Patents
Literature
203 results about "Current sense amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
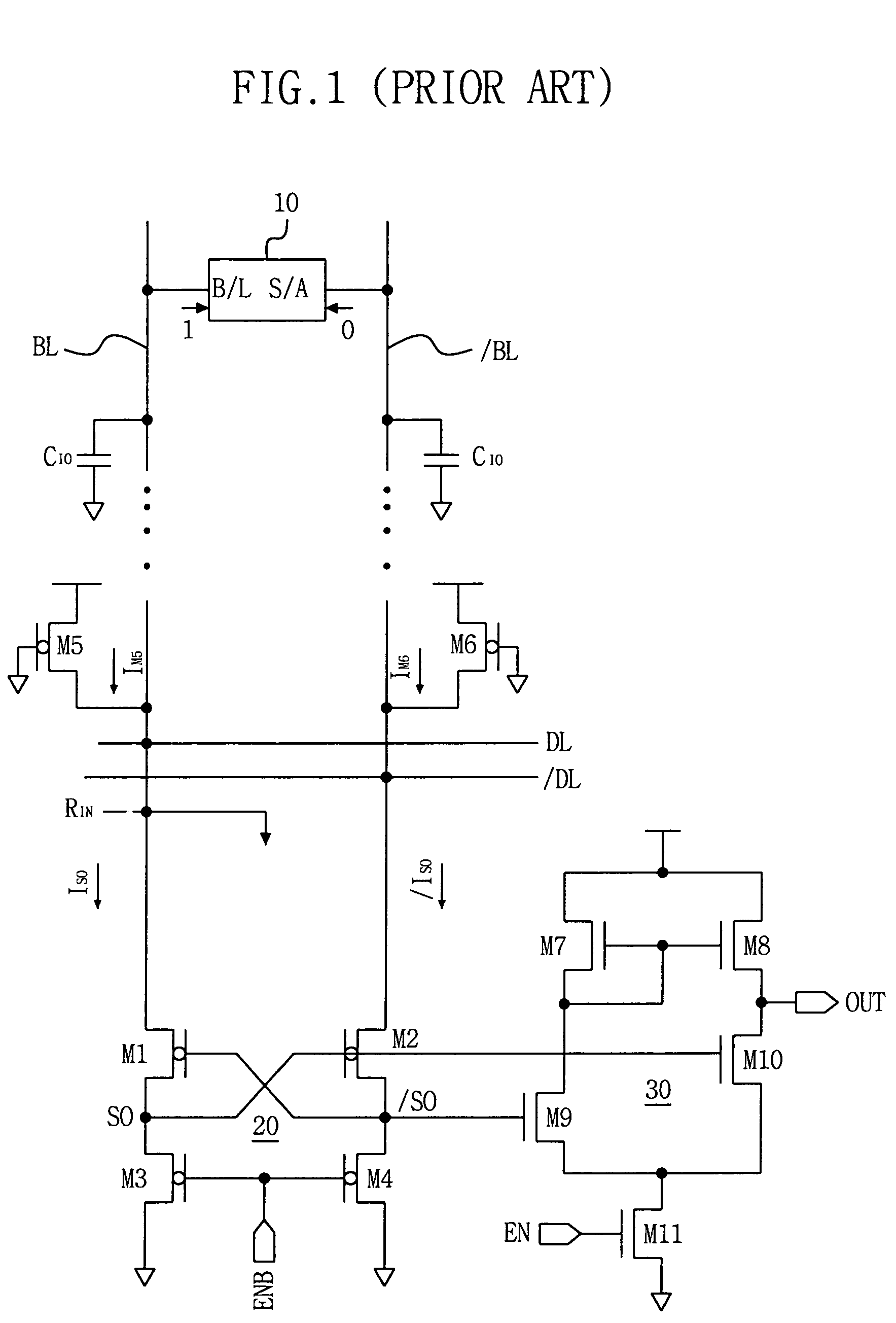
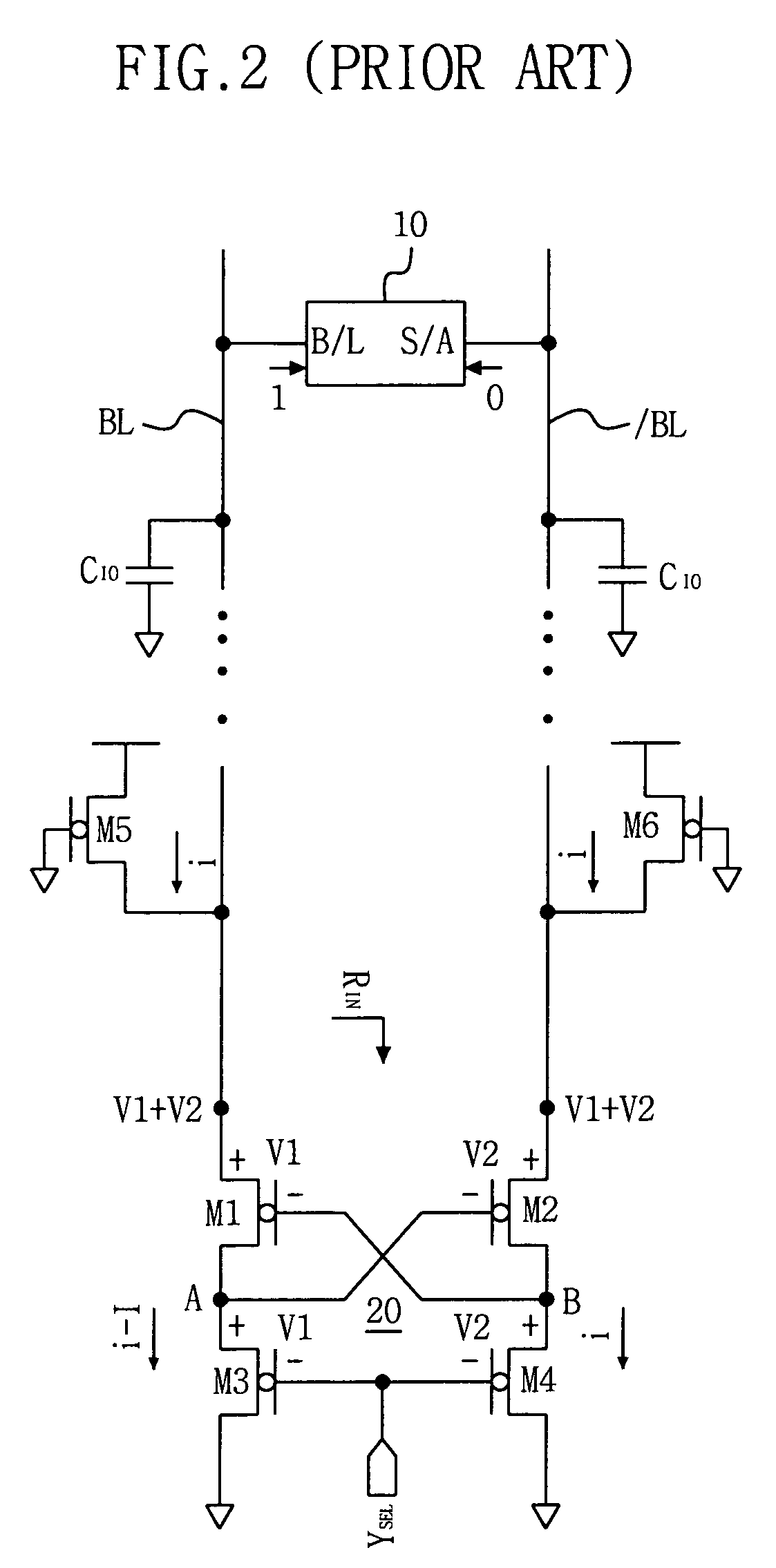
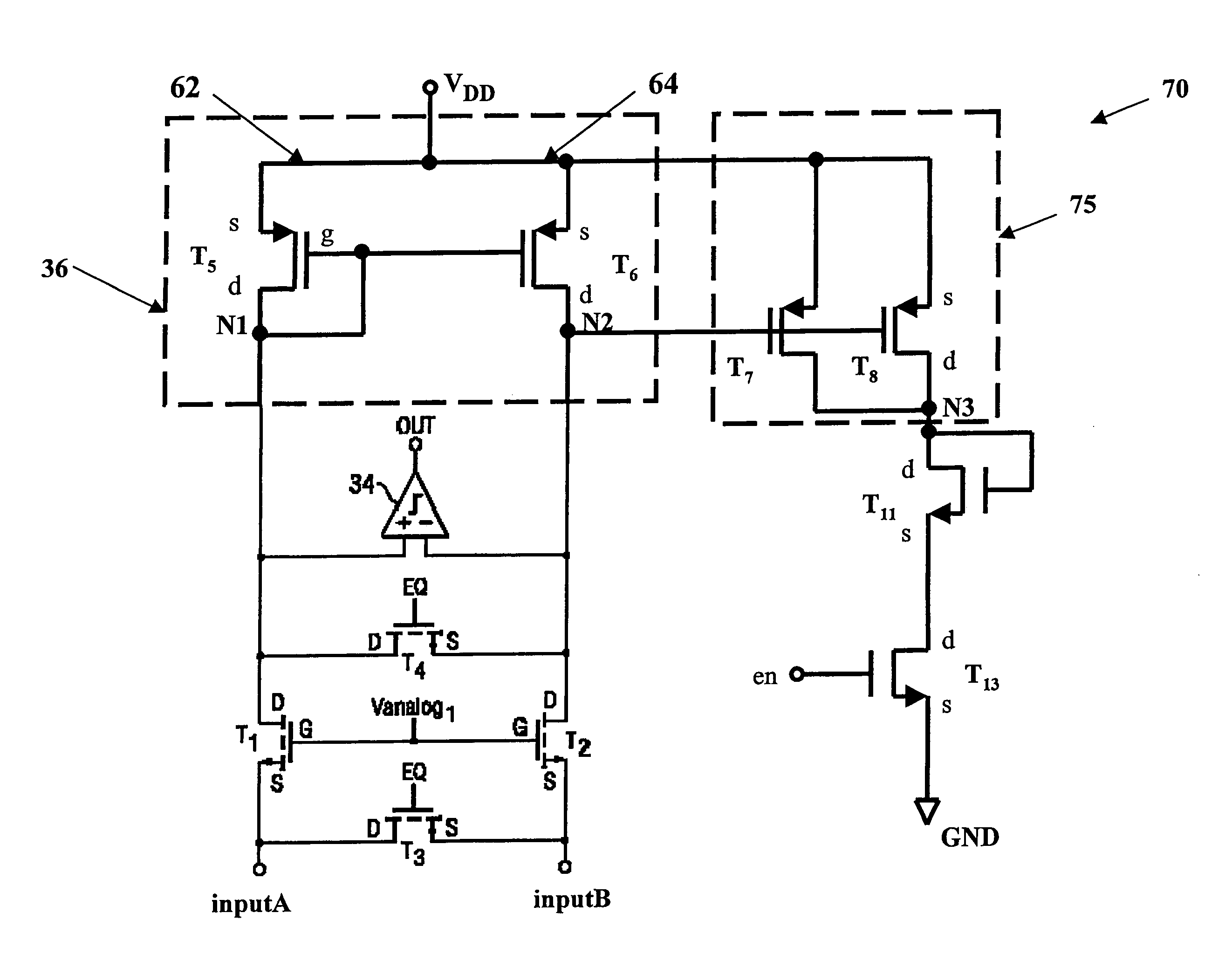
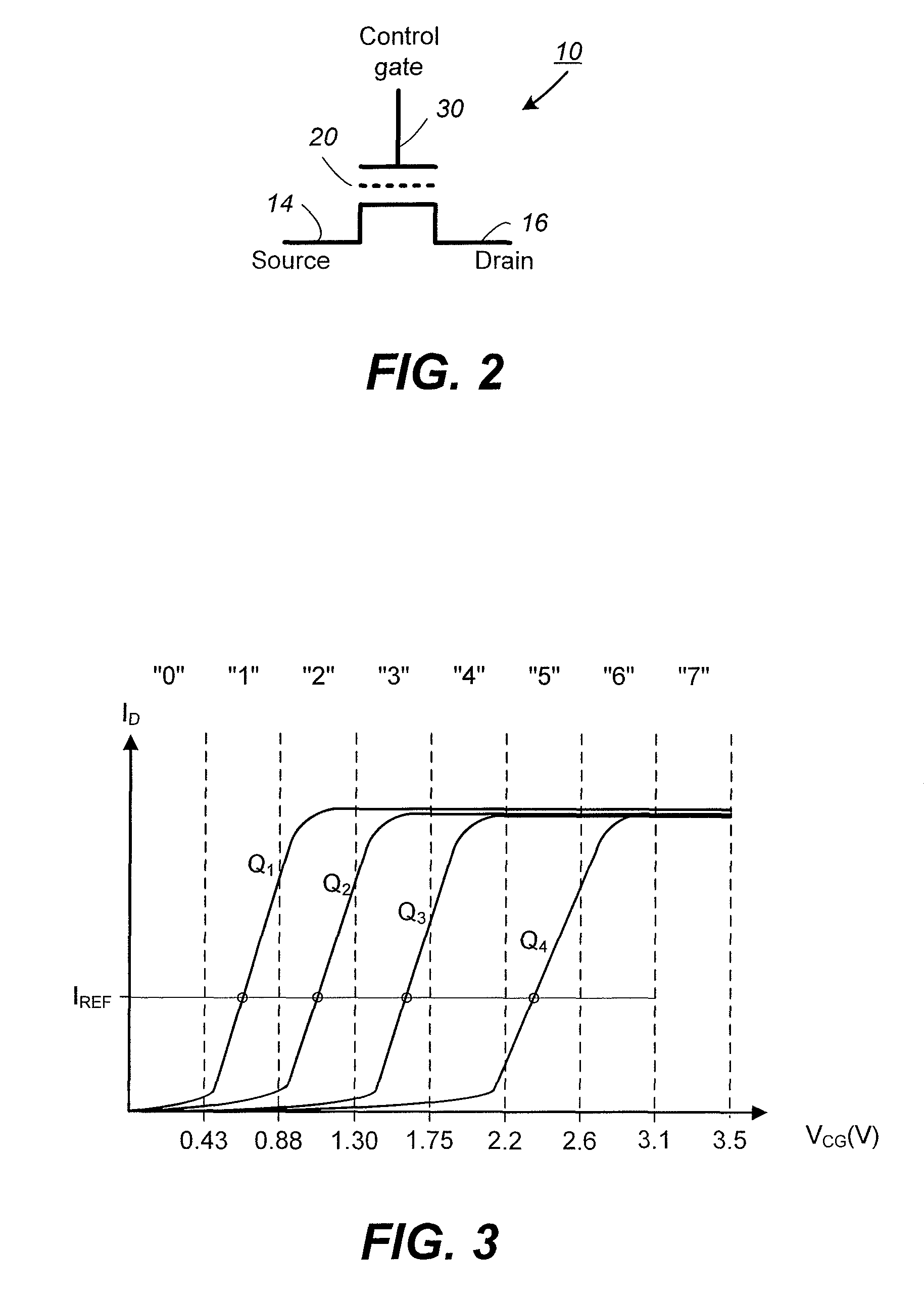
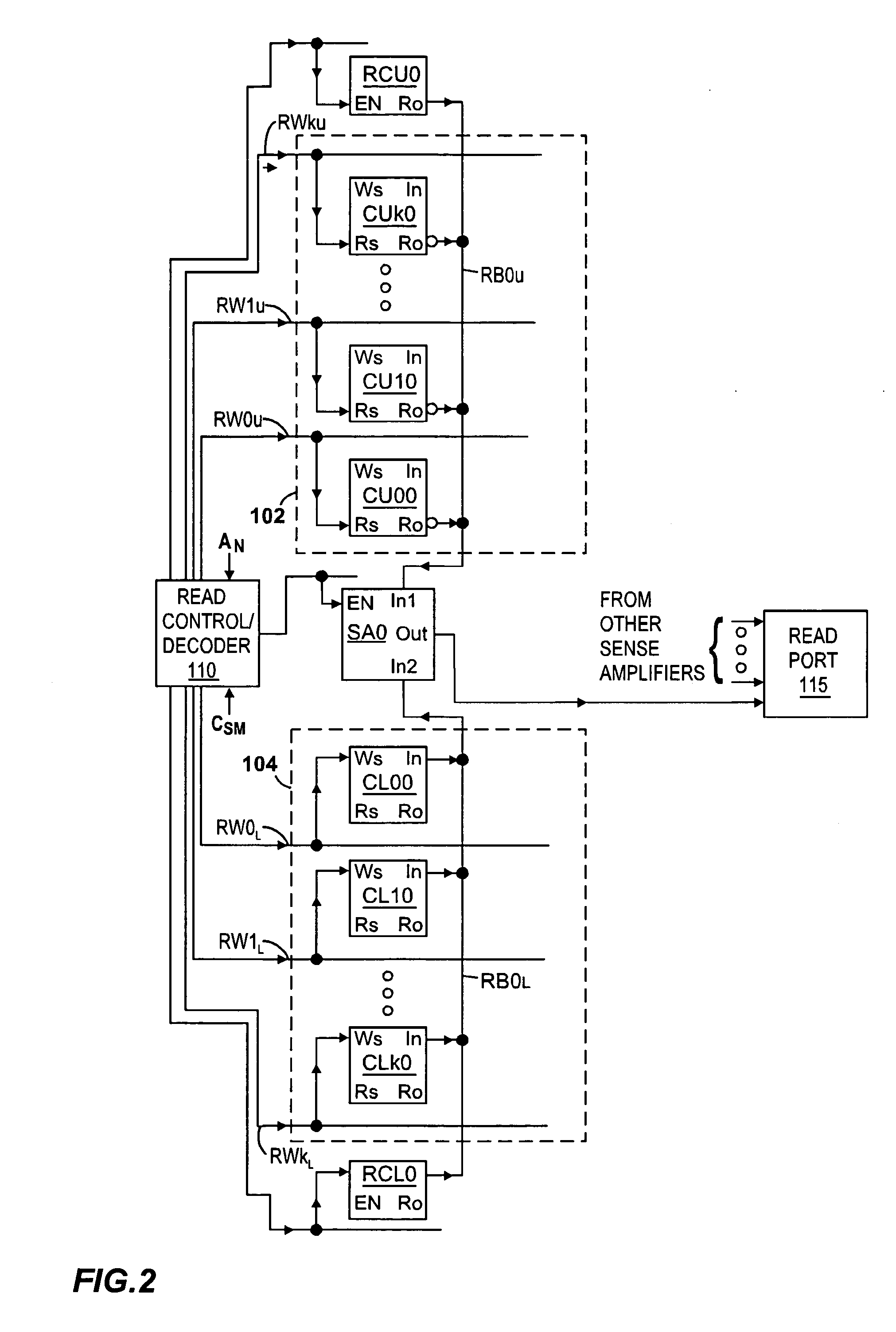
Current sense amplifiers (also called current shunt amplifiers) are special-purpose amplifiers that output a voltage proportional to the current flowing in a power rail. They utilize a "current-sense resistor" to convert the load current in the power rail to a small voltage, which is then amplified by the current-sense amplifiers. The currents in the power rail can be in the range of 1 A to 20 A, requiring the current-sense resistor to be a resistor typically in the range of 1 to 100 mΩ. These amplifiers are designed to amplify a very small "sense voltage" of 10 to 100 mV, in the presence of very large common-mode voltages of 5 to 30 V. DC precision (low input offset voltage) and high common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR) are distinguishing characteristics of these amplifiers. Some current sense amplifiers measure current flowing in a single direction; bidirectional amplifiers measure current flow in both directions through the sense resistor.
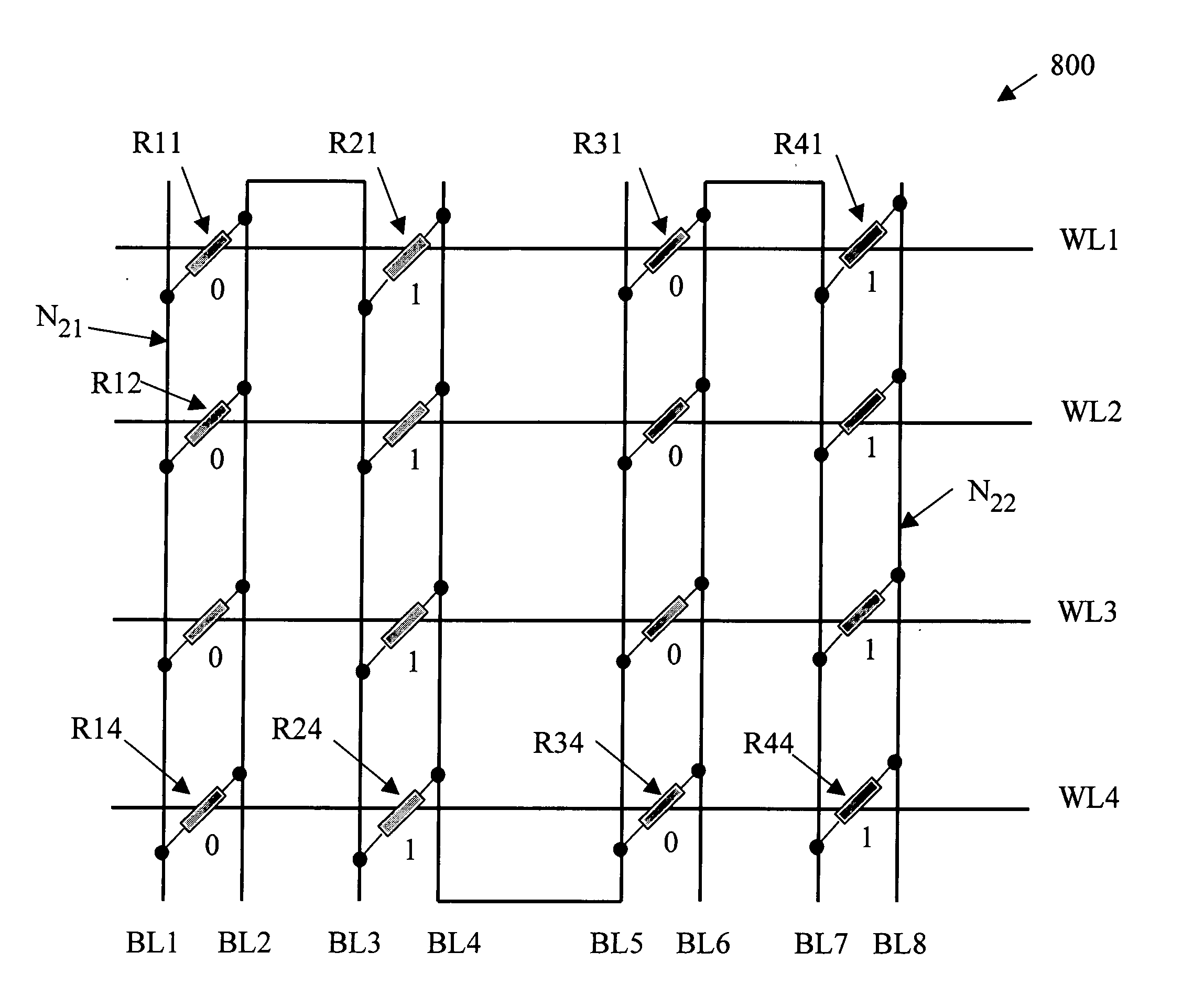
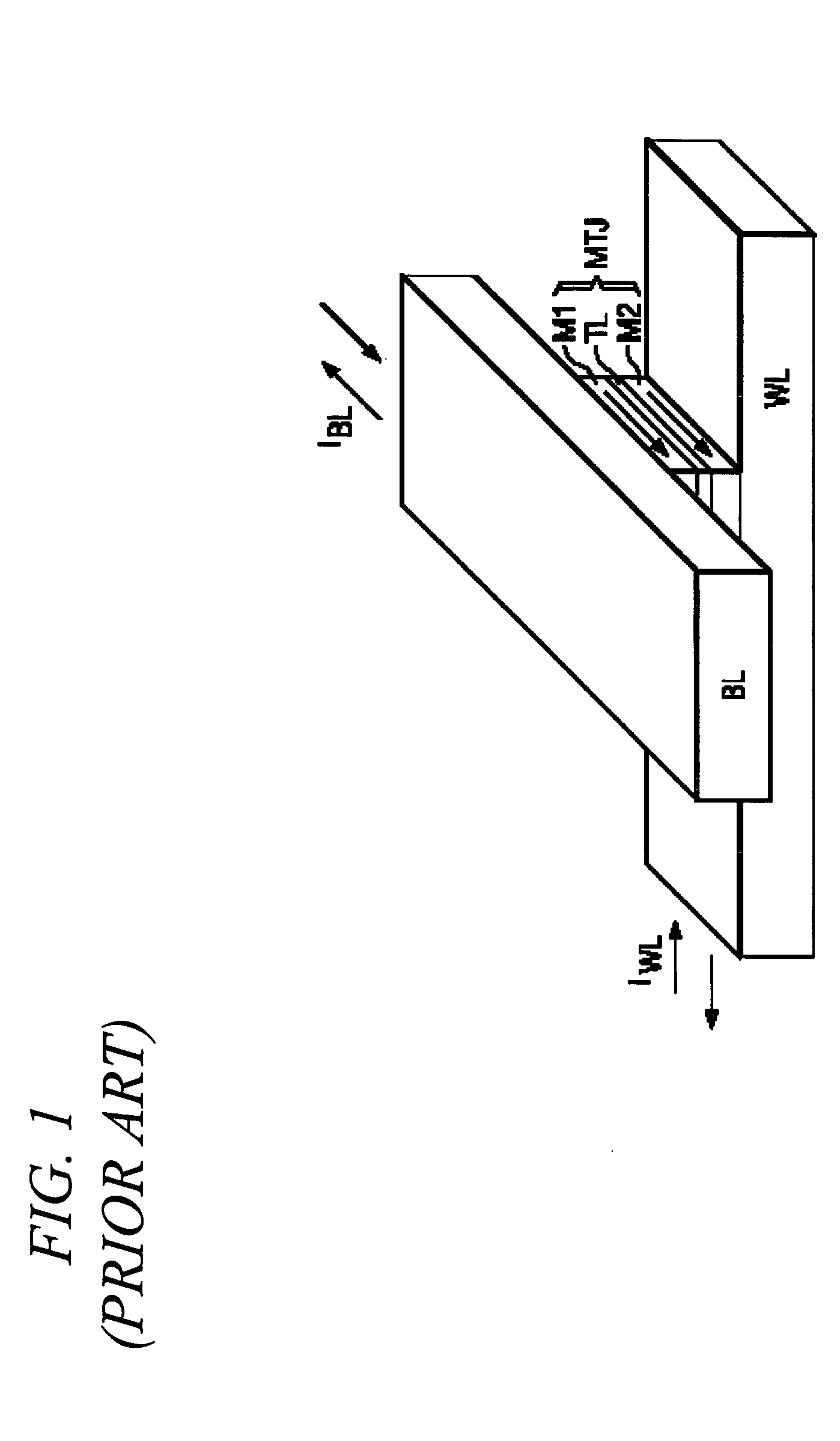
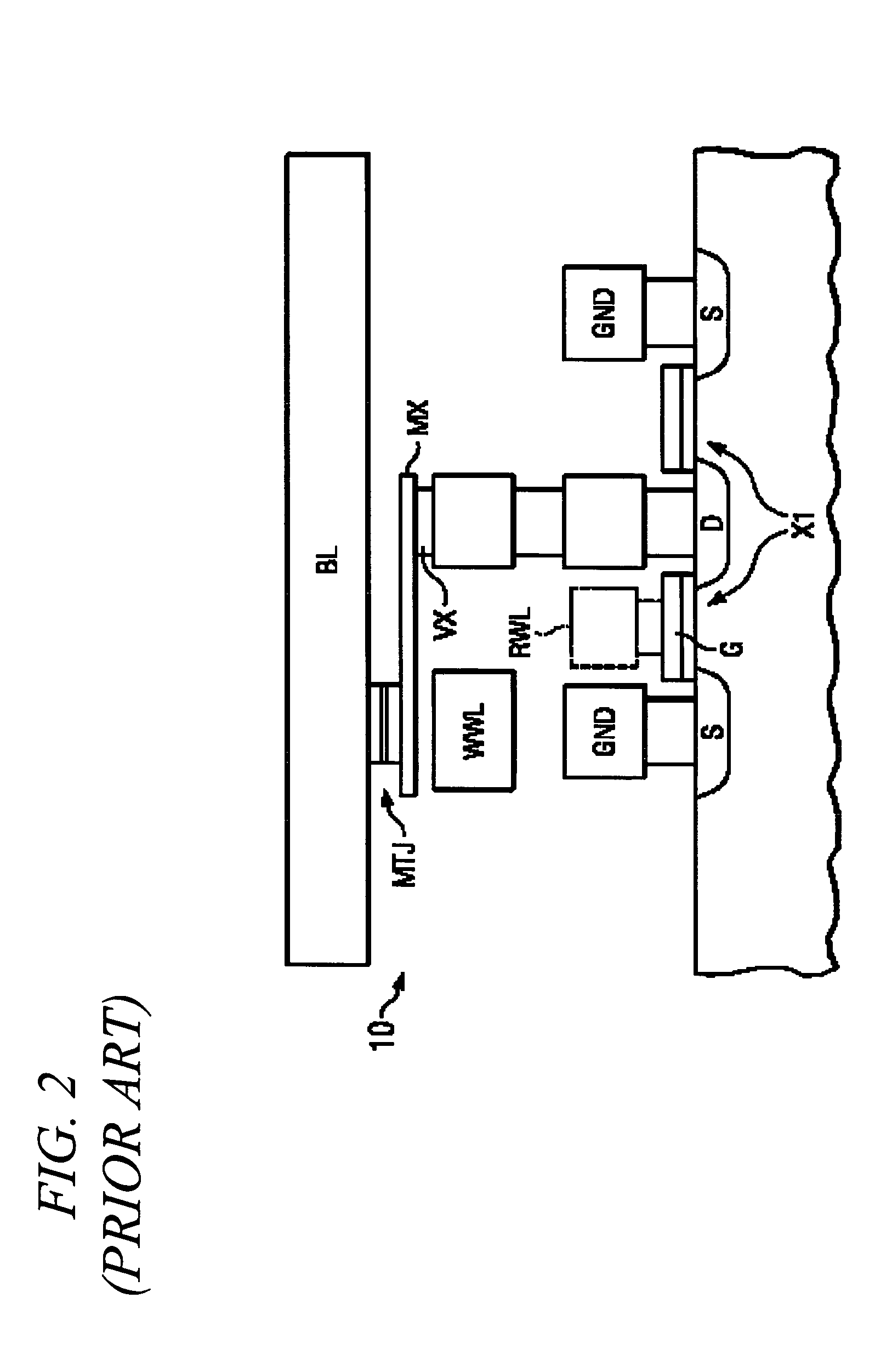
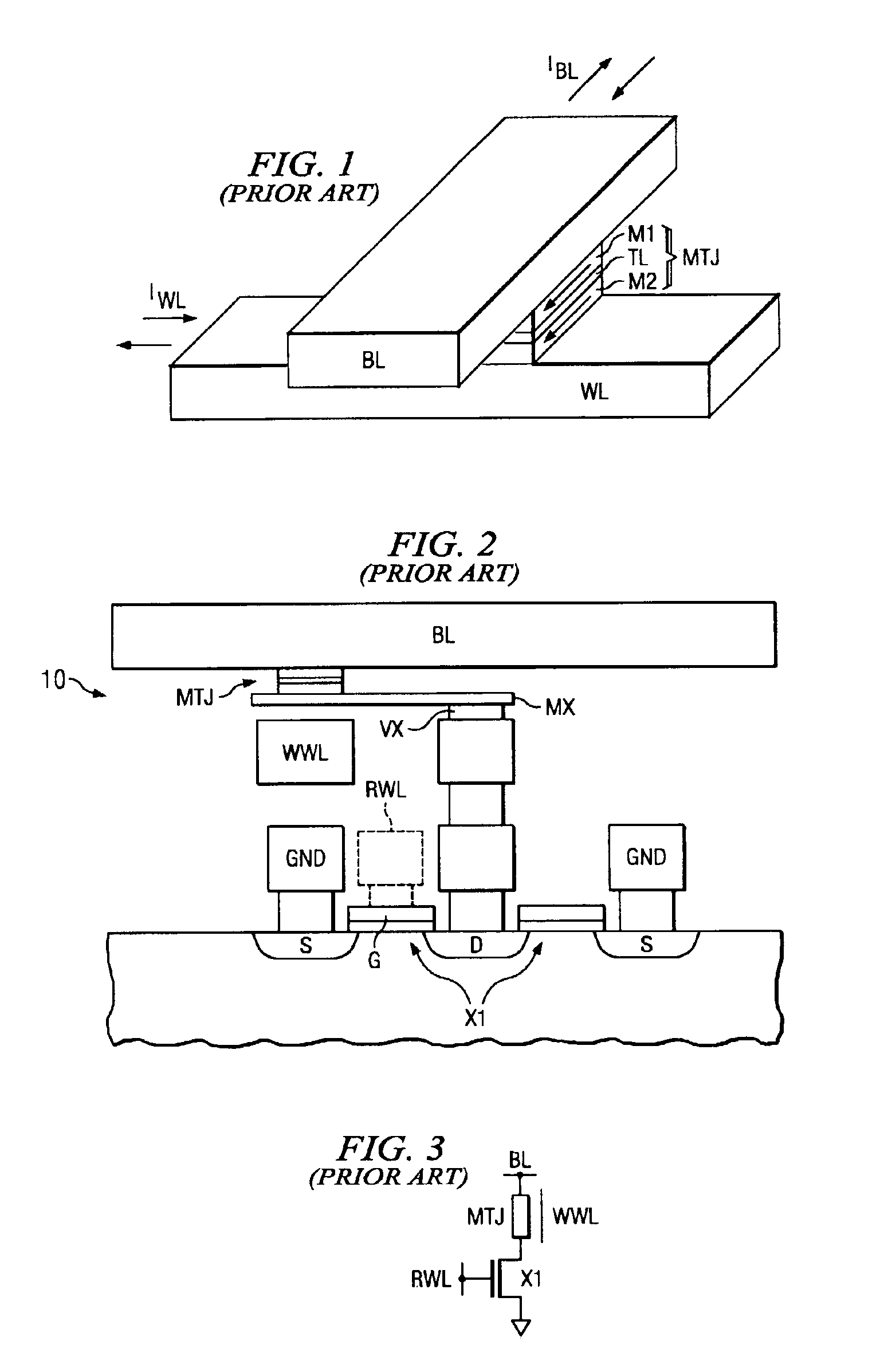
Reference current source for current sense amplifier and programmable resistor configured with magnetic tunnel junction cells
InactiveUS20060092689A1Improve reliabilityWithout compromising device design marginDigital storageAudio power amplifierReference current
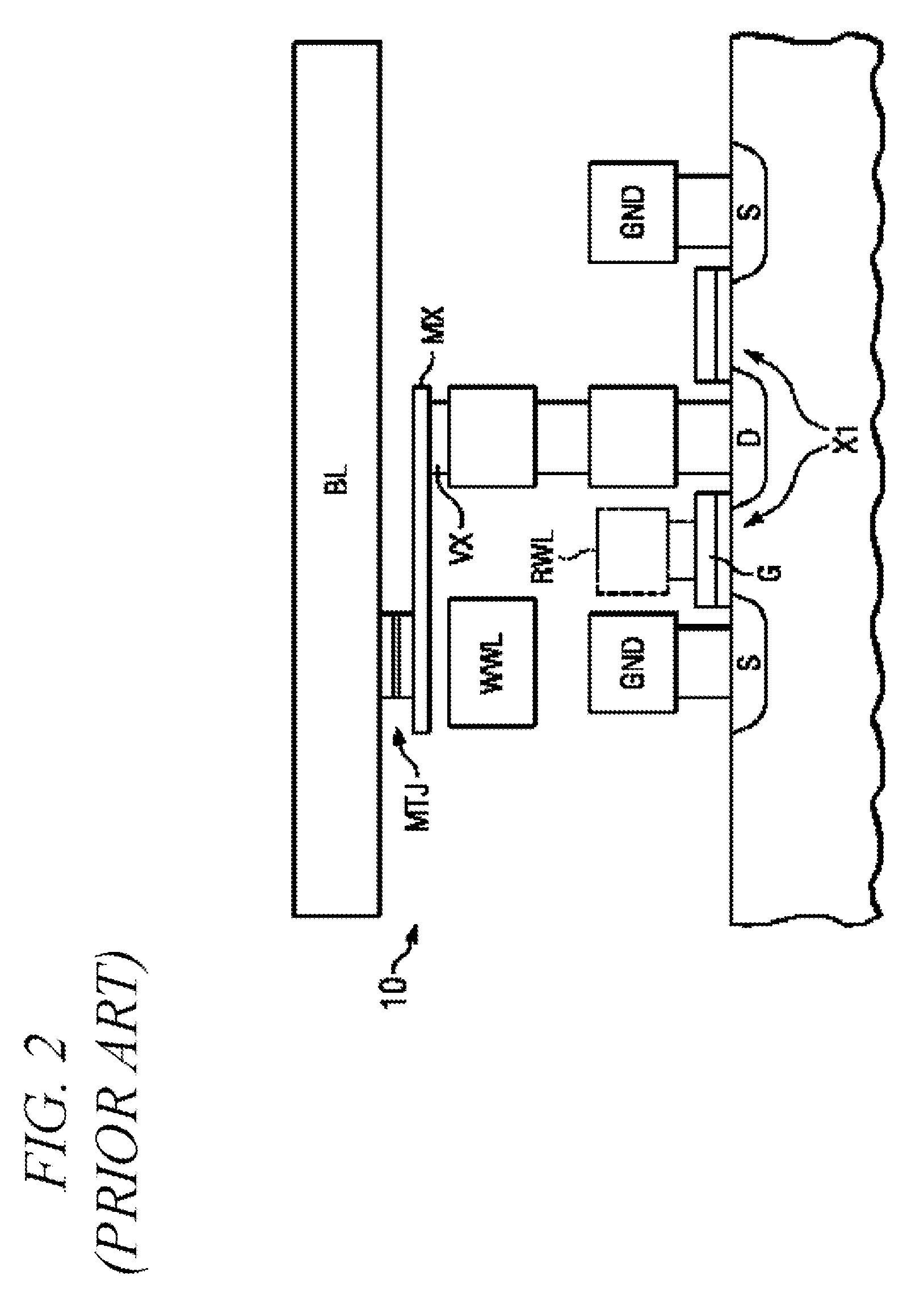
A reference current source for a magnetic memory device is preferably configured with magnetic tunnel junction cells and includes more than four reference magnetic memory cells to improve reliability of the magnetic memory device and to reduce sensitivity at a device level to individual cell failures. The reference current source includes a large number of magnetic memory cells coupled in an array, and a current source provides a reference current dependent on the array resistance. In another embodiment a large number of magnetic memory cells are coupled to current sources that are summed and scaled to produce a reference current source. A current comparator senses the unknown state of a magnetic memory cell. In a further embodiment, an array of magnetic memory cells is configured to provide a non-volatile, adjustable resistance. In a further embodiment, the array of magnetic memory cells is configured with a tap to provide a non-volatile, adjustable potentiometer.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Integrated Circuit, Method of Operating an Integrated Circuit, Method of Manufacturing an Integrated Circuit, Memory Module, Stackable Memory Module
InactiveUS20080002481A1Improve performanceIncrease speedCurrent/voltage measurementDigital storageCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
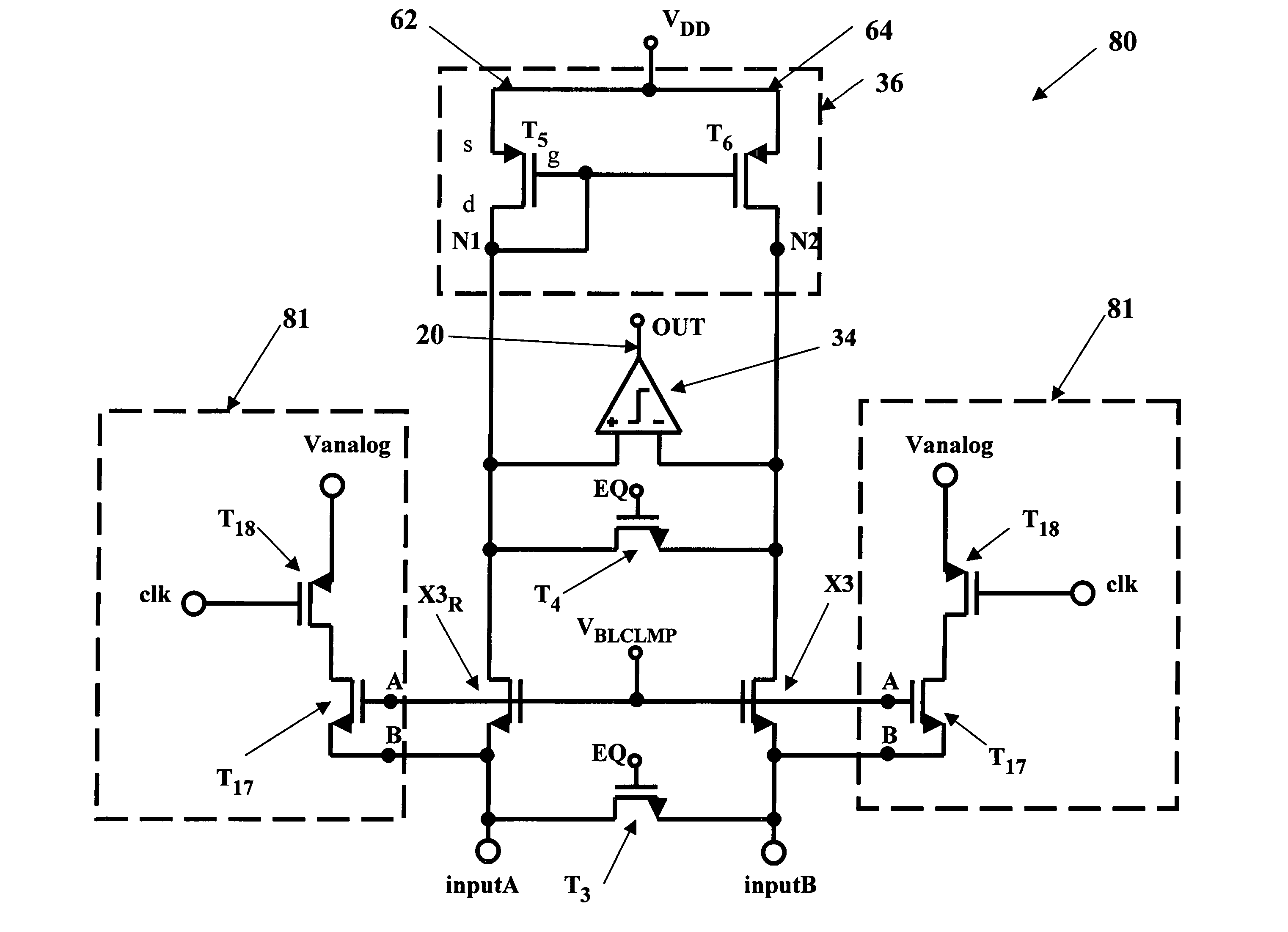
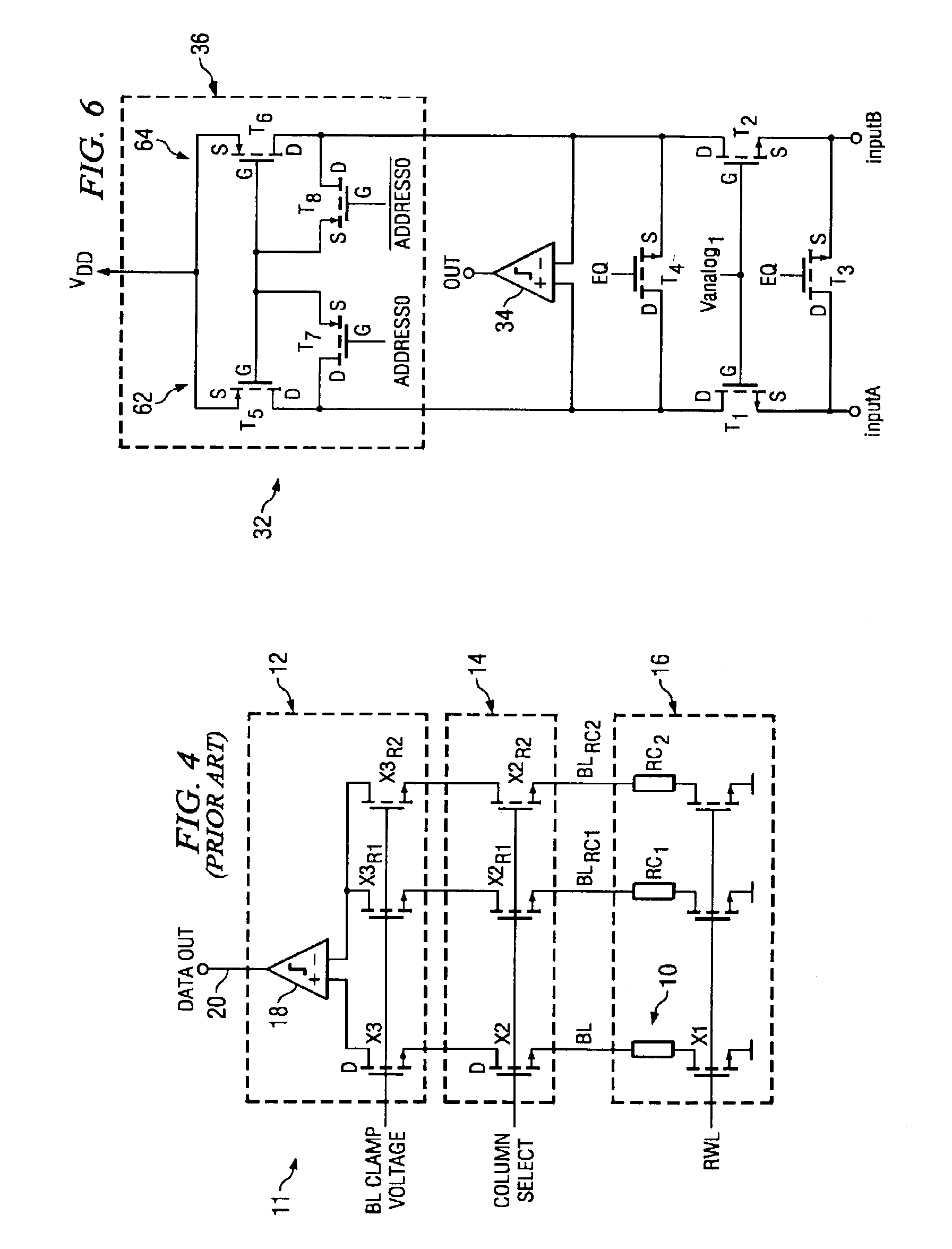
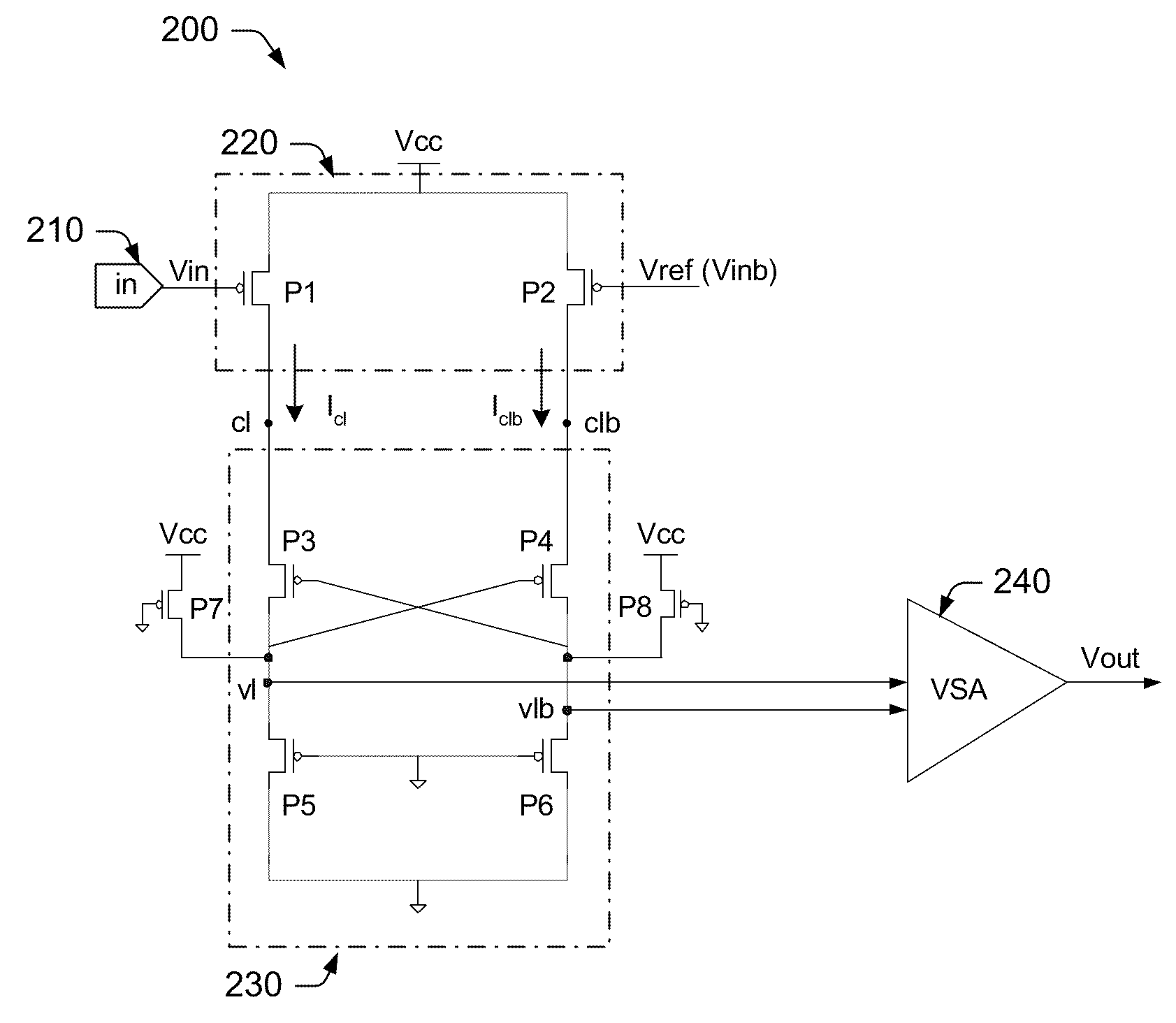
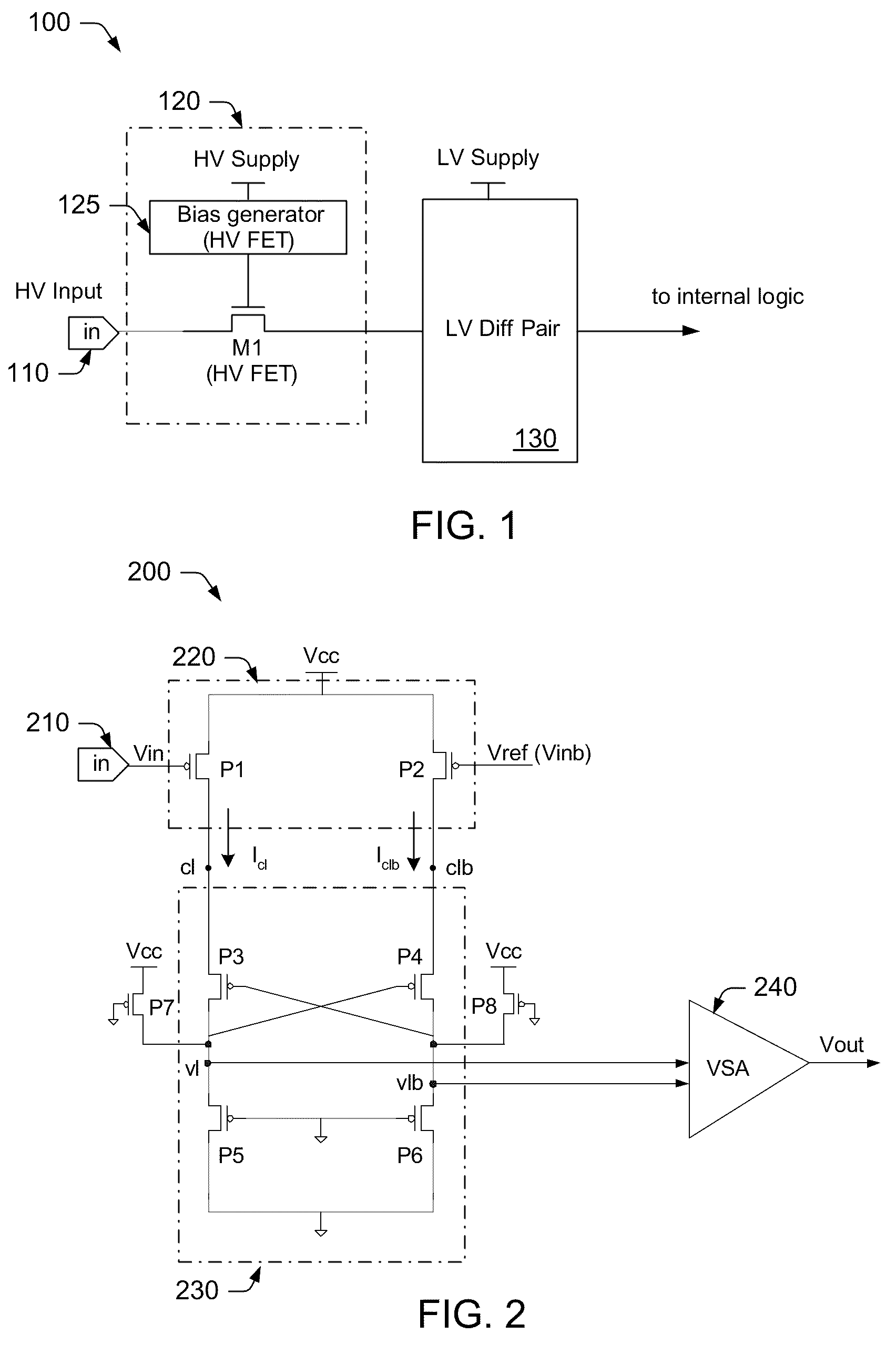
