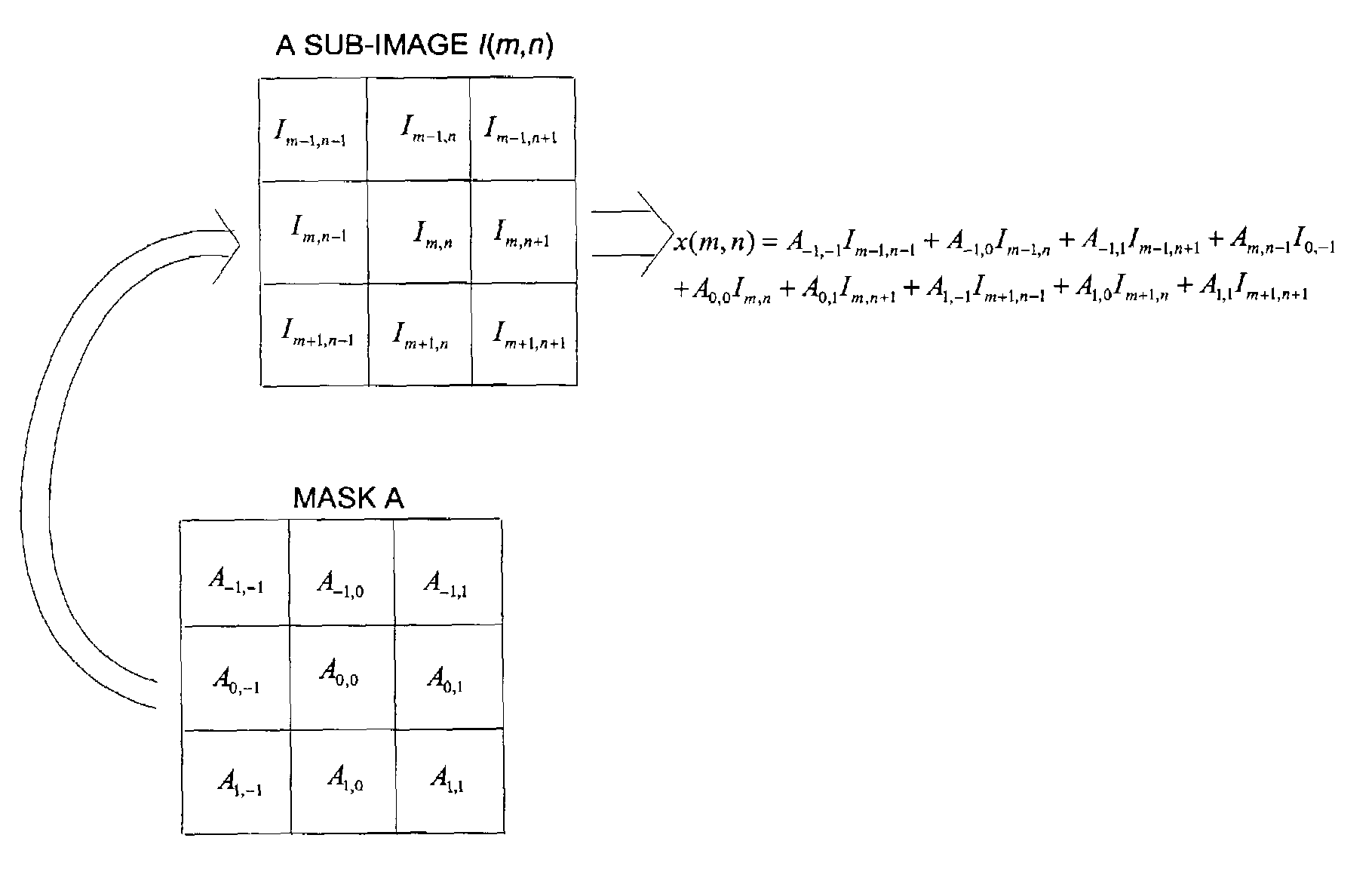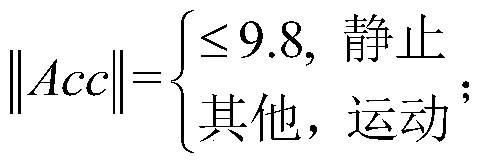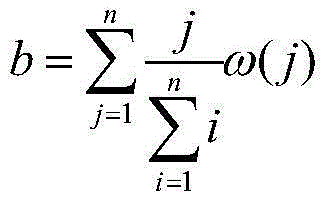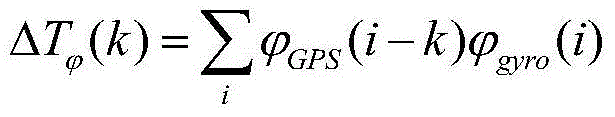Patents
Literature
356 results about "Average filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
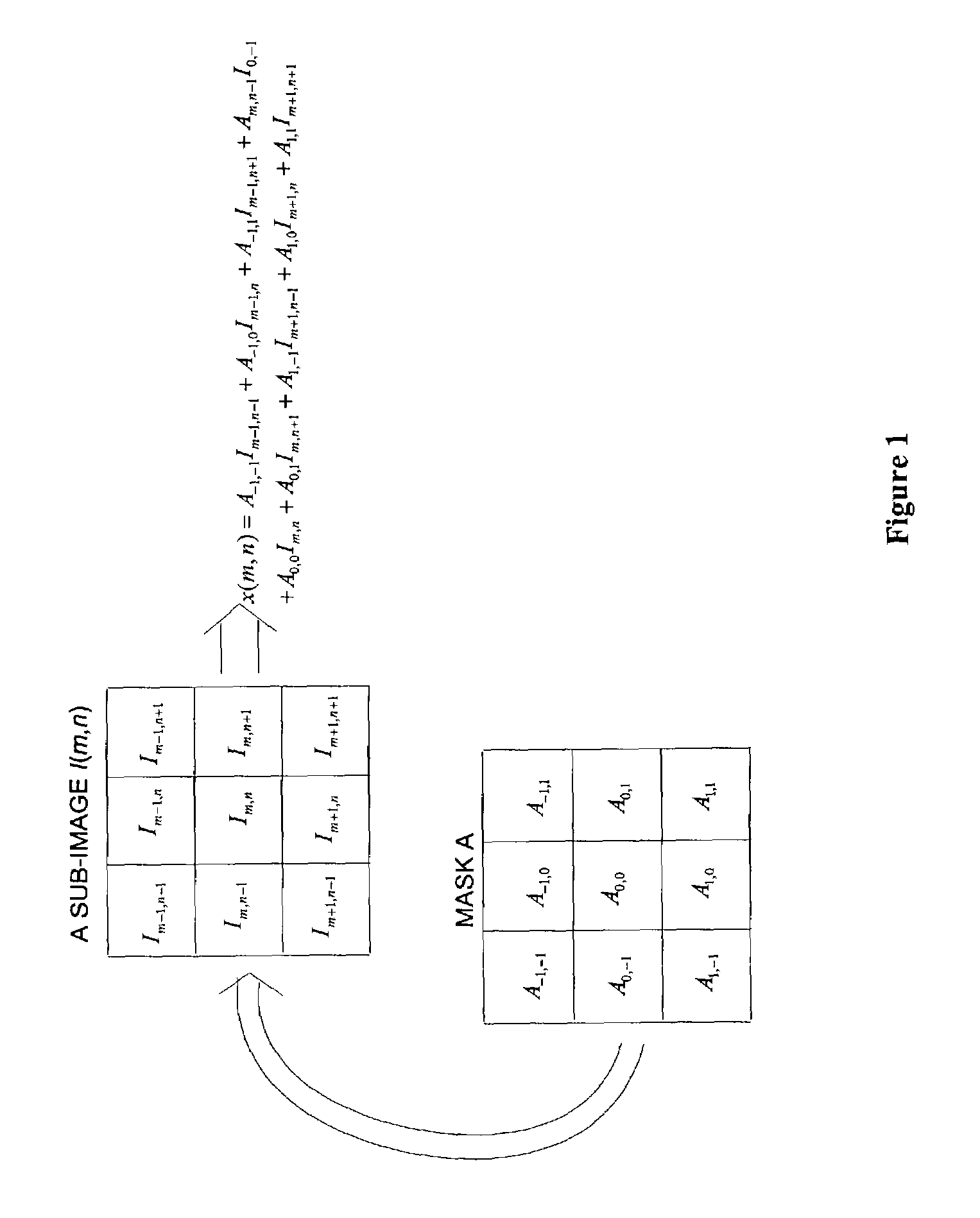
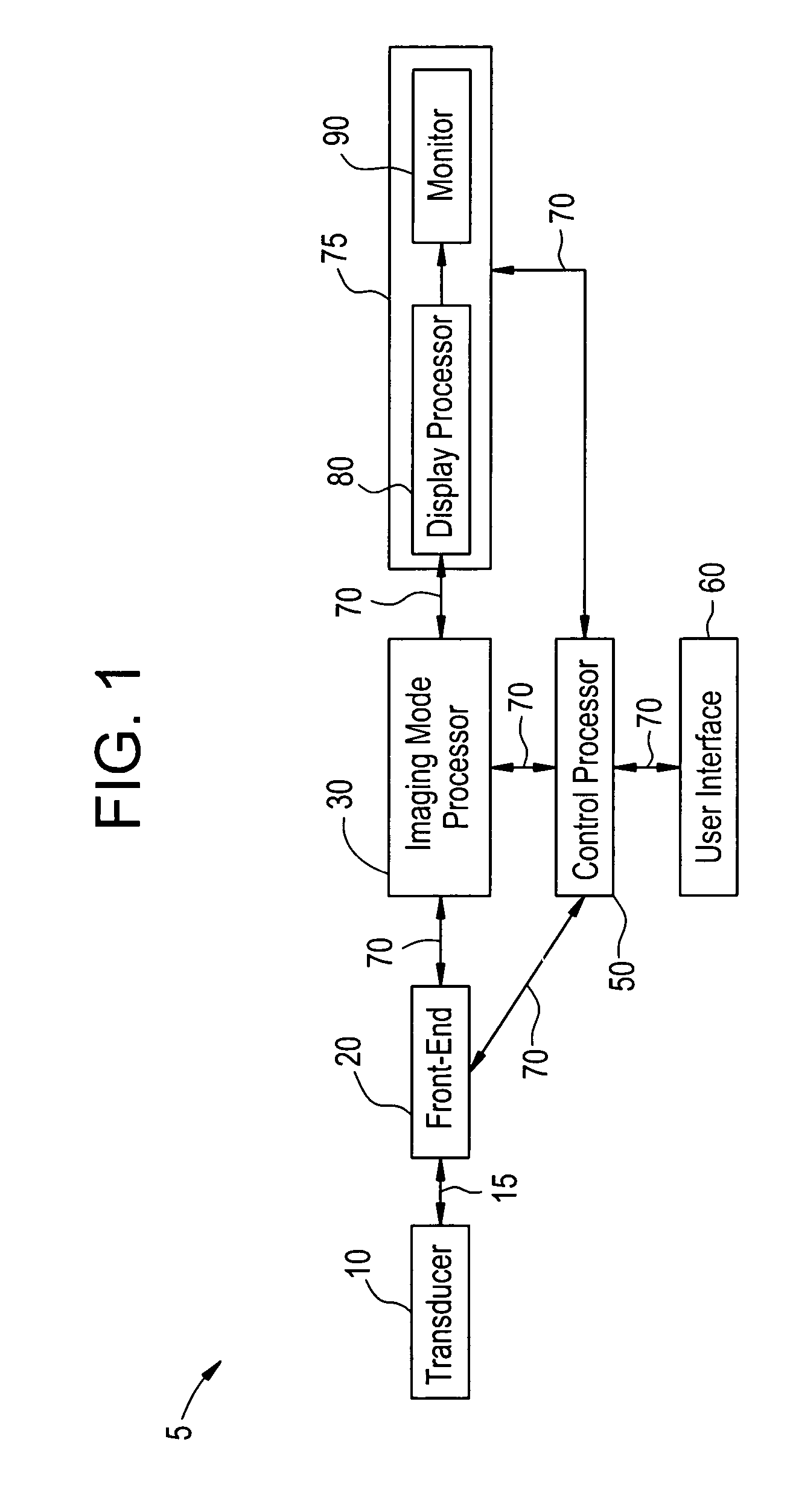
Color imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20120293695A1Accurate estimateSuppress generationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageAverage filter
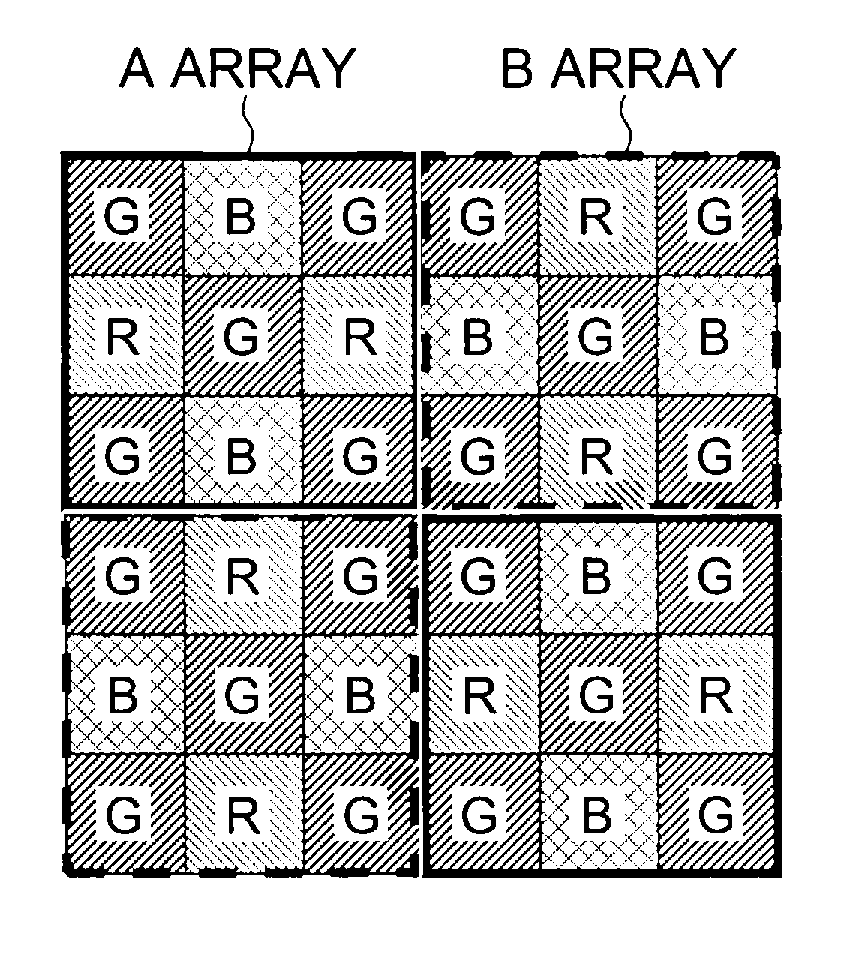
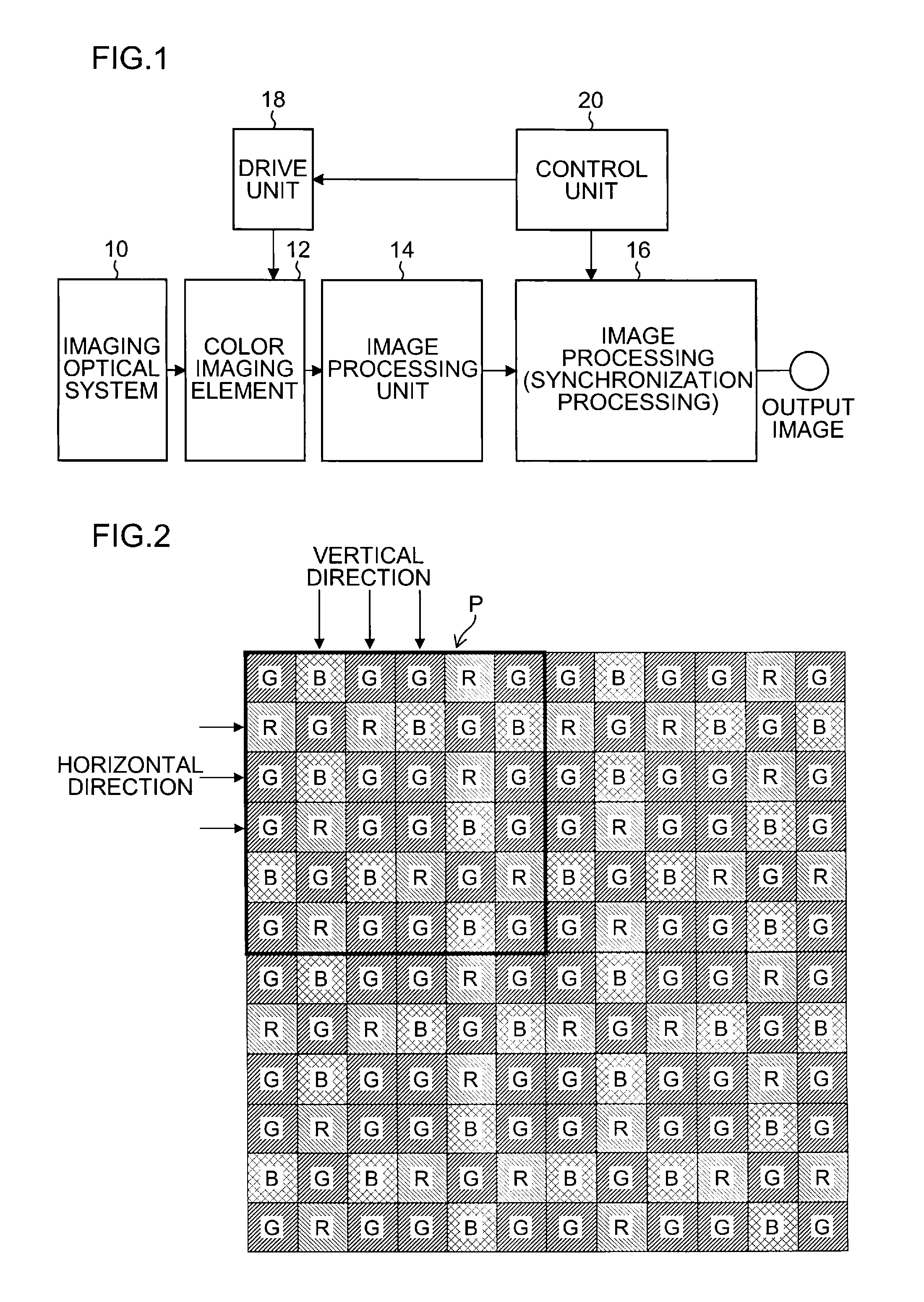
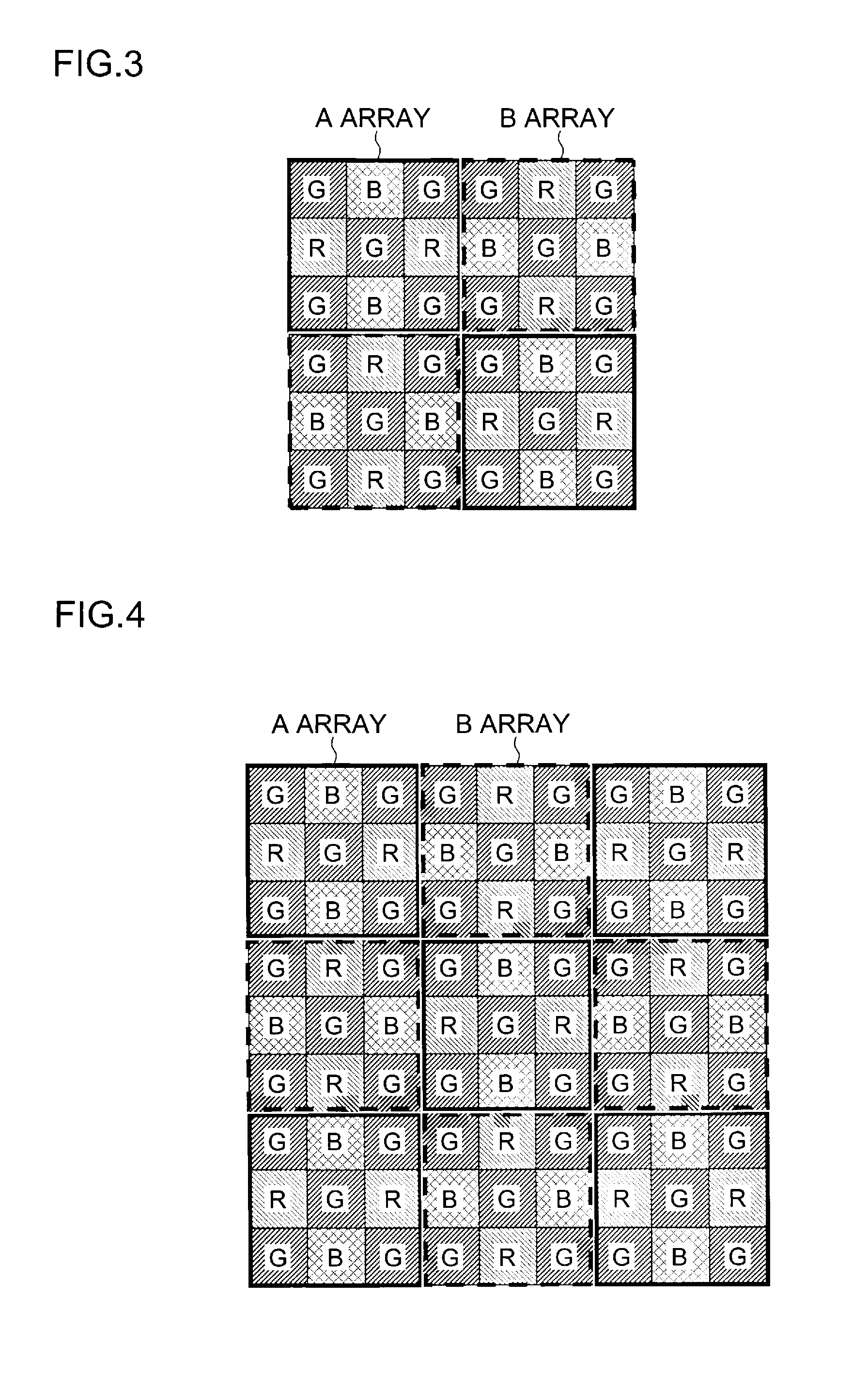
A color imaging apparatus comprising: a single-plate color imaging element including color filters arranged on pixels arranged in horizontal and vertical directions where all colors are arranged in each line in the directions; weighted average filters with filter coefficients set in a local area extracted from a mosaic image acquired from the color imaging element corresponding to the weighted average filters so that proportions of sums of the filter coefficients of each color in the lines in the horizontal and vertical directions are equal; a weighted average calculation unit that calculates weighted average values of each color; a demosaicking processing unit that calculates a pixel value of another color at a pixel position of a target pixel of demosaicking processing and that interpolates a pixel value of the target pixel based on a color ratio or a color difference of the calculated weighted average values to calculate the pixel value.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Perception-based image retrieval
InactiveUS6865302B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalAverage filterPattern perception
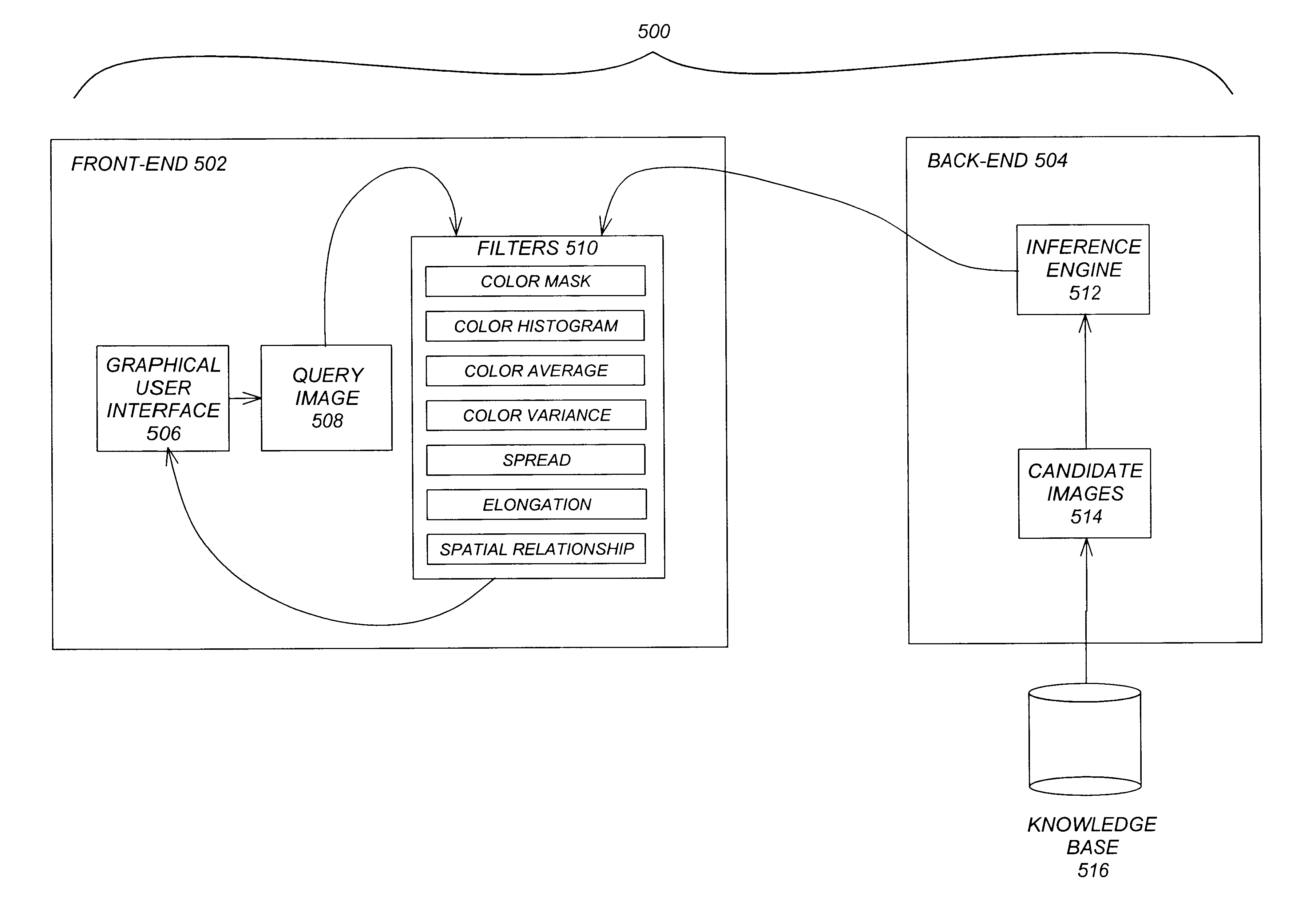
A content-based image retrieval (CBIR) system has a front-end that includes a pipeline of one or more dynamically-constructed filters for measuring perceptual similarities between a query image and one or more candidate images retrieved from a back-end comprised of a knowledge base accessed by an inference engine. The images include at least one color set having a set of properties including a number of pixels each having at least one color, a culture color associated with the color set, a mean and variance of the color set, a moment invariant, and a centroid. The filters analyze and compare the set of properties of the query image to the set of properties of the candidate images. Various filters are used, including: a Color Mask filter that identifies identical culture colors in the images, a Color Histogram filter that identifies a distribution of colors in the images, a Color Average filter that performs a similarity comparison on the average of the color sets of the images, a Color Variance filter that performs a similarity comparison on the variances of the color sets of the images, a Spread filter that identifies a spatial concentration of a color in the images, an Elongation filter that identifies a shape of a color in the images, and a Spatial Relationship filter that identifies a spatial relationship between the color sets in the images.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
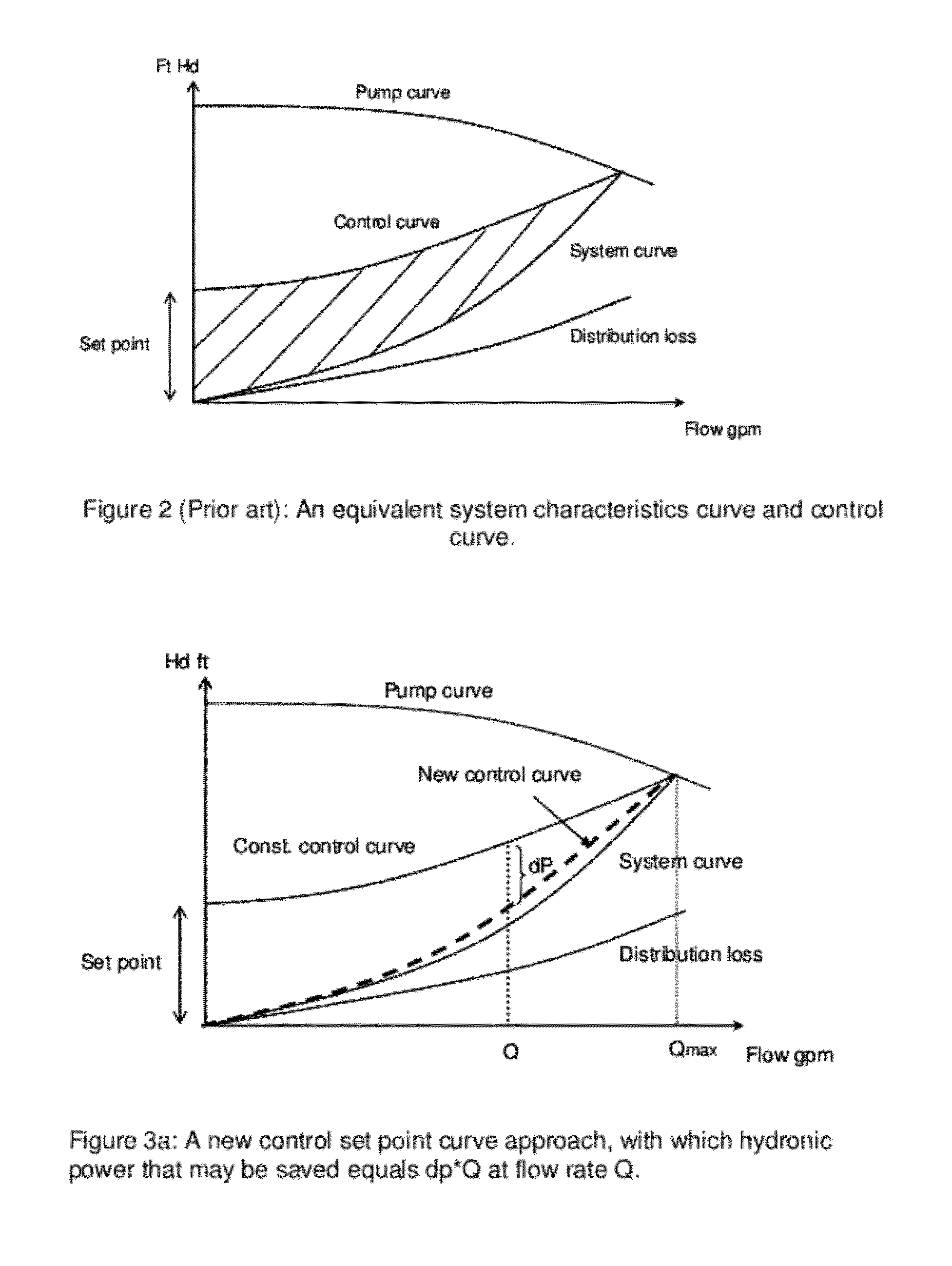
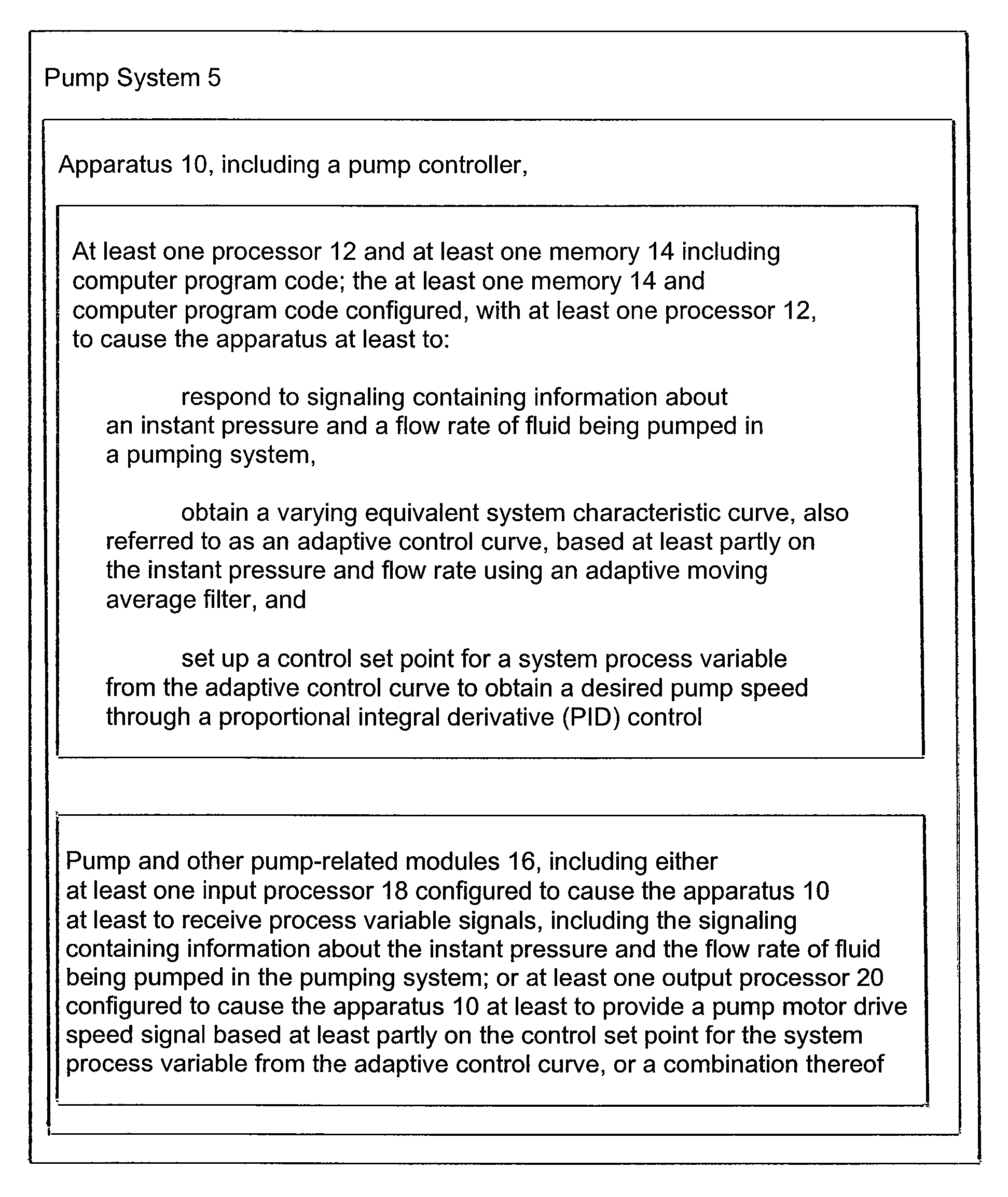
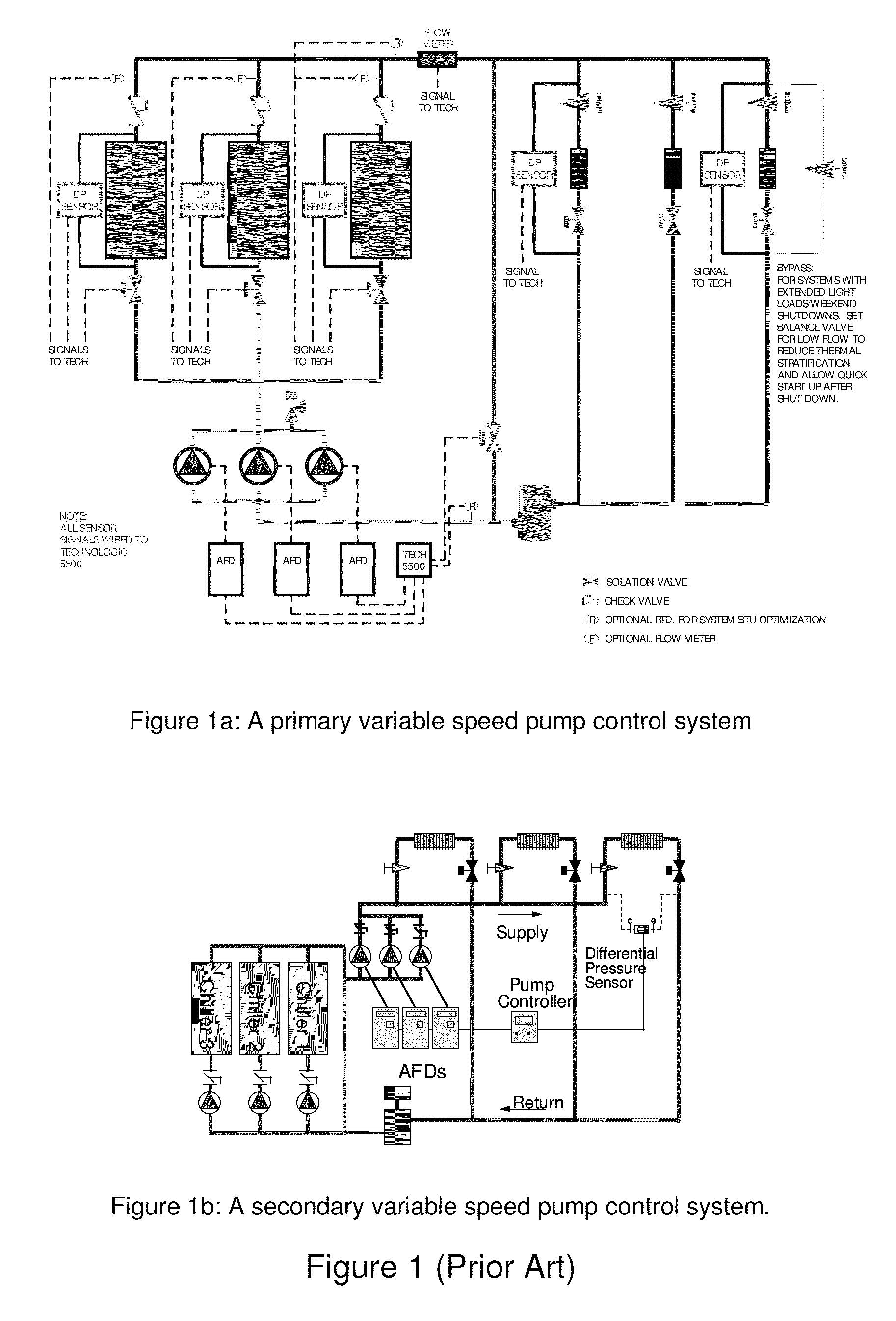
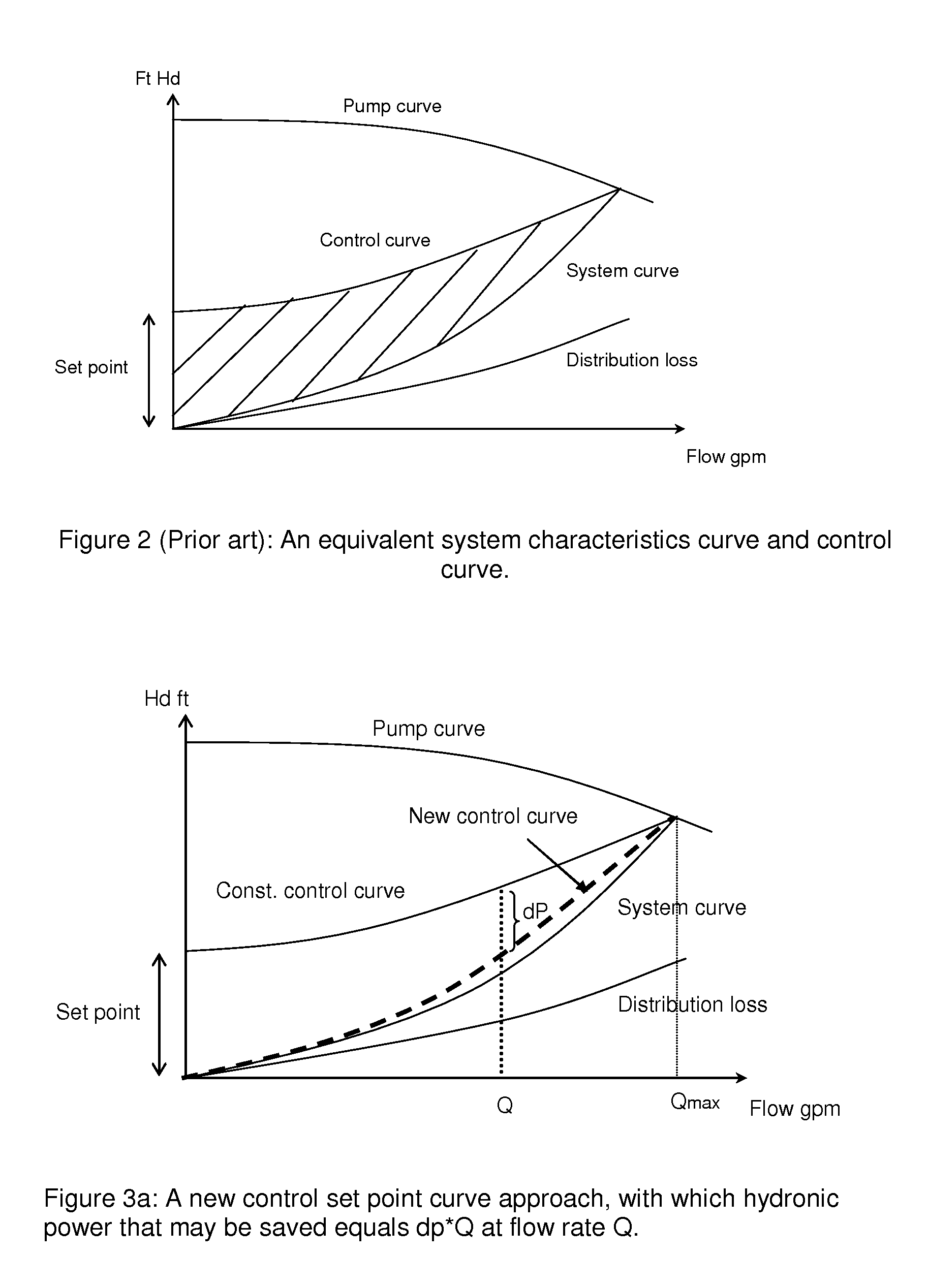
Method and Apparatus for Pump Control Using Varying Equivalent System Characteristic Curve, AKA an Adaptive Control Curve
ActiveUS20120173027A1Reduce energy consumptionReduce operating costsFlow control using electric meansFluid pressure control using electric meansMoving averageAverage filter
The present invention provides, e.g., apparatus comprising at least one processor; at least one memory including computer program code; the at least one memory and computer program code being configured, with at least one processor, to cause the apparatus at least to: respond to signaling containing information about an instant pressure and a flow rate of fluid being pumped in a pumping system, and obtain an adaptive control curve based at least partly on the instant pressure and flow rate using an adaptive moving average filter. The adaptive moving average filter may be based at least partly on a system flow equation: SAMAt=AMAF(Qt / √{square root over (ΔPt)}), where the function AMAF is an adaptive moving average filter (AMAF), and the parameters Q and ΔP are a system flow rate and differential pressure respectively. The at least one memory and computer program code may be configured to, with the at least one processor, to cause the apparatus at least to obtain an optimal control pressure set point from the adaptive control curve with respect to an instant flow rate or a moving average flow rate as SPt=MA(Qt) / SAMAt, where the function MA is a moving average filter (MA), to obtain a desired pump speed through a PID control.
