Patents
Literature
724 results about "Switching power converter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
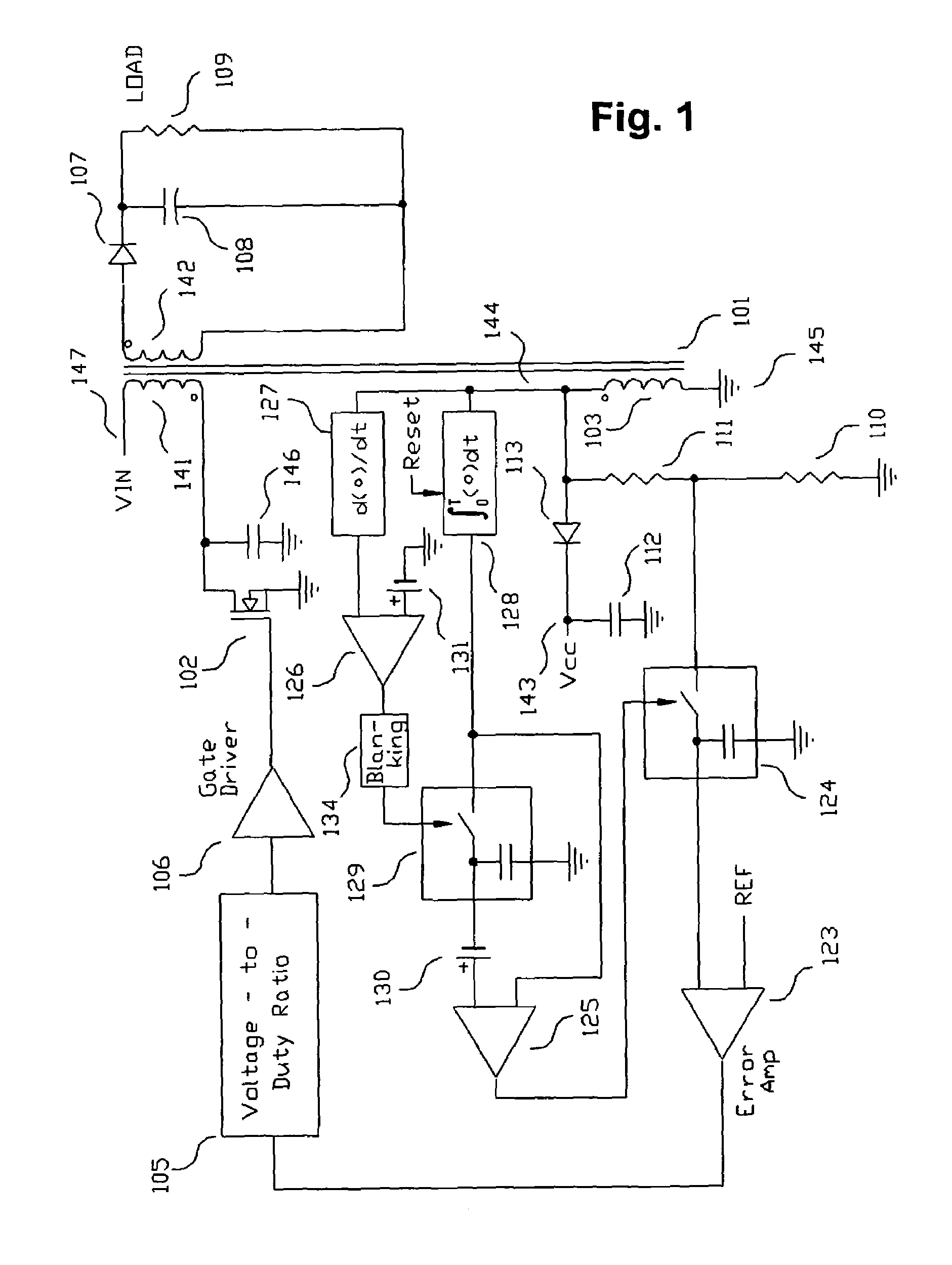
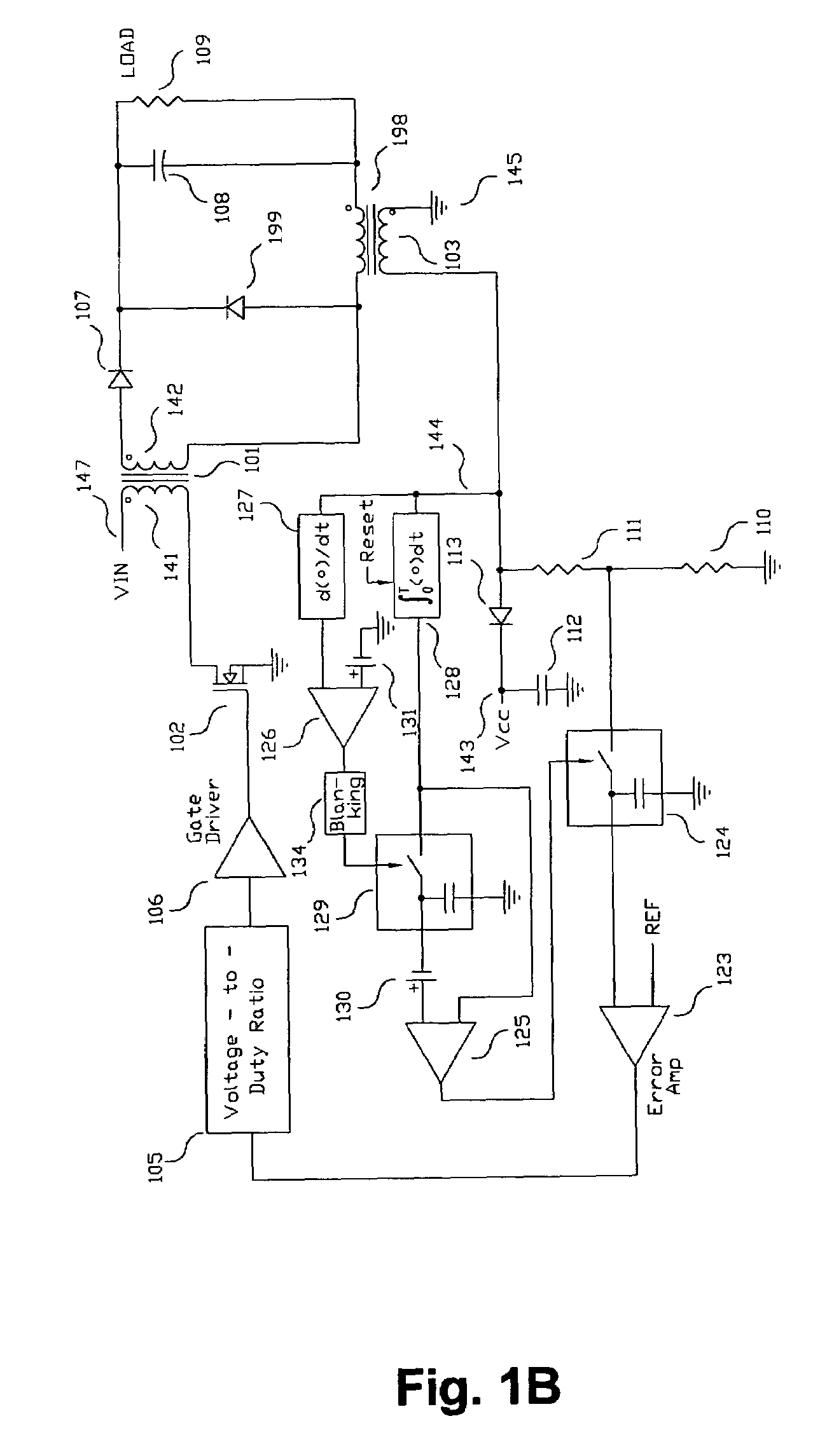
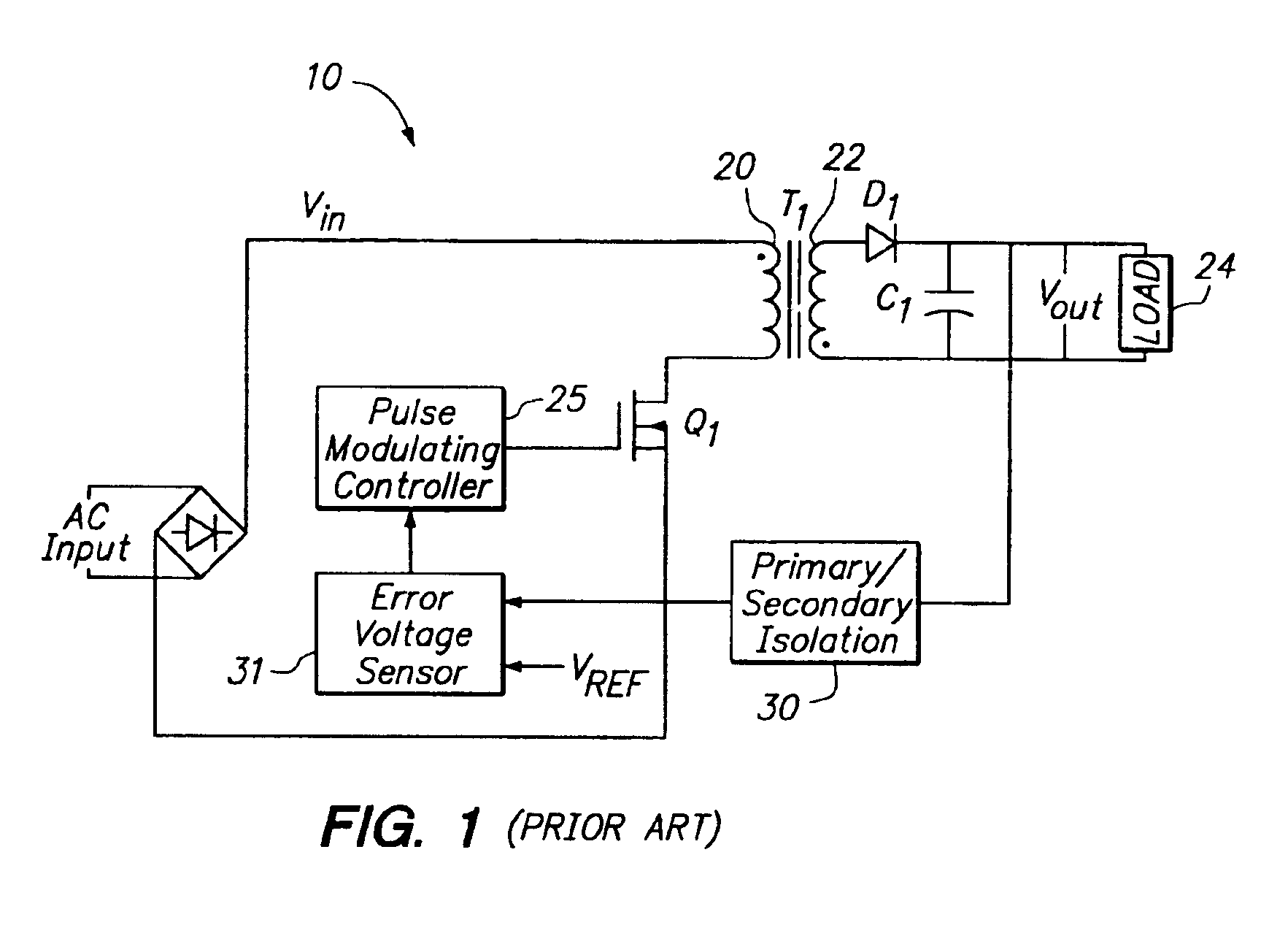
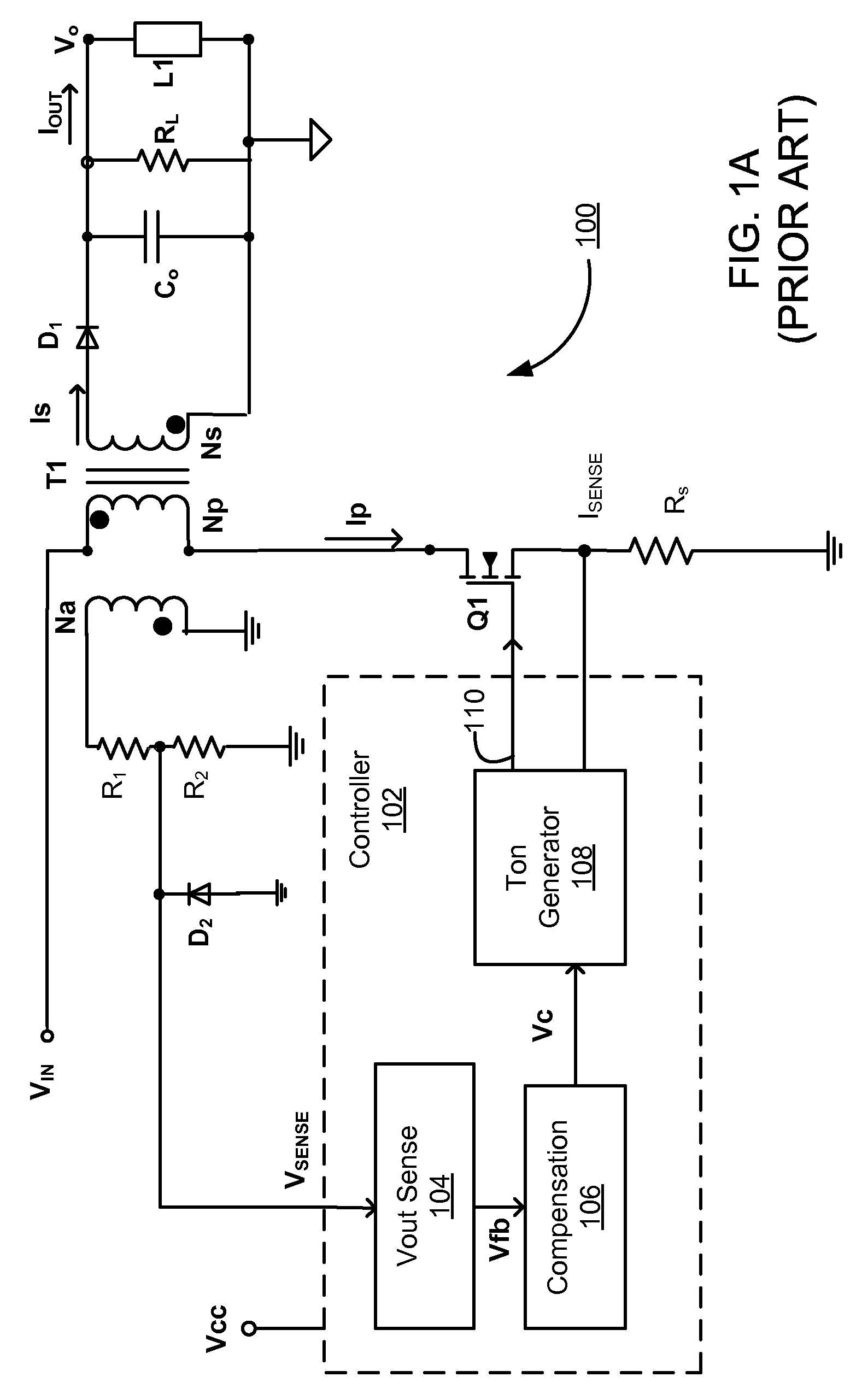
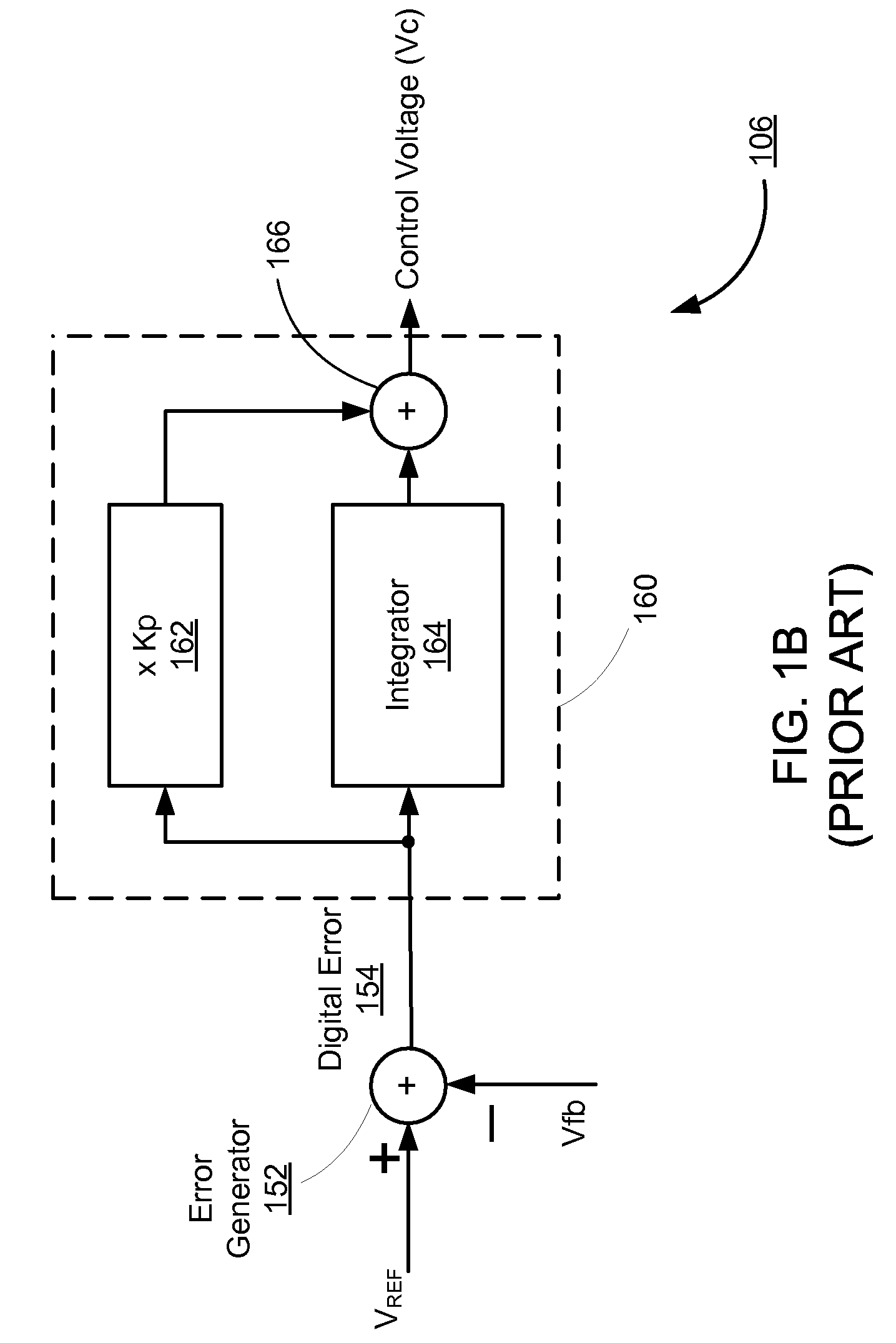
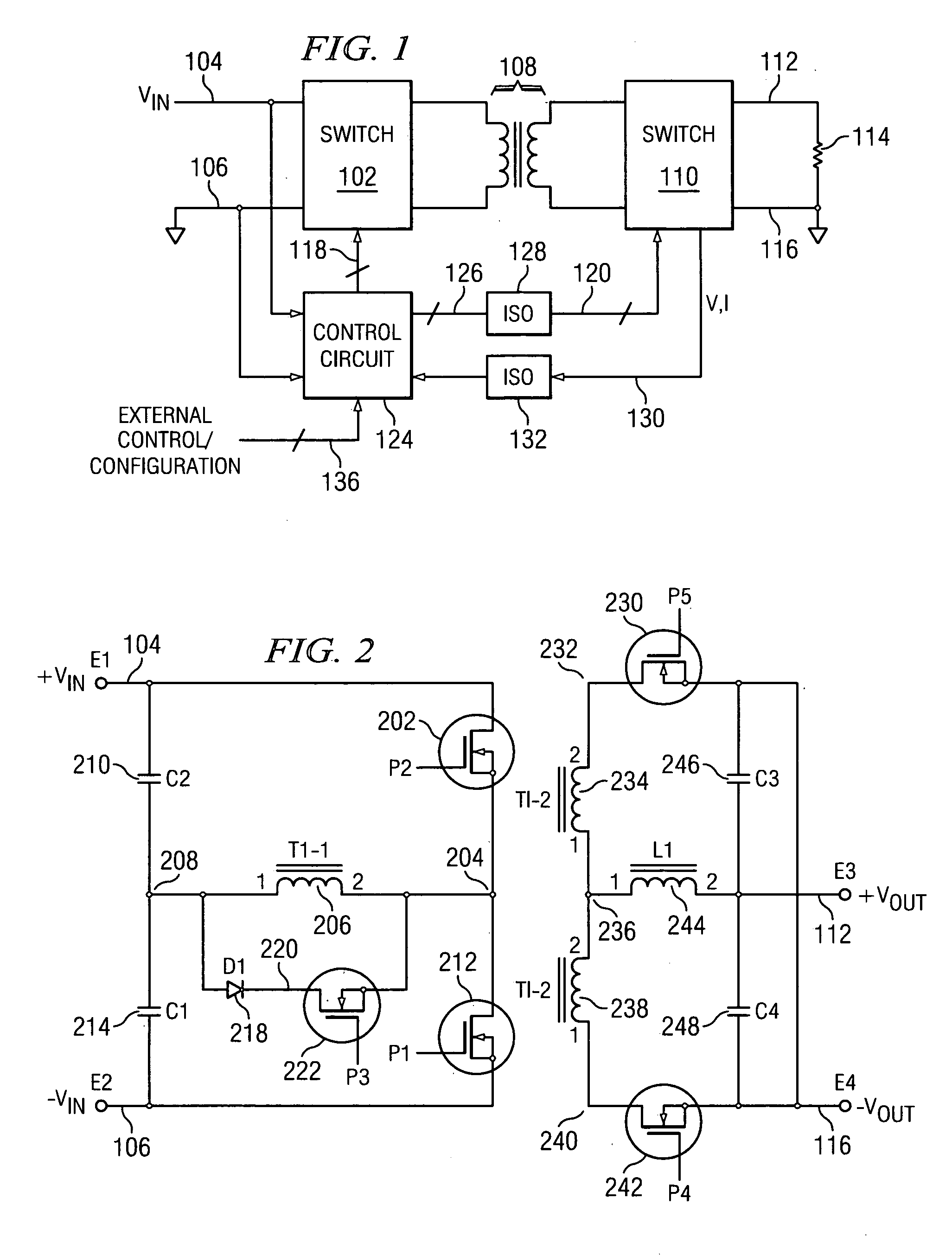
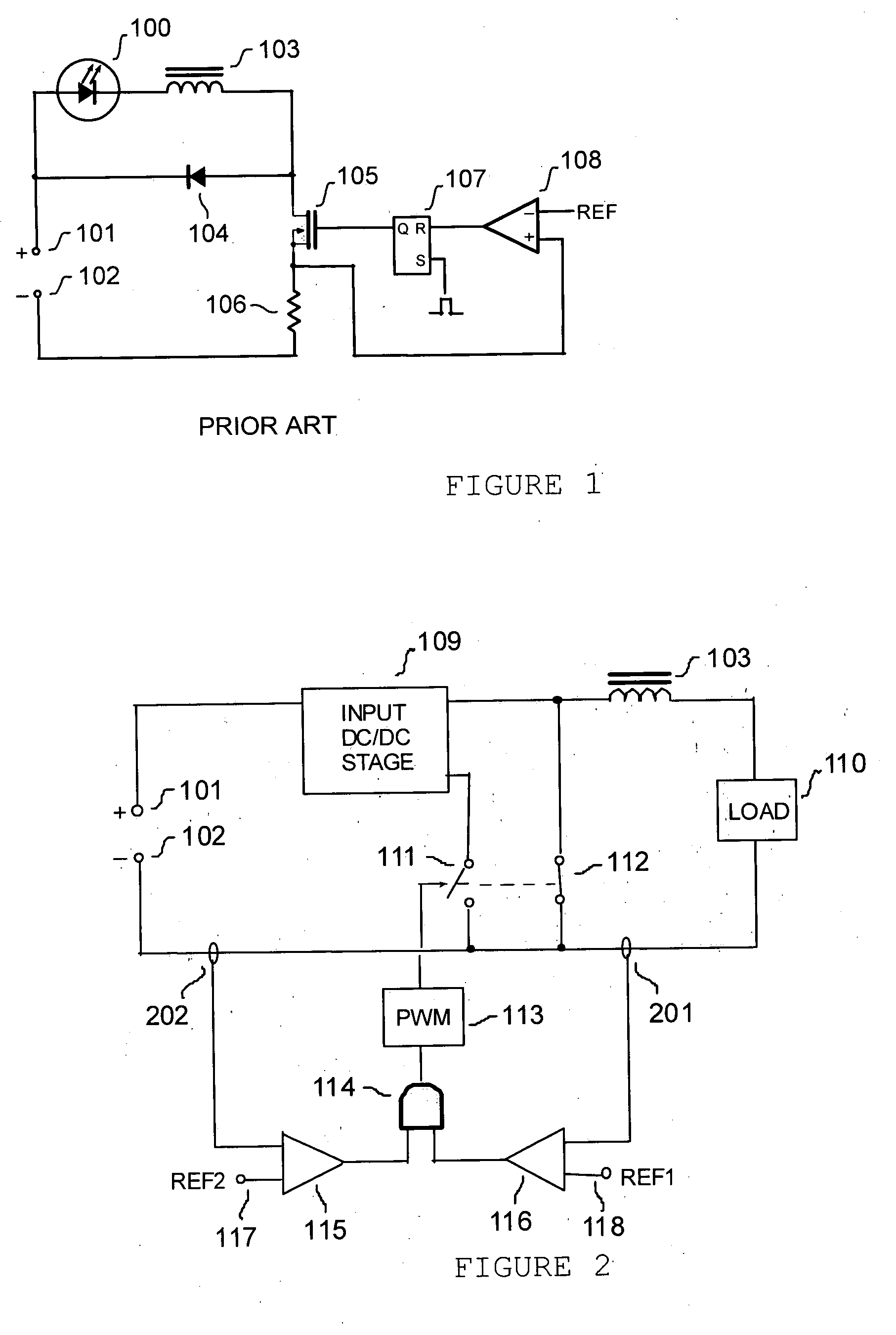
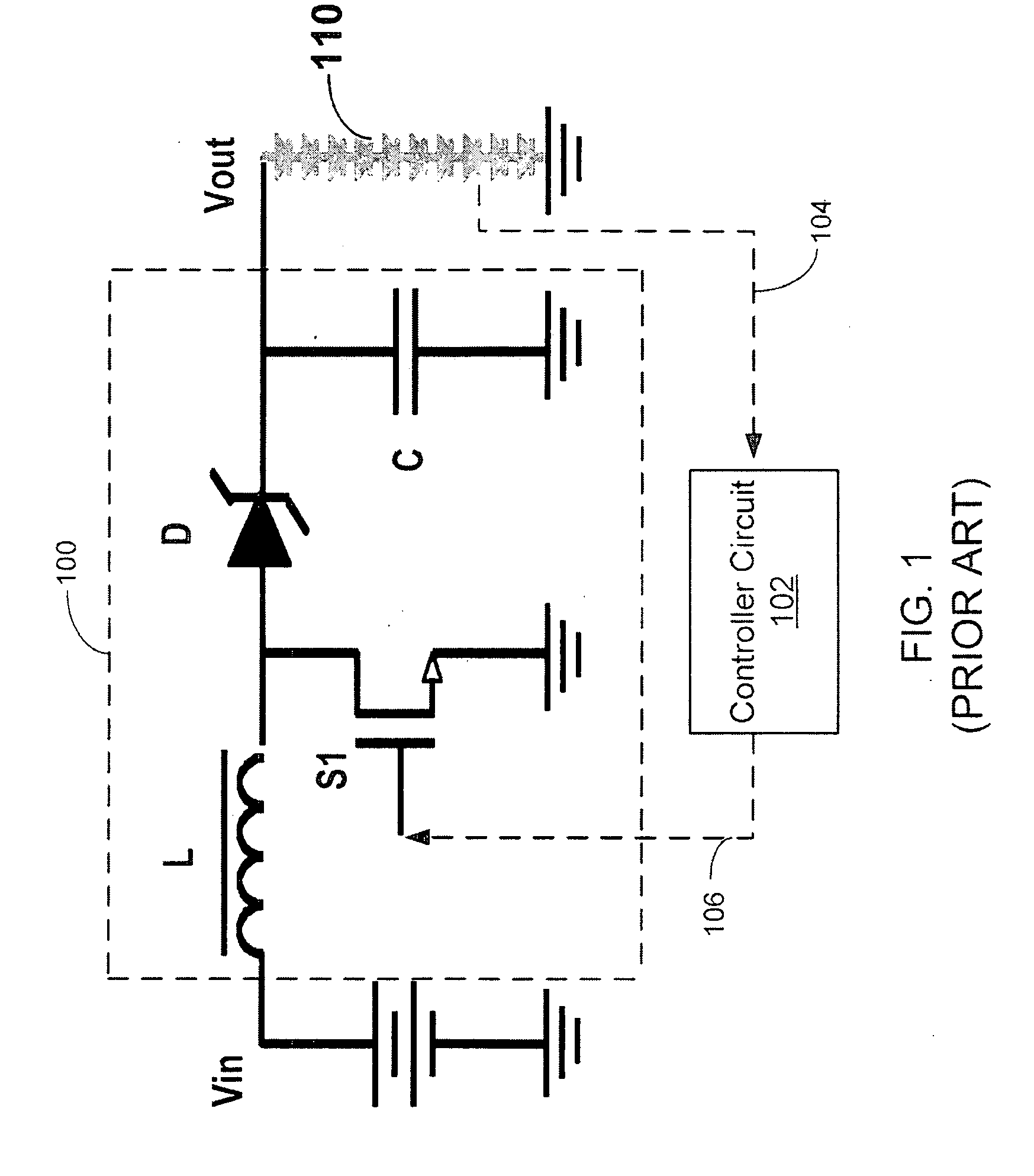
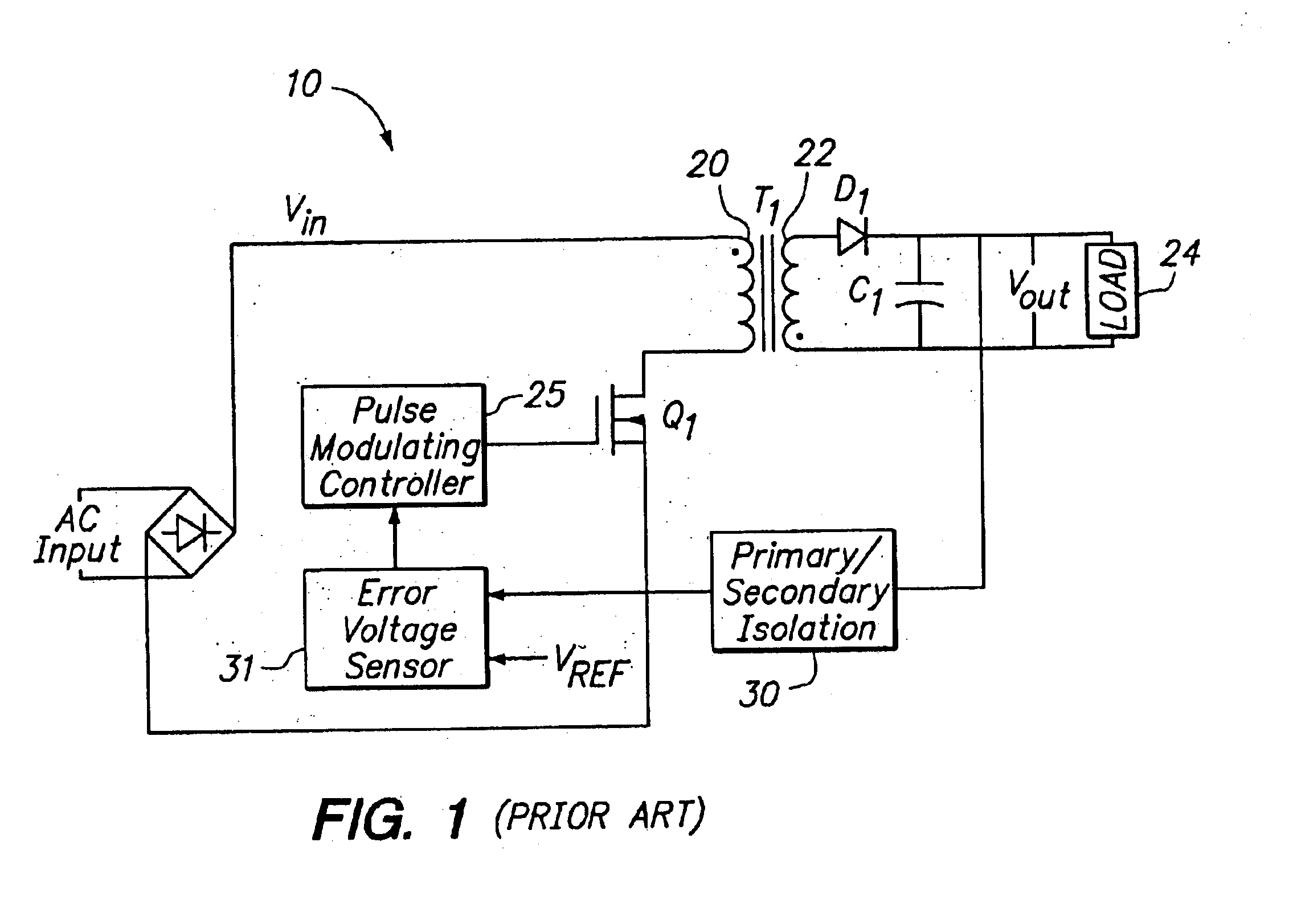
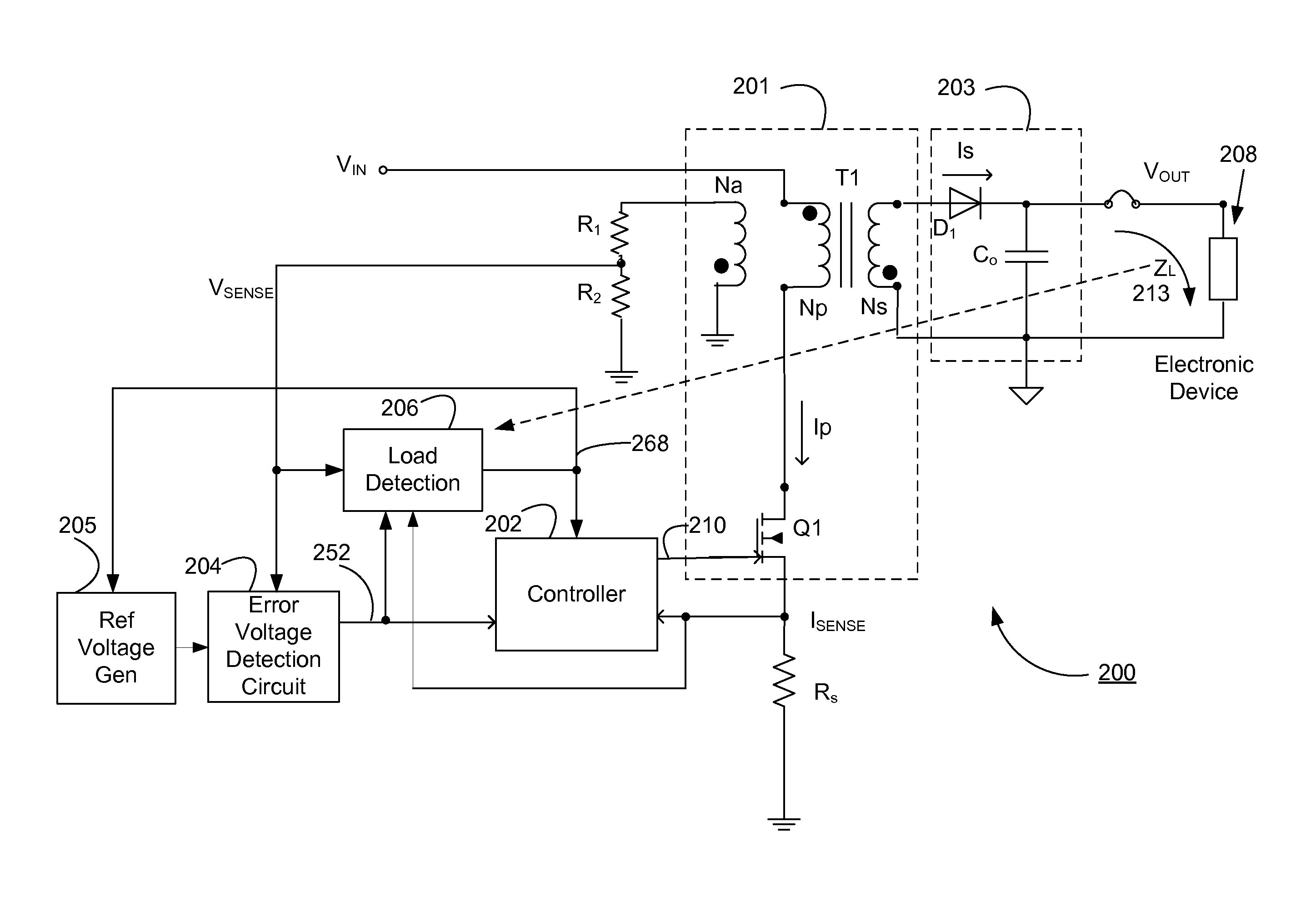
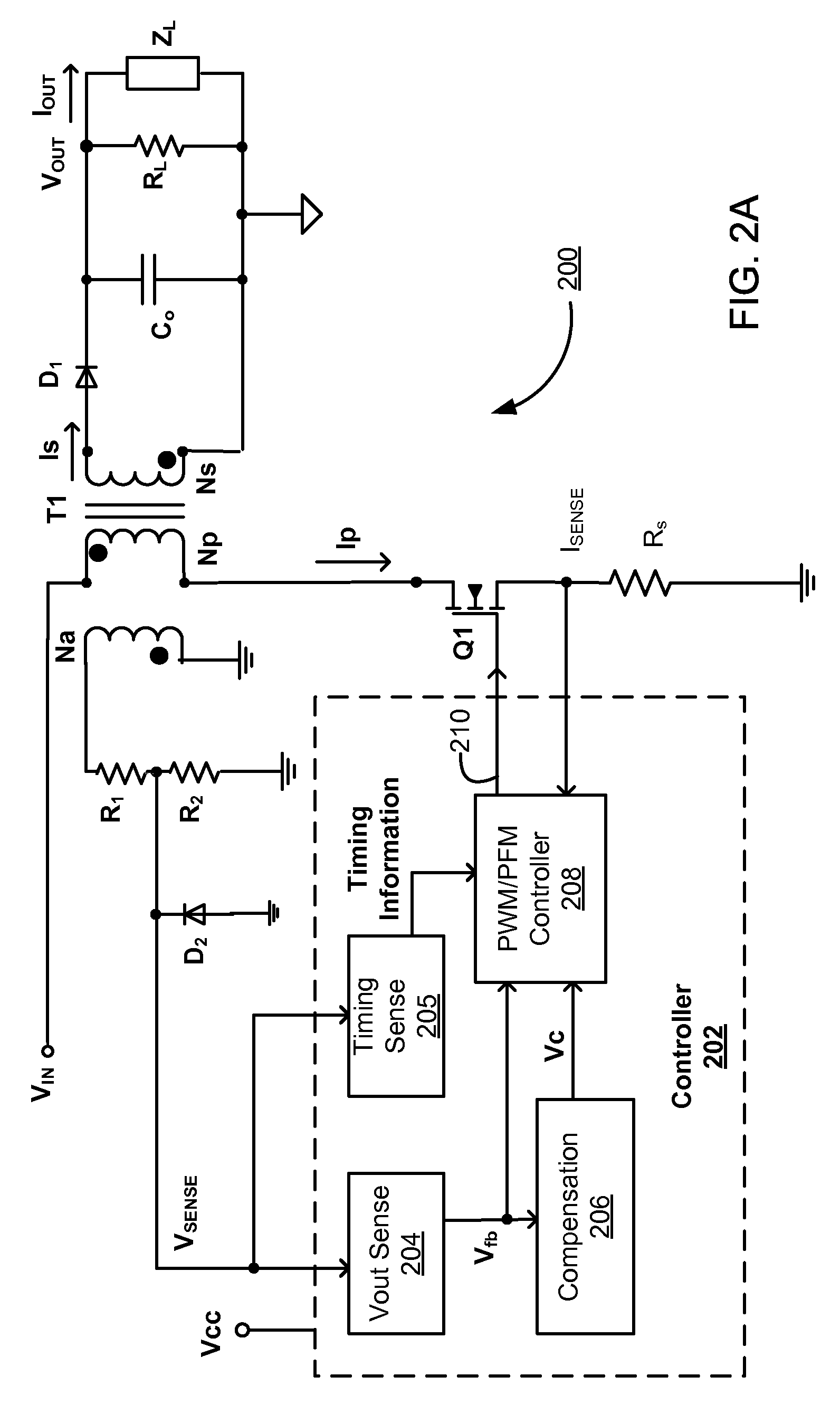
Switching power converter and method of controlling output voltage thereof using predictive sensing of magnetic flux
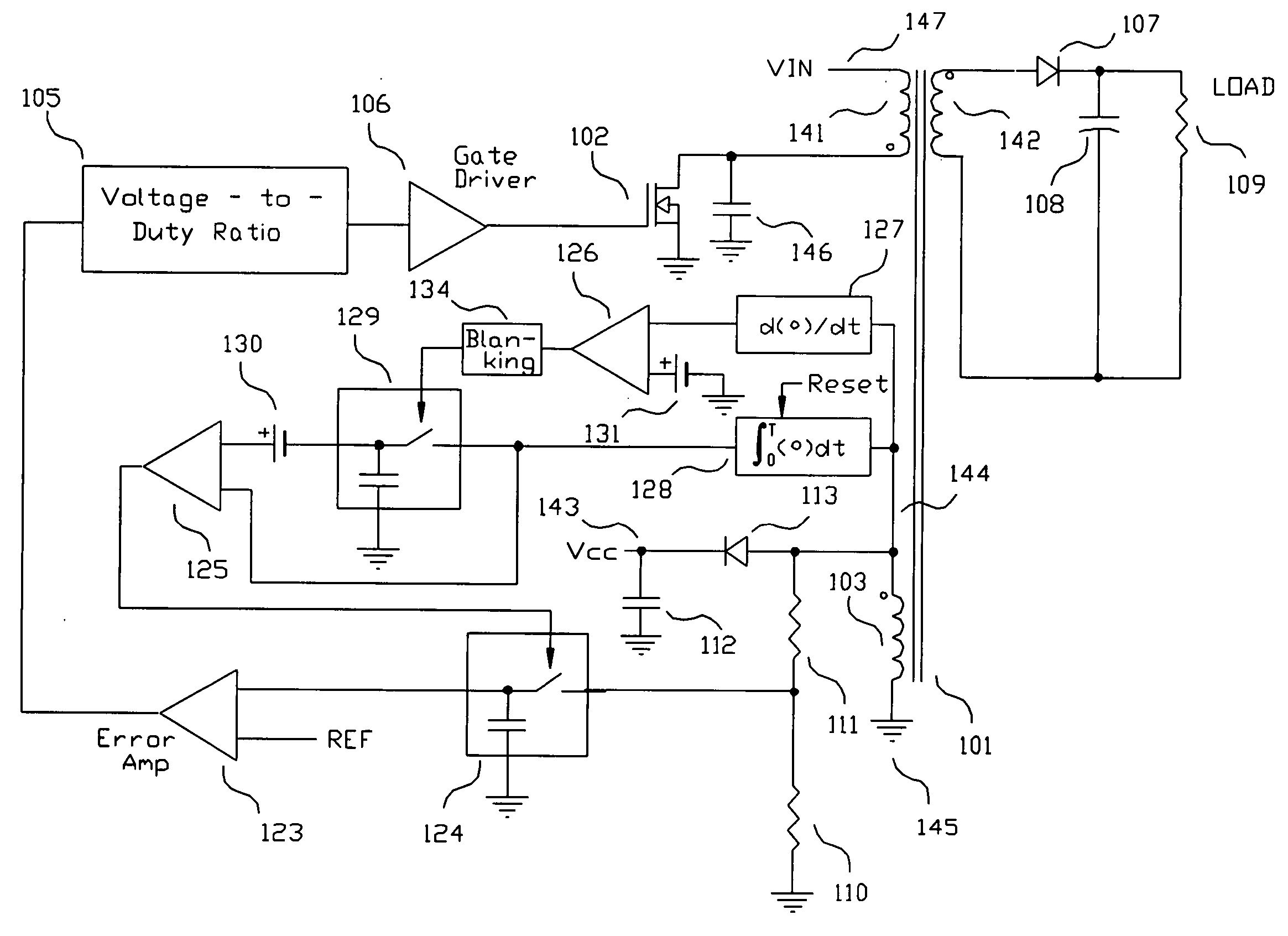
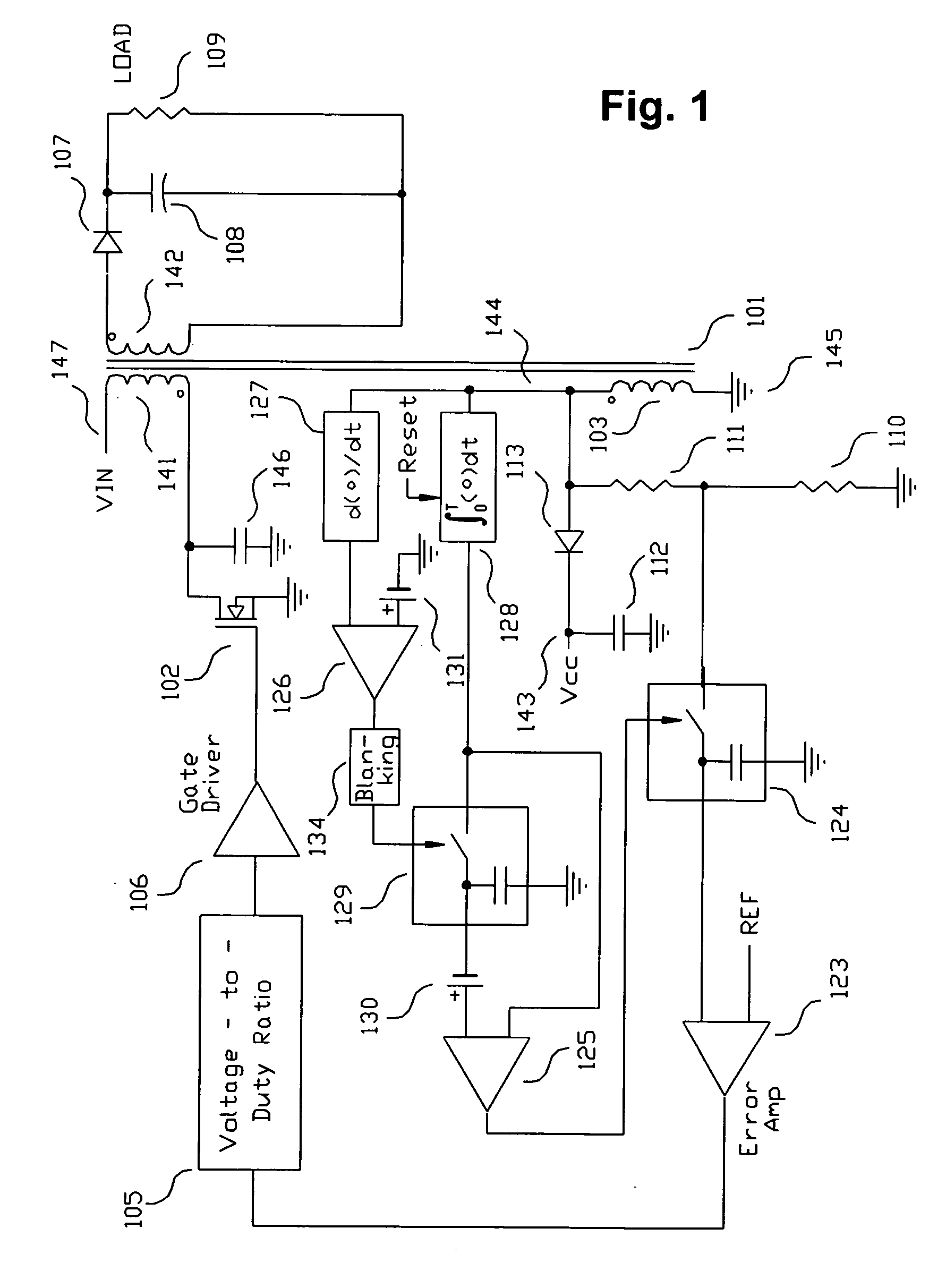
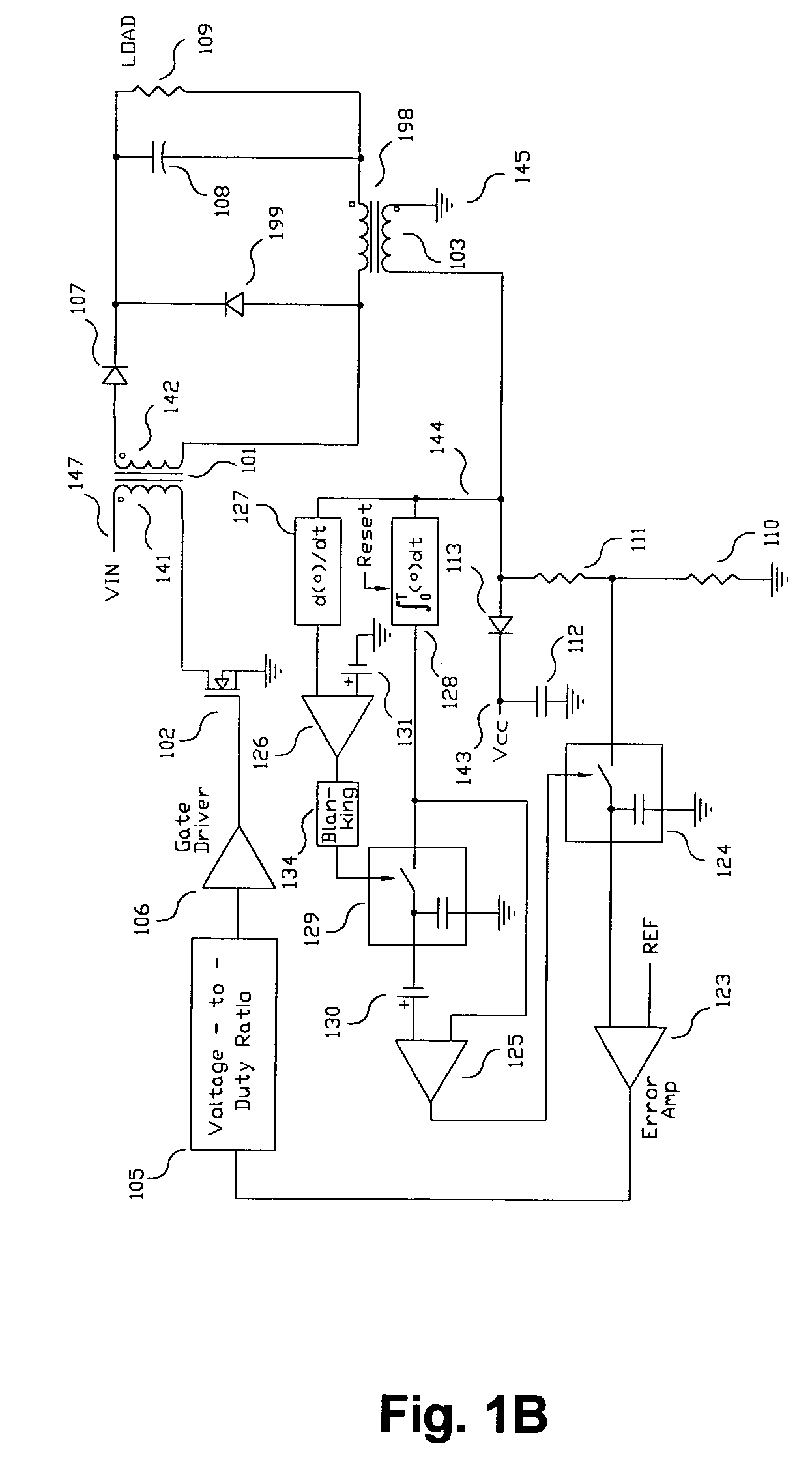
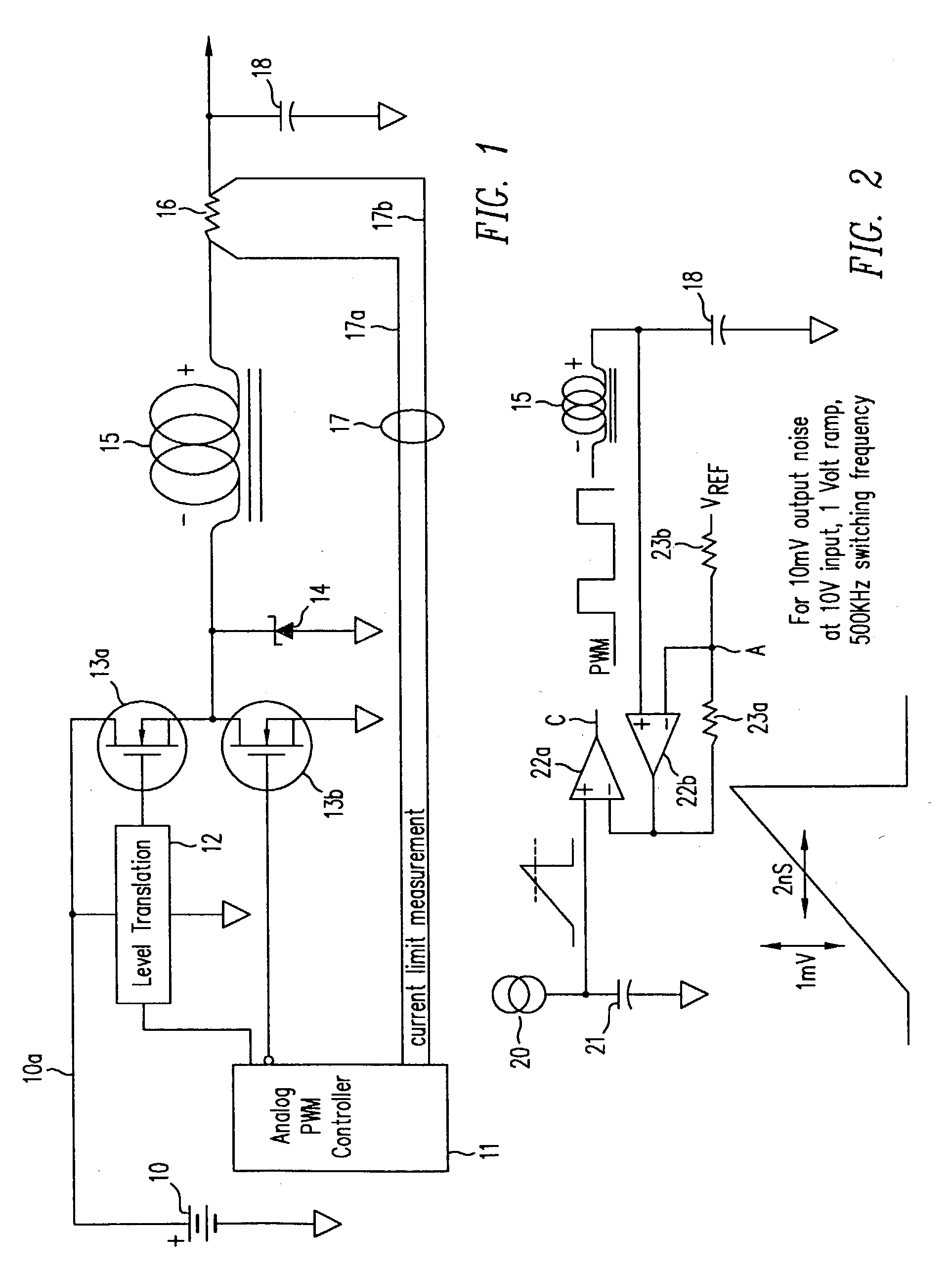
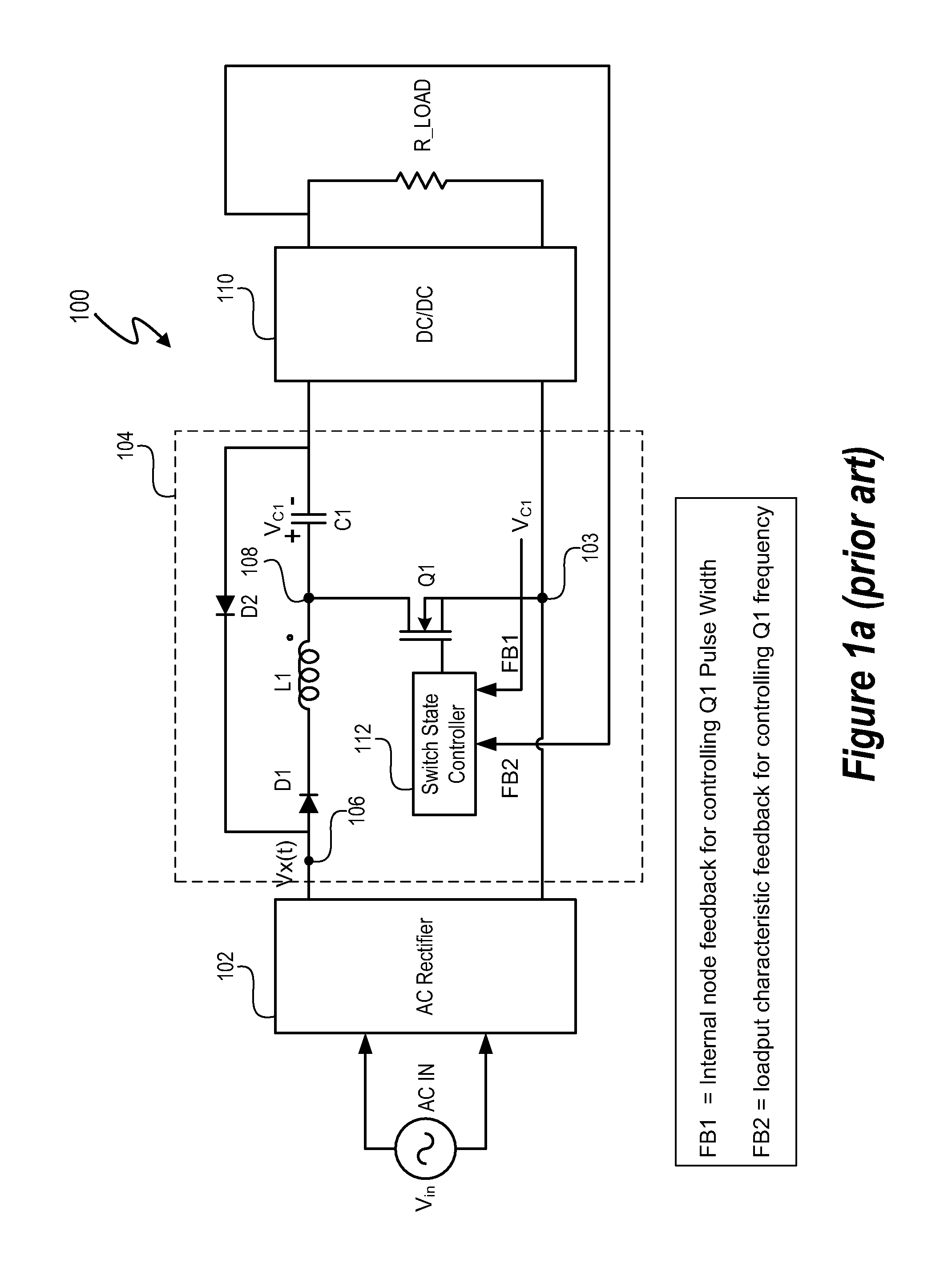
A switching power converter and method of controlling an output voltage thereof using predictive sensing of magnetic flux provides a low-cost switching power converter via primary-side control using a primary-side winding. An integrator generates a voltage that represents flux within a magnetic element by integrating a primary-side winding voltage. A detection circuit detects the end of a half-cycle of post-conduction resonance that occurs in the power magnetic element subsequent to zero energy level in the power magnetic element. The integrator voltage