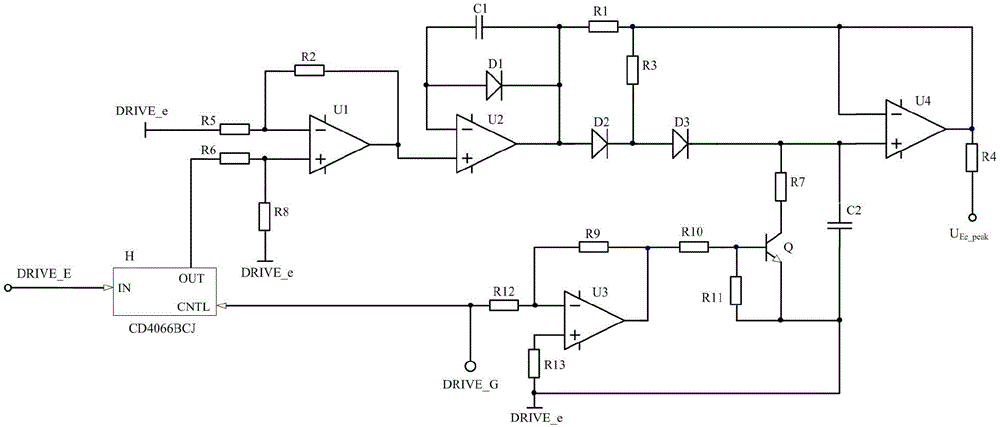
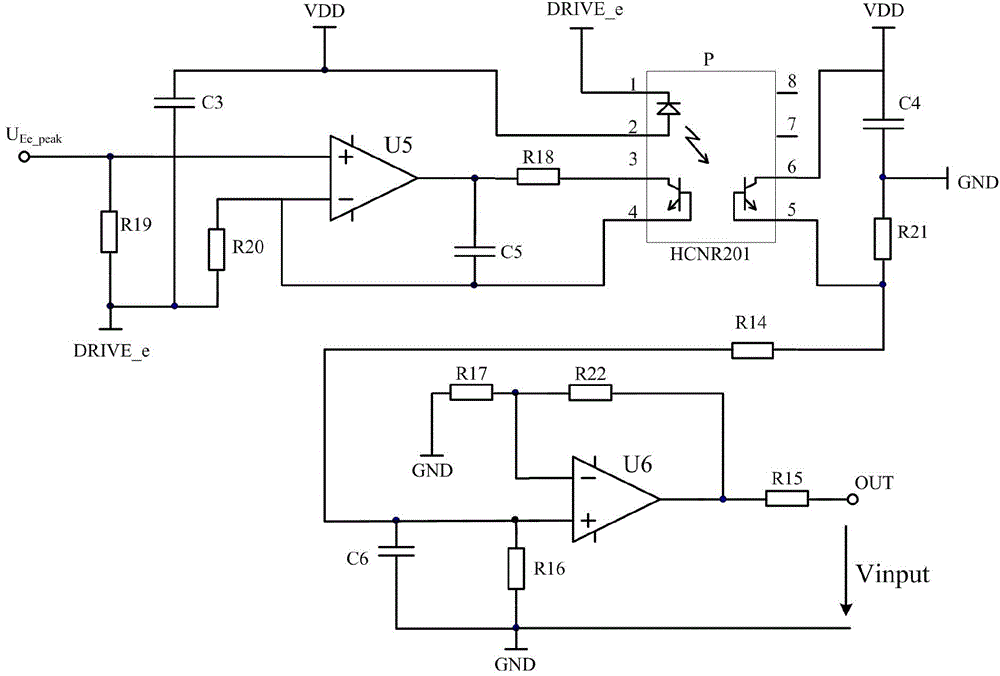
Patents
Literature
1097 results about "Reverse recovery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
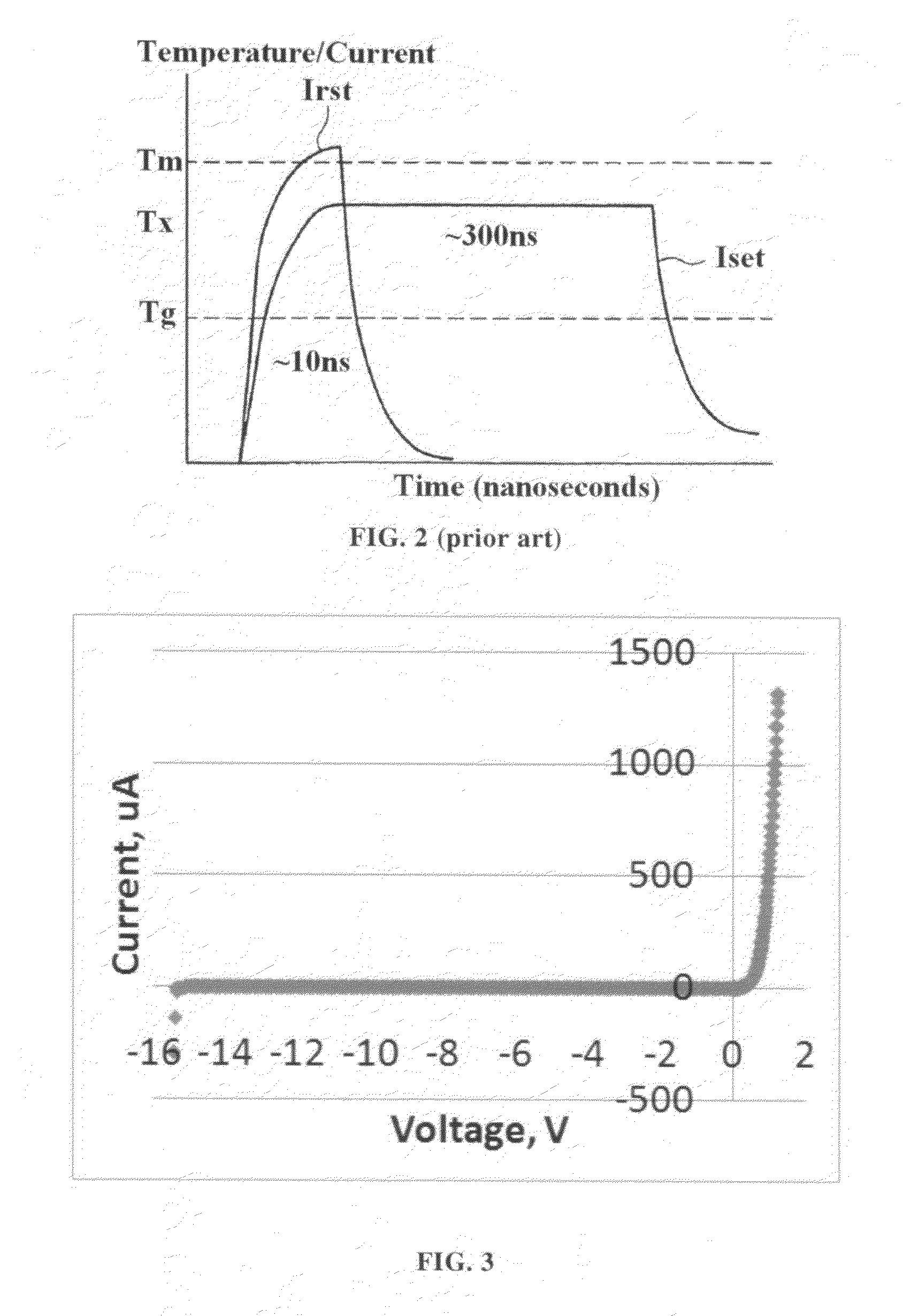
Reverse recovery time (trr) The time interval between the instant when the current passes through zero when changing from the forward direction to the reverse direction and, after reverse current reaches its peak value I RM(REC), the instant when.
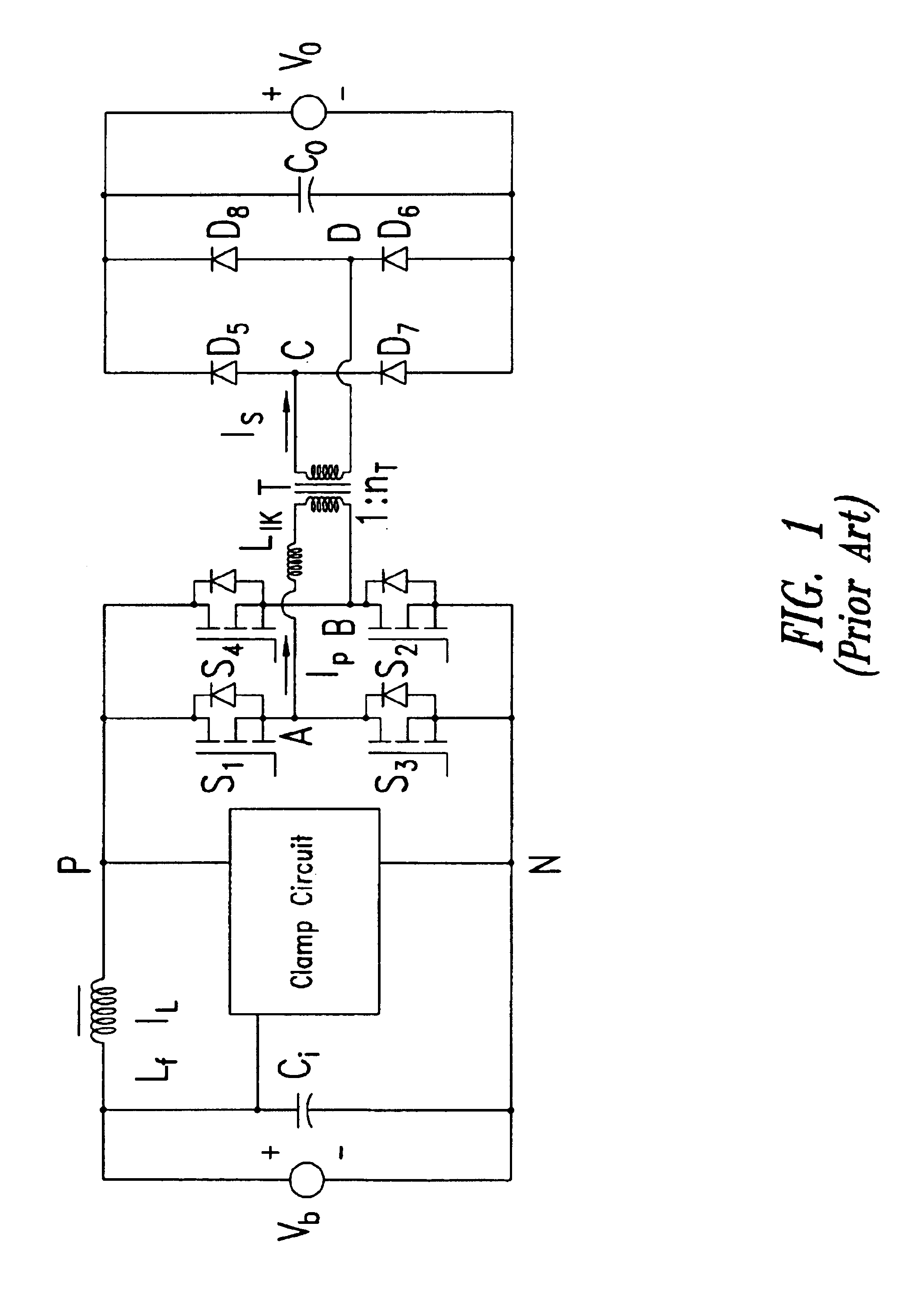
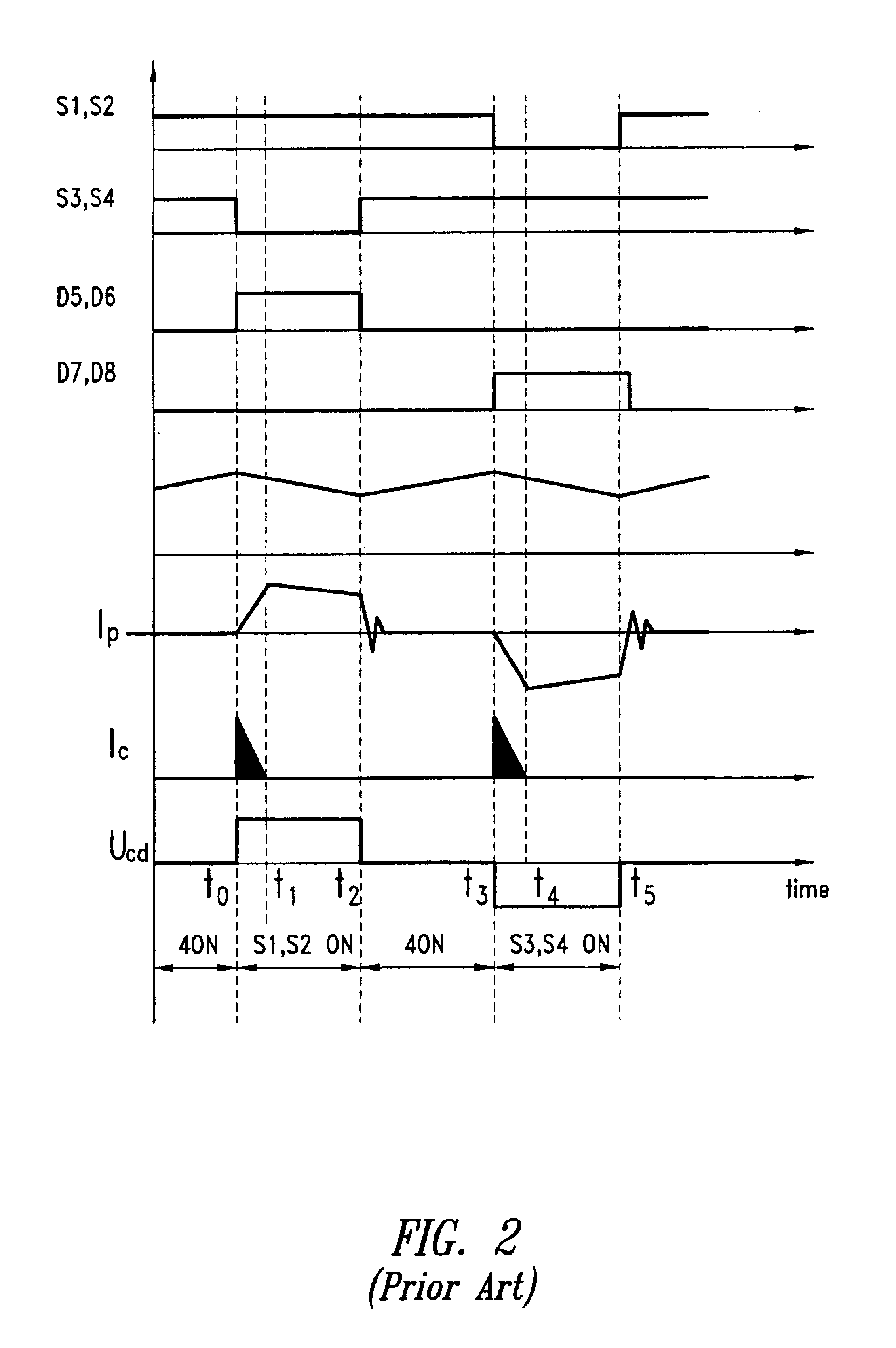
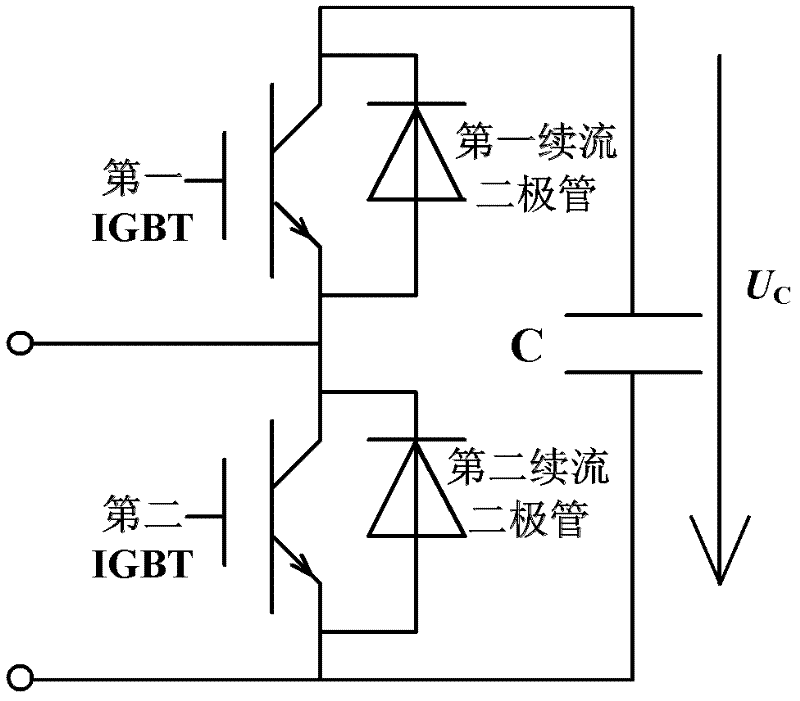
Universal Power Converter
ActiveUS20080013351A1Increased electric lossIncrease lossEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionReverse recoveryInductor
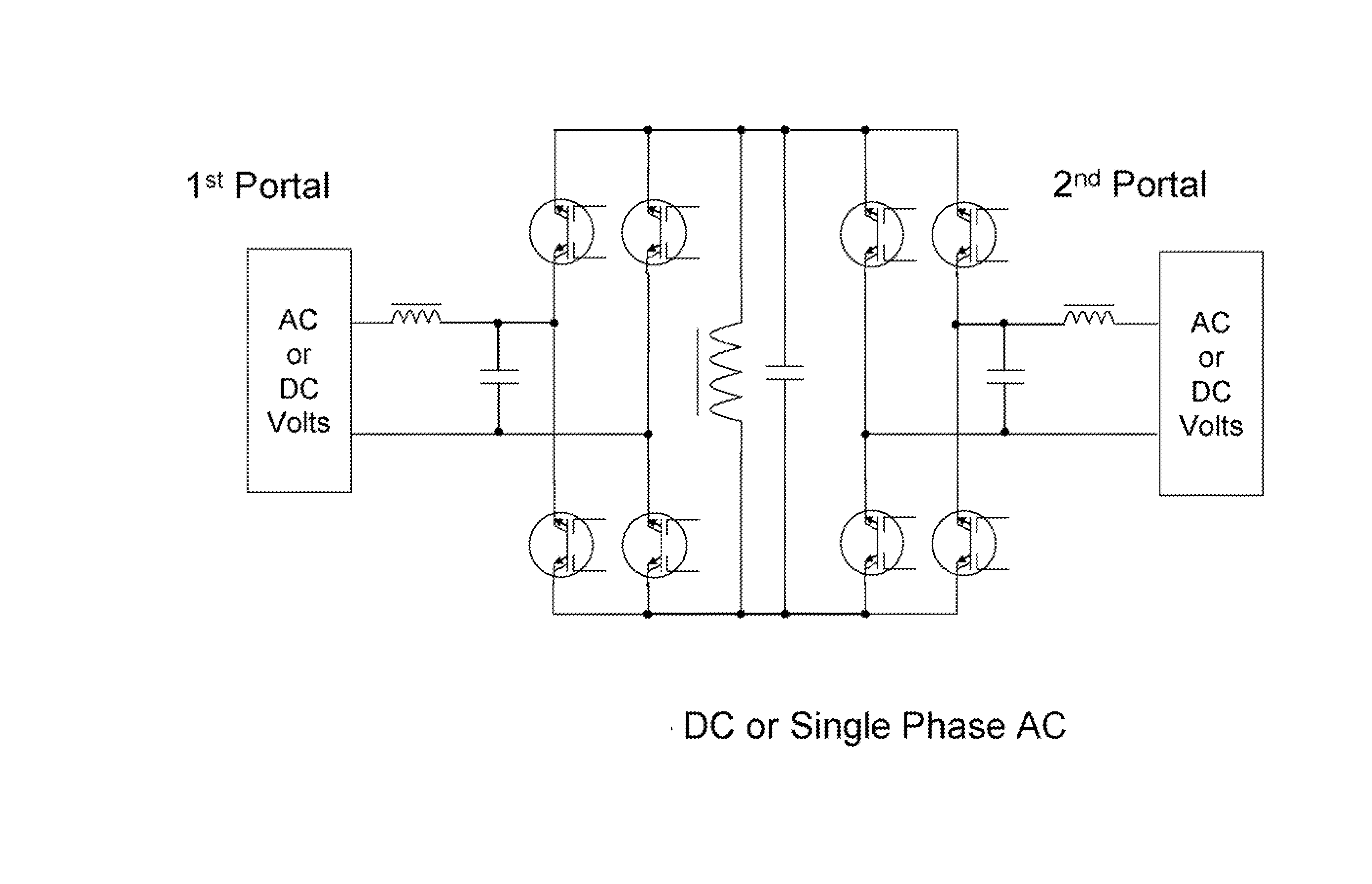
Methods and systems for transforming electric power between two or more portals. Any or all portals can be DC, single phase AC, or multi-phase AC. Conversion is accomplished by a plurality of bi-directional conducting and blocking semiconductor switches which alternately connect an inductor and parallel capacitor between said portals, such that energy is transferred into the inductor from one or more input portals and / or phases, then the energy is transferred out of the inductor to one or more output portals and / or phases, with said parallel capacitor facilitating “soft” turn-off, and with any excess inductor energy being returned back to the input. Soft turn-on and reverse recovery is also facilitated. Said bi-directional switches allow for two power transfers per inductor / capacitor cycle, thereby maximizing inductor / capacitor utilization as well as providing for optimum converter operation with high input / output voltage ratios. Control means coordinate the switches to accomplish the desired power transfers.
