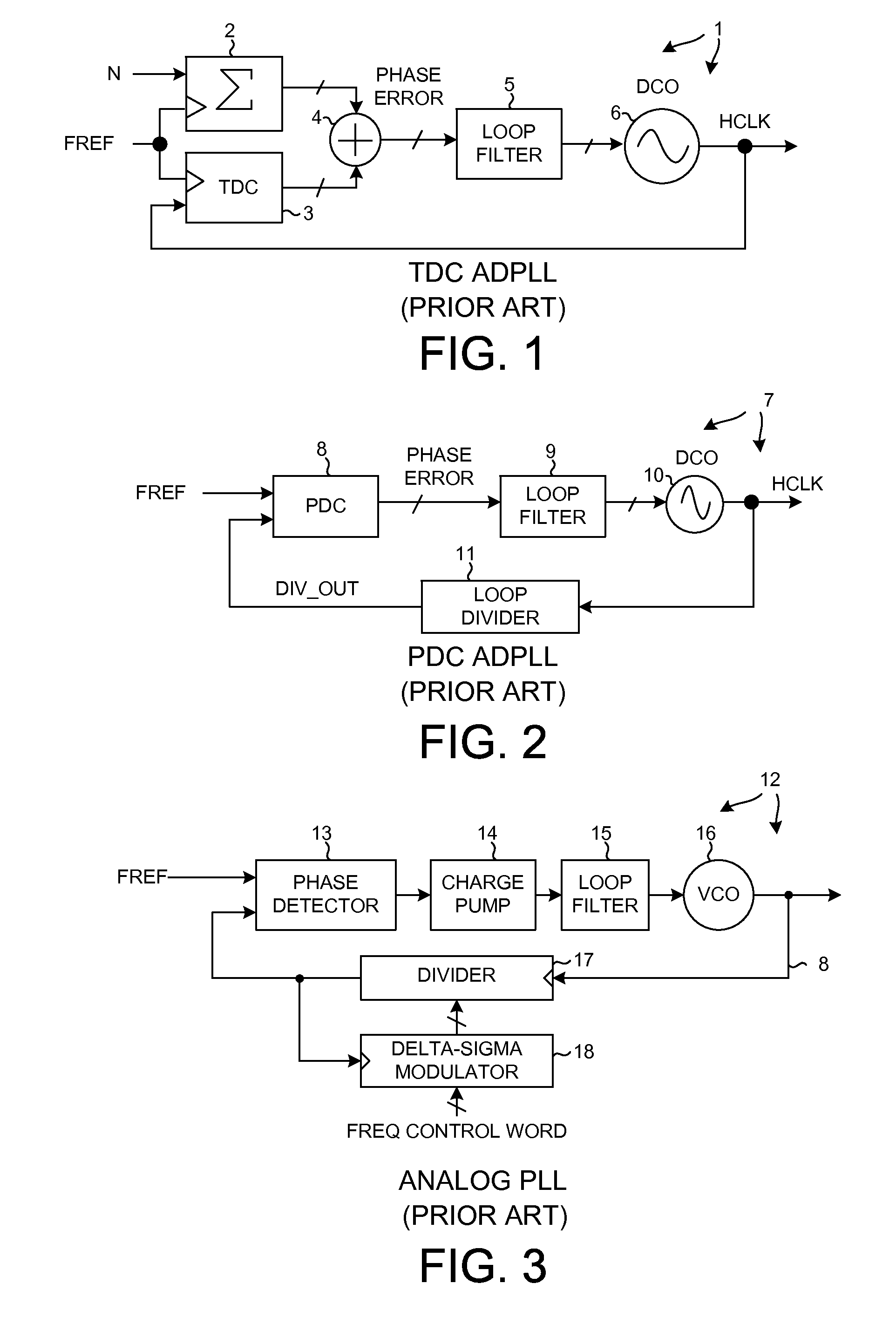
InactiveUS20110090998A1Increase costReduce noisePulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationDigital tuningVoltage amplitude
A Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) includes a Phase-to-Digital Converter (PDC), a programmable digital loop filter, a Digitally-Controlled Oscillator (DCO), and a loop divider. Within the PDC, phase information is converted into a stream of digital values by a charge pump and an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC). The stream of digital values is supplied to the digital loop filter which in turn supplies digital tuning words to the DCO. A number of types of ADCs can be used for the ADC including a continuous-time delta-sigma oversampling Digital