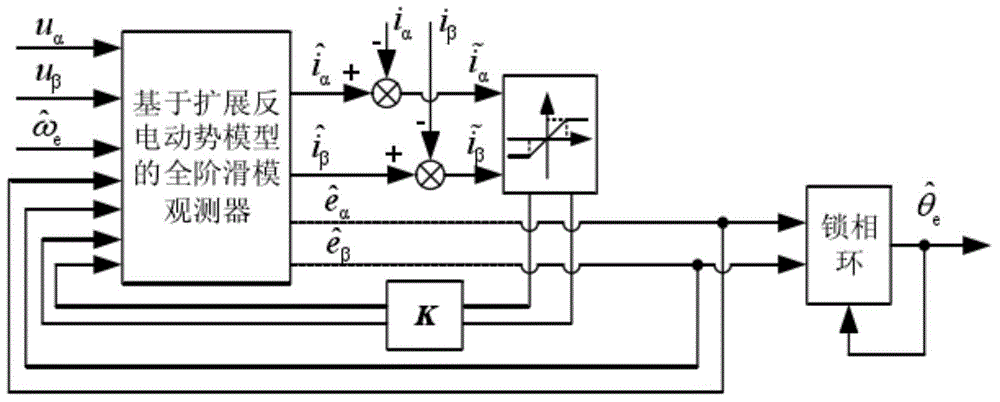
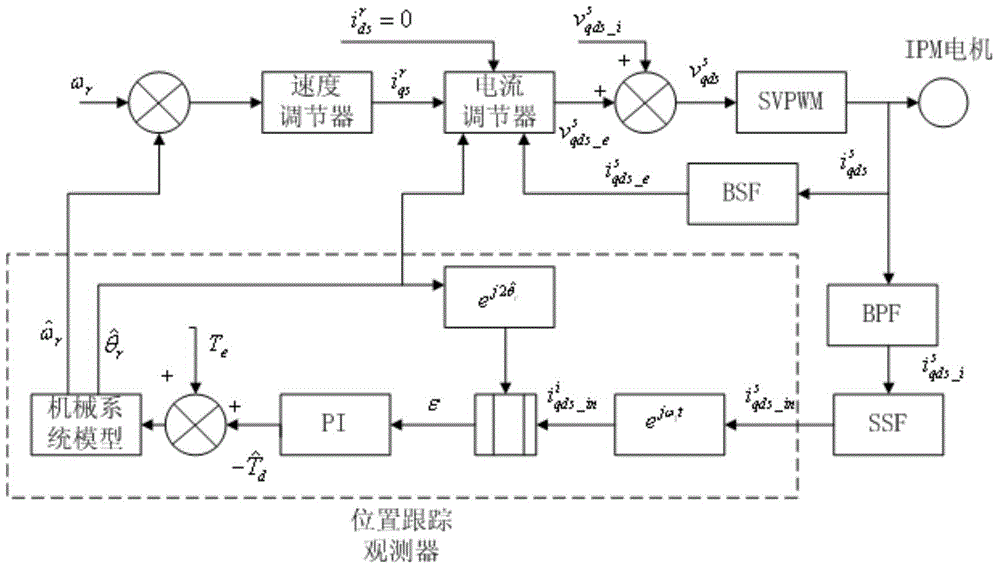
Patents
Literature
579 results about "Rotor angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
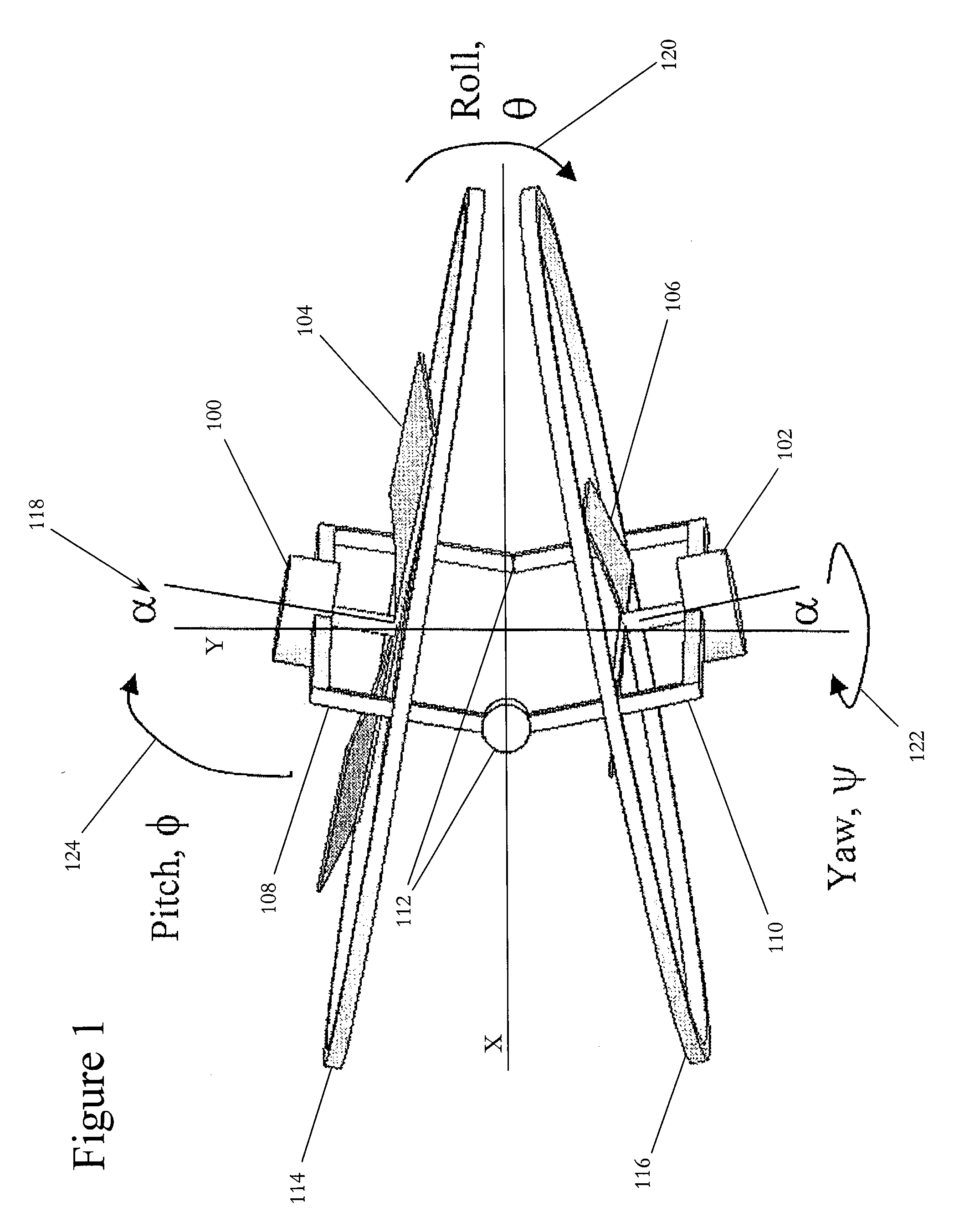
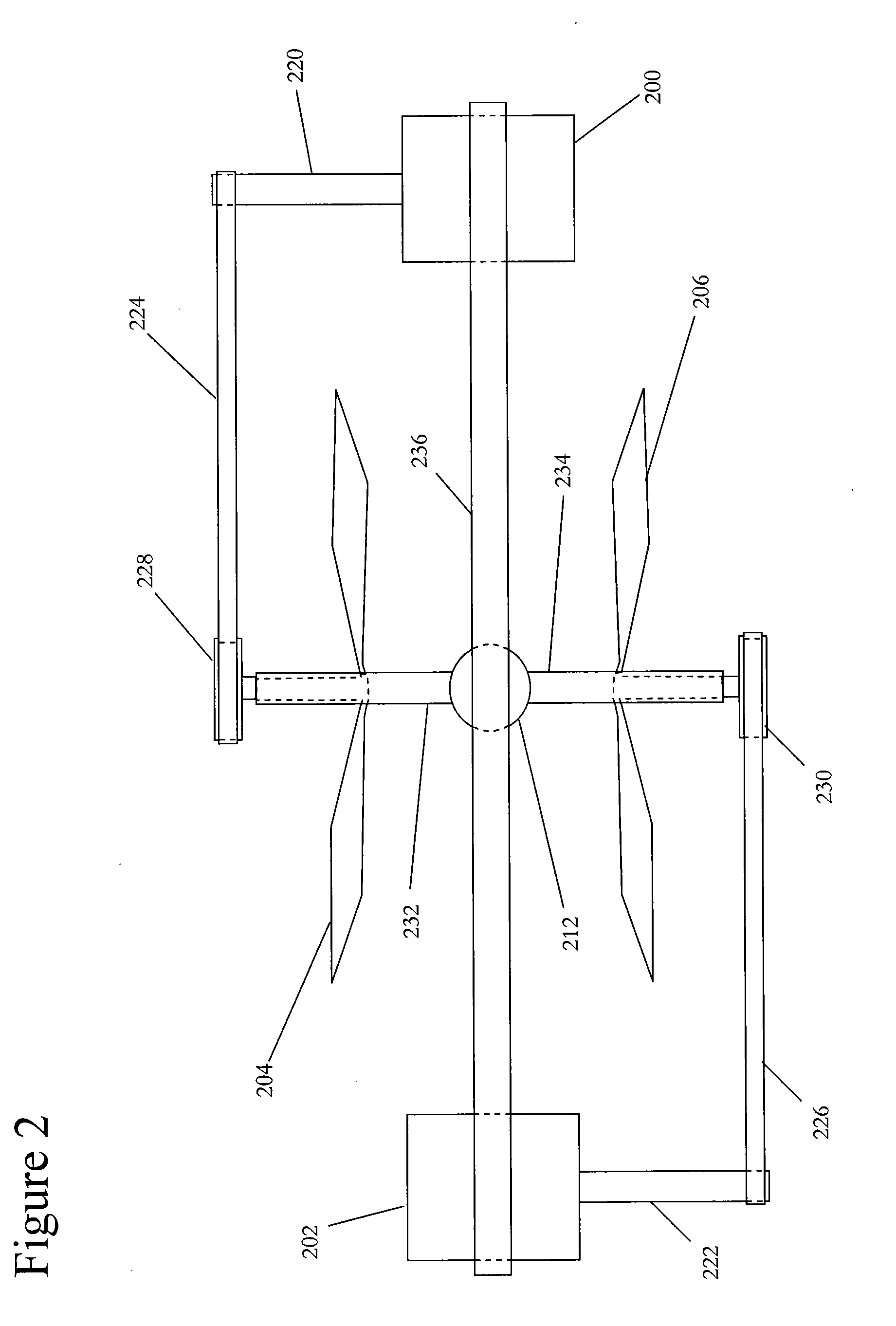
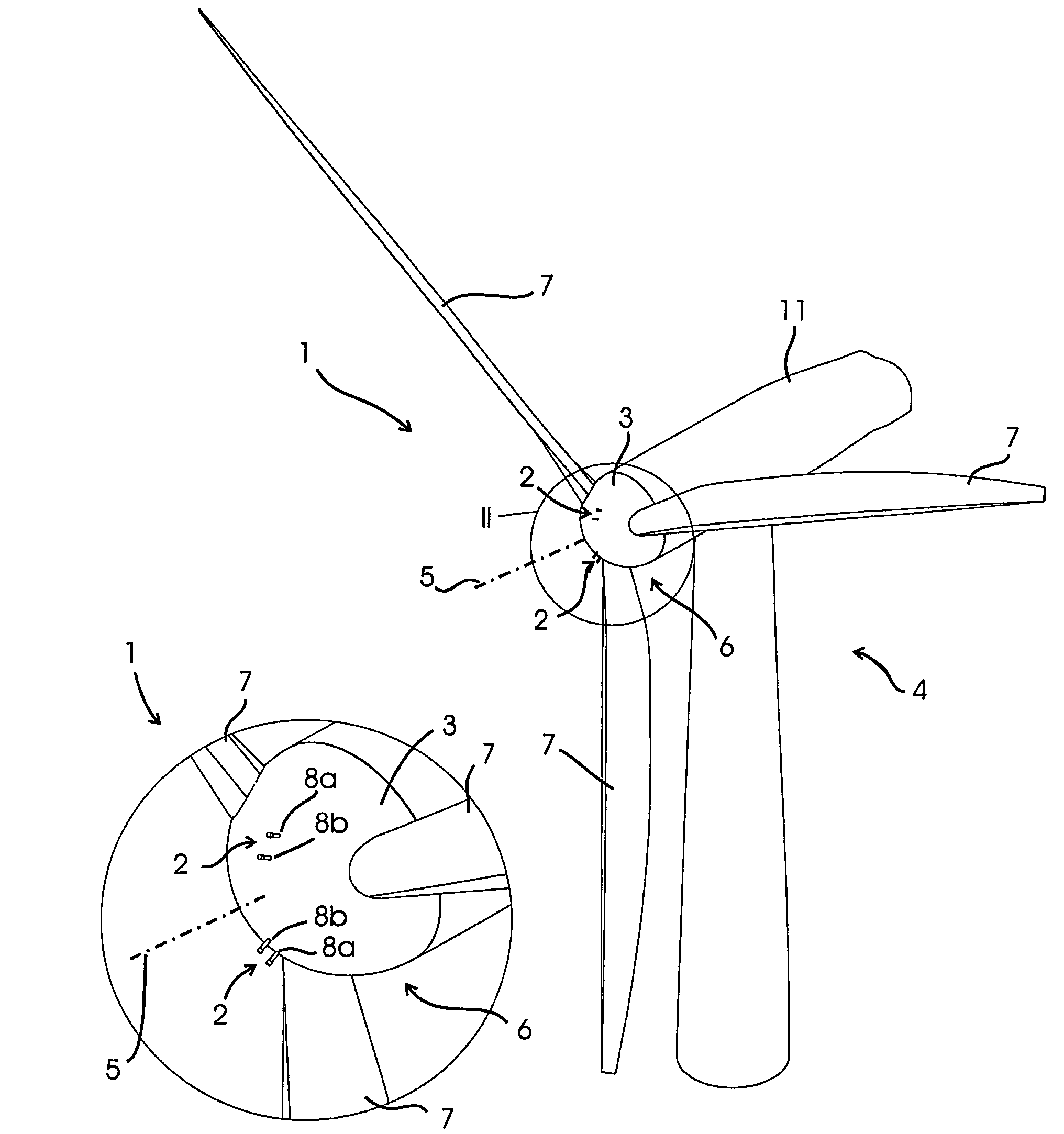
Rotor angle is the amount of turn or change in position, regarding angular measurement, made by a rotor: it can be measured as an arc length(if radius is known), or usually the use of degree, radian, gradian.
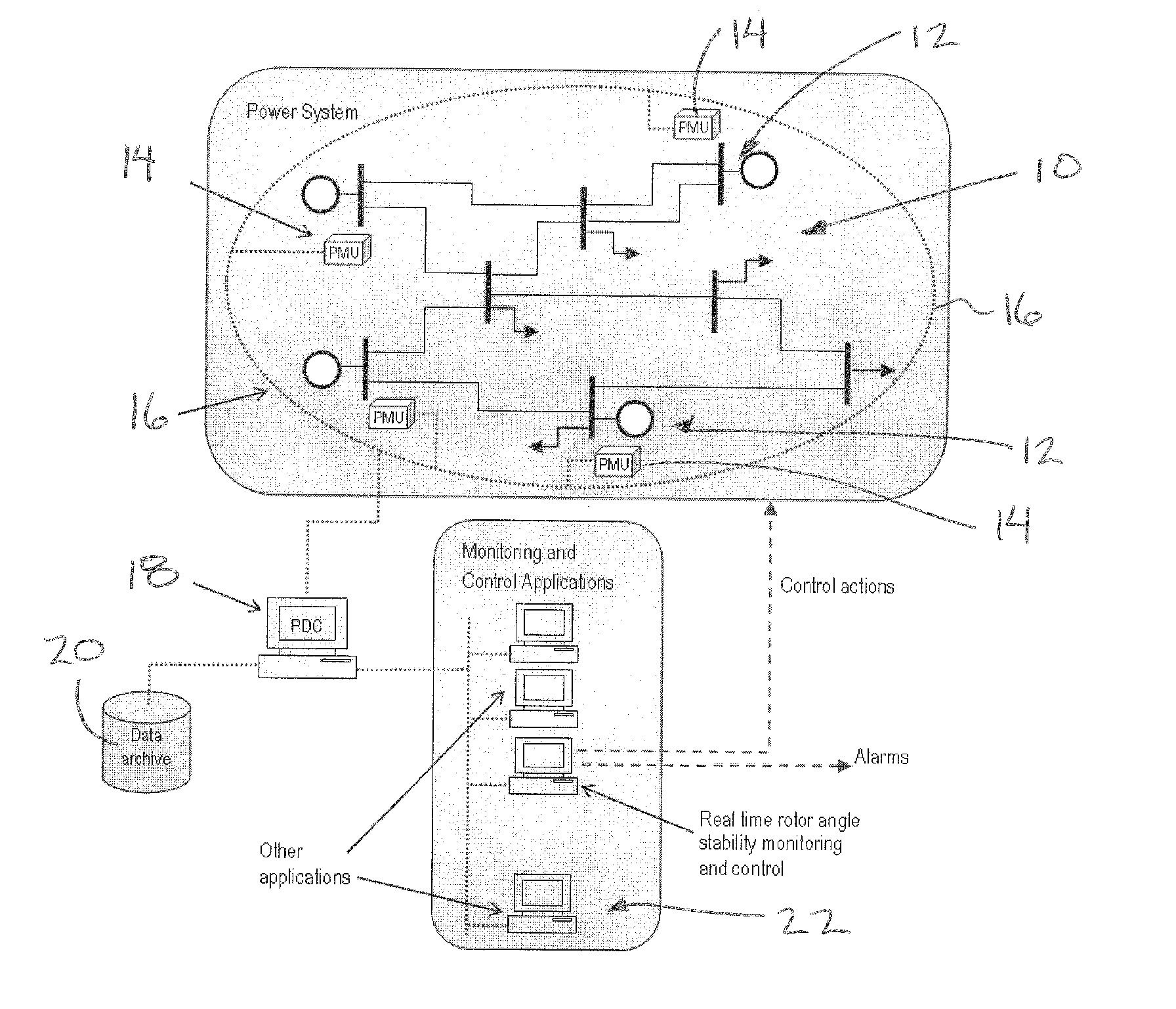
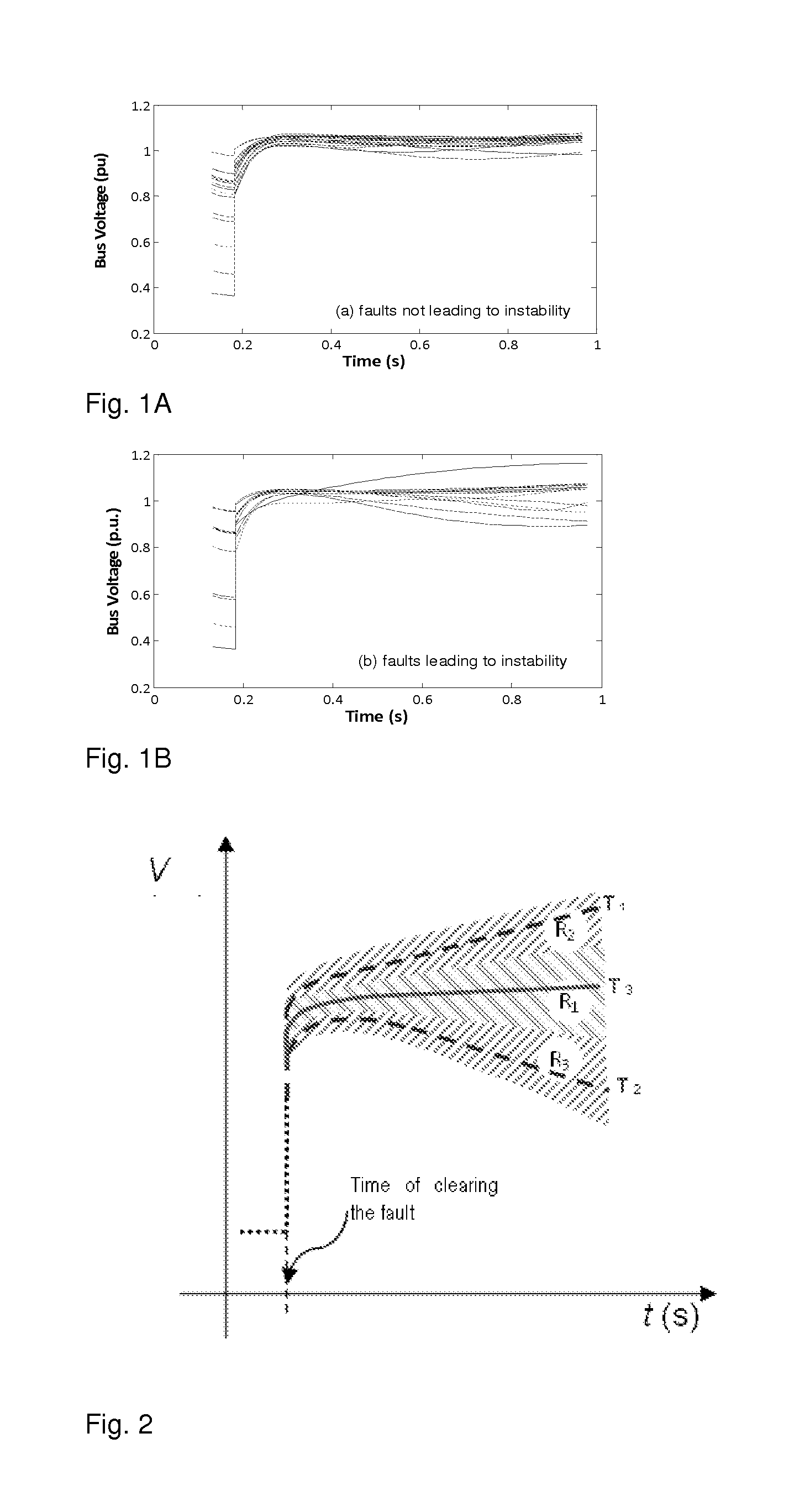
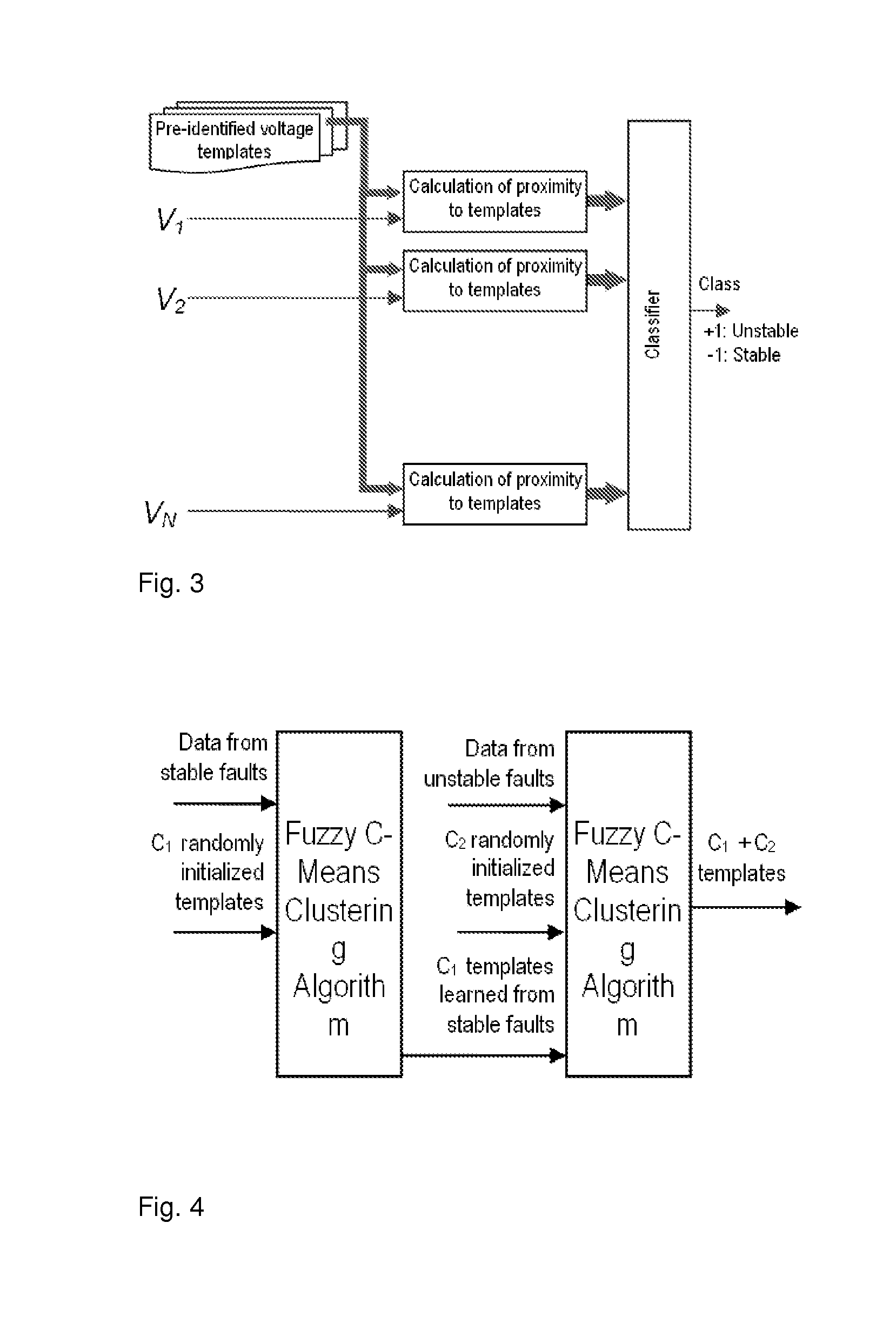
Rotor Angle Stability Prediction Using Post Disturbance Voltage Trajectories
ActiveUS20110022240A1Level controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDisturbance voltageSupport vector machine classifier
A new method for predicting the rotor angle stability status of a power system immediately after a large disturbance is presented. The proposed two stage method involves estimation of the similarity of post-fault voltage trajectories of the generator buses after the disturbance to some pre-identified templates and then prediction of the stability status using a classifier which takes the similarity values calculated at the different generator buses as inputs. The typical bus voltage variation patterns after a disturbance for both stable and unstable situations are identified from a database of simulations using fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm. The same database is used to train a support vector machine classifier which takes proximity of the actual voltage variations to the identified templates as features.