is stored at the end of the half-cycle and is used to determine a sampling point prior to or equal to the start of post-conduction resonance in a subsequent switching cycle of the power converter. The primary-side winding voltage is then sampled at the sampling point, providing an indication of the output voltage of the power converter by which the output voltage of the converter can be controlled.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
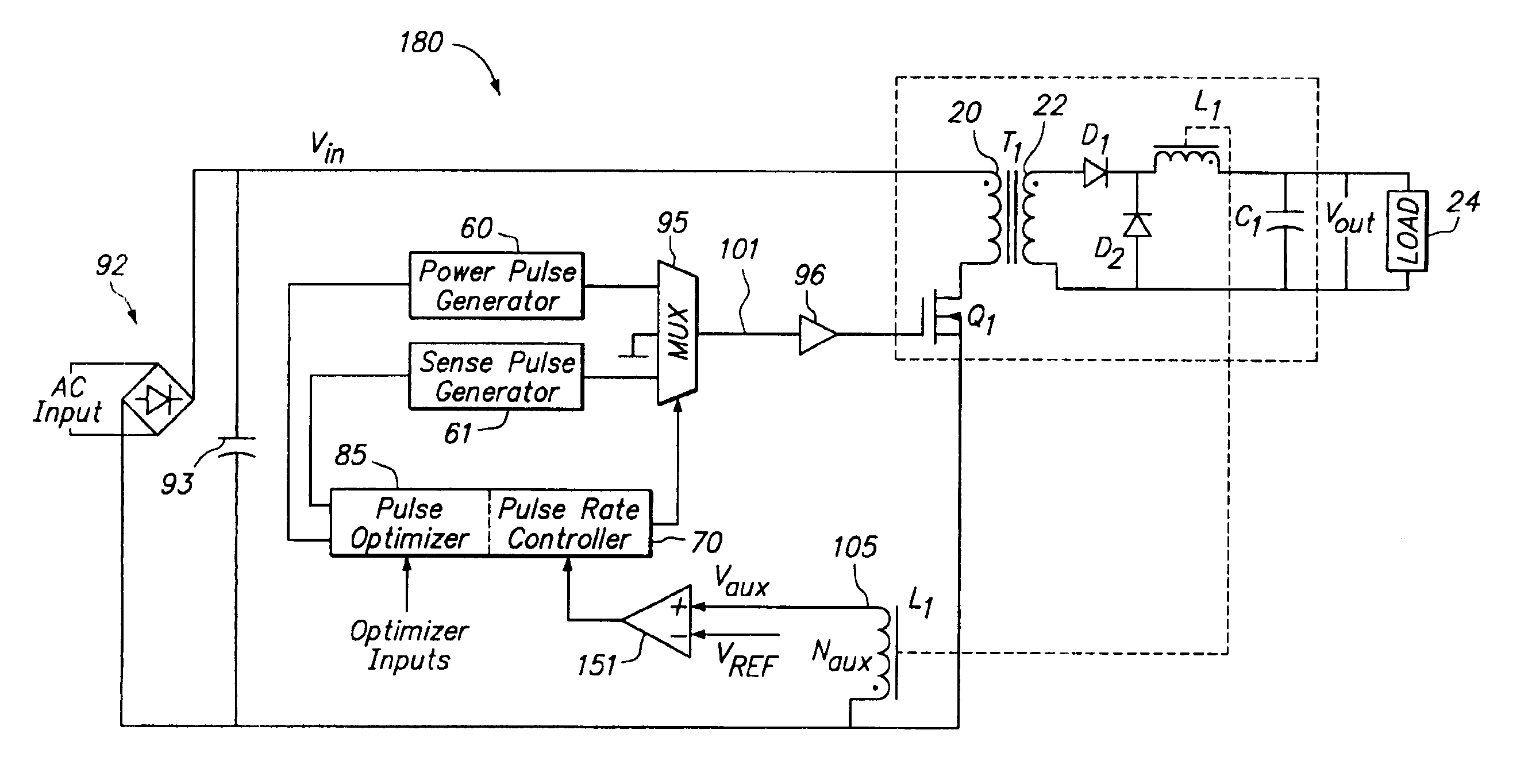
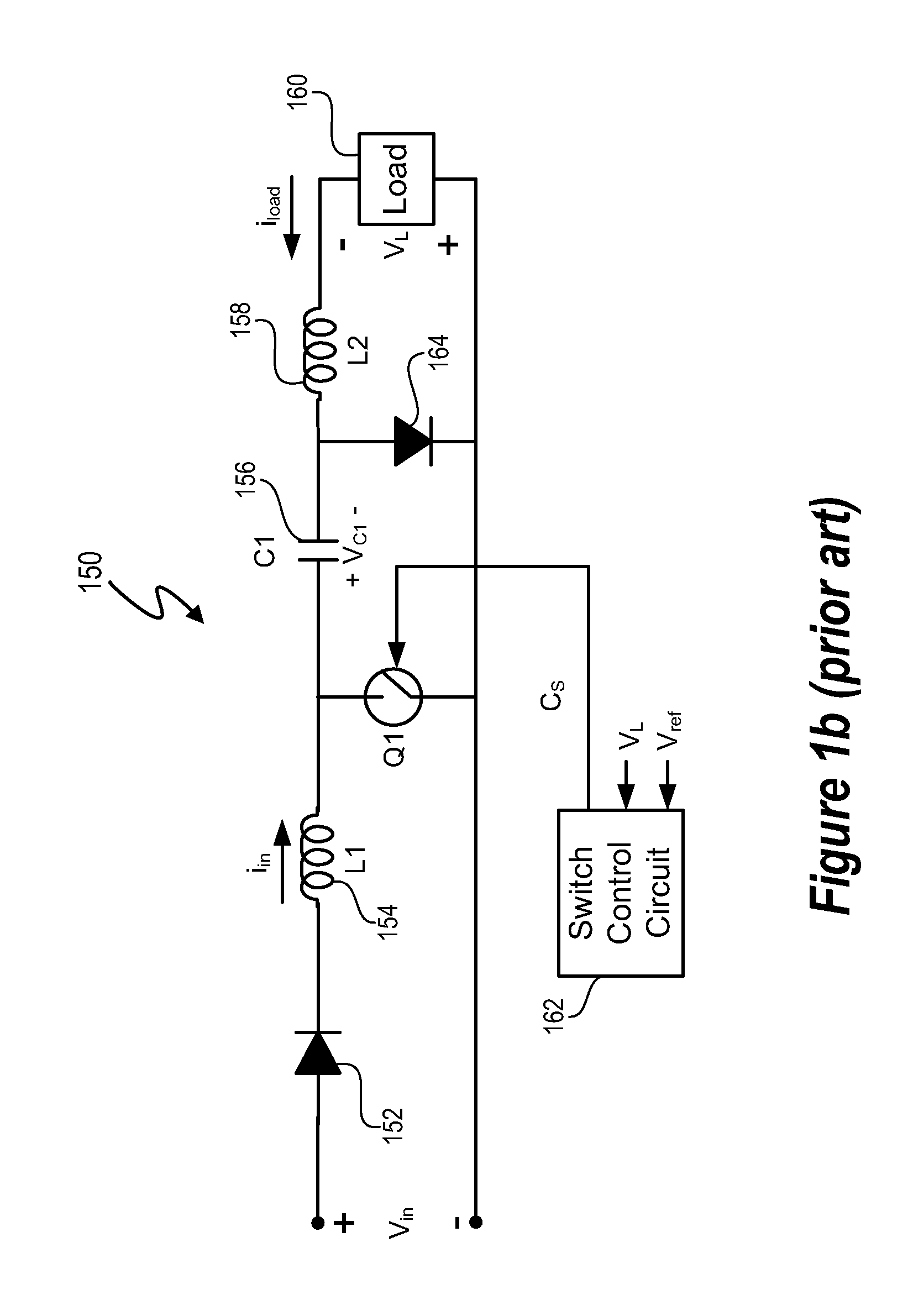
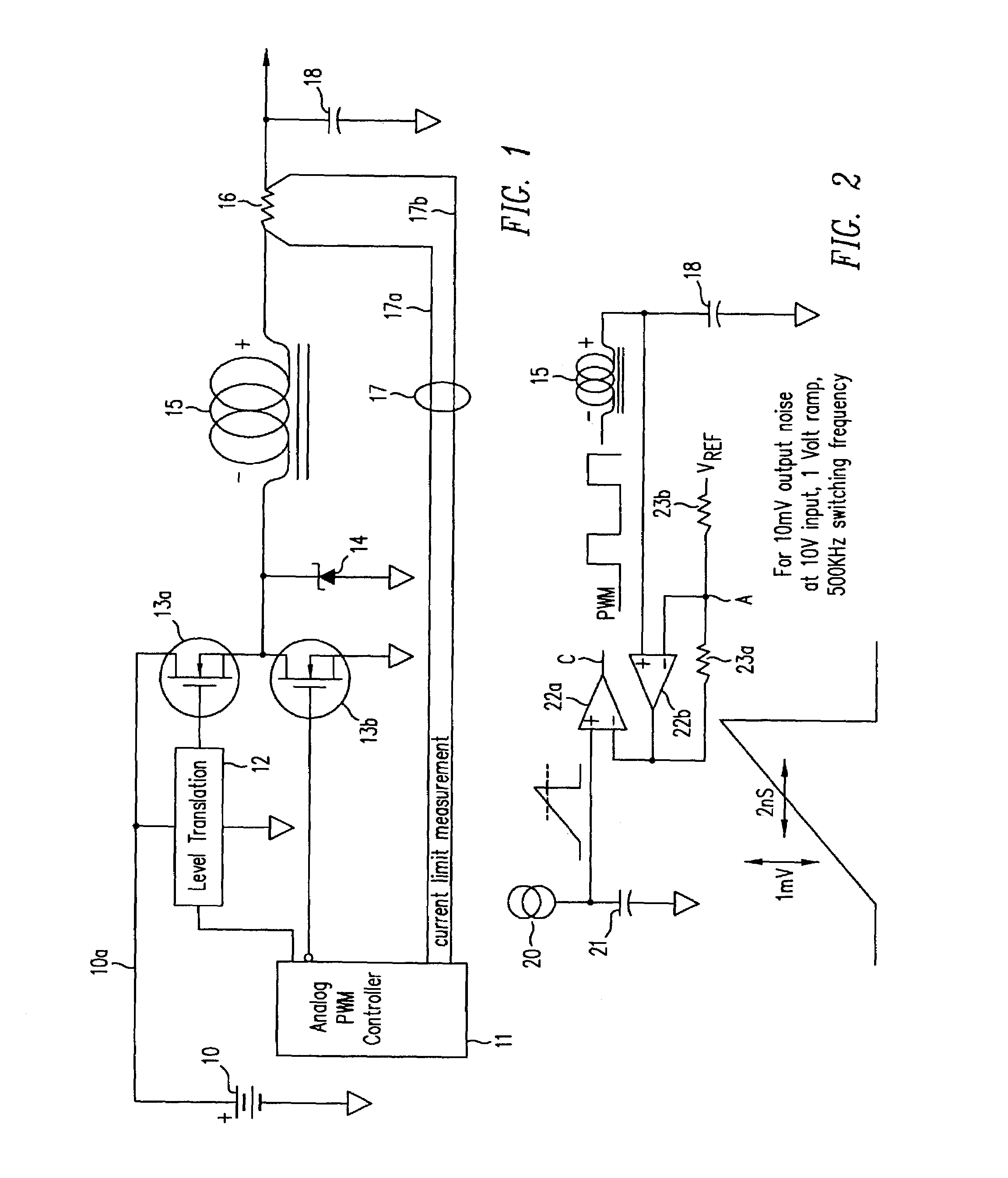
Method of driving a power converter by using a power pulse and a sense pulse
InactiveUS6894911B2Efficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEngineeringVoltage
A method of regulating voltage at an output of a switching power converter, the converter comprising a switch and pulse generation circuitry, the pulse generation circuitry producing one or more drive signals for cycling the switch ON and OFF, wherein if the switch is cycled ON and OFF according to a cycle of a drive signal, power is transferred from a source to a load. The method includes sensing an output voltage feedback signal, comparing the sensed feedback signal to a reference at a determined time during a cycling of the switch, and regulating an output voltage at the load by controlling whether a cycle of one of the drive signals cycles the switch in response to the comparison.
