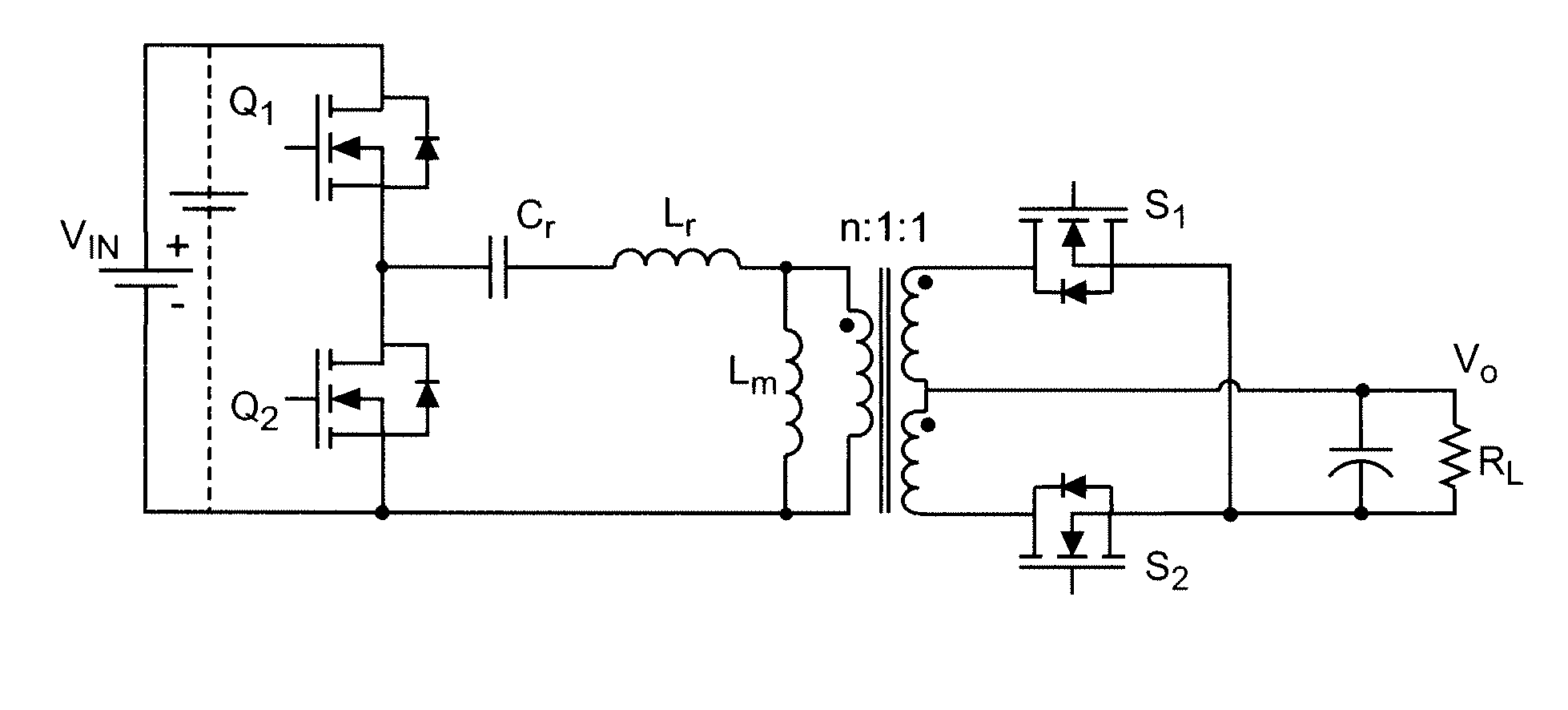
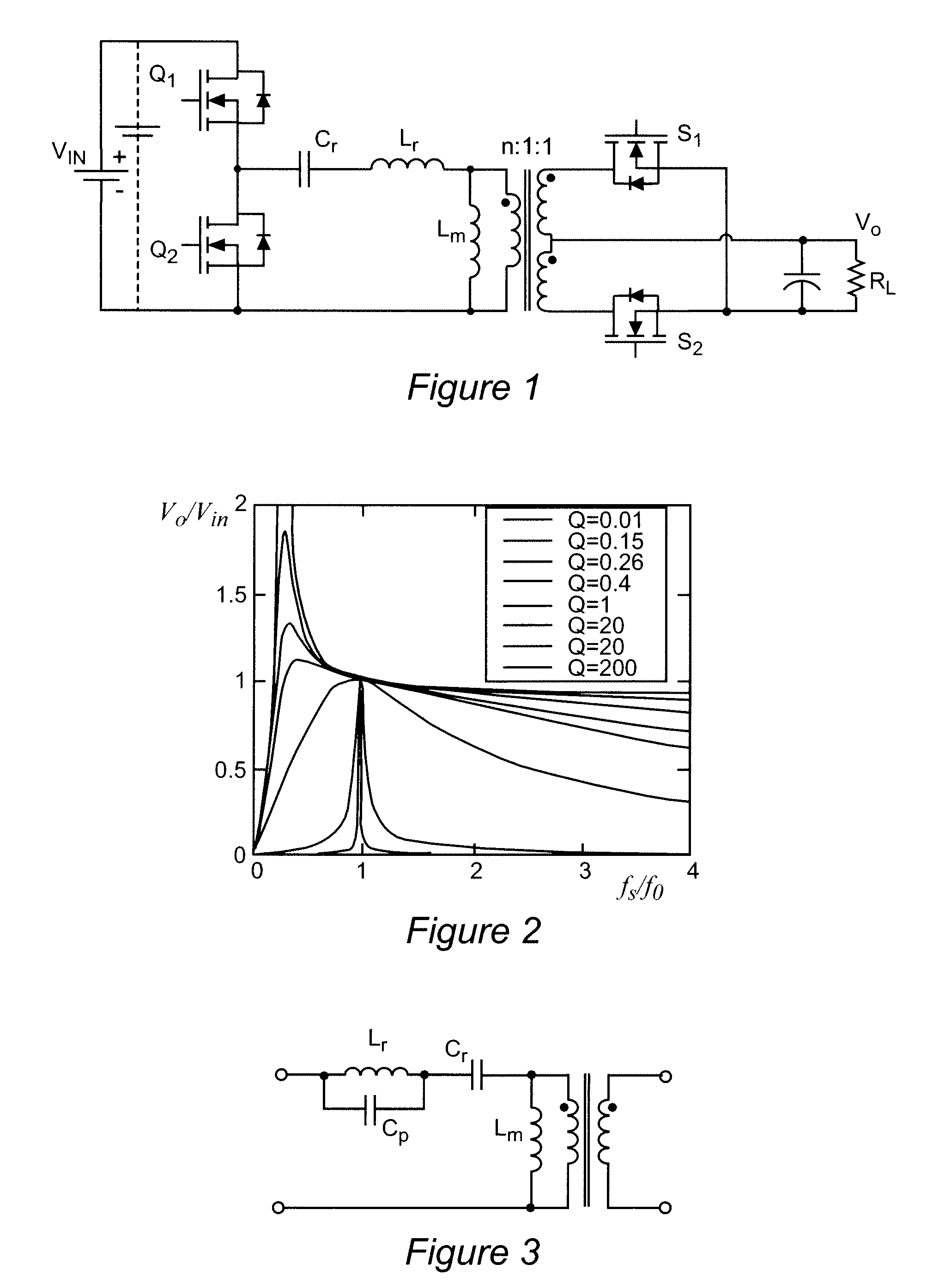
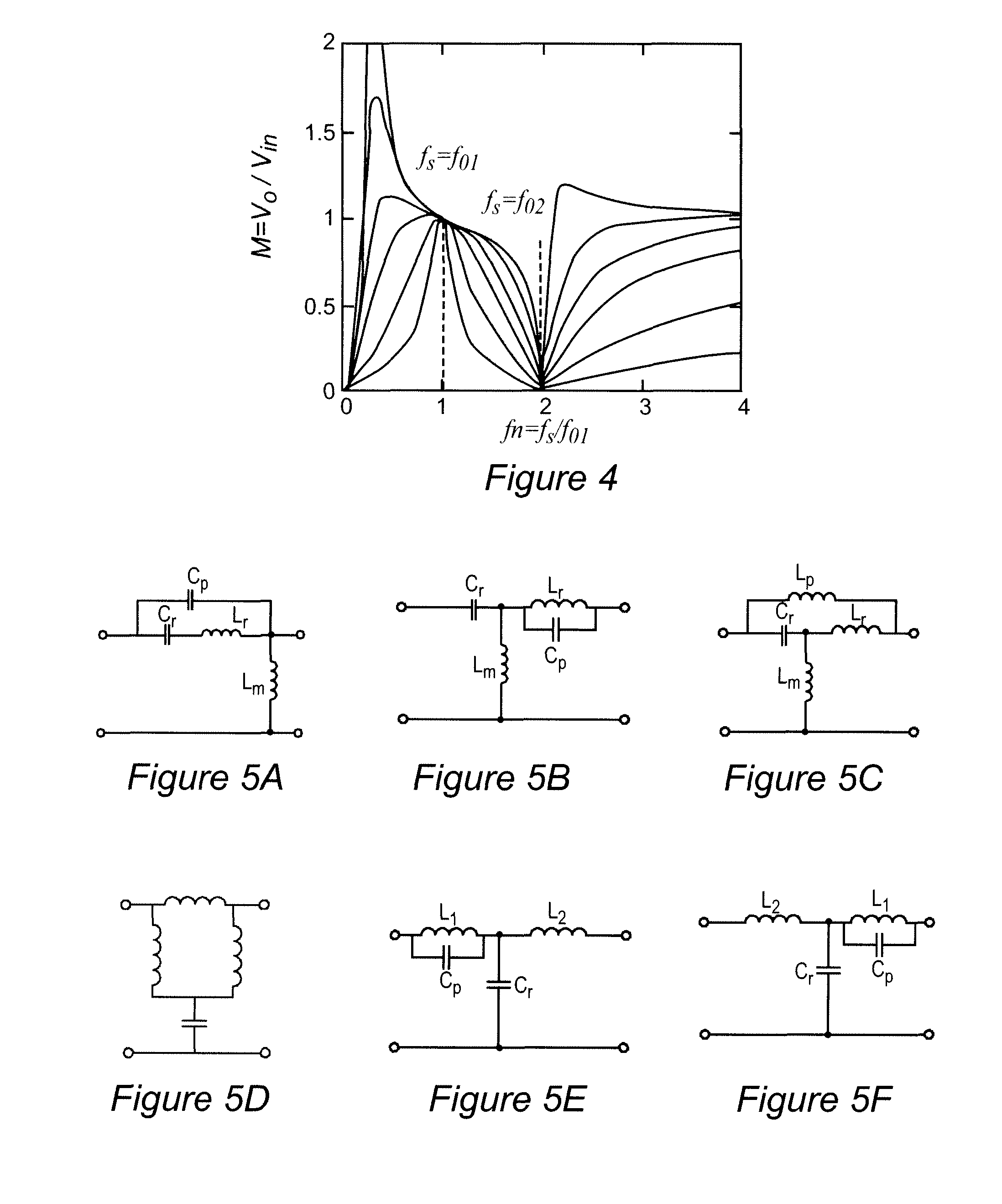
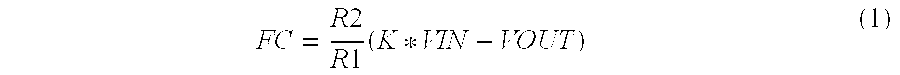Patents
Literature
180 results about "Switching frequency control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
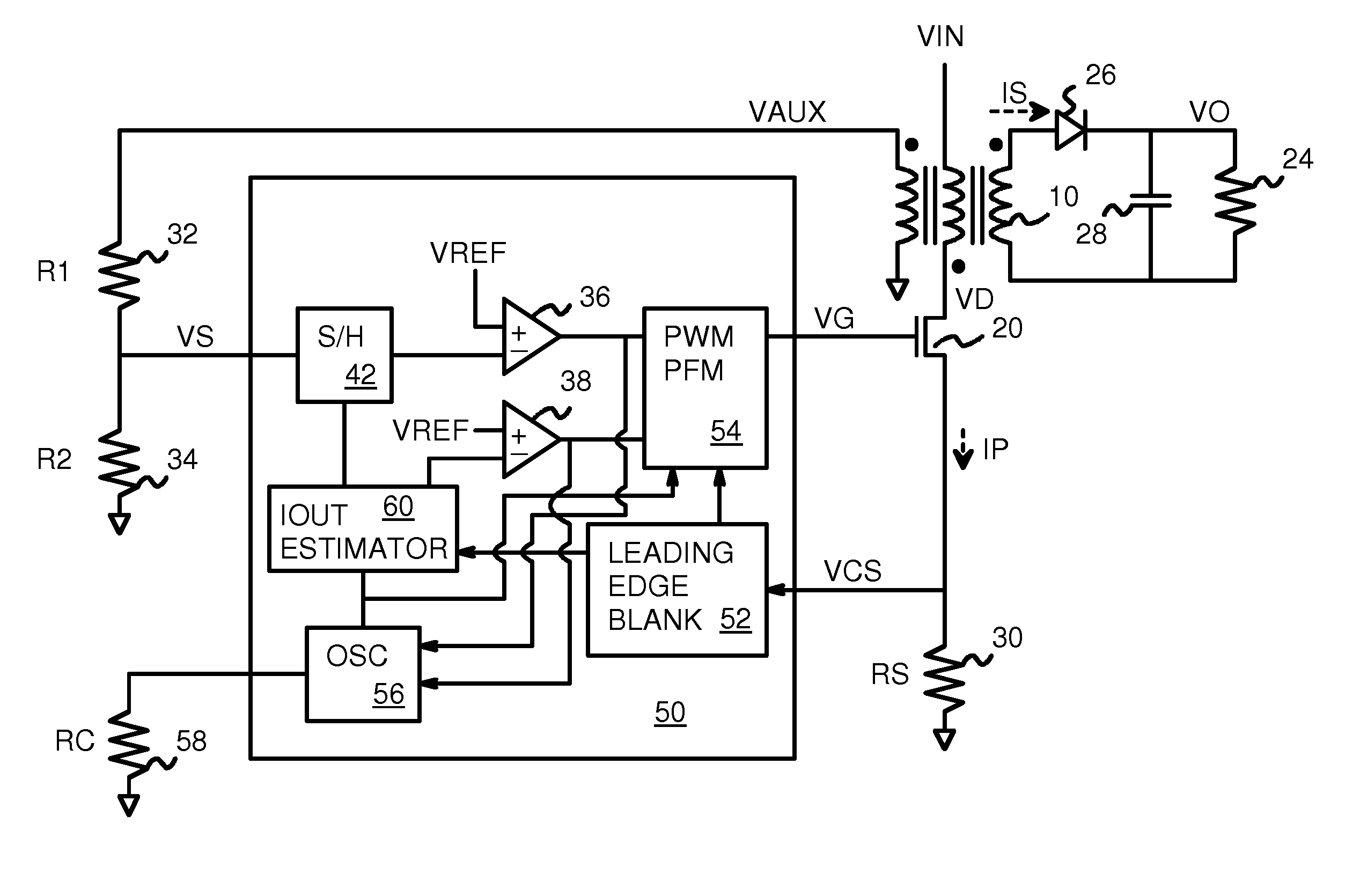
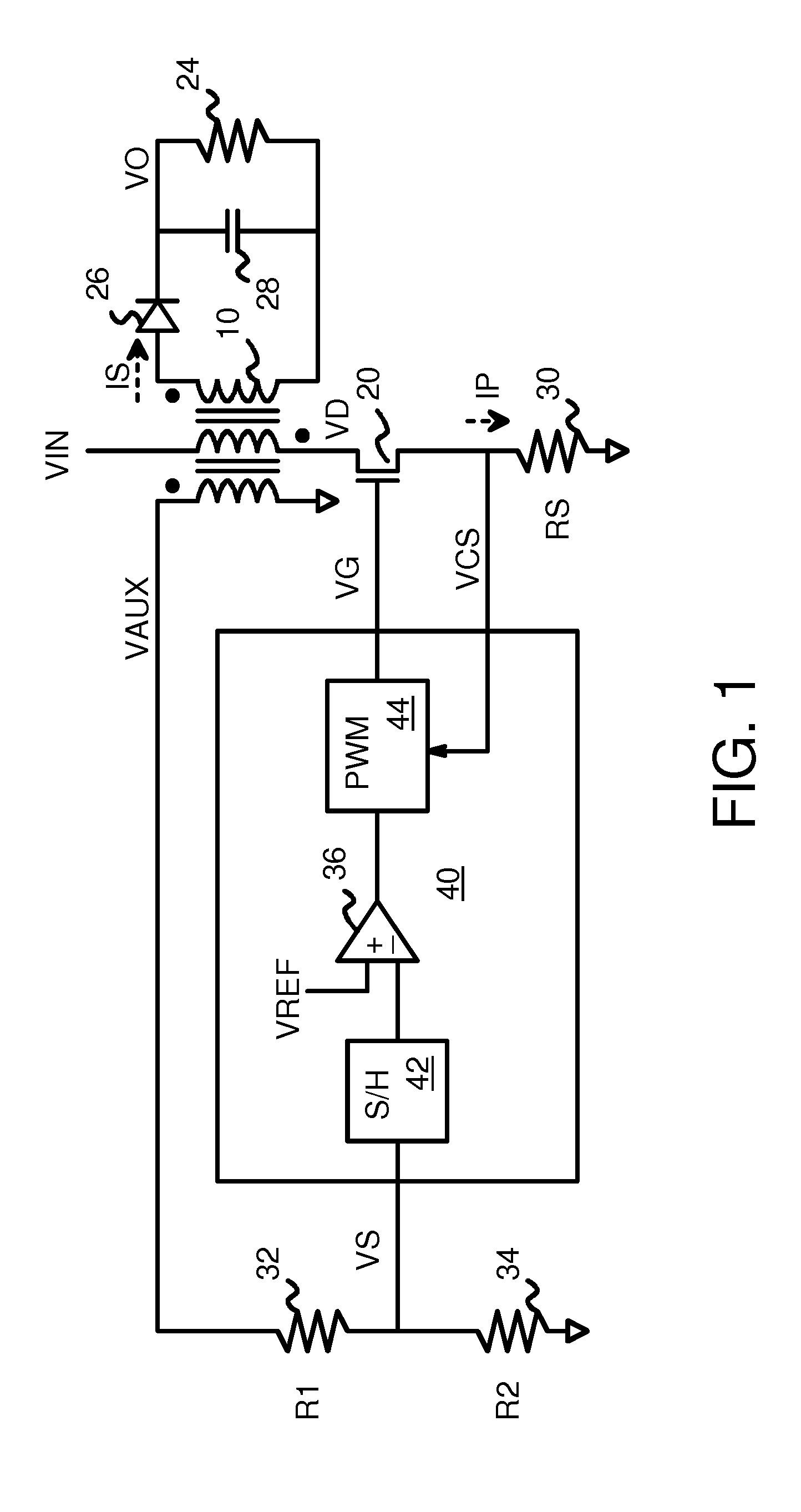
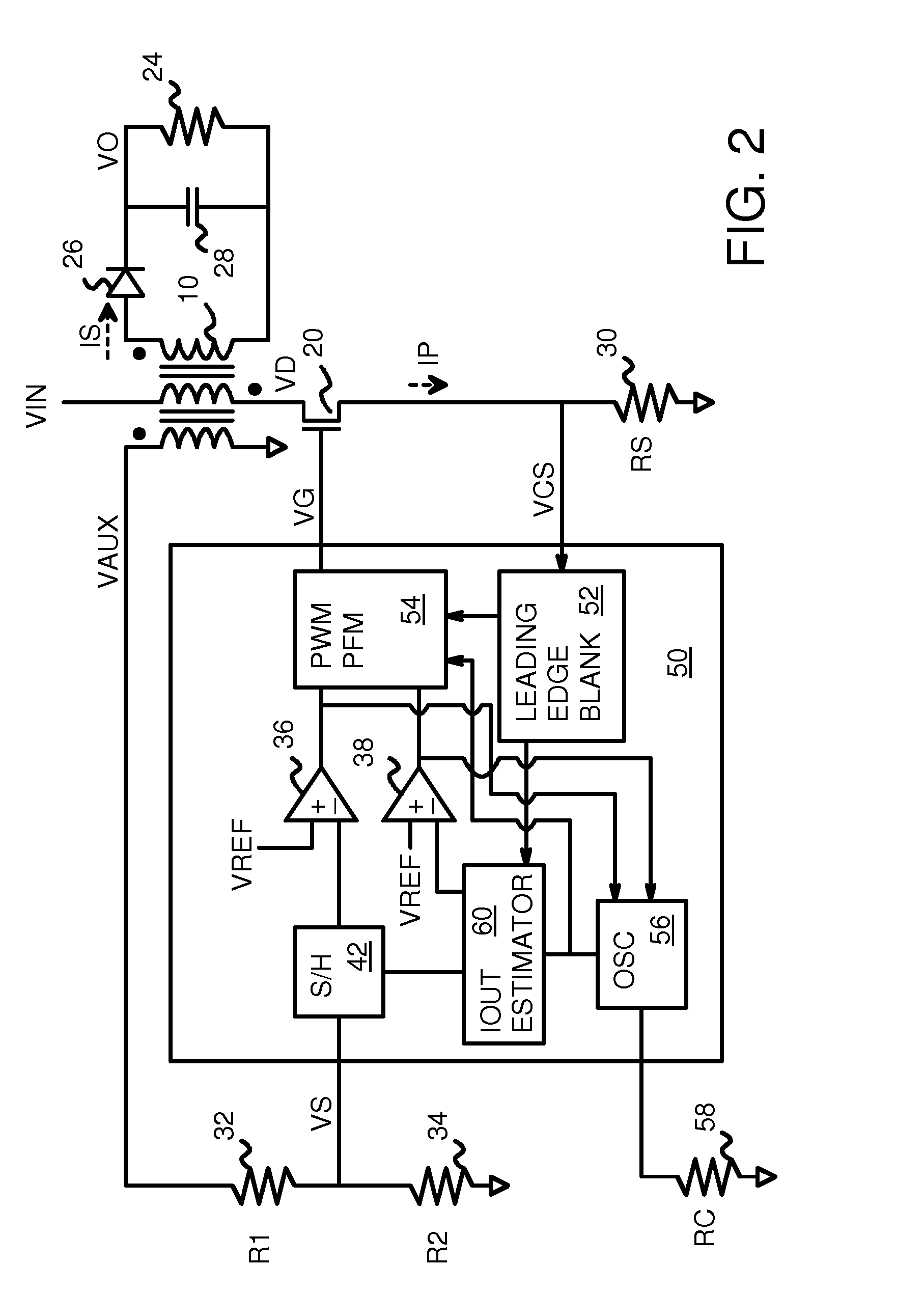
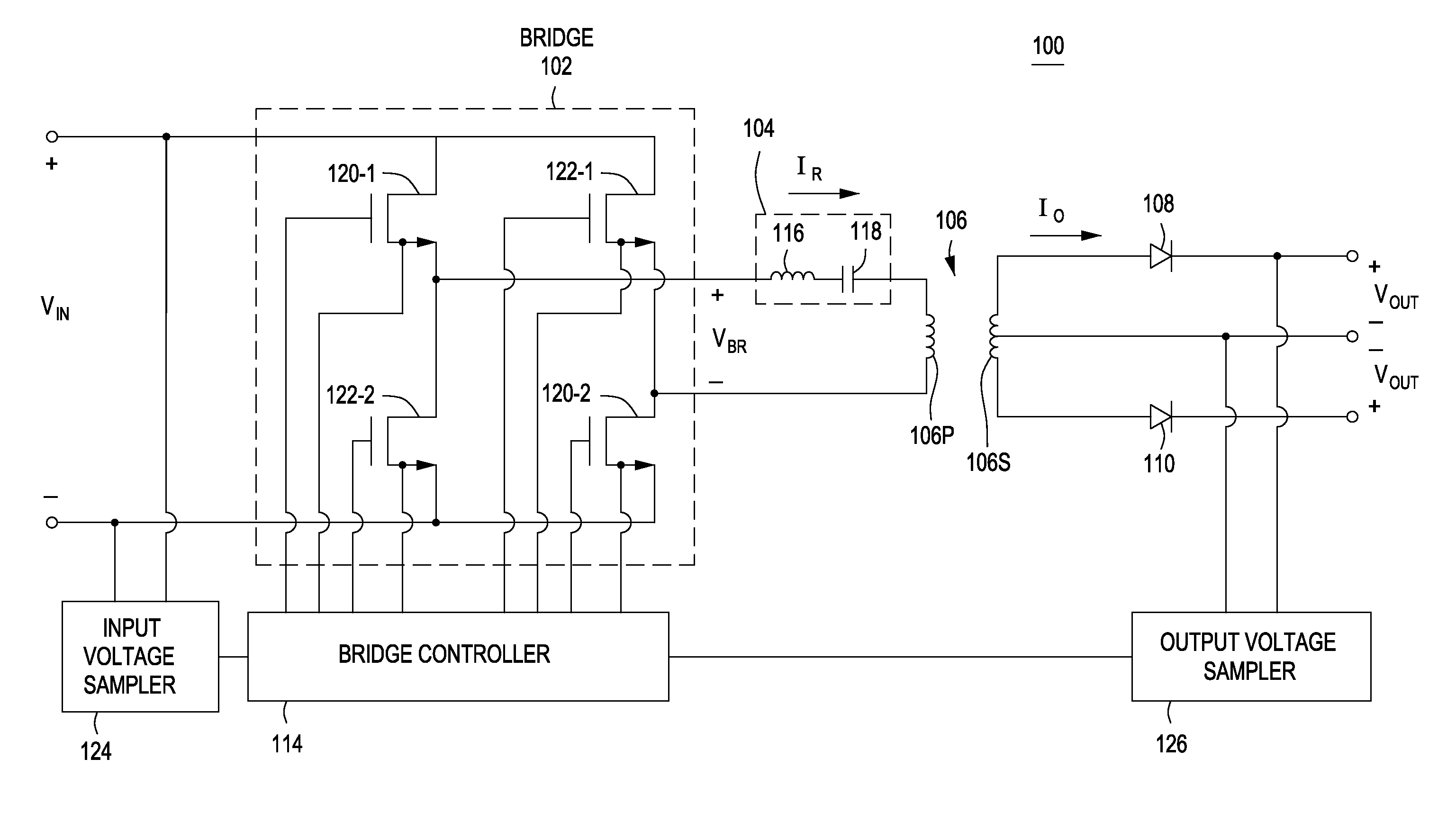
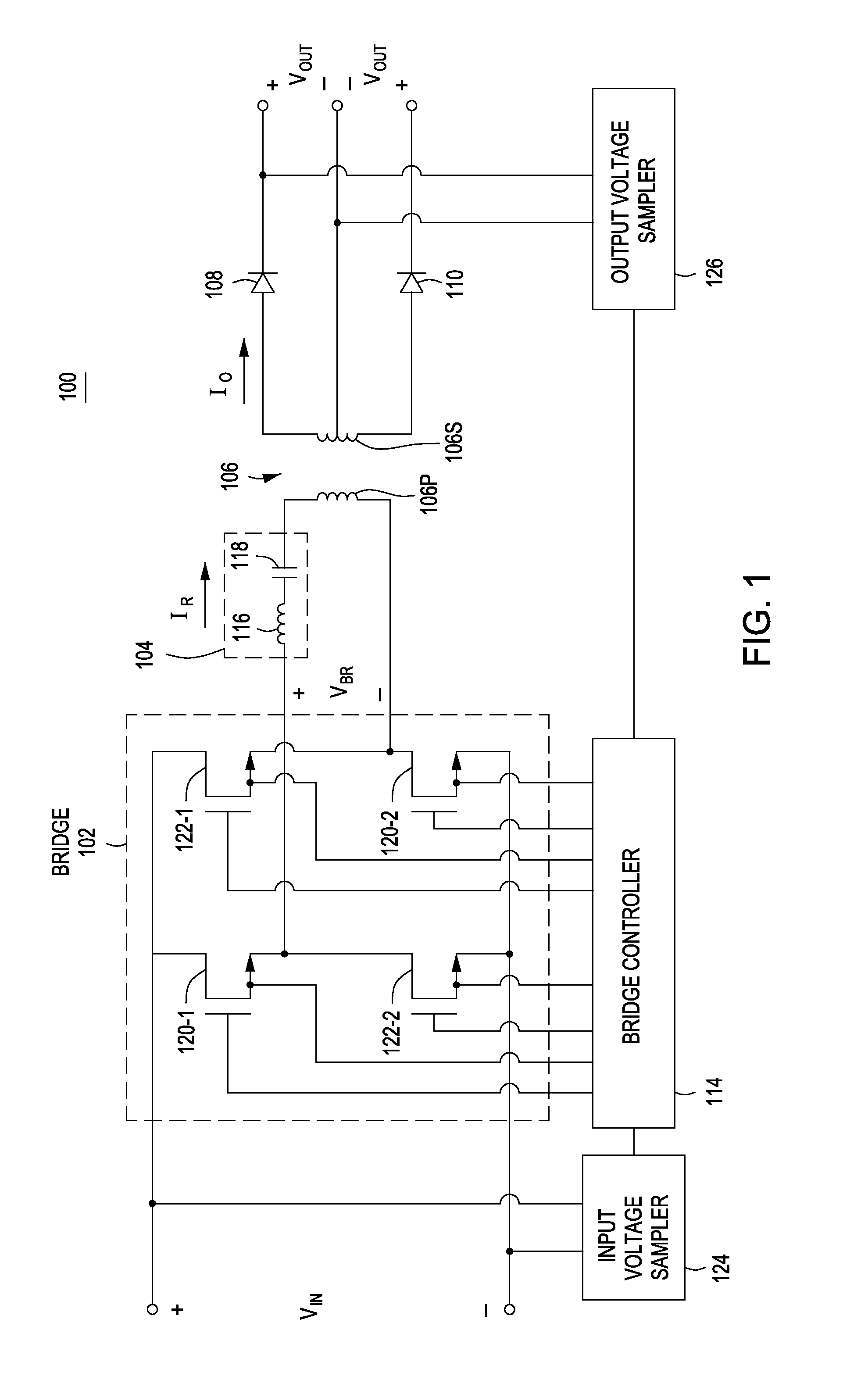
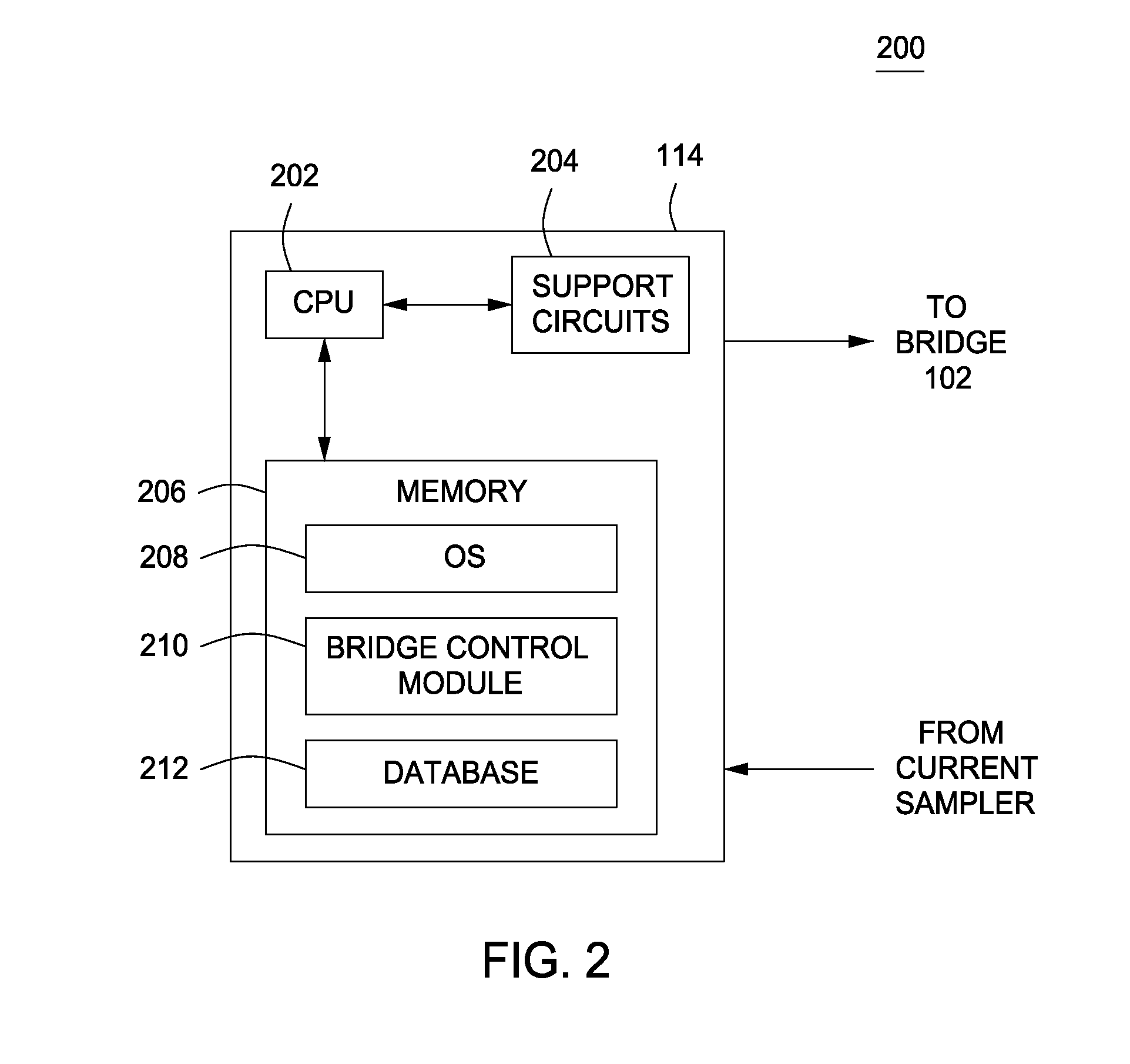
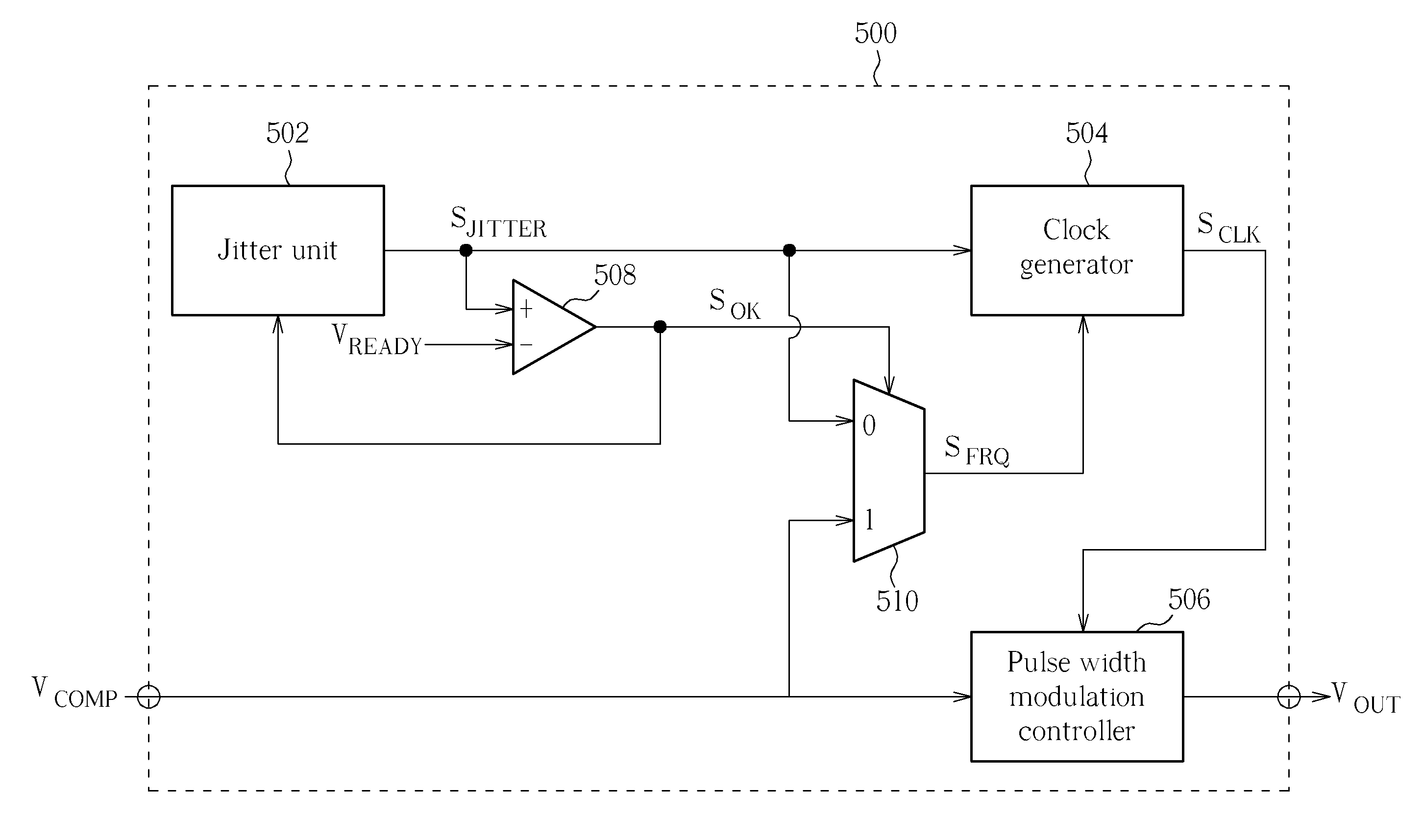
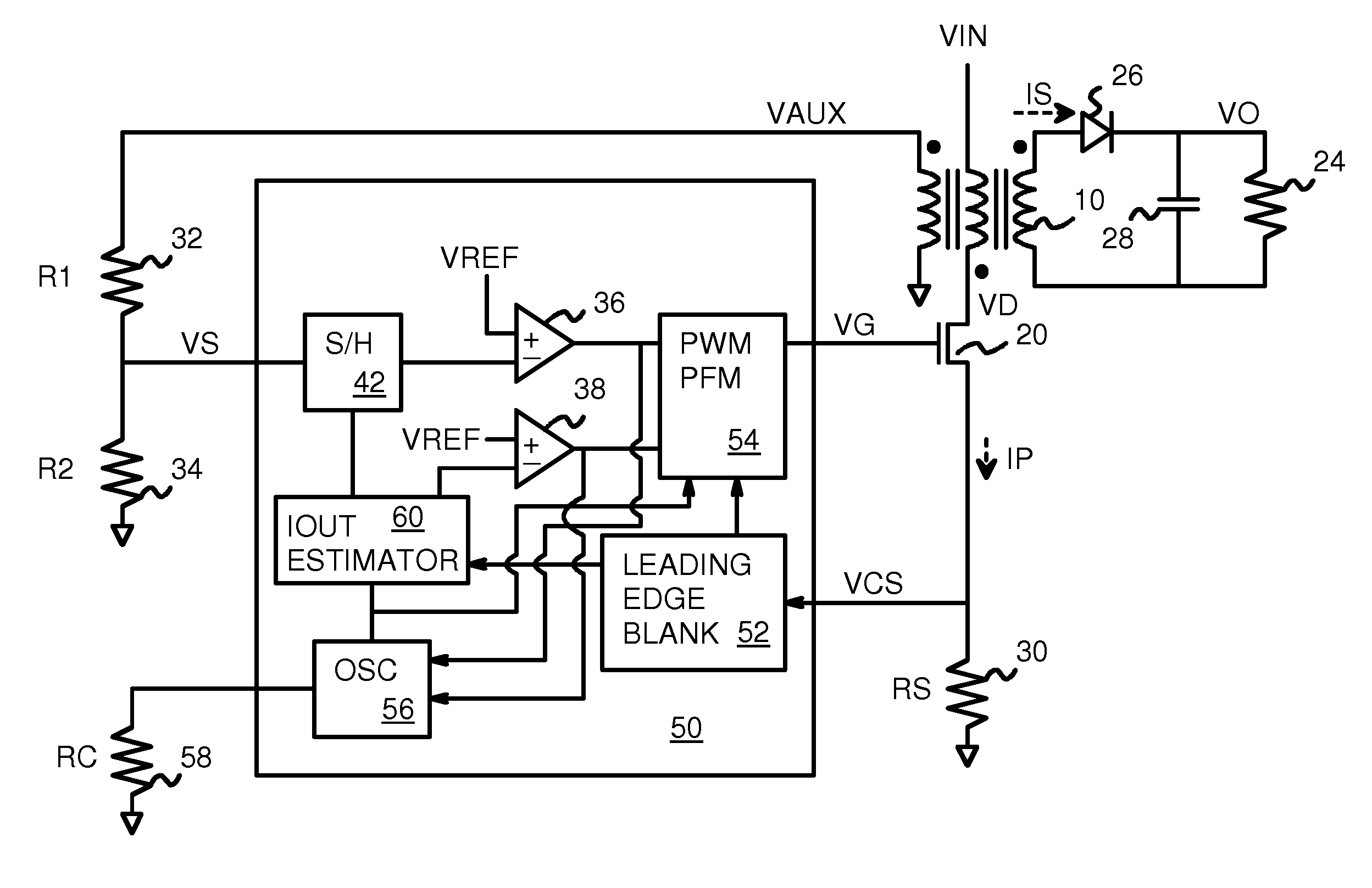
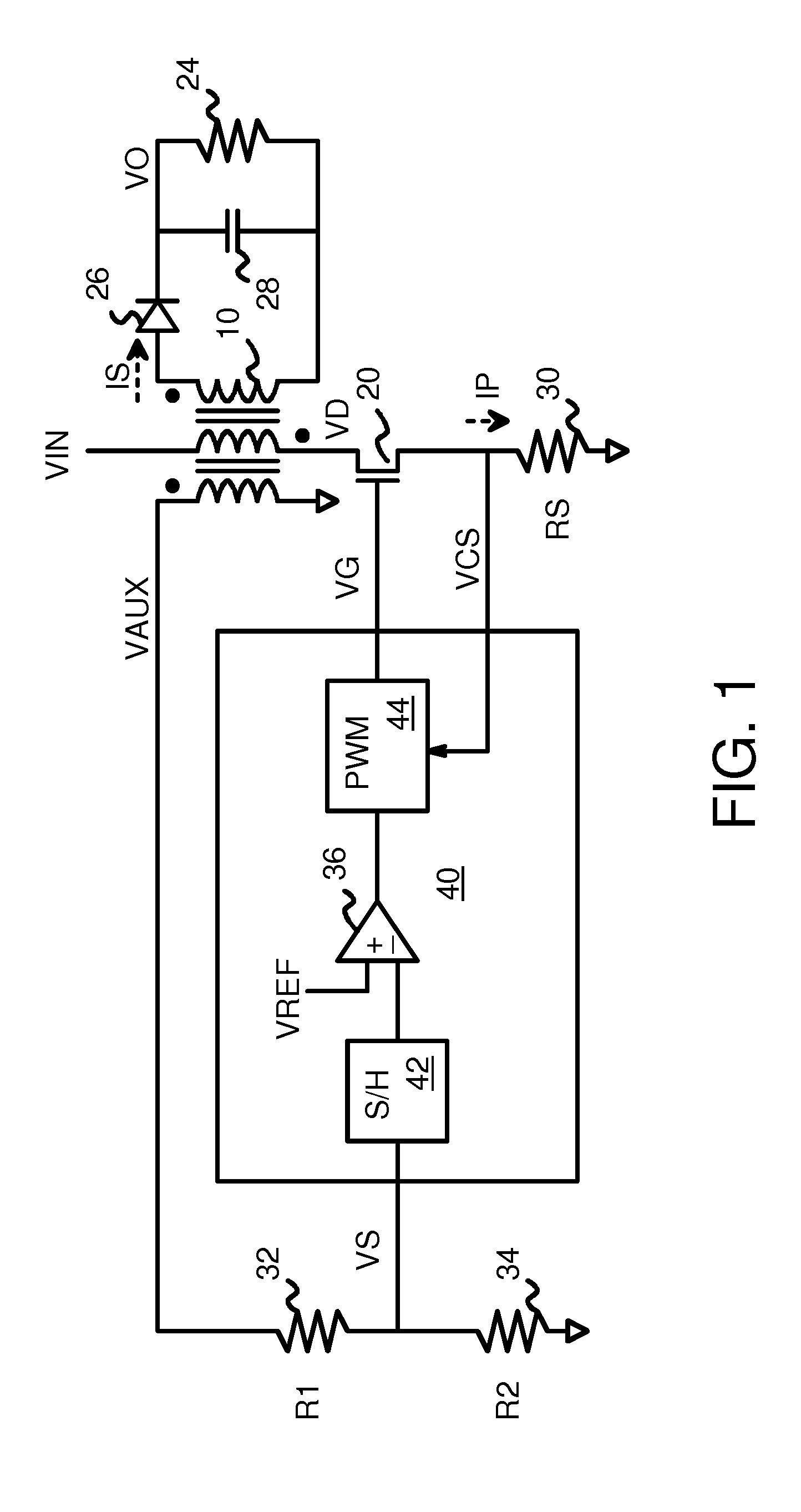
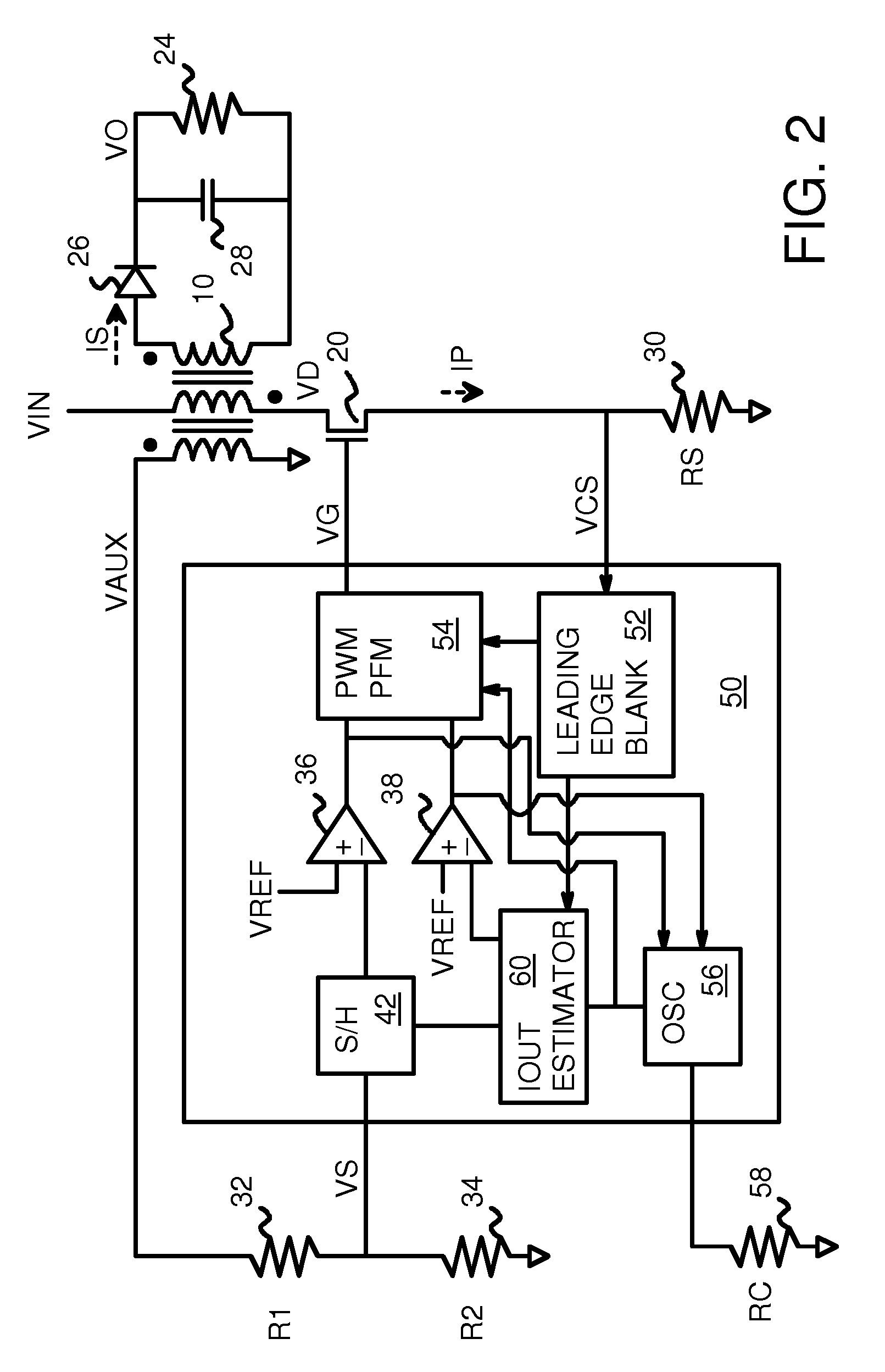
Output Current Estimation for an Isolated Flyback Converter With Variable Switching Frequency Control and Duty Cycle Adjustment for Both PWM and PFM Modes
InactiveUS20130294118A1Dc-dc conversionDifferential amplifiersTransformerSwitching frequency control
A fly-back power converter has a current-estimating control loop that senses the primary output current in a transformer to control the secondary output. A primary-side control circuit switches primary current through the transformer on and off. A discharge time when a secondary current through an auxiliary winding of the transformer is flowing is generated by sampling a voltage divider on an auxiliary loop for a knee-point. A normalized duty cycle is calculated by multiplying the discharge time by a current that is proportional to the switching frequency and comparing to a sawtooth signal having the switching frequency. The peak of a primary-side voltage is sensed from the primary current loop and converted to a current and multiplied by the normalized duty cycle to generate an estimated current. An error amp compares the estimated current to a reference to adjust the oscillator frequency and peak current to control primary switching.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Multi-Element Resonant Converters
InactiveUS20090303753A1Improved power transferRaise transfer toEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionBand-pass filterSwitching frequency control
A resonant switched power converter having switching frequency controlled in response to an output voltage thereof achieves over-current protection such as at start-up or under short circuit conditions using a resonant tank circuit which provides a notch filter in addition to a band pass filter. A additional band pass filter provided in the resonant tank circuit achieves increased power transfer to a load and reduced circulating resonant currents and conduction losses. The inductances of the preferred LCLCL tank circuit or other tank circuit with two pass band filters and a notch filter may be integrated into a single electrical component.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Switching frequency control of switched capacitor circuit using output voltage droop
A frequency control circuit including a controlled oscillator and an amplifier circuit is disclosed for providing a clock signal to a switched capacitor circuit which divides an input voltage to provide an output voltage. The controlled oscillator has a frequency control input receiving a frequency control signal and an output for providing the clock signal at a frequency based on the frequency control signal. The amplifier circuit has an input for receiving the output voltage and an output providing the frequency control signal based on droop of the output voltage. In one embodiment, the amplifier circuit adjusts the frequency control signal to optimize efficiency of the switched capacitor circuit over a voltage range of the output voltage, which changes based on load level.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Multi-element resonant converters
