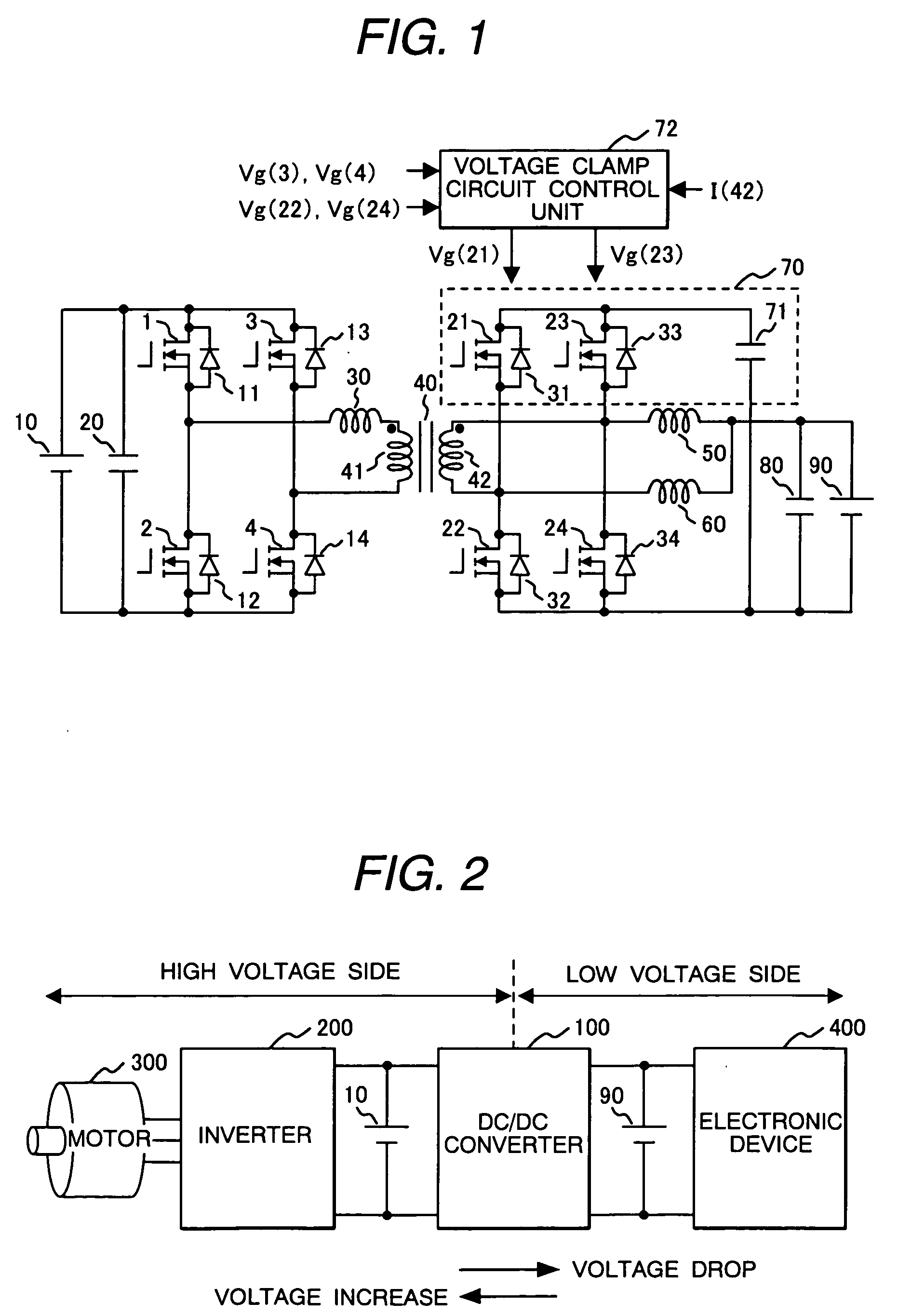
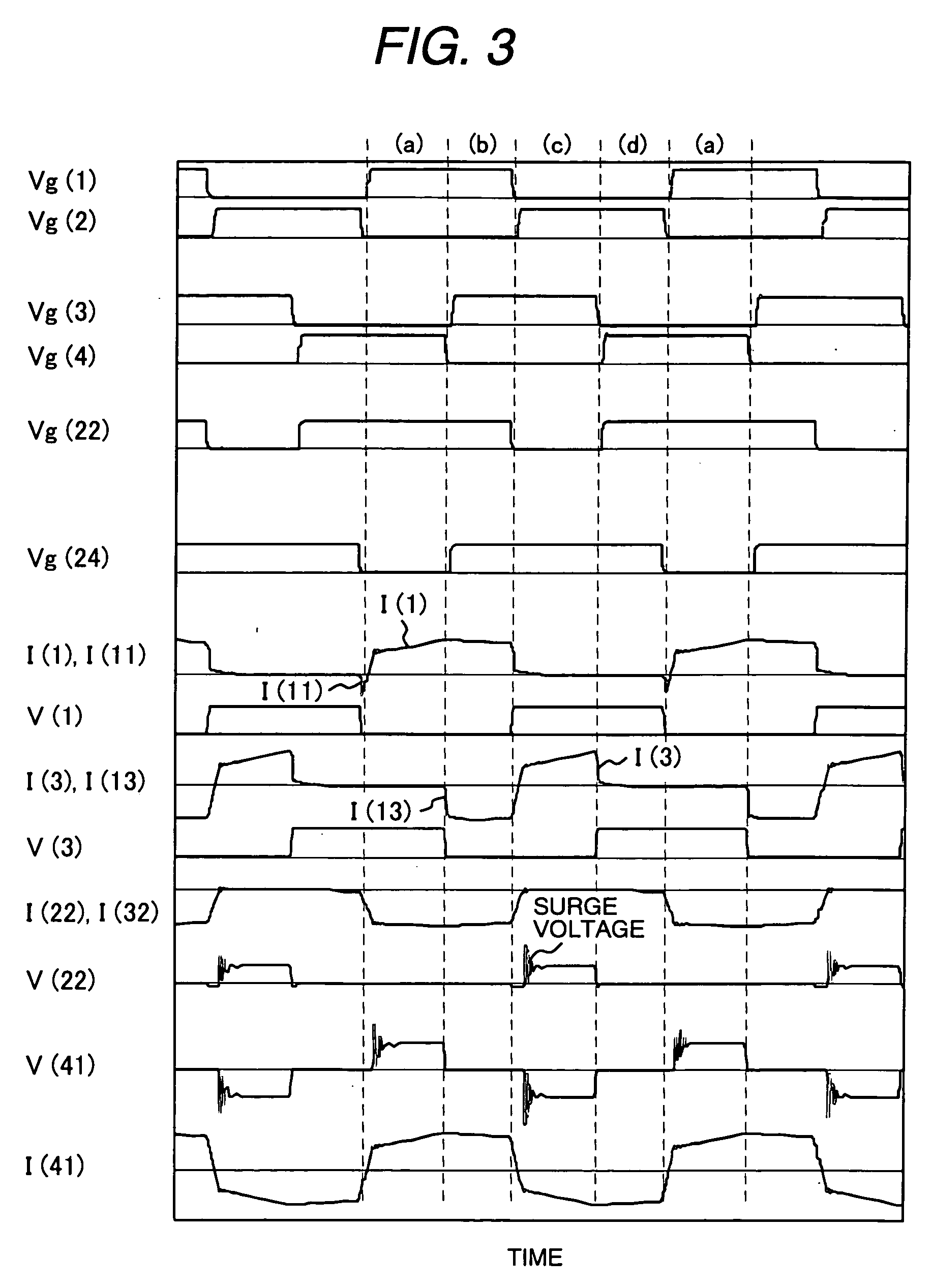
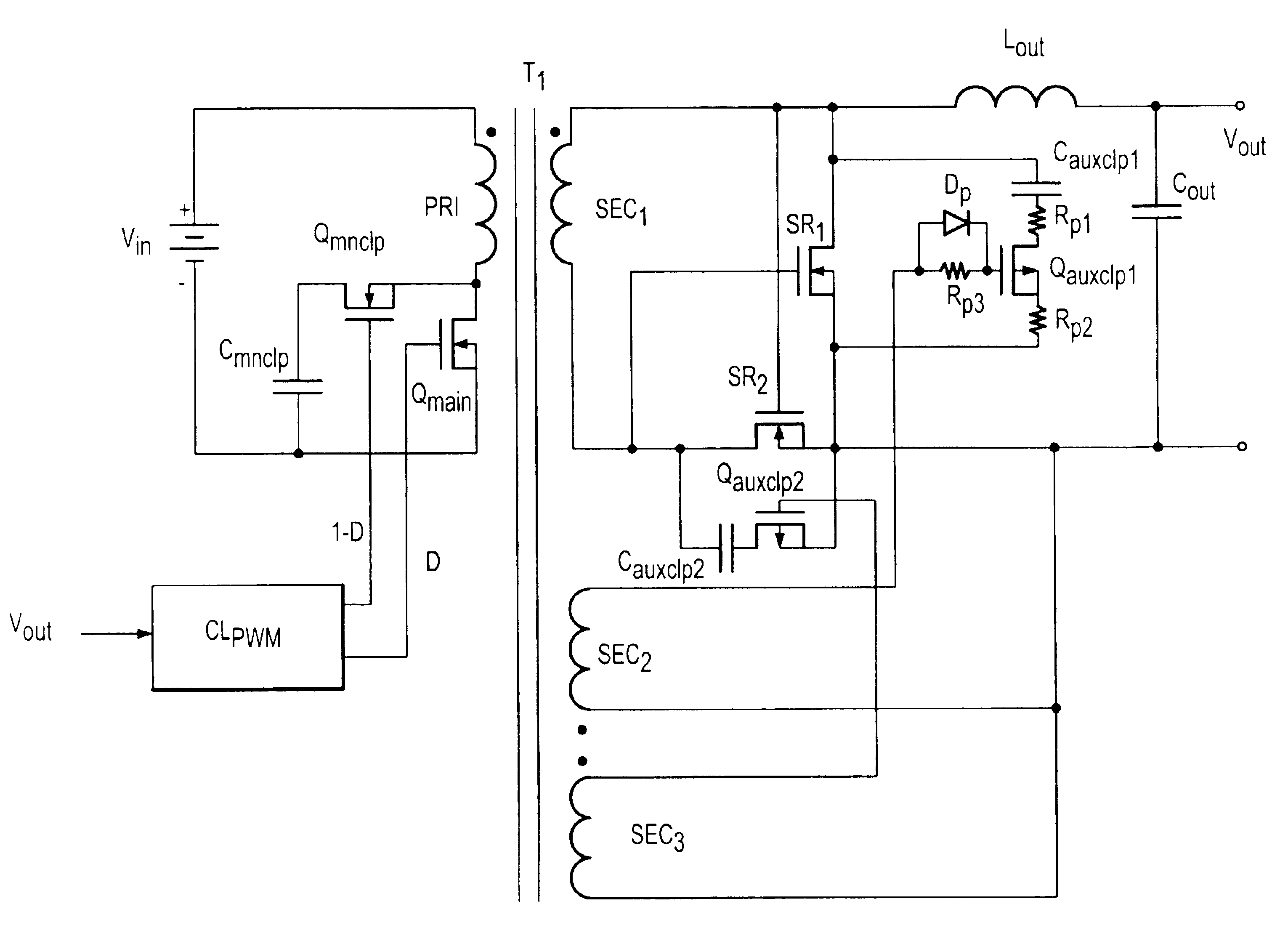
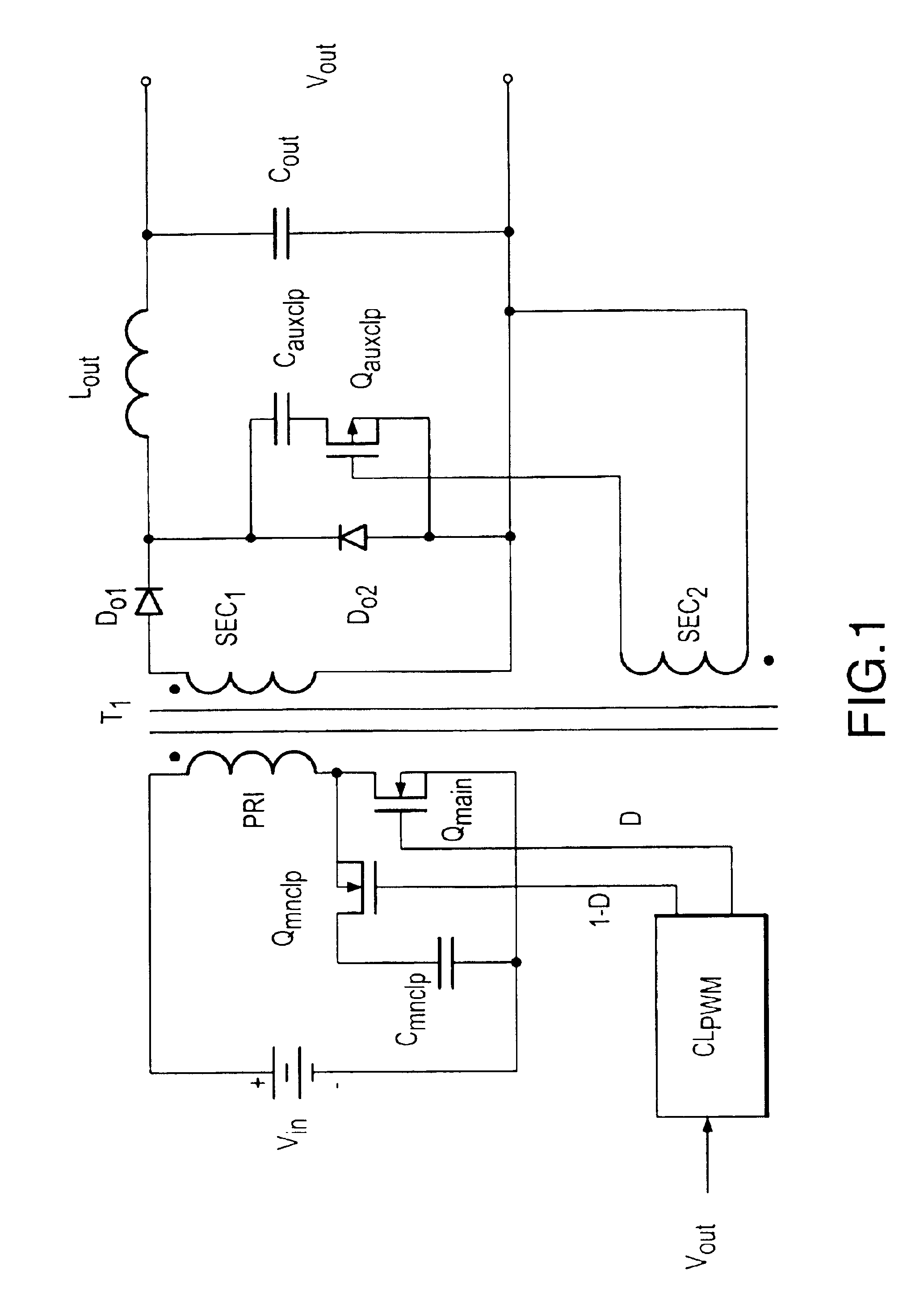
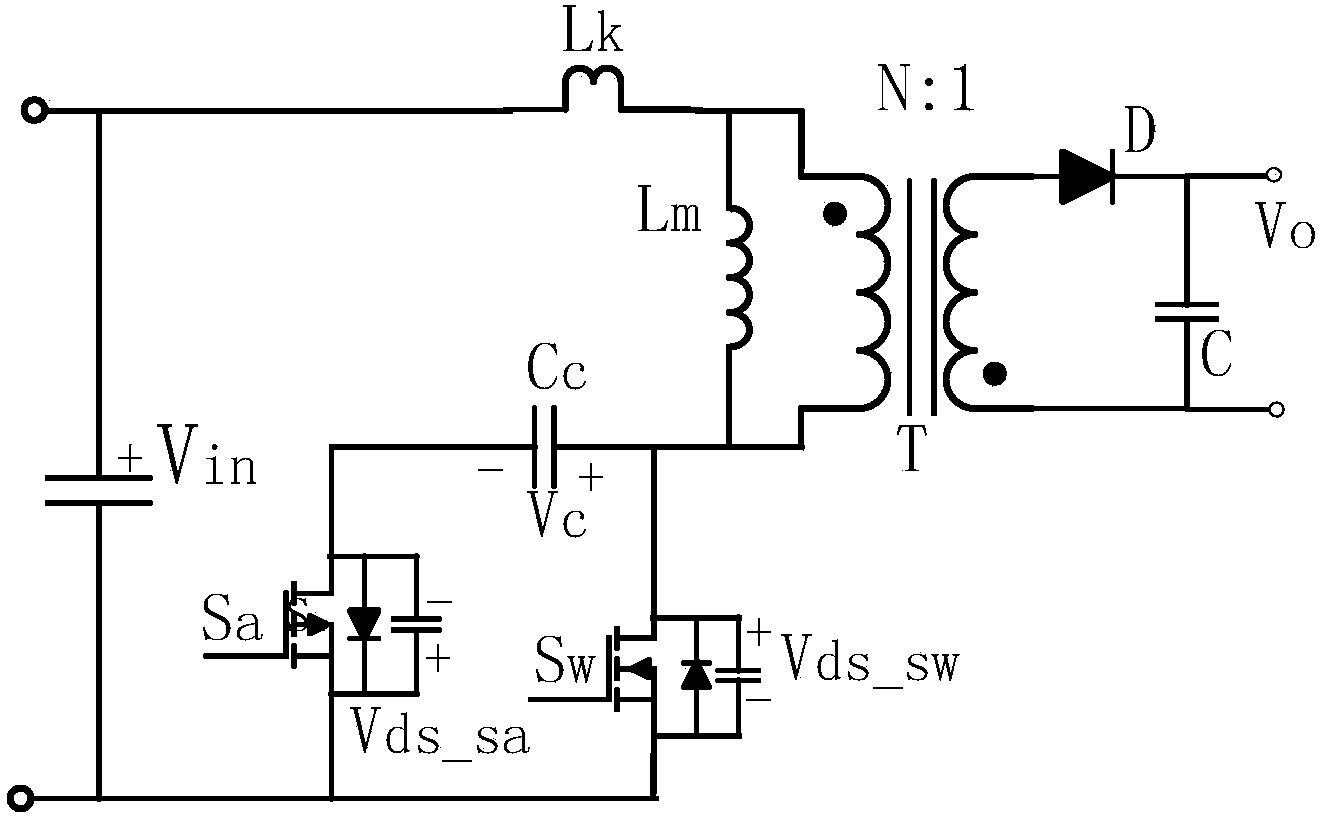
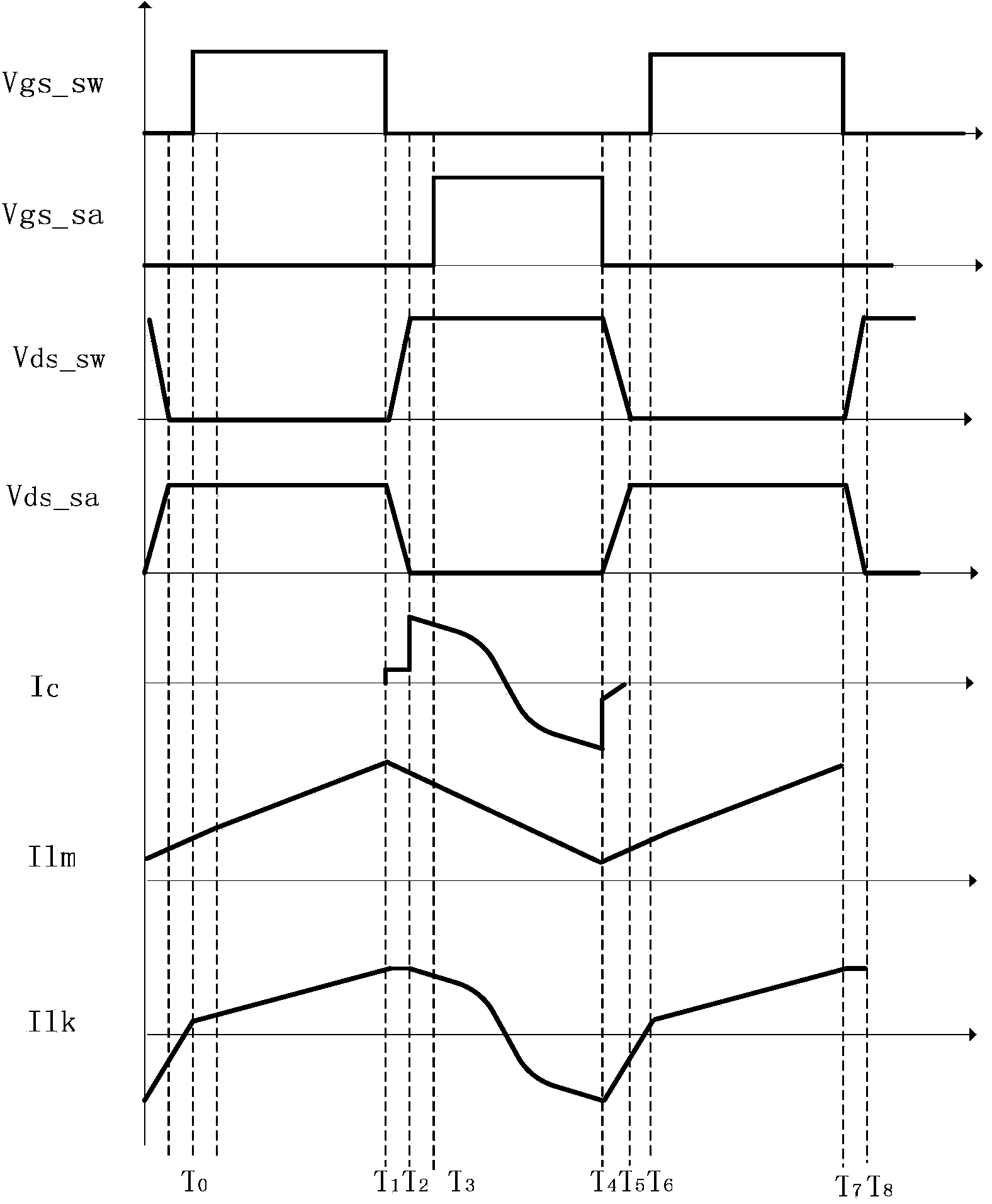
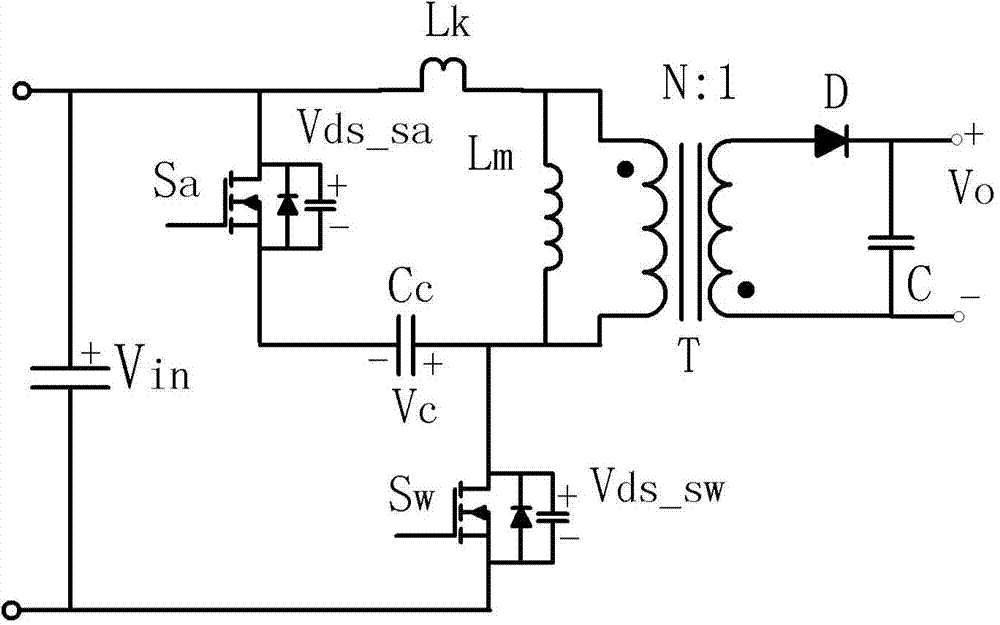
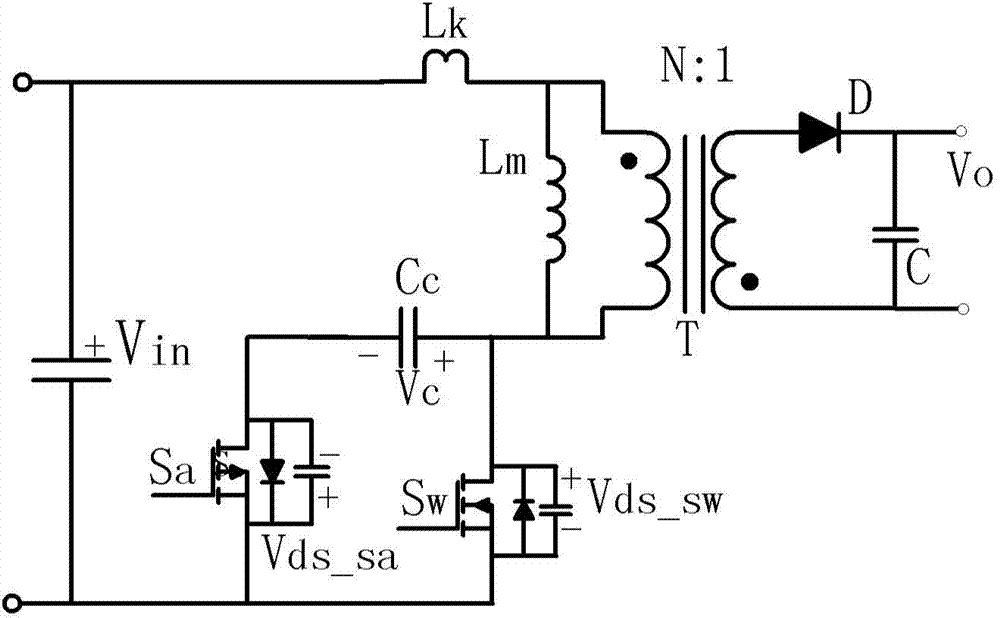
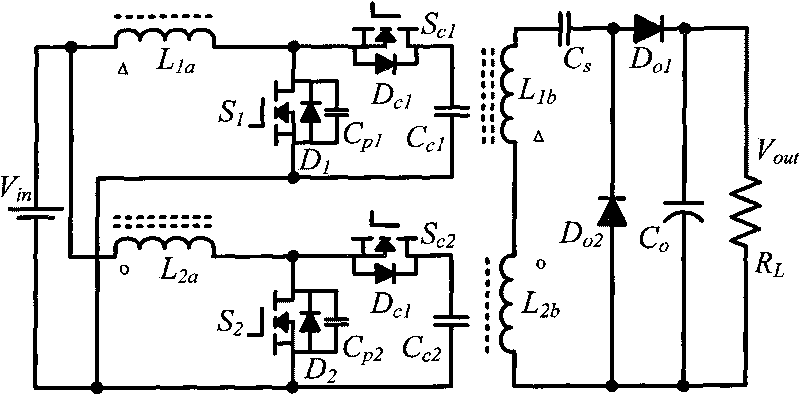
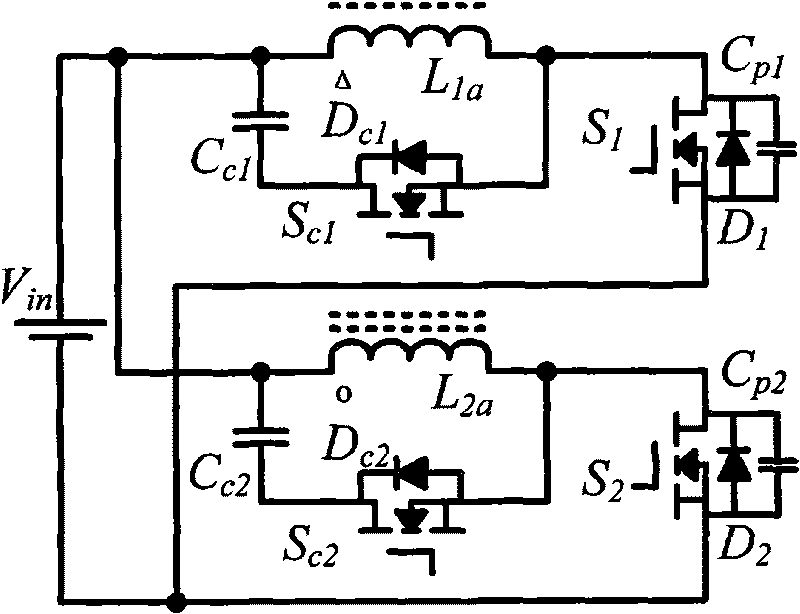
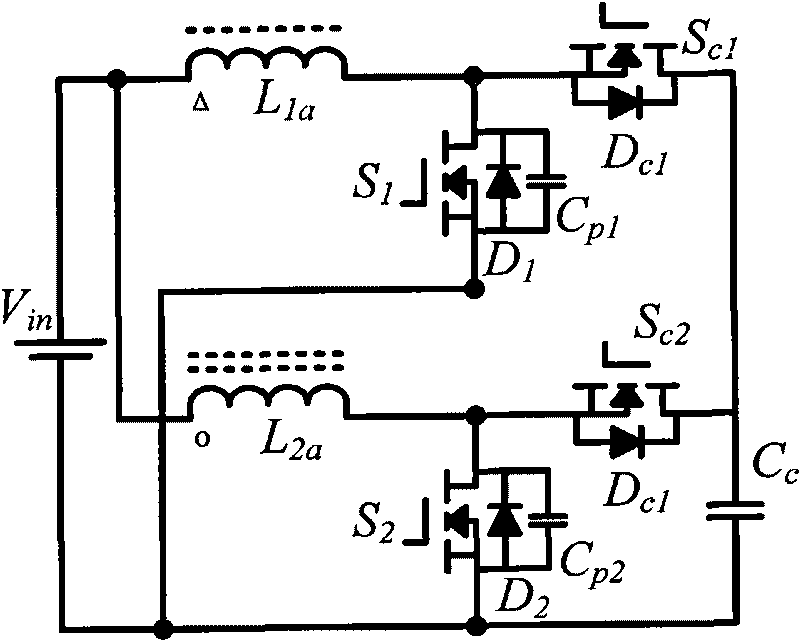
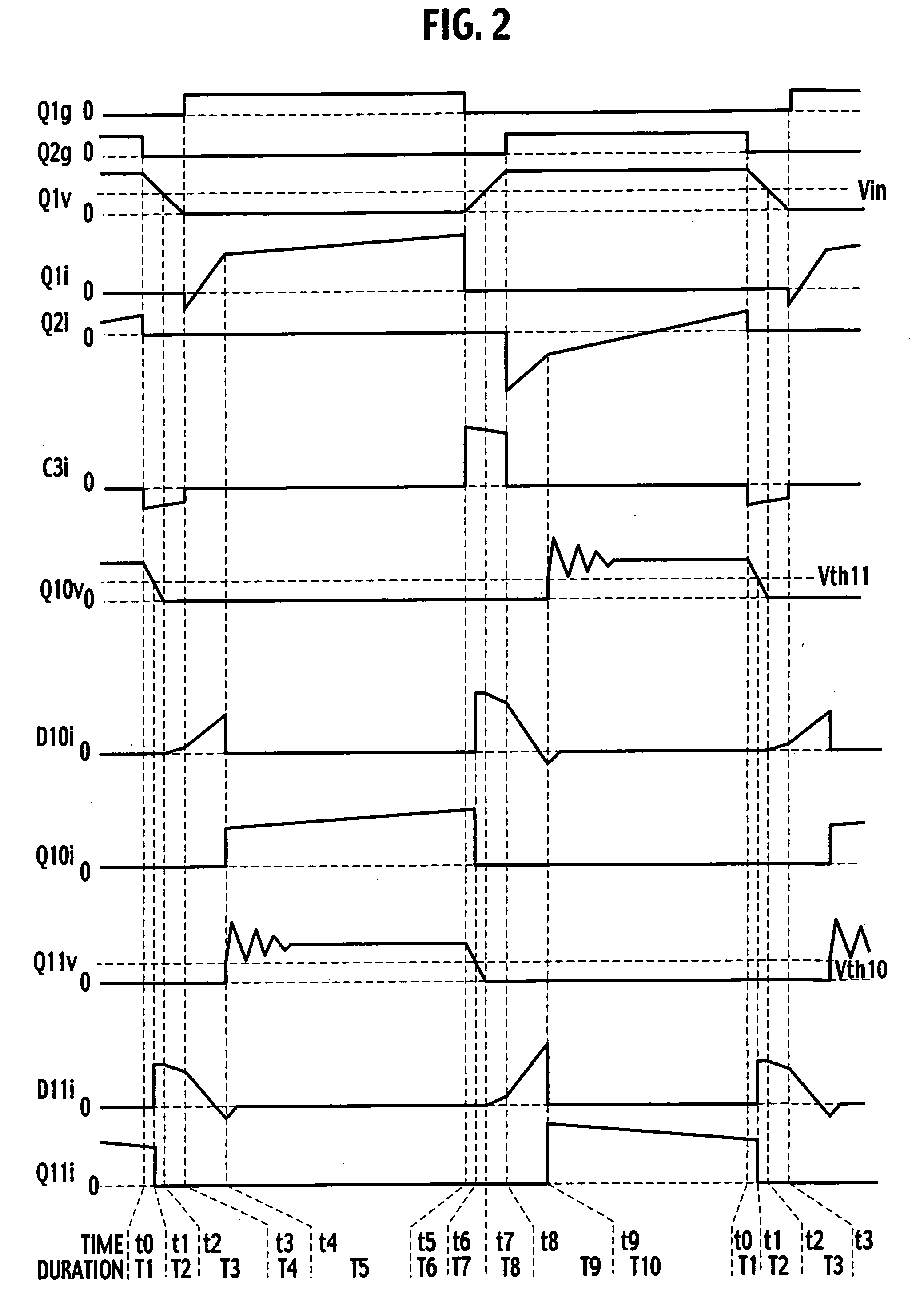
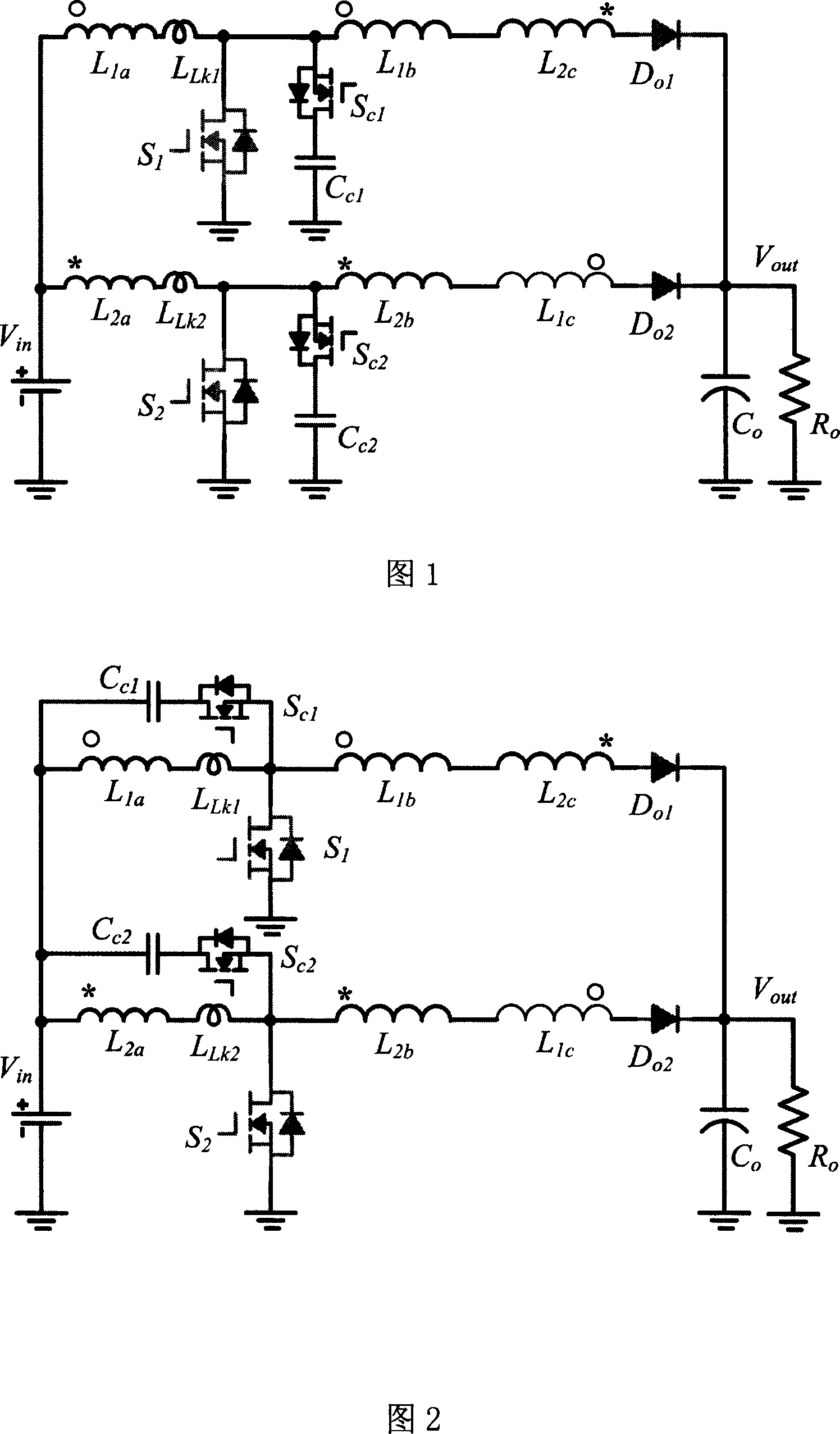
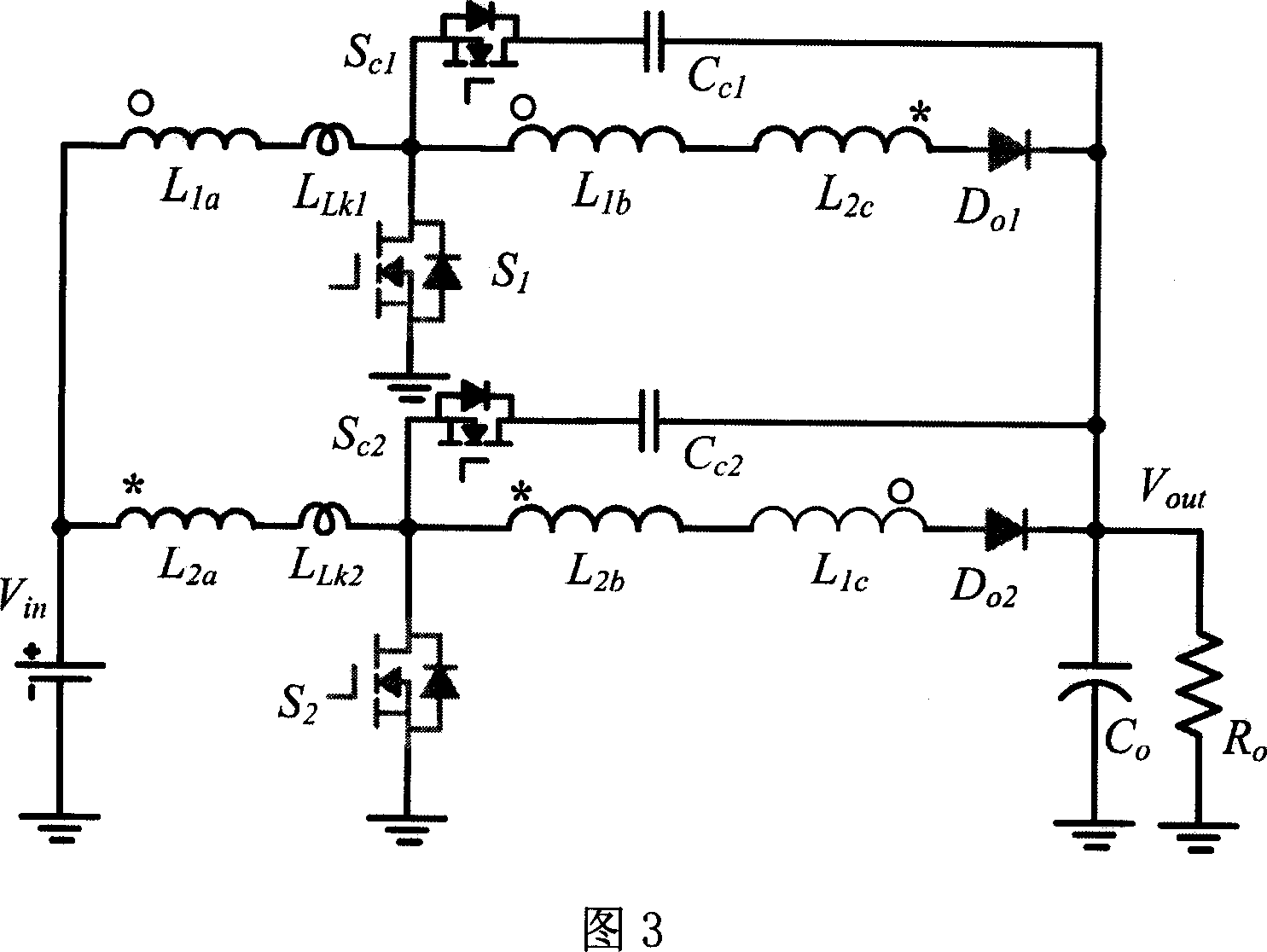
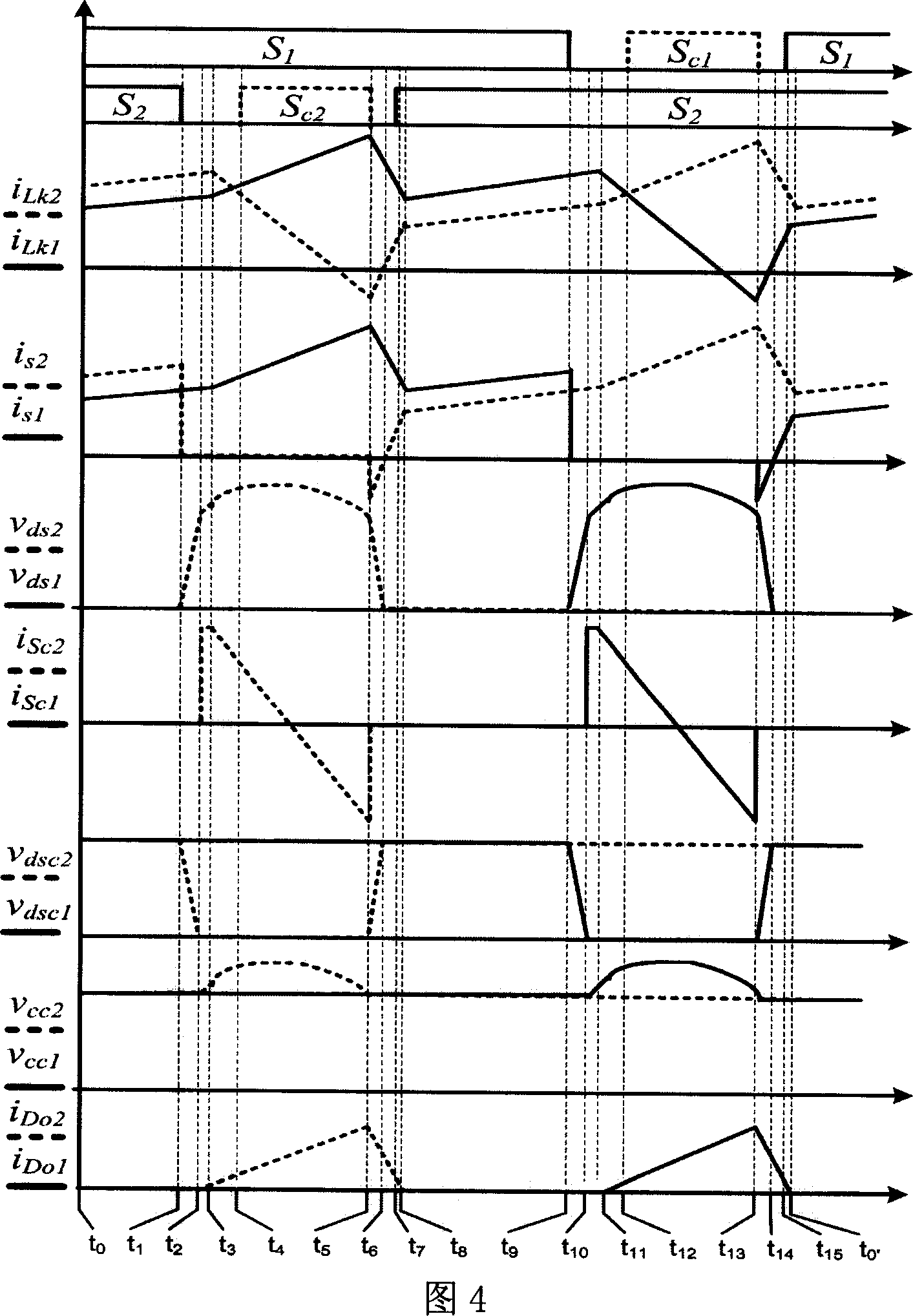
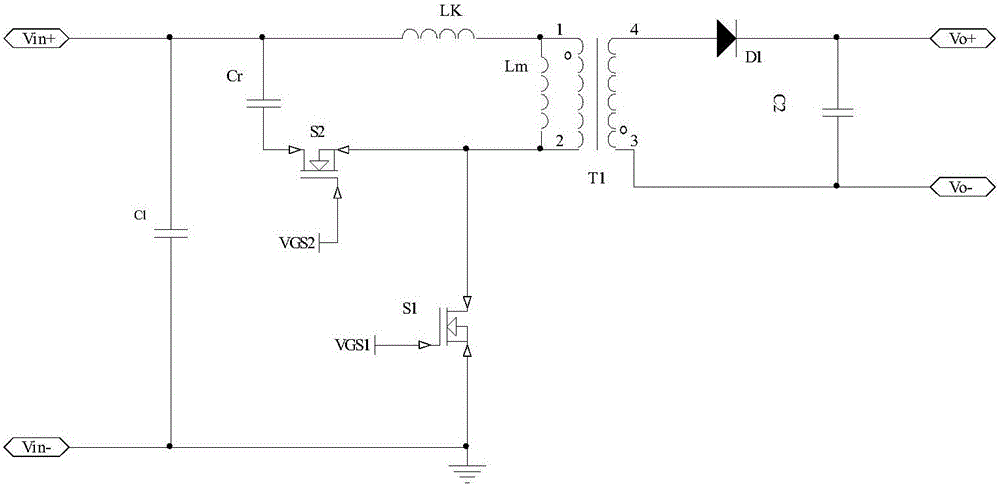
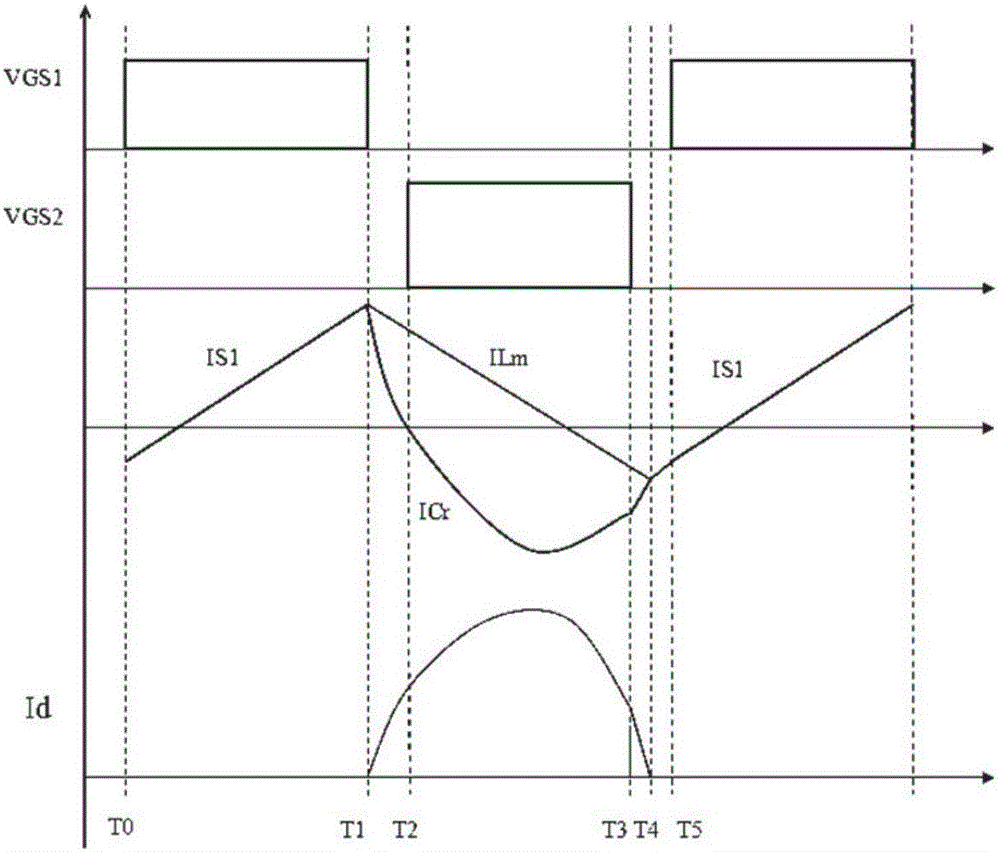
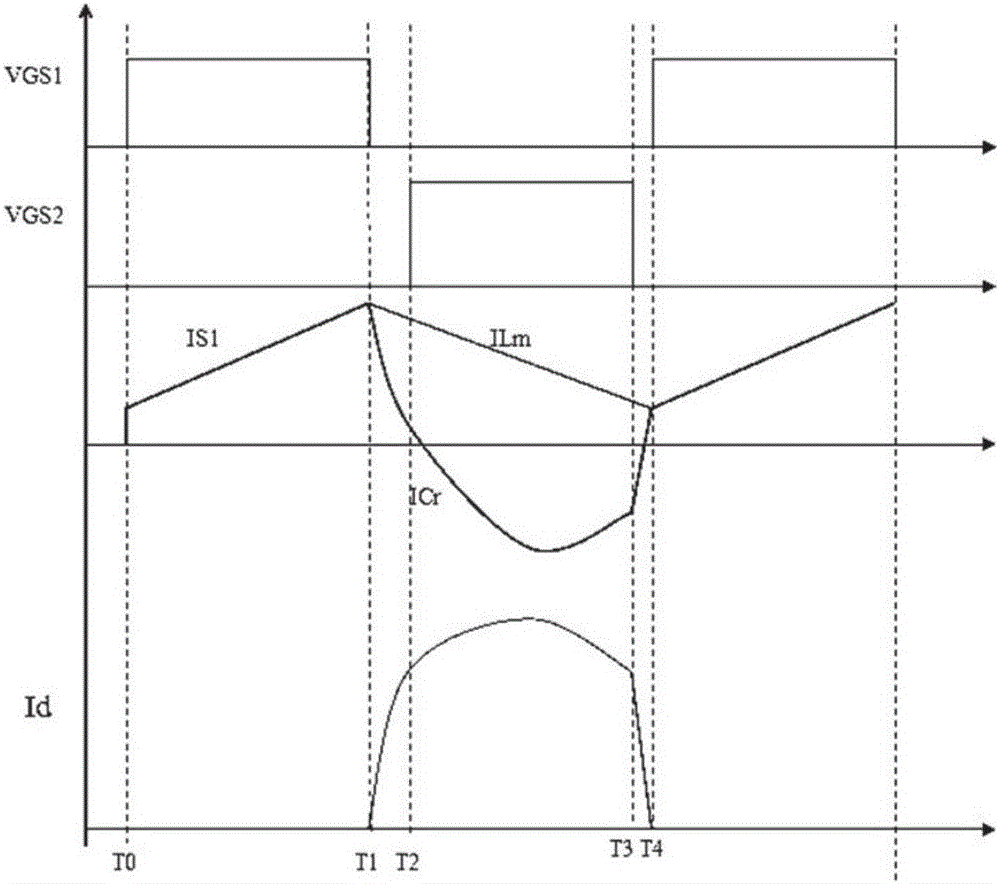
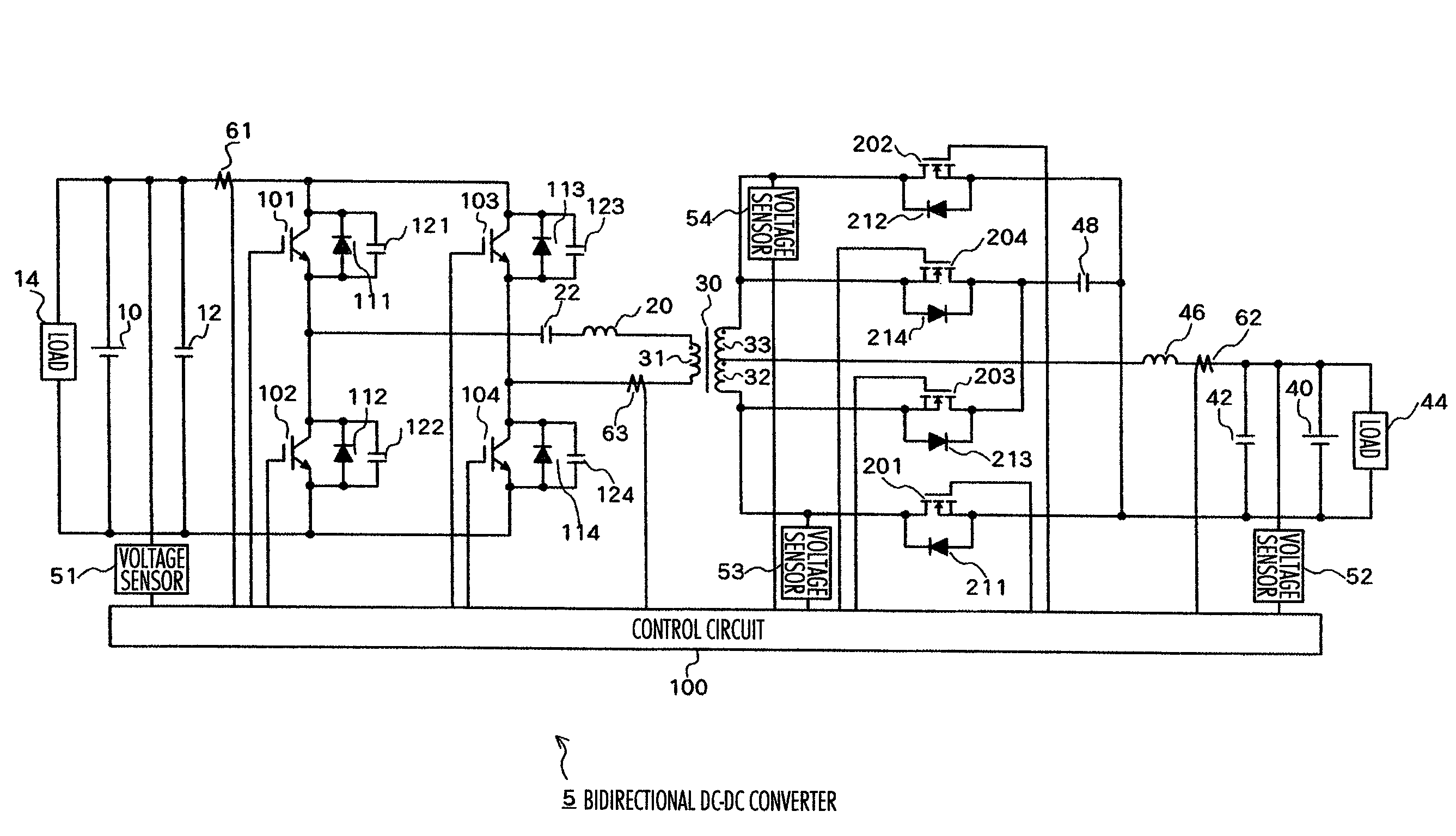
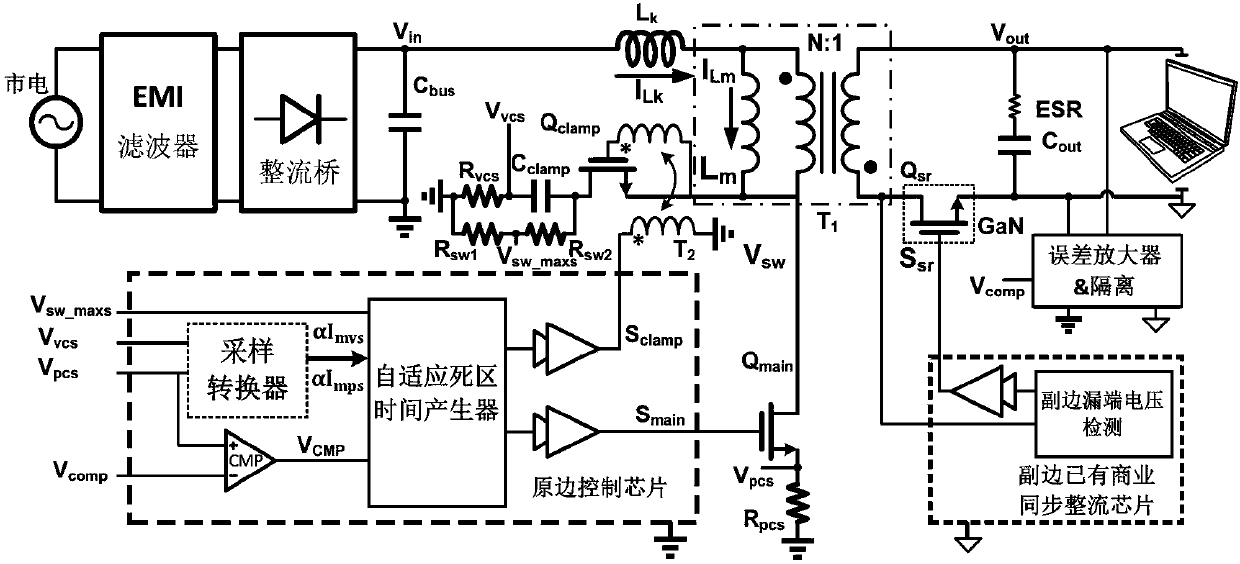
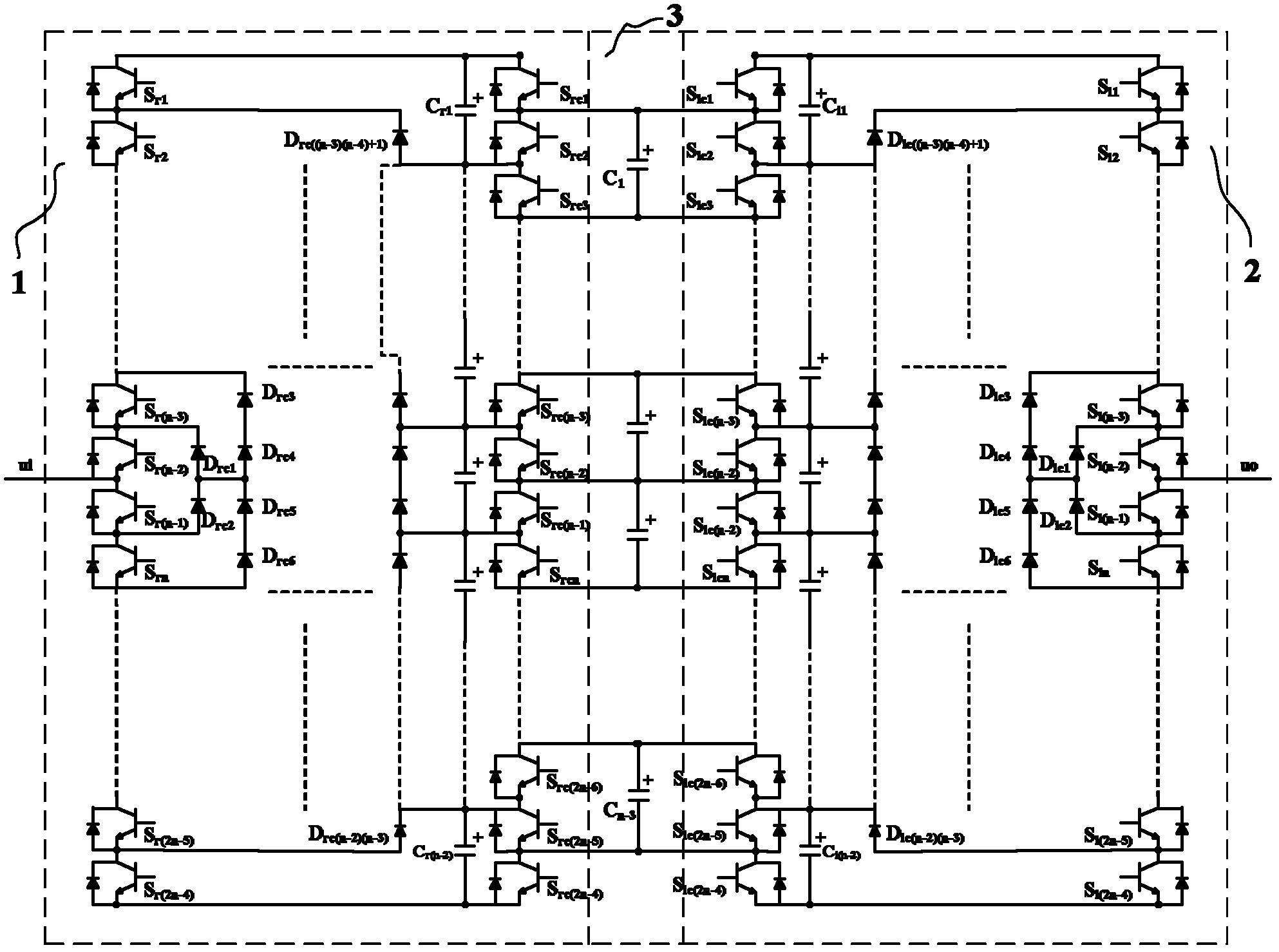
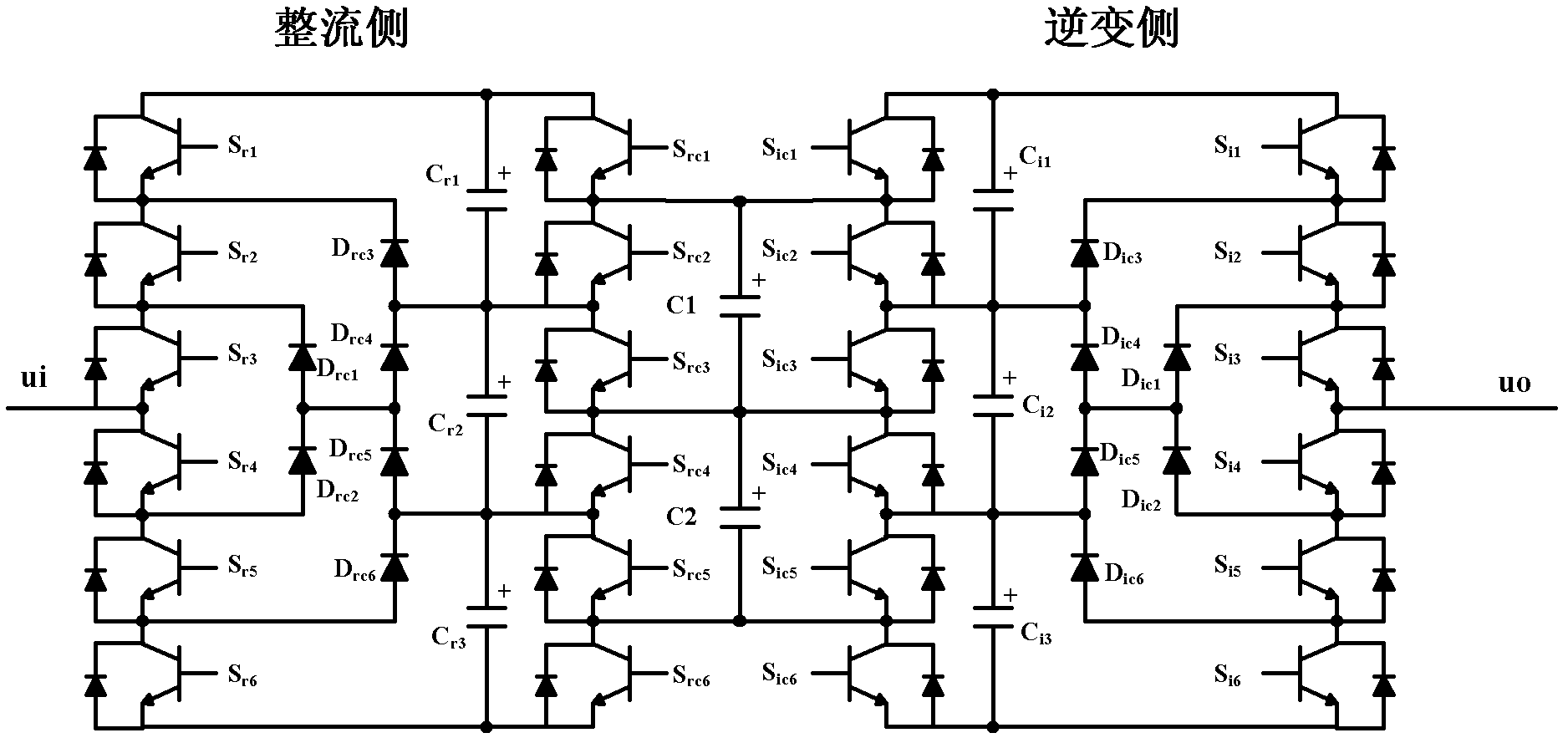
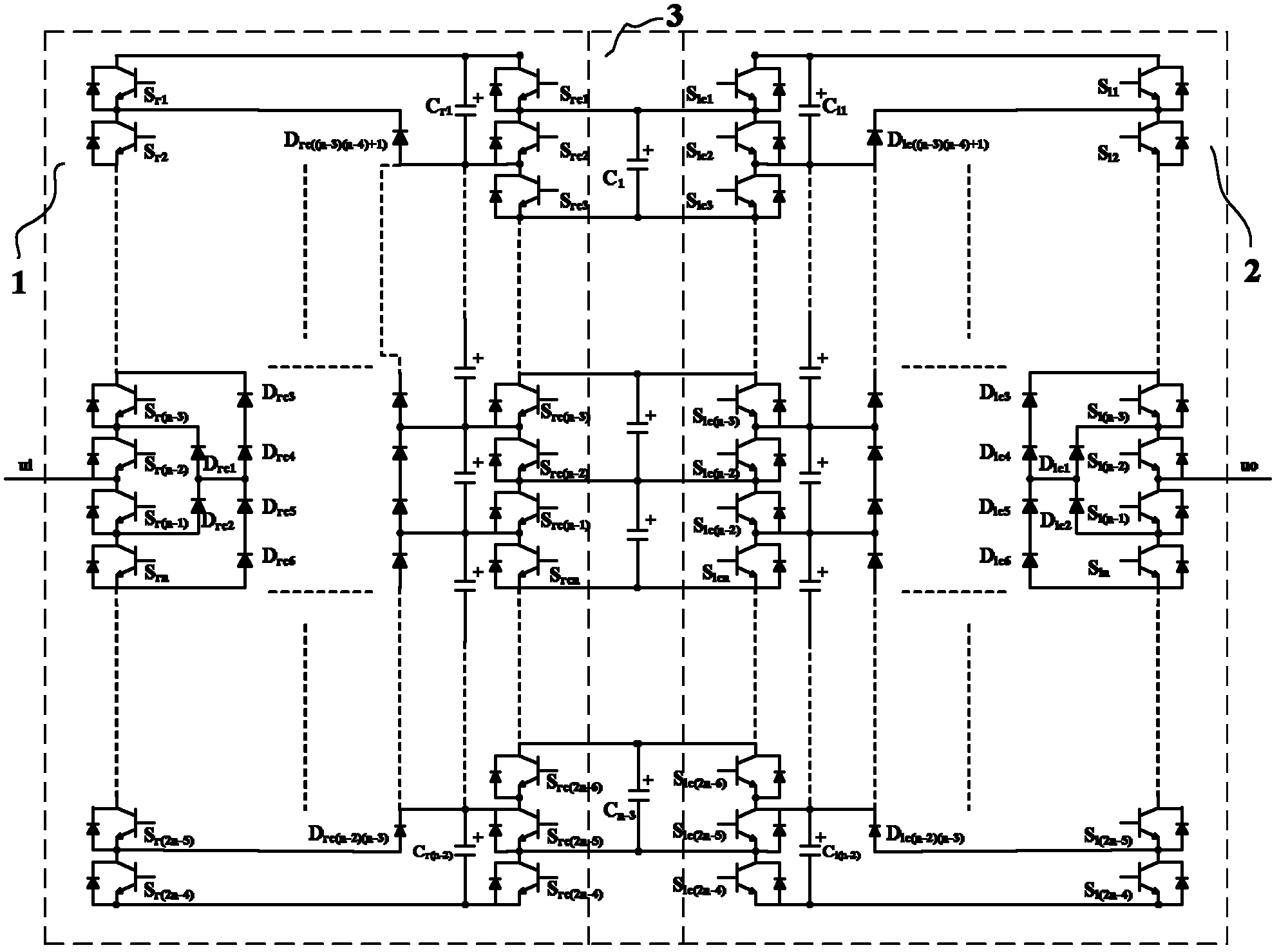
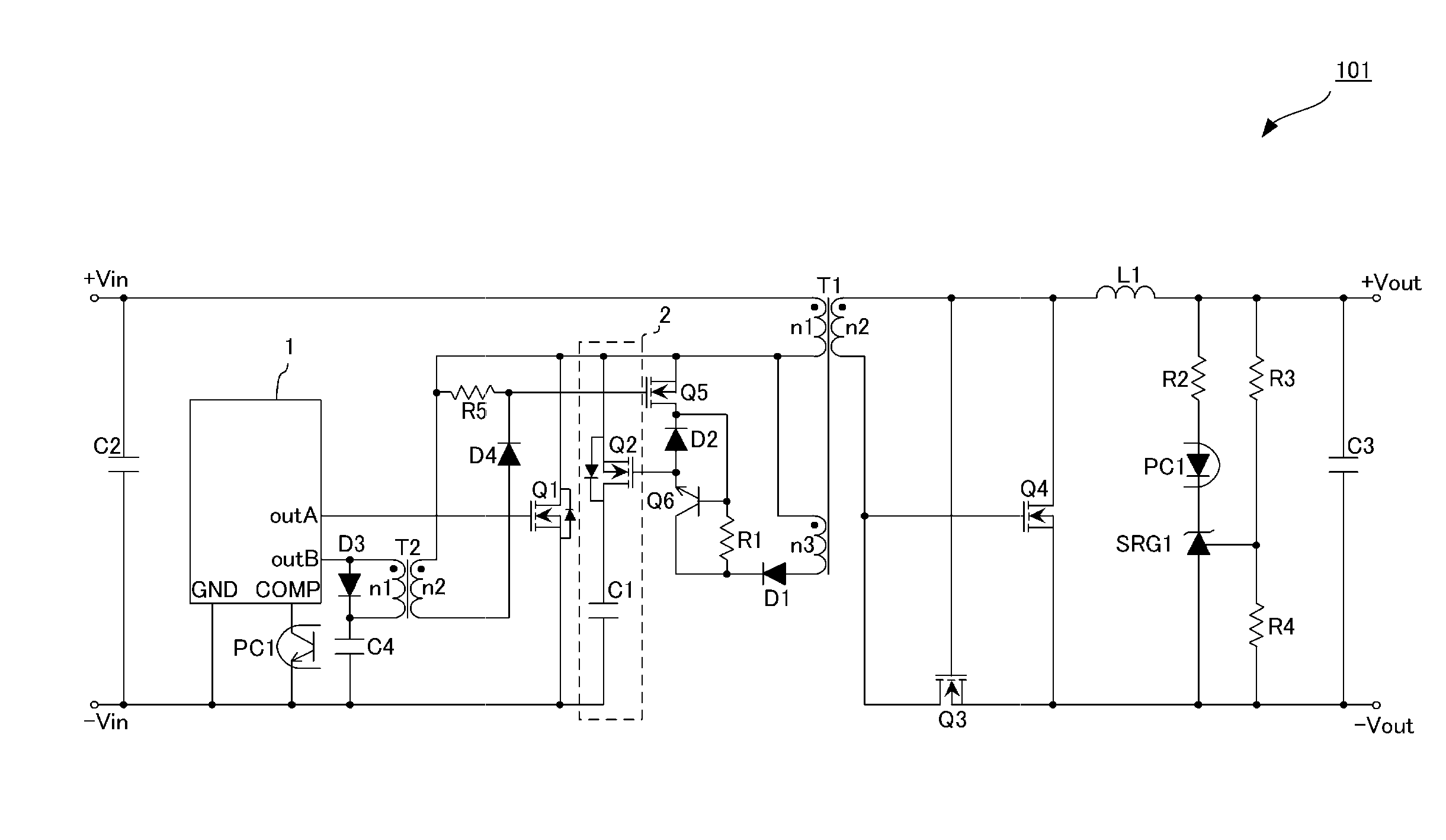
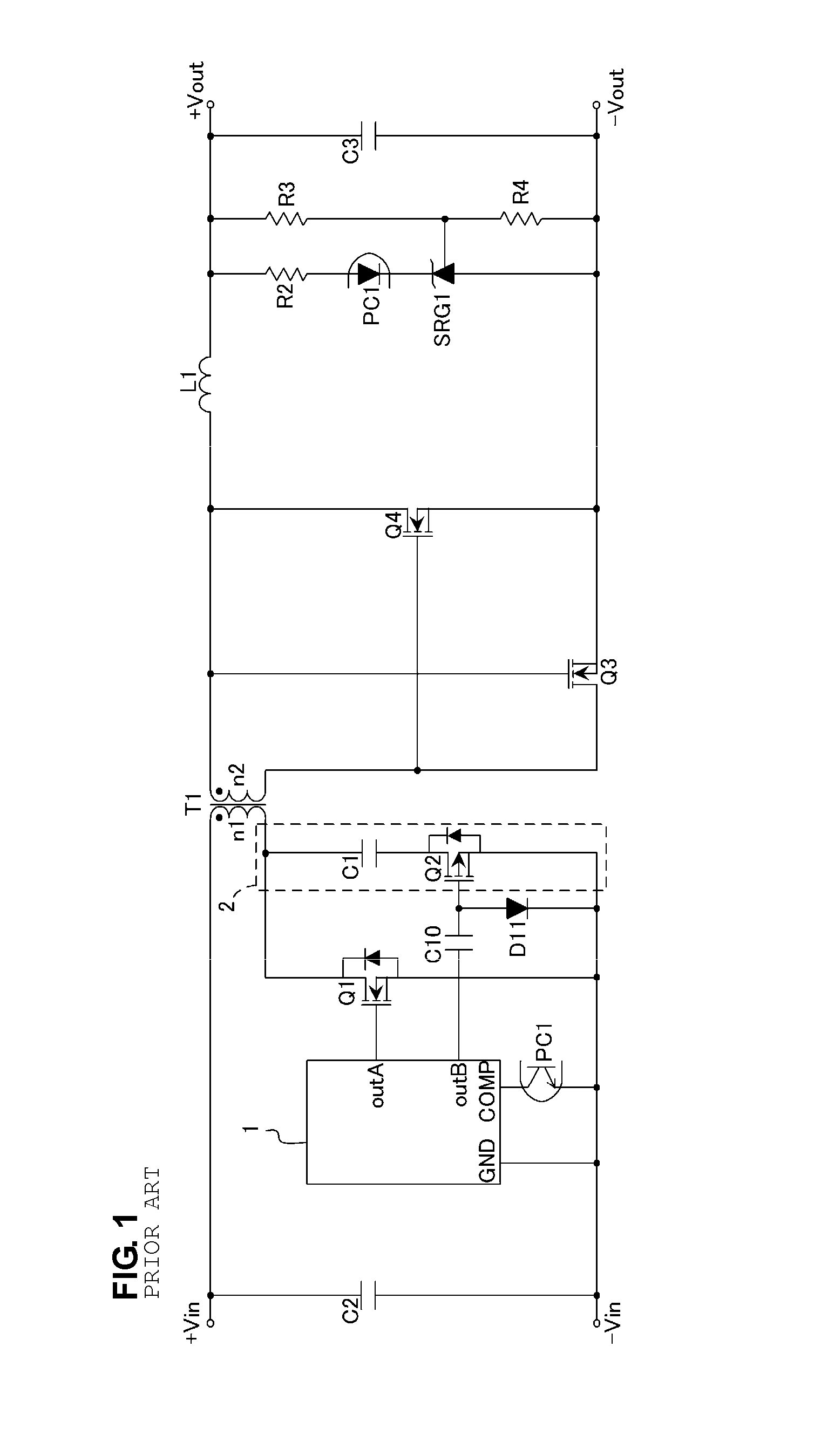
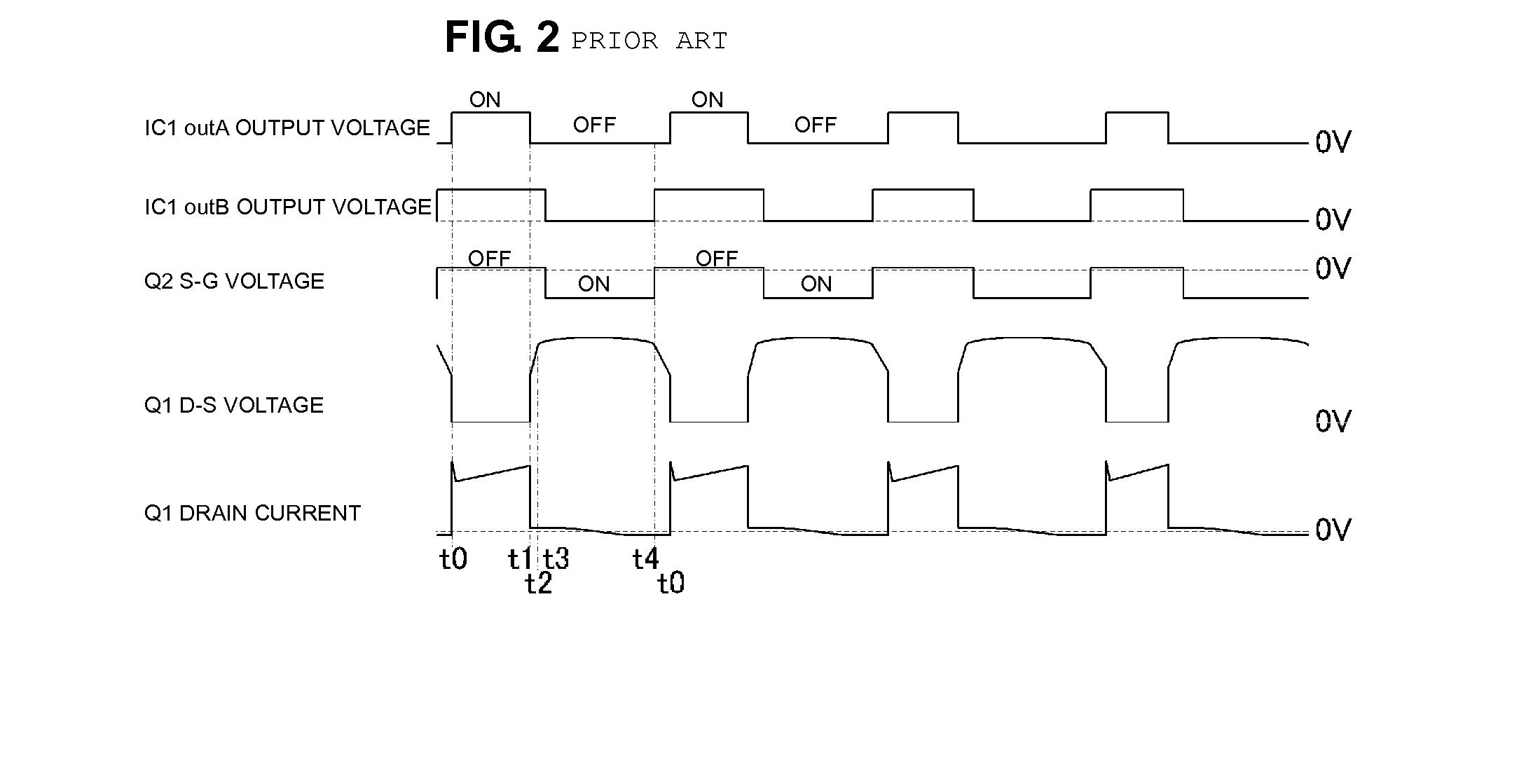
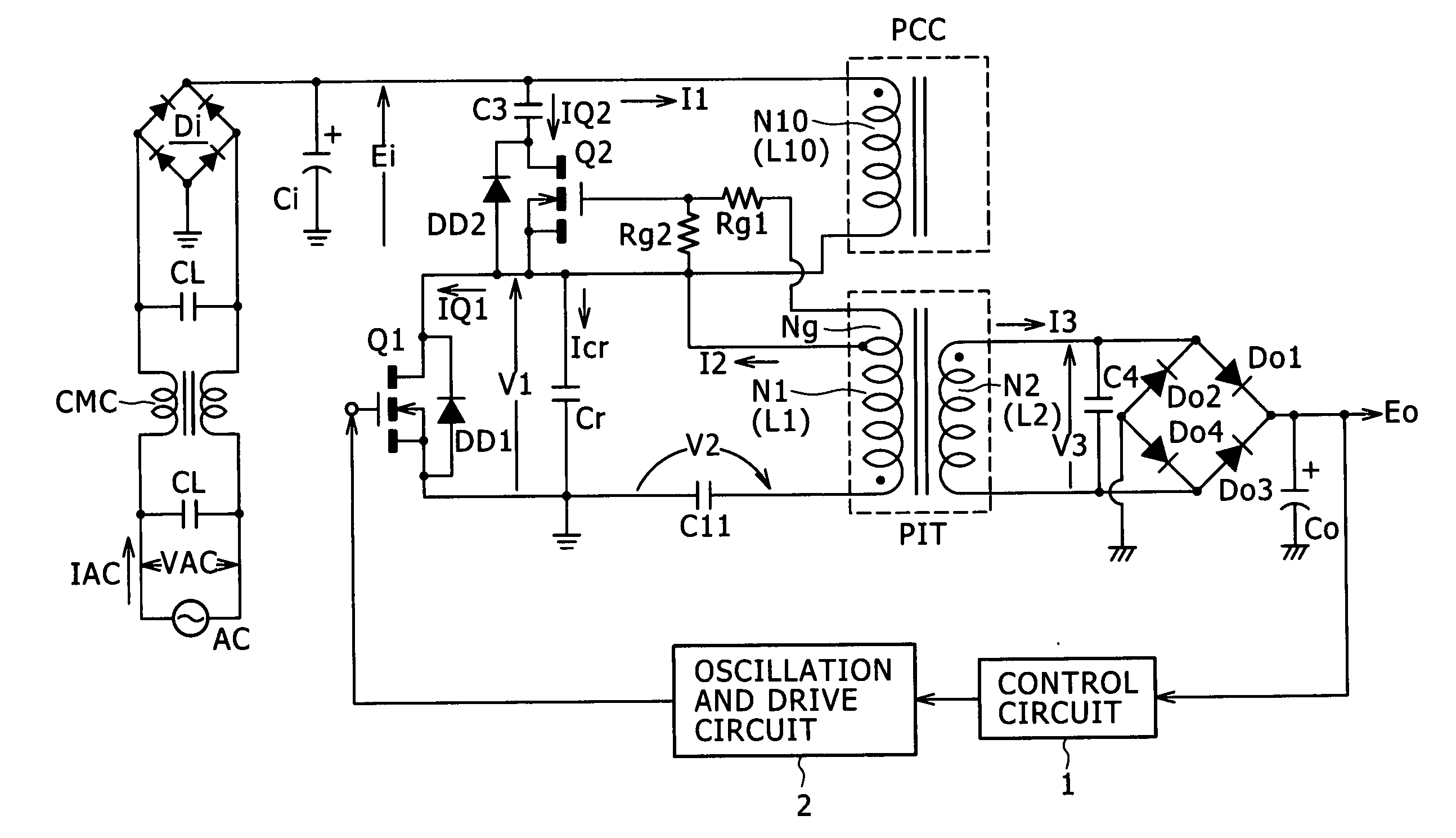
