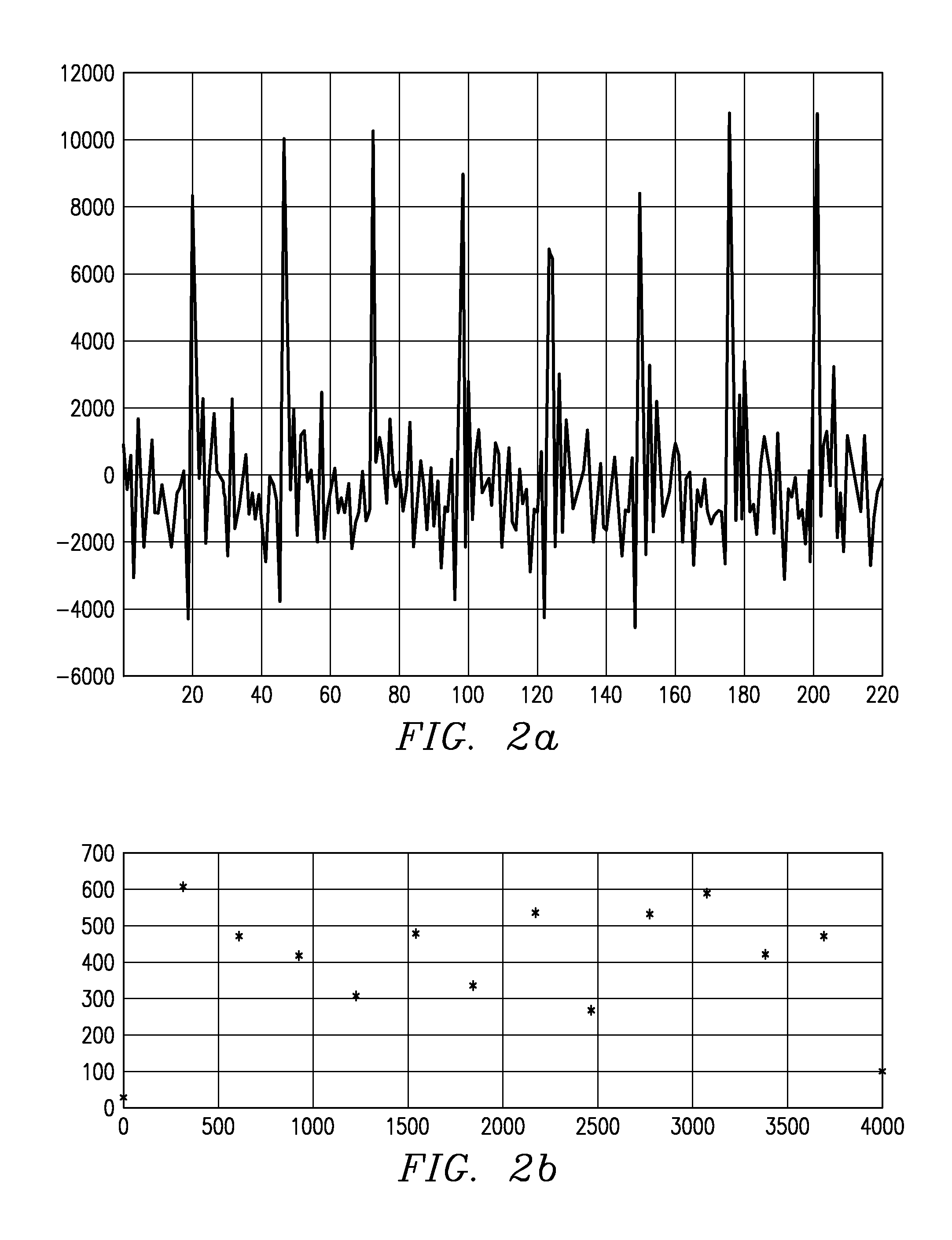
Patents
Literature
565 results about "Zero phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
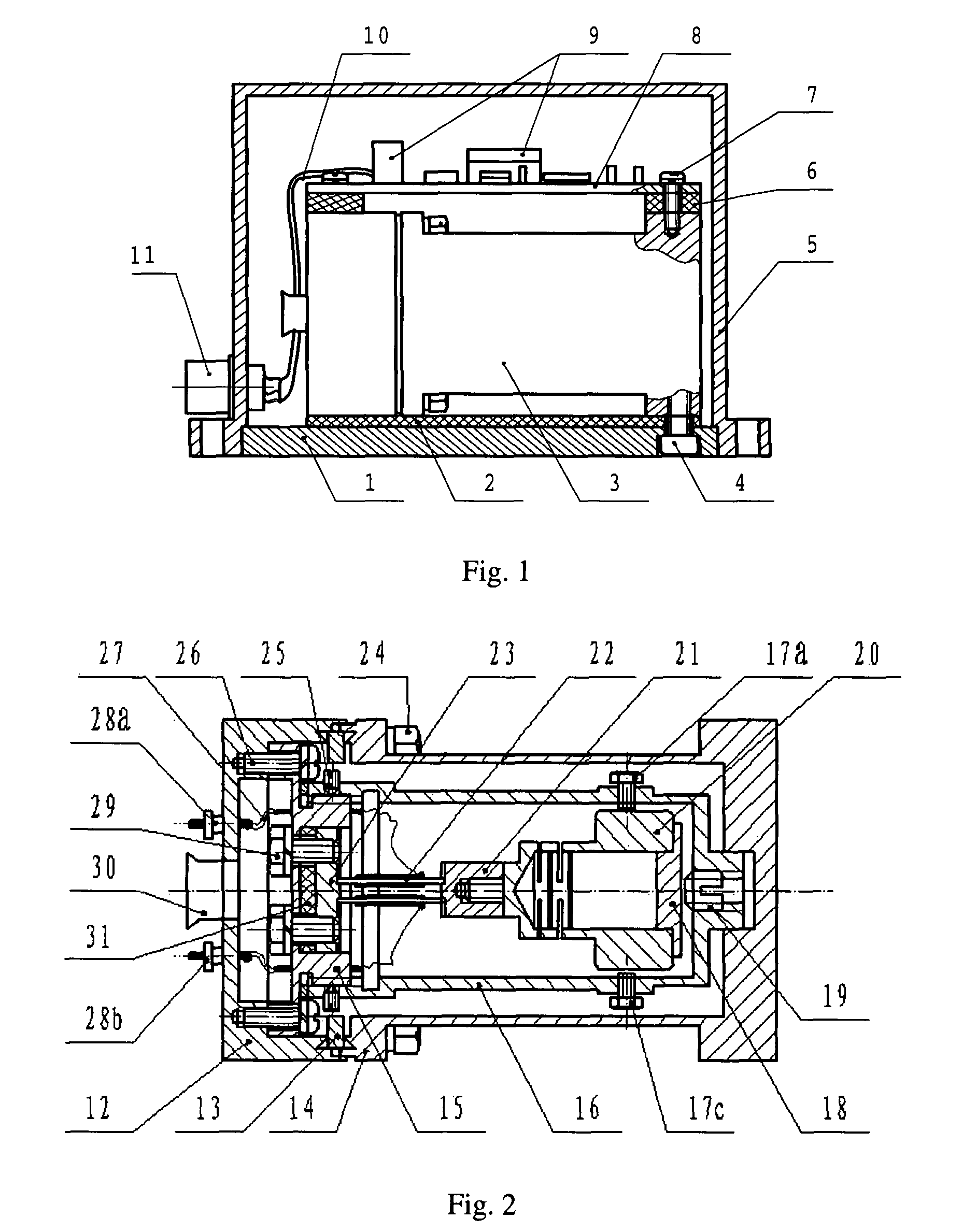
Method for analyzing signal waveform and analyzing vehicle dynamic characteristic
ActiveUS7523011B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceResistance/reactance/impedenceVehicle dynamicsWaveform analysis
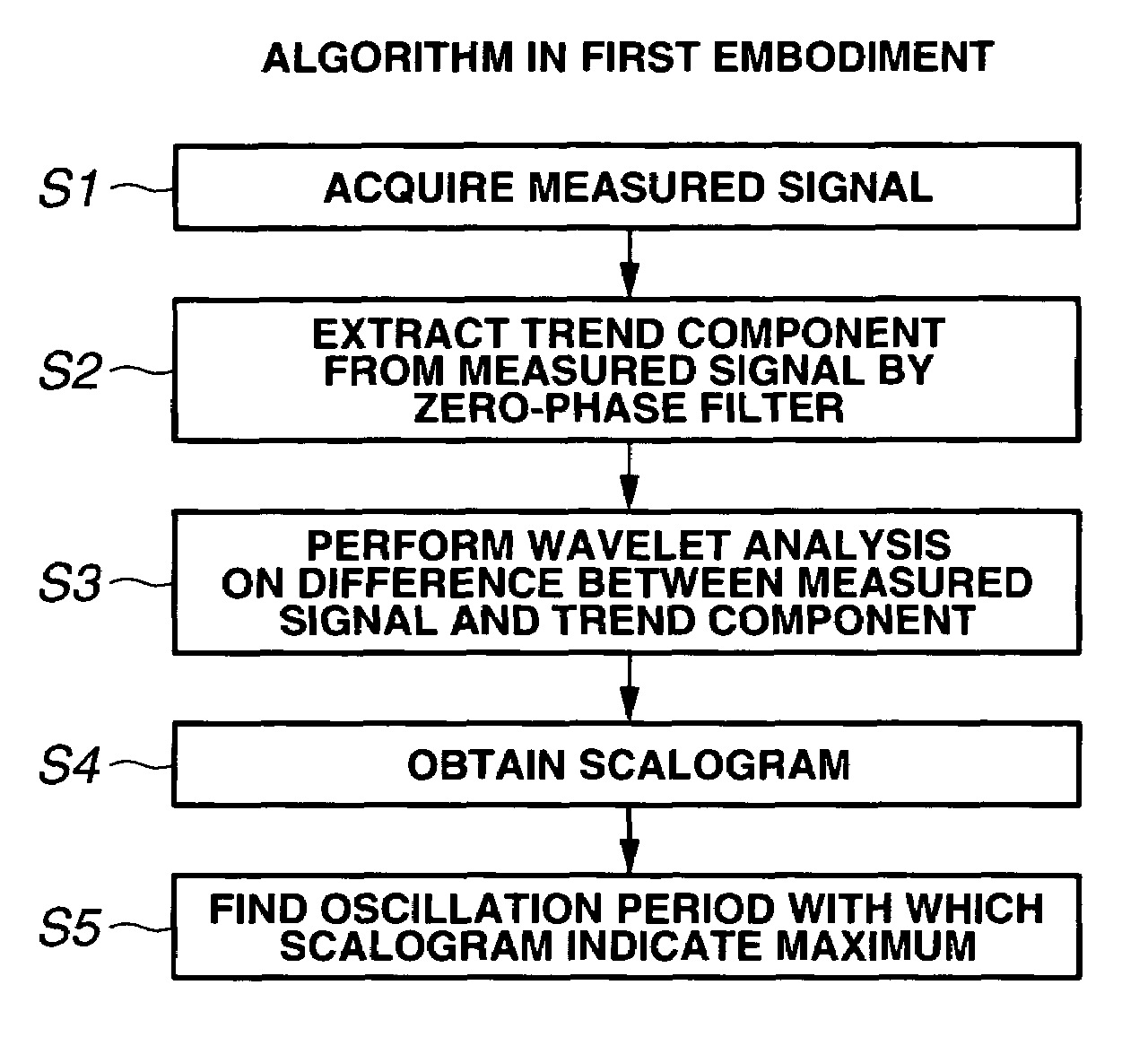
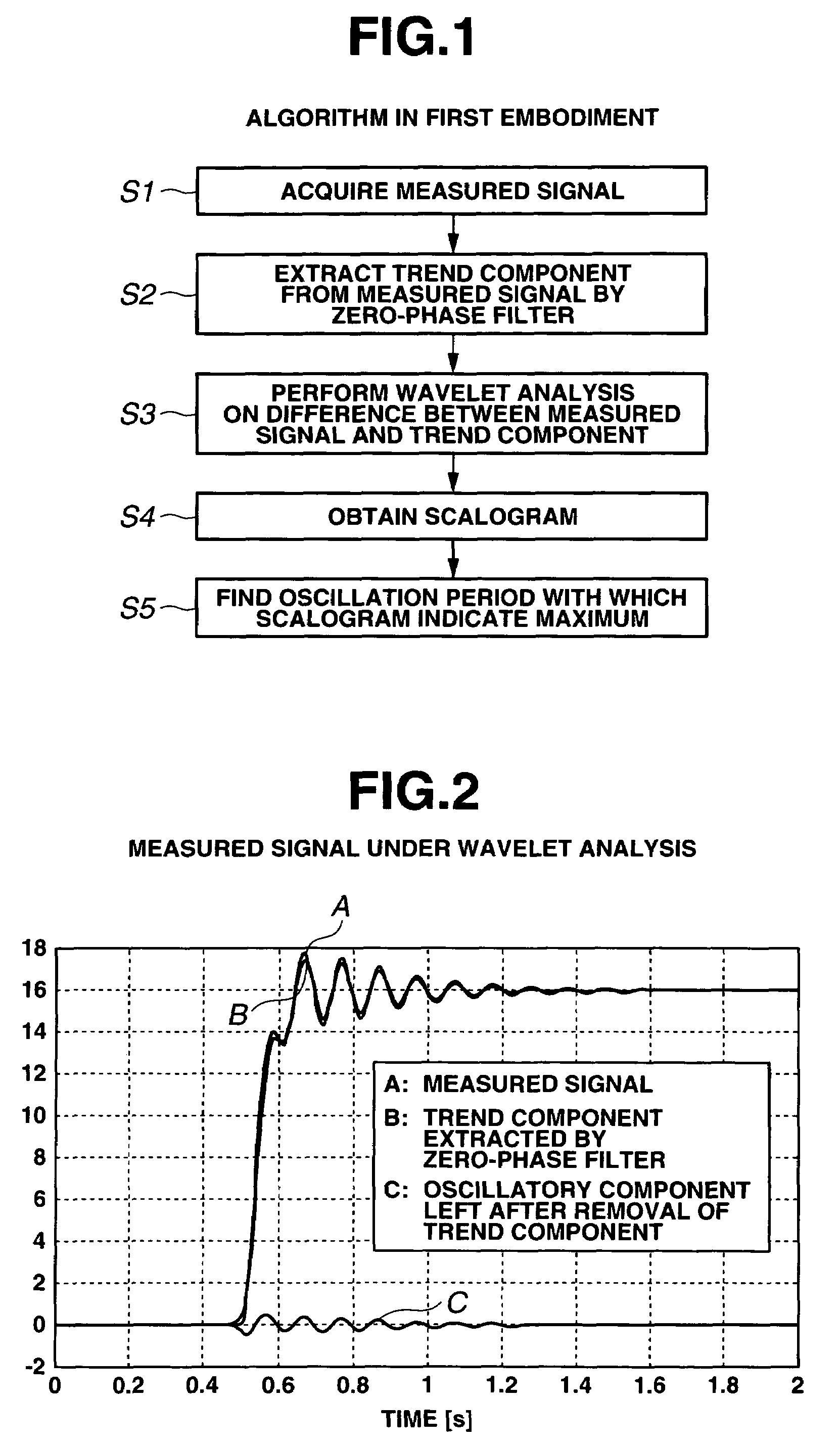
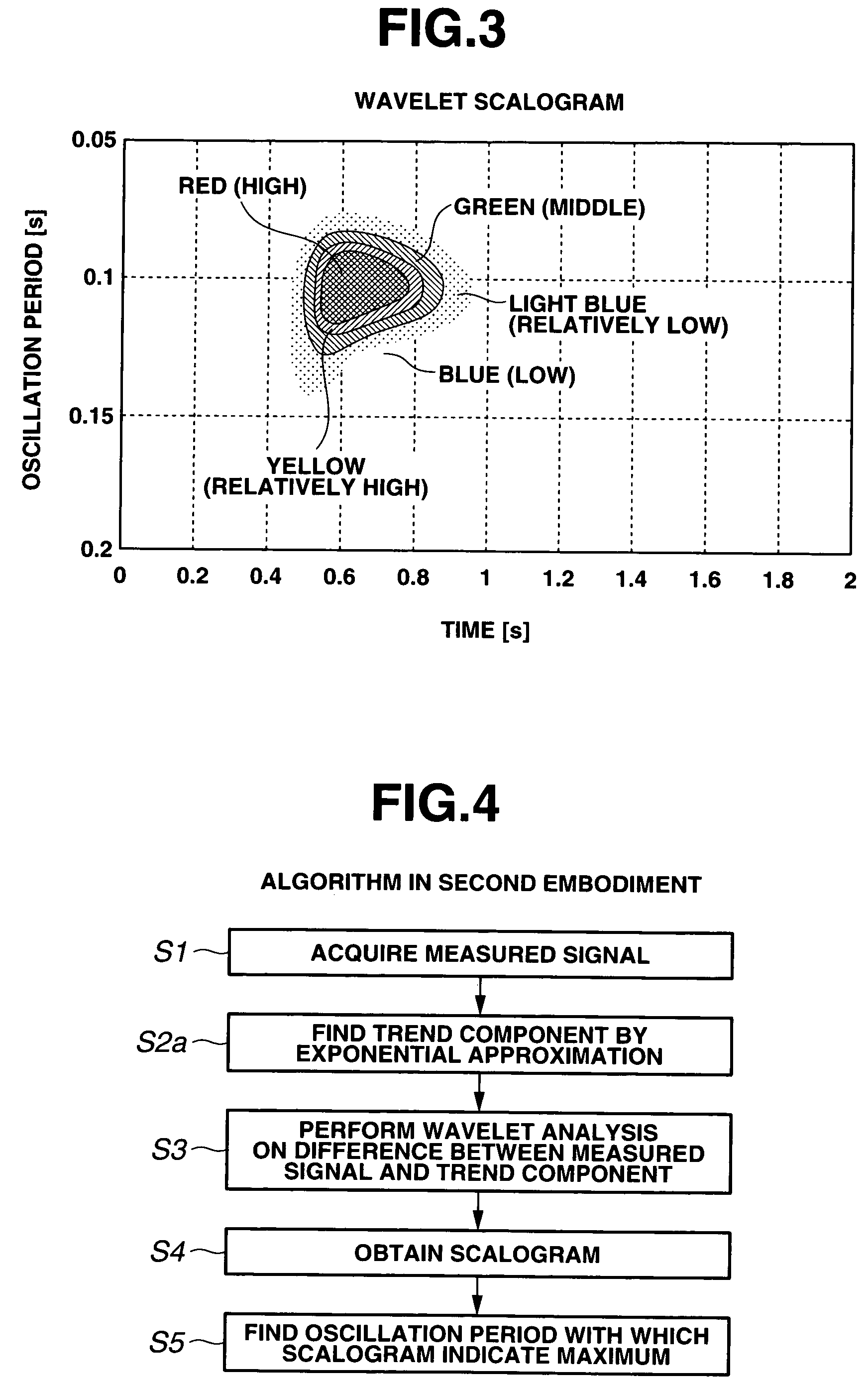
A signal waveform analysis method includes: determining a trend component of an object signal by applying a zero-phase filter to the object signal; determining an oscillatory component of the object signal by removing the trend component from the object signal; determining a wavelet scalogram by performing a wavelet analysis on the oscillatory component; and determining an oscillation period of the object signal with which the wavelet scalogram indicates a maximum. The signal waveform analysis method is employed to evaluate vehicle dynamic characteristics.
Owner:MEIDENSHA ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD +1
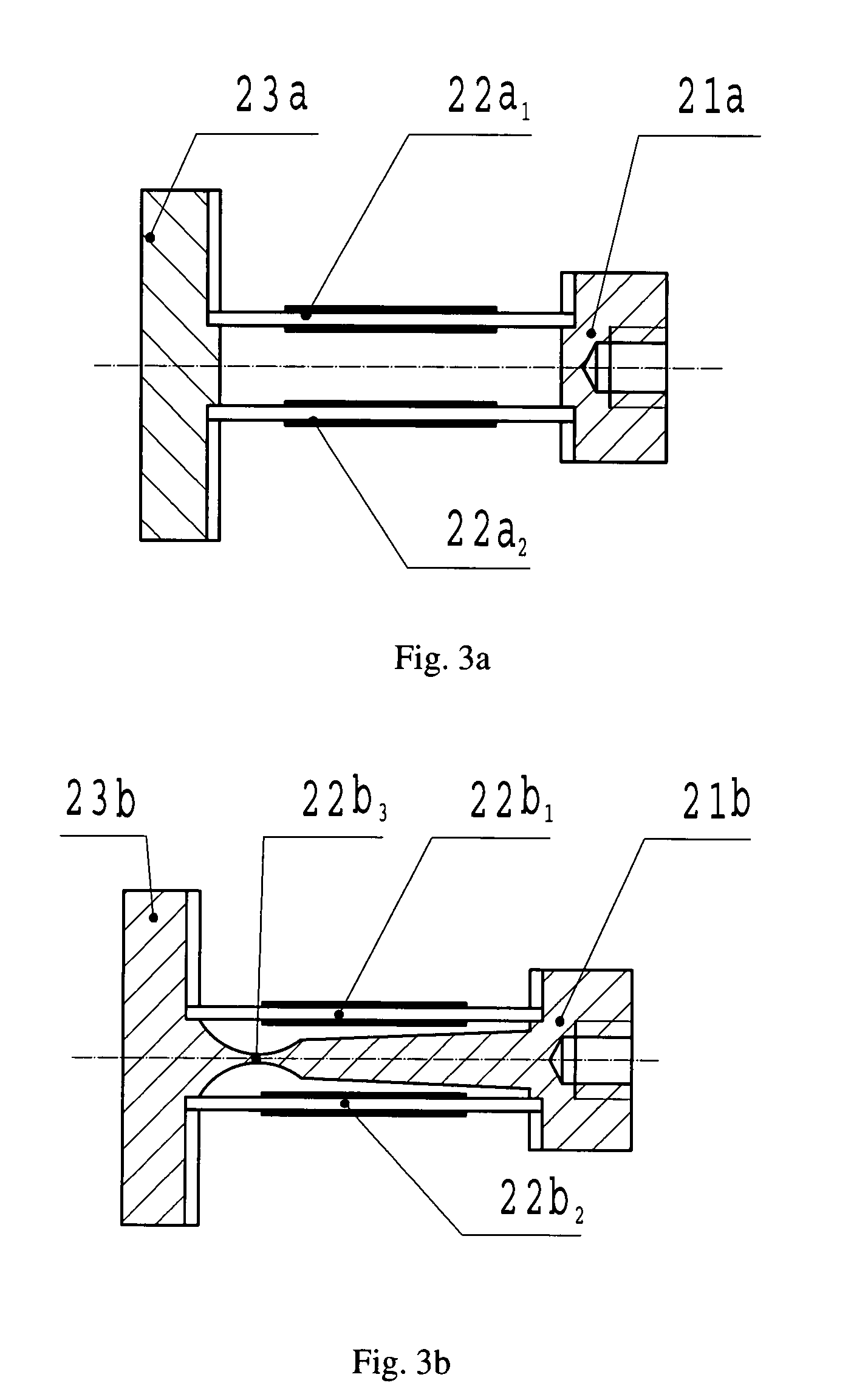
Piezoelectric quartz accelerometer
InactiveUS7716985B2High linearizationHigh resolutionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed/acceleration/shock instrument detailsAccelerometerSignal processing circuits
A piezoelectric quartz accelerometer includes a sensitive element, a signal processing circuit, a base, an outer case, and a socket, wherein the sensitive element includes two round piezoelectric quartz wafers, and a supporting frame, wherein the two round piezoelectric quartz wafers are symmetrically mounted on both sides of the center axial line of the supporting frame; the sensitive element further includes an axial shock buffer unit and a transverse retaining unit for protecting overload of the two round piezoelectric quartz wafers; the signal processing circuit includes an oscillation circuit for obtaining frequency signal, a frequency differential forming circuit for extracting signal, a phase lock and times frequency circuit for amplifying signal, compensating zero phase, compensating non-linearization and compensating temperature, and an output circuit.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION TECH INST
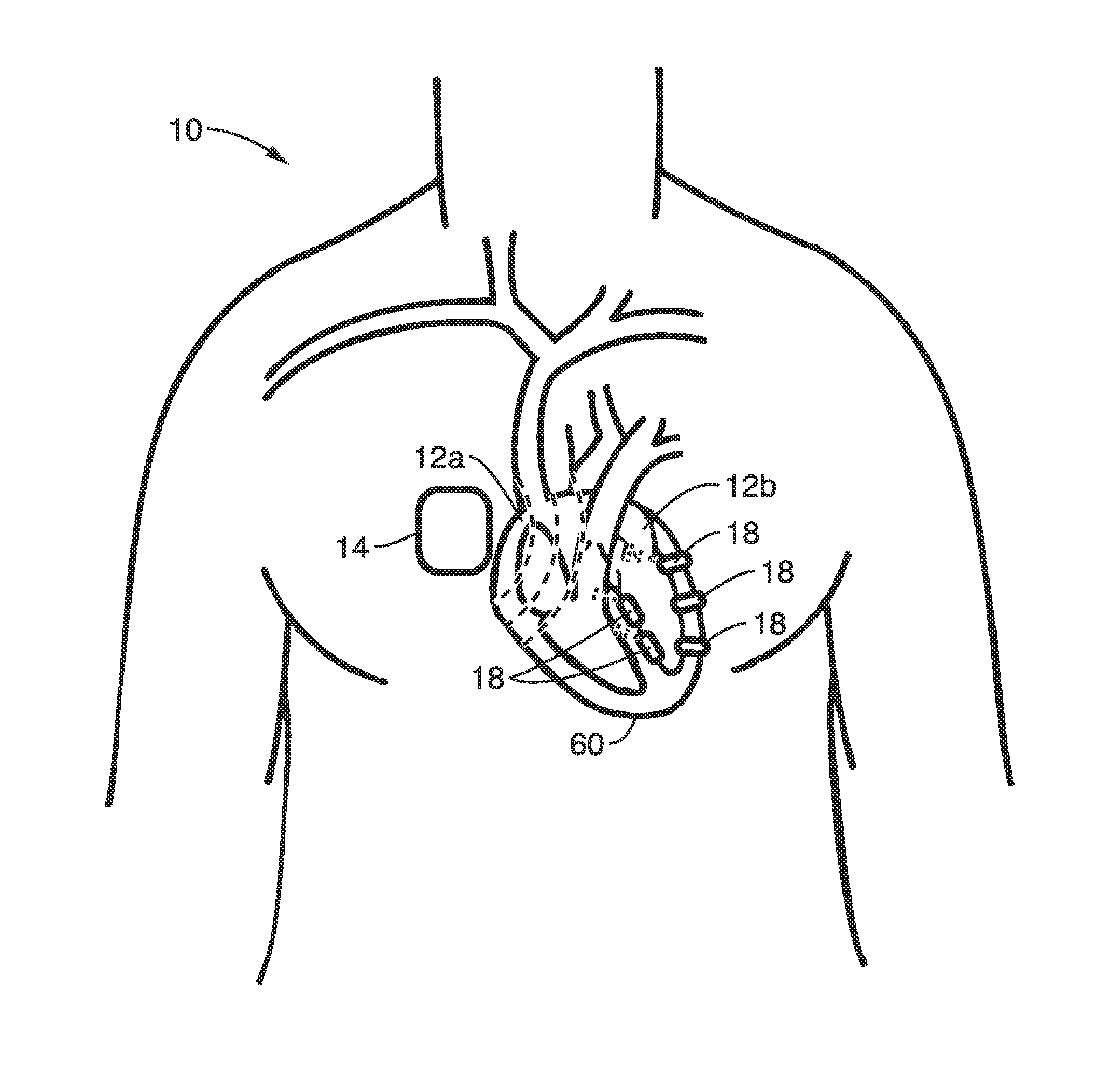
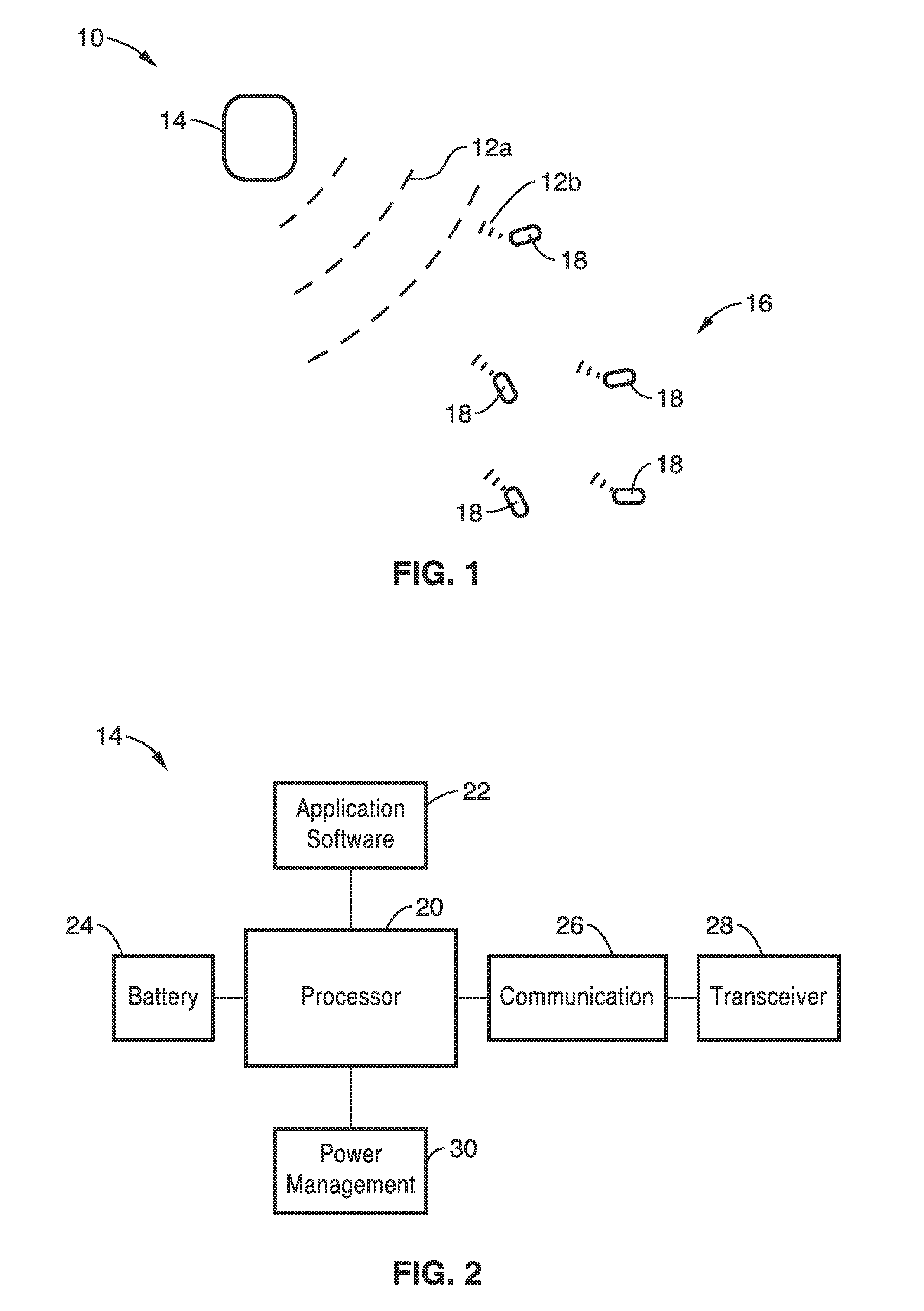
Intelligent self-organizing electrode stimulation delivery system
InactiveUS8977358B2Effective treatmentLower energy requirementsHeart stimulatorsZero phaseBiological activation
An electrode stimulation delivery system is described having a unit and a network of wireless remote electrodes configured for implantation within a plurality of spaced apart locations in the tissue, e.g. myocardium, of a patient. The control unit is configured to be positioned at or subcutaneous to the patient's skin, and includes a processor, an antenna configured for delivering RF energy in proximity to the plurality of wireless remote electrodes, and programming executable on the processor for wirelessly communicating to the network of wireless remote electrodes via the delivered RF energy to individually control pacing of the plurality of wireless remote electrodes. Each of the plurality of wireless remote electrodes comprises a metamaterial-based biomimetic harvesting antenna comprising a Van Atta array zero-phase transmission lines to receive the RF energy to power activation of the plurality of wireless remote electrodes.