ADC and a Successive Approximation ADC. The voltage signal on the charge pump output is a small amplitude midrange voltage signal. The small voltage amplitude of the signal leads to numerous advantages including improved charge pump linearity, reduced charge pump noise, and lower supply voltage operation of the overall PLL.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
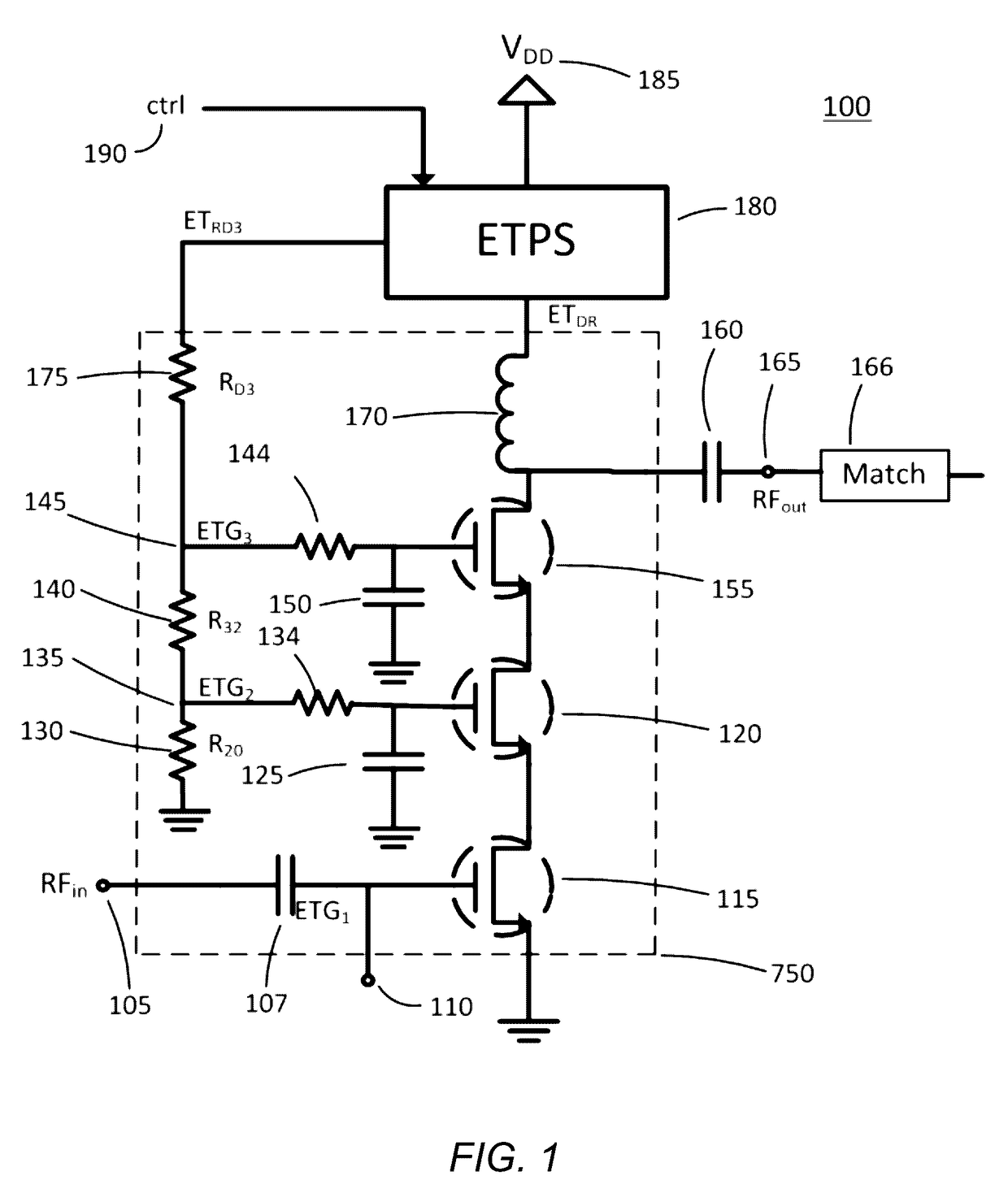
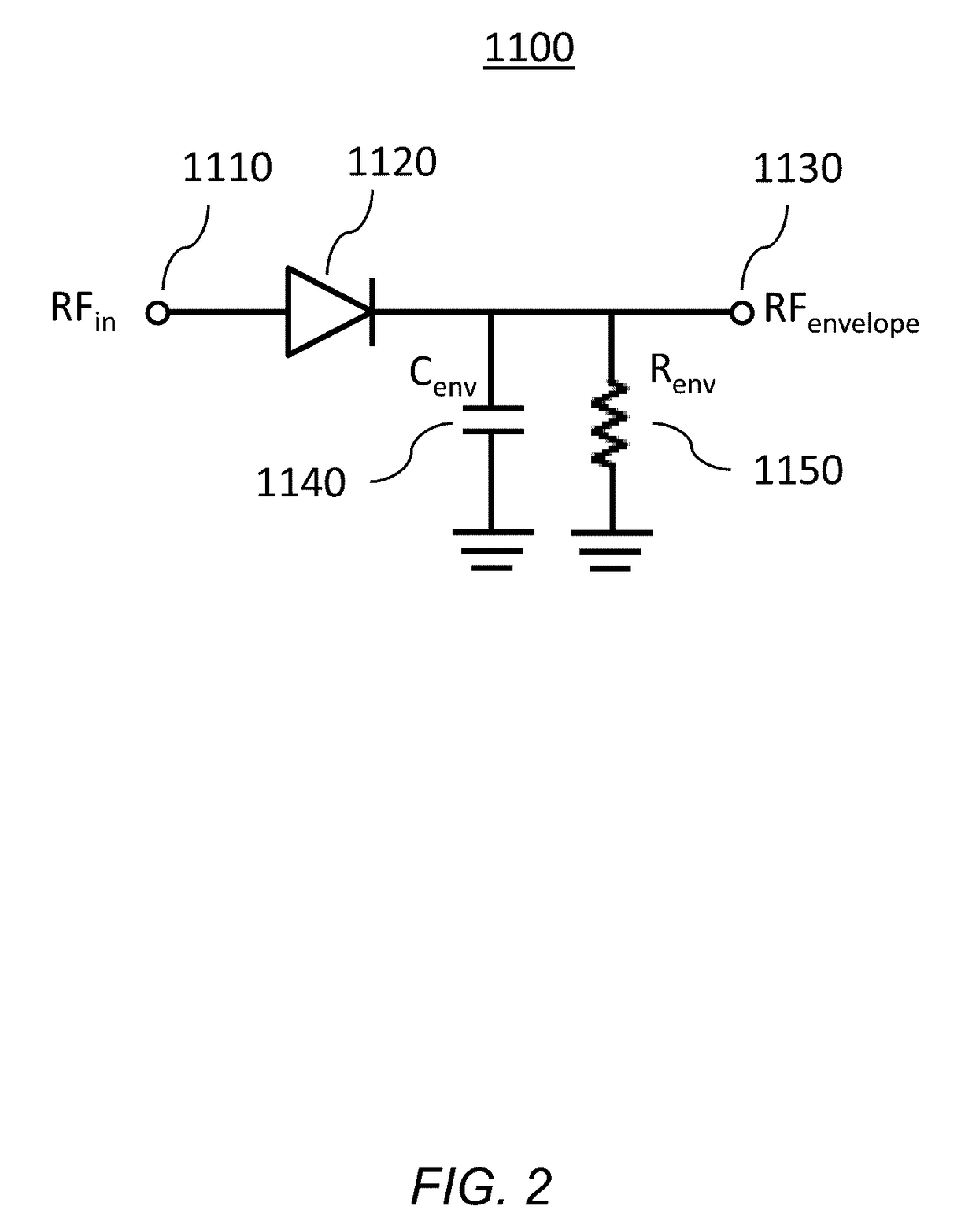
Error driven RF power amplifier control with increased efficiency
ActiveUS7466195B2Reduce power supply voltageImprove efficiencyNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAc componentsAudio power amplifier
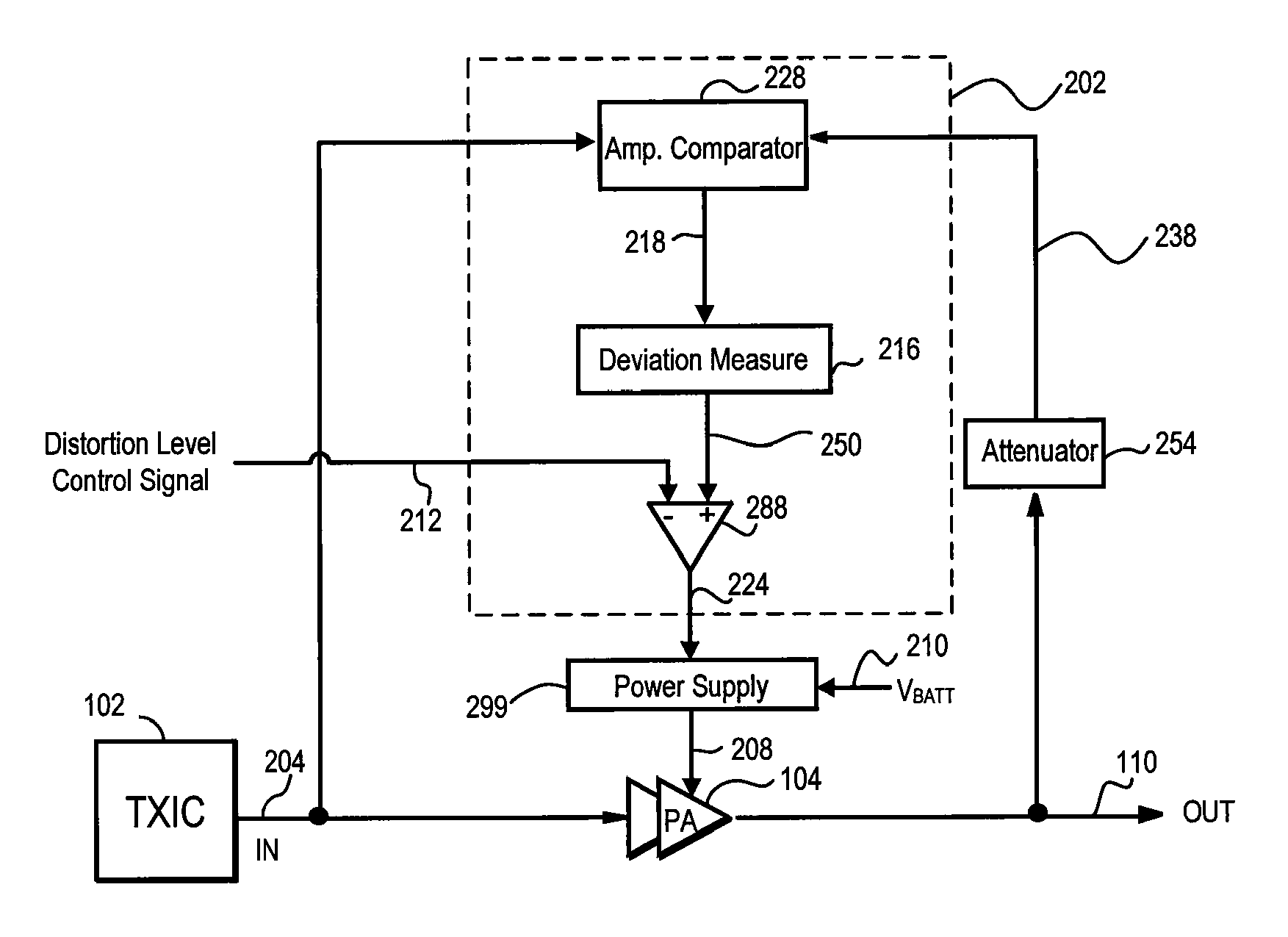
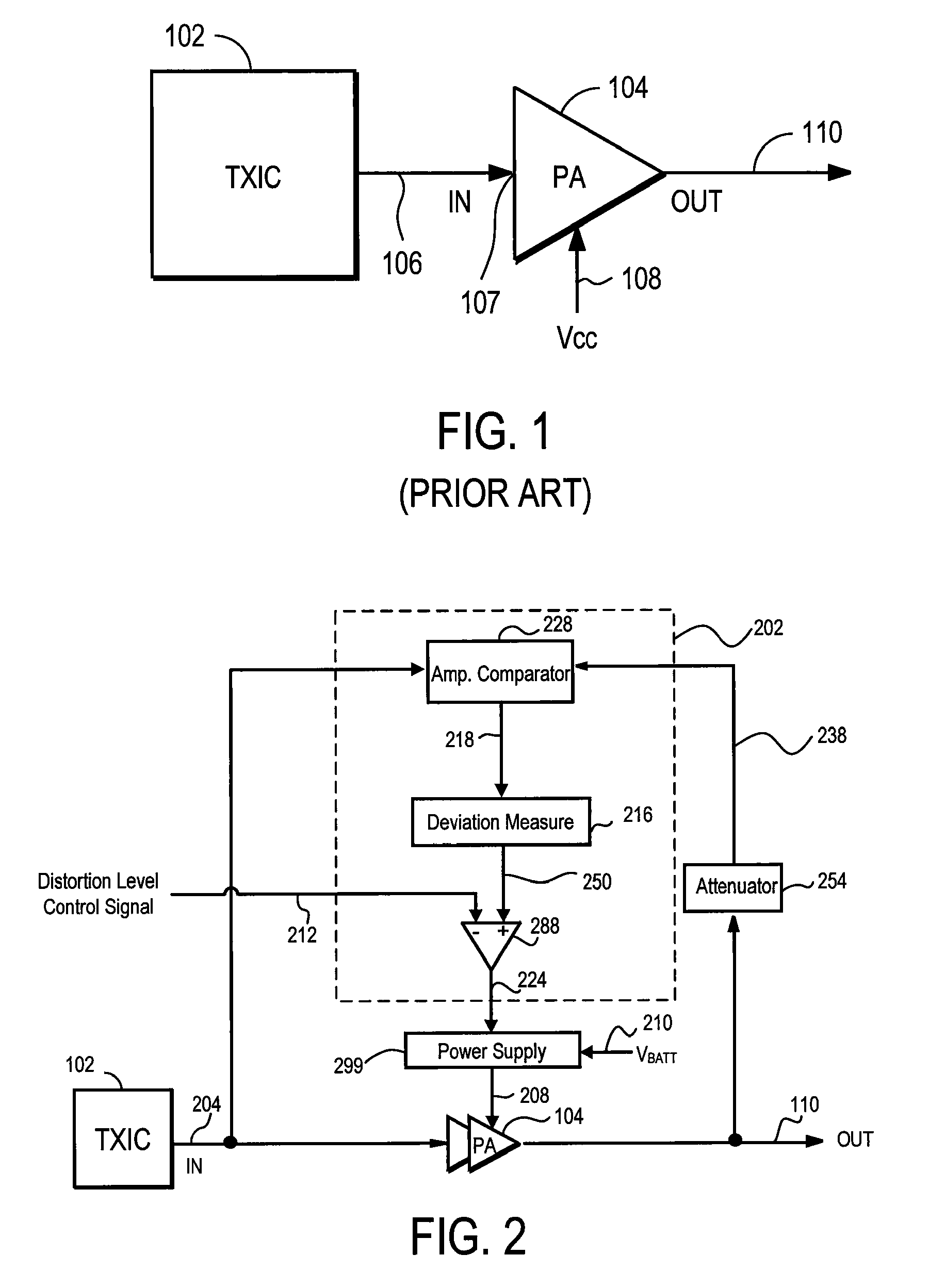
