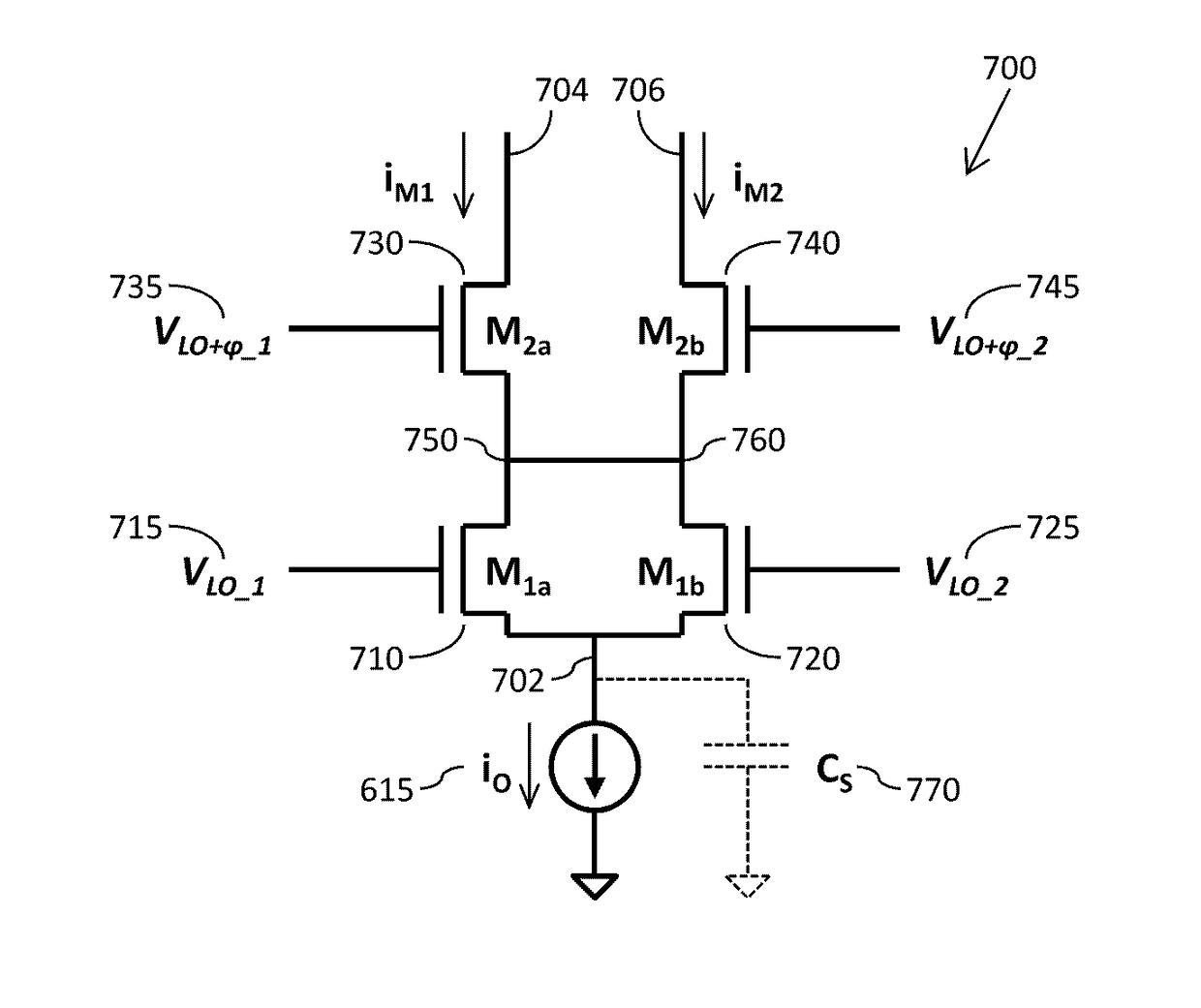
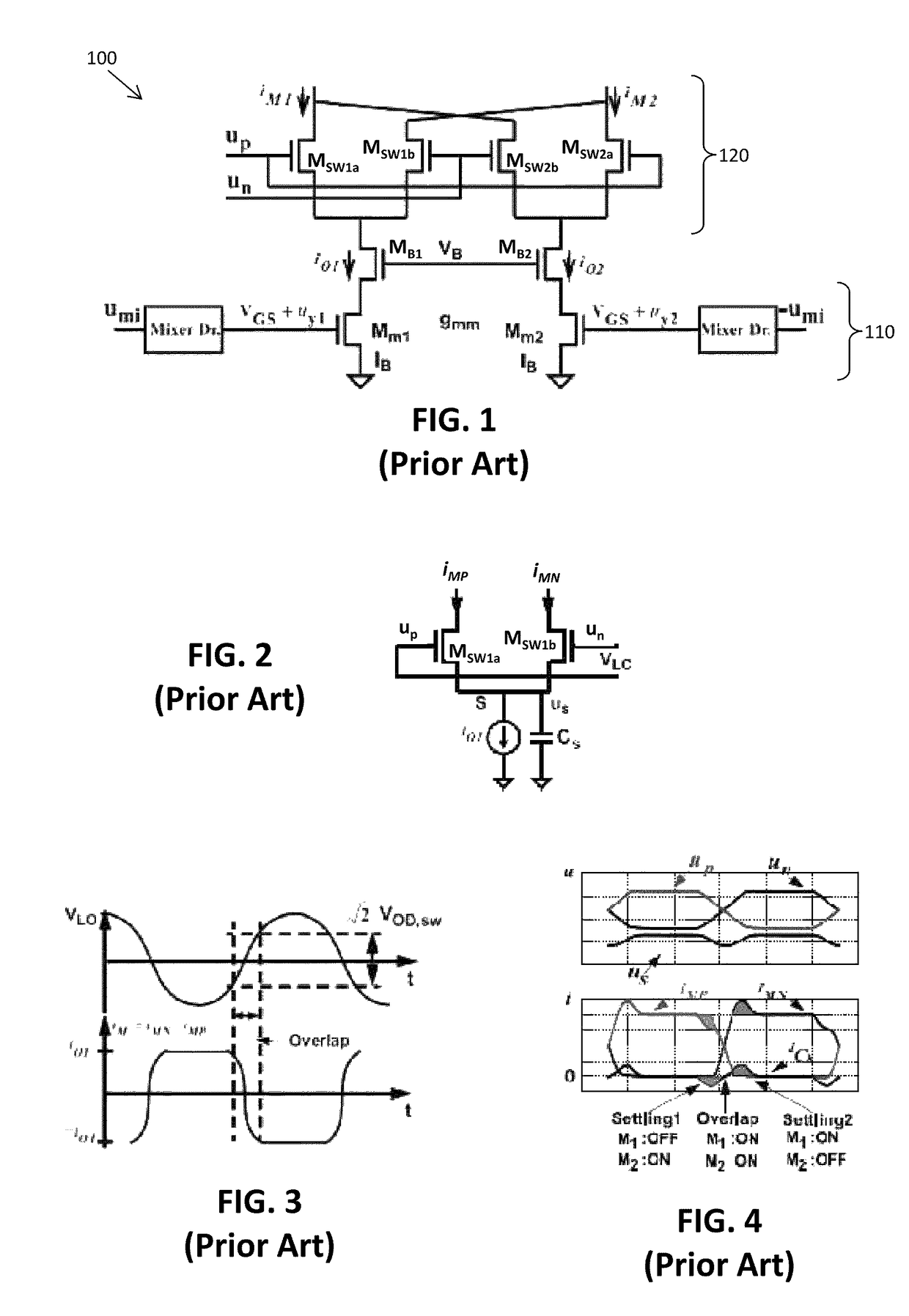
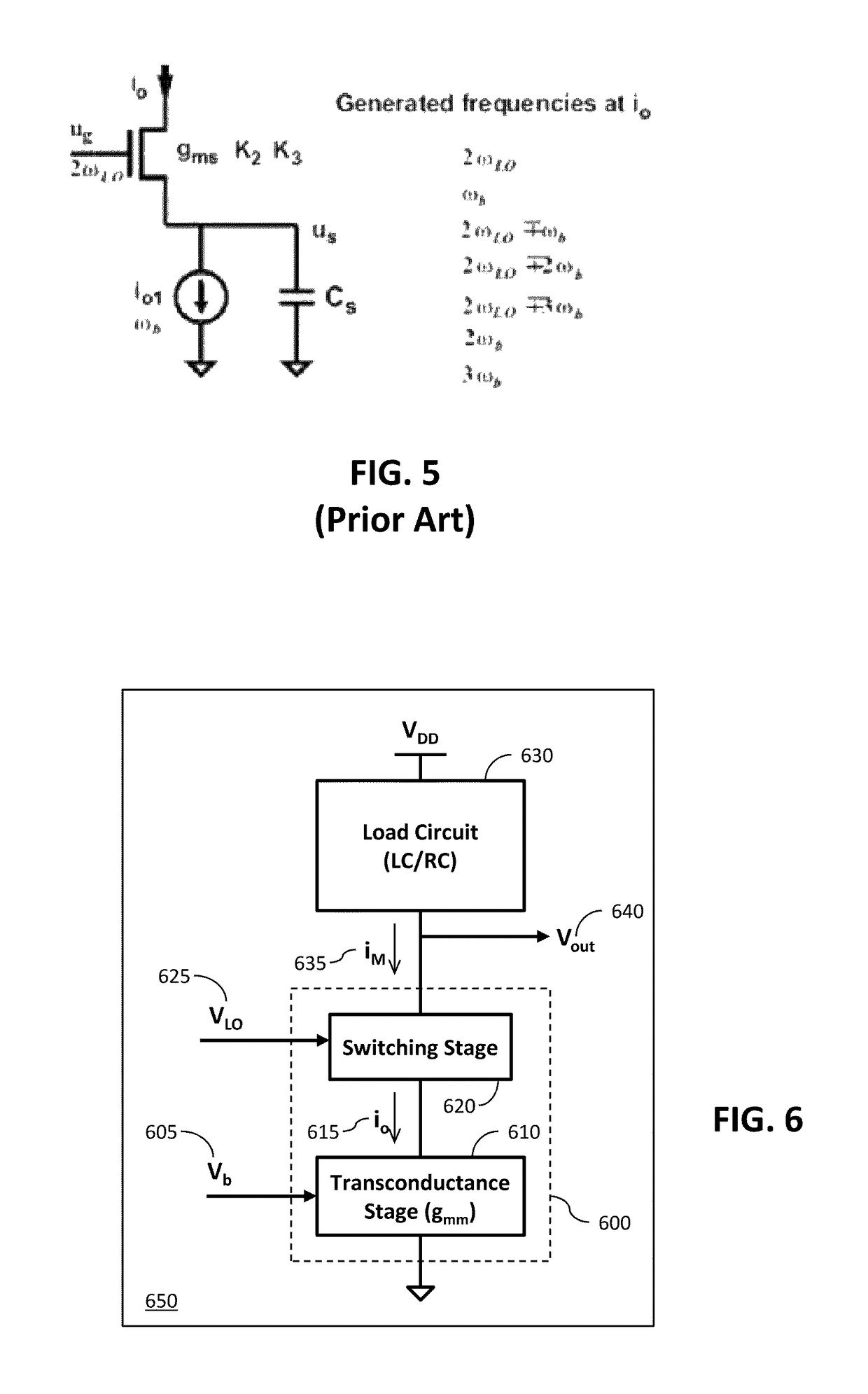
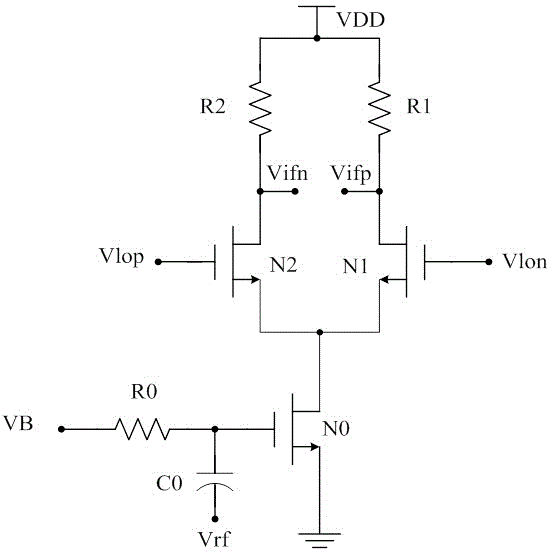
Patents
Literature
57 results about "Active mixer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
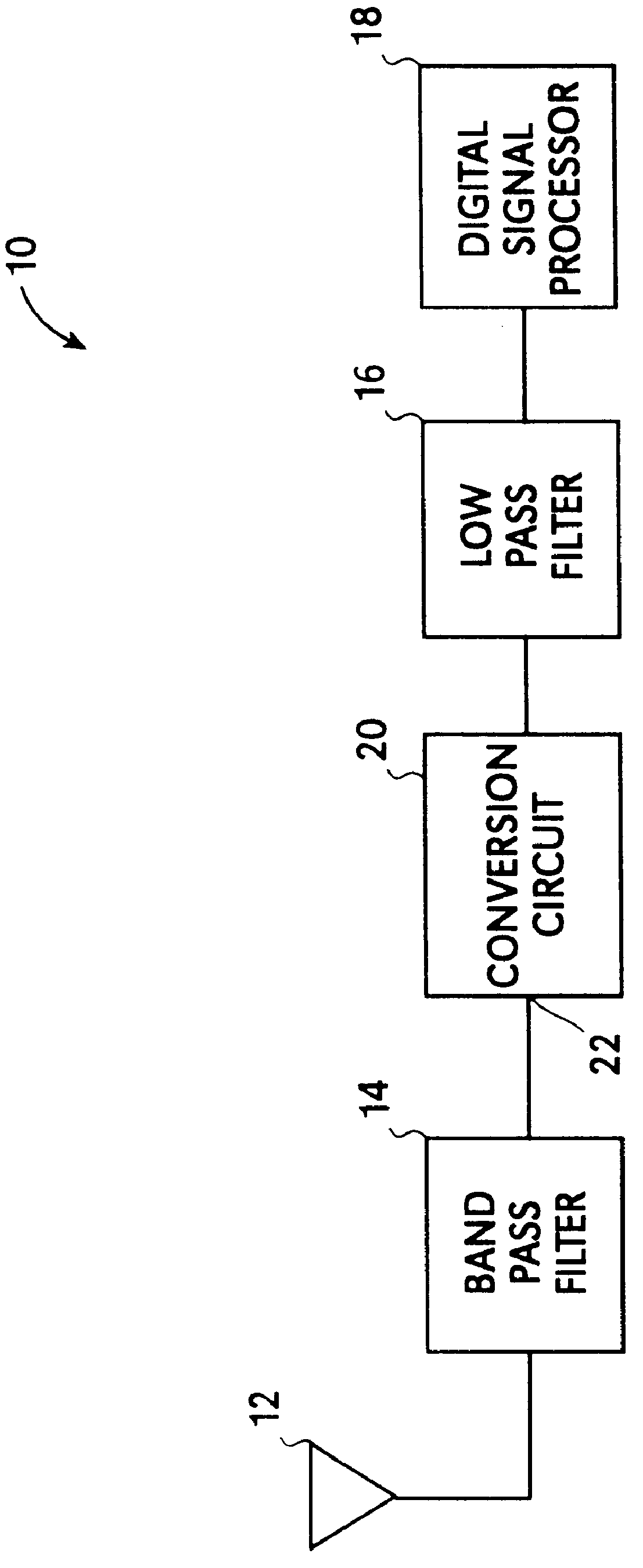
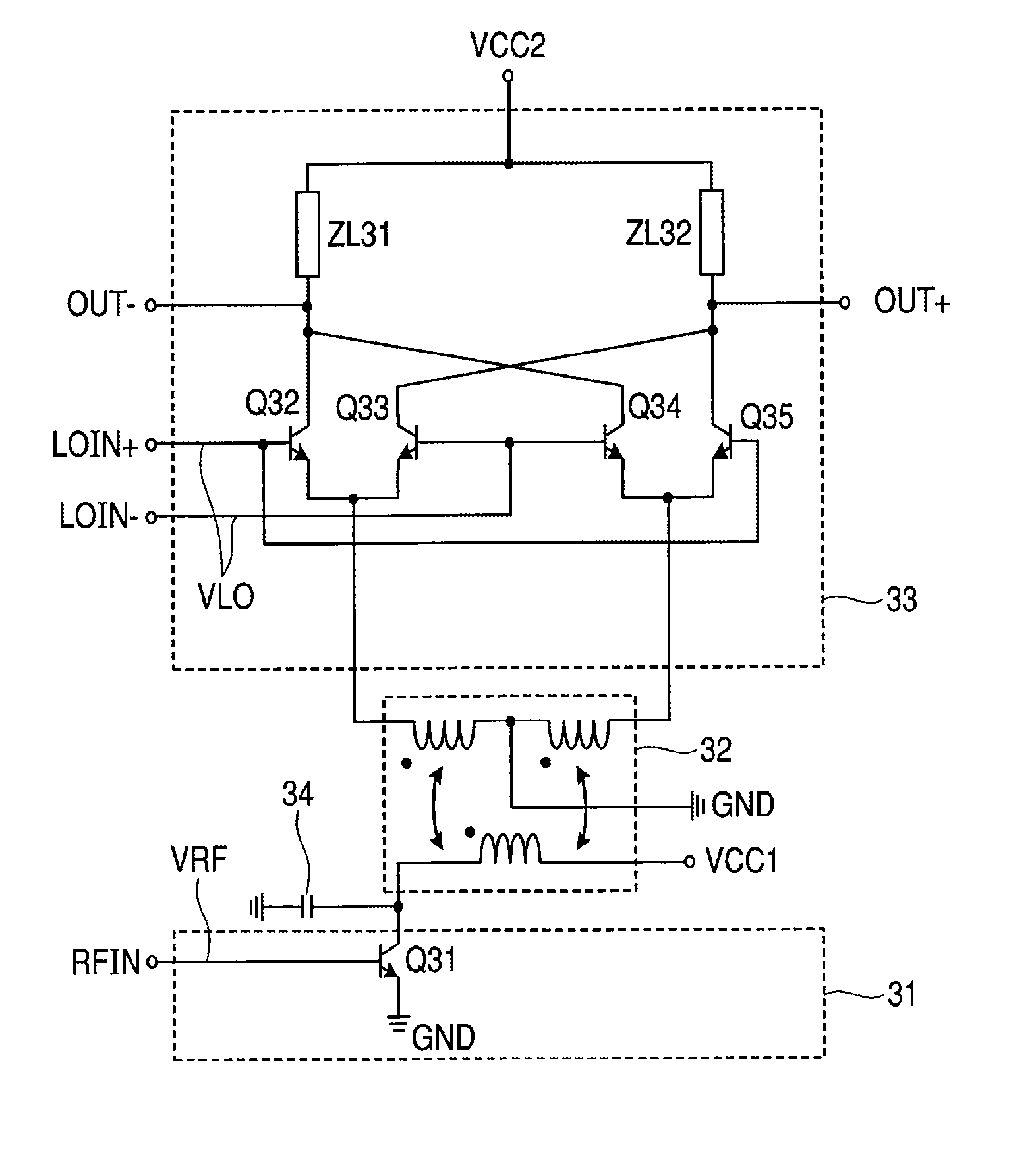
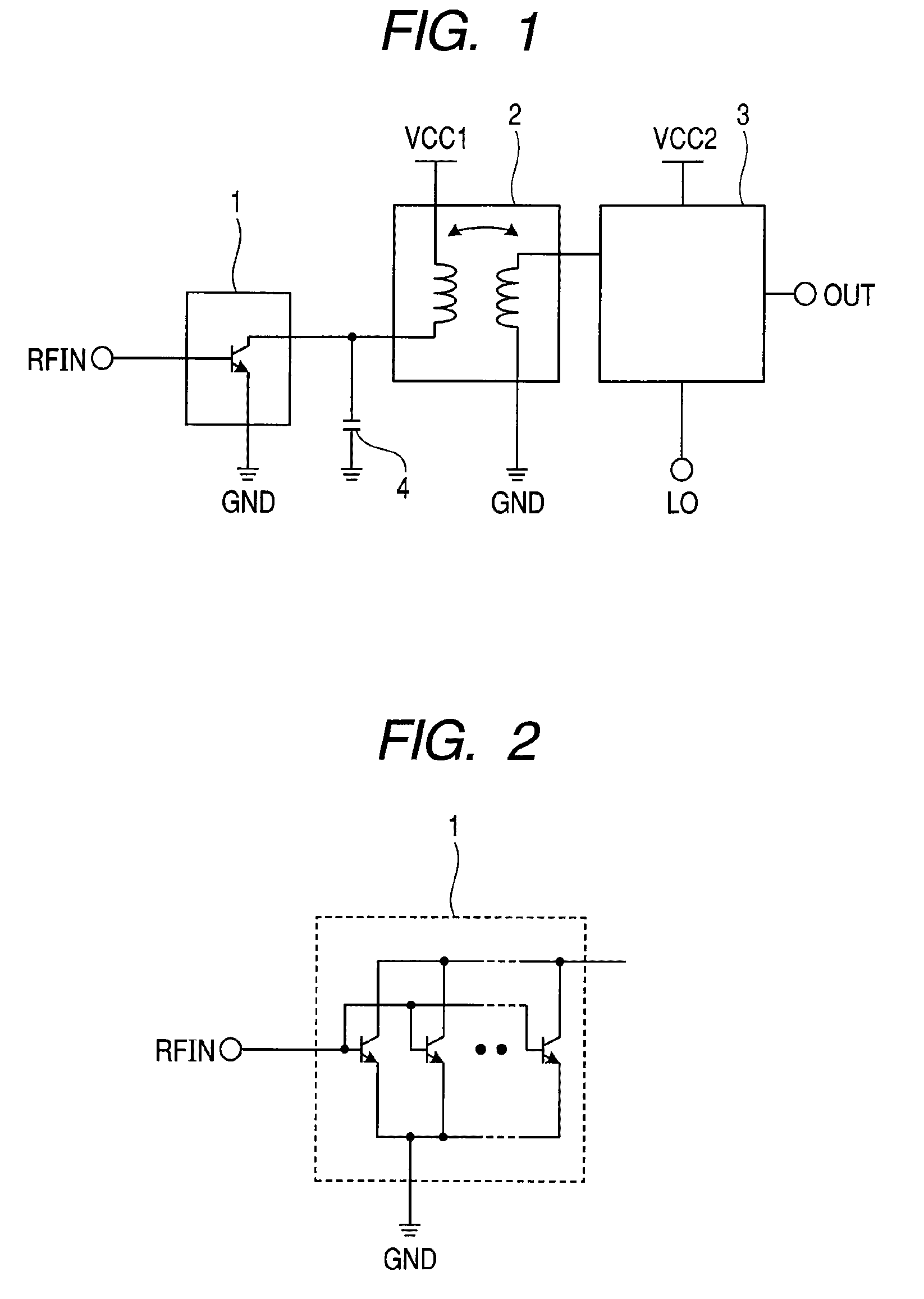
Direct conversion receiver with reduced even order distortion
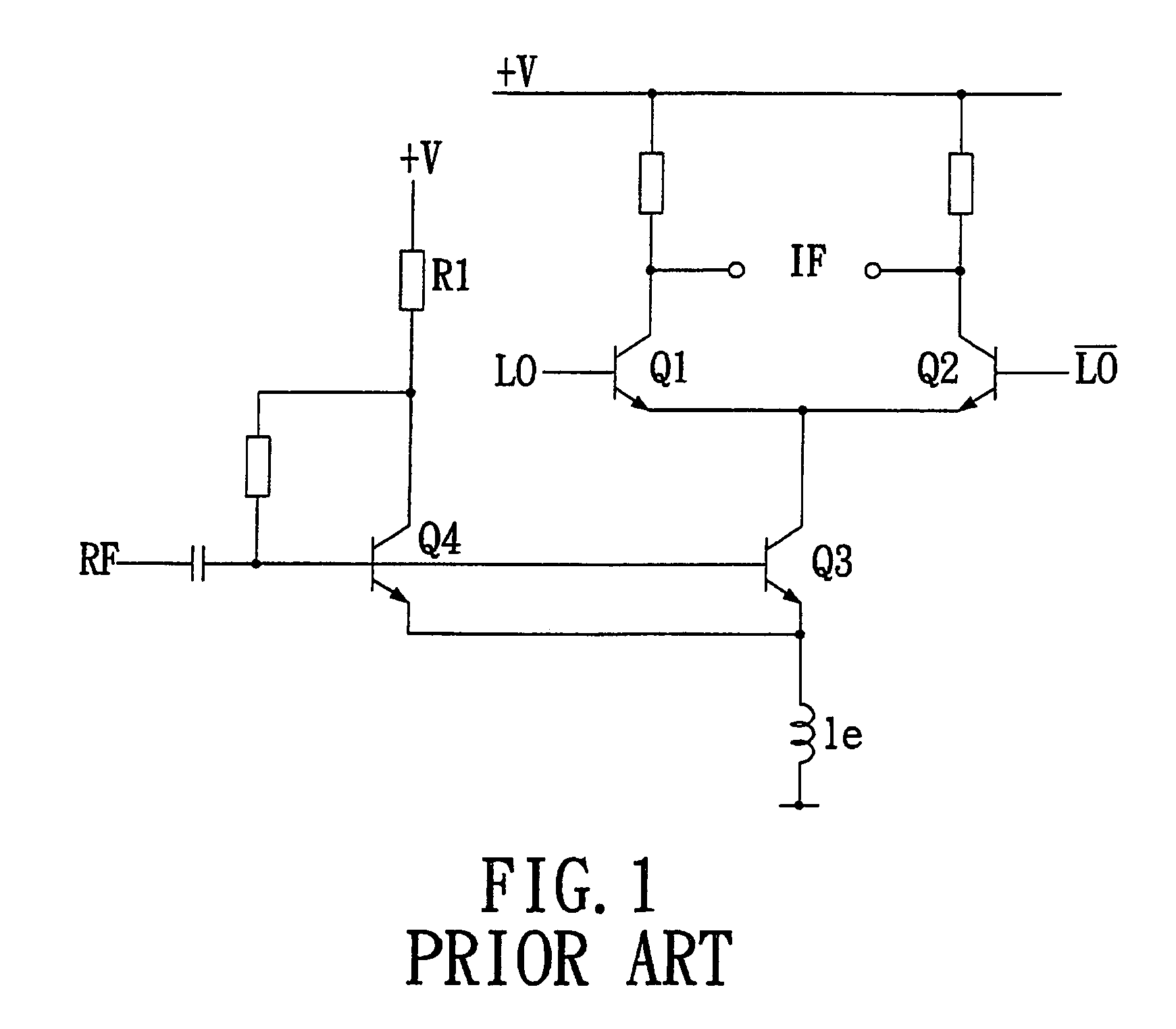
InactiveUS6021323AReduce distortion problemsReduces even order distortionModulation transference balanced arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPhase currentsLinear component
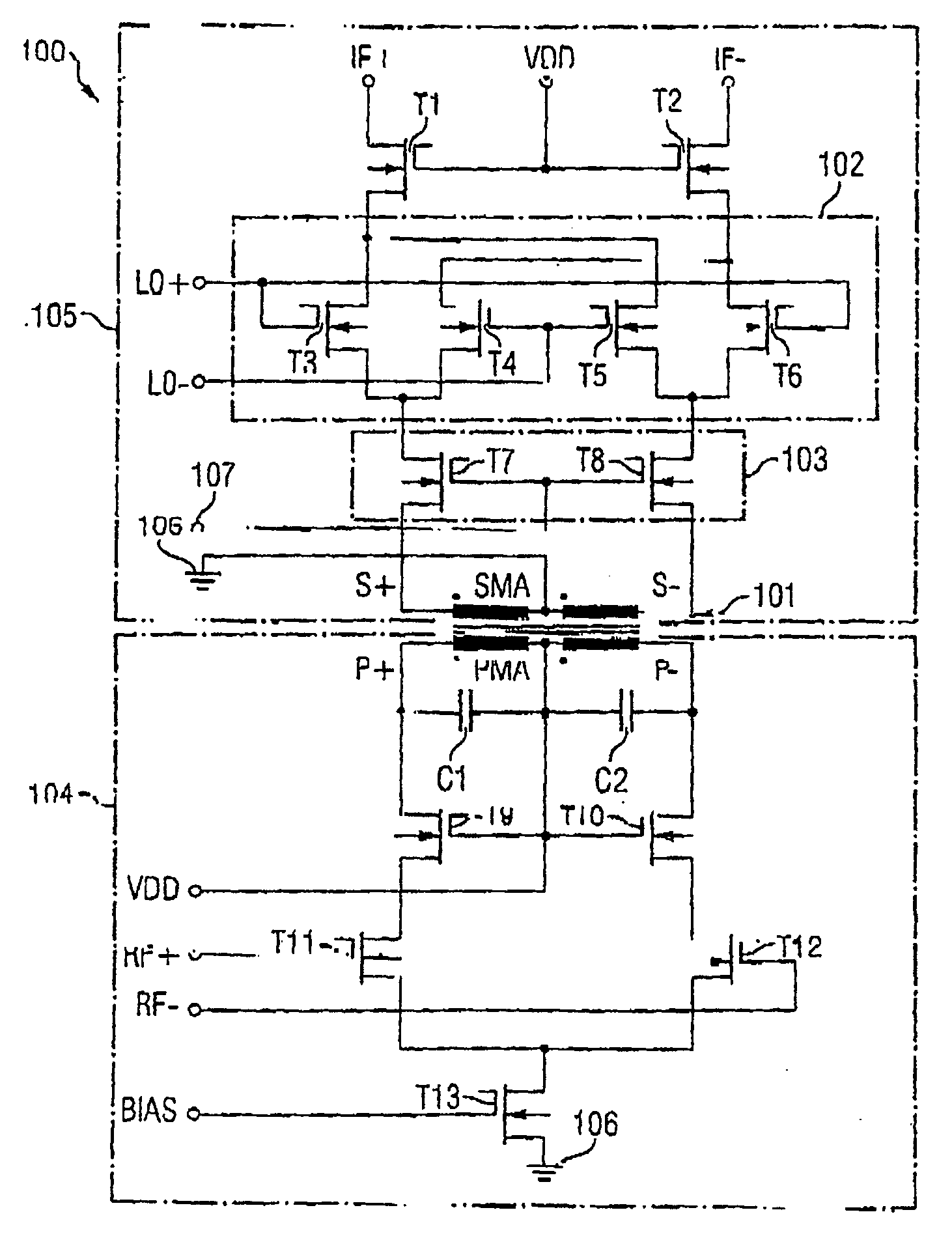
A mixer for use in a direct conversion receiver includes a compensating differential amplifier which injects equal amplitude opposite phase currents with respect to even order distortion currents. The compensating differential amplifier utilizes an ideal current source. The mixer is an active mixer which utilizes four switching transistors. The even order distortion is introduced by non-linear components which demonstrate strong off-channel signals.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
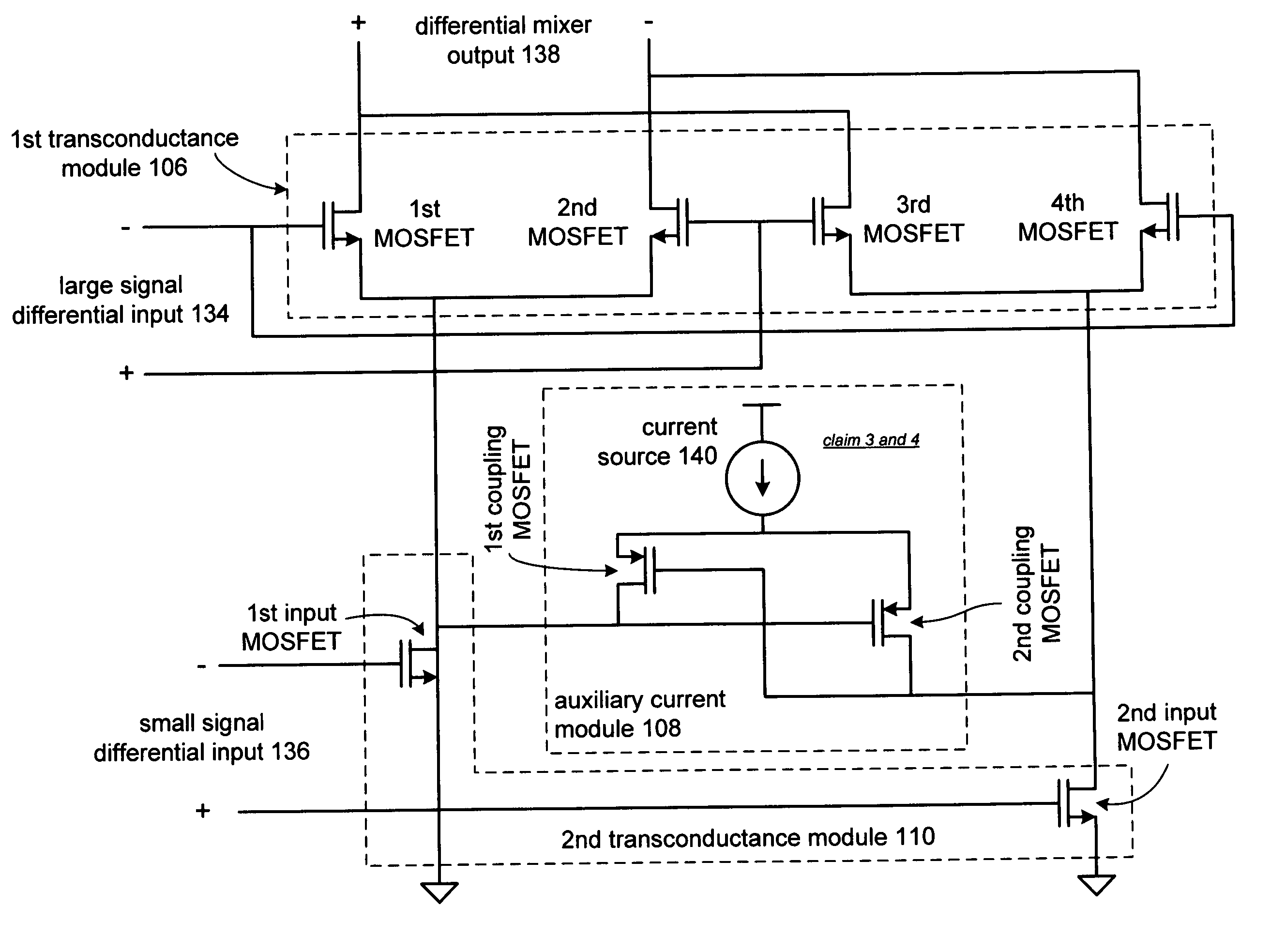
Reducing active mixer flicker noise
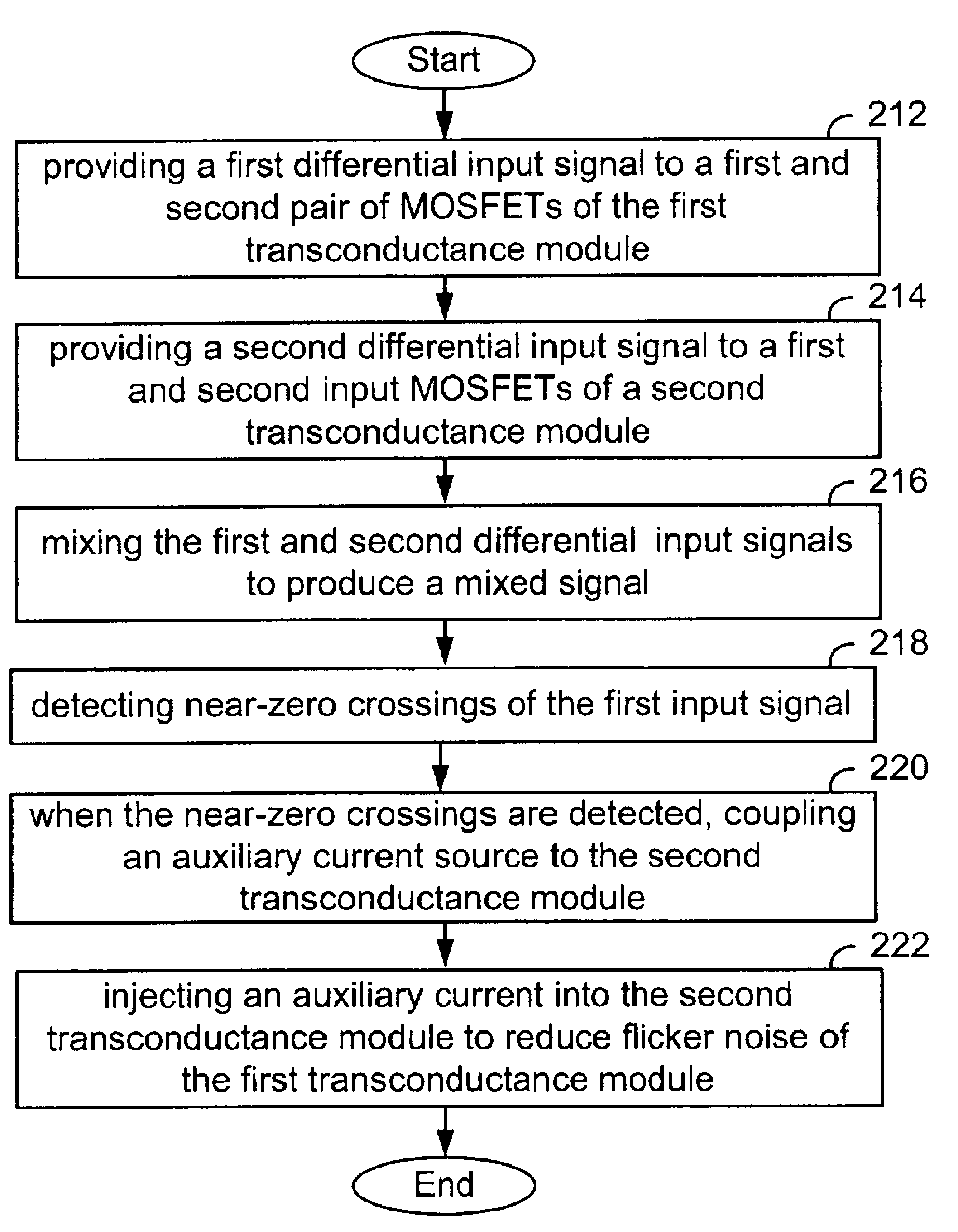
InactiveUS20050164671A1Reduces and eliminates flicker noiseReduces and eliminates any flicker noiseModulation transference balanced arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceMOSFETFrequency mixer
A mixer is disclosed that includes first and second transconductance modules that, in one embodiment, includes MOSFETs configured to receive a plurality of signals that are to be mixed and a selectively coupled auxiliary current source to inject an auxiliary current into the second transconductance module approximately at or near a zero-crossing point in order to reduce flicker noise and other noise introduced into an output signal during switching. Accordingly, as a first transconductance module approaches a zero-crossing, auxiliary current is injected to reduce the current produced therefrom thereby reducing flicker noise. In a differential mixer, the amount of current produced from a transistor pair to which the signal cycle is being switched is also reduced thereby reducing noise from the transistor pair that is turning on for the next portion of a signal cycle.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Magnetic mixing apparatus