Owner:FLUID HANDLING
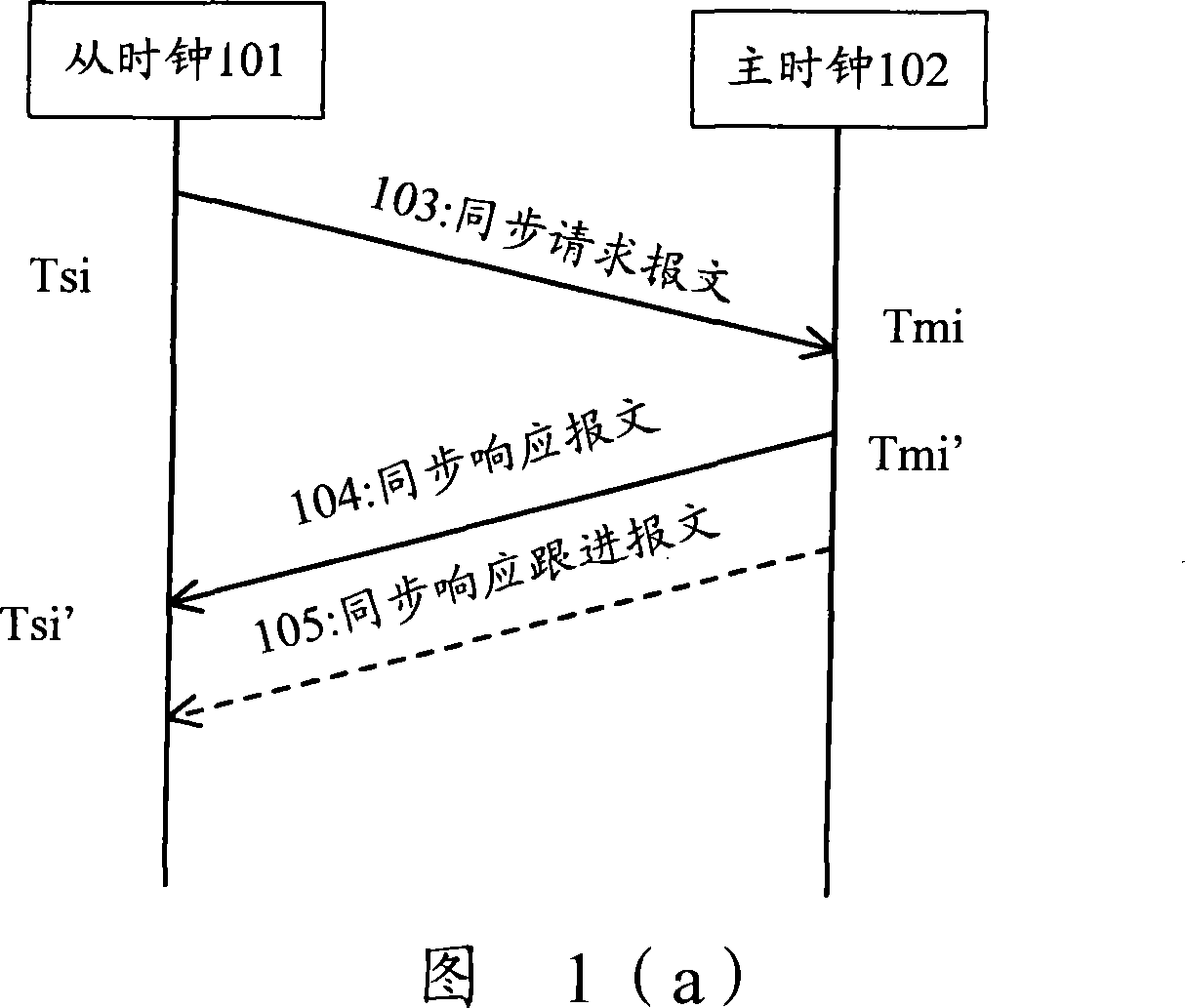
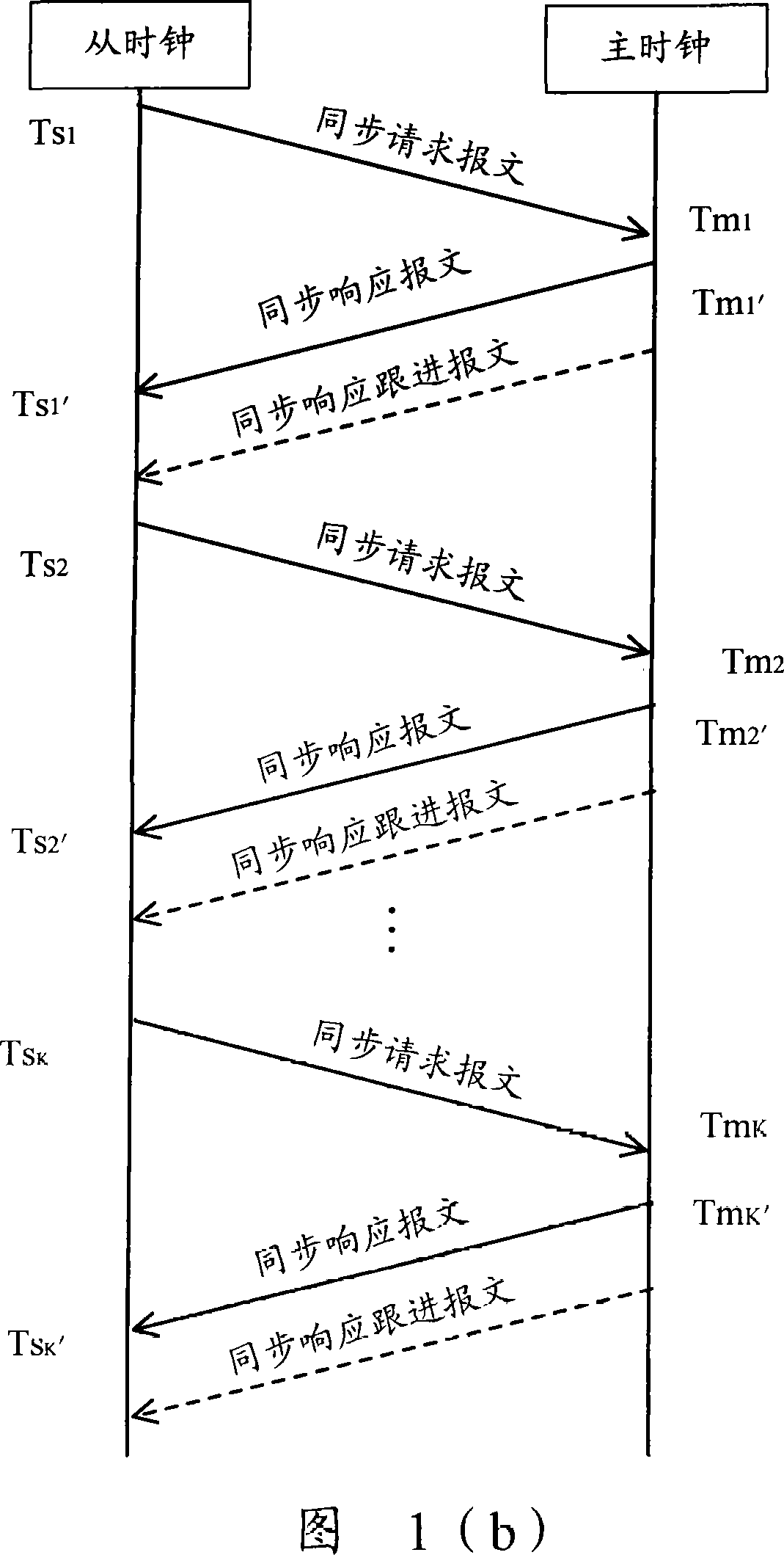
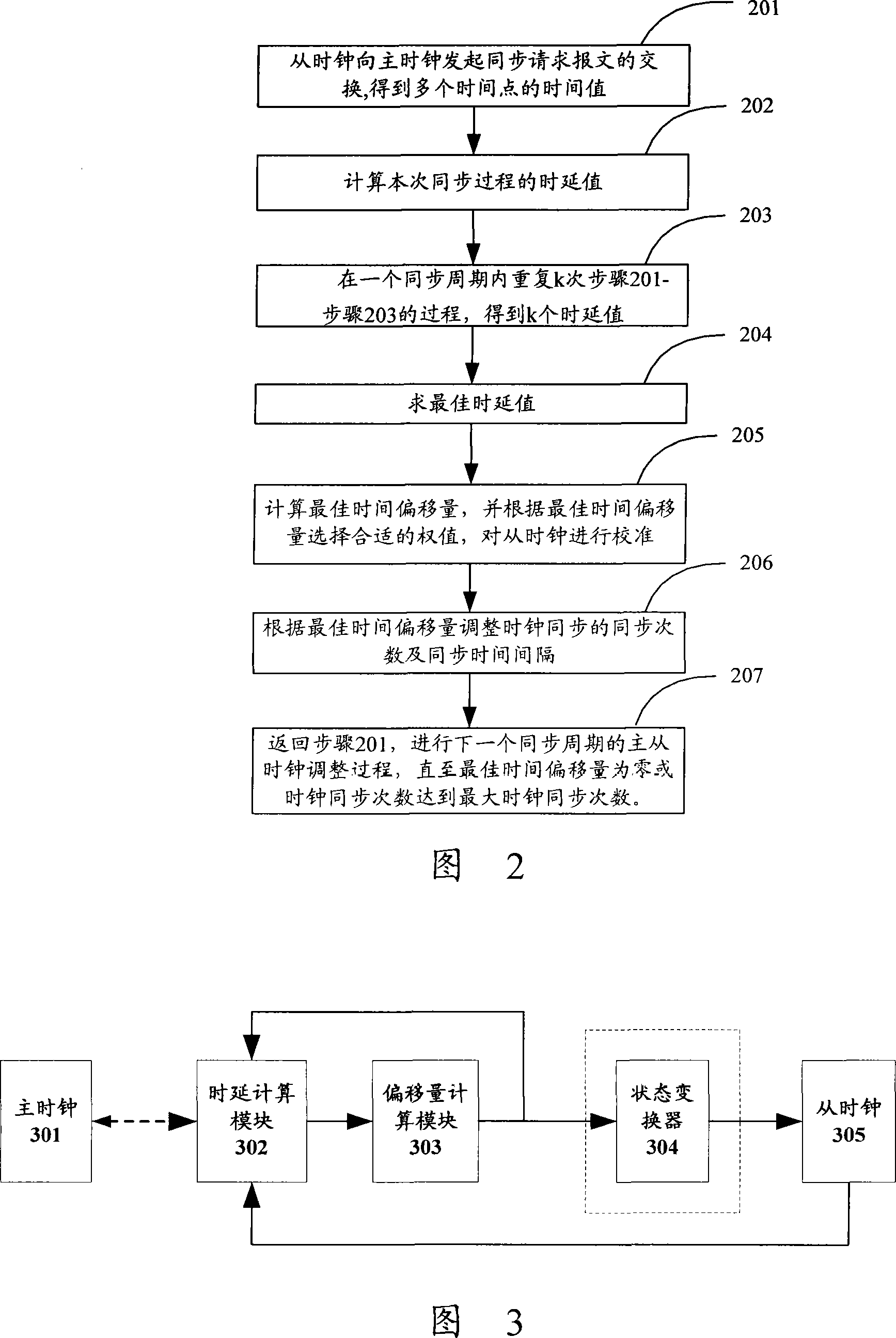
Method and apparatus for master-salve clock synchronization
InactiveCN101227246AEliminate delay errorsHigh synchronization accuracyTime-division multiplexTransmissionAverage filterSlave clock
The invention discloses a method and a device for synchronizing a master clock and a slave clock, the method comprises: sending synchronous request message to the master clock for many times in a simultaneous cycle by the slave clock, recording the corresponding the time value, then, utilizing a median average filtering algorithm to obtain the optimum time migration amount, utilizing the time migration amount to adjust the slave clock, eliminating the delay inequality which is caused by stochastic disturbance and burst interference of a network communication channel between the master clock and the slave clock, guaranteeing the stability of slave clock signals, and increasing the synchronous preciseness of the master clock and the slave clock.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Reduction of moiré in screened images using hierarchical edge detection and adaptive-length averaging filters
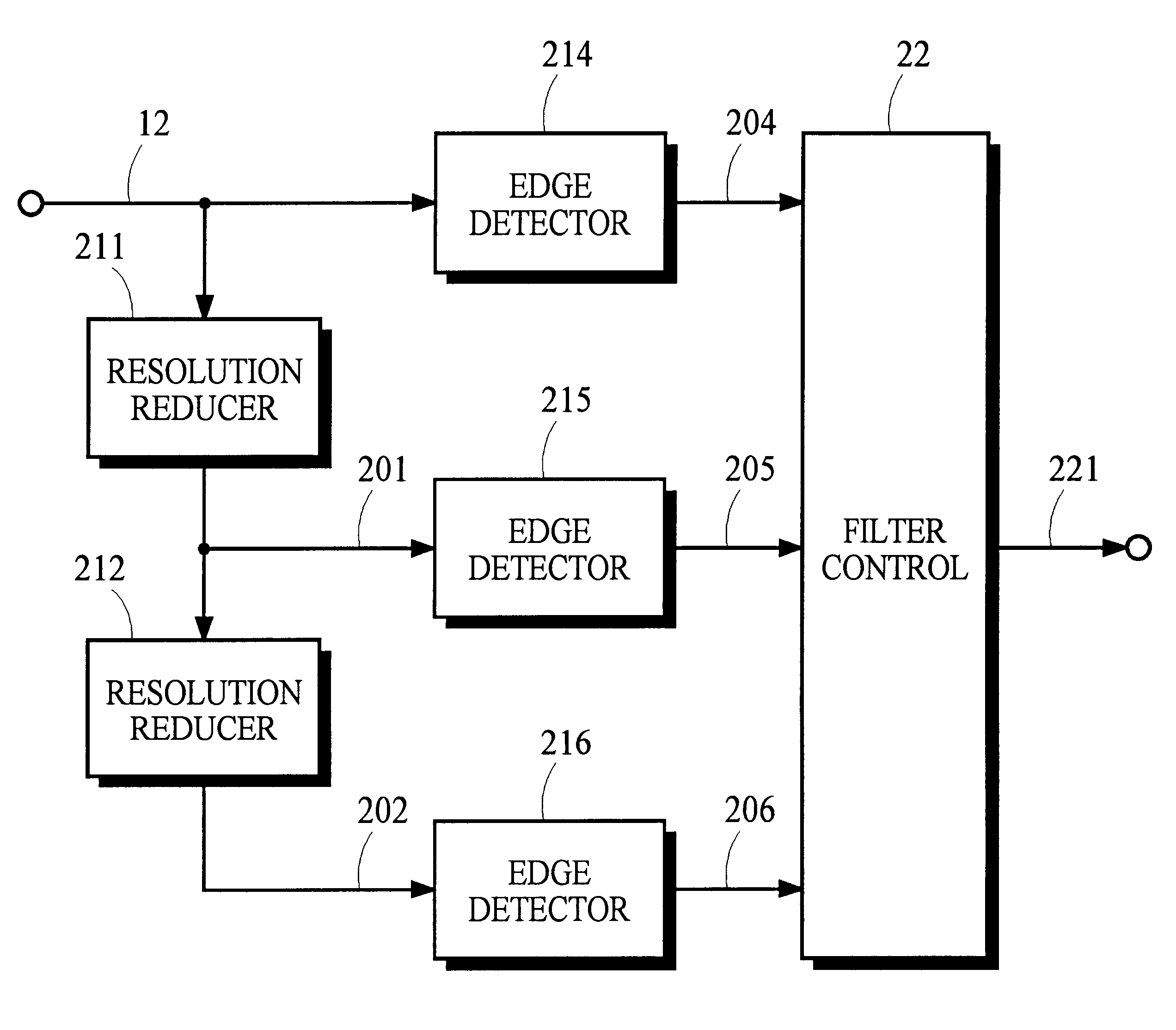
InactiveUS6233060B1Modest and memory resourceLow-cost implementationImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersAverage filterImage resolution
In an image reproduction system, an image processor analyzes a hierarchy of image representations of different resolutions to detect edges. In regions having edges that are detected in all hierarchical representations, little or no filtering is applied to the image. In regions having no edges or edges that are detected in only the highest-resolution representation, greater amounts of filtering are applied to the image. In regions having edges detected in two or more but not all hierarchical representations, an intermediate amount of filtering is applied to the image. In preferred embodiments, two-dimensional averaging filters of varying size are applied to the image. The size of the averaging filter is selected according to the number of hierarchical representations in which an edge is detected.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
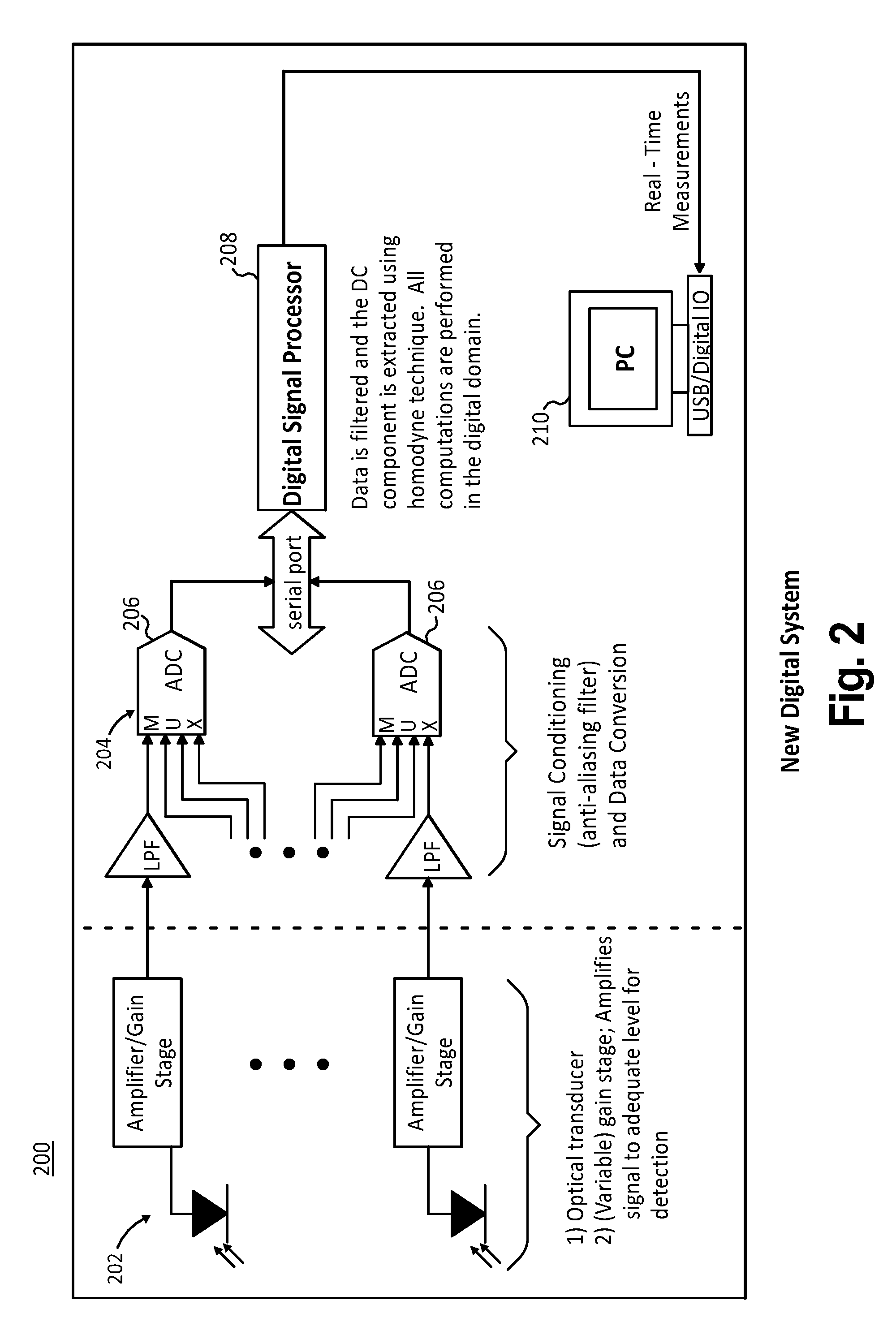
Digital signal processor-based detection system, method, and apparatus for optical tomography
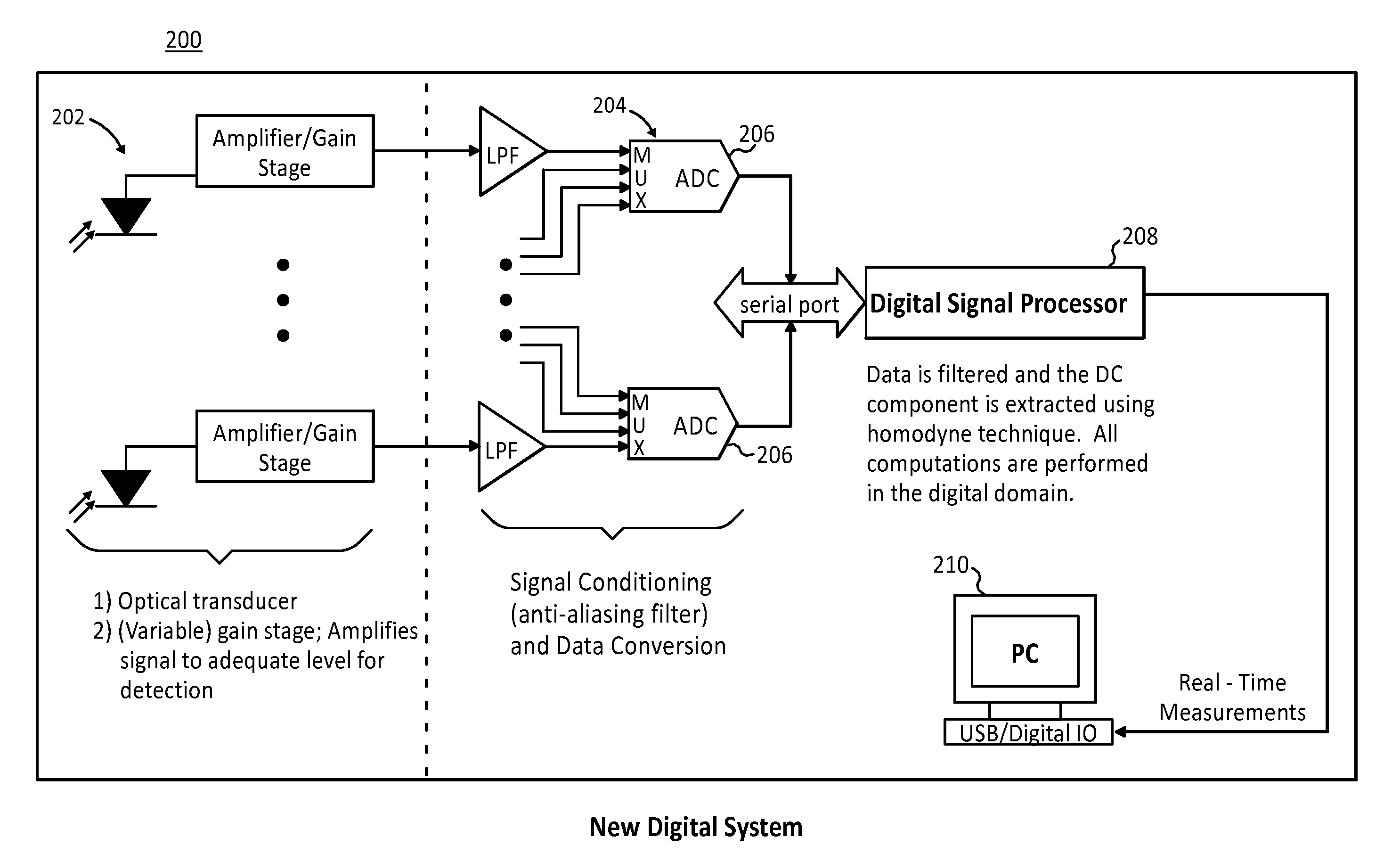
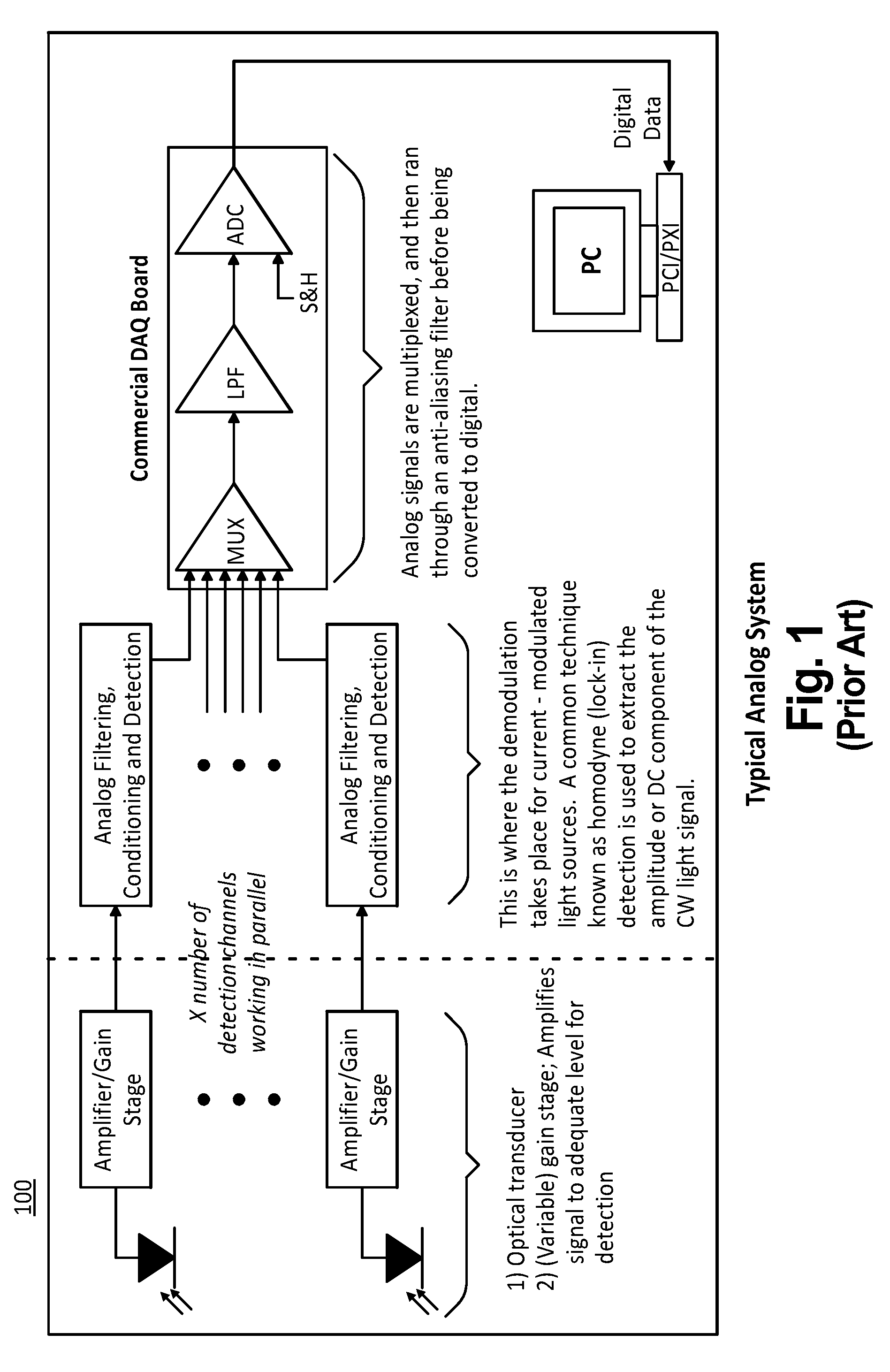
ActiveUS7463362B2Easy accessScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansDigital signal processingAverage filter
The present invention provides systems, methods and apparatuses that perform digital detection for use in optical tomography. Methods and systems are provided in which digital lock-in detection is performed using an algorithm that employs a phase-independent quadrature technique. Methods and systems are provided in which a unique manipulation of an ordinary averaging filter optimized for sources discrimination and the consequent sampling constraints is presented as a novel filtering scheme for the lock-in detection. Systems and apparatuses are provided which include a digital signal processor which performs digital lock-in detection and an integrated complex programmable logic device for timing control. Apparatuses are provided which include an instrument having an integrated digital signal processor for performing digital processing and detection for use in optical tomography.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
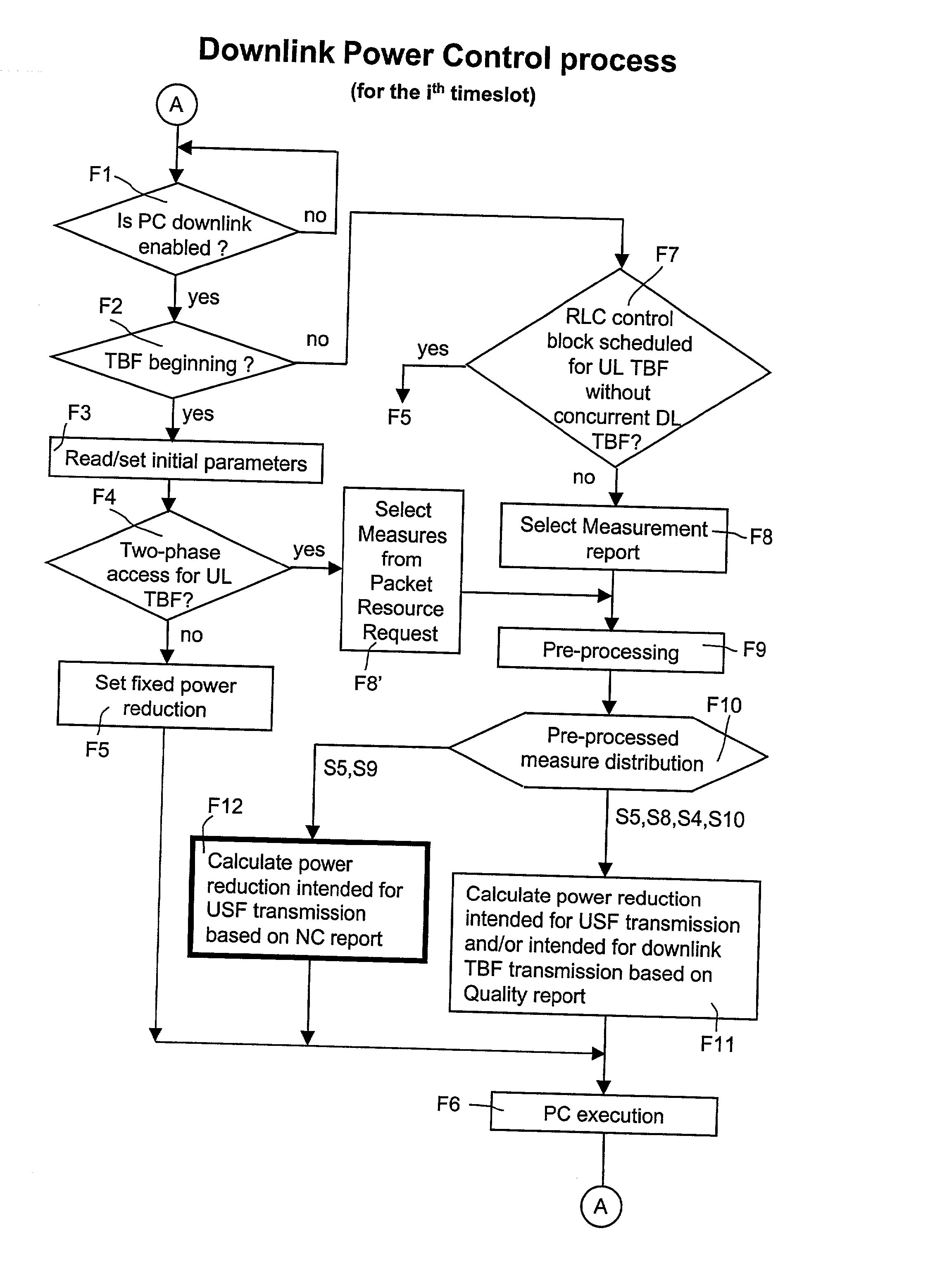
Method to perform downlink power control in packet switching cellular systems with dynamic allocation of the RF channel
InactiveUS20030054850A1Minimize unsuccessfulGreat data-ratesEnergy efficient ICTPower managementAverage filterDownlink power control
