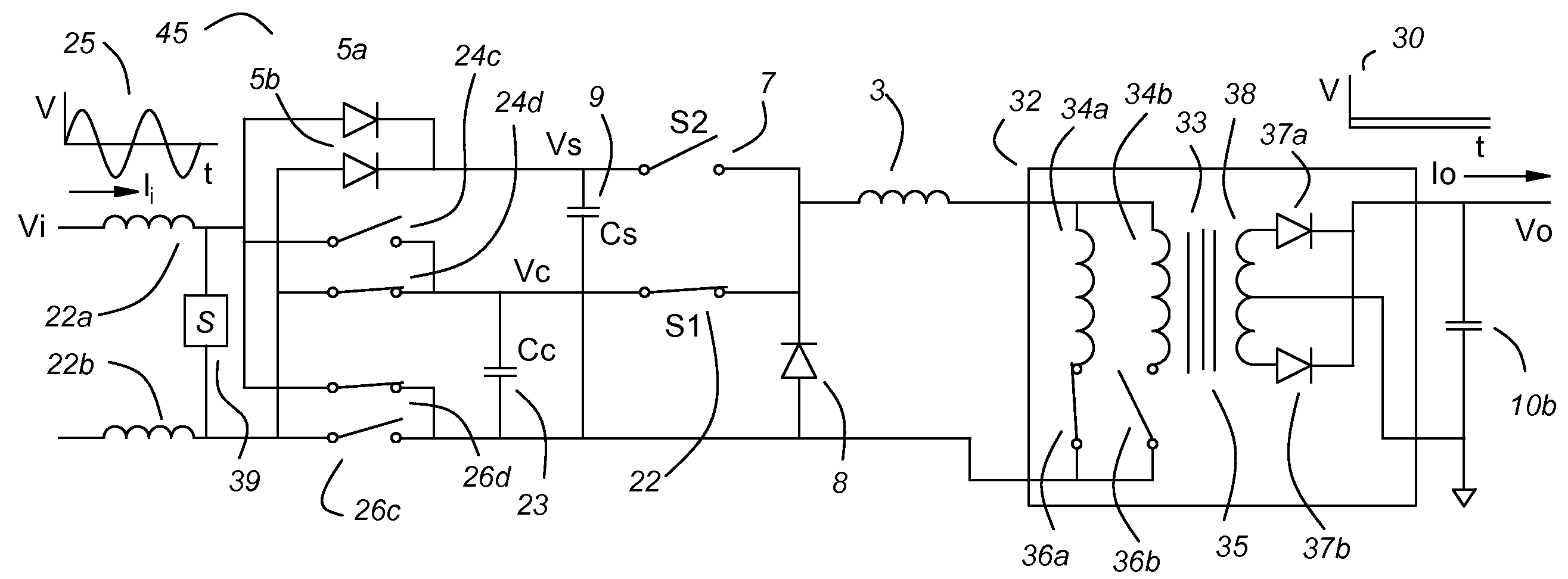
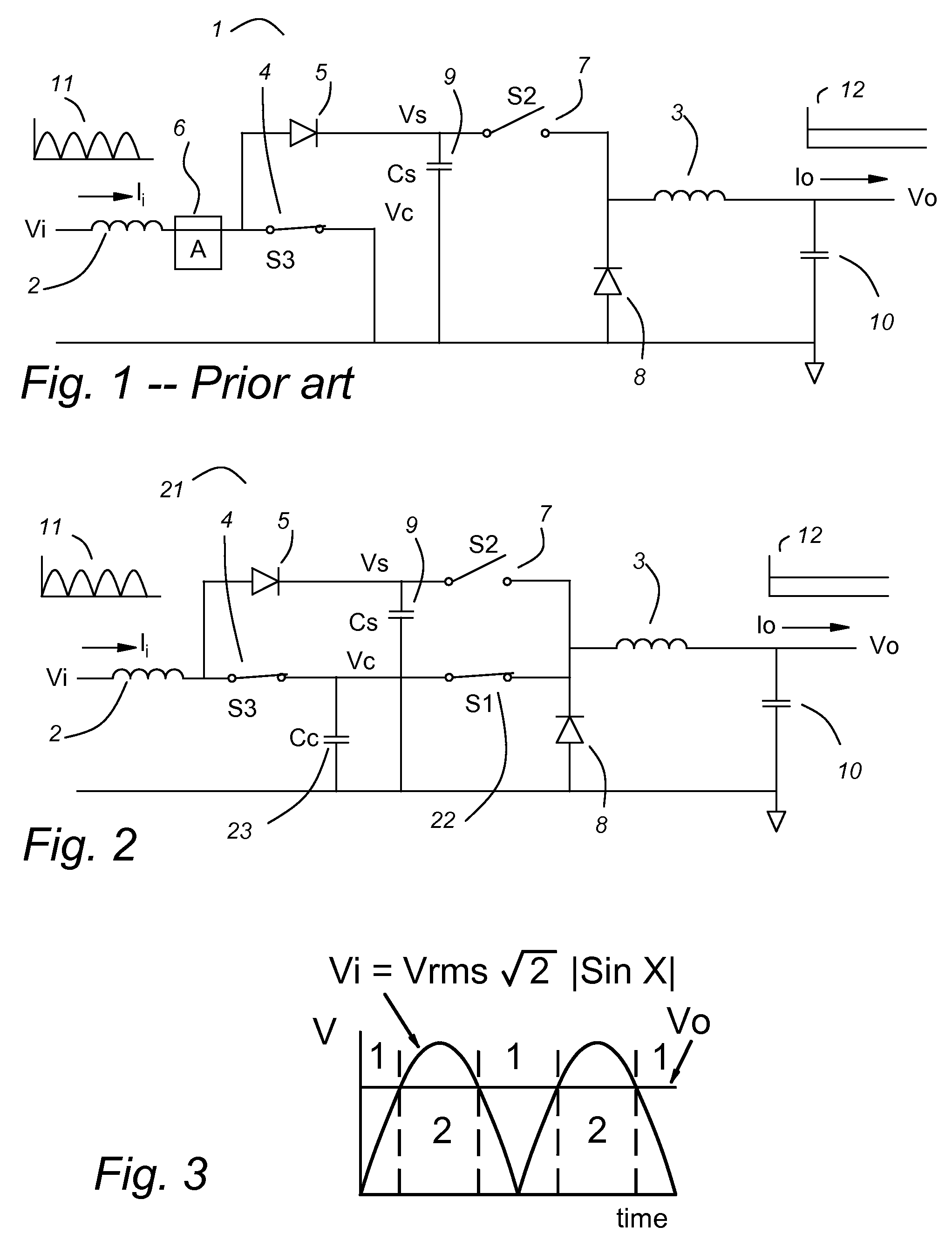
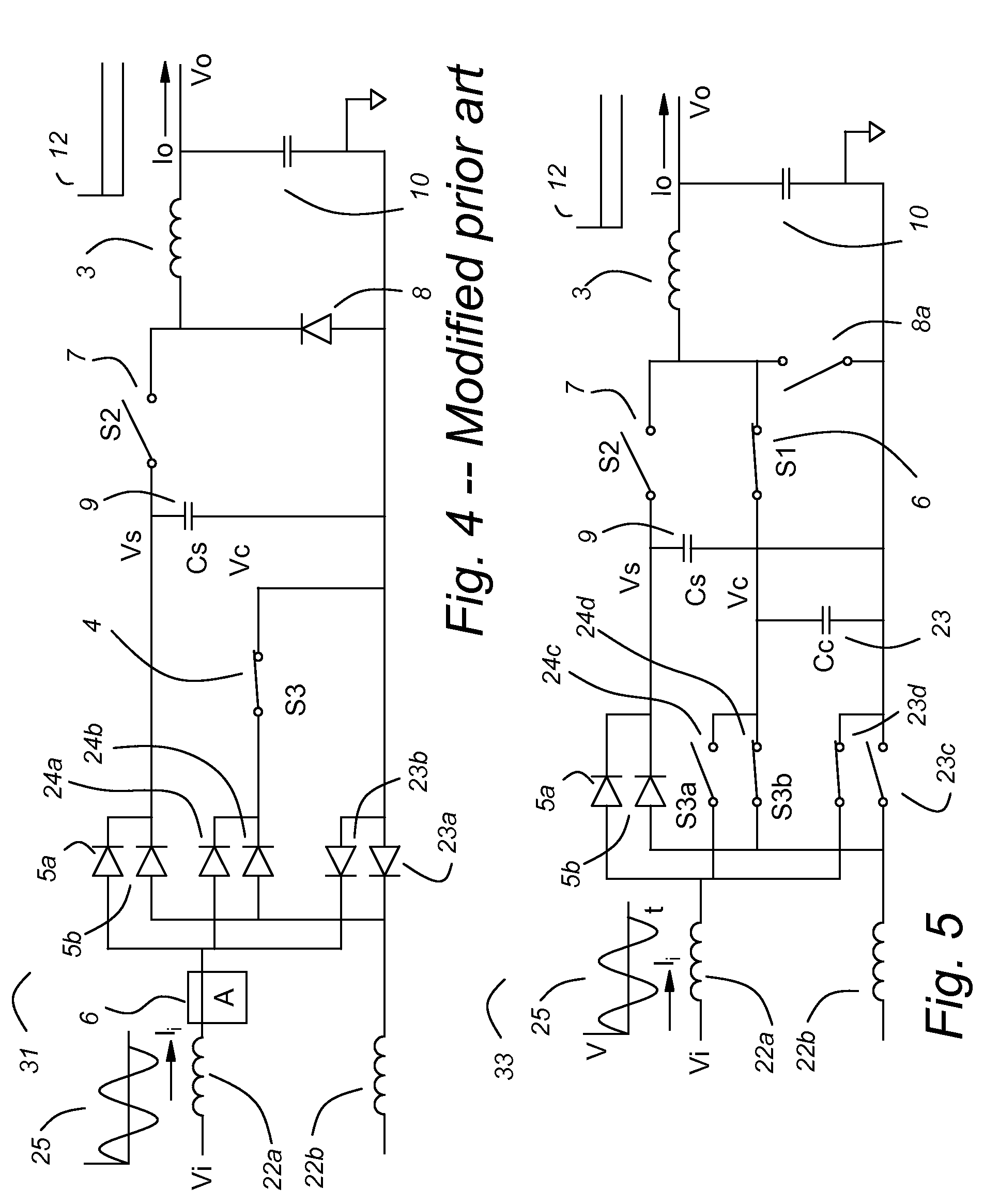
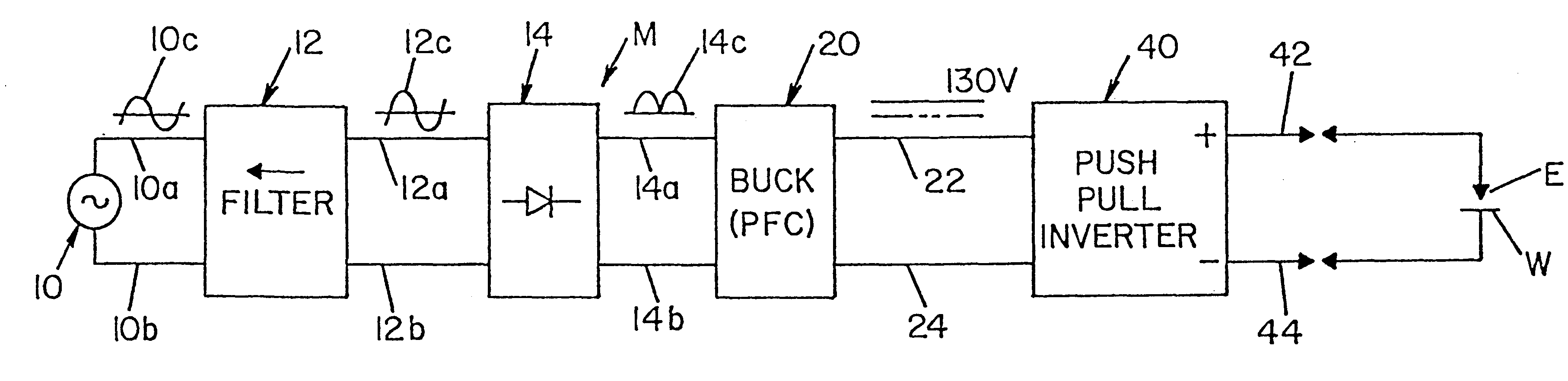
Patents
Literature
1146 results about "DC-to-DC converter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
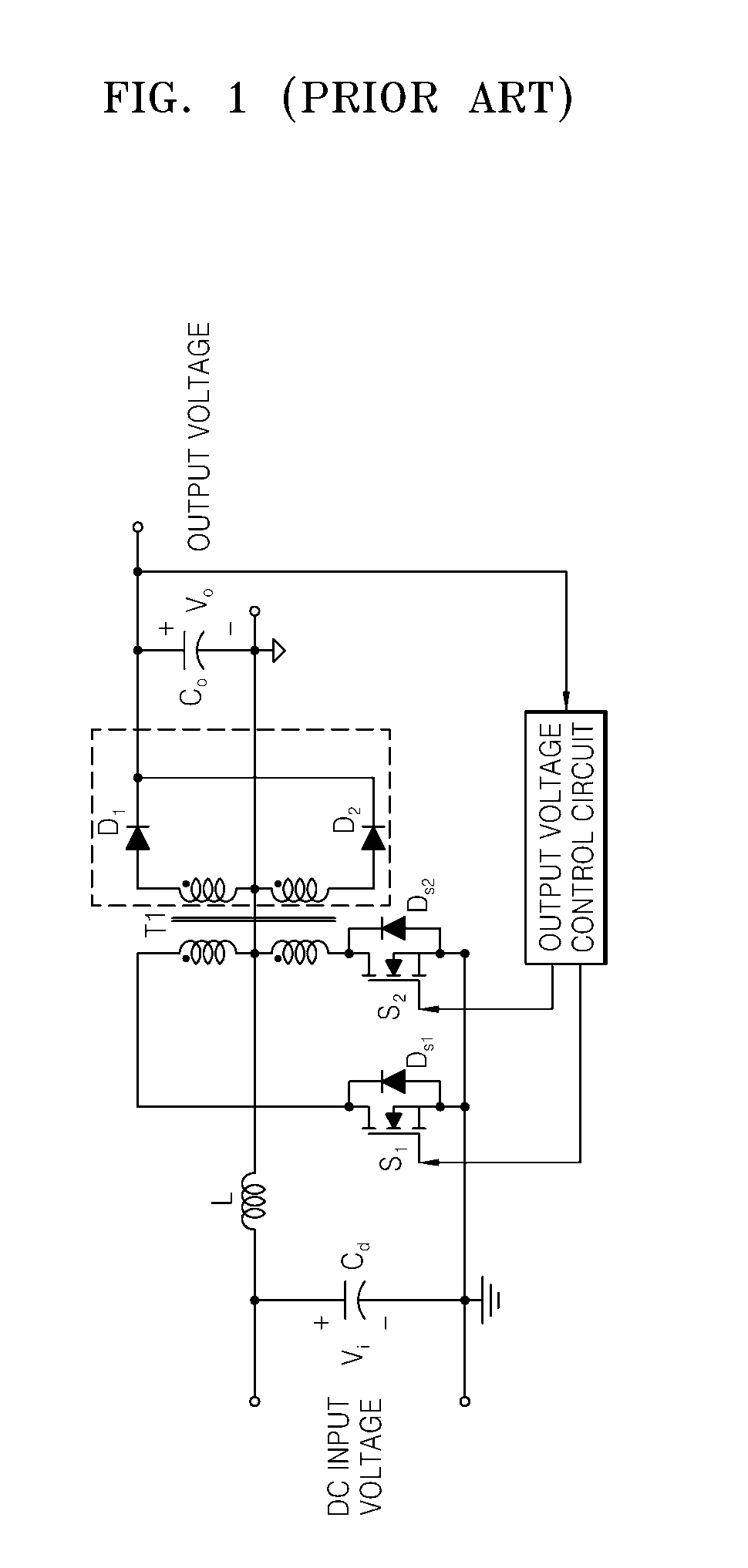
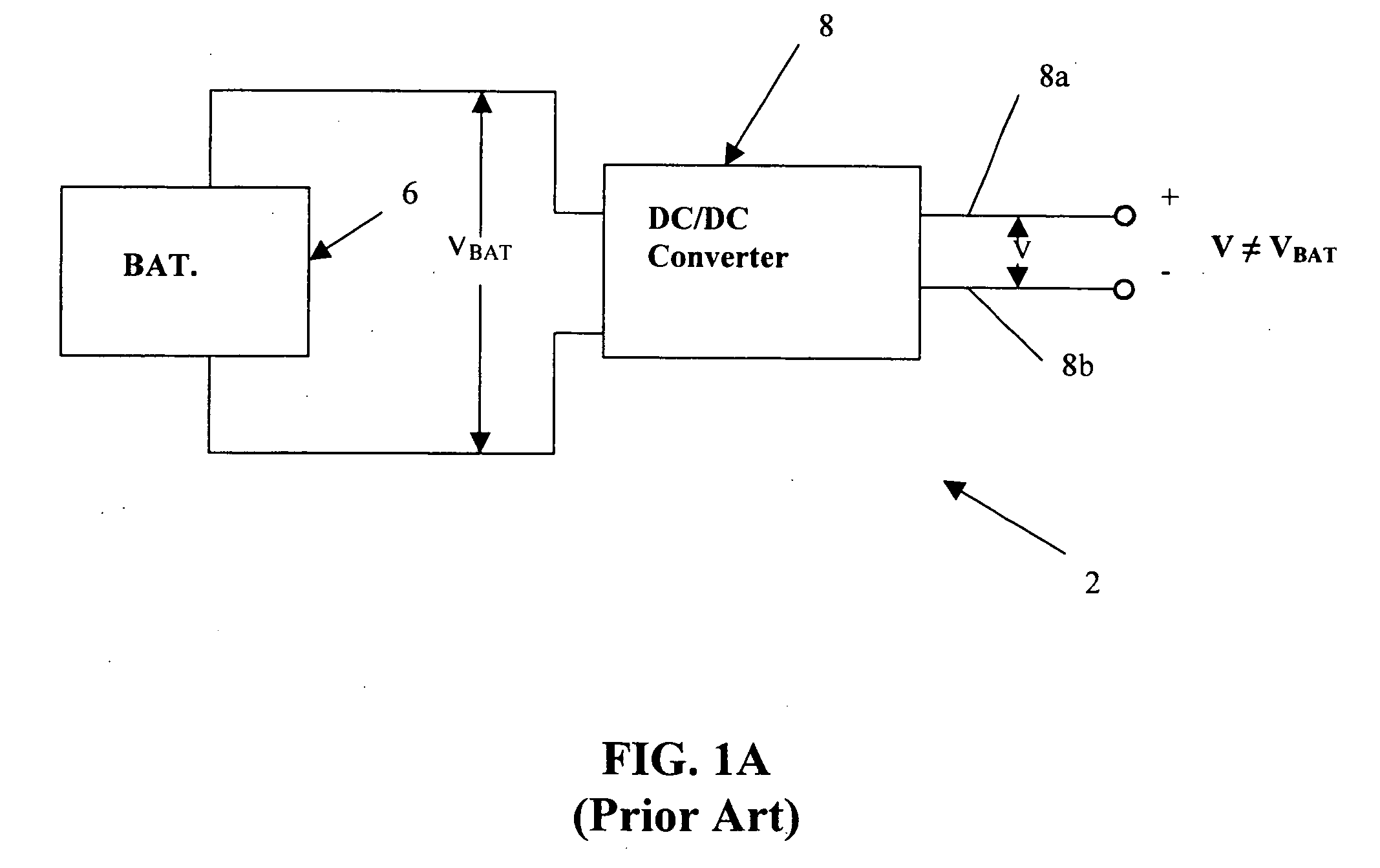
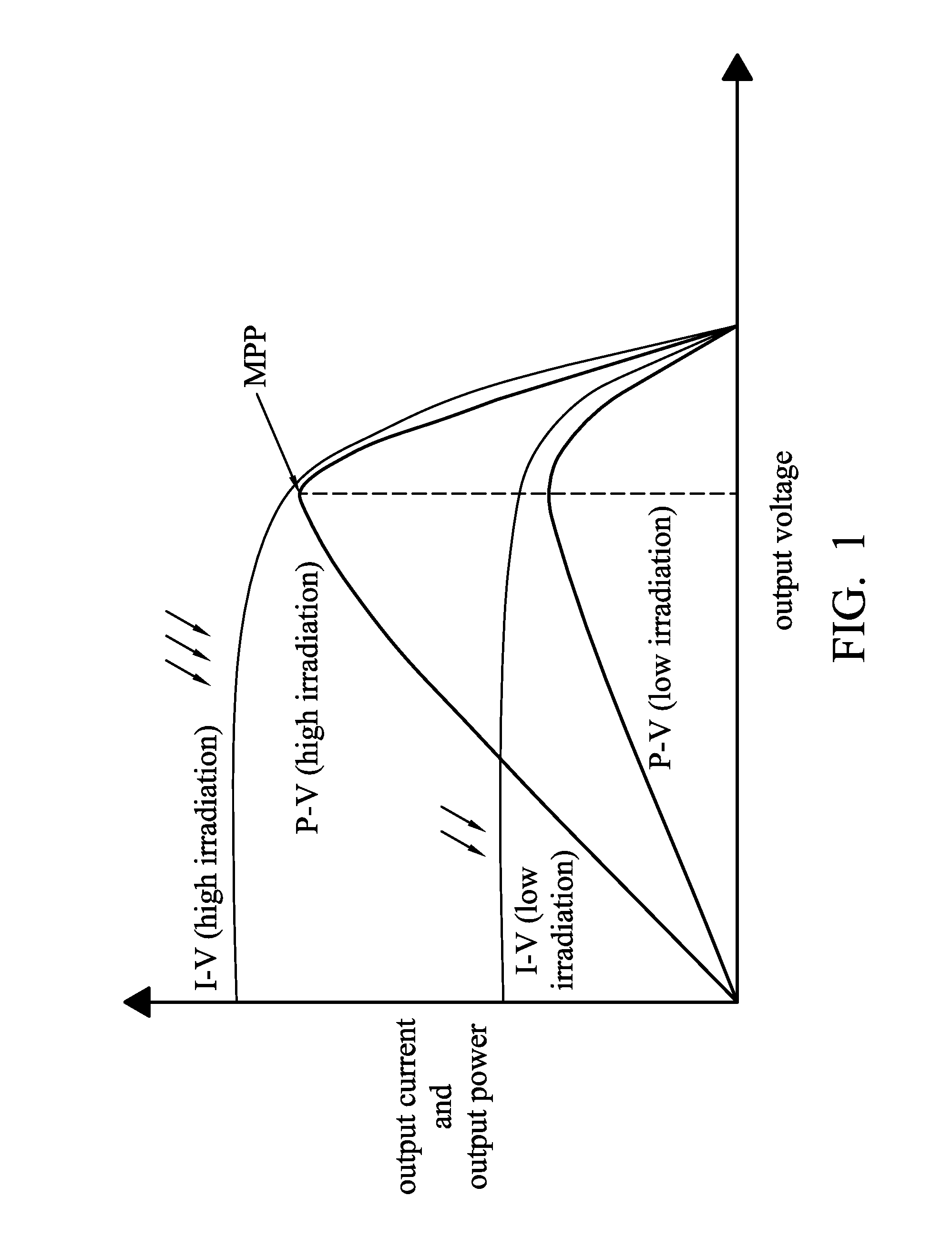
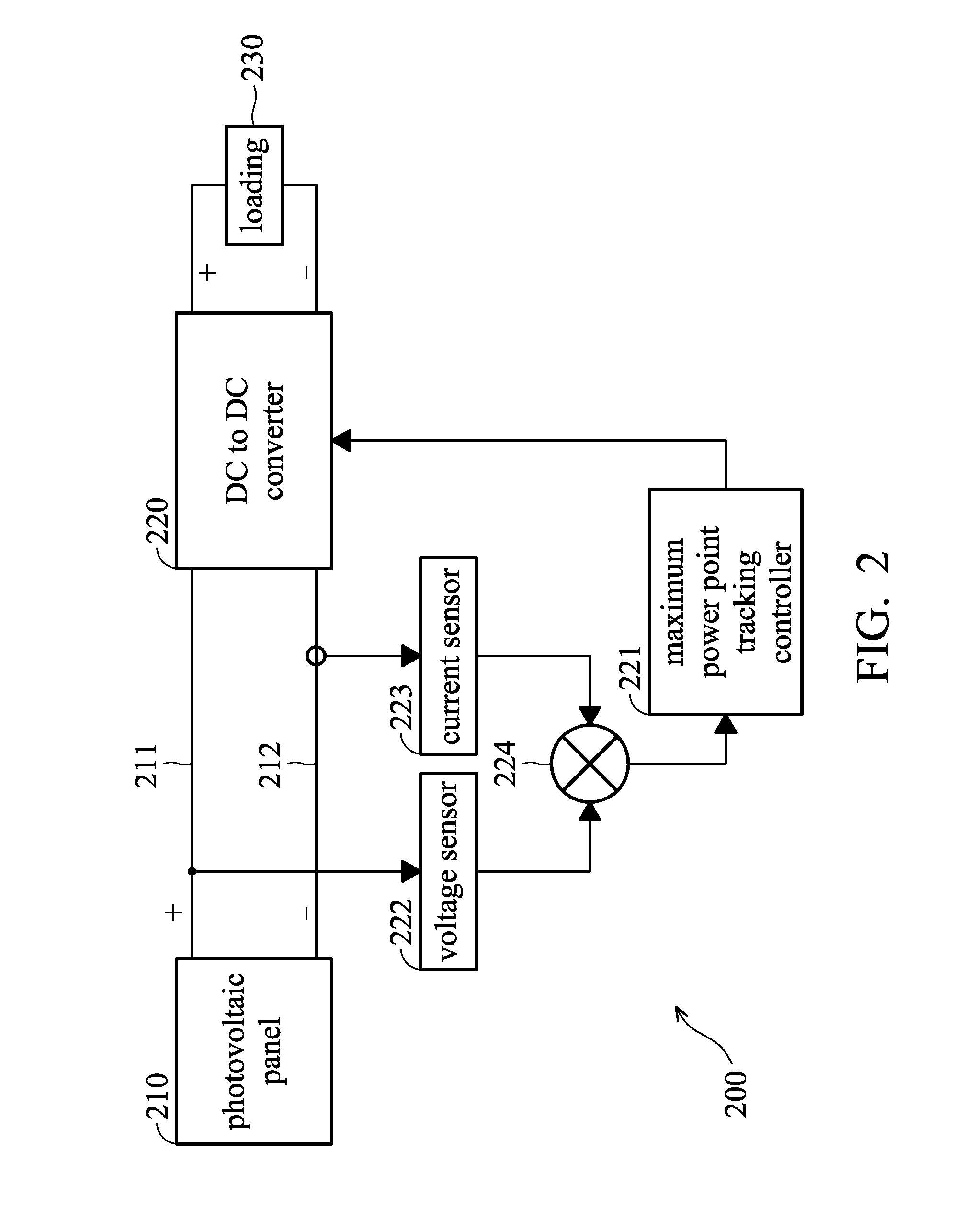
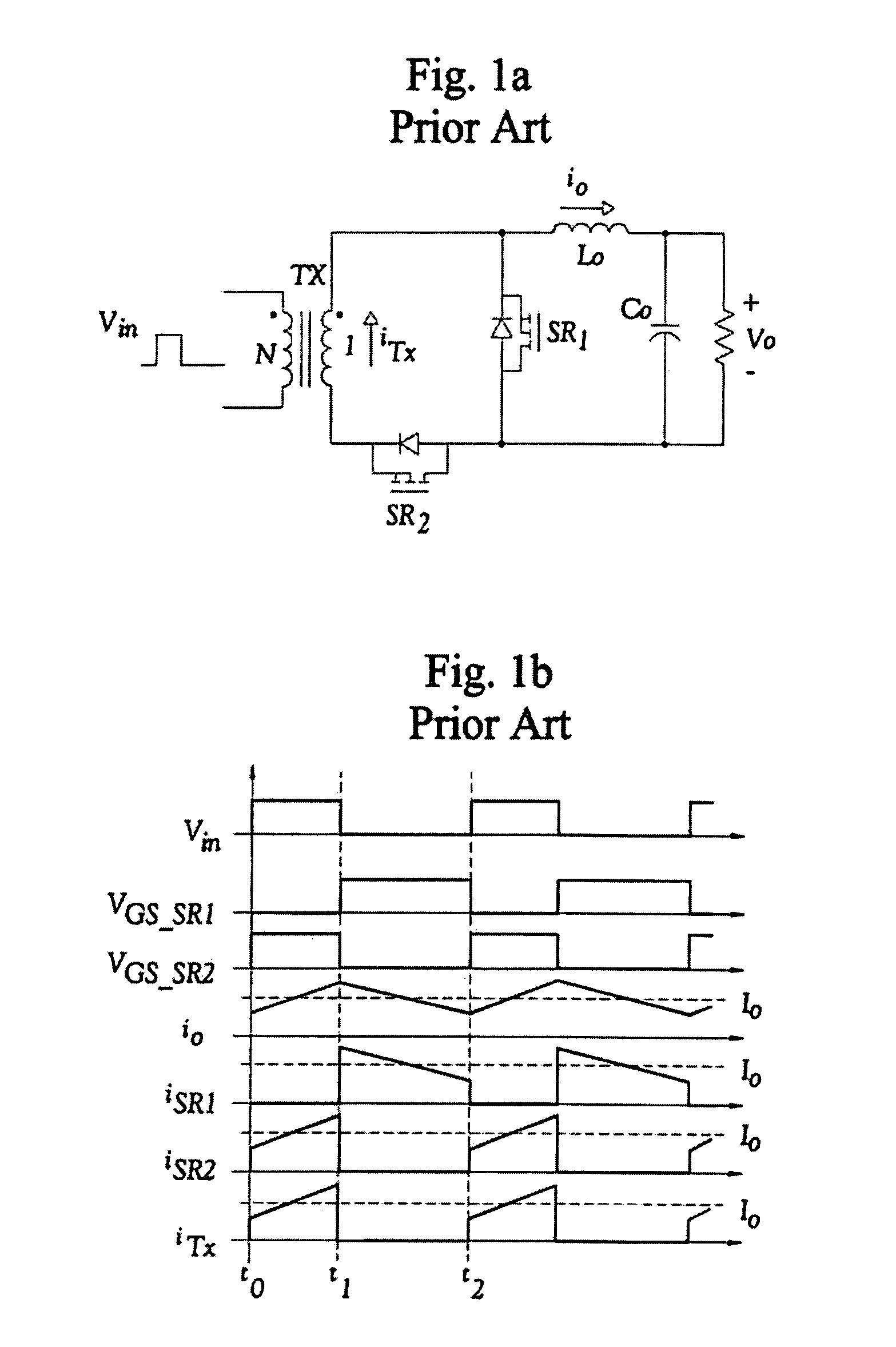
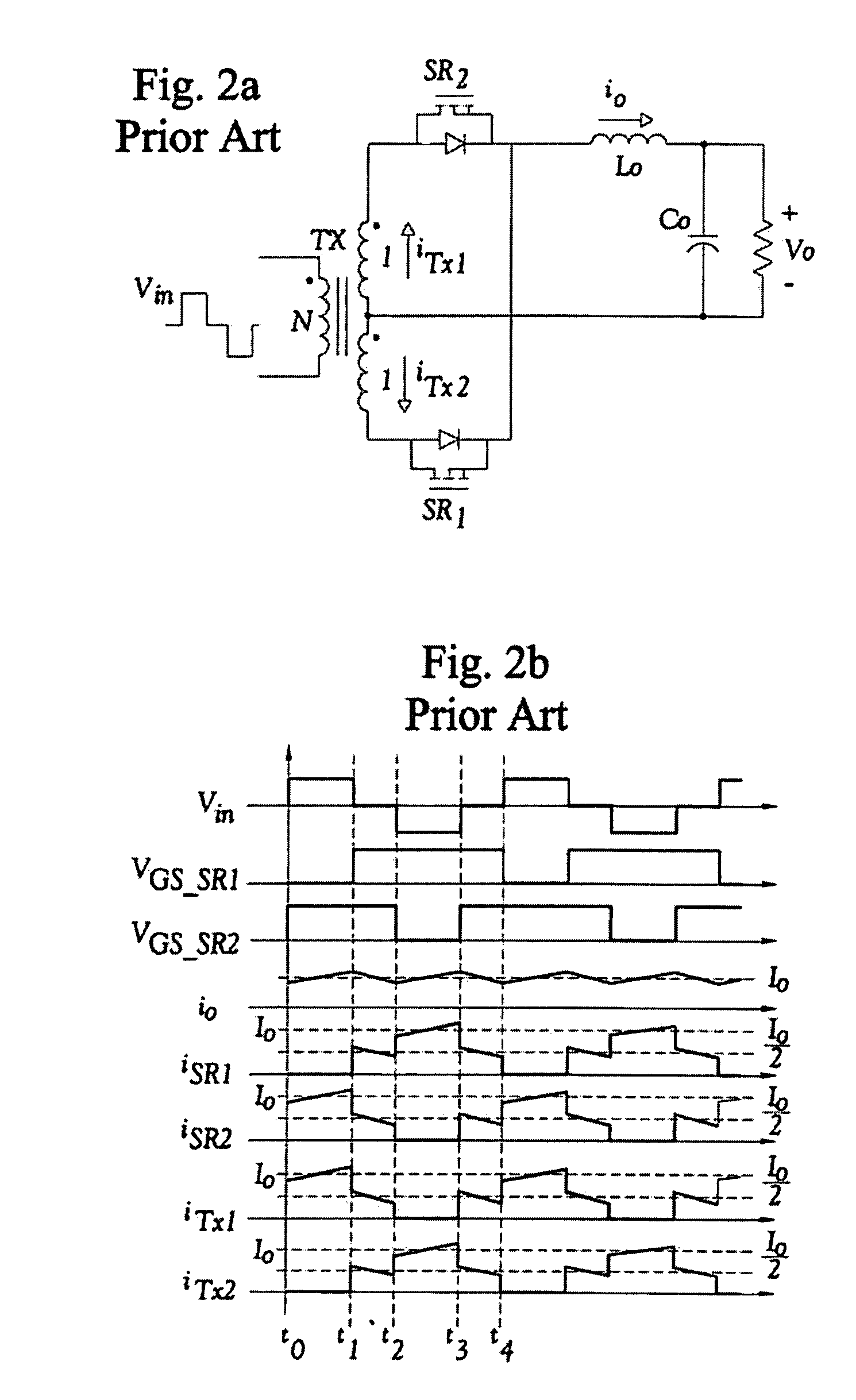
A DC-to-DC converter is an electronic circuit or electromechanical device that converts a source of direct current (DC) from one voltage level to another. It is a type of electric power converter. Power levels range from very low (small batteries) to very high (high-voltage power transmission).