InactiveUS7742318B2Raise transfer toEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionBand-pass filterSwitching frequency control
A resonant switched power converter having switching frequency controlled in response to an output voltage thereof achieves over-current protection such as at start-up or under short circuit conditions using a resonant tank circuit which provides a notch filter in addition to a band pass filter. A additional band pass filter provided in the resonant tank circuit achieves increased power transfer to a load and reduced circulating resonant currents and conduction losses. The inductances of the preferred LCLCL tank circuit or other tank circuit with two pass band filters and a notch filter may be integrated into a single electrical component.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Method and apparatus for controlling resonant converter output power
ActiveUS20120294045A1Dc network circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionSwitching frequency controlResonant converter
A method and apparatus for controlling power conversion. In one embodiment, the method comprises computing a voltage ratio based on a voltage conversion in a resonant converter; comparing the voltage ratio to a threshold; and controlling, independent of switching frequency of the resonant converter, power output from the resonant converter based on whether the voltage ratio satisfies the threshold.
Owner:ENPHASE ENERGY
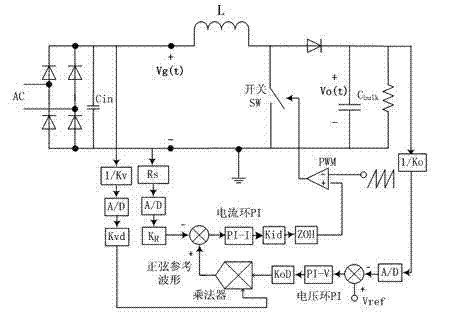
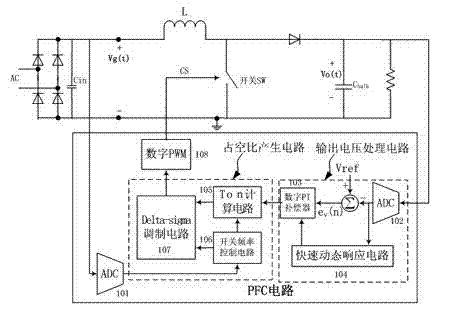
PFC (power factor correction) circuit based on delta-sigma modulation technique and duty ratio control method thereof
InactiveCN102255490AQuick responseIncrease powerEfficient power electronics conversionPower conversion systemsFrequency spectrumActive power factor correction
The invention provides a PFC (power factor correction) circuit based on a delta-sigma modulation technique and a duty ratio control method thereof. The PFC circuit comprises an input voltage ADC (analog to digital converter), a duty ratio generation circuit, an output voltage processing circuit and a digital pulse width modulation circuit in electrical connection, wherein the duty ratio generation circuit comprises a switching frequency control circuit, a Ton counting circuit and a delta-sigma modulation circuit in electrical connection; and the output voltage processing circuit comprises an output voltage ADC, a digital PI (proportional integral) compensator and a rapid dynamic response circuit in electrical connection. The delta-sigma modulation technique is utilized in the PFC circuit to realize the duty ratio control method. According to the invention, the response speed of the input voltage change can be improved, the iL waveform of the input inductive current is adjusted, the frequency spectrum of the pulse width signal is shaped, the power factor is improved and the output voltage is stabilized.