Owner:CET GRP SA +1
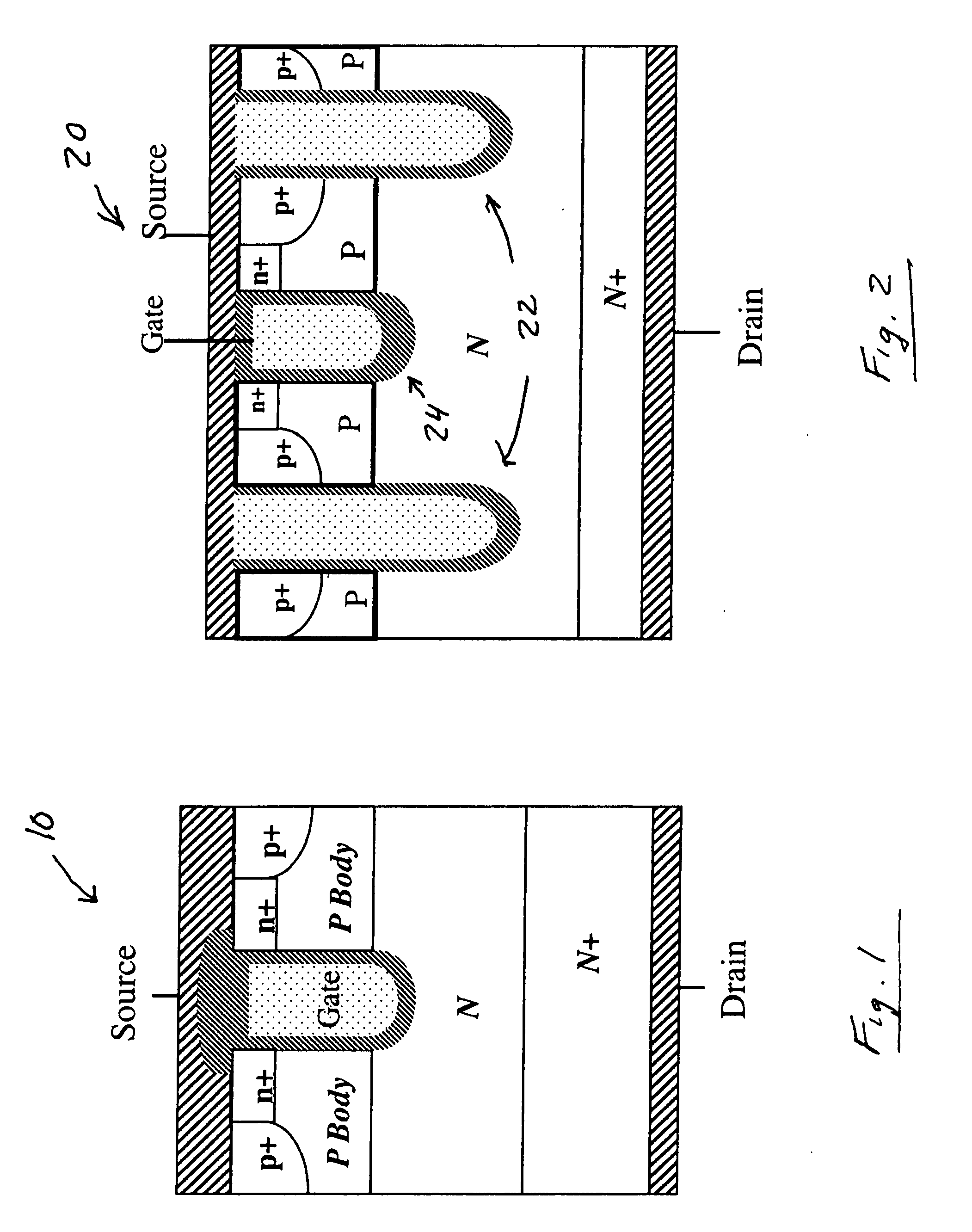
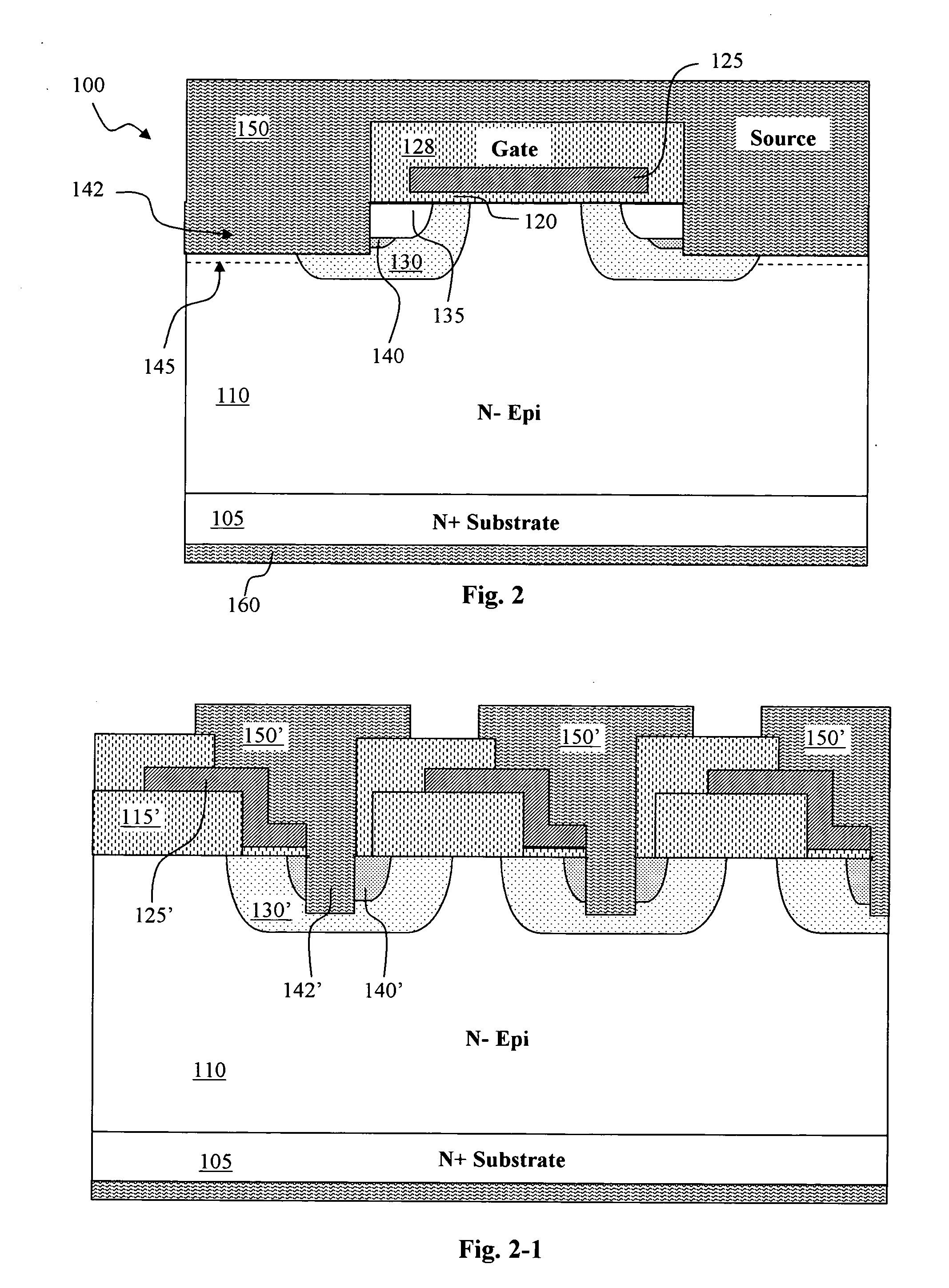
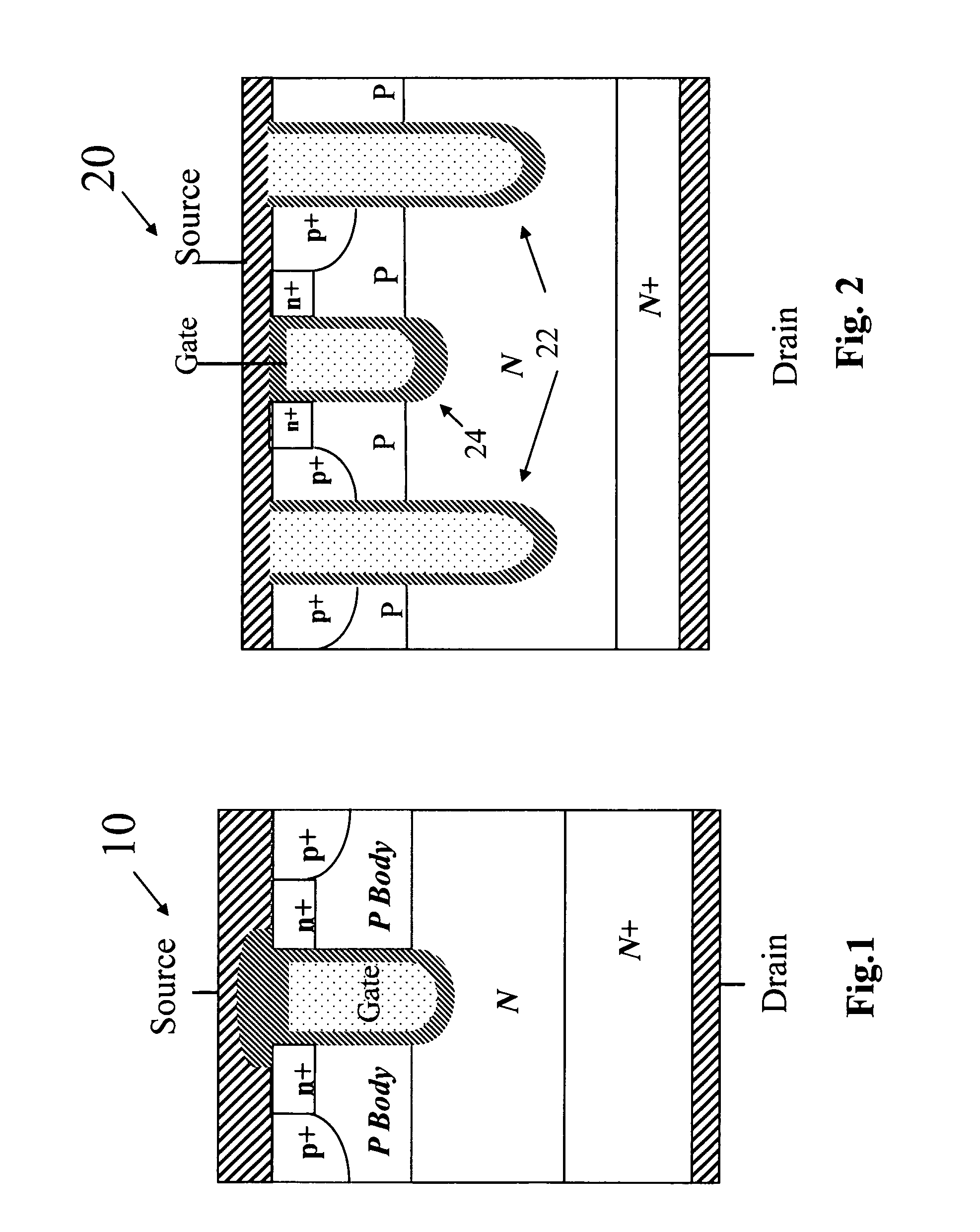
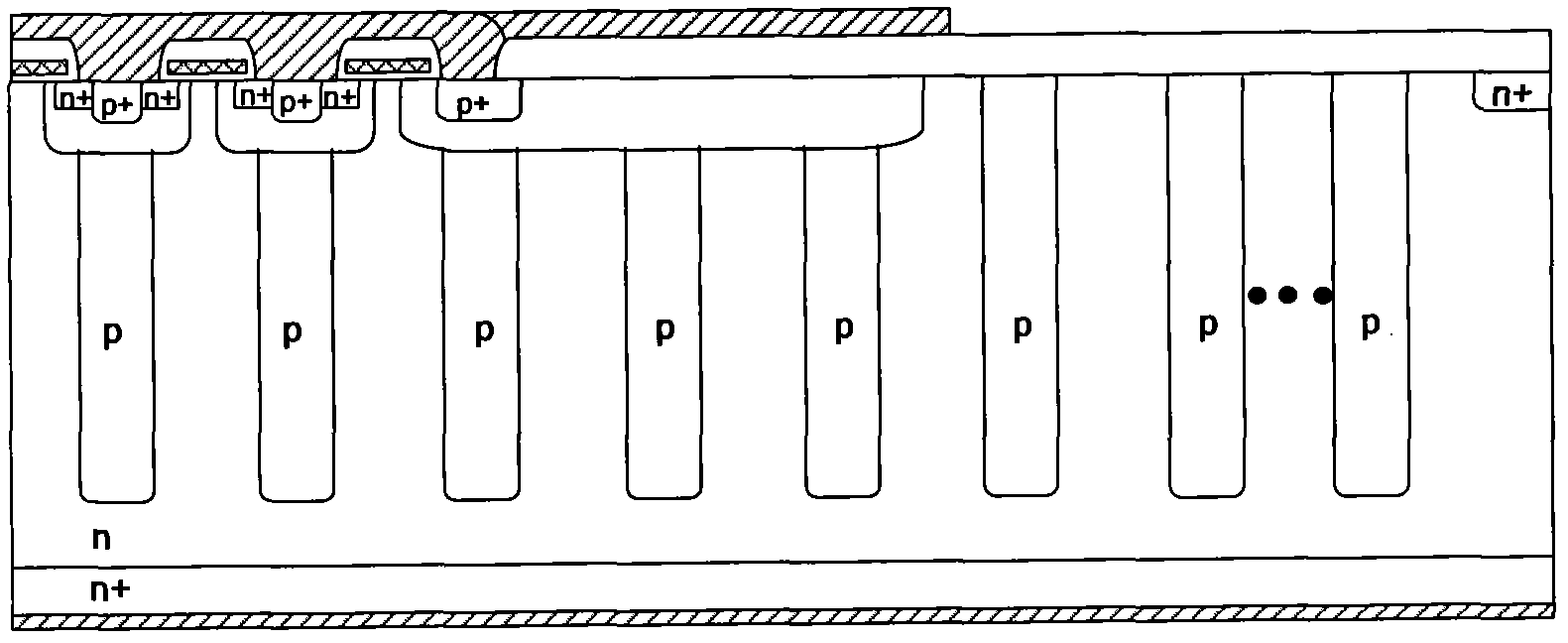
Power MOSFET with recessed field plate
ActiveUS20080073707A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrench mosfetReverse recovery
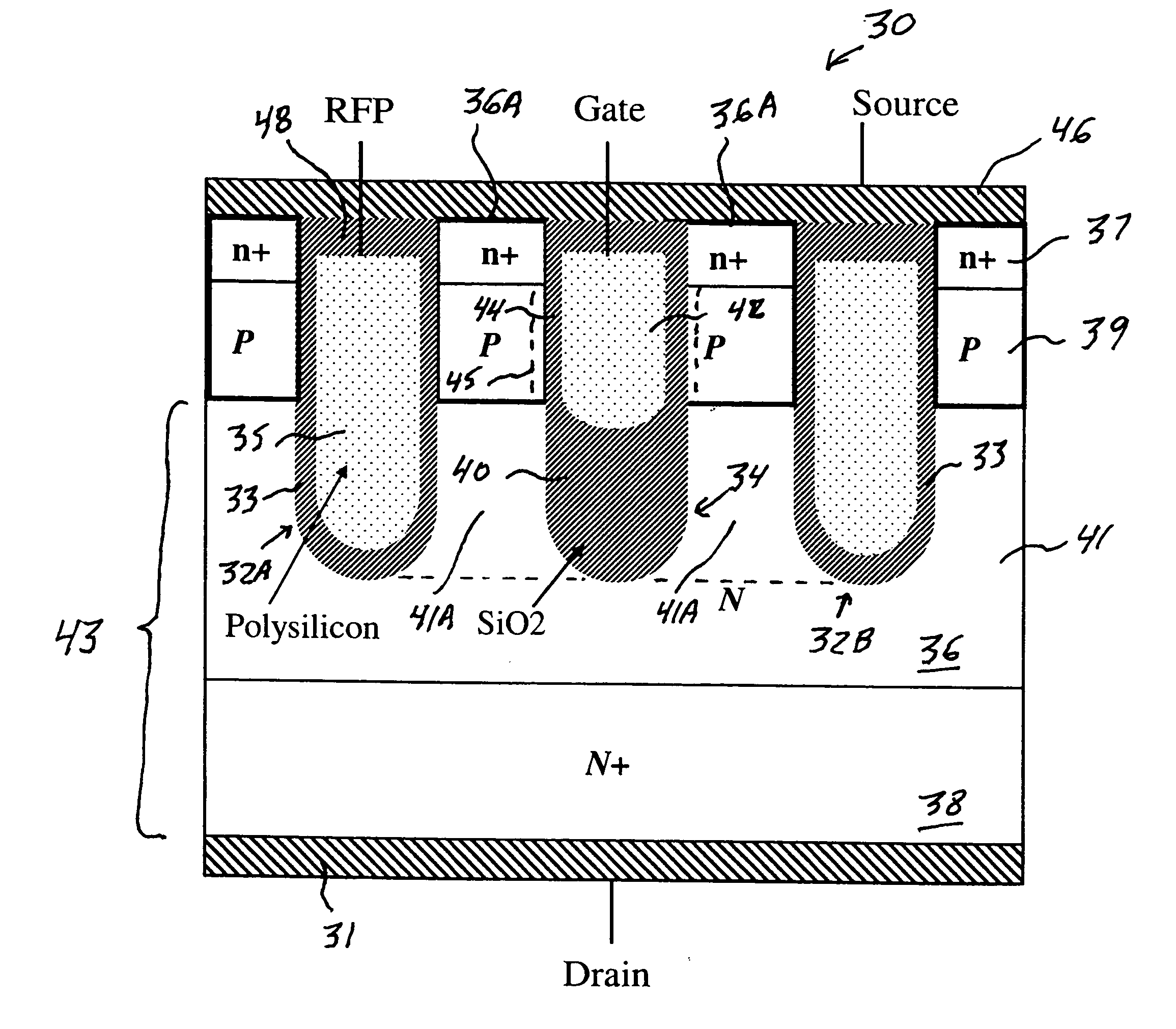
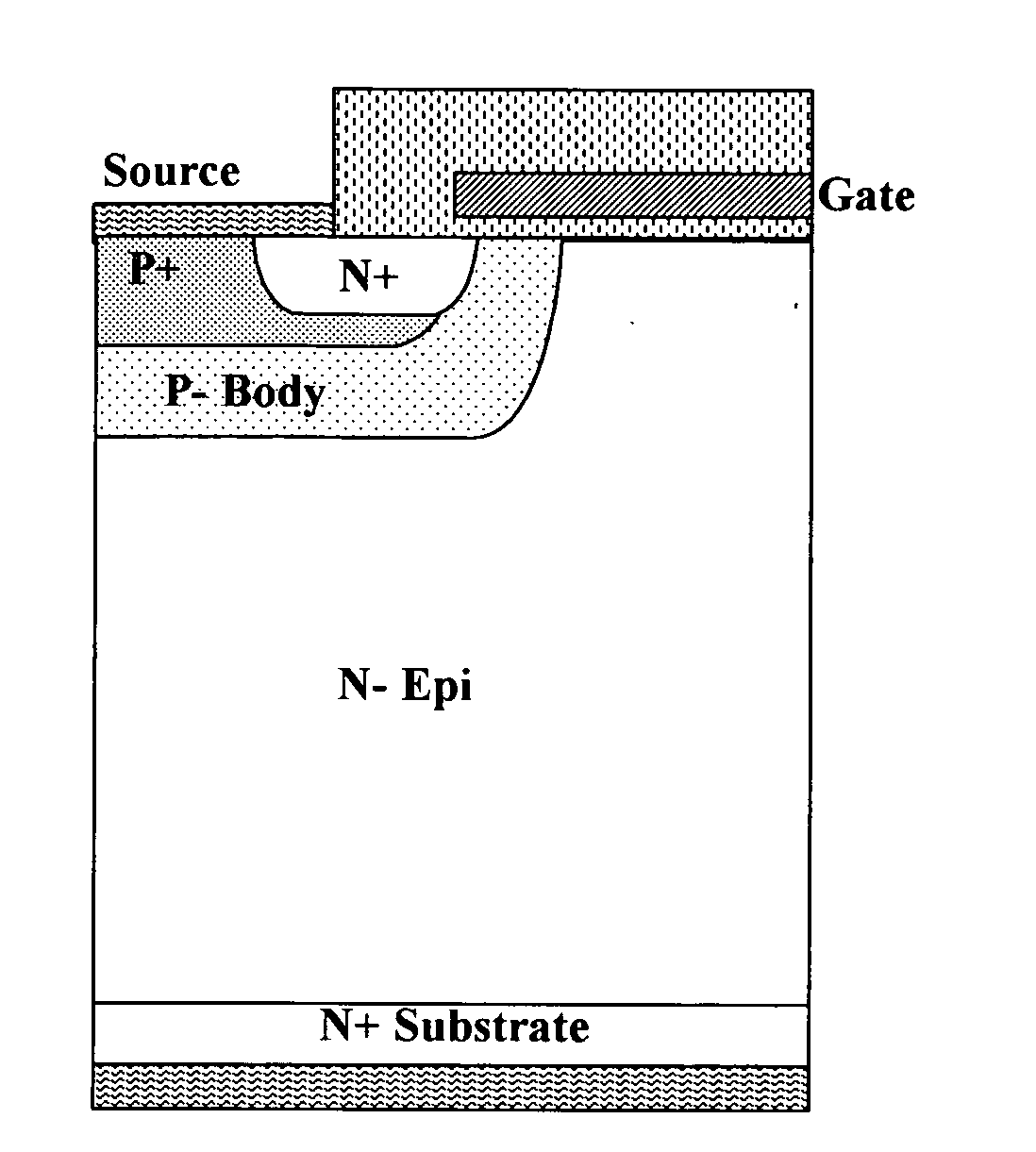
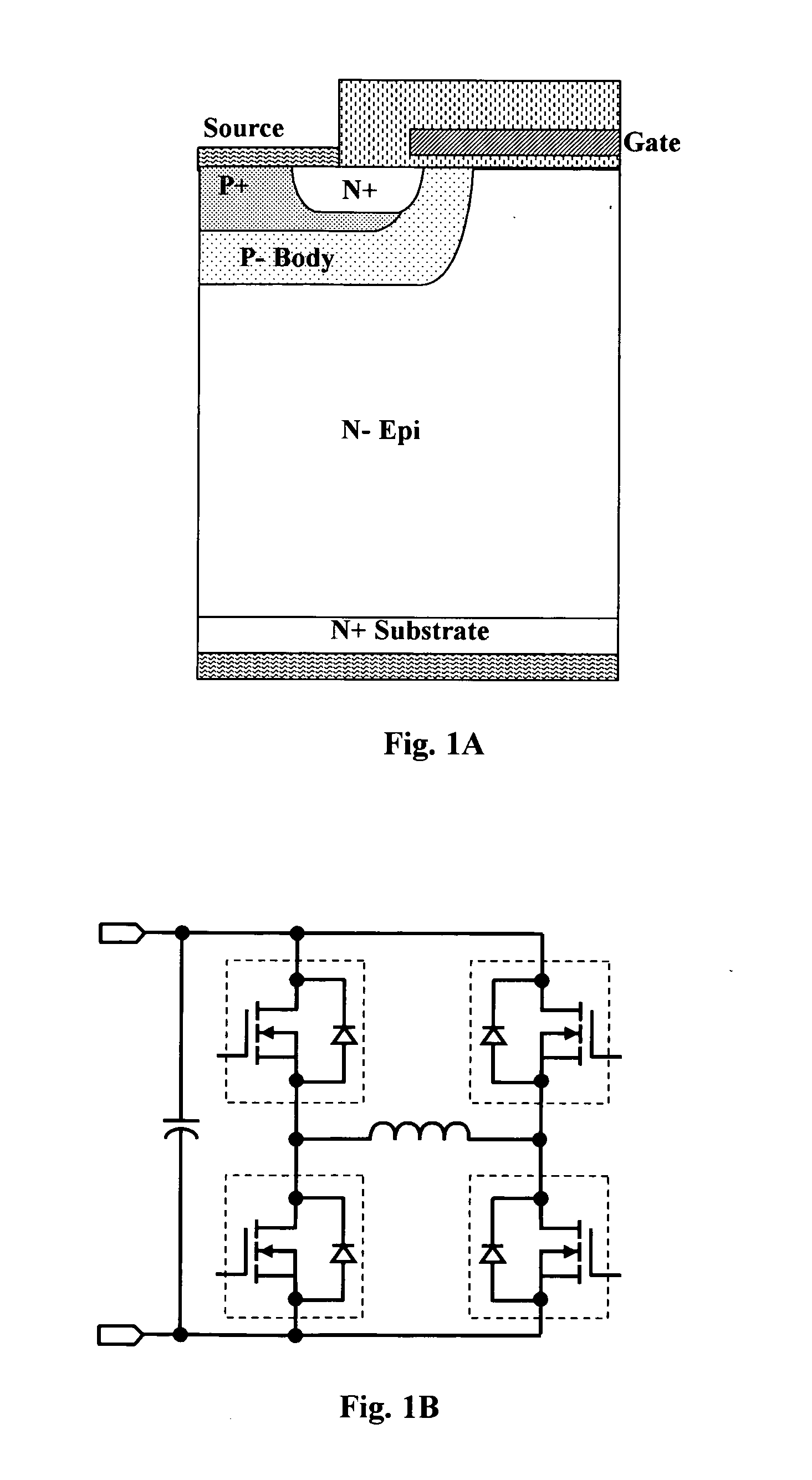
A trench MOSFET contains a recessed field plate (RFP) trench adjacent the gate trench. The RFP trench contains an RFP electrode insulated from the die by a dielectric layer along the walls of the RFP trench. The gate trench has a thick bottom oxide layer, and the gate and RFP trenches are preferably formed in the same processing step and are of substantially the same depth. When the MOSFET operates in the third quadrant (with the source / body-to-drain junction forward-biased), the combined effect of the RFP and gate electrodes significantly reduces in the minority carrier diffusion current and reverse-recovery charge. The RFP electrode also functions as a recessed field plates to reduce the electric field in the channel regions when the MOSFET source / body to-drain junction reverse-biased.
Owner:MAXPOWER SEMICON INC
Universal Power Conversion Methods
InactiveUS20080031019A1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionEngineeringElectric power
Methods and systems for transforming electric power between two or more portals. Any or all portals can be DC, single phase AC, or multi-phase AC. Conversion is accomplished by a plurality of bi-directional conducting and blocking semiconductor switches which alternately connect an inductor and parallel capacitor between said portals, such that energy is transferred into the inductor from one or more input portals and / or phases, then the energy is transferred out of the inductor to one or more output portals and / or phases, with said parallel capacitor facilitating “soft” turn-off, and with any excess inductor energy being returned back to the input. Soft turn-on and reverse recovery is also facilitated. Said bi-directional switches allow for two power transfers per inductor / capacitor cycle, thereby maximizing inductor / capacitor utilization as well as providing for optimum converter operation with high input / output voltage ratios. Control means coordinate the switches to accomplish the desired power transfers.
