Patents
Literature
816 results about "Shunt capacitance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The shunt capacitance is the total capacitance of the device itself. across it's terminals. The load capacitance is **normally** the loading capacitance required. to operate the device nominally.
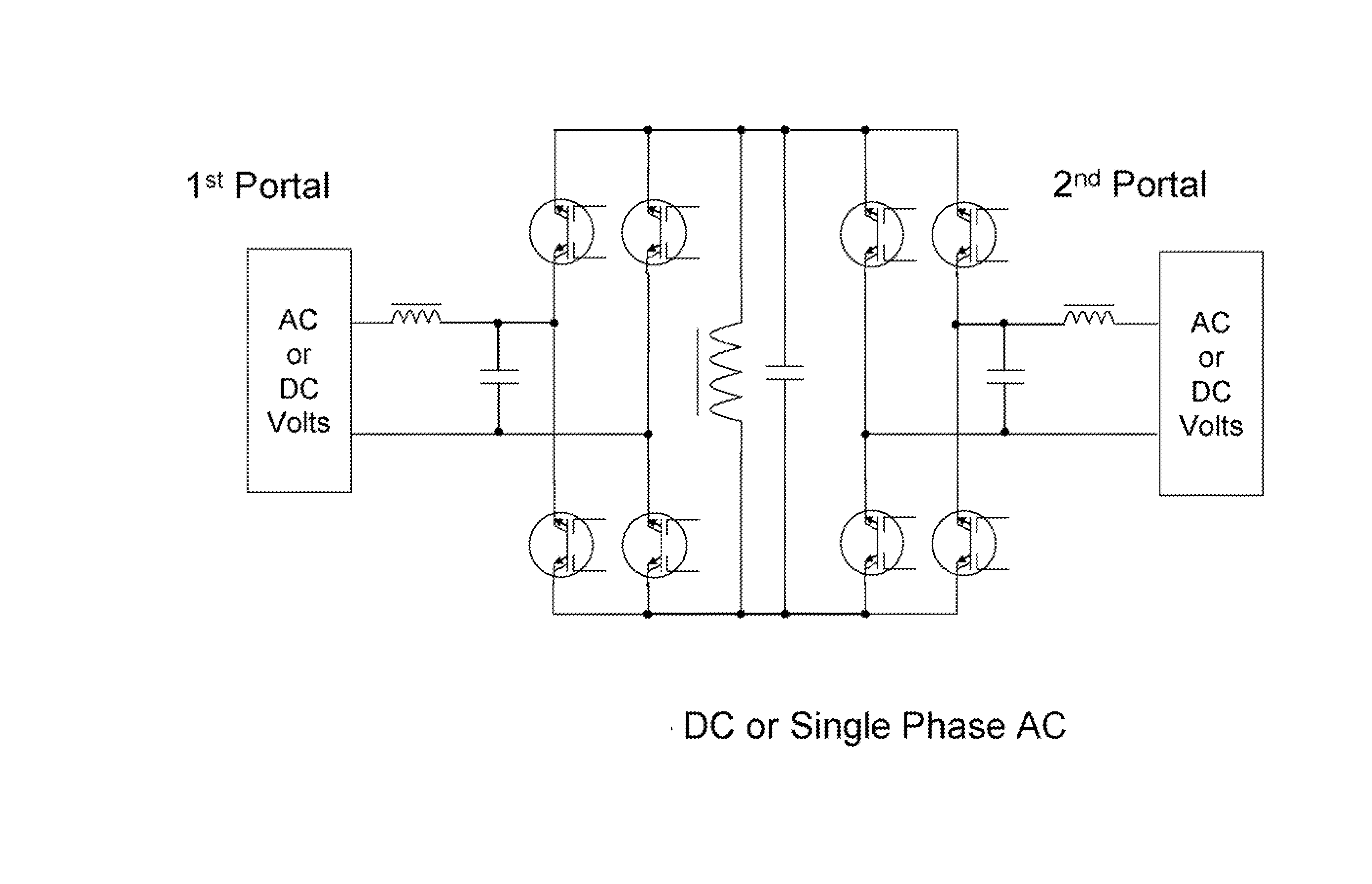
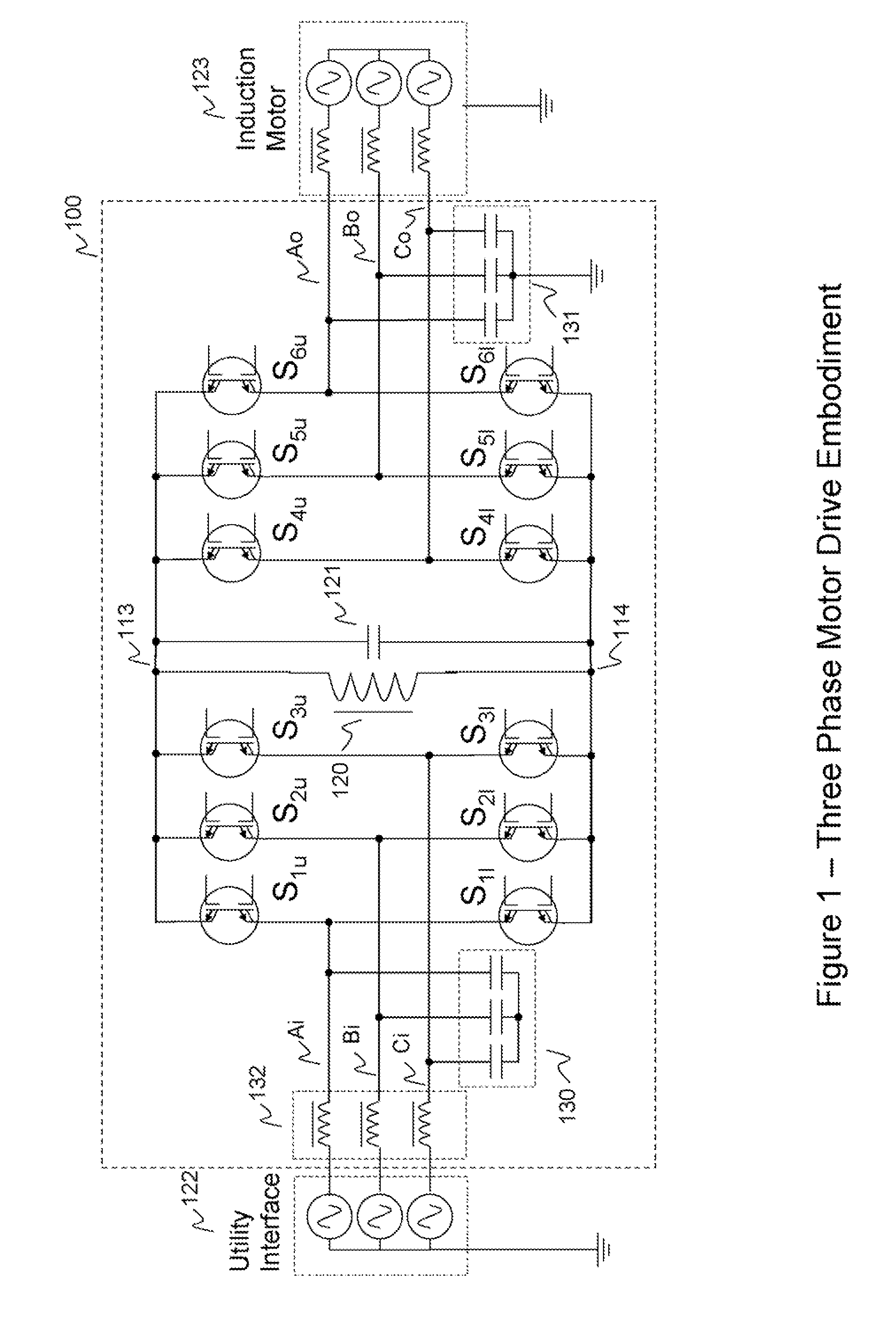
Universal Power Converter
ActiveUS20080013351A1Increased electric lossIncrease lossEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionReverse recoveryInductor
Methods and systems for transforming electric power between two or more portals. Any or all portals can be DC, single phase AC, or multi-phase AC. Conversion is accomplished by a plurality of bi-directional conducting and blocking semiconductor switches which alternately connect an inductor and parallel capacitor between said portals, such that energy is transferred into the inductor from one or more input portals and / or phases, then the energy is transferred out of the inductor to one or more output portals and / or phases, with said parallel capacitor facilitating “soft” turn-off, and with any excess inductor energy being returned back to the input. Soft turn-on and reverse recovery is also facilitated. Said bi-directional switches allow for two power transfers per inductor / capacitor cycle, thereby maximizing inductor / capacitor utilization as well as providing for optimum converter operation with high input / output voltage ratios. Control means coordinate the switches to accomplish the desired power transfers.
Owner:CET GRP SA +1
Tank filters adaptable for placement with a guide wire, in series with the lead wires or circuits of active medical devices to enhance MRI compatibility
InactiveUS20080161886A1Reduce sensitivityReduce heatMultiple-port networksAnti-noise capacitorsEngineeringInductor
A tank filter is provided for a lead wire of an active medical device (AMD). The tank filter includes a capacitor in parallel with an inductor. The parallel capacitor and inductor are placed in series with the lead wire of the AMD, wherein values of capacitance and inductance are selected such that the tank filter is resonant at a selected frequency. A passageway through the tank filter permits selective slidable passage of a guide wire therethrough for locating the lead wire in an implantable position. The Q of the inductor may be relatively maximized and the Q of the capacitor may be relatively minimized to reduce the overall Q of the tank filter to attenuate current flow through the lead wire along a range of selected frequencies. In a preferred form, the tank filter is integrated into a TIP and / or RING electrode for an active implantable medical device.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
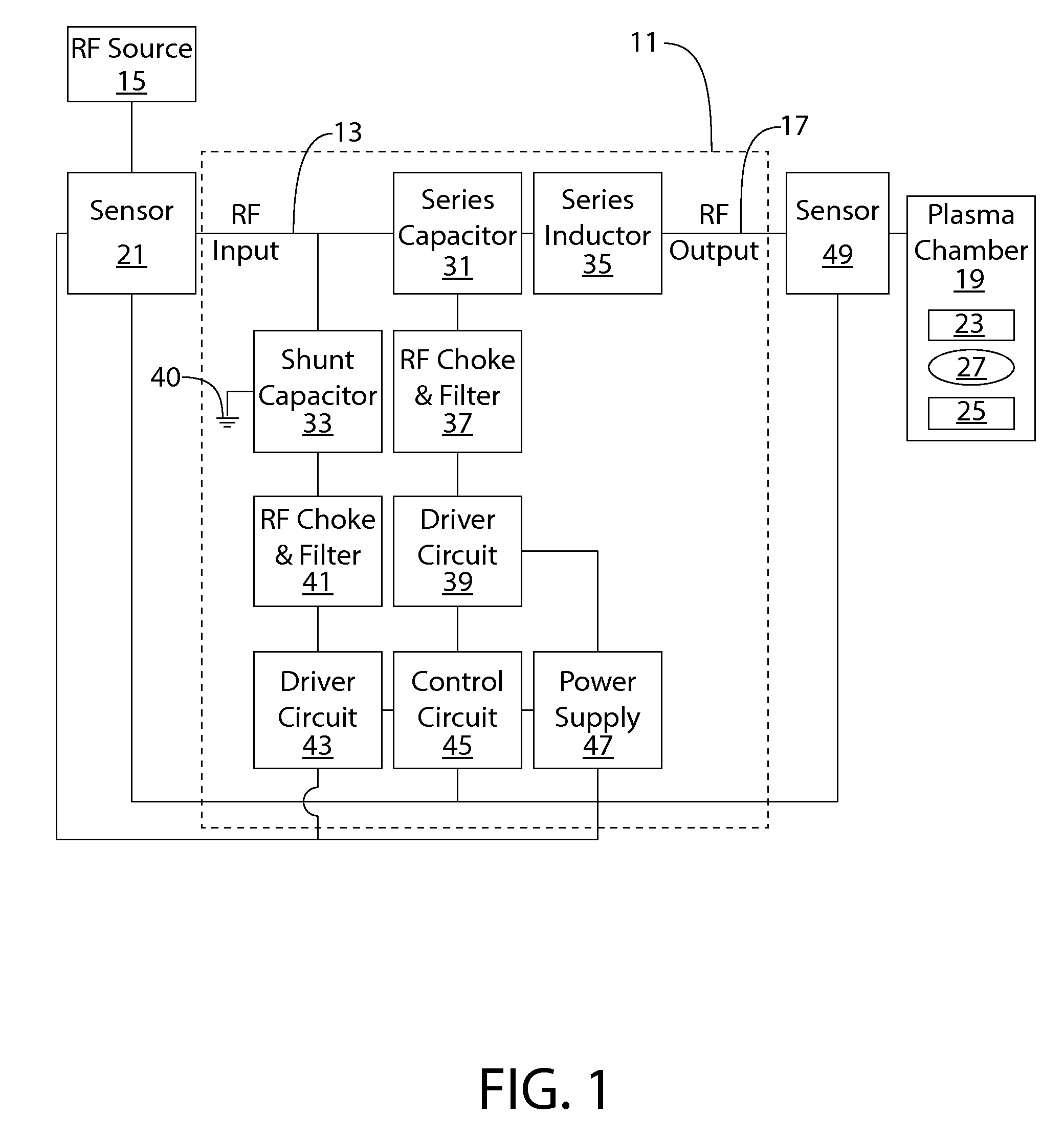
RF impedance matching network
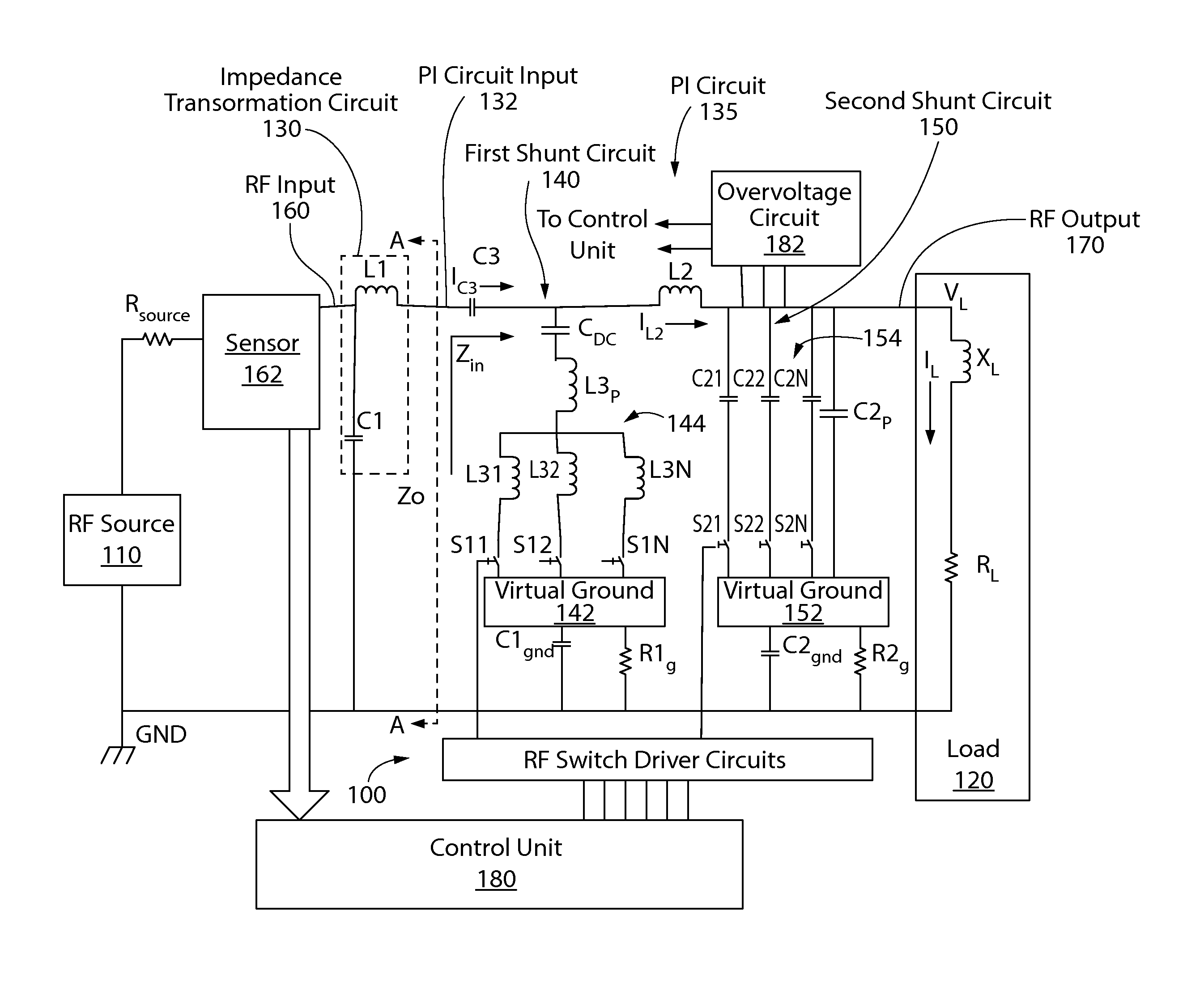
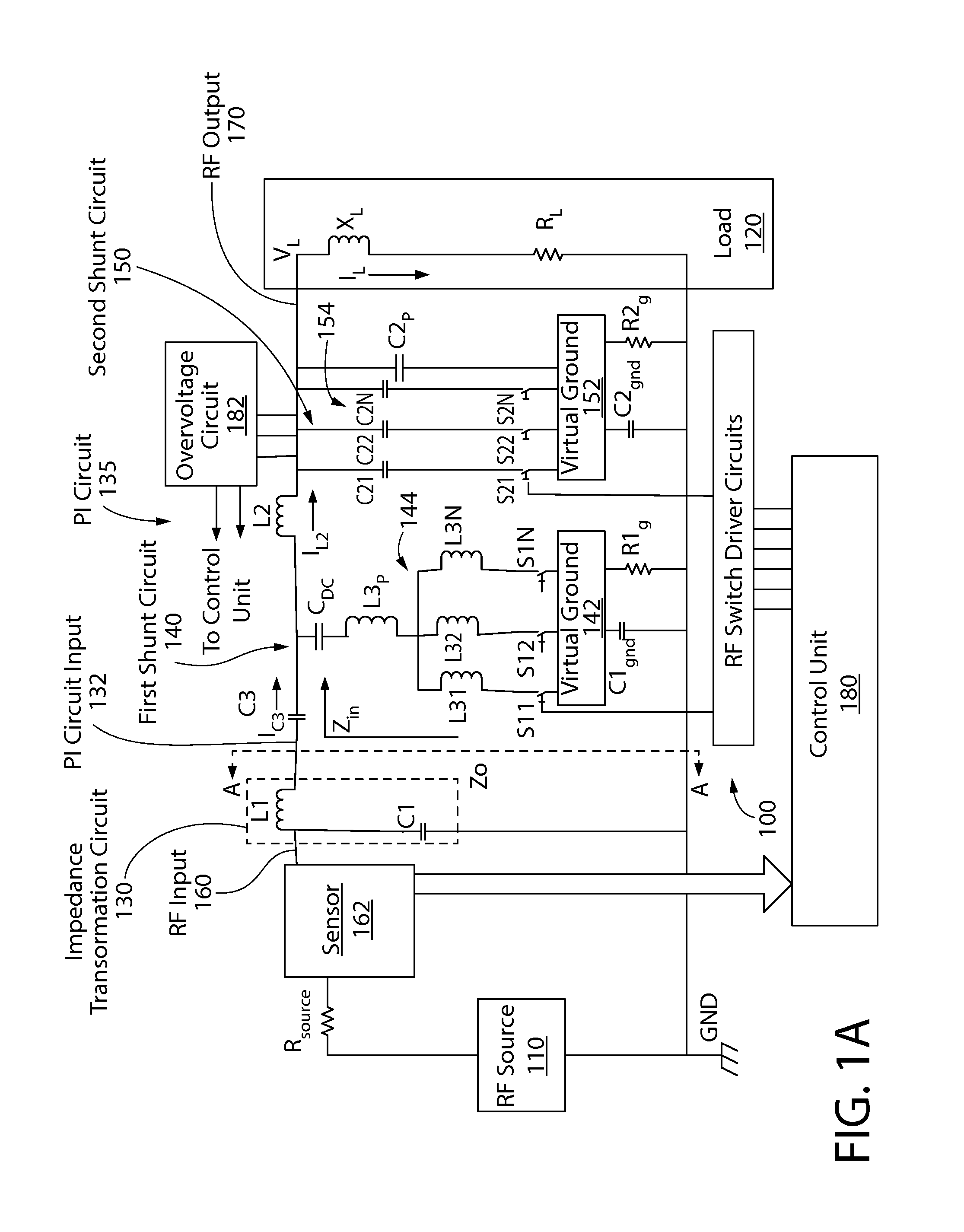
An RF impedance matching network includes a transformation circuit configured to provide a transformed impedance; a first shunt circuit in parallel to the RF input, the first shunt circuit including a first shunt variable capacitance component comprising (a) a plurality of first shunt capacitors coupled in parallel, and (b) a plurality of first shunt switches coupled to the plurality of first shunt capacitors and configured to connect and disconnect each of the plurality of first shunt capacitors to a first virtual ground; and a second shunt variable capacitance component including (a) a plurality of second shunt capacitors coupled in parallel, and (b) a plurality of second shunt switches coupled to the plurality of second shunt capacitors and configured to connect and disconnect each of the plurality of second shunt capacitors to a second virtual ground.