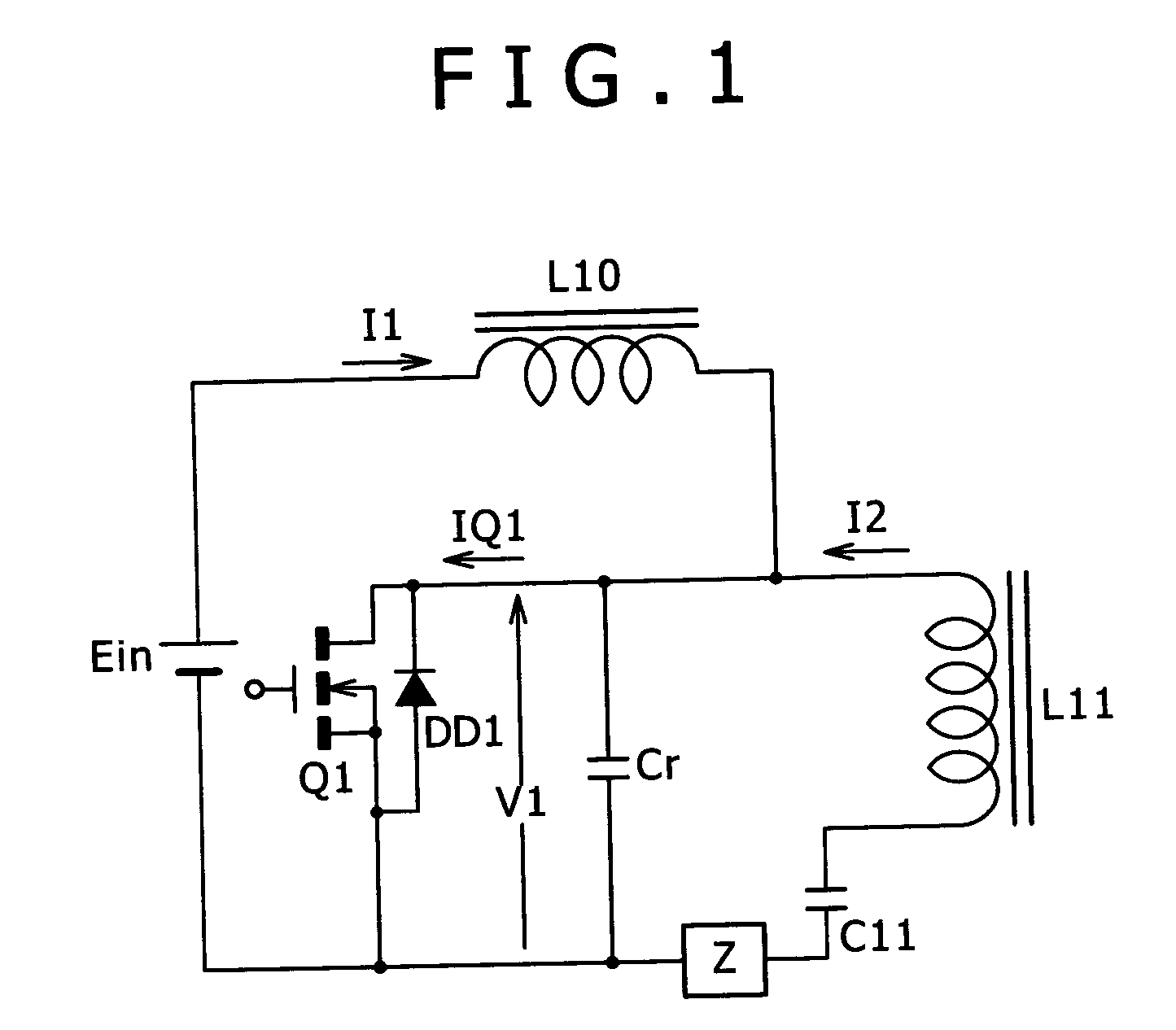
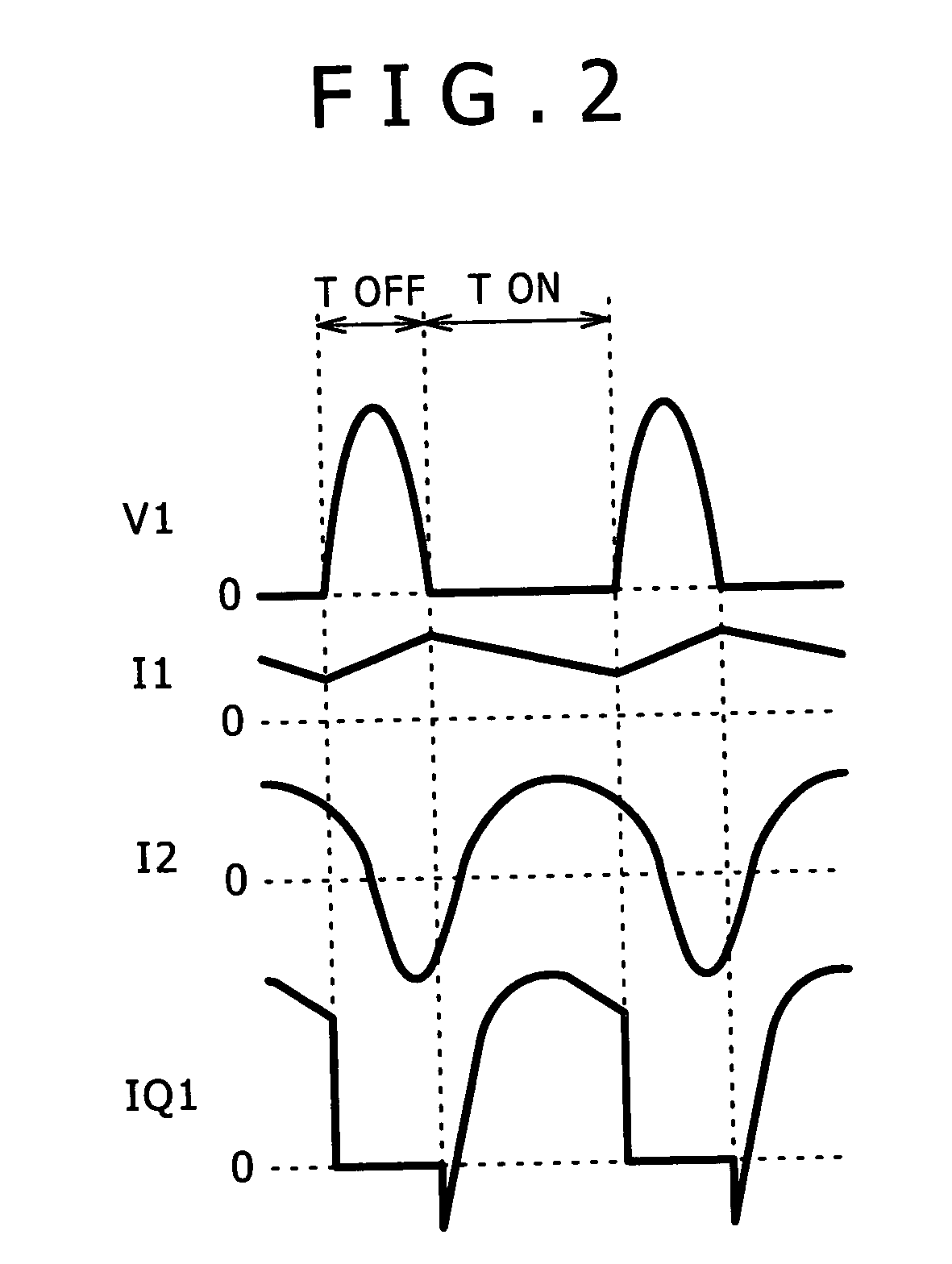
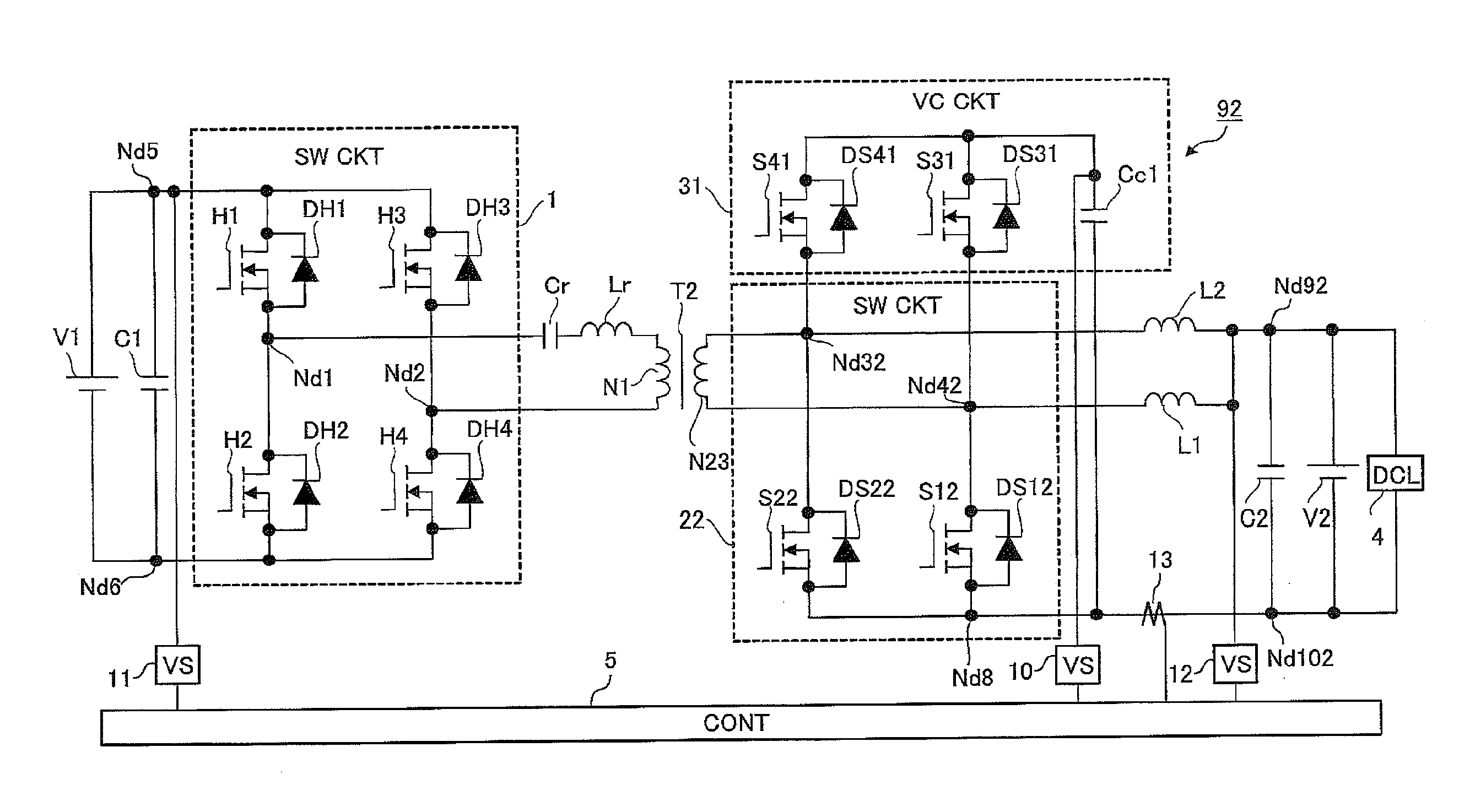
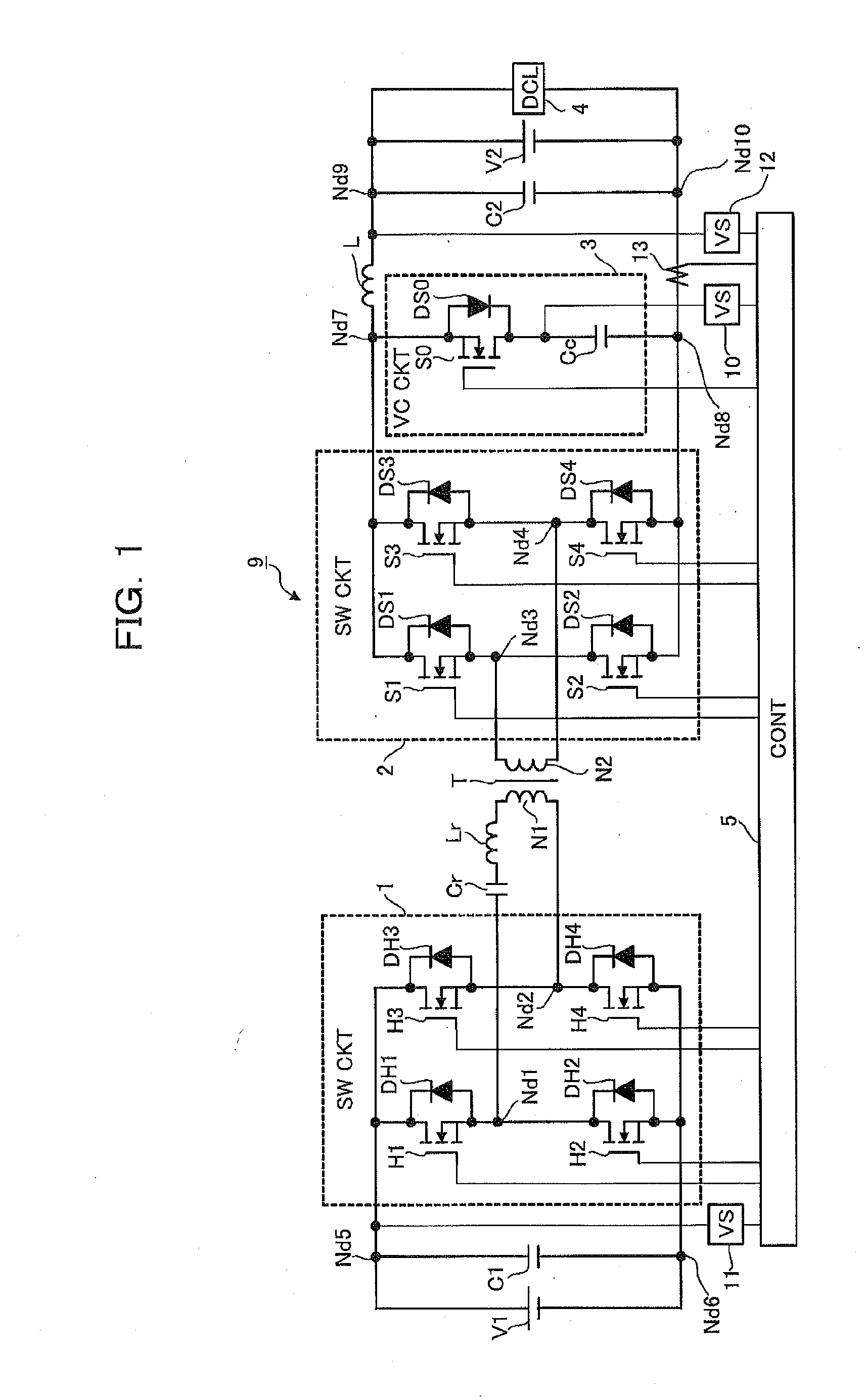
Patents
Literature
218 results about "Clamp capacitor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
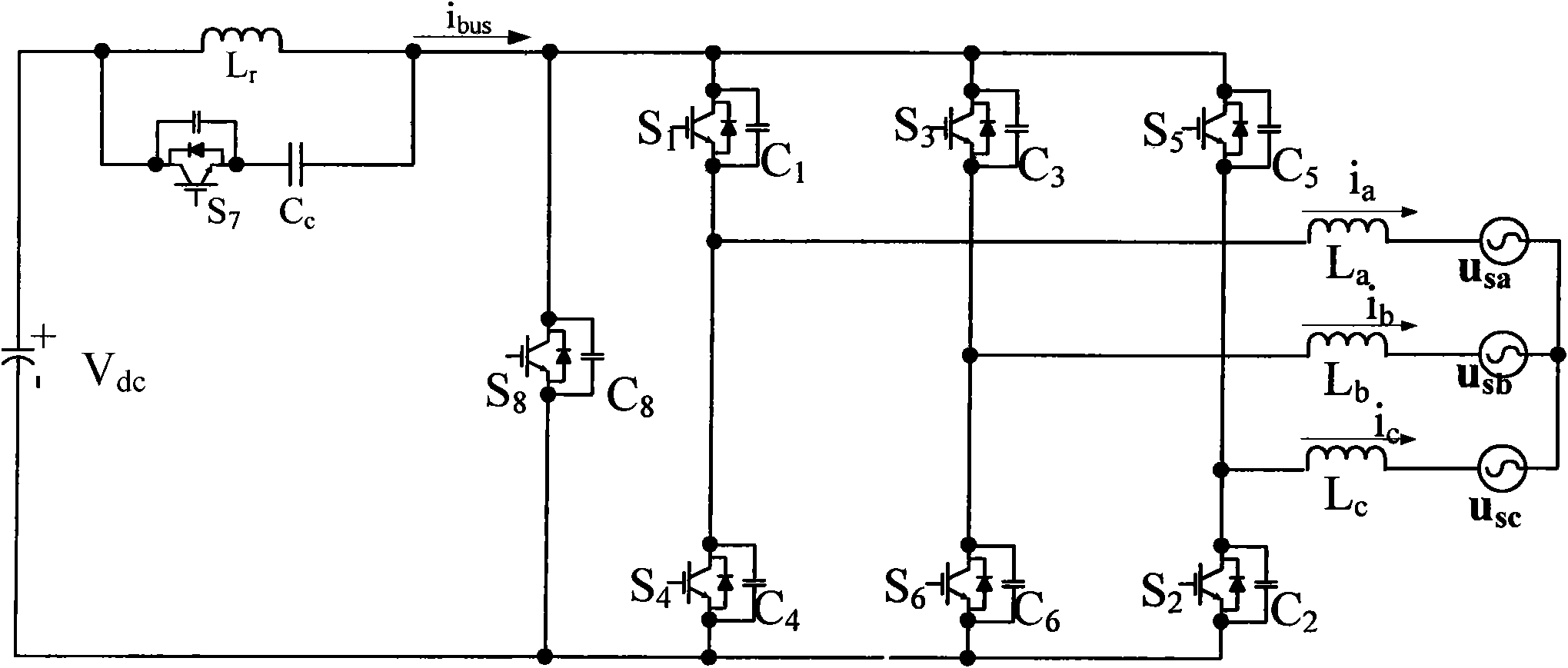
Dual bridge matrix converter
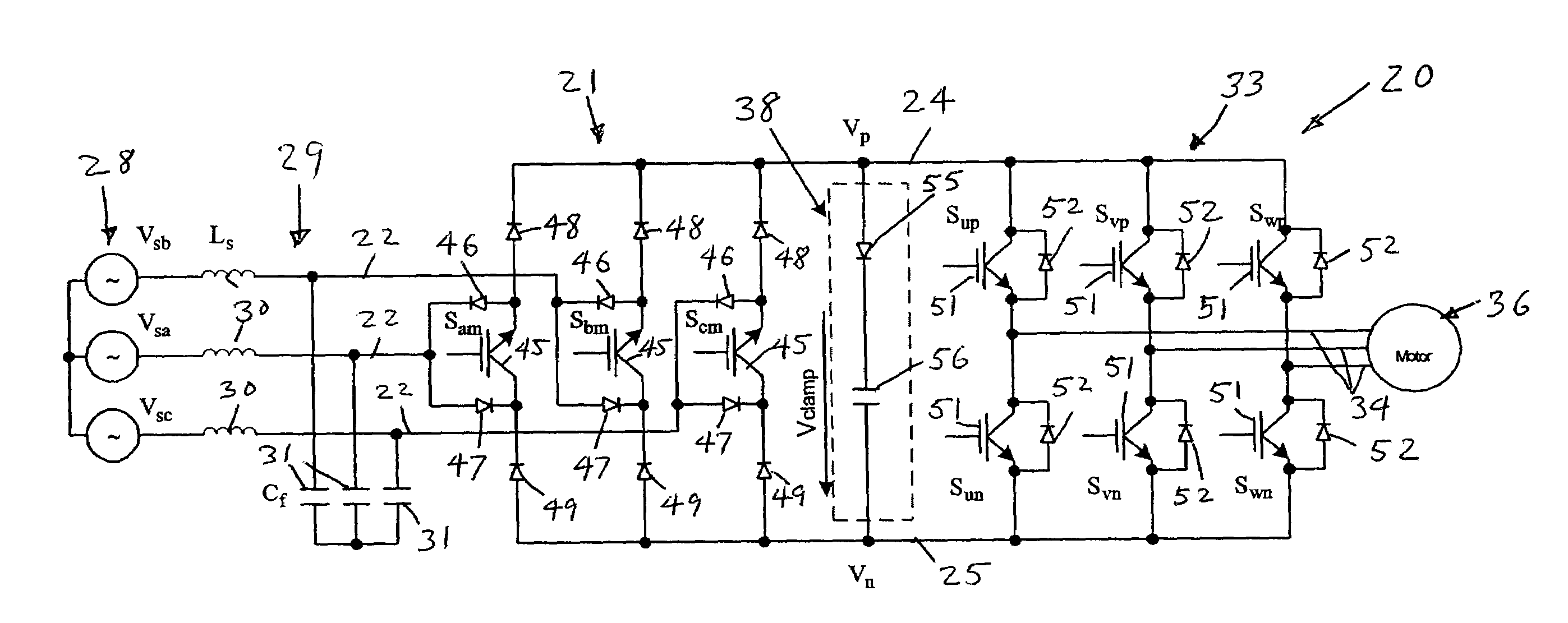
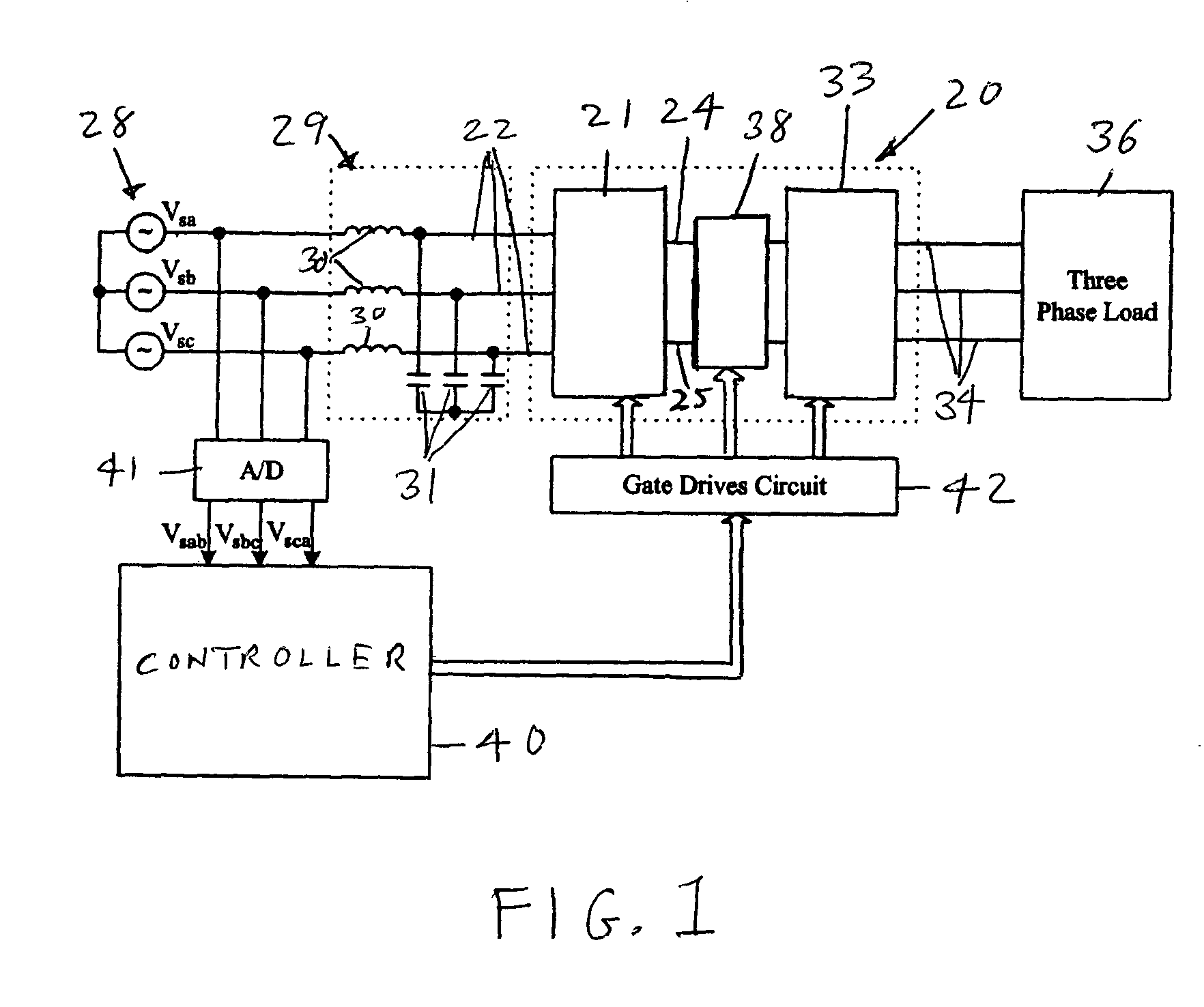
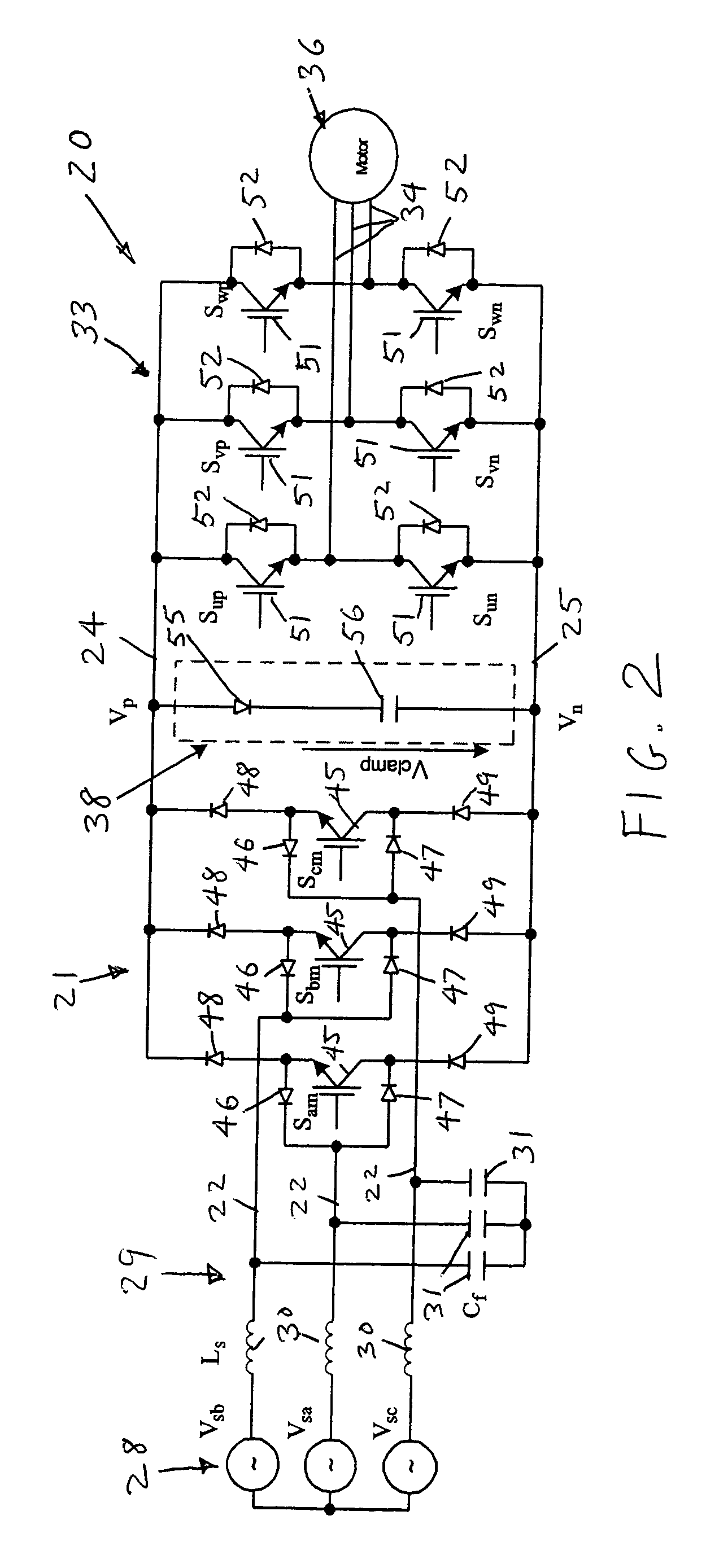
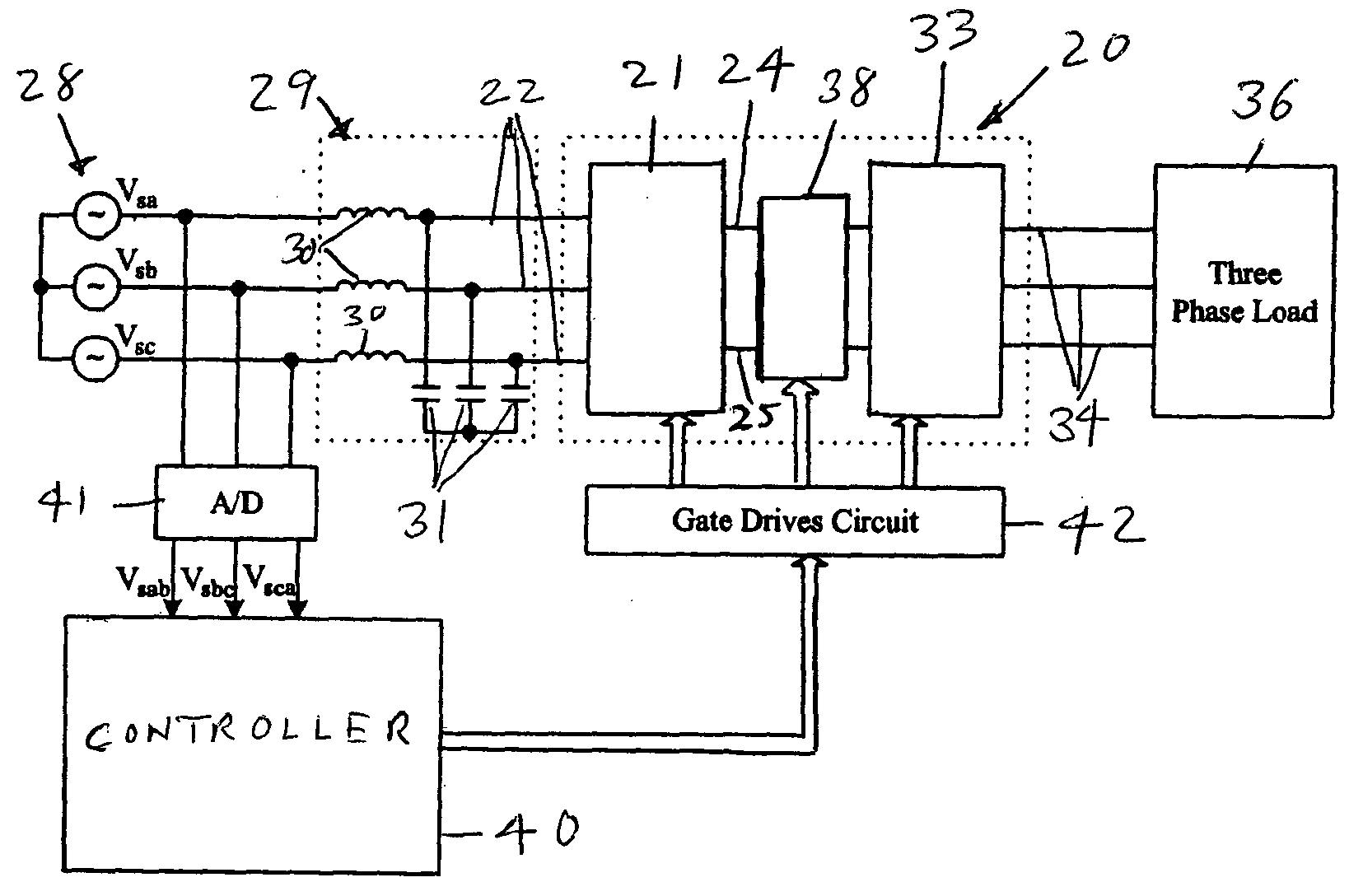
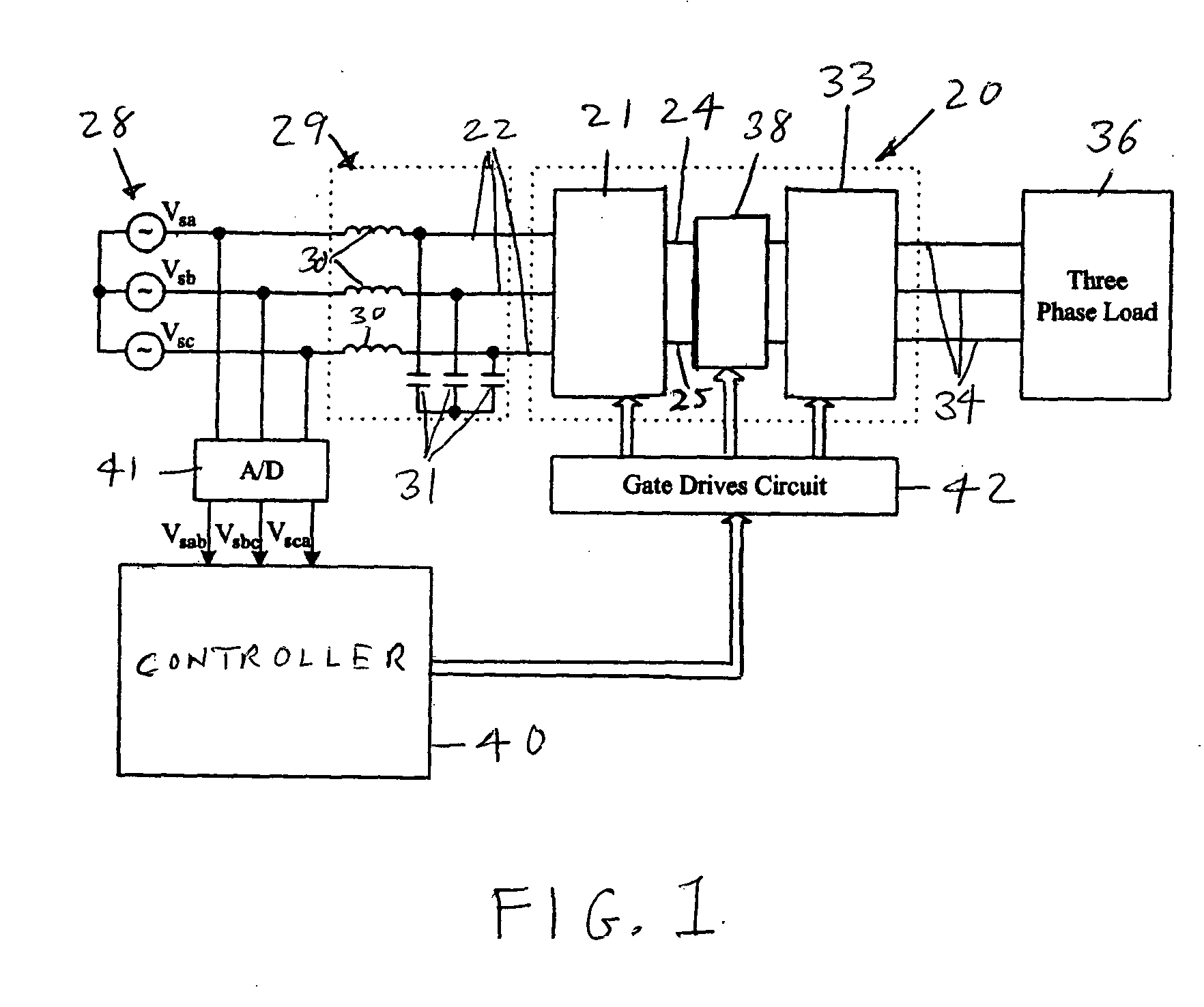
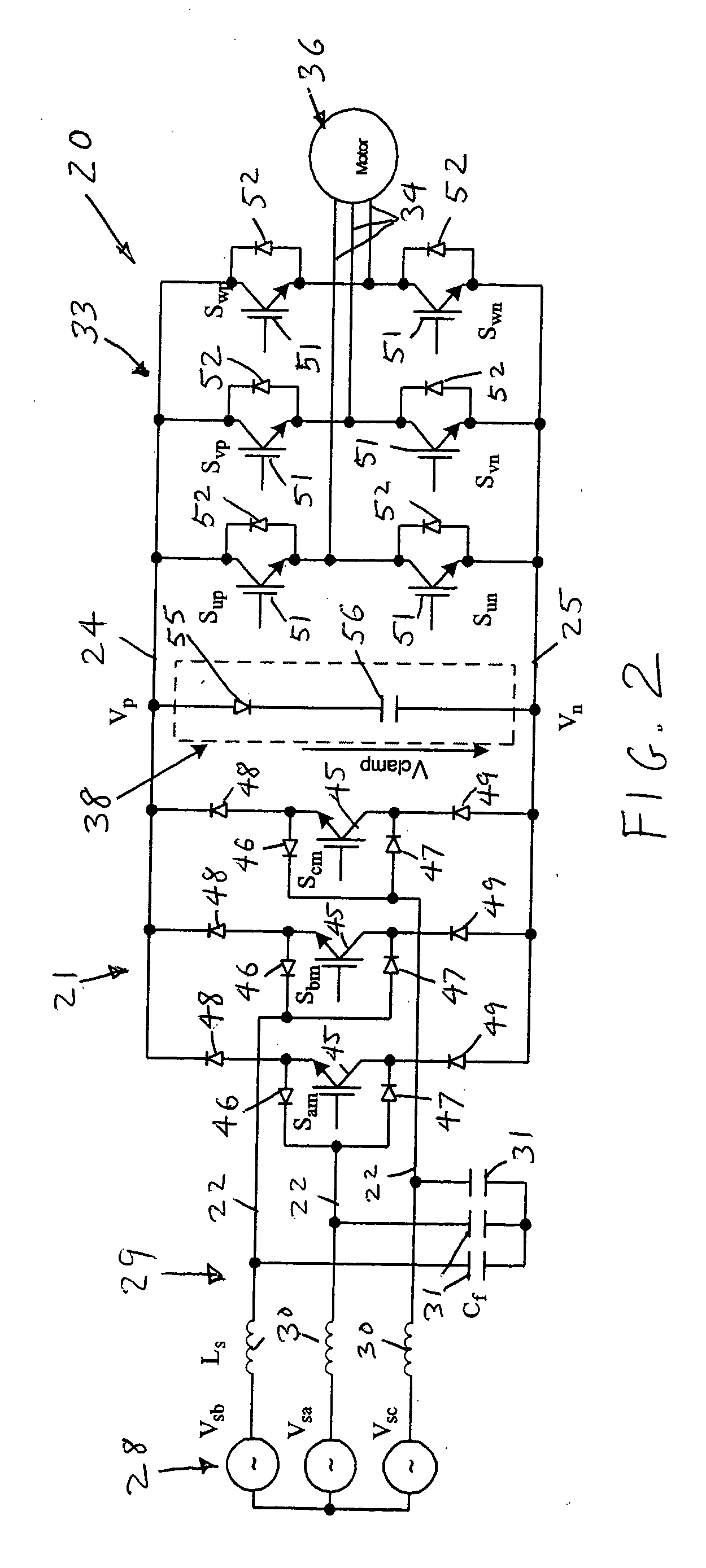
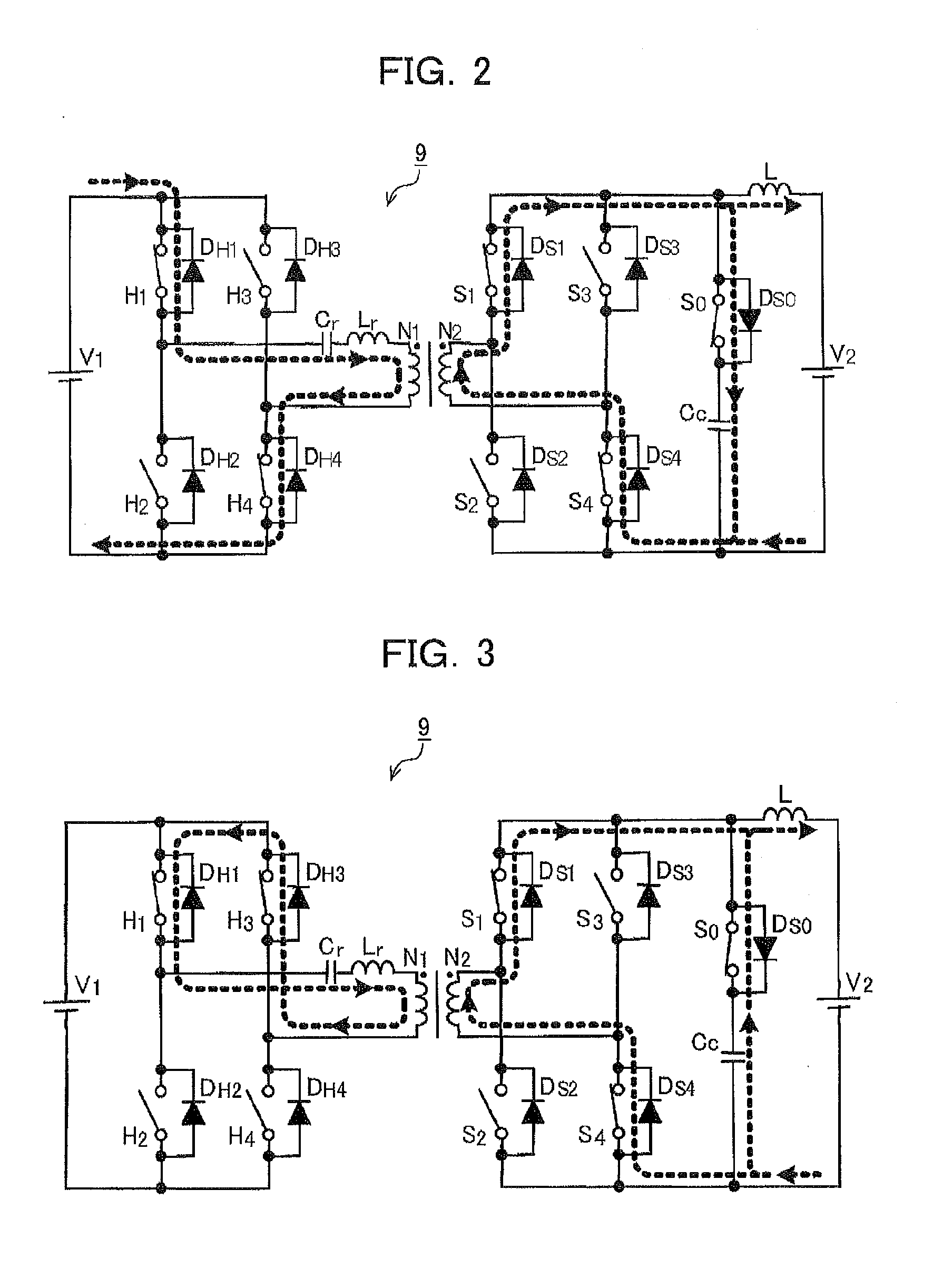
ActiveUS6995992B2Reduce and eliminate voltage spikeSmall and inexpensiveConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc circuit to reduce harmonics/ripplesMatrix convertersClamp capacitor
A dual bridge matrix converter has a line-side converter with controllable switches that receives AC power and provides unidirectional power to high and low DC link lines, and a load-side converter which receives the power from the DC link lines and