Patents
Literature
582 results about "Input resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
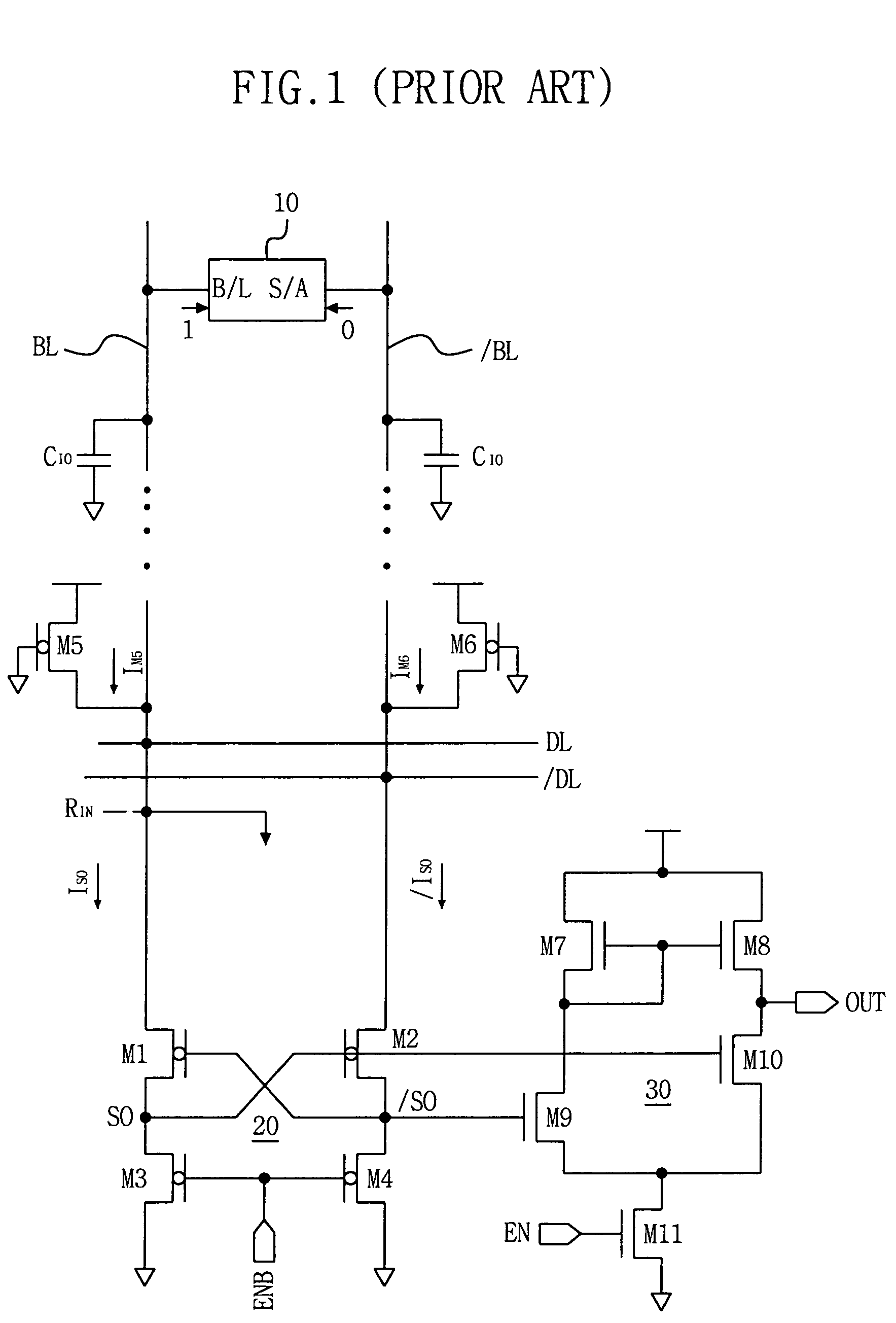
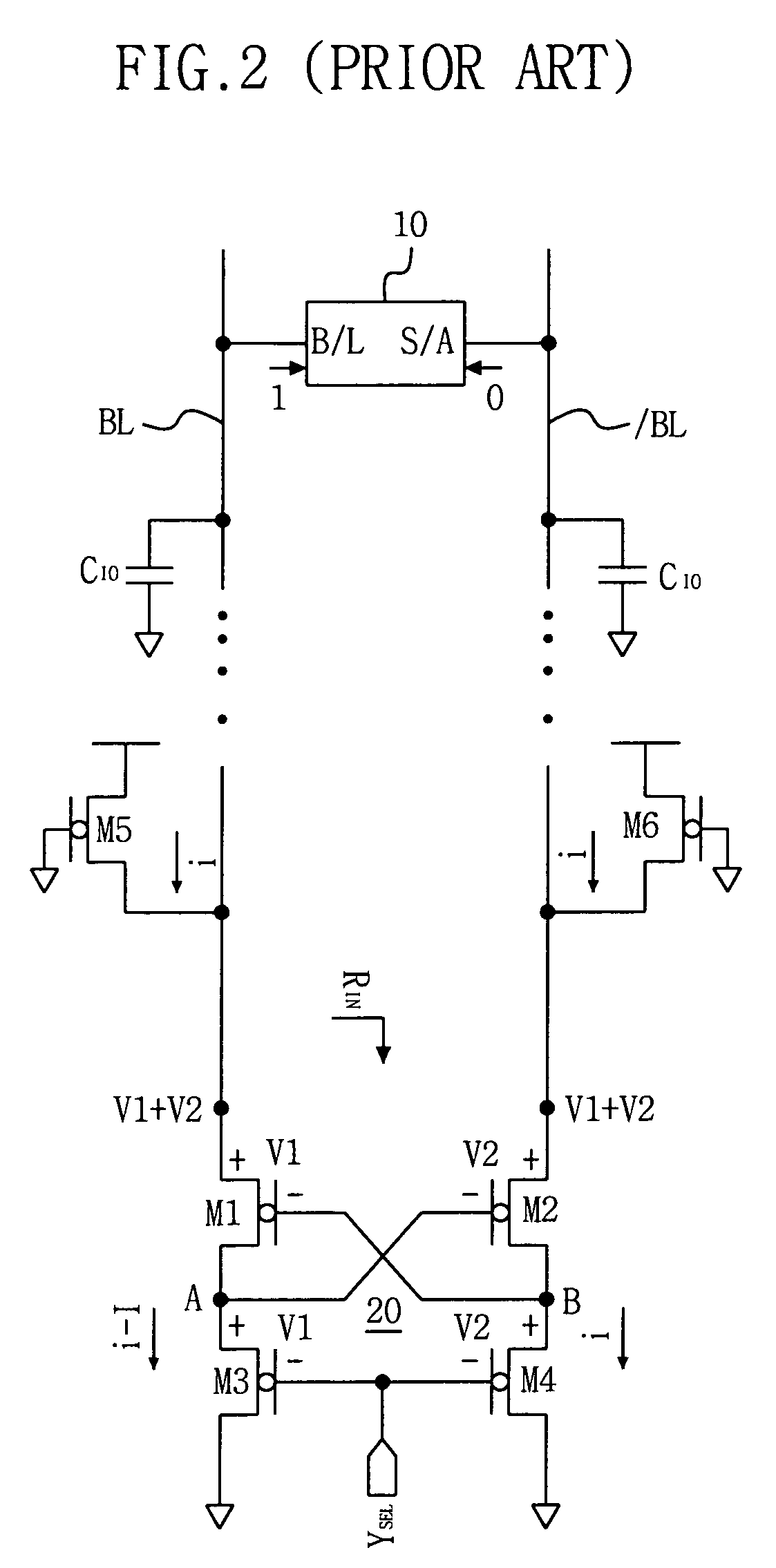
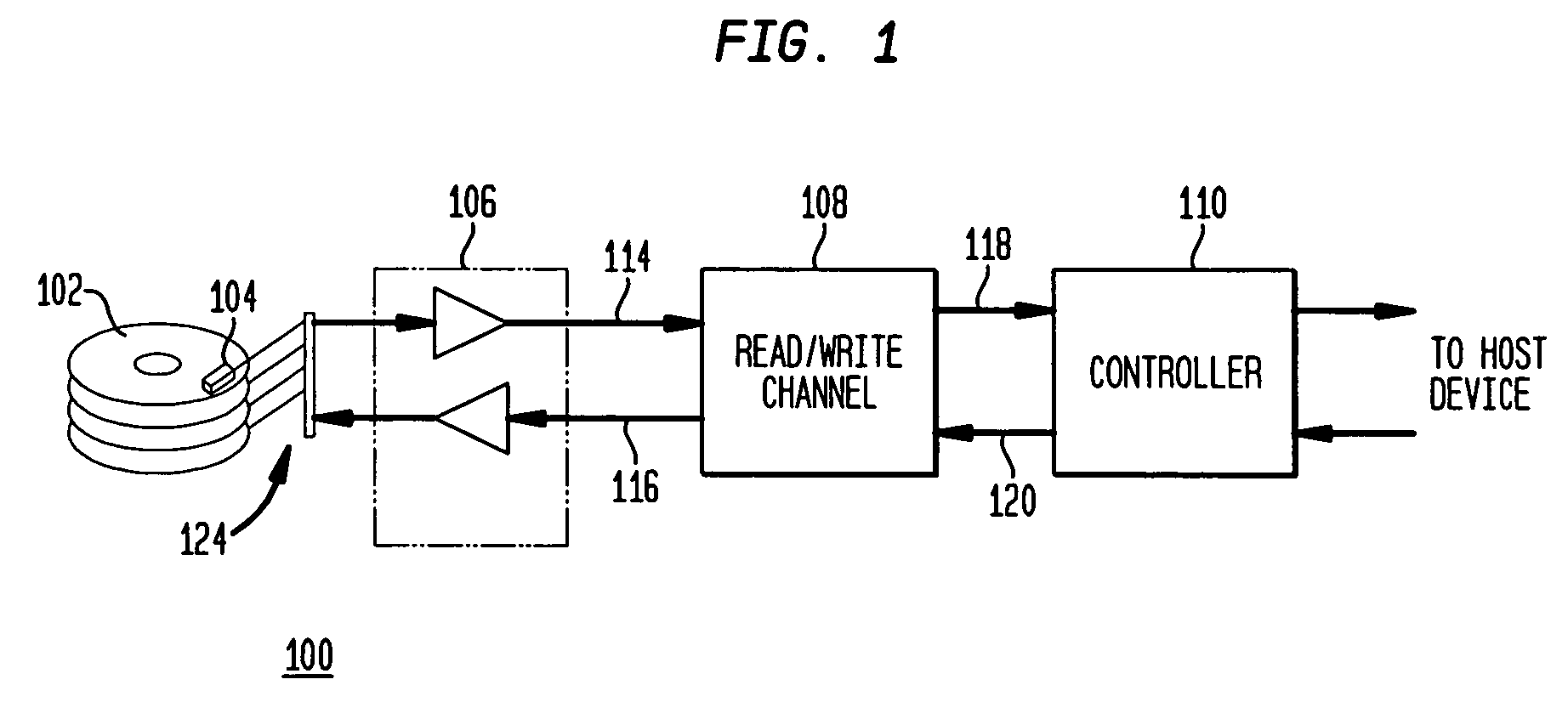
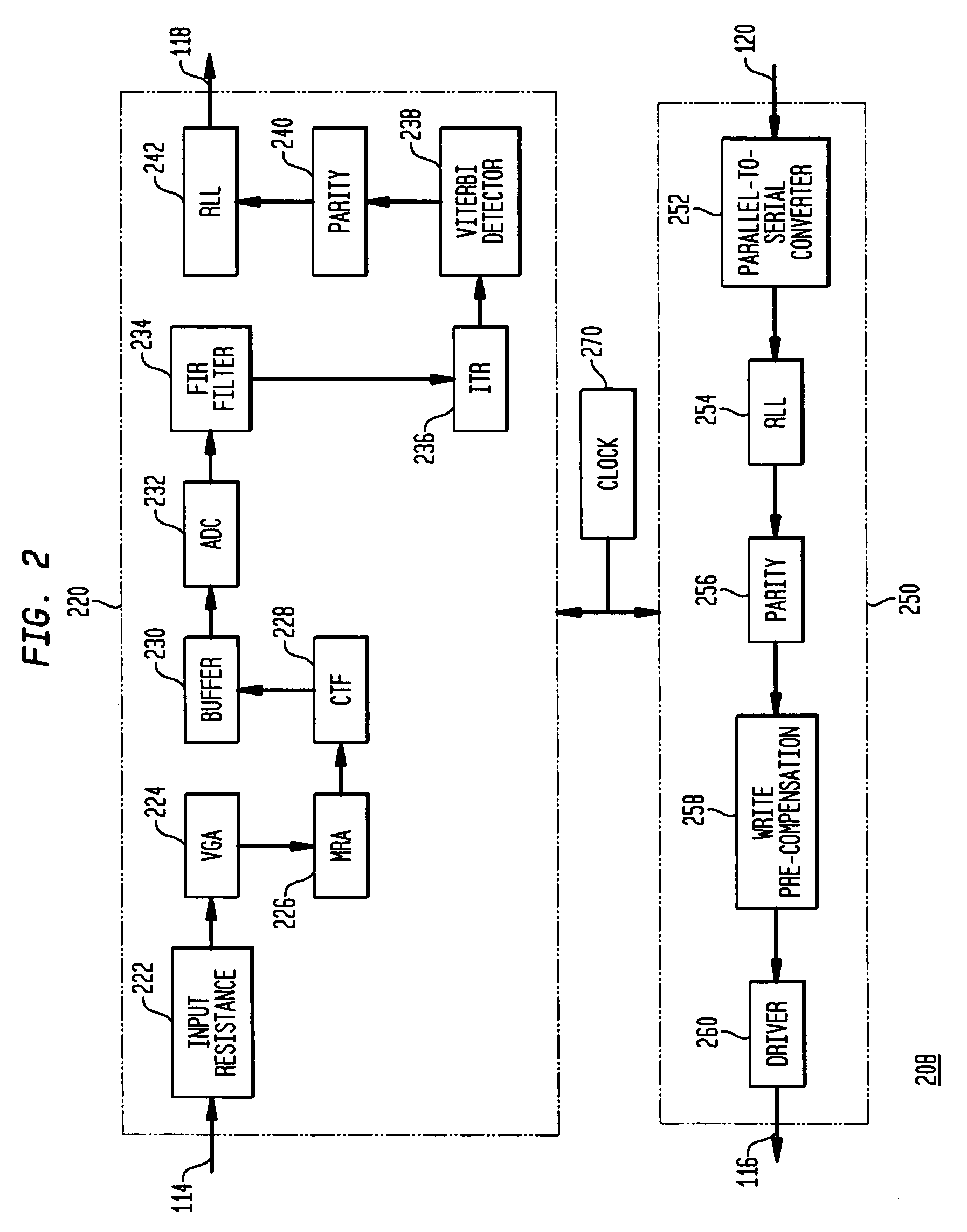
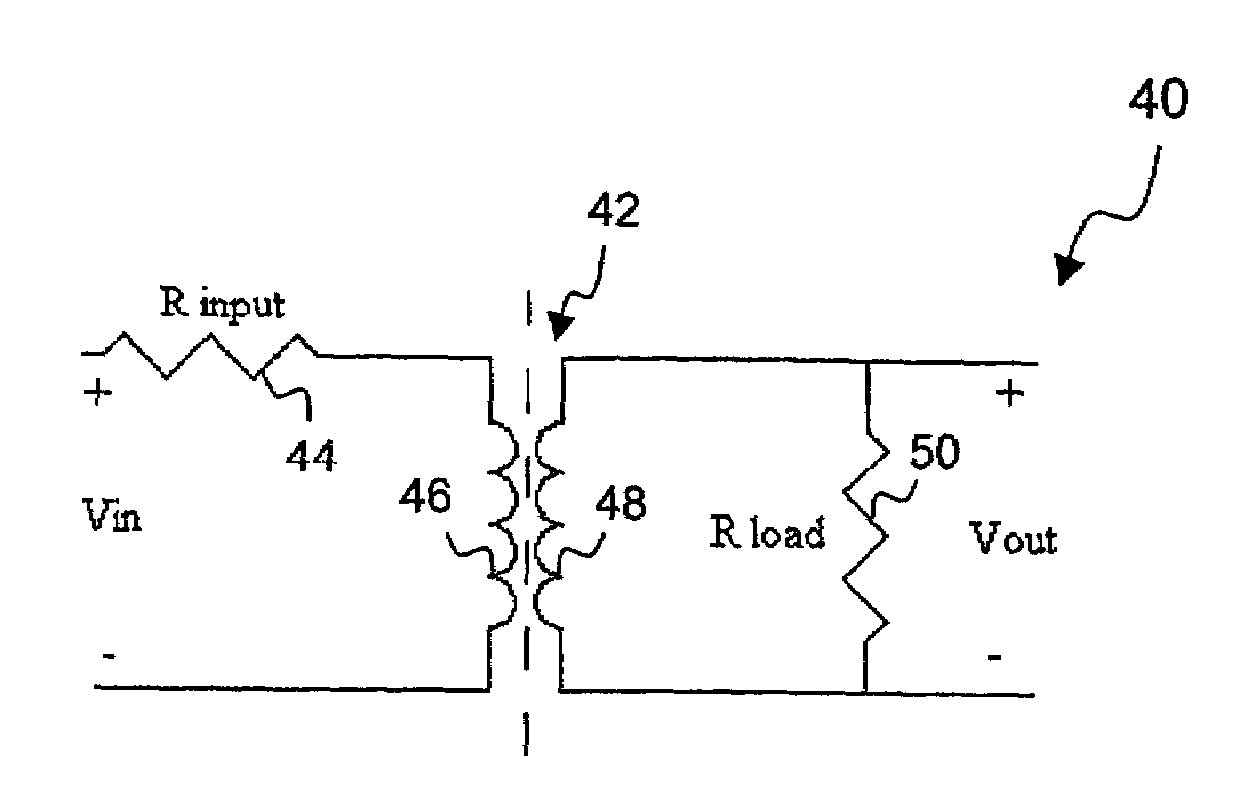
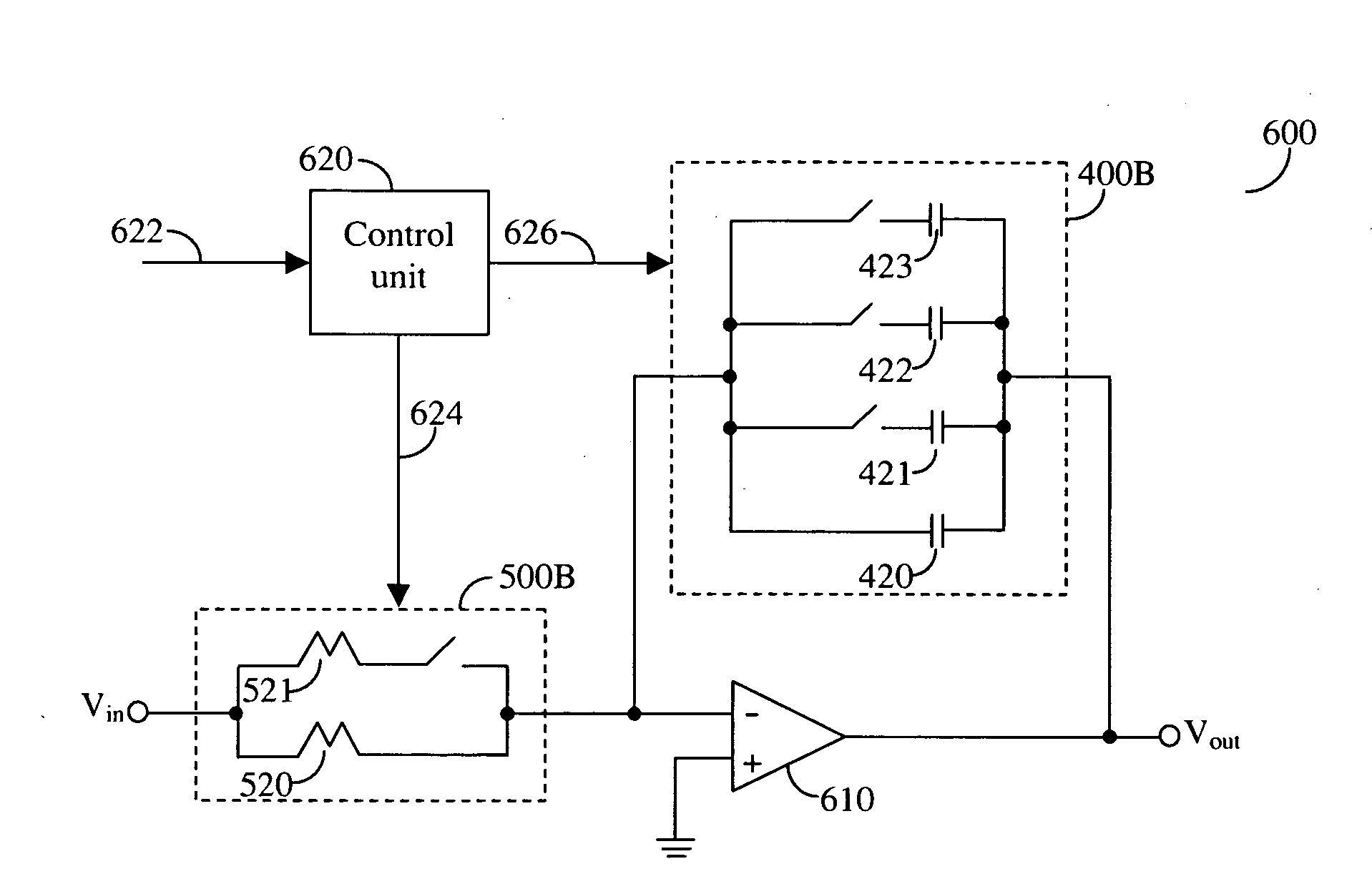
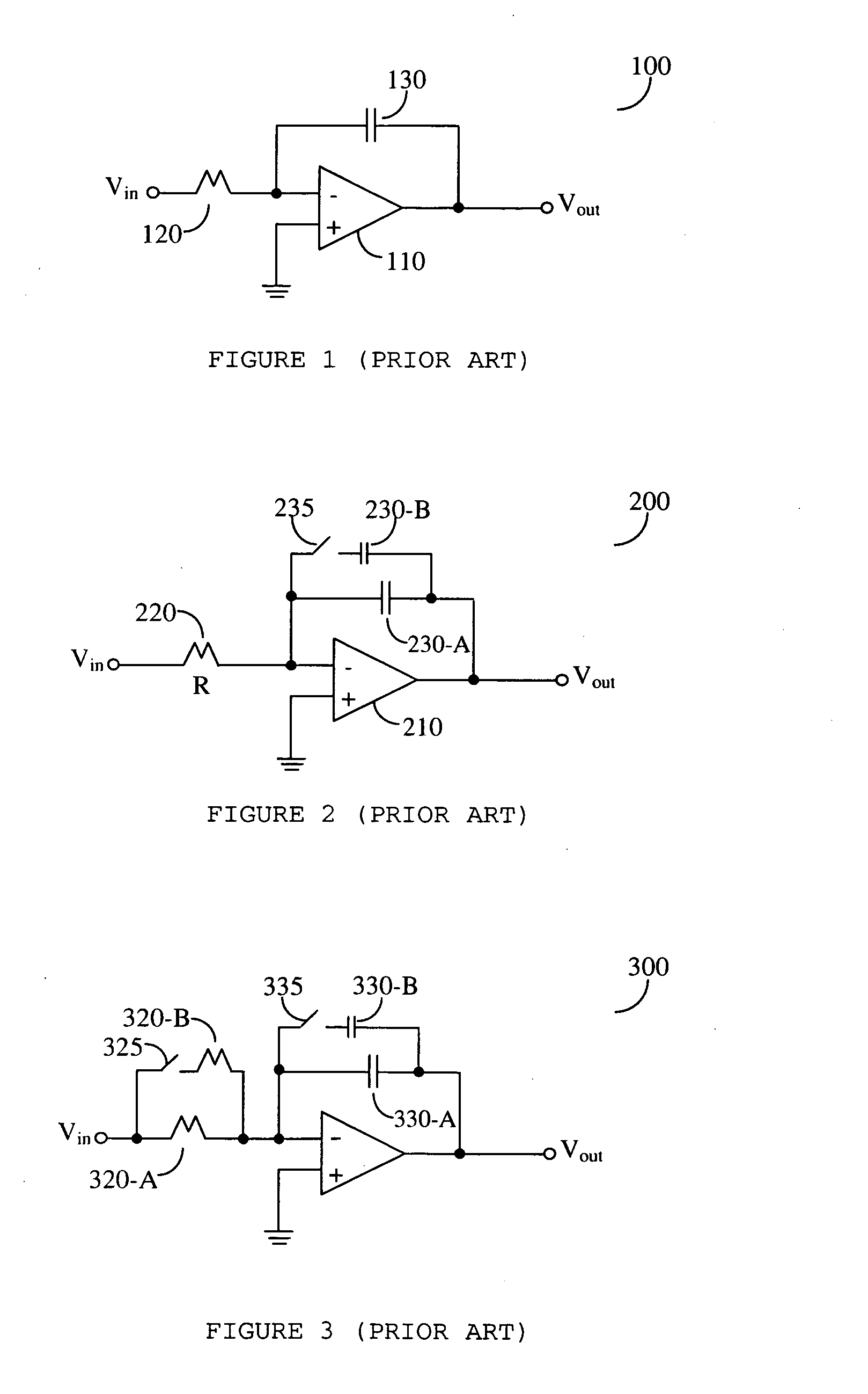
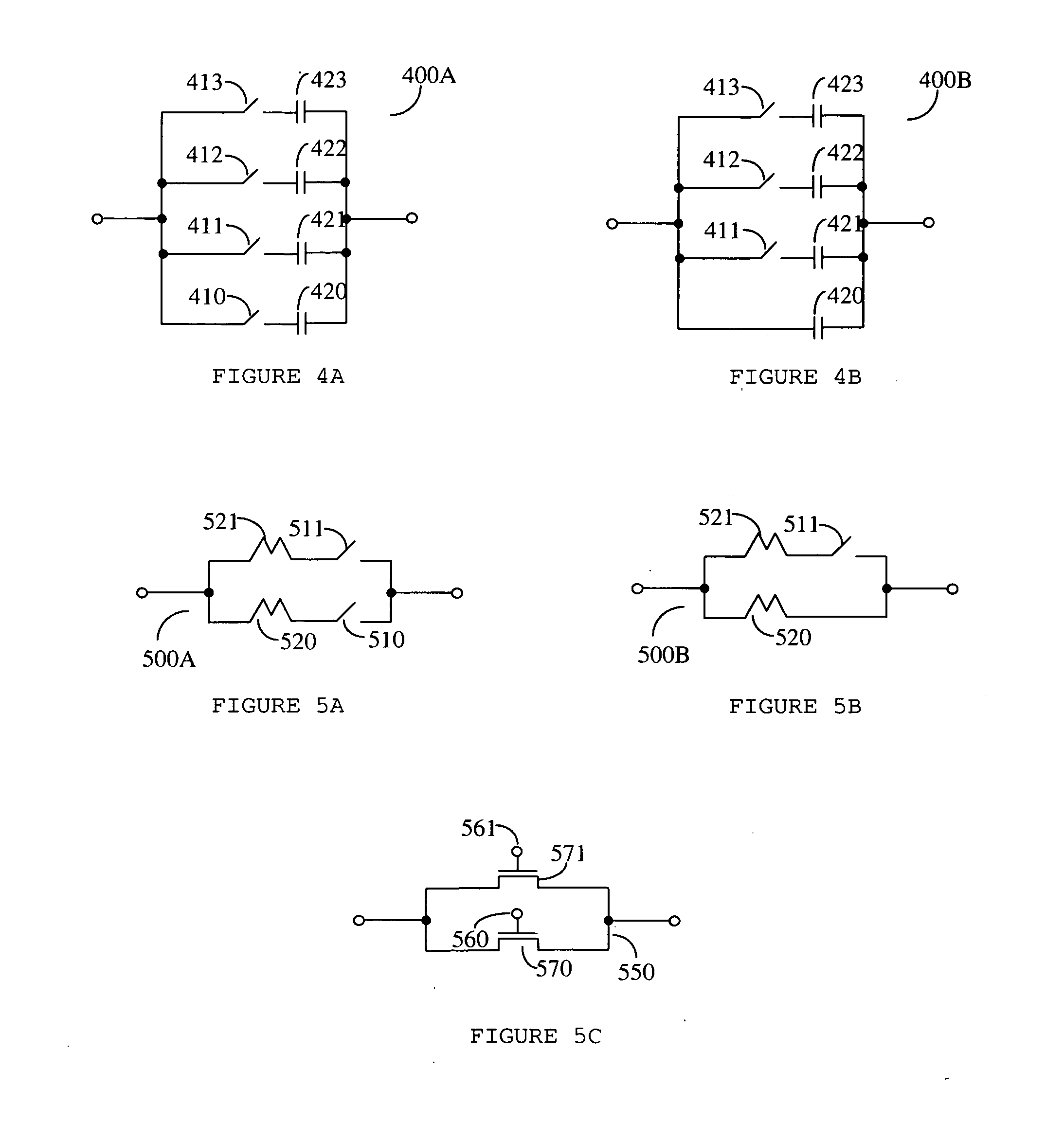
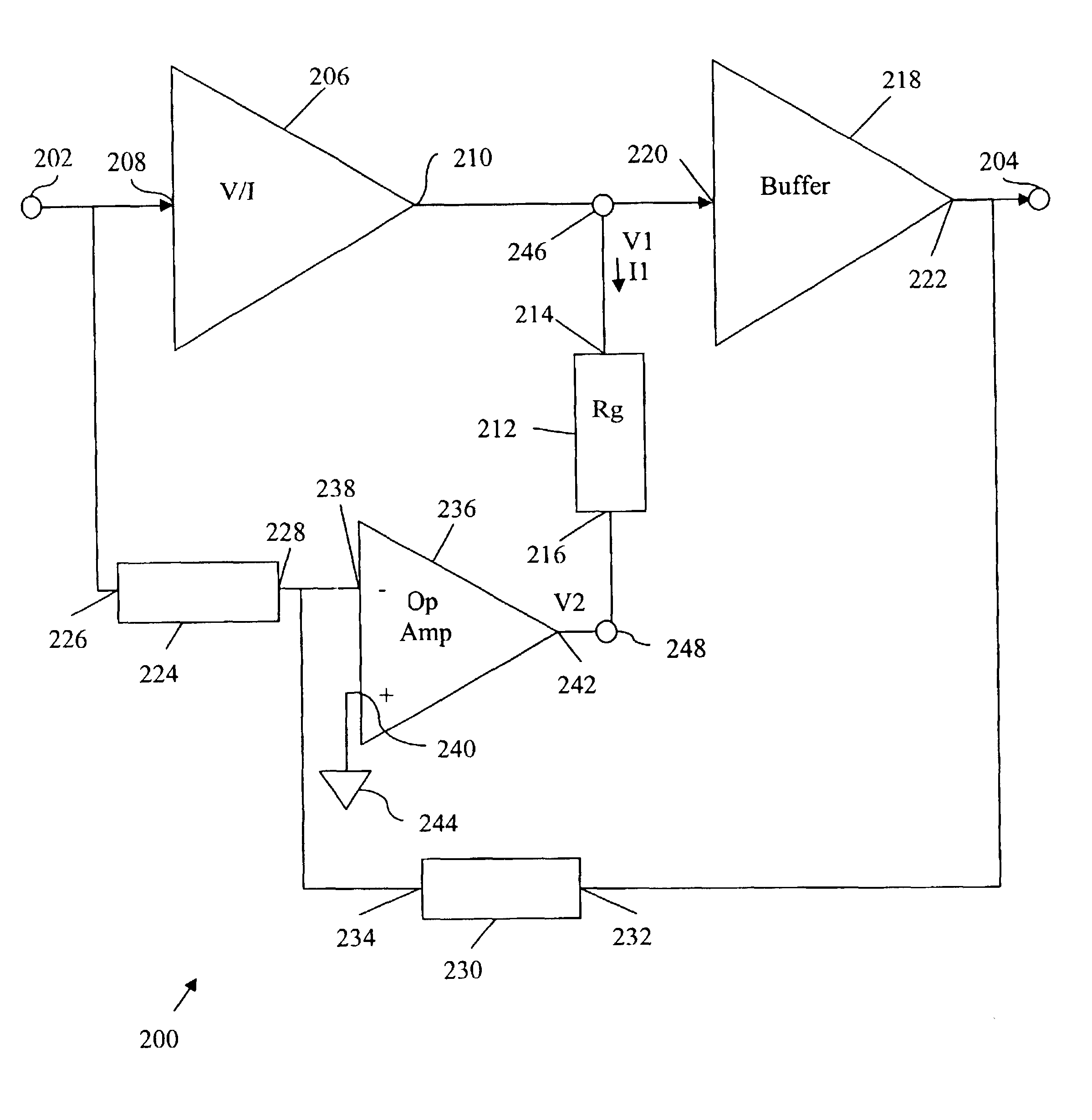
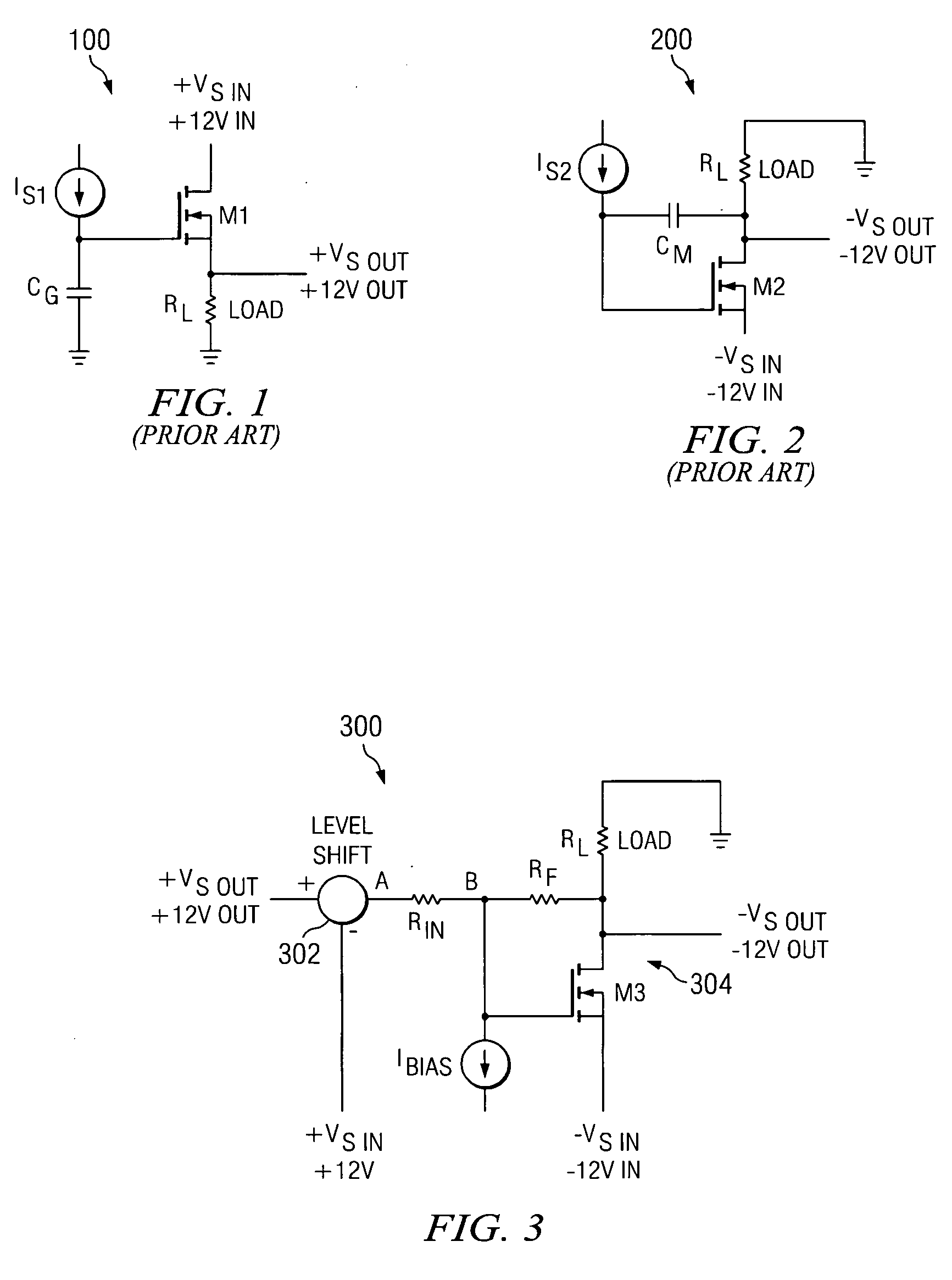
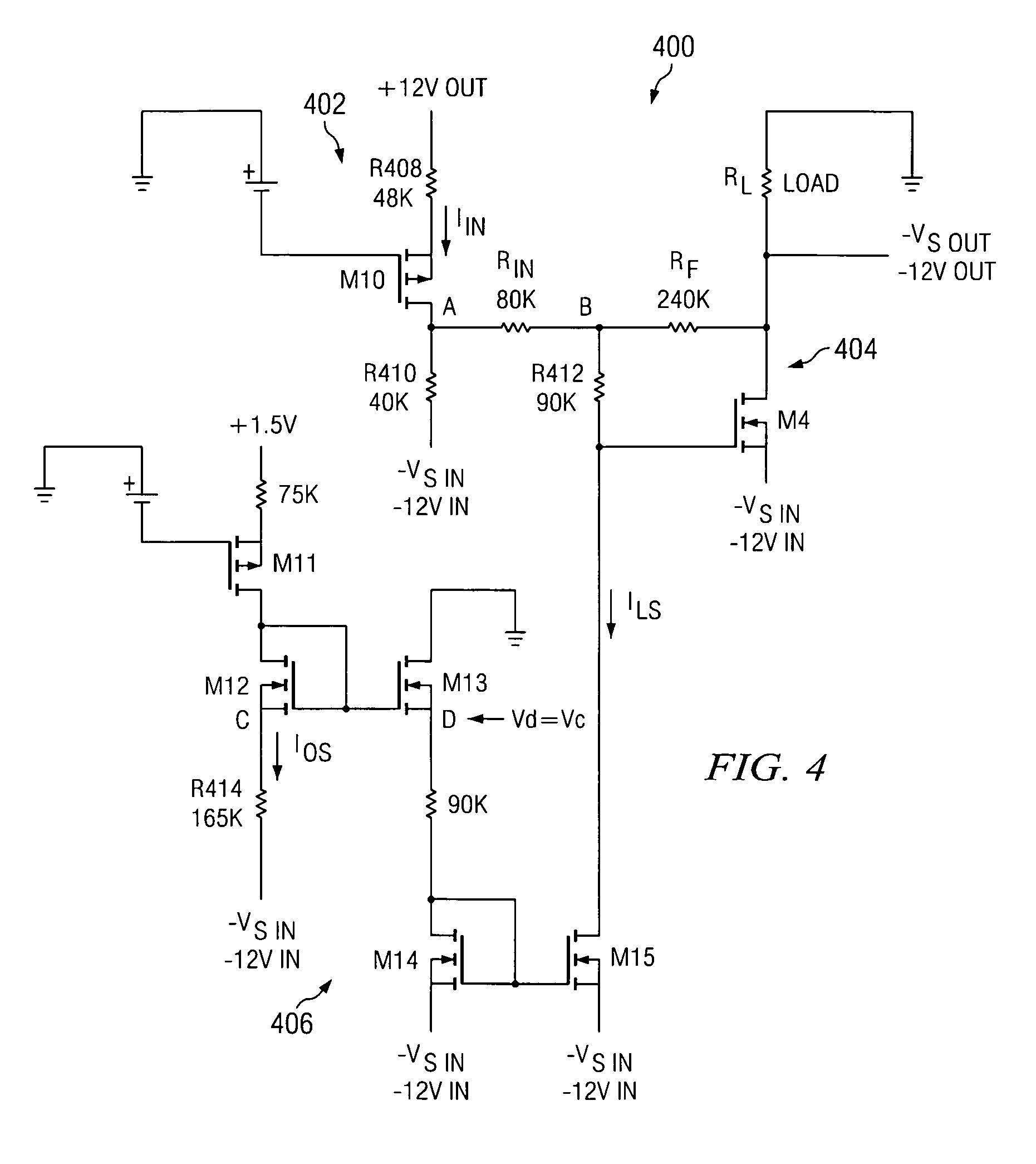
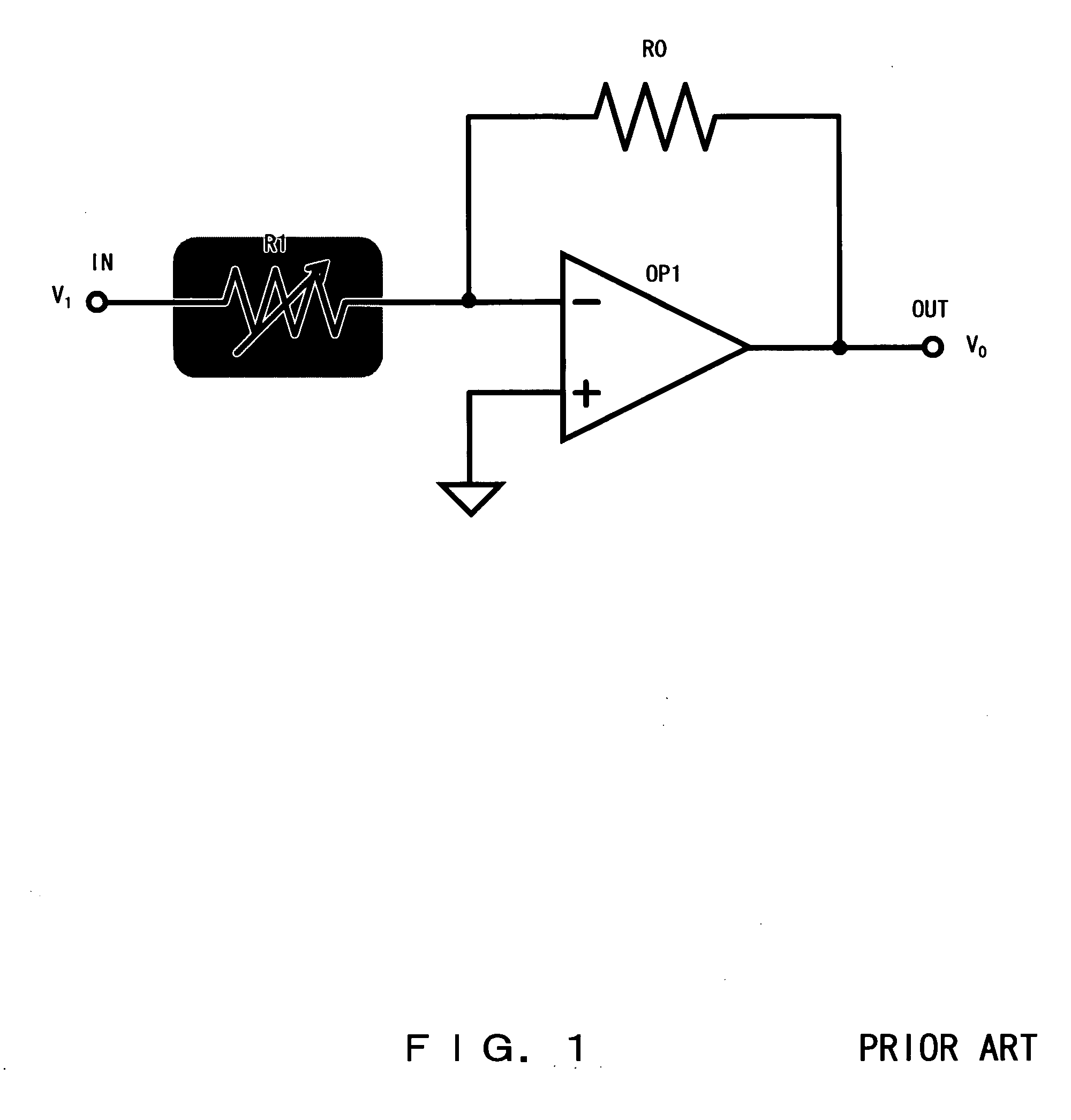
Input Resistance: The input resistance is the resistance seen by the current source or voltage source which drives the circuit. For example, returning to the circuit in Fig.