An integrated circuit has a current sense amplifier that includes a voltage comparator having a first input, a second input and an output; a first clamping device coupled between the first input of the voltage comparator and a first input signal node, a second clamping device coupled between the second input of the voltage comparator and a second input signal node, a current mirror having a first side and a second side, the current mirror first side including a first transistor coupled between a voltage source and the first clamping device and the current mirror second side including a second transistor coupled between the voltage source and the second clamping device, and a sensing scheme including an actively balanced capacitance coupled to the source and drain of the second transistor.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Integrated circuit, method of operating an integrated circuit, method of manufacturing an integrated circuit, memory module, stackable memory module
InactiveUS7433253B2Design and efficient manufactureAccurate balanceCurrent/voltage measurementDigital storageCapacitanceEngineering
An integrated circuit has a current sense amplifier that includes a voltage comparator having a first input, a second input and an output; a first clamping device coupled between the first input of the voltage comparator and a first input signal node, a second clamping device coupled between the second input of the voltage comparator and a second input signal node, a current mirror having a first side and a second side, the current mirror first side including a first transistor coupled between a voltage source and the first clamping device and the current mirror second side including a second transistor coupled between the voltage source and the second clamping device, and a sensing scheme including an actively balanced capacitance coupled to the source and drain of the second transistor.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Sample and hold technique for generating an average of sensed inductor current in voltage regulators
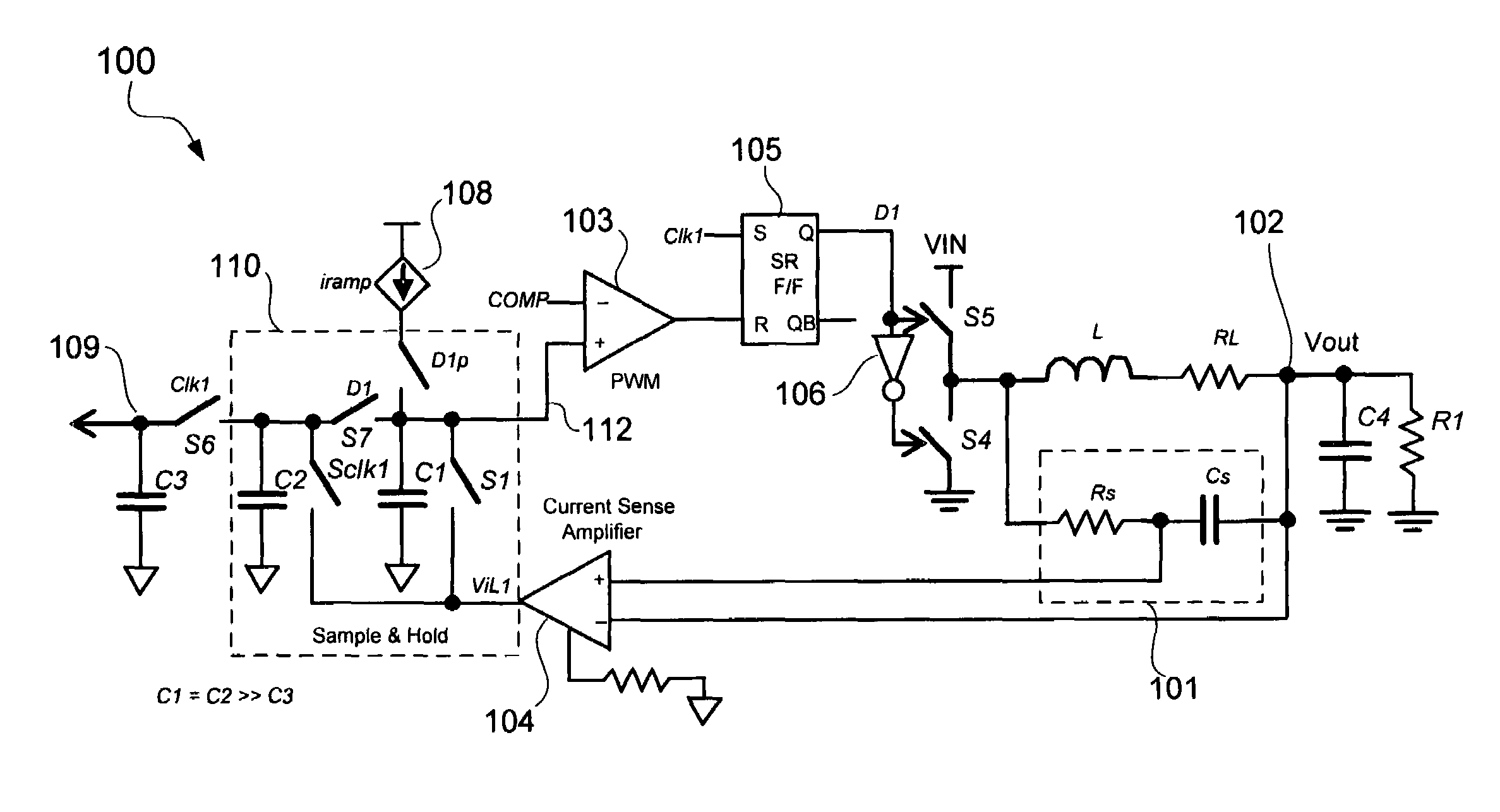
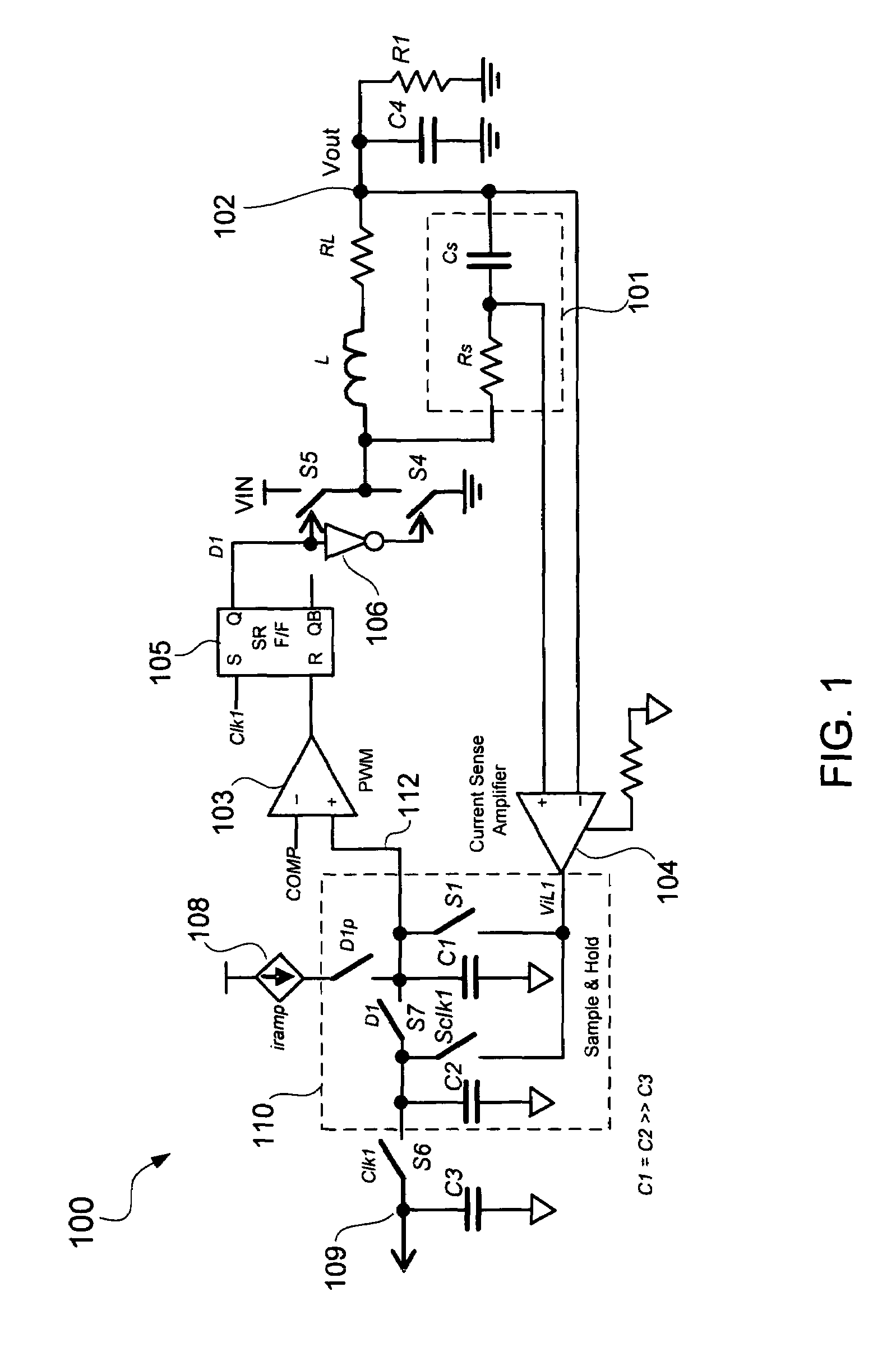
A sample and hold inductor current sense configuration senses inductor current flowing through an output inductor of a voltage regulator and generates an average of the sensed inductor current. The average of the sensed inductor current may be generated from samples of peaks and valleys of the sensed inductor current. For example, the peak of the sensed inductor current may be stored in a first capacitor and the valley of the sensed inductor current may be stored in a second capacitor. The first and second capacitors may be coupled together to generate the average of the sensed inductor current. The average of the sensed inductor current may be provided to a droop control circuit to control droop of an output voltage of the voltage regulator. An input offset voltage of a current sense amplifier sensing the inductor current may be calibrated between samplings of the sensed inductor current.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
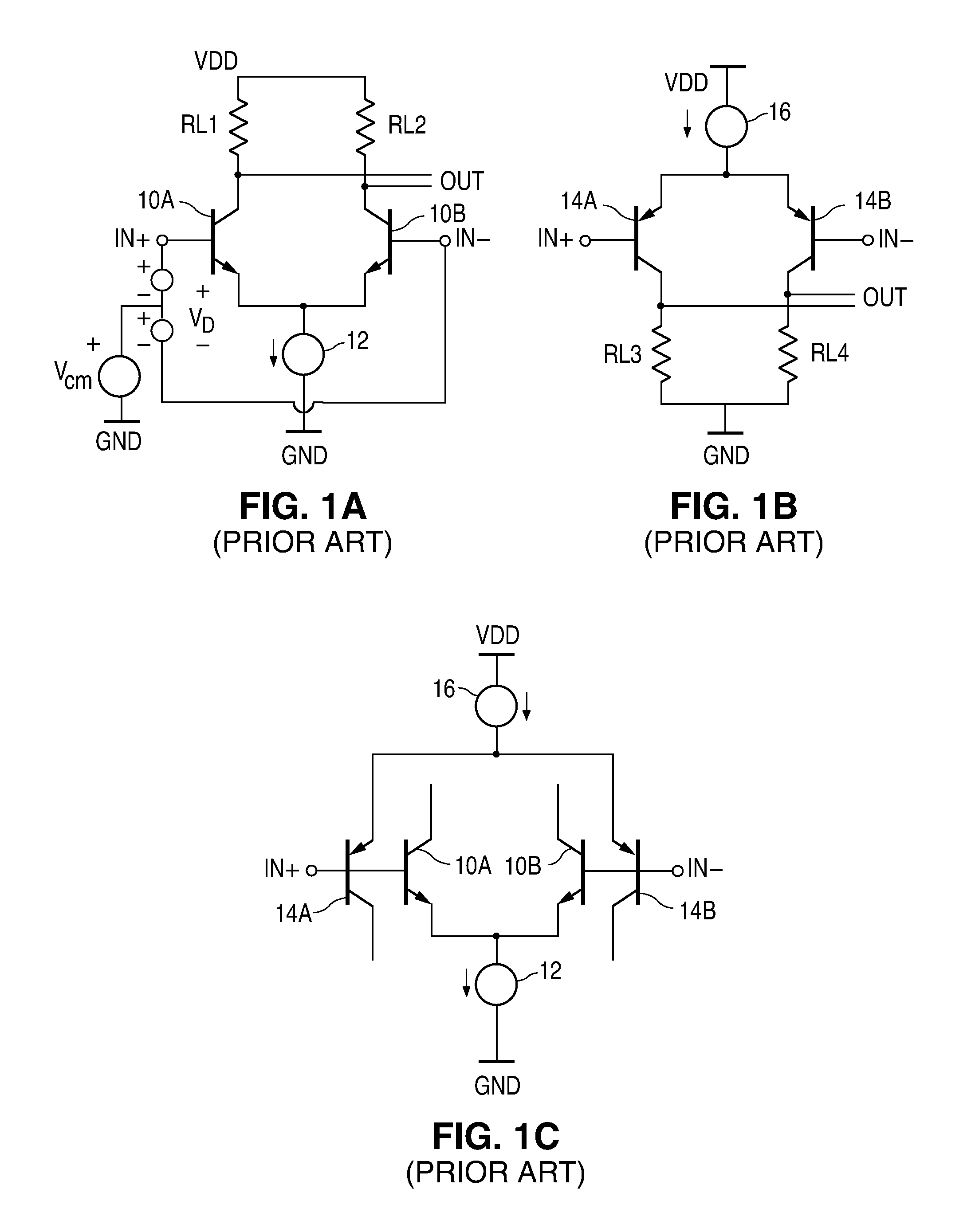
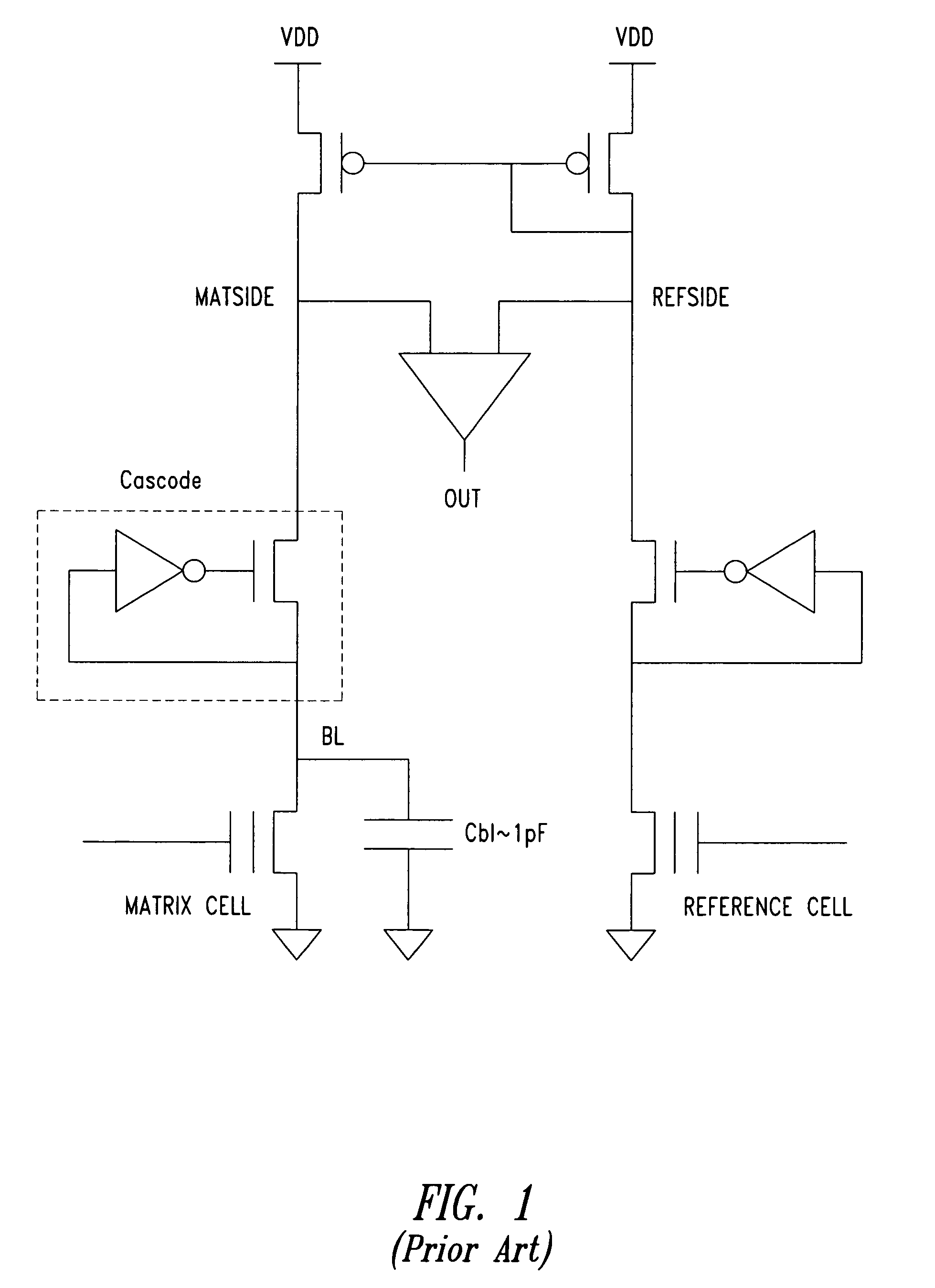
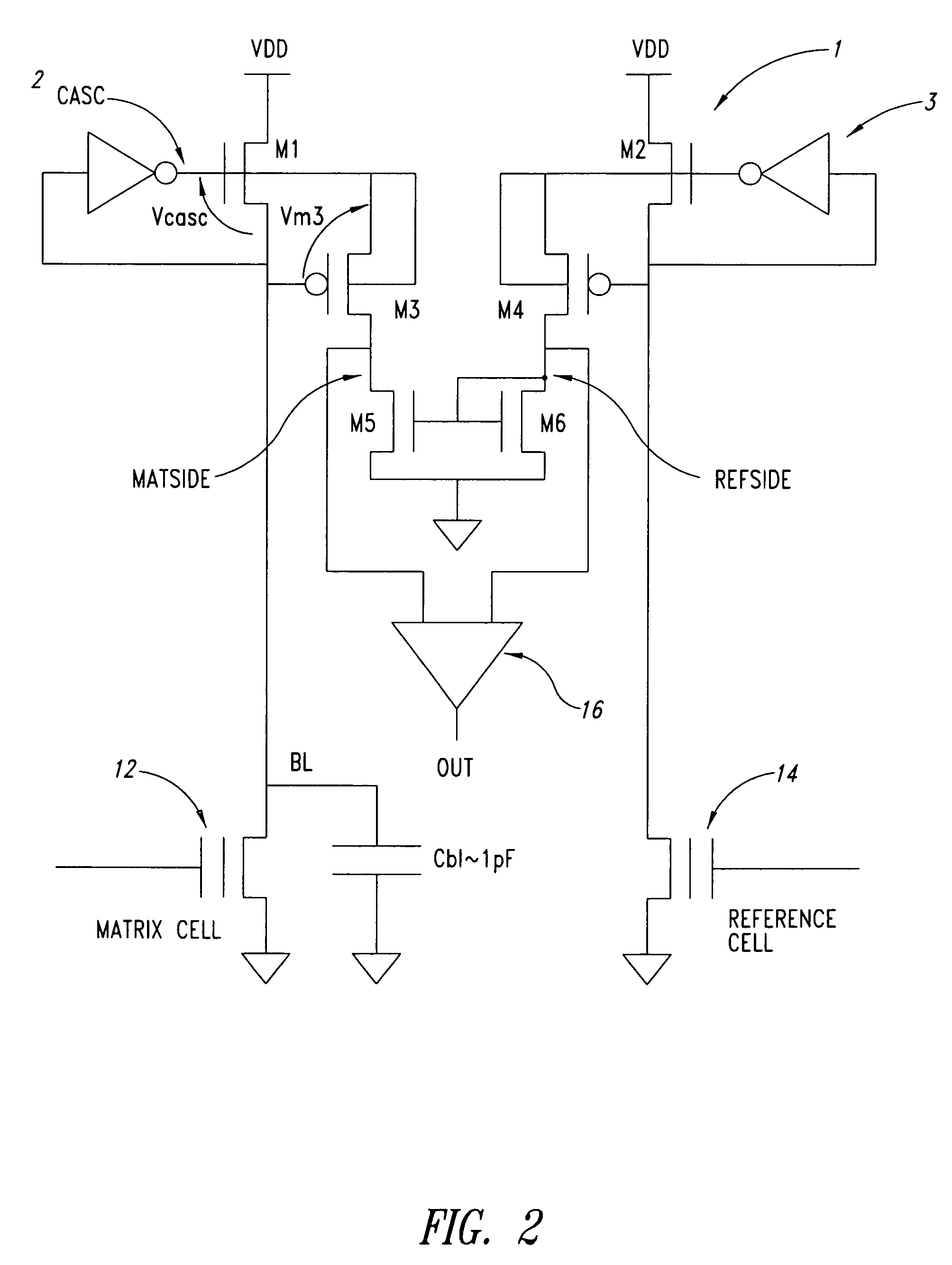
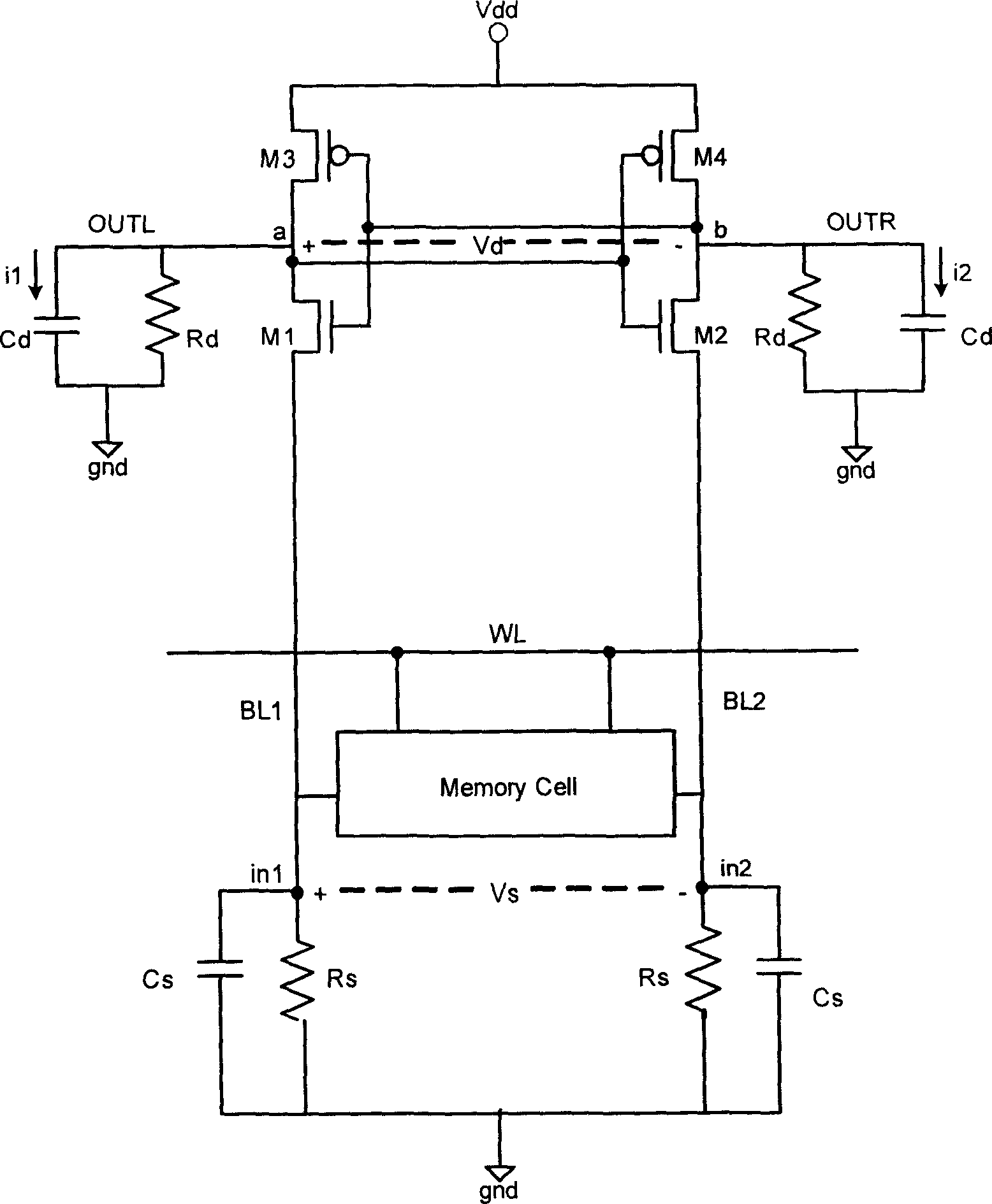
Current sense amplifier
InactiveUS20060050584A1Improve performanceIncrease speedCurrent/voltage measurementDigital storageCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
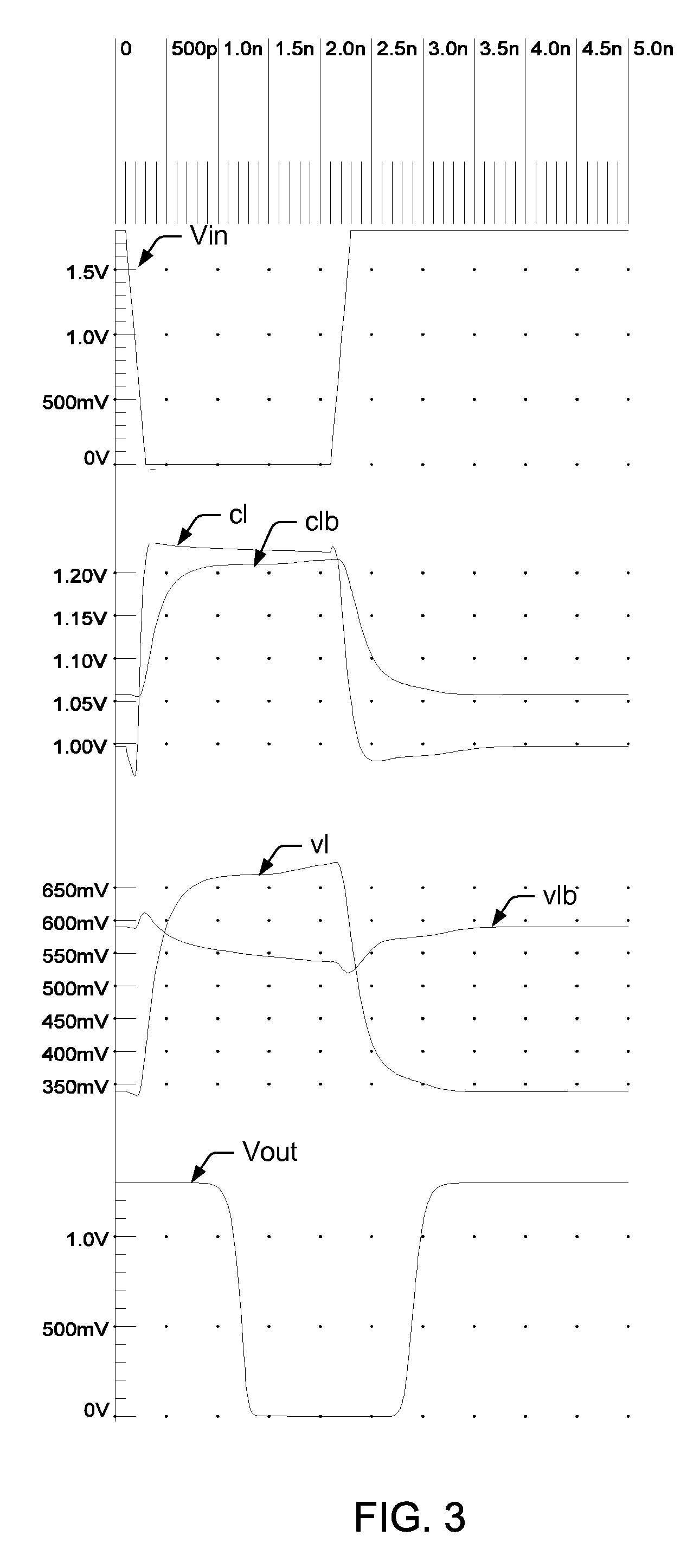