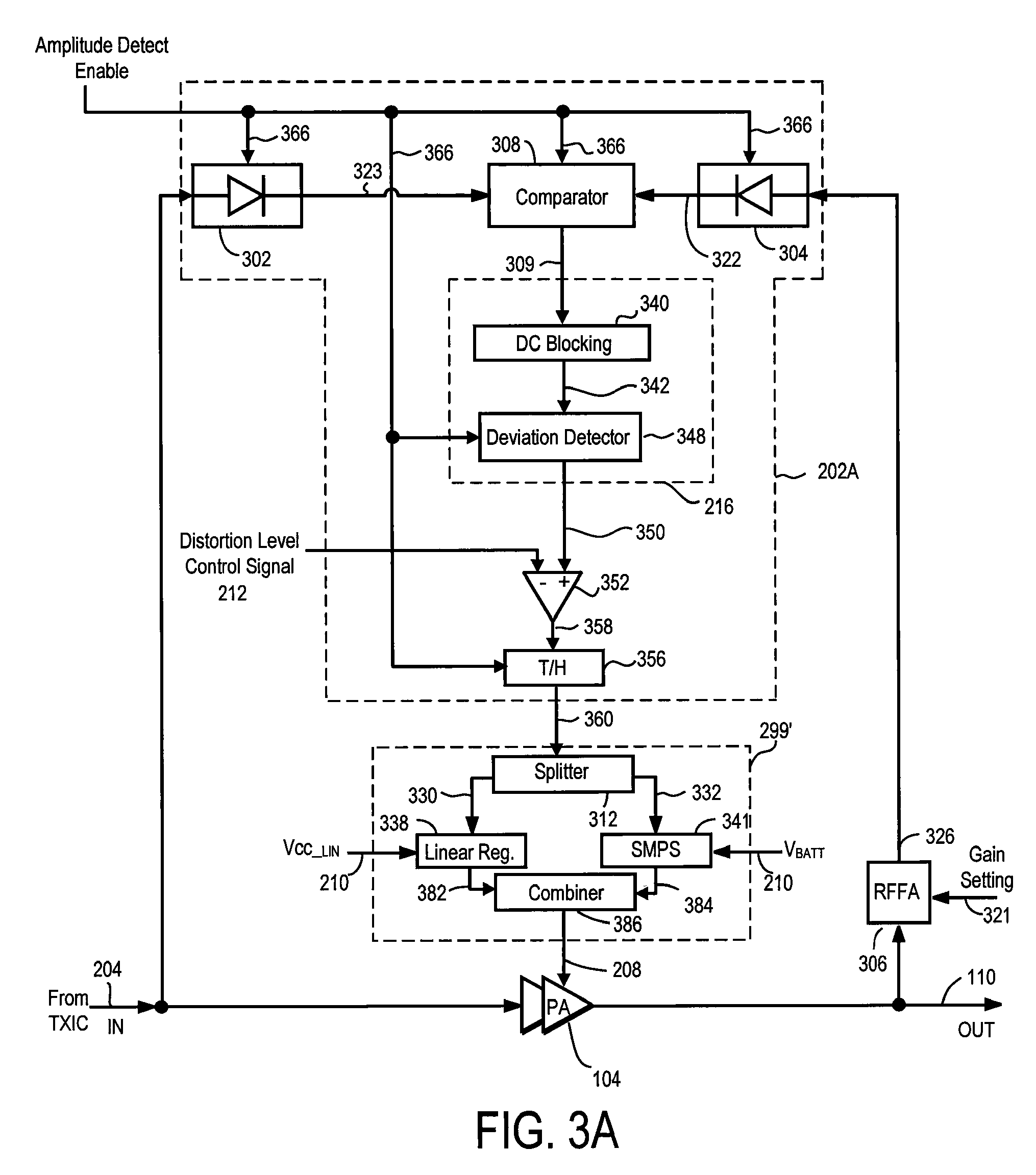
A power amplifier controller for adjusting a supply voltage to a power amplifier. The power amplifier controller adjusts the supply voltage so that distortion in an RF output signal corresponds to a predetermined limit. An amplitude error signal is generated by the power amplifier controller which represents a difference between an RF output signal and an attenuated RF output signal. The AC components of the amplitude error signal are processed to generate a deviation signal that represents the distortion in the RF output signal. The supply voltage to the power amplifier is increased when the deviation signal exceeds a distortion level control signal, and decreased when the deviation signal drops below the distortion level control signal.