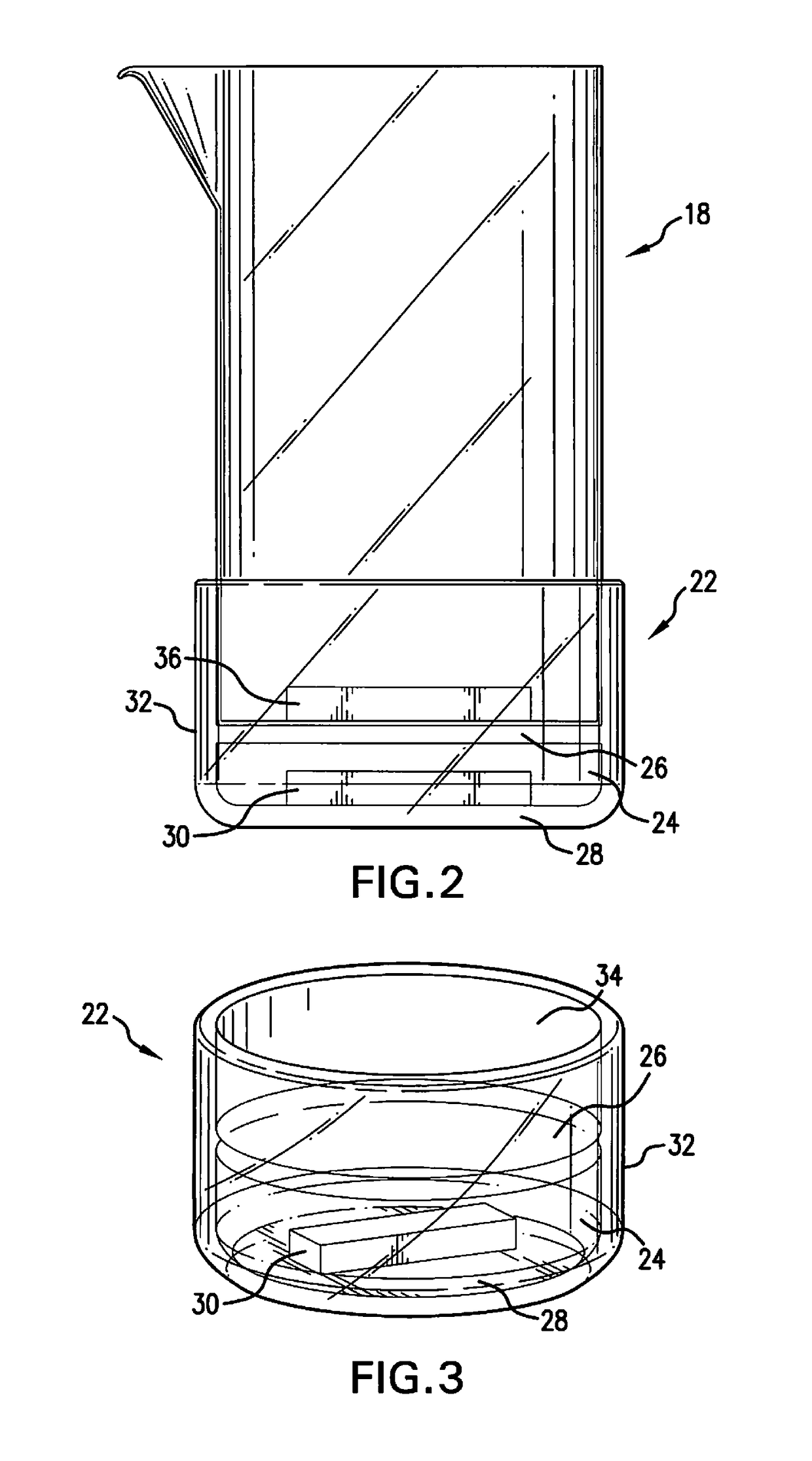
InactiveUS20180199760A1Reduce frictionSmall surface areaTransportation and packagingMixersMagnetic tension forceActive mixer
A container having a captive rotatable magnet to induce spinning of a separate unattached stirring implement placed in the container. The captive rotatable magnet may be part of an active mixer attached to the container. It may also be passively housed in a chamber in the bottom of the container to be spun under the influence of an external mixer to transmit by coupling the spinning to the separate spinning implement. The stirring implement is magnetically retained within the container during the pouring of a mixed substance.
Owner:RAISON INVESTMENTS INC
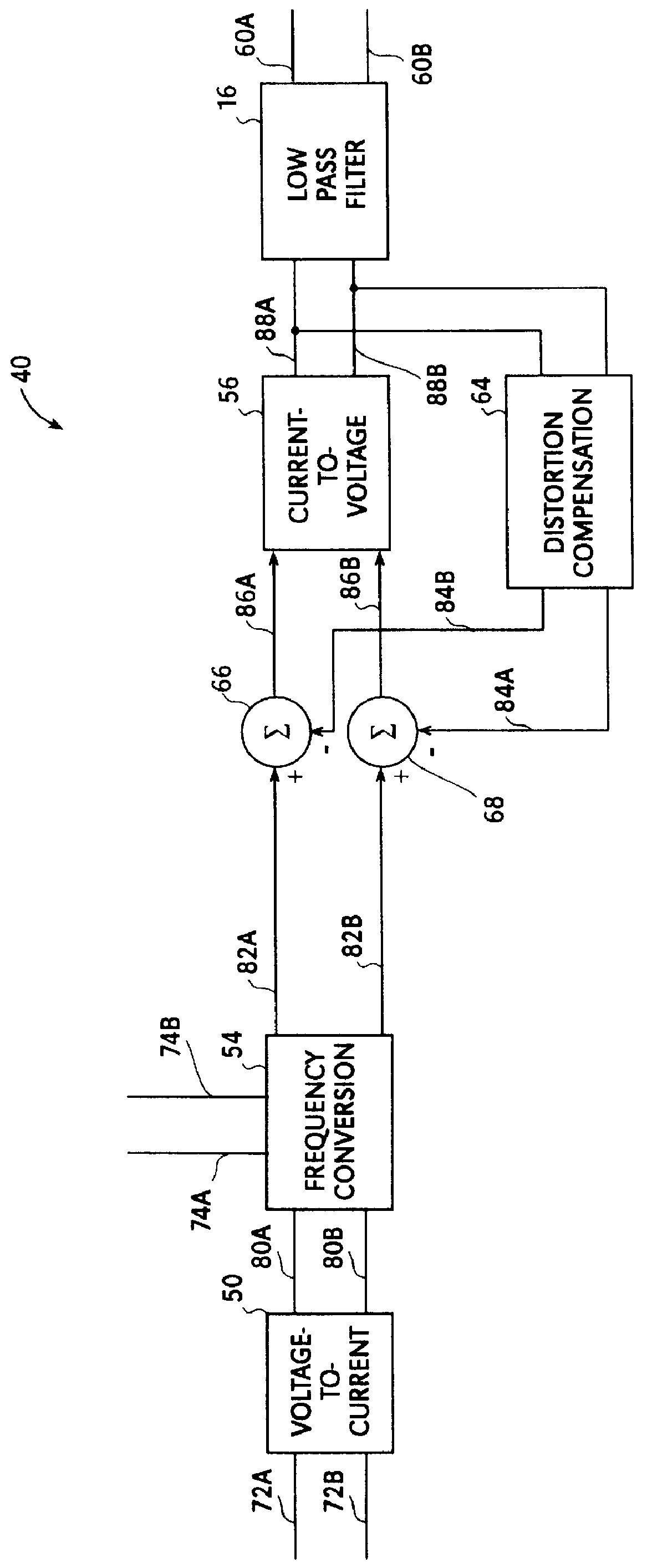
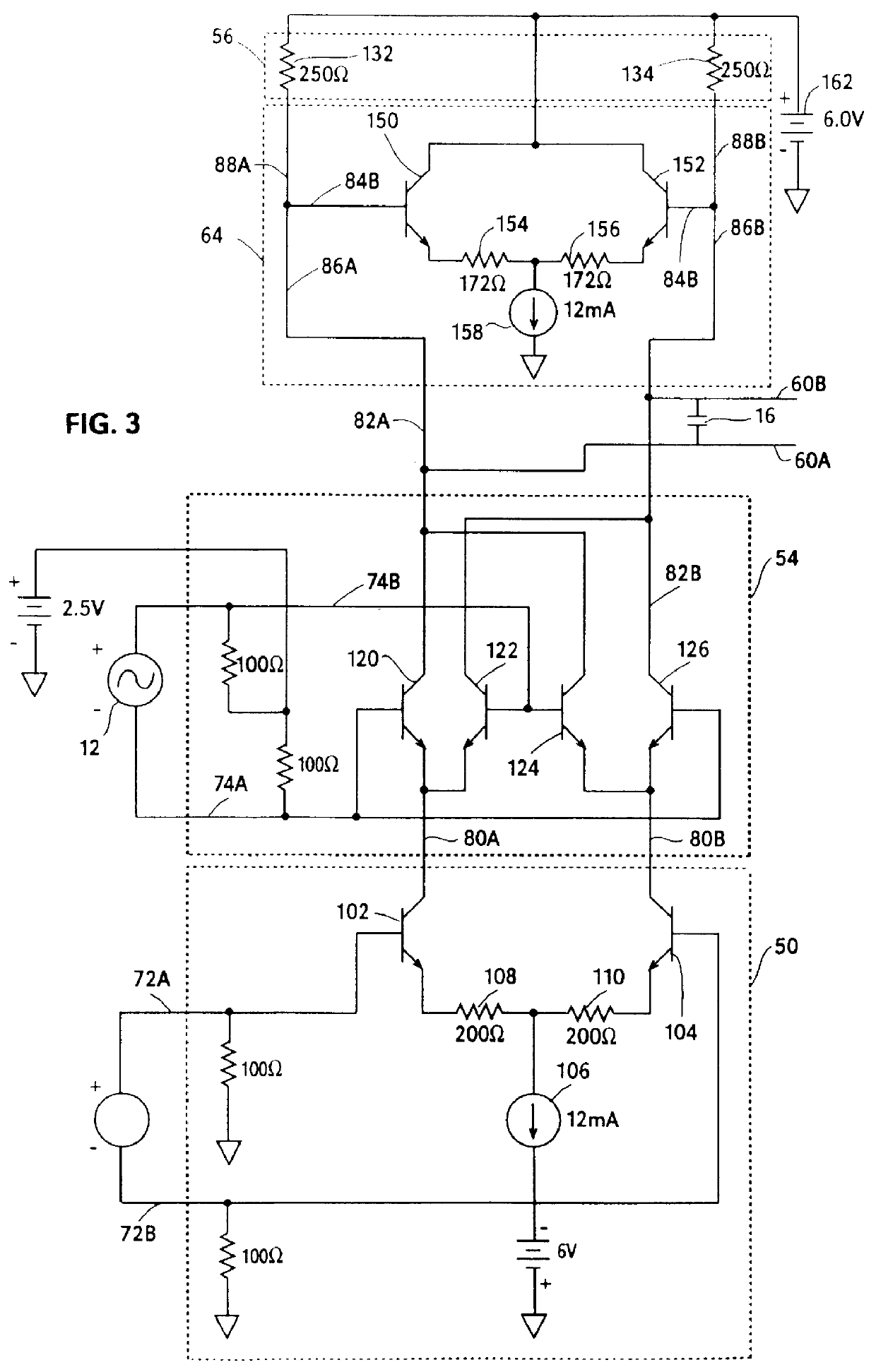
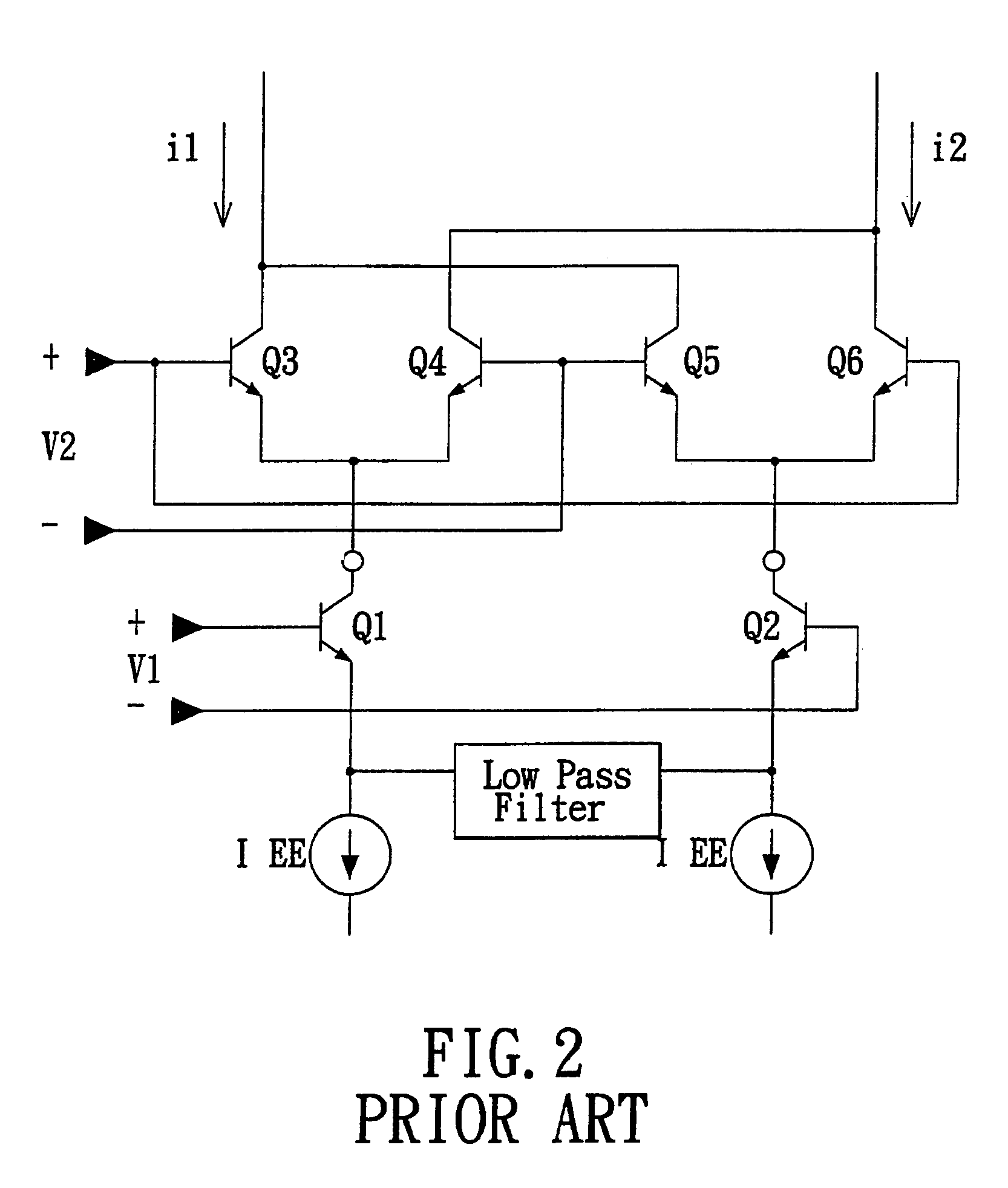
Method for reducing IM2 noise in a down conversion circuit
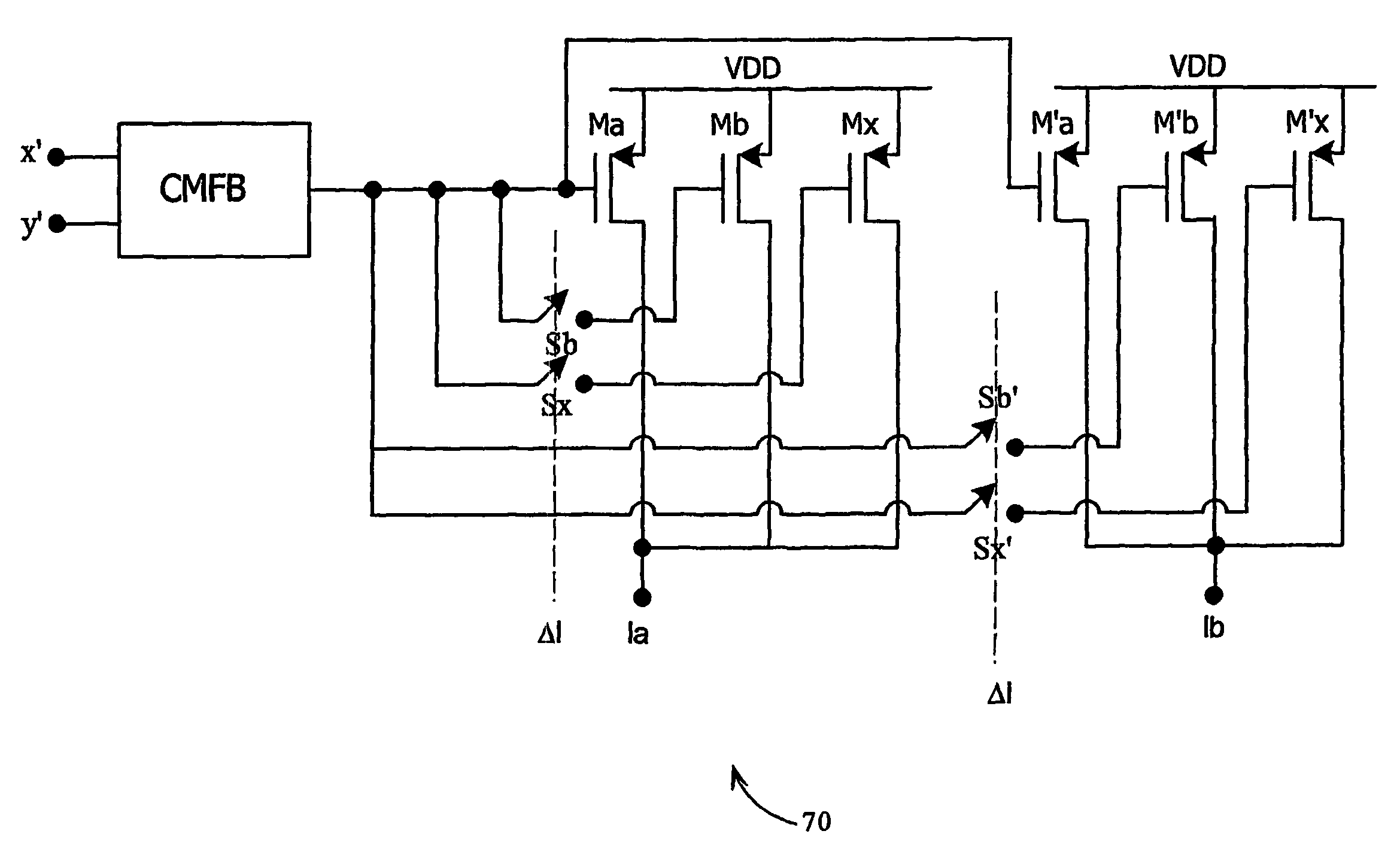
InactiveUS7263344B2Modulation transference balanced arrangementsDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionActive mixerEngineering
The present invention relates generally to communications, and more specifically to a method and apparatus for minimizing DC offset and second-order modulation products (IM2 noise) while demodulating RF signals. The principle of the invention can be applied to differential, down-conversion circuits (50) consisting of two differential mixers (54, 56) in series, a follows: a pair of current sources Ia and Ib are used to provide current to positive and negative channels of the first differential mixer (54). Providing current to the amplifying transistors of the first mixer (54) reduces the current drawn through the active mixer switches, reducing the noise generated. The current sources 1a and 1b are trimmed in a complementary manner where 1a=I+Delta1, and 1b=Delta1. The value of Δ1 can be determined in a number of manners; for example, it could be established by testing after the circuit has been fabricated, and the value stored on-chip, for future use.