A high-speed current sense amplifier has complementary reference cells and load devices that eliminate capacitive mismatch contributions. The current sense amplifier includes a voltage comparator, a first clamping device coupled between a first input of the voltage comparator and a first input signal node. The first clamping device is coupled to a reference voltage. A second clamping device is coupled between the second input of the voltage comparator and a second input signal node. The second clamping device is also coupled to the reference voltage. A current mirror is coupled between the first and second input of the voltage comparator and is coupled to an active capacitance balancing circuit. The active capacitance balancing circuit may be combined with the voltage comparator. Equalization devices may be coupled between the first and second inputs of the voltage comparator, and between the first input signal node and the second input signal node.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
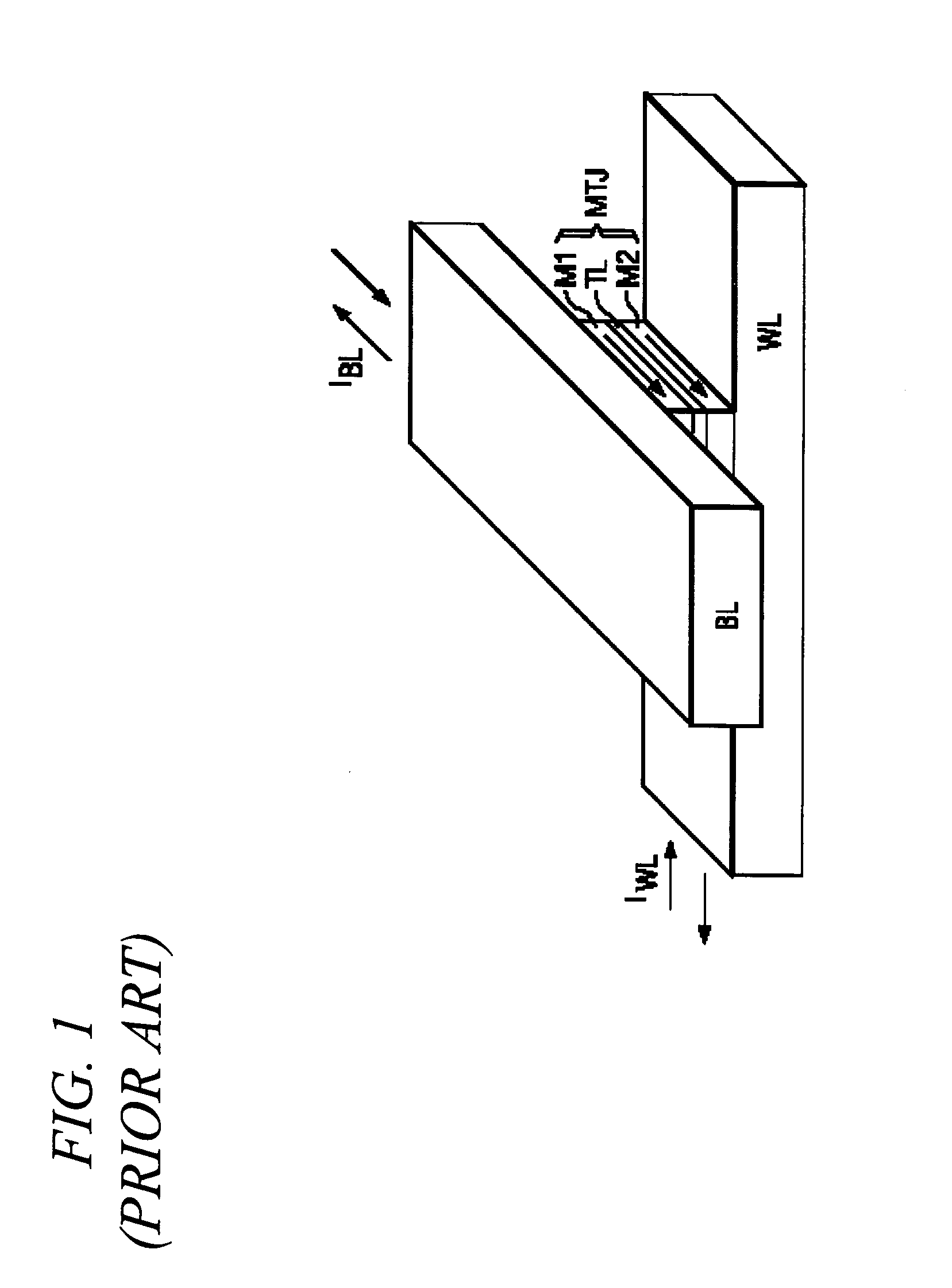
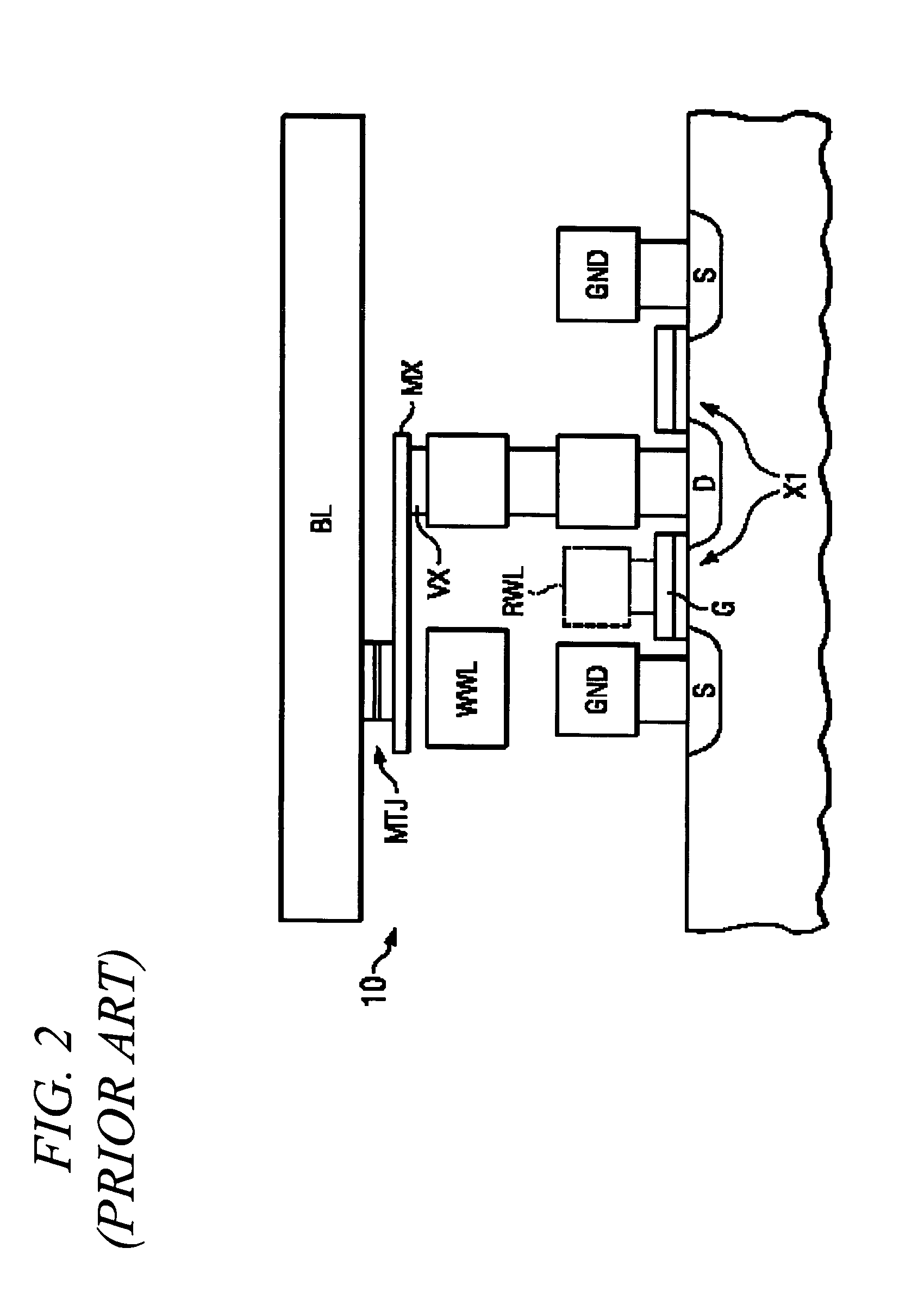
Sense amplifier bitline boost circuit
ActiveUS7161861B2Increase available currentHigh densityDigital storageAudio power amplifierHemt circuits
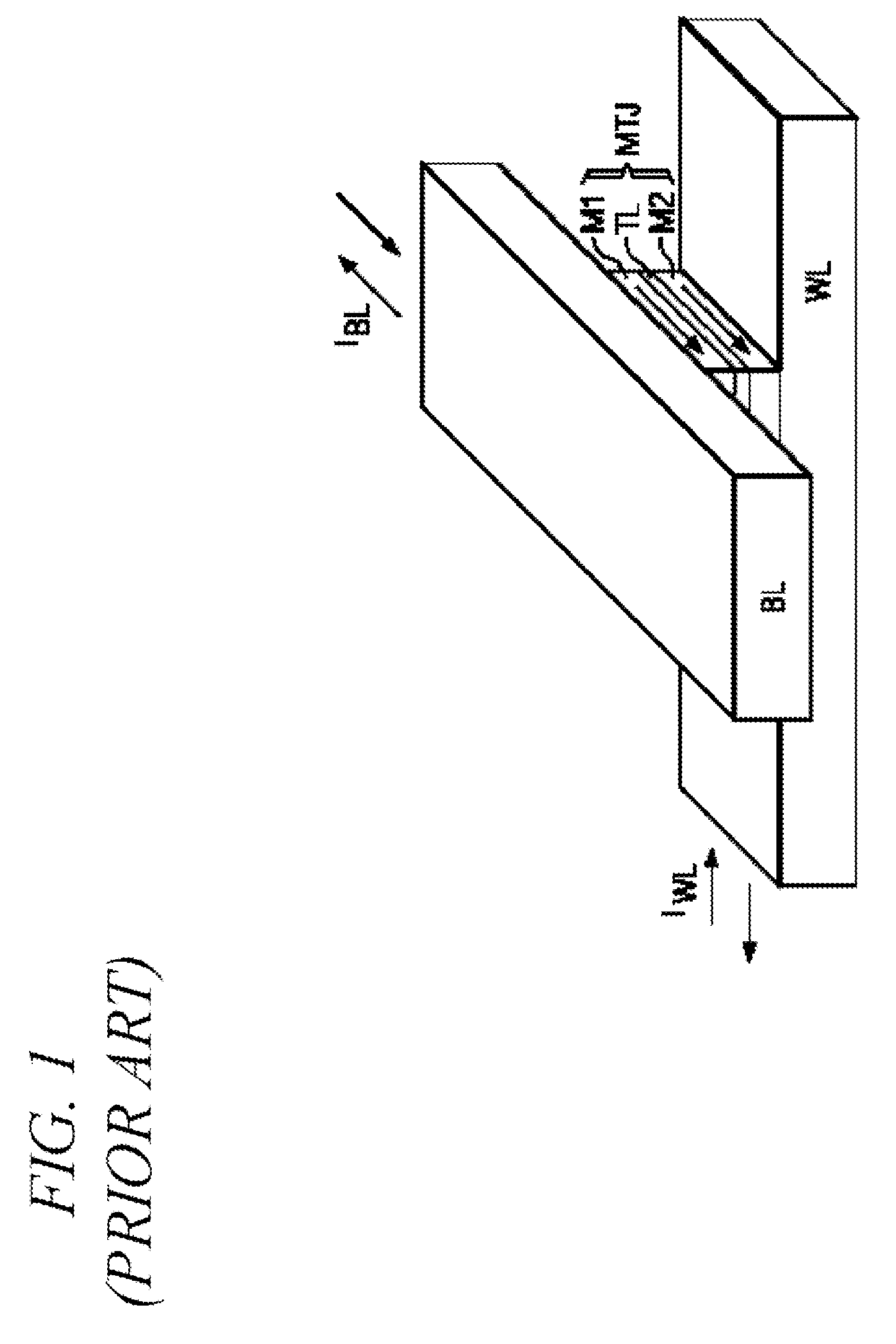
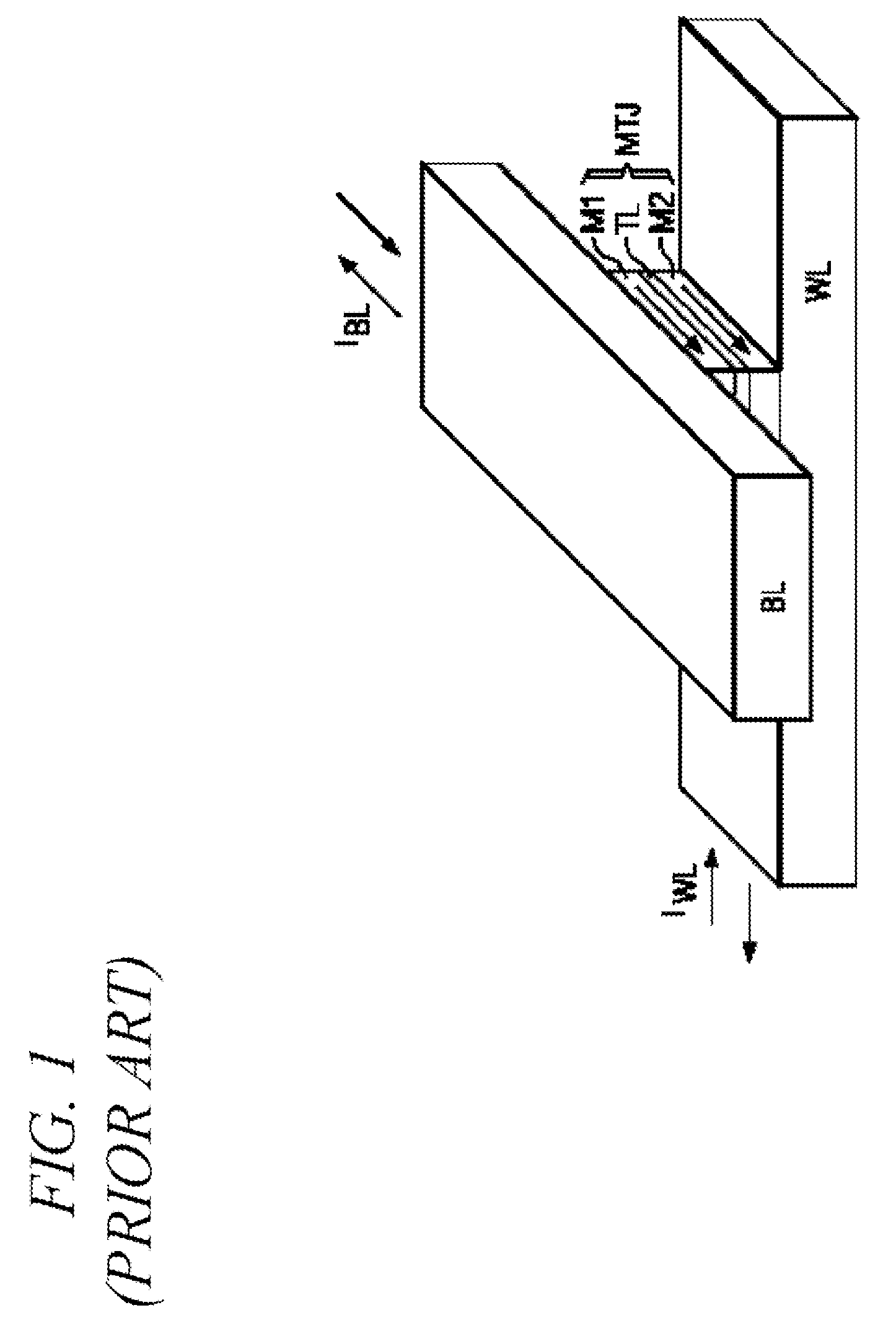
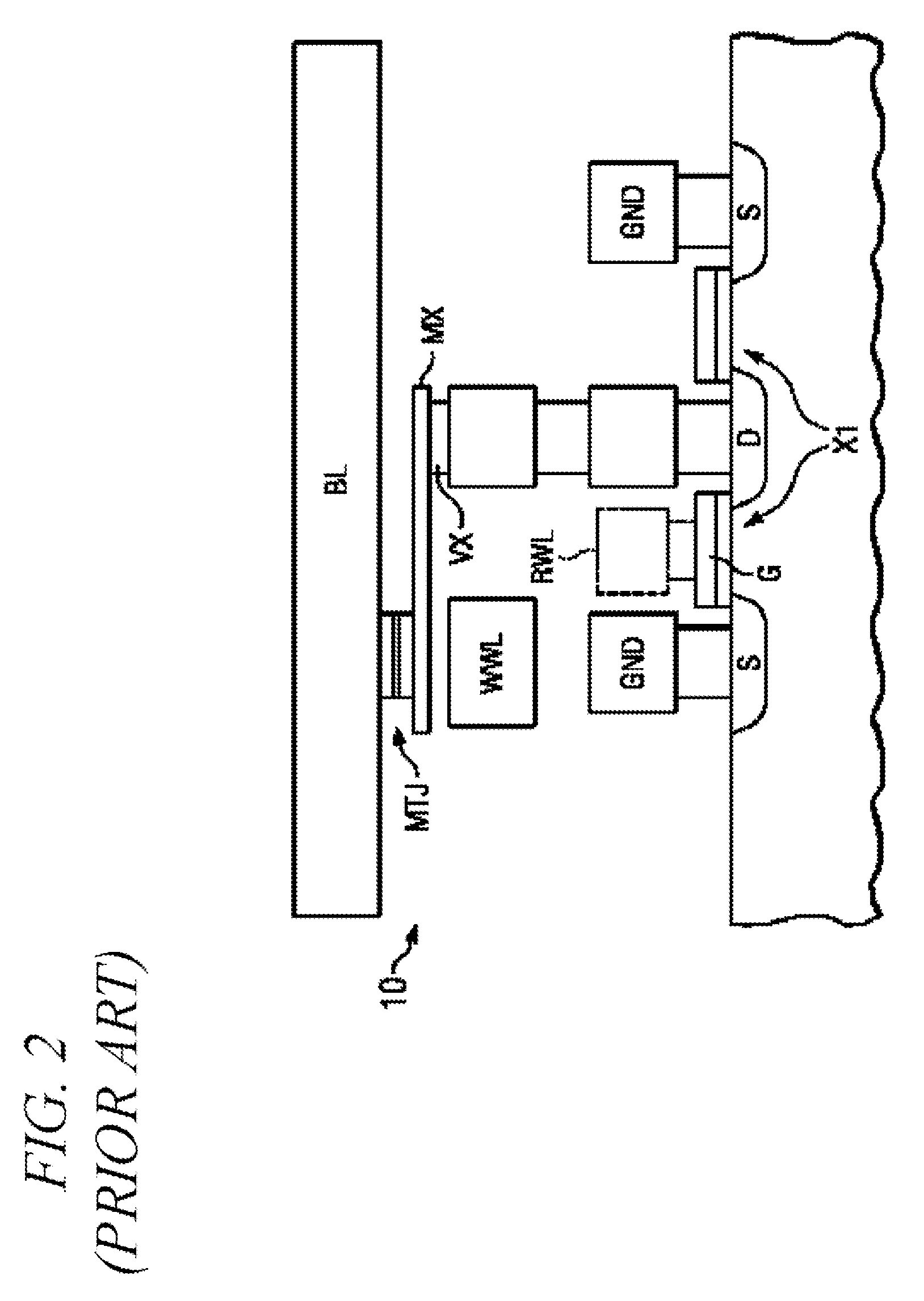
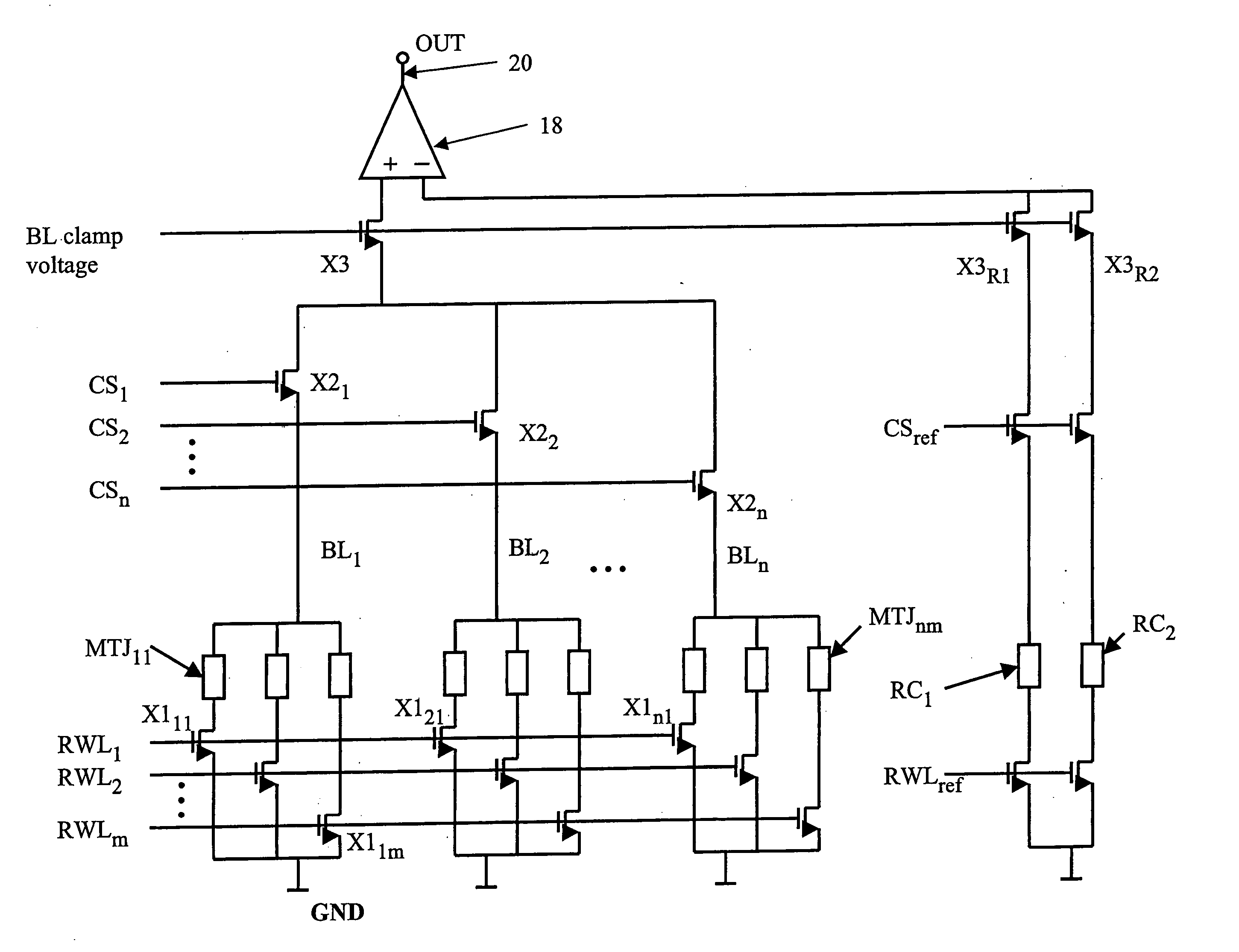
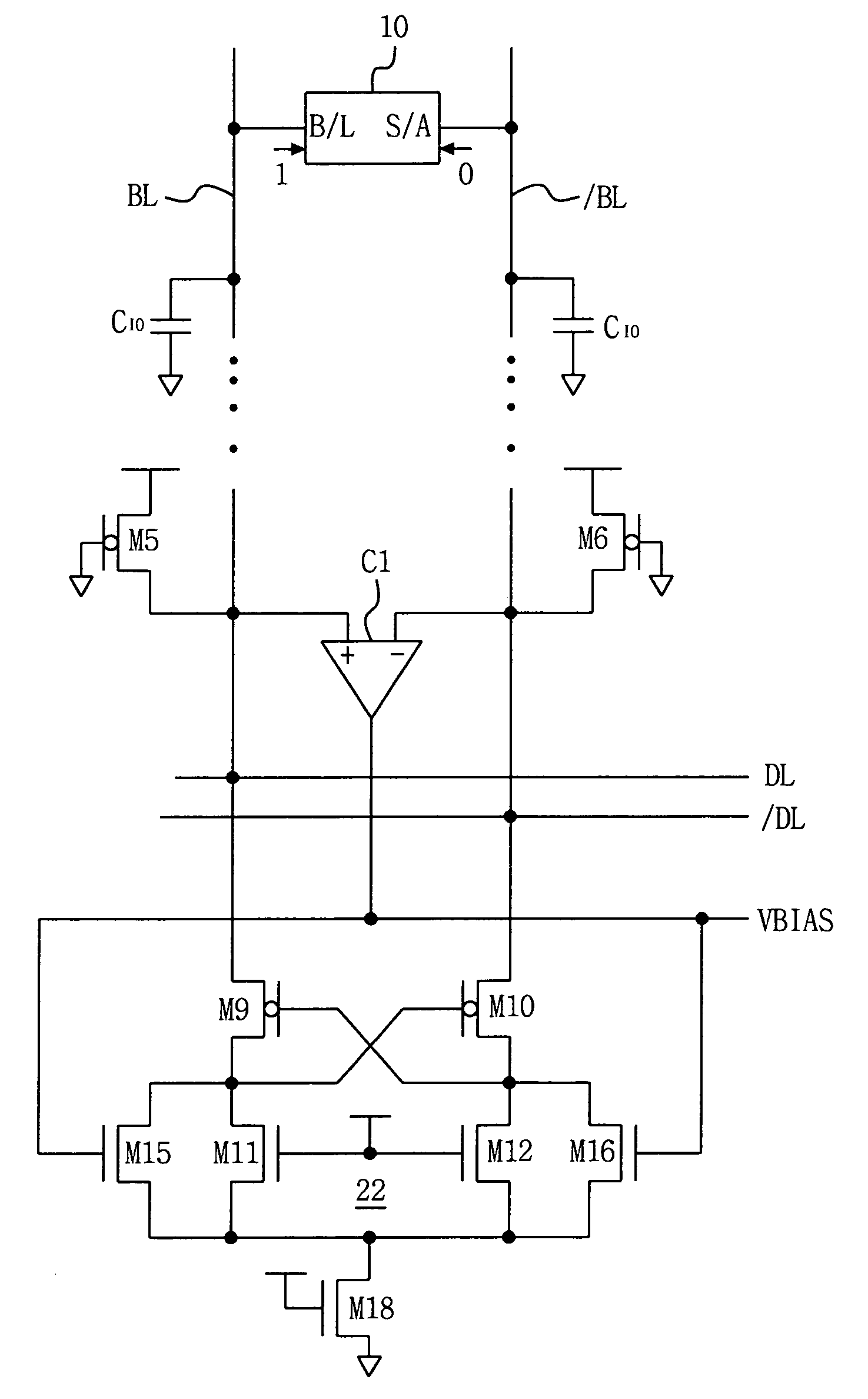
A current sense amplifier including clamping devices and a current mirror is configured to sense the resistance of an MTJ memory cell utilizing a bitline boost circuit to shorten the charging time for parasitic circuit capacitance. The bitline boost circuit includes a source follower coupled to a reference voltage and a switch coupled to another voltage source. The switch is enabled to conduct during an initial period of sensing the resistance of the memory cell. The source follower in the bitline boost circuit is configured to clamp the voltage of an input signal at substantially the same level as the clamping devices, and to provide additional current to shorten the period for charging parasitic capacitance. The resulting current sense amplifier can be used to implement a memory device with fast and reliable read times and low manufacturing cost.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
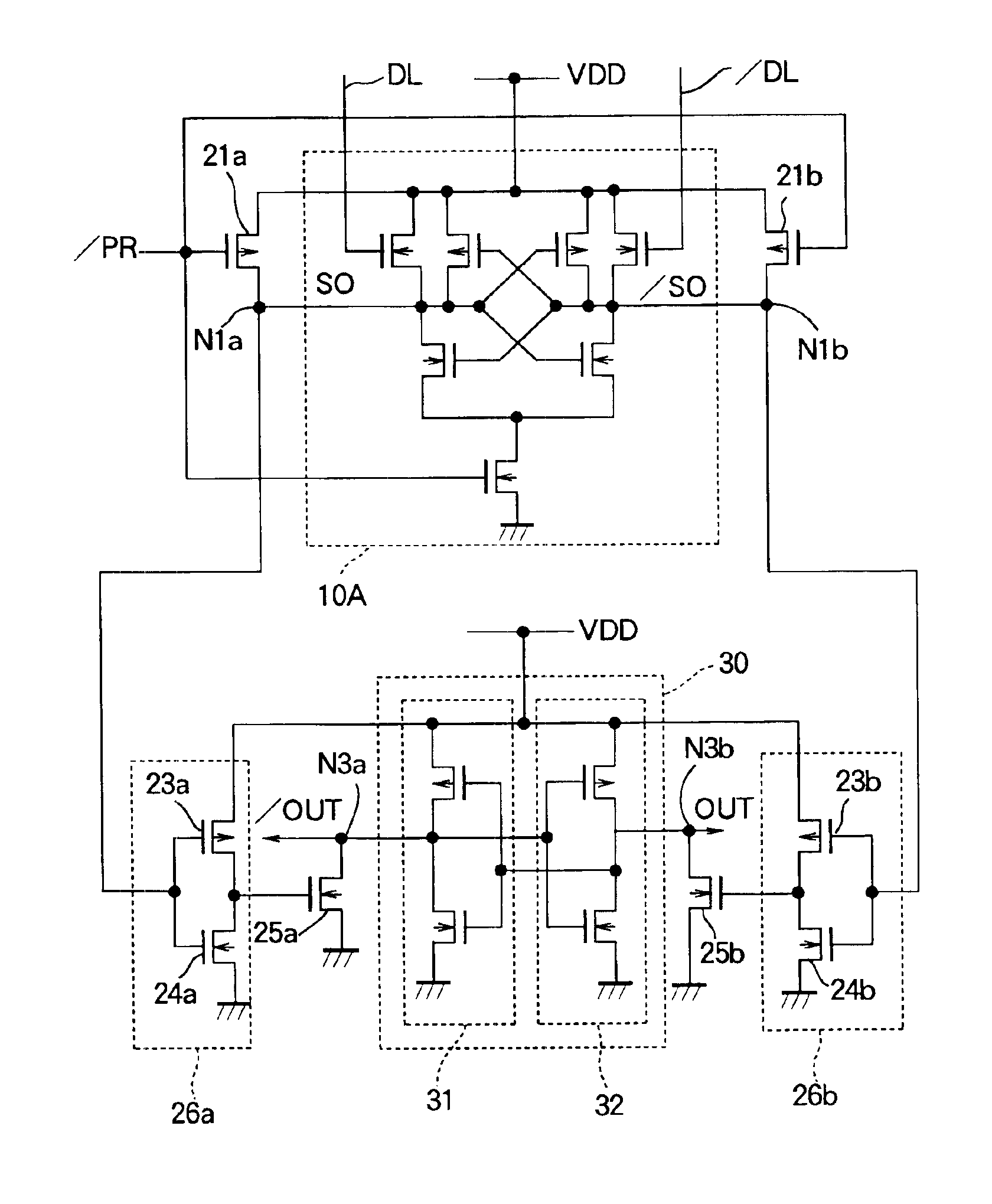
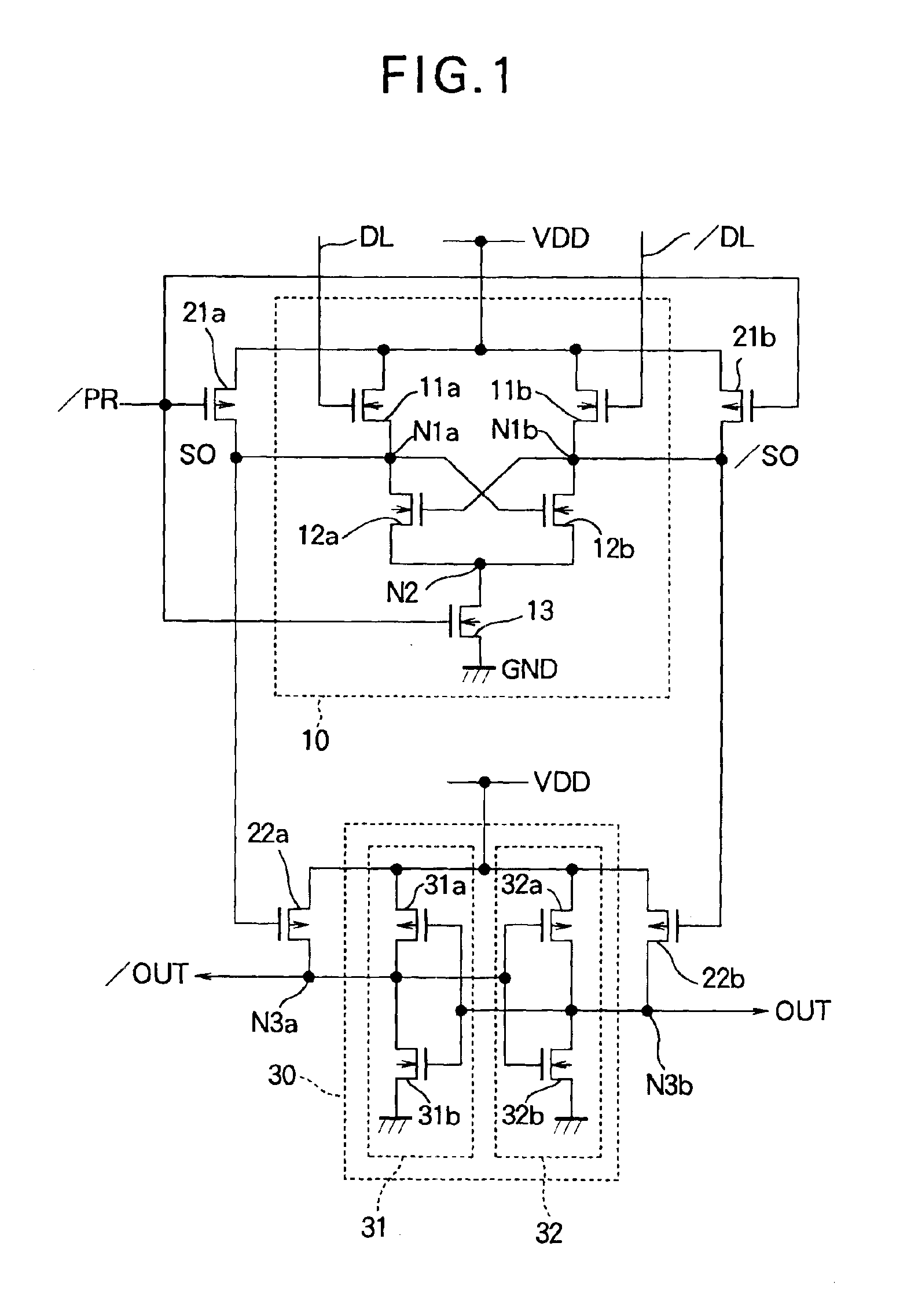
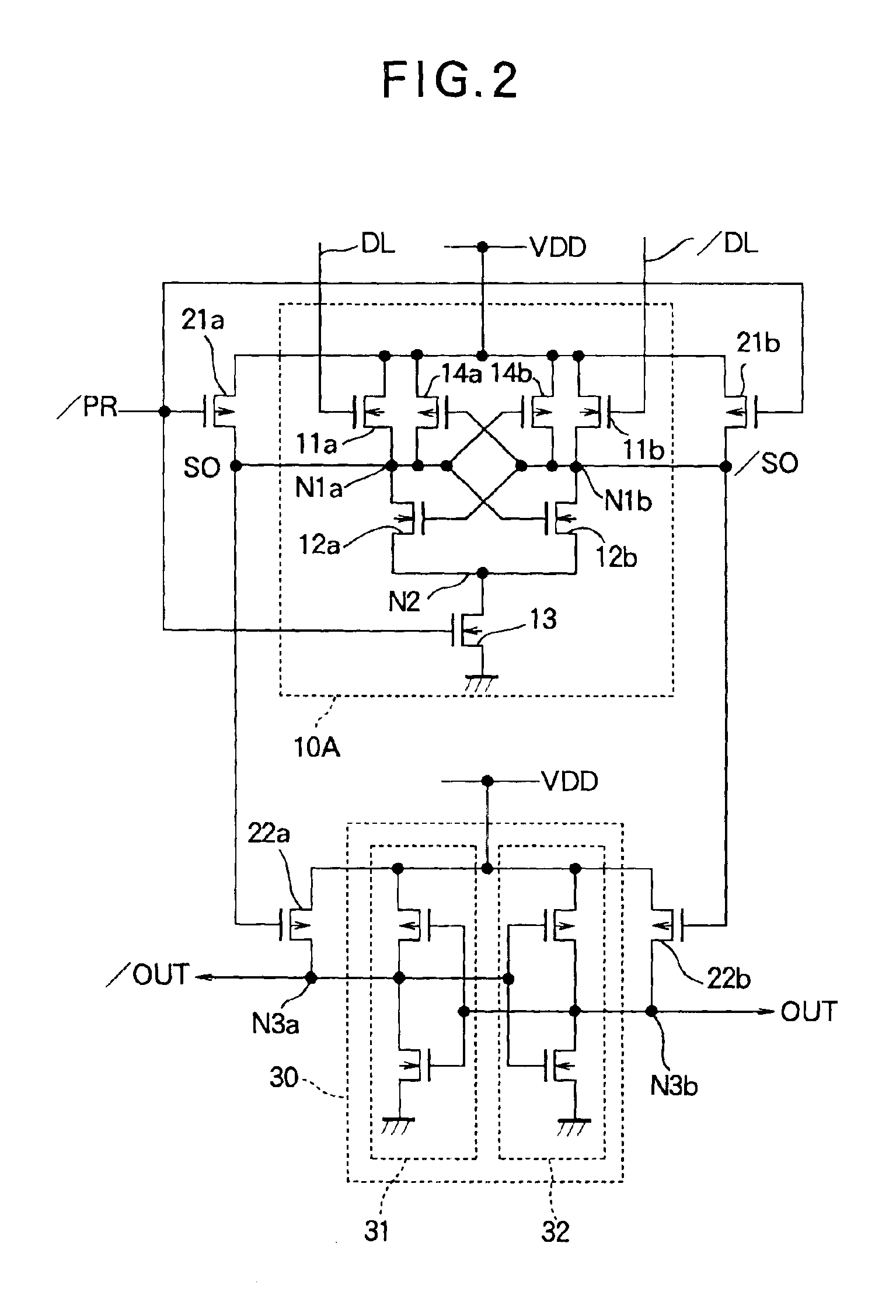
Current sense amplifier
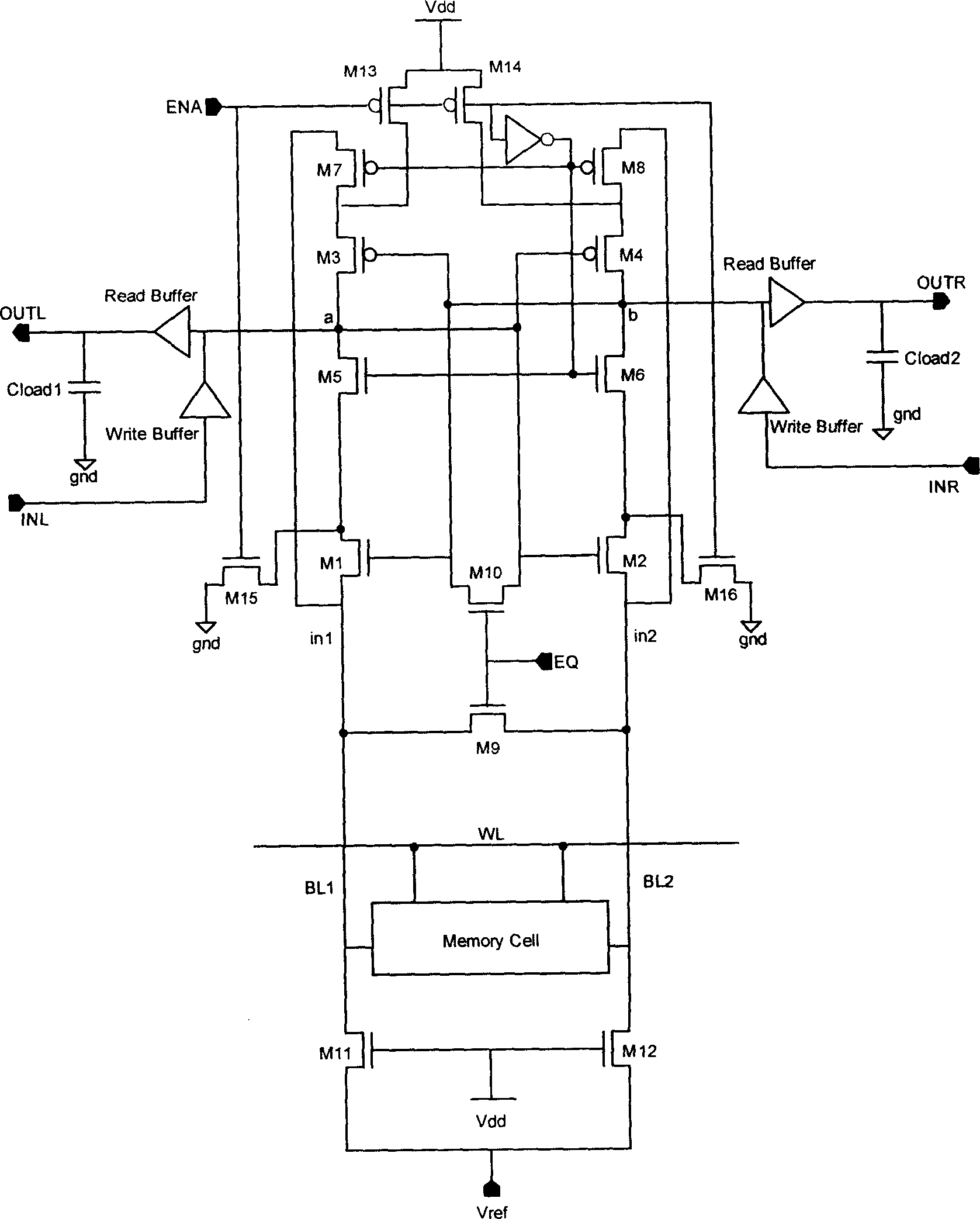
InactiveUS6946882B2Useful in sensing currentEliminate architecture-related capacitive mismatch contributionsCurrent/voltage measurementDigital storageCapacitanceVoltage reference
A symmetrical high-speed current sense amplifier having complementary reference cells and configurable load devices that eliminates architecture-related capacitive mismatch contributions. The current sense amplifier is adapted for use in a symmetric sensing architecture and includes a configurable load device. The current sense amplifier includes a voltage comparator, a first clamping device coupled between a first input of the voltage comparator and a first input signal, the first clamping device being coupled to a reference voltage. A second clamping device is coupled between the second input of the voltage comparator and a second input signal, the second clamping device being coupled to the reference voltage. The load device may comprise a current mirror that is coupled between the first and second input of the voltage comparator. The current mirror may be configurable by select transistors. Alternatively, the load device may be a hard-wired current mirror, and a multiplexer may be used to select whether the first input signal or the second input signal is connected to a first or second side of the current mirror. Configurable dummy loads may be added at appropriate nodes to optimize the capacitive load and increase the speed of the amplifier. Equalization devices may be coupled between the first and second inputs of the voltage comparator, and between the first input signal and the second input signal.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Switching regulator