Owner:HERCULES TECH GROWTH CAPITAL
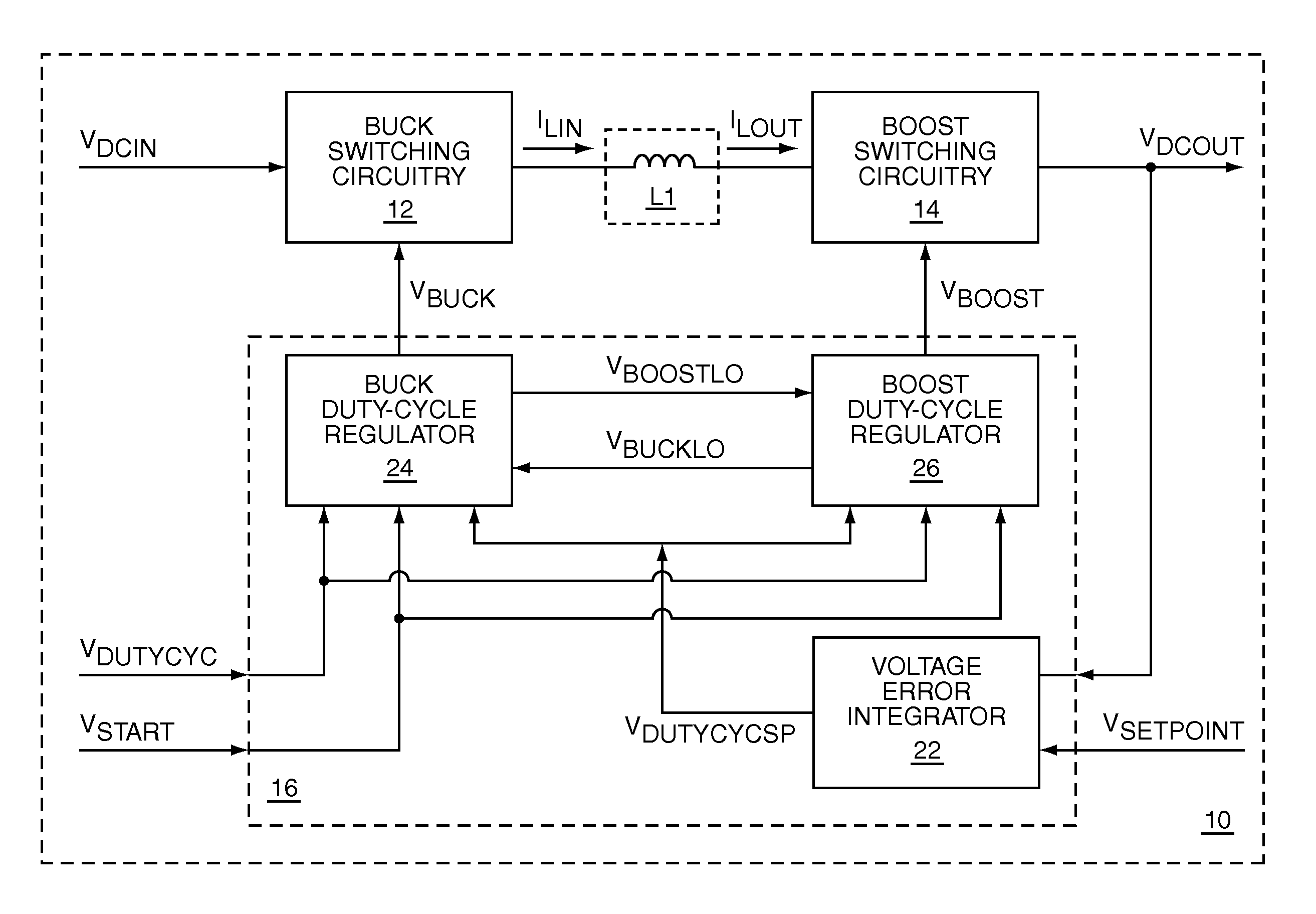
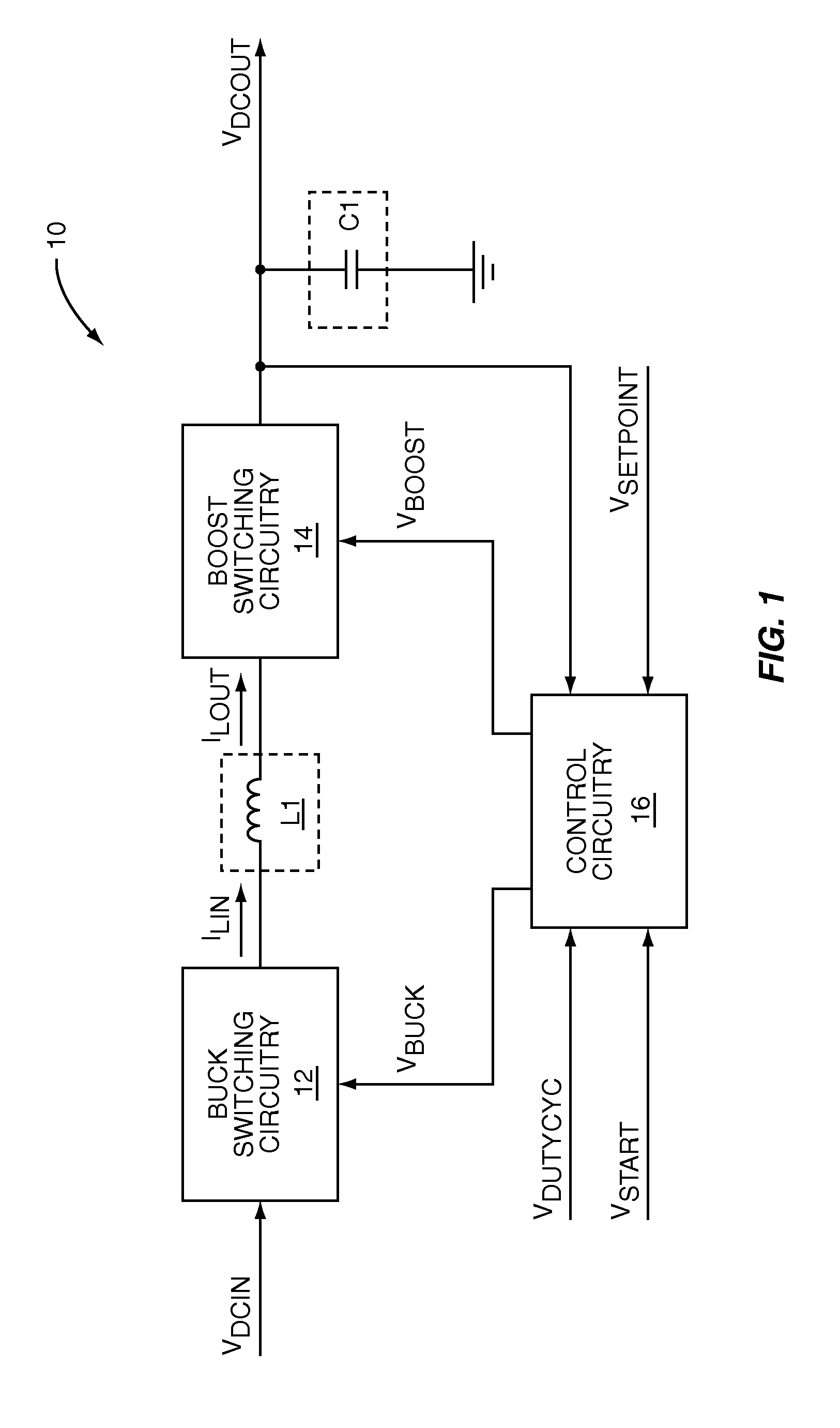
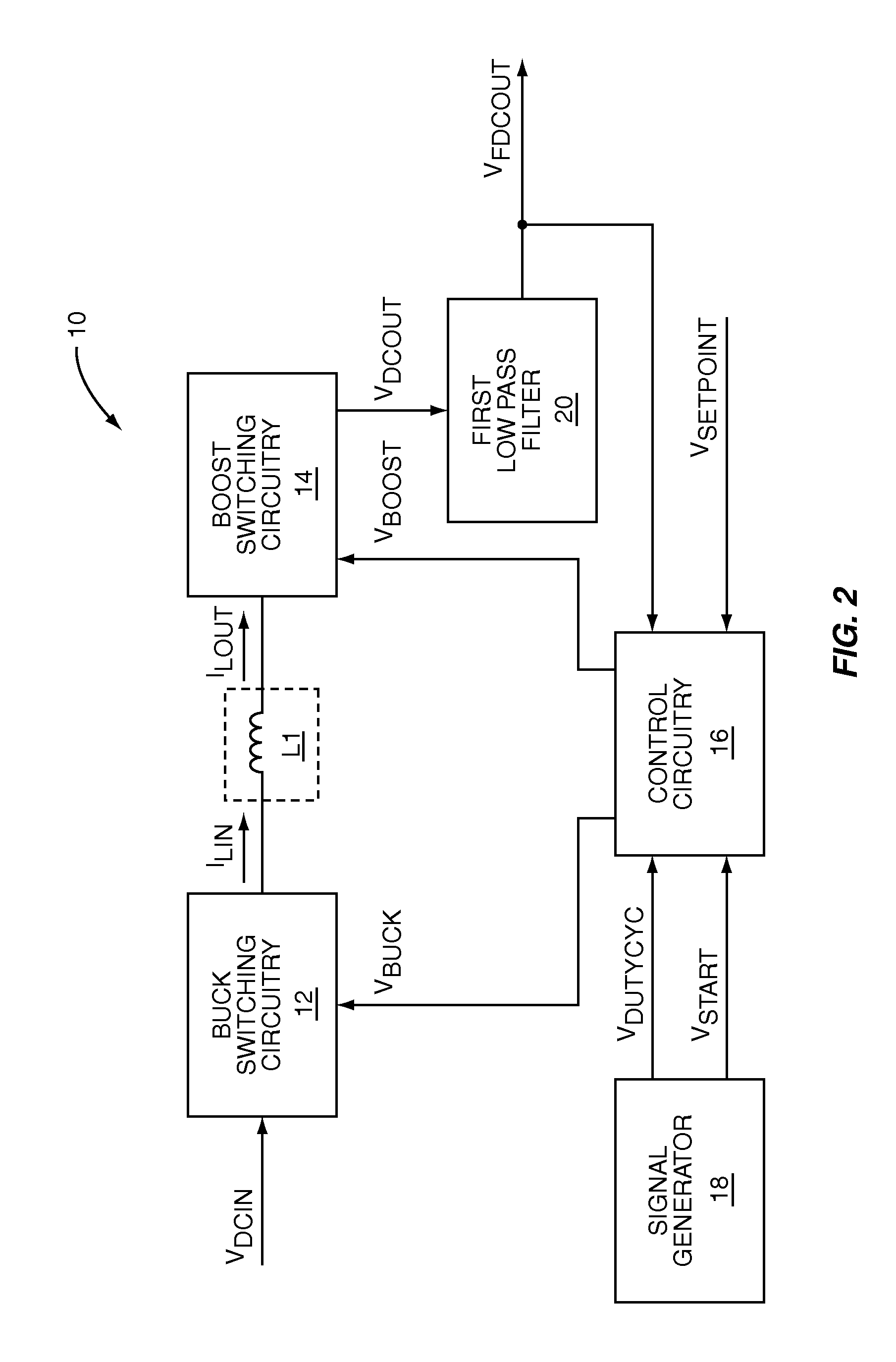
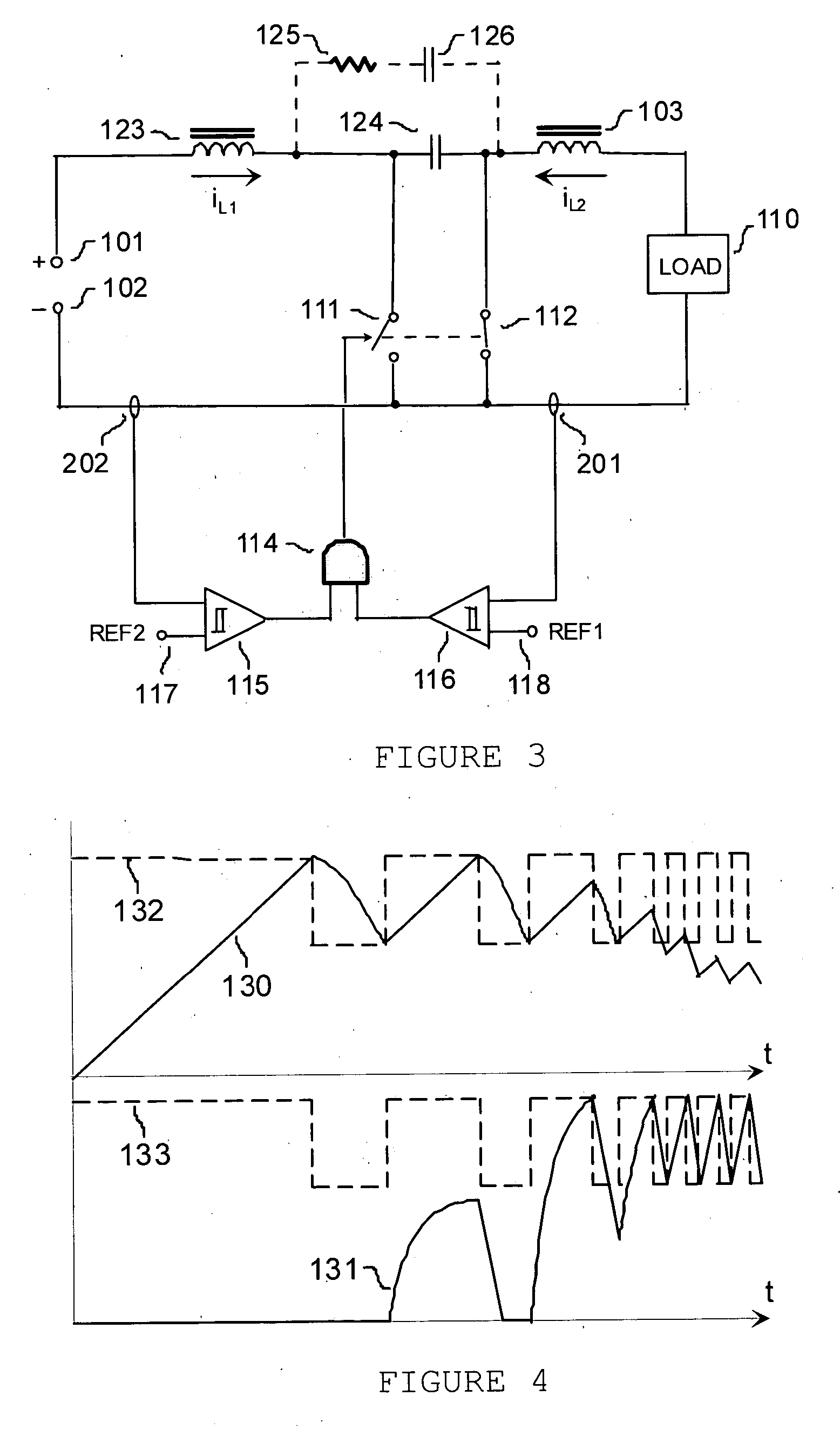
Switching power converter that supports both a boost mode of operation and a buck mode of operation using a common duty-cycle timing signal
ActiveUS7336056B1Remove overlapSmooth transitEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionIntegratorBuck converter
The present invention is a switching power converter that supports both a boost mode of operation and a buck mode of operation, uses one energy storage element, transitions smoothly between boosting and bucking, and avoids simultaneous boosting and bucking. The switching power converter uses a common duty-cycle timing signal and a common duty-cycle setpoint signal to provide a smooth transition between boosting and bucking, and to eliminate overlap between boosting and bucking. A voltage input error integrator is used to integrate out errors between an output voltage and a setpoint voltage to provide the common duty-cycle setpoint signal. Duty-cycle error integrators are used to integrate out errors between the common duty-cycle setpoint signal and the actual duty-cycle of either the buck converter or the boost converter. Non-overlapping boost operating and buck operating ranges are provided by the common duty-cycle setpoint signal.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Power converter circuitry and method
InactiveUS20040135560A1Easy to makeBatteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionControl systemEngineering
A control system and method for simultaneously regulating the operation of a plurality of different types of switching power converters. The system utilizes in regulating the power converters sampled data and nonlinear feedback control loops.
Owner:EXAR CORP
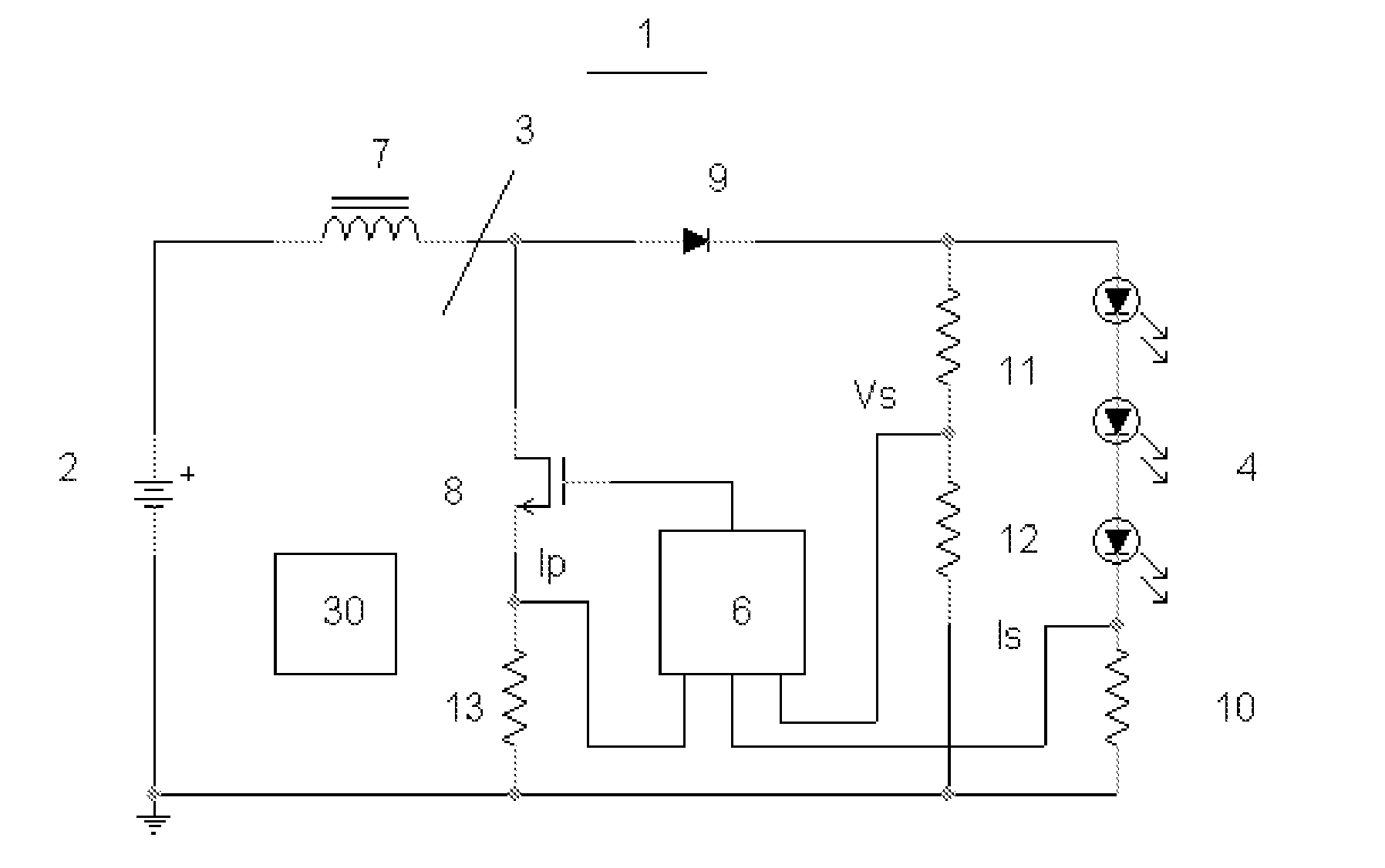
System and Method for Driving LED
ActiveUS20070285031A1Accurate estimateLow costElectroluminescent light sourcesDc-dc conversionAverage currentPeak value
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Detecting Light Load Conditions and Improving Light Load Efficiency in a Switching Power Converter
ActiveUS20100208500A1Minimize switching lossesReduce switching frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLow loadVoltage regulation
A switching power converter detects low load conditions based on the ratio of a first peak current value for peak current switching in constant voltage regulation mode to a second peak current value for peak current switching in constant current regulation mode. The power supply load is considered to have a low load if the ratio is lower than a predetermined threshold. Once a low load condition is detected, the switching frequency of the switching power converter is reduced to a level that minimizes switching loss in the power converter. In addition, the switching power converter also adjusts the switching frequency according to the sensed input line voltage. An offset is added to the switching period to reduce the switching frequency of the switching power converter, as the input line voltage is increased.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
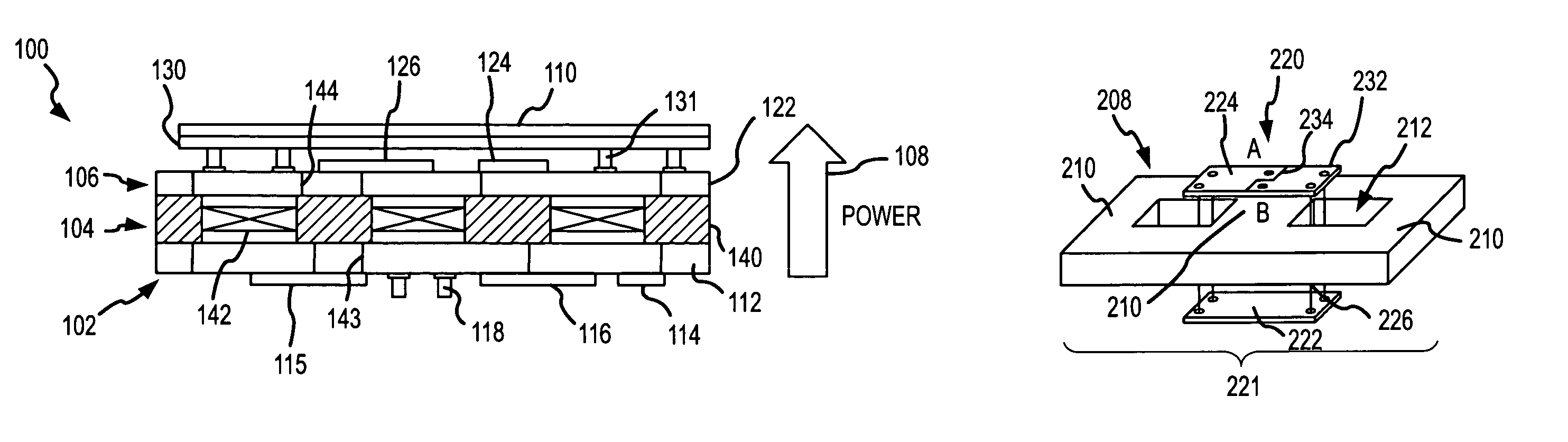
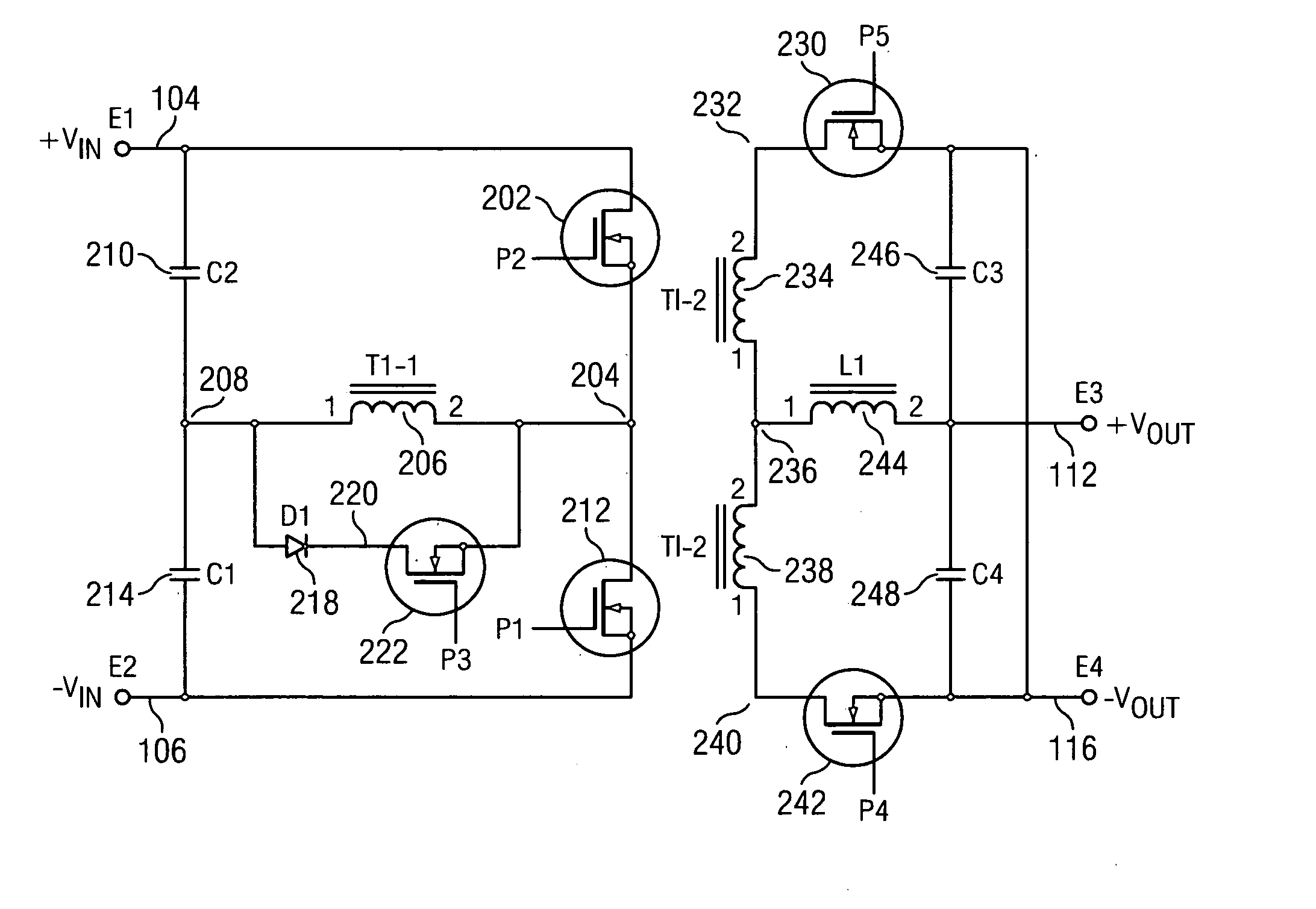
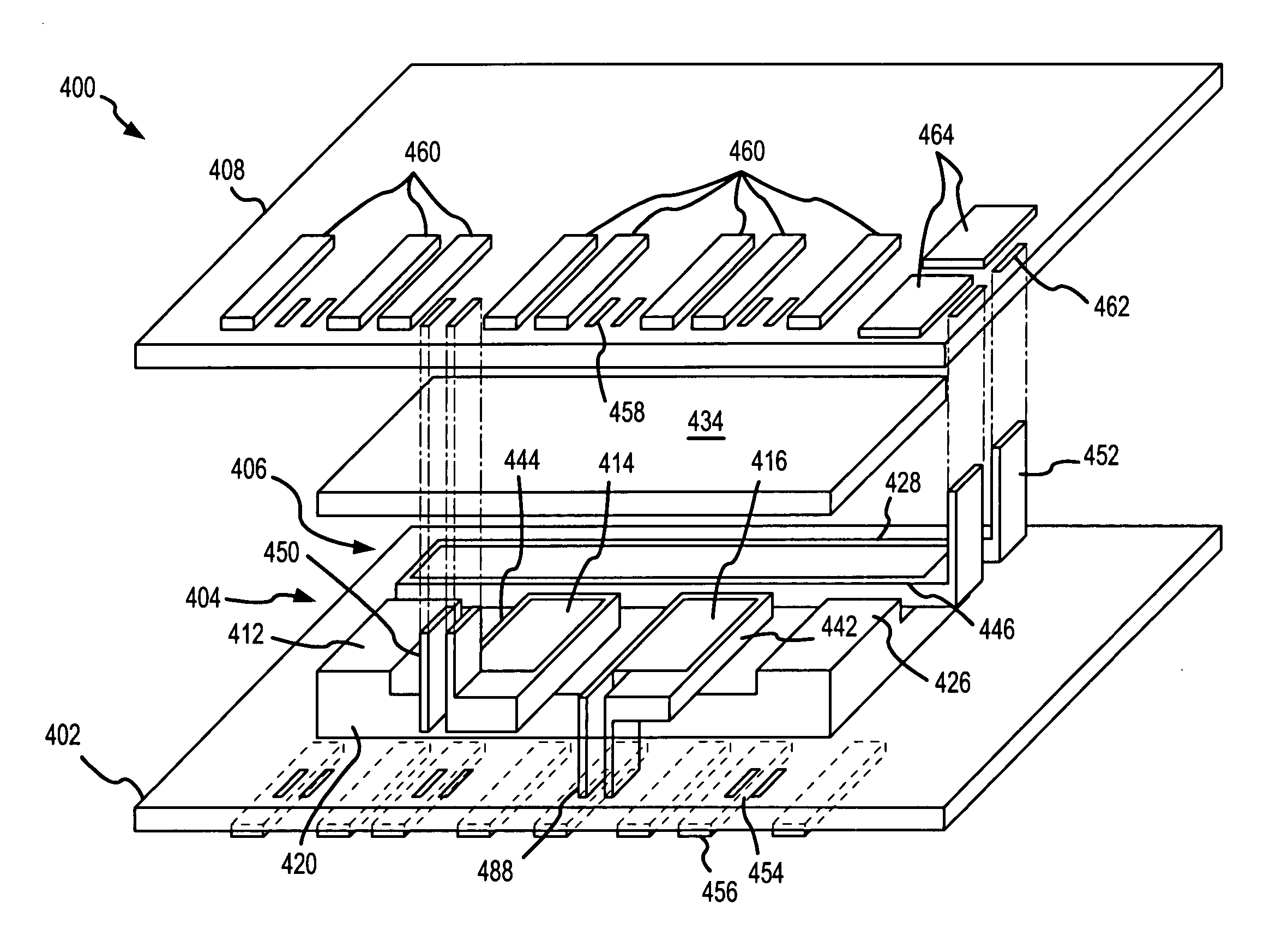
Vertically packaged switched-mode power converter
ActiveUS7012414B1Tight regulationFast transient responseTransformersConversion constructional detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceCellular architecture
A vertically packaged cellular power converter solves the problems associated with conventional designs and paves the way for a cellular circuit architecture with ultra-low interconnect resistance and inductance. The vertical packaging results in a power flow in the vertical direction (from the bottom to the top) with very short internal interconnects, thereby minimizing the associated conduction losses and permitting high conversion efficiency at high currents. The cellular architecture is ideally suited for generating multiple supply voltages.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