Owner:NORTH DAKOTA STATE UNIV RES FOUND +1
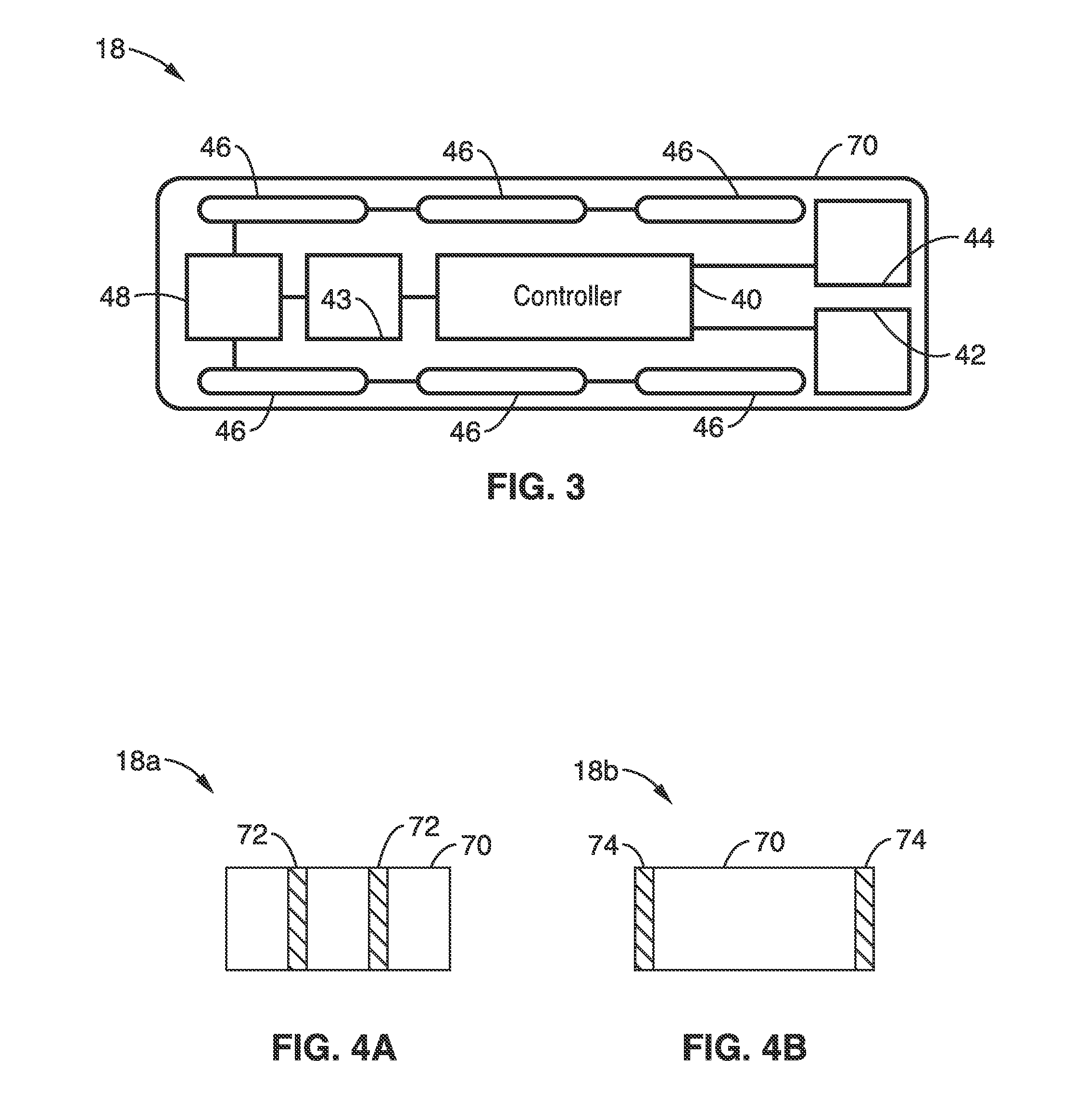
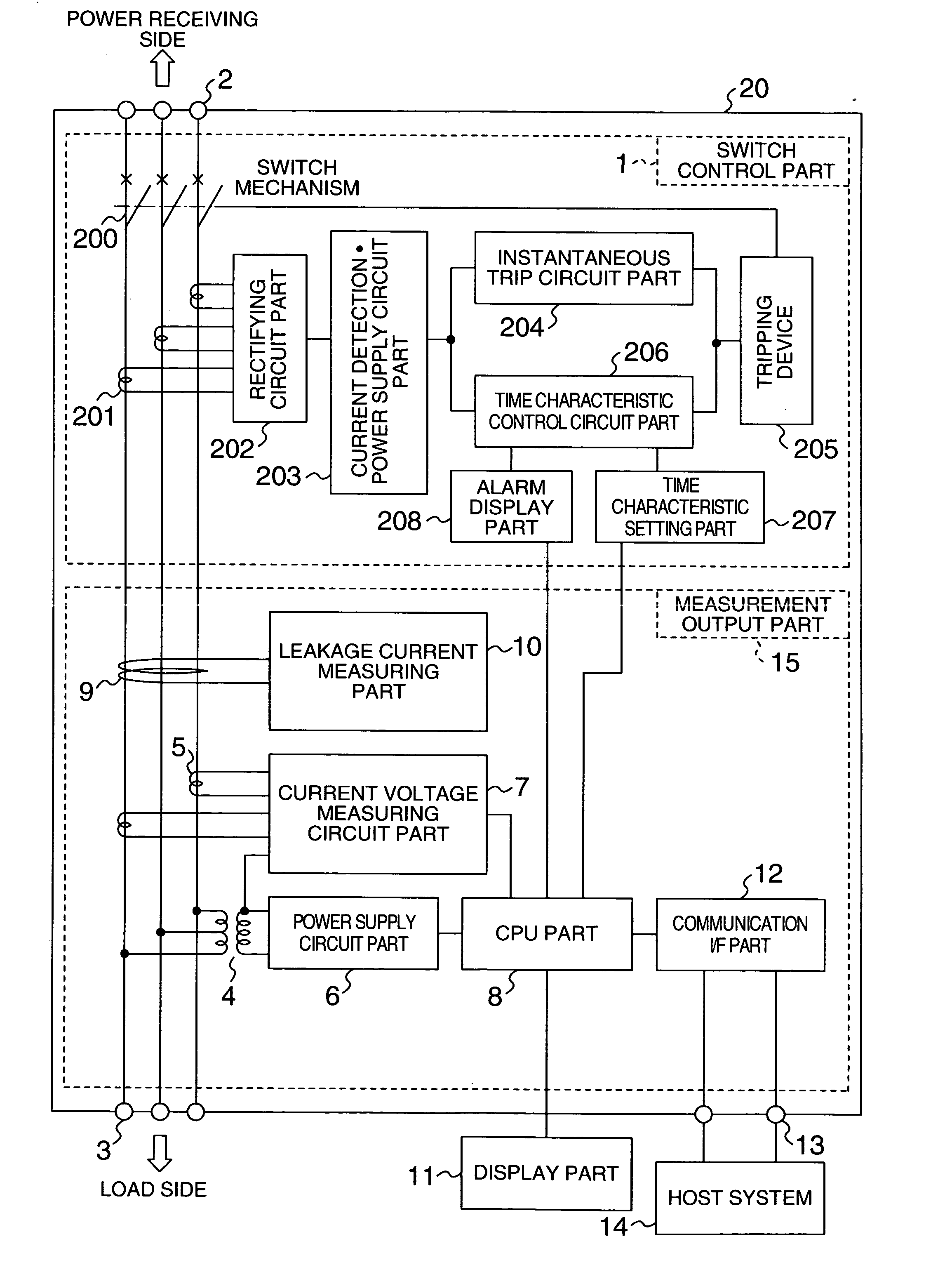
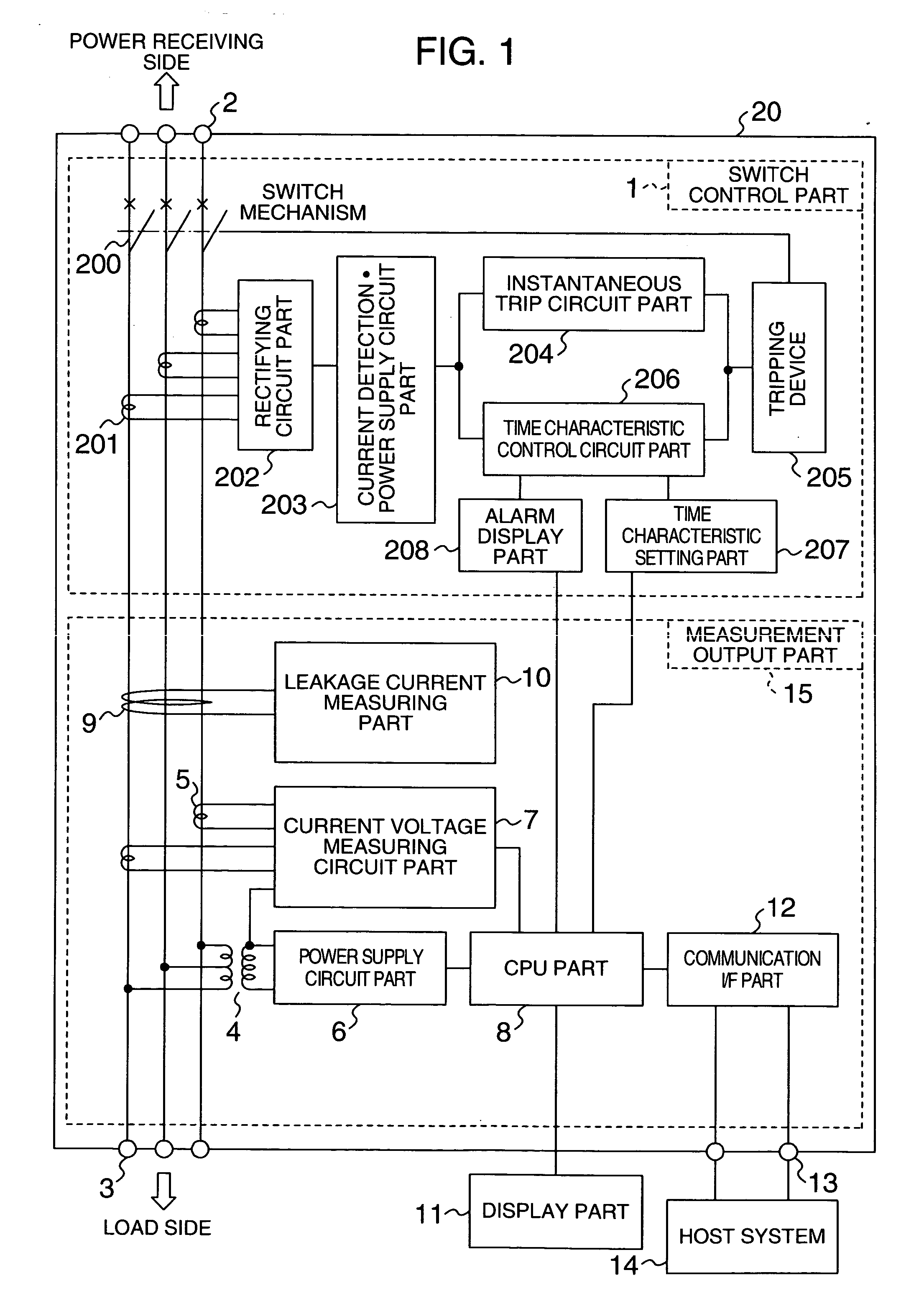
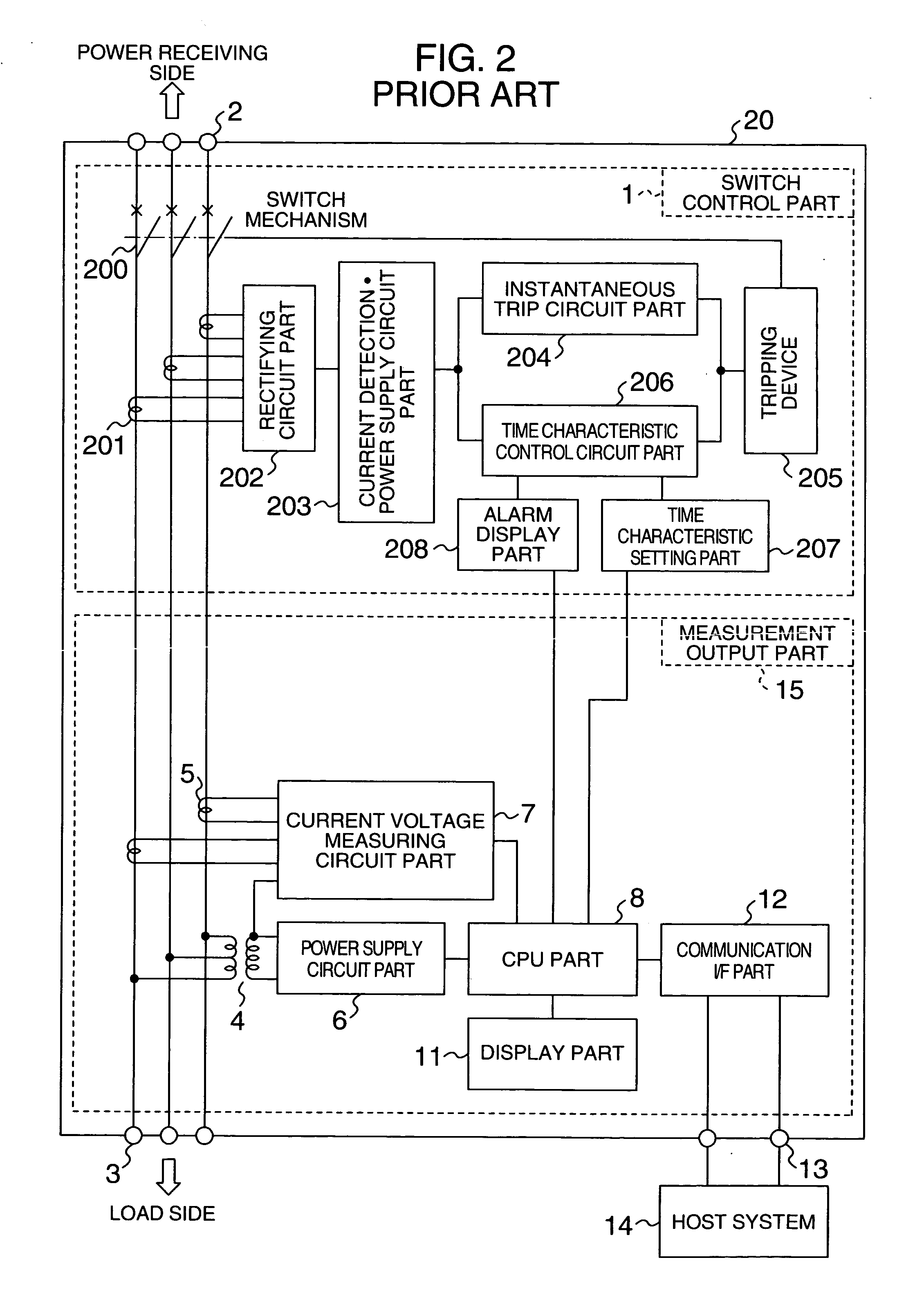
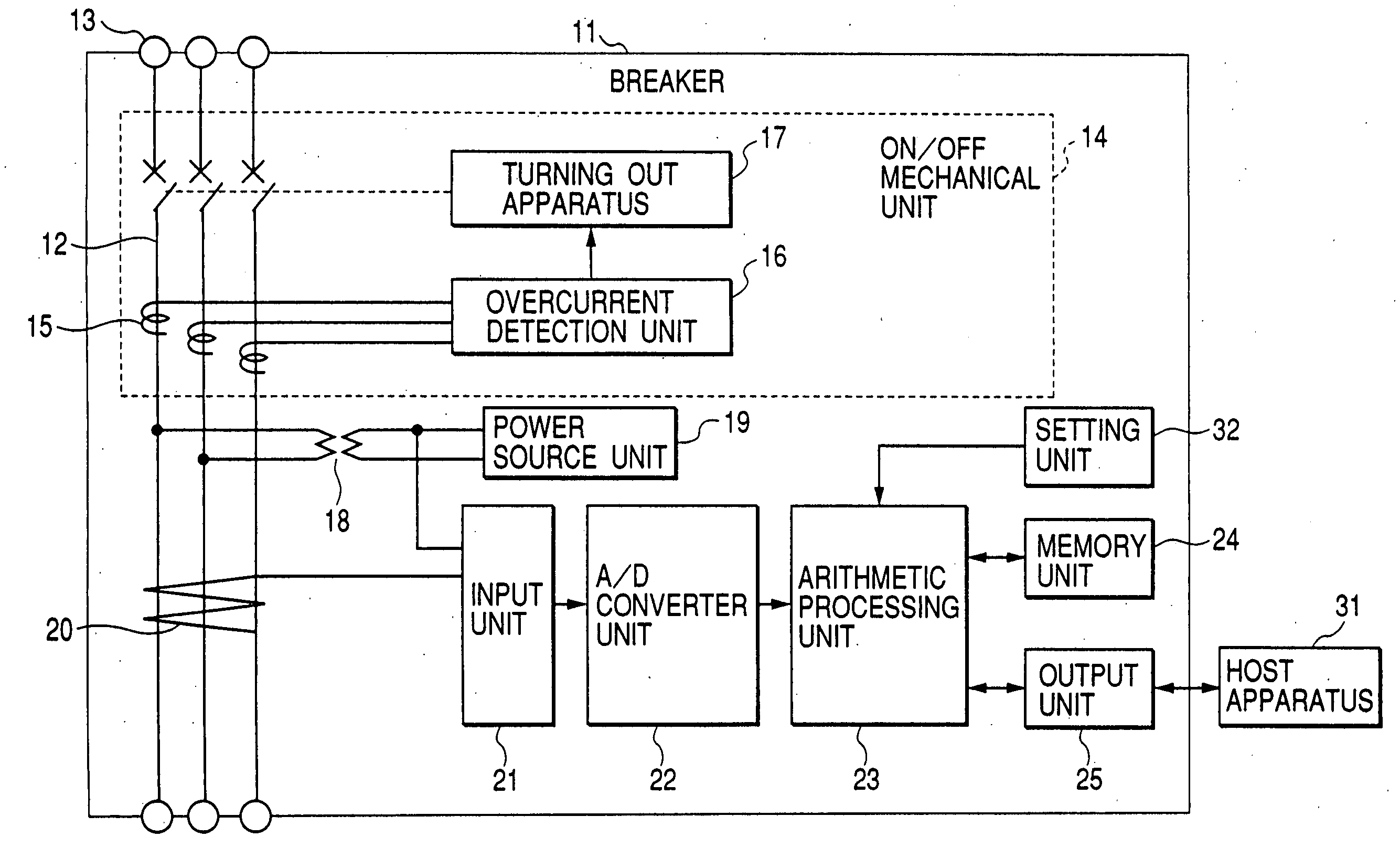
Leakage monitoring system
InactiveUS20050225909A1Easy CalibrationImprove reliabilitySwitch operated by current/voltage unbalanceElectric switchesZero phaseMonitoring system
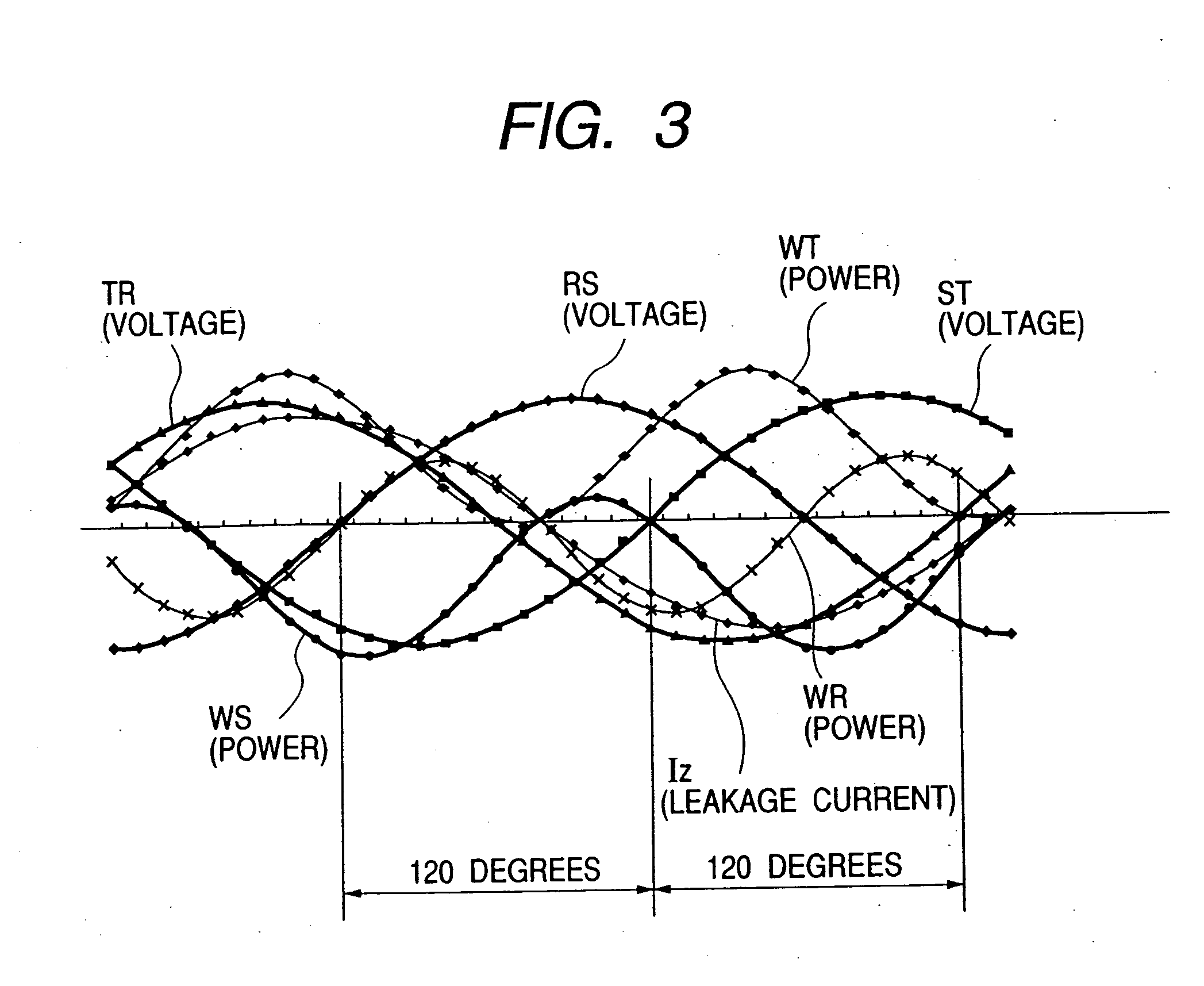
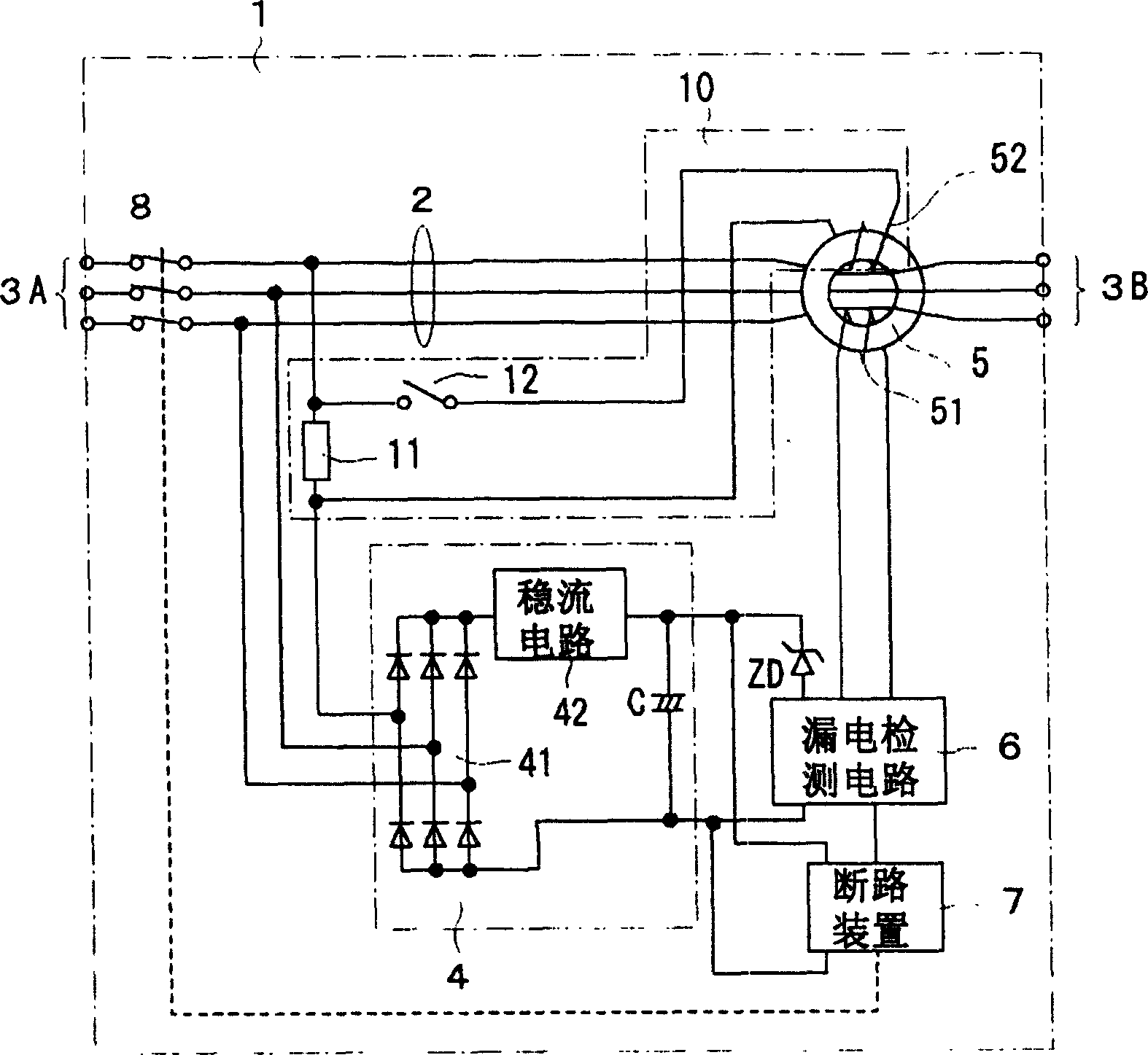
The system makes it possible to monitor various electrical variables by using a simple structure at low cost with ease and with high reliability by a circuit breaker which jointly includes a current transformer to detect current, a transformer to detect voltage, and a zero-phase current transformer to detect leakage current, in addition to the switch controller to perform the basic function of the circuit breaker. Moreover, the system also provides a function to display various measured values, obtained as described above, by a display unit that can be detached and installed separately from the measuring section to display data sent in digital form by data transmission.
Owner:HITACHI IND EQUIP SYST CO LTD
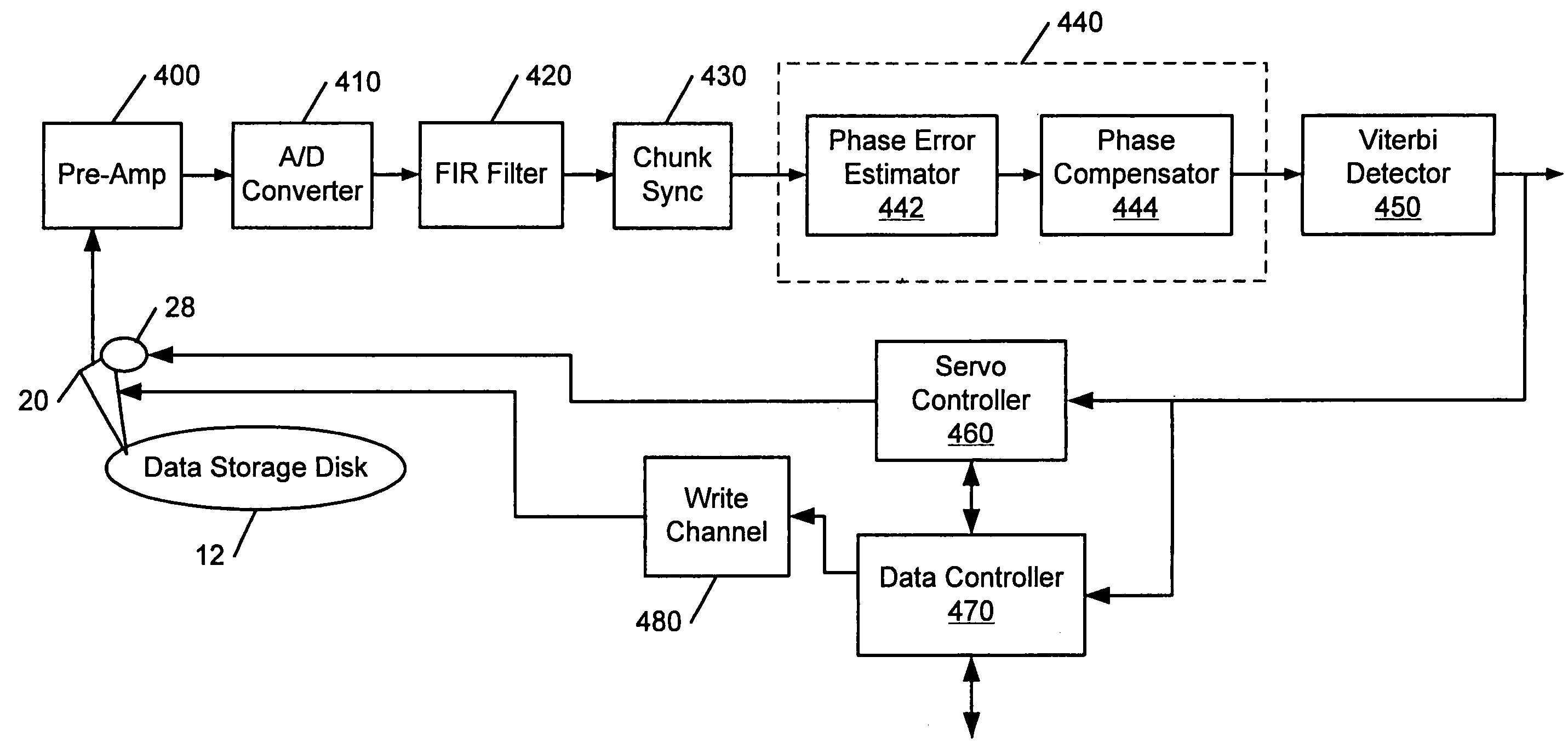
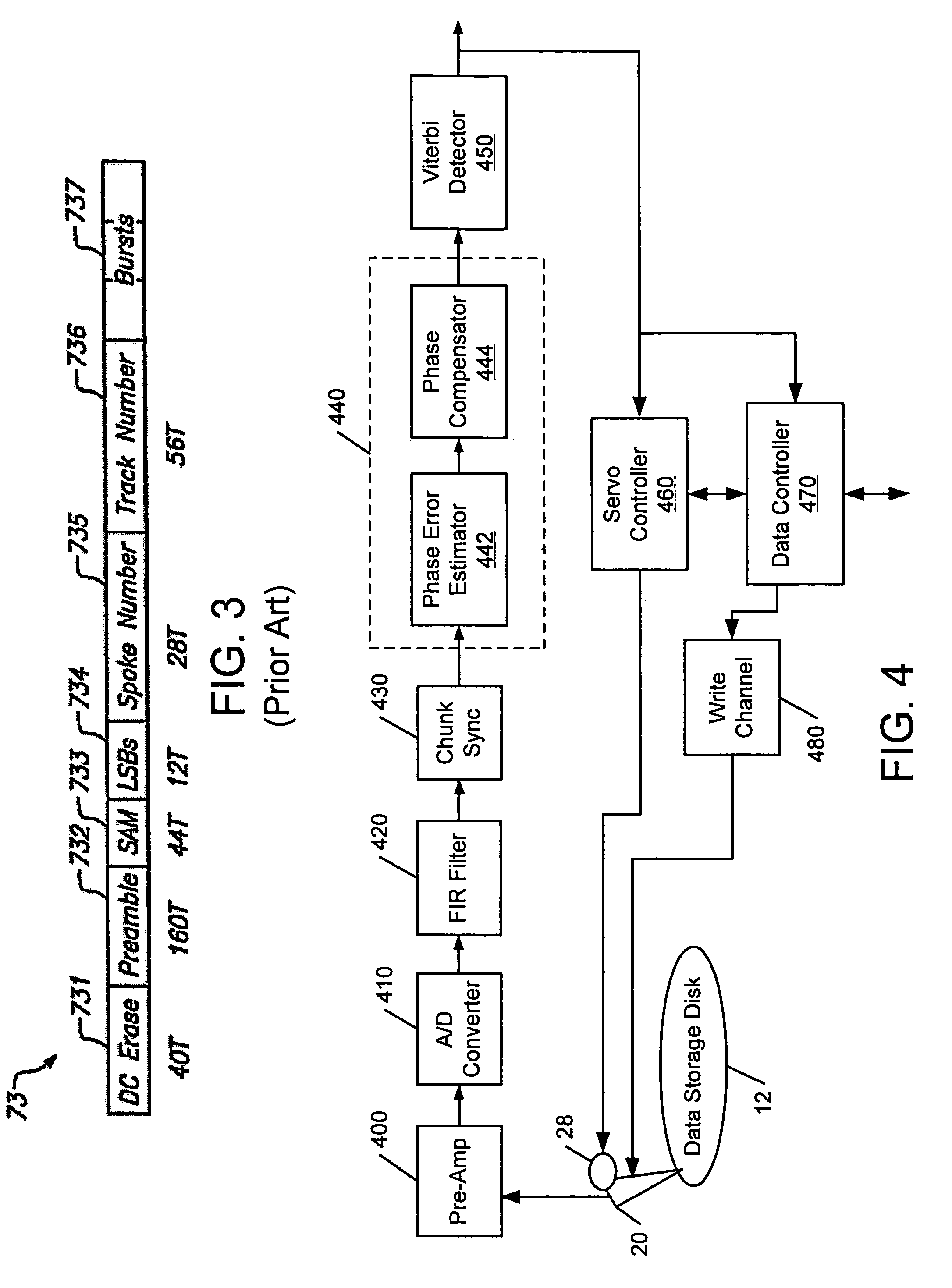
Disk drive that compensates for phase incoherence between radially adjacent servo tracks and methods thereof
Methods of compensating for radial incoherence in servo information that is read from adjacent servo tracks that have a phase offset relative to one another on a data storage disk of a disk drive are provided. While a transducer is seeking to a target track, the transducer generate a servo information signal that has a first component from servo information read from a first servo track on the disk and a second component from servo information read from a second servo track that is radially adjacent to the first servo track. The servo information in the first and second servo tracks are offset by a non-zero phase error relative to one another and are in a same servo sector on the disk. The servo information signal is sampled to generate a series of sampled servo values. A phase error of a group of the sampled servo values is determined. The sampled servo values are compensated in response to the determined phase error to generate compensated servo values with at least reduced phase error.