Owner:ASM AMERICA INC
High frequency printed circuit board via
A printed circuit board (PCB) via, providing a conductor extending vertically between microstrip or stripline conductors formed on separate layers of a PCB, includes a conductive pad surrounding the conductor and embedded within the PCB between those PCB layers. The pad's shunt capacitance and the magnitudes of capacitances of other portions of the via are sized relative to the conductor's inherent inductance to optimize frequency response characteristics of the via.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
High frequency MOSFET switch
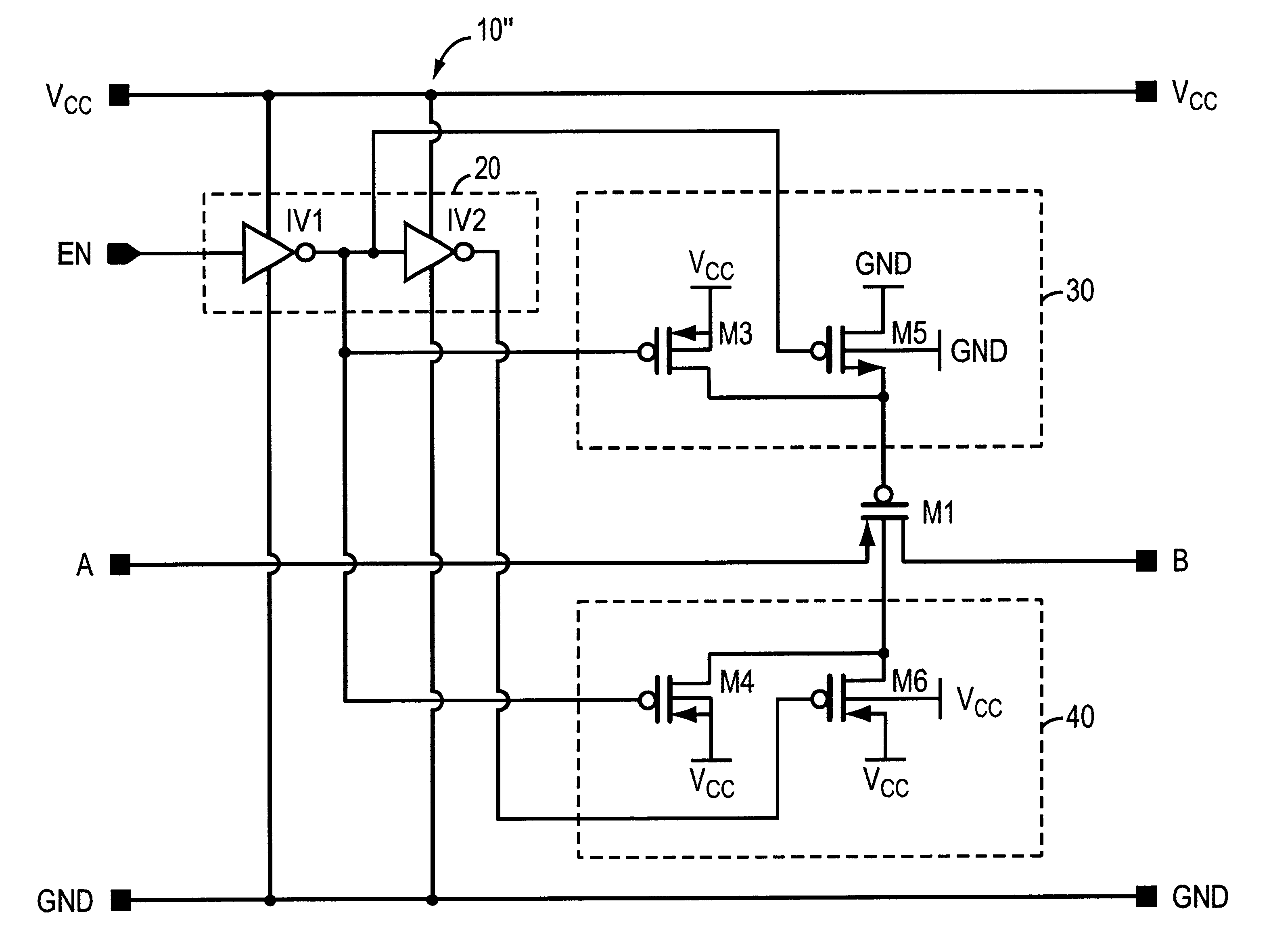
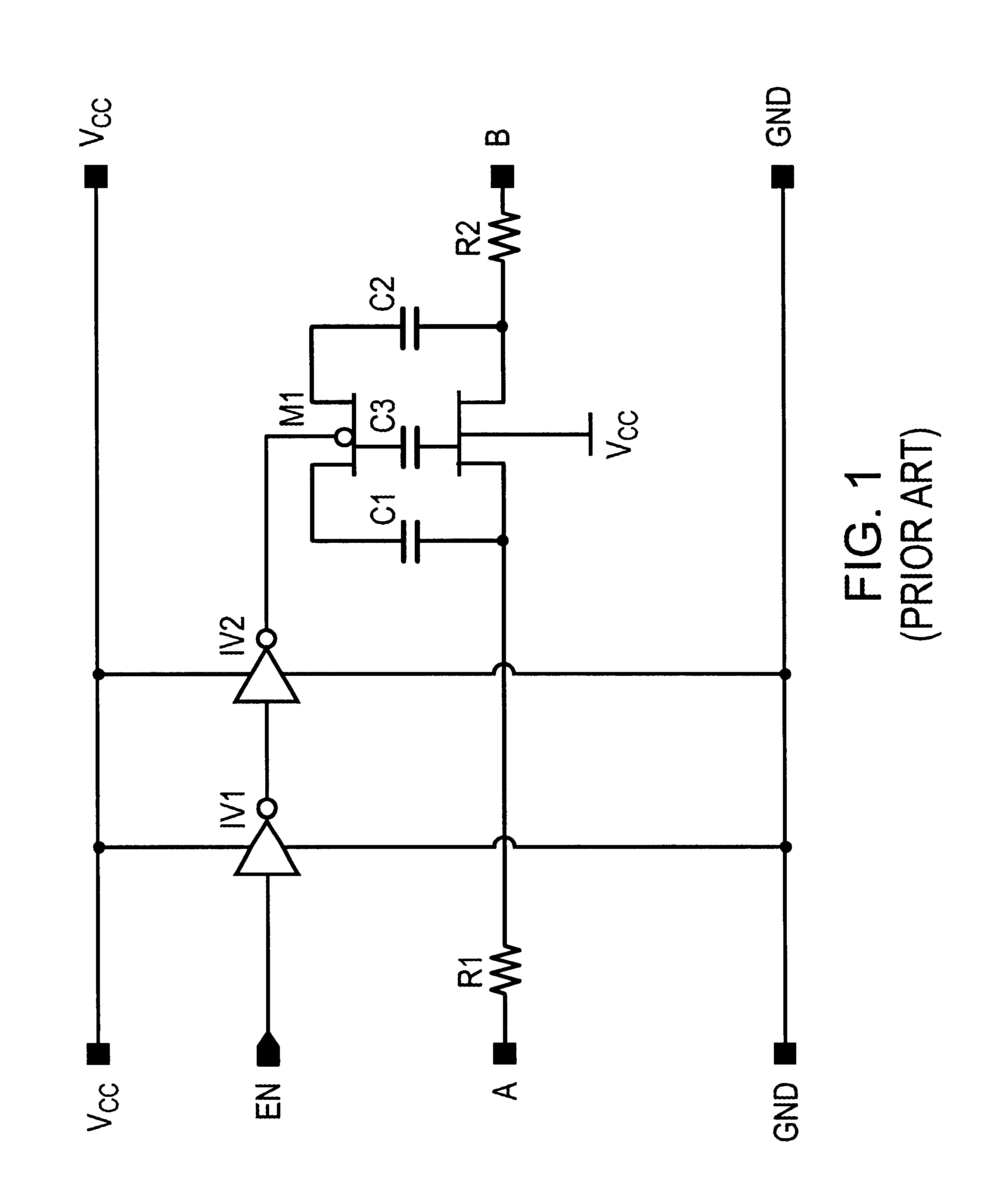
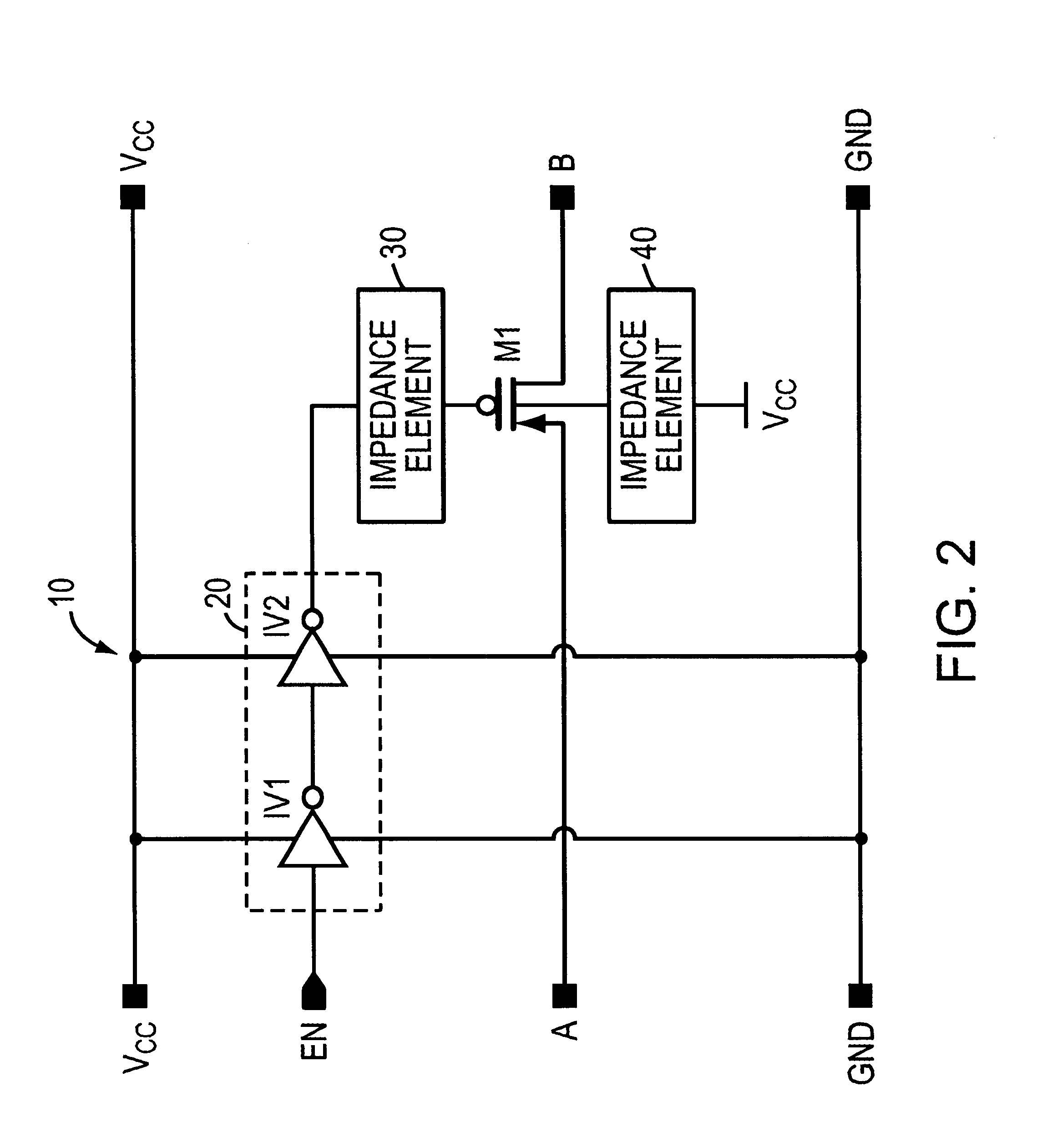
A high-frequency switch circuit having an MOS pass gate or transfer transistor. The switch circuit of the invention includes a first impedance element coupled to the gate of the transfer transistor and, preferably, an alternative second impedance element coupled to the bulk of the transfer transistor. One or both of the impedance elements substantially negates the low-parasitic shunt capacitance associated with the transfer transistor that controls signal attenuation under high frequency operation. The impedance element is coupled in series with that parasitic capacitance to increase substantially the impedance of that pathway, thereby increasing substantially the passable bandwidth. The impedance element may simply be a resistor. The switch circuit is suitable for use in an array of applications, including signal propagation in computing systems, routers, and flat panel screen displays.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Universal Power Conversion Methods
InactiveUS20080031019A1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionEngineeringElectric power
Methods and systems for transforming electric power between two or more portals. Any or all portals can be DC, single phase AC, or multi-phase AC. Conversion is accomplished by a plurality of bi-directional conducting and blocking semiconductor switches which alternately connect an inductor and parallel capacitor between said portals, such that energy is transferred into the inductor from one or more input portals and / or phases, then the energy is transferred out of the inductor to one or more output portals and / or phases, with said parallel capacitor facilitating “soft” turn-off, and with any excess inductor energy being returned back to the input. Soft turn-on and reverse recovery is also facilitated. Said bi-directional switches allow for two power transfers per inductor / capacitor cycle, thereby maximizing inductor / capacitor utilization as well as providing for optimum converter operation with high input / output voltage ratios. Control means coordinate the switches to accomplish the desired power transfers.
Owner:CET GRP SA +1
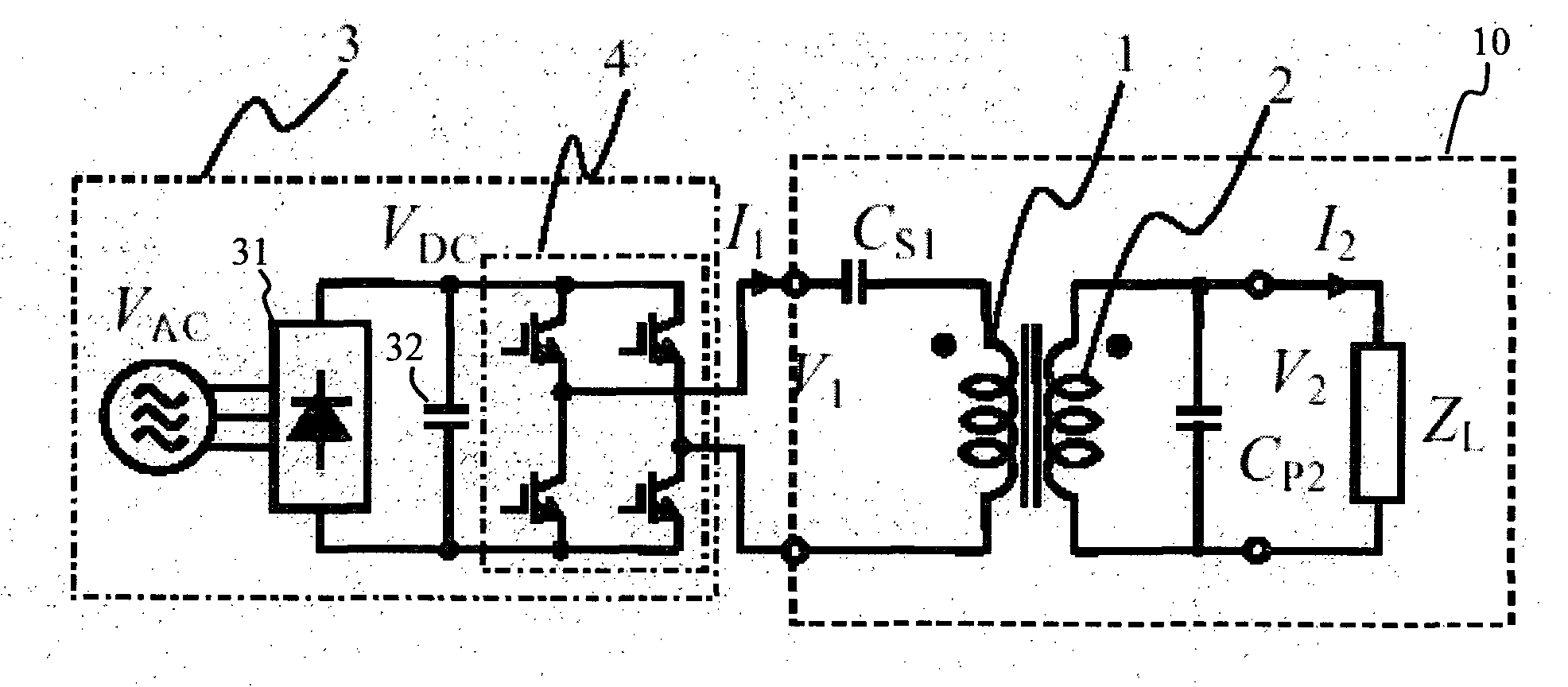
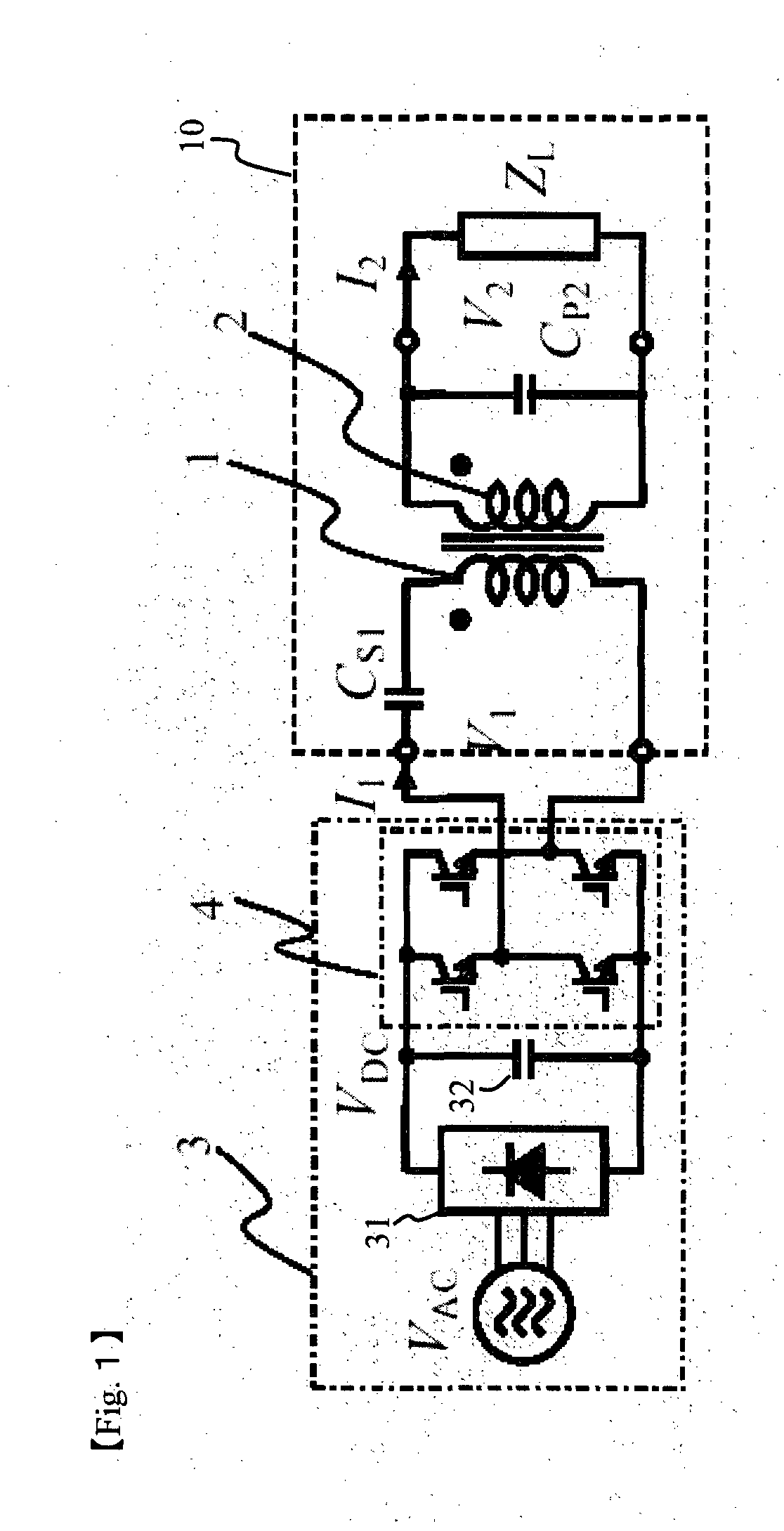
Non-contact power feeder
InactiveUS20100033156A1Improve conversion efficiencySimple designConversion with intermediate conversion to dcCircuit arrangementsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
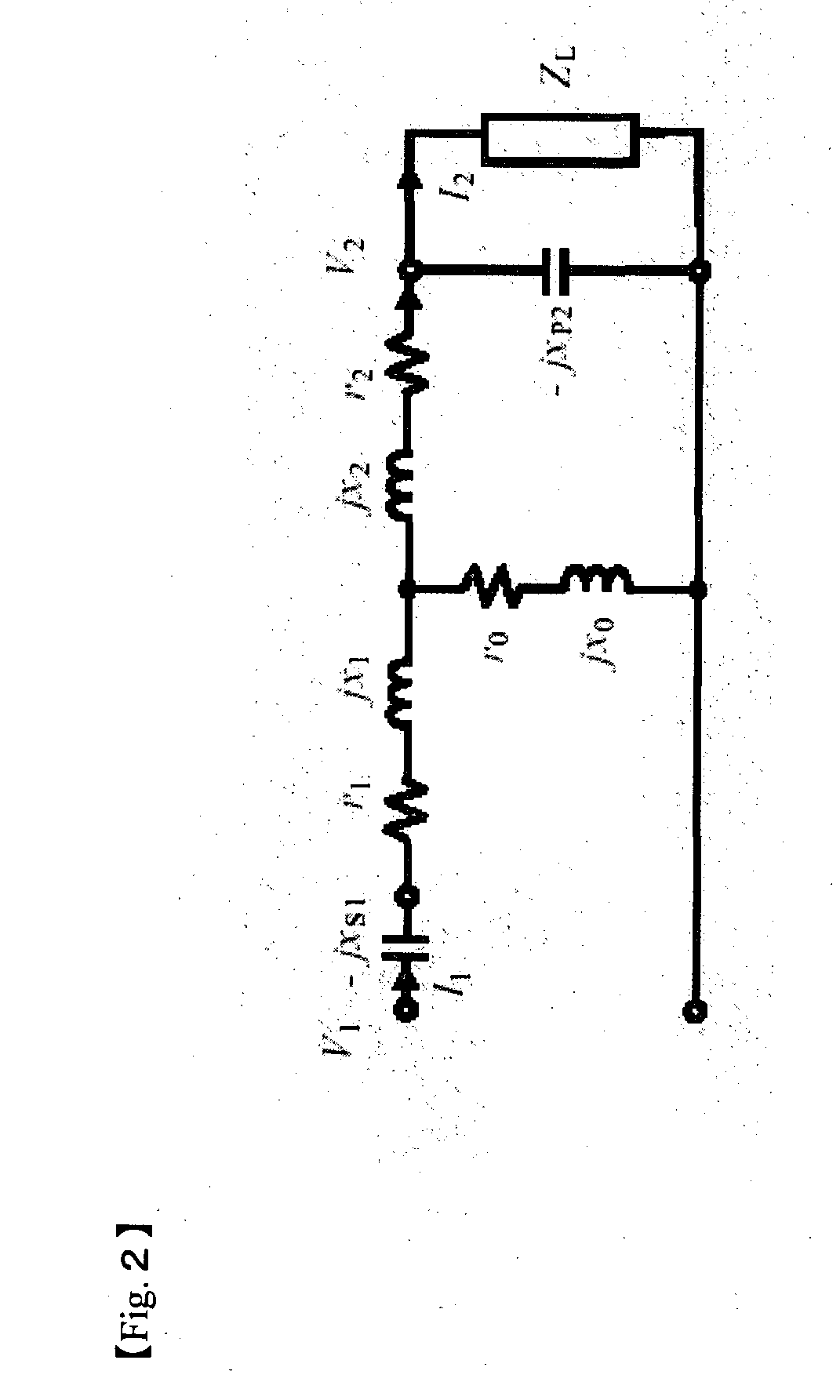
[Problems] To provide a non-contact power feeder that is high efficient and high power factor and has no load dependence.[Means for Solving Problems] A series capacitor Cs1 is connected to a primary winding 1 driven by an AC power supply 3 and a parallel capacitor Cp2 is connected to a secondary winding 2. The capacitance Cp is set to Cp≈1 / {2πf0×(x0+x2)} and the capacitance Cs converted to the primary side is set to Cs≈(x0+x2) / {2πf0×(x0×x1+x1×x2+x2×x0)}, where f0 is the frequency of the power supply, x1 is a primary leakage reactance of the primary winding 1, x2 is a secondary leakage reactance of the secondary winding 2 converted to the primary side and x0 is an excitation reactance converted to the primary side. By setting Cp and Cs to the above values, the transformer of the non-contact power feeder is substantially equivalent to an ideal transformer. If it is driven by a voltage type converter, the output voltage (=load voltage) becomes substantially constant voltage regardless of the load. In case of a resistive load (ZL=R), the power factor of the power supply output always remains 1 even if the load may vary.