InactiveUS20130207625A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionVoltage referenceSupply current
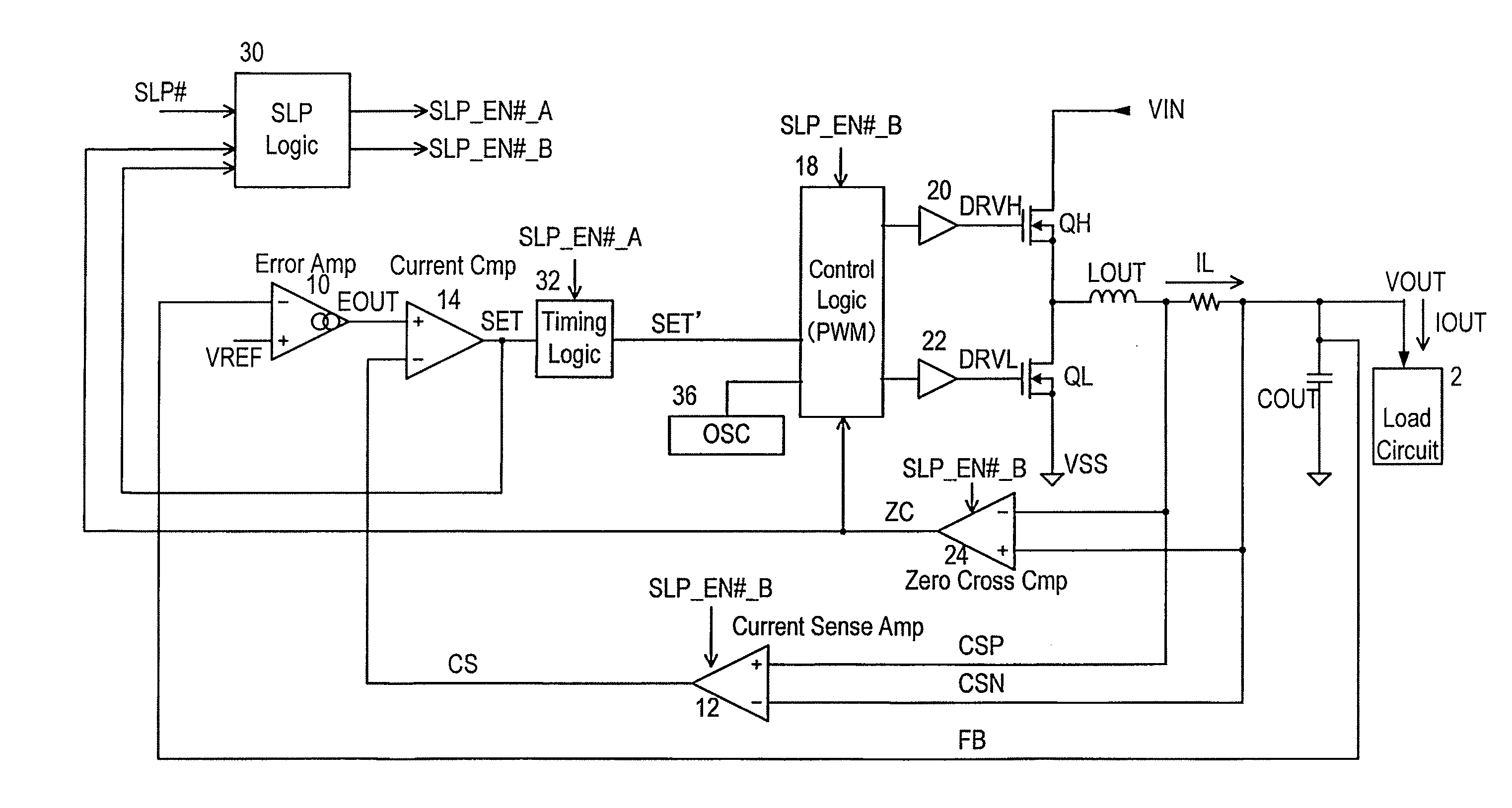
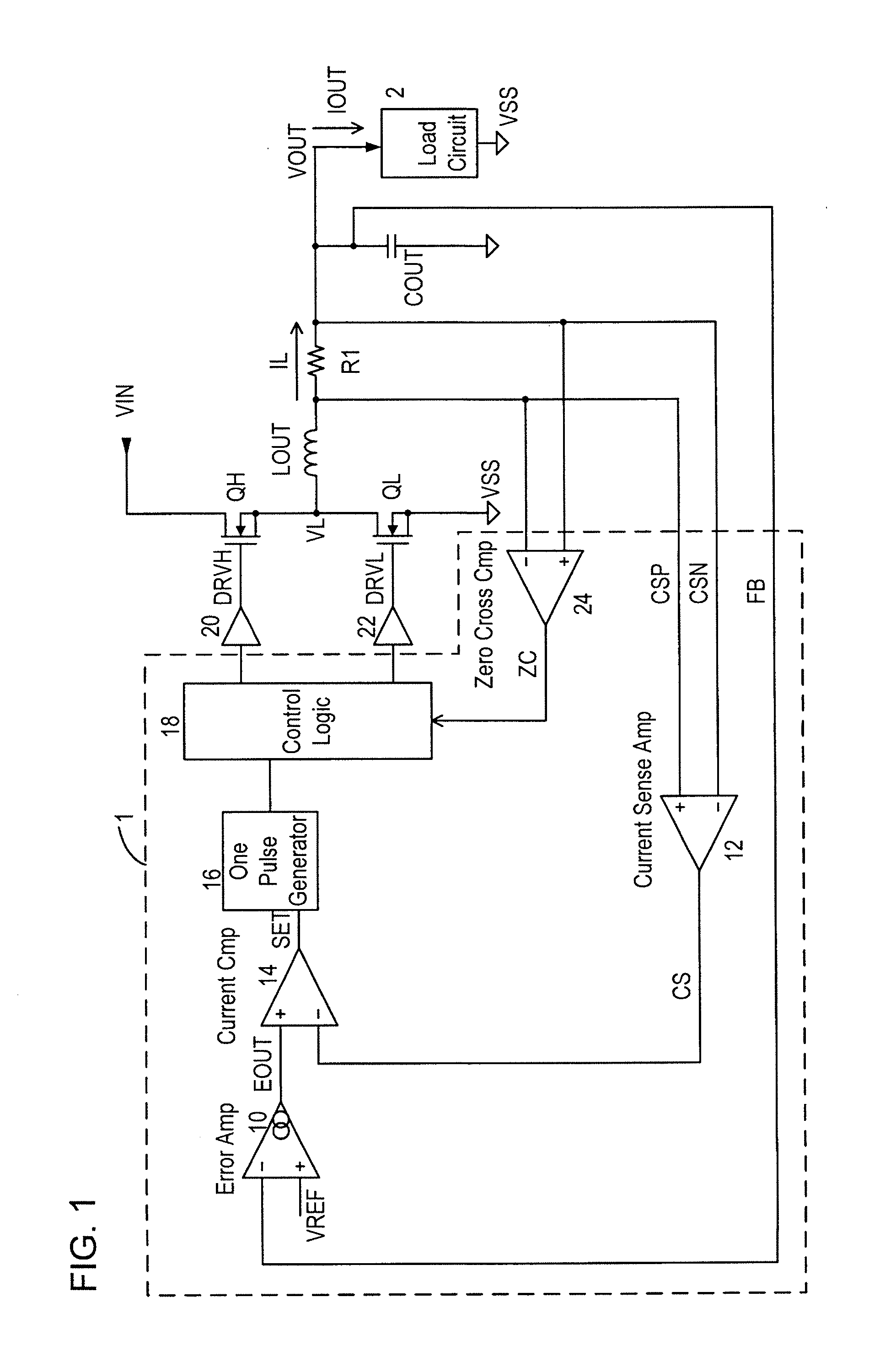
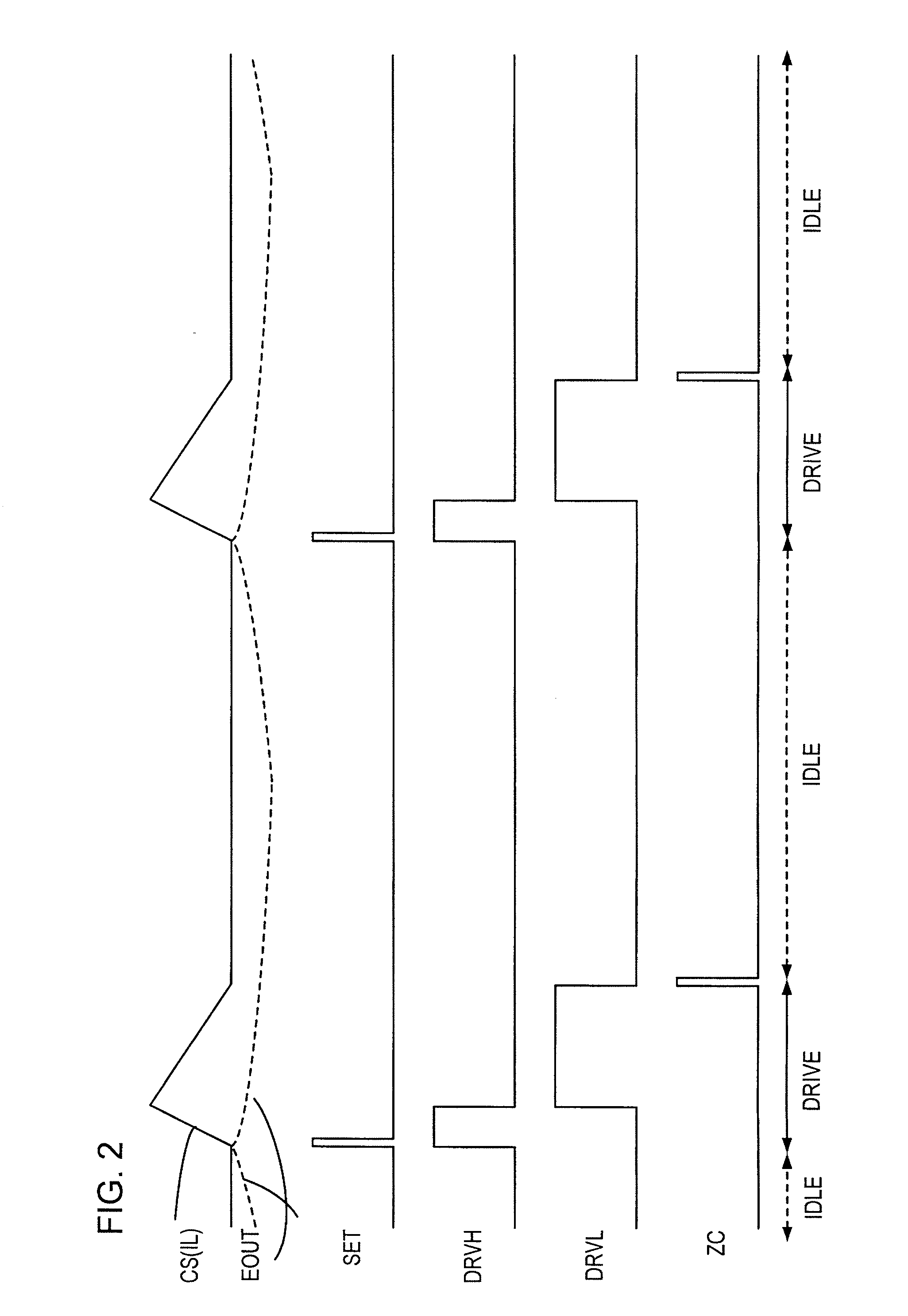
A switching regulator controls an output transistor supplying current to an inductor and generates a second supply voltage from a first supply voltage. The switching regulator has: an error amplifier amplifying a difference between the second supply voltage and a reference voltage; a current sense amplifier converting an inductor current into voltage; a current comparator comparing an output voltages of the error amplifier and the current sense amplifier, so as to output a trigger signal when the second supply voltage decreases; a pulse generation circuit generating a control pulse to drive the first output transistor in response to the trigger signal; and a sleep control circuit, during a sleep period by a sleep signal supplied from a load side, suspending operation of the current sense amplifier or the pulse generation circuit, and tentatively resuming the suspended operation in response to the trigger signal, and thereafter suspending the operation again.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Current sense amplifier circuits having a bias voltage node for adjusting input resistance
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Current sense amplifier
InactiveUS7251178B2Faster sensingDesign and efficient manufactureCurrent/voltage measurementDigital storageCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A high-speed current sense amplifier has complementary reference cells and load devices that eliminate capacitive mismatch contributions. The current sense amplifier includes a voltage comparator, a first clamping device coupled between a first input of the voltage comparator and a first input signal node. The first clamping device is coupled to a reference voltage. A second clamping device is coupled between the second input of the voltage comparator and a second input signal node. The second clamping device is also coupled to the reference voltage. A current mirror is coupled between the first and second input of the voltage comparator and is coupled to an active capacitance balancing circuit. The active capacitance balancing circuit may be combined with the voltage comparator. Equalization devices may be coupled between the first and second inputs of the voltage comparator, and between the first input signal node and the second input signal node.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
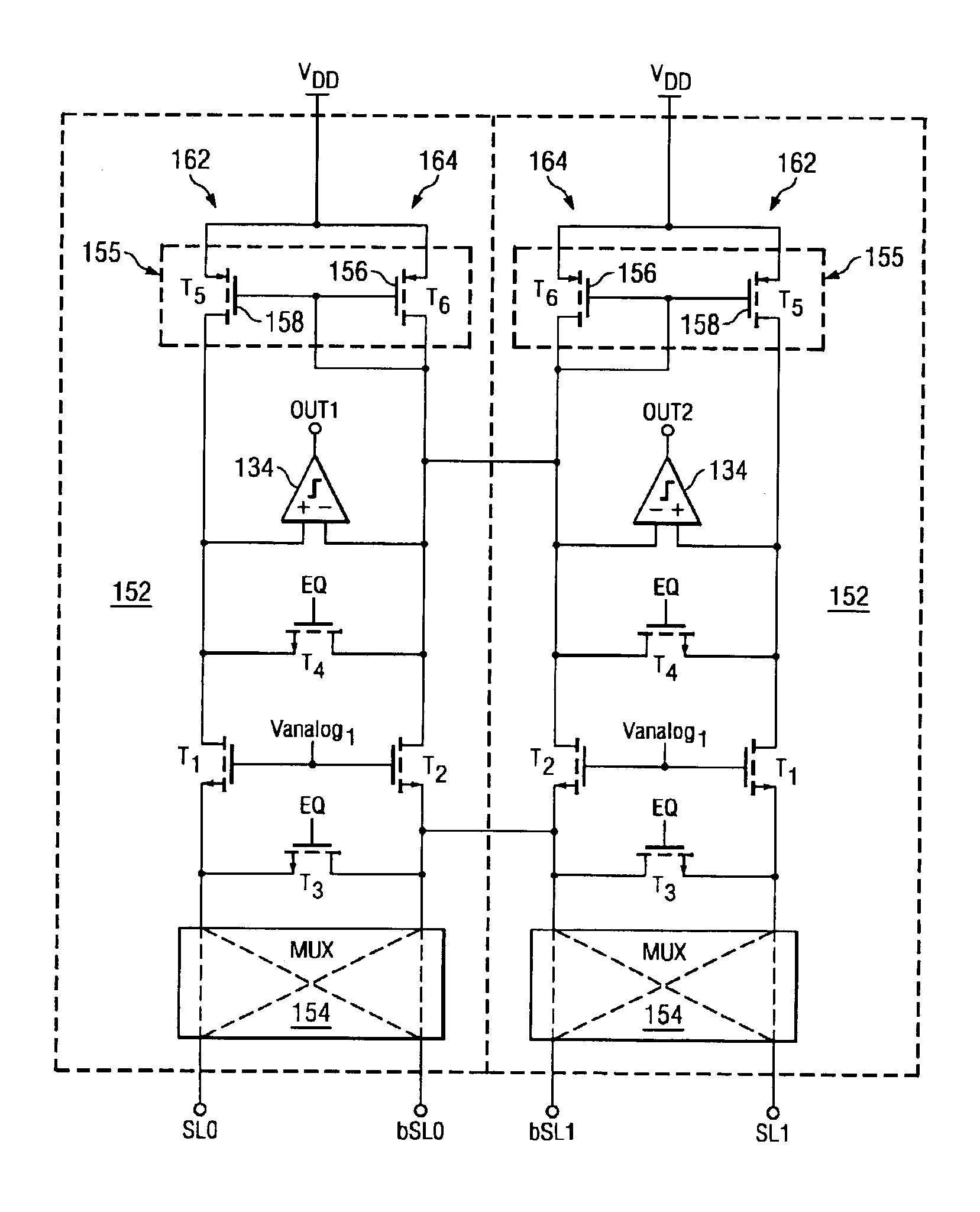
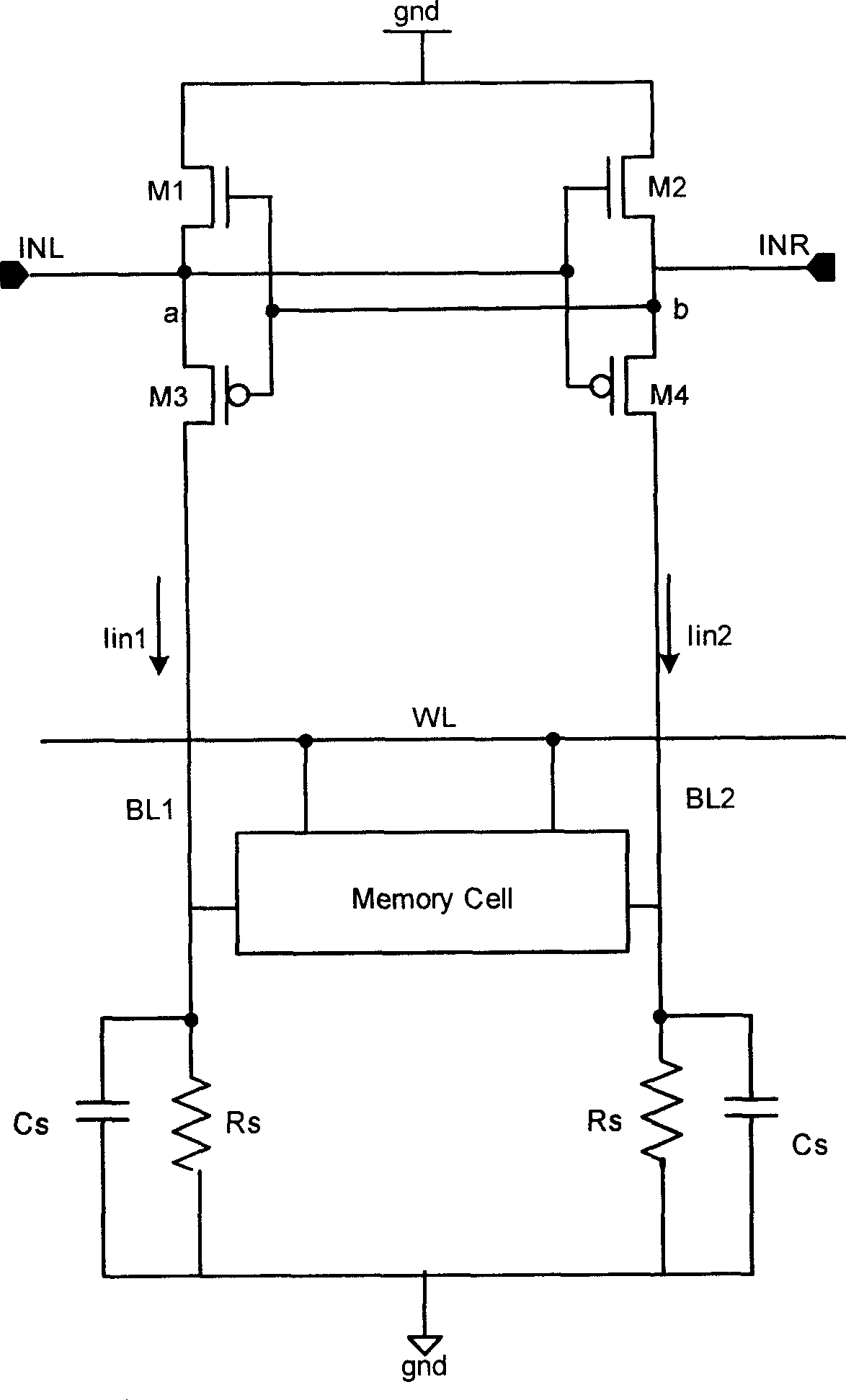
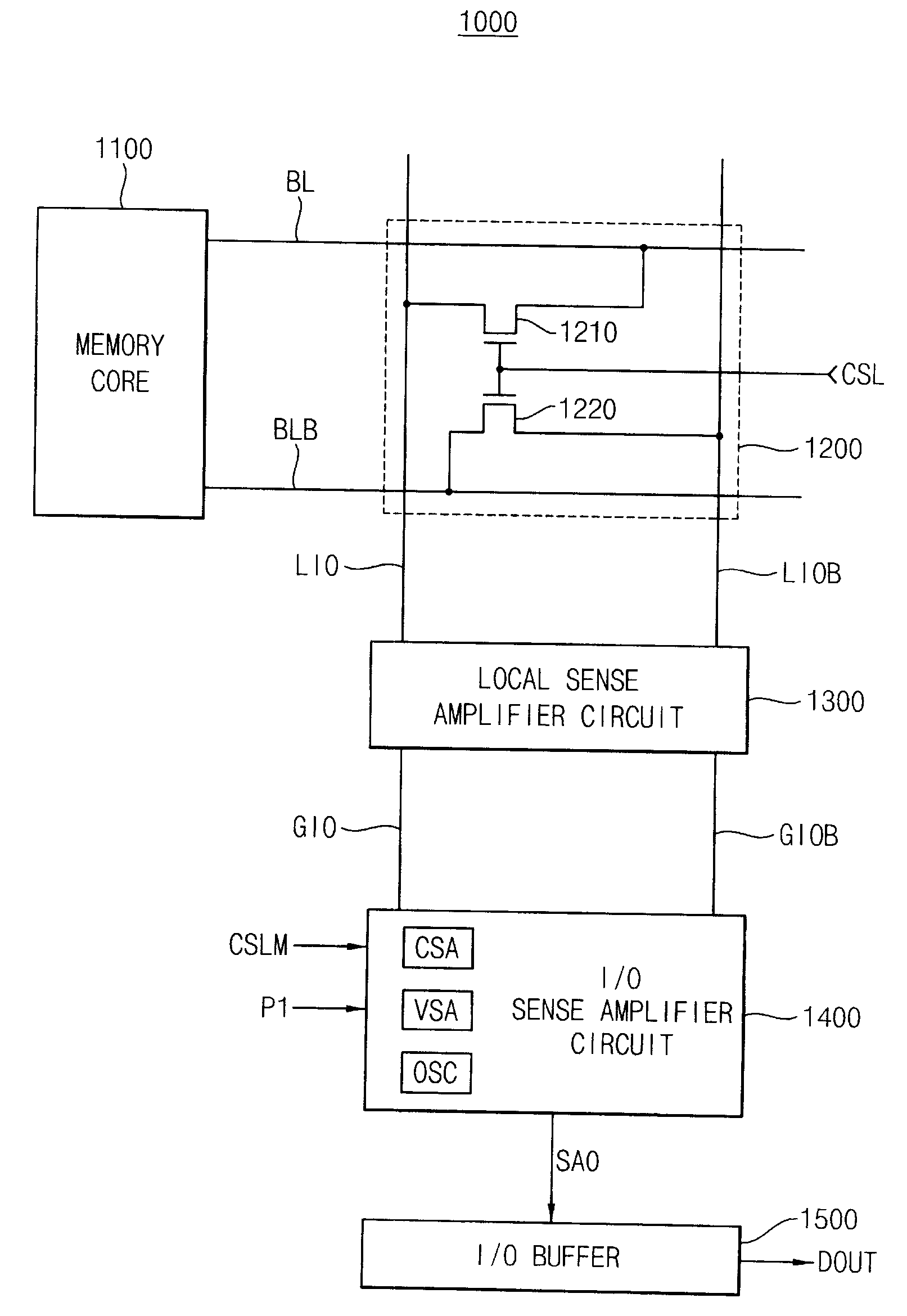
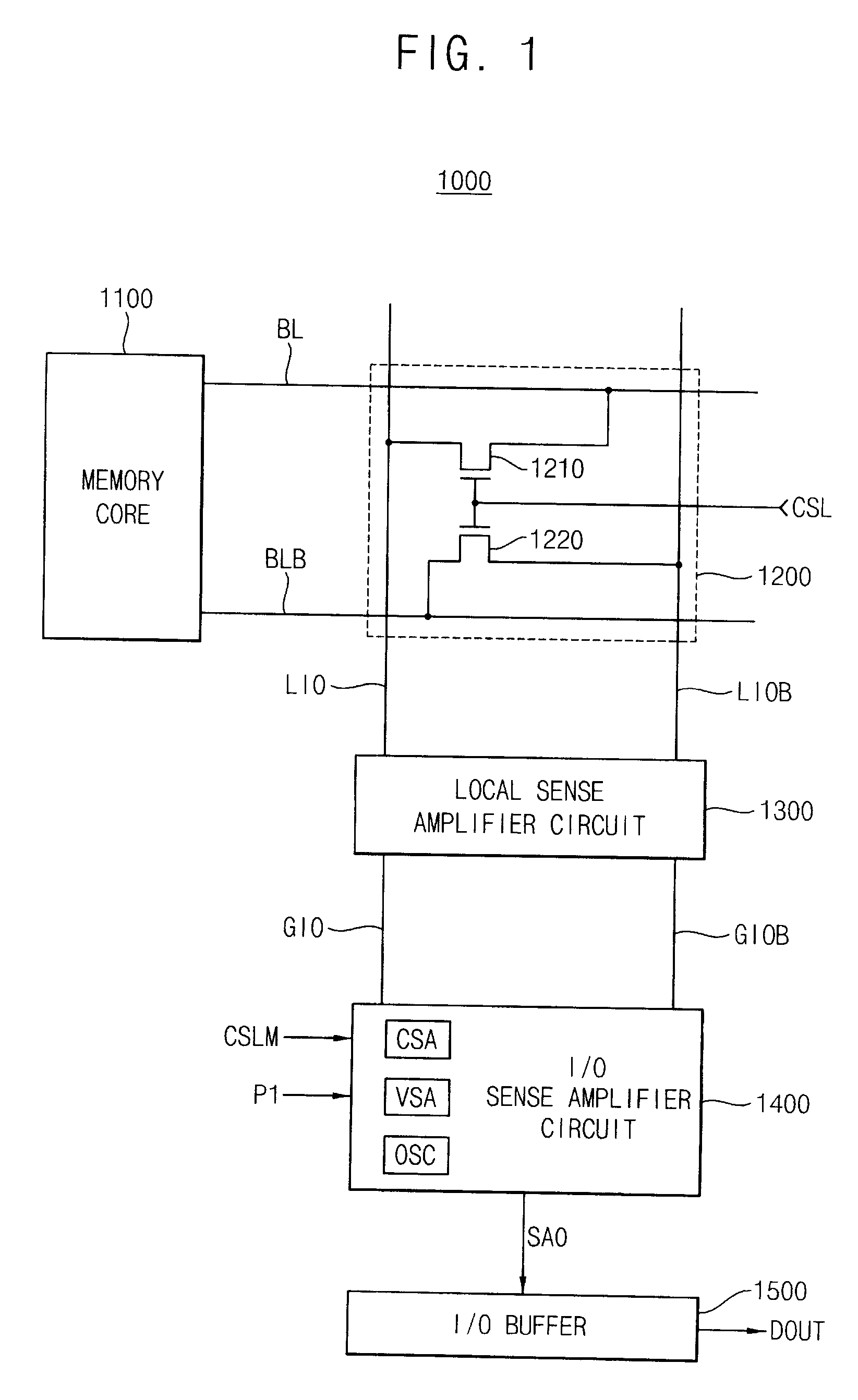
Low voltage data path and current sense amplifier
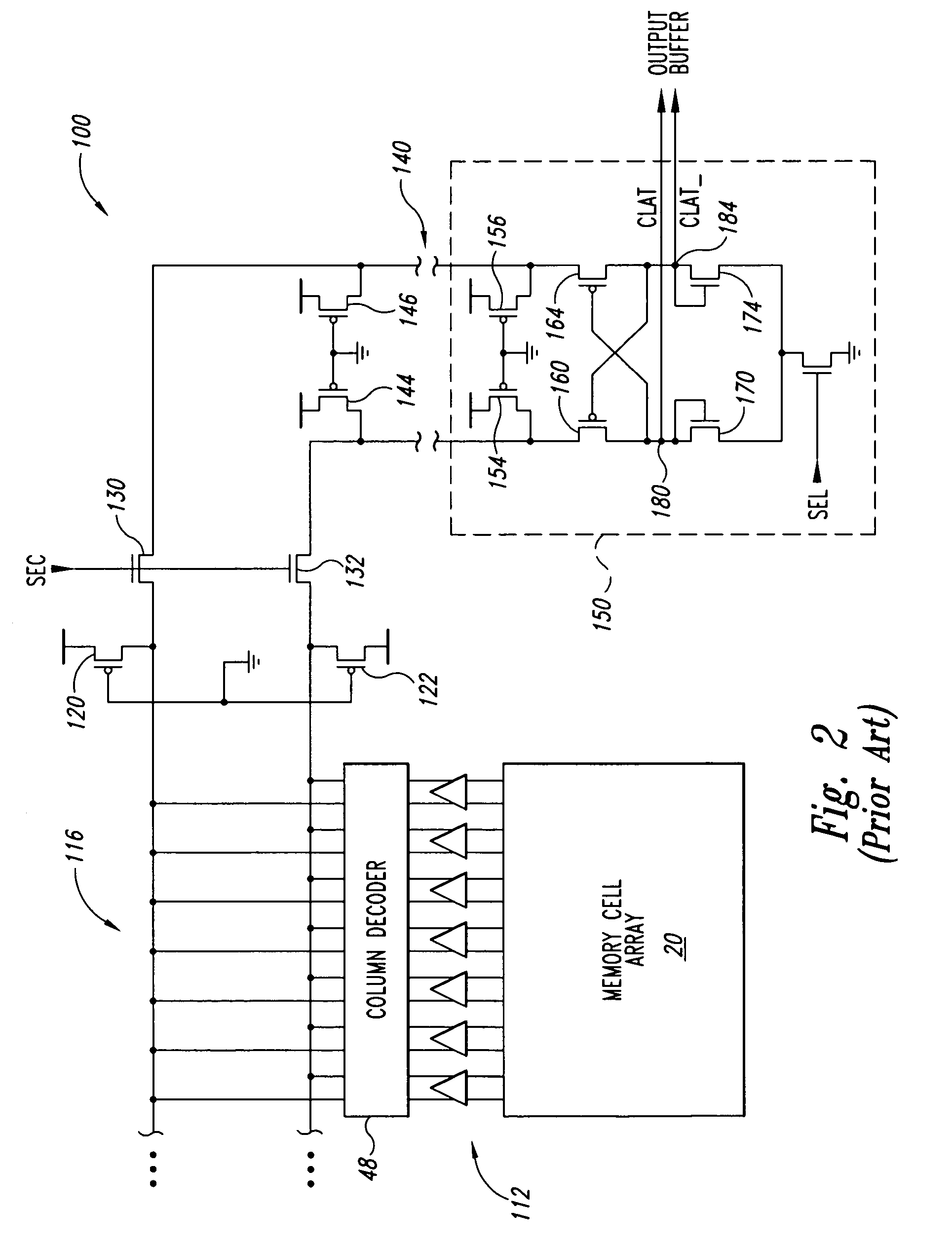
A data path including a local input / output (LIO) line and a global input / output (GIO) line coupled together through an input / output (IO) line coupling circuit. The coupling circuit is coupled to an internal voltage supply, and couples and decouples signal lines of the GIO line from the supply terminal according to read data coupled to the LIO line. The GIO line is coupled to a current sense amplifier to generate output voltage signals that are coupled to an output buffer. An example of a current sense amplifier coupled to the GIO line includes first and second load circuits and first and second n-channel MOS (NMOS) transistors coupled to a respective load circuit. The gates of NMOS transistors are cross coupled, and input current signals are coupled to source terminals of the NMOS transistors and the output voltage signals are coupled from the drain terminals of the NMOS transistors.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