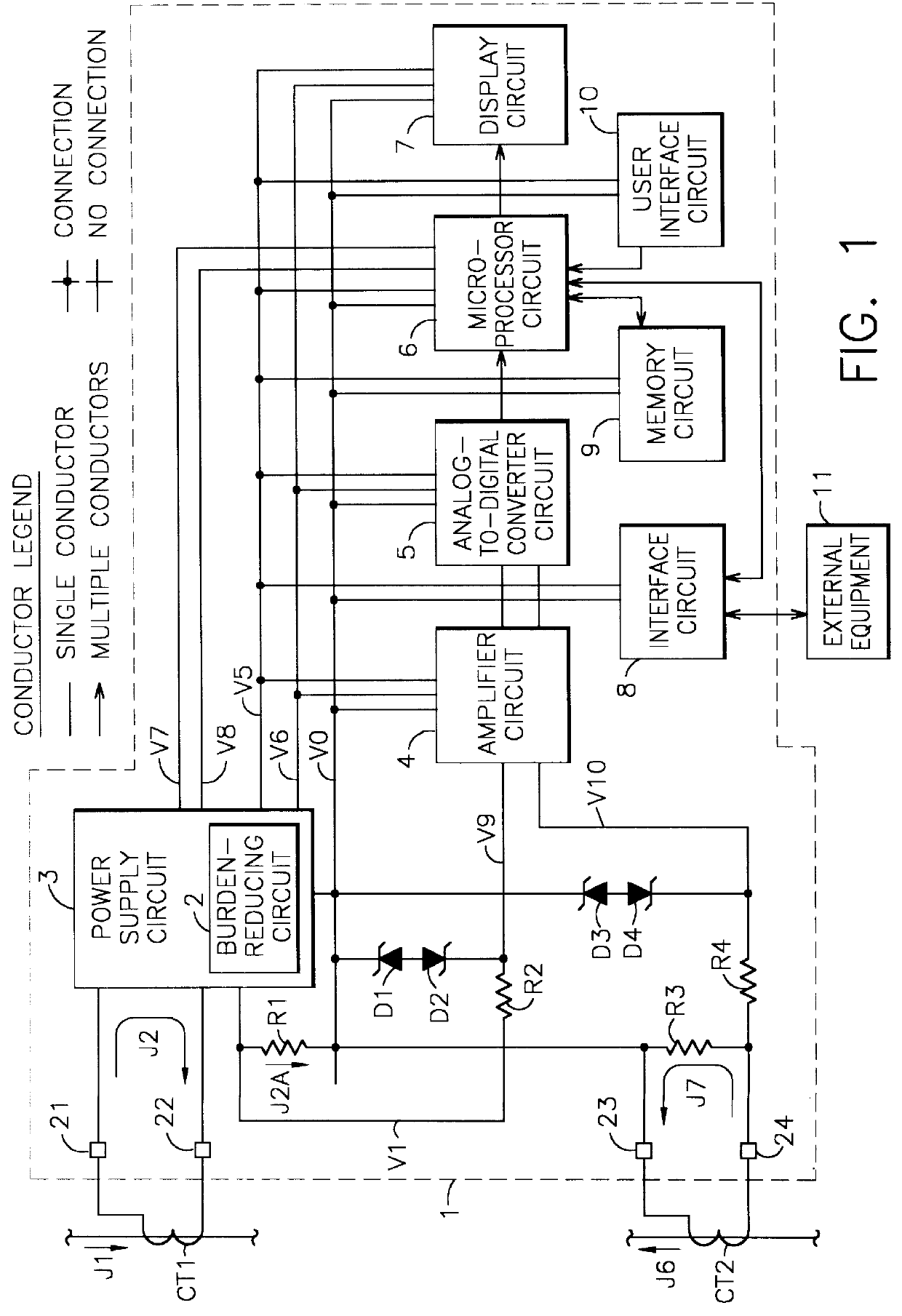
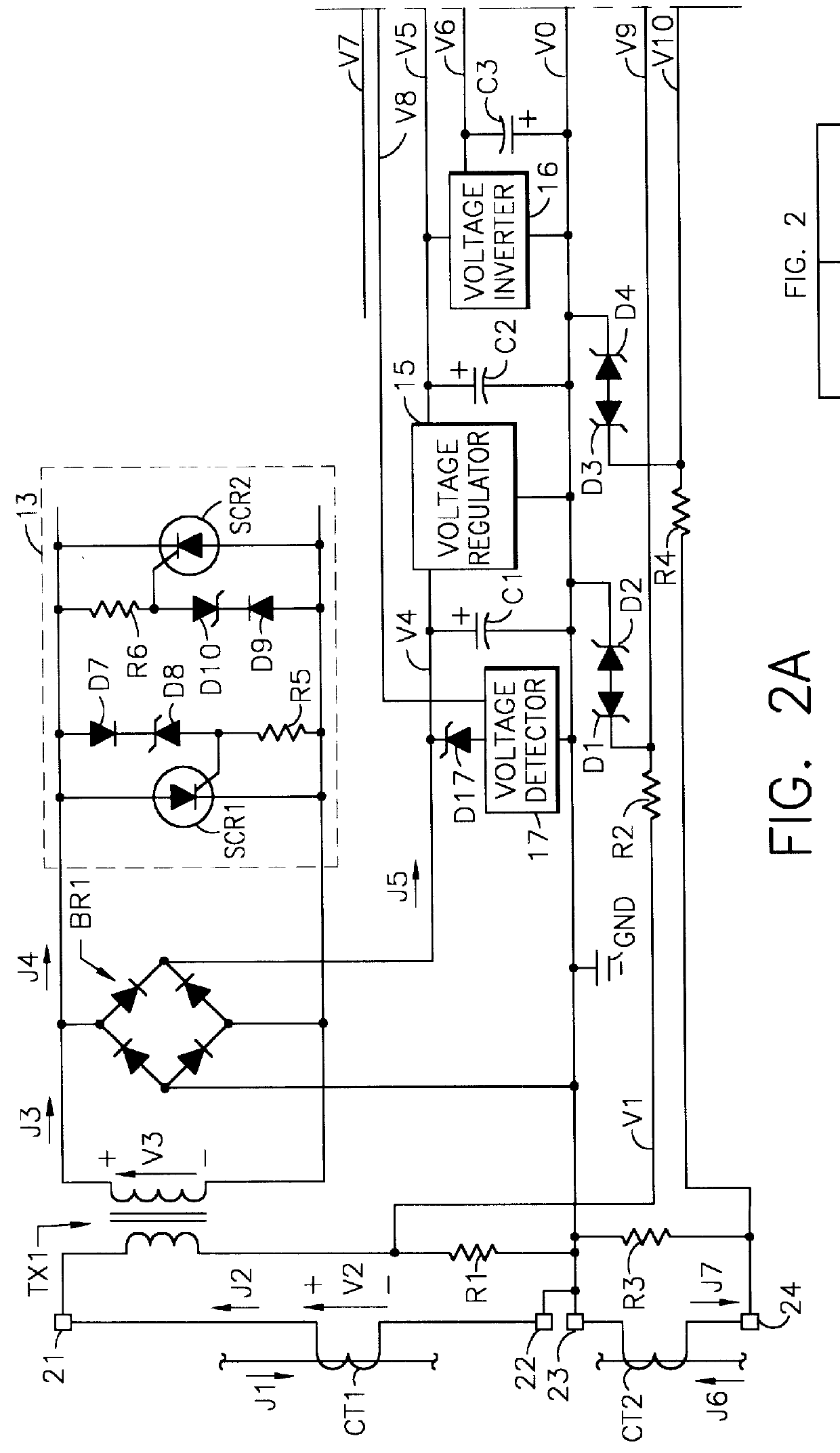
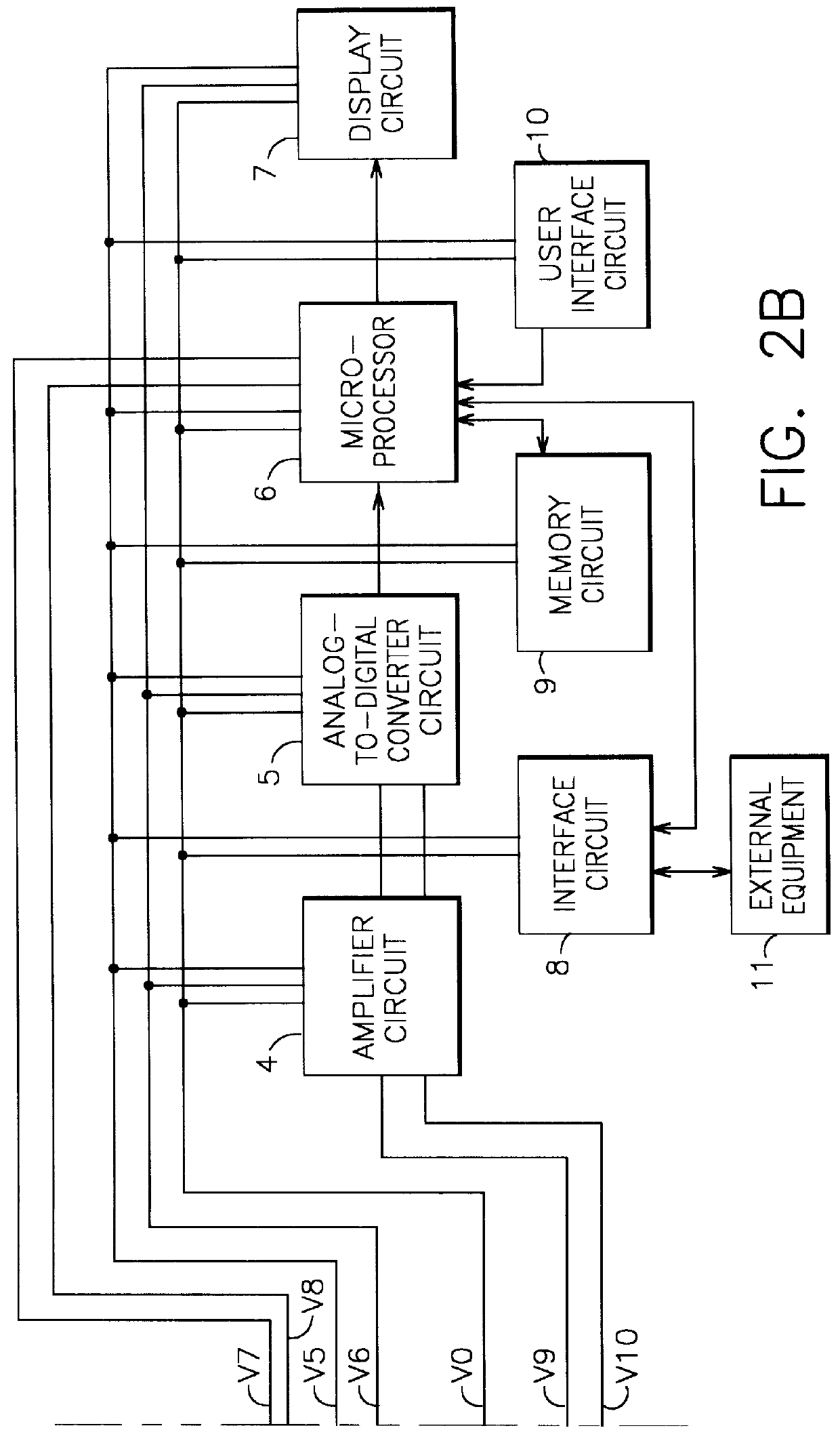
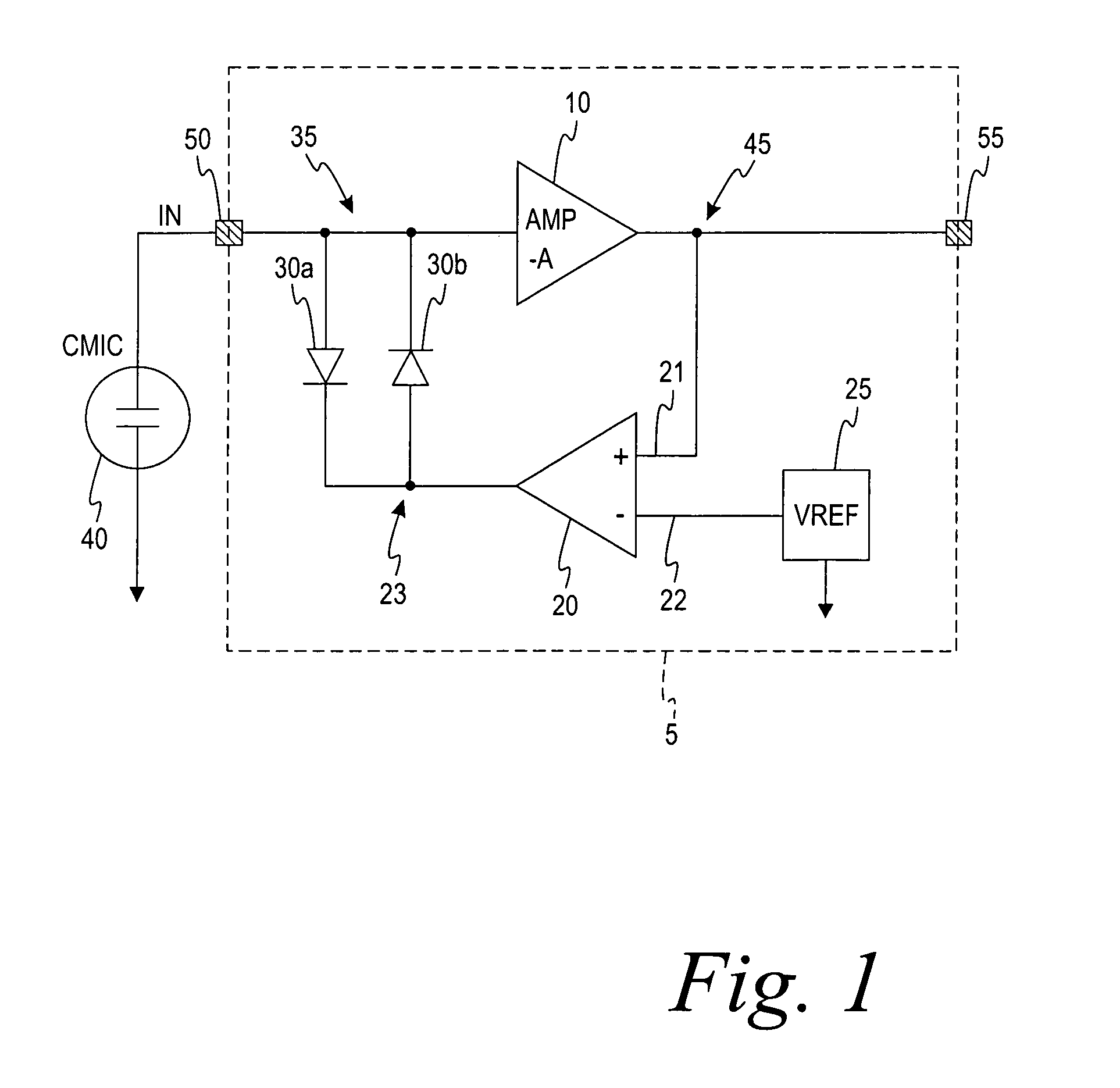
Self-powered current monitor
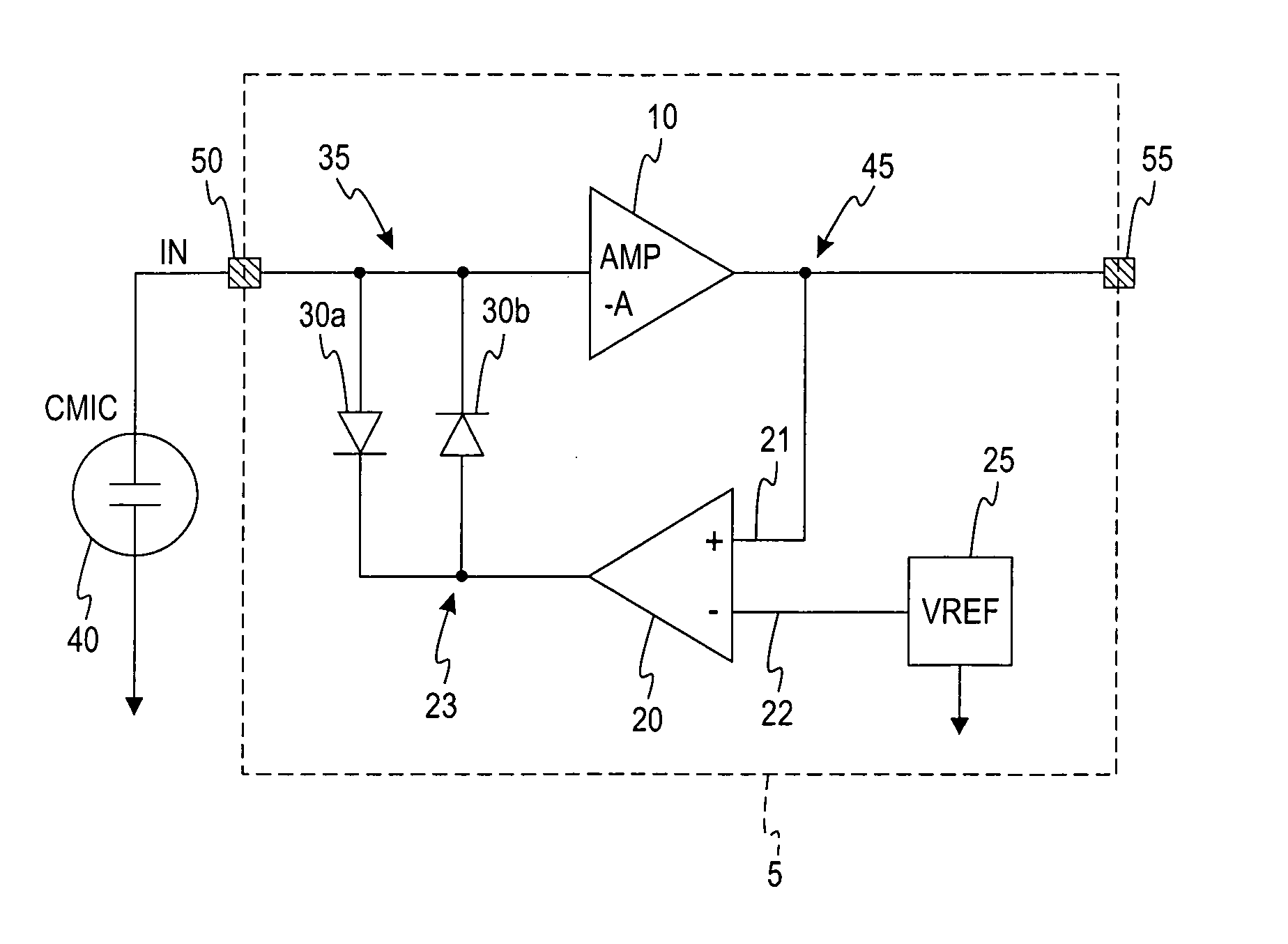
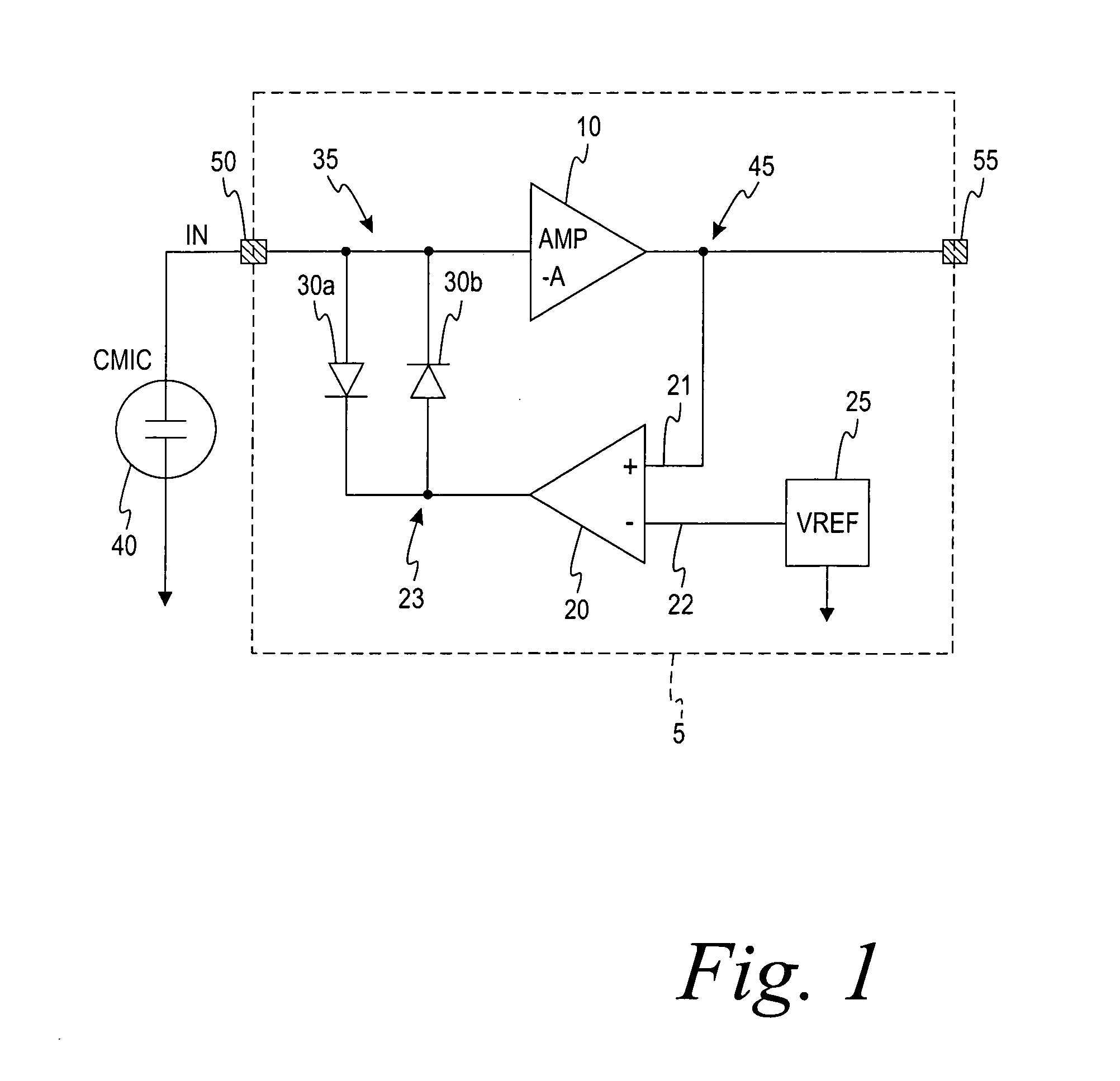
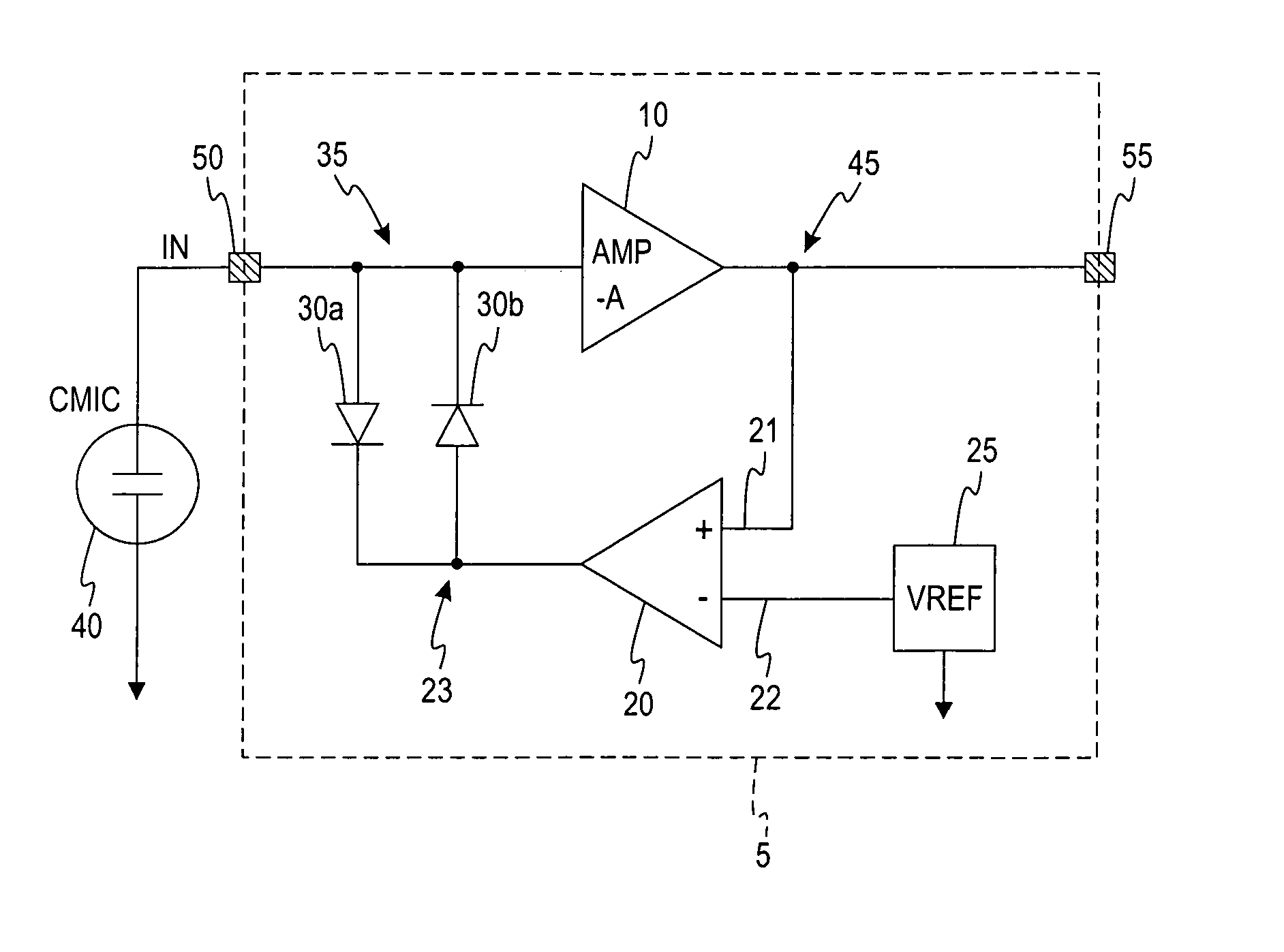
A self-powered current monitor for monitoring current in electric power systems. Various data relating to input currents may be displayed, such as current magnitude, current demand, and harmonics levels. Operating power is derived from one or more of the input currents. The power supply configuration may include a burden-reducing means to reduce the burden on input current sources during sampling of the input currents. The self-powered current monitor (1) includes a power supply section (3), input resistors (R1 and R3), an analog-to-digital converter circuit (5), a microprocessor circuit (6), a memory circuit (9), and a display circuit (7). Optional features include a burden-reducing circuit (2), input circuit protective elements (D1, D2, D3, D4, R2, and R4), an amplifier circuit (4), a user interface circuit (10), and an interface circuit (8) for communication to other equipment.