Owner:ICERA CANADA ULC
Reducing active mixer flicker noise
InactiveUS6889037B2Reduce and eliminate flicker noiseImprove output signal qualityModulation transference balanced arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceMOSFETFrequency mixer
A mixer is disclosed that includes first and second transconductance modules that, in one embodiment, includes MOSFETs configured to receive a plurality of signals that are to be mixed and a selectively coupled auxiliary current source to inject an auxiliary current into the second transconductance module approximately at or near a zero-crossing point in order to reduce flicker noise and other noise introduced into an output signal during switching. Accordingly, as a first transconductance module approaches a zero-crossing, auxiliary current is injected to reduce the current produced therefrom thereby reducing flicker noise. In a differential mixer, the amount of current produced from a transistor pair to which the signal cycle is being switched is also reduced thereby reducing noise from the transistor pair that is turning on for the next portion of a signal cycle.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
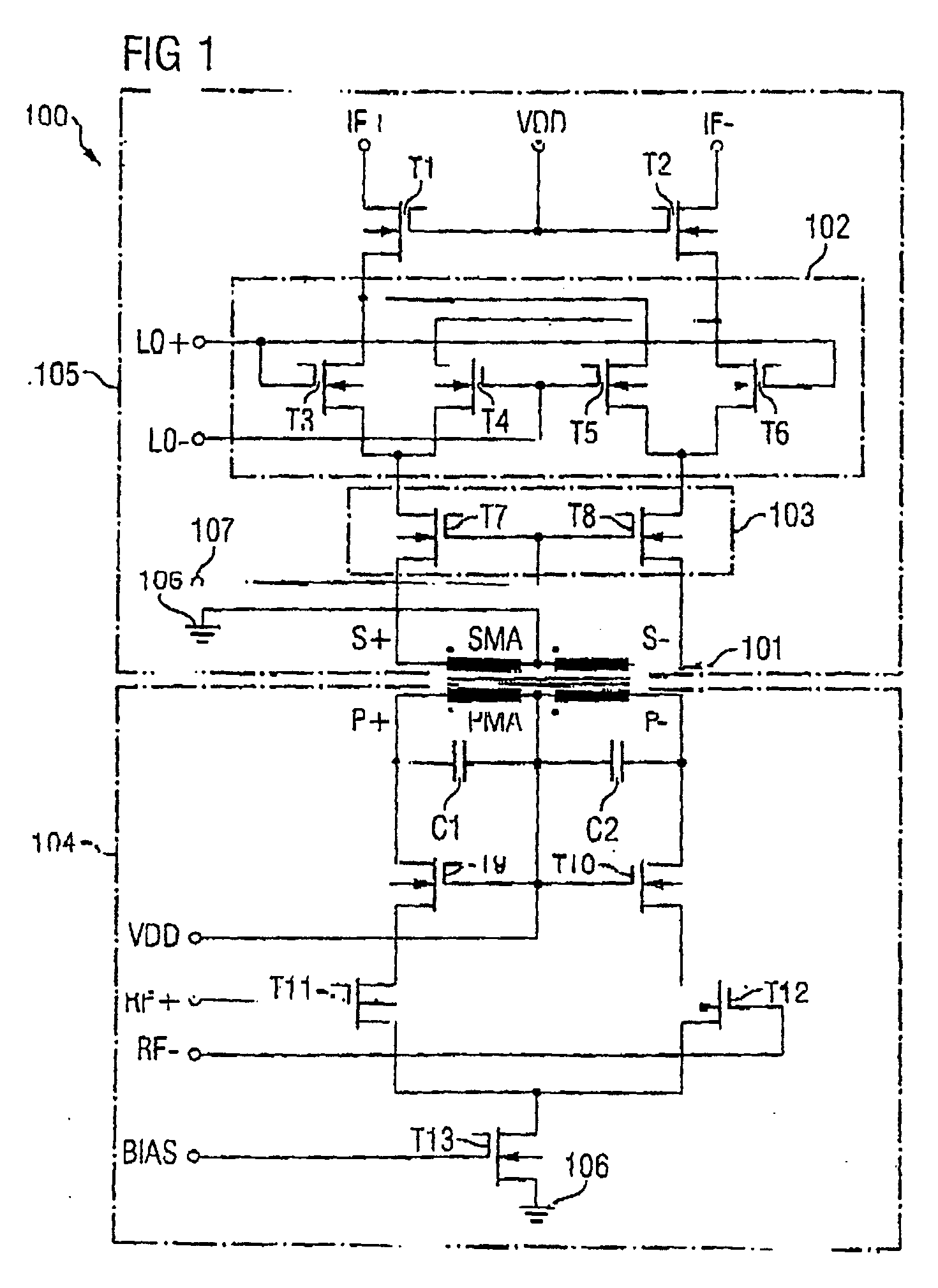
Integrated circuit having a mixer circuit
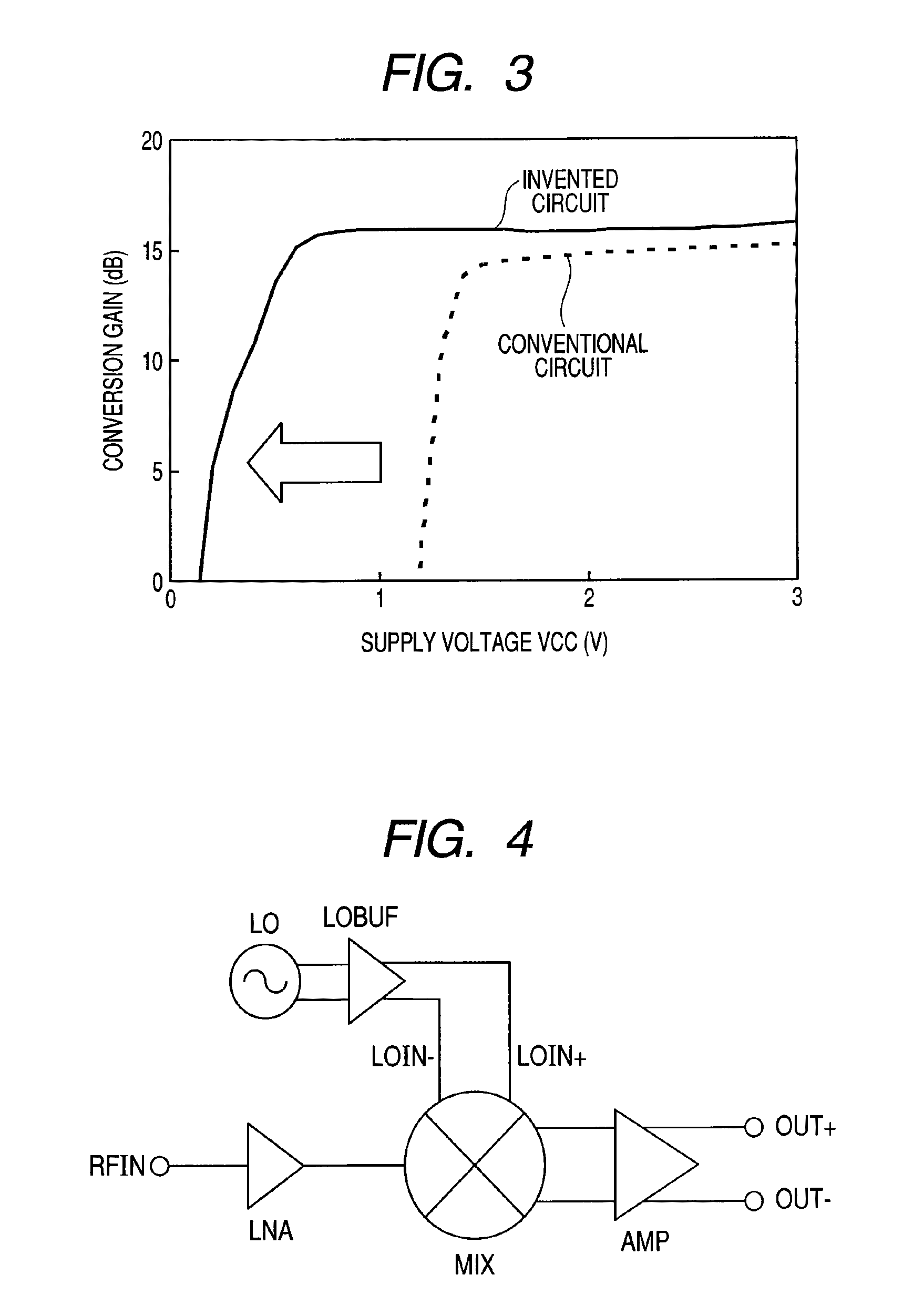
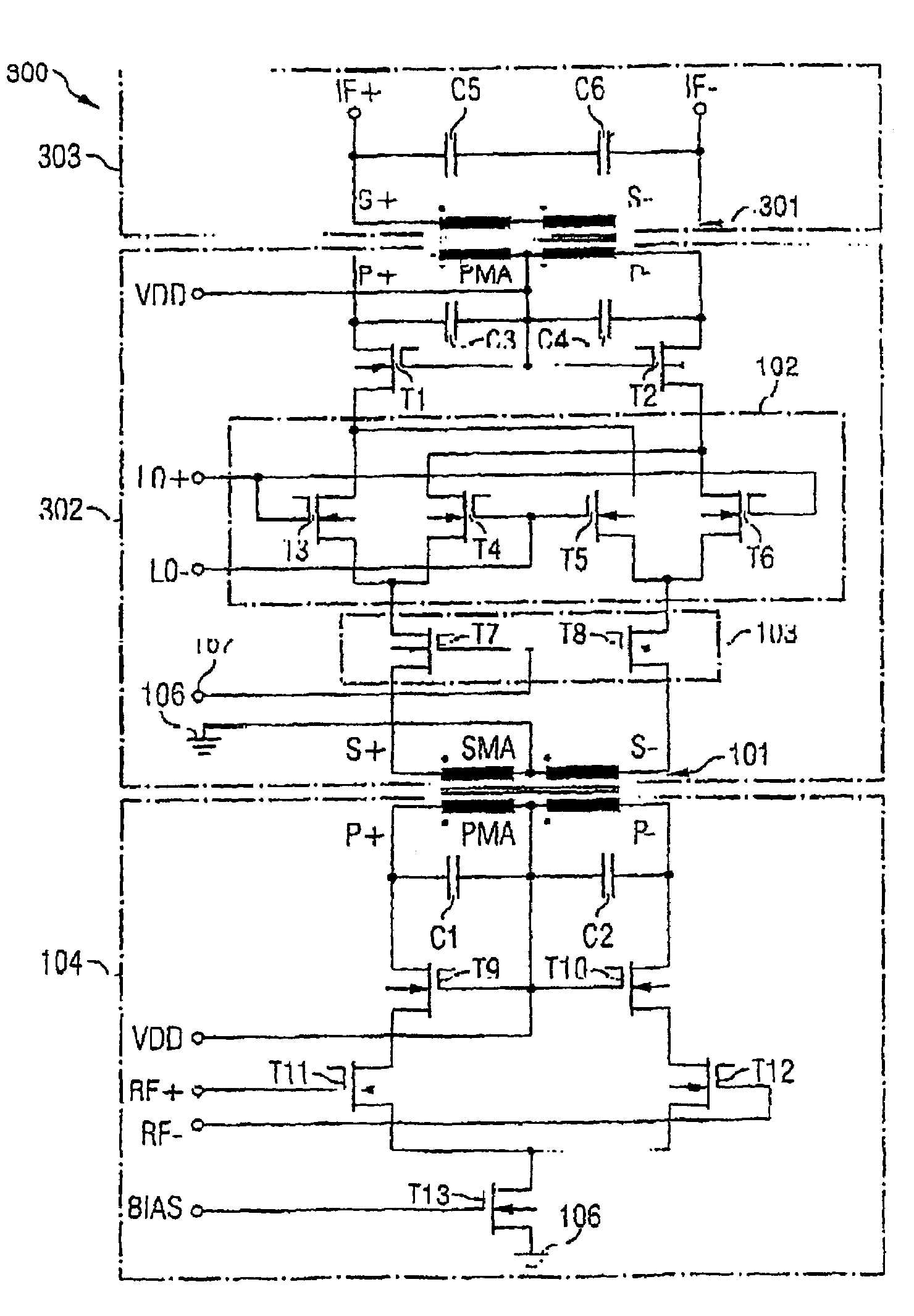
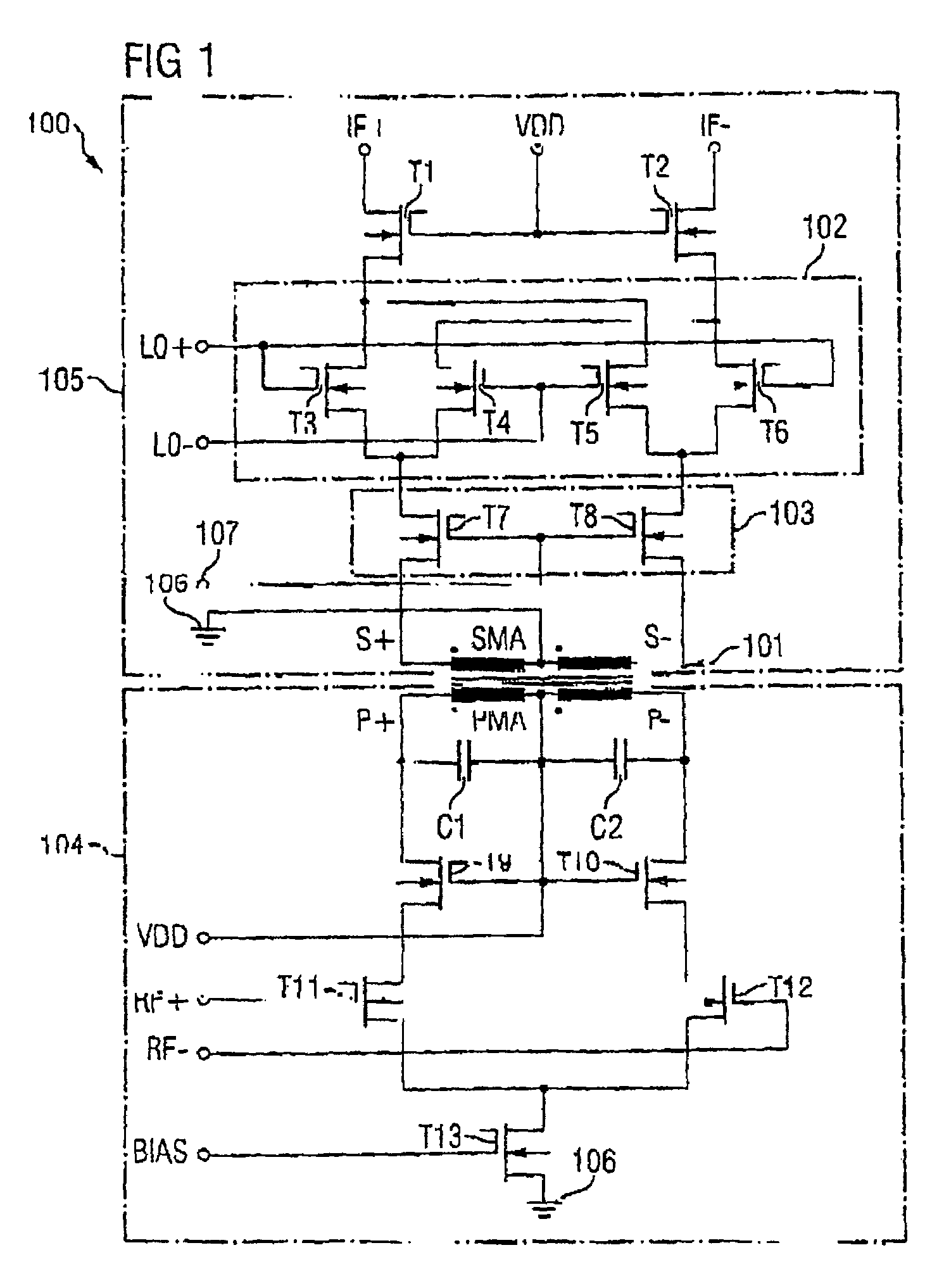
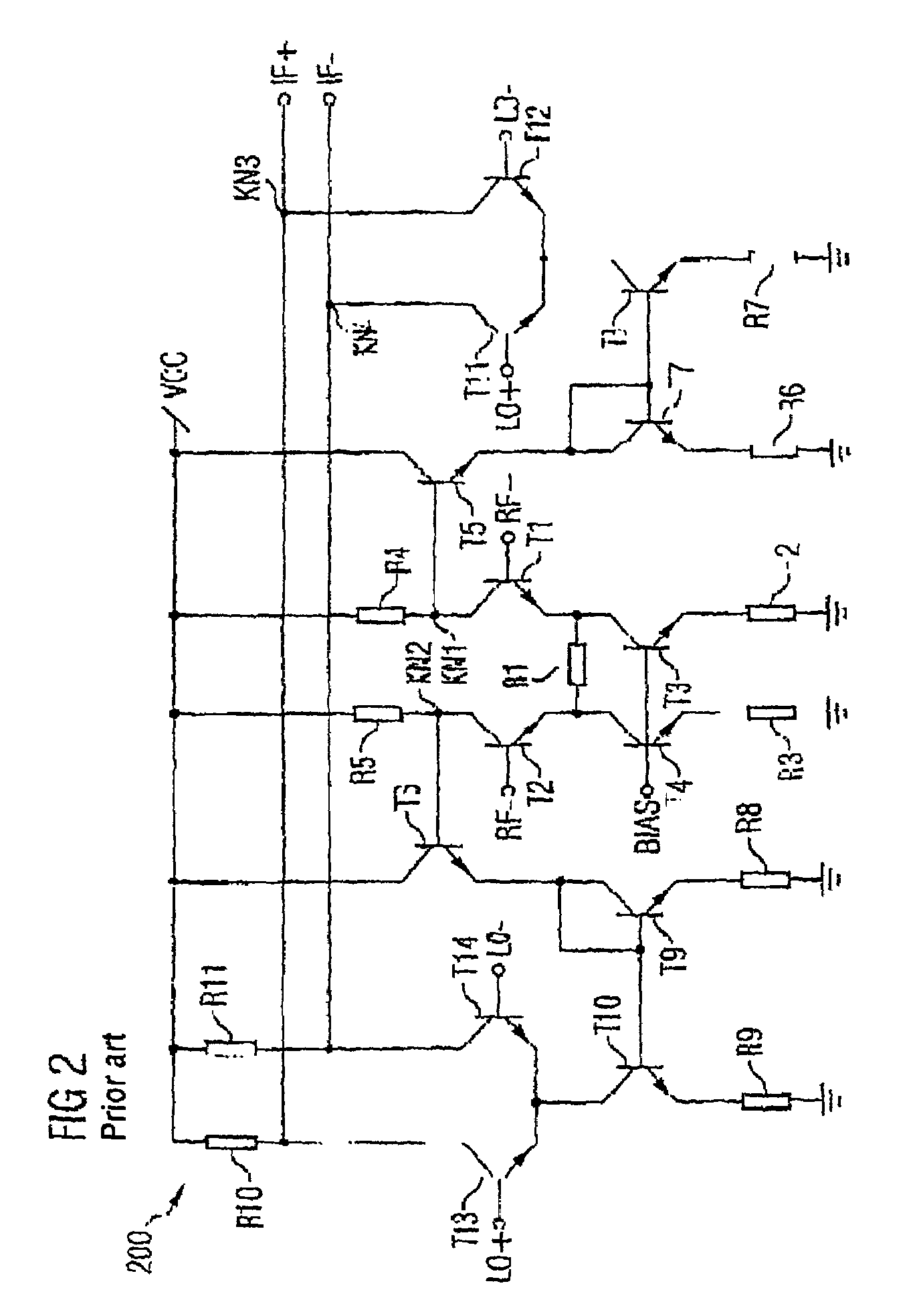
ActiveUS20050118979A1Reduce stepsLow working voltageModulation transference balanced arrangementsComputations using contact-making devicesTransformerIntermediate frequency
Integrated circuit including a mixer circuit, which has a first circuit section, a second circuit section, and a transformer. The first circuit section has two radiofrequency terminals. The second circuit section has two reference oscillator terminals, an active mixer unit with a signal-amplifying unit, and two intermediate frequency terminals. The active mixer unit and the signal-amplifying unit have a common current path. The transformer directly electrically decouples the two radiofrequency terminals from the active mixer unit, and couples the first circuit section and the second circuit section together such that each of the two circuit sections is separately supplied with a full operating voltage of the integrated circuit. The integrated circuit may additionally include a second transformer connected between the active mixer unit and the two intermediate frequency terminals.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Gilbert cell mixer with automatic optimal bias and harmonic wave control
InactiveCN102394566AReduce areaModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesCapacitanceTransceiver
The invention, which belongs to the radio frequency integrated circuit design technology field, more particularly relates to a Gilbert cell mixer with automatic optimal bias and harmonic wave control. The mixer comprises a basic Gilbert frequency mixing unit, an optimal bias circuit and a harmonic wave control circuit. The Gilbert frequency mixing unit consists of a transconductance level, a switch level, and a load level. The optimal bias circuit includes duplication or reduction with a same proportion of a transconductance-level device of the Gilbert frequency mixing unit, a resistor chain, and operational amplifiers, wherein weak currents flow through the resistor chain and the operational amplifiers form two feedback loops. A middle point of the resistor chain in the optimal bias circuit provides a direct current bias for a transconductance tube in the Gilbert frequency mixing unit. And the harmonic wave control circuit is composed of an adjustable active inductance and a harmonic wave control capacitor; and the harmonic wave control circuit is connected to a drain terminal of the transconductance tube of the Gilbert frequency mixing unit. According to the invention, accuracy of a generated optimal bias is optimized; and a secondary harmonic wave feedback effect is overcome. Besides, the Gilbert cell mixer with automatic optimal bias and harmonic wave control is suitable for application to a wireless communication transceiver circuit needing an active mixer with high linearity.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Micromachined diagnostic device with controlled flow of fluid and reaction
This invention relates to a micromachined microfluidics diagnostic device that comprises one or multiple assaying channels each of which is comprised a sample port, a first valve, a reaction chamber, a second valve, a fluid ejector array, a third valve, a buffer chamber, a capture zone and a waste chamber. Each of these device components are interconnected through microfluidic channels. This invention further relates to the method of operating a micromachined microfluidic diagnostic device. The flow of fluid in the microchannels is regulated through micromachined valves. The reaction of sample analytes with fluorescent tags and detection antibodies in the reaction chamber are enhanced by the micromachined active mixer. By ejecting reaction mixture onto the capture zone through micromachined fluid ejector array, the fluorescent tagged analytes bind with capturing antiodies on capture zone. The fluid ejector array further ejects buffer fluid to wash away unbound fluorescent tags.