provides AC power to output lines. A clamp circuit is connected across the DC link lines and includes a series connected diode and a capacitor. Negative DC link current will be conducted through the clamp diode to charge the clamp capacitor to avoid voltage spikes on the DC link lines. A controllable switch may be connected in parallel with the clamp diode and is turned on when the voltage across the clamp capacitor is above a threshold that is greater than the normal peak-to-peak AC input voltage. The switch is turned off when the voltage across the clamp capacitor is lower than the threshold voltage.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Isolated bidirectional DC-DC converter
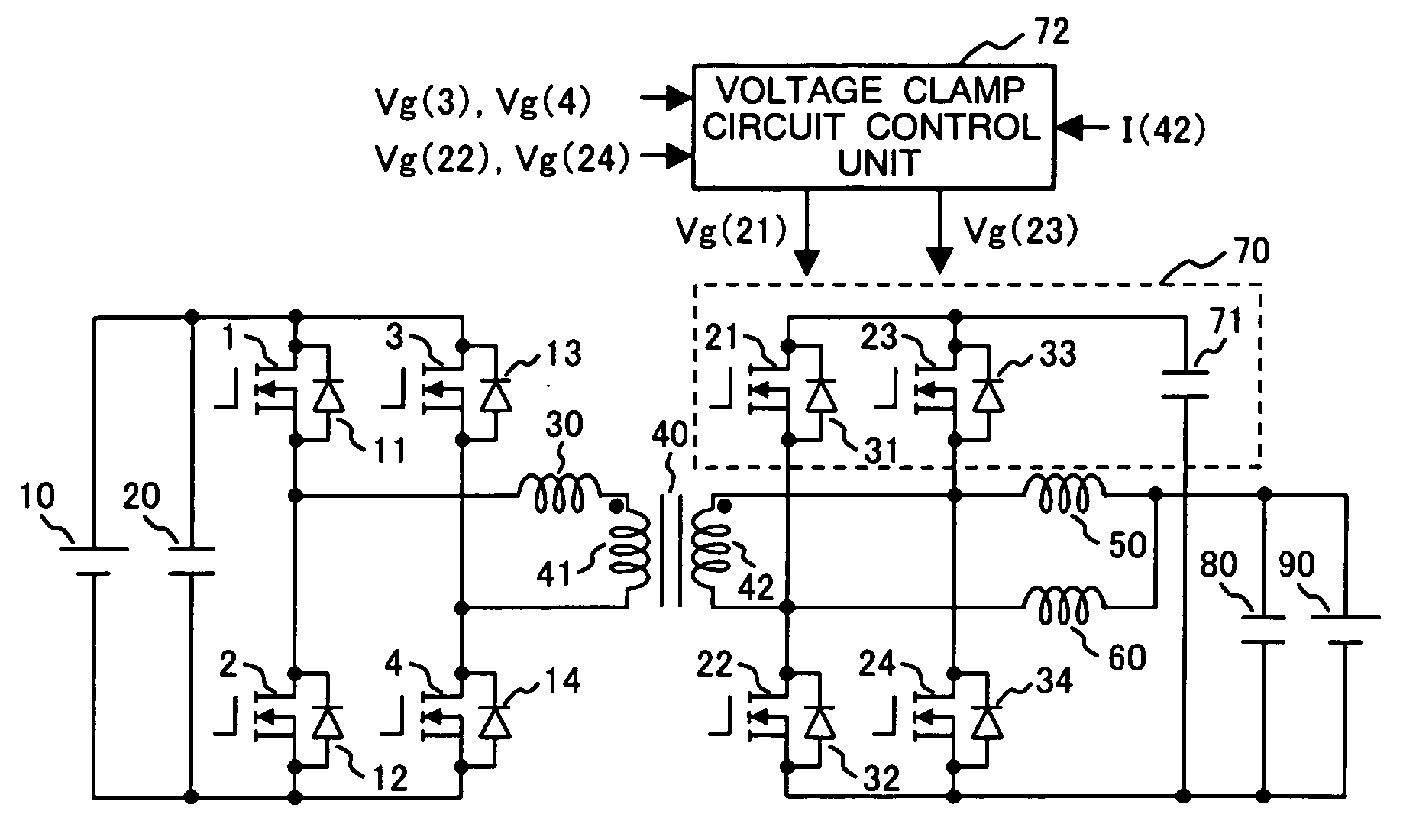
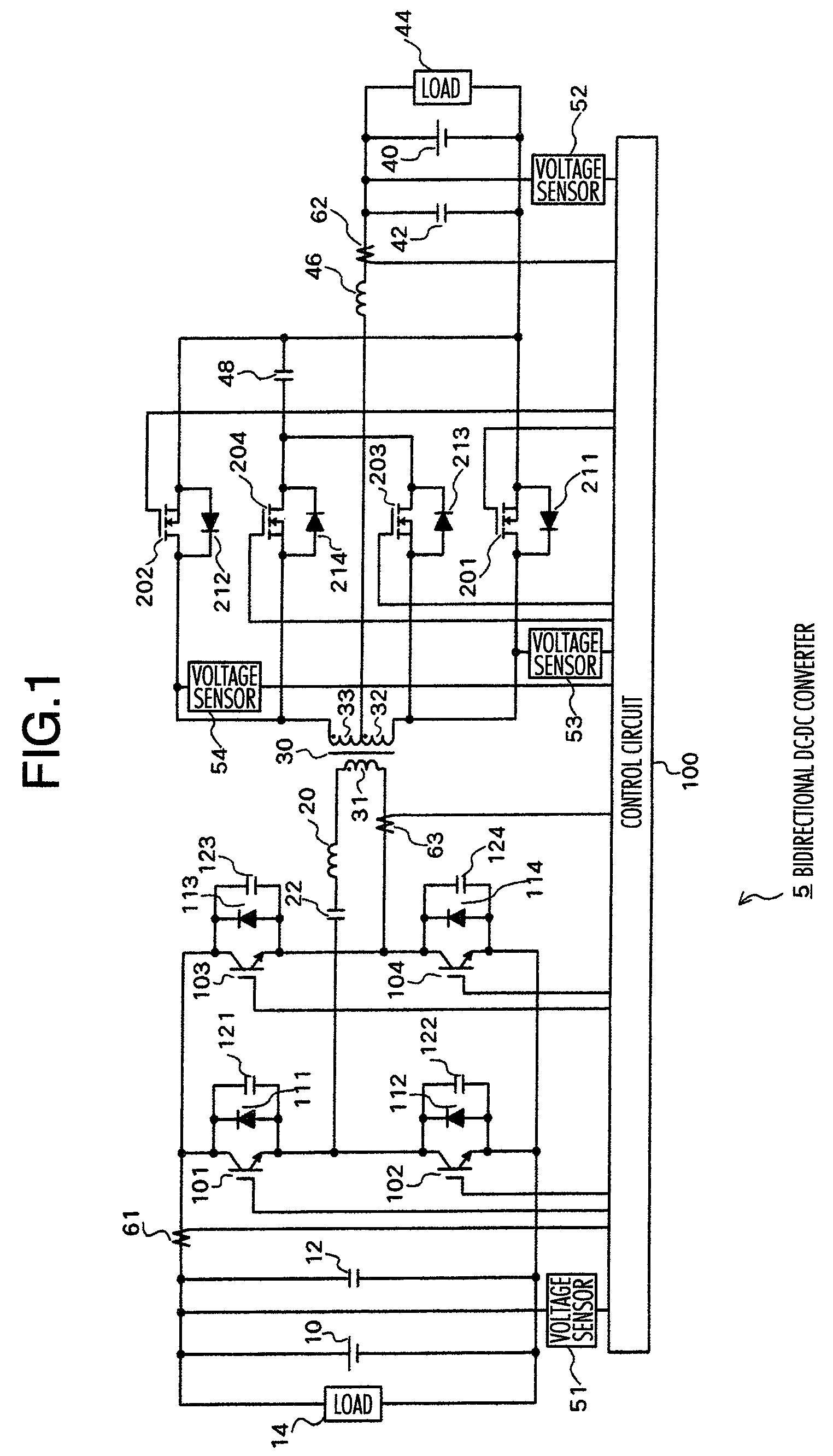
ActiveUS20060139823A1Total current dropReduce lossesEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionClamp capacitorLow noise
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
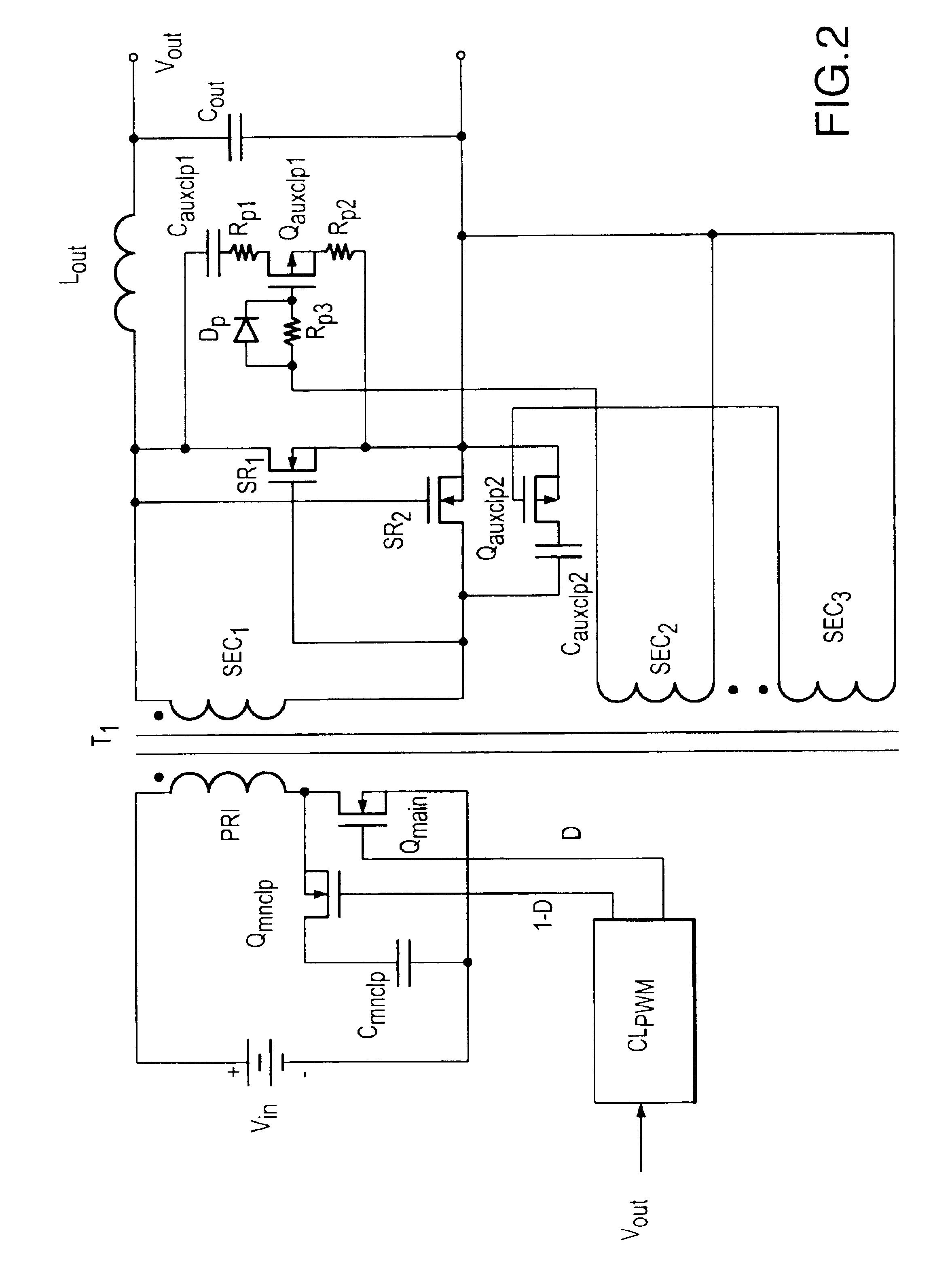
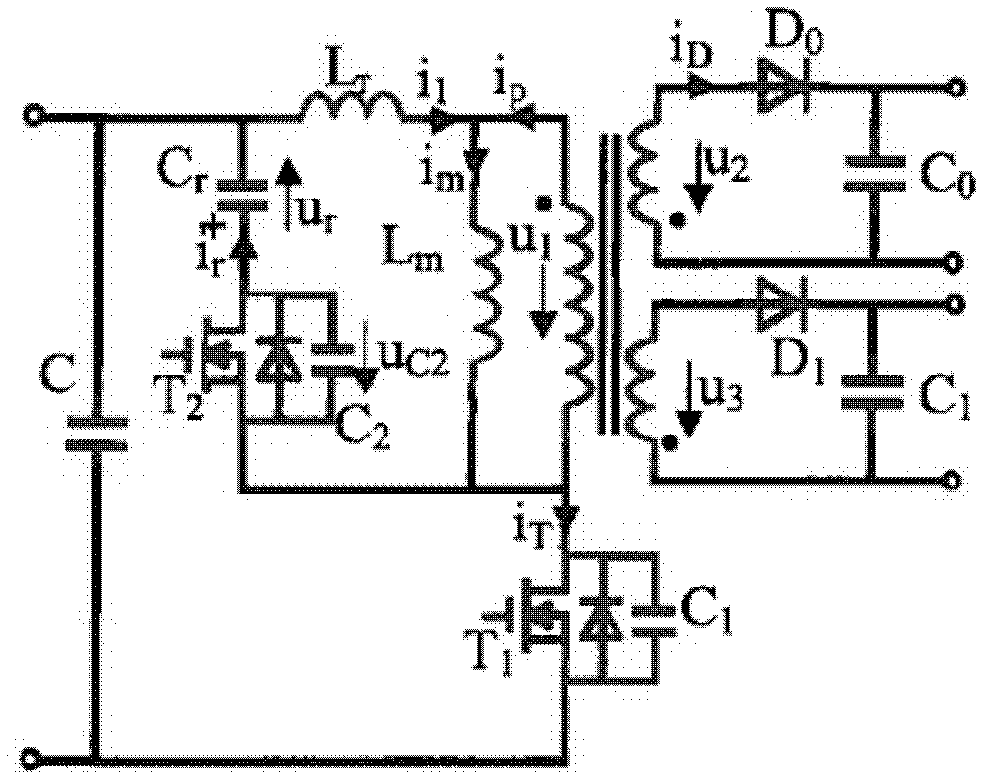