Digital calibration with lossless current sensing in a multiphase switched power converter
ActiveUS20060001408A1Accurate currentImprovement of regulation of powerDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationNoise generationVoltage regulation
Disclosed is a multi-phase power regulator that accurately senses current at a load in a lossless manner and adjusts the power supplied to the load based on the sensed current. Also disclosed is a method of calibrating a multiphase voltage regulator by applying a known calibration current at the load and determining actual current values by the difference in measured values between when the known calibration current is applied and when it is not applied. The accurate current is determined at a known temperature and accurate temperature compensation is provided by a non-linear digital technique. Each phase of the multi-phase power regulator is individually calibrated so that balanced channels provide accurate power to the load. Also disclosed is a calibration method with minimal noise generation.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
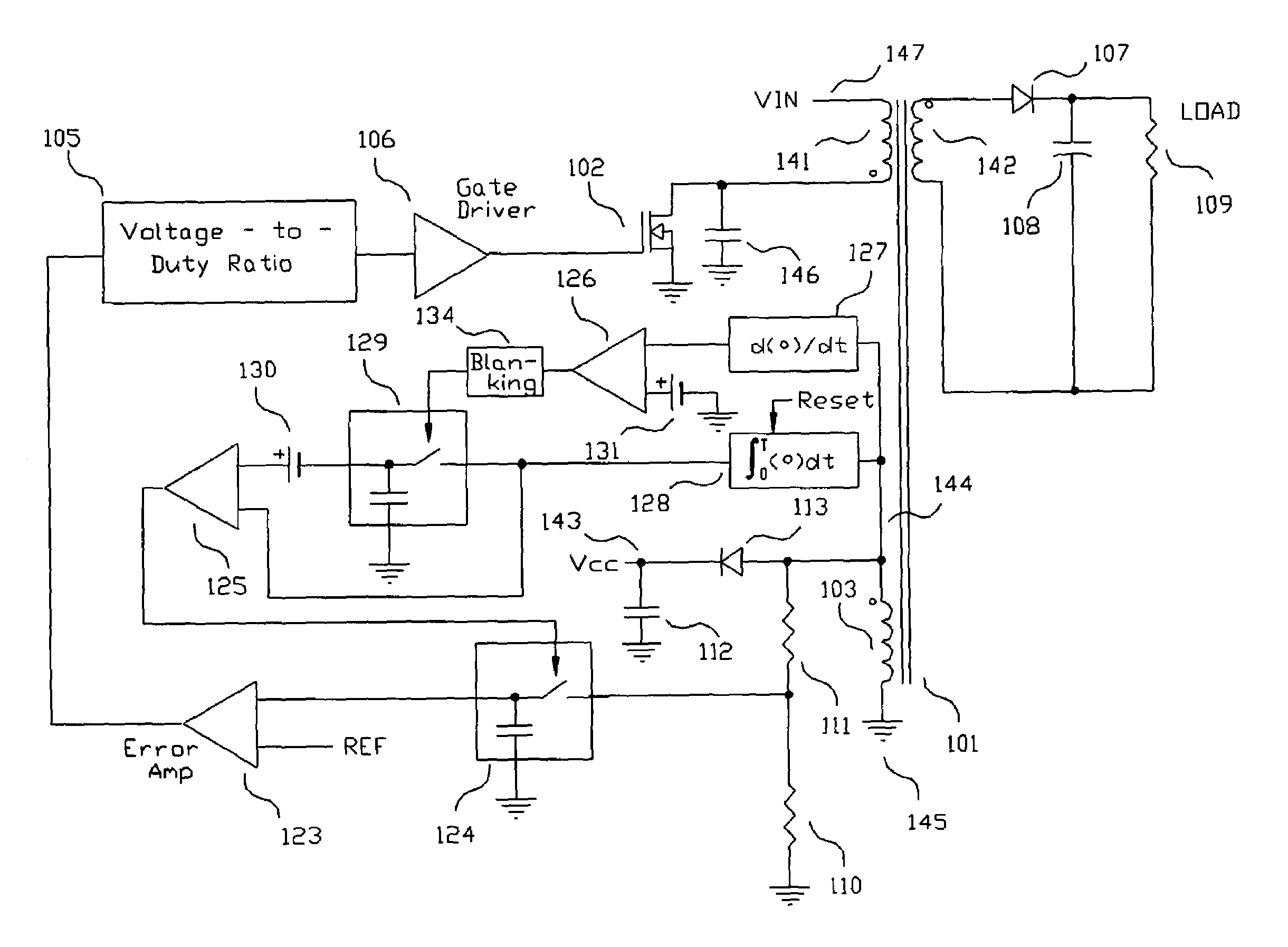
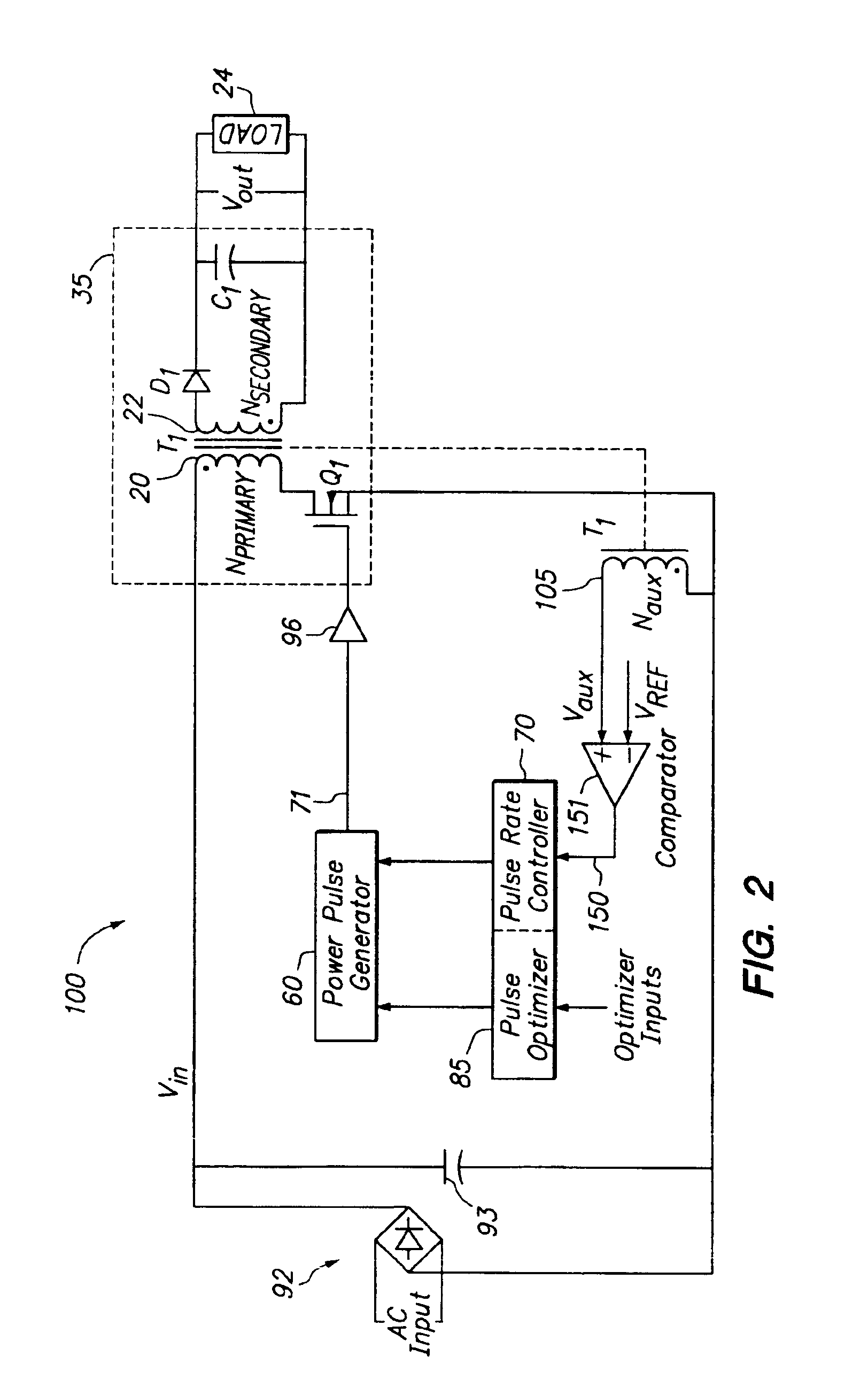
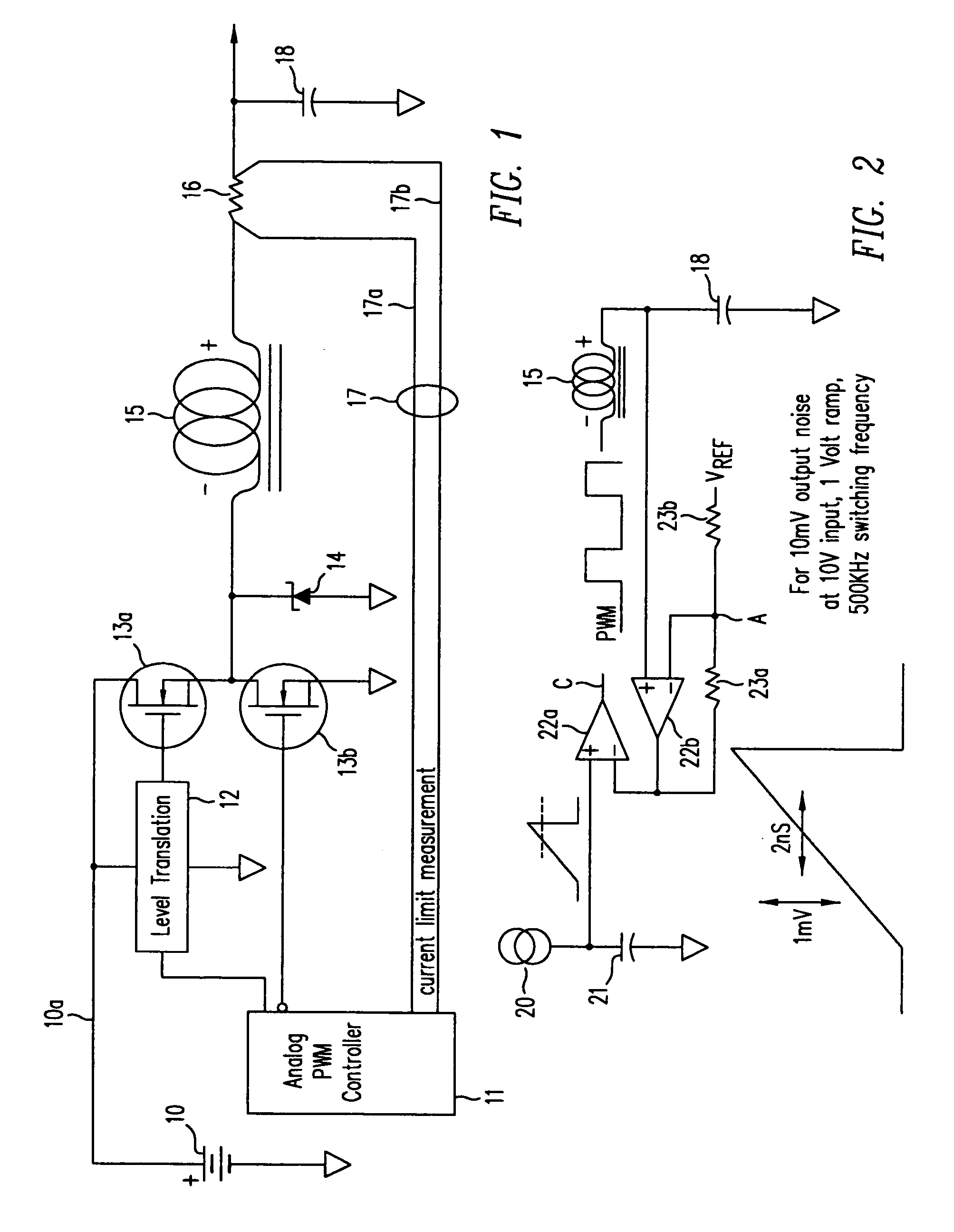
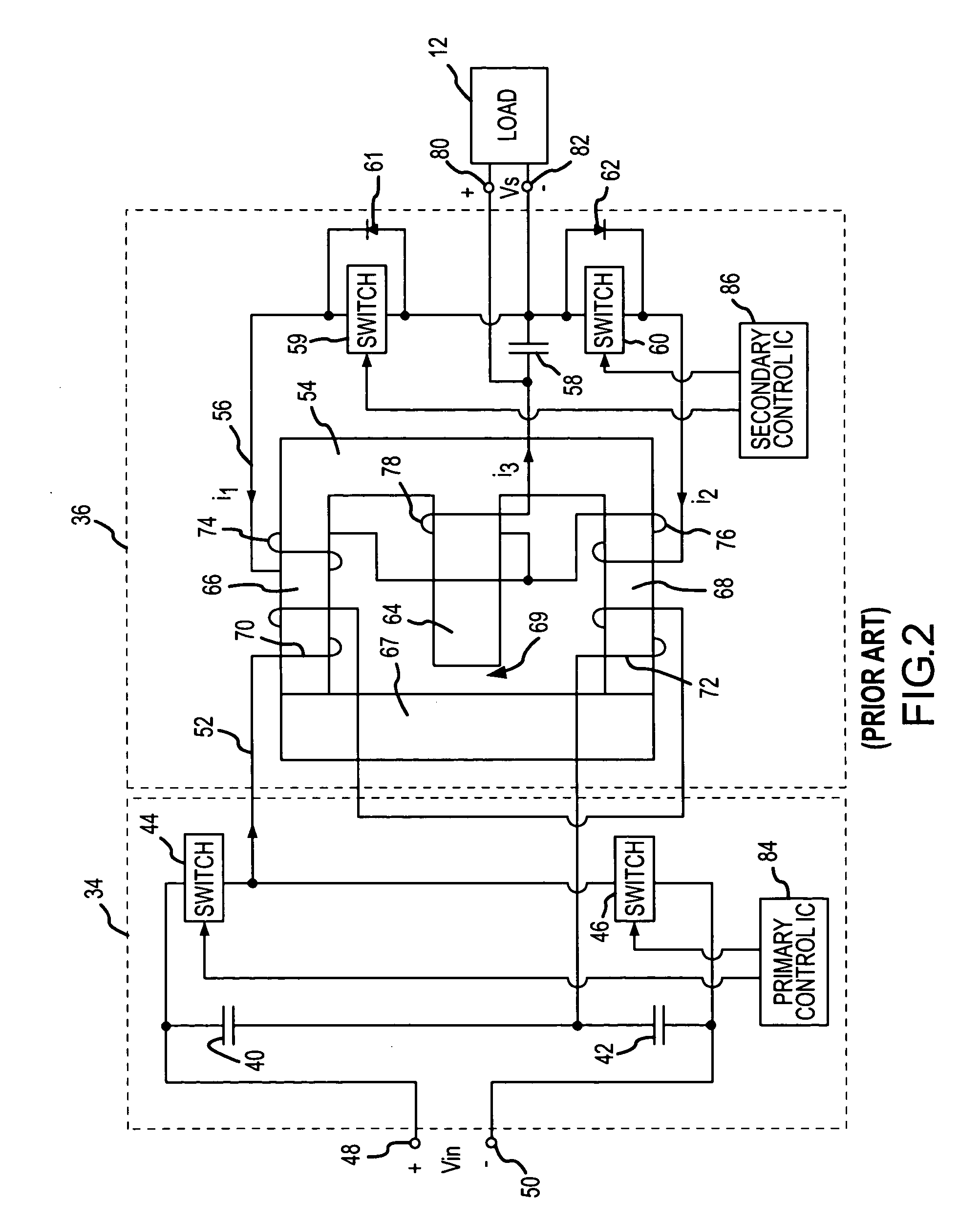
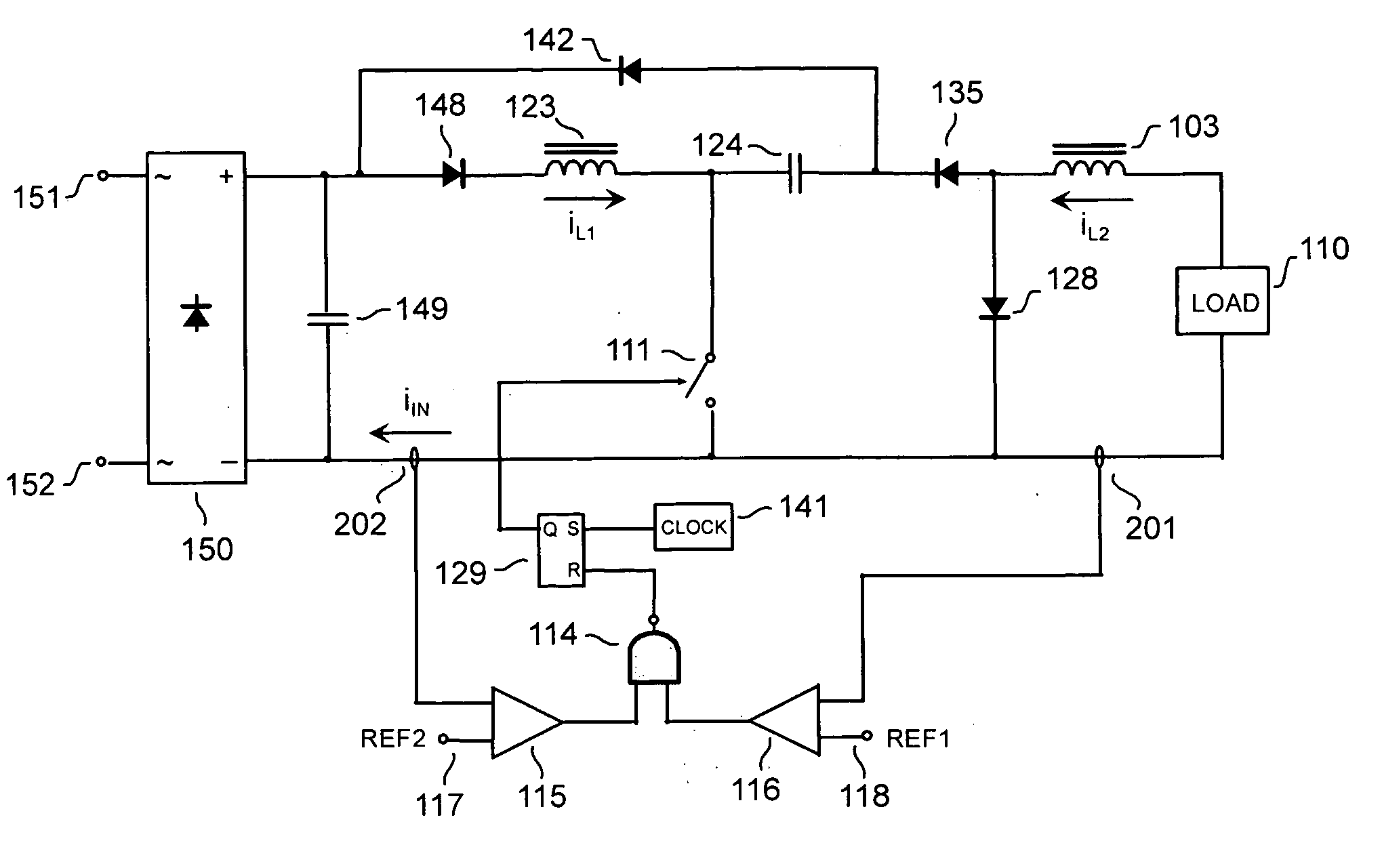
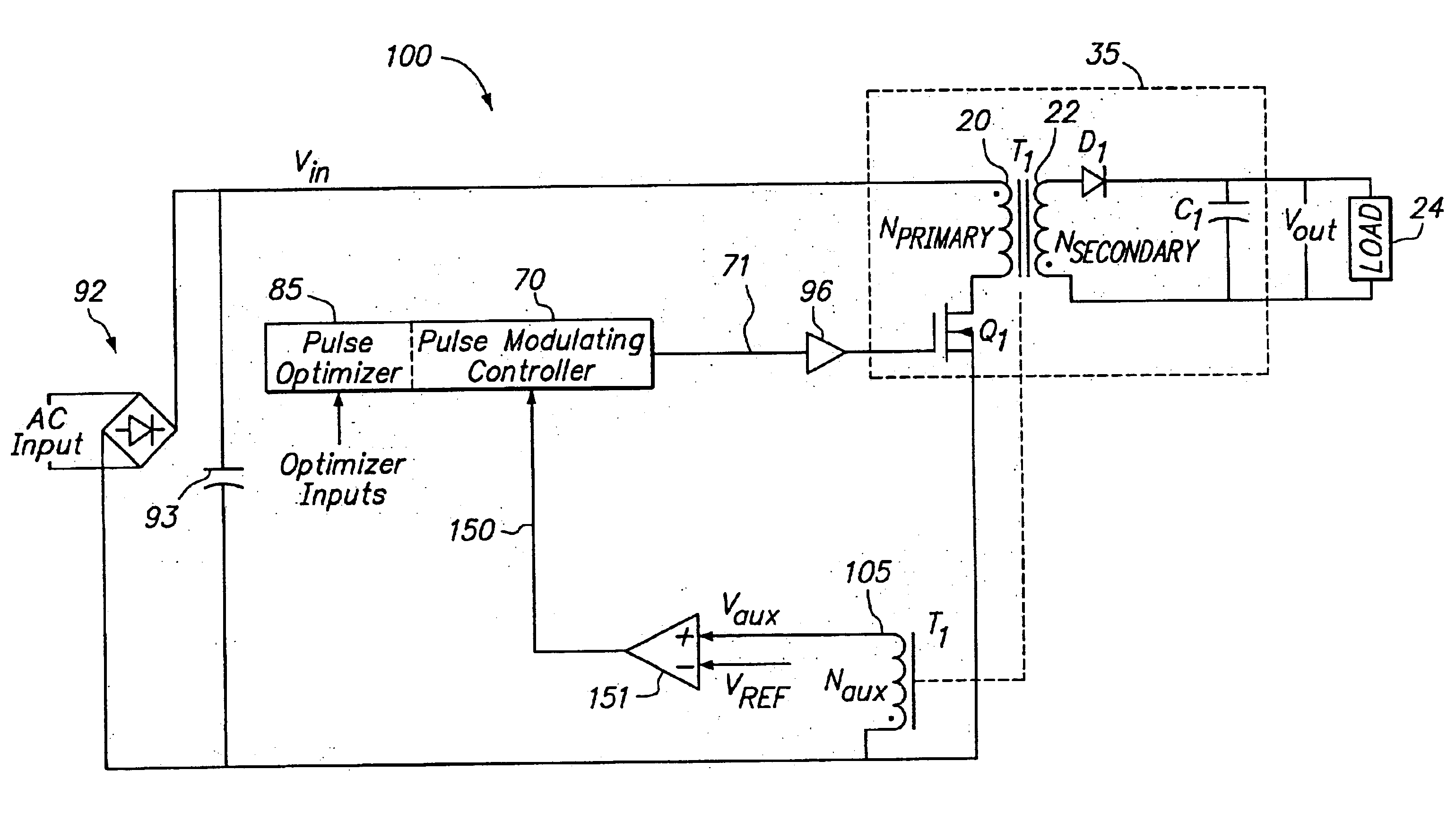
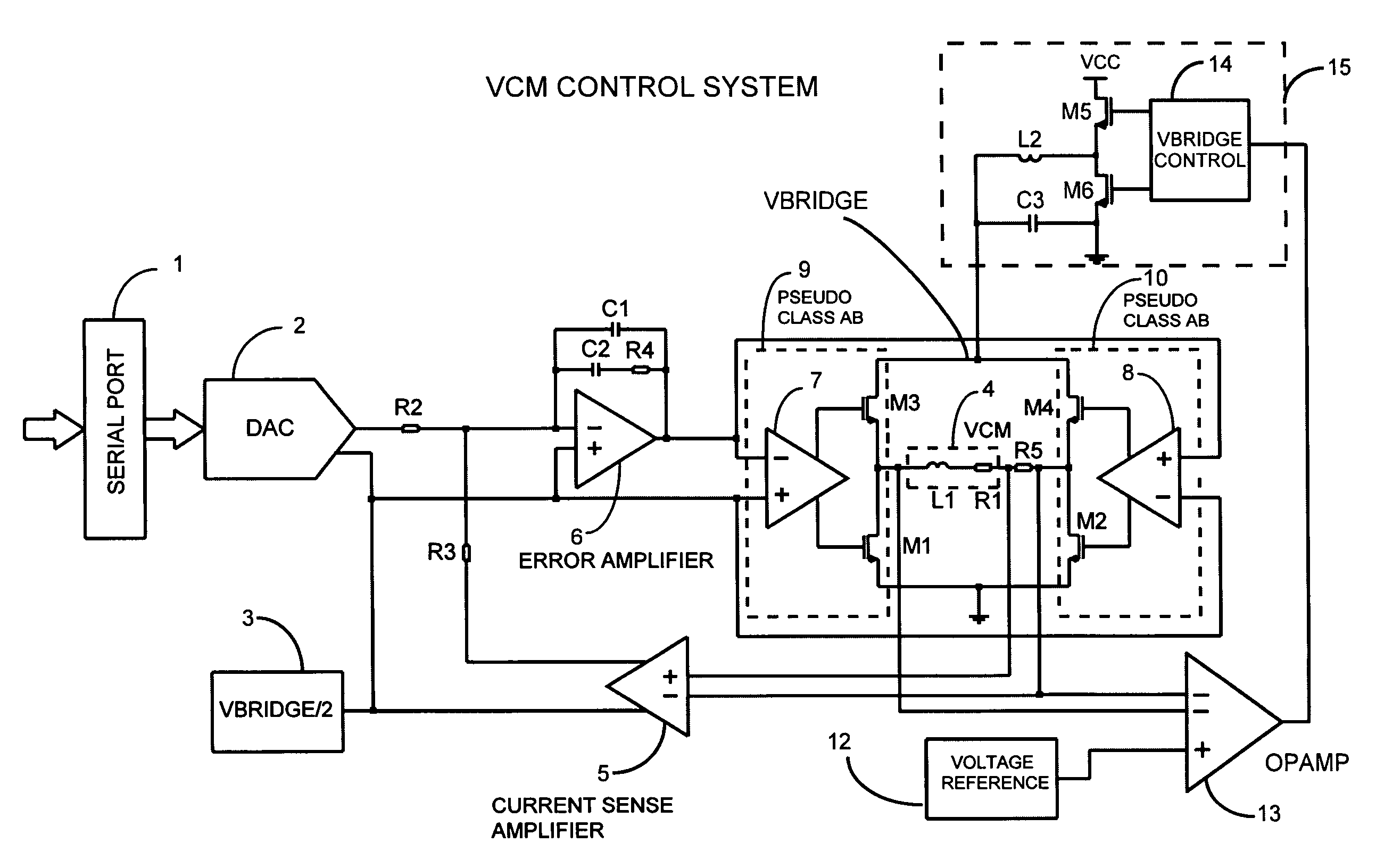
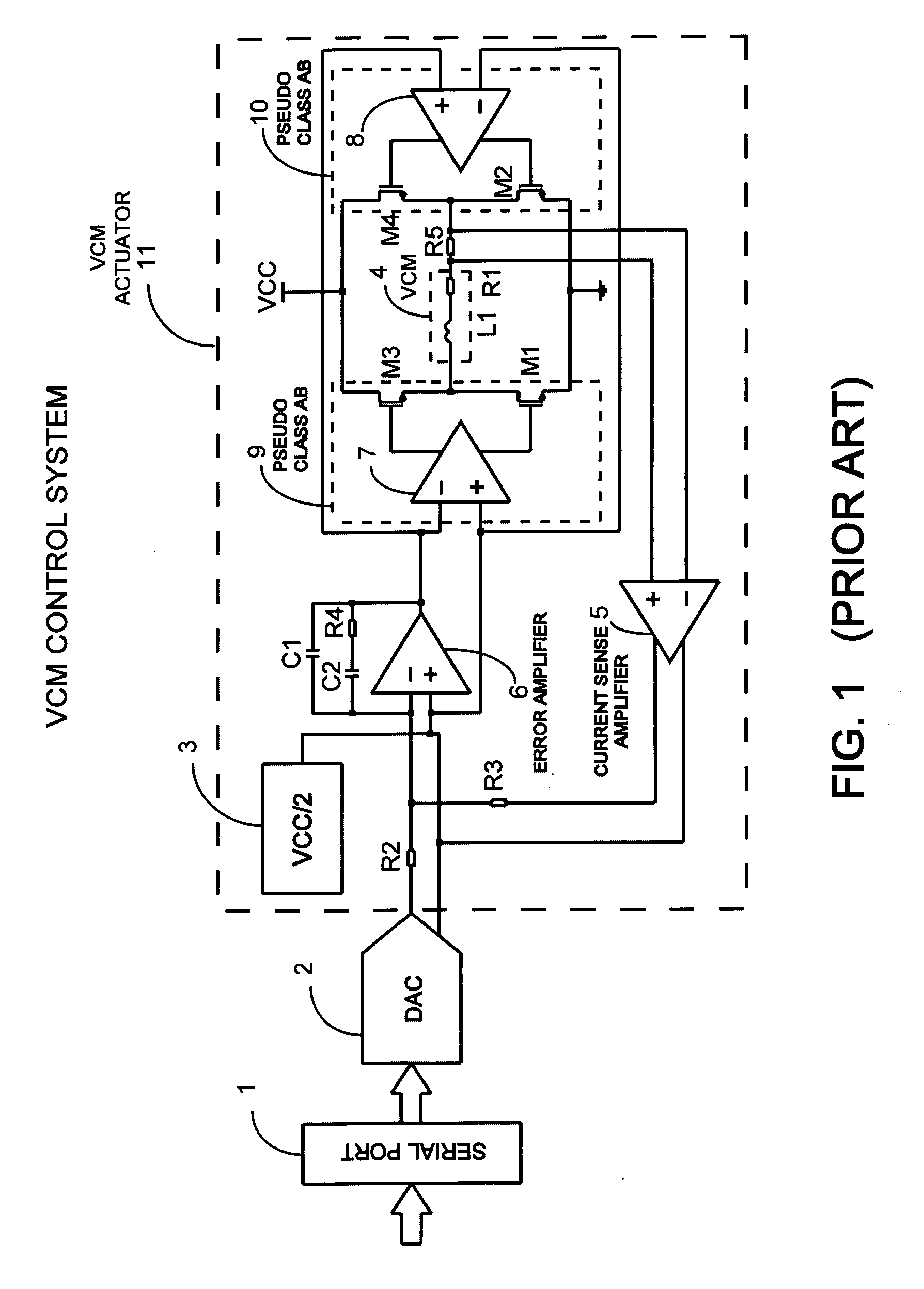
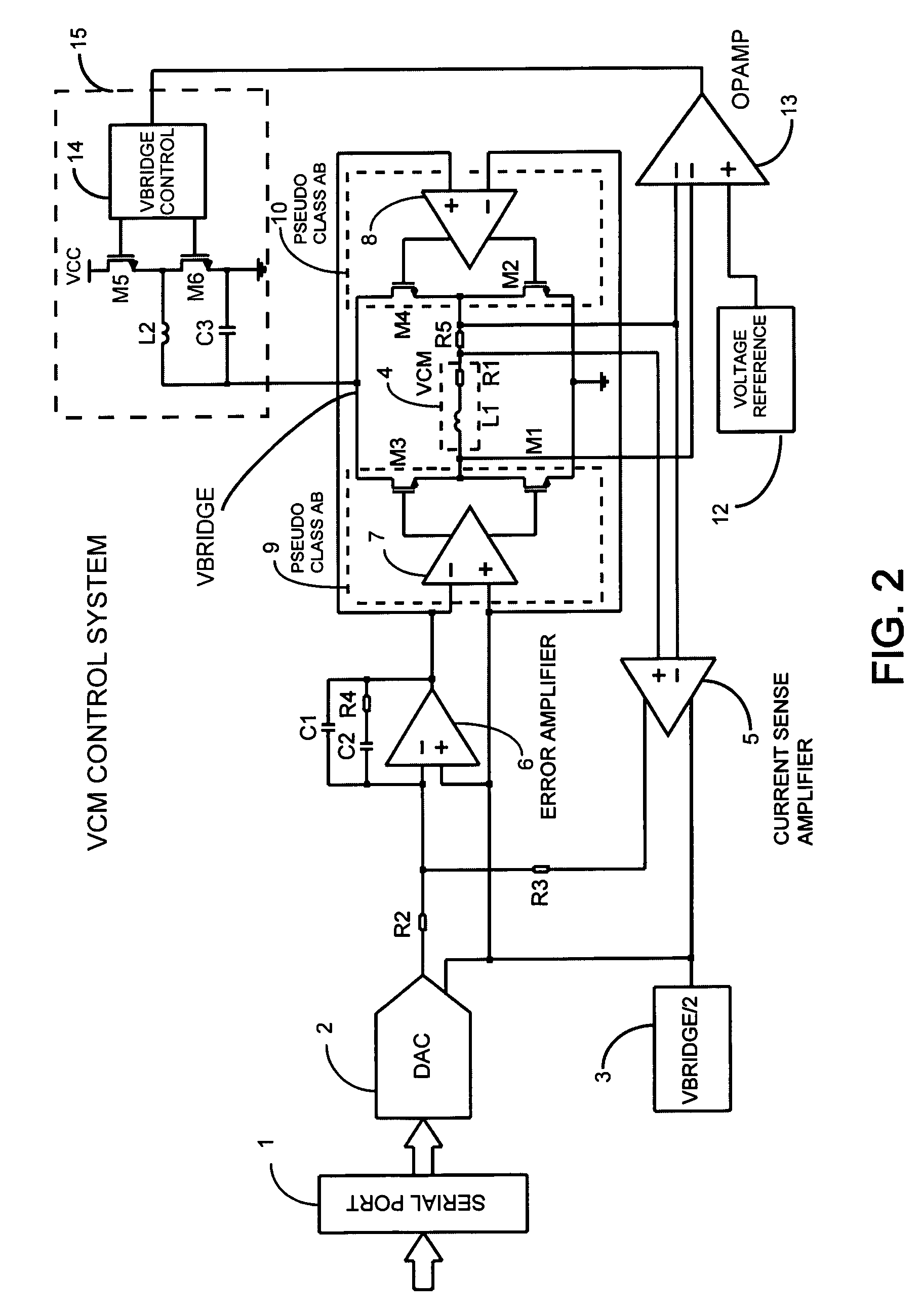
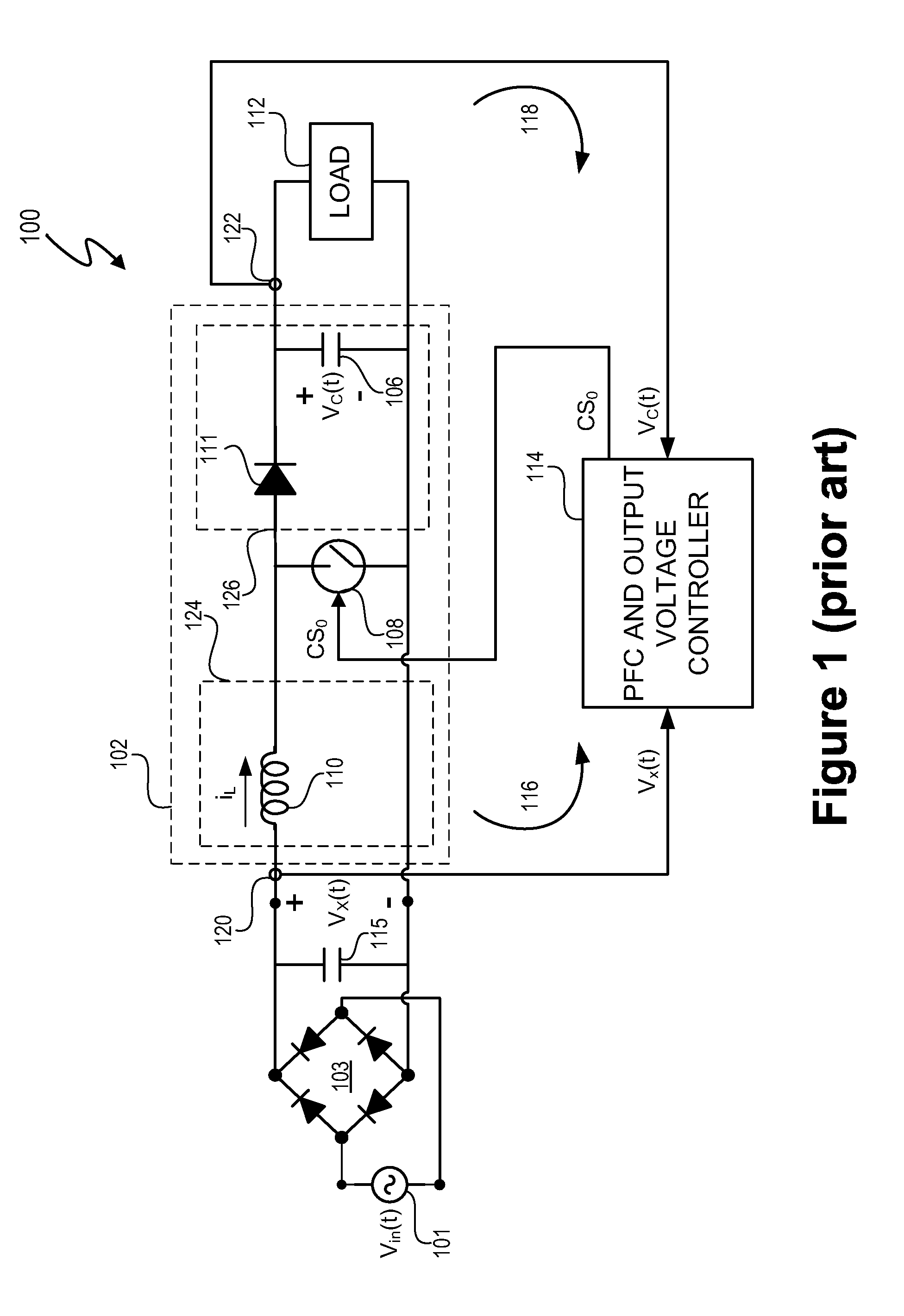
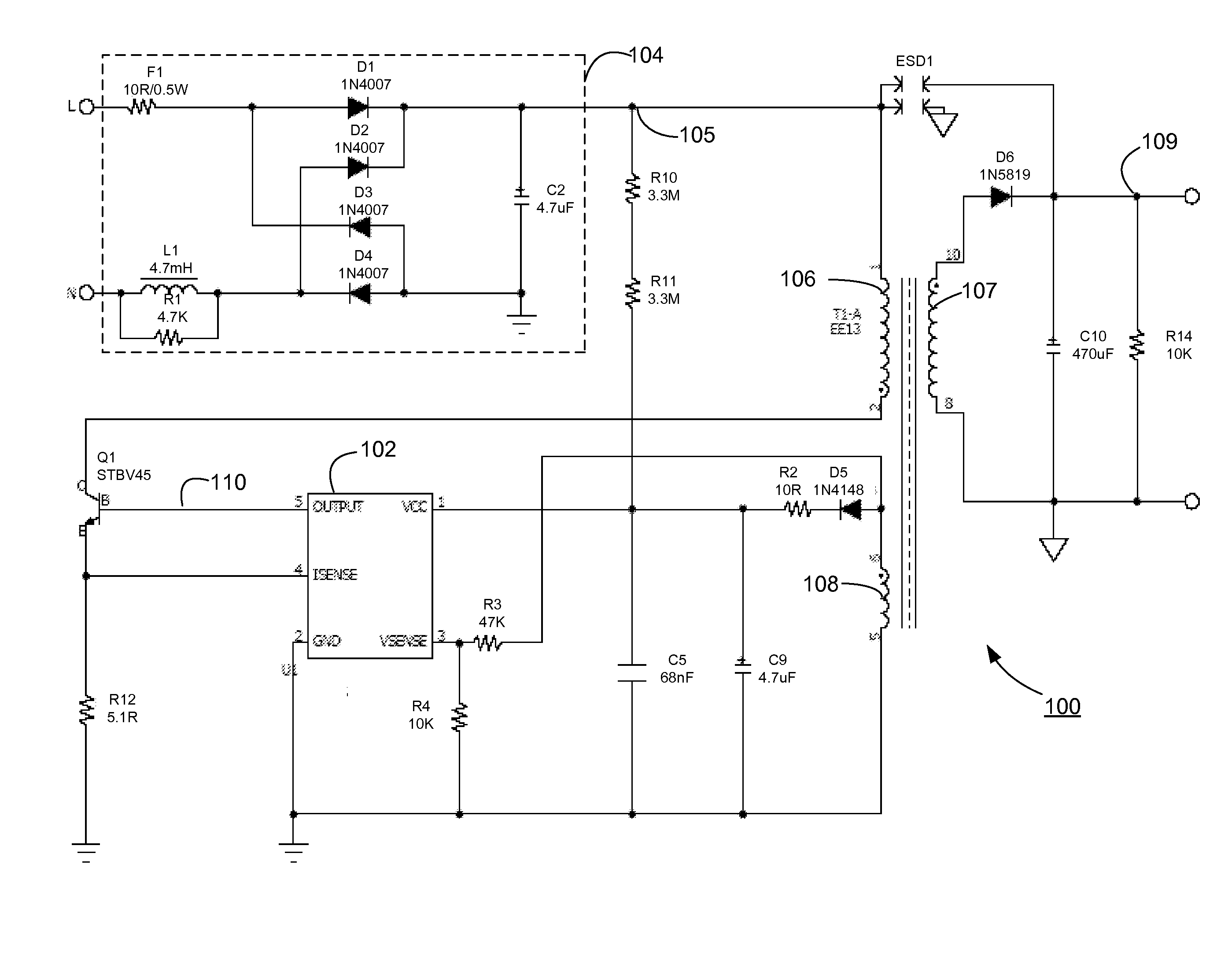
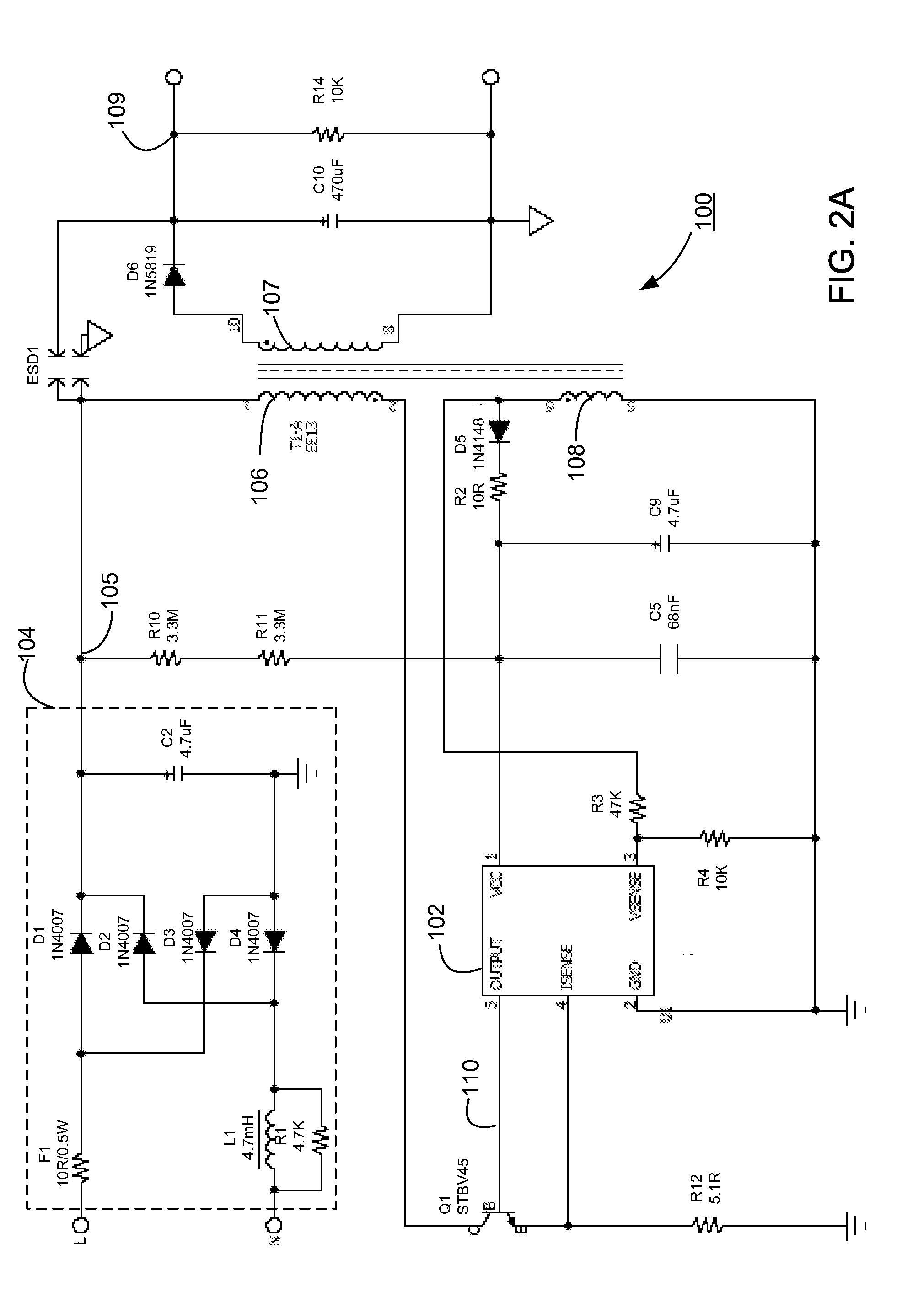
Switching power converter and method of controlling output voltage thereof using predictive sensing of magnetic flux
ActiveUS20050073862A1Improve immunityDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationIntegratorSwitching cycle
A switching power converter and method of controlling an output voltage thereof using predictive sensing of magnetic flux provides a low-cost switching power converter via primary-side control using a primary-side winding. The power converter has improved immunity to parasitic phenomena and other variations within the power converter components. An integrator is used to generate a voltage analog that represents magnetic flux within a power magnetic element via an integration of a voltage on a primary-side winding of the power magnetic element. A detection circuit detects the end of a half-cycle of post-conduction resonance that occurs in the power magnetic element subsequent to the energy level in the power magnetic element reaching zero. The voltage of the integrator is stored at the end of the post-conduction resonance half-cycle and is used to determine a sampling point prior to or equal to the start of post-conduction resonance in a subsequent switching cycle of the power converter (which is the predicted zero-energy storage point of the power magnetic element). The primary-side winding voltage is then sampled at the sampling point, providing an indication of the output voltage of the power converter. By predicting the zero-magnetic-energy storage point, the output voltage of a power converter operating in discontinuous or boundary conduction mode can be accurately controlled without being affected by parasitic phenomena or variations in circuit performance over time, input voltage and temperature.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Power converter circuitry and method
InactiveUS20040095020A1Easy to makeBatteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionControl systemEngineering
A control system and method for simultaneously regulating the operation of a plurality of different types of switching power converters. The system utilizes in regulating the power converters sampled data and nonlinear feedback control loops.