Owner:MICROPOINT BIOTECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
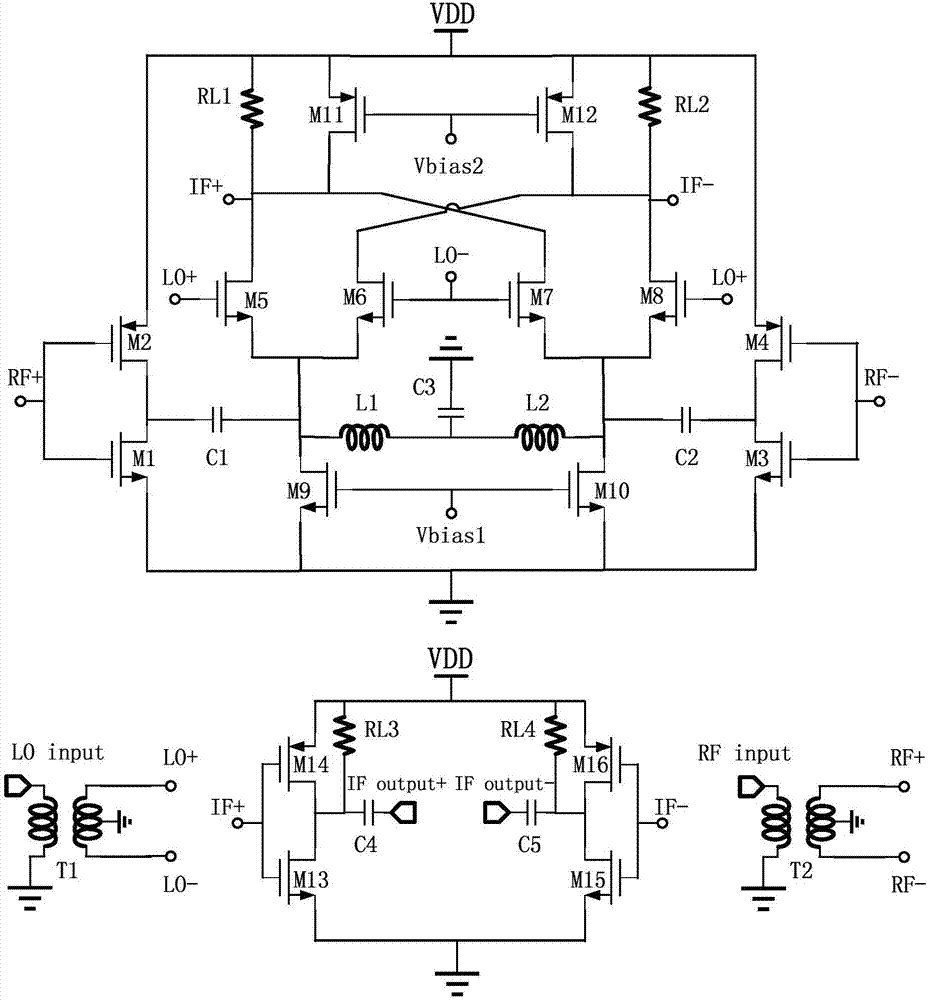
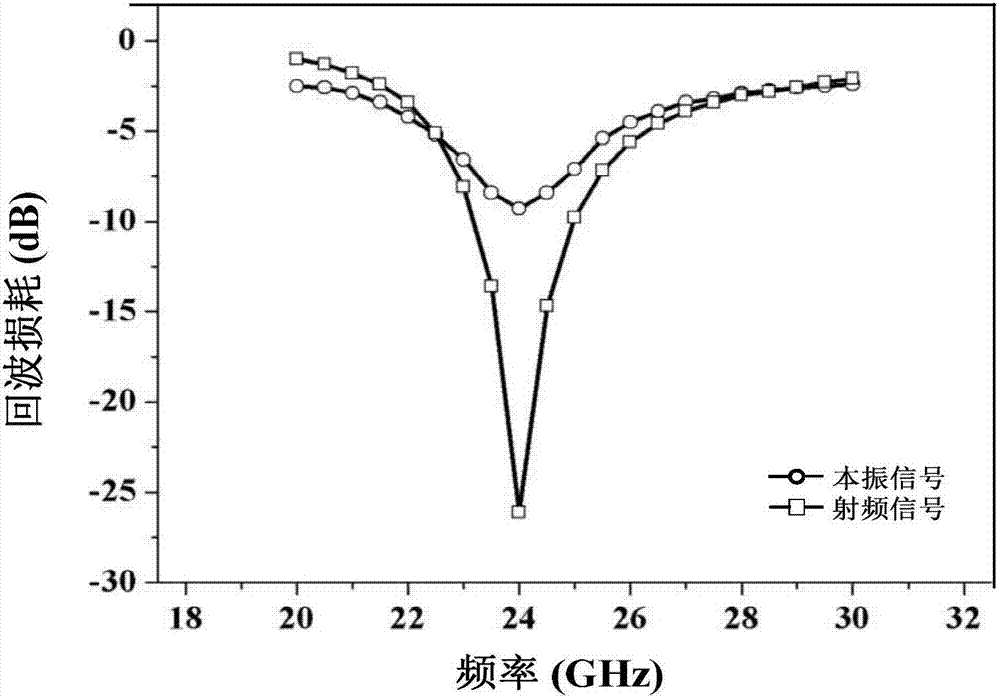
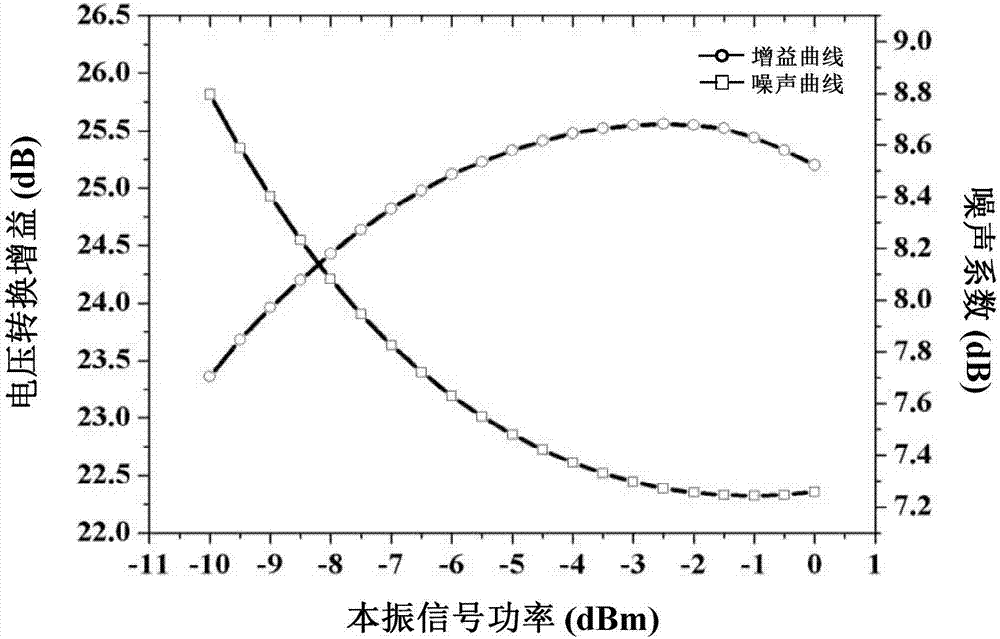
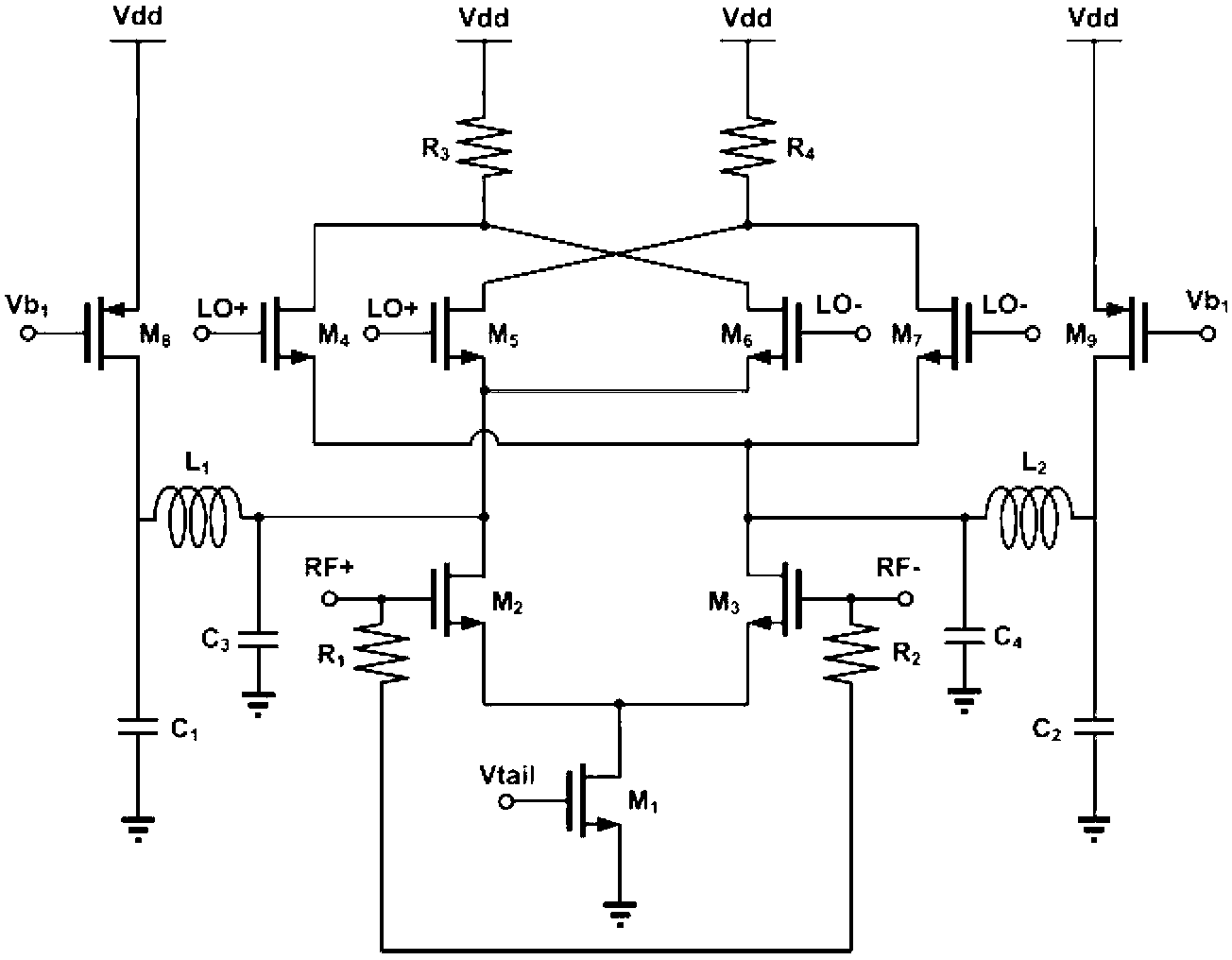
Folding double balance active mixer of K wave band
ActiveCN107040217ABig bias currentLarge transconductance parameterModulation transference balanced arrangementsFrequency mixerParasitic capacitance
The invention relates to the mixer technology, and specifically relates to a folding double balance active mixer of K wave band. The folding double balance active mixer of K wave band includes a first balance-imbalance converter T1, a second balance-imbalance converter T2, a first transconductance amplification circuit, a second transconductance amplification circuit, a first current source circuit, a second current source circuit, a switch level circuit, a load level circuit, a first buffer circuit and a second buffer circuit. The folding double balance active mixer of K wave band solves the compromise problem between structural noise, gain and linearity of a traditional mixer, and can effectively improve the overall performance index of the mixer. The folding double balance active mixer of K wave band can improve the gain and reduce the noise. The folding double balance active mixer of K wave band obtains the relatively ideal switching performance and greater output amplitude space, and can expand the linearity of the circuit. The folding double balance active mixer of K wave band can further improve the gain and the noise performance by eliminating the influence of parasitic capacitance. Moreover, when the folding double balance active mixer of K wave band drives the post 50 ohm load, the signal amplitude cannot be attenuated.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
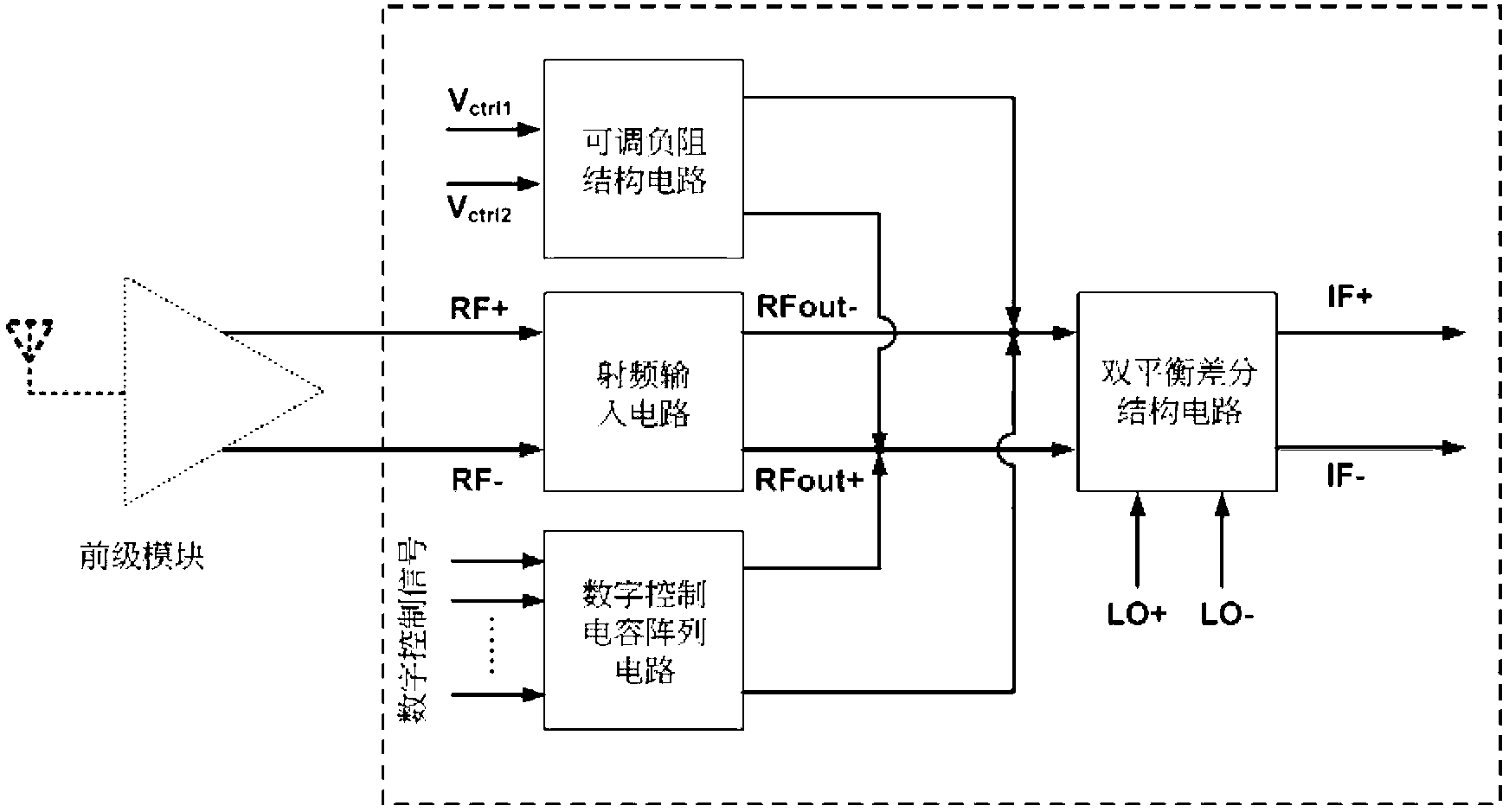
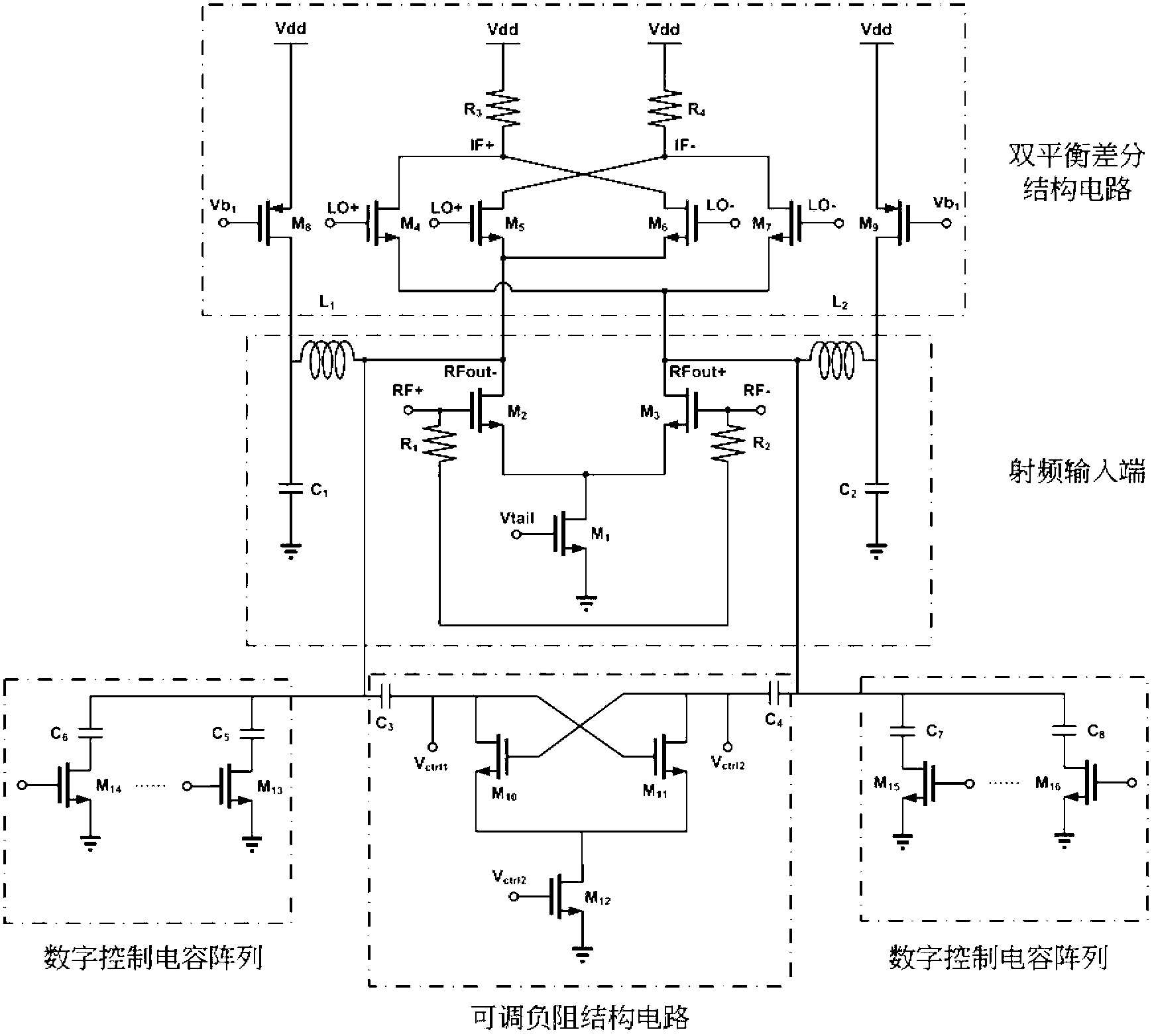
Adjustable negative resistance structure-based multimode multi-channel mixer
InactiveCN103236821AImprove conversion gainReduce flicker noiseModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesIntermediate frequencyEngineering
The invention provides an adjustable negative resistance structure-based multimode multi-channel mixer, which comprises a radio frequency input circuit, an adjustable negative resistance circuit, a digital control capacitor array circuit and a double-balanced differential structure circuit, wherein two input ports of the radio frequency input circuit are connected with radio frequency signals RF+ and RF-, and an output port of the radio frequency input circuit is directly connected with ports RFout+ and RFout-; the negative resistance size of the adjustable negative resistance circuit is controlled by two levels Vctrll and Vctrl, and an output end of the adjustable negative resistance circuit is connected with the RFout+ and the RFout-; an input port of the digital control capacitor array circuit is controlled by a digital signal, and two output ports of the digital control capacitor array circuit are connected with the RFout+ and the RFout-; and radio frequency current signals are input into the double-balanced differential structure circuit through the RFout+ and the RFout-, and are mixed with local oscillation signals LO+ and LO- to output intermediate-frequency signals IF+ and IF- to be then input into a rear-end module. By the adjustable negative resistance circuit, the equivalent parallel resistance of a capacitor array is eliminated, a noise coefficient is reduced, the gain of an active mixer is improved, the working frequency of the mixer can be controlled by a digital end, and the requirements of a broadband multi-channel system are met.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Active mixer circuit and a receiver circuit or a millimeter-wave communication unit using it
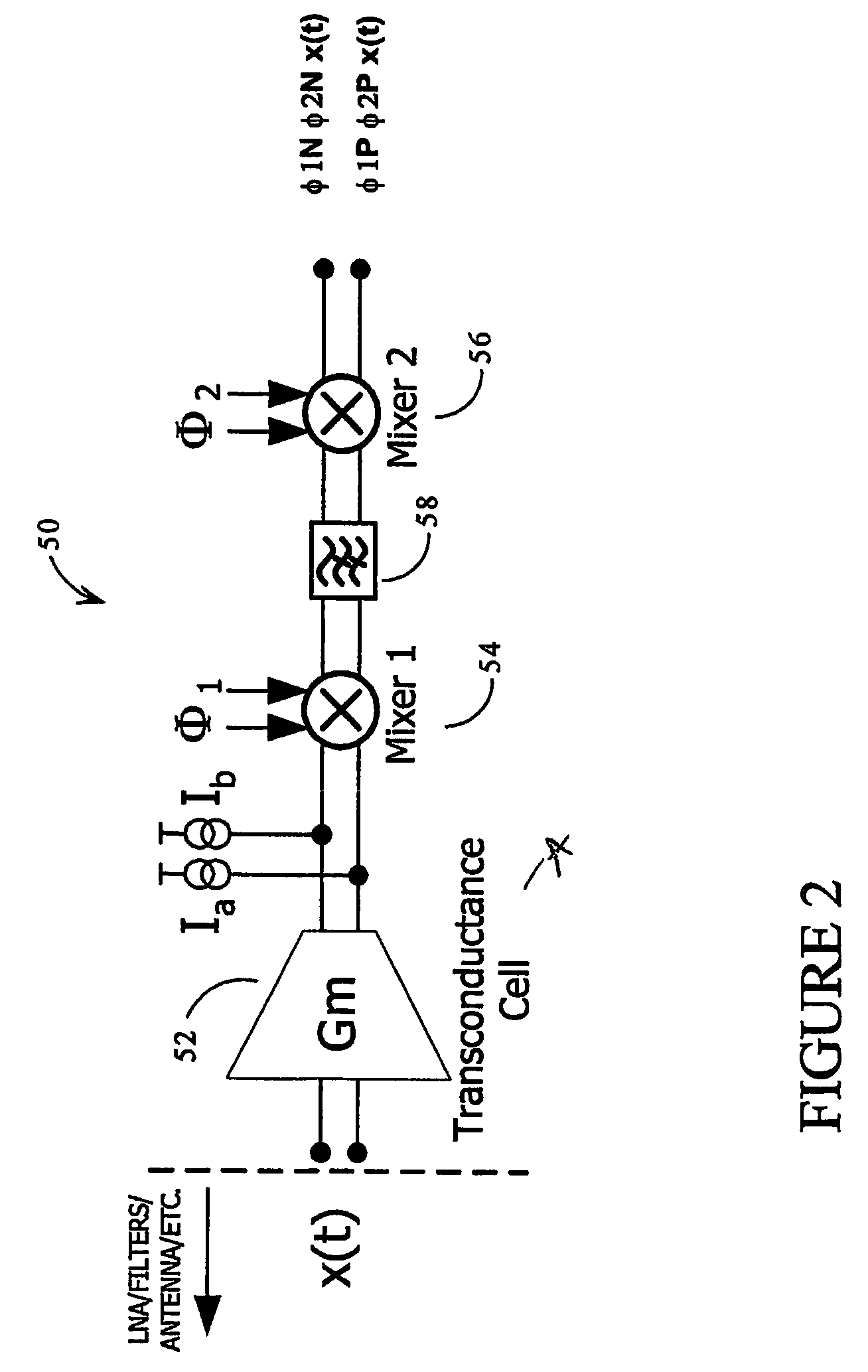
ActiveUS8121579B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce deteriorationTransmissionMulti-frequency-changing modulation transferenceLow noiseLow voltage
The present invention provides a semiconductor integrated circuit including an active mixer circuit that is operated at low voltage, low noise, and low power consumption. It includes a transconductance amplifier, a transformer, and a multiplier, connects a transformer between the transconductance amplifier and the multiplier, and separates between the transconductance amplifier and the multiplier with respect to direct current inside the transformer. Further, each of the tranconductance amplifier and the multiplier is configured of transistors that are single-stacked between the supply voltage terminal and ground terminal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
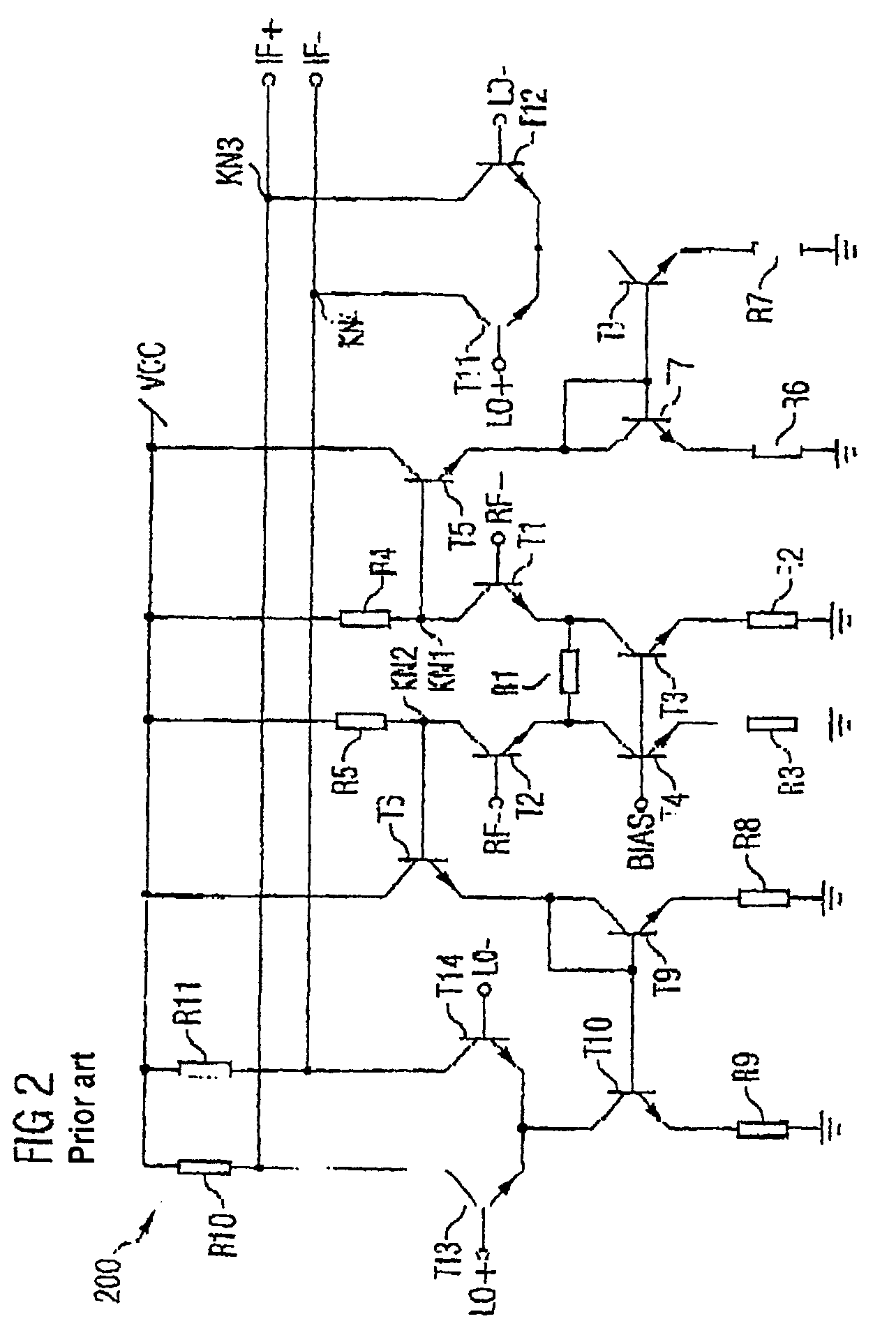
Integrated circuit having a mixer circuit
InactiveUS7509111B2Low working voltageReduce parasitic capacitanceModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmissionFrequency mixerTransformer
Owner:INTEL CORP
Feed-forward amplifier loop control utilizing if signal processing
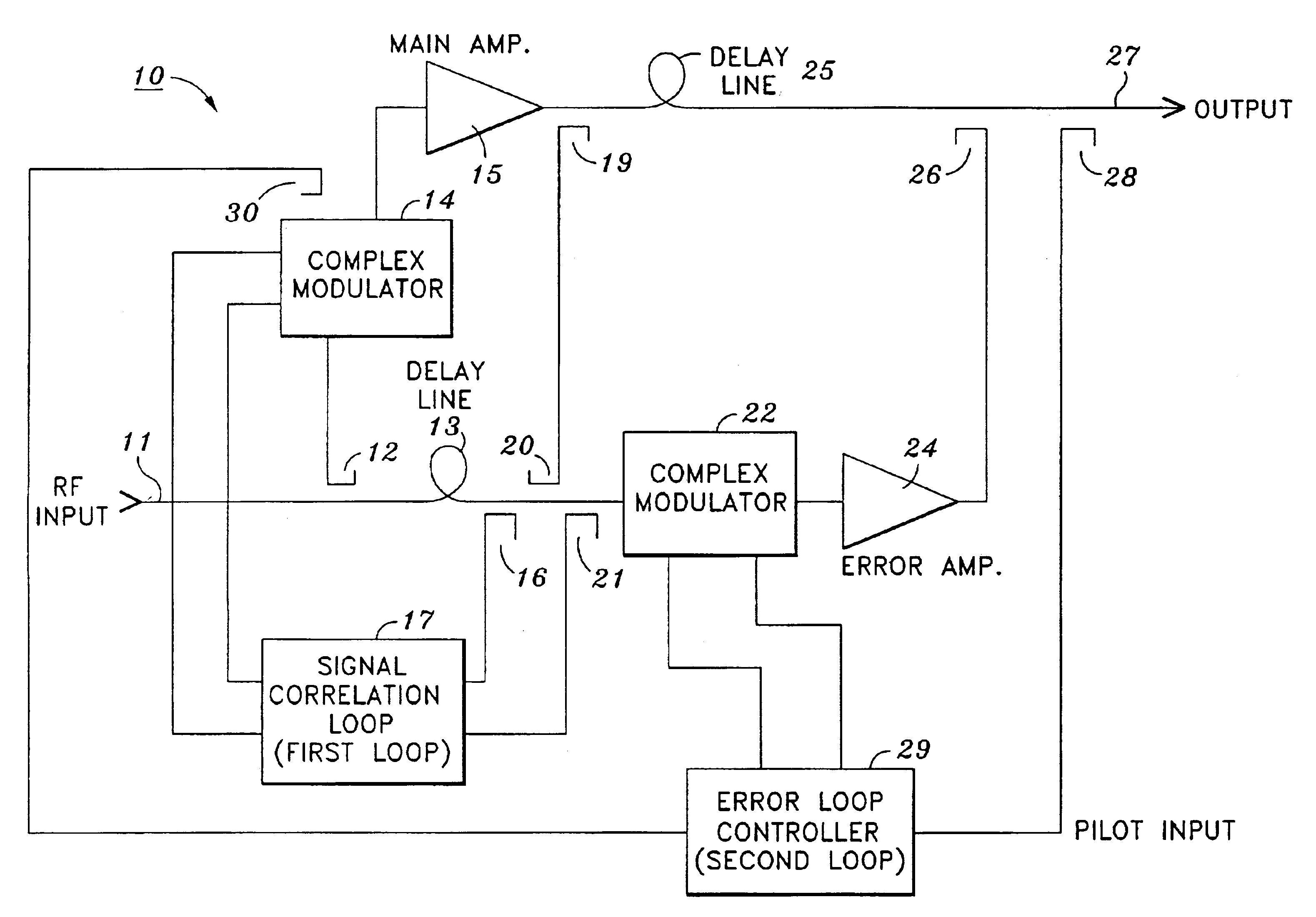
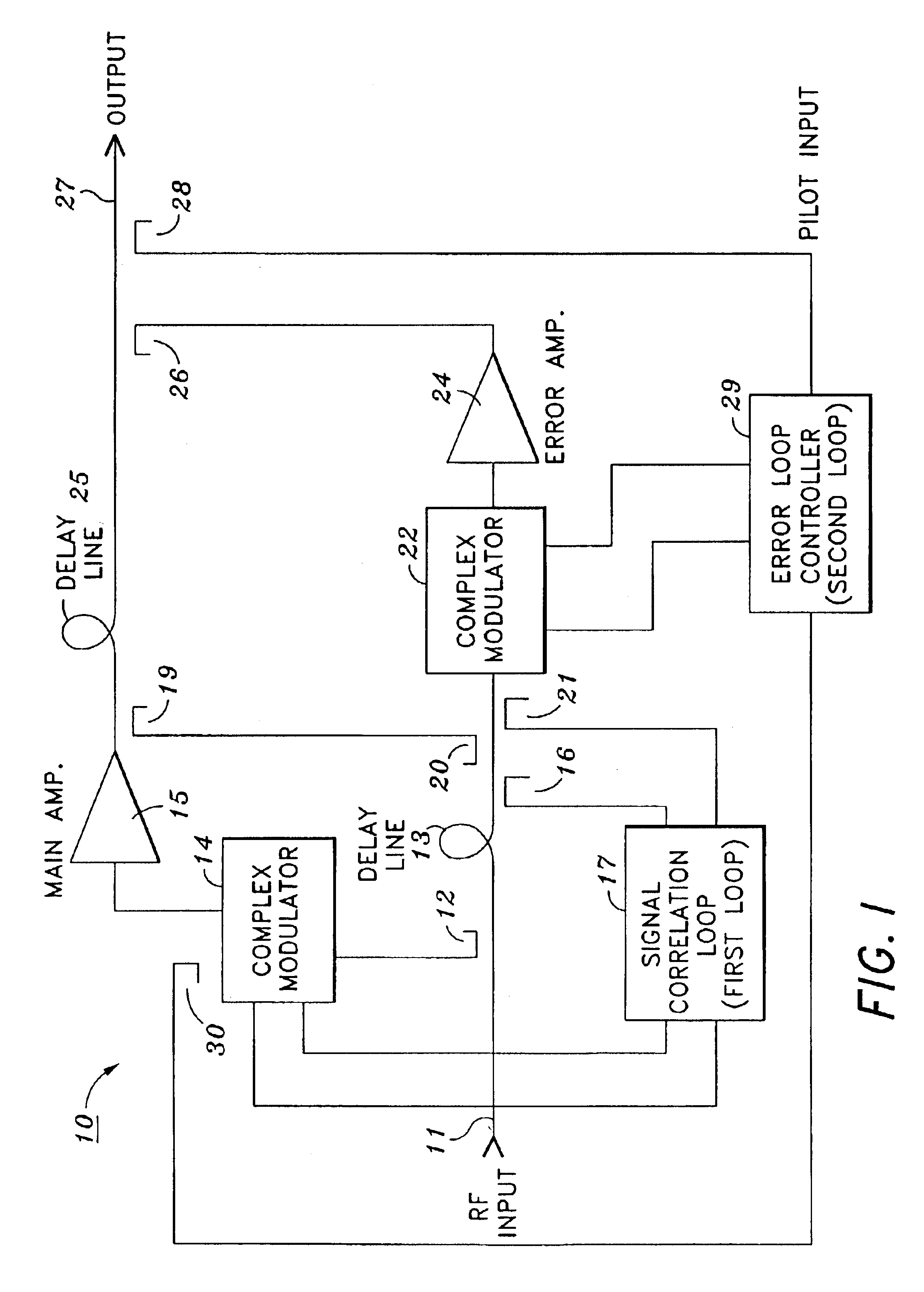
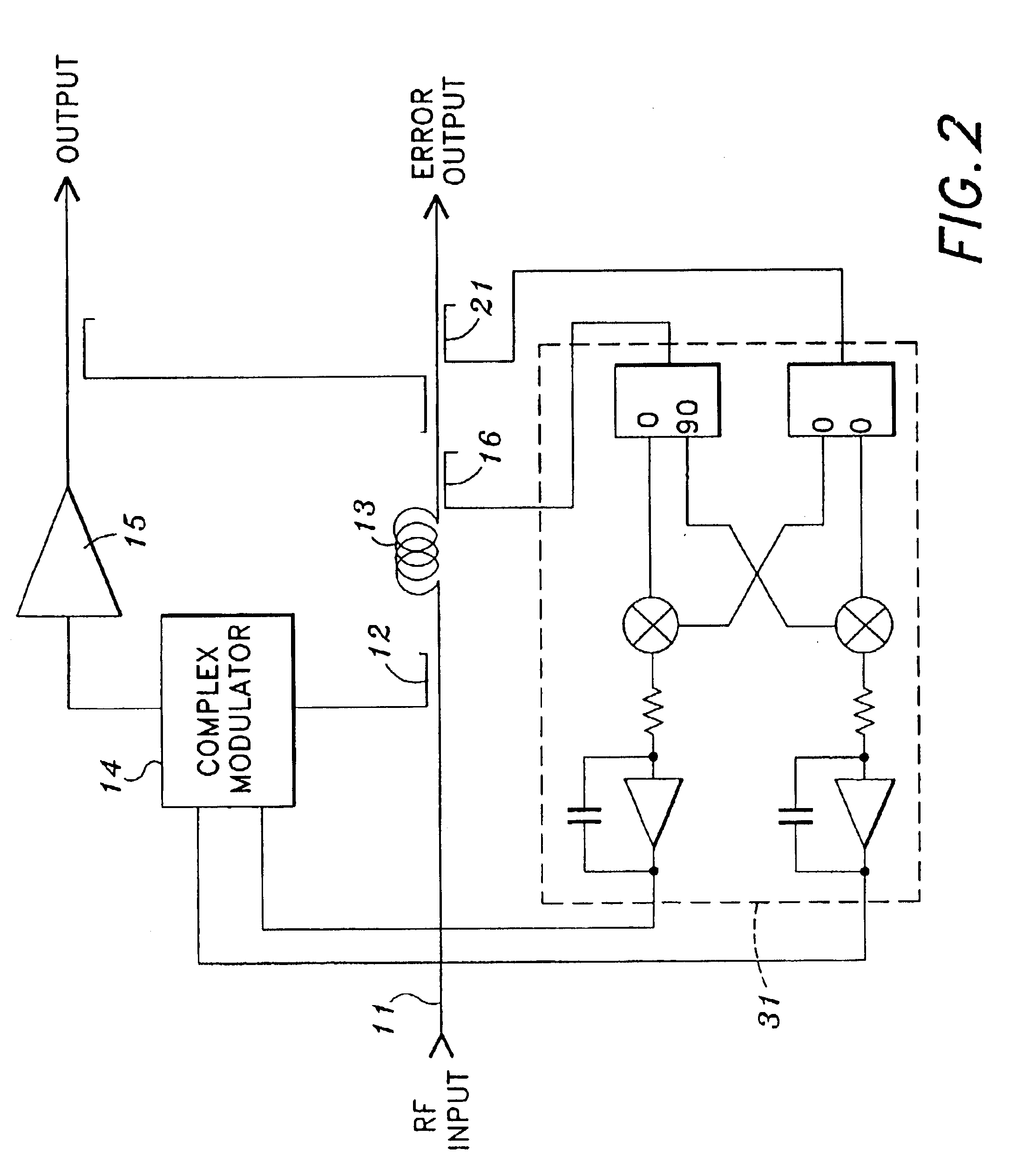