Auxiliary active clamp circuit, a method of clamping a voltage of a rectifier switch and a power converter employing the circuit or method
InactiveUS6882548B1Easy to useTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionActive clampClamp capacitor
The present invention is directed to an auxiliary active clamp circuit and a method of clamping a voltage of a rectifier switch associated with a power converter. The power converter includes a main active clamp circuit associated with a main power switch coupled to a primary winding of a transformer and a rectifier switch coupled to a secondary winding of the transformer. The main power switch conducts during a main conduction period of the power converter and the rectifier switch conducts during an auxiliary conduction period of the power converter. In one embodiment, the auxiliary active clamp circuit includes an auxiliary clamp capacitor, coupled across the rectifier switch, that stores a clamping voltage substantially equal to an off-state voltage of the rectifier switch. The auxiliary active clamp circuit also includes an auxiliary clamp switch, coupled in series with the auxiliary clamp capacitor, that receives a drive signal from a secondary winding and conducts during the main conduction period thereby clamping a voltage across the rectifier switch at about the clamping voltage.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
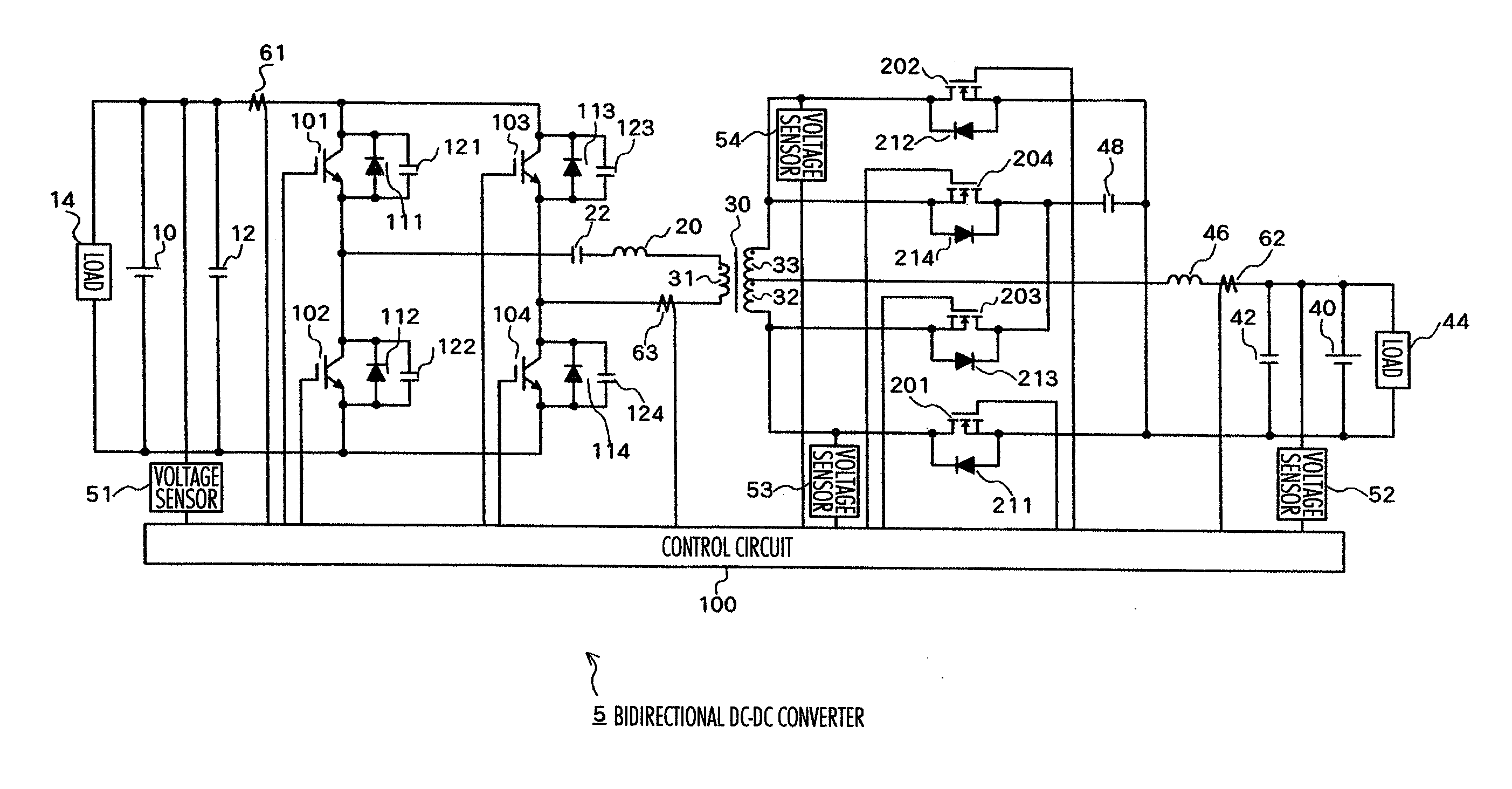
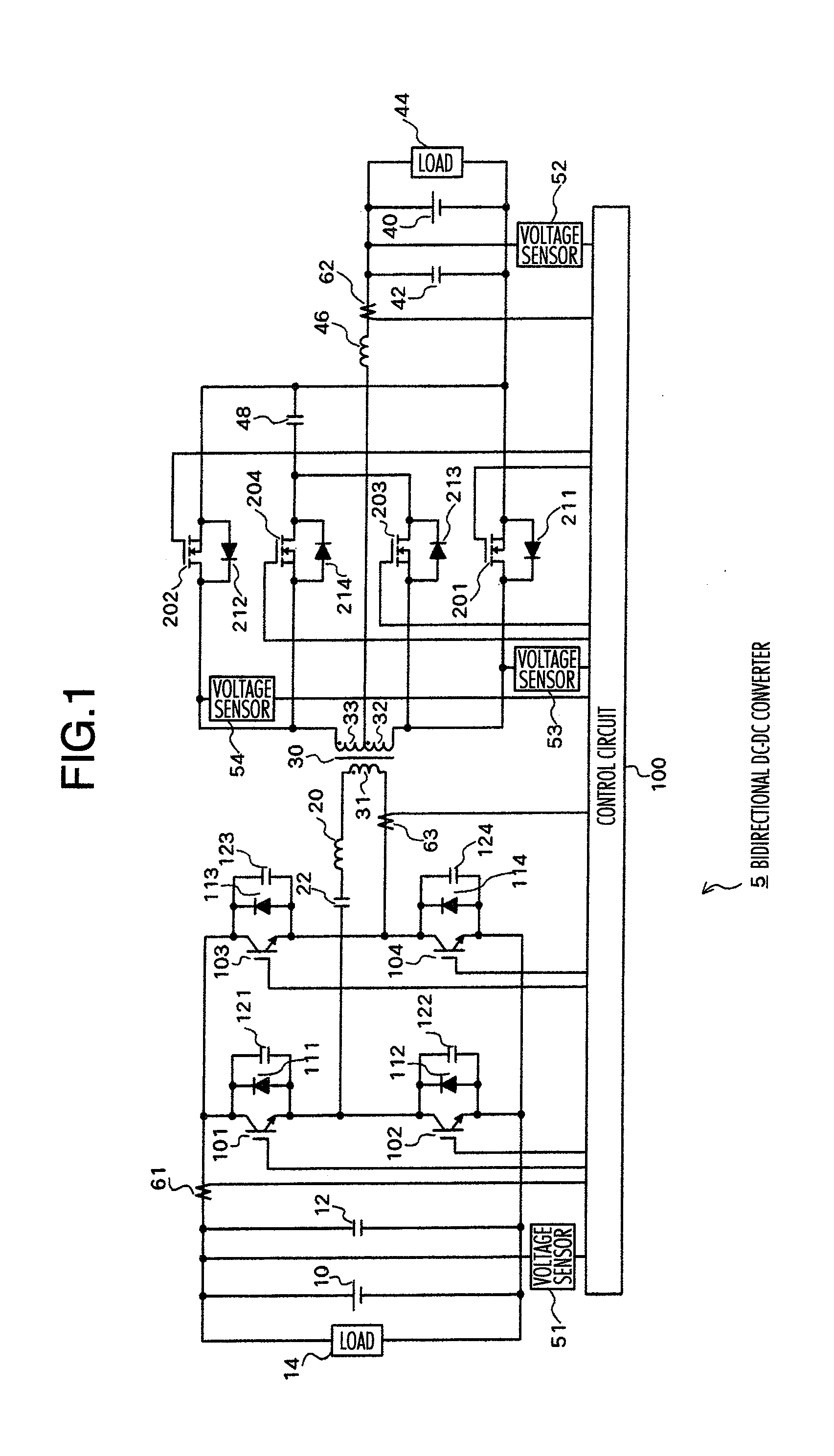
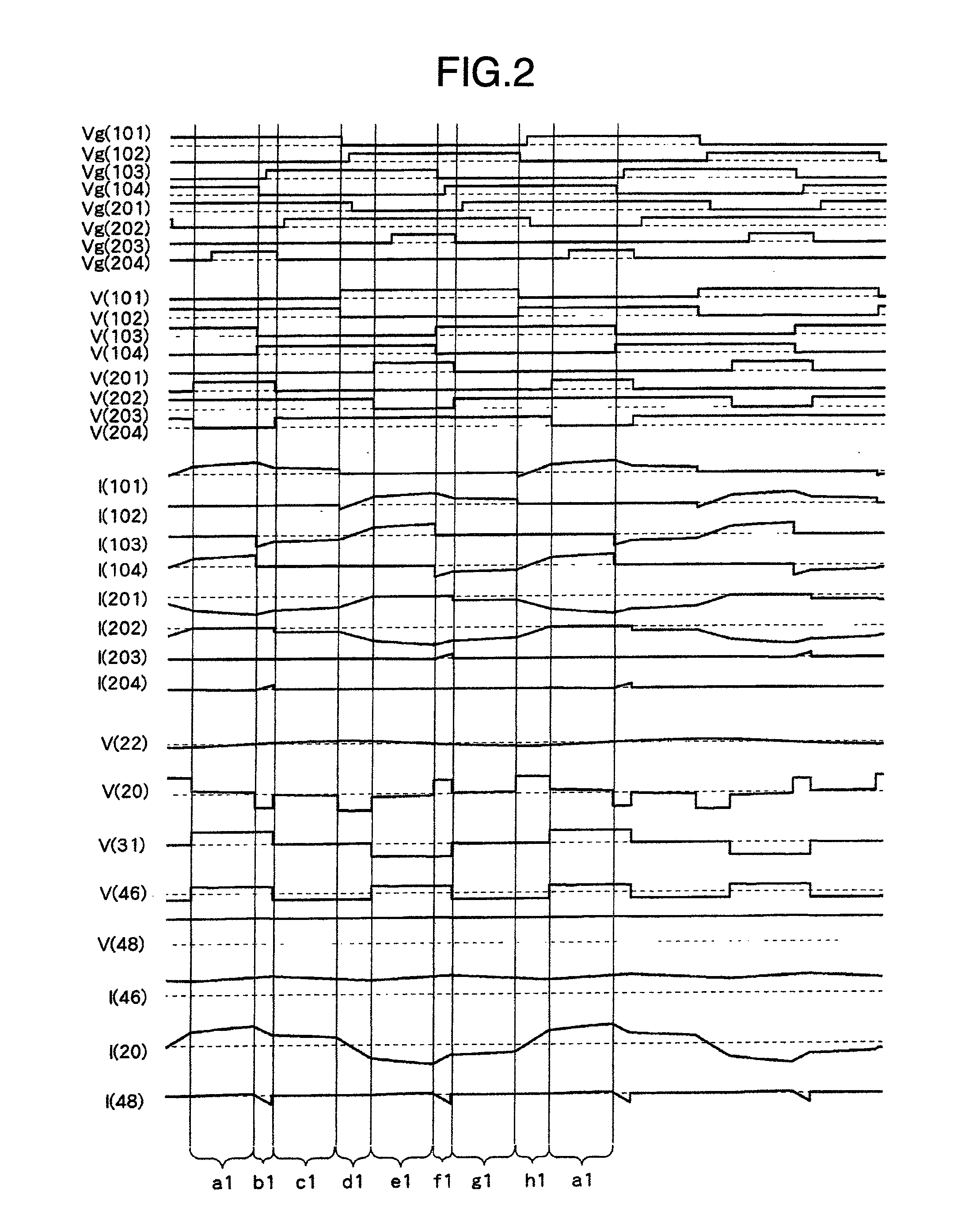
Bi-directional dc-dc converter and method for controlling the same
InactiveUS20090059622A1Large electric powerEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionClamp capacitorDc dc converter
A bi-directional DC-DC converter has a transformer for connecting a voltage type full bridge circuit connected to a first power source and a current type switching circuit connected to a second power source. A voltage clamping circuit constructed by switching elements and a clamping capacitor is connected to the current type switching circuit. The converter has a control circuit for cooperatively making switching elements operative so as to control a current flowing in a resonance reactor.