Owner:佛山市南海赛威科技技术有限公司
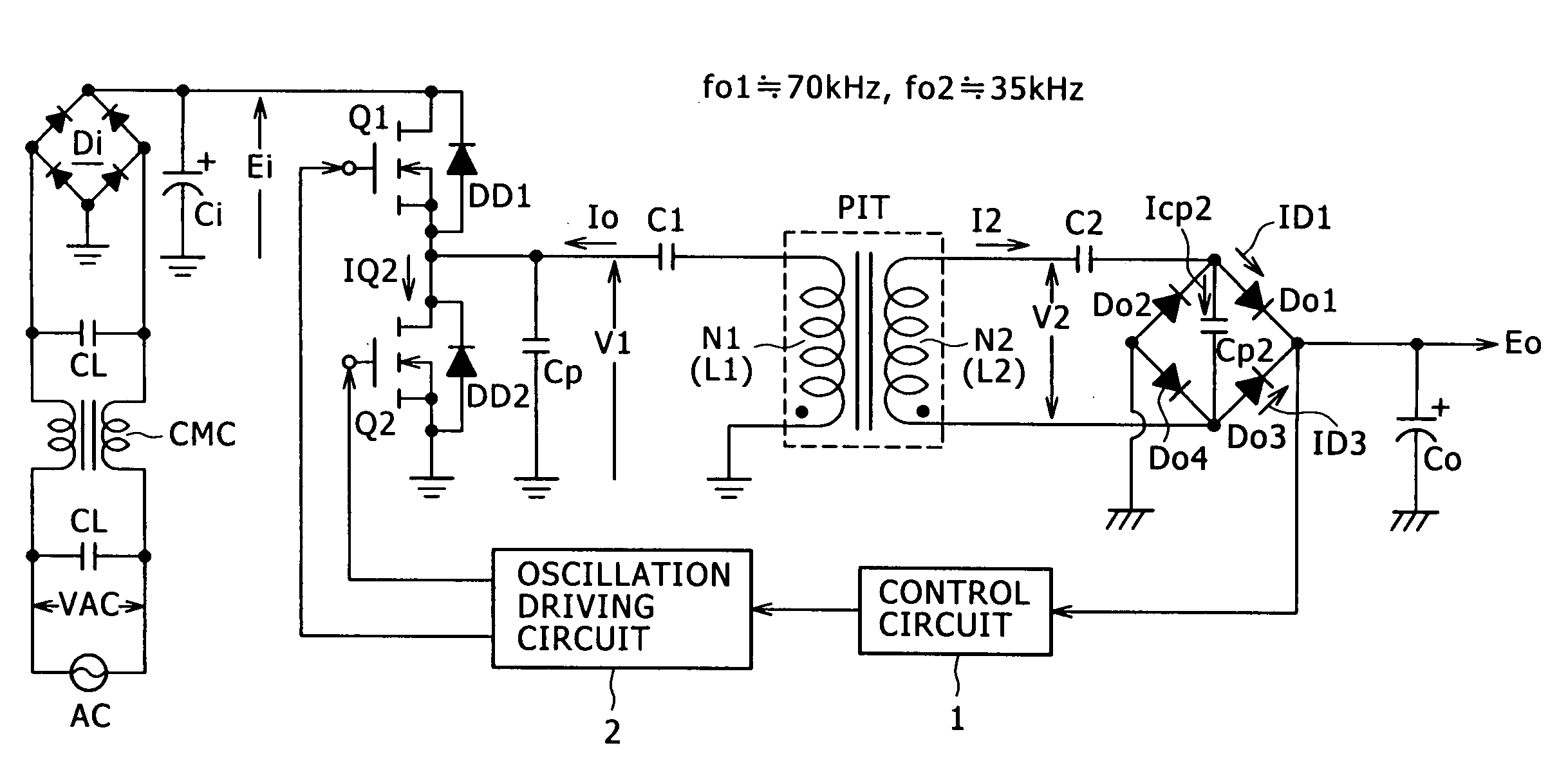
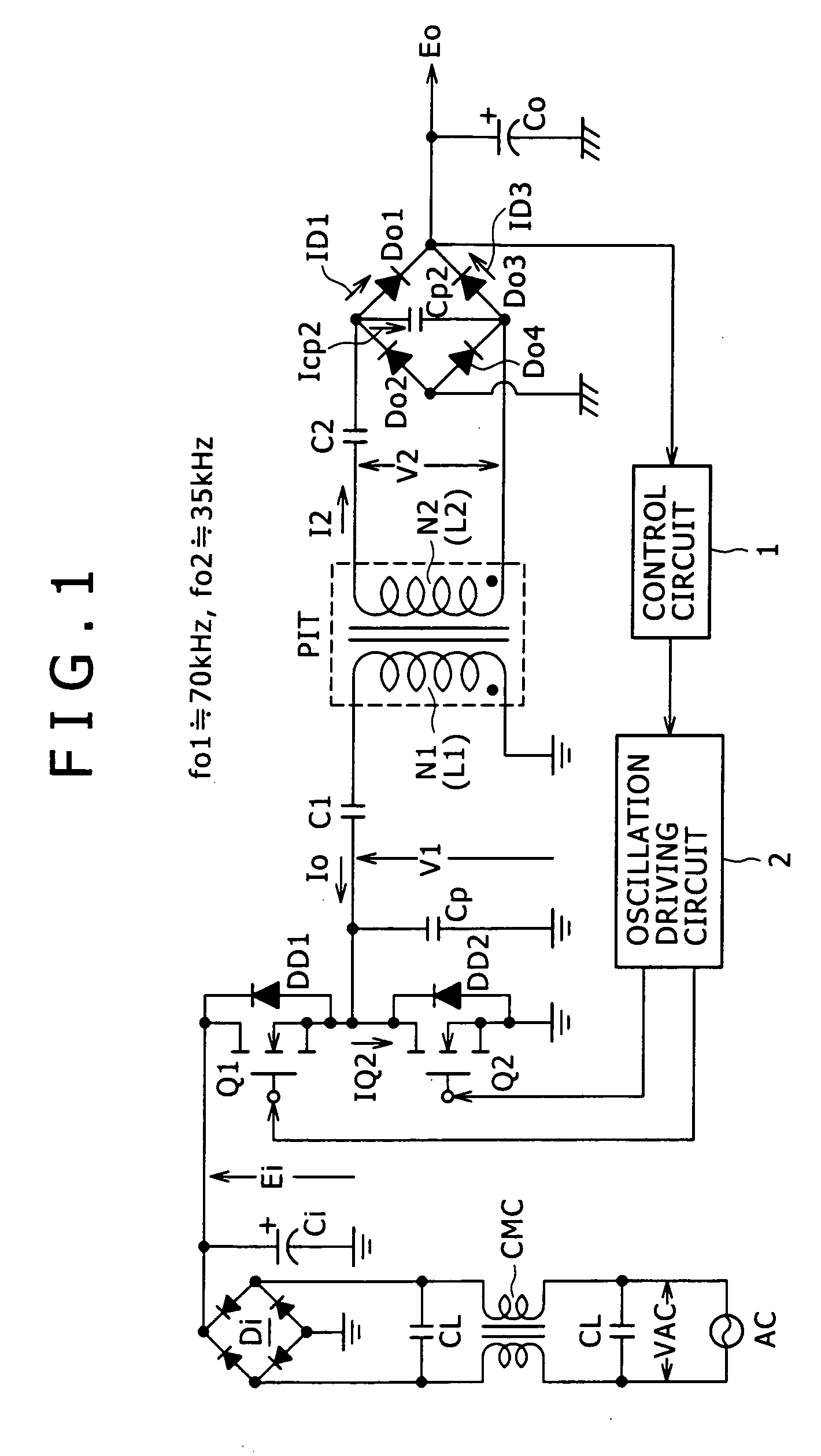
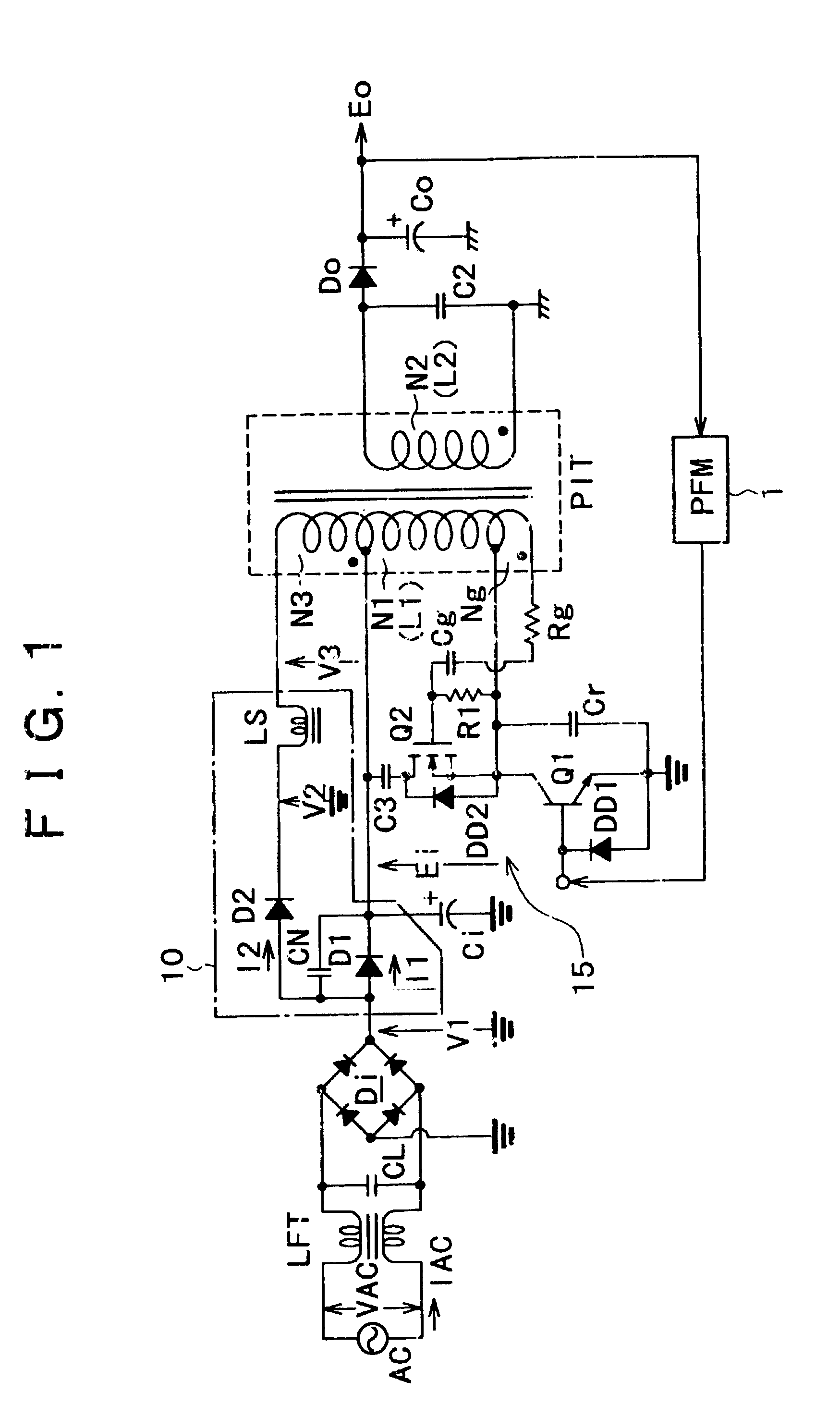
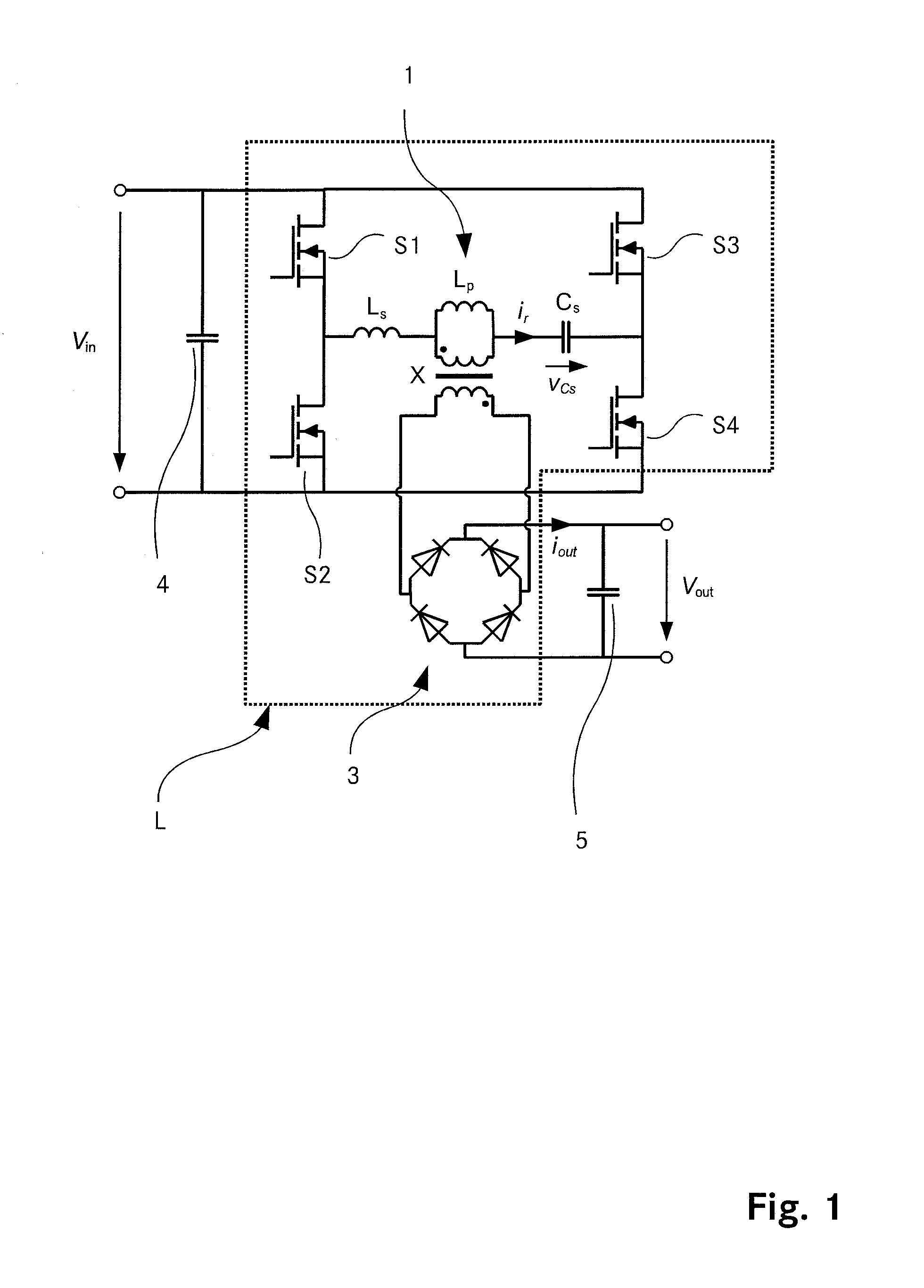
Switching power supply circuit
InactiveUS20050270805A1Improve reliabilityConstant reliabilityEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionCouplingResonance
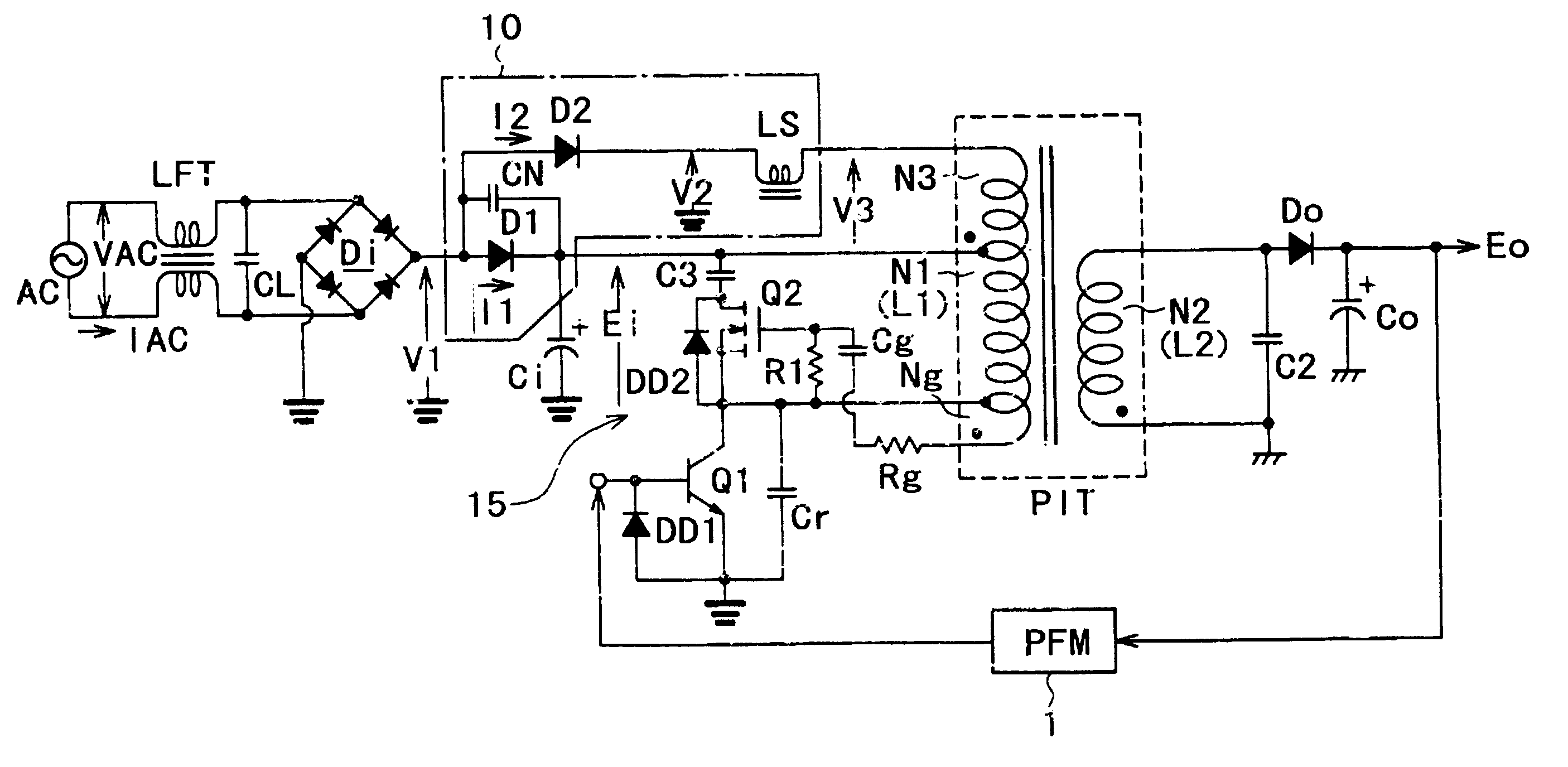
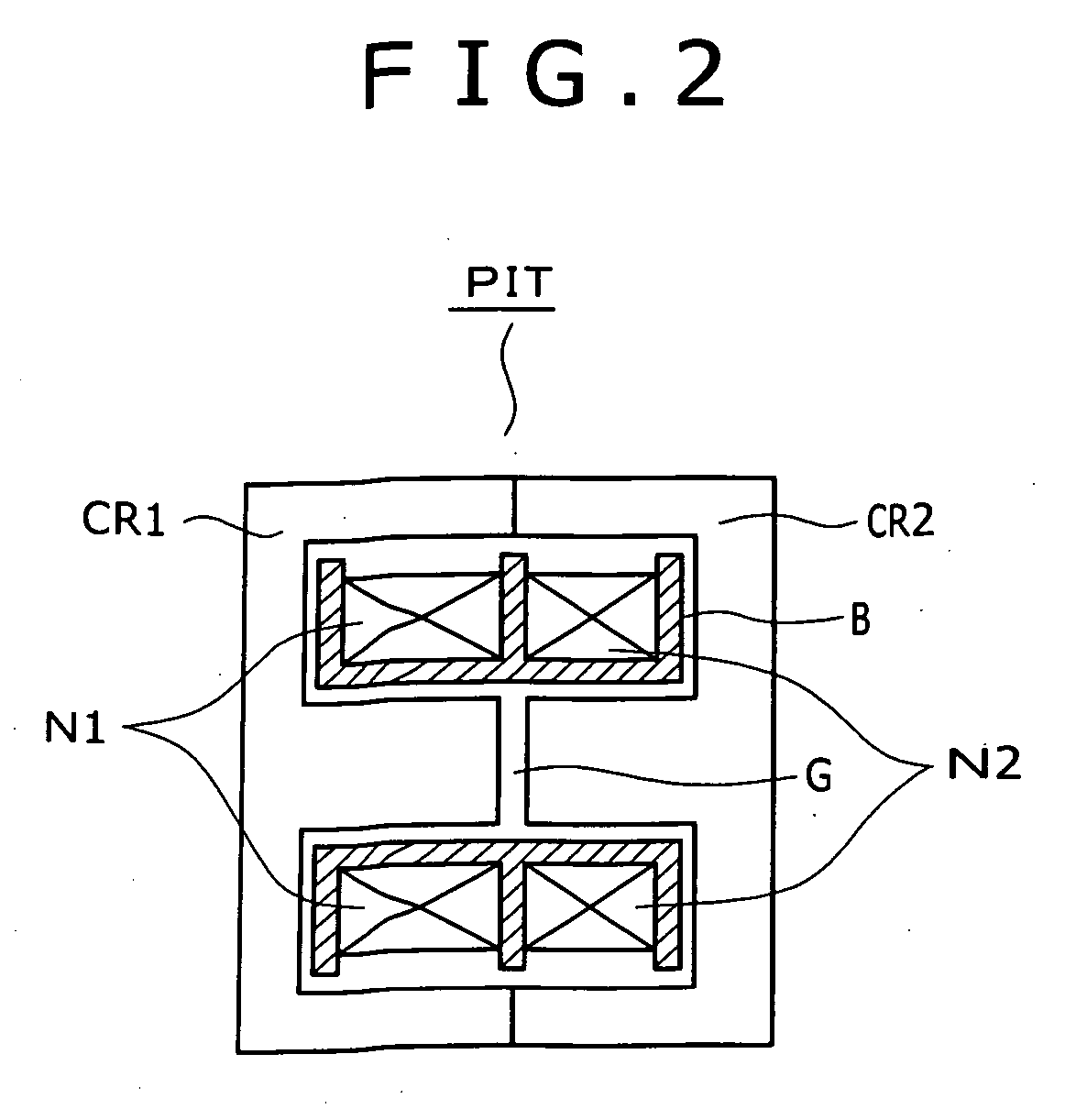
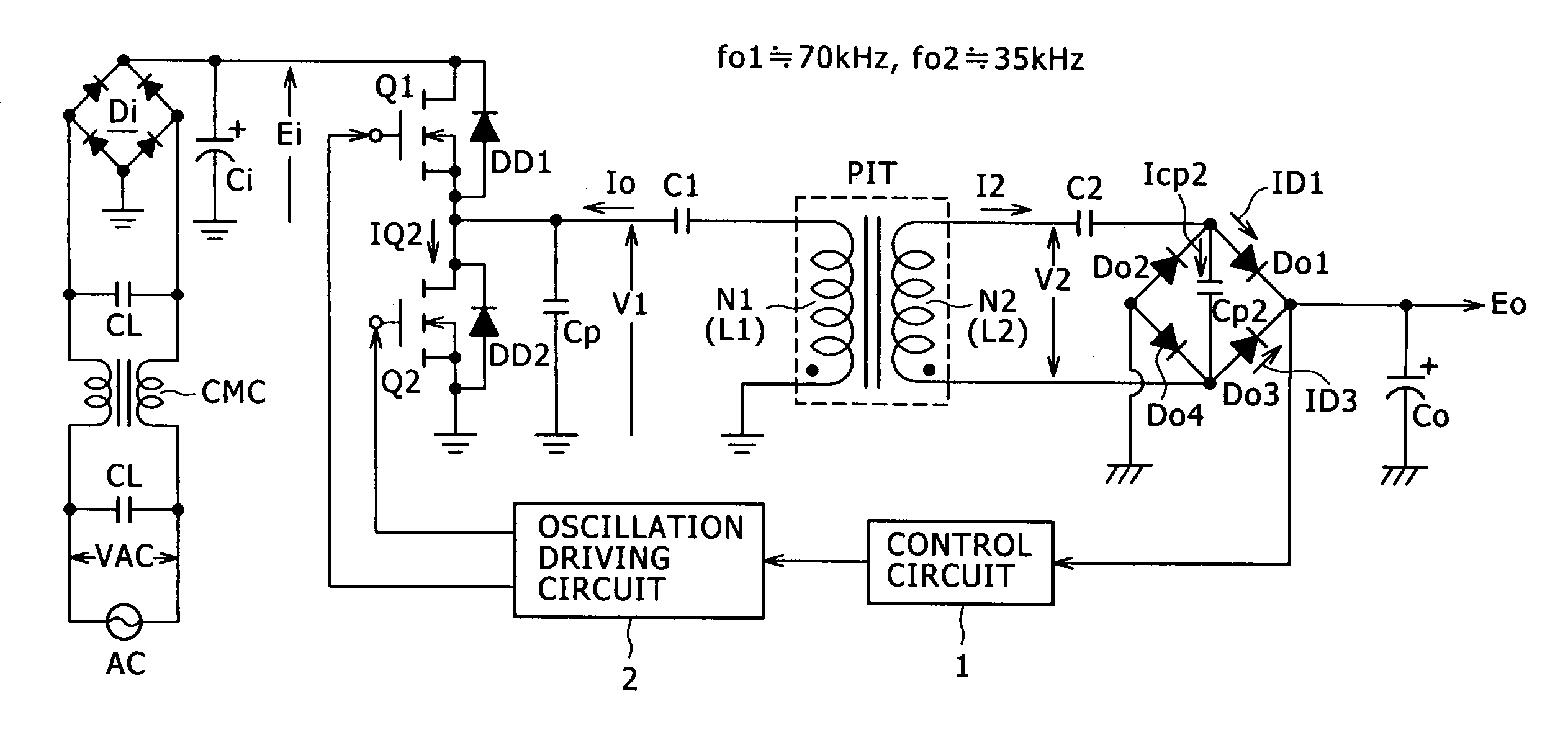
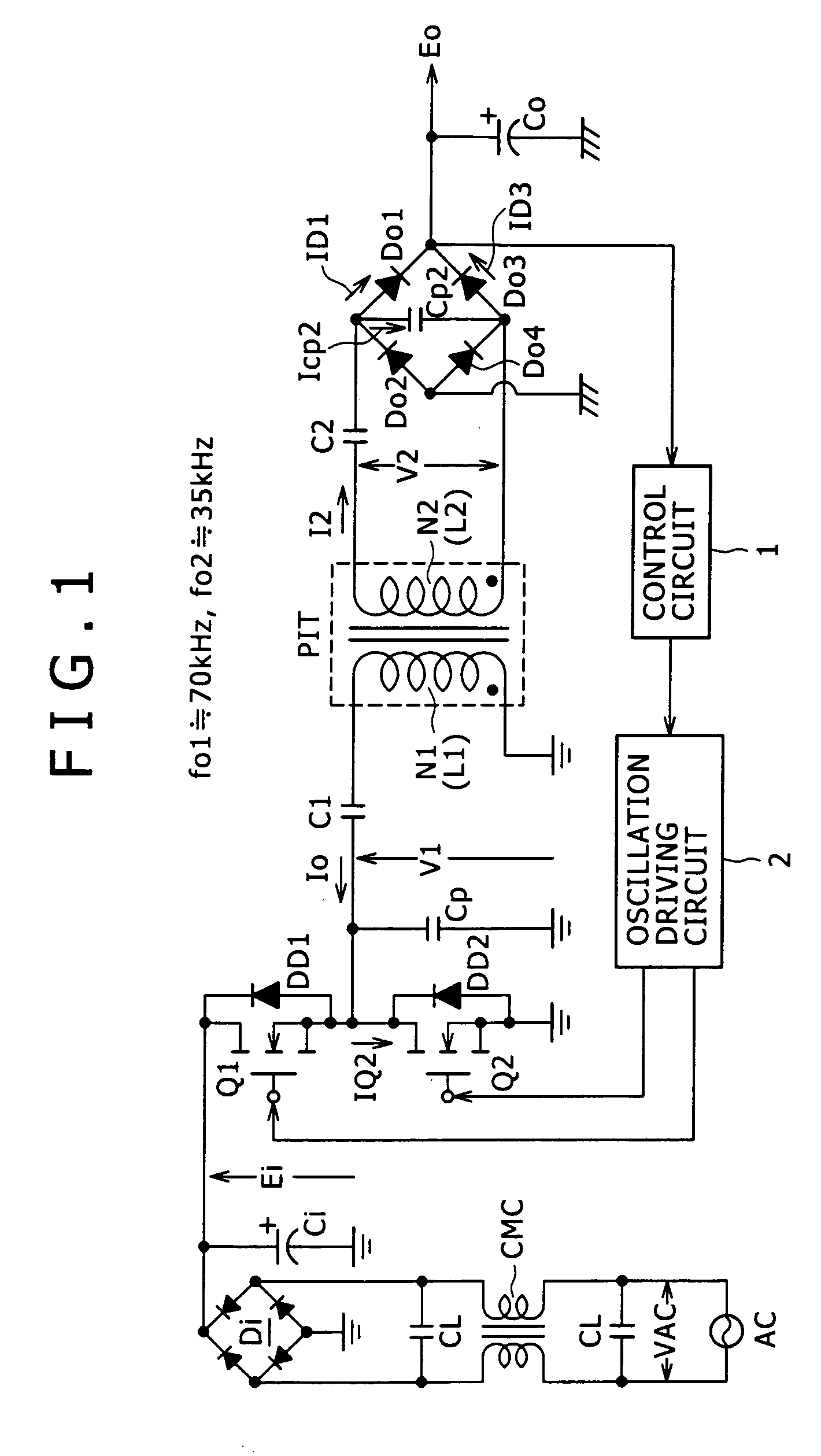
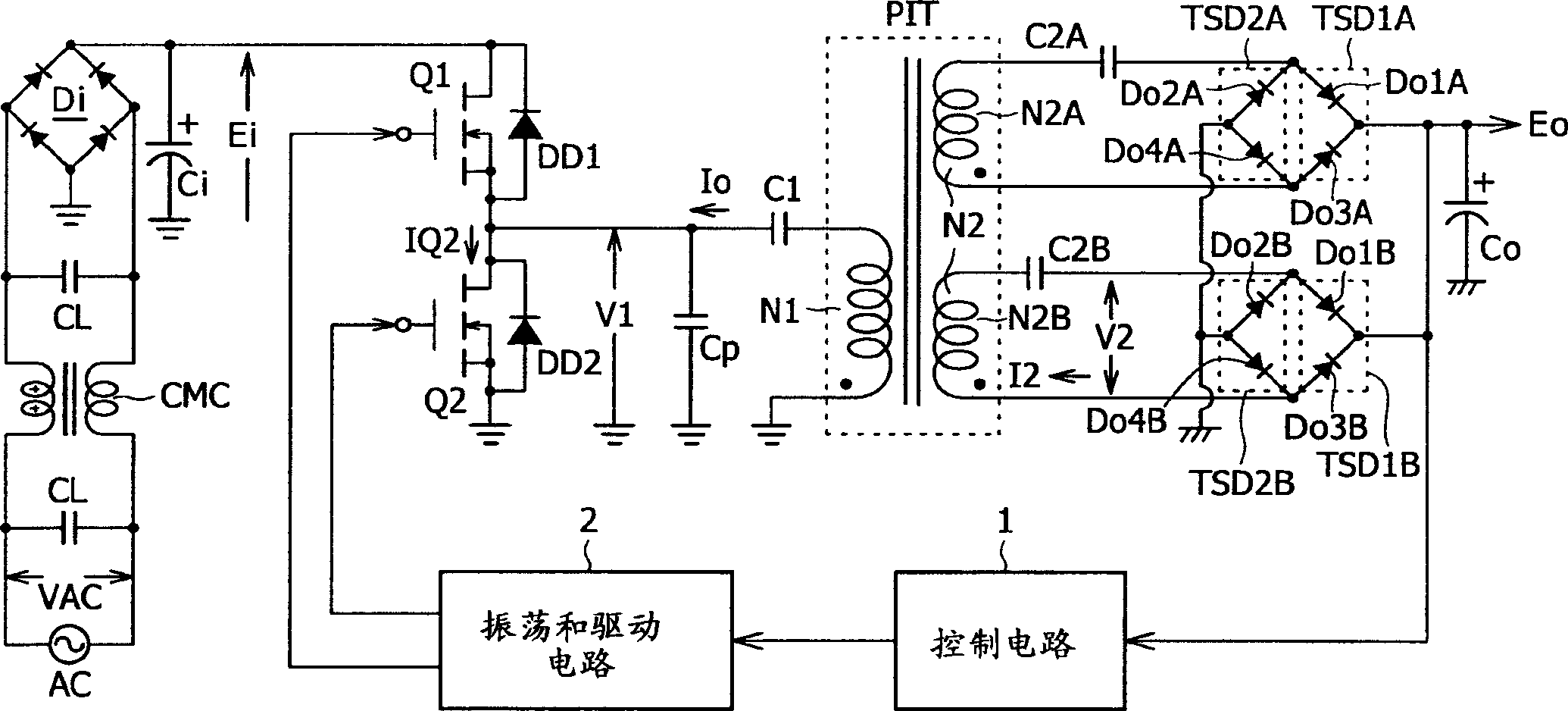
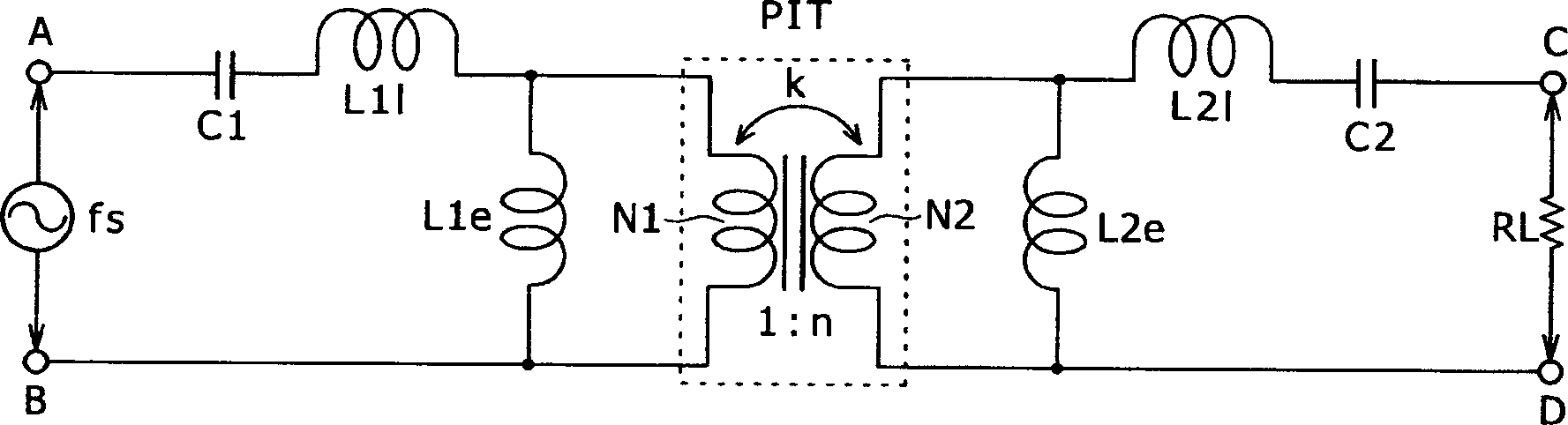
The present invention provides a power supply circuit performing constant voltage control by switching frequency control and achieving minimization of a necessary control range of the switching frequency control and implementation of a configuration ready for a wide range. A switching power supply circuit includes a switching circuit, a switching driving unit, an insulating converter transformer, a primary side series resonance circuit, a secondary side series resonance circuit, a secondary side DC output voltage production unit, a constant voltage control circuit, and a composite coupling coefficient setting mechanism.
