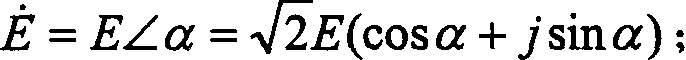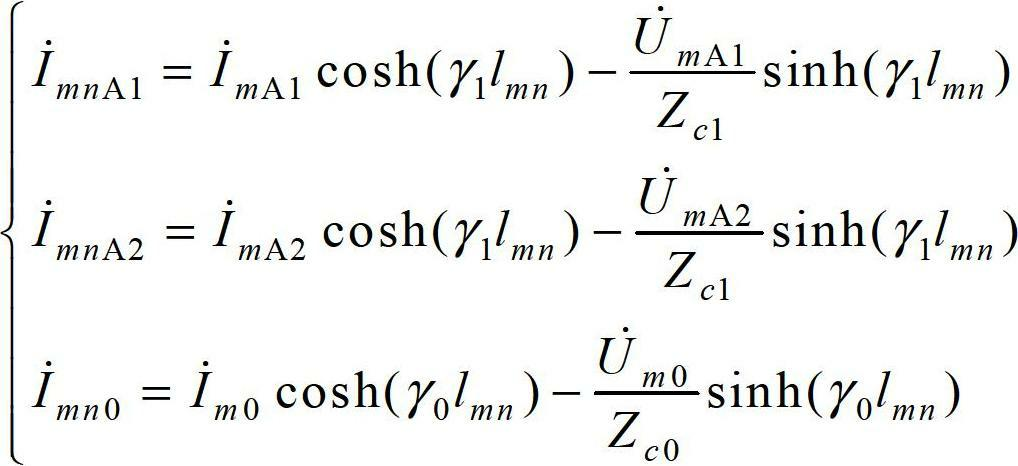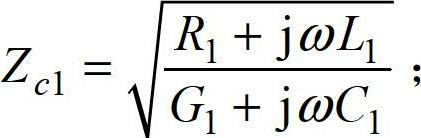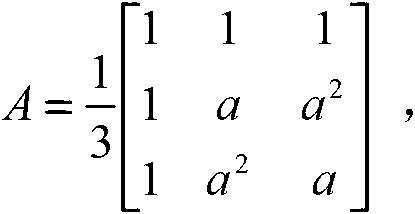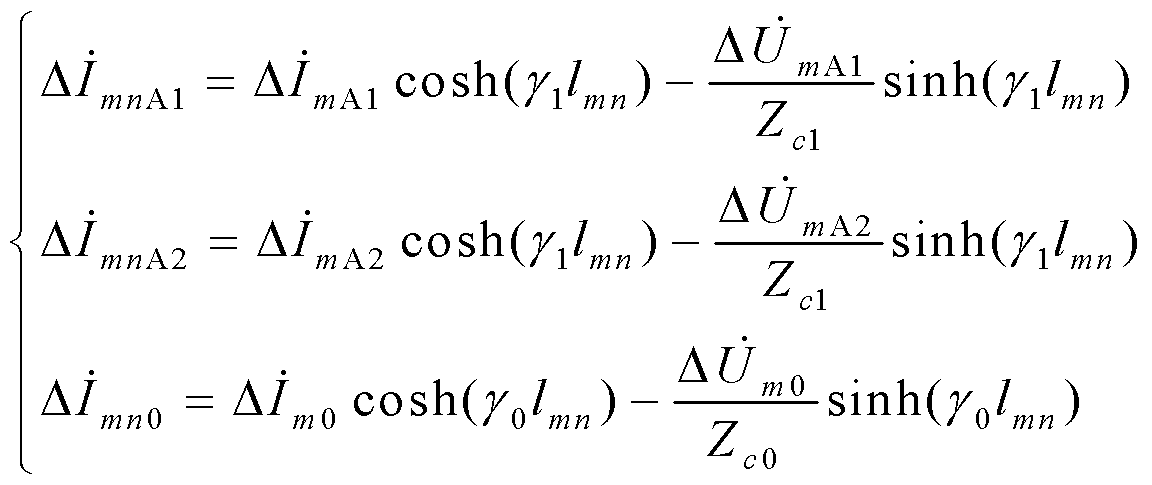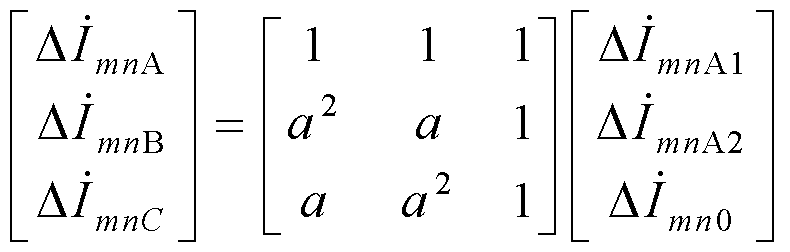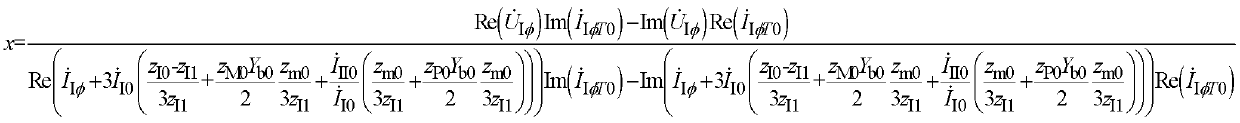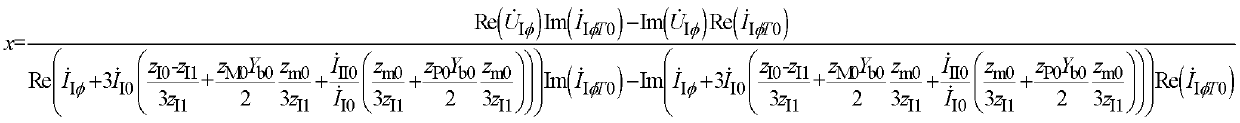Patents
Literature
285 results about "Symmetrical components" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electrical engineering, the method of symmetrical components simplifies analysis of unbalanced three-phase power systems under both normal and abnormal conditions. The basic idea is that an asymmetrical set of N phasors can be expressed as a linear combination of N symmetrical sets of phasors by means of a complex linear transformation.
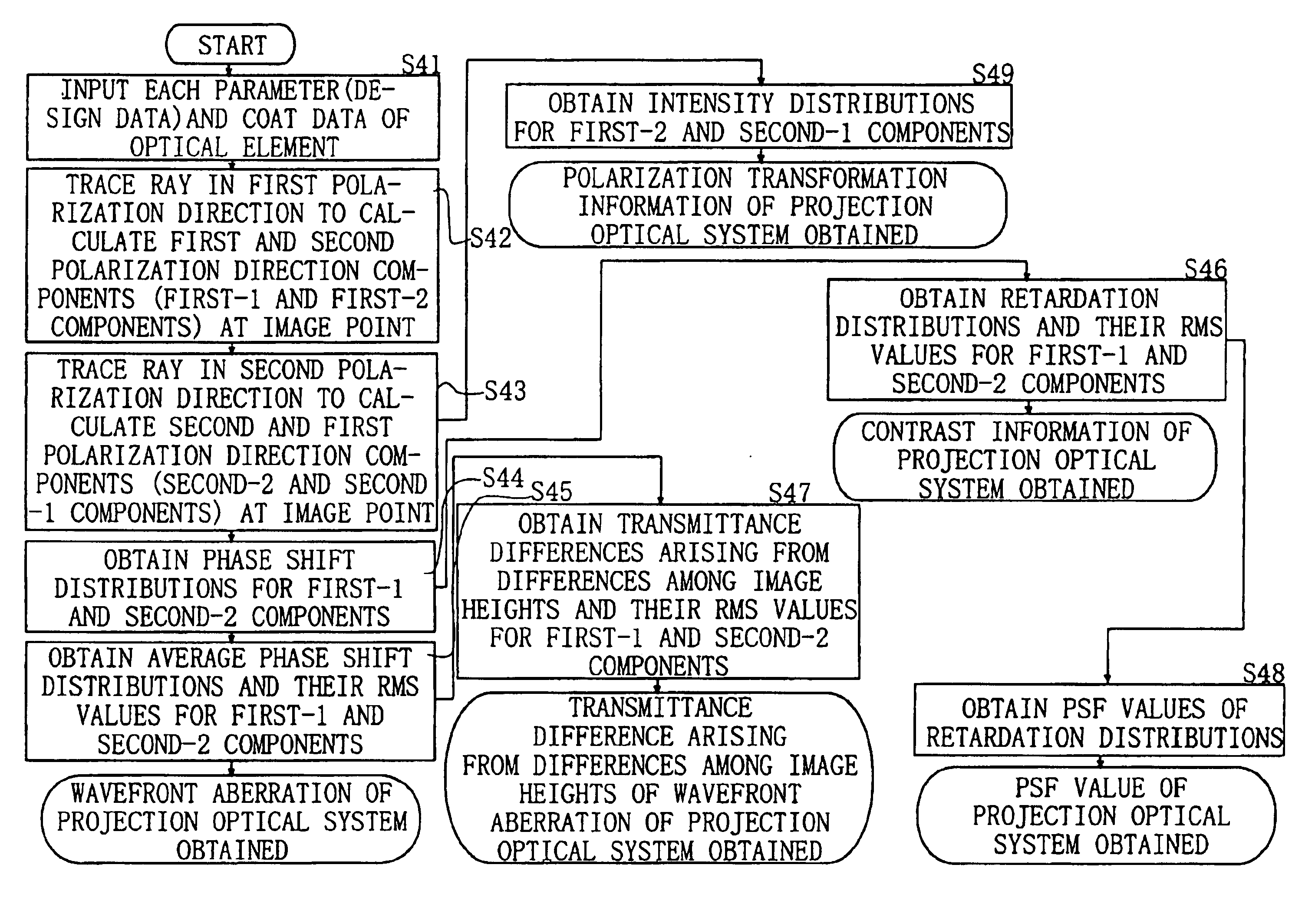
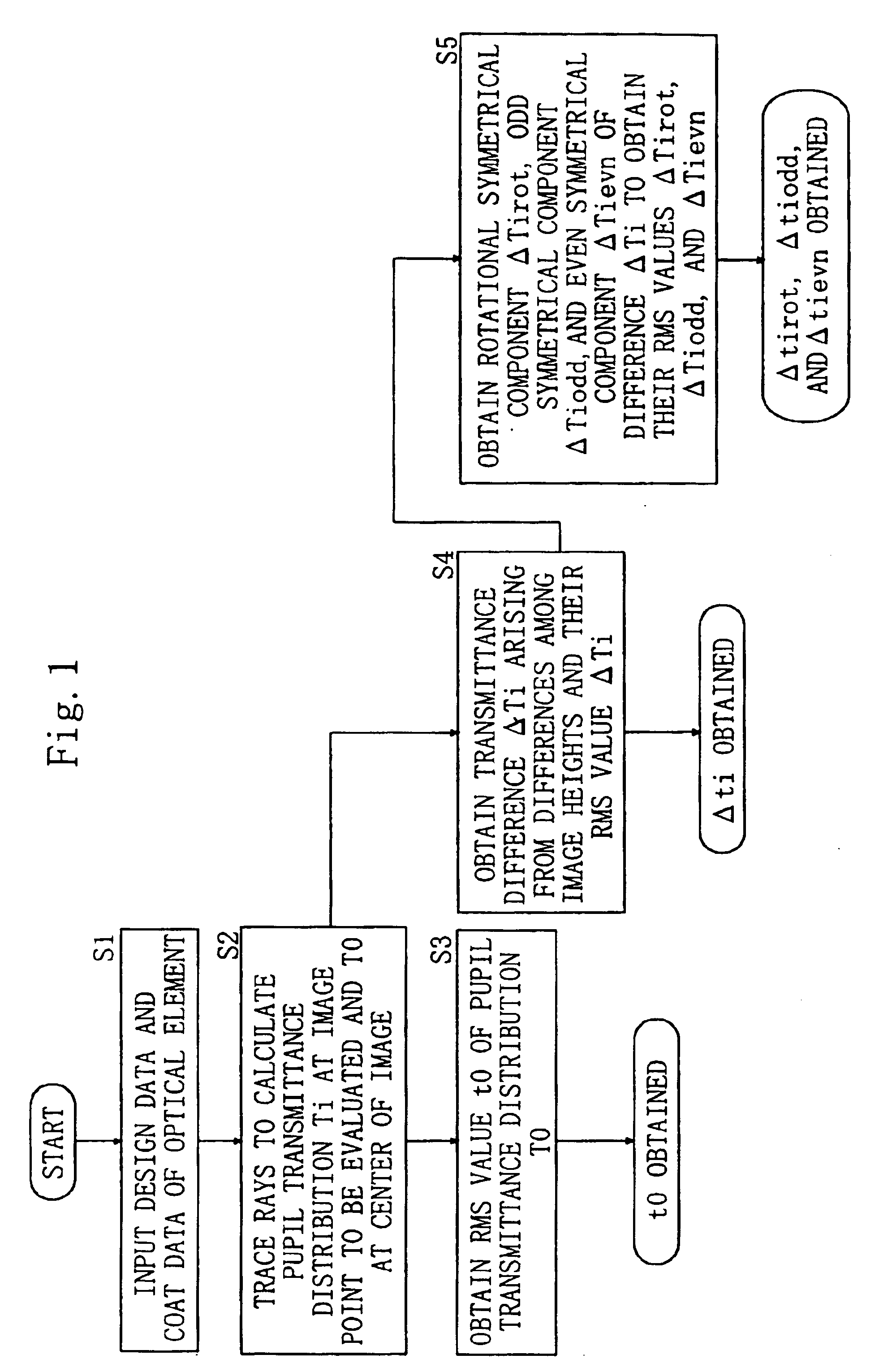
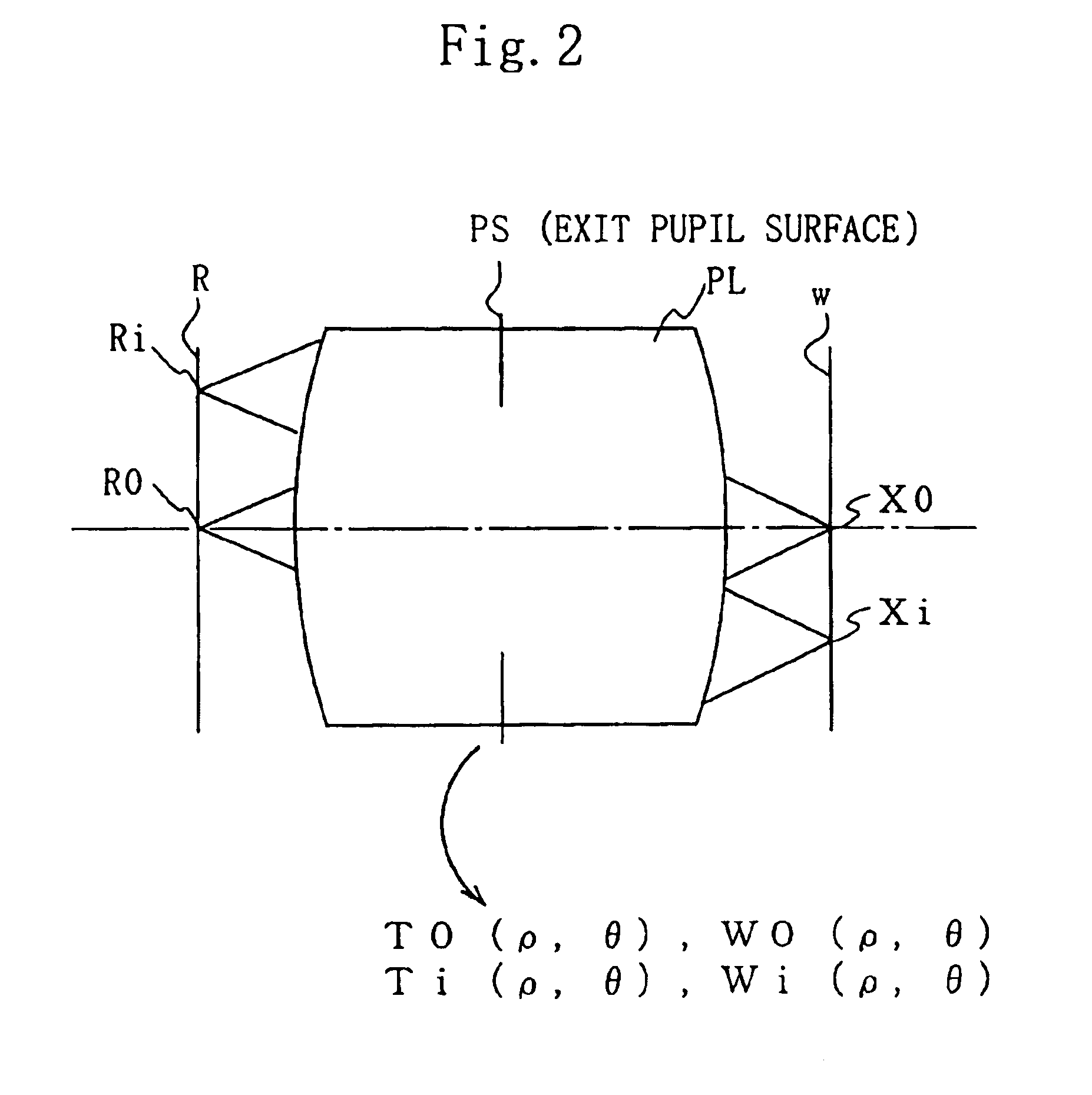
Method for evaluating image formation performance
The present invention accomplishes an evaluation of image formation performance in which the influence of a coat is accurately reflected. According to the present invention, for the evaluation of image formation performance of an optical system obtained is a pupil transmittance distribution (a distribution of light transmittance on an exit pupil surface) of a light beam that enters an image point to be evaluated of the optical system. At least one of a rotational symmetrical component, an odd symmetrical component, and an even symmetrical component is extracted from the obtained pupil transmittance distribution as an evaluation index.