Owner:MAXTOR
Resonant converter and control method thereof
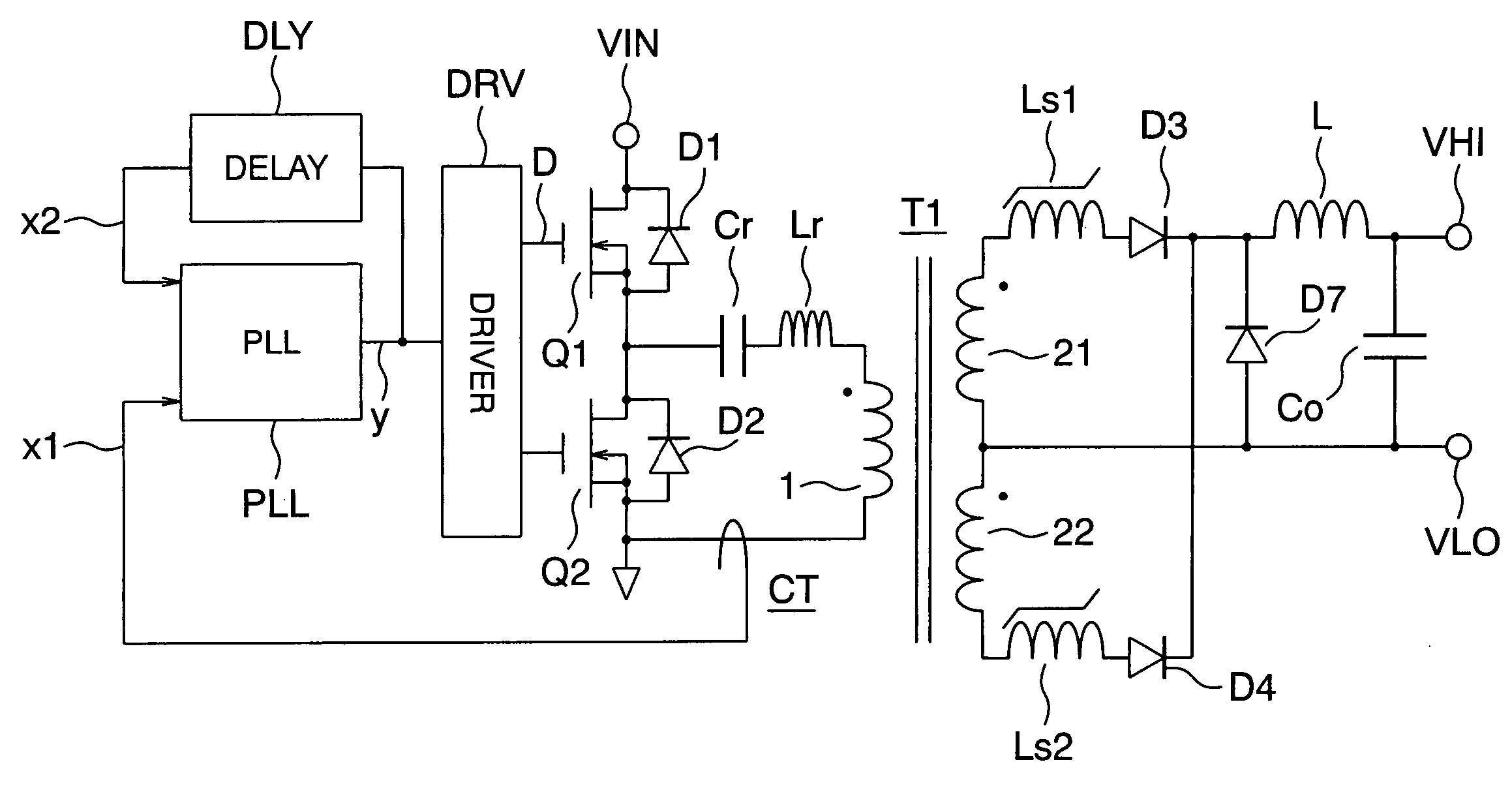
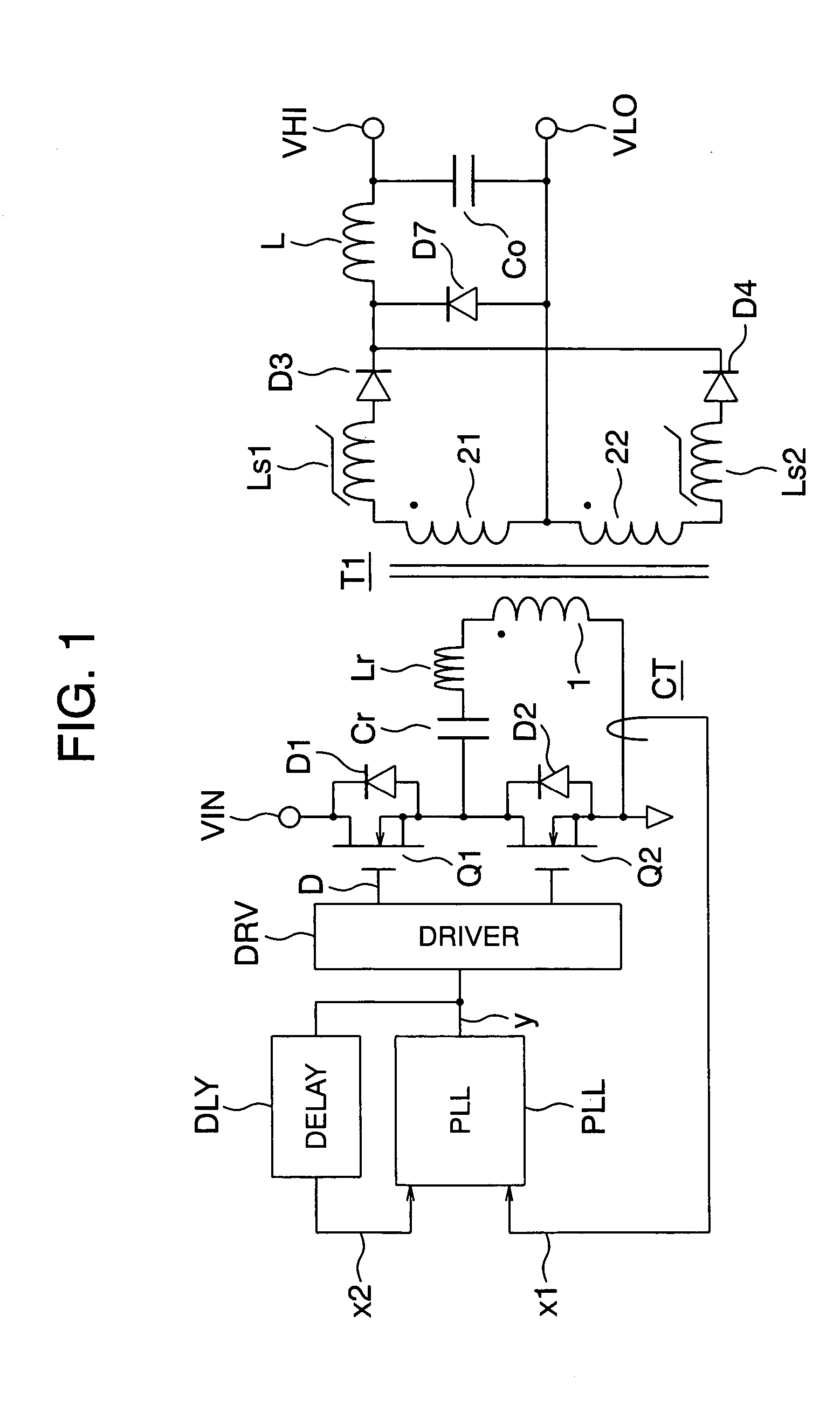
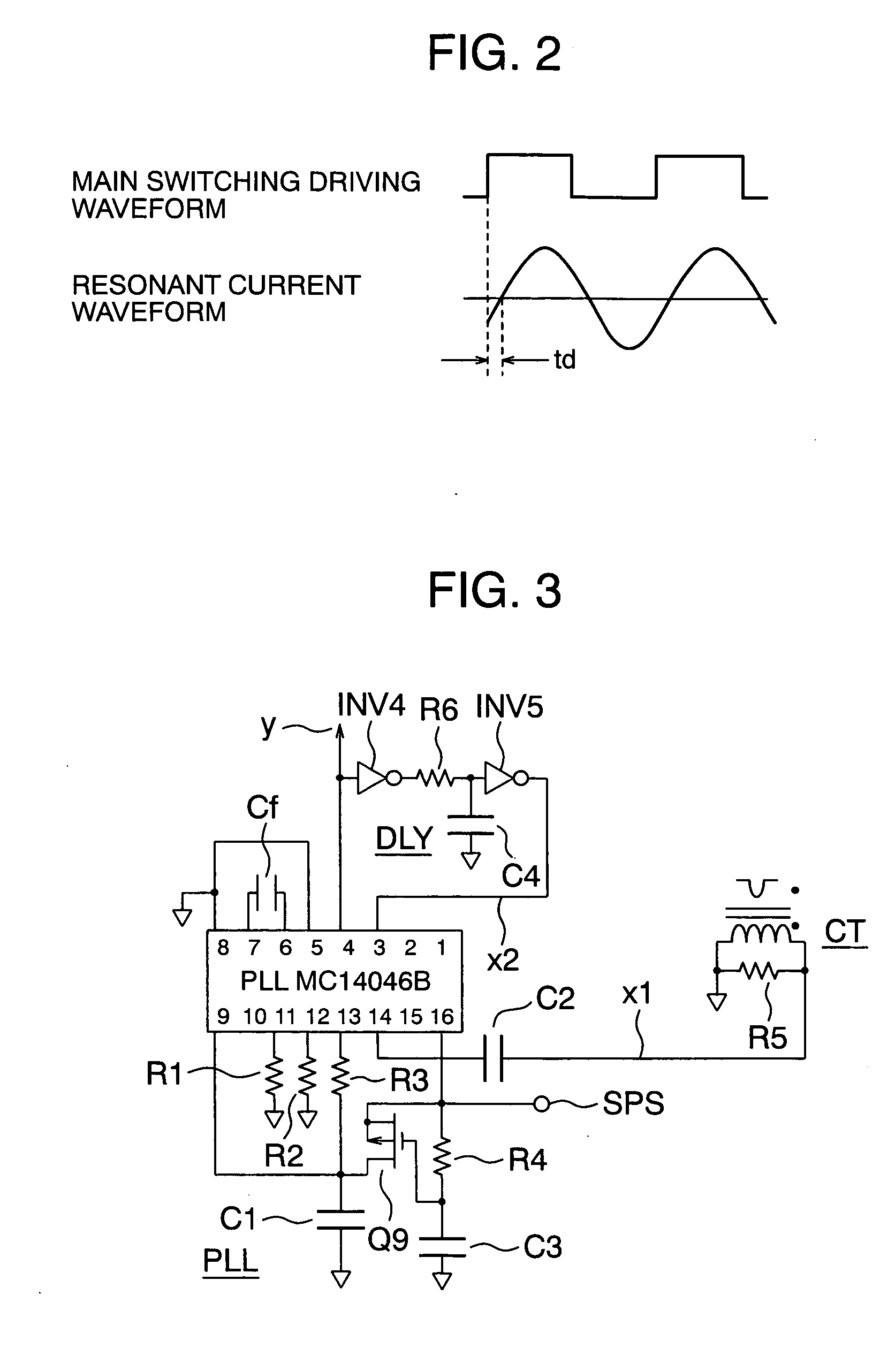
InactiveUS20050099827A1Simple designReliable soft switching operationAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionSoft switchingZero phase
A resonant converter which can realize its easy design, eliminate the need for its adjustment, realize reliable soft switching operation, and increase an efficiency. A driver DRV of a main switching device uses a PLL circuit PLL to apply frequency tracking control in such a manner that a driving frequency fsw is made to track a resonant frequency fr (or 1 / N thereof, N being an odd number) and that the phase of the driving frequency fsw leads the current zero phase of the resonant frequency fr always by a desired time. As a result, such an optimum condition can be kept that the main switching device is triggered immediately before the zero-cross point of a resonant current. Thus the resonant converter which can always satisfy the optimum operational conditions, realize soft switching operation, and increase an efficiency can be realized with an easy design and a manufacturing adjustment-free arrangement.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
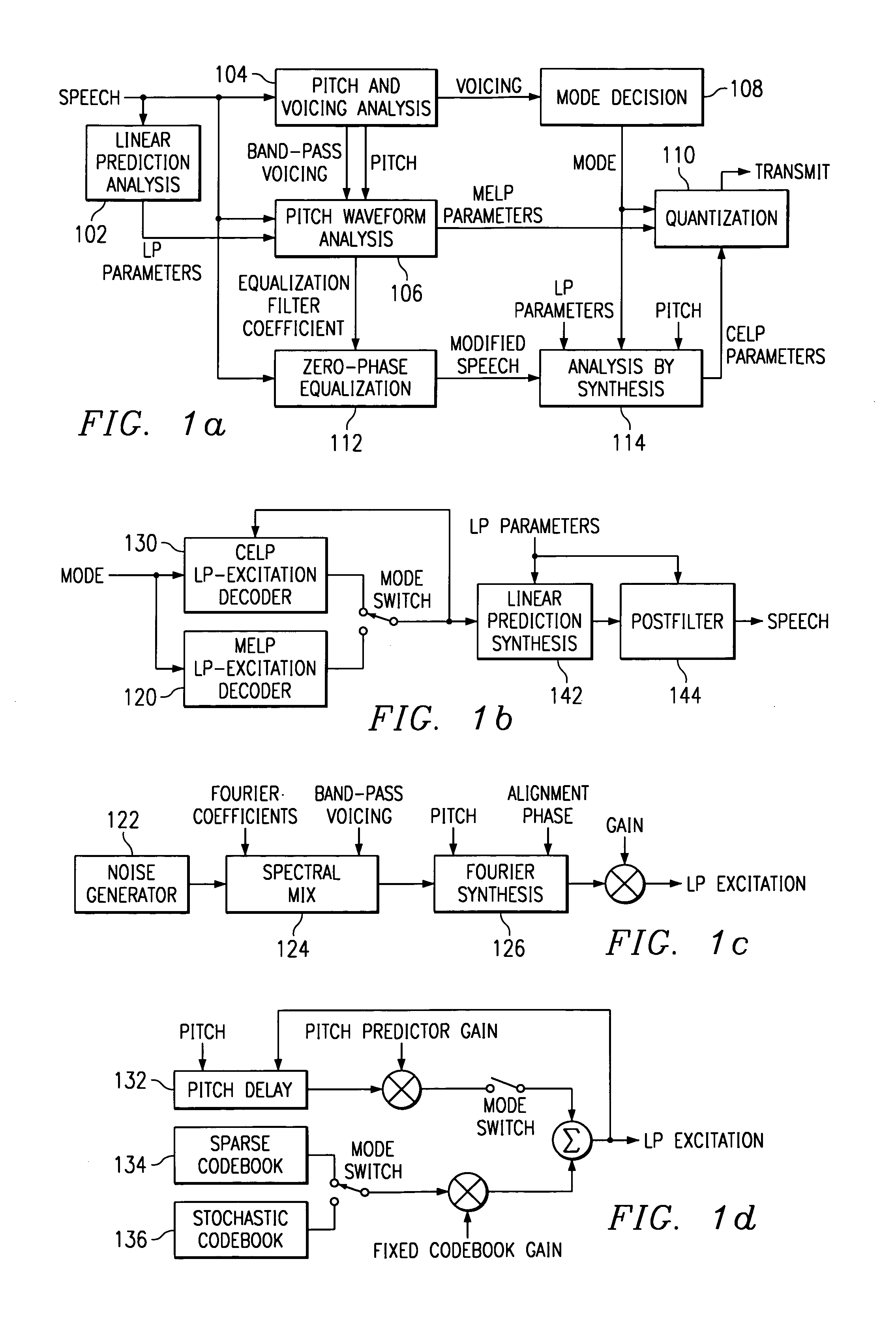
Hybrid speech coding and system
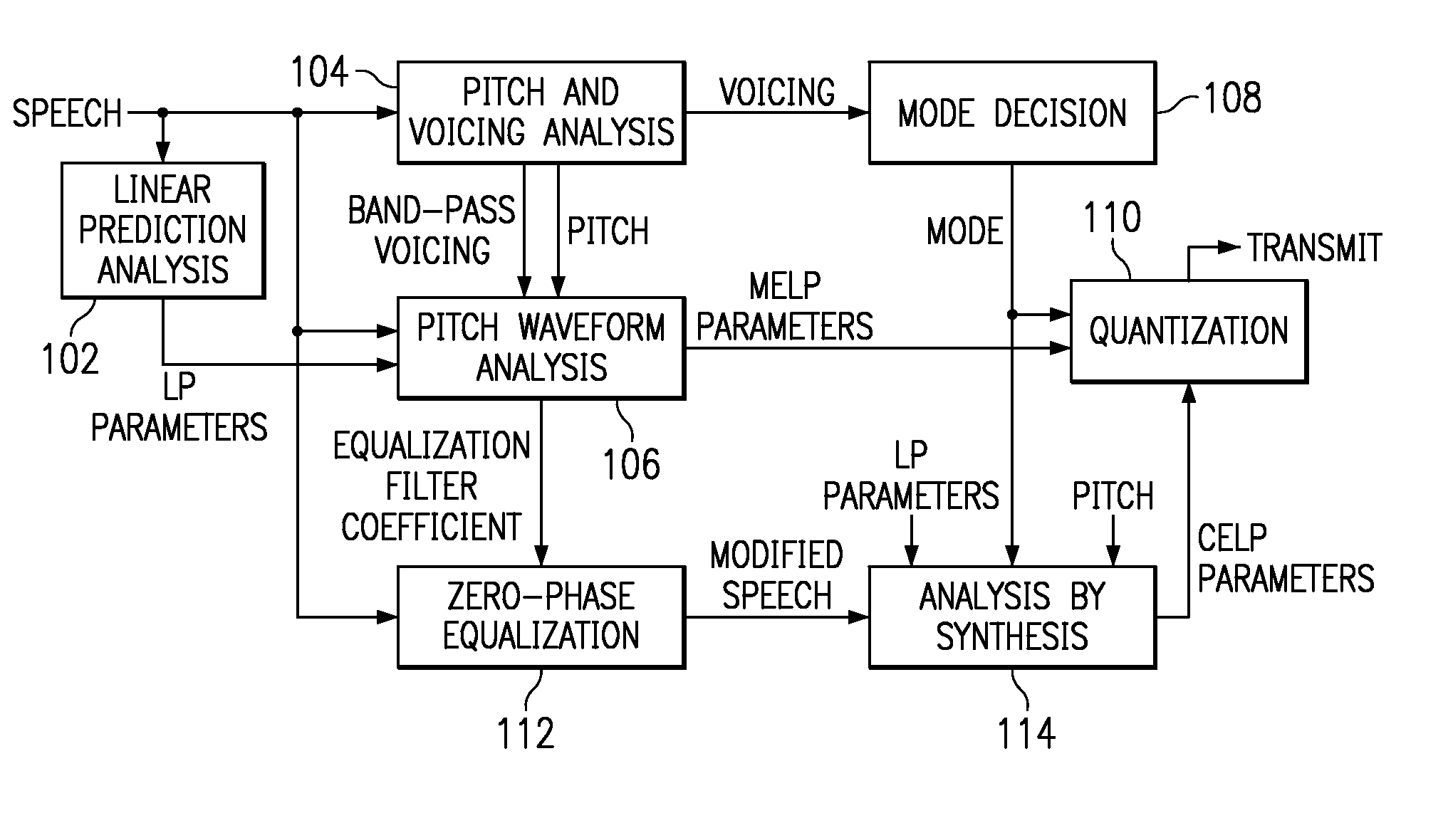
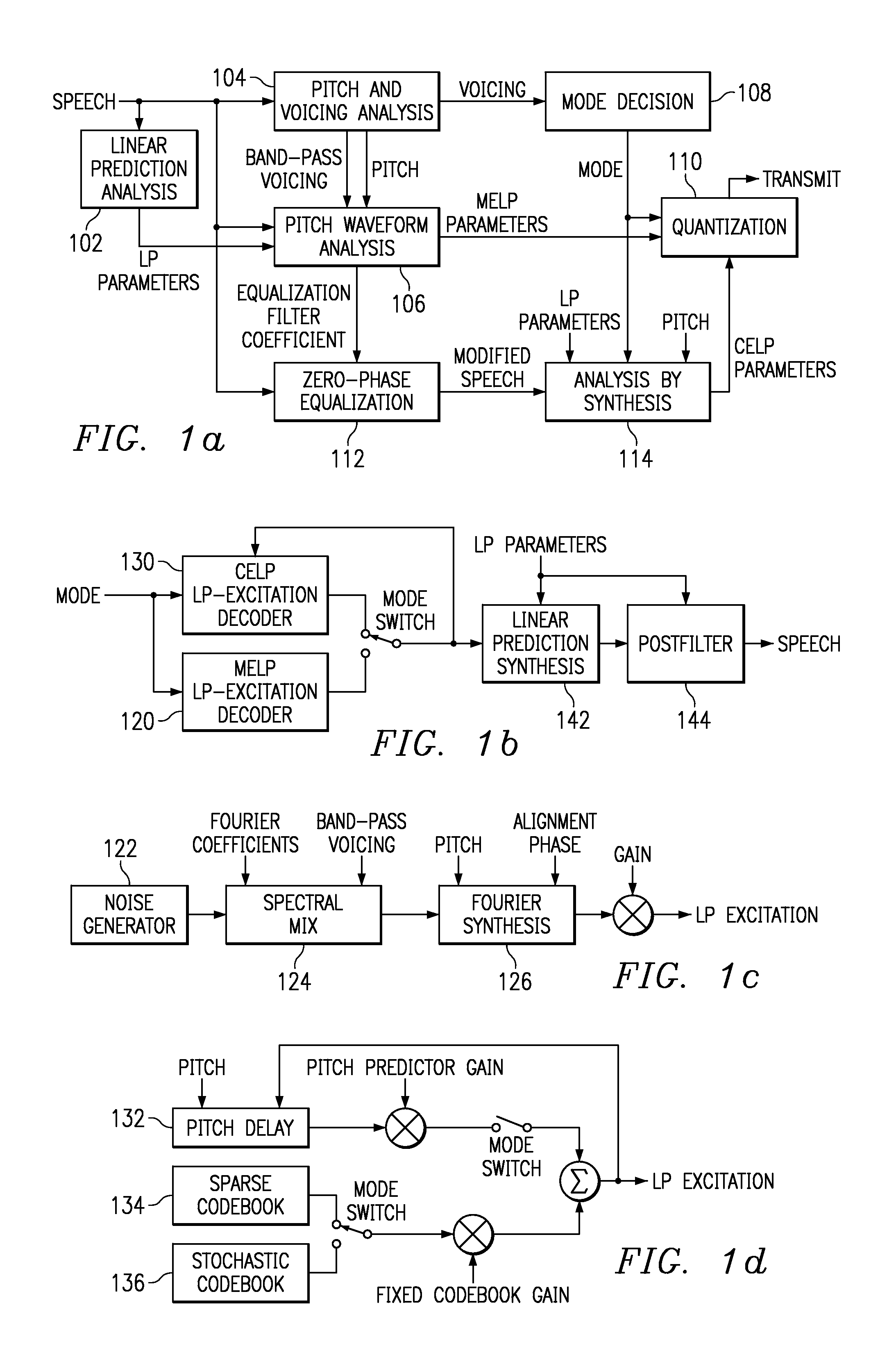
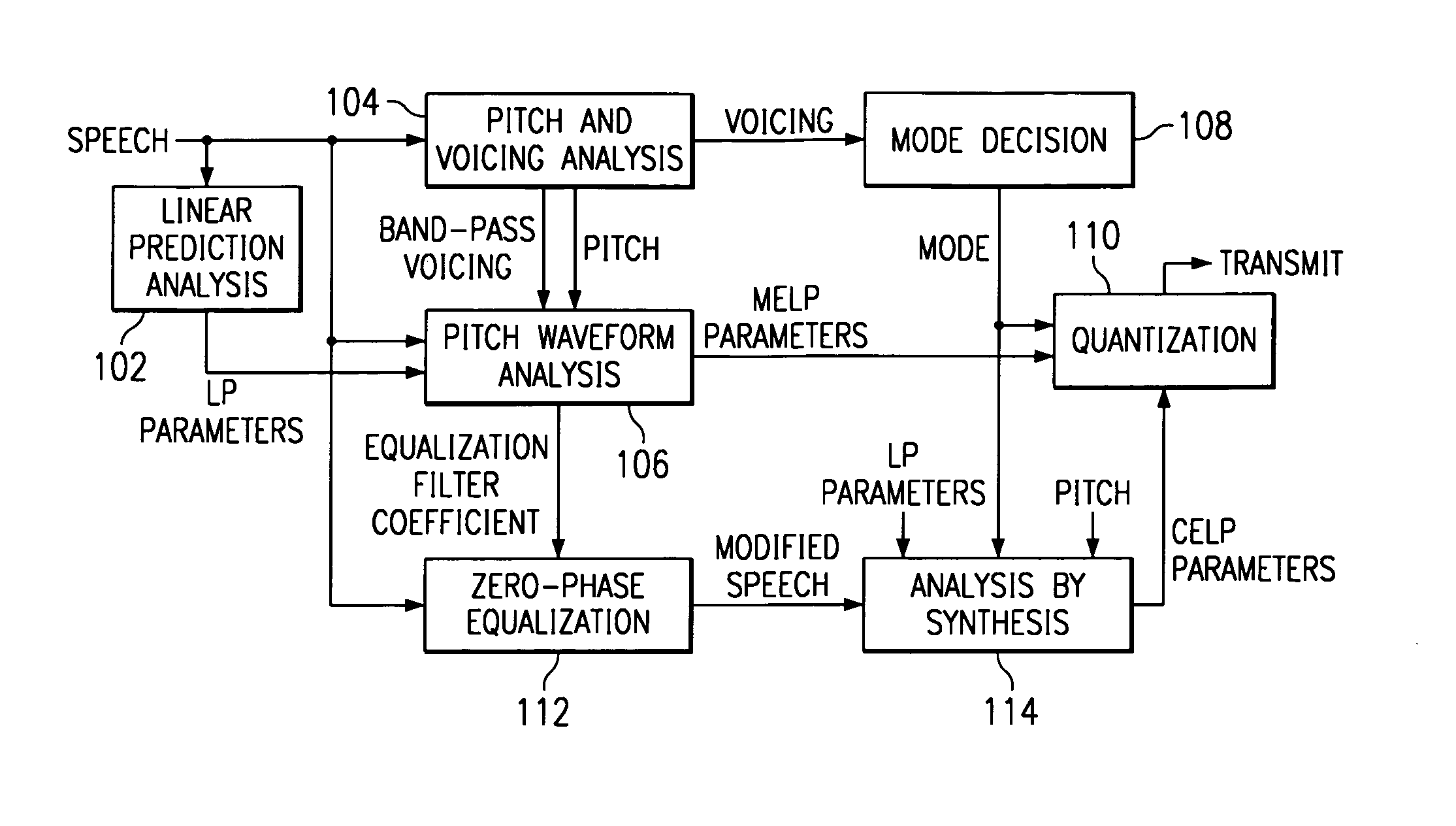
InactiveUS7222070B1Improve performanceEnhance the waveform coderSpeech analysisWaveform codingZero phase
Linear predictive speech coding system with classification of frames and a hybrid coder using both waveform coding and parametric coding for different classes of frames. Phase alignment for a parametric coder aligns synthesized speech frames with adjacent waveform coder synthesized frames. Zero phase alignment of speech prior to waveform coding aligns synthesized speech frames of a waveform coder with frames synthesized with a parametric coder. Inter-frame interpolation of LP coefficients suppresses artifacts in resultant synthesized speech frames.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
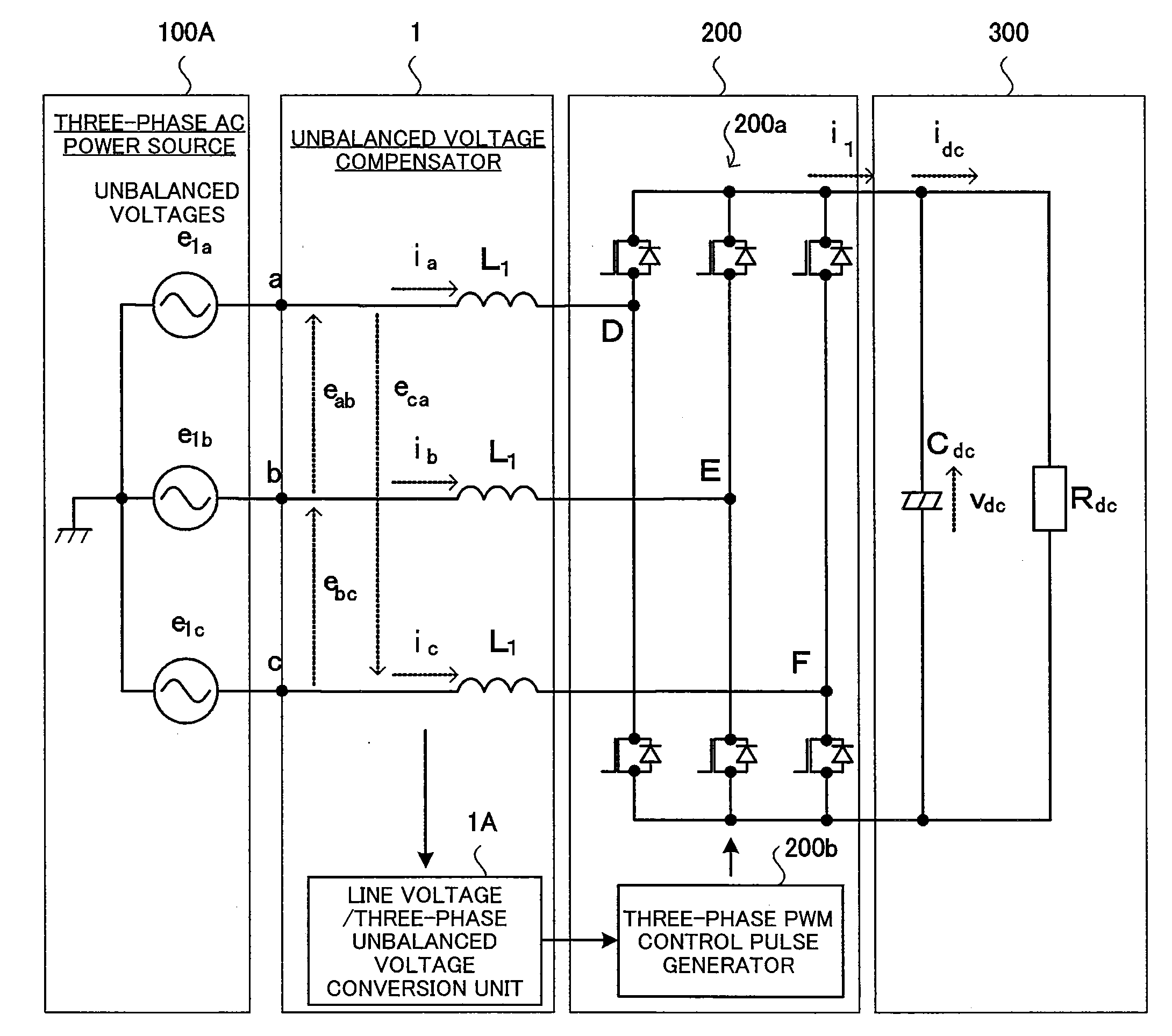
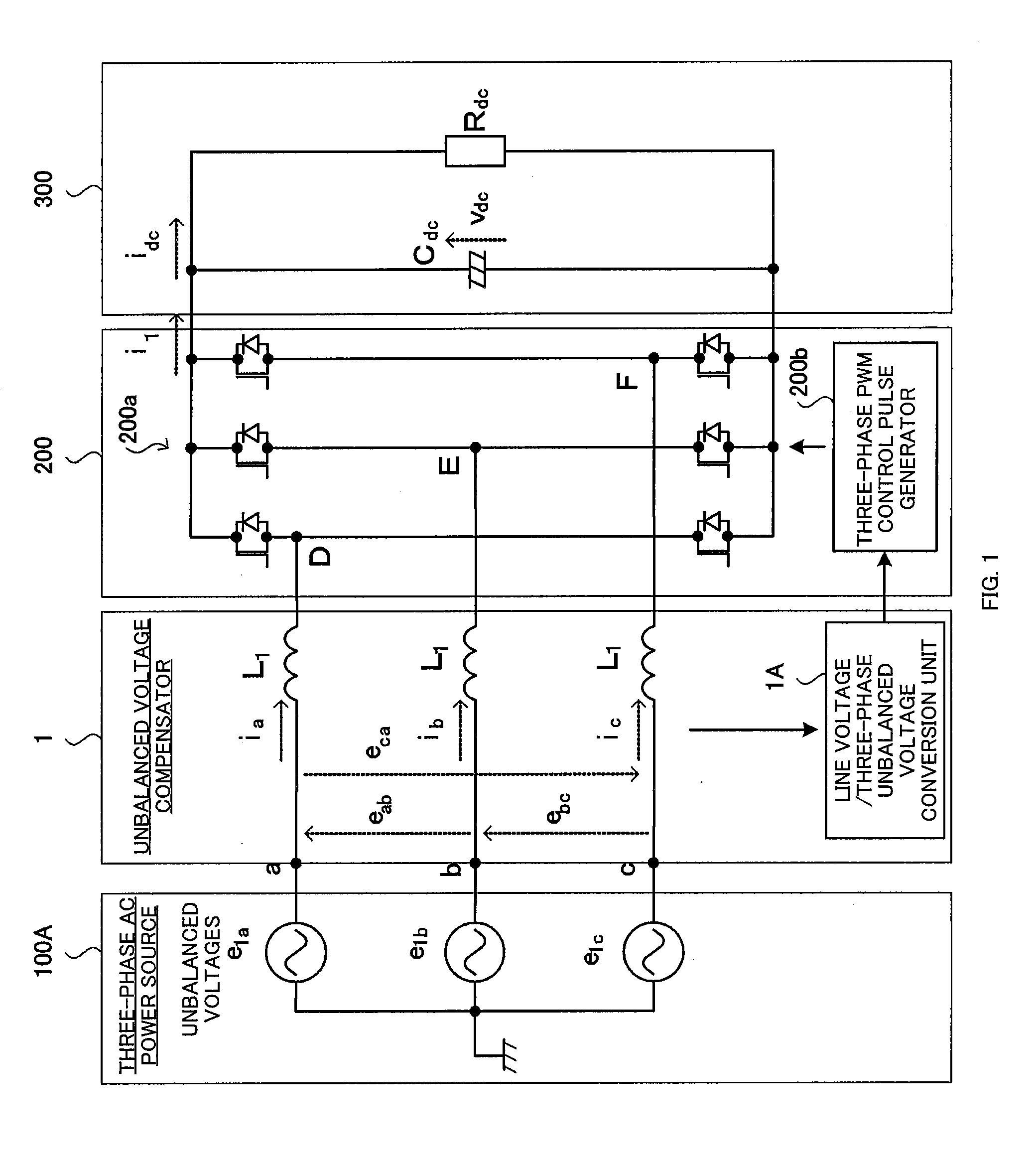
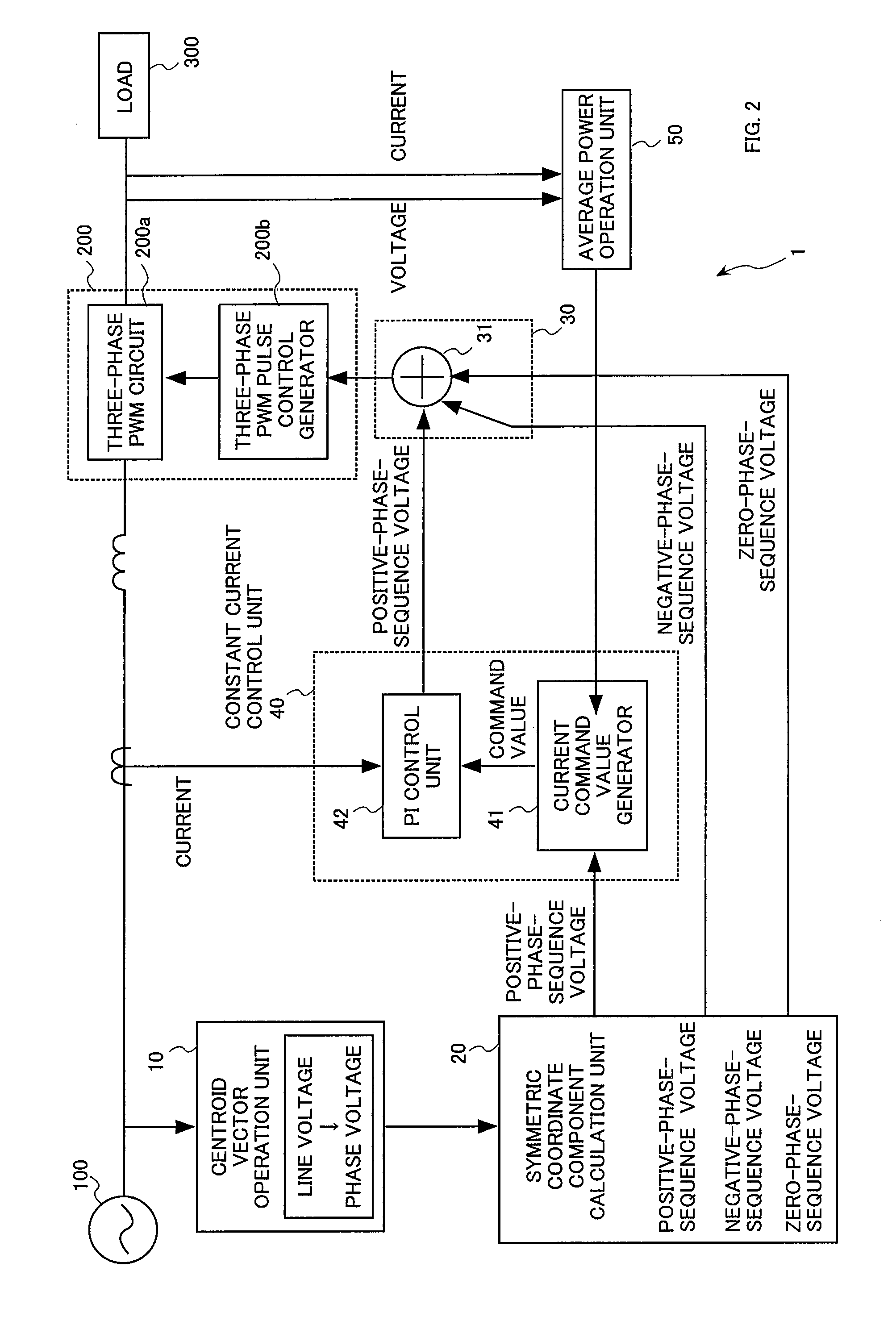
Unbalanced voltage compensation method, unbalanced voltage compensator, three-phase converter control method, and controller of three-phase converter
ActiveUS20110134669A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcControl signalThree phase converter
In compensating for unbalanced voltages of three-phase AC, instantaneous values of wye-phase voltages 120° out of phase with each other are obtained from line voltages using a centroid vector operation, symmetrical component voltages of three-phase balanced system are obtained from the instantaneous values of wye-phase voltages, a compensation signal to compensate unbalanced voltages of three-phase AC is generated from zero-phase-sequence voltage of symmetrical component voltages is generated, wye-phase voltages 120° out of phase, the unbalanced voltages of which are compensated, are obtained from the compensation signal and the symmetrical component voltages, a control signal of a PWM conversion is generated based on the compensated wye-phase voltage compensated, and the unbalanced voltages of three-phase AC are compensated. The amount of time to compensate the three-phase unbalanced voltages required for detecting an unbalance of voltages and generating a control signal can be shortened.