The invention discloses a method to perform downlink Power Control in packet switching cellular systems with dynamic allocation of the RF channel, such as GPRS / EGPRS. The performances concern a scenario in which a radio block transmitted from the Base Station (BTS) on a downlink channel has to be received from at least two MSs simultaneously, a first MS being the addressee of the data / control packet on the downlink TBF while the second MS being the addressee of the Uplink State Flag (USF) for scheduling transmission of the next data / control packet from an uplink TBF to an uplink shared channel. First MS transmits to the BTS a first measurement report including measures of BCCH level and interference level on all the timeslots, while the second MS transmits a NC report including measures of BCCH level only, that because detailed interference measure on the downlink channel are prevented due the absence of a concurrent downlink TBF. The measures are averaged in as many running average filters and the averages compared with target thresholds to find a first and a second power reduction intended for USF and packet transmission respectively. A final power reduction is selected from the two for the next PC execution step. Target threshold for the first MS's averaged measures is a C / I value which provides maximum achievable net throughput independently of Coding Scheme. Target threshold for the second MS depends on CS of the USF flag in a way that when the mean value of the level measures is equal to the threshold a fixed probability takes place that the USF flag is decoded with success. The network, in the capacity of the BSC and PCU, counts successfully and unsuccessfully blocks received uplink upon transmission of the scheduled USFs for that uplink TBF, being the lack of a scheduled block noticed by the network. If successfully counting reaches a fixed maximum counting before, then an increment of the first power reduction is decided, while in case the maximum unsuccessfully counting is reached before a decrement of the first power reduction is instead decided (FIG. 10).
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
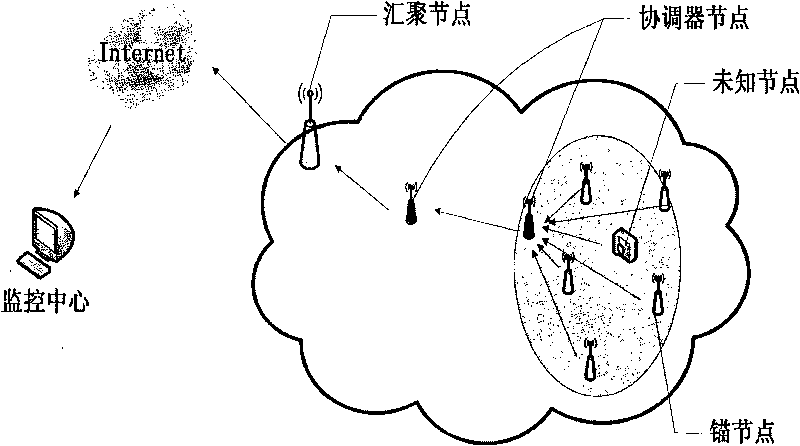
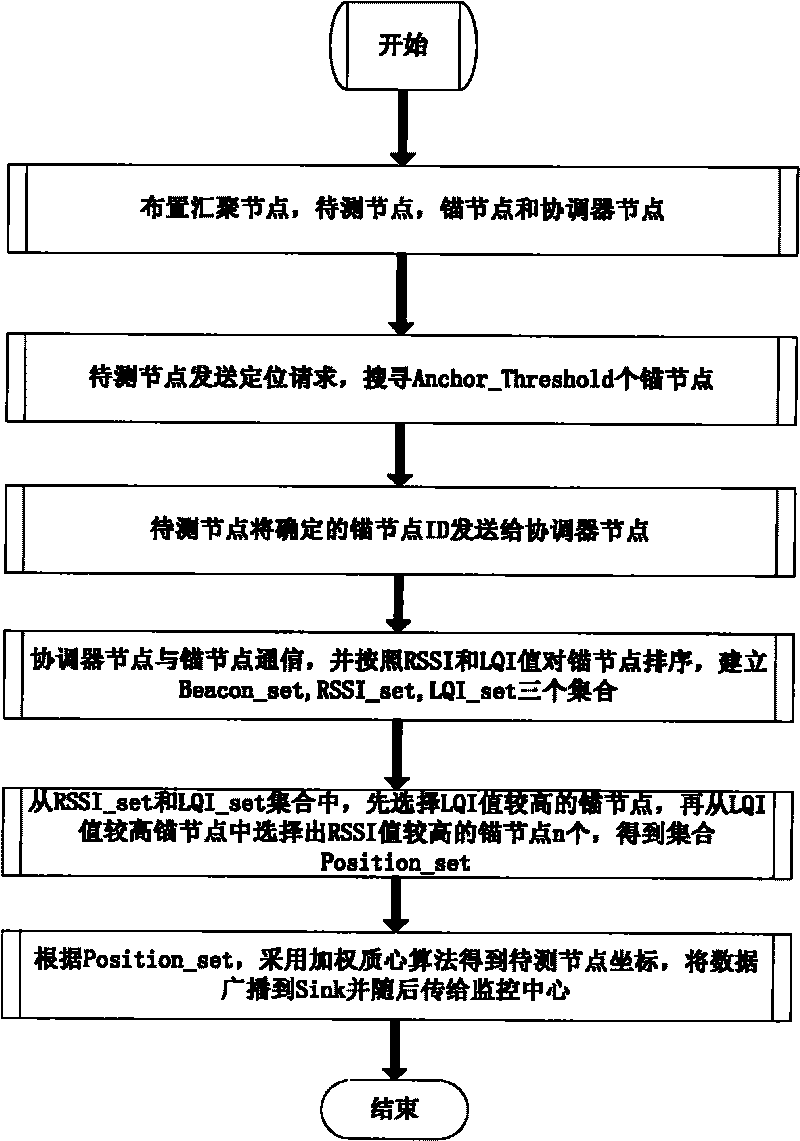
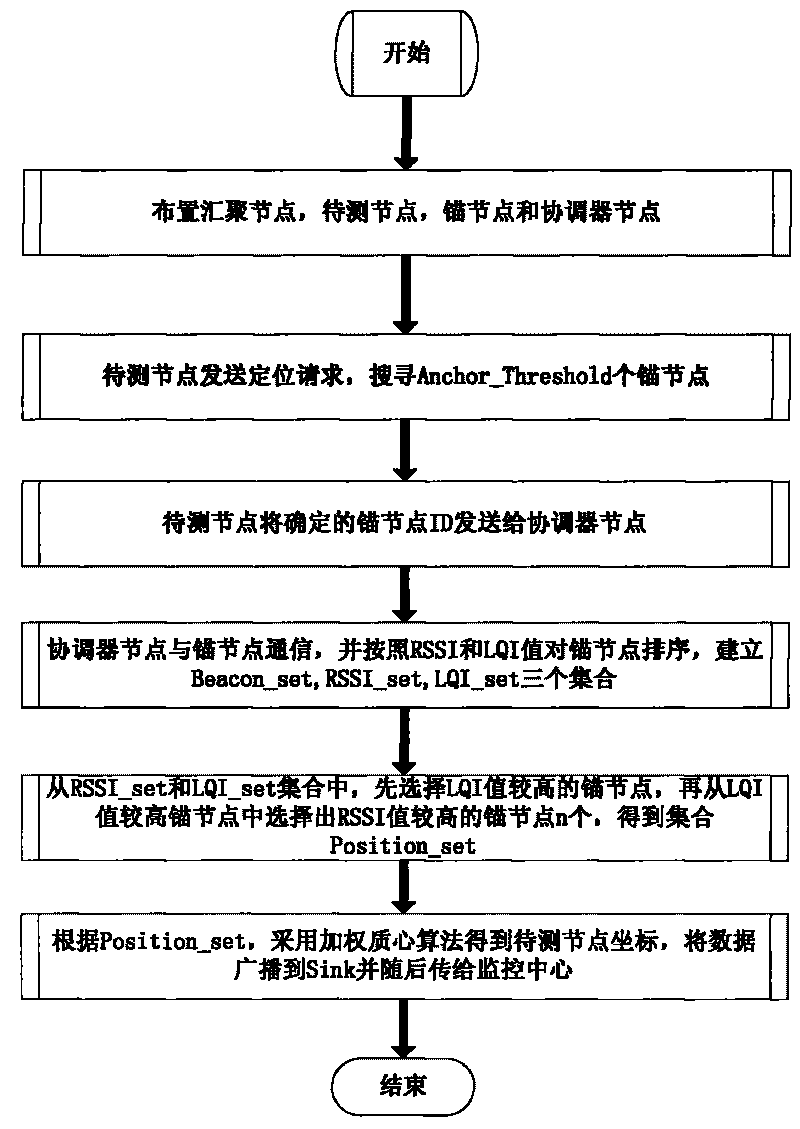
Positioning method of weighted wireless sensor network nodes based on RSSI and LQI
InactiveCN101715232AEasy to implementSave hardware resourcesNetwork topologiesComputation complexityRound complexity
The invention relates to a positioning method of weighted wireless sensor network nodes based on an RSSI and an LQI, which is characterized in that (1) the parameters of the RSSI and the LQI, which can be acquired easily from a hardware register, are used for positioning, thus the method can be realized easily and has few required hardware resources; (2) an LQI ranging model obtained by fitting experimental data is combined with an RSSI ranging model to select anchor nodes; and (3) an RSSI value and an LQI value which pass through an average filter are weighted and combined, an improved weighted centroid algorithm is used for estimating the positions of nodes to be detected, the data is broadcasted to cluster nodes, and then, the data is uploaded to a monitoring centre through a wired network. The positioning method of invention has the advantages of high positioning accuracy without being influenced by the environment easily, easy implementation of hardware, lower cost and smaller computation complexity.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for pump control using varying equivalent system characteristic curve, AKA an adaptive control curve
ActiveUS8700221B2Reduce consumptionReduce stepsError preventionTransmission systemsMoving averageAverage filter
The present invention provides, e.g., apparatus comprising at least one processor; at least one memory including computer program code; the at least one memory and computer program code being configured, with at least one processor, to cause the apparatus at least to: respond to signaling containing information about an instant pressure and a flow rate of fluid being pumped in a pumping system, and obtain an adaptive control curve based at least partly on the instant pressure and flow rate using an adaptive moving average filter. The adaptive moving average filter may be based at least partly on a system flow equation:SAMAt=AMAF(Qt / √{square root over (ΔPt)}),where the function AMAF is an adaptive moving average filter (AMAF), and the parameters Q and ΔP are a system flow rate and differential pressure respectively. The at least one memory and computer program code may be configured to, with the at least one processor, to cause the apparatus at least to obtain an optimal control pressure set point from the adaptive control curve with respect to an instant flow rate or a moving average flow rate asSPt=MA(Qt) / SAMAt,where the function MA is a moving average filter (MA), to obtain a desired pump speed through a PID control.