Owner:RAJAPAKSE ATHULA
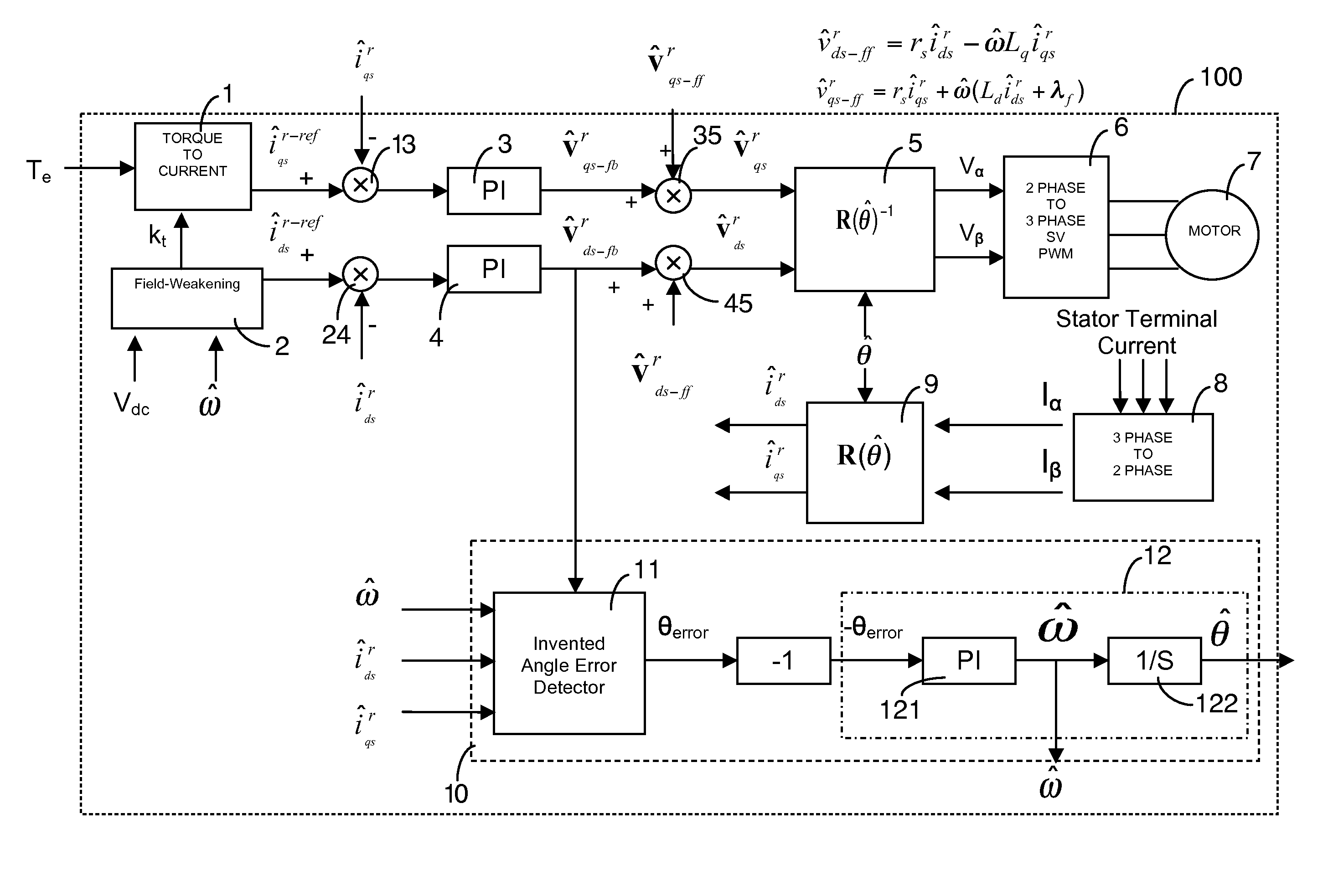
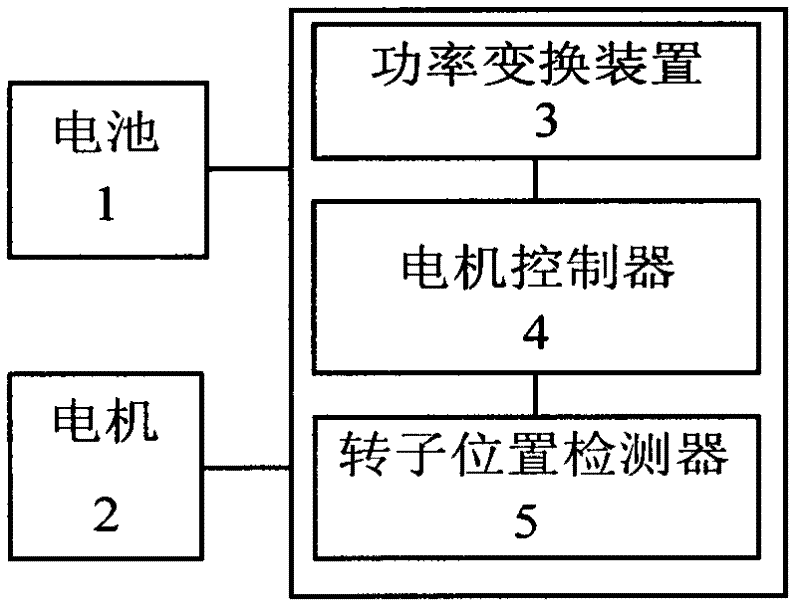
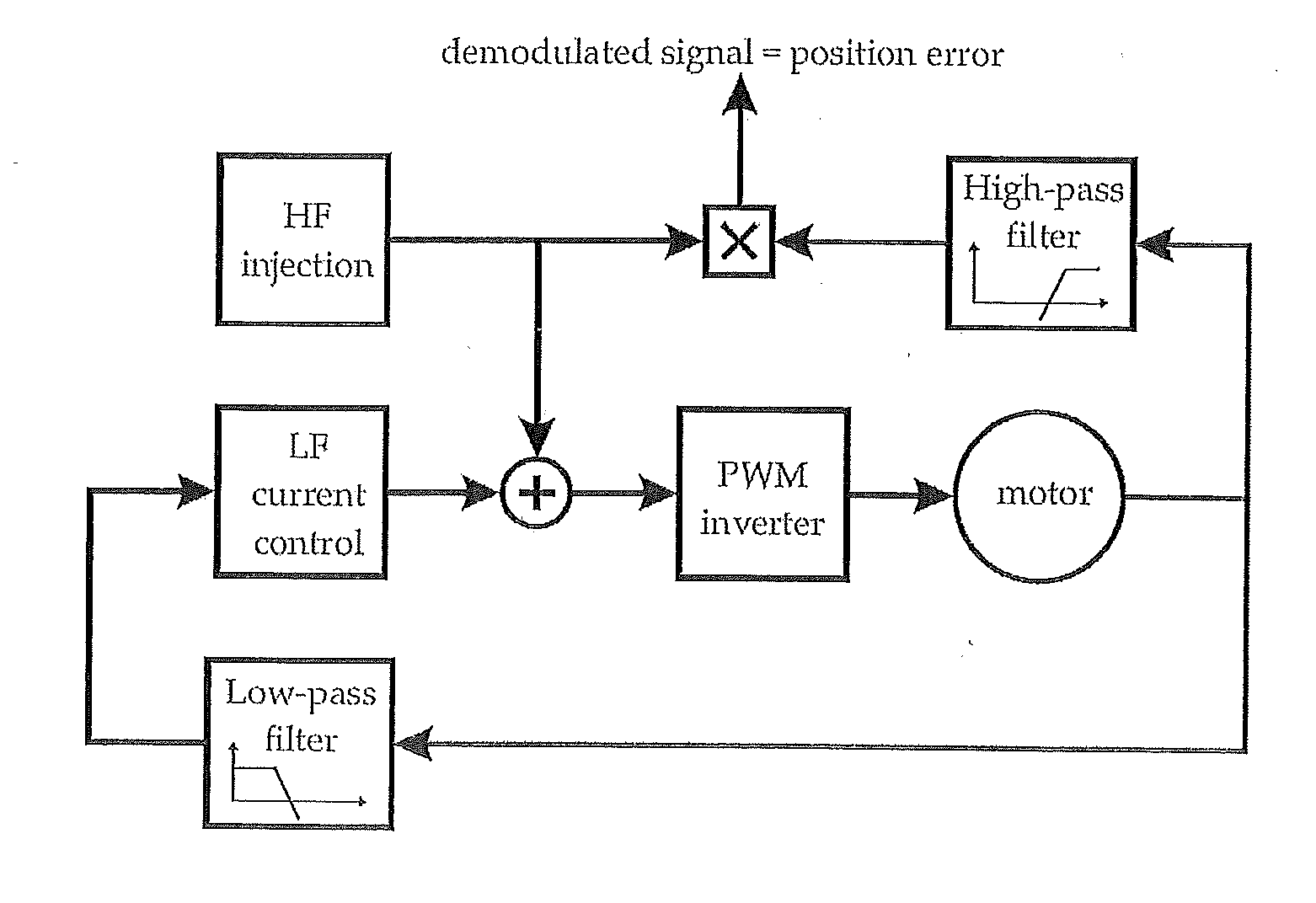
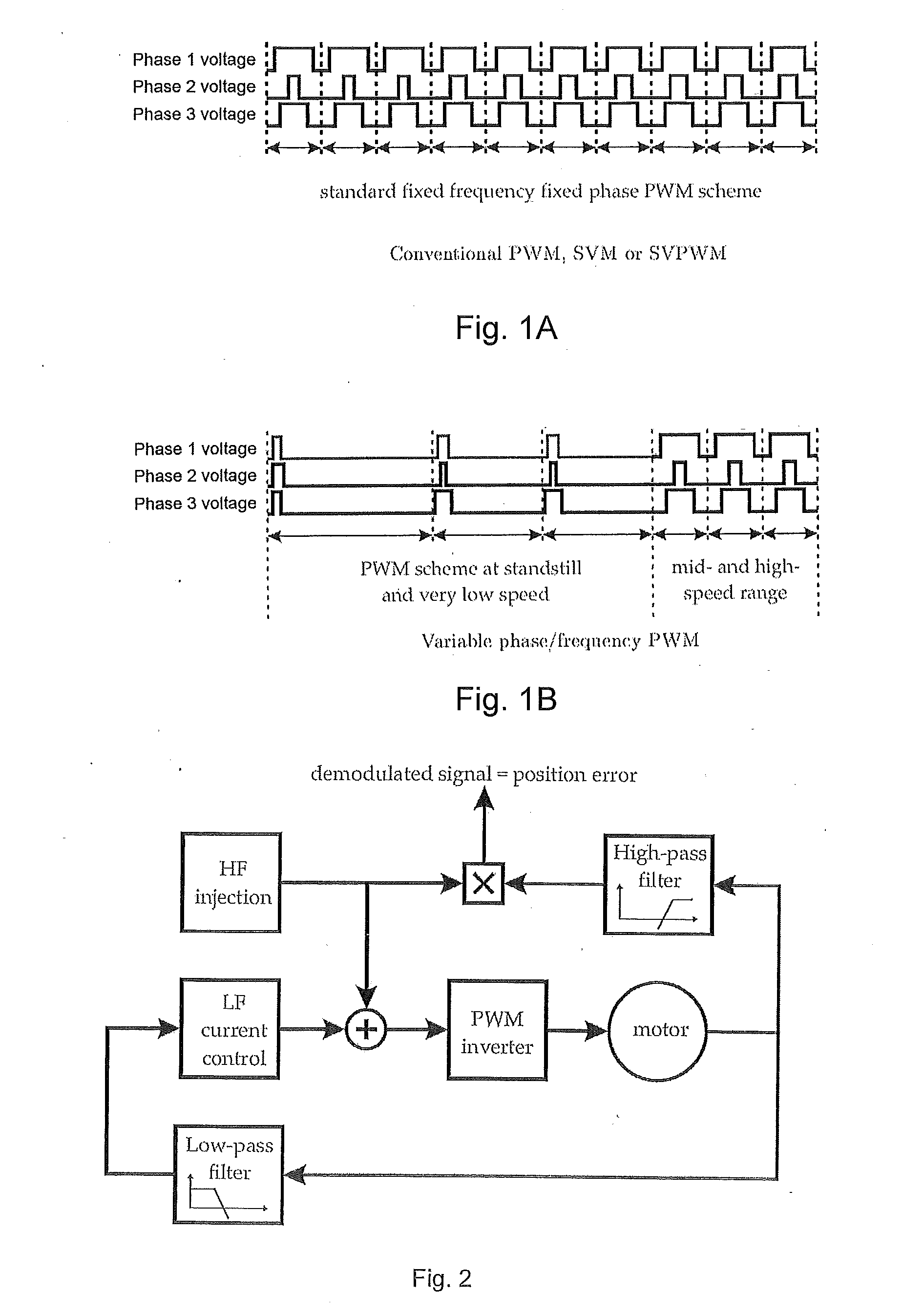
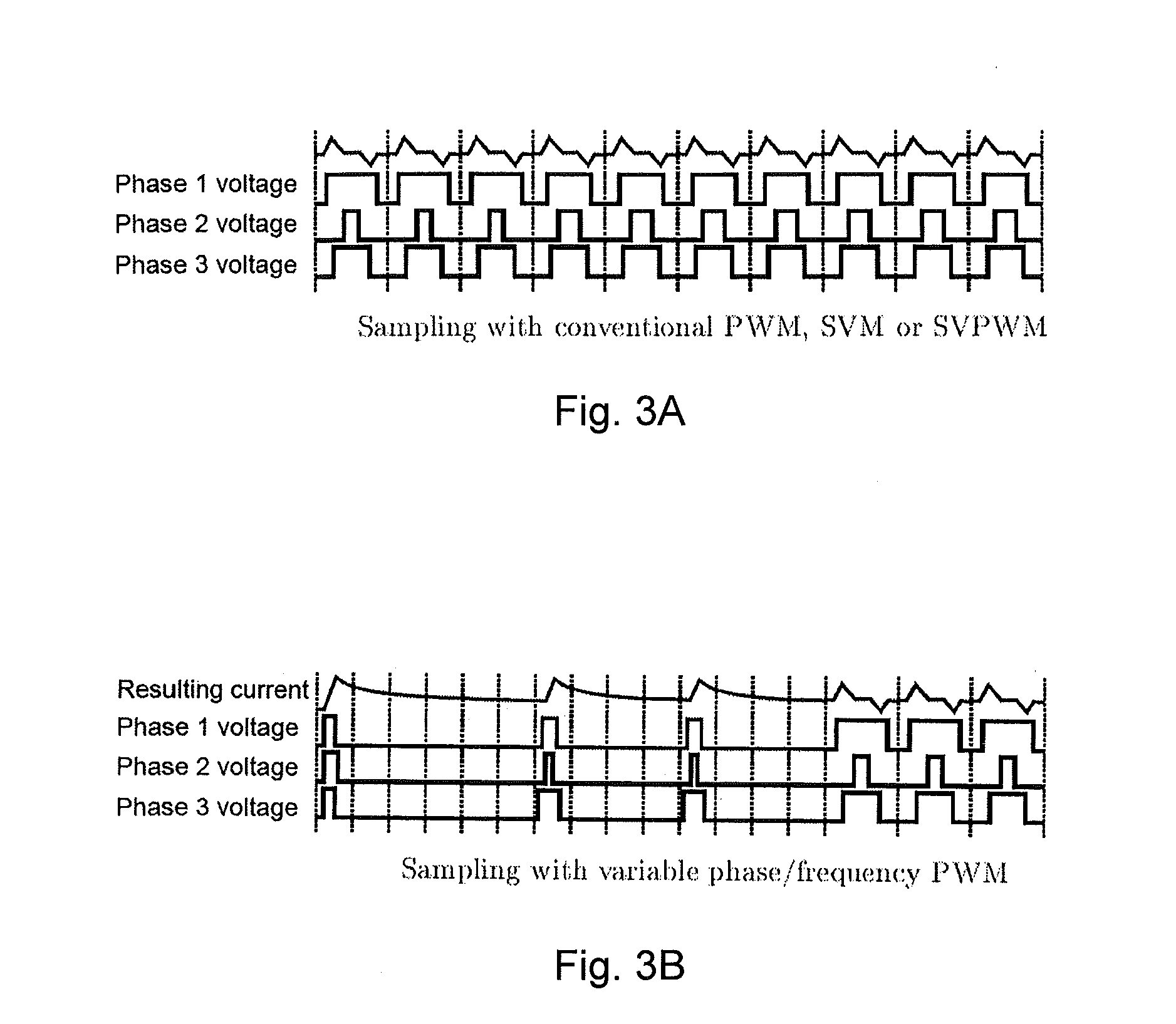
Position-sensorless control system and method of operation for a synchronous motor
InactiveUS20100109584A1Well formedMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlSynchronous motorControl system
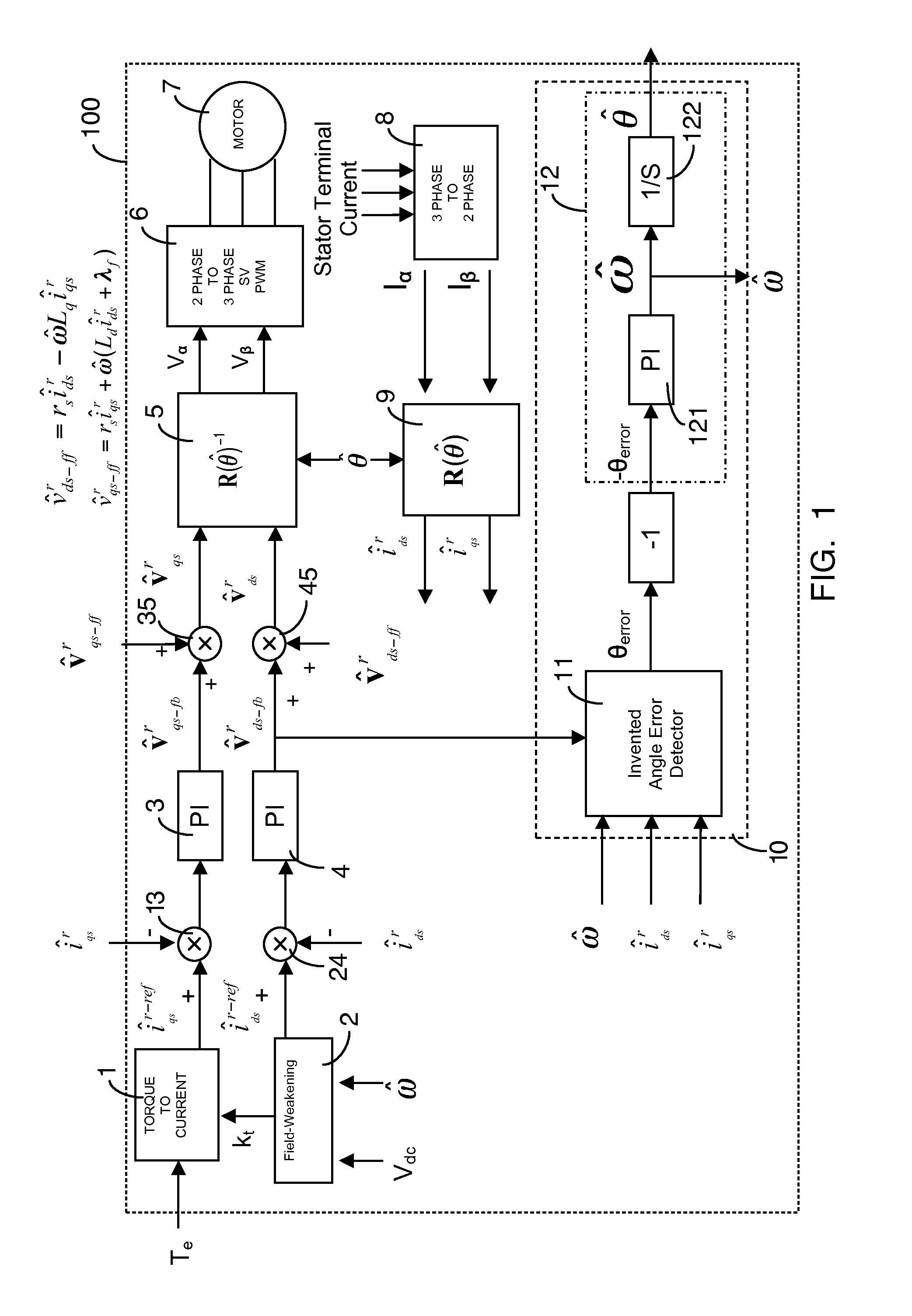
This invention provides an advanced position and velocity estimation scheme used in a position-sensorless control system for synchronous operation of an electric motor. The system includes an electric motor having a stator and a rotor; an inverter for powering the electric motor; and a controller for controlling the inverter. The controller utilizes a control system comprising a rotor angle and angular velocity estimation block; an estimated angle error detector block; a field-weakening block; and a torque-to-current converter block, all of which operate to generate control commands for operation of the motor.
Owner:R & D DYNAMICS
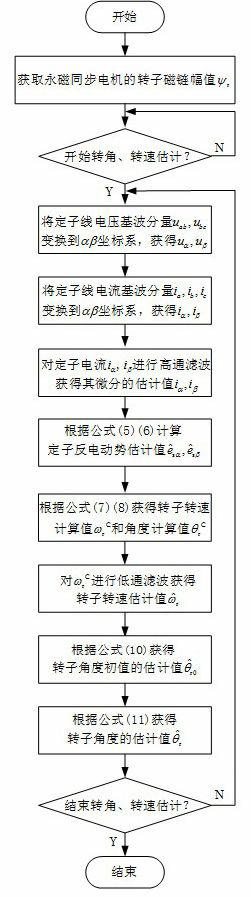
Speed sensor-less method for estimating rotor angle and revolving speed of permanent-magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN102437813AImprove dynamic performanceEasy to debugElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsStator voltageSynchronous motor
The invention relates to the technical field of electric transmission and control, in particular to a speed sensor-less method for estimating the rotor angle and the revolving speed of a permanent-magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps: a. obtaining the rotor flux linkage amplitude Psi<r> of a permanent-magnet synchronous motor; b. transforming a stator voltage fundamental component to be under an alpha beta coordinate system to obtain u<alpha> and u<beta>; c. transforming the stator current fundamental component to be under the alpha beta coordinate system to obtain i<alpha> and i<beta>; d. carrying out highpass filtering on stator current i<alpha> and i<beta> under the alpha beta coordinate system, and obtaining the differential estimation value sum of the stator current; e. obtaining a stator counter electromotive force estimation value; f. obtaining a rotor revolving speed calculation value omega<rC> and a rotor angle calculation value theta<rC>; g. carrying out lowpass filtering on the rotor revolving speed calculation value omega<rC> to obtain a rotor revolving speed estimation value; h. obtaining the estimation value of a rotor angle starting value; and i. obtaining a rotor angle estimation value. The method has the advantages that only forward calculation, instead of a feedback channel, exists in the method for estimating the rotor angle and revolving speed, and except filter delaying, no dynamic regulation process exists.