Owner:NIKON CORP
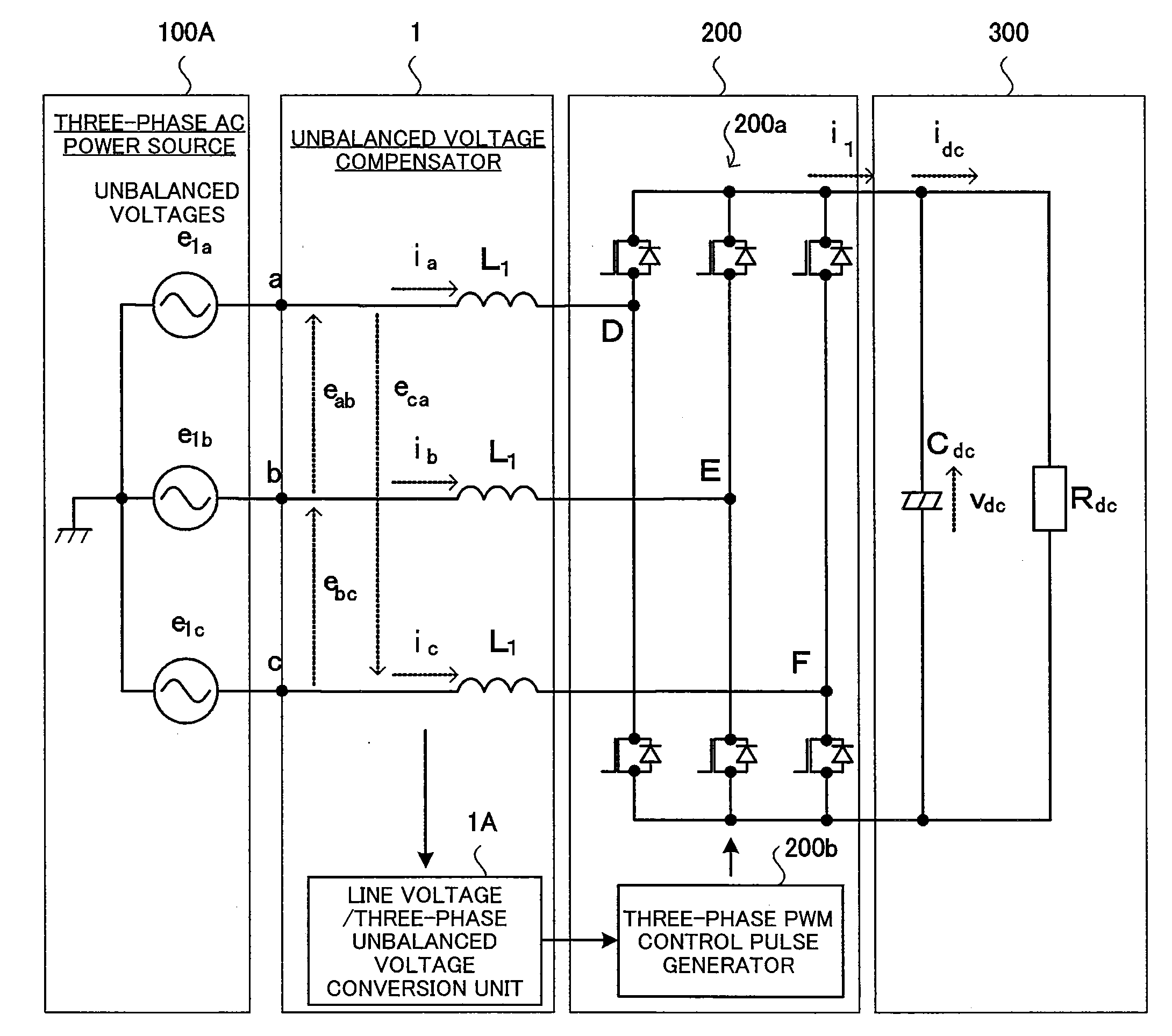
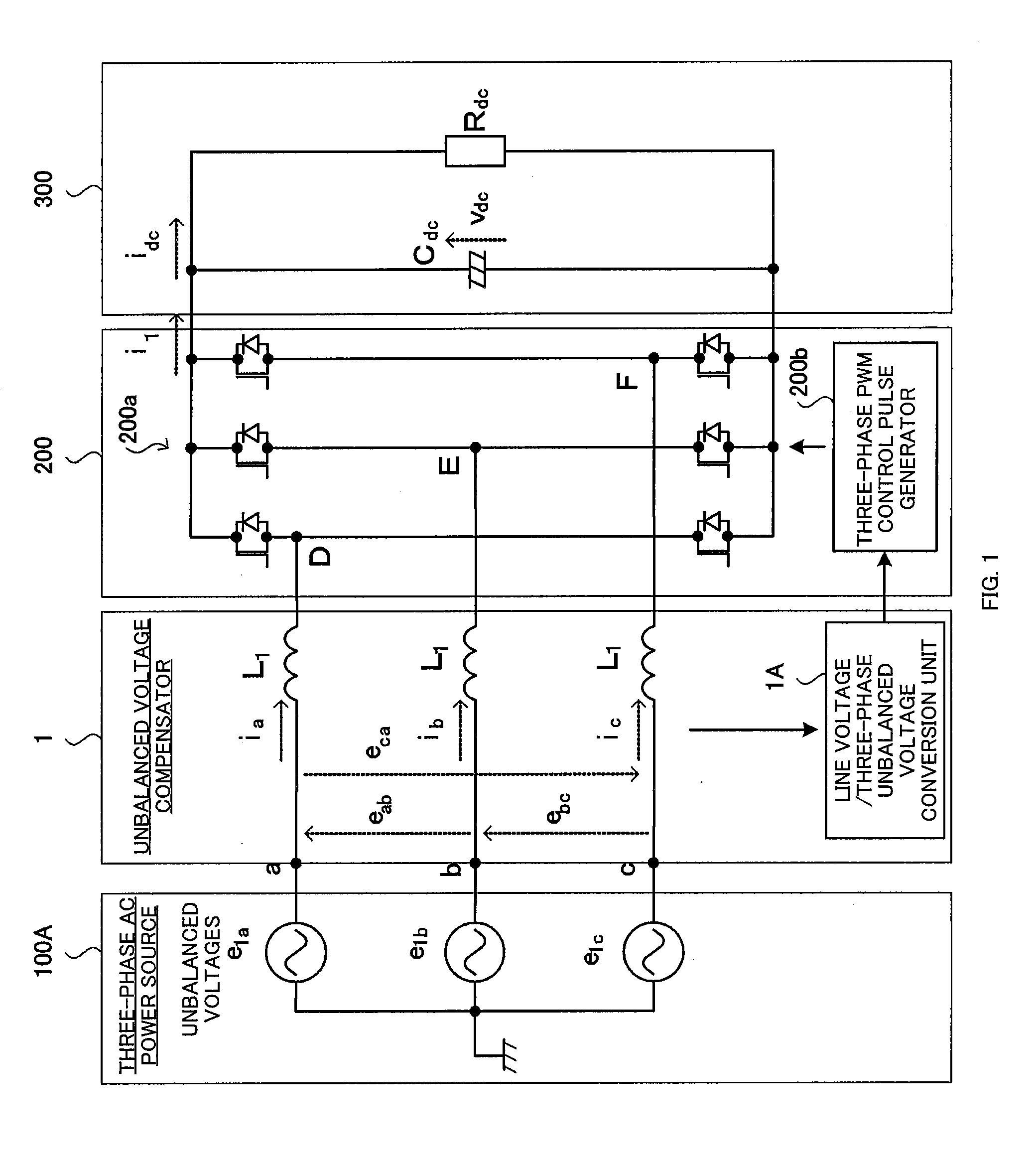
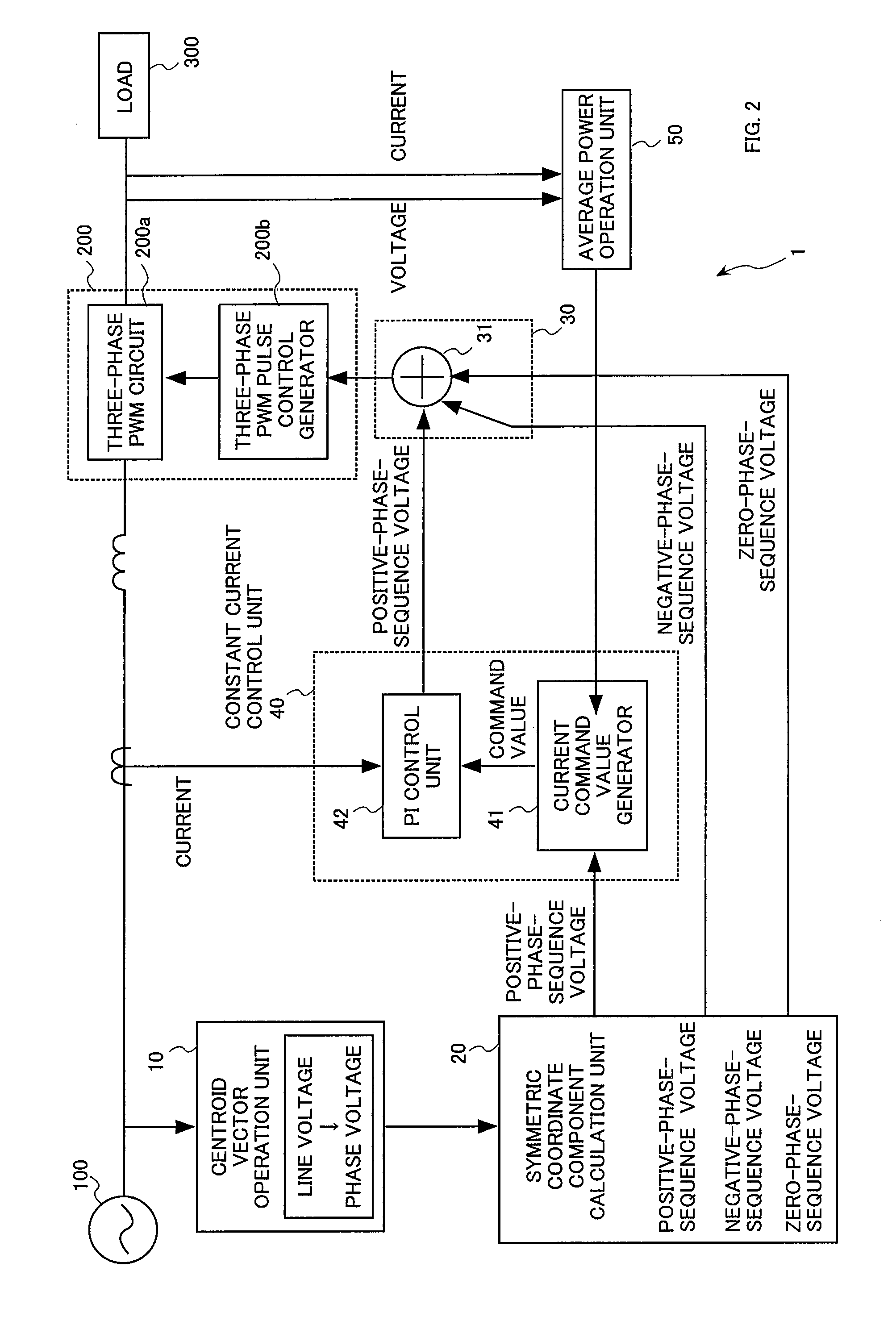
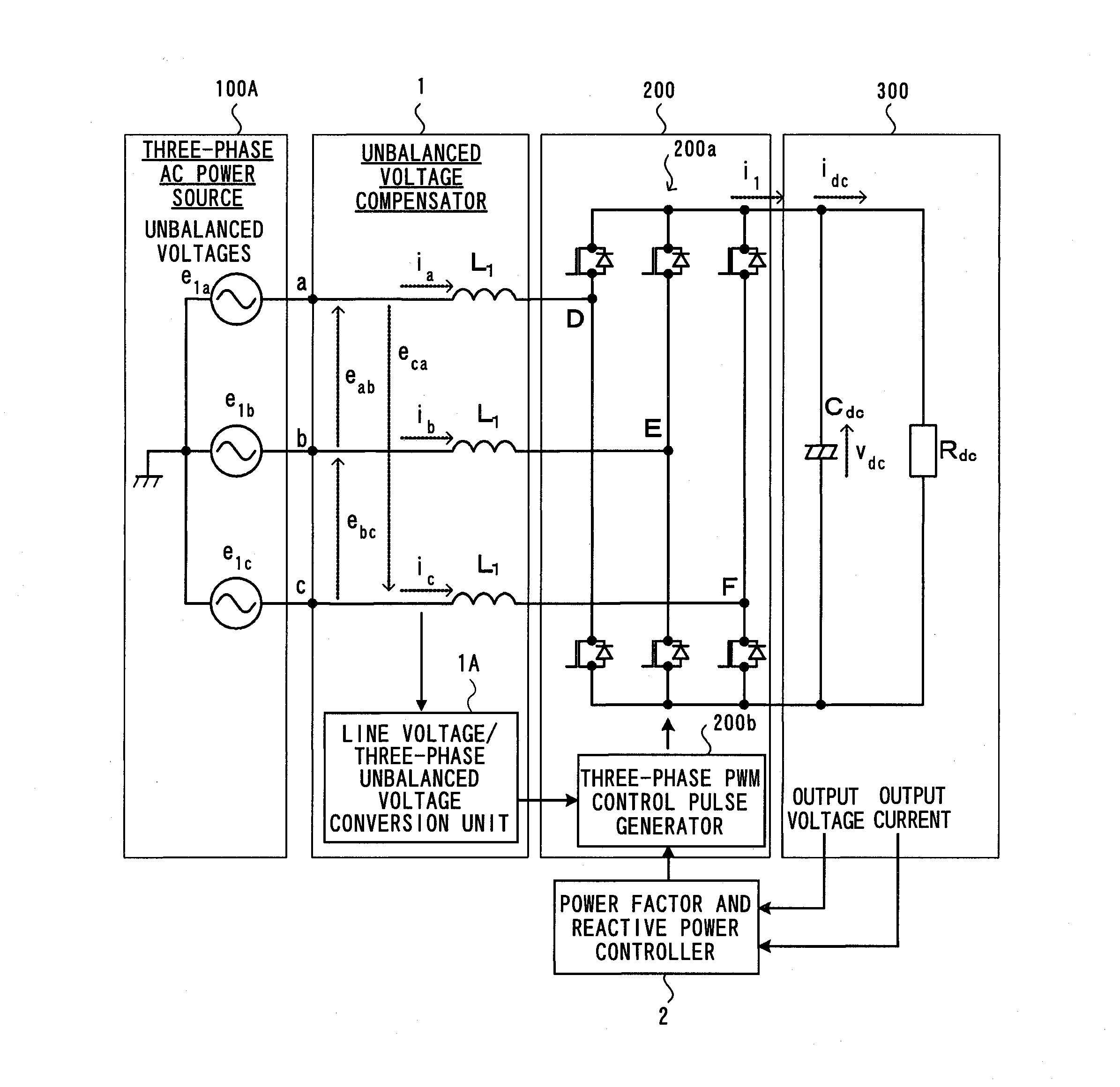
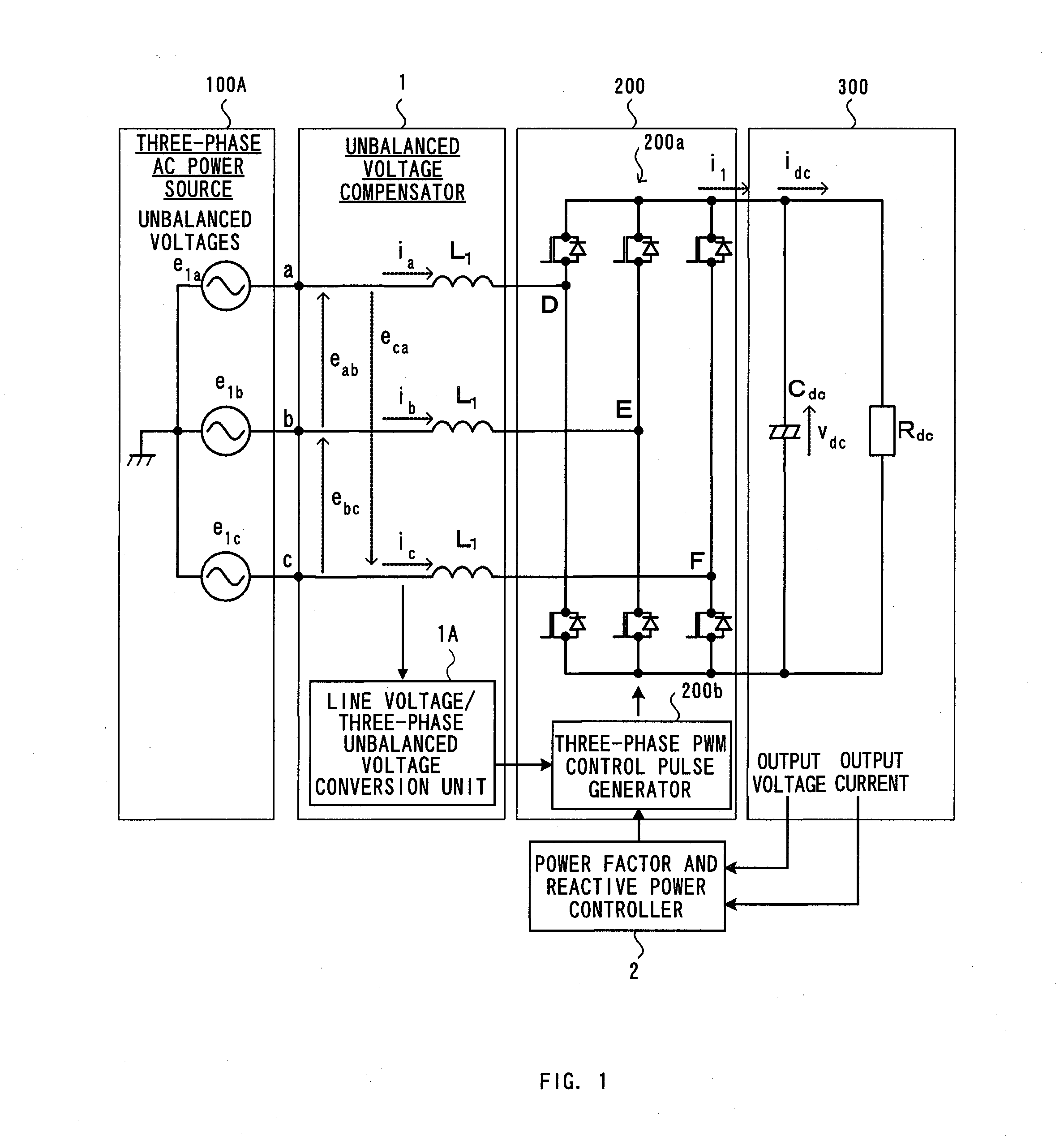
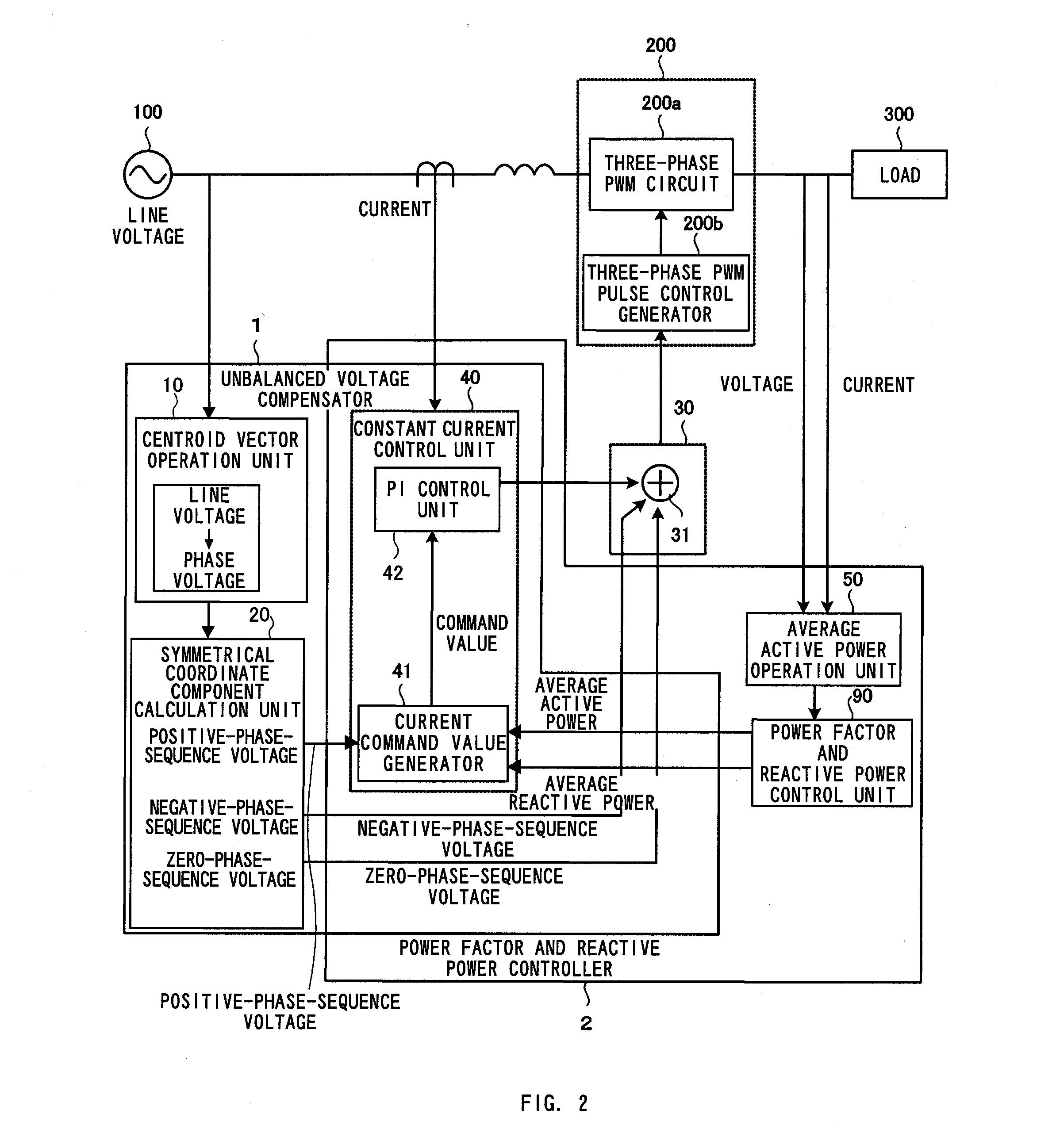
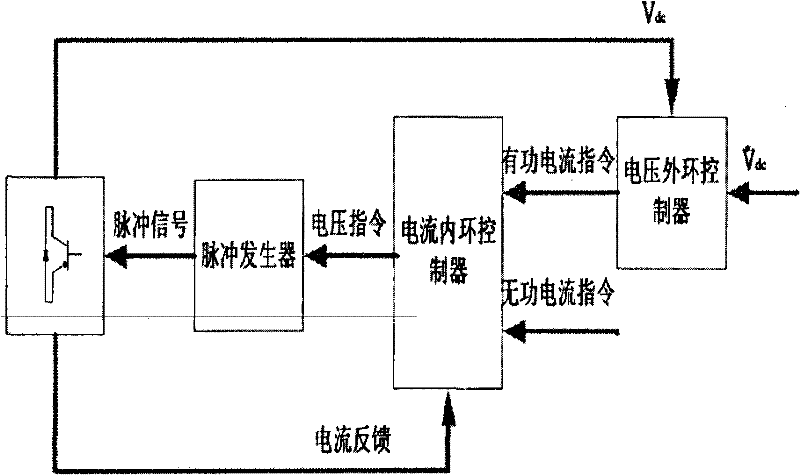
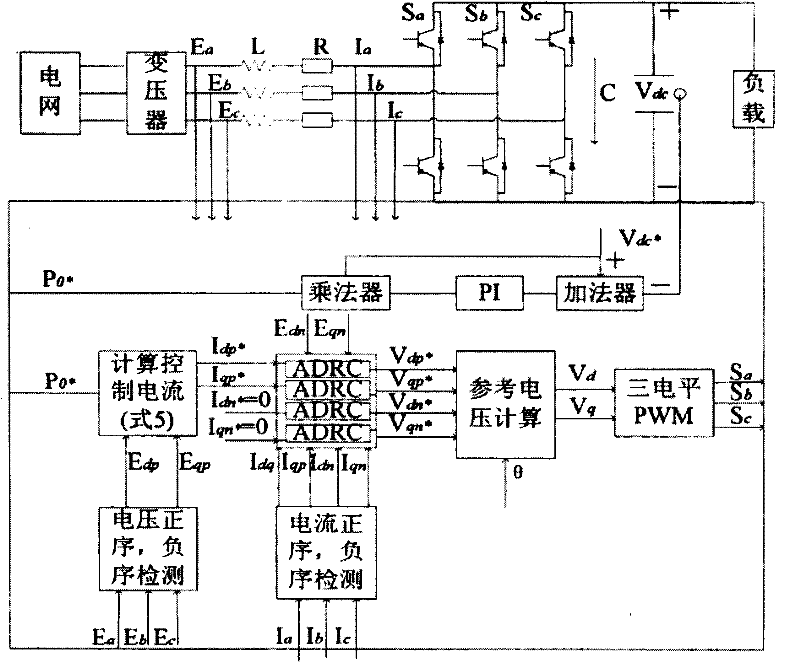
Unbalanced voltage compensation method, unbalanced voltage compensator, three-phase converter control method, and controller of three-phase converter
ActiveUS20110134669A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcControl signalThree phase converter
In compensating for unbalanced voltages of three-phase AC, instantaneous values of wye-phase voltages 120° out of phase with each other are obtained from line voltages using a centroid vector operation, symmetrical component voltages of three-phase balanced system are obtained from the instantaneous values of wye-phase voltages, a compensation signal to compensate unbalanced voltages of three-phase AC is generated from zero-phase-sequence voltage of symmetrical component voltages is generated, wye-phase voltages 120° out of phase, the unbalanced voltages of which are compensated, are obtained from the compensation signal and the symmetrical component voltages, a control signal of a PWM conversion is generated based on the compensated wye-phase voltage compensated, and the unbalanced voltages of three-phase AC are compensated. The amount of time to compensate the three-phase unbalanced voltages required for detecting an unbalance of voltages and generating a control signal can be shortened.
Owner:KYOSAN ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
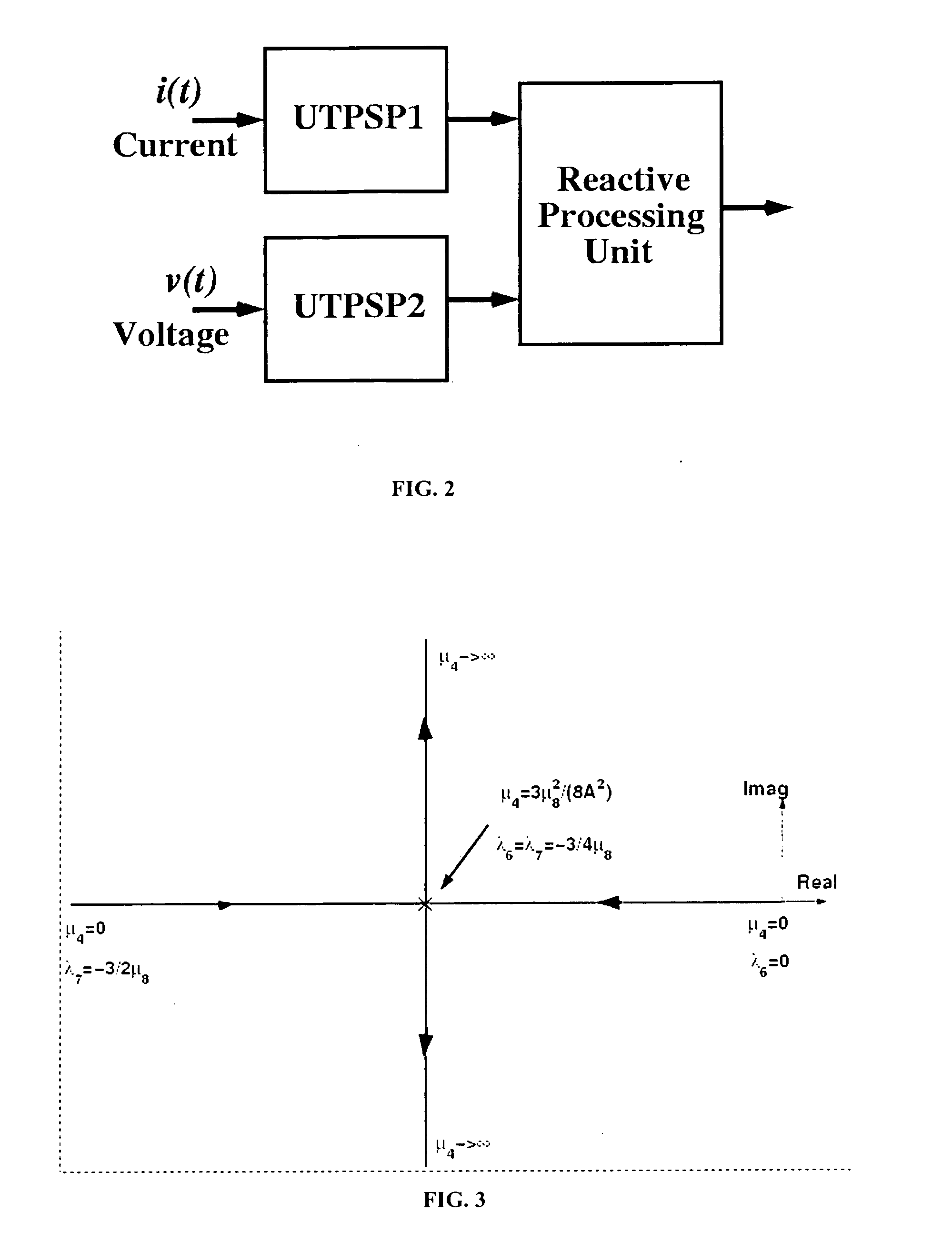
Three-phase power signal processor
InactiveUS20050231871A1Improve accuracyEasy to implementElectric devicesPulse automatic controlPower qualityAdaptive filter
A Three-phase Power Signal Processor (TPSP) is disclosed for general three-phase power system applications. The TPSP is developed based on the concepts from adaptive filter and dynamical systems theories. The structure of the TPSP is unified as it provides a multiplicity of the signals and pieces of information without the need to change, modify, or enhance the structure or to impose excessive computational time or resource requirements. The presented TPSP receives a set of three-phase measured signals, which can be voltage, current, magnetic flux, etc, and provides (1) the instantaneous and steady-state symmetrical components, (2) the fundamental components, (3) the peak values (magnitudes) of the symmetrical components, (4) the frequency and its rate of change, (5) the synchronization signal(s) and zero-crossing instants, (6) the phase-angles of the symmetrical components, and (7) the disturbance signatures. Two or more TPSP units, when properly augmented, further provide (8) the individual harmonic components, (9) the inter-harmonics, (10) the instantaneous real and reactive current components, (11) the total harmonic distortion, dc-offset, and power factor. The TPSP can serve as the building block for various signal processing requirements encountered in the context of power system applications including power systems control, protection, monitoring, and power quality.
Owner:KARIMI GHARTEMANI MASOUD M K
Method for controlling power factor of three-phase converter, method for controlling reactive power of three-phase converter, and controller of three-phase converter
ActiveUS20120212191A1Easy to controlRapid responseEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionControl powerControl signal
In power conversion according to the three-phase converter, symmetrical component voltage values of a balanced system are calculated from wye-phase voltages on the three-phase AC input side of the three-phase converter. On the DC output side thereof, the power factor is set, an average active power value is calculated from an output voltage value and an output current value, and an average reactive power is calculated from the set power factor. On the basis of the symmetrical component voltage values, the average active power, and the active reactive power, a compensation signal for compensating for unbalanced voltages of the three-phase AC voltages and a control signal for controlling the power factor are generated, and according to the compensation signal and the control signal, a control signal for outputting DC is generated.