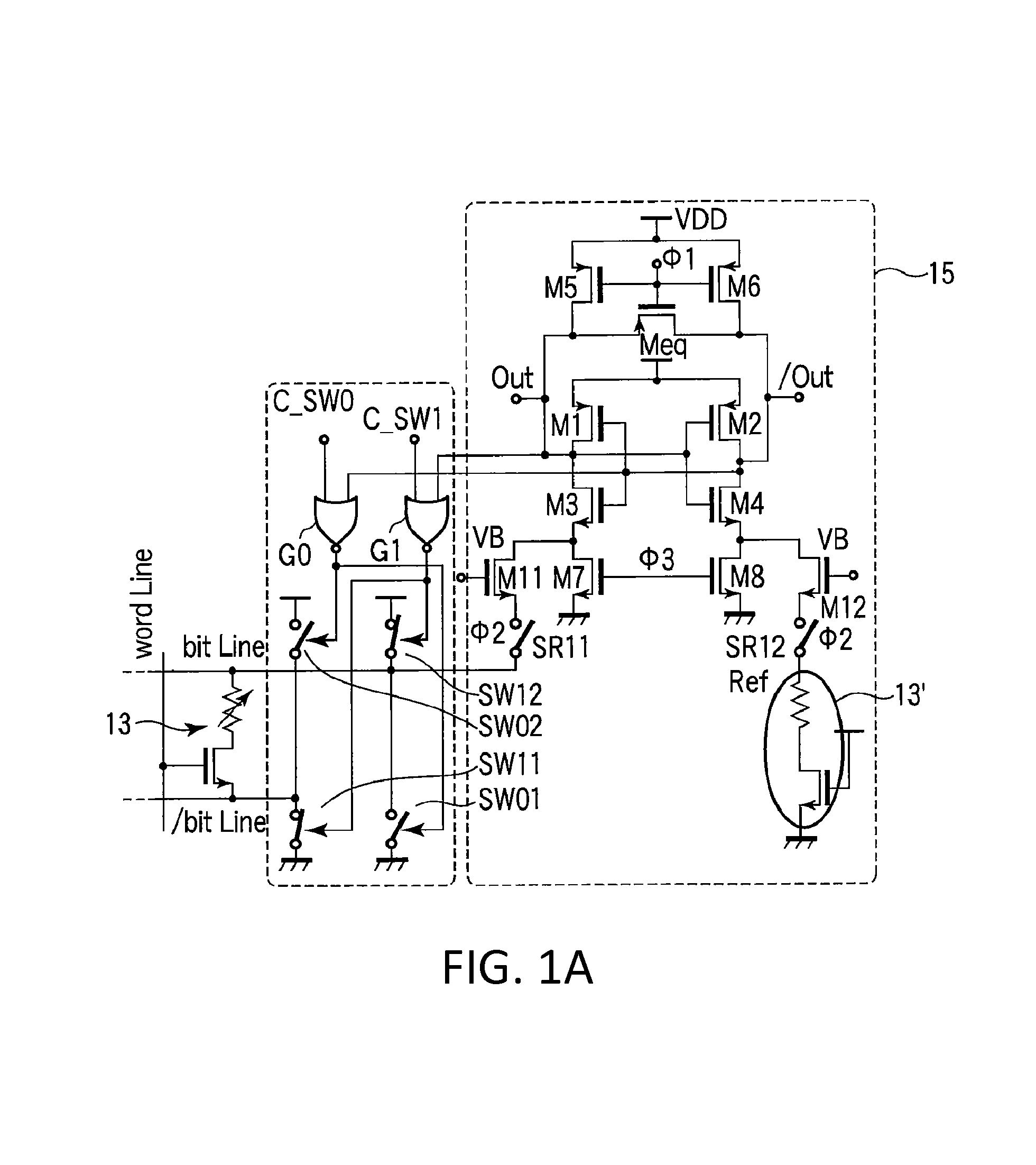
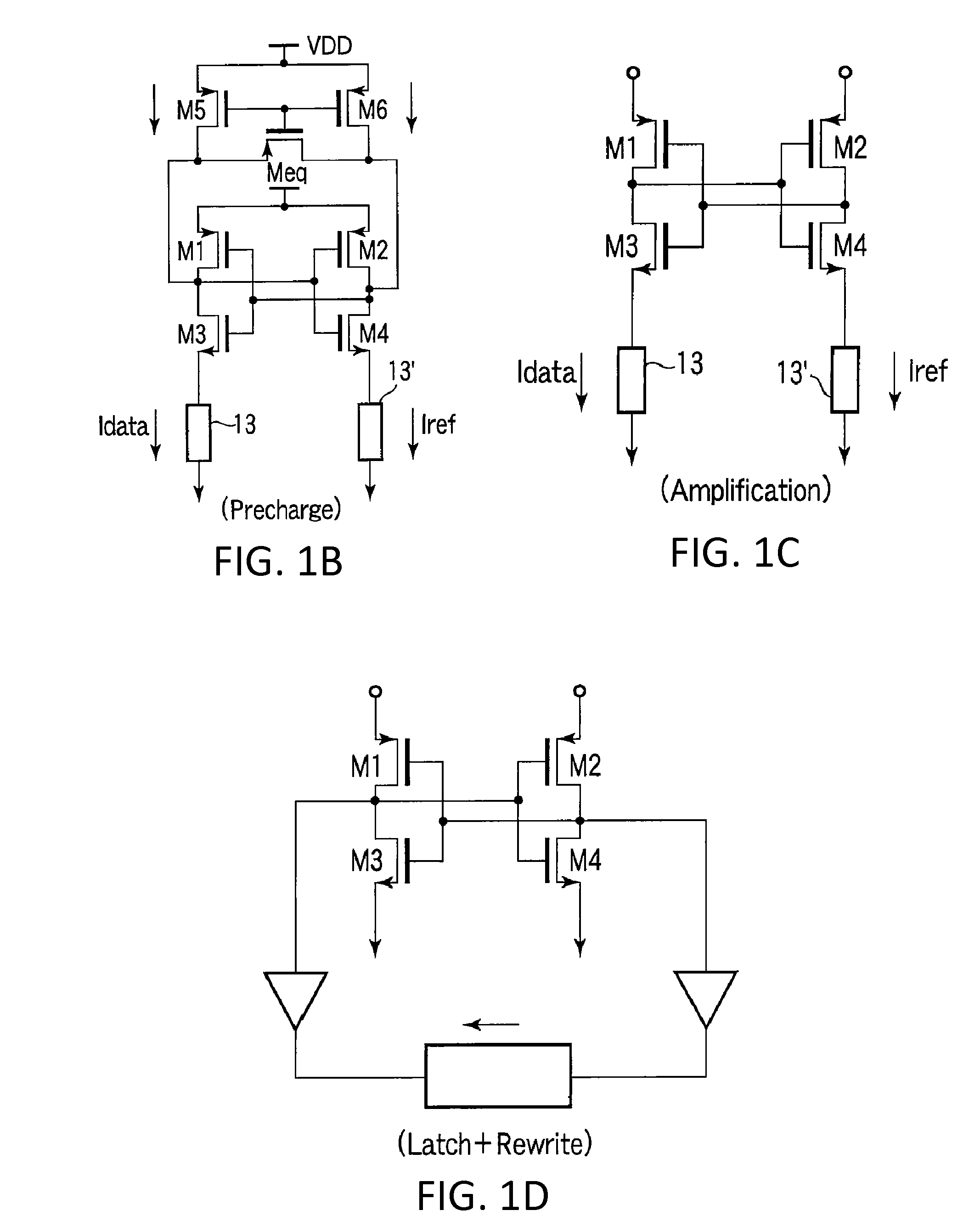
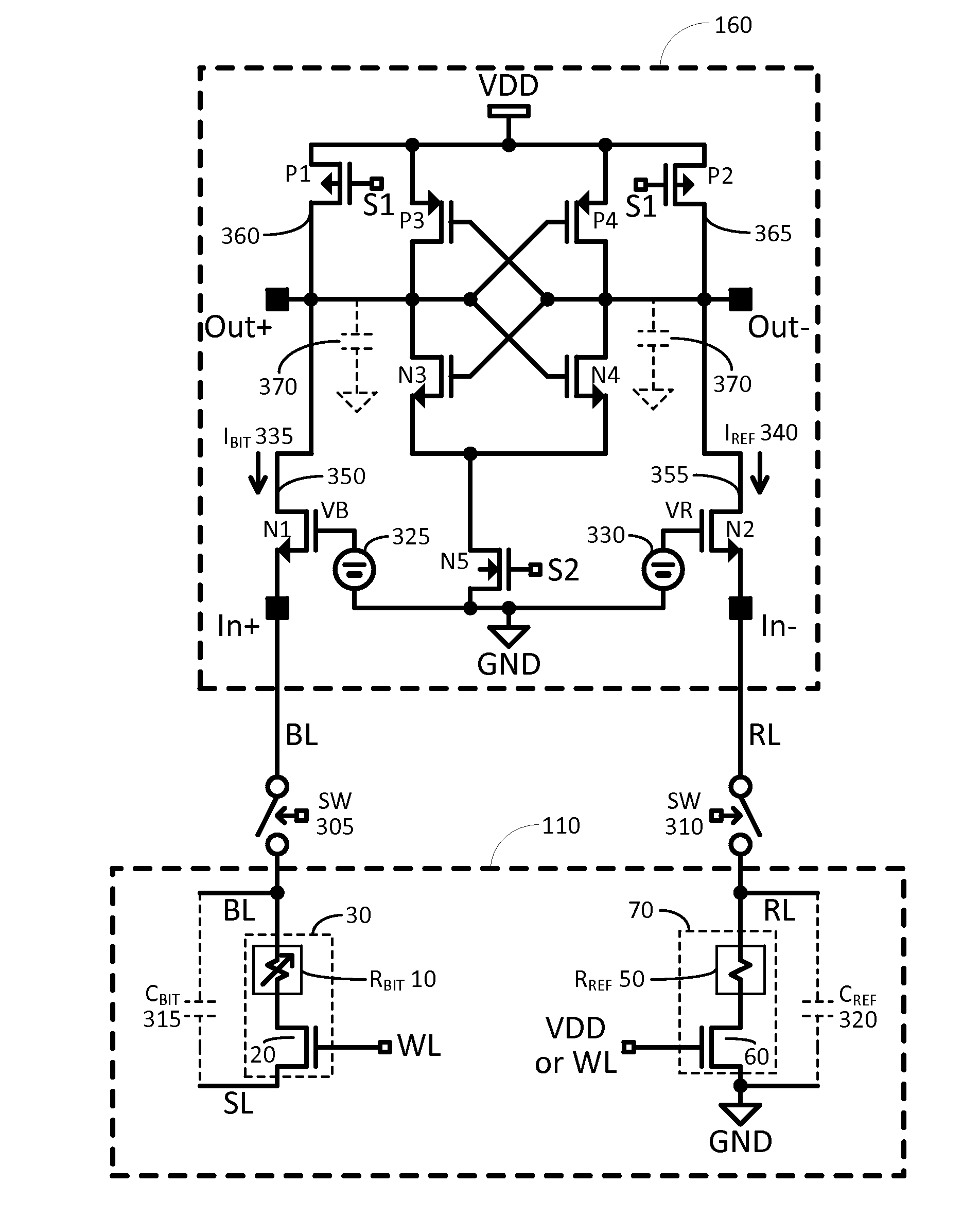
Sense amplifier circuitry for resistive type memory
Example embodiments include a resistive type memory current sense amplifier circuit including differential output terminals, first and second input terminals, pre-charge transistors, and current modulating transistors coupled directly to the pre-charge transistors. The pre-charge configuration provides high peak currents to charge the bit line and reference line during a “ready” or “pre-charge” stage of operation of the current sense amplifier circuit. The current modulating transistors are configured to operate in a saturation region mode during at least a “set” or “amplification” stage. The current modulating transistors continuously average a bit line current and a reference line current during the “set” or “amplification” stage, thereby improving noise immunity of the circuit. During a “go” or “latch” stage of operation, a logical value “0” or “1” is latched at the differential output terminals based on positive feedback of a latch circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Parallel power supply with active droop current sharing circuit having current limiting function
ActiveUS7541793B2Dc-dc conversionElectric light circuit arrangementAudio power amplifierCurrent limiting
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) PUBLIC CO LTD +1
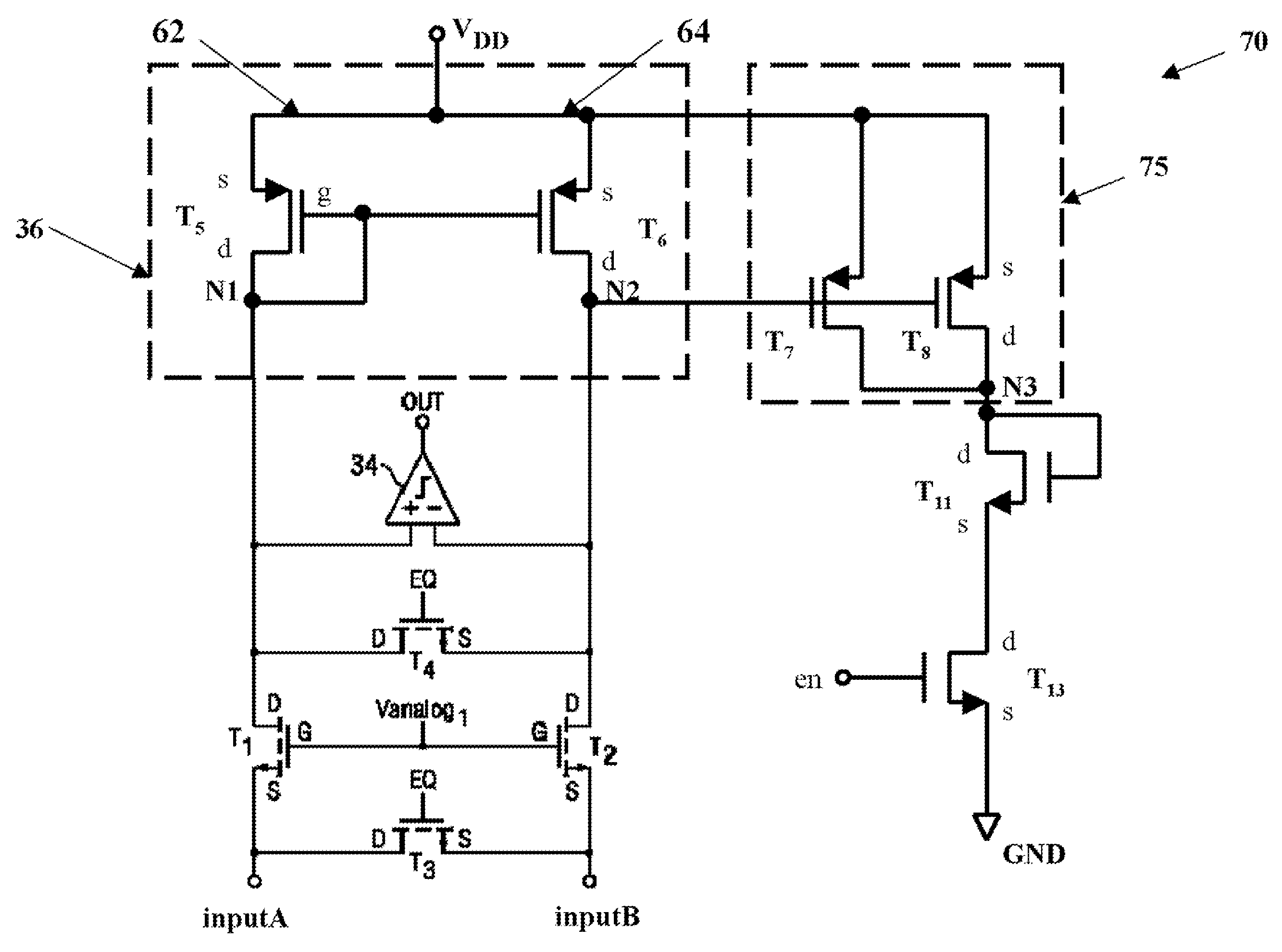
Current sense amplifier having bipolar common mode input range
ActiveUS20130135047A1Differential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesAudio power amplifierOperation mode
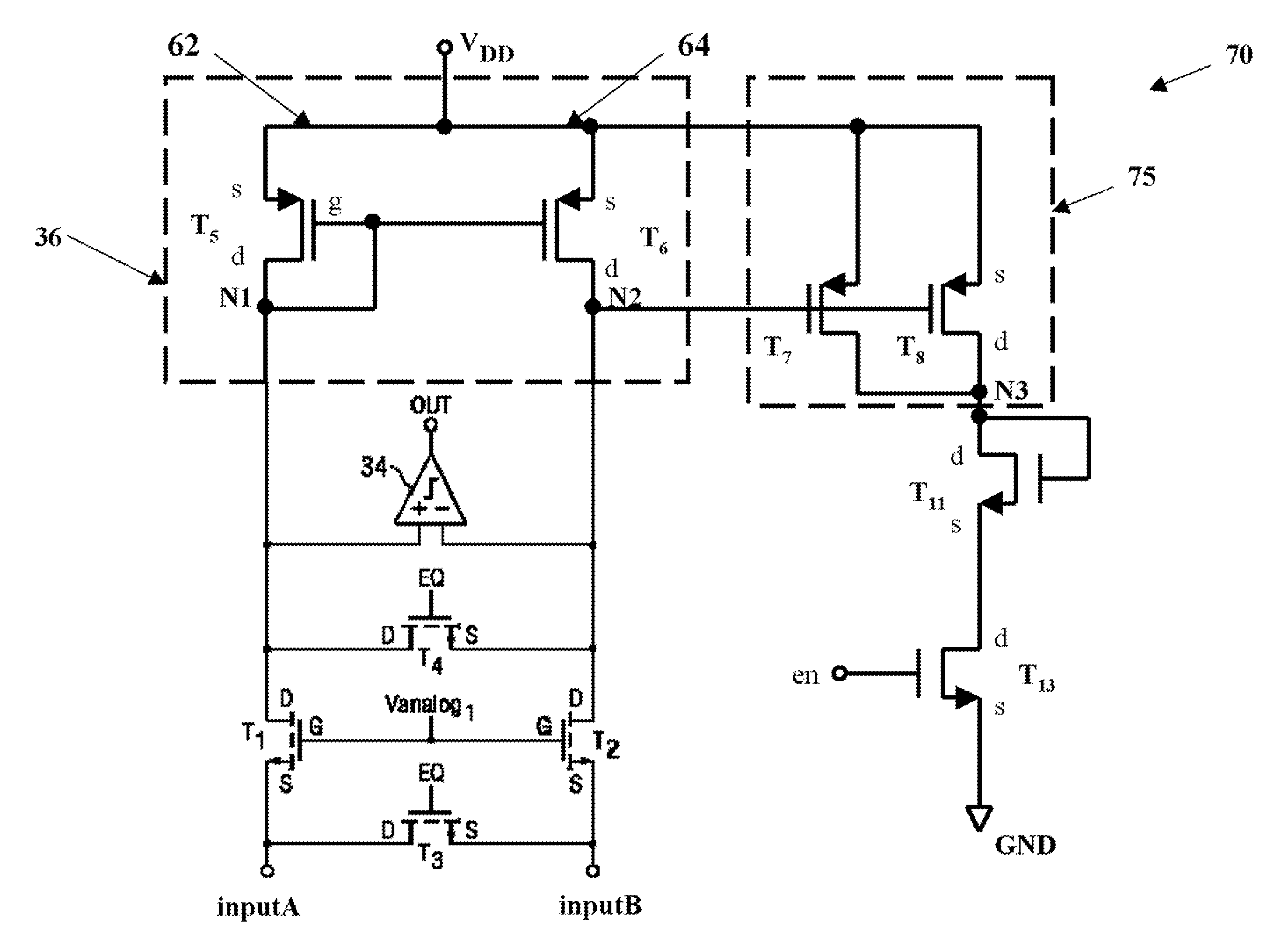
An amplifier configuration including first and second amplifier inputs and a bias input adapted to receive a common mode signal indicative of a common mode input voltage. First and second amplifier input stage sections, each having first and second inputs coupled to respective ones of the first and second amplifier inputs, are provided. Operating mode circuitry switches the amplifier configuration between first and second operating modes in response to the common mode signal, where in the first operating mode the first and second amplifier input stage sections are active and inactive, respectfully and where in the second operating mode the first and second amplifier input stage sections are inactive and active, respectfully. The active first and second amplifier input stage sections are capable of operating with common mode voltages in excess of the upper and lower power supply rails, respectively.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Sense amplifier circuitry for resistive type memory
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
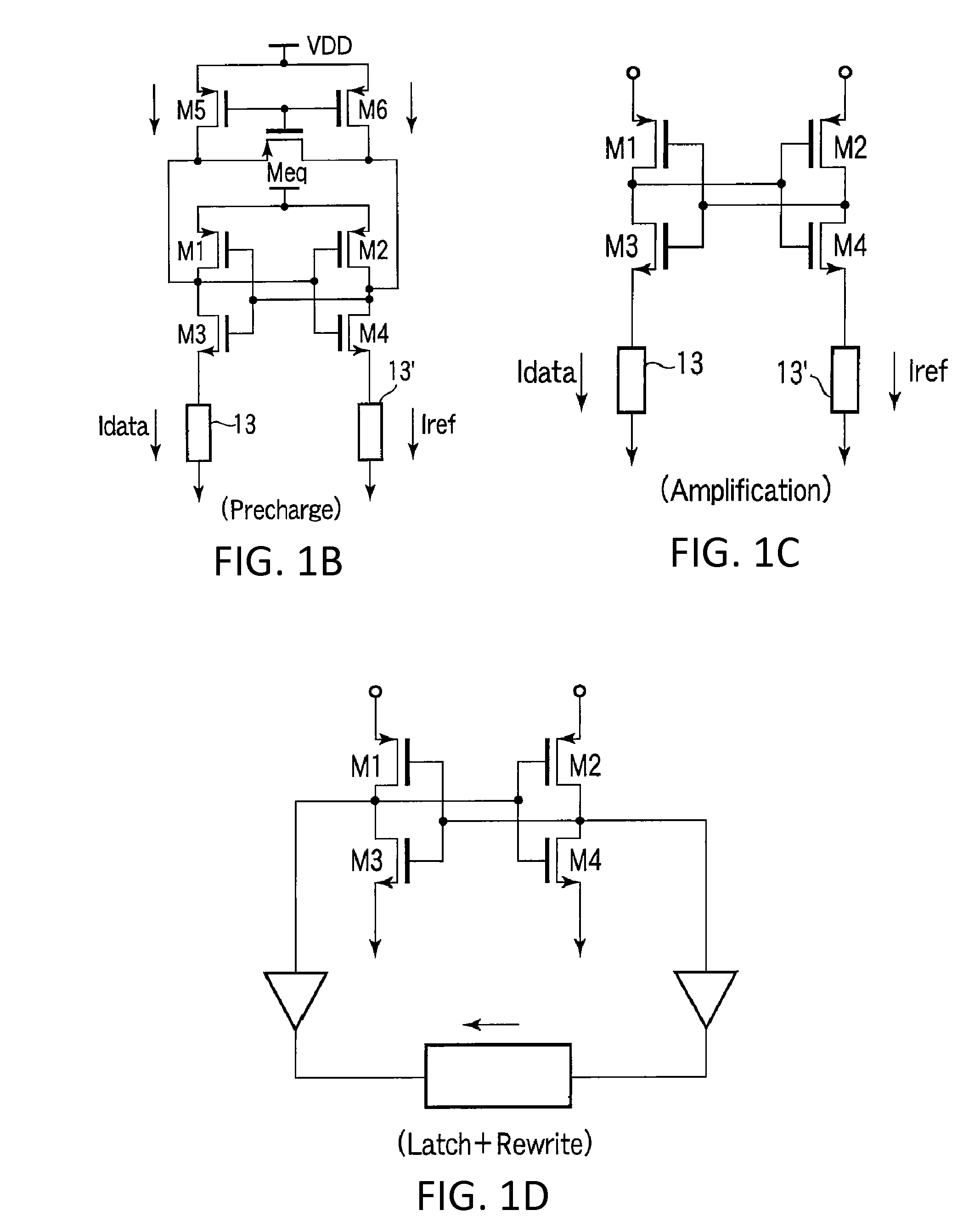
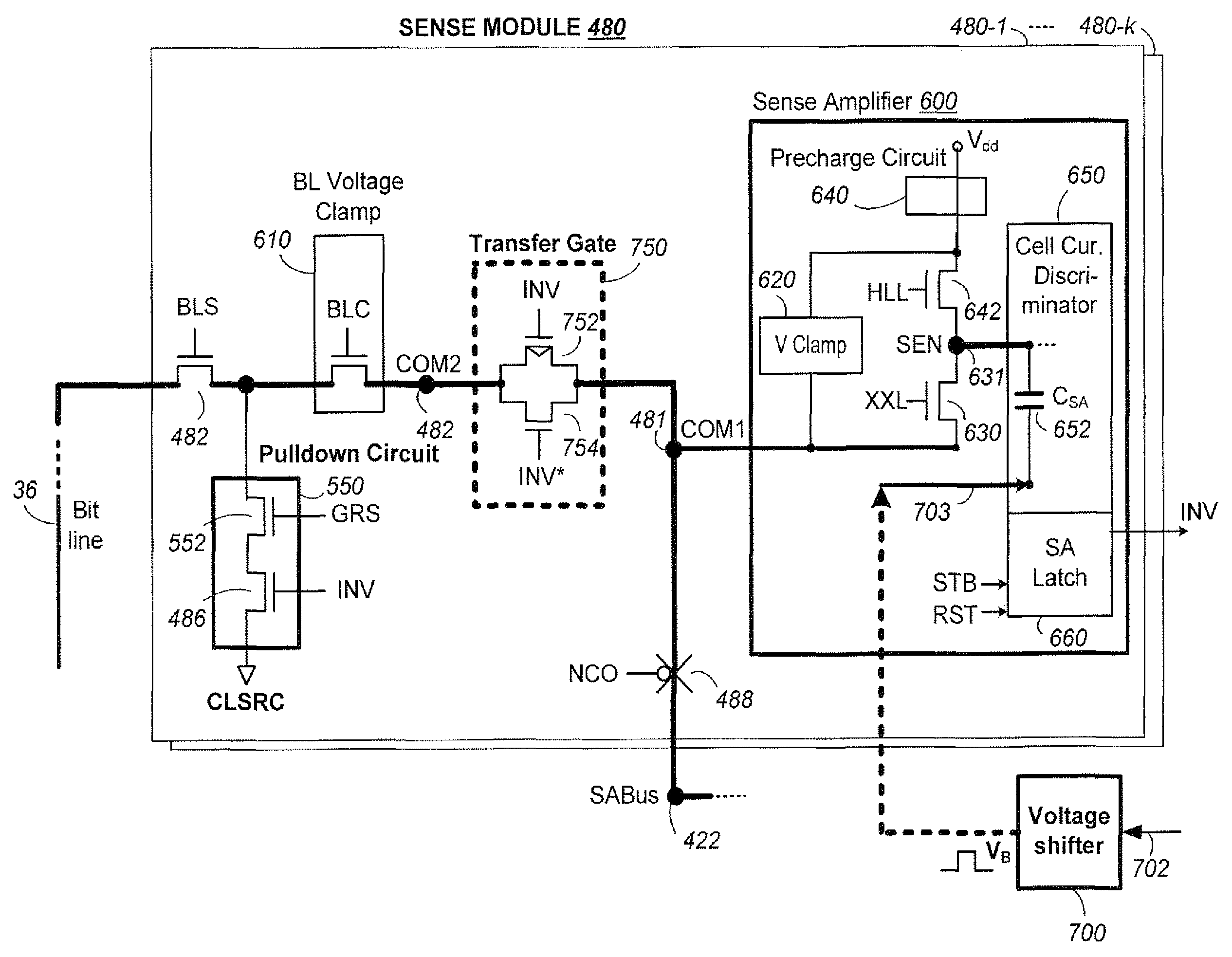
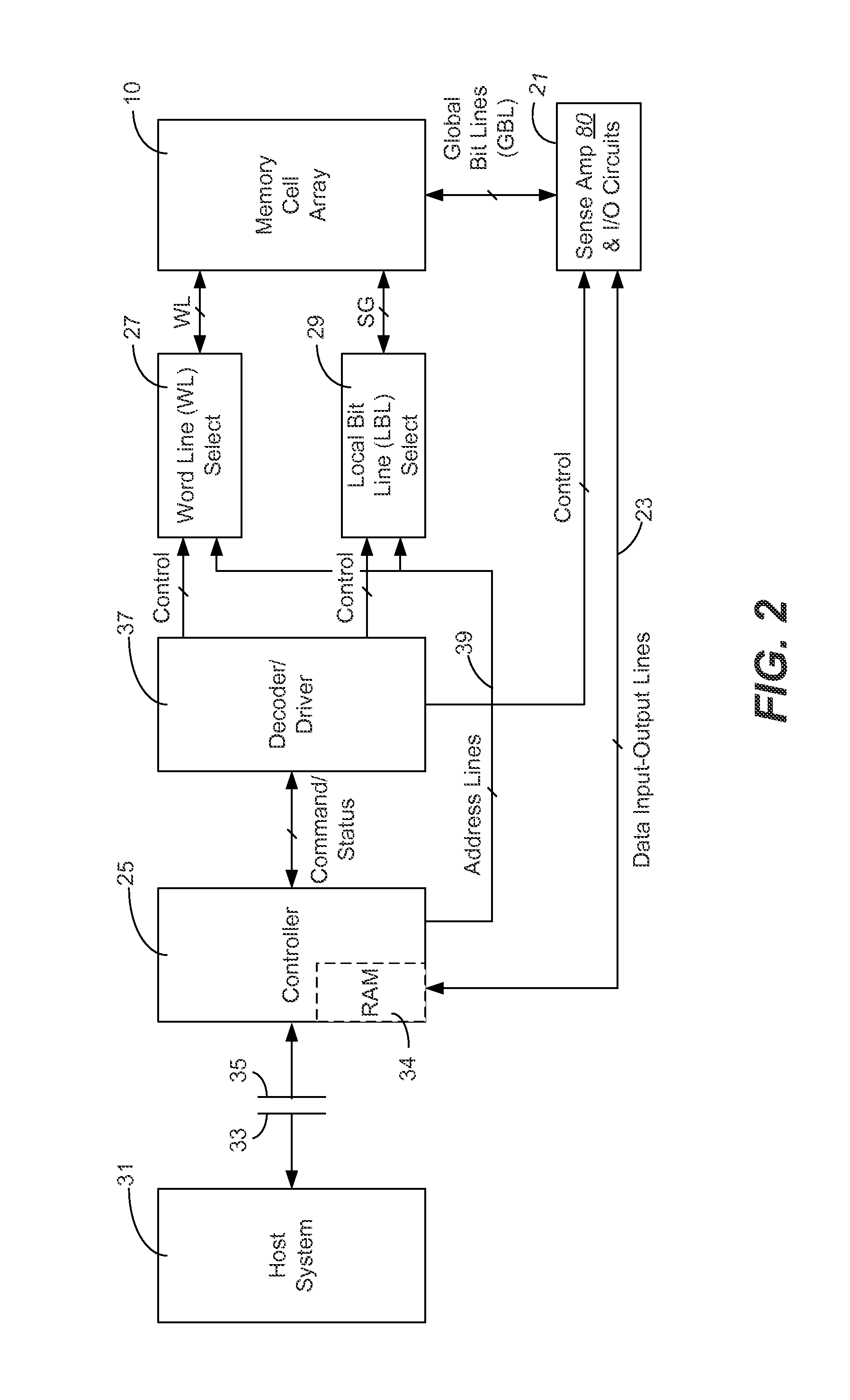
Nonvolatile memory with a current sense amplifier having a precharge circuit and a transfer gate coupled to a sense node