Owner:CET GRP SA +1
Soft switching interleaved power converter
ActiveUS6979980B1Reduce switching lossesReduced loss diode reverse-recovery lossApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationSoft switchingReverse recovery
There is provided by this invention soft switching interleaved power converters that are suitable for high power and high voltage applications such as plasma processing. They have greatly reduced switching losses and diode reverse-recovery losses which allows operation at high switching frequencies. The peak values of the reverse-recovery currents of the diodes are substantially less then their peak forward operating currents. The power converters incorporate power converter cells that comprise a plurality of switching assemblies that are operated with an interleaved switching pattern, and that are each connected to an input terminal of an inductor assembly that also has a common terminal. The inductance between each pair of input terminals is less than the inductance between each input terminal and the common terminal of the inductor assembly.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
Three-Level Active Neutral Point Clamped Zero Voltage Switching Converter
ActiveUS20120218785A1Improve efficiencyHigh level conversionEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionThree levelSwitching cycle
A main circuit of a three-level active neutral point clamped voltage source converter having a pair of additional main switches provides two paths between an output node and a neutral point in which one of the paths involves only switches of an inner pair of switches that are operated at a high frequency. An auxiliary circuit operating at a high frequency for only a brief period during each high frequency switching cycle selects the path involving only the inner switches and provides operation with zero voltage switching and avoids reverse recovery of diodes connected antiparallel with the main and additional main switches. Accordingly, turn-on switching losses in the main switches is avoided and the voltage source converter can be operated at increased frequency to allow reduction in size of magnetic components and full potential power transfer to be achieved.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
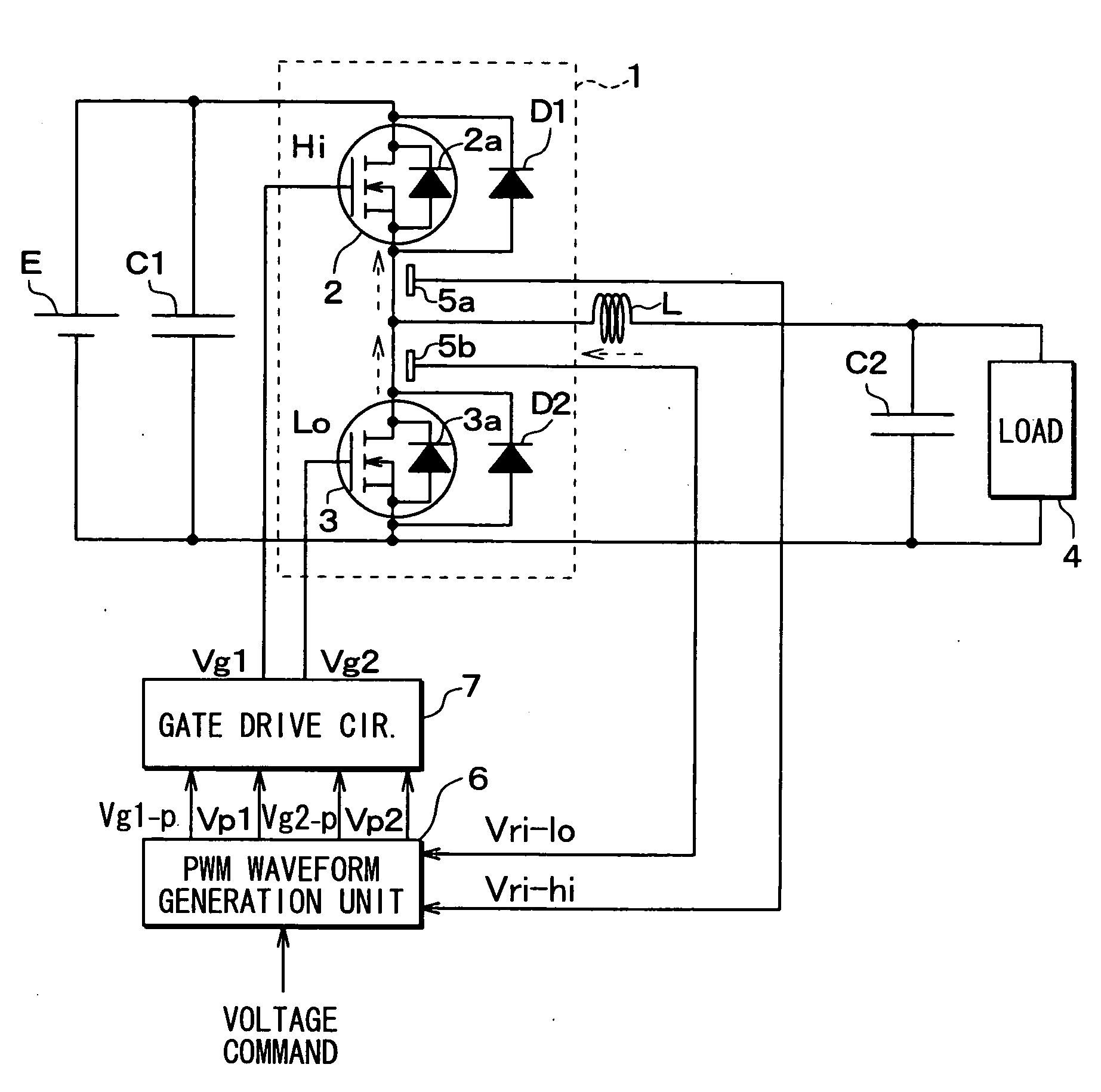
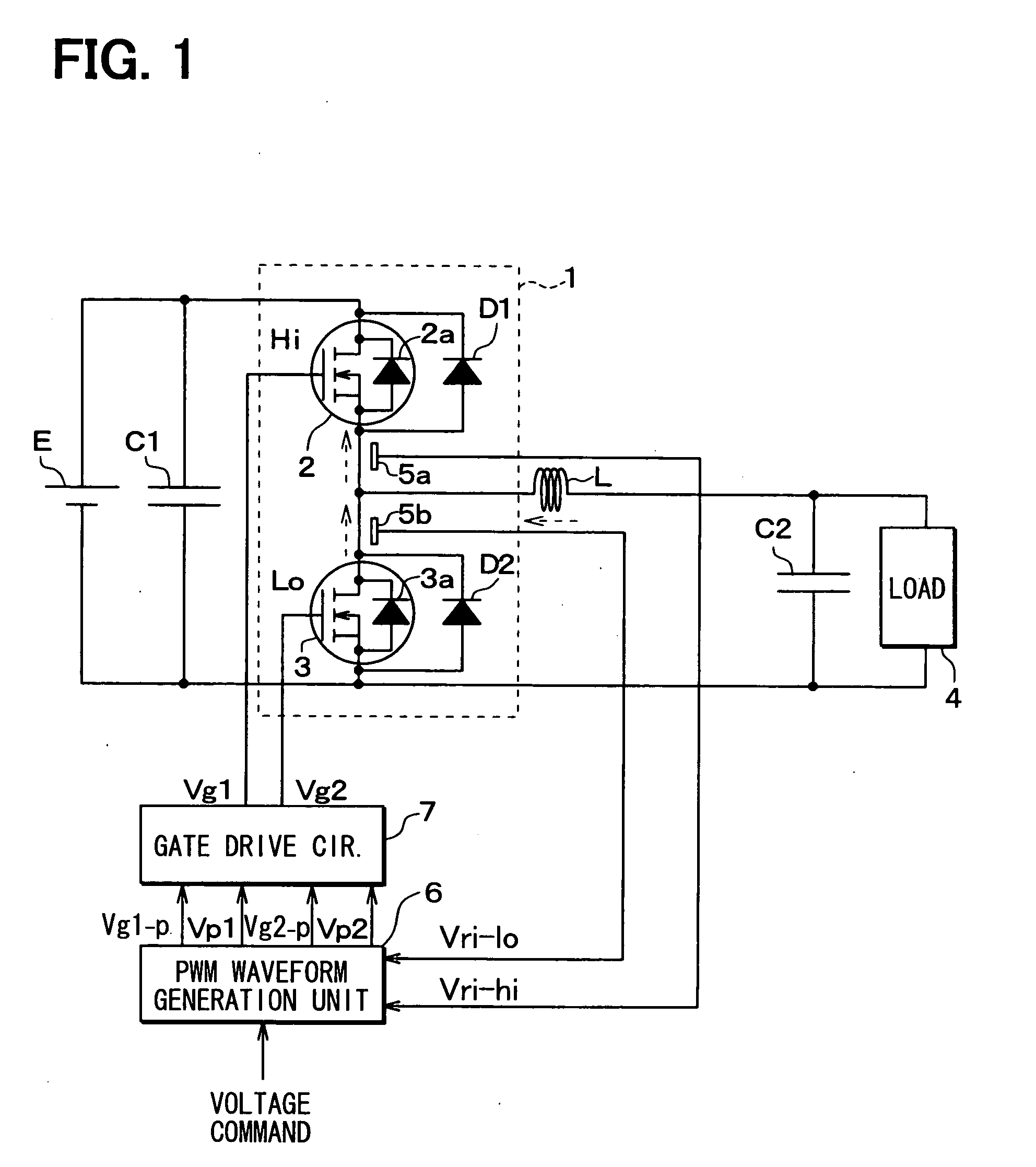
Gate Drive Circuit
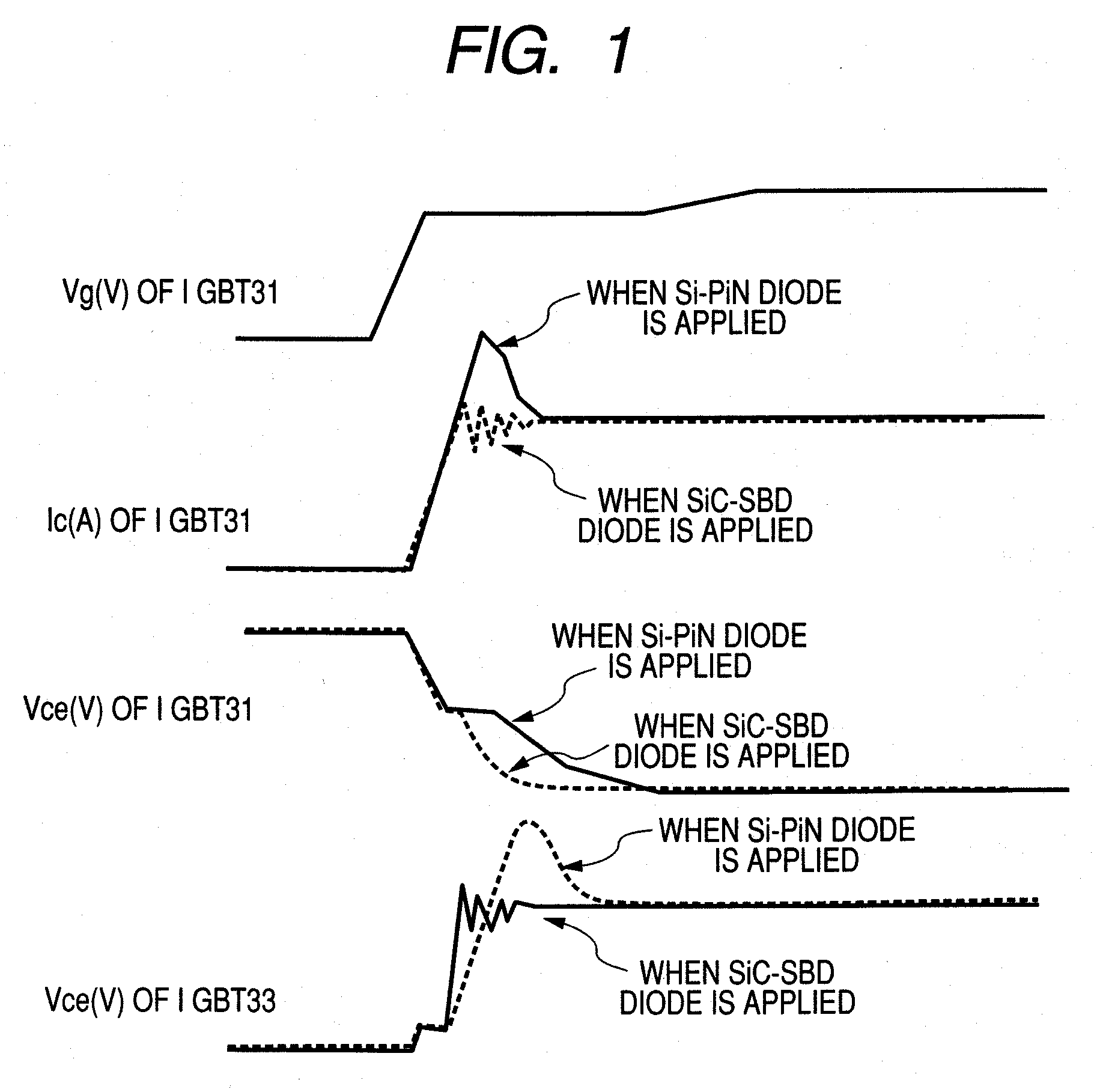
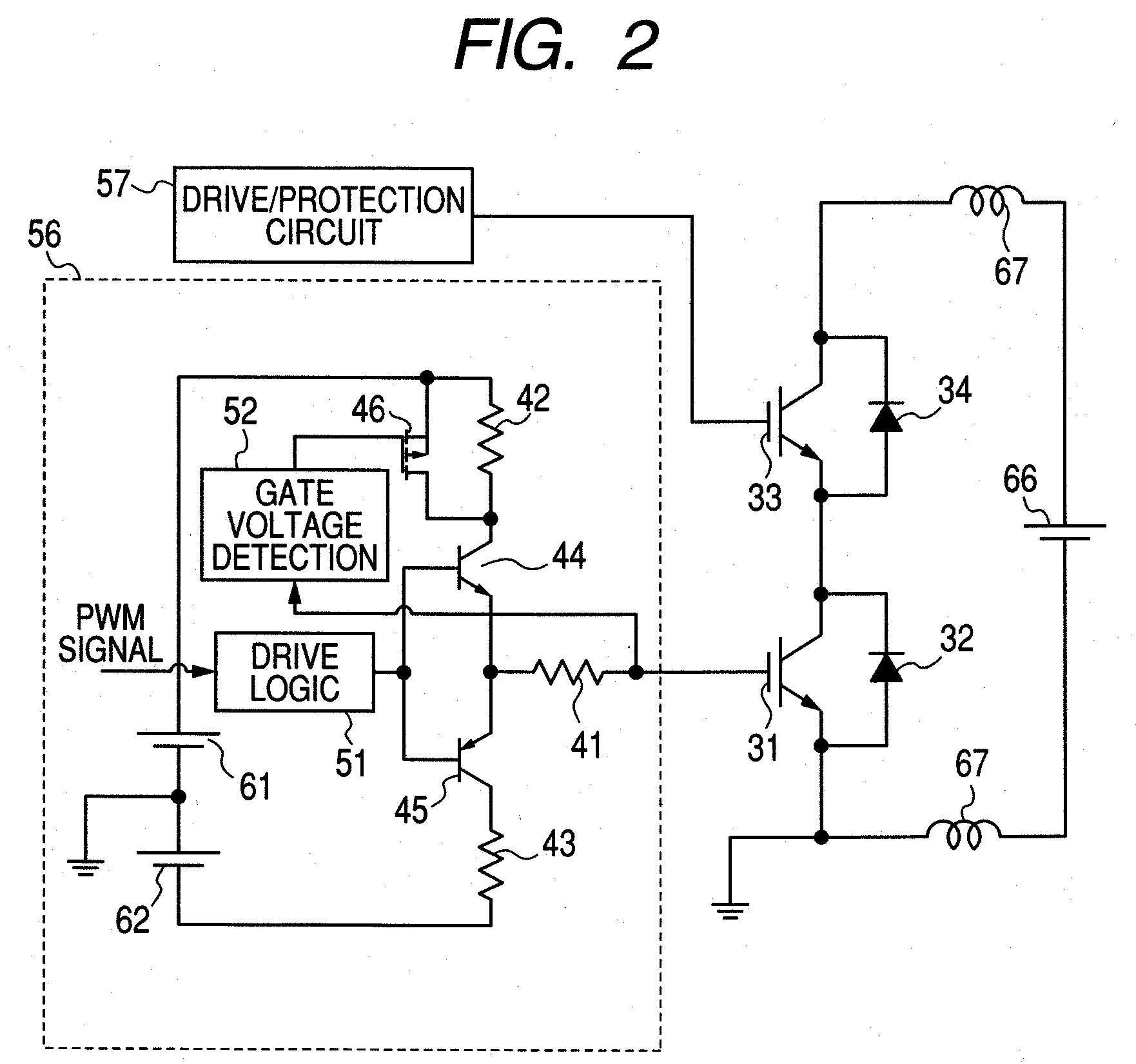
InactiveUS20080122497A1Reduce power lossReduce noiseElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorDriver circuitReverse recovery
A subject of the present invention is to reduce noise caused by ringing or the like while reducing turn-on power loss of the element and reverse recovery loss of the diode in a switching circuit of a power semiconductor element to which a SiC diode having small recovery current is connected in parallel.A means for solving the problem is to detect gate voltage and / or collector voltage of the power semiconductor switching element and change gate drive voltage in several stages based on the detected value.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
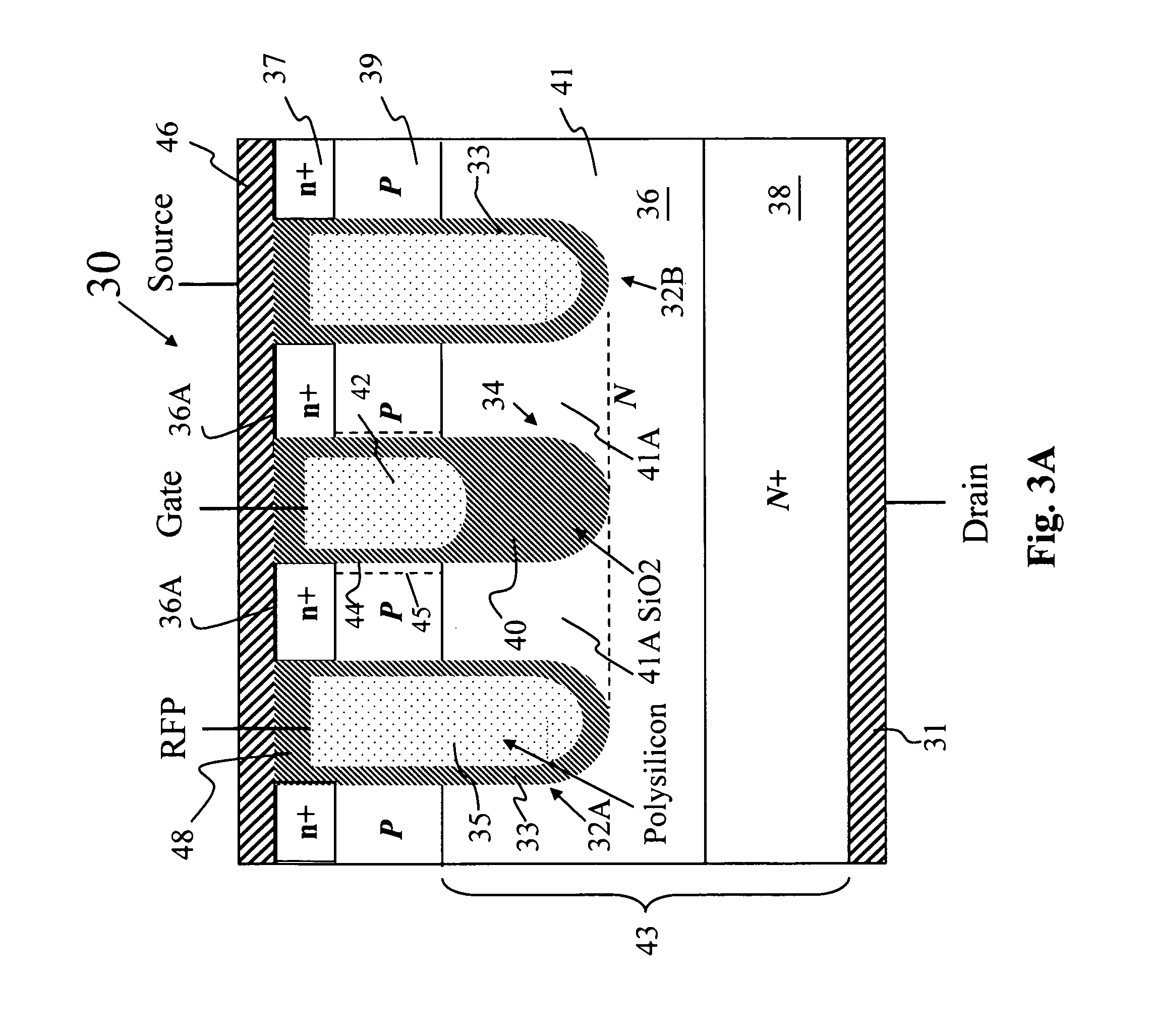
High voltage MOSFET diode reverse recovery by minimizing P-body charges
ActiveUS20110073906A1Improve configurationImprove methodSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeHigh concentrationDopant
This invention discloses a method for manufacturing a semiconductor power device in a semiconductor substrate comprises an active cell area and a termination area. The method comprises the steps of a) growing and patterning a field oxide layer in the termination area and also in the active cell area on a top surface of the semiconductor substrate b) depositing and patterning a polysilicon layer on the top surface of the semiconductor substrate at a gap distance away from the field oxide layer; c) performing a blank body dopant implant to form body dopant regions in the semiconductor substrate substantially aligned with the gap area followed by diffusing the body dopant regions into body regions in the semiconductor substrate; d) implanting high concentration body-dopant regions encompassed in and having a higher dopant concentration than the body regions e) applying a source mask to implant source regions having a conductivity opposite to the body region with the source regions encompassed in the body regions and surrounded by the high concentration body-dopant regions; and f) etching contact trenches into the source, body contact, and body regions.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
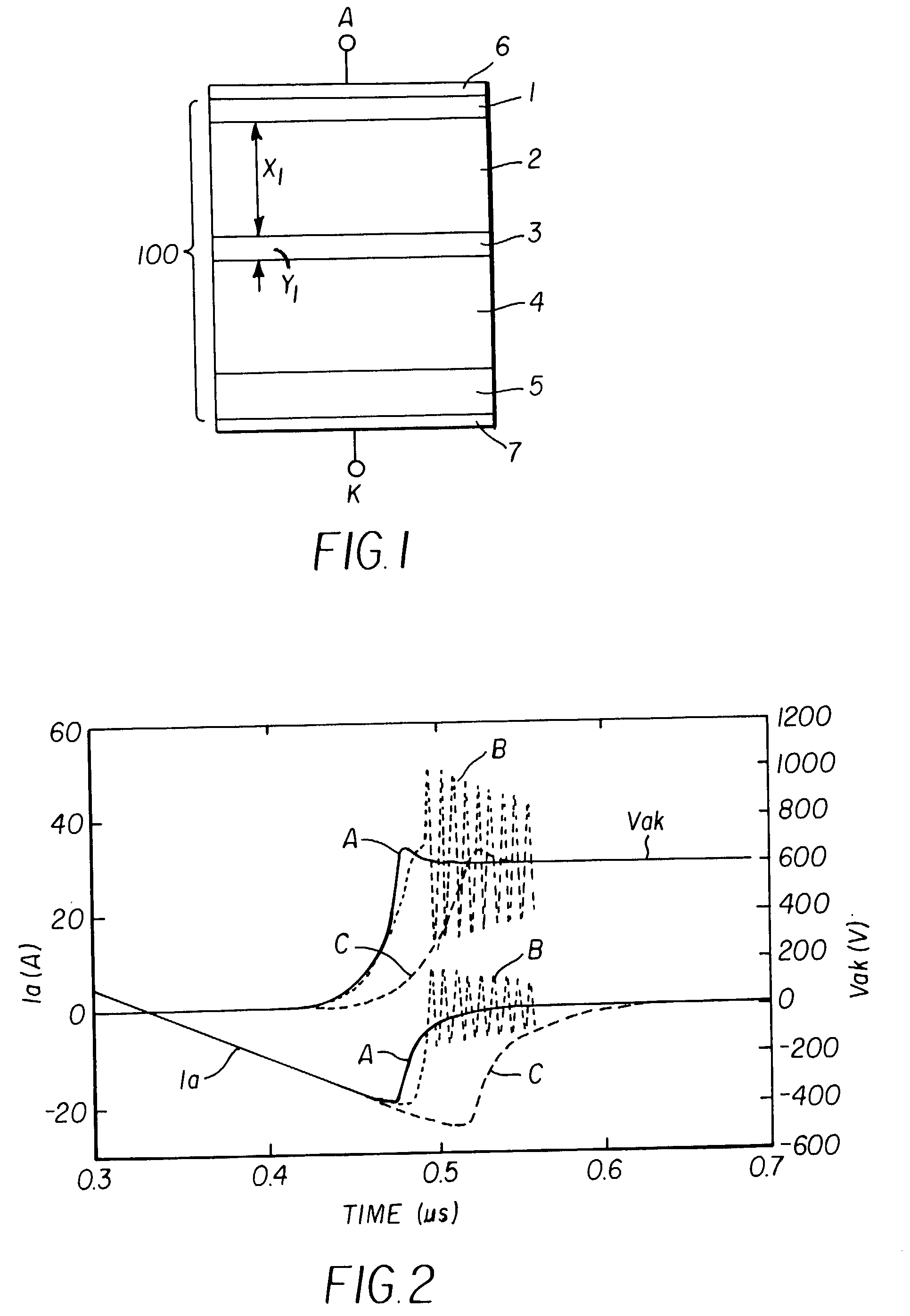
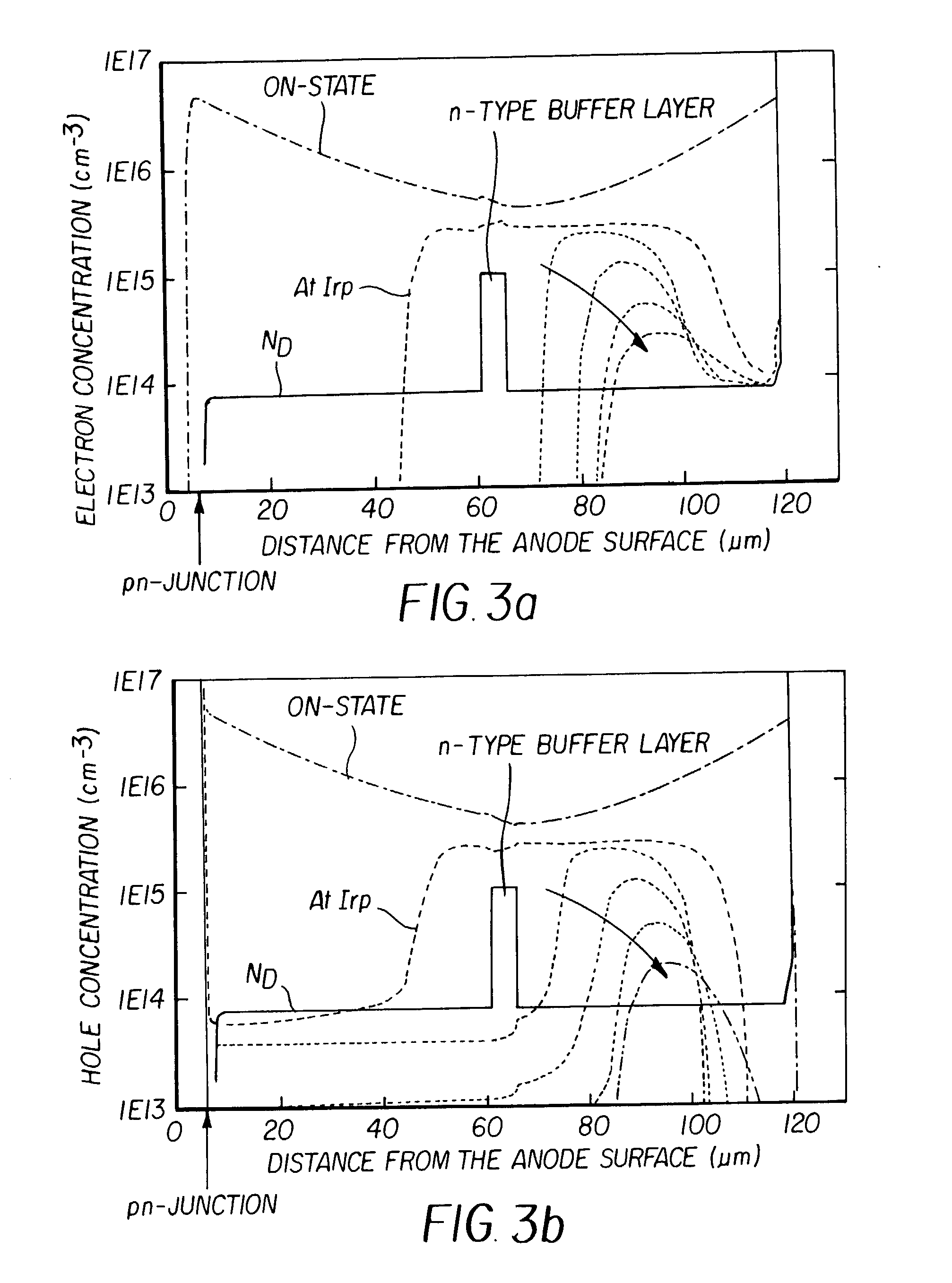
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20020130331A1ThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsReverse recoveryShortest distance
A semiconductor device, such as a pin diode, includes a first drift layer, a second drift layer, an anode layer on the first drift layer, and a buffer layer formed between the first and second drift layers. The shortest distance from the pn-junction between the anode layer and the buffer layer, and the thickness of the buffer layer are set at the respective values at which a high breakdown voltage is obtained, while reducing the tradeoff relation between the soft recovery and the fast and low-loss reverse recovery.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Soft transition converter
InactiveUS6862195B2Total current dropReduce reverse recovery lossEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcSoft switchingFull bridge
The present invention is a circuit and method for reducing switching and reverse recovery losses in the output rectifiers while creating zero voltage switching conditions for the primary switchers. There are described two output configurations, one employing a soft commutation inductor element a bridge rectifier and a output filter capacitor, the second using a soft commutation inductor element a rectification-filtering bridge composed by two capacitors and two capacitors. Both secondary circuits can be driven by three primary circuits. A first circuit is a full bridge with phase shift control, and a second circuit is a half bridge topology with an additional bydirectional switch which achieves two goals, on to get soft switching commutation across all the primary switches, the second to create the right waveforms in the secondary suitable with the claims in this invention. The third topology is a phase shifted two transistors forward. The circuits claimed in this invention can provide soft commutation across the primary switching elements and secondary rectifier means, clamping the voltage across the rectifiers to the output voltage eliminating the need for snubbers circuits both in primary and the secondary section.