Owner:KYOSAN ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
Phased array antenna having integral calibration network and method for measuring calibration ratio thereof
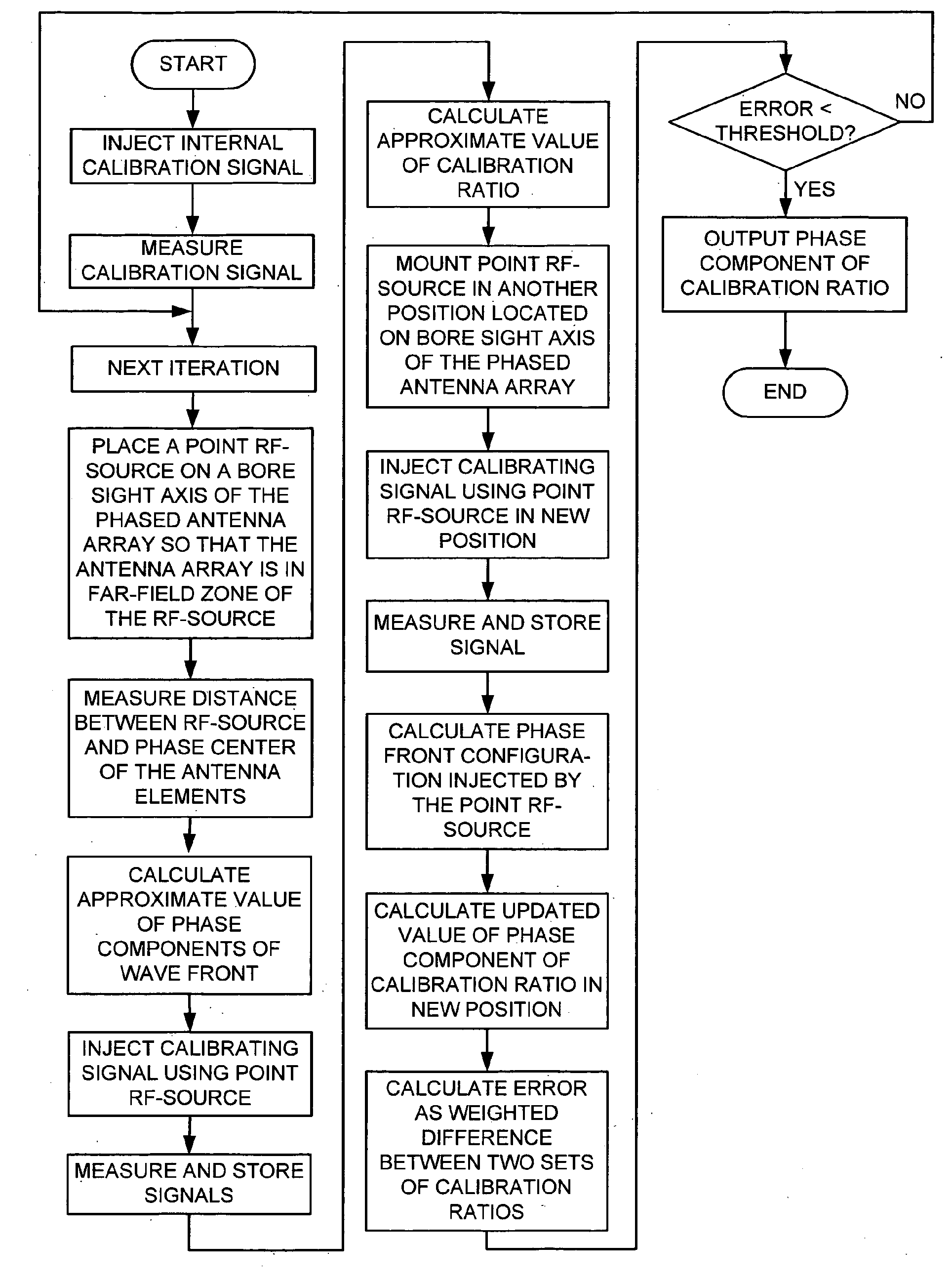
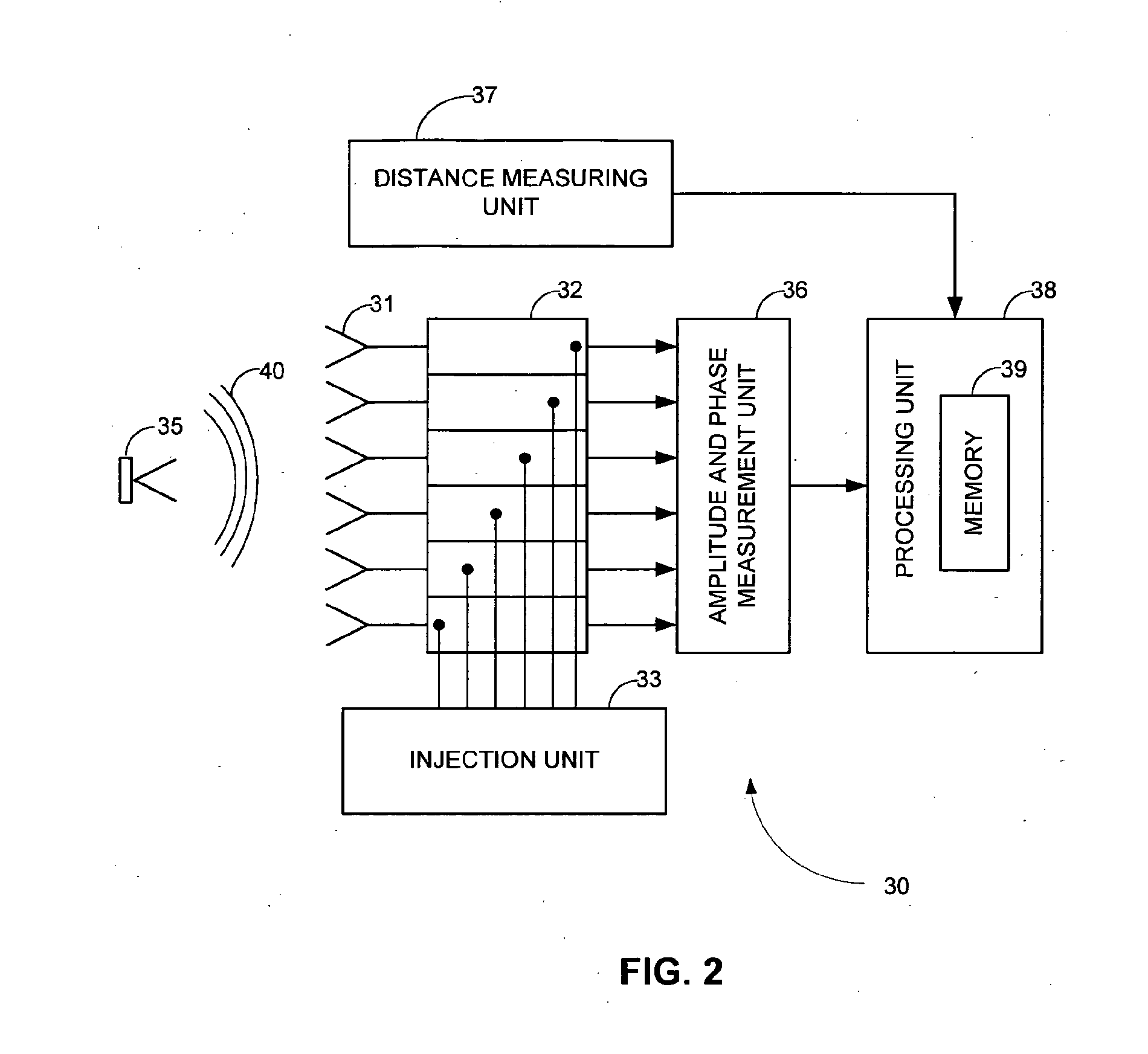
ActiveUS20110122016A1Calibration expensive and complexCost-effectiveWave based measurement systemsAntennasPhase differenceZero phase
A phased antenna arrangement and a method for estimating the calibration ratio of an active phased antenna having a plurality of phased array antenna elements are described. The phased antenna arrangement includes a plurality of antenna elements, a plurality of receiving channels, an injection unit for injection of calibrating signals into the receiving channels, a point RF-source, located in a far field zone, a distance measurement unit, an amplitude and phase measurement unit and a data processing unit. The method comprises injecting an internal calibrating signal having a known amplitude and phase to each antenna element. An external calibration signal from a stationary RF-source is sequentially injected to all of the phased array antenna elements so that different phases of the external calibration signal arrive at each of the antenna elements. The differences in phases of the external calibration signal reaching the antenna elements are compensated so as compute an effective signal amplitude that would reach all of the antenna elements at zero phase difference. Calibration ratio is calculated as the ratio between the amplitude of the internal calibrating signal to the effective signal amplitude of the external calibration signal.
Owner:ELTA SYST LTD
Hybrid speed coding and system
Linear predictive speech coding system with classification of frames and a hybrid coder using both waveform coding and parametric coding for different classes of frames. Phase alignment for a parametric coder aligns synthesized speech frames with adjacent waveform coder synthesized frames. Zero phase alignment of speech prior to waveform coding aligns synthesized speech frames of a waveform coder with frames synthesized with a parametric coder. Inter-frame interpolation of LP coefficients suppresses artifacts in resultant synthesized speech frames.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
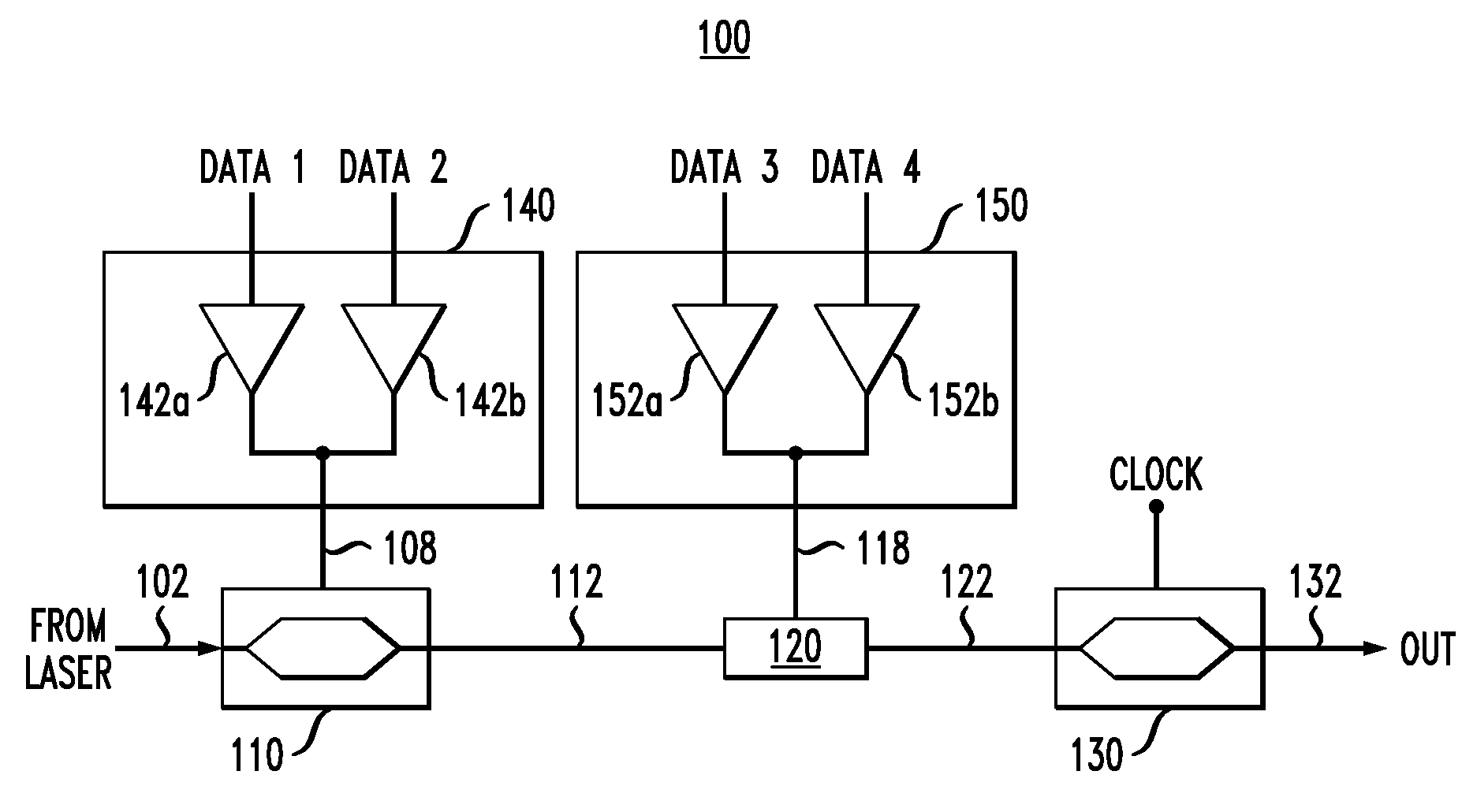
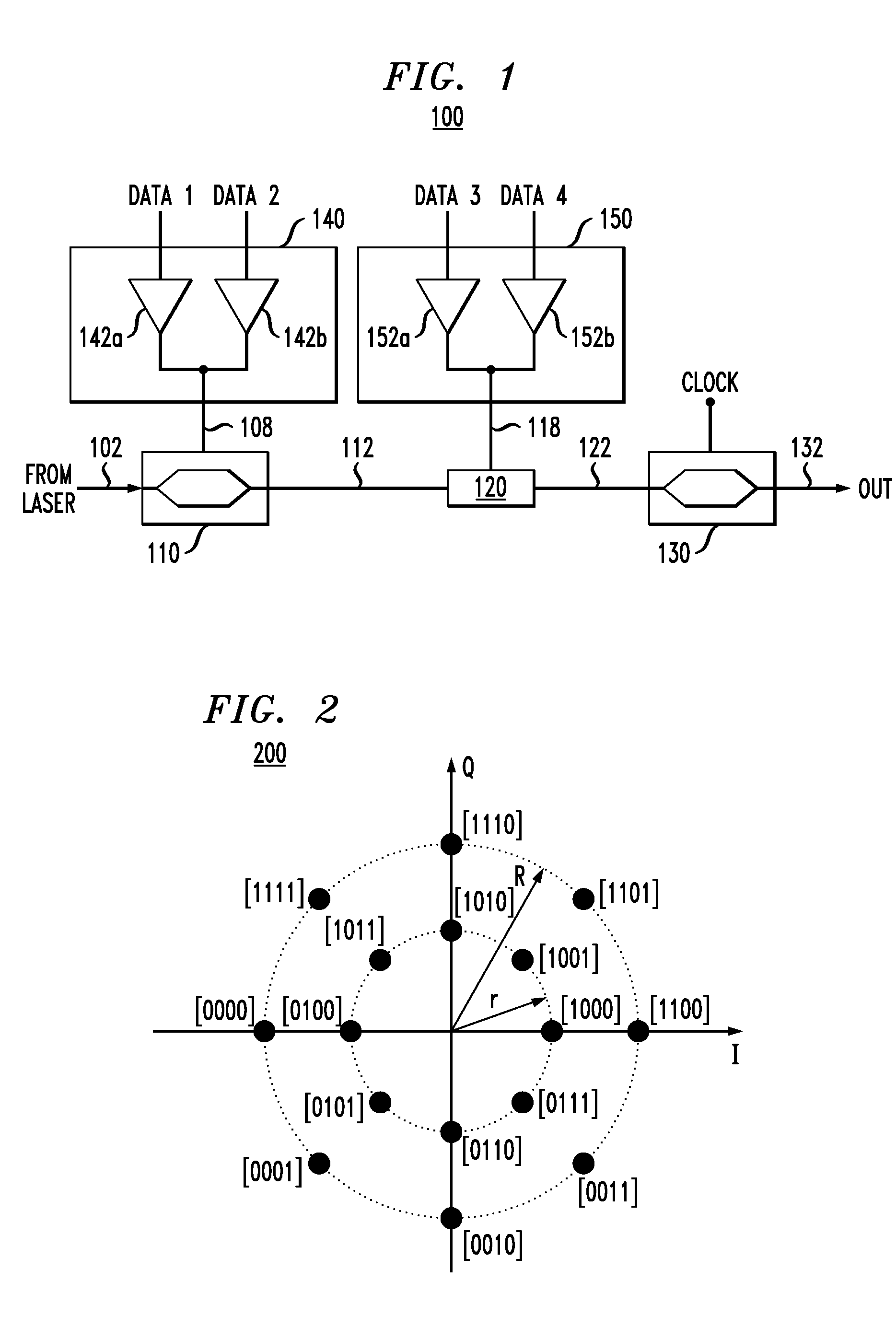
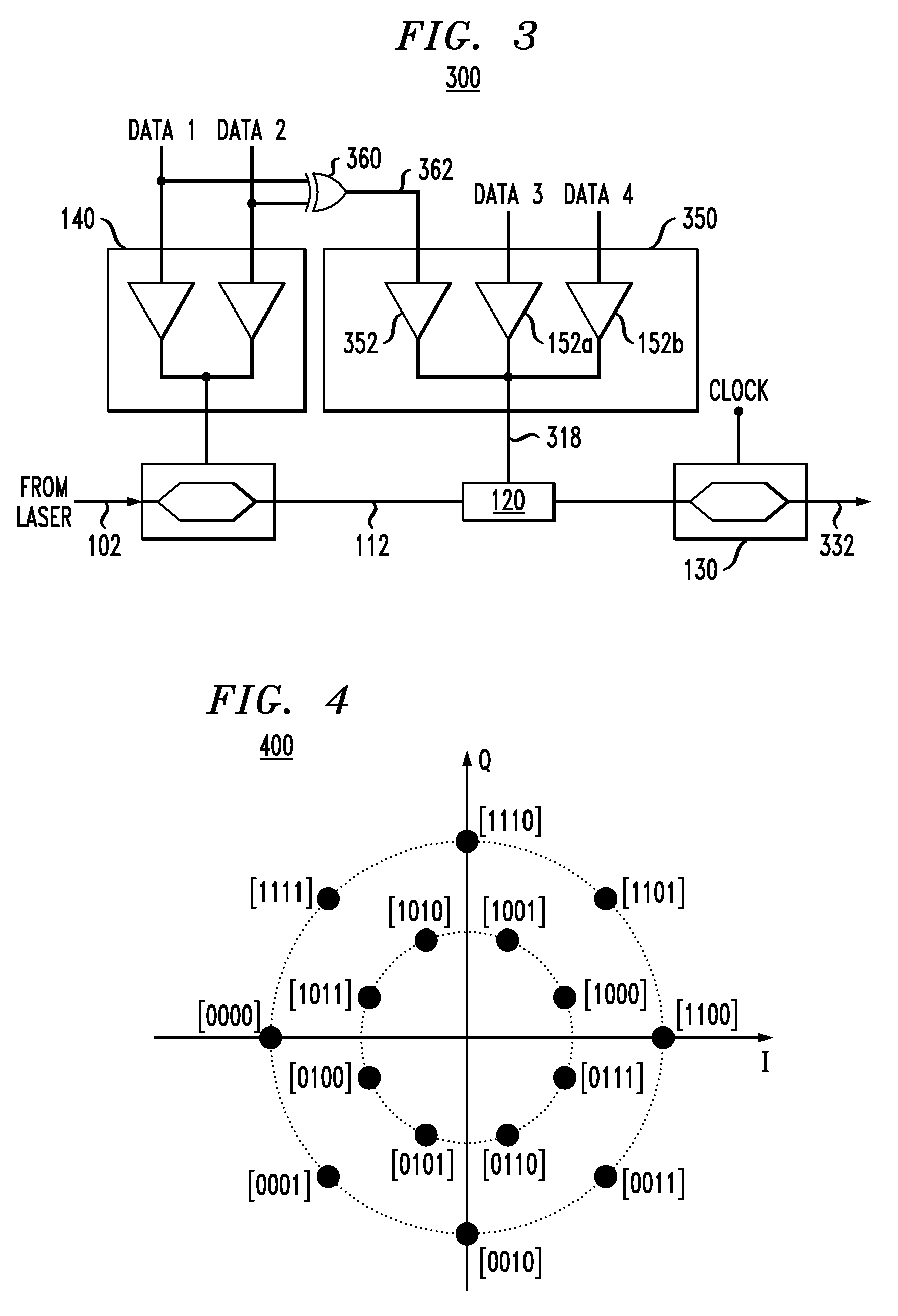
Optical modulator for higher-order modulation
According to one embodiment of the invention, a 16-QAM optical modulator has a Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM) coupled to a drive circuit that drives the MZM based on two electrical binary signals. The output of the MZM corresponds to an intermediary constellation consisting of four constellation points arranged on a straight line in the corresponding in-phase / quadrature-phase (I-Q) plane. Two of these constellation points correspond to a zero phase, and the remaining two constellation points correspond to a phase of π radian. The 16-QAM optical modulator further has a phase shifter that modulates the output of the MZM based on two additional electrical binary signals. The resulting optical output signal corresponds to a star 16-QAM constellation, which is produced by incremental rotation of the intermediary constellation.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
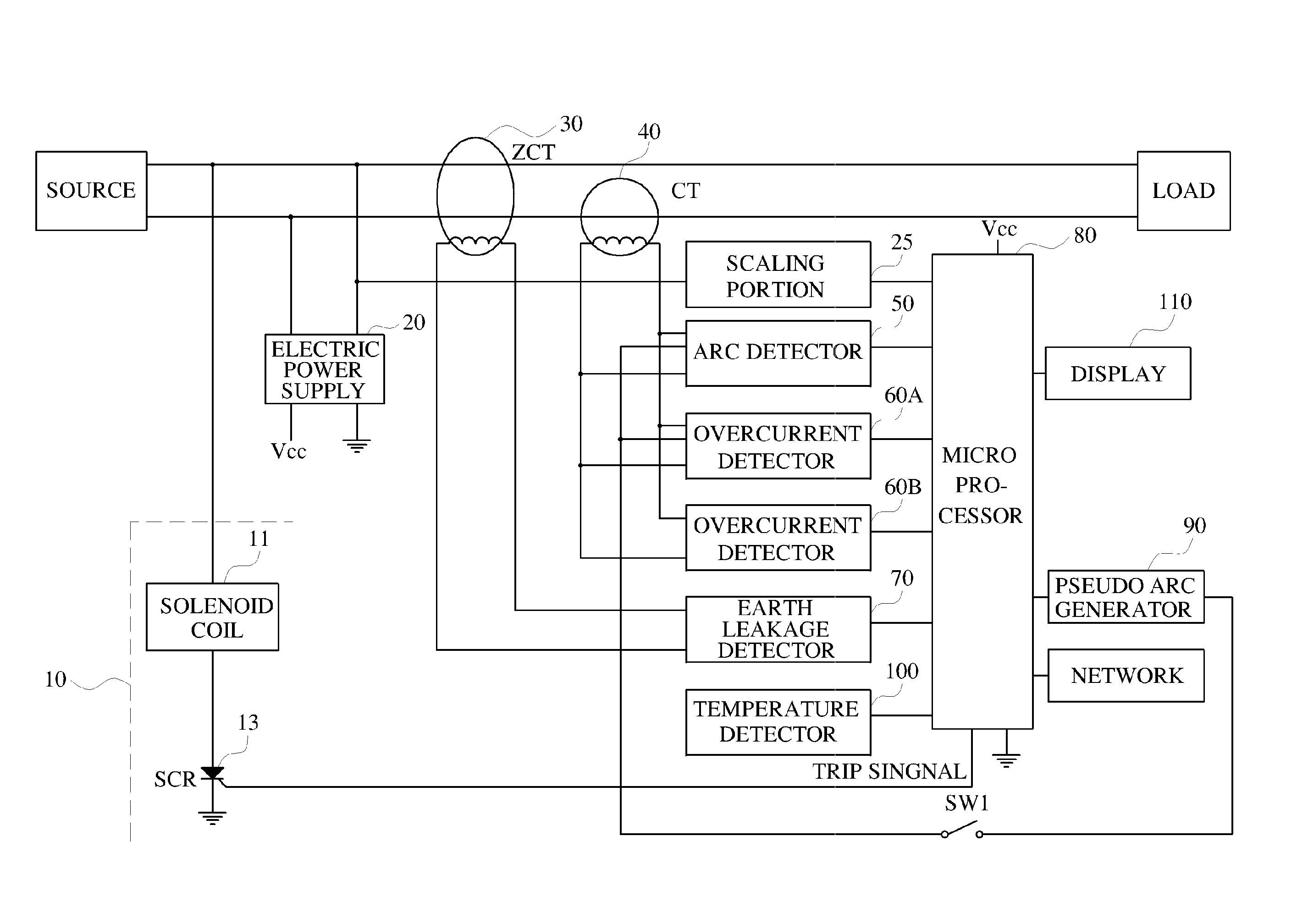
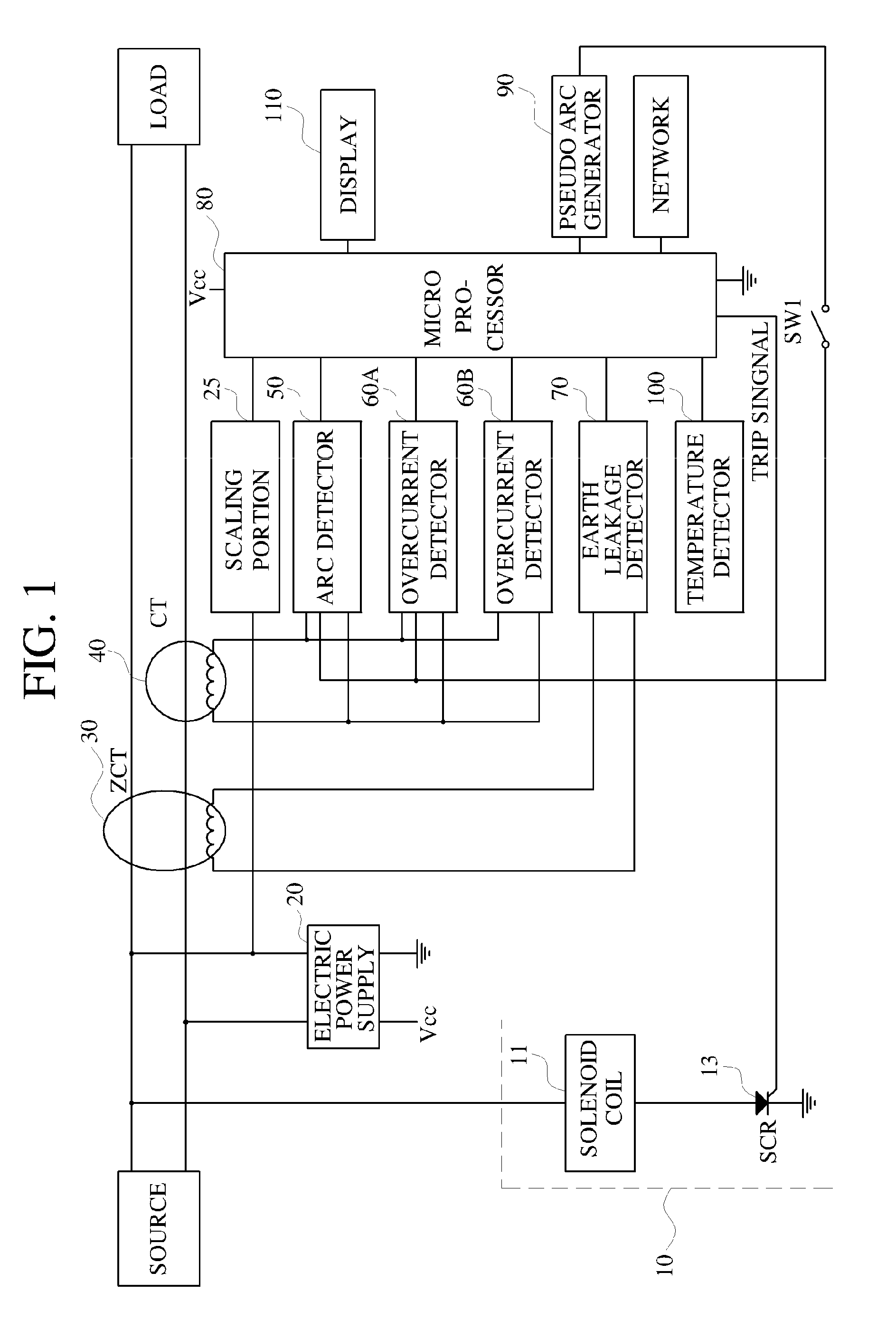
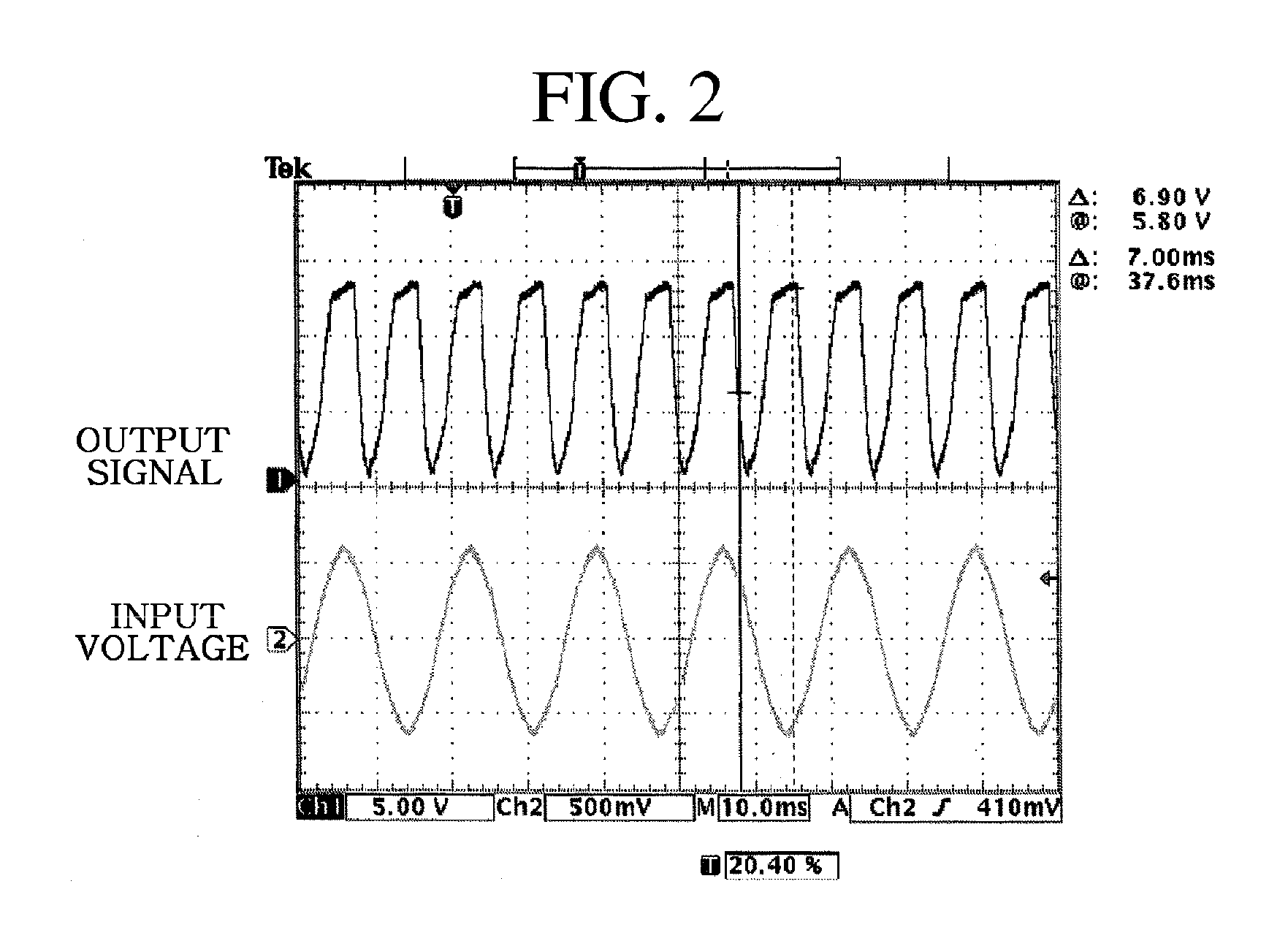
Composite type electric circuit breaker and method thereof
ActiveUS20100324747A1Maximize efficiencyPrevents electric accidents and occurrence of fire more accuratelyMechanical power/torque controlTesting dielectric strengthZero phaseEngineering
A composite electric circuit breaker, and method thereof, is configured to detect signals regarding arc faults, overcurrent, and earth leakage. Arcs and electric currents are detected by a current transformer and earth leakage is detected by a zero phase current transformer. A variation of electric current, the number of arcs which are generated per a unit time, a present electric current value, and electric current earth leakage are combined to judge whether arc faults occur to then interrupt an electric power supply. Temperature is measured on a printed circuit board, and if temperature rise occurs, the electric power supply is interrupted, and an interruption cause is displayed. Electric accidents and occurrence of fires are prevented simultaneously and more accurately. The interruption causes can be confirmed, analyzed and externally monitored through a network, to thus maximize efficiency of electric management.
