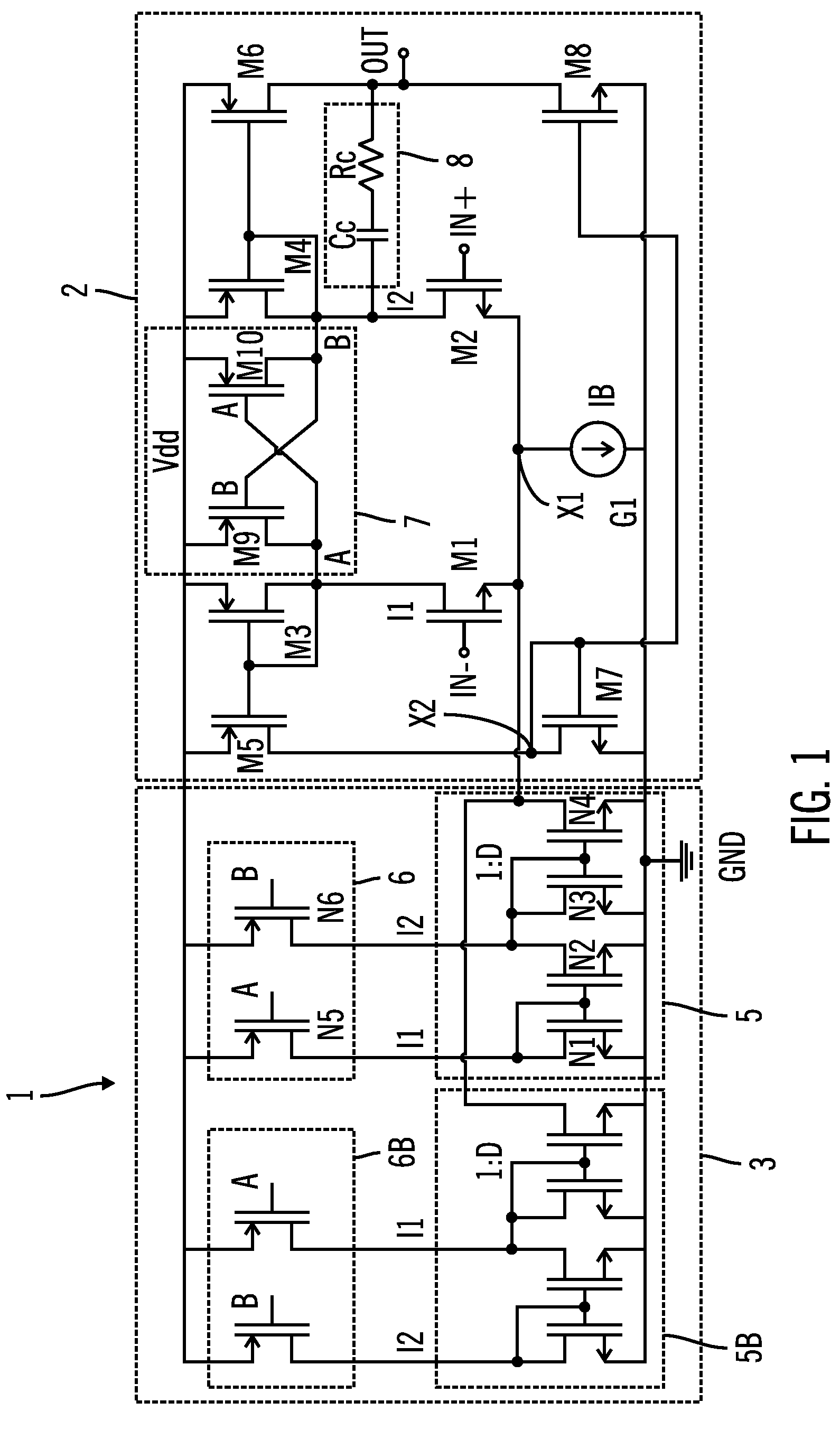
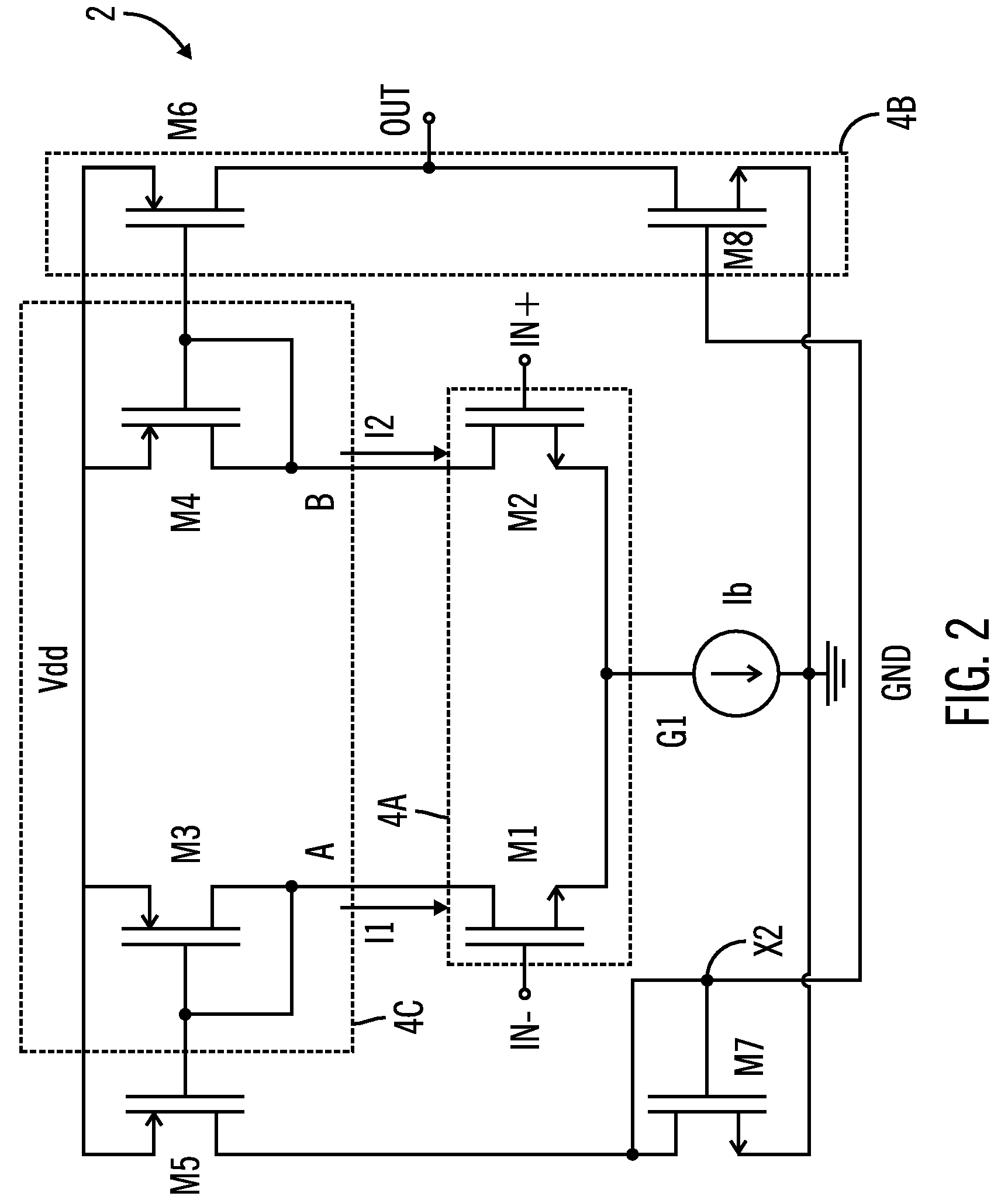
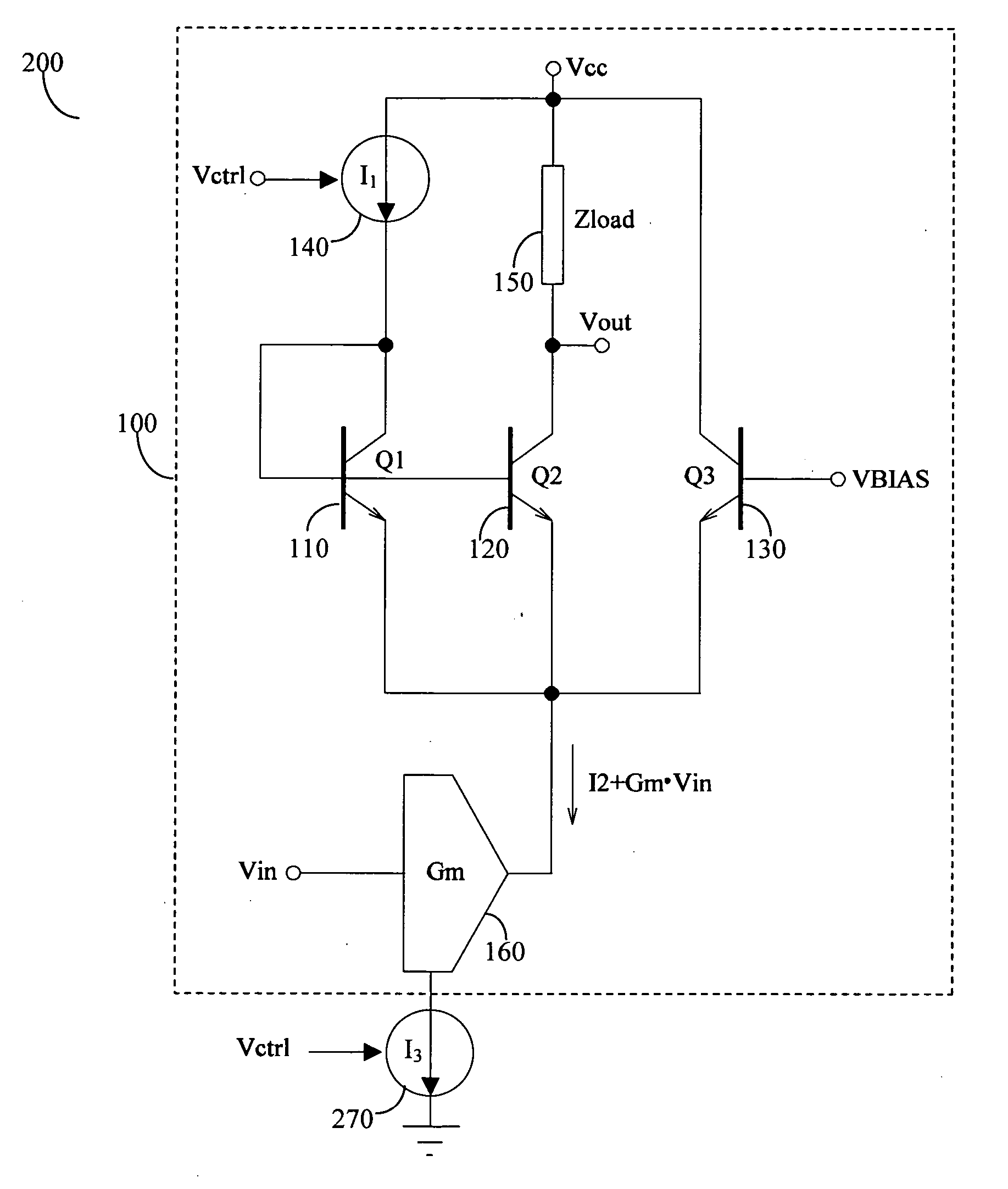
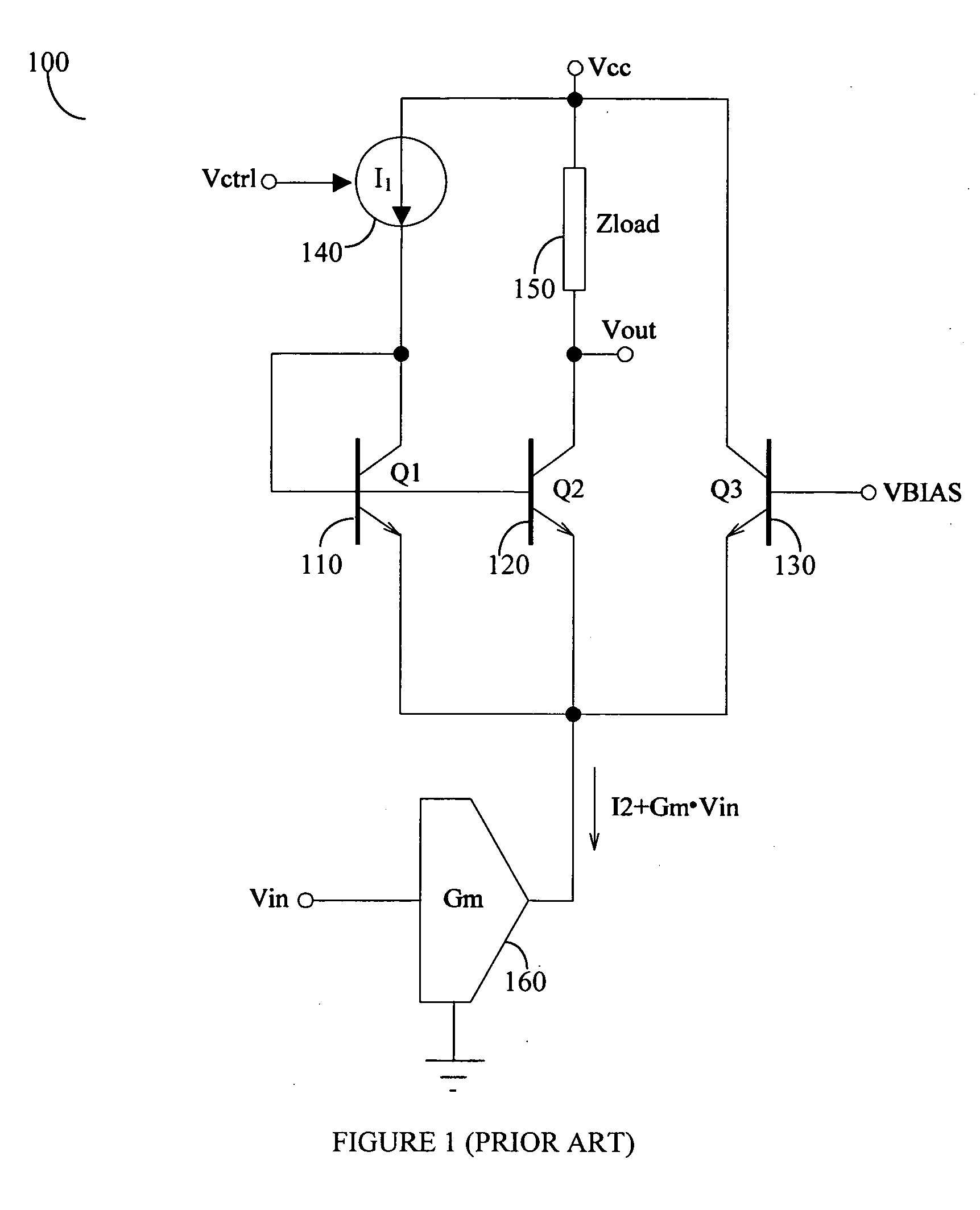
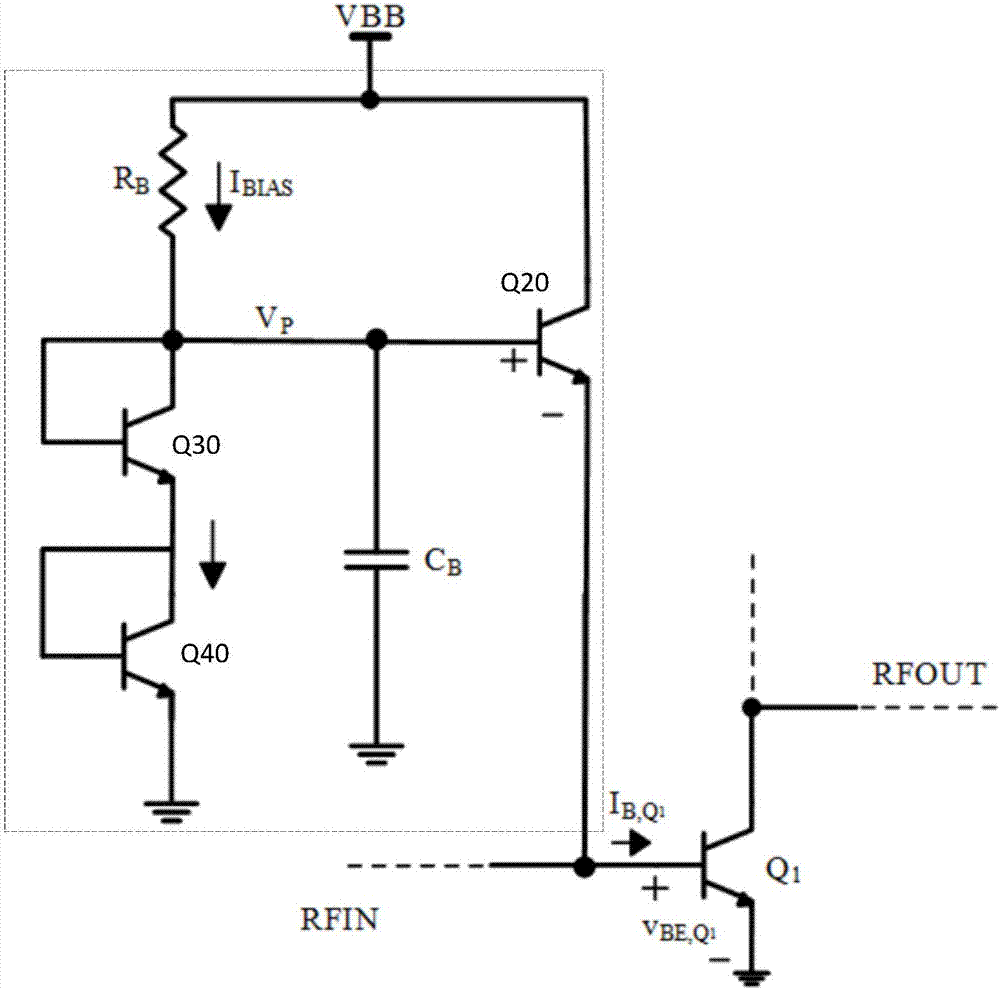
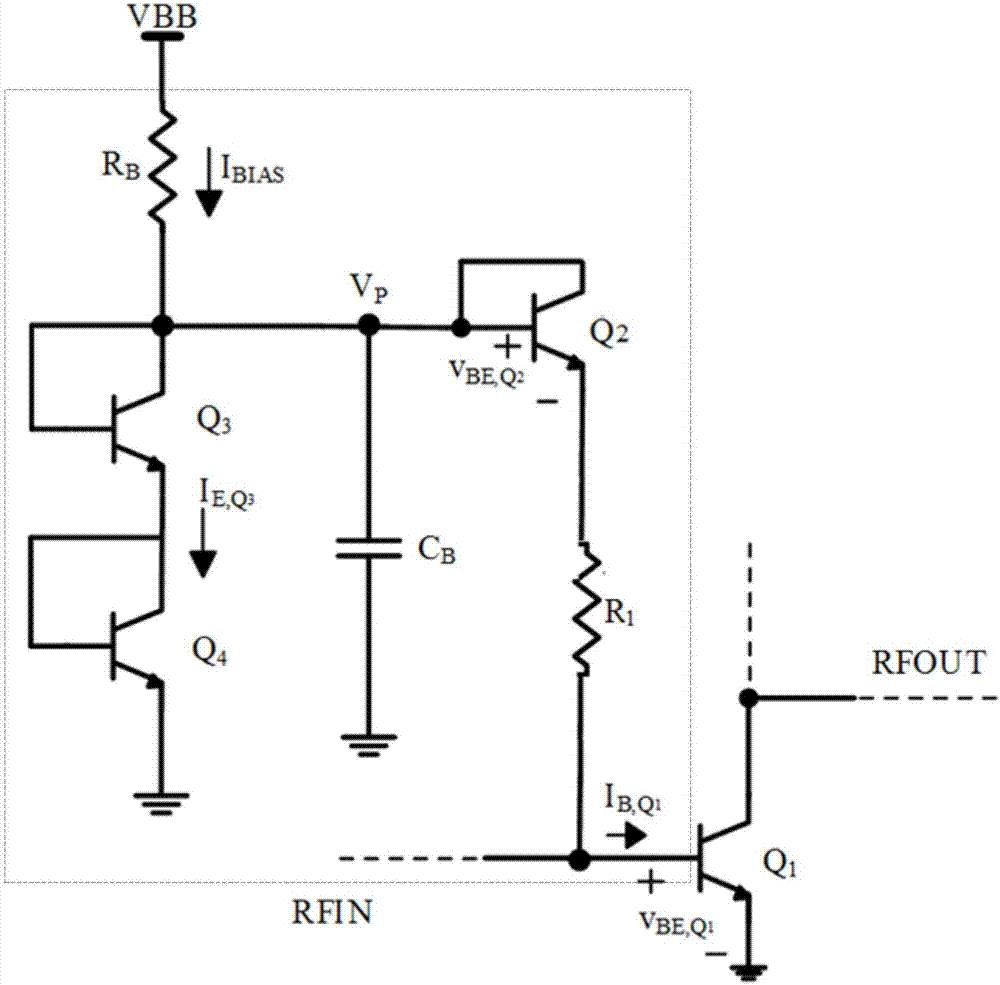
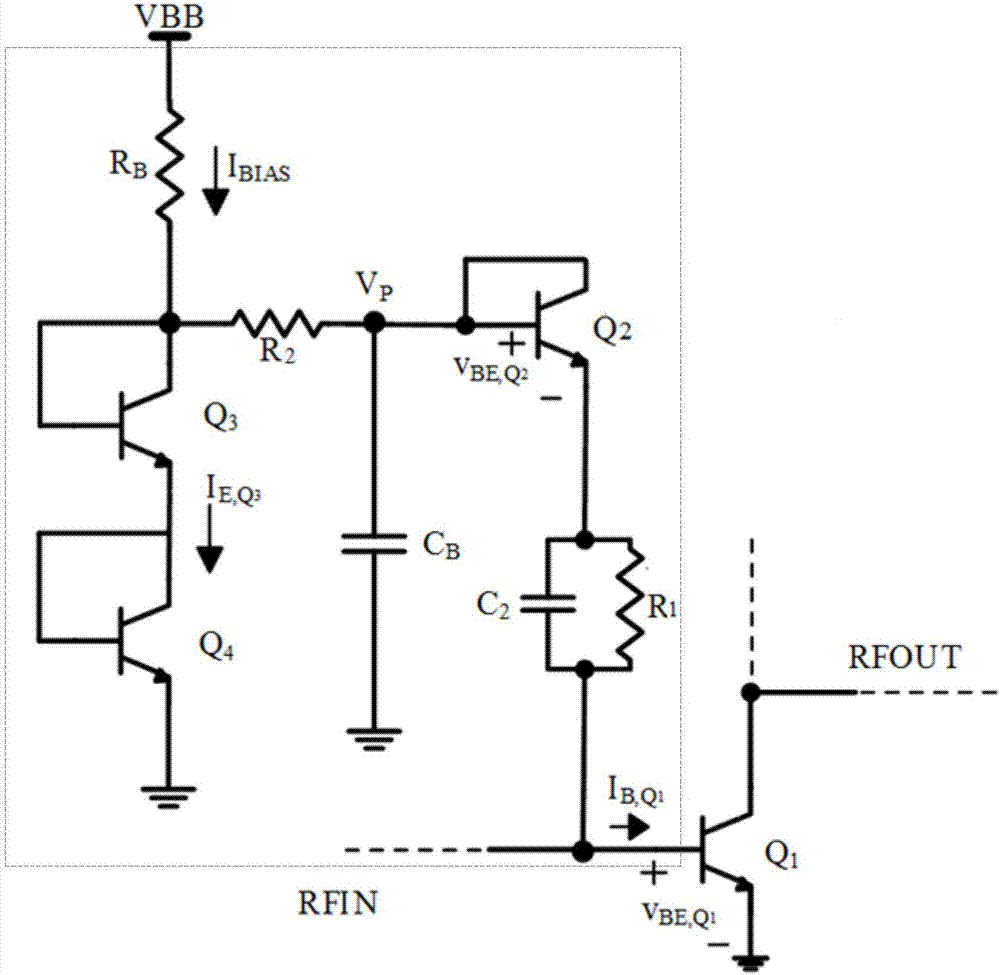
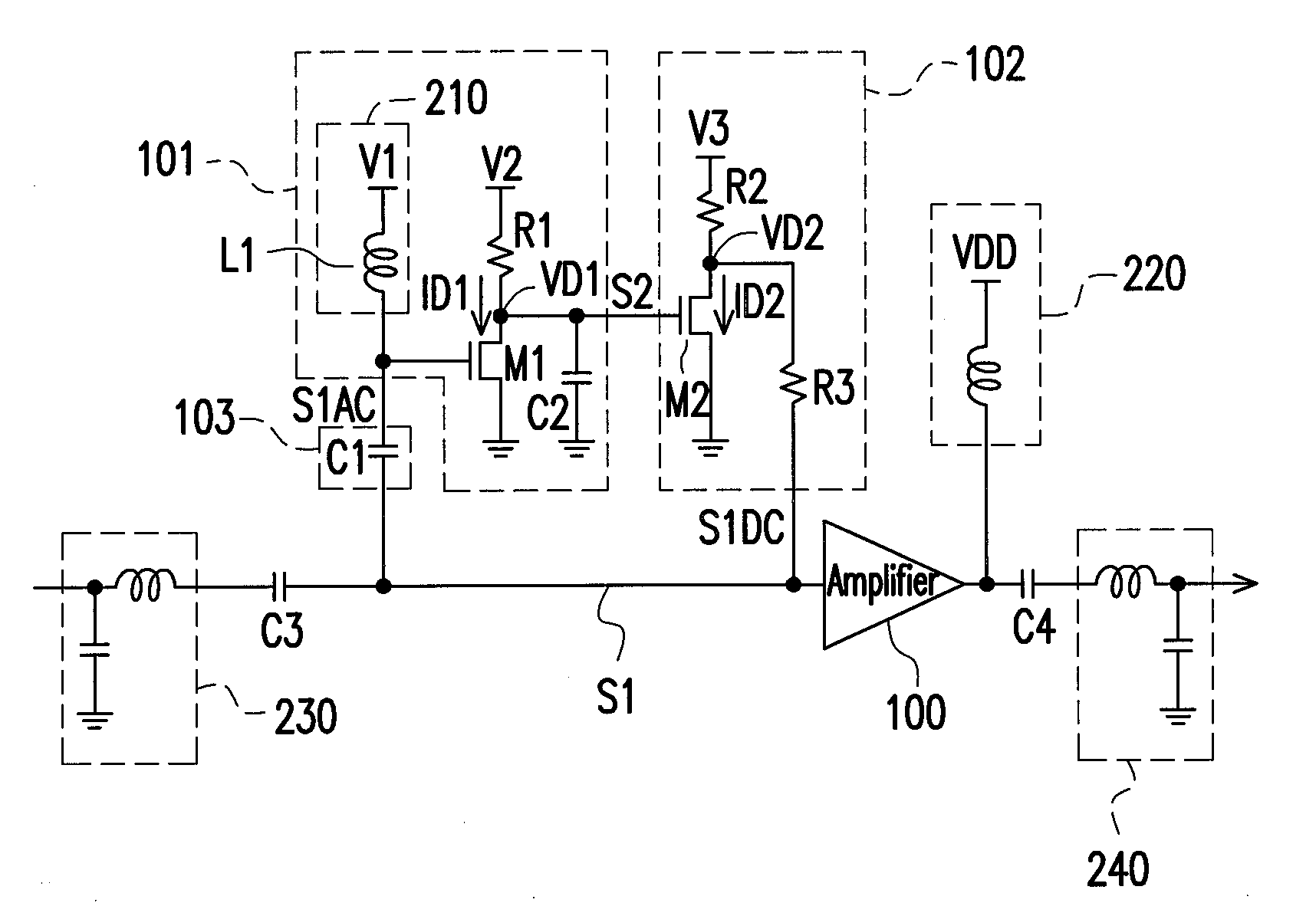
Patents
Literature
79 results about "Adaptive bias" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Adaptive bias is the idea that the human brain has evolved to reason adaptively, rather than truthfully or even rationally, and that cognitive bias may have evolved as a mechanism to reduce the overall cost of cognitive errors as opposed to merely reducing the number of cognitive errors, when faced with making a decision under conditions of uncertainty.