Owner:DONGFANG ELECTRIC CORP LTD
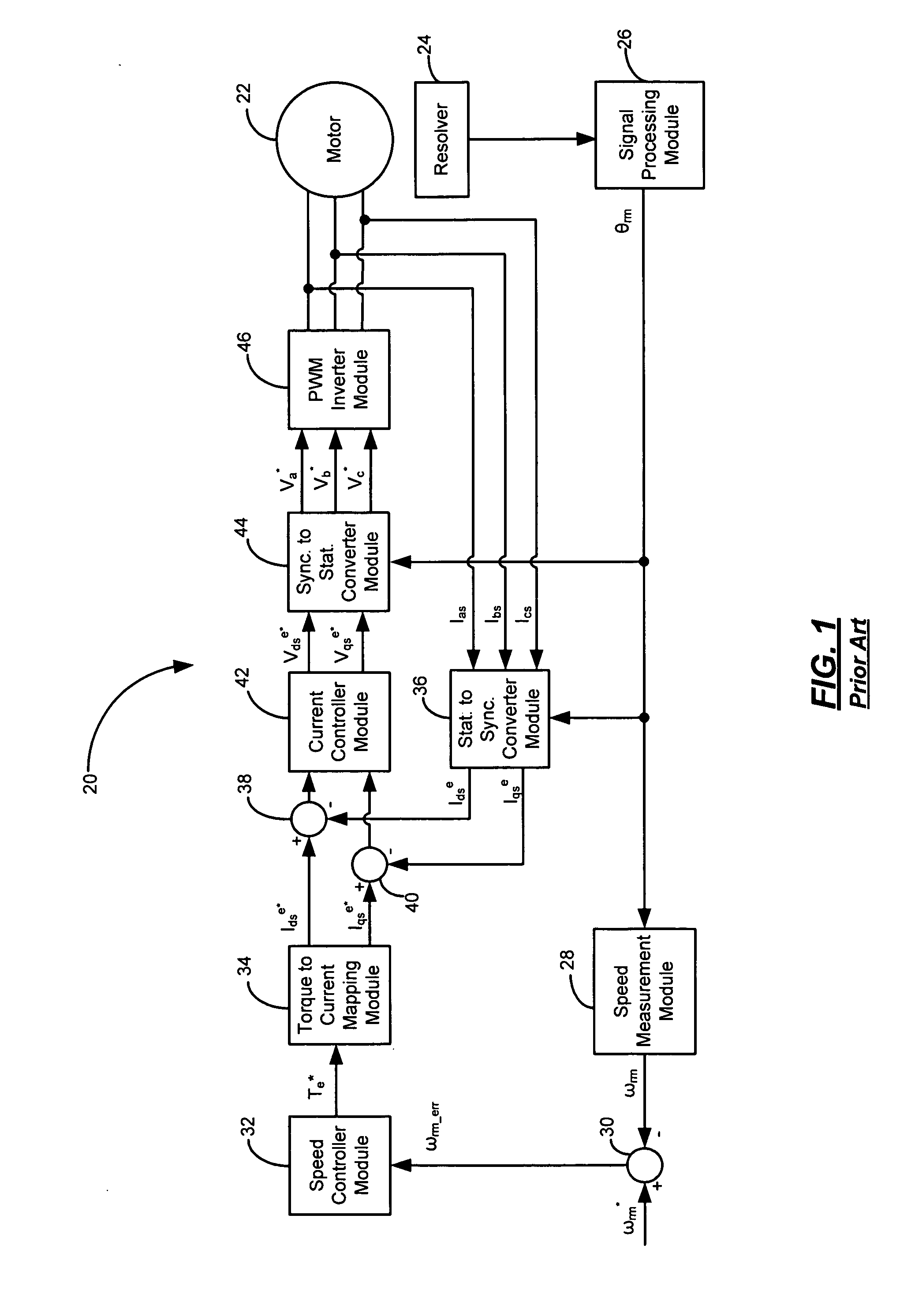
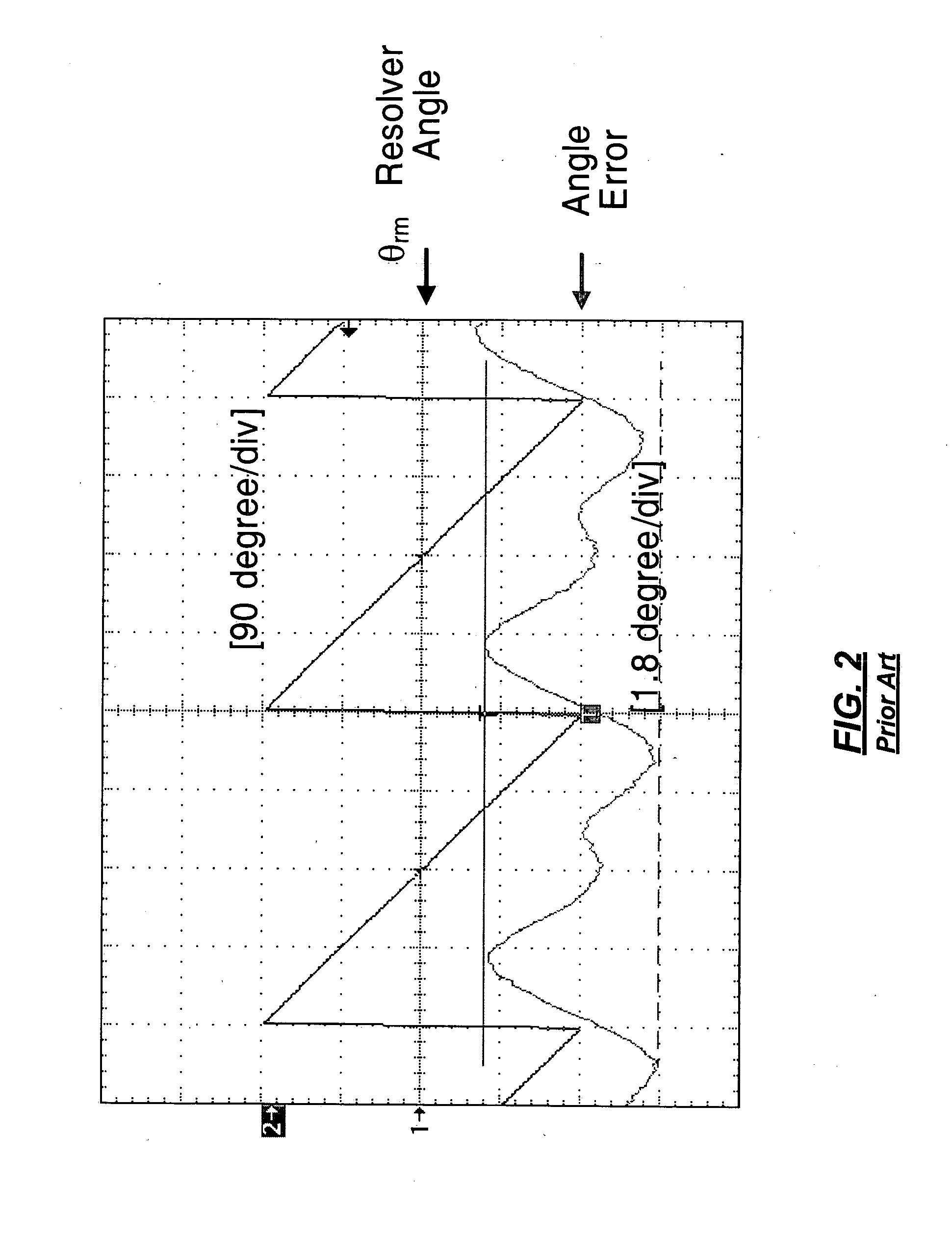
Digital signal processing of resolver rotor angle signals
InactiveUS20020173931A1Digital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsDigital signal processingEngineering
An apparatus and method for determining the angular position of a rotor. The rotor is a part of a resolver used to determine the position of a shaft, or the like, in operation in a system such as a shaft in a missile gimbal. A digital signal processor is used advantageously to reduce cost. The inherently poorer performance of a data sampling approach in the presence of noise, as compared to the prior art tracking converter approach, is overcome by novel application of the digital signal processor and related circuitry.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method for detecting rotor position in non position sensor switch magnetic resistance motor
InactiveCN101436843AReduce manufacturing costReduce production processDevices using electric/magnetic meansElectronic commutatorsMotor controlHome appliance
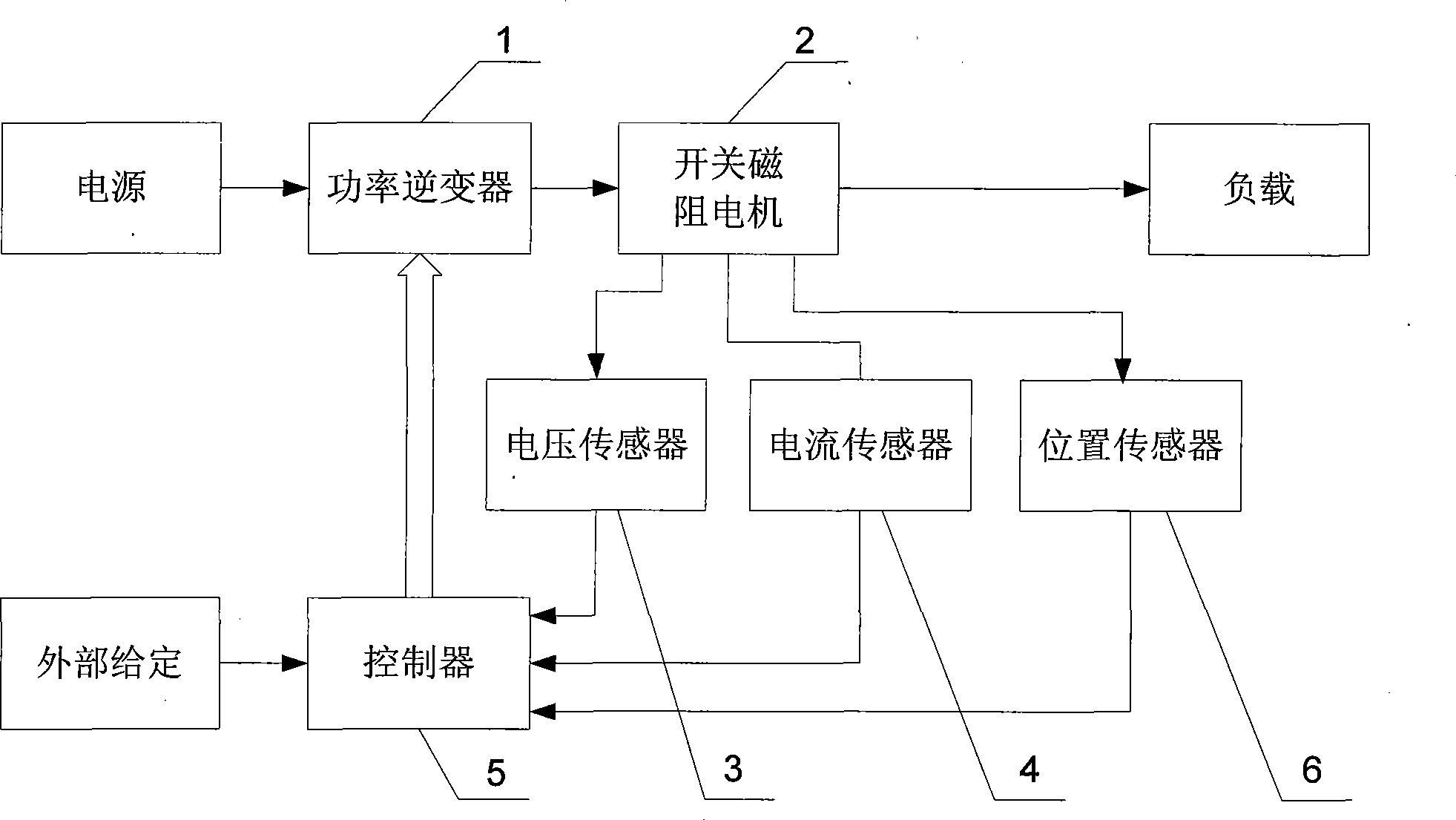
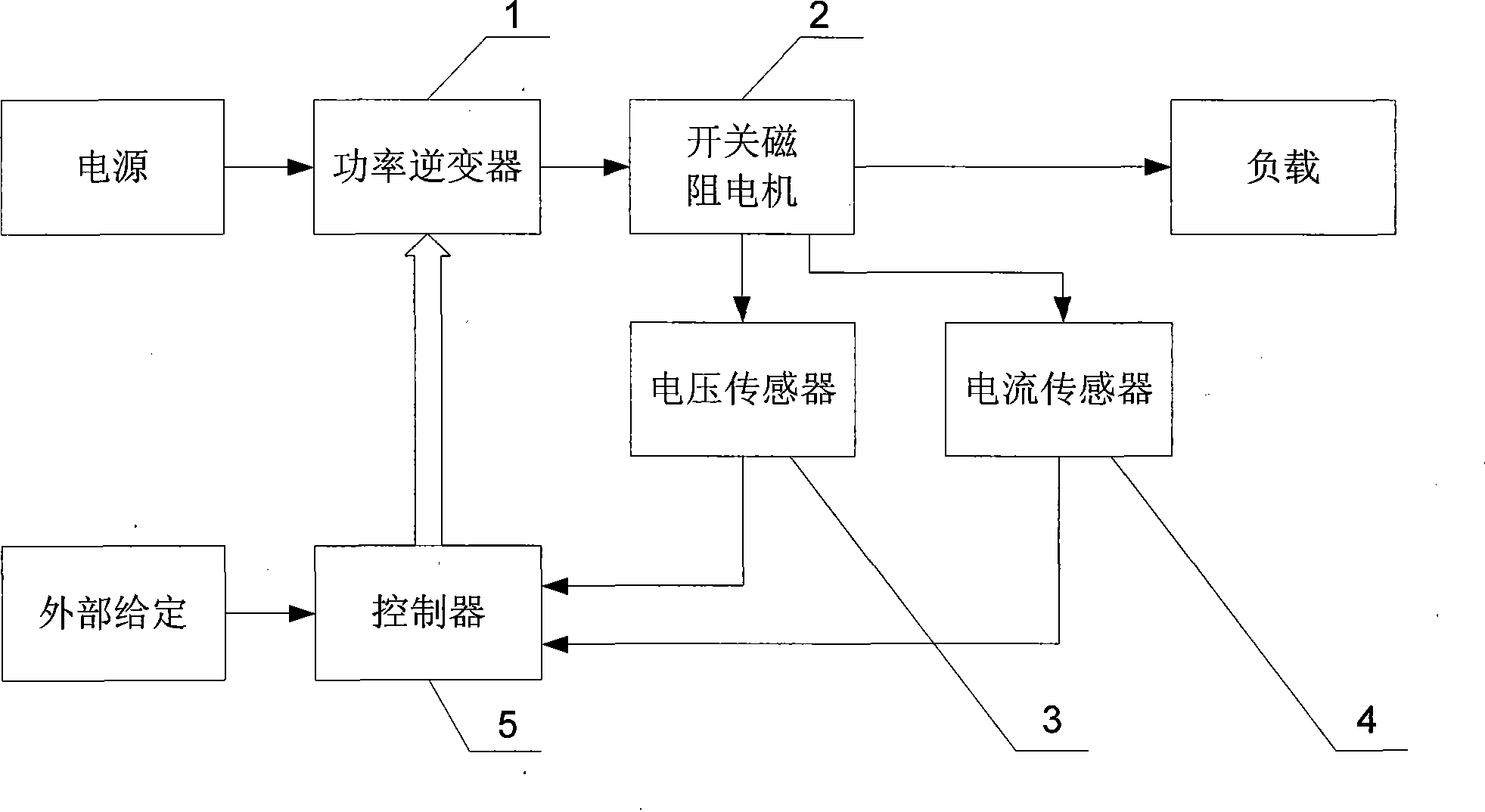
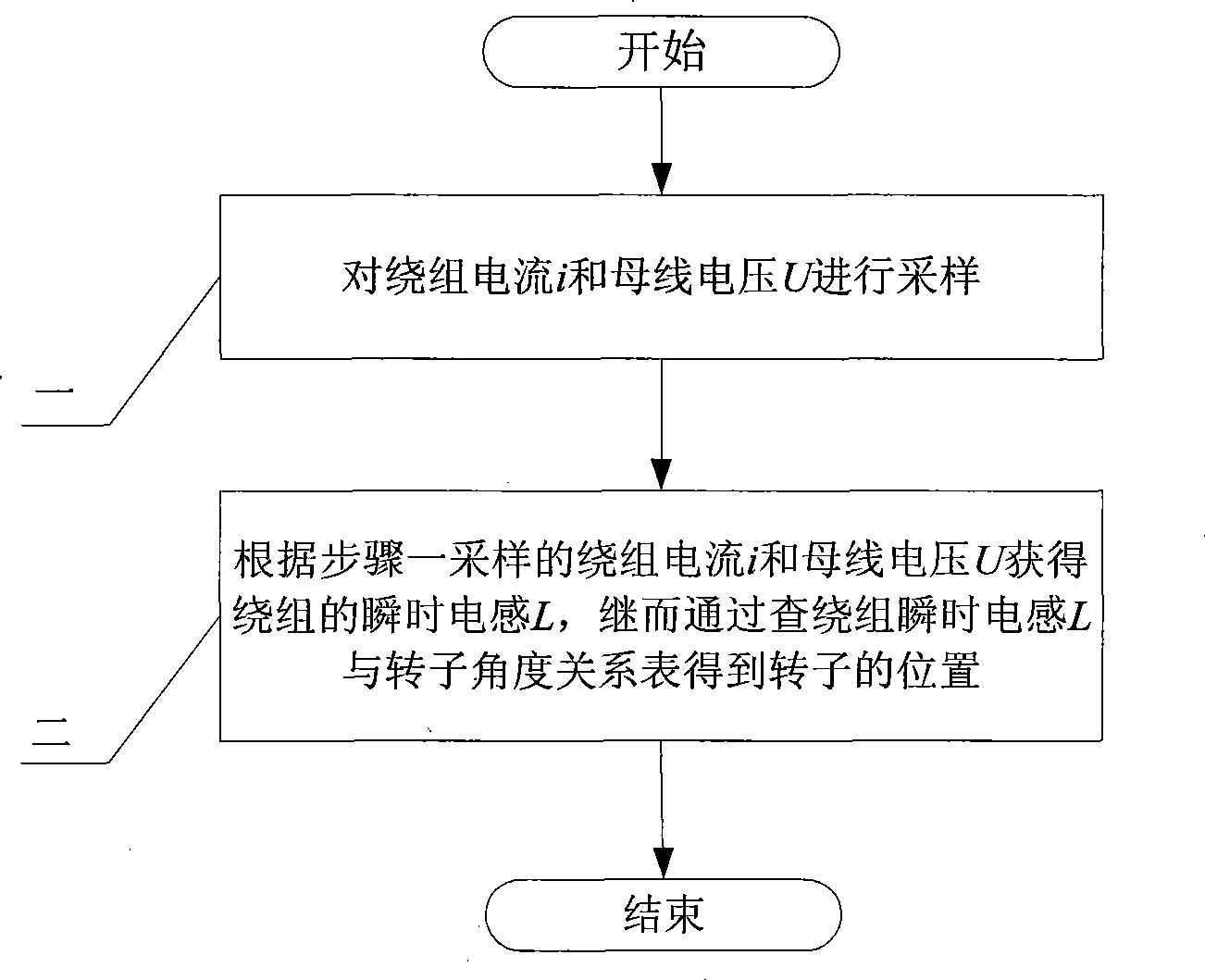
The invention provides a method for detecting rotor position of a switch reluctance motor without a position sensor, and belongs to the field of motor control. The invention aims at solving the problems existing in the prior method for indirectly detecting the rotor position that resisting moment and moment harmonic components occur in the motor rotor so that the efficiency of a motor system is reduced. The method comprises the following steps: 1, winding current i and busbar voltage U are sampled; and 2, according to the winding current in step one, instantaneous inductance (L) of the winding is acquired, and by looking up the winding instantaneous inductance (L) and rotor angle relation table, the rotor position is acquired. The method can lower manufacturing process of the switch reluctance motor, and has good application prospect in oil fields, coal mines, elevators, home appliances and the like.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Counter-rotational inertial control of rotorcraft
A rotorcraft with two counter-rotating rotors and method for inertially controlling the rotorcraft. The rotorcraft includes a hinged frame configured such that at least one inter-rotor angle of the two counter-rotating rotors is controlled by at least one actuated hinge of the hinged frame and the rotational axes of the two counter-rotating rotors are substantially collinear when the actuated hinge is in a fully open position. The sum of the magnitudes of torque applied to the two counter-rotating rotors is varied to control the lift of the rotorcraft. The difference of the magnitudes of torque applied to the two counter-rotating rotors is varied to control the yaw of the rotorcraft. The at least one inter-rotor angle is varied using the at least one actuated hinge to control the pitch and / or roll of the rotorcraft.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method and apparatus to determine the wind speed and direction experienced by a wind turbine