Owner:ARCONTEK CO LTD
Failure line selection method of small current ground system by using simulation after zero mode current measure
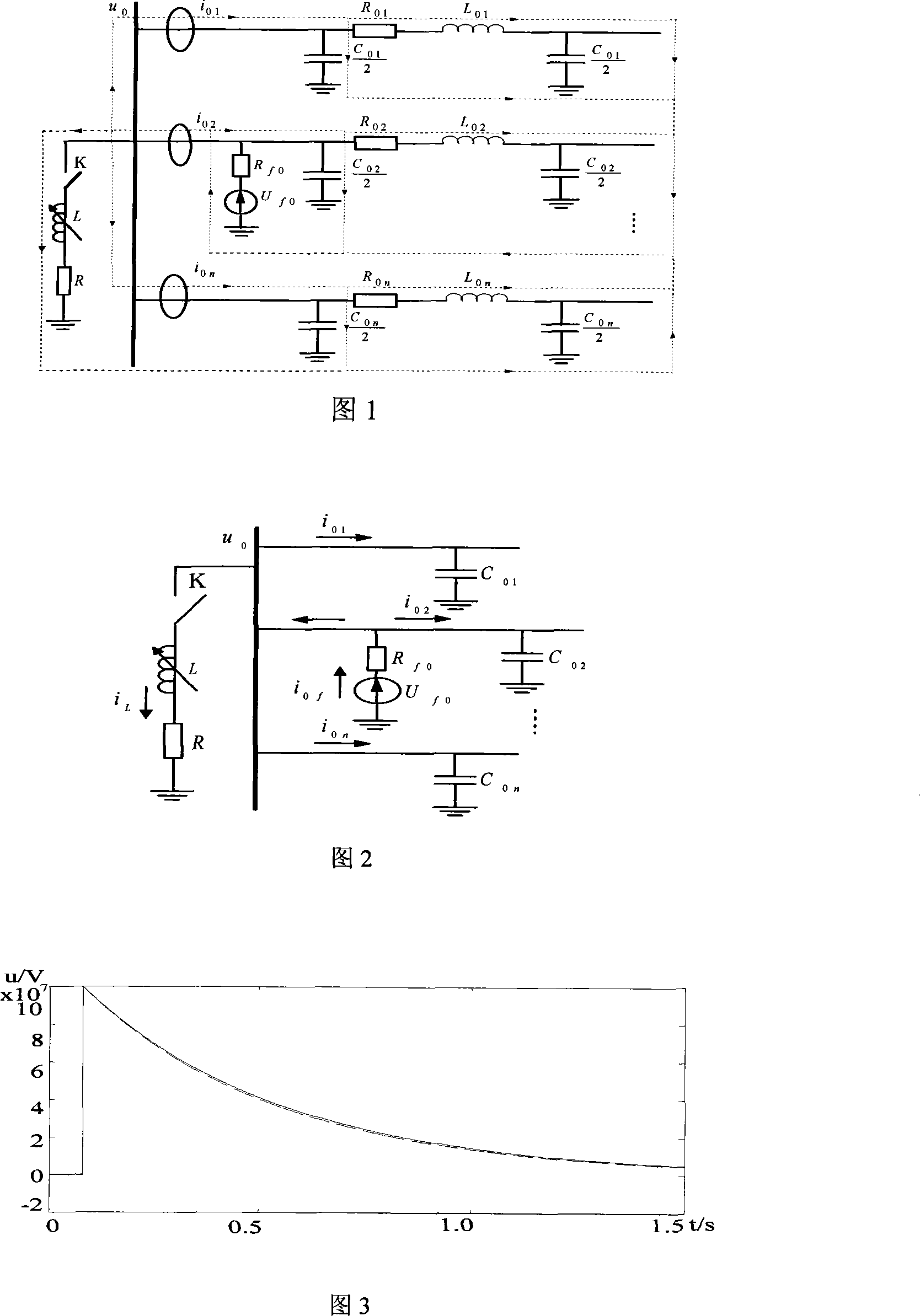
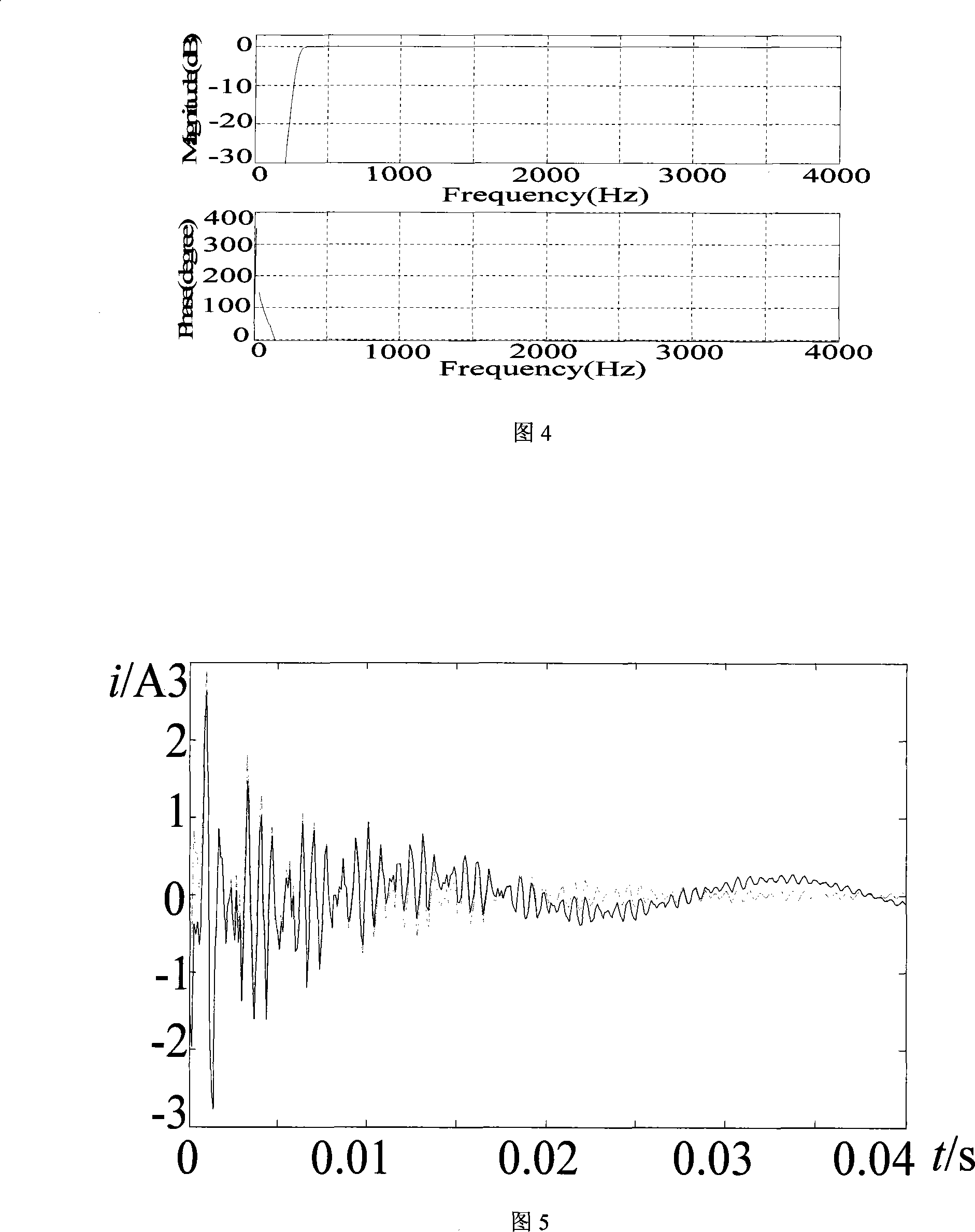
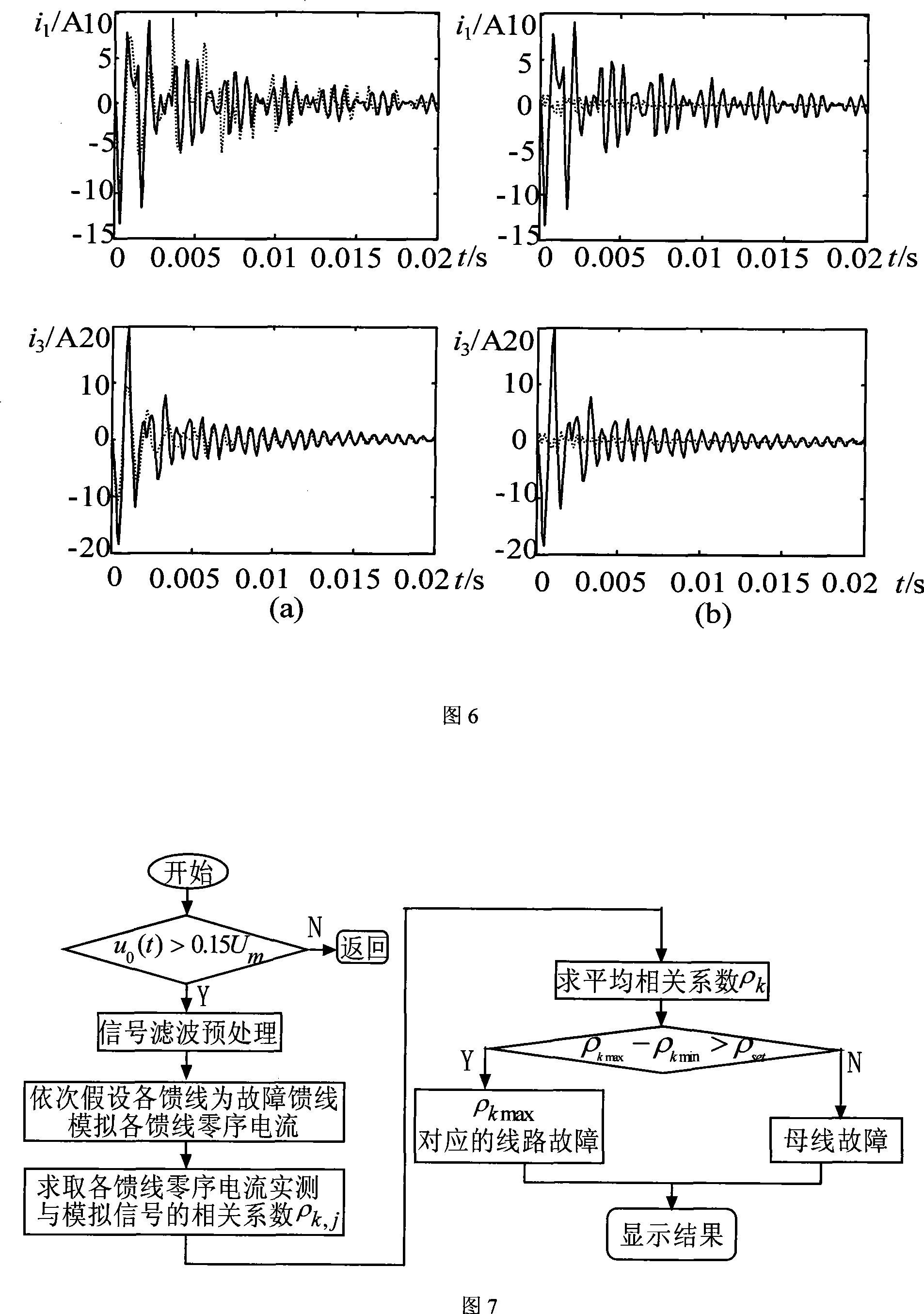
InactiveCN101242097AOvercome the influence of small fault transient currentRealize correct line selectionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCapacitanceEngineering
The invention provides a fault route-selecting method by using small current grounding system simulated by measured zero-mode current. The method includes following steps: when a generatrix zero-mode voltage instantaneous value is over the limit, a fault route-selecting is started and recorded immediately; zero-phase shift digital wave filter is used to obtain a high-frequency transient weight of each feed line zero-mode current; orderly the feed line is supposed to be fault feed line, the rest of the high-frequency transient weight of the feed line zero-mode current is quantificationally solved by using the measured simulative method according to the supposed high-frequency transient weight of the feed line zero-mode current and each feed line zero-order distributing capacitance parameter; the actual-measured wave shape and simulative wave shape of the high-frequency transient weight of the feed line zero-mode current are analyzed and a average relative coefficient of the actual-measured wave shape and simulative wave shape of the high-frequency transient weight of the feed line zero-mode current are solved, the route-selecting criterion is formed to achieve the fault route selection. The principle analysis and simulation indicate that route selection of this method is accurate and reliable.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
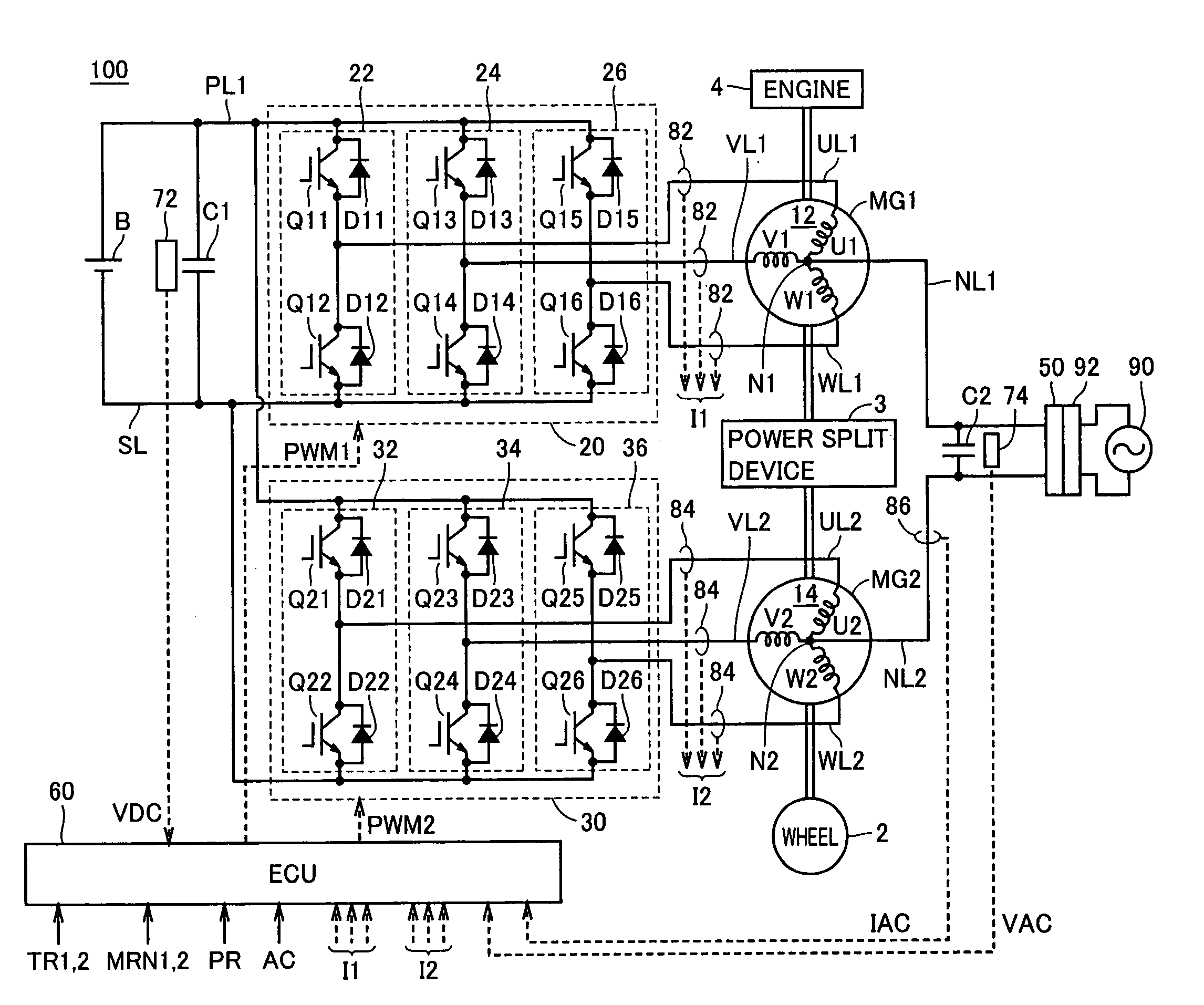
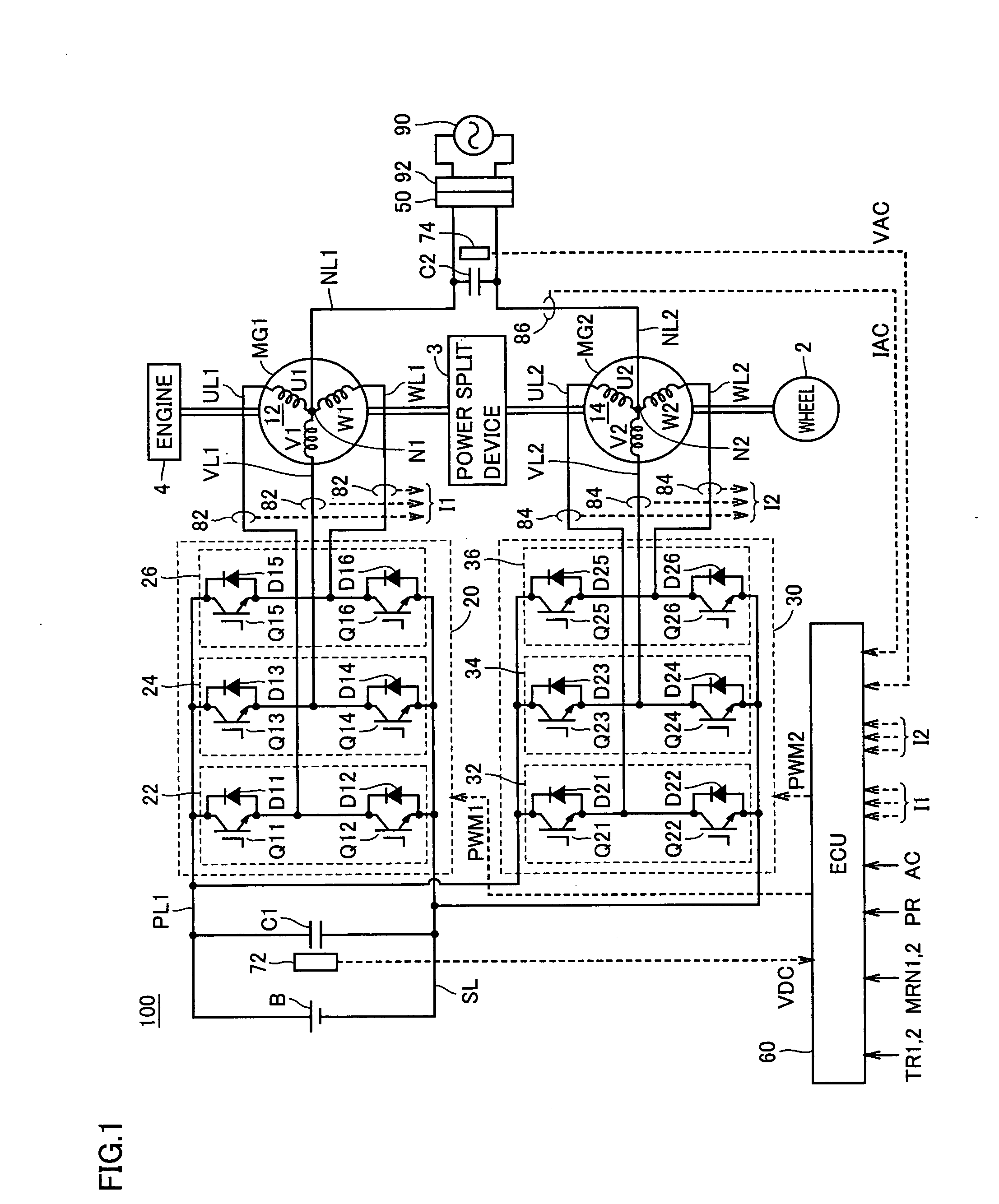
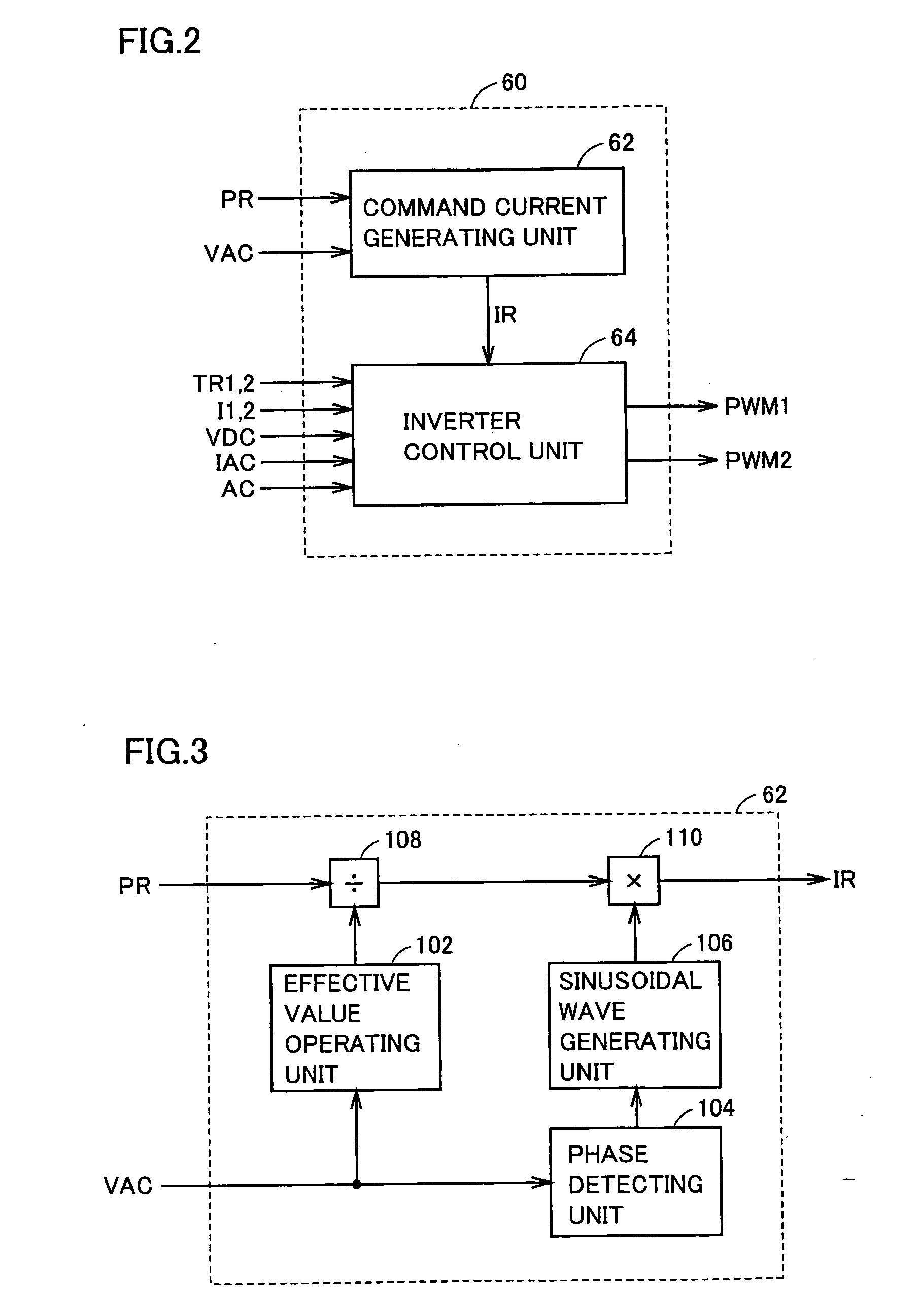
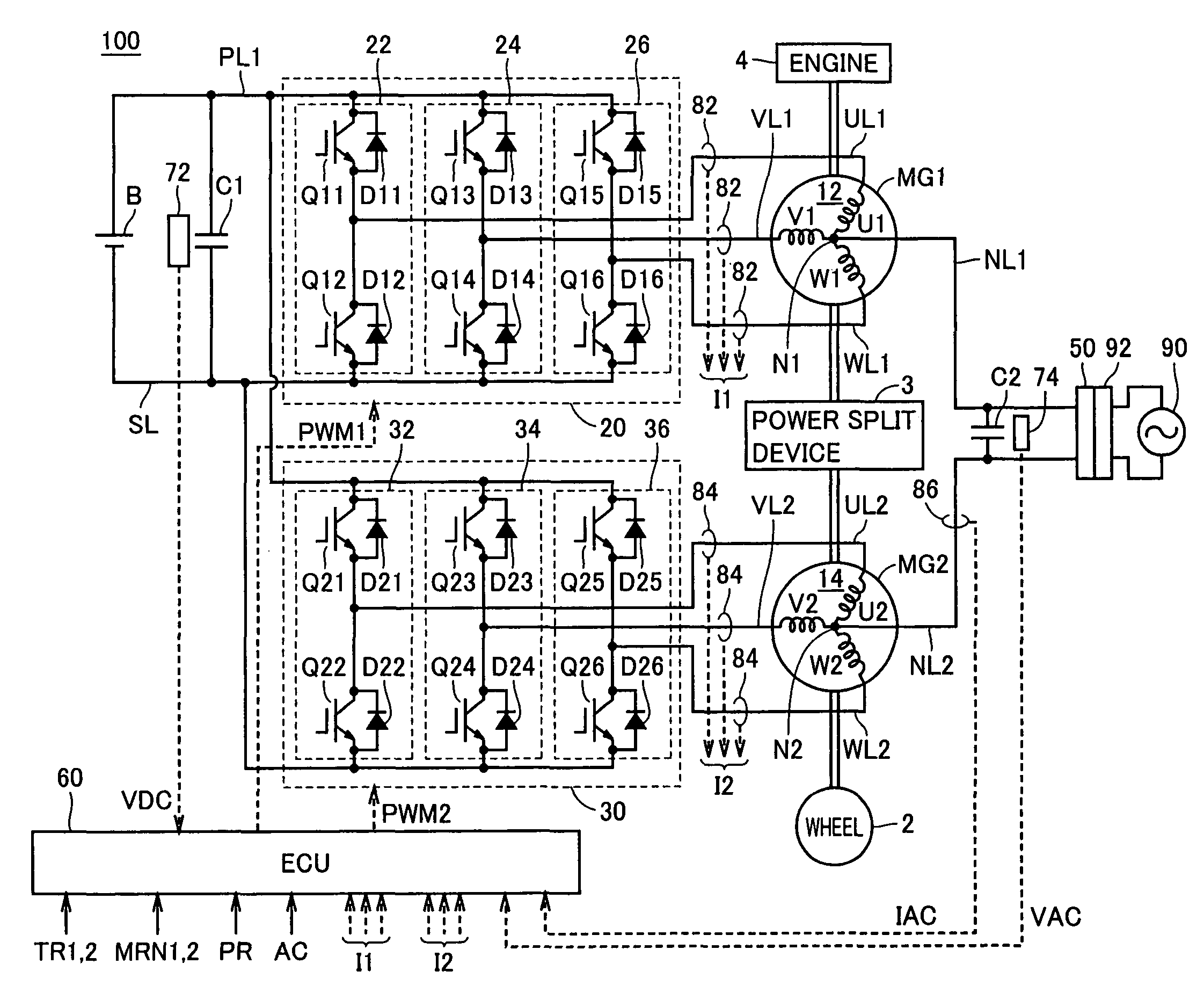
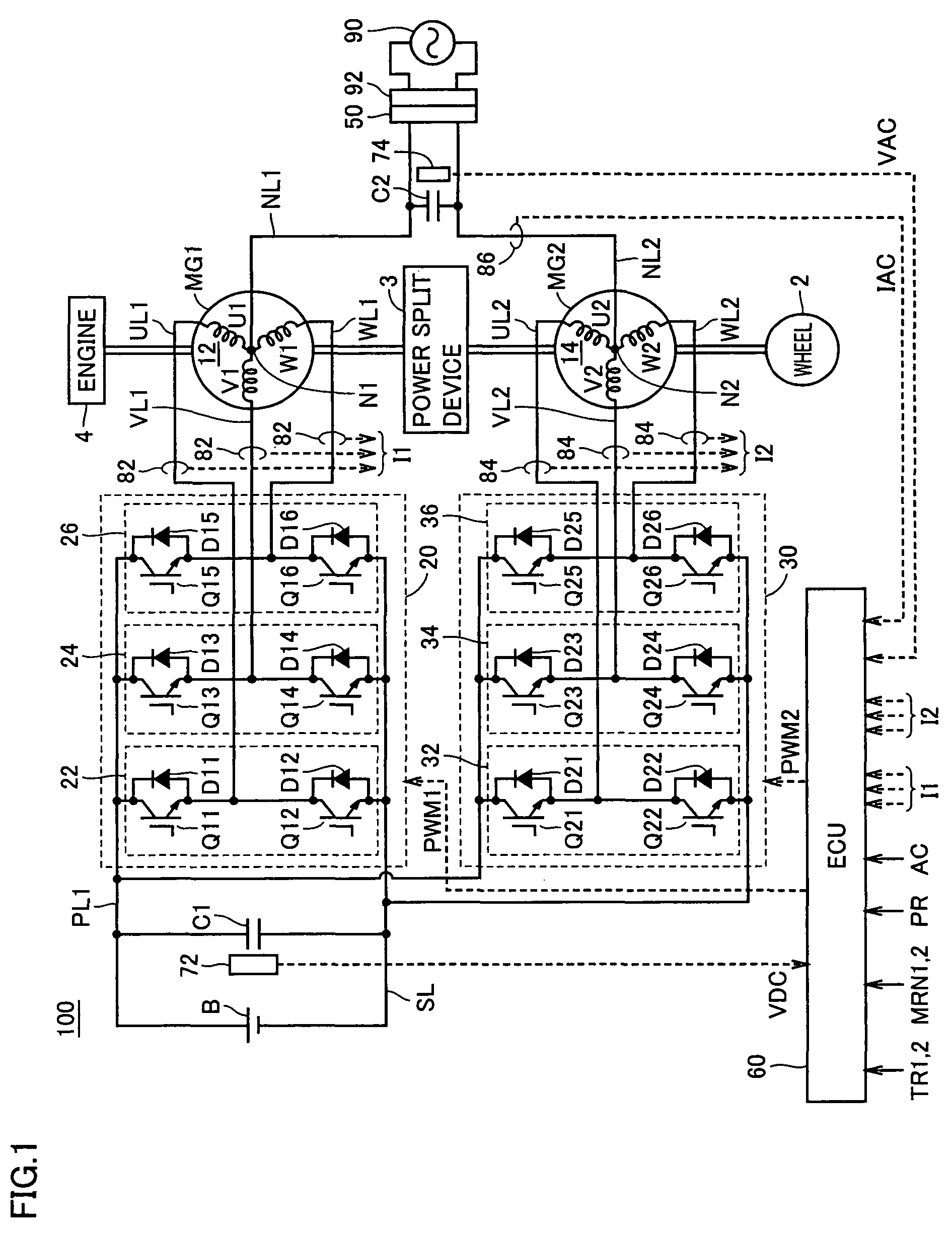
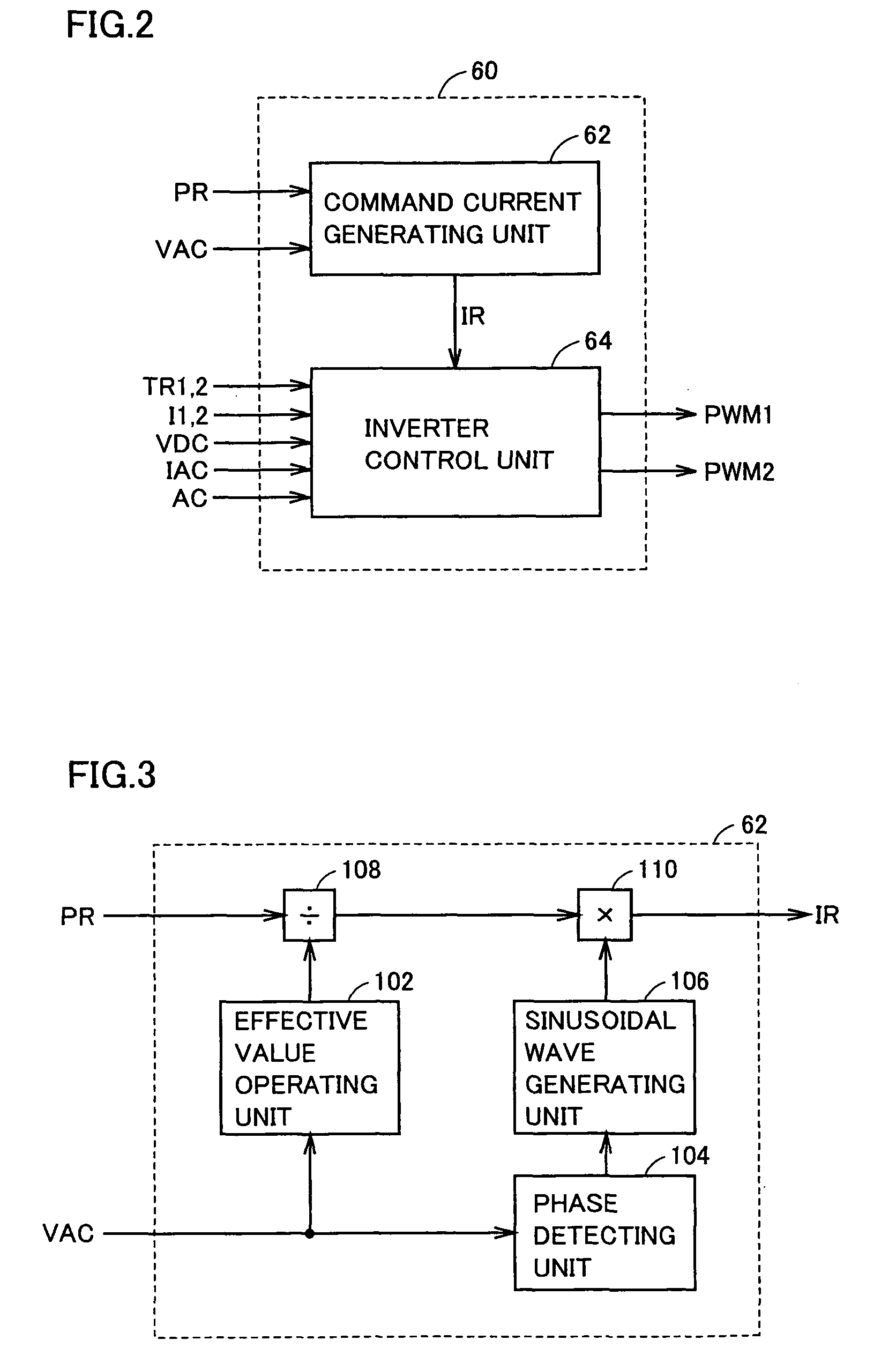
Power Controller and Vehicle Equipped with Power Controller
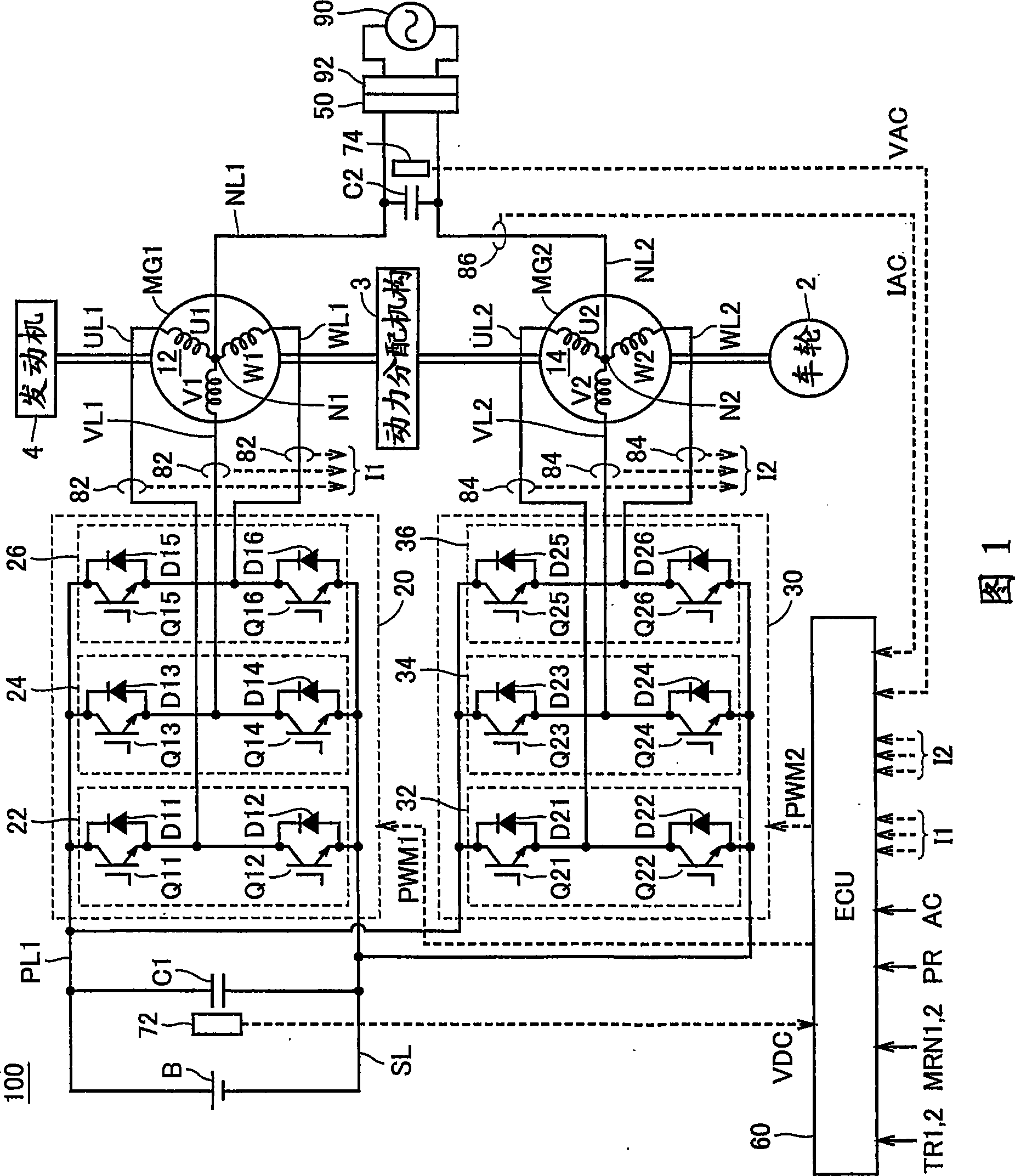
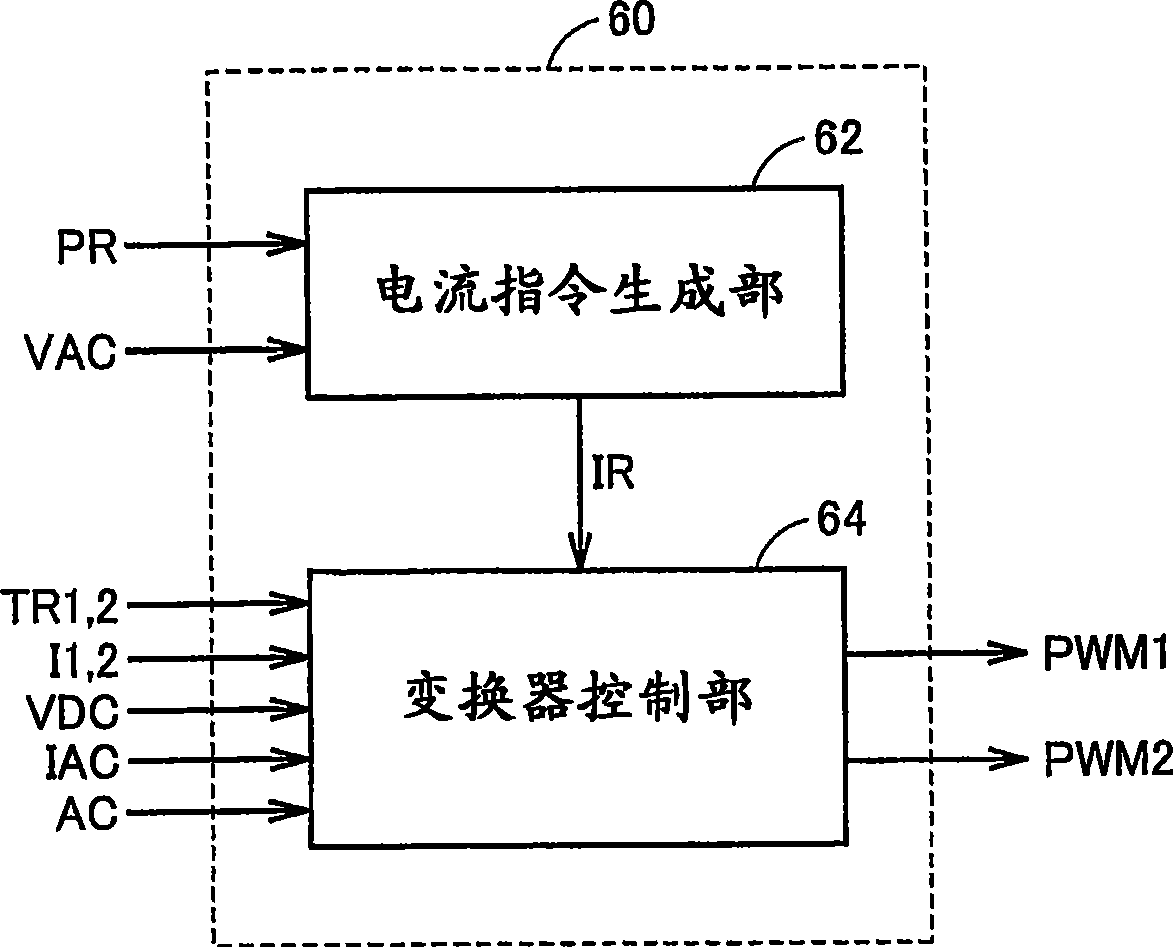
InactiveUS20090067205A1Reduce in quantityAvoid componentsAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPower controllerPower flow
An ECU detects an effective value and phase of a voltage from a commercial power supply, based on a voltage from a voltage sensor. Further, ECU generates a command current, which is a command value of current caused to flow through power lines and in-phase with the voltage of the commercial power supply, based on the detected effective value and the phase and on a charge / discharge power command value for a power storage device. Then, ECU controls zero-phase voltage of inverters based on the generated command current.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
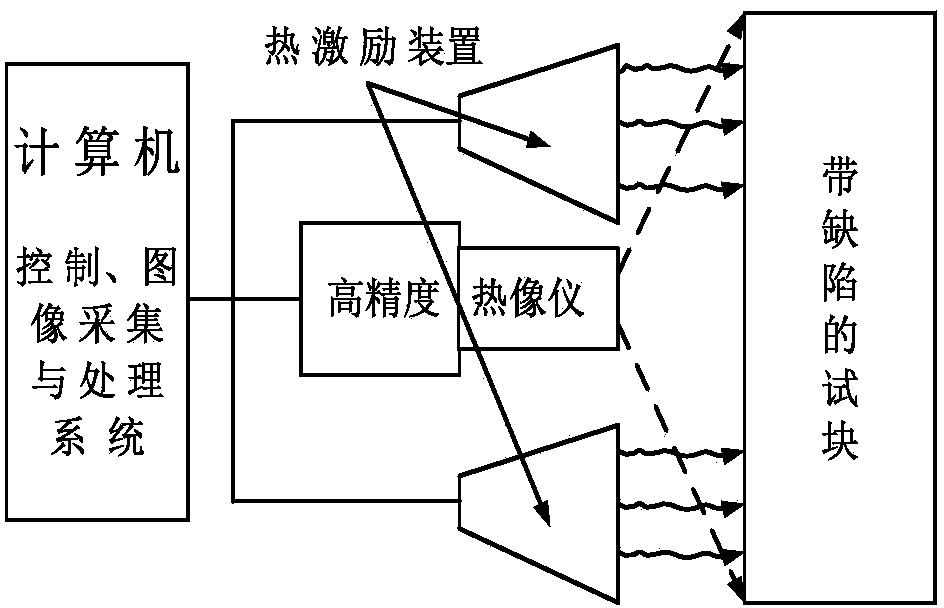
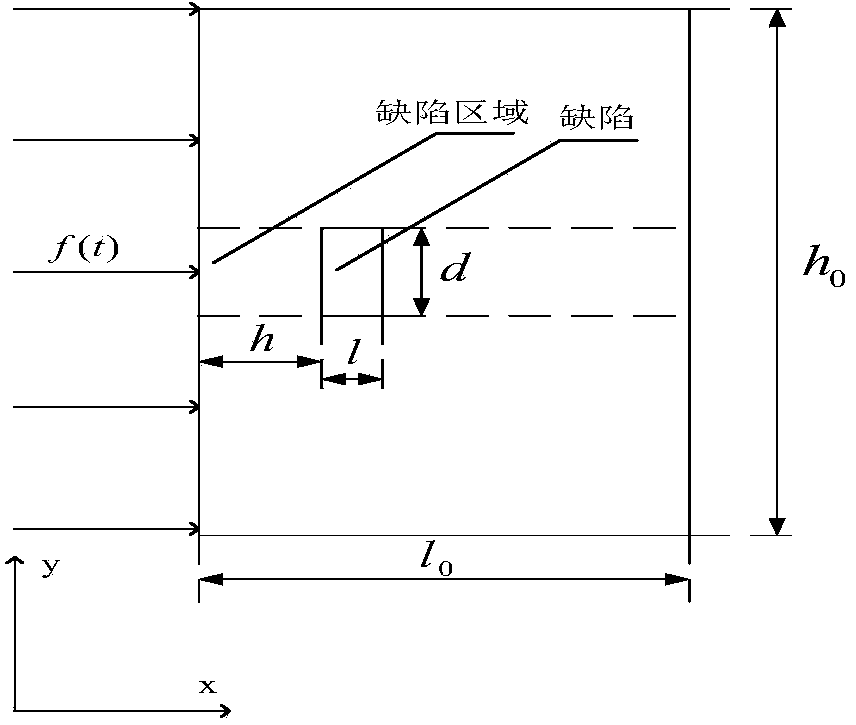
Non-destructive detection method of pulse-excited infrared thermal wave phase of fixed viewing field
InactiveCN104359944AEasy to detectFlexible useMaterial flaws investigationFrequency spectrumImage sequence
The invention relates to a non-destructive detection method of pulse-excited infrared thermal wave phase of a fixed viewing field. The non-destructive detection method comprises the following steps: comprehensively applying a multiple-modulation Zoom-FFT refining spectrum method, a thermal-wave data fitting extension method and a zero-phase digital filter method, and carrying out high-accuracy spectral analysis on acquired continuous equally-spaced infrared thermal-wave image sequences before and after thermal excitation, thus quickly obtaining precise ultralow-frequency thermal-image phase diagram and amplitude diagram, and further realizing detection and recognition for defects or damages of equipment. Compared with the prior art, the non-destructive detection method has the beneficial effects that not only can the acquisition frequency, the acquisition time, the acquisition frame number and the refining degree of analysis of thermal images be flexibly set, but also the detection speed, the refining degree and the precision degree can be increased by ten times respectively, the multiplied increase of the detection effect and the detection depth of the defects also can be realized, simultaneously the requirement for computer hardware is also reduced, so that the method is flexible in use, is especially suitable for non-destructive detection of the infrared thermal wave on site and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:PLA SECOND ARTILLERY ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY
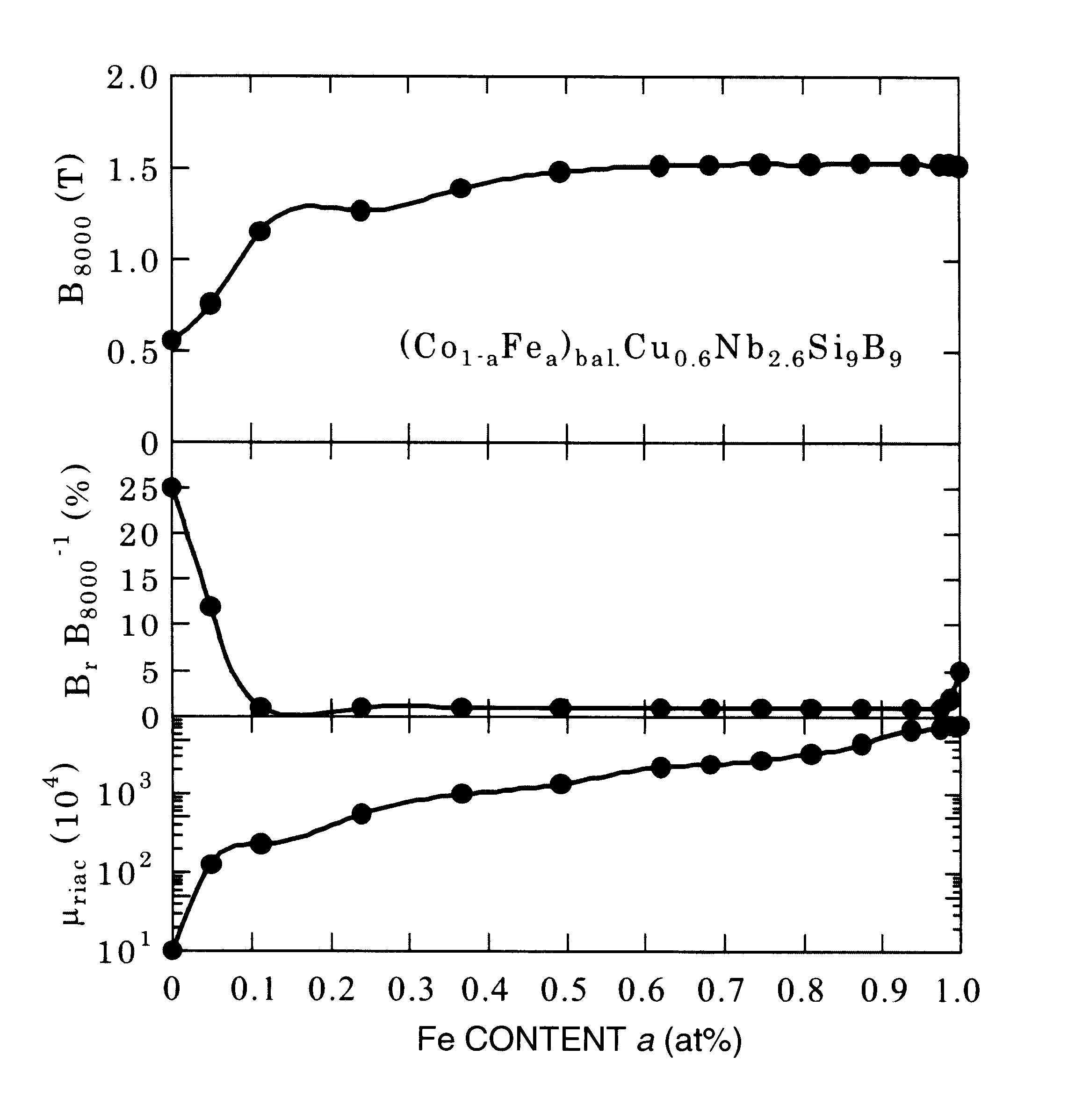
Co-based magnetic alloy and magnetic members made of the same
Disclosed is a Co-base magnetic alloy excellent in high-frequency magnetic properties, of which chemical composition is represented by the following general formula, by atomic %, (Co1-aFea)100-y-cM'yX'c, where M' is at least one element selected from the group consisting of V, Ti, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Sc, Ta and W; X' is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Si and B; and a, y and c are defined by the formulas of a<0.35, 1.5<=y<=15, and 4<=c<=30, respectively. At least a part of the alloy structure of the alloy consists of crystal grains having an average grain size of not more than 50 nm. The alloy has a relative initial permeability of not more than 2000. It is suitably used for members of countermeasure against noise such as zero phase reactors for large current and electromagnetic shielding materials, inverter transformers, choke coils for active filters, antennas, smoothing choke coils, power supplies for lasers, pulse power magnetic members for accelerators.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Self-adaptive filtering method of dynamic axle weighing signal of vehicle