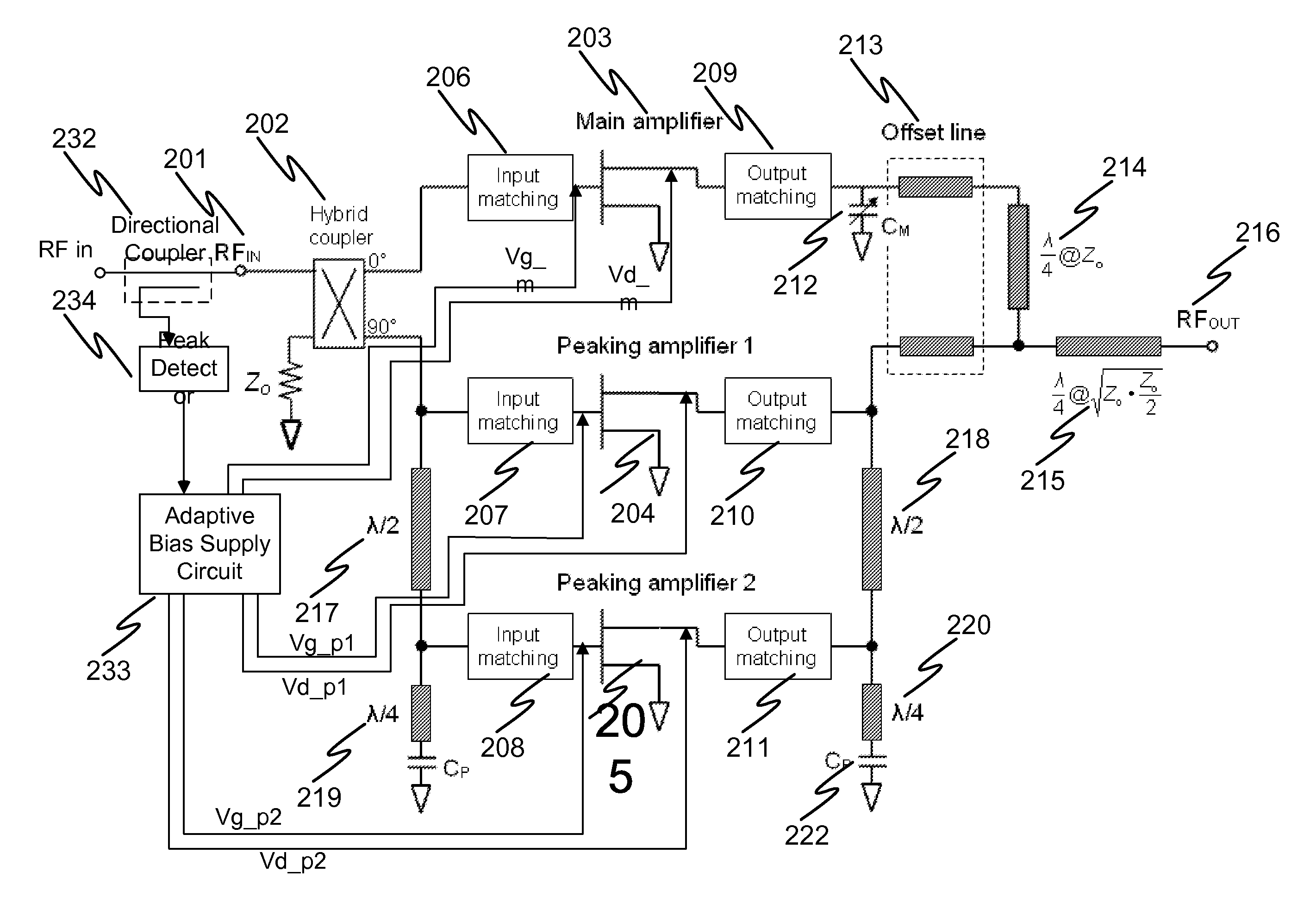
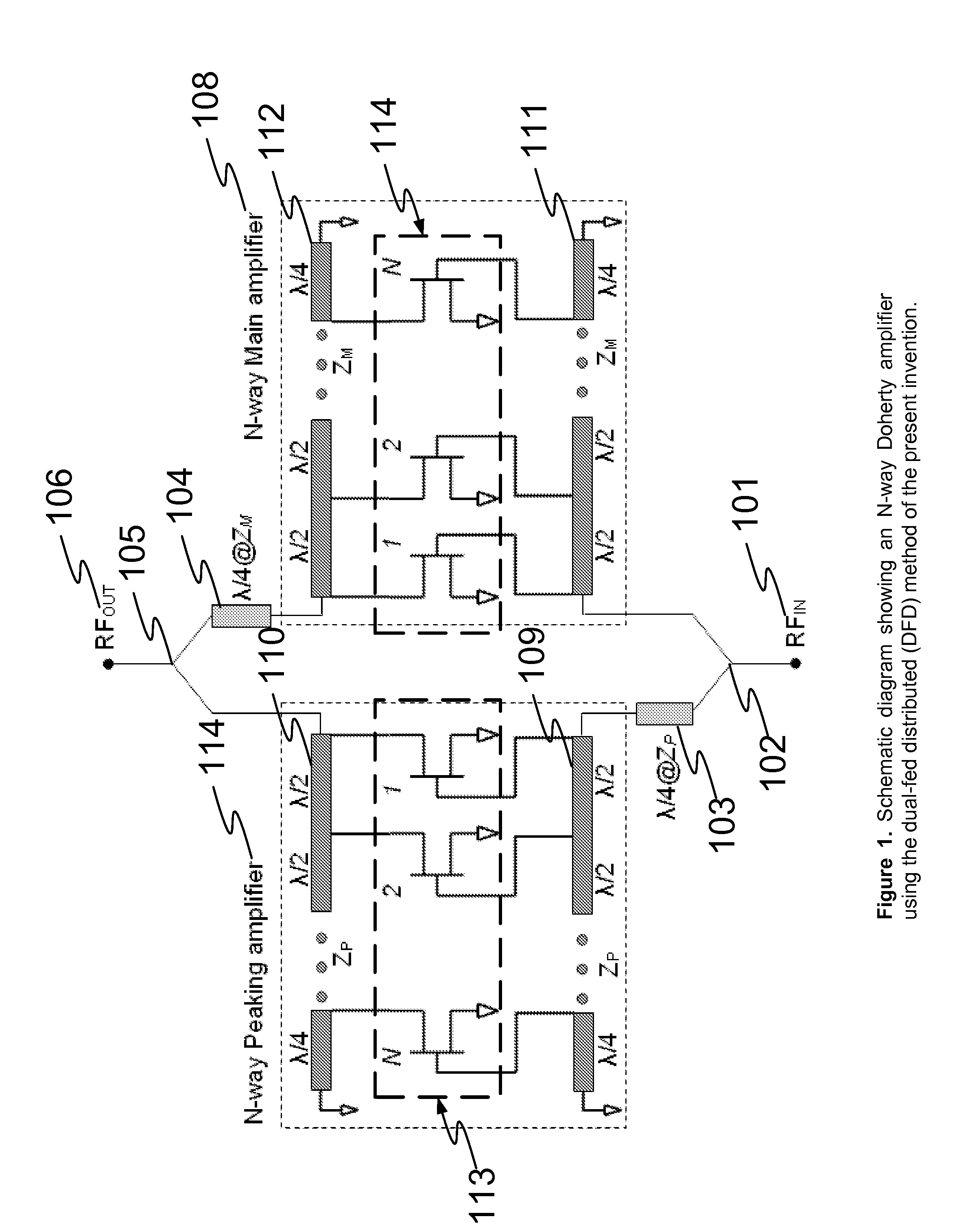
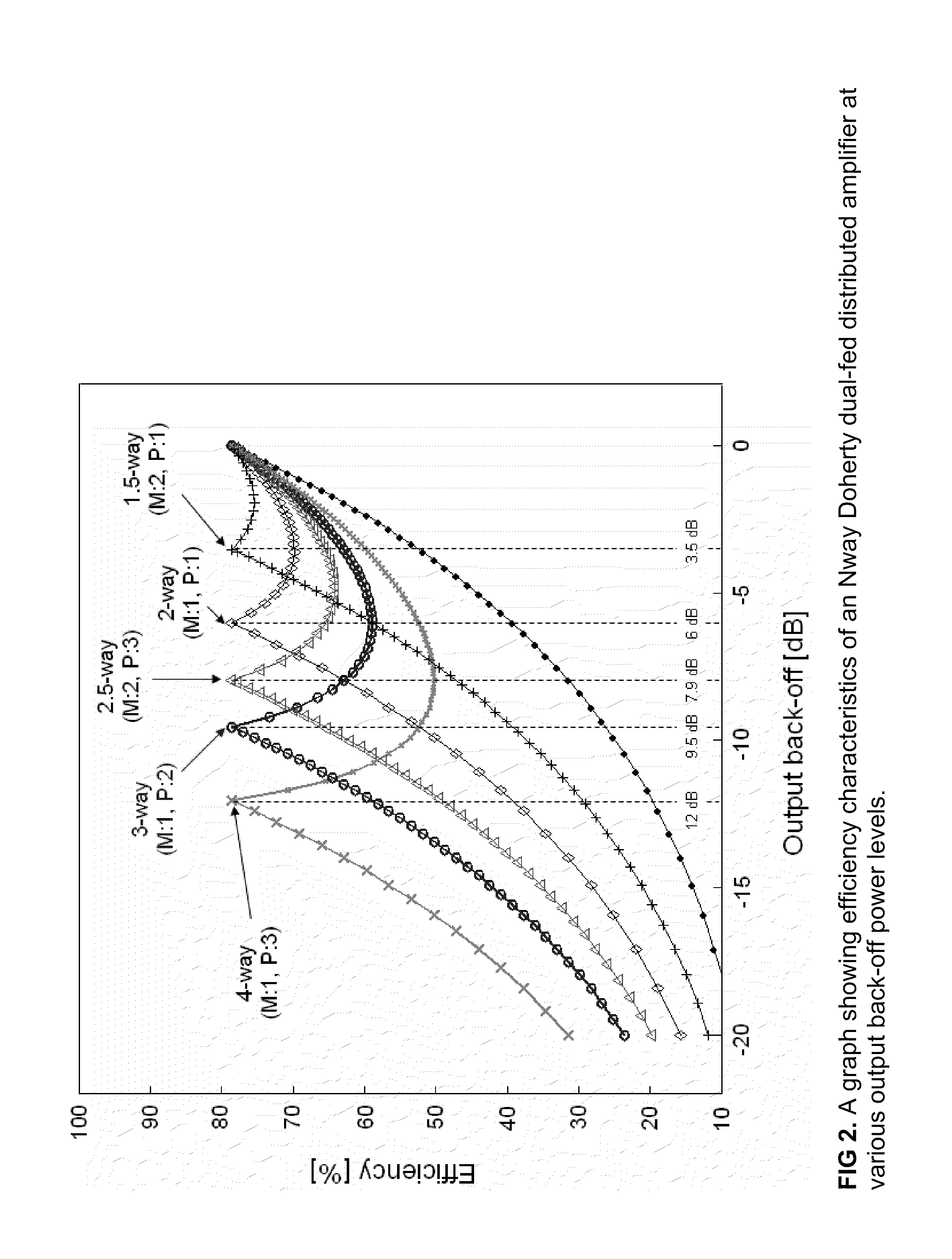
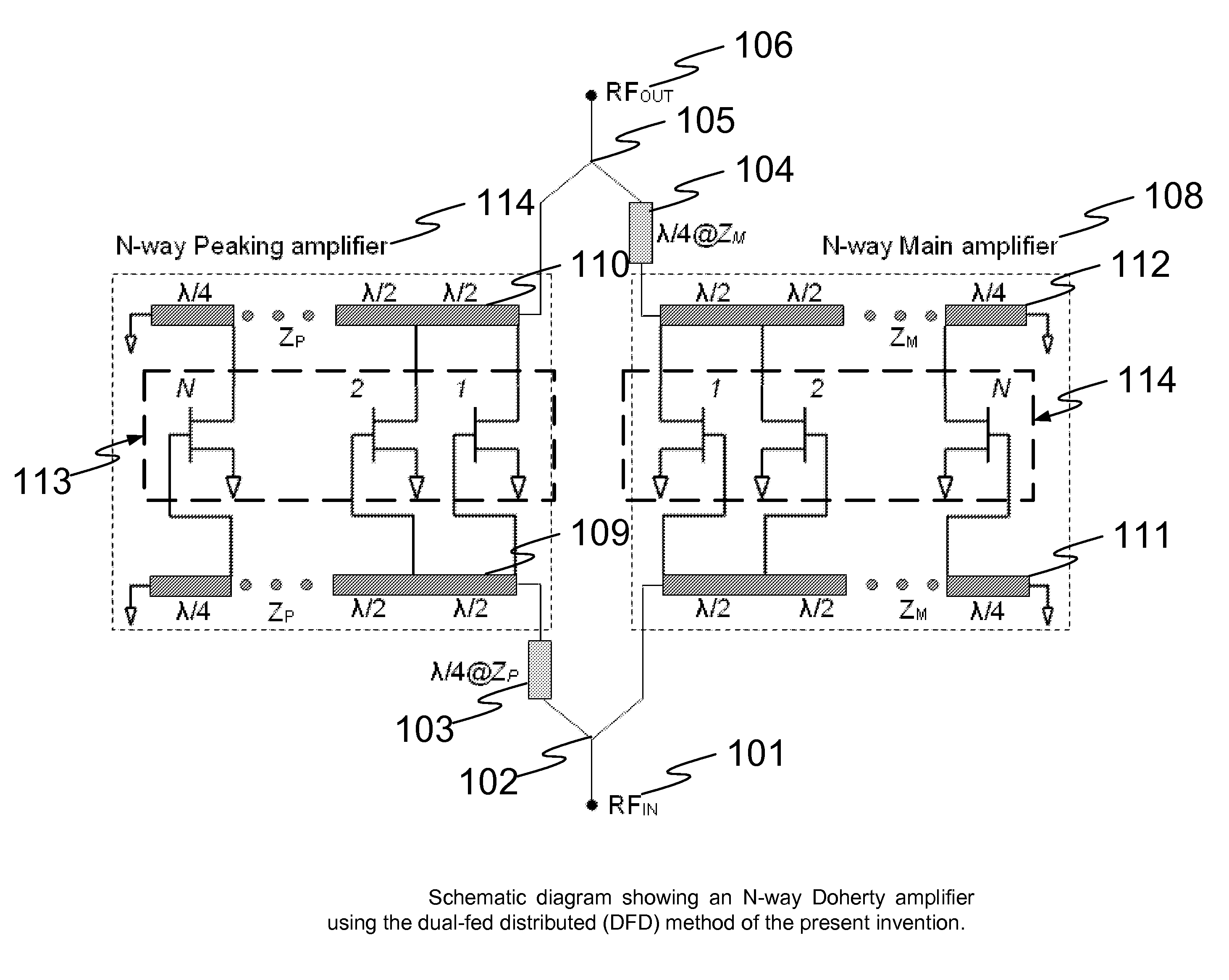
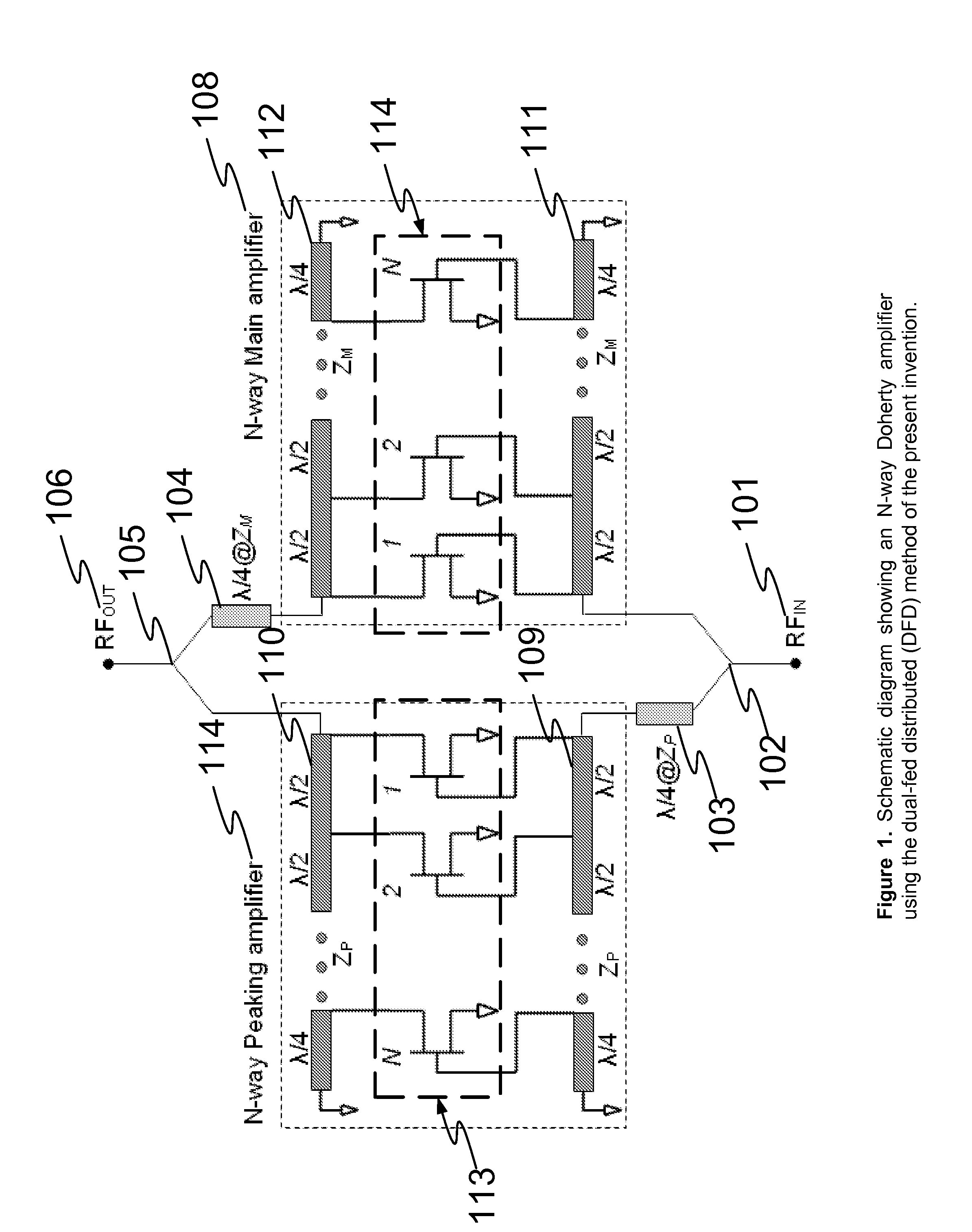
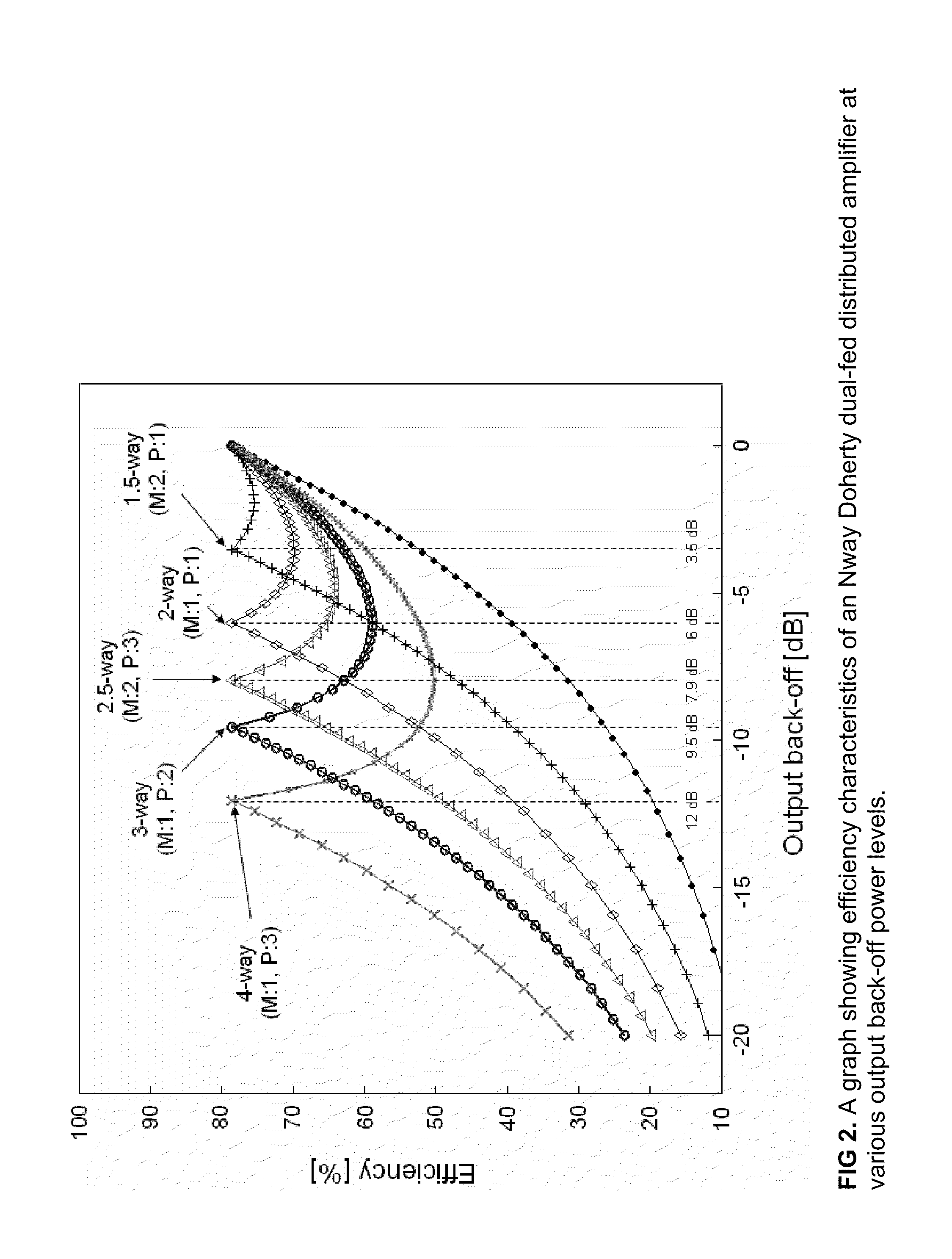
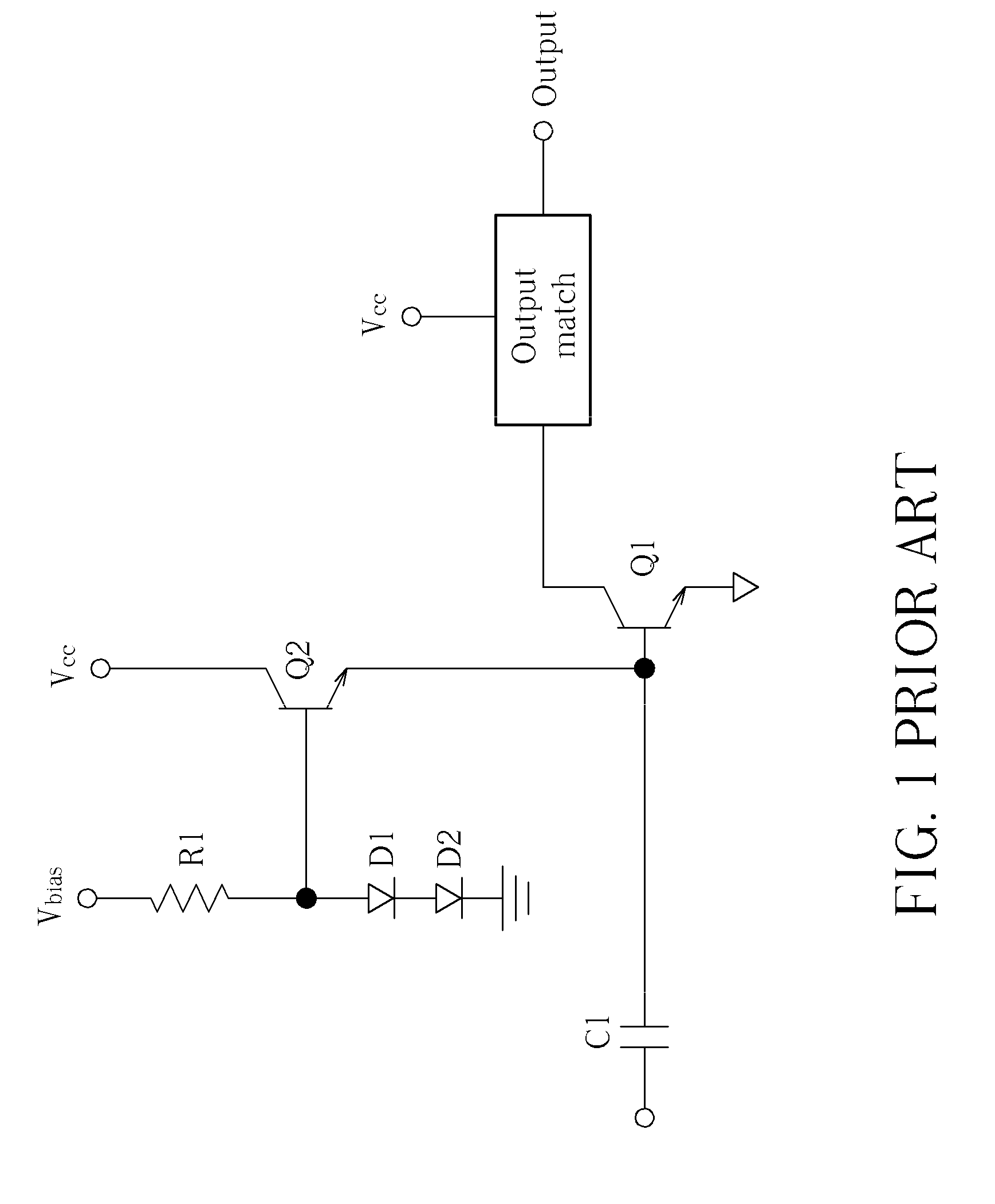
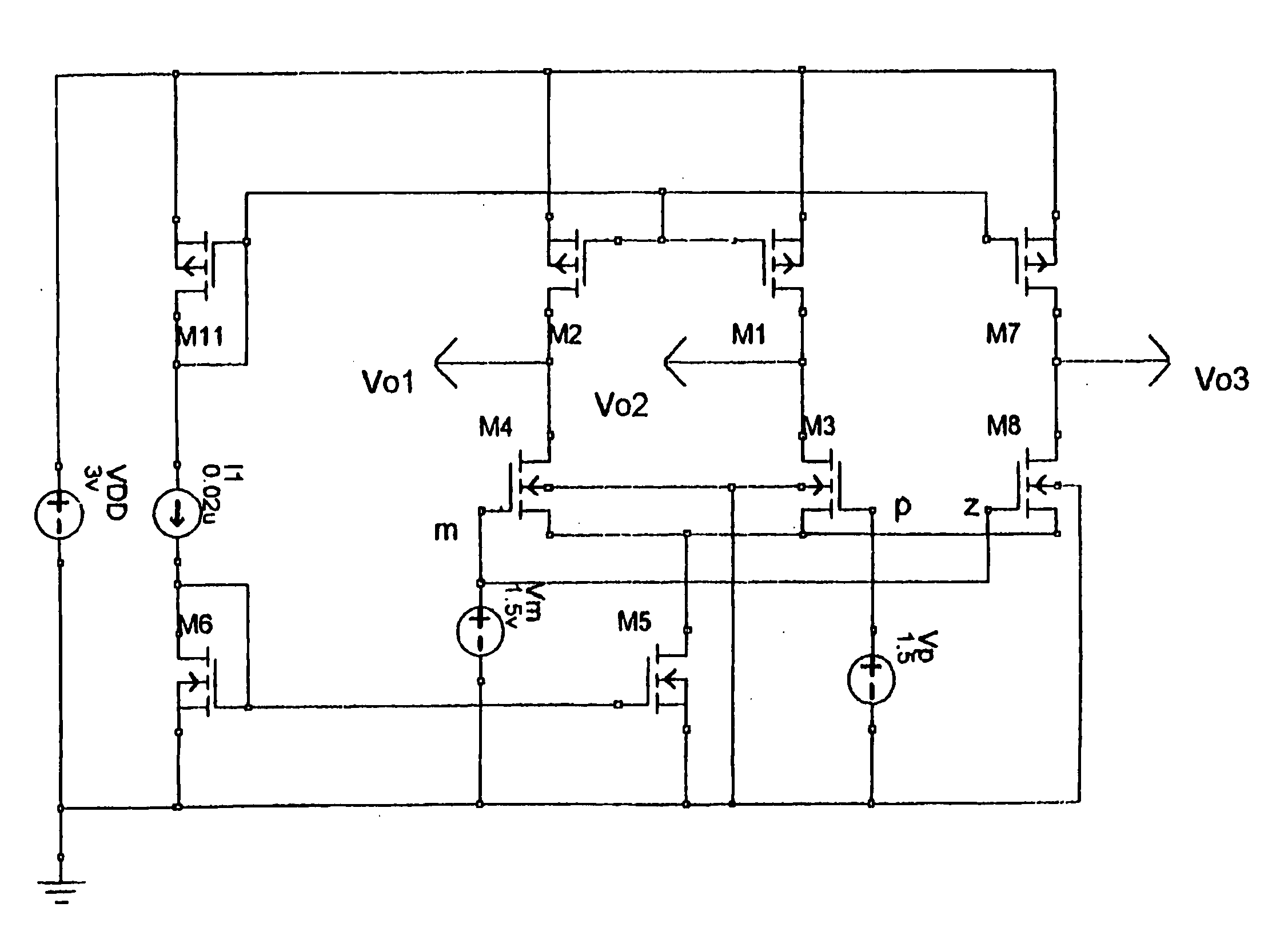
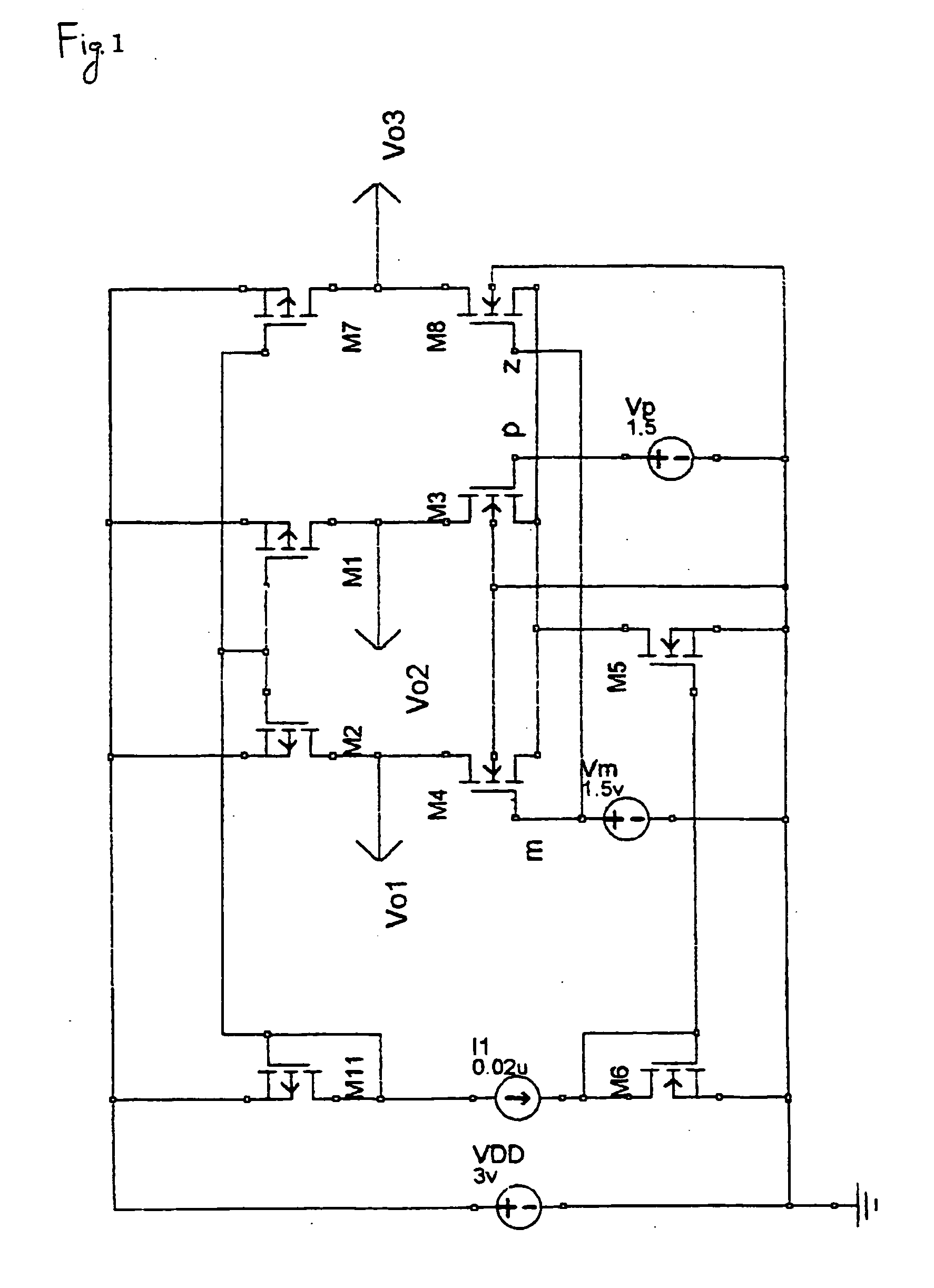
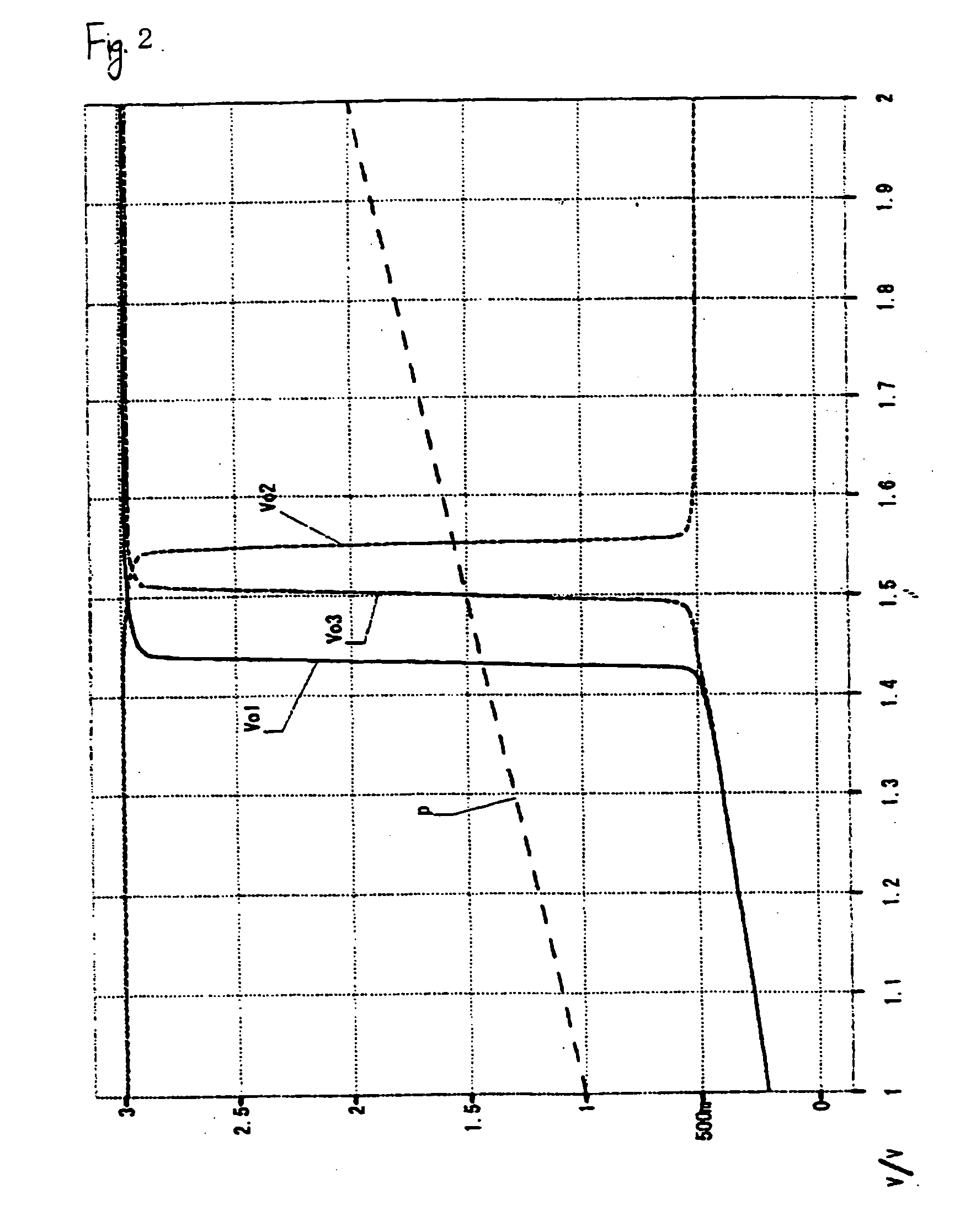
N-way Doherty distributed power amplifier with power tracking
ActiveUS8274332B2Improve performanceIncrease productionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsAdaptive biasMultiplexing
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
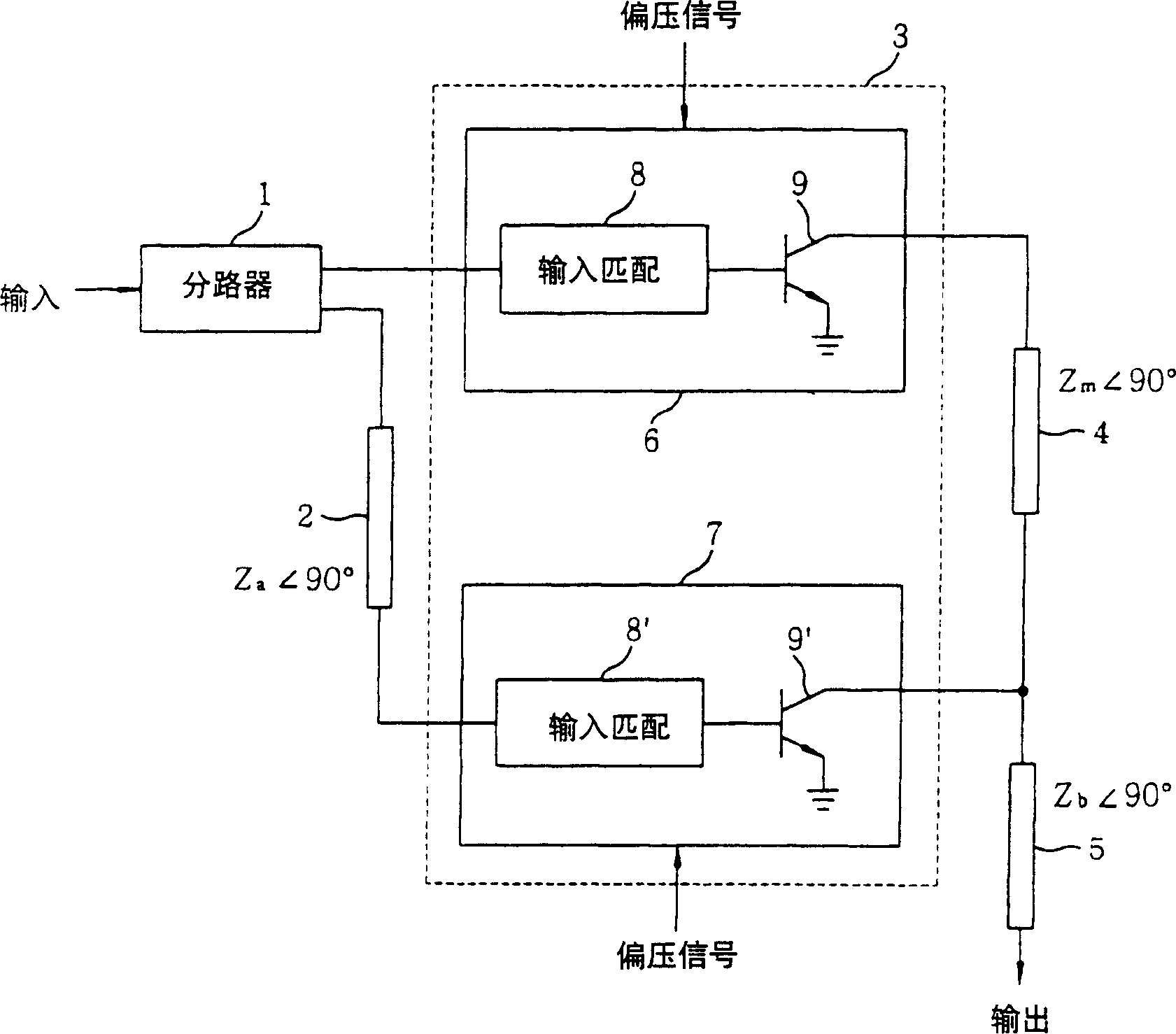
N-Way Doherty Distributed Power Amplifier with Power Tracking
ActiveUS20100176885A1Improve performanceIncrease productionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsAdaptive biasMultiplexing
A power amplifier using N-way Doherty structure with adaptive bias supply power tracking for extending the efficiency region over the high peak-to-average power ratio of the multiplexing modulated signals such as wideband code division multiple access and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing is disclosed. In an embodiment, the present invention uses a dual-feed distributed structure to an N-way Doherty amplifier to improve the isolation between at least one main amplifier and at least one peaking amplifier and, and also to improve both gain and efficiency performance at high output back-off power. Hybrid couplers can be used at either or both of the input and output. In at least some implementations, circuit space is also conserved due to the integration of amplification, power splitting and combining.