Owner:EXAR CORP
Power converter circuitry and method
InactiveUS20040095118A1Easy to makeBatteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionControl systemEngineering
A control system and method for simultaneously regulating the operation of a plurality of different types of switching power converters. The system utilizes in regulating the power converters sampled data and nonlinear feedback control loops.
Owner:EXAR CORP
Multi-Element Resonant Converters
InactiveUS20090303753A1Improved power transferRaise transfer toEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionBand-pass filterSwitching frequency control
A resonant switched power converter having switching frequency controlled in response to an output voltage thereof achieves over-current protection such as at start-up or under short circuit conditions using a resonant tank circuit which provides a notch filter in addition to a band pass filter. A additional band pass filter provided in the resonant tank circuit achieves increased power transfer to a load and reduced circulating resonant currents and conduction losses. The inductances of the preferred LCLCL tank circuit or other tank circuit with two pass band filters and a notch filter may be integrated into a single electrical component.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
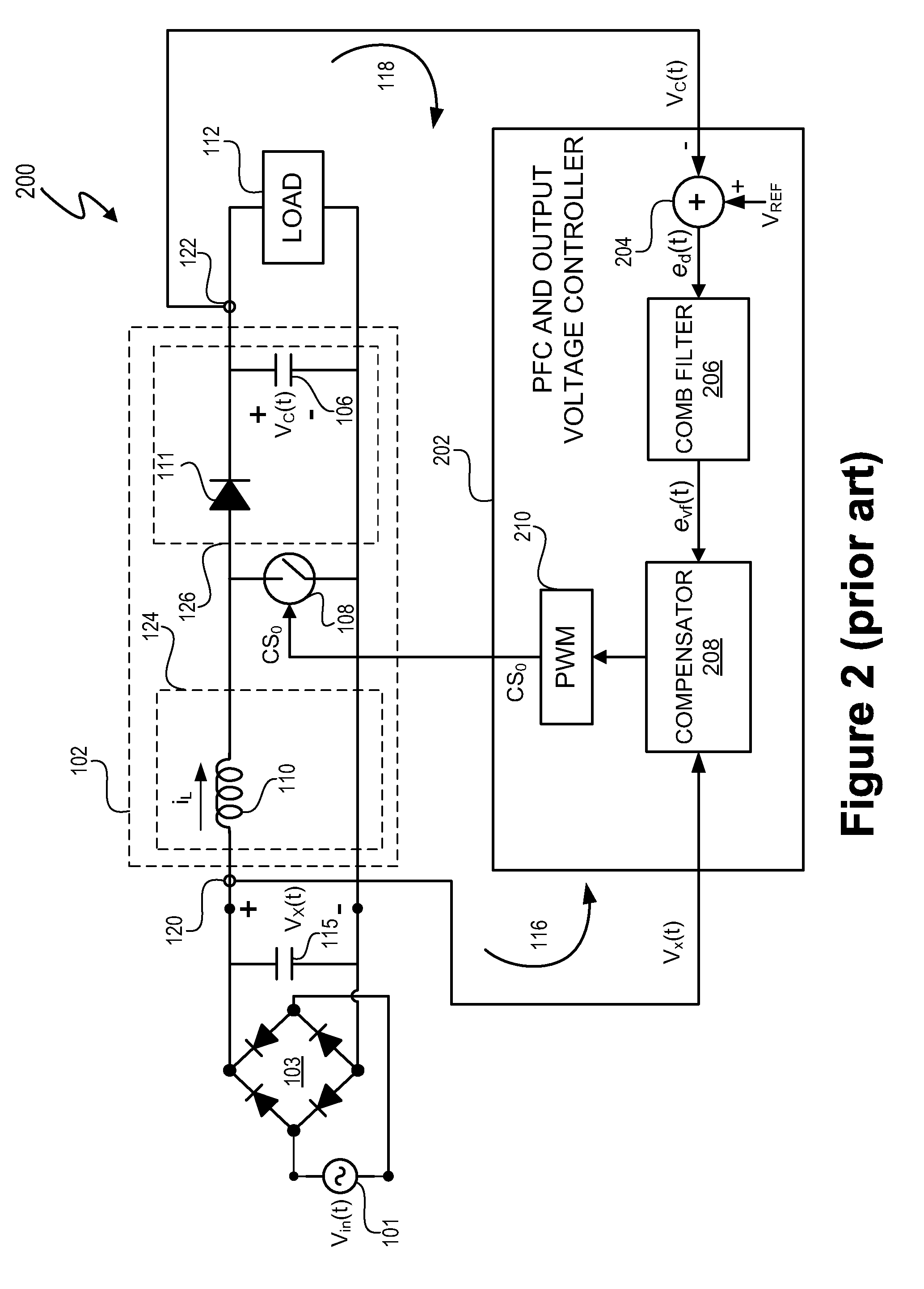
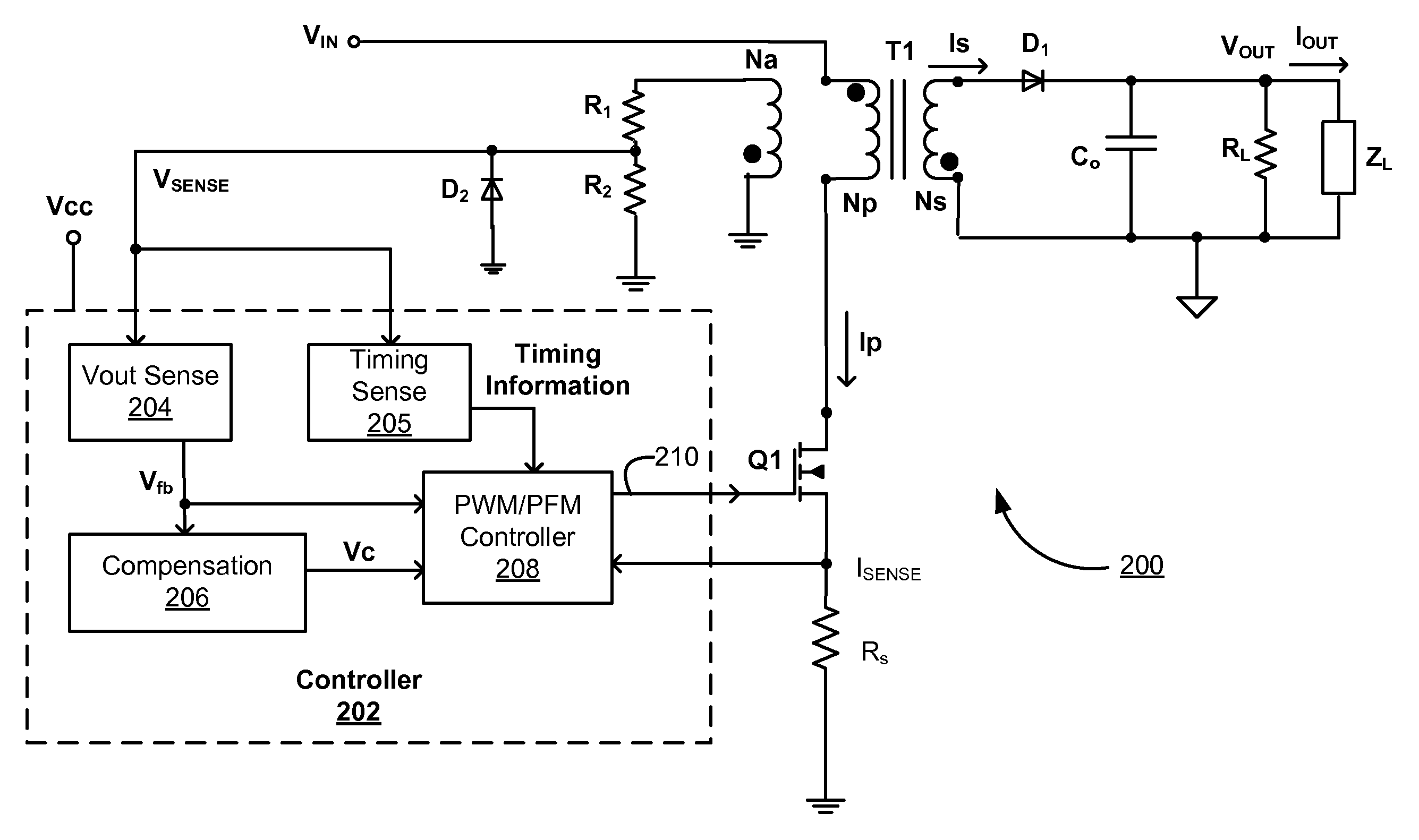
Switching power converter and control system
ActiveUS8076920B1Efficient power electronics conversionElectroluminescent light sourcesEnergy transferControl signal
A switching power converter tracks a time-varying input voltage during each cycle of the input voltage to provide power factor correction. The switching power converter includes a switch with a frequency and duty cycle modulated control signal. The switch controls the transfer of energy between the input and output of the switching power converter. The frequency of the control signal is greater than a frequency of the input signal. The control signal frequency is modulated during each cycle of the input voltage so that energy transferred from the switching power tracks the energy supplied to the switching power converter.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
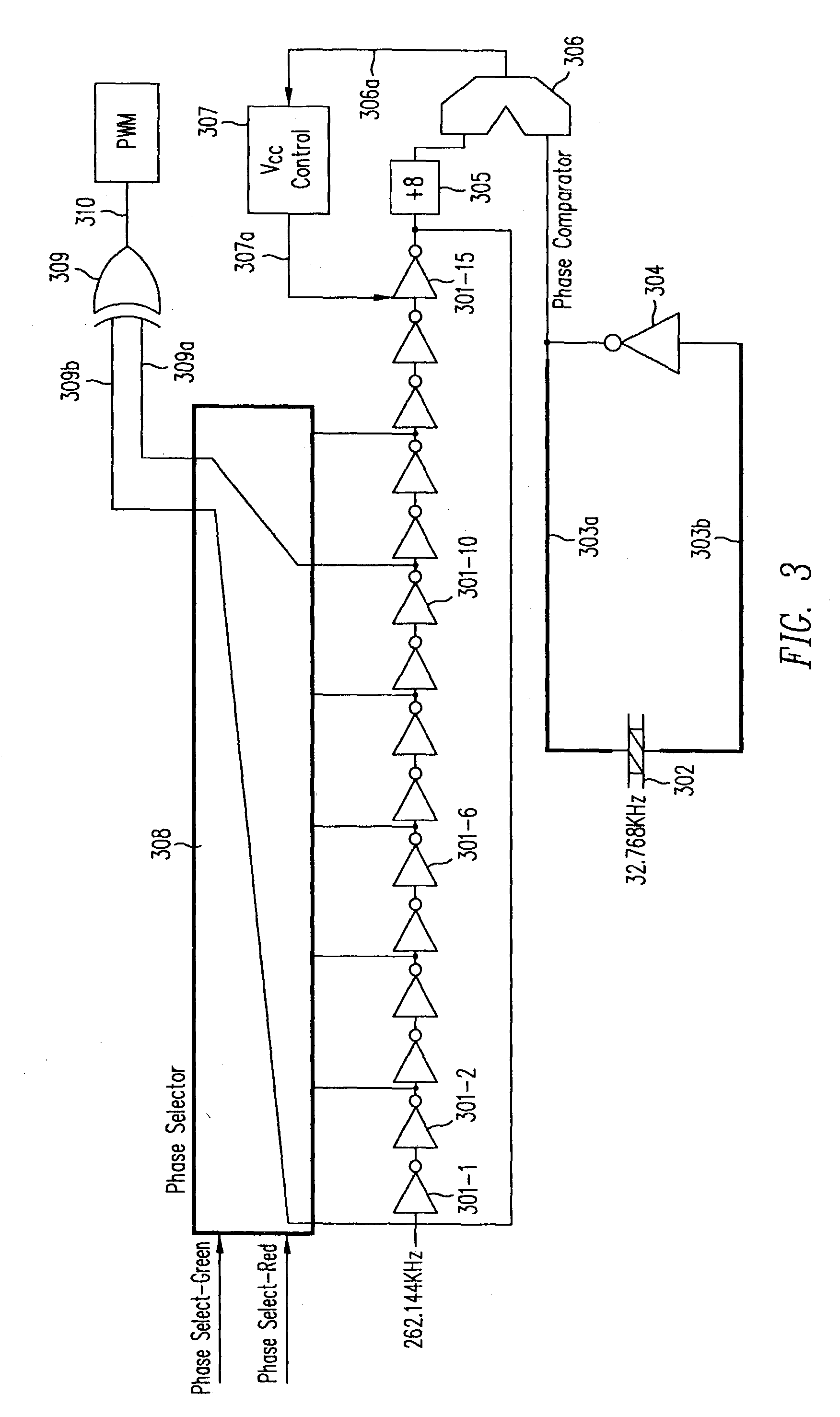
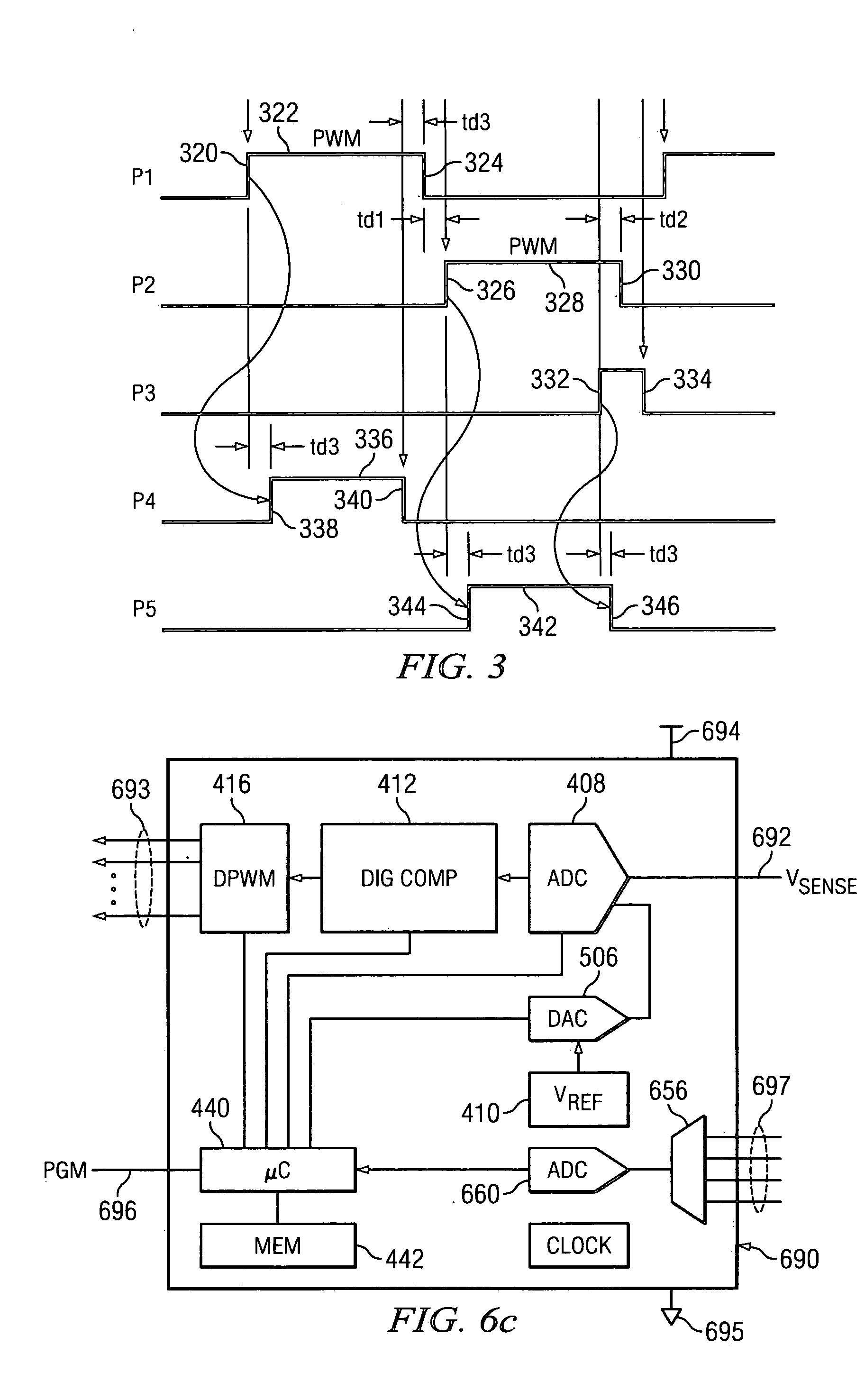
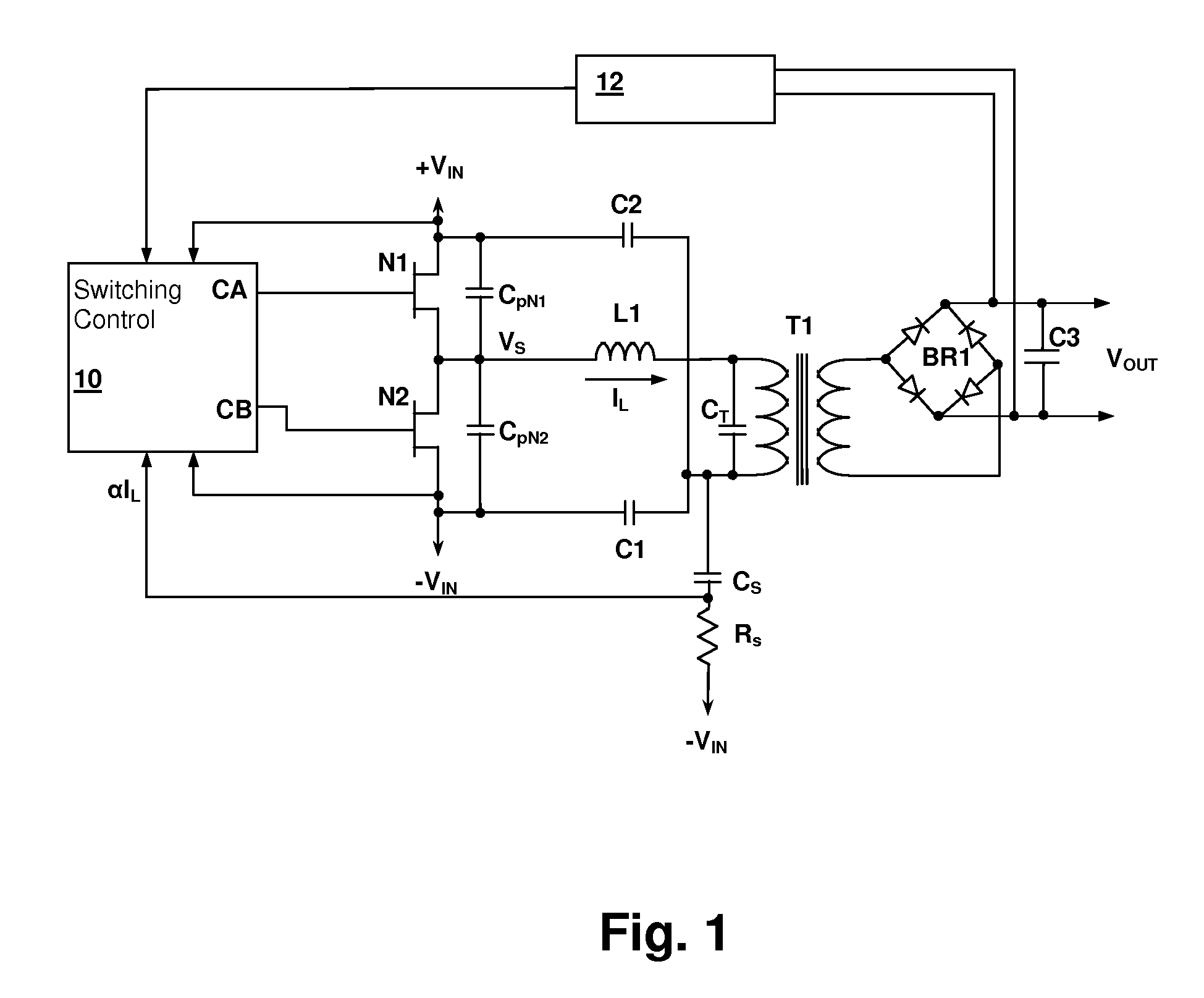
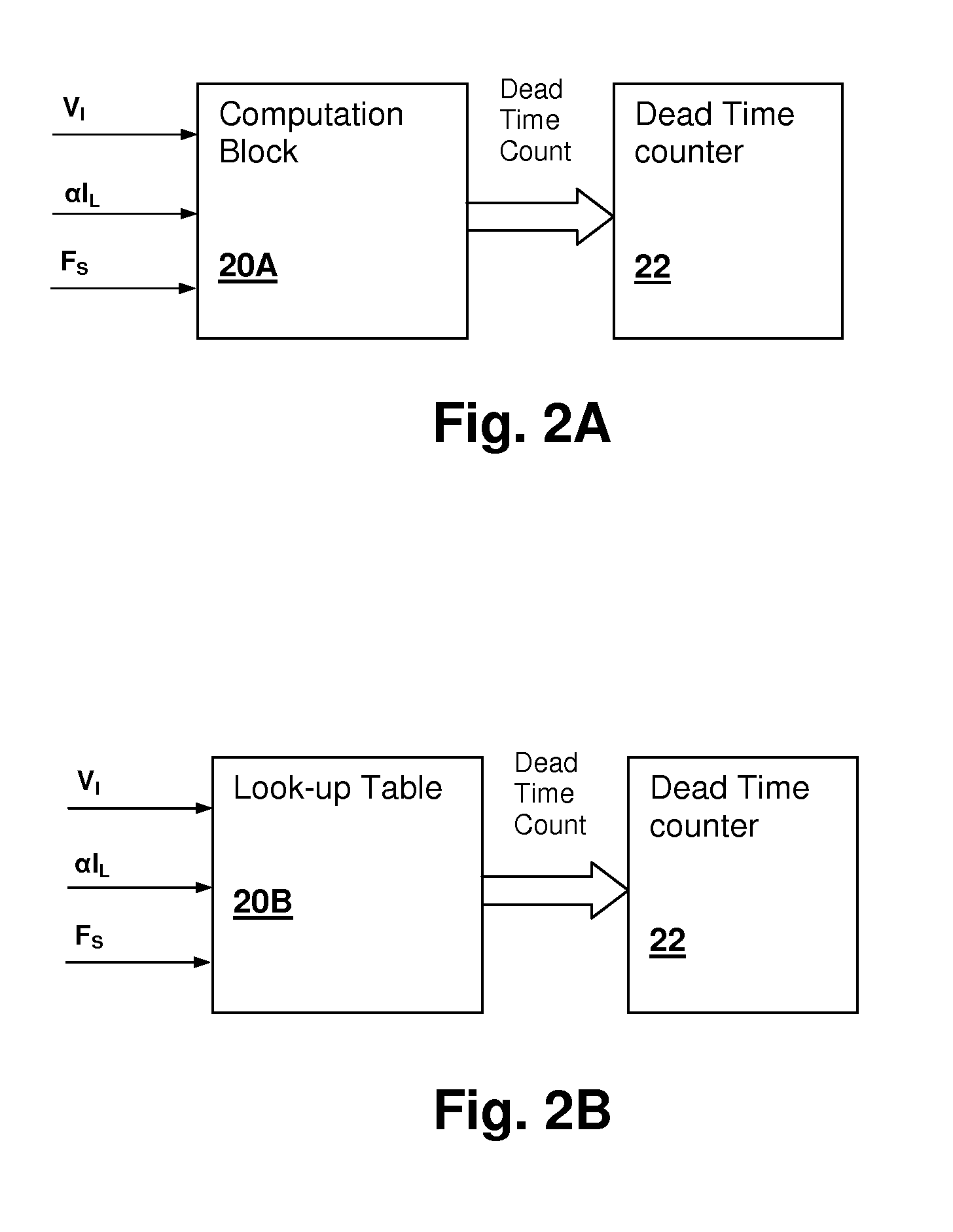
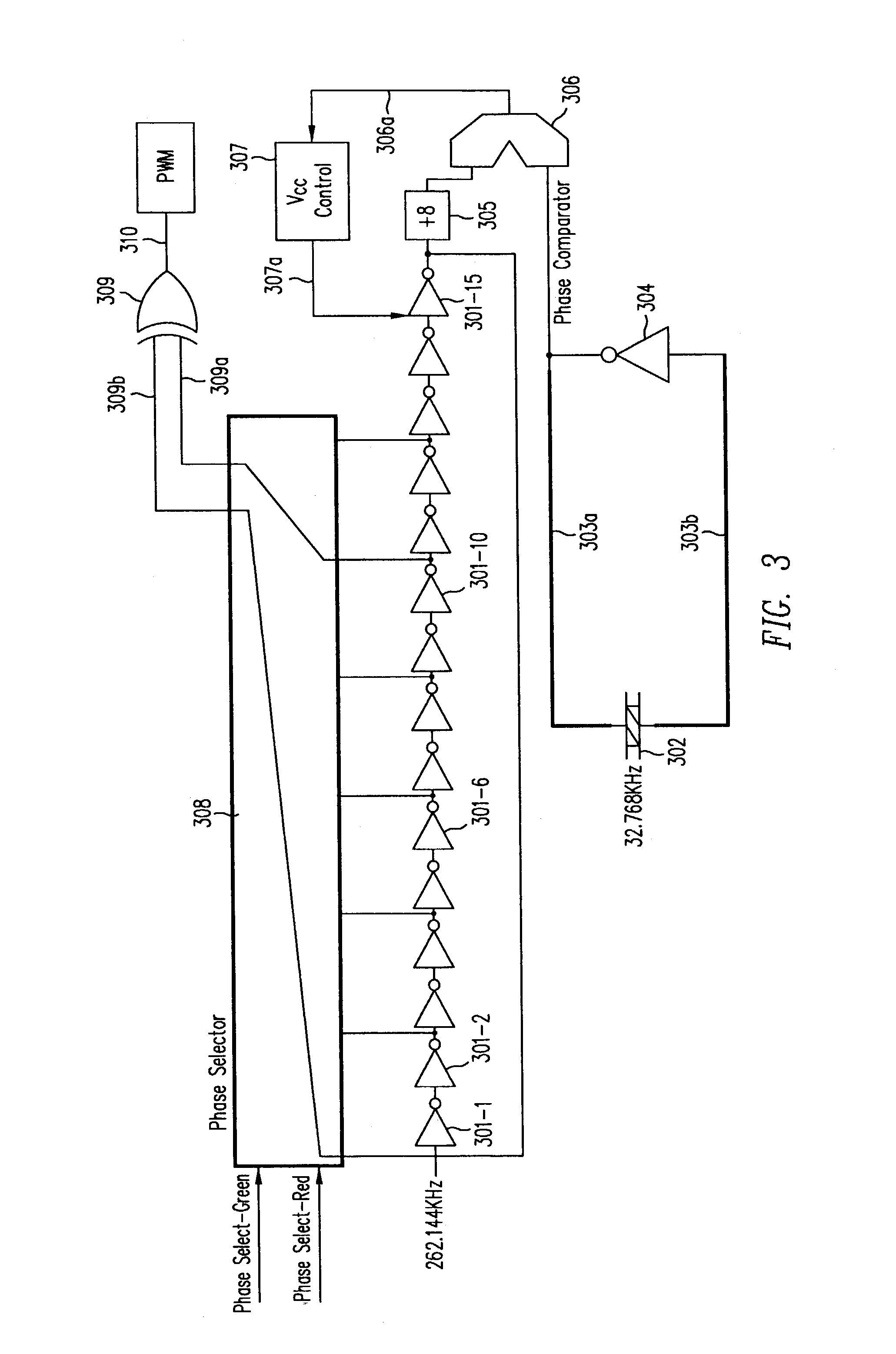
Digital PWM controller for digital power supply having programmable dead times
A system for controlling a switching power converter and includes a digital controller that receives an analog signal representing the output DC voltage of the power converter for comparison to a desired output voltage level and generates switching control signals to control the operation of the power supply to regulate the output DC voltage to said desired output voltage level. At least two of the switching control signals having a dead time between a first edge of a first control signal and a second edge of a second control signal. The dead time is programmable such that the second edge of the second control signal may occur at a selected point in time either before or after the first edge of the first control signal.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Vertically packaged switched-mode power converter
ActiveUS20060038549A1Tight regulationFast transient responseTransformersConversion constructional detailsCellular architectureElectrical resistance and conductance
A vertically packaged cellular power converter solves the problems associated with conventional designs and paves the way for a cellular circuit architecture with ultra-low interconnect resistance and inductance. The vertical packaging results in a power flow in the vertical direction (from the bottom to the top) with very short internal interconnects, thereby minimizing the associated conduction losses and permitting high conversion efficiency at high currents. The cellular architecture is ideally suited for generating multiple supply voltages.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