Owner:KYOSAN ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
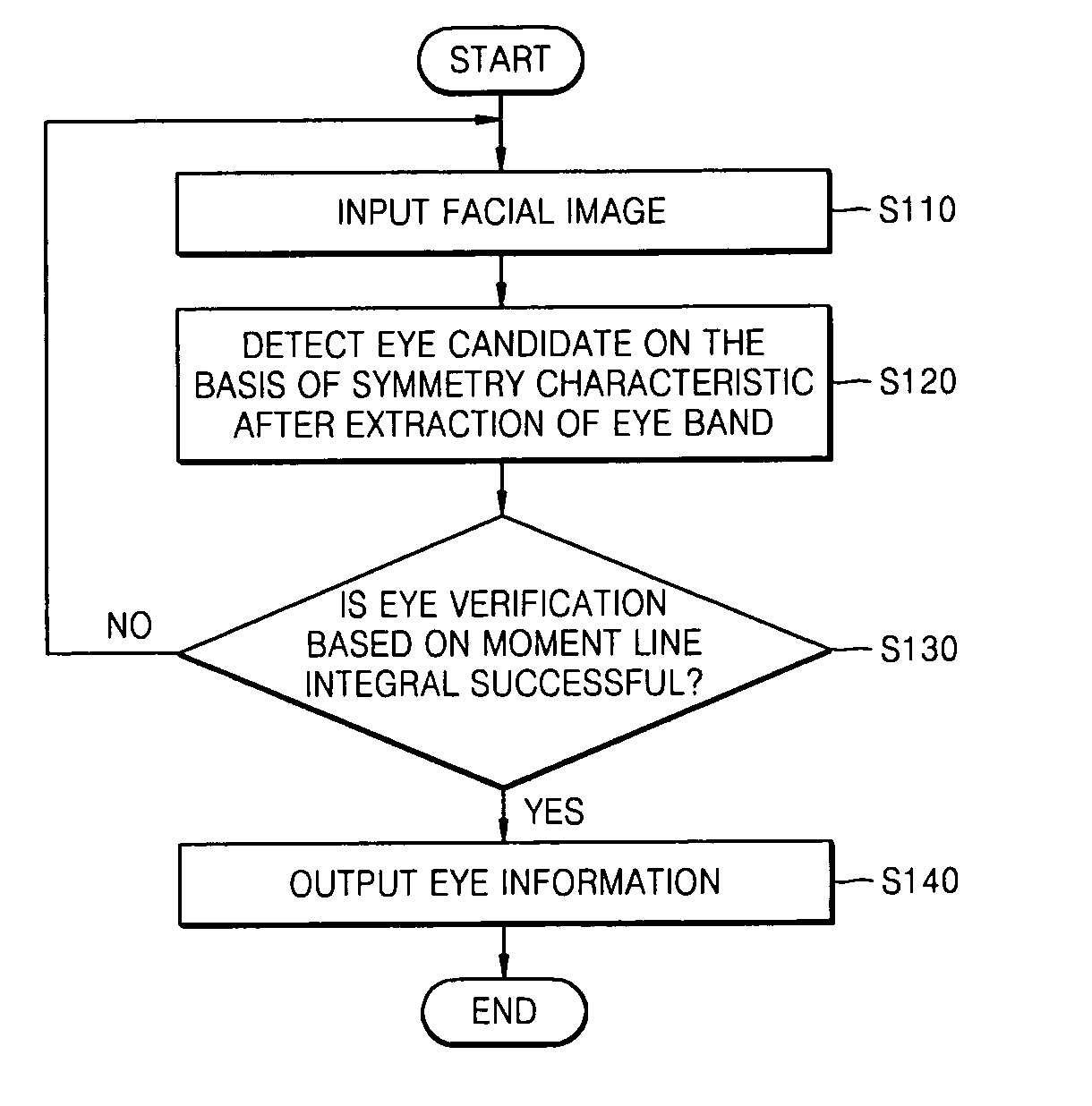
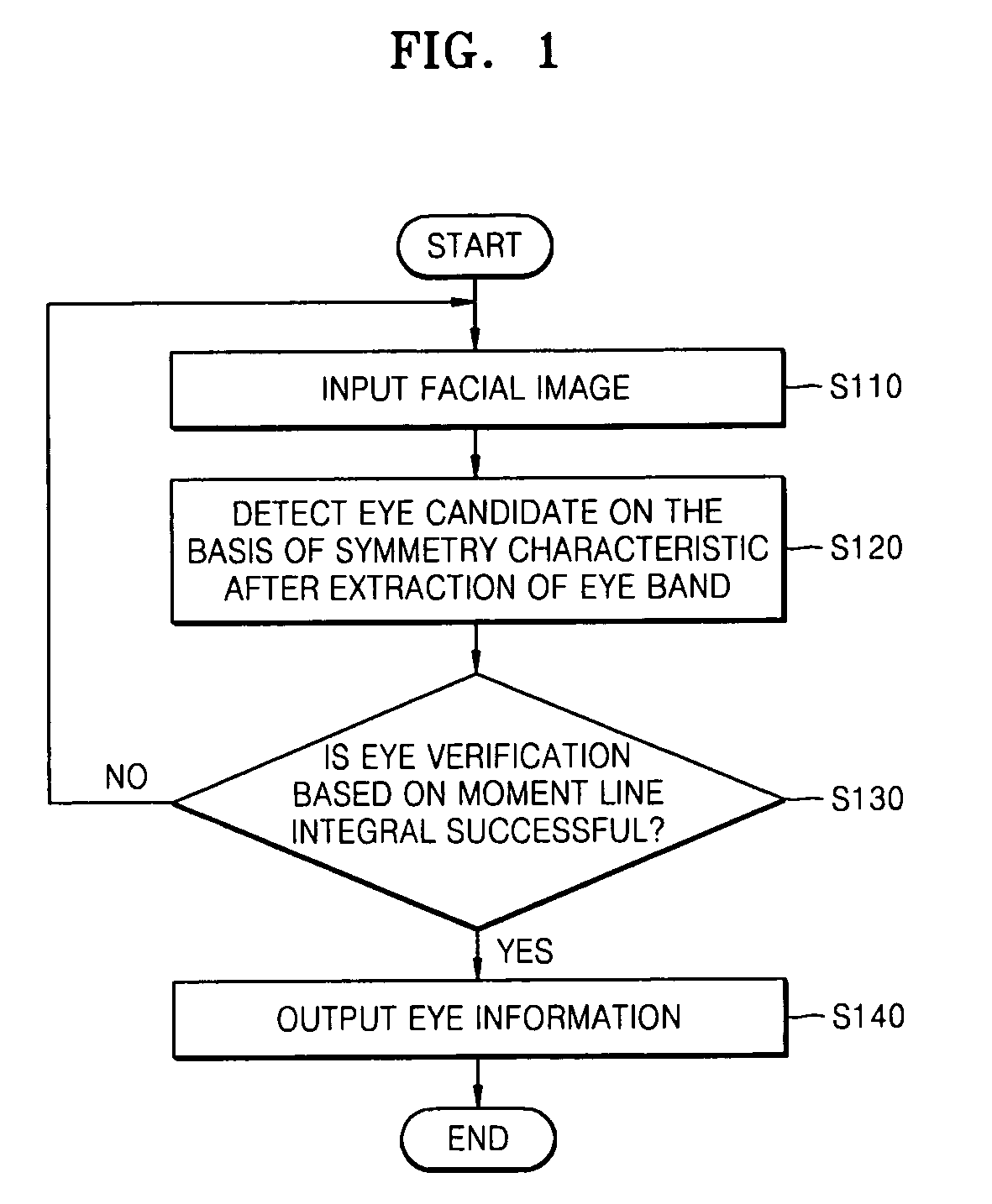
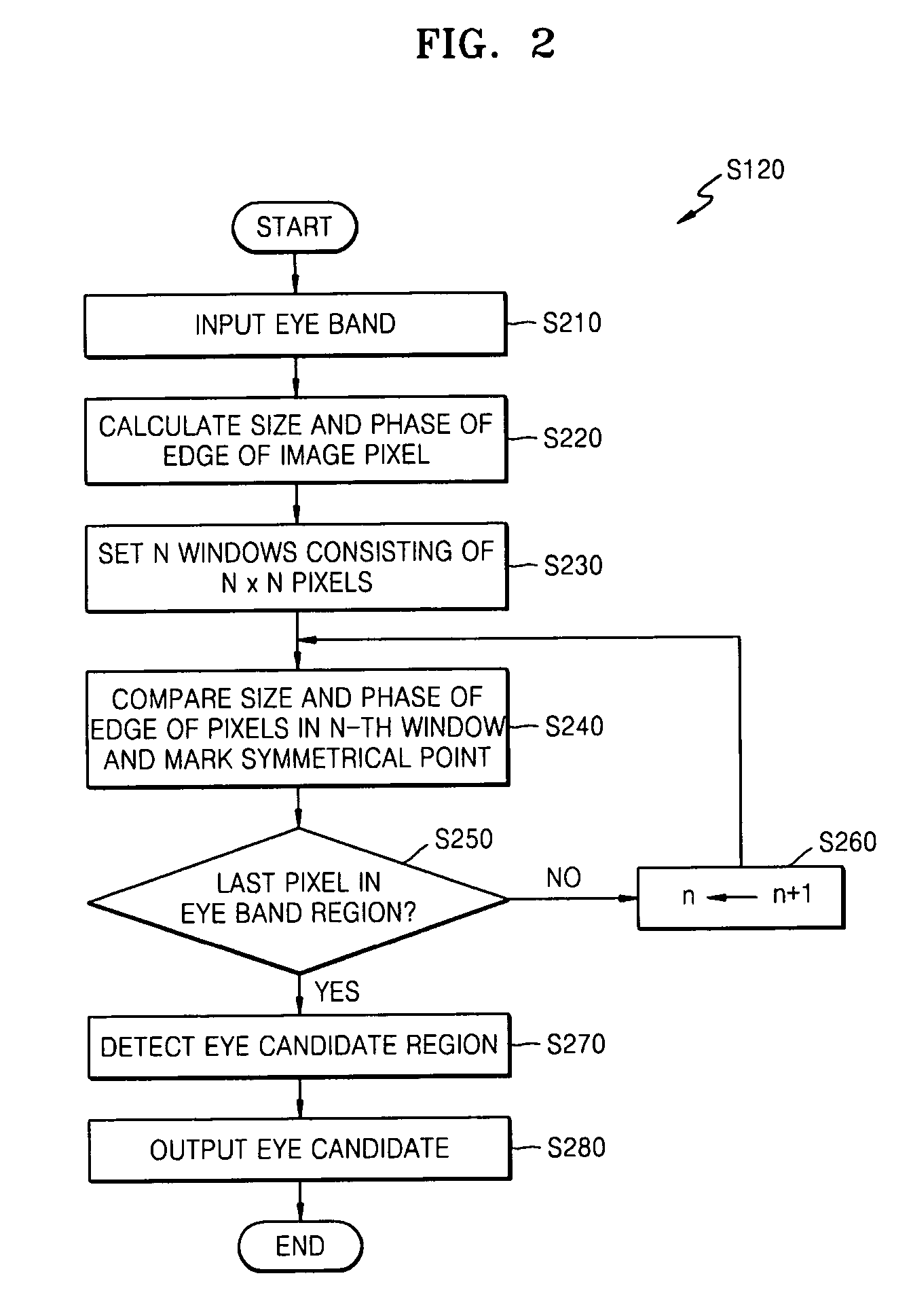
Method and apparatus of detecting eye using symmetry and moment characteristics of object
InactiveUS20060222215A1Prevent false detectionReliable detectionImage analysisAcquiring/recognising eyesSymmetrical componentsComputer science
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
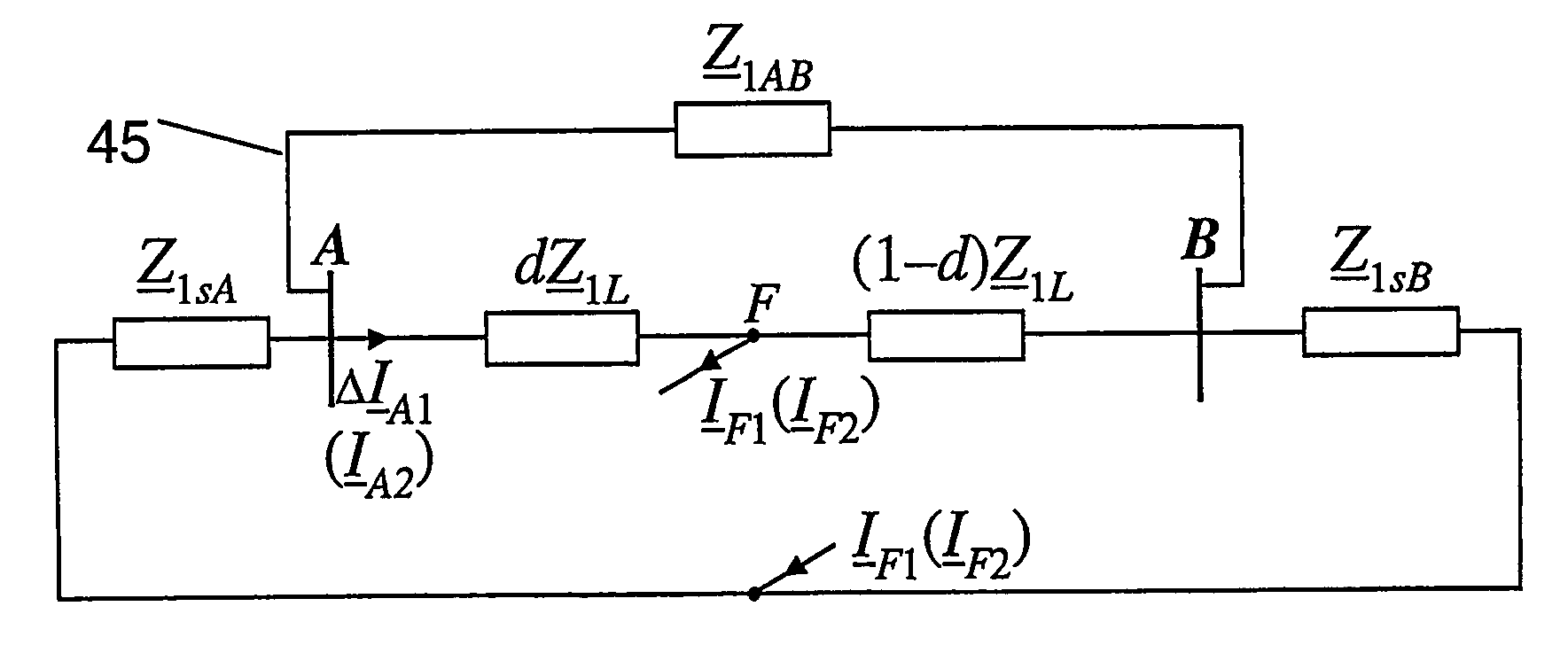
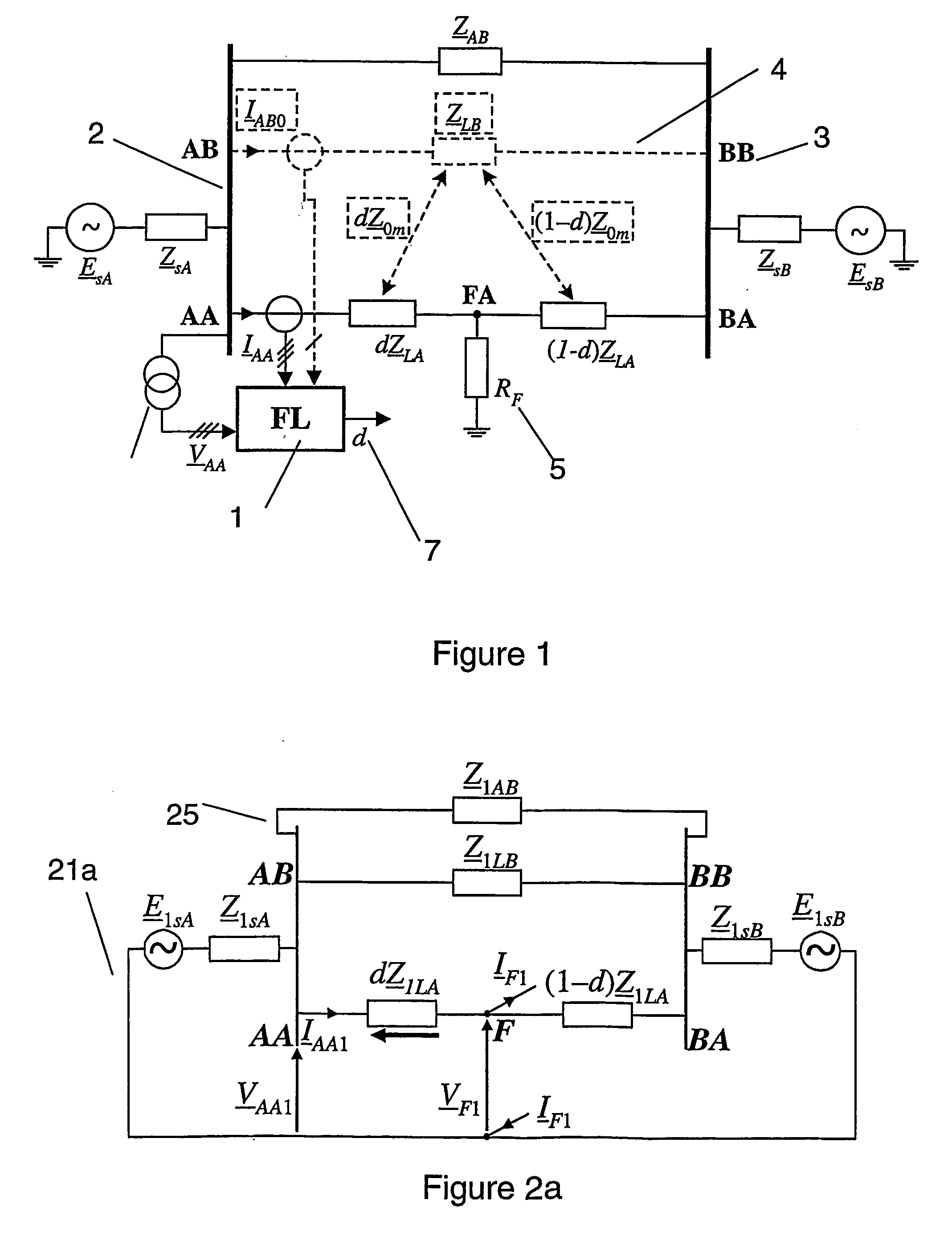
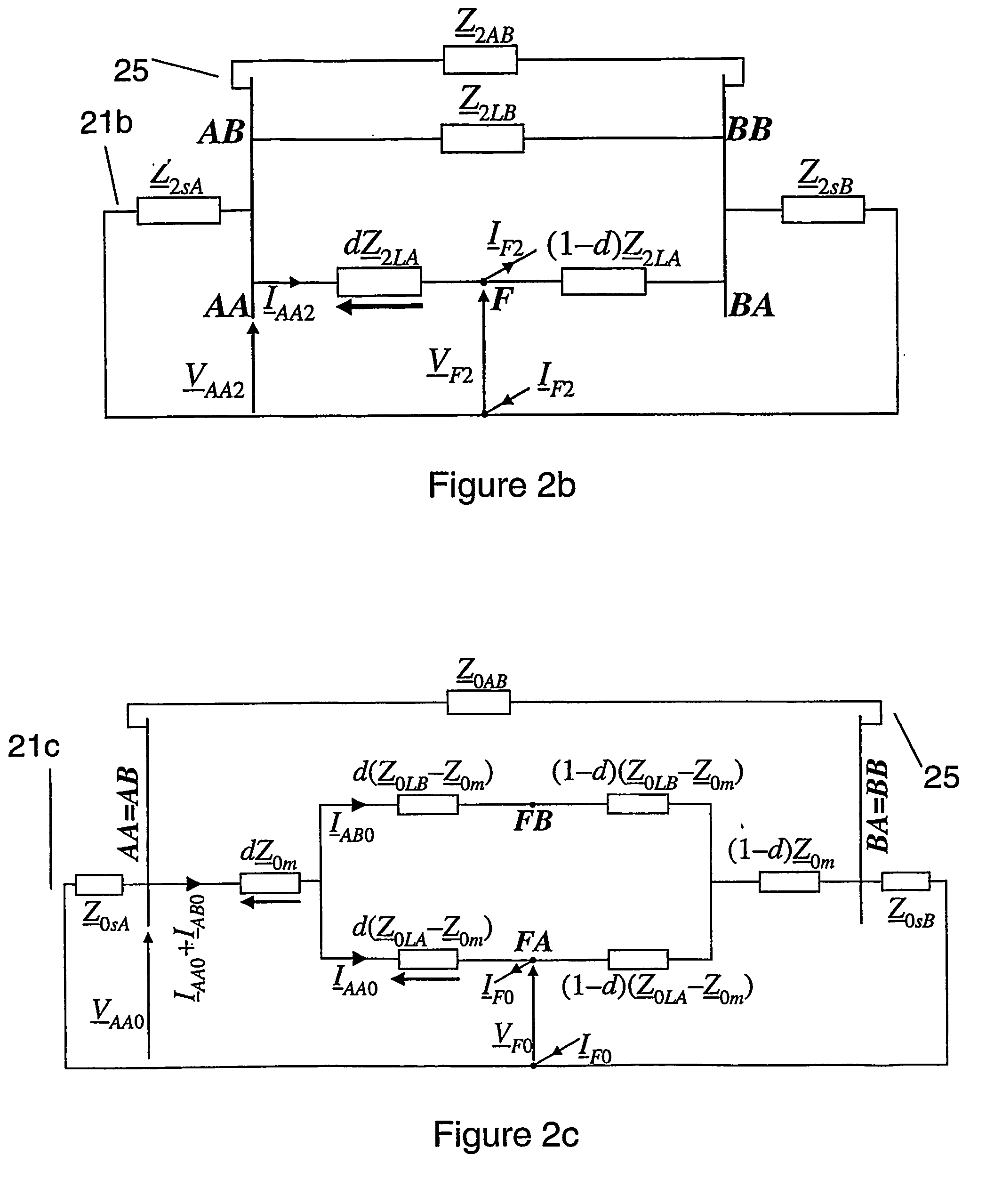
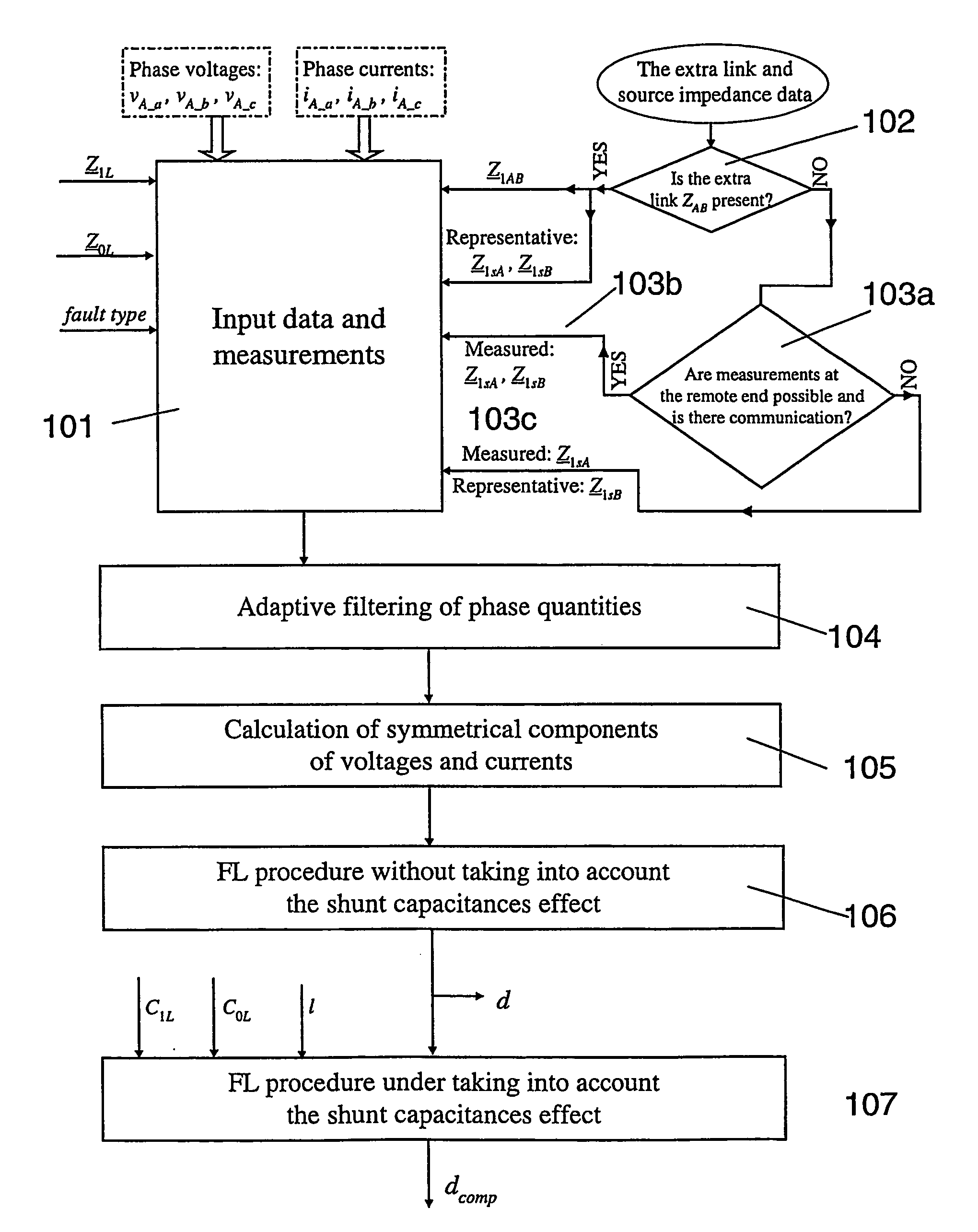
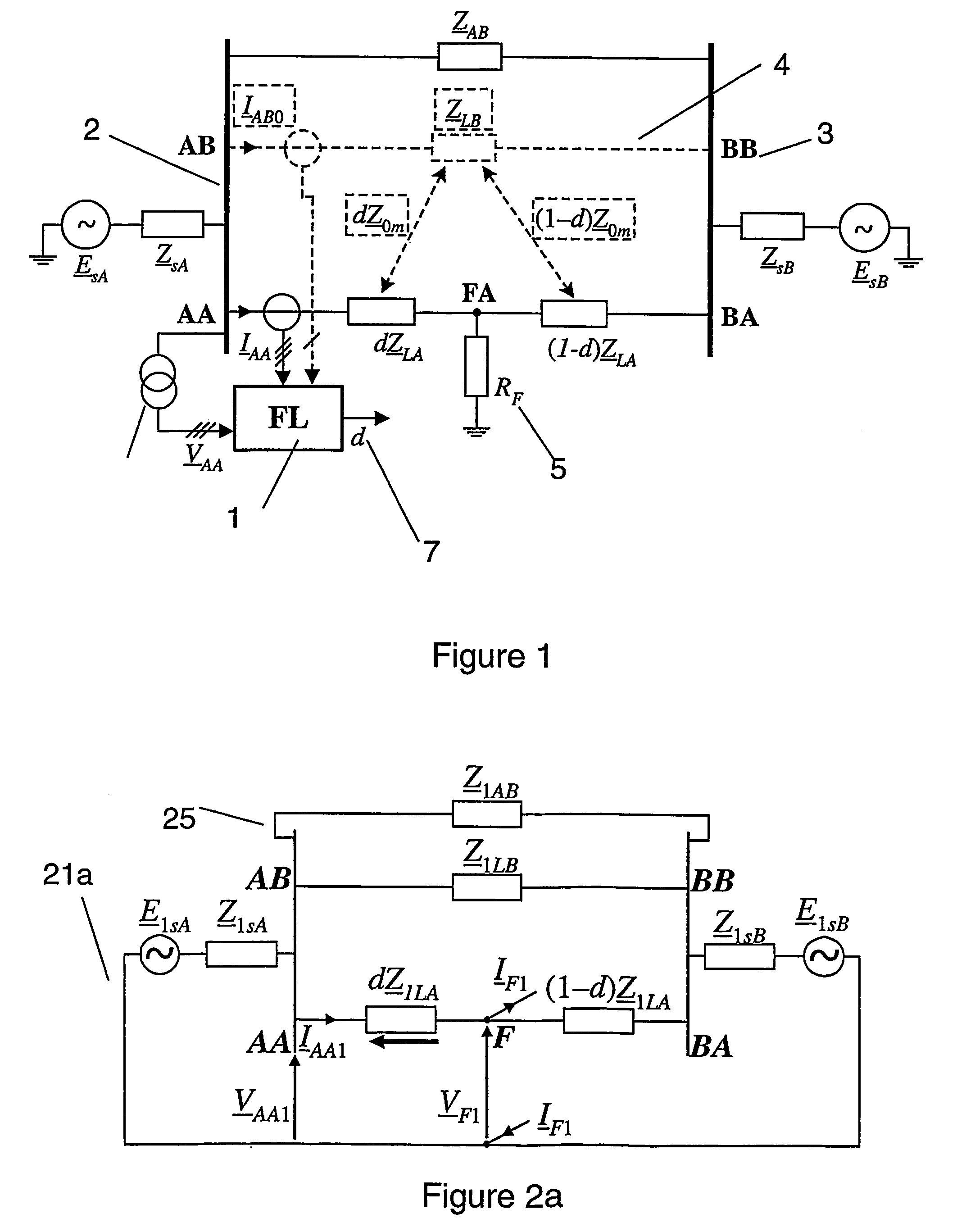
Fault location using measurements of current and voltage from one end of a line
InactiveUS20060097728A1Improve accuracyShunt capacitance is facilitatedFault location by conductor typesEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionSymmetrical componentsElectrical impedance
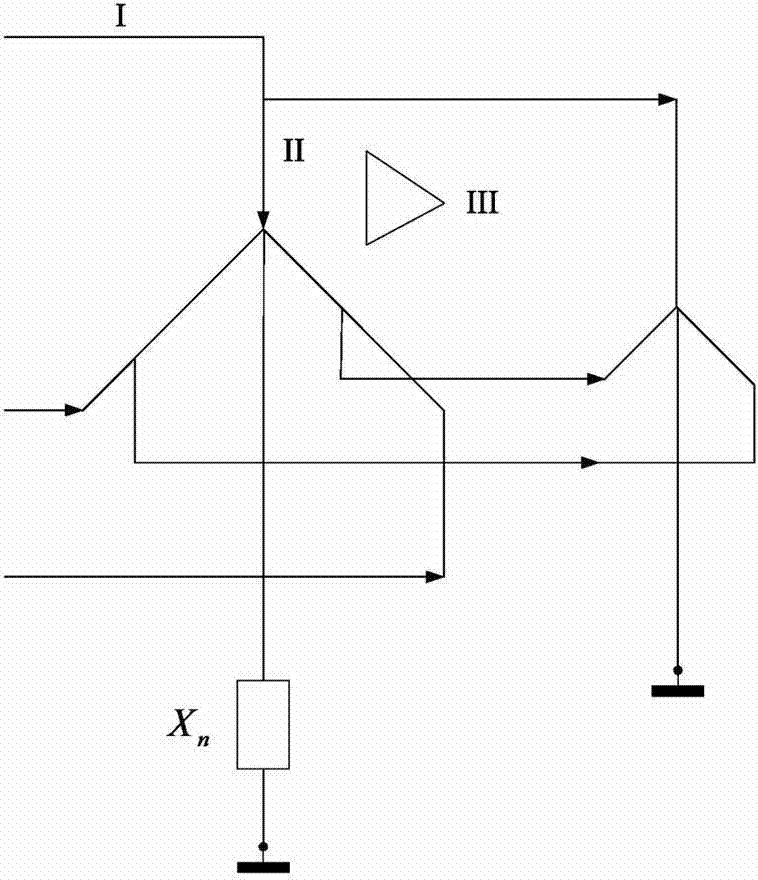
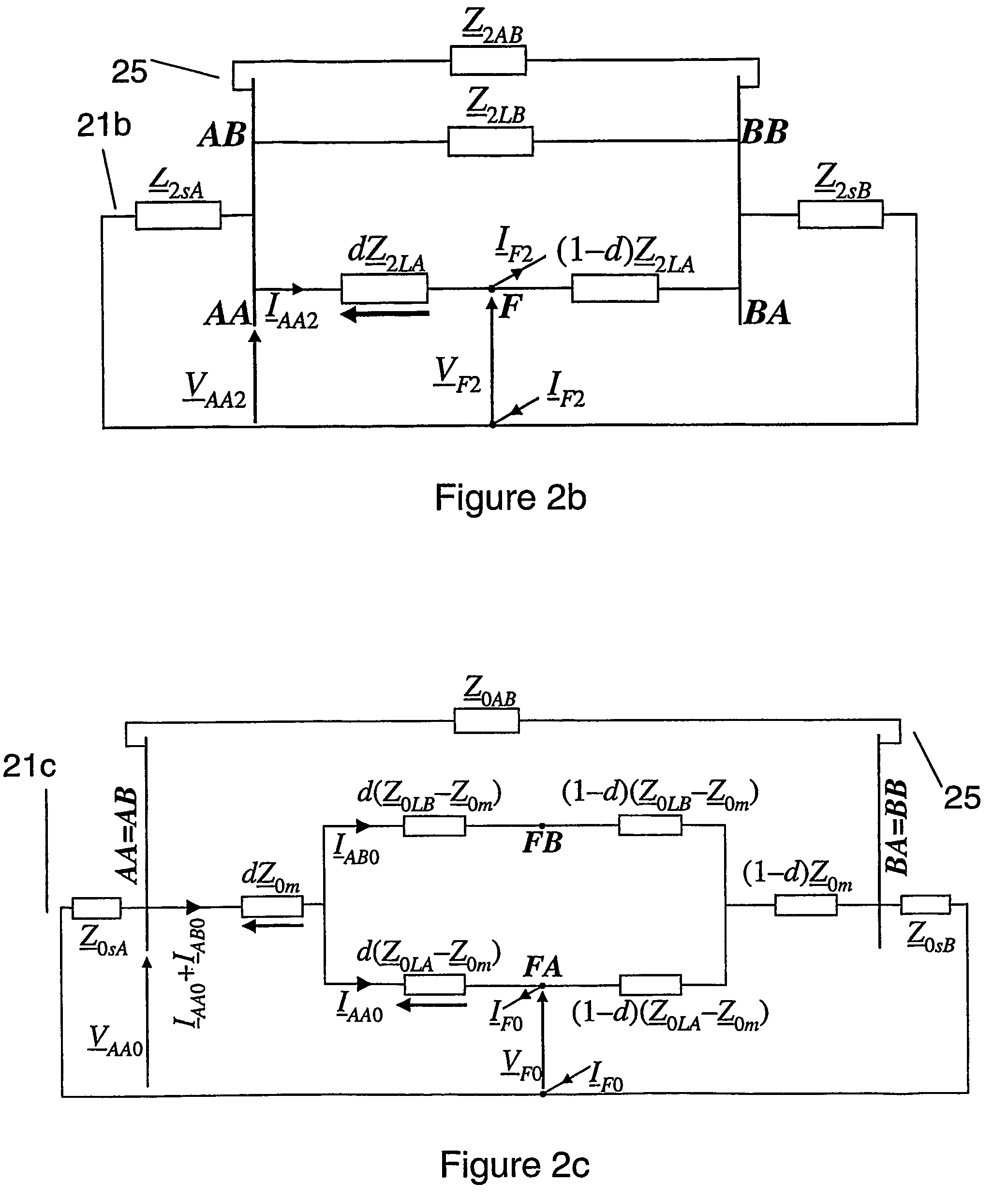
A method to locate a fault from one end of a section of a power line utilizing measurements of current, voltage and angles between the phases at a first end of said section. Symmetrical components of currents are calculated for the current and voltage measurement at the first end. A value of impedance is calculated for an extra link between the terminals with the impedance for the positive sequence equal to: (Z_1 LB&AB=Z_1LBZ_1ABZ_1LB+Z_1AB) where:Z1AB=impedance for the positive sequence of the extra link, Z1LA=positive-sequence impedance of the healthy line. A compensation is determined for the shunt capacitance with the aid of an equation of the form: B2comp<sub2>—< / sub2>1(dcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1)2+B1comp<sub2>—< / sub2>1dcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1+B0comp<sub2>—< / sub2>1=0 where: B2comp<sub2>—< / sub2>1=A2<sub2>—< / sub2>Recomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1A00<sub2>—< / sub2>Imcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1−A2<sub2>—< / sub2>Imcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1A00<sub2>—< / sub2>Recomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1 B1comp<sub2>—< / sub2>1=A1<sub2>—< / sub2>Recomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1A00<sub2>—< / sub2>Imcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1−A1<sub2>—< / sub2>Imcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1A00<sub2>—< / sub2>Recomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1 B0comp<sub2>—< / sub2>1=A0<sub2>—< / sub2>Recomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1A00<sub2>—< / sub2>Imcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1−A0<sub2>—< / sub2>Imcomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1A00<sub2>—< / sub2>Recomp<sub2>—< / sub2>1. The zero-sequence current is determined from the healthy line of a section of parallel power lines. A distance to a fault is calculated for the parallel line section. The distance to the fault from the first end is calculated using a quadratic equation of the form: B2d2+B1d+B0=0 where: B2=A2<sub2>—< / sub2>ReA00<sub2>—< / sub2>Im−A2<sub2>—< / sub2>ImA00<sub2>—< / sub2>Re B1=A1<sub2>—< / sub2>ReA00<sub2>—< / sub2>Im−A1<sub2>—< / sub2>ImA00<sub2>—< / sub2>Re B0=A0<sub2>—< / sub2>ReA00<sub2>—< / sub2>Im−A0<sub2>—< / sub2>ImA00<sub2>—< / sub2>Re.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
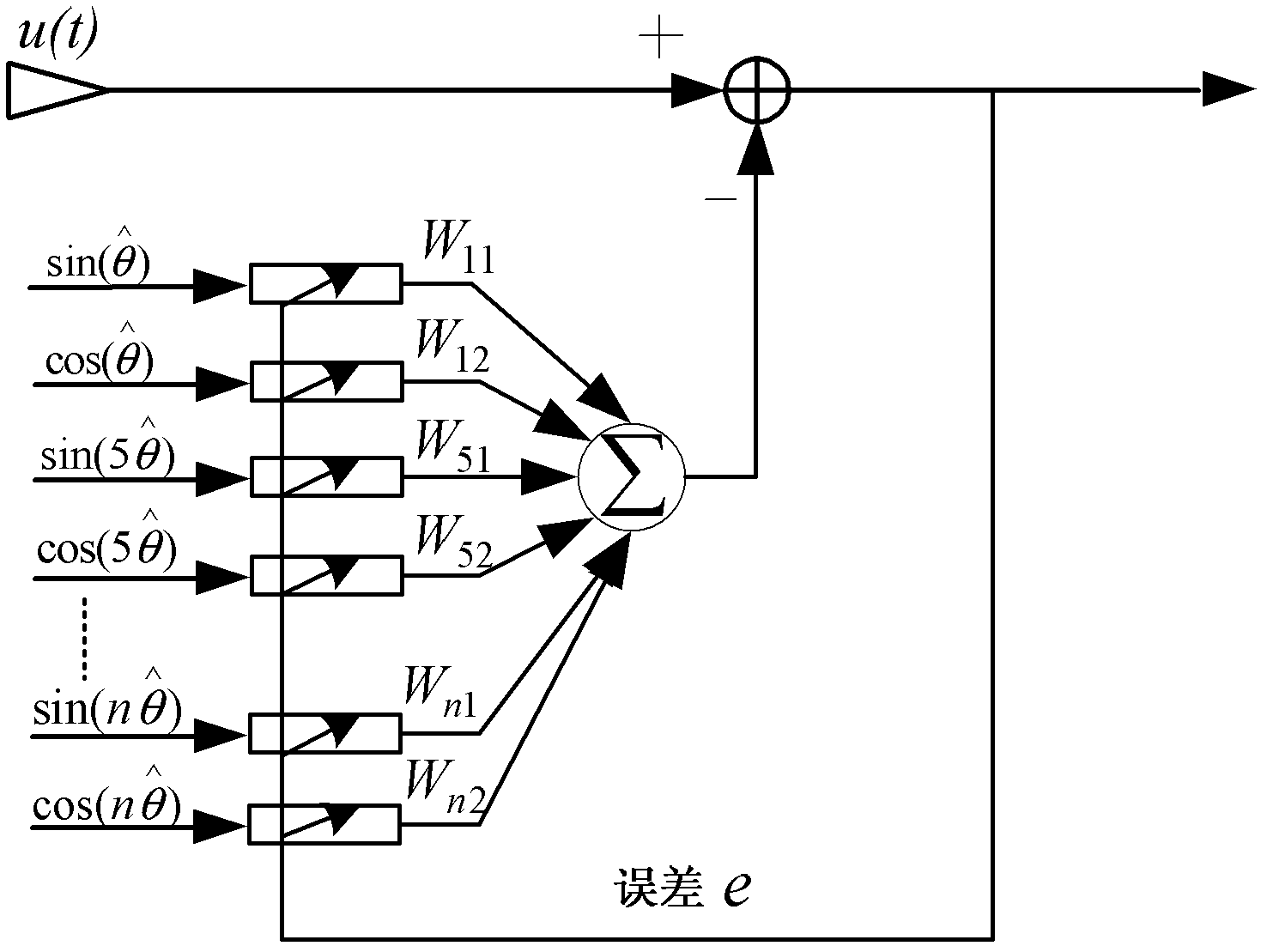
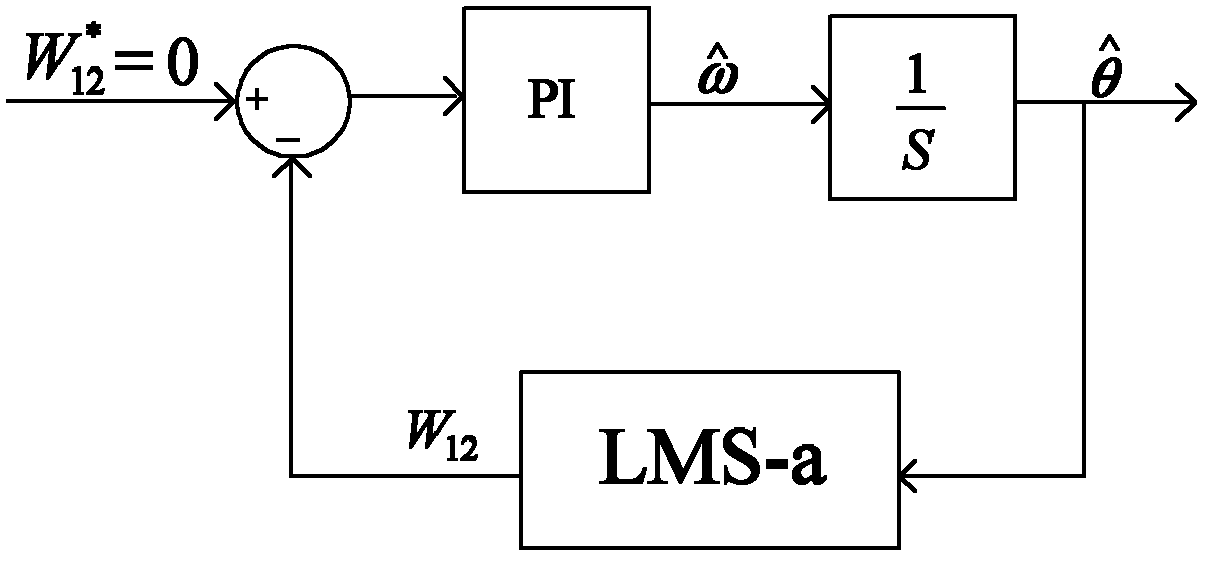
Method for detecting fundamental component and harmonic component of voltage of power grid
InactiveCN102401858AAccurate detectionImprove robustnessSpectral/fourier analysisMean squareHarmonic
The invention discloses a method for detecting a fundamental component and a harmonic component in voltage of a power grid, which relates to the field of signal processing and solves the problem that the traditional method for detecting the fundamental component and the harmonic component in the voltage has low accuracy. The method comprises the following steps of: designing a wave trap according to an LMS (Least Mean Square) algorithm; separating out the fundamental component and the sub-harmonic components from voltage of power grid by using the wave trap to obtain the fundamental component and the sub-harmonic components in the phase voltage; taking an error signal in the obtained fundamental component in the phase A voltage as a feedrear of a phase locked loop, and using the phase locked loop to obtain an estimation value of a power grid voltage frequency and an estimation value of the phase; and according to the obtained fundamental component and the sub-harmonic components in the phase voltage, using a symmetrical component method to detect positive sequence, negative sequence and zero sequence information of the fundamental component and the sub-harmonic components, taking the information as the detection results, and finishing the detection of the fundamental component and the harmonic component in the voltage of the power grid. The method is suitable for the detection of the fundamental component and the harmonic component in the voltage of the power grid.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Diagnosis method for single-phase line breakage grounding complex fault type of power distribution network based on zero sequence voltage