Owner:FLUID HANDLING
Weighted absolute difference based noise reduction method and apparatus
The invention is a method and apparatus for reducing noise in an image. The method and apparatus involves calculating a plurality of directional operators, comparing the directional operators to a predetermined threshold, and applying a filter responsive to the comparing. The method and apparatus computes the directional operators by taking a weighted sum of the absolute differences between a target pixel and its surrounding pixels. The comparison signals to the method or apparatus the existence of a line or edge. If the method or apparatus detects no edge or line, the method applies a smoothing or averaging filter. If the method or apparatus detects an edge or line, the method applies a median filter in the direction with a minimum directional difference.
Owner:PIXELWORKS
Bivariate nonlocal average filtering de-noising method for X-ray image
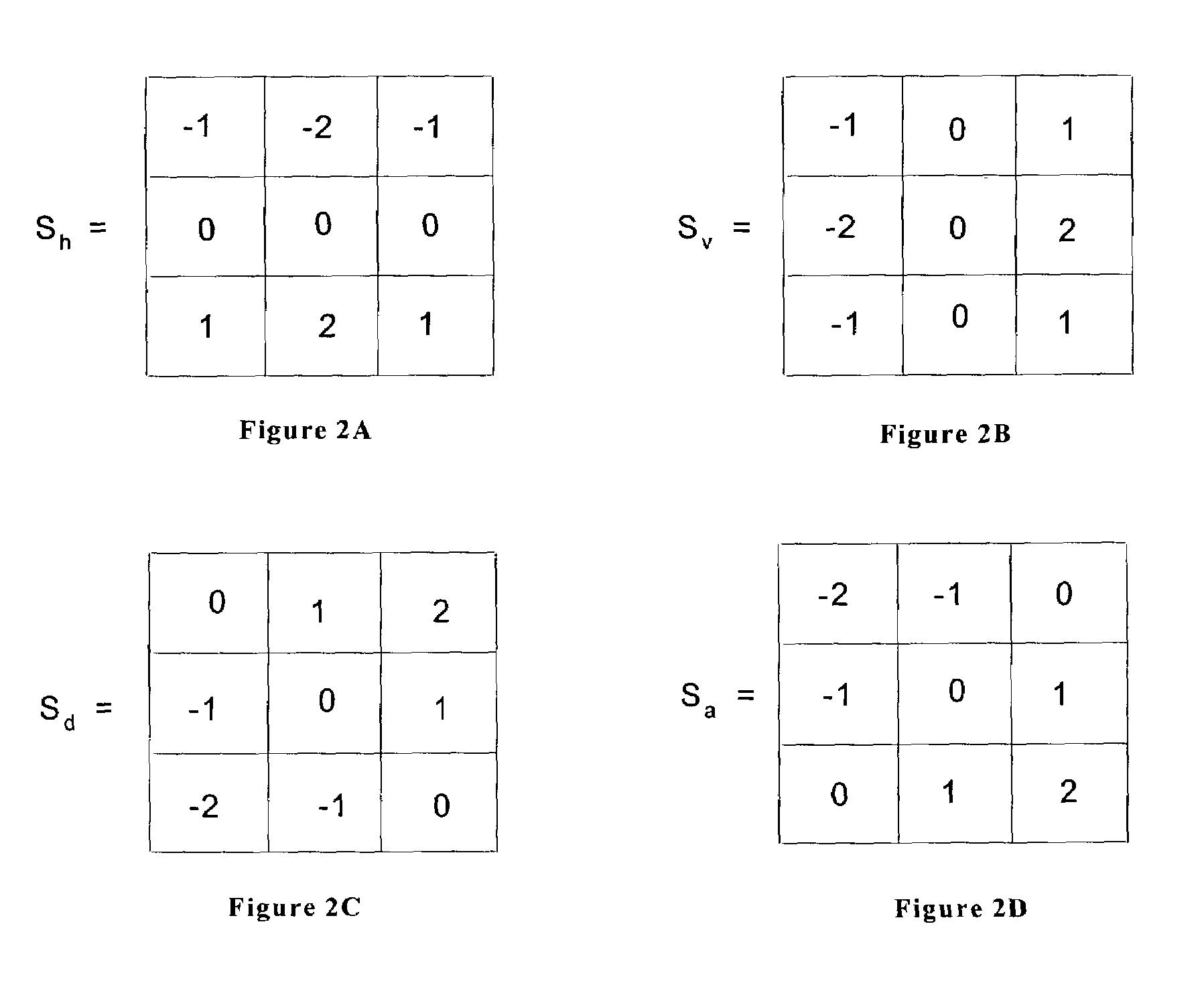
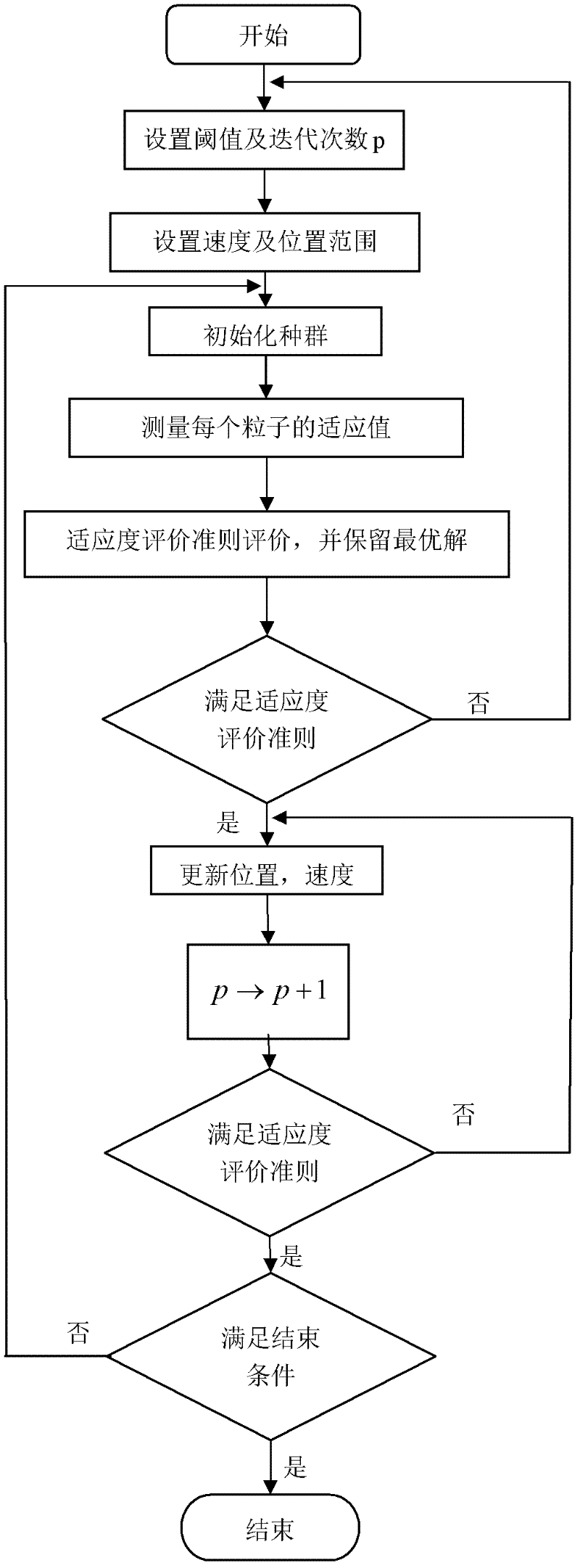
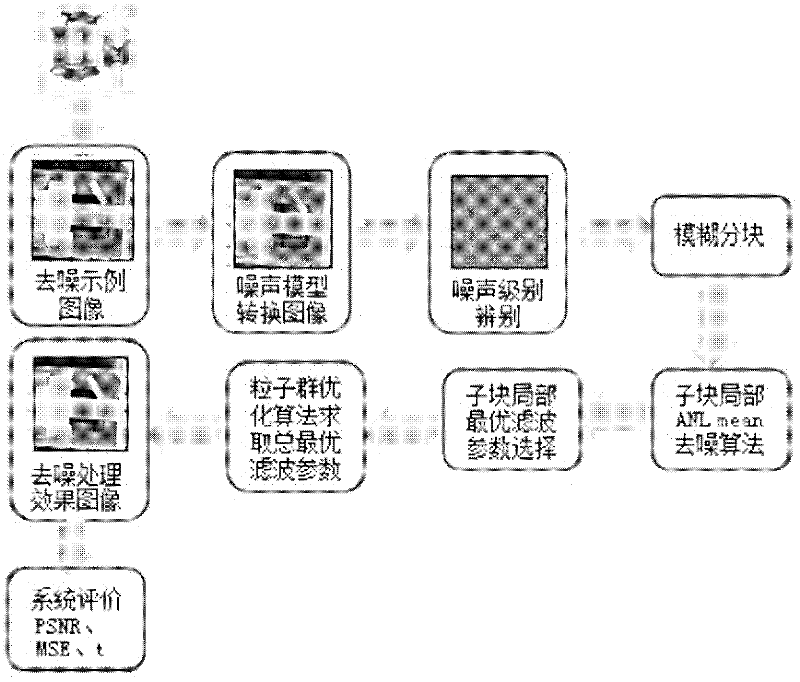
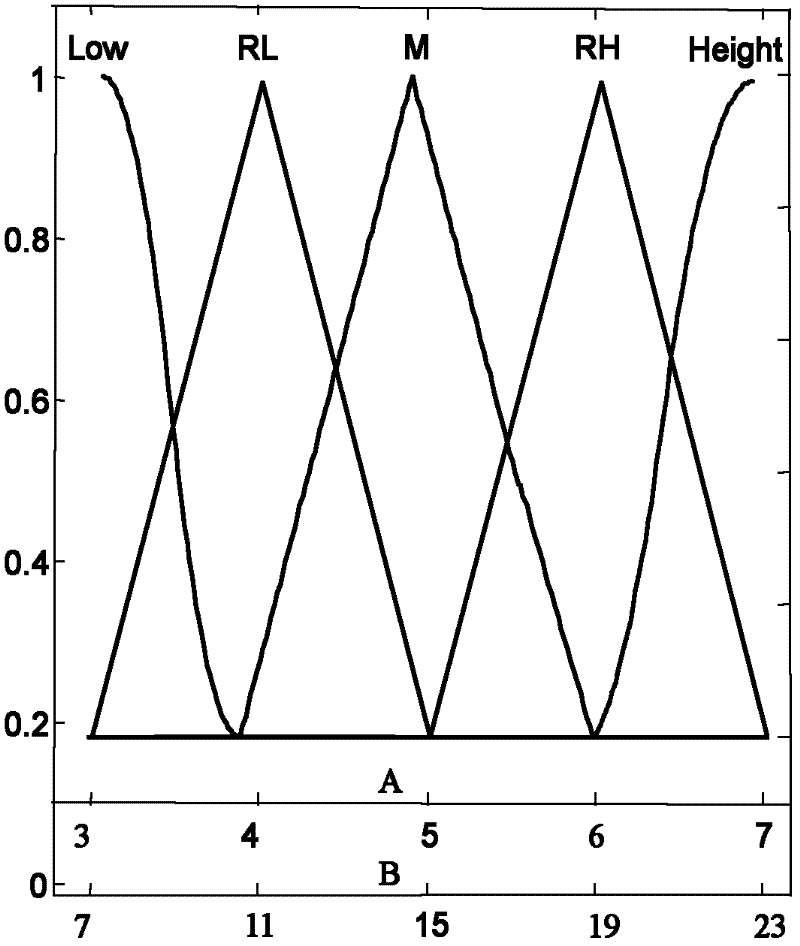
The invention provides a bivariate nonlocal average filtering de-noising method for an X-ray image. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) a selecting method of a fuzzy de-noising window; and 2) a bivariate fuzzy adaptive nonlocal average filtering algorithm. The method has the beneficial effects that in order to preferably remove the influence caused by the unknown quantum noise existing in an industrial X-ray scan image, the invention provides the bivariate nonlocal fuzzy adaptive non-linear average filtering de-noising method for the X-ray image, in the method, a quantum noise model which is hard to process is converted into a common white gaussian noise model, the size of a window of a filter is selected by virtue of fuzzy computation, and a relevant weight matrix enabling an error function to be minimum is searched. A particle swarm optimization filtering parameter is introduced in the method, so that the weight matrix can be locally rebuilt, the influence of the local relevancy on the sample data can be reduced, the algorithm convergence rate can be improved, and the de-noising speed and precision for the industrial X-ray scan image can be improved, so that the method is suitable for processing the X-ray scan image with an uncertain noise model.
Owner:YUN NAN ELECTRIC TEST & RES INST GRP CO LTD ELECTRIC INST +1
Filter technique based numerical control system acceleration and deceleration control method
ActiveCN101211177ASolve Vibration ProblemsReduce vibrationDigital technique networkNumerical controlMoving averageAverage filter
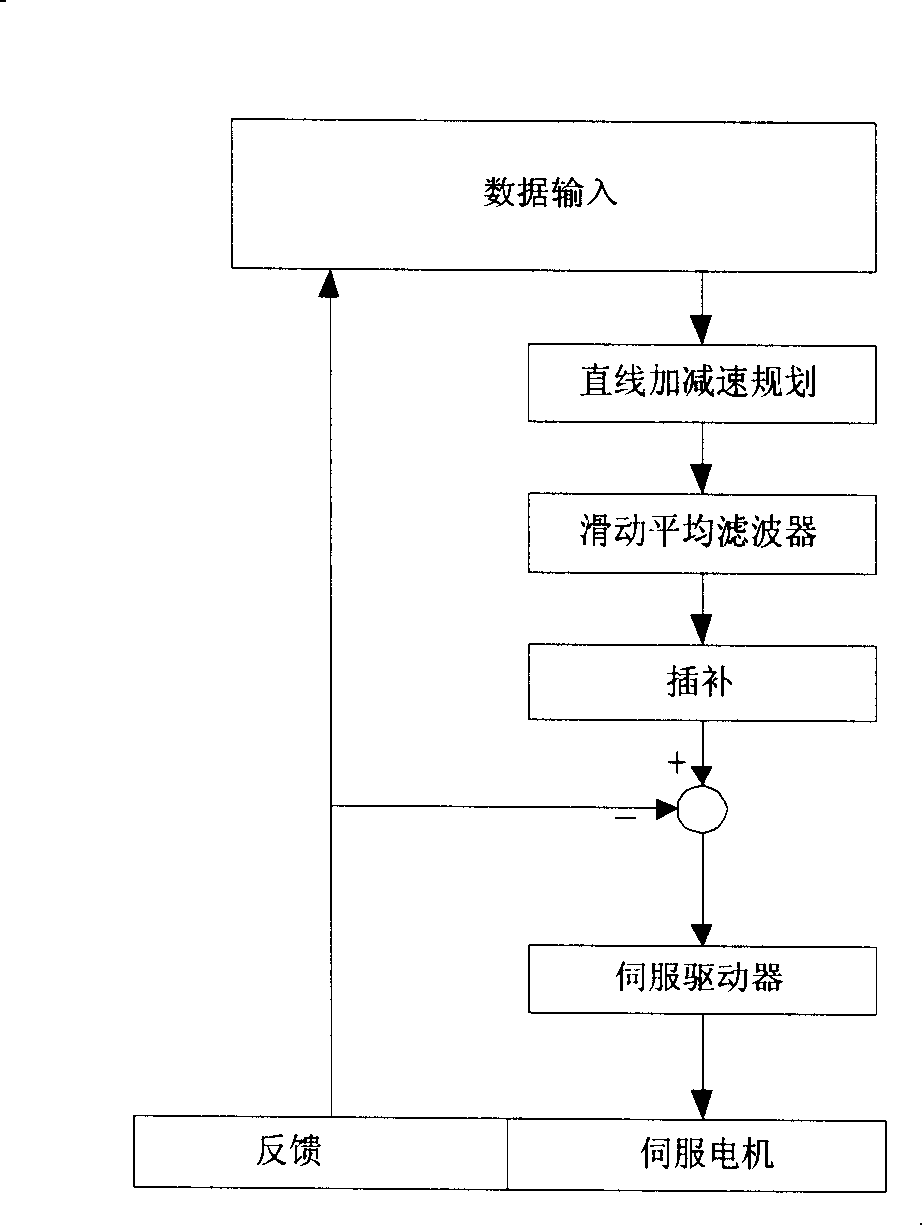
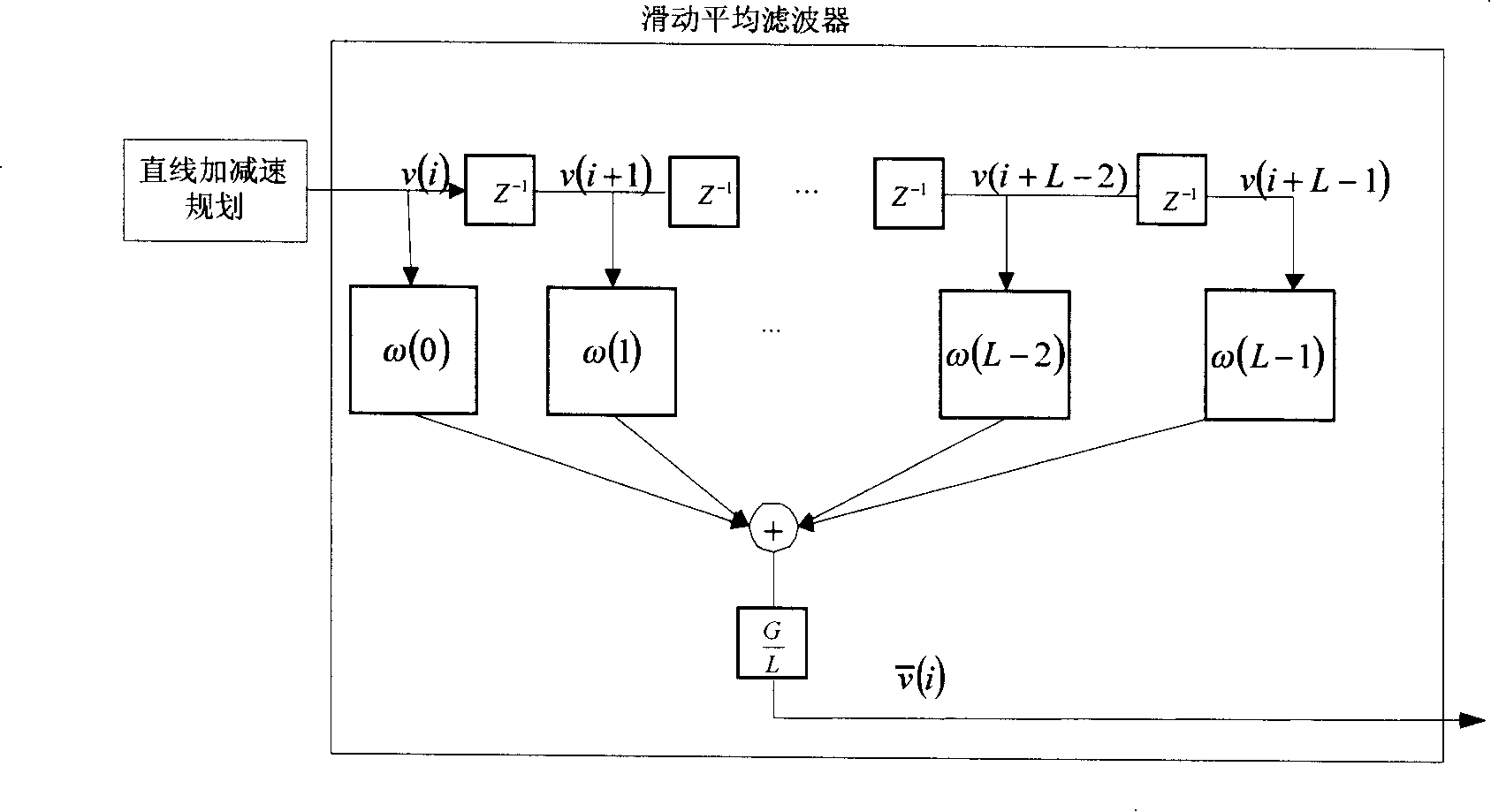
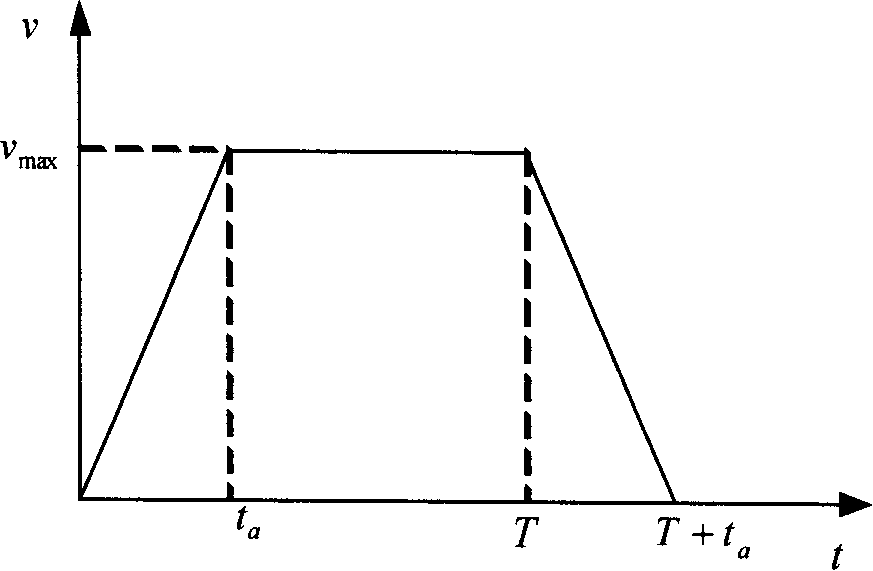
The invention relates to an acceleration or deceleration control method of numerical control system based on filter technique, which comprises the following steps: planning straight acceleration or deceleration by using the inputted workpiece program data; performing moving average filtering and filter compensation on the planned speed of the straight acceleration or deceleration to obtain a new planned speed value and a position value; performing interpolation on the position value; transmitting the interpolated position value to a servo driver in order to control a servomotor; wherein the moving average filtering of the planned speed of the straight acceleration or deceleration is implemented by adding a moving average filter after planning the straight acceleration or deceleration to control sudden changes of an accelerated speed, particularly comprising the following steps: calculating the speed with a method of planning the moving average filtering speed; changing the smooth degree of the straight acceleration or deceleration by selecting filter length (i.e. controlling the magnitude and the shape of the accelerated speed); and calculating a planned position according to the speed after filtering. The invention solves the vibration problem of a numerically-controlled machine tool during movement, and has the advantages of easy implementation, good compatibility and good flexibility.
Owner:SHENYANG GOLDING NC & INTELLIGENCE TECH CO LTD
Filtering method for IMU multi sensor data fusion
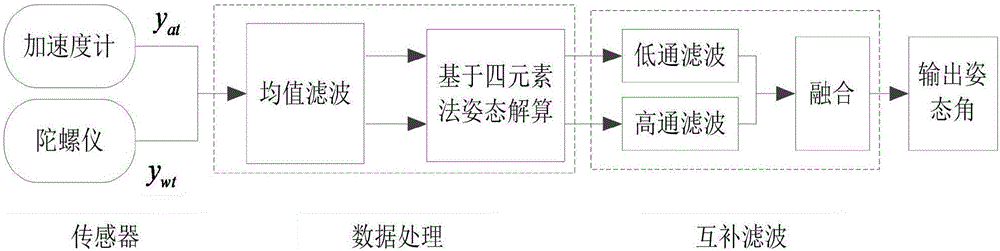
InactiveCN106482734AHigh measurement accuracyImprove dynamic performanceNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMathematical modelComplementary filter
The present invention provides a filtering method for IMU multi sensor data fusion, firstly data is collected, aircraft attitude data can be acquired by an IMU inertial measurement unit comprising a gyroscope, an accelerometer and other multiple sensors, and a sensor output information mathematical model expression formula can be established; output data processing is performed, and the output data processing mainly includes removal of interference information and noises by use of slide average filter and resolution of the rotation angle of each sensor based on a four element method; a high-pass filter and a low-pass filter are combined, PI control parameters are added into a low-pass filtering part, proportionality coefficient variable Kp and integral coefficient variable KI are introduced for design of an error correction negative feedback of a second order complementary filter so as to realize the data fusion of each sensor, and finally attitude angles are outputted. By introduction and setting of the PI control parameters, a negative-feedback-containing second order complementary filter algorithm is designed to fuse the information of each sensor to improve the measurement accuracy and dynamic performance of the system.