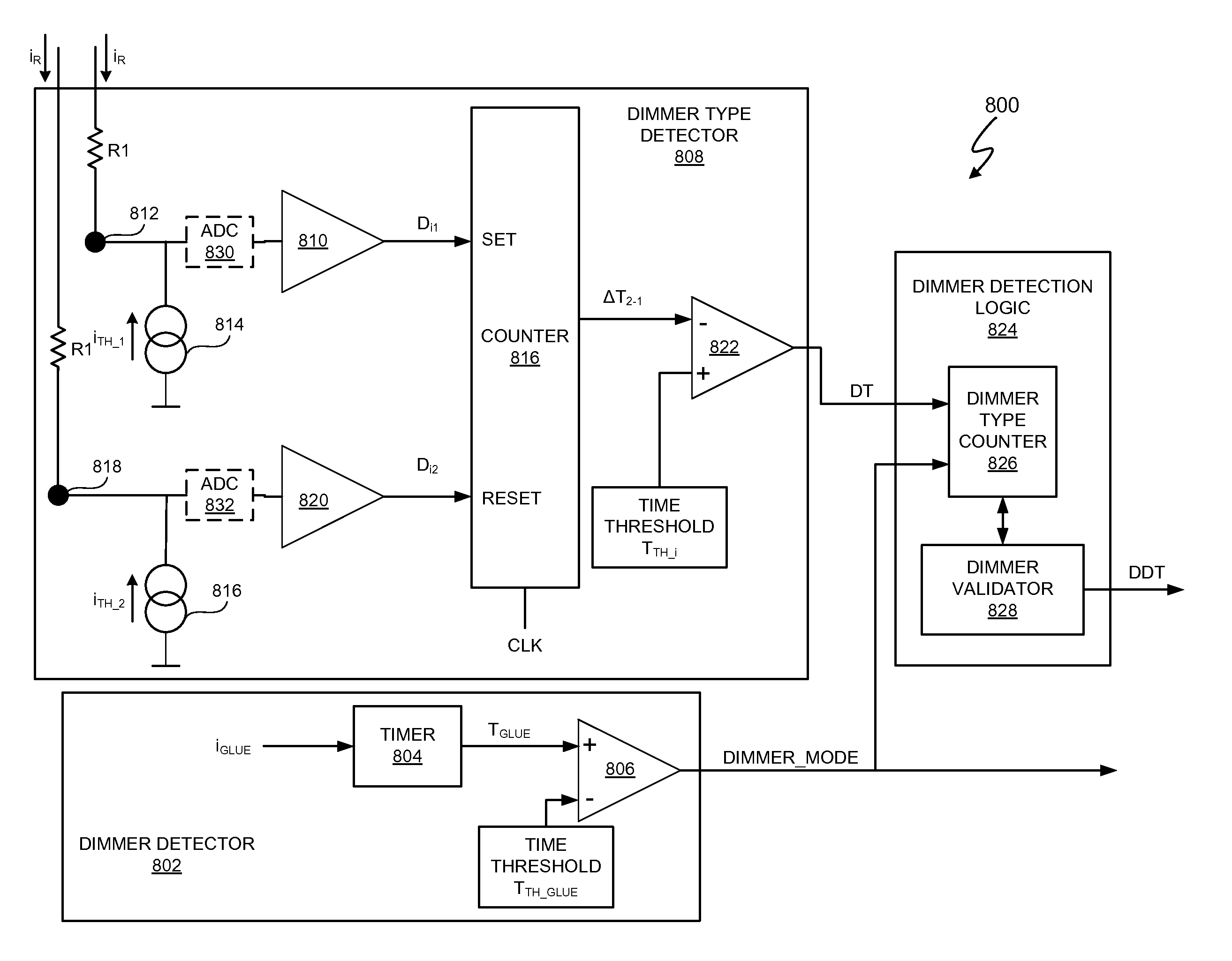
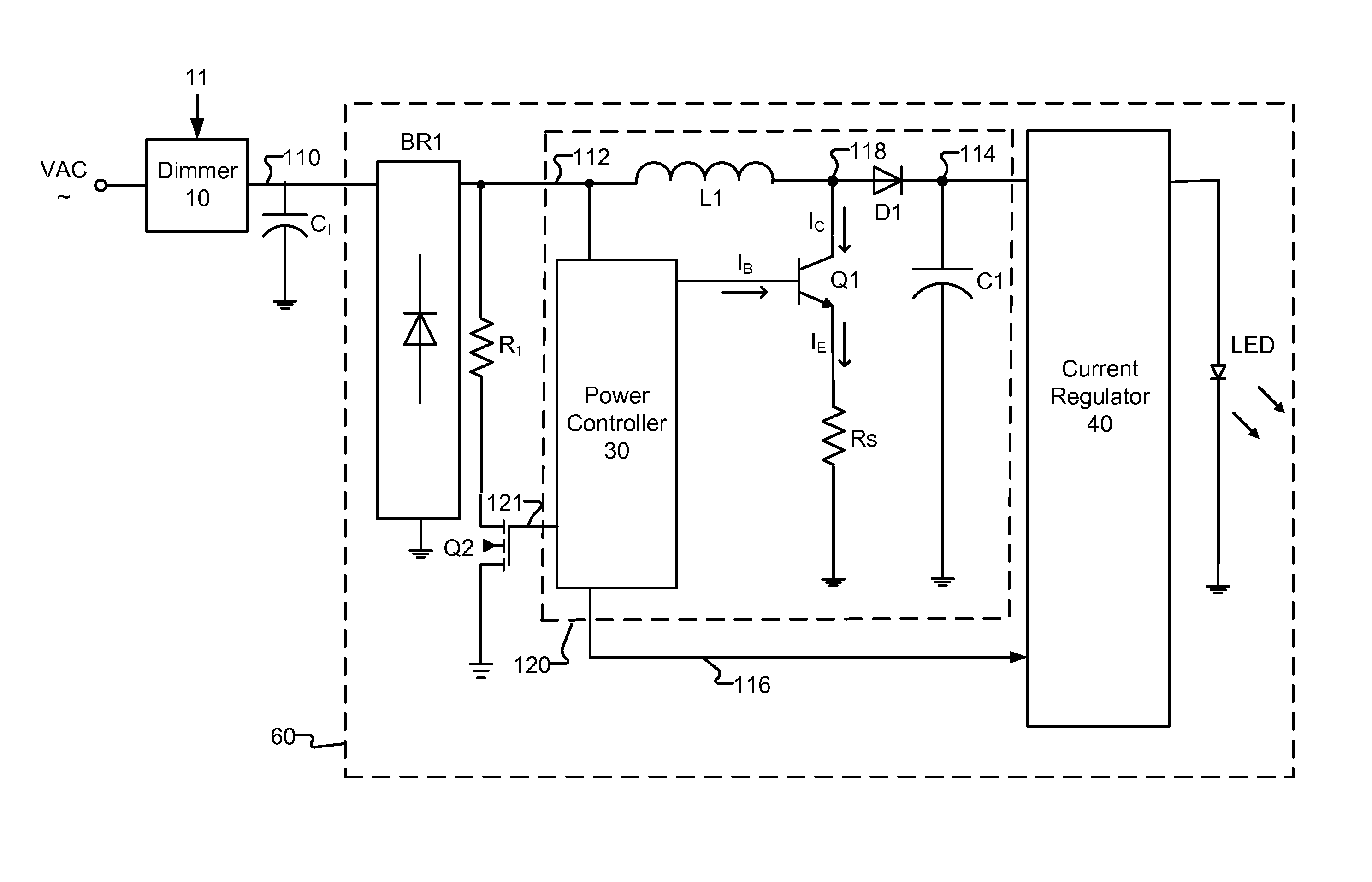
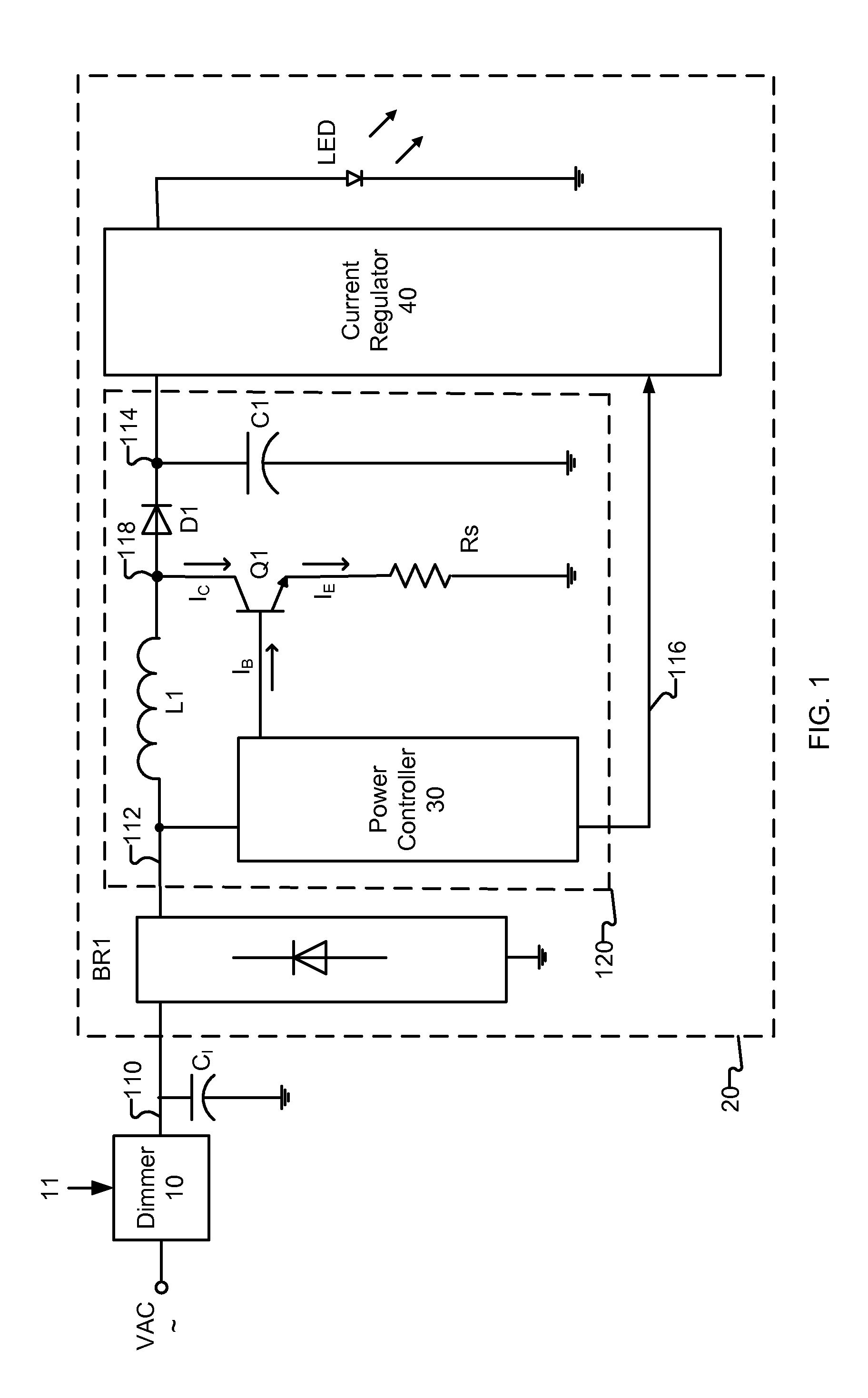
Dimmer detection
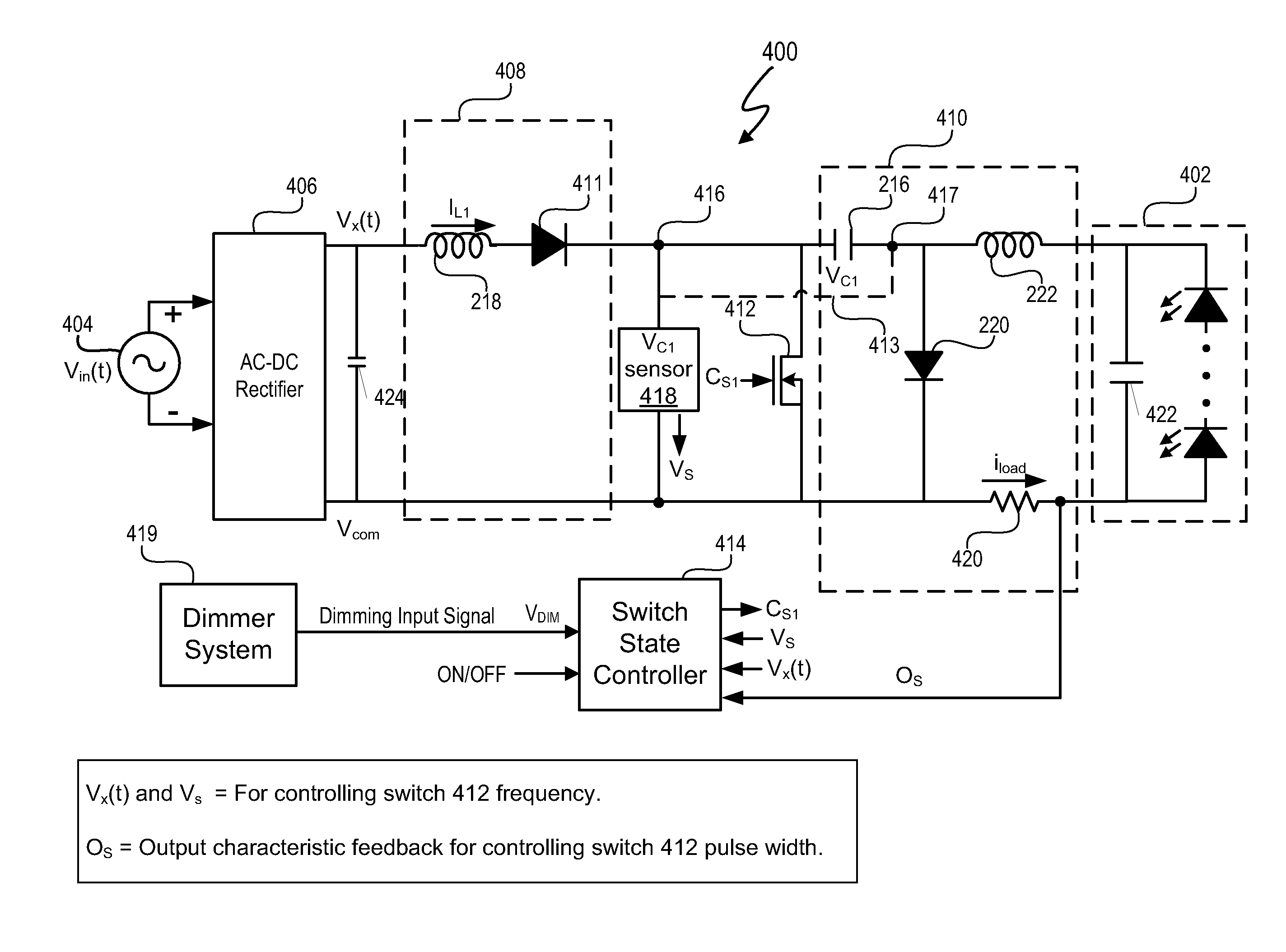
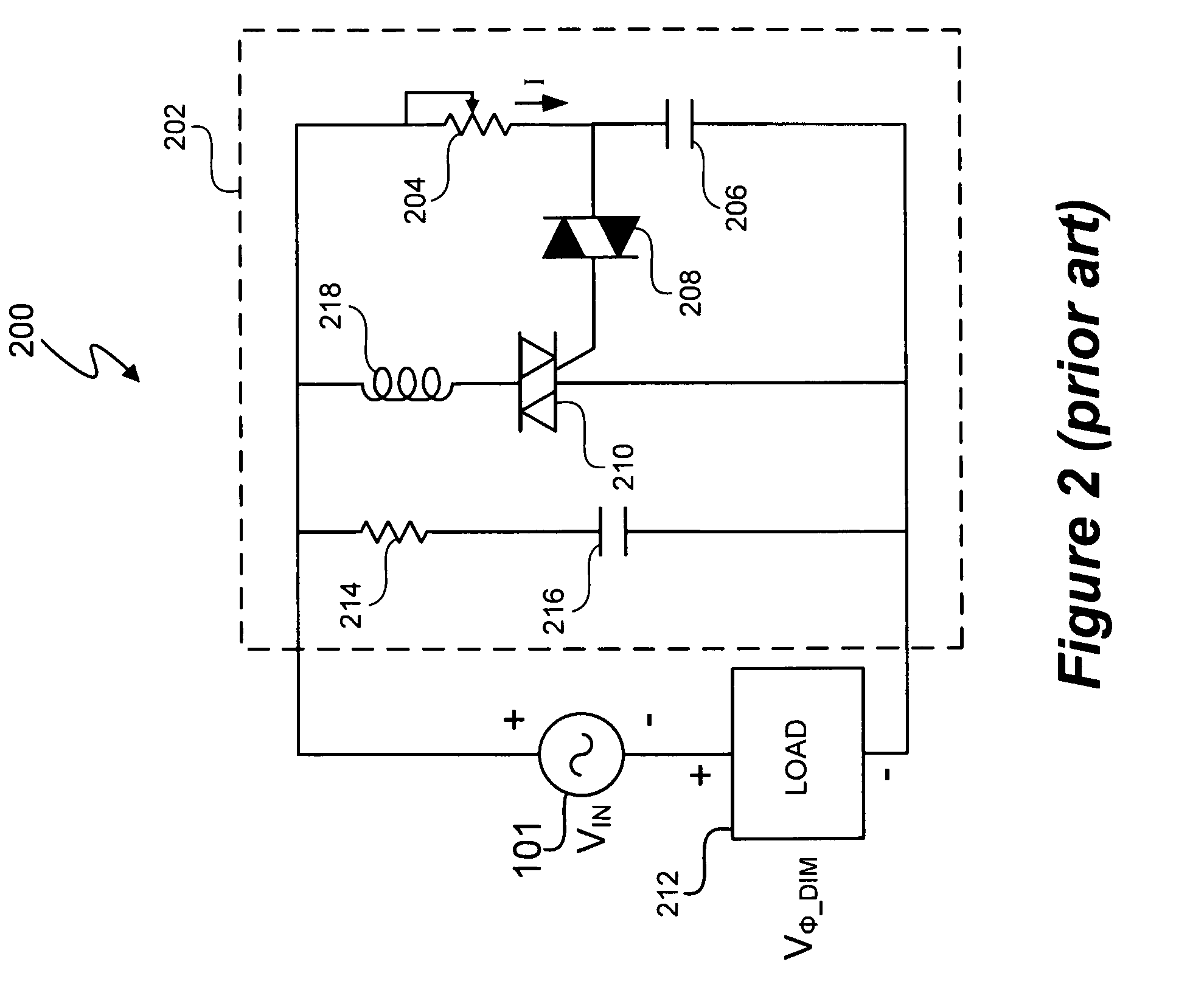
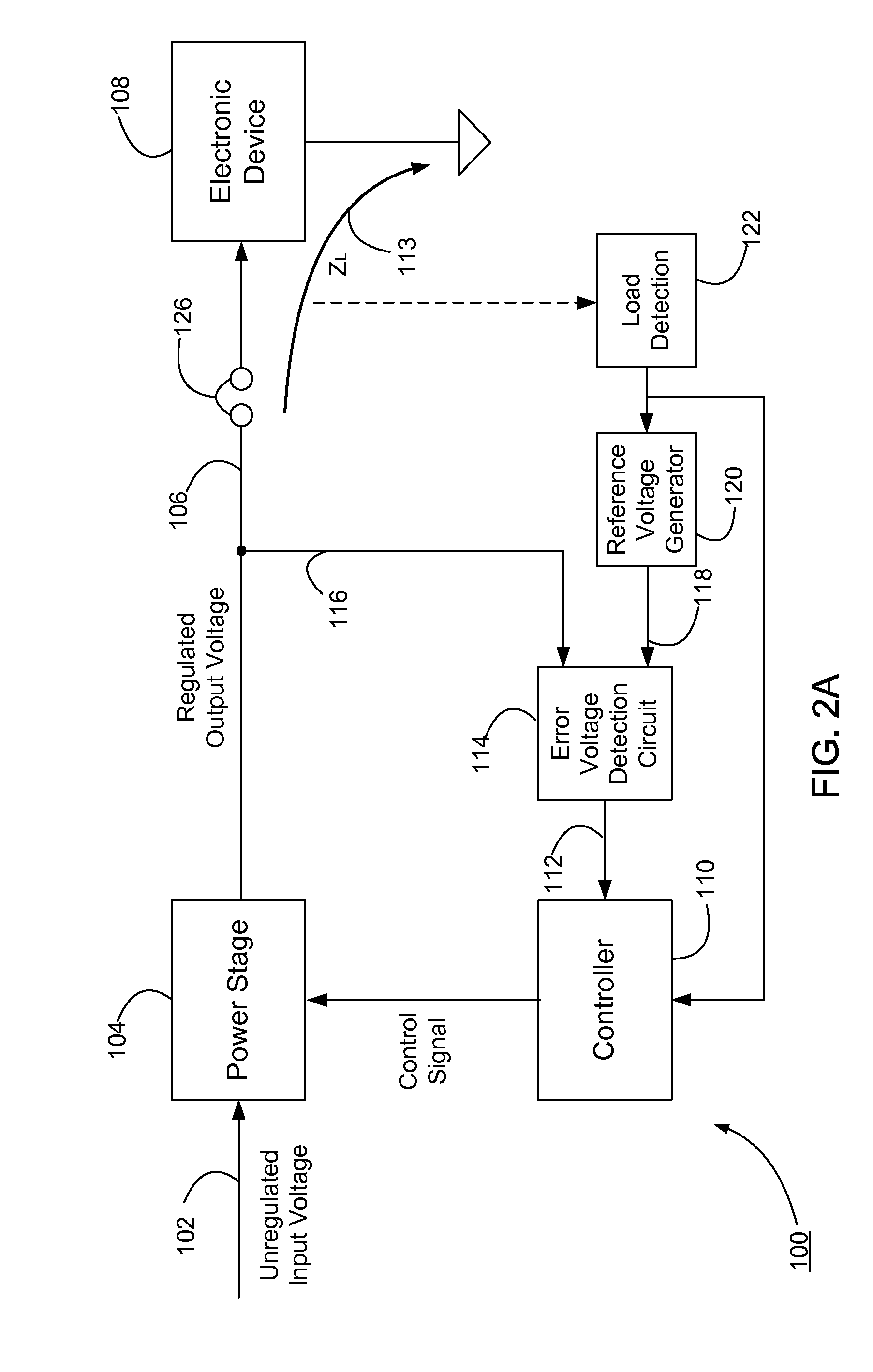
In at least one embodiment, a lighting system receives an input signal, such as a supply voltage, that can be affected by a dimmer. The supply voltage can be affected by a dimmer when, for example, a dimmer phase cut (i.e. chopped) the supply voltage. A dimmer detection system of the lighting system determines if a dimmer is affecting the supply voltage. In at least one embodiment, the dimmer detection system also determines a type of the dimmer, such as detecting if the dimmer is a leading edge or trailing edge dimmer. In at least one embodiment, the dimmer detection system provides dimmer type data to one or more other circuits such as a switching power converter controller. The one or more other circuits utilize the dimmer type data to affect their operation.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Method and apparatus for controlling output current of a cascaded DC/DC converter
ActiveUS20060113975A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCascade converterEngineering
A circuit and a method for controlling output current of cascaded switching power converters having a buck type output stage are disclosed. The circuit comprises two comparators for sensing input and output current, a logic gate for processing the output states of the comparators, and a pulse width modulator circuit for receiving the output of the logic gate and for controlling a switching power converter in accordance with this output. The method comprises simultaneous monitoring current in the stages of the converter, comparing the currents to the corresponding reference levels, generating the corresponding error signals, and controlling a pulse-width modulator circuit of a switching converter in accordance with these error signals.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
LED driver with multiple feedback loops
ActiveUS20090322234A1Quick controlAccurate currentElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLoop controlPower switching
An LED driver includes at least two interlocked closed feedback loops. One feedback loop controls the duty cycle of the on / off times of a switch connected in series to the LED string, and the other feedback loop controls the duty cycle of the on / off times of a power switch in the switching power converter that provides a DC voltage applied to the LED string. The LED driver of the present invention achieves fast control of the LED brightness and current sharing among multiple LED strings simultaneously in a power-efficient and cost-efficient manner.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
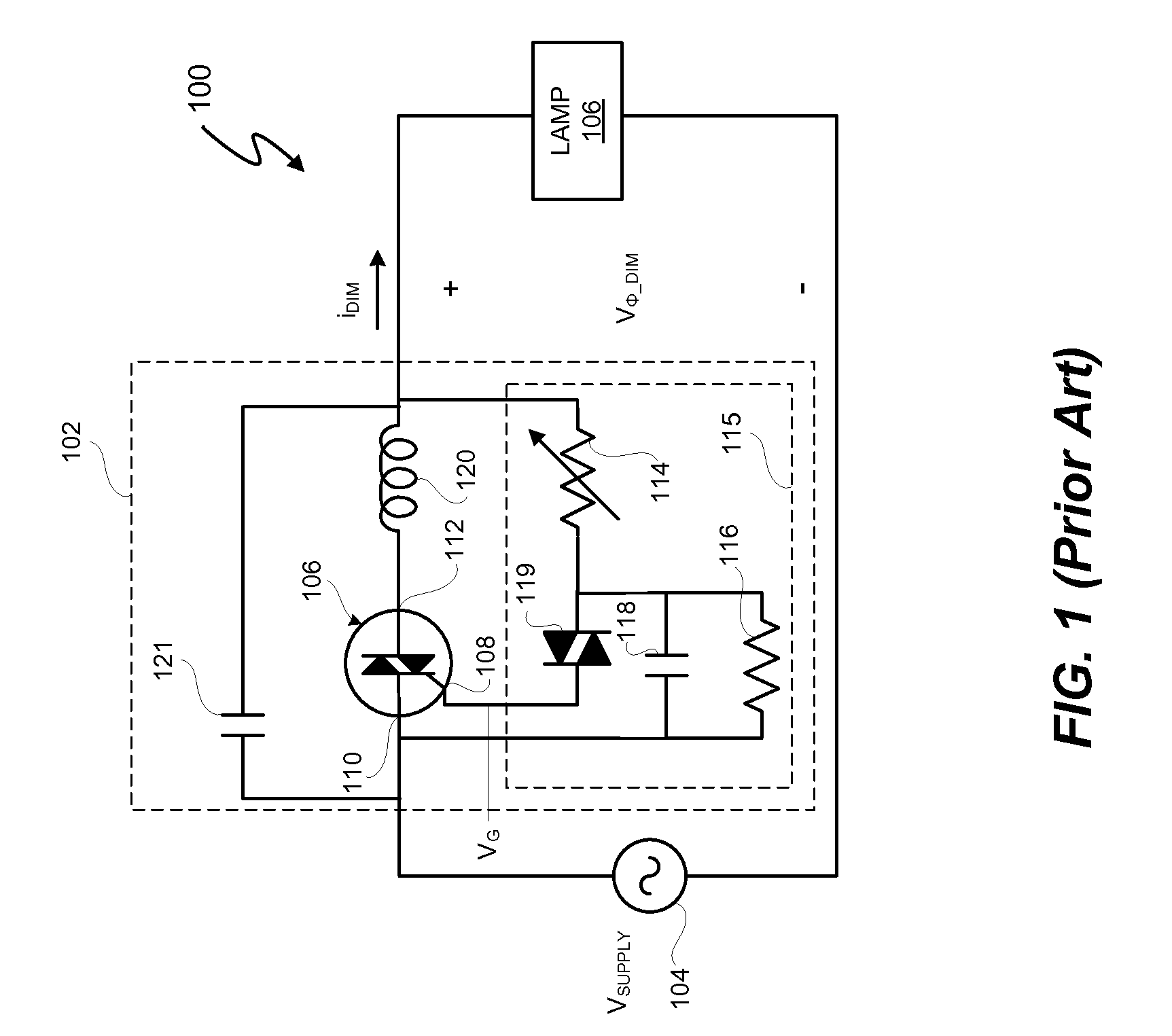
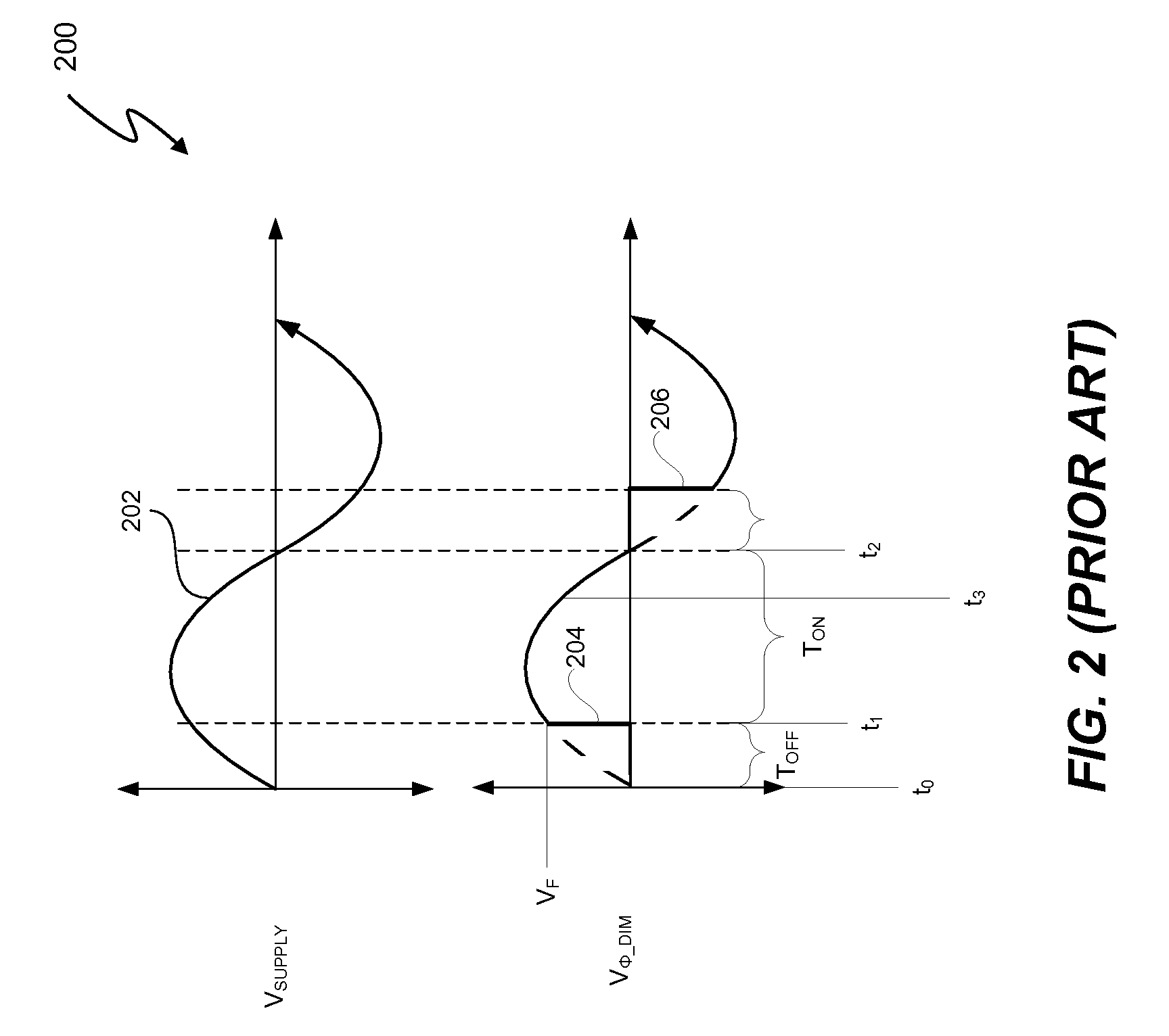
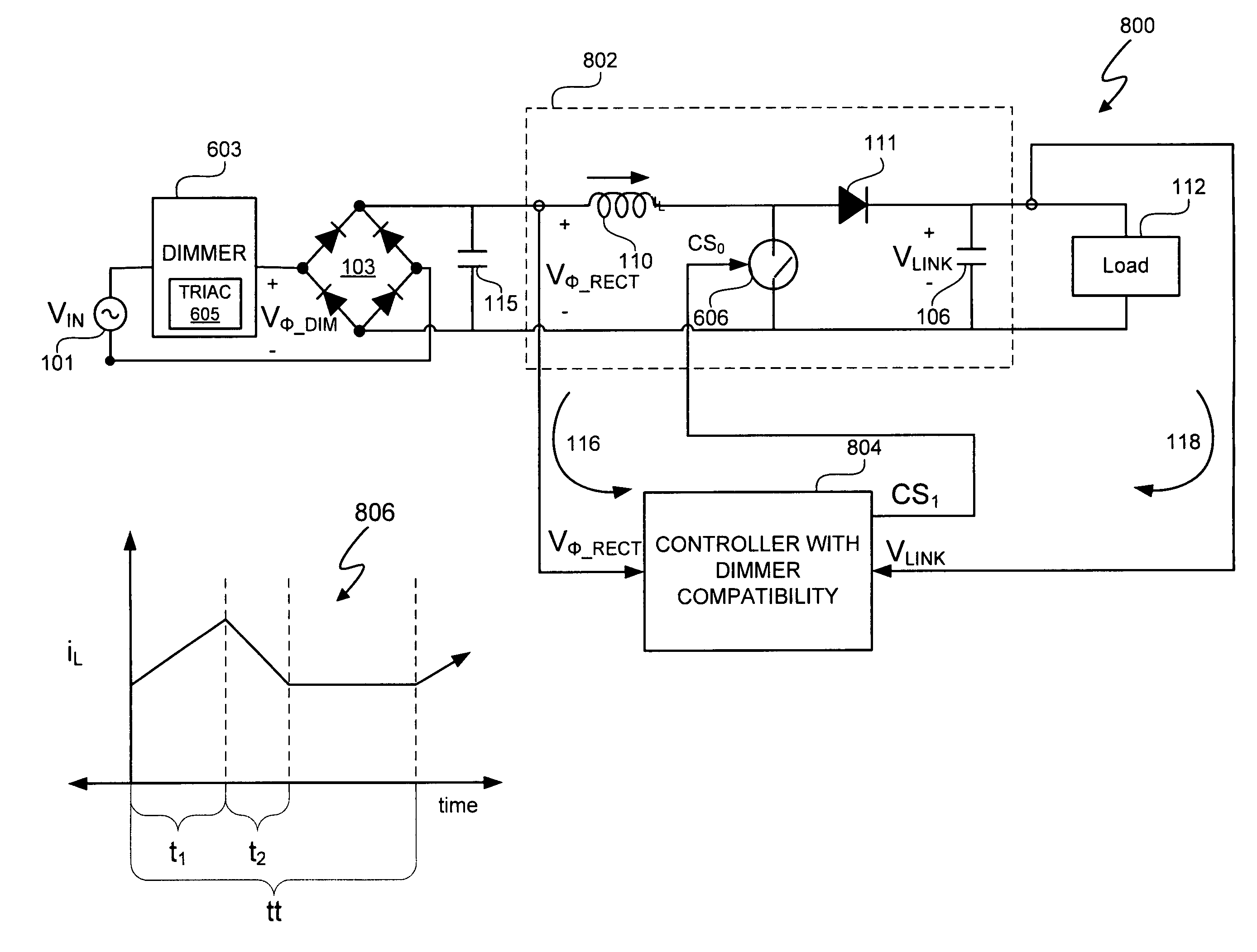
Switching power converter control with triac-based leading edge dimmer compatibility
In at least one embodiment, a controller allows triac-based dimmer to properly function and dim a load whose voltage is regulated by a switching power converter. In at least one embodiment, the switching power converter includes a switch to control voltage conversion of an input voltage to the switching power converter, wherein phase delays are introduced in the input voltage by a triac-based dimmer during a dimming period. In at least one embodiment, the controller is configured to control the switch of the switching power converter to establish an input resistance of the switching power converter during a dimming portion of the input voltage, wherein the input resistance allows the triac-based dimmer to phase modulate a supply voltage to the dimmer so that an output voltage of the dimmer has a substantially uninterrupted phase delay during each half-cycle of the supply voltage during the dimming period.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