Owner:SAITAMA UNIVERSITY
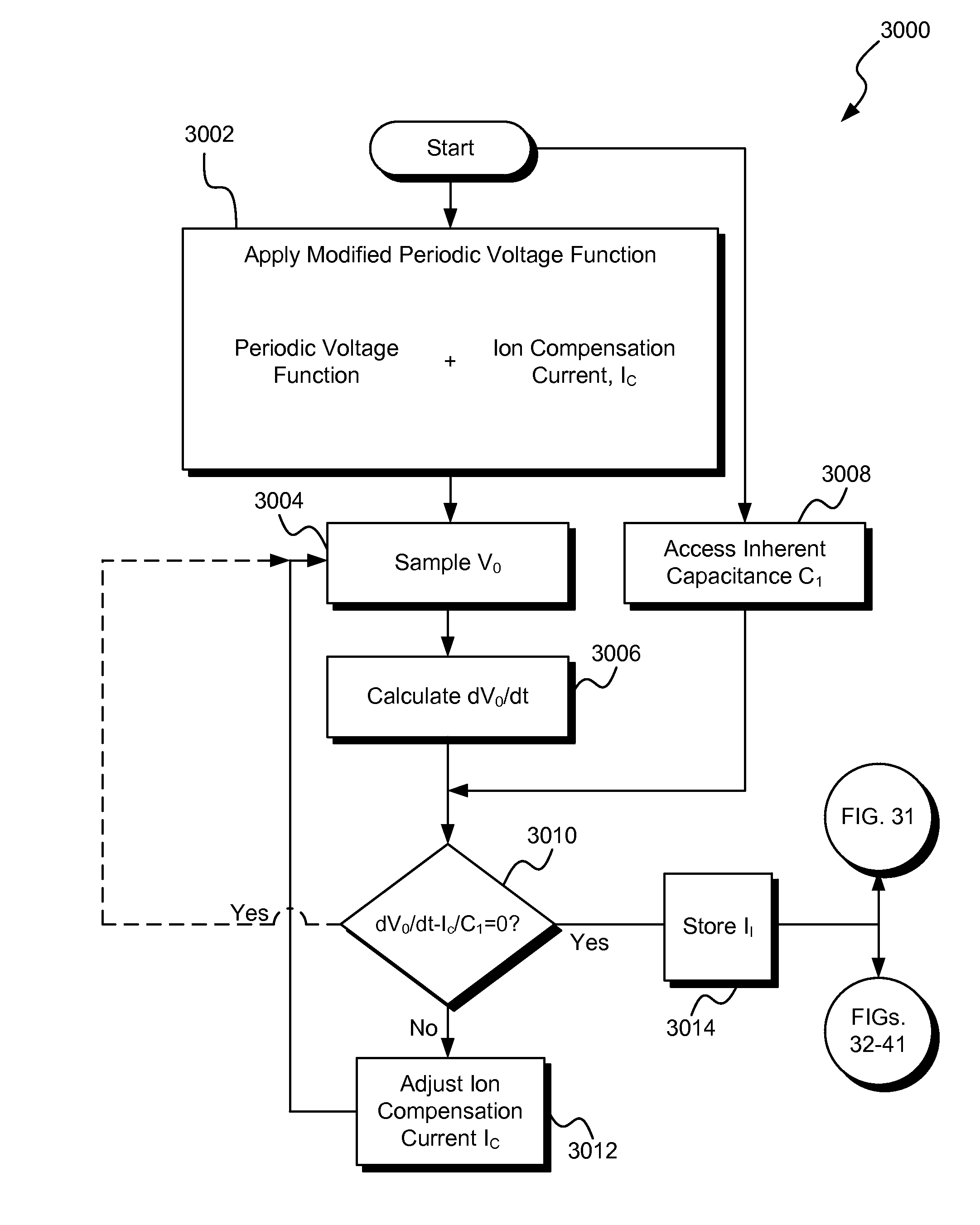
Systems and methods for calibrating a switched mode ion energy distribution system
Systems, methods and apparatus for regulating ion energies and ion energy distributions along with calibrating a bias source and a plasma processing chamber are disclosed. An exemplary method includes applying a periodic voltage function to a load emulator, which emulates electrical characteristics of a plasma load and associated electronics such as an e-chuck. The load emulator can be measured for various electrical parameters and compared to expected parameters generated by the bias source. Differences between measured and expected values can be used to identify and correct faults and abnormalities in the bias supply, the chamber, or a power source used to ignite and sustain the plasma. Once the bias supply is calibrated, the chamber can be calibrated by measuring and calculating an effective capacitance comprising a series and parallel capacitance of the substrate support and optionally the substrate.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
LED retrofit lamp with shunt capacitors across rectifier diodes for use with a ballast
ActiveUS20150351171A1Extend lamp lifeSave energyElectrical apparatusElectric circuit arrangementsShunt capacitorsRectifier diodes
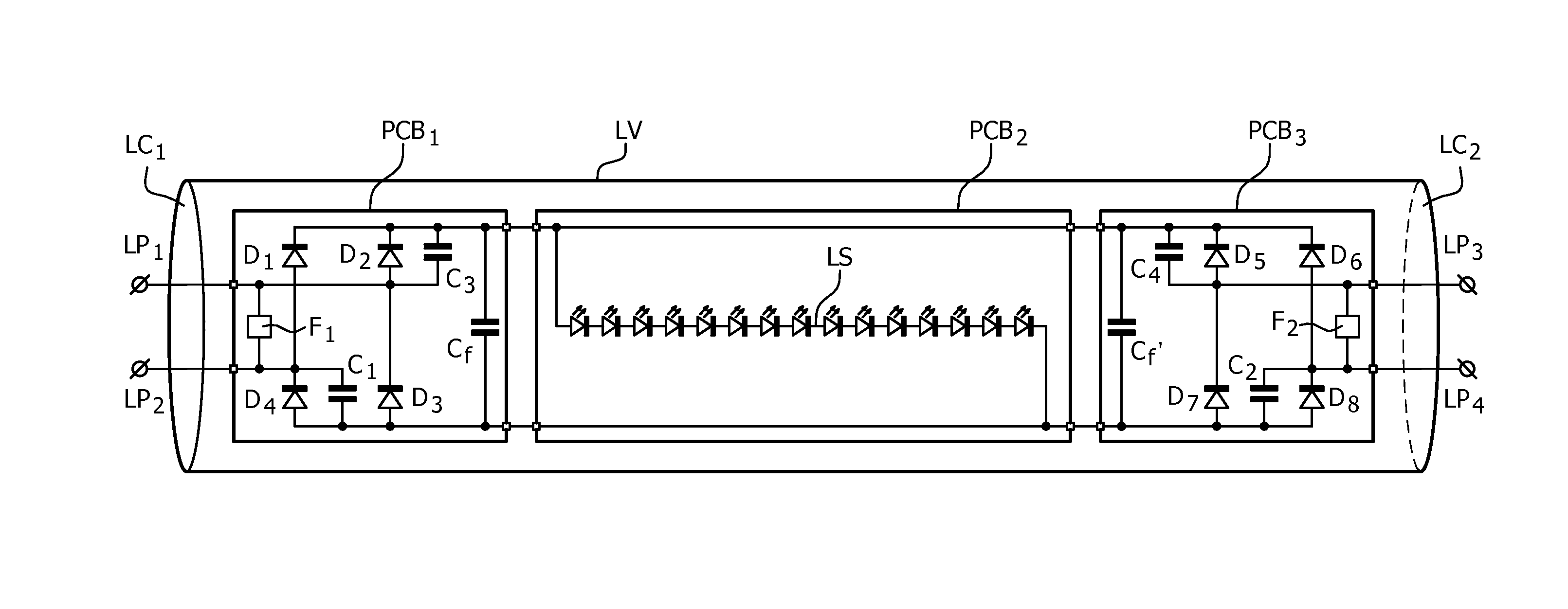
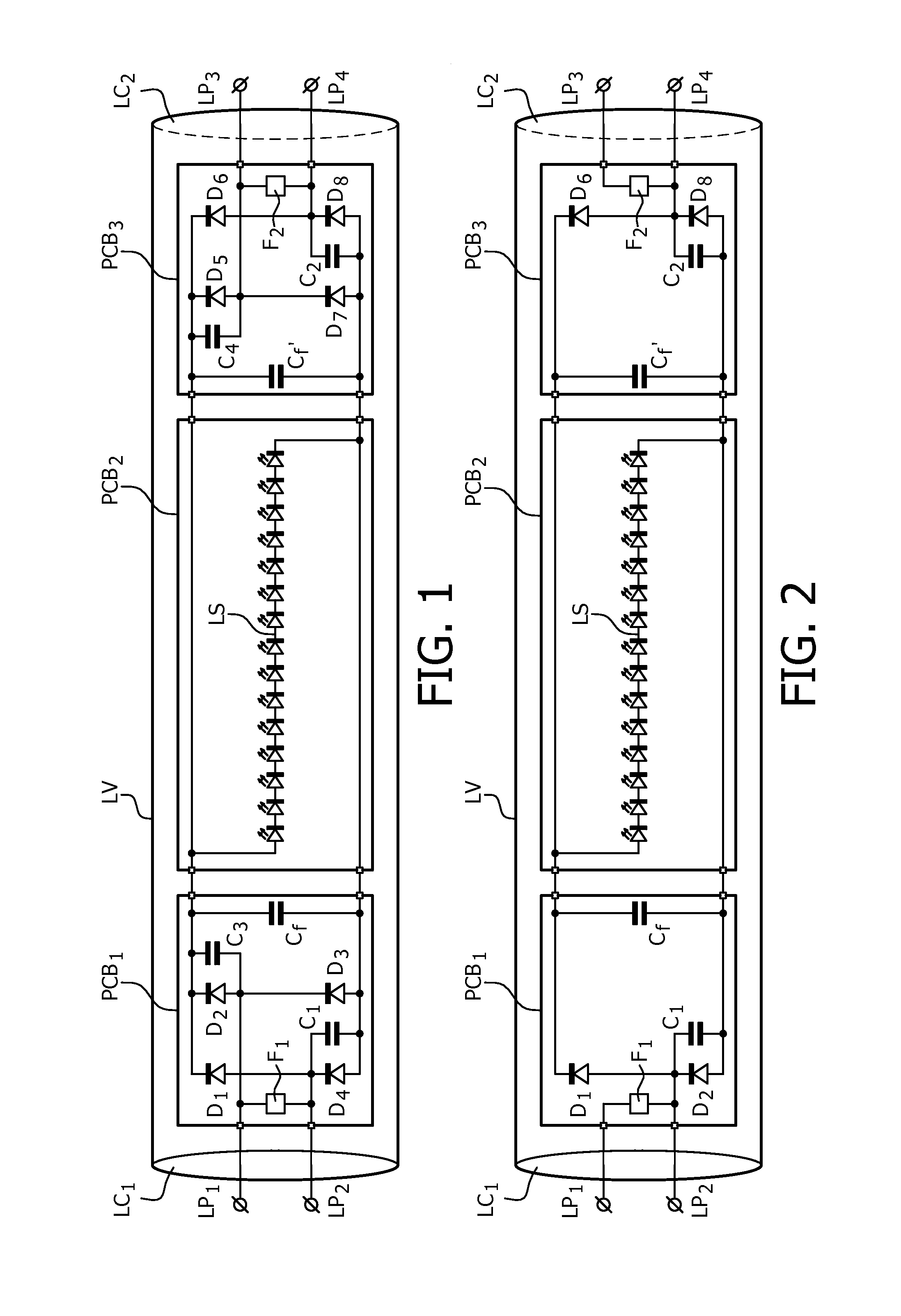
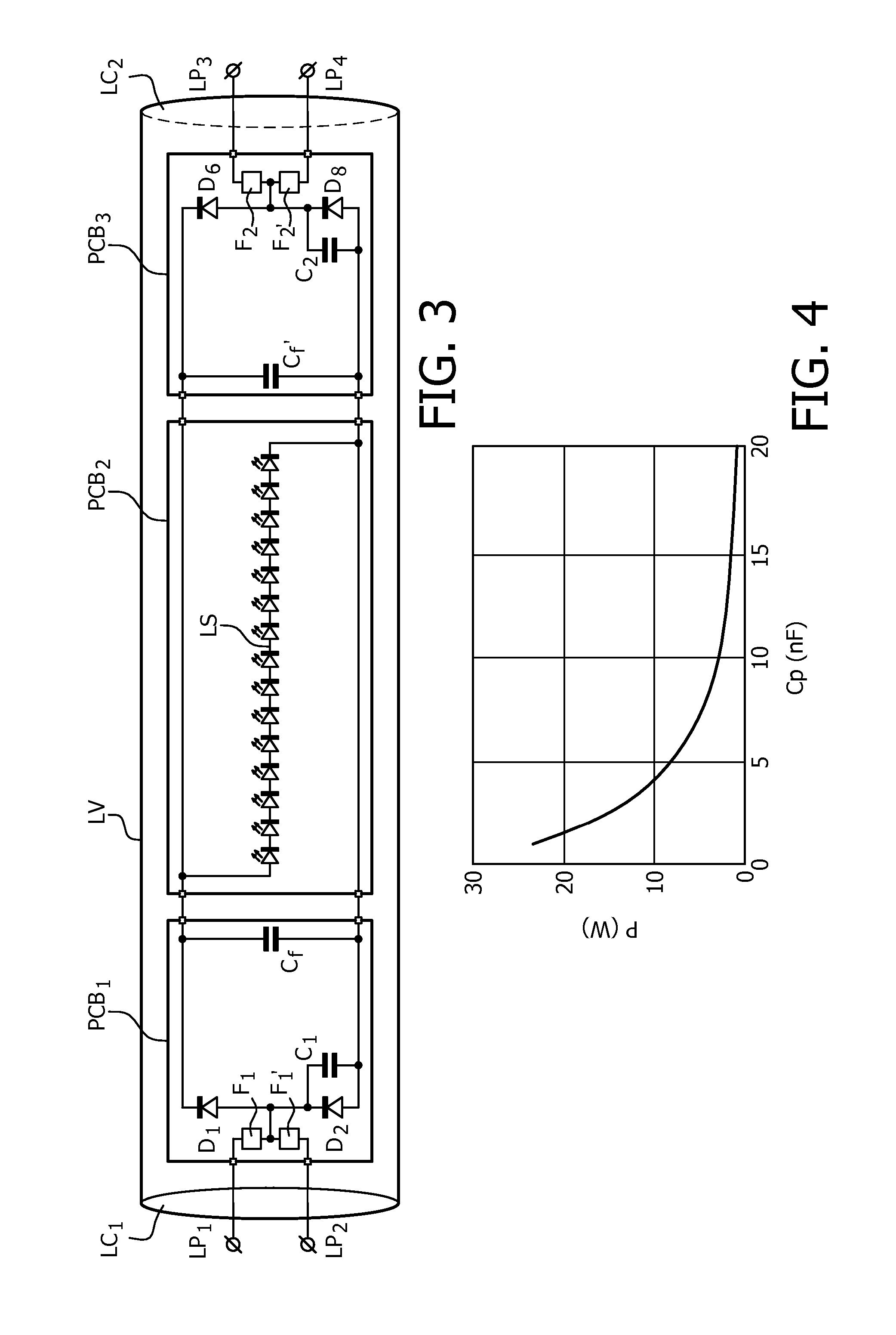
The invention relates to LED replacement lamp suitable for operation with a high frequency fluorescent lamp ballast, comprising—a LED load (LS) comprising a series arrangement of LEDs,—a first lamp end circuit comprising—a first lamp pin (LP1) and a second lamp pin (LP2) for connection to a first lamp connection terminal comprised in the high frequency fluorescent lamp ballast,—a first rectifier (D1-D4; D1,D2) equipped with at least one input terminal coupled to the second lamp pin and with first and second output terminals coupled to respective ends of the LED load, the first rectifier comprising at least two diodes, one of which is shunted by a first capacitor (C1),—a second lamp end circuit comprising—a third lamp pin (LP3) and a fourth lamp pin (LP4) for connection to a second lamp connection terminal comprised in the high frequency fluorescent lamp ballast,—a second rectifier (D5-D8, D5, D6) equipped with at least one input terminal coupled to the fourth lamp pin and with first and second output terminals coupled to respective ends of the LED load, the second rectifier comprising at least two diodes, one of which is shunted by a second capacitor (C2), wherein the first capacitor and the second capacitor form a series arrangement coupled between the second lamp pin and the fourth lamp pin.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
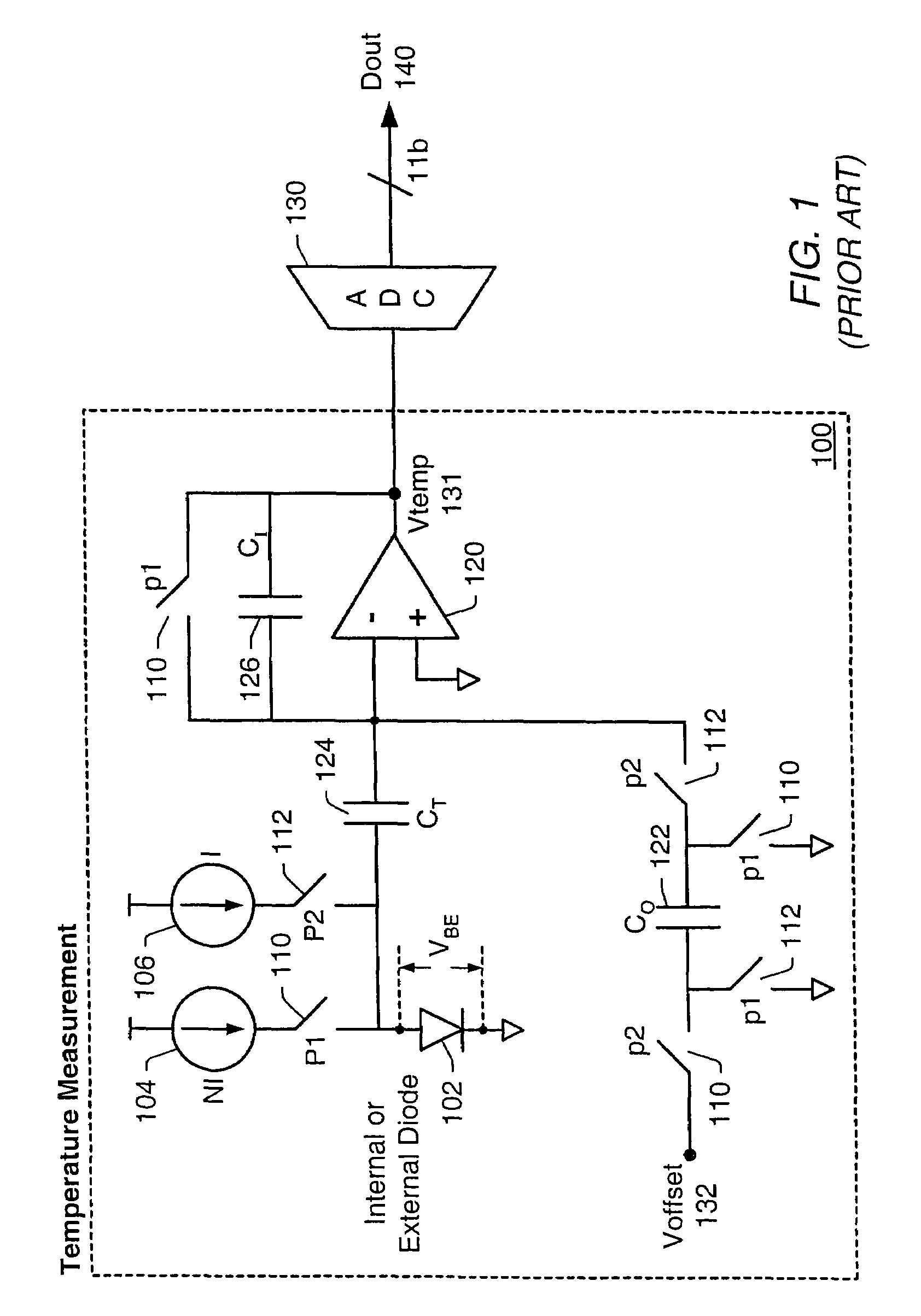
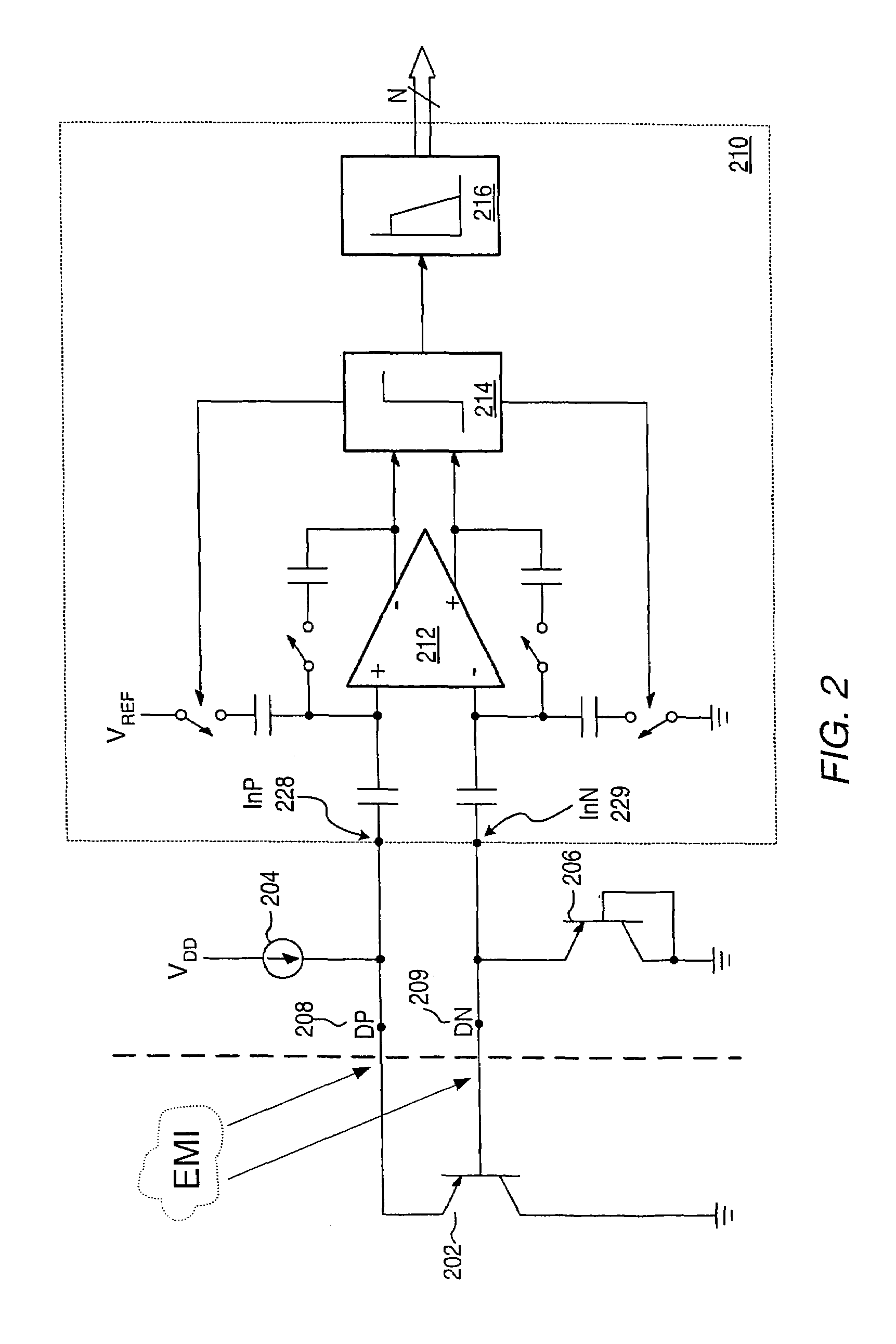
Proportional settling time adjustment for diode voltage and temperature measurements dependent on forced level current
ActiveUS7429129B2Increase conversion rateMinimizing temperature measurementThermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionAc componentsShunt capacitors
A temperature sensor circuit and system providing accurate digital temperature readings using a local or remote temperature diode. In one set of embodiments a change in diode junction voltage (ΔVBE) proportional to the temperature of the diode is captured and provided to an analog to digital converter (ADC), which may perform required signal conditioning functions on ΔVBE, and provide a digital output corresponding to the temperature of the diode. DC components of errors in the measured temperature that may result from EMI noise modulating the junction voltage (VBE) may be minimized through the use of a front-end sample-and-hold circuit coupled between the diode and the ADC, in combination with a shunt capacitor coupled across the diode junction. The sample-and-hold-circuit may sample VBE at a frequency that provides sufficient settling time for each VBE sample, and provide corresponding stable ΔVBE samples to the ADC at the ADC operating frequency. The ADC may therefore be operated at its preferred sampling frequency rate without incurring reading errors while still averaging out AC components of additional errors induced by sources other than EMI.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Integrated broadband ceramic capacitor array
InactiveUS6970341B1Effective wideband performanceImprove performanceMultiple fixed capacitorsFixed capacitor electrodesCeramic capacitorEngineering
A monolithic capacitor structure includes opposed and overlapping plates within a dielectric body, which are arranged to form a lower frequency, higher value capacitor. Other conductive structure is located either inside the dielectric body or on an external surface thereof and is effective to form a higher frequency, lower value capacitor in parallel with the lower frequency, higher value capacitor. The resulting array of combined series and parallel capacitors integral with the dielectric body provides effective wideband performance in an integrated, cost-effective structure.
Owner:DEVOE DANIEL +2
Forward-flyback isolated type boost inverter realized by coupling inductors and application thereof
ActiveCN101702578AIncrease profitReduce volumeApparatus with intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationClamp capacitorResonance
The invention discloses a forward-flyback isolated type boost inverter realized by coupling inductors and application thereof, comprising two power switch tubes, two auxiliary switch tubes, four anti-parallel diodes, a switch tube parallel capacitor, two clamp capacitors, two switch capacitors, two output diodes and two coupling inductors respectively provided with two windings. The invention realizes zero-voltage switching on of the power switch tubes through the resonance of the leakage inductance of the two coupling inductors and the switch tube parallel capacitor, absorbs the voltage peak switched off by the switch tubes caused by the leakage inductance and realizes energy lossless transfer by utilizing a clamp circuit comprising the anti-parallel diodes of the switch tubes and the two clamp capacitors, realizes the high gain output of the inverter by utilizing the serial connection of the second windings of the two coupling inductors, further improves the gain of the inverter and lowers the output voltage stress of the diodes by utilizing the switch capacitors and realizes the output zero-current switching off of the diodes by utilizing the leakage inductance of the coupling inductors.