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
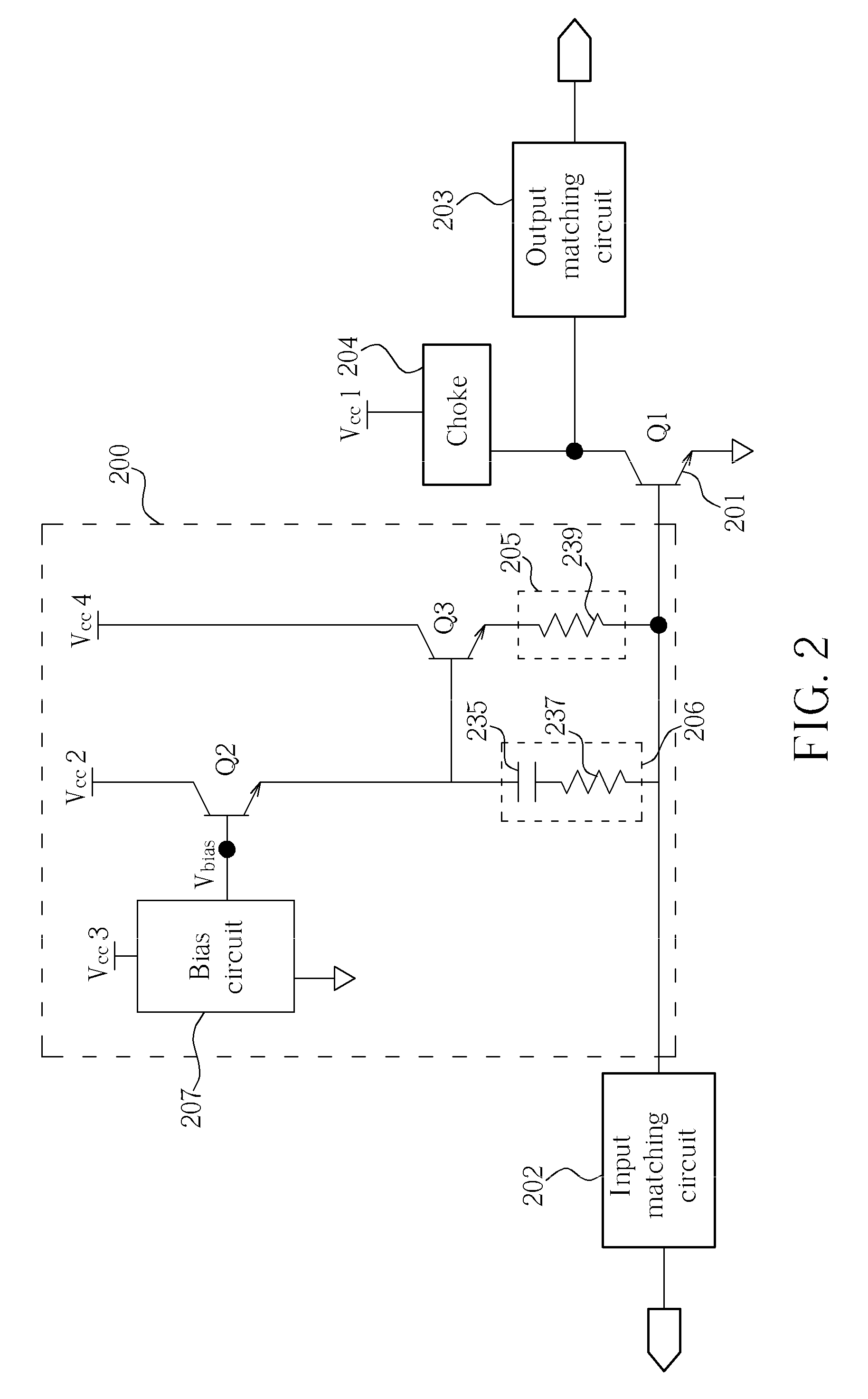
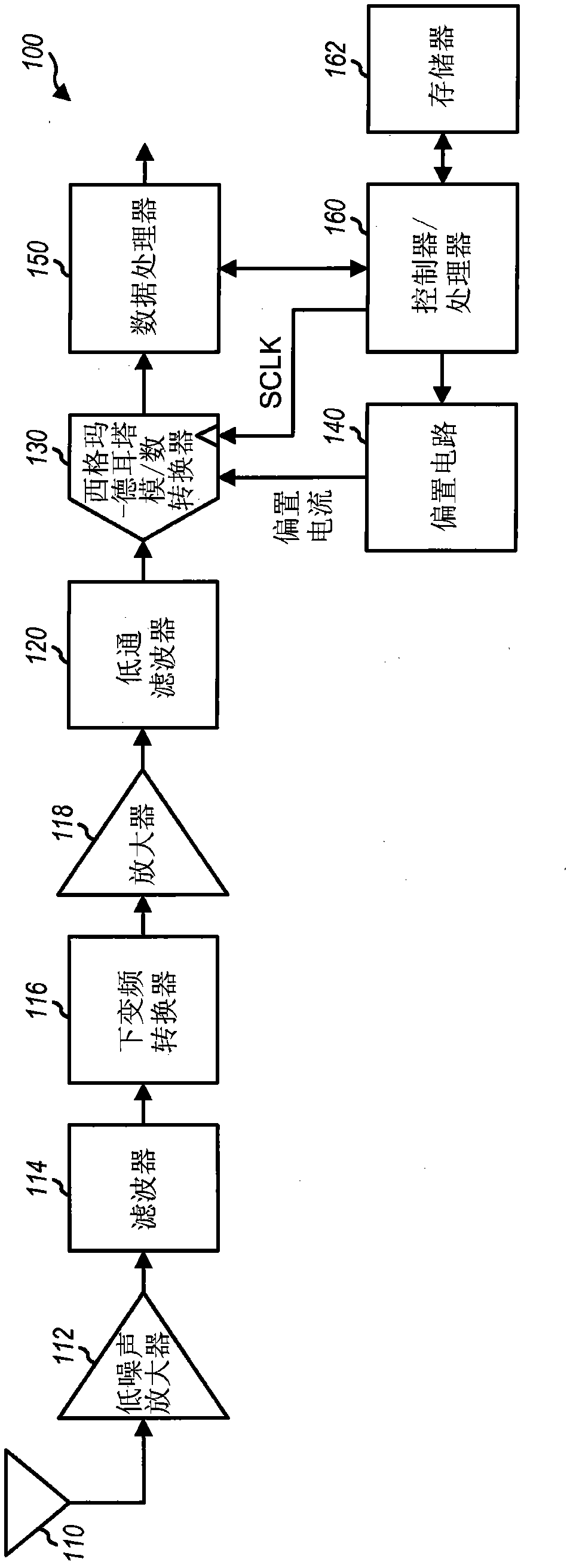
Adaptive bias current circuit and method for amplifiers
ActiveUS7567123B2High currentHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlElectrical resistance and conductanceAdaptive bias
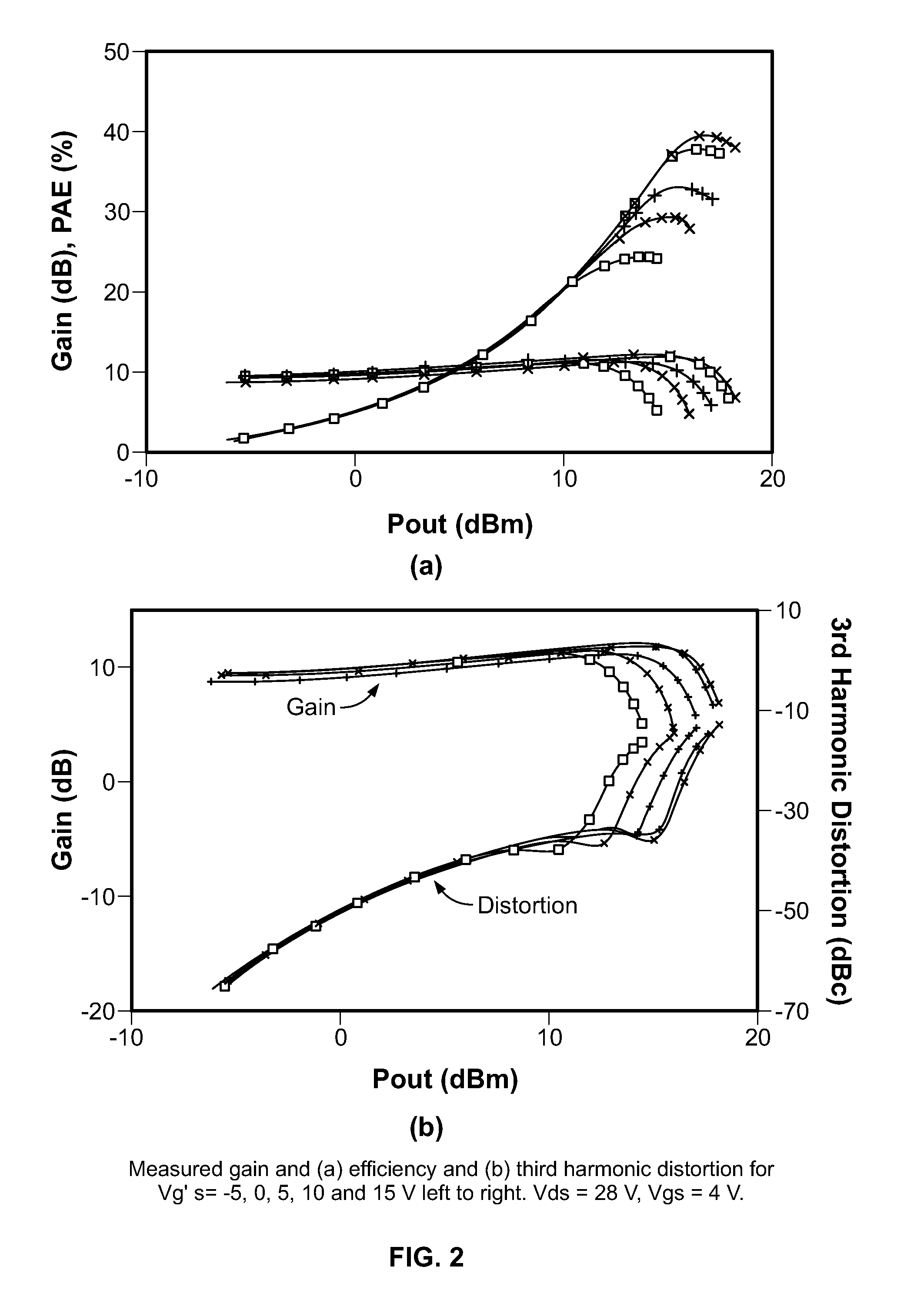
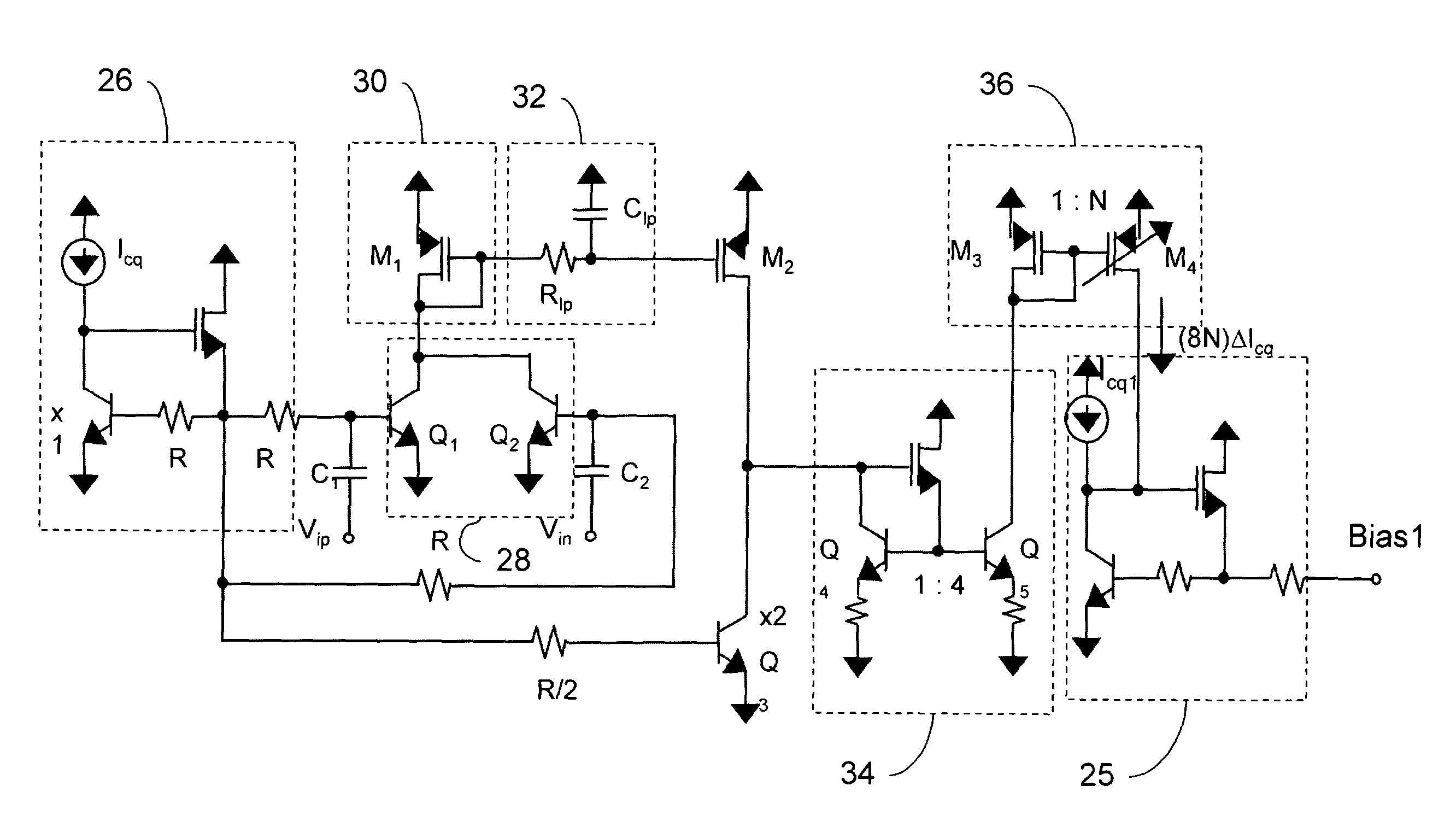
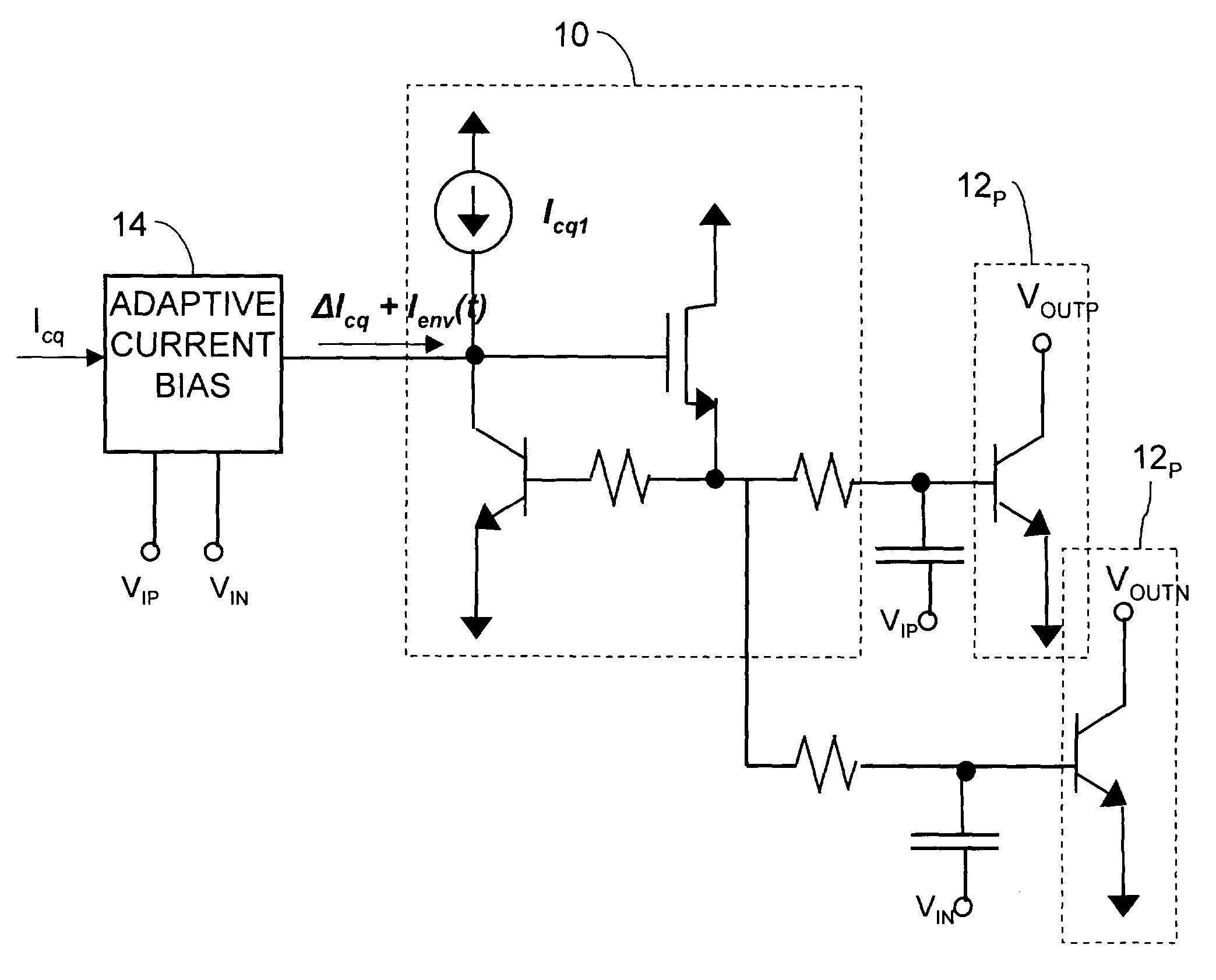
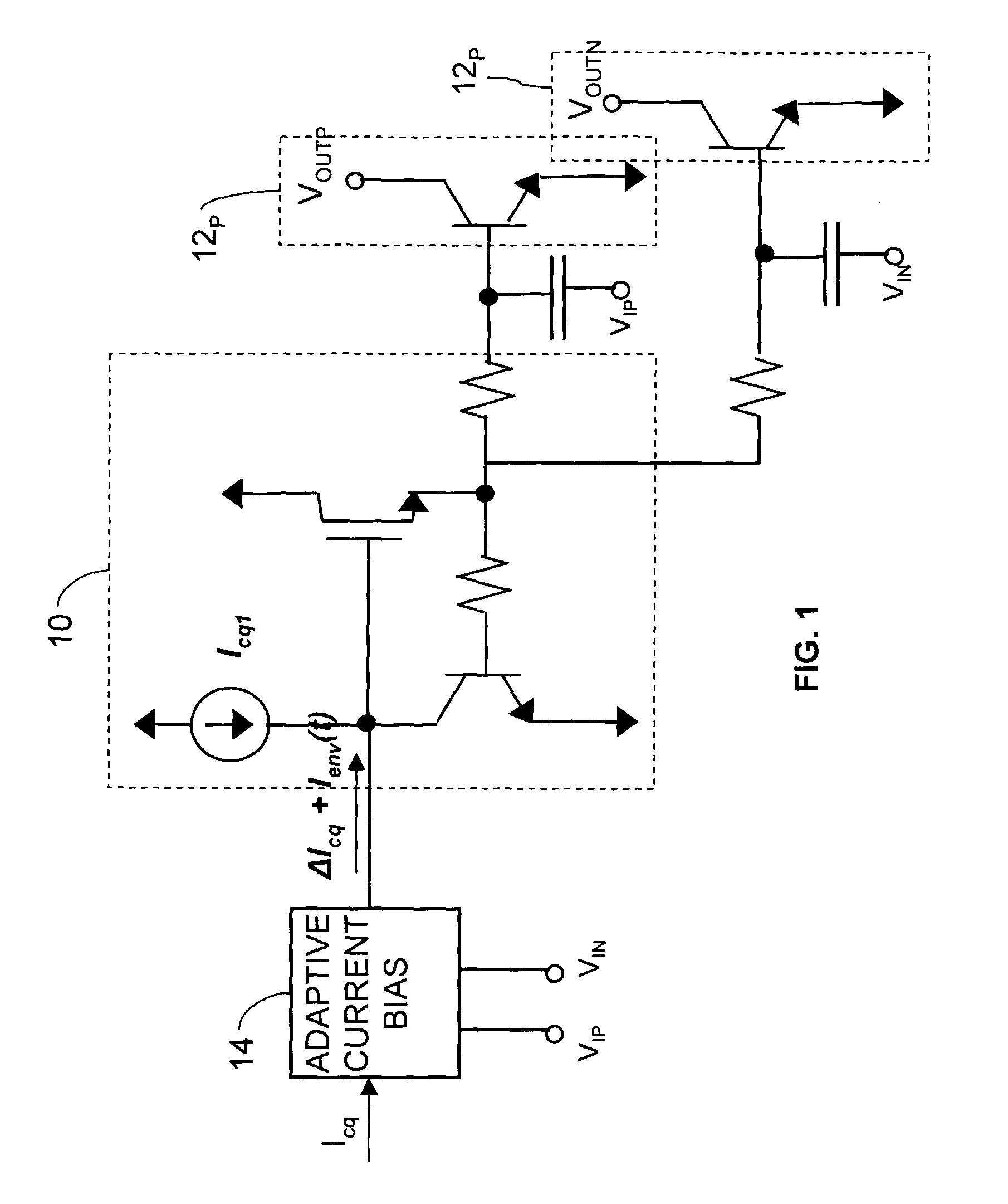
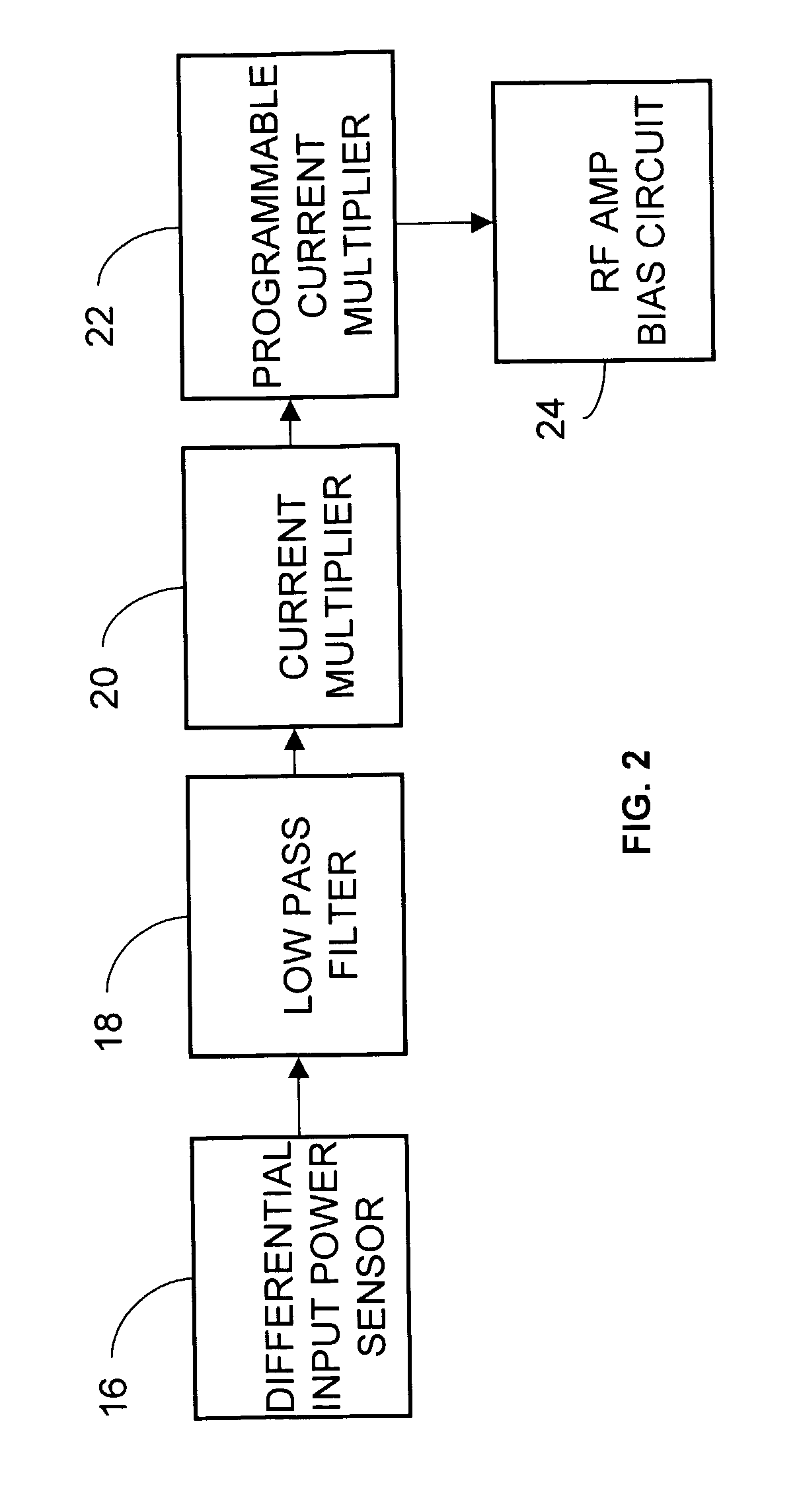
An adaptive bias method and circuits for amplifiers that provide a substantial current boost based at least partly upon a sensed input power of an amplifier circuit. Methods and circuits of the invention provide an additional bias current based upon the sensed input power. Circuits of the invention may be simple, area-efficient, low-power, stable and digitally-programmable. In addition, methods and circuits of the invention may be used with a number of amplifier circuit configurations, including amplifiers having either inductor and / or resistive degeneration.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Adaptive Bias Current Circuit and Method for Amplifiers
ActiveUS20070252646A1High currentHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAdaptive biasElectrical resistance and conductance
An adaptive bias method and circuits for amplifiers that provide a substantial current boost based at least partly upon a sensed input power of an amplifier circuit. Methods and circuits of the invention provide an additional bias current based upon the sensed input power. Circuits of the invention may be simple, area-efficient, low-power, stable and digitally-programmable. In addition, methods and circuits of the invention may be used with a number of amplifier circuit configurations, including amplifiers having either inductor and / or resistive degeneration.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
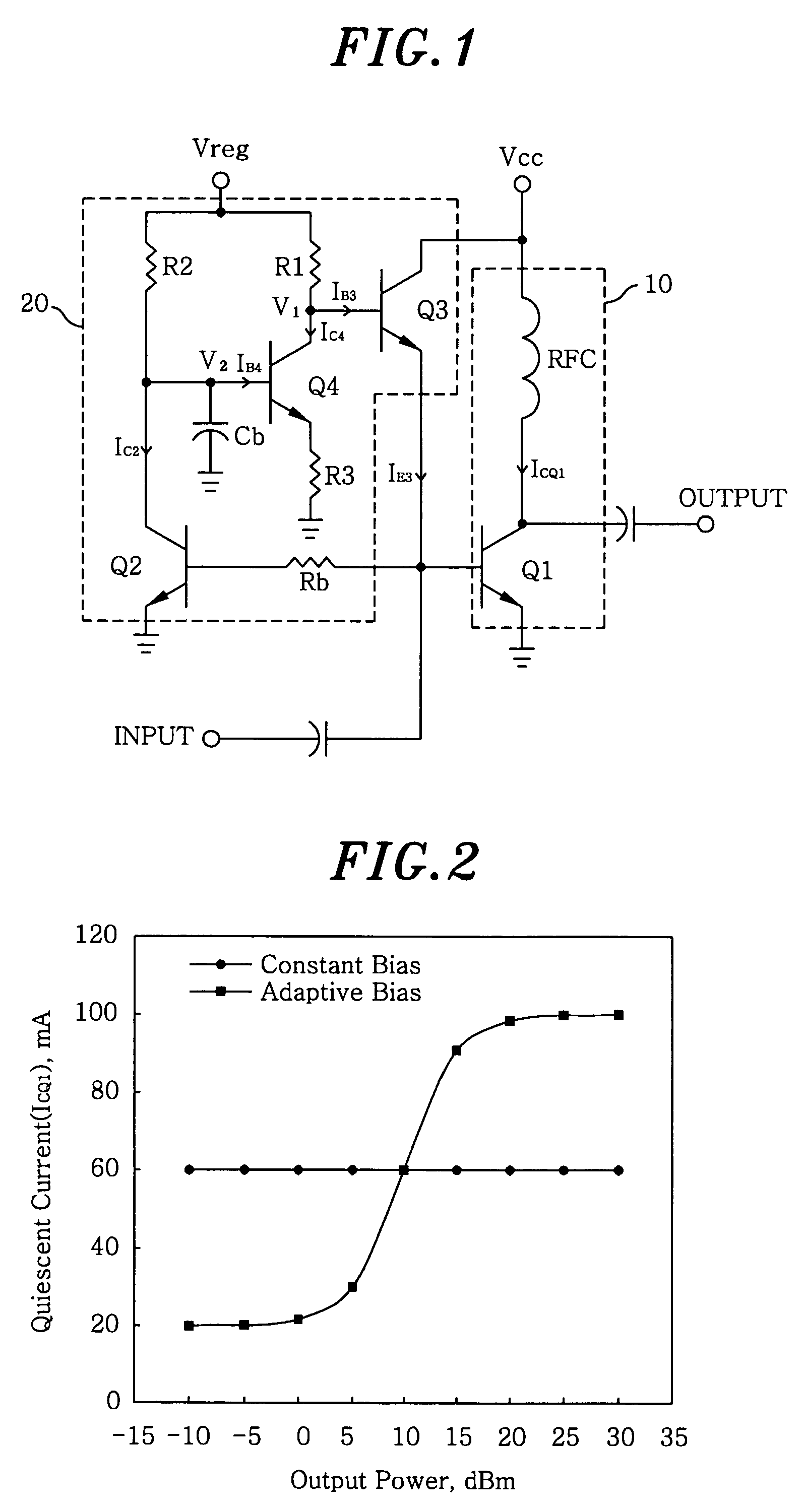
Adaptive bias circuit for a power amplifier
InactiveUS7005923B2Effective controlImprove power added efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationGain controlAdaptive biasDriving current
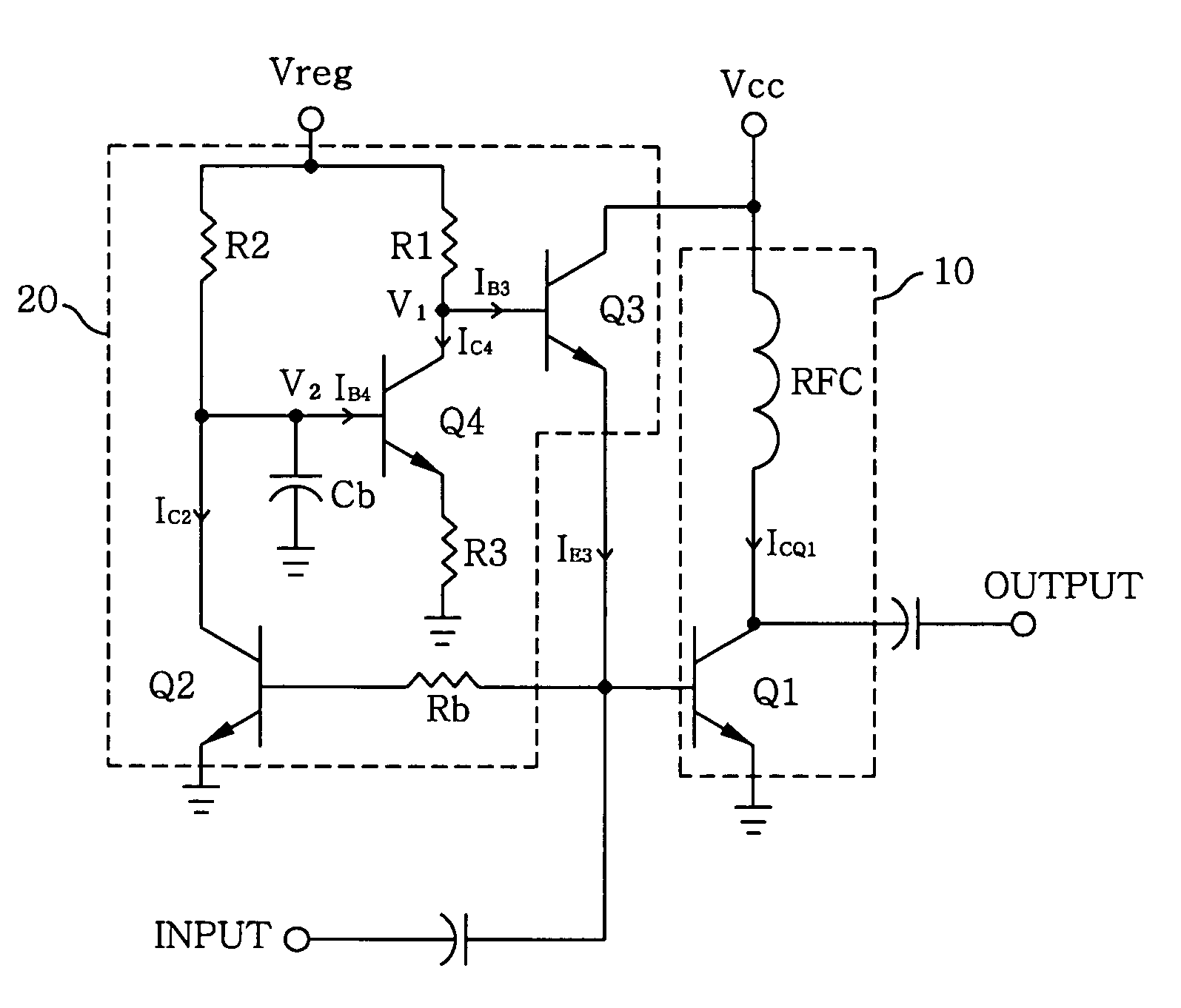
An adaptive bias circuit is provided for an amplifier module including a RF power amplifier for amplifying an input signal to generate an output signal, wherein the bias circuit receives the input signal to adjust a driving current to control a quiescent current of the RF power amplifier. The adaptive bias circuit includes means for providing the driving current to the bias circuit and means for drawing a bypass current from the providing means to reduce the driving current in response to the input signal, wherein the quiescent current is reduced when the driving current is reduced and the bypass current increases when the input signal is reduced.