Owner:EDEL THOMAS G
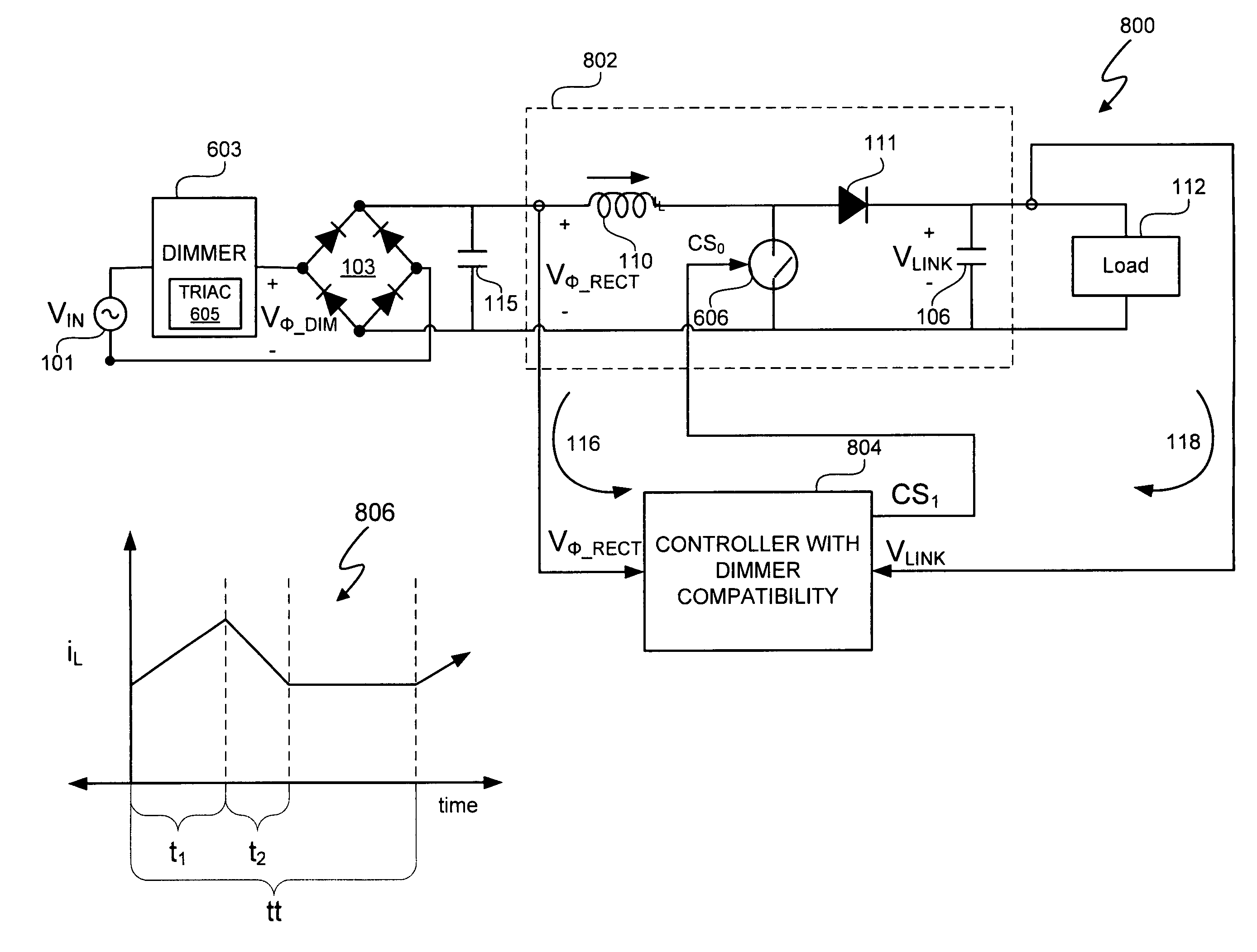
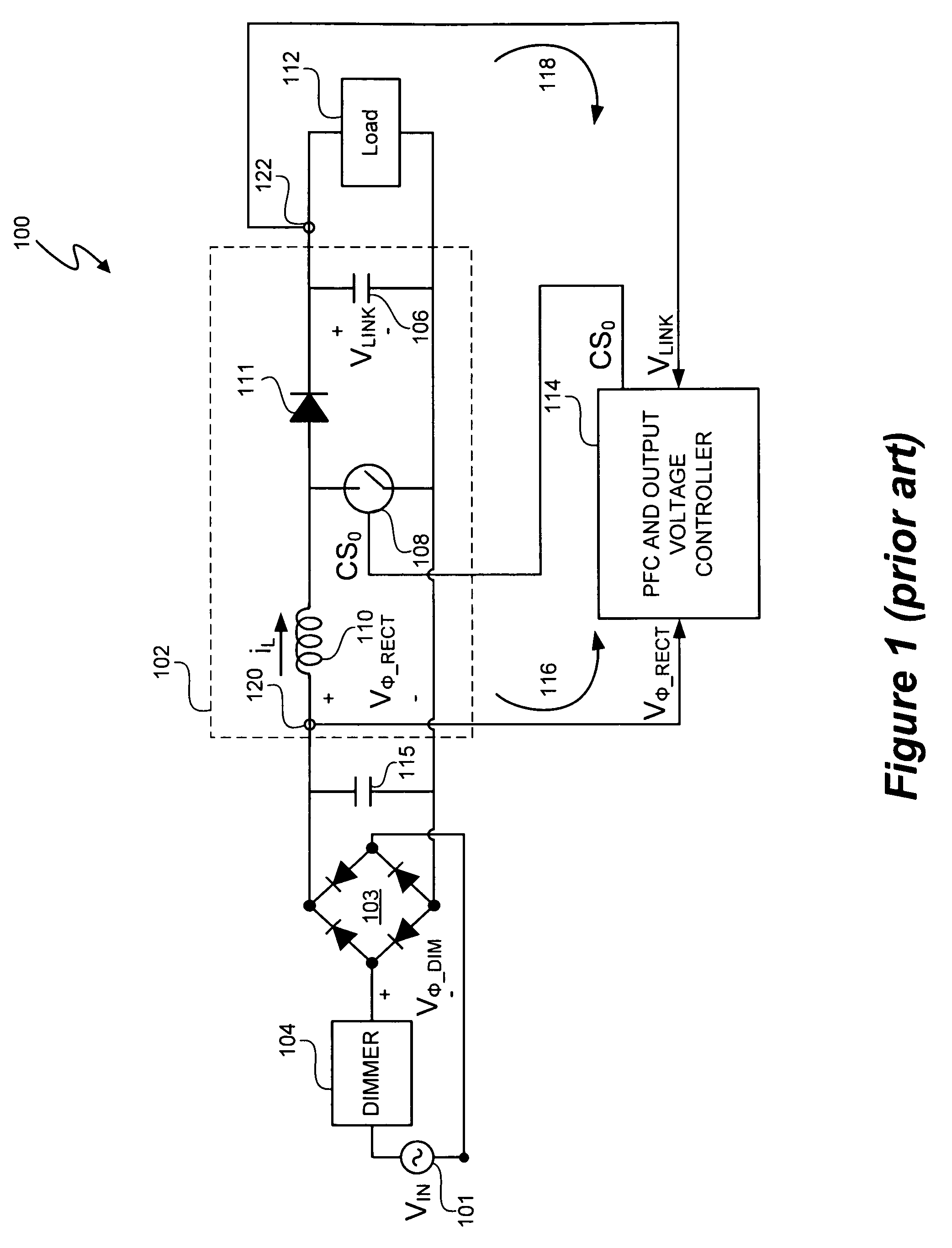
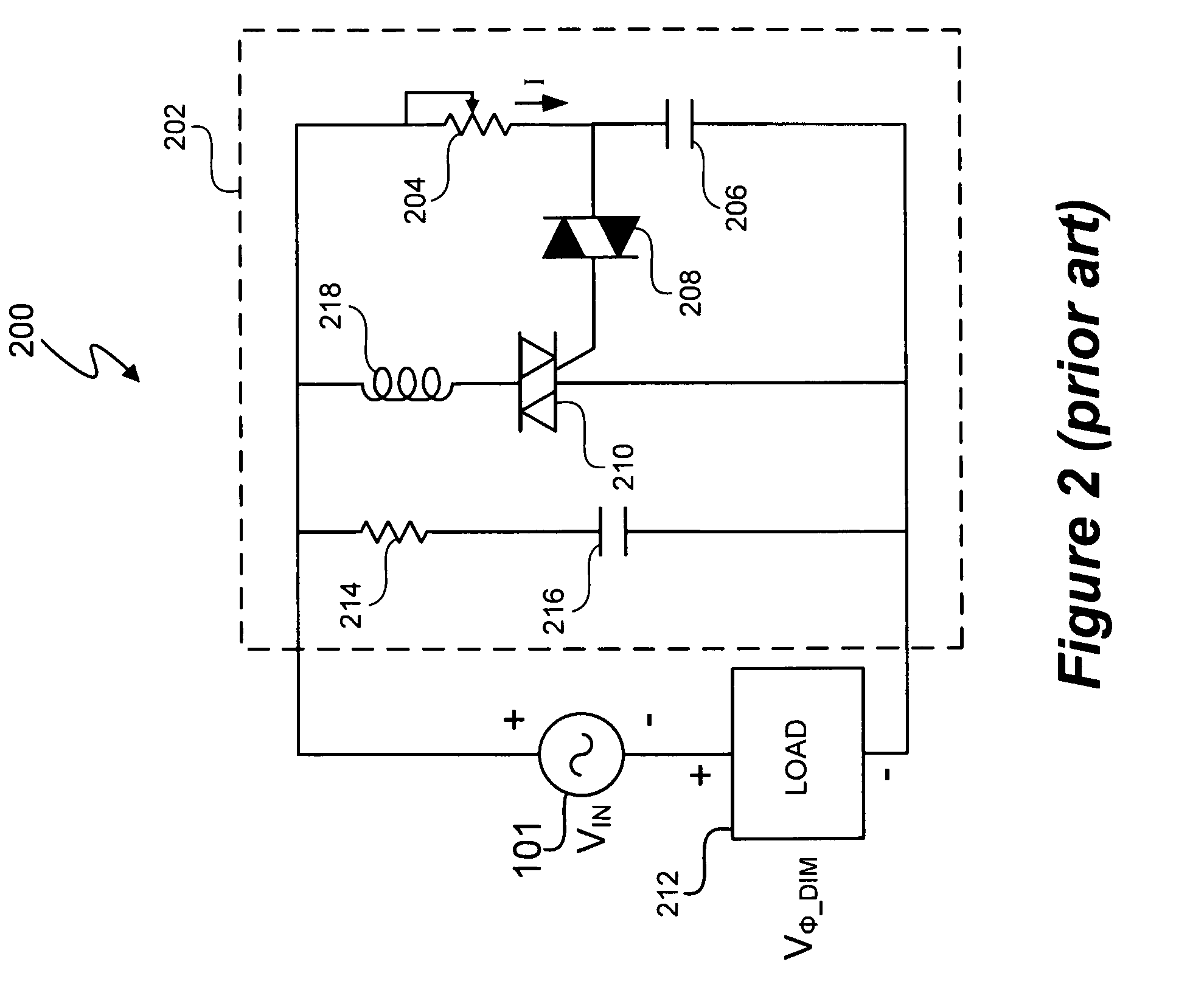
Switching power converter control with triac-based leading edge dimmer compatibility
In at least one embodiment, a controller allows triac-based dimmer to properly function and dim a load whose voltage is regulated by a switching power converter. In at least one embodiment, the switching power converter includes a switch to control voltage conversion of an input voltage to the switching power converter, wherein phase delays are introduced in the input voltage by a triac-based dimmer during a dimming period. In at least one embodiment, the controller is configured to control the switch of the switching power converter to establish an input resistance of the switching power converter during a dimming portion of the input voltage, wherein the input resistance allows the triac-based dimmer to phase modulate a supply voltage to the dimmer so that an output voltage of the dimmer has a substantially uninterrupted phase delay during each half-cycle of the supply voltage during the dimming period.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
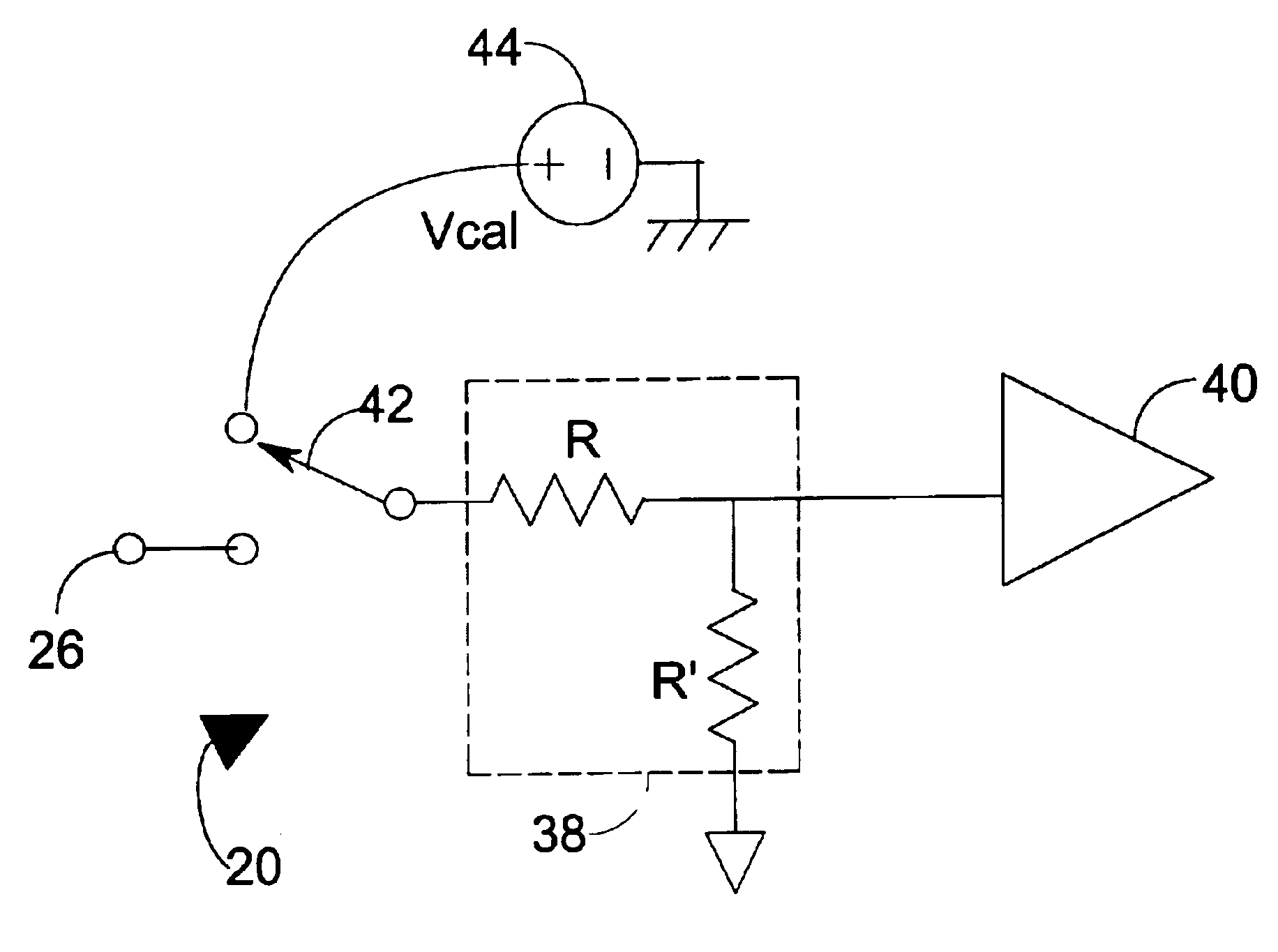
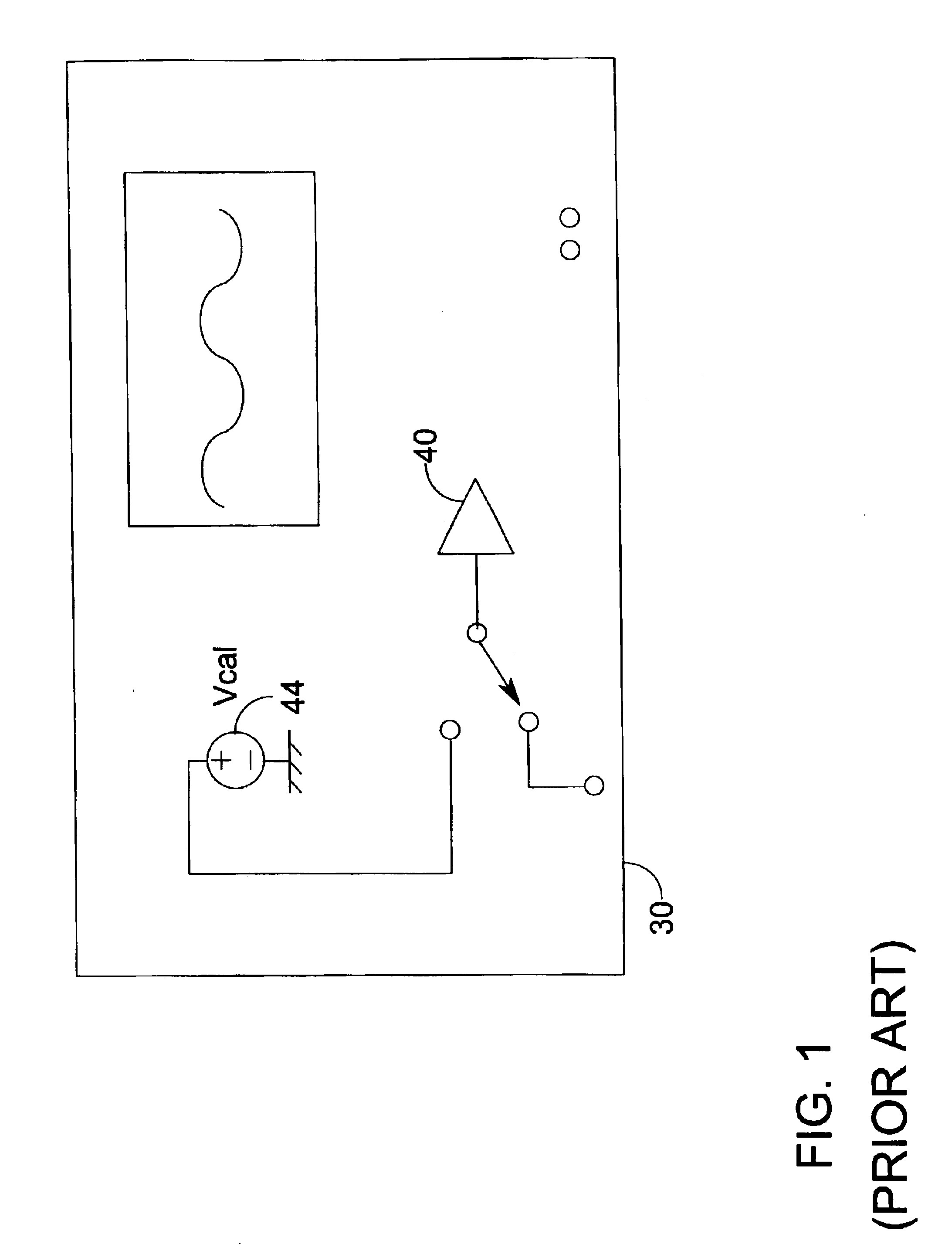
Self-calibrating electrical test probe
InactiveUS6870359B1Easy to understandElectronic circuit testingElectrical measurement instrument detailsEngineeringCalibration test
A self-calibrating test probe system of the present invention does not require probing head removal and replacement. Using the system of the present invention, the test probe and / or the entire system (including a testing instrument) may be calibrated or may self-calibrate while the probing head remains connected to an electrical component under test. The self-calibrating electrical testing probe system includes calibration circuitry including at least one input resistor, at least one relay, and at least one known calibration reference signal. If the test probe is an active test probe, the calibration circuitry may also include at least one amplifier. Each relay has a first position that provides signal access to a testing signal from an electrical component under test and a second position that provides signal access to the known calibration reference signal. Using the present invention, the error of the test probe and / or system is determined and compensated. Exemplary methods by which error compensation may be provided includes, for example, amplifying the testing signal, creating a correction table of correction values and adding an appropriate value from the correction table, or mathematically compensating.
Owner:TELEDYNE LECROY
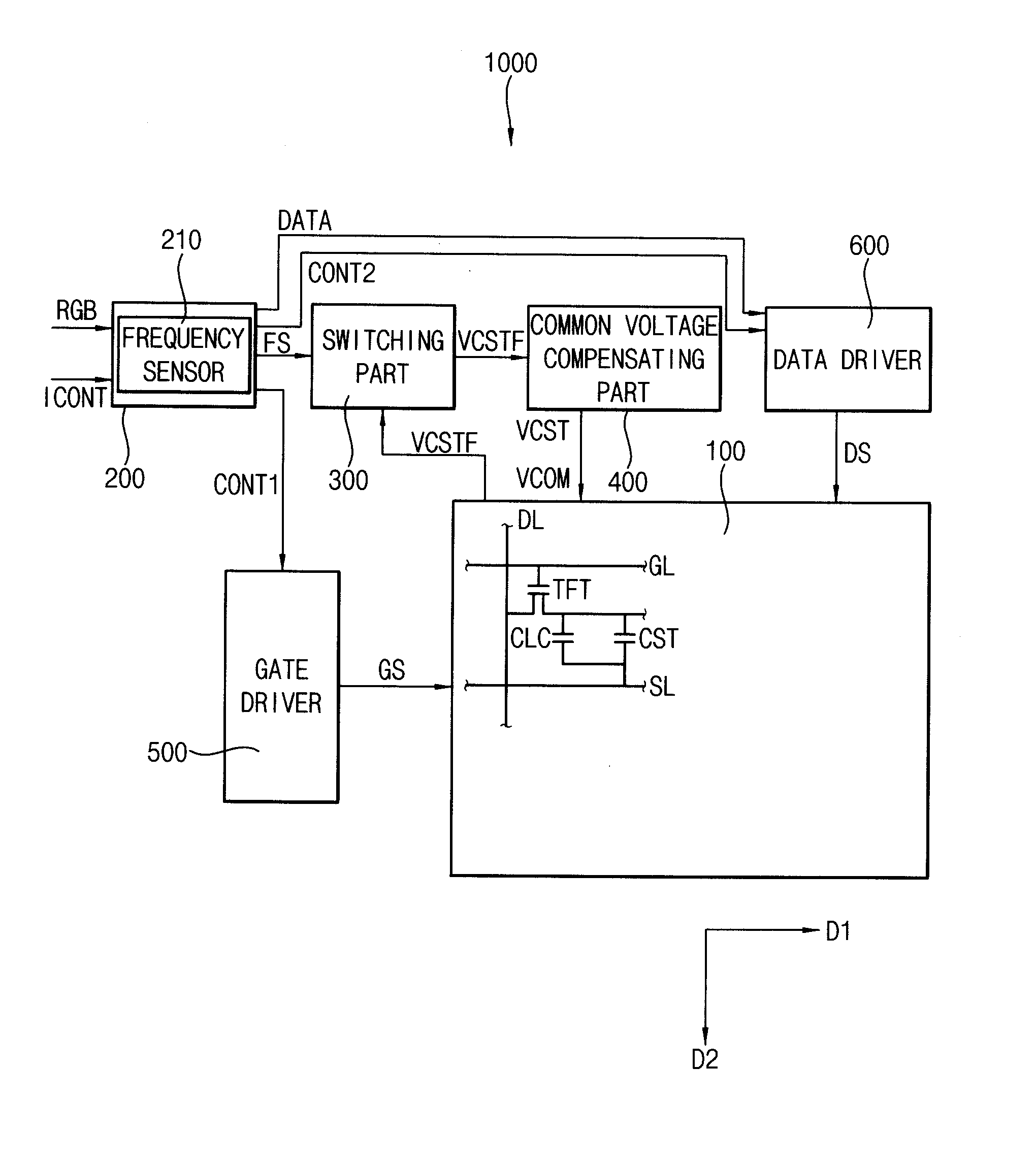
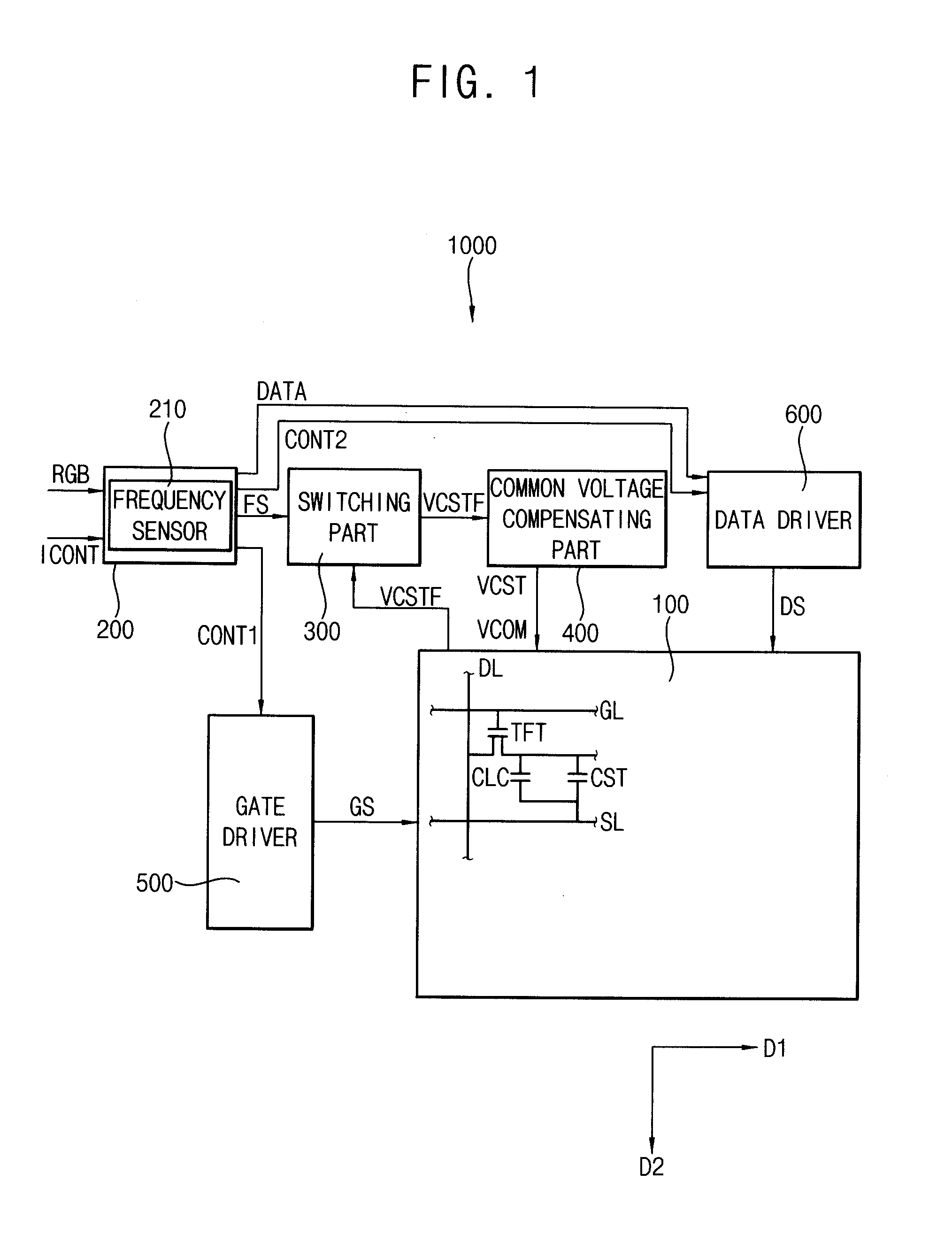
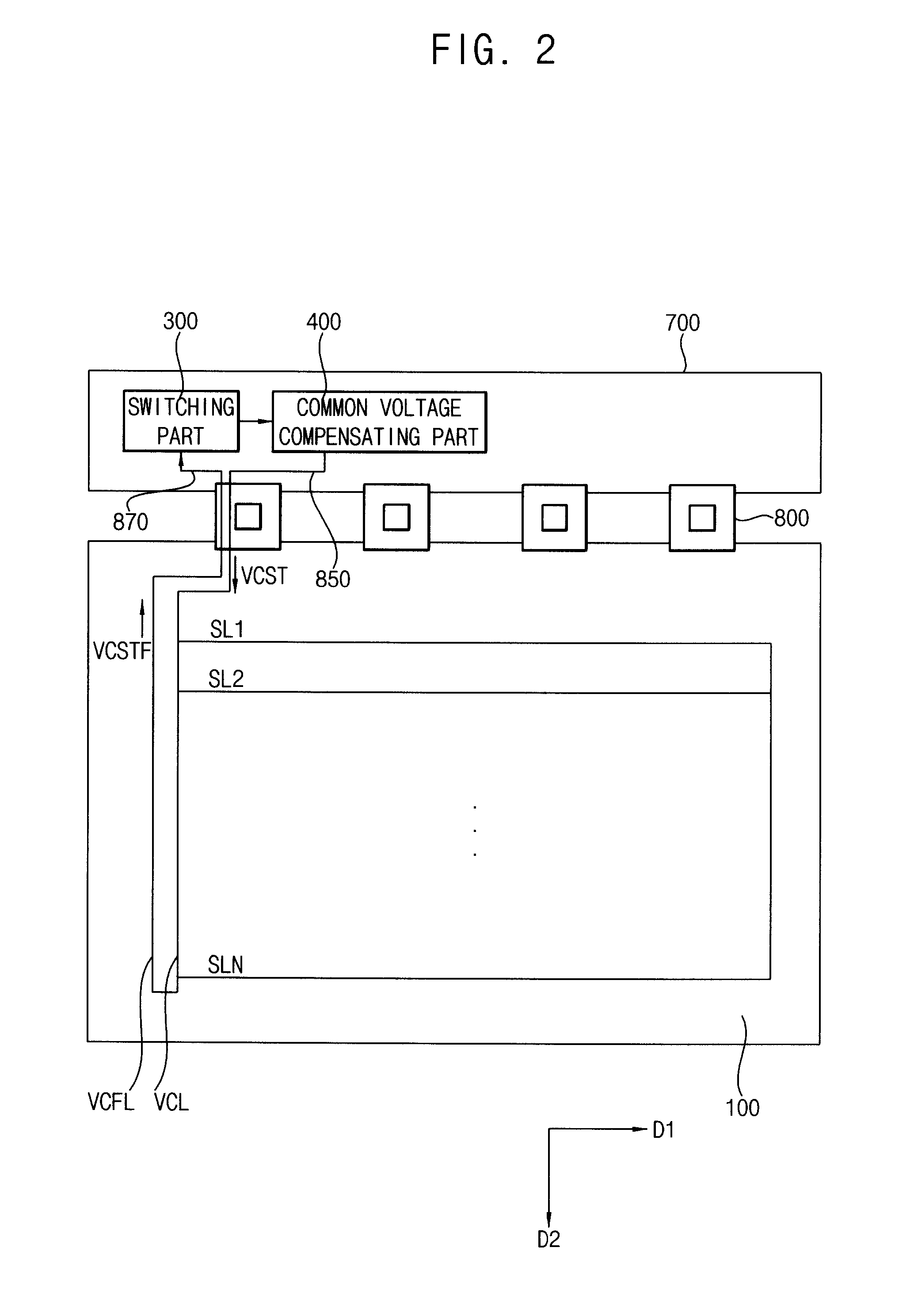
Method of driving display panel and display apparatus for performing the same
InactiveUS20120162184A1Improve display qualityLower resistanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
A method of driving a display panel includes applying a common voltage to the display panel, sensing a frequency of the display panel to generate a frequency signal, adjusting a gain of an operational amplifier based on the frequency signal, receiving a feedback common voltage from the display panel, and compensating the common voltage using an input resistor, the operational amplifier and a feedback resistor based on the feedback common voltage to apply the compensated common voltage to the display panel. The operational amplifier includes an inverting input terminal connected to the input resistor, a non-inverting input terminal to which a reference common voltage is applied and an output terminal. The feedback resistor is between the inverting input terminal and the output terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
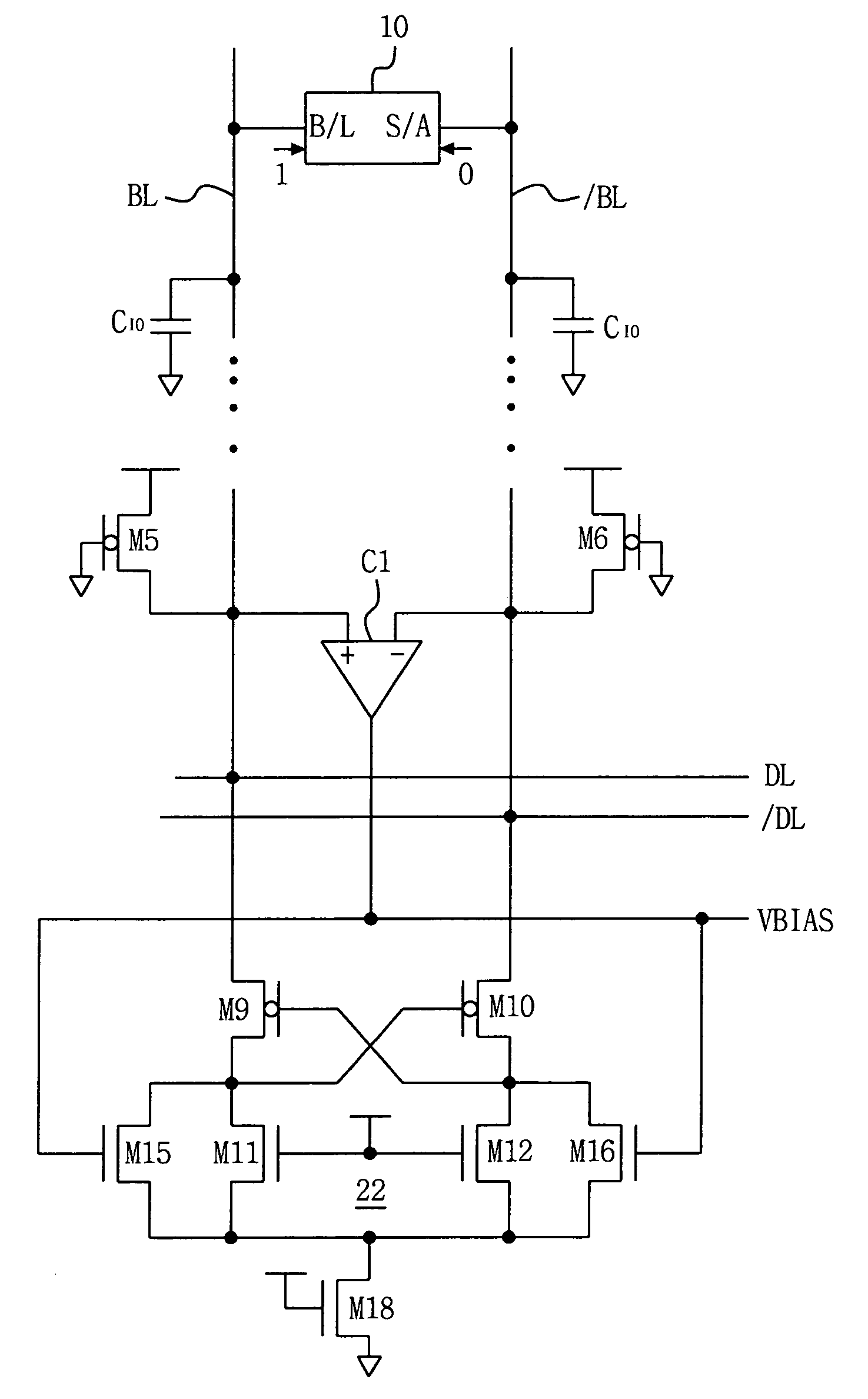
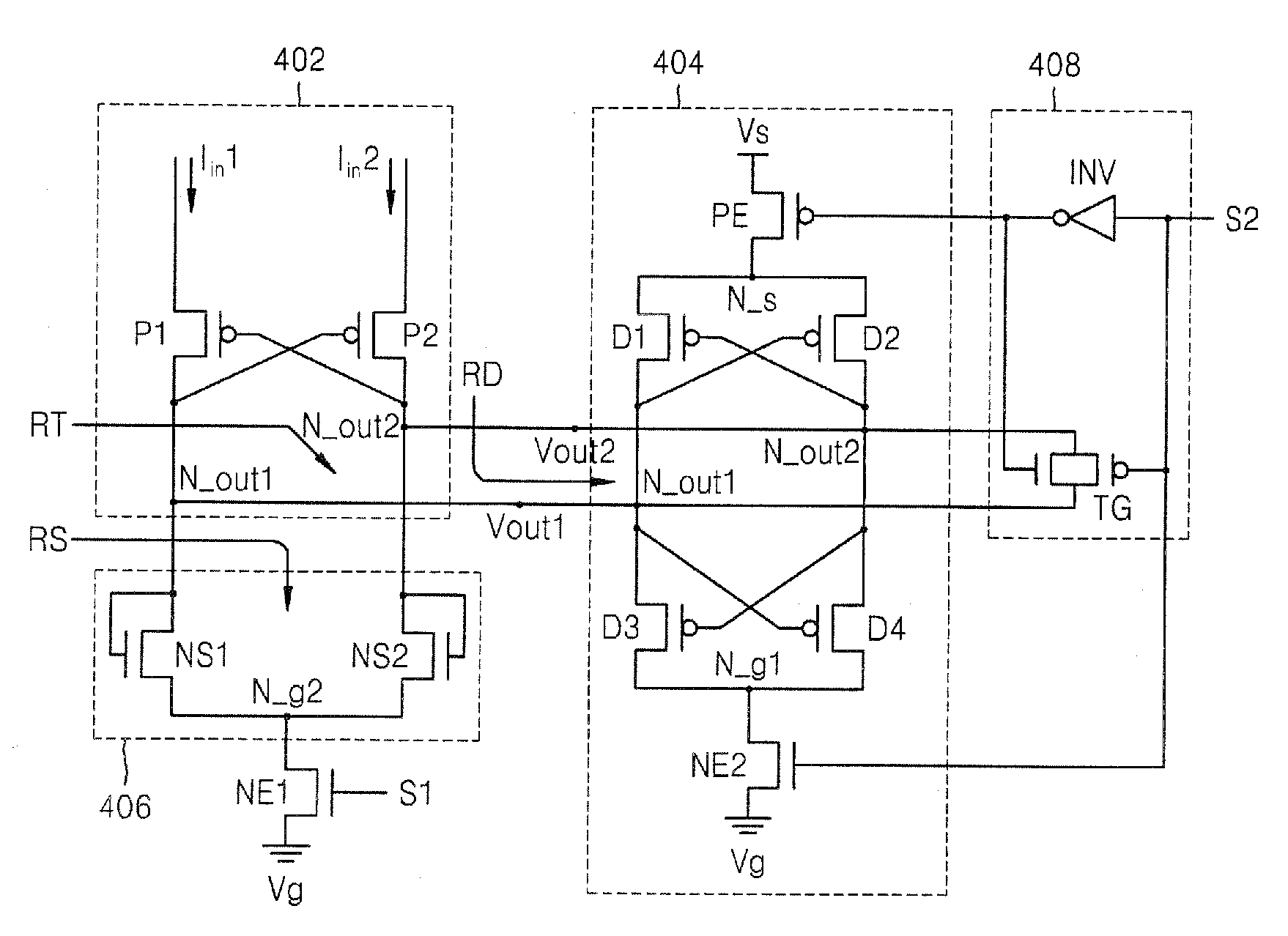
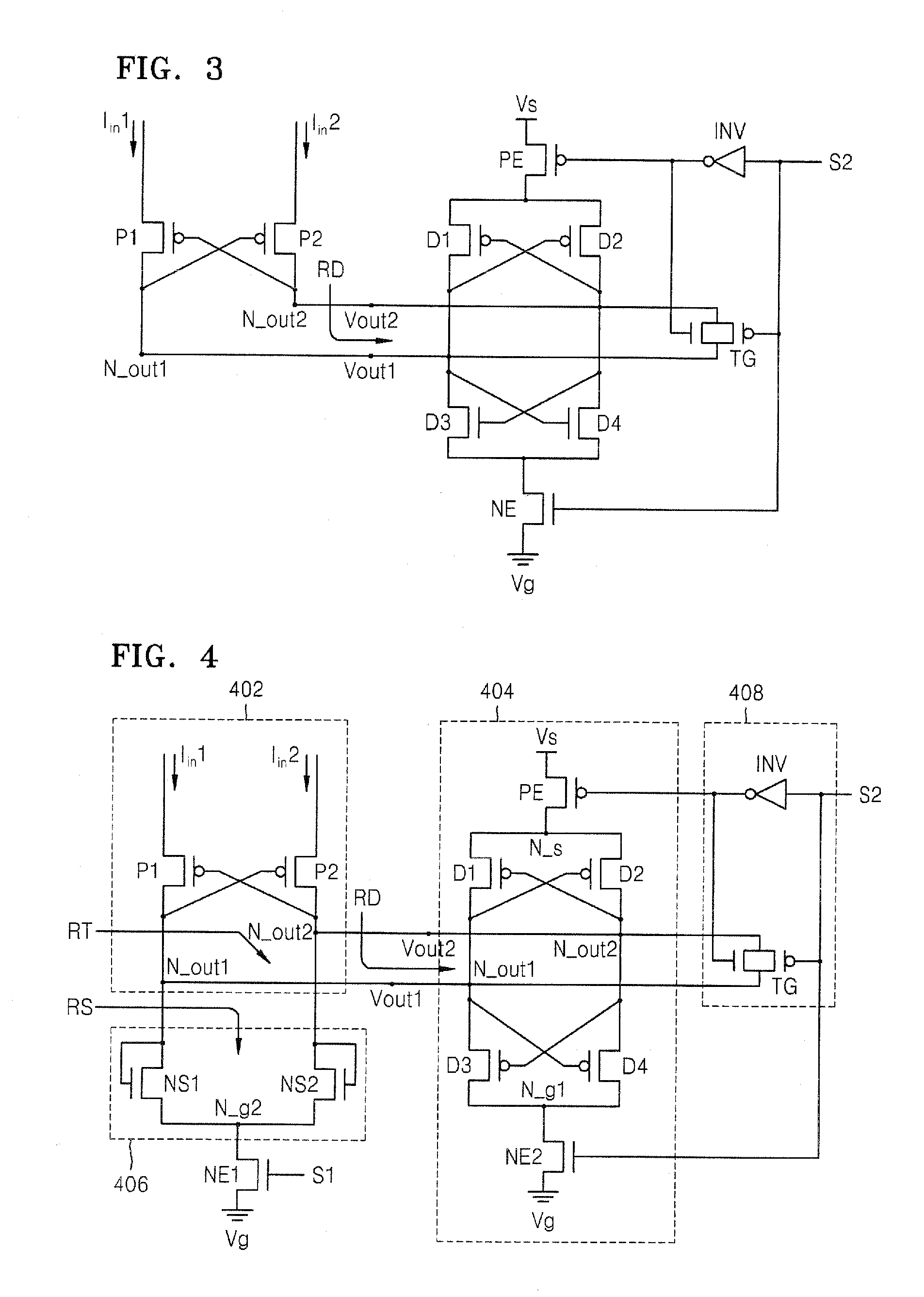
Current sense amplifier circuits having a bias voltage node for adjusting input resistance
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
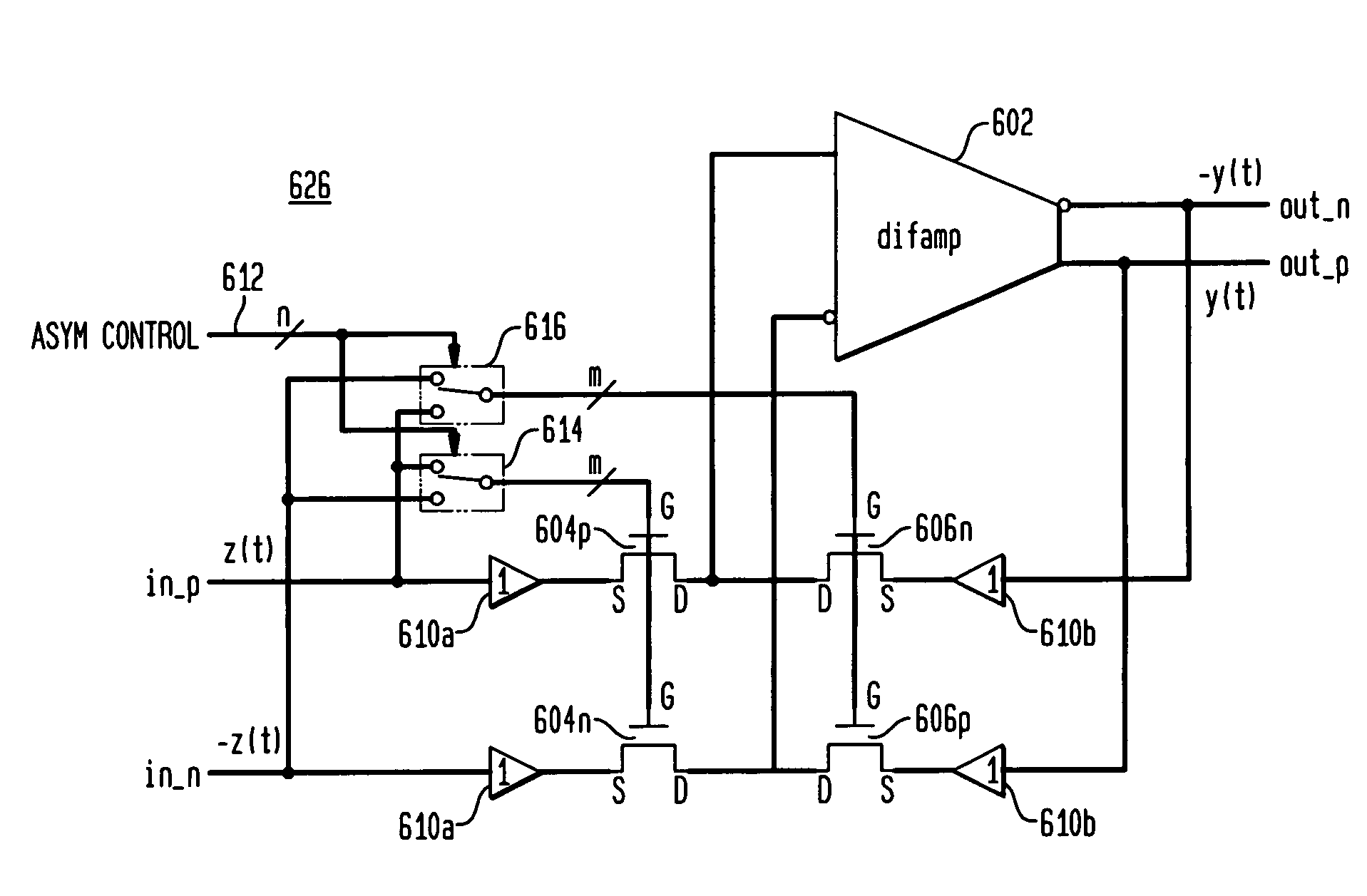
Asymmetry correction for magneto-resistive heads
ActiveUS7092180B2Accurate signalPulse automatic controlRecord information storageAudio power amplifierHemt circuits
An asymmetry-reducing circuit adapted to process an input signal having positive and negative pulses of different amplitudes and generate a corresponding balanced signal having positive and negative pulses of substantially uniform amplitudes. The asymmetry-reducing circuit balances the input signal by providing signal contributions corresponding to the second and third orders of the input signal. In a representative embodiment, the asymmetry-reducing circuit includes a differential amplifier and a plurality of arrayed MOS transistors connected to its inputs and outputs such that source-to-drain conductance of the transistors provides input and feedback resistances to the amplifier. A switch set selectively couples the fingers (gates) of the transistors to the input signal to modulate the source-to-drain conductance with said signal such that the input and feedback resistances change in a complementary manner. Advantageously, circuits of the invention can correct signal asymmetry within a relatively wide asymmetry range.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Automatic gain control amplifier for canceling direct current offset
ActiveCN102790596AThe process deviation and other factors have little influenceSimple structureGain controlCapacitanceProcess deviations
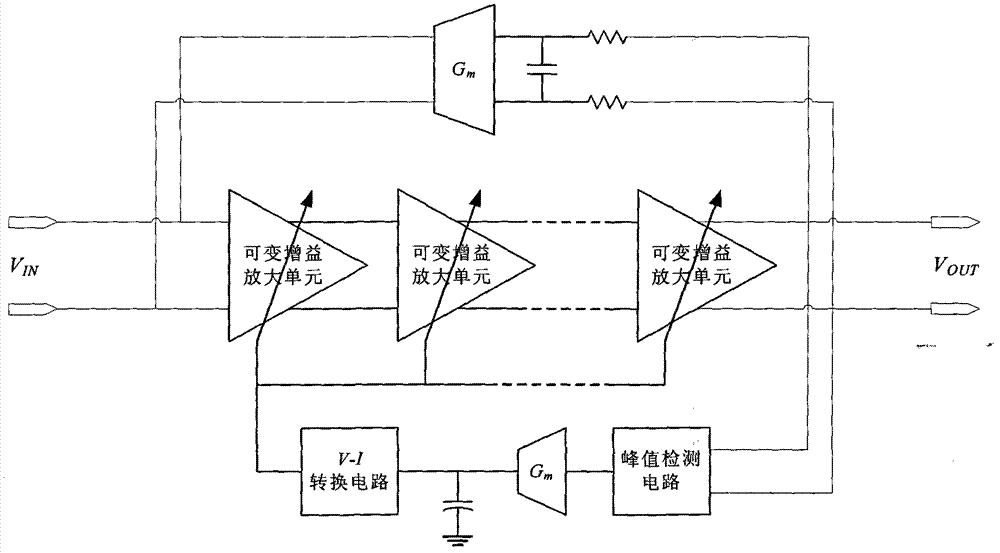
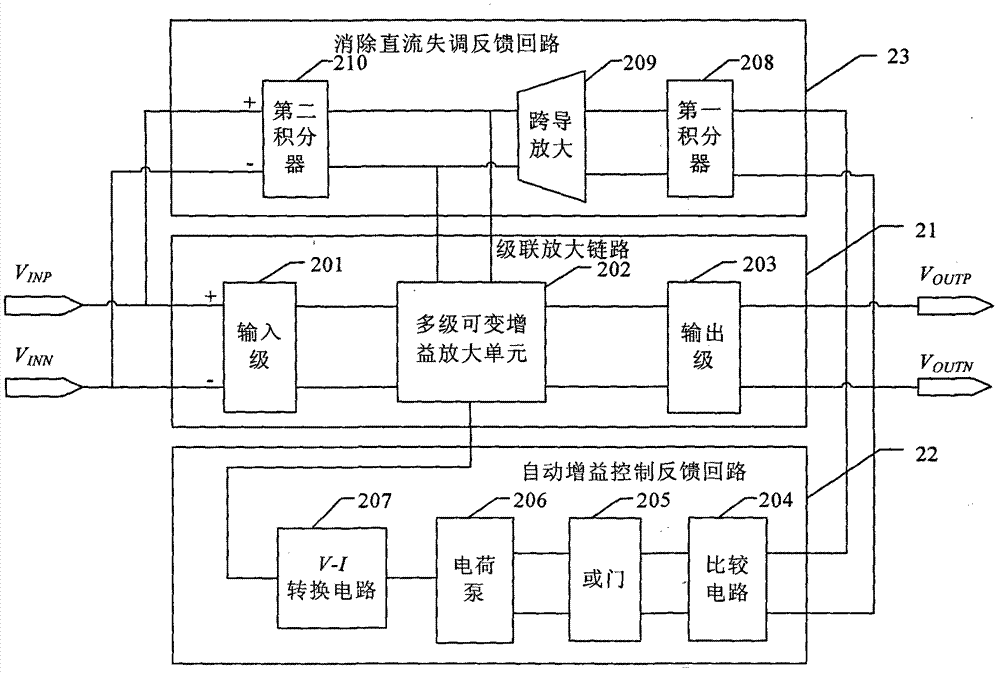
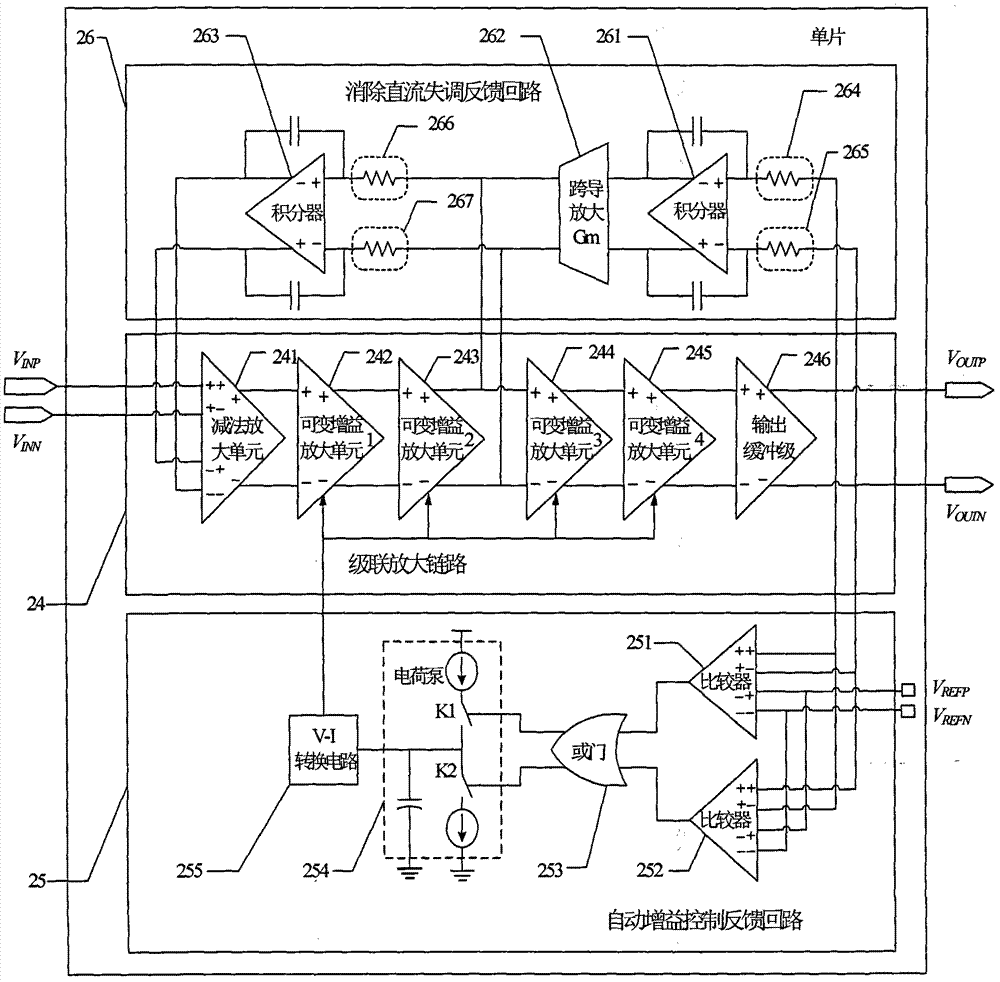