Energy conversion apparatus
InactiveUS20140159667A1Maximize energy conversion efficiencyMaximize efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric powerInput impedanceEngineering
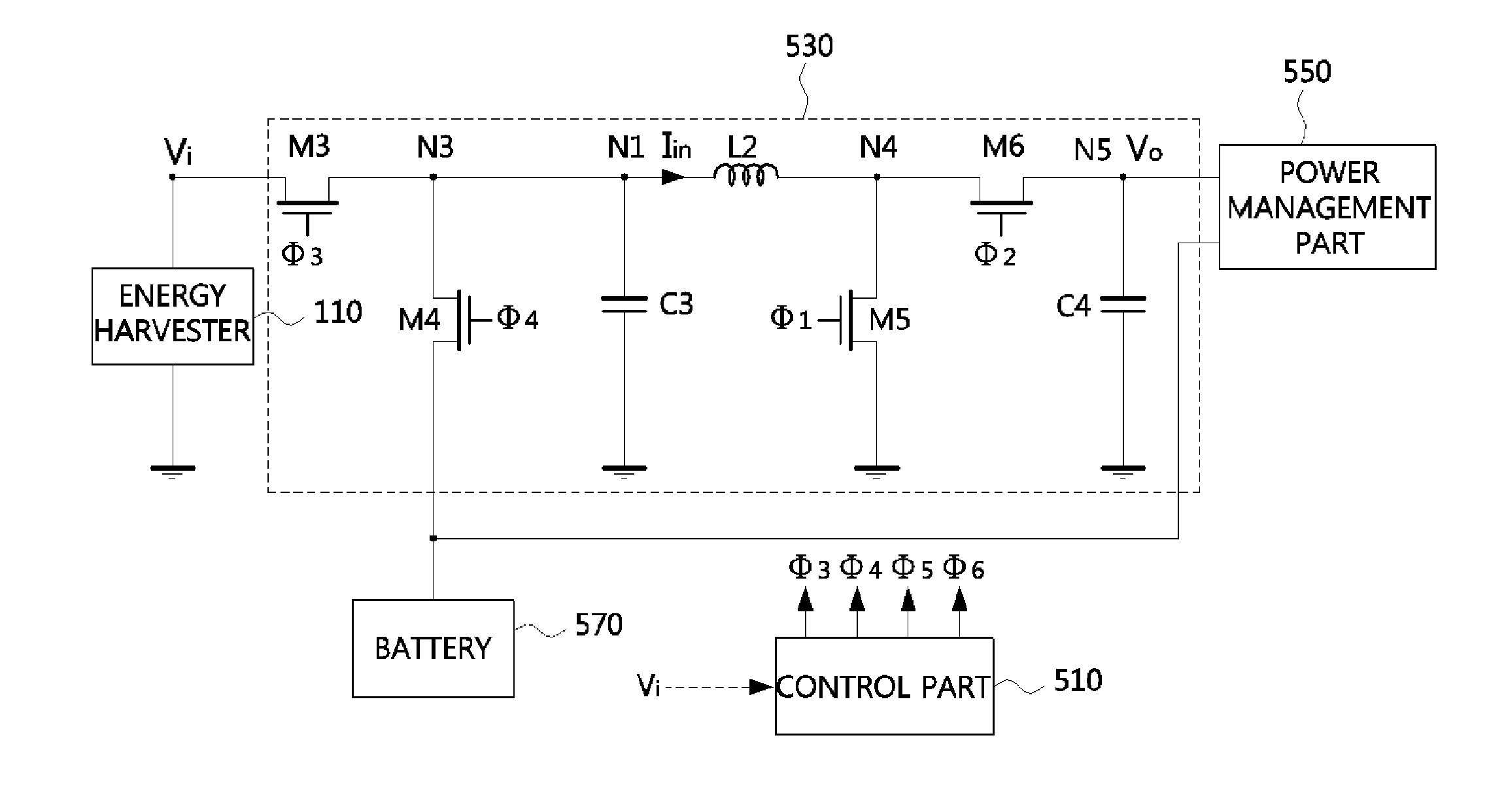
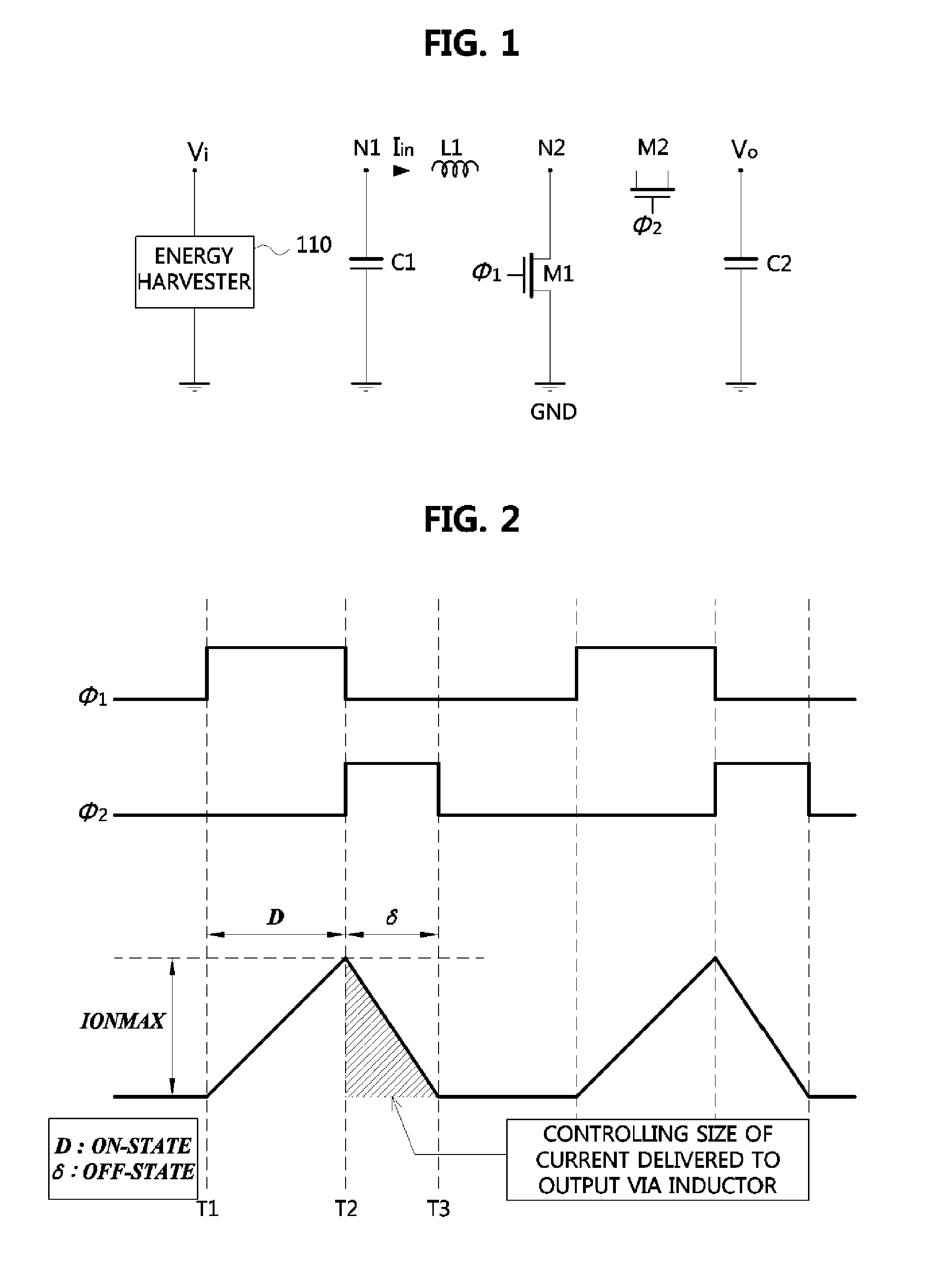
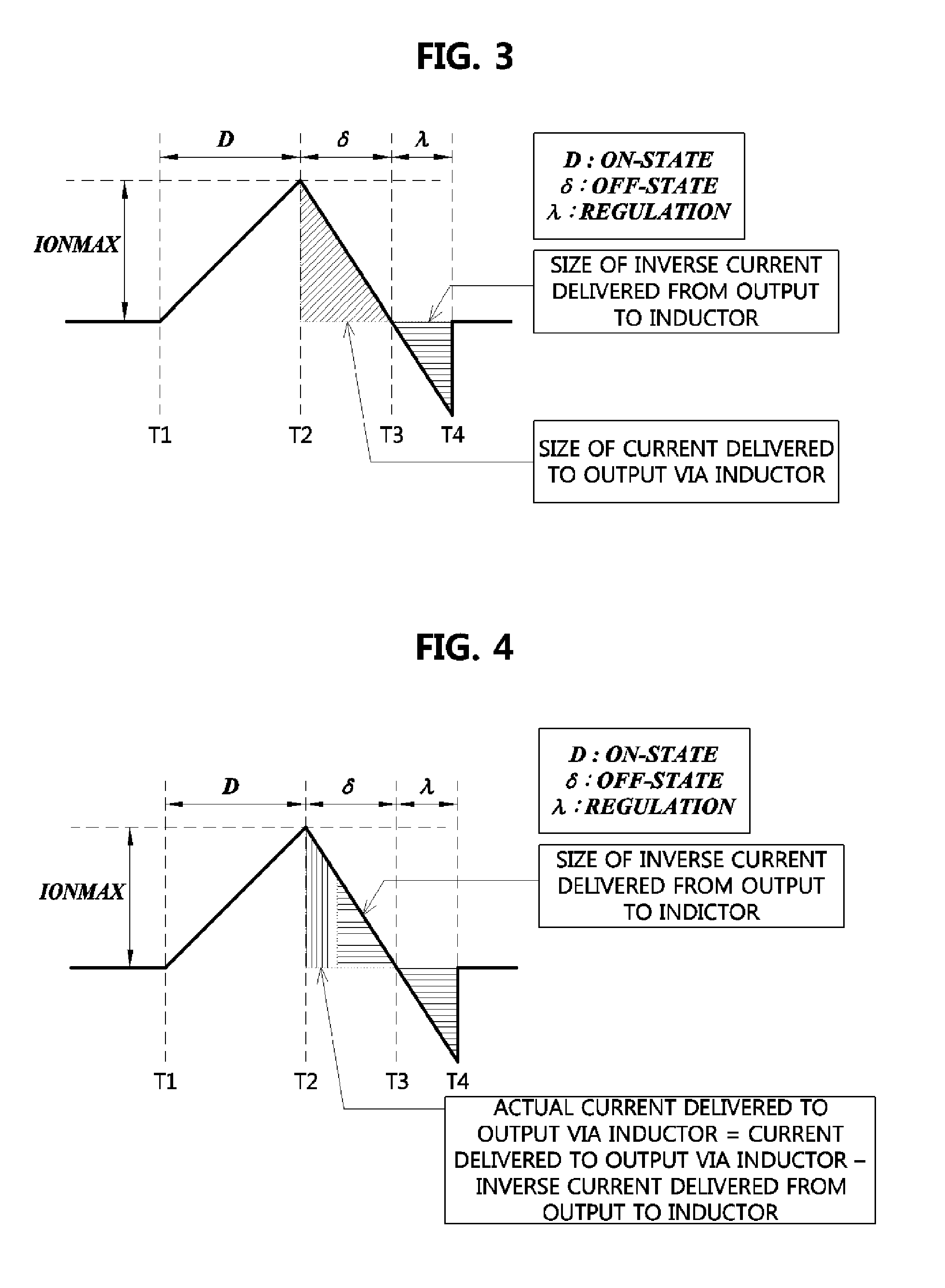
Disclosed is an energy conversion apparatus. An energy conversion apparatus may comprise a control part controlling a length of a first time duration in which input current is inputted and accumulated, a length of a second time duration in which the accumulated current is provided to a load, and a length of a third time duration in which inverse current flows; and a DC-to-DC converter including an inductor, a output capacitor, and at least one switching element, wherein the input current is accumulated during the first time duration by switching the at least one switching element according to a control of the control part so as to perform input impedance matching, and the DC-to-DC convert provides a current corresponding to a difference between the accumulated current provided during the second time duration and the inverse current flowing from the output capacitor during the third time duration to the load.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
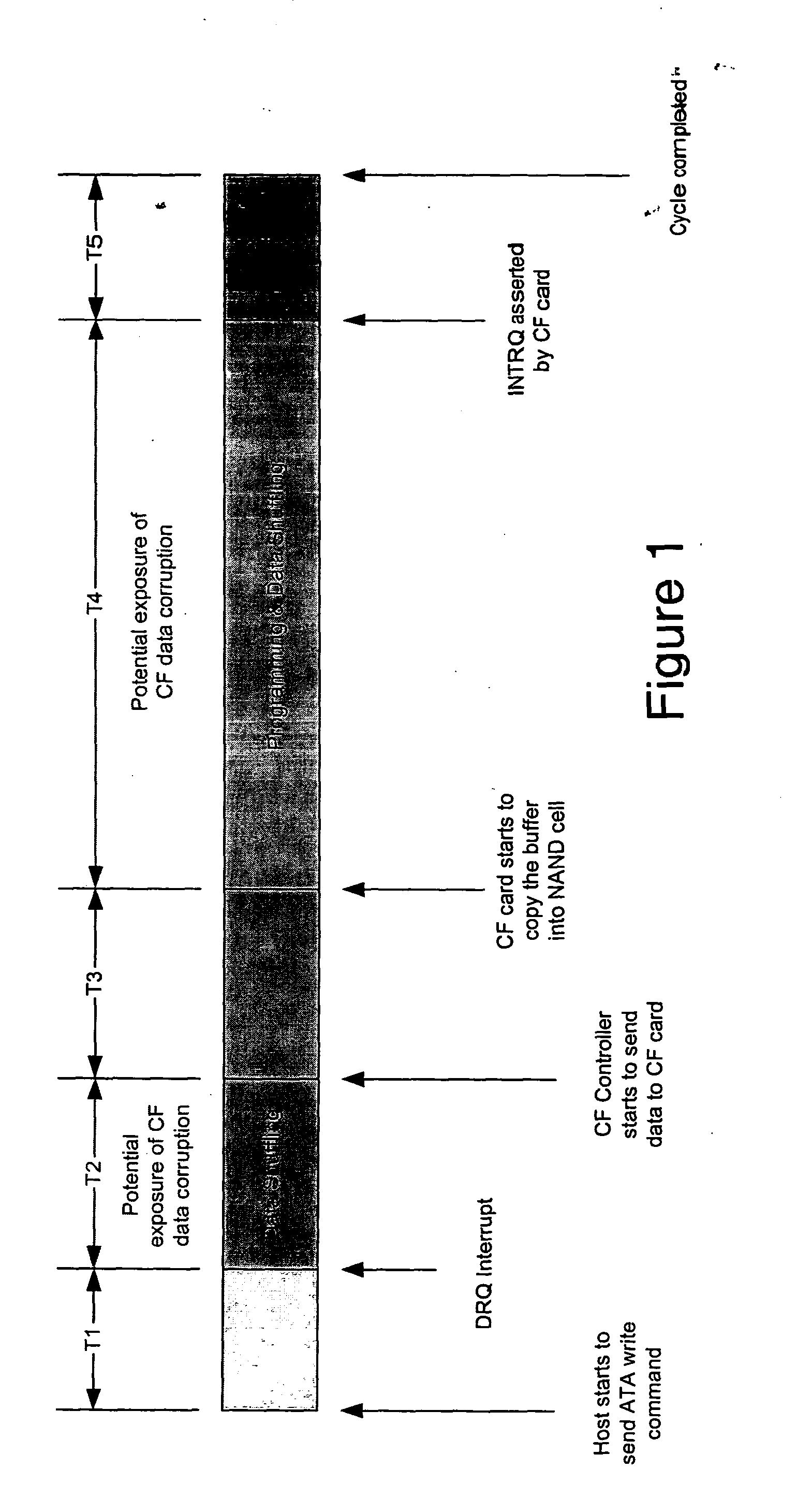
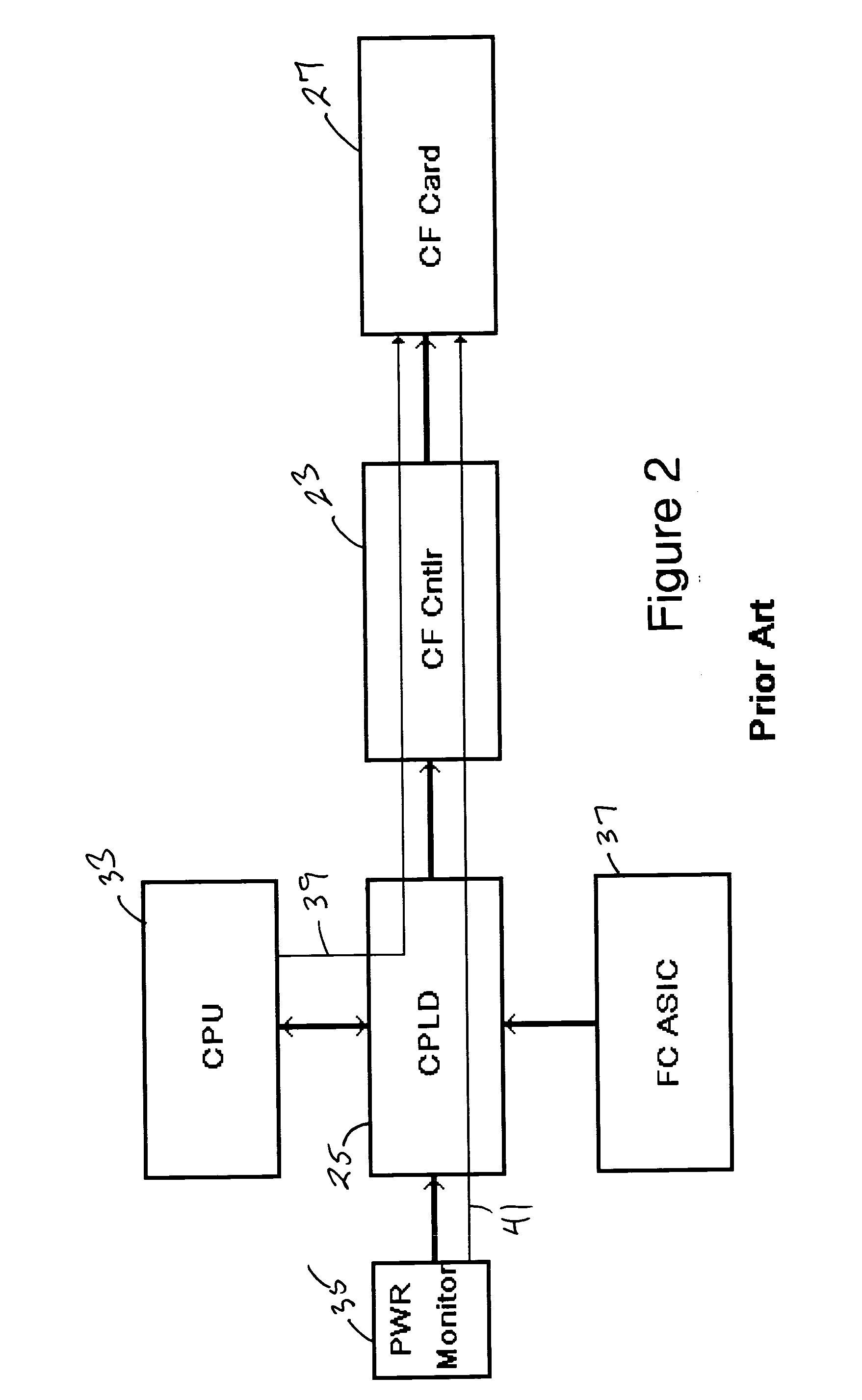
Apparatus for reducing data corruption in a non-volatile memory
InactiveUS20050024968A1Loss and corruption can be preventedEliminate requirementsReliability increasing modificationsRead-only memoriesTime segmentData Corruption
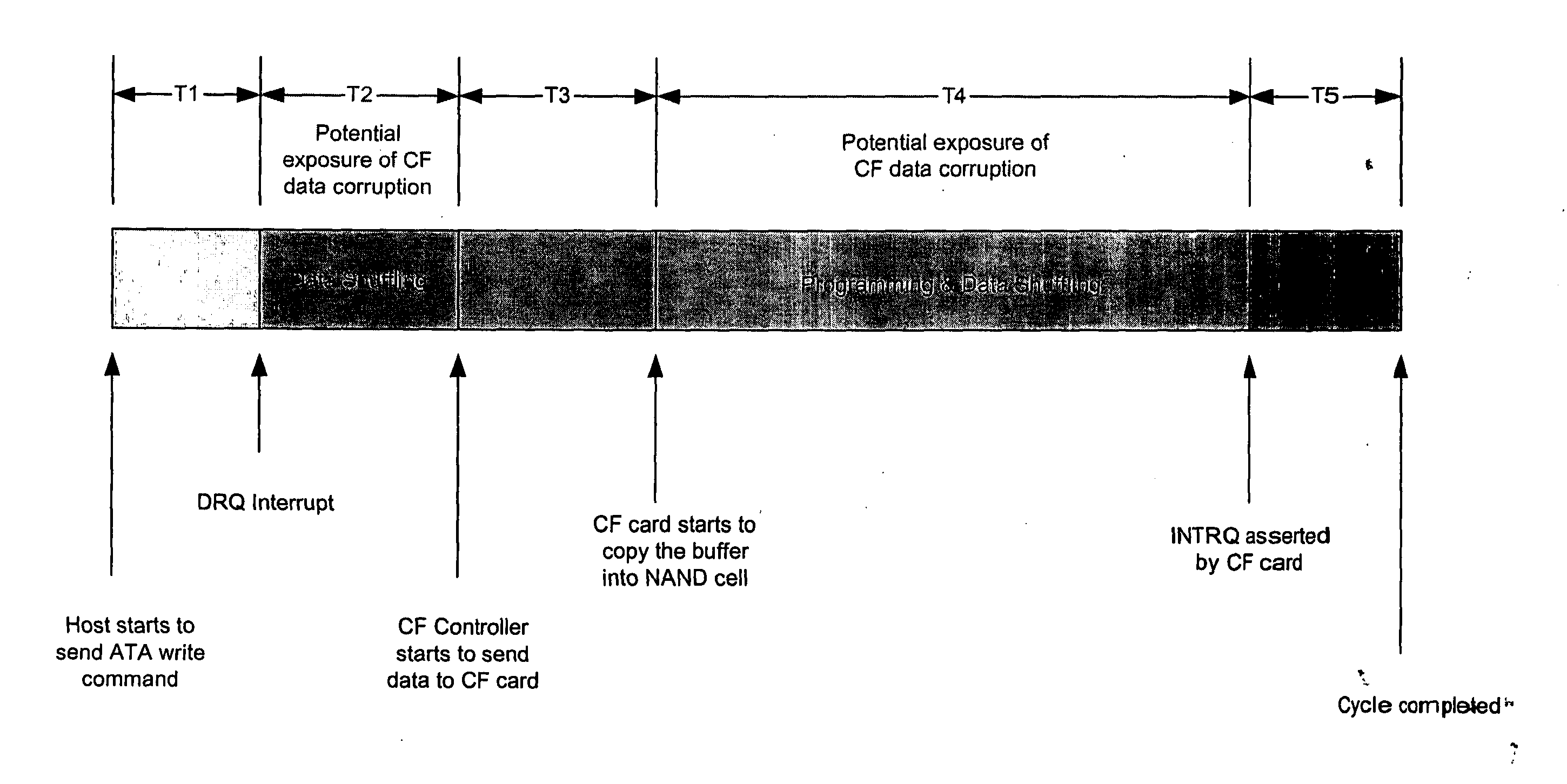
The loss of data and / or the corruption of data that may occur in flash memory when a reset signal is received during a memory write cycle is prevented by delaying reset signals sent to the flash memory for a time period sufficient for a write cycle to be completed. The loss of data and / or the corruption of data that may occur in flash memory when the power supply is interrupted during a write cycle is prevented by providing a DC-to-DC converter with one or more large capacitors in parallel with its input as the power supply to the flash memory. If the system power supply fails or is interrupted, the discharge of the capacitor(s) delays the voltage decay at the input of the DC-to-DC converter such that the output of the DC-to-DC converter remains within tolerance for a time sufficient for the flash memory to complete a write cycle.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Circuit for maintaining hold-up time while reducing bulk capacitor size and improving efficiency in a power supply
InactiveUS20050030772A1Improve efficiencyReducing voltage operating rangeEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceDc dc converter
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
Switched constant current driving and control circuit
ActiveUS20060001381A1Full dimming without large power lossesConstant currentElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesControl signalInput control
The driving and control device according to the present invention provides a desired switched current to a load including a string of one or more electronic devices, and comprises one or more voltage conversion means, one or more dimming control means, one or more feedback means and one or more sensing means. The voltage conversion means may be a DC-to-DC converter for example and based on an input control signal converts the magnitude of the voltage from the power supply to another magnitude that is desired at the high side of the load. The dimming control means may comprise a switch such as a FET, BJT, relay, or any other type of switching device, for example, and provides control for activation and deactivation of the load. The feedback means is coupled to the voltage conversion means and a current sensing means and provides a feedback signal to the voltage conversion means that is indicative of the voltage drop across the current sensing means which thus represents the current flowing through the load. The current sensing means may comprise a fixed resistor, variable resistor, inductor, or some other element which has a predictable voltage-current relationship and thus will provide a measurement of the current flowing through the load based on a collected voltage signal. Based on the feedback signal received, the voltage conversion means can subsequently adjust its output voltage such that a constant switched current is provided to the load.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
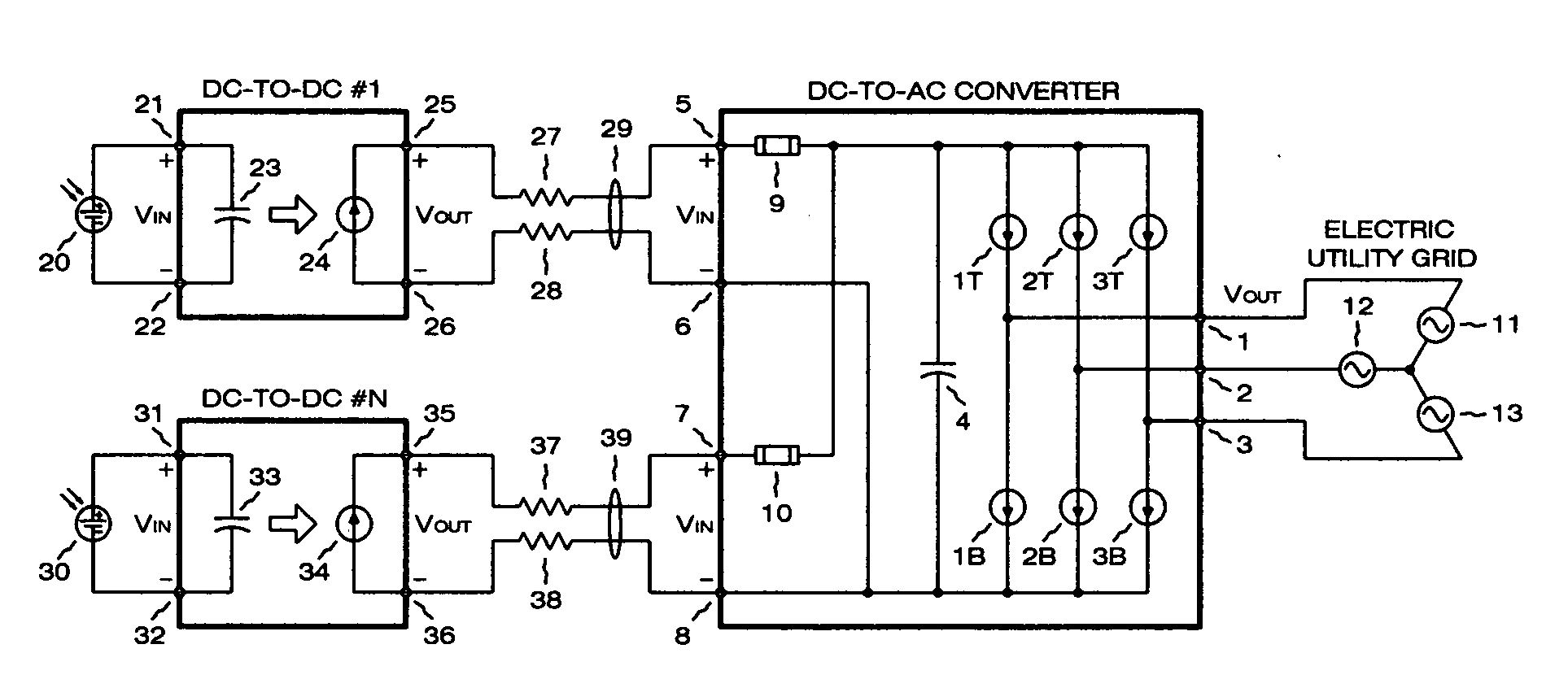
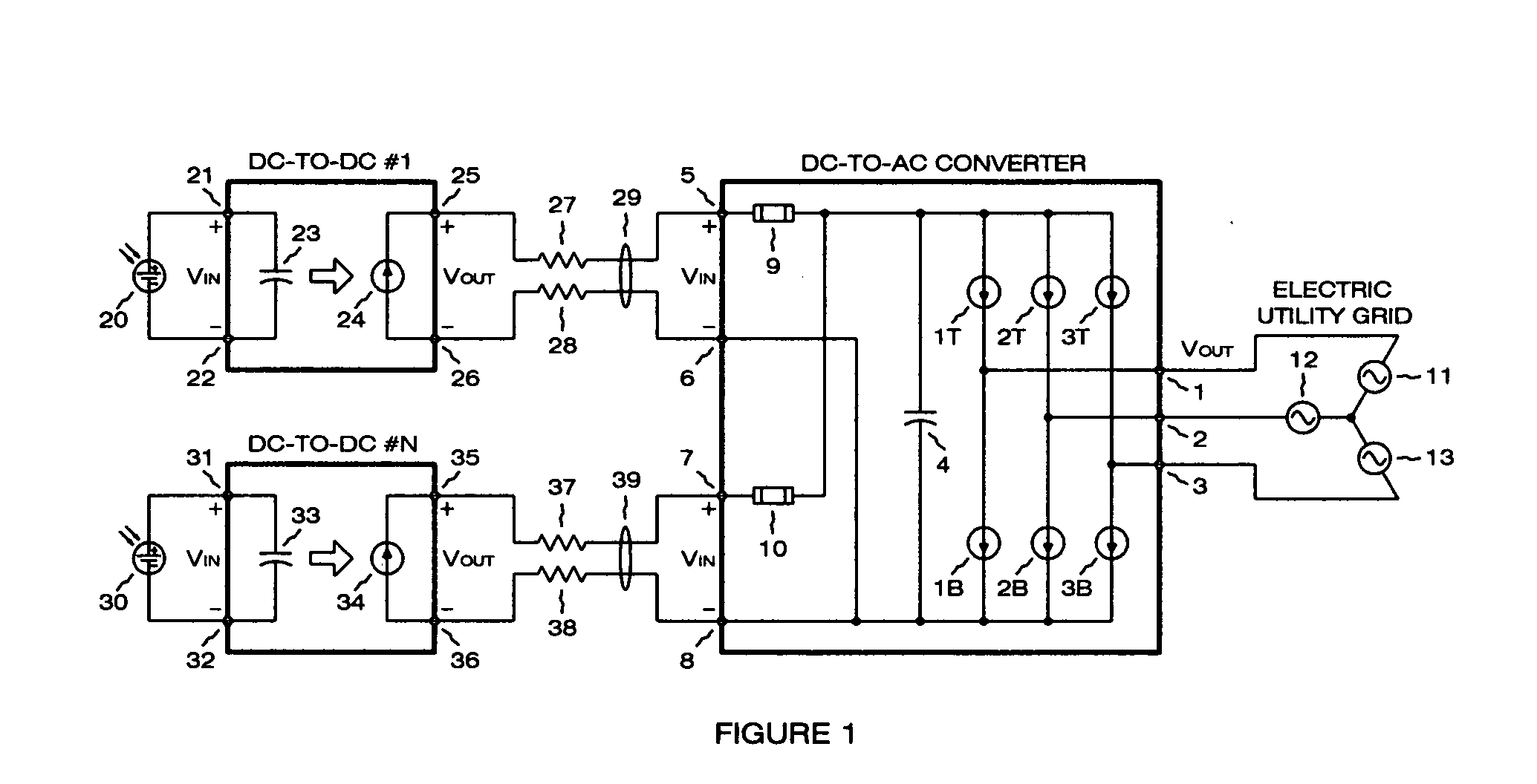
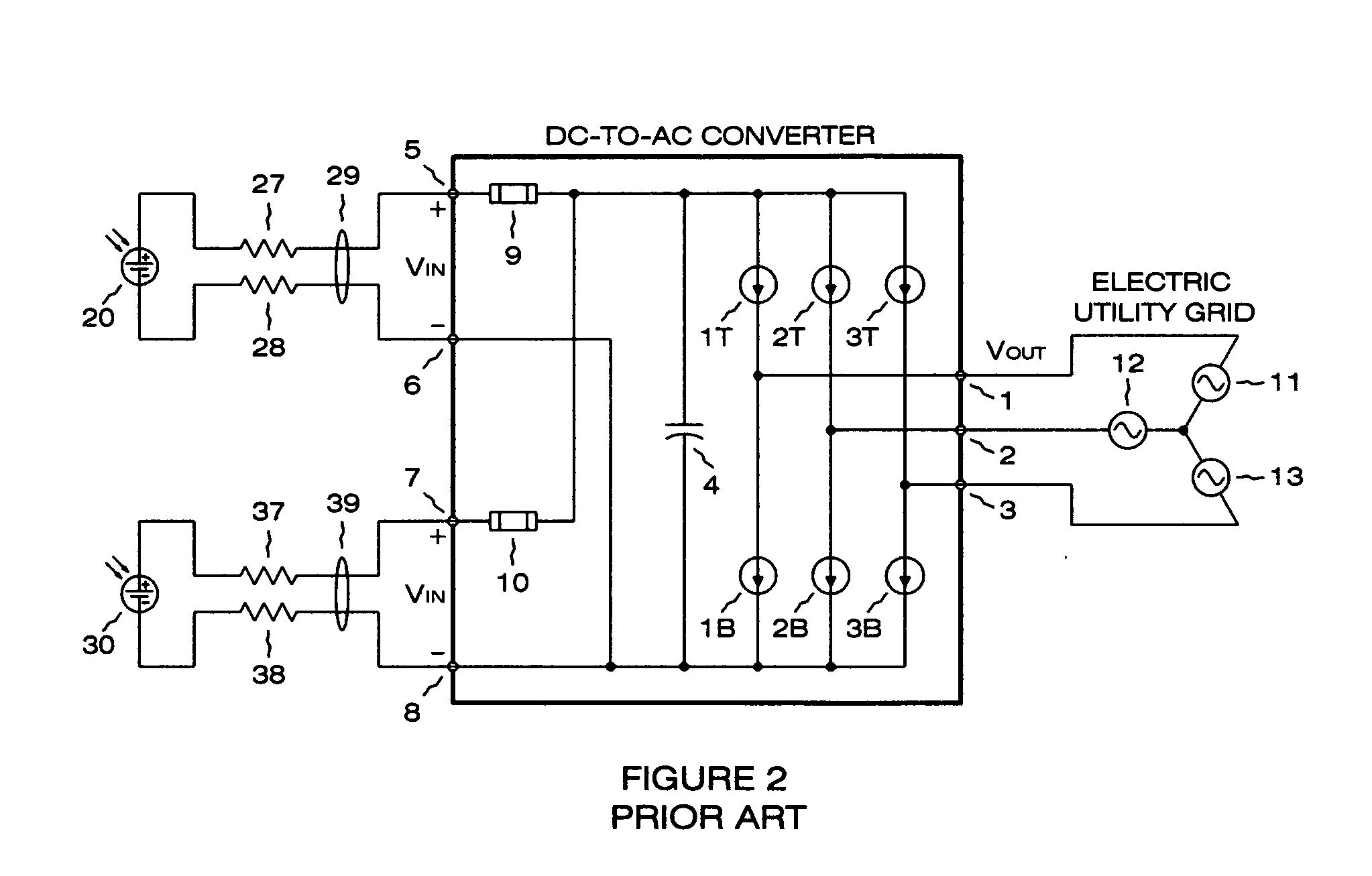
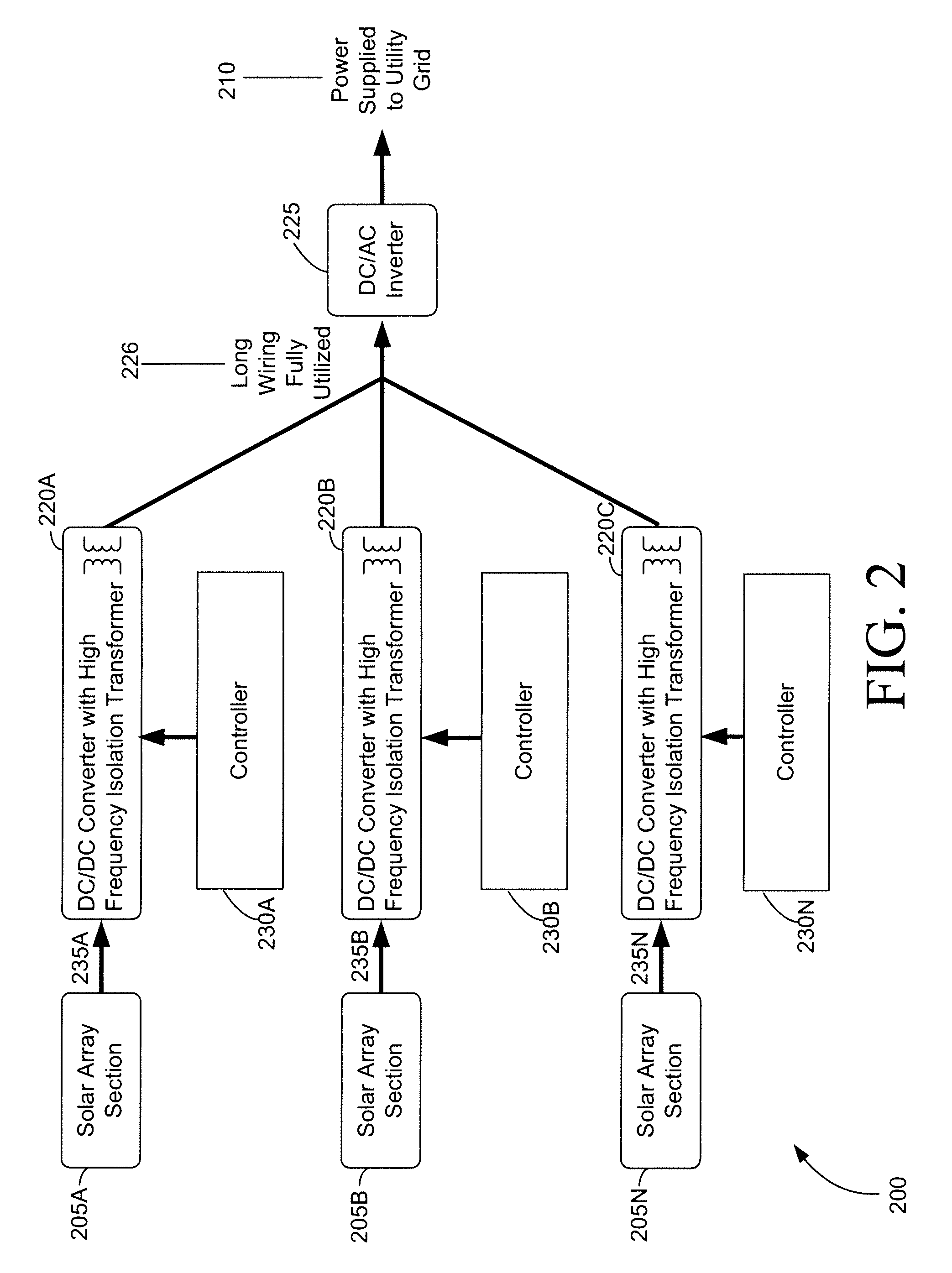
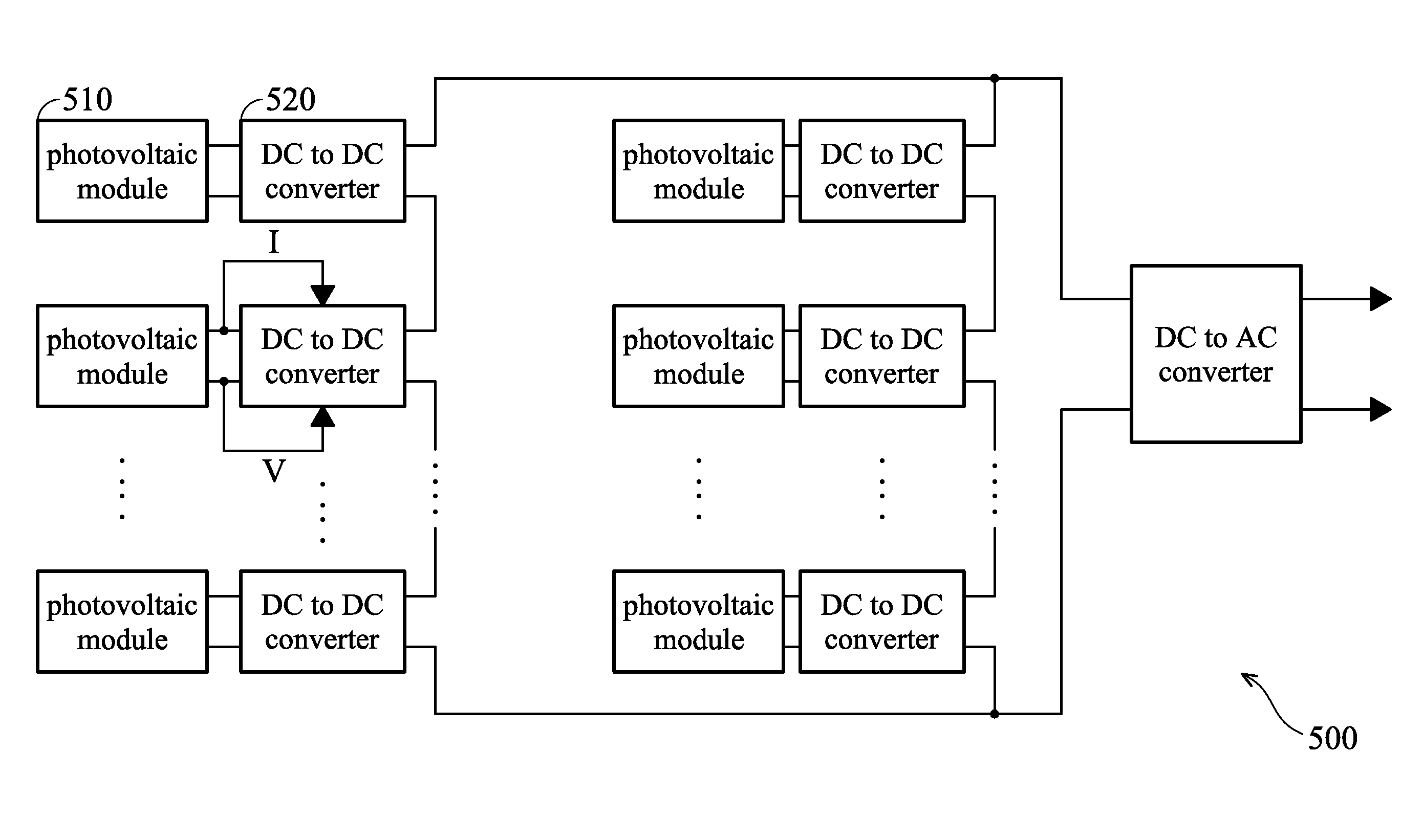
Photovoltaic power plant with distributed DC-to-DC power converters
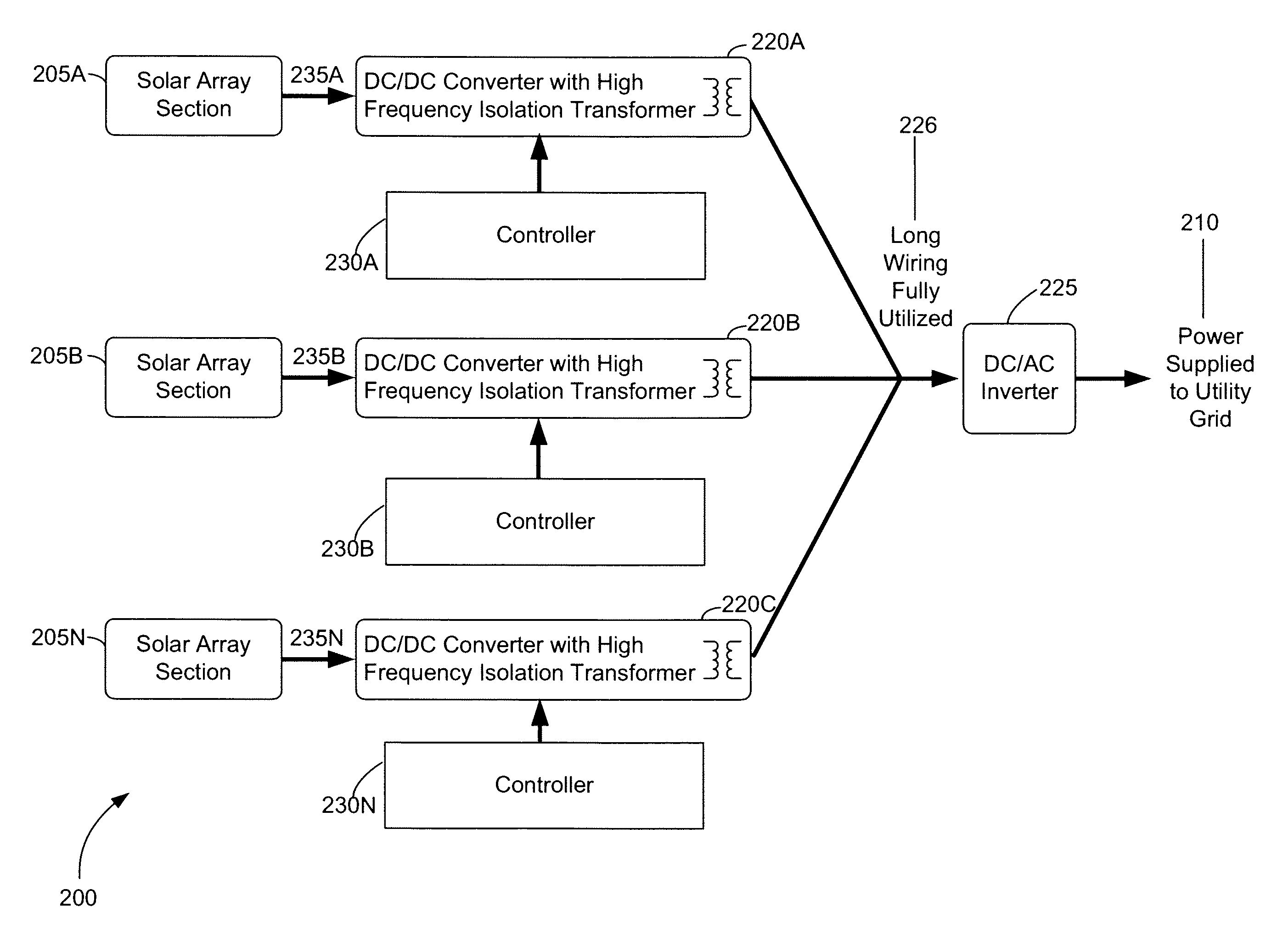
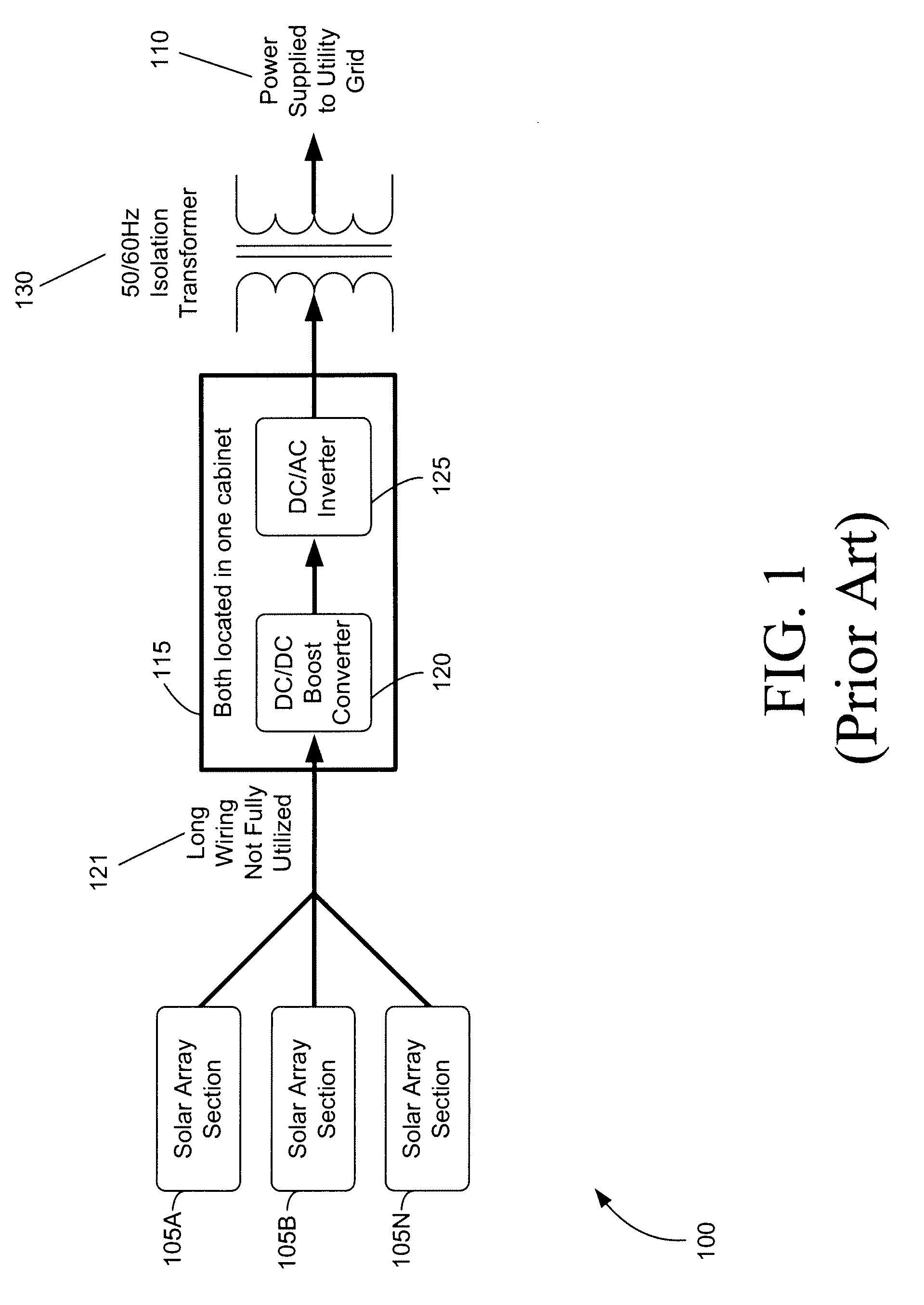