Owner:HOYMILES POWER ELECTRONICS INC
Gate drive method and apparatus for reducing losses in the switching of MOSFETs
InactiveUS6992520B1Reduces and eliminates consequenceLower impedanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETLower limit
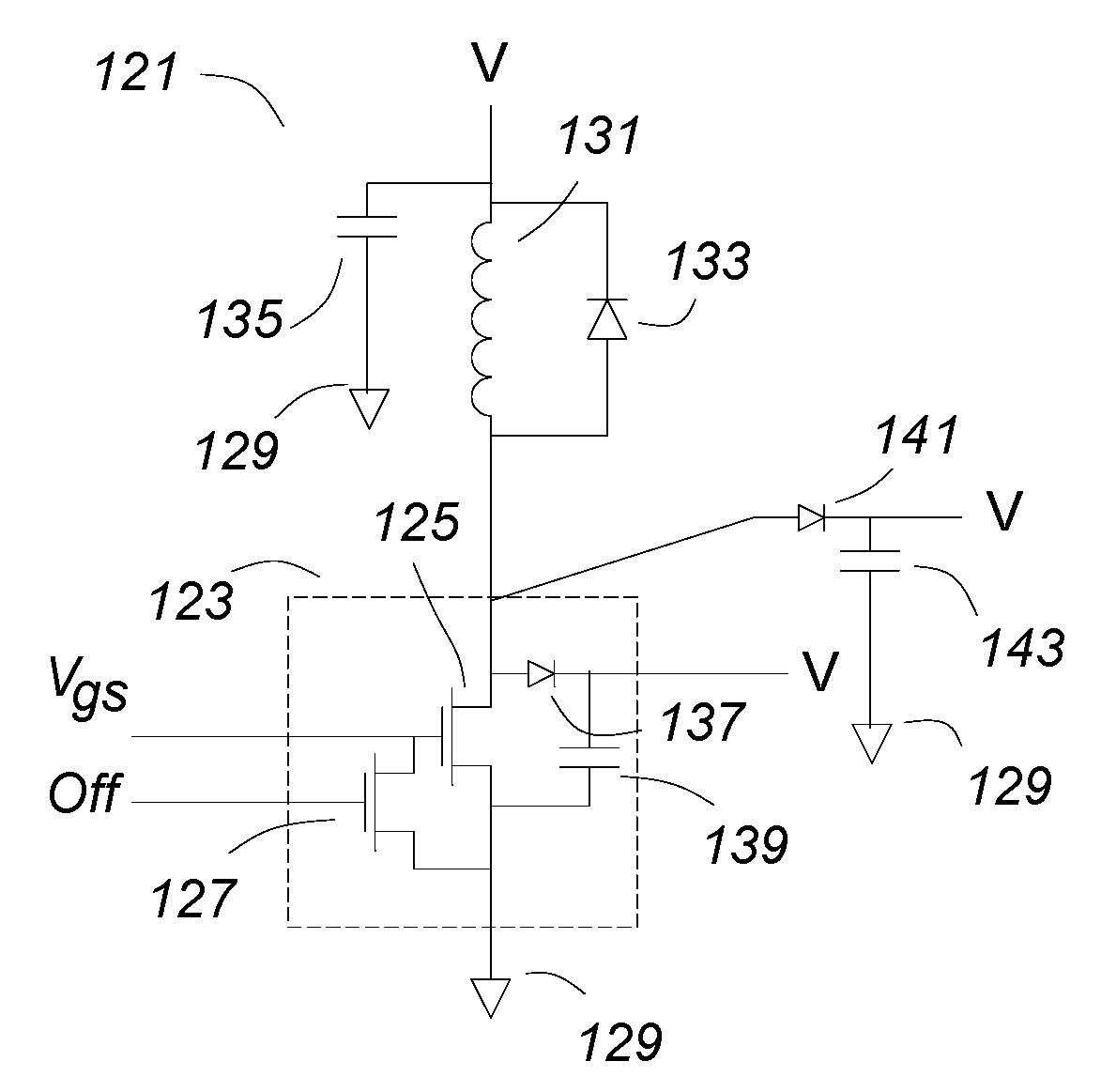
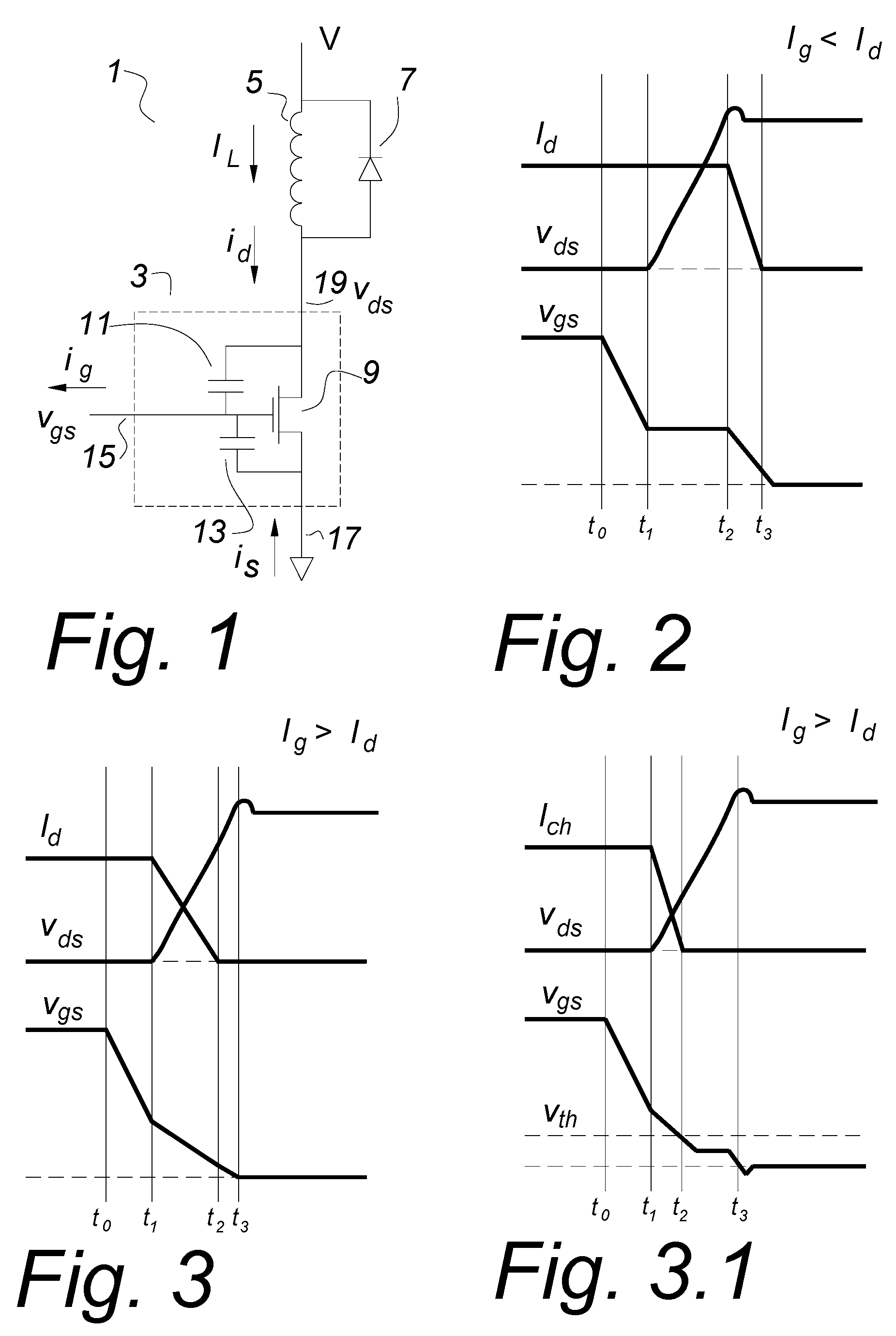
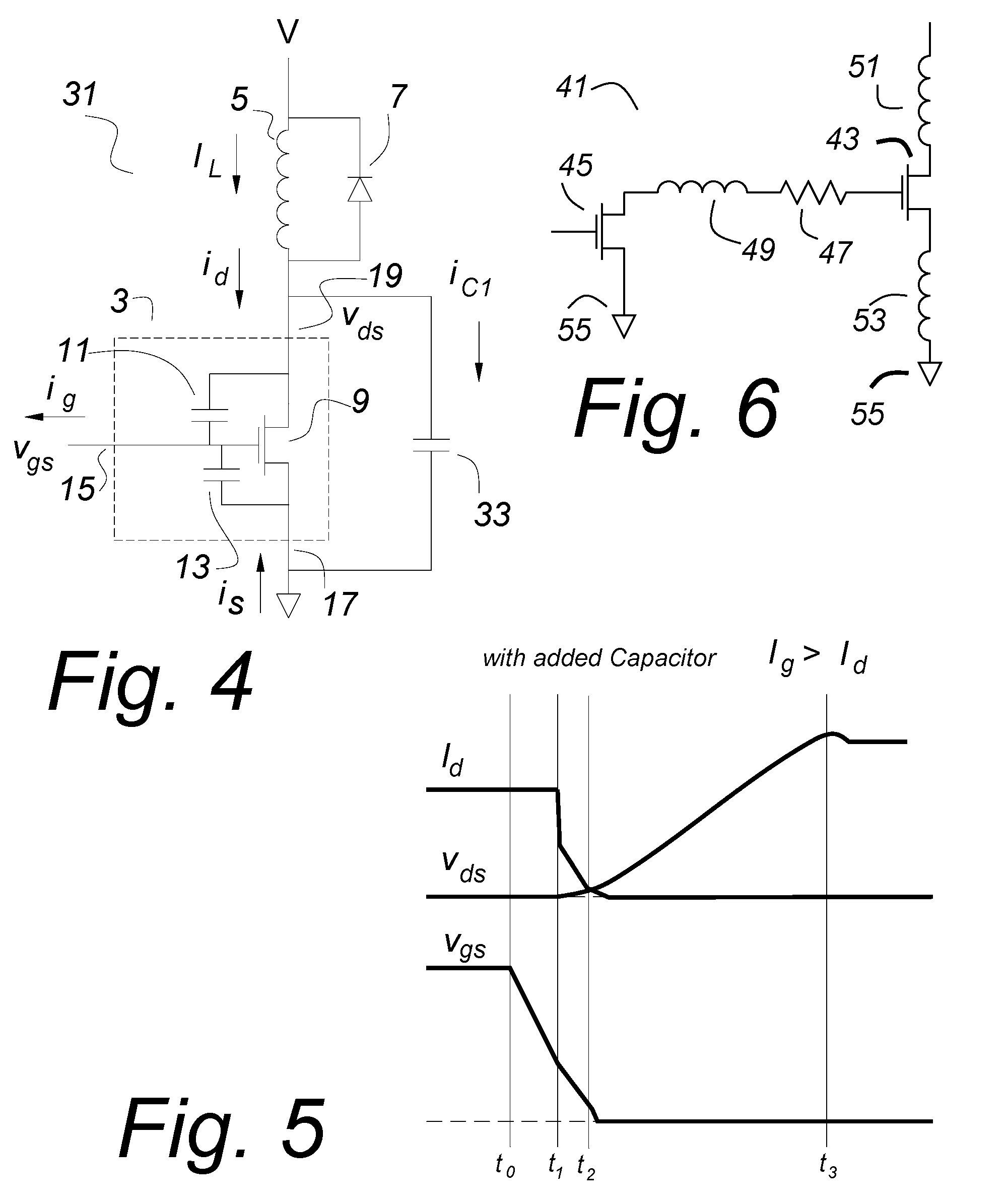
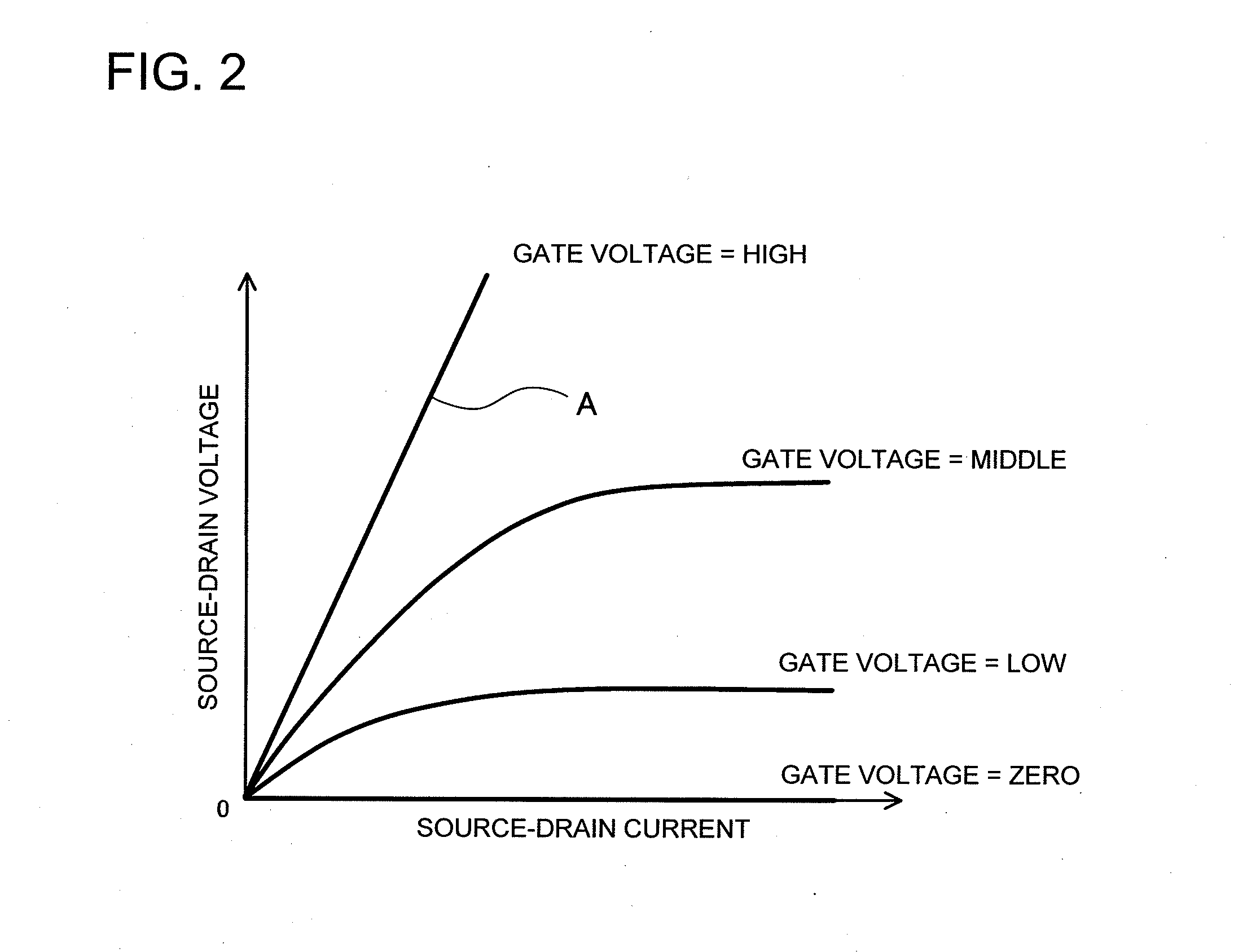
Usually, in power converters, the load on a MOSFET is inductive, and the current cannot change rapidly. The drain current is the upper limit of the Miller current, so that if the gate current is larger than the drain current, the gate capacitance will continue to discharge and there can be no Miller shelf. If a parallel capacitor is used with a MOSFET, once the drain voltage starts to rise, the load current divides, placing a new lower limit on the Miller current. To drive a MOSFET with a gate current that exceeds the drain current, the circuit impedances have to be very low, suggesting a new geometry and packaging arrangement for the MOSFET and gate drive. A compatible gate turn of circuit is also disclosed.
Owner:HERBERT EDWARD
RF impedance matching network
ActiveUS9196459B2Shorten the timeImpedence matching networksMultiple-port networksPlasma impedanceControl signal
An RF impedance matching network includes an RF input; an RF output configured to operably couple to a plasma chamber; a series electronically variable capacitor (“series EVC”), the series EVC electrically coupled in series between the RF input and the RF output; and a shunt electronically variable capacitor (“shunt EVC”), the shunt EVC electrically coupled in parallel between a ground and one of the RF input and the RF output; a control circuit to control the series variable capacitance and the shunt variable capacitance, wherein the control circuit is configured to determine the variable plasma impedance of the plasma chamber, determine a series capacitance value and a shunt capacitance value, and generate a control signal to alter at least one of the series variable capacitance and the shunt variable capacitance; wherein the alteration is caused by at least one of a plurality of switching circuits.