InactiveUS6897723B2Easy to controlImprove shielding effectAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLoop controlControl signal
An amplifier arrangement including a main amplifier to which feed-forward cancellation is applied, where the amplifier arrangement comprises an input for receiving signals to be amplified, an output for providing an amplified input signal, a pilot signal modulation circuit to generate a CW frequency shifted pilot signal, a mixer down for converting the pilot signal to an IF signal, and a sampling circuit for digitally sampling the IF signal. The amplifier arrangement includes a signal cancellation loop and a distortion cancellation loop each acting as an independent control function for minimizing pilot signal. The signal cancellation loop utilizes a Cartesian loop method for controlling the signal cancellation loop for sensing both phase and amplitude information simultaneously. The Cartesian loop uses a high frequency active mixer, which is a dual cross coupled differential pairs of devices capable of operating with input signals from near DC to 2.4 GHz, for control of the signal cancellation loop.
Owner:INTEL CORP
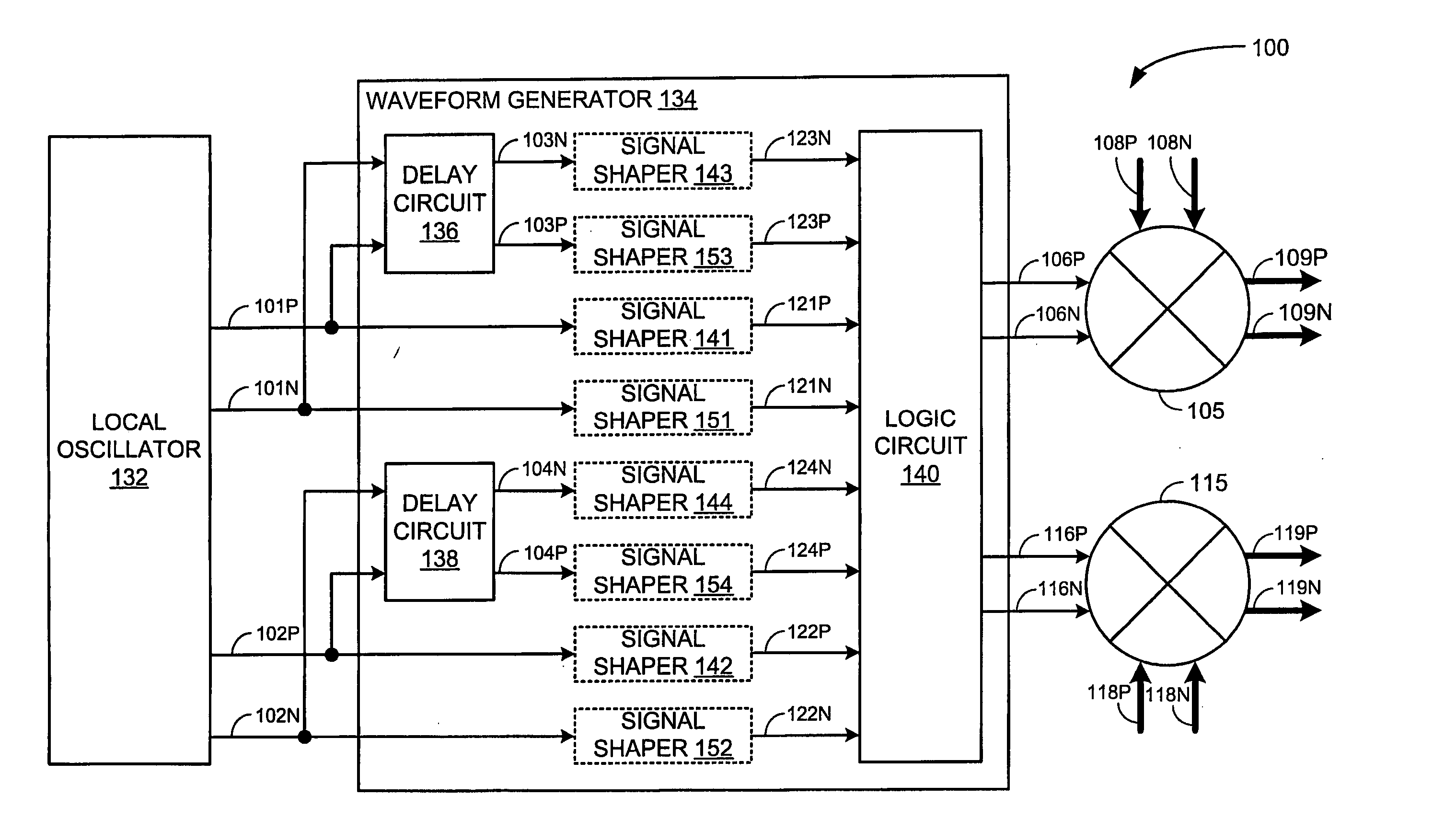
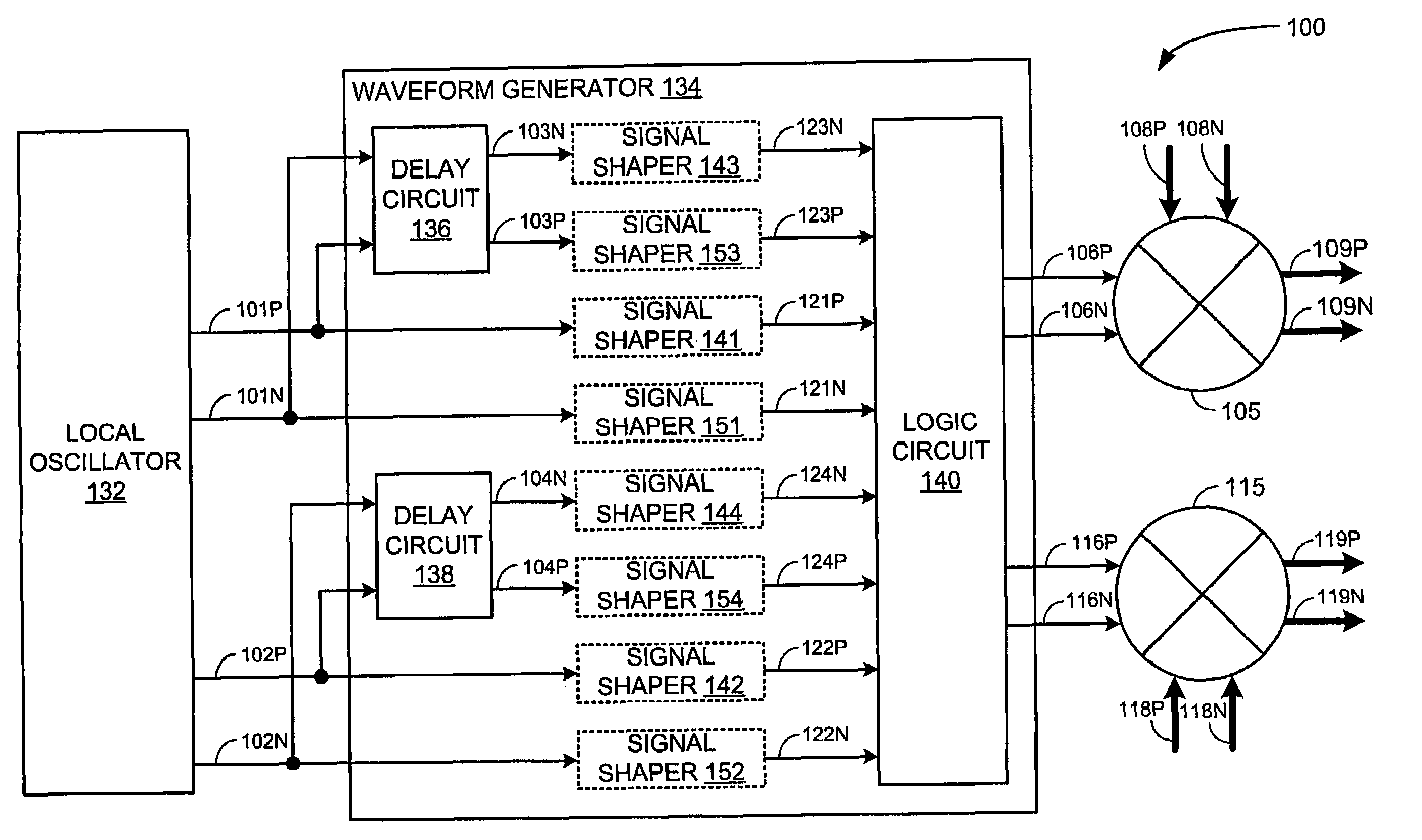
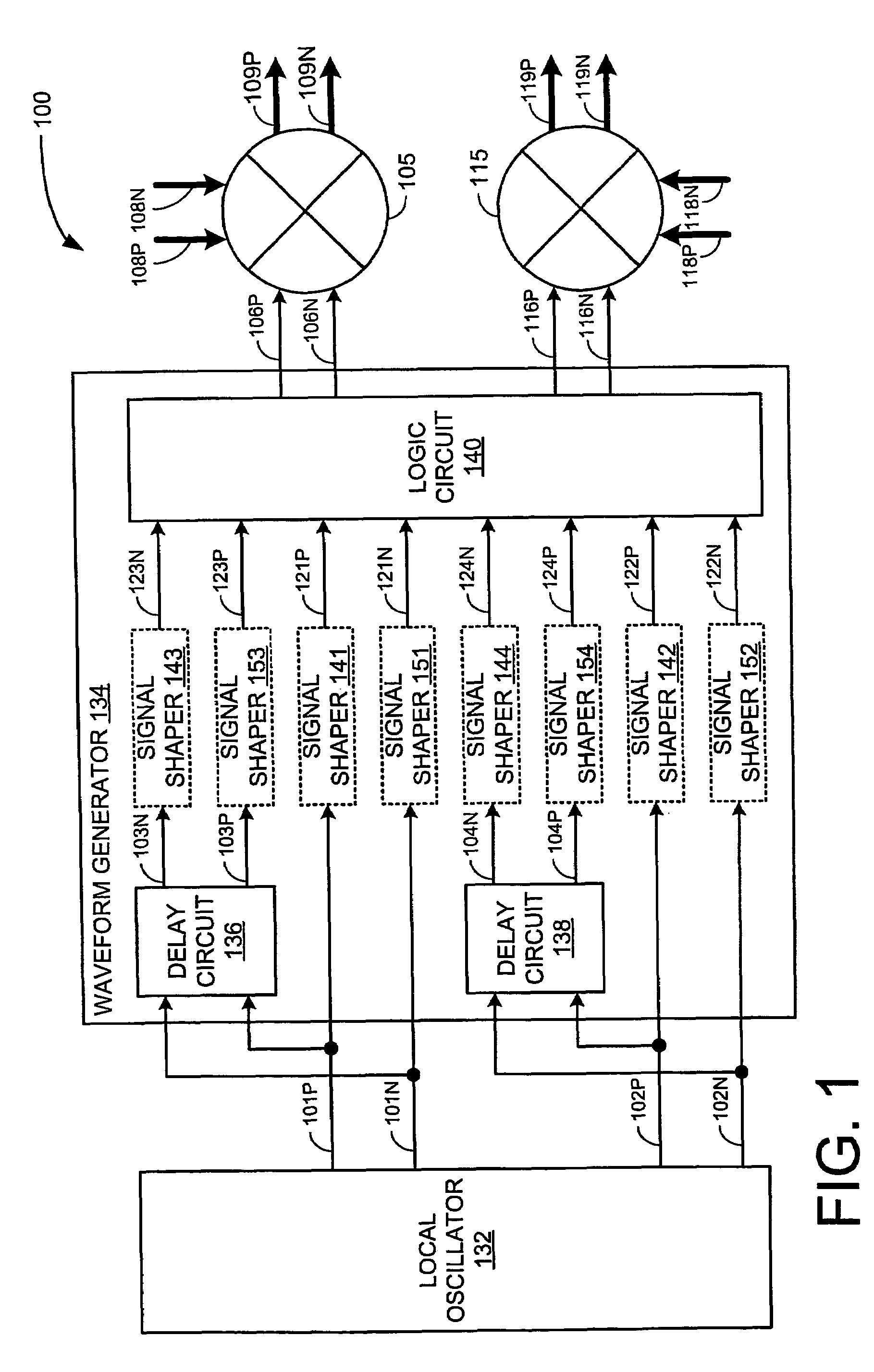
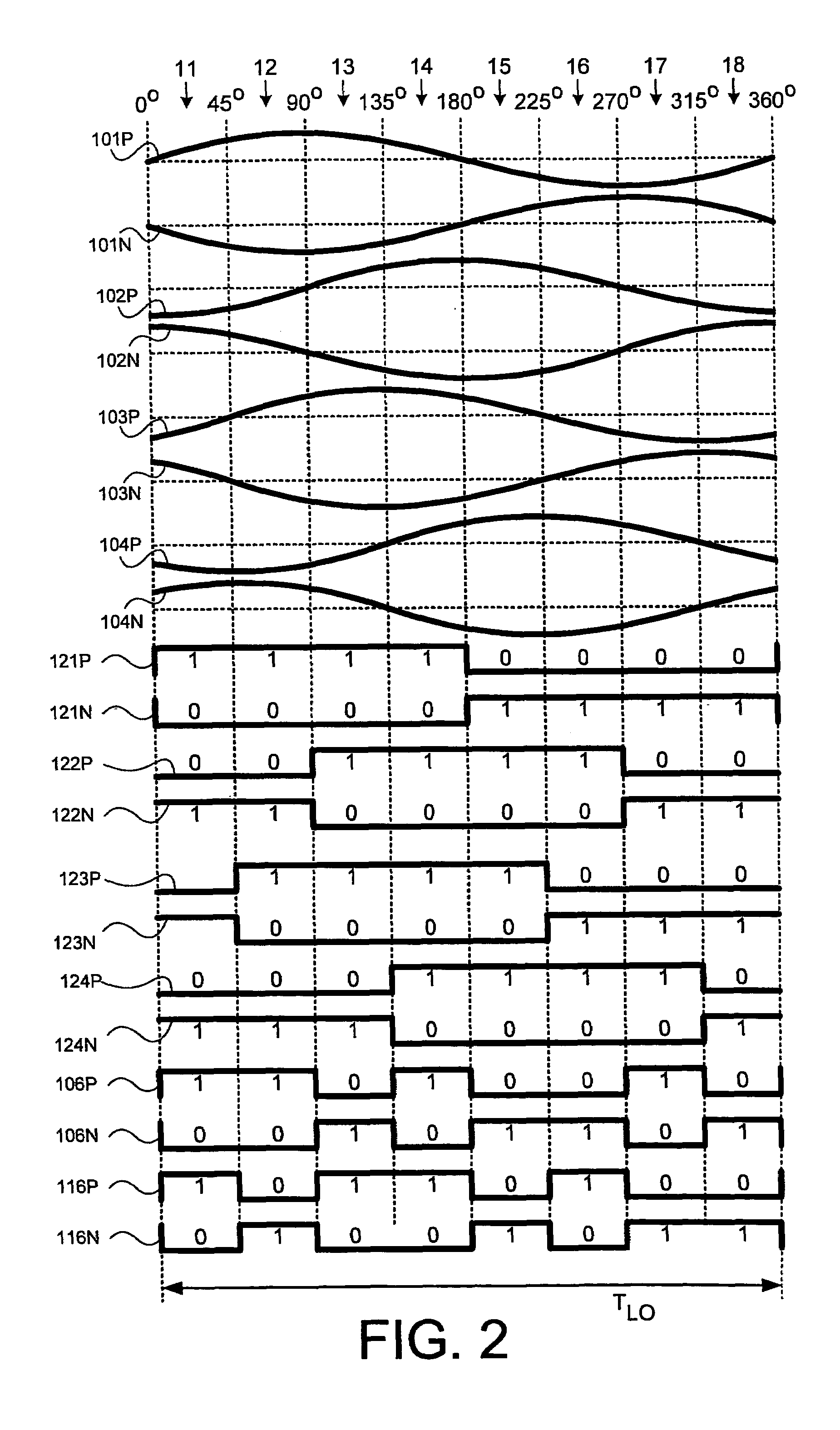
Integrated circuit and methods for third sub harmonic up conversion and down conversion of signals
ActiveUS20050215215A1Modulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmissionFrequency spectrumGilbert cell
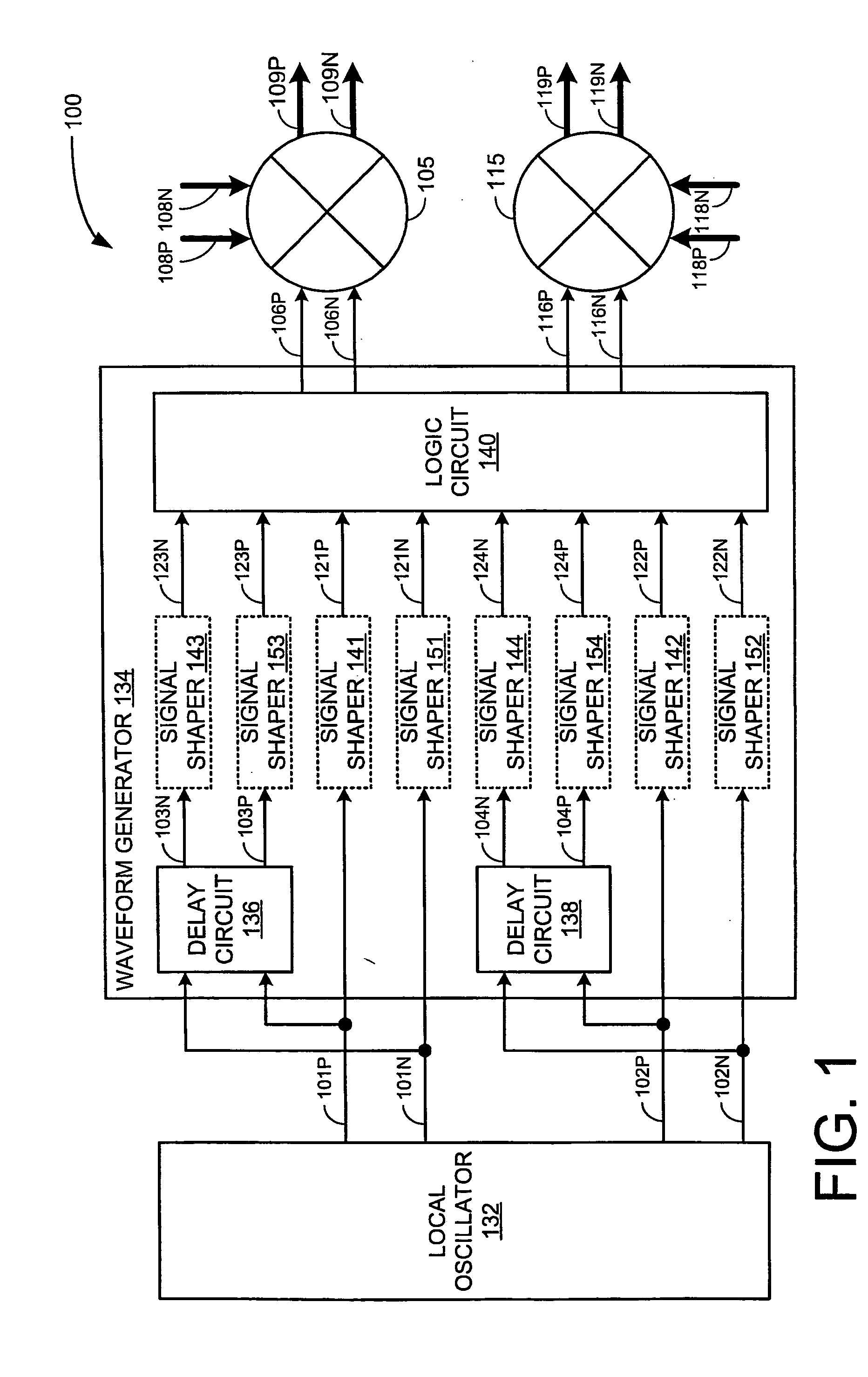
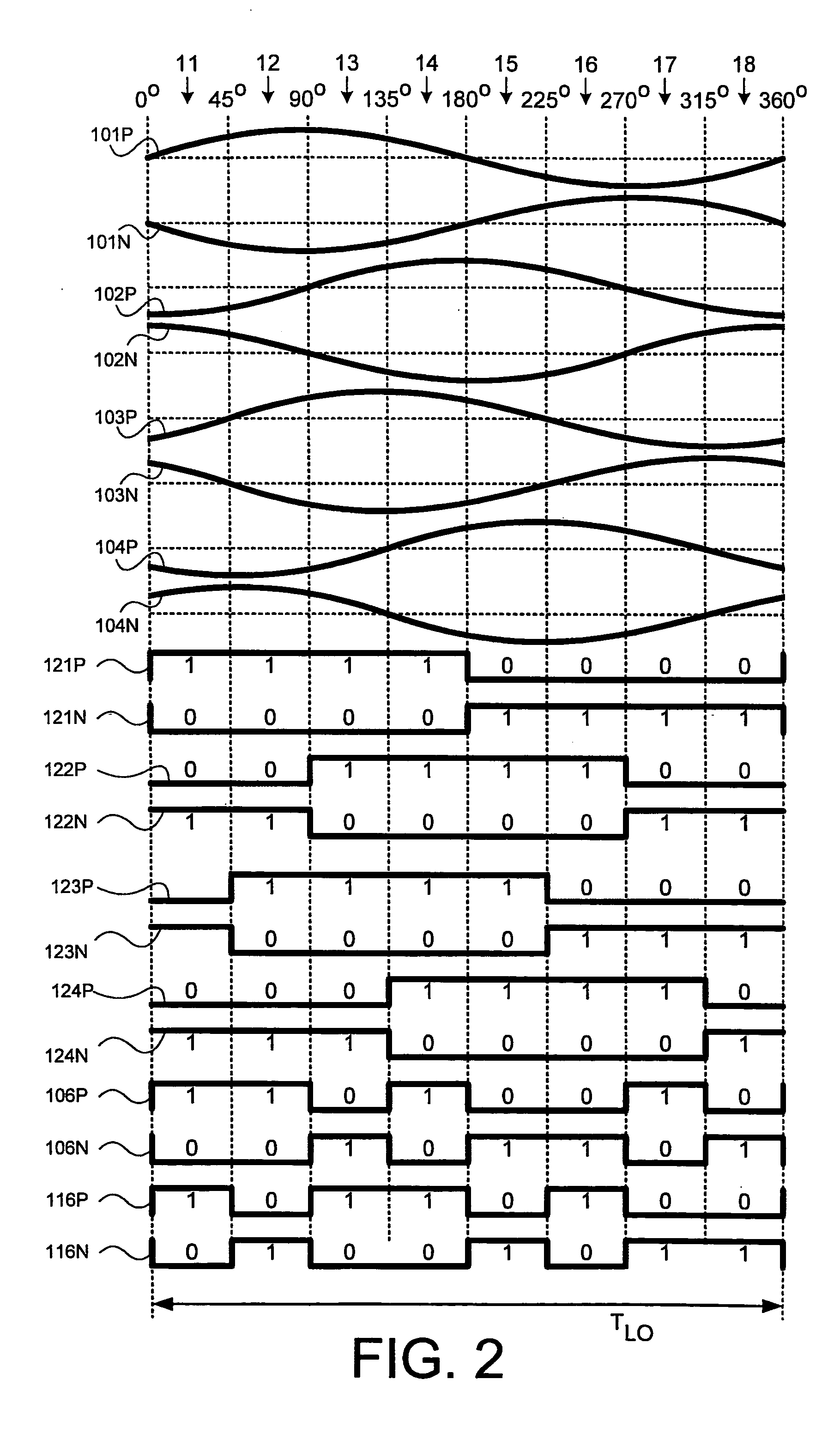
An integrated circuit may include a receiver and / or a transmitter that performs third order sub-harmonic conversion. The integrated circuit may include a Gilbert cell active mixer with three or more serially-connected transistors in each of the mixer's four branches. Alternatively, the integrated circuit may include a quad-ring passive resistive mixer with three or more serially-connected transistors in each of the mixer's four branches. Alternatively, the integrated circuit may include a logic circuit and a mixer. The logic circuit may apply logic operations to periodic logic signals having a local frequency and to delayed versions thereof to produce reference signals having a dominant spectral component at three times the local frequency. The mixer may mix input signals with the reference signals to produce output signals having a dominant spectral component at three times the local frequency less a center frequency of the input signals.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
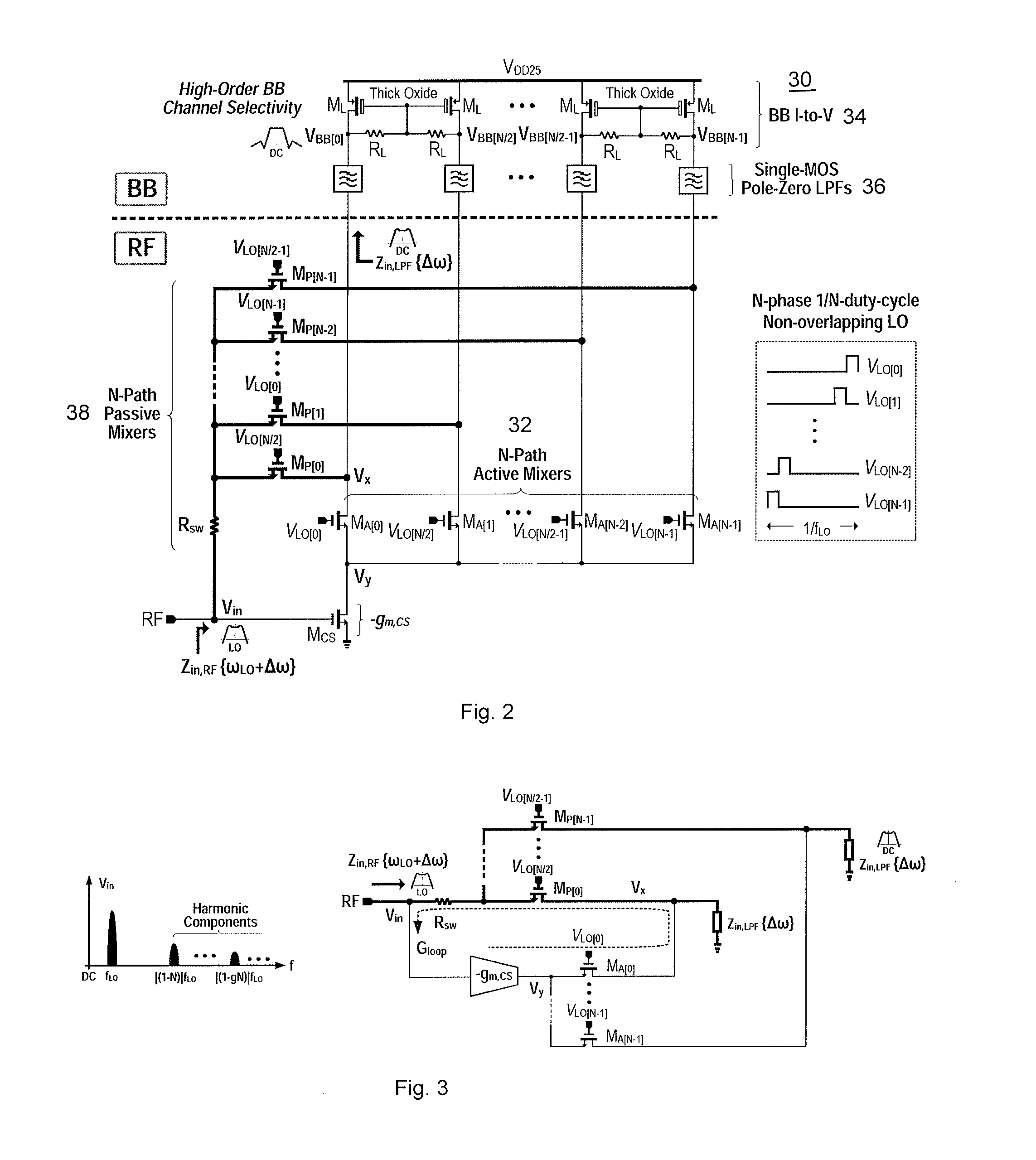
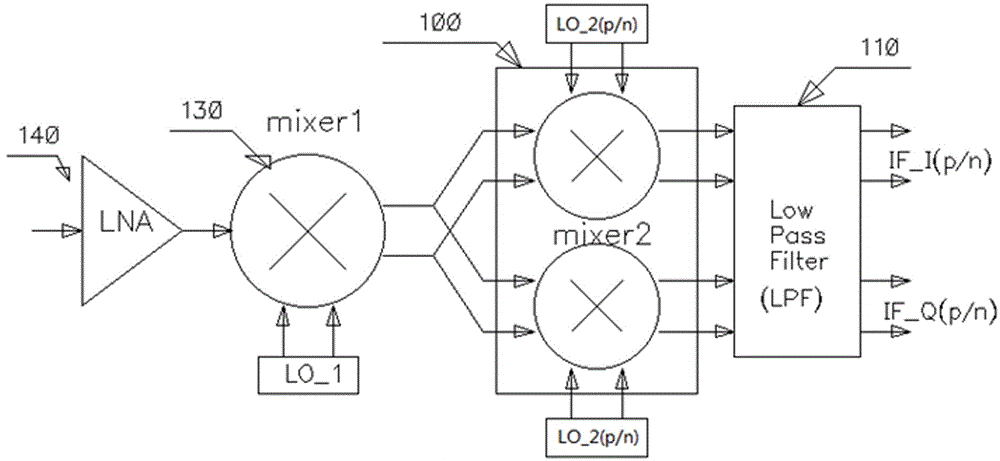
RF-to-BB-current-reuse wideband receiver with parallel N-path active/passive mixers
ActiveUS9356636B1Improve linearityImprove power efficiencyModulation transference balanced arrangementsAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesBandpass filteringLow voltage
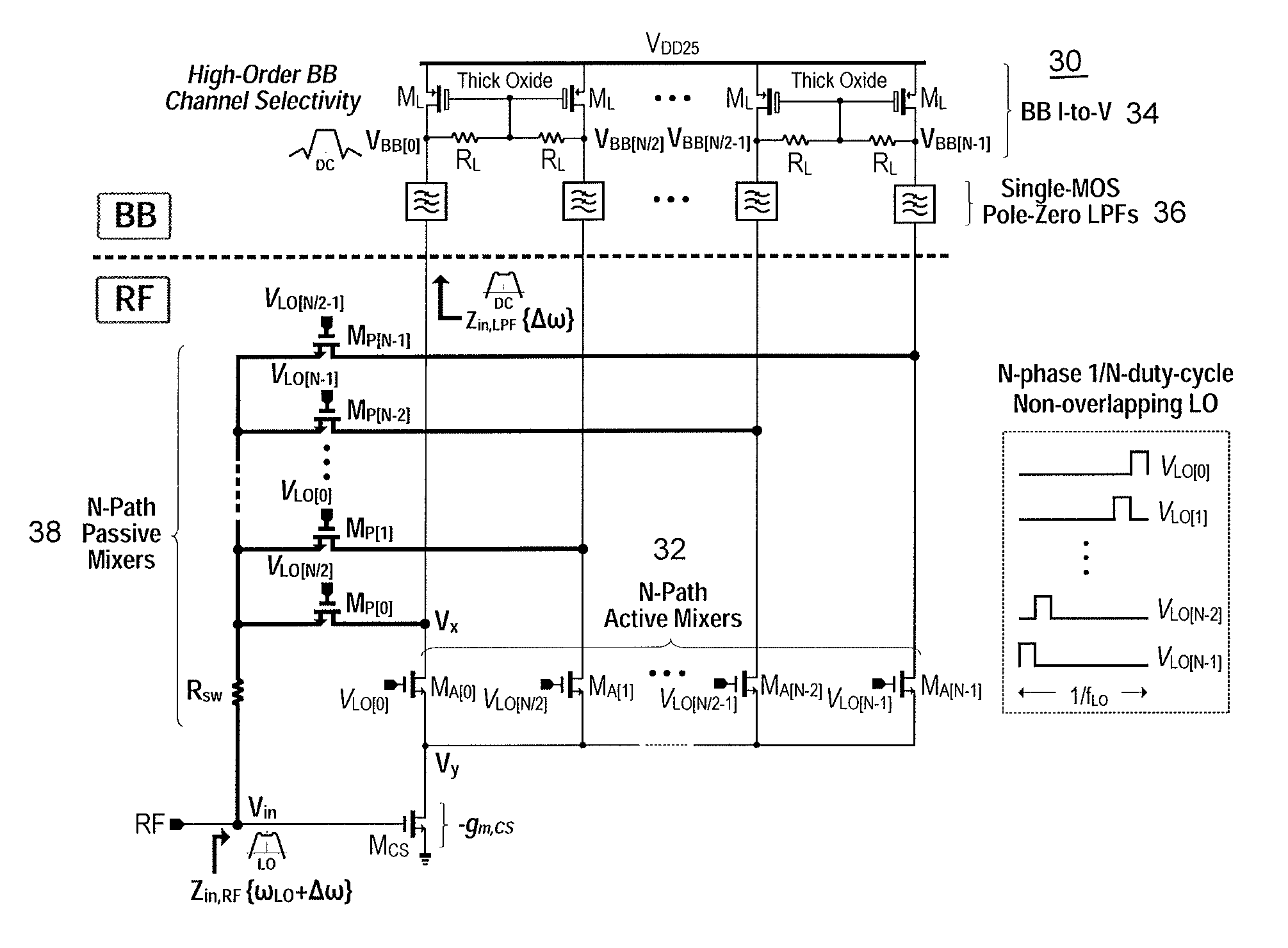
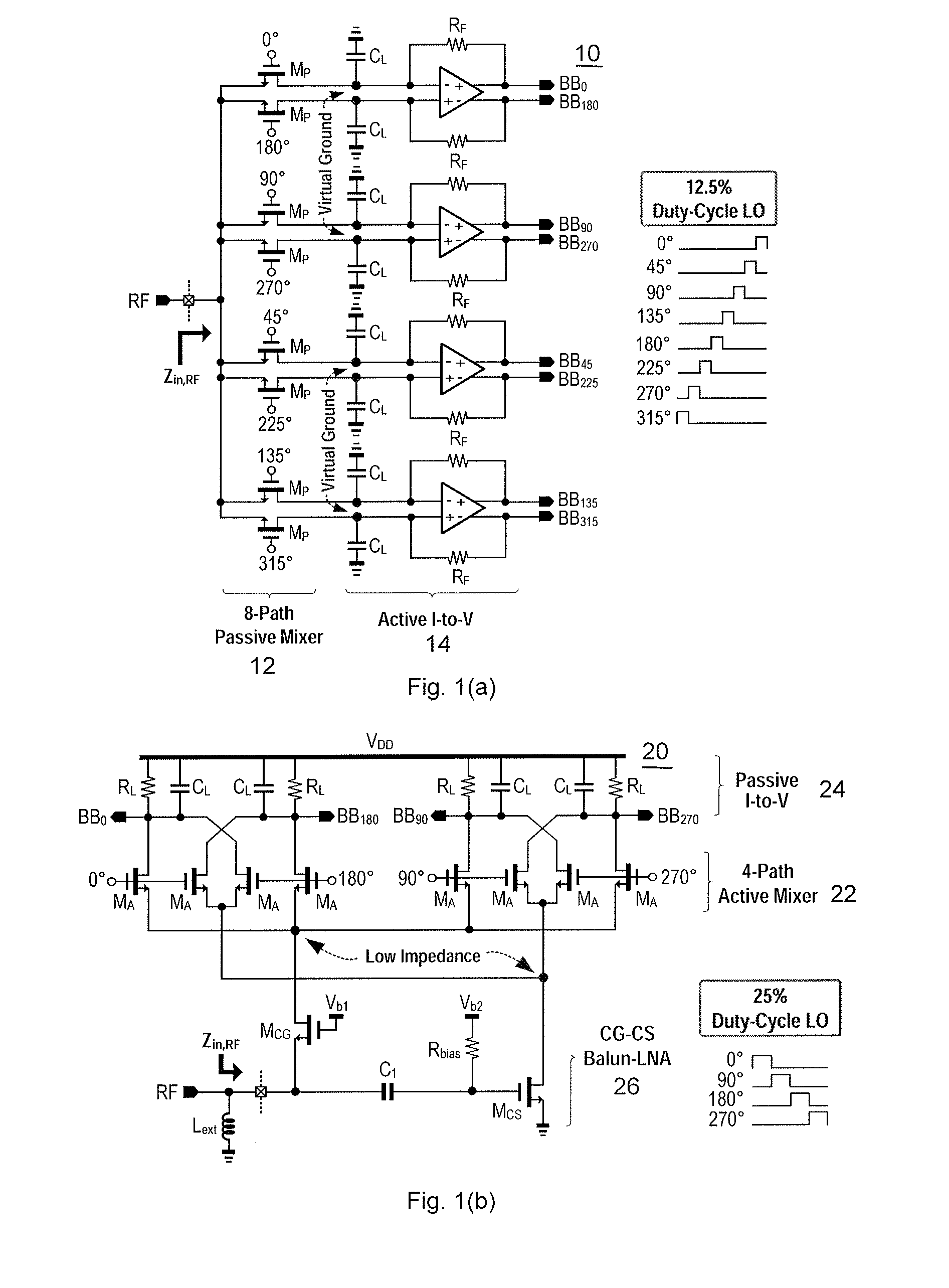
A single-ended-input current-reuse wideband receiver comprising (1) a stacked Radio Frequency to Baseband (RF-to-BB) front-end with an 8-path active mixer realizing RF amplification, harmonic-recombination (HR) down-conversion, and BB filtering in the current domain for better linearity and power efficiency; (2) a feedforward 8-path passive mixer enabling LO-defined input impedance matching without external components, while offering frequency-translated bandpass filtering and noise cancelling; (3) a single-MOS pole-zero lowpass filter (LPF) permitting both RF and BB filtering at low voltage headroom consumption, while easing the tradeoff between the in- / out-of-band linearity; and (4) a BB-only two-stage HR amplifier boosting the 3rd and 5th harmonic rejection ratios (HRR3,5) with low hardware intricacy.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MACAU
Integrated circuit and methods for third sub harmonic up conversion and down conversion of signals
ActiveUS7340233B2Modulation transference balanced arrangementsComputing operation arrangementsFrequency spectrumGilbert cell
An integrated circuit may include a receiver and / or a transmitter that performs third order sub-harmonic conversion. The integrated circuit may include a Gilbert cell active mixer with three or more serially-connected transistors in each of the mixer's four branches. Alternatively, the integrated circuit may include a quad-ring passive resistive mixer with three or more serially-connected transistors in each of the mixer's four branches. Alternatively, the integrated circuit may include a logic circuit and a mixer. The logic circuit may apply logic operations to periodic logic signals having a local frequency and to delayed versions thereof to produce reference signals having a dominant spectral component at three times the local frequency. The mixer may mix input signals with the reference signals to produce output signals having a dominant spectral component at three times the local frequency less a center frequency of the input signals.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
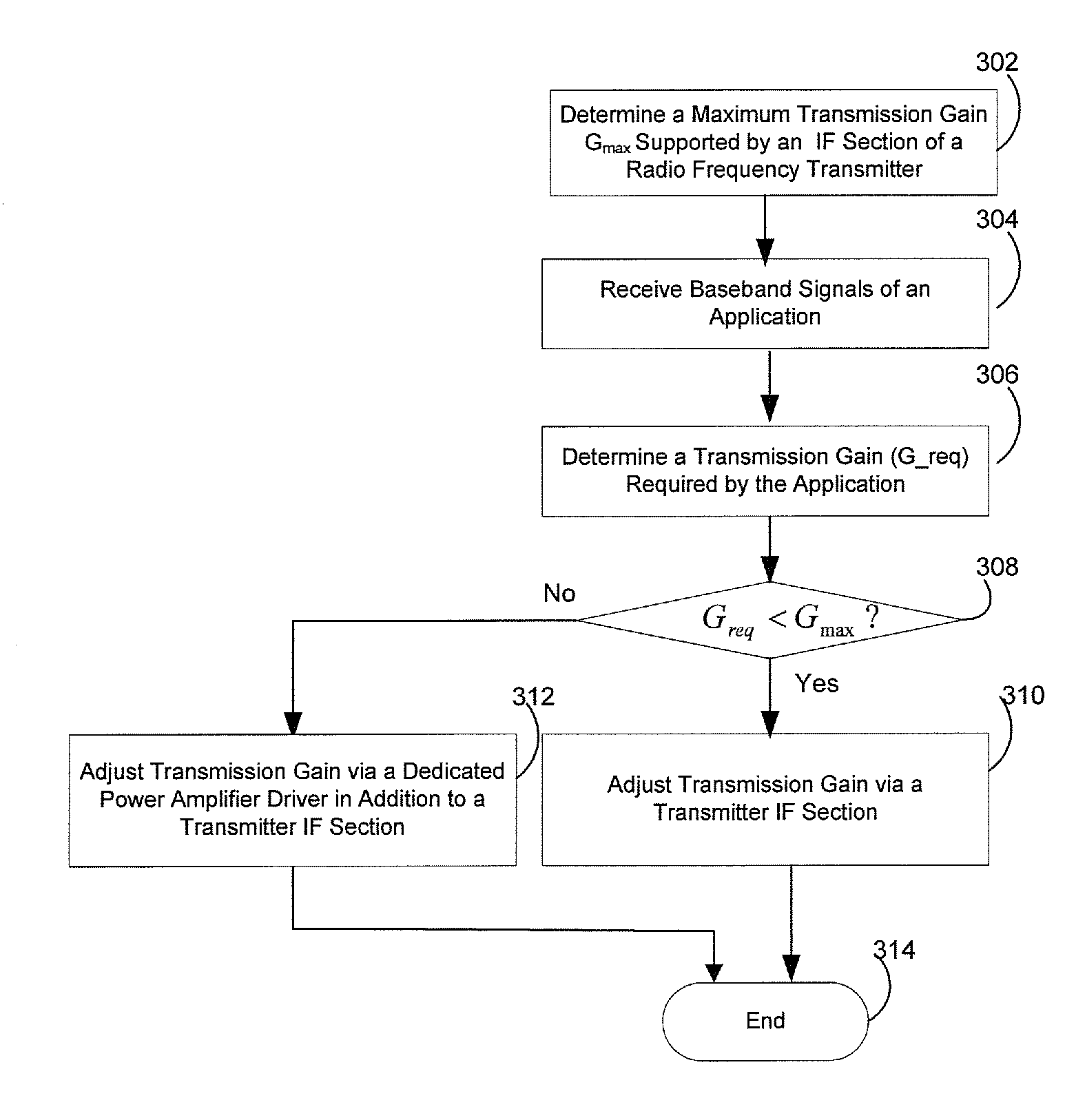
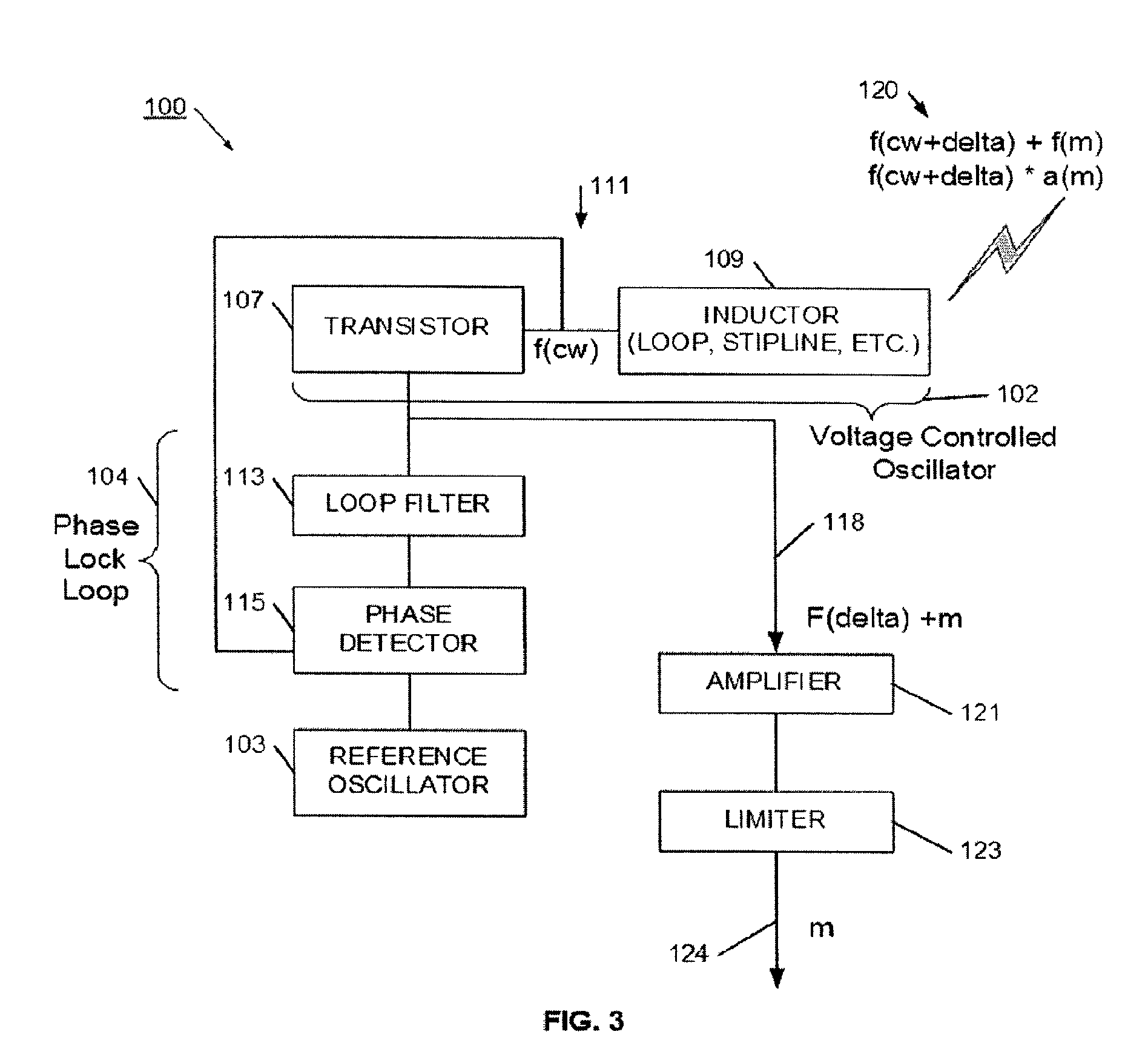