The invention discloses a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) automatic gain control amplifier for canceling direct current offset. The CMOS automatic gain control amplifier comprises a cascade amplification link, an automatic gain control feedback loop and a direct current offset canceling feedback loop. The cascade amplification link uses multistage variable gain amplification units for cascading and can achieve high gain and enlarge high gain dynamic ranges. The automatic gain control feedback loop uses a charge pump structure and has the advantages that the automatic gain control feedback loop is less influenced by process deviation and temperature deviation, is capable of accurately detecting narrow-band and wide-band signal amplitude and is suitable for achieving CMOS processes. The direct current offset canceling feedback loop uses two-stage negative feedback loops, and each of the two-stage negative feedback loops uses an integrator as low-pass negative feedback; an active device is used as an integrator input resistor, and an equivalent resistor is provided with characteristics of temperature compensation; and the automatic gain control amplifier for canceling the direct current offset is capable of effectively canceling the direct current offset superposed by a preceding stage circuit and the direct current offset of the amplification link and is provided with a lower high pass corner frequency and a higher integrated level, and the automatic gain control amplifier for canceling the direct current offset is small in low-frequency signal loss and requires no off-chip passive devices (high value resistors or capacitors and the like). The automatic gain control amplifier is applicable to wireless communication receivers with zero intermediate frequency structures in the CMOS processes.
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
Amplifier circuit for capacitive transducers
ActiveUS20050151589A1Load minimizationLow noise amplification/bufferingAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierEngineering
An amplifier circuit for capacitive transducers, such as miniature electret or condenser microphones, wherein the amplifier circuit comprises bias control means adapted to improve settling of the amplifier circuit. Another aspect of the invention relates to a miniature condenser microphone and a monolithic integrated circuit comprising an amplifier circuit according to the present invention. The present invention provides amplifier circuits of improved performance by resolving traditionally conflicting requirements of maintaining a large input resistance of the amplifier circuit to optimize its noise performance and provide fast settling of the amplifier circuit.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Amplifier circuit for capacitive transducers
ActiveUS7634096B2Load minimizationLow noise amplification/bufferingAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierCondenser microphone
An amplifier circuit for capacitive transducers, such as miniature electret or condenser microphones, wherein the amplifier circuit comprises bias control means adapted to improve settling of the amplifier circuit. Another aspect of the invention relates to a miniature condenser microphone and a monolithic integrated circuit comprising an amplifier circuit according to the present invention. The present invention provides amplifier circuits of improved performance by resolving traditionally conflicting requirements of maintaining a large input resistance of the amplifier circuit to optimize its noise performance and provide fast settling of the amplifier circuit.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
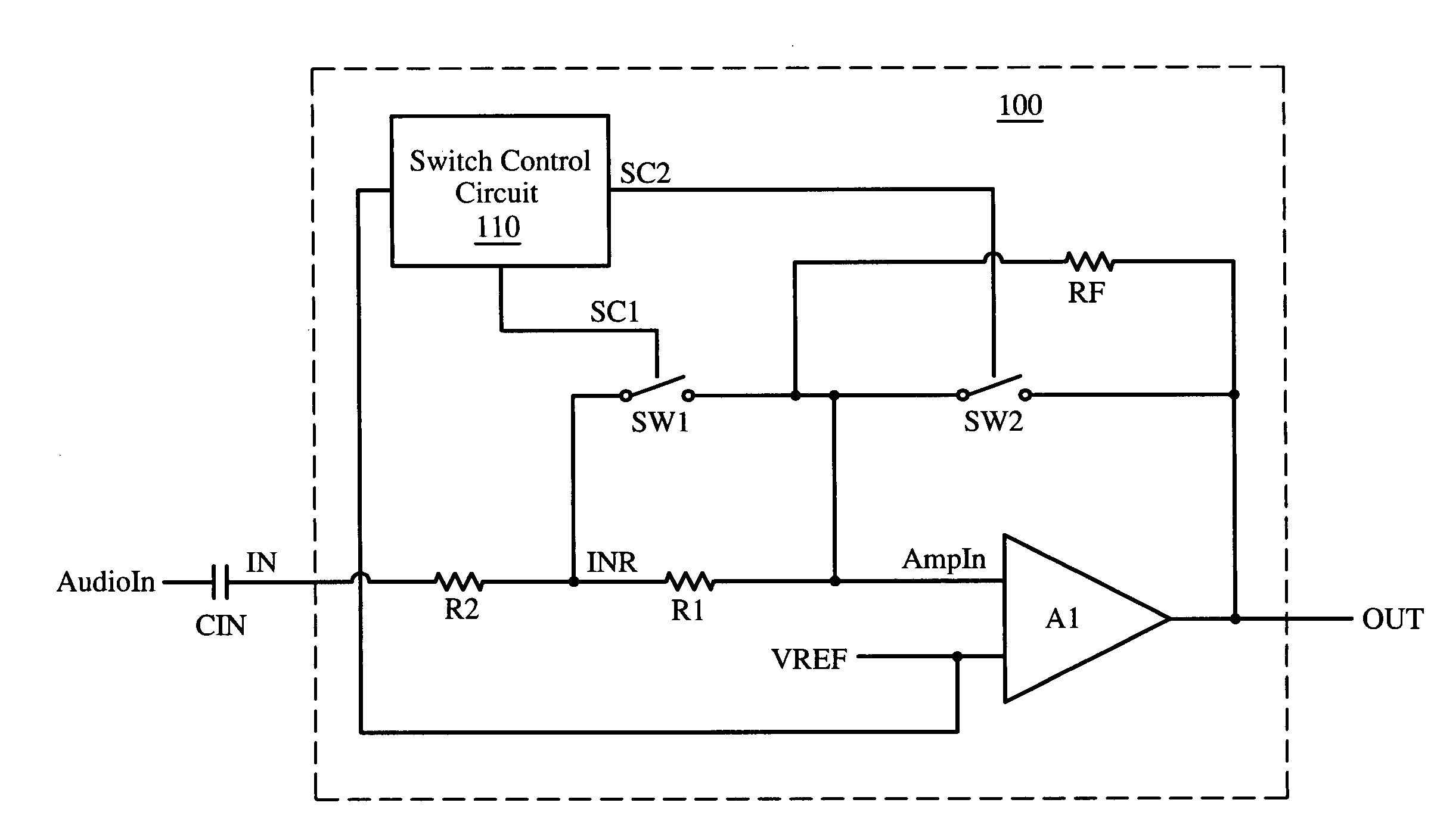
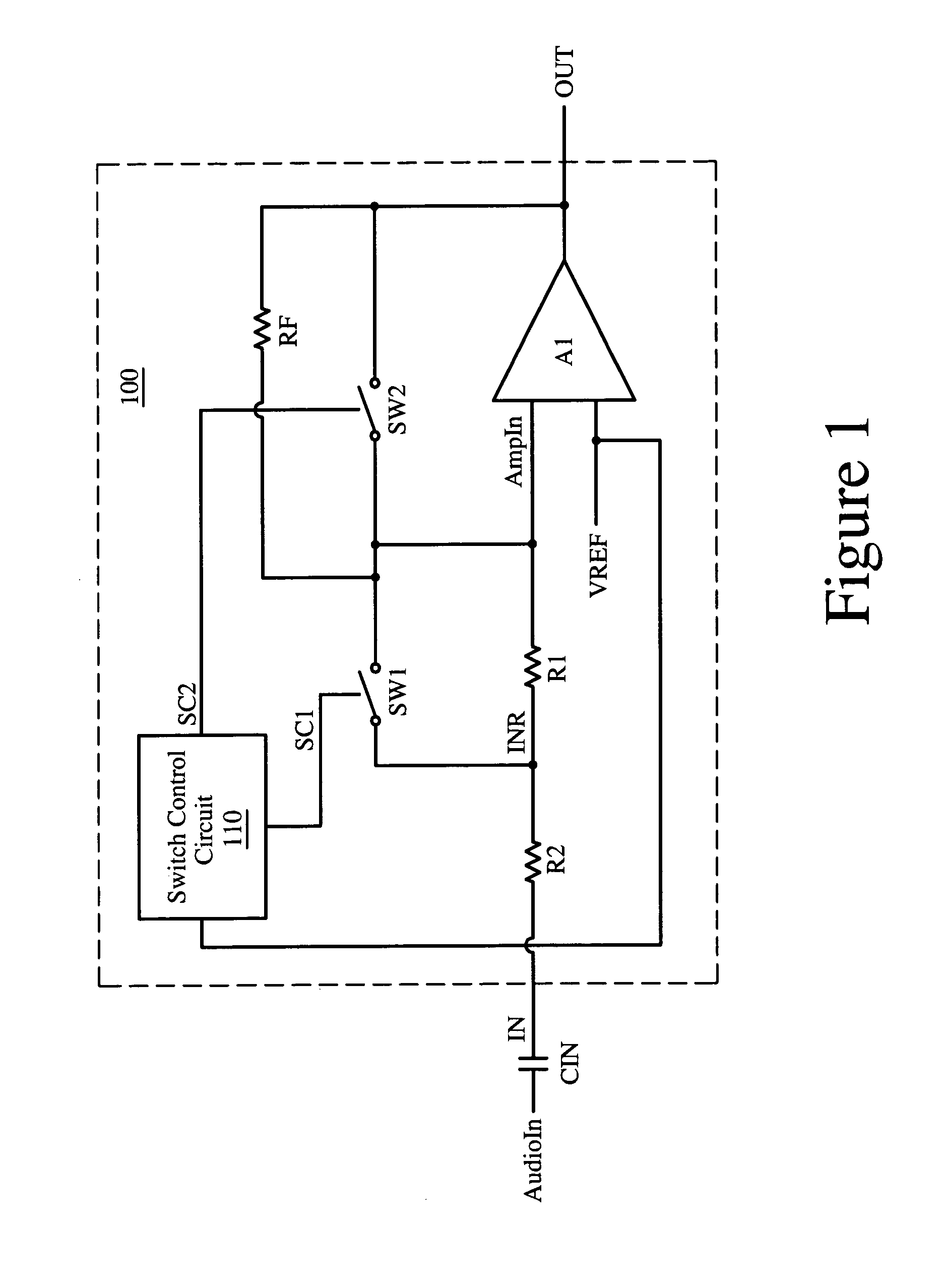
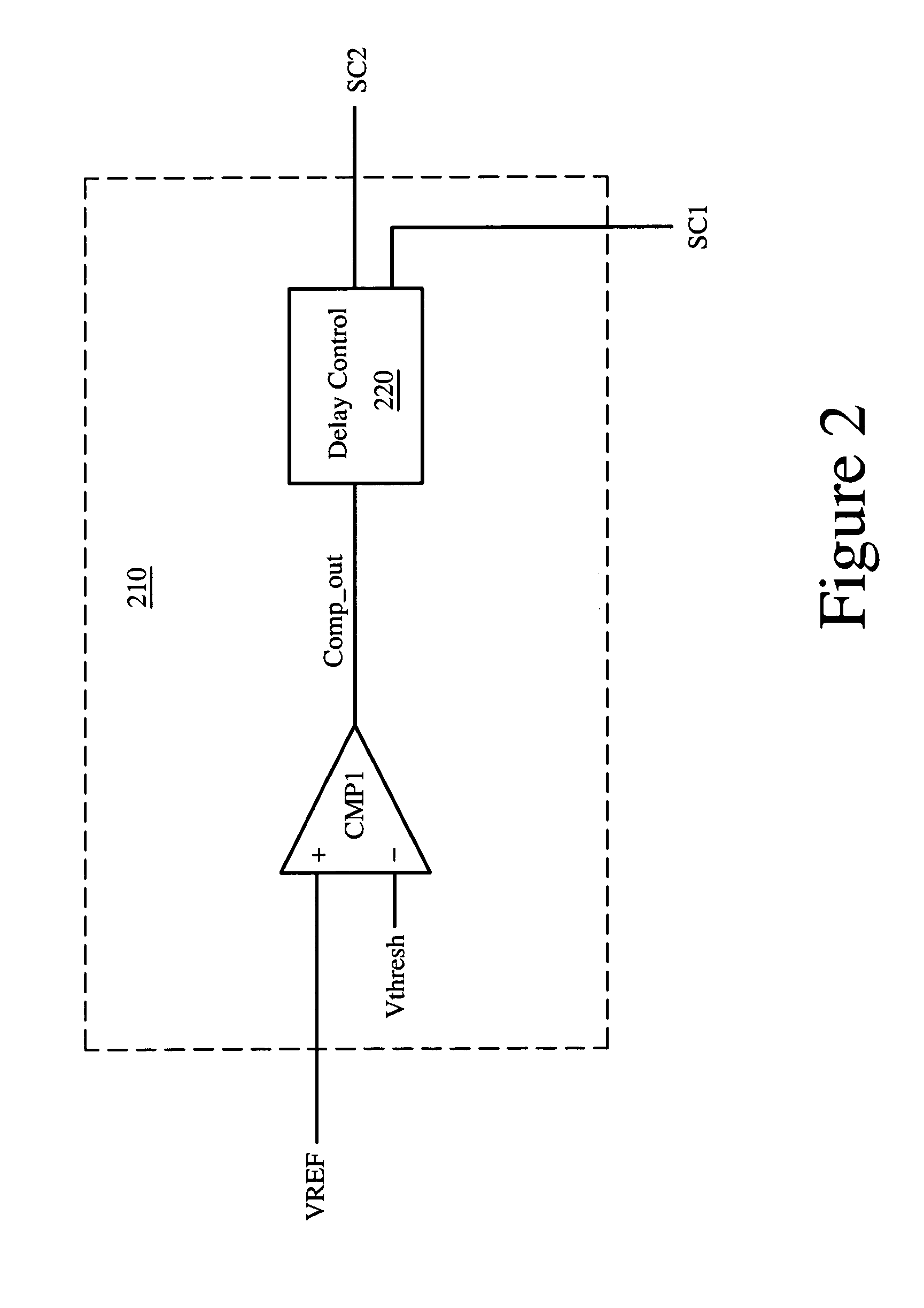
Apparatus and method for pop-and-click suppression with fast turn-on time
ActiveUS7164312B1Amplifier modifications to raise efficiencyTransmission noise suppressionCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A circuit for audio amplification includes an amplifier and a first input resistor. The amplifier is arranged to provide an amplifier output signal that is based, in part, on a capacitively-coupled audio input signal. The capacitively-coupled audio input signal is based, in part, on an input RC value. The input RC value is given by the input capacitance times the input resistance. The input resistance is reduced during the turn-on in order to achieve a fast turn-on time with minimal pop-and-click noise. Also, the input resistance is increased to its normal value after the turn-on so that full audio fidelity is substantially maintained during normal operation.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
System and method for acquiring voltages and measuring voltage into and electrical service using a non-active current transformer
InactiveUS7075288B2Accurate measurementWide input voltage rangeMeasurement using dc-ac conversionMaterial nanotechnologyEngineeringConductor Coil
A voltage acquisition circuit for sensing input voltage signals in each phase of an electrical service includes a non-active current transformer configuration that is operable over a wide input voltage range. The current transformer configuration includes primary and secondary windings, an input resistor and a burden resistor across which an output voltage is defined. The input resistor may be relatively large, such as on the order of about one MΩ and the transformer core may have a nanocrystalline core characterized by predictable magnetic properties versus varied transformer flux levels. This operational predictability facilitates phase compensation via digital filtering or otherwise for any phase shift induced between input and output voltages of the current transformer.