Owner:INFORMATION & COMM UNIV EDUCATIONAL FOUND
Circuit and method for reducing overshoots in adaptively biased voltage regulators
ActiveUS7982448B1Reduce overshootCurrent is limitedElectric variable regulationAdaptive biasVoltage regulation
Disclosed are a circuit and a method for adaptively biasing a voltage regulator with minimal output overshoot. The circuit includes an adaptive bias current mirror circuit further including a first transistor and a second transistor, the first transistor and the second transistor having source nodes coupled to a drain node of the first transistor. The circuit includes a common node coupled to the source node of the first transistor and the source node of the second transistor, wherein a source degenerate resistor is coupled to the adaptive bias current mirror circuit and is coupled to the common node and wherein the source degenerate resistor is configured to limit an output peak current of the voltage regulator circuit.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
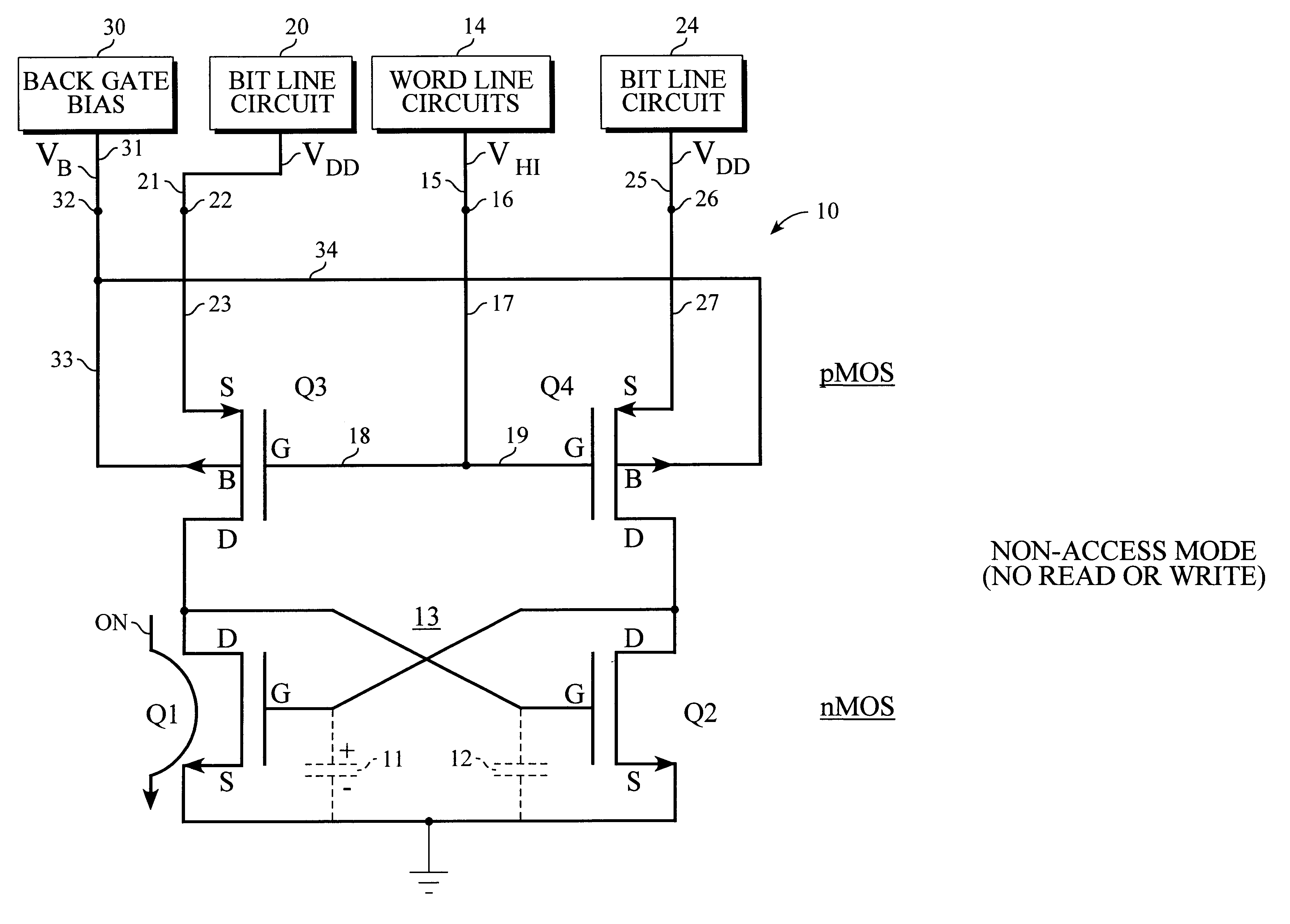
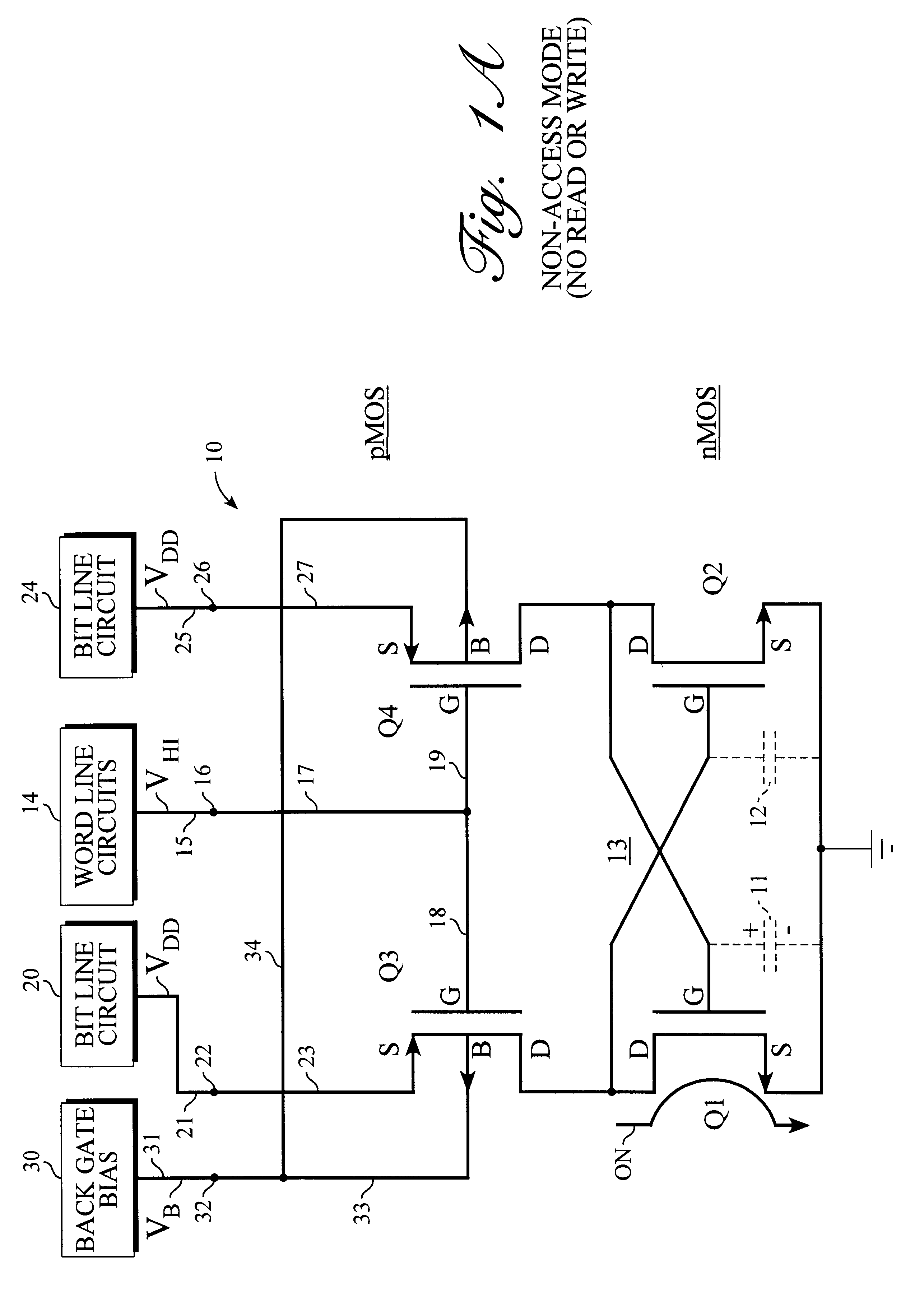
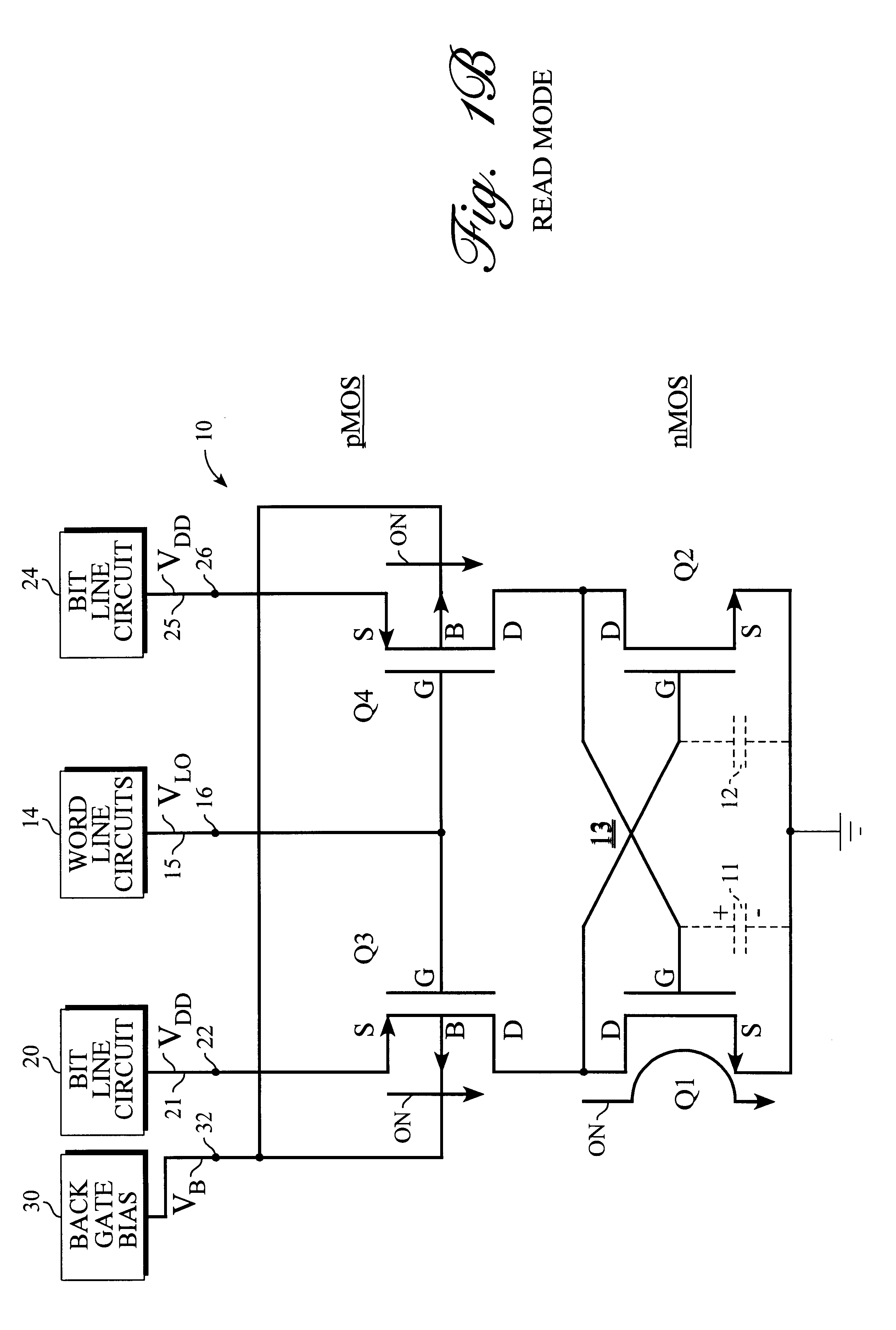
Static random access memory (RAM) systems and storage cell for same
A method of continuously replenishing a four-transistor static RAM storage cell is described. Such method comprises biasing both the back gate terminals and the normal gate terminals of the two bit line coupling transistors in the static RAM storage cell to voltage levels for causing a flow of small compensating currents through such coupling transistors when they are in a standby or non-access condition. Such small compensating currents are supplied to the two storage transistors in the storage cell for replenishing leakage of charge from the parasitic capacitance in the storage cell. The bias voltages arc supplied by adaptive bias circuits which adjust the bias voltages to track changes in the leakage of charge from the parasitic cell capacitance.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
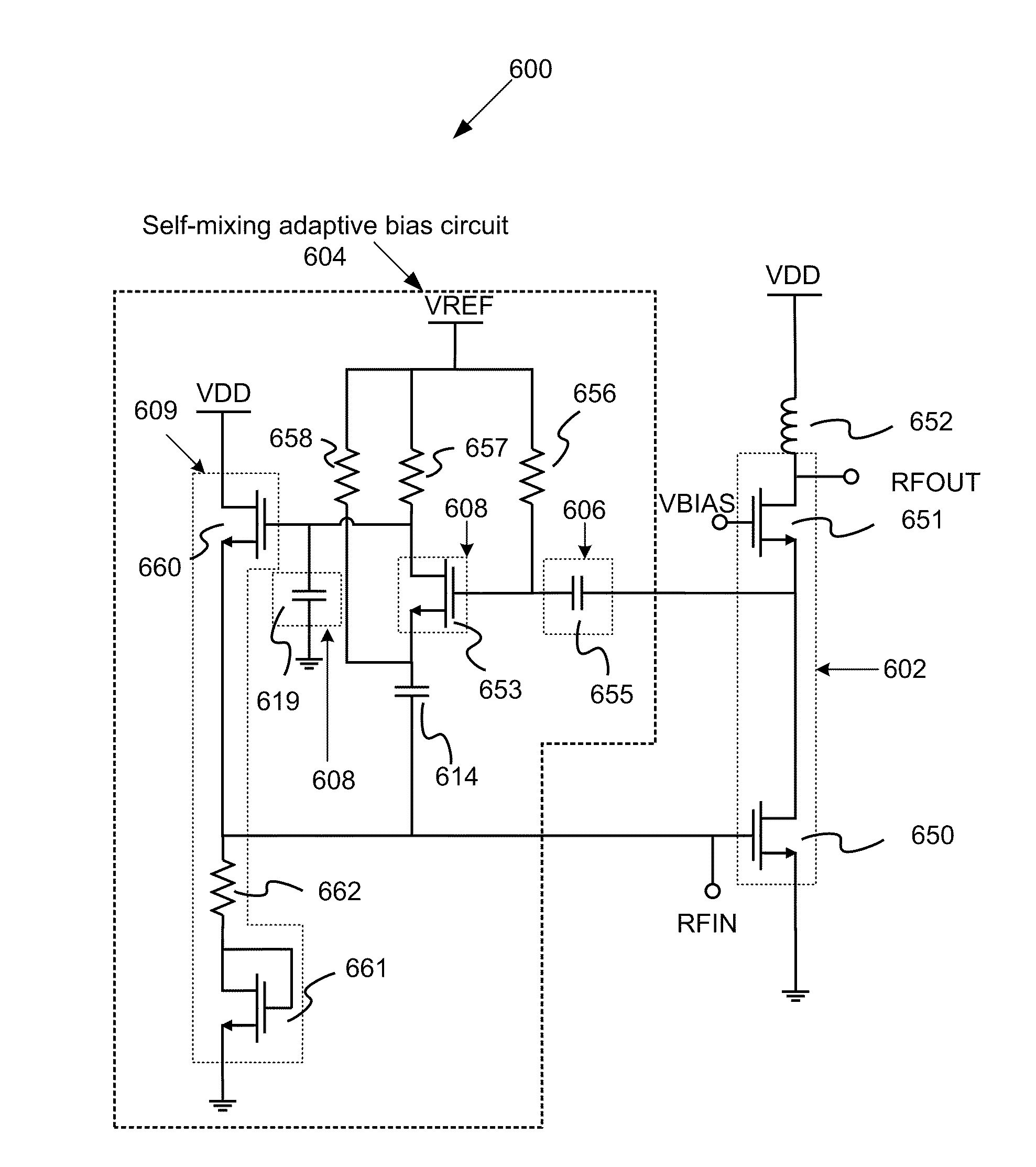
Systems and methods for self-mixing adaptive bias circuit for power amplifier
ActiveUS20100156536A1Improve linearityGain controlAmplififers with field-effect devicesAdaptive biasAudio power amplifier
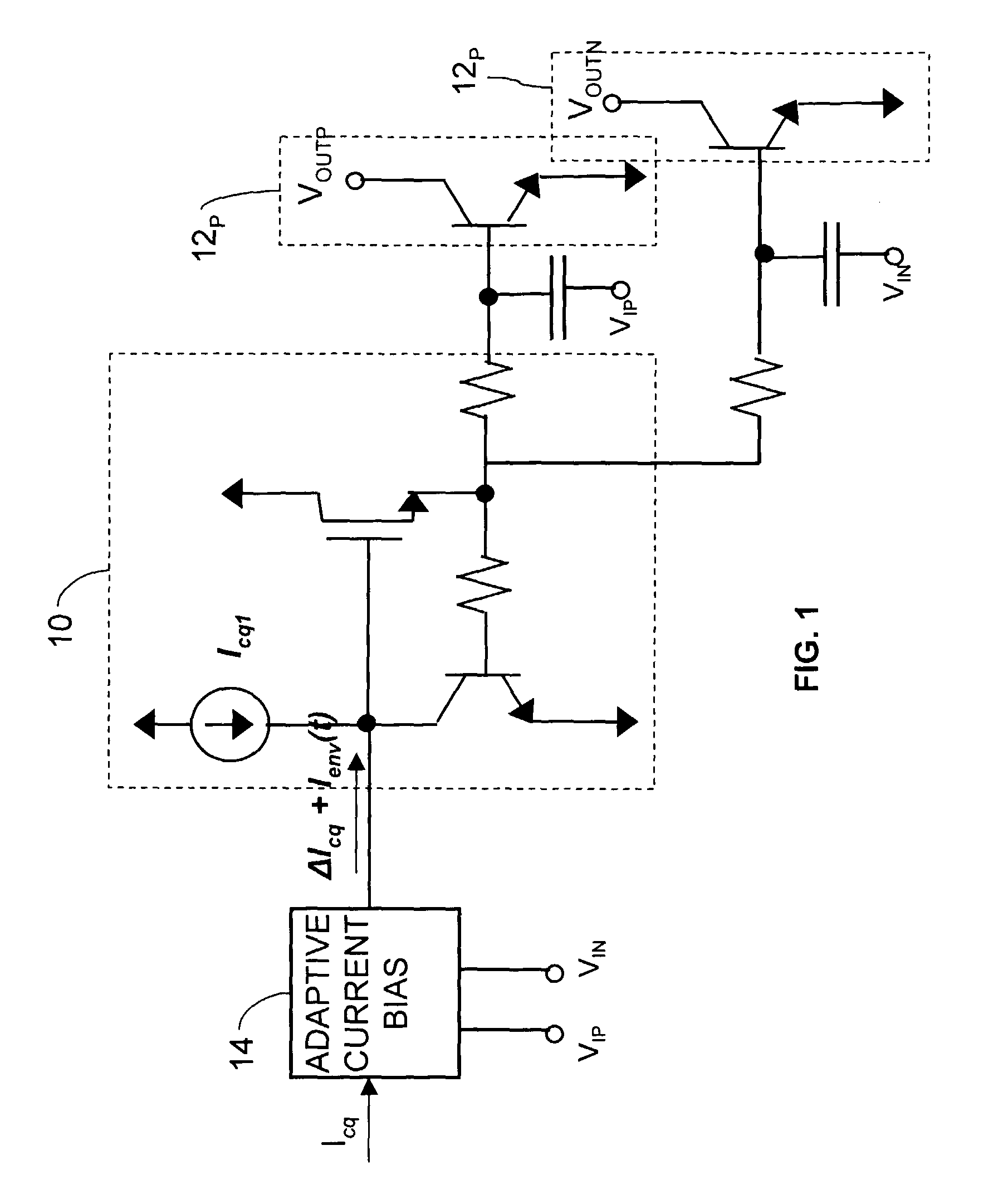
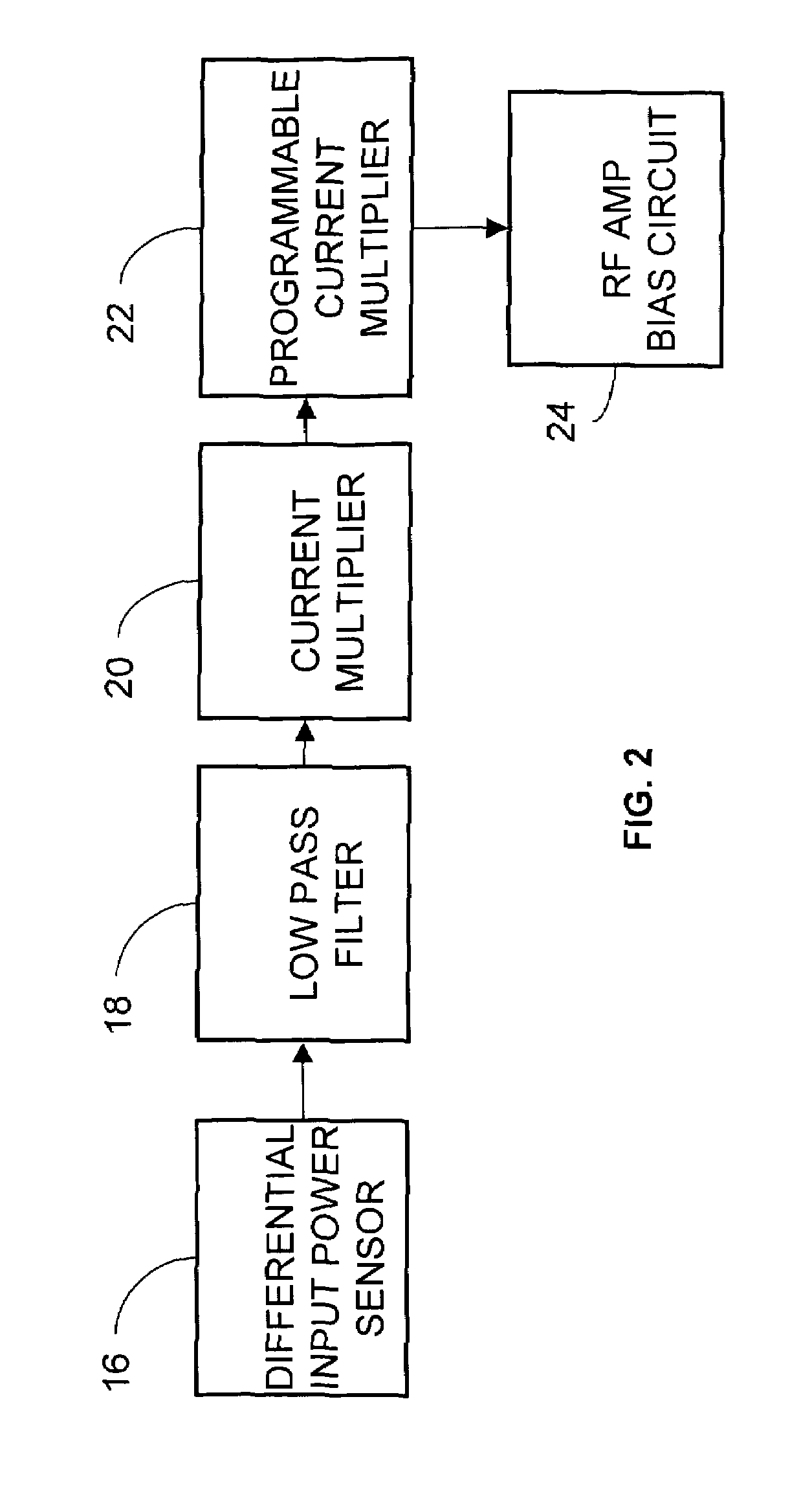
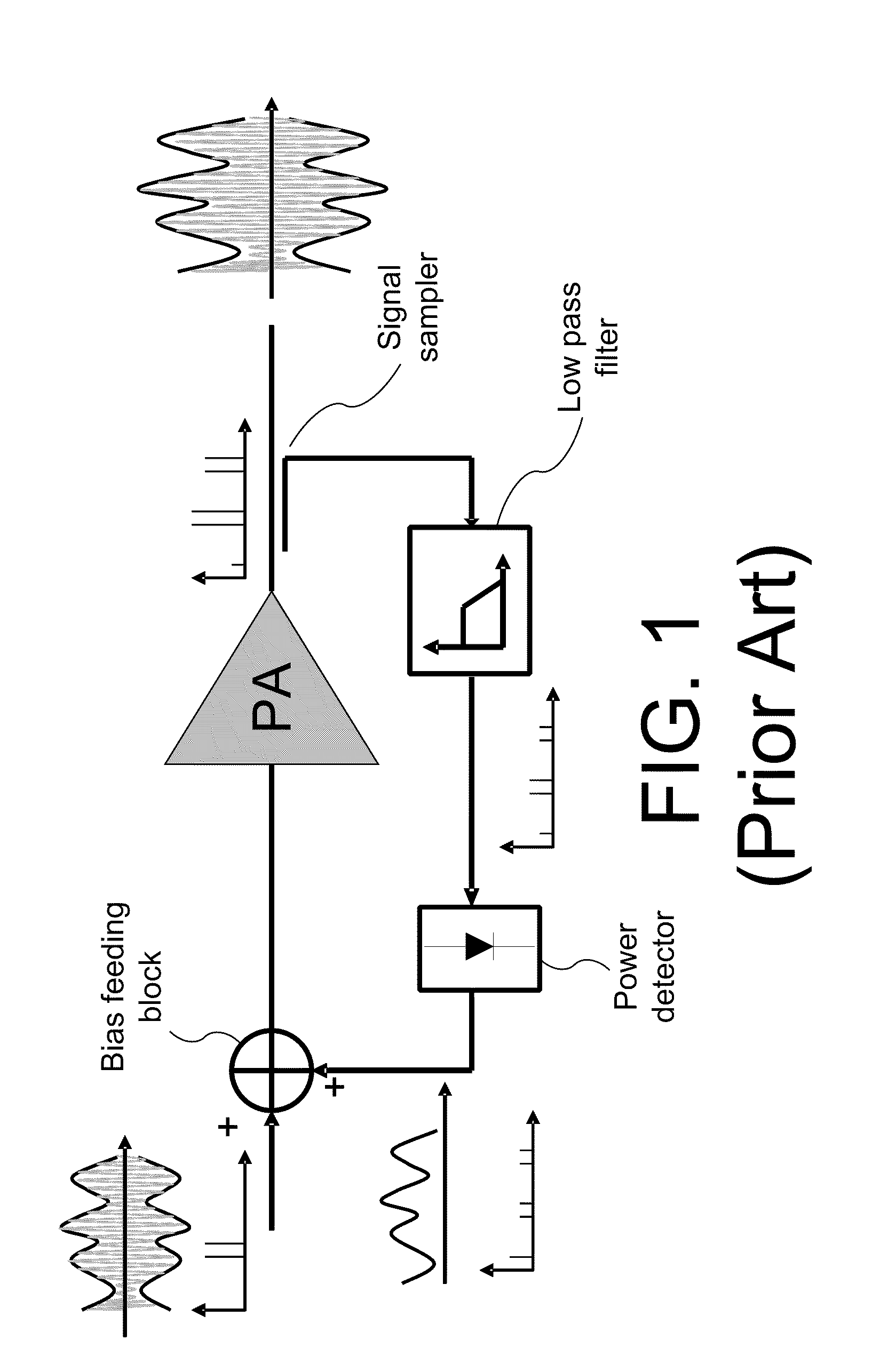
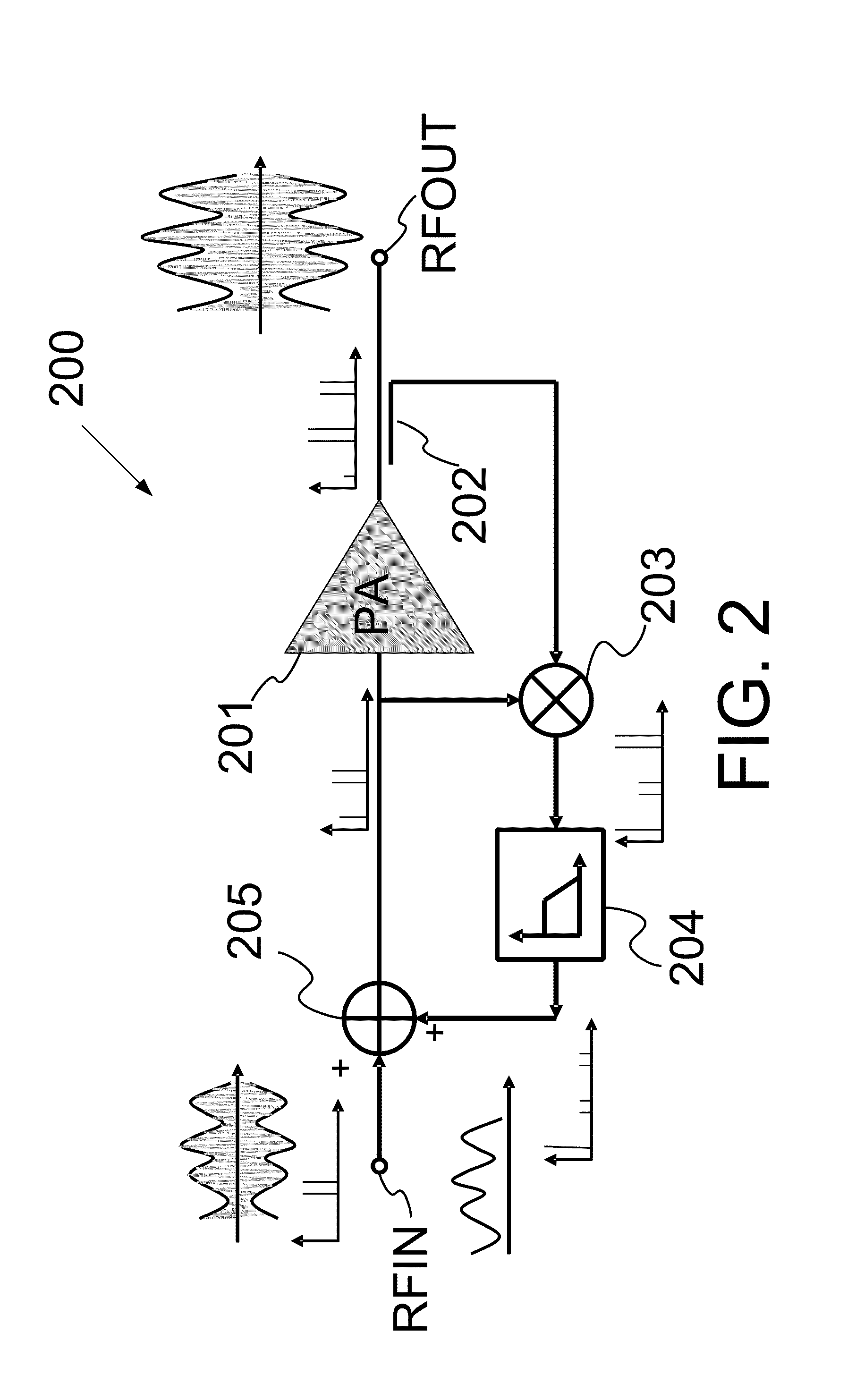
Systems and methods for providing a self-mixing adaptive bias circuit that may include a mixer, low-pass filter or a phase shifter, and a bias feeding block. The self-mixing adaptive bias circuit may generate an adaptive bias signal depending on input signal power level. As the input power level goes up, the adaptive bias circuit increases the bias voltage or bias current such that the amplifier will save current consumption at low power operation levels and obtain better linearity at high power operation levels compared to conventional biasing techniques. Moreover, the adaptive bias output signal can be used to cancel the third-order intermodulation terms (IM3) to further enhance the linearity as a secondary effect.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
Systems and methods for an adaptive bias circuit for a differential power amplifier
InactiveUS20100148871A1Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationPower amplifiersAdaptive biasCommon emitter
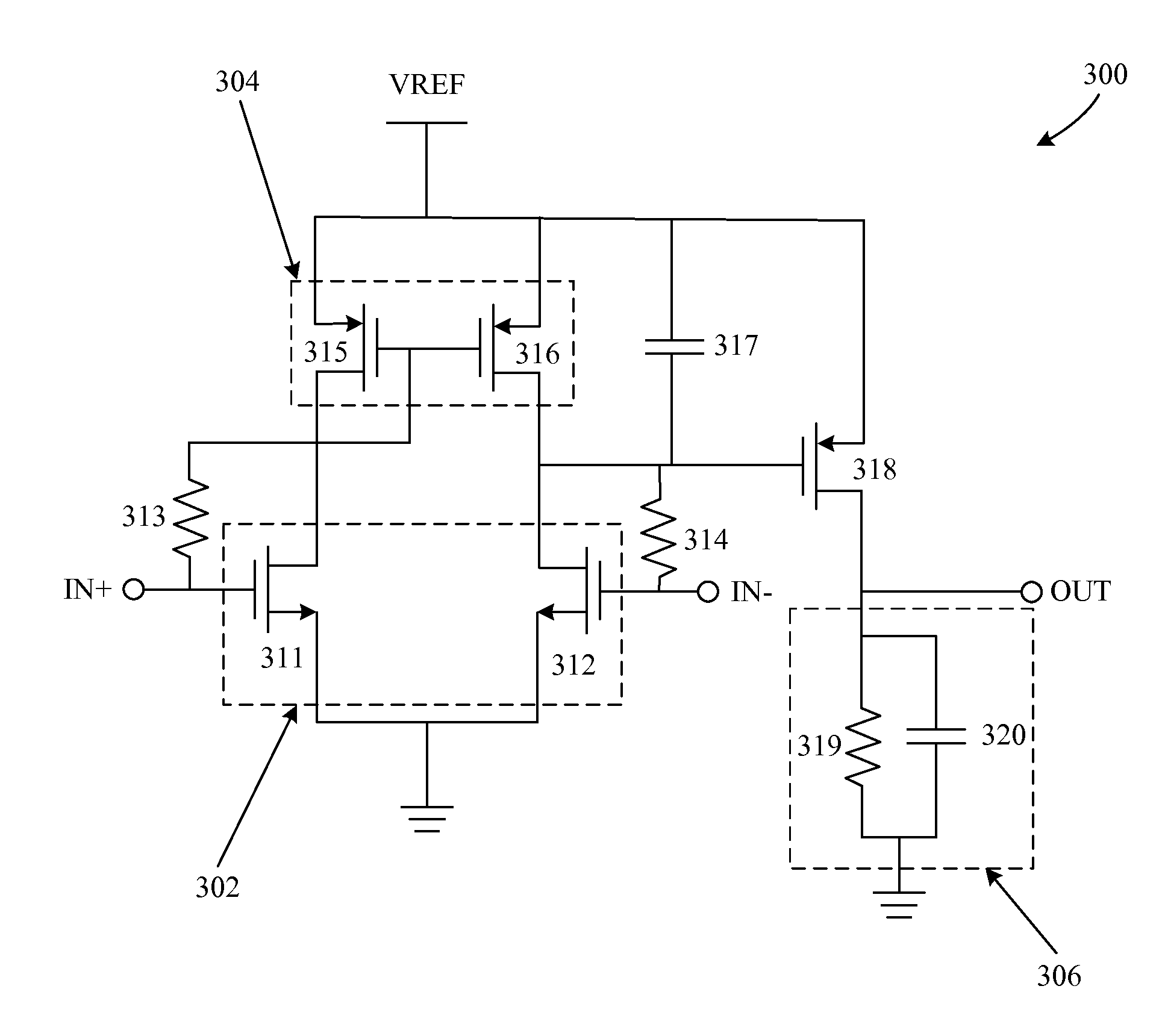
Systems and methods for providing an adaptive bias circuit that may include a differential amplifier, low-pass filter, and common source amplifier or common emitter amplifier. The adaptive bias circuit may generate an adaptive bias output signal depending on input signal power level. As the input power level goes up, the adaptive bias circuit may increase the bias voltage or bias current of the adaptive bias output signal. A power amplifier (e.g., a differential amplifier) may be biased according to the adaptive bias output signal in order to reduce current consumption at low power operation levels.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
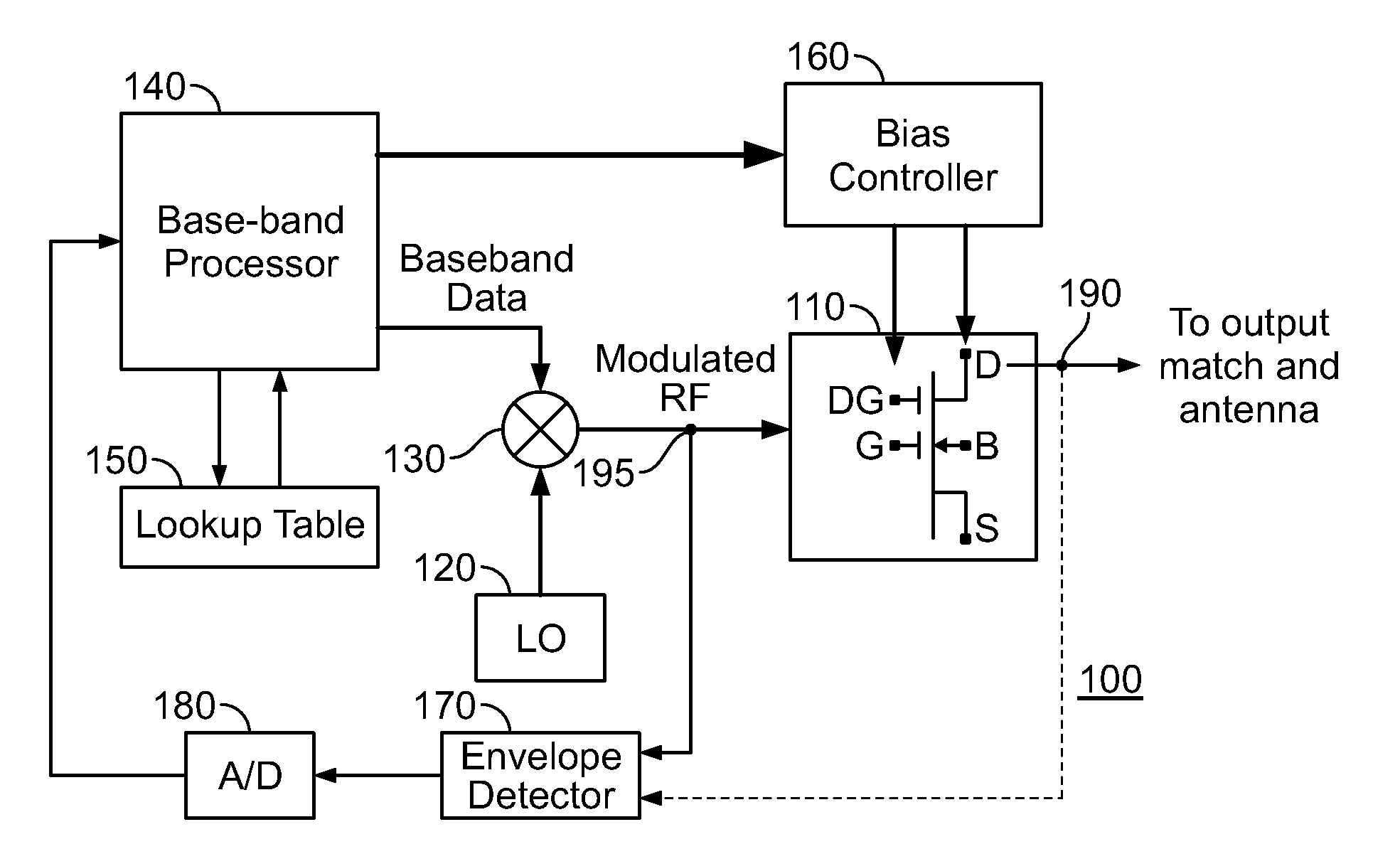
Doherty amplifier utilizing adaptive bias control
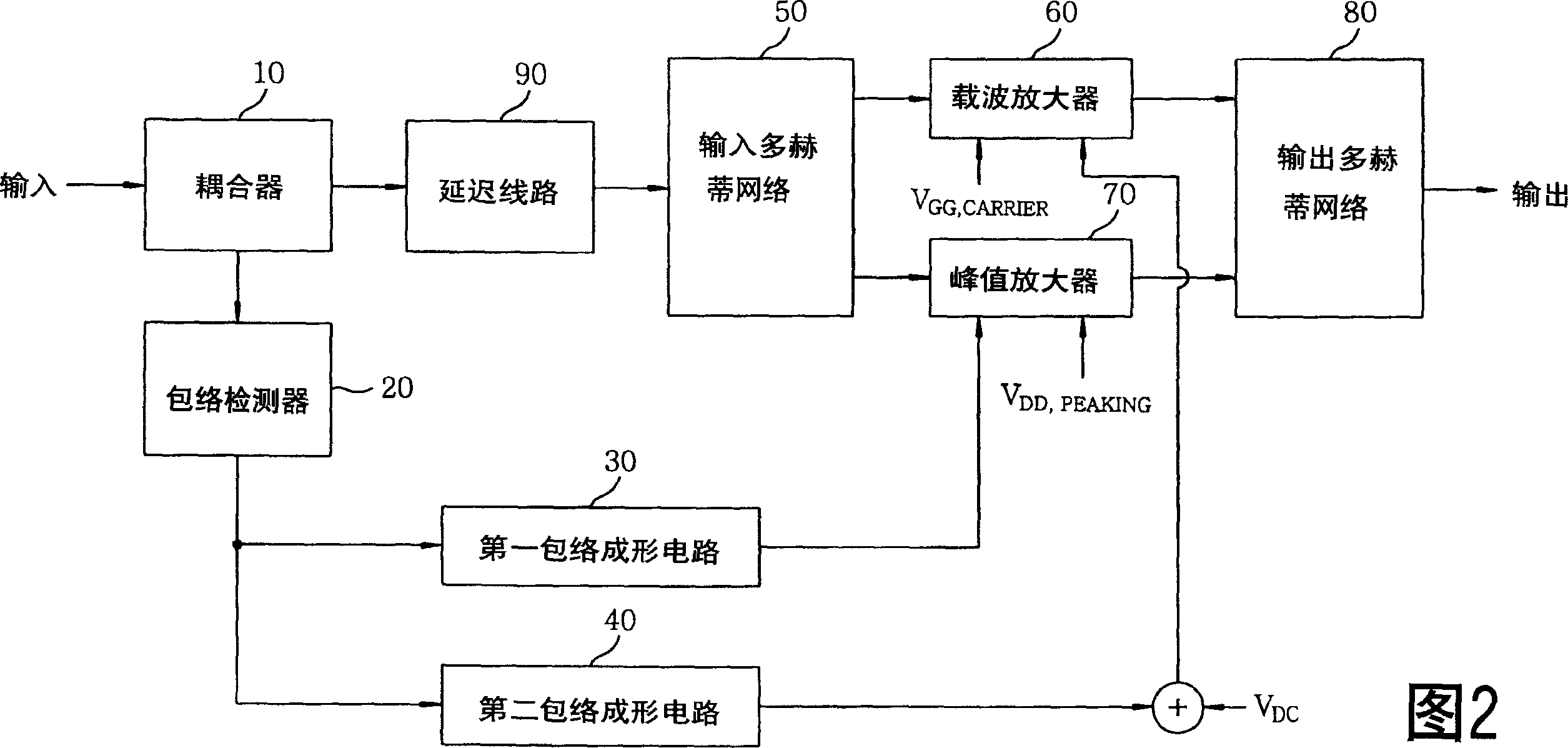
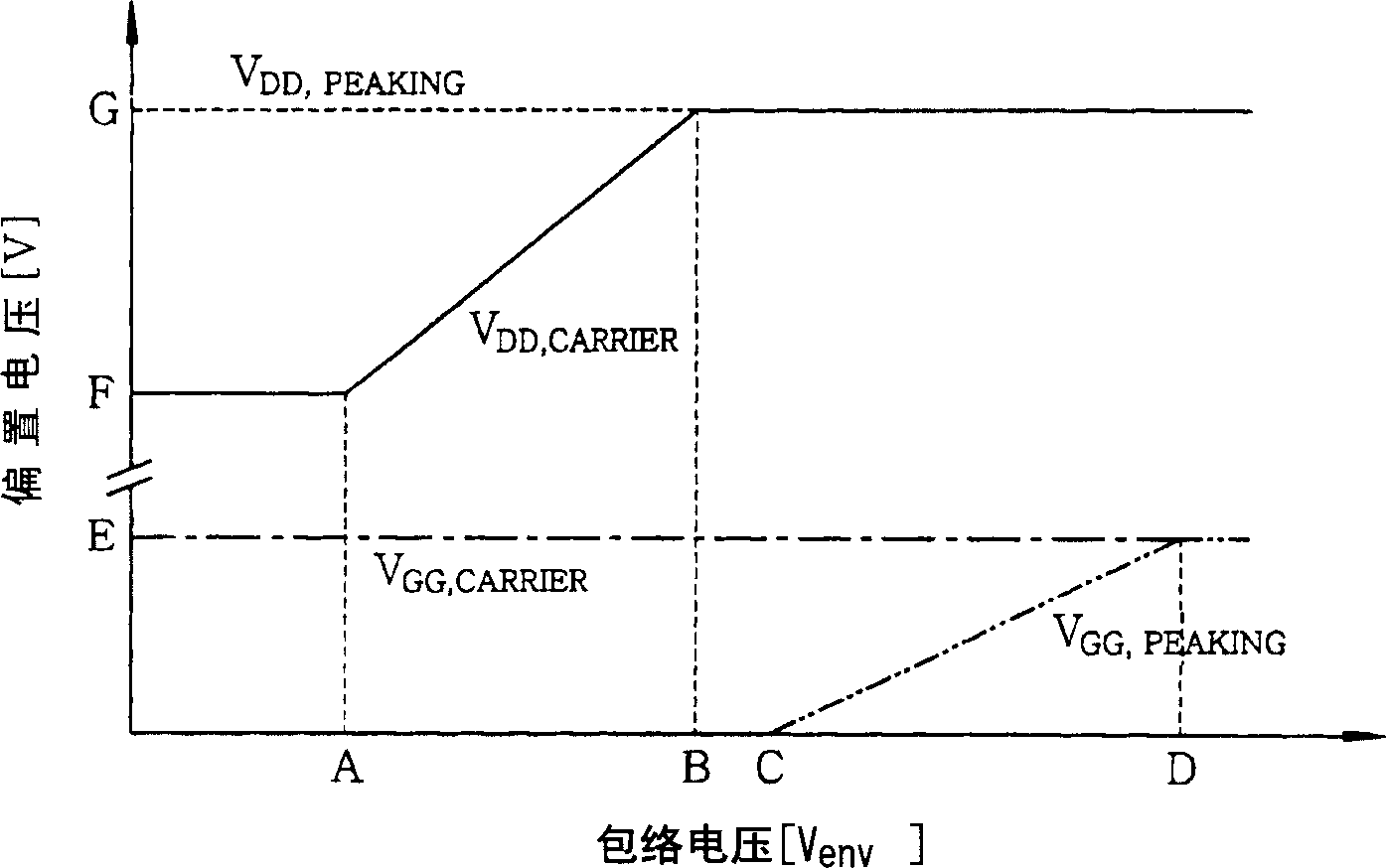
InactiveCN1527478AImprove linearityMaximize efficiencyAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAdaptive biasAudio power amplifier
An amplifier circuit using an adaptive bias control comprises an envelope detector for detecting an envelope of an input signal from a coupler, envelope shaping circuits for transforming of the envelope voltage from the envelope detector. The one transformed envelope voltage is applied to a drain bias for the peaking amplifier and the other is add by VDC to be applied to a gate bias for the carrier amplifier. In the Doherty amplifier, the gate voltage of the peaking amplifier and the drain voltage of the peaking amplifier are controlled in accordance with the input signal envelope to maximize efficiency with a desired linearity.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Operational amplifier of class AB