ActiveCN106872852AVersatileOffset angle characteristics are not affected by voltage levelFault location by conductor typesPhase differenceSymmetrical components
The invention discloses a diagnosis method for a single-phase line breakage grounding complex fault type of a power distribution network based on a zero sequence voltage, and the method comprises the steps: setting a start value of the zero sequence voltage through determining a small current grounding mode; extracting voltage sampling data of each phase of N cyclic waves before a line breakage moment and N cyclic waves after a fault moment, and calculating and obtaining the phase difference relation between the phase of the fault phase voltage before the fault and the phase of the steady-state zero sequence voltage after the fault and a reference function as the criterion through the FFT and a symmetrical component algorithm; judging whether the zero sequence voltage exceeds the start value or not: carrying out the extraction if the zero sequence voltage exceeds the start value and judging whether the phase difference between the phase of the zero sequence voltage and the phase of the fault phase voltage before the fault is corresponding to a load side grounding range of the criterion or not: determining that the fault is a single line breakage and load side grounding fault if the phase difference is corresponding to the load side grounding range of the criterion, or else determining that the fault is a single line breakage and power side grounding fault. The method is good in universality, and is suitable for power distribution networks at various voltage levels, wherein the neutral points of the power distribution networks are not grounded or the power distribution networks are grounded through arc suppression coils. Moreover, the deviation angle is not affected by the voltage level.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Method for compensating dynamic three-phase imbalance load and compensator
InactiveCN1450704APolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionPolyphase network asymmetry reductionElectric power systemSymmetrical components
A method for compensating dynamic three-phase unbalanced loadsand and its device characterizing in sampling values of line voltage and load line current of two sample points at the connecting place of the compensation device and the system to compute related sine signal basic wave symmetric component, then to calculate positive and negative sequential compensator threephase equal susceptance, thesum of which is the three-phase susceptance value for compensating load unbalance and providing reactive current for the load, the susceptance reference value to be converted to a control angle signal and an order of the thyristor switched capacitor to be sent to the pulse generation plate and the condenser zero-cross trigger plate for controlling two devices.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
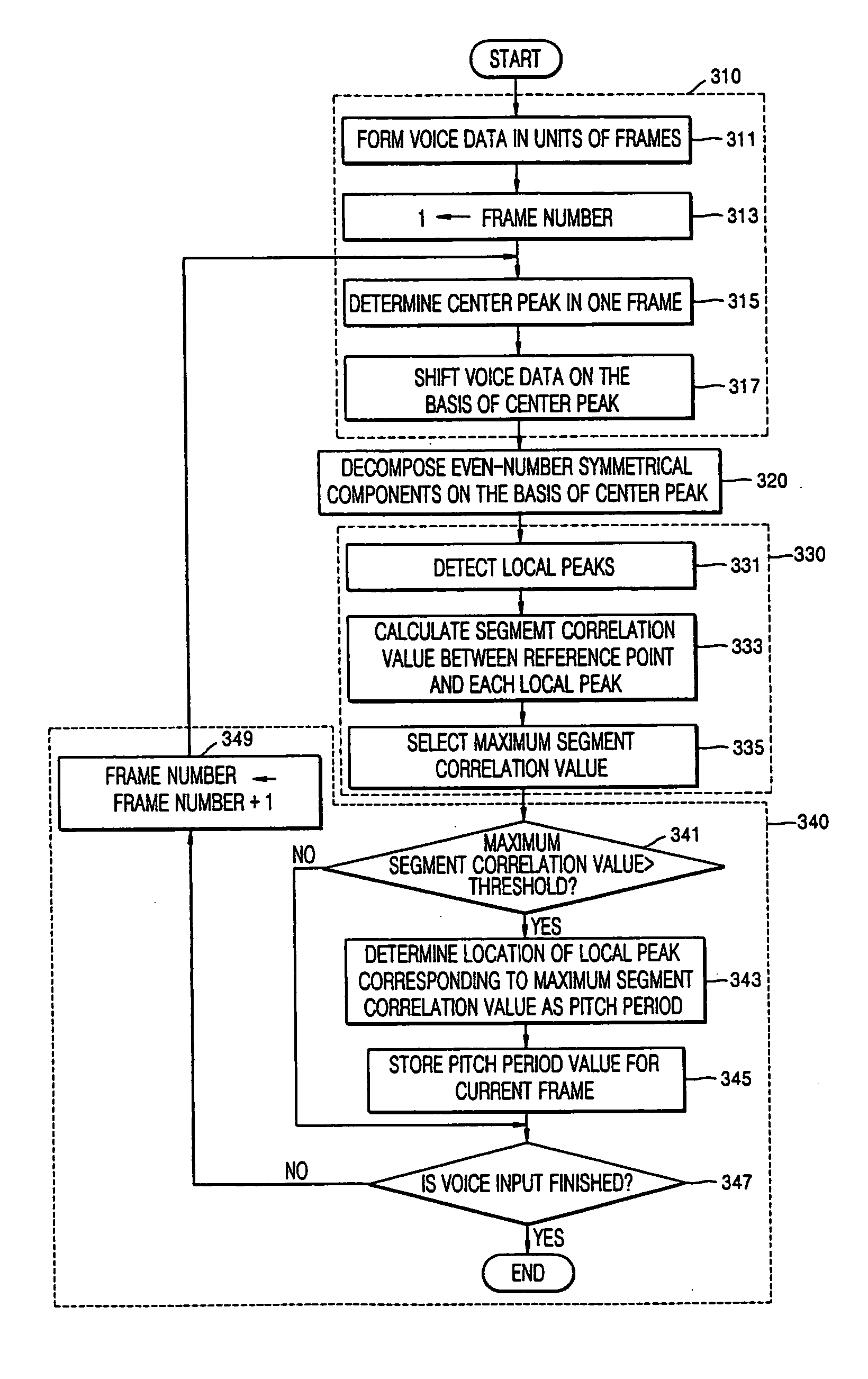
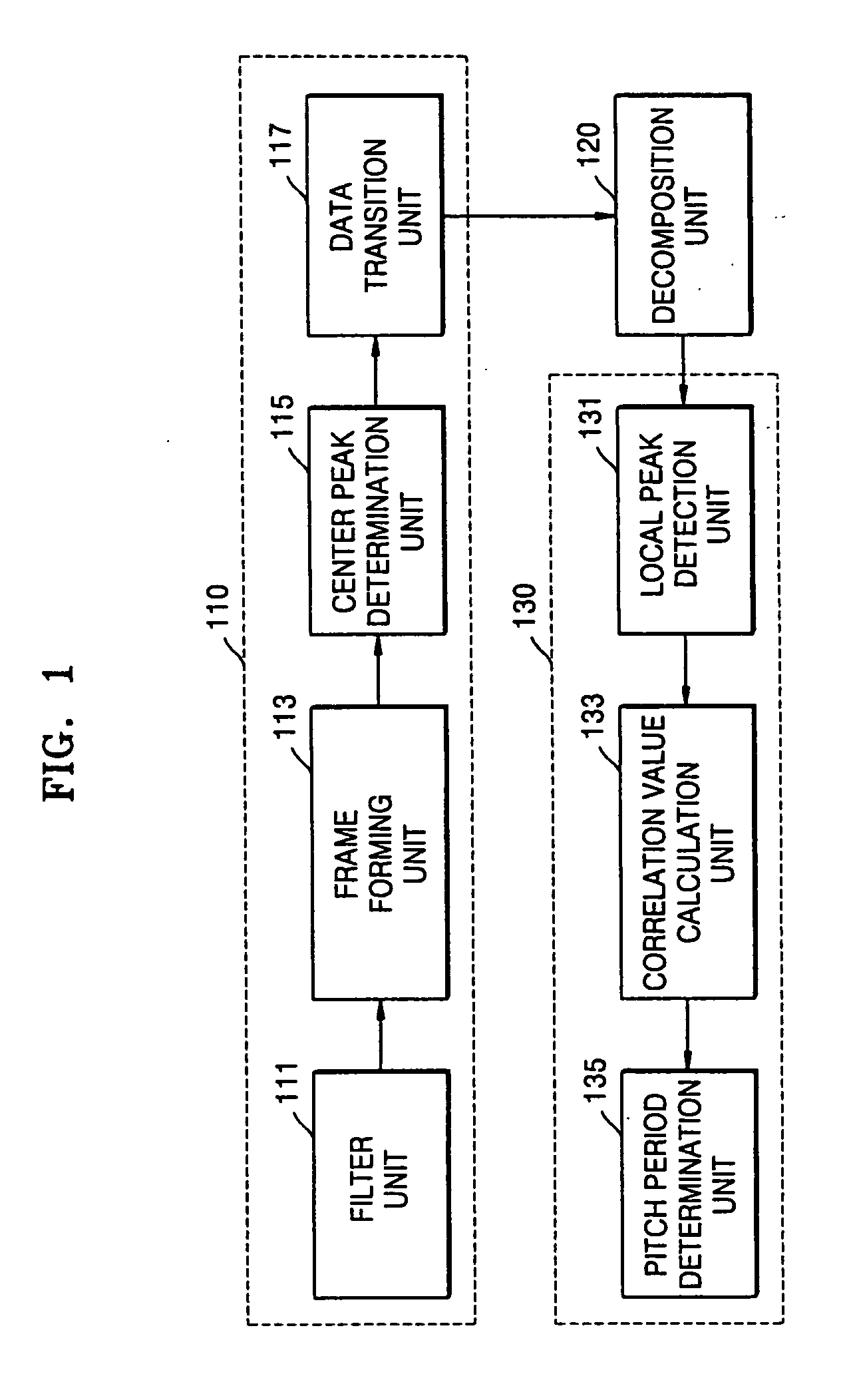
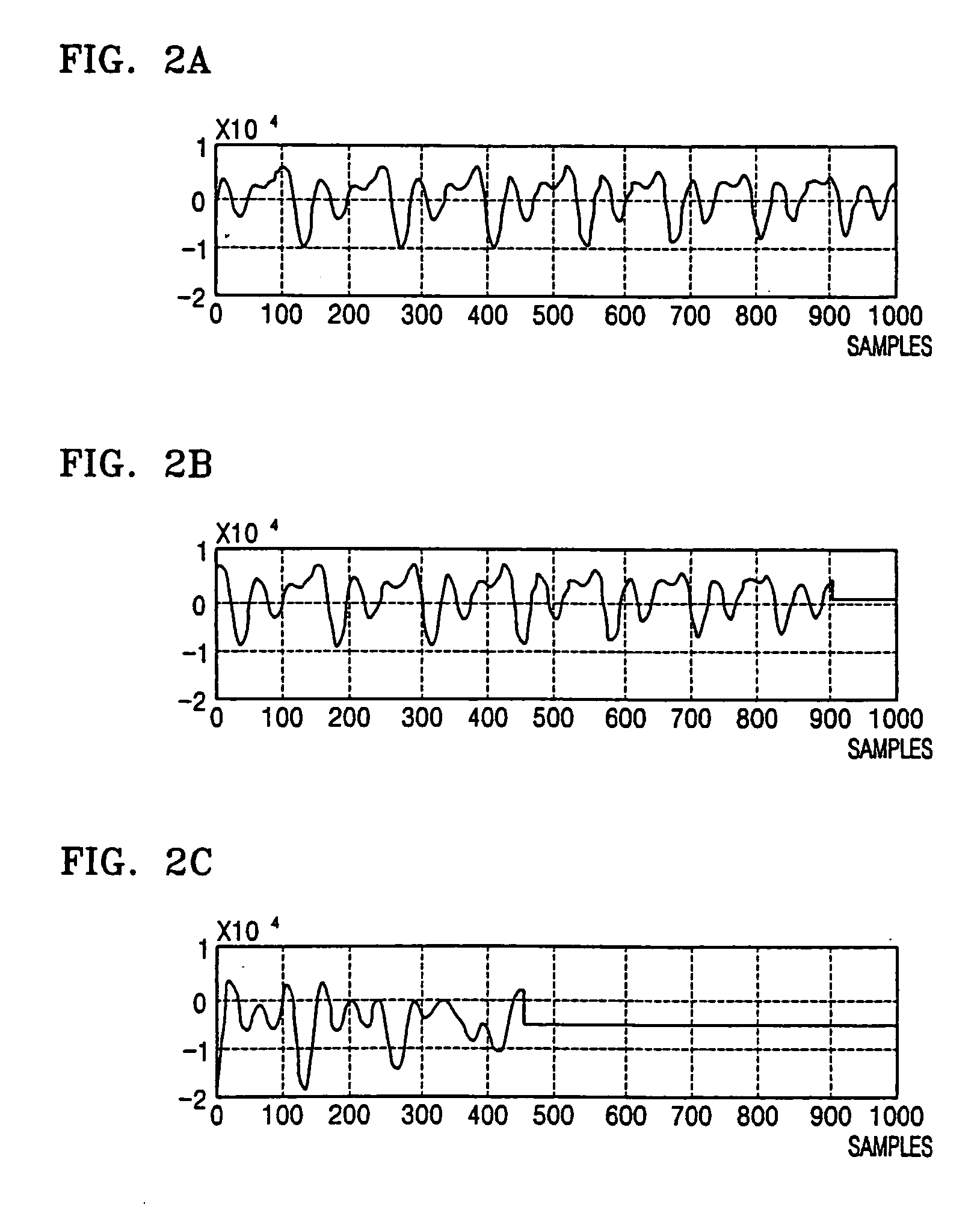
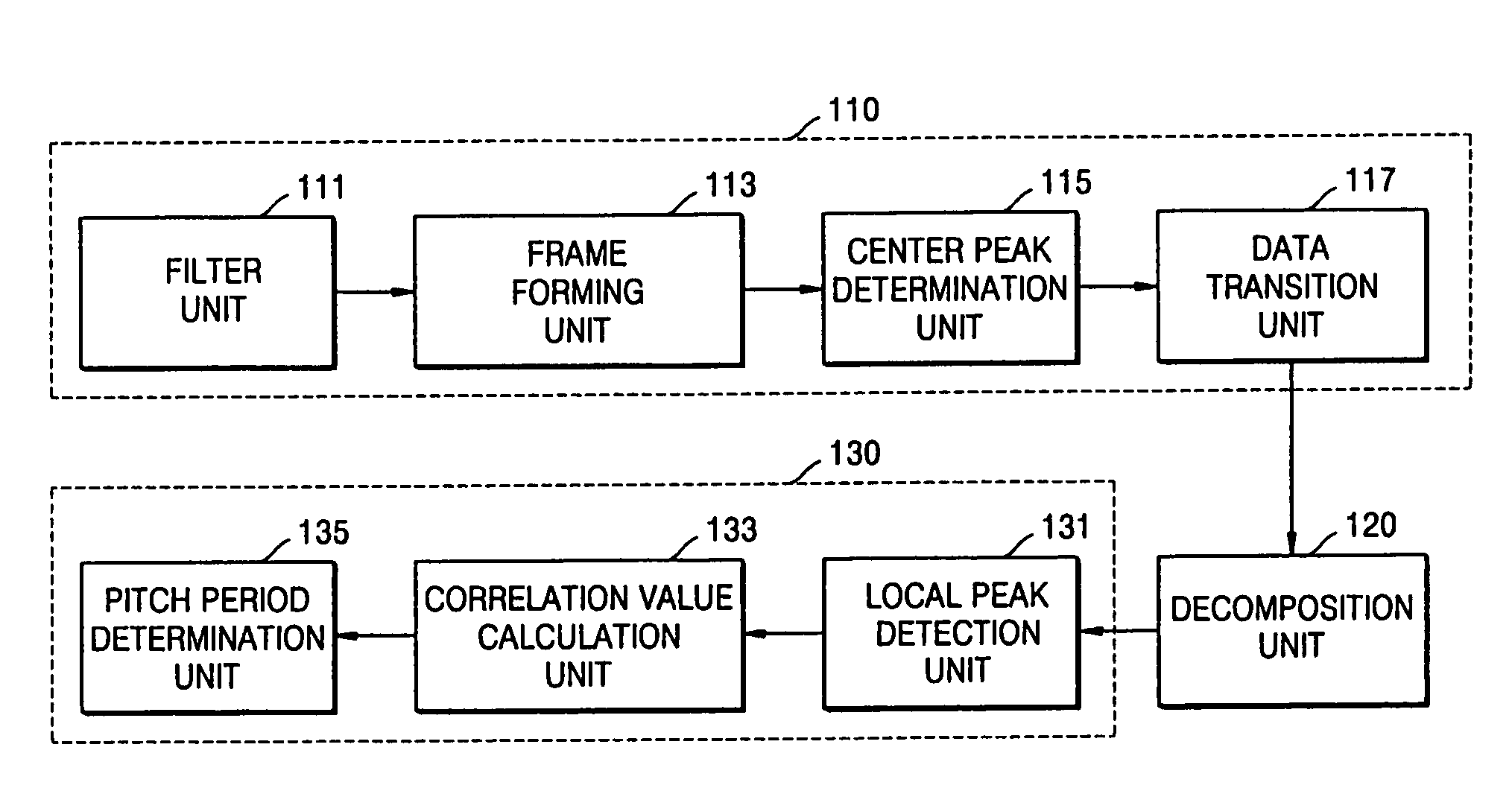
Pitch detection method and apparatus
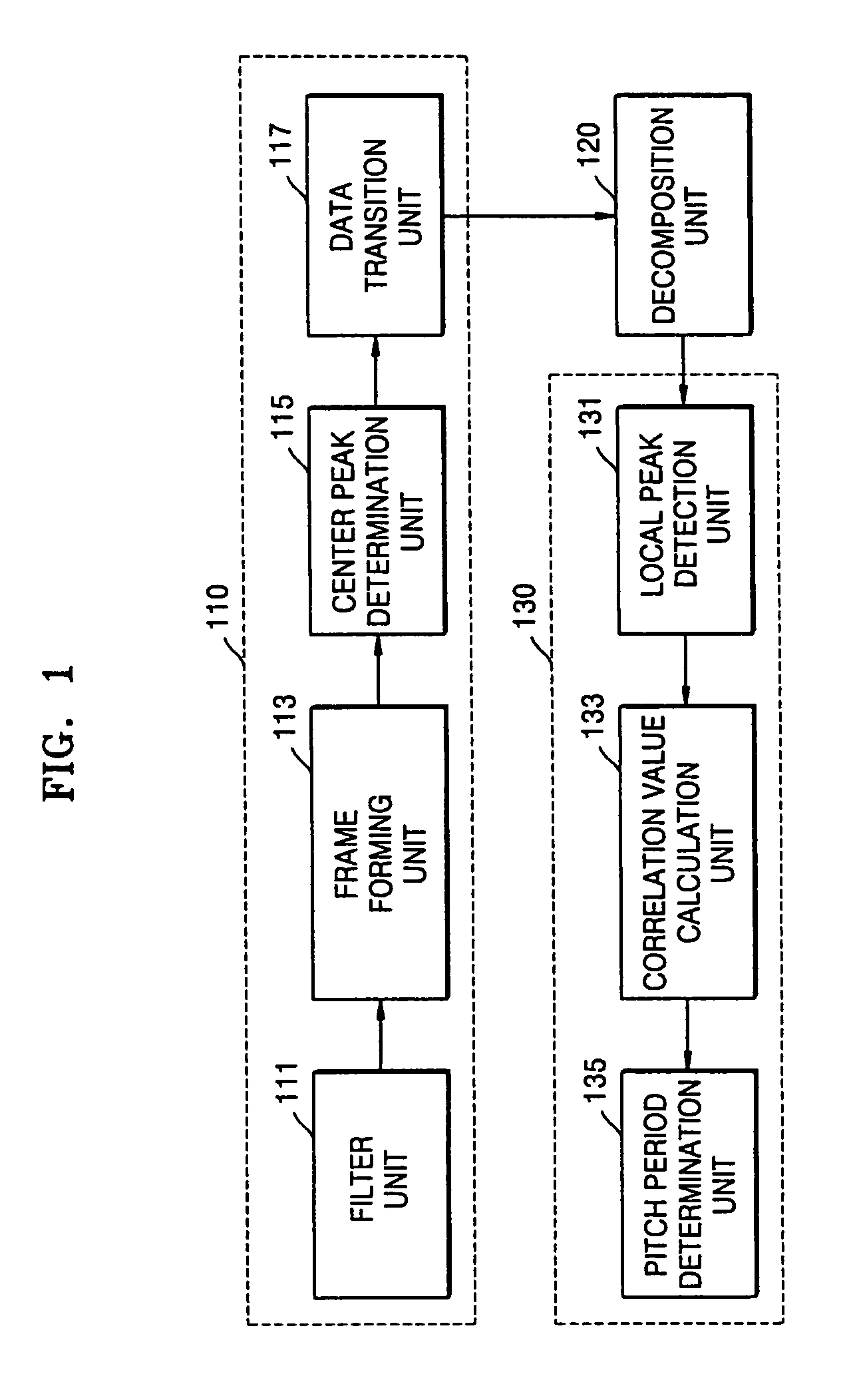
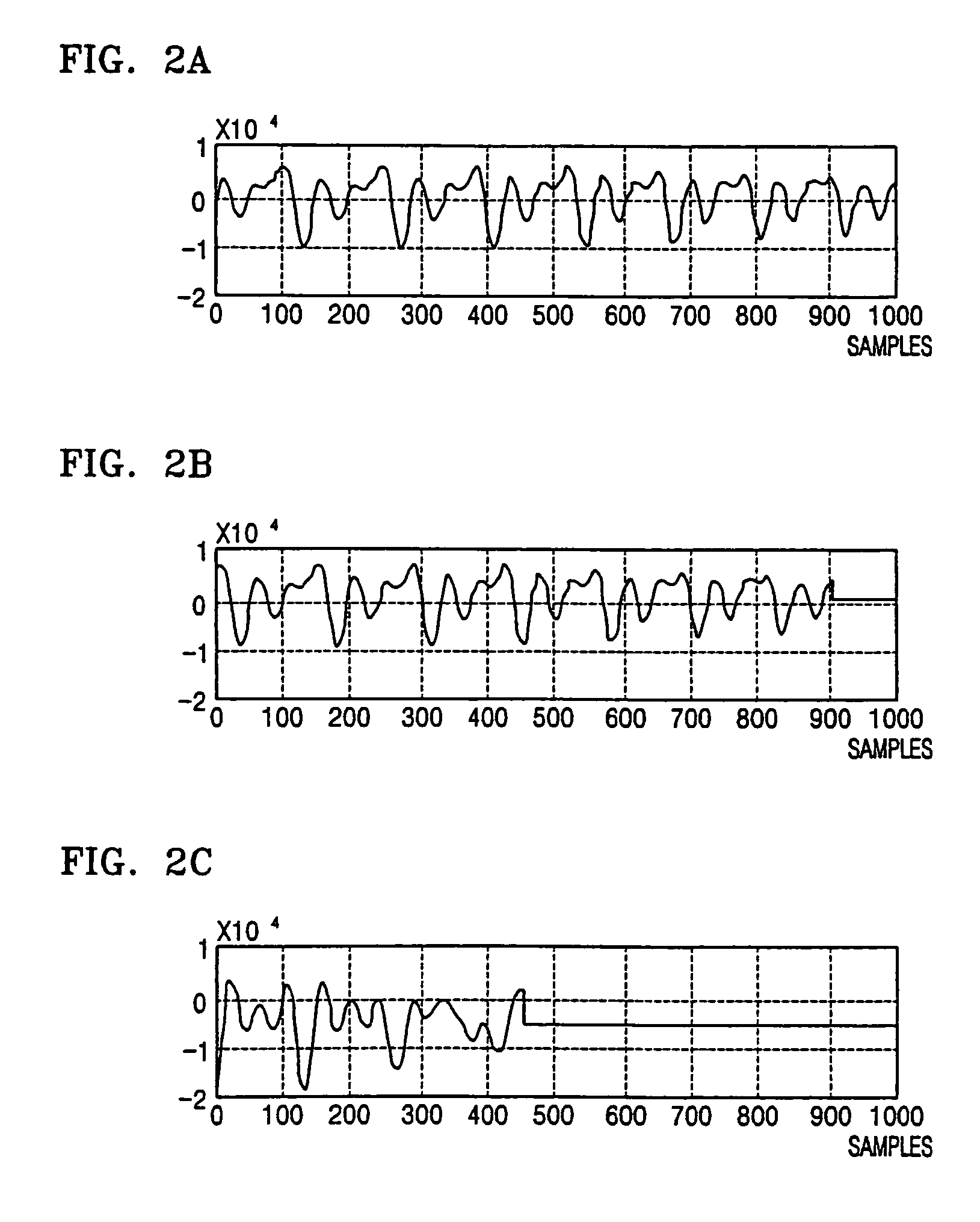
A pitch detection method and apparatus, the pitch detection apparatus includes: a data rearrangement unit which rearranges voice data on the basis of a center peak of the voice data included in a single frame; a decomposition unit which decomposes rearranged voice data into even symmetrical components on the basis of a center peak; a pitch determination unit which obtains a segment correlation value between a reference point and at least one or more local peaks in relation to even symmetrical components, and determines the location of a local peak corresponding to a maximum segment correlation value among the obtained segment correlation values, as a pitch period.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
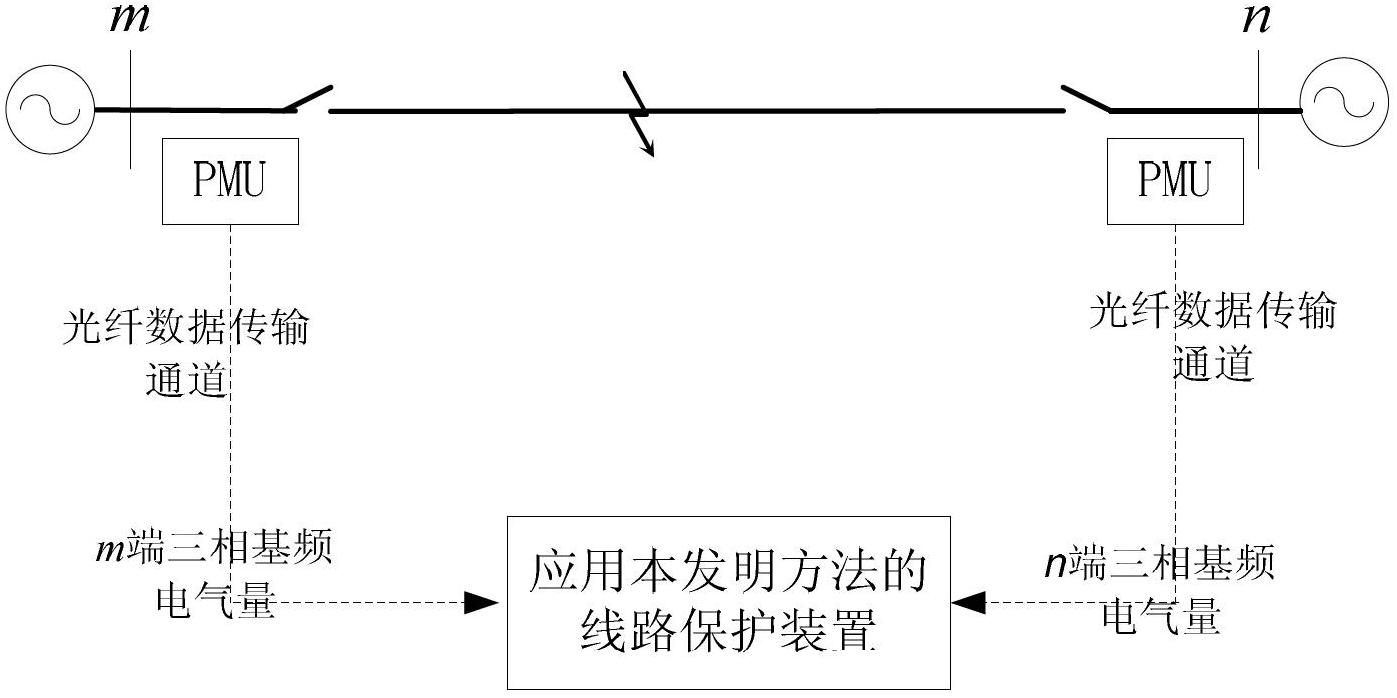
Ultra high-voltage alternating current transmission line protection method based on all-component differential coefficient matrix