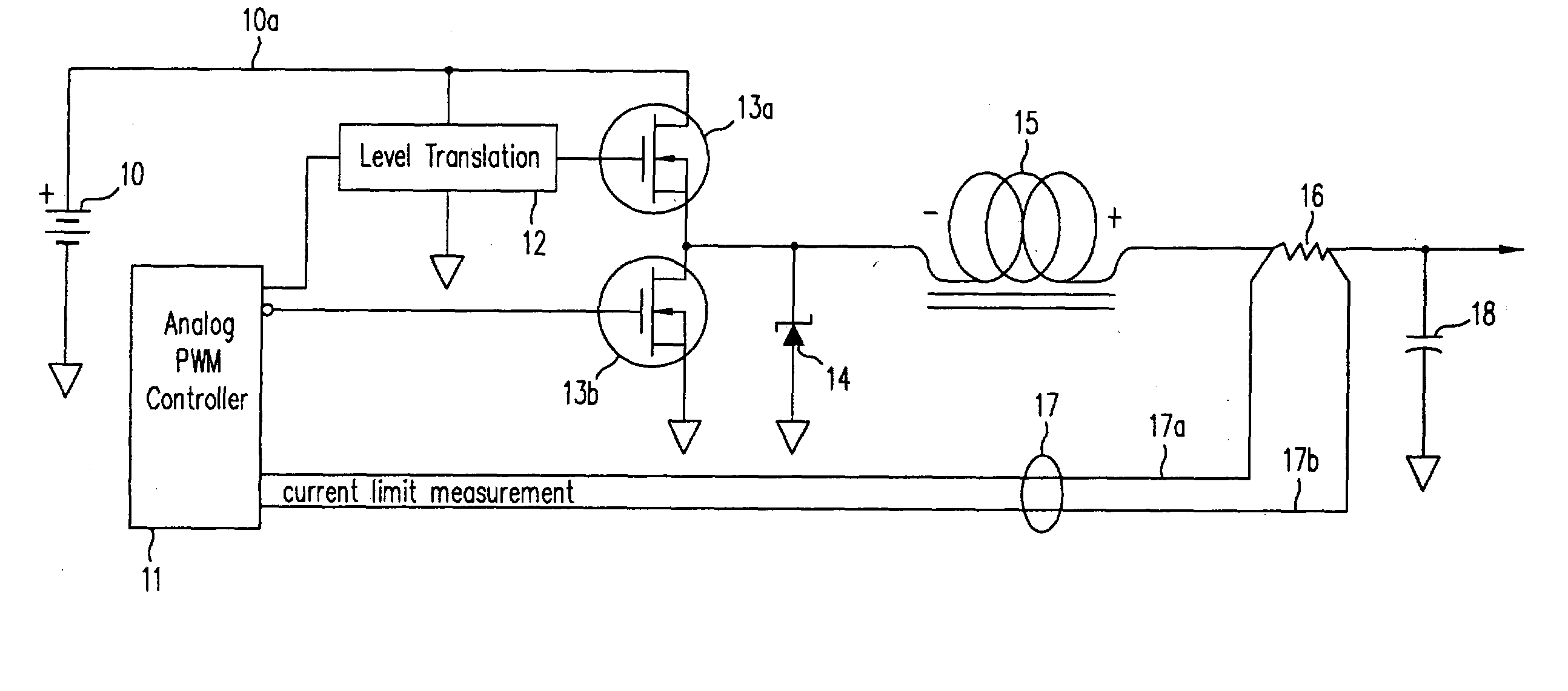
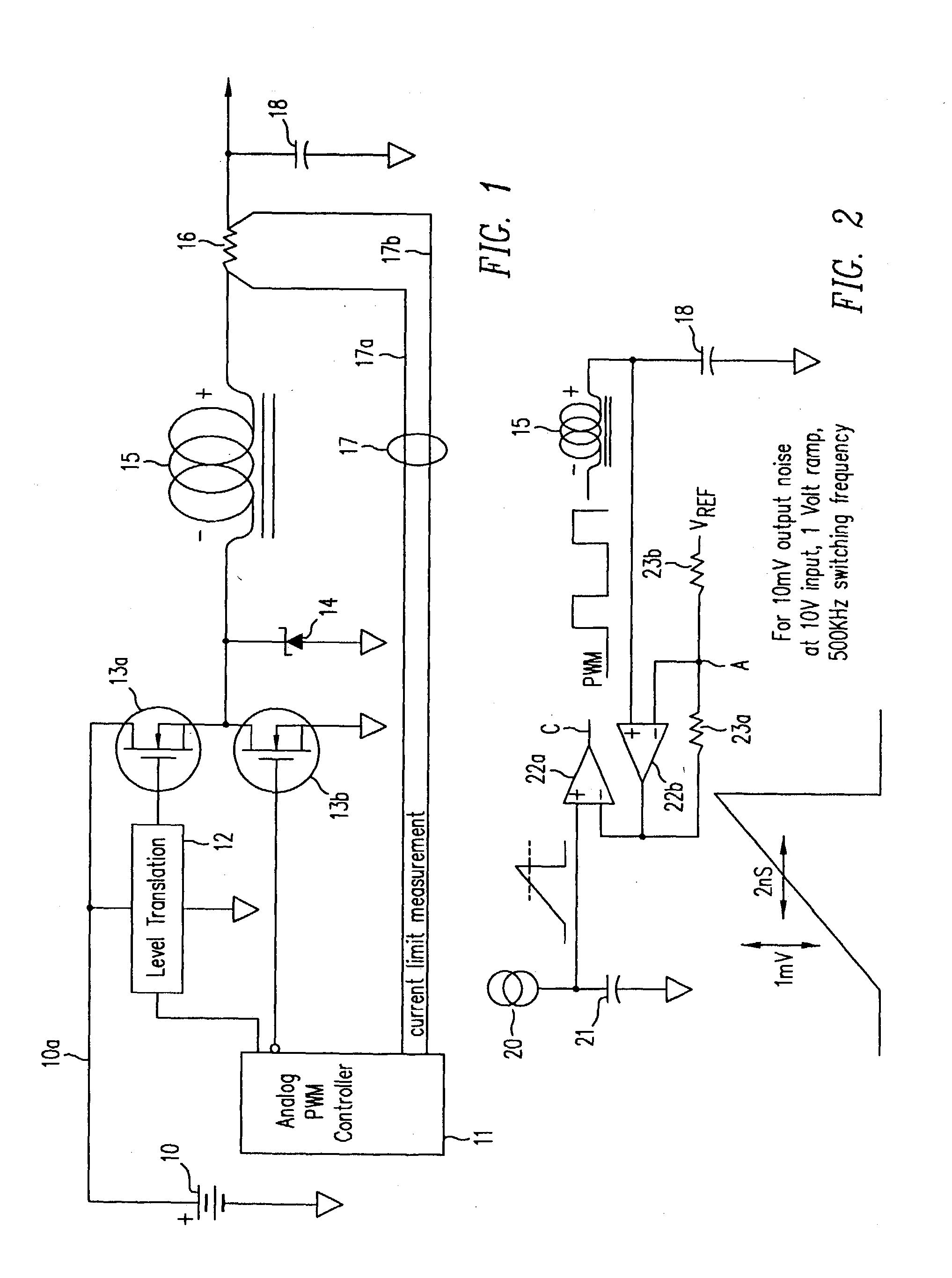
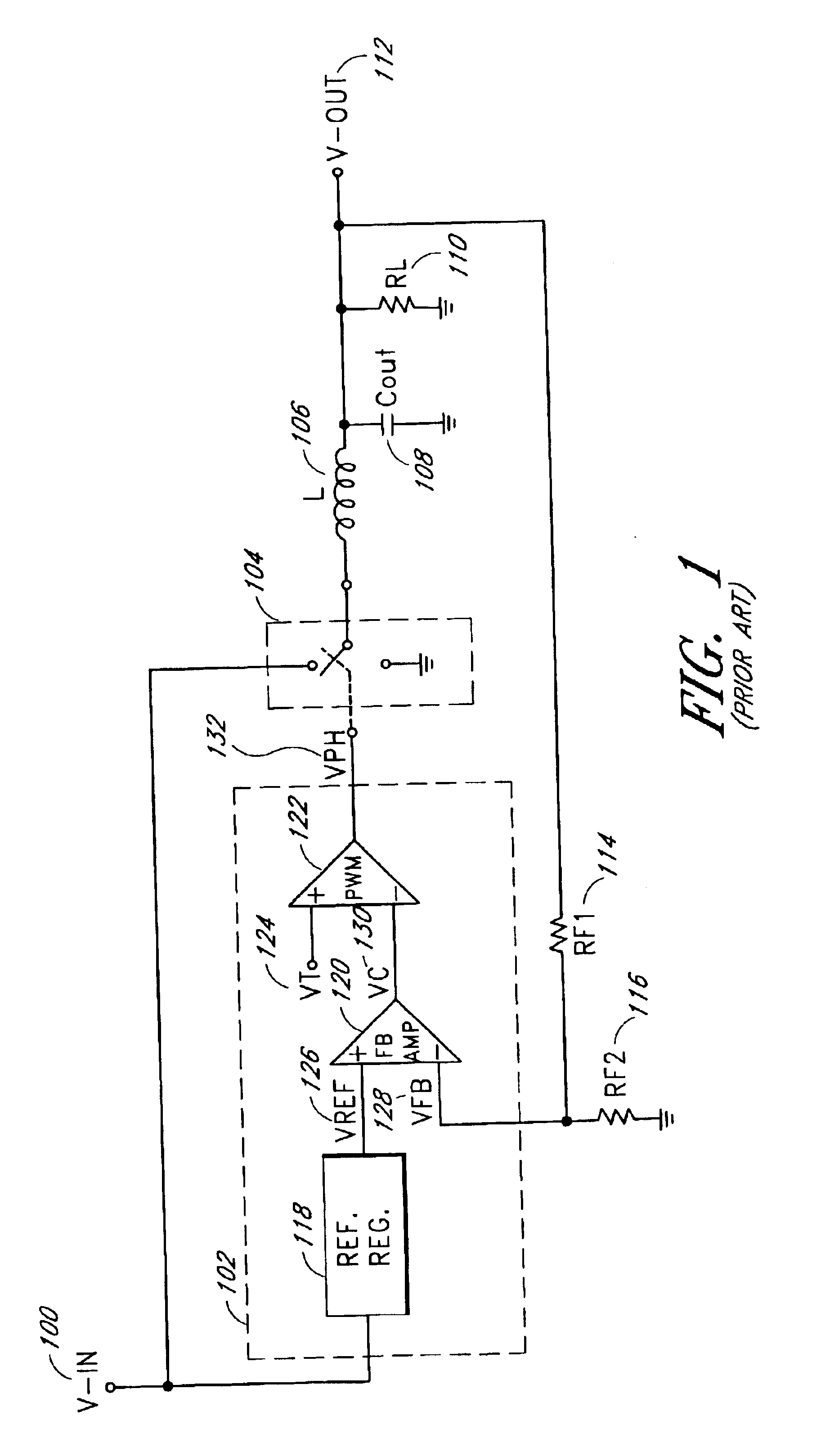
PWM power converter controlled by transistion detection of a comparator error signal
InactiveUS6900995B2Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcApparatus without intermediate ac conversionComparatorError signal
Owner:HERCULES TECH GROWTH CAPITAL
Switching power converter with load impedance detection
ActiveUS20100195355A1Reduce output voltageReduce power lossEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionVoltage referenceEngineering
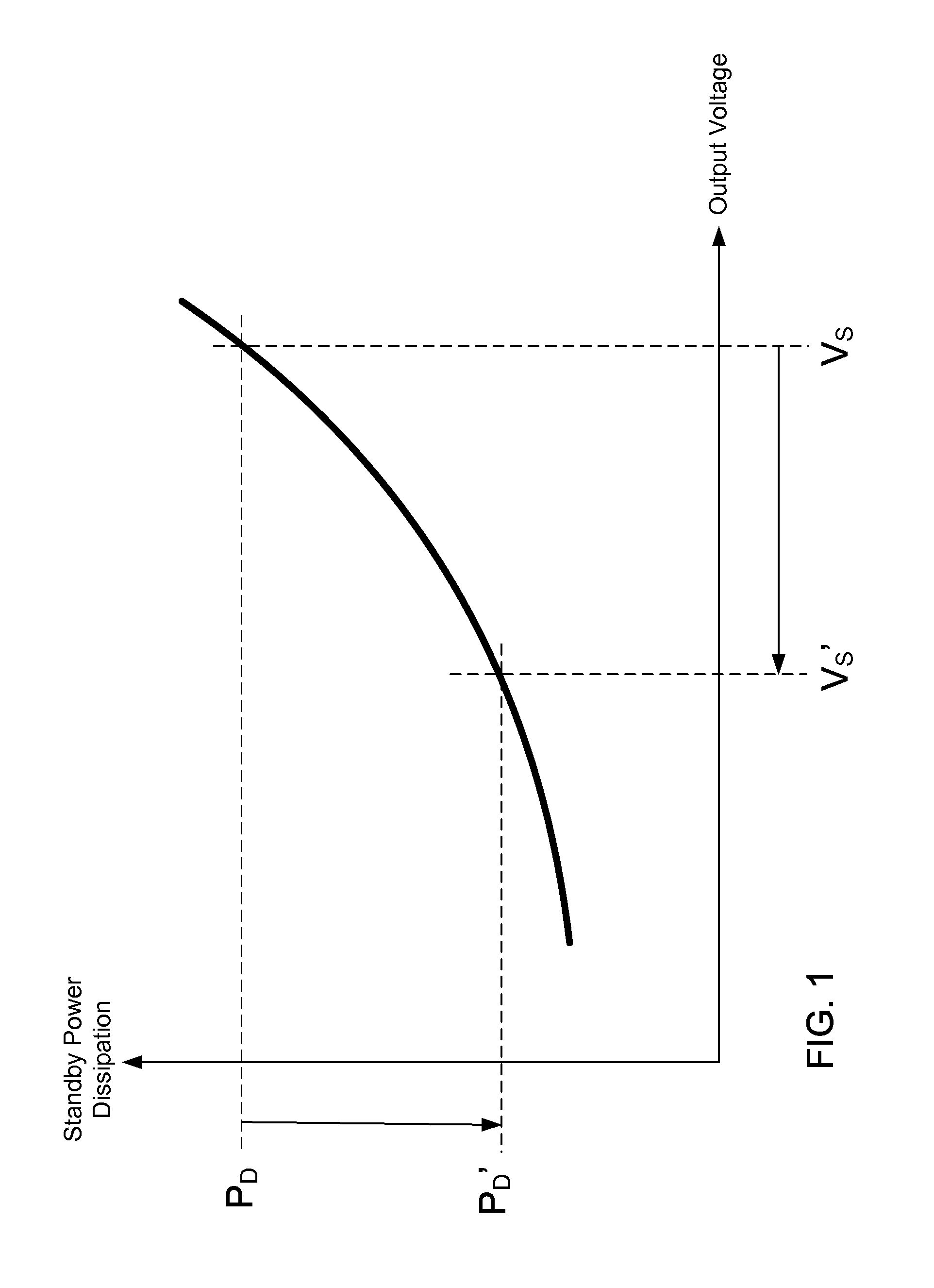
In a switching power converter, no-load condition is detected based on a variety of parameters including the output current, primary current, transformer reset time, and switching period. Once the no-load condition is detected, the switching power converter enters stand-by mode, in which the reference voltage corresponding to the target regulated output voltage of the switching power converter is lowered to a low stand-by value or the switching power converter is shut down for a predetermined duration. As a result, power loss during the stand-by mode of the switching power converter can be reduced significantly.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
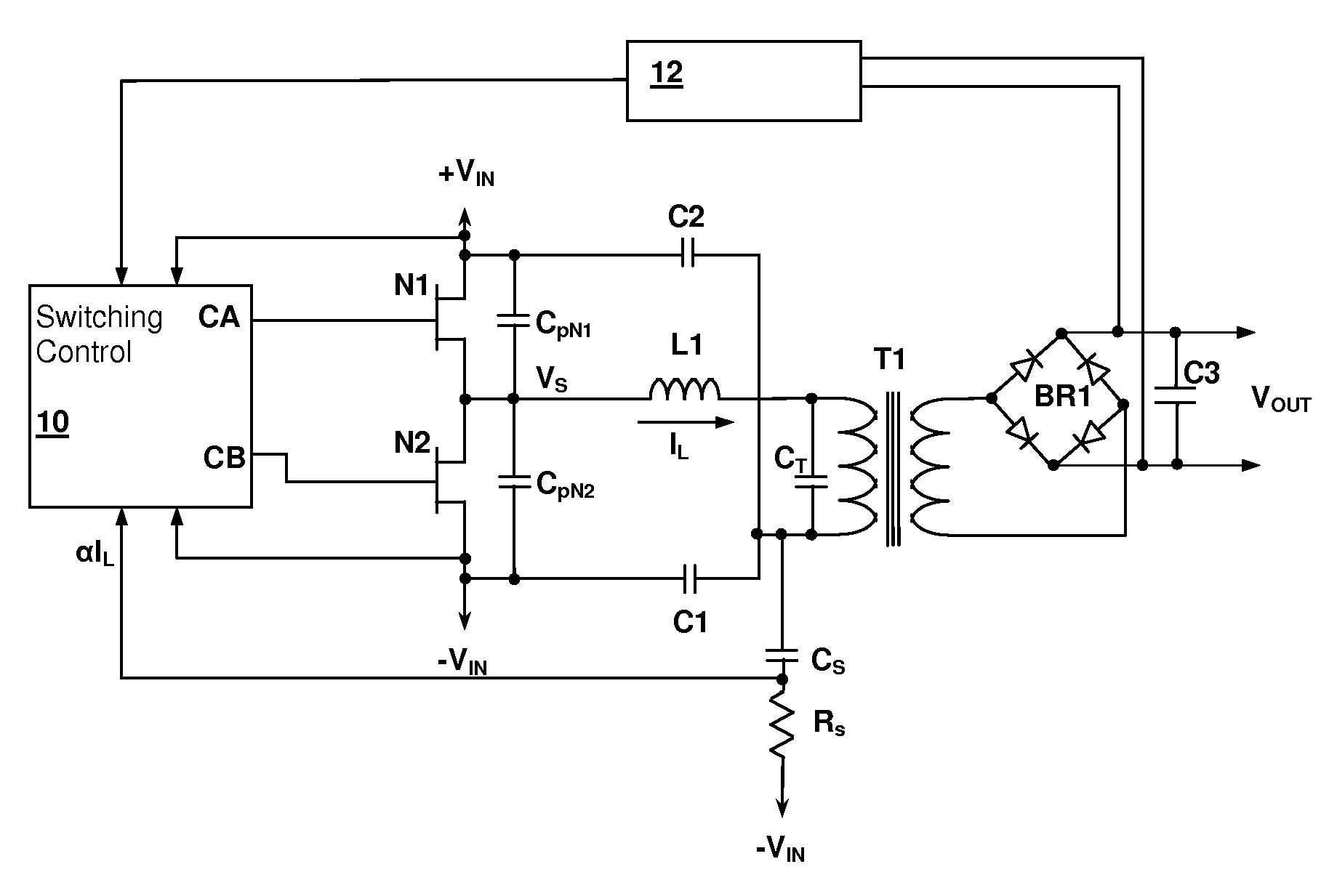
Resonant switching power converter with adaptive dead time control
InactiveUS20100020569A1Improve efficiencyRelieve pressureTransformersEfficient power electronics conversionTransverterEngineering
A resonant switching power converter having adaptive dead time control provides improved efficiency along with reduced EMI / audible noise and component stresses. A dead time between pulses generated by a switching circuit is adaptively set in conformity with a value of the input voltage to the resonant switching power converter and an indication of a magnitude of the current passing through inductive element of the resonant tank of the converter. The indication of the current magnitude may be the switching frequency of the converter, or a measure of line or load current levels. The dead time can be obtained from a look-up table or computed from the current magnitude and input voltage values.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
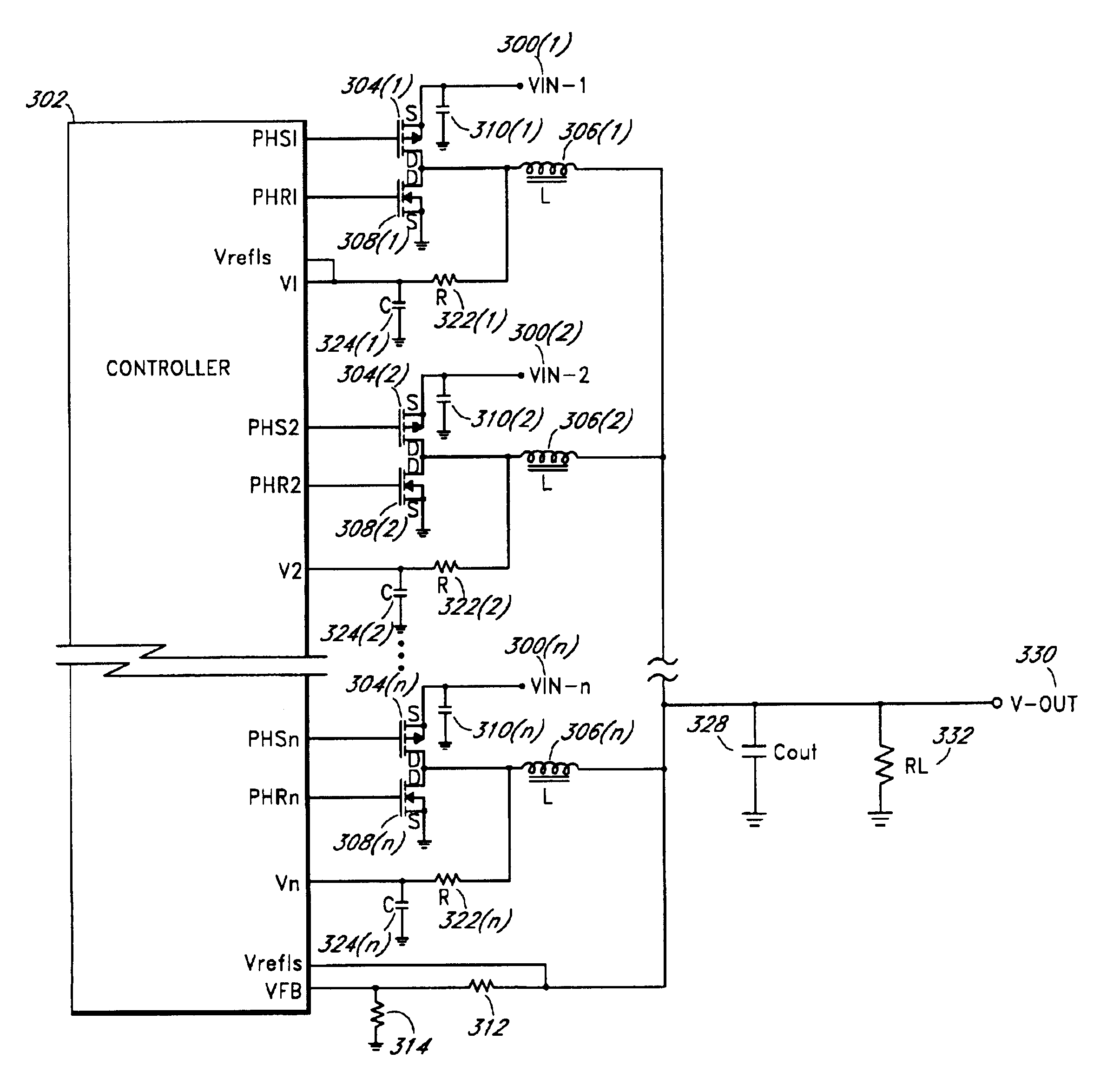
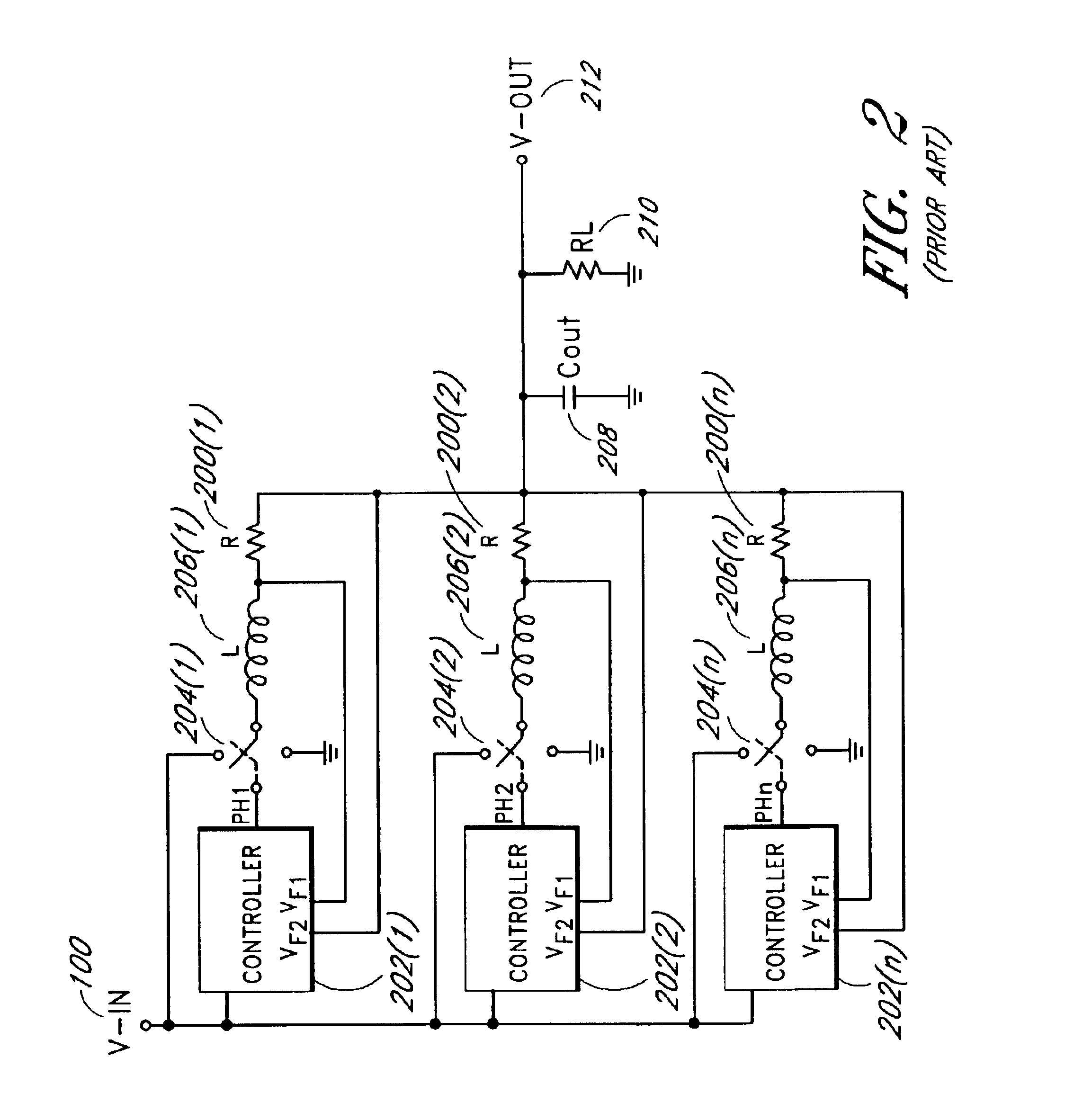
Method and apparatus for load sharing in a multiphase switching power converter
InactiveUS7005835B2Improve reliabilityLow costDc-dc conversionDc source parallel operationPeer-to-peerDC-to-DC converter
A plurality of single-phase synchronizing converter automatically synchronize on a peer-to-peer basis. Each synchronizing converter is configured as a DC-to-DC converter. The synchronizing converters operate in parallel as a multi-phase converter. A common bus between the synchronizing converters includes a sync line and a common phase control line. Proper phasing automatically occurs when power is applied, and the phasing changes automatically as converters are added or removed. When the system powers up, the converters arbitrate for phase position. The phasing positions are random, but the phasing is relatively symmetrical regardless of the number of phases. In one embodiment, a hot-swappable converter module can be plugged into any location of a parallel multiphase bus to produce a common output voltage. When an additional module is plugged in, the converters readjust their phases to maintain phase symmetry. In one embodiment, each module shares a substantially equal portion of the output load.