Owner:ITRON
High linearity and low noise CMOS mixer and signal mixing method
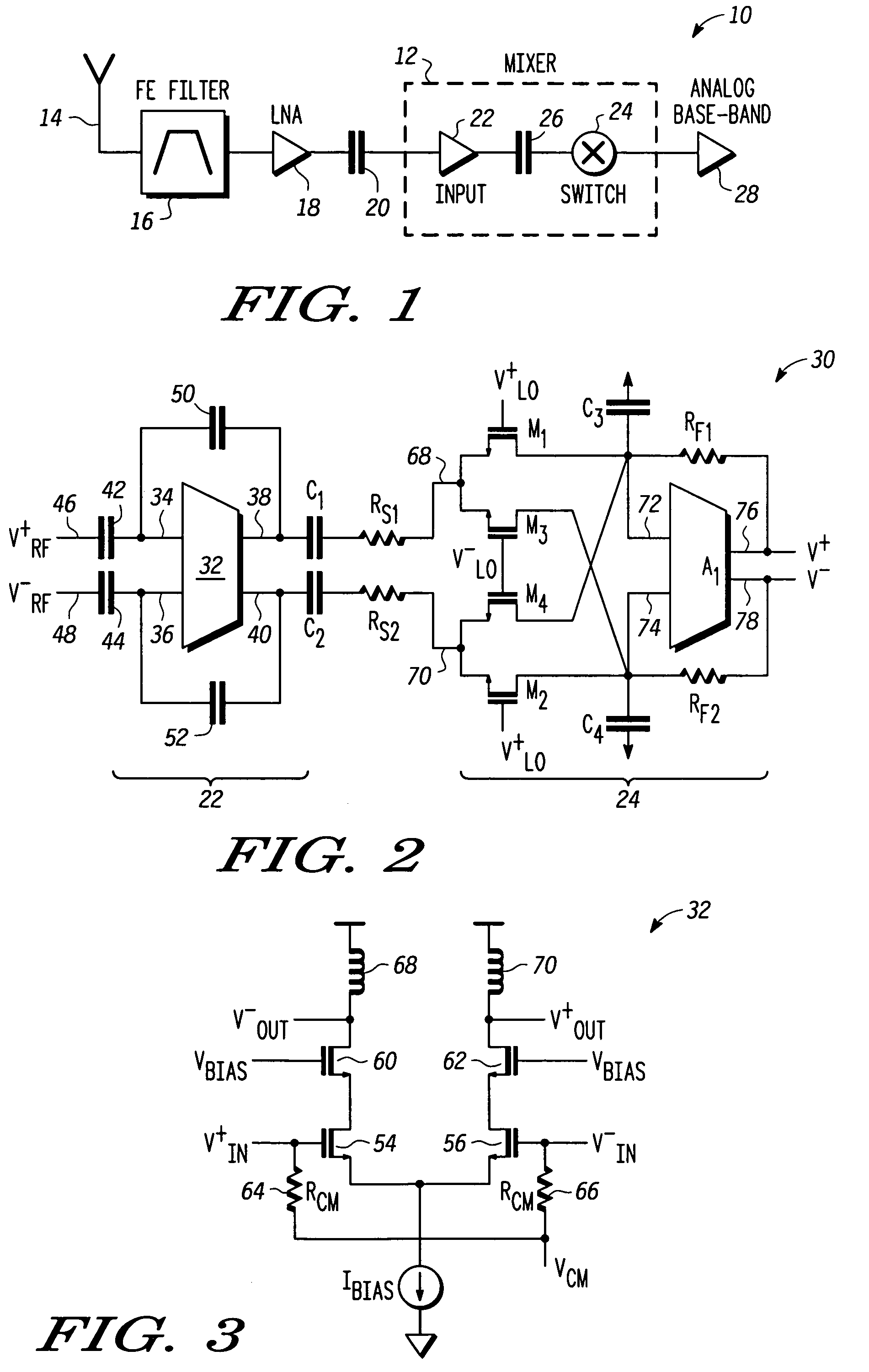
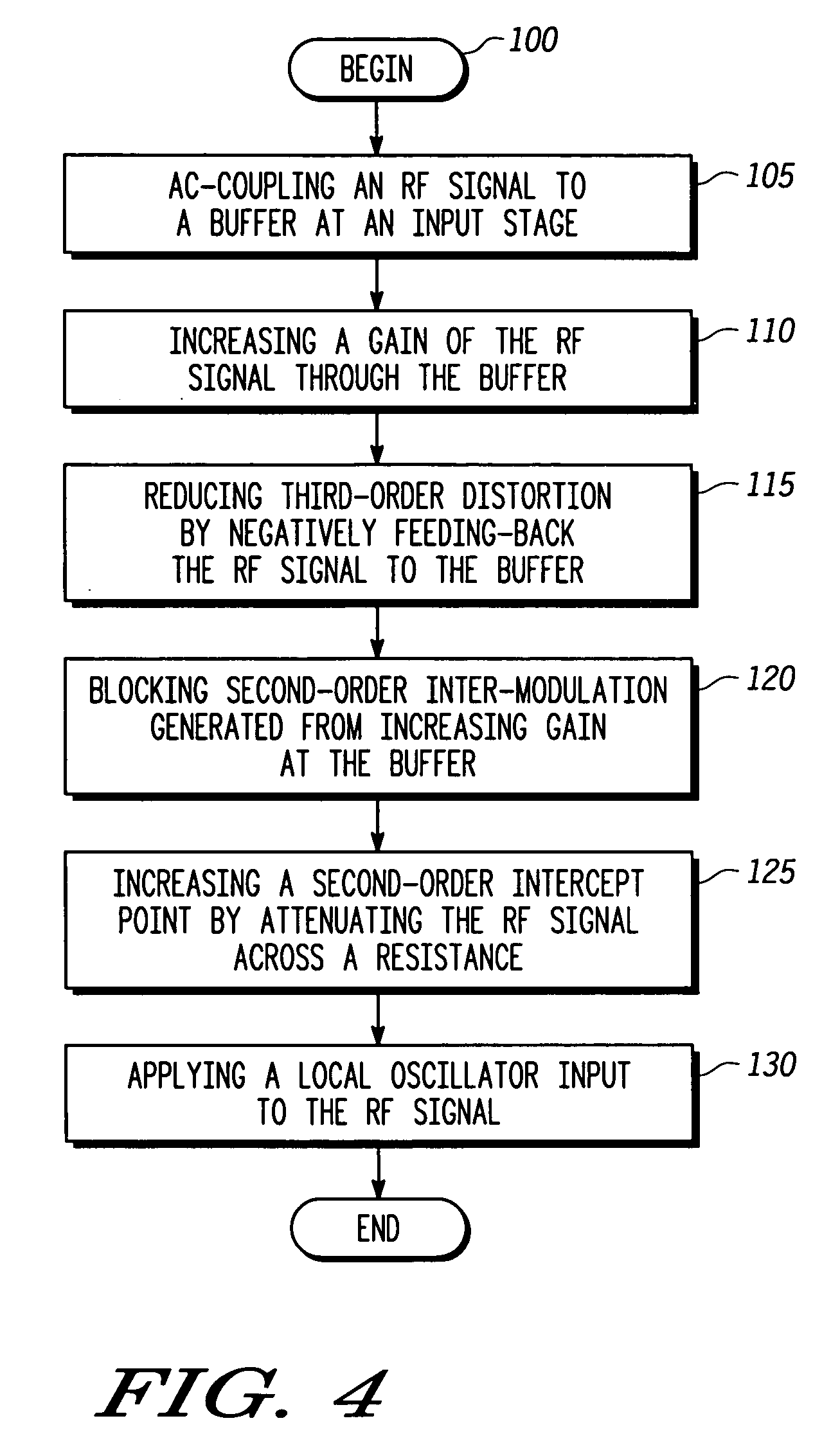
ActiveUS7177616B2Improve linearityReduce noiseModulation transferenceRadio transmissionLow noiseNegative feedback
Method and apparatus are provided for high linearity and low noise communication signal mixing. The apparatus includes a high linearity low noise mixer having an input stage coupled to a switch stage by a series-coupled blocking capacitance and input resistance. The input stage includes a buffer with negative feedback, and the switch stage includes a transistor based switch network connected to an amplifier that has feedback resistance and shunting capacitance. The method includes AC coupling an RF signal, increasing a gain of the RF signal, reducing third-order distortion by negatively feeding-back the RF signal, blocking IM2 generated from said gain increasing step, increasing a second-order input intercept point (IIP2) by attenuating the RF signal across a resistance, and applying a local oscillator input to the RF signal.
Owner:APPLE INC
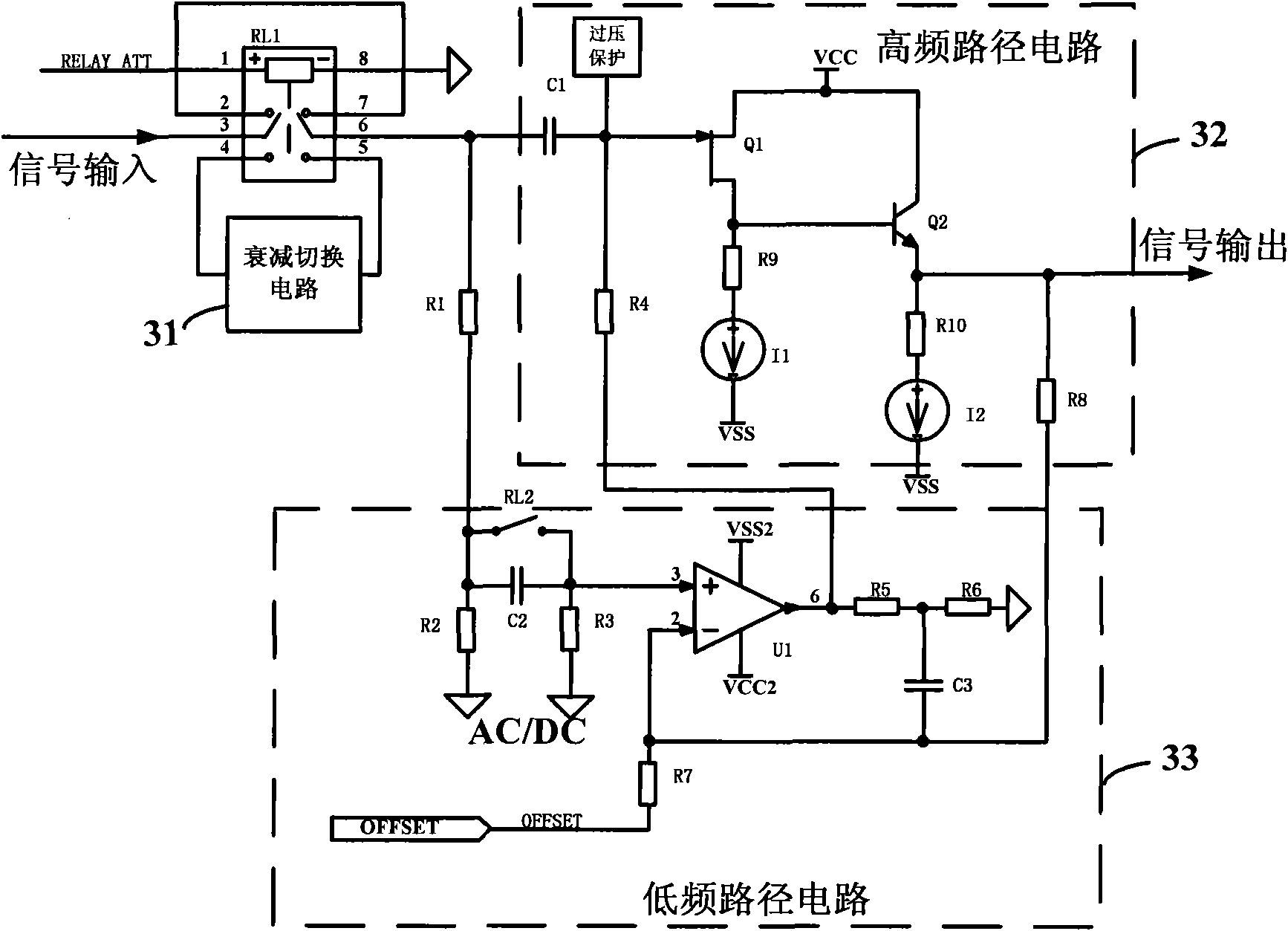
Oscilloscope with high-frequency path and low-frequency path separation circuit
The invention discloses an oscilloscope with a high-frequency path and low-frequency path separation circuit, comprising a high-frequency path and low-frequency path separation circuit. The high-frequency path and low-frequency path separation circuit comprises an attenuation switch circuit, a high-frequency path circuit and a low-frequency path circuit, wherein the input signal of the oscilloscope enters the attenuation switch circuit and is switched by a double-pole-double-throw switch in the attenuation switch circuit; then the input signal enters the high-frequency path circuit and the low-frequency path circuit; the input signal of the oscilloscope is output respectively from the high-frequency path circuit and the low-frequency path, the ratio of a high-frequency output signal and a high-frequency input signal is 1:1, the ratio of a low-frequency output signal and a low-frequency input signal is 1:1, i.e. the ratio of signal input and signal output is 1:1 follow; and thus, the separation process of high-frequency components and low-frequency components is finished. The invention realizes an oscilloscope input circuit with high input resistance, low input capacitance, high DC(Direct Current) precision, high input pressurization, big bandwidth, low noise, large signal input shift range and good frequency response flatness.
Owner:RIGOL
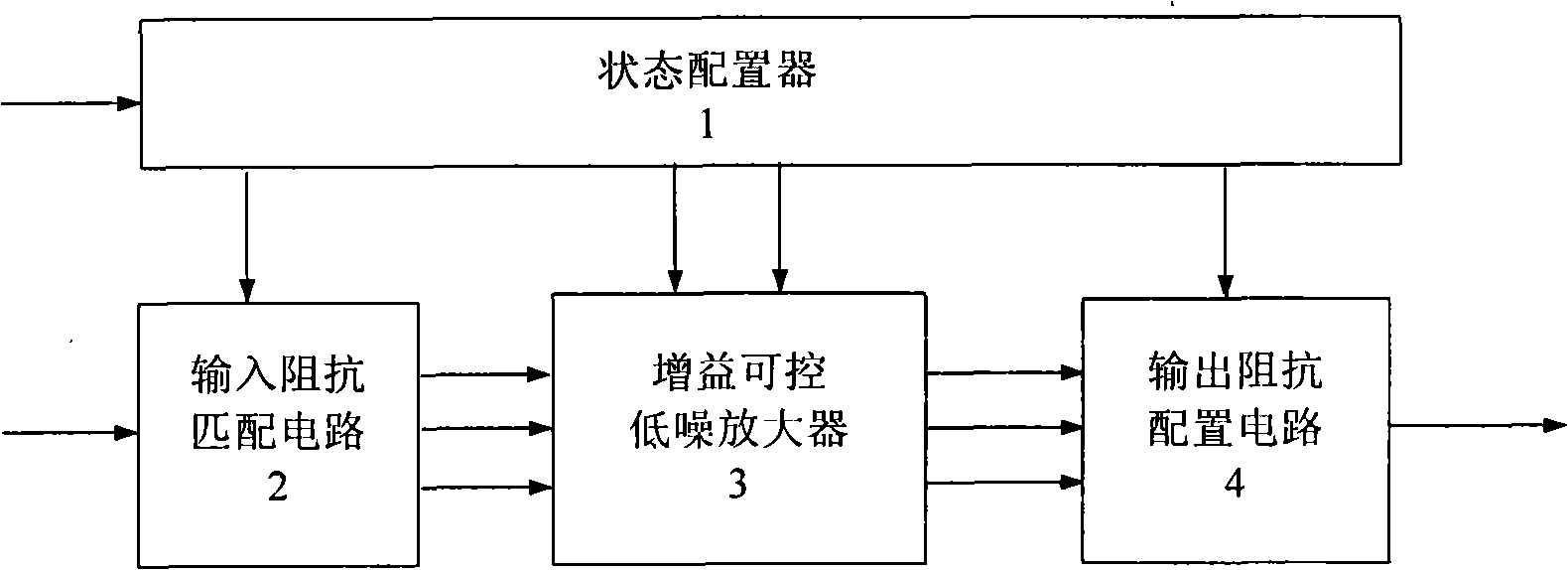
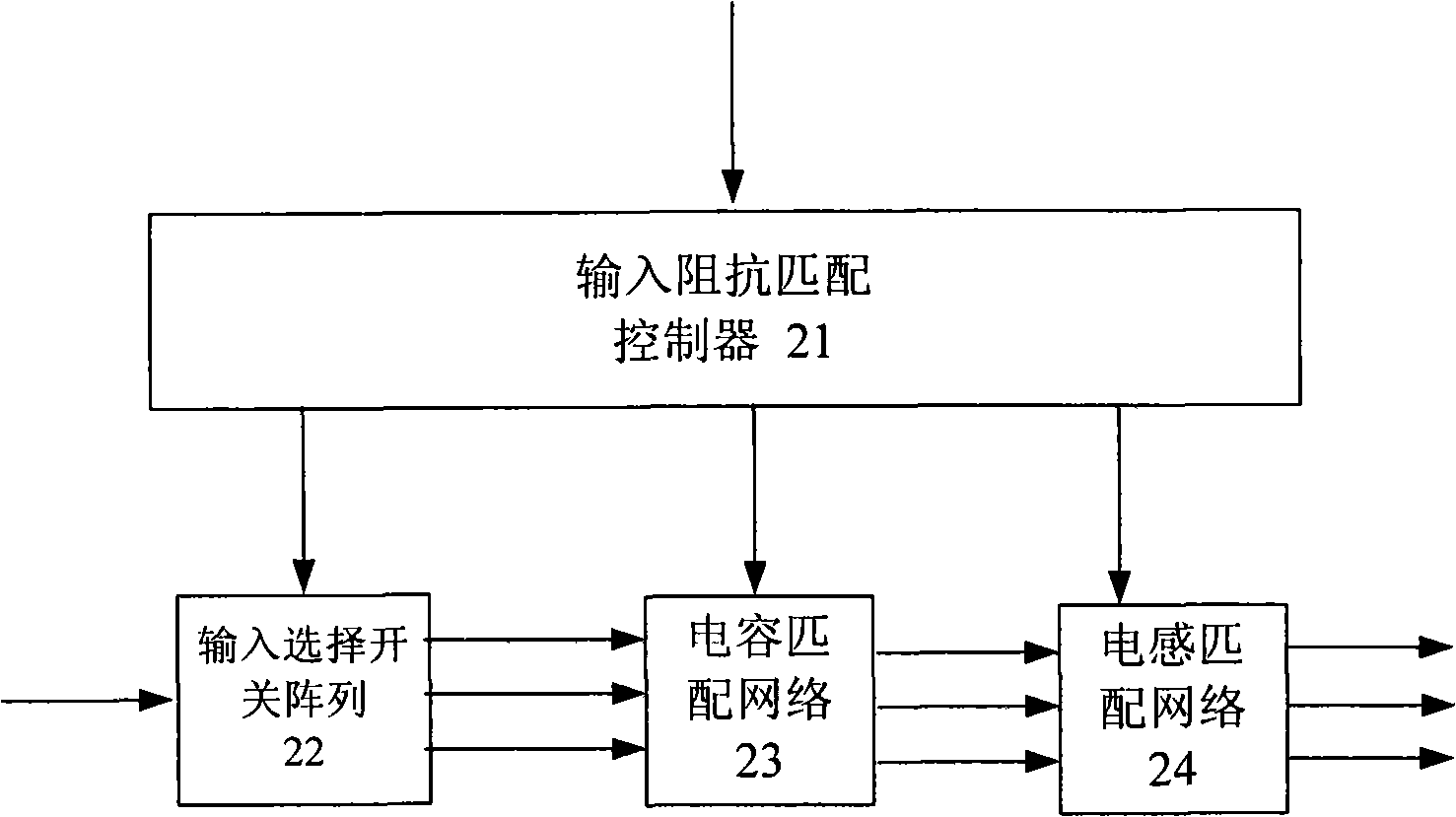
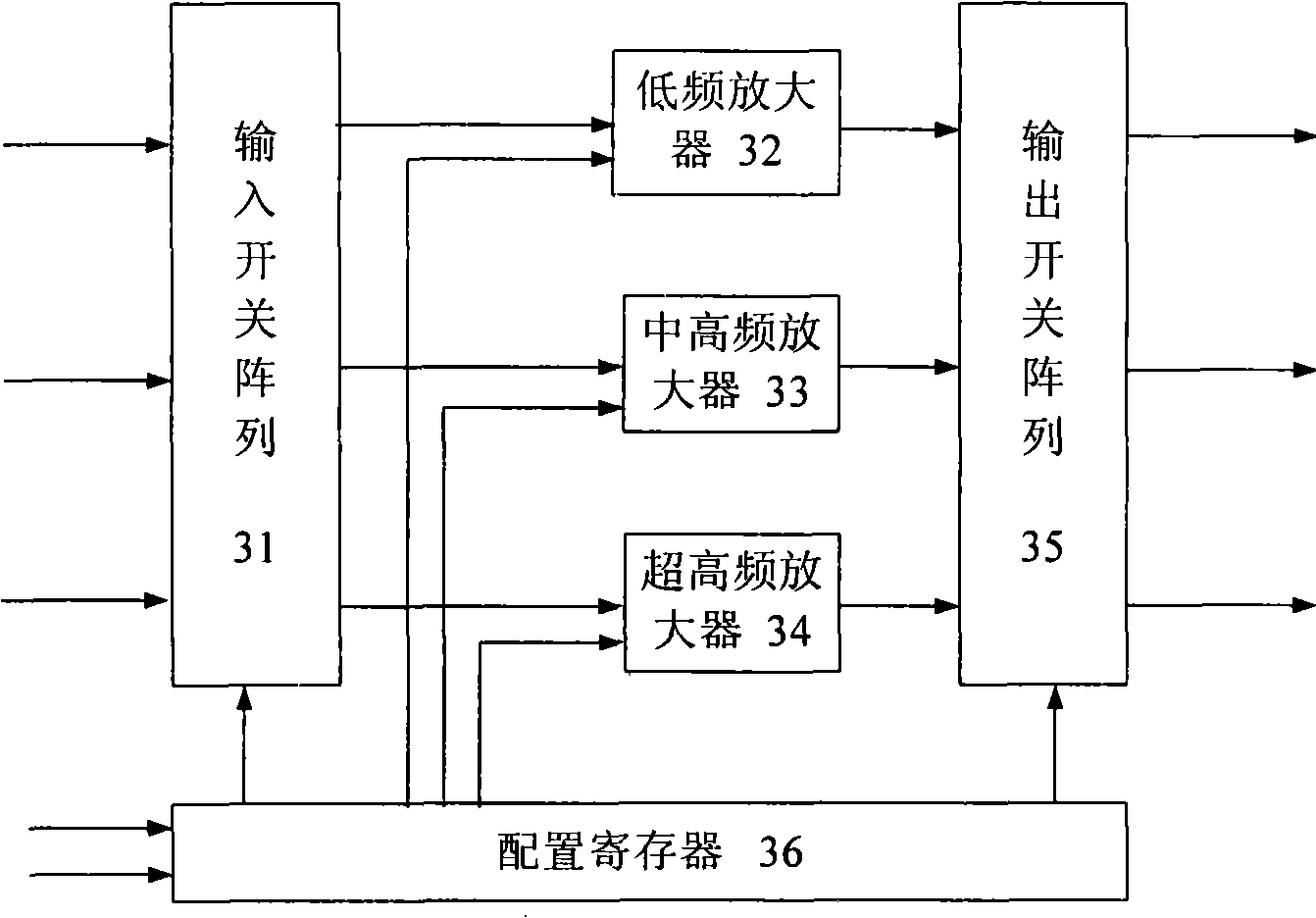
Gain-controllable wide-band low-noise amplifier
ActiveCN101316095AMeet performance requirementsReduce areaMultiple-port networksAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTransceiverWireless transceiver
The invention provides a gain-controllable wide-frequency low-noise amplifier, wherein, a state configuration device is used for generating input and output configuration signals, gains and wave section switch control signals, respectively controlling an input resistance matching circuit, a gain-controllable wide-frequency low-noise amplifier and an output resistance matching circuit, and setting suitable input resistance, amplifier gain, working bandwidth and output resistance. RF input signals can be transmitted with maximum efficiency to the gain-controllable amplifier through the input resistance matching circuit and generate little energy reflection. Subsequently, owing to the self-adaptability of the amplifier gain, the amplifier adjusts the self-gain according to the input RF signal amplitude, leads the output voltage to be stable, and ensures the normal operation of the sub-step circuit. Owing to the existence of the output resistance matching circuit, the system output signal can be transmitted to the sub-step circuit with the maximum efficiency, thus ensuring the working efficiency of the circuit. The gain-controllable wide-frequency low-noise amplifier of the invention can be applied to the wireless transceiver with different resistance antennas and different working frequency protocols, and can carry out the self-adaptability gain adjustment.
Owner:WUHAN SYNTEK CO LTD
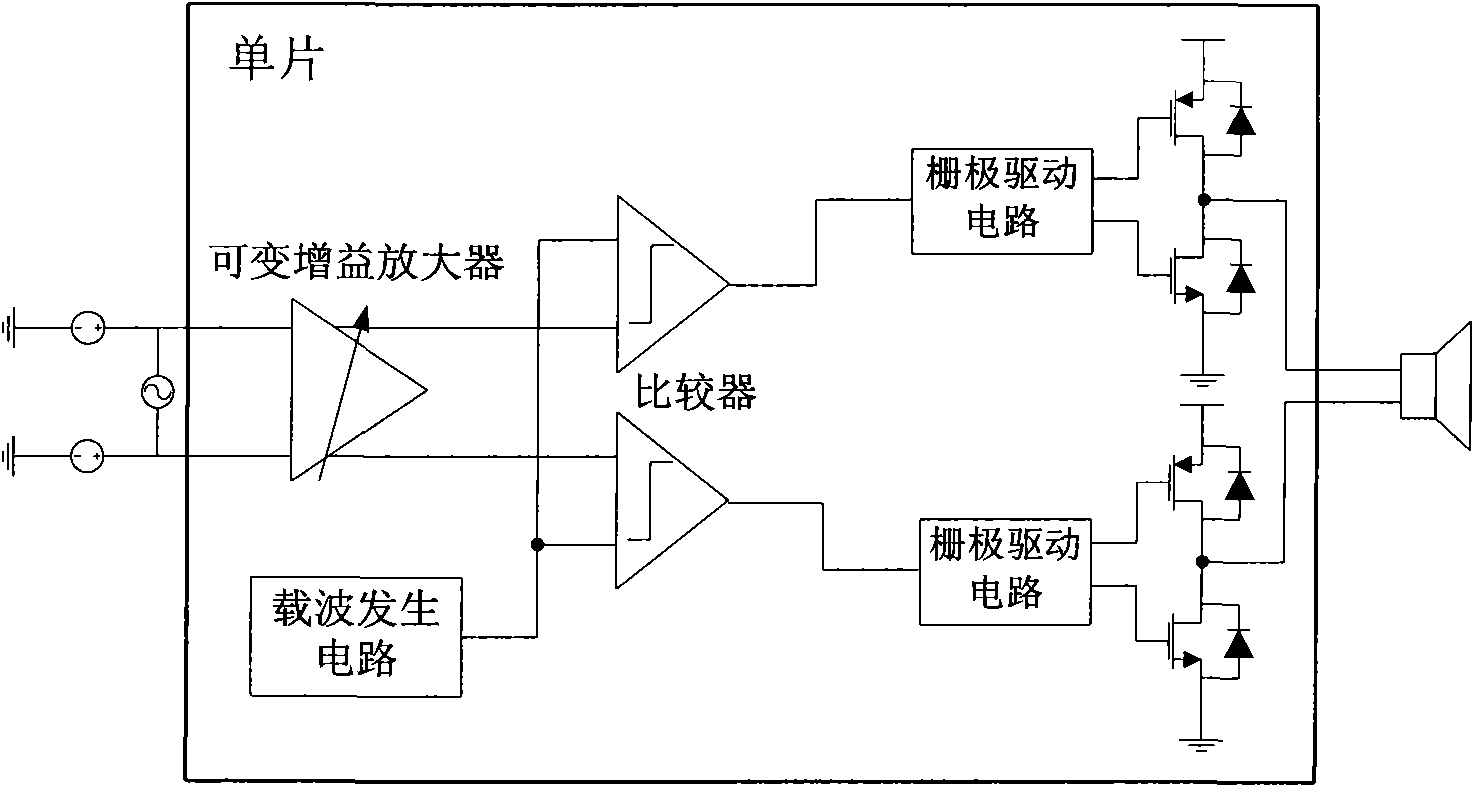
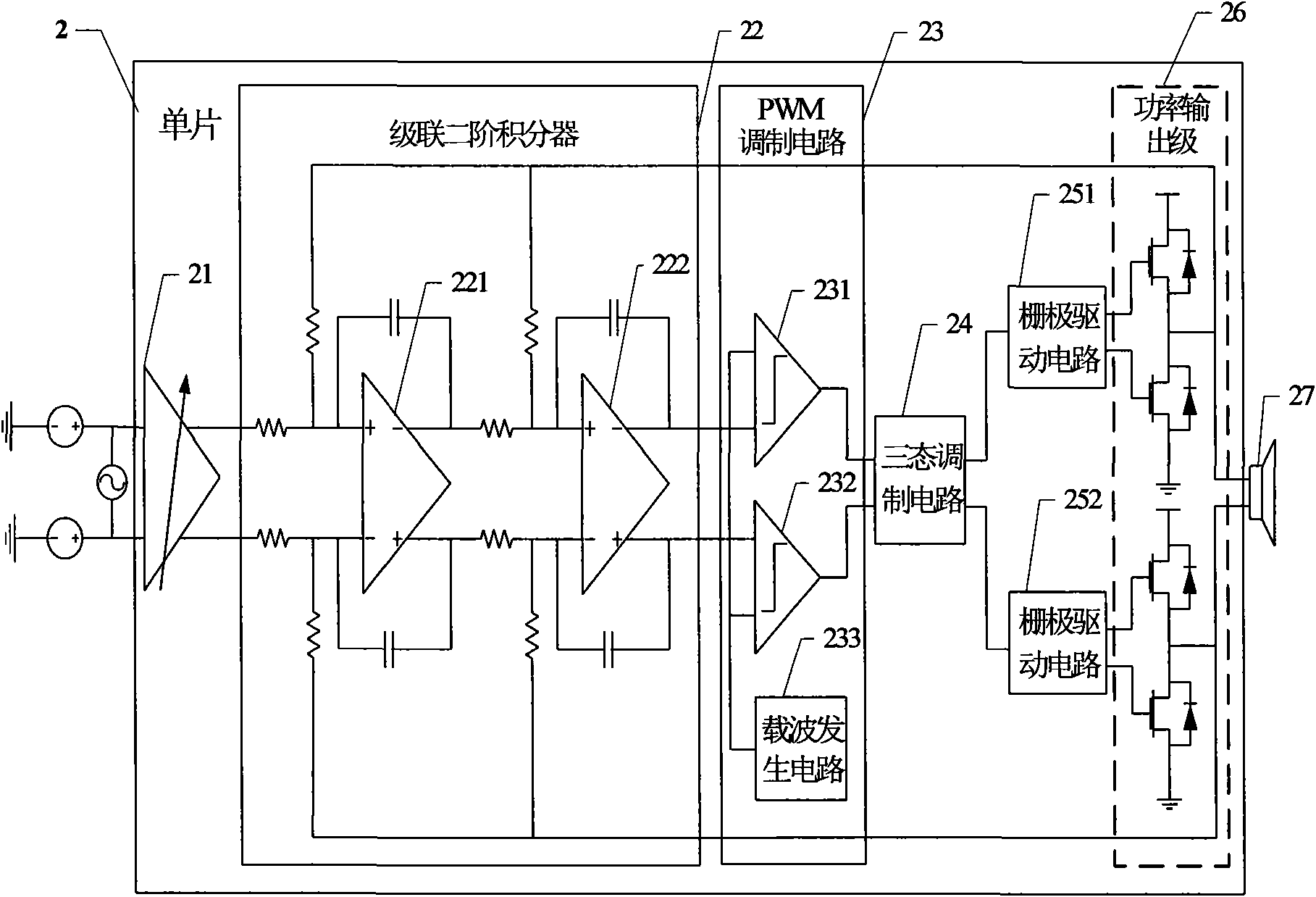
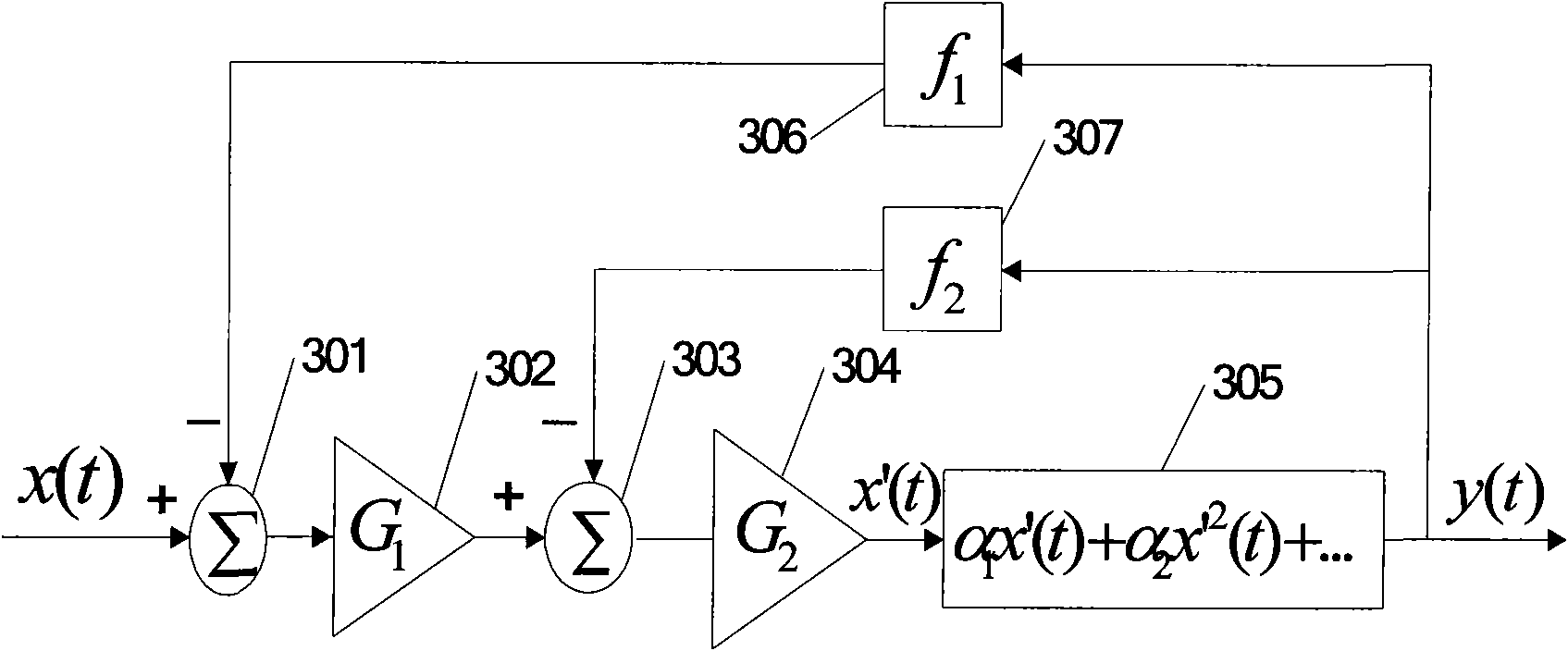
High-performance D type audio power amplifier with high-order multipath feedback structure
InactiveCN101847968AAvoid inability to guarantee stabilityImprove performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceIntegratorTotal harmonic distortion
The invention discloses a high-performance D type audio power amplifier adopting high-order multipath feedback structure, which comprises a prepositive variable gain amplifier, an integrator, a pulse width modulation (PWM) circuit, a three-state regulating circuit, a grid driving circuit and a power output stage. The integrator is in a two-order structure formed by cascade connection of two stages of integrators, and two paths of feedback are introduced to form a higher-order double-feedback loop, thereby effectively increasing the loop gain and the out-off-band attenuation, and obviously improving the suppression ratio of total harmonic distortion and noise to power sources and other main properties in the range of audio frequency band (22Hz-22KHz). By introducing two paths of voltage negative feedback and comprehensively considering the input dynamic range, the signal-to-noise ratio and stability factors, the ratio of two stages of feedback coefficients can be regulated by regulating the ratio of the input resistance and the feedback resistance of two stages of integrators, thereby ensuring the stability of a system. The D type audio power amplifier with the structure has the characteristics of high integration level and high performance and can be widely applied to the fields of portable equipment, consumer electronics and the like.