Owner:HITACHI INFORMATION & TELECOMM ENG LTD
Voltage clamping system and method for a DC/DC power converter
InactiveUS6314002B1Efficient recyclingReduce switchingEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCapacitanceClamp capacitor
A voltage boost power converter circuit, having an input inductor, active switch, and a transformer having primary, secondary and auxiliary windings. A clamping capacitor and a first passive switch are in series across the primary winding. The auxiliary winding and a second passive switch are in series, connected to the node between the clamping capacitor and first passive switch. The active switch is connected between ground the primary winding. A bulk capacitor forms a series loop including the active switch and primary winding. The method efficiently resets a the transformer, by transferring power to a load through the primary winding, and discharging a clamping capacitor through a separate inductively linked winding of the transformer during an ON state; and clamping the active switch voltage with the clamping capacitor, charging the clamping capacitor with a leakage inductance of the transformer, and charging the bulk capacitor during an OFF state.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NORTH AMERICA
Flyback converter and control method of flyback converter
ActiveCN104300795AGuaranteed efficiencyReduce distractionsDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationClamp capacitorCapacitance
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH
Non-complementary flyback active clamp converter
ActiveCN103795260AImprove reliabilityImplement non-complementary controlDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationActive clampCapacitance
The invention discloses a non-complementary flyback active clamp converter. The non-complementary flyback active clamp converter comprises a transformer, a main switching tube, a clamp switching tube, a clamp capacitor and a drive module. The drive module outputs main drive signals to the drive end of the main switching tube, and the driving signals are used for controlling the main switching tube to be alternately switched on and switched off. The drive module outputs clamp drive signals to the drive end of the clamp switching tube. The clamp drive signals and the main drive signals have the same period. Each period comprises a first pulse signal which is generated when the switching-on state of the main switching tube is converted to the switching-off state, a second pulse signal which is generated when the main switching tube is in the switching-off state, and a signal which is generated at the remaining time and used for controlling the switching-on and the switching-off of the clamp switching tube, wherein the first pulse signal and the second pulse signal are independent of each other and both used for controlling the switching-on and the switching-off of the clamp switching tube. By the adoption of the non-complementary flyback active clamp converter, it is guaranteed that a high-frequency current generated when the clamp capacitor is charged fully flows through the clamp switching tube and avoids a backward diode of the clamp switching tube.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH
Three-phase three-level soft-switched pfc rectifiers
ActiveUS20130235626A1Low rateReduce conduction lossAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionClamp capacitorThree level
A low input-current-harmonic three-phase three-level boost rectifier includes an input stage for receiving a three-phase input voltage in relation to a neutral node and an output stage adapted to couple to at least one load. The rectifier further includes one or more switching converter stages, each having a plurality of serially-connected switches coupled to the neutral node, one of the serially-connected switches operating with a fixed duty cycle while the other of the serially-connected switches operating with a variable duty cycle, the fixed duty cycle being a substantially 50% duty cycle and the variable duty cycle being less than or equal to a substantially 50% duty cycle. The serially-connected switches are coupled to clamping diodes and clamping capacitors. The rectifier further includes one or more controllers adapted to vary the switching frequency and / or duty cycle of the plurality of switches based on at least one of a condition of the at least one load or the input voltage and includes one or more decoupling stages, each including one or more inductive elements adapted to inductively decouple the output stage from at least one of the one or more switching converter stages.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Forward-flyback isolated type boost inverter realized by coupling inductors and application thereof
ActiveCN101702578AIncrease profitReduce volumeApparatus with intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationClamp capacitorResonance
The invention discloses a forward-flyback isolated type boost inverter realized by coupling inductors and application thereof, comprising two power switch tubes, two auxiliary switch tubes, four anti-parallel diodes, a switch tube parallel capacitor, two clamp capacitors, two switch capacitors, two output diodes and two coupling inductors respectively provided with two windings. The invention realizes zero-voltage switching on of the power switch tubes through the resonance of the leakage inductance of the two coupling inductors and the switch tube parallel capacitor, absorbs the voltage peak switched off by the switch tubes caused by the leakage inductance and realizes energy lossless transfer by utilizing a clamp circuit comprising the anti-parallel diodes of the switch tubes and the two clamp capacitors, realizes the high gain output of the inverter by utilizing the serial connection of the second windings of the two coupling inductors, further improves the gain of the inverter and lowers the output voltage stress of the diodes by utilizing the switch capacitors and realizes the output zero-current switching off of the diodes by utilizing the leakage inductance of the coupling inductors.
Owner:HOYMILES POWER ELECTRONICS INC
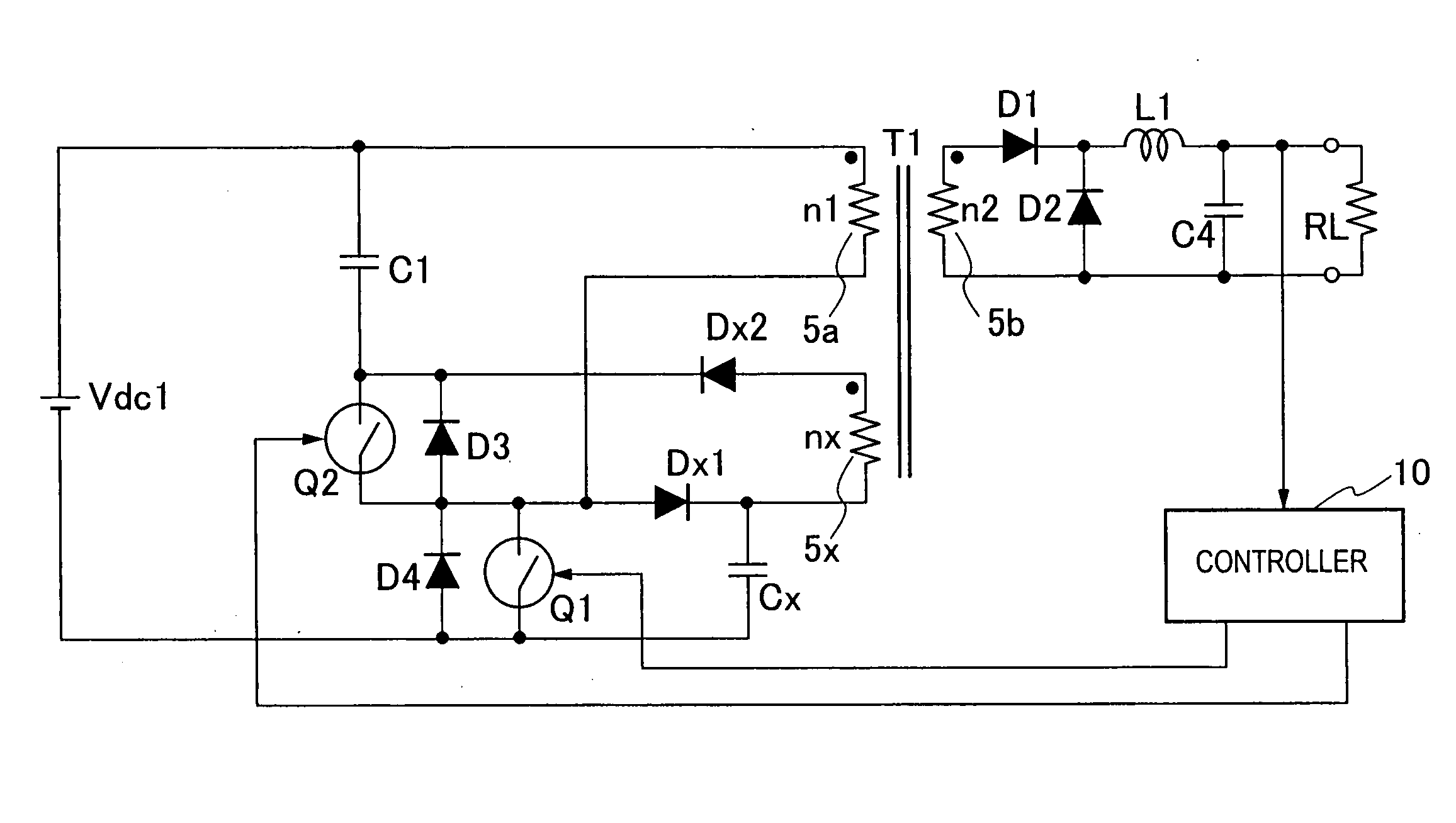
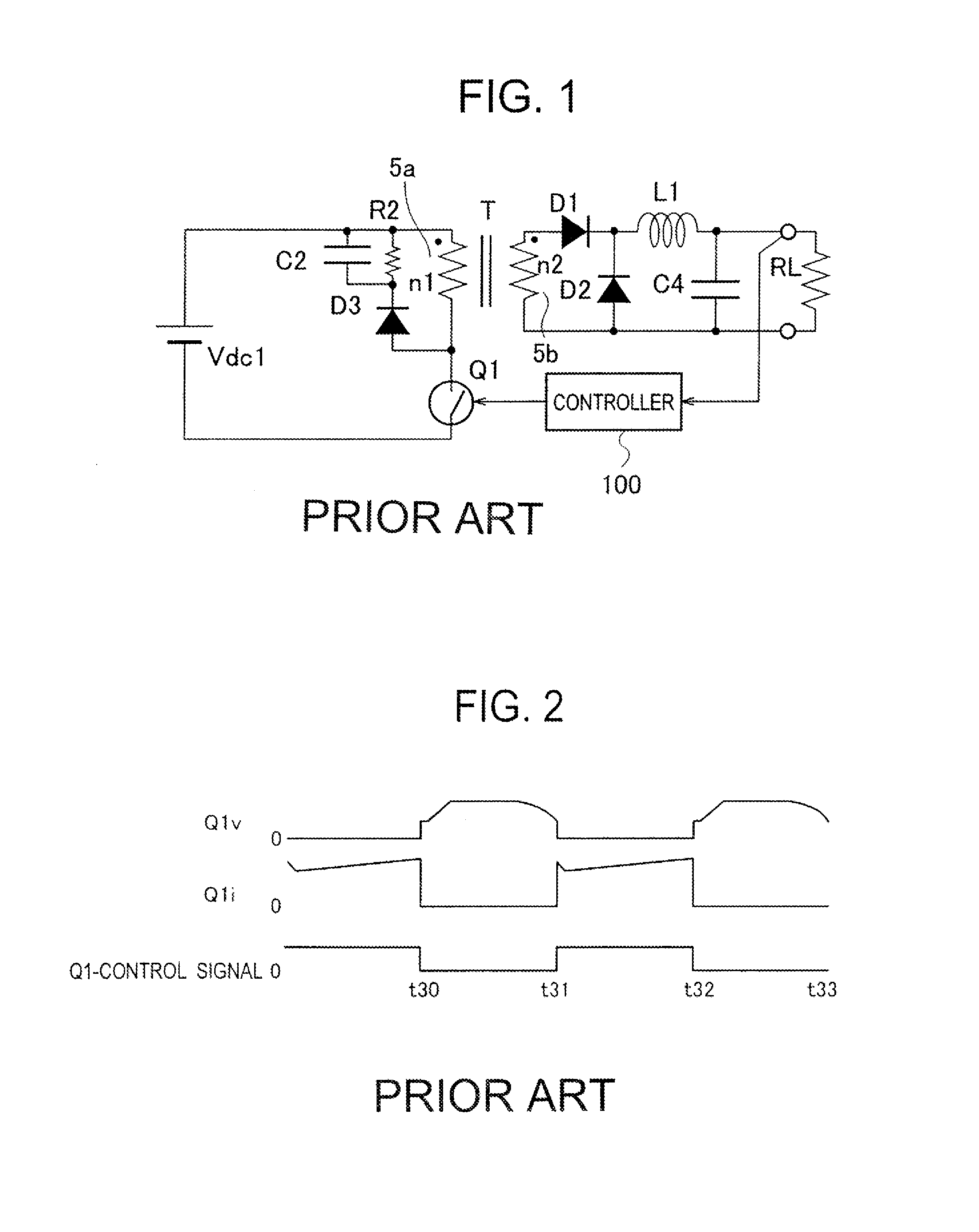
Switching power supply apparatus
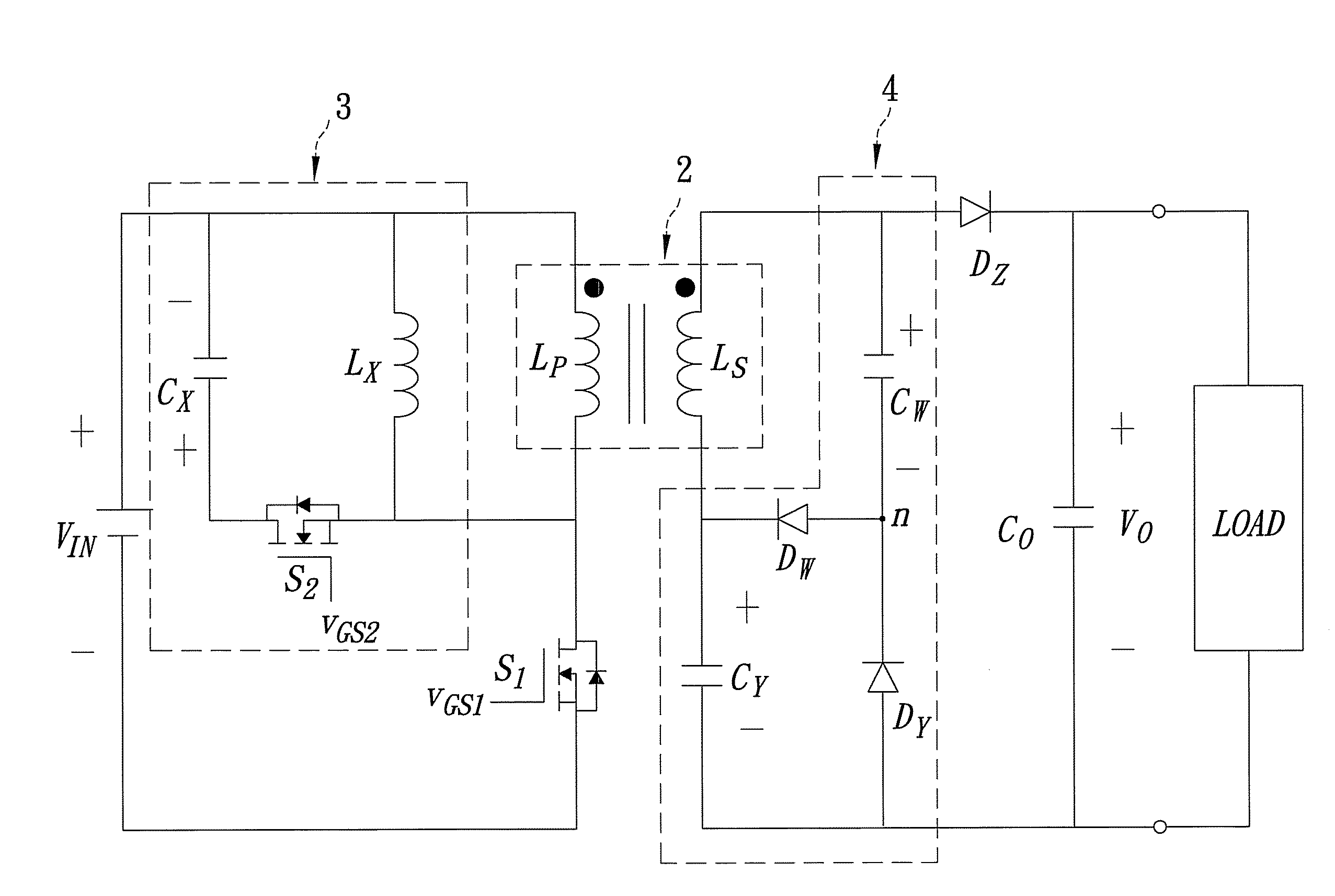
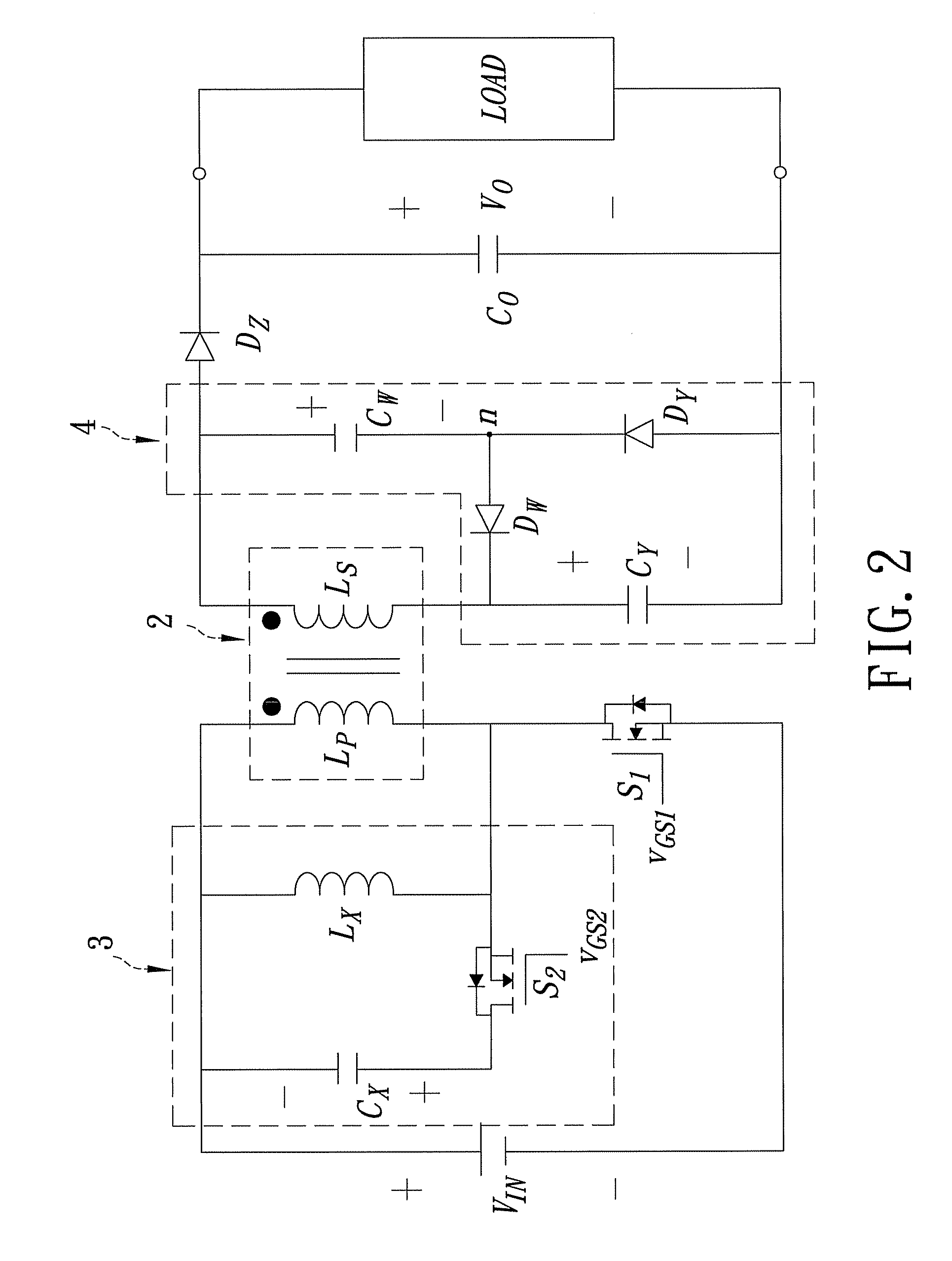
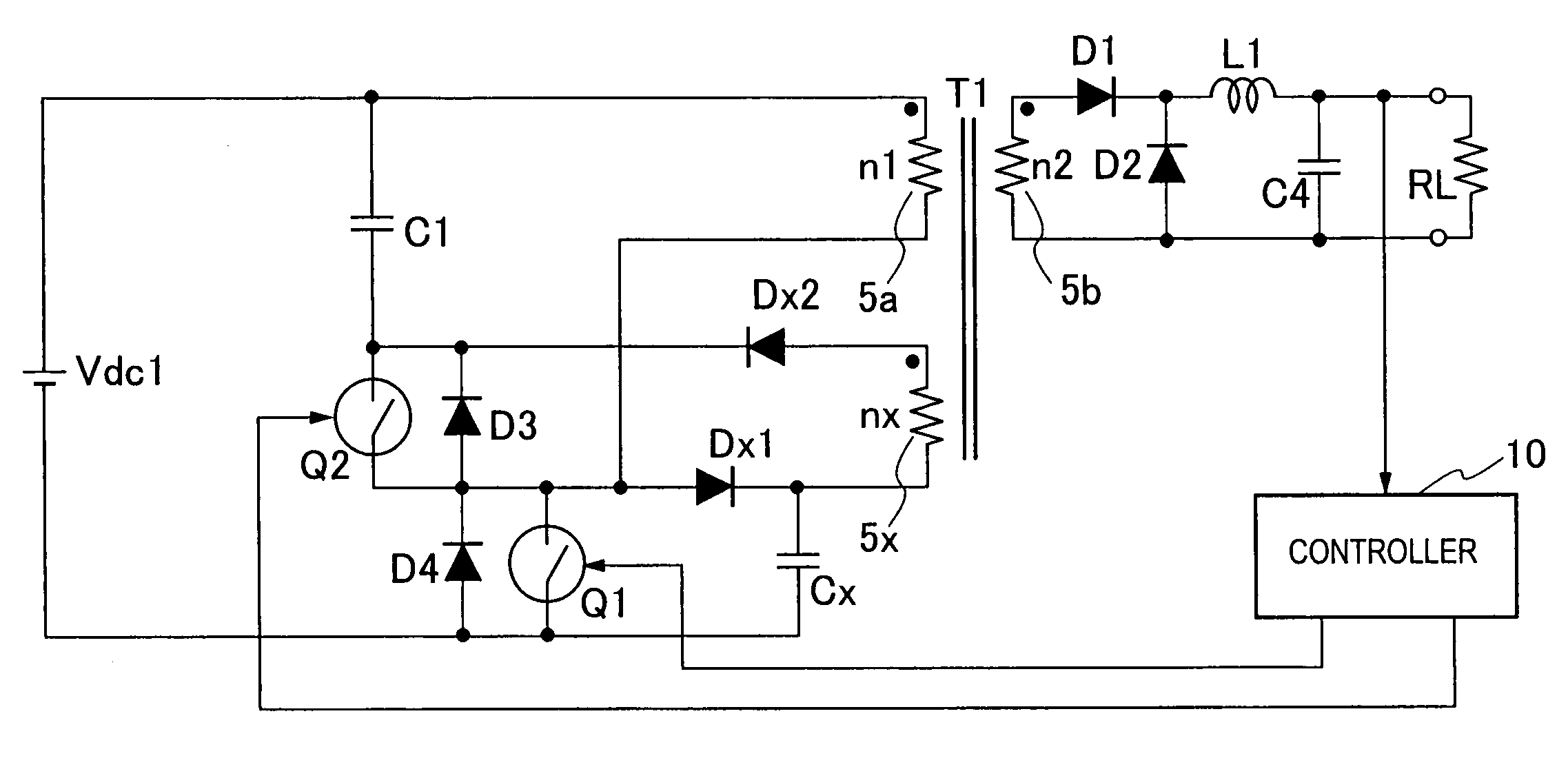
InactiveUS20060187688A1Increase usageSmall sizeEmergency protective circuit arrangementsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsClamp capacitorSnubber capacitor
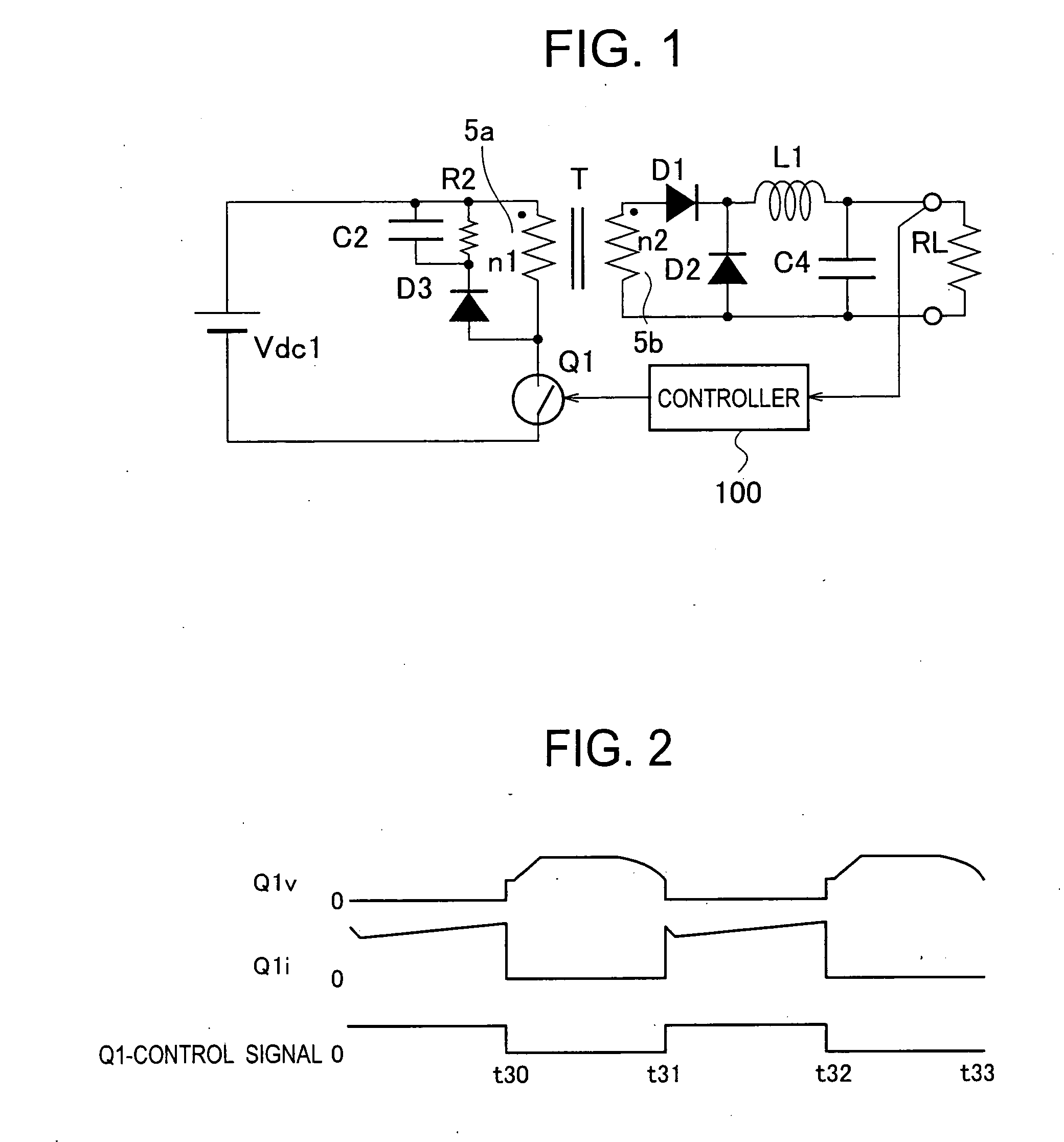
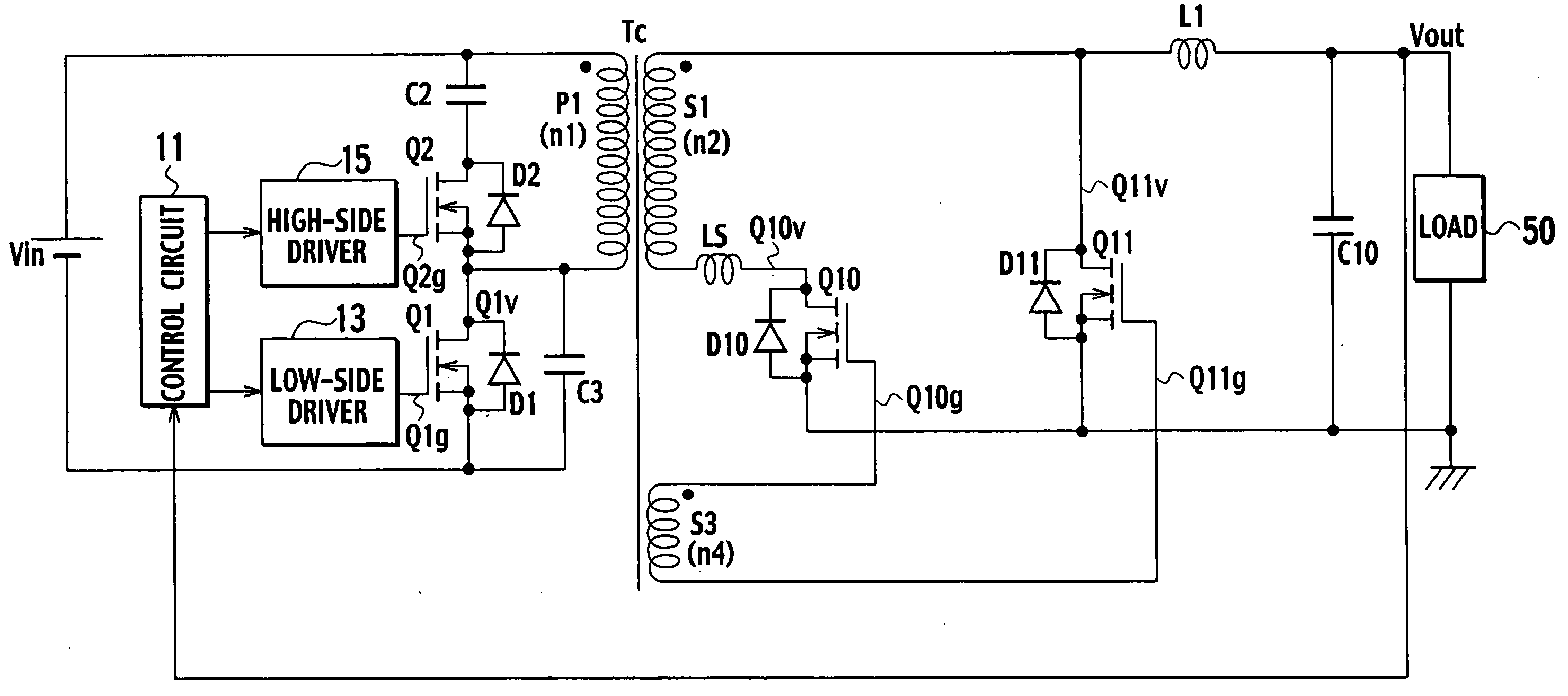
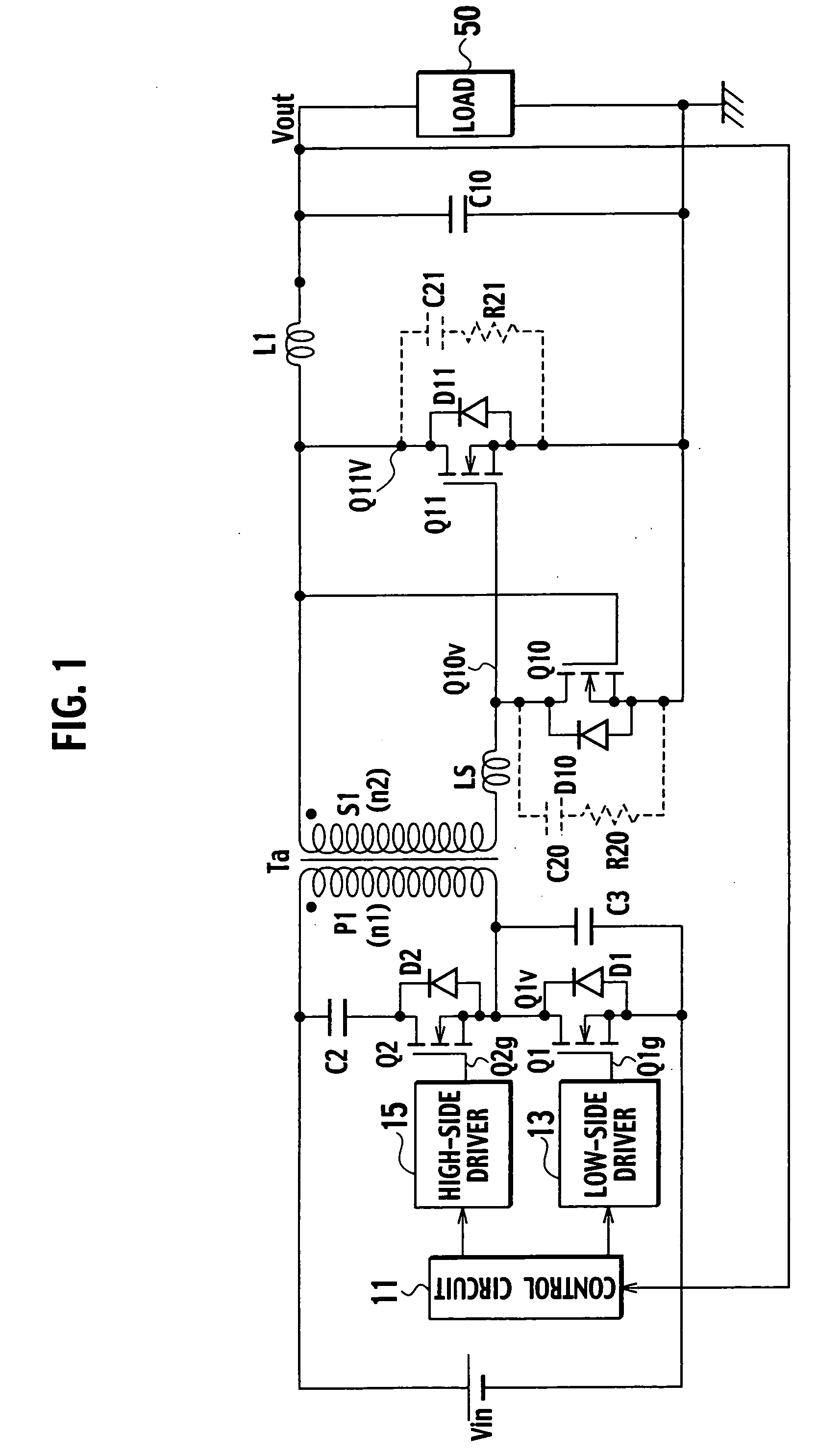
A switching power source apparatus can reduce the size of a transformer and realize the zero-voltage switching of a switch. The apparatus is compact, highly efficient, and low in noise. The apparatus has a series circuit connected to each end of a DC power source (Vdc1) and including a primary winding (5a) of a transformer (T) and a main switch (Q1), a rectifying-smoothing circuit to rectify and smooth a voltage that is outputted from a secondary winding (5b) when the main switch (Q1) is turned on, a series circuit connected to each end of the primary winding (5a) and including an auxiliary switch (Q2) and a clamp capacitor (C1), a series circuit connected to each end of the main switch (Q1) and including a diode (Dx1) and a snubber capacitor (Cx), a series circuit connected to a node between the diode (Dx1) and the snubber capacitor (Cx) and a node between the auxiliary switch (Q2) and the clamp capacitor (C1) and including an auxiliary winding (5x) and a diode (Dx2), and a control circuit (10) to alternately turn on / off the main switch (Q1) and auxiliary switch (Q2). When the main switch (Q1) is turned on, the snubber capacitor (Cx) is discharged through the auxiliary winding (5x) to the clamp capacitor (C1). When the main switch (Q1) is turned off, the snubber capacitor (Cx) is charged, to relax the inclination of a voltage increase of the main switch (Q1).