ActiveUS7576610B2Reduce power consumptionEnhanced DC-gainDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesAdaptive biasAudio power amplifier
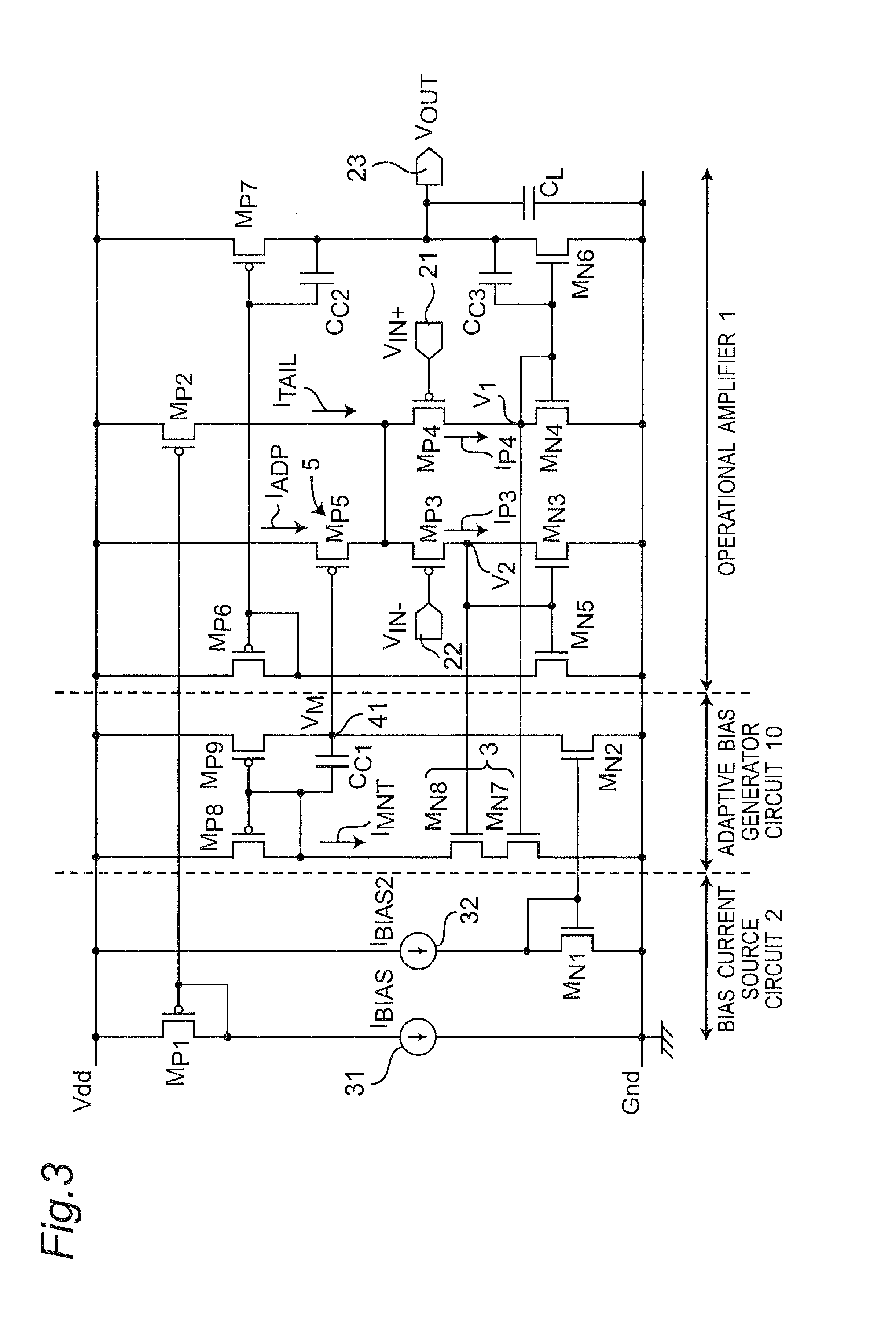
A class AB operational amplifier is provided that includes first and second input transistors respectively coupled between first and second internal nodes and a first common node, first and second input stage load transistors diode connected and respectively coupled between a first voltage reference and the first and second internal nodes, first and second output transistors coupled in series between the first voltage reference and a second voltage reference, a tail current generator coupled between the first common node and the second voltage reference, an adaptive bias block coupled between the first and second voltage references and coupled to the first common node, and a positive feedback network coupled between the first voltage reference and the first and second internal nodes. Also provided is an integrated circuit having at least one such operational amplifier.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Linear-in-dB variable gain amplifiers with an adaptive bias current
ActiveUS20060132237A1Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationGain controlAdaptive biasAudio power amplifier
Linear-in-dB current-steering VGAs with an adaptive bias current operable so that as the gain of the amplifier decreases, the DC current consumption also decreases. The modified VGA circuits result in power consumption savings, which are of particular value in wireless (battery powered) applications.
Owner:THETA IP
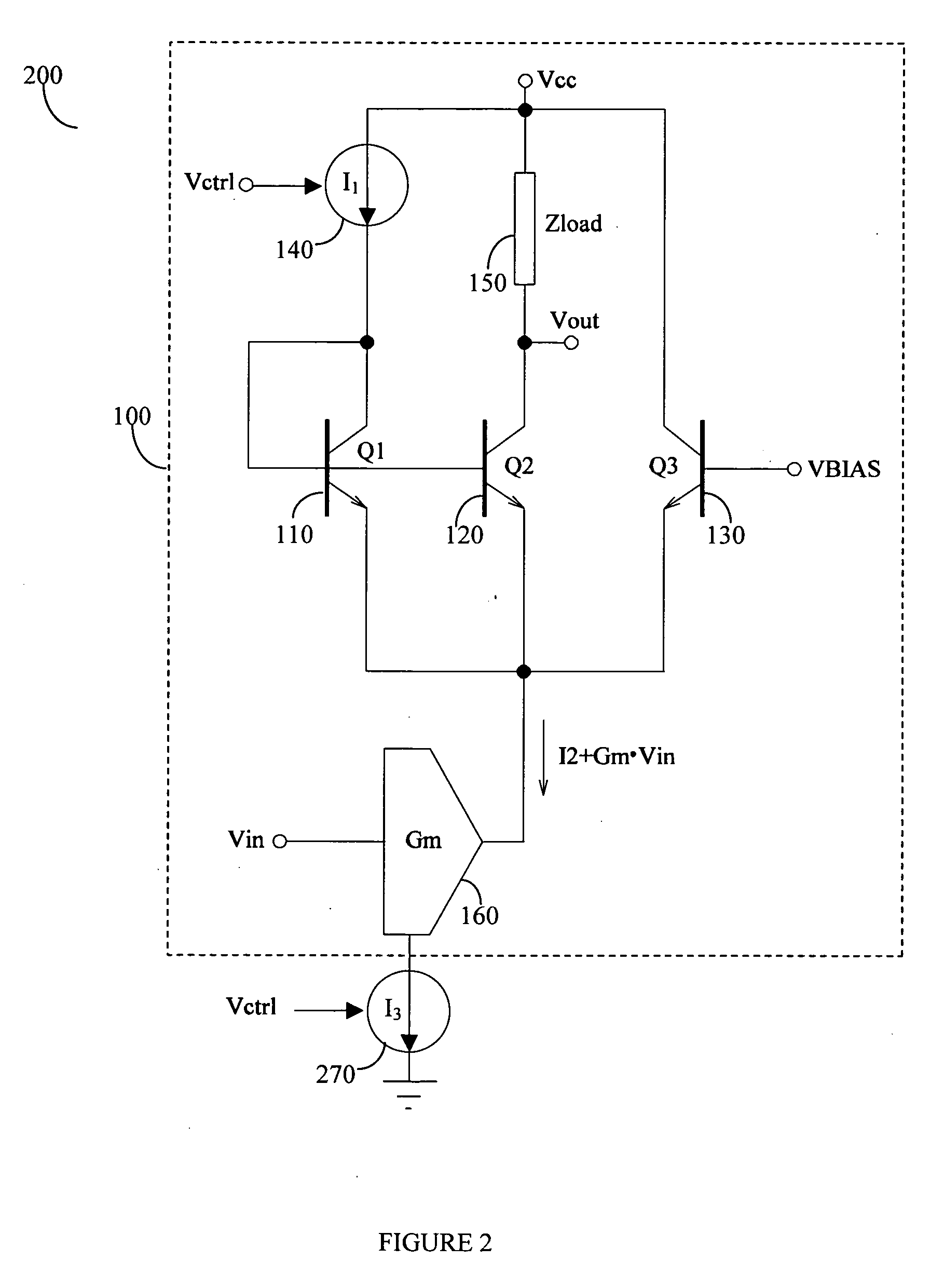
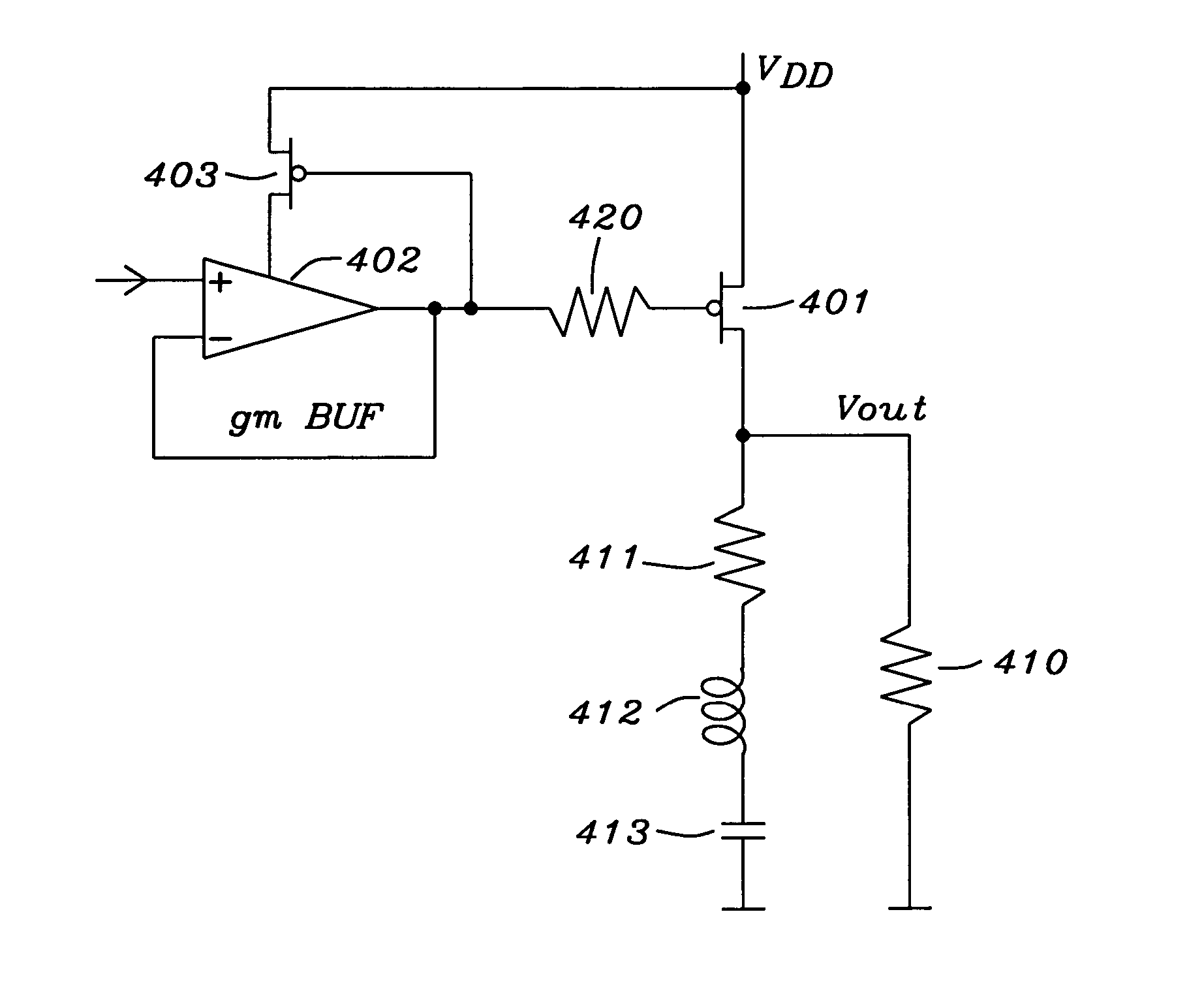
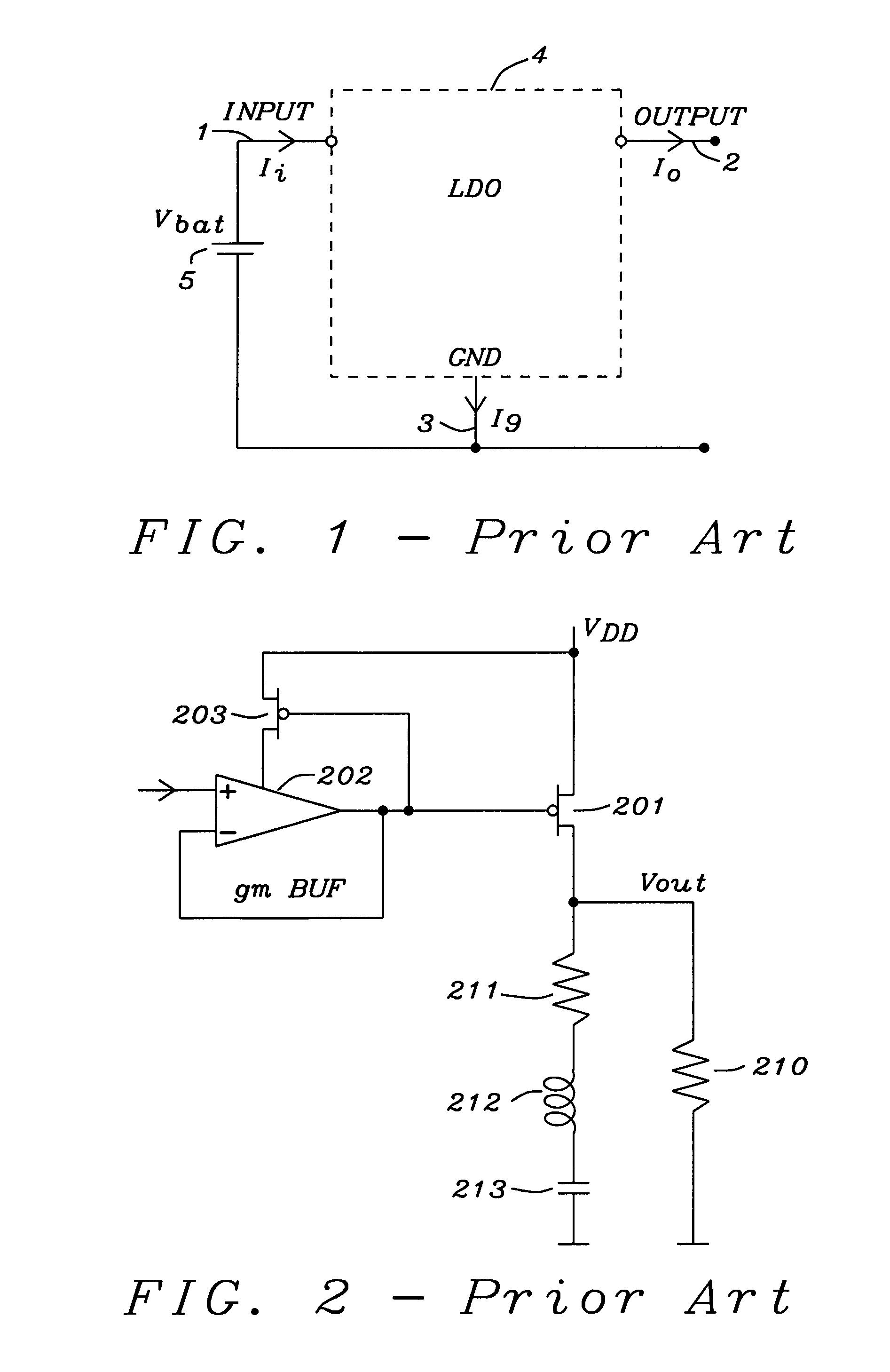
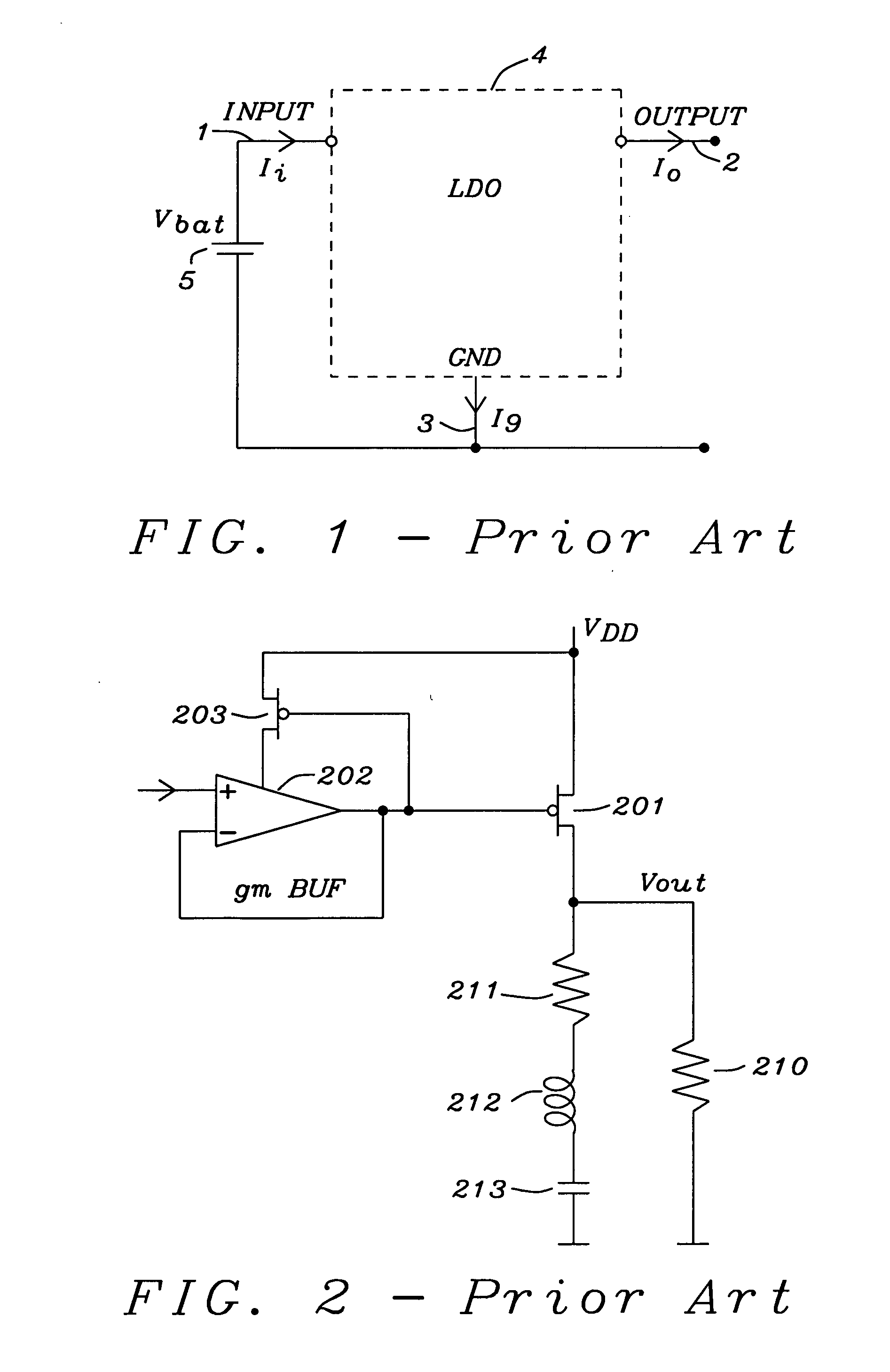
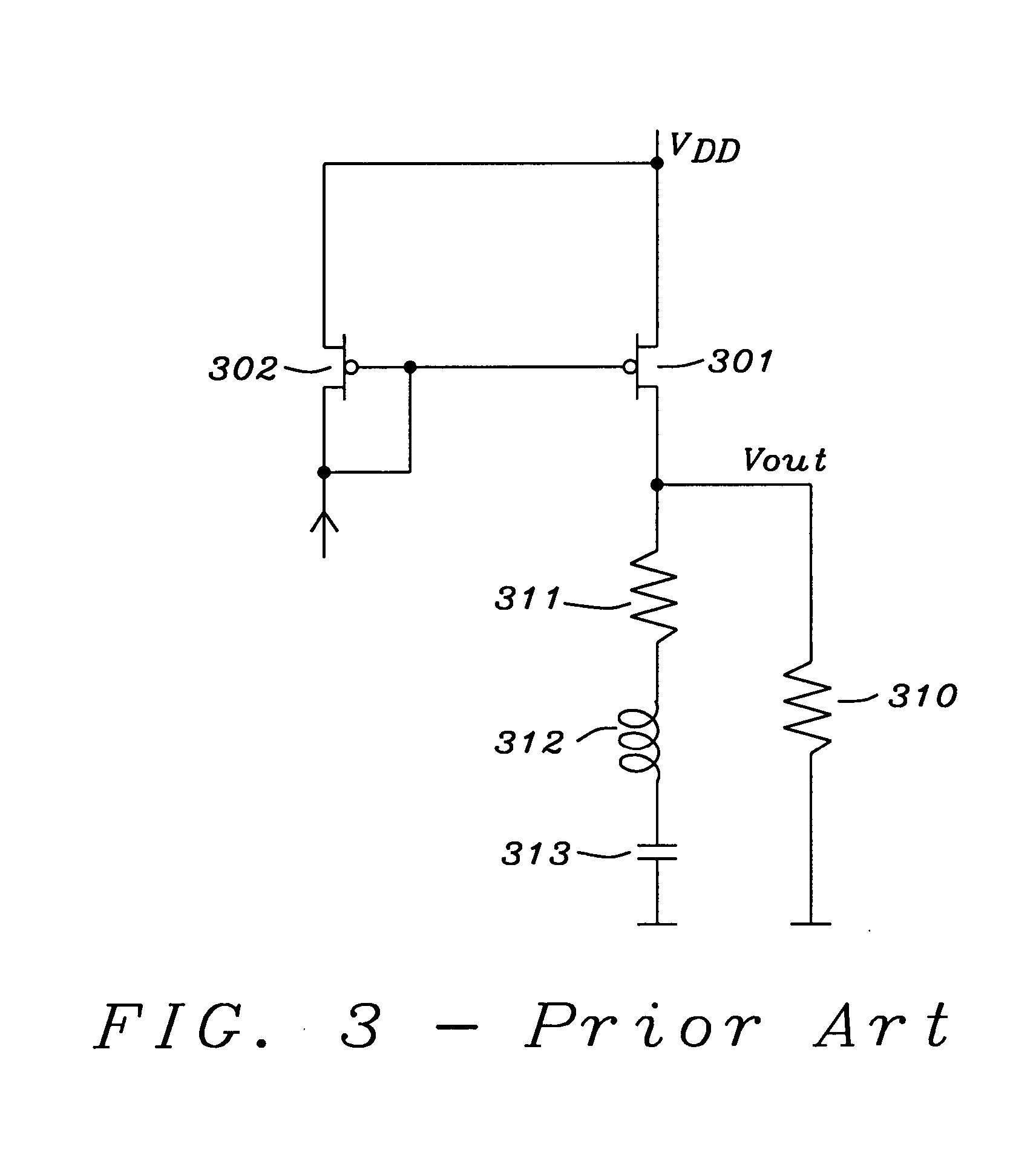
Frequency compensation scheme for low drop out voltage regulators using adaptive bias
ActiveUS7030677B2Improve stabilityCurrent consumptionPulse automatic controlPulse shapingAdaptive biasCapacitance
A method and circuits to improve the stability of low dropout voltage regulators having an adaptive biased driving stage. Said improvement of stabilization is valid through the total range of output current possible. A serial impedance is added to the gate capacitance of the PMOS pass device of said LDO. Said serial impedance could be a resistor or a transistor. In case of low load currents said impedance is not dominating, for high load currents said impedance keeps the gate pole close to the resonance frequency of the output tank. In case of medium load currents, wherein the inner resistance of the driving stage is about equal to said serial impedance, the gate pole could get too low. This problem is solved by reducing said serial impedance by shunting. Said shunting can be performed stepwise depending on the size of the load current. A special circuitry detects the condition of medium load currents and can initialize the shunting of said serial impedance accordingly in order to keep the gate pole on the optimum frequency.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
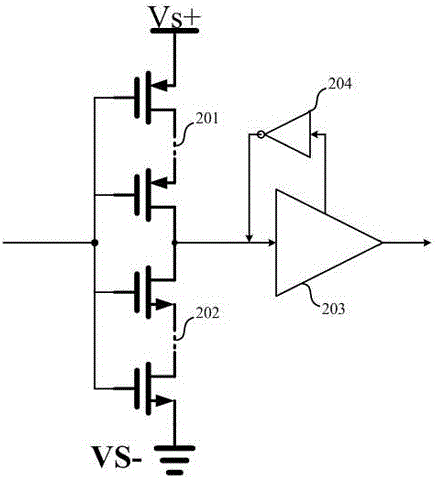
Comparator circuit provided with differential amplifier making logical judgment by comparing input voltage with reference voltage
ActiveUS20110210762A1Shorten judgment timeIncrease speedMultiple input and output pulse circuitsInstant pulse delivery arrangementsAdaptive biasPower flow
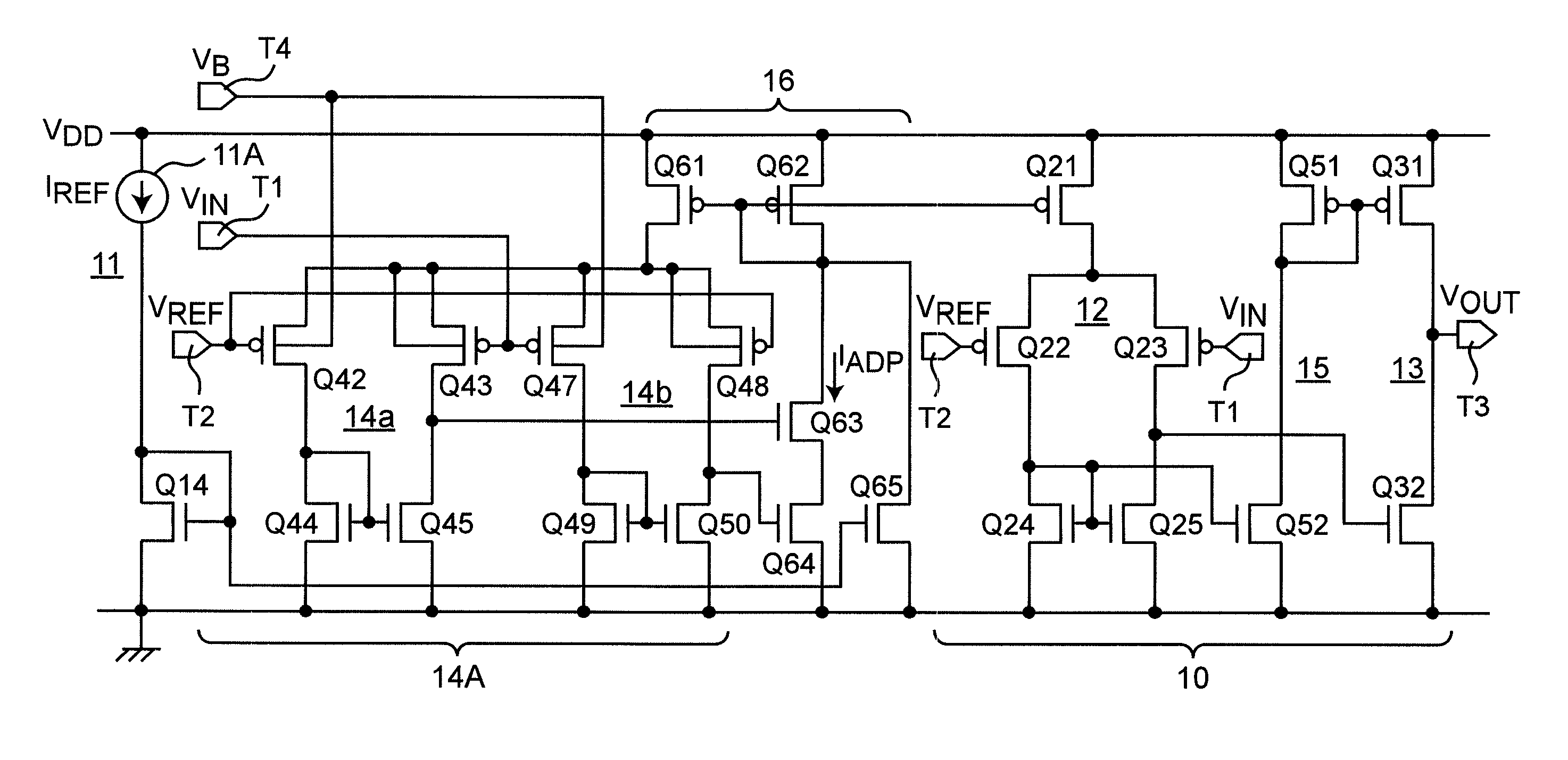
In a comparator circuit having a differential amplifier, which makes a logical judgment by comparing an input voltage with a reference voltage, generates and outputs a resulting output voltage thereof, a current source generates and supplies a bias current of a predetermined minute current to the differential amplifier, and a first inverter circuit inverts a differential voltage from the differential amplifier. An adaptive bias current generator circuit detects the bias current of the current source, and a through current of the first inverter circuit. The adaptive bias current generator circuit generates and supplies an adaptive bias current for executing adaptive bias current control to the differential amplifier to allow the differential amplifier to operate with the bias current upon no logical judgment, and to allow the differential amplifier to operate by using the adaptive bias current obtained by increasing the bias current upon logical judgment.