Owner:ASM AMERICA INC
Implantable medical device lead incorporating a conductive sheath surrounding insulated coils to reduce lead heating during MRI
InactiveUS20110034983A1Reduce couplingReduce heatInternal electrodesExternal electrodesDevice implantConductive polymer
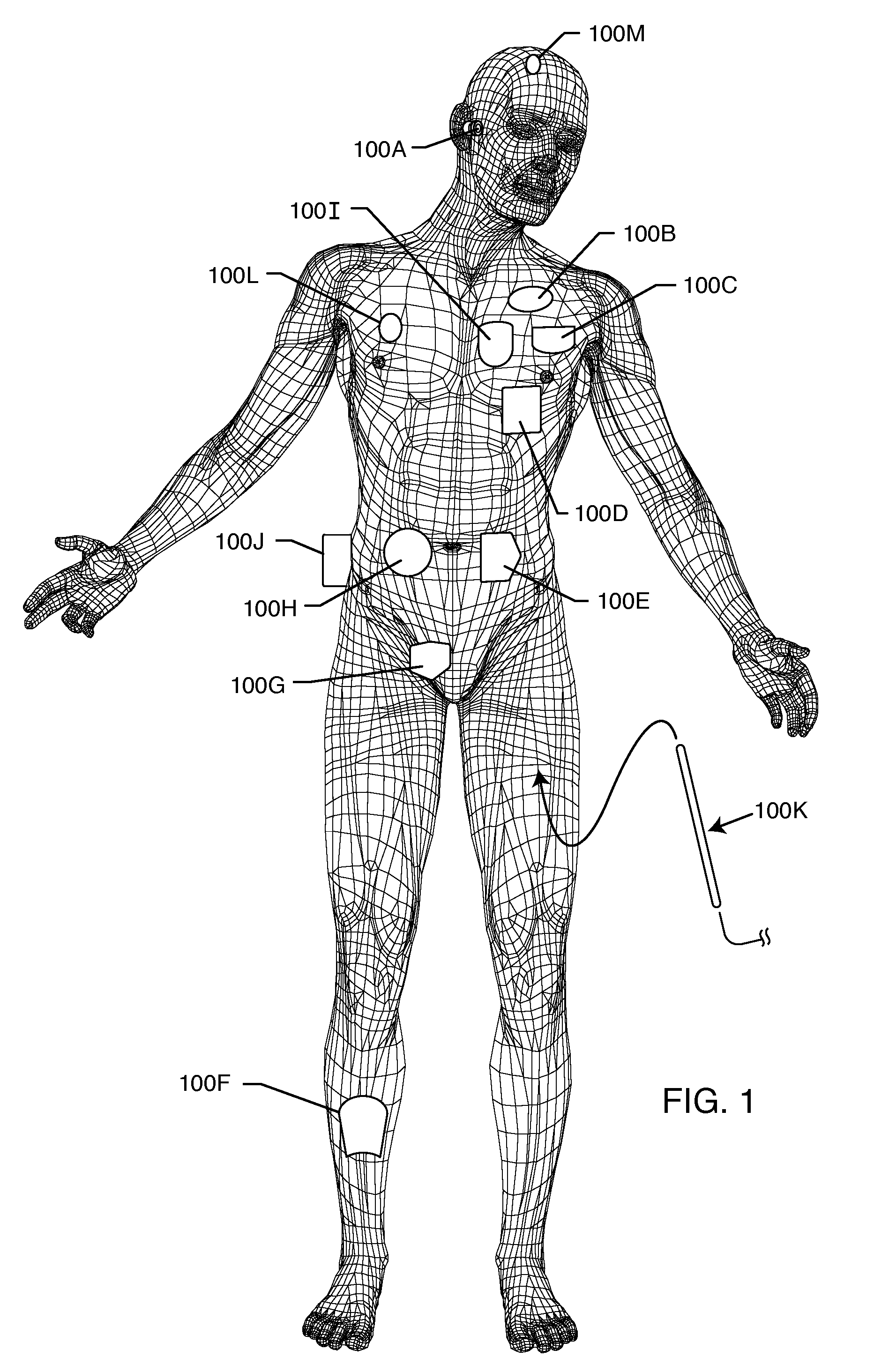
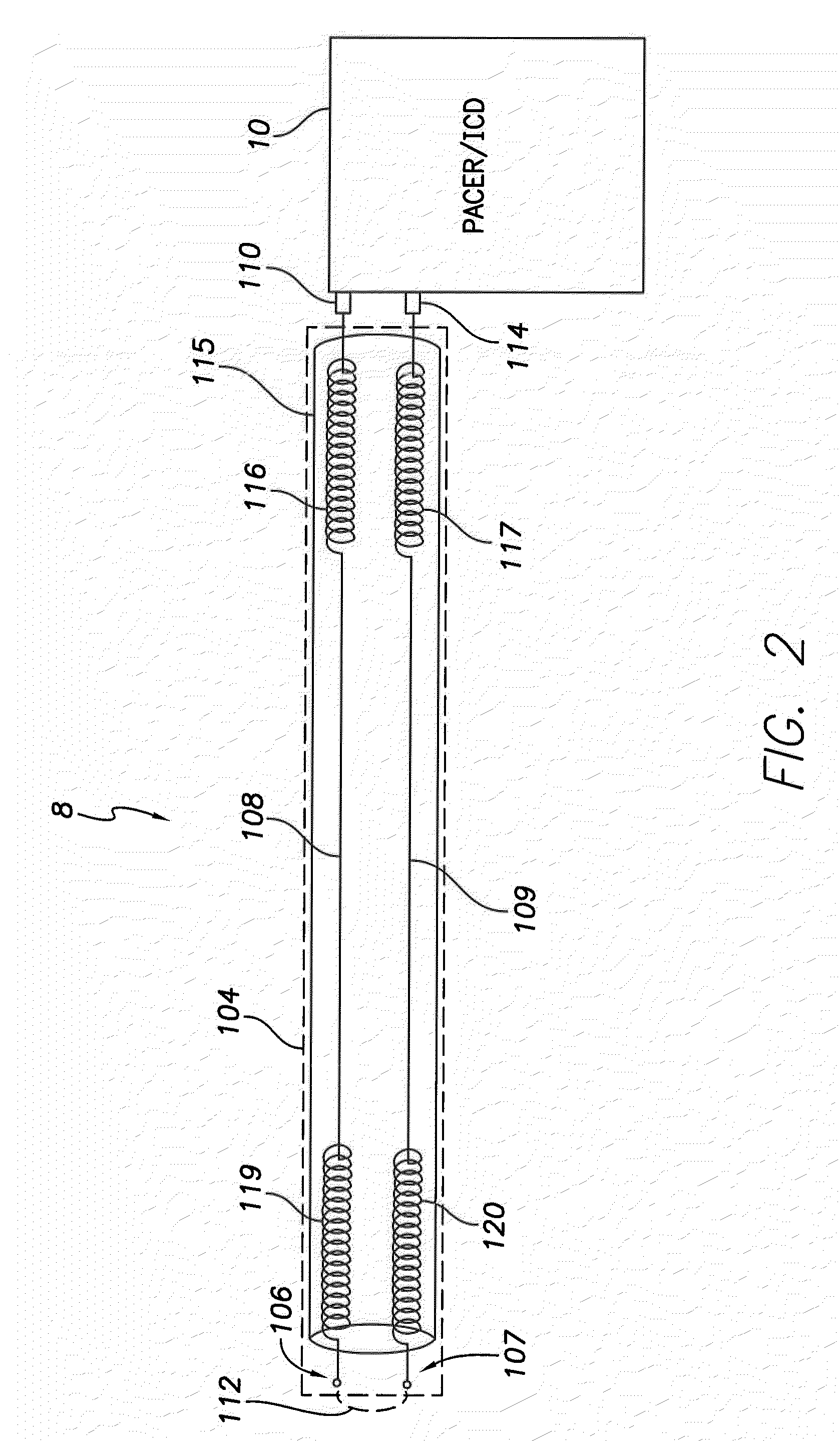
A conducting sheath is provided along at least a portion of an implantable medical device lead, and preferably along substantially its entire length, for mitigating heating problems arising during magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) procedures, particularly problems arising due to a problem described herein as the “coiling effect.” During device implant, the clinician may elect to wrap or coil excess proximal portions of leads around or under the medical device being implanted. Thereafter, during MRI procedures, shunt capacitance may develop between the housing of the implantable device and insulated coils within the proximal portions of the lead that are near the device, resulting in greater lead heating during the MRI. The conducting sheath helps suppress induced currents and also reduces or eliminates shunt capacitance. The conducting sheath may be, for example, formed using a metal mesh or a conducting polymer tube incorporating non-ferrous metal powders. The sheath may be formed in ¼ wavelength segments.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method of determining plasma ion density, wafer voltage, etch rate and wafer current from applied bias voltage and current
ActiveUS20060278608A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesImpedance matchingShunt capacitance
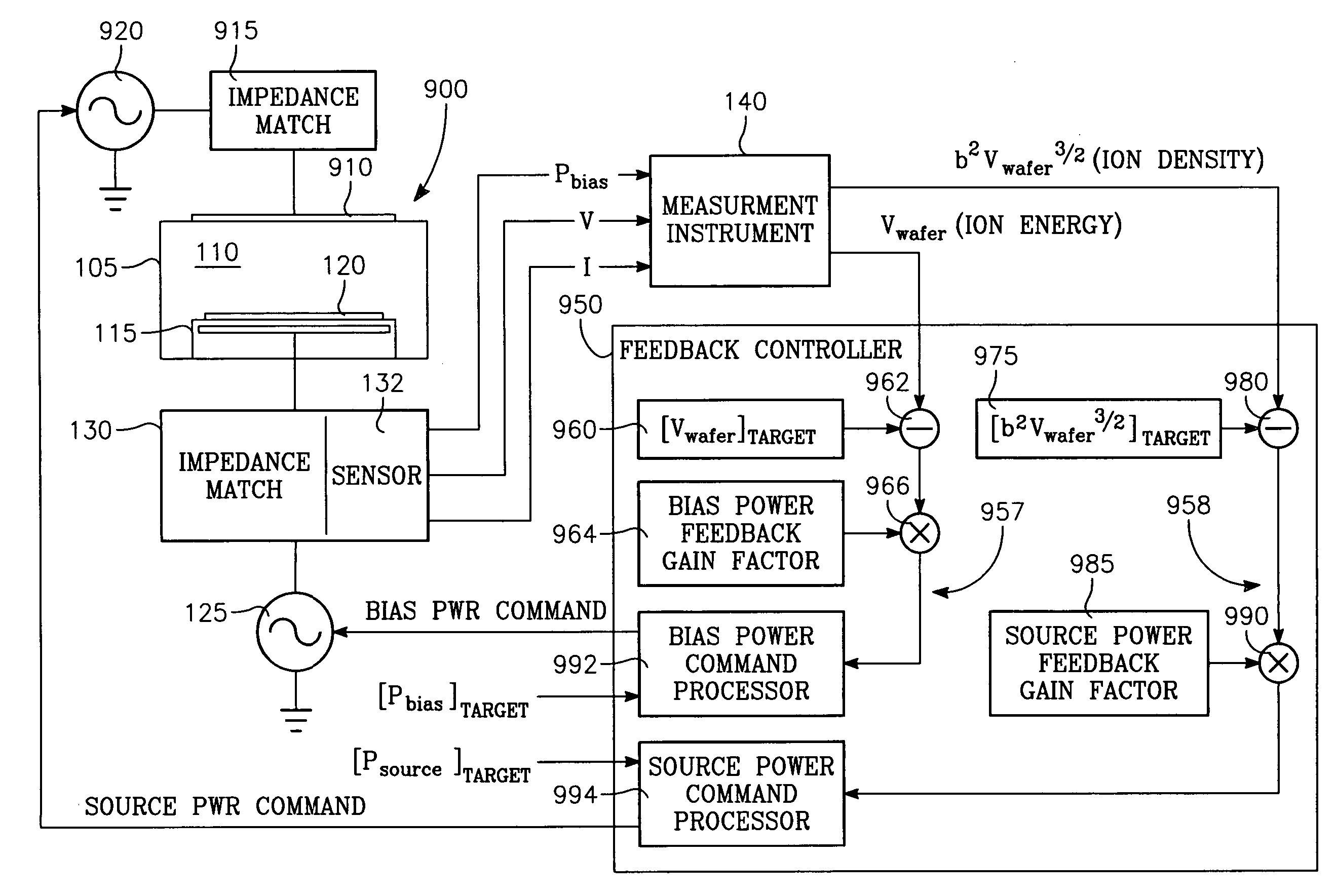
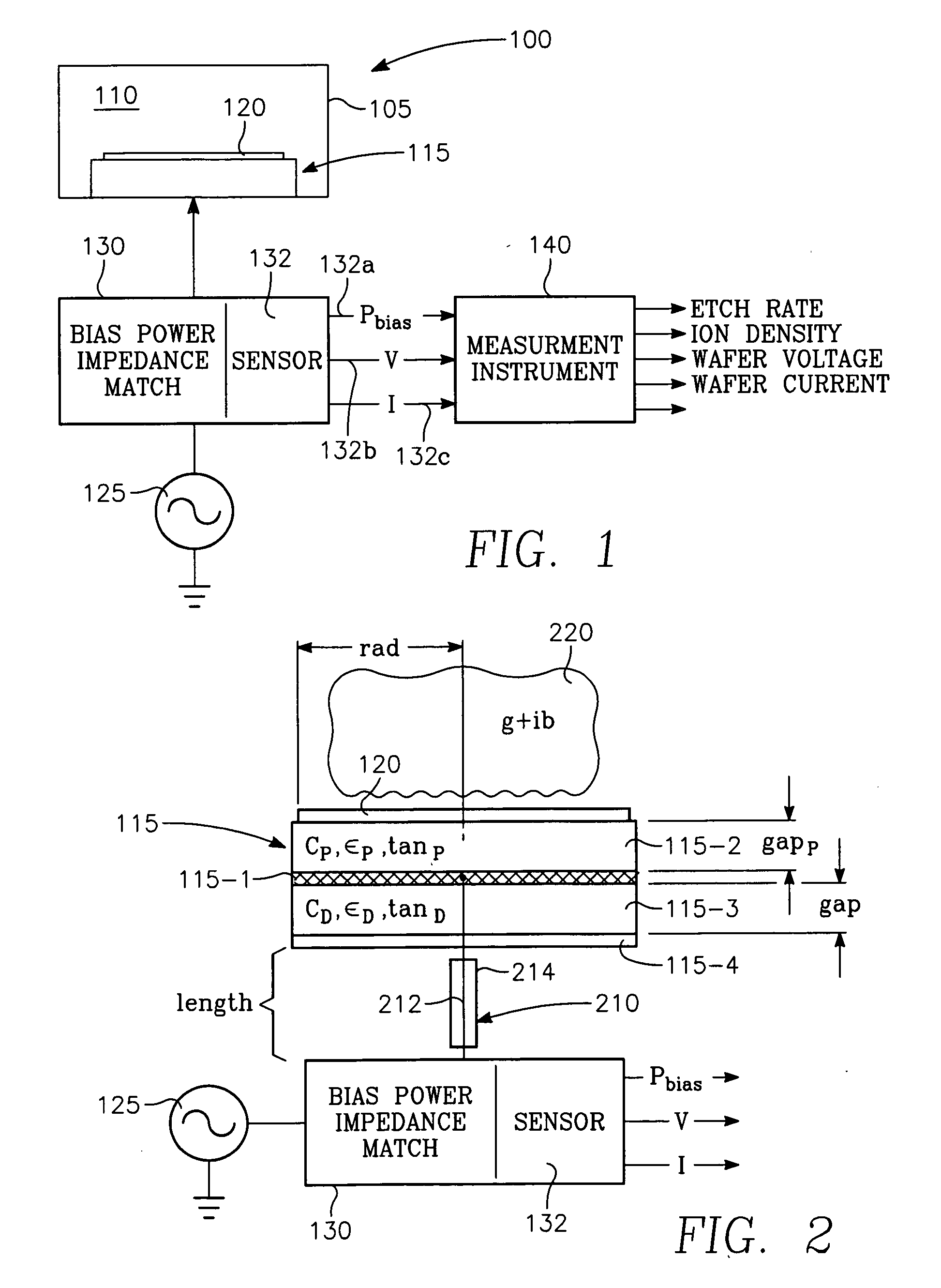
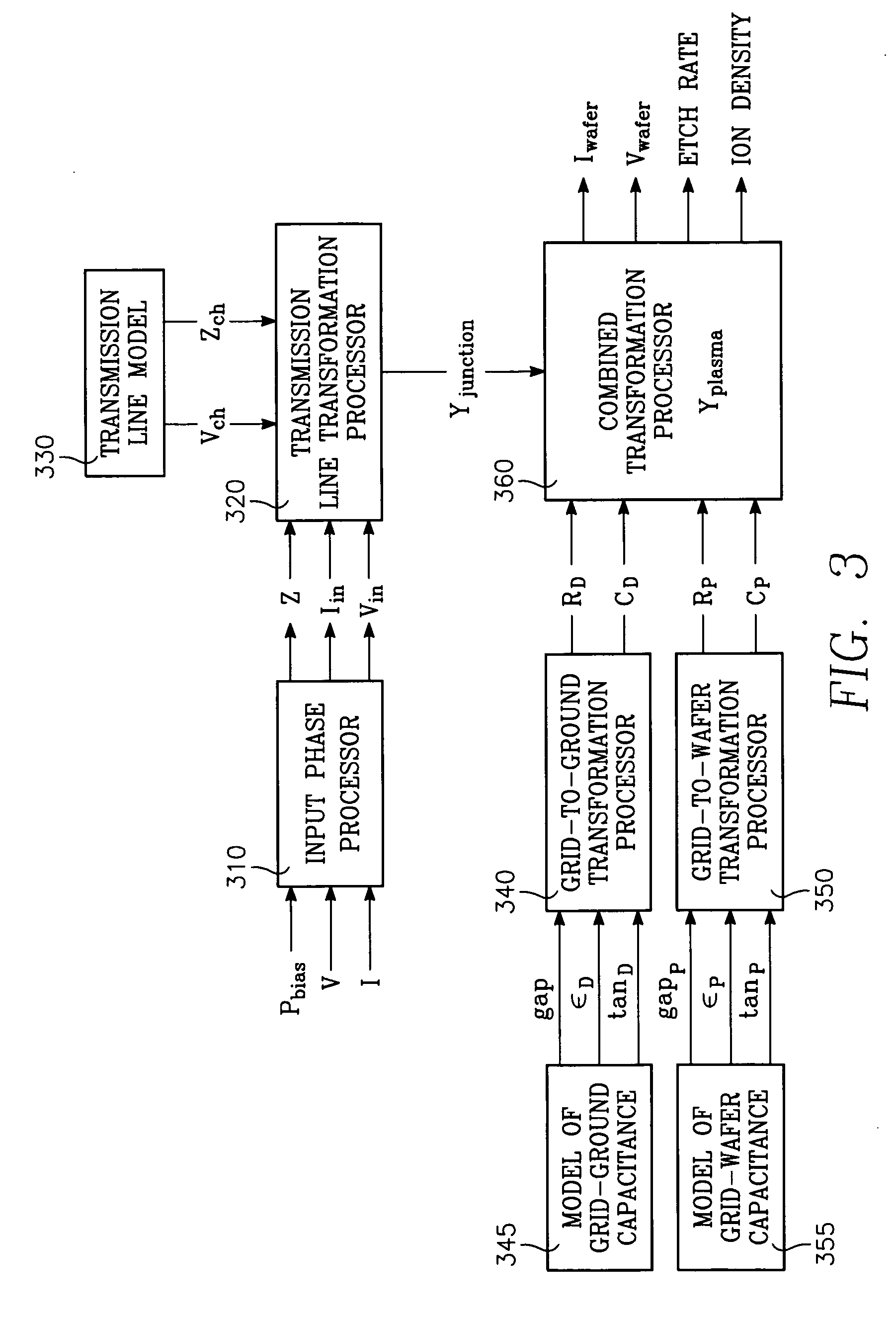
Plasma parameters such as plasma ion density, wafer voltage, etch rate and wafer current in the chamber are determined from external measurements on the applied RF bias electrical parameters such as voltage and current. The method includes sensing RF parameters corresponding to an input impedance, an input current and an input voltage at the input of the impedance match element to a transmission line coupled between the bias generator and the wafer pedestal. The method continues by computing a junction admittance of a junction between the transmission line and the electrode within the wafer pedestal from the input impedance, input current and input voltage and from parameters of the transmission line. The method further includes providing shunt electrical quantities of a shunt capacitance between the electrode and a ground plane, and providing load electrical quantities of a load capacitance between the electrode and a wafer on the pedestal. The method further includes computing at least one of the plasma parameters from the junction admittance, the shunt electrical quantities, the load electrical quantities and a frequency of RF bias power applied to the electrode.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
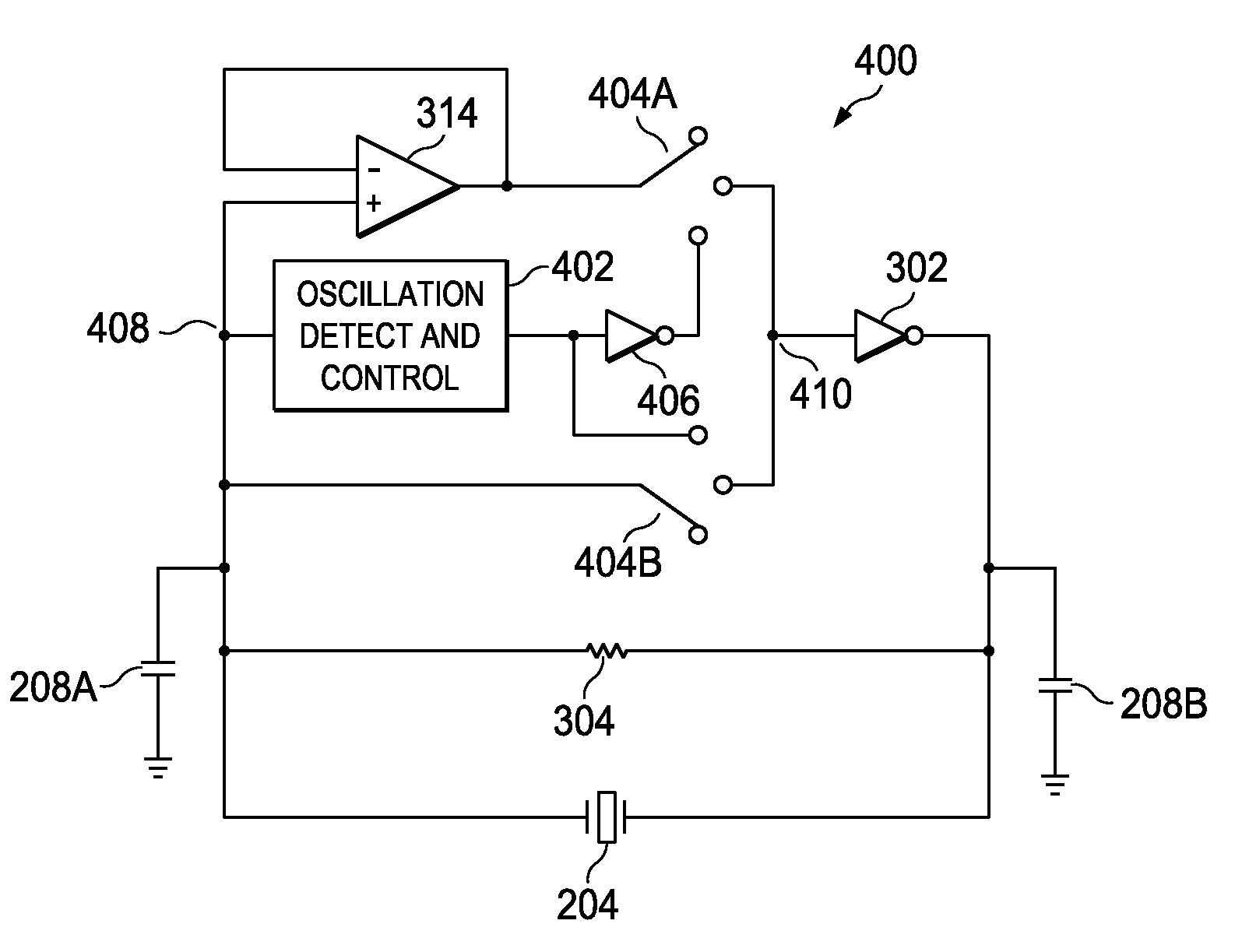
Fast start-up crystal oscillator
ActiveUS20110037527A1Reduce startup timeImprove the immunityPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsStart up timeSnubber
An exemplary fast start-up crystal oscillator with reduced start-up time. The exemplary oscillator reduces the start-up time (i.e., the time taken to attain sustained stable oscillations after the power is turned on) by increasing the negative resistance of a circuit. Increasing the negative resistance increases the rate of growth of the oscillations, thereby reducing start-up time. The exemplary crystal oscillator includes a gain stage with negative resistance. A crystal with shunt capacitance is placed in the feedback loop of the gain stage. A buffer is coupled to the gain stage such that it blocks the crystal shunt capacitance from loading the gain stage, effectively increasing the negative resistance of the gain stage. Further, an oscillation detection and control circuit is coupled between the crystal and the gain stage. The oscillation detection and control circuit connects the buffer during start-up, and disconnects the buffer once an oscillation signal attains sustained stable oscillations.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Integrated broadband ceramic capacitor array
InactiveUS7307829B1Effective wideband performanceImprove performanceMultiple fixed capacitorsFixed capacitor electrodesCeramic capacitorEngineering
A monolithic capacitor structure includes opposed and overlapping plates within a dielectric body, which are arranged to form a lower frequency, higher value capacitor. Other conductive structure is located either inside the dielectric body or on an external surface thereof and is effective to form a higher frequency, lower value capacitor in parallel with the lower frequency, higher value capacitor. The resulting array of combined series and parallel capacitors integral with the dielectric body provides effective wideband performance in an integrated, cost-effective structure.
Owner:DEVOE DANIEL +2
Fault location using measurements of current and voltage from one end of a line
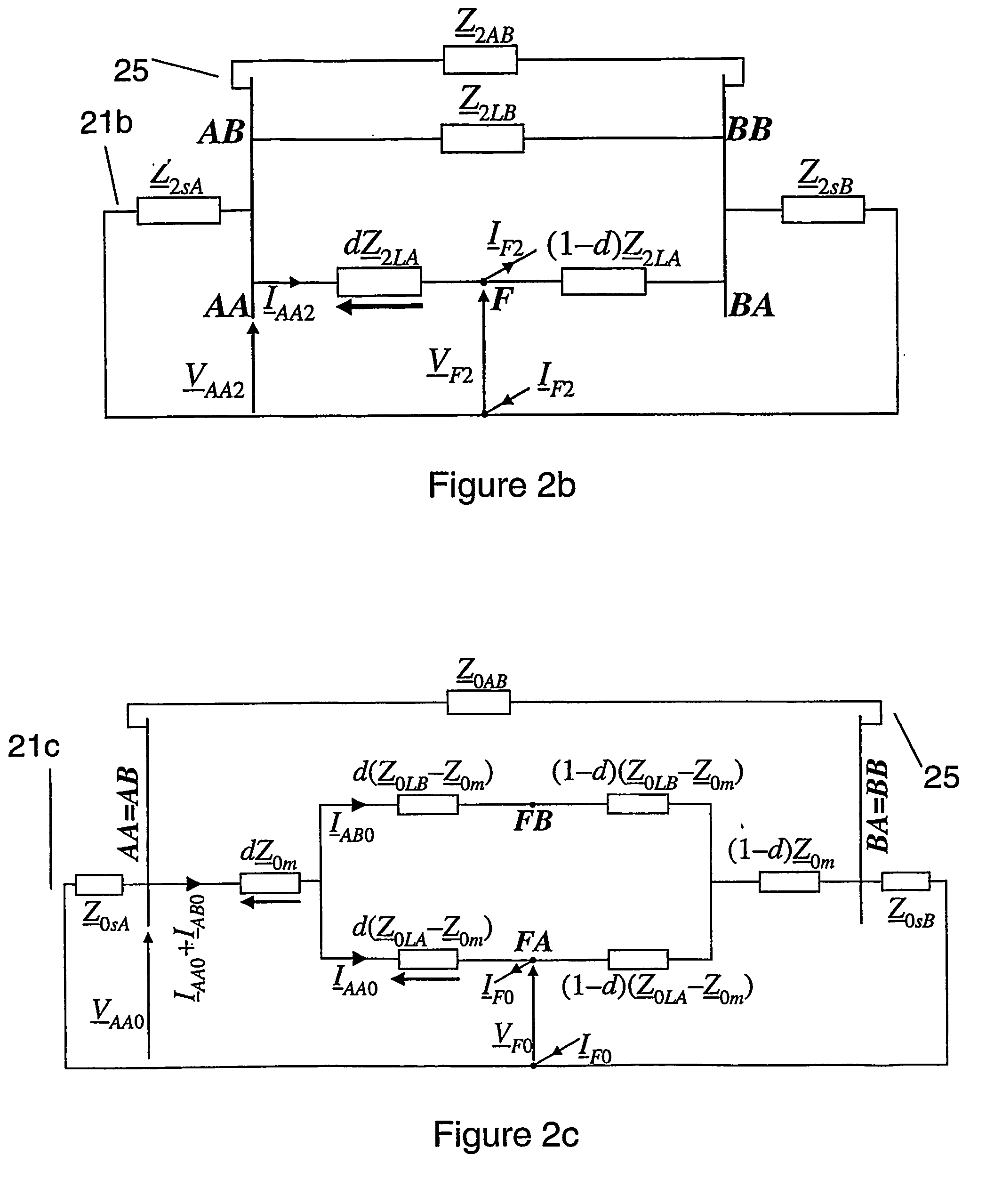
InactiveUS20060097728A1Improve accuracyShunt capacitance is facilitatedFault location by conductor typesEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionSymmetrical componentsElectrical impedance
A method to locate a fault from one end of a section of a power line utilizing measurements of current, voltage and angles between the phases at a first end of said section. Symmetrical components of currents are calculated for the current and voltage measurement at the first end. A value of impedance is calculated for an extra link between the terminals with the impedance for the positive sequence equal to: (Z_1 LB&AB=Z_1LBZ_1ABZ_1LB+Z_1AB) where:Z1AB=impedance for the positive sequence of the extra link, Z1LA=positive-sequence impedance of the healthy line. A compensation is determined for the shunt capacitance with the aid of an equation of the form: B2comp<sub2>—< / sub2>1(dcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1)2+B1comp<sub2>—< / sub2>1dcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1+B0comp<sub2>—< / sub2>1=0 where: B2comp<sub2>—< / sub2>1=A2<sub2>—< / sub2>Recomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1A00<sub2>—< / sub2>Imcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1−A2<sub2>—< / sub2>Imcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1A00<sub2>—< / sub2>Recomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1 B1comp<sub2>—< / sub2>1=A1<sub2>—< / sub2>Recomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1A00<sub2>—< / sub2>Imcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1−A1<sub2>—< / sub2>Imcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1A00<sub2>—< / sub2>Recomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1 B0comp<sub2>—< / sub2>1=A0<sub2>—< / sub2>Recomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1A00<sub2>—< / sub2>Imcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1−A0<sub2>—< / sub2>Imcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1A00<sub2>—< / sub2>Recomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1. The zero-sequence current is determined from the healthy line of a section of parallel power lines. A distance to a fault is calculated for the parallel line section. The distance to the fault from the first end is calculated using a quadratic equation of the form: B2d2+B1d+B0=0 where: B2=A2<sub2>—< / sub2>ReA00<sub2>—< / sub2>Im−A2<sub2>—< / sub2>ImA00<sub2>—< / sub2>Re B1=A1<sub2>—< / sub2>ReA00<sub2>—< / sub2>Im−A1<sub2>—< / sub2>ImA00<sub2>—< / sub2>Re B0=A0<sub2>—< / sub2>ReA00<sub2>—< / sub2>Im−A0<sub2>—< / sub2>ImA00<sub2>—< / sub2>Re.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Active clamp zero voltage soft switch high gain booster staggered parallel converter
InactiveCN101022244AIncrease output gainImprove circuit efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionClamp capacitorActive clamp
This invention discloses active clamp zero-voltage soft switch high gain boost staggered parallel converters including two power switch tubes, two clamp switch tubes, two clamp capacitors, two continuing flow diodes and two coupled inductors, in which, each of the two coupled inductors includes three windings, which utilizes the second and third windings of the two coupled inductors to realize high gain output of the converter, utilizes a serial circuit composed of the two clamp switch tubes and two clamp capacitors to absorb and transfer harmlessly the leak energy of the two coupled inductors and realizes turn on of zero voltage of two power switch tubes and zero voltage turn-off of them utilizing the parallel capacitors of the two switch tubes to further realize zero-voltage turn on and off of the two clamp switch tubes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Multi-band antenna structure
ActiveUS20050116869A1Lengthening radiating elementShorten the lengthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandEngineering
The invention provides a multi-band antenna structure for use in a wireless communication system. The antenna structure includes integrated inductive elements and capacitive elements that function as a tuned circuit to allow the antenna structure to operate in multiple frequency ranges. In particular, the capacitive elements electromagnetically couple to the inductive elements. The capacitive elements provide the inductive elements with parallel capacitance at a given set of frequencies, thereby providing the antenna structure with frequency selectivity. At a particular frequency range, the inductive elements act as short circuits, thereby lengthening the radiating elements, which radiate energy at the particular frequency. At another frequency range, the inductive components act as open circuits, virtually shortening the radiating elements in order to radiate the higher frequencies. In this manner, the multi-band antenna structure operates within multiple frequency ranges.