Sensing circuits for sensing a conduction current of a memory cell among a group of non-volatile memory cells being sensed in parallel and providing the result of the sensing to a data bus are presented. A precharge circuit is coupled to a node for charging the node to an initial voltage. An intermediate circuit is also coupled to the node and connectable to the memory cell, by which current from the precharge circuit can be supplied to the memory cell. The circuit also includes a comparator circuit to perform a determination of the conduction current by a rate of discharge at the node; a data latch coupled to the comparator circuit to hold the result of this determination; and a transfer gate coupled to the data latch to supply a latched result to the data bus independently of the node. This arrangement improves sensing performance and can help to eliminate noise on the analog sensing path during sensing and reduce switching current.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Low-power high-PSRR current-mode microphone pre-amplifier system and method
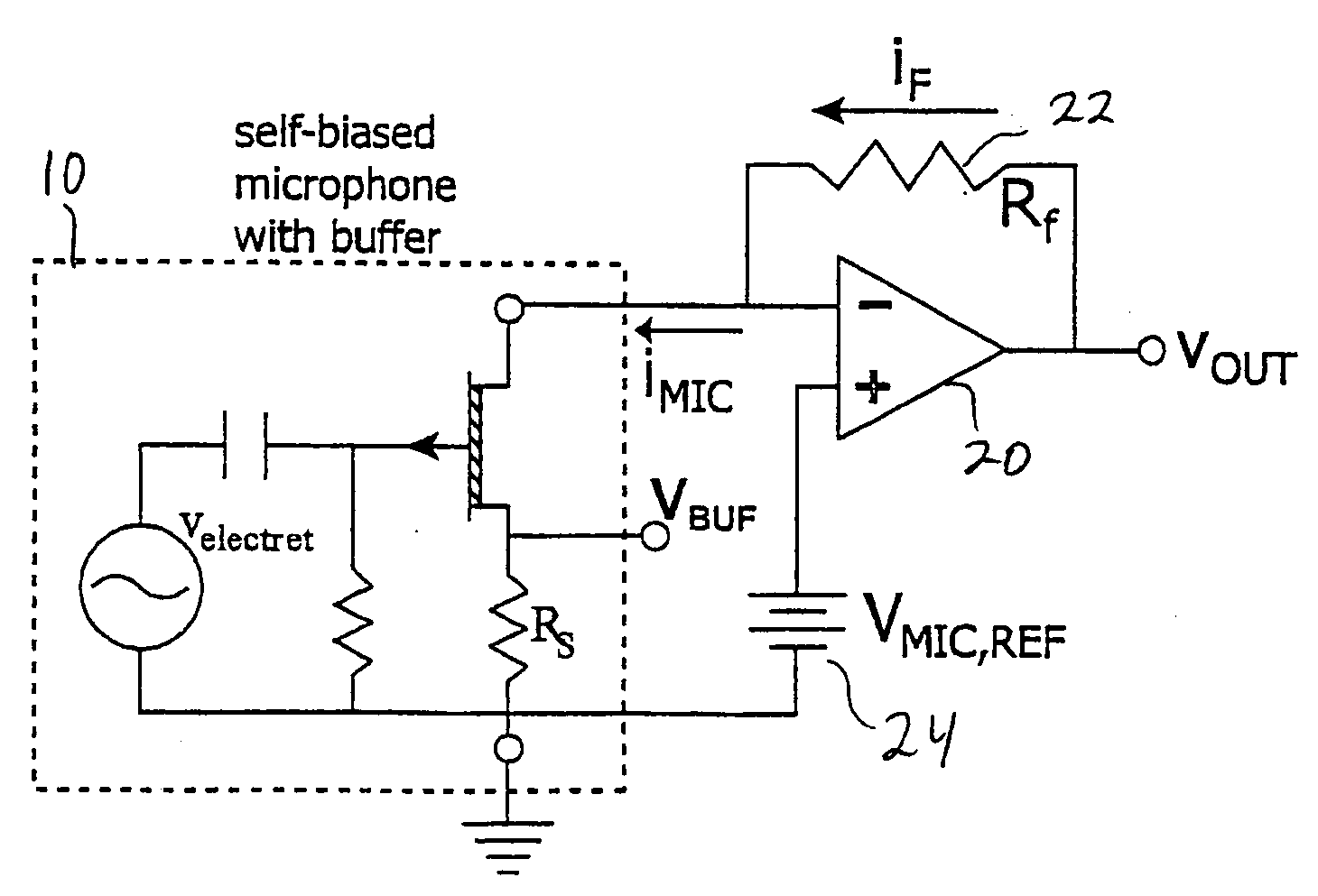
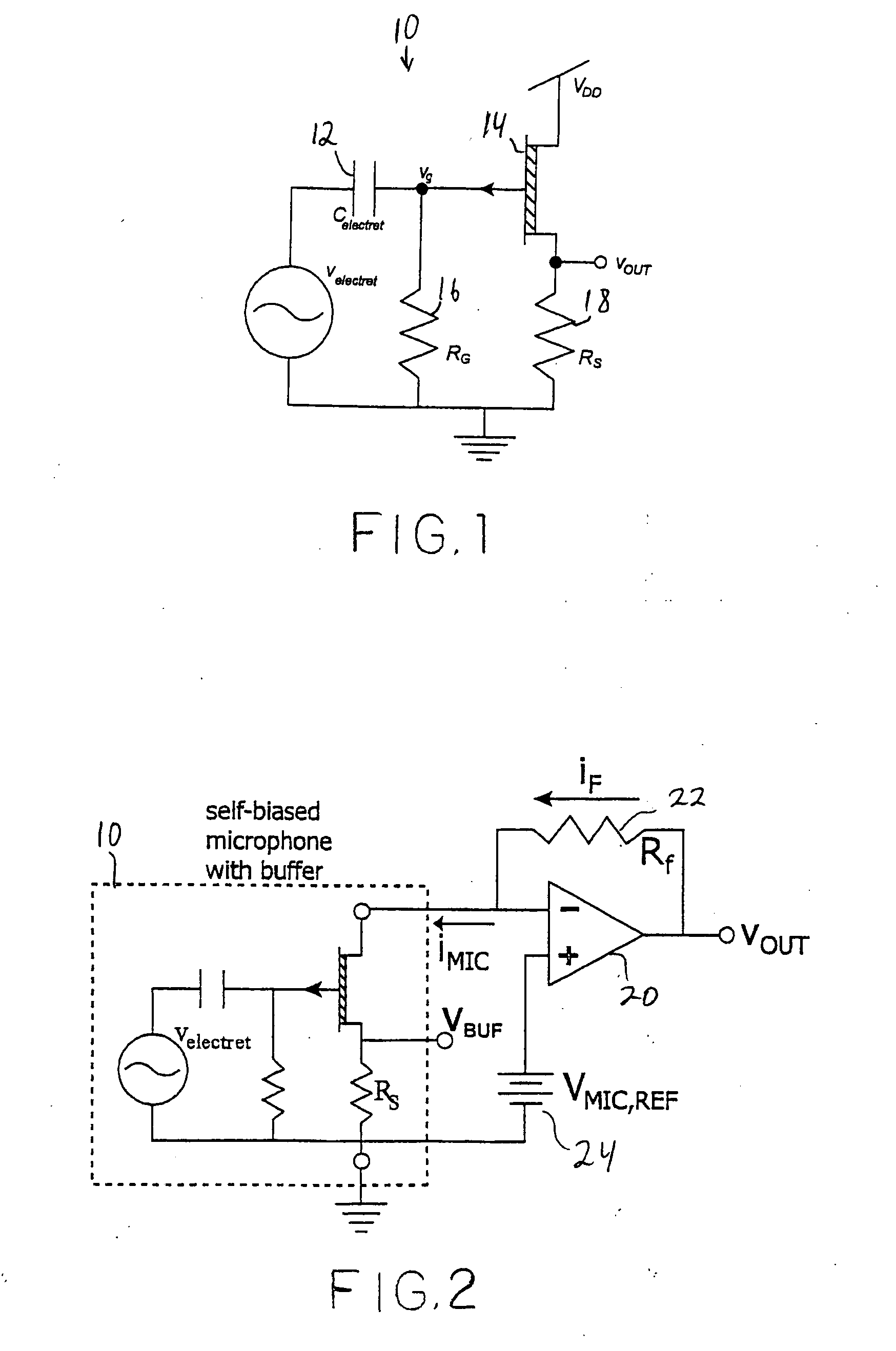
A low power high dynamic range microphone amplification system is disclosed. The system includes a current sensing amplifier for receiving an input current signal representative of auditory information and for providing an amplifier output signal. The current sensing amplifier includes a DC bias network that includes a cascode filter.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
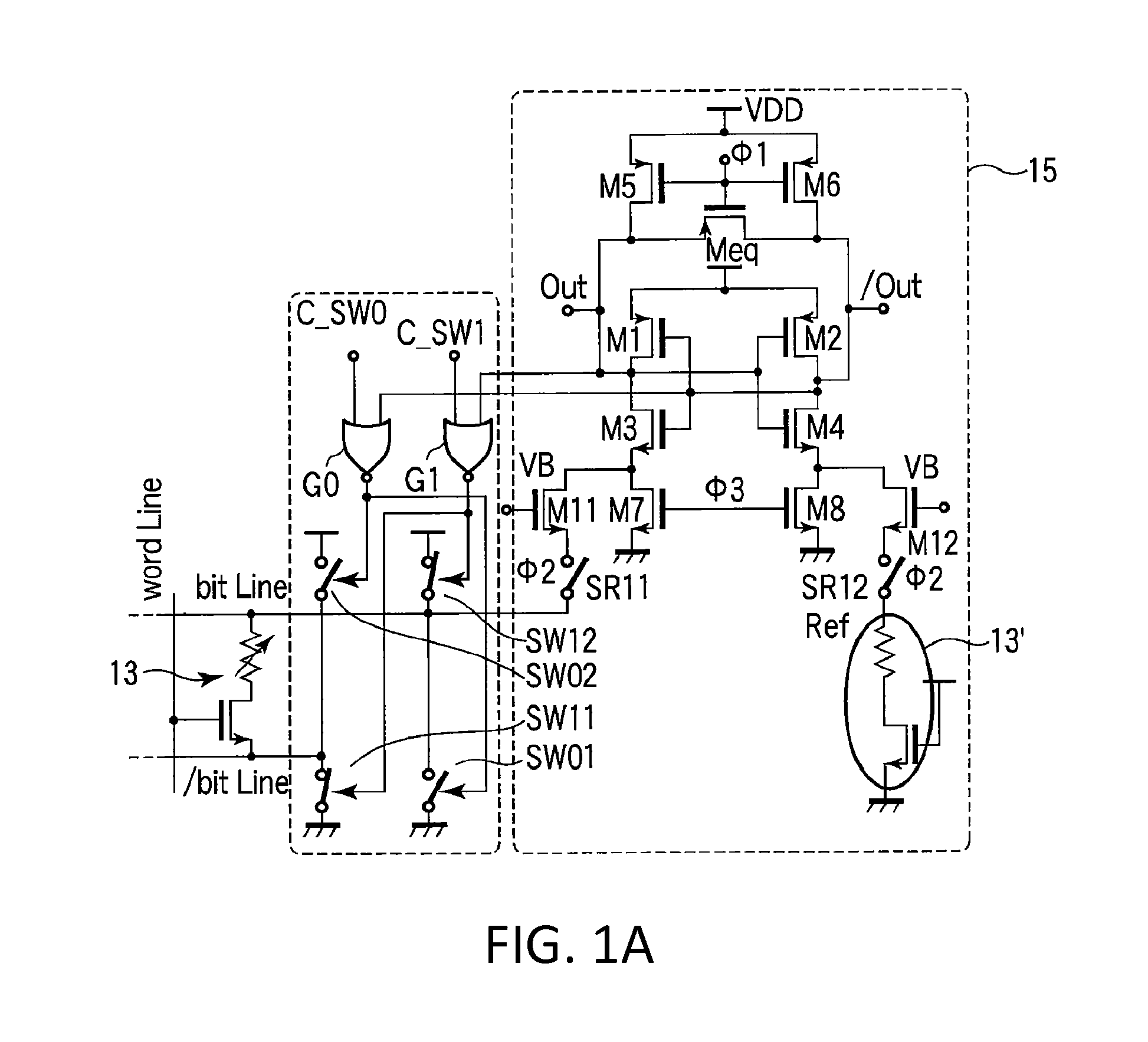
Current sense amplifier for low voltage applications with direct sensing on the bitline of a memory matrix
A current sense amplifier, in particular for low voltage applications, of the type incorporated in a memory electronic device and including a differential amplifier having inputs respectively associated with a matrix circuit leg, connected to a cell to be sensed, and a reference circuit leg, connected a reference cell. At least the matrix circuit leg has a first MOS transistor to which an inverter is connected in a cascode configuration and a first input of the differential amplifier corresponding to the matrix circuit leg is coupled to a conduction terminal of the first MOS transistor and to the bitline of the memory matrix by a second MOS transistor.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
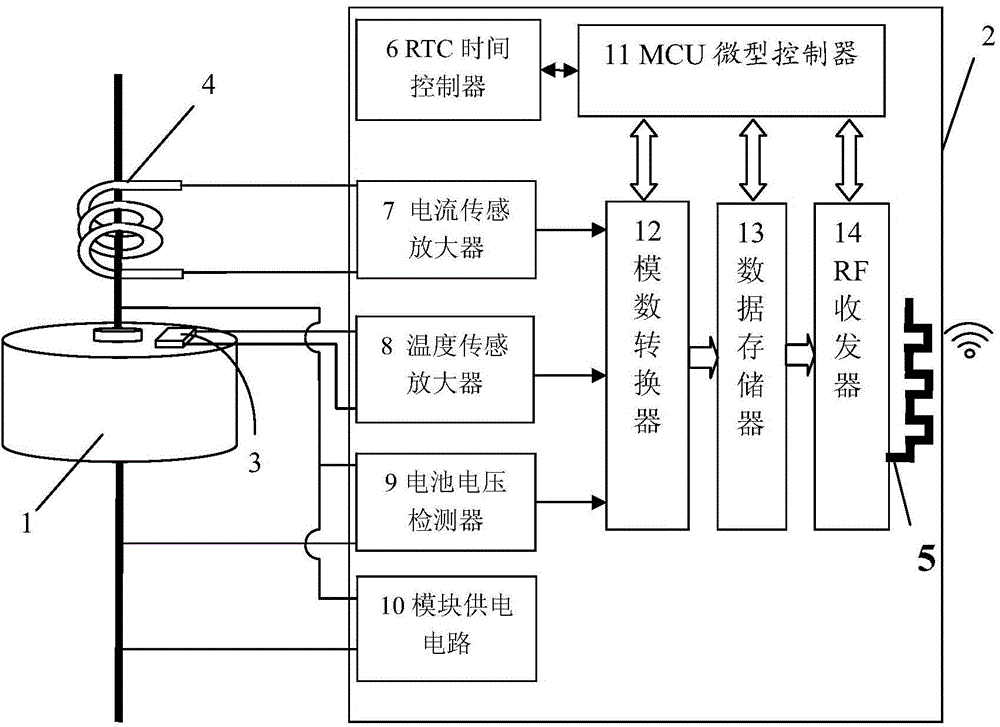
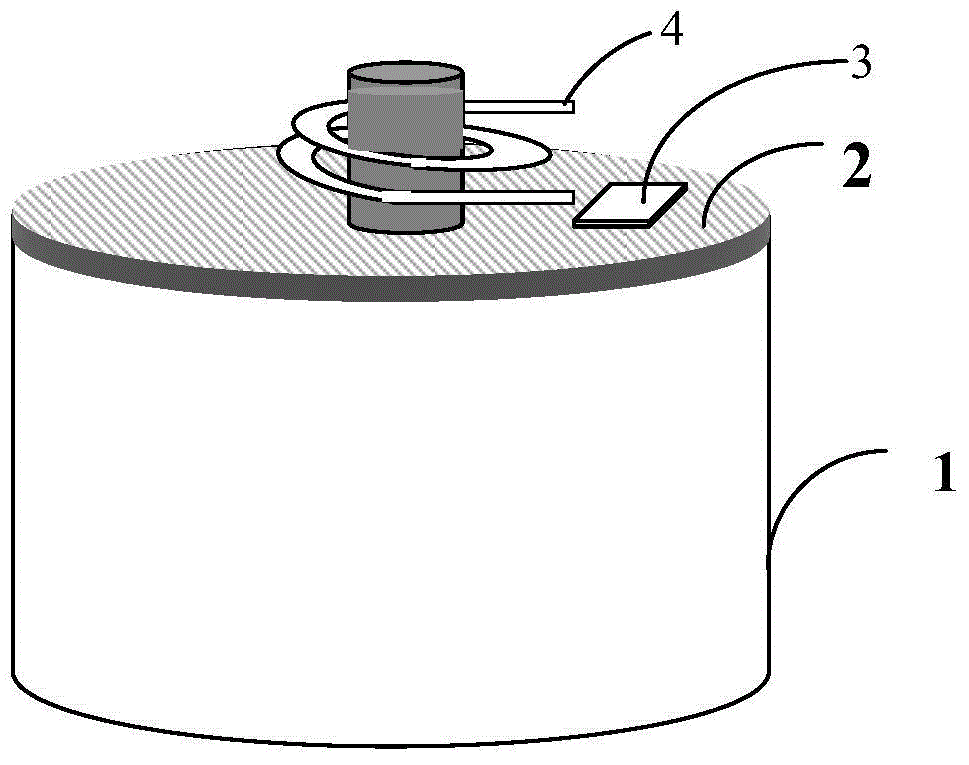
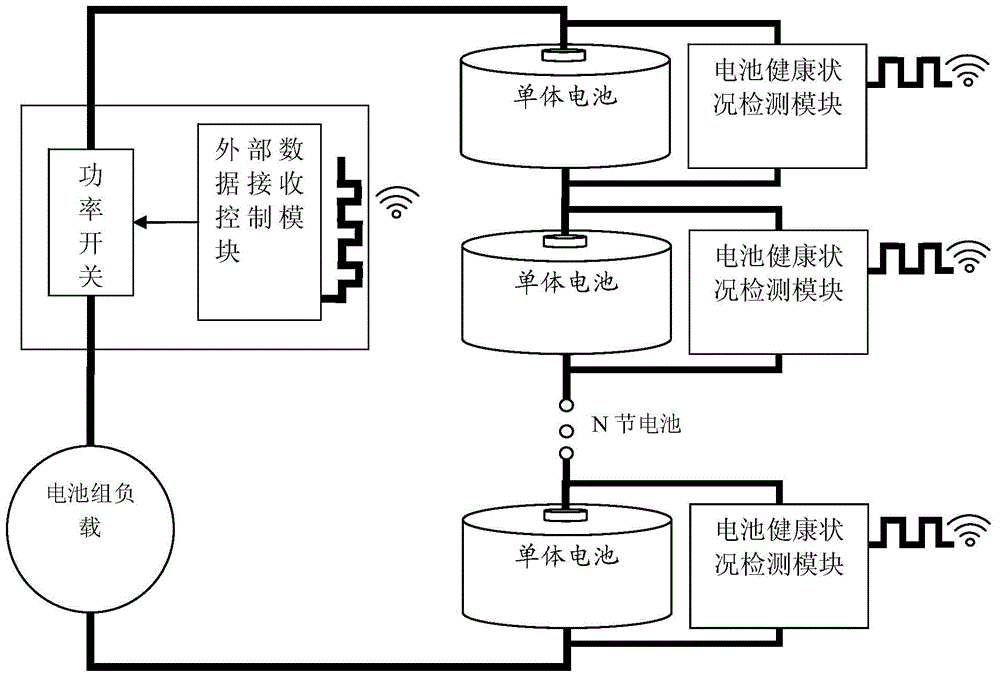
Battery health condition detection module, system thereof and battery with detection module
ActiveCN104914383AFlexible configurationReliable communicationElectrical testingDetector circuitsElectrical battery
The present invention provides a battery health condition detection module and a battery with a detection module. The problem of the health state monitoring of each single battery in a battery pack is solved, the voltage, current, battery capacity and temperature state monitoring of the single battery in the battery pack is carried out, and the detection module and each single battery are made into an integrated battery with the detection module which is integratedly formed. The invention also provides a battery health condition detection system, the measurement and record data obtained by the detection module is sent to an external data receiving and controlling system in a wireless mode, the external data receiving control system carries out analysis processing, and even the battery pack is sealed, the monitoring of the health condition of each single battery in the battery pack by the external data receiving and controlling system is not affected. The battery health condition detection module comprises a current sensing amplifier circuit, a battery voltage detector circuit, a temperature sensing amplifier circuit, an RTC time controller, a micro control unit, and a module power supply circuit.