ActiveCN102694375AAccurate identificationReliable actionEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionDifferential coefficientHigh resistance
The invention discloses an ultra high-voltage alternating current transmission line protection method based on an all-component differential coefficient matrix, comprising the following steps that the fundamental frequency electric amount on both ends of an ultra high-voltage alternating current transmission line is measured; the positive, negative and zero sequence current amount on the other end is calculated from that on one end of the line with a long line equation; the fundamental frequency current amount on the other end is calculated through a symmetrical component method; and then a differential coefficient matrix is calculated. A fault type is judged according to the values of all elements of the differential coefficient matrix, and a fault phase is enabled to be correctly tripped. The method is applicable to protecting the whole fault process of the ultra high-voltage alternating current transmission line; and particularly when the ultra high-voltage alternating current transmission line has a single-phase high-resistance grounding short-circuit fault, the method can accurately identify and correctly trip the fault phase, and circuit breakers on both ends of other two normal phase lines are reliable without working.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Quadrupole ion trap with switchable multipole fractions
InactiveUSRE36906E1Great massSwitch over the various operating states quicklyStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometrySymmetrical components
An ion trap is provided in which higher multipole field fractions can be switched on and off and, in addition, can be electrically tuned. Specifically, the electrodes of an ideally shaped ion trap are divided into rotationally symmetrical component electrodes positioned facing the interior of the ion trap on a hyperboloidal surface with rotationally symmetry.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH
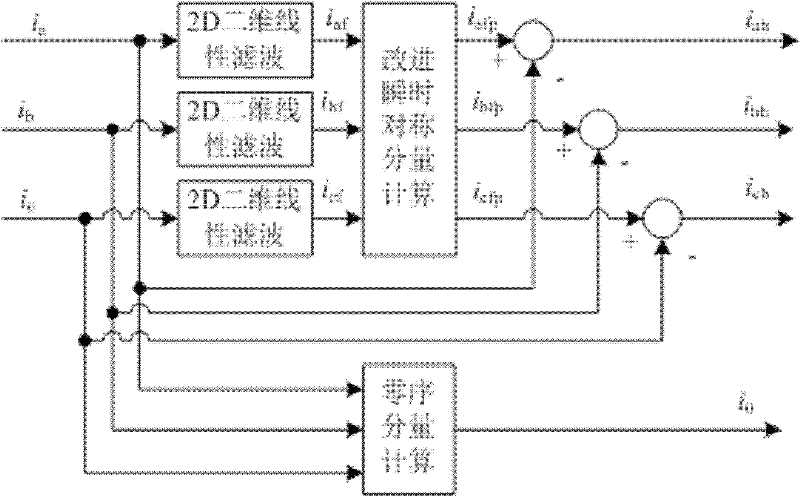
Instantaneous symmetrical component method-based current detection method for distribution static synchronous compensator (DSTATCOM)
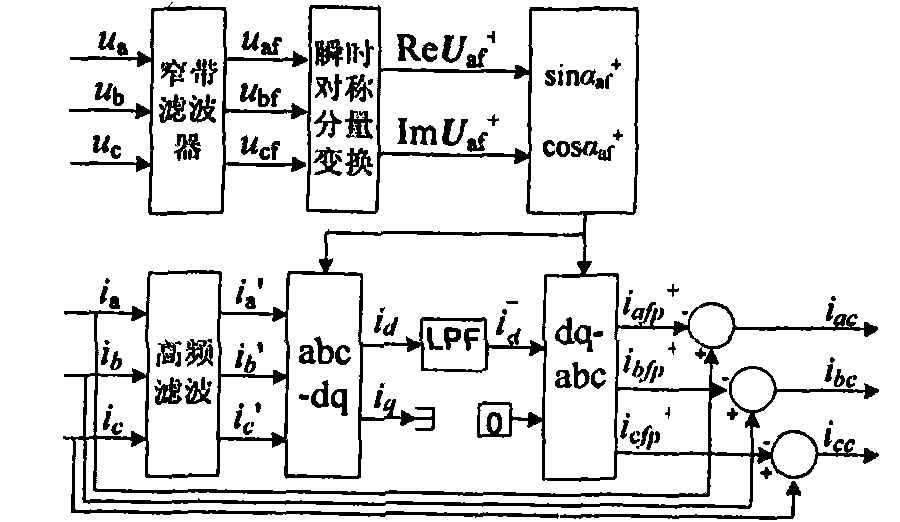
InactiveCN102081114AAvoid look-up processQuick checkReactive/real component measurementsPhase locked loop circuitSymmetrical components
The invention discloses an improved instantaneous symmetrical component method-based current detection method for a distribution static synchronous compensator (DSTATCOM), which comprises the following steps of: 1, determining a symmetrical component method and a method for expressing an instantaneous value in a phasor time domain; 2, determining the instantaneous value; 3, implementing the improved instantaneous symmetrical component method; 4, establishing a model by adopting a MATLAB simulation tool to perform simulation analysis on a conclusion; 5, filtering, converting and processing data; and 6, subtracting obtained three phases of positive fundamental active currents iafp<+>, ibfp<+> and icfp<+> from a load current to obtain required comprehensive compensation command currents iac, ibc and icc comprising harmonic components, negative sequence components and reactive components. The method avoids a complex phase shift circuit, a phase locked loop circuit, and an address generator and a table lookup process of sine and cosine function table, and eliminates errors and faults caused thereby.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Method and device of fault location
InactiveUS7283915B2Improve fault location accuracyImprove accuracyFault location by conductor typesSystems intergating technologiesSymmetrical componentsThree-phase
The present invention relates to a method for location of a fault utilizing unsynchronized measurements of three phase voltages and currents acquired at the line terminals without synchronization. Phasors for symmetrical components of the measured quantities are determined and used in the fault location algorithm. According to one embodiment, positive sequence phasors of post-fault quantities are used for estimation of the distance to fault and it is distinctive that such an estimation of a distance to fault is performed without essentially involving iterative techniques. In this embodiment, the fault location algorithm step is performed regardless of the fault type. In later steps, the type of fault may be obtained. According to another embodiment of the invention, at the occurrence of a fault, the type of fault is determined. If it is determined that it is not a three-phase balanced fault, negative sequence phasors are used for the estimation of the distance to fault. On the other hand, if it is a three-phase balanced fault, the incremental positive sequence phasors are used.