Owner:DSP GROUP
Power supply device having precharging function
InactiveUS20110234177A1Reduce resistanceQuickly prechargedBatteries circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionEngineeringControl circuit
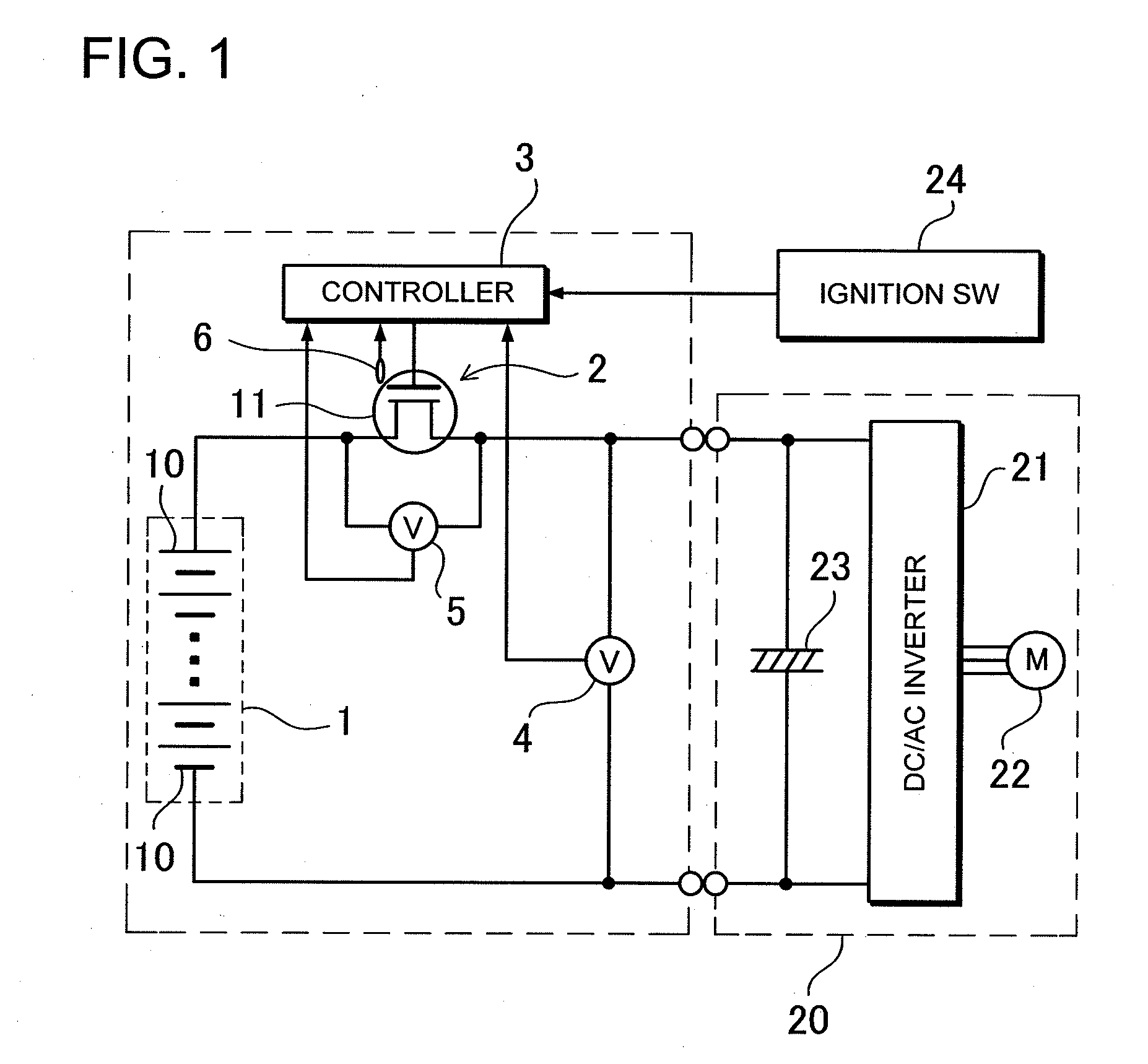
A power supply device includes a battery 1, an output switch 2 connecting the battery 1 to a load 20, and a control circuit 3 controlling the output switch 2. The output switch 2 is a semiconductor switching element 11 having controllable ON resistance. In the power supply device, the ON resistance of the semiconductor switching element 11 is controlled by the control circuit 3 so that the ON resistance in a precharge state is set larger than the ON resistance in an electrically-conducted state. The parallel capacitor 23 of the load 20 is precharged in the precharge state. After the parallel capacitor 23 of the load 20 is precharged, the load 20 is supplied with power from the battery 1 with the semiconductor switching element 11 being brought into the electrically-conducted state in which the ON resistance of the semiconductor switching element 11 is smaller than the precharge state.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
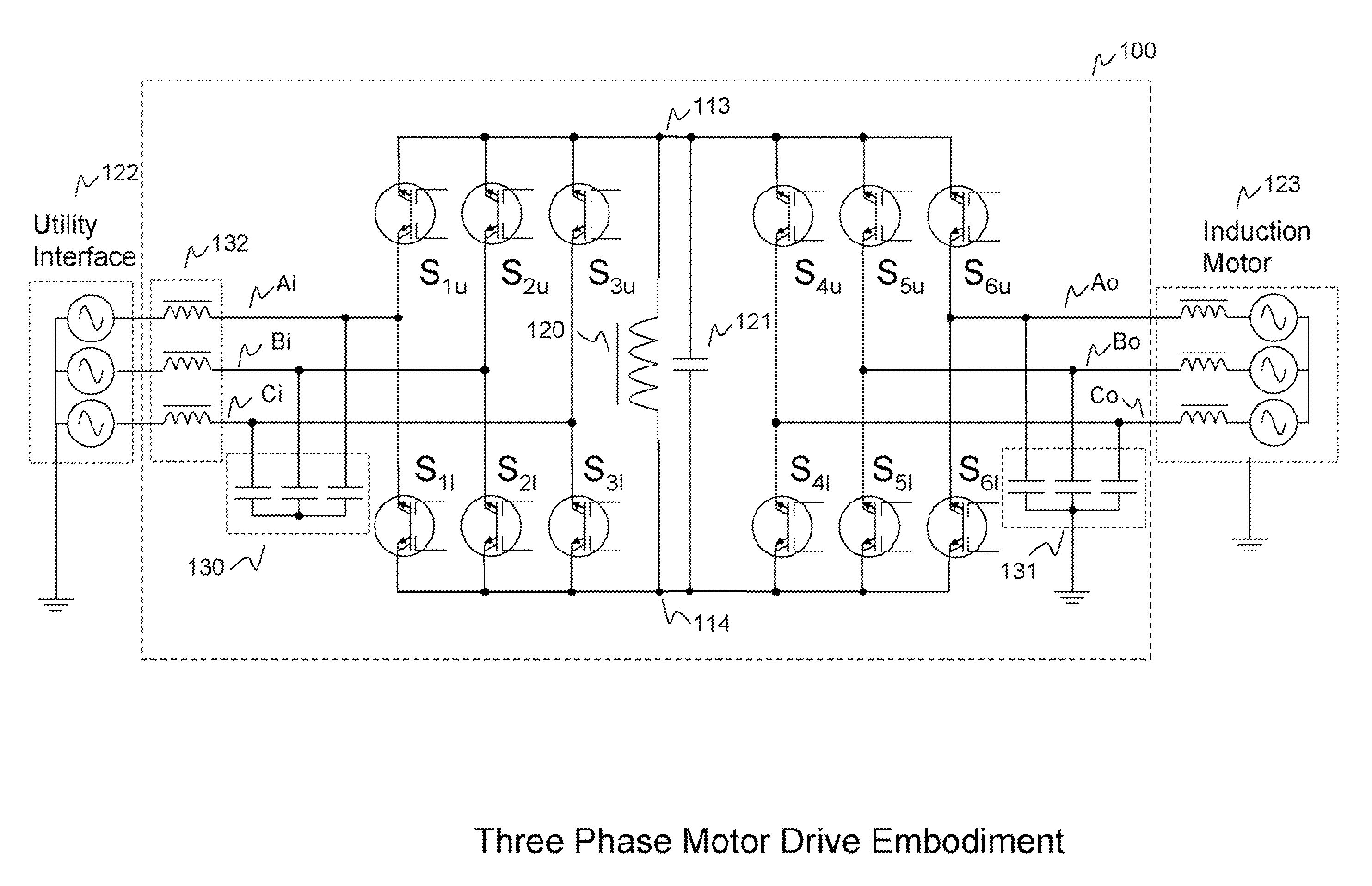
Composite active clamped 3-phase A.C-D.C power factor correction transformer
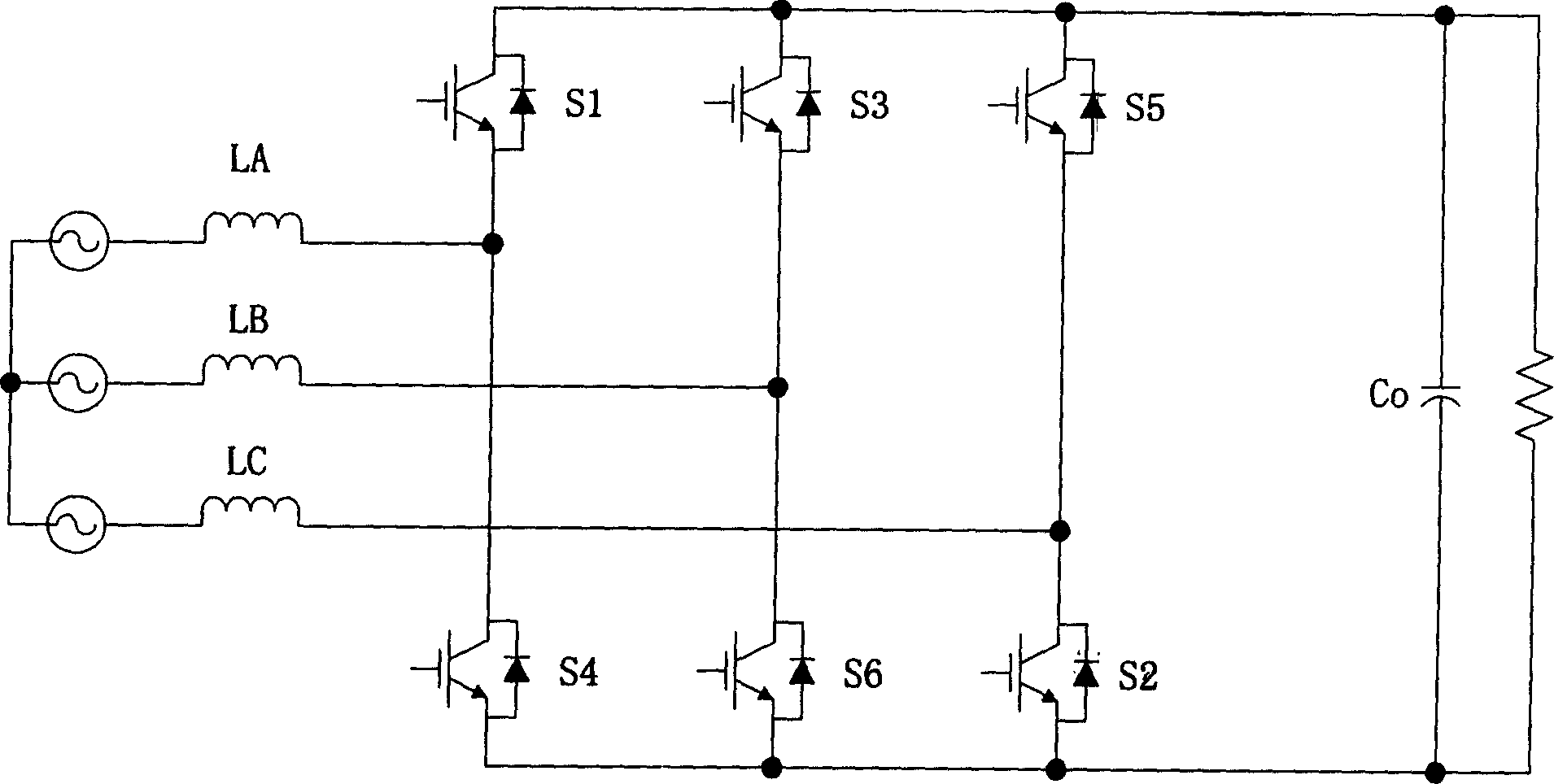
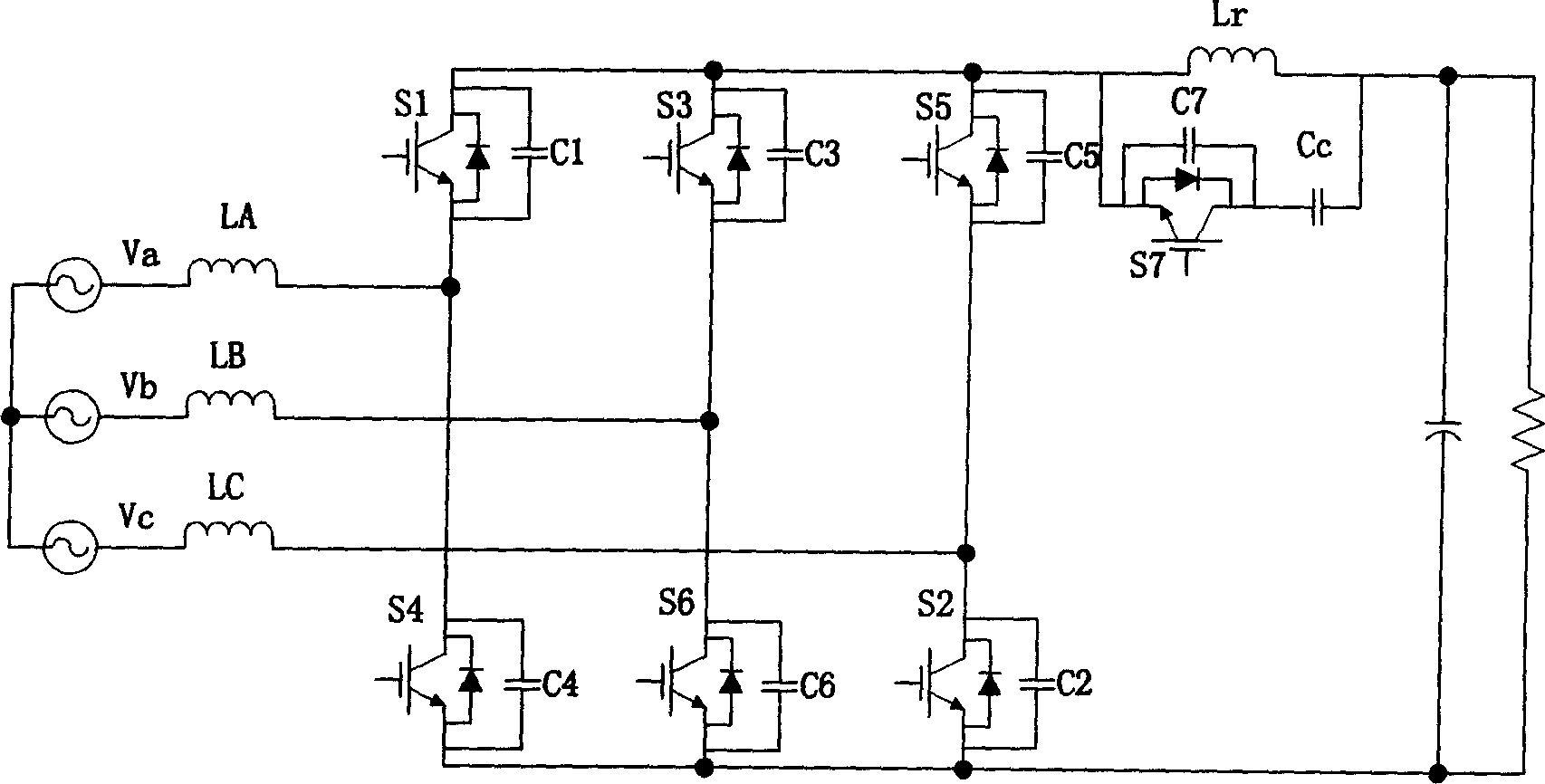
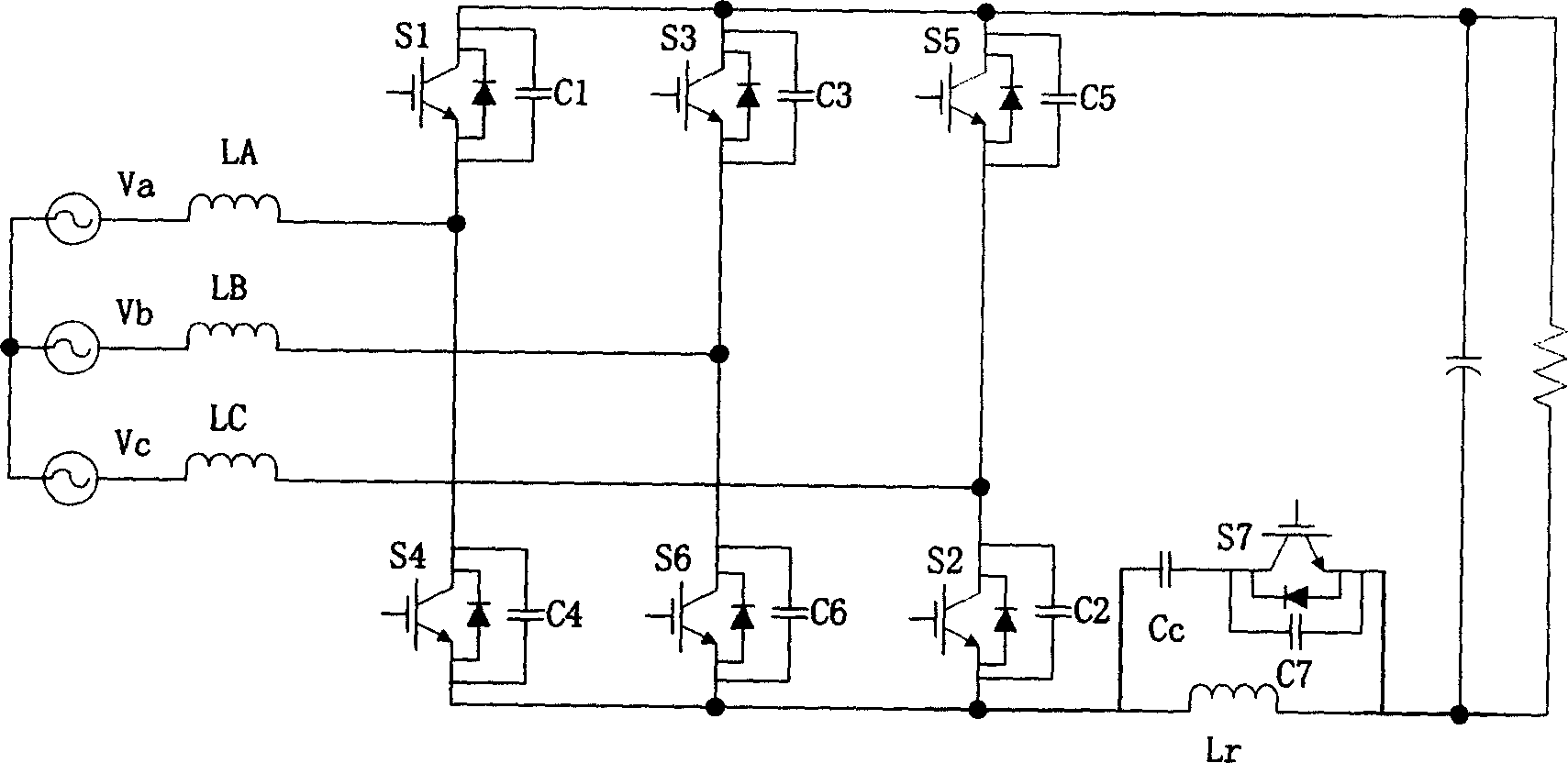
ActiveCN1564447ASimple structureReduce lossEfficient power electronics conversionEnergy industryTransformerDC-BUS
The converter includes six pieces of three phase bridge arm including full controlled main switch with diode connected in inverted parallel, input inductance connected between power source and middle point of each phase bridge arm, and output capacitance connected to output end of three phase bridge arm. Characters are that capacitance is connected to six main switches respectively. Resonant inductance is connected to DC bus of three-phase bridge arm and output capacitance. Cascaded circuit of auxiliary switch and clamping capacitance is cross-connected on two ends of resonant inductance. Two ends of the auxiliary switch are connected to diode in inverted parallel as well as connected to capacitance. Features of the converter are simple structure, restraining backward recovery of diode connected in inverted parallel, realization of soft switch and high efficiency of circuit.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
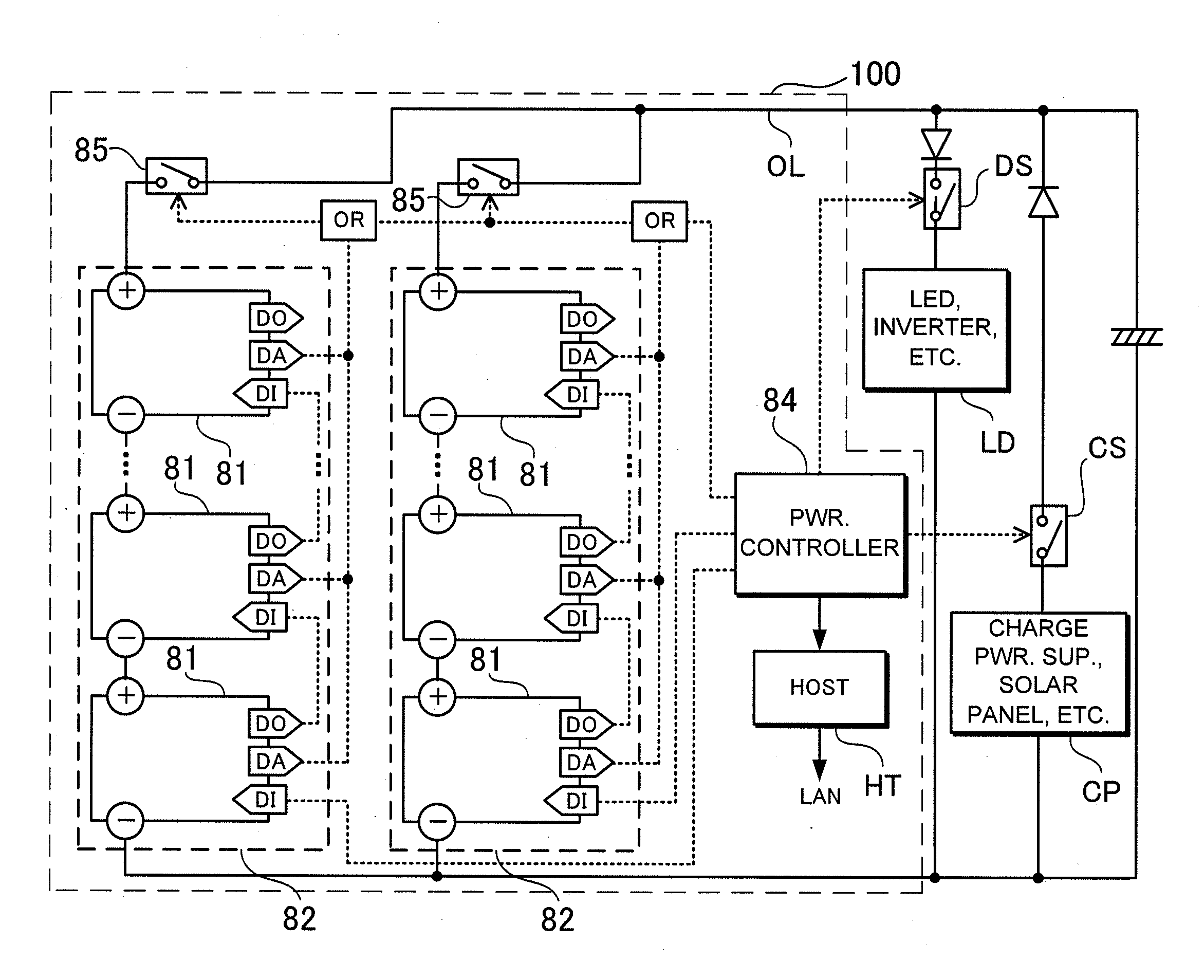
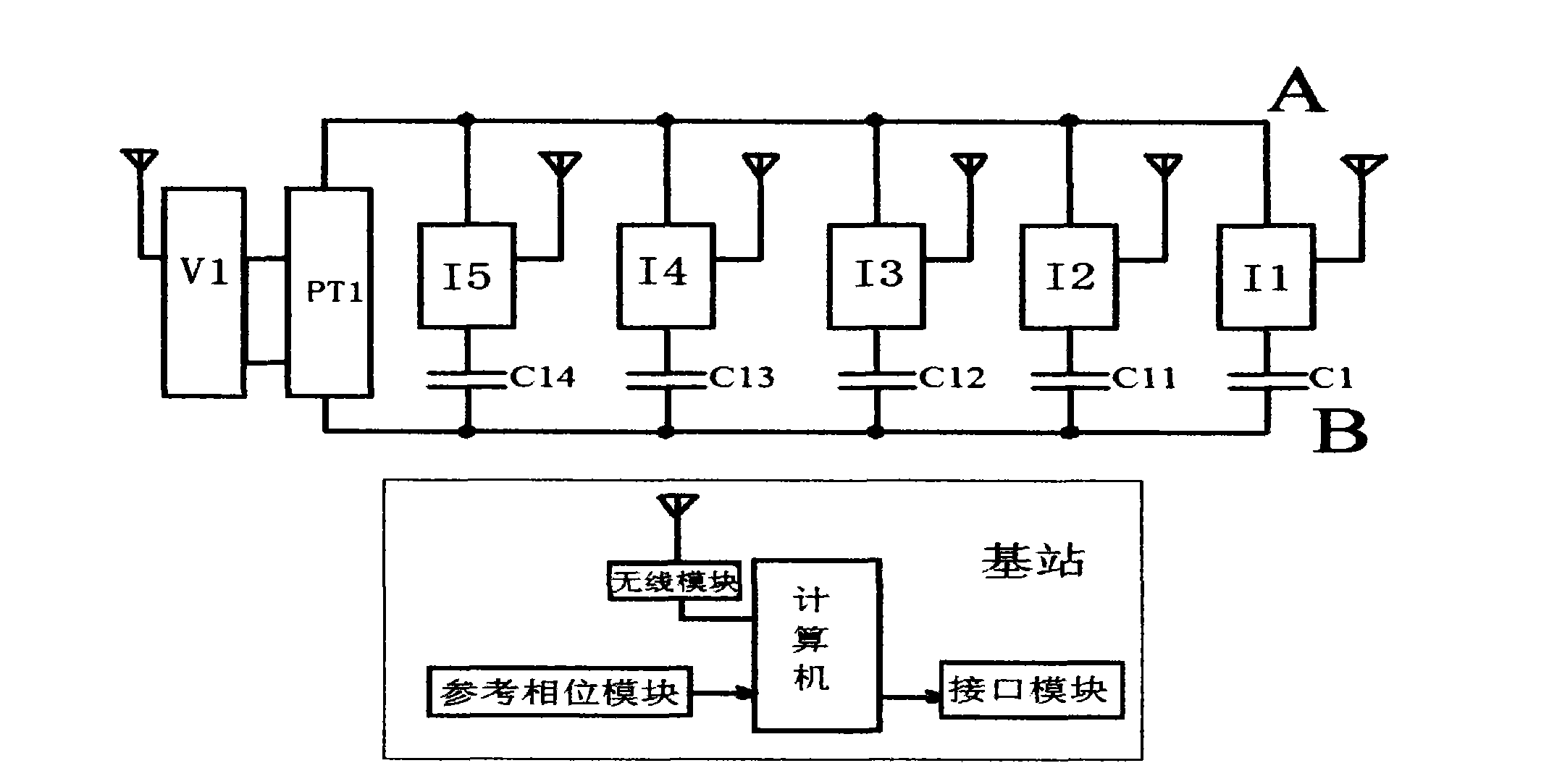
Transformer substation capacitor on-line monitoring method and device based on wireless mode