ActiveCN101105411ASuppress interferenceAccurate detectionDigital technique networkSpecial purpose weighing apparatusVehicle dynamicsPhase distortion
The invention relates to a self-adapting method for filtering vehicle dynamic shaft load signal, aiming to effectively eliminate weighing error due to vehicle dynamic load and remarkably improve the vehicle weighing accuracy. The invention processes the original shaft load signal by zero phase offset and low-pass filtering, so as to eliminate white noise interference and inhibit phase distortion of the shaft load signal during low-pass filtering process. The invention also adopts optimized cut-off to the original weighing signal by searching average value of extreme points of shaft load signal, so as to better inhibit gravitation impulse interference in the weighing signal. Further, the invention decomposes the weighing signal by empirical mode decomposition method, meanwhile, adopts end point continuation method in empirical mode decomposition, so as to eliminate end effect, effectively inhibit the generation of false mode and make the decomposed result relatively true. The invention eliminates low-frequency interference through empirical mode decomposition, so as to obtain true shaft load signal.
Owner:西安航天三沃机电设备有限责任公司
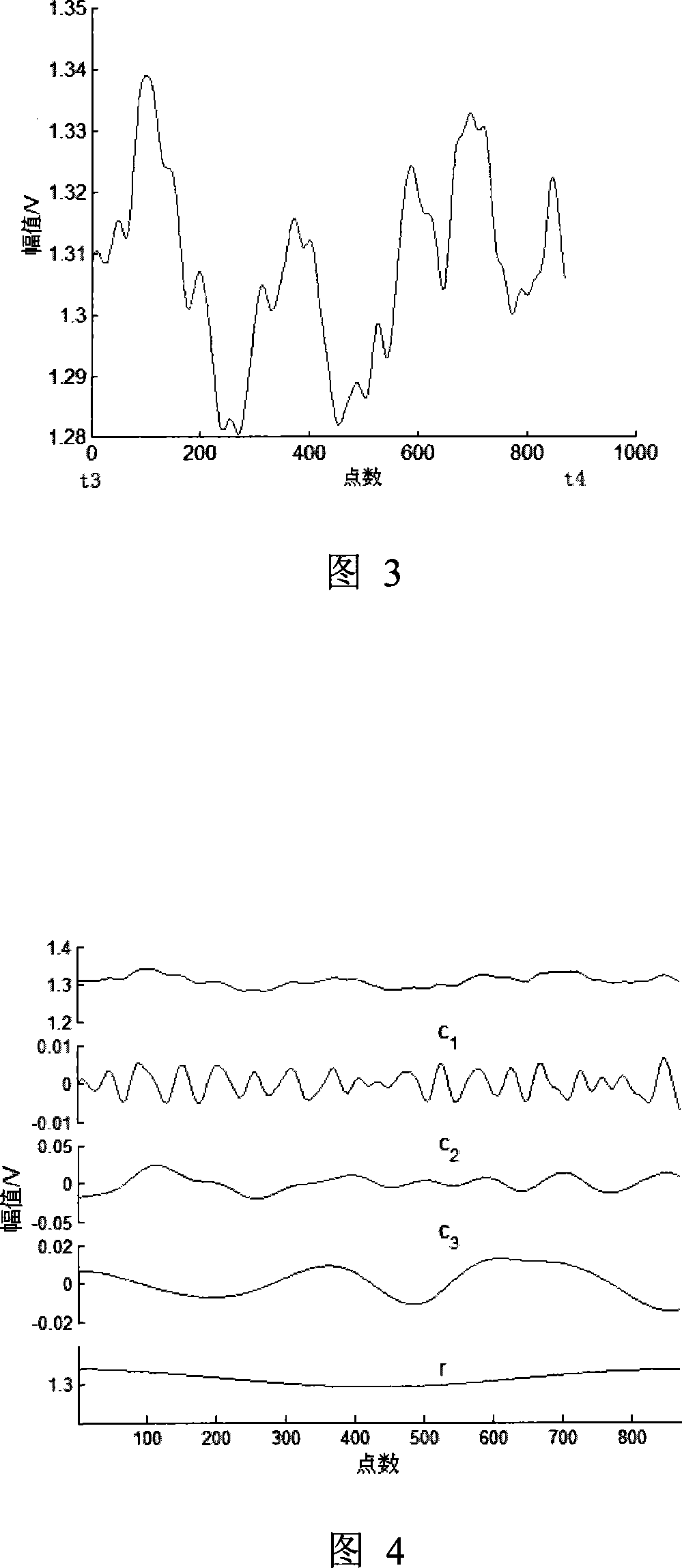
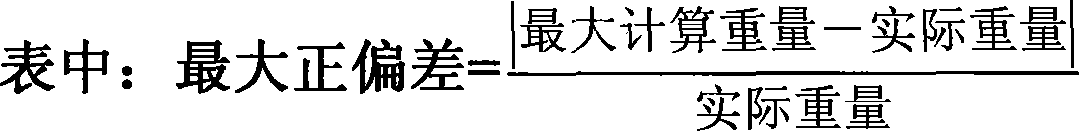
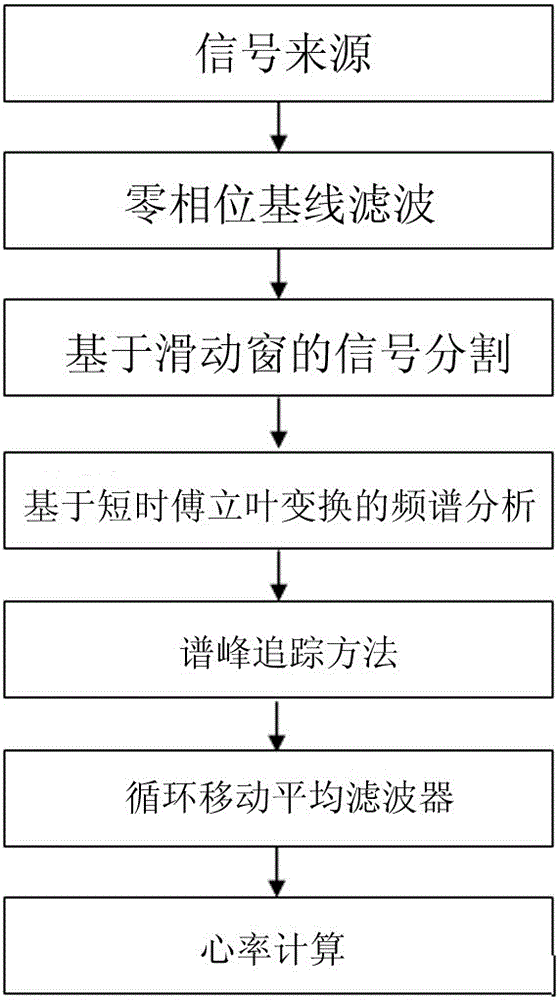
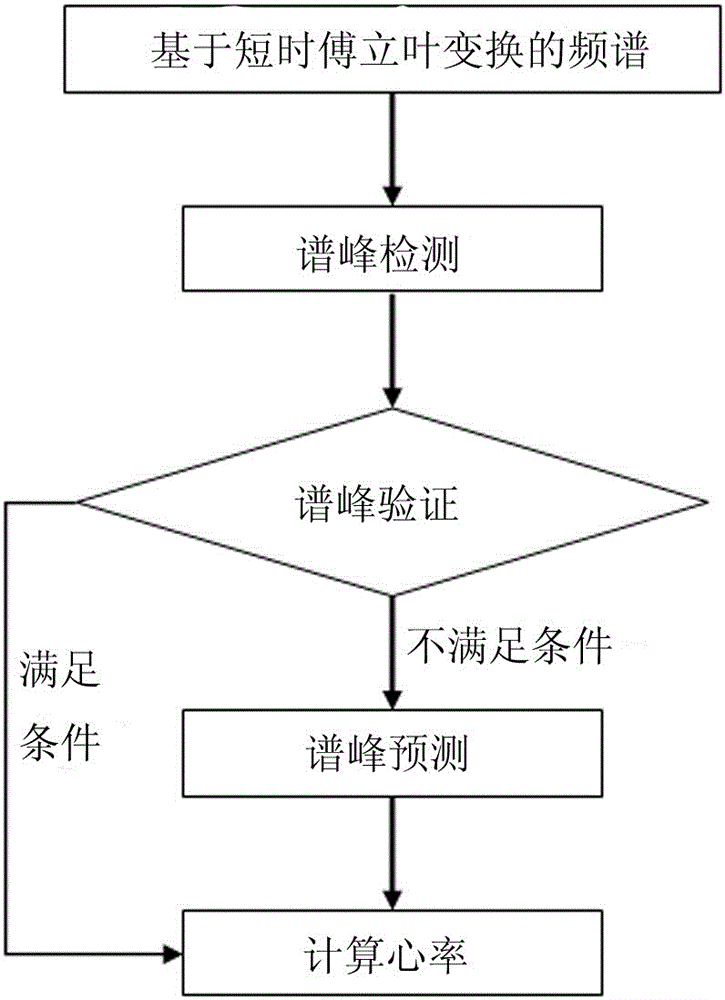
Motion state heart rate monitoring method based on photoplethysmography and spectrum analysis
ActiveCN105105737ARealize health monitoringEasy to knowMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateFrequency spectrumAverage filter
The invention relates to motion state heart rate monitoring, in particular to a motion state heart rate monitoring method based on photoplethysmography and a spectrum analysis. The method comprises the following steps: performing zero-phase base line filtering on a source signal; partitioning a processed signal by a sliding window method; obtaining a frequency spectrum by a short-time Fourier transformation method; finding out a spectrum peak representing heart rate data by a spectrum peak tracing method to obtain the heart rate data; processing the heart rate data by a calculatedly moving mean filter to obtain a final heart rate result. The motion state heart rate monitoring method is simple in design and efficient; by monitoring and the analysis of the method, a user can acquire the heart rate data under a motion state. The motion state heart rate monitoring method can be applied to wearable equipment so as to realize healthy monitoring of the heart rate and has higher application value.
Owner:南京盟联信息科技股份有限公司
Time-frequency synchronization joint estimation method based on multi-carrier receiver of digital television media broadcast (DTMB) system
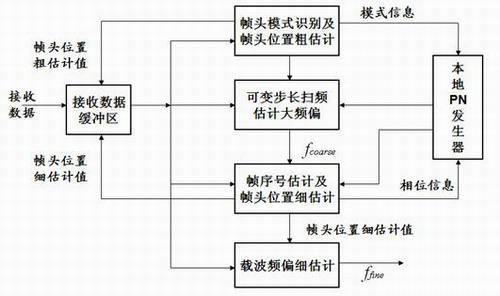
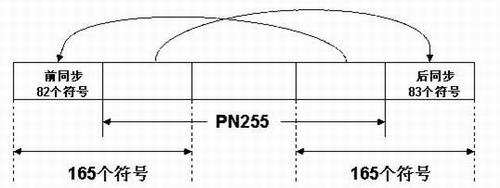
InactiveCN102143117ASharedHave identityBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsPattern matchingEstimation methods
The invention relates to a time-frequency synchronization joint estimation method based on a multi-carrier receiver of a digital television media broadcast (DTMB) system. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: step 1, carrying out frame header mode recognition and frame header position coarse estimation; step 2, generating a pseudorandom noise (PN) sequence A of a zero phase matched with the frame header mode by a local PN generator, and carrying out carrier frequency offset estimation by utilizing a step-variable frequency sweeping method; step 3, correlating received data with the PN sequence A after compensation carrier is subjected to large frequency offset, so as to estimate a serial number of a frame; generating a PN sequence B of a matched phase matched with the frame header mode, and then correlating the PN sequence B with the received data so as to obtain a frame header position fine estimation value; and step 4, carrying out self-correlation on the frame header position according to the frame header position fine estimation value so as to obtain a carrier frequency offset fine estimation value, and summarizing a carrier frequency large offset estimation value and the carrier frequency offset fine estimation value so as to obtain a final carrier frequency offset estimation value. In the invention, the time-frequency synchronization joint estimation method based on the multi-carrier receiver of the DTMB system is used, thereby facilitating the realization of share of operation data and parameters and reducing the arithmetic labor.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Power controller and vehicle equipped with power controller
ActiveCN101454958AEfficient chargingIncrease powerBatteries circuit arrangementsAC motor controlPower controllerCapacitance
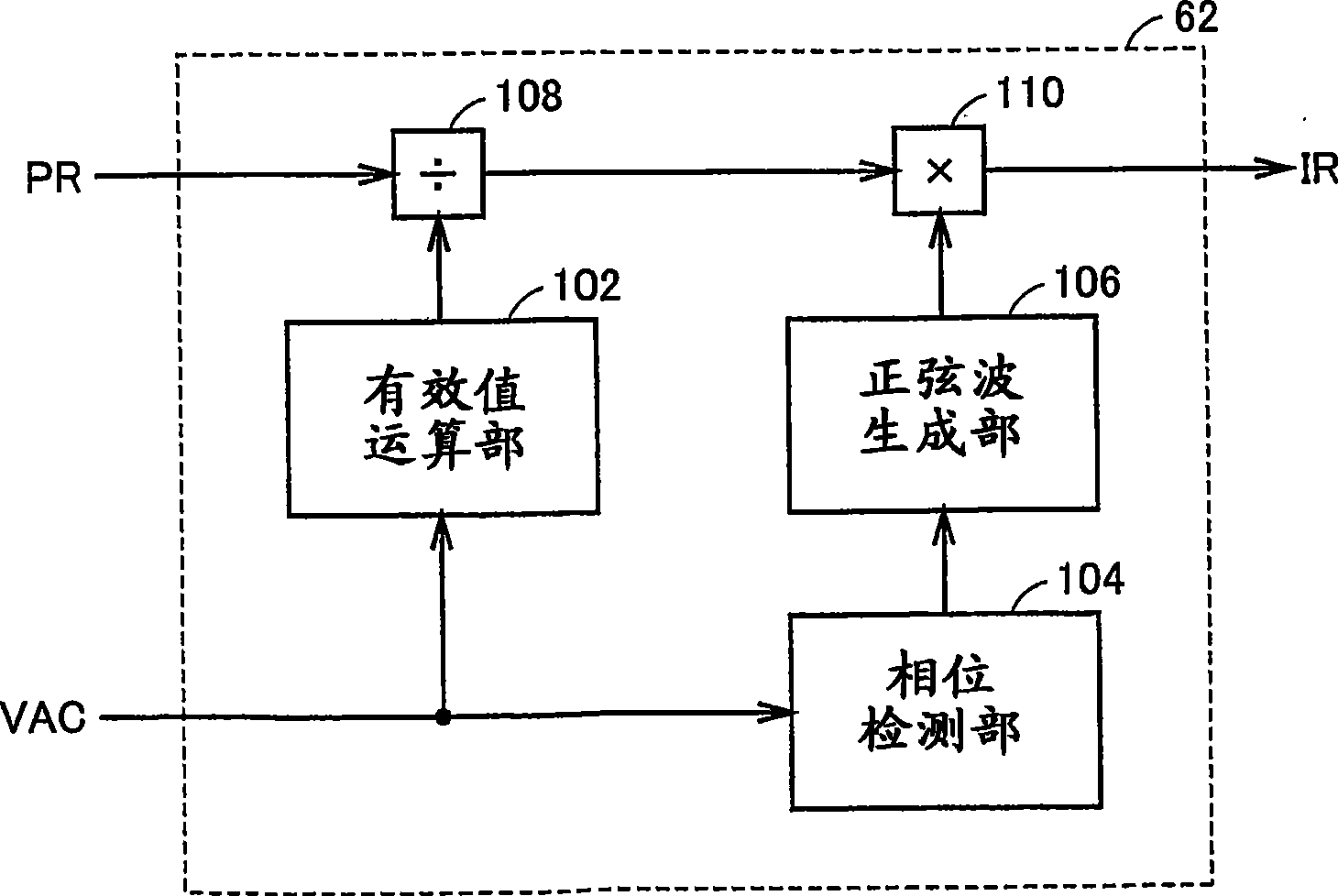
An ECU (60) detects an effective value and phase of a voltage from a commercial power supply (90), based on a voltage (VAC) from a voltage sensor (74). Further, ECU (60) generates a command current (IR), which is a command value of current (IAC) caused to flow through power lines (NL1, NL2) and in-phase with the voltage of the commercial power supply (90), based on the detected effective value and the phase and on a charge / discharge power command value (PR) for a power storage device (B). Then, ECU (60) controls zero-phase voltage of inverters (20, 30) based on the generated command current (IR).