Owner:ABB POWER GRIDS SWITZERLAND AG
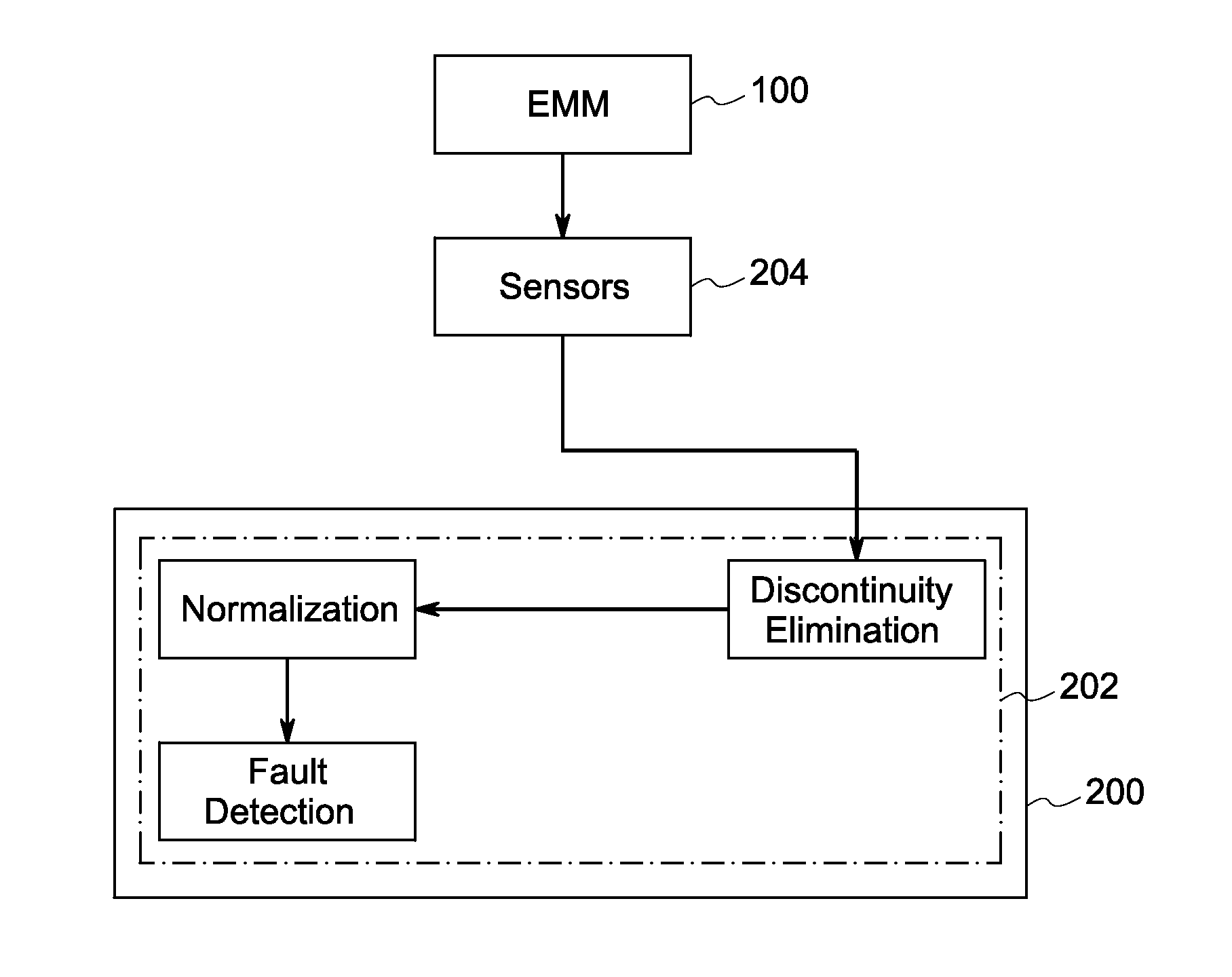
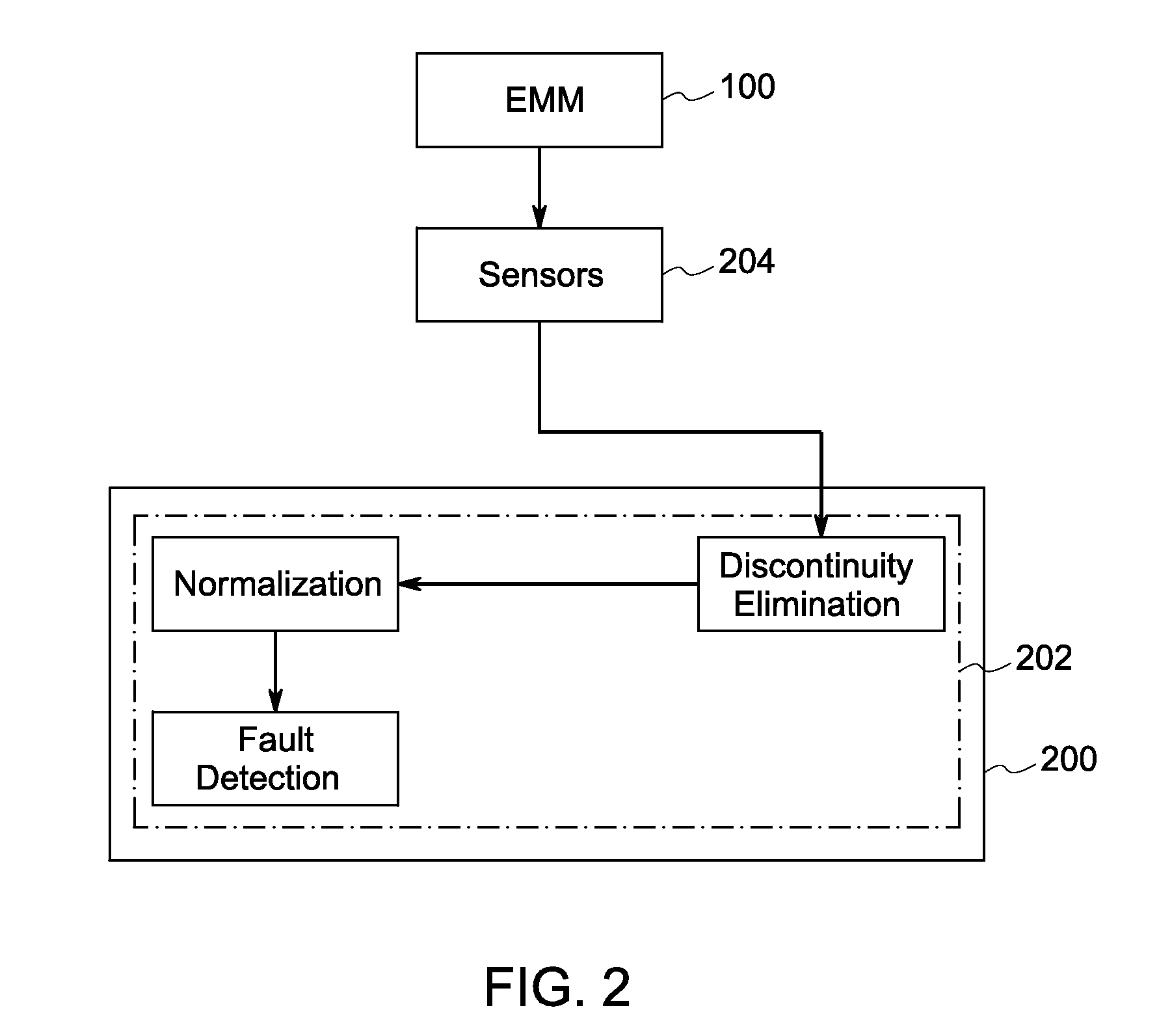
Broken rotor bar detection based on current signature analysis of an electric machine
InactiveUS20140303913A1Electric motor controlSpecial data processing applicationsElectric machineSymmetrical components
A method for detection of rotor bar faults in an electric machine is provided. The method includes acquiring electrical signals from the electric machine that are representative of the operative condition of the machine. The symmetrical components from the electrical signals are eliminated by squaring an instantaneous value of each data point from the electrical signals and summing the squared values. The method further includes the step of eliminating discontinuities in the electrical signals by applying a window function to compute weighted representation of the squared values. Furthermore, the method includes the step of normalizing the weighted representation to obtain spectral information. The faults in the rotor bar are detected by analyzing the spectral information obtained after normalization.
Owner:GE ENERGY POWER CONVERSION TECH
Pitch detection method and apparatus
A pitch detection method and apparatus, the pitch detection apparatus includes: a data rearrangement unit which rearranges voice data on the basis of a center peak of the voice data included in a single frame; a decomposition unit which decomposes rearranged voice data into even symmetrical components on the basis of a center peak; a pitch determination unit which obtains a segment correlation value between a reference point and at least one or more local peaks in relation to even symmetrical components, and determines the location of a local peak corresponding to a maximum segment correlation value among the obtained segment correlation values, as a pitch period.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
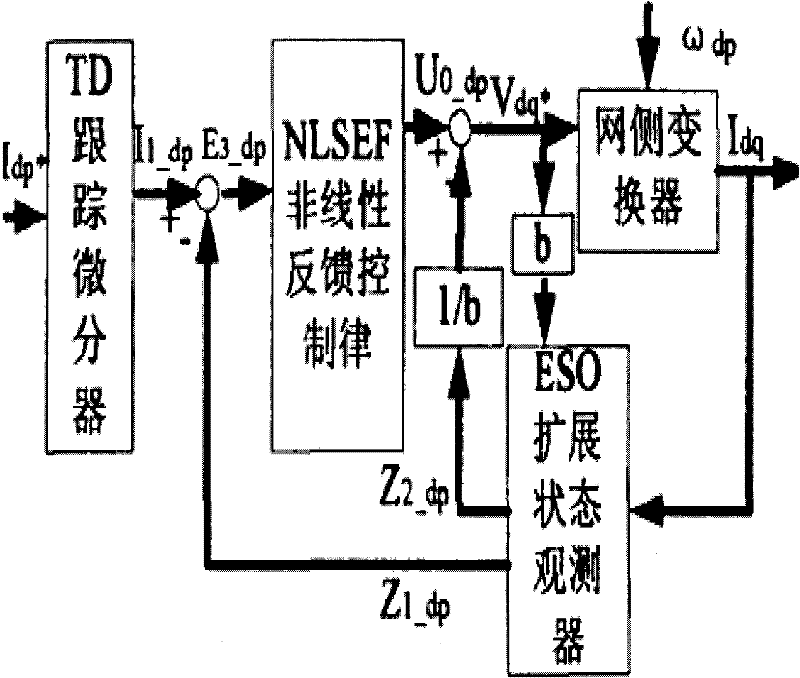
Voltage unbalanced mathematical model-based control strategy for brushless double-feed motor grid-side converter
InactiveCN102055205AImprove control efficiencyHarmonic suppressionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower conversion systemsVoltage vectorInterference resistance
The invention relates to a voltage unbalanced mathematical model-based control strategy for a brushless double-feed motor grid-side converter. Unbalanced voltage vectors are decomposed into balanced positive sequence components, negative sequence components and zero sequence components by utilizing a symmetrical component method; a mathematical model of the grid-side converter is created when the voltage is unbalanced; and the problems of coupling terms and external disturbance existing in the grid-side converter are observed and compensated by utilizing an expansion state observer and a self anti-interference control theory. A nonlinear control method designed in the invention can inhibit the harmonic wave problem of the grid-side converter under the voltage unbalanced condition very well, and has the advantages of strong anti-interference capability, favorable robustness, and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Linear filter-based harmonic current detection method in three-phase four-wire system
InactiveCN102253266AReduce computationThe detection method is simpleCurrent/voltage measurementHarmonicSymmetrical components
The invention discloses a linear filter-based harmonic current detection method in a three-phase four-wire system. According to the method, a structural characteristic of the three-phase four-wire system is considered; according to the idea of an adaptive notch filter (ANF), a two-dimensional linear sine filter is obtained after rotation transformation on the basis of a minimum variance principleand a gradient decent method; fundamental currents of all phases are respectively separated from an actual measured current by the two-dimensional linear sine filter; and then a symmetrical fundamental wave positive sequence component is obtained by utilizing a modified instantaneous symmetric component calculation method; after calculation of the fundamental wave positive sequence component withthe original actual measured current, a harmonic component of a load current, a fundamental negative sequence component and a zero sequence component are drawn off. Compared with the prior art, a technique employed in the linear filter-based harmonic current detection method in the three-phase four-wire system provided of the invention enables the method to have the following advantages that: themethod is simple with a small amount of computation and it is not needed to carry out complicated rotation transformation and trigonometric function calculation; the method has a good real-time performance and high detection precision; and a harmonic current and a reactive current and a neutral current in the three-phase four-wire system can be detected on the condition of unsymmetrical nonlinearload and nonideal voltage.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
Three-phase decoupling load flow calculation method of power distribution network based on path matrix
ActiveCN102842907AAvoid calculationSmall amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsAc network circuit arrangementsComponent LoadLoop analysis
The invention discloses a three-phase decoupling load flow calculation method of a power distribution network based on a path matrix. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, adopting a symmetrical component method to perform sequence component decoupling on a three-phase unbalanced power distribution network to obtain zero sequence, a power distribution sequence network with positive sequence and negative sequence, and adopting a loop-analysis method based on the path matrix to perform one-phase-sequence component load flow calculation to obtain load flows of the three-sequence networks; and secondly, transforming sequence network load flows in a phase component mode by an inverse transformation principle of the symmetrical component method to obtain three-phase load flows. By using the method, a three-phase unbalanced power distribution network system is decoupled into zero sequence, positive sequence and negative sequence networks, so that large matrix manipulation in the three-phase load flow calculation is avoided, the calculated amount is decreased, and the calculation efficiency is improved. The method has the advantages of clear calculation process, simple programming and fast calculation speed. Finally, a 6-busbar test example verifies the correctness and good convergence; and the method is good in generality and practical applicability.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
SVG negative sequence and zero sequence current compensation method based on improved instantaneous symmetrical component method
ActiveCN106532736AAvoid imprecisionGuaranteed three-phase symmetryFlexible AC transmissionPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionTime domainTime delays
The invention discloses an SVG negative sequence and zero sequence current compensation method based on an improved instantaneous symmetrical component method. An instantaneous value is determined by using the improved symmetrical component method and a trigonometric function decomposition method of the instantaneous value in a phasor time domain; the method comprises the following steps: decomposing the system into a positive, negative and zero three-sequence network to obtain positive, negative and zero three-sequence components without delay, making the SVG to emit reactive current and harmonic current requiring compensation in a power grid by positive sequence current control, and compensating negative sequence and zero sequence components generated by unbalance of three-phase loads by negative sequence and zero sequence current control; and when the volume of the SVG is limited, preferably compensating the negative sequence and zero sequence components to ensure the maximum compensation of the reactive components. By adoption of the SVG negative sequence and zero sequence current compensation method disclosed by the invention, the defects of time delay in the traditional instantaneous symmetrical component method is overcome, the flexibility of the SVG compensation ability is given play, the three-phase symmetry of a common node is preferably ensured, the actual demands of the power distribution system are satisfied, and the psychological expectations of industrial users are also satisfied.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Three-phase decoupling power flow calculation method for power distribution network containing multiple transformer branches