ActiveUS7347668B2Simple and robust and low cost apparatusLow computing performancePropellersWind motor controlNacelleEngineering
Owner:ROMO WIND AG
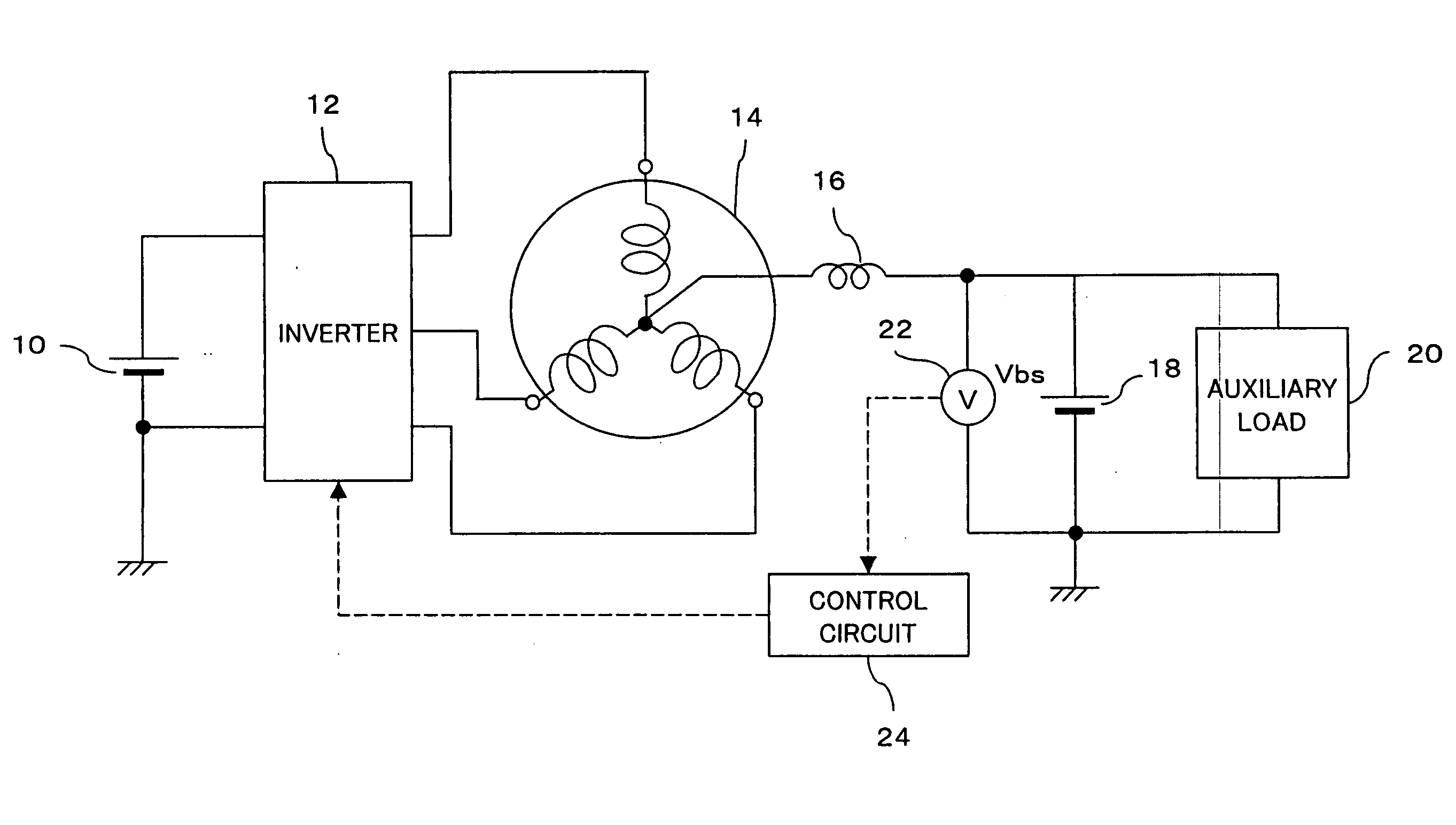
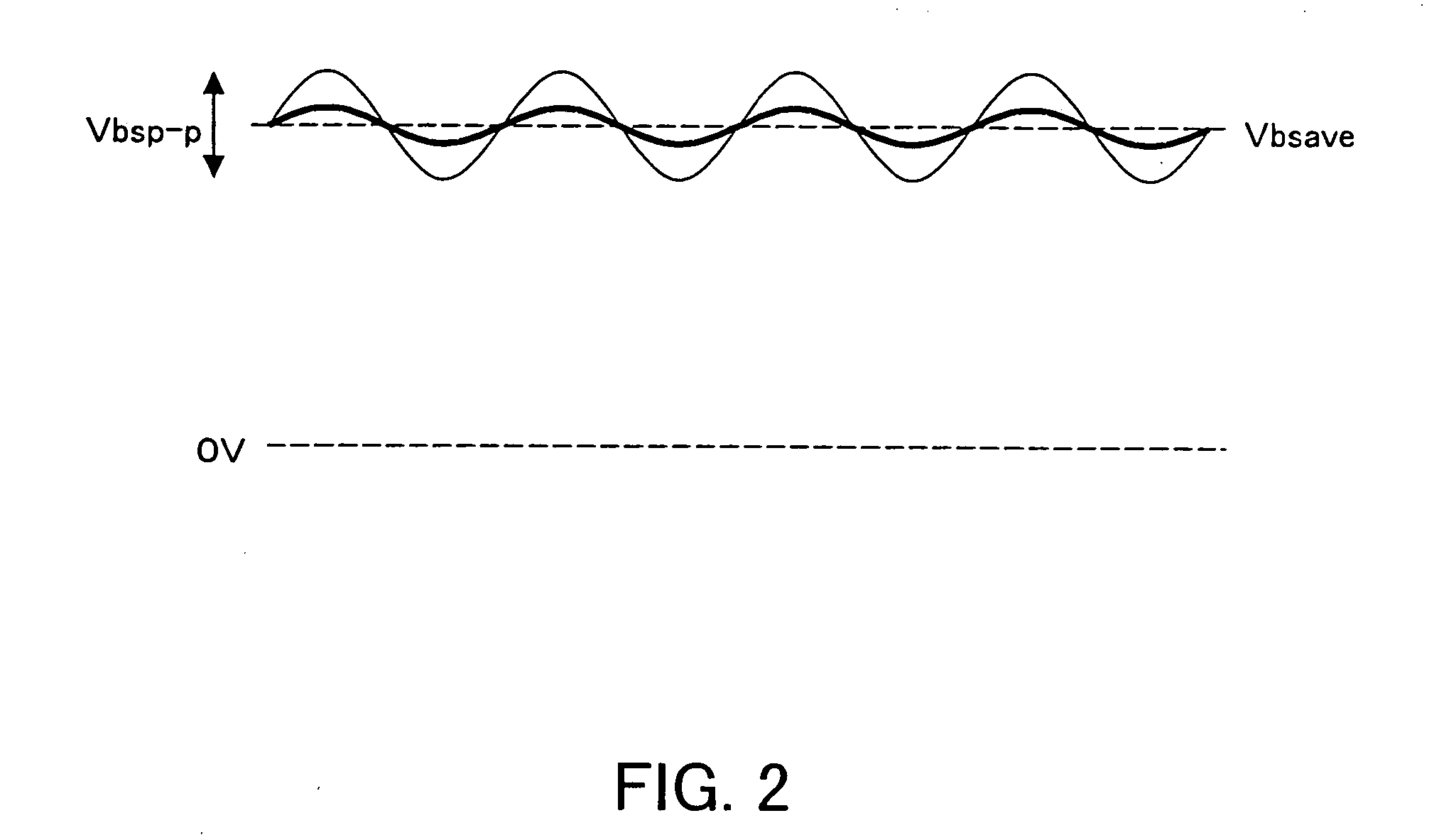
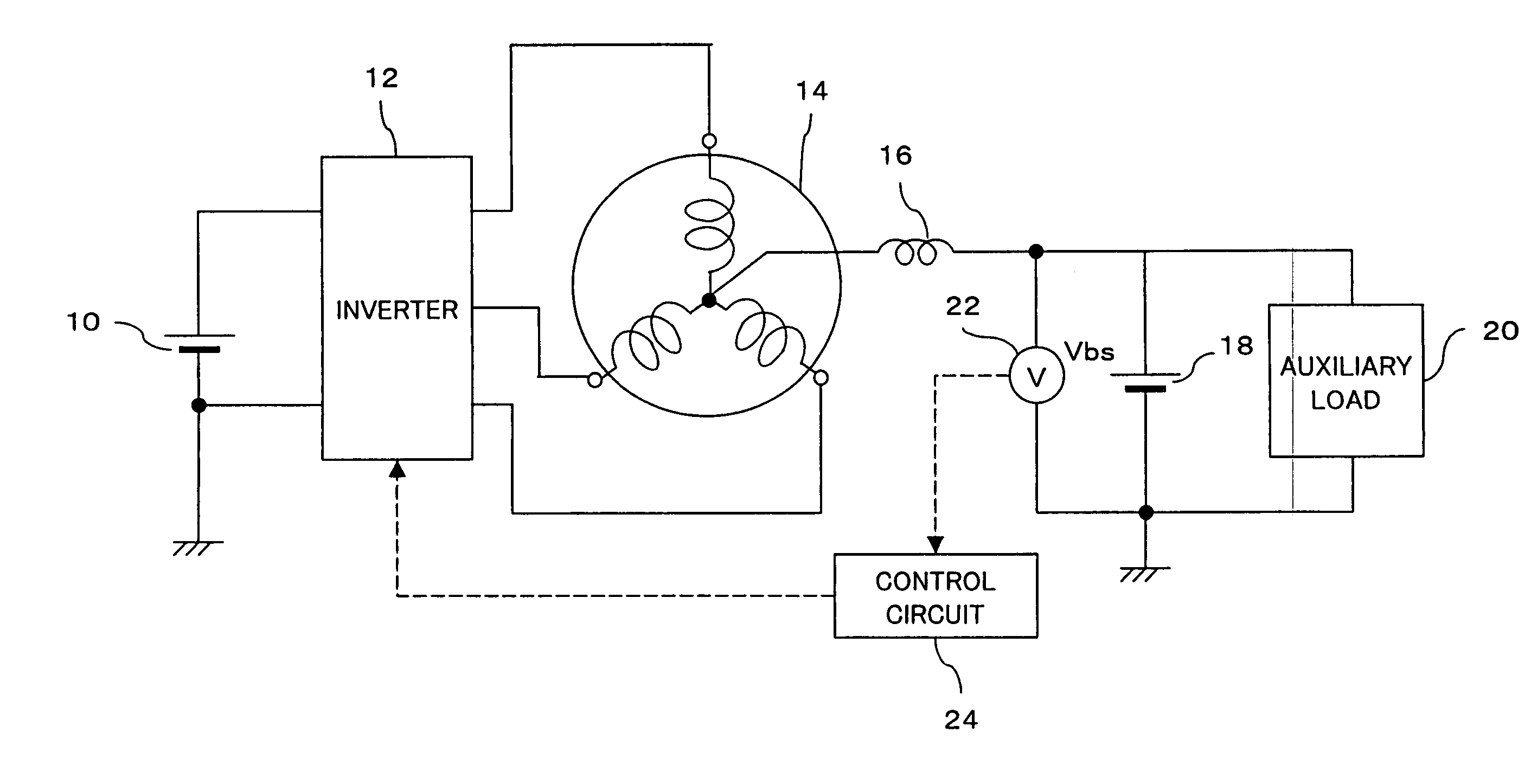
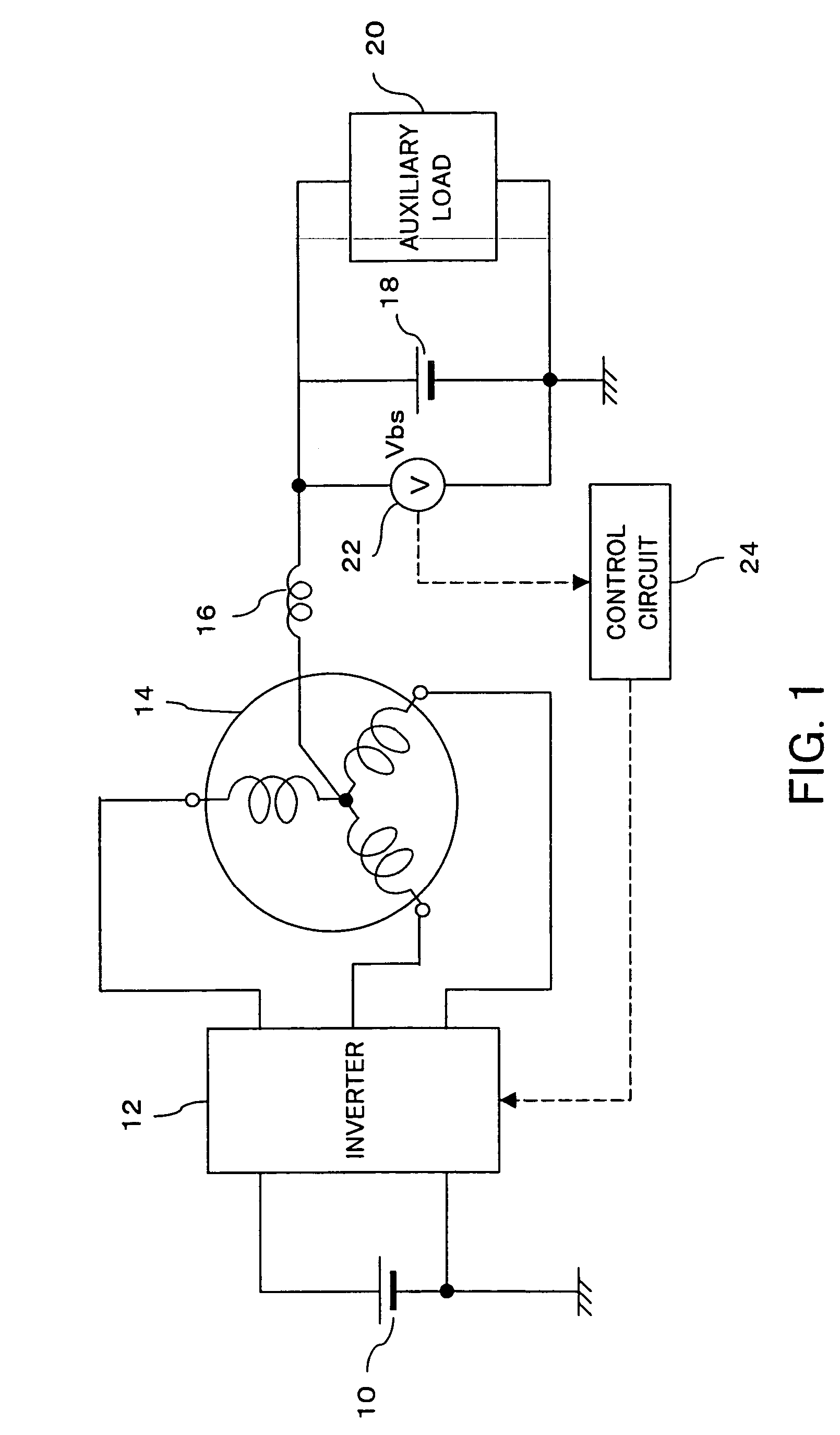
Method and system for detecting the disconnection of an auxiliary power suppply from a poly-phase motor
InactiveUS20050258796A1Limited rangeAvoid problemsSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlPhase currentsVoltmeter
To a neutral point of a motor is connected a positive electrode of an auxiliary battery and an auxiliary load. Voltage on a power supply line to the auxiliary load, a neutral point voltage, is detected, and disconnection of the auxiliary battery is determined when an increase of ripples in the neutral point voltage is detected. When a voltmeter cannot be used, control of the neutral point voltage is continued by measuring current of the auxiliary battery and performing control such that the current value becomes 0. A resolver is further provided on the motor for detecting the rotor angle with high accuracy. A control circuit generates, in accordance with an output of the resolver, a voltage control signal for each phase current having the same amplitude as the carrier amplitude during startup, and compares the voltage control signal to carrier to obtain a gate signal having the same frequency as the carrier frequency. In switching of the inverter, due to this gate signal, periods in which all phases are on or off are reduced, thereby preventing a large neutral point current.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
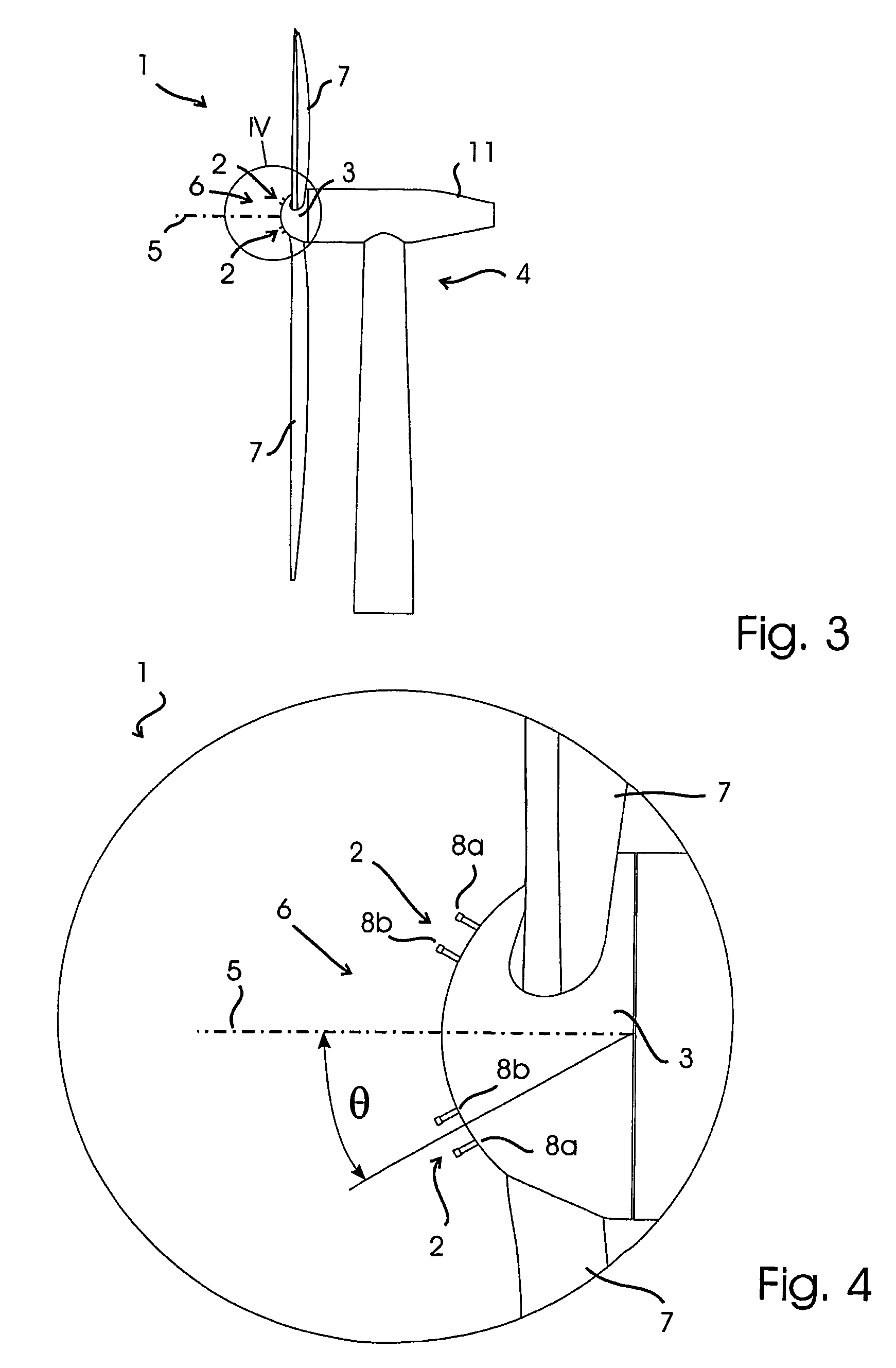
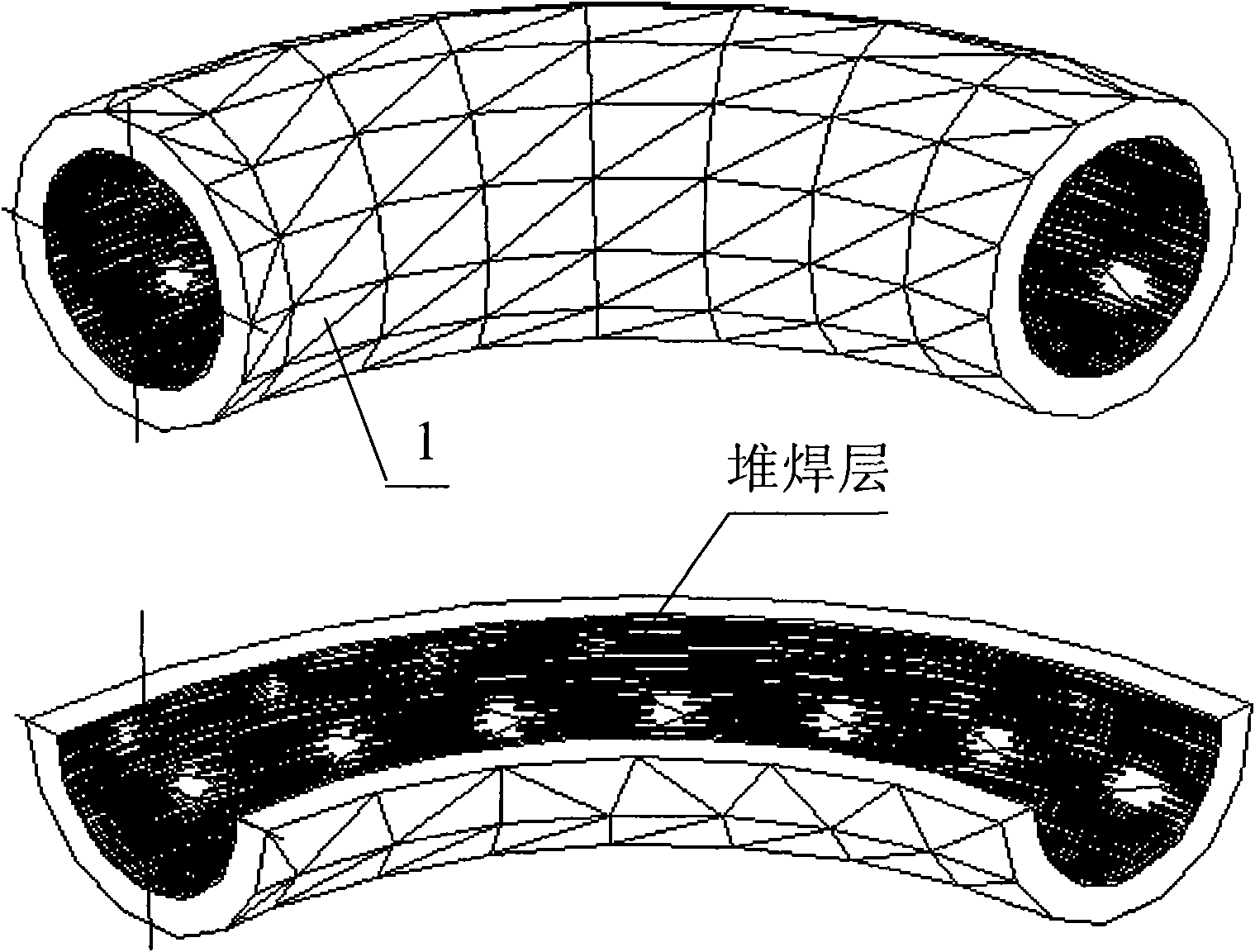
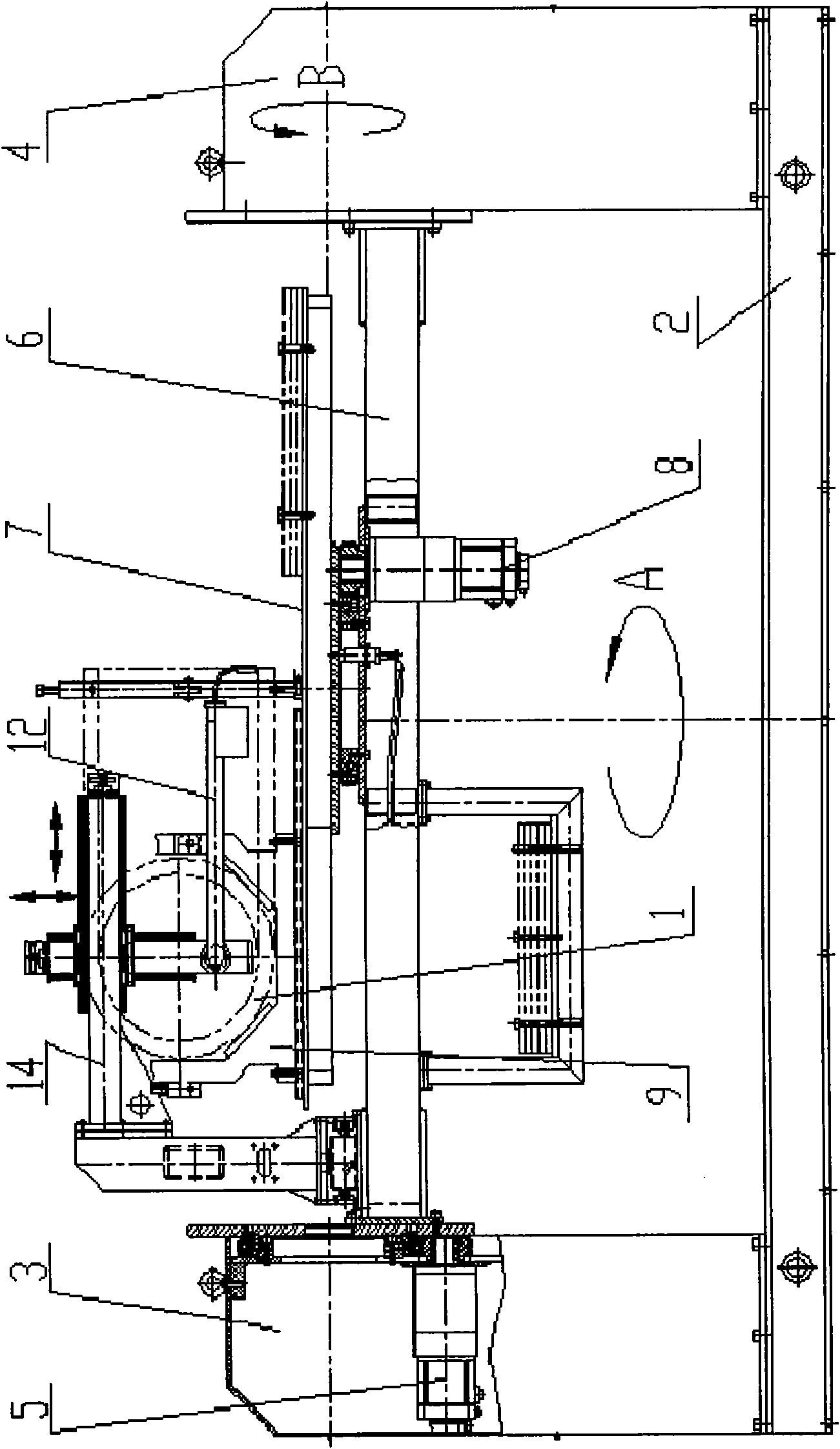
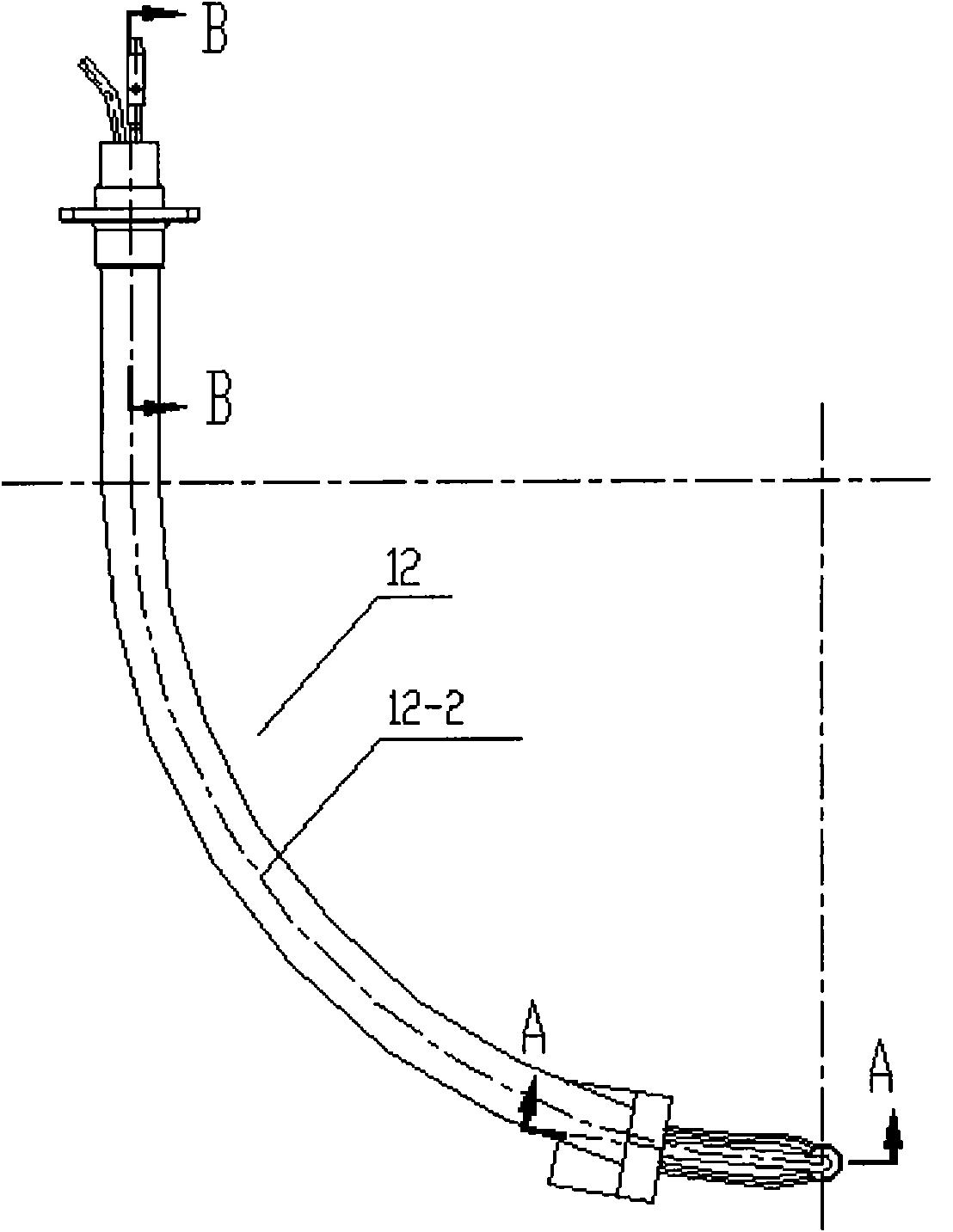
Automatic surfacing device of inner wall anticorrosion layer of 90-degree bent pipe and automatic surfacing method thereof
The invention provides an automatic surfacing device of an inner wall anticorrosion layer of a 90-degree bent pipe and an automatic surfacing method thereof, belonging to the technical field of automatic surfacing and solving the technical problems of long surfacing period and hardly guaranteed surfacing quality of the inner wall anticorrosion layer of a 90-degree bent pipe in a heavy type pressure vessel in the background art. In the automatic surfacing device and the automatic surfacing method, the rotor angle and the displacement of a welding gun head (12-1) is completed through the rotation of a rotary angle motor (12-3) and the displacement of a three-dimensional guide rail (14), the rotation of an overturn motor (5) enables the 90-degree bent pipe to rotate, the swinging of a swinging motor (8) enables the welding gun head (12-1) to carry out surfacing at a certain speed, accordingly, the previous factors enable the inner wall of the 90-degree bent pipe to realize high-efficiency and high-quality surfacing. The invention is mainly used for the surfacing of the inner wall of the 90-degree bent pipe in the heavy type pressure vessel with the working environment of high temperature, high pressure and corrosion medium contacting.