A solar photovoltaic plant is disclosed where a number of distributed DC-to-DC converters are used in conjunction with a central DC-to-AC converter. Each DC-to-DC converter is dedicated to a portion of the photovoltaic array and tracks the maximum power point voltage thereof. The DC-to-DC converters also boost the photovoltaic voltage and regulate a DC output current for transmission to the central DC-to-AC converter. Five distinct advantages are had over the prior art. First, efficiencies in intra-field power collection are greatly improved by transferring power at higher DC voltages. Second, the number of independent photovoltaic maximum power point trackers in the power plant can be increased, in a cost effective manner, to optimize the overall photovoltaic array energy harvest. Third, each DC-to-DC converter output “looks” like a current source at the input of the DC-to-AC converter and therefore can be easily paralleled. Fourth, the current source nature of the DC-to-DC converter outputs enables the DC-to-AC converter to operate with a minimum, fixed DC bus voltage to provide maximum DC-to-AC power conversion efficiencies. And fifth, each distributed DC-to-DC converter can isolate a faulted portion of the photovoltaic array while the remainder of the array continues producing power.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
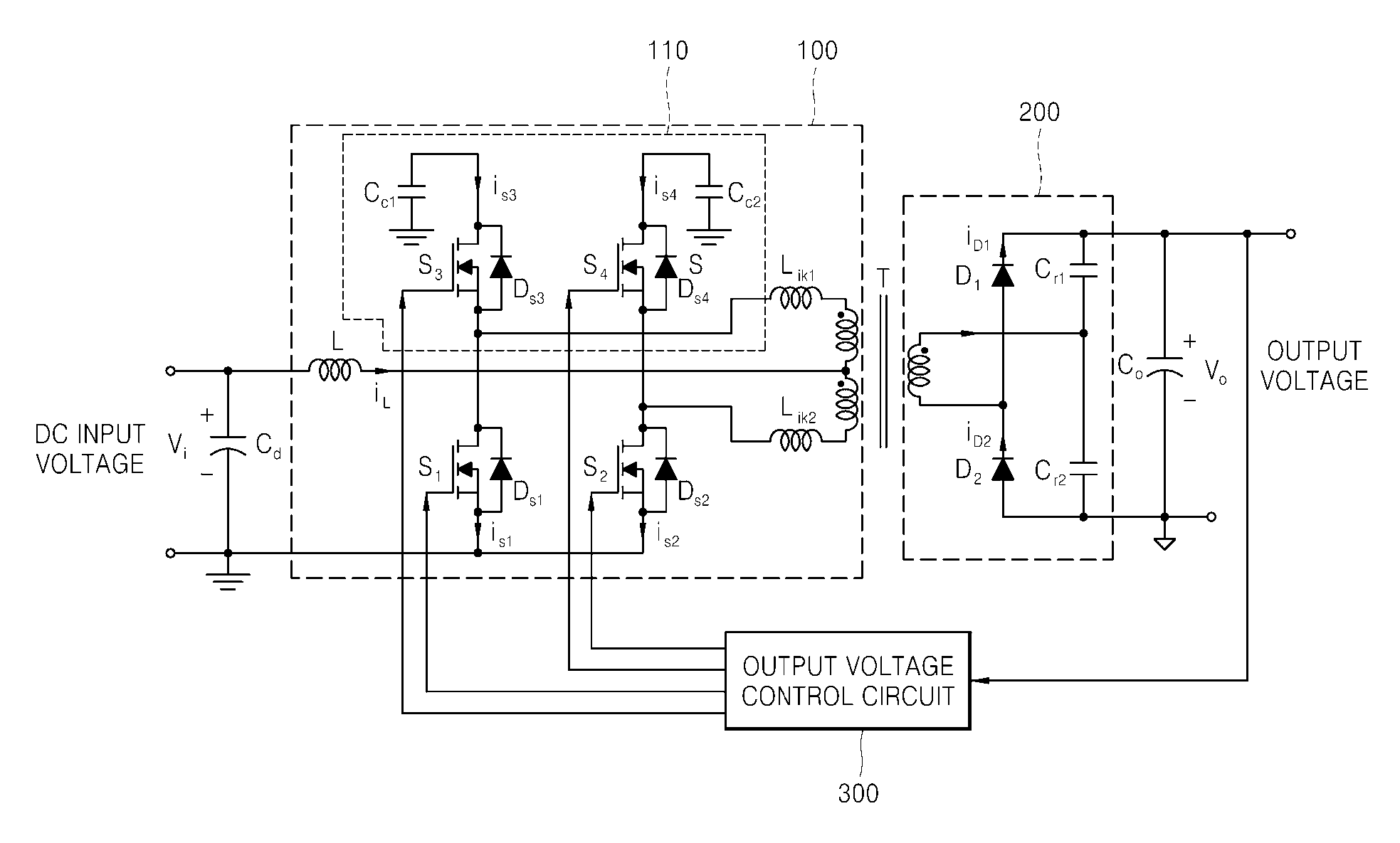
Active-clamp current-source push-pull dc-dc converter
InactiveUS20070247877A1Improve power conversion efficiencyReduce voltage stressEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionFull wavePush pull
Provided is a current-source push-pull DC-DC converter using an active clamp circuit for reusing energy of leakage inductances by not only diodes on a secondary side of a transformer being zero-current switched using a series-resonant full-wave rectifier, but also the active clamp circuit on a primary side of the transformer, which provides a discharge path of the energy stored in the leakage inductances, increases power conversion efficiency even for a wide input voltage range and reduces a switch voltage stress as compared to a conventional current-source push-pull circuit by operating even for a duty ratio below 0.5 by flowing a current of an input inductor through capacitors of the active clamp circuit when both main switches are off.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Novel Solar Power Circuits
InactiveUS20110210611A1Reducing eliminating riskAvoid flowDc source parallel operationPhotovoltaic energy generationPower flowReverse current
Particular embodiments of the inventive technology disclosed herein seek to reduce or eliminate the risk of damage to components of photovoltaic power circuits such as solar arrays. Aspects of the inventive technology, in embodiments, utilize diode to prevent reverse current flow in the event of application of a voltage to a power supply string which would otherwise effect such flow. Prevention of such reverse current flow may preclude voltages that would otherwise damage reverse current sensitive devices such as switches that may form part of a voltage limiting DC to DC converter.
Owner:AMPT
Battery controller and method for controlling a battery
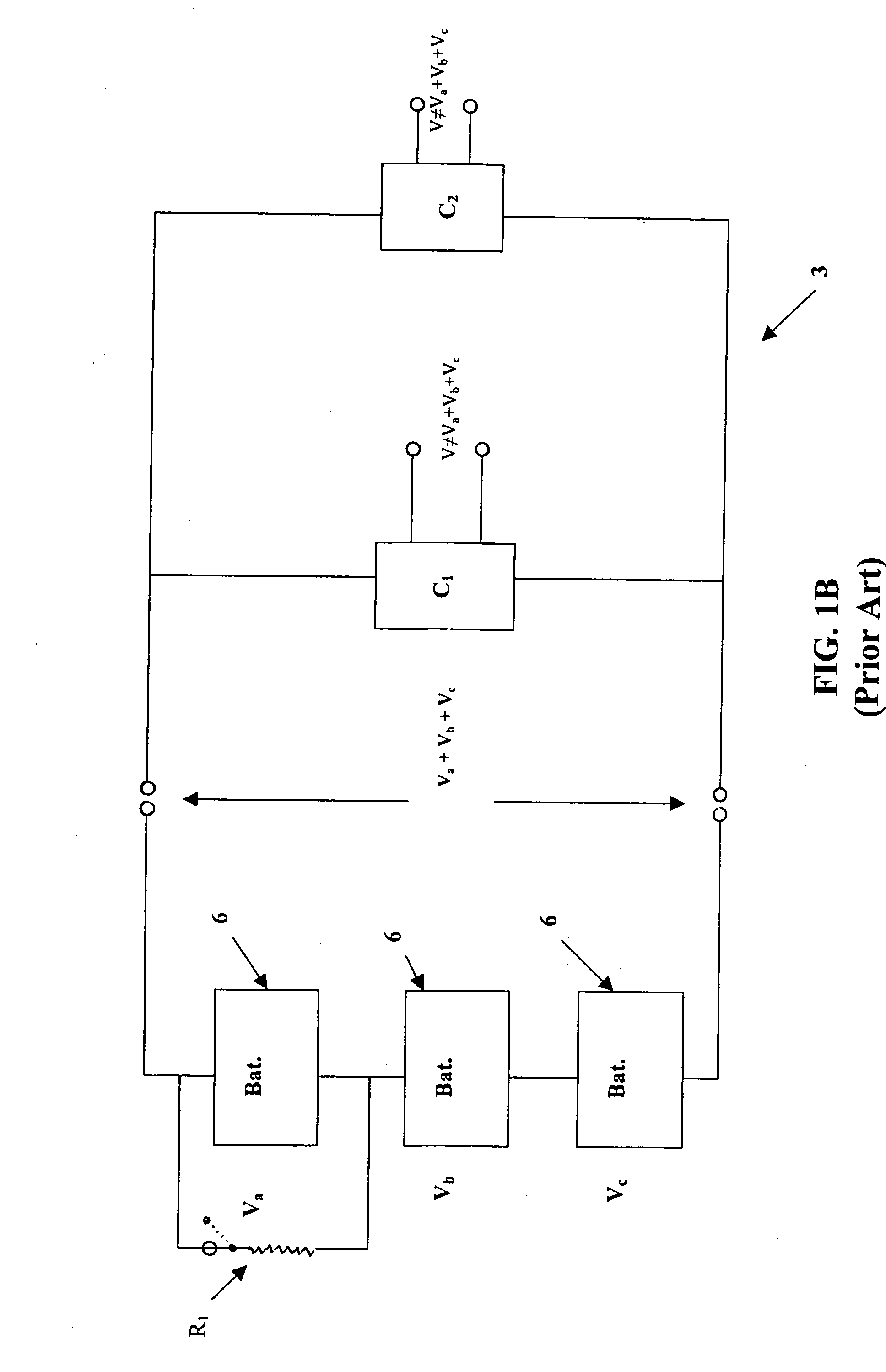
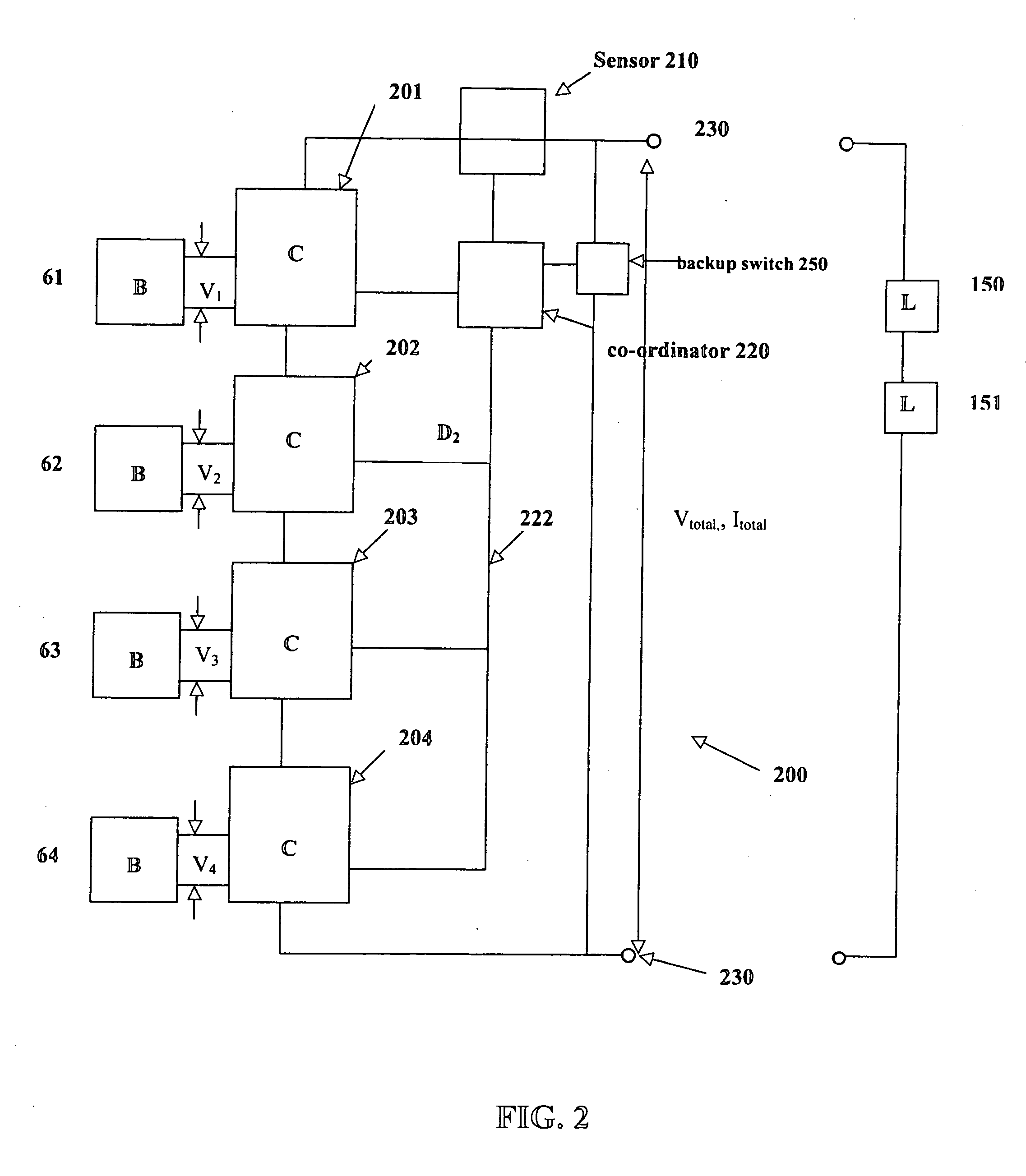
ActiveUS7282814B2Process economyMore energyDc network circuit arrangementsCharge equalisation circuitElectricityEngineering
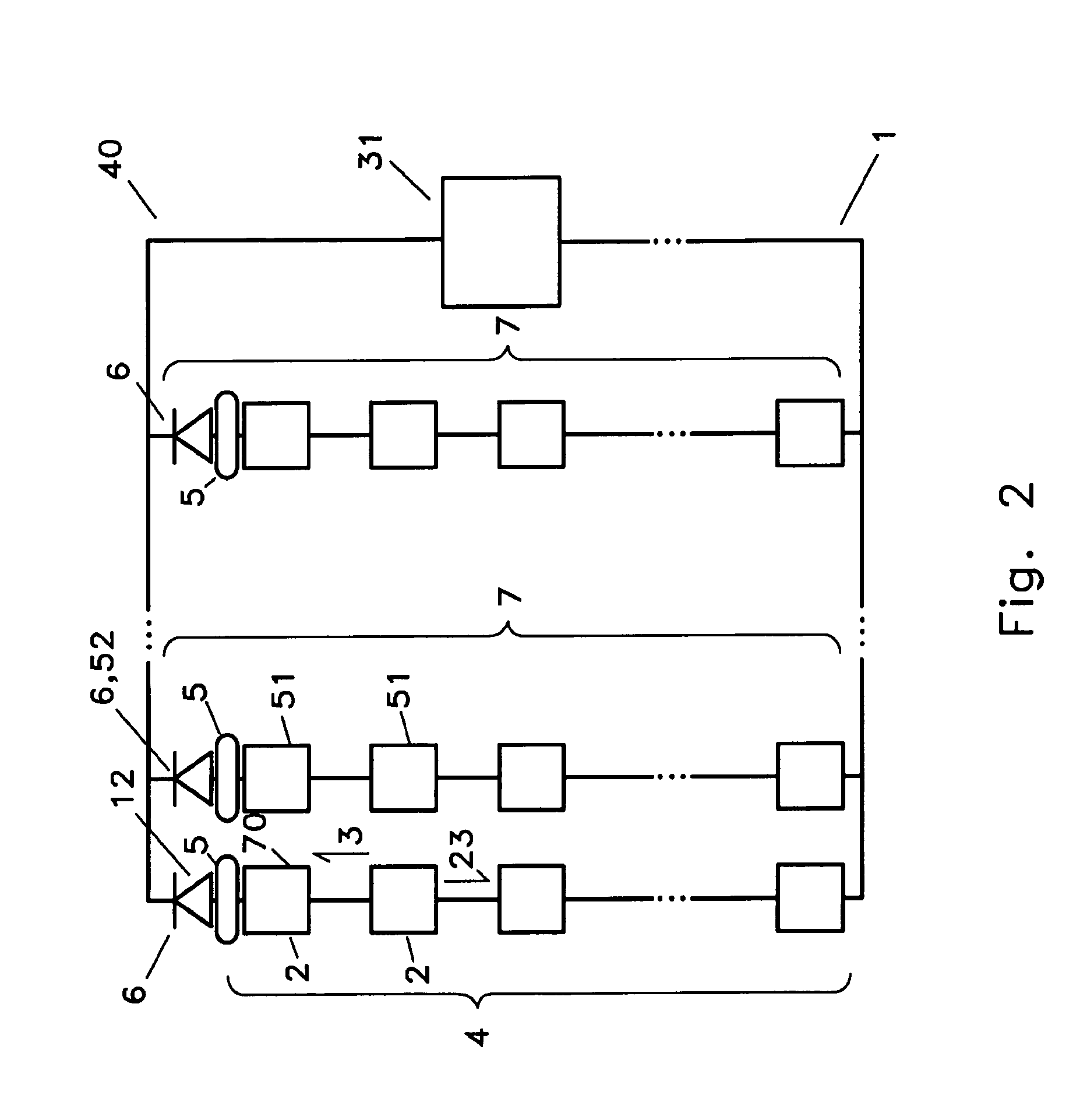
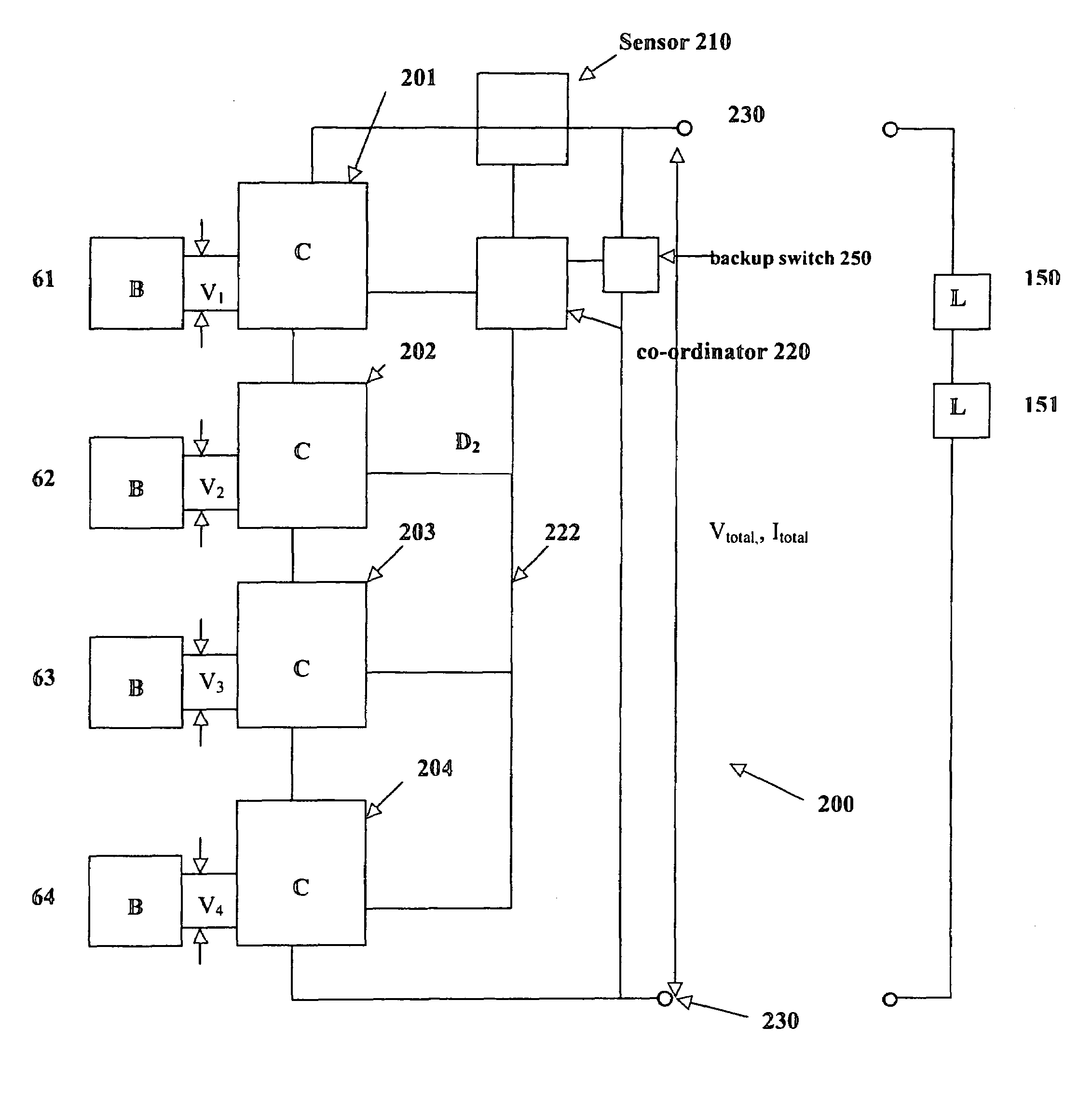
A battery controller for charging and discharging a plurality of batteries is disclosed. The battery controller has a plurality of direct current to direct current (DC to DC) converters connected to each other in series. Each battery of a plurality of batteries is electrically connectable to a respective DC to DC converter. A co-ordinator connected to each of the plurality of DC to DC converters controls charging and discharging of the battery electrically connected to the respective converter. The co-ordinator can also control charging and discharging of any one of the batteries to ensure that the battery retains sufficient electrical capacity, and, to increase the longevity of the respective batteries. Because each battery is electrically connected to a respective DC to DC converter, the energy from one battery can be used to charge another battery in order to monitor battery characteristics including energy capacity of each battery. Each of the DC to DC converters is selected to operate preferably below 30 volts while the total voltage of the entire battery system can be much more than 30 volts depending on the number of DC to DC converters placed in series.
Owner:ELECTROVAYA
Circuit for Rendering Energy Storage Devices Parallelable
InactiveUS20120274145A1Increase capacityEasy to recycleSecondary cellsDc source parallel operationBattery state of chargeElectrical battery
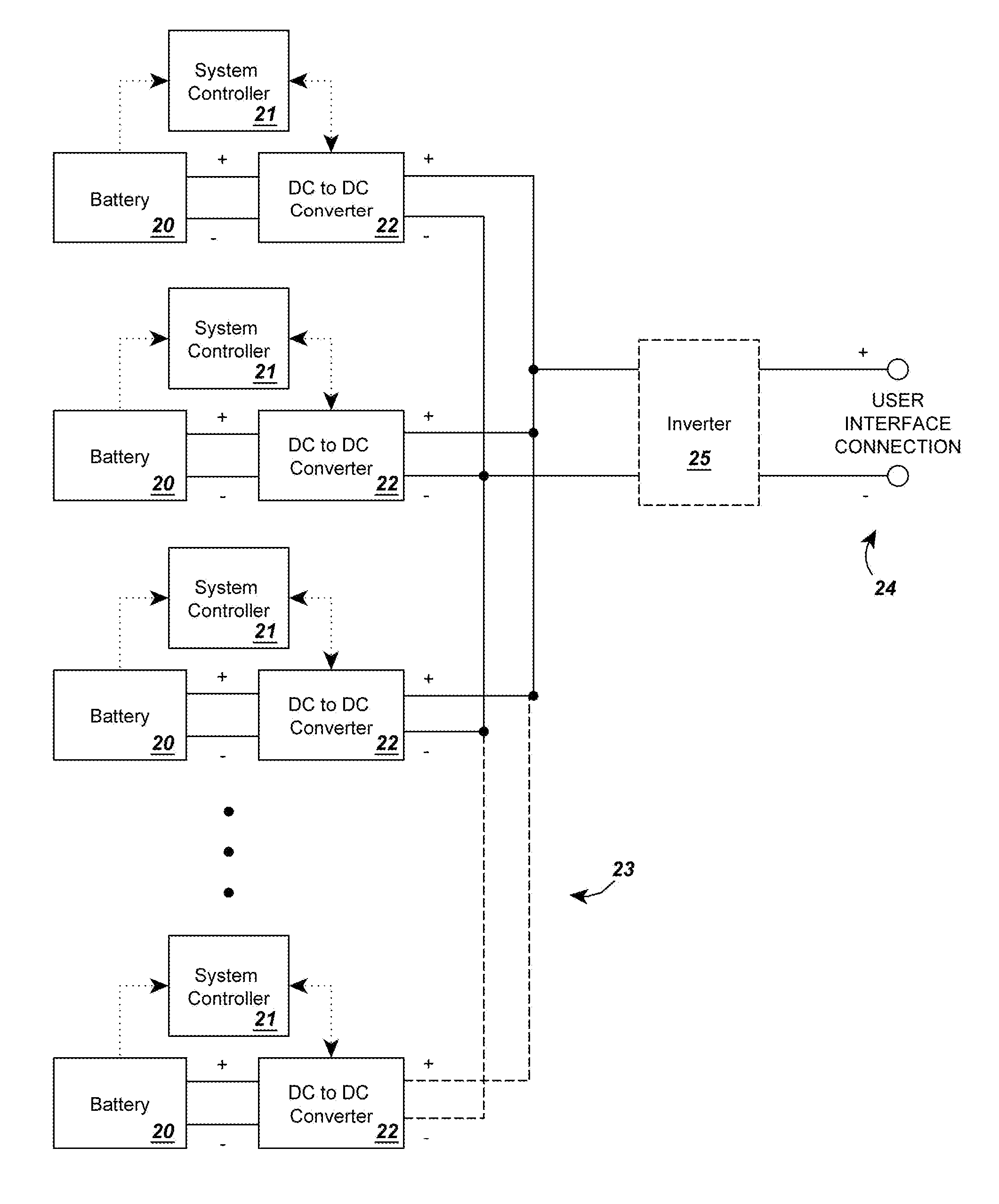
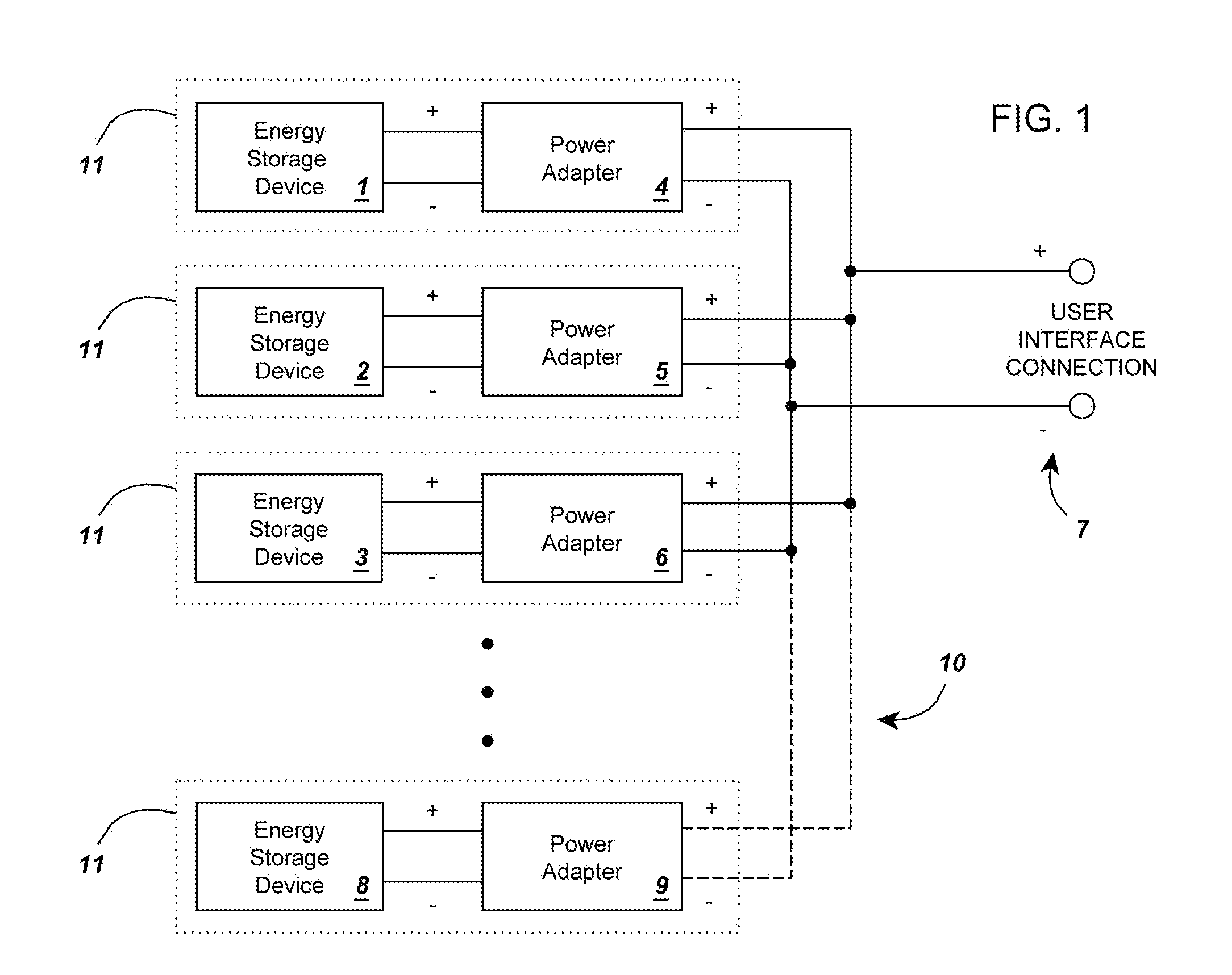
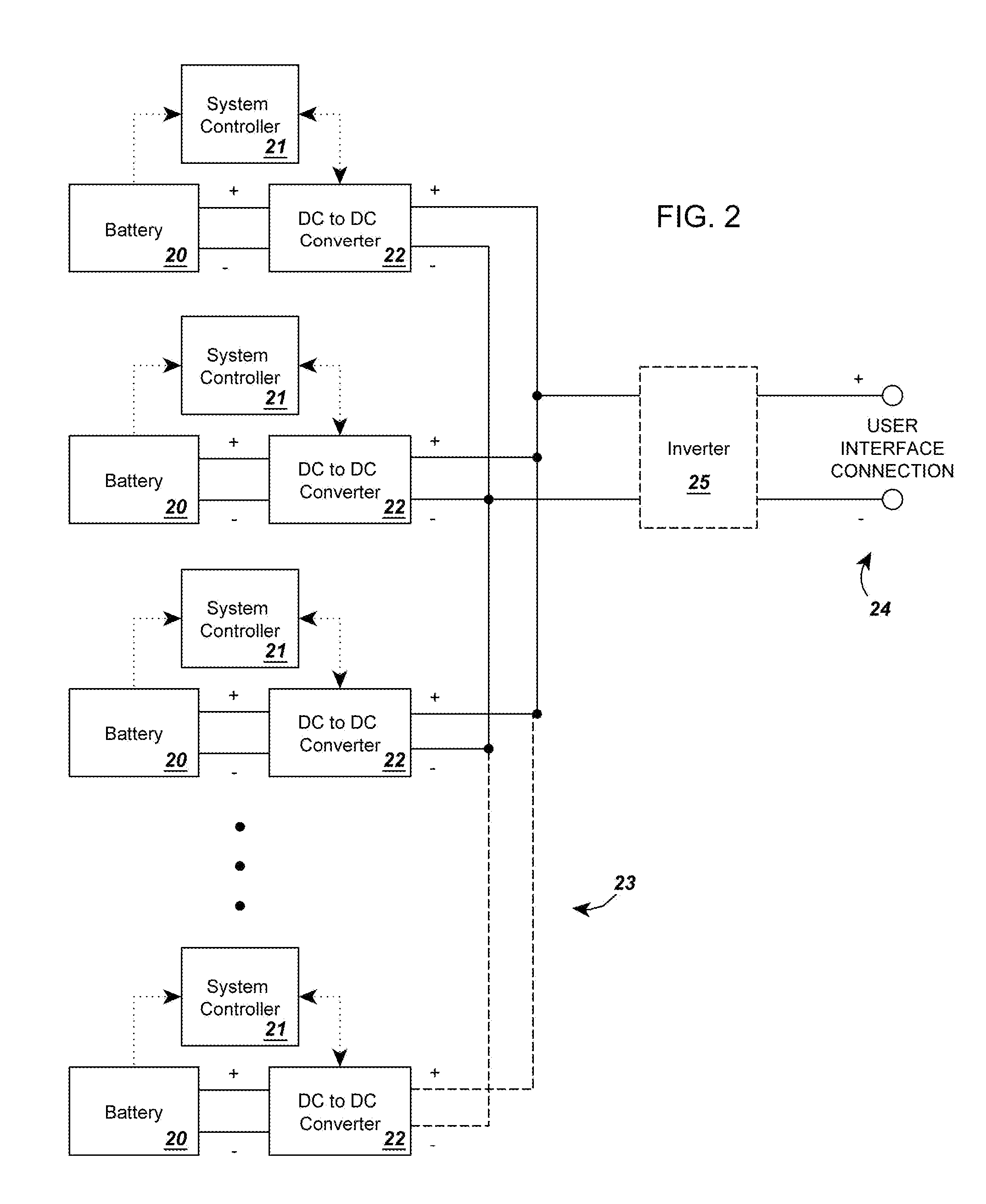
A circuit for rendering an energy storage device parallelable comprised of an energy storage device connected to a power adapter that converts the potential of the energy storage device into a potential that follows a predetermined function of the state of charge of the energy storage device. When multiple assemblies are paralleled, they may be charged and discharged as a whole with individual storage devices maintaining equal states of charge. The energy storage devices can be batteries with different cell counts, configurations, and energy discharge profiles. In some cases, the power adapters are comprised of DC to DC converters and system controllers that are used to translate each battery's energy discharge profile into a user-determined energy discharge profile that is a predictable function of the battery's state of charge and independent of temperature or other external conditions.