Owner:SONY CORP
Frequency compensation scheme for low drop out voltage regulators using adaptive bias
ActiveUS20050040799A1Improve stabilityCurrent consumptionPulse automatic controlPulse shapingCapacitanceAdaptive bias
A method and circuits to improve the stability of low dropout voltage regulators having an adaptive biased driving stage. Said improvement of stabilization is valid through the total range of output current possible. A serial impedance is added to the gate capacitance of the PMOS pass device of said LDO. Said serial impedance could be a resistor or a transistor. In case of low load currents said impedance is not dominating, for high load currents said impedance keeps the gate pole close to the resonance frequency of the output tank. In case of medium load currents, wherein the inner resistance of the driving stage is about equal to said serial impedance, the gate pole could get too low. This problem is solved by reducing said serial impedance by shunting. Said shunting can be performed stepwise depending on the size of the load current. A special circuitry detects the condition of medium load currents and can initialize the shunting of said serial impedance accordingly in order to keep the gate pole on the optimum frequency.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR
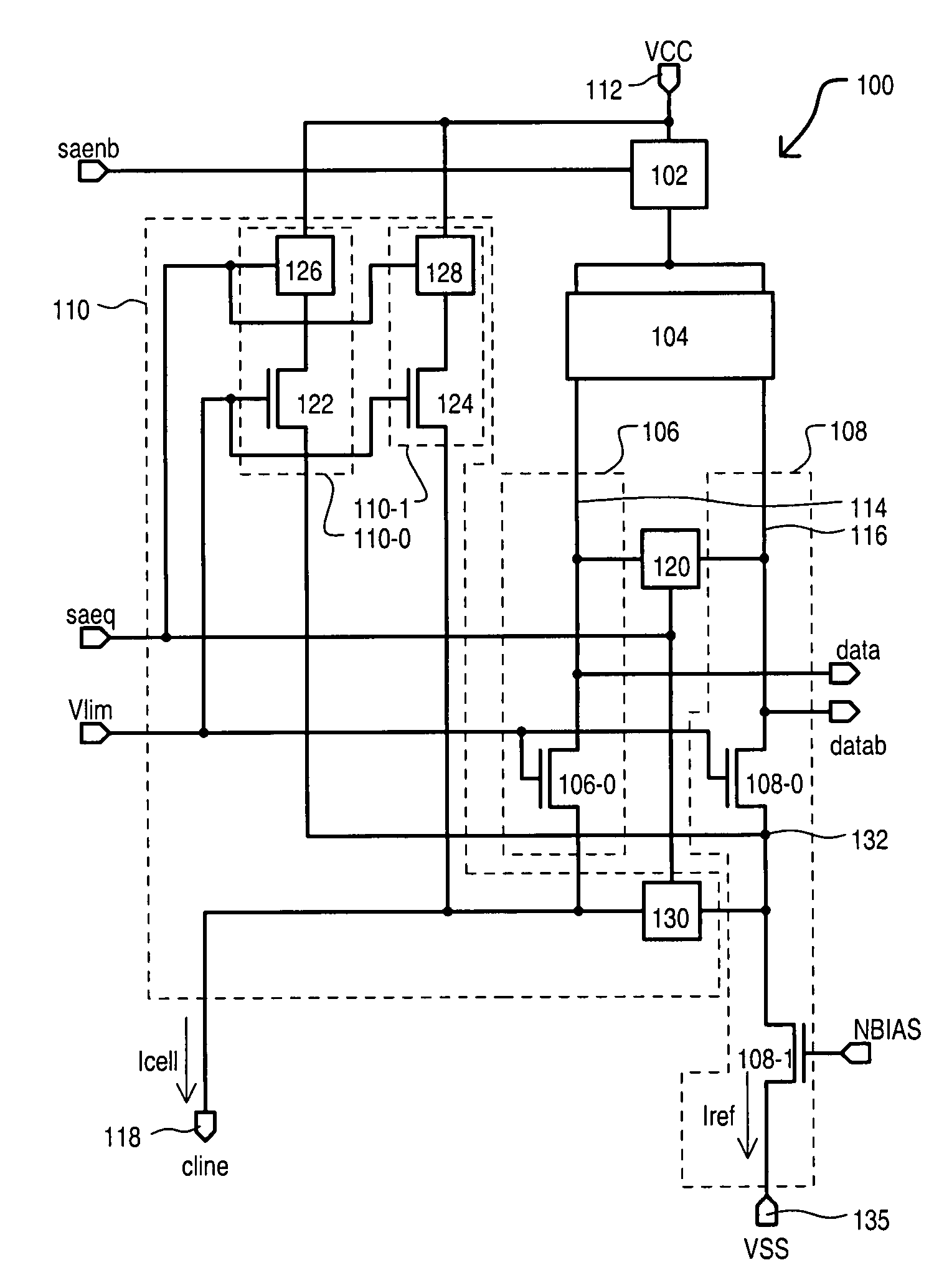
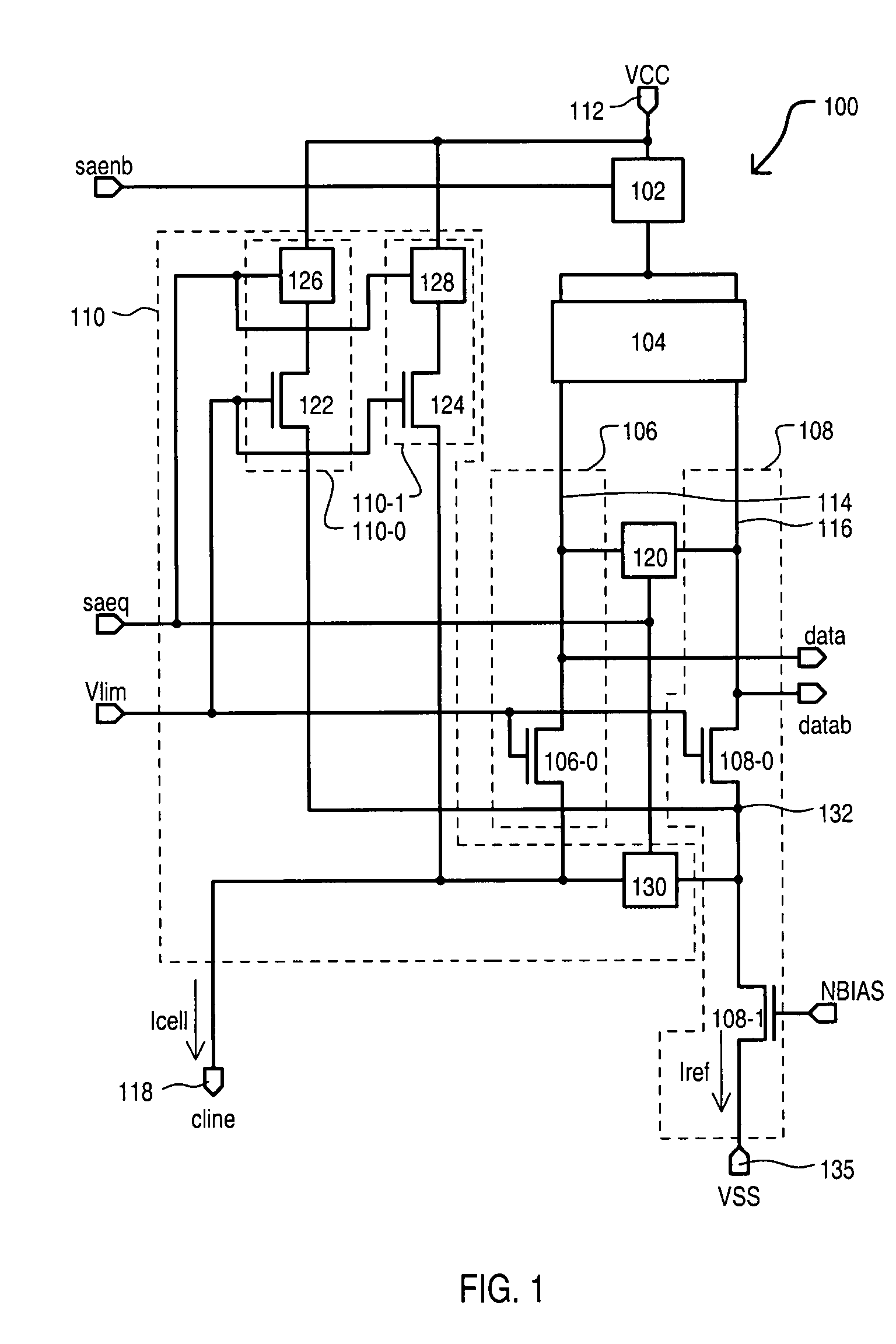
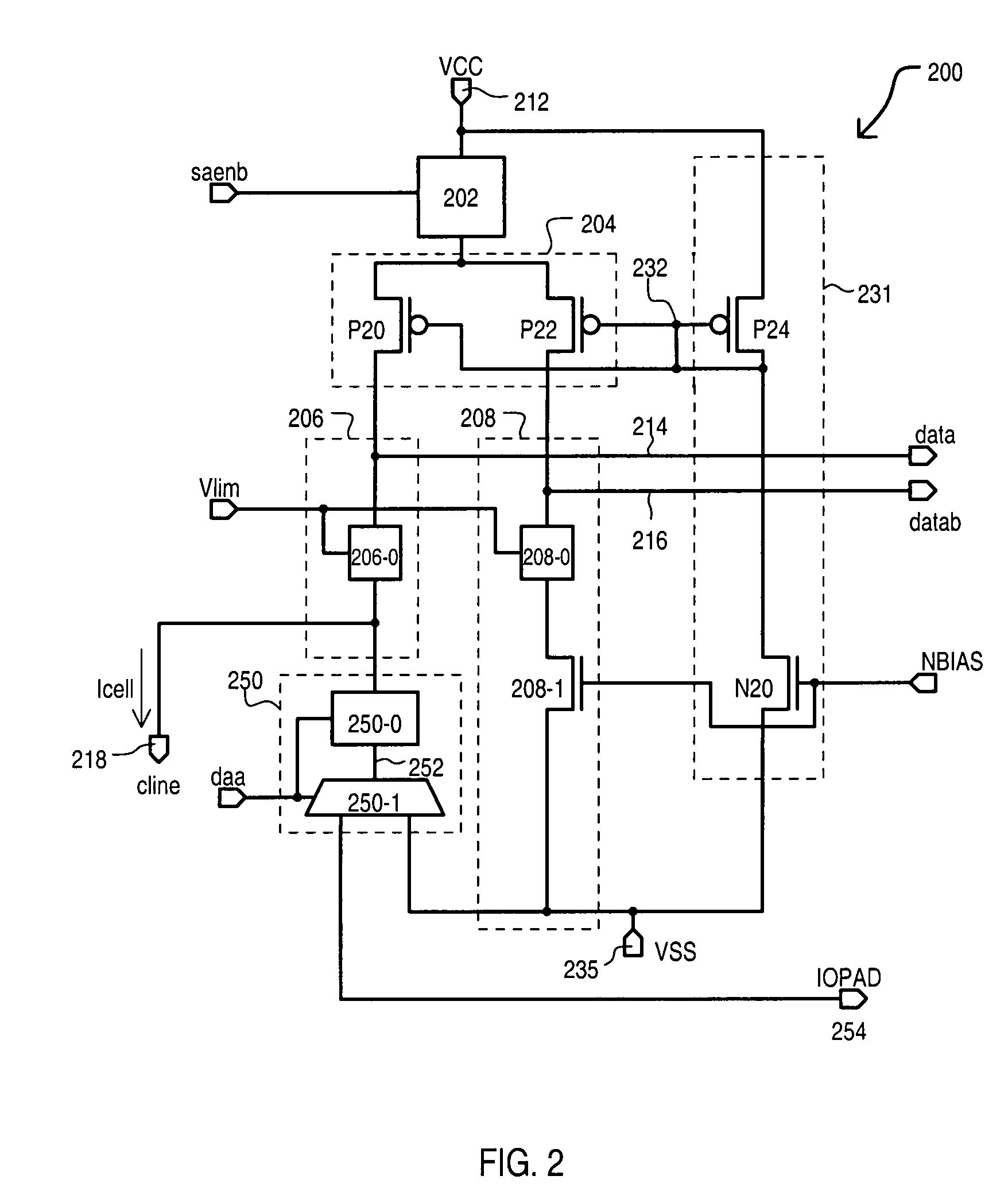
Adaptive current sense amplifier with direct array access capability
A current sense amplifier can include an active load circuit having a first load device and second load device coupled in parallel to a first power supply node. A first load device and second load device can provide an impedance that varies according to a potential at a load control node. A reference current circuit can be coupled between the first load device and a second power supply node that includes a current reference section that provides an impedance according to a bias voltage. A data current circuit can be coupled between the second load device and a plurality of memory cells. An adaptive bias circuit can be coupled between the first power supply and the second power supply node and can include a bias section coupled to the load control node that provides an impedance according to the bias voltage.
Owner:LONGITUDE FLASH MEMORY SOLUTIONS LTD
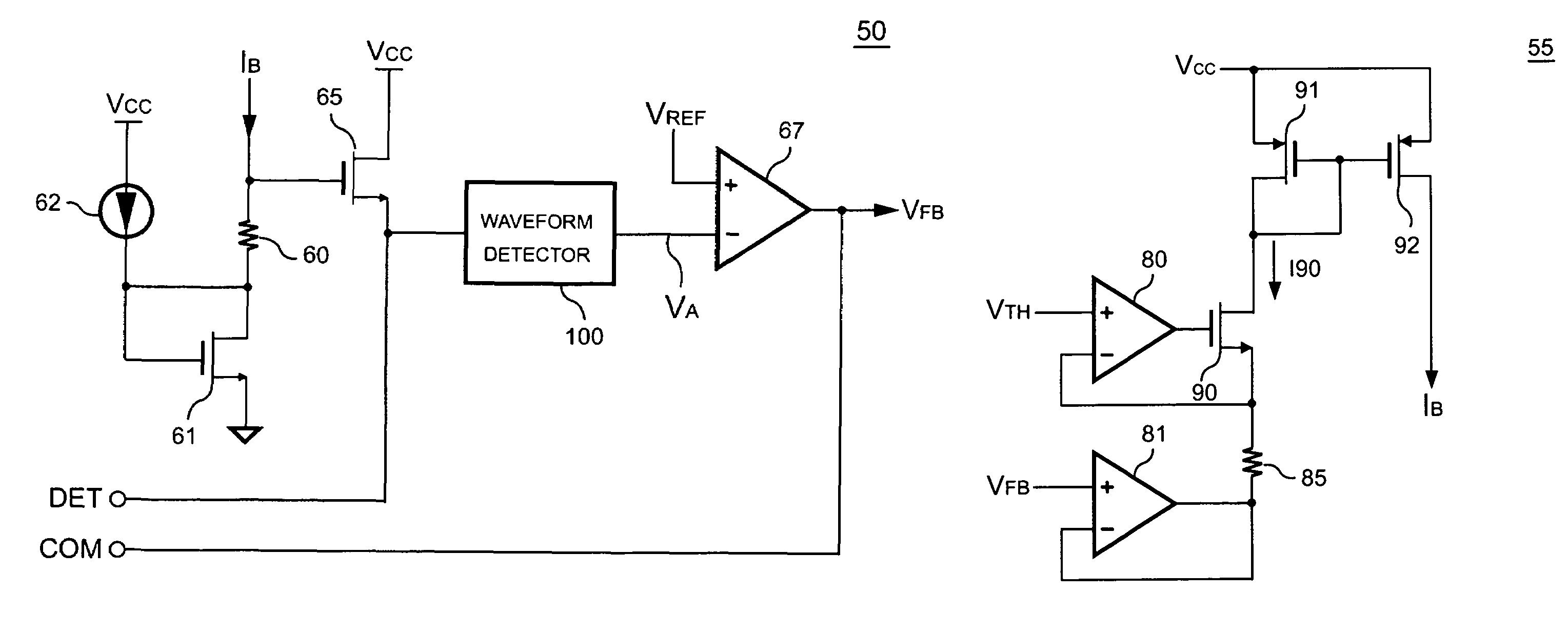
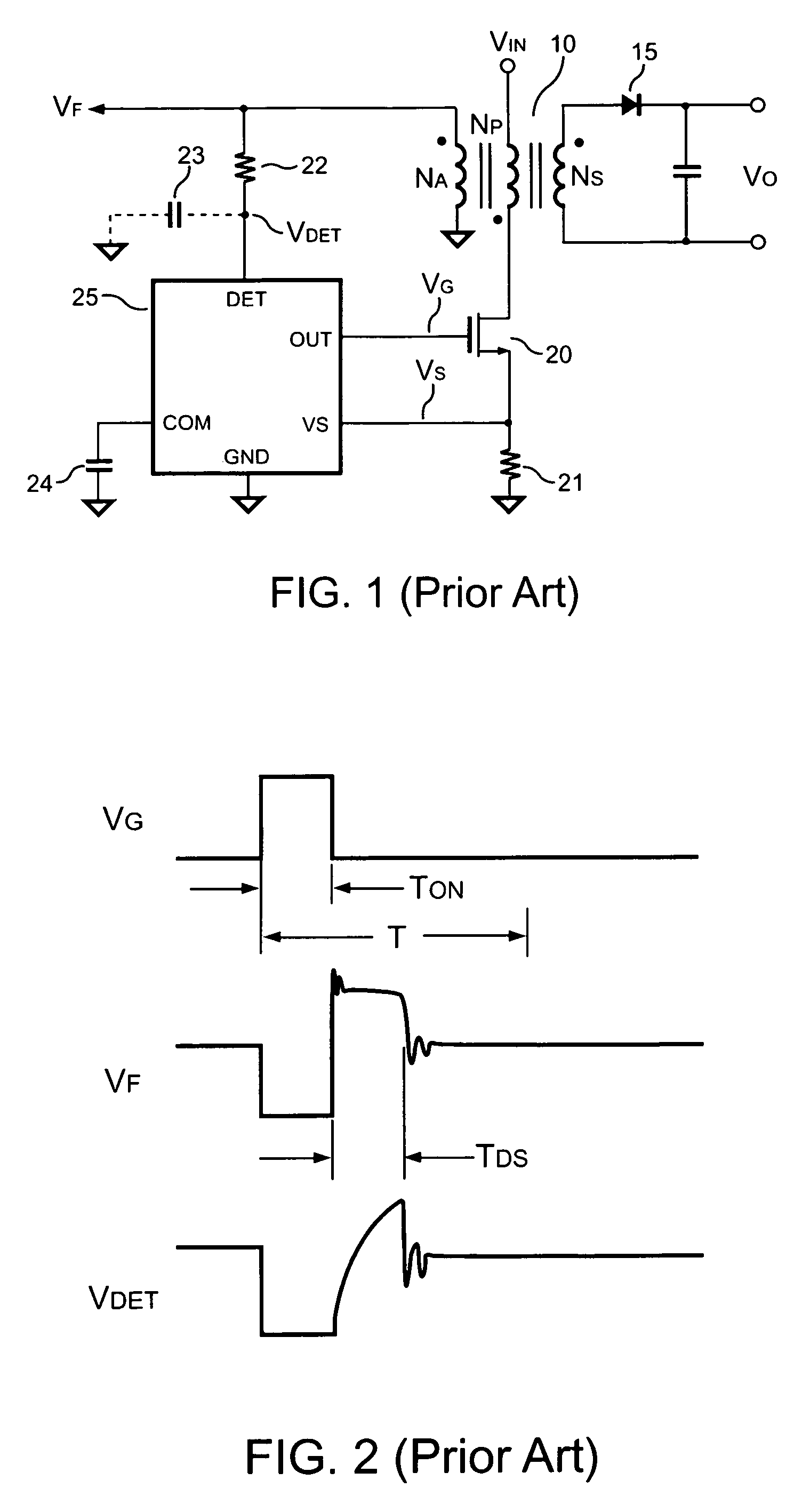
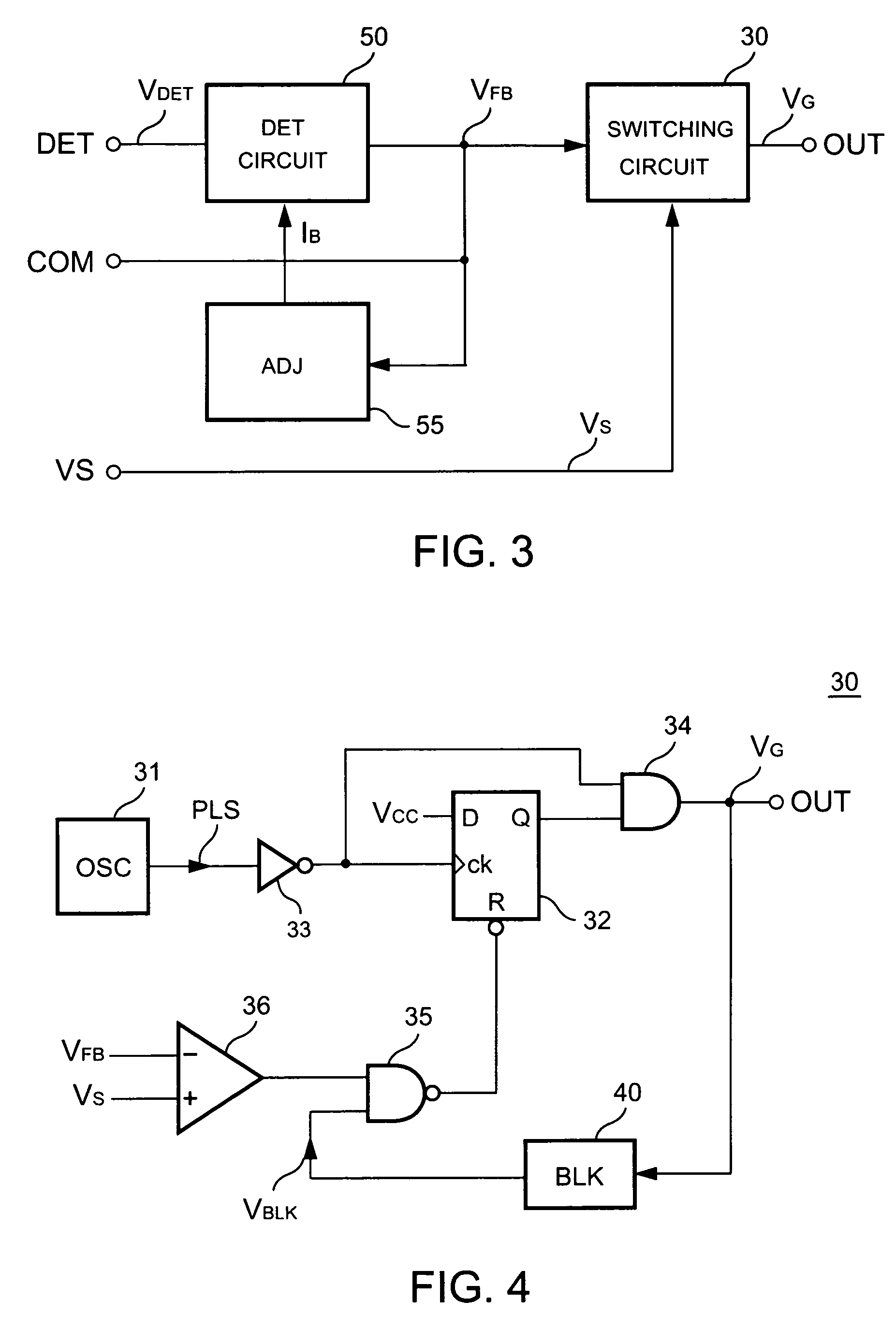
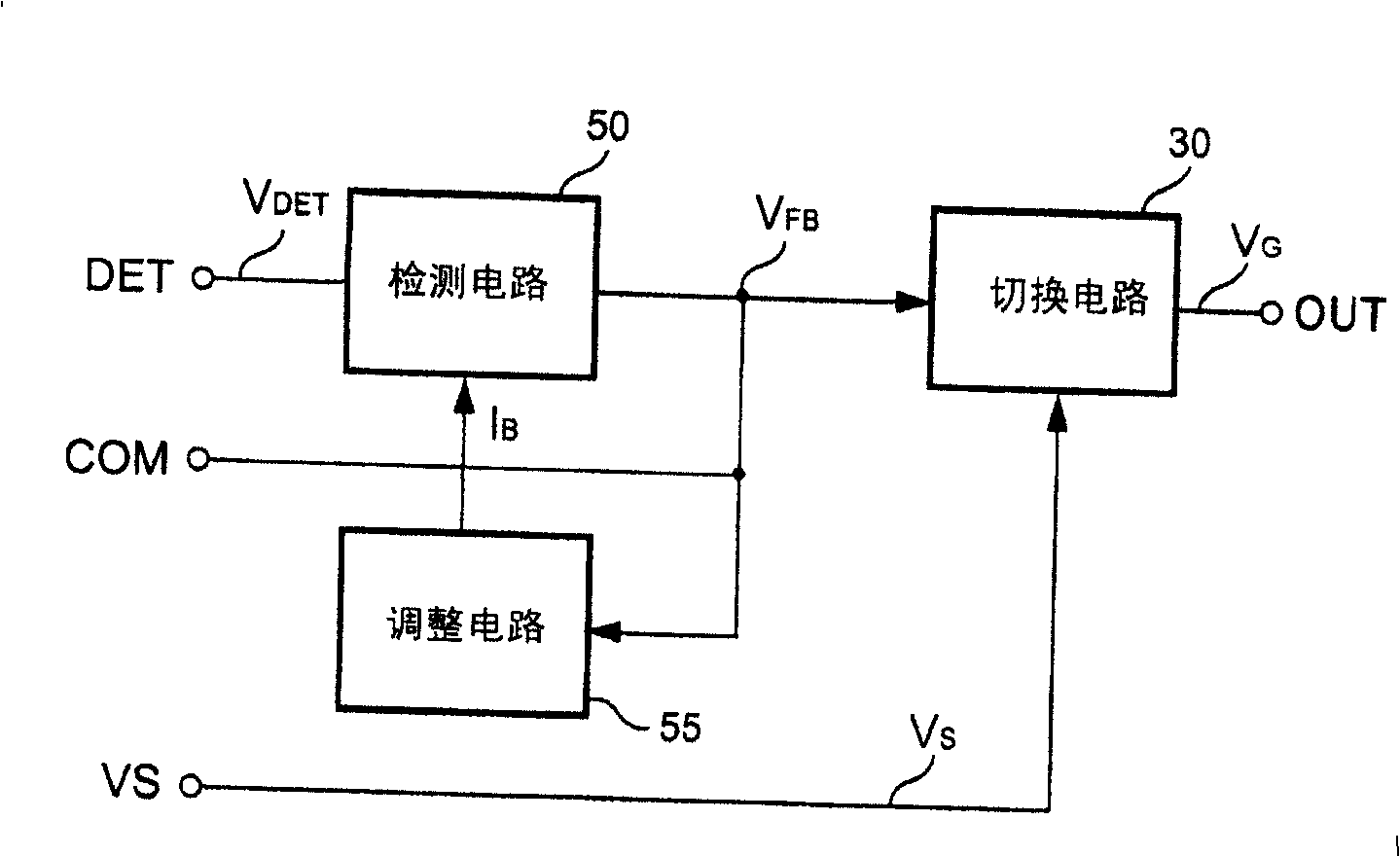
Control circuit of power converter having adaptive bias for detecting reflected voltage of transformer
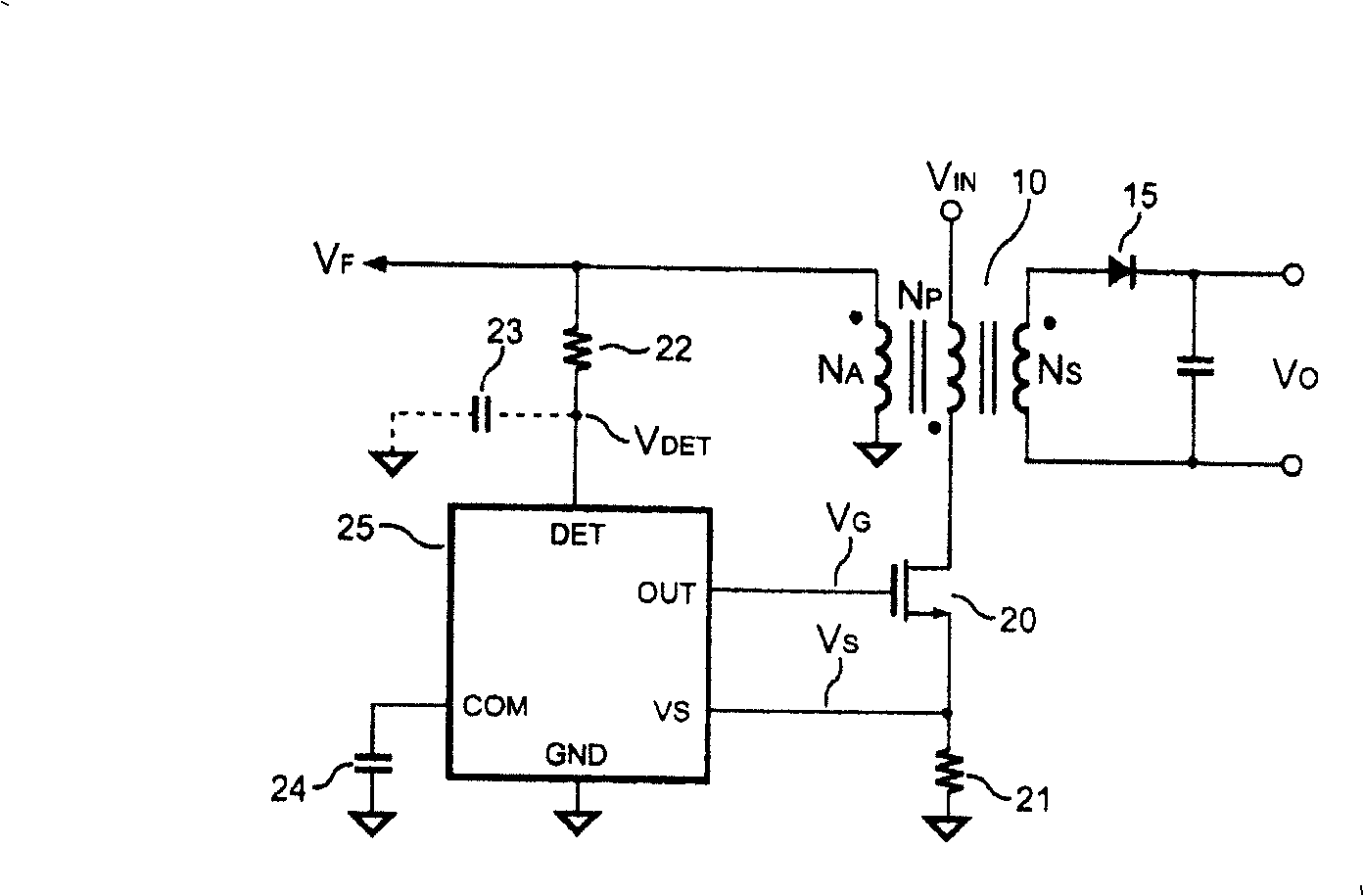
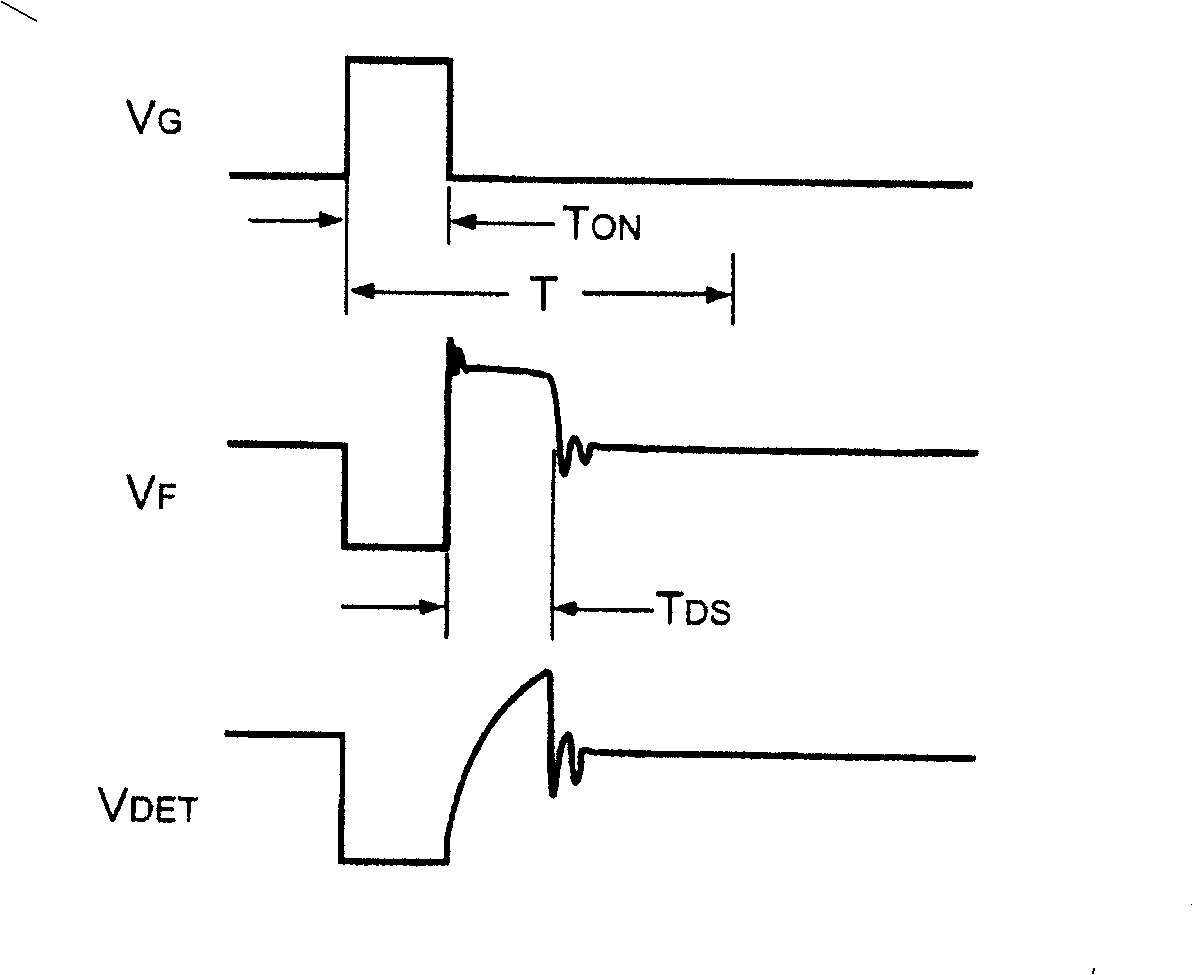
ActiveUS7492613B2Prevent Waveform DistortionEasy to detectTransformersDc-dc conversionAdaptive biasTransformer
A control circuit for detecting the reflected voltage of a transformer is provided. A detection circuit is developed for sampling the reflected voltage. Because the pulse width of the reflected voltage is narrower at light load, a bias circuit is utilized for producing a bias signal to help the reflected voltage detection. Furthermore, a blanking circuit ensures a minimum pulse width of the reflected voltage.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Adaptive bias circuit with low loss and temperature compensation, and wireless transmitting system
ActiveCN107171647AImprove thermal performanceSuppression temperatureAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