Owner:HARBIN WELDING INST LTD
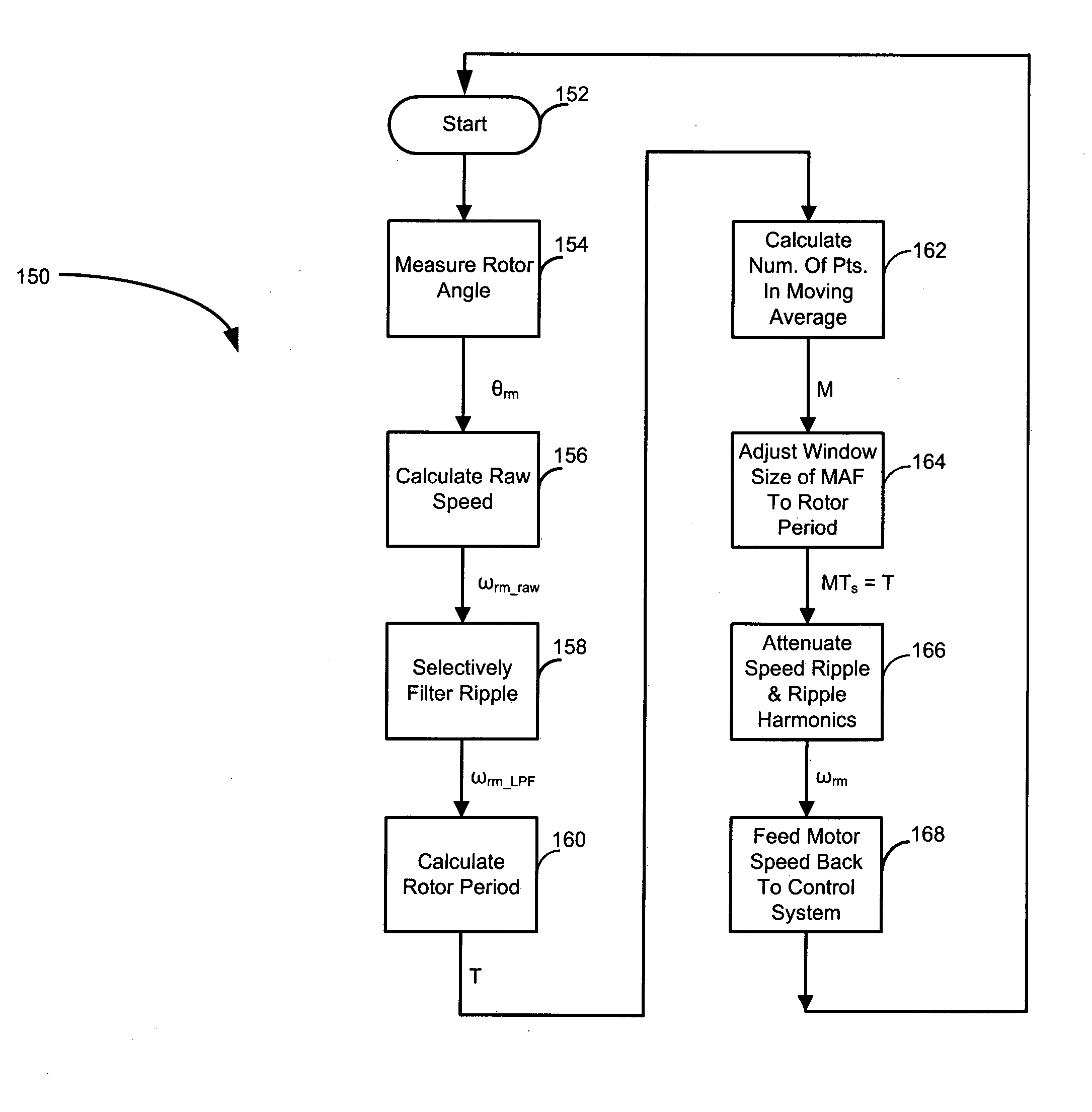
Speed measurement system for speed control of high-speed motors
InactiveUS20070043528A1Speed measurement using accelerationVector control systemsMoving averageAverage filter
A system for measuring speed of a high-speed motor using a moving average filter. A position sensor generates a rotor position signal. A signal processing module determines a rotor angle from the rotor position signal. A speed observer module calculates a raw speed of the motor from the rotor angle. A filter module selectively generates a filtered speed of the motor from the raw speed of the motor. A frequency-to-period converter module calculates a rotor period from one of the raw speed of the motor and the filtered speed of the motor. A divider module calculates number of points in a moving average from the rotor period. A moving average filter module adjusts a window size of the moving average to the rotor period. A moving average filter removes ripple and harmonics of the ripple from the raw speed of the motor.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Device and method for observing rotor position in motor control
InactiveCN102347726AGuaranteed uptimeAvoid lostElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl vectorPosition angle
The invention relates to a method and device for observing and controlling a rotor position in motor control. According to the method and the device, an initial position angle of a motor rotor can be observed; angular errors caused by an imprecise assembled angle of a Hall sensor can be eliminated by online discrimination of software; a real-time speed detection program is provided to eliminate an angular accumulated error caused by imprecision of an angular speed omega; a rotor position angle can be precisely tracked in a motor vector control operation process, the rotor angle is prevented form overflowing, and self-detection of the motor in reverse rotation can be realized; and when a certain sensor has a fault, a system can judge a fault point per se and performs self-adaption to achieve the function of still normally running. According to the device and the method, independence on a hardware circuit is reduced, observation and real-time tracking of the rotor position angle can be realized, the function of fault judgment of the system can be used for protecting the motor, and loss caused by motor locking or running out is prevented. The device has a great practical value in the fields of electric vehicles and precise machine tools, and has the advantages of reliability in operation, low cost and wide application range.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
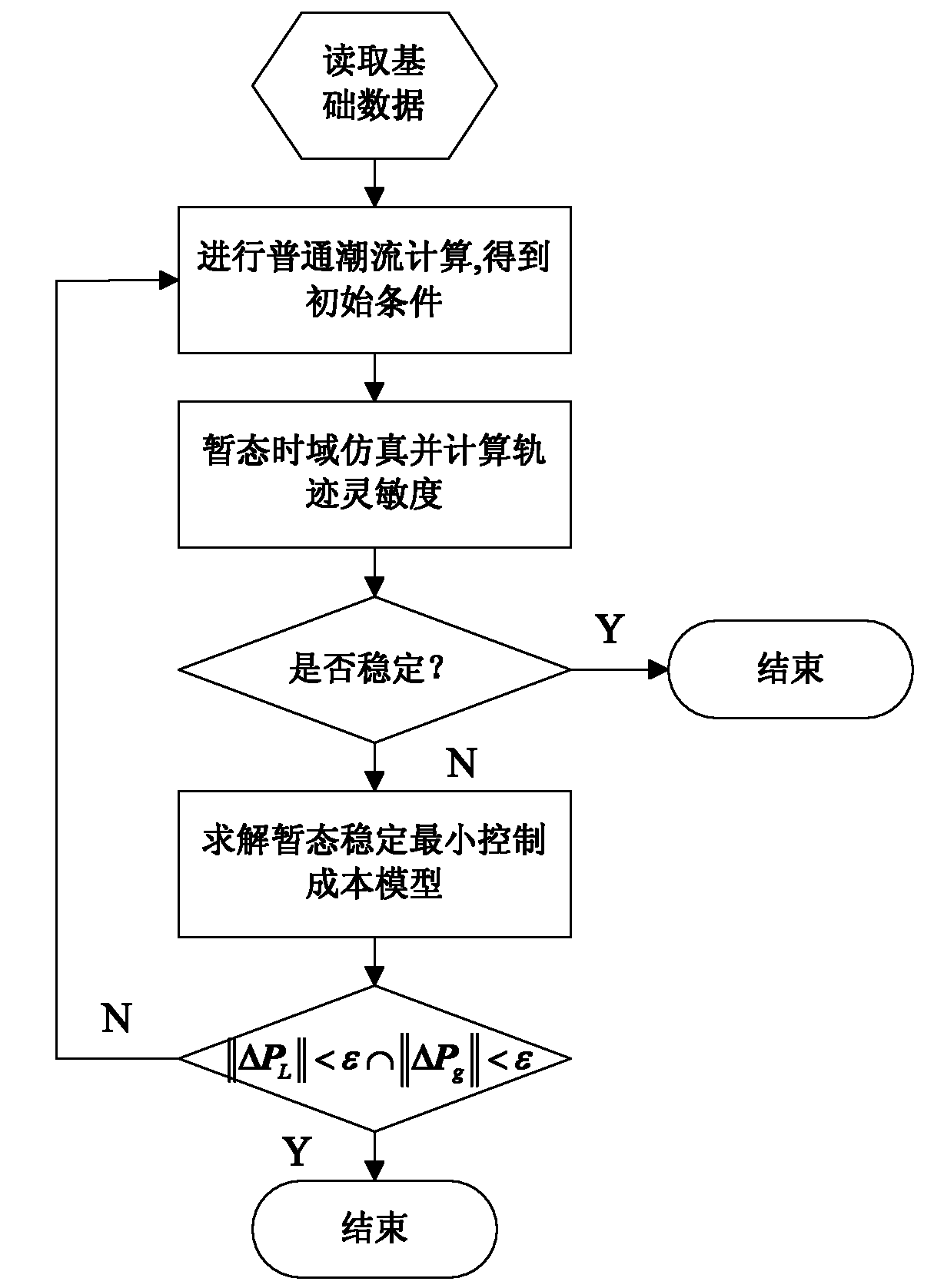
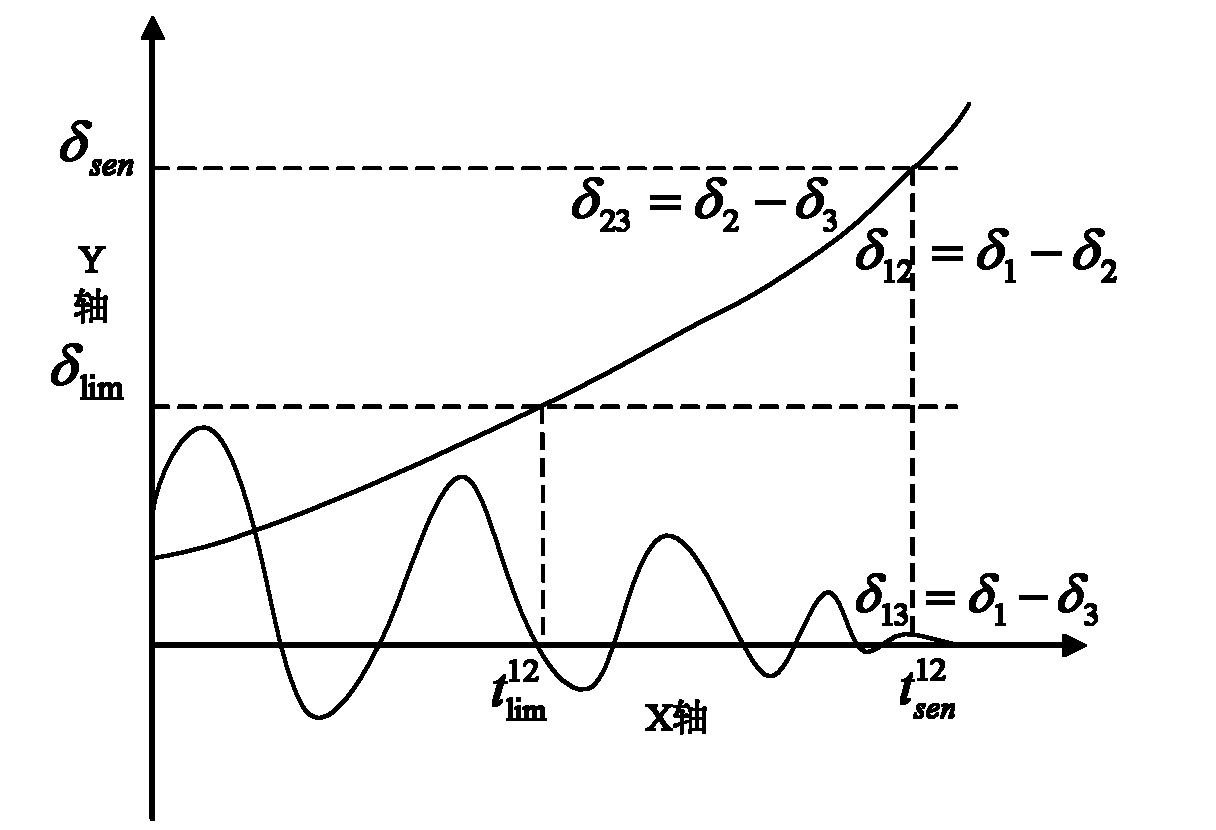
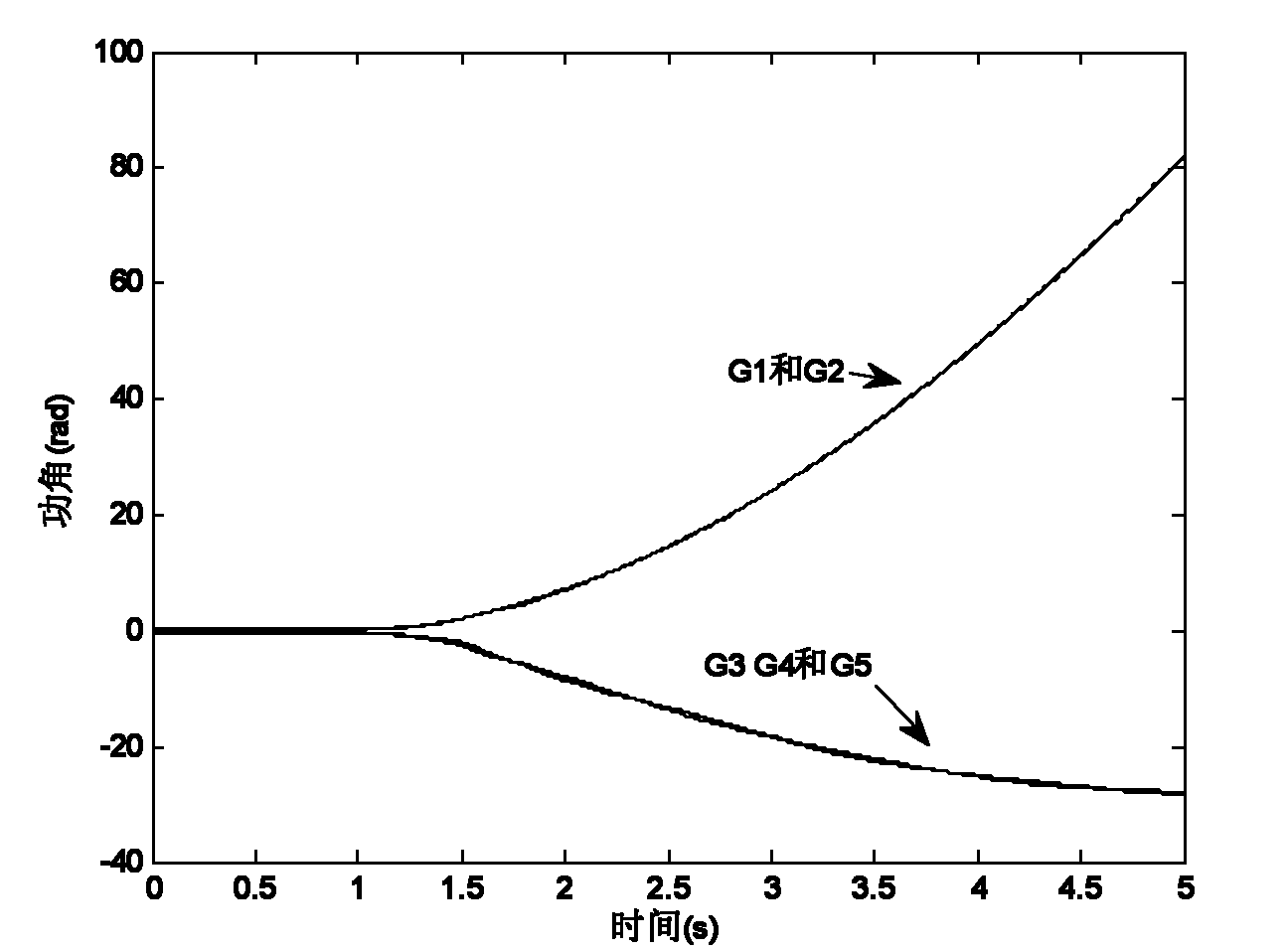
Fault loss estimation method for risk assessment of transient rotor angle stability
ActiveCN101969199ASmall amount of calculationAc network circuit arrangementsTransient stateTime domain
The invention relates to fault loss estimation of a power network and provides a practical and effective fault loss estimation method for the risk assessment of transient rotor angle stability. In the technical scheme adopted by the invention, the fault loss estimation method for the risk assessment of the transient rotor angle stability comprises the following steps of: performing the ordinary power flow calculation to obtain the initial condition; performing transient time domain simulation and calculating trace sensitivity; if instability is determined, resolving a transient stability minimum control cost model; and if the convergence conditions that the absolute value of delta PL is less than epsilon and that the absolute value of delta Pg is less than epsilon are not met, repeating the previous steps. The method is mainly applied to the fault loss estimation and management of the power network.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
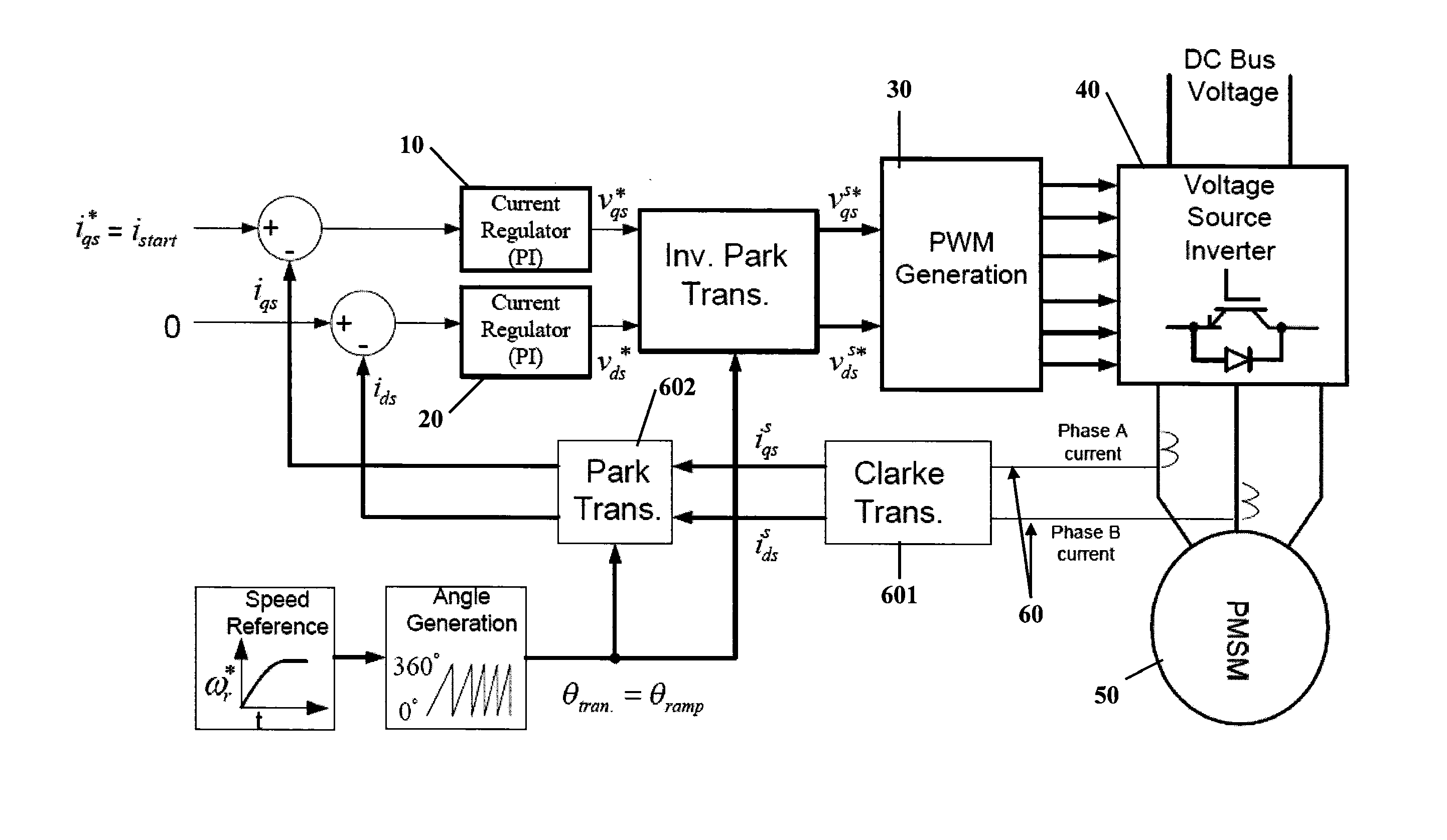
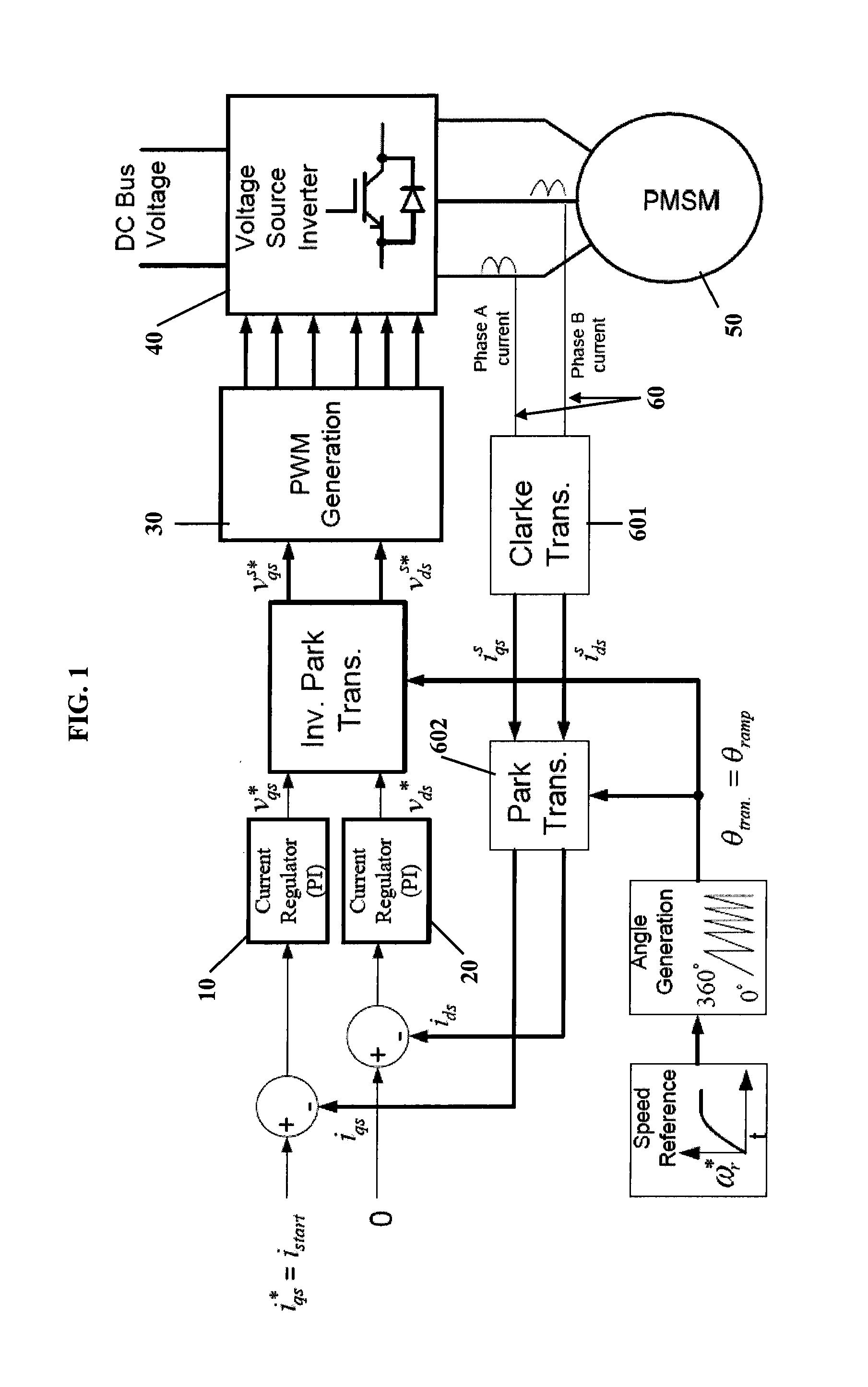
Method for smooth motor startup
ActiveUS20140152212A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersLoop controlClosed loop
A method of conducting smooth motor startup is provided and includes operating a motor in an open loop control scheme at startup, operating the motor in a closed loop sensorless control scheme at a time after startup and transitioning between the open loop control scheme and the closed loop control scheme by reducing a difference between an estimated rotor angle of the motor and a commanded ramping angle of the motor.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
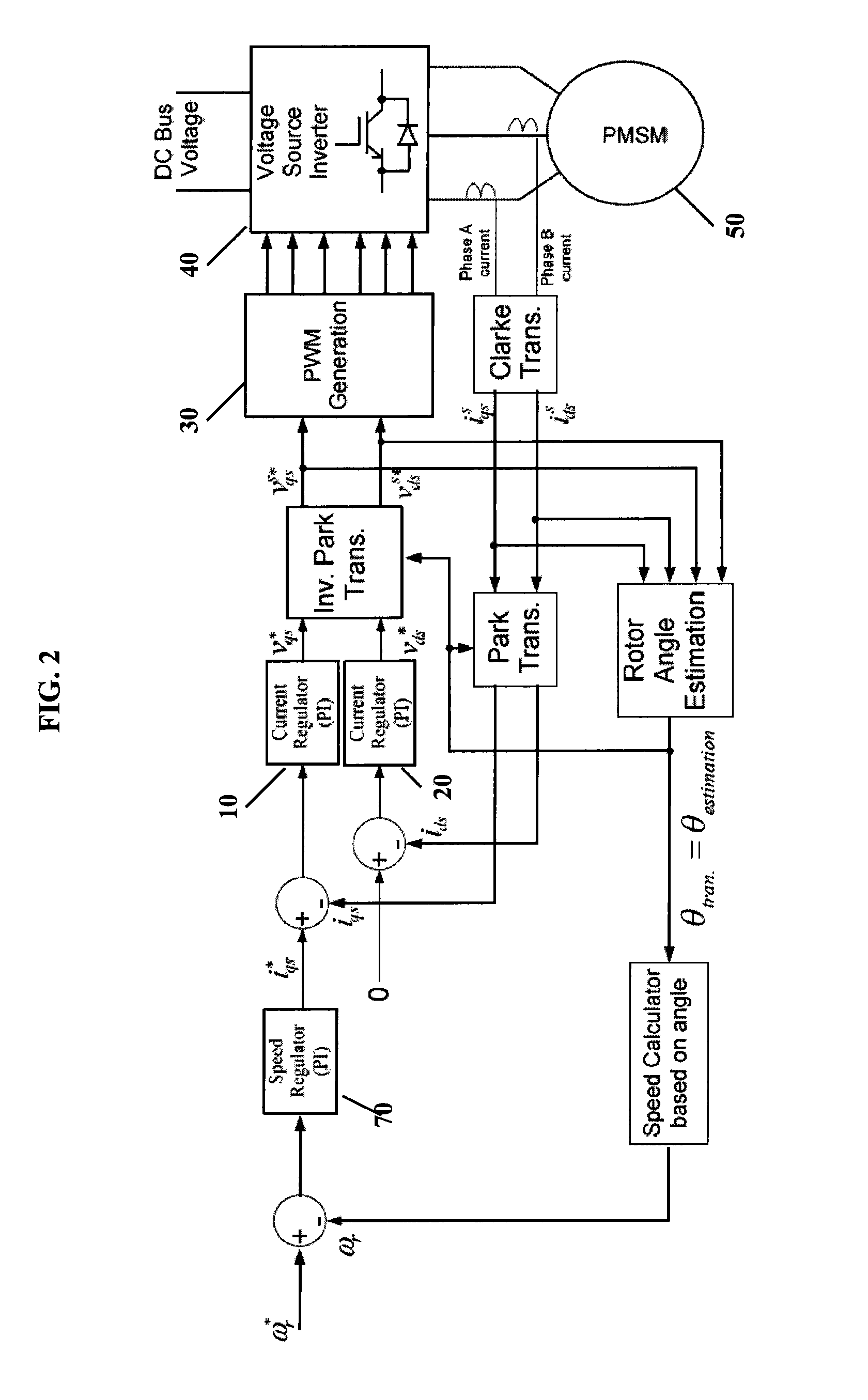
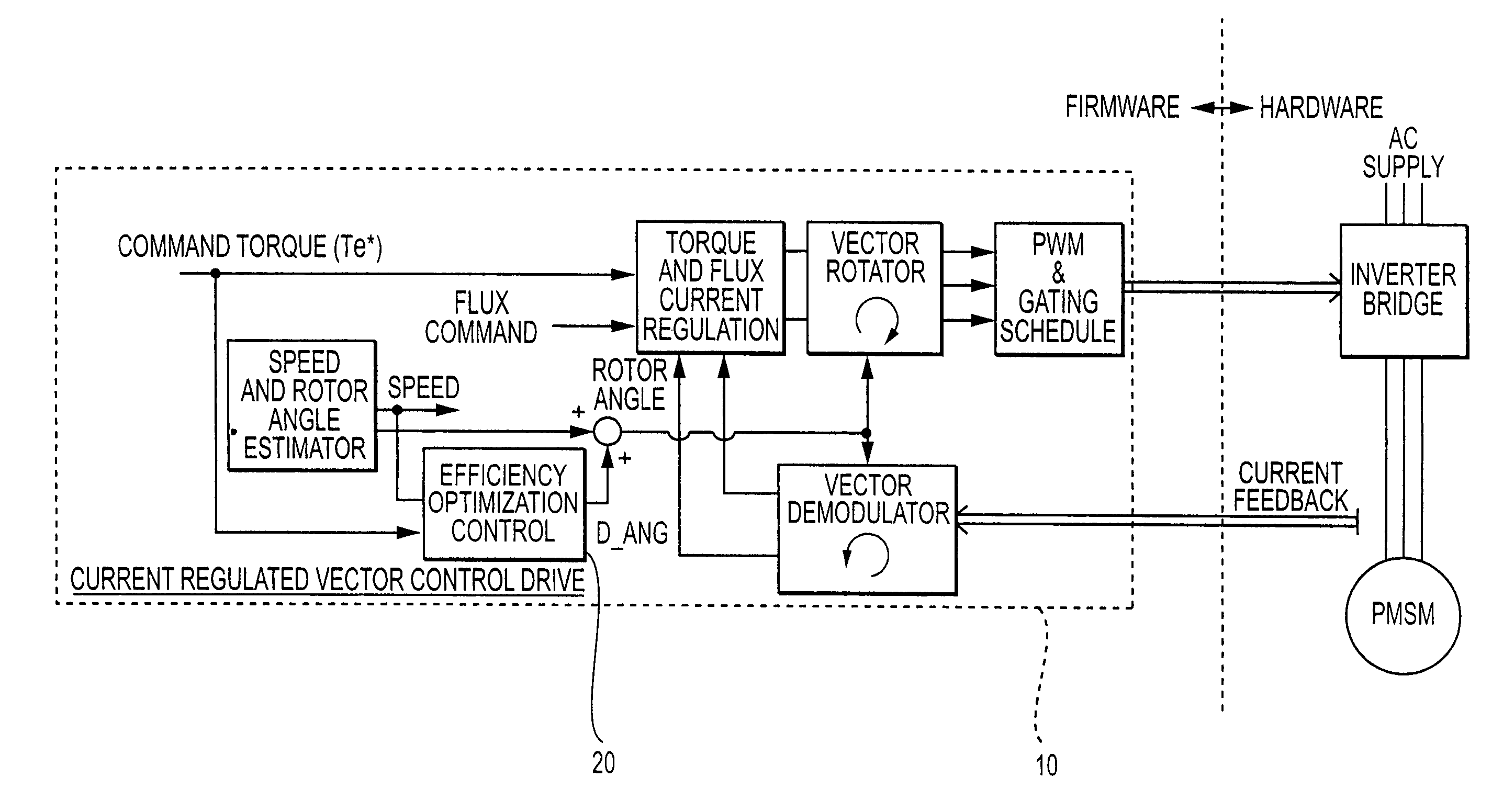
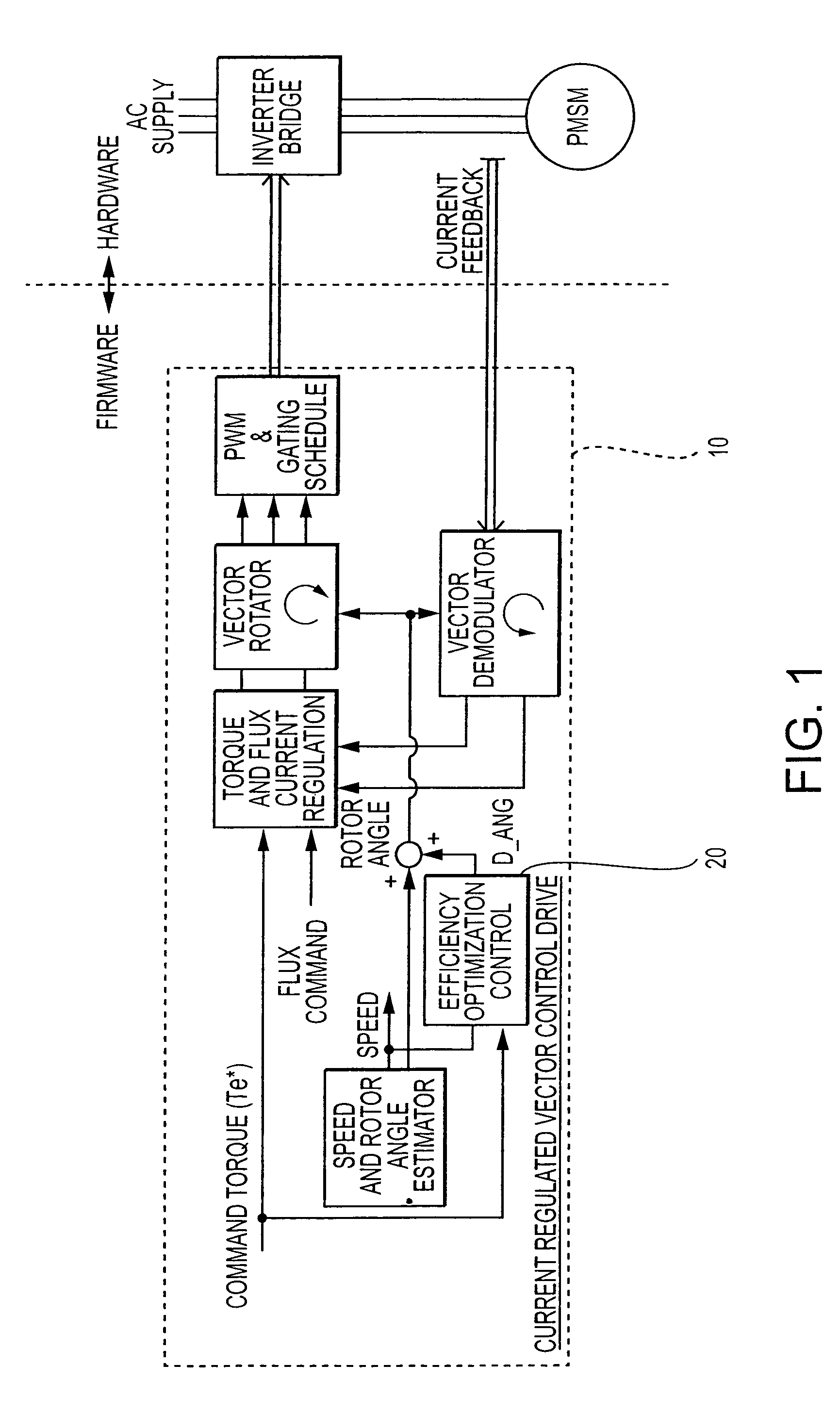