Owner:ENGIE STORAGE SERVICES NA LLC
Battery controller and method for controlling a battery
ActiveUS20050194937A1Process economyMore energy efficientDc network circuit arrangementsCharge equalisation circuitElectricityBattery system
A battery controller for charging and discharging a plurality of batteries is disclosed. The battery controller has a plurality of direct current to direct current (DC to DC) converters connected to each other in series. Each battery of a plurality of batteries is electrically connectable to a respective DC to DC converter. A co-ordinator connected to each of the plurality of DC to DC converters controls charging and discharging of the battery electrically connected to the respective converter. The co-ordinator can also control charging and discharging of any one of the batteries to ensure that the battery retains sufficient electrical capacity, and, to increase the longevity of the respective batteries. Because each battery is electrically connected to a respective DC to DC converter, the energy from one battery can be used to charge another battery in order to monitor battery characteristics including energy capacity of each battery. Each of the DC to DC converters is selected to operate preferably below 30 volts while the total voltage of the entire battery system can be much more than 30 volts depending on the number of DC to DC converters placed in series.
Owner:ELECTROVAYA
Systems, Methods, and Apparatus for Converting DC Power to AC Power
ActiveUS20100277001A1Dc network circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationElectricityEngineering
Embodiments of the invention can provide systems, methods, and an apparatus for converting direct current (DC) power to alternating current (AC) power. According to one embodiment, a system for converting DC power to AC power can be provided. The system can include a DC power source electrically coupled to a DC-to-DC converter. The DC power source can be associated with a first ground, and the DC-to-DC converter can be operable to isolate the power provided by the DC power source from the first ground. The DC-to-DC converter can be further operable to condition the DC power and to provide the conditioned DC power to an inverter. The inverter can receive the conditioned DC power and can convert the conditioned DC power to AC power. The AC power can be associated with a second ground and can be provided to at least one load electrically coupled to the inverter.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
DC power source conversion modules, power harvesting systems, junction boxes and methods for DC power source conversion modules
InactiveUS20120161526A1Dc network circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationComputer moduleEngineering
A DC power source conversion module is provided, including a DC power source module and a DC to DC conversion module. The DC to DC conversion module includes a DC to DC converter and a control module. The DC to DC converter is powered by the DC power source module to generate an output signal. The control module senses a responding signal of the DC to DC conversion module and controls the DC to DC converter according to the sensed responding signal, such that the DC power source conversion module is operated at a predetermined output power, in which the responding signal responds to the output signal of the DC to DC converter.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
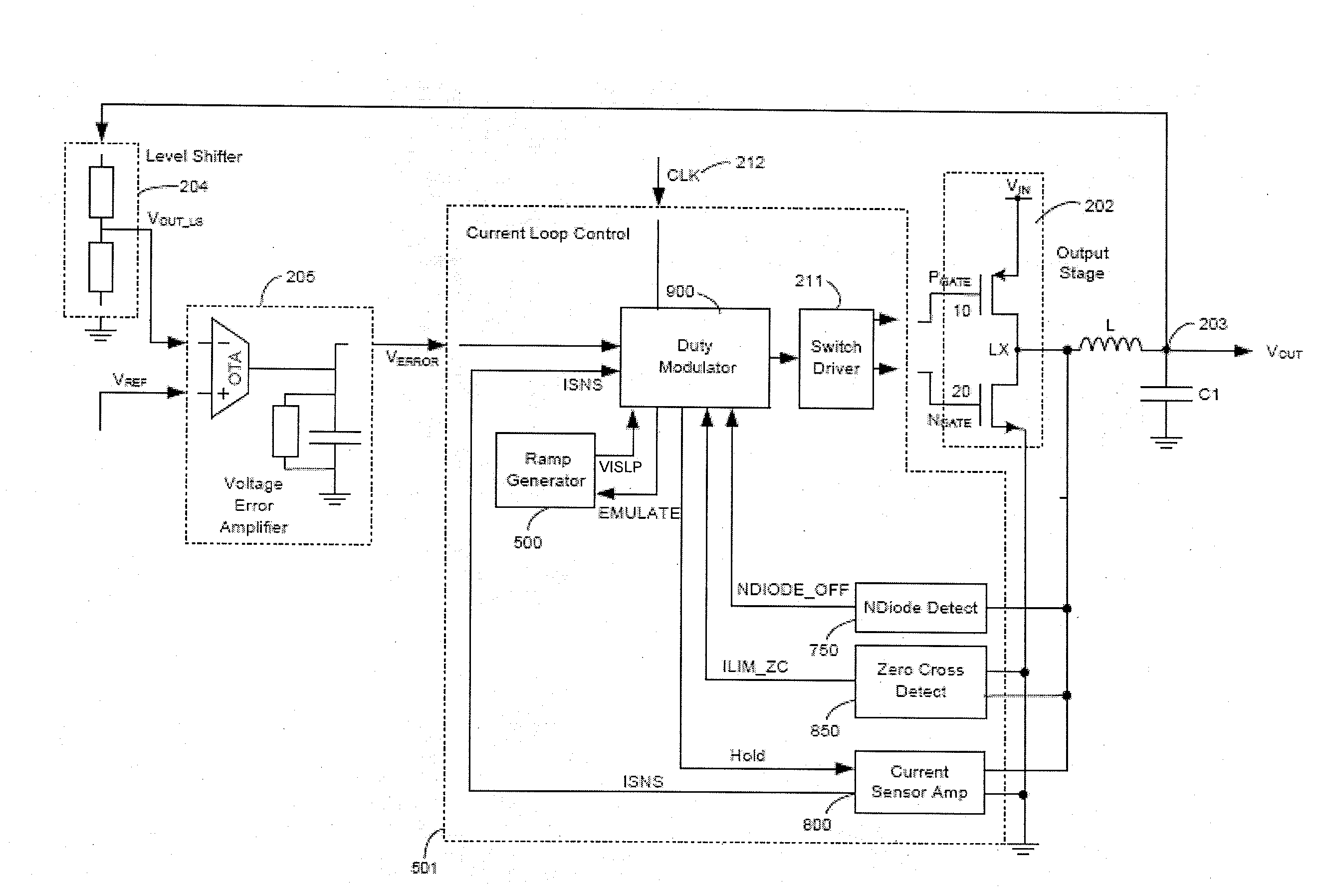
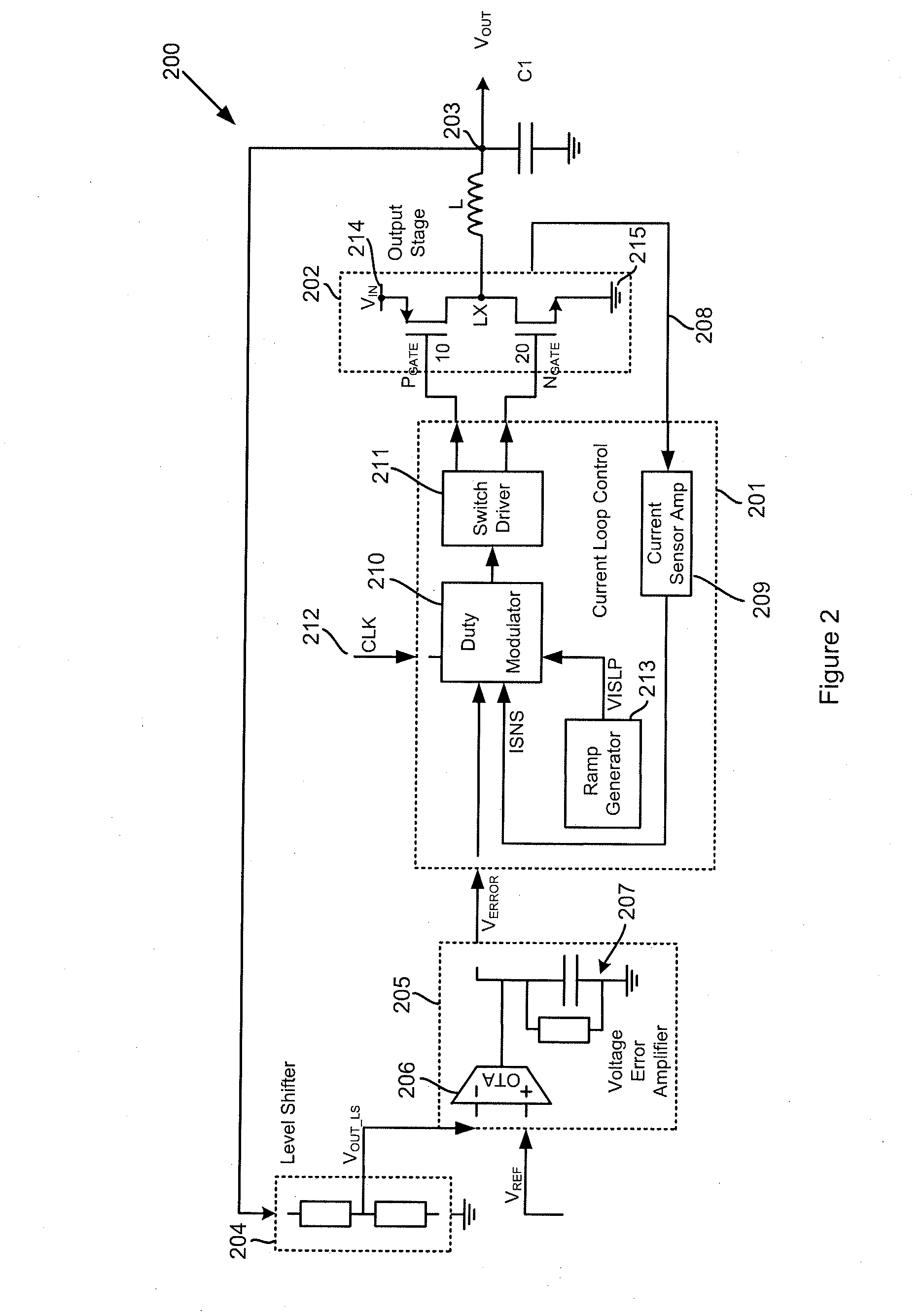
Dc-dc converters
ActiveUS20110018516A1Easy to controlTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionDc dc converterPower flow
Methods and apparatus for control of DC-DC converters. The DC-DC converter is operable so that the low side supply switch may be inhibited from turning on in a cycle following the high side supply switch turning off. Turn on of the low side switch is inhibited if the time between turn off of the high side switch and the inductor (L) current reaching zero is less than a predetermined duration. Inhibiting the low side switch from turning on can prevent the inductor current from going negative, which would reduce the efficiency of the converter. When turn on of the low side switch is inhibited the inductor current flows through a parallel path, such as a parasitic body diode associated with the low side switch, which allows current flow in one direction only.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
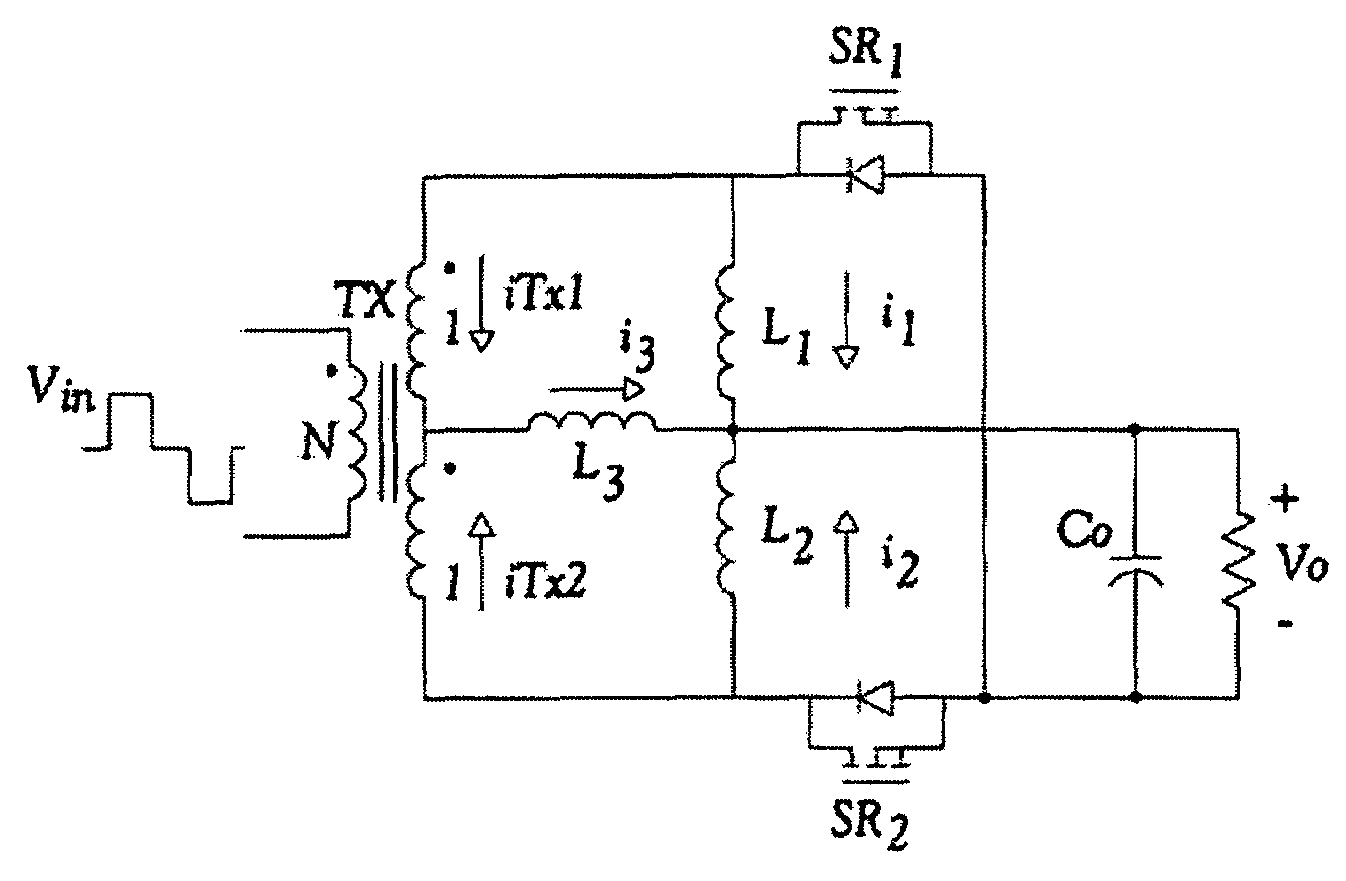
Isolated DC-DC converters with high current capability
ActiveUS7471524B1Improved thermal managementSimplified magnetic designAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionStable stateDc dc converter
A DC-to-DC converter having a transformer with a primary and a tapped secondary, two serial output filter inductors connected parallel with the secondary, a center output filter inductor connected between the secondary tap and serial output inductors, two serially connected switches connected in parallel with the two output inductors for receiving a signal to control operation of the switches during steady state and an output load connected between the serial connection of the serial output inductors and serial switching devices. The transformer primary side connected with double-ended primary-side topologies. The transformer secondary and output filers configured to form a current tripler rectifier, current quadtupler rectifier or current N-tuper rectifier. The output filter inductors evenly share output current resulting in reduction of current and thermal stress during high current application and the rectification topology has simple driving for synchronous rectifier application without increasing complexity of control and operation of primary-side topologies.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
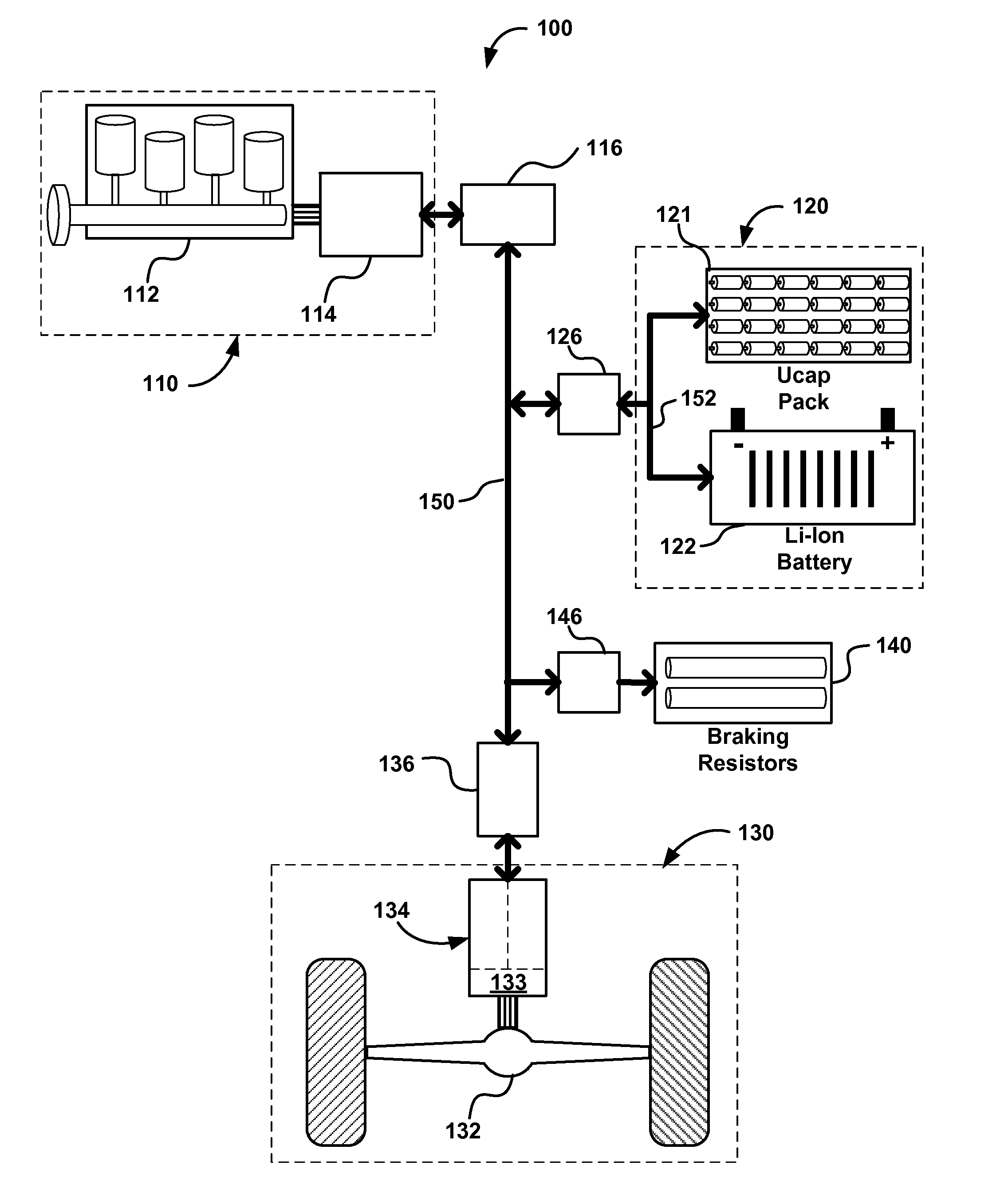
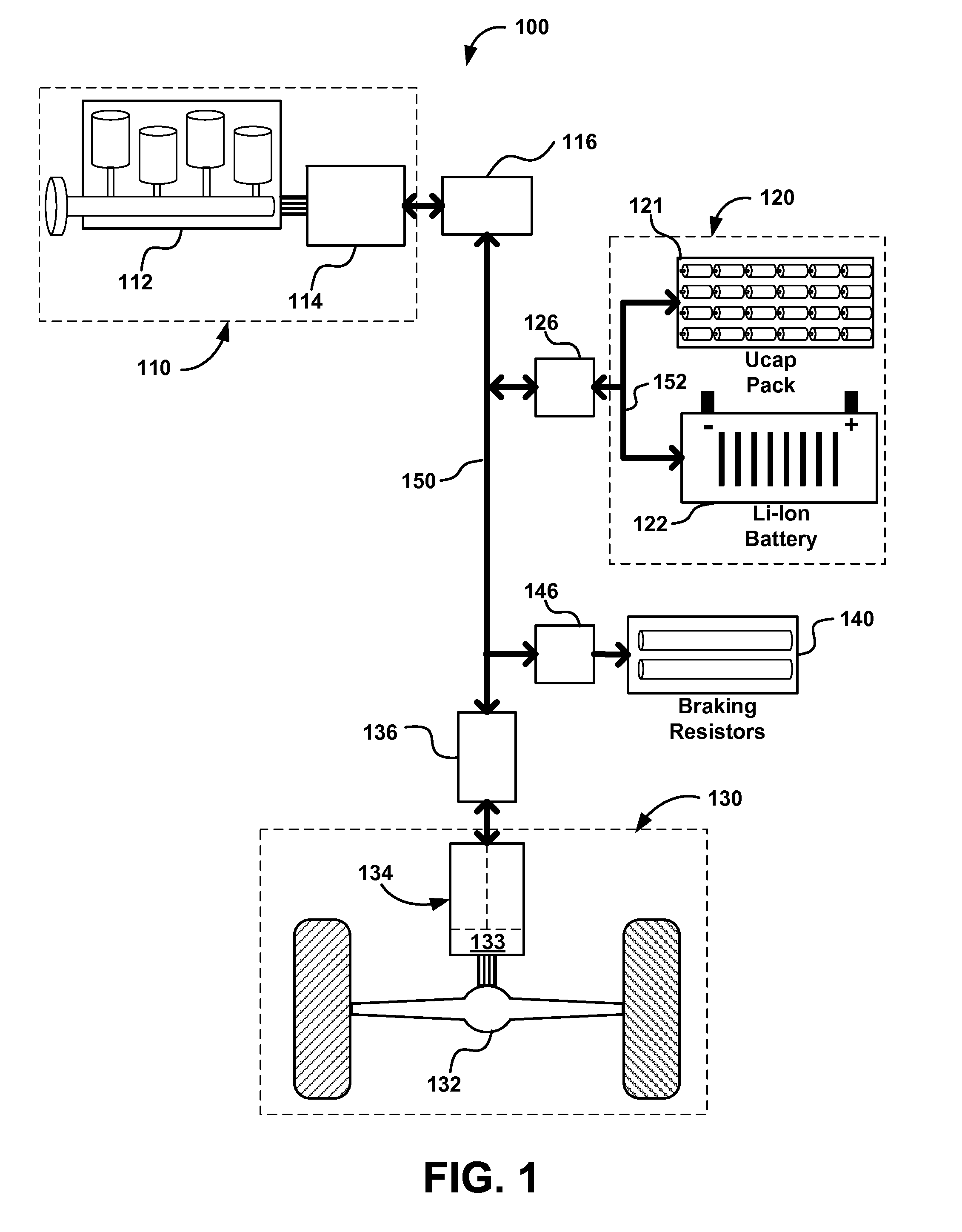
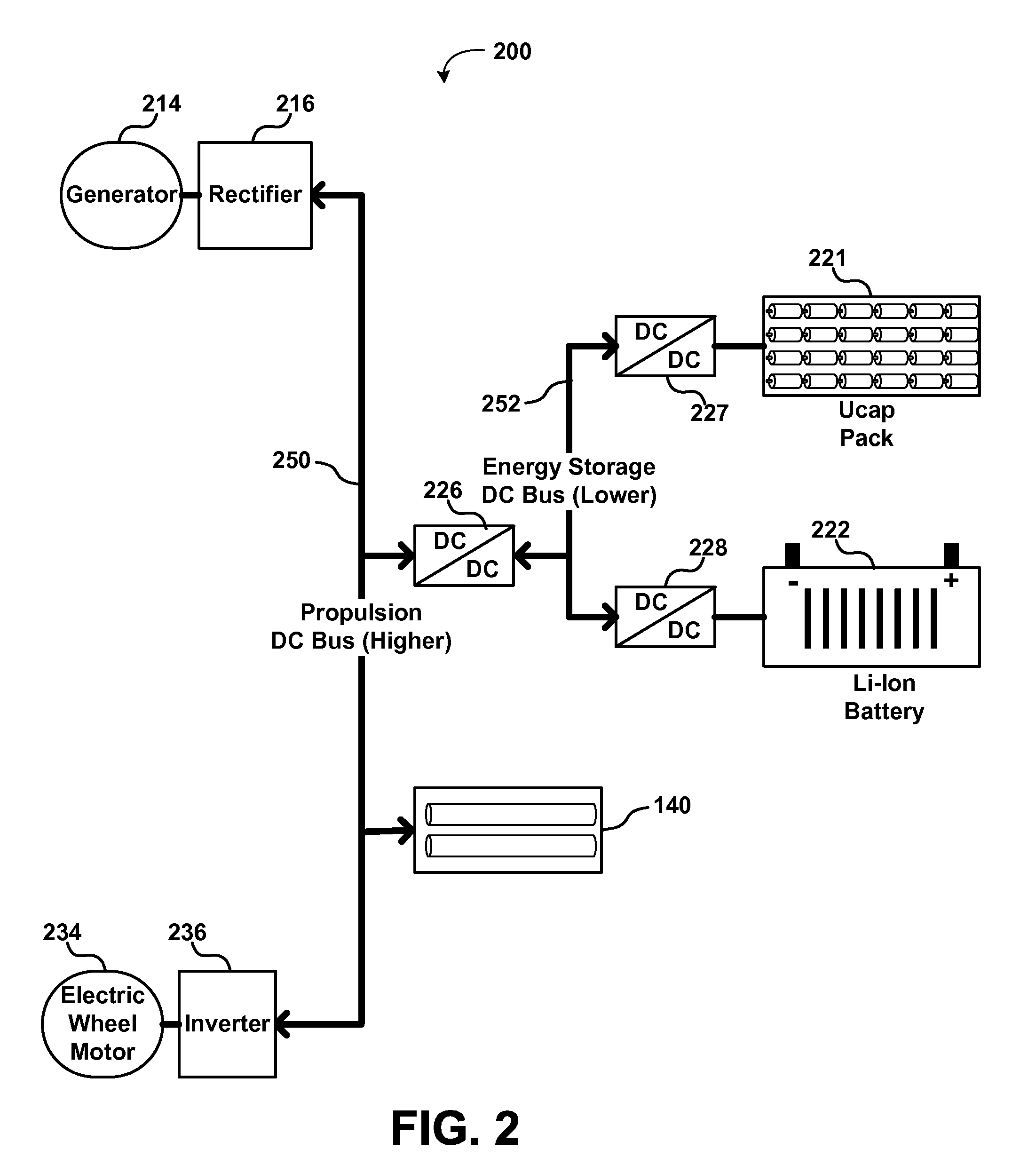
Propulsion Energy Storage Control System and Method of Control
InactiveUS20110100735A1Efficient and inexpensive and reliableElectrodynamic brake systemsPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsElectricityControl system
A propulsion energy storage control system and method of control interspersed between a heavy duty hybrid-electric drive system and its propulsion energy storage. The control system having an energy storage DC bus, electrical interfaces to the drive system and a plurality of propulsion energy storage subsystems, DC-to-DC converters at each interface, and a controller configured to operate each DC-to-DC converter independently such that power flow may charge, discharge, and shuttle between the plurality of propulsion energy storage subsystems.