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Single stage isolated ac/dc power factor corrected converter
ActiveUS20170025962A1Improve efficiencyReduce the burden onEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionClamp capacitorSingle stage
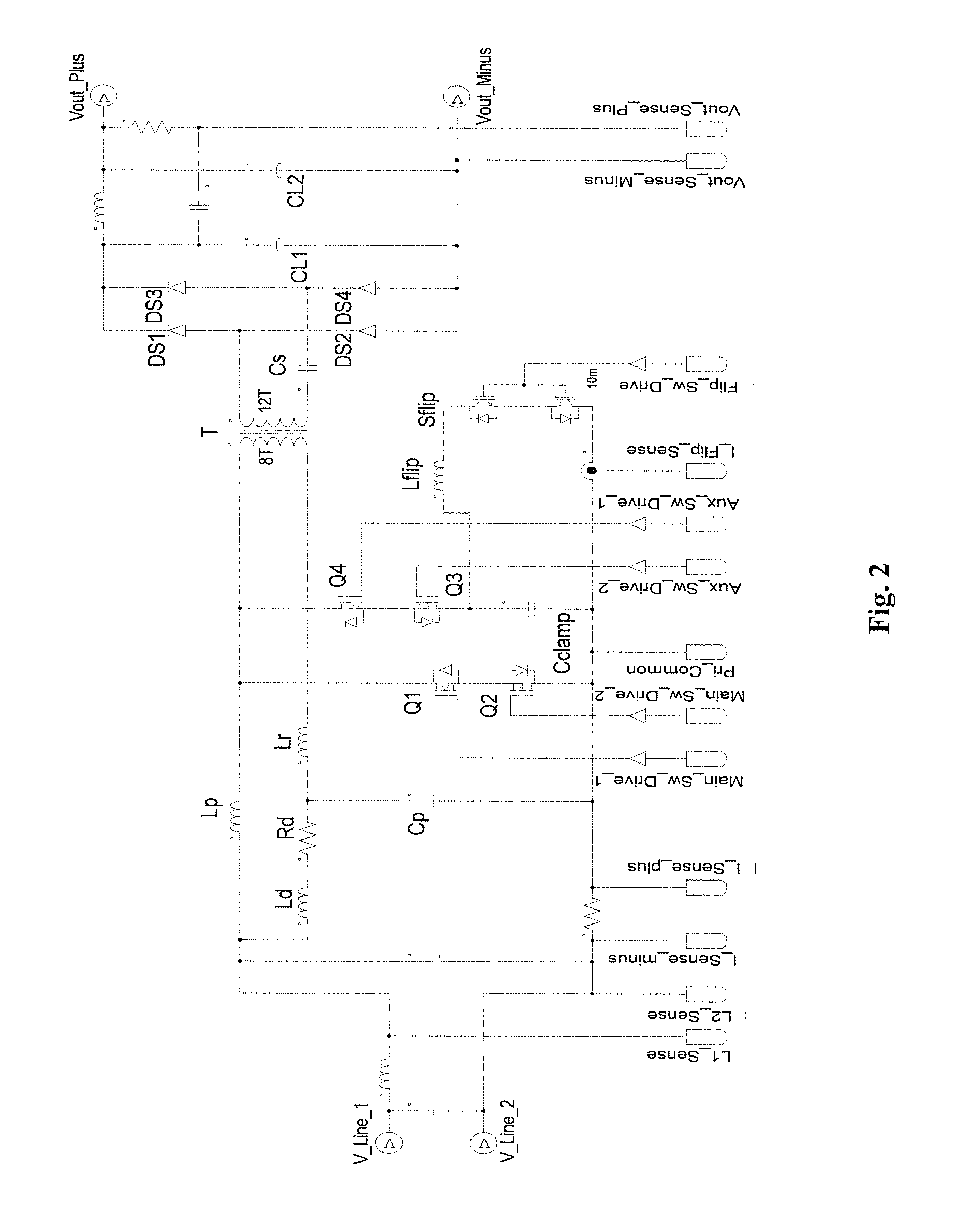
Two versions of an isolated single stage converter AC / DC Power Factor Corrected (PFC) converter topology have been invented. One is with a full bridge rectifier at its input and the other is a True Bridgeless version. The two versions of the topology feature new configurations and circuitry including a simplified damper circuit and a clamp capacitor flipping circuit and control methods that allow them to realize improved single stage isolated power factor converters which are suitable for high power operation, features Zero Voltage Switching to maximize conversion efficiency and to minimize Electro-Magnetic Interference generation, does not need an additional circuit to limit the inrush current, achieves reasonably low input current Total Harmonic Distortion (THD), and is easy to control. The second version provides a true bridgeless single stage isolated power factor converter with even higher efficiency and lower input current THD.
Owner:DAVIDSON CHRISTOPHER DONOVAN
Dual bridge matrix converter
ActiveUS20050099829A1Reduce and eliminate high voltage spikeSmall and inexpensiveConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc circuit to reduce harmonics/ripplesMatrix convertersClamp capacitor
A dual bridge matrix converter has a line-side converter with controllable switches that receives AC power and provides unidirectional power to high and low DC link lines, and a load-side converter which receives the power from the DC link lines and provides AC power to output lines. A clamp circuit is connected across the DC link lines and includes a series connected diode and a capacitor. Negative DC link current will be conducted through the clamp diode to charge the clamp capacitor to avoid voltage spikes on the DC link lines. A controllable switch may be connected in parallel with the clamp diode and is turned on when the voltage across the clamp capacitor is above a threshold that is greater than the normal peak-to-peak AC input voltage. The switch is turned off when the voltage across the clamp capacitor is lower than the threshold voltage.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Voltage-clamp power converters
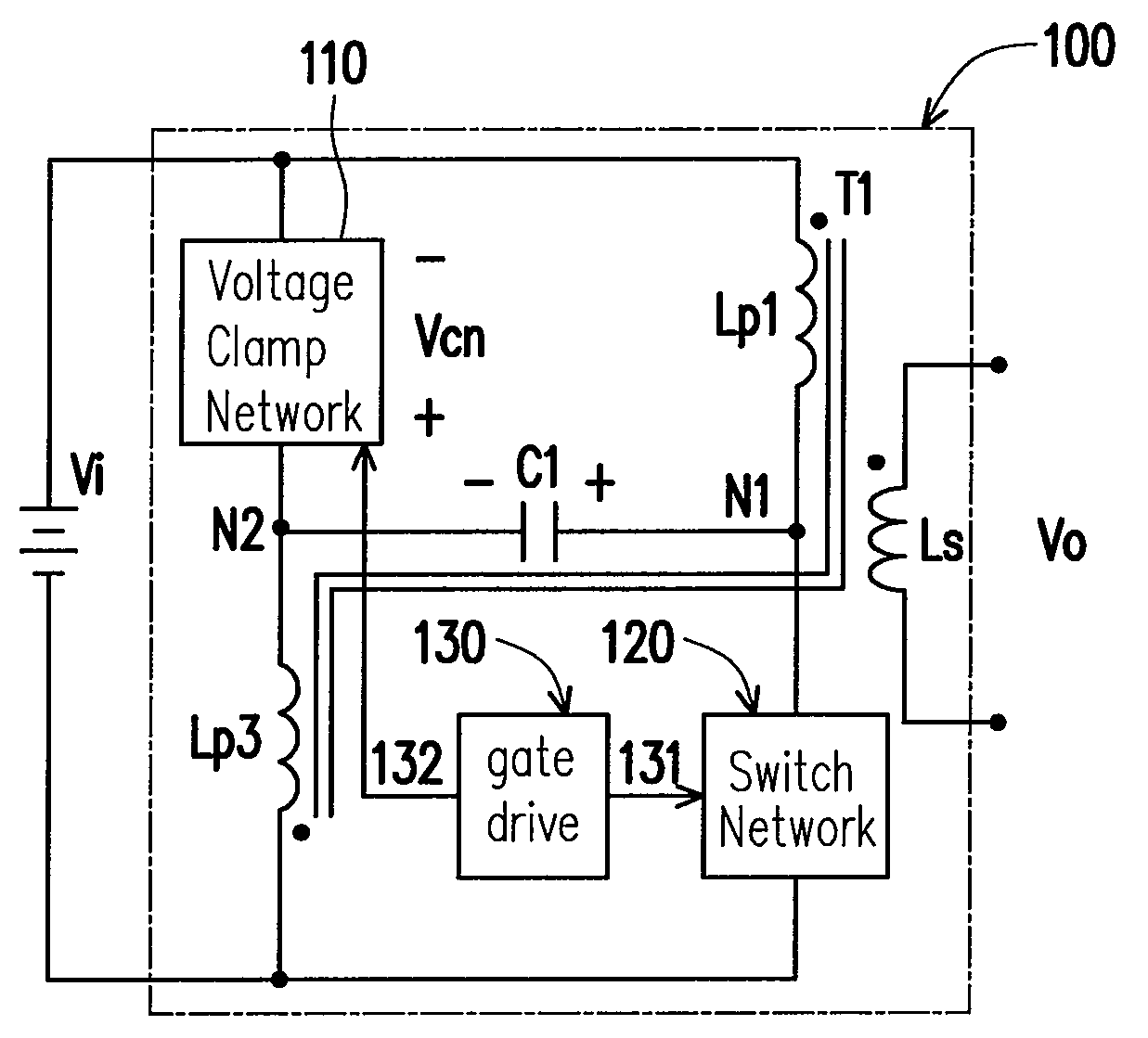
InactiveUS20090257254A1Reduced input current rippleReduce EMI problemsEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionMOSFETClamp capacitor
Several inversion circuits used to convert a DC input to an AC output comprise two series circuits, at least one clamp capacitor, and at least one transformer. Each of the series circuits is in parallel with the DC input. The first series circuit includes one switch network and at least one transformer primary. The second series circuit includes one voltage-clamp network and at least one transformer primary. At least one clamp capacitor couples the first and the second series circuits, and is attached to each series circuit at a node between the respective transformer primary winding. The voltage-clamp network may be implemented with two of the three sub-circuits connected in series: a diode, a resister-capacitor-diode, and a MOSFET-capacitor.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Isolated bidirectional DC-DC converter
ActiveUS7638904B2Effectively miniaturizedTotal current dropEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionClamp capacitorConverters
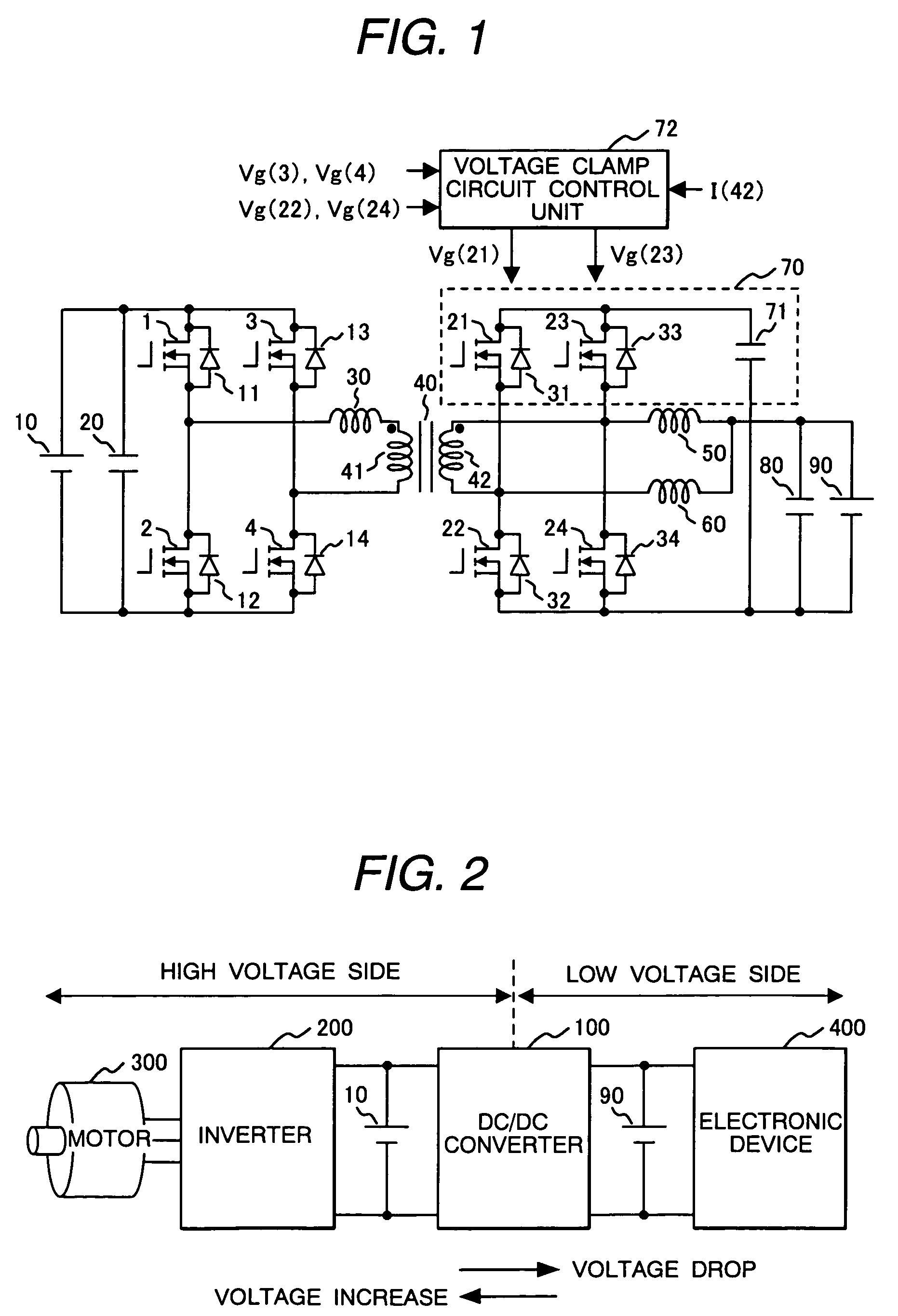
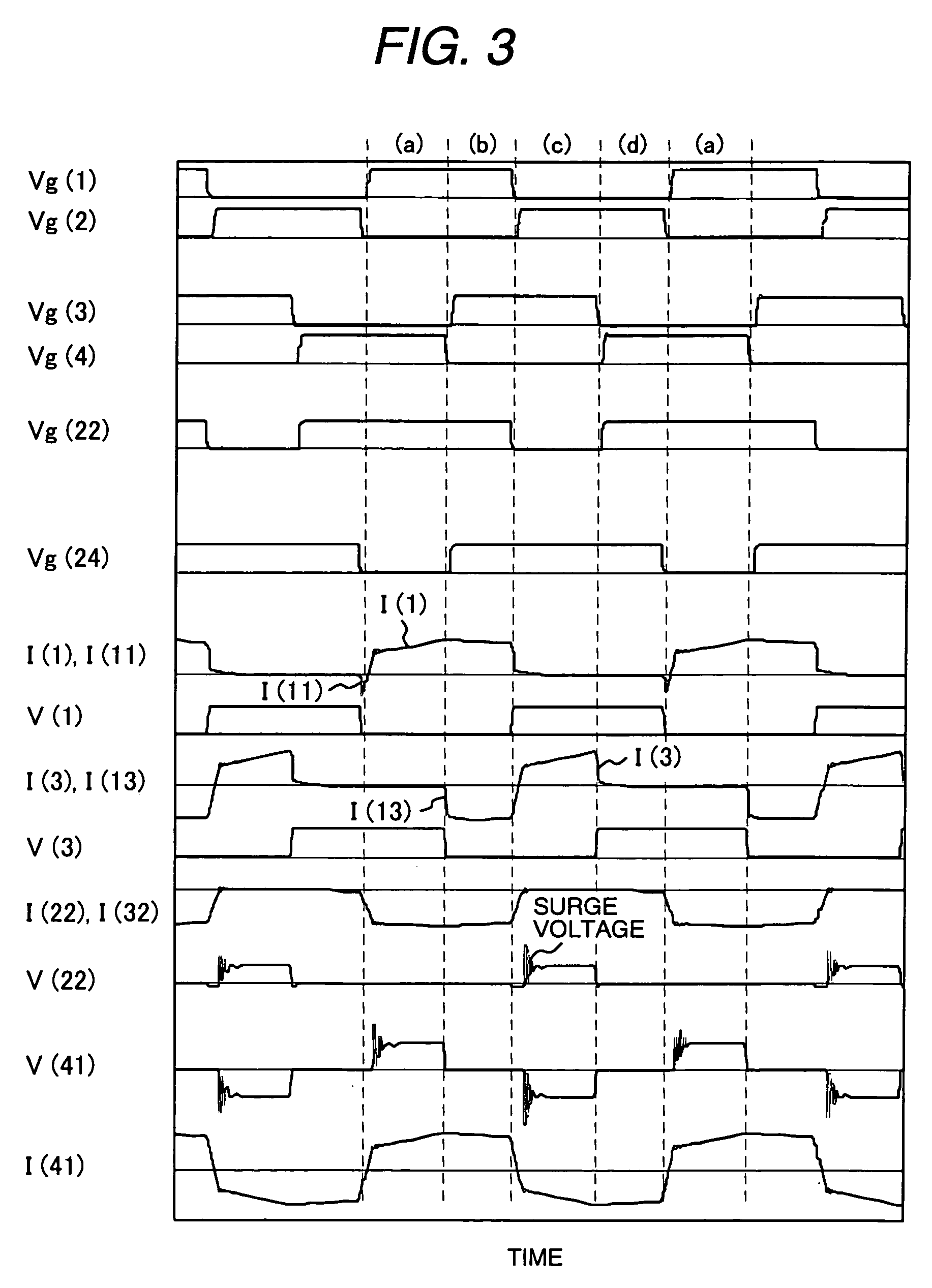
The DC-DC converter connects a first and a second switching circuit for converting power mutually between direct current and alternating current respectively to a first DC power source and a second DC power source and has a transformer between the AC terminals thereof. Here, between the AC terminals of the second switching circuit and the negative pole terminal of the DC power source, a voltage clamp circuit composed of a series unit of switching devices with a reverse parallel diode and a clamp condenser is connected.An isolated bidirectional DC-DC converter which prevents a reduction in a circulating current at time of buck and an occurrence of a surge voltage at time of voltage boost and realizes highly efficiency, low noise, and miniaturization is provided.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
DC converter
InactiveUS20060209571A1Drive stabilityImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionClamp capacitorEngineering
A DC converter has a transformer with loosely coupled primary and secondary windings, a main switch connected in series with the primary winding of the transformer, and a series circuit connected to ends of one of the primary winding and main switch. The series circuit includes a clamp capacitor and an auxiliary switch. The main and auxiliary switches are alternately turned on / off so that a voltage of the secondary winding of the transformer is synchronously rectified with synchronous rectifiers and is smoothed with smoothing elements, to provide a DC output. The DC converter also includes a tertiary winding provided for the transformer, tightly coupled with the primary winding, and configured to generate a voltage that drives the synchronous rectifiers.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Active clamp zero voltage soft switch high gain booster staggered parallel converter
InactiveCN101022244AIncrease output gainImprove circuit efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionClamp capacitorActive clamp
This invention discloses active clamp zero-voltage soft switch high gain boost staggered parallel converters including two power switch tubes, two clamp switch tubes, two clamp capacitors, two continuing flow diodes and two coupled inductors, in which, each of the two coupled inductors includes three windings, which utilizes the second and third windings of the two coupled inductors to realize high gain output of the converter, utilizes a serial circuit composed of the two clamp switch tubes and two clamp capacitors to absorb and transfer harmlessly the leak energy of the two coupled inductors and realizes turn on of zero voltage of two power switch tubes and zero voltage turn-off of them utilizing the parallel capacitors of the two switch tubes to further realize zero-voltage turn on and off of the two clamp switch tubes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
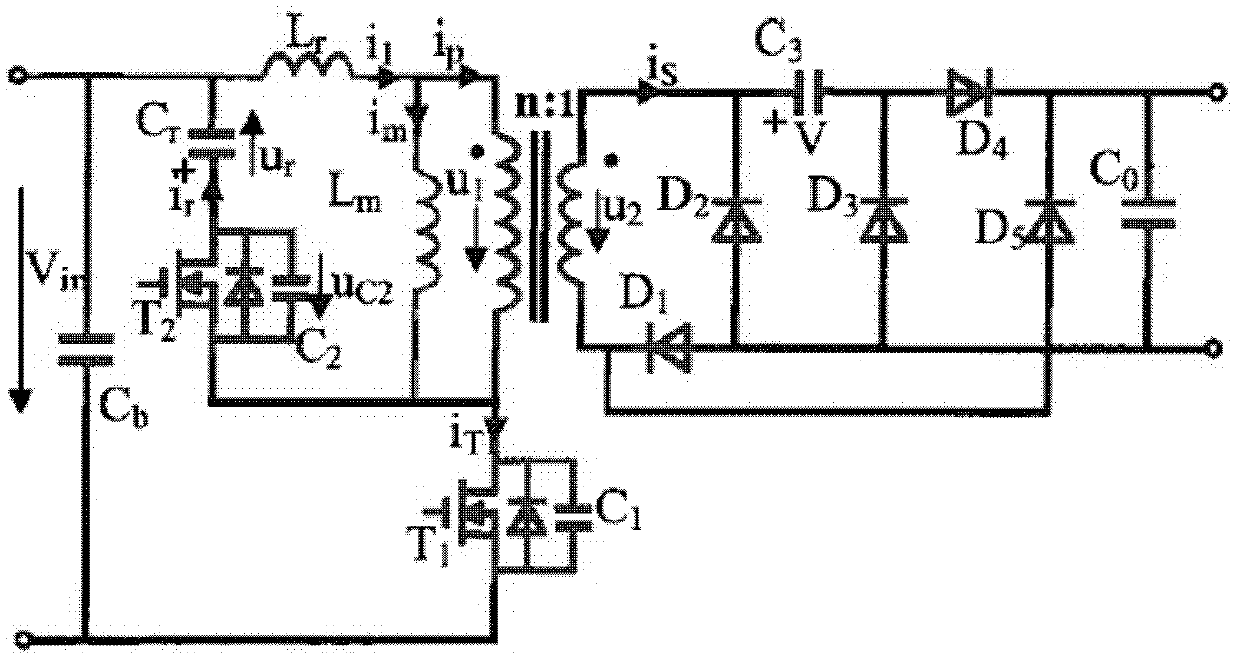
Active clamp flyback circuit and control method thereof
ActiveCN106059313AGuaranteed not to reverse positiveReduce voltageEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionClamp capacitorCapacitance
The invention relates to the field of switching converters, and particularly relates to a flyback active clamp-type switching converter control circuit and a control method thereof. The active clamp flyback circuit of the invention can realize reduced frequency and ZVS, and comprises a main power circuit, a clamp circuit, and an output rectification filter circuit, wherein a transformer and a main switching tube are connected to form the main power circuit; a clamp switching tube and a clamp capacitor and a clamp diode are connected to form the clamp circuit; and an output rectification diode and an output capacitor are connected to form the output rectification filter circuit. In comparison with the prior art, reduced frequency in light load can be realized, and the control scheme is flexible; switching loss in no load and loss of a transformer winding and switching tube inner resistance caused by a current effective value are little, no-load power consumption is greatly reduced, and the light-load efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN NANYUN MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
Bi-directional DC-DC converter and method for controlling the same
InactiveUS7848118B2Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionClamp capacitorDc dc converter
A bi-directional DC-DC converter has a transformer for connecting a voltage type full bridge circuit connected to a first power source and a current type switching circuit connected to a second power source. A voltage clamping circuit constructed by switching elements and a clamping capacitor is connected to the current type switching circuit. The converter has a control circuit for cooperatively making switching elements operative so as to control a current flowing in a resonance reactor.