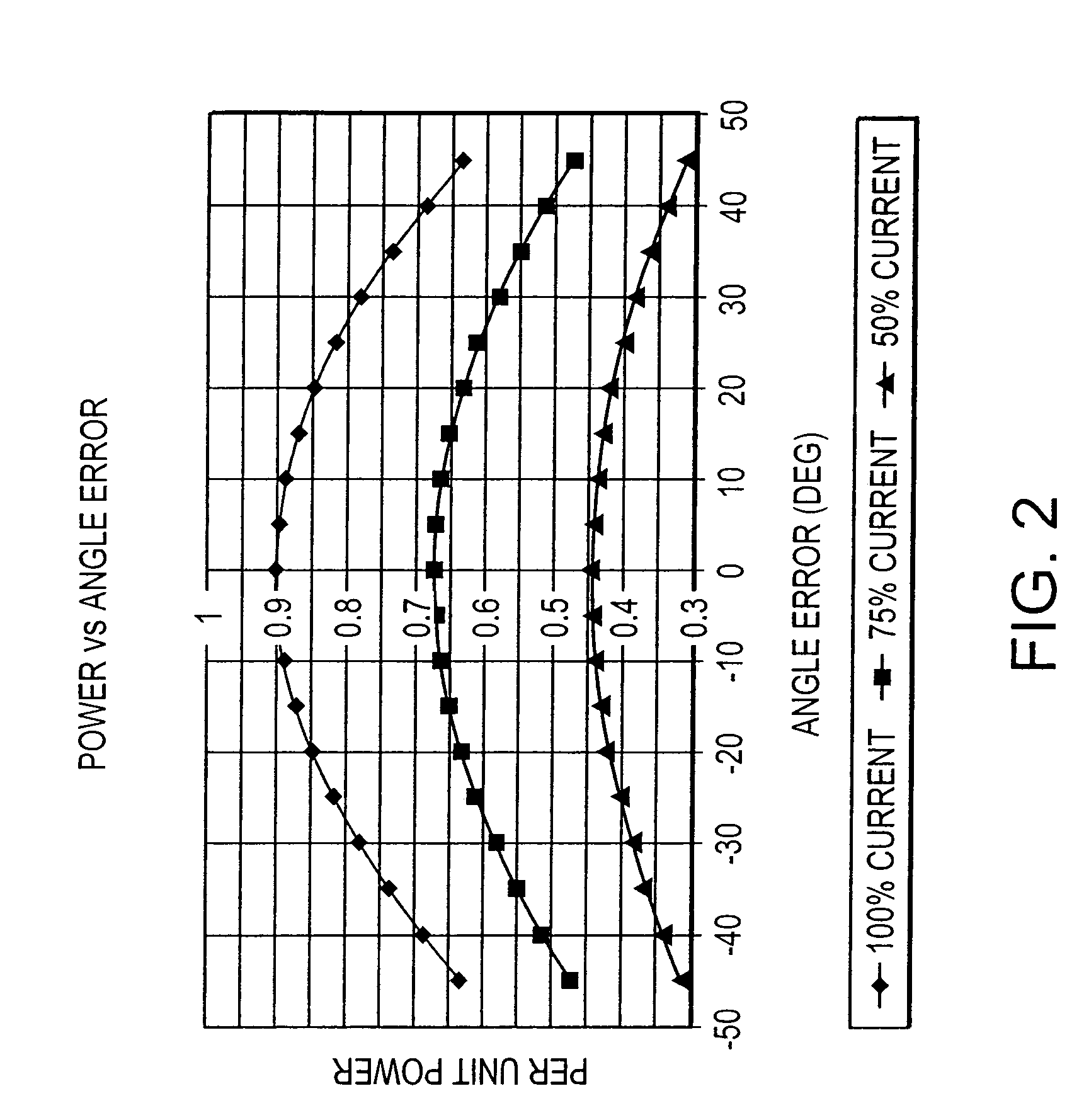
Efficiency optimization control for permanent magnet motor drive
InactiveUS6979967B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlPermanent magnet motorRotor angle
A method and system for modifying an estimated rotor angle for improved efficiency in a PMSM drive system. A module monitors a run command, a torque command, and an estimated speed; and in response thereto, generates an output correction angle for modifying the estimated rotor angle. The output correction angle may be added to the estimated rotor angle. The output correction angle may be generated only for predetermined conditions of said run command, torque command, and speed. In particular, the output correction angle may be generated (1) when the run command is asserted, (2) when the torque command is above a predetermined level, and (3) when variations in the speed are within predetermined limits.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
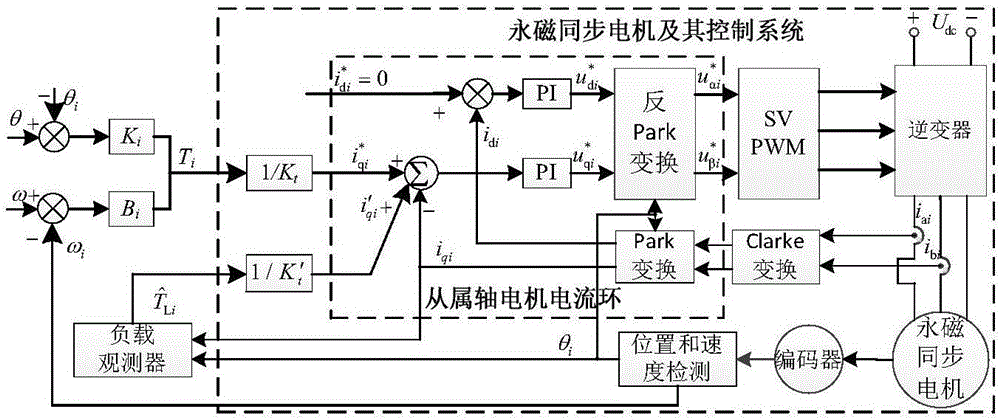
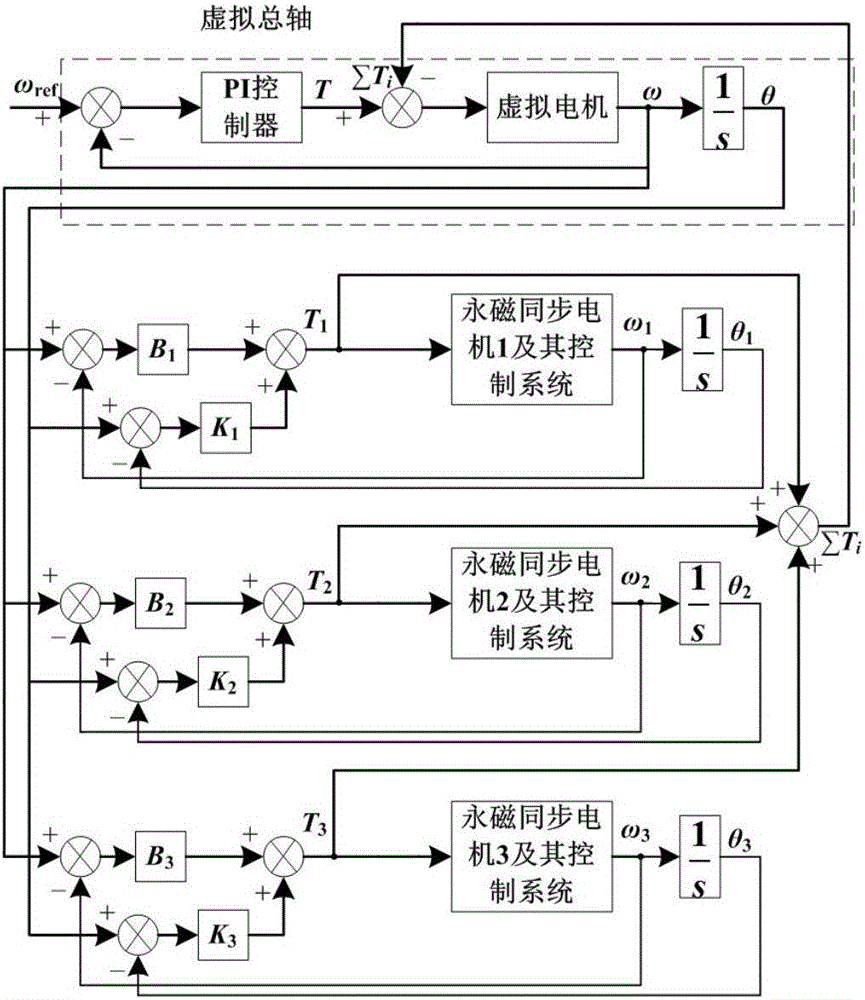
Load observer-based virtual line shaft control method for multiple permanent magnet synchronous motors
ActiveCN106208865AImprove robustnessAvoid uncertaintyVector control systemsMultiple motor speed/torque controlMotor speedPhase currents
The invention belongs to the field of multi-motor speed cooperation control. Synchronous operation among various subordinate shafts is coordinated; the dynamic relationship among various shafts is also really reflected; meanwhile, the robustness of a system is further improved; and load torque measurement values are fed forwards to current rings of subordinate shaft motors. According to the technical scheme, by a load observer-based virtual line shaft control method or multiple permanent magnet synchronous motors, the system comprises n permanent magnet synchronous motors and a virtual motor; DC voltage and phase current output by a rectifier bridge are collected by an AD conversion interface in a microprocessor; a rotor angle position thetai of an ith permanent magnet synchronous motor is detected through a rotor position sensor, and meanwhile, a rotating speed omegai of the ith permanent magnet synchronous motor is calculated; alpha-axis reference voltage and beta-axis reference voltage are generated; and finally a six-pulse drive control signal of an inverter is output by employing a voltage space vector pulse width modulation SVPWM method. The load observer-based virtual line shaft control method is mainly applied to the occasion of multi-motor speed cooperation control.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Counter-rotational inertial control of rotorcraft
A rotorcraft with two counter-rotating rotors and method for inertially controlling the rotorcraft. The rotorcraft includes a hinged frame configured such that at least one inter-rotor angle of the two counter-rotating rotors is controlled by at least one actuated hinge of the hinged frame and the rotational axes of the two counter-rotating rotors are substantially collinear when the actuated hinge is in a fully open position. The sum of the magnitudes of torque applied to the two counter-rotating rotors is varied to control the lift of the rotorcraft. The difference of the magnitudes of torque applied to the two counter-rotating rotors is varied to control the yaw of the rotorcraft. The at least one inter-rotor angle is varied using the at least one actuated hinge to control the pitch and / or roll of the rotorcraft.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Equipment and method for measuring the offset angle of a resolver in a synchronous electric machine
InactiveCN102906989ARealize measurementSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsPhase currentsElectric machine
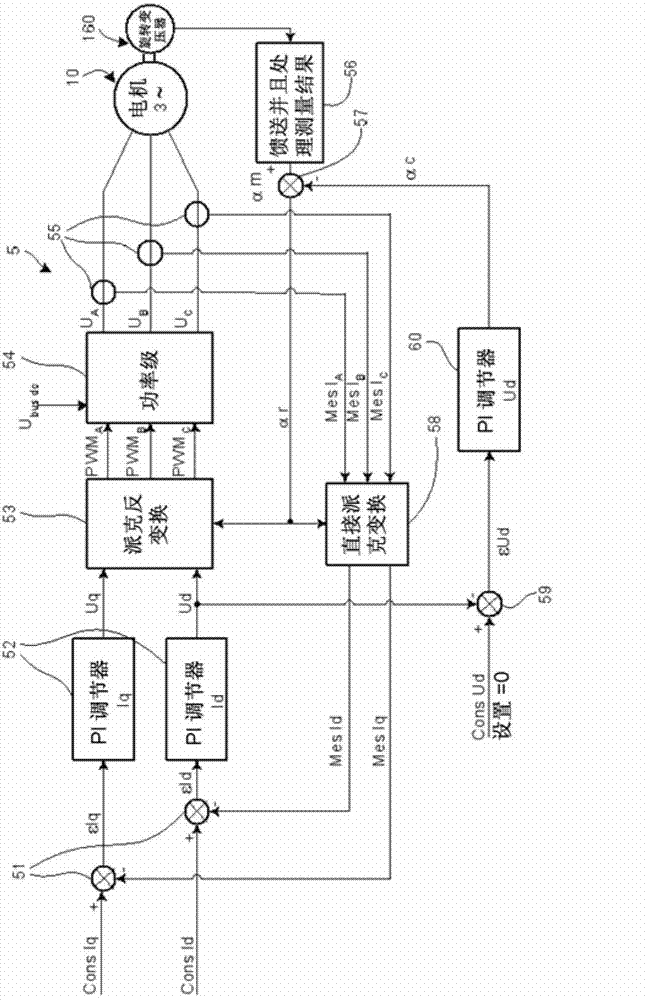
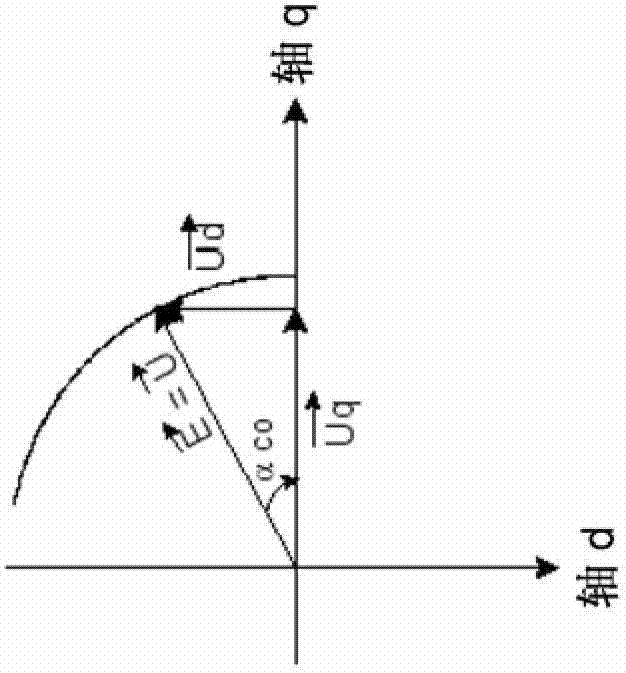
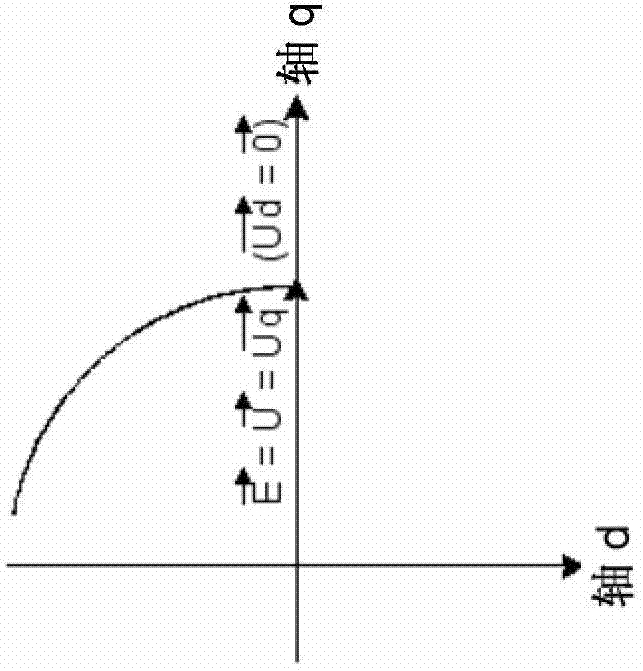
The invention relates to equipment comprising a first calculation unit (53) for carrying out a inverse Park transform on the basis of the voltages (Uq and Ud) at the output of the PI current controllers (52), outputting electric-voltage set-point signals (PWMA, PWMB et PWMC) into a power stage (54) powered by a line on which a DC voltage (Ubus-dc) is available. The power stage (54) generates a three-phase voltage system (UA, UB and UC) for powering the electric machine (10). The equipment comprises a signal-processing unit (56) that provides an angle measurement (am). A second calculation unit (58) uses the phase currents (Mes IA, Mes IB and Mes lC) and the rotor angle (ar) to output values (MesId and MesIq) used by the first calculation unit (53). A PI voltage controller (60) outputs an angle (ac) for adjusting the setting error by adjusting a set value for the voltage (Ud).