Owner:湖南优象科技有限公司
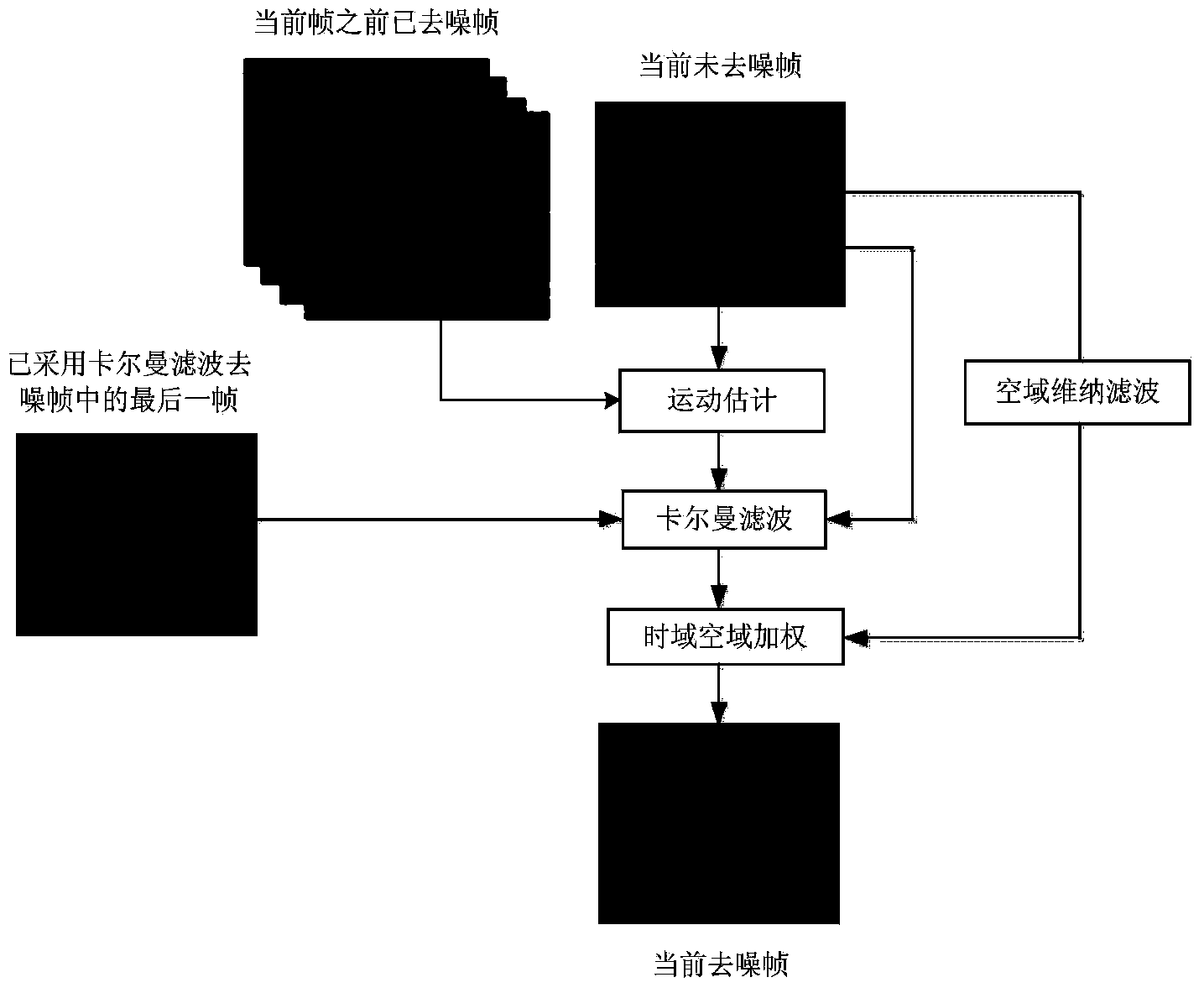
Video de-noising method based on structure tensor and Kalman filtering
The invention provides a video real-time de-noising method based on a structure tensor and Kalman filtering. The method includes the following steps that an image frame to be processed at the current moment is acquired, and n frames of images which are before the current frame and have been stored and de-noised; the image frame to be processed at the current moment is pre-filtered with an average filter; based on the structure tensor, movement of the current image frame is estimated by fully utilizing close time and space relations between the image frame to be processed at the current moment and adjacent image frames before the image frame to be processed at the current moment; based on the movement estimation result, de-noising is performed in a time domain with a Kalman filtering method; de-noising is performed in a space domain with a Wiener filtering method; two de-noised images are synthesized, and the final de-noised image is acquired through weighting. With the method, high-noise video can be de-noised, and a good de-noising effect is achieved; besides, because complicated interactive calculation does not exist, achievement of hardware such as FPGAs is facilitated, and real-time the high-noise video can be de-noised.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Motion state heart rate monitoring method based on photoplethysmography and spectrum analysis
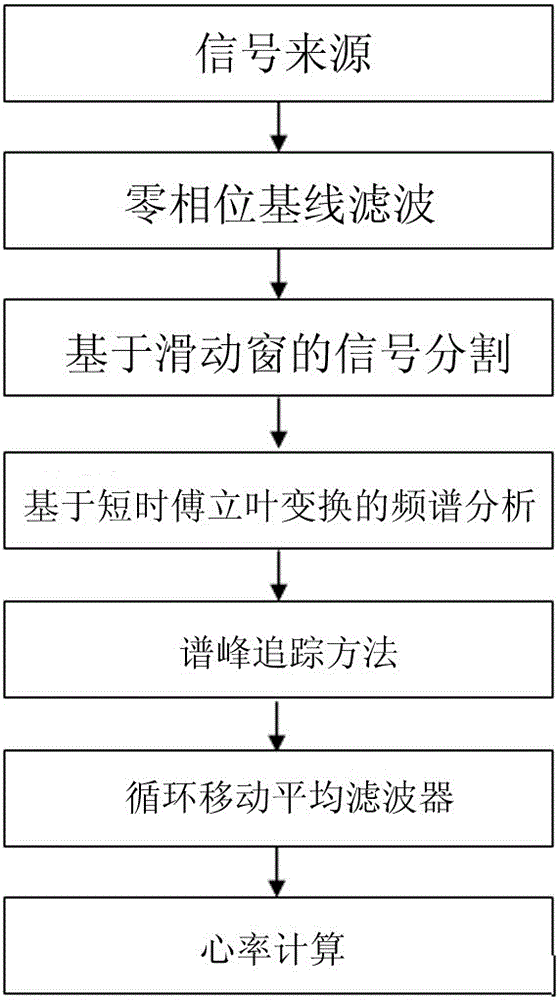
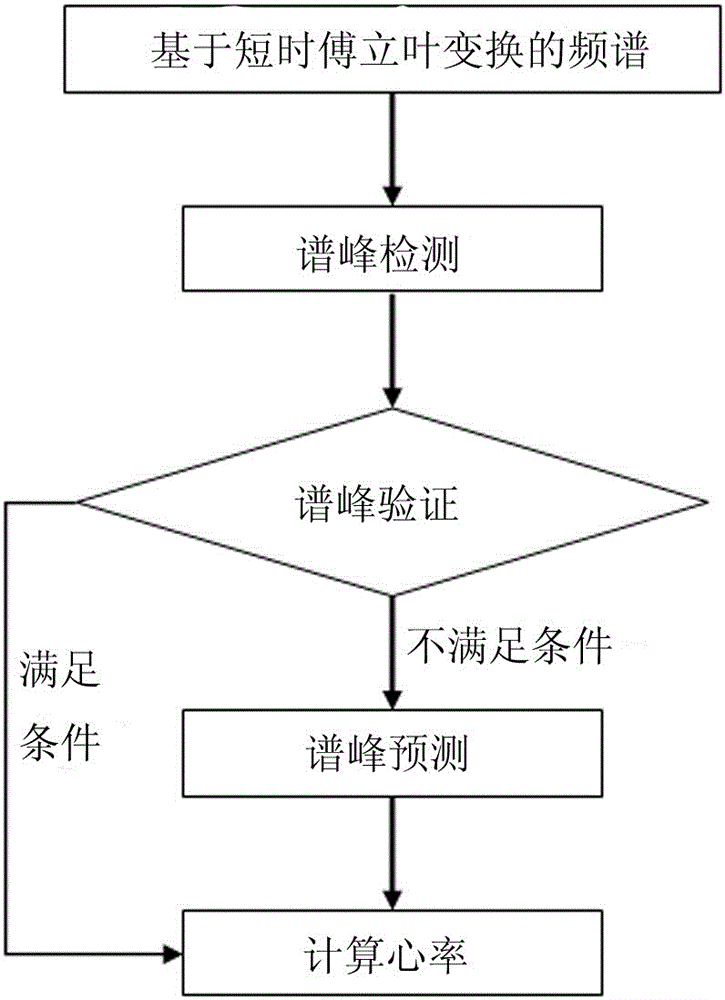
ActiveCN105105737ARealize health monitoringEasy to knowMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateFrequency spectrumAverage filter
The invention relates to motion state heart rate monitoring, in particular to a motion state heart rate monitoring method based on photoplethysmography and a spectrum analysis. The method comprises the following steps: performing zero-phase base line filtering on a source signal; partitioning a processed signal by a sliding window method; obtaining a frequency spectrum by a short-time Fourier transformation method; finding out a spectrum peak representing heart rate data by a spectrum peak tracing method to obtain the heart rate data; processing the heart rate data by a calculatedly moving mean filter to obtain a final heart rate result. The motion state heart rate monitoring method is simple in design and efficient; by monitoring and the analysis of the method, a user can acquire the heart rate data under a motion state. The motion state heart rate monitoring method can be applied to wearable equipment so as to realize healthy monitoring of the heart rate and has higher application value.
Owner:南京盟联信息科技股份有限公司
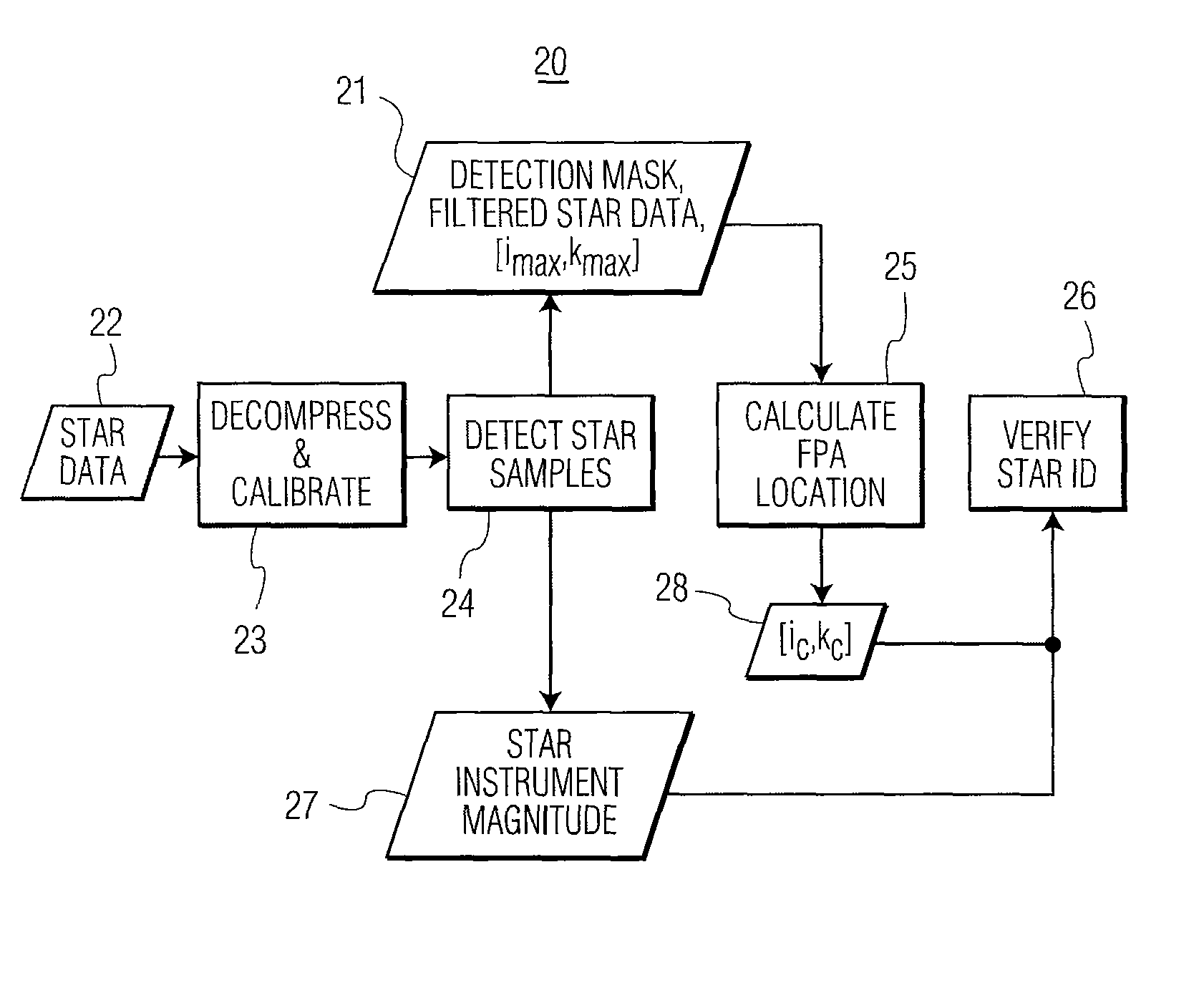
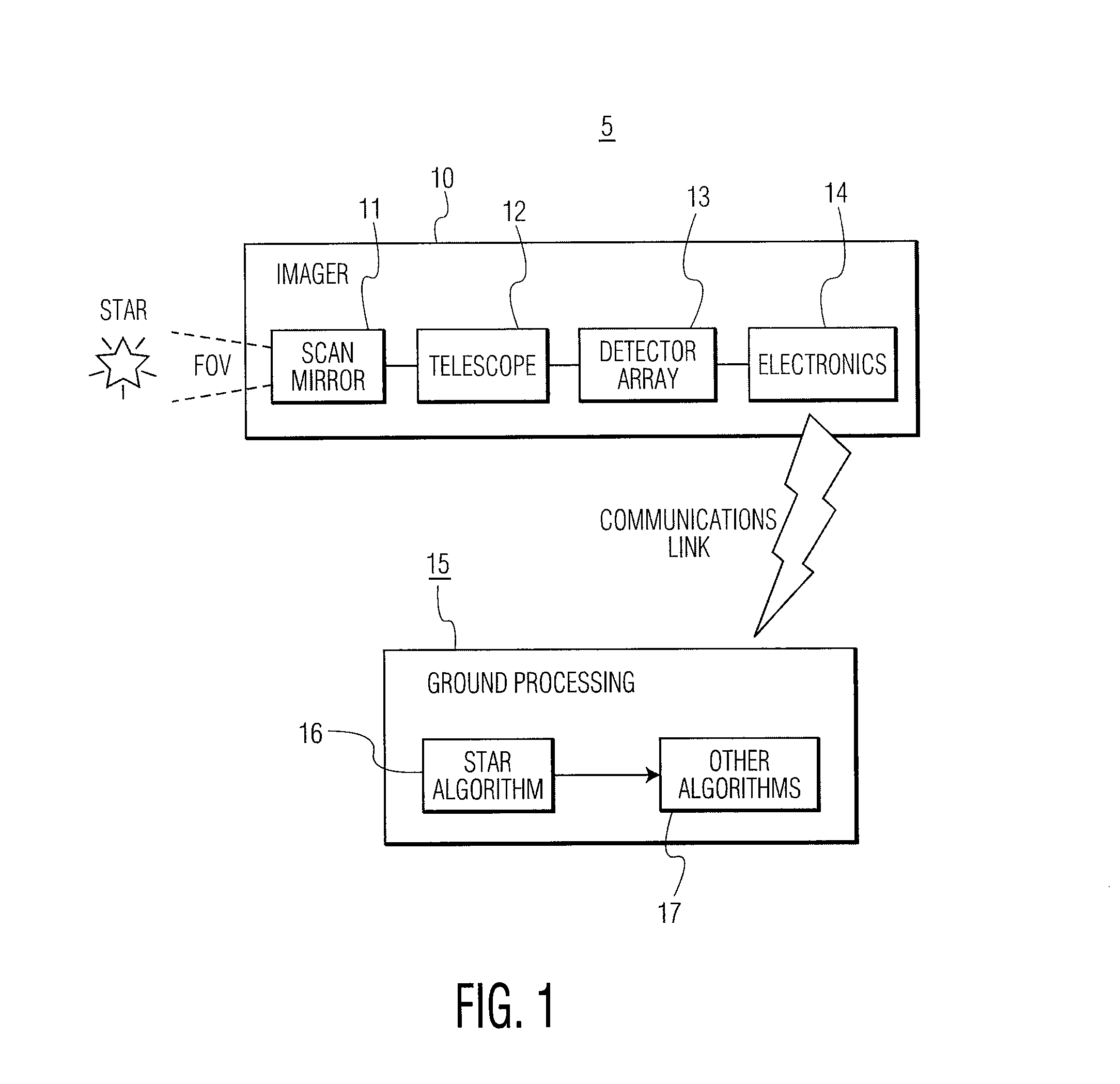
Star sensing for an earth imaging sensor
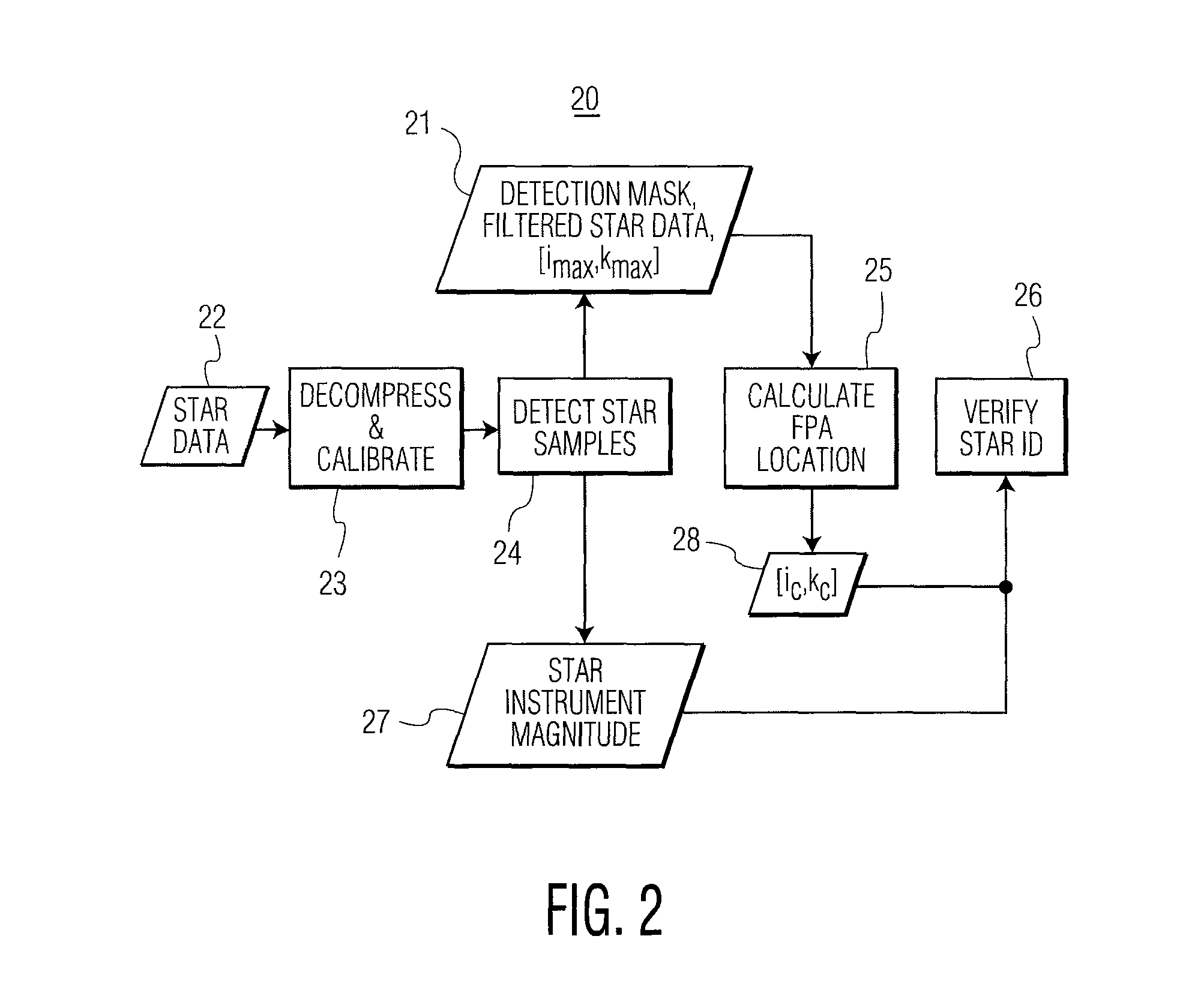
ActiveUS8218013B1Reduce spikesTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAverage filterDetector array
A star sensor includes (a) a scan mirror for scanning at least one star; (b) a detector array, coupled to the scan mirror, for detecting the one star; and (c) a processor, coupled to the detector array. The processor includes a first filter configured to reduce noise spikes in the detected one star, and provide a detection mask of filtered data. Also included is a second filter configured to reduce non-contiguous samples in the detection mask. A centroid calculator is included to determine a location of the one star, after the first and second filtering. The first filter includes a median filter, followed by an averaging filter, both configured to filter the one star in an along-scan direction of the scan mirror. The first filter includes another median filter, which is configured to filter the detected one star in the cross-scan direction of the scan mirror. An adder is included to subtract (a) output data from the other median filter from (b) output data from the averaging filter and provide filtered star data to the second filter.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
System and method for a vector difference mean filter for noise suppression
InactiveUS20060103892A1Suppress noiseReduce noiseImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionAverage filter
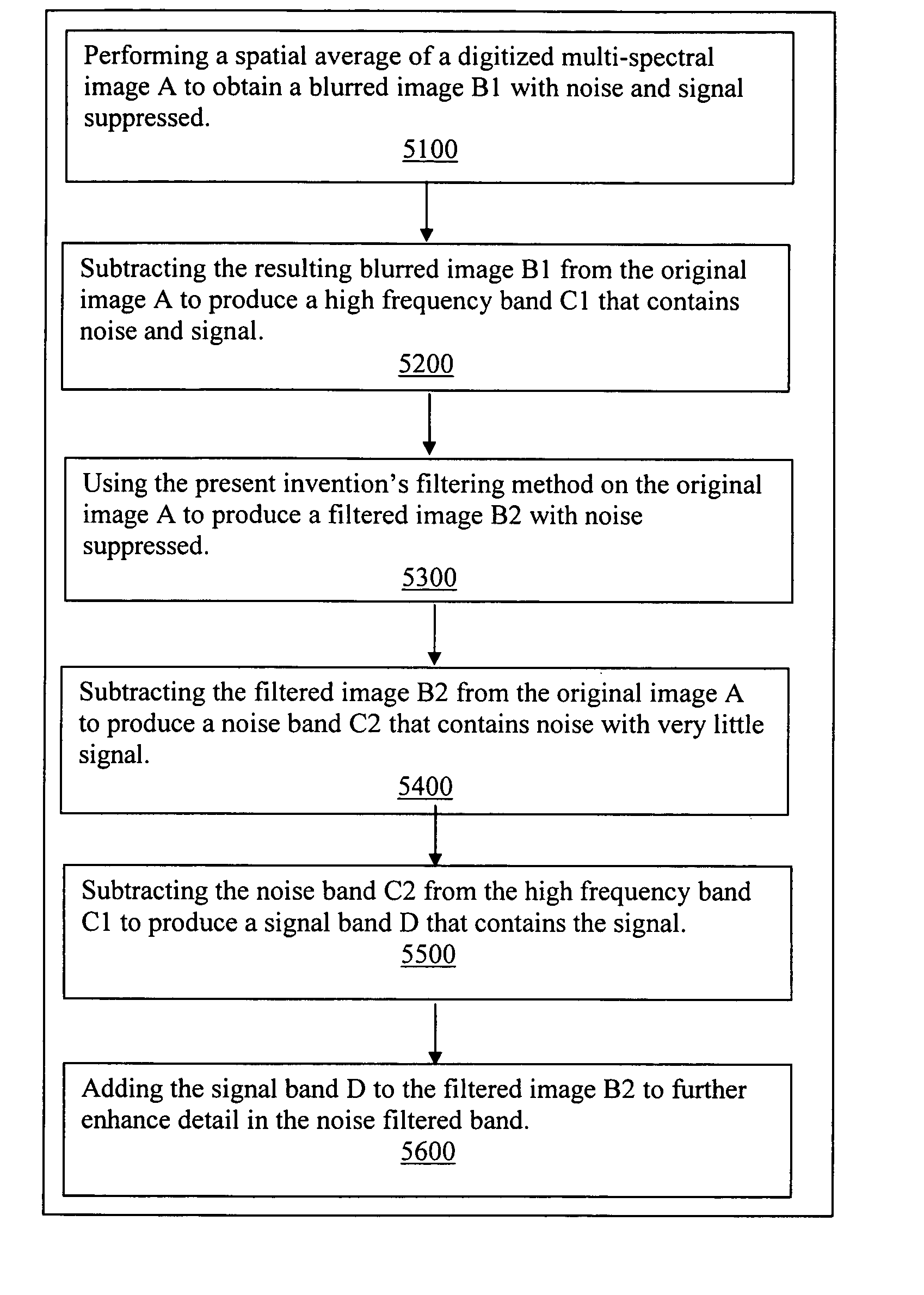
Reduction of noise in digitized multi-spectral images is provided by filtering based on vector values rather than independent scalar values. Vector values refer to a pixel with two or more values. For this method, a metric is defined for pixel vector magnitude. A sliding processing kernel is also defined, with a specified shape, a specified number of pixels to be included in the kernel, and a specified value contrast threshold to avoid distorting edges and fine details. The metric and kernel are used to select pixels for computing filtering of the center pixel in a kernel. A statistical measurement is computed, for example by mean averaging the specified pixels, and the resulting value is made the value of the center pixel of the kernel. The filtering process is applied throughout the image by making each pixel the center of a processing kernel.