Owner:QUANTANCE
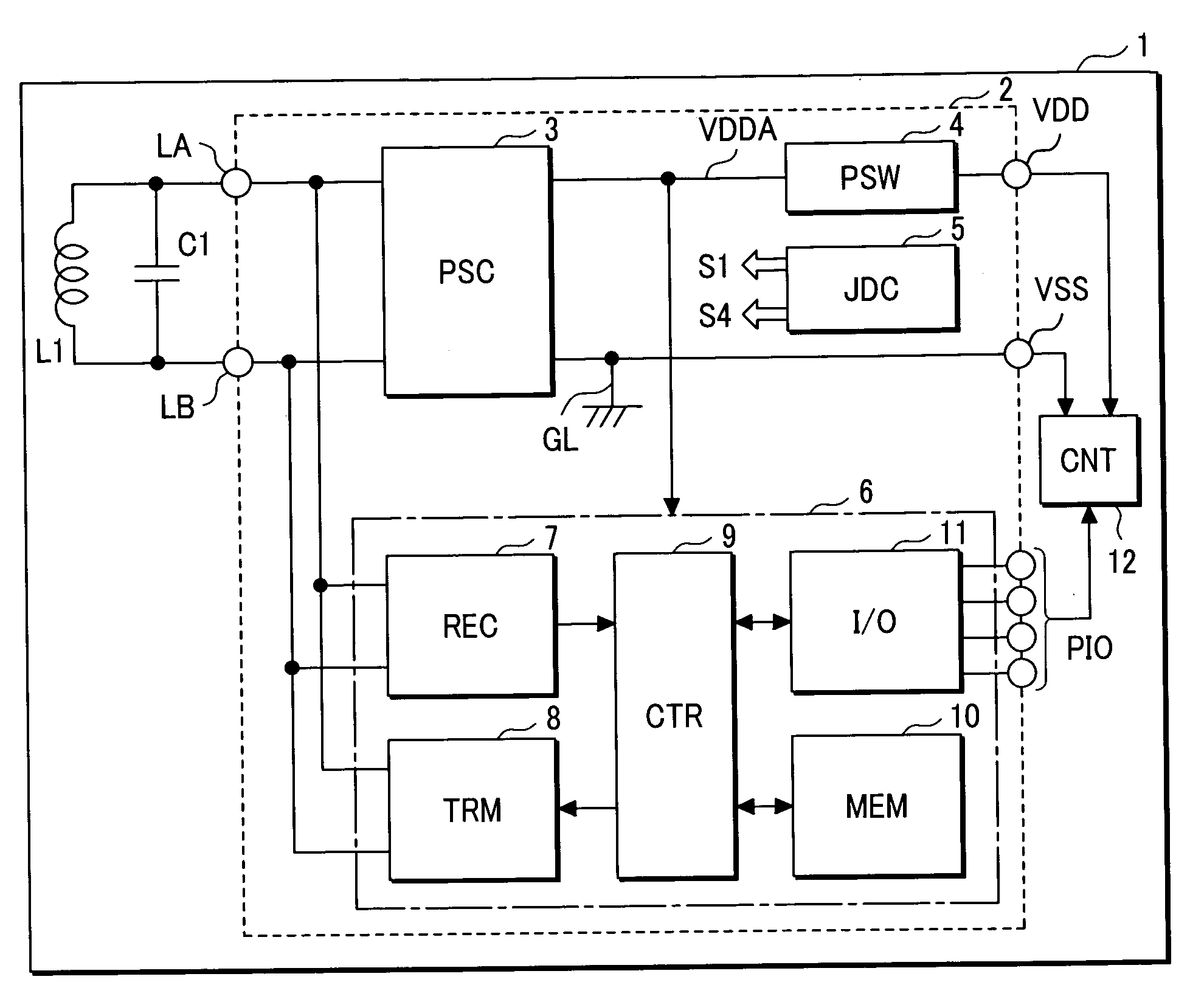
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and IC card equipped with the same
ActiveUS20070127185A1Reduce decreaseSmall sizeDigital data processing detailsHardware monitoringPower switchingSemiconductor
There is a need for turning off a transistor in a power supply switch circuit irrespective of relative potential relationship between a contact power supply terminal and an internal power supply line and making it possible to decrease an on-resistance of an MOS transistor without increasing the size of the MOS transistor constituting the power supply switch circuit. The power supply switch circuit is comprised of two PMOS transistors whose gate terminals connect with two pull-up circuits. A charge pump circuit generates a negative voltage and is connected to a pull-down circuit. The pull-down circuit is connected to the gate terminals in common. During a contactless operation, the pull-up circuit short-circuits one gate terminal to a contact power supply terminal VDD and the other gate terminal to an internal power supply line VDDA. During a contact operation, the pull-up circuit supplies both gate terminals with a negative voltage from the charge pump circuit.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
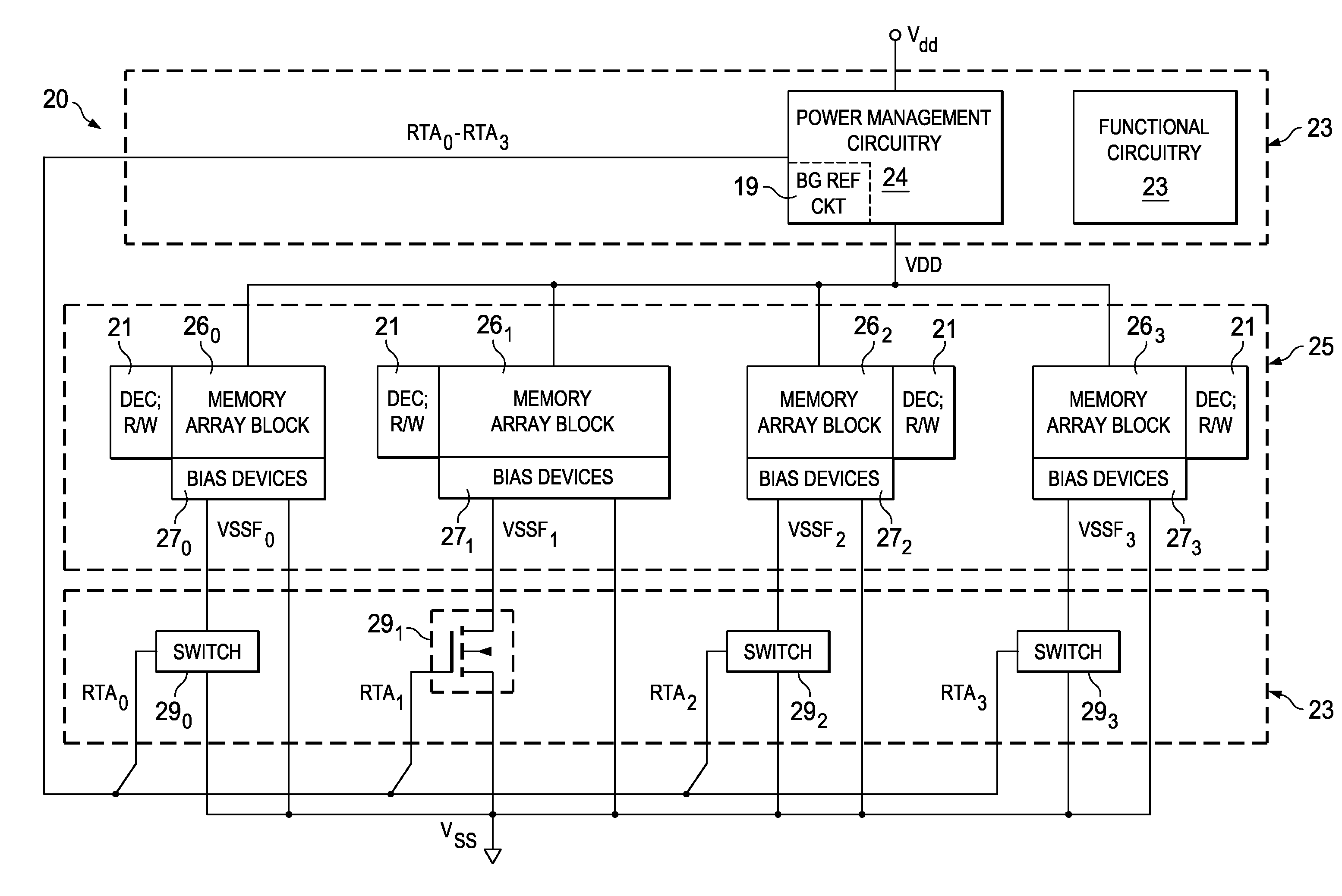