Owner:DELTA ENERGY SYST SWITZERLAND
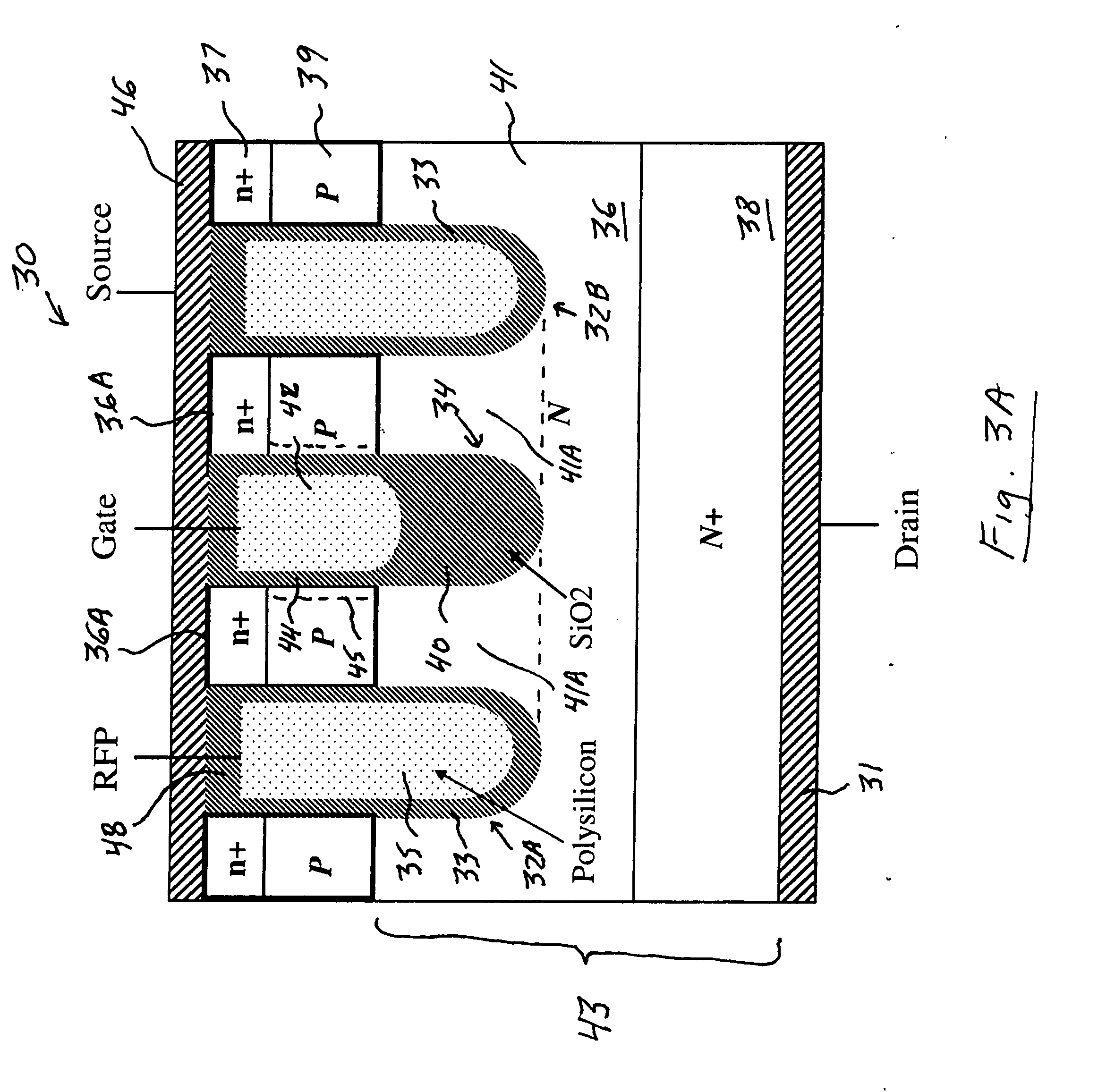
Power MOSFET with recessed field plate
ActiveUS7843004B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrench mosfetReverse recovery
A trench MOSFET contains a recessed field plate (RFP) trench adjacent the gate trench. The RFP trench contains an RFP electrode insulated from the die by a dielectric layer along the walls of the RFP trench. The gate trench has a thick bottom oxide layer, and the gate and RFP trenches are preferably formed in the same processing step and are of substantially the same depth. When the MOSFET operates in the third quadrant (with the source / body-to-drain junction forward-biased), the combined effect of the RFP and gate electrodes significantly reduces in the minority carrier diffusion current and reverse-recovery charge. The RFP electrode also functions as a recessed field plates to reduce the electric field in the channel regions when the MOSFET source / body to-drain junction reverse-biased.
Owner:MAXPOWER SEMICON INC
Method for controlling vertical type MOSFET in bridge circuit
ActiveUS20080265975A1Reduce diode power lossImprove featuresTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionMOSFETReverse recovery
A method for controlling a vertical type MOSFET in a bridge circuit is provided to reduce diode power loss and improve a reverse recovery characteristic. The method includes controlling a forward voltage of a built-in diode of the vertical type MOSFET to be a first forward voltage by setting a gate voltage of the vertical MOSFET to a first gate voltage, so that the vertical type MOSFET is switched into a first off mode; and controlling the forward voltage of the built-in diode of the vertical type MOSFET to be a second forward voltage by setting the gate voltage of the vertical MOSFET to a second gate voltage, so that the vertical type MOSFET is switched into a second off mode.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Interleaved soft switching bridge power converter
InactiveUS7423894B2Reduce switching lossesReduce recoveryConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionMotor driveReverse recovery
An interleaved soft switching bridge power converter comprises switching poles operated in an interleaved manner so as to substantially reduce turn-on switching losses and diode reverse-recovery losses in the switching pole elements. Switching poles are arranged into bridge circuits that are operated so as to provide a desired voltage, current and / or power waveform to a load. By reducing switching turn on and diode reverse recovery losses, soft switching power converters of the invention may operate efficiently at higher switching frequencies. Soft switching power converters of the invention are well suited to high power and high voltage applications such as plasma processing, active rectifiers, distributed generation, motor drive inverters and class D power amplifiers.
Owner:ADVANCED ENERGY IND INC
Method and apparatus for fault detection of series diodes in rectifiers
ActiveUS20110216449A1Minimize potentialEasy to detectDiode testingEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentReverse recoveryEngineering
A method and apparatus for fault detection of series diodes in rectifiers is disclosed, wherein the voltages across one or both of the individual diodes, and / or the voltage across the pair of diodes are measured to determine a ratio between two of those voltages. The ratio is then analyzed to determine if a fault (e.g., a short circuit or an open circuit) is present. In some embodiments, circuitry can be included to compensate for the normal variations in diode characteristics (e.g., reverse leakage current, reverse recovery charge) between the pair of series diodes to minimize the potential for erroneous fault detection.
Owner:ACCUMETRICS INC +1
Converter circuit and control method for same
InactiveCN1682445AConduction cancellationShort reverse recovery timeDc-dc conversionElectronic switchingReverse recoveryFlyback diode
In known converter circuits switching losses occur, which are caused by reverse-recovery currents of a freewheeling diode. To reduce said switching losses it is proposed by the invention to drive the switching elements such that, upon switching from the second to the first switching element, the timing is controlled in such a manner that the shoot through currents and the conduction of the freewheeling diode are kept at a low value or, better still, are precluded. As regards the control mechanism, it is proposed to turn on the first switching element later if shoot through currents occur, and to turn on the first switching element sooner if conduction of the freewheeling diode occurs. Here, a time of overlap may be provided during which both switching elements are simultaneously conducting. For the control mechanism, the voltage across a switching element can be used as a measured input value.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Zero-voltage-switching DC-DC converters with synchronous rectifiers
ActiveCN101047335AEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceDc dc converter
A DC-DC converter includes an inductor, a synchronous rectifier (SR) connected to the inductor, and an active switch connected to the inductor and the SR. An active resonant tank (ART) cell is connected to the SR or a transformer in parallel such that a resonant capacitor of the ART cell is charged through the active switch and discharged through the synchronous rectifier so that during a switch transition period energy is pumped out of the resonant capacitor by activating the ART cell to eliminate reverse recovery switching loss and achieve Zero Voltage Switching (ZVS).