Owner:SONY CORP
Current ripple real-time prediction model-based three-level voltage source variable switching frequency control method
InactiveCN106385196ASimple Prediction Calculation ProcessFew parametersAc-dc conversionThree levelFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a current ripple real-time prediction model-based three-level voltage source variable switching frequency control method. According to the control method, a current ripple real-time prediction module and a switching cycle updating module are established; and with a current ripple peak value adopted as a control object, the switching cycle of an inverter is updated in real time through using a current ripple real-time prediction model. With the three-level voltage source variable switching frequency control method adopted, the switching frequency of the inverter changes in real time, and therefore, compared with a traditional constant switching frequency PWM control algorithm, the control method of the invention can significantly decrease average switching frequency and greatly reduce the switching loss of the inverter; and since the switching frequency change range of the inverter is wide, spectrum distribution is broader, and a harmonic current peak value can be effectively reduced, and conducted EMI (electro-magnetic interference) can be effectively improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Simplified model forecasting control method of network voltage unbalance three-level rectifier
InactiveCN103956919ASimplified Predictive Control AlgorithmReduce search timesAc-dc conversion without reversalSimulationElectric network
The invention belongs to the field of converter control, and relates to a simplified model forecasting control method of a network voltage unbalance three-level rectifier. The simplified model forecasting control method of the network voltage unbalance three-level rectifier comprises the steps that (1) positive and negative sequence separation is carried out on three-phase network voltage and current to obtain positive and negative sequence components; (2) coordinate transformation is carried out on three-phase positive sequence voltage and current to obtain positive sequence voltage and current under a two-phase static coordinate system; (3) according to the three-phase positive sequence voltage, three levels are changed into two levels in an order reduction mode through reference voltage; (4) an active power reference value and a current reference value are calculated; (5) a current forecasting value of the rectifier, a direct current side capacitance voltage forecasting value and the changing number of switching elements are calculated; (6) current control, neutral-point potential control and switching frequency control are forecast according to a model, and the best switching state is selected. The simplified model forecasting control method of the network voltage unbalance three-level rectifier can effectively suppress double-frequency fluctuation of input power of the rectifier, lower the switching frequency of the elements, shorten circulation calculation time, control neutral-point potential balance, and improve the operation efficiency of the system.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Dimming of LED driver
A dimmable LED driver circuit comprises a resonant DC-DC converter coupled to an output circuit. The converter comprises a half bridge or full bridge switching circuit coupled to a resonant circuit. An output of the resonant circuit is rectified and fed to the output circuit. The output circuit may comprise at least one LED series or shunt switch for switching an LED unit on and off. A control circuit controls the switches of the switching circuit at a variable switching frequency. The control circuit is also configured for controlling the switching circuit for amplitude modulating the converter and for pulse-width modulating the converter at a first pulse-width modulation frequency lower than the switching frequency. The control circuit is may further be configured for controlling the switching of the LED switch at a second pulse-width modulation frequency lower than the switching frequency.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
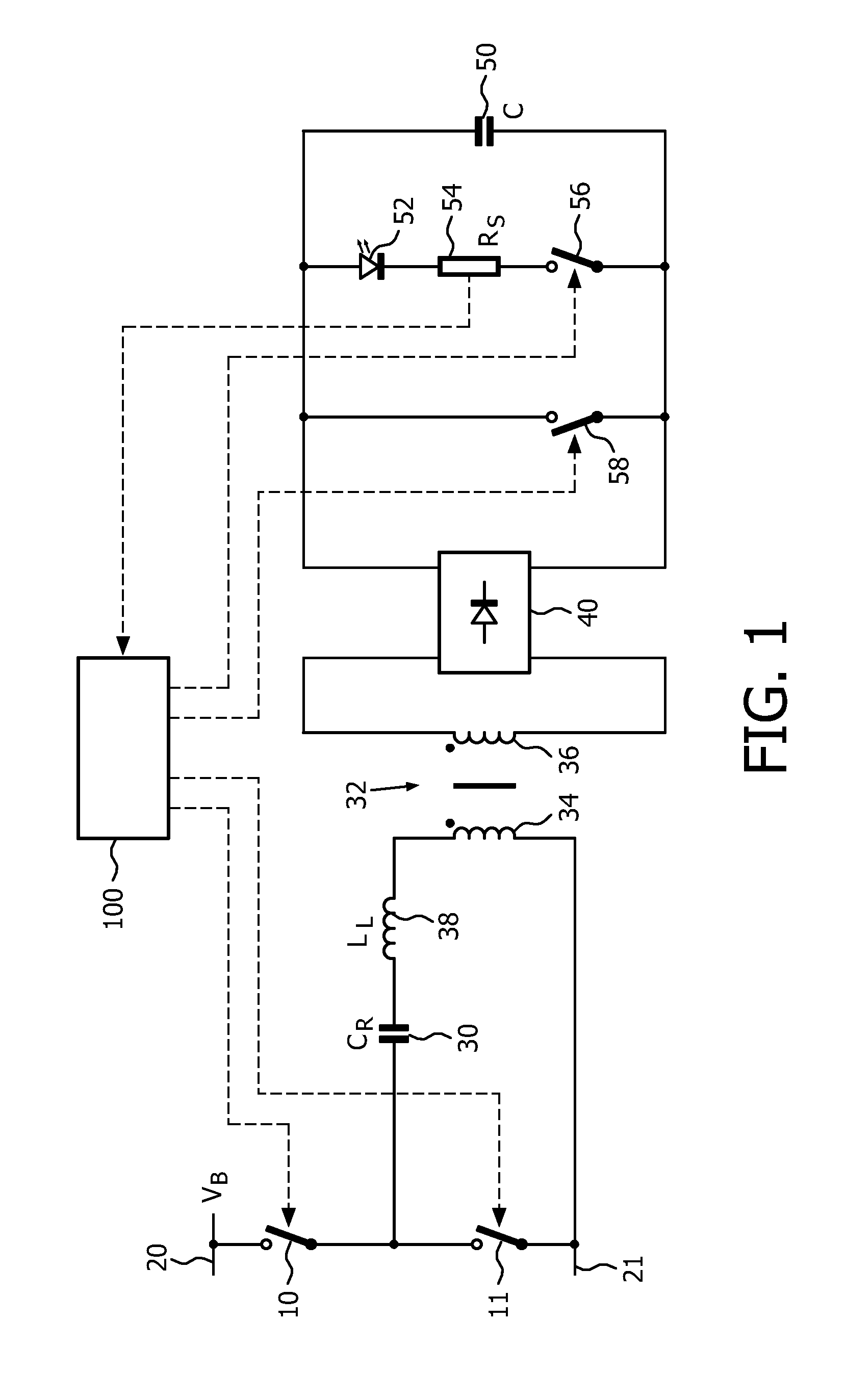
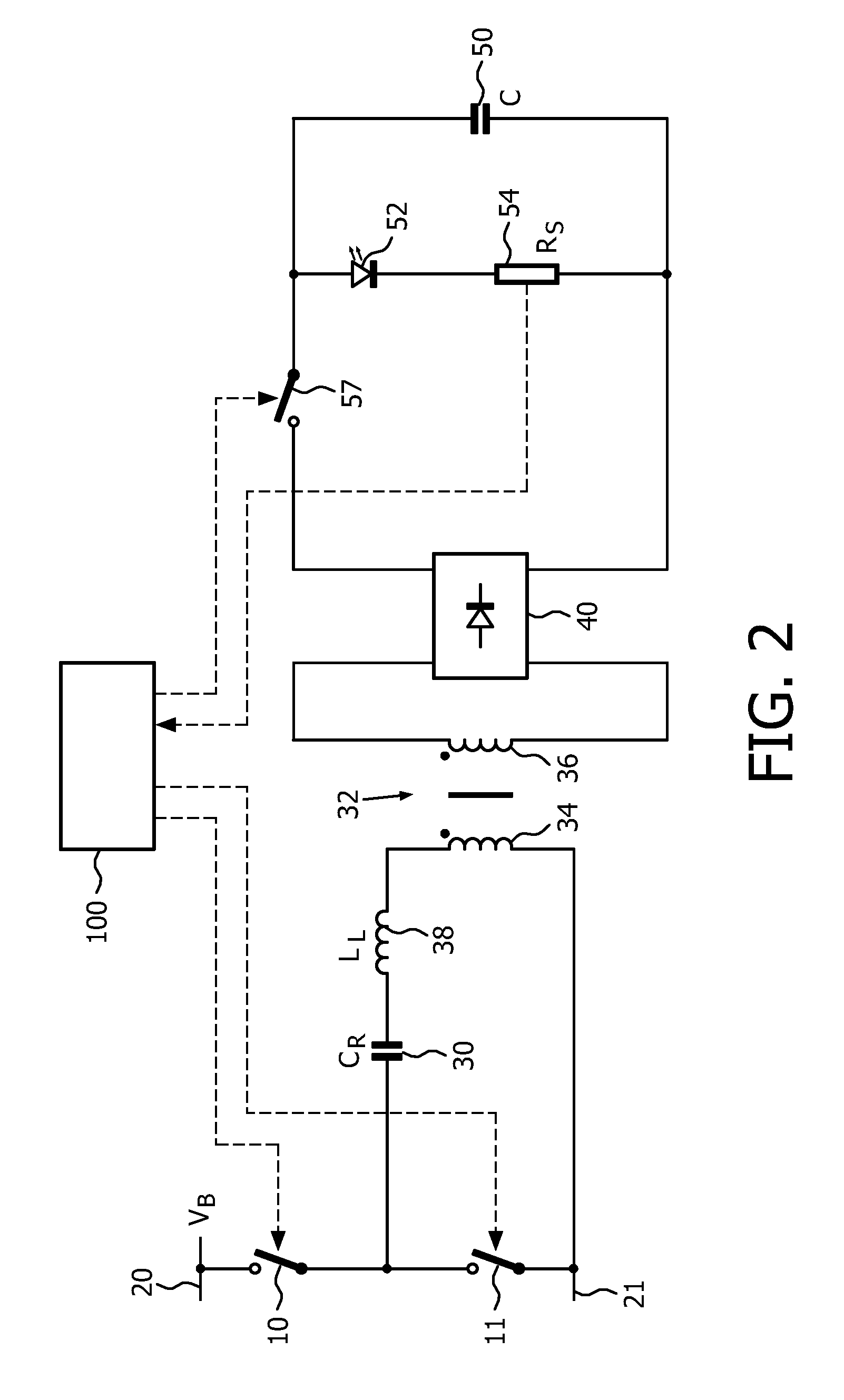
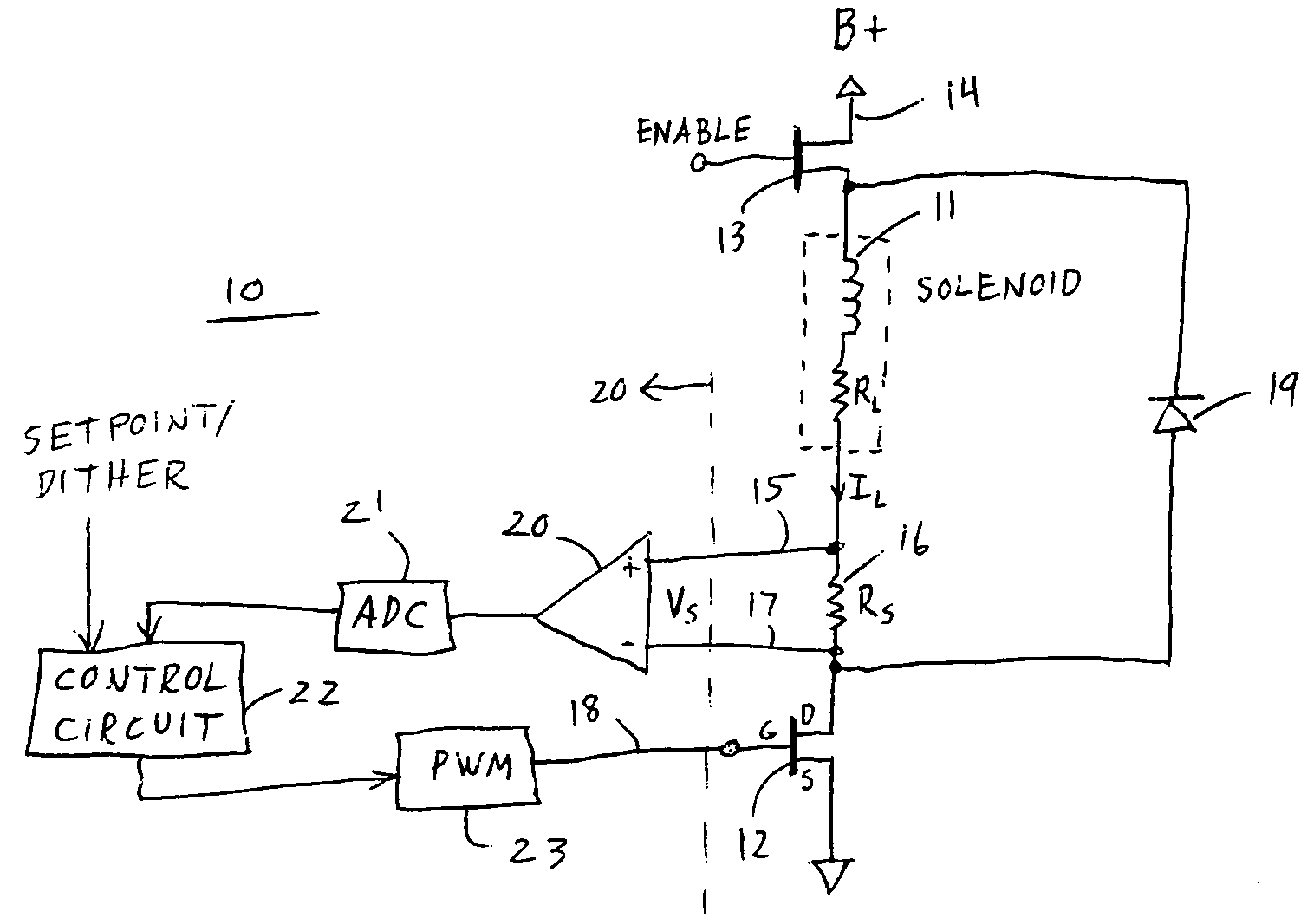
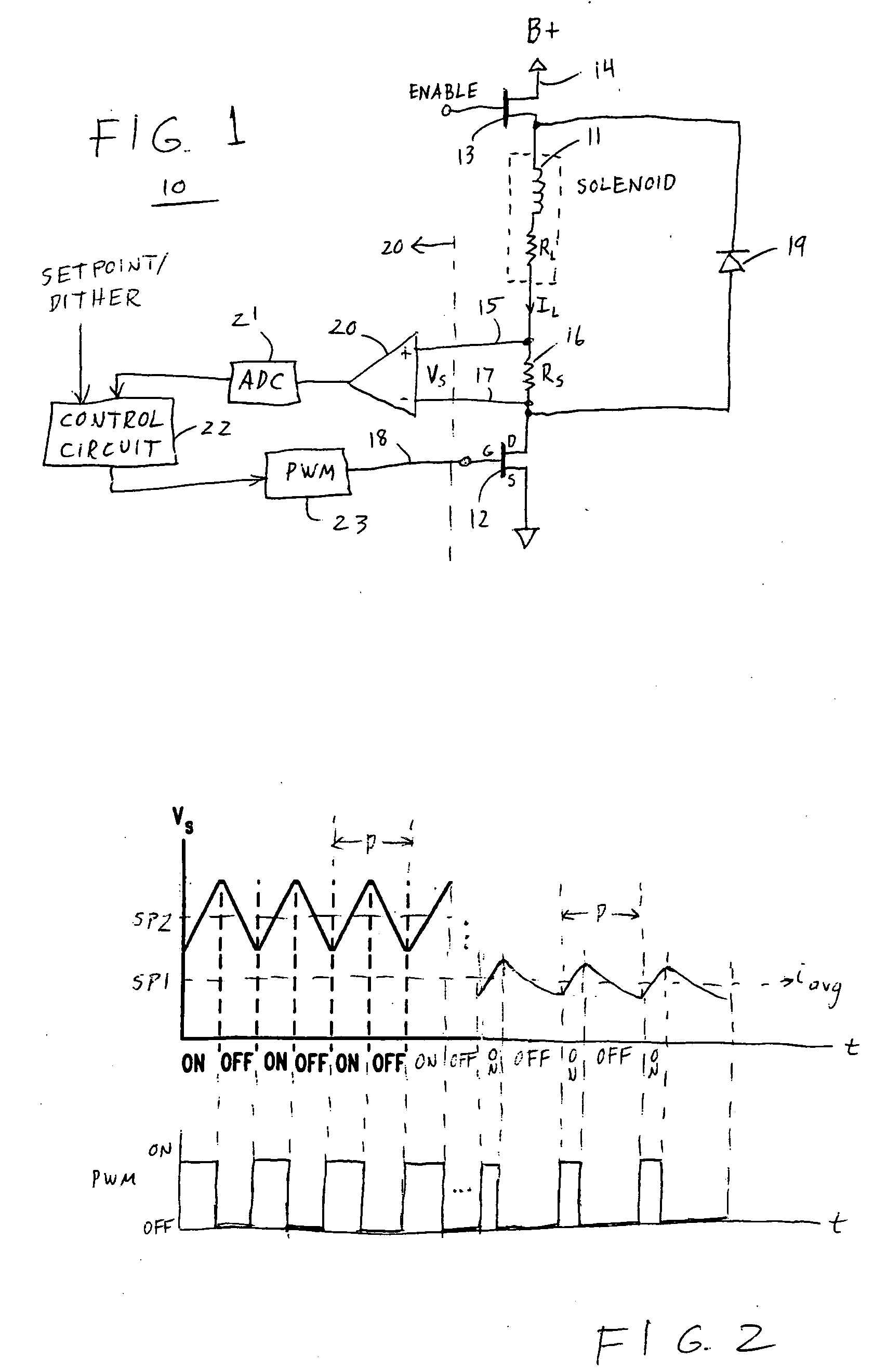
Frequency-controlled load driver for an electromechanical system
ActiveUS20050180084A1Easy to changeElectric switchesElectromagnetic relaysDriver circuitTransient mode
A frequency-controlled load driver circuit includes a steady-state and a transient operational mode. A switching driver switches a load current to a solenoid at a set switching frequency during a steady-state operational mode. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) oversamples a sense resistor voltage an integer number of times within each period of the switching frequency. A control circuit sets the switching frequency of the driver during the steady-state operational mode by providing predetermined switching times. The control circuit disables switching during the transient mode. Dither can be applied during the steady-state mode.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
Heat-fixing device
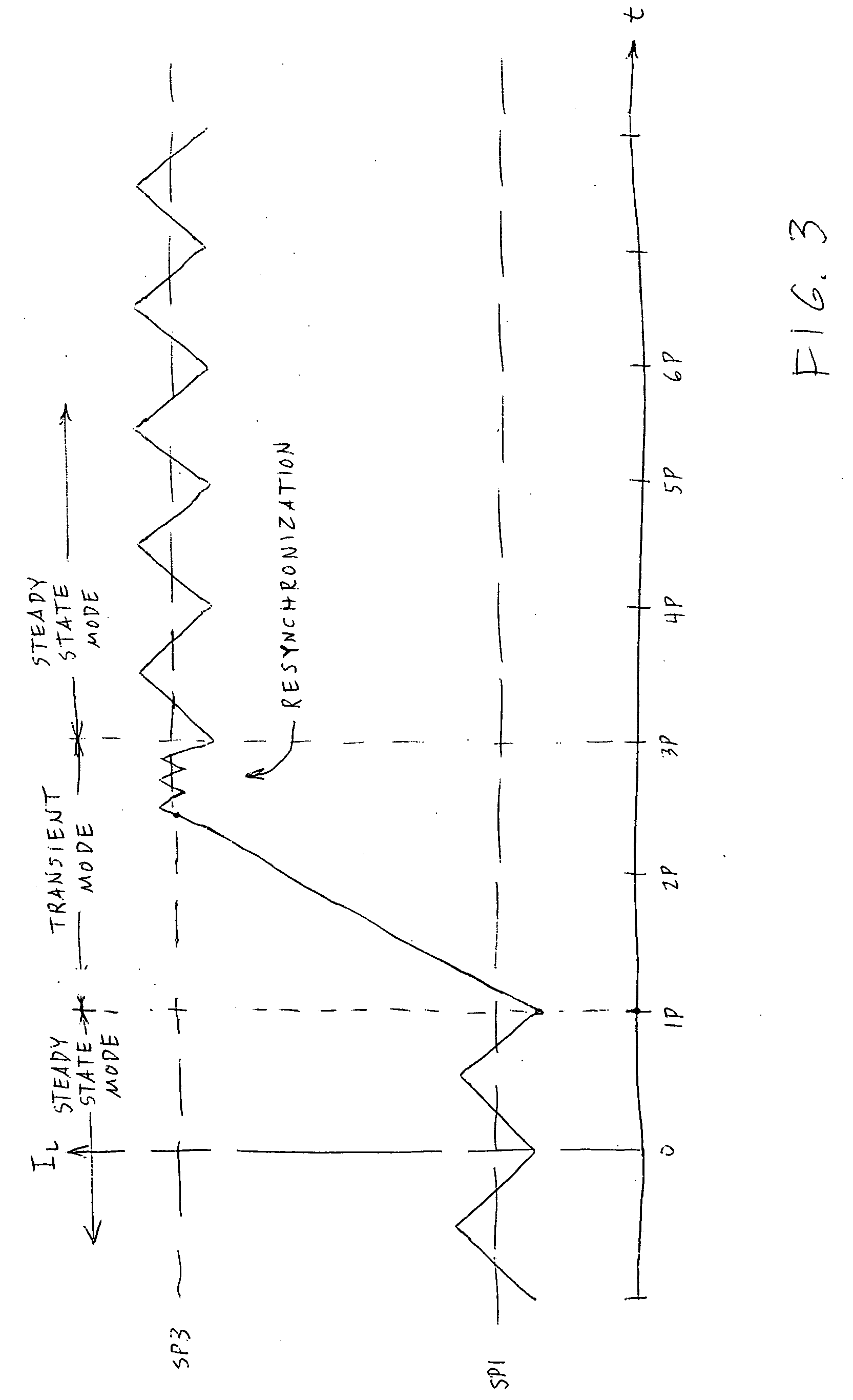
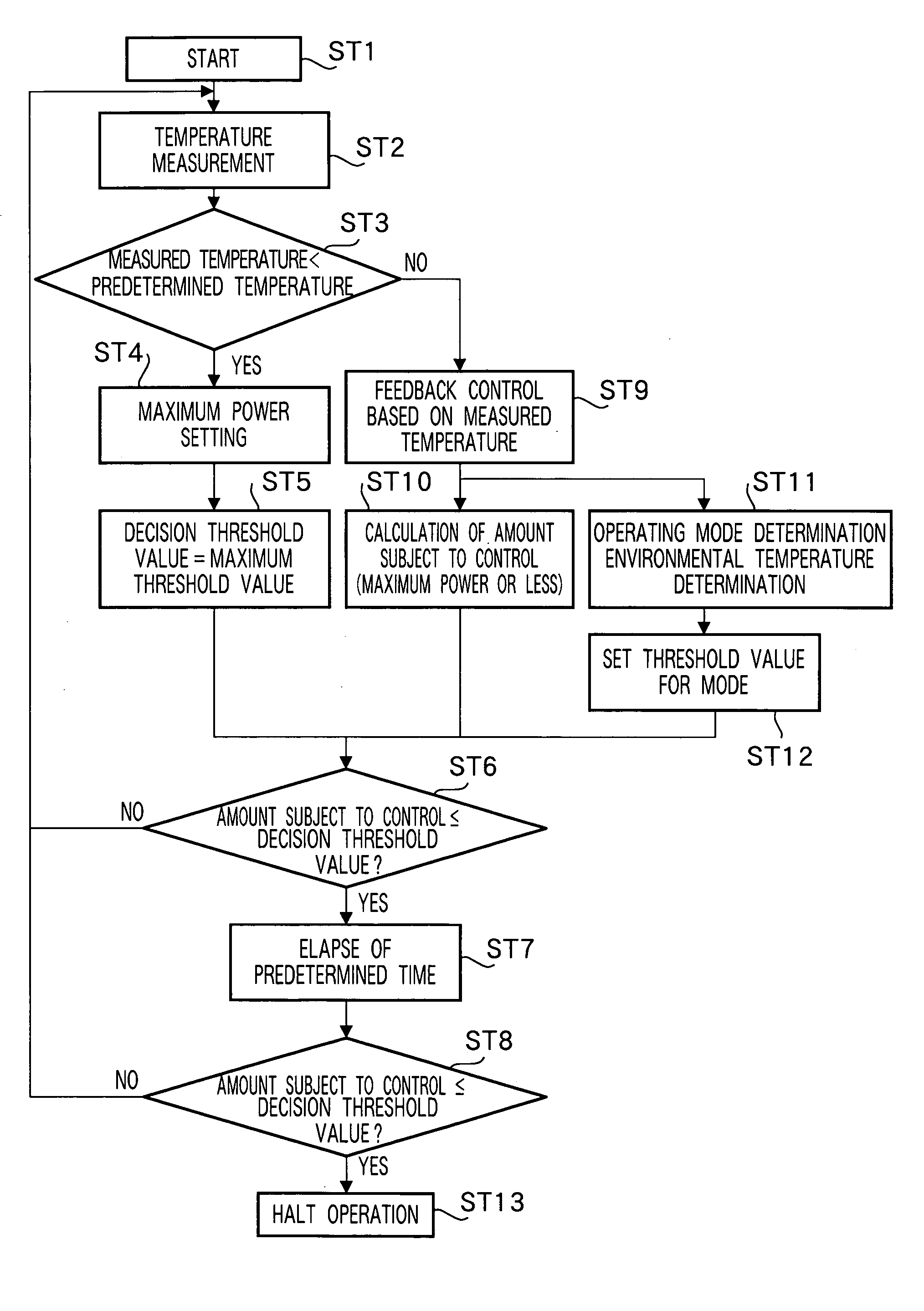
A heat-fixing apparatus is provided that enables a rise in temperature of a heating member to be closely tracked, and an excessive rise in temperature of the heating member to be obviated, a simple configuration and irrespective of differences in the operating mode, such as immediately after a rise in temperature or during continuous operation. Different threshold values are set in accordance with different modes, such as a warm-up mode and a fixing operation mode. Threshold decisions on a switching frequency controlled by a frequency control section are made using different threshold values, according to the mode. A switching frequency of switching elements are varied so that power necessary in each mode is supplied to an exciting coil. An excessive rise in temperature is prevented in each mode by halting a switching element drive in accordance with the threshold decision.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Control circuit of a switched-mode power converter and method thereof
ActiveUS20120300499A1Lower levelImprove the level ofDc-dc conversionPulse shapingSwitching frequency controlEngineering
A method for controlling voltage crossing a power switch of a switched-mode power converter is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of: controlling a switch frequency of a power switch of a switched-mode power converter to a first frequency as activating the switched-mode power converter; and changing the switch frequency of the power switch to a second frequency after a specific amount of time; wherein the first frequency is lower than the second frequency.