InactiveCN102842908AFast convergenceOptimize calculation speedSpecial data processing applicationsAc network circuit arrangementsBalancing networkSymmetrical components
The invention discloses a three-phase decoupling power flow calculation method for a power distribution network containing multiple transformer branches. According to the characteristics of basically symmetrical three-phase line parameters, unbalanced three-phase load and the tree structure of the power distribution network, the method comprises the following steps: performing sequence component decoupling on the three-phase unbalanced network of the power distribution network by a symmetrical component method; in a power distribution three-sequence network model, transforming the transformer branches into the common branches by a phase transformation technology; and calculating the sequence network power flow of the power distribution system by a path matrix-based loop analysis method and transforming sequence component power flow into phase component power flow by an inverse transformation principle so as to realize three-phase decoupling power flow calculation of the three-phase unbalanced system of the power distribution network containing multiple transformer branches and reduce calculated quantity. The method is clear in calculation process, simple in programming and high in calculation speed. The correctness and high convergence property of the method are verified through 34 bus test calculation examples. The method has high generality and practicability.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +1
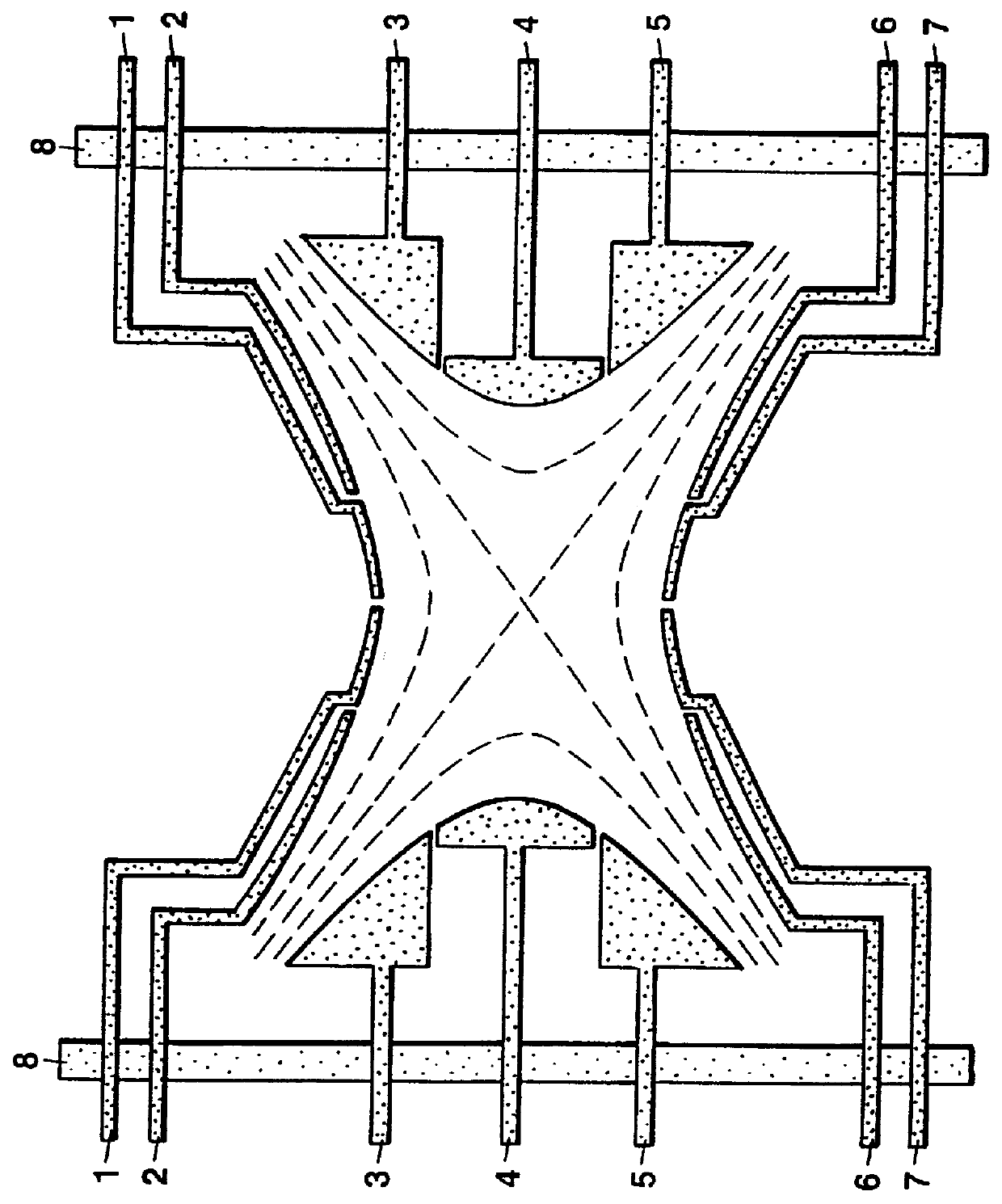
Generation of periodic structures on rotationally symmetrical components
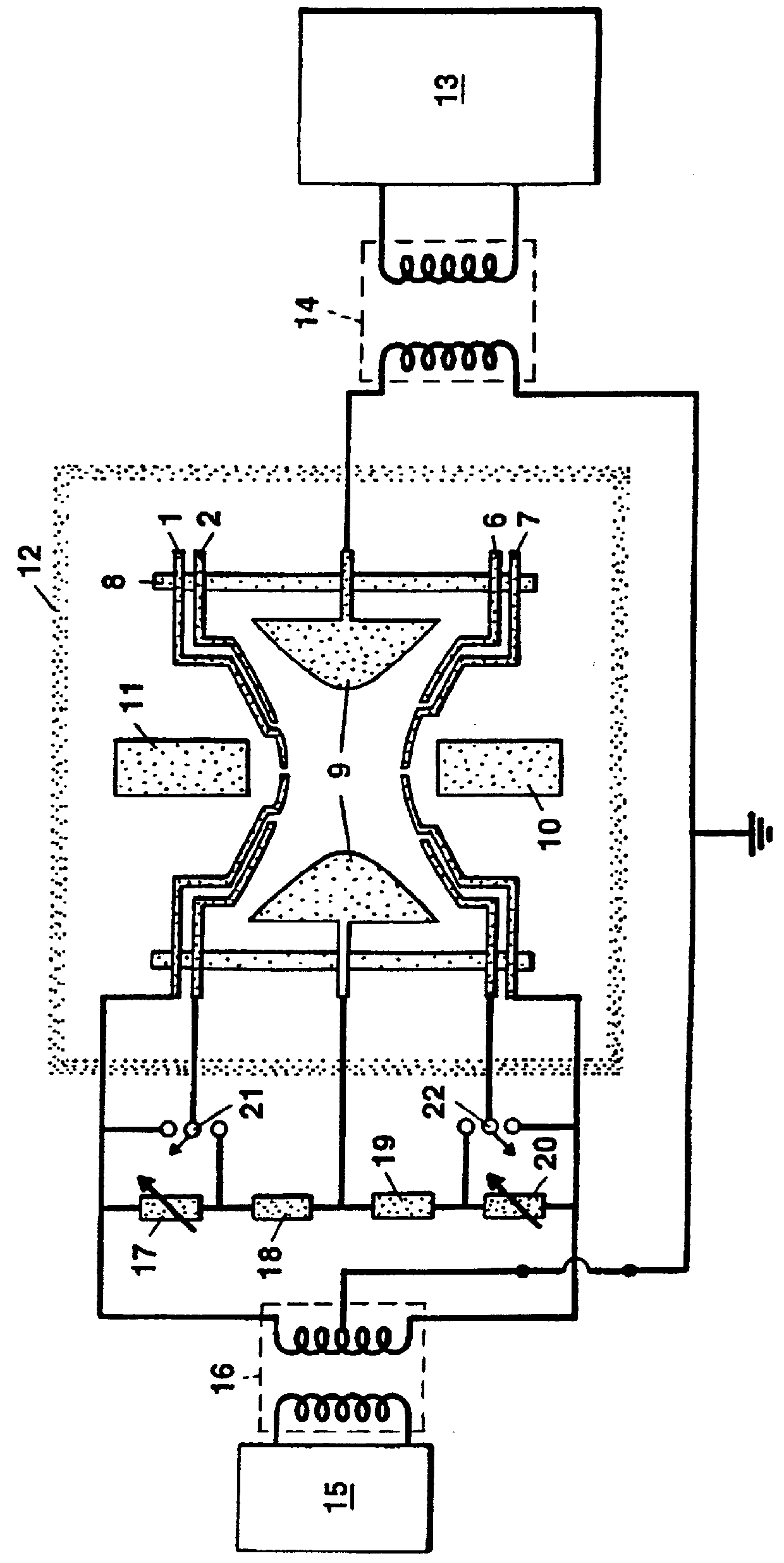
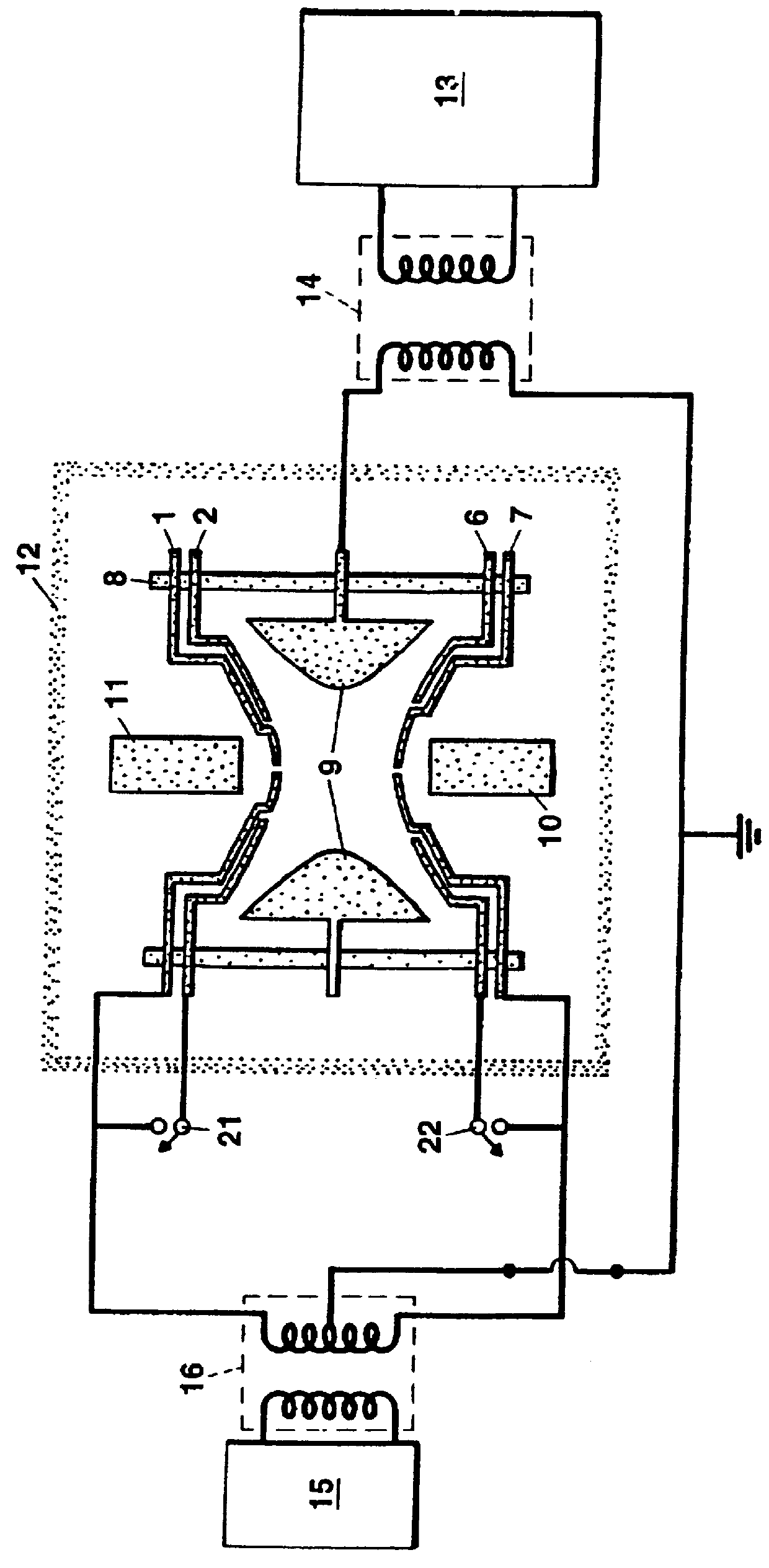
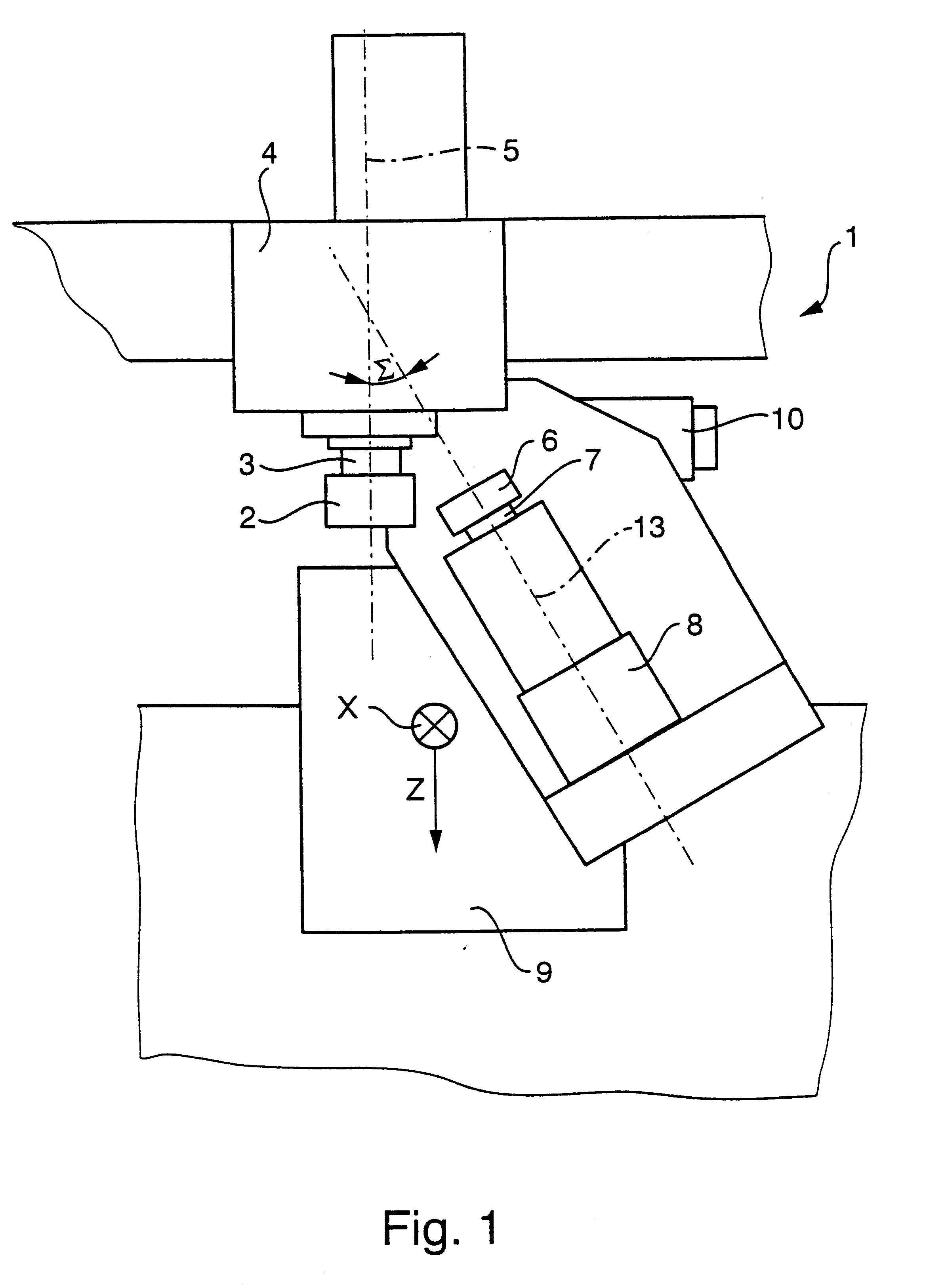
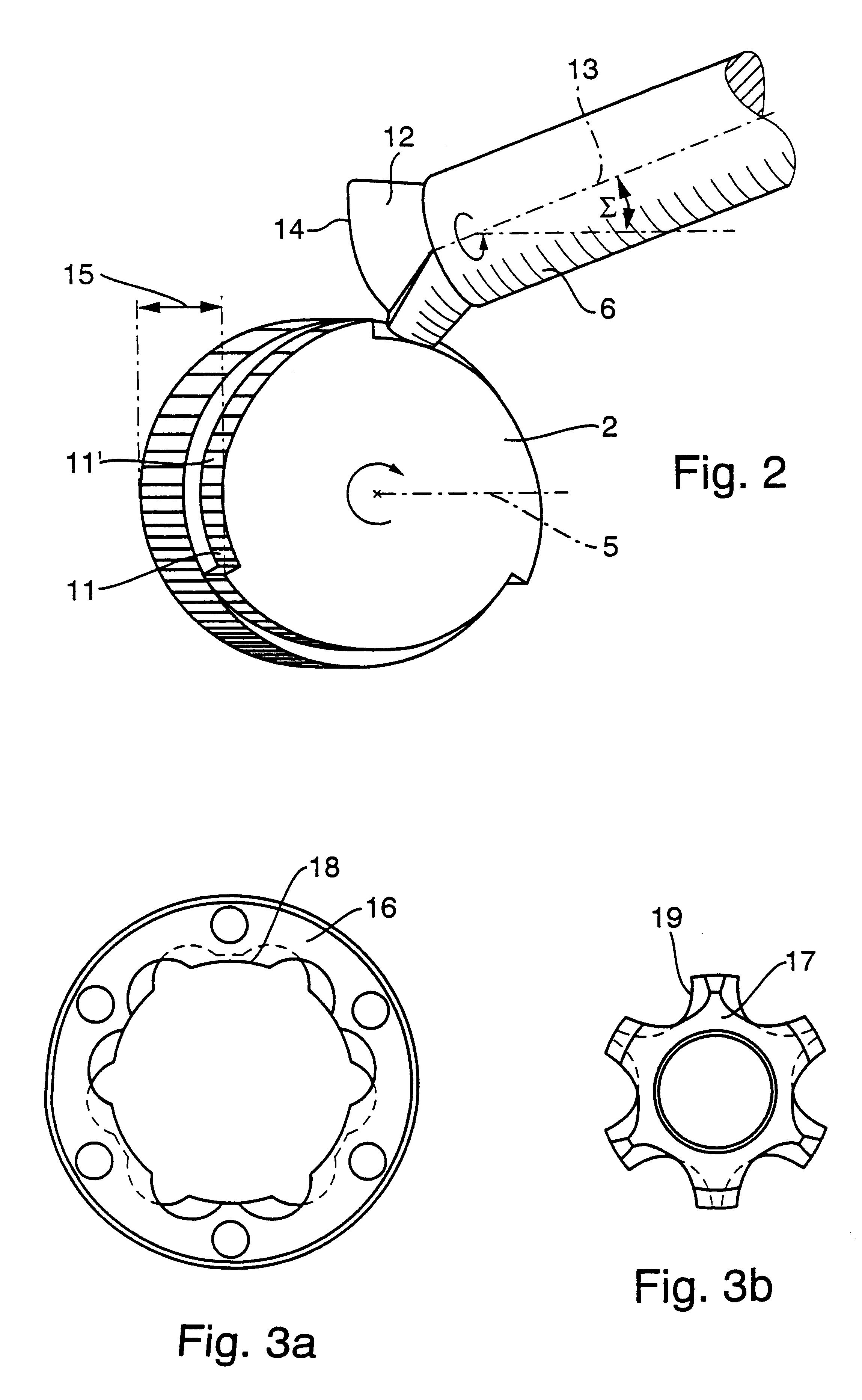
InactiveUS6394718B1Highly precise, quick and cost-effectiveFast processingPlaning/slotting machinesMilling machinesSymmetrical componentsEngineering
The invention relates to the generation of periodic profiles on at least approximately rotationally symmetrical blanks, such as, for example, the generation of shaft-hub connection profiles such as circular wedge profiles, splined shaft profiles, etc., on shaft or hub blanks. To this end, the use of generating skiving is proposed, which permits the production of any desired periodic profiles on rotationally symmetrical blanks and is far superior to rival processes with regard to the productive machining time.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Ultra-high-voltage transmission line relay protection method based on break variable differential coefficient matrix
ActiveCN103296650ACorrect and reliable identificationRealize relay protection functionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDifferential coefficientCapacitance
The invention discloses an ultra-high-voltage transmission line relay protection method based on a break variable differential coefficient matrix. The method includes by utilizing a distributed parameter model, computing three-phase current break variables of the other end of an ultra-high-voltage transmission line by positive, negative and zero-sequence voltage break variables and current break variables of one end of the ultra-high-voltage transmission line and positive, negative and zero-sequence current break variables of the other end of the ultra-high-voltage transmission line by the aid of a symmetrical component method, further computing the break variable differential coefficient matrix, forming protection criterions according to size relationships of elements of the break variable differential coefficient matrix, and distinguishing fault phases of the ultra-high-voltage transmission line. The distributed parameter model is used as a physical model and unaffected by distributed capacitance current, and the method is applicable to any voltage classes and in particular to ultra-high-voltage transmission lines.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
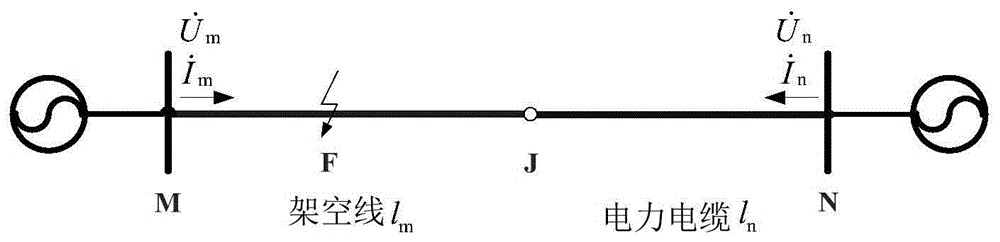
Double-end range finding method for single-phase earth fault of overhead-cable mixed line
ActiveCN105759178AEliminates the effects of attenuating DC componentsComputationally efficientFault location by conductor typesIterative searchSymmetrical components
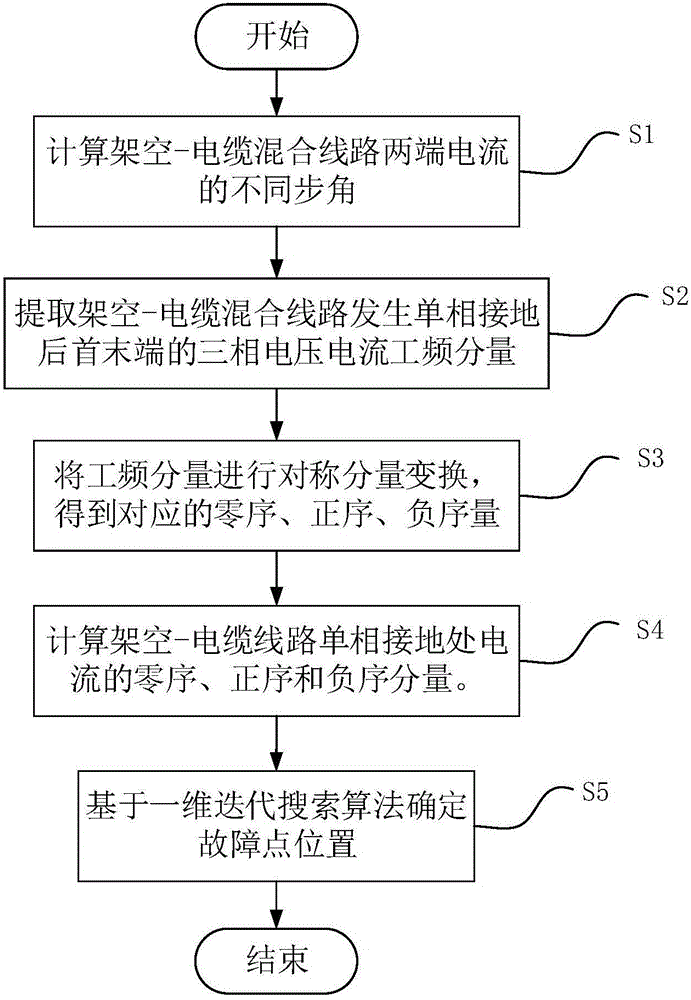
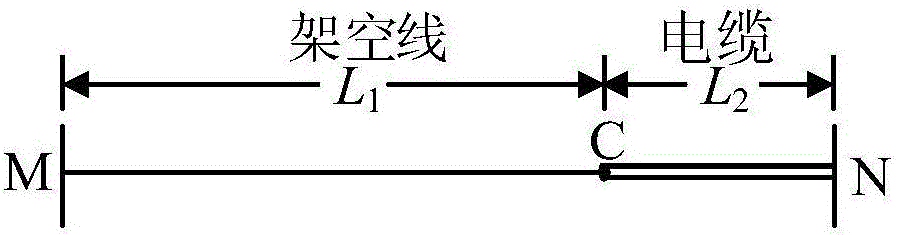
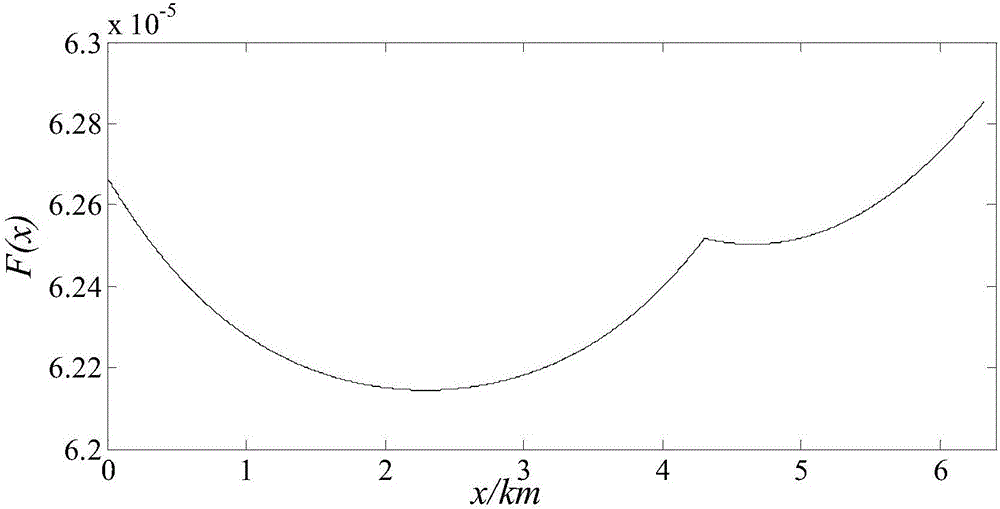
The invention relates to a double-end range finding method for a single-phase earth fault of an overhead-cable mixed line. The method comprises: according to positive-sequence components of three-phase voltages and currents of a front end and a tail end in a normal condition of an overhead-cable mixed line, non-synchronized angles delta of currents at the two ends of the overhead-cable mixed line are calculated; power frequency components of the three-phase voltages and currents at the front end and the tail end of the overhead-cable mixed line after a single-phase earth fault are extracted by using a differential fourier algorithm; symmetric component conversion is carried out on the power frequency components of the three-phase voltages and currents at the front end and the tail end of the overhead-cable mixed line after the single-phase earth fault to obtain sequence components of the voltages and currents at the front end and the tail end of the overhead-cable mixed line after the single-phase earth fault; a sequence component of the single-phase earth fault current of the overhead-cable mixed line is calculated; and the fault point position is determined based on a one-dimensional iterative searching algorithm. Compared with the prior art, the provided method has characteristics of accurate range finding and high efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
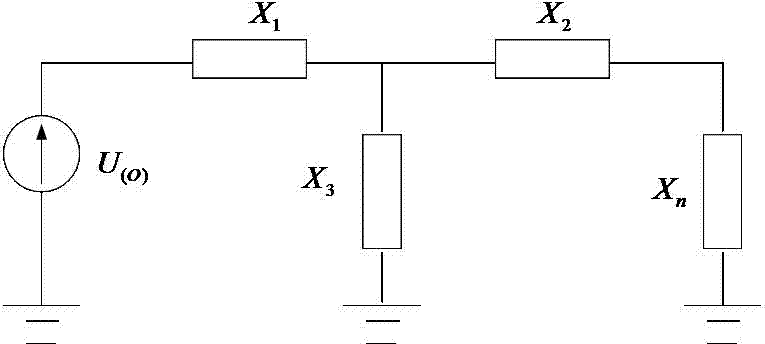
Small reactance value choose method during ultrahigh voltage autotransformer neutral point grounding in small reactance mode
InactiveCN104767195AEasy to calculate the resistance valueGuaranteed reliabilityEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectricityAutotransformer
The invention discloses a small reactance value choose method during ultrahigh voltage autotransformer neutral point grounding in a small reactance mode. According to the principle that during neutral point grounding through an electric reactor, the ratio of the reactance value Xn of the neutral point to the zero-sequence reactance value X0 of a transformer is less than or equal to 1 / 3, according to the symmetrical component analytical method and specific boundary conditions of a dissymmetric short-circuit, by means of a BPA short-circuit current calculation procedure, a high-voltage side bus and a low-voltage side bus of a ultrahigh voltage autotransformer in a transformer substation are subjected to one-phase grounded short-circuit current calculation to choose a suitable reactance value, during the neutral point grounding through the electric reactor, the ratio of the reactance value Xn of the neutral point to the zero-sequence reactance value X0 of the transformer is less than or equal to 1 / 3, namely, Xn / X0<=1 / 3, the guarantee is provided for the reliability of monitoring the normal operation during the autotransformer neutral point grounding in a small reactance mode, and the wide practical significance is achieved.