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
Car power source apparatus
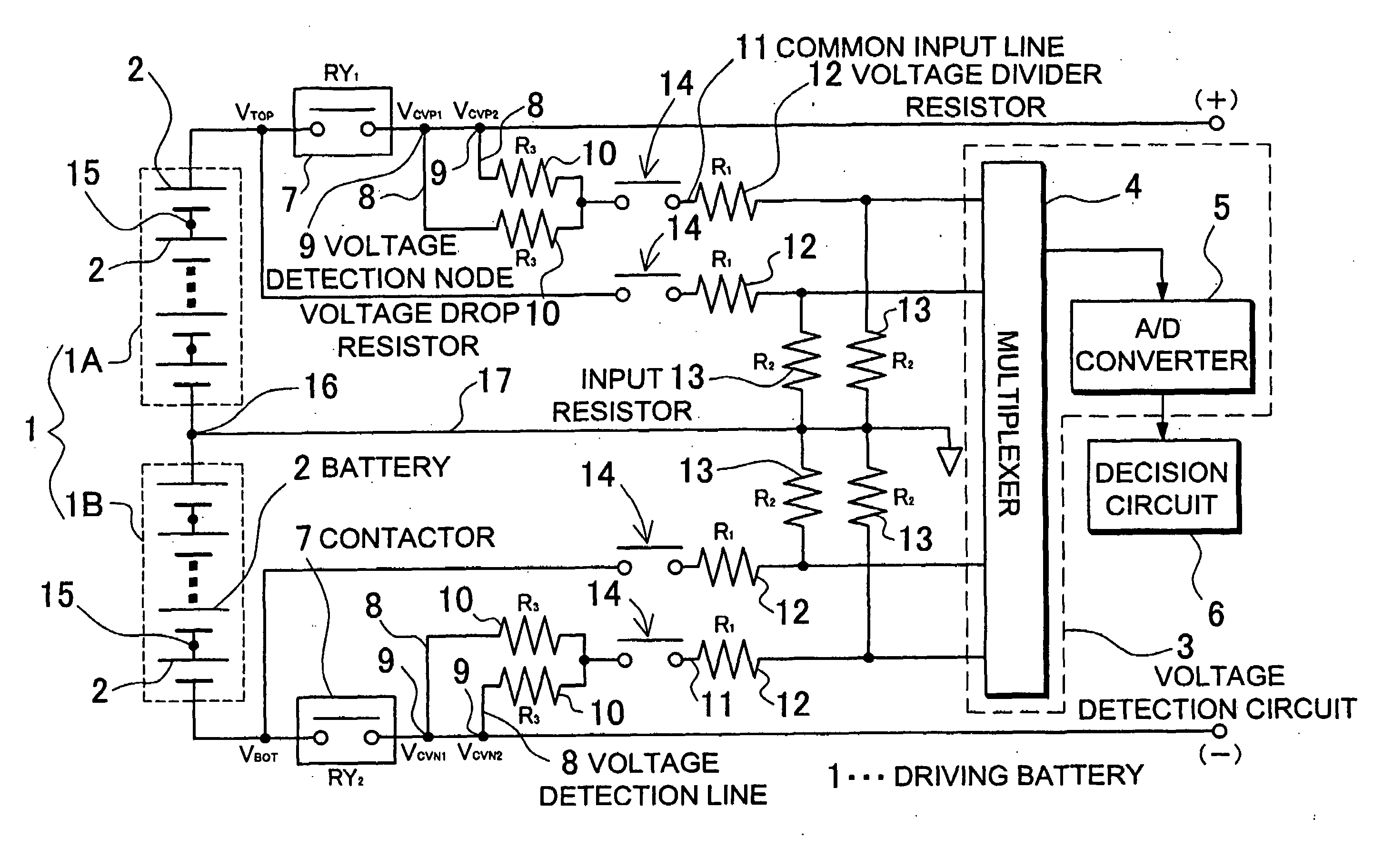
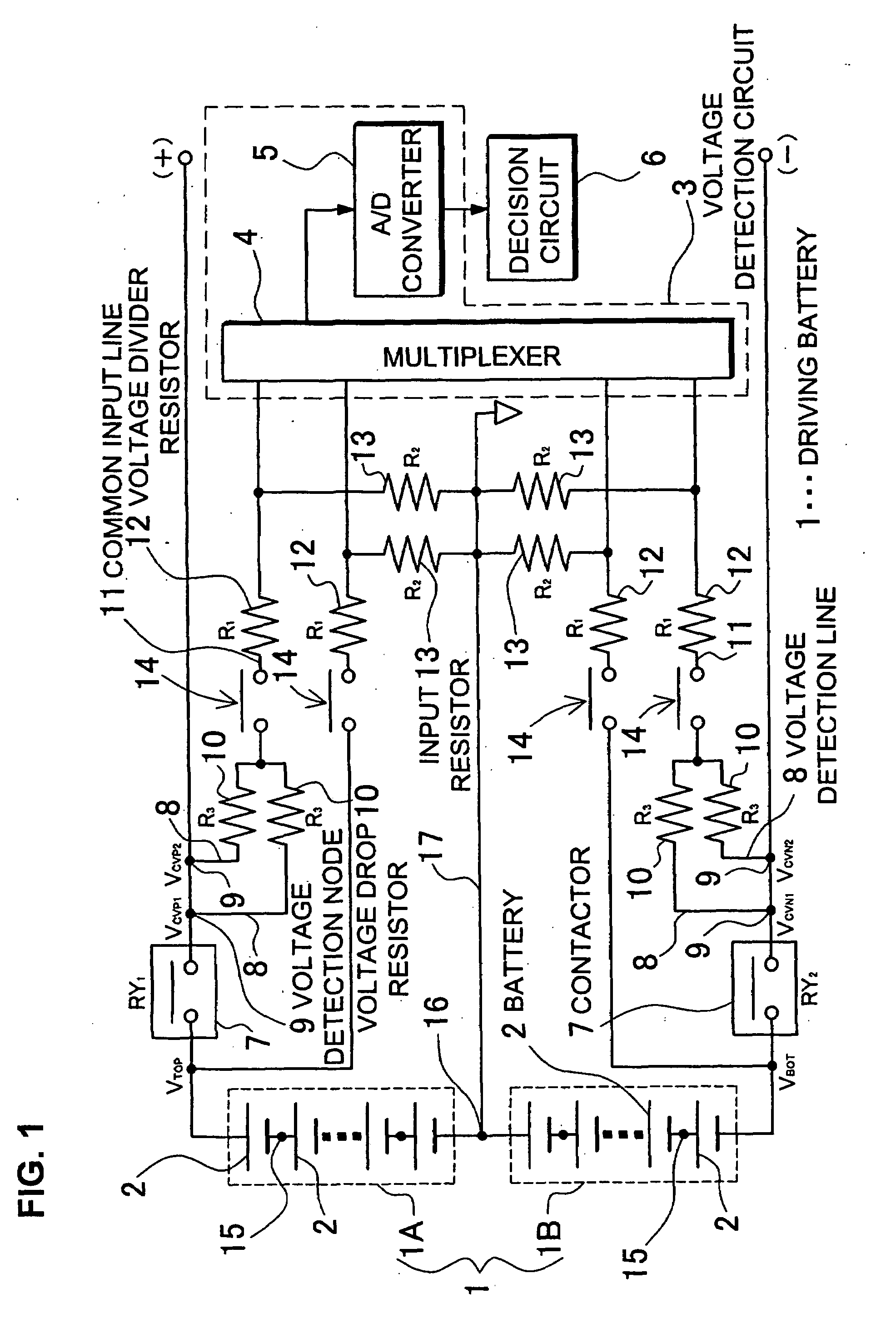
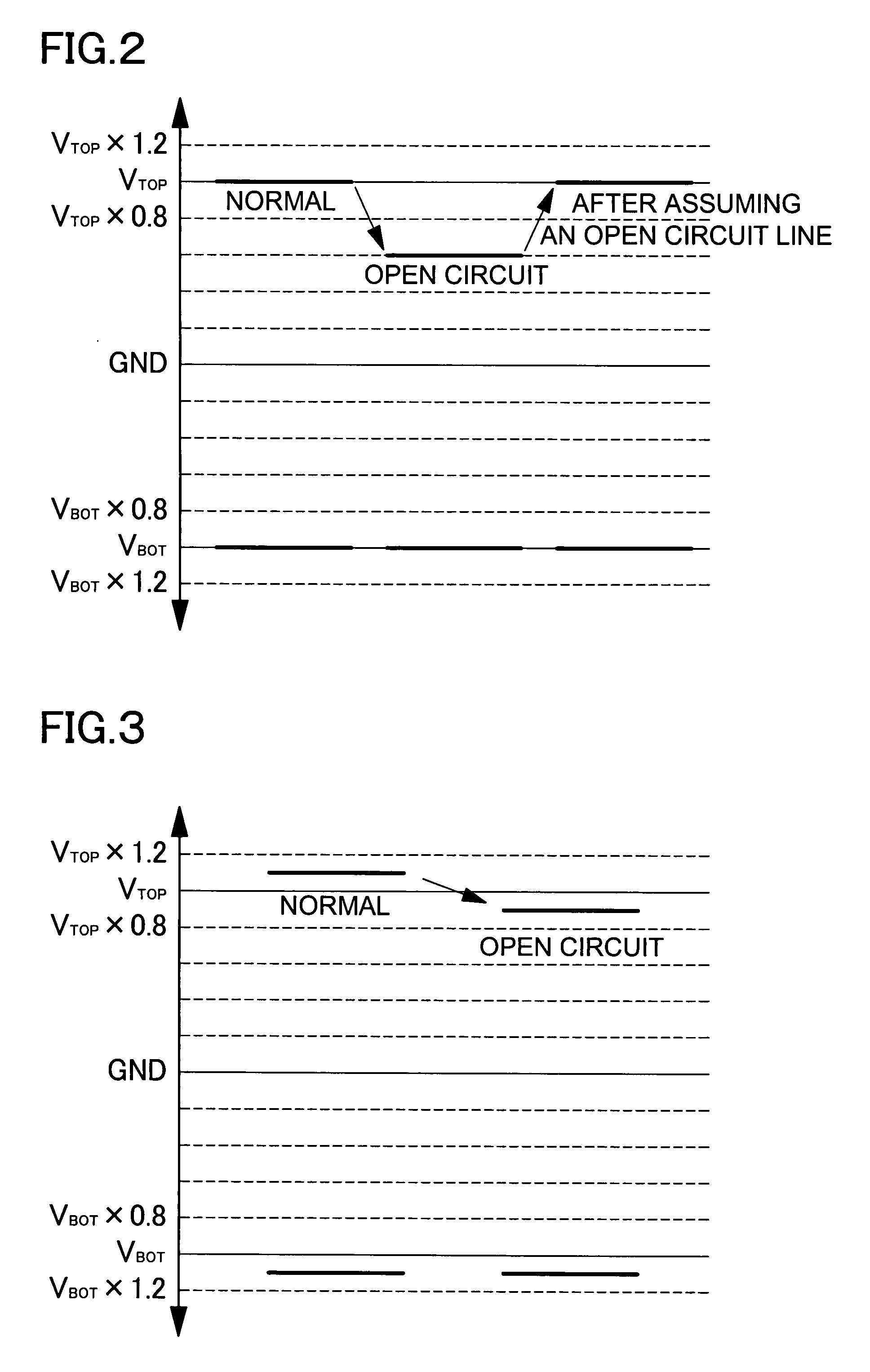
ActiveUS20080079434A1Measurement is droppedBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric devicesDecision circuitVoltage drop
The car power source apparatus is provided with a driving battery 1 that supplies power to the car's electric motor, a voltage detection circuit 3 that measures the voltage of batteries 2 in the driving battery 1, a plurality of voltage detection lines 8 connected in parallel between the input-side of the voltage detection circuit 3 and driving battery 1 voltage detection nodes 9, and a decision circuit 6 that determines if a voltage detection line 8 is open circuited from the voltage measured by the voltage detection circuit 3. Each voltage detection line 8 has a voltage drop resistor 10 connected in series. The voltage detection circuit 3 is provided with input resistors 13 on its input-side. The car power source apparatus makes computations on the voltage measured by the voltage detection circuit 3, which is from the voltage divider formed by the input resistor 13 and voltage drop resistors 10, to detect voltage detection line 8 open circuit.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Circuit and method for weak current detection
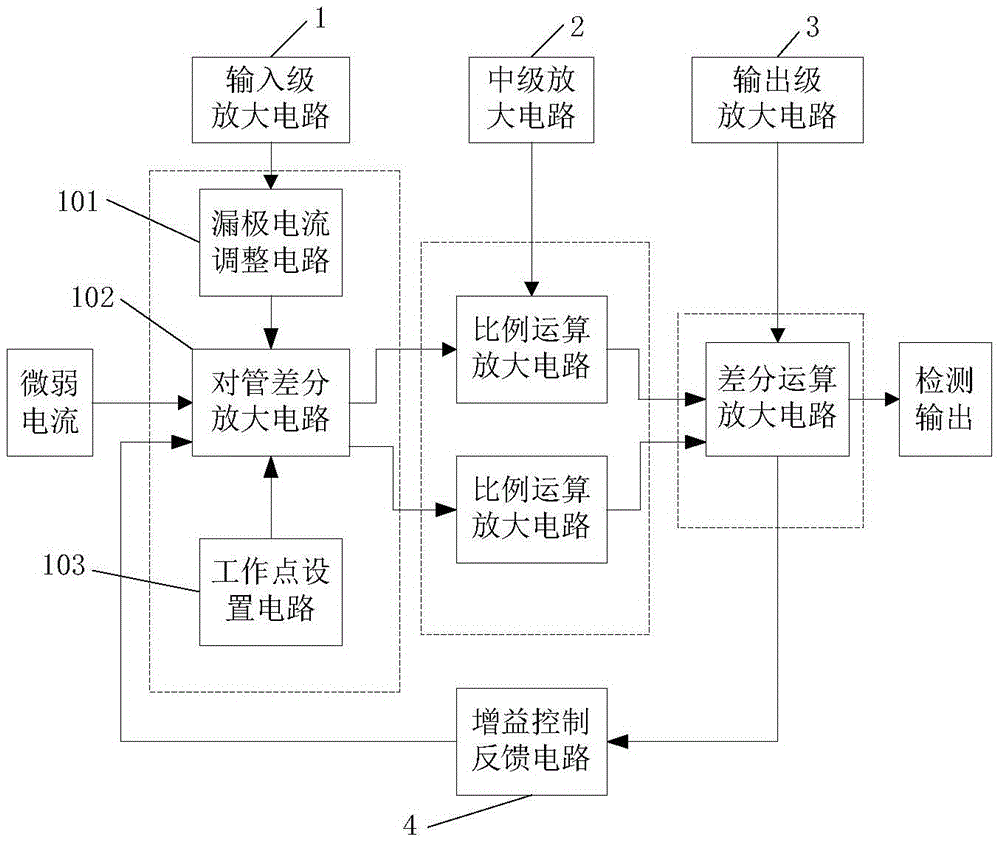
InactiveCN105548654ALarge measuring rangeHigh measurement accuracyCurrent measurements onlyEngineeringWeak current
The invention discloses a circuit and a method for weak current detection and belongs to the current detection field. Geminate field effect transistors are employed by an input end to form a difference amplifier, and I-V conversion of a weak current is carried out; a voltage signal after conversion is sent to two sets of proportion operation circuits having symmetric in-phase input modes for proportion operation amplification; difference operation amplification of the voltage signal after proportion operation amplification is carried out, and a difference operation amplification voltage magnitude is measured. According to the method and the device, the junction type geminate field effect transistors are employed to form the difference amplifier as an input level, so input impedance is improved, and the relatively high common-mode inhibition ratio is acquired; the precise proportion operation circuit structures in the symmetric in-phase input modes are employed as the middle level, input impedance is further improved, and measurement precision is improved; the multiple operation amplifier difference amplification detection technology is employed, conflicts of useful-signal weakness and relatively high common-mode interference can be effectively solved, and high gain, high input resistance and the high common-mode inhibition ratio of the detection circuit are realized.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
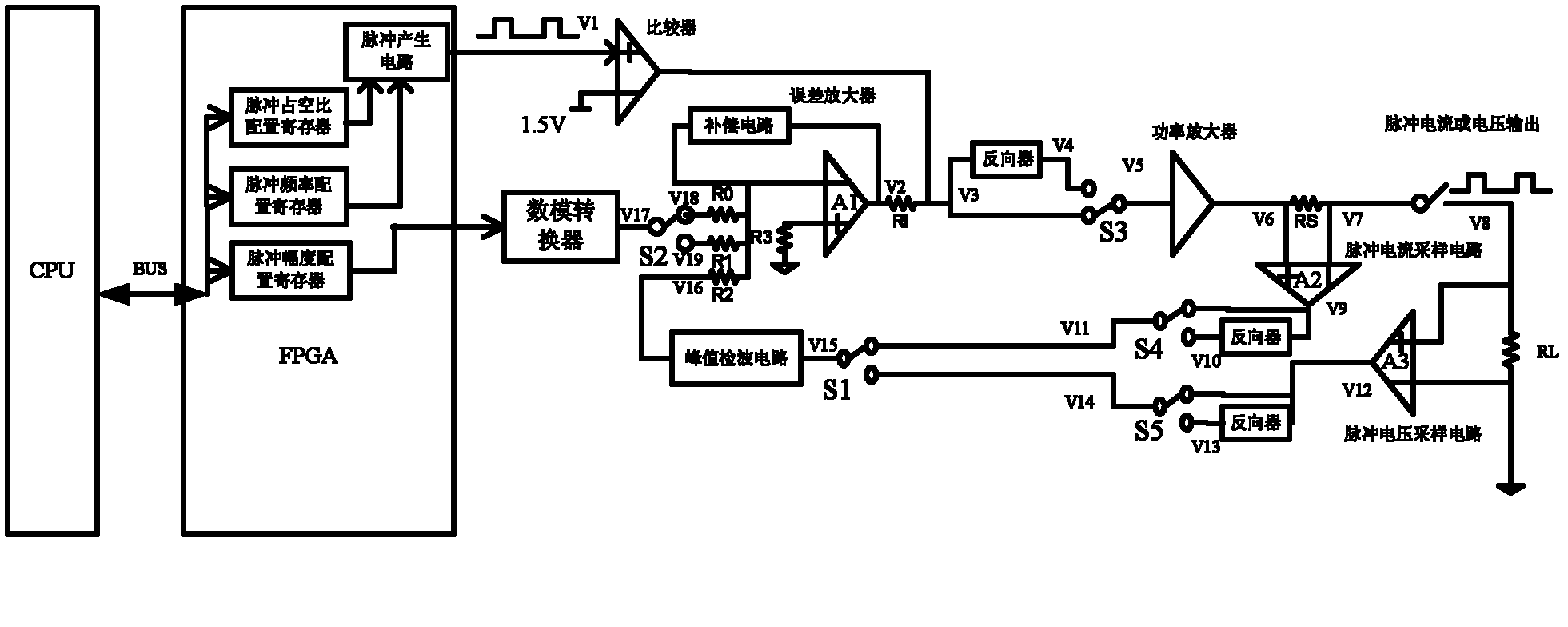
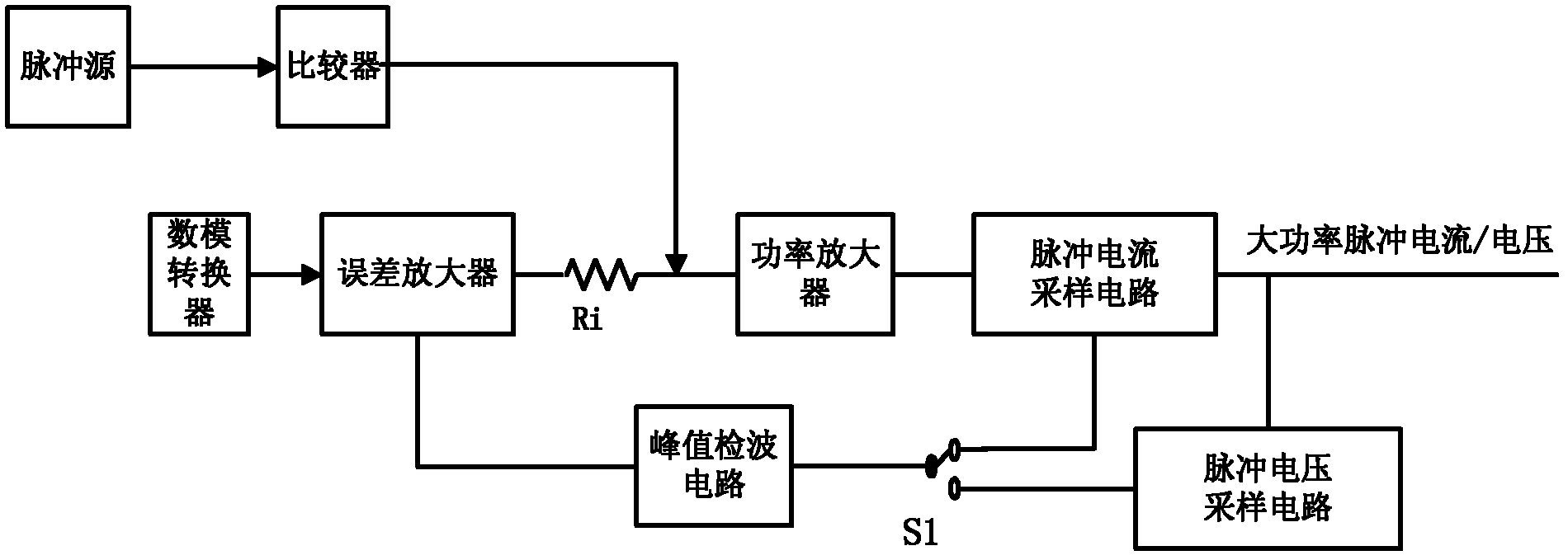
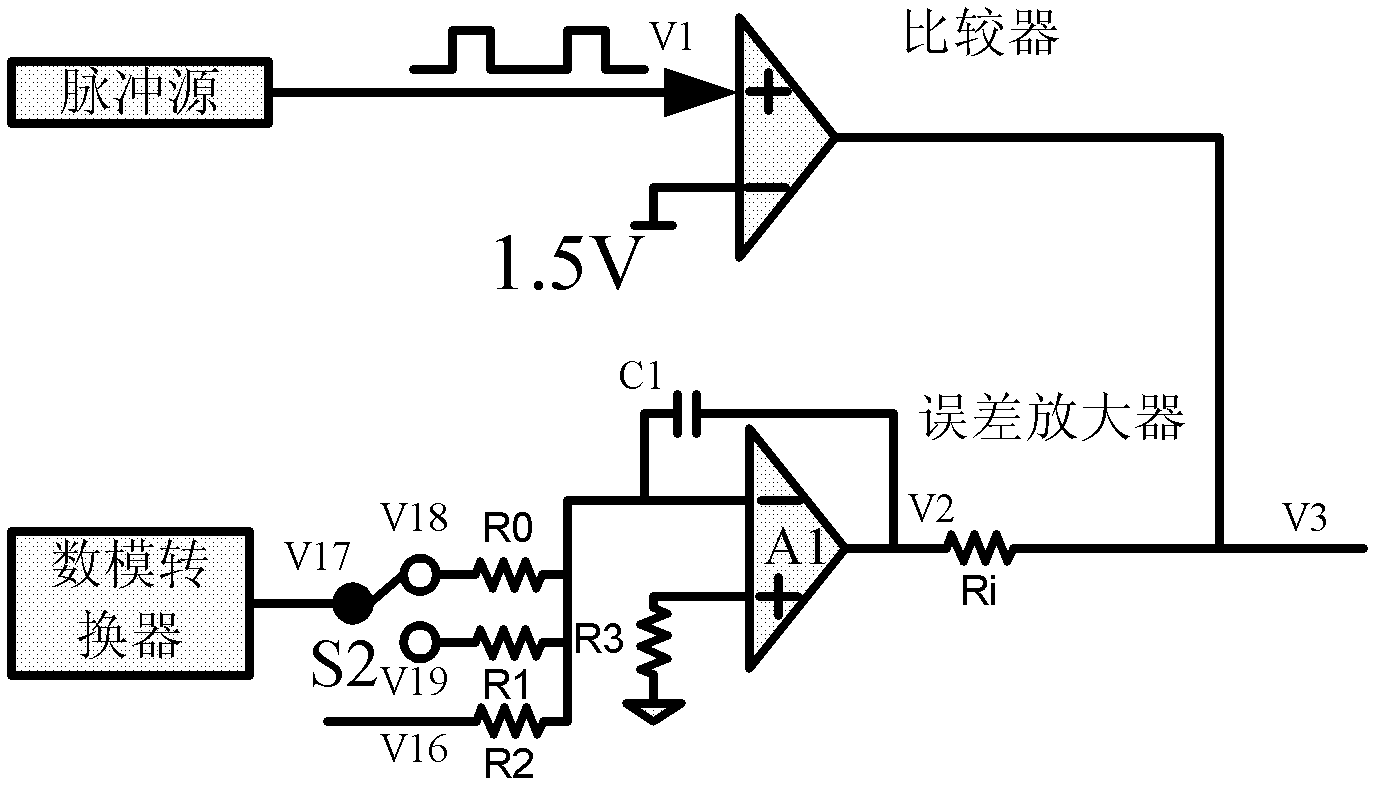
A High Power Pulse Current/Voltage Generating Circuit
InactiveCN102291104AMeet the testAmplitude adjustableElectric pulse generatorNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a high-power pulse current / voltage generating circuit with programmable pulse width, duty ratio and pulse amplitude, wherein a digital-analog converter, an error amplifier, a power amplifier, a pulse current sampling circuit, a pulse voltage sampling circuit, a pulse current / voltage sampling selection switch and a peak detecting circuit are formed into a negative feedback loop. The amplitude analog signal output by the digital-analog converter is compared with the pulse peak obtained by the peak detecting circuit in the error amplifier; and the pulse peak is equal to the amplitude analog signal output by the digital-analog converter in the negative feedback loop. The power amplifier is connected with the output end of the comparator and is connected with the output end of the error amplifier through an input resistor; the comparator adjusts the frequency and duty ratio of the output high-power current / voltage under the control of the periodic pulse signal output by the pulse source, thus, the pulse width, the duty ratio and the pulse amplitude of the output pulse current / voltage of the high-power pulse current / voltage generating circuit can be adjusted.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multi-port cross-connected multi-level cascode differential amplifier
InactiveUS7161429B2Increasing current gain and input impedance and bandwidthReduce input currentAmplifier combinationsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceCross connectionInput impedance
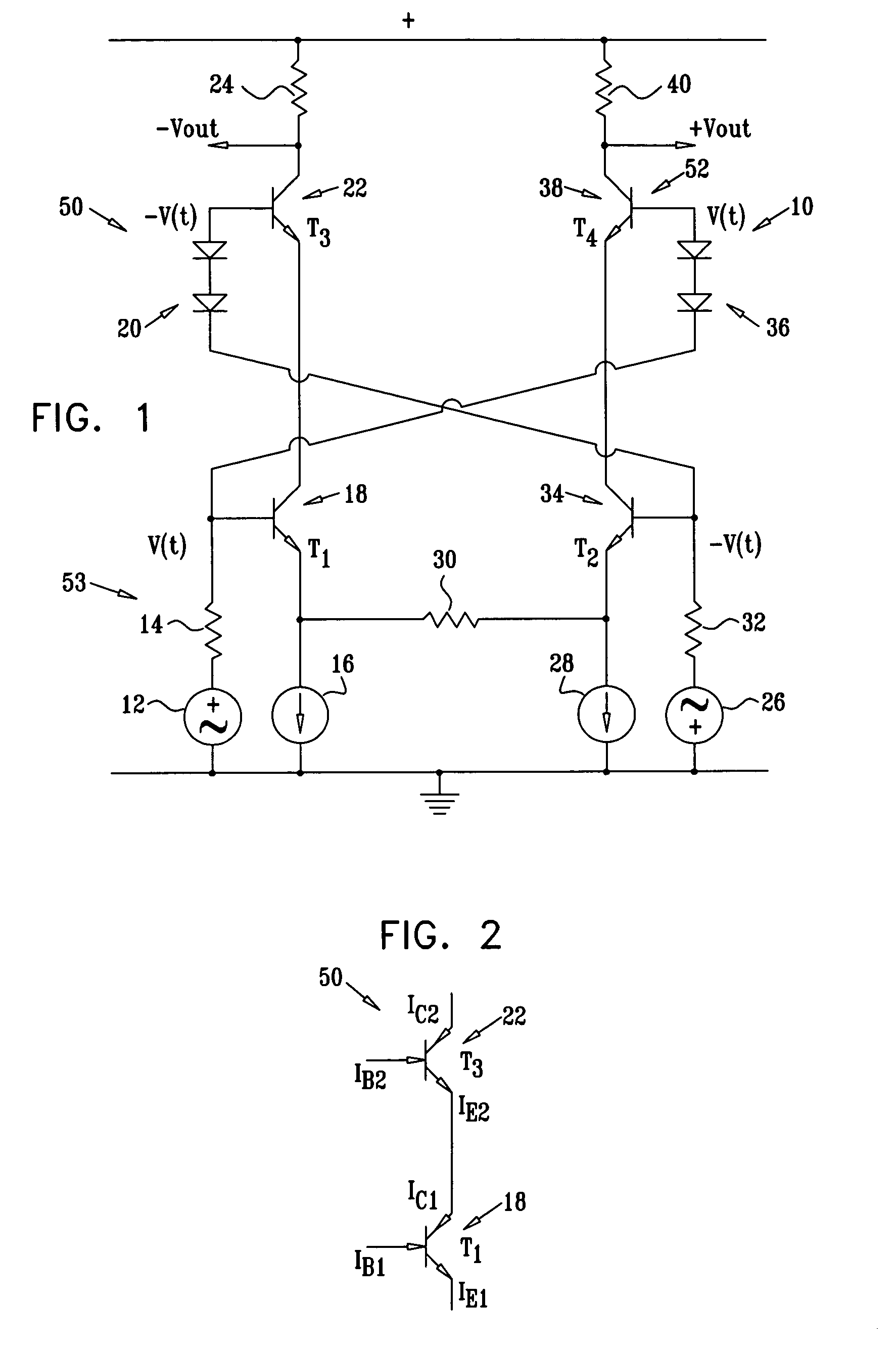
A differential cascode amplifier has first and second cascode circuits, driven by two differential signal sources including input resistances.The first cascode circuit includes a first input transistor having a first collector, a first emitter, and a first base, and a first output transistor having a second collector, a second base, and a second emitter coupled to the first collector. The second cascode circuit includes a second input transistor having a third collector, a third emitter, and a third base, and a second output transistor having a fourth collector, a fourth base, and a fourth emitter coupled to the third collector. The amplifier has a first connection connecting the first base to the fourth base, and a second connection connecting the second base to the third base.This cross-connected differential cascode architecture provides doubled output bandwidth and current gain (in dB), further increasing input impedance and output swing.