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing thereof
InactiveUS6979874B2Reduce the amount requiredImprove pressure resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallic electrodeReverse recovery
A plurality of p anode regions are formed at one surface of an n− substrate. A trench is formed in each p anode region. An ohmic junction region is formed between an anode metallic electrode and the p anode region. The p anode region has a minimum impurity concentration at a portion near the ohmic junction region which enables ohmic contact. A cathode metallic electrode is formed at the other surface of the n− substrate with an n+ cathode region interposed. Accordingly, a semiconductor device which has an improved withstand voltage and in which the reverse recovery current is reduced can be obtained.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
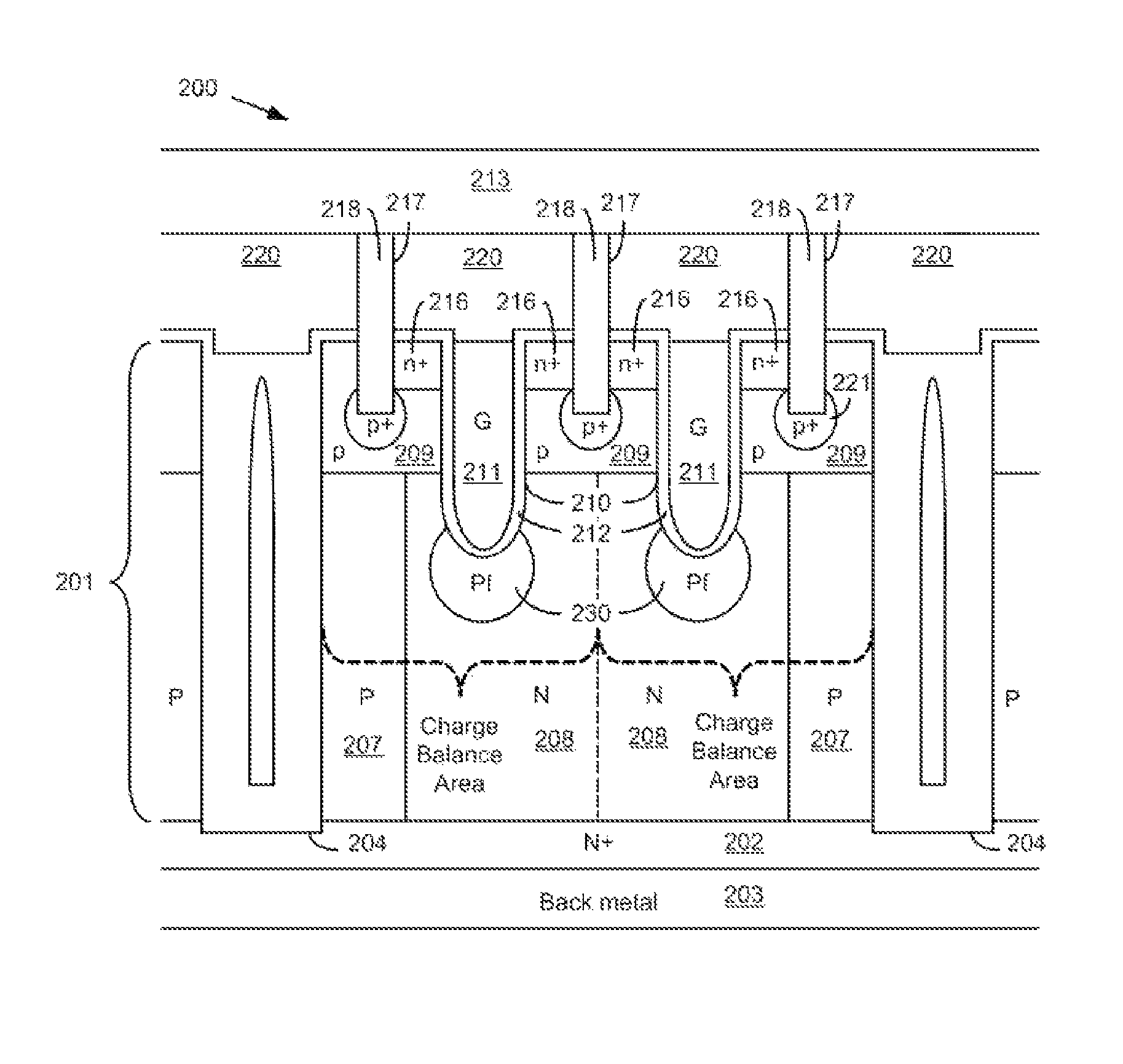
Super junction device
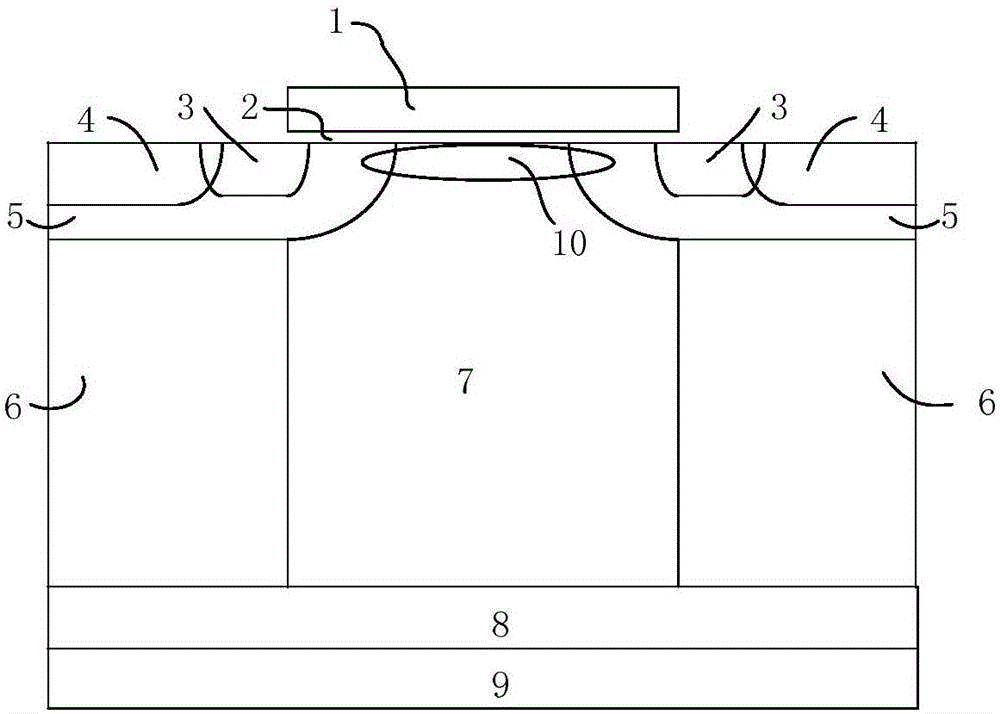
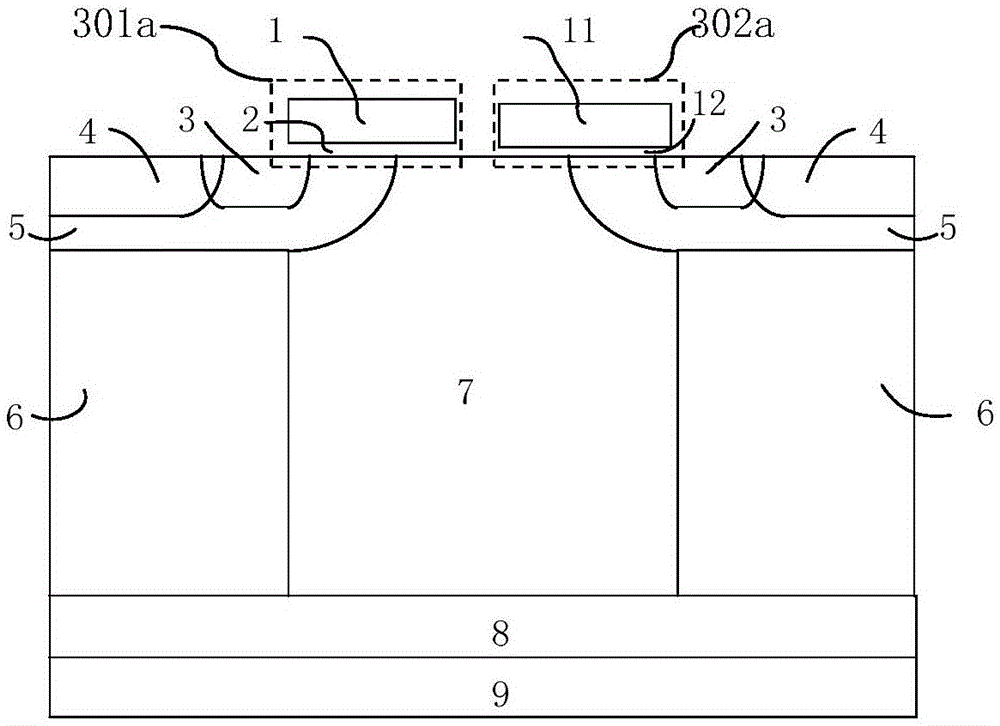
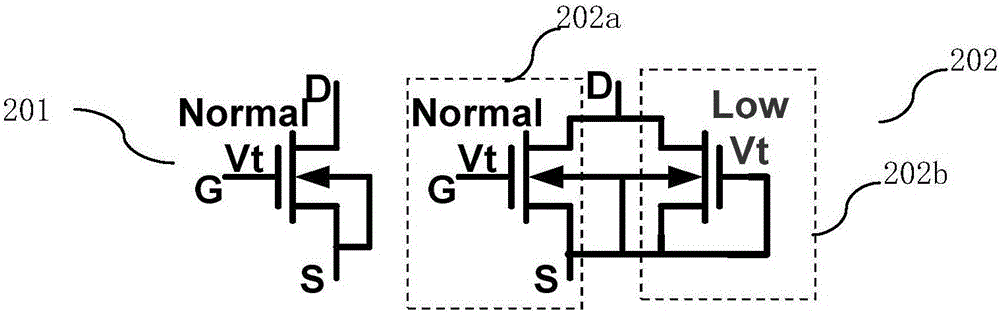
The invention discloses a super junction device, which comprises a gate structure I and a gate structure II which are separated from each other, wherein the gate structure I comprises a gate dielectric layer I and an electrode material I; the gate structure II comprises a gate dielectric layer II and an electrode material II; the electrode material I is connected to a gate; the electrode material II is connected to a source; threshold voltage I, of forming a channel I, of the gate structure I is greater than threshold voltage II, of forming a channel II, of the gate structure II; when the super junction device is positively conducted, the voltage applied to the gate is greater than the threshold voltage I, the channel I is conducted, the channel II is cut off and a parasitic body diode is cut off; when the super junction device is reversely conducted, the voltage applied to the gate is smaller than the threshold voltage I, the channel I is cut off, the parasitic body diode is positively conducted, the threshold voltage II is required to be smaller than a positive conduction voltage drop of the parasitic body diode and the channel II is conducted. The hole concentration of an N-type column surface region is reduced through conduction of the channel II, so that the maximum reverse recovery current of the super junction device is reduced.
Owner:上海鼎阳通半导体科技有限公司
Super Junction VDMOS device
InactiveCN101950759AGood reverse recovery characteristicsReduced process line width requirementsSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceReverse recovery
The invention discloses a Super Junction VDMOS device, which belongs to the technical field of semiconductor power devices. In the invention, a trench Schottky contact structure is introduced on the basis of the Super Junction VDMOS device with a flat Schottky contact structure. The trench Schottky contact structure is that: a polycrystalline gate electrode is divided into two sections above an N-type pillar area; meanwhile, the area, which is between the two sections of the polycrystalline gate electrode, of a metal source electrode is extended downward to the N-type pillar area and forms the trench Schottky contact structure on the surface contacted with the N-type pillar area. In addition, the two ends of the metal source electrode may have a trench ohmic contact structure. The Super Junction VDMOS device provided by the invention has an excellent reverse recovery property; with a requirement of the same reverse recovery property, the requirement on the wide of a process line in the preparation of the device is lowered, and the size of the element is smaller; and the trench ohmic contact structure can reduce the contact resistance of the device and improve the radiation performance of the device. The two trench structure can use the same mask plate, and thus, the manufacturing cost of the device does not increase obviously.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Power converters having capacitor resonant with transformer leakage inductance
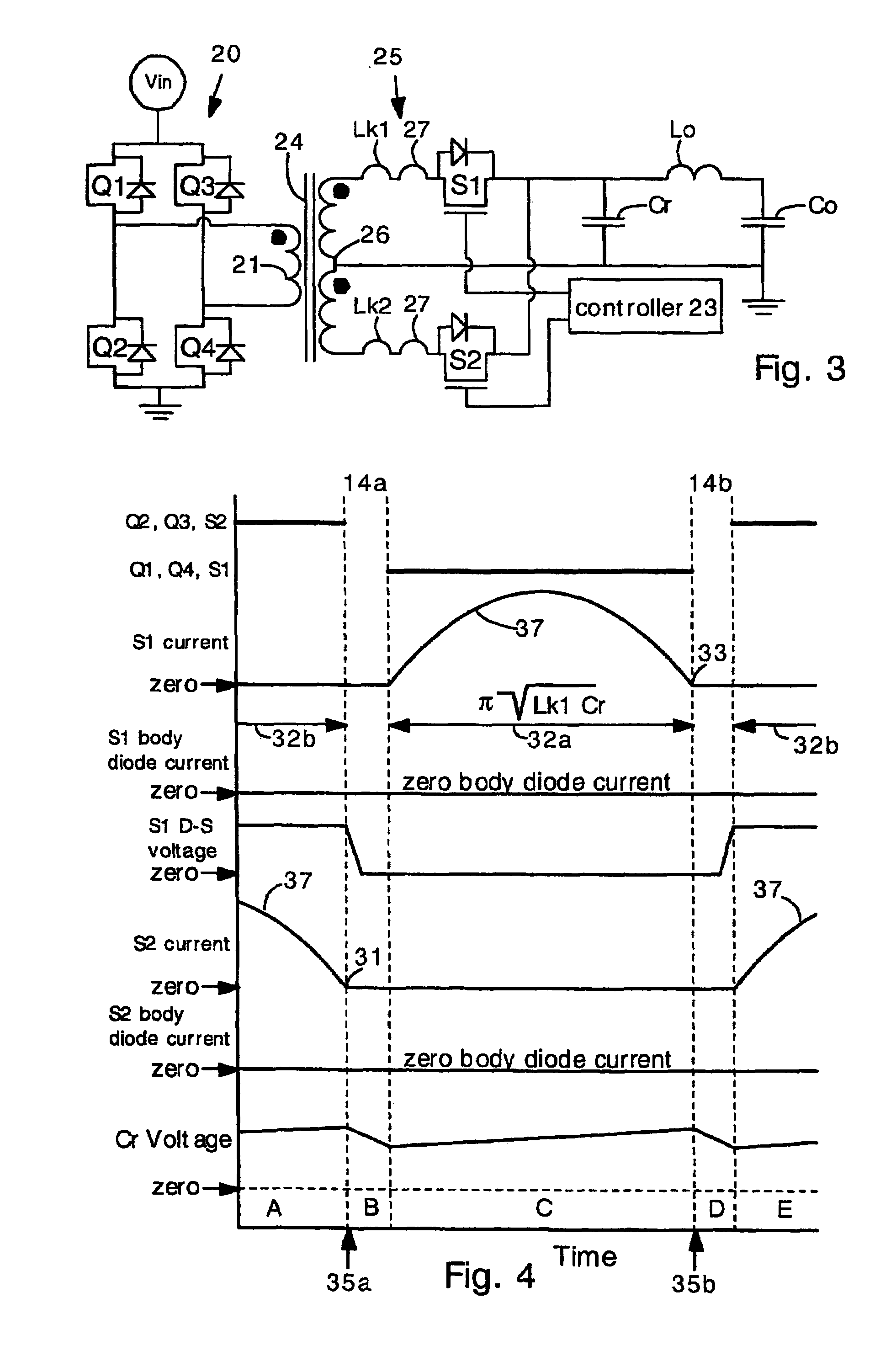
Power converters having reduced body diode conduction loss, reduced reverse recovery loss and lower switching noise, among other benefits, have a resonant capacitor Cr connected across an unfiltered output. The resonant capacitor Cr resonates with the leakage inductance Lk of the transformer. The resonant capacitor and leakage inductance are selected such that ½ a LC resonance period is equal to an ON time of each secondary switch S1 S2. The resonance provides zero current switching for secondary switches S1 S2, eliminates zero body diode conduction during dead times, and eliminates reverse recovery losses in the secondary switches. The present invention is applicable to many different circuit topologies such as full bridge, active clamp forward, push-pull forward, and center-tap secondary. The present converters provide high energy conversion efficiency and high frequency operation.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Active clamping forward-flyback converter
ActiveCN101692595AReduce voltage stressIncrease profitApparatus with intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceVoltage spike
The invention discloses an active clamping forward-flyback converter, which is provided with a primary side clamping resonant circuit comprising a series branch consisting of a clamping switching tube and a primary side clamping capacitor, wherein the series branch is connected with an original-level winding of the primary side of an isolation transformer in parallel or is connected in serial between a start end of the original-level winding of the primary side of the isolation transformer and a negative terminal of a direct current power supply; and a contravariant switching tube works in a ZVS state, and a secondary rectification circuit is one of a forward-flyback working rectification loop and a flyback working rectification loop. The active clamping forward-flyback converter can enter two different operation modes to achieve a large adjustment range of input and output voltages, reduce reverse steady-state voltages and reverse recovery resonance voltage spikes of a primary side switching tube and a secondary rectifier diode and the voltage stress and the switching loss of the primary side switching tube, and improve the efficiency. The active clamping forward-flyback converter is particularly suitable to be widely applied in the occasions with a very wide input voltage fluctuation range and a wide and high output voltage, in which semiconductors cannot withstand high voltages.
Owner:SANTAK ELECTRONICS SHENZHEN
Totem-pole bridgeless power factor correction circuit
InactiveCN102130580AWon't breakShort reverse recovery timeEfficient power electronics conversionEnergy industryPower flowBusbar
The invention discloses a totem-pole bridgeless power factor correction circuit which comprises a switching tube series branch and a rectifier diode series branch, and also comprises two series diodes and two parallel diodes, wherein the switching tube series branch is provided with a first switching tube and a second switching tube, the rectifier diode series branch is provided with a first rectifier diode and a second rectifier diode, the two series diodes are respectively serially connected between the first switching tube and a negative busbar and between the second switching tube and a positive busbar, the two parallel diodes are respectively connected in parallel between a common terminal of the first switching tube and the positive busbar and between the common terminal of the second switching tube and the negative busbar, wherein reverse recovery time of the parallel diodes corresponding to the first switching tube is less than that of the first switching tube, and reverse recovery time of the parallel diodes corresponding to the second switching tube is less than that of the second switching tube. Because reverse recovery characteristics of the parallel diodes are better, a reverse recovery current is smaller without damaging the totem-pole bridgeless power factor correction (PFC) circuit working in a CCM (Coincident-Current Memory) mode.