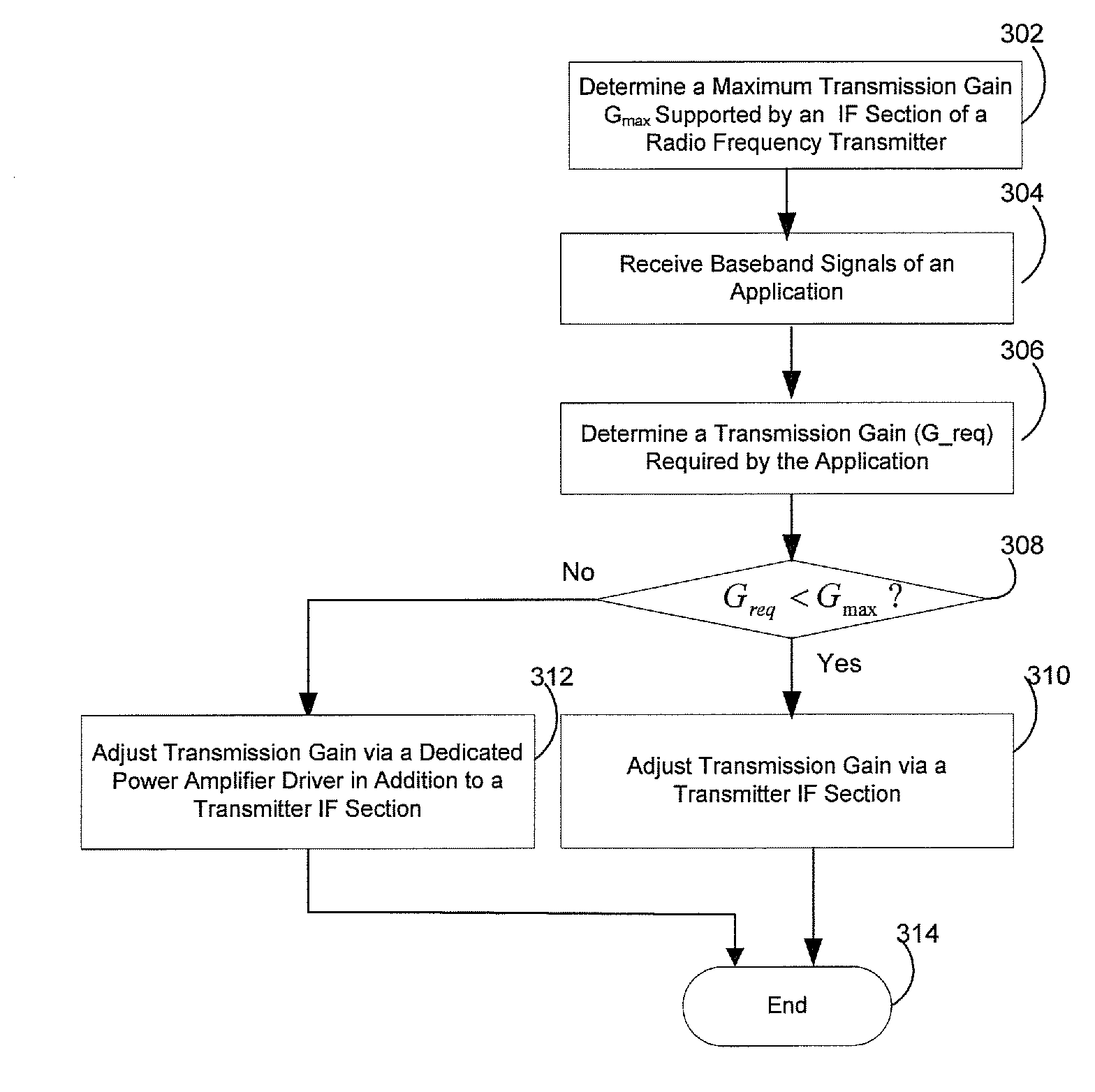
Method and system for a dynamic transmission gain control using a dedicated power amplifier driver in a radio frequency transmitter
A transmitter RF front-end integrated on a single substrate is enabled to determine whether associated IF amplification stage provides a required transmission gain for transmitting an output signal of an application. A dedicated power amplifier driver within the transmitter RF front-end is configured to provide additional gain, when needed based on the determination, to meet the required transmission gain for transmitting the output signal. The associated IF amplification stage comprises an upconversion mixer and a lowpass filter (LPF). The upconversion mixer may be implemented as an active mixer or a passive mixer. The upconversion mixer and the dedicated power amplifier driver are enabled to operate in 2.44 gigahertz. A maximum gain provided by the associated intermediate frequency (IF) amplification stage for transmitting the output signal is determined to decide the additional gain provided by the dedicated power amplifier driver by comparing with the required transmission gain.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
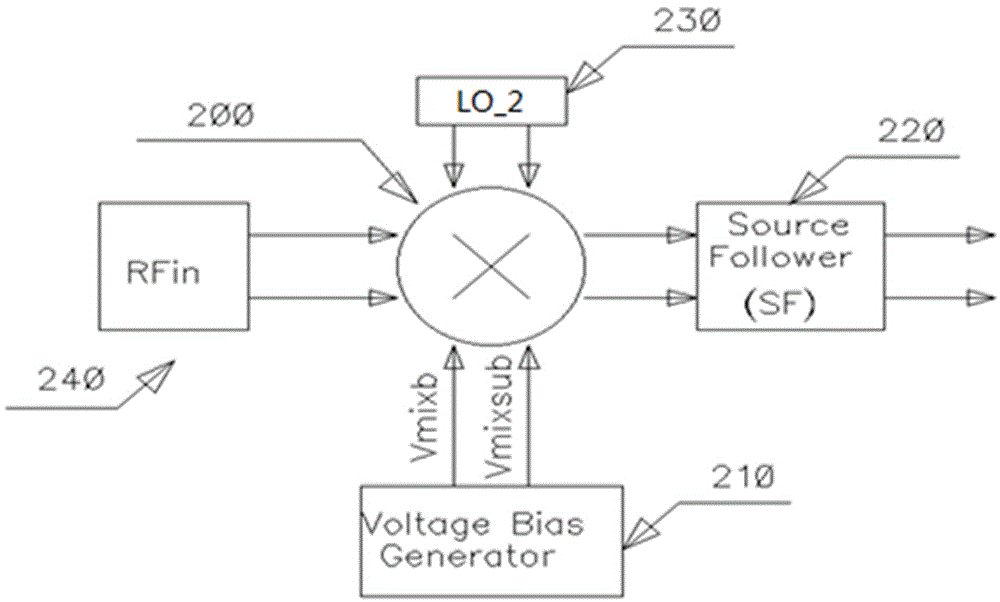
Enhanced broadband operation of an active mixer
ActiveCN110063027AModulation transferenceOscillations generatorsFrequency mixerIntermediate frequency
Methods, systems, and devices for wireless communication are described for enhanced broadband operation of an active mixer. In an example, the apparatus may include an active mixer that converts between radio frequency (RF) signals and intermediate frequency (IF) signals based at least in part on an alternating current (AC) local oscillator (LO) signal, wherein a direct current (DC) current generated within the active mixer is dependent in part on a bias voltage and the AC LO signal. The apparatus may include a mixer biasing circuit that generates the bias voltage for the active mixer, a magnitude of the bias voltage having an inverse relationship to an amplitude of the AC LO signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Low-power low-cost and high-linearity voltage mode passive mixer
ActiveCN106603014AReduce power consumptionLow costModulation transference balanced arrangementsHigh level techniquesLocal oscillator signalIntermediate frequency
The invention relates to a low-power low-cost and high-linearity voltage mode passive mixer which is arranged on the signal communication channel of a radio frequency receiver to serve as a second mixer of the radio frequency receiver. Through circuits, the mixer is arranged between a first mixer and a low-pass filter. The mixer of the invention consists of two structure-identical frequency mixing circuits. The radio frequency signal outputted from the first mixer is pre-mixed with the local oscillator signals in the frequency mixing circuits respectively to output an intermediate frequency signal which is subjected to filtering of the low-pass filter. The local oscillator signal in each frequency mixing circuit adopts an I / Q (in-phase / quadrature) square wave signal whose duty ratio stands at 25%. With the two frequency mixing circuits, I / Q frequency conversion can be realized. The mixer of the invention can solve the shortcomings represented by the second mixer in the form of a voltage type active mixer and a current type passive mixer in a second frequency conversion structured receiver in the prior art. At the same time, the mixer of the invention also features as a low-power, low-cost, high linearity, and wideband radio frequency receiver.
Owner:HANGZHOU CANAANTEK COMM TECH +1
S-band high-linearity, low-noise and low-gain down-conversion active mixer
InactiveCN104518736AAdjust gainAdjust Linearity PerformanceModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLow noiseFrequency mixer
The invention discloses an S-band high-linearity, low-noise and low-gain down-conversion active mixer. The structure of the mixer is based on a Gilbert-type unit. The invention further discloses a local oscillator drive circuit so as to provide a good local oscillator input signal and improve overall circuit performance. The mixer has the advantages of low power consumption, high linearity and low noise, and linearity and noise performance of the mixer are improved under the condition of low gain.
Owner:CHENGDU AIJIELONG INFORMATION TECH
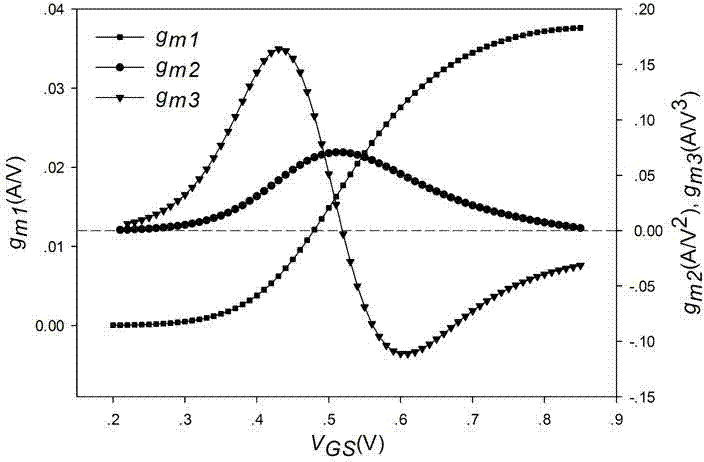
Method capable of improving low-frequency flicker noise and high-gain characteristic and active mixer
InactiveCN103187928AModulation transference balanced arrangementsIntermediate frequencyFrequency mixer
The invention discloses an active mixer with low-frequency flicker noise and a high-gain characteristic. In the prior art, a traditional Gilbert active mixer has the problems that flicker noise is loud, and compromise of noise and gain exists, so that the traditional Gilbert active mixer cannot meet the requirement of a present receiver to a high-performance mixer, especially to zero intermediate frequency receivers and low intermediate frequency receivers. Aiming at the defects, the active mixer with low-frequency flicker noise and the high-gain characteristic reduces the mixer flicker noise by reducing direct current which flows through a traditional Gilbert active mixer switch pipe, and by the adoption of input transconductance generated by the current, the contradictory problem that the flicker noise and the gain exist in traditional active mixer performance optimization is solved, so that the high-performance active mixer which is low in flicker noise and high in gain is achieved.