Owner:MICROSEMI CORP ANALOG MIXED SIGNAL GRP LTD
Power converter circuitry and method
InactiveUS7365661B2Different output voltageEasy to makeAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsControl systemEngineering
A control system and method for simultaneously regulating the operation of a plurality of different types of switching power converters. The system utilizes in regulating the power converters sampled data and nonlinear feedback control loops.
Owner:EXAR CORP
Class H Drive
InactiveUS20080310046A1Increase the switching frequencyImprove motor efficiencySynchronous motors startersDC motor speed/torque controlAudio power amplifierDigital analog converter
A method for driving a load by using an output stage amplifier in full bridge configuration whose supply is modulated by means of a fast switching power converter, controlled in order to maintain the stage's output common mode at its minimum voltage, is presented. The modulation of the switching power converter output is obtained by a feedback control system regulating directly the voltage of the bridge output stage terminals. This bridge unipolar class H stage allows driving the load with high accuracy and improved efficiency without introducing switching noise and EMI at the load terminals typical of PWM driving. This method can be applied with the same benefits to class AB, pseudo class AB or to class A output stages. When this method is associated with an imposed current driving approach and with a current oversampling digital to analog converter the resulting advantages are very significant for accurate motor control applications.
Owner:MENEGOLI PAOLO +1
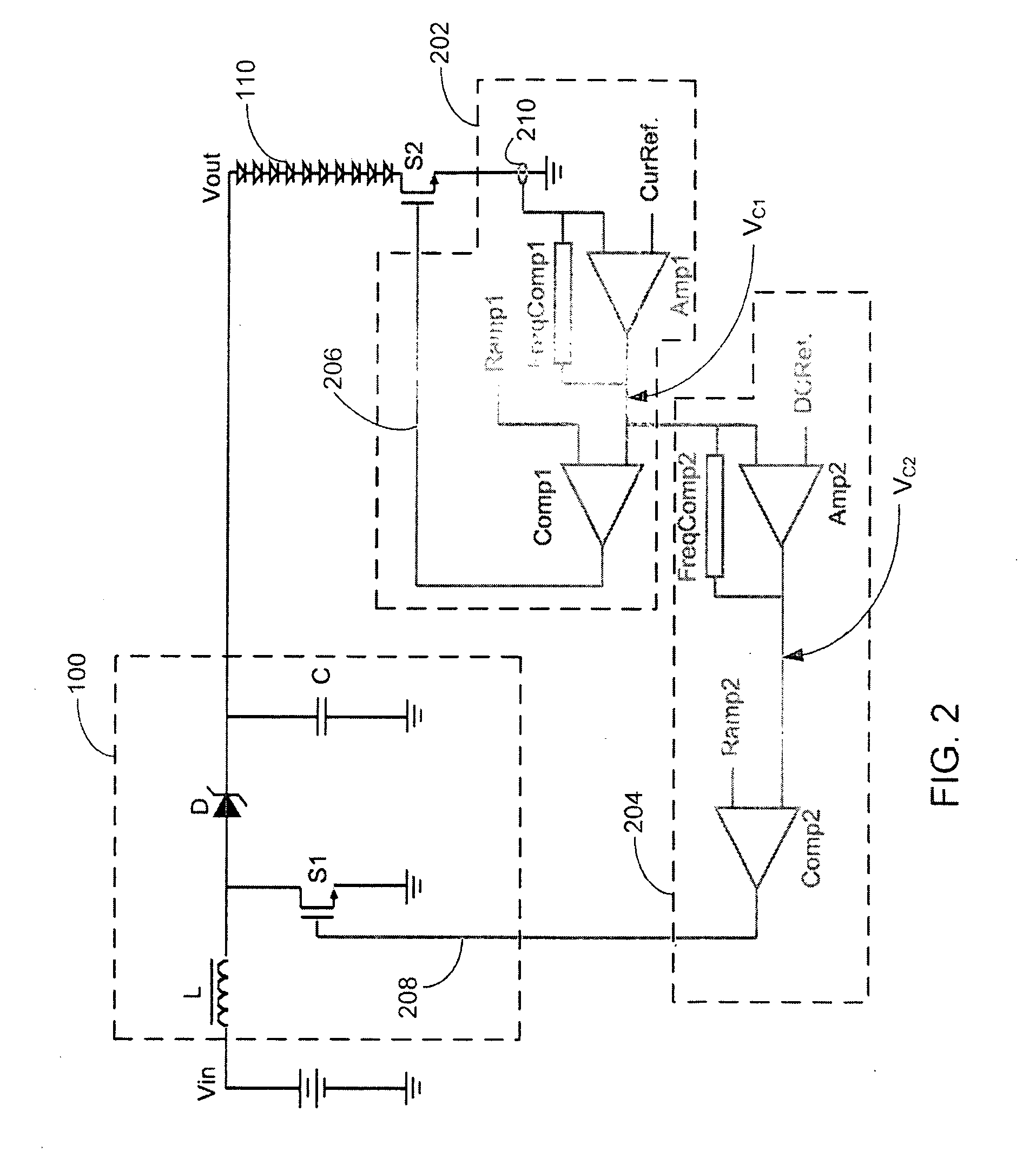
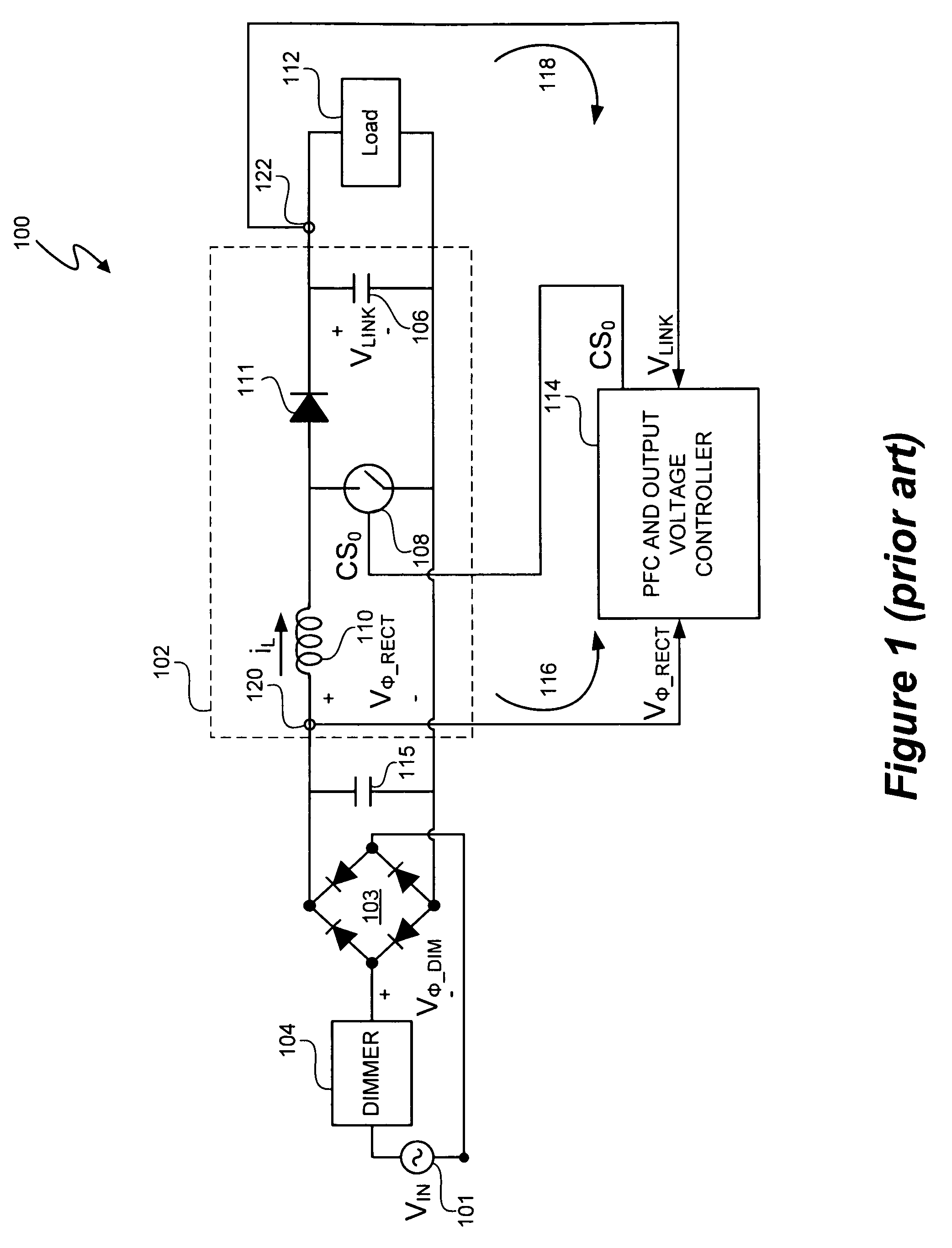
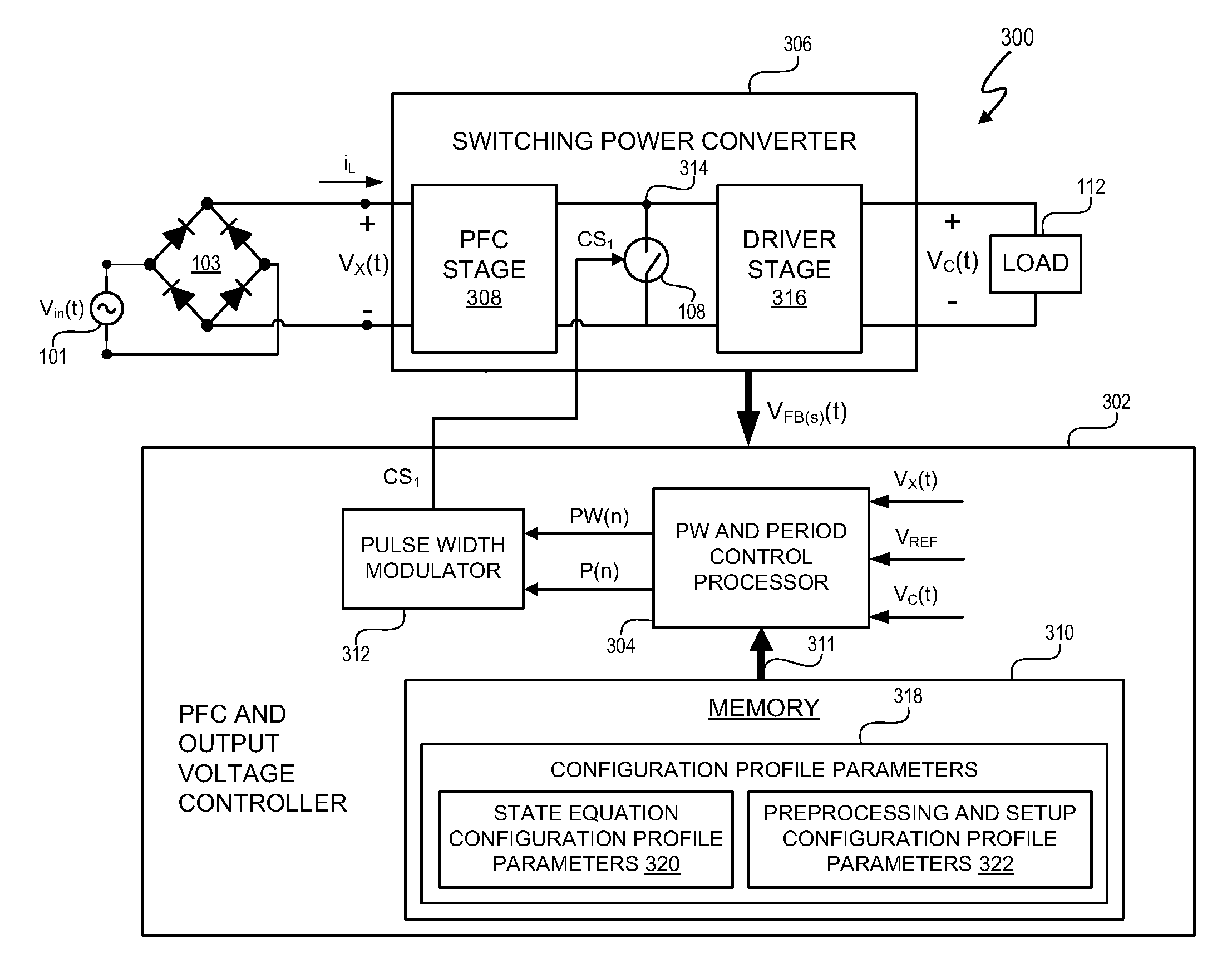
Programmable power control system
InactiveUS20080272747A1Efficient power electronics conversionAnalogue conversionPower control systemControl signal
A power control system includes a switching power converter and a programmable power factor correction (PFC) and output voltage controller. The programmable PFC and output voltage controller generates a control signal to control power factor correction and voltage regulation of the switching power converter. In at least one embodiment, the control signal is a pulse width modulated signal. The programmability of the PFC and output voltage controller provides the programmable PFC and output voltage controller flexibility to operate in accordance with programmable parameters, to adapt to various operating environments, and to respond to various operating exigencies. In at least one embodiment, the programmable PFC and output voltage controller includes a state machine to process one or more programmable, operational parameters to determine the period and pulse width states of the control signal.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Power dissipation monitor for current sink function of power switching transistor
ActiveUS20130241427A1Precise functionElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPower controllerPower switching
The embodiments disclosed herein describe a method of a power controller for monitoring for unsafe operating conditions of a drive transistor in a switching power converter of a LED lamp system by predicting the power dissipation of the drive transistor based on knowledge of the current through the drive transistor and a continuous observation of the voltage across the drive transistor. When the drive transistor approaches unsafe operating conditions, the power controller turns off the drive transistor.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Power converter circuitry and method
InactiveUS20040095264A1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsControl systemEngineering
A control system and method for simultaneously regulating the operation of a plurality of different types of switching power converters. The system utilizes in regulating the power converters sampled data and nonlinear feedback control loops.
Owner:EXAR CORP
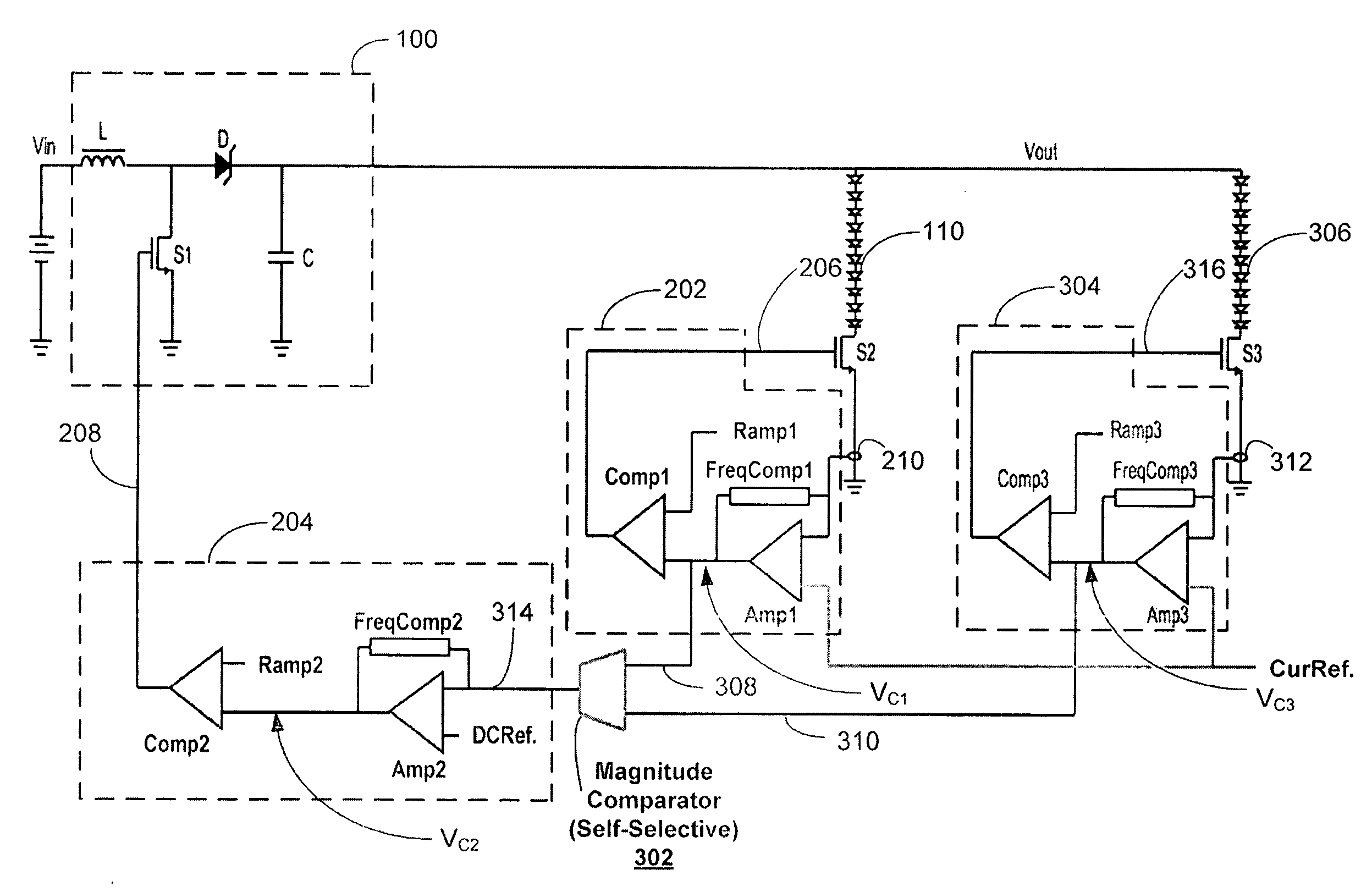
Adaptive multi-mode digital control improving light-load efficiency in switching power converters
ActiveUS20100164455A1Improve switching power converter light-load efficiencyImprove light load efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionFrequency levelEngineering
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR
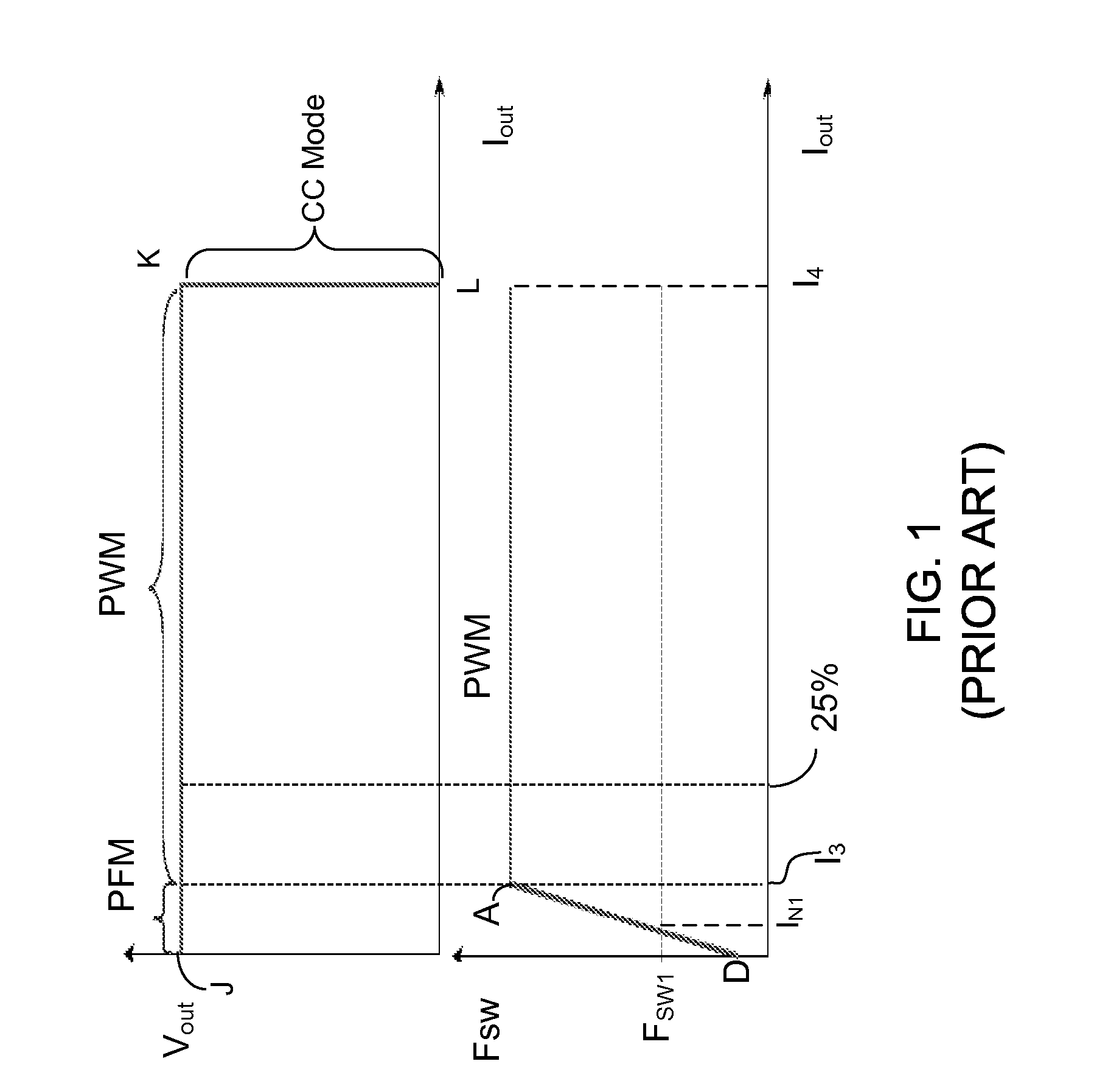
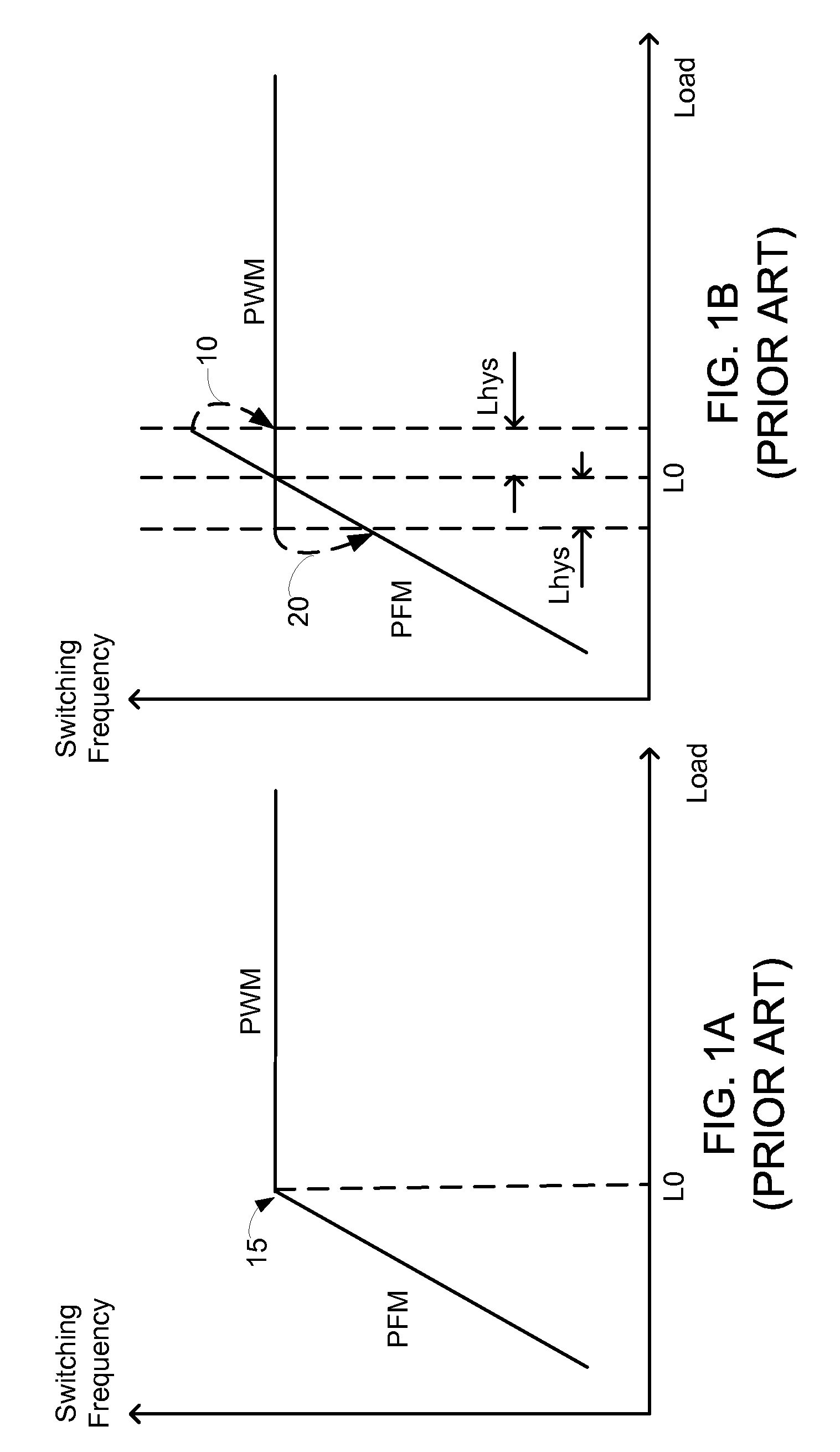
Adaptive control for transition between multiple modulation modes in a switching power converter
ActiveUS8018743B2TransitionLow output rippleEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionVoltage rangeSelf adaptive
In a switching power converter, PWM mode and PFM mode are separated into two independent control sections with the control voltage range in each control section determined independently. Each of the PWM and PFM modulation modes cannot operate continuously beyond its boundaries, thereby forming a control gap between the two control sections within which no continuous operation is allowed. In order to supply a load condition within the control gap, the power supply operates at the two boundaries of the control gap. Transition between PWM and PFM modes occurs fast, with low output voltage ripple. No limitation needs to be imposed on the control voltage range in each of the PWM and PFM control sections, because the control parameters in the PWM and PFM control sections need not be matched to one another, due to separation of the PWM and PFM modes by the control gap.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com