Owner:MICHELIN & CO (CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN)
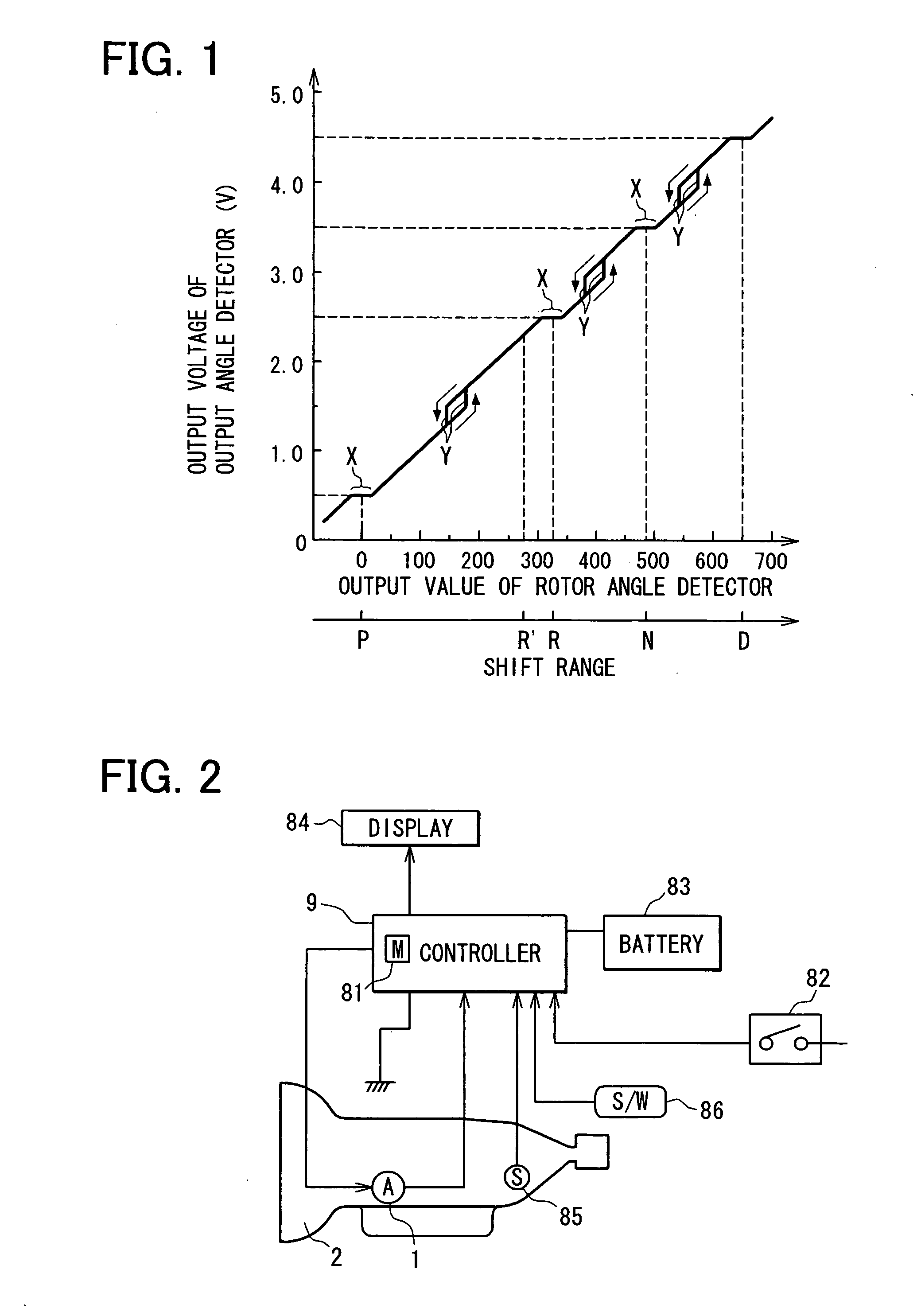
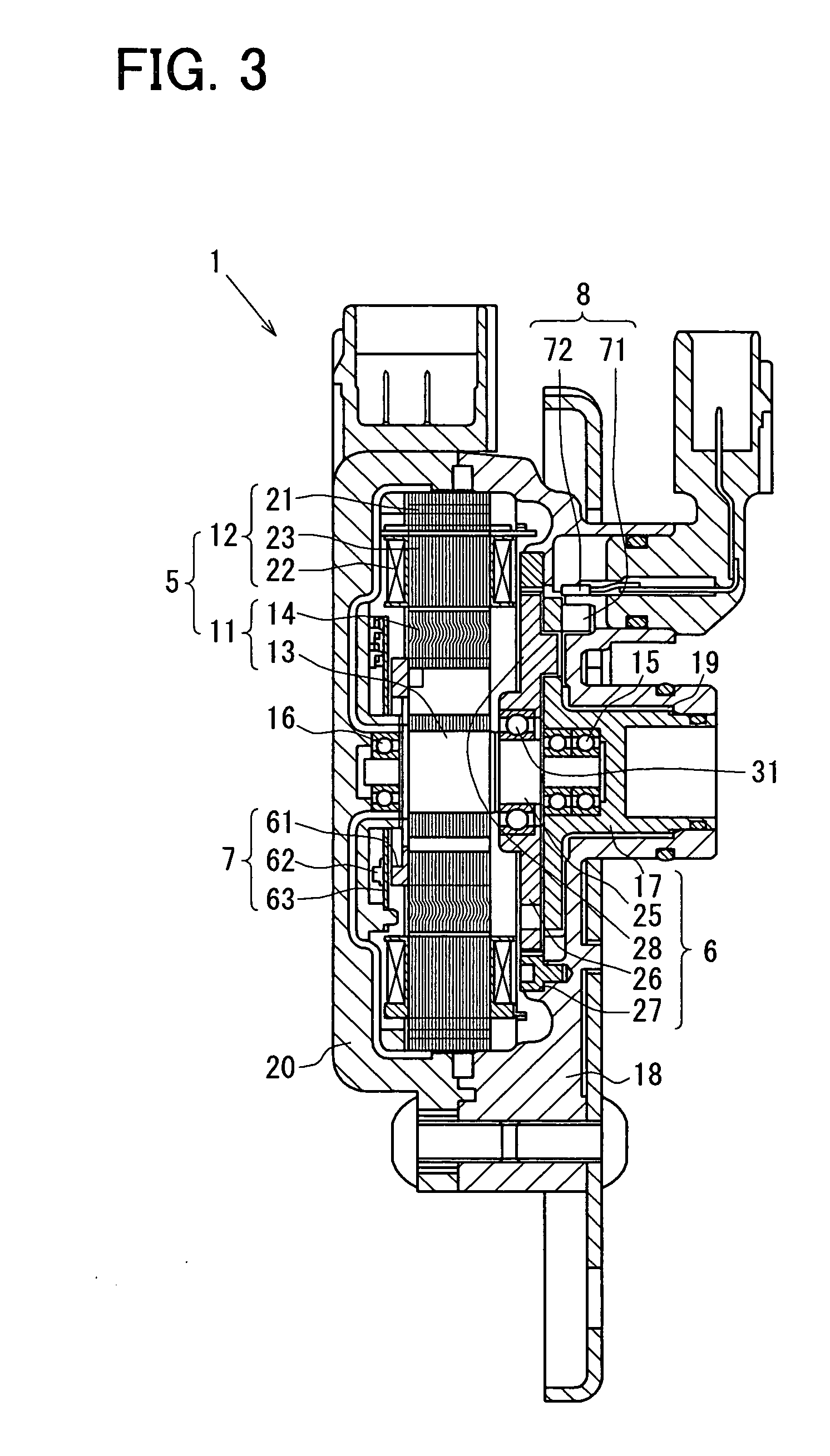
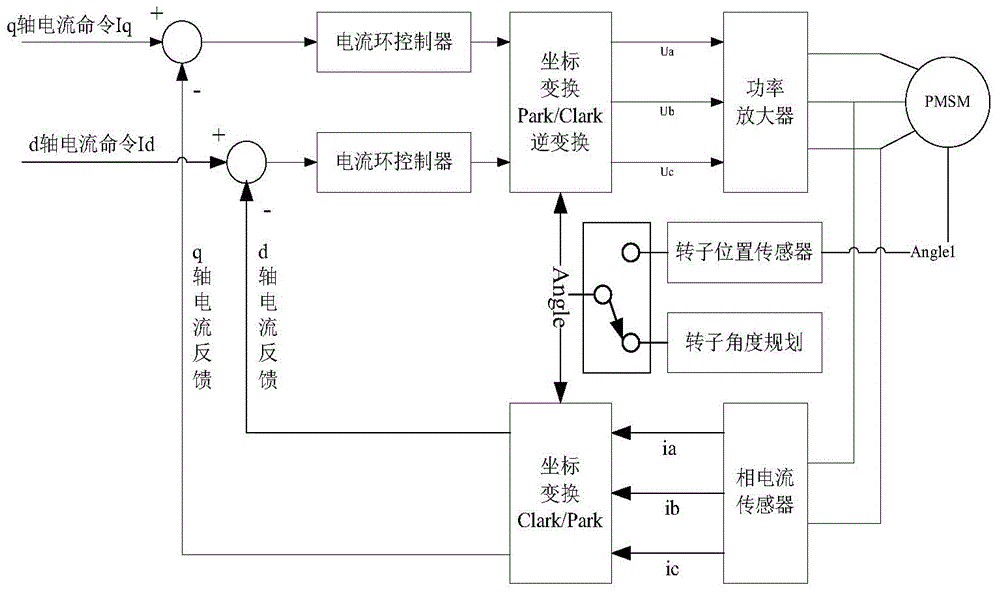
Shift range switching apparatus
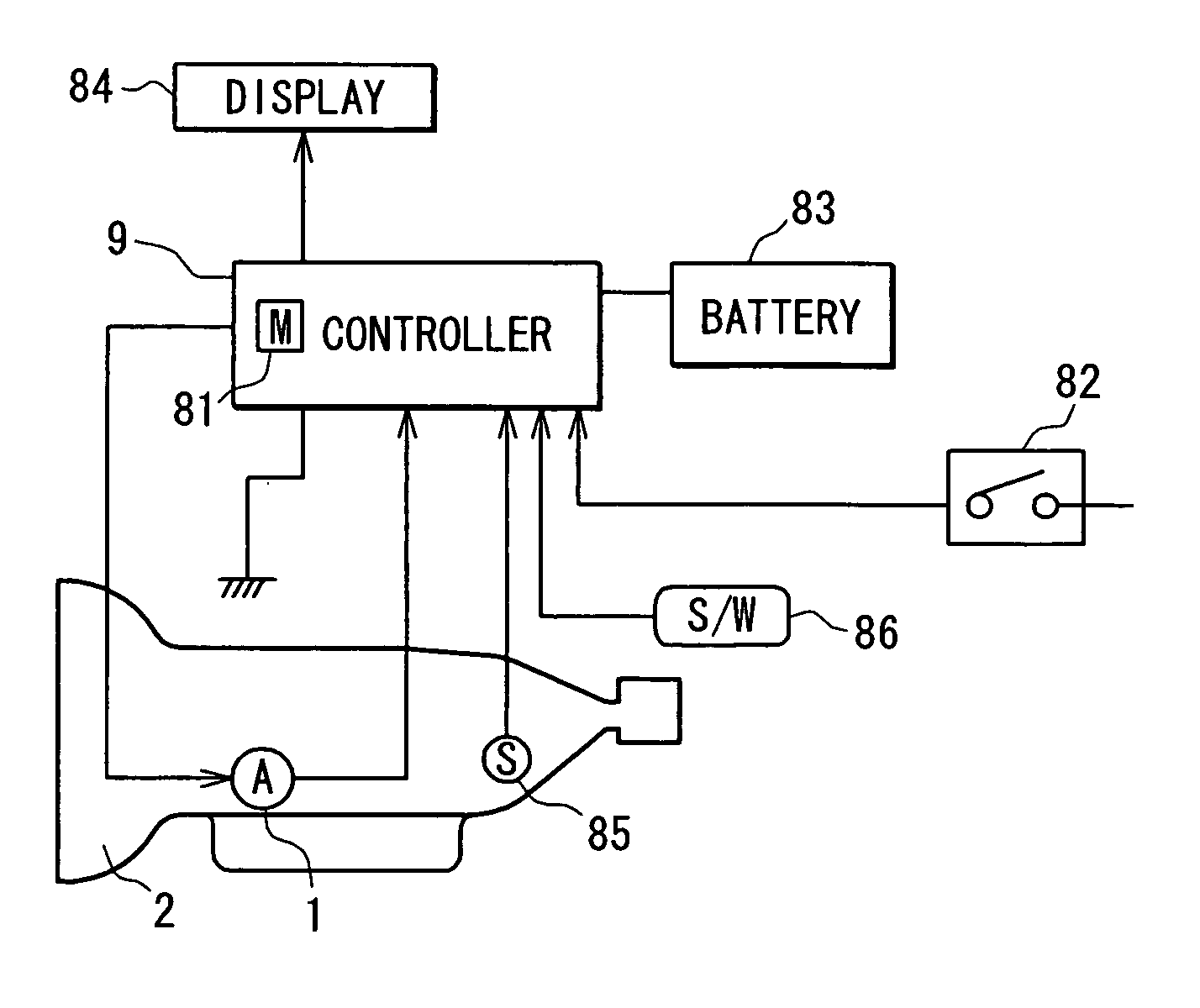
ActiveUS20070046243A1DC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlPosition dependentMotor controller
By utilizing a mechanical backlash generated between an electric actuator and a shift range switching mechanism, a specific region is obtained, in which a variation in the output shaft angle is relatively small with respect to a variation in rotor angle. In this specific range, an actual shift range position is calculated, whereby the rotor angle that the motor controller recognizes is corrected so as to relate the actual shift range position. A deviation between the rotor angle and the actual shift range is corrected, so that the shift range switching is precisely performed.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Zero-position correction system and method of PMSM rotor
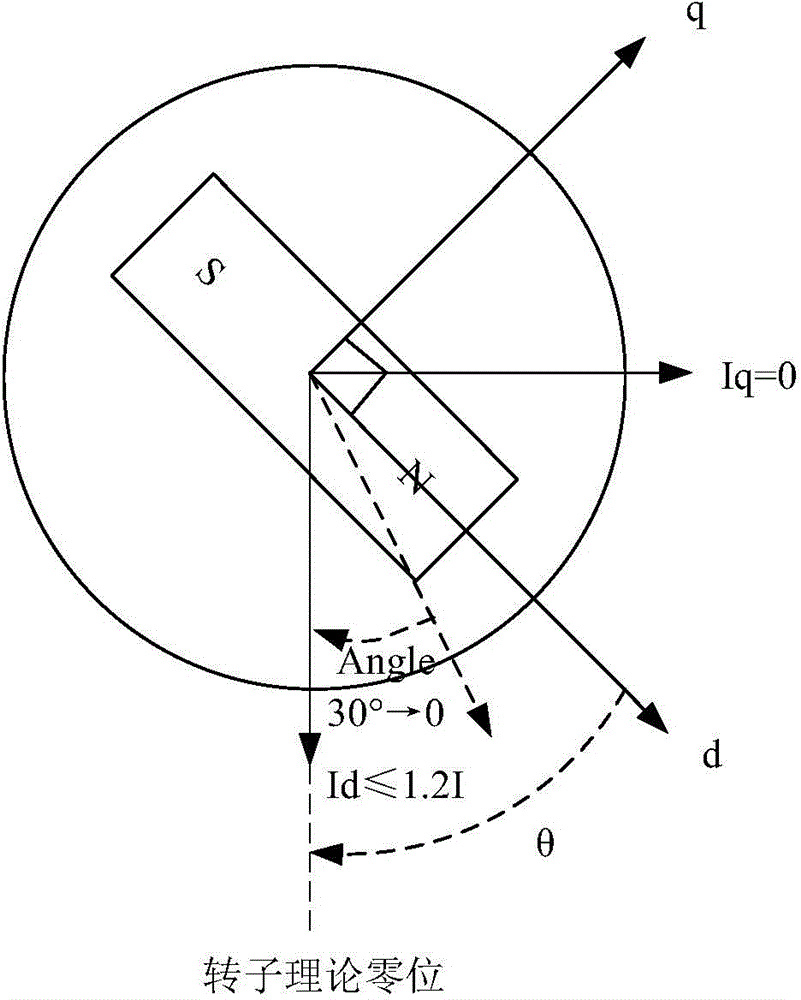
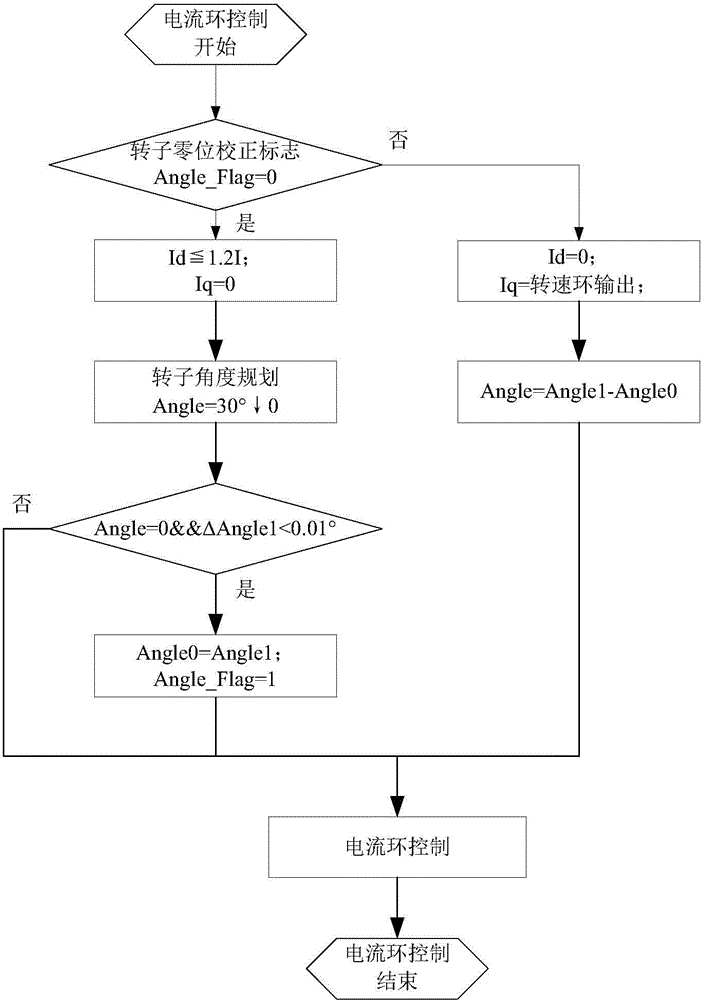
InactiveCN104836506AEasy to controlAchieve correctionElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPhase currentsAngular degrees
The invention relates to a zero-position correction system and method of a PMSM rotor, and belongs to the technical field of motor servo control. The q shaft current in a motor control branch is set as 0, the d shaft current is controlled within 1.2 times of rated current, the using angle in given sector control is decreased gradually from 30 to 0 degree, and thus, the PMSM motor is changed from an angle theta to a theoretical zero position; whether the PMSM rotor reaches a final stable position is determined, and the angle when the PMSM rotor is at the final stable position is used as the zero-position correction angle of the rotor; and the rotor angle measured in the process that the correction angle is compensated for motor control is used as the practical rotor angle, and zero-position correction of the rotor is realized. The correction method in the invention is simple and easy to implement, and can effectively solve the problems that operation is complex, the versatility is low and the phase current is not easy to control in zero-position correction of the PMSM rotor in the prior art.