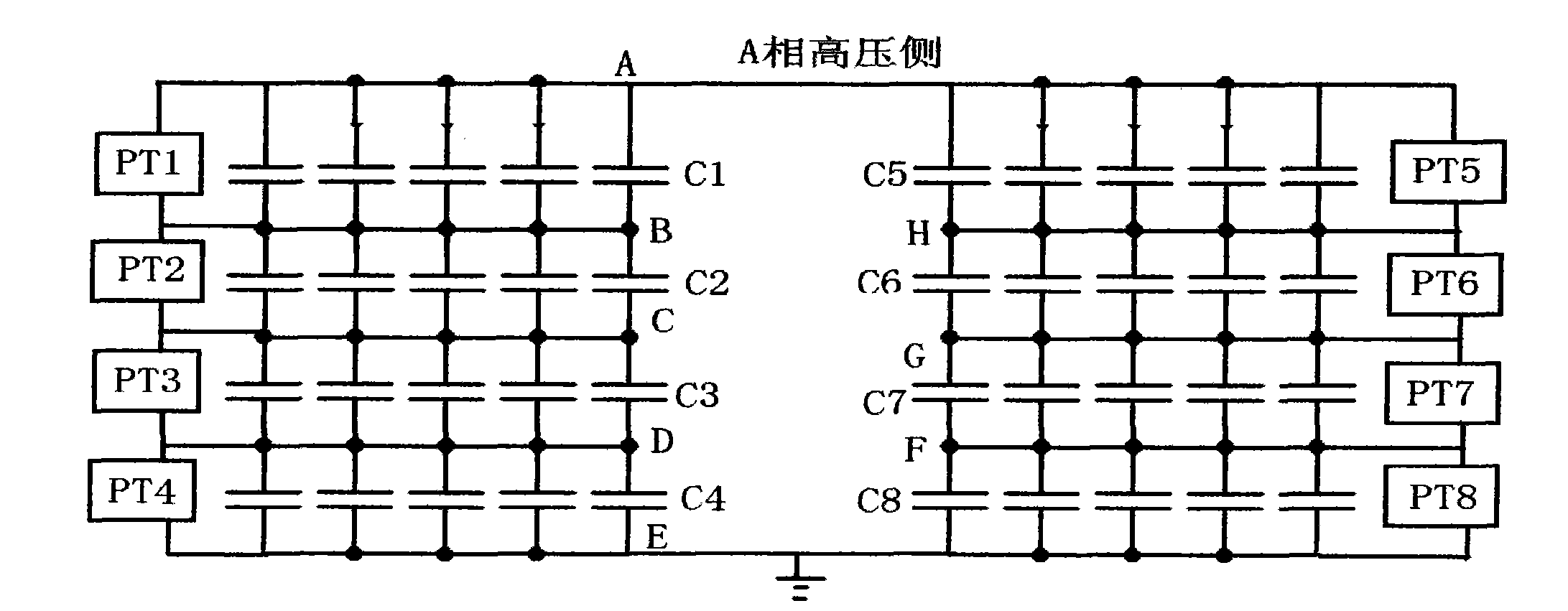
ActiveCN102680799ARealize data queryImplement fault diagnosisTransmission systemsResistance/reactance/impedenceFrequency spectrumCapacitor voltage
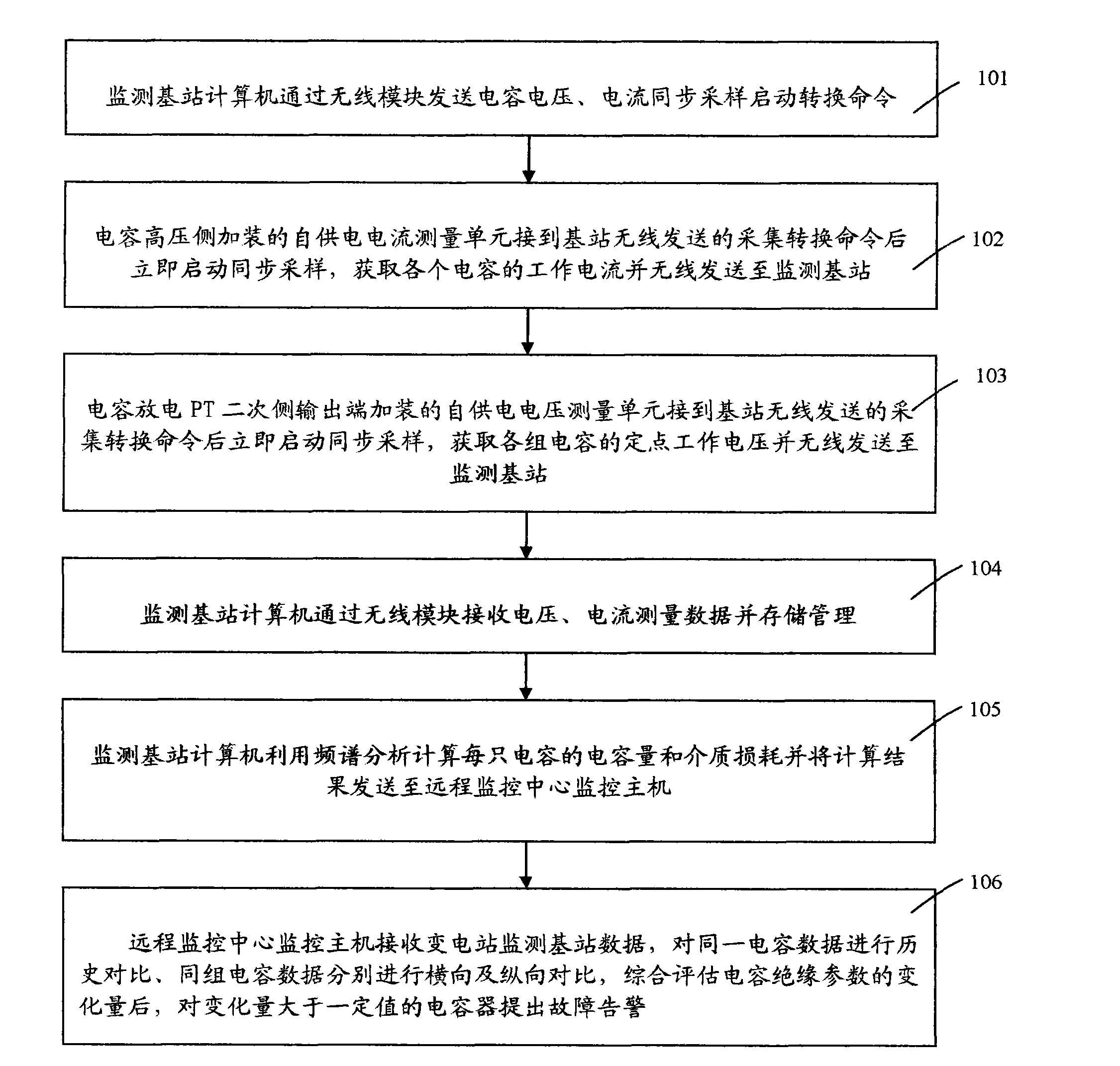
The invention belongs to the technical field of electric power equipment on-line monitoring, and in particular relates to a transformer substation capacitor on-line monitoring method and device based on a wireless mode, wherein the method mainly comprises the following steps: designing and additionally arranging a self-electricity-supplying current measuring unit at the high-voltage side of each capacitor, additionally arranging a self-electricity-supplying voltage measuring unit at the secondary side output end of an electricity discharge PT (potential transformer) of each group of parallel capacitors, acquiring the working voltage and current of each capacitor, and sending the obtained working voltage and current of each capacitor wirelessly to a monitoring base station; monitoring an internally-built computer and a wireless module of the base station; sending a capacitor voltage and current synchronous sampling starting conversion command, receiving, storing and managing measurement data, calculating the capacitance and medium loss of each capacitor by utilizing spectrum analysis, sending the calculated result to a monitoring host machine of a remote monitoring center for comprehensive estimation and analysis, and giving out a fault alarm for the capacitors with the variation greater than a certain value.
Owner:山东惠工电气股份有限公司
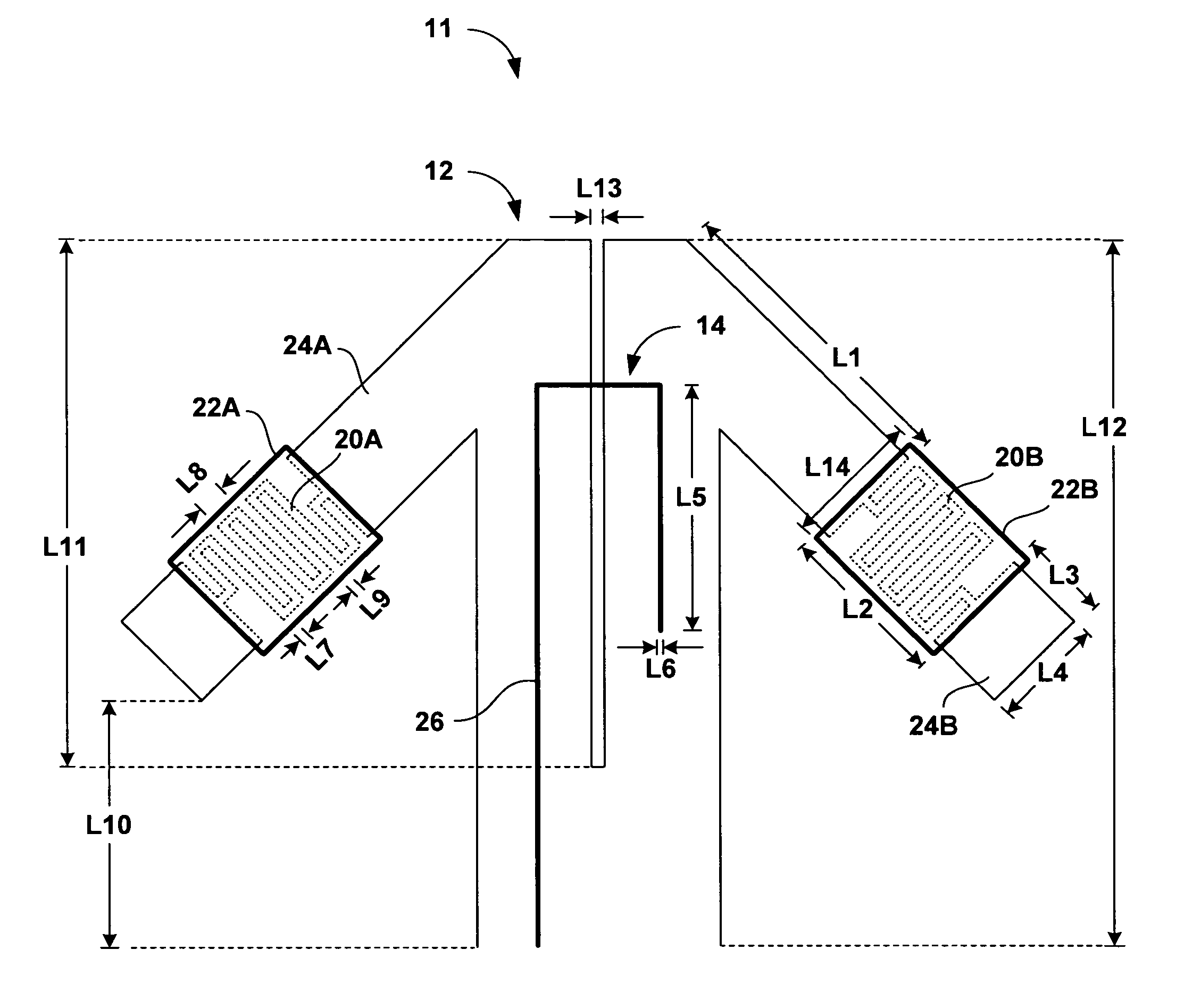
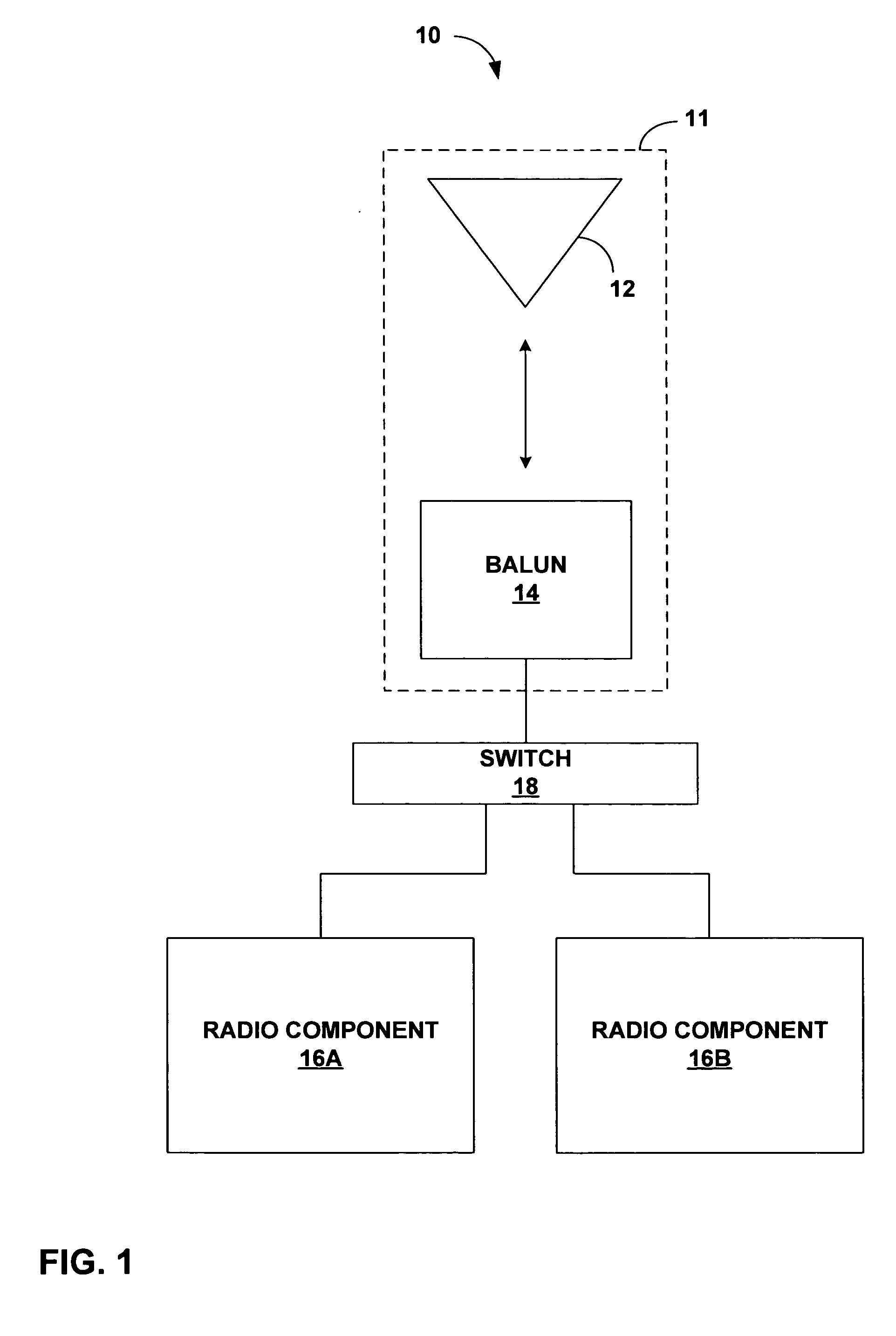
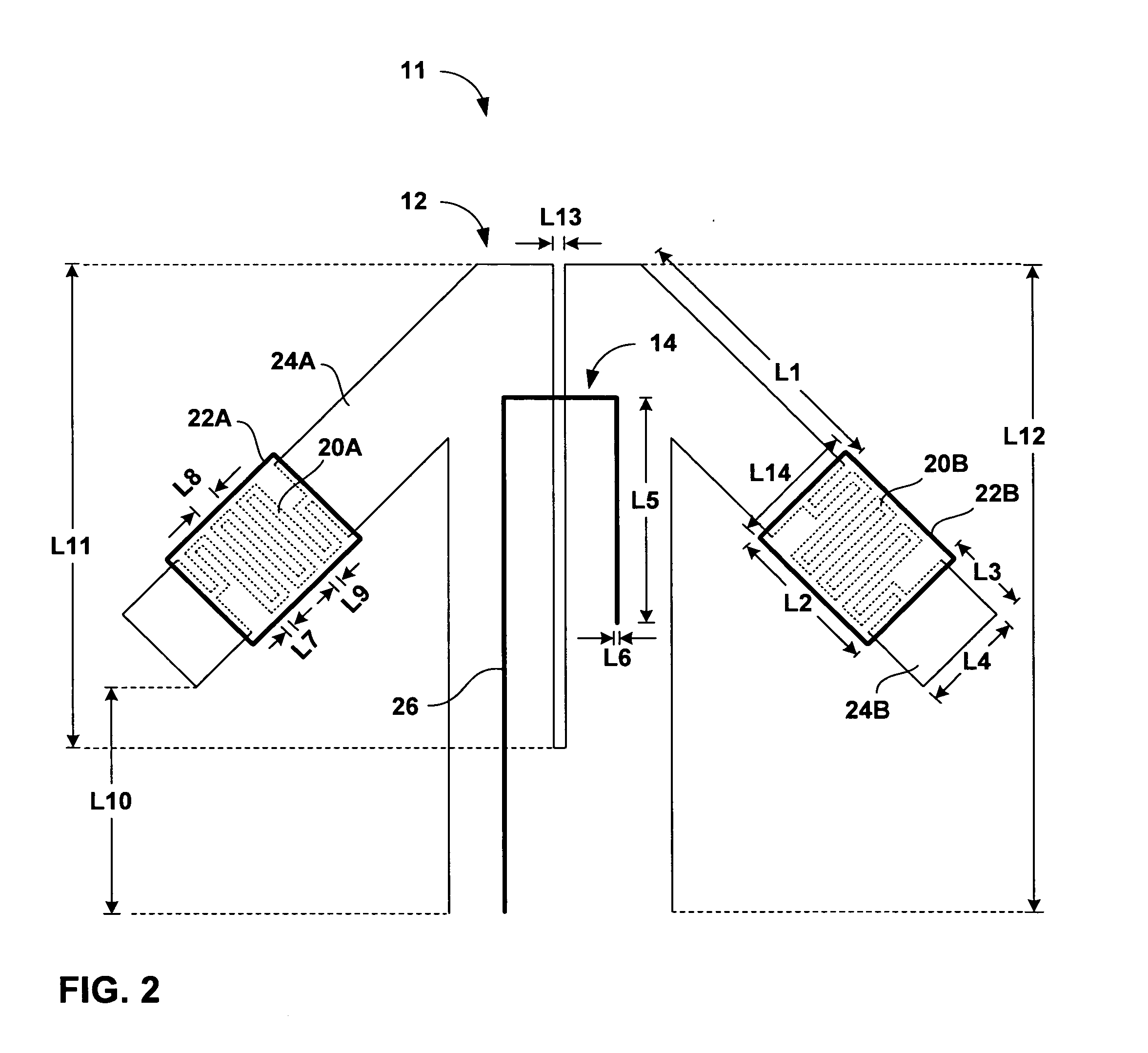
Miniaturised half-wave balun
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method and apparatus for switching of parallel capacitors in an HID bi-level dimming system using voltage suppression
InactiveUS6856101B1Accurately clamp voltageAvoid overall overheatingElectric light circuit arrangementElectric discharge lampsEngineeringPeak value
Switching of parallel capacitors in an HID bi-level lighting control system is accomplished through use of transient voltage suppression across an electronic relay for discharge of residual charge from a switched capacitor when combined peak voltage exceeds clamping voltage, thereby allowing maximum switch voltage rating to be lower than is possible through the use of conventional switching methods and circuitry. The invention contemplates method and apparatus permitting capacitive switching at voltage levels higher than are possible in conventional capacitive switching arrangements including capacitive switching arrangements used in lighting control systems.