Owner:SOZOTEK
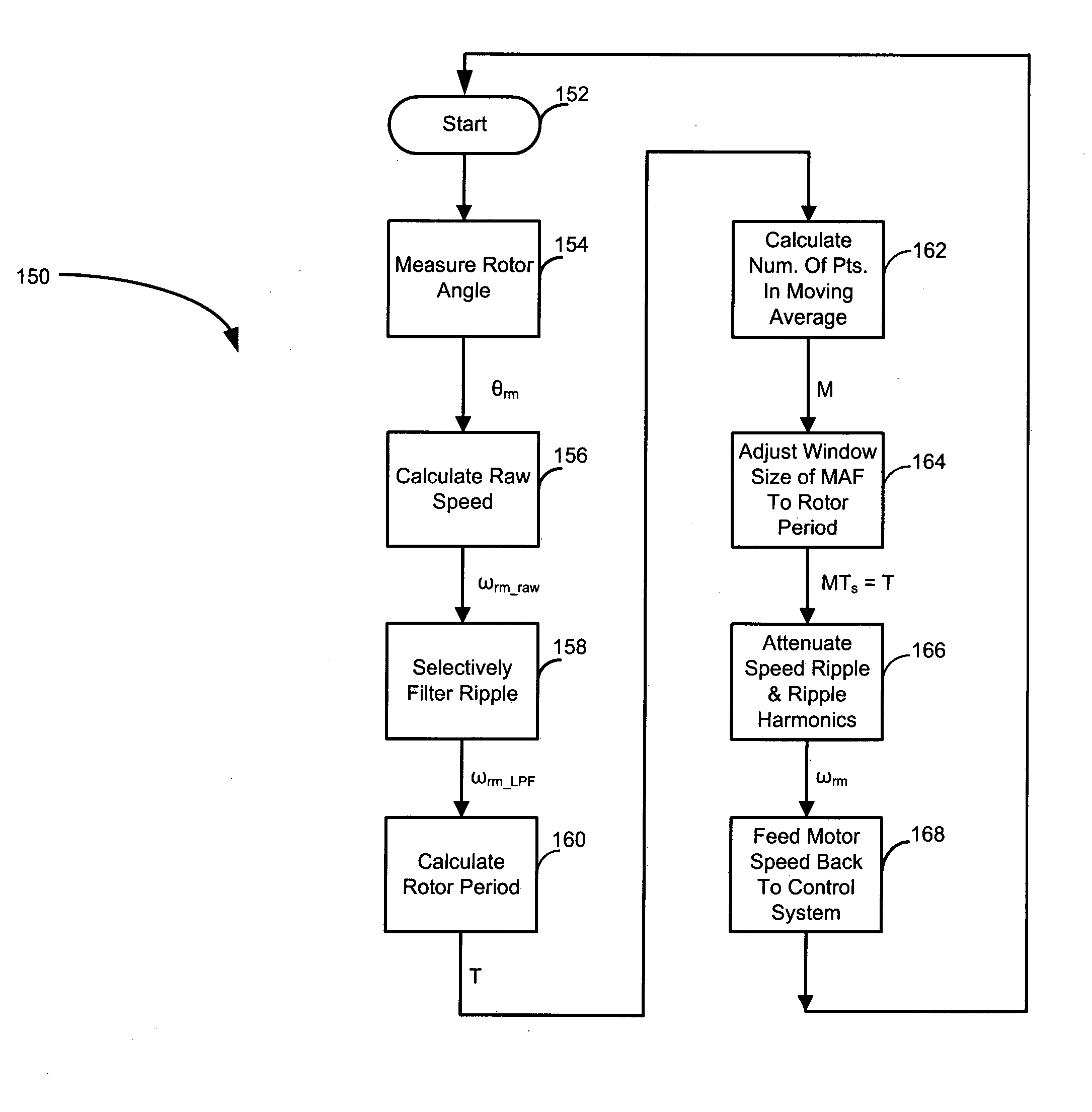
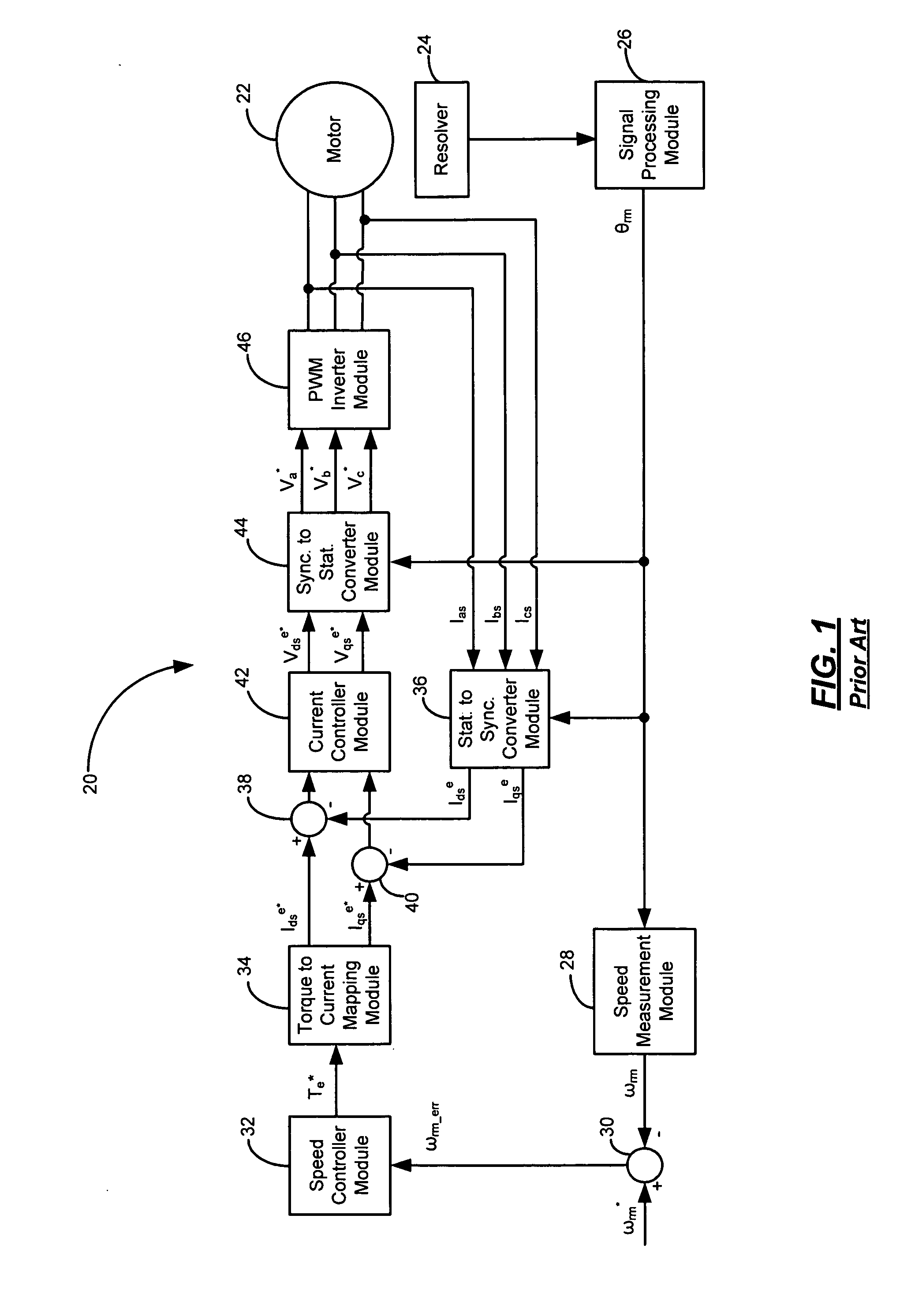
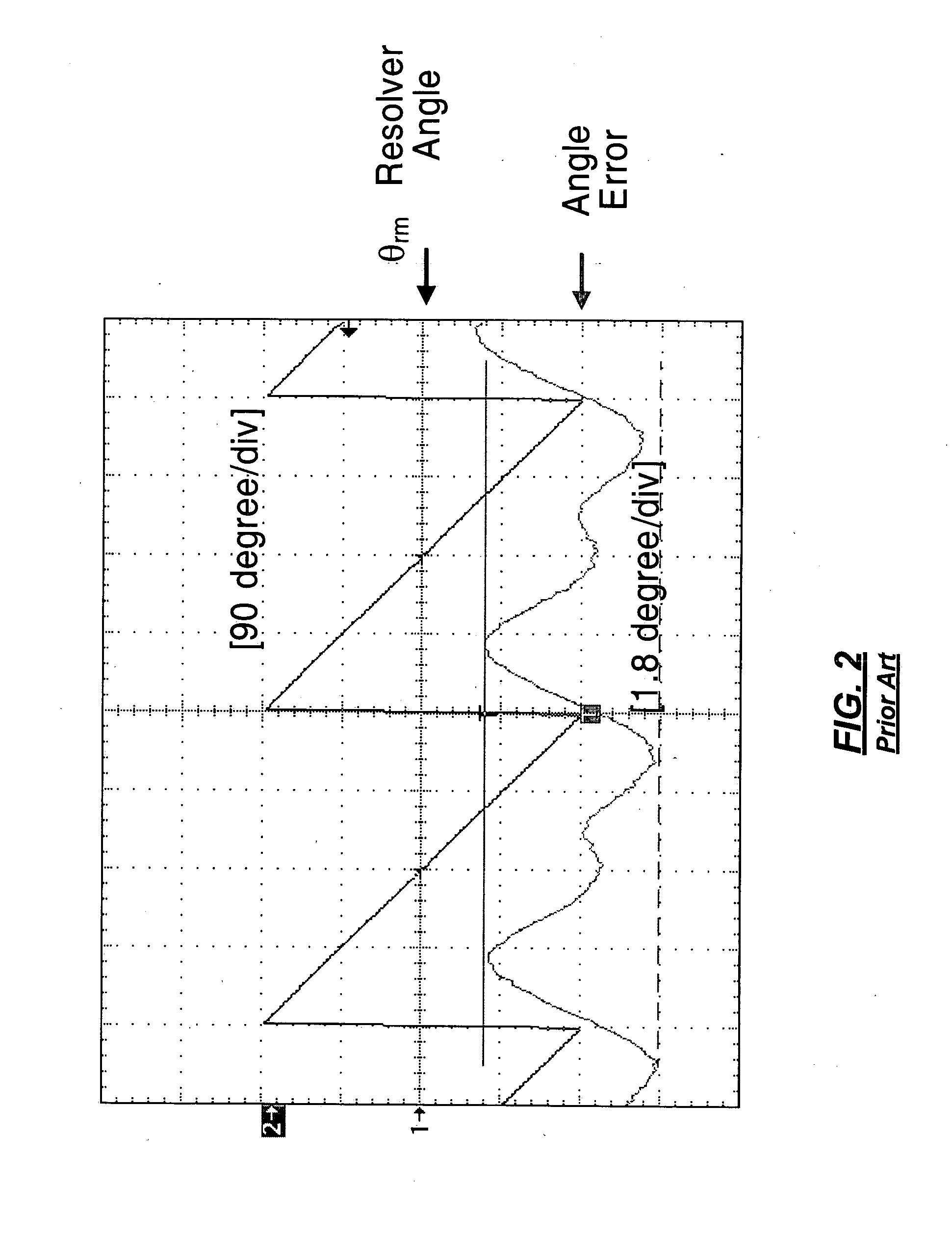
Speed measurement system for speed control of high-speed motors
InactiveUS20070043528A1Speed measurement using accelerationVector control systemsMoving averageAverage filter
A system for measuring speed of a high-speed motor using a moving average filter. A position sensor generates a rotor position signal. A signal processing module determines a rotor angle from the rotor position signal. A speed observer module calculates a raw speed of the motor from the rotor angle. A filter module selectively generates a filtered speed of the motor from the raw speed of the motor. A frequency-to-period converter module calculates a rotor period from one of the raw speed of the motor and the filtered speed of the motor. A divider module calculates number of points in a moving average from the rotor period. A moving average filter module adjusts a window size of the moving average to the rotor period. A moving average filter removes ripple and harmonics of the ripple from the raw speed of the motor.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
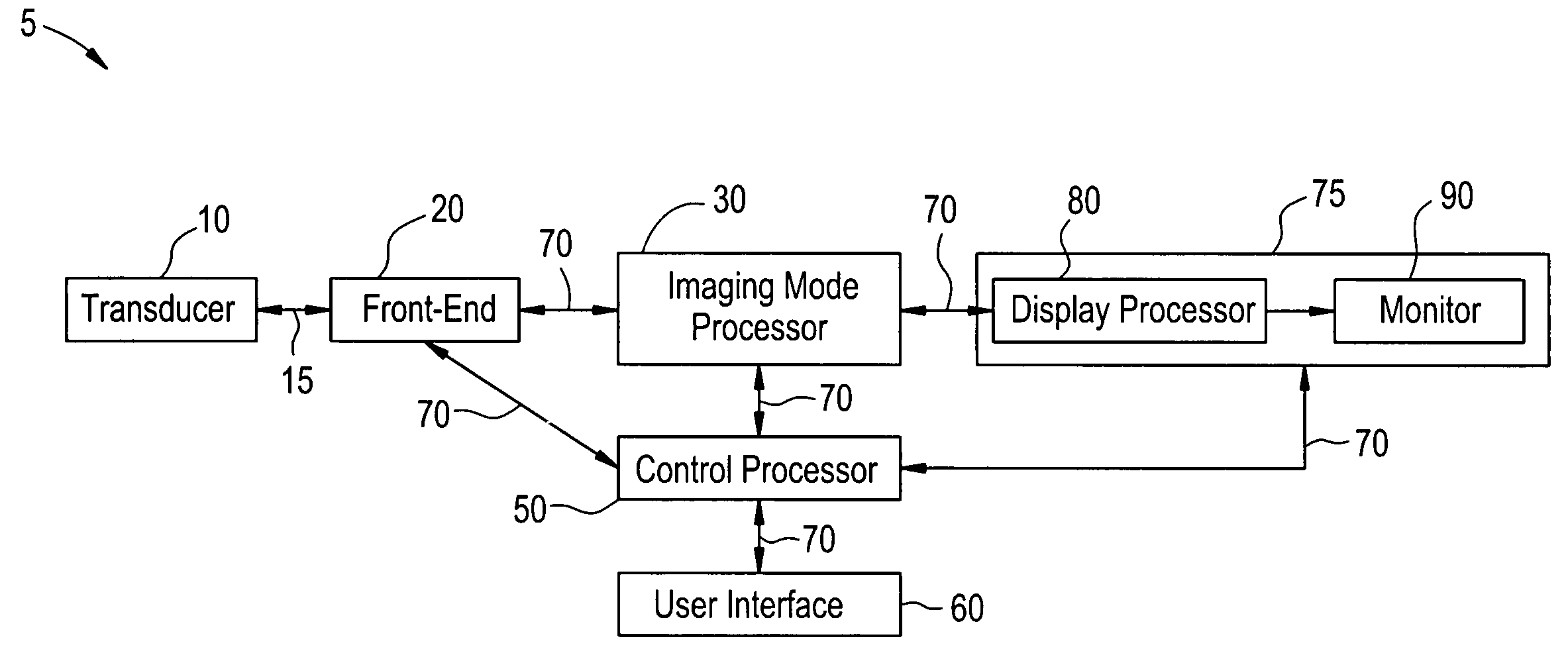
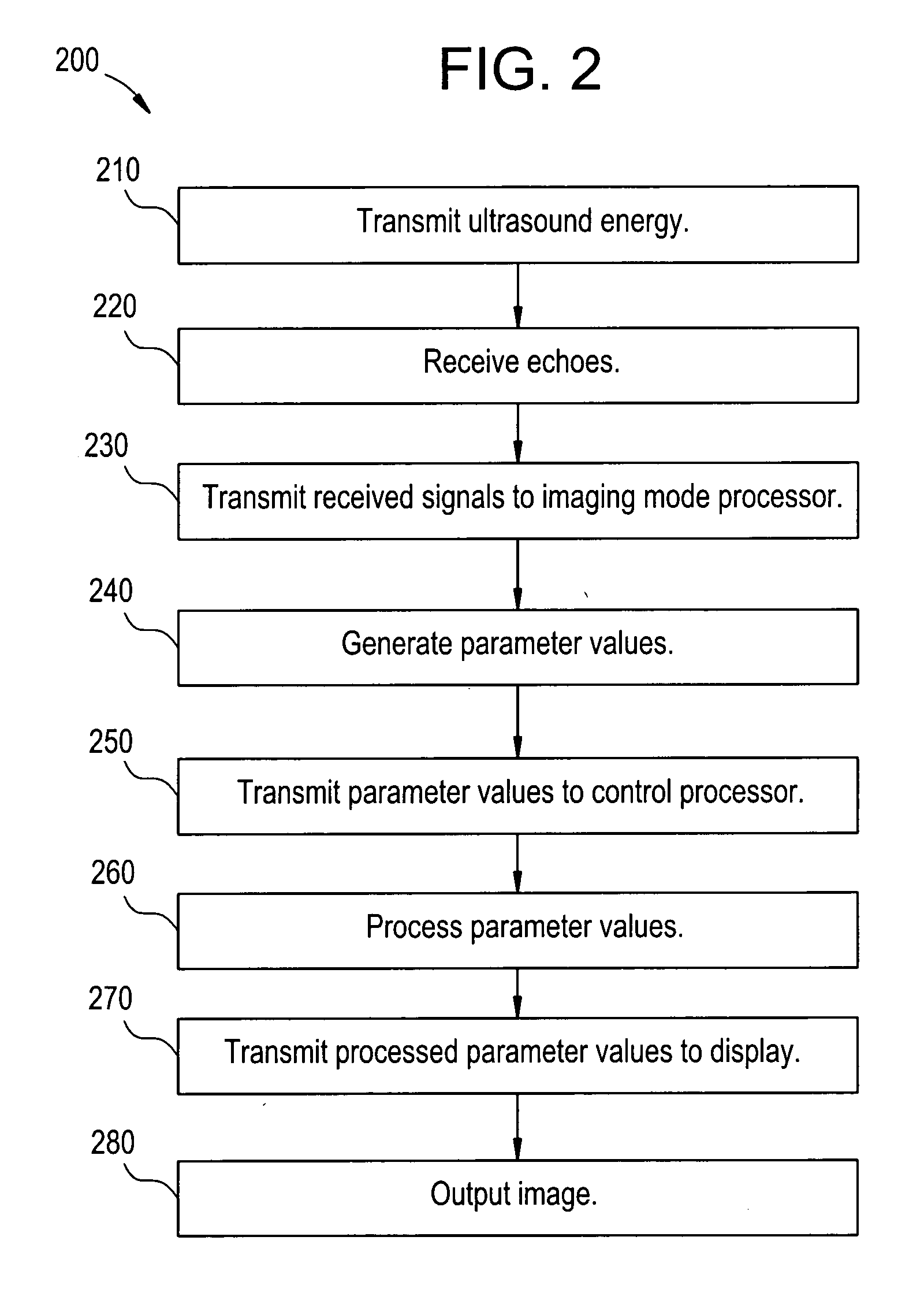
Method and apparatus for single transmission Golay coded excitation
InactiveUS20050096544A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsFinite impulse responseFirst pathway
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide a method and system for improved ultrasound imaging using single transmission coded excitation. Certain embodiments include encoding a first ultrasound beam with a first code, transmitting the first ultrasound beam on a first path, encoding a second ultrasound beam with a second code, transmitting the second ultrasound beam on a second path and receiving echo signals from the first and second ultrasound beams. The codes may be complimentary Golay codes or other complimentary codes. The first and second paths may be adjacent scan lines. The method may also include match filtering the echo signals with corresponding matched filters. Match filtered echo signals along adjacent scan lines may be filtered, such as with a lateral averaging filter or other finite impulse response filter. Alternate complementary code transmission helps preserve or improve frame rate while maintaining signal-to-noise ratio improvement and range lobe cancellation.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
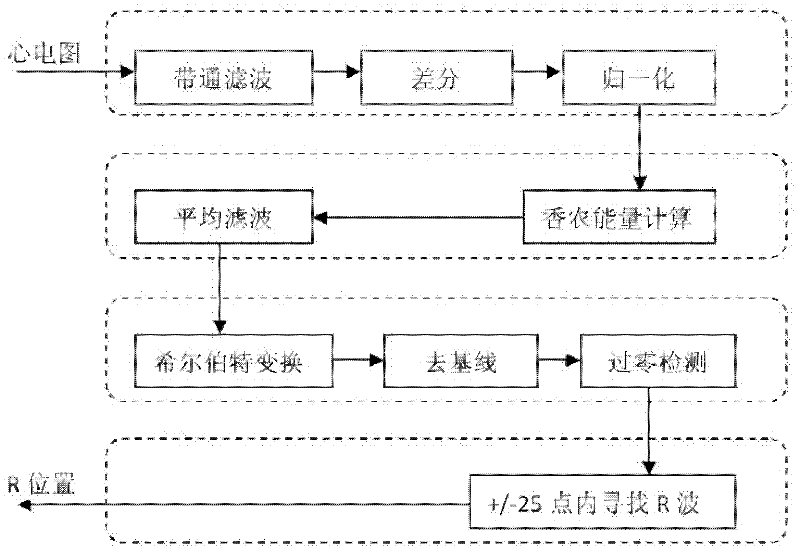
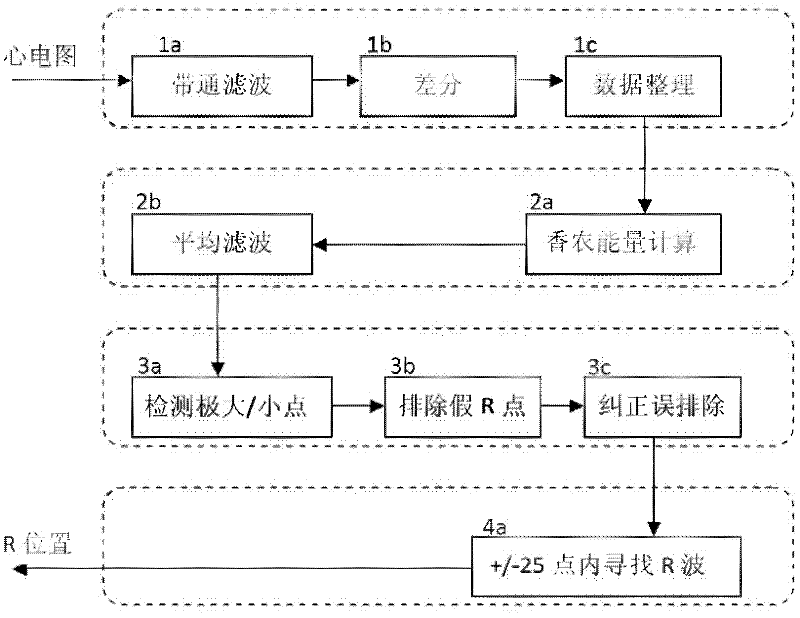
Electrocardiogram R wave detection method
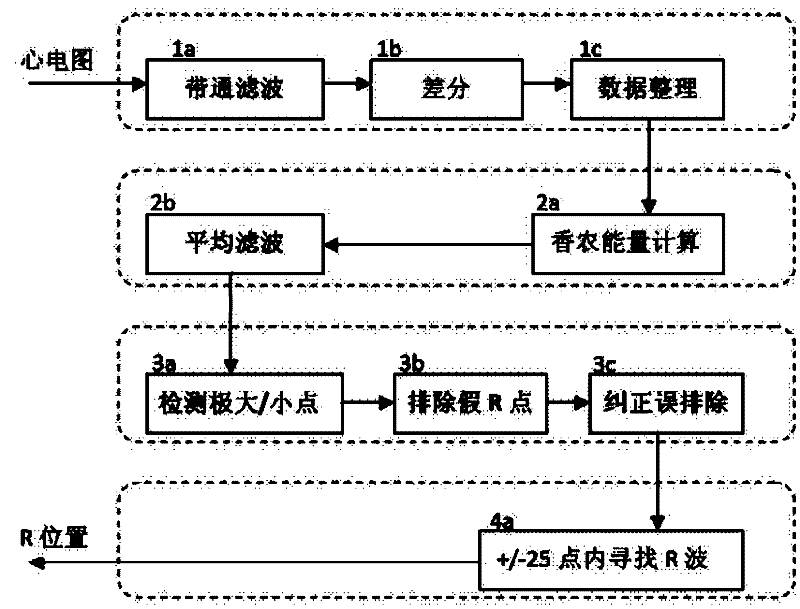
InactiveCN102379694AOvercoming delayOvercoming detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAverage filterAlgorithm
The invention discloses an electrocardiogram R wave detection method. The method comprises the following steps: filtering an input electrocardiogram signal by a band pass filter, and performing phase compensation; performing differential processing; performing data reduction on a differential signal by adopting linear variation; performing Shannon energy conversion by using a formula d(n)*d(n)*log(d(n)*d(n)); filtering by using an average filter, and performing phase compensation; detecting a maximum point and a minimum point, eliminating a fault R point, and correcting a falsely eliminated point to obtain a position of approximate R wave; and searching the position of true R in a range of periphery of the position of the approximate R wave + / - 25 points. By using the method, the problems of time delay and asystole detection unavailability in the conventional R wave detection method can be solved, and the method can be used for analyzing real-time electrocardiogram to reduce time delay and reduce required memory space, so that the accuracy rate is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
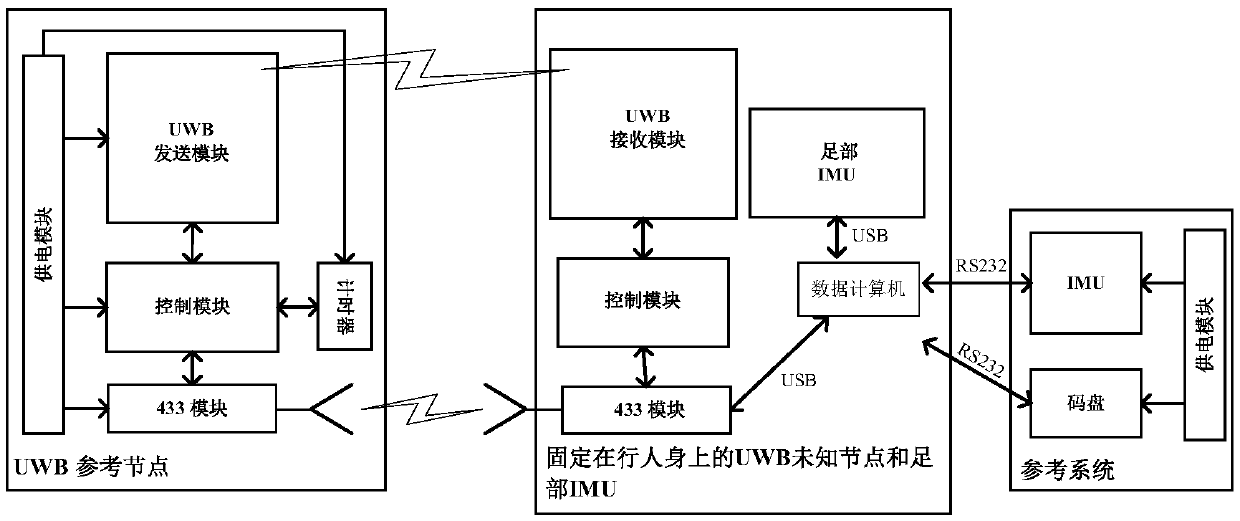
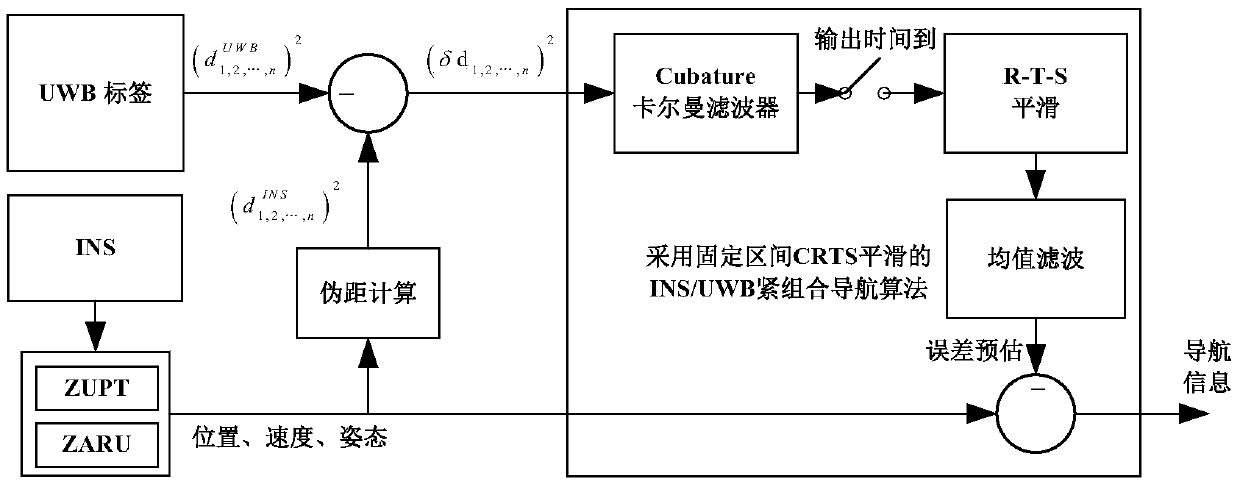
Tightly coupled INS/UWB integrated navigation system and method adopting fixed-interval CRTS smoothing
ActiveCN105509739ANavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsCubature kalman filterNavigation system
The invention discloses a tightly coupled INS / UWB integrated navigation system and method adopting fixed-interval CRTS smoothing. The navigation system comprises an inertial navigation system (INS), a UWB radio tag, UWB wireless reference nodes, a reference system and a data processing system, wherein the inertial navigation system (INS) and the UWB radio tag are arranged on shoes of a pedestrian; the UWB wireless reference nodes and the reference system are arranged at a set position; the inertial navigation system (INS), the UWB radio tag and the reference system are connected with the data processing system respectively; the data processing system comprises a local data fusion filter, a Cubature Kalman Filter (CKF), a pseudo-distance data processing module, an RTS smoothing module and an average filtering module. The tightly coupled INS / UWB integrated navigation system and method has the benefits that the possibility of introducing truncation errors due to omitting of higher terms of Taylor expansion in a conventional tightly coupled integrated navigation model is effectively decreased.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Synchronous detection method and device, and sensor signal detector
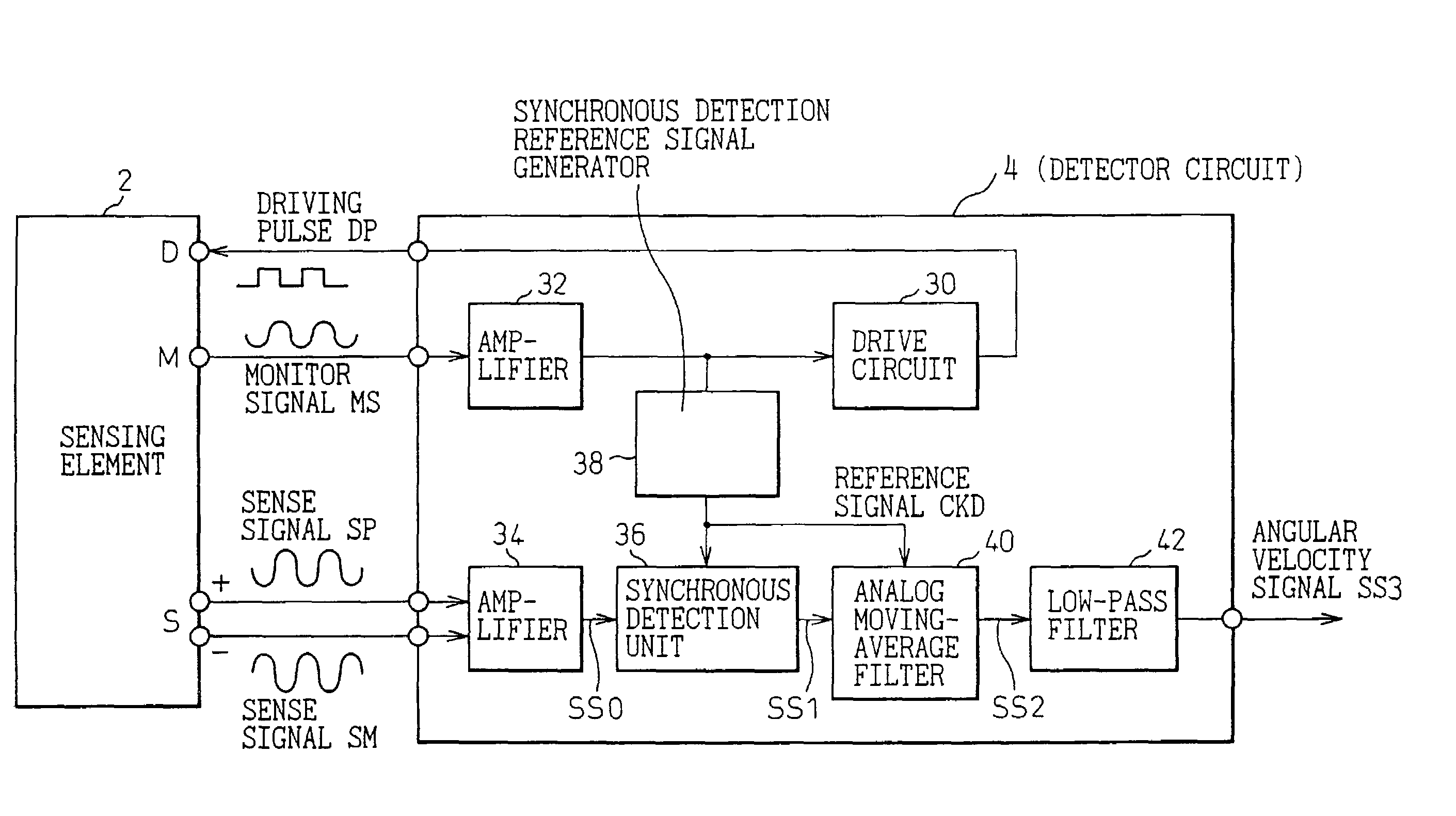
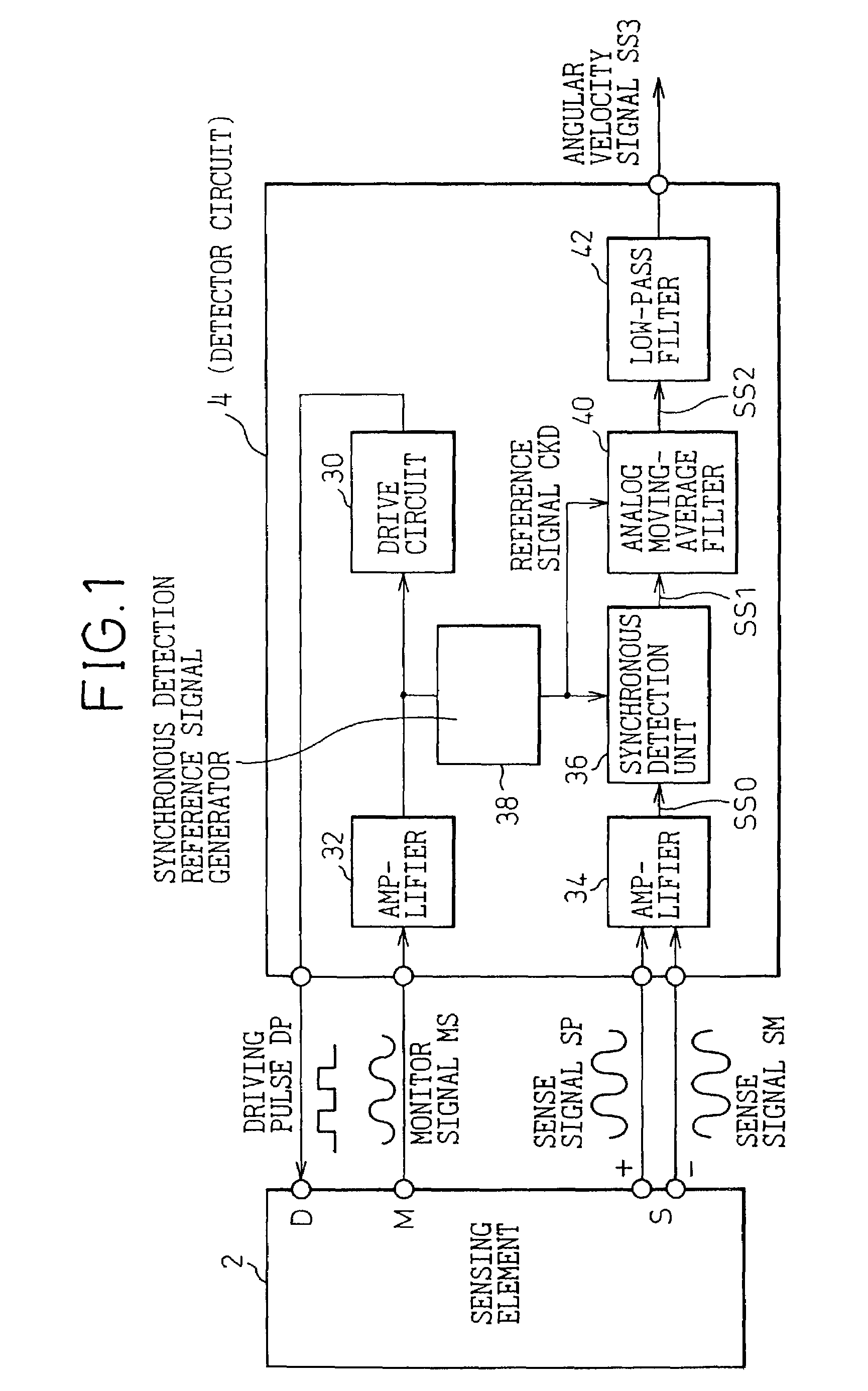
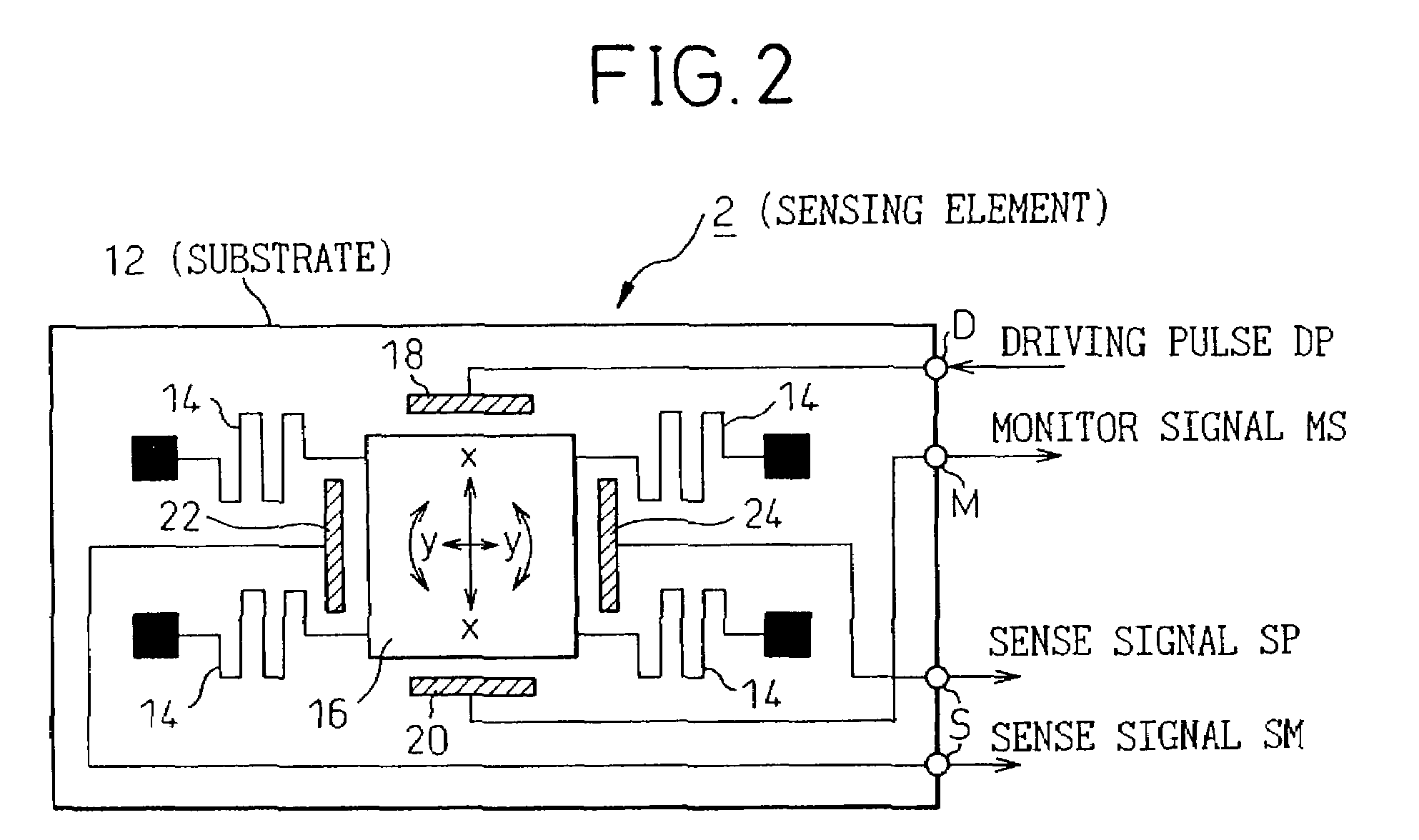
ActiveUS7068744B2Effectively minimizedMinimize high-frequency noiseAcceleration measurement using interia forcesError preventionMoving averageGyroscope
The present invention is intended to efficiently minimize high-frequency noise stemming from synchronous detection without the necessity of a low-pass filter that requires a large time constant. A vibratory gyroscope includes a synchronous detection unit that detects a sense signal sent from a sensing element using a reference signal synchronous with a monitor signal. In the vibratory gyroscope, an analog moving-average filter that produces a moving average of the detection signal by sampling the detection signal during one cycle of the reference signal is used to remove high-frequency noise components from the detection signal, which is detected to be synchronous with the reference signal, without the necessity of a CR filter that requires a large time constant. Consequently, unnecessary noise components whose frequencies are equal to the frequency of the reference signal and those of its harmonics, and which stem from synchronous detection, can be efficiently attenuated owing to an infinite attenuation frequency band offered by the analog moving-average filter.
Owner:DENSO CORP
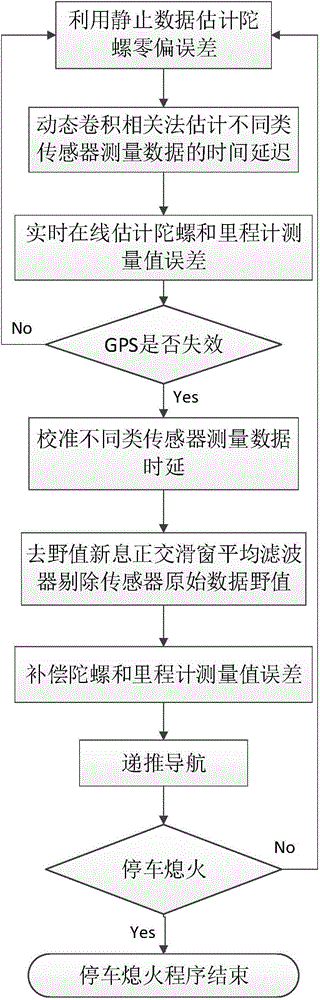
Vehicle-mounted integrated navigation method of resisting to failure of global positioning system
InactiveCN103983997AImprove estimation accuracySmall dispersionNavigation by terrestrial meansSatellite radio beaconingGyroscopeTime delays