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Rotary electric system designed to utilize zero-phase circuit
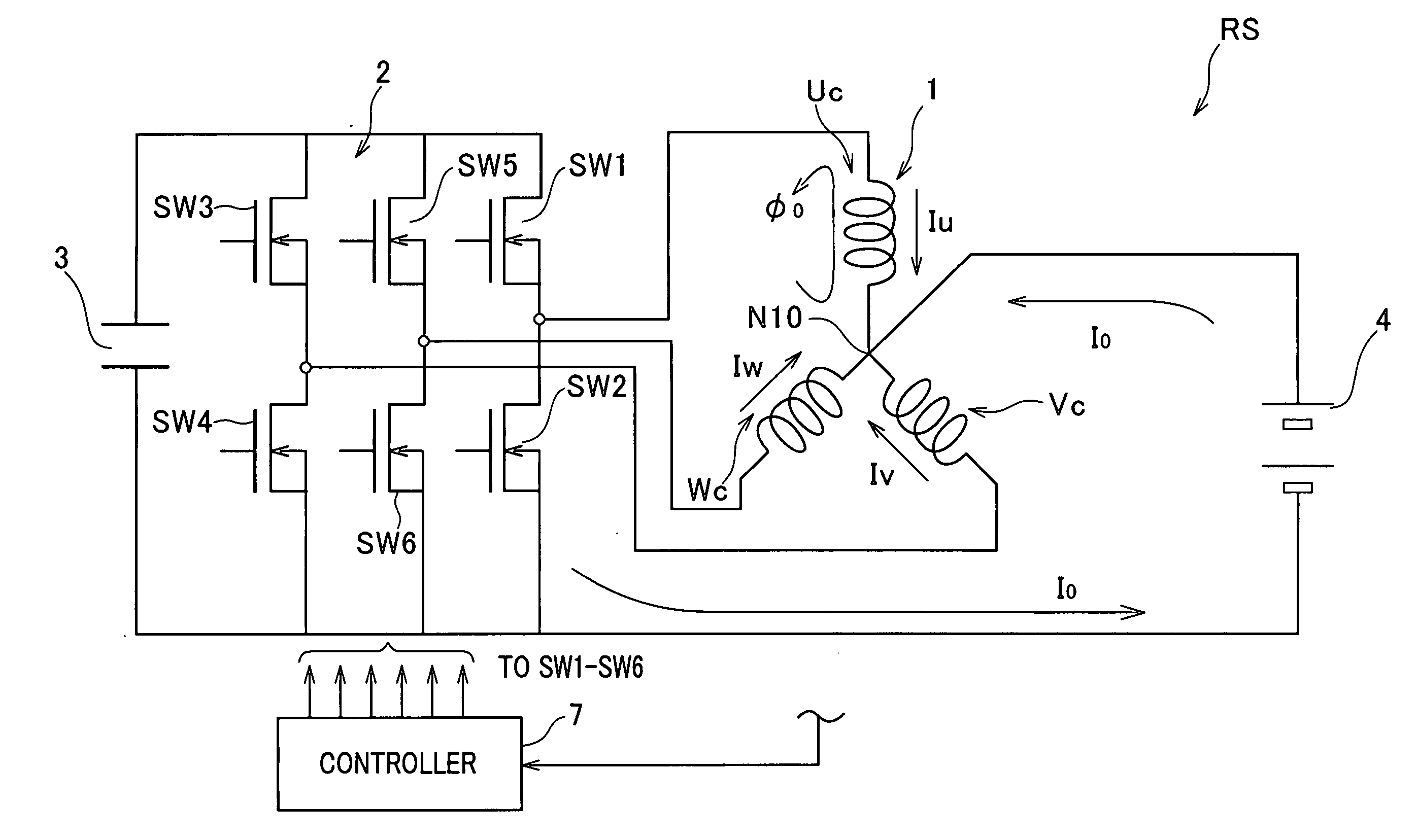
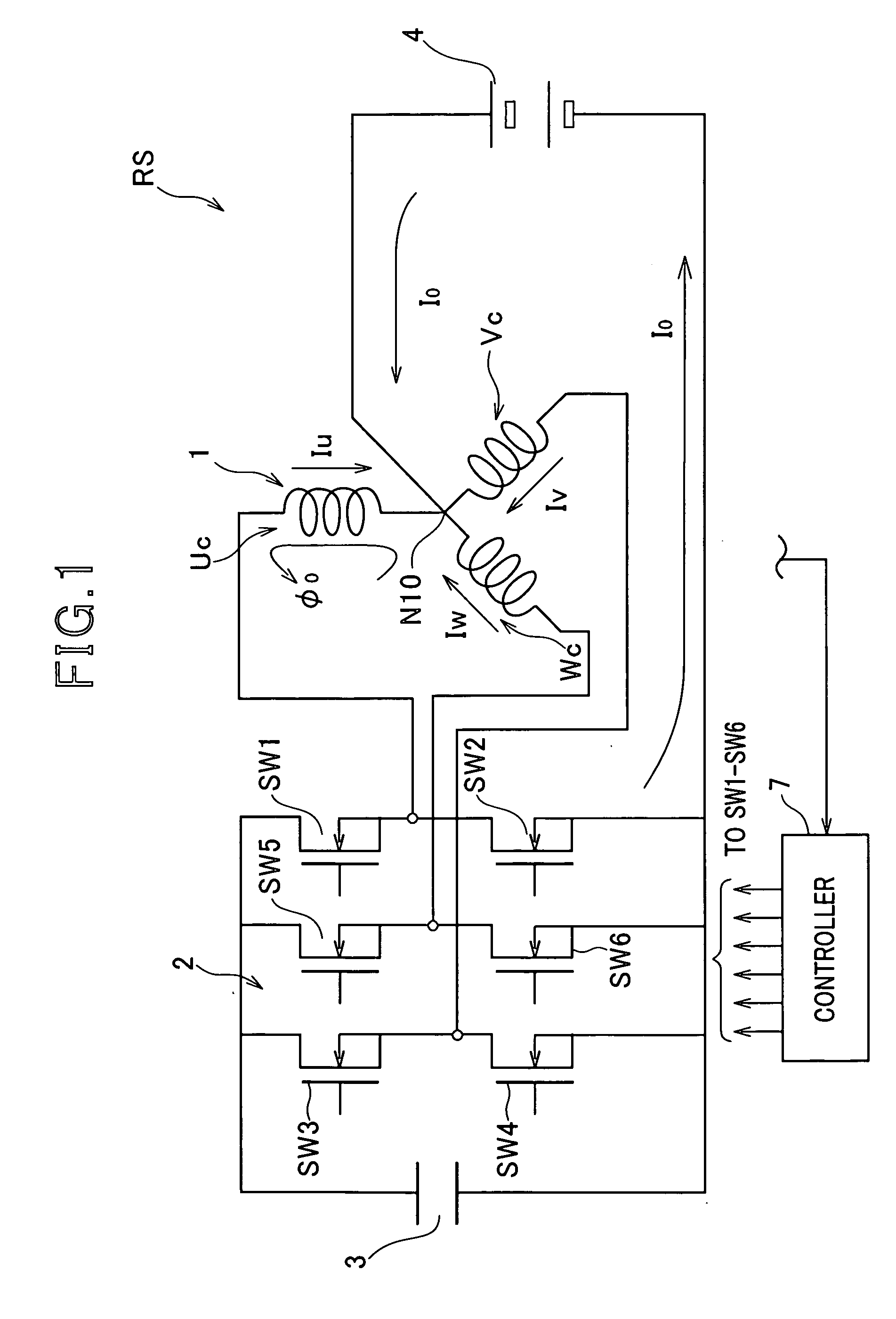
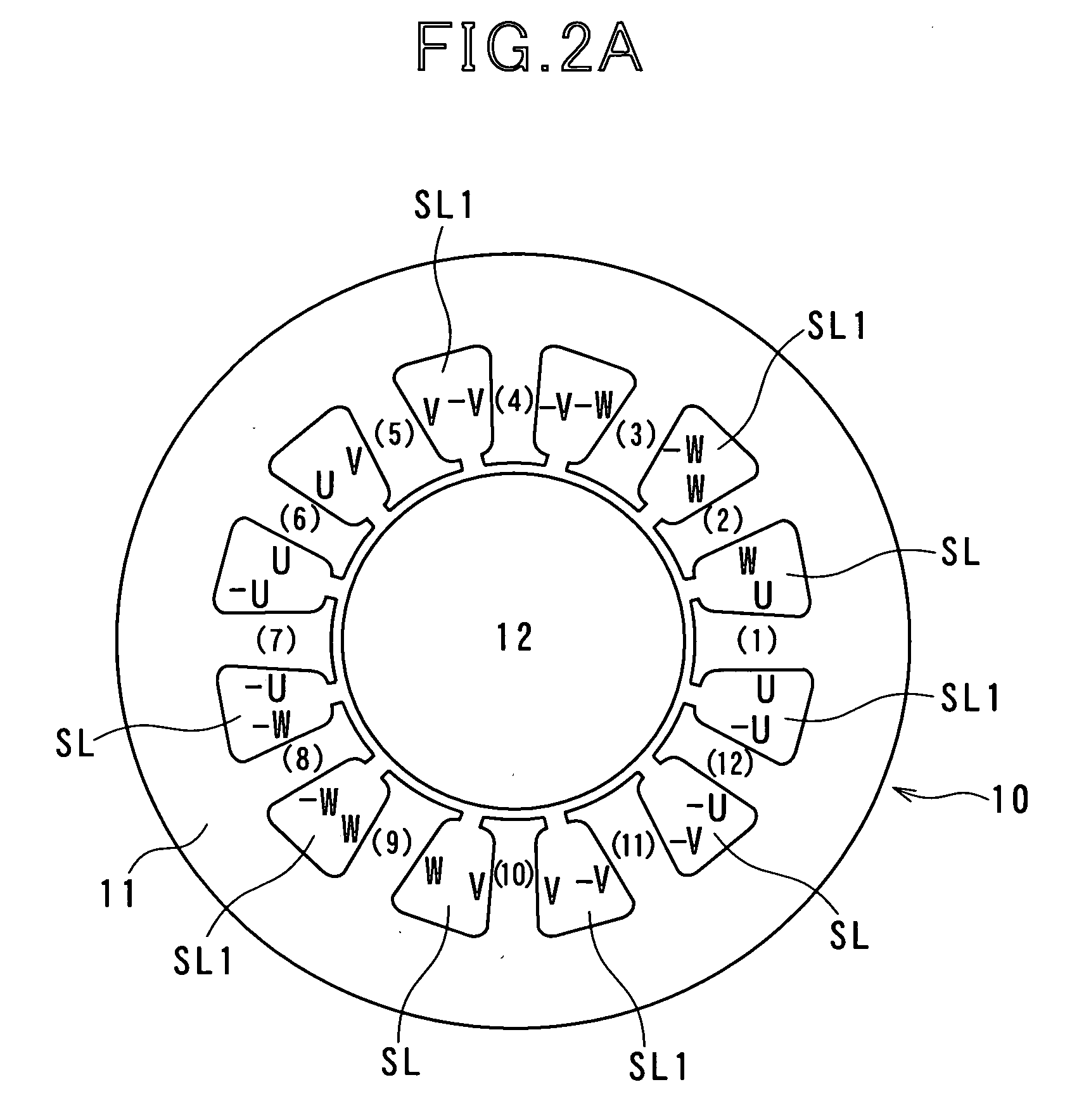
InactiveUS20080278102A1Good effectCreate torqueBatteries circuit arrangementsSynchronous motors startersSystems designElectric machine
In a rotary electric system, a rotary electric machine is provided with an armature core and star-connected multiphase windings with a neutral point wound in the armature core. Each of the star-connected multiphase windings has a predetermined winding configuration that prevents, when a zero-phase current is supplied from a direct current power source to the star-connected multiphase windings via the neutral point, a zero-phase magnetic flux created in the armature core based on the zero-phase current flowing in each phase winding of the star-connected multiphase windings from being cancelled out by a zero-phase magnetic flux created in the armature core based on the zero-phase current flowing in another one phase winding of the star-connected multiphase windings.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Power controller and vehicle equipped with power controller
InactiveUS7891451B2Avoid componentsAvoid generatingAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPower controllerZero phase
An ECU detects an effective value and phase of a voltage from a commercial power supply, based on a voltage from a voltage sensor. Further, ECU generates a command current, which is a command value of current caused to flow through power lines and in-phase with the voltage of the commercial power supply, based on the detected effective value and the phase and on a charge / discharge power command value for a power storage device. Then, ECU controls zero-phase voltage of inverters based on the generated command current.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
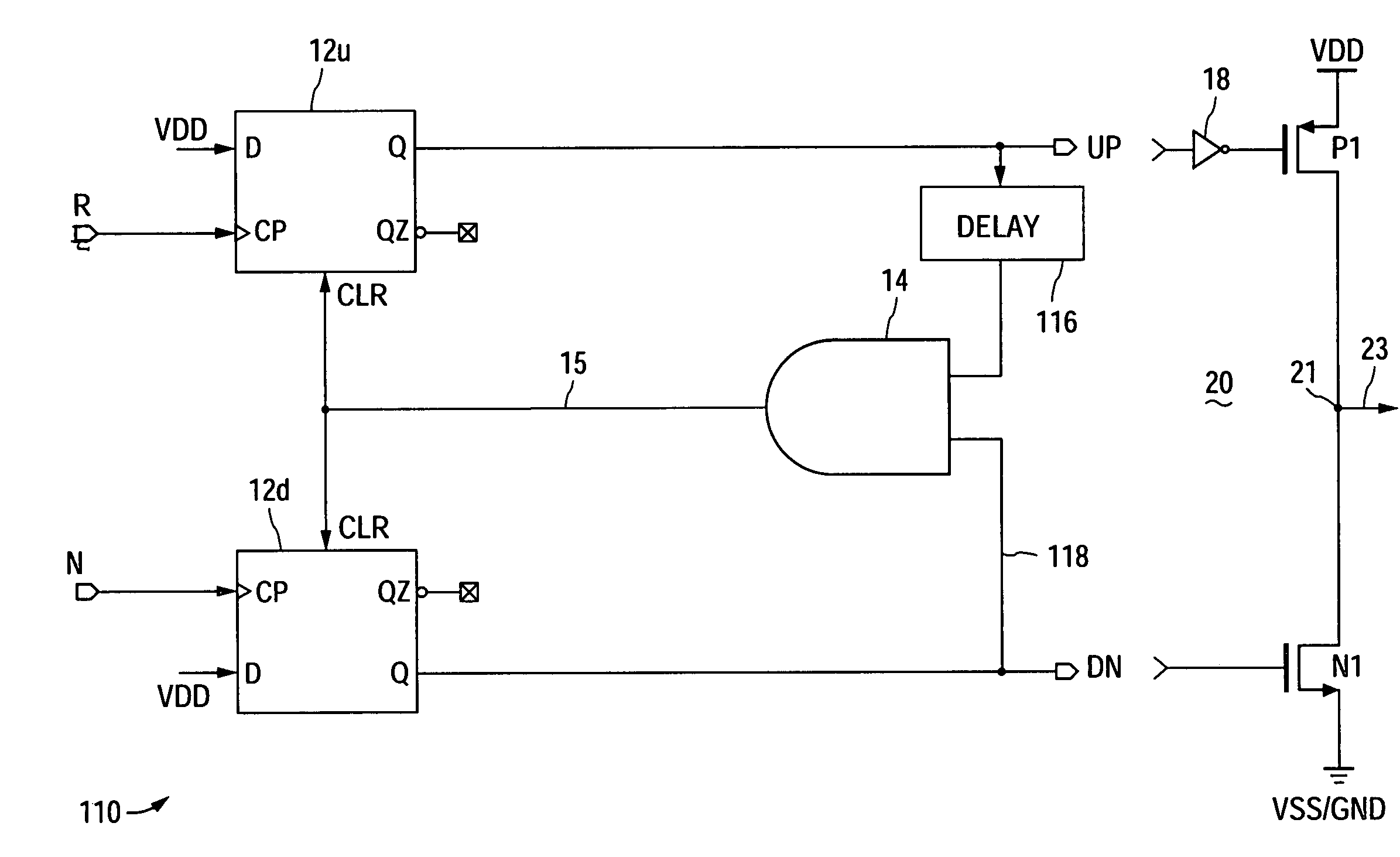
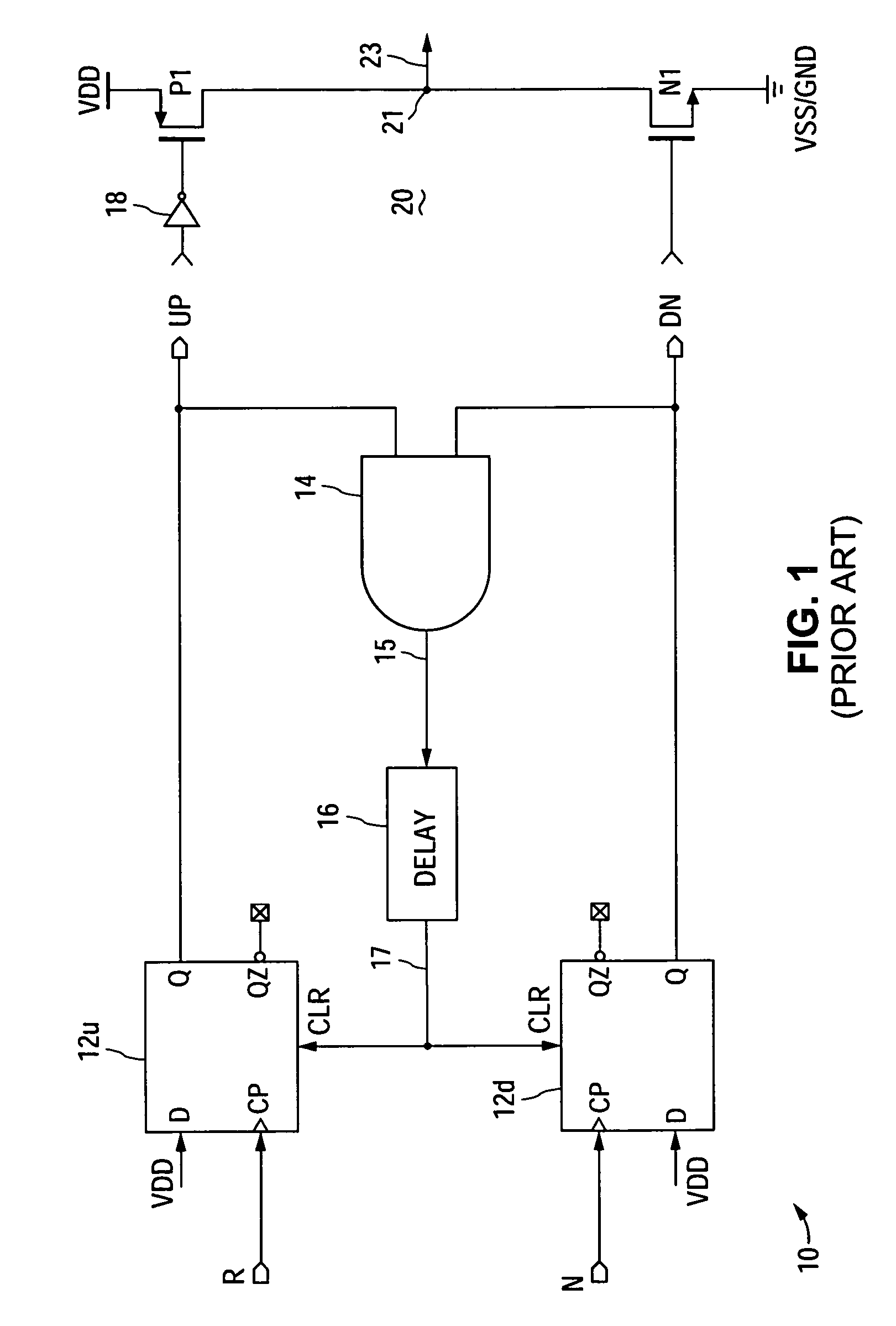
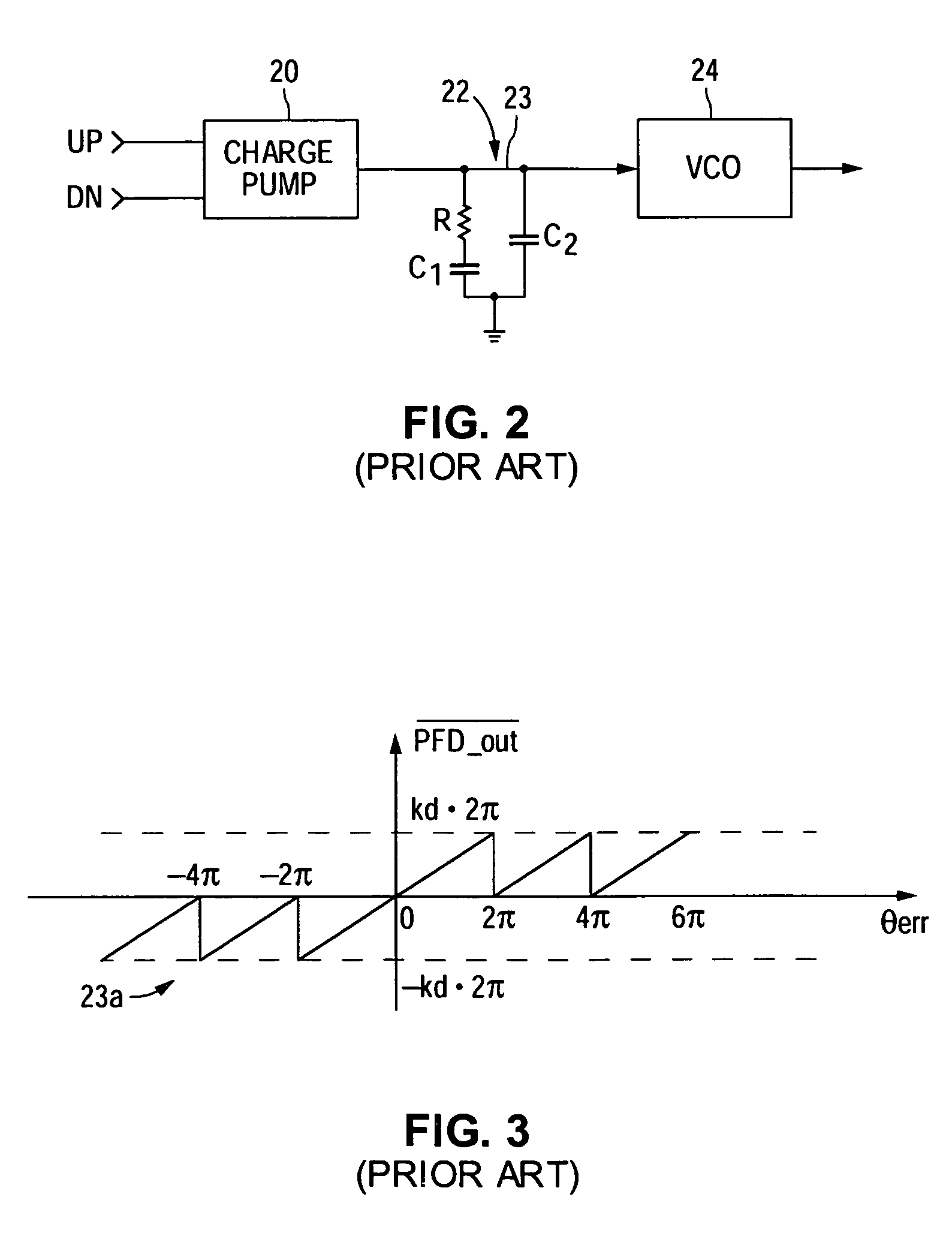
Phase-frequency detector with linear phase error gain near and during phase-lock in delta sigma phase-locked loop
ActiveUS7092475B1Pulse automatic controlOscillations comparator circuitsNon symmetricPhase difference
A phase-frequency detector (PFD) having substantially linear phase error gain within a predetermined phase error range centered about zero phase error when used in a delta sigma phase-locked loop (PLL). The output signals (e.g., charge pump control signals), which are also used to reset the input circuitry, are fed back with asymmetrical signal delays, thereby causing one of the output signals to remain in an asserted state for a substantially constant time duration at least during when a difference between the reference and feedback signal phases is within a predetermined phase difference range centered about zero phase difference.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
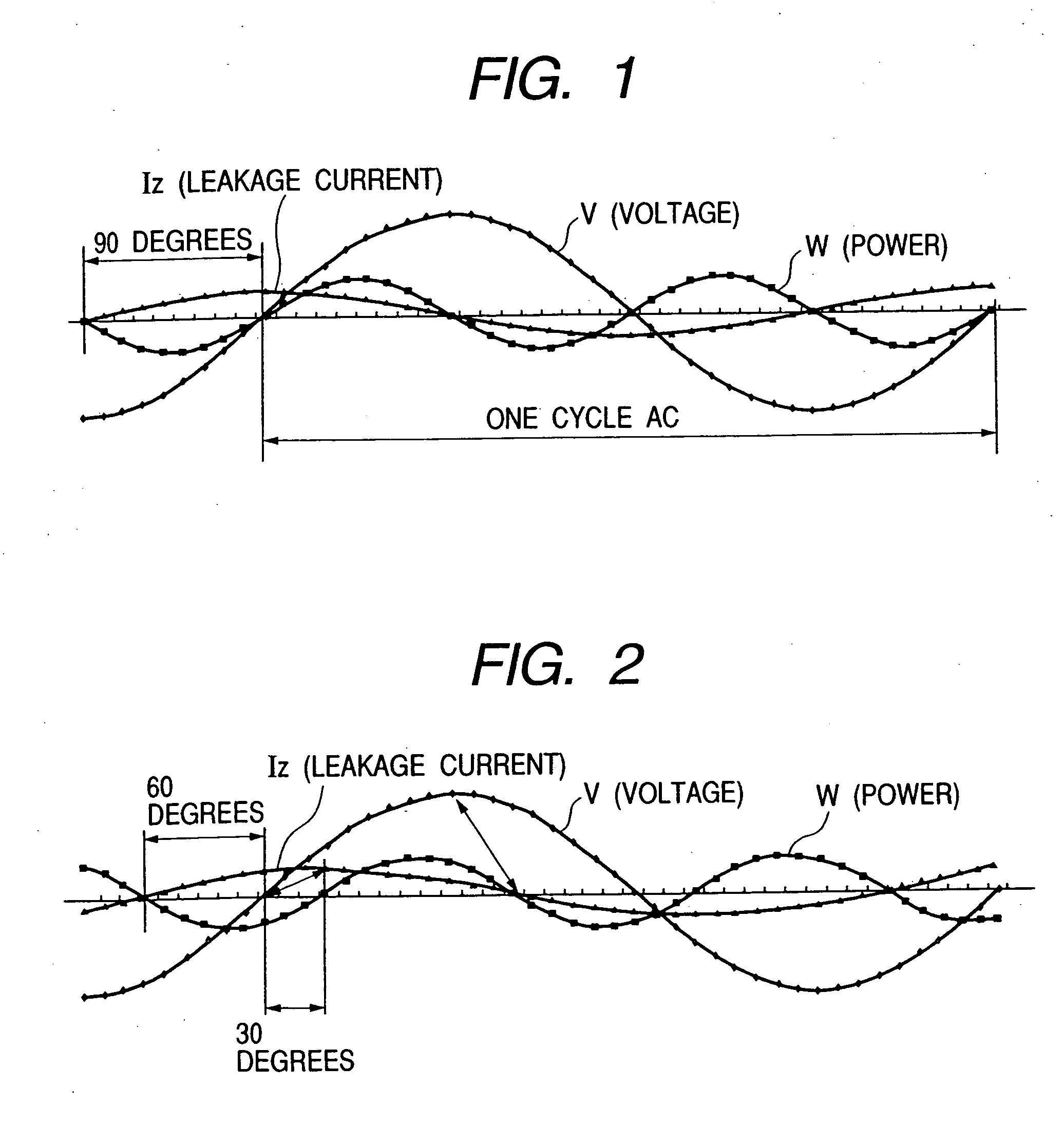
Leakage current or resistance measurement method, and monitoring apparatus and monitoring system of the same
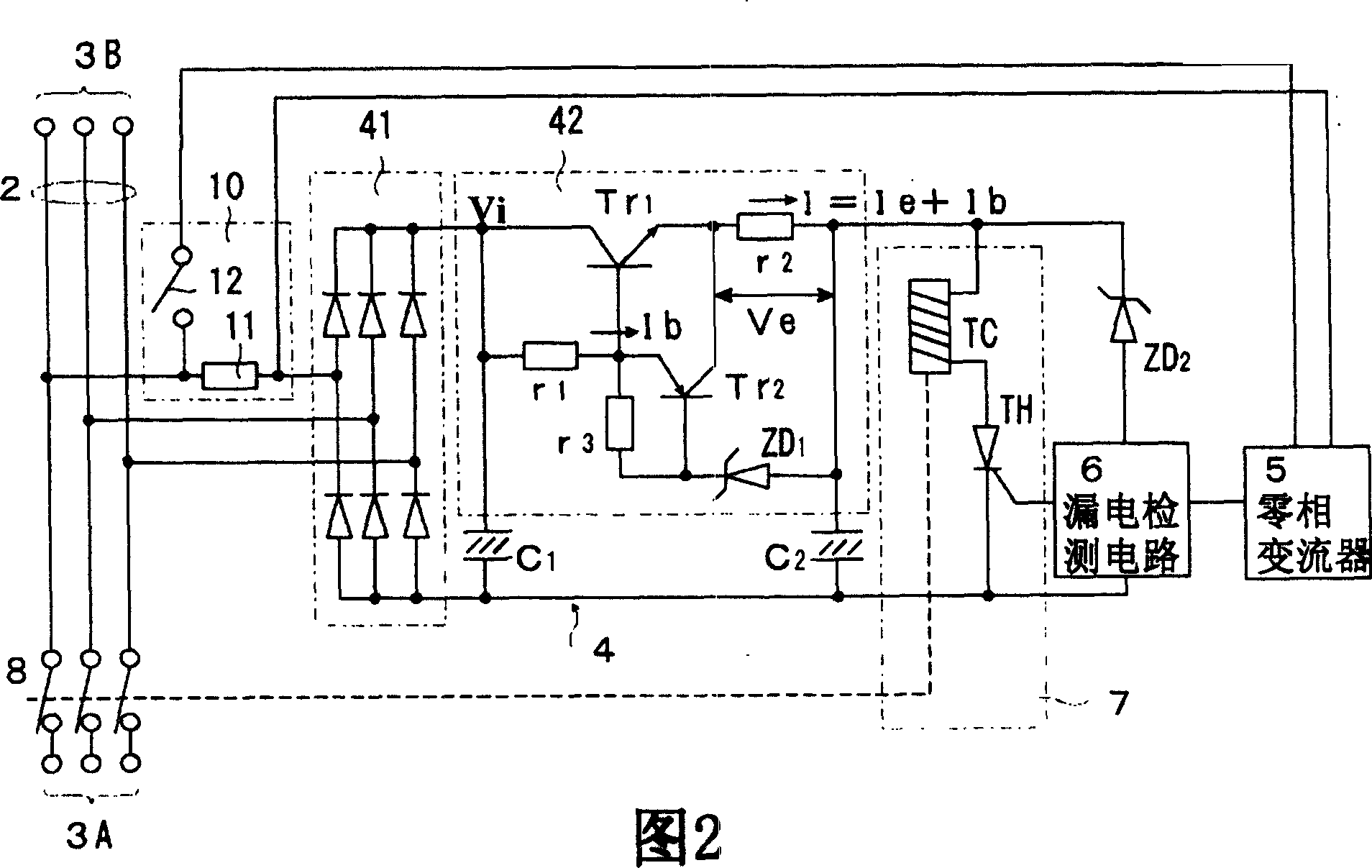
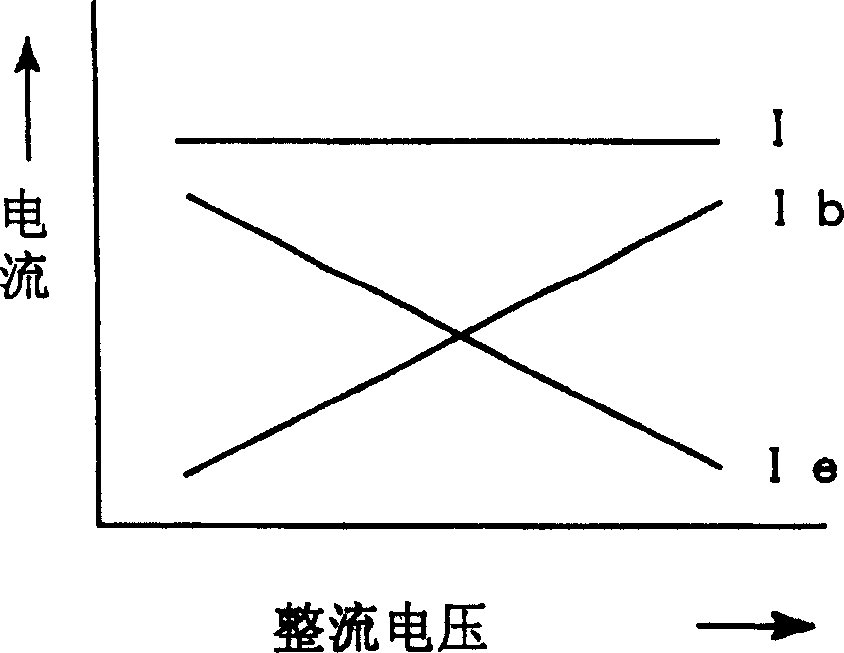
InactiveUS20060020406A1Improve reliabilityAvoid failureCurrent/voltage measurementSpecial data processing applicationsDigital dataEngineering
A measurement method is disclosed for measuring the resistance component leakage current included in the leakage current and the resistance value that is an insulation resistance to monitor the insulation state of a distribution system. The signal waveform of at least one AC cycle is sampled in the resistance component leakage current measurement from the leakage current signal and the voltage signal of a current transformer of target measurement circuit, and the resistance component leakage current is measured by dividing the average of integrated value of the instantaneous leakage current values and the instantaneous voltage values by the square root of average of squared instantaneous voltage values. A zero-cross detecting circuit for detecting a voltage zero-crossing point of the target measurement circuit and outputting a sampling start signal is provided, voltage digital data of the sine wave form whose effective value is 1 and the output signal of the zero-phase current transformer are sampled, and the products of multiplication are averaged by synchronizing the sampled output signal value and the voltage digital data to obtain an active leakage component current of leakage currents.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Residual current circuit breaker
InactiveCN1622414ASmall shapeReduce usageSwitch operated by current/voltage unbalanceSwitch operated by earth fault currentsElectrical resistance and conductanceDc current
The invention discloses a leakage circuit breaker which has a simple and small structure of a test circuit and can simultaneously perform accurate leakage tests. As a power supply circuit for supplying power to the leakage detection circuit in the leakage circuit breaker, a power supply circuit with a constant current circuit that converts the AC current supplied from the main circuit into a DC current and supplies a constant DC current to the leakage detection circuit is used, and the test resistance The elements are arranged in series in the circuit connecting the main circuit and the AC input end of the current stabilizing circuit, and the test coil of the zero-phase converter is connected to both ends of the resistance element through a test switch to form a leakage test circuit.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC FA COMPONENTS & SYST CO LTD
Power feed control device
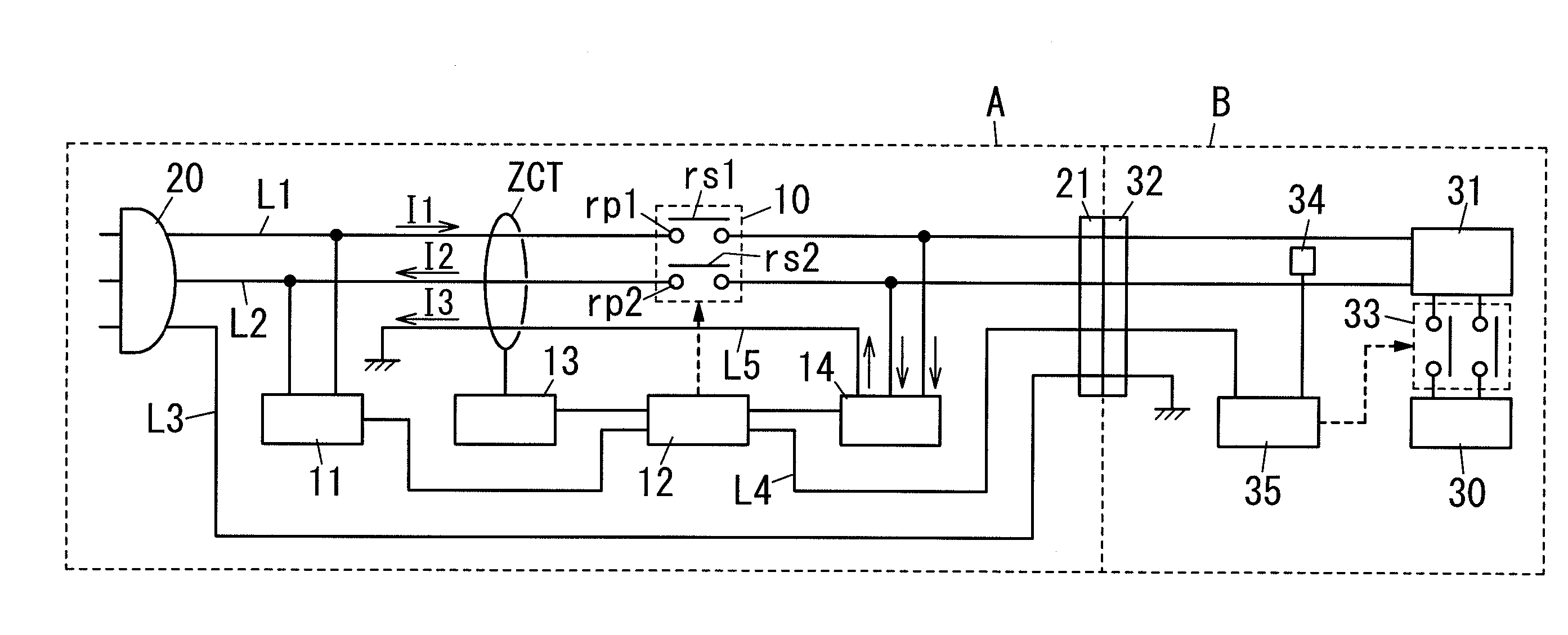
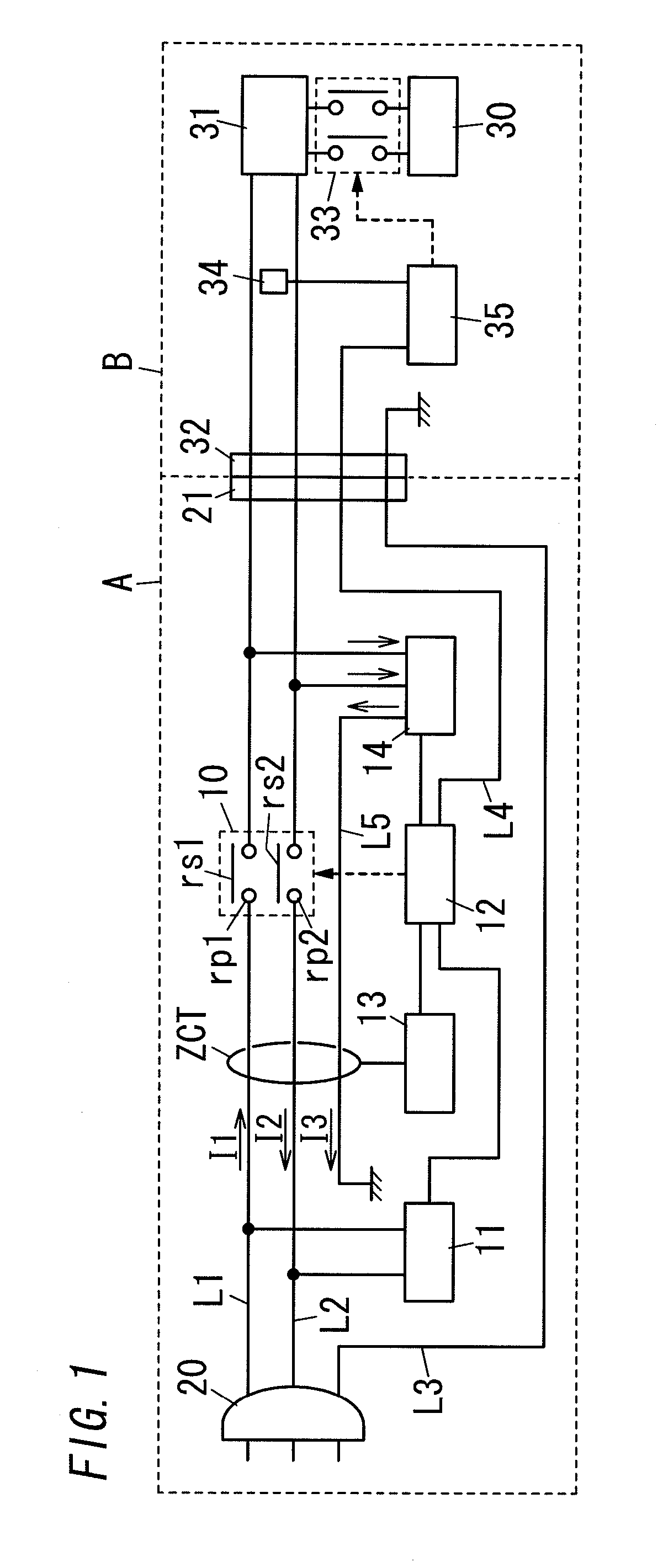
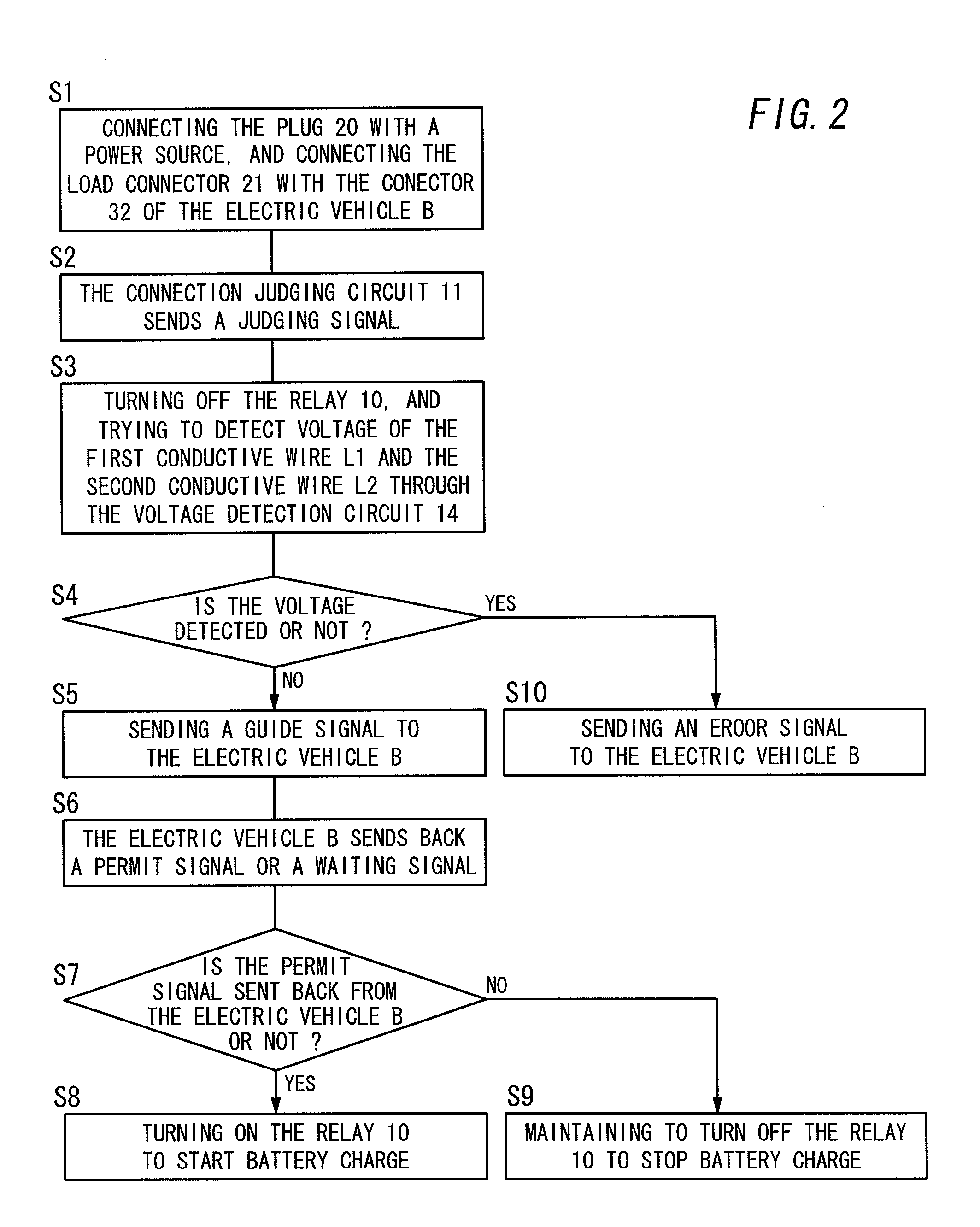
ActiveUS20110122536A1Accurately detect occurrenceAccurate detectionCharging stationsElectric devicesZero phaseEngineering