Owner:双竞科技有限公司
High speed low power consumption current sensitive amplifier
InactiveCN1716448AReduced voltage swingReduce power consumptionDigital storageCapacitanceEngineering
The present invention belongs to the field of integrated circuit technology, and is especially one kind of current mode sense amplifier for embedded SRAM. The current mode sense amplifier consists of mainly bit line clamp circuit, cross coupling inverter, equalizing circuit and I / O buffer. The sense amplifier can realize both the read operation and the write operation on SRAM unit by means of the differential current signal, rather than traditional differential voltage signal, resulting in very small bit line voltage swing and effectively lowered memory read / write power consumption. Simulation result shows that the sense amplifier has delay insensitive on capacitance variance.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
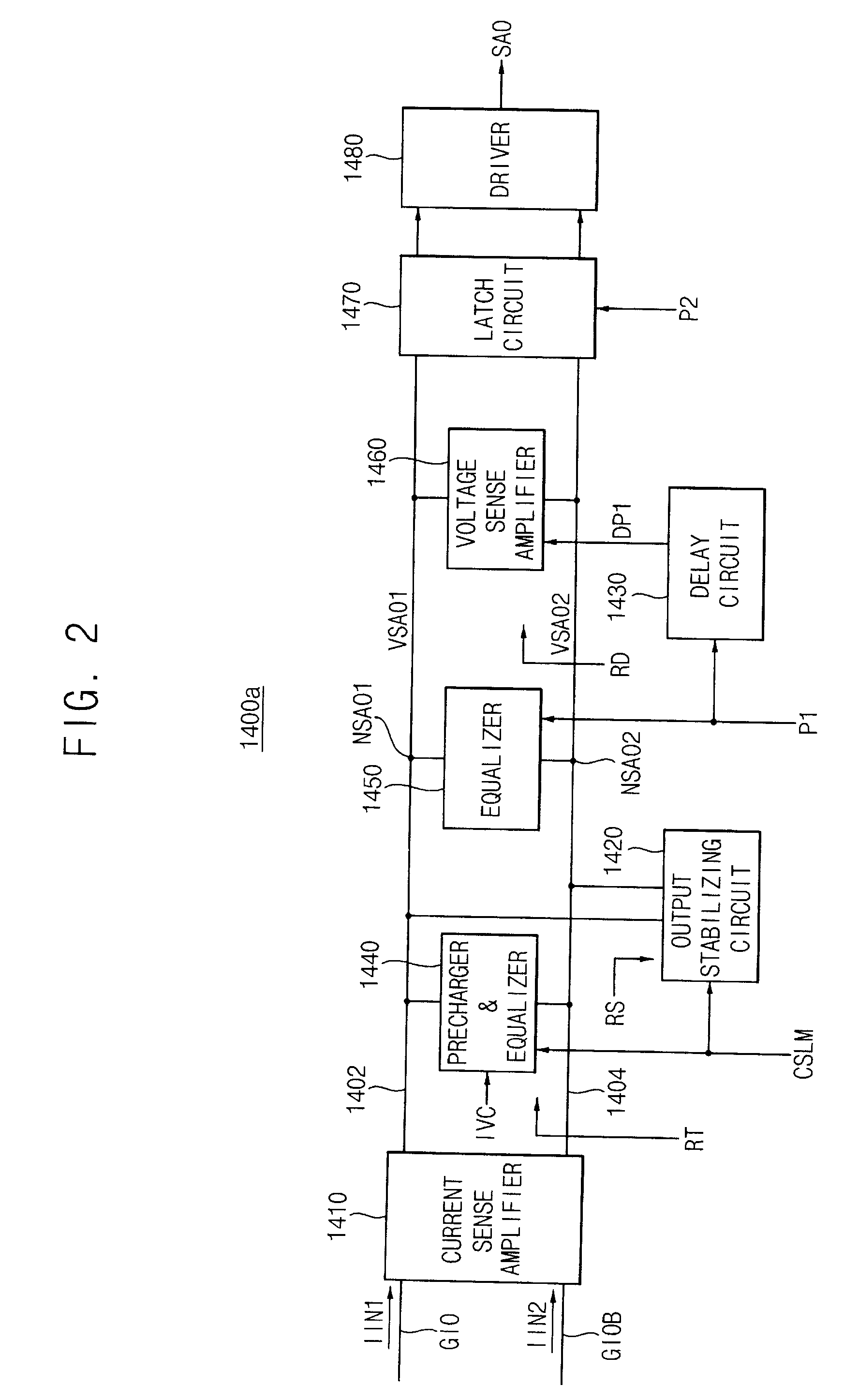
Sense amplifier and semiconductor memory device having the same
ActiveUS20090010086A1High amplification gainShorten induction timeCurrent/voltage measurementRead-only memoriesAudio power amplifierSemiconductor chip
A sense amplifier circuit includes a current sense amplifier, a voltage sense amplifier, and an output stabilizing circuit. The current sense amplifier amplifies differential input currents to generate differential output voltages and provides the differential output voltages to a sense amplifier output line pair. The voltage sense amplifier is coupled to the sense amplifier output line pair to amplify the differential output voltages on the sense amplifier output line pair. The voltage sense amplifier is activated at the time later than a time of activation of the current sense amplifier. The output stabilizing circuit is coupled to the sense amplifier output line pair to stabilize the differential output voltages on the sense amplifier output line pair. The output stabilizing circuit has a positive input resistance. Accordingly, the sense amplifier circuit reduces power consumption and an occupied area on a semiconductor chip.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
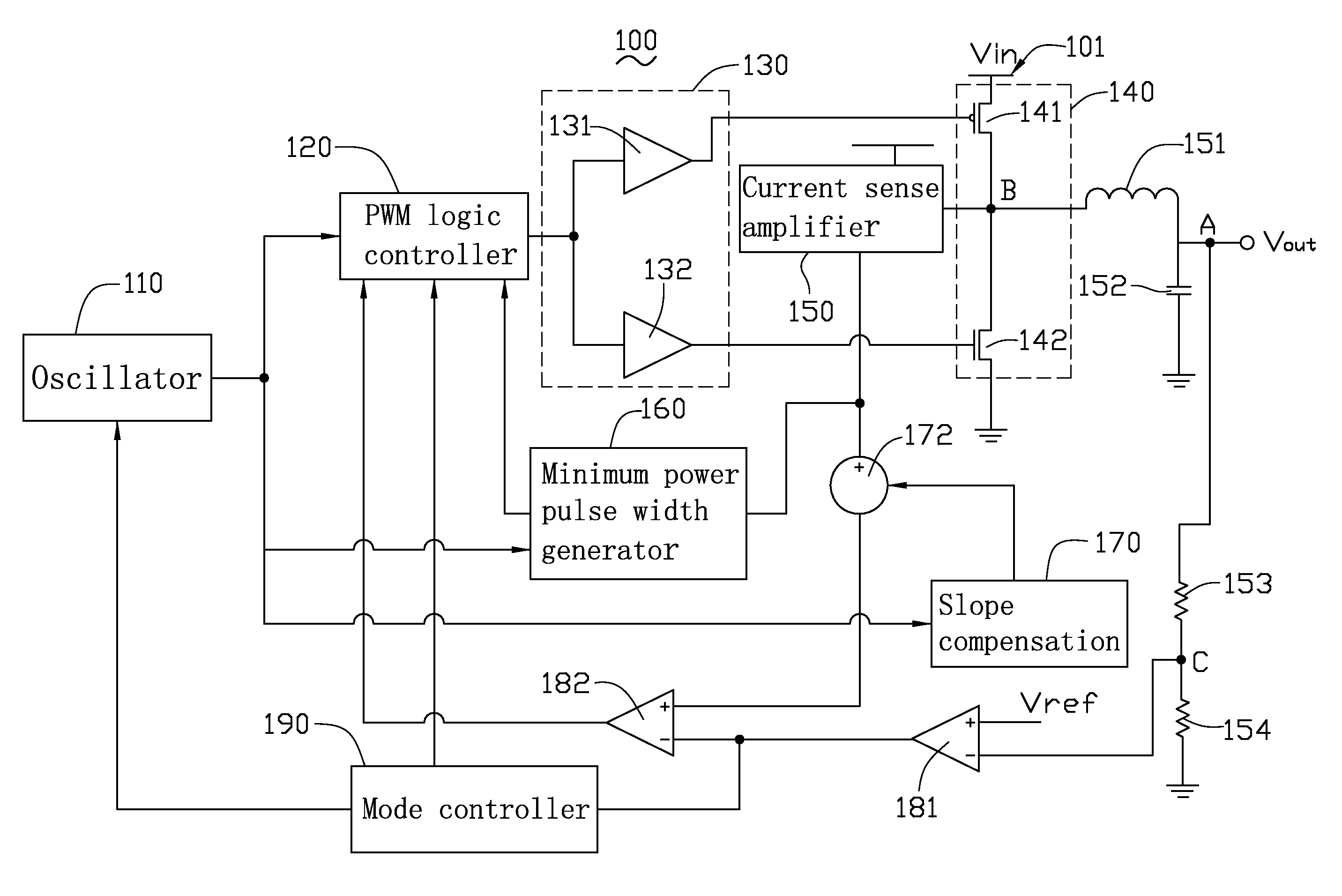
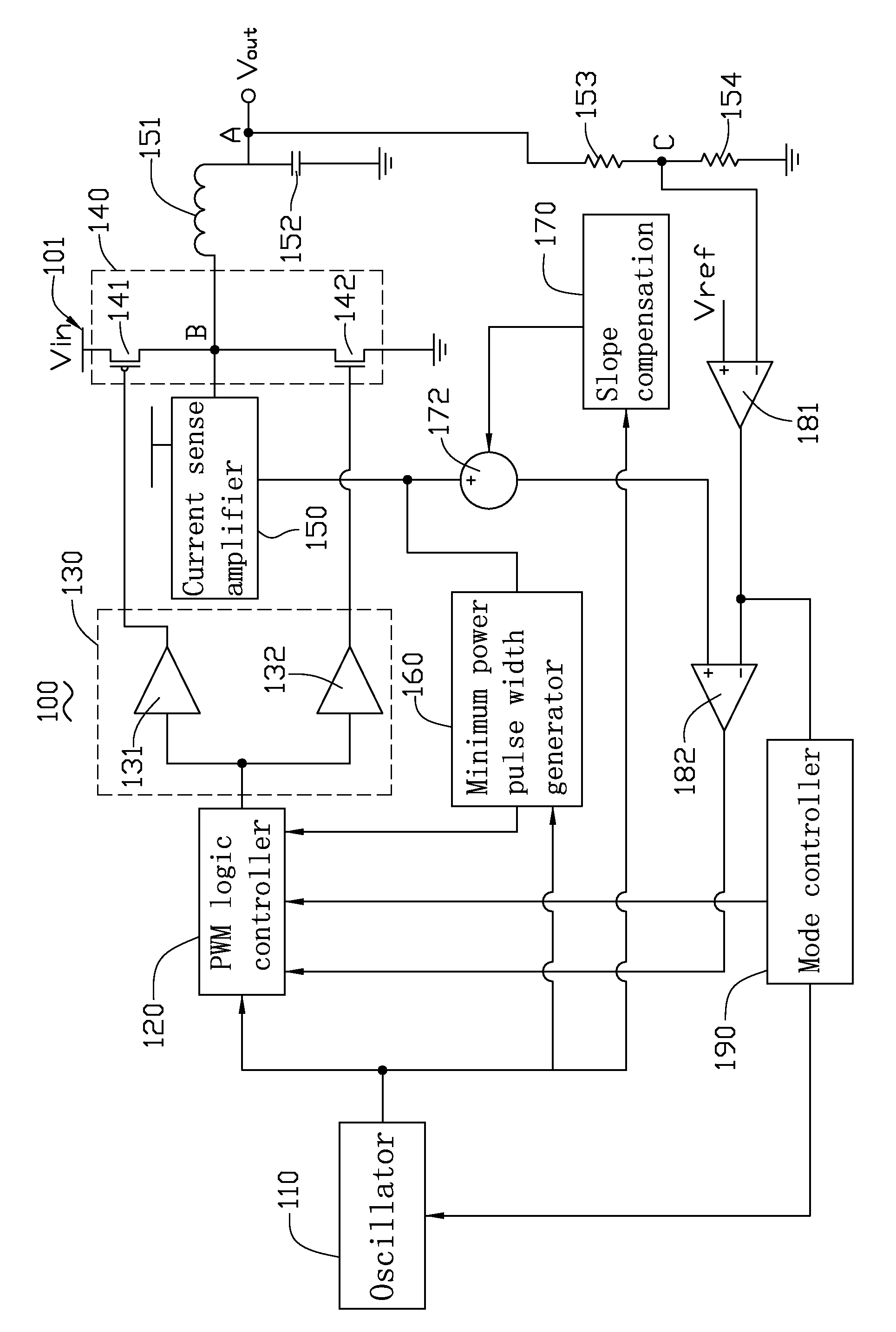
Switching regulator
An exemplary switching regulator, is provided. The switching regulator includes an oscillator, a PWM logic controller, an inductor, a capacitor, a switch, a driver, a current sense amplifier, and a minimum power pulse width generator. The current sense amplifier and the minimum power pulse width generator compose a first feedback loop for generating a first feedback signal to the PWM logic controller.
Owner:FITIPOWER INTEGRATED TECH INC
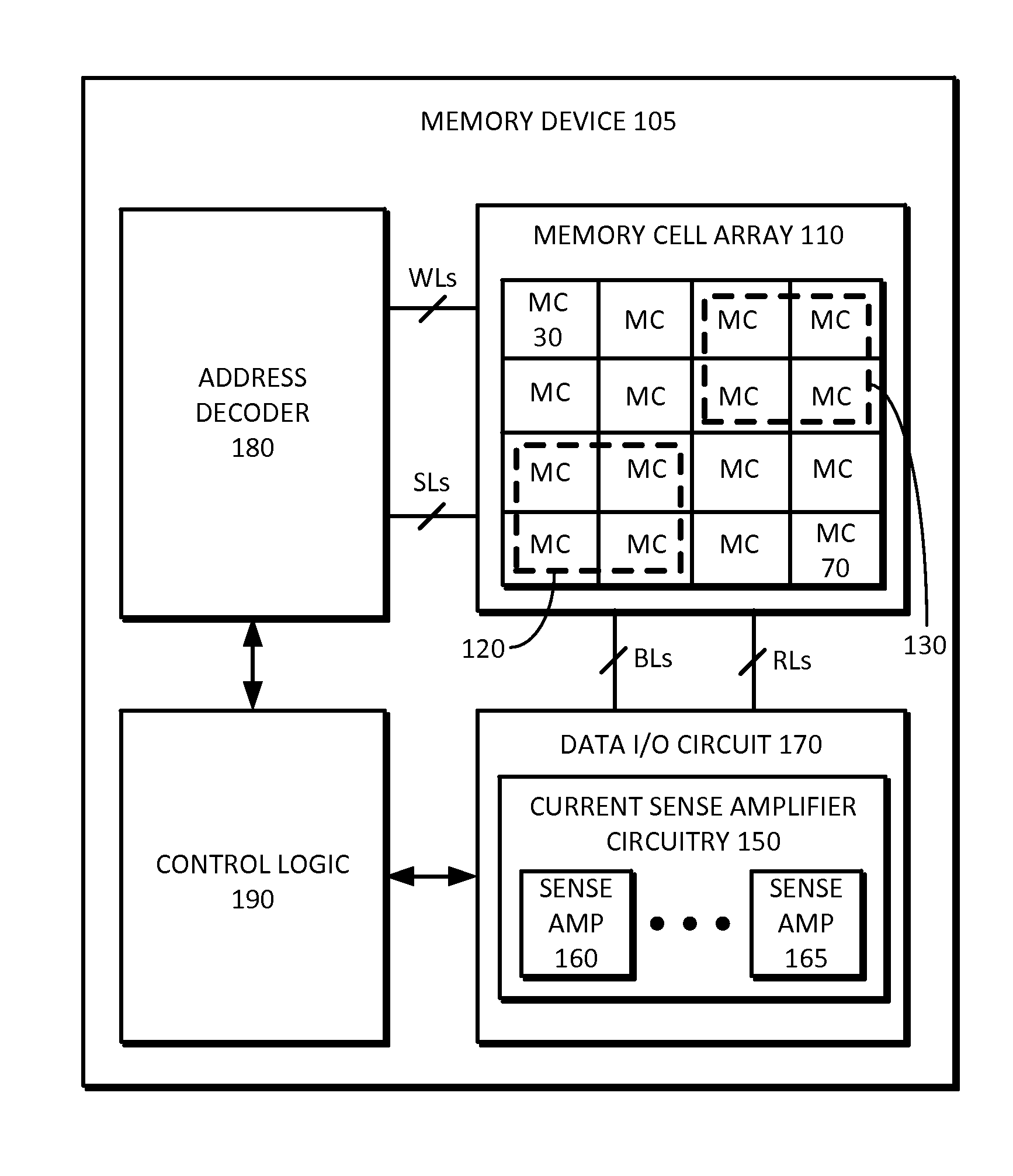
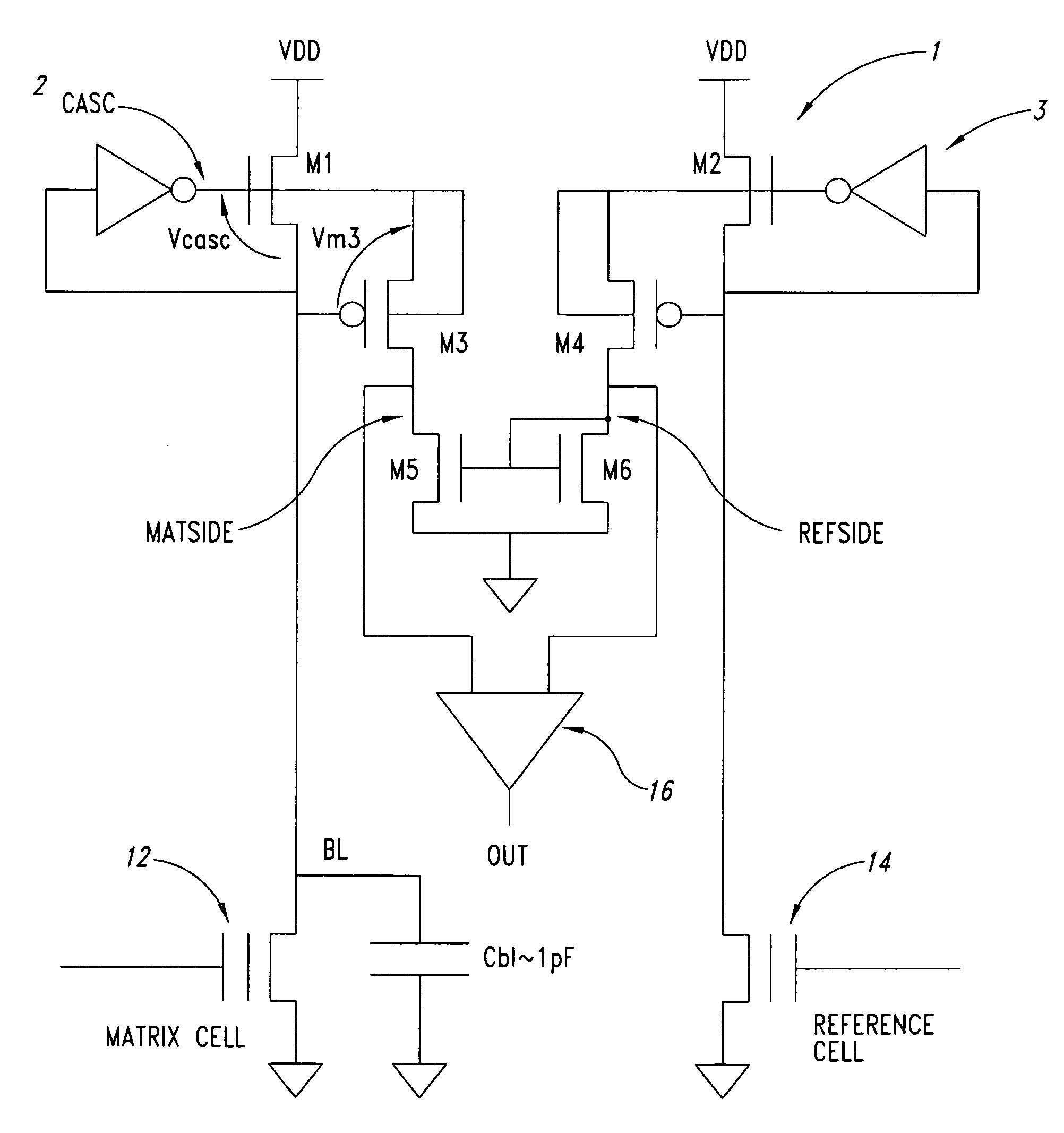
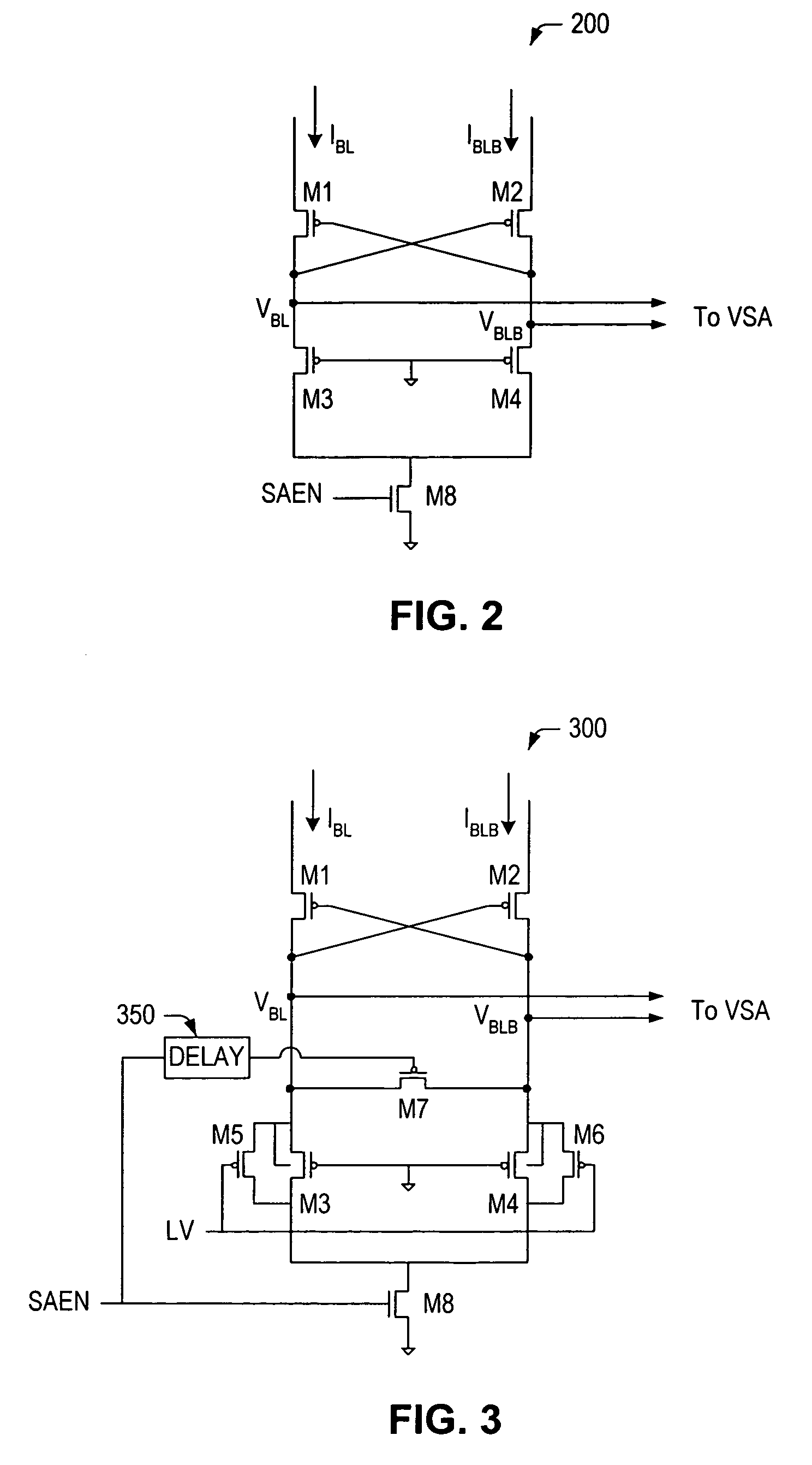
Memory device, current sense amplifier, and method of operating the same
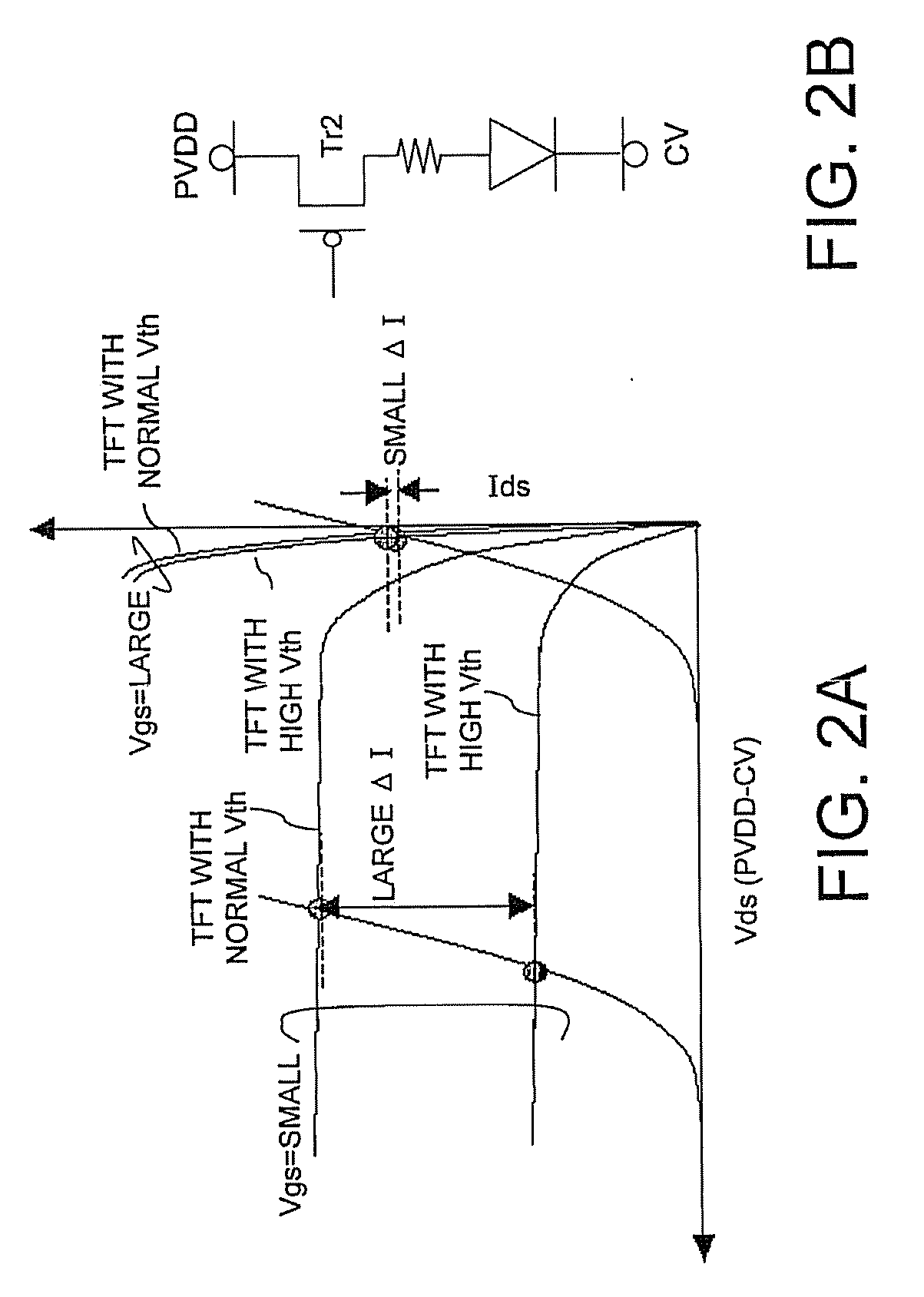
InactiveUS7616513B1Improving mismatch toleranceImprove circuit stabilityRead-only memoriesDigital storageAudio power amplifierTime segment
A memory device, current sense amplifier and method of operating the same are disclosed herein. In accordance with one embodiment, the current sense amplifier circuit may include a pair of cross-coupled transistors, a pair of output nodes and a first pair of load transistors. The pair of cross-coupled transistors may be coupled for receiving a pair of differential currents and for generating a pair of differential voltages, which may then be supplied to the pair of output nodes. The first pair of load transistors may have mutually-connected gate terminals, mutually-connected drain terminals, and a source terminal coupled to a different one of the output nodes. In a unique aspect of the invention, an equalization transistor may coupled between the pair of output nodes for equalizing the pair of differential voltages for a predetermined amount of time at the beginning of a sense cycle. As such, the equalization transistor may be added to prevent the current sense amplifier circuit from generating erroneous results during the predetermined time period.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
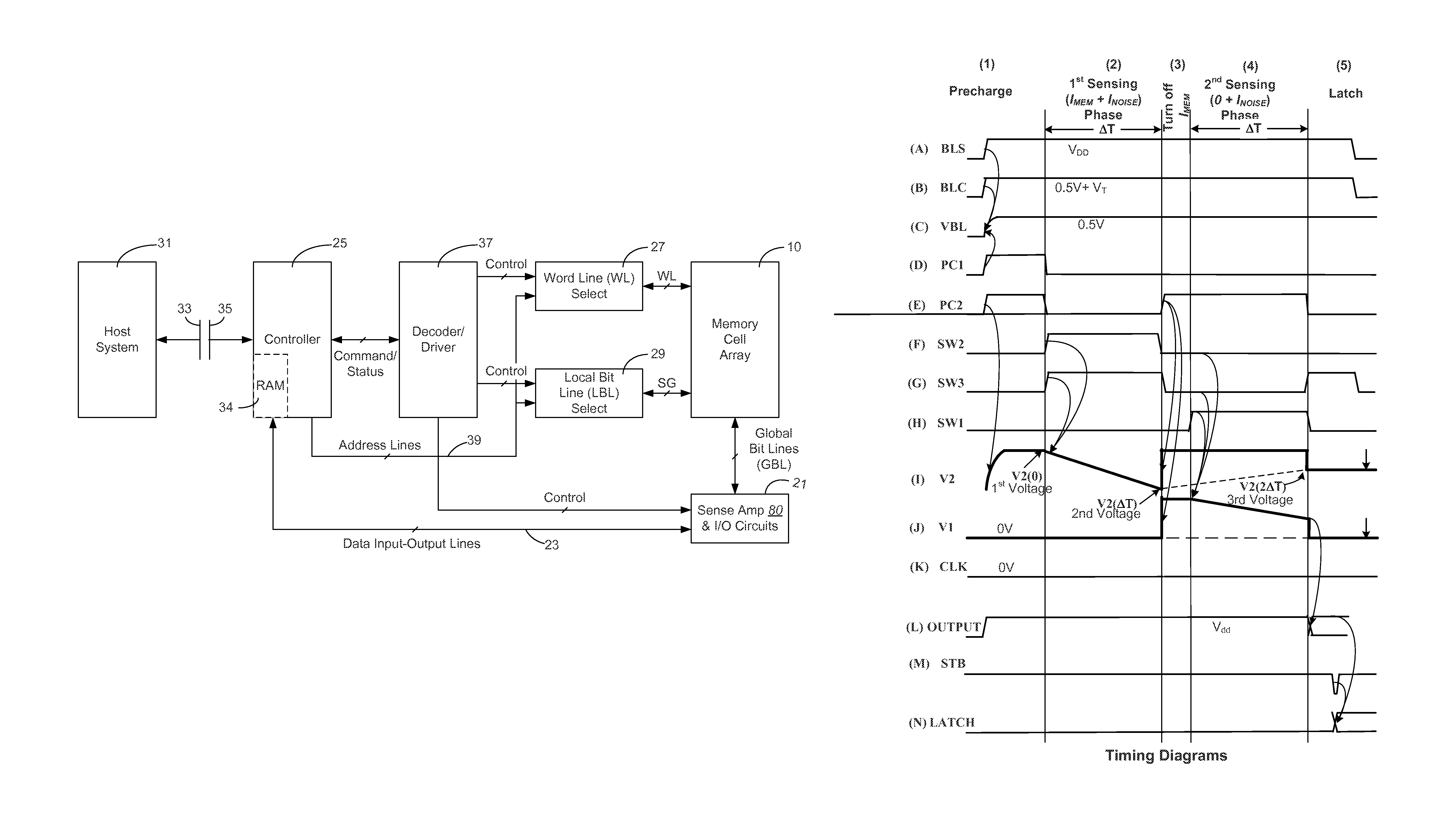
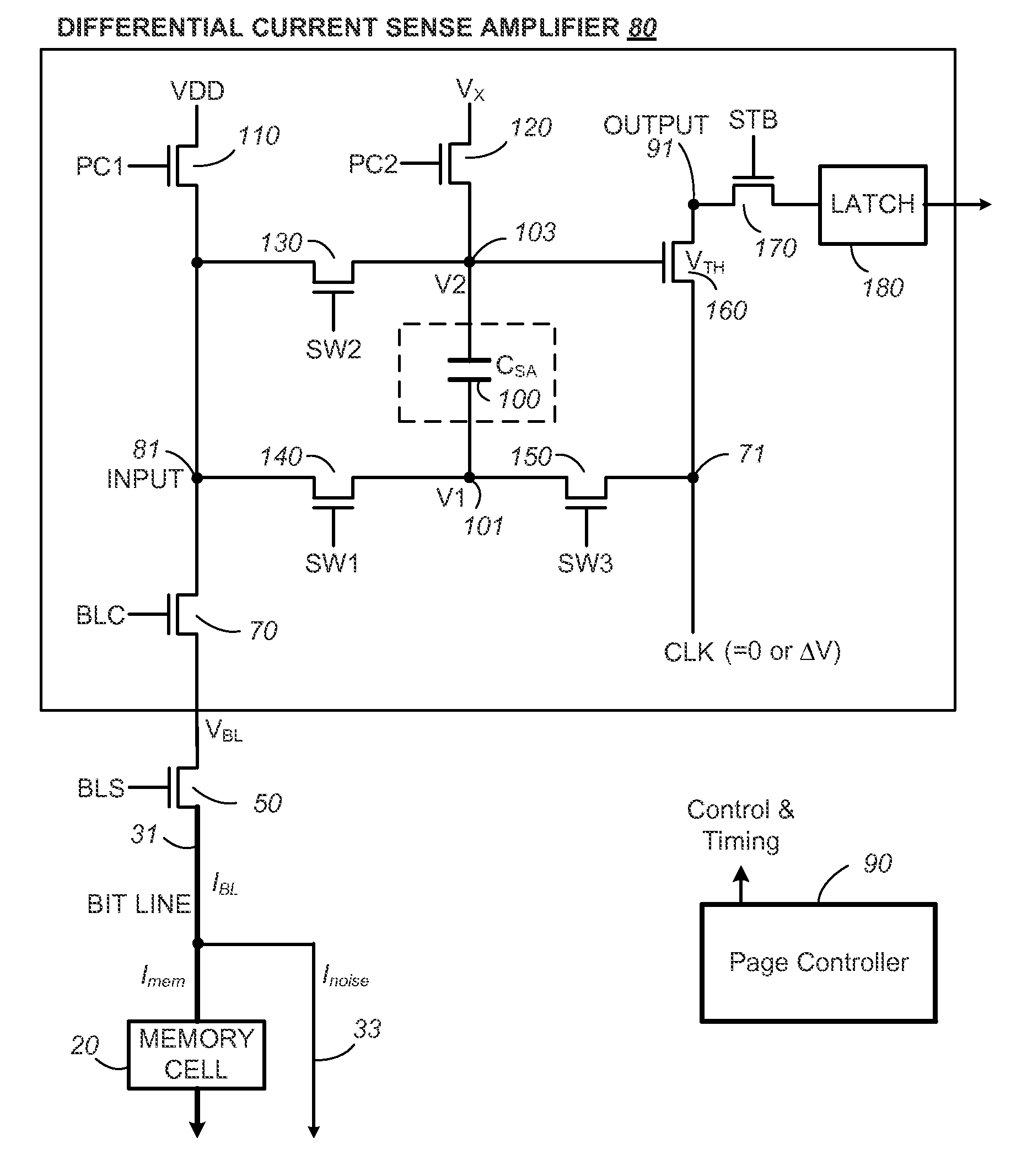
Differential current sense amplifier and method for non-volatile memory
ActiveUS9123430B2Effectively subtractingMinimise currentRead-only memoriesDigital storageEngineeringSense amplifier
The selected bit line in a non-volatile memory carries a cell conduction current to be measured and also a leakage current or noise due to weak coupling with neighboring array structures. In a first phase, a sense amplifier senses the bit line current by discharging a capacitor with the combined current (cell conduction current plus the leakage current) over a predetermined time. In a second phase, the cell conduction current is minimized and significantly the leakage current in the selected bit line is used to recharge in tandem the capacitor in a time same as the predetermined time, effectively subtracting the component of the leakage current measured in the first sensing phase. The resultant voltage drop on the capacitor over the two sensing phases provides a measure of the cell conduction current alone, thereby avoiding reading errors due to the leakage current present in the selected bit line.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Differential current sense amplifier and method for non-volatile memory
ActiveUS20140369132A1Effectively subtractingAvoid reading errorsRead-only memoriesDigital storageEngineeringSense amplifier