Owner:NATIONZ TECH INC
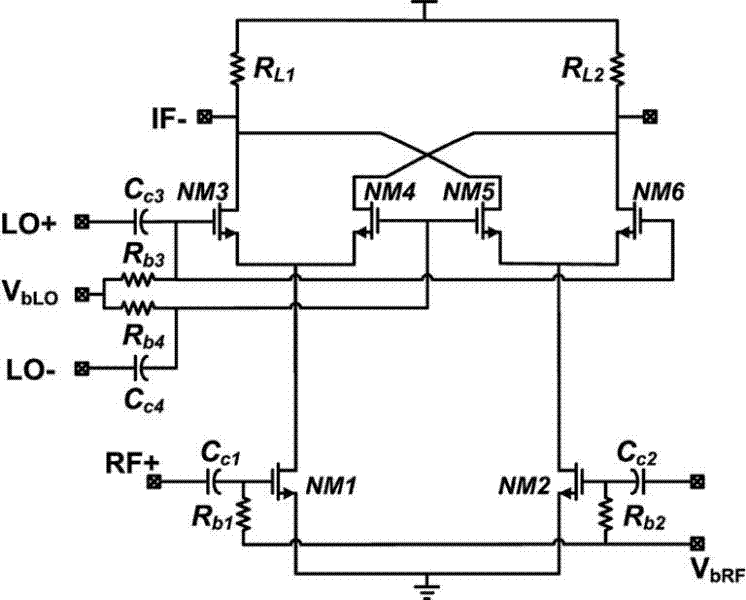
Switching circuit, integrated circuit, active mixer circuit and method thereof
ActiveCN105720923AElectronic switchingMulti-frequency-changing modulation transferencePhase shiftedFrequency mixer
There is provided a switching circuit for an active mixer. The switching circuit comprises a first pair of parallel switching devices and a second pair of parallel switching devices. The first and second pairs of parallel switching devices are arranged in a stacked configuration between an input node at which an input current comprising a first input frequency signal is received and a pair of differential output nodes. The first pair of switching devices are controlled by a second input frequency signal. The second pair of switching devices are controlled by a phase-shifted counterpart of the second input frequency signal. A common node between the first switching devices of the first and second pairs of switching devices is electrically coupled to a common node between the second switching devices of the first and second pairs of switching devices.
Owner:MEDIATEK SINGAPORE PTE LTD SINGAPORE
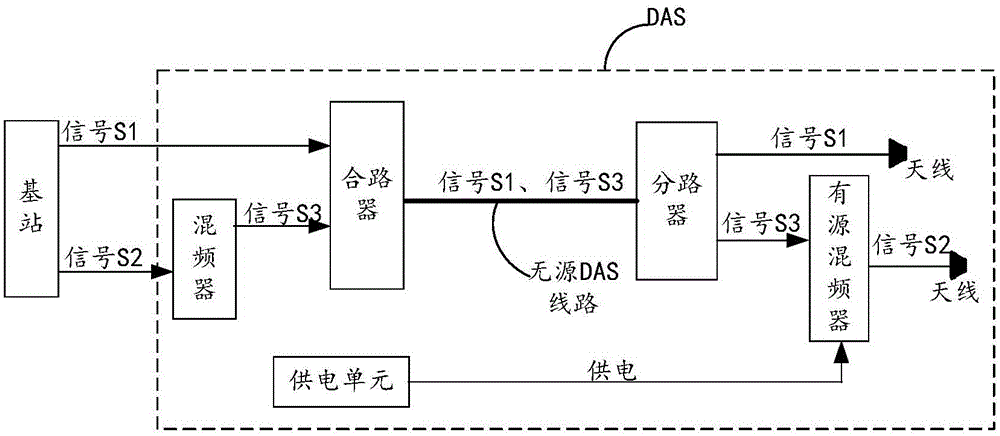
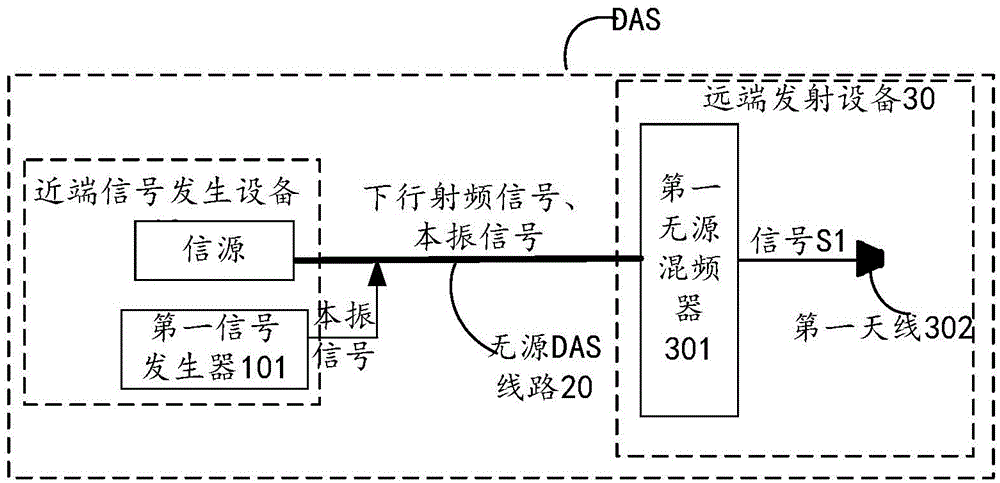
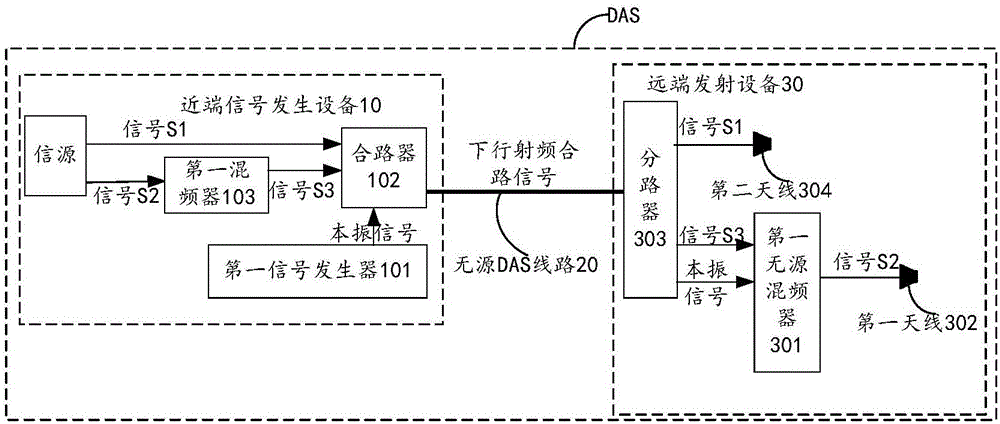
Distributed antenna system and signal transmitting method
The invention discloses a distributed antenna system DAS and a signal transmitting method, and relates to the communication technology field. Problems such as large construction difficulty and high costs caused by realization of power supply of an active mixer on the far end of the DAS are solved. The DAS comprises a source, a first signal generator, a first passive mixer, and a first antenna. The first signal generator is used to generate a first local oscillation signal, and is used to transmit the first local oscillation signal to the first passive mixer by a passive DAS line. The first passive mixer is used to receive the first local oscillation signal and a downlink radio frequency signal having a second radio frequency band. The first passive mixer is used for the mixing processing of the received downlink radio frequency signal having the second radio frequency band by using the first local oscillation signal to form a first downlink radio frequency signal having a first radio frequency band, and is used to transmit the first downlink radio frequency signal having the first radio frequency band to the first antenna. The first antenna is used to transmit the received first downlink radio frequency signal having the first radio frequency band.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Active mixer and active mixing method
ActiveUS9350297B2Modulation transference balanced arrangementsComputing operation arrangementsLoad circuitElectricity
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
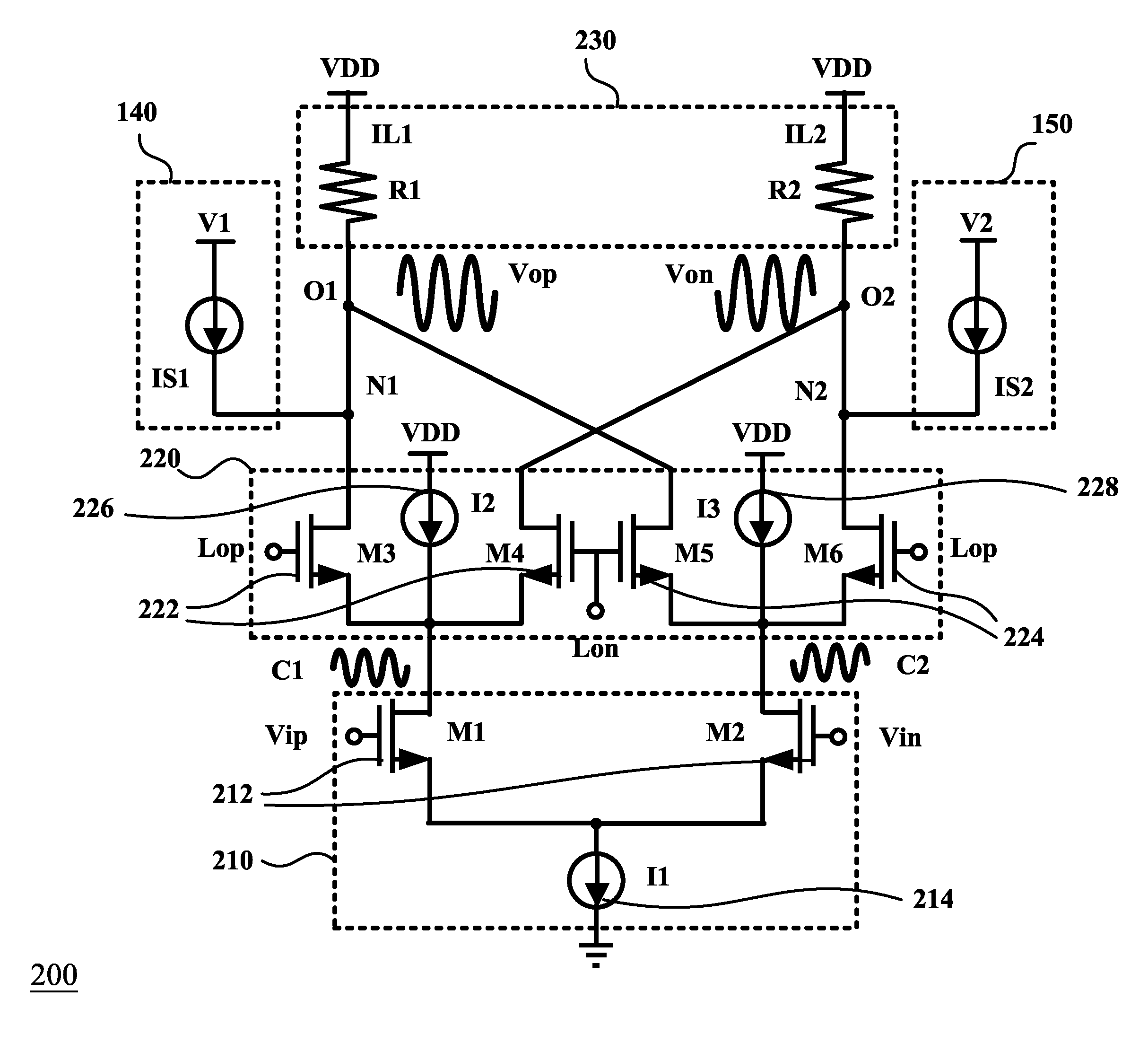
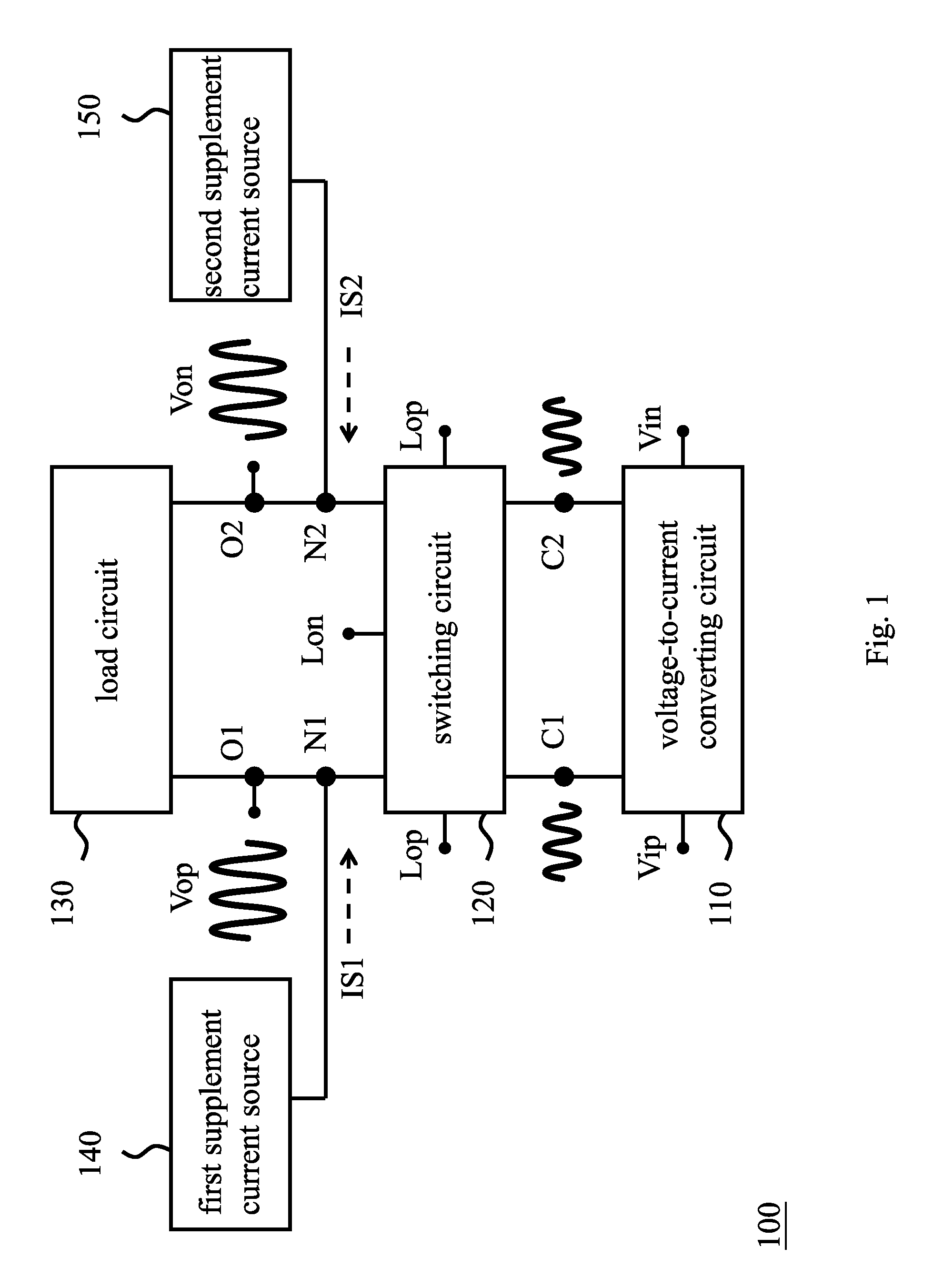
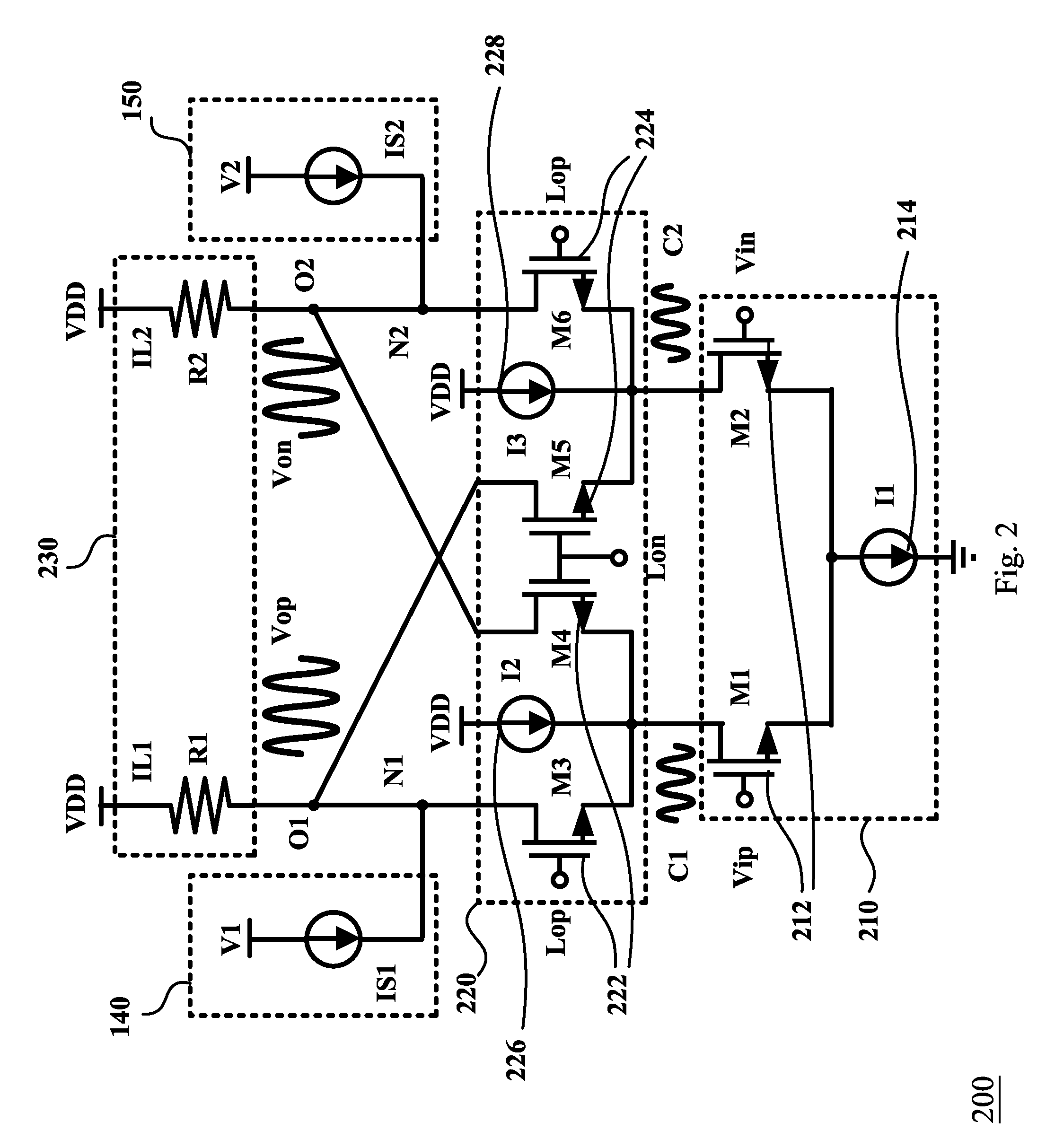
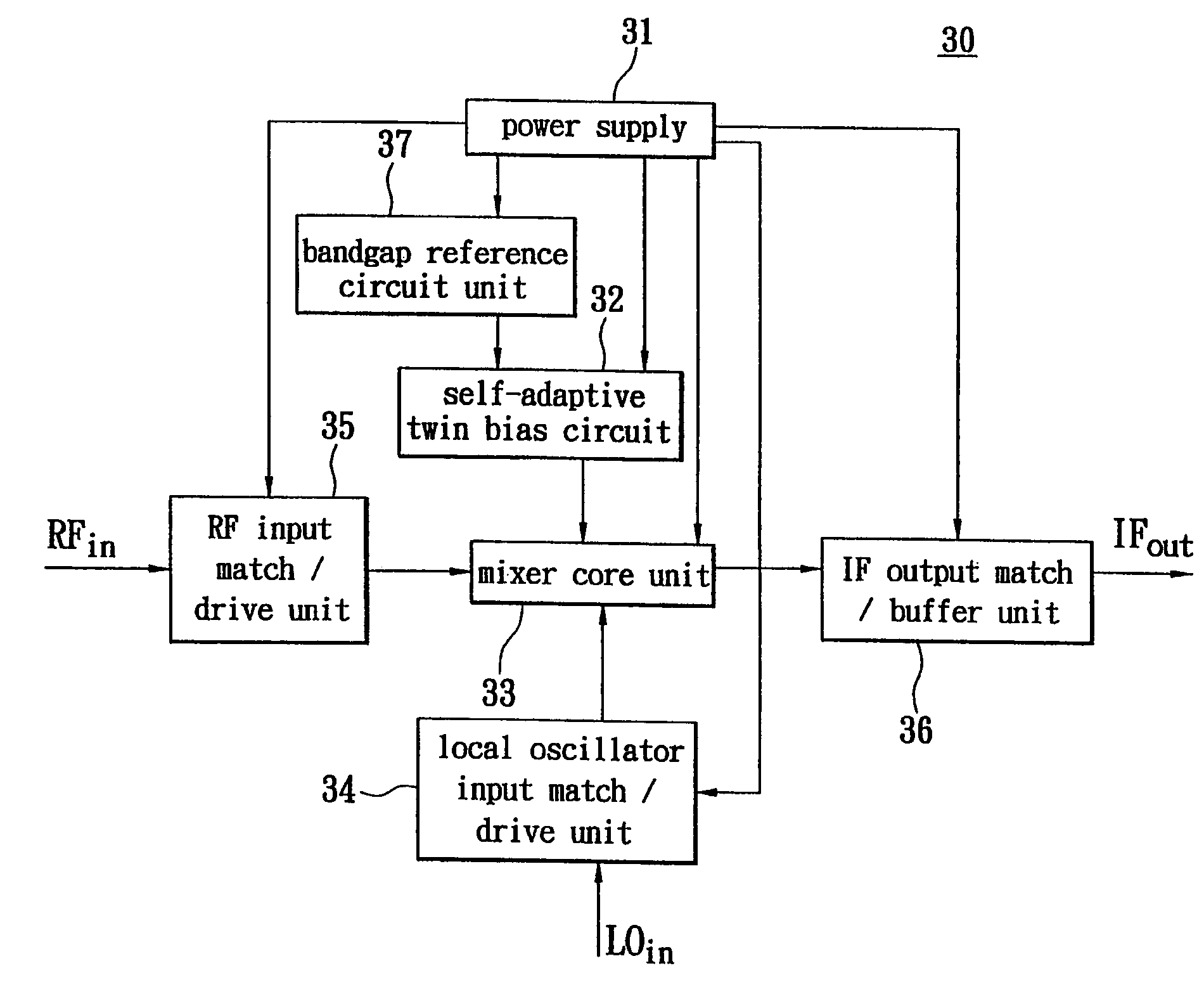
Active mixer with self-adaptive bias feedback
ActiveUS7437131B2Improve linearityGood temperature responseResonant long antennasModulation transferenceTemperature responseMicrowave
An active mixer with self-adaptive bias feedback is described and resolves a poor linearity, inconvenient design of a bias circuit, and other defects of a conventional mixer. The dual self-feedback bias structure according to this invention is used. The active mixer with self-adaptive bias feedback has a power supply, an RF input match / drive unit, a local oscillator input match / drive unit, a mixer core unit, a self-adaptive twin bias circuit and an IF output match / buffer unit. This invention improves the linearity of a conventional mixer and does not affect other characteristics. There are fewer components in this invention; an area of the mixer is thus smaller. Further, this invention may improve temperature response, increase yield factor, and lower unit cost. The dual self-feedback bias structure is designed for further application to other semiconductor manufacturing processes, components, and microwave products.
Owner:RICHWAVE TECH CORP
Simplified radio frequency receiver
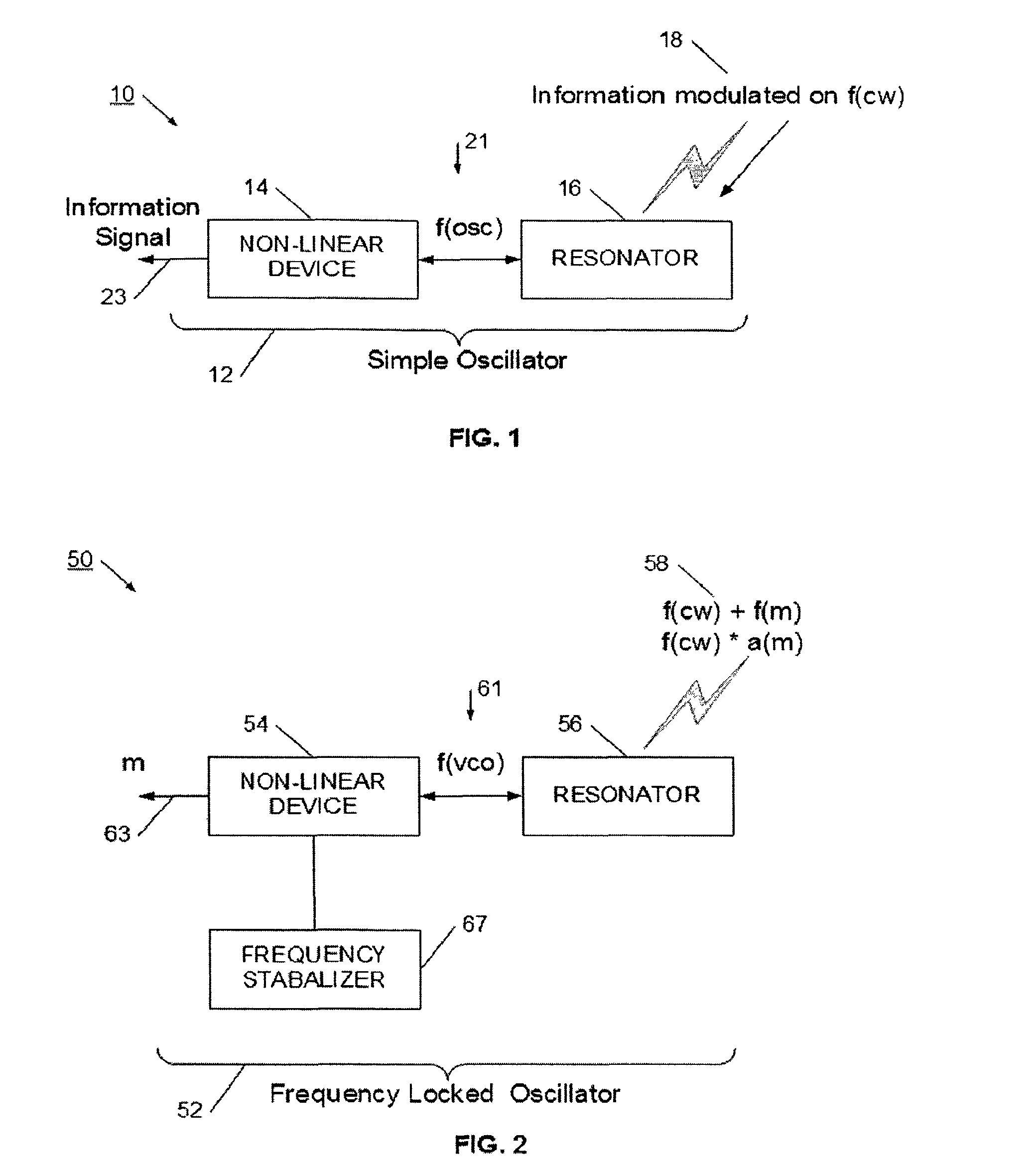
InactiveUS20120184234A1Efficient constructionLess powerPower managementRadio transmissionTuned radio frequency receiverCarrier frequency offset
An oscillator is provided that is arranged to function as a simplified receiver. The oscillator has a resonator portion and a non-linear portion, which cooperate to generate an oscillating signal. The resonator portion is positioned to receive a modulated signal. In one configuration, the oscillator operates at a frequency offset from the frequency of the carrier for the modulated signal. In this simple arrangement, the oscillator functions as an active mixer, and generates a product output signal. The output signal is extracted from a high impedance point of the oscillator's non-linear device. The output signal is a demodulated or mixed signal, and may be further processed to detect a data signal.