Owner:HITACHI INFORMATION & TELECOMM ENG LTD
A soft switching conversion device based on a flyback converter
ActiveCN107896062AEliminate OscillationAchieve zero voltage turn-onEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionPower topologyClamp capacitor
The invention provides a soft switching conversion device based on a flyback converter. On the basis of the conventional Flyback converter power topology, a clamp branch consisting of a controllable power clamper tube and a clamp capacitor is connected to a drain end of a main power tube in series; a primary side chip of the conversion device receives information such as the peak excitation current, the valley bottom excitation current and the maximum voltage of switching nodes of a converter power loop and generates ideal drive dead time varying with an input voltage and a load condition to control the main power tube and the clamper tube, so that the voltage oscillation of the drain end of the power tube caused by leakage inductance can be completely eliminated. Owing to the basically loss-free soft switching technology of the MOS tube active clamp, the stable clamp voltage value and the primary-side and auxiliary-side full working conditions, the device can work at a high frequency(> 1MHz) and can greatly increase the power density of a power adapter when being applied to the adapter.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Mixed clamping back-to-back multi-level AC-DC-AC switching circuit
InactiveCN102223080ARealize dynamic self-balancingSolve balance problemsDc network circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionClamp capacitorCapacitor voltage
The invention discloses a mixed clamping back-to-back multi-level AC-DC-AC switching circuit. The mixed clamping back-to-back multi-level AC-DC-AC switching circuit comprises two groups of multi-level switching circuits and a direct current bus capacitor link connected with the two groups of multi-level switching circuits; and the level number of the direct current bus capacitor link is more than or equal to 4. By the mixed clamping back-to-back multi-level AC-DC-AC switching circuit, the dynamic self-balance between all direct current bus capacitors and clamping capacitors can be realized and equal capacitor voltage can be obtained so that the champing capacitors and the direct current bus capacitors complete multi-level boost output and a good condition for the expansion of the capacitance of direct current bus capacitors is created at the same time. The mixed clamping back-to-back multi-level AC-DC-AC switching circuit bears a high-power high-voltage load on the premise of guaranteeing system reliability and good harmonic output characteristics, is flexible in control, quite low in loss, has efficient performance, can realize bidirectional flow and mutual control compensation of reactive power and active power, and is very suitable for alternating current speed regulation or a power grid interconnection technique of different distributed power generating systems.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
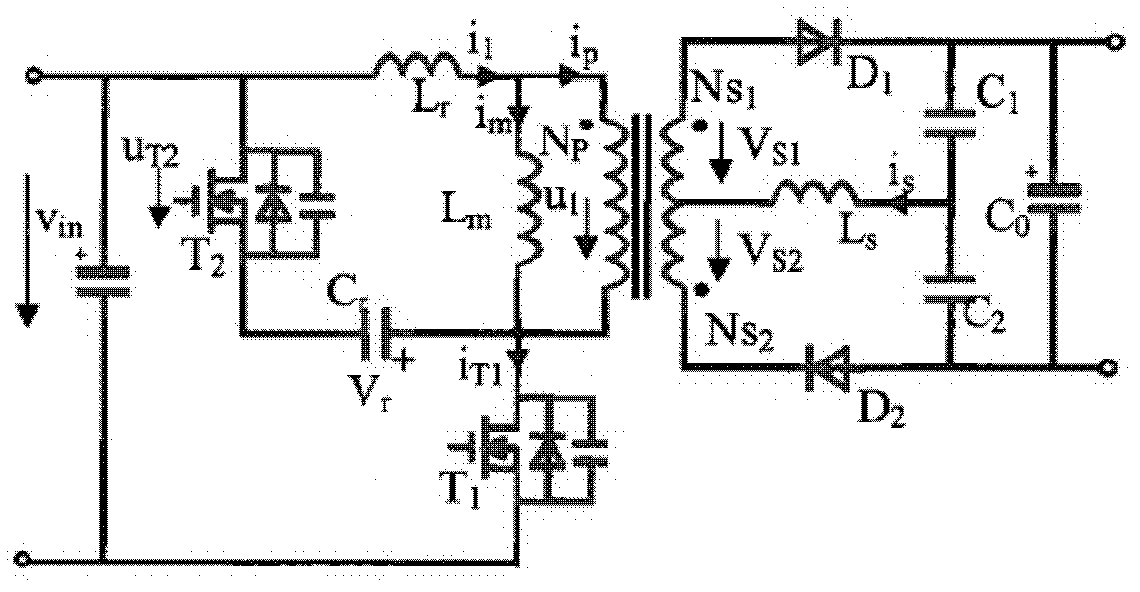
High-efficiency and low-cost forward-flyback DC-DC (direct current-direct current) converter topology
InactiveCN102891608AAvoid voltage spikesAvoid lossEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionClamp capacitorDc dc converter
The invention relates to a high-efficiency and low-cost forward-flyback DC-DC (direct current-direct current) converter topology. The forward-flyback DC-DC converter topology comprises a transformer, a main switch tube, a clamp circuit, a first rectification switch tube, a second rectification switch tube, an LC resonance circuit and an output capacitor, wherein a primary winding of the transformer is connected in series with the main switch tube between a first input end and a second input end; the clamp circuit consisting of a clamp capacitor and a clamp switch tube which are connected in series is connected in parallel with the primary winding or the main switch tube; a secondary winding of the transformer comprises a forward winding and a flyback winding; one end making the current flow into the primary winding is a dotted end of the primary winding; the secondary side of the transformer is connected in a manner that: the dotted end of the forward winding is connected to the first output terminal through the first rectification switch tube, and the dotted end of the flyback winding is connected to the second output terminal through the second rectification switch tube; the LC resonance circuit is connected to the first output terminal and the second output terminal and the unlike ends of the forward winding and the flyback winding so as to switch on or switch off the first rectification switch tube and the second rectification switch tube at zero current; and the output capacitor is connected between the first output terminal and the second output terminal.
Owner:SANTAK ELECTRONICS SHENZHEN
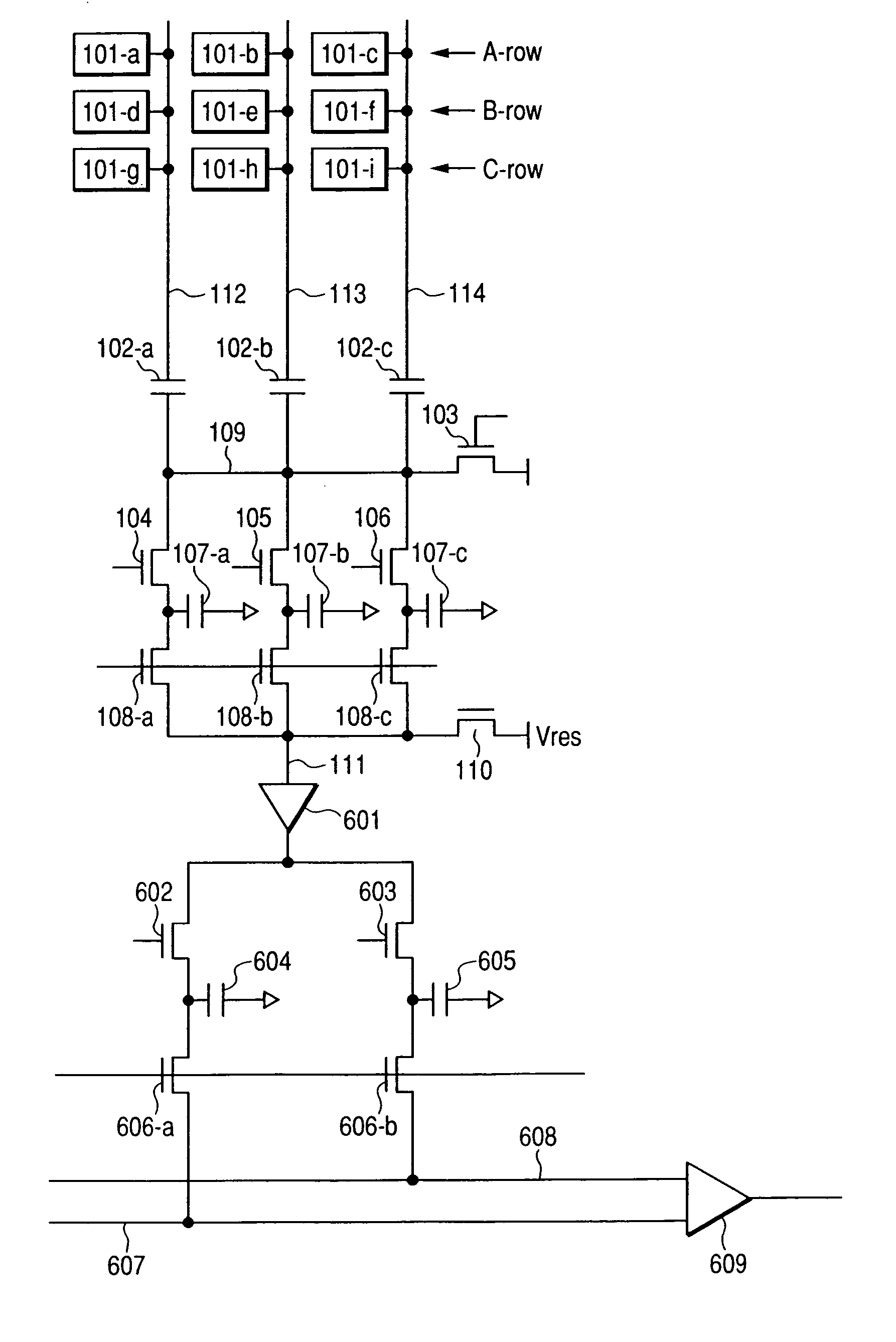
Solid-state image pickup device and camera
ActiveUS20050270393A1Suppress random noiseRemove reset noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsClamp capacitorAudio power amplifier
The number of necessary sampling and holding capacitors is reduced. A solid-state image pickup device has signal lines to which photoreceiving elements are connected, a clamp circuit that has clamp capacitors in which one terminal is connected to the signal lines and the other terminals are short-circuited, has a switch for applying a reference voltage to the other terminals by the clamping operation, and adds signals from the plurality of photoreceiving elements provided in the row direction along with the clamping operation, adding means (switches and capacitors) which is connected to the other terminals of the clamp capacitors, adds addition signals of the respective photoreceiving element rows outputted from the other terminals and adds the signals of the plurality of photoreceiving elements provided in the column direction; an amplifier connected to the adding means; a switch for resetting the input side of the amplifier; and circuit means (switches and capacitors) for outputting an offset of the amplifier and the signal from the amplifier.
Owner:CANON KK
Soft switching three-phase gird-connected inverter additionally provided with freewheeling path
InactiveCN101951186ASimple structureReduce lossAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsClamp capacitorPower factor
The invention discloses a soft switching three-phase gird-connected inverter additionally provided with a freewheeling path, which comprises an inverter direct current power supply, a three-phase bridge arm formed by six full-control master switches with antiparallel diodes, and output filter inductors respectively connected between the midpoint of each phase of the bridge arm and an alternating current grid, wherein the three-phase bridge arm is connected with a full-control switch with an antiparallel diode, the full-control switch and the six master switches of the three-phase bridge arm are respectively connected with a capacitor in parallel, an auxiliary switch with an antiparallel diode and a serial branch of a clamp capacitor are accessed between the inverter direct current power supply and a direct current bus of the three-phase bridge arm, and a resonance inductor Lr is bridged at two ends of the serial branch, and the auxiliary switch is connected in parallel with the capacitor. The invention is simple in structure, can suppress the reverse recovery of the diodes, and reduces the electromagnetic interference. All switches of the inverter realize zero-voltage switching-on, thus the inverter has the advantages of little switching loss and high circuit efficiency. The inverter can realize control of power factors and harmonic waves for output grid-connected current, and can be used in a grid-connected inverter in various power supplies.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
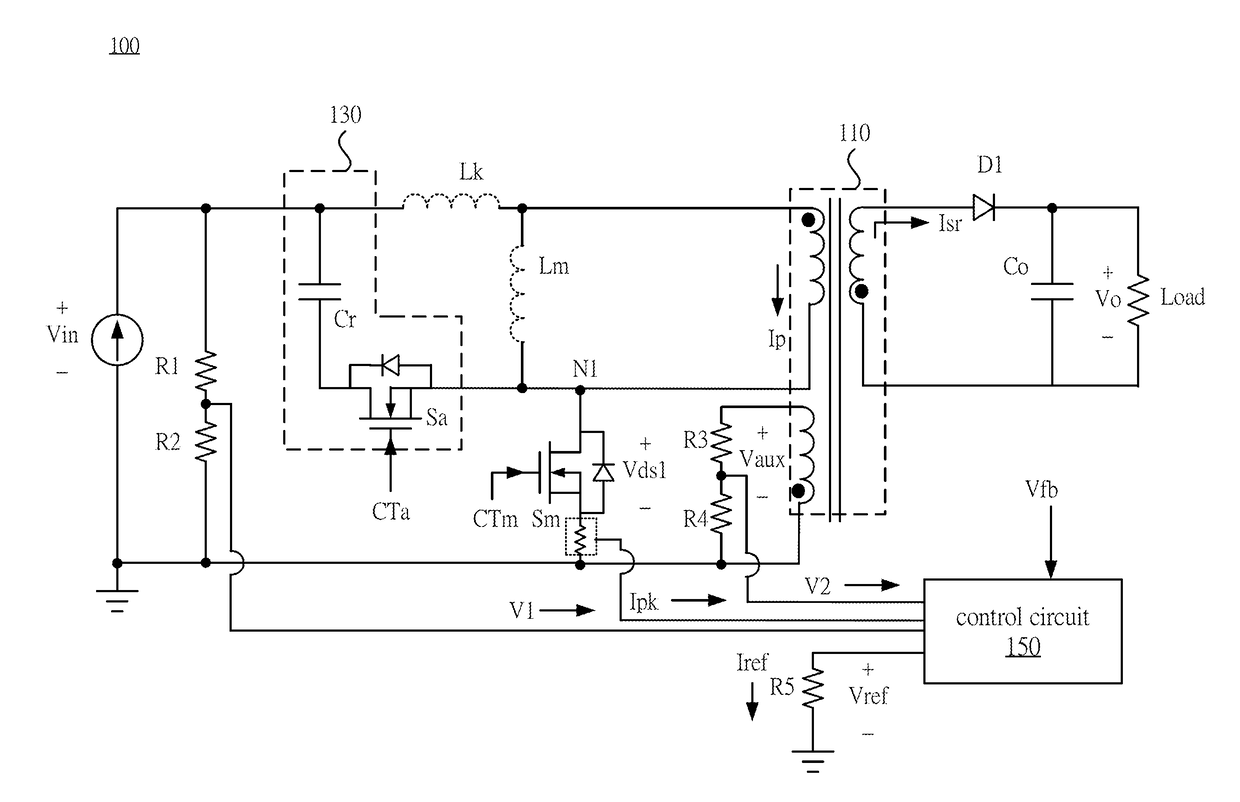
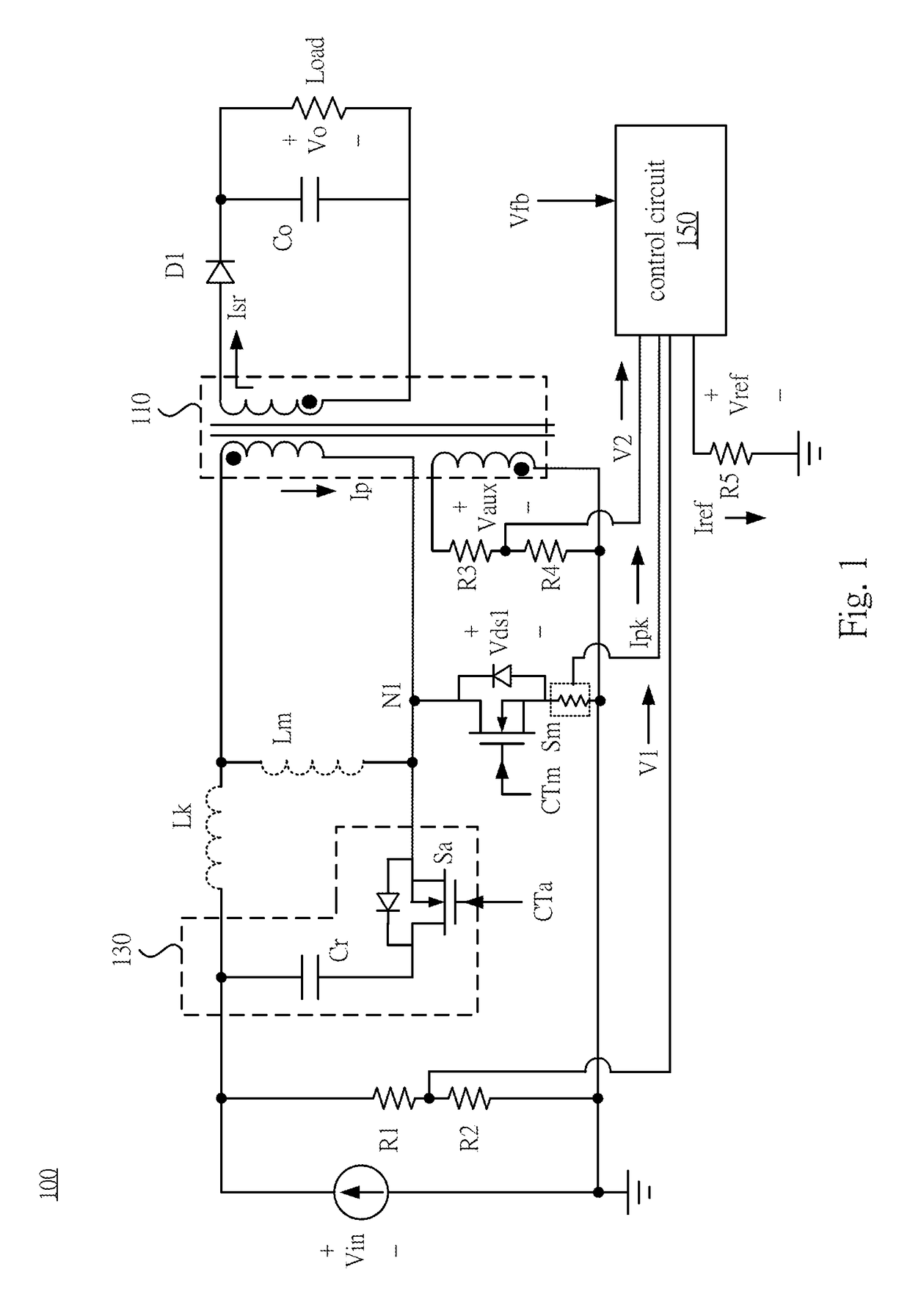
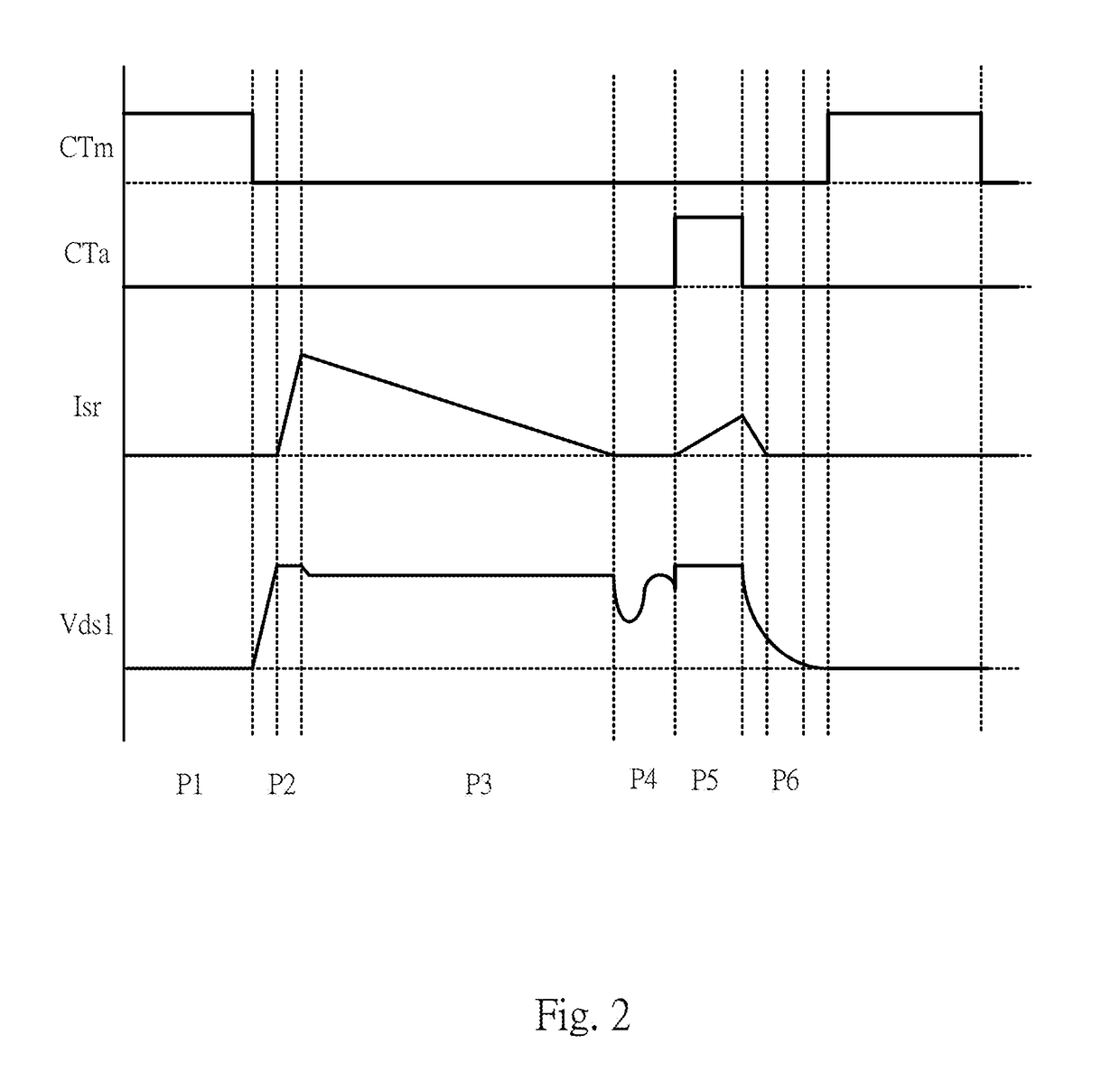
Converter and control method thereof
ActiveUS20180062529A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionActive clampClamp capacitor
A converter includes a transformer, a main switch, an active clamp circuit, and a control circuit. The transformer includes a primary winding and a secondary winding, and is configured to receive an input voltage and output an output voltage to a load. The main switch is coupled between the primary winding and a primary ground terminal. The active clamp circuit includes an auxiliary switch and a clamp capacitor. The auxiliary switch is coupled to the clamp capacitor in series, and the active clamp circuit is coupled in parallel to the two terminals of the primary winding or the main switch, and is configured to clamp the voltage across the main switch when it is OFF. The control circuit outputs an auxiliary switch control signal to turn on the auxiliary switch when the voltage across the main switch is at its first peak of the resonant voltage.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Isolated switching power supply device
ActiveUS20100188872A1Increased power capacityIncrease costEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionClamp capacitorSecondary circuit
An isolated switching power supply device includes a main transformer having a primary coil on a primary circuit side and a secondary coil on a secondary circuit side. On the primary circuit side are disposed an input smoothing capacitor, a switching control circuit, a high-side driver, a low-side power switch, a high-side power switch, capacitors, and edge signal-generating circuits. A symmetrical control half bridge converter is thus provided. The secondary circuit side has a voltage clamping circuit including a clamp capacitor, a clamp switch and a diode.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Switching power supply circuit
InactiveUS20070076443A1Low costSmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionClamp capacitorLeakage inductance
A switching power supply circuit includes a switching element, a converter transformer, a secondary-side rectifying and smoothing circuit, a switching element control unit, a choke coil, a primary-side series resonant circuit, a primary-side parallel resonant circuit, and a series circuit. The switching element implements switching for a direct-current (DC) voltage to convert the voltage into an alternating-current (AC) voltage. The choke coil is supplied with the voltage and is connected to one winding end of the primary winding and one terminal of the switching element. The primary-side series resonant circuit connects a primary-side series resonant capacitor, having a resonant frequency dominated by a leakage inductance. The primary-side parallel resonant circuit connects a primary-side parallel resonant capacitor in parallel to the switching element, having a resonant frequency. The series circuit is formed of a clamp capacitor and an auxiliary switch element which conducts in a non-conducting period of the switching element.
Owner:SONY CORP
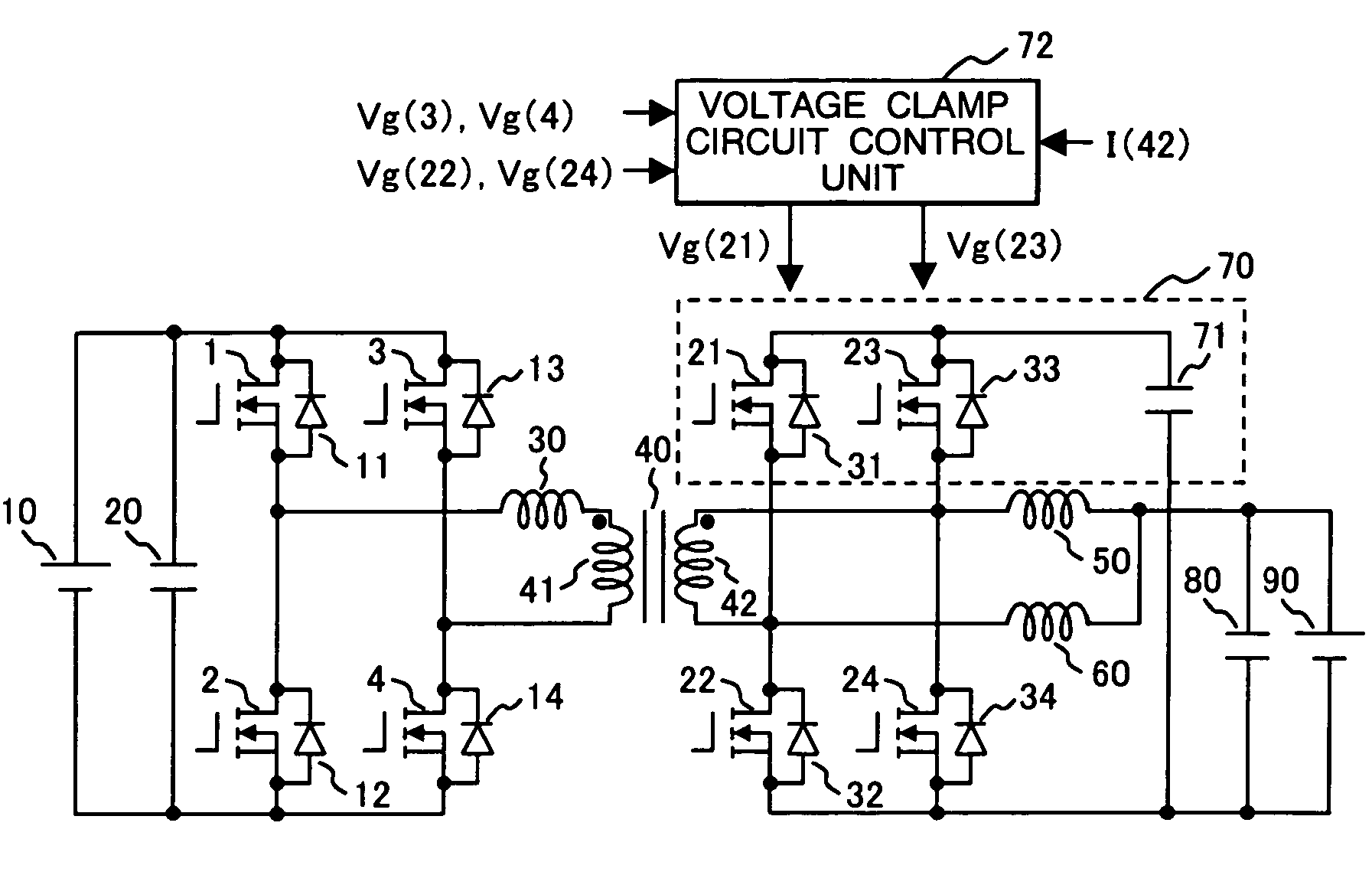
Dc-dc converter, secondary battery charge and discharge system, and method of controlling dc-dc converter
ActiveUS20150214847A1Short time intervalLow costBatteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionClamp capacitorBattery charge
In a DC-DC converter, a smoothing capacitor is connected between DC terminals of the switching circuit, and a smoothing capacitor and a voltage clamp circuit are connected between DC terminals of a switching circuit, the voltage clamp circuit including the switching device and the clamp capacitor. The smoothing capacitors are connected to the DC power sources) in parallel, respectively. The winding of the switching circuit is magnetically coupled to the winding of the switching circuit by the transformer. The DC-DC converter performs a discharging operation for discharging the clamp capacitor between at least one of the step-down operation and a step-up operation and a step-up operation performed thereafter.
Owner:HITACHI INFORMATION & TELECOMM ENG LTD
Hybrid-clamped three-electric-level three-phase four-wired photovoltaic system based on 3D-SPWM (three-dimensional sinusoidal pulse width modulation)
ActiveCN103023070AEnsure balanceReduce leakage currentAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsCapacitanceClamp capacitor
The invention relates to a hybrid-clamped three-electric-level three-phase four-wired photovoltaic system based on 3D-SPWM (three-dimensional sinusoidal pulse width modulation). By the use of a 3D-SPWM control method, system leak current is reduced effectively, neutral-point potential balance is guaranteed, balance of outputting three-phase voltage by the photovoltaic system in independent operation is guaranteed, and balance of three-phase grid-connecting current in grid-connecting operation is guaranteed. In addition, neutral current can be lowered effectively by controlling zero-sequence component. The photovoltaic system comprises three-phase bridge arms connected in parallel. Each bridge arm comprise four IGBTs (insulated gate bipolar transistors) connected in series, a neutral point of each phase bridge arm is connected with a corresponding resistor through a filter, and the resistors are grounded. A pair of a capacitor C1 and a capacitor C2 in series connection are connected at an input end of each bridge arm in parallel, the capacitors C1 and the capacitors C2 are connected with an acquisition photovoltaic array. A pair of diodes are connected between the first IGBT and the fourth IGBT of each bridge arm in series,and neutral points of the capacitors C1 and the capacitors C2 are grounded. In addition, clamped capacitors Cxi are connected on each pair of diodes in parallel, wherein i is equal to a, b and c. The IGBTs are controlled by a control circuit in a 3D-SPWM manner to balance potential at the neutral points.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Boost Device For Voltage Boosting
ActiveUS20100277955A1Boost voltageOvercomes drawbackAc-dc conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsClamp capacitorTransformer
A boost device boosts an input voltage to an output voltage across an output capacitor, and includes an output diode coupled to the output capacitor, and a transformer coupled to a first switch, a clamp circuit and a boost circuit. The clamp circuit is coupled across a first winding of the transformer, and includes a clamp capacitor coupled in series to a second switch. The output capacitor is capable of being charged through the output diode with an induced voltage across a second winding of the transformer. The boost circuit is capable of being charged with the induced voltage across the second winding, and of charging the output capacitor so as to boost the output voltage across the output capacitor.
Owner:HUNGKUANG UNIV
Switching power source apparatus
InactiveUS7130204B2Reduce rateIncrease in sizeTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsClamp capacitorCapacitance
A switching power source apparatus can reduce the size of a transformer and realize the zero-voltage switching of a switch. The apparatus is compact, highly efficient, and low in noise. The apparatus has a series circuit connected to each end of a DC power source (Vdc1) and including a primary winding (5a) of a transformer (T) and a main switch (Q1), a rectifying-smoothing circuit to rectify and smooth a voltage that is outputted from a secondary winding (5b) when the main switch (Q1) is turned on, a series circuit connected to each end of the primary winding (5a) and including an auxiliary switch (Q2) and a clamp capacitor (C1), a series circuit connected to each end of the main switch (Q1) and including a diode (Dx1) and a snubber capacitor (Cx), a series circuit connected to a node between the diode (Dx1) and the snubber capacitor (Cx) and a node between the auxiliary switch (Q2) and the clamp capacitor (C1) and including an auxiliary winding (5x) and a diode (Dx2), and a control circuit (10) to alternately turn on / off the main switch (Q1) and auxiliary switch (Q2). When the main switch (Q1) is turned on, the snubber capacitor (Cx) is discharged through the auxiliary winding (5x) to the clamp capacitor (C1). When the main switch (Q1) is turned off, the snubber capacitor (Cx) is charged, to relax the inclination of a voltage increase of the main switch (Q1).
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com