Retain-Till-Accessed Power Saving Mode in High-Performance Static Memories
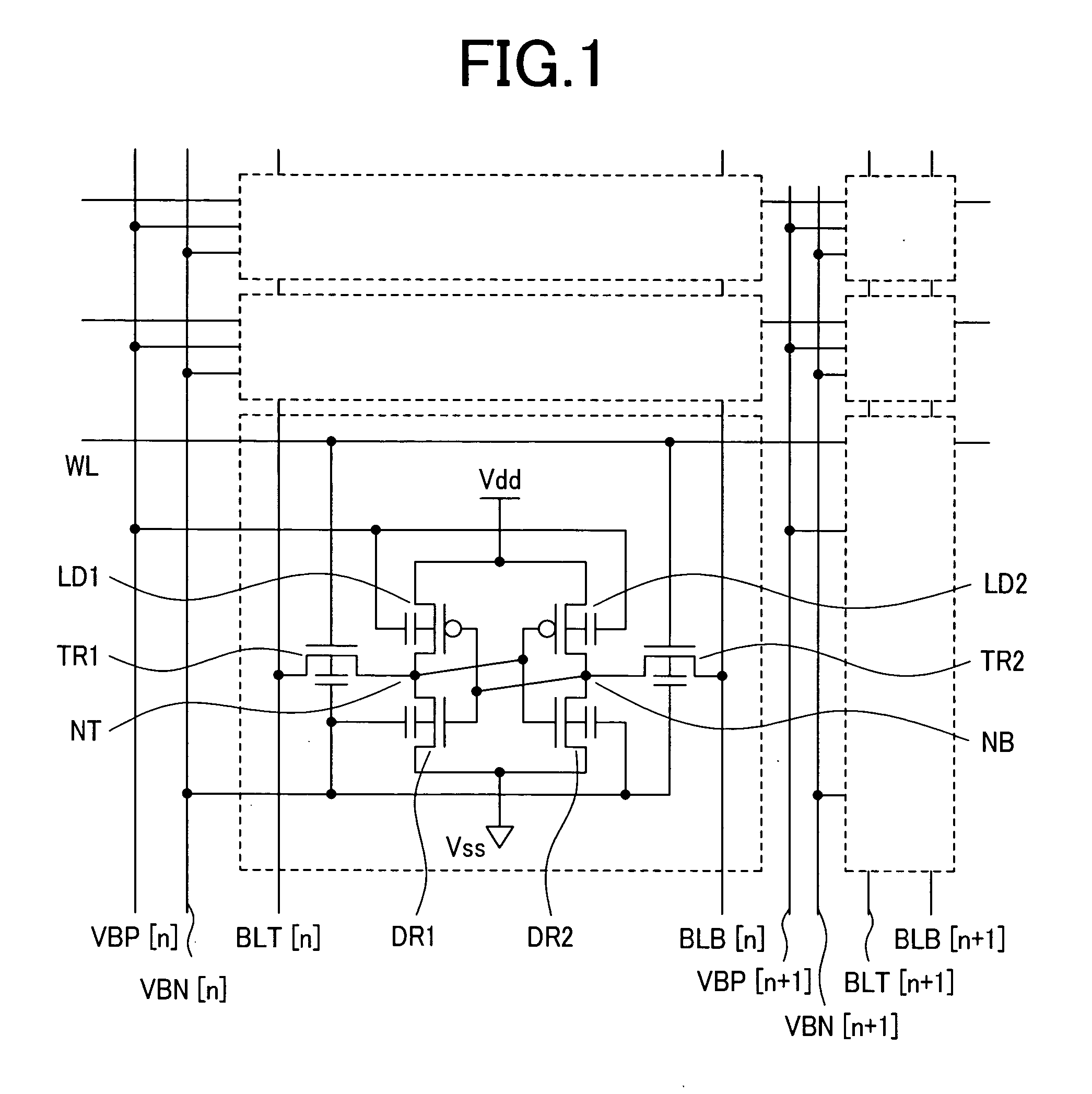
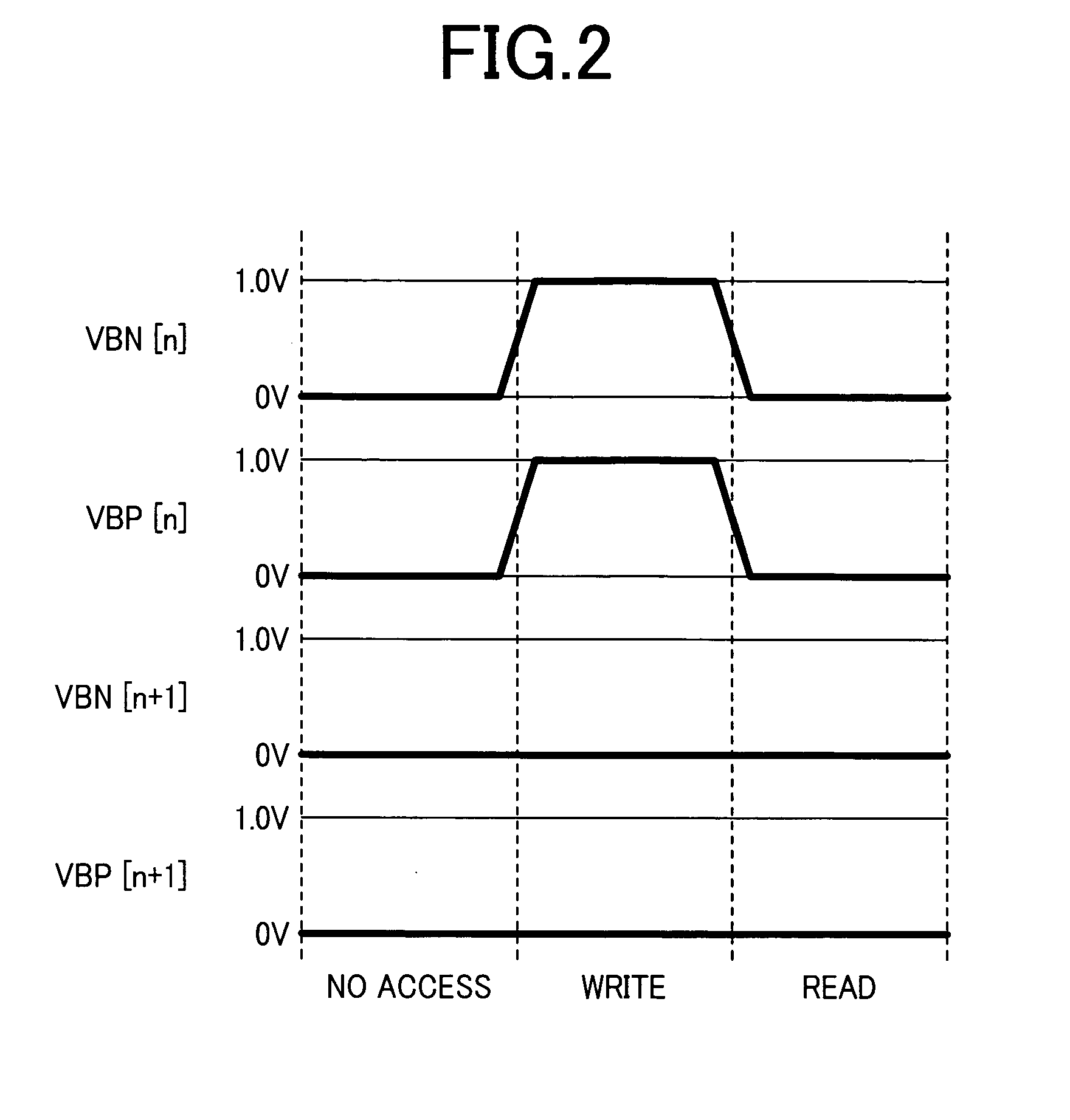
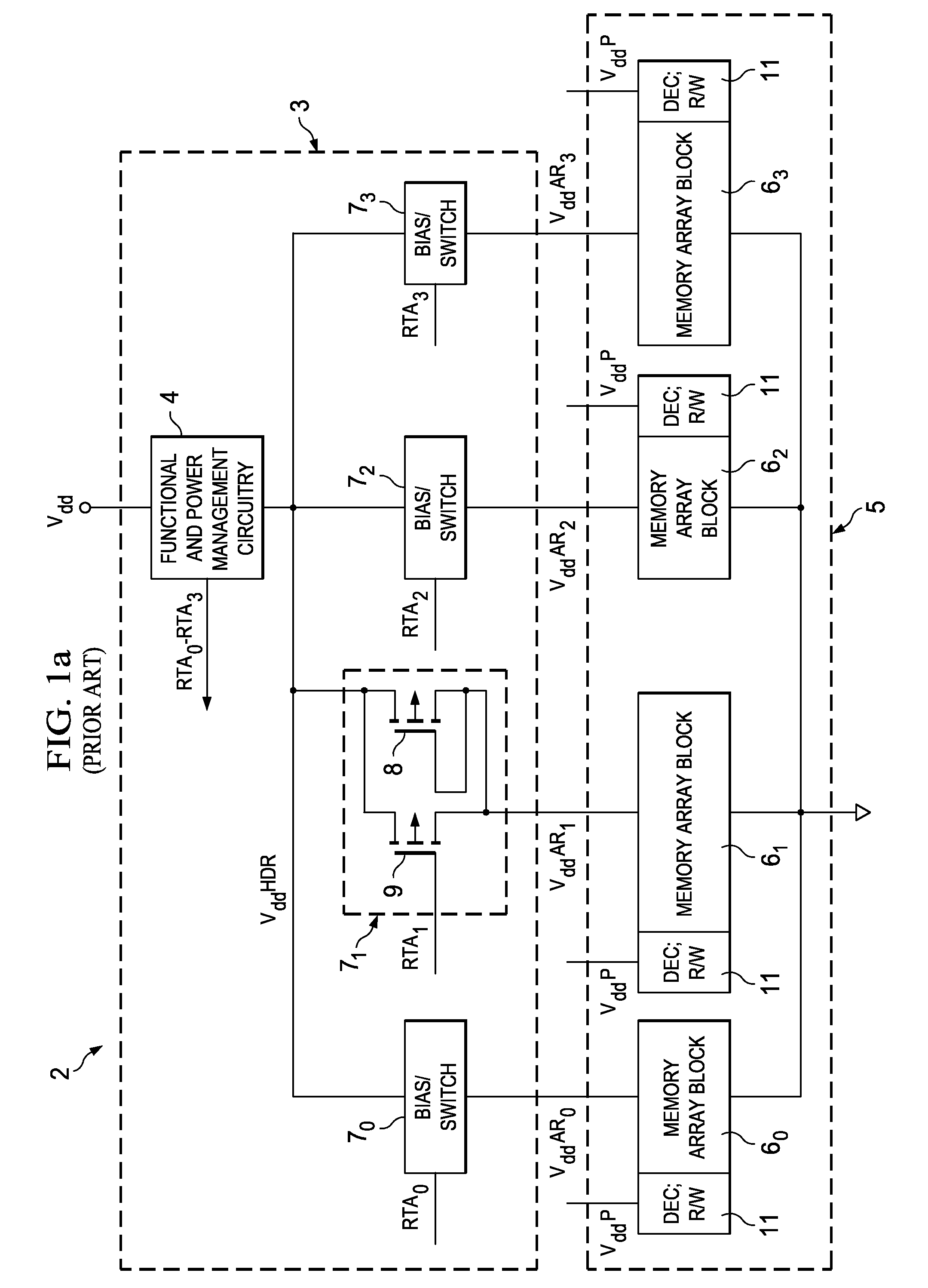
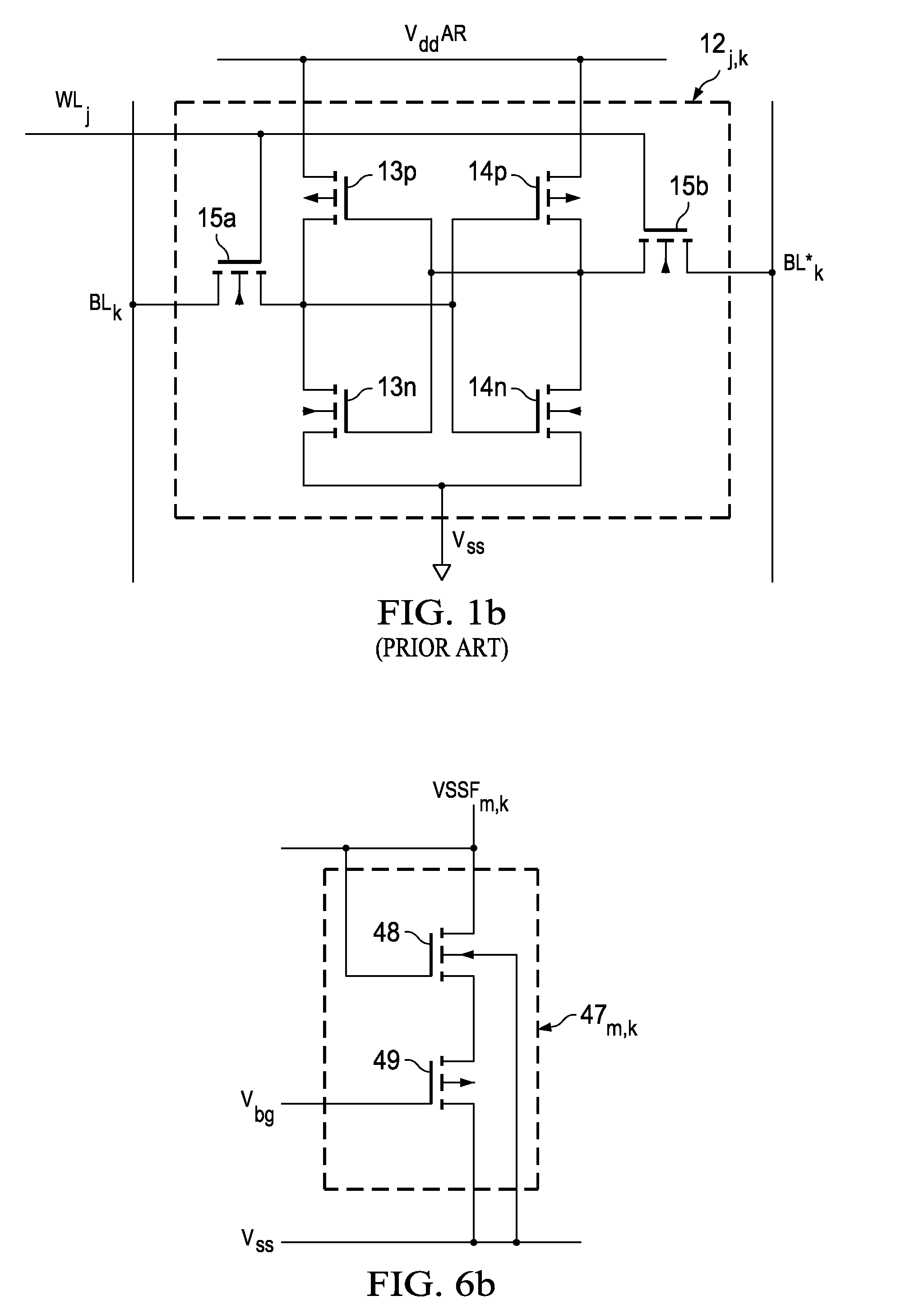
ActiveUS20110261609A1Reduced power supply voltageHigh performance static random accessDigital storagePower savingSram cell
Bias circuitry for a static random-access memory (SRAM) with a retain-till-accessed (RTA) mode. The memory is constructed of multiple memory array blocks, each including SRAM cells of the 8-T or 10-T type, with separate read and write data paths. Bias devices are included within each memory array block, for example associated with individual columns, and connected between a reference voltage node for cross-coupled inverters in each memory cell in the associated column or columns, and a ground node. In a normal operating mode, a switch transistor connected in parallel with the bias devices is turned on, so that the ground voltage biases the cross-coupled inverters in each cell. In the RTA mode, the switch transistors are turned off, allowing the bias devices to raise the reference bias to the cross-coupled inverters, reducing power consumed by the cells in that mode.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
High-speed laser array driver
InactiveUS20020064193A1Reduce power consumptionReduce power supply voltageSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsCapacitancePhotodetector
A method and apparatus for driving lasers. An example laser driving system includes a laser current controller for providing a modulation signal and a bias signal. The modulation signal and bias signal is used by a plurality of high-speed current drivers that accept the modulation signal and the bias signal and produce a plurality of laser drive signals. The example system also has a disable input that disconnects power from a high-speed current driver when the high-speed current driver is not in use. The exemplary system develops the modulation and bias signals by feeding back a signal developed from detection of laser light from one of the lasers driven by the system. The laser may be a data laser or a control laser that is modulated by a signal having a lower frequency than the data lasers. If a control laser is used then the photodetector circuit used for feedback can have a lower frequency response because of the lower frequency of the control laser signal. The photodetector system may also employ a peak detector capacitor discharge circuit where a large capacitance is simulated by having the capacitor discharge through the base of a transistor have a current source in the emitter circuit.