The selected bit line in a non-volatile memory carries a cell conduction current to be measured and also a leakage current or noise due to weak coupling with neighboring array structures. In a first phase, a sense amplifier senses the bit line current by discharging a capacitor with the combined current (cell conduction current plus the leakage current) over a predetermined time. In a second phase, the cell conduction current is minimized and significantly the leakage current in the selected bit line is used to recharge in tandem the capacitor in a time same as the predetermined time, effectively subtracting the component of the leakage current measured in the first sensing phase. The resultant voltage drop on the capacitor over the two sensing phases provides a measure of the cell conduction current alone, thereby avoiding reading errors due to the leakage current present in the selected bit line.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
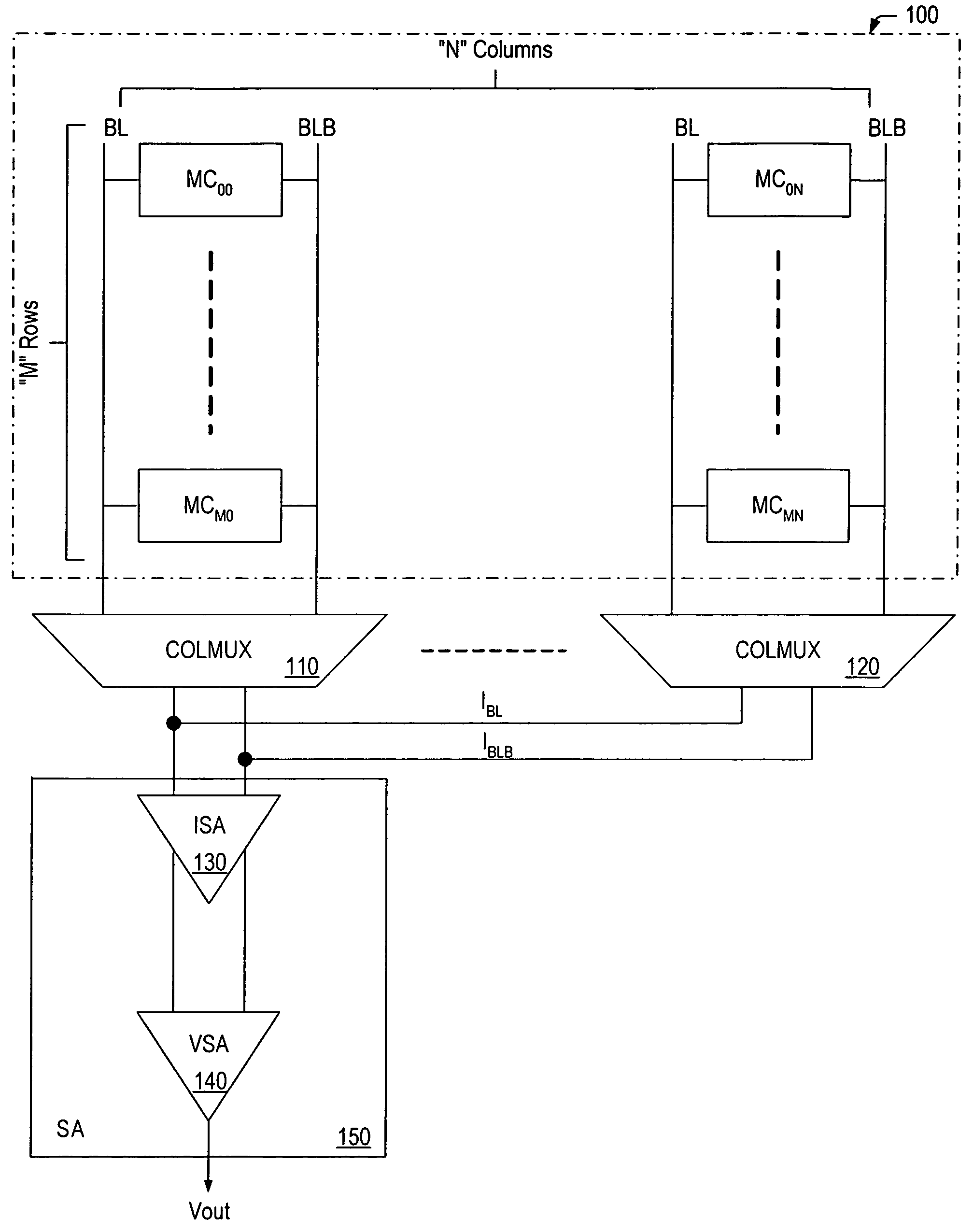
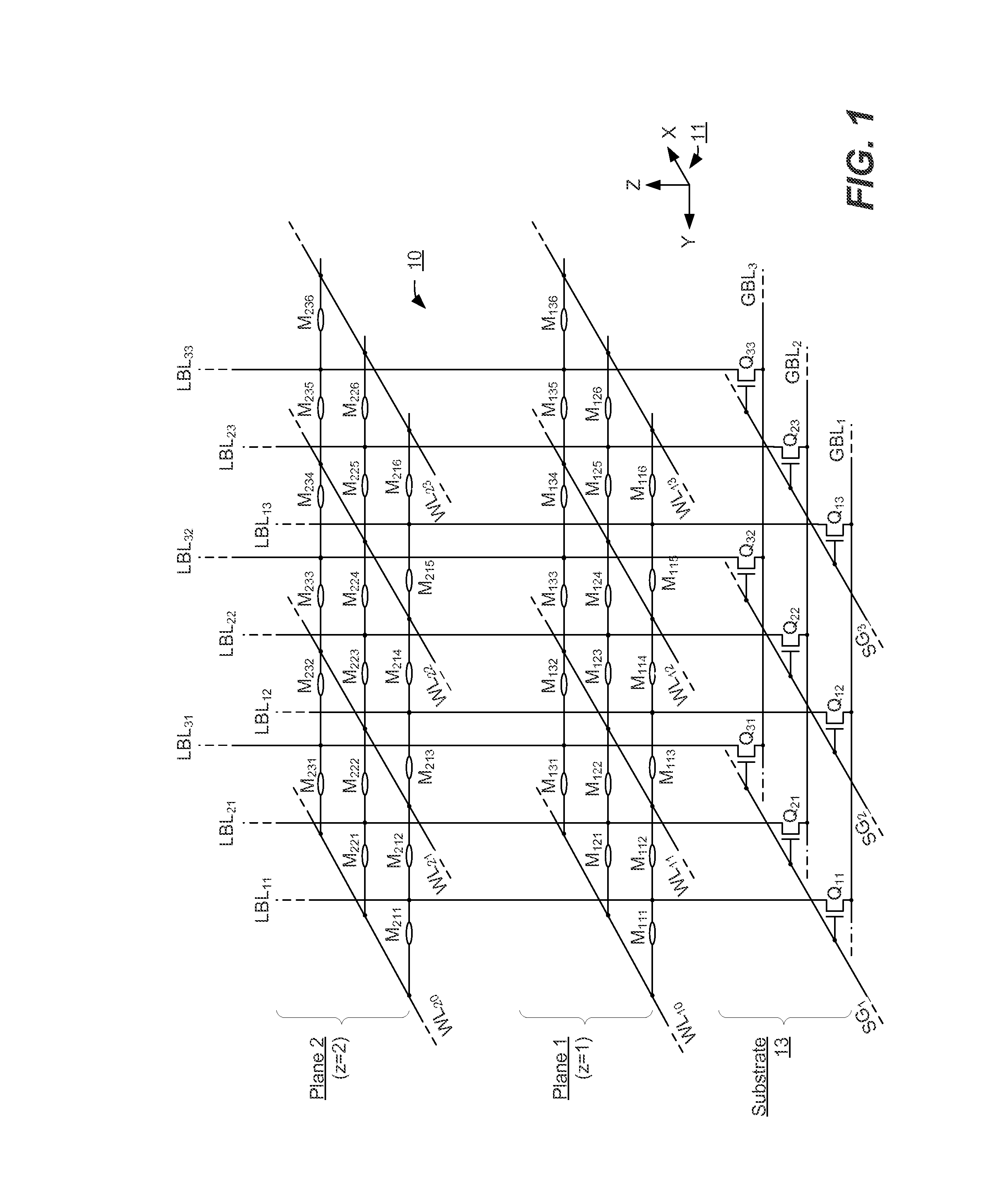
Differential current-mode sensing methods and apparatuses for memories
Disclosed is a memory architecture where current sense amplifiers are used instead of voltage sense amplifiers, and where the memory cells normally disposed along a single bit line are divided between two half bit lines. Each half bit line is coupled to a respective input of the current sense amplifier. When one of the memory cells is selected for reading, it couples a current related to its stored data state to the half bit line that it is coupled to. During this operation, a reference current is generated on the other half bit line. Also disclosed are novel current sense amplifiers.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
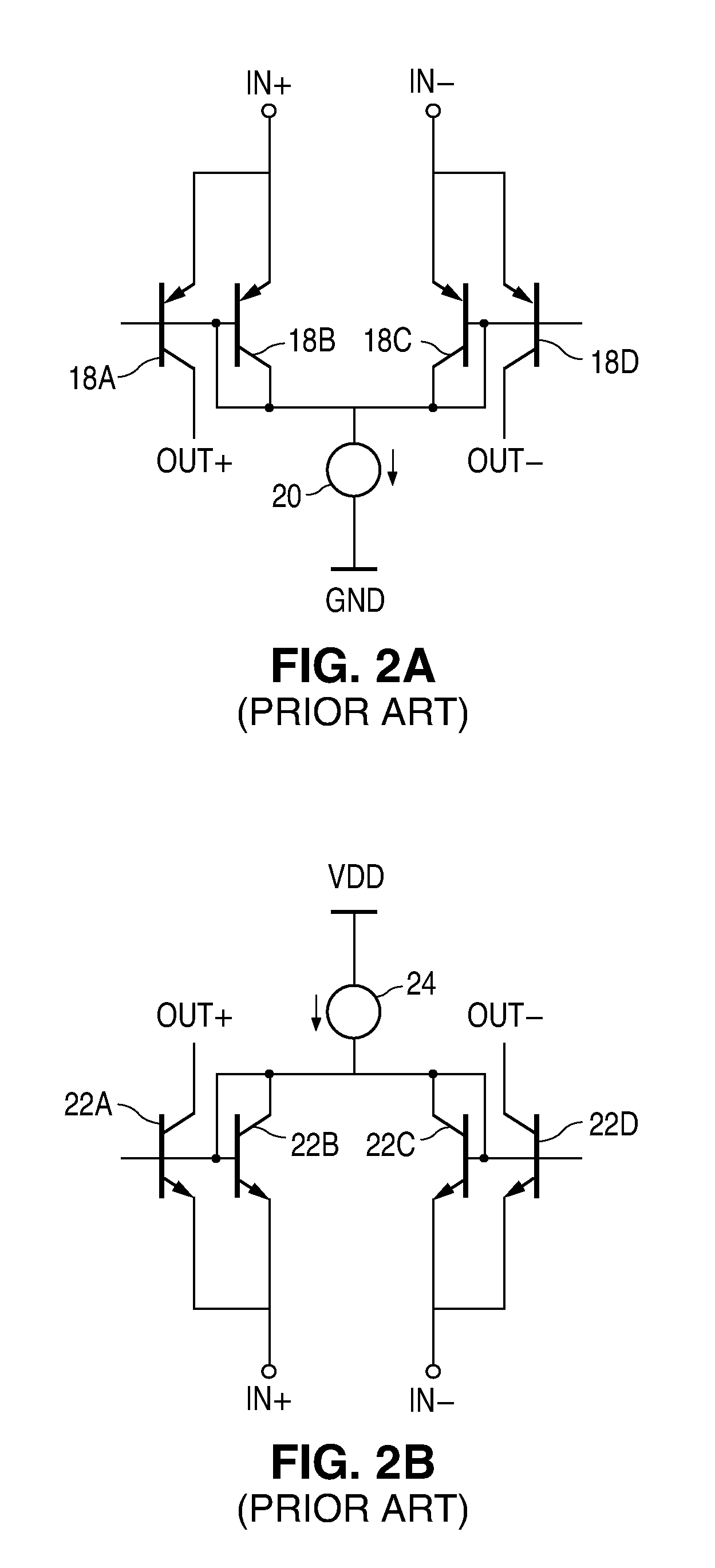
High-speed cross-coupled sense amplifier
InactiveUS6885222B2Avoid delayIncrease potential differenceMultiple input and output pulse circuitsCurrent/voltage measurementAudio power amplifierPotential difference
A sense amplifier has a pair of internal nodes that are precharged to a power-supply level. A first pair of n-channel transistors supplies current to the internal nodes responsive to a pair of data signals, both of which are initially high. When one of the data signals begins falling toward the low level, the corresponding n-channel transistor immediately reduces the current supplied to one of the internal nodes. A second pair of n-channel transistors, cross-coupled to the internal nodes, amplifies the resulting potential difference between the internal nodes, thereby pulling down the potential of one of the internal nodes. An output signal is generated from one or both of the internal nodes. The output signal is obtained quickly, because amplification begins without delay.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Low voltage interface circuit
ActiveUS7956641B1Avoid gate oxide degradation/breakdownHighly robustPulse automatic controlCurrent/voltage measurementAudio power amplifierLow voltage
An improved interface circuit is provided herein for translating a relatively high input voltage into a relatively low output voltage using only low voltage transistors and a single, low voltage power supply. According to one embodiment, the interface circuit includes a power supply, a pair of input transistors with source terminals coupled together for receiving a relatively low voltage from the power supply, and a current sense amplifier with a pair of input terminals, each coupled to a drain terminal of a different one of the pair of input transistors for receiving a pair of differential currents and for generating a pair of differential voltages therefrom.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
LED (Light-Emitting Diode) lamp and electronic breaker thereof
ActiveCN104078919AArrangements responsive to excess currentMeasurement using digital techniquesElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
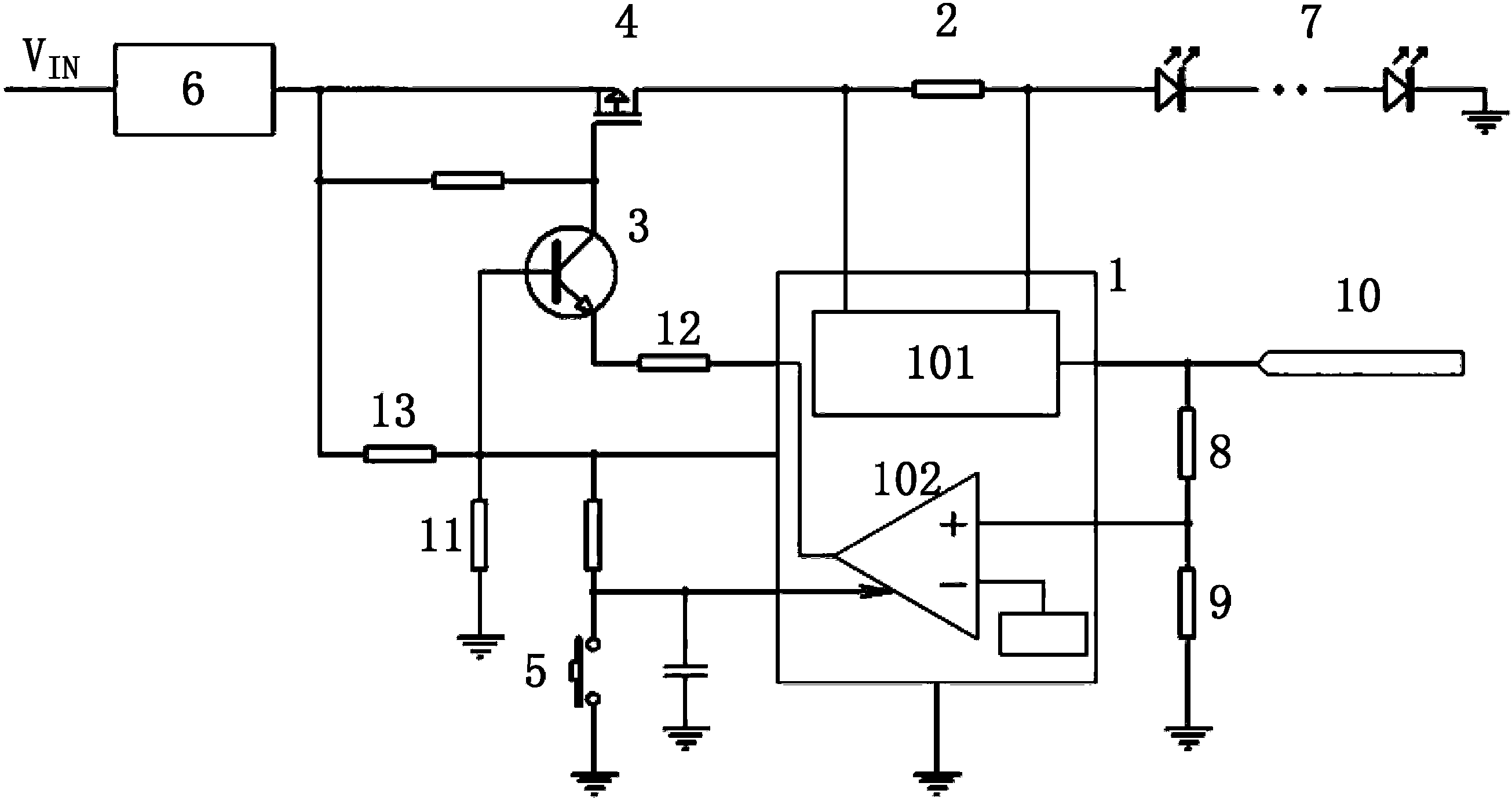
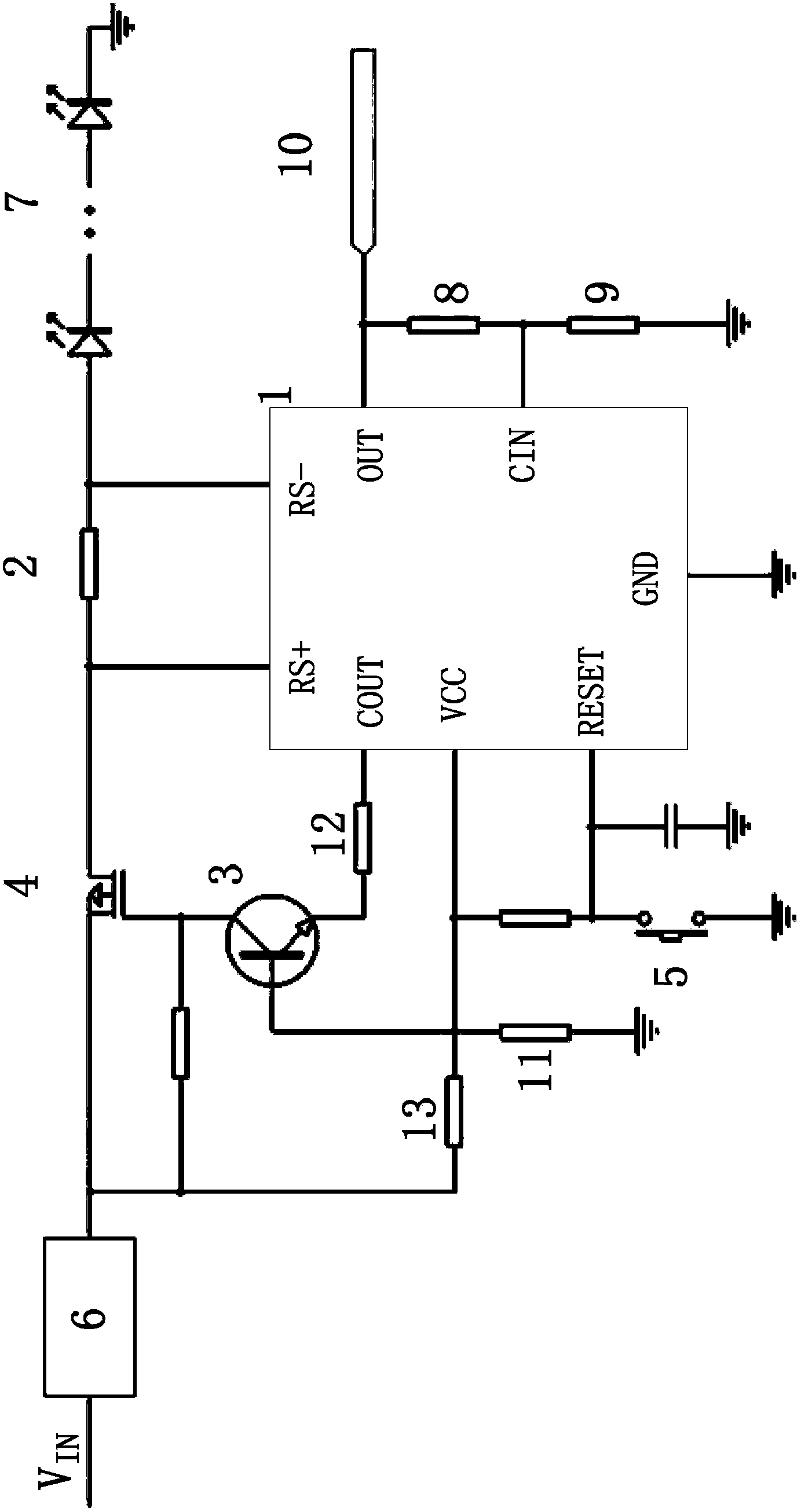
The invention provides an LED (Light-Emitting Diode) lamp and an electronic breaker thereof. The electronic breaker is connected in series between a power supply input end and the LED lamp, and comprises a sampling resistor, a field effect transistor and a current detection chip, wherein one end of the sampling resistor is coupled with the LED lamp; a source electrode of the field effect transistor is coupled with the power supply input end; a grid electrode of the field effect transistor is coupled with the other end of the sampling resistor; the current detection chip comprises a current detection amplifier and a voltage comparator; two detection pins of the current detection amplifier are coupled with the two ends of the sampling resistor respectively; an output pin of the current detection amplifier is coupled with an LED alternating-direct (AD) current conversion port, and earthed by a resistance voltage-dividing network; and a locking output pin of the voltage comparator is coupled with a drain electrode of the field effect transistor. The electronic breaker limits current on the LED lamp, timely disconnects a power supply and a load in case of overcurrent, and can detect real-time working current of an LED.
Owner:OCEANKING DONGGUAN LIGHTING TECH +2
Electroluminescence display apparatus
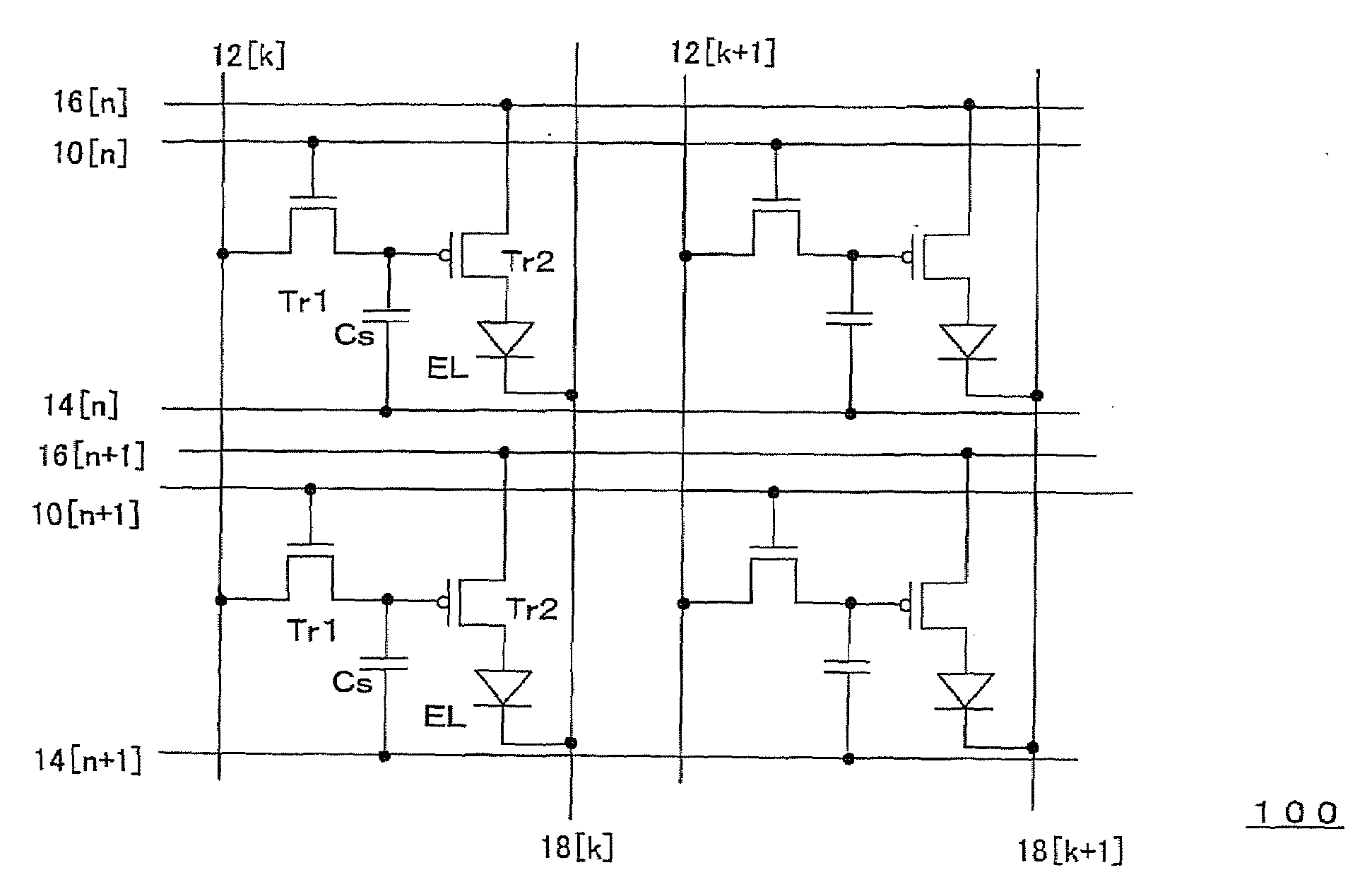
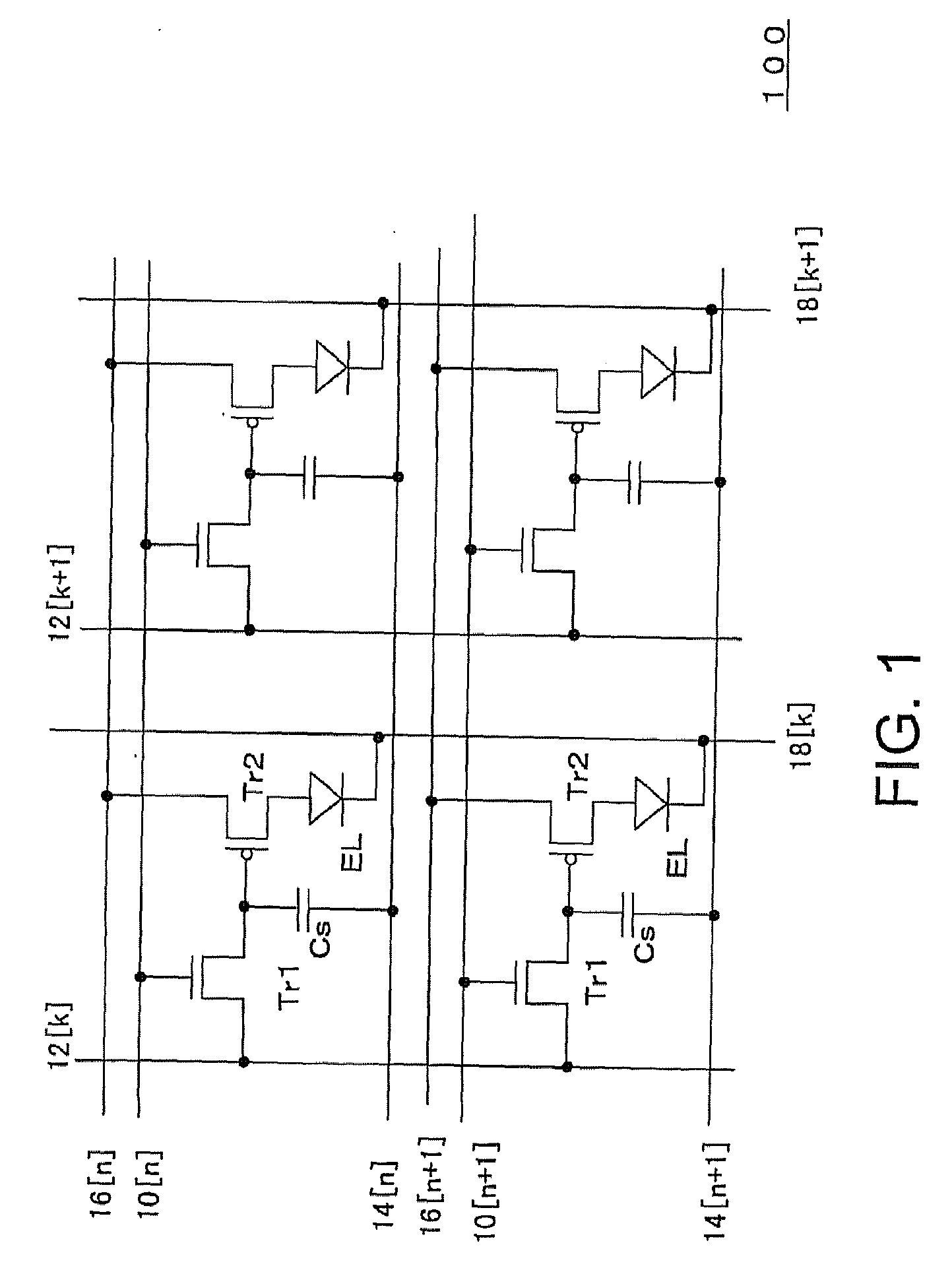
ActiveUS20080238834A1Speedily carry out measurement of a display variationElectroluminescent light sourcesMaterial analysis by optical meansDriving currentElectricity
During a blanking period of a video signal, an element driving transistor for controlling a drive current supplied to an EL element is operated in its saturation region to thereby set the EL element to an emission level, and a current flowing through the EL element at that time is detected. Each current detector includes a current detection amplifier and a successive approximation type AD converter, and a DA converter of the successive approximation type AD converter is commonly shared among a plurality of the AD converters. With this arrangement, sufficient AD converting speed can be attained while using a simple structure to execute current detection for correcting display variations.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com