Owner:IBM CORP
High-efficiency linear LINC transmitter
InactiveCN101651459AIncreased average synthesis efficiencyAchieving High Efficiency Linear AmplificationRadio transmissionQuadrature modulationControl signal
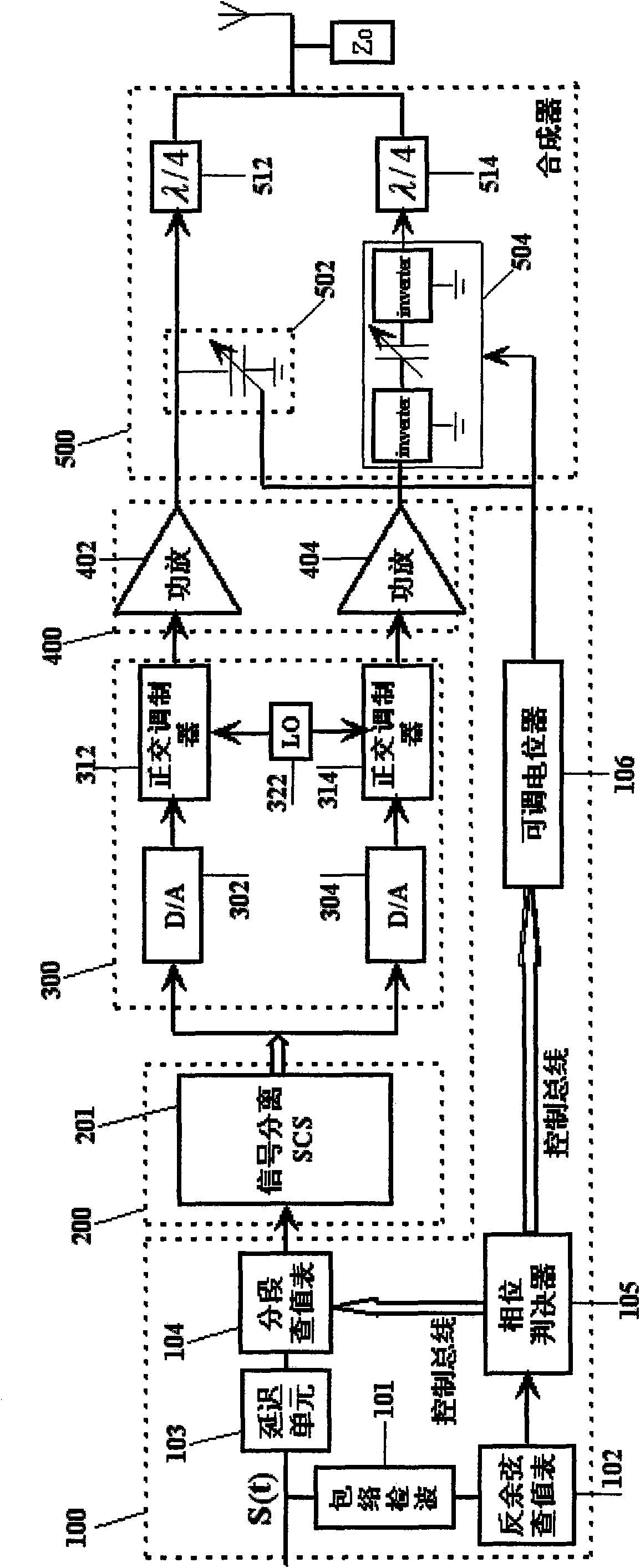
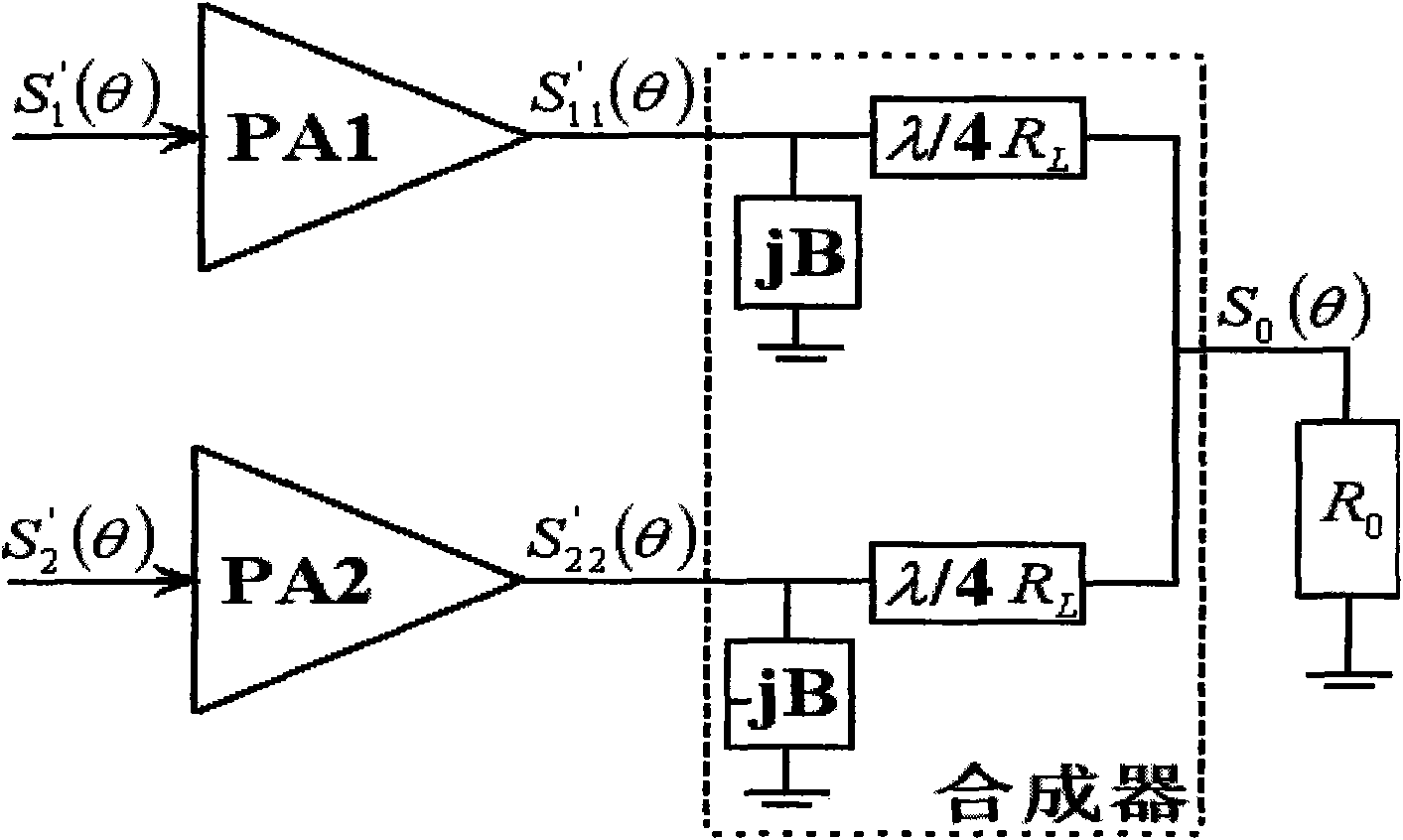
The invention provides a high-efficiency linear LINC transmitter which comprises a signal preprocessing unit, a signal separation unit, an analogue upconversion unit, an amplifying processing unit and a vector resultant unit, wherein the signal preprocessing unit finishes the segmenting pre-distortion processing for inputted signals and the control of a synthesizer; the signal separation unit divides the signals after pre-distortion into two ways of constant envelope phase-modulated signals; the analogue upconversion unit converts the two ways of separated digital baseband signals into analogue signals, and carries out quadrature modulation to radio frequency; the amplifying processing unit amplifies the power of the two ways of radio frequency signals; and the vector resultant unit synthesizes and outputs the power of the two ways of signals. The signal preprocessing unit can calculate an equilibrium angle theta during signal separation according to the amplitude of the inputted signals and divide the interval of the equilibrium angle theta before signal separation to generate different control signals so as to ensure that the input resistance of the synthesizer changes along with the equilibrium angle theta. In order to guarantee that the LINC transmitter has high linear index, the invention also carries out segmenting pre-distortion processing on the inputted signals according to the interval of the equilibrium angle theta.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
variable gain amplifier
InactiveCN102270972ALower input resistanceMinimize the effect of op amp feedback resistor valuesGain controlVariable-gain amplifierAudio power amplifier
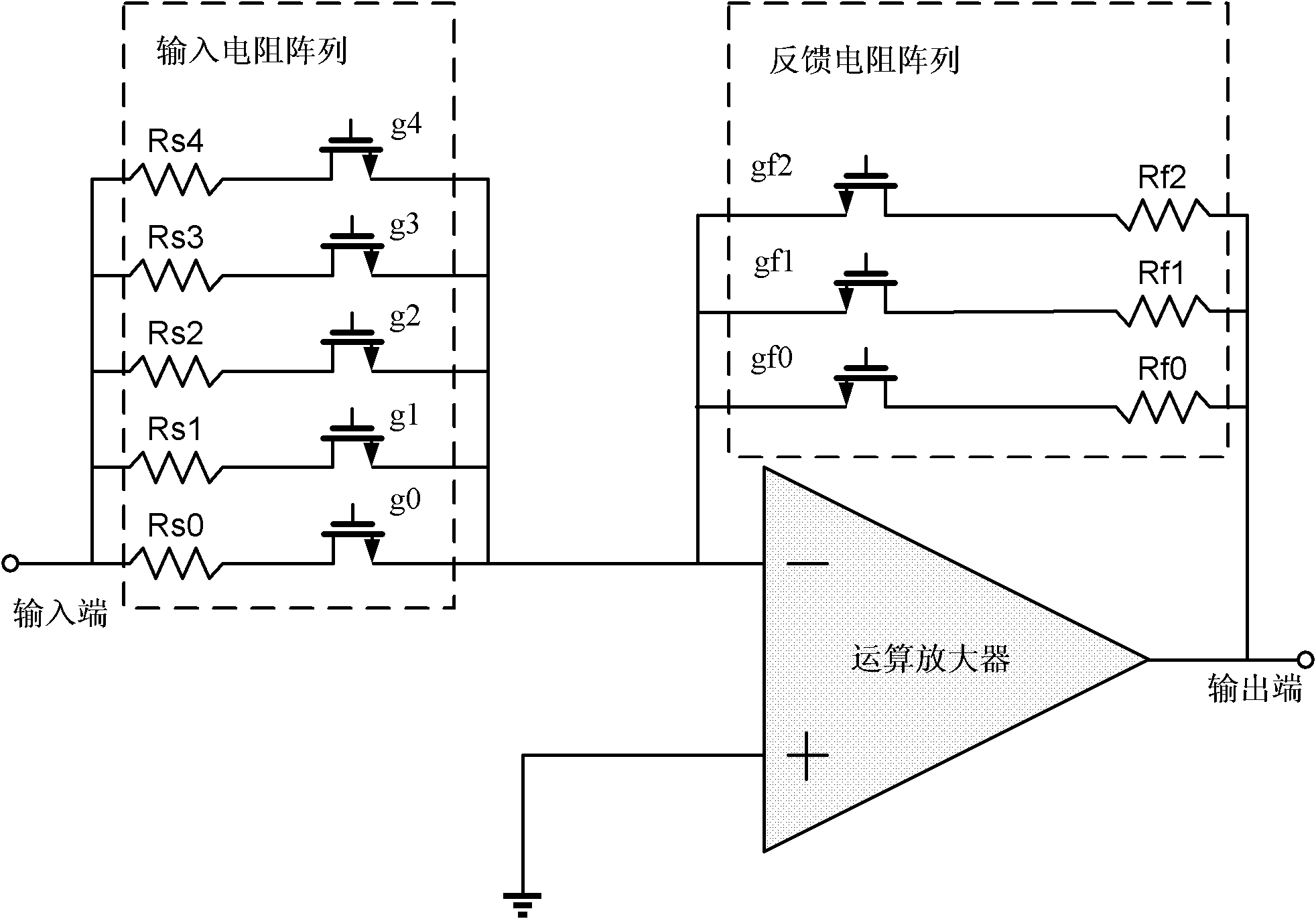
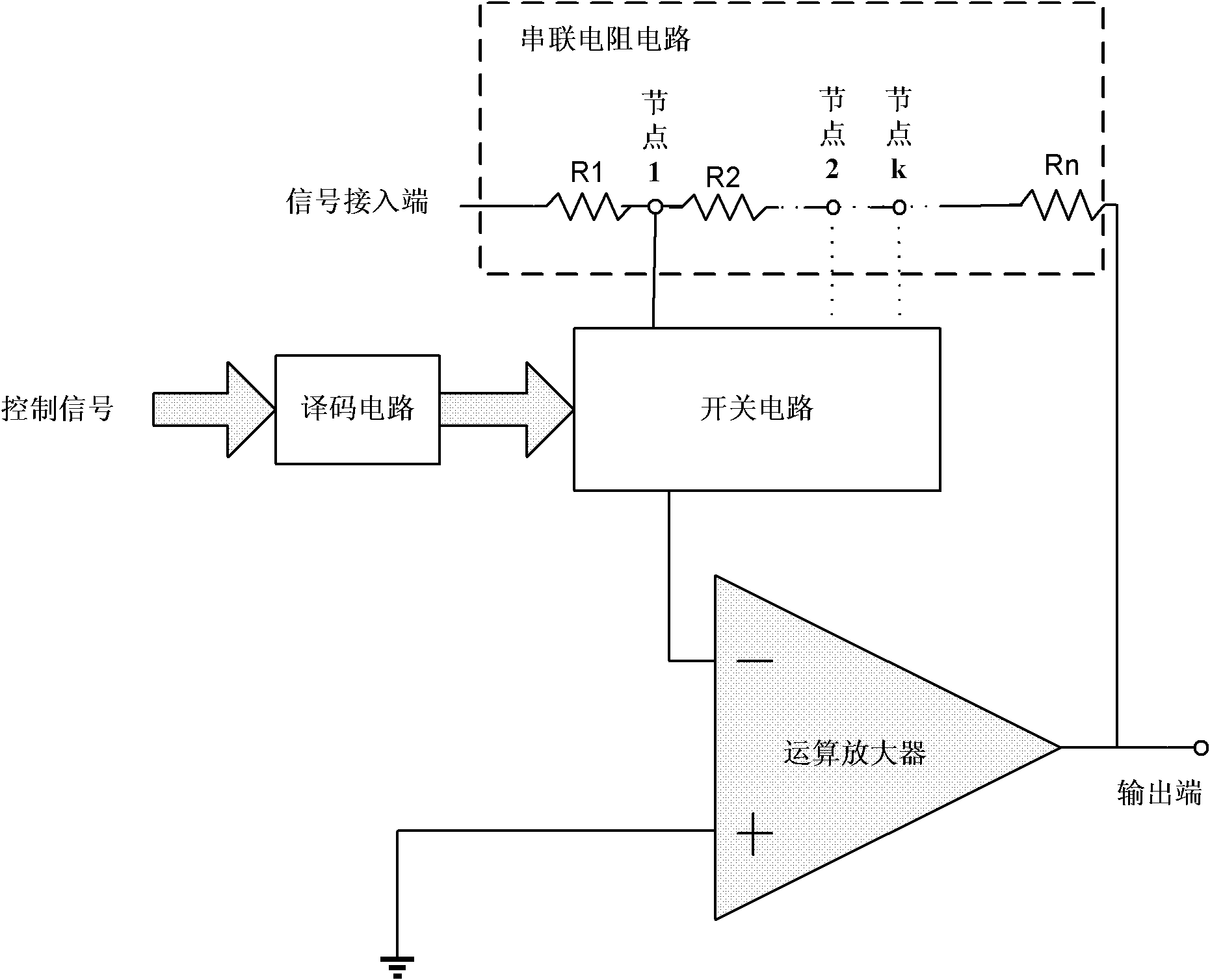
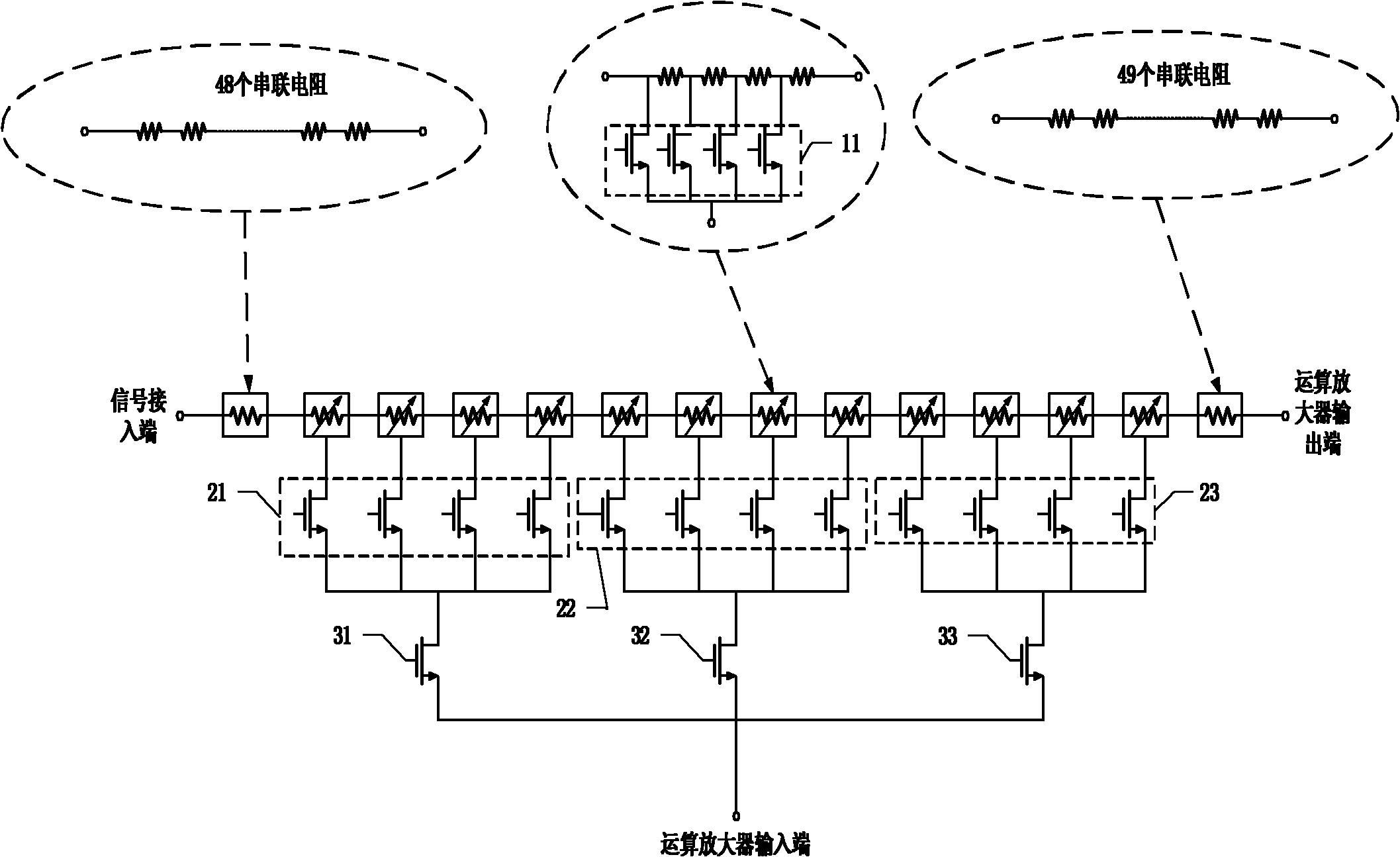
The present invention provides a variable gain amplifier, which includes: an operational amplifier; at least one series resistor circuit with one end as a signal input end and the other end connected to the output end of the operational amplifier, and a plurality of resistors connected in series; and A switch circuit connected to multiple nodes of each series resistor circuit and an input terminal of the operational amplifier is used to control the on-off of multiple nodes of each serial resistor circuit and an input terminal of the operational amplifier, so that each Part of the resistance in a series resistance circuit is used as the input resistance of the operational amplifier, and the rest of the resistance is used as the feedback resistance of the operational amplifier; and a decoding circuit is used to decode the input control signal and output it for controlling the operational amplifier. The opening and closing signals of the opening and closing of the plurality of controlled switches. The invention has the advantages of removing the switch circuit from the signal path, thereby eliminating the influence of the on-resistance of each switch on the input impedance and feedback impedance of the operational amplifier, and improving the linearity of the gain.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINPUZHEN MICROELECTRONICS
Programmable filters and methods of operation thereof
InactiveUS20080100374A1Active element networkOscillations generatorsSoftware engineeringInput impedance
Programmable filters are used for the purpose of changing the filter cutoff frequency as may be necessary for the operation of a wireless transmitter or receiver. Frequencies may be changed by selecting a desirable value of a capacitor and / or a resistor. The programmable filter controls the frequency according to the disclosed method. Furthermore, in order to reduce the area consumed by the programmable filter a three-dimensional layout is used. In accordance with the disclosed invention it is possible to program the input of the programmable filter to have a higher or lower input resistance as may be required while maintaining the desired programmed cutoff frequency by switching the respective capacitors in a capacitor bank, thereby combining the elements needed for frequency programmability and input impedance level selection.
Owner:THETA MICROELECTRONICS
Electronic amplifier
InactiveUS6731165B1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierOperational amplifier
An amplifier that accurately amplifies signals over a wide bandwidth, including DC, has a voltage-to-current converter, a feed-forward resistive element, a buffer, an input resistive element, a feedback resistive element, and an operational amplifier. A first end of the feed-forward resistive element is coupled to an output of the voltage-to-current converter and to an input of the buffer. A first end of the input resistive element is coupled to an input to the voltage-to-current converter. A first end of the feedback resistive element is coupled to an output of the buffer. An inverting input of the operational amplifier is coupled to a second end of the input resistive element and to a second end of the feedback resistive element. A noninverting input of the operational amplifier is coupled to ground, and an output of the operational amplifier is coupled to a second end of the feed-forward resistive element.
Owner:MARZ DANIEL J
High voltage supply sensing high input resistance operational amplifier input stage
InactiveUS6914485B1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplififers with field-effect devicesMOSFETLow voltage
A high voltage operational amplifier input stage utilizes a pair of low voltage p-type MOSFET input devices configured to operate at a common mode voltage. The input stage operates between positive and negative voltage supply rails. Common mode bipolar transistor feedback loops force drains of the MOSFETs to track corresponding source potentials. MOSFET substrate connections are maintained at a predetermined level above (or below, depending on the power supply sensing arrangement) the common mode voltage of the input stage to ensure power supply sensing capability. The input stage has a common mode range which includes the supply rail potential, and which tolerates a total supply voltage that exceeds the MOSFET breakdown voltage. The effective threshold voltage of the input devices is increased above the nominal threshold value to sustain the linear operation of the input stage.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Control device for variable speed electric motors, particularly for power tools
InactiveUS20060113930A1Reduce sensitivityQuantity of light is reducedAC motor controlField or armature current controlHand heldEngineering
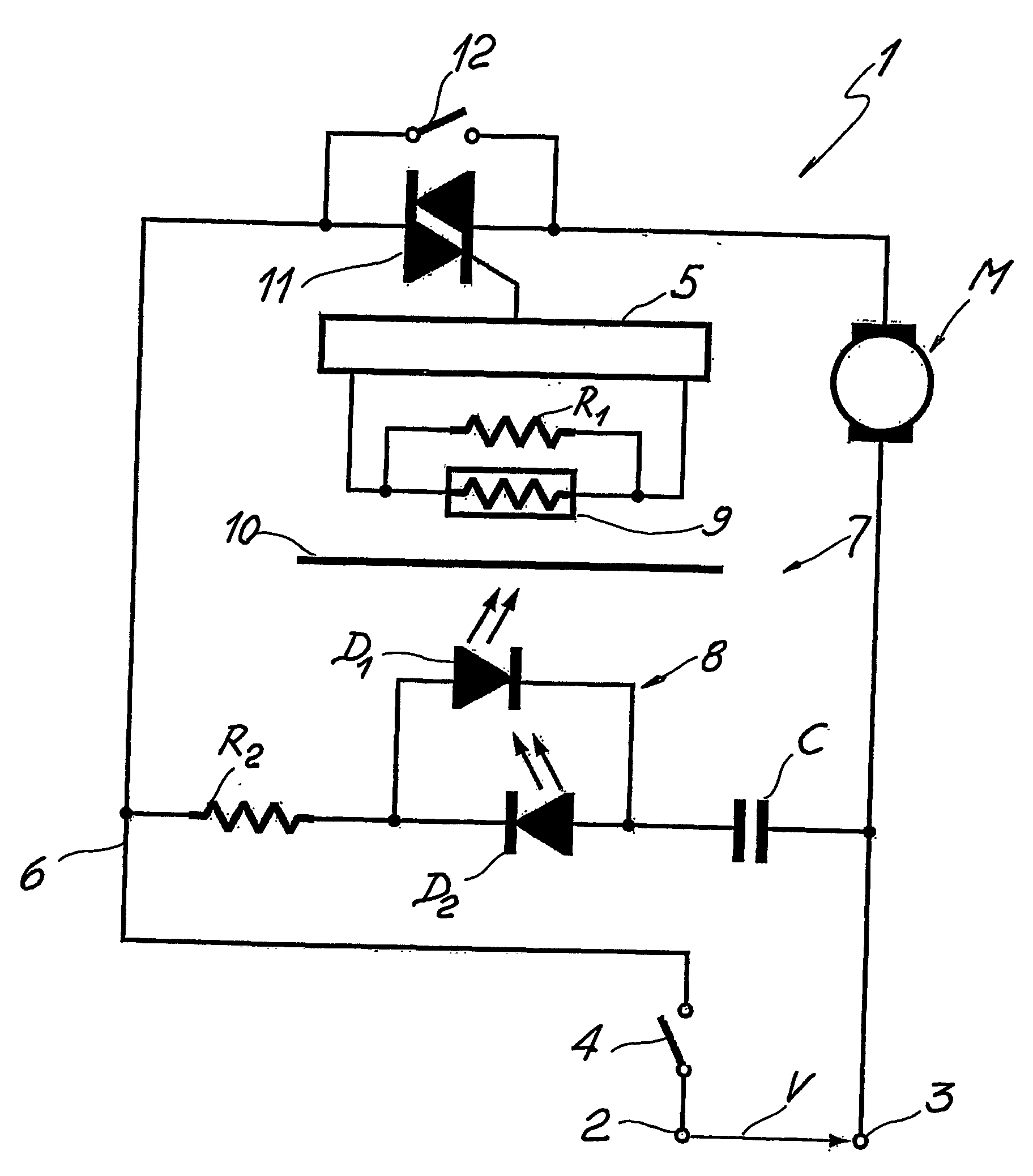
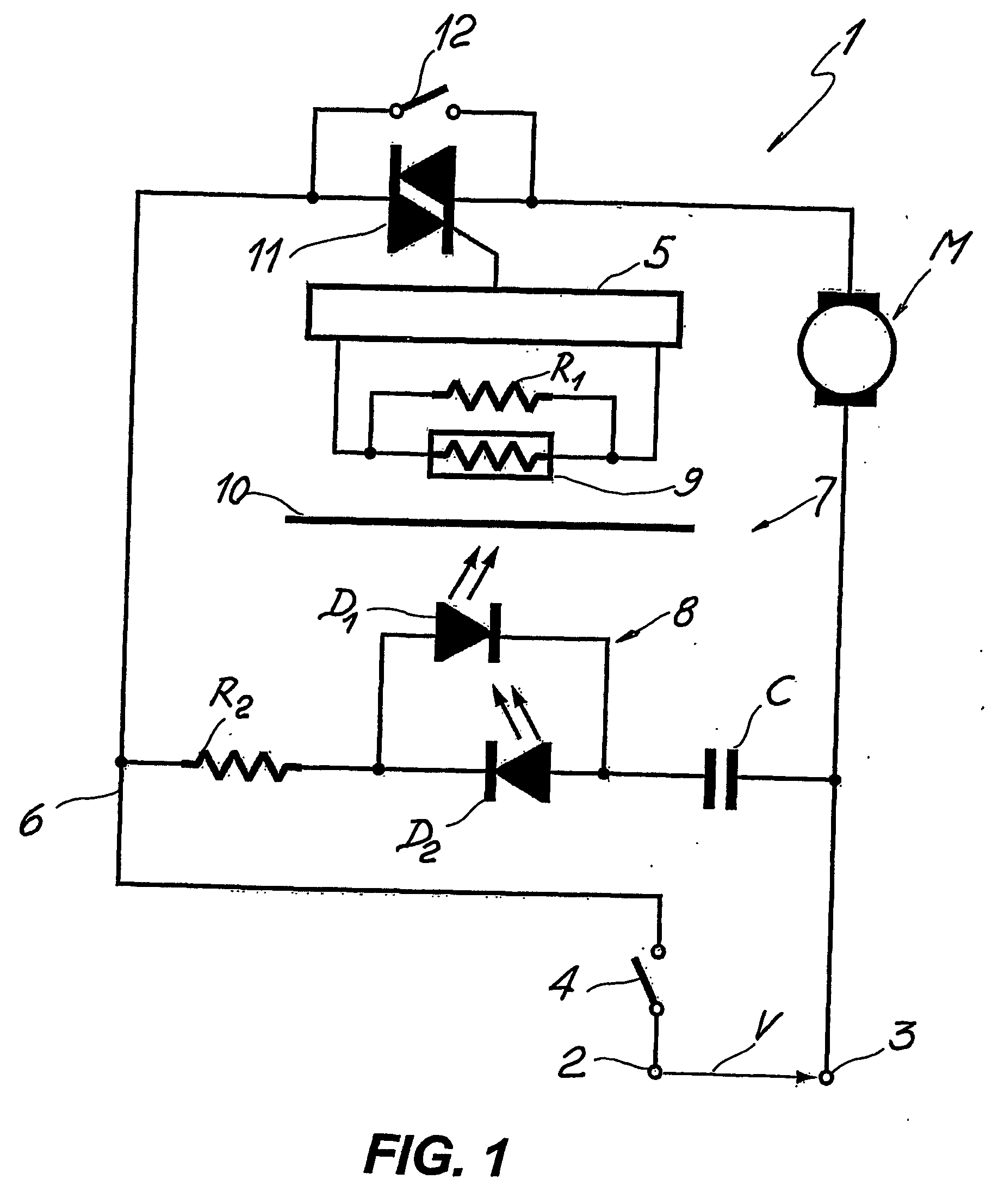
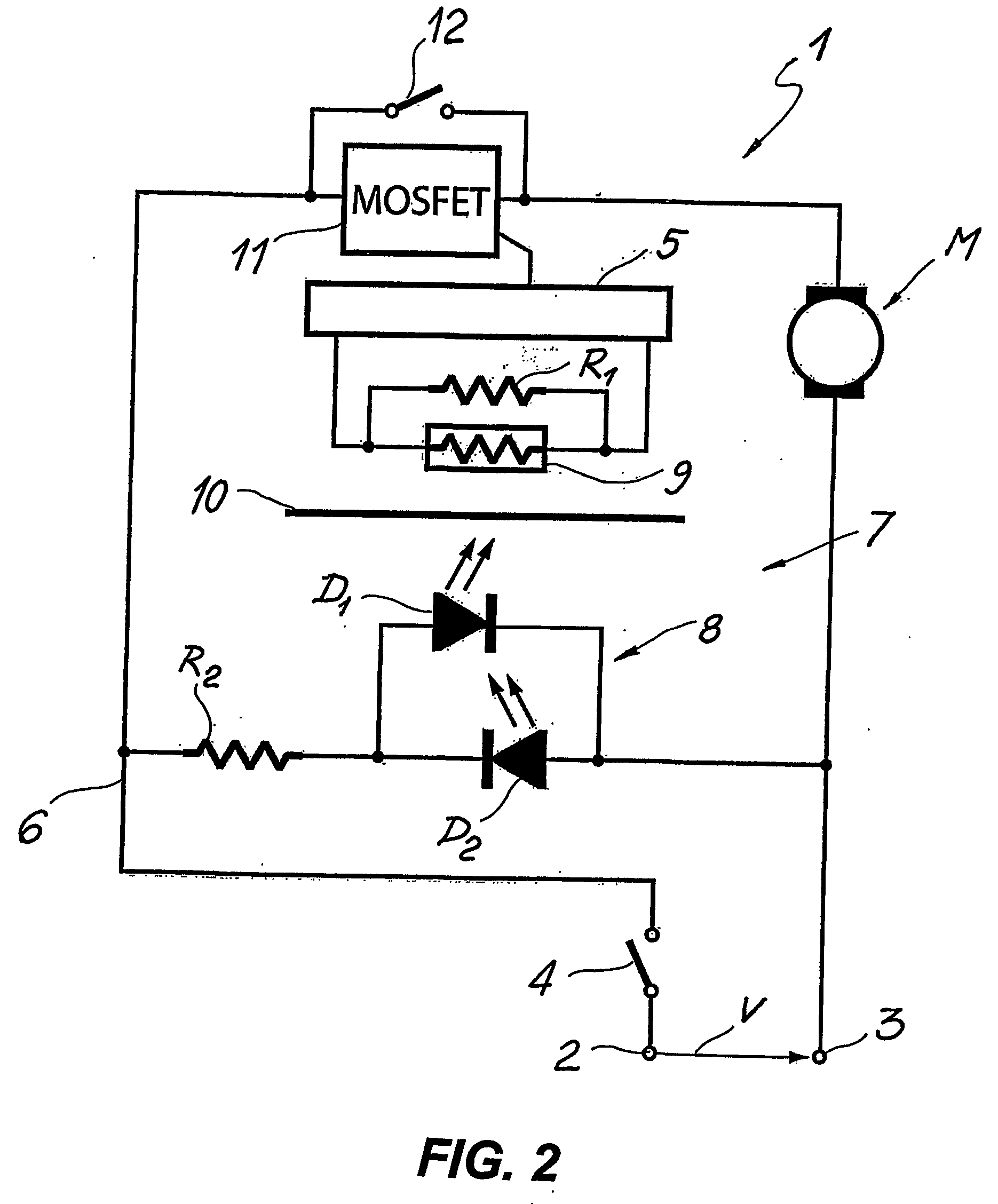
A device for controlling variable speed electric motors, particularly for hand held power tools and other miniaturised electrically powered apparatuses, comprises an electronic driver unit (5) connectable to the terminals (2, 3) of an electric power source for supplying electric current to at least one electric motor (M) and an optical switch device (7) for triggering the electronic driver unit (5). The optical switch device (7) comprises light emitting means (8) and light transducer means (9) for detecting and converting light into an electric variable signal. The light transducer means (9) are operatively connected to the electronic driver unit (5) for controlling the electric motor (M). The light emitter means (8) comprise at least one white light, high brightness LED (D1, D2) connected in parallel to the electric power line terminals (2, 3) by means of a miniaturised power circuit. The miniaturised power circuit comprises at least one resistor (R2) when said at least one electric motor (M) is a DC motor, and a capacitive phase displacement power supply (C, R2) when said electric motor is an AC motor. The capacitive phase displacement power supply (C, R2) comprises at least one capacitor (C) and an input resistor (R2) adapted to supply said diodes (D1, D2) with a threshold voltage.