The invention provides a vehicle-mounted integrated navigation method of resisting to failure of a global positioning system, and relates to a GPS-failure-resisting integrated navigation method suitable for a vehicle-mounted low-cost integrated navigation system. The vehicle-mounted integrated navigation method of resisting to failure of the GPS comprises the following steps that firstly, relative time delay of measurement data of different types of sensors is estimated with the dynamic convolution correlation method, and output data of three types of sensors which are the GPS, a gyroscope and the speed sensor are corrected according to the relative time delay; secondly, outliers of original data of the three types of sensors are removed through an outlier-removing innovation orthogonality sliding window average filter, and the discrete degree of the data is reduced; thirdly, error coefficients of the gyroscope and the speed sensor are estimated online in real time in the effective status of the GPS, and compensation for the error coefficients is conducted; fourthly, when failure of the GPS occurs, the recursive algorithm is started and the position information and course information are given. According to the vehicle-mounted integrated navigation method of resisting to failure of the GPS, the problem that error drifting of the vehicle-mounted low-cost gyroscope and the speed sensor is rapid is solved, position and course accuracy is improved obviously, and the vehicle-mounted integrated navigation method of resisting to failure of the GPS can be used for various vehicle-mounted navigation systems comprising GPSs, gyroscopes and speed sensors.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
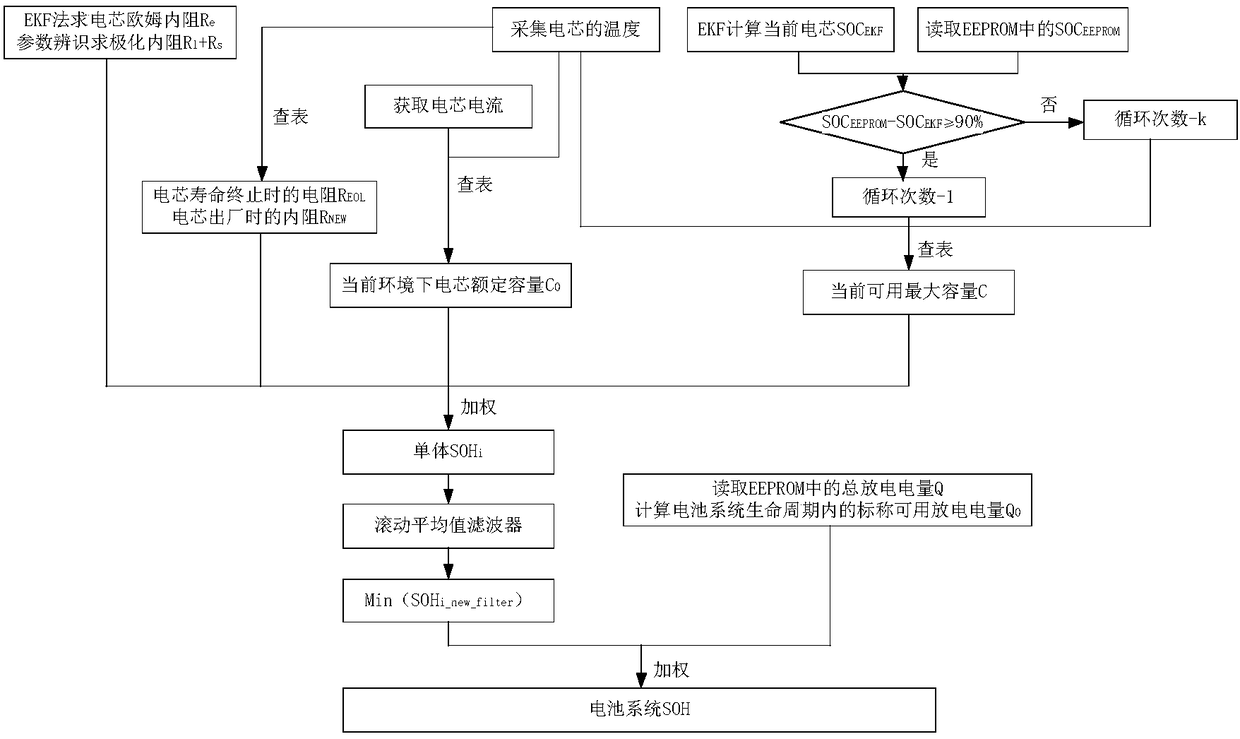
Method for estimating SOH of battery
InactiveCN108549032AEstimated results are accurateElectrical testingState of healthInternal resistance
The invention discloses a method for estimating the state of health (SOH) of a battery. The method comprises: a rated capacity of a current electric core in a current environment is obtained by a temperature and charge and discharge rates; an SOC value of the current electric core is calculated; a corresponding residual cycle index is obtained; a current available maximum capacity of the electriccore is obtained; a resistance value REOL at the end of the life of the electric core and an internal resistance value of the electric core going out of the factory are acquired; according to a second-order RC ring model, an actual internal resistance of the electric core is calculated; a single healthy state of an ith battery at a current time is calculated; filter calculation is carried out on the single healthy state SOHi of the ith battery at the current time by a rolling average filter; a nominal available discharge electricity quantity in the battery system life cycle is obtained; and the SOH of the battery system is calculated. According to the invention, estimation of the state of health of the battery is carried out by integrating parameters of the single battery and the battery system; and because of consideration of influence factors like the temperature, the cycle number and the internal resistance for SOH estimation of the battery, the estimation result accuracy is improved.
Owner:BEIJING ZHIXING HONGYUAN AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
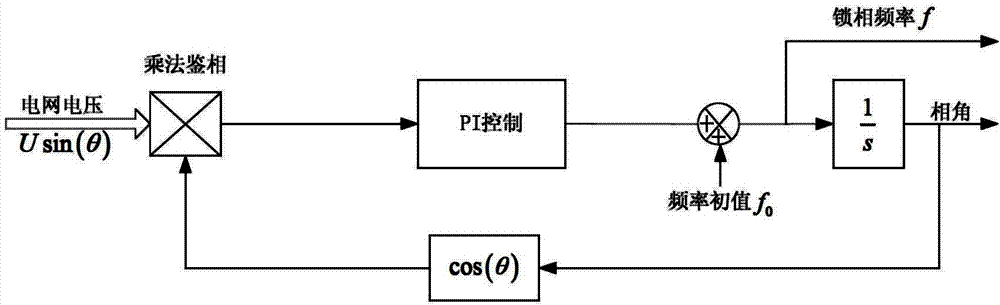
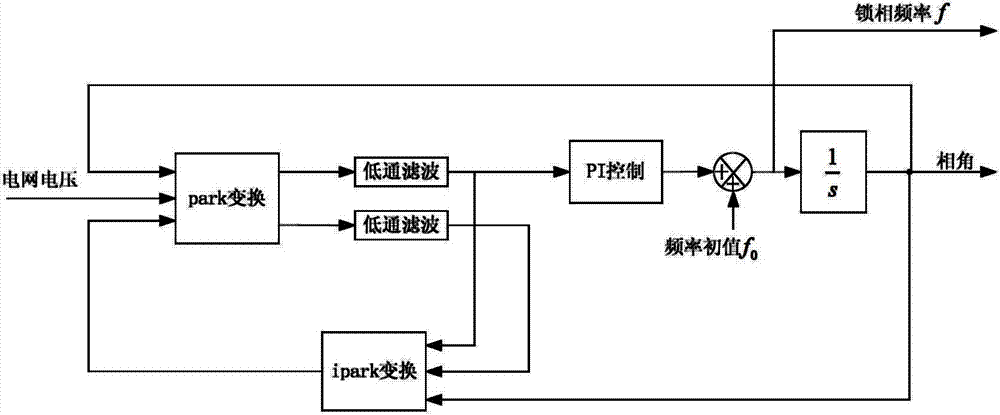
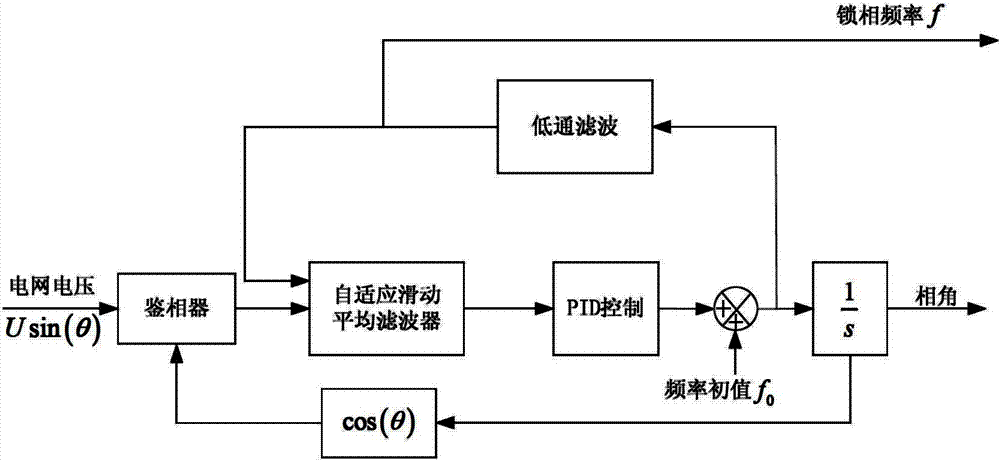
Self-adaptive grid-tied converter single phase soft phase-locked loop
ActiveCN102904568AGuaranteed speedGuaranteed dynamic performancePulse automatic controlMoving averageDiscriminator
The invention discloses a self-adaptive grid-tied converter single phase soft phase-locked loop. The self-adaptive grid-tied converter single phase soft phase-locked loop comprises a phase discriminator, a low pass filter, a loop filter and an integrator module, wherein the loop filter is composed of a self-adaptive moving average filter and a proportion integration differentiation (PID) regulator, the phase discriminator is a multiplication phase discriminator, an input signal is a trigonometric function of an output angle of power grid voltage and a phase-locked loop, and an output signal is transmitted into the moving average filter; an input signal of the moving average filter is output of the phase discriminator and output of the low pass filter, and the output signal is transmitted to the PID regulator; and an input signal of the PID regulator is an output signal of the moving average filter, and the output signal is transmitted into the low pass filter and the integrator module. The self-adaptive grid-tied converter single phase soft phase-locked loop has the advantages that the loop filter is improved, effects of secondary ripple and harmonic voltage on phase lock result in the steady state are eliminated, and simultaneously the rapidity of the phase lock is guaranteed.
Owner:西安奥特迅电力电子技术有限公司 +2
Method of down-chain power control in packet switching cellular system
InactiveCN1395375AAvoid uncertaintyReduce failurePower managementEnergy efficient ICTAverage filterDownlink power control
The invention discloses a method to perform downlink Power Control in packet switching cellular systems with dynamic allocation of the RF channel, such as GPRS / EGPRS. The performances concern a scenario in which a radio block transmitted from the Base Station (BTS) on a downlink channel has to be received from at least two MSs simultaneously, a first MS being the addressee of the data / control packet on the downlink TBF while the second MS being the addressee of the Uplink State Flag (USF) for scheduling transmission of the next data / control packet from an uplink TBF to an uplink shared channel. First MS transmits to the BTS a first measurement report including measures of BCCH level and interference level on all the timeslots, while the second MS transmits a NC report including measures of BCCH level only, that because detailed interference measure on the downlink channel are prevented due the absence of a concurrent downlink TBF. The measures are averaged in as many running average filters and the averages compared with target thresholds to find a first and a second power reduction intended for USF and packet transmission respectively. A final power reduction is selected from the two for the next PC execution step. Target threshold for the first MS's averaged measures is a C / I value which provides maximum achievable net throughput independently of Coding Scheme. Target threshold for the second MS depends on CS of the USF flag in a way that when the mean value of the level measures is equal to the threshold a fixed probability takes place that the USF flag is decoded with success. The network, in the capacity of the BSC and PCU, counts successfully and unsuccessfully blocks received uplink upon transmission of the scheduled USFs for that uplink TBF, being the lack of a scheduled block noticed by the network. If successfully counting reaches a fixed maximum counting before, then an increment of the first power reduction is decided, while in case the maximum unsuccessfully counting is reached before a decrement of the first power reduction is instead decided (fig.10).