Owner:MAINTENANCE COMPANY OF STATE GRID XINJIANG ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY
Fault location using measurements of current and voltage from one end of a line
InactiveUS7298149B2Good estimateShunt capacitance is facilitatedFault location by conductor typesEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionSymmetrical componentsEngineering
A method to locate a fault from one end of a section of a power line utilizing measurements of current, voltage and angles between the phases at a first end of said section. Symmetrical components of currents are calculated for the current and voltage measurement at the first end. A value of impedance is calculated for an extra link between the terminals with the impedance for the positive sequence. A compensation is determined for the shunt capacitance. The zero-sequence current is determined from the healthy line of a section of parallel power lines. A distance to a fault is calculated for the parallel line section. The distance to the fault from the first end is calculated. The fault is located utilizing the calculate distances.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Ac electric quantity measuring device
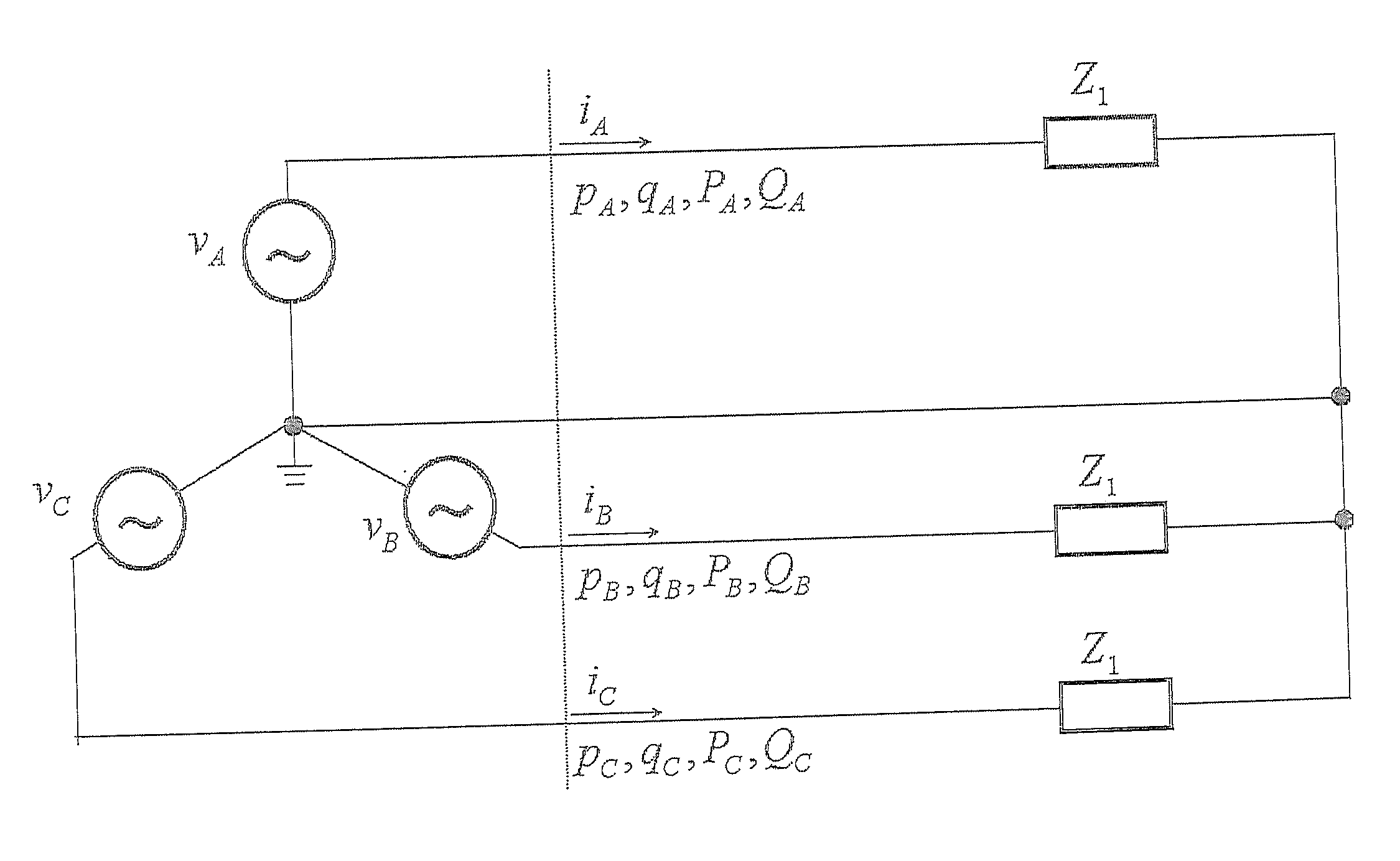
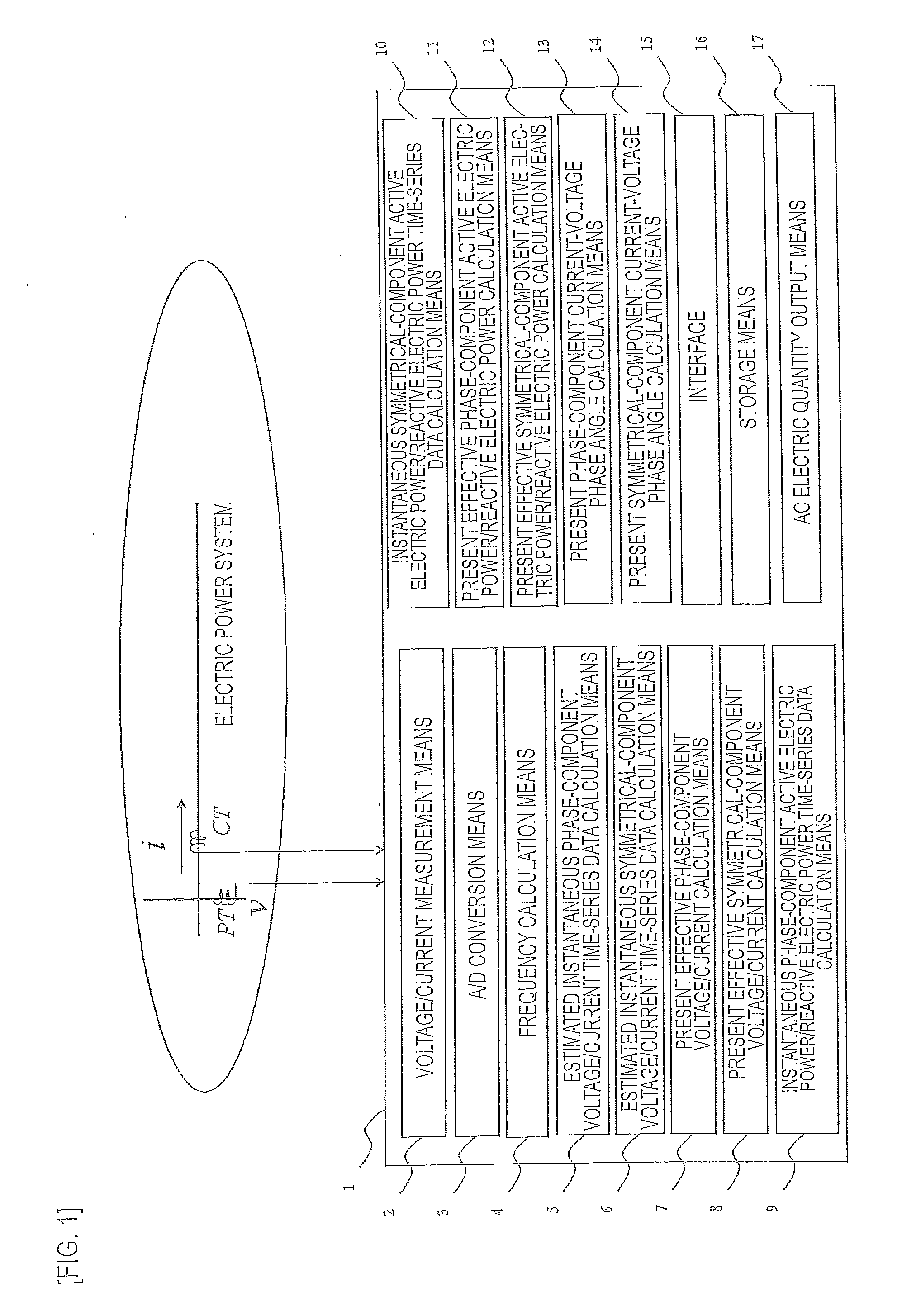
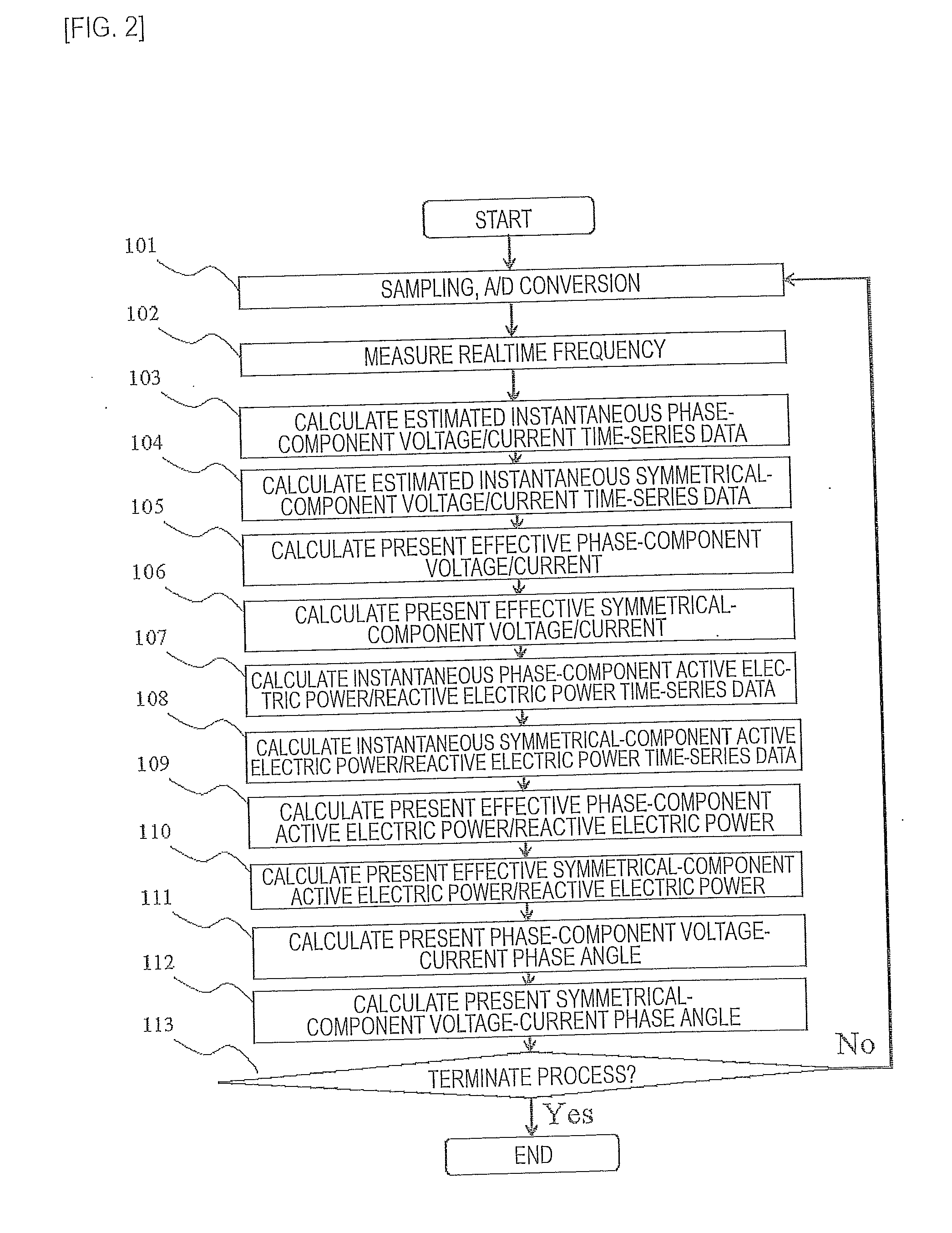
ActiveUS20100019758A1Improve electrical performanceLow costCurrent/voltage measurementDigital variable/waveform displayMeasurement deviceElectric power system
In the present invention, a measured realtime accurate frequency is used to determine estimated instantaneous voltage / current time-series data for each phase component in accordance with the least-squares method. The estimated instantaneous voltage / current time-series data are used to determine effective voltage, effective current, instantaneous active electric power, instantaneous reactive electric power, effective active electric power, and effective reactive electric power of each phase component and symmetrical component. The measured AC electric quantities are applied to any type of electric power system control / protection apparatus.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
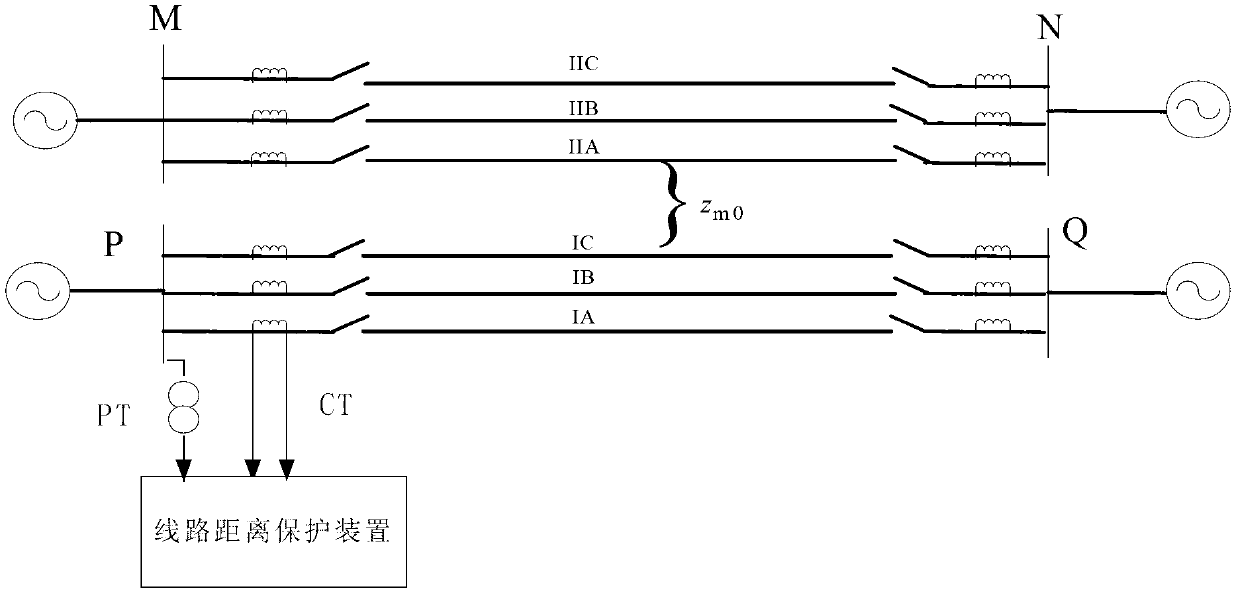
Grounding fault distance protecting method of double circuit lines on same tower
The invention discloses a grounding fault distance protecting method of double circuit lines on the same tower. The grounding fault distance protecting method of the double circuit lines on the same tower comprises the steps of estimating the phase of voltages of a grounding fault point by using a fault syntropy zero sequence current phase, directly calculating a fault distance x according to the fact that the voltage drop of a protecting mounting portion to the grounding fault point is in linear relation with the fault distance, and comparing the size relationship of the fault distance x and a protection setting range xset. If a I circuit line of the double circuit lines on the same tower is in single-phase grounding fault, and the fault distance x is smaller than the protection setting range xset, the I circuit line of the double circuit lines on the same tower is protected to send an action tripping signal. If a II circuit line of the double circuit lines on the same tower is in single-phase grounding fault, and the fault distance x is smaller than the protection setting range xset, the II circuit line of the double circuit lines on the same tower is protected to send the action tripping signal. According to the grounding fault distance protecting method of the double circuit lines on the same tower, a symmetrical component method and a six-sequence component method are used comprehensively, and accurate measuring of the fault distance of the single-phase grounding fault of the single circuit line of the double circuit lines on the same tower is achieved.
Owner:STATE GRID FUJIAN ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD +3
Fault positioning method for overhead line-high voltage cable mixing line
ActiveCN105044551ACalculation speedNot affected by transition resistanceFault locationInformation technology support systemVoltage amplitudeSymmetrical components
The present invention provides a fault positioning method for an overhead line-high voltage cable mixing line, comprising the steps of: (1) respectively measuring three-phase voltage and current phasors of M and N end points at two sides of the line, respectively calculating negative sequence voltages, negative sequence currents, positive sequence voltages and positive sequence currents of the two sides through a symmetrical component method; (2) judging a fault type according to the negative sequence voltages; (3) if the fault type is asymmetric fault, respectively calculating a negative sequence voltage amplitude of each point along the line through the three-phase voltage and current phasors of two-terminal electrical quantities M and N sides, and determining that the points with the equal negative sequence voltage amplitude are fault points; (4) if the fault type is three-phase symmetrical fault, performing fault positioning through a method for comparing positive sequence voltage amplitude variations, and determining that the points with the equal positive sequence voltage amplitude variation are fault points. The fault positioning method of the present invention aims at parameter characteristics of the overhead line-high voltage cable mixing line, does not require synchronous two-terminal electrical quantities, does not need to perform fault section judgment in advance, does not have a pseudo root identification problem, and can adopt various quick search algorithms in the process of fault position search.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
PMU data-based identification method for single electric transmission line zero-sequence parameter robustness
InactiveCN103869184AReduce adverse effectsEasy to operateCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical testingSymmetrical componentsPower grid
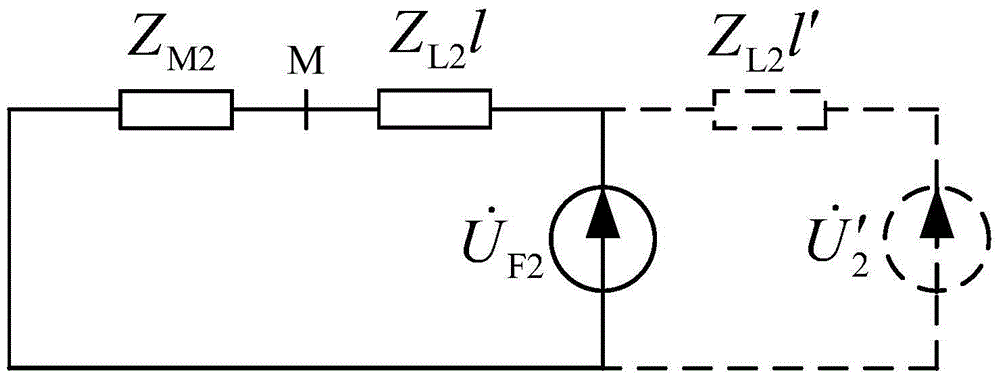
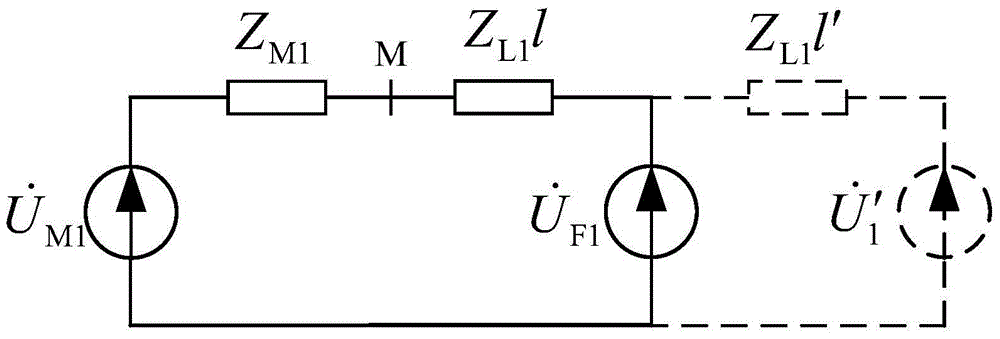
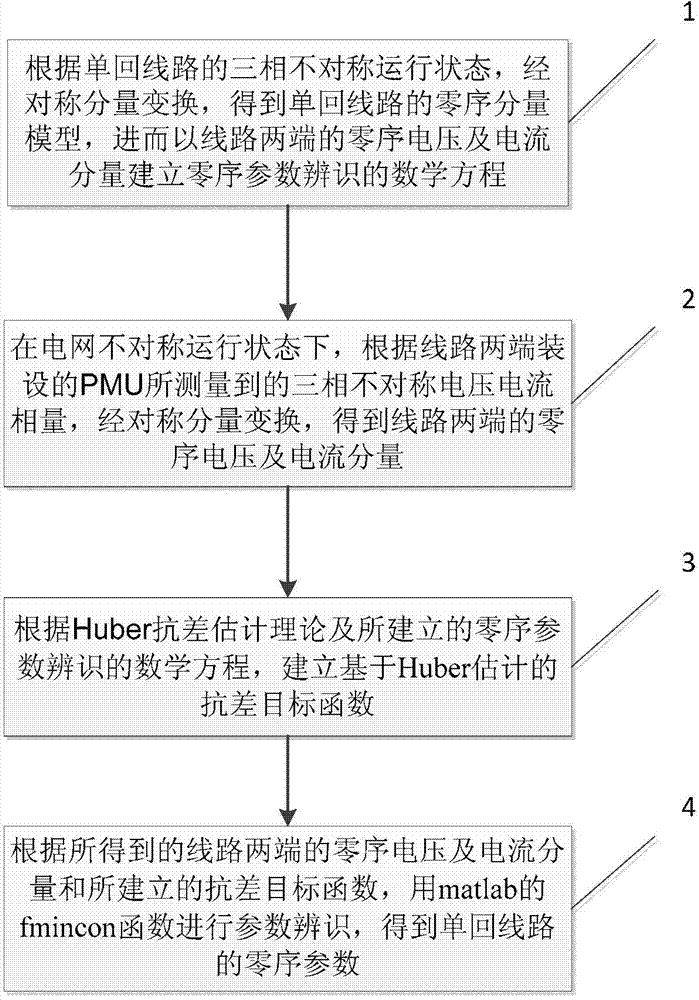
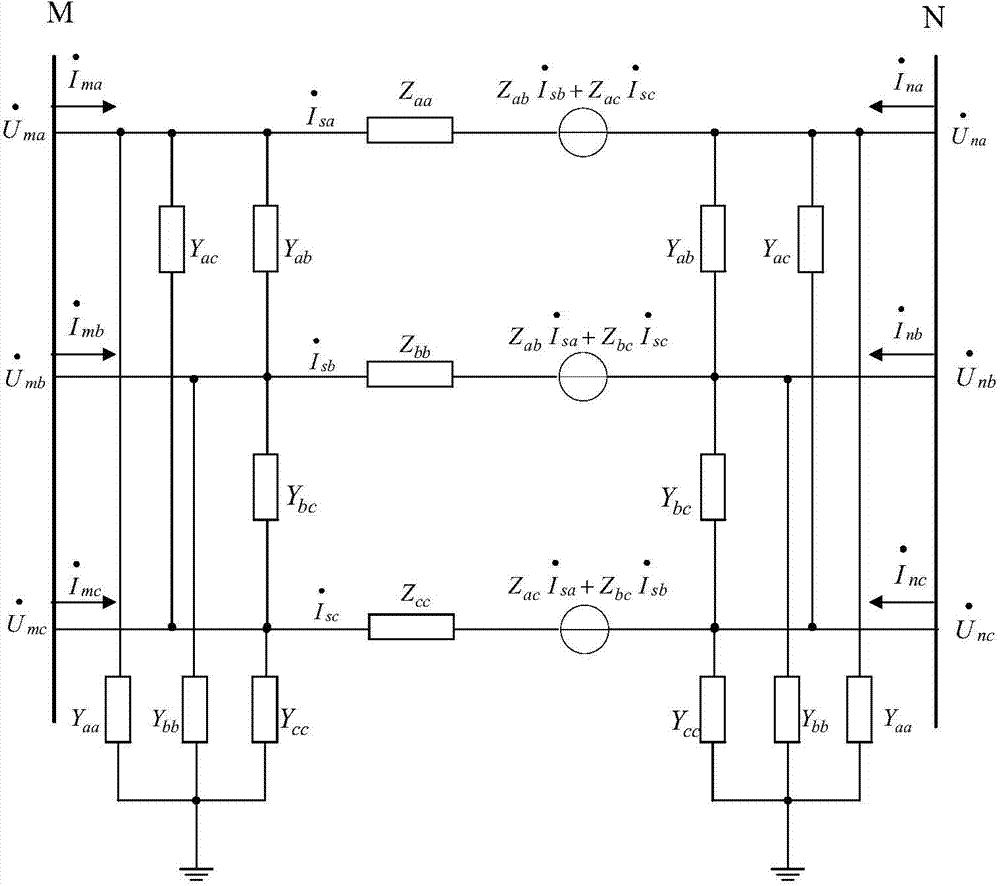
A PMU data-based identification method for single electric transmission line zero-sequence parameter robustness comprises the following steps that firstly, according to the three-phase unsymmetrical operation state of a single electric transmission line, a zero-sequence equivalent model of the single electric transmission line is obtained through symmetrical component transformation, and further a mathematical equation for zero-sequence parameter identification is constructed by using the zero-sequence voltage and current components on the two ends of the single electric transmission line; secondly, under the unsymmetrical operation state of a power grid, the zero-sequence voltage and current components on the two ends of the single electric transmission line are obtained according to three-phase unsymmetrical voltage and current phasors measured by PMUs arranged on the two ends of the single electric transmission line through symmetrical component transmission; thirdly, a Huber estimation-based robustness target function is established according to the Huber robustness estimation theory and the constructed mathematical equation for zero-sequence parameter identification; lastly, parameter identification is performed by using the fmincon function of the matlab according to the obtained zero-sequence voltage and current components on the two ends of the single electric transmission line and the established robustness target function, and thus the zero-sequence parameter of the single electric transmission line is obtained.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com