Owner:POSITEC GROUP
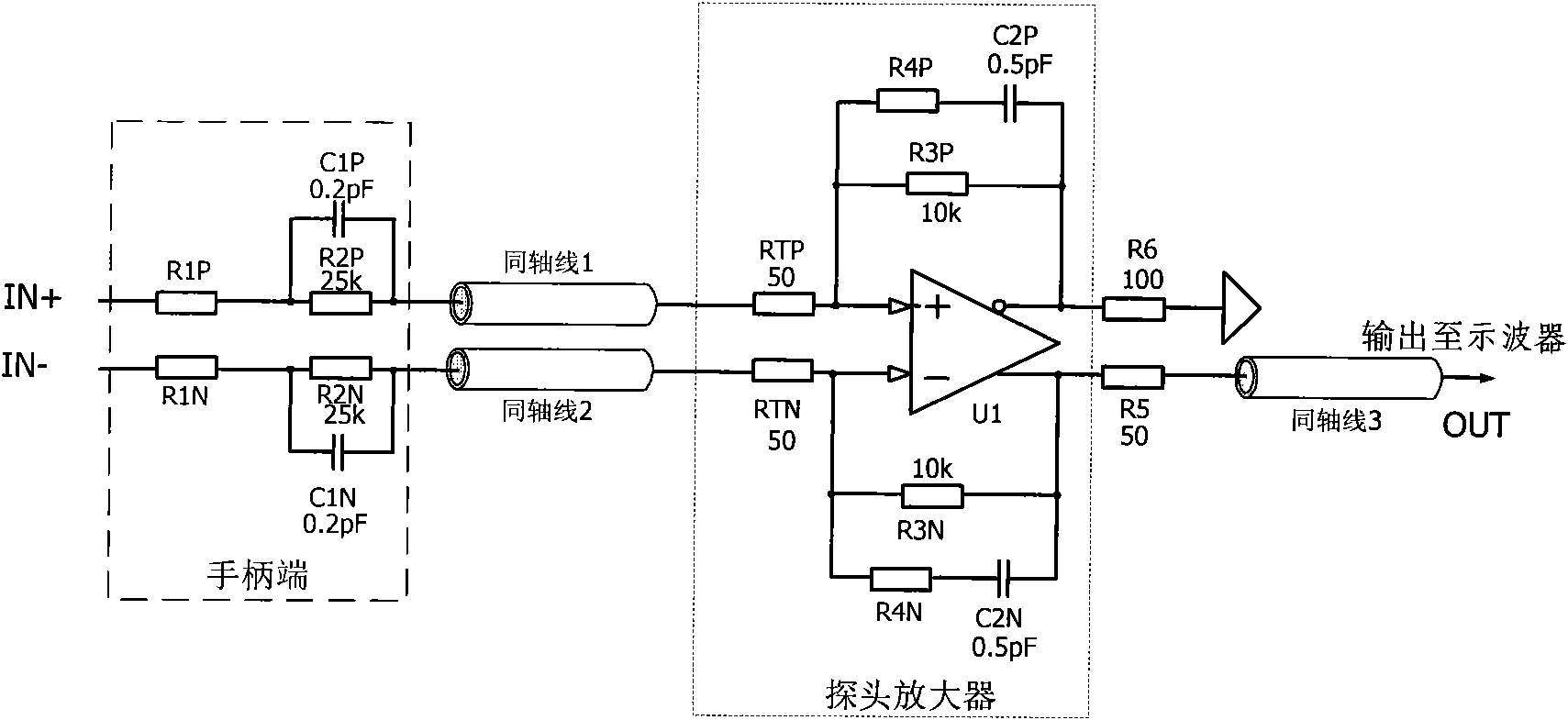
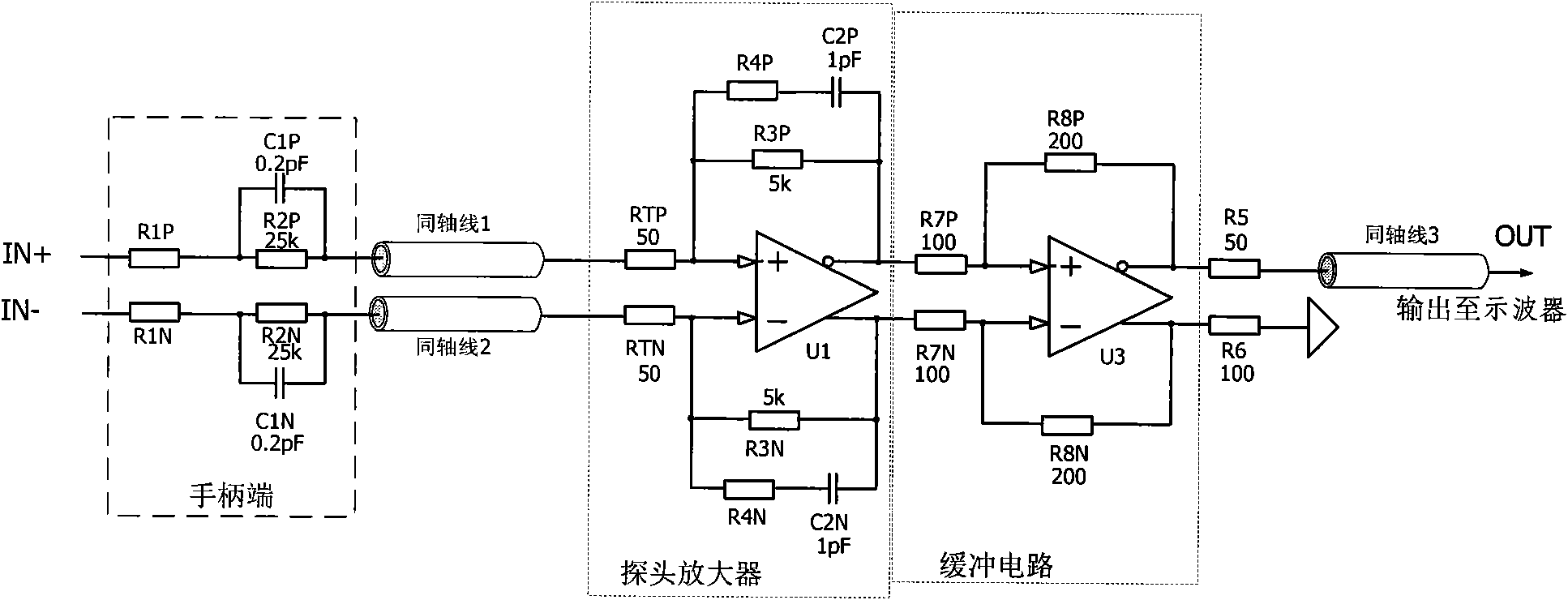
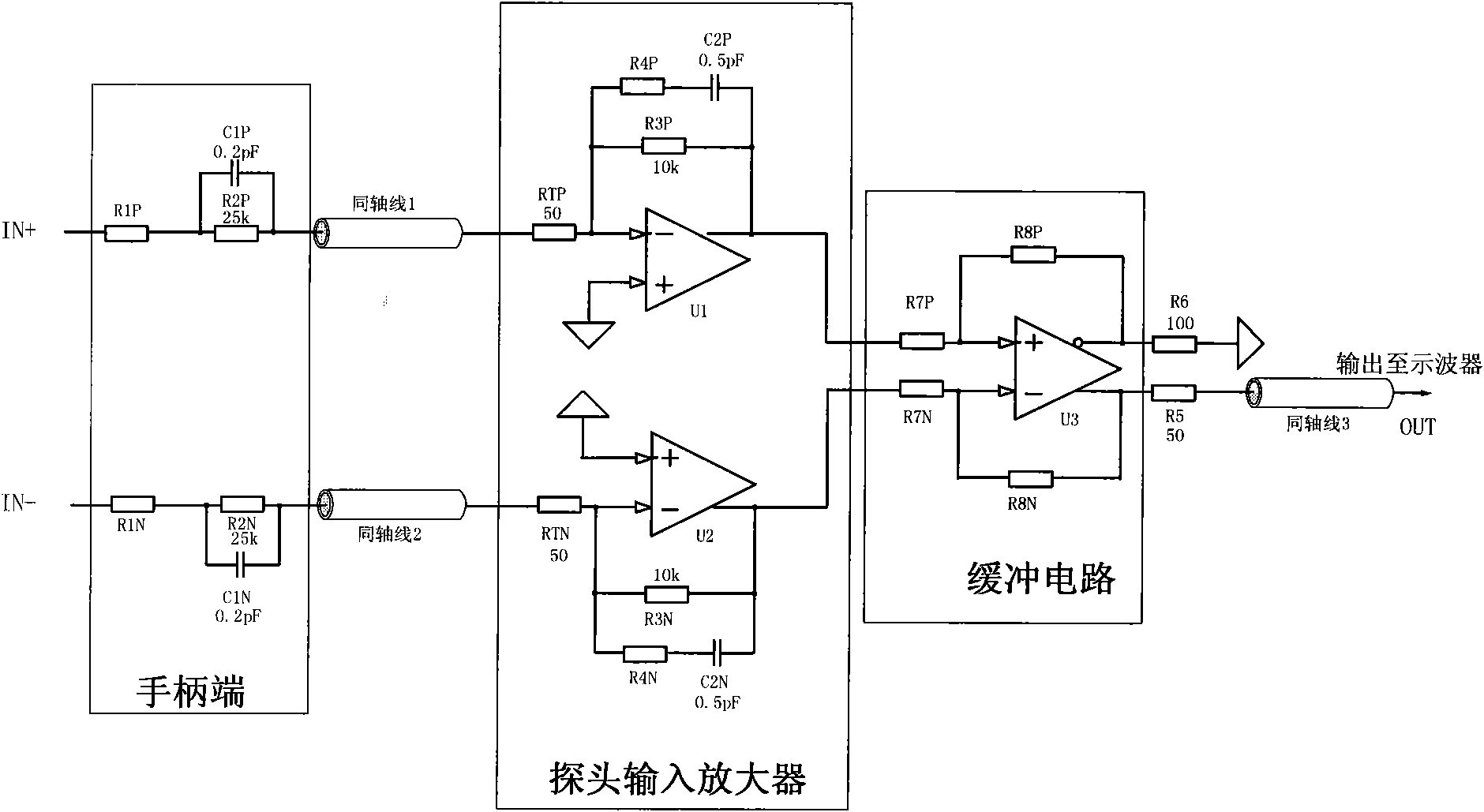
Active differential voltage probe
ActiveCN102053177AHigh input resistanceReduce input capacitanceElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention provides an active differential voltage probe composed of a handle end, a coaxial line and a probe amplifier. The active differential voltage probe provided by the invention has the advantages of higher input resistance, extremely low input capacitance and wider detection bandwidth after the circuit structure is improved. The interference of the probe to a measured signal is less, thus a distortionless detection signal is obtained. Besides, according to the invention, the detection performance of the probe can be further improved by adopting a multipolarity amplifier design method, thus the influence of the length of a probe line on the probe is less, and the frequency response of the probe is good.
Owner:RIGOL
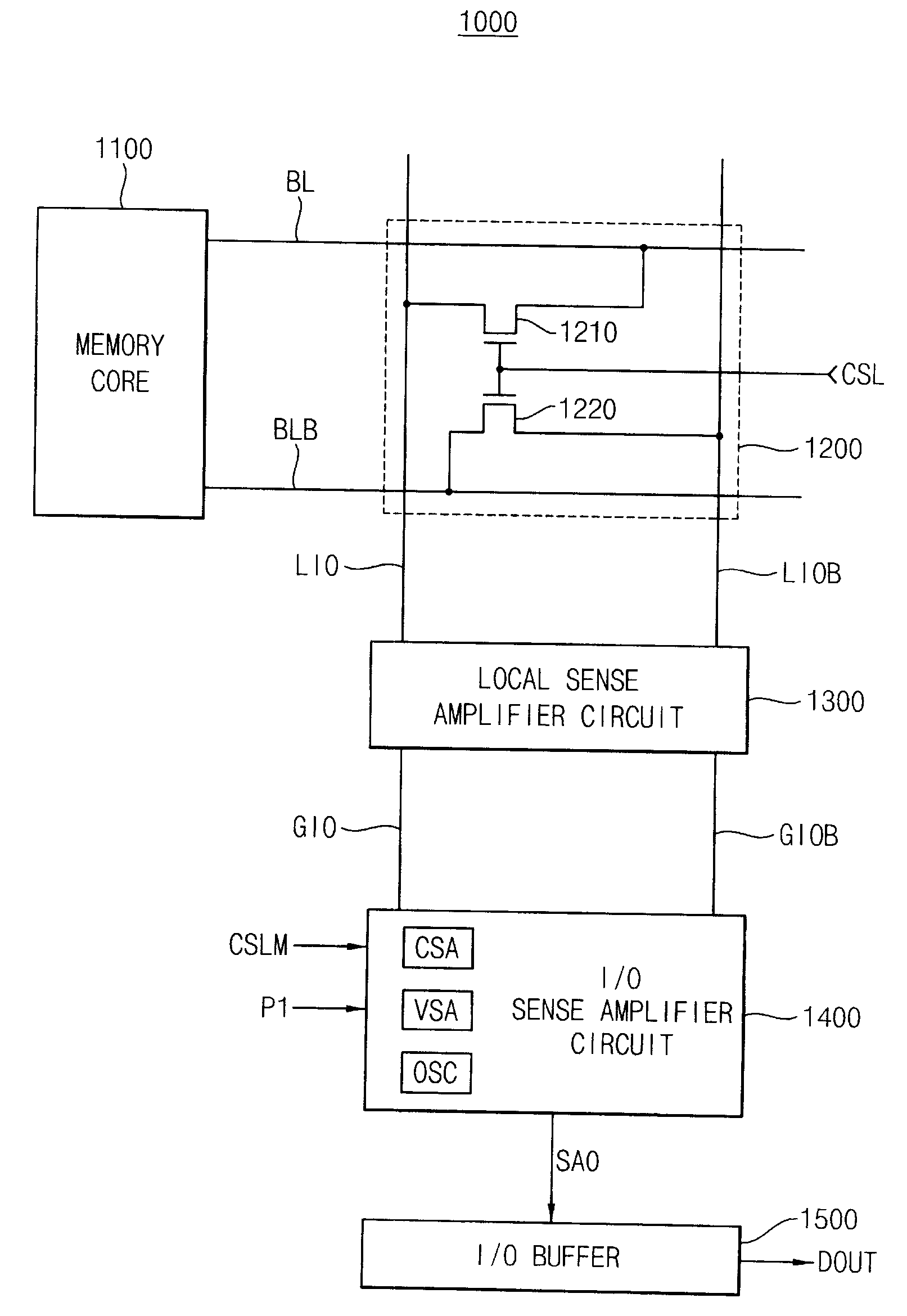
Sense amplifier and semiconductor memory device having the same
ActiveUS20090010086A1High amplification gainShorten induction timeCurrent/voltage measurementRead-only memoriesAudio power amplifierSemiconductor chip
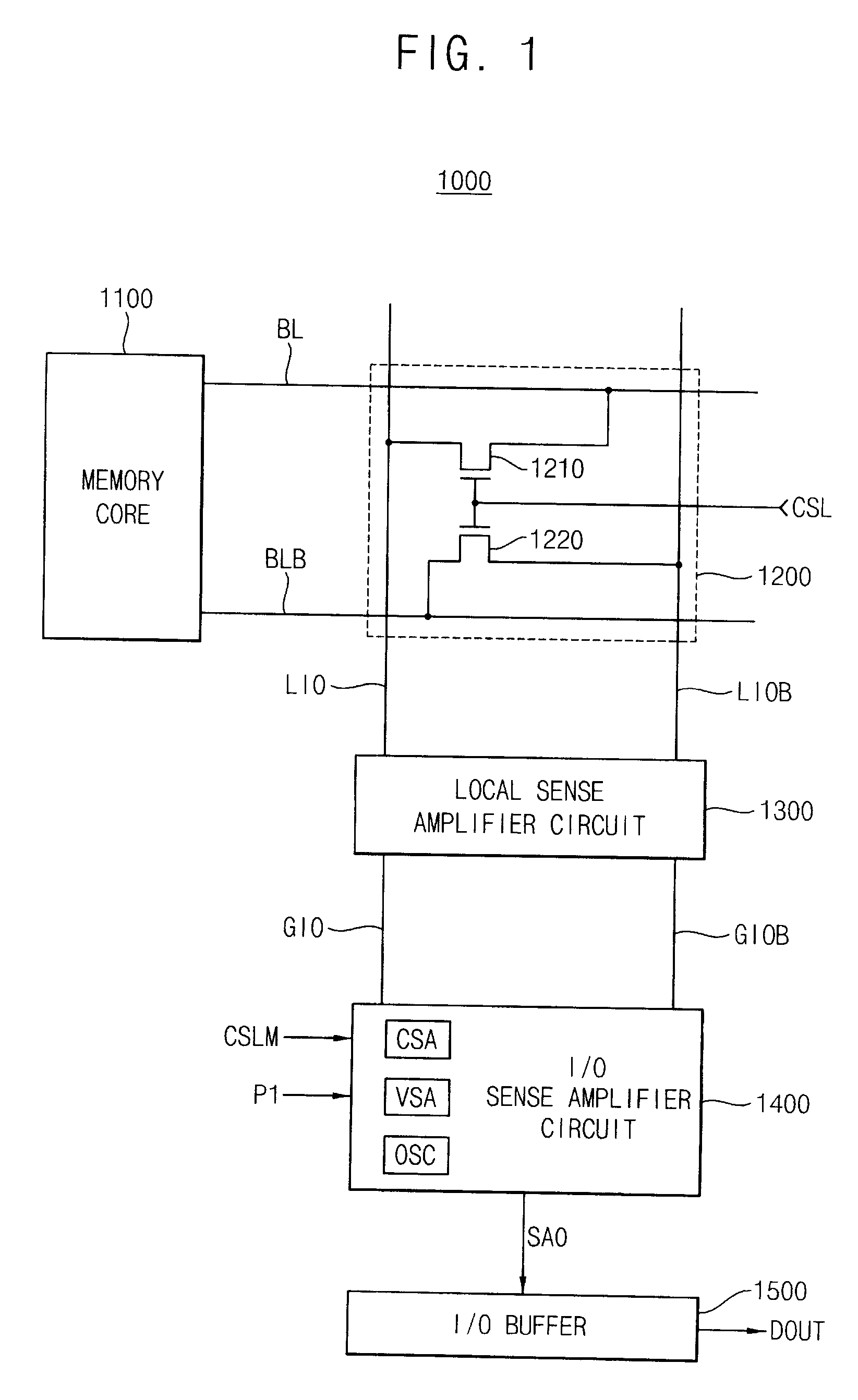
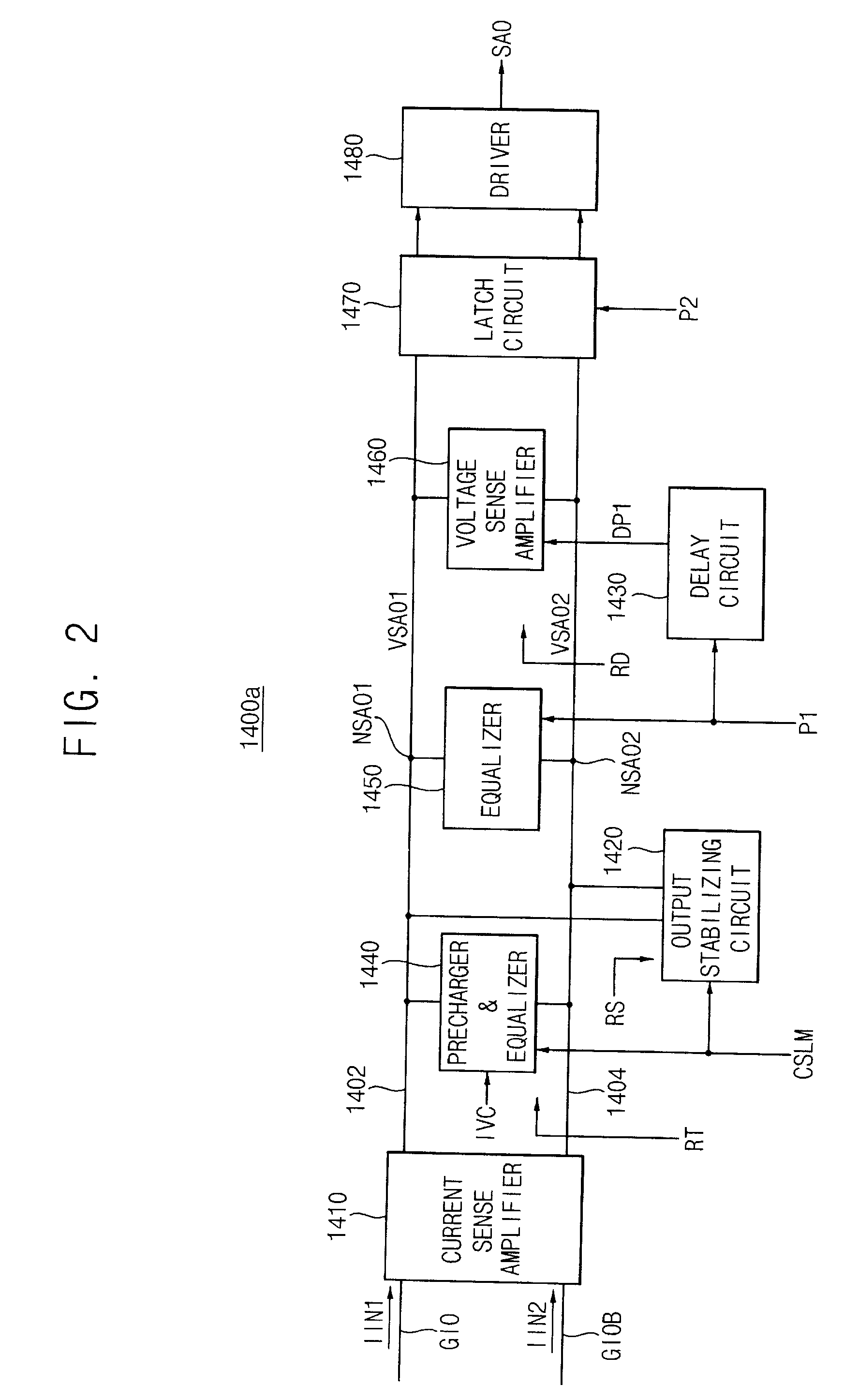
A sense amplifier circuit includes a current sense amplifier, a voltage sense amplifier, and an output stabilizing circuit. The current sense amplifier amplifies differential input currents to generate differential output voltages and provides the differential output voltages to a sense amplifier output line pair. The voltage sense amplifier is coupled to the sense amplifier output line pair to amplify the differential output voltages on the sense amplifier output line pair. The voltage sense amplifier is activated at the time later than a time of activation of the current sense amplifier. The output stabilizing circuit is coupled to the sense amplifier output line pair to stabilize the differential output voltages on the sense amplifier output line pair. The output stabilizing circuit has a positive input resistance. Accordingly, the sense amplifier circuit reduces power consumption and an occupied area on a semiconductor chip.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Linear voltage tracking amplifier for negative supply slew rate control
ActiveUS20050052209A1Low costAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationElectric analogue storesLevel shiftingAudio power amplifier
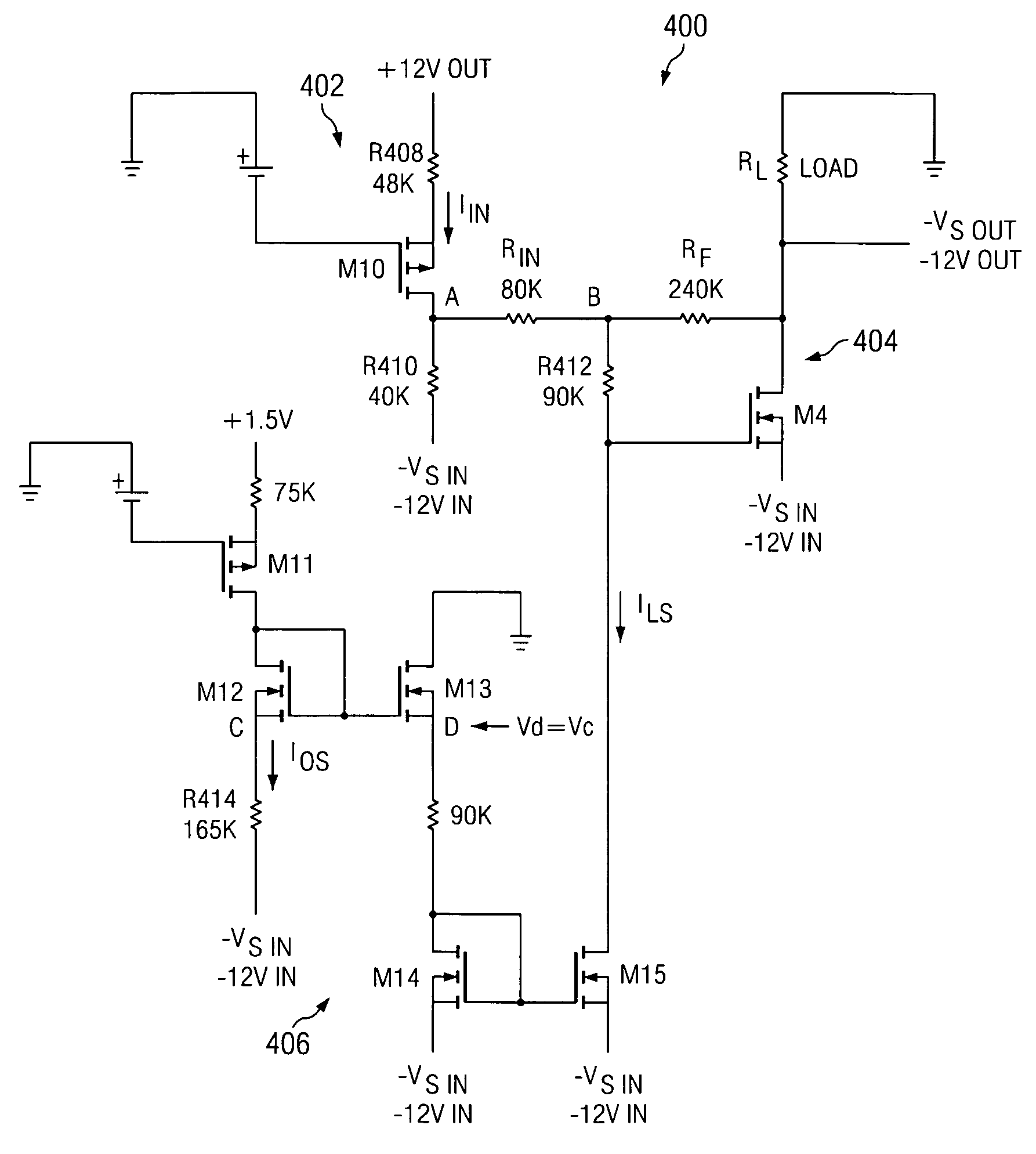
Circuitry is provided for controlling the slew rate of a negative output supply. The slew rate control circuitry includes an NMOS FET, a feedback resistor connected across the drain and the gate of the NMOS FET, an input resistor connected to the gate of the NMOS FET, level shifting circuitry connected between a positive output supply voltage and the input resistor, and a bias current source connected to the gate of the NMOS FET. A negative input supply voltage is connected to the source of the NMOS FET, and the negative output supply voltage is provided across a load connected to the drain of the NMOS FET. As the positive supply voltage ramps up from 0 to +VS, the level shifter provides a voltage to the input resistor that ramps up from −VS to 0 volts. Further, the drain voltage of the NMOS FET ramps down from 0 to −VS, thereby providing a negative output supply voltage −VS with a slew rate that linearly tracks the slew rate of the master positive output supply.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Stable sense amplifier
InactiveUS20080048728A1Stable differential amplifying operationHigh differential amplification gainCurrent/voltage measurementDigital storageAudio power amplifierSense amplifier
In an embodiment, a sense amplifier can perform a stable differential amplifying operation while having a high differential amplification gain. The sense amplifier comprises a current sense amplification unit, a voltage difference amplification unit, and an output stabilization unit. The current sense amplification unit receives differential input currents and generates differential output voltages corresponding to the differential input currents. The voltage difference amplification unit amplifies a voltage level difference between the differential output voltages through positive feedback using cross-coupled transistors. The output stabilization unit connects output stabilizing elements having a positive input resistance in parallel with the voltage difference amplification unit having a negative input resistance to stabilize the output of the voltage difference amplification unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Variable gain amplifier circuit and filter circuit
ActiveUS20080197924A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
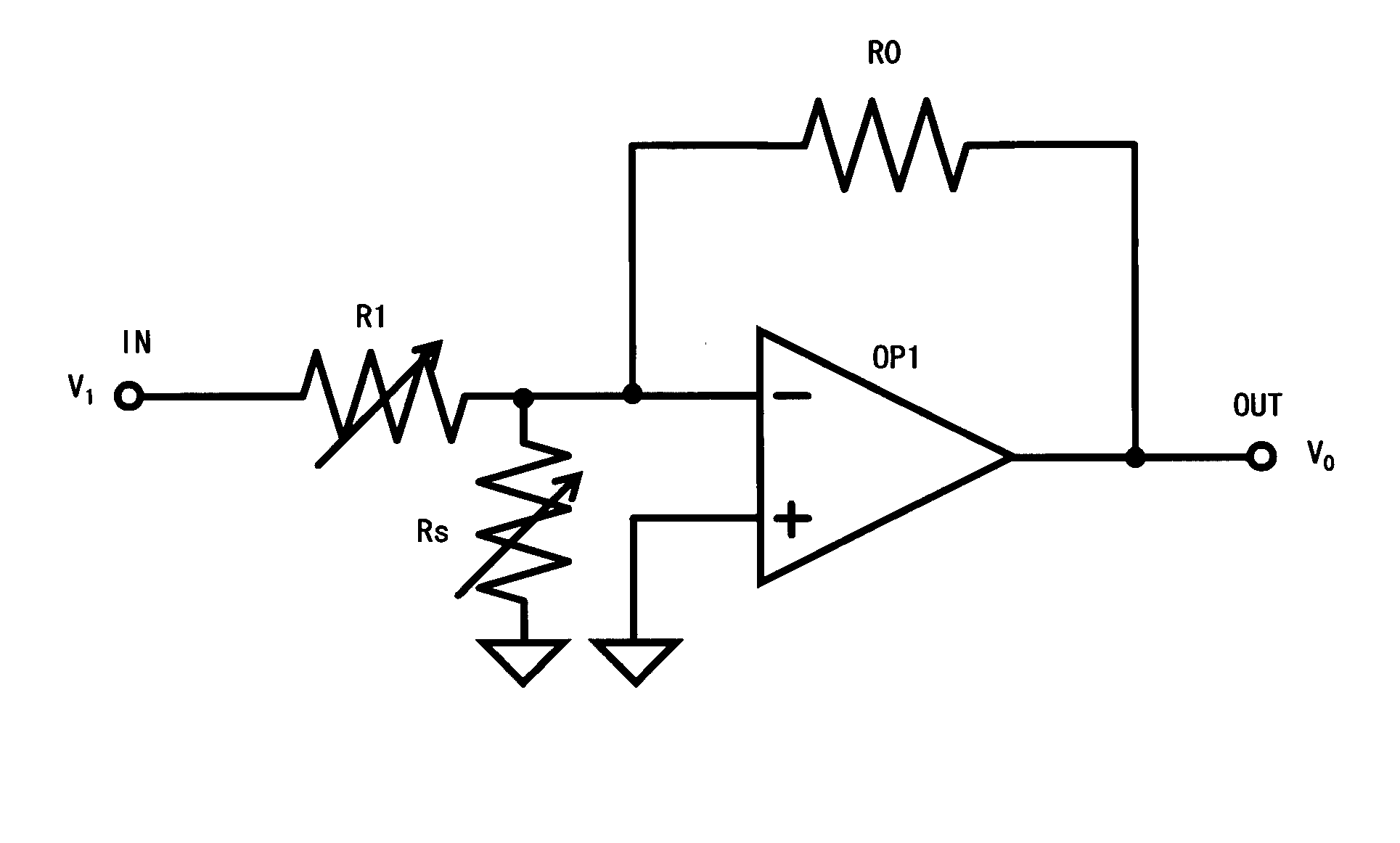
This variable gain amplifier is provided with an operational amplifier. The non-inversion input terminal of the operational amplifier is connected to a reference potential. A feedback resistor is connected between the output terminal and inversion input terminal of the operational amplifier. An input resistor is inserted between the inversion input terminal of the operational amplifier and the input terminal of the variable gain amplifier circuit. An adjustment resistor is connected between the inversion input terminal of the operational amplifier and the reference potential. The resistance value of the adjustment resistor is controlled in such a way as to maintain constant against the resistance value change a combined resistance value in its parallel connection with the input resistor when changing the resistance value of the input resistor.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com