Owner:SHEPPARD MULLIN RICHTER & HAMPTON
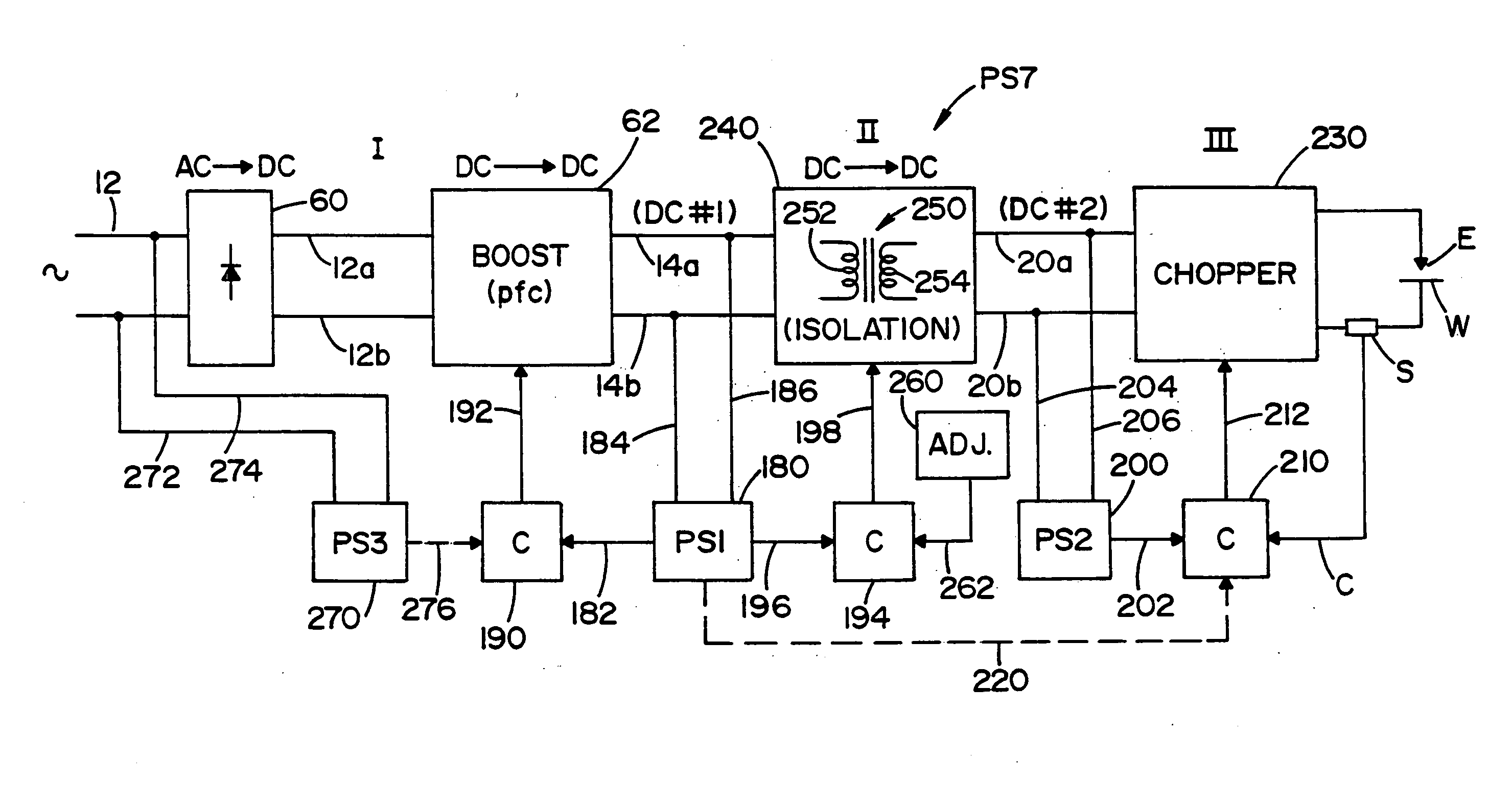
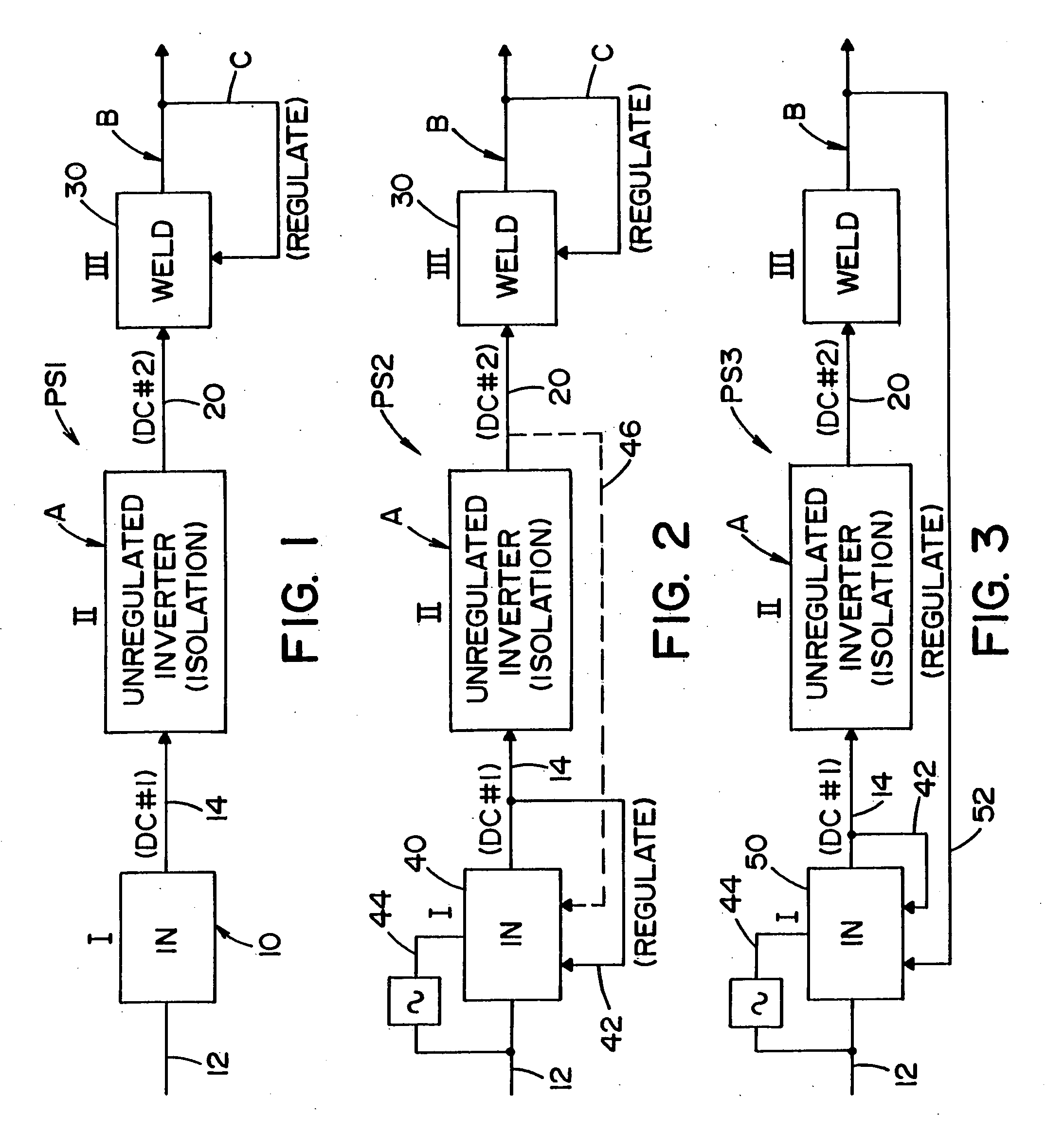
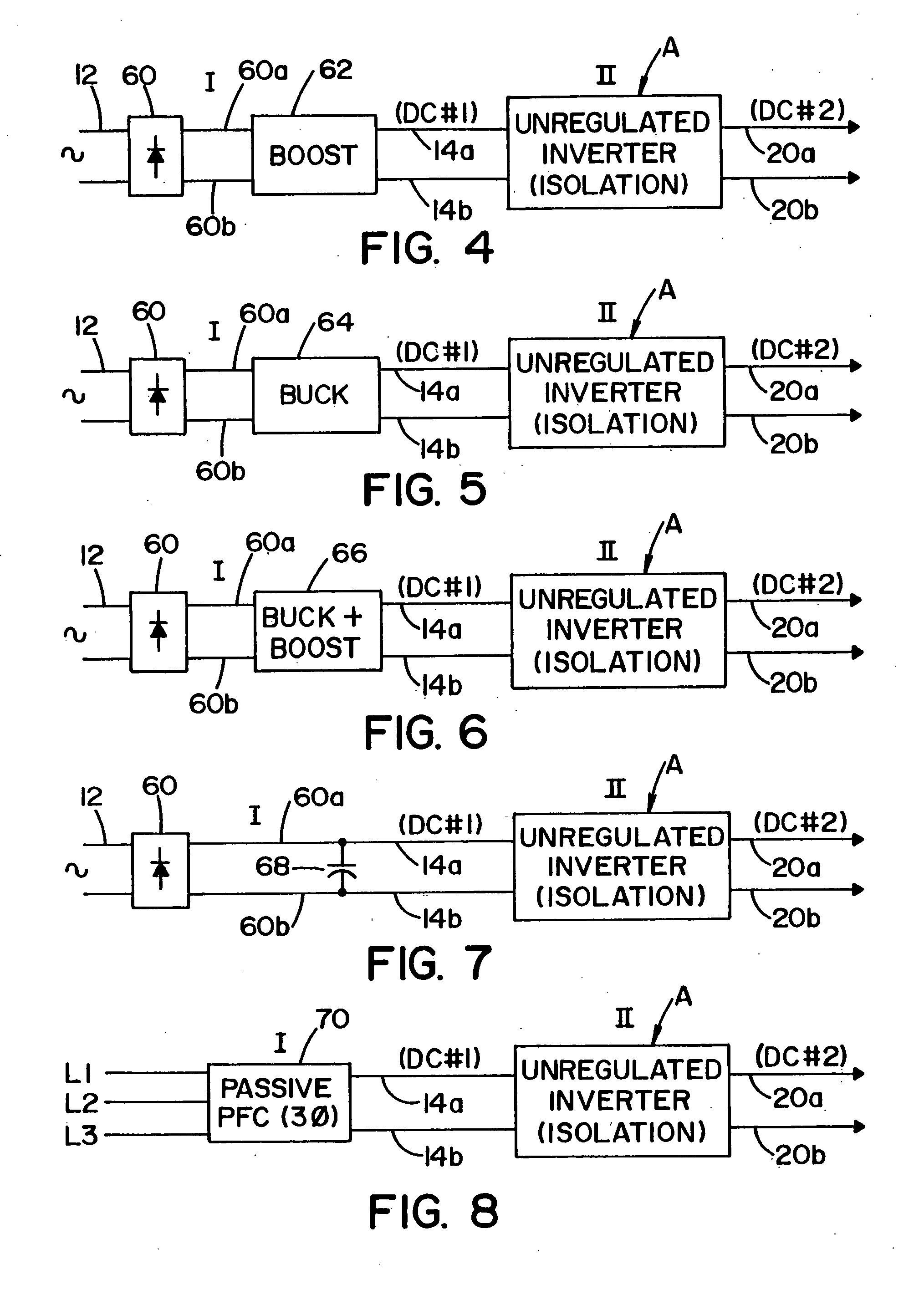
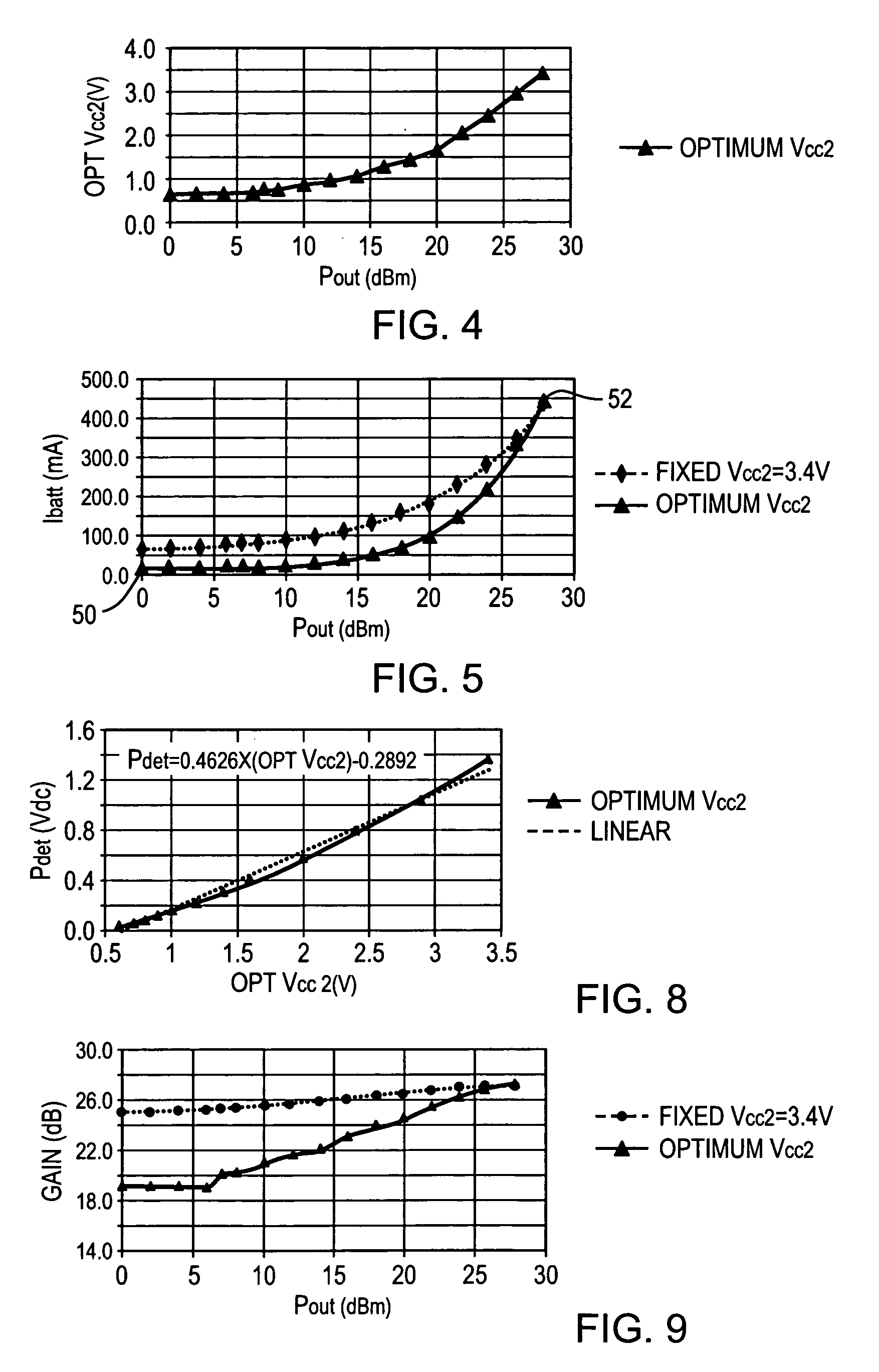
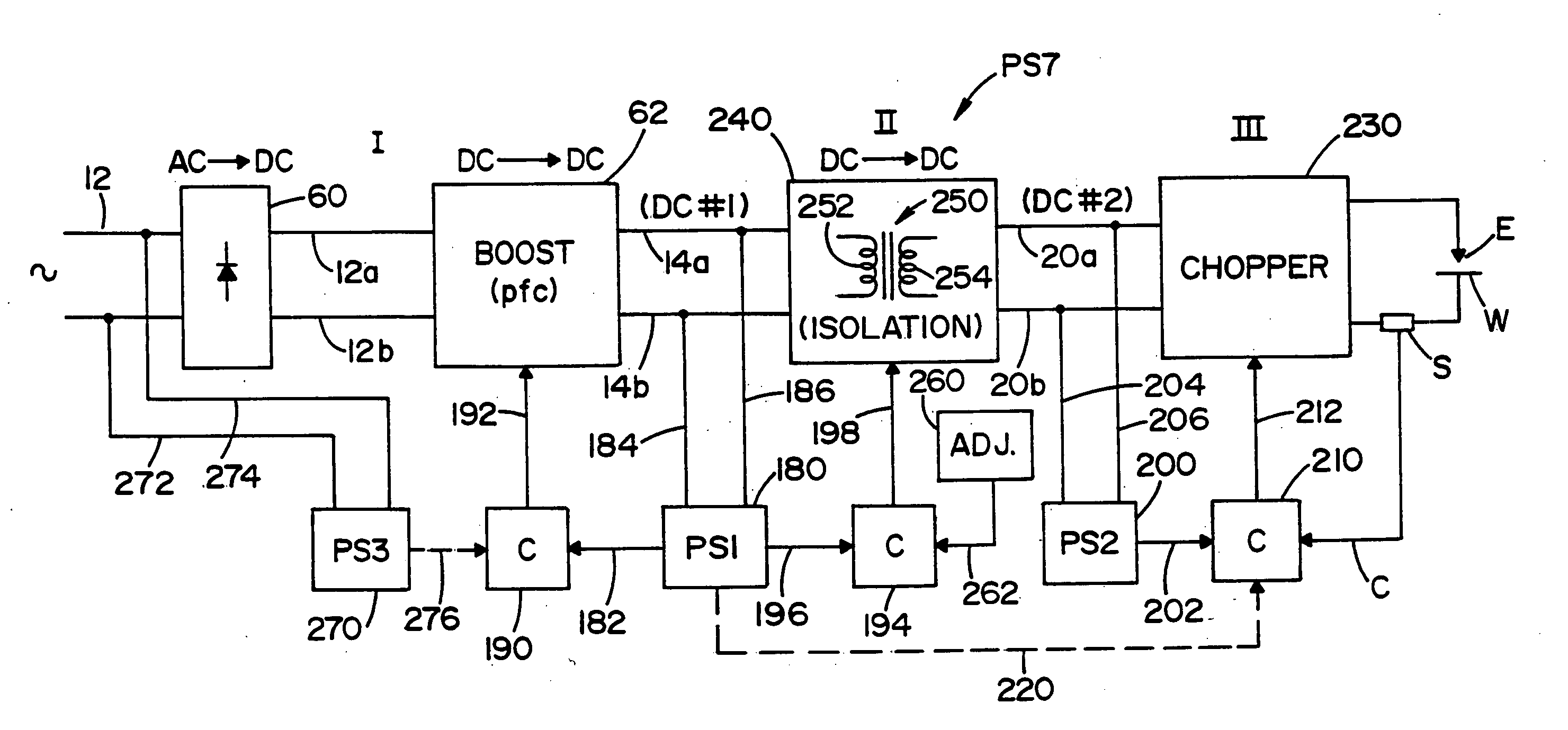
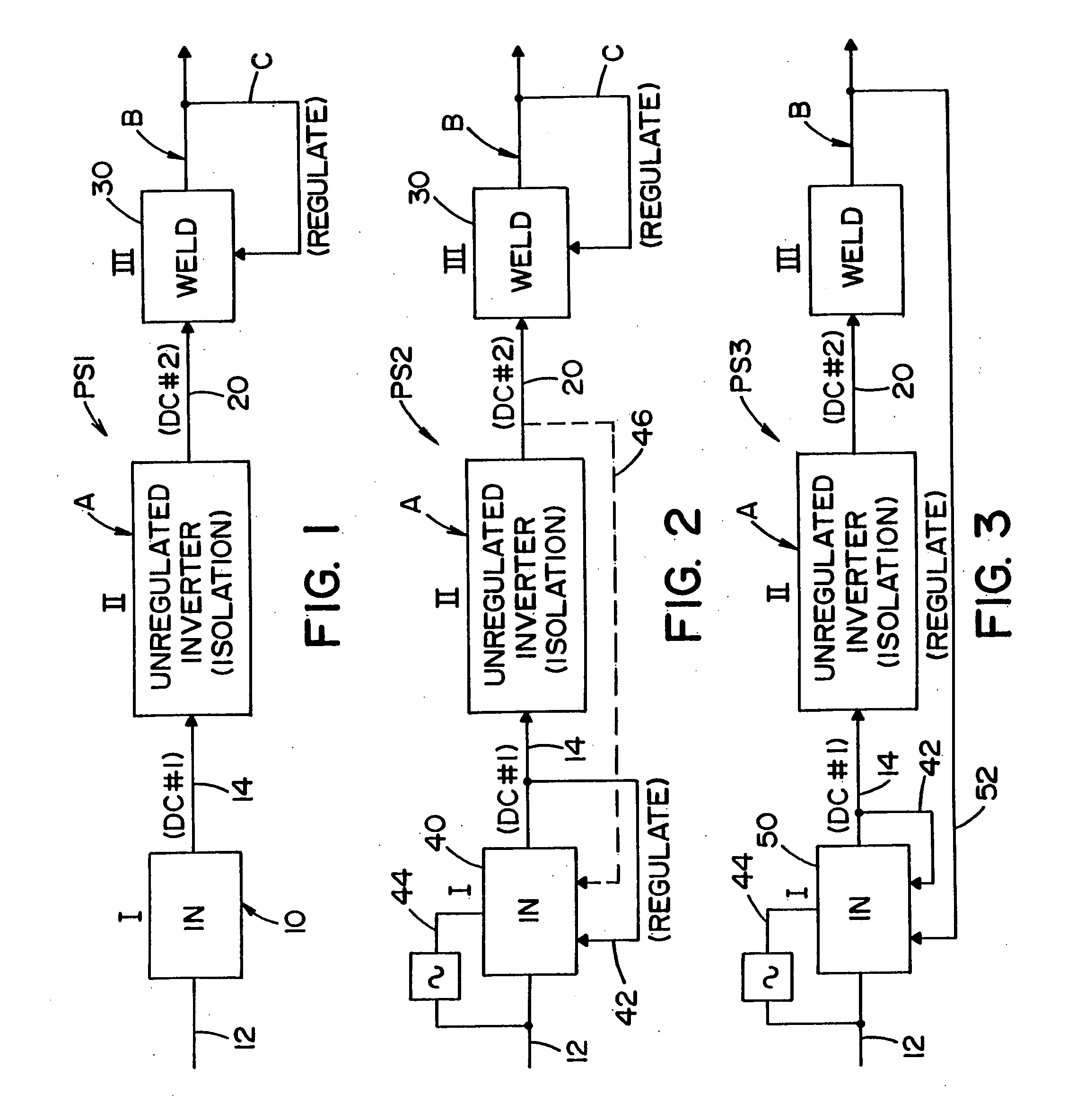
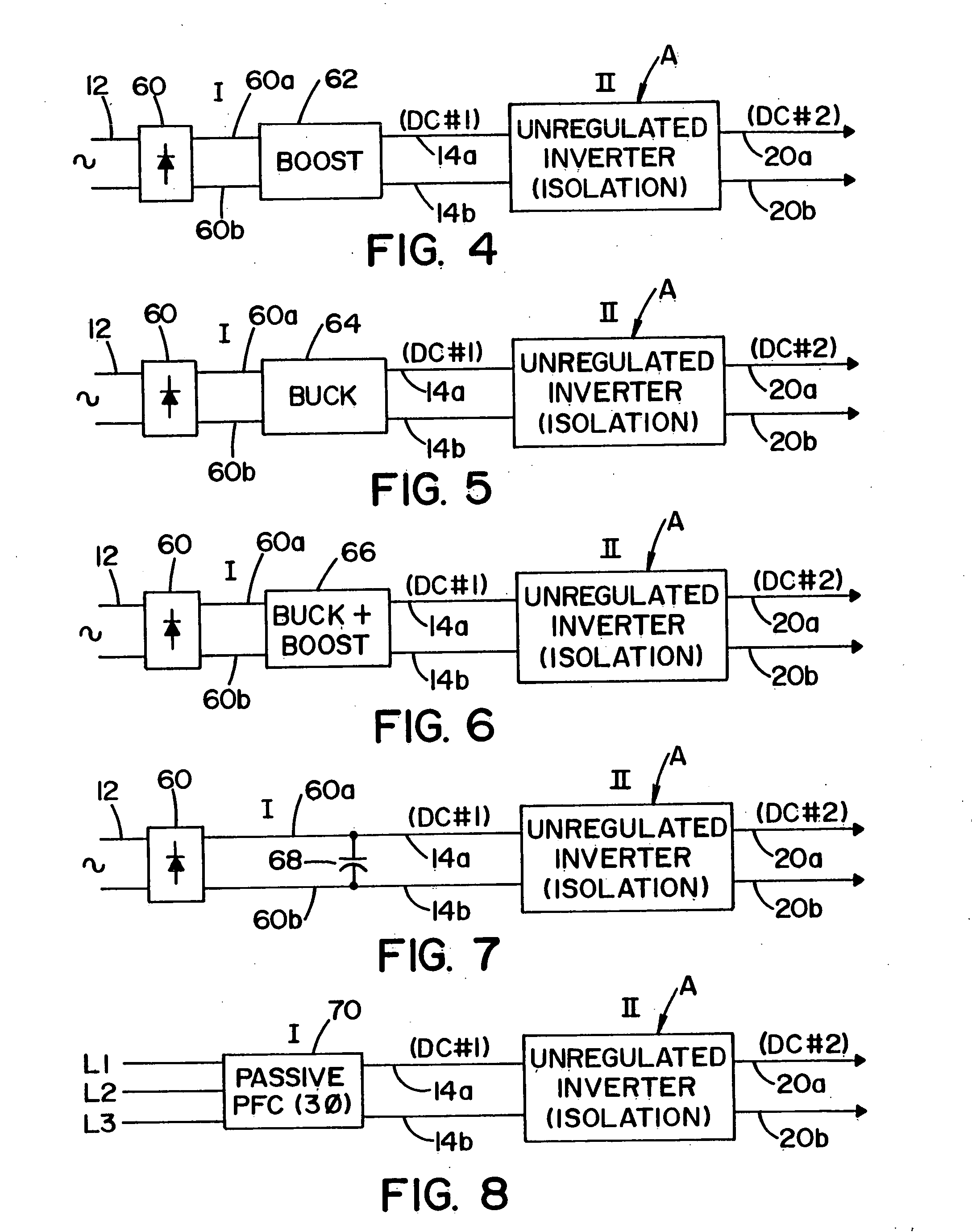
Three stage power source for electric ARC welding
ActiveUS20060213890A1Fast switching speedImprove portabilityEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionSoft switchingEngineering
A three stage power source for an electric arc welding process comprising an input stage having an AC input and a first DC output signal; a second stage in the form of an unregulated DC to DC converter having an input connected to the first DC output signal, a network of switches switched at a high frequency with a given duty cycle to convert the input into a first internal AC signal, an isolation transformer with a primary winding driven by the first internal high frequency AC signal and a secondary winding for creating a second internal high frequency AC signal and a rectifier to convert the second internal AC signal into a second DC output signal of the second stage, with a magnitude related to the duty cycle of the switches; and, a third stage to convert the second DC output signal to a welding output for welding wherein the input stage has a regulated DC to DC converter with a boost power switch having an active soft switching circuit.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
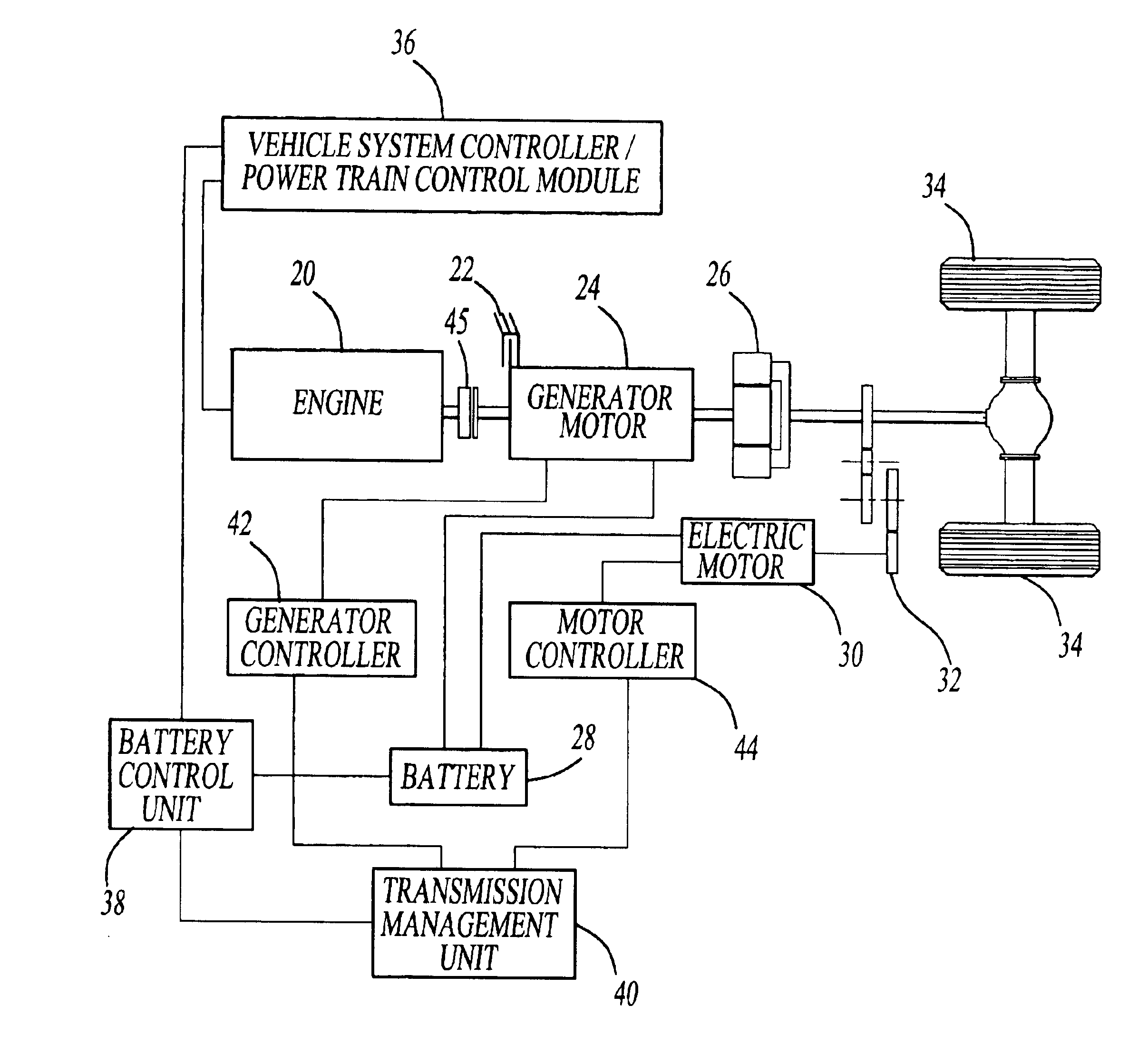
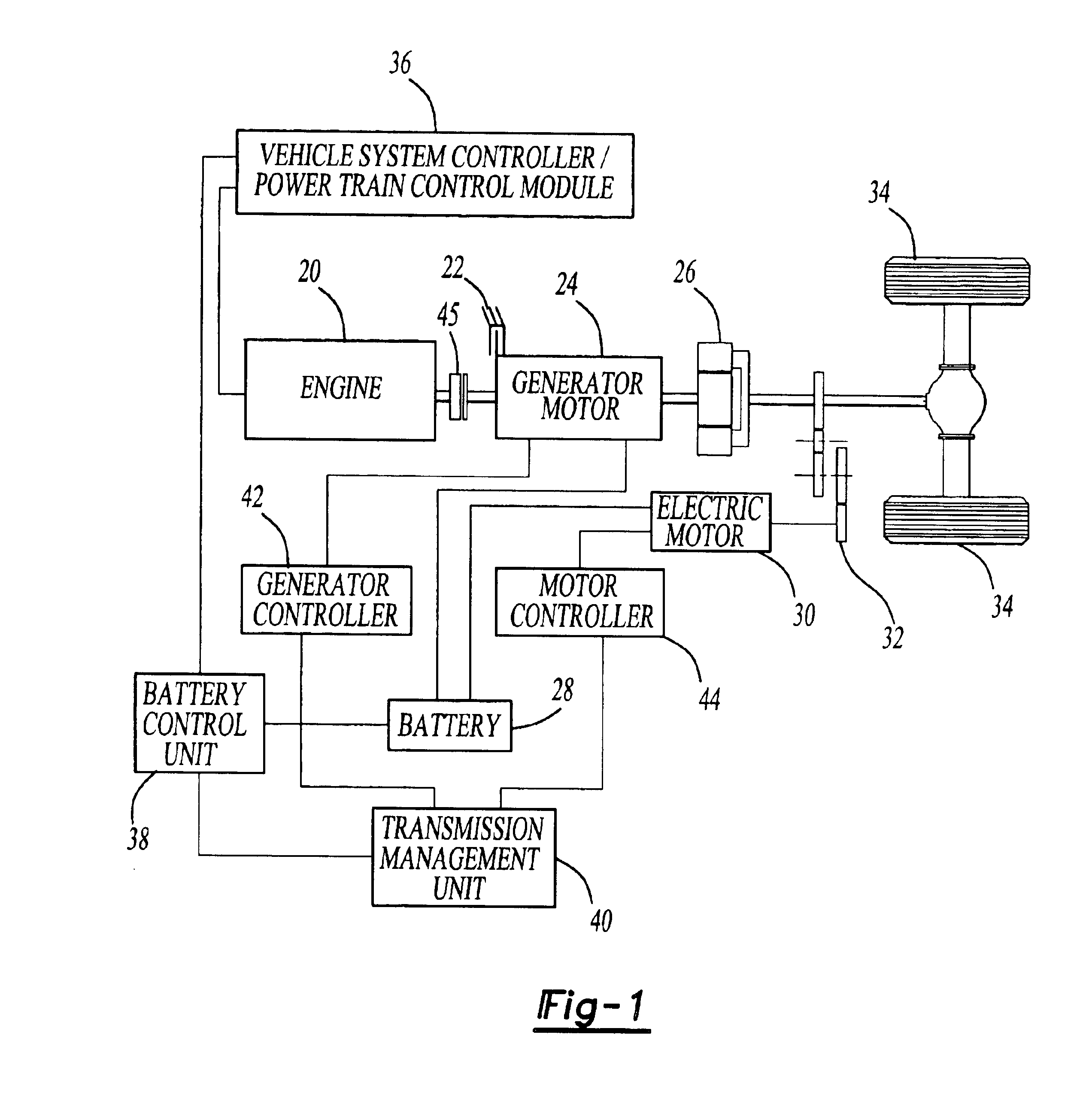
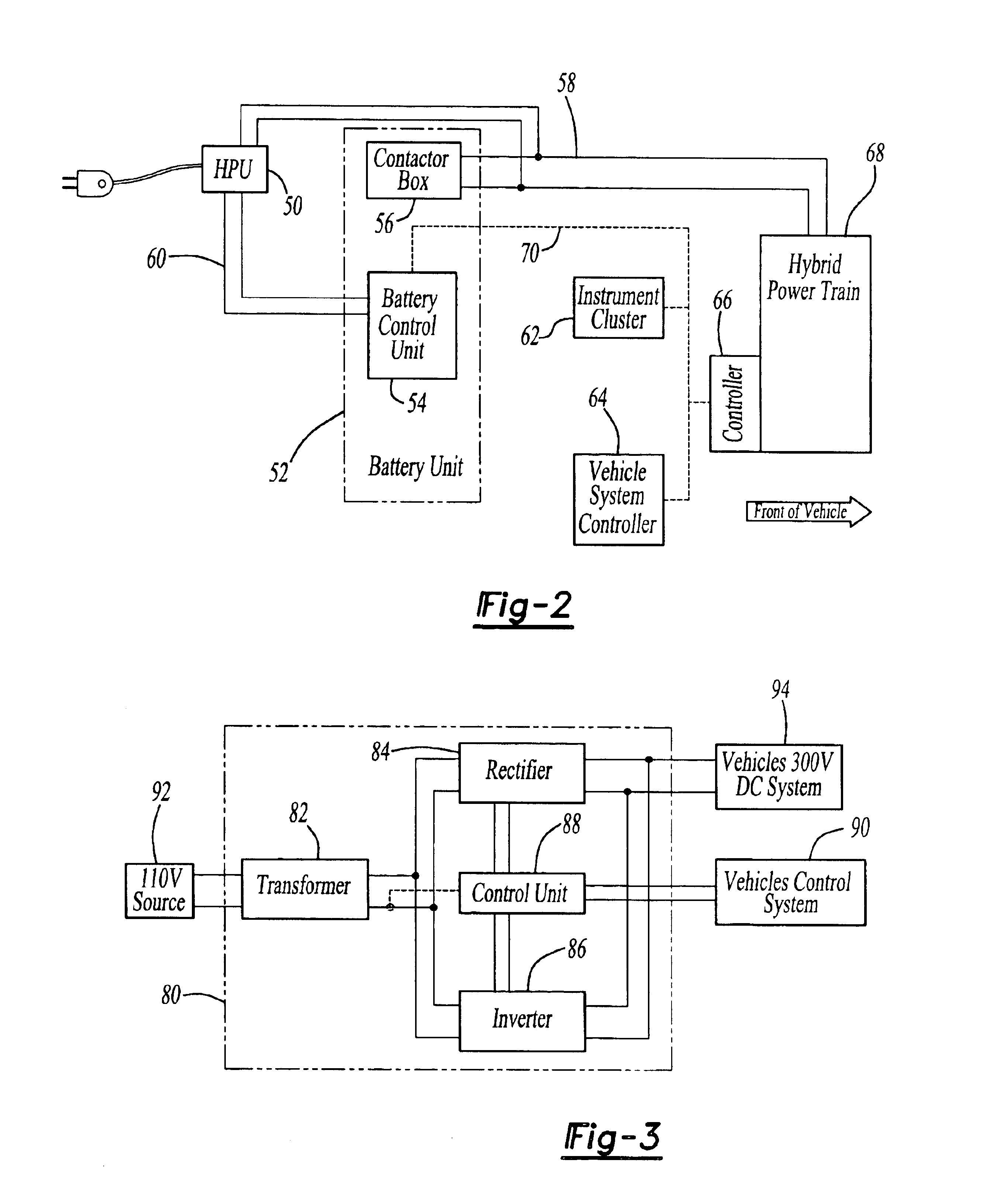
HEV charger/generator unit
The present invention provides an apparatus, system, and method of utilizing a Home Power Unit ("HPU") which functions as a battery charger for a Hybrid Electric Vehicle ("HEV") or as a generator, utilizing the HEV's electrical power to operate external electrical devices. In its simplest form, the HPU comprises a Transformer, inverter means, rectifier means, a control unit, connection means to the HEV and external electrical loads or sources and switching means to change operation between charger and generator function. Alternative embodiments of the present invention utilize the HEV's existing components thereby avoiding component redundancy within the HPU. Specifically, in the first alternative embodiment, the inverter means are utilized within the vehicle, therefore, requiring only filter and transformer to be added to the vehicle. In the second alternative embodiment, the vehicle's DC-to-DC Converter is utilized as opposed to implementing a transformer. Therefore, only an inverter and filter are added to the system.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
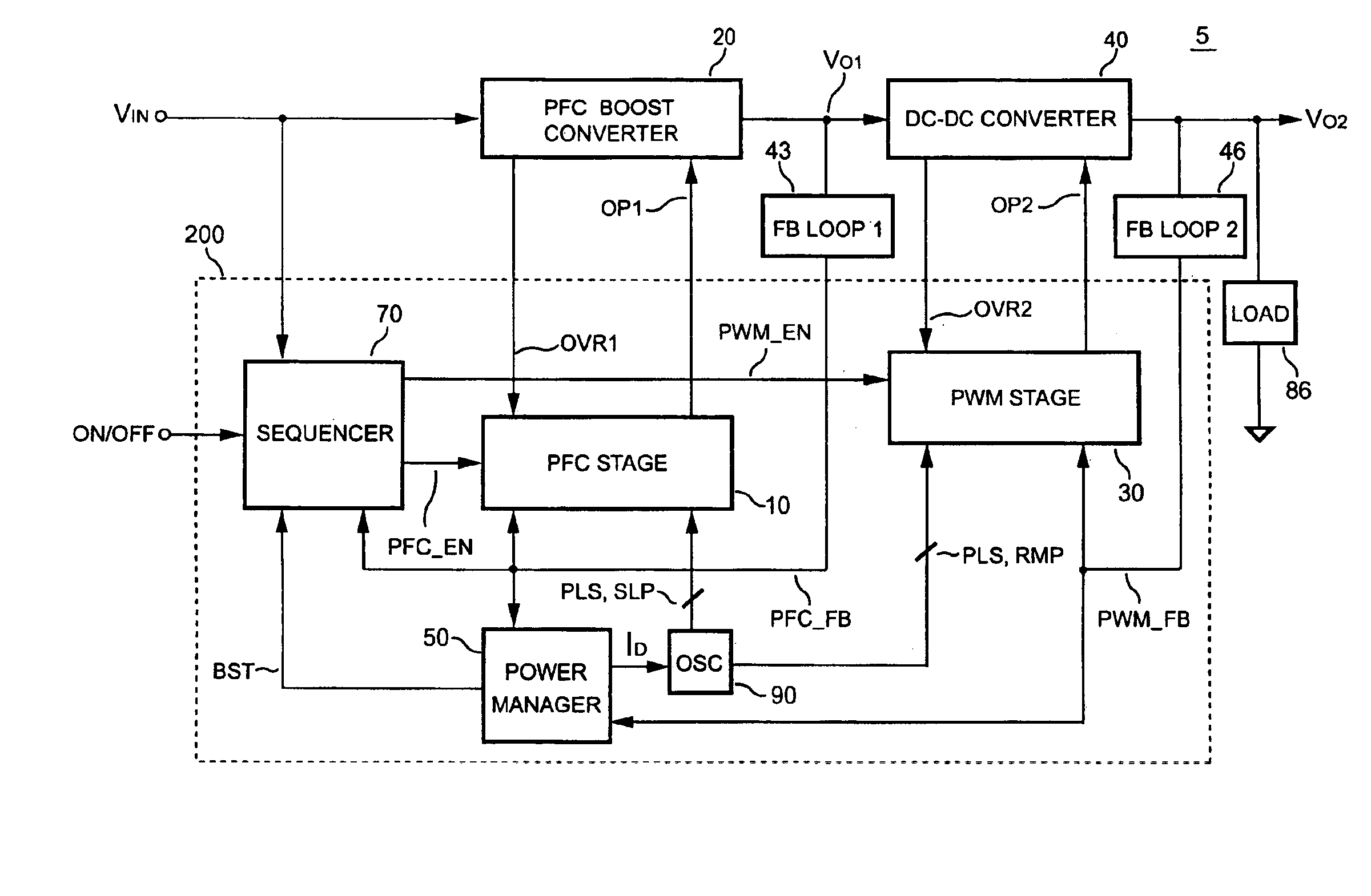
PFC-PWM controller having interleaved switching
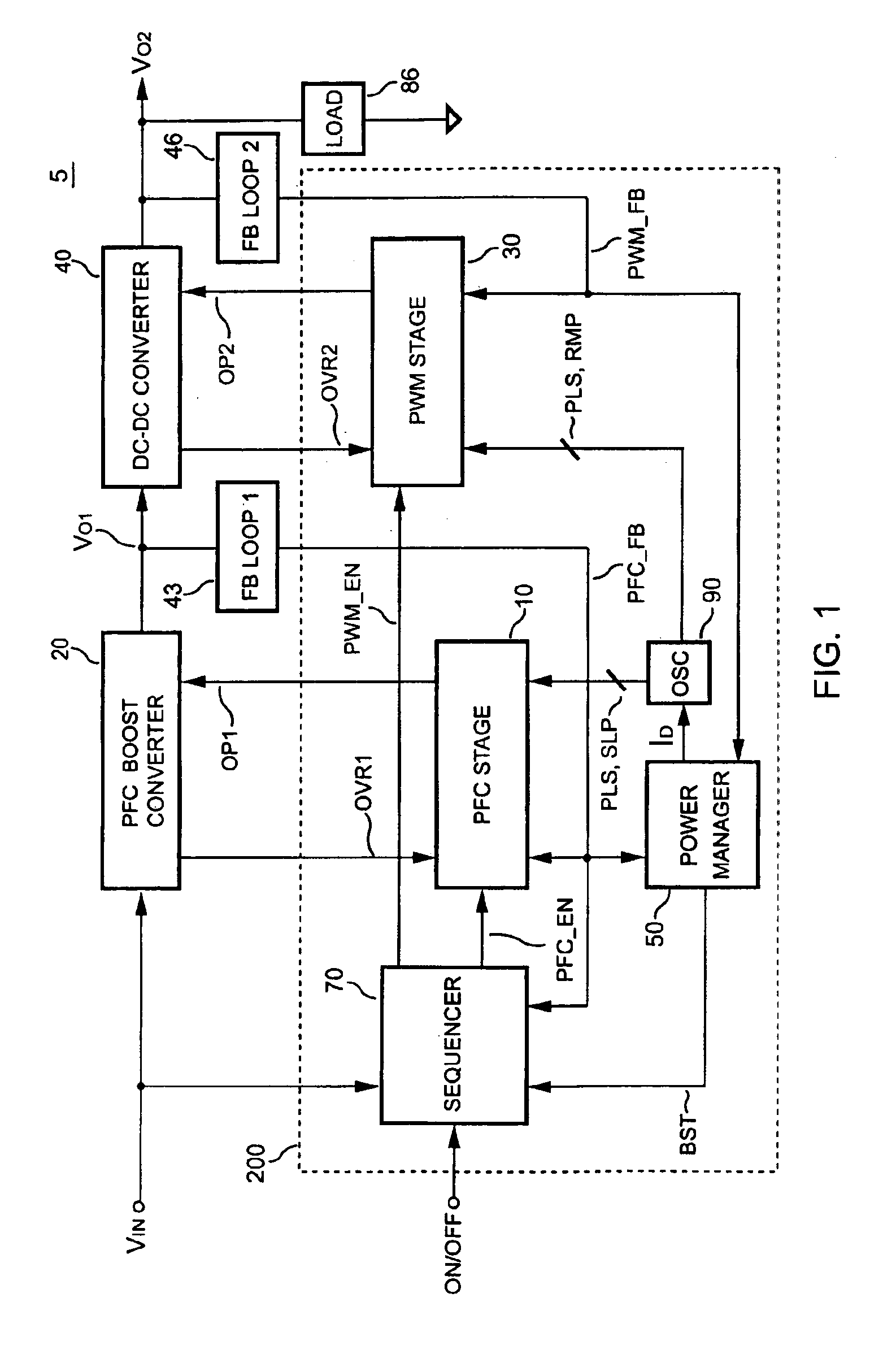
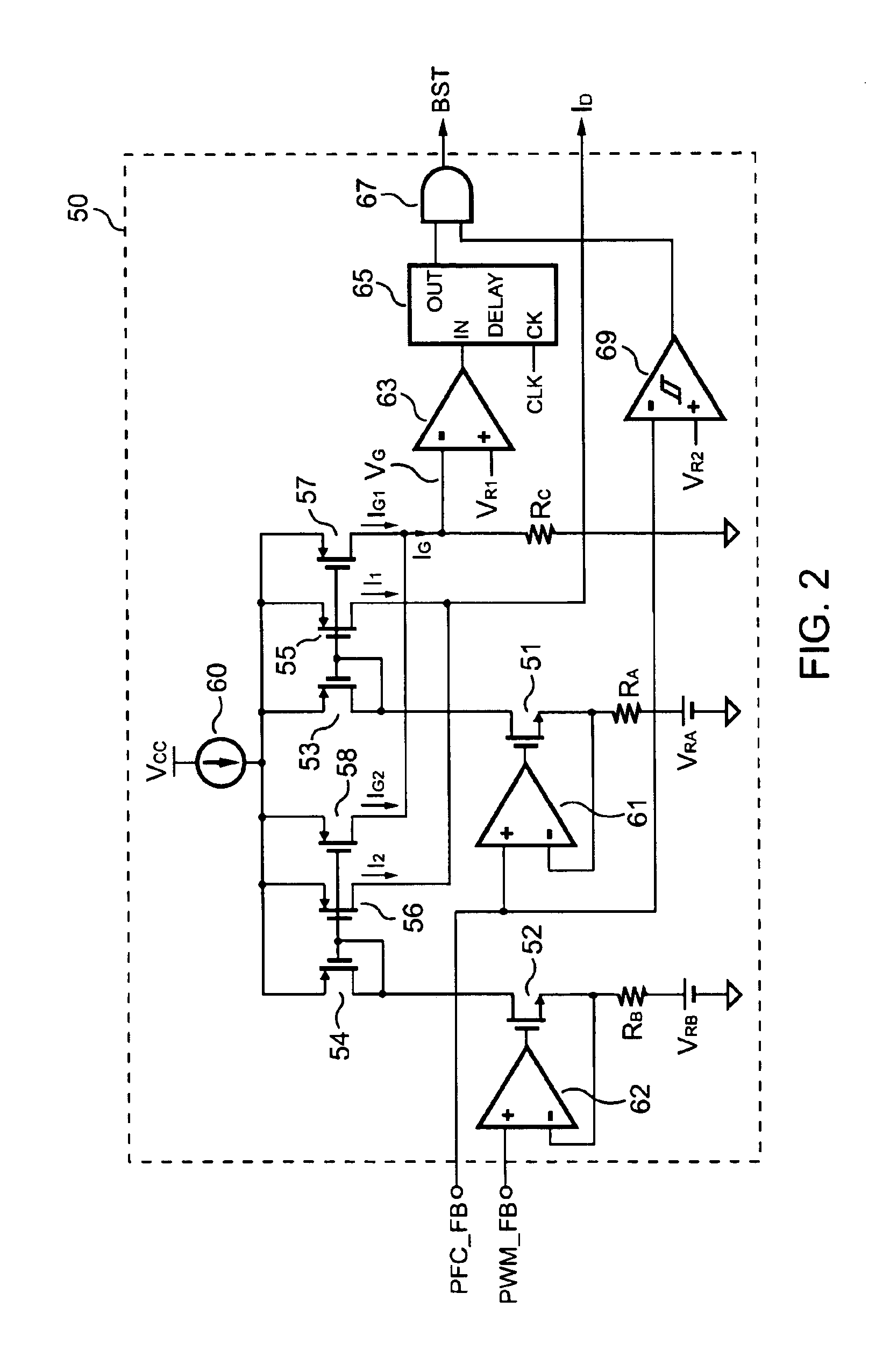
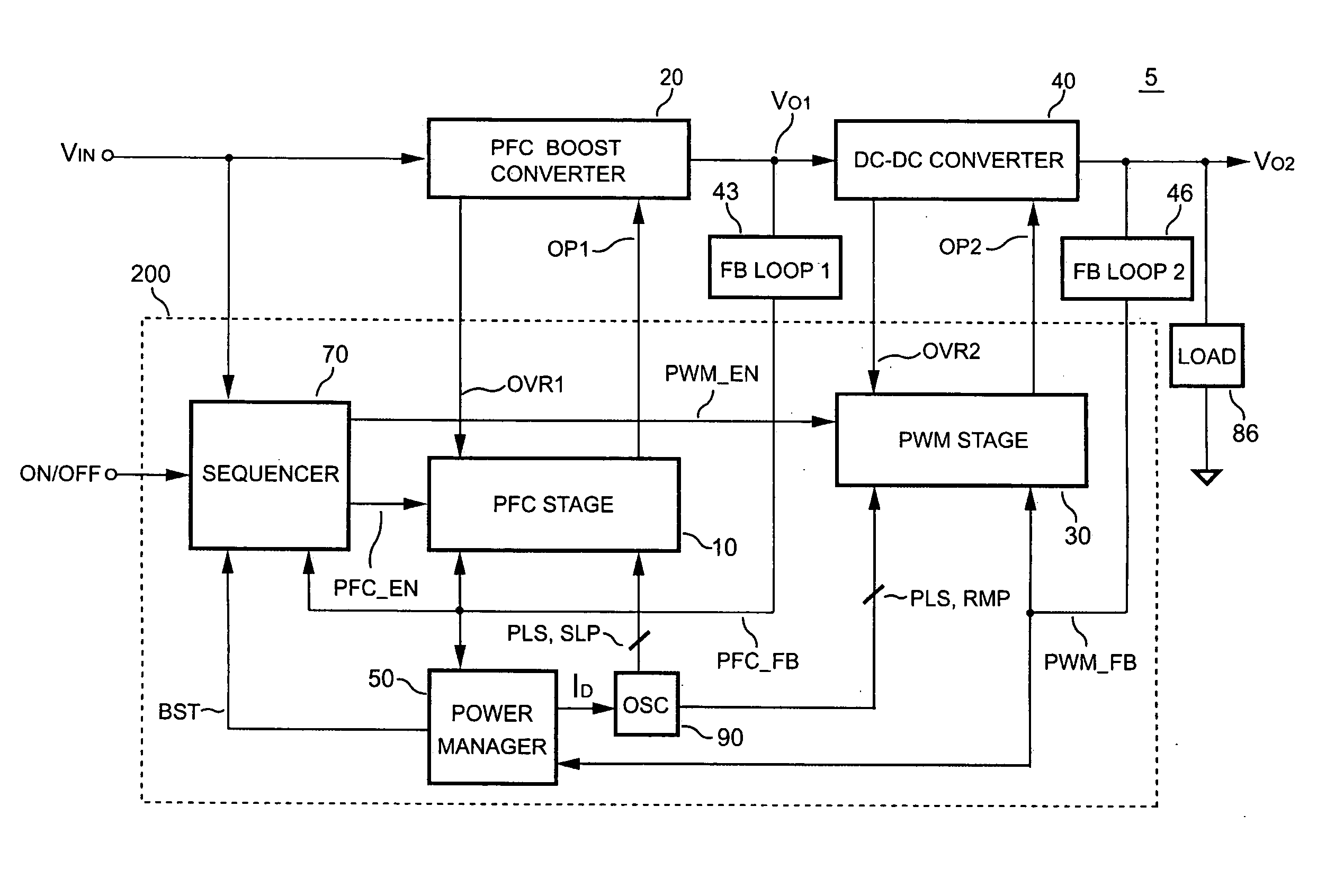
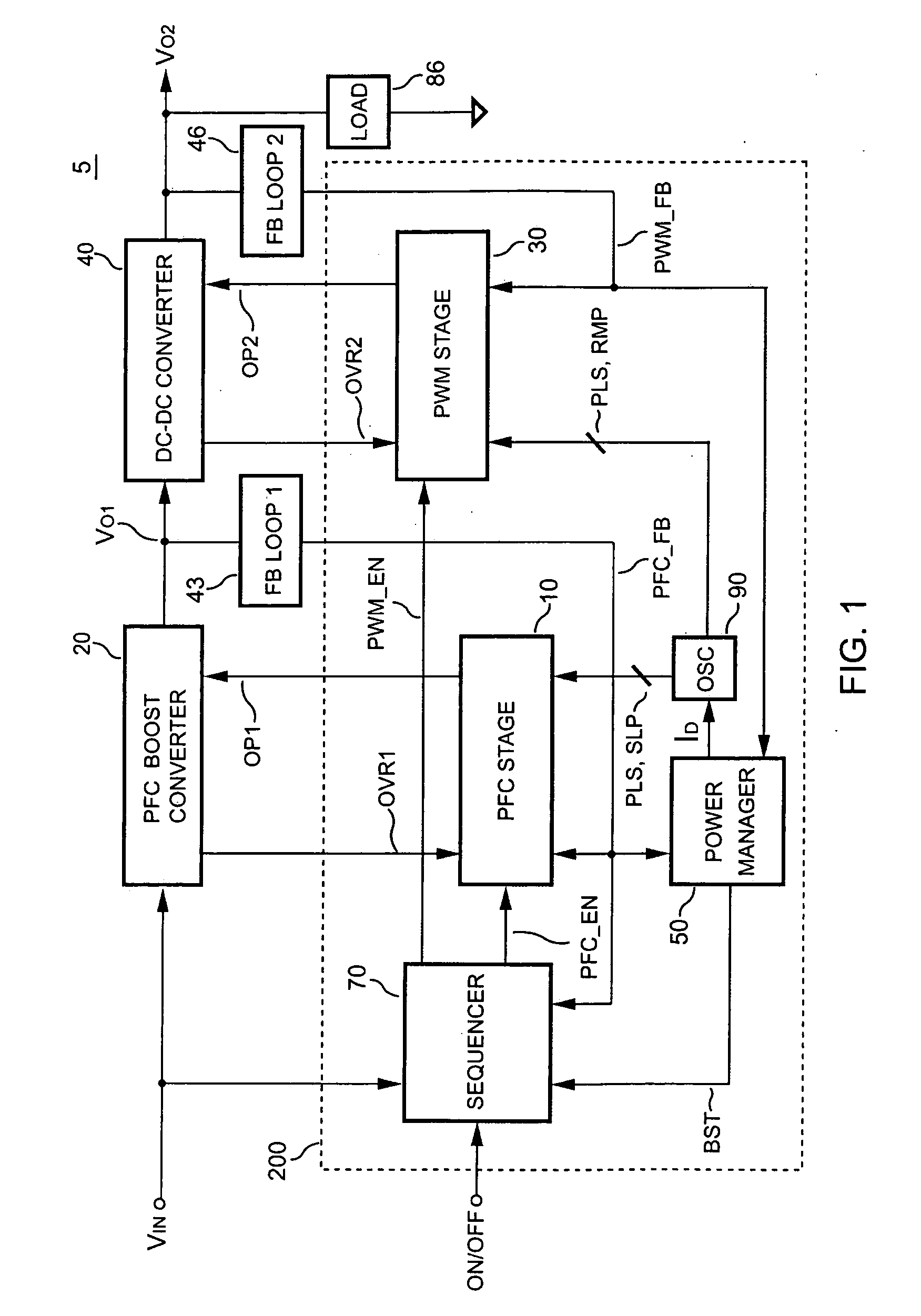
InactiveUS6903536B2Reduce switching noiseIncrease the pulse widthEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDead timeSwitching signal
The present invention discloses a PFC-PWM controller having interleaved switching. A PFC stage generates a PFC signal for switching a PFC boost converter of a power converter. A PWM stage generates a PWM signal for switching a DC-to-DC converter of the power converter. The PFC-PWM controller includes a power manager for generating a discharge current and a burst-signal. Under light-load conditions, the discharge current decreases in proportion to a load of the power converter. The burst signal is utilized to disable the PFC signal in a suspended condition for power saving. A pulse width of the pulse-signal ensures a dead time to spread switching signals, such as the PFC and PWM signals, and reduces switching noise. When the discharge current decreases, the pulse width of the pulse-signal will increase and a frequency of the pulse-signal will decrease correspondingly. This further reduces power consumption under light-load and zero-load conditions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
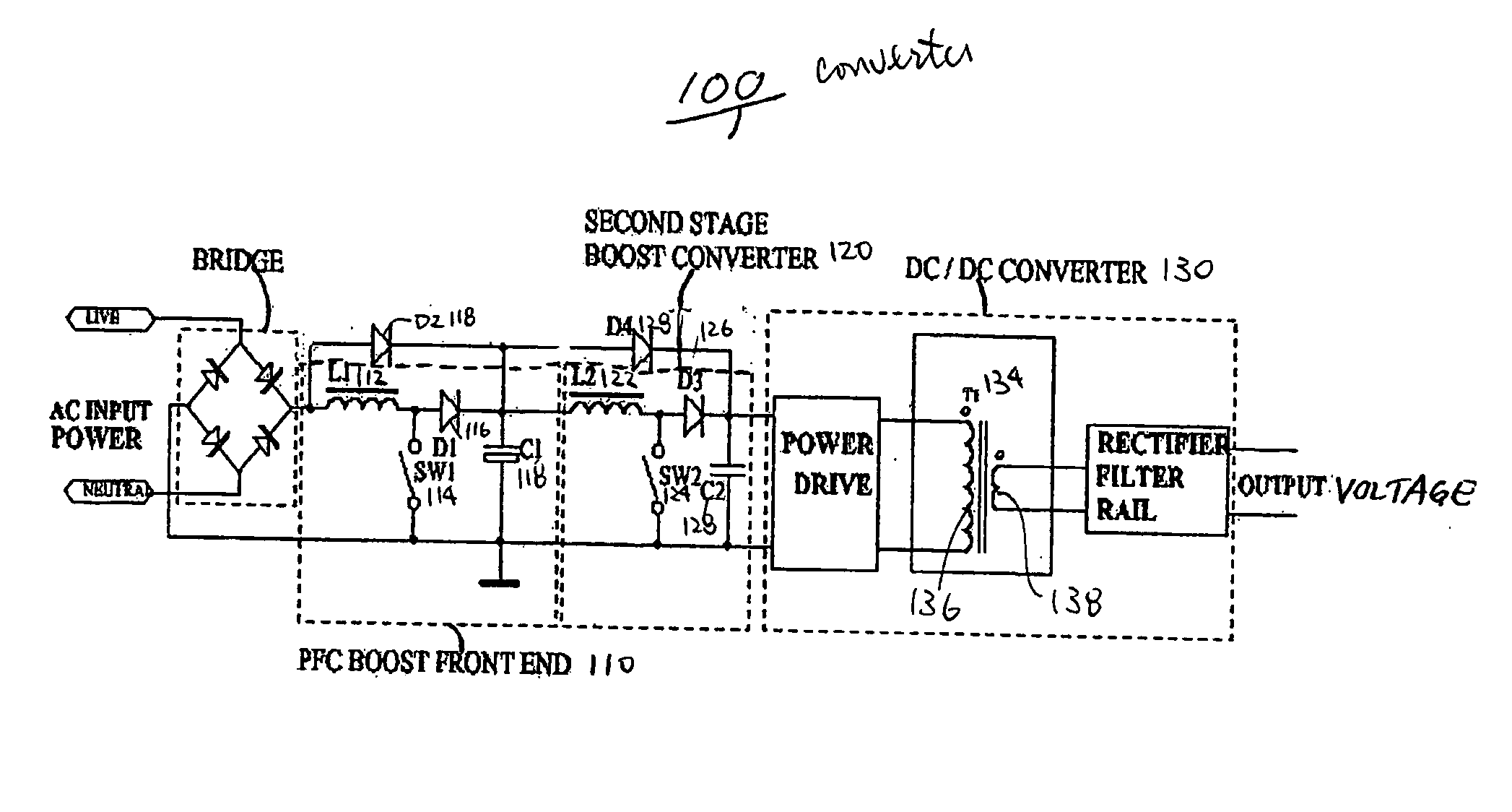
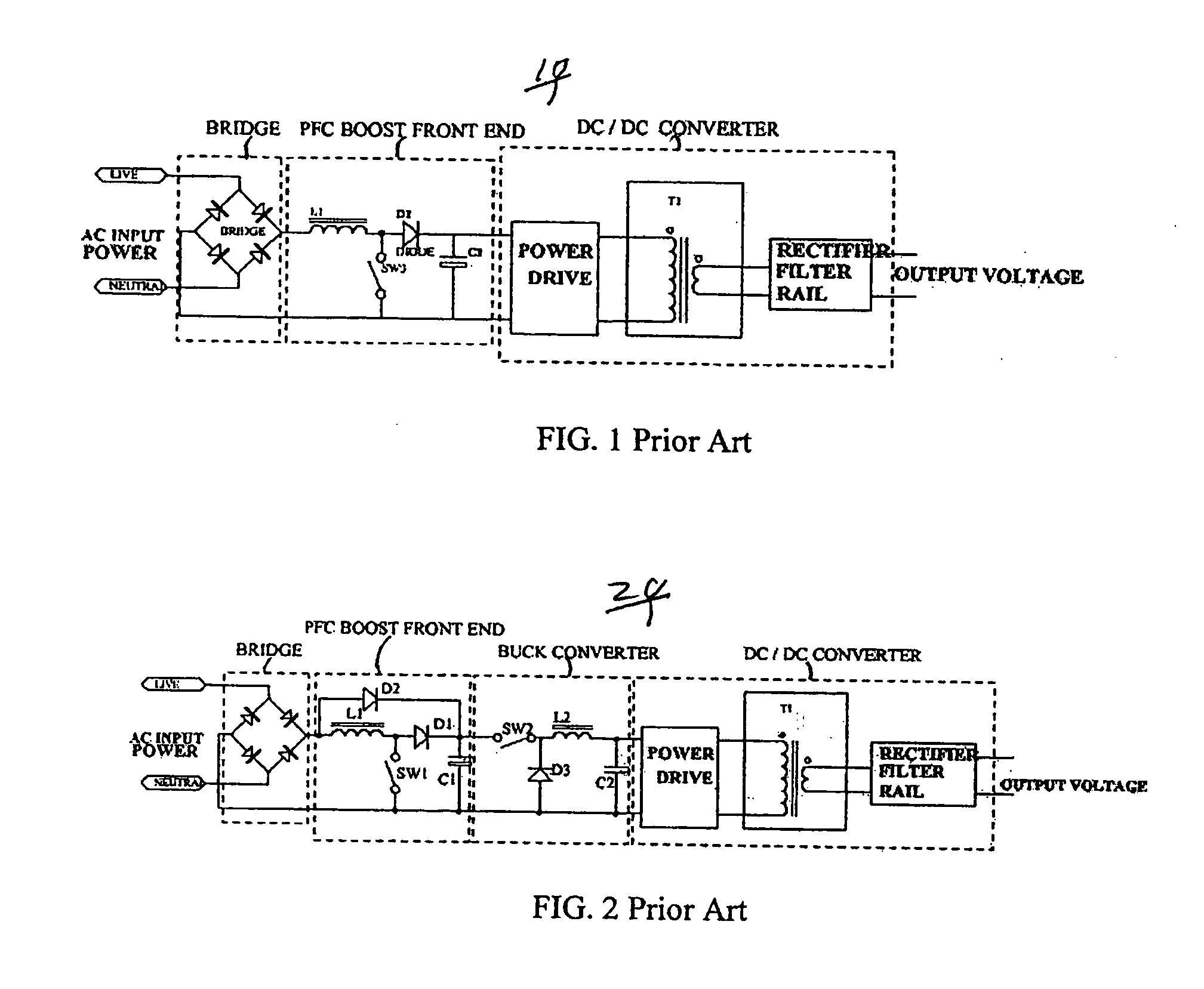
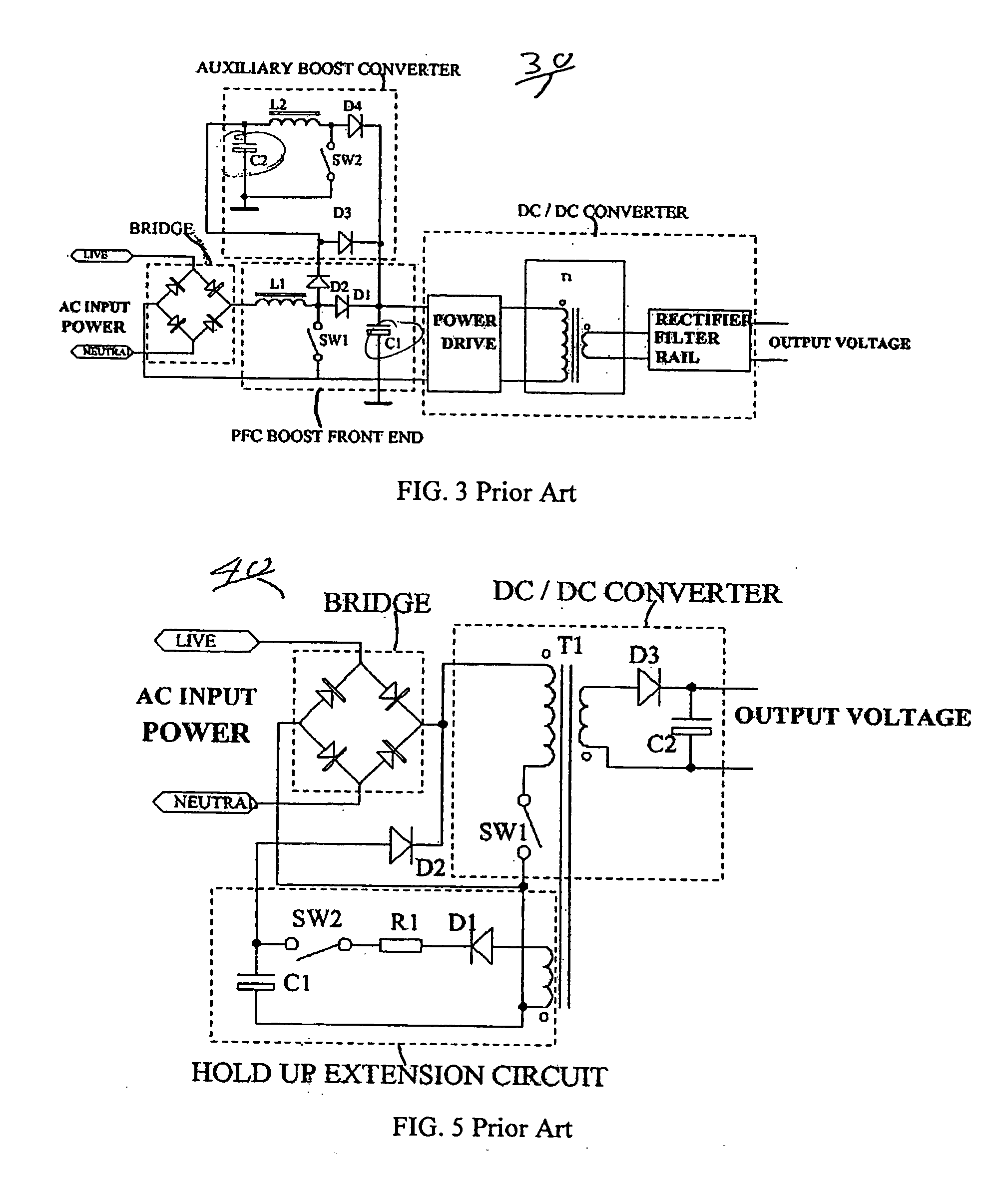
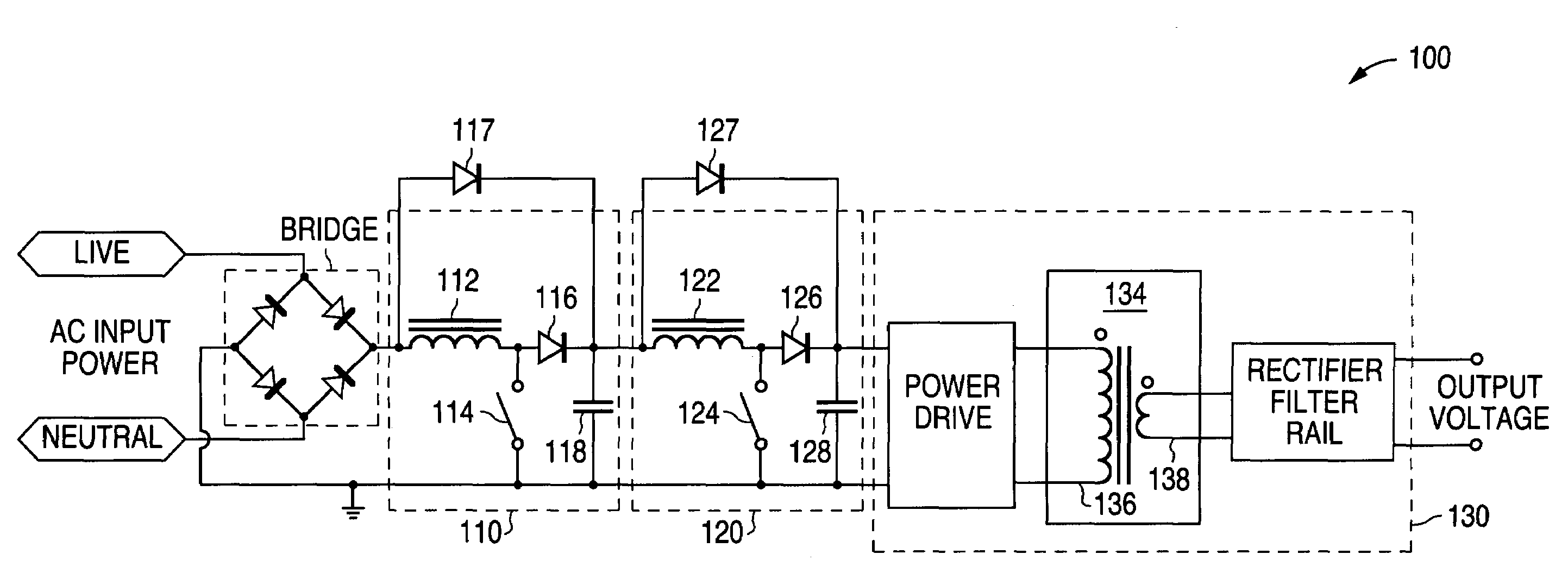
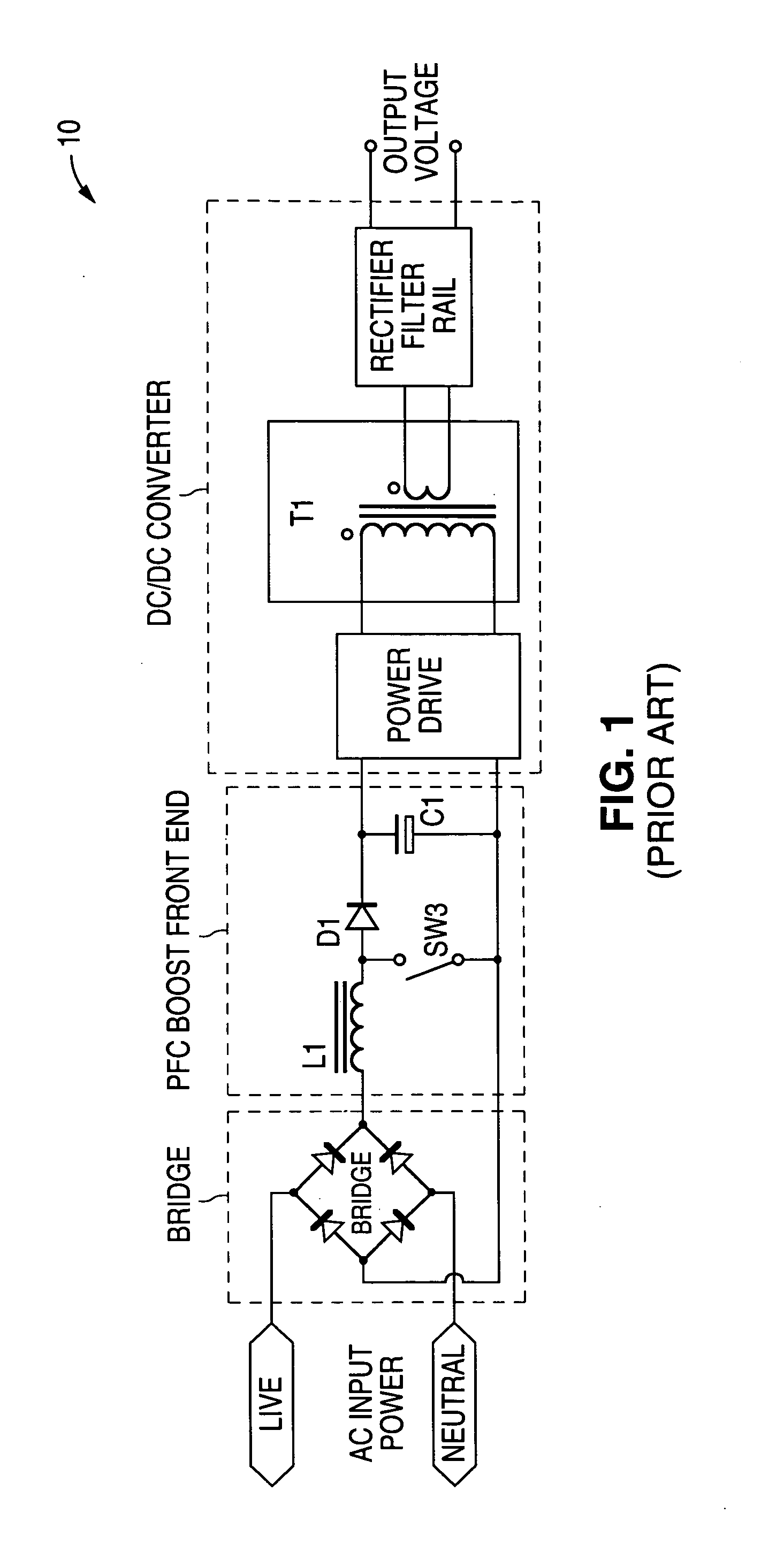
Circuit for maintaining hold-up time while reducing bulk capacitor size and improving efficiency in a power supply
InactiveUS7061212B2Improve efficiencyReduces peak current and voltage stressEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceDc dc converter