Owner:LEADTREND TECH
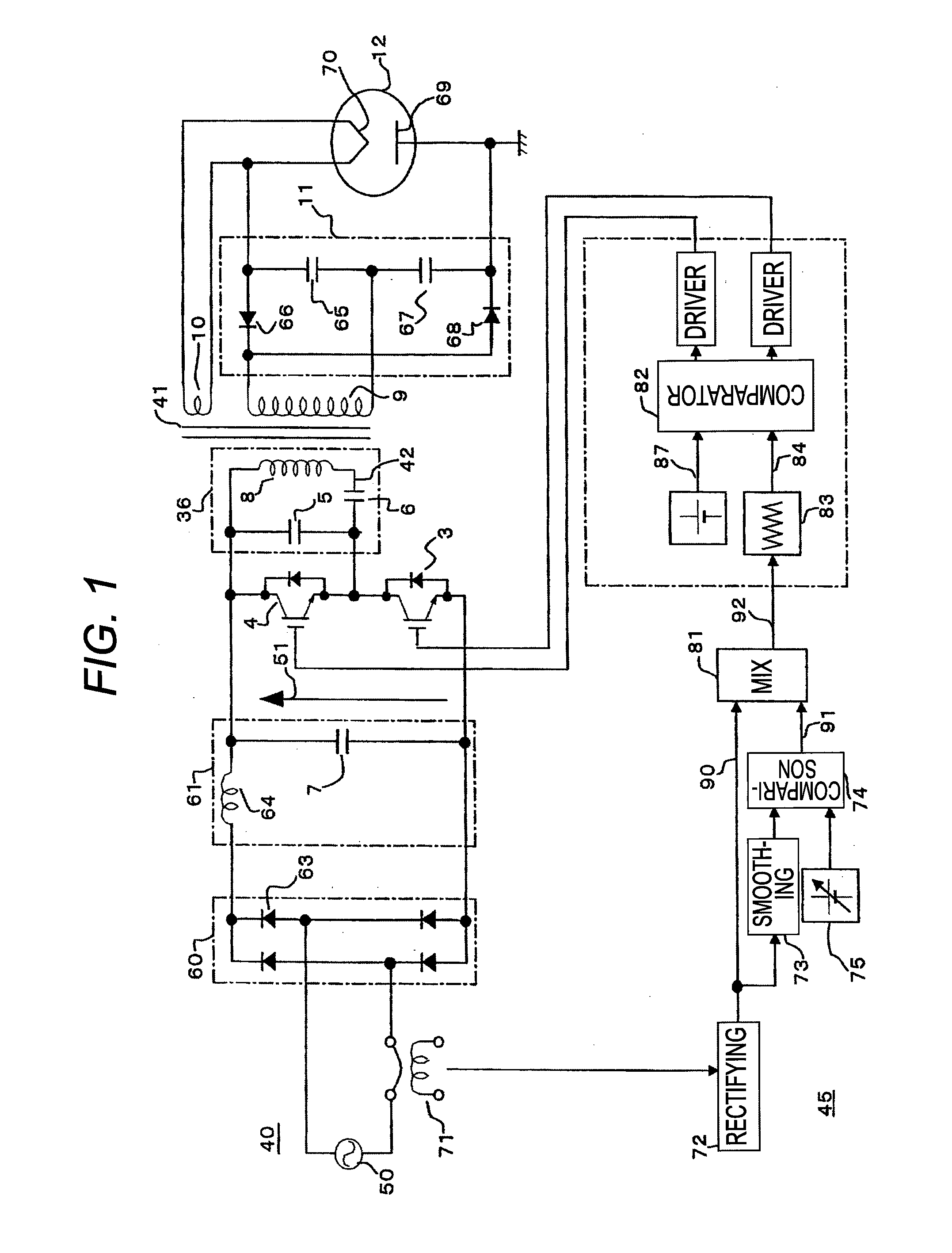
Switching power supply circuit
InactiveUS6839245B2Increase conduction angleImprove power factorAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionActive clampResonance
A switching power supply circuit ready for worldwide use is disclosed which suppresses a variation of a pulse voltage to be fed back when the alternating-current input varies. The switching power supply circuit includes a composite resonance type converter of a switching frequency control scheme wherein a voltage resonance pulse voltage generated in a primary side voltage resonance converter is fed back to a rectification diode through a high speed diode and an inductance or a transformer. An active clamp circuit is provided on the primary side to clamp the voltage resonance pulse voltage.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and system for operating a motor to reduce noise in an electric vehicle
Methods and systems for operating a motor coupled to an electrical bus in a vehicle are provided. Selected resonant frequencies of the electrical bus are determined. The selected resonant frequencies include a low resonant frequency and a high resonant frequency. Power is provided to the motor through at least one switch operating at a switching frequency. The switching frequency is controlled as a function of a rate of operation of the motor.; The function is characterized by one of a first substantially linear portion having a first slope when the switching frequency is less than or equal to a selected switching frequency and a second substantially linear portion having a second slope if the switching frequency is greater than the selected frequency, the selected switching frequency being greater than the low resonant frequency and a substantially linear portion having a y-intercept being greater than the low resonant frequency.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Output current estimation for an isolated flyback converter with variable switching frequency control and duty cycle adjustment for both PWM and PFM modes
A fly-back power converter has a current-estimating control loop that senses the primary output current in a transformer to control the secondary output. A primary-side control circuit switches primary current through the transformer on and off. A discharge time when a secondary current through an auxiliary winding of the transformer is flowing is generated by sampling a voltage divider on an auxiliary loop for a knee-point. A normalized duty cycle is calculated by multiplying the discharge time by a current that is proportional to the switching frequency and comparing to a sawtooth signal having the switching frequency. The peak of a primary-side voltage is sensed from the primary current loop and converted to a current and multiplied by the normalized duty cycle to generate an estimated current. An error amp compares the estimated current to a reference to adjust the oscillator frequency and peak current to control primary switching.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
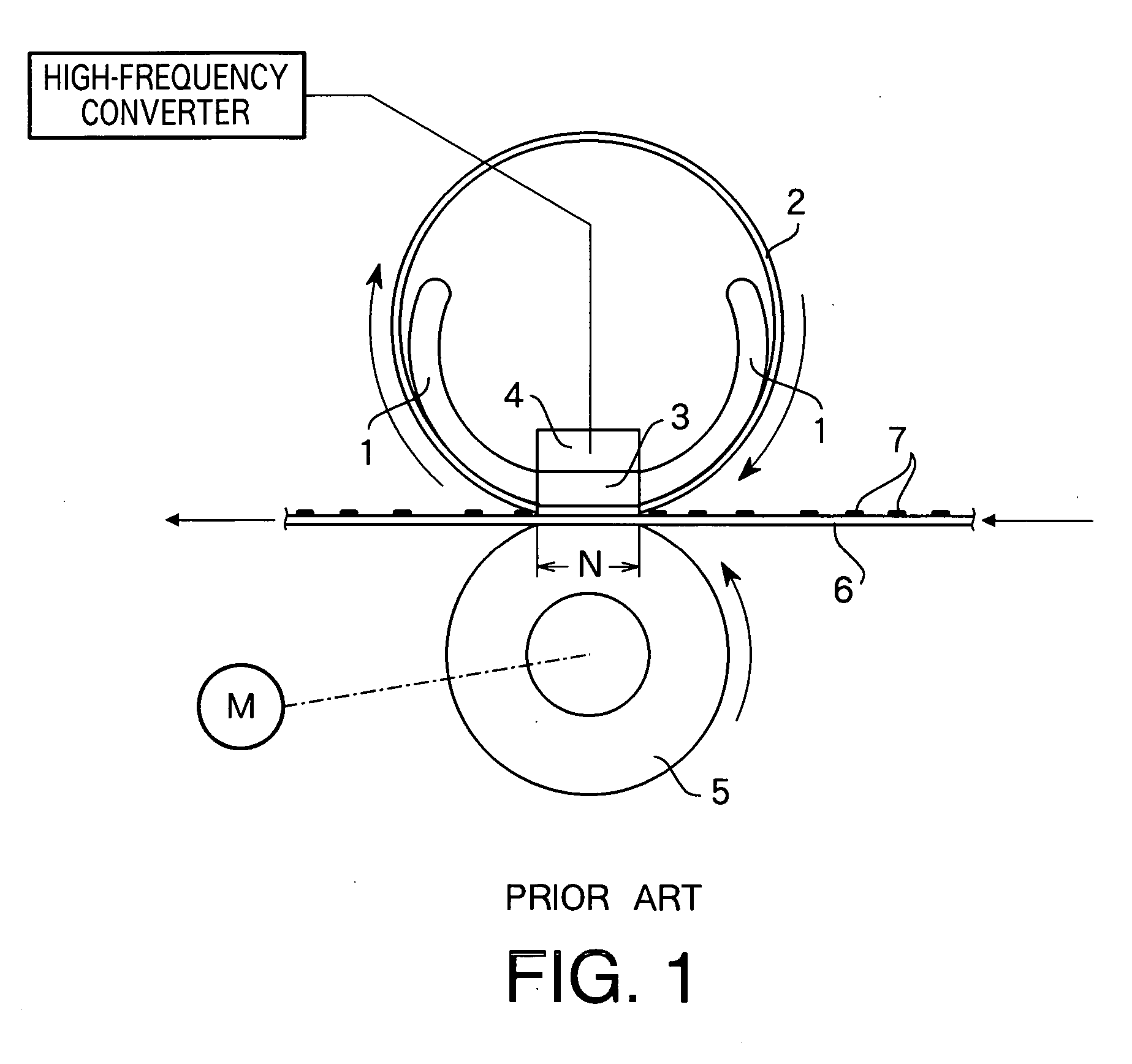
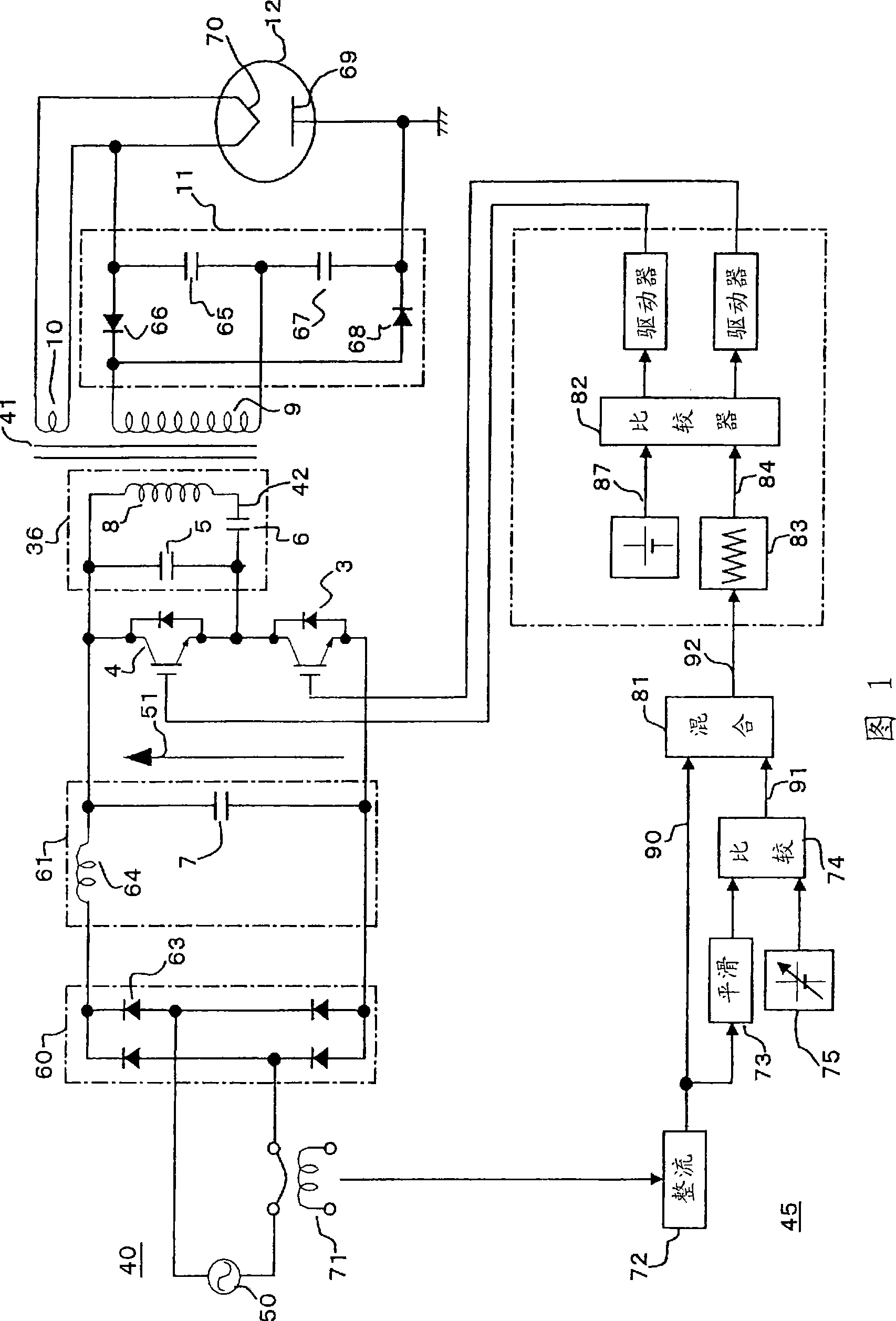
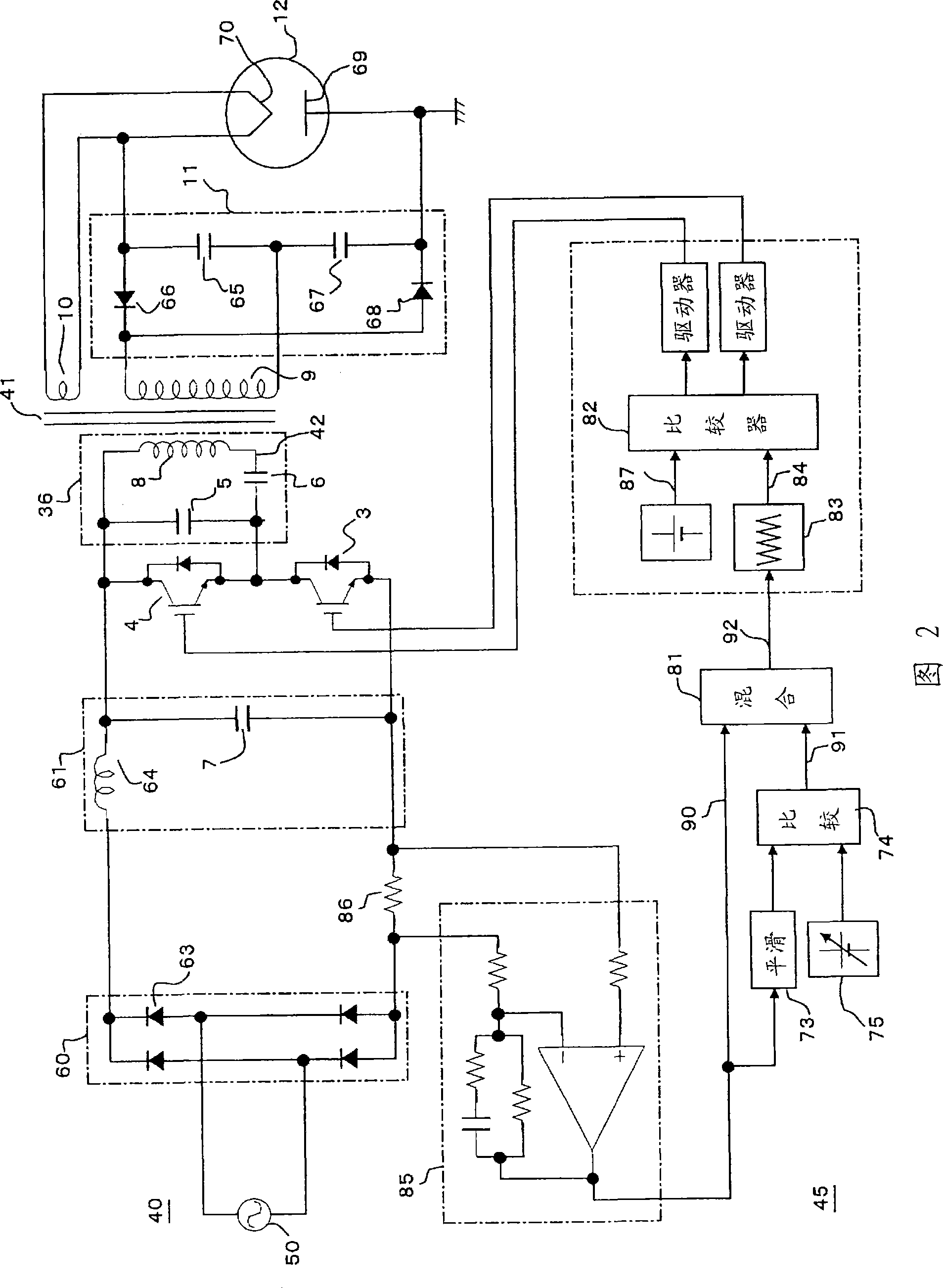
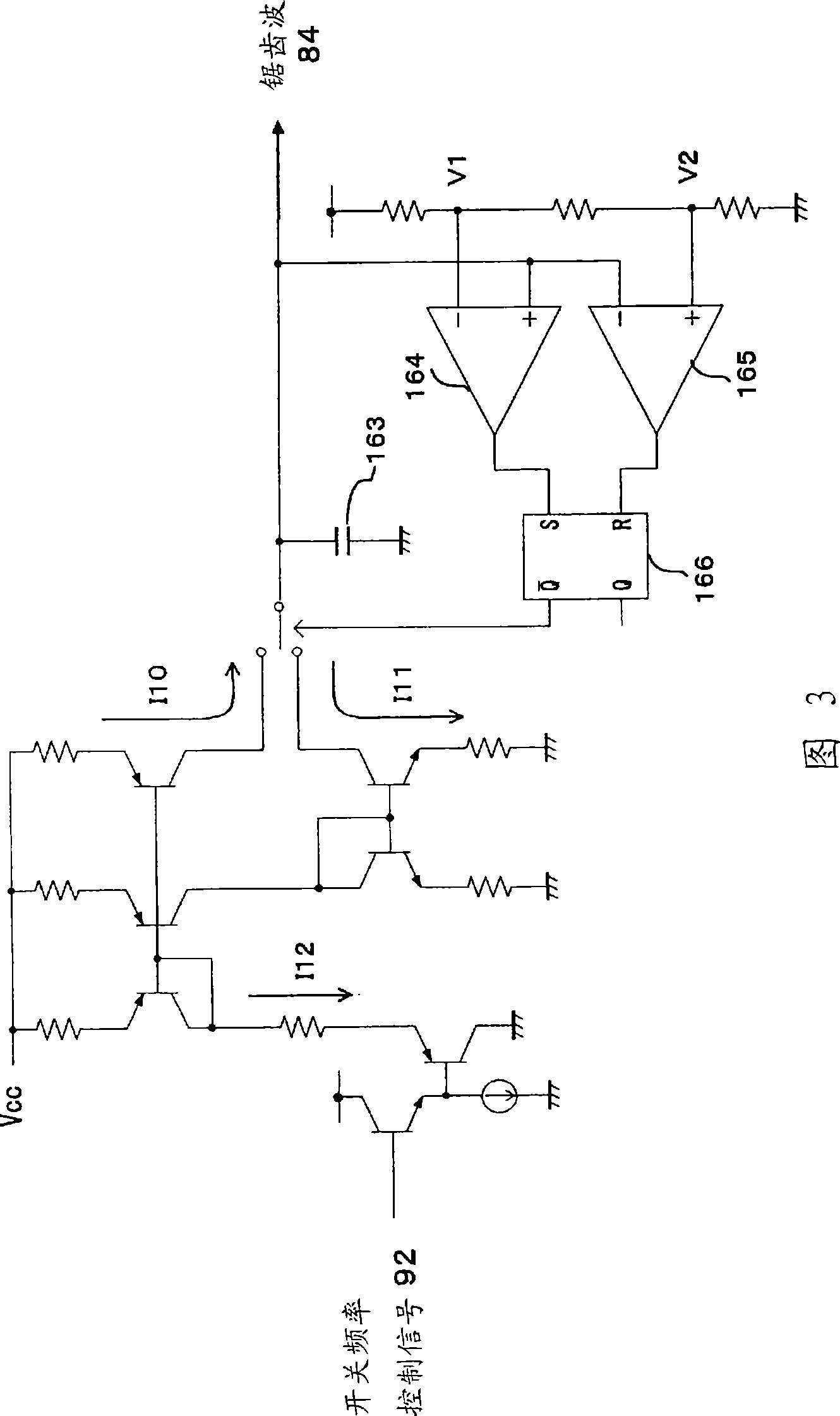
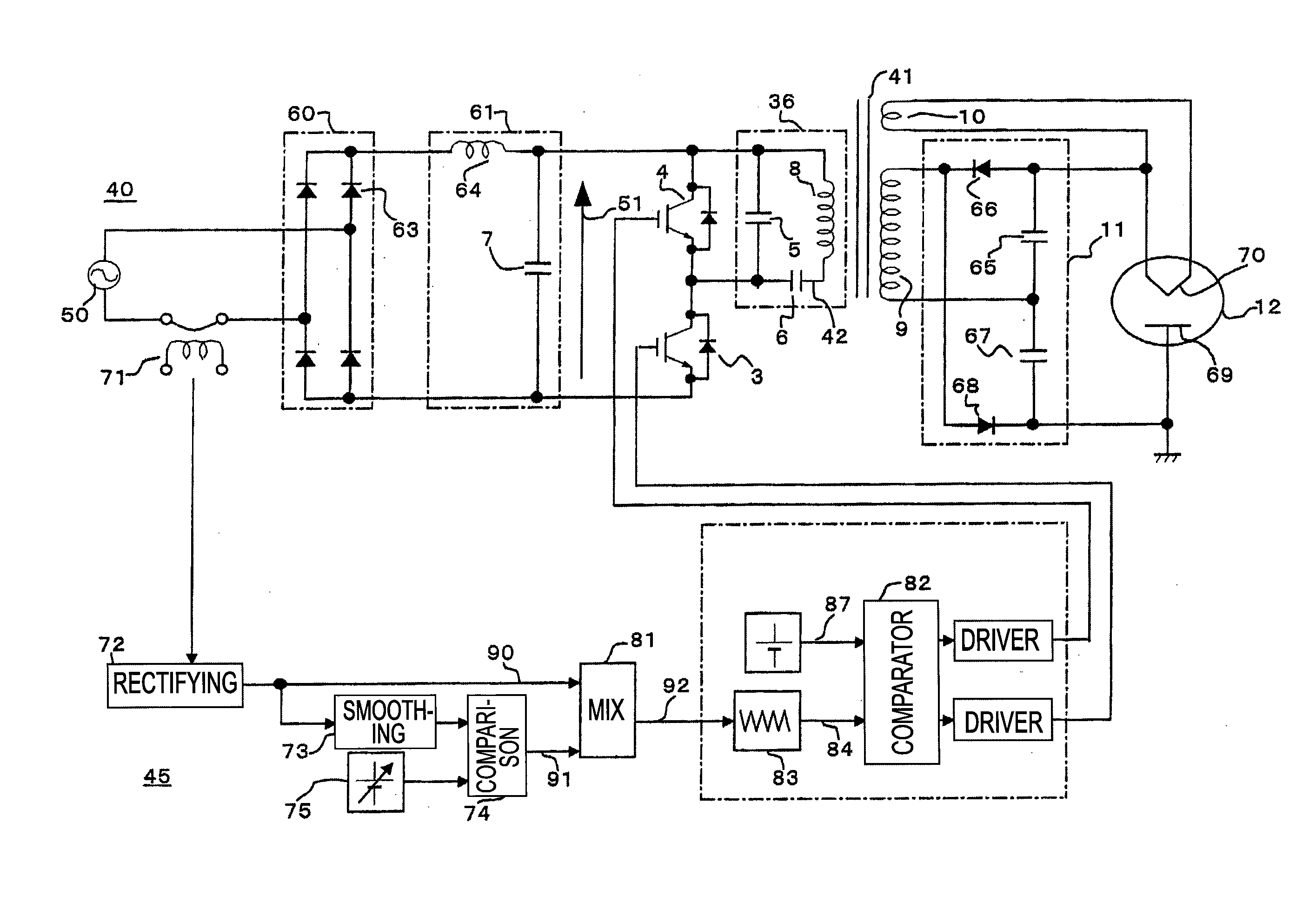
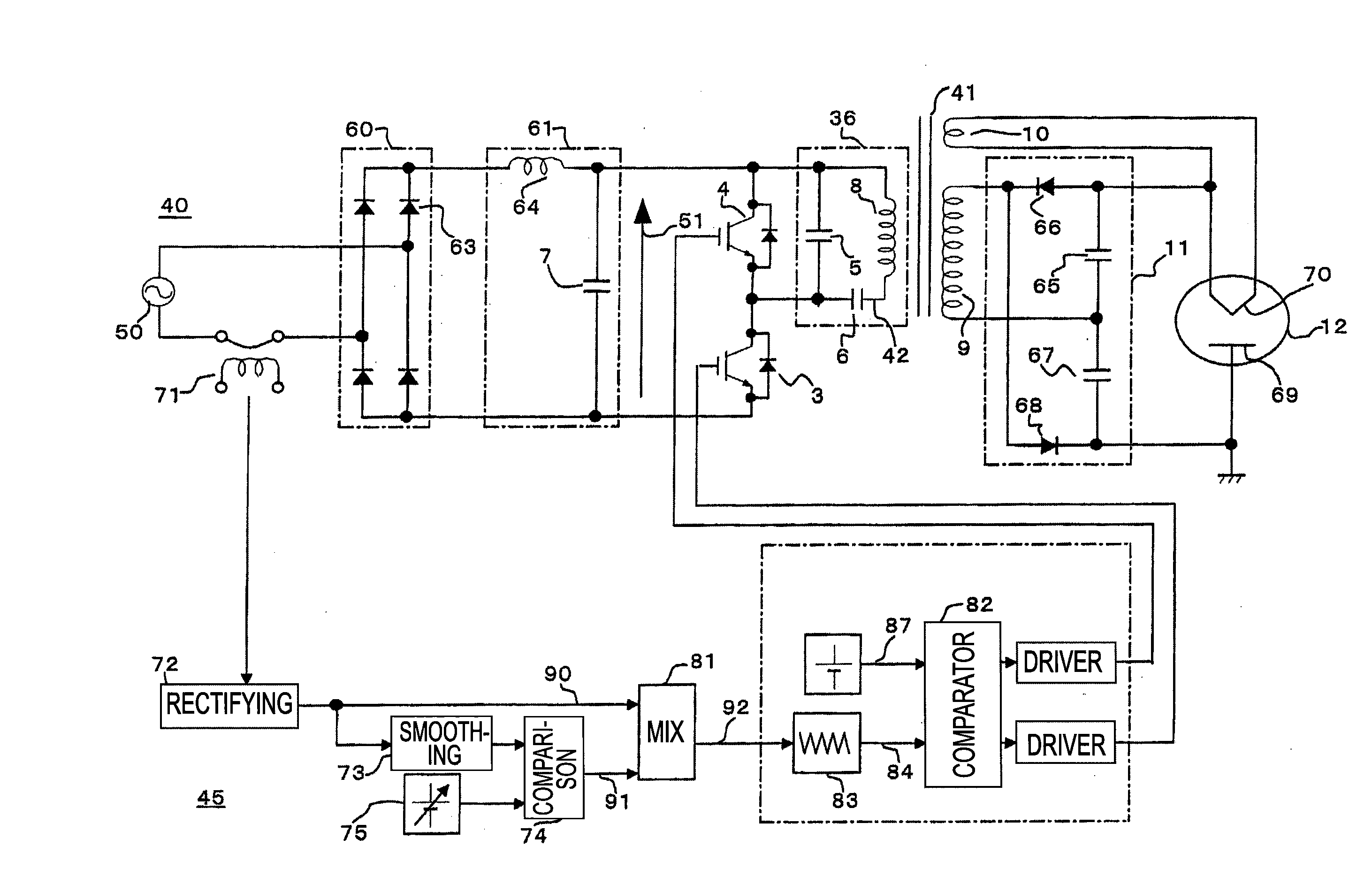
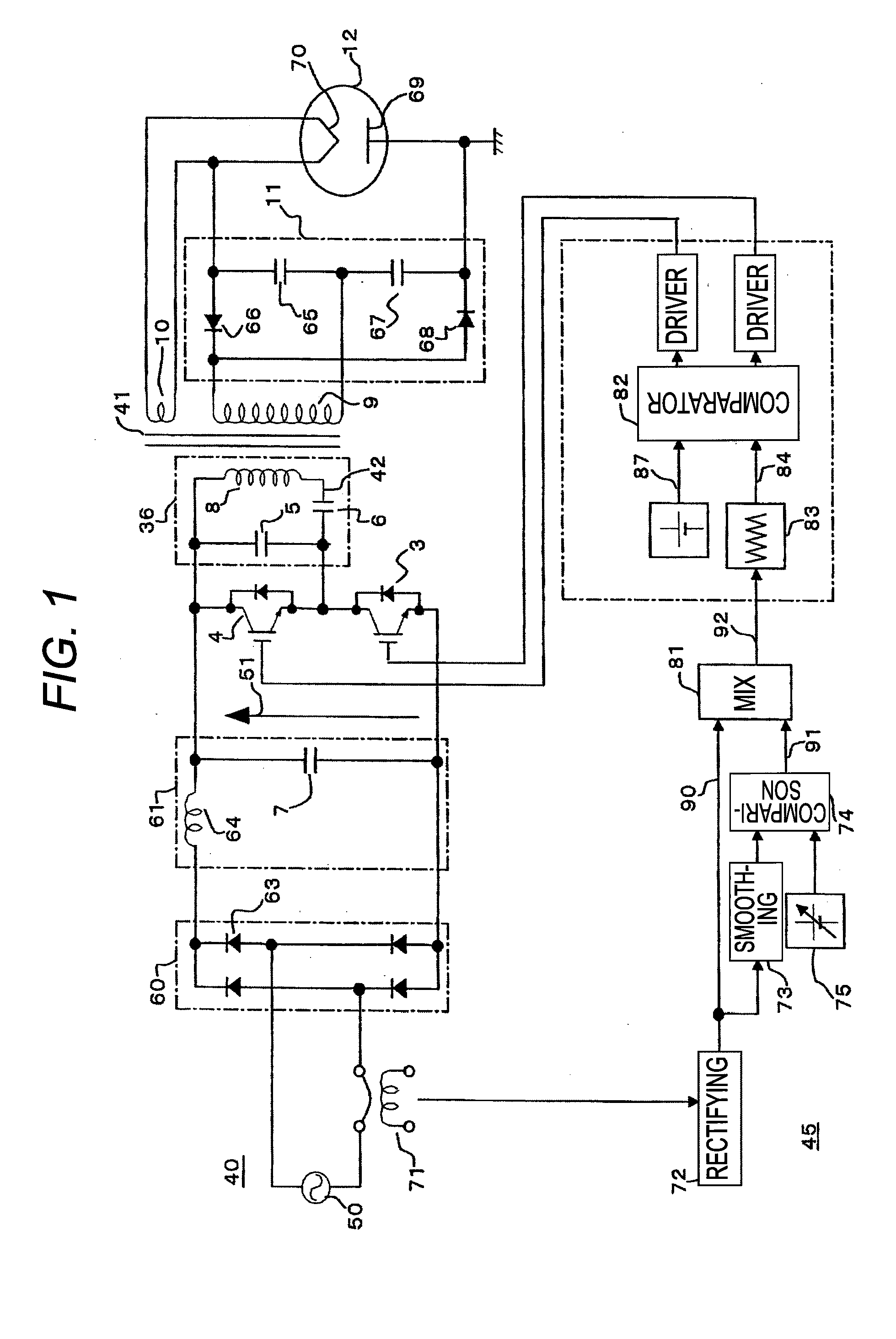
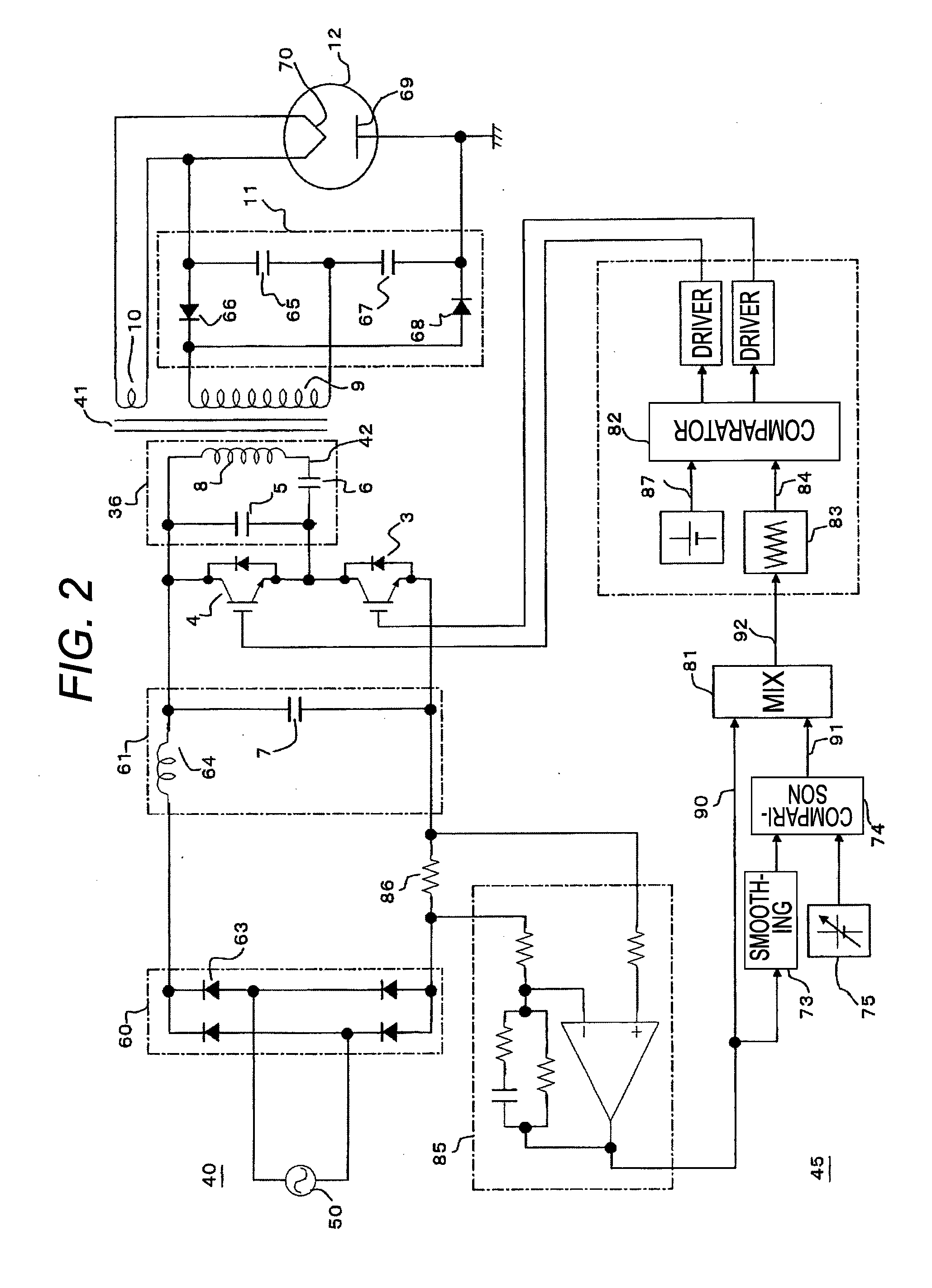
Power control apparatus for high frequency dielectric heating and control method employed by the power control apparatus
ActiveCN101461283ASuppress transient fluctuationsReduce startup timeMicrowave heatingDomestic cooking appliancesHigh frequency powerEngineering
Provided is a power control apparatus for high frequency dielectric heating, which is not affected by magnetron types, fluctuations of characteristics, power supply voltages and the like. The power control apparatus is provided with input current detecting sections (71, 72) for detecting an input current to an inverter circuit (10), which rectifies (31) an alternating current power supply voltage (20) and converts it into high-frequency power by performing high-frequency switching. A switching frequency control signal (92) wherein input current waveform information (90) from the input current detecting section and power control information (91) are mixed, is converted into a drive signal of semiconductor switching elements (3, 4) of the inverter circuit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Power control unit for high-frequency dielectric heating and control method thereof