Owner:OPTICAL COMM PRODS
Design concept for SRAM read margin
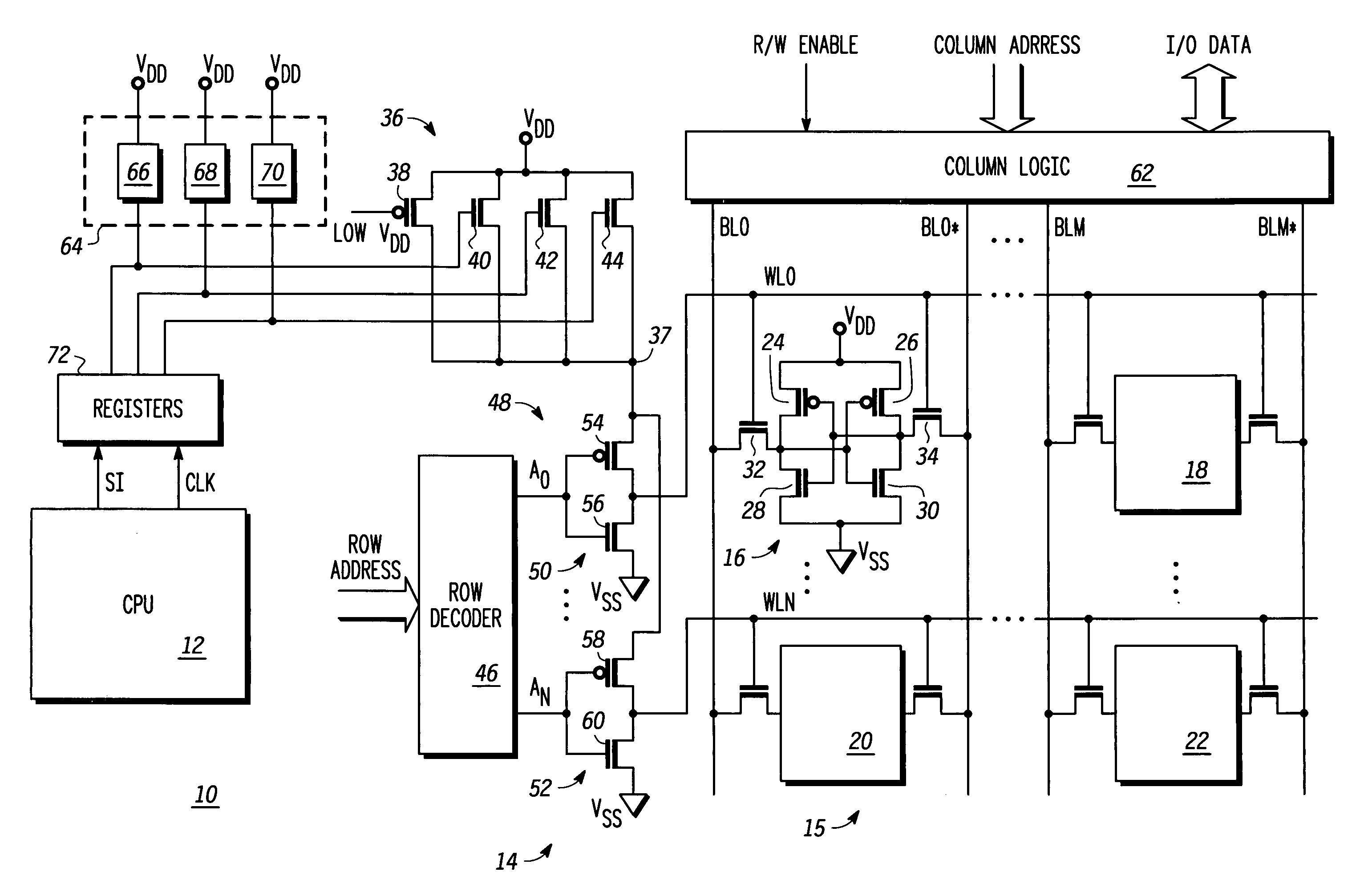
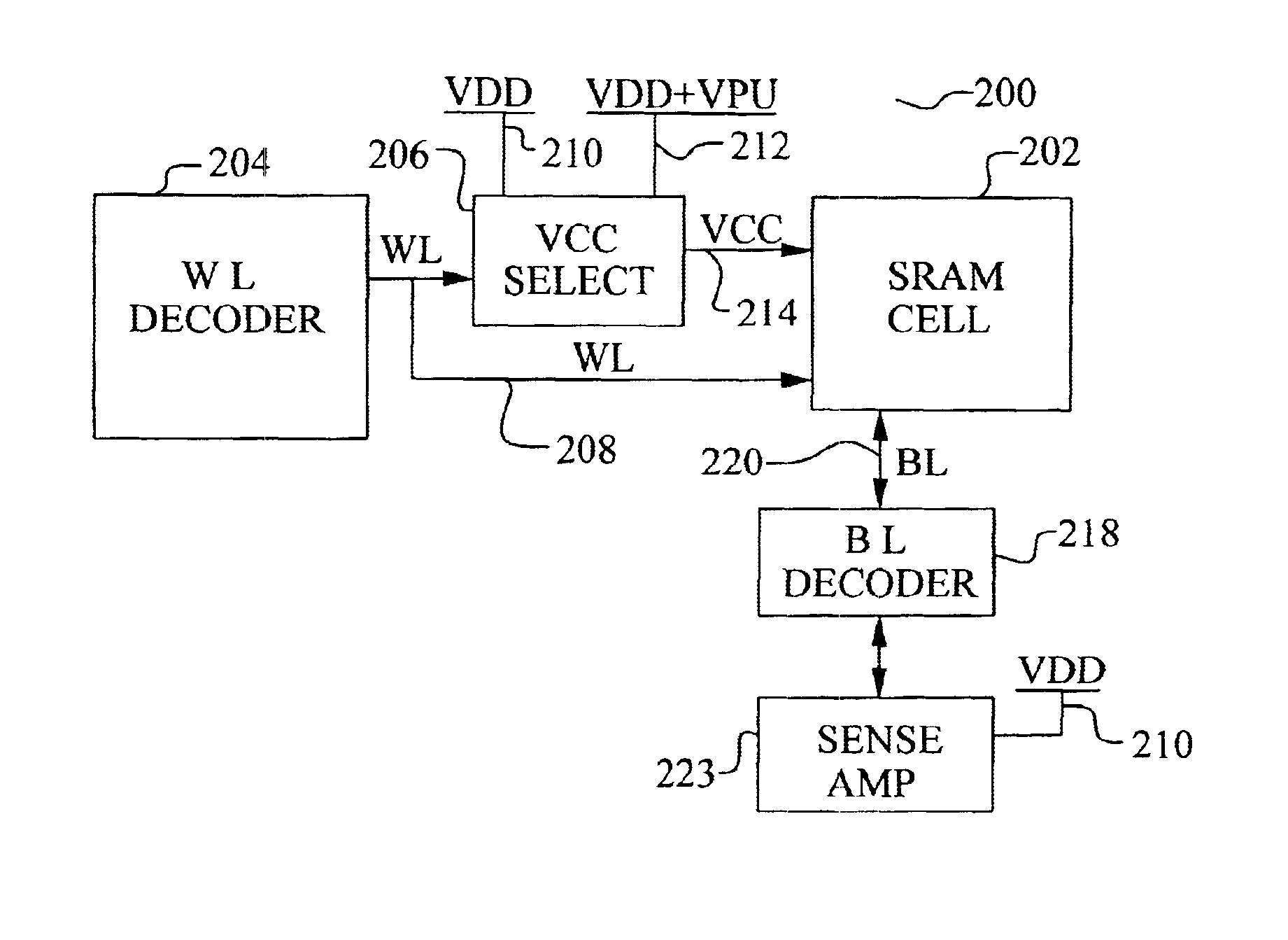
InactiveUS6891745B2Increases reading marginReduce power supply voltageDigital storageSram cellVoltage
A new method to improve the reading margin in a SRAM memory array is achieved. The method comprises providing an array of SRAM cells. Each SRAM cell has a power supply terminal. A first voltage is forced on the power supply terminal of a first SRAM cell that is selected for reading. A second voltage is forced on the power supply terminal of a second SRAM cell that is not selected for reading. The first voltage does not equal the second voltage. A new SRAM device featuring this method is disclosed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Drive circuit, light emitting diode head, and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20080292344A1Transistor area can be reducedReduce power supply voltageStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentAudio power amplifier
A drive circuit includes a drive element for driving a driven element; a correction data input section for adjusting a drive current of the driven element; a resistor having an end portion connected to ground; and a control voltage generation section for generating a direction value of the drive current. The control voltage generation section includes a calculation amplifier having a first input terminal for receiving a standard voltage, a second input terminal, and an output terminal; a first conductive type transistor having a first terminal, a second terminal connected to the ground, and a control terminal connected to the output terminal; and a current-mirror circuit including a control side transistor and a follower side transistor. The control side transistor has a current output terminal connected to the first terminal. The follower side transistor has a current output terminal connected to another end portion of the resistor and the second input terminal.