A circuit that utilizes most of the energy stored in the bulk capacitor of an AC to DC or DC to DC converter power supply by providing an intermediate converter between a first stage boost converter and a DC-DC converter. When the bulk voltage starts to fall during the hold-up time, the intermediate converter boosts the falling voltage to maintain the regulated DC input to the DC to DC converter while reducing the operating range and increasing the operating duty cycle, so as to increase efficiency, reduce peak current and voltage stresses. The circuit also reduces the size of the output filter components and reduces the size of the bulk capacitance by up to half.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
Electric ARC welder and plasma cutter
InactiveUS6023037AReduce Harmonic DistortionImprove power factorAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcFull waveTransformer coupling
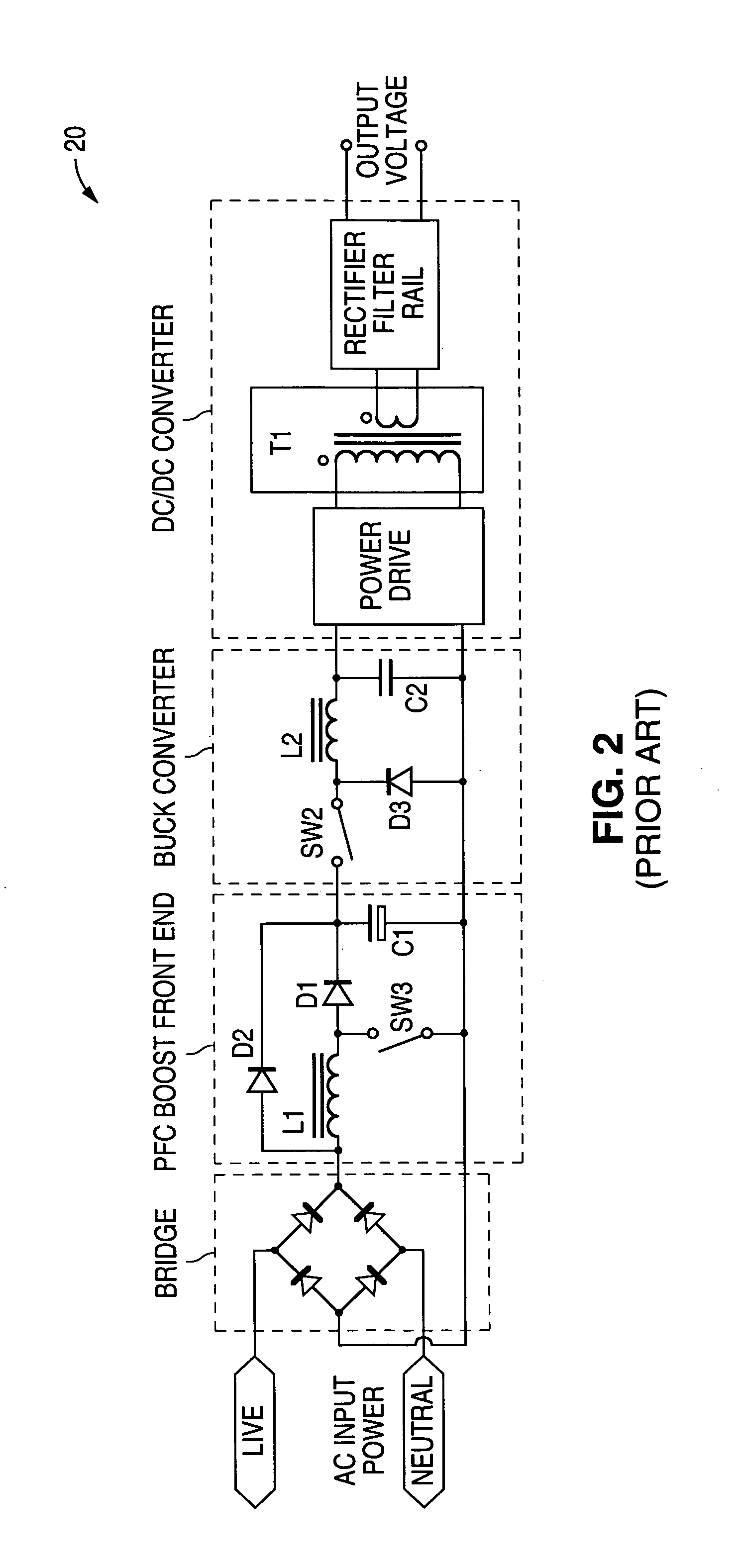
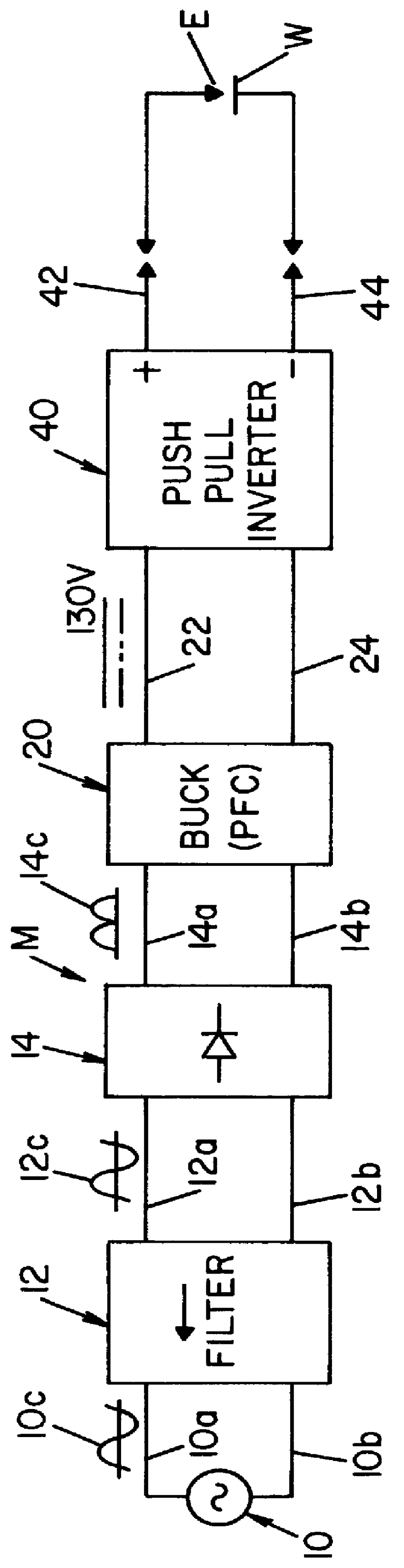
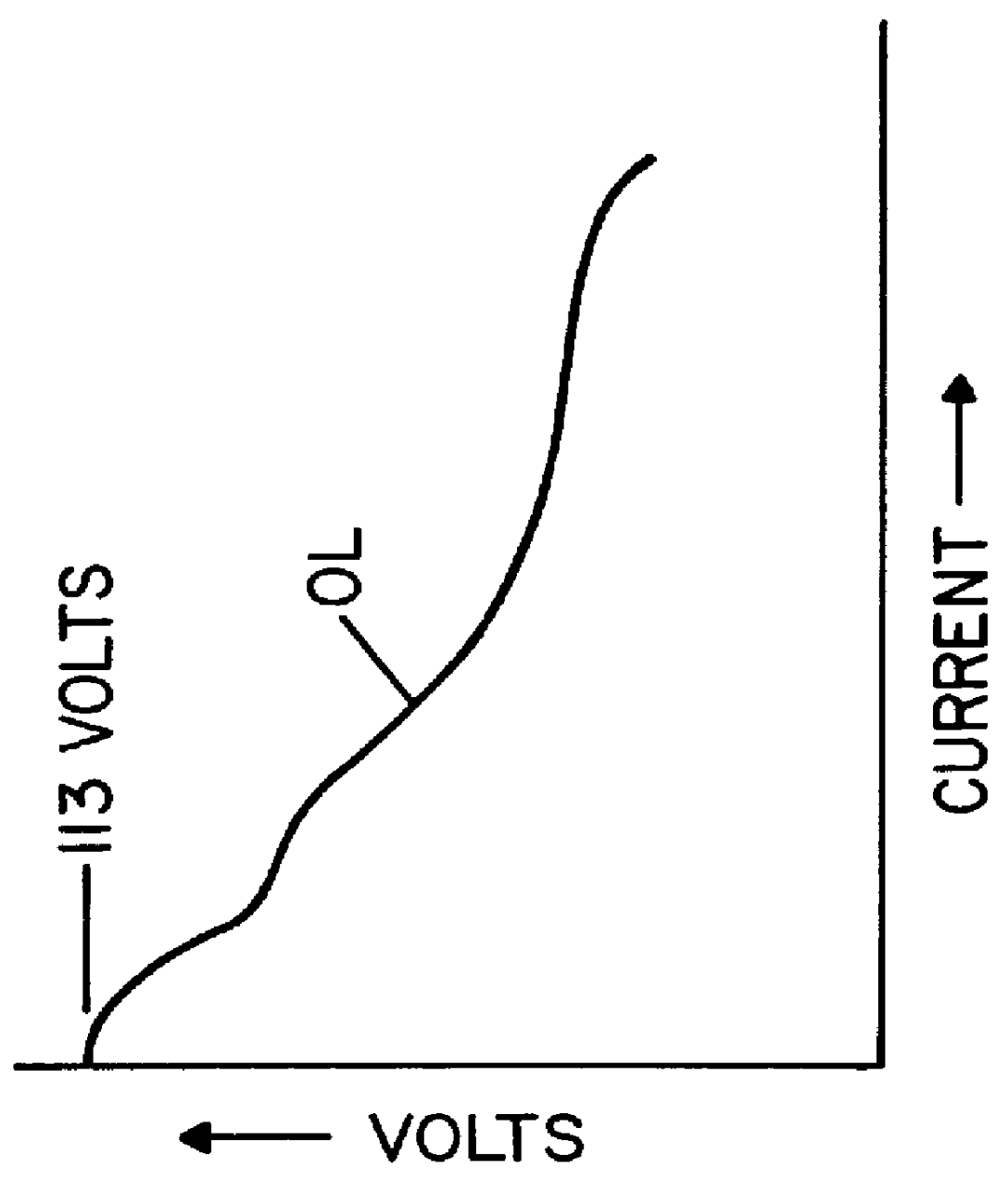
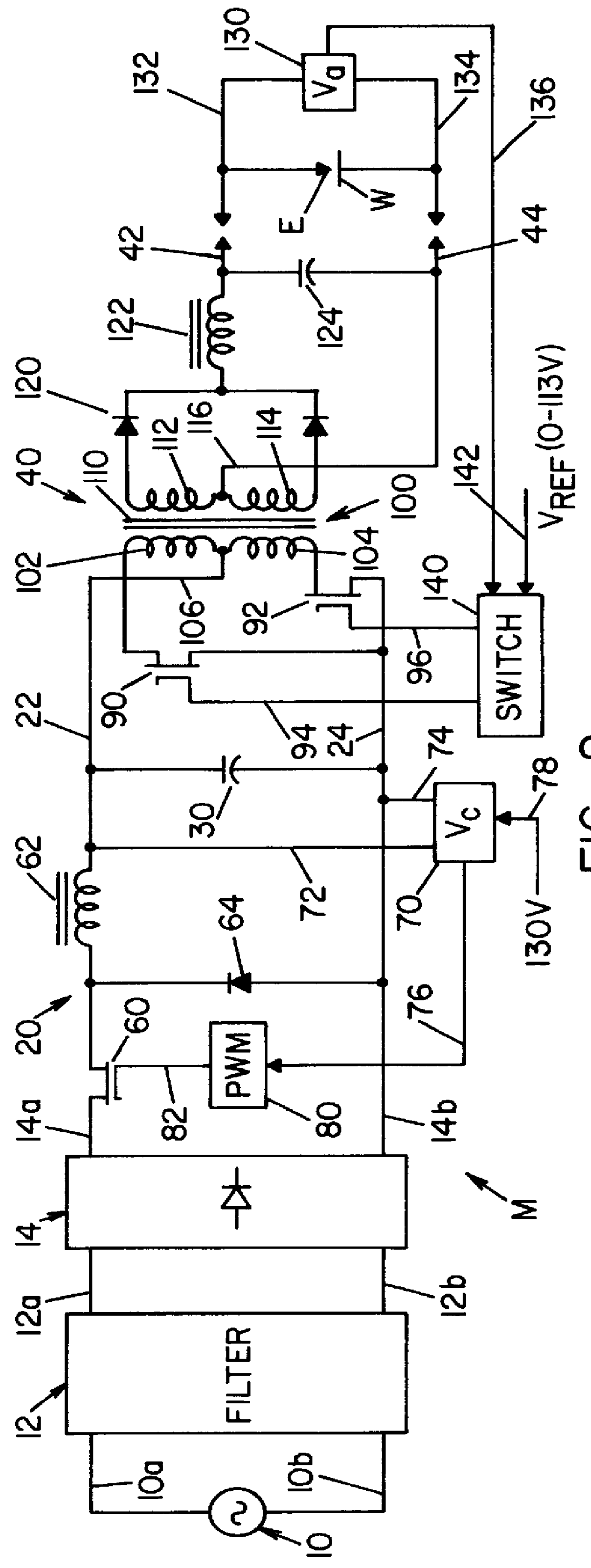
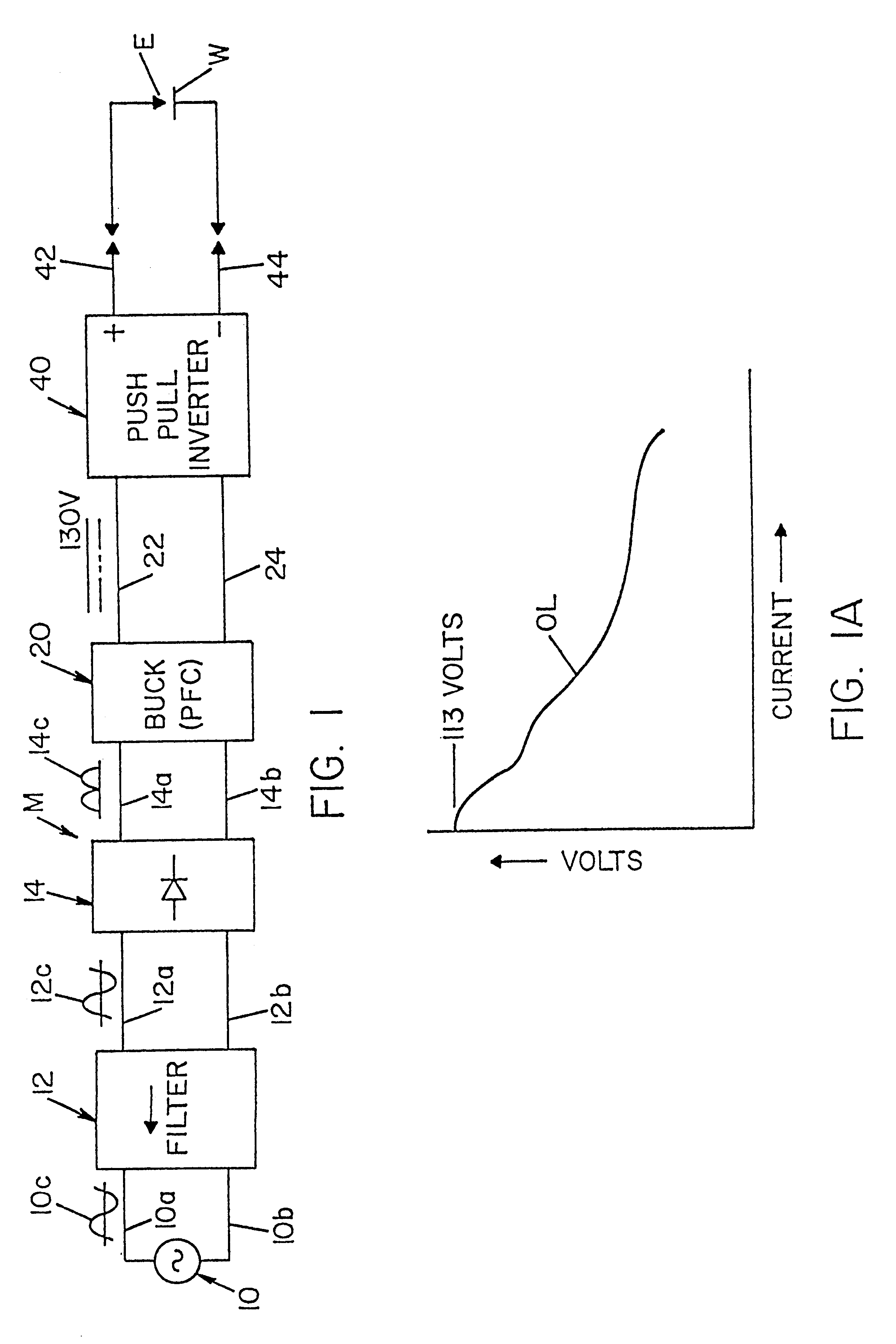
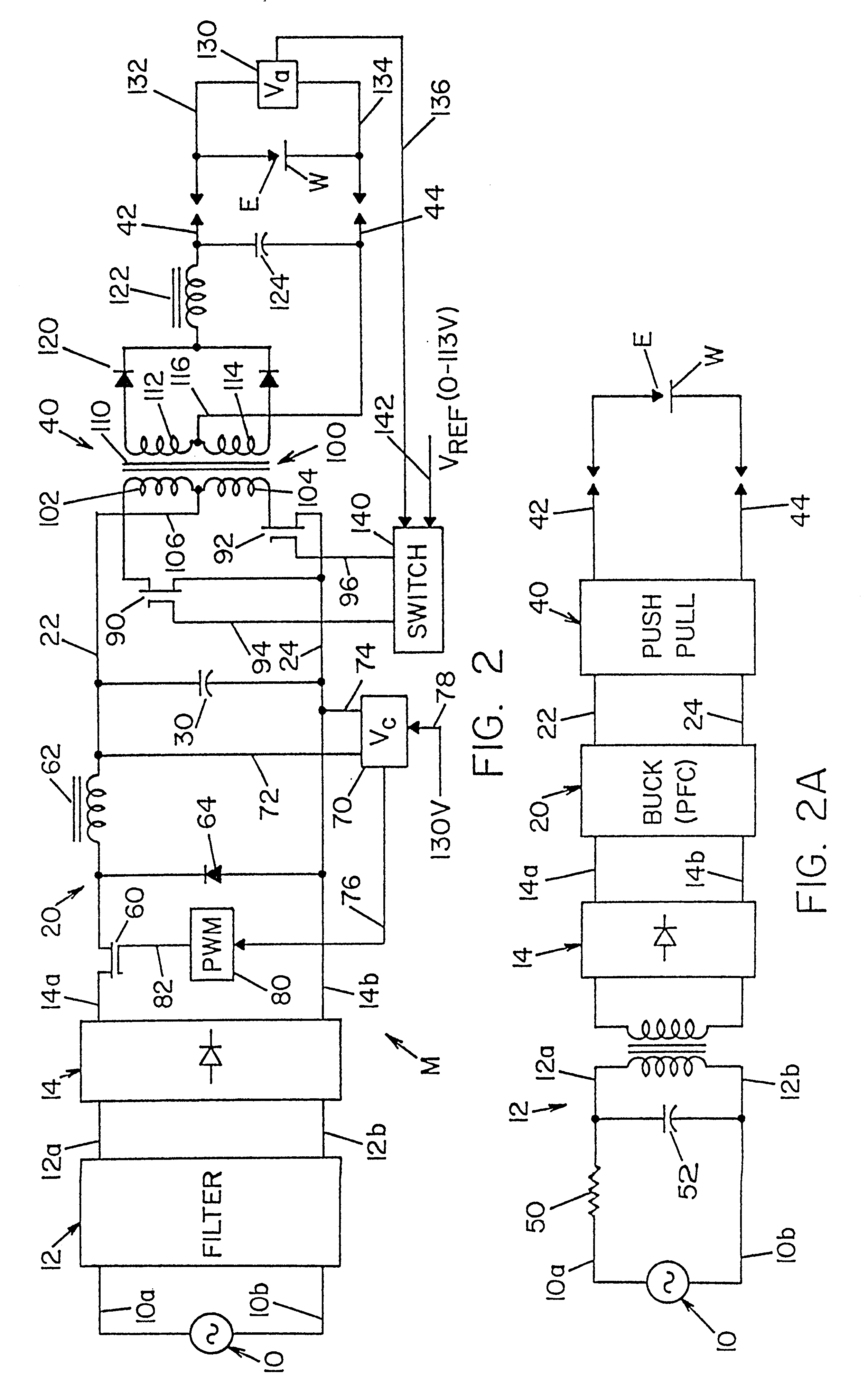
A single phase power supply module for electric arc welders and plasma arc cutters comprising: a single phase input stage; positive and negative output terminals; a full wave rectifier connected to the input stage for rectifying the single phase voltage at the input stage; a buck converter type power factor correcting circuit for controlling current flow from the input stage to the rectifier, which buck converter has an output capacitor regulated to an intermediate voltage in the range of 100-150 volts; and, a high speed DC to DC converter having an internal transformer coupling applying voltage across the output terminals and means for regulating the applied voltage to an output voltage in the range of 0-113 volts. The module is universal and several can be connected in parallel, in series or to switch networks to construct several welders or cutters.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Power factor corrected single-phase AC-DC power converter using natural modulation
InactiveUS7564706B1Reduce lossesMost efficientAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionLevel shiftingElectric power system
A power factor corrected (pfc) ac-dc converter has a modified boost input and a modified buck output. Unlike the prior art boost input, the boost switch returns to the output, not to ground. Unlike the prior art buck output stage, a third switch connects to the input. This allows much of the input current to pass through the converter to the output. There is no input current measurement, but nearly ideal power factor correction is achieved through “natural modulation.” A preferred pfc ac-dc converter uses a variable dc-dc transformer on its output, as a post regulator, to provide dielectric isolation and to provide voltage level shifting. The output of the pfc ac-dc converter has the control characteristics of a buck converter, so it is a natural mate for the variable dc-dc transformer. An ac-dc buck converter is most efficient at its maximum duty cycle. It cannot regulate for a lower input voltage, but it can reduce its duty-cycle to control for higher input voltages. A variable dc-dc transformer is most efficient at its maximum ratio. It cannot regulate for a higher input voltage, but it can reduce its effective turns ratio to control for a lower input voltage. With a small overlap in their control ranges, both parts of the power system can operate at maximum efficiency. The variable dc-dc transformer controls the output voltage for nominal and low input voltage. The ac-dc buck converter limits over-voltage transients.
Owner:HERBERT EDWARD
Electric arc welder and plasma cutter
InactiveUS6177645B1Reduce Harmonic DistortionImprove power factorAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcFull waveEngineering
A single phase power supply module for electric arc welders and plasma arc cutters comprising: a single phase input stage; positive and negative output terminals; a full wave rectifier connected to the input stage for rectifying the single phase voltage at the input stage; a buck converter type power factor correcting circuit for controlling current flow from the input stage to the rectifier, which buck converter has an output capacitor regulated to an intermediate voltage in the range of 100-150 volts; and, a high speed DC to DC converter having an internal transformer coupling applying voltage across the output terminals and means for regulating the applied voltage to an output voltage in the range of 0-113 volts. The module is universal and several can be connected in parallel, in series or to switch networks to construct several welders or cutters.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Pfc-pwm controller having interleaved switching