InactiveUS20090272735A1Suppress transient fluctuationsSimple configurationMicrowave heatingDomestic cooking appliancesHigh frequency powerElectric power
A power control unit for a high-frequency dielectric heating not affected by variations in the magnetron type or characteristic, and power supply voltage fluctuation, etc., is provided. The power control unit for a high-frequency dielectric heating has an input current detection section 71, 72 for detecting input current of an inverter 10 for rectifying 31 an AC power supply voltage 20, performing high-frequency switching of the voltage, and converting the voltage to high-frequency power. The power control unit for a high-frequency dielectric heating converts a switching frequency control signal 92 provided by mixing input current waveform information 90 and power control information 91 into a drive signal of a semiconductor switching element 3, 4 of the inverter.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
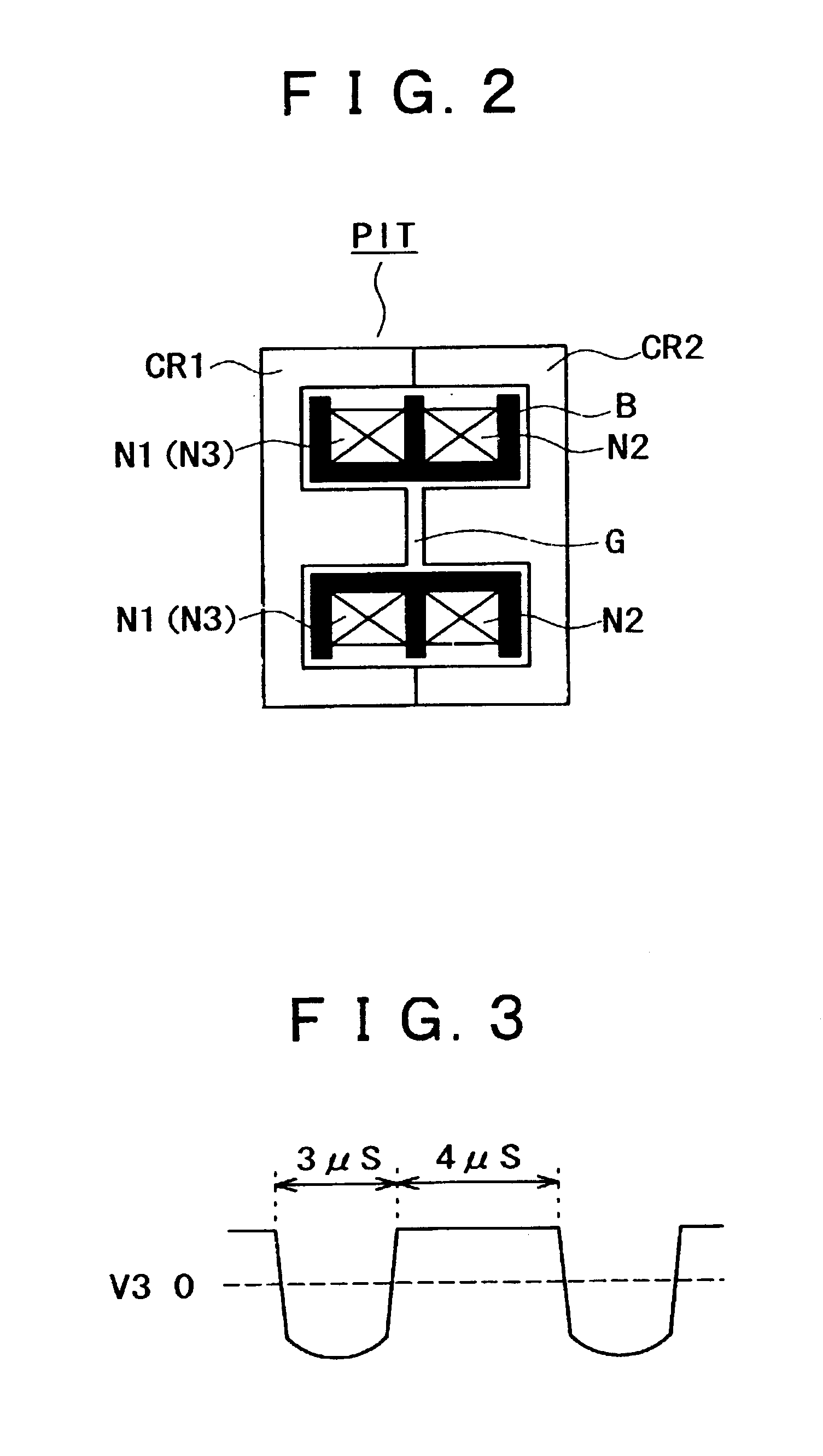
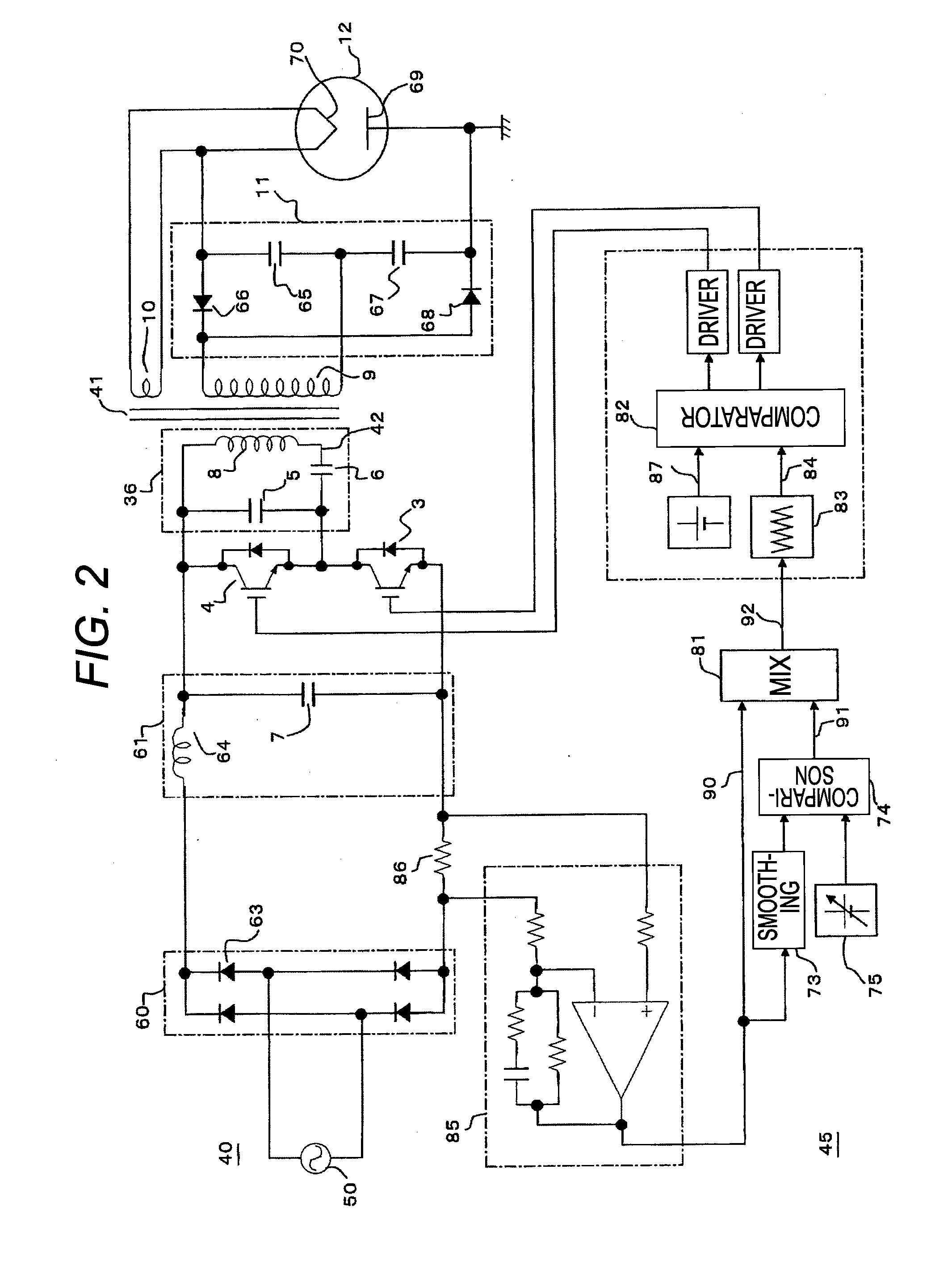
Switching power supply circuit
InactiveUS20060209576A1Improve power supply reliabilitySmall sizeTelevision system detailsEfficient power electronics conversionVoltage pulseEngineering
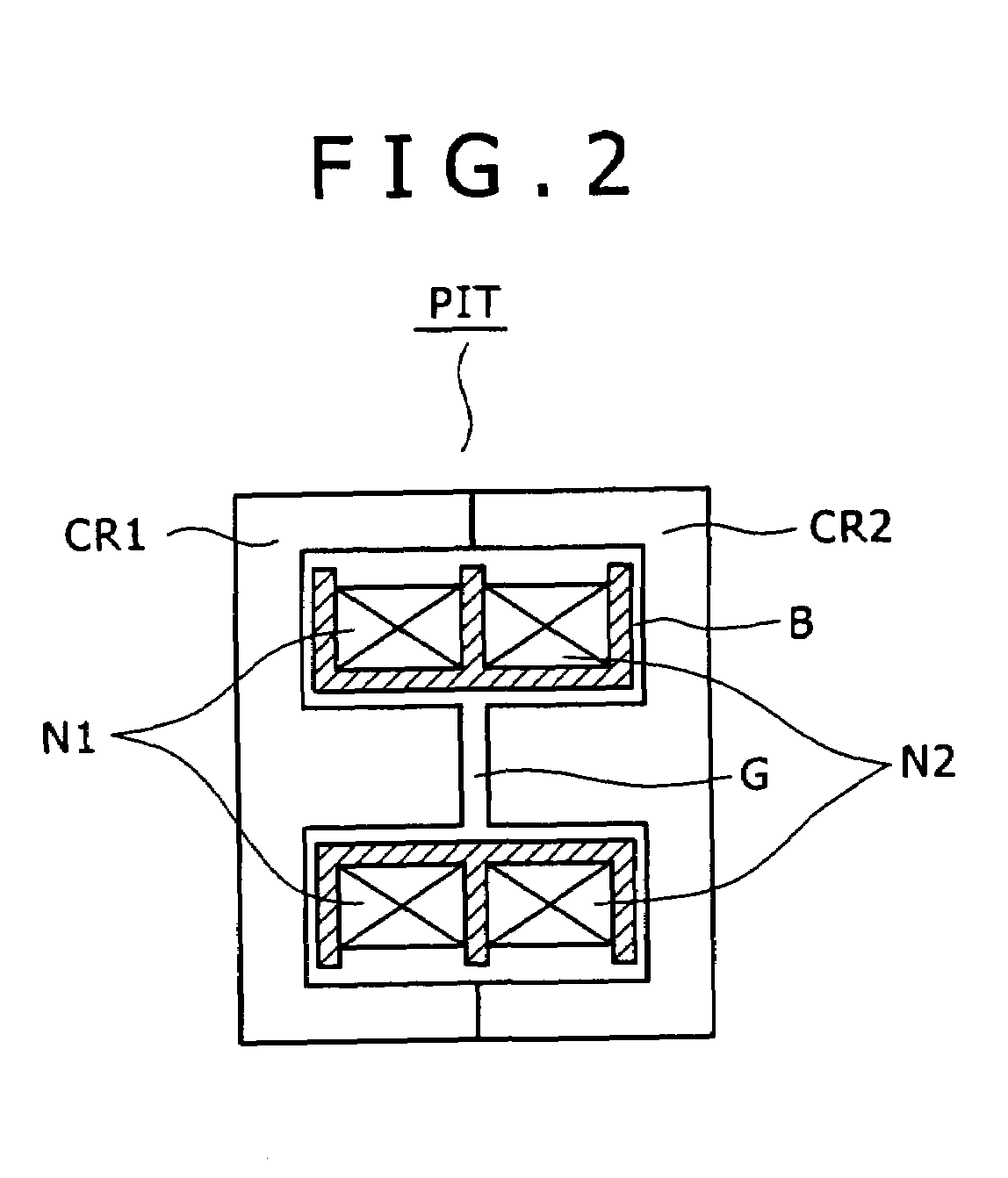
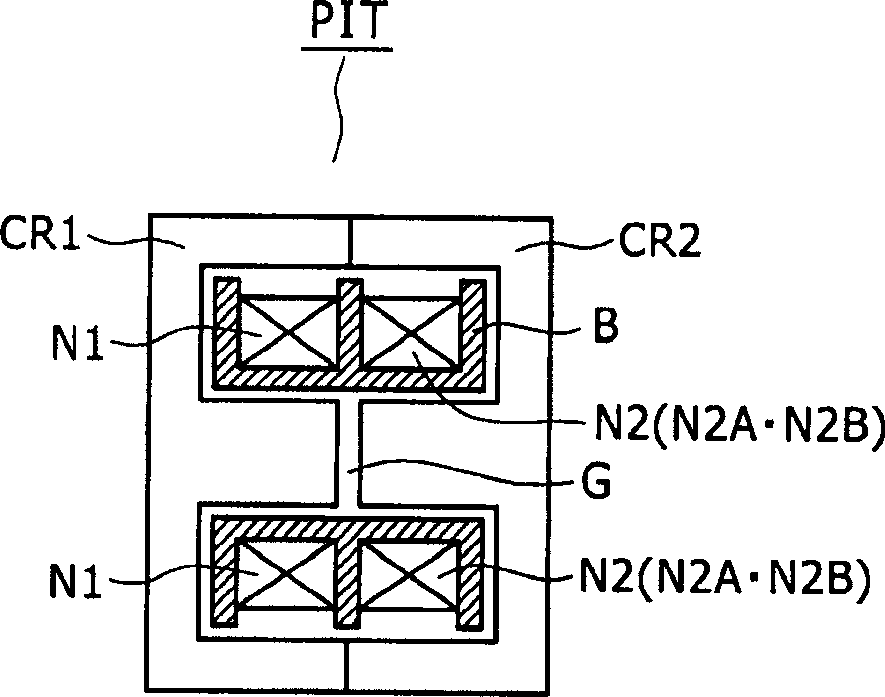
A wide-range compatible voltage resonant converter provides high efficiency and allows use of low-breakdown-voltage products for a circuit. The voltage resonant converter is provided with a secondary-side parallel resonant circuit and a secondary-side series resonant circuit, and a loose coupling state is established in which the coupling coefficient of an isolation converter transformer is about 0.7 or less. Thus, a constant-voltage control characteristic is obtained as a sharp unimodal characteristic, which narrows the switching frequency control region required for stabilization of an output voltage. In addition, a primary-side parallel resonant frequency, a secondary-side parallel resonant frequency and a secondary-side series resonant frequency are set so that a favorable power conversion efficiency is obtained. Moreover, an active clamp circuit is provided to suppress the peak level of a resonant voltage pulse to thereby allow use of low-breakdown-voltage products for a switching element and so on.
Owner:SONY CORP
Switching power supply circuit
InactiveUS7110268B2Reduce controlEasy to getEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionCouplingResonance
Owner:SONY CORP
Power control unit for high-frequency dielectric heating and control method thereof
InactiveUS20100155395A1Stable outputSuppress transient fluctuationsMicrowave heatingDomestic cooking appliancesHigh frequency powerEngineering
A power control unit for a high-frequency dielectric heating not affected by variations in the magnetron type or characteristic, and power supply voltage fluctuation, etc., is provided. The power control unit for a high-frequency dielectric heating has an input current detection section 71, 72 for detecting input current of an inverter 10 for rectifying 31 an AC power supply voltage 20, performing high-frequency switching of the voltage, and converting the voltage to high-frequency power. The power control unit for a high-frequency dielectric heating converts a switching frequency control signal 92 provided by mixing input current waveform information 90 and power control information 91 into a drive signal of a semiconductor switching element 3, 4 of the inverter.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
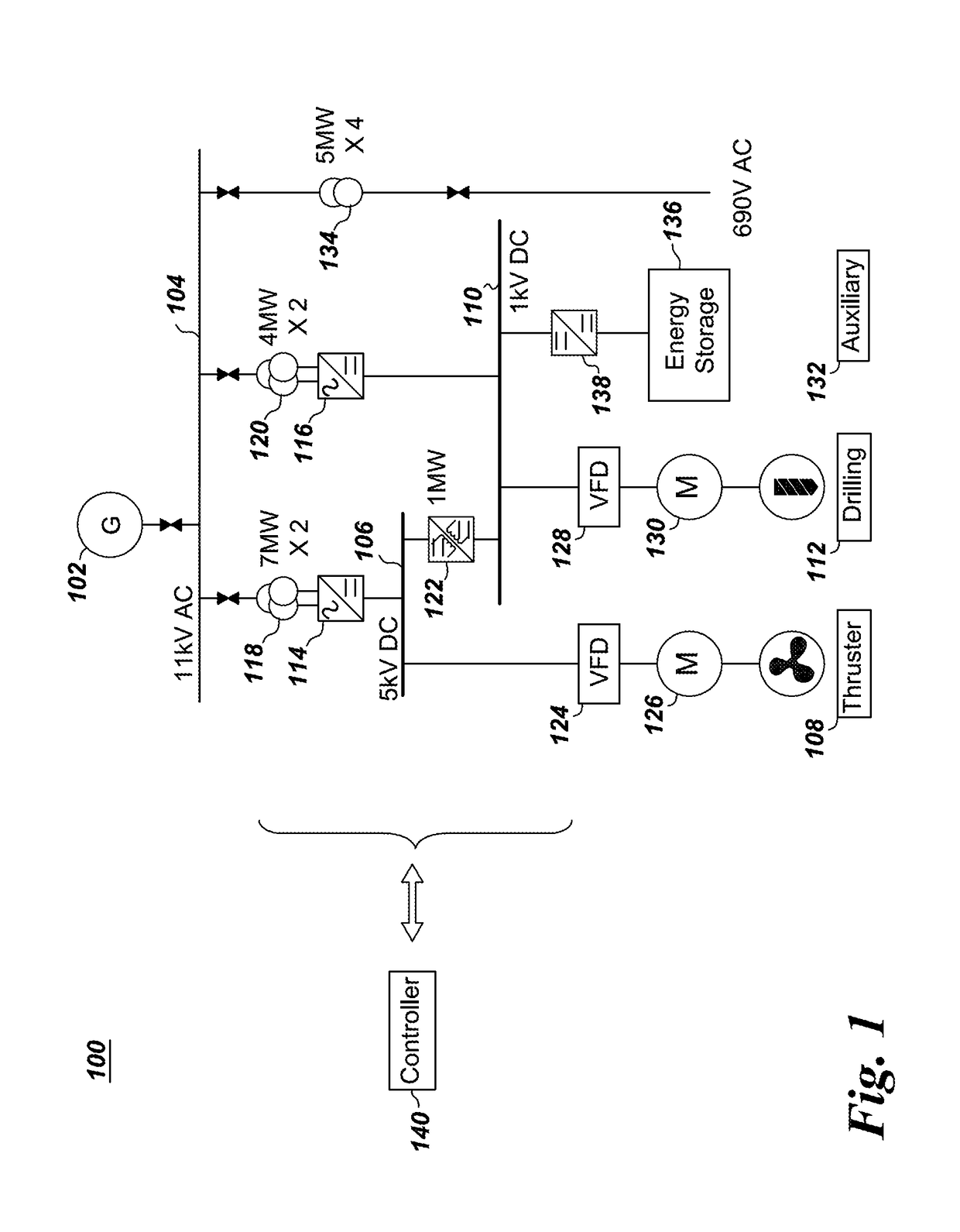
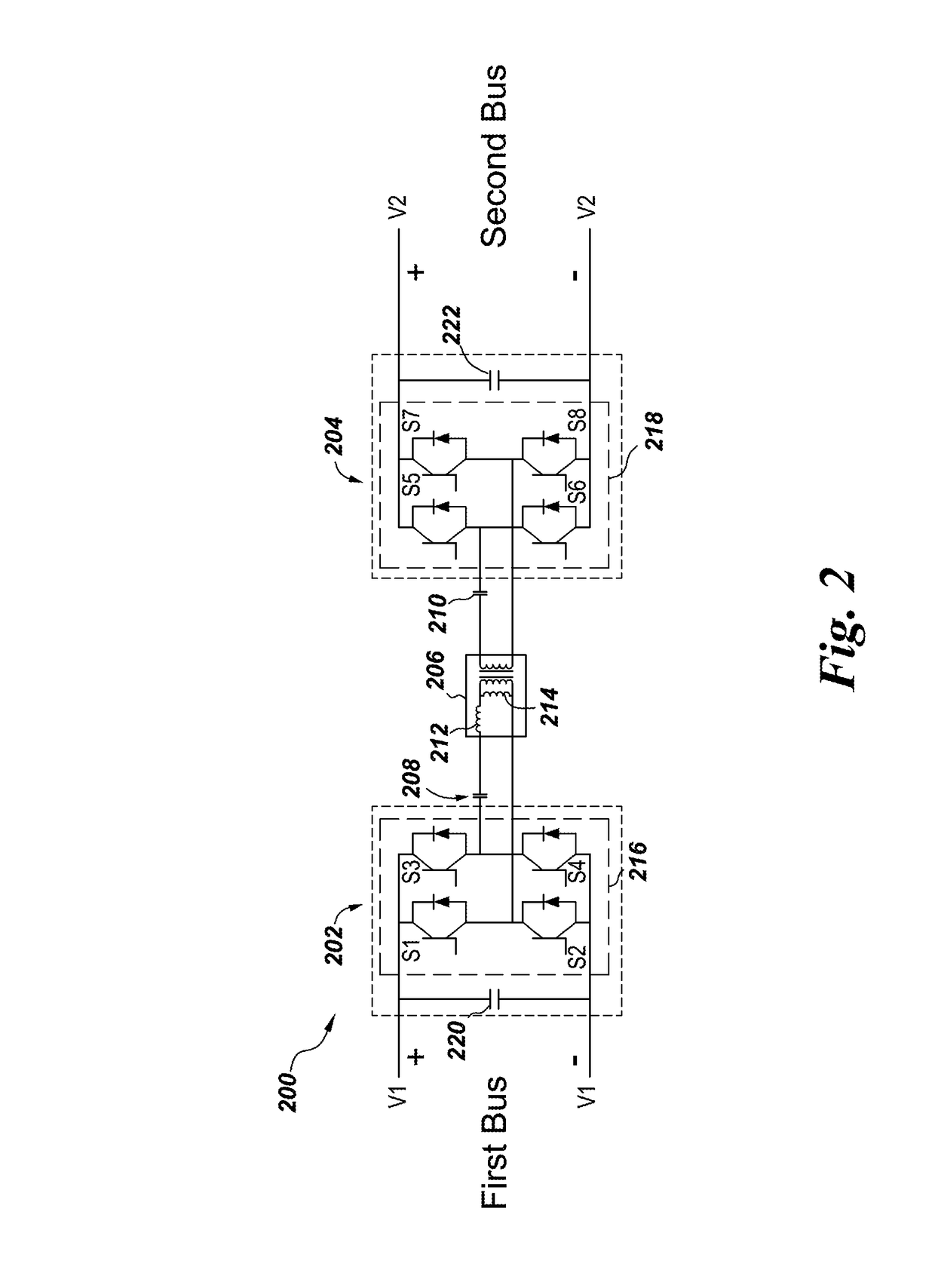
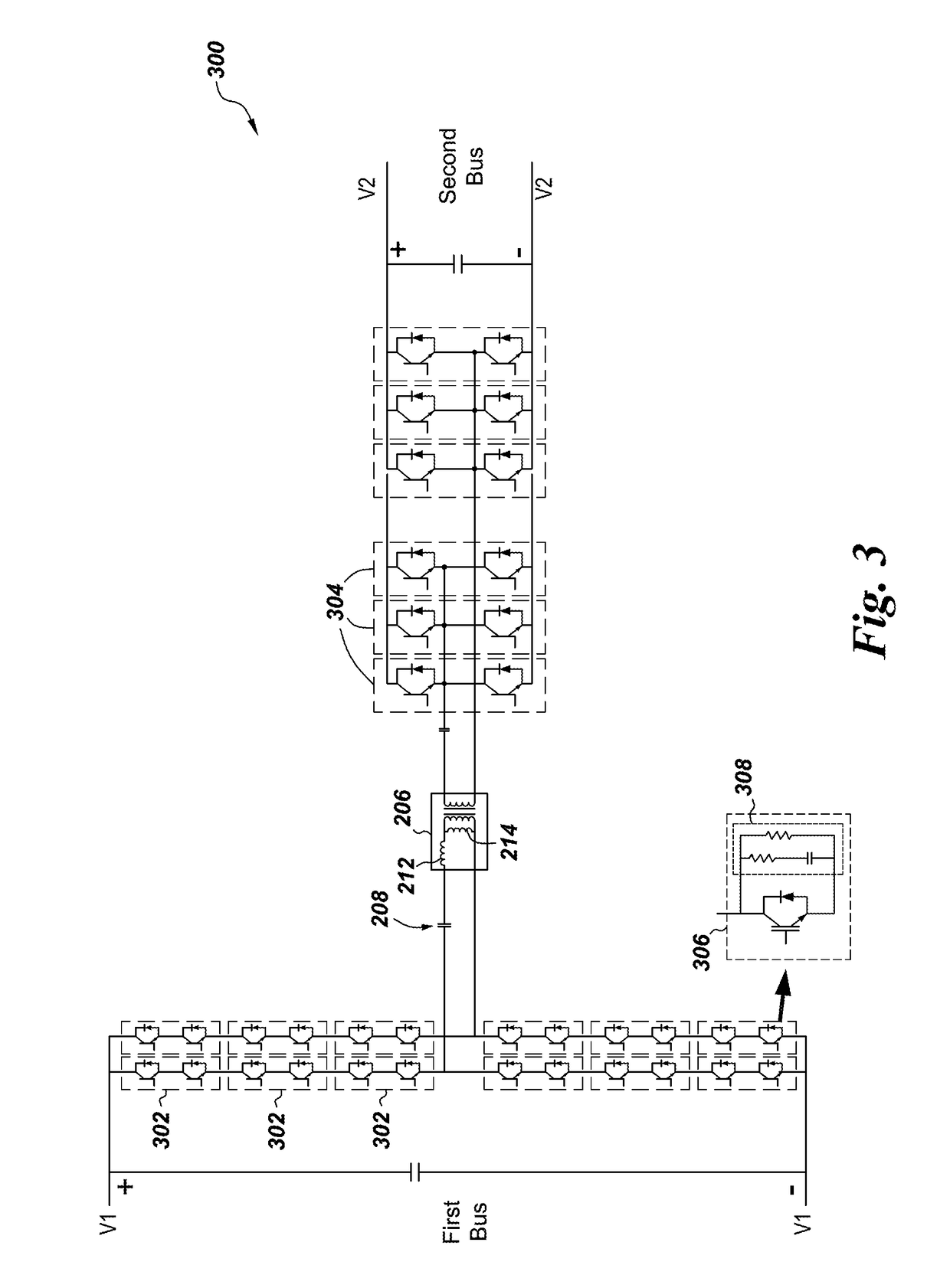
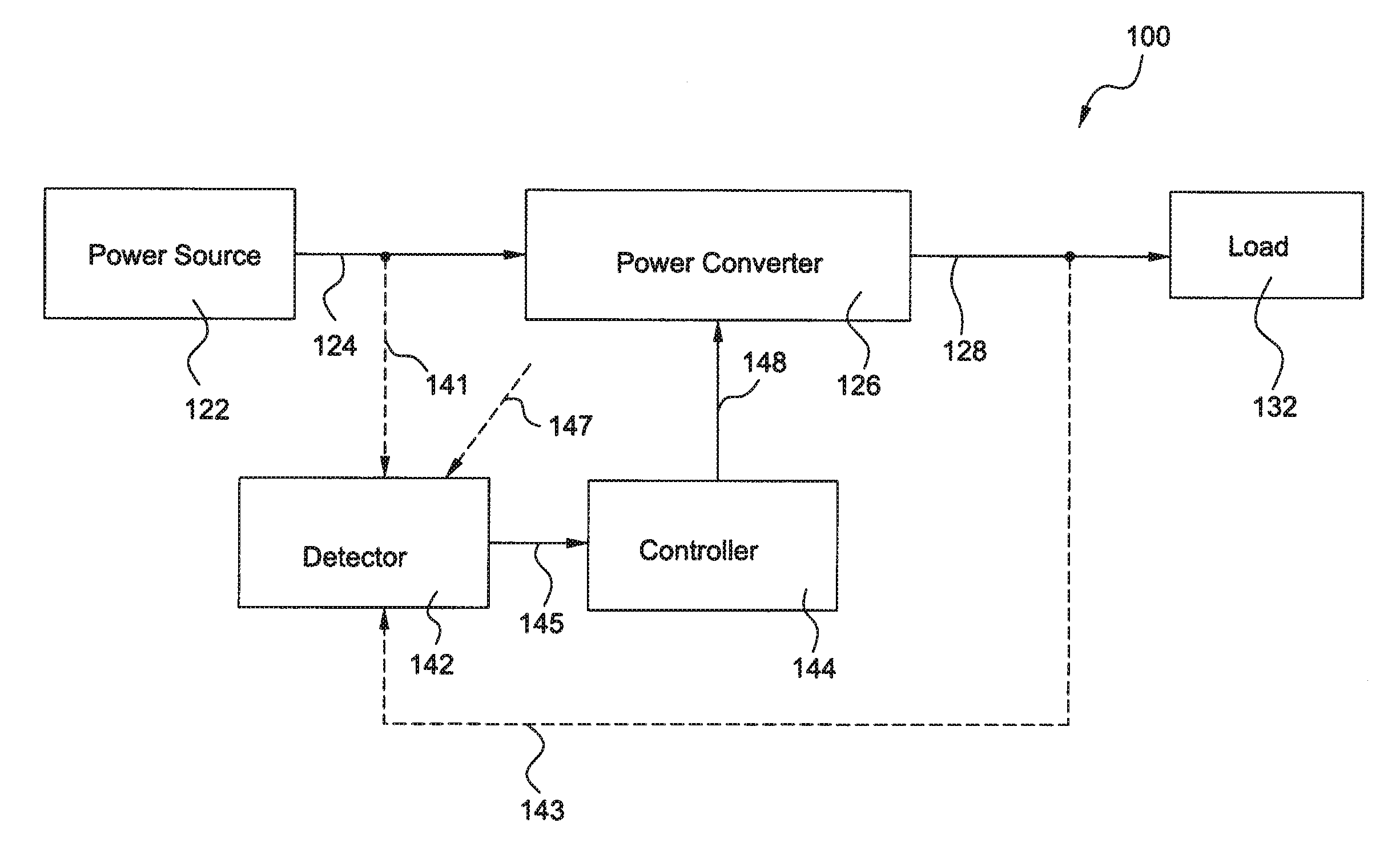
System and method for operating a DC to DC power converter