A branch wire L5 from the voltage detection circuit 14 is inserted in the zero-phase-sequence current transformer ZCT in the direction from the load side to the external power supply side. For this configuration, the zero-phase-sequence current transformer ZCT is to detect unbalance of the sum of current flowing in the first and second conductive wires L1, L2 and the current flowing in the branch wire L5. Therefore, the present invention can accurately detect occurrence of electrical leakage.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Gas ultrasonic flowmeter intermittent excitation and signal processing method and system based on adjacent peak maximum difference value
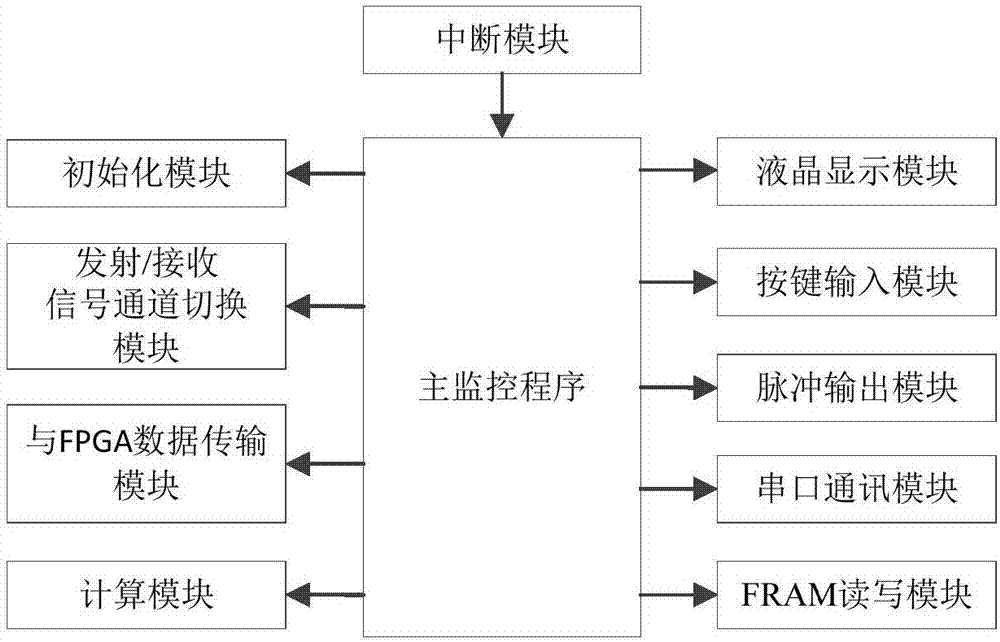
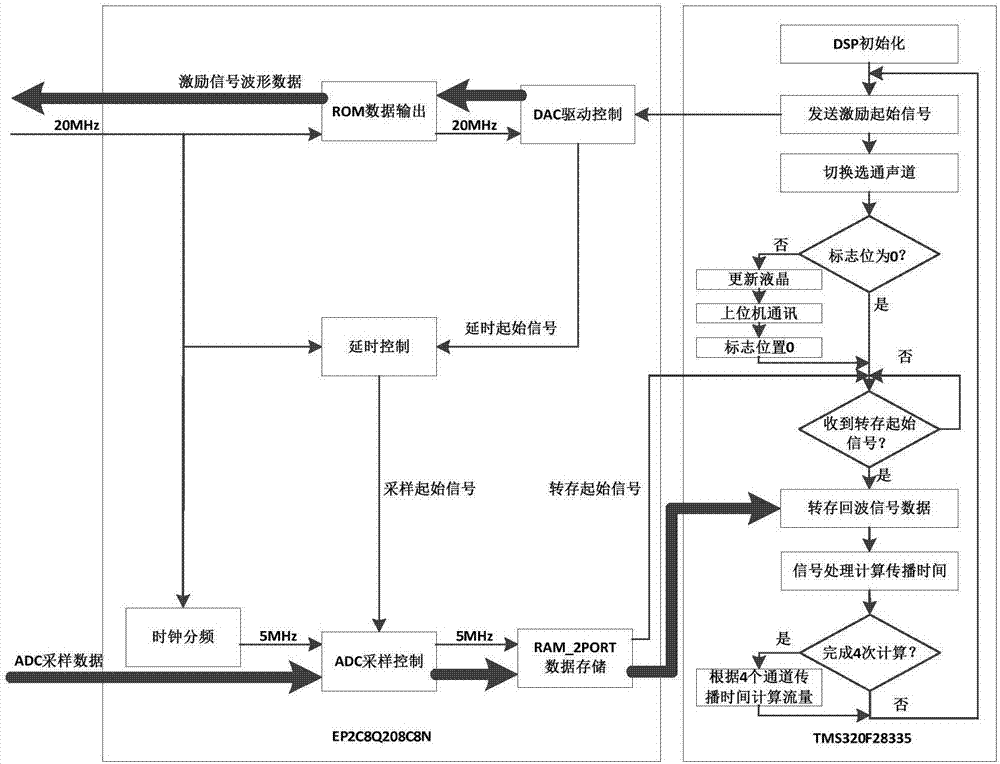
Disclosed is a gas ultrasonic flowmeter intermittent excitation and signal processing system based on an adjacent peak maximum difference value. An ultrasonic transmitting transducer is excited through intermittent excitation signals (continuous non-coding excitation signals are transmitted one time, and then transmitted again after a certain period of time), and an ultrasonic signals are generated; when a receiving transducer receives ultrasonic signals, the signals are converted into echo signals; then, zero phase filtering is performed on the received echo signals, a characteristic wave corresponding to the maximum difference value of adjacent peaks in the echo signals is found, a mean value of eight zero crossing points behind the characteristic waves is adopted as a characteristic point, ultrasonic signal down flow and reverse flow transmitting time is determined, and the gas flow is calculated.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Boring, milling machine primed by straight-line driven portal shaped in zero phase on beam of magnetic suspension
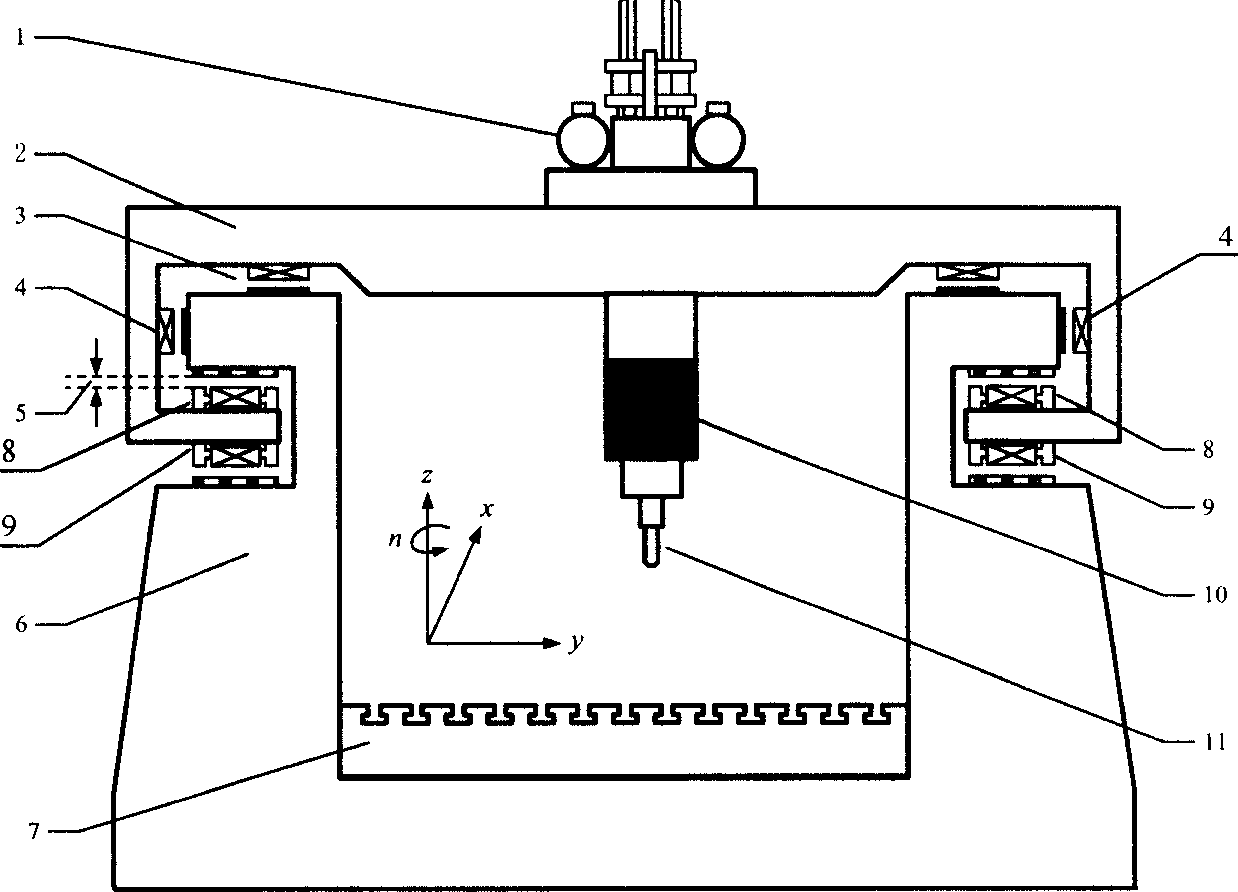
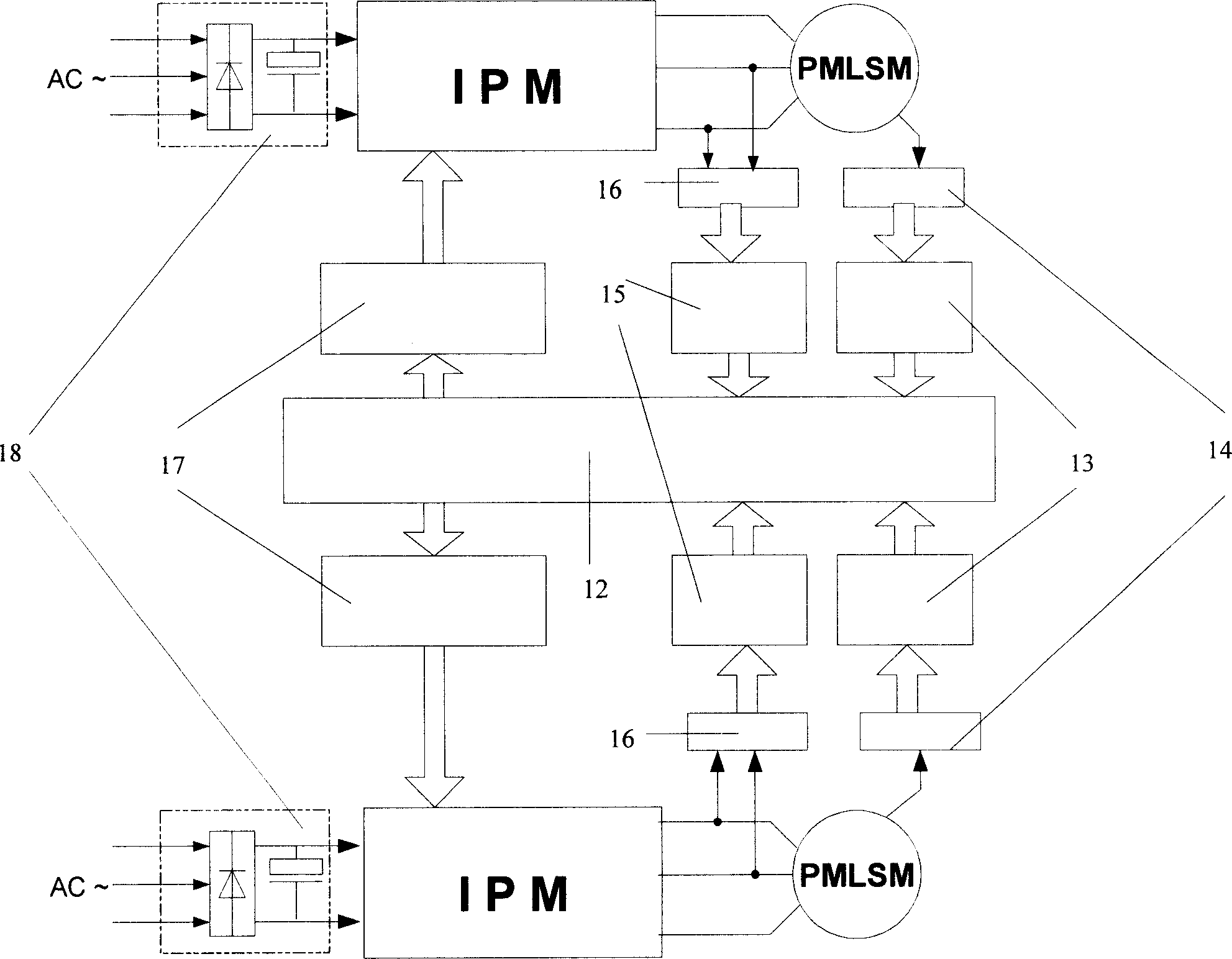
InactiveCN1915587AFast and accurate traceabilityImprove robustnessOther manufacturing equipments/toolsControl using feedbackMotor driveSynchronous control
A movable boring-milling machine is composed of a magnetically suspended transverse beam, a straight-line motor driven gantry, movable machine-tool and control circuit unit including the control circuit for the synchronous drive of dual straight-line motos and the control circuit for controlling the height of transverse beam. Its control method includes the synchronous control to dual straight-line motor by improved master-slave synchronous drive, and controlling the suspended height of said transverse beam.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
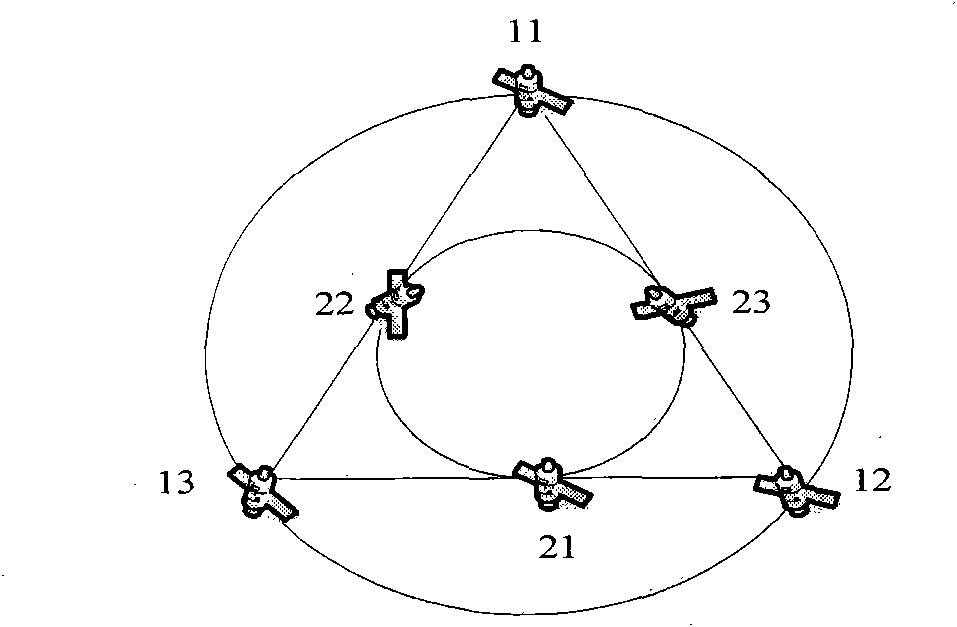
Low-orbit/middle-orbit double-layer satellite optical network structure system and design calculation method
InactiveCN101604996ATopologically stableSimplified routingElectromagnetic network arrangementsZero phaseNetwork structure
The invention discloses a low-orbit / middle-orbit double-layer satellite optical network structure system. Global coverage low-orbit satellite constellation designed on the basis of a coverage zone method and middle-orbit satellite constellation form a double-layer satellite optical network structure system. The system is connected with at least 76 satellites, wherein, a low-orbit satellite layer is provided with at least 7 orbits, and each orbit is connected with at least 10 satellites; a middle-orbit satellite layer is composed of an outer orbit and an inner orbit, wherein, the outer orbit is respectively connected with the satellites, and the inner orbit is respectively connected with the satellites. The calculation method is as follows: calculating the radius theta of a single satellite covering circle; calculating the halfangle psi of the covering zone; calculating delta B; calculating alpha'; calculating sin alpha; and calculating the distribution of P orbits on the equator. The structure is stable topological structure, the changes of inter-satellite links pitch angle and azimuth angle are smaller than the changes of the inter-satellite links pitch angle and the azimuth angle of the non-zero phase constellation, satellite switch is reduced, satellite-carried resources are saved, and management of the low-orbit satellite layer is effectively strengthened; the middle-orbit satellite constellation is least affected by space radiation, and the system life cycle is lengthened.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Electric leak breaker for self-test
InactiveUS20050243484A1Avoid inconvenienceEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEmergency protection for supplying operative powerLow voltageZero phase
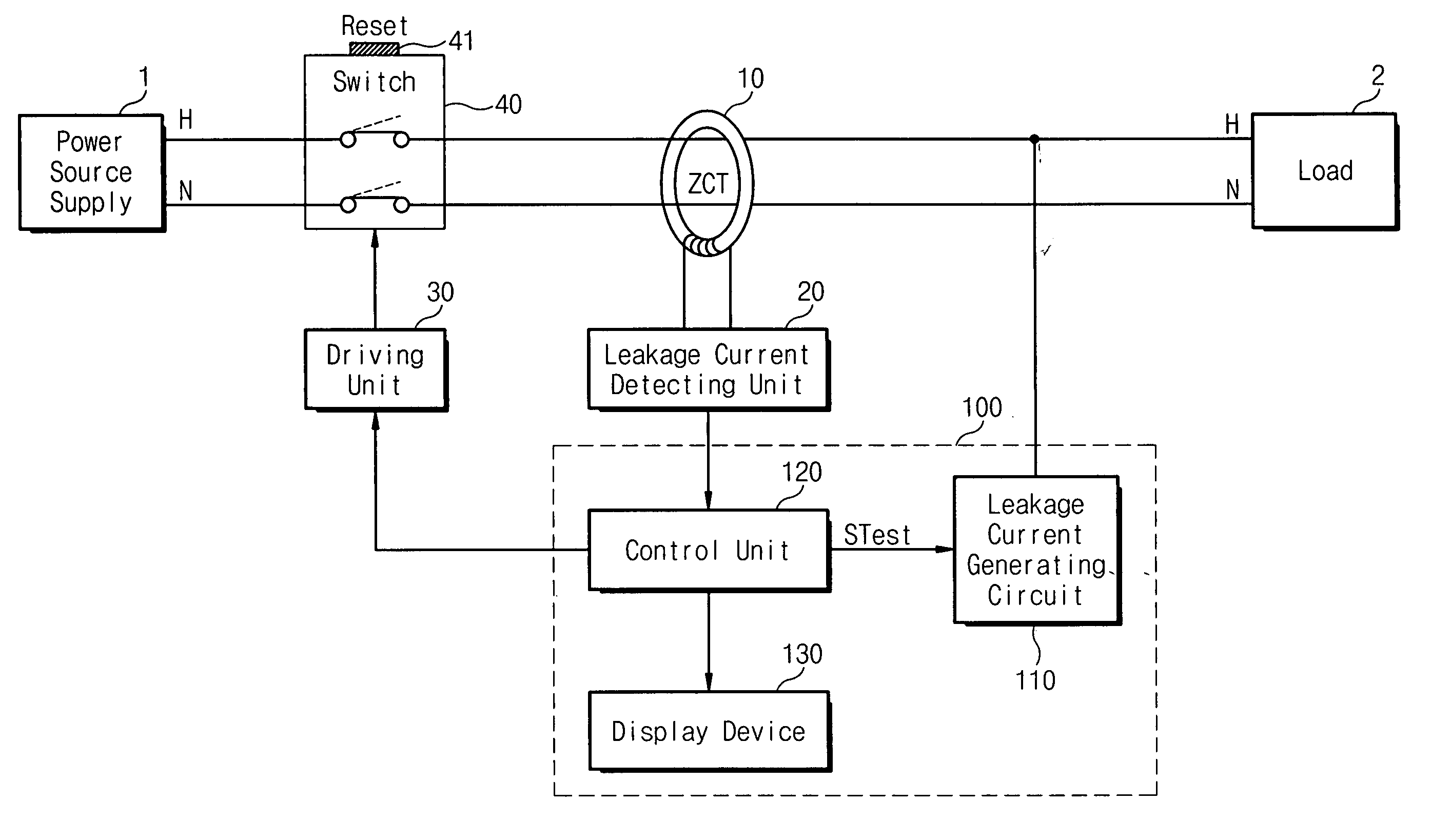
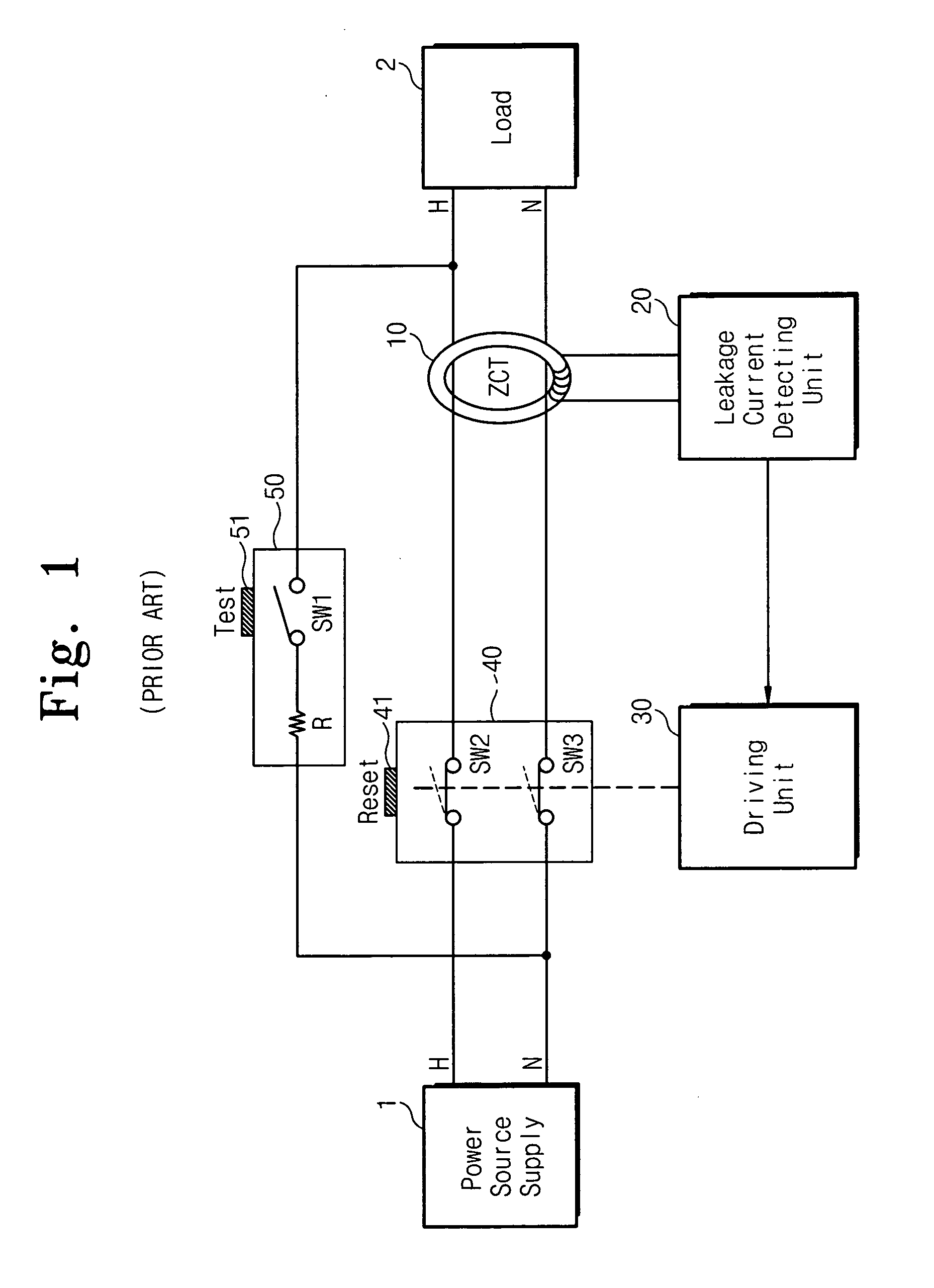
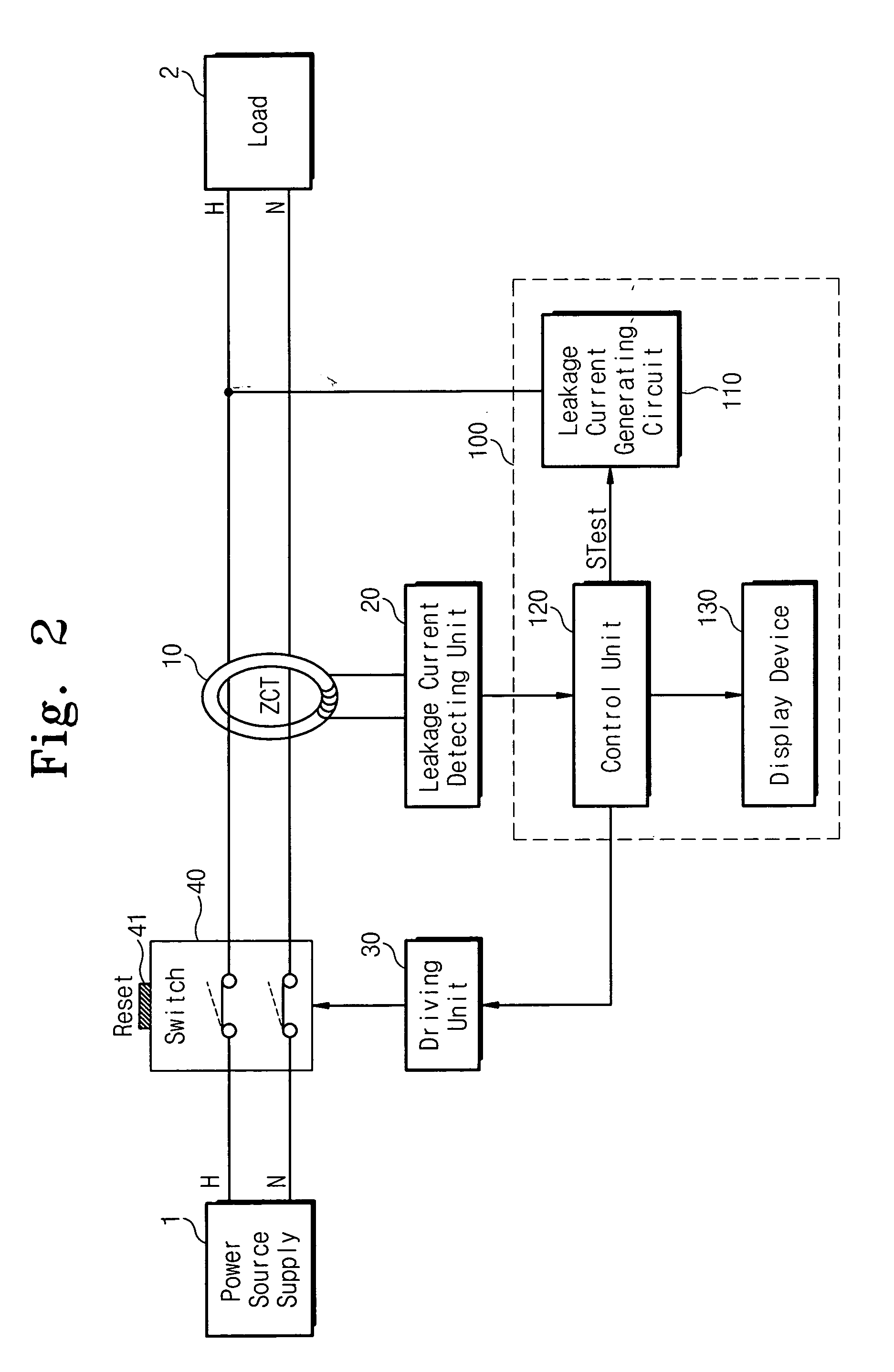
The present invention disclosed herein is an electric leak breaker for self-test. The electric leak breaker for self-test comprises power supply lines for connecting a power source supply with a load; a zero-phase current transformer installed on the power supply lines and for sensing a current difference between the power supply lines; a leakage current detecting unit connected to the zero-phase current transformer for detecting whether a leakage current occurs to generate a detection signal; a driving unit for making the power supply lines broken when a critical voltage or a voltage higher than the critical voltage is provided; and a self-test unit for periodically inducing the leakage current at the power supply lines to test whether the leakage detecting unit is normally operating, and for providing a lower voltage than the critical voltage to the driving unit to test whether the driving unit is normally operating in a self-test operation. According to the present invention, it is possible to periodically test the electric leak breaker as well as to overcome an inconvenience to push a reset button.
Owner:CHE IL ELECTRIC WIREING DEVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com