Owner:EMERSON NETWORK POWER ENERGY SYST NORTH AMERICA
Device and method of commutation control for an isolated boost converter
InactiveUS6937483B2Reduce wasteImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationVoltage spikeReverse recovery
A device and method of commutation control for an isolated boost converter provides a unique commutation logic to limit voltage spikes by utilizing switches on the secondary side to minimize a mismatch between current in the inductor and current in the leakage inductance of the transformer when commutation takes places. To minimize this mismatch, the current in the leakage inductance is preset at a certain level that approaches the current in the inductor prior to the commutation, thus significantly reducing the power rating for a clamp circuit and enabling use of a simple passive clamp circuit. In addition, through unique timing of the turn-on of the secondary switches, soft switching conditions are created that eliminate turn-on losses and the reverse recovery problems of free-wheeling diodes.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
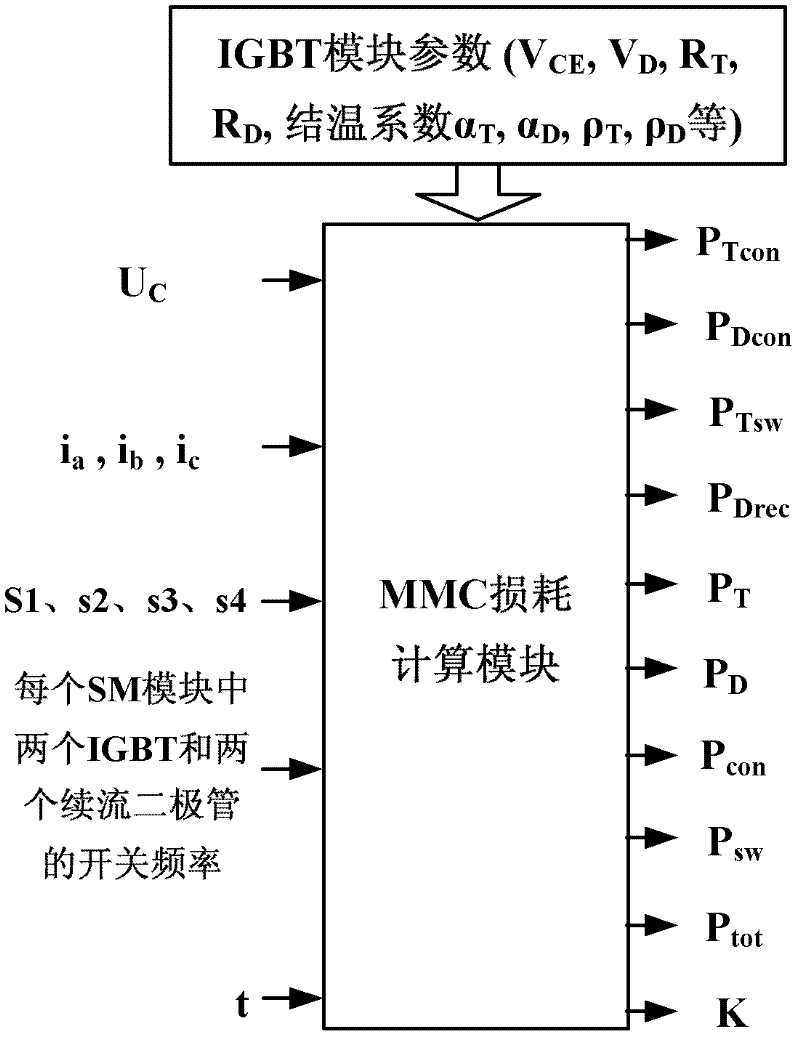
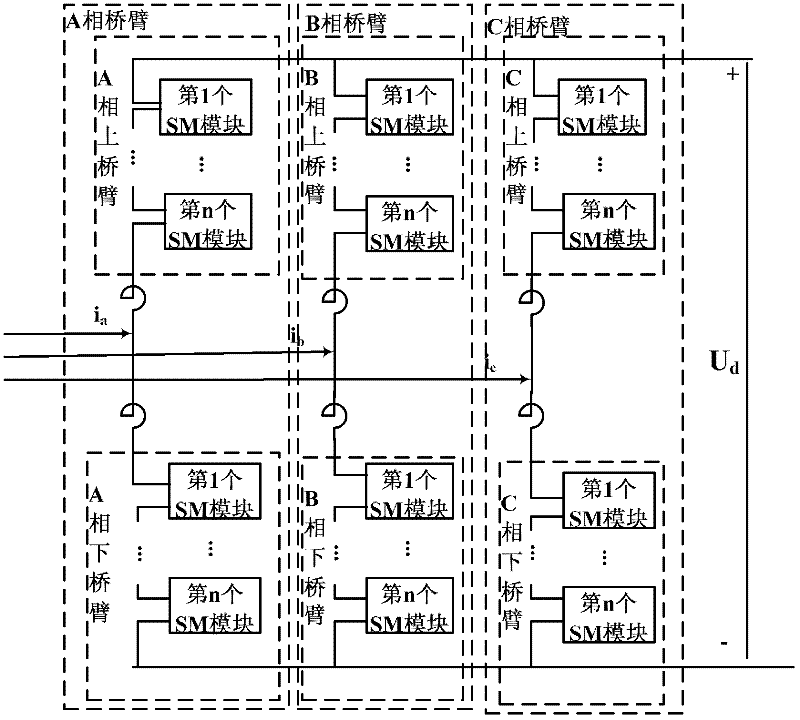
Online loss calculation method for modular multilevel converter
InactiveCN102570864ARealize online computingEasy to observeAc-dc conversion without reversalResource utilizationFlyback diode
The invention discloses an online loss calculation method for a modular multilevel converter (MMC), and belongs to the field of power transmission and distribution. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) calculating the conduction loss of two insulated gate bipolar transistors (LGBT) and two flywheel diodes in each sub-module (SM); 2) calculating the switching loss of the two IGBTs and the reverse recovery loss of the two flywheel diodes in each SM; and 3) calculating related loss by using a loss calculation module. The method has the advantages that: 1, the complexity of manual measurement and calculation is effectively avoided when the MMC has a great number of modules, workload is greatly reduced, and the method is fast and convenient; 2, the online calculation of the loss of the MMC is realized, and the method is wide in application range, and can be applied to the loss calculation of an MMC system in any operating state; and 3, modular packaging is facilitated, a floor area is saved, the utilization rate of resources is increased, and the output of a platform comprises various kinds of loss and loss ratios, so that the method is direct and clear, and staff can conveniently observe the running state of the system at any time.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Semiconductor device structures and related processes
ActiveCN102007584AIncrease the on-resistanceImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETDopant
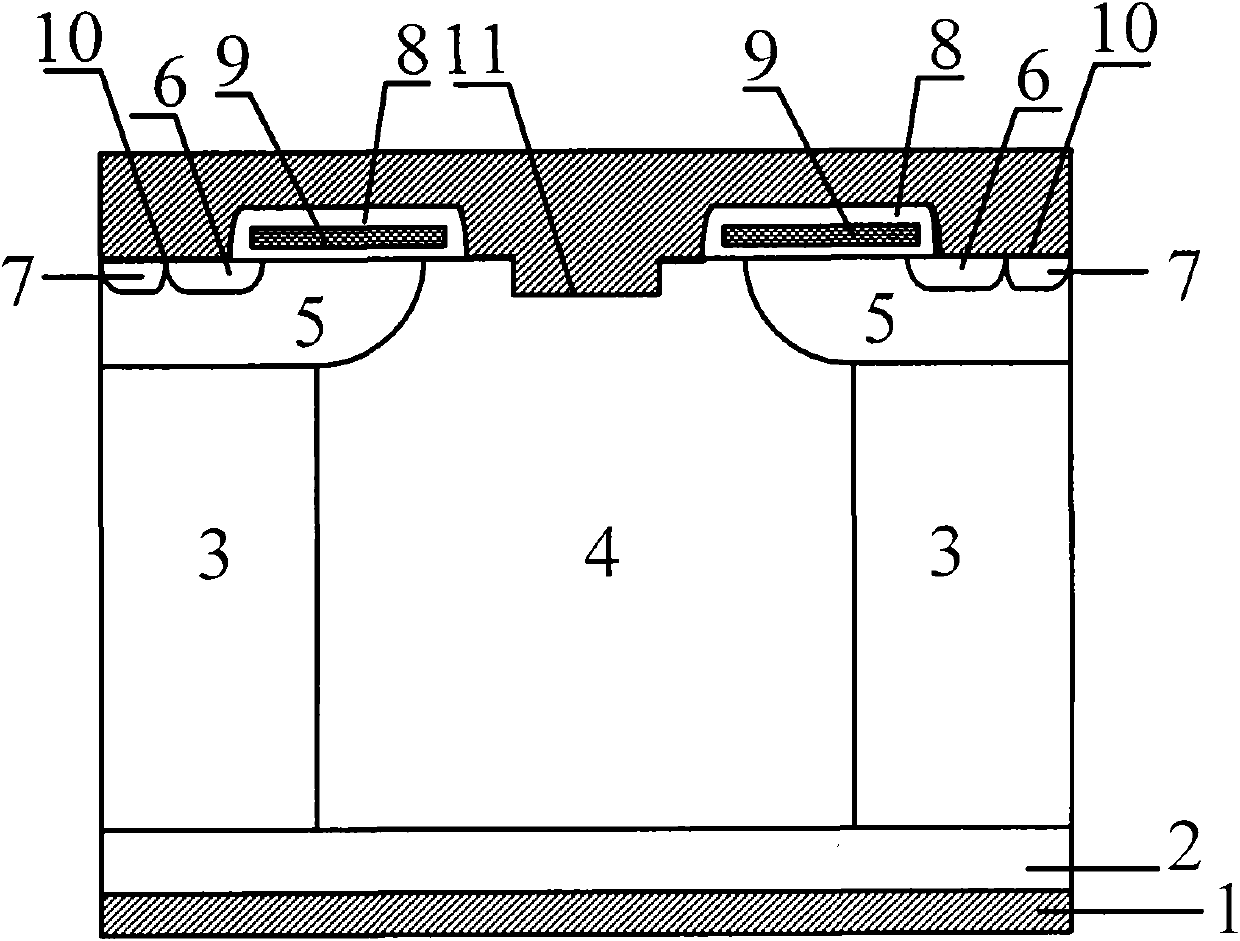
Improved highly reliable power RFP structures and fabrication and operation processes. The structure includes plurality of localized dopant concentrated zones beneath the trenches of RFPs, either floating or extending and merging with the body layer of the MOSFET or connecting with the source layer through a region of vertical doped region. This local dopant zone decreases the minority carrier injection efficiency of the body diode of the device and alters the electric field distribution during the body diode reverse recovery.
Owner:MAXPOWER SEMICON INC
Semiconductor device
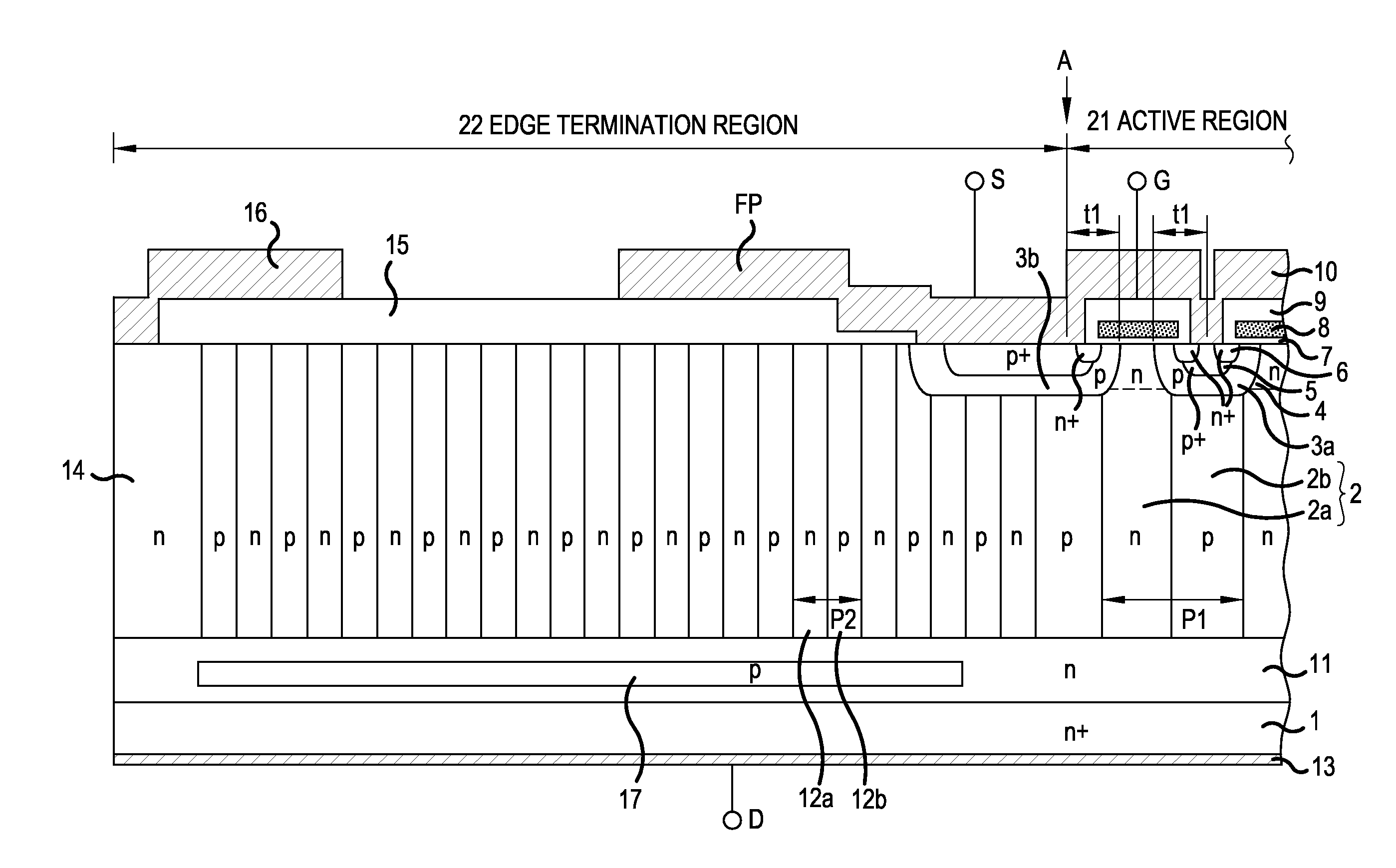
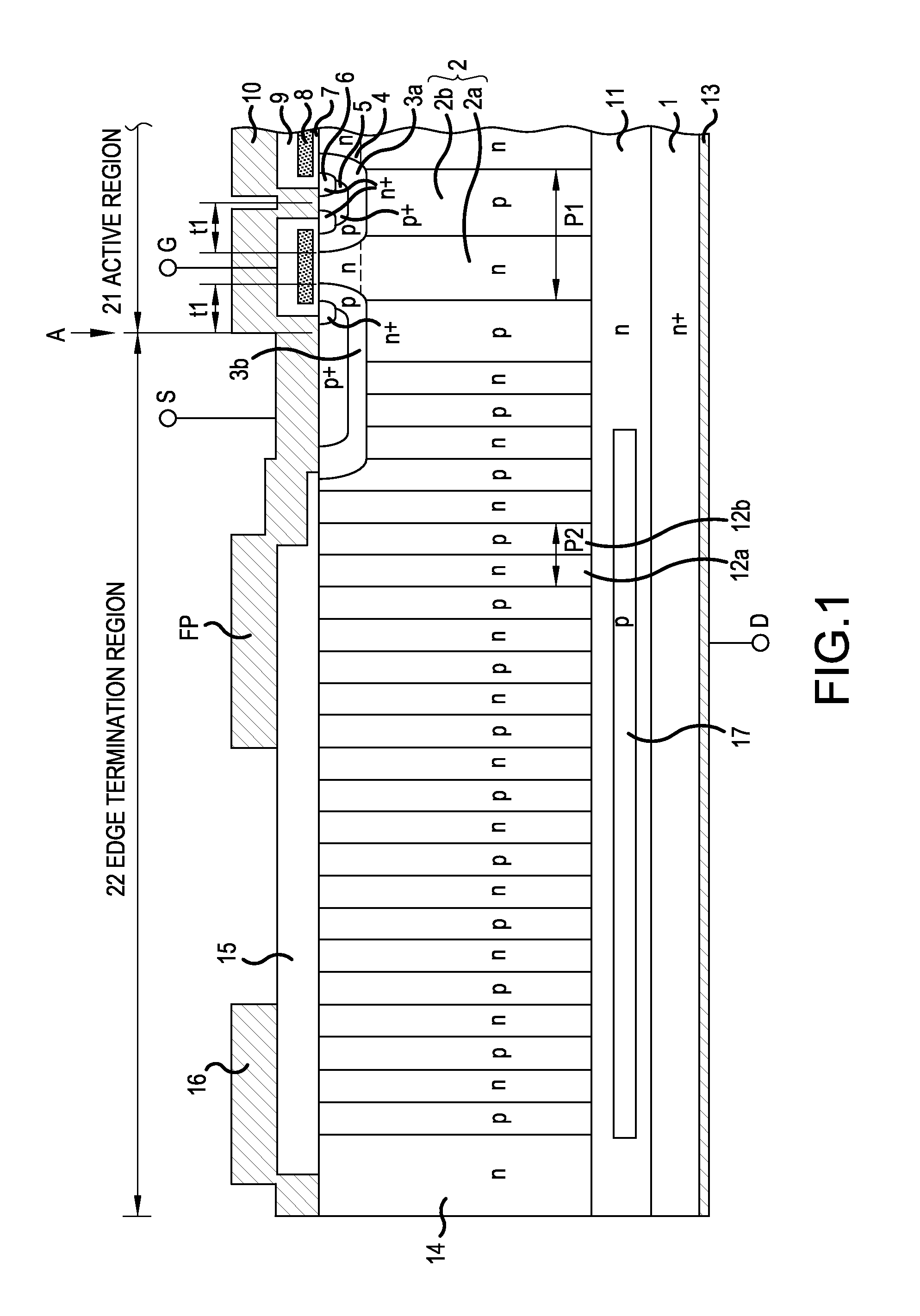
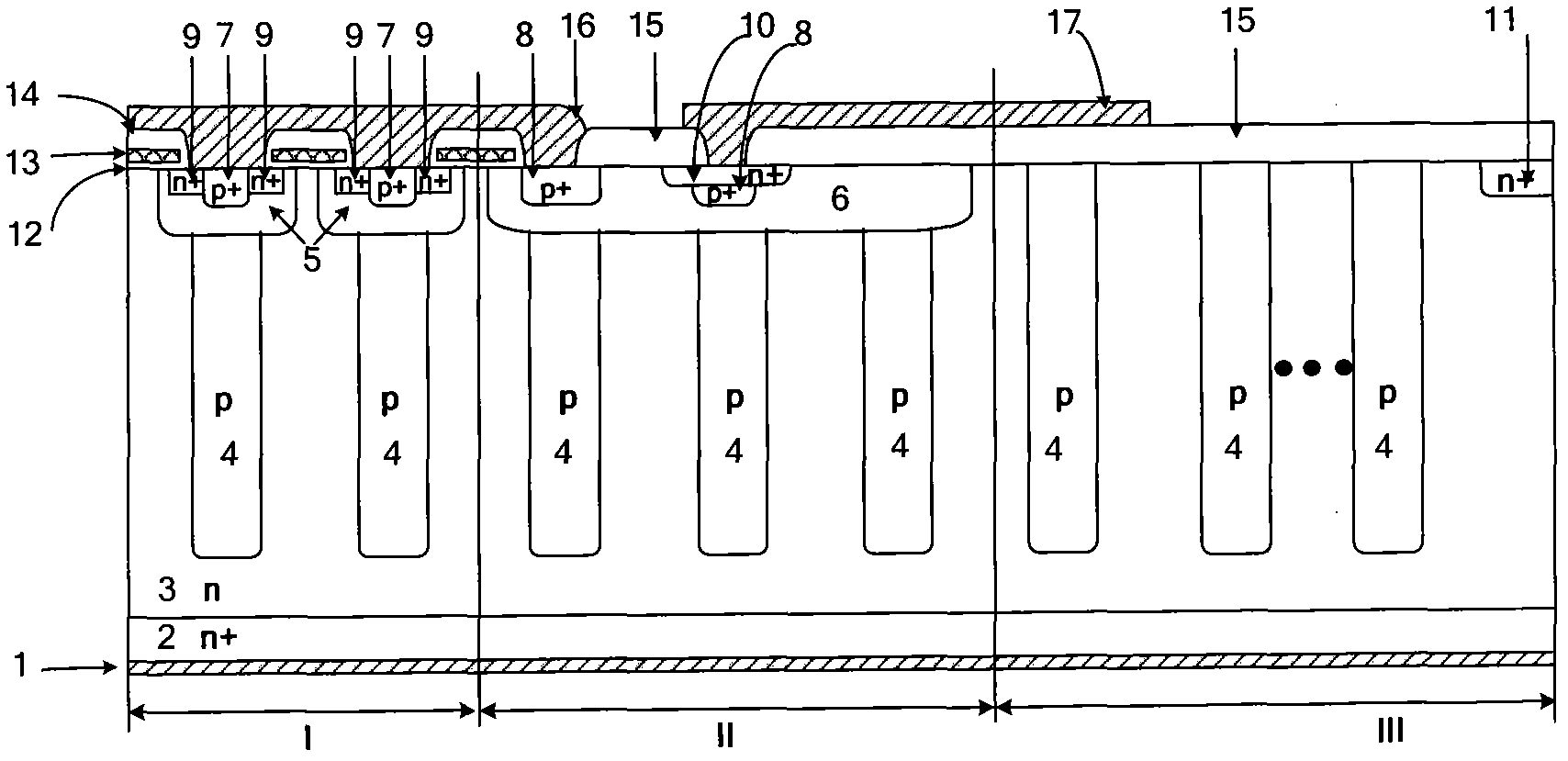
ActiveUS20140197477A1Reduce in quantityImproved reverse recovery capabilitySemiconductor devicesReverse recoverySemiconductor
A superjunction semiconductor device is disclosed in which the tradeoff relationship between on-resistance and breakdown voltage is improved greatly so that reverse recovery capability is improved. A drain drift portion substantially corresponds to a portion just under p-base regions serving as an active region and forms a first parallel pn structure in which a first n-type region and a first p-type region are joined to each other alternately and repeatedly. A drain drift portion is surrounded by edge termination region including a second parallel pn structure. Edge termination region is formed such that second n-type and p-type regions oriented consecutively to the first parallel pn structure of the drain drift portion are joined to each other alternately and repeatedly. N-buffer layer is provided between first and second parallel pn structures and n+ drain layer. P-buffer layer is provided selectively inside n-buffer layer in edge termination region.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Rapid superjunction longitudinal double-diffusion metal oxide semiconductor transistor
InactiveCN101969073AExpand quicklyImprove pressure resistanceSemiconductor devicesDouble diffusionEngineering