A direct current (DC) to DC power converter includes a first bus converter for converting a first DC bus voltage into a first high frequency AC voltage and a second bus converter for converting a second high frequency alternating current (AC) voltage into a second DC bus voltage. The DC to DC converter also includes a resonant circuit for coupling the first bus converter and the second bus converter and a controller for providing switching signals to the first bus converter and the second bus converter to operate the power converter in a soft switching mode. The controller includes a switching frequency controller for determining a switching frequency signal for the power converter based on a reference output current and a phase shift controller for determining a phase shift signal for the power converter. When the reference output current is lower than the a first load current value the switching frequency signal is maintained at a first switching frequency and the phase shift is determined according to the reference output current. Further, when the reference output current is above a second load current value the switching frequency signal is maintained at a second switching frequency and the phase shift is determined according to the reference output current. When the reference output current is between the first load current value and the second load current value, the switching frequency signal is adjusted according to a value of the reference output current and the phase shift is determined based on the switching frequency, the reference output current and perturbations in the output current.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Llc balancing
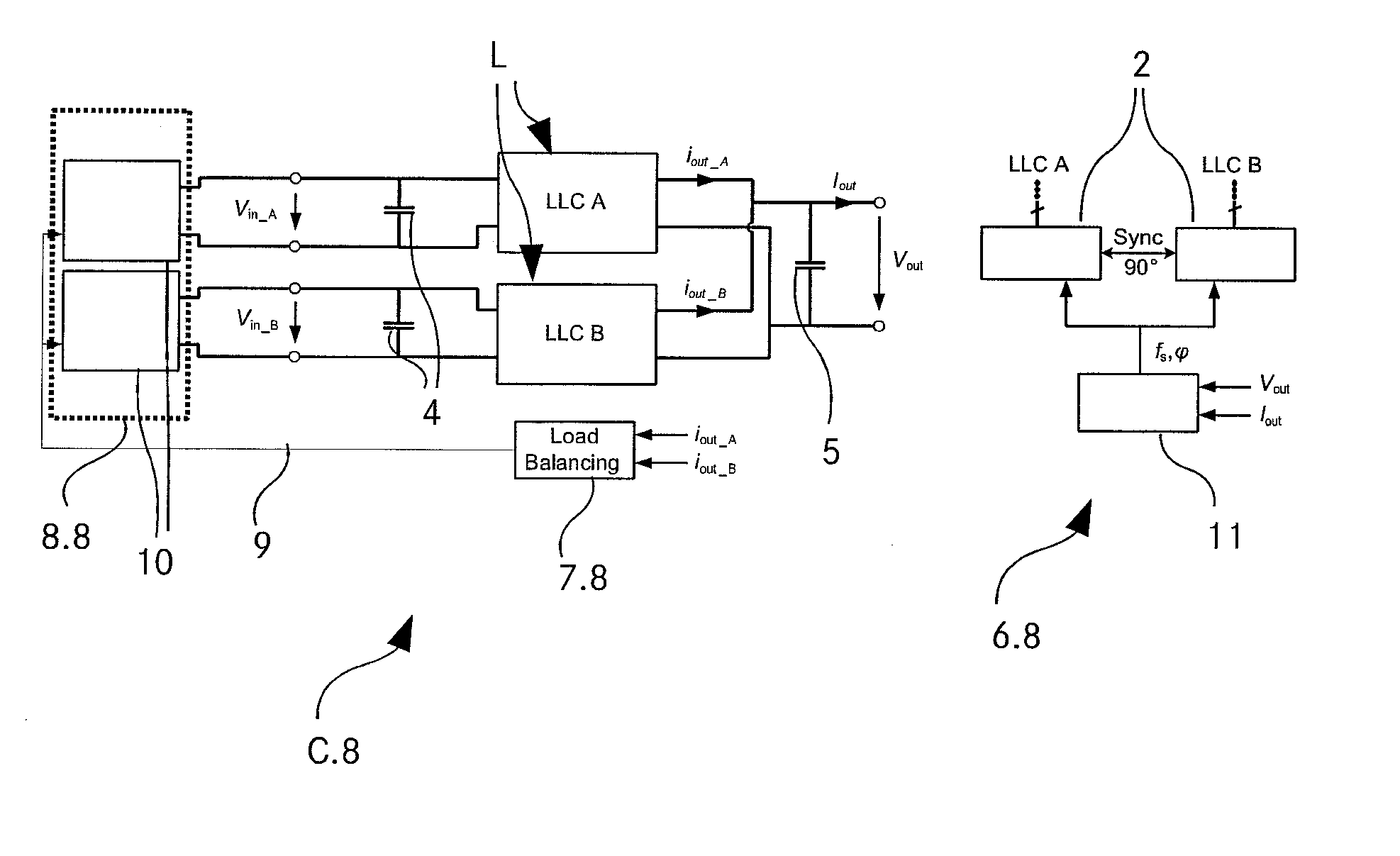
ActiveUS20140009985A1Overcome unbalanced loadingImprove reliabilityEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionPhase shift controlSwitching frequency control
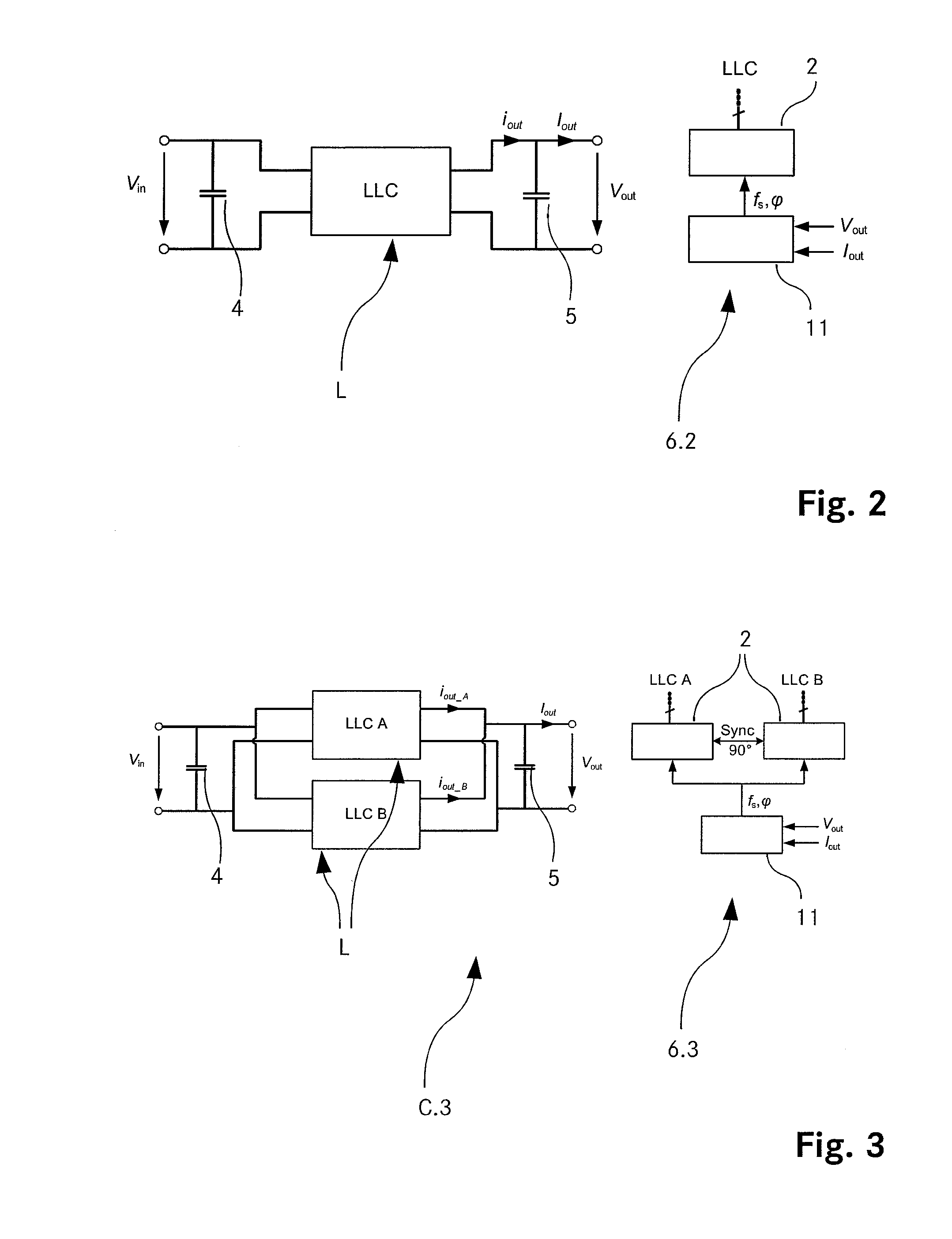
A converter arrangement (C.5, C.7, C.8, C.9, C.11, C.12) with at least two single LLC converters (L), a pulse generator (2) per single LLC converter (L) wherein each pulse generator (2) is configured to supply switching pulses to one single LLC converter (L) and an output controller (11) configured to use switching frequency control and / or phase-shift control to control the pulse generators (2) comprises a load balancing control (7.5, 7.7, 7.8, 7.9, 7.11, 7.12) for overcoming unbalanced loading of the converter arrangement (C.5, C.7, C.8, C.9, C.11, C.12).
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) PUBLIC CO LTD
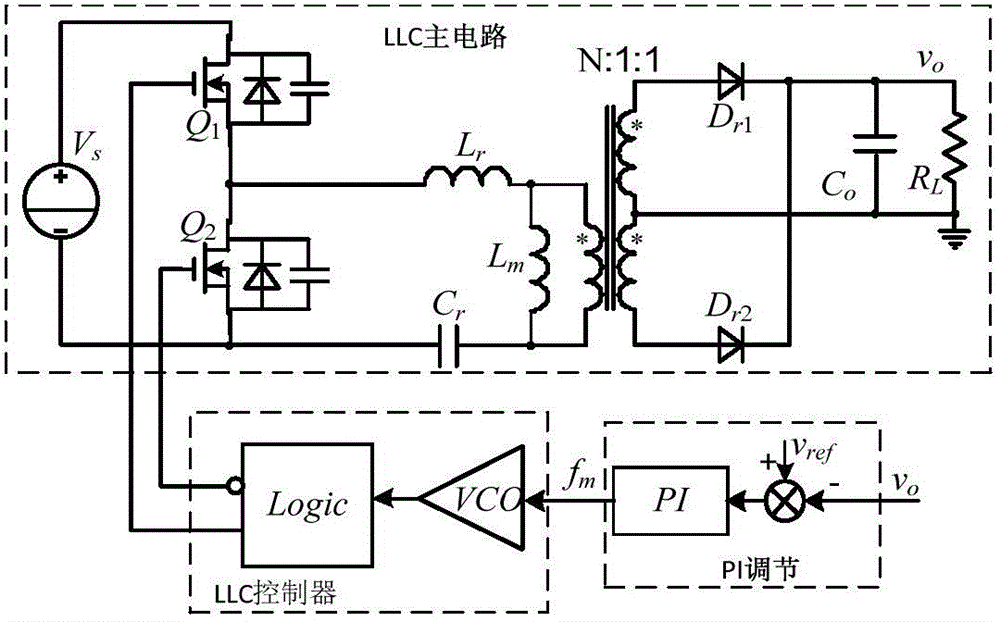
Resonant converting device
ActiveCN103840646AEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalSwitching frequency control
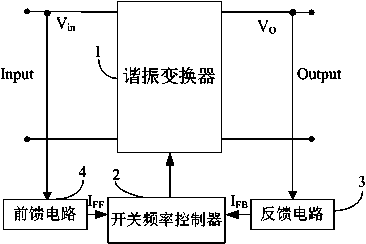
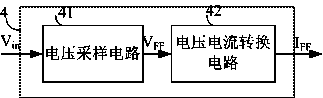
The invention discloses a resonant converting device. A feedforward circuit is added into the device. The feedforward comprises a voltage sampling module and a voltage-current conversion module. The voltage sampling module samples a ripple of an input voltage of a resonant converter and provides a sampled value for the voltage-current conversion module, which converts the sampled value into a current signal. The ripple of the input voltage of the device is sampled and converted into the current signal representing a control signal for controlling switch frequency, and the current signal is fed forward to a switch frequency controller for controlling the direction of change of an output gain to be opposite to the direction of fluctuation of the input voltage, so that the device can filter the ripple, an output voltage is not affected by the ripple of the input voltage, and the ripple is relatively small.
Owner:FSP POWERLAND TECH
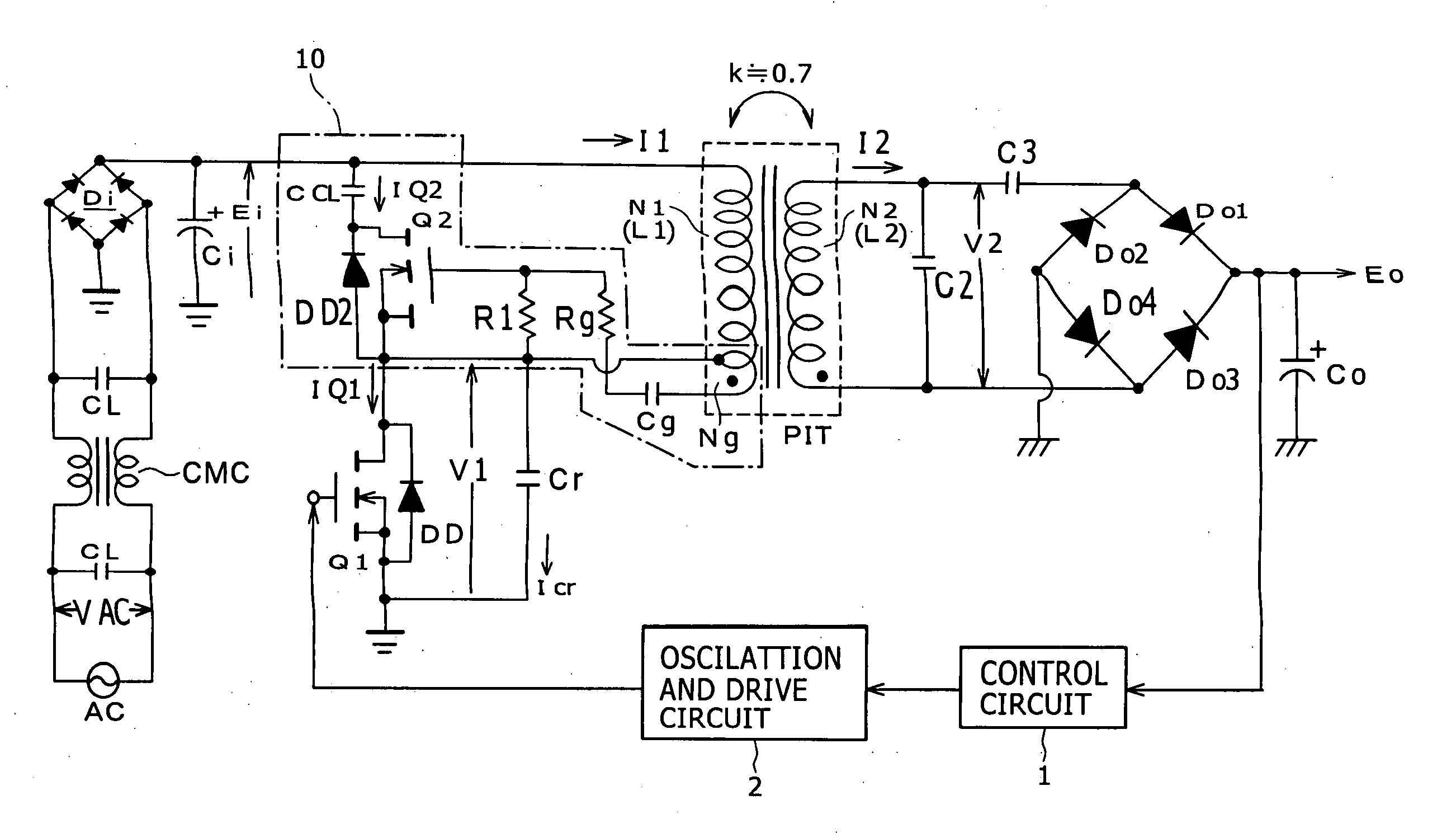
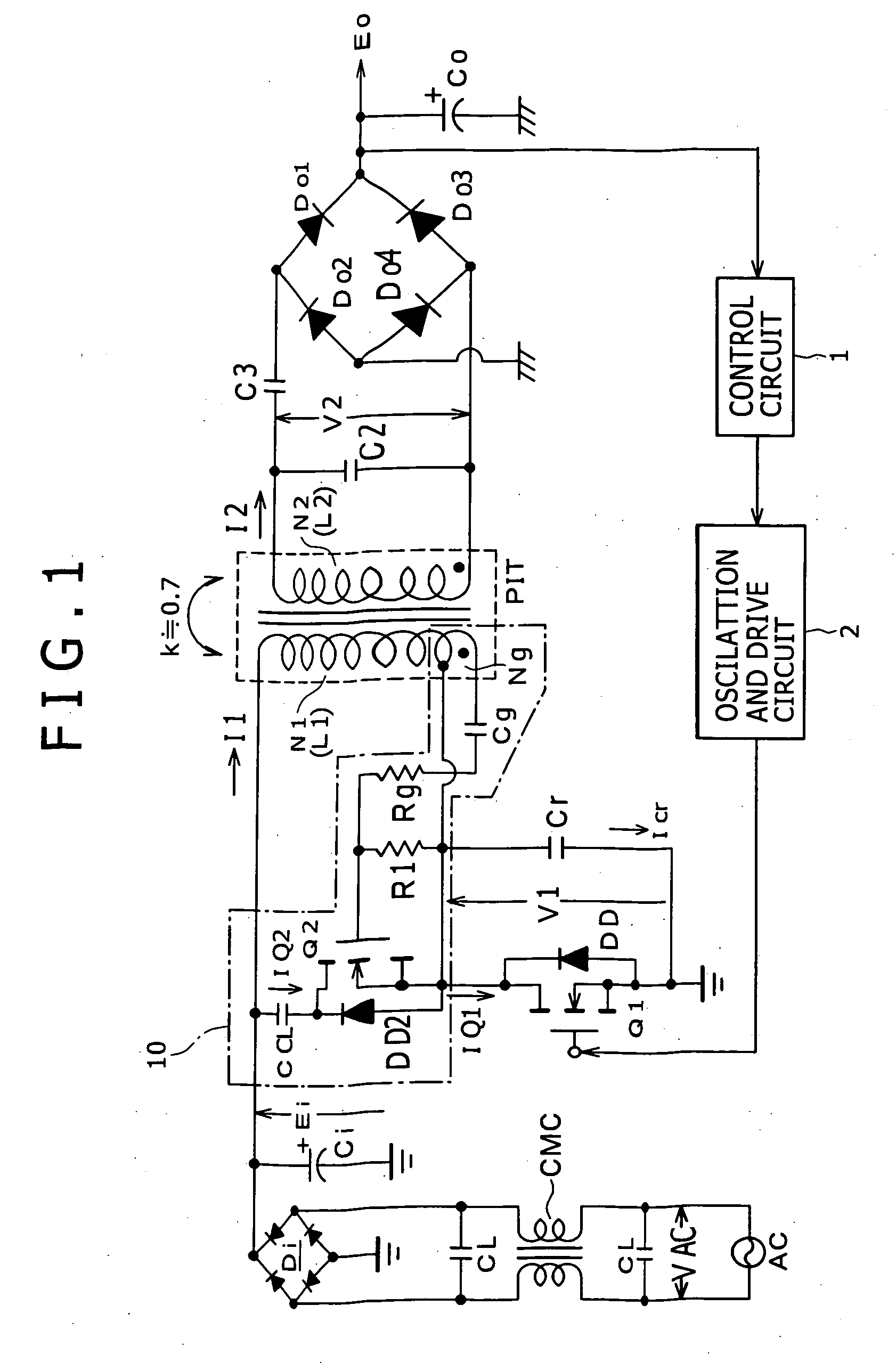
Switching power supply circuit
InactiveCN1750376AImprove responsibilityLower levelEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionElectromagnetic couplingResonance
A power supply circuit is disclosed which performs constant voltage control by switching frequency control and is ready for a wide range while the necessary control range of the switching frequency control is reduced. The circuit includes a primary side series resonance circuit forming a current resonance type converter, and a secondary side series resonance circuit formed from secondary windings and secondary side series resonance capacitors while a coupling type resonance circuit by electromagnetic coupling of an insulating converter transformer is formed. To obtain a single-humped characteristic from the coupling type resonance circuit, a gap of approximately 1.6 mm is formed in the core of the insulating converter transformer so as to achieve a coupling coefficient of 0.65 or less. A secondary side DC output voltage is produced from outputs of the secondary windings so as to cope with a heavy load condition.