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
Six-axes robot kinetic parameter identification method based on neural network
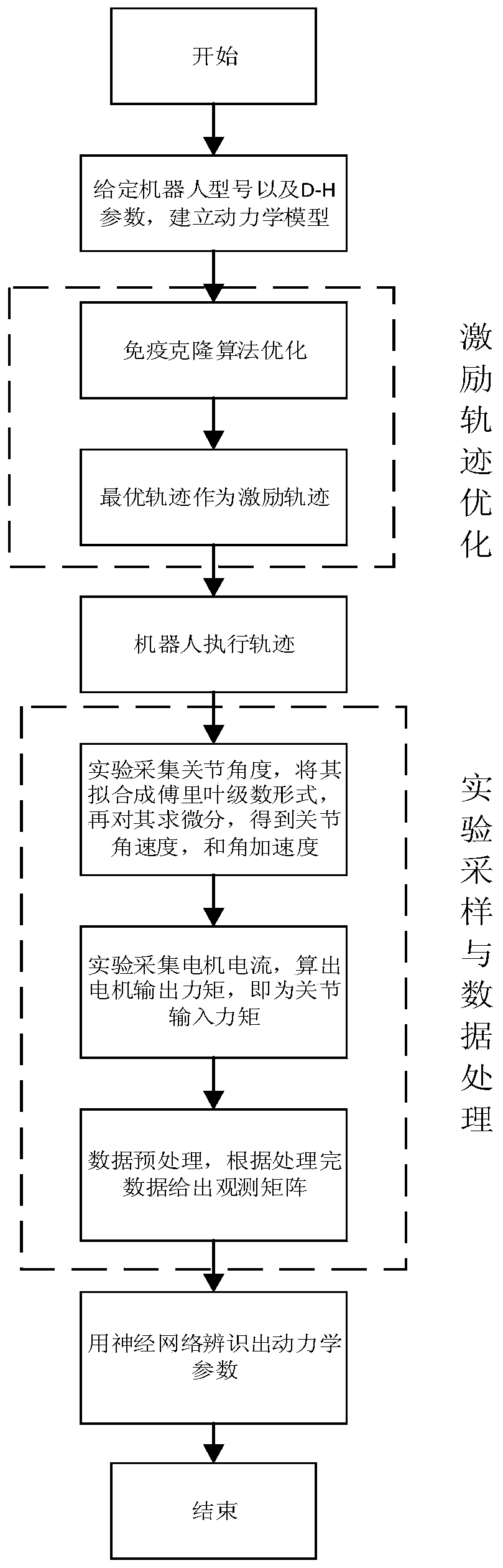
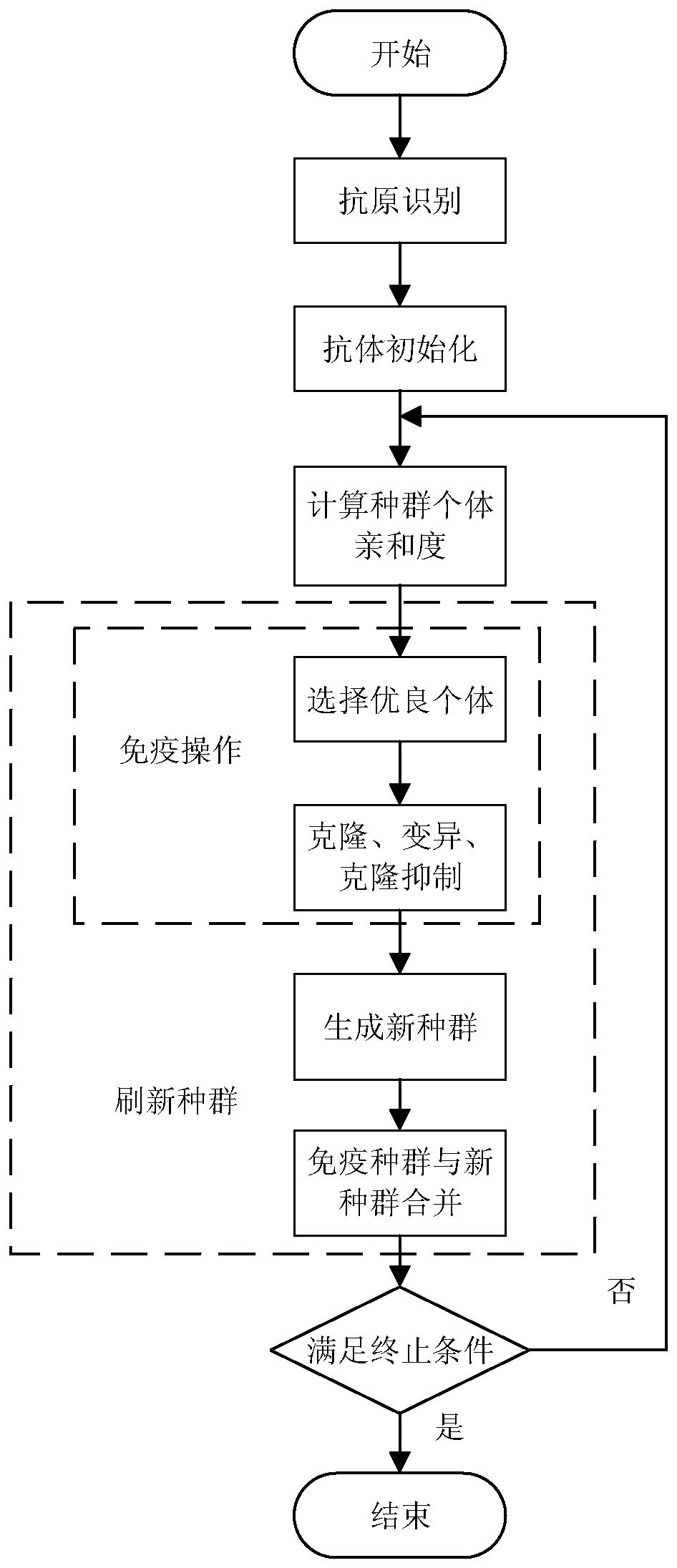
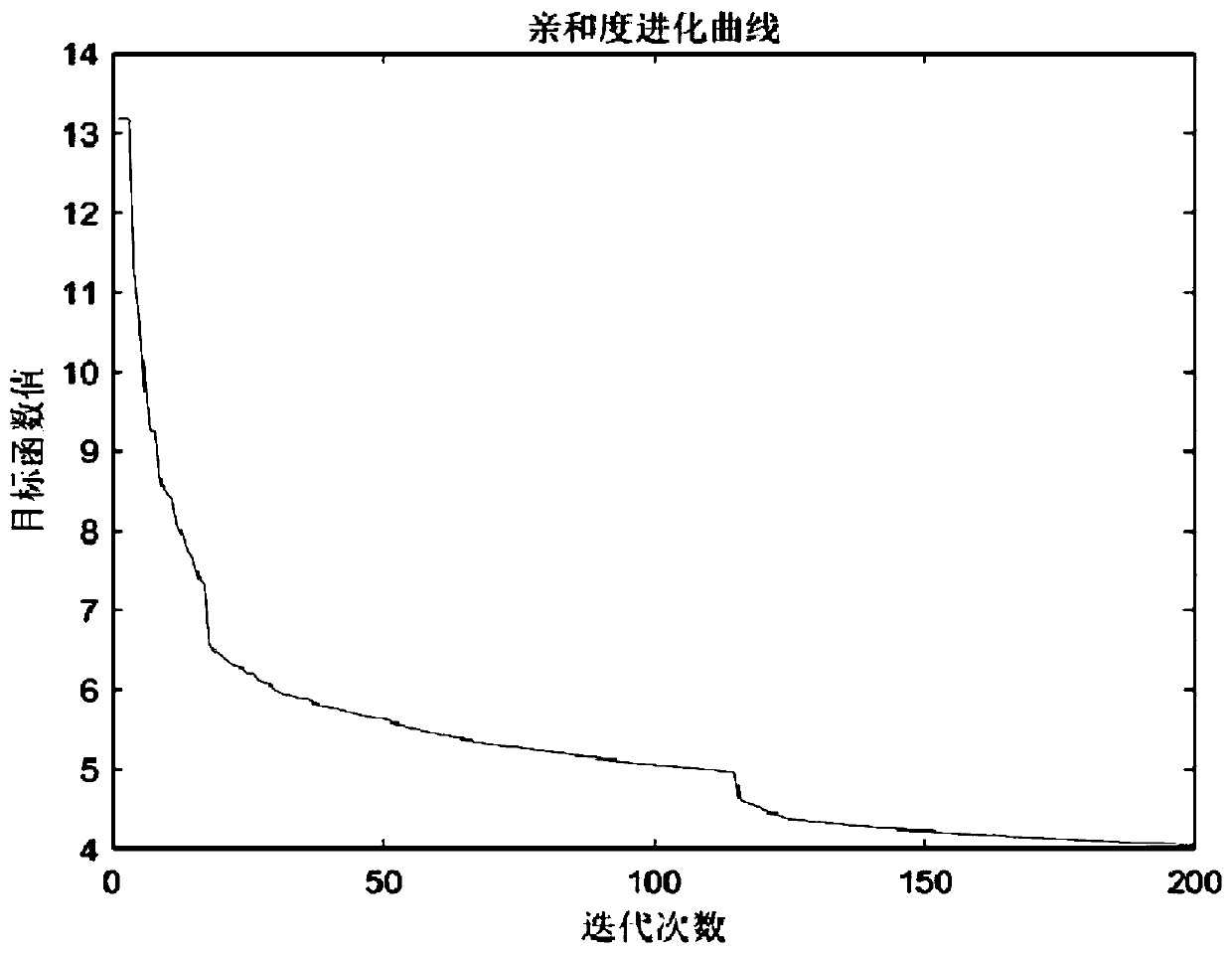
ActiveCN109773794AFast convergenceSuppress random disturbanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsAverage filterObservation matrix
The invention discloses a six-axes robot kinetic parameter identification method based on a neural network. The six-axes robot kinetic parameter identification method comprises the following steps that firstly, robot kinetic modeling and linearization are conducted; secondly, motivation trajectory optimization is conducted, and specifically a motivation trajectory is optimized through an artificial immune algorithm; thirdly, experiment sampling is conducted, specifically a robot moves along the motivation trajectory, and multiple sets of observation matrices and joint torque are obtained as experiment data; fourthly, data processing is conducted, the data collected in an experiment are preprocessed through a three standard deviation norm and a median average filter method, and the influence brought by data noise is lowered; fifthly, kinetic parameter estimation is conducted, and kinetic parameters are estimated through the neural network; and sixthly, parameter verification is conducted, the robot follows an executable trajectory different from the motivation trajectory, experiment data are sampled again, theoretical joint torque is predicted according to kinetic parameters obtained by identification, and reliability of the identified kinetic parameters is evaluated with the torque residual root.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Video noise reduction method using adaptive spatial and motion-compensation temporal filters
ActiveUS7729555B2Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionAverage filter
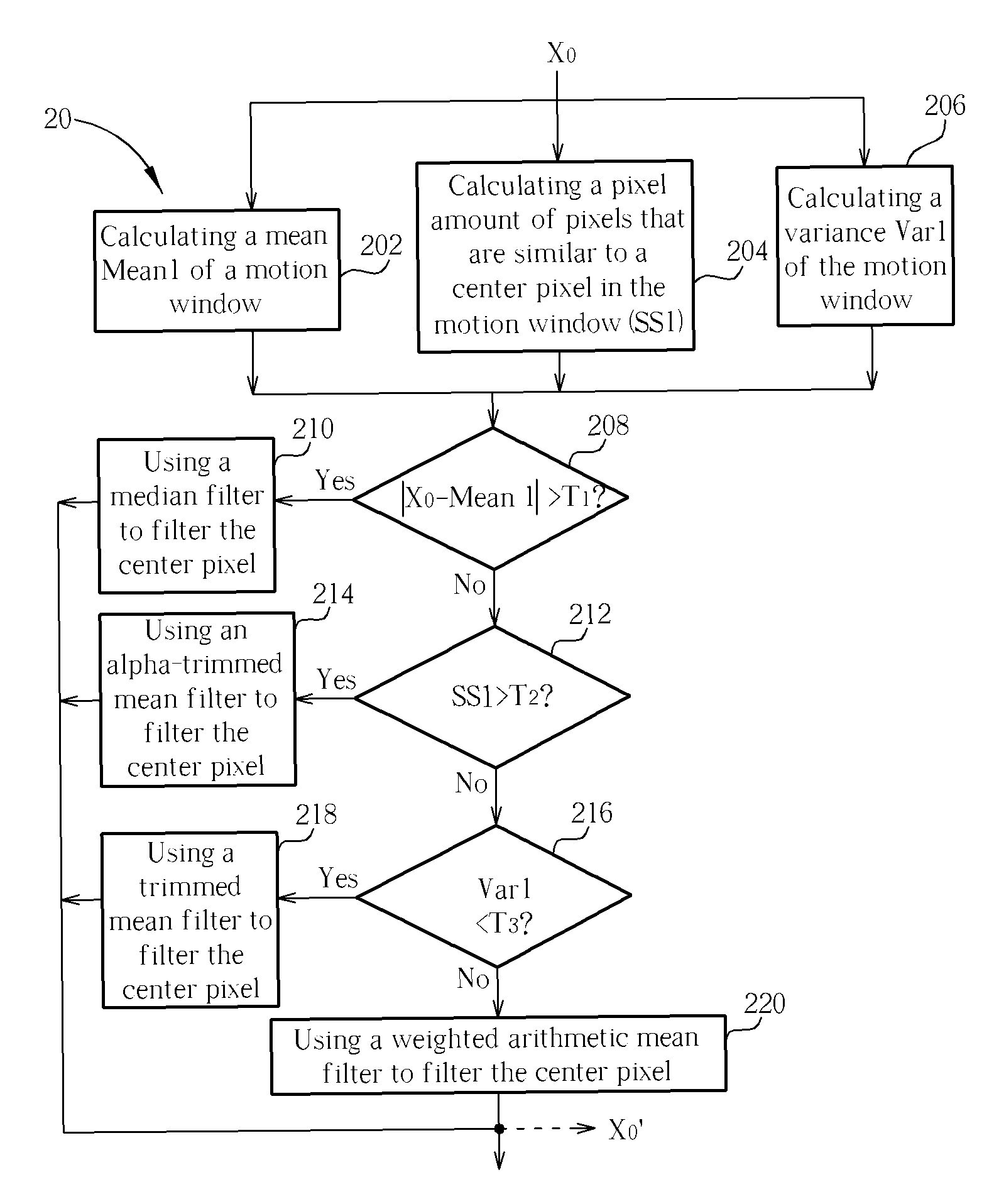
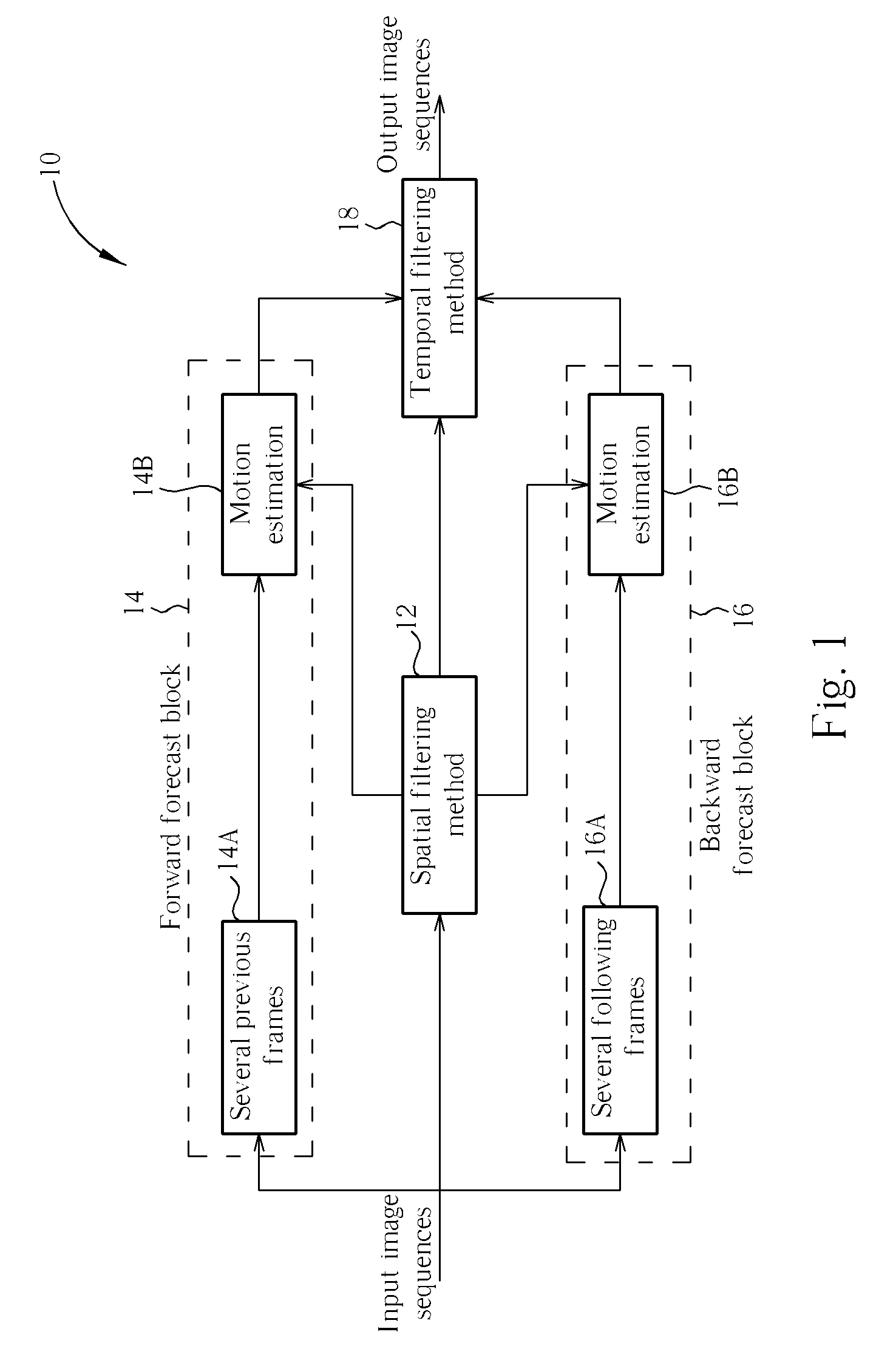
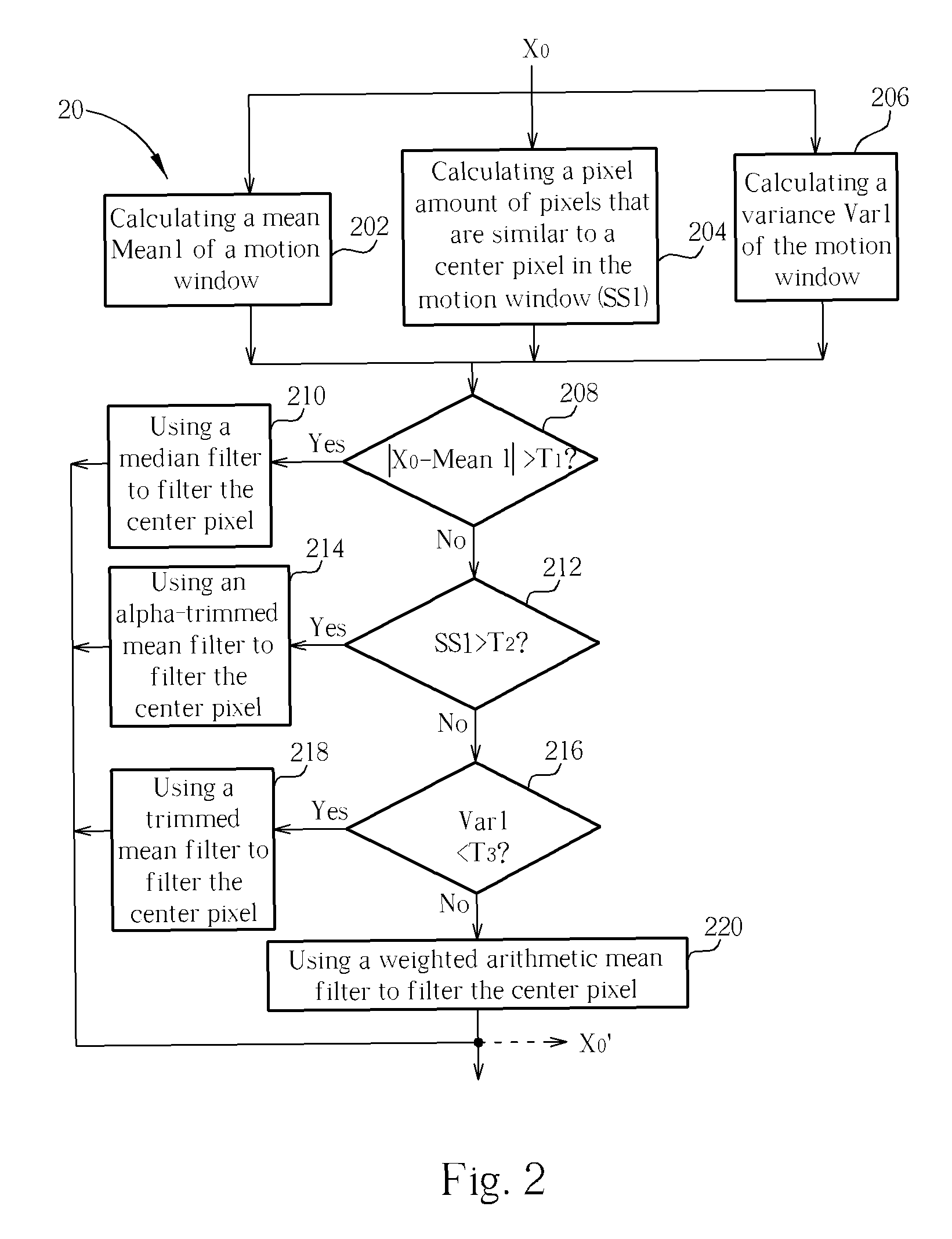
A method includes calculating a mean of a plurality of pixels of a motion window, calculating a pixel amount of pixels similar to a center pixel, calculating a variance of the pixels, determining whether a difference between the center pixel and the mean is greater than a first predetermined value, determining whether the pixel amount similar to the center pixel is greater than a second predetermined value if the difference between the center pixel and the mean is not greater than the first predetermined value, determining whether the variance is smaller than a threshold value if the pixel amount similar to the center pixel is not greater than the second predetermined value, and filtering the center pixel according to a result of determining whether the variance is smaller than the threshold value. Finally, temporal weighted mean filters involving motion estimation are used for motion compensation in images after spatial filtering.
Owner:HUPER LAB
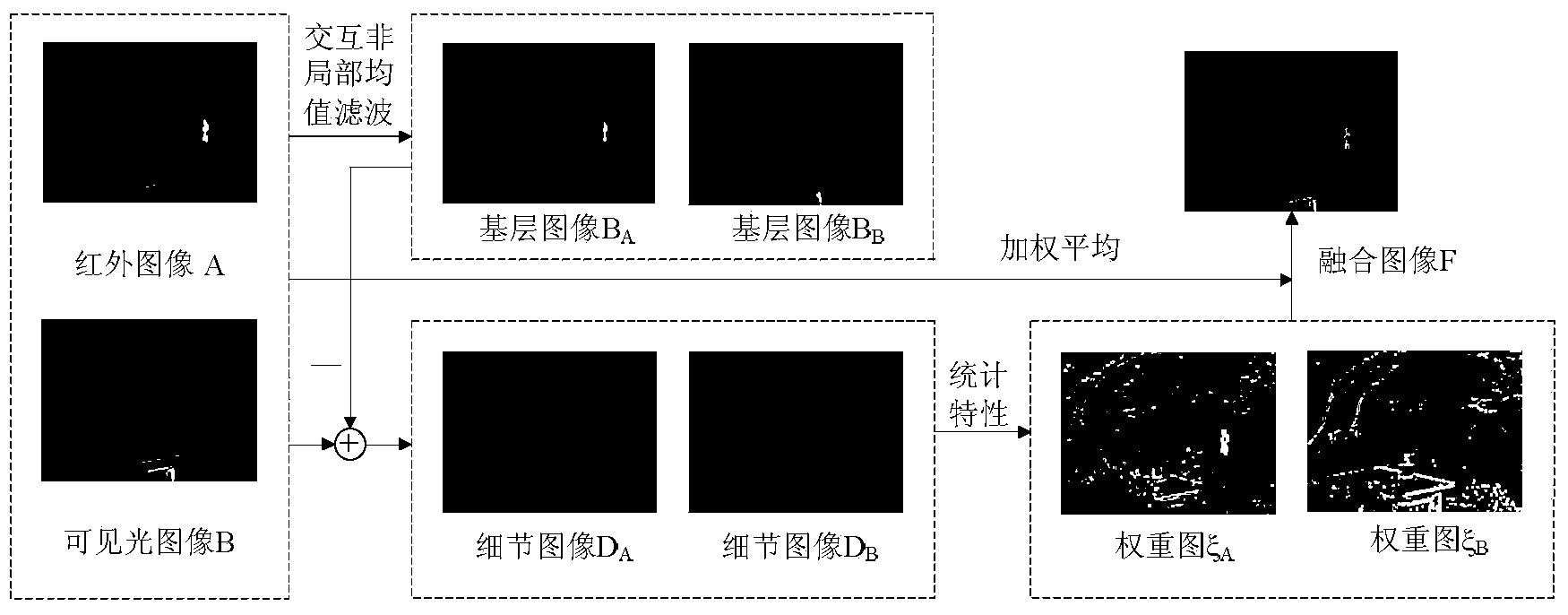
Infrared light image and visible light image fusion method based on interactive non-local average filtering
The invention relates to an infrared light image and visible light image fusion method based on interactive non-local average filtering. The method mainly aims to solve the problems that a fused image obtained through an existing infrared light image and visible light image fusion method is low in definition, contrast and spatial resolution. The method comprises the implementation steps of (1) carrying out interactive non-local average filtering on an input infrared light image and an input visible light image to obtain base layer images; (2) subtracting the corresponding base layer image from the infrared light image to obtain a detail image of the infrared light image, and subtracting the corresponding base layer image from the visible light image to obtain a detail image of the visible light image; (3) calculating the neighboring window statistical characteristics of the detail images to obtain a fusion weight plot of the infrared light image and a fusion weight plot of the visible light image; (4) enabling the fusion weight plot of the infrared light image and the fusion weight plot of the visible light image to act on the infrared light image and the visible light image respectively, and carrying out weight fusion on the infrared light image and the visible light image which have undergone action of the corresponding fusion weight plots to obtain a fused image. By means of the infrared light image and visible light image fusion method based on interactive non-local average filtering, the fused image high in definition, contrast and spatial resolution can be obtained, and the fusion effect is good. The infrared light image and visible light image fusion method based on interactive non-local average filtering can be used in the fields of human vision, machine cognition and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI RONGJUN TECH
Retinex image enhancing method and system
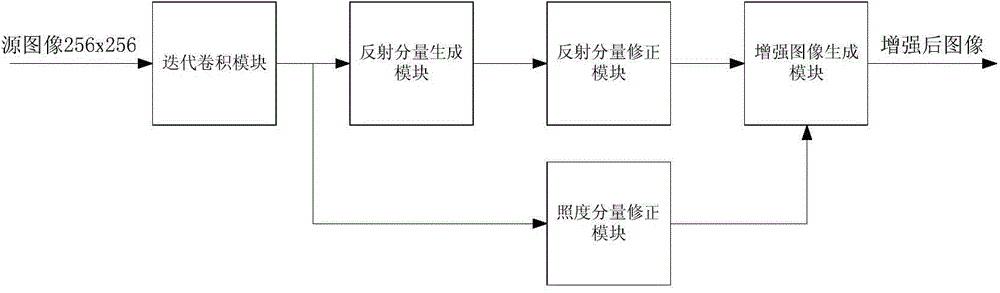
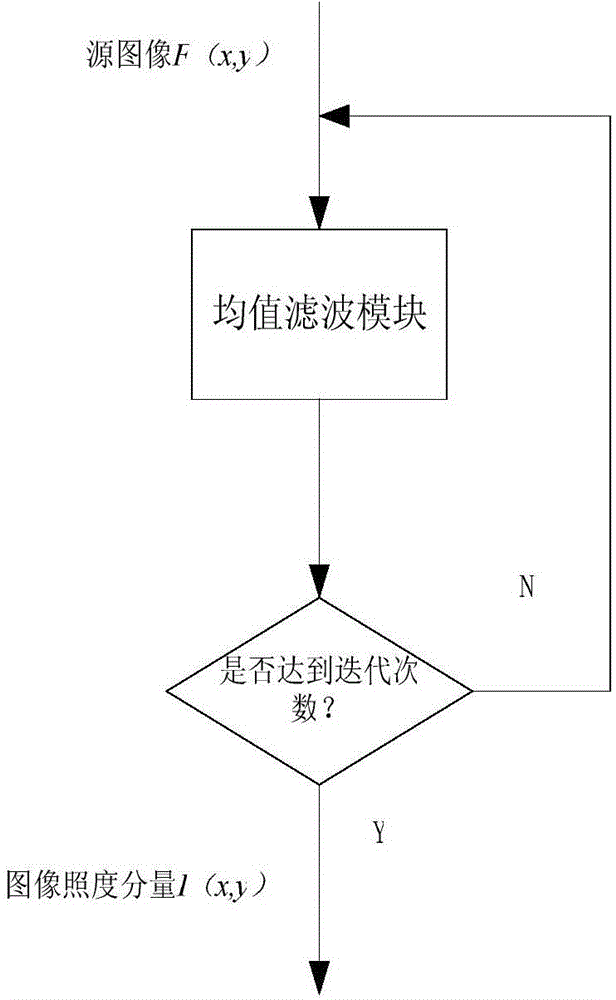
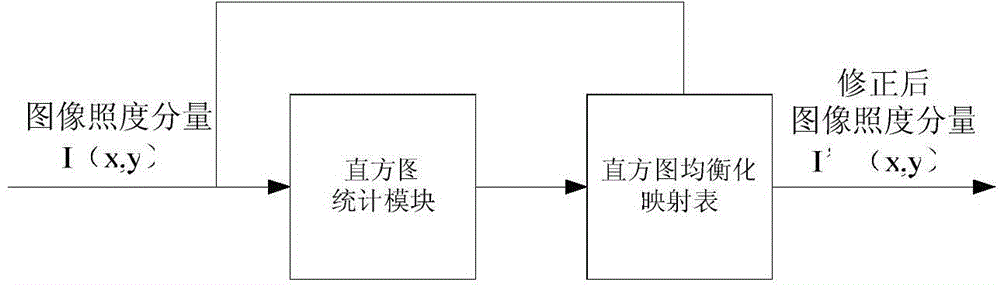
The invention provides a Retinex image enhancing method and a Retinex image enhancing system. The Retinex image enhancing method comprises the steps of: carrying out repeated average filtering iteration on a video source image acquired by a video camera to generate an image illuminance component; acquiring an image reflection component according to the source image and the image illuminance component; correcting the image illuminance component and the image reflection component; and calculating to obtain an image after Retinex image enhancement according to the corrected image illuminance component and the corrected image reflection component. The Retinex image enhancing system comprises an iterative convolution module, a reflection component generation module, an illuminance component correction module, a reflection component correction module and an enhanced image generation module, wherein the modules are implemented on an FPGA. The Retinex image enhancing method and the Retinex image enhancing system can be used for carrying out self-adaptive enhancement on images of different types, and ensure the real-time performance of image enhancement.
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com