The invention relates to a rapid superjunction longitudinal double-diffusion metal oxide semiconductor transistor which comprises a cell area, a terminal area and a transition area, wherein the terminal area is arranged at the outermost periphery of a chip; the transition area is positioned between the cell area and the terminal area; the bottoms of the cell area, the transition area and the terminal area (III) are provided with drain electrode metal; a heavy doping n-type silicon substrate is arranged on the drain electrode metal and used as a drain area of the chip; an n-type doping epitaxial layer is arranged on the heavy doping n-type silicon substrate; and a discontinuous p-type doping columnar semiconductor area is arranged in the n-type doping epitaxial layer. The rapid superjunction longitudinal double-diffusion metal oxide semiconductor transistor is characterized in that an n-type heavy doping semiconductor area is arranged in a second p-type doping semiconductor area in the transition area, and the surface of the n-type heavy doping semiconductor area is provided with a contact hole which is connected with a metal layer to form a ground contact electrode of the chip. The invention can effectively reduce the reverse recovery charge of a device and improve the reverse recovery characteristics under the conditions of not increasing the process cost or changing the main parameter of the device.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method of cross-point memory programming and related devices
A reverse recovery current of a diode is used for programming a cross-point memory. Programming of a crossbar memory device, comprising a diode with preferably short charge carriers lifetime and a storage element by keeping the device at one polarity for a period of time and then switching it from first polarity to second polarity (e.g., forward to reverse polarity of the diode). Programming occurs due to diode's reverse recovery current. The value and duration of the recovery current pulse are selected to program the storage element into one of plurality of electrically distinguish states by variation of the level of current flowing through the device in the first polarity of applied bias voltage, by variation of the speed for changing the bias voltage from first polarity to second polarity, and by steady state value of the second polarity voltage applied to the device in one or more embodiments.
Owner:SAVRANSKY SEMYON D
Fast switching super-junction trench MOSFETs
ActiveUS8829607B1Increase concentrationPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesTrench mosfetReverse recovery
A fast switching super-junction trench MOSFET is disclosed having a floating region formed underneath each gate trench and surrounding at least bottom of each the gate trench, which has a parasitic body diode with superior reverse recovery characteristics.
Owner:HSIEH FU YUAN +1
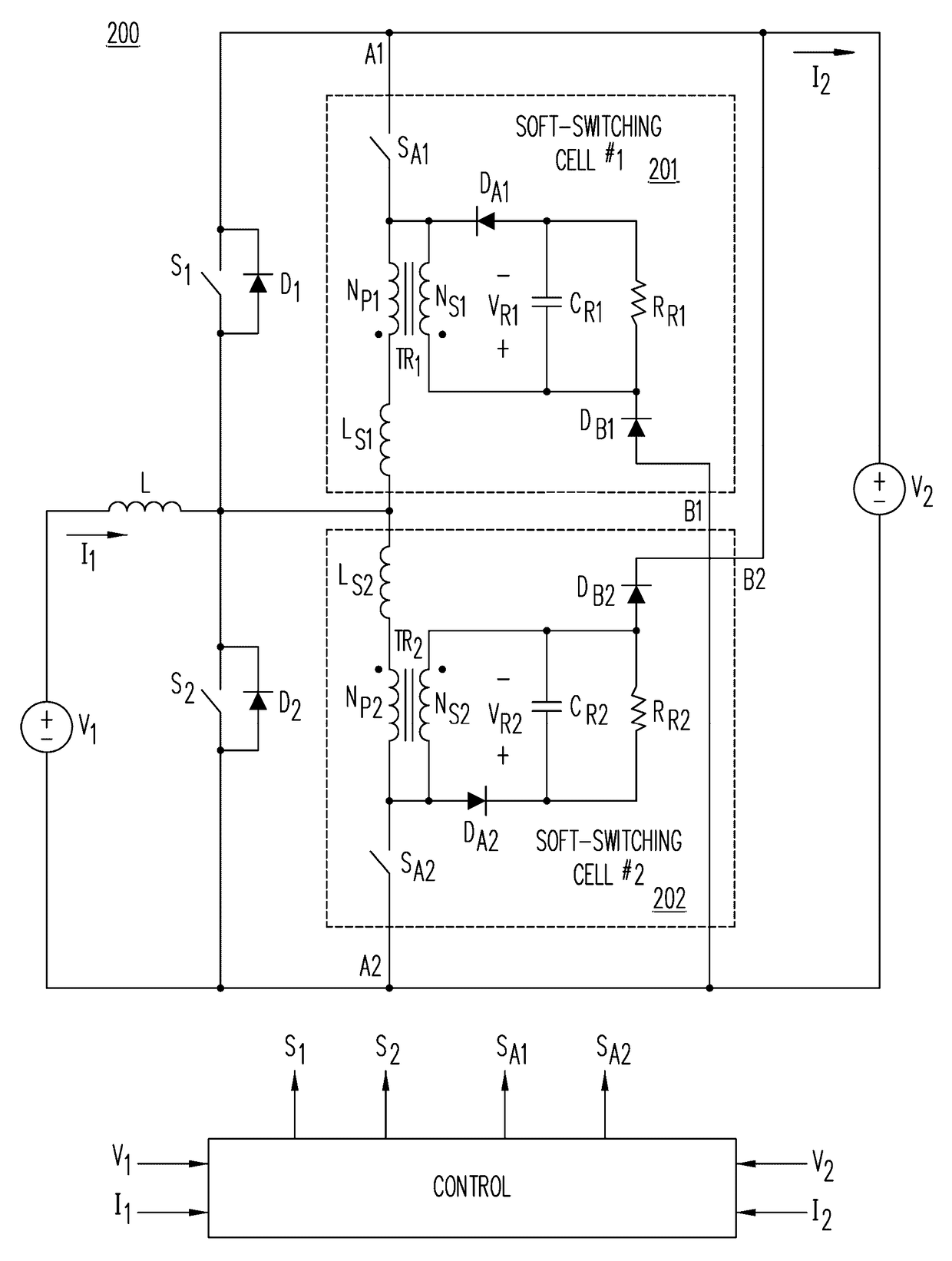
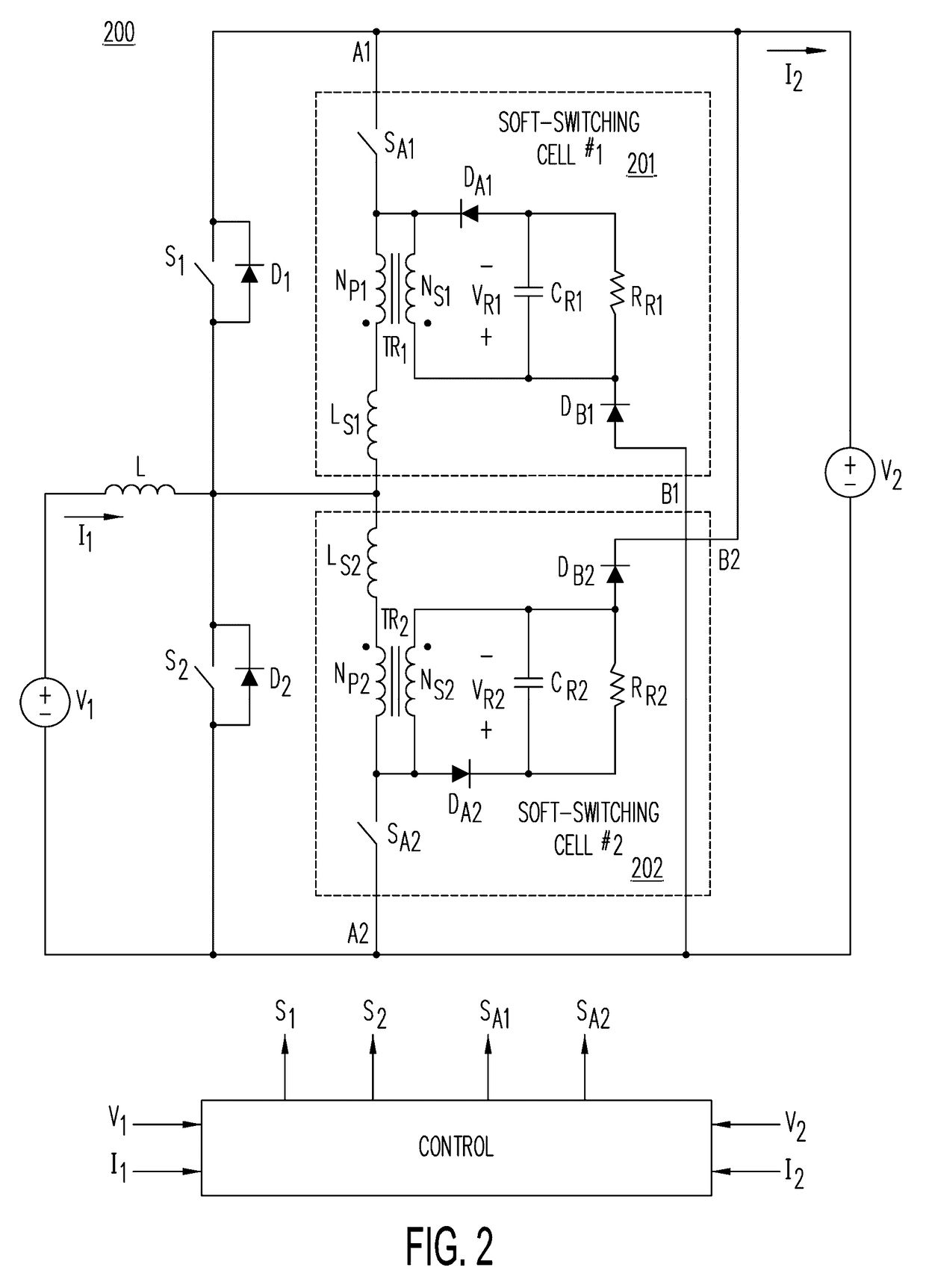
Soft-switched bidirectional buck-boost converters
ActiveUS20170163163A1Reduce switching lossesMinimize reverse-recovery lossEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTransformerActive switch
A bidirectional buck-boost converter includes at least one soft-switching cell to reduce switching losses by providing soft-switching of all semiconductor devices. A soft-switching cell comprises an active switch coupled in series with an inductor, a two-winding transformer, and a reset-voltage circuit. The soft-switching cells enable the buck and boost rectifiers to turn off with a controlled turn-off rate of their current to minimize their reverse-recovery losses, the power-controlling buck and boost switch to turn on with zero-voltage switching (ZVS), and the switch of the soft-switching cell to turn off with zero-current switching (ZCS).
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
On-line detection system and method for work junction temperature of power diode module
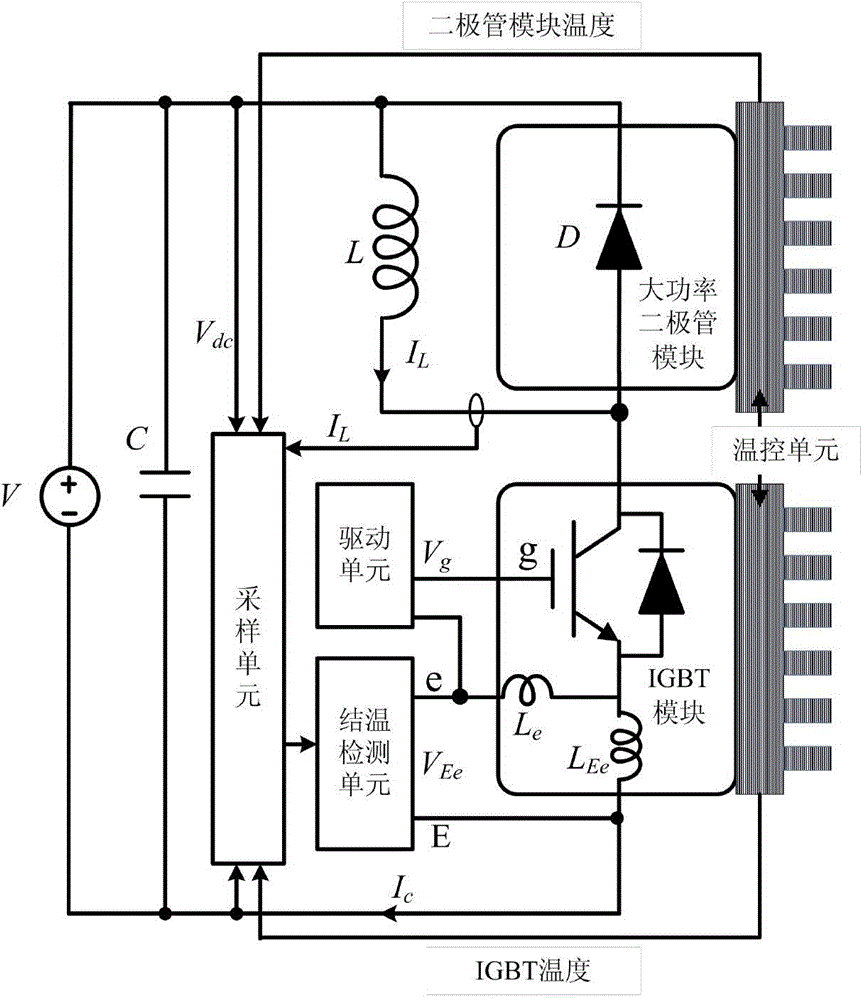
ActiveCN104090224AHigh precisionImprove real-time performanceElectrical testingSpecial data processing applicationsControl signalLow voltage
The invention discloses an on-line detection system and method for the work junction temperature of a power diode module. According to the on-line detection system and method, on-off of an active switch device is controlled to enable the power diode module to be switched in the turn-on state and the turn-off state. When the power diode module is switched to be turned off from being turned on, currents flowing through the power diode module are converted to a complementary switch tube, the reverse recovery currents of the power diode module can generate corresponding induced voltages on a stray inductor of a conversion circuit, and the induced voltages are related to the reverse recovery currents of the power diode module and also comprise the temperature information of the power diode module. According to the on-line detection system and method for the work junction temperature of the power diode module, the variation condition of the reverse recovery currents comprising the temperature information can be measured on the complementary switch tube only by one low-voltage amplitude detection circuit, and additional high-voltage passive auxiliary elements are of no need. While a driving circuit sends control signals, variation voltages caused by the reverse recovery currents are captured, and high precision and real-time performance are achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com