Owner:SONY CORP
System and method for converter switching frequency control
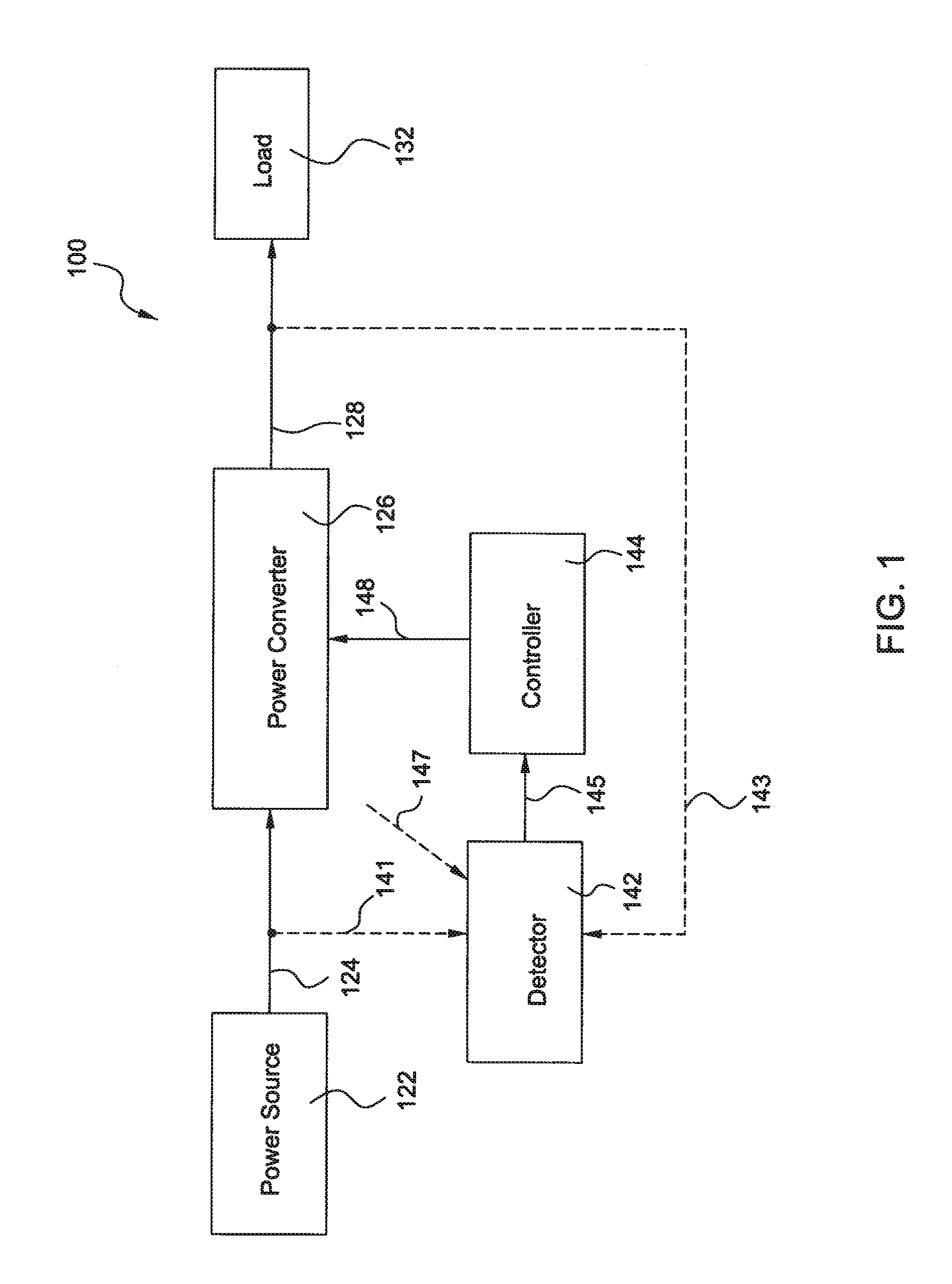
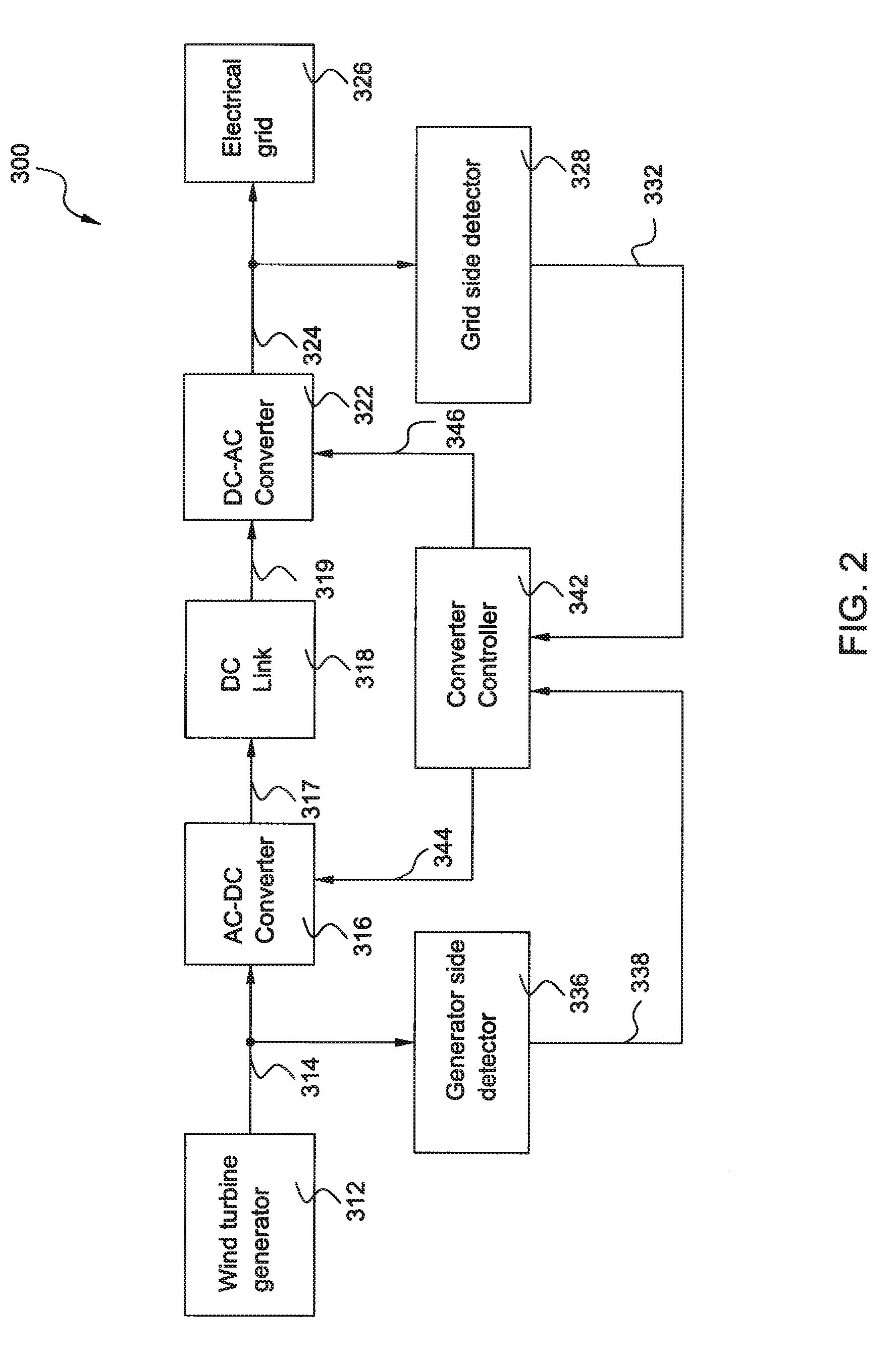
ActiveUS9190923B2Wind motor controlEfficient power electronics conversionOperational systemControl system
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
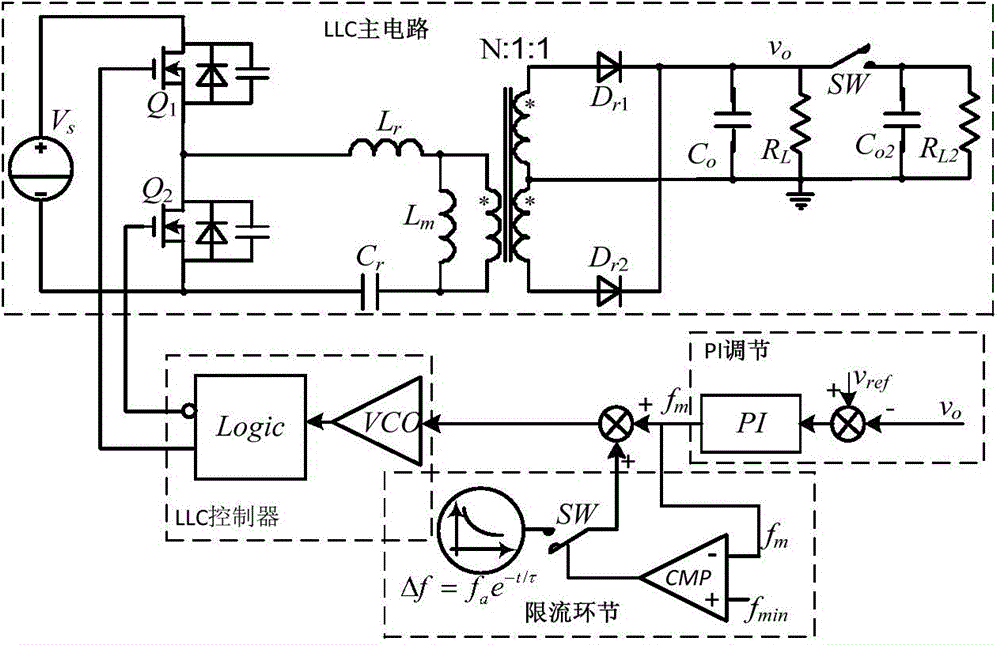
Current-limiting method and current-limiting circuit of LLC resonant converter
ActiveCN104638895APrevent misoperation of overcurrent protectionSampling interference is smallDc-dc conversionEnergy industryCapacitanceCurrent limiting
The invention discloses a current-limiting method and a current-limiting circuit of an LLC resonant converter. According to the current-limiting method, the controlled quantity of switching frequency output in a PI adjusting step is detected so as to judge whether a frequency modulation step is added for current-limiting operation. The provided current-limiting circuit comprises a comparing trigger circuit and a current injection circuit. The current-limiting circuit can correspondingly adjust the switching frequency of the LLC resonant converter under the working condition of abruptly adding resistance-capacitance load, thus limiting the current shock of a resonant circuit, protecting the power element of the resonant circuit and solving the false triggering problem of overcurrent protection. According to the current-limiting method and the current-limiting circuit for frequency modulation, the structure is simple, the cost is low, the response speed of frequency modulation is high under the condition of abruptly adding resistance-capacitance load, and the current of the resonant circuit can be limited in an expected current set value.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Thermal controller
InactiveUS20140225659A1Improve reliabilityUtilization capacitySolid-state devicesElectronic switchingJunction temperatureSwitching frequency control
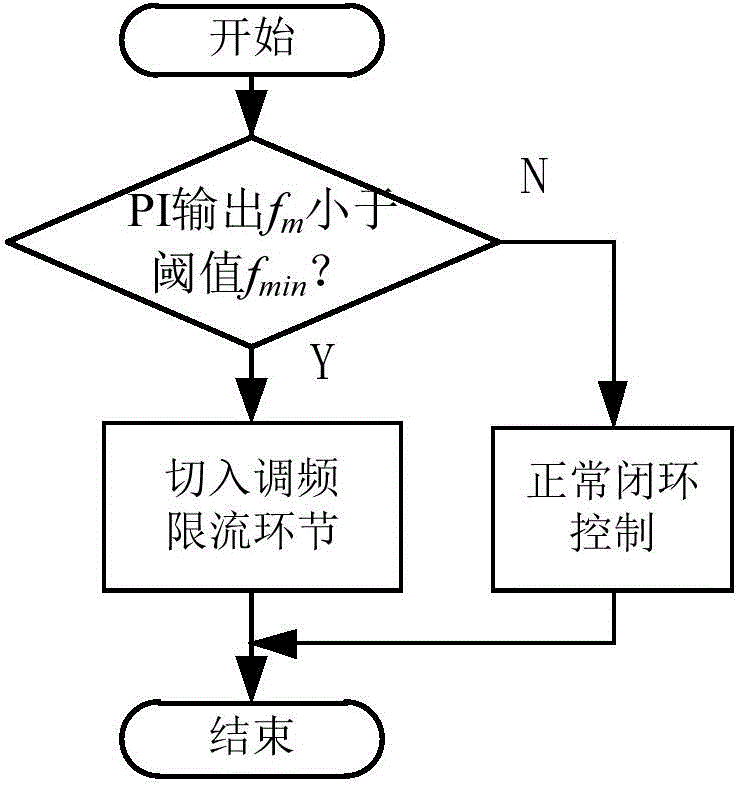
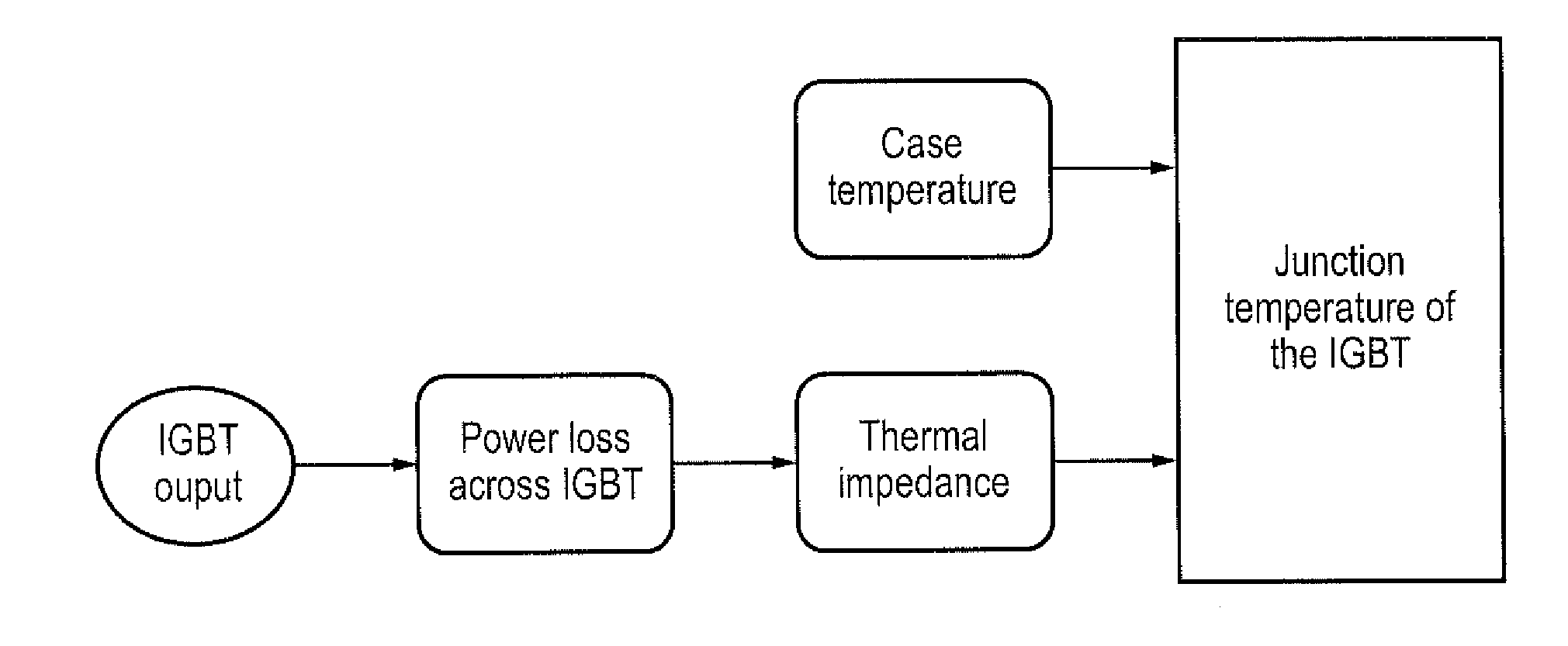
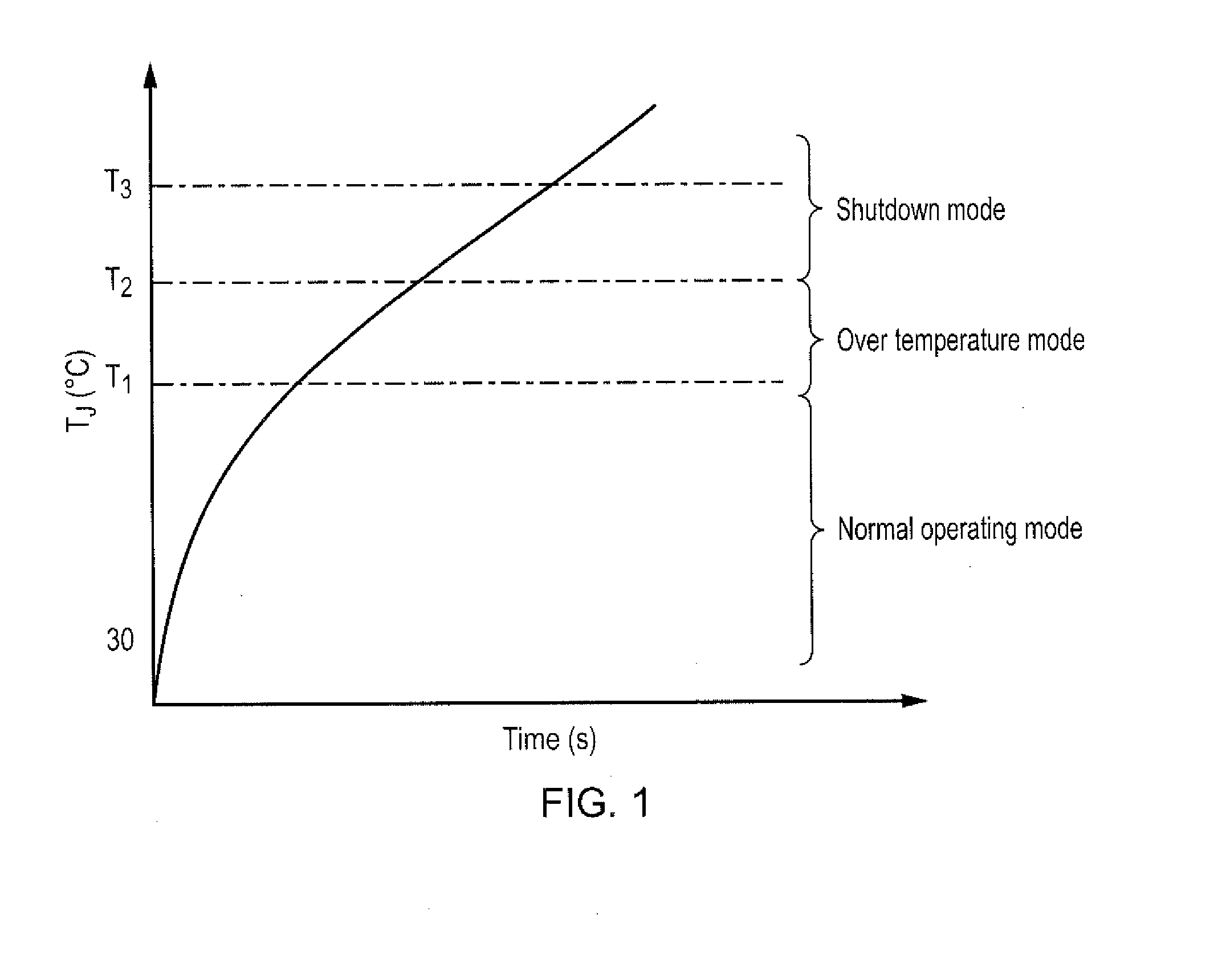
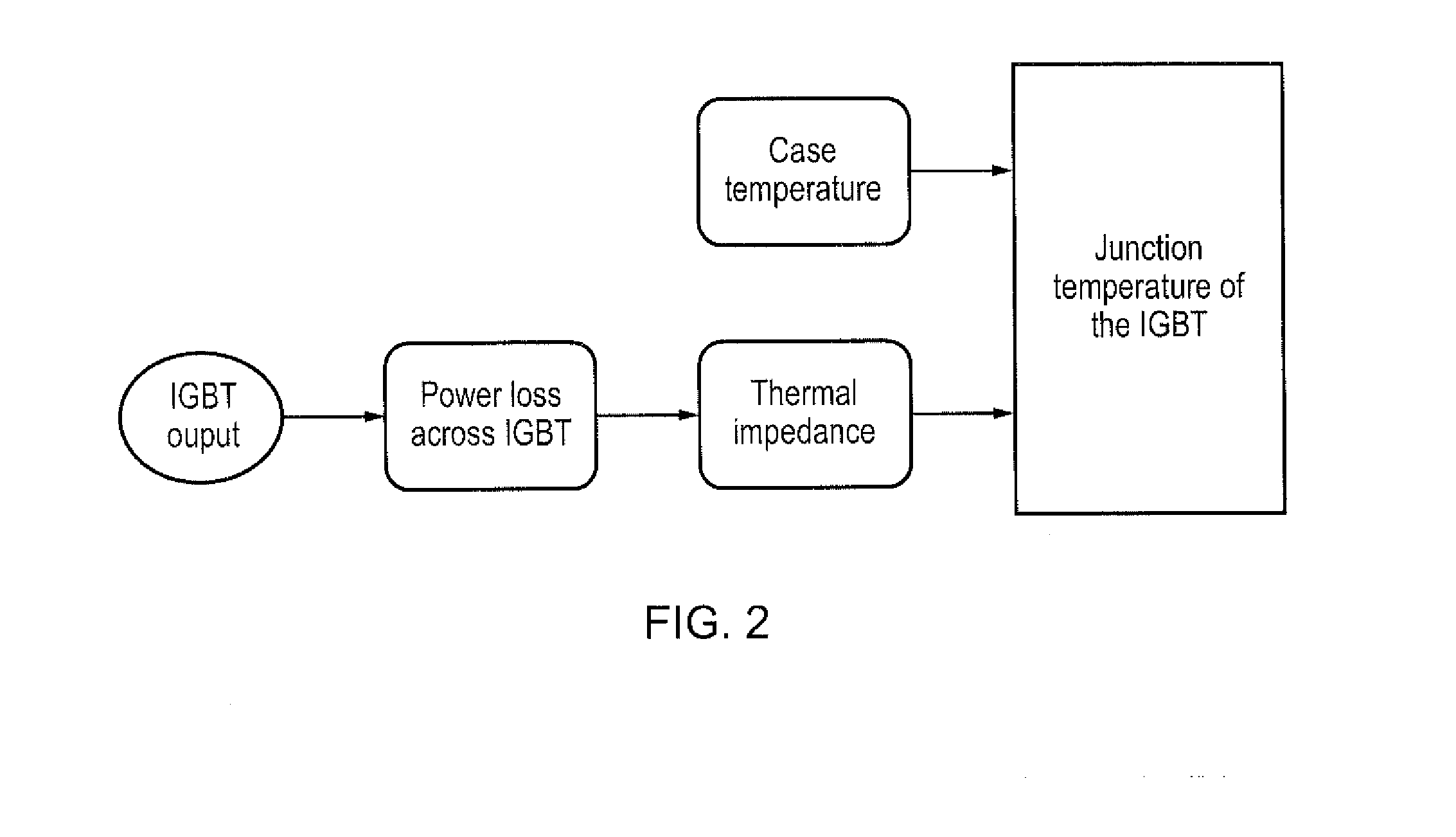
A thermal controller for driving a gate control unit of a gate-driven semiconductor switching device, the thermal controller comprising a junction temperature estimation module for generating an estimated junction temperature for the switching device, a gate voltage control module for modifying a gate voltage of the switching device, a switching frequency control module for modifying a switching frequency of the switching device, and a duty cycle control module for modifying the duty cycle of the switching device. In use, the thermal controller is adapted to activate one of the gate voltage control module, switching frequency control module and duty cycle control module dependent upon the estimated junction temperature in order to maintain the actual junction temperature below a pre-determined limit.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Panoramic photographing system on automobile
InactiveCN103312987ALow costEasy maintenanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSwitching frequency controlImaging processing
The invention discloses a panoramic photographing system on an automobile. The panoramic photographing system comprises a high-speed camera, a camera support, a camera electronic switch, an automobile speed synchronous controller, a motor, a motor controller and an image processing module. The high-speed camera can take a preset quantity of pictures within a preset angle range by the aid of the camera electronic switch. The automobile speed synchronous controller is used for regulating power outputted by the motor controller according to a current automobile speed. The high-speed camera takes the pictures and then is closed according to a preset switch frequency under the control of the camera electronic switch, and the switch frequency is relevant to the rotation speed of the motor. The image processing module digitally combines the preset quantity of pictures within the preset angle range into panoramic pictures, and the panoramic pictures are stored in a memory.
Owner:KAIPING ZHONGLV IND
DC-DC converter
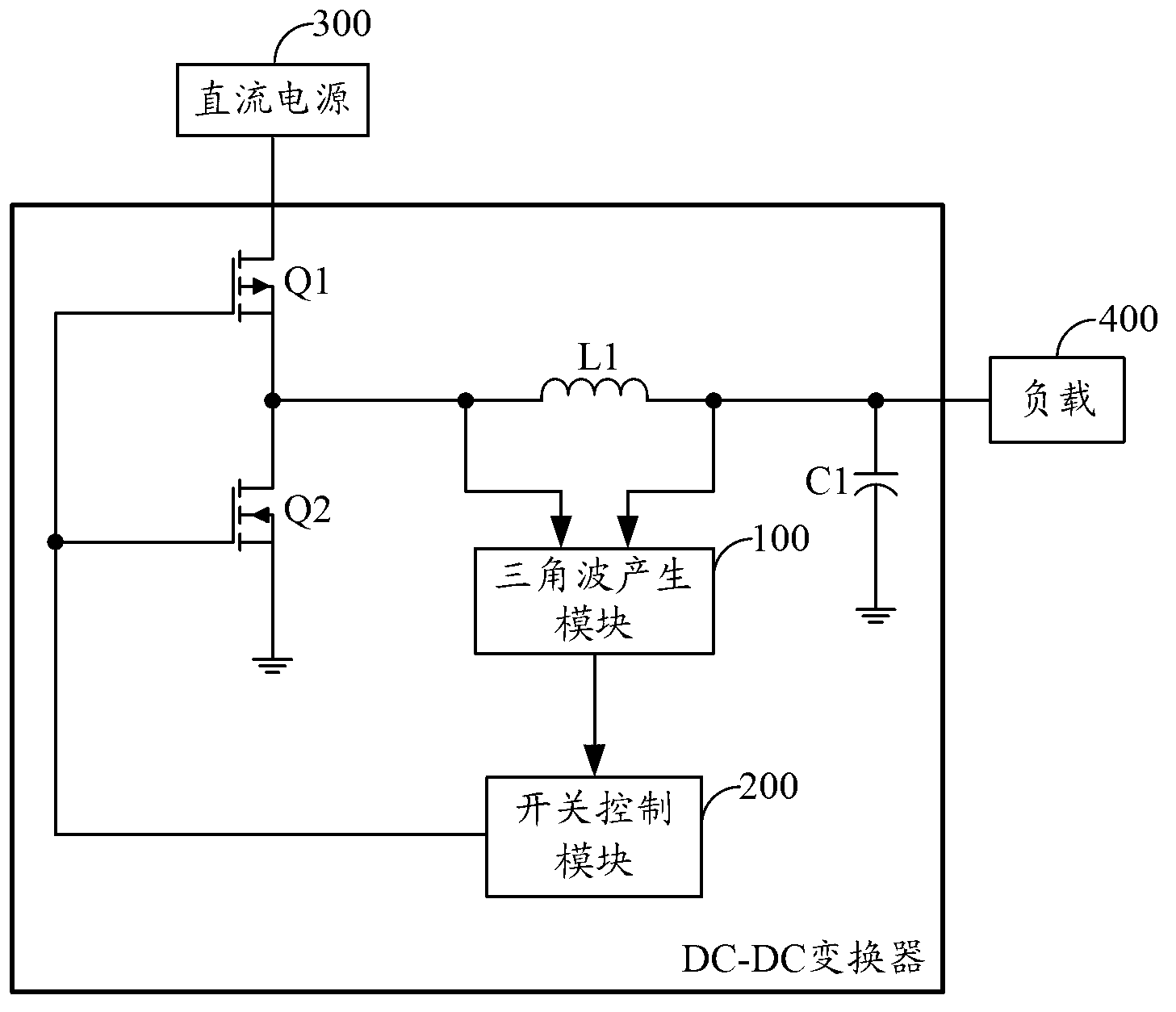
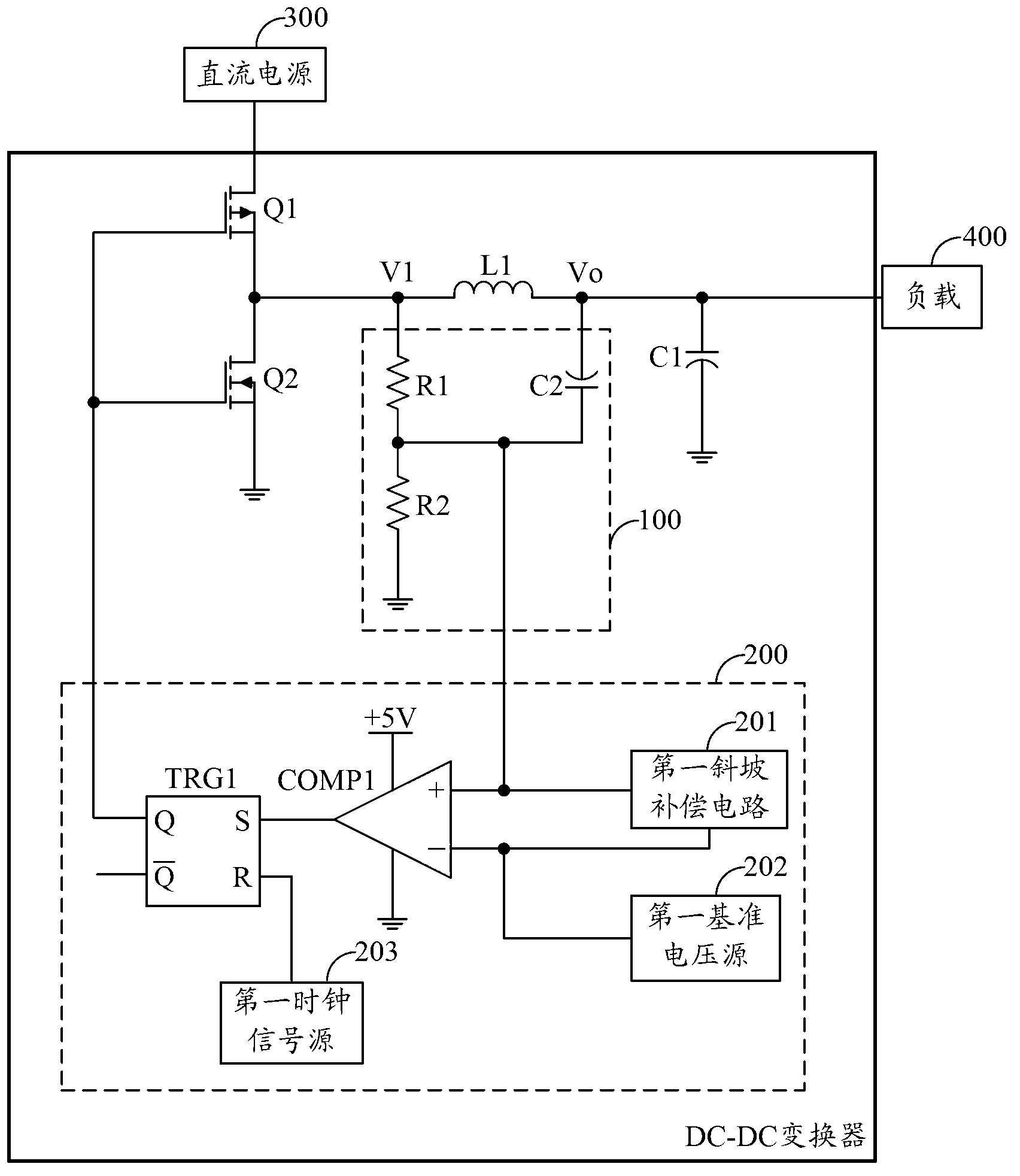
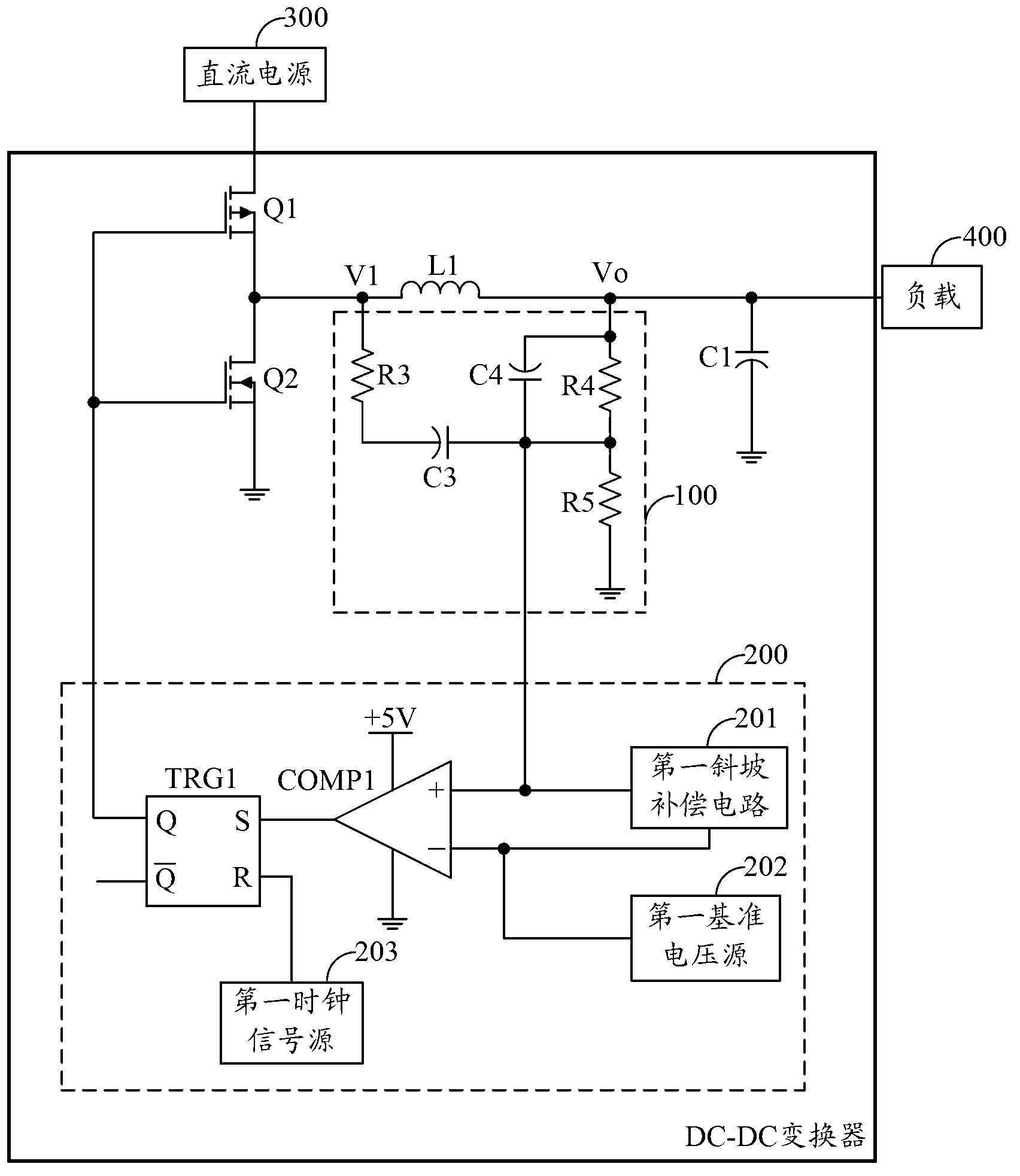
ActiveCN103227566ASimple circuit structureImprove noise immunityDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringP channel
The invention is applied to the field of direct current (DC) conversion, and provides a DC-DC converter. The DC-DC converter comprising a triangular wave generation module and a switch control module is adopted, the triangular wave generation module generates a triangular wave signal according to voltage across an energy storage inductor L1, and the switch control module outputs a control level according to a clock signal generated in the switch control module and the triangular wave signal to control a PMOS (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) power tube and an NMOS (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) power tube to perform switching operation according to the preset switching frequency, so that fixed switching frequency control on the PMOS power tube and the NMOS power tube is achieved; a circuit structure of the DC-DC converter is simplified on the premise that voltage conversion is performed on DC; the noise immunity is raised; a packaging area occupied by the DC-DC converter in a chip integration design process is reduced; and the cost of a chip is further lowered.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com