Owner:AVAAK
Method and system for a dynamic transmission gain control using a dedicated power amplifier driver in a radio frequency transmitter
A transmitter RF front-end integrated on a single substrate is enabled to determine whether associated IF amplification stage provides a required transmission gain for transmitting an output signal of an application. A dedicated power amplifier driver within the transmitter RF front-end is configured to provide additional gain, when needed based on the determination, to meet the required transmission gain for transmitting the output signal. The associated IF amplification stage comprises an upconversion mixer and a lowpass filter (LPF). The upconversion mixer may be implemented as an active mixer or a passive mixer. The upconversion mixer and the dedicated power amplifier driver are enabled to operate in 2.44 gigahertz. A maximum gain provided by the associated intermediate frequency (IF) amplification stage for transmitting the output signal is determined to decide the additional gain provided by the dedicated power amplifier driver by comparing with the required transmission gain.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Switching circuit
ActiveUS9634609B2Reduce impactModulation transference balanced arrangementsElectronic switchingPhase shiftedActive mixer
There is provided a switching circuit for an active mixer. The switching circuit comprises a first pair of parallel switching devices and a second pair of parallel switching devices. The first and second pairs of parallel switching devices are arranged in a stacked configuration between an input node at which an input current comprising a first input frequency signal is received and a pair of differential output nodes. The first pair of switching devices are controlled by a second input frequency signal. The second pair of switching devices are controlled by a phase-shifted counterpart of the second input frequency signal. A common node between the first switching devices of the first and second pairs of switching devices is electrically coupled to a common node between the second switching devices of the first and second pairs of switching devices.
Owner:MEDIATEK SINGAPORE PTE LTD SINGAPORE
Low voltage low power consumption active mixer
ActiveCN105337579ADoes not consume quiescent voltageWeakening rangeModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesCapacitanceLocal oscillator signal
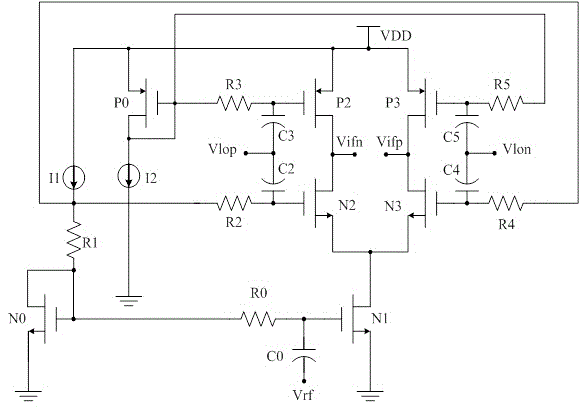
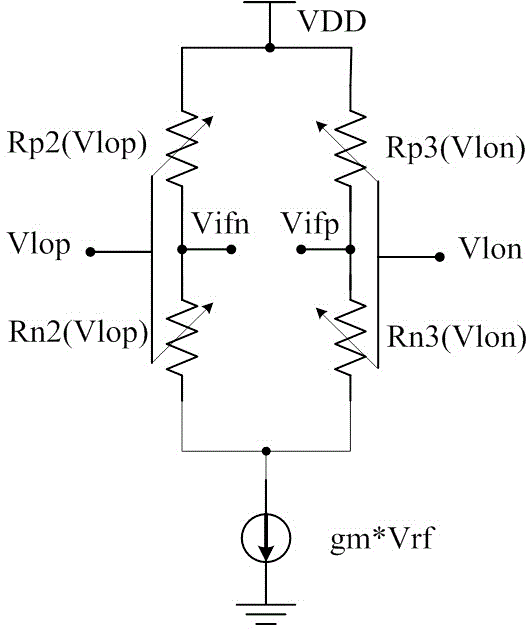
The invention relates to a single-balanced active mixer that can work at a low power voltage. The active mixer comprises an alternating current coupling capacitor C0 of a radio frequency (RF) input signal (Vrf), a direct current bias resistor R0, an input tube N1 and a bias tube N0 thereof, and also comprises a metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) tube N2, an MOS tube N3, an MOS tube P2 and an MOS tube P3 that are used as loads. The N2 and P2 are connected to a positive local oscillator signal (Vlop) through capacitors C2 and C3. The N3 and P3 are connected to a negative local oscillator signal (Vlon) through capacitors C4 and C5. A P0 provides direct current bias for grids of load tubes P2 and P3. A resistor R1 provides bias for grids of the load tubes N2 and N3, and the bias resistor R1 and the bias tube N0 are in the same current path, so that the bias voltages of the N2 and N3 are slightly higher than that of the N1. Through adoption of the active mixer, the problem that the existing active mixer is hard to work at an extreme low voltage is solved, and the active mixer has lower power consumption.
Owner:NANJING NENGRUI AUTOMATION EQUIP
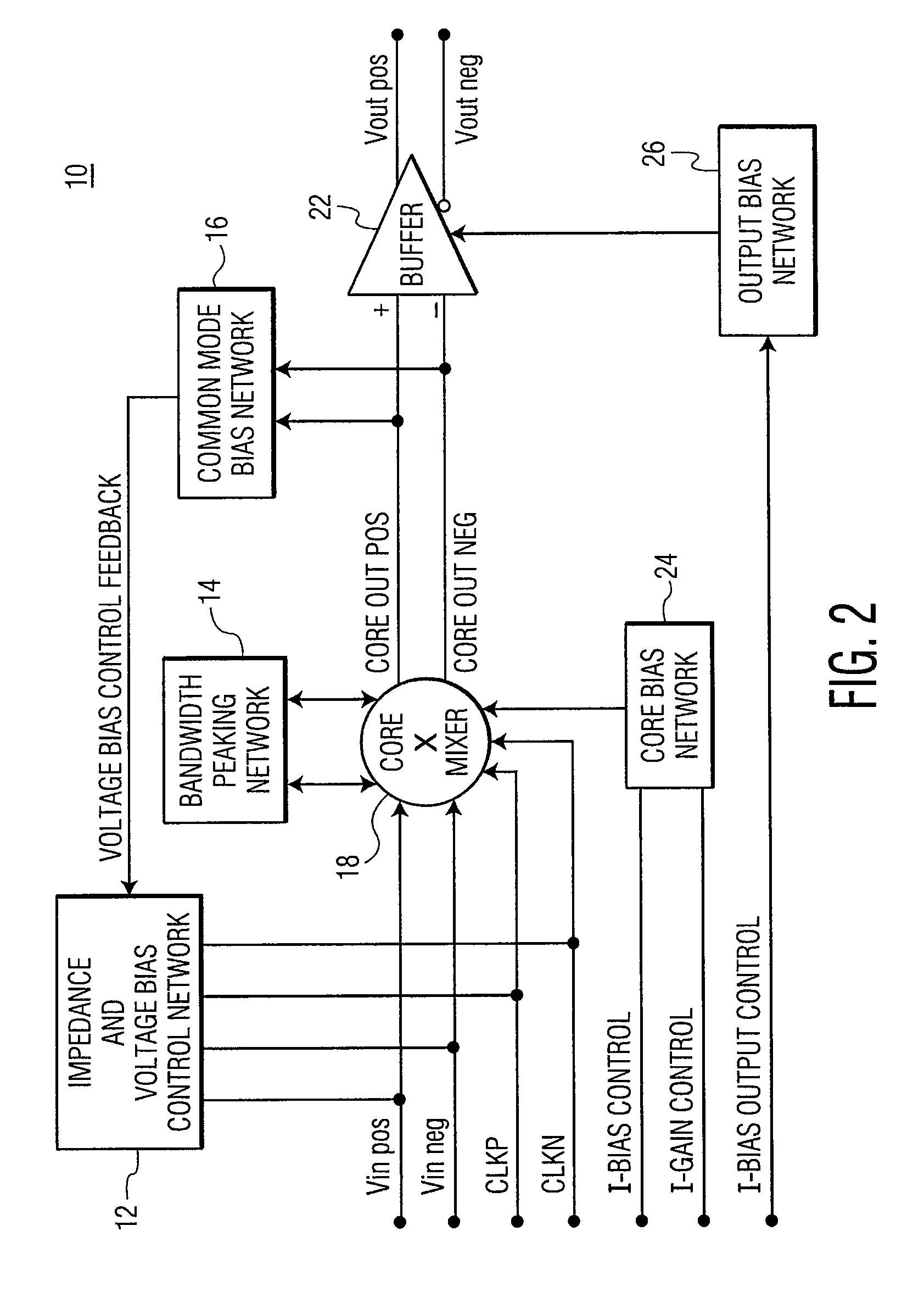
Ultra wide band, differential input/output, high frequency active mixer in an integrated circuit
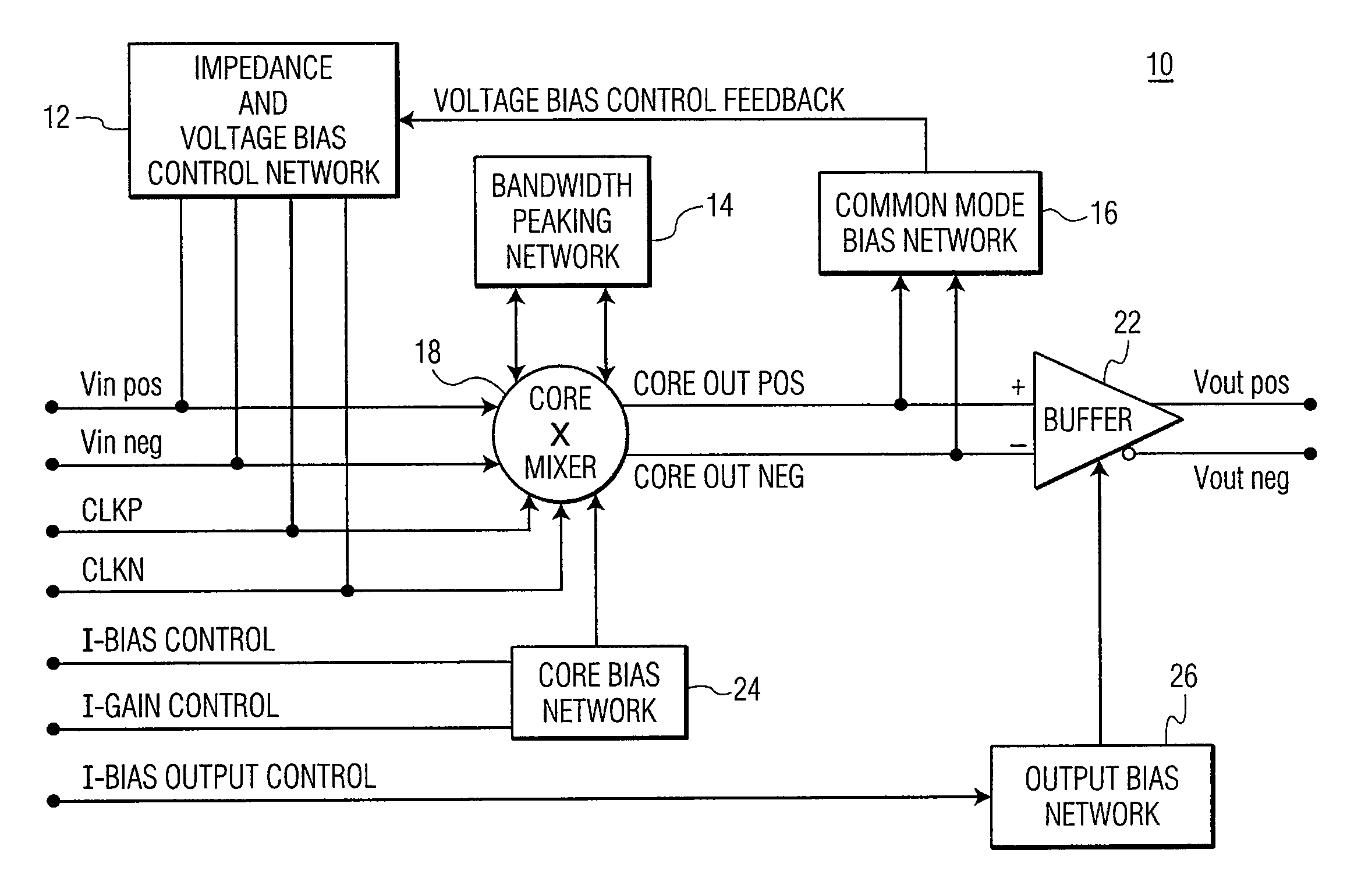
A wideband mixer includes a core mixer having input terminals and output terminals for, respectively, receiving differential input signals and providing amplified differential output signals. A steering module is coupled to the core mixer for receiving differential reference signals and providing bi-phase modulated amplified differential output signals. The core mixer is configured to provide a value of gain between the differential input signals and the differential output signals. A bandwidth peaking network is coupled to the core mixer and includes (a) a first coil and a first resistor connected in series and (b) a second coil and a second resistor connected in series. The first coil and resistor and the second coil and resistor, respectively, are coupled to the core mixer for receiving the amplified differential output signals. The bandwidth peaking network is configured to increase the frequency bandwidth of the core mixer.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com