The invention discloses an adaptive bias circuit with low loss and temperature compensation. The adaptive bias circuit comprises a first NPN type triode having a current mirror structure, a second NPN type triode, a transistor, a bias capacitor and a first resistor. By means of a specific circuit connecting structure, the potential of the bias capacitor can be kept unchanged when the input power is increased and does not exceed the critical value, therefore the current of the collector of a power tube is increased with the increase of the input power, and when the input power is further increased and exceeds the critical value, the potential of the bias capacitor is reduced, therefore the current of the collector of the power tube is reduced with the increase of the input power and finally trends to be stable. In addition, the temperature of the power tube can be compensated by the first resistor to improve the thermal temperature. The invention further discloses a wireless transmitting system comprising the above circuit, and the beneficial effects are as mentioned above.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Power amplifier
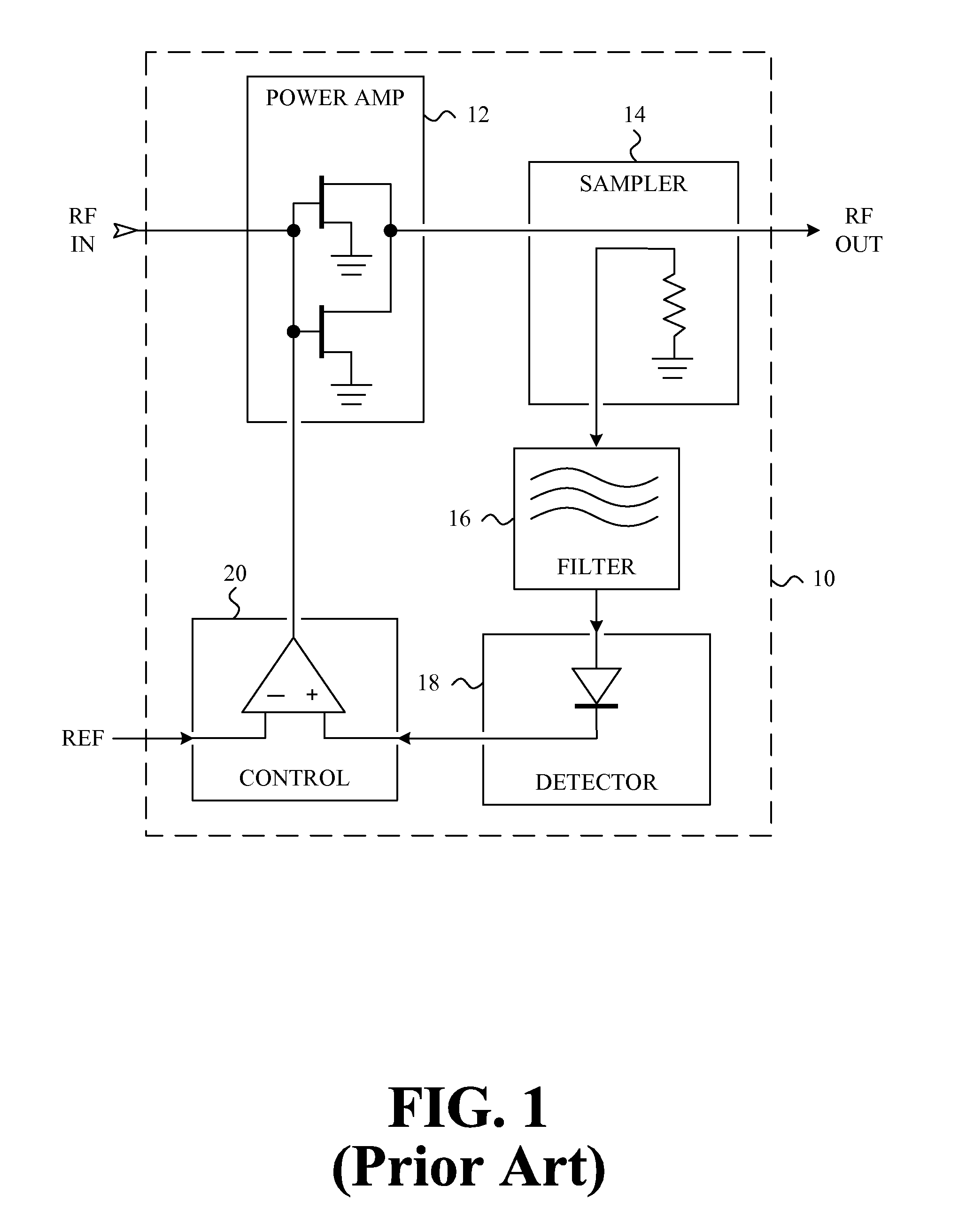
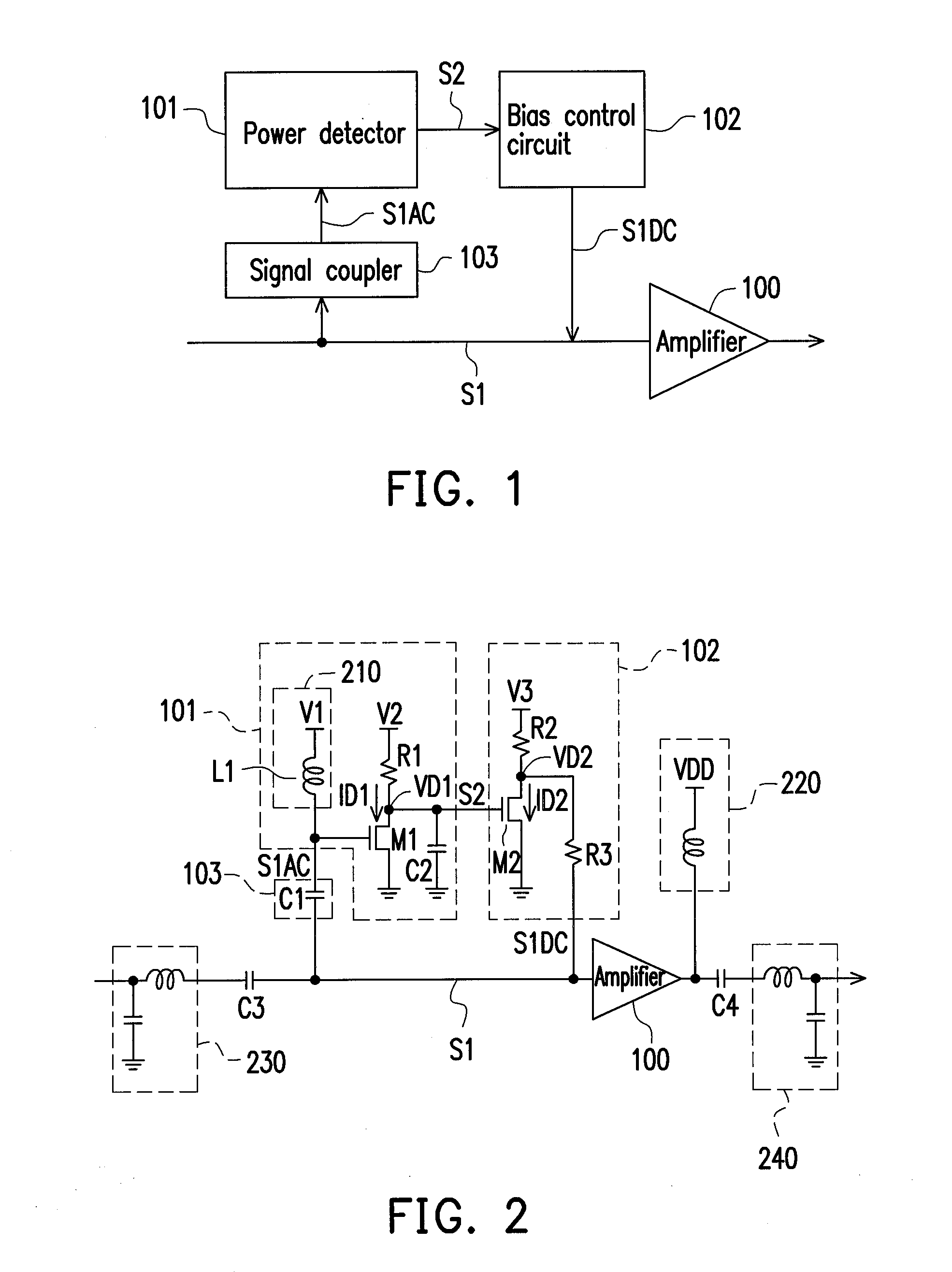
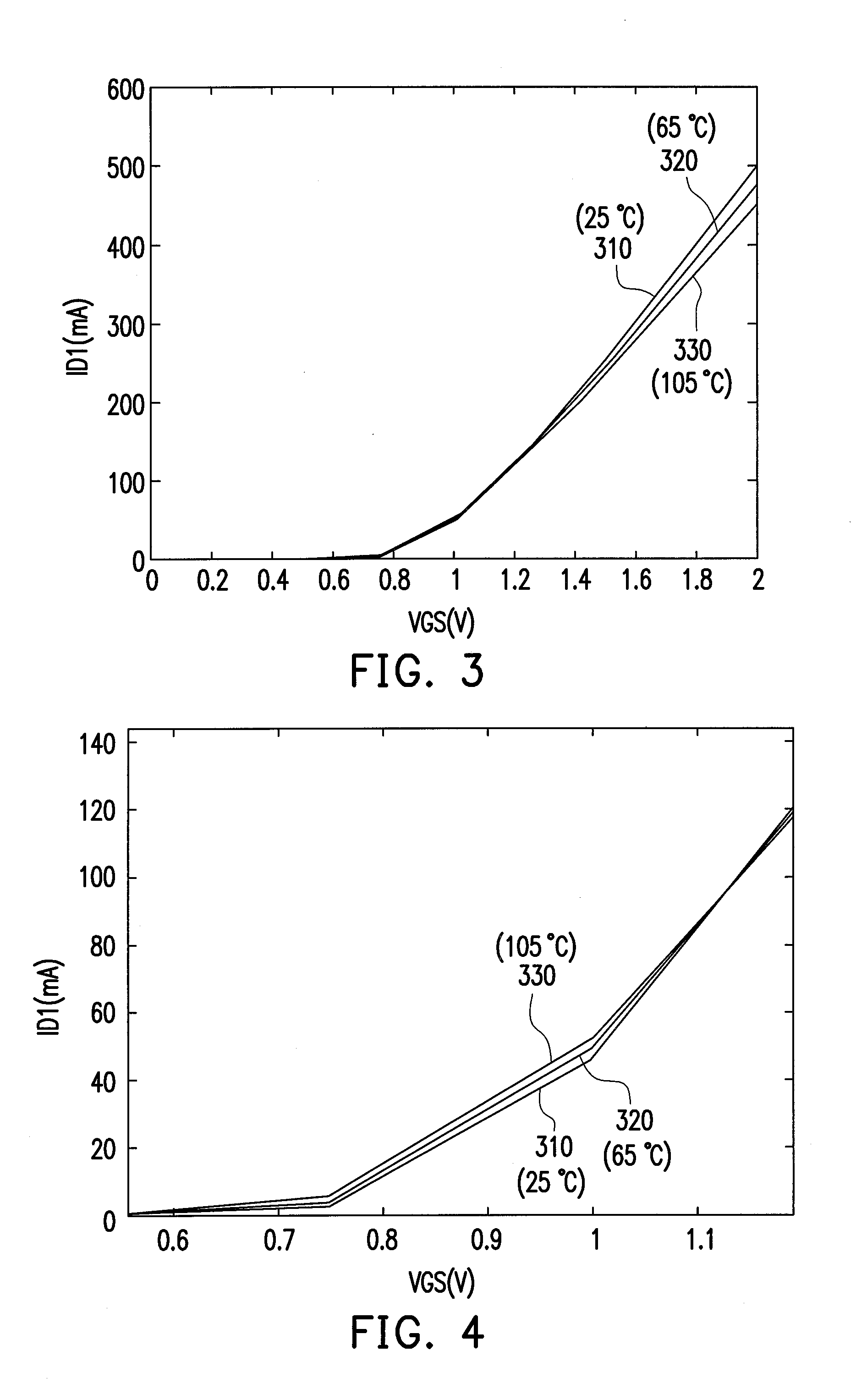
ActiveUS20110090011A1Improve power efficiencyImprove efficiencyGain controlAmplifier detailsAdaptive biasAudio power amplifier
An adaptive bias power amplifier including an amplifier, a signal coupler, a power detector and a bias control circuit is provided. The signal coupler is connected to an input terminal of the amplifier. The power detector is connected to the signal coupler, and detects an input power of the amplifier via the signal coupler. The bias control circuit is connected to an output terminal of the power detector and the input terminal of the amplifier. The bias control circuit adjusts a gate bias of the amplifier in accordance with a detecting result of the power detector.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
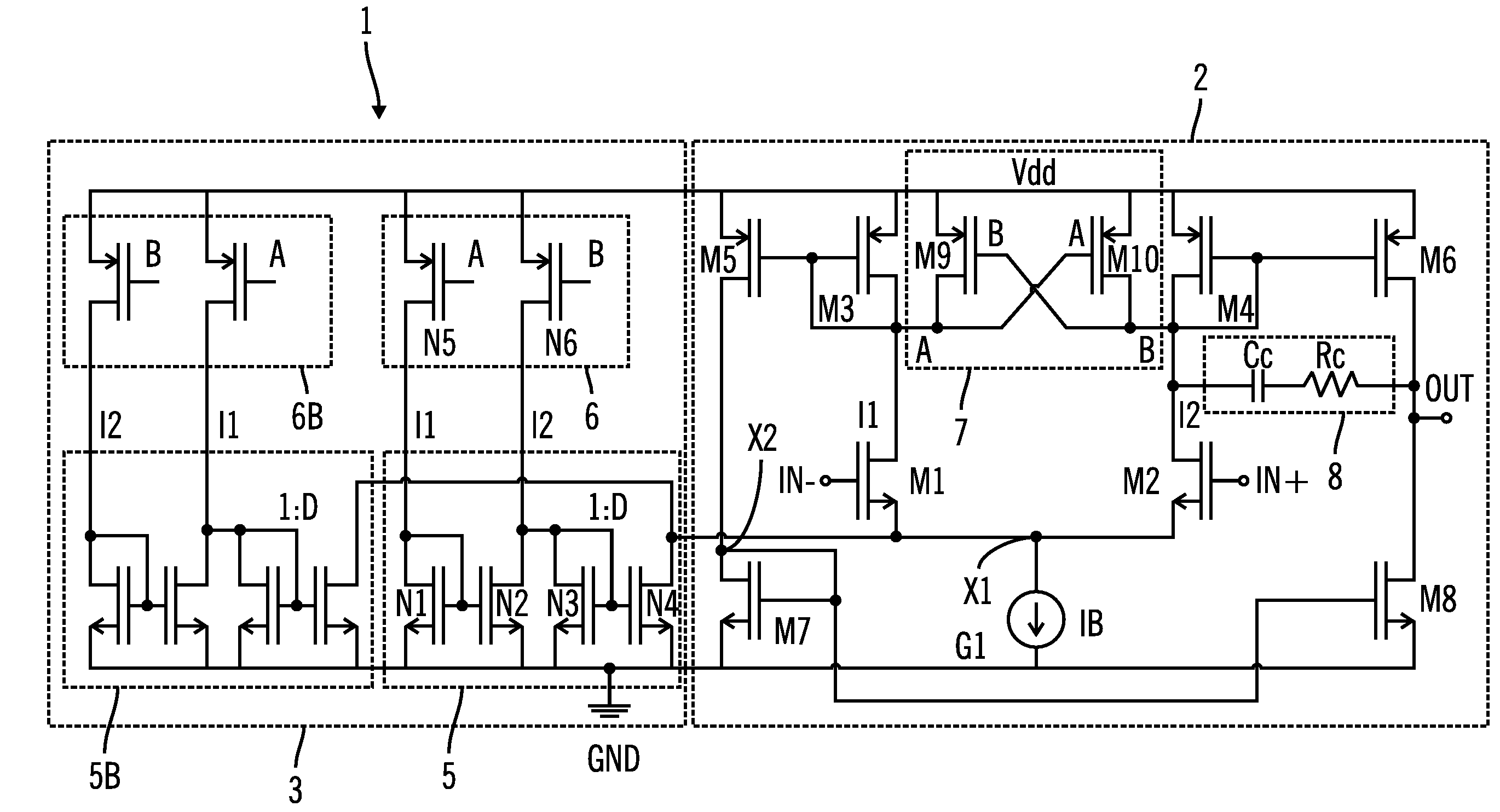
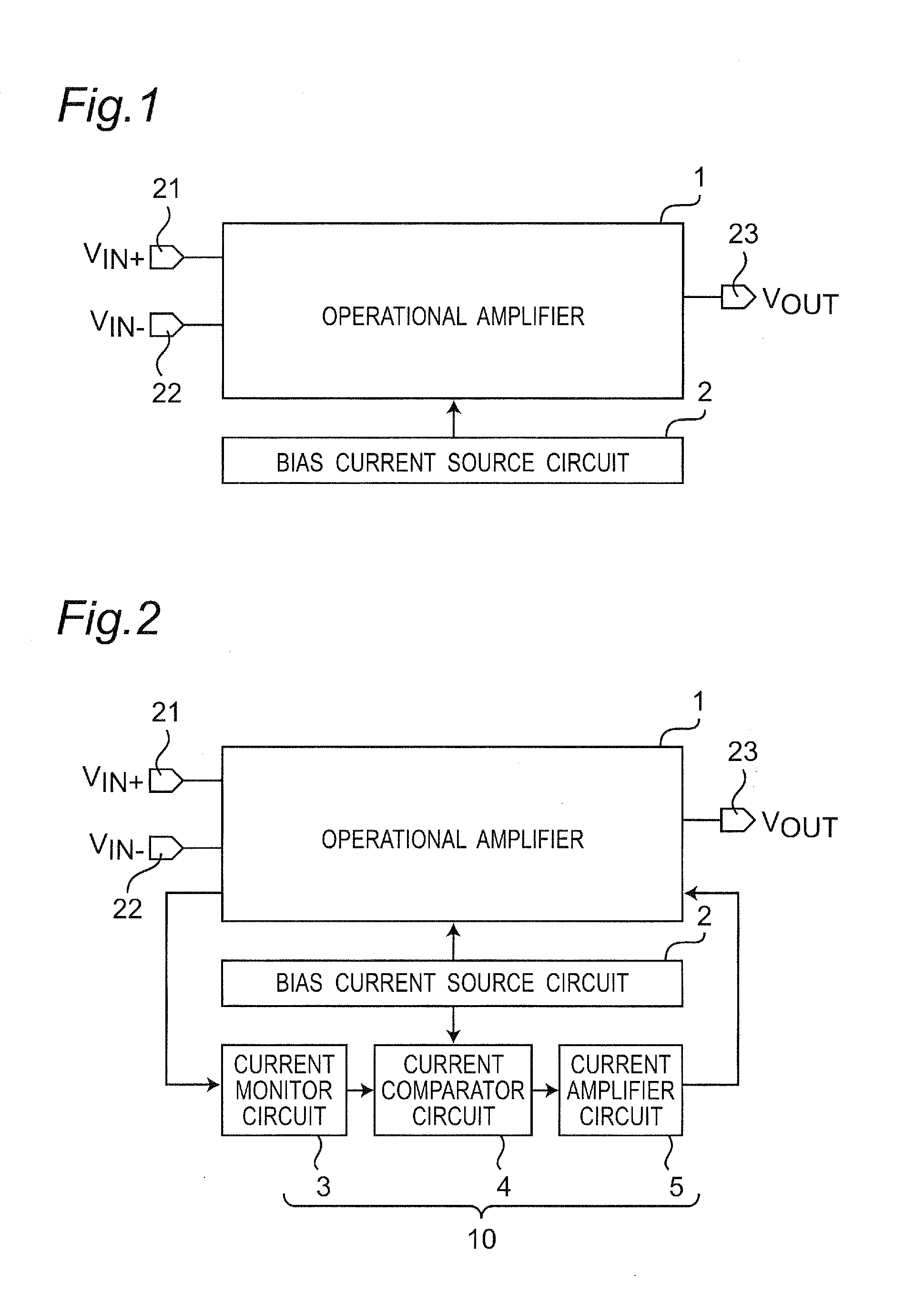
Differential amplifier circuit with ultralow power consumption provided with adaptive bias current generator circuit
ActiveUS20130194039A1Reduced operating requirementsConsuming operationDifferential amplifiersAmplifier detailsAdaptive biasEngineering
A differential amplifier circuit includes a differential operational amplifier that includes a differential pair circuit and operates based on a constant bias current supplied from a bias current source circuit, and the differential amplifier circuit includes a bias current generator circuit. A current monitor circuit detects two currents flowing through the differential pair circuit in correspondence with differential input voltages inputted to the differential pair circuit, and detect a minimum current of the two currents for a difference voltage of the differential input voltages as a monitored current. A current comparator circuit compares the monitored current with the constant bias current. A current amplifier circuit amplifies a voltage corresponding to the comparison result, and controls currents flowing through the differential pair circuit based on an amplified voltage, and the bias current generator circuit performs negative feedback adaptive control such that the bias current increases as the monitored current decreases.