ActiveUS20050099164A1Reduce switching noiseImproper operationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringPwm signals
The present invention discloses a PFC-PWM controller having interleaved switching. A PFC stage generates a PFC signal for switching a PFC boost converter of a power converter. A PWM stage generates a PWM signal for switching a DC-to-DC converter of the power converter. The PFC-PWM controller includes a power manager for generating a discharge current and a burst-signal. Under light-load conditions, the discharge current decreases in proportion to a load of the power converter. The burst signal is utilized to disable the PFC signal in a suspended condition for power saving. A pulse width of the pulse-signal ensures a dead time to spread switching signals, such as the PFC and PWM signals, and reduces switching noise. When the discharge current decreases, the pulse width of the pulse-signal will increase and a frequency of the pulse-signal will decrease correspondingly. This further reduces power consumption under light-load and zero-load conditions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Direct mode pulse width modulation for DC to DC converters
InactiveUS20070063681A1Simple control circuitFast transient responseEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCapacitanceEngineering
A DC to DC converter has an inverter, an inductor, a voltage sensor, a comparator, a clock generator, a driver and an output capacitor. The inverter converts an input voltage into a square-wave voltage. The inductor is electrically connected to an output of the inverter. The voltage sensor is electrically connected to the inductor and derives a sense voltage. The comparator compares the sense voltage and a reference voltage. The clock generator generates a reference clock pulse. The driver is triggered by the reference clock pulse and switches the inverter according to an output of the comparator. The output capacitor is electrically connected between the voltage sensor and the ground.
Owner:AMAZION ELECTRONICS
Apparatus and method for driving laser diodes
InactiveUS20060291512A1Fast rise timeImprove efficiencyLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersCapacitanceMode control
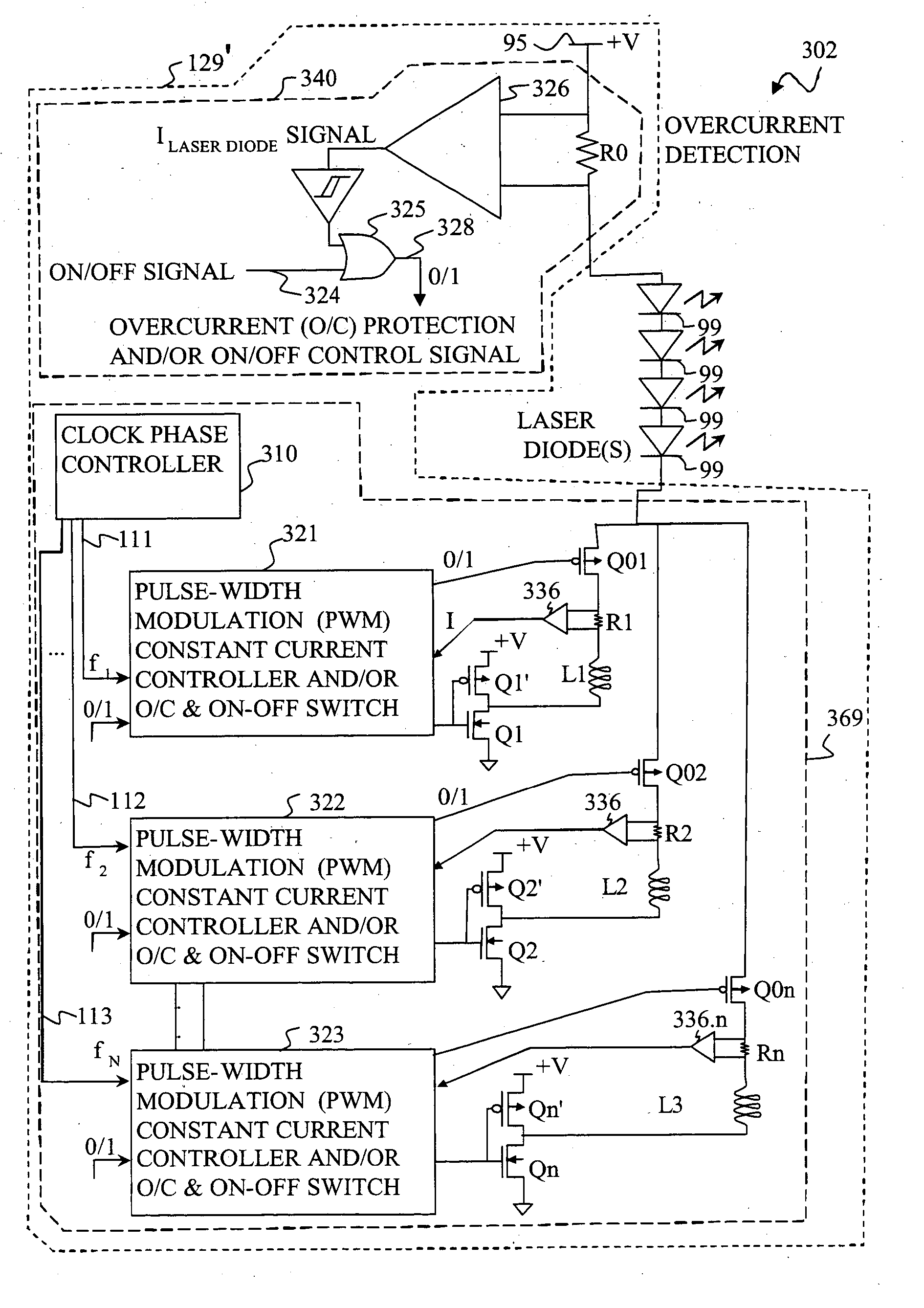
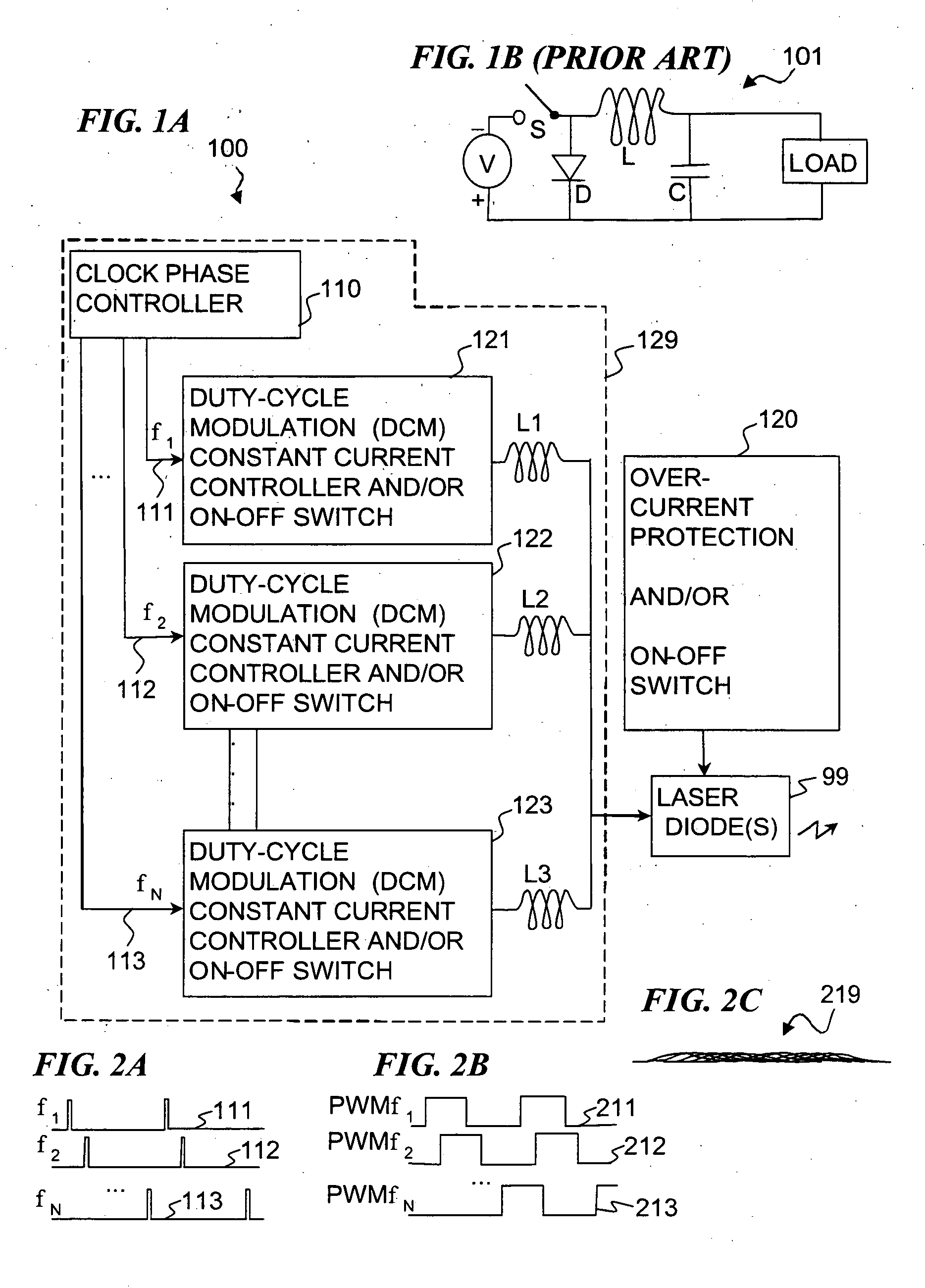
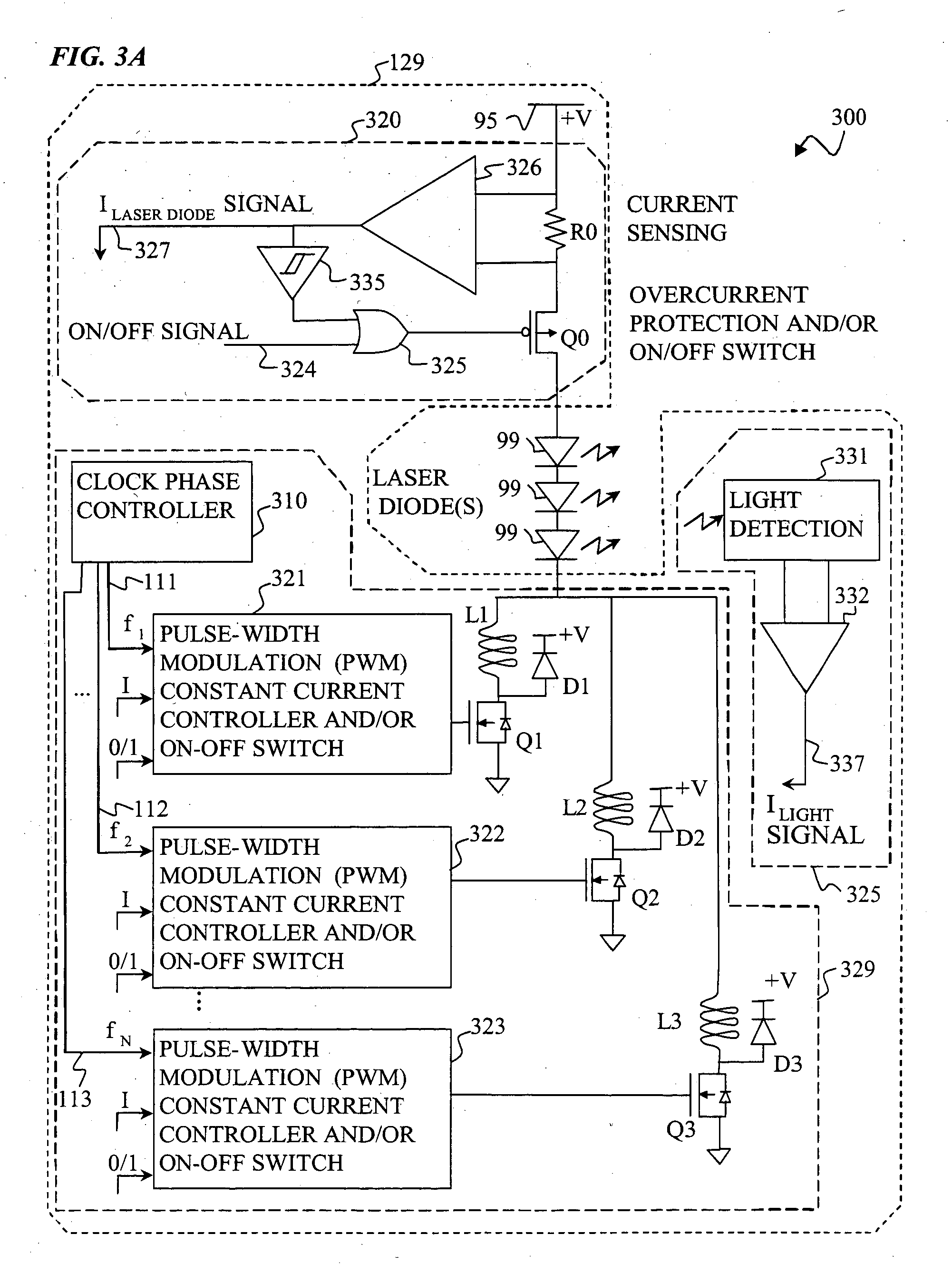
Apparatus and method for driving laser diodes with electrical power in pulsed operation. Pulsed power, for example using pulse-width modulation, is applied through an inductor in one or more parallel regulator circuits having little or no output capacitance to provide a high-efficiency laser-diode-driver power supply. Some embodiments that use two or more parallel regulator circuits in the laser-diode driver, drive each from a different phase of a clock signal. Some embodiments provide a first DC-to-DC converter has a relatively high-voltage input (e.g., about 275 volts, 0.75 amps) and an intermediate output of e.g., 11 to 15 volts, 15 to 11 amps used to charge a storage capacitor, and a second DC-to-DC converter diode driver having one or more parallel circuits (each having, e.g., a PWM switching-mode controller and its respective switch, inductor, and diode) to turn on, regulate, and turn off a constant laser-diode current through one or more laser diodes.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
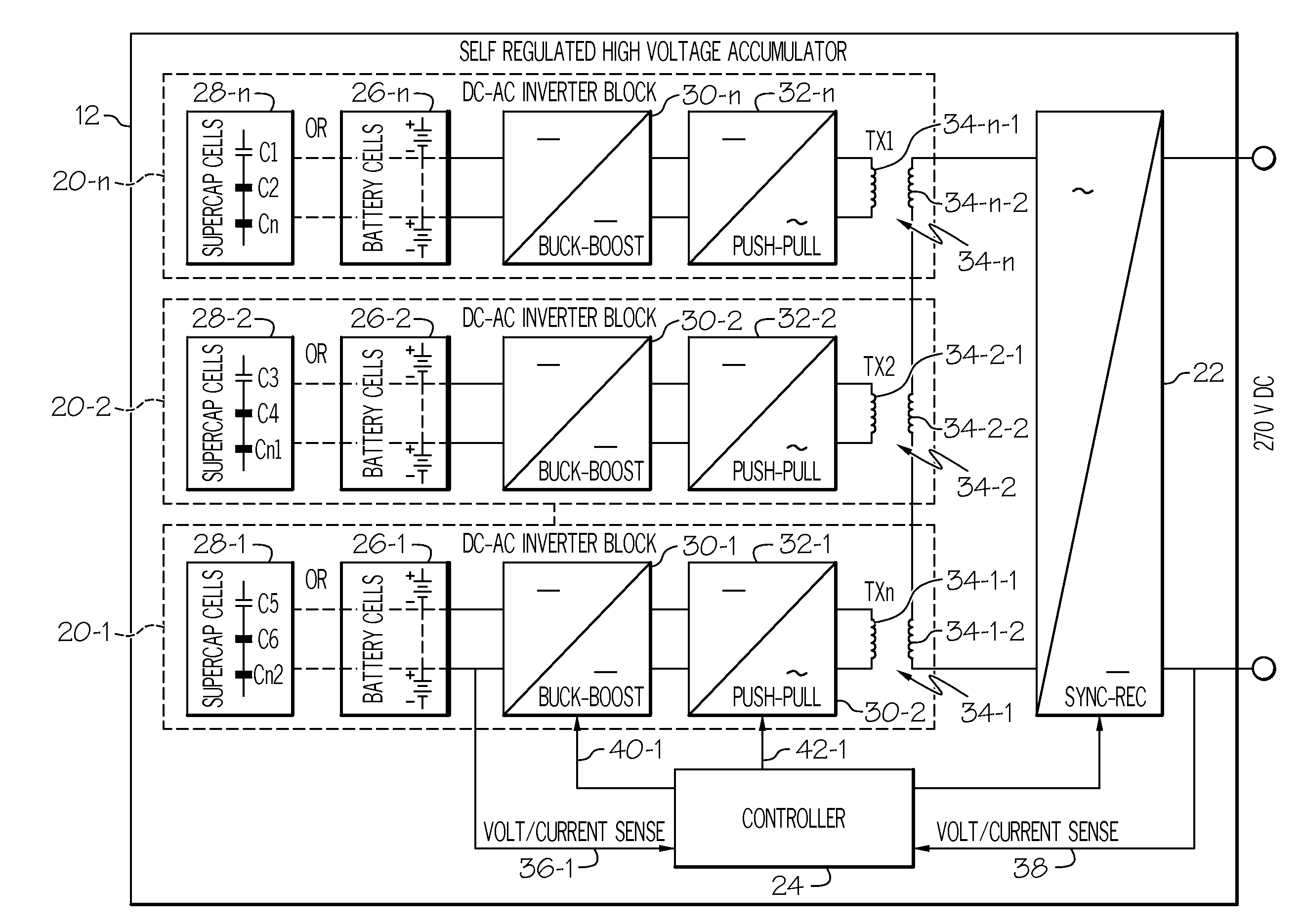
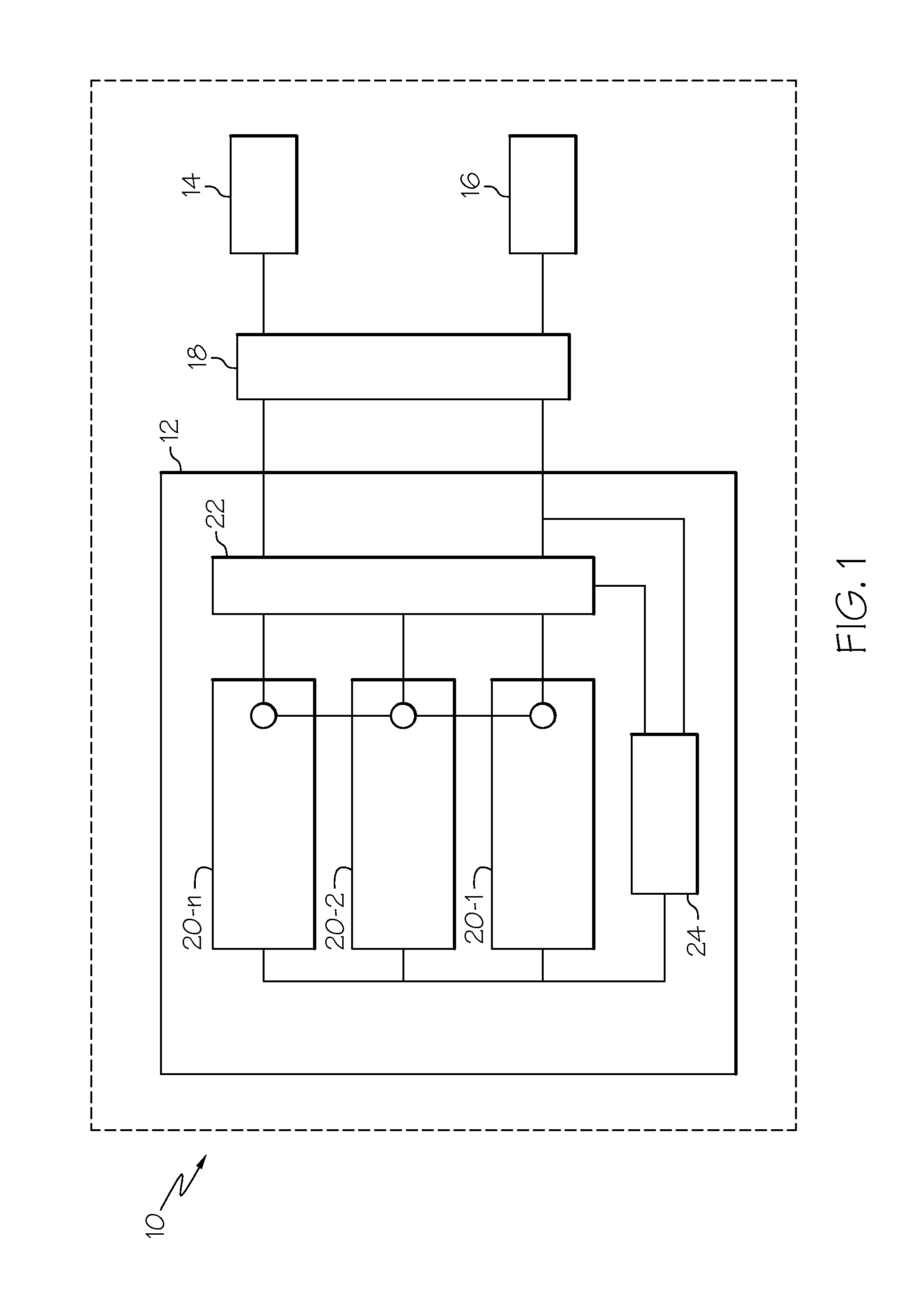
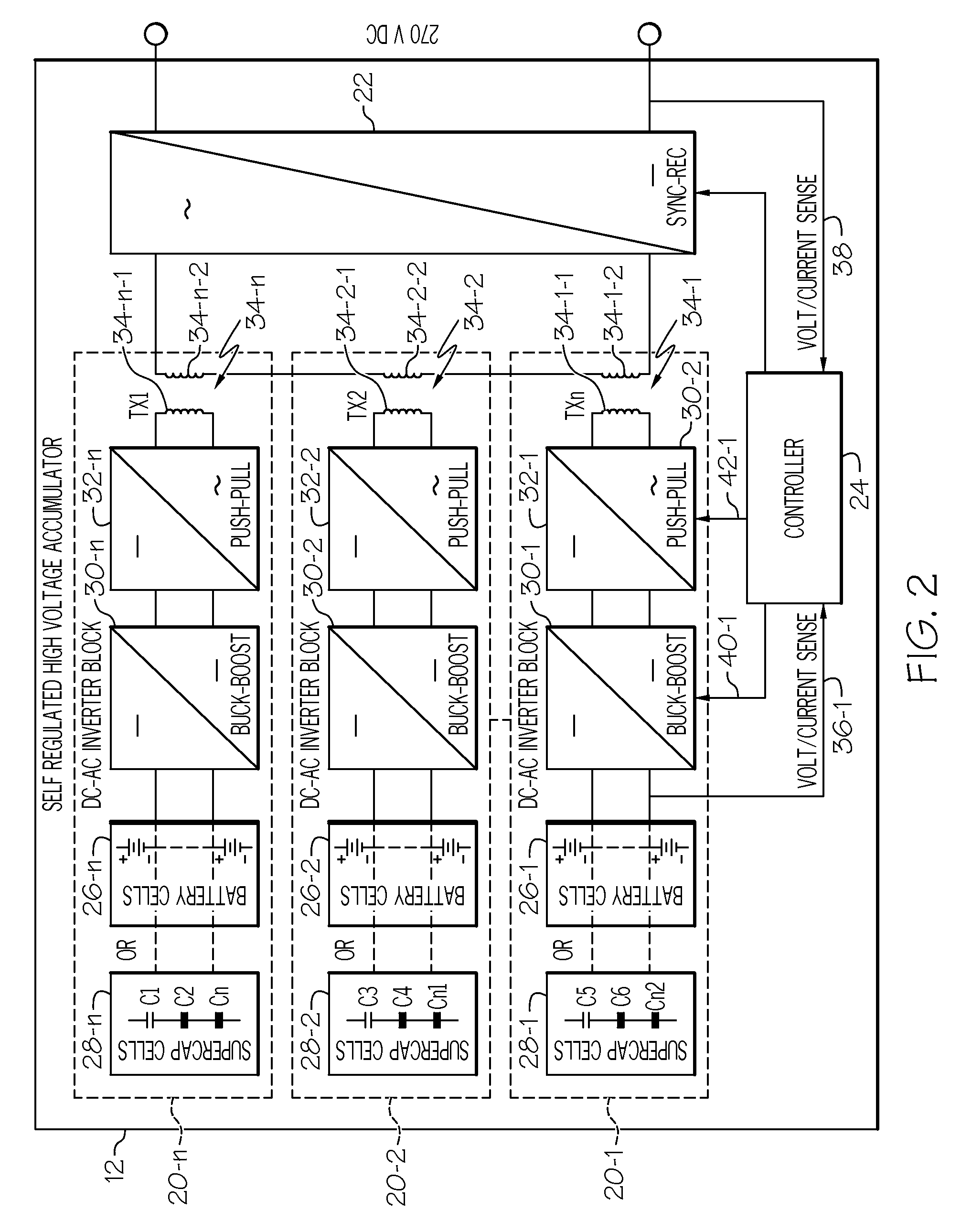
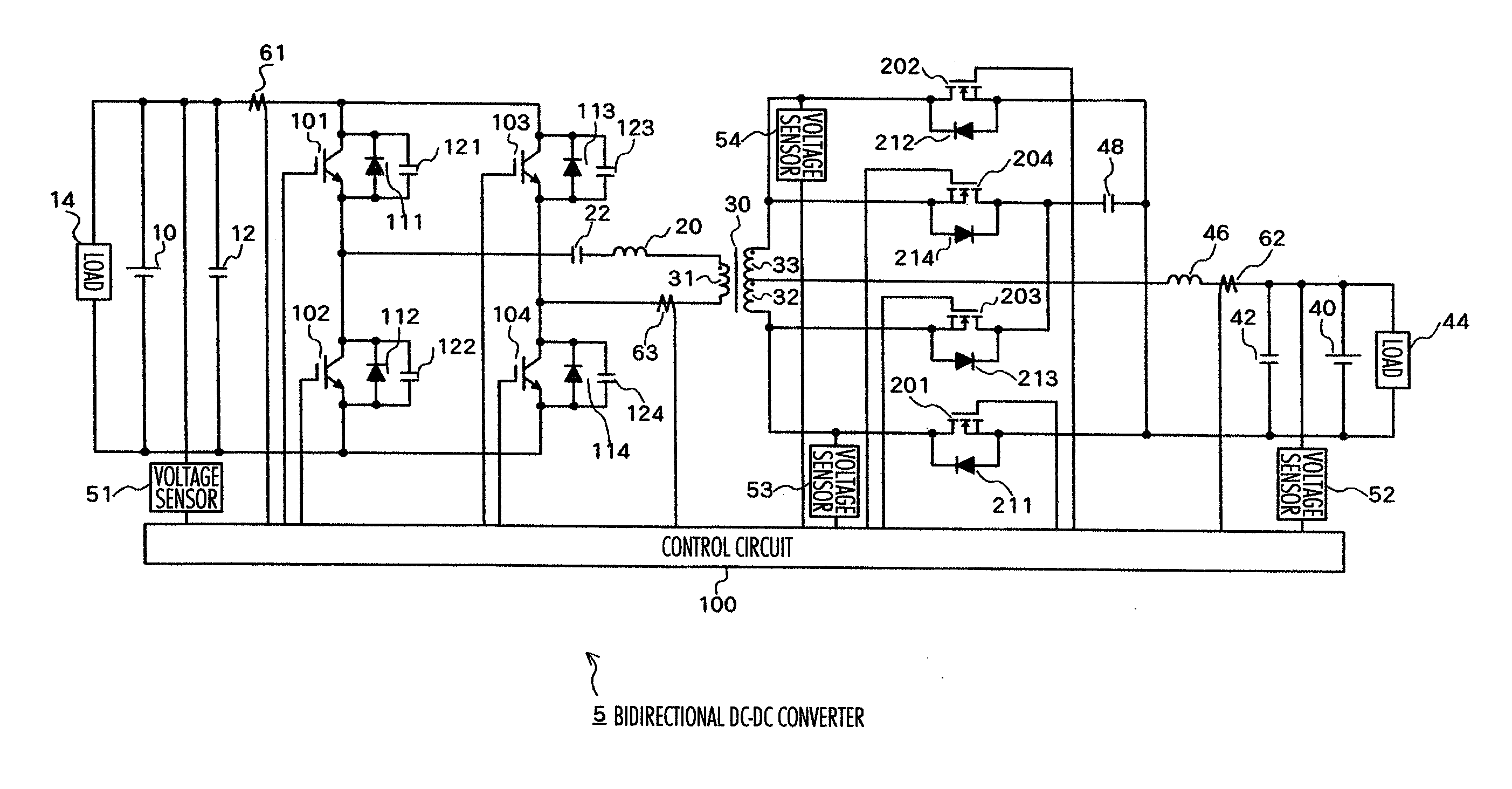
High voltage electric accumulators with internal distributed dc-dc converters for self regulation and protection
ActiveUS20120104861A1Electric signal transmission systemsDc network circuit arrangementsTransformerEngineering
A power management system may employ a power source, a distribution system between the power source and electrical loads and an energy accumulator. The accumulator may comprise a plurality of energy processing blocks. Each block may have a limited number of energy storage cells connected in series to produce first voltage. A second higher output voltage from the accumulator may be achieved though integrated DC-DC, DC-AC and AC-DC conversion with intermediate boost of AC voltage through high frequency transformers. Bidirectional power flow may be achieved with high efficiency during charge and discharge of the accumulator. Secondary windings of the transformers may be connected with one another in series so that the accumulator can transfer energy between the distribution system and any one or all of the energy processing units in a fault-tolerant and efficient manner.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