Owner:ABL IP HLDG
Virtual-capacitor-based power sharing control method for micro-grid inverter parallel connection
ActiveCN105226727ANo need for additional communicationLow costSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsVoltage amplitudePower inverter
The invention discloses a virtual-capacitor-based power sharing control method for micro-grid inverter parallel connection. The method is characterized in that a voltage amplitude value and a phase angle value are obtained by using a power outer ring of a power outer ring control algorithm; and a virtual capacitor algorithm is added to obtain an output voltage amplitude value and a phase angle instruction, and dual-closed-ring control of the output voltage and the capacitive current is carried out. According to the virtual capacitor algorithm, parallel capacitor characteristics of output terminals of inverters are simulated by a control algorithm and the output voltages and reactive powers of the inverters are adjusted; and a virtual capacitance value is obtained by calculation based on outputted reactive powers of all inverters and a capacitance sagging formula. According to the invention, interconnection communication among inverters and connecting impedance detection are not required; the line impedance voltage drop can be compensated in a self-adaption mode; and reactive power sharing capabilities and output voltage precision of all inverters can be improved.
Owner:黄山科创中心有限责任公司
Soft switching three-phase gird-connected inverter additionally provided with freewheeling path
InactiveCN101951186ASimple structureReduce lossAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsClamp capacitorPower factor
The invention discloses a soft switching three-phase gird-connected inverter additionally provided with a freewheeling path, which comprises an inverter direct current power supply, a three-phase bridge arm formed by six full-control master switches with antiparallel diodes, and output filter inductors respectively connected between the midpoint of each phase of the bridge arm and an alternating current grid, wherein the three-phase bridge arm is connected with a full-control switch with an antiparallel diode, the full-control switch and the six master switches of the three-phase bridge arm are respectively connected with a capacitor in parallel, an auxiliary switch with an antiparallel diode and a serial branch of a clamp capacitor are accessed between the inverter direct current power supply and a direct current bus of the three-phase bridge arm, and a resonance inductor Lr is bridged at two ends of the serial branch, and the auxiliary switch is connected in parallel with the capacitor. The invention is simple in structure, can suppress the reverse recovery of the diodes, and reduces the electromagnetic interference. All switches of the inverter realize zero-voltage switching-on, thus the inverter has the advantages of little switching loss and high circuit efficiency. The inverter can realize control of power factors and harmonic waves for output grid-connected current, and can be used in a grid-connected inverter in various power supplies.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
High efficiency dc/dc converter and controller
ActiveUS20150138841A1Boost voltageEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionElectric forceElectric power transmission
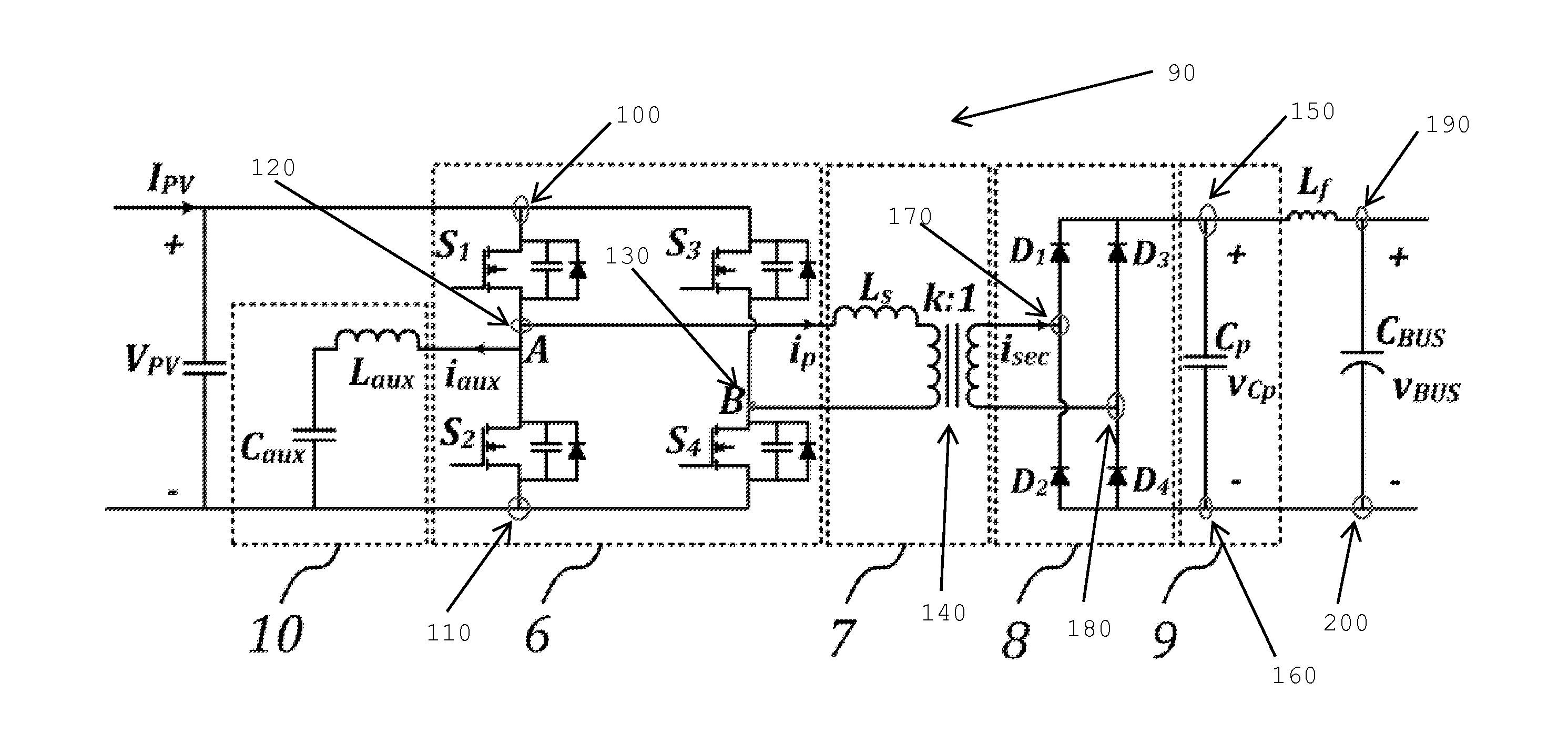
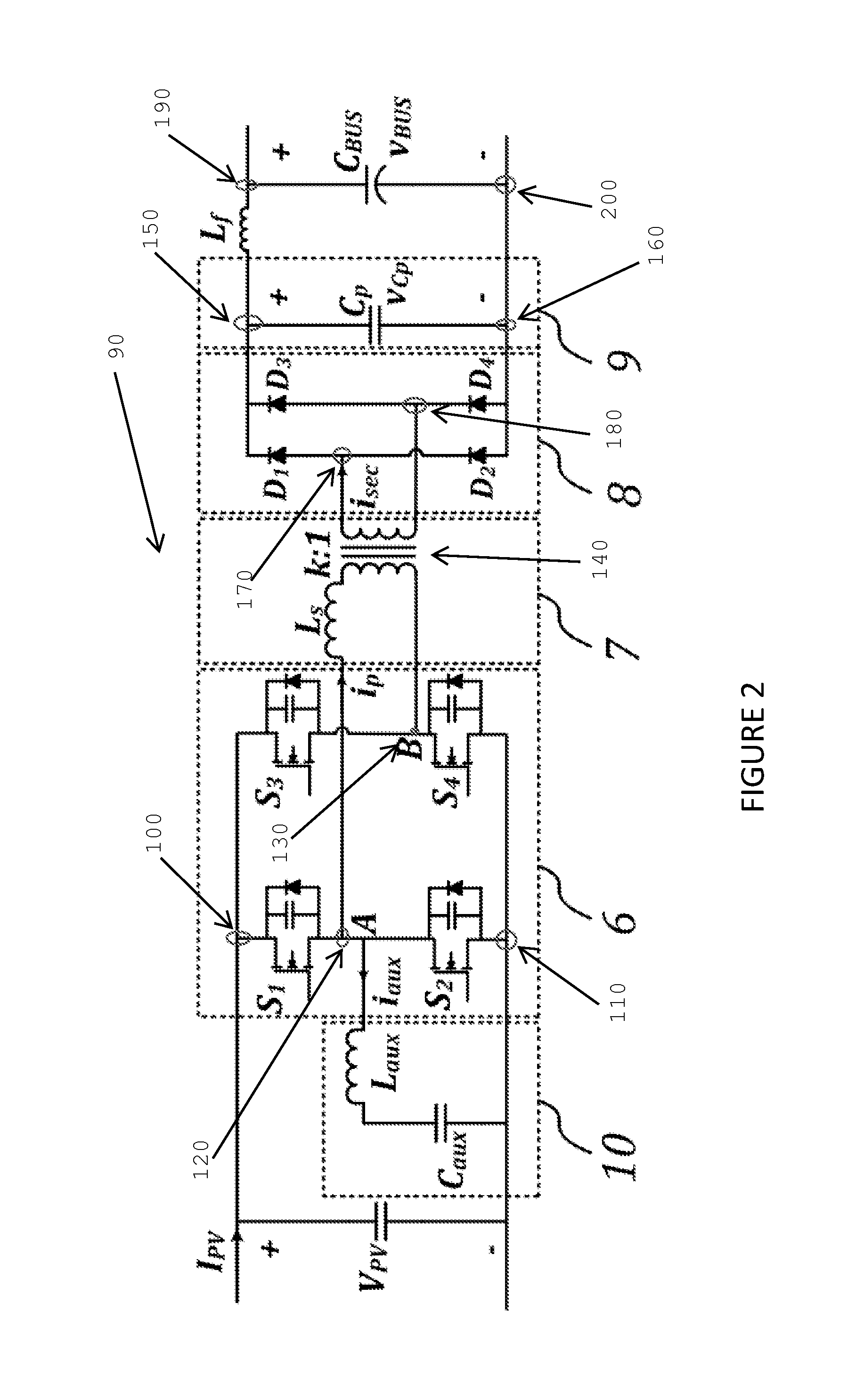
Systems, methods, and devices for use in a DC / DC converter. A circuit uses a full-bridge power semiconductor subcircuit along with a high power transformer subcircuit, a diode bridge subcircuit, and a parallel capacitor to provide galvanic isolation and boost the voltage from a power source such as a photovoltaic panel. To ensure zero voltage switching for the power semiconductors, either a passive auxiliary subcircuit or an inductor coupled in parallel to a transformer in the transformer subcircuit may be used. A controller which derives its timing signals from the transformer primary current is used to control the timing of the power semiconductors in the circuit. The circuit and its controller allows for self-adjusting regardless of load and uses the entire switching cycle to be used for power transfer.
Owner:SPARQ SYST INC
Class-E radio frequency power amplifier with feedback control
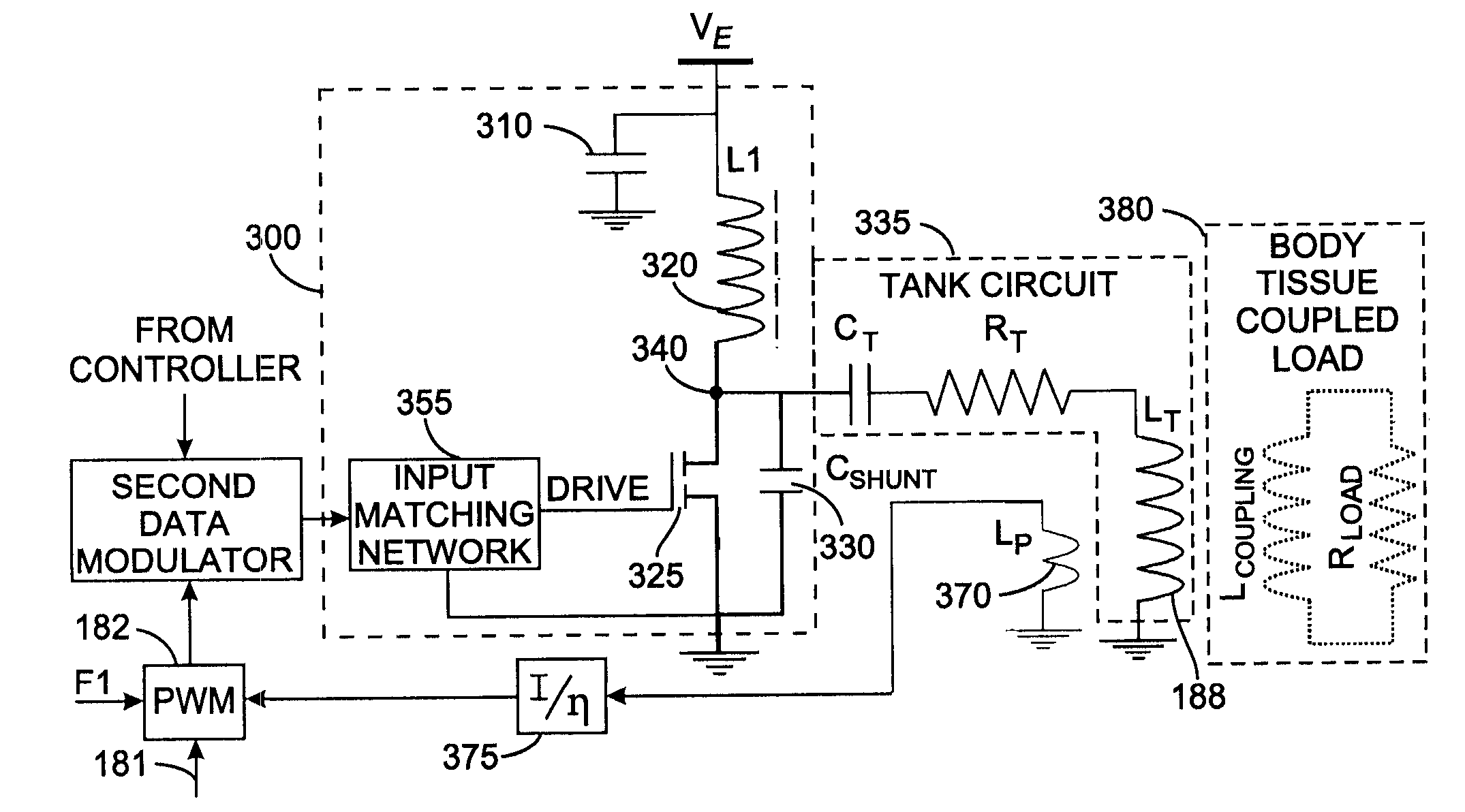
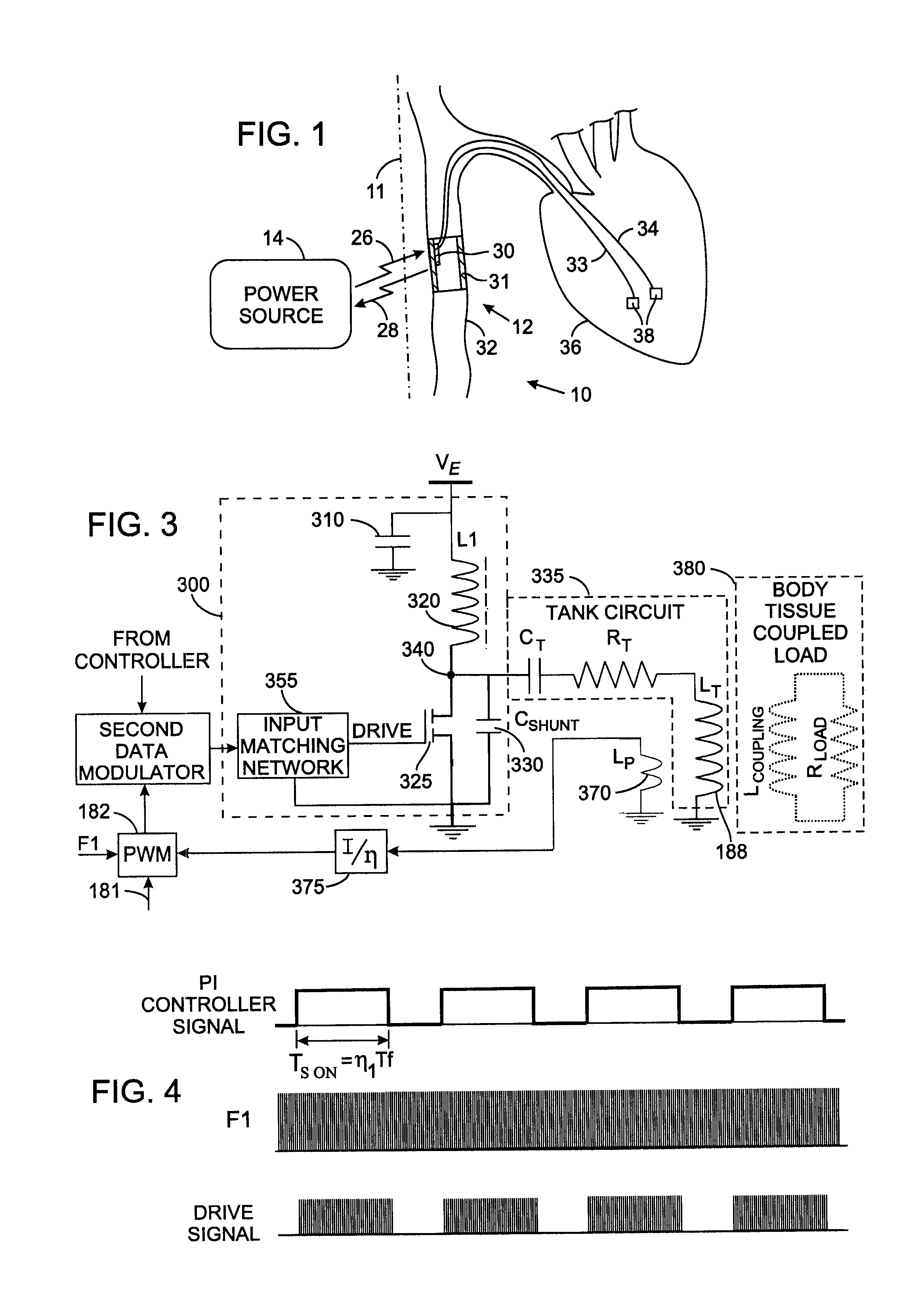
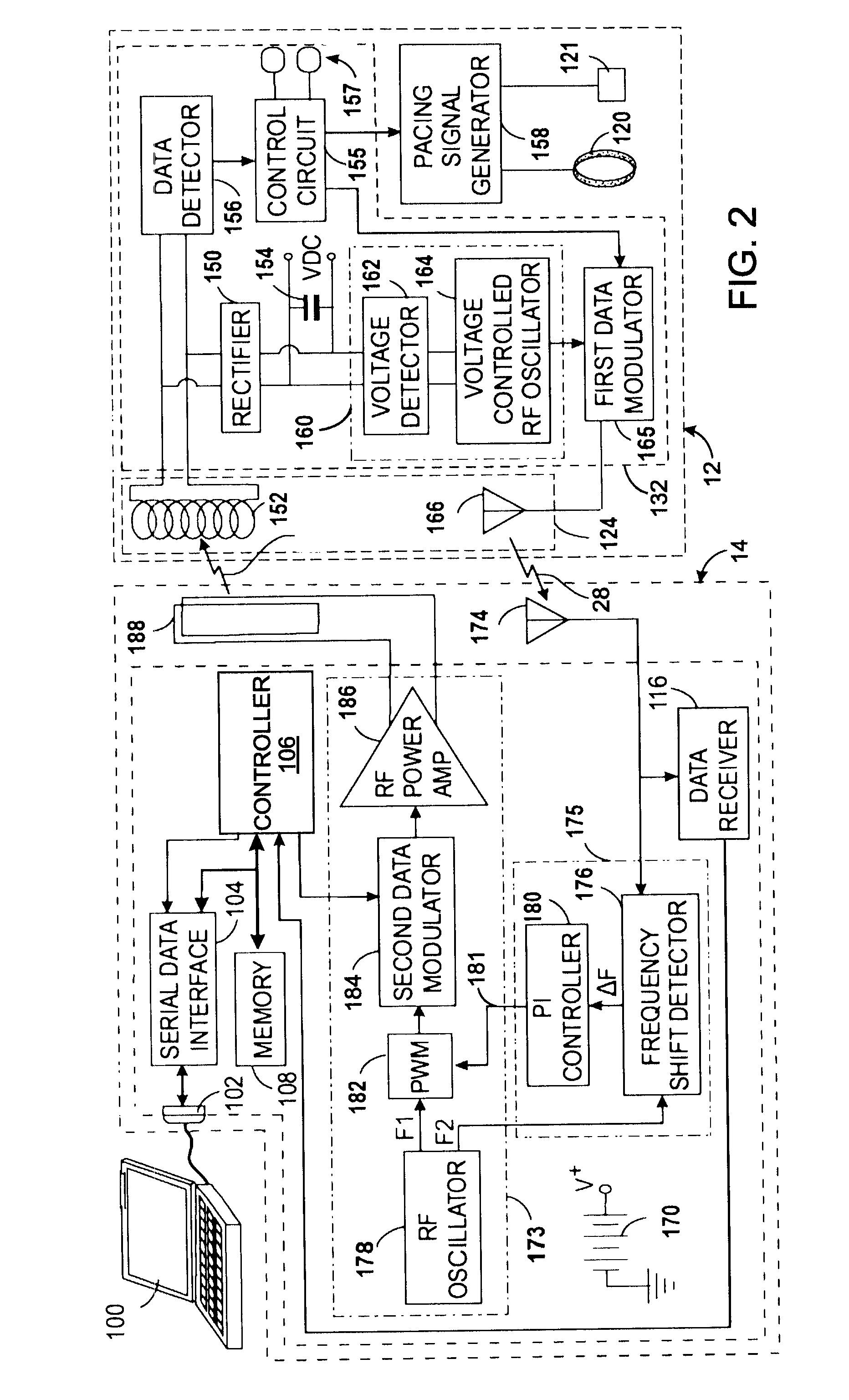
InactiveUS7535296B2ElectrotherapyNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsShunt capacitorsAudio power amplifier
A Class-E power amplifier includes a choke and a switch connected in series between a source of a supply voltage and circuit ground and connected to an inductively coupled coil. An output node of the amplifier is formed between choke and the switch and connected to a transmitter antenna. A shunt capacitor couples the amplifier's output node to the circuit ground. A feedback signal, indicating an intensity if the signal at the amplifier output node is used to vary the input signal to the Class-E power amplifier and thereby control operation of the switch.
Owner:KENERGY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com