Owner:SONY CORP
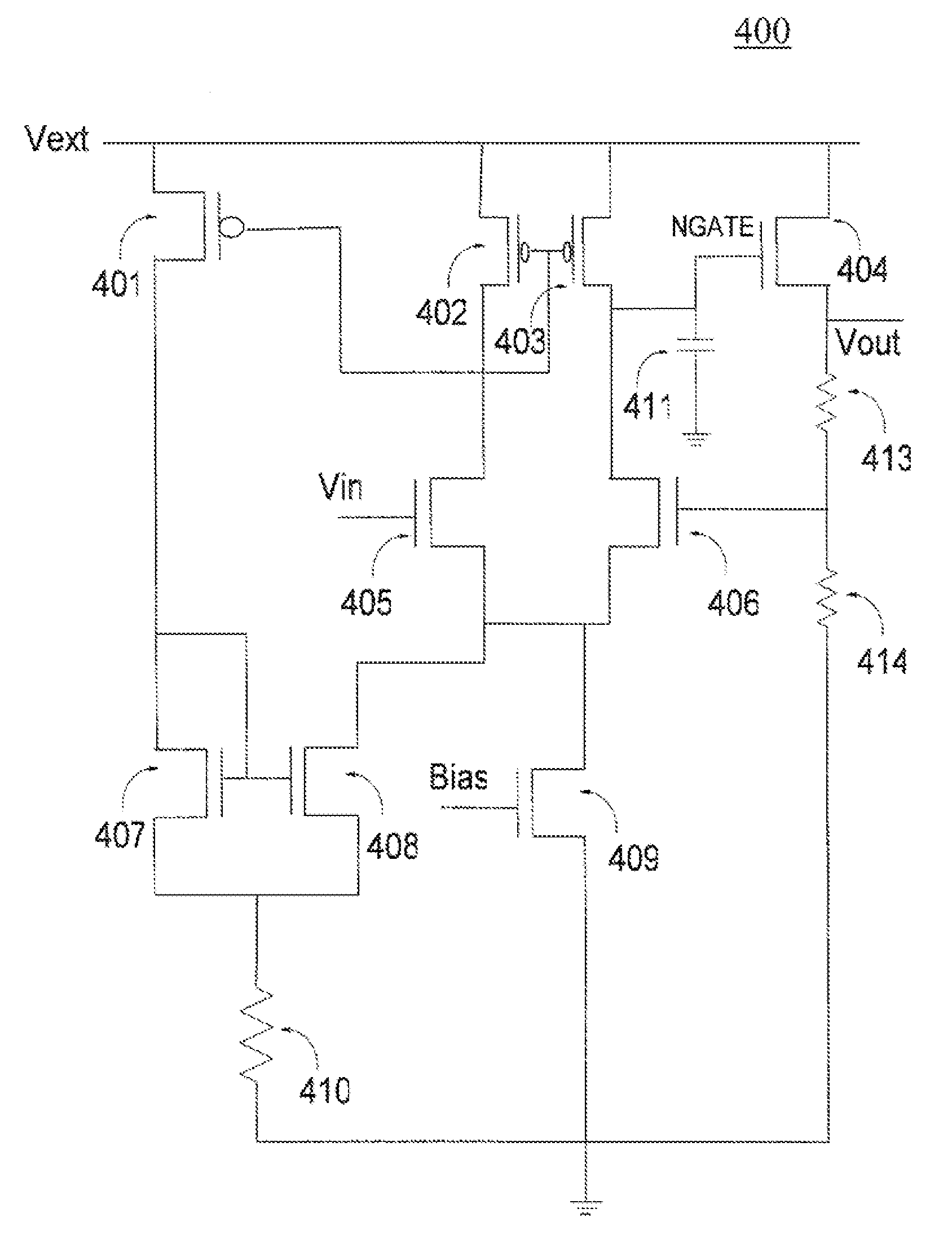
Adaptive bulk-bias technique to improve supply noise rejection, load regulation and transient performance of voltage regulators
InactiveUS20190041885A1Increased output current capabilityImprove PSRElectric variable regulationAdaptive biasVoltage regulation
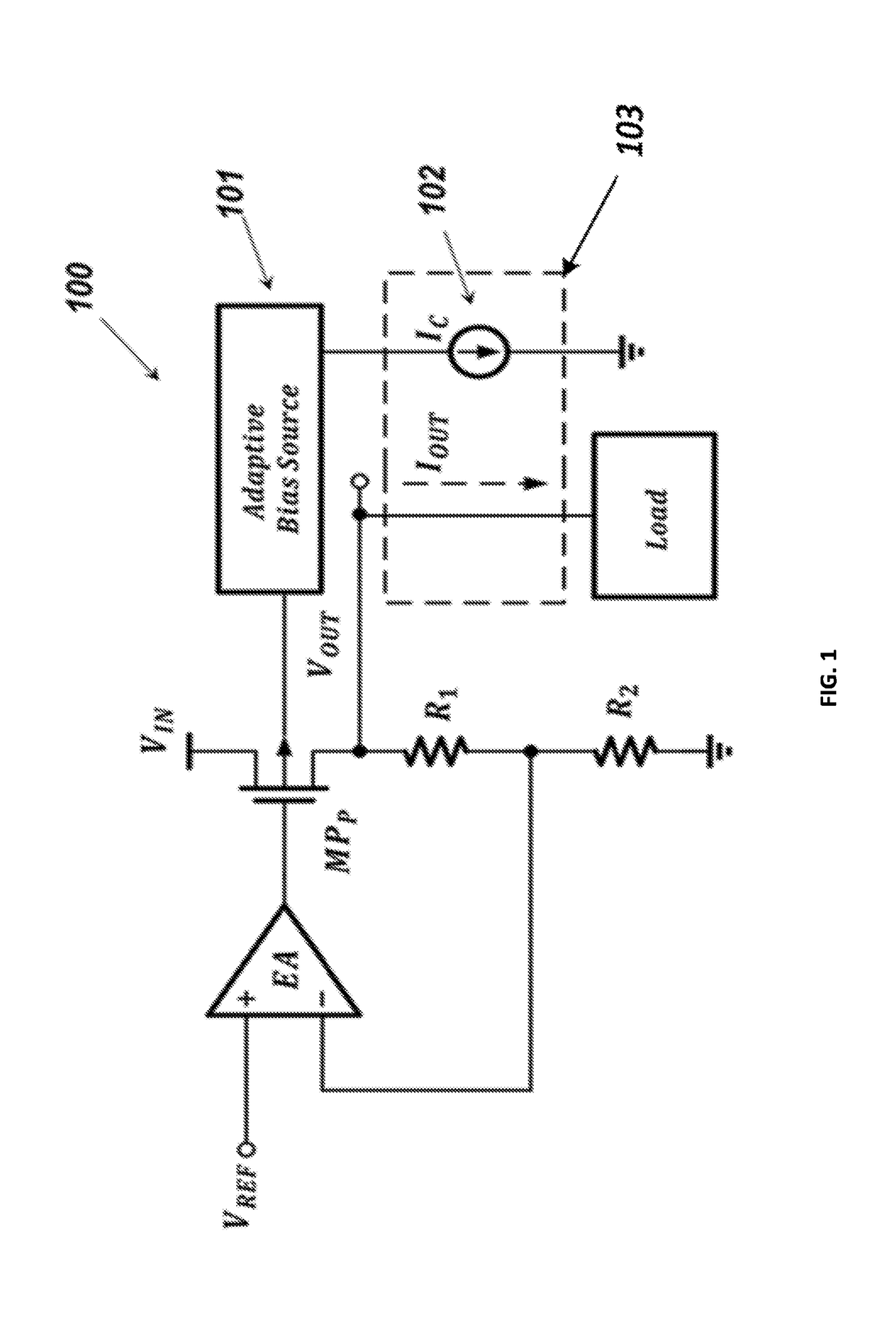
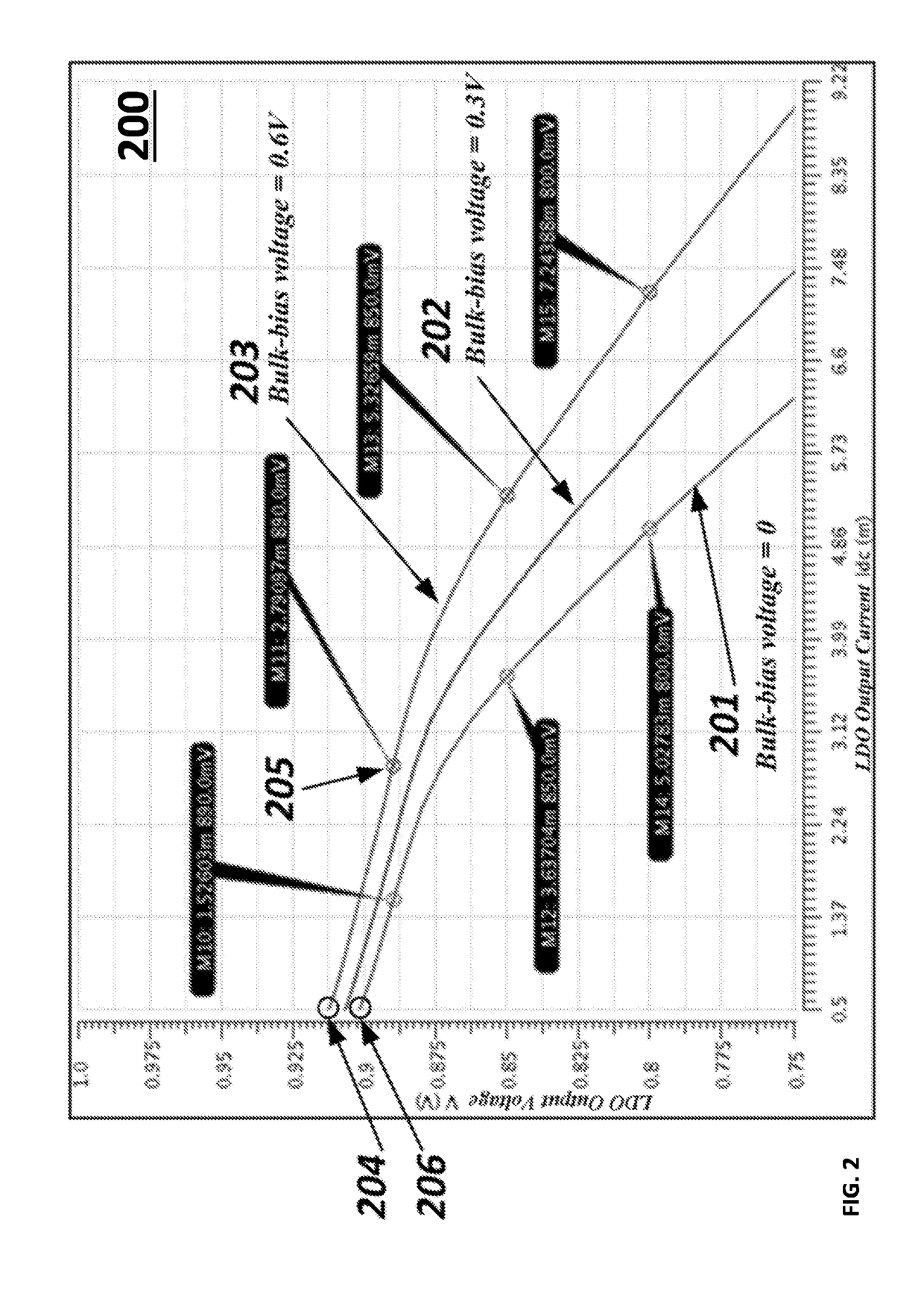
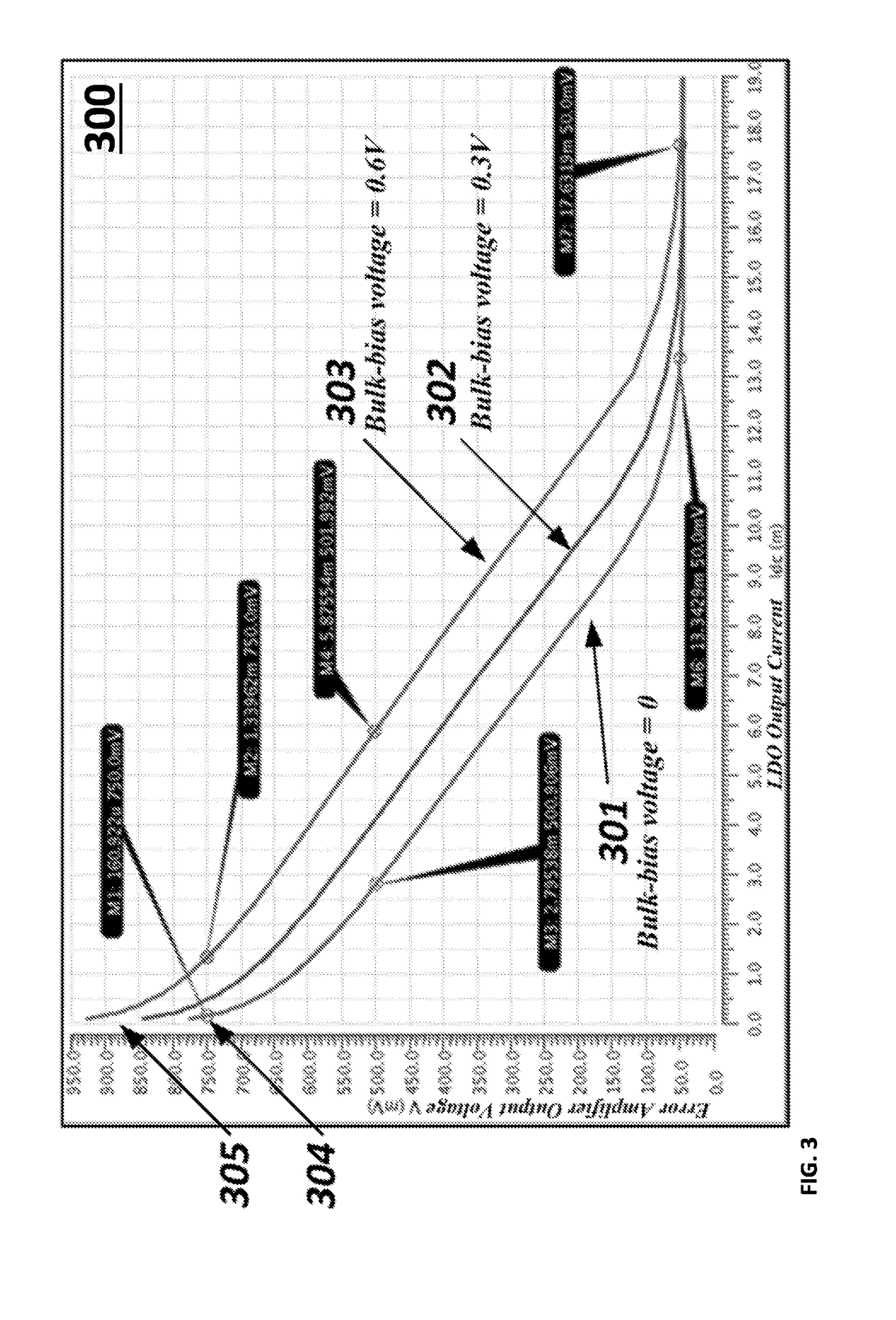
A low-dropout (LDO) voltage regulator includes an adaptive bias source for generating a bulk-bias signal to a pass device in the LDO voltage regulator, wherein the adaptive bias source generates the bulk-bias signal based on a signal obtained at an output of the LDO voltage regulator. The signal includes a current signal, which is proportional to a current at the output of the LDO voltage regulator, and / or a feedback signal from a feedback path connected between the adaptive bias source and the output of the LDO voltage regulator for sensing negative and / or positive spikes.
Owner:VIDATRONIC
Comparator circuit provided with differential amplifier making logical judgment by comparing input voltage with reference voltage
ActiveUS8330499B2Reducing logical judgment timeReduced operating requirementsMultiple input and output pulse circuitsInstant pulse delivery arrangementsAdaptive biasComparators circuits
In a comparator circuit having a differential amplifier, which makes a logical judgment by comparing an input voltage with a reference voltage, generates and outputs a resulting output voltage thereof, a current source generates and supplies a bias current of a predetermined minute current to the differential amplifier, and a first inverter circuit inverts a differential voltage from the differential amplifier. An adaptive bias current generator circuit detects the bias current of the current source, and a through current of the first inverter circuit. The adaptive bias current generator circuit generates and supplies an adaptive bias current for executing adaptive bias current control to the differential amplifier to allow the differential amplifier to operate with the bias current upon no logical judgment, and to allow the differential amplifier to operate by using the adaptive bias current obtained by increasing the bias current upon logical judgment.
Owner:SONY CORP
Adaptive bias circuit and system thereof
Owner:RICHWAVE TECH CORP
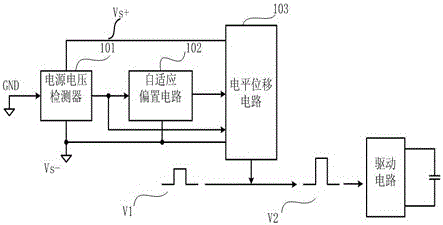
Positive and negative voltage dynamic bias level shifting circuit based on negative voltage detection and band-gap reference
ActiveCN106330171AImprove reducibilityLogic circuit interface arrangementsAdaptive biasLevel shifting
The invention discloses a positive and negative voltage dynamic bias level shifting circuit based on negative voltage detection and band-gap references, comprising a power supply voltage detector, an adaptive bias circuit and a level shifting circuit, wherein the power supply voltage detector is used for detecting the negative power supply voltage and positive power supply voltage of a chip, respectively comparing the negative power supply voltage and the positive power supply voltage with a ground level, and outputting a negative power supply voltage signal when the positive power supply voltage reaches a set value and the negative power supply voltage reaches a threshold; the adaptive bias circuit is used for adaptively adjusting bias current according to the negative power supply voltage signal and the power supply voltage; and the level shifting circuit is used for implementing level shifting on a driving signal according to the positive power supply voltage, the negative power supply voltage signal and the bias current to obtain a switch signal which cannot be changed with the power supply voltage and has fixed rising and falling edge delays. According to the positive and negative voltage dynamic bias level shifting circuit disclosed by the invention, the signal transmission distortion caused by power supply voltage changes even the negative voltage can be solved, and thus high reducibility of the signals in a level shifting process under high-speed signal transmission can be improved.
Owner:成都启臣微电子股份有限公司
Adaptive bias current generator methods and Apparatus
ActiveUS20080284406A1Reduce power consumptionDc network circuit arrangementsWelding electric supplyAdaptive biasCapacitance
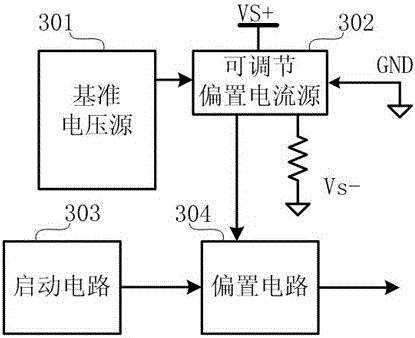
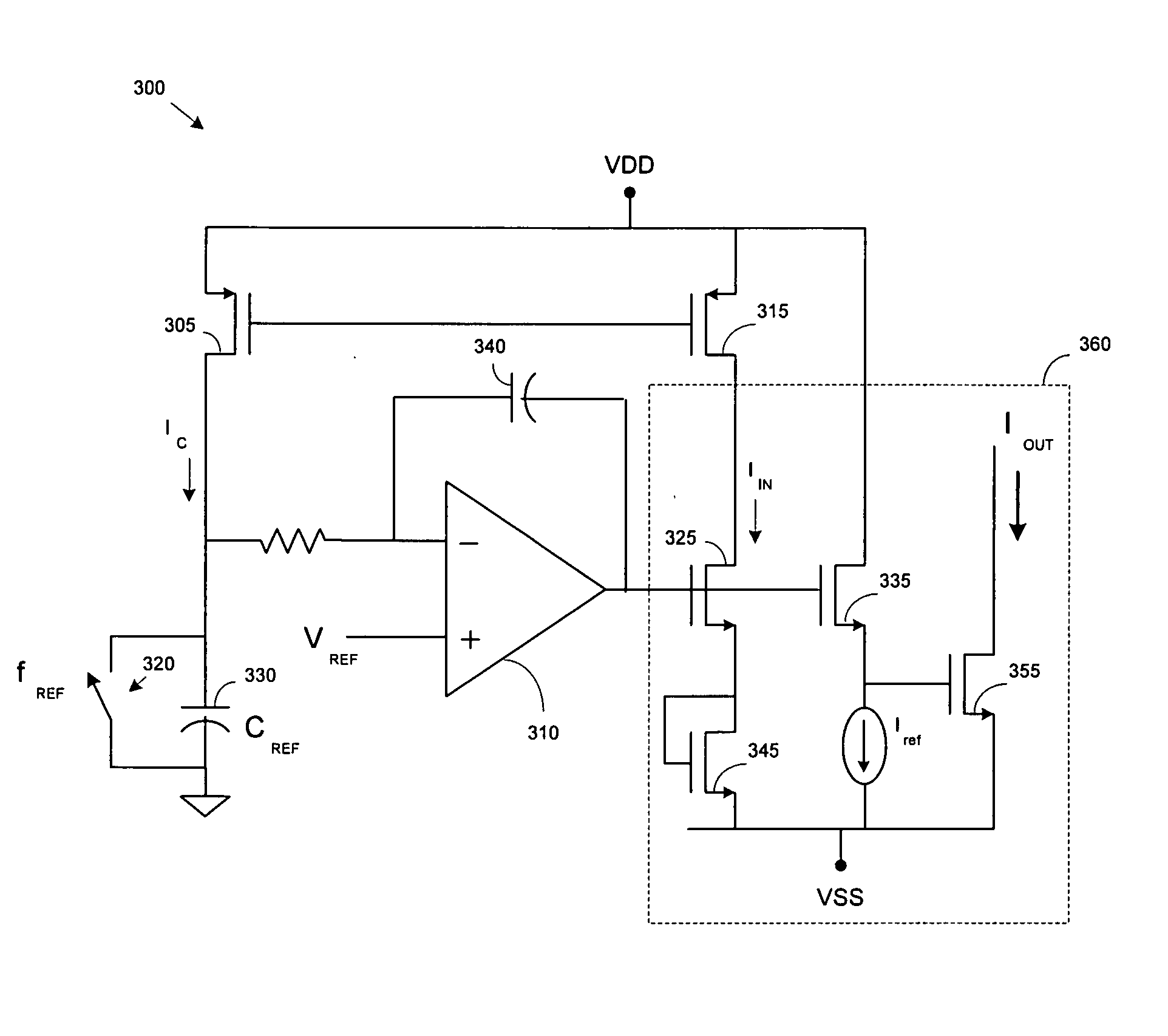
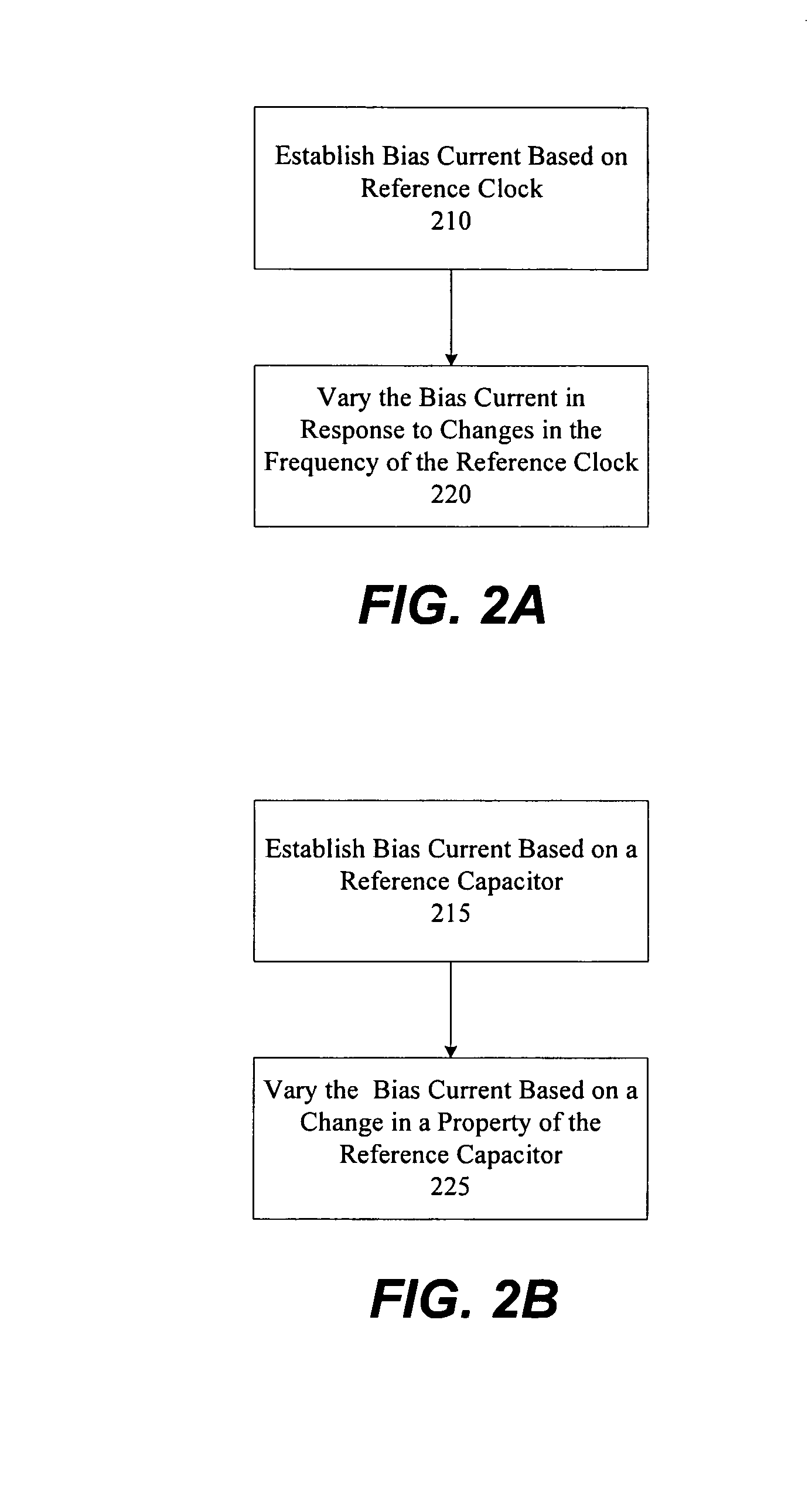
In one aspect, a method of reducing power consumption in a circuit by adaptive bias current generation of a bias current configured to bias, at least in part, at least one amplifier of the circuit is provided. The method comprises establishing the bias current based, at least in part, on a reference frequency of a reference clock providing a clock signal to at least one component of the circuit, and changing the bias current in response to a change in the reference frequency of the at least one reference clock, the bias current being change non-linearly with respect to the change in the reference frequency of the at least one reference clock. In another aspect, the method comprises establishing the bias current based, at least in part, on a capacitance of a reference capacitor, and changing the bias current in response to a change in the capacitance of the reference capacitor such that the bias current is changed non-linearly with respect to changes in the capacitance of the reference capacitor.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Multi-input differential circuit
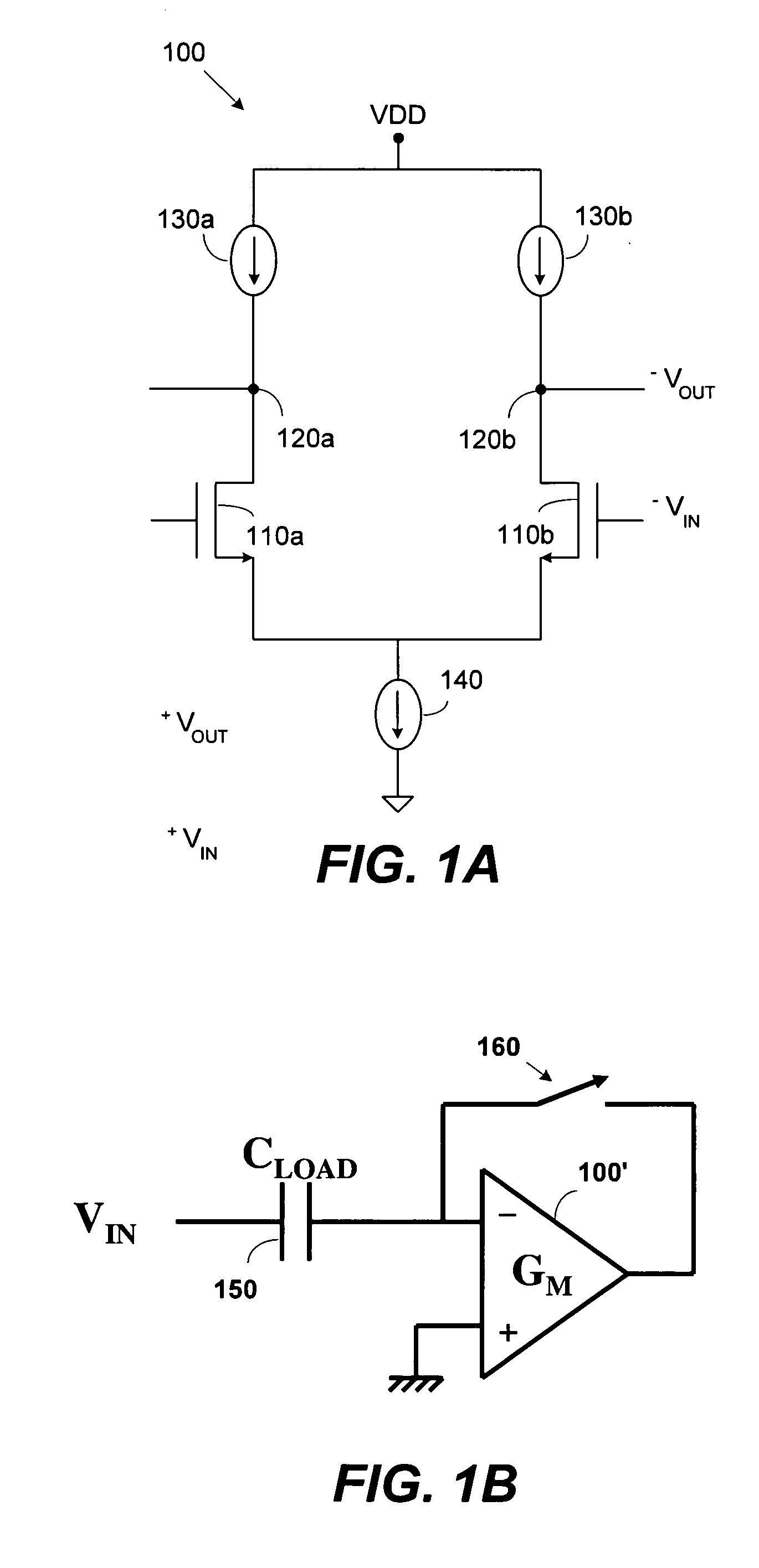
InactiveUS20050017761A1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyMulti inputAdaptive bias
The invention provides a NANO-ampere operable differential circuit by means of a few additional components. The multi-input differential circuit consists of more than three input elements that are connected to the same tail node, and an adaptive bias current control circuit. Applications of this multi-input differential circuit, which are, for instance comparators and voltage followers, do have a very low operation current at a normal operation mode. The proposed differential circuit is applicable for all kinds of analog complex circuits to attain nano-power operation.
Owner:NANOPOWER SOLUTION
Adaptive bias current generation for switched-capacitor circuits
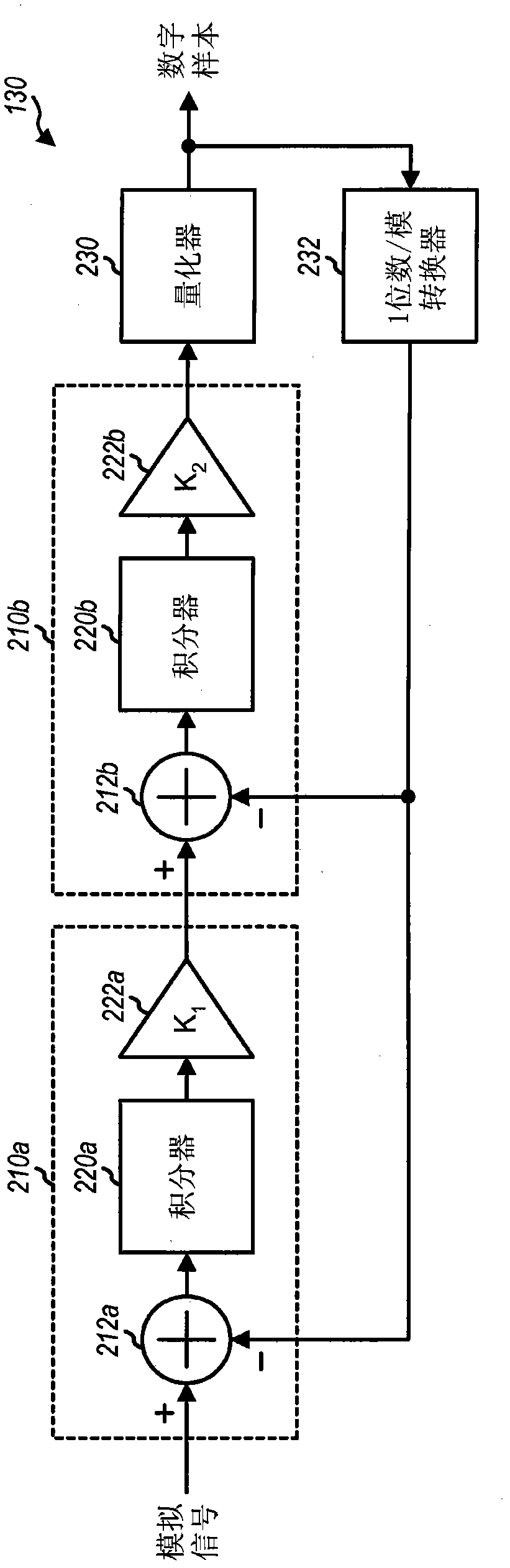
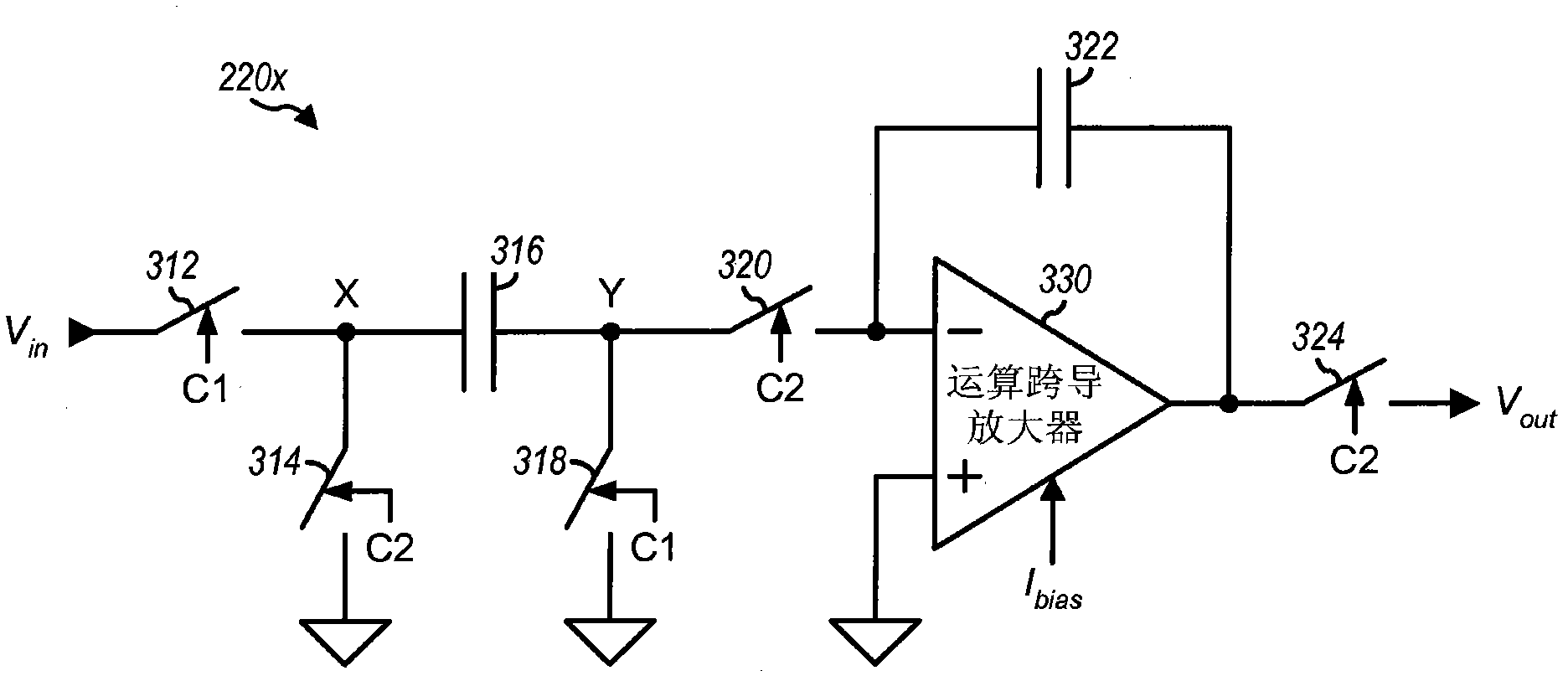
InactiveCN102113208AAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAnalogue conversionAdaptive biasAudio power amplifier
Techniques for adaptively generating bias current for a switched-capacitor circuit are described. The switched-capacitor circuit charges and discharges at least one switching capacitor at a sampling rate and may be a ADC that digitizes an analog signal at the sampling rate and provides digital samples. The switched-capacitor circuit may support multiple modes associated with different sampling rates. A bias circuit generates a bias current for the switched-capacitor circuit to be proportional to the sampling rate for a selected mode, to provide a bandwidth proportional to the sampling rate for an operational transconductance amplifier (OTA) within the switched-capacitor circuit, and to track changes in the switching capacitor(s) due to variations in integrated circuit (IC) process and temperature. The settling time of the switched-capacitor circuit may track with the multiple modes and across IC process and temperature variations.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Control circuit for power converter with adaptive bias
The invention discloses control circuit for detecting reflected voltage of transformer. The detecting circuit is in use for sampling reflected voltage. Since pulse width of reflected voltage is narrower under state of light load, thus, using biasing circuit generates biasing signal to help to detect reflected voltage. Besides, blanking circuit ensures minimum pulse width of reflected voltage.
Owner:SYST GEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com