Owner:OKI DATA CORP
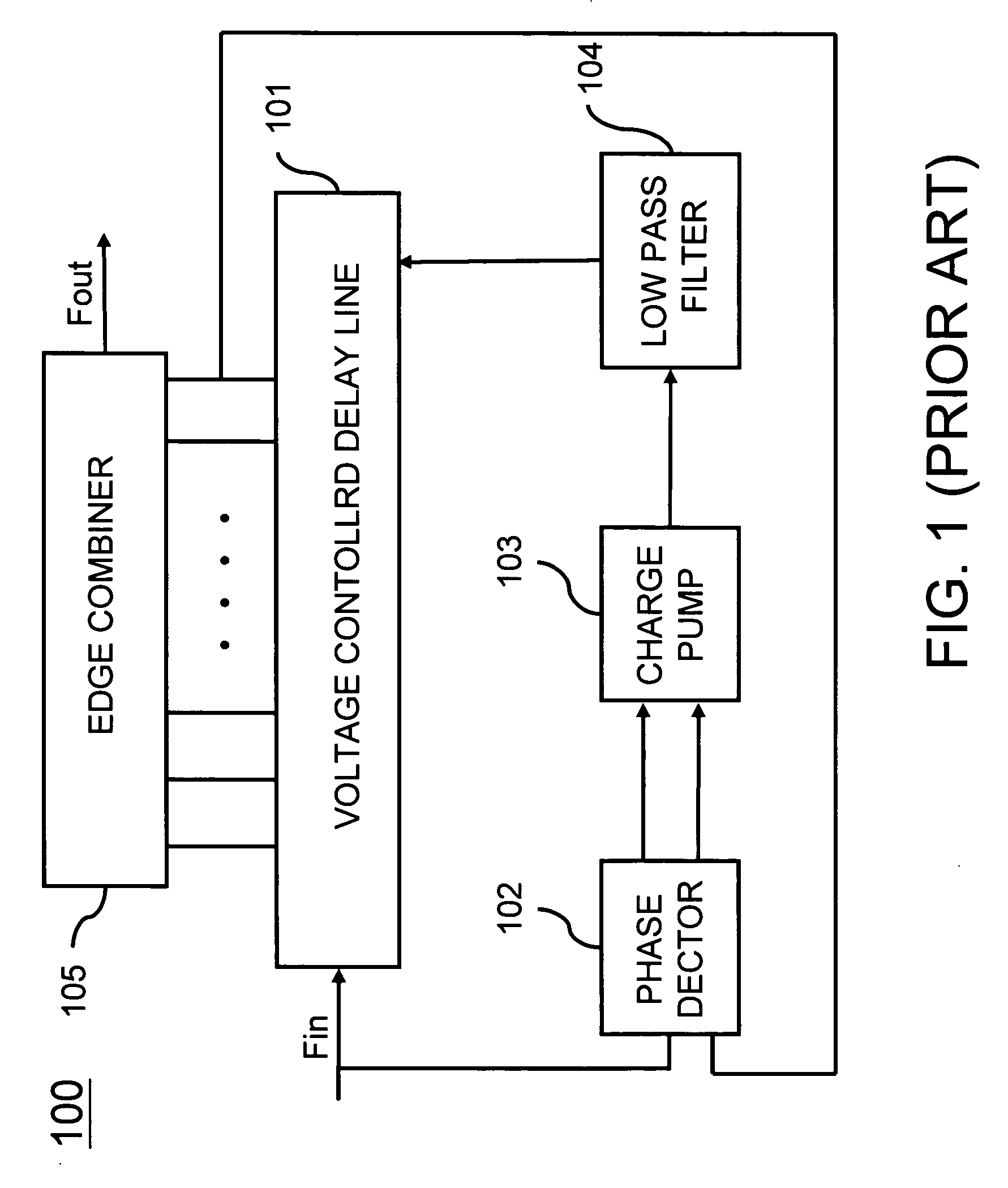
DLL-based programmable clock generator using a threshold-trigger delay element circuit and a circular edge combiner
InactiveUS20070030041A1Reduced out jitterImprove linearityPulse automatic controlPulse manipulationClock generatorVoltage
A DLL-based programmable clock generator using a threshold-trigger delay element and an edge combiner is proposed. A threshold-trigger delay element with full swing complementary output signals consumes no dc power. It exhibits small delay error resulting reduced out jitter. It also increases the linearity of delay time versus control voltage. The circular edge combiner can multiply the input signal at a lower supply voltage. The rise and fall time of output signal are more symmetrical. It also present the multiplication factor of the clock generator can be easy to choose with the increasing of the number of delay elements.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
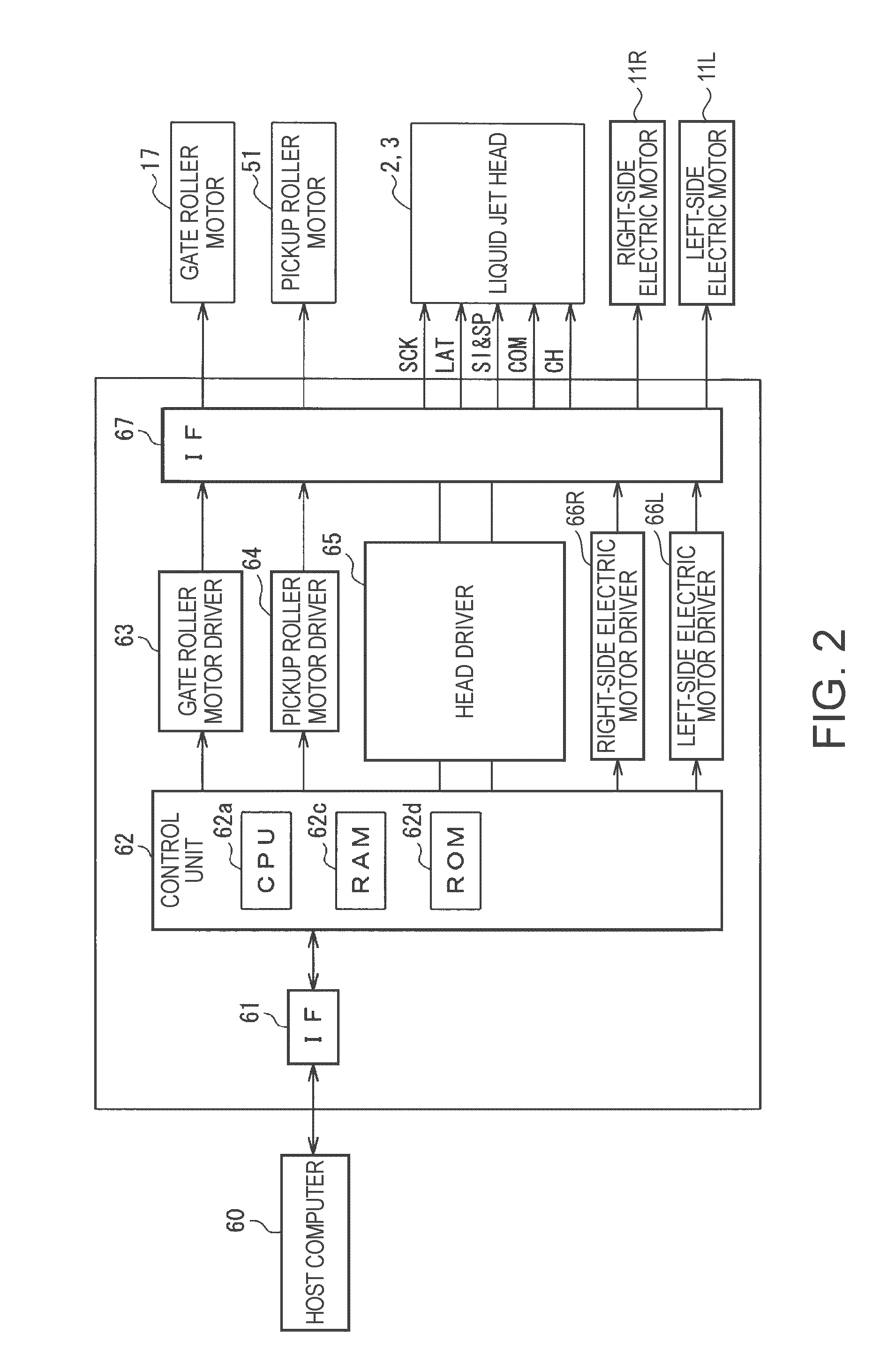
Liquid jet apparatus and printing apparatus
InactiveUS20100188452A1Order of a low pass filter can be decreasedReduce orderOther printing apparatusLiquid jetAudio power amplifier
A liquid jet apparatus of the invention includes a drive waveform generator that generates a drive waveform signal, a modulator that pulse-modulates the drive waveform signal so as to produce a modulated signal, a digital power amplification circuit that amplifies the power of the modulated signal so as to produce an amplified digital signal, and a low pass filter that smoothes the amplified digital signal so as to produce a drive signal. The digital power amplification circuit includes multiple stages of digital power amplifiers each including a pair of switching elements that are push-pull-connected. The amplified digital signal is a multi-value signal that reaches a larger number of steps of electric potentials than the number of digital power amplifiers.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com