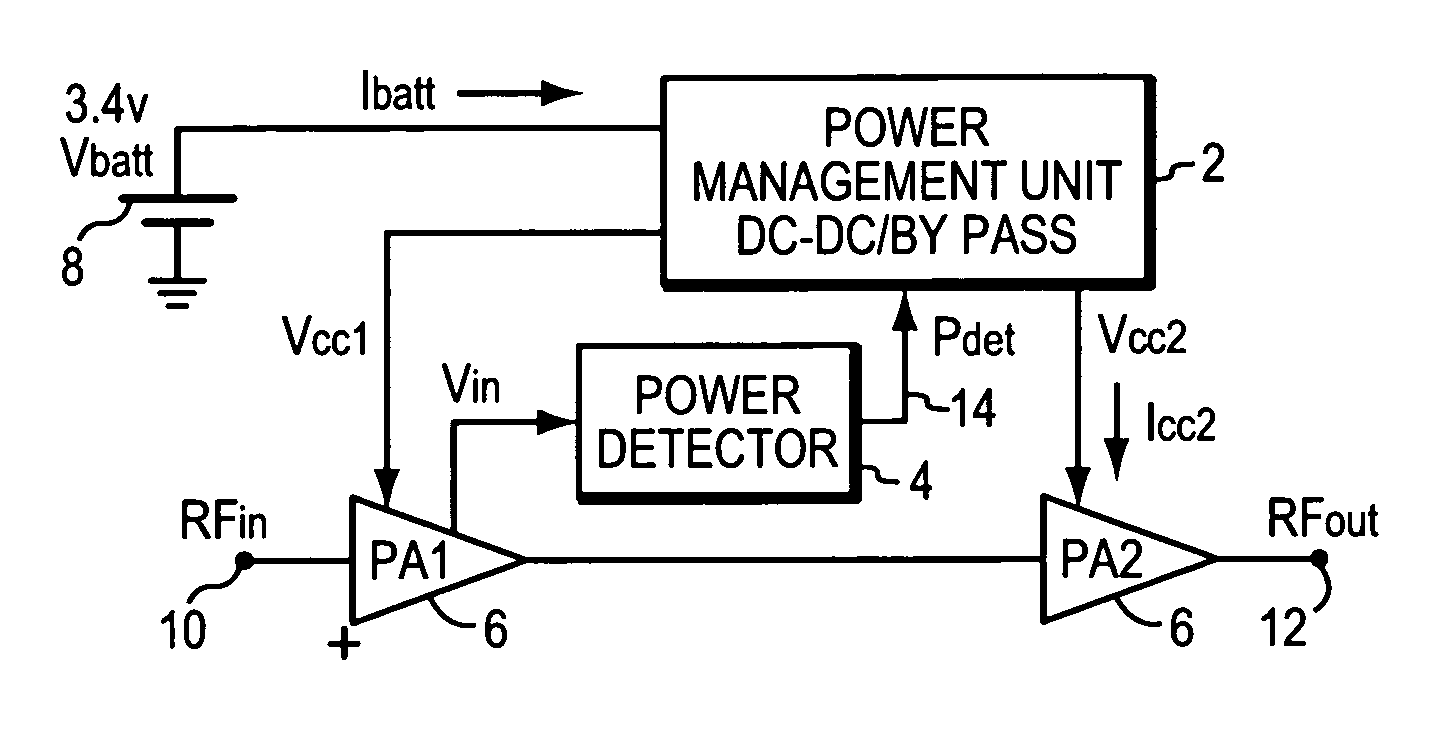
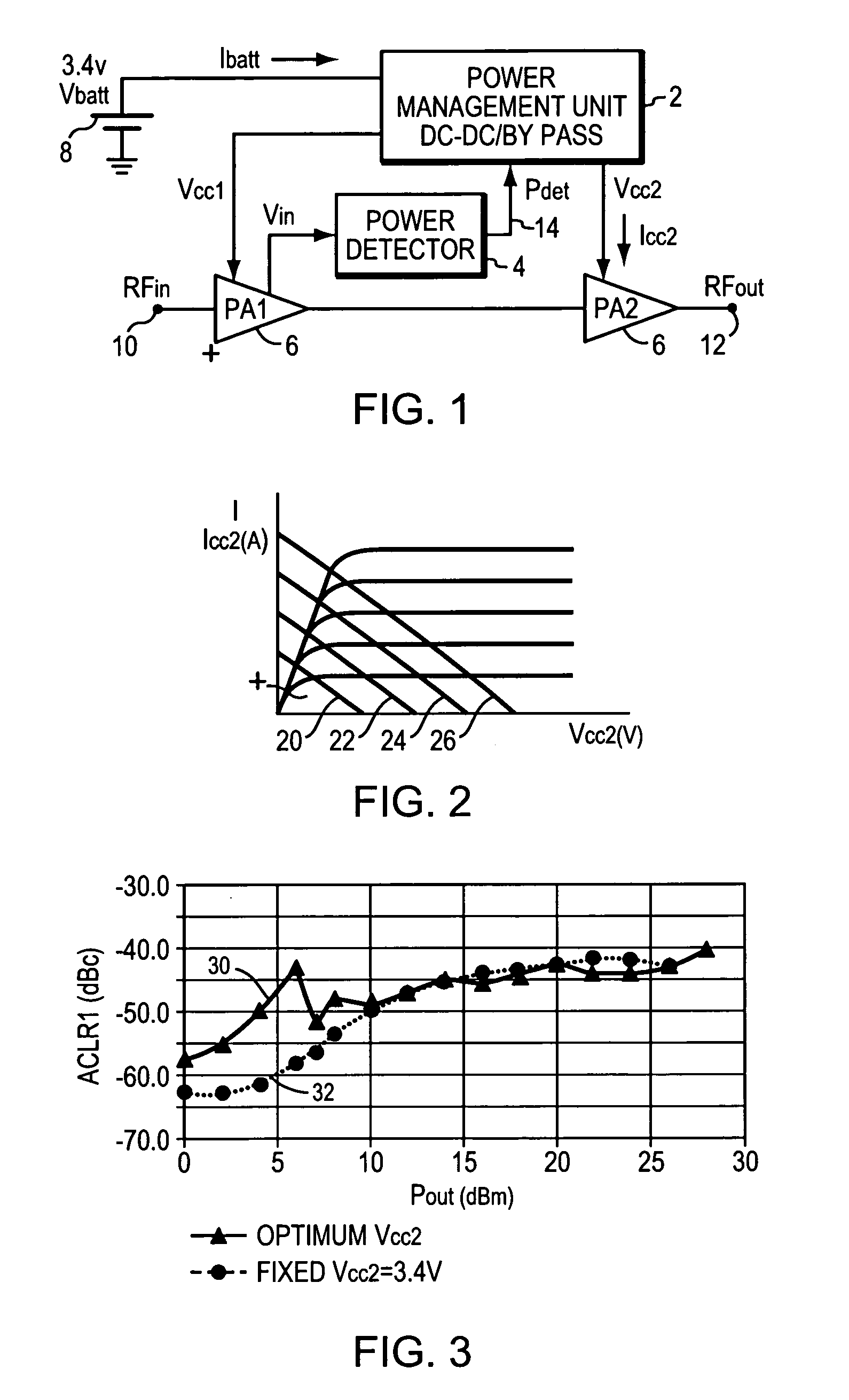
Power amplifier with close-loop adaptive voltage supply
InactiveUS20070182490A1Conserve battery lifeReduce current consumptionGain controlAmplifier detailsControl signalPower detector
A two- (or multi) stage power amplifier receives a variable RF input signal, and outputs an optimized. RF output signal from, for example, a mobile handset. The output power level from the handset is predetermined, as known in the art, by the received control signal from a base station. The first power amplifier stage amplifies the variable RF input signal and outputs an RF signal, Vin, to a power detector circuit and an RF signal to the second or next amplifier stage. The power detect circuit amplifies the Vin signal and rectifies that signal with a linearly biased diode and provides a detect signal to a DC to DC converter. The converter responds by providing an optimum voltage bias, which is linearly related to the DC voltage detect signal from the power detector, to the output stage, and, if desired, to the first and / or other stages of the power amplifier that optimizes the output power level while meeting the required linearity specification. The battery current consumption is optimized through this automatic, dynamically control of the supply voltage for the power amplifier at each output power level through the DC to DC converter.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Modular power source for electric ARC welding and output chopper
ActiveUS20060175313A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalArc welding apparatusEngineeringConductor Coil
A three stage power source for an electric arc welding process comprising an input stage having an AC input and a first DC output signal; a second stage in the form of an unregulated DC to DC converter having an input connected to the first DC output signal, a network of switches switched at a high frequency with a given duty cycle to convert the input into a first internal AC signal, an isolation transformer with a primary winding driven by the first internal high frequency AC signal and a secondary winding for creating a second internal high frequency AC signal and a rectifier to convert the second internal AC signal into a second DC output signal of the second stage; with a magnitude related to the duty cycle of the switches and, a third stage to convert the second DC output signal to a welding output for welding wherein the input stage and the second stage are assembled into a first module and the third stage is assembled into a second module connectable to the first module.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
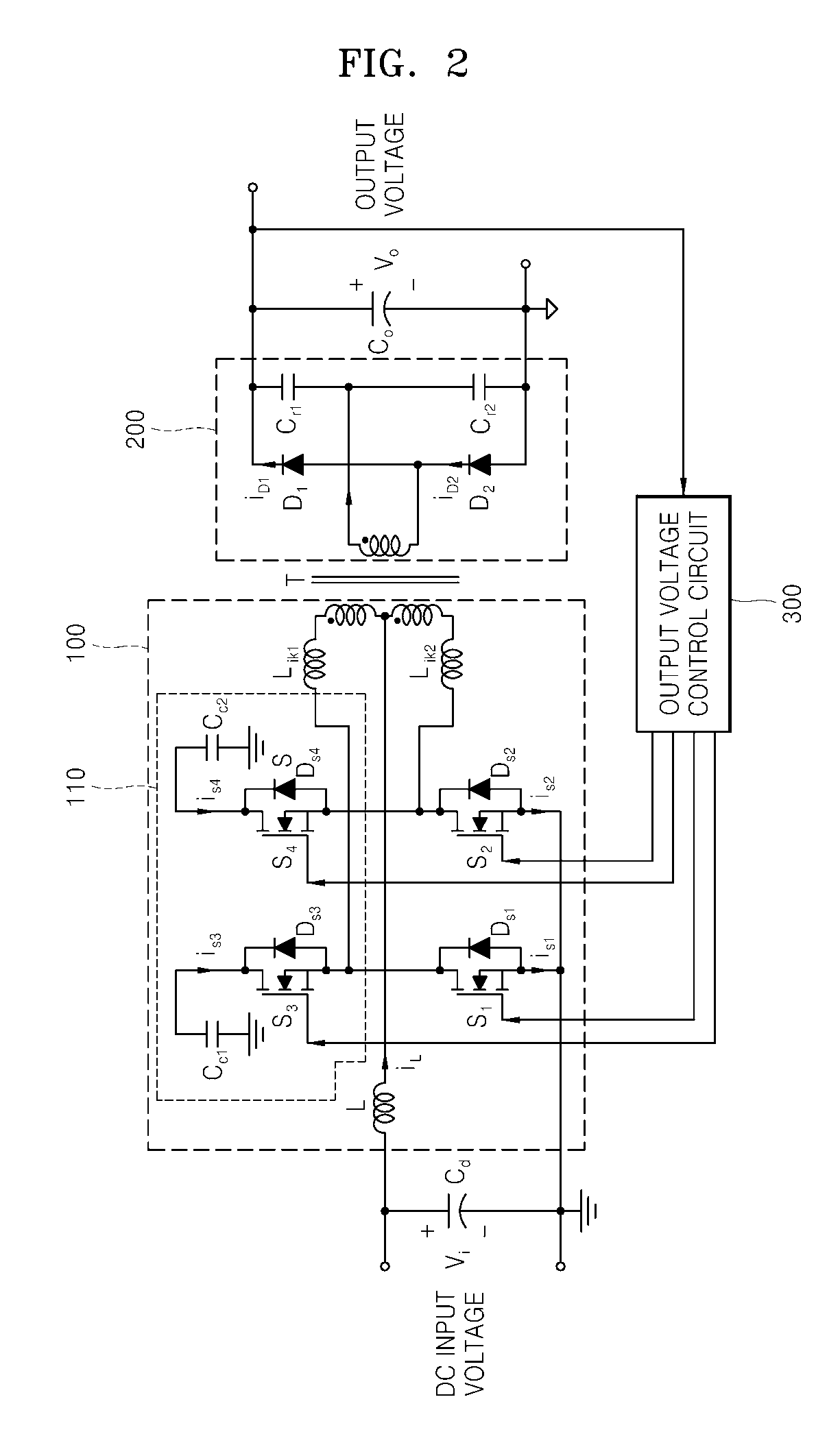
DC-DC converter
ActiveUS20050047175A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterNegative power
In a DC to DC converter, first and second primary windings are magnetically coupled to a first secondary winding. Third and fourth primary windings are magnetically coupled to a second secondary winding. The first and second primary windings are magnetically coupled to the first secondary winding. The third and fourth primary windings are magnetically coupled to the second secondary winding. The first and third primary windings are coupled in series to form a first coil member. The second and fourth primary windings are coupled in series to form a second coil member. One end of the first coil member is coupled to the first positive power line. A first switching element is coupled between the first negative power line and the other end of the first coil member. A first capacitor is coupled between the first negative terminal and one end of the second coil member.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
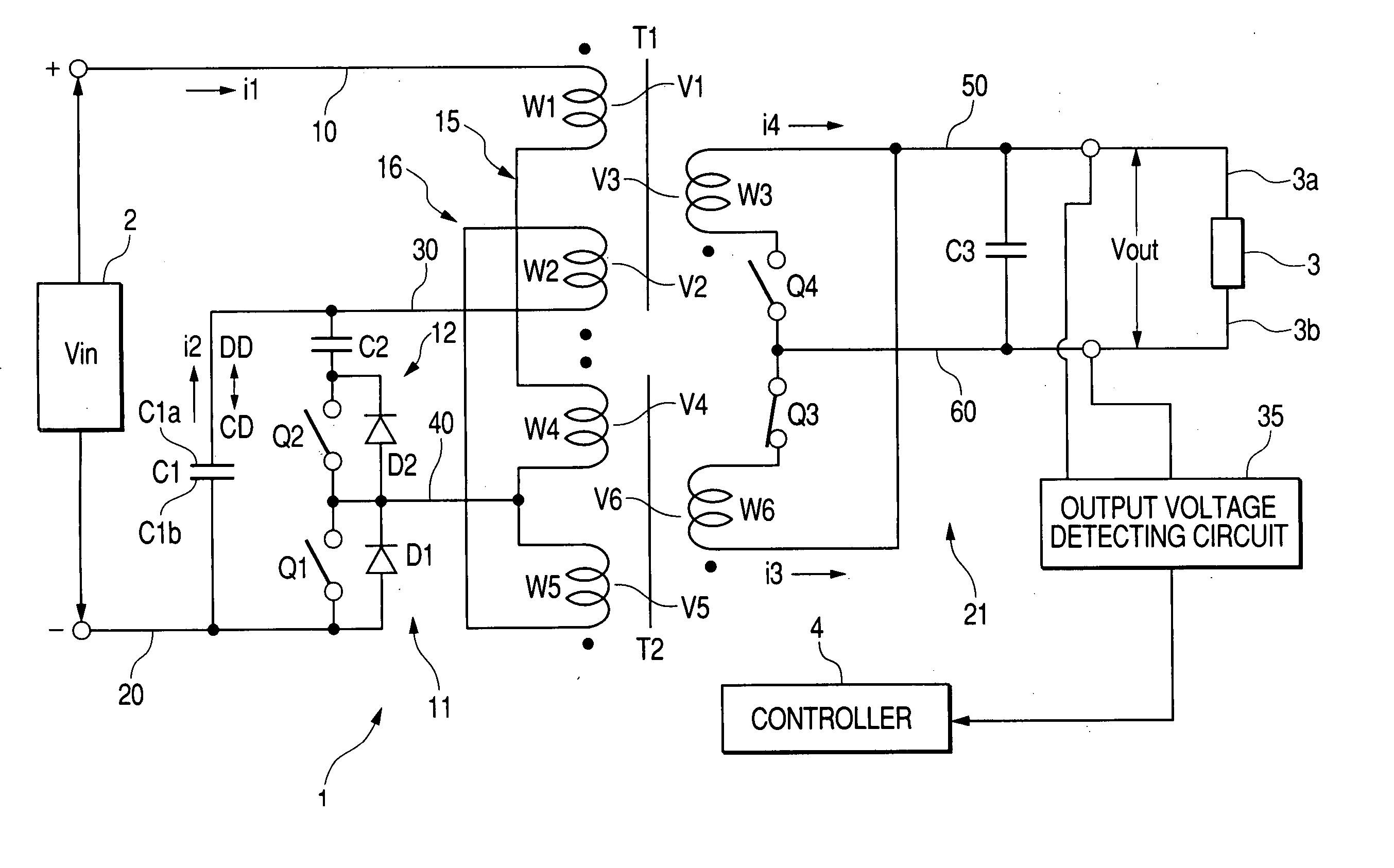
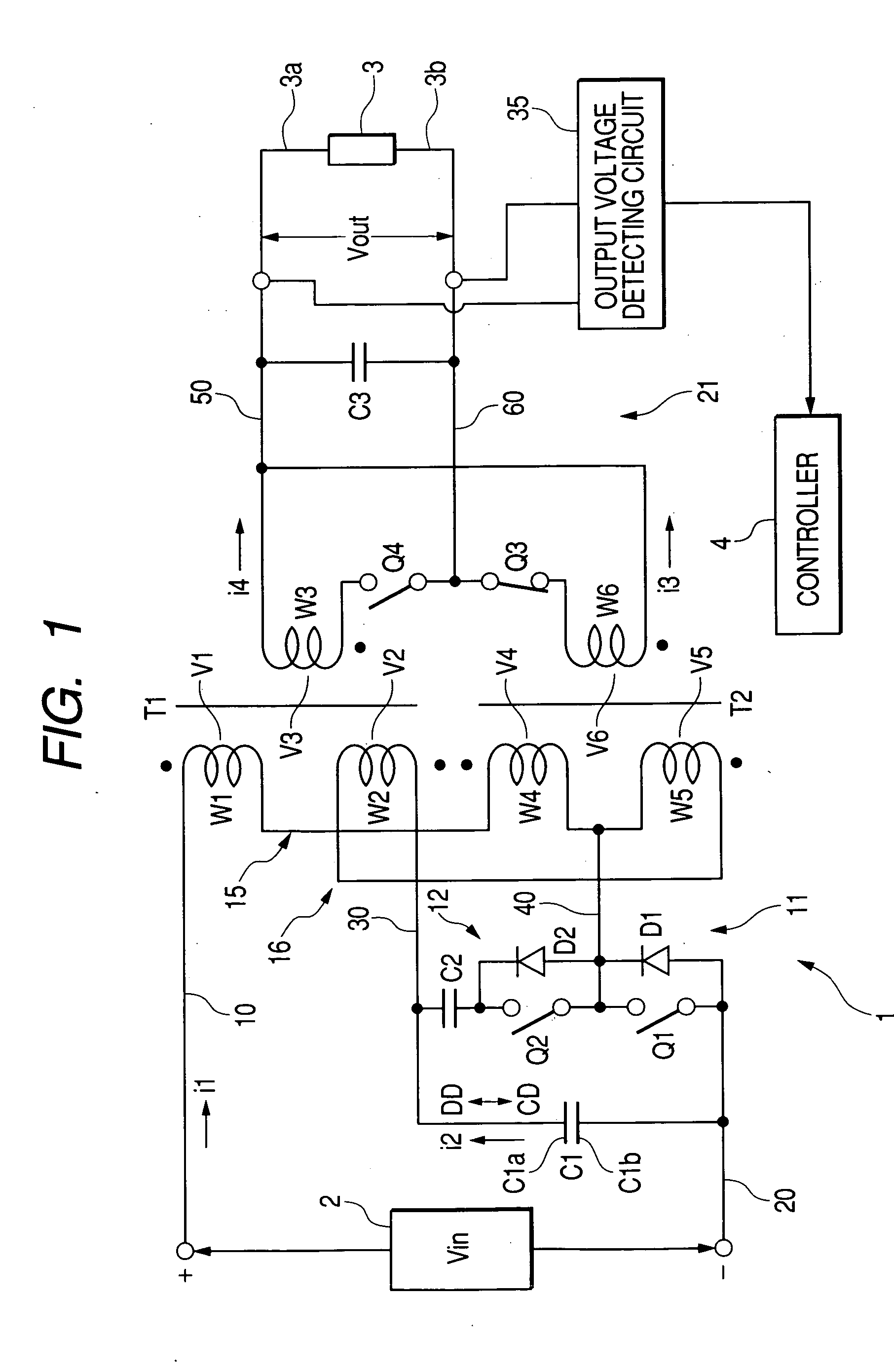
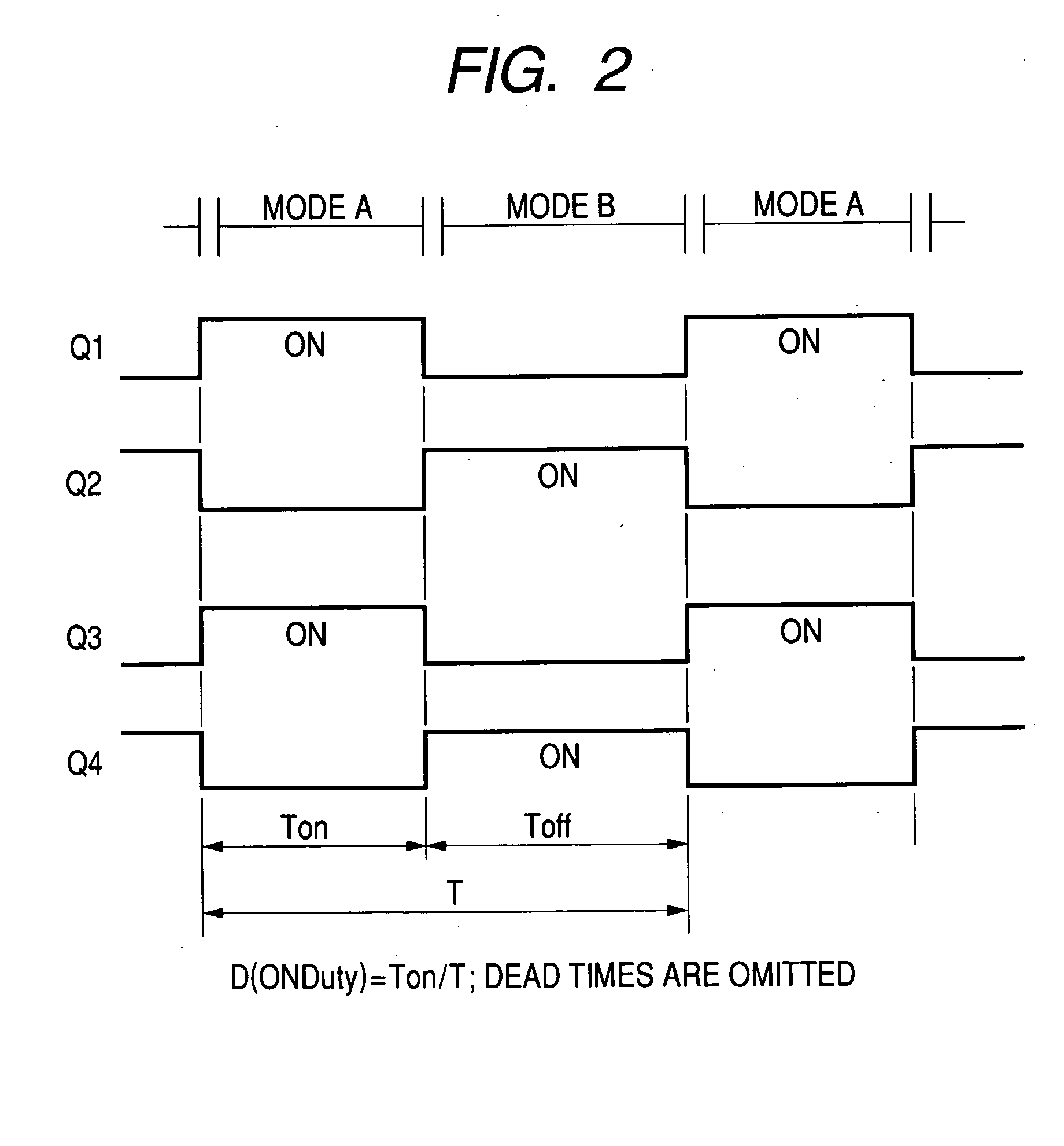
Bi-directional dc-dc converter and method for controlling the same
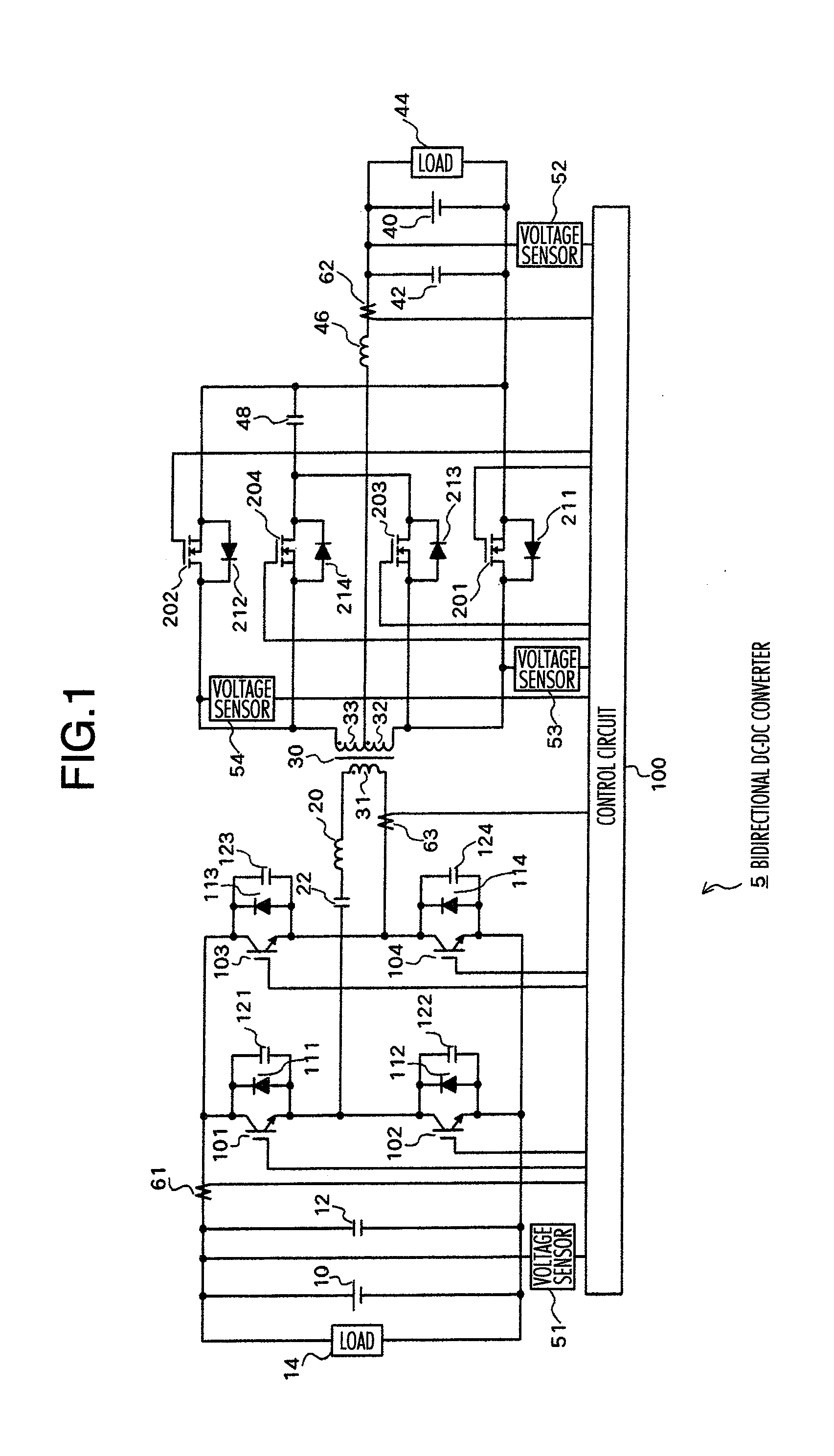
InactiveUS20090059622A1Large electric powerEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionClamp capacitorDc dc converter
A bi-directional DC-DC converter has a transformer for connecting a voltage type full bridge circuit connected to a first power source and a current type switching circuit connected to a second power source. A voltage clamping circuit constructed by switching elements and a clamping capacitor is connected to the current type switching circuit. The converter has a control circuit for cooperatively making switching elements operative so as to control a current flowing in a resonance reactor.
Owner:HITACHI INFORMATION & TELECOMM ENG LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com