Owner:XUJI GRP +2
Digital signal processing of resolver rotor angle signals
InactiveUS6754610B2Increase the amount of calculationLow costDigital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsDigital signal processingEngineering
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Salient pole type permanent magnet synchronous motor position sensor-free control method and device
InactiveCN104868814ASolve technical problemsImprove reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPhase currentsLow speed
The invention discloses a salient pole type permanent magnet synchronous motor position sensor-free control method and device. The method includes the following steps that: when a salient pole type permanent magnet synchronous motor operates in a high-speed operation mode, voltage and phase current at the motor end are acquired and are transformed into voltage and current under an alpha-beta coordinate system, so that a counter electromotive force can be estimated, and therefore, a rotor angular position can be obtained; when the salient pole type permanent magnet synchronous motor operates in a low-speed or zero-speed mode, symmetrical three-phase high-frequency rotating voltage is injected into a stator winding; rotor position information can be obtained through the interaction of the symmetrical three-phase high-frequency rotating voltage and the salient poles of the motor; and the rotor angular position or the rotor position information are substituted into a weighted equation of a linking algorithm, so that current rotor position and speed can be estimated. The control method of the invention is not only suitable for high speed, but also suitable for low speed and zero speed, and can increase the reliability of motor driving.
Owner:BEIJING POWER MACHINERY INST
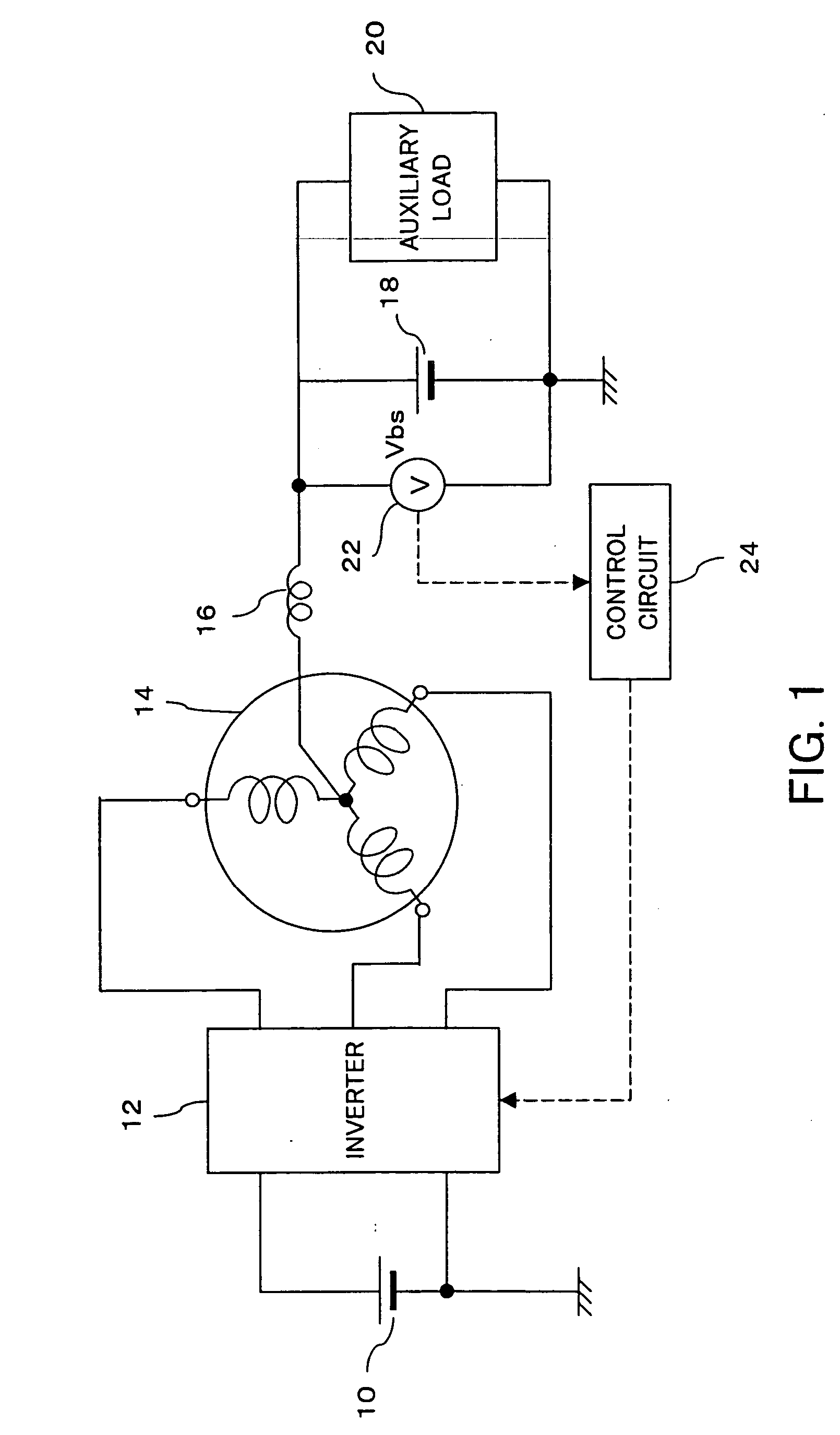
Method and system for detecting the disconnection of an auxiliary power supply from a poly-phase motor
InactiveUS7098624B2Significant changeEfficient detectionSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlPhase currentsElectrical battery
To a neutral point of a motor is connected a positive electrode of an auxiliary battery and an auxiliary load. Voltage on a power supply line to the auxiliary load, a neutral point voltage, is detected, and disconnection of the auxiliary battery is determined when an increase of ripples in the neutral point voltage is detected. When a voltmeter cannot be used, control of the neutral point voltage is continued by measuring current of the auxiliary battery and performing control such that the current value becomes 0. A resolver is further provided on the motor for detecting the rotor angle with high accuracy. A control circuit generates, in accordance with an output of the resolver, a voltage control signal for each phase current having the same amplitude as the carrier amplitude during startup, and compares the voltage control signal to carrier to obtain a gate signal having the same frequency as the carrier frequency. In switching of the inverter, due to this gate signal, periods in which all phases are on or off are reduced, thereby preventing a large neutral point current.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for on-line fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control of position signals of switch reluctance motor
ActiveCN103414408AEasy to implementGuaranteed uptimeTorque ripple controlCommutation monitoringFault tolerancePosition angle
The invention provides a method for on-line fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control of position signals of a switch reluctance motor. A position sensor detects the rotation position of a three-phase 12 / 8 pole rotor in real time, the relative position of the rotor of the motor is determined according to a built-up sequence of three paths of feedback position signals and a trigger edge, then a position angle q of the rotor is calculated, and by combination with a current energizing phase, fault position signals and fault types can be diagnosed in an on-line mode; under the fault state, invalid phase changing actions are rebuilt, correct phase changing operations are conducted, fault tolerance and recovery control over the position signals are conducted, the continuous operation of the motor after the fault is achieved, and the correct cut-in of the position signals when the fault recovery is performed is achieved. The method is convenient to achieve and reliable in operation, in the diagnosis process, the rotor position angle q is amended in each rotor angle cycle, an accumulative error can not be produced, and the accumulative influence on the output performance of a system does not exist; the method can diagnose the fault position signals and the fault types in the on-line mode and enable the system to rapidly recover normal stable operation, and the reliability of the system is improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
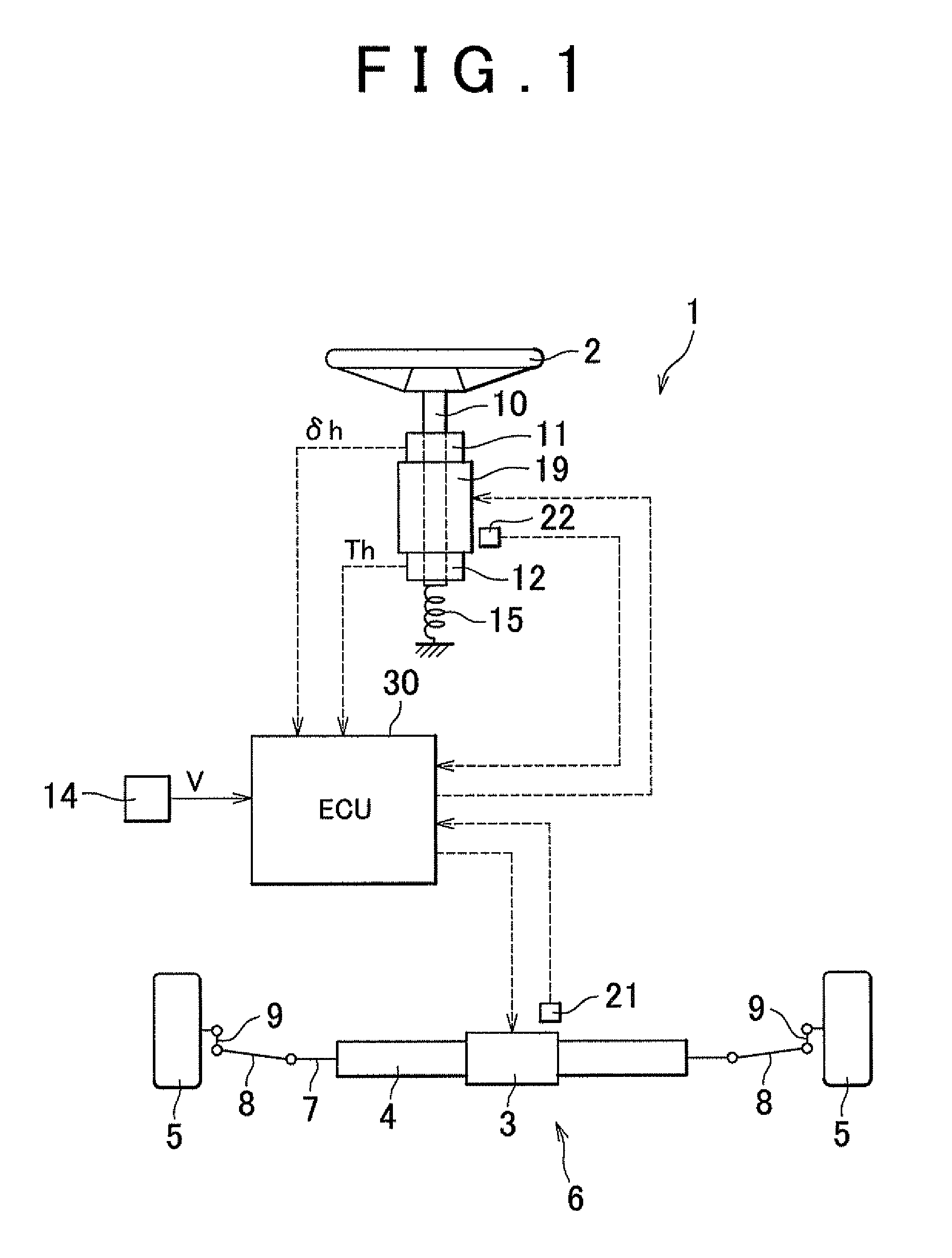
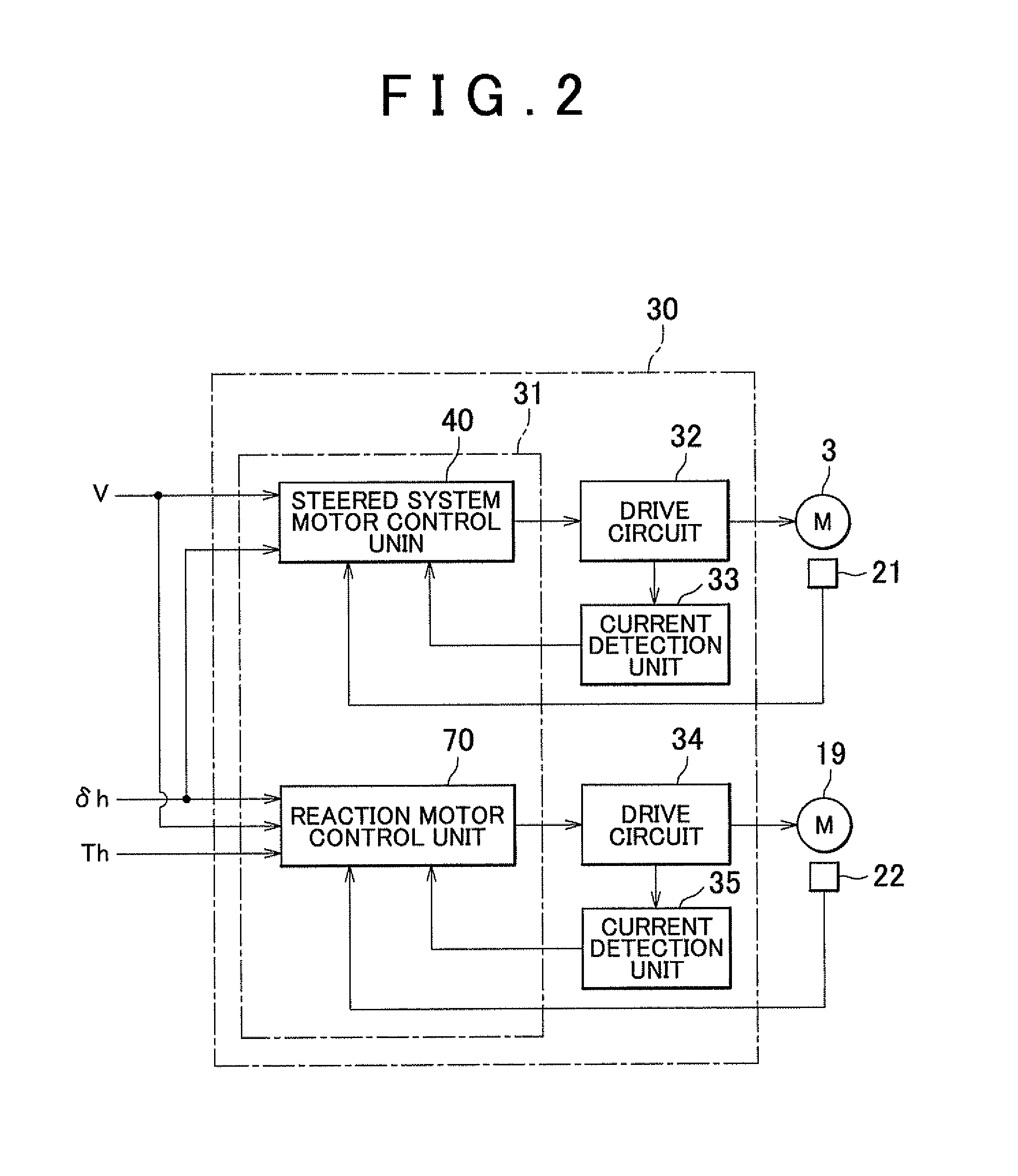
Vehicle steering system
InactiveUS20130138300A1Single motor speed/torque controlSteering initiationsSignal onAngular degrees
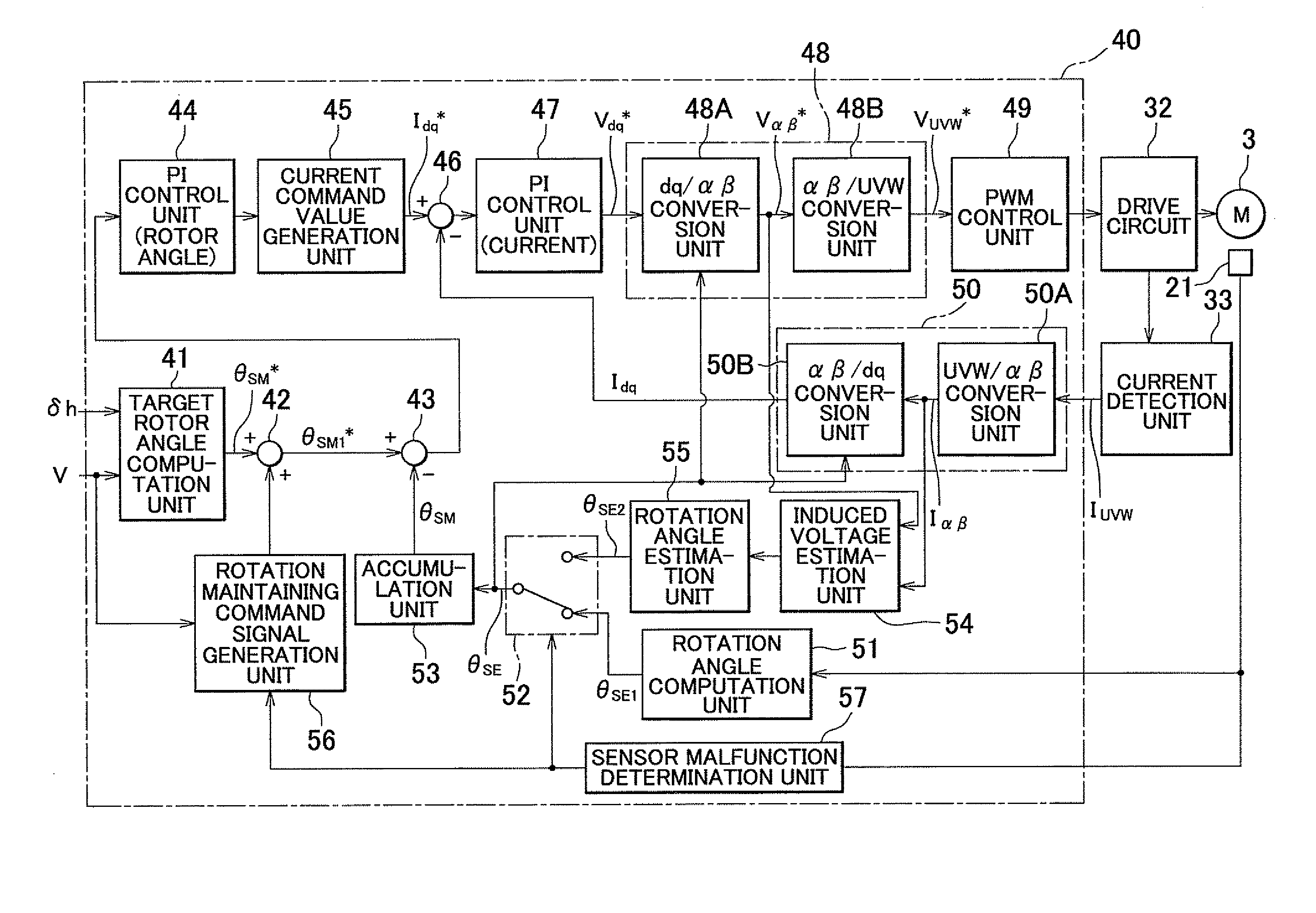
In a vehicle steering system, when a sensor malfunction determination unit detects a malfunction of a rotation angle sensor, the sensor malfunction determination unit changes a control mode from a first control mode to a second control mode. In the second control mode, an actual rotor angle (mechanical angle) (θSM) of a steered system motor is computed on the basis of a second rotor angle (electric angle) (θSE2) estimated by a rotation angle estimation unit. Then, feedback control is executed such that the actual rotor angle (θSM) converges to a target rotor angle (θSM1*) that is obtained by superimposing a rotation maintaining command signal on a target rotor angle (θSM*) computed by a target rotor angle computation unit.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
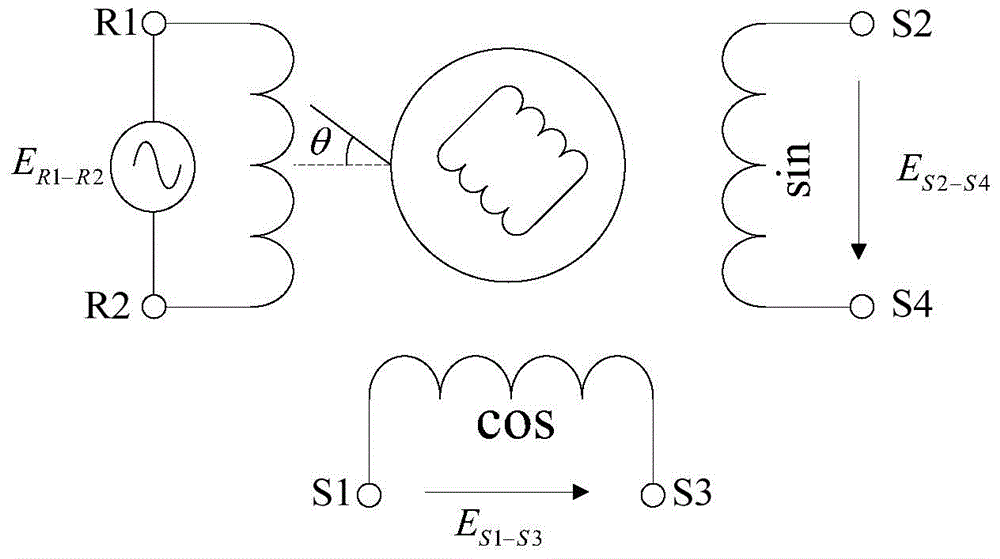
Multi-turn memory rotary transformer decoding circuit and position calculating method thereof
InactiveCN105222814AComplete the decoding functionConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyElectricityElectric machine
A multi-turn memory rotary transformer decoding circuit and a position calculating method thereof. A rotary transformer exciting circuit generates a sinusoidal excitation signal to be applied to a primary exciting winding, a rotary transformer output signal acquisition circuit samples an output voltage value of a secondary induction winding, a position calculating circuit calculates according to the output voltage value of the secondary induction winding of the rotary transformer to obtain the motor rotor angle, the motor rotor speed and the number of turns of the motor rotor, and a power management circuit can still provide electric energy for the multi-turn memory rotary transformer decoding circuit under the outage condition of external power supply. The multi-turn memory rotary transformer decoding circuit provided by the invention provides motor multi-turn absolute angle information while providing high-precision motor rotor angle information and rotating speed information, and can still complete a function of decoding rotary transformer information under the condition that a system is powered down.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST +1
Signal conditioning apparatus and method for determination of permanent magnet motor rotor position
ActiveUS20080048599A1Fast trackSimple technologyElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersLow speedCurrent amplitude
An apparatus and method for estimating rotor angle information for the control of permanent magnet AC motors having sinusoidal current excitation. The disclosed motor drive can provide full load operation at very low speeds including zero speed without the use of a shaft position sensing device. The rotor angle is estimated through injection of high frequency current, and rotor angle is extracted by a signal-conditioning algorithm, which utilizes current amplitude differential to discriminate the rotor angle. Rotor angle magnetic axis orientation (North or South pole) at startup is detected by comparing time average current ripple (at signal injection frequency) content between two different levels of d-axis current injection.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Method and apparatus for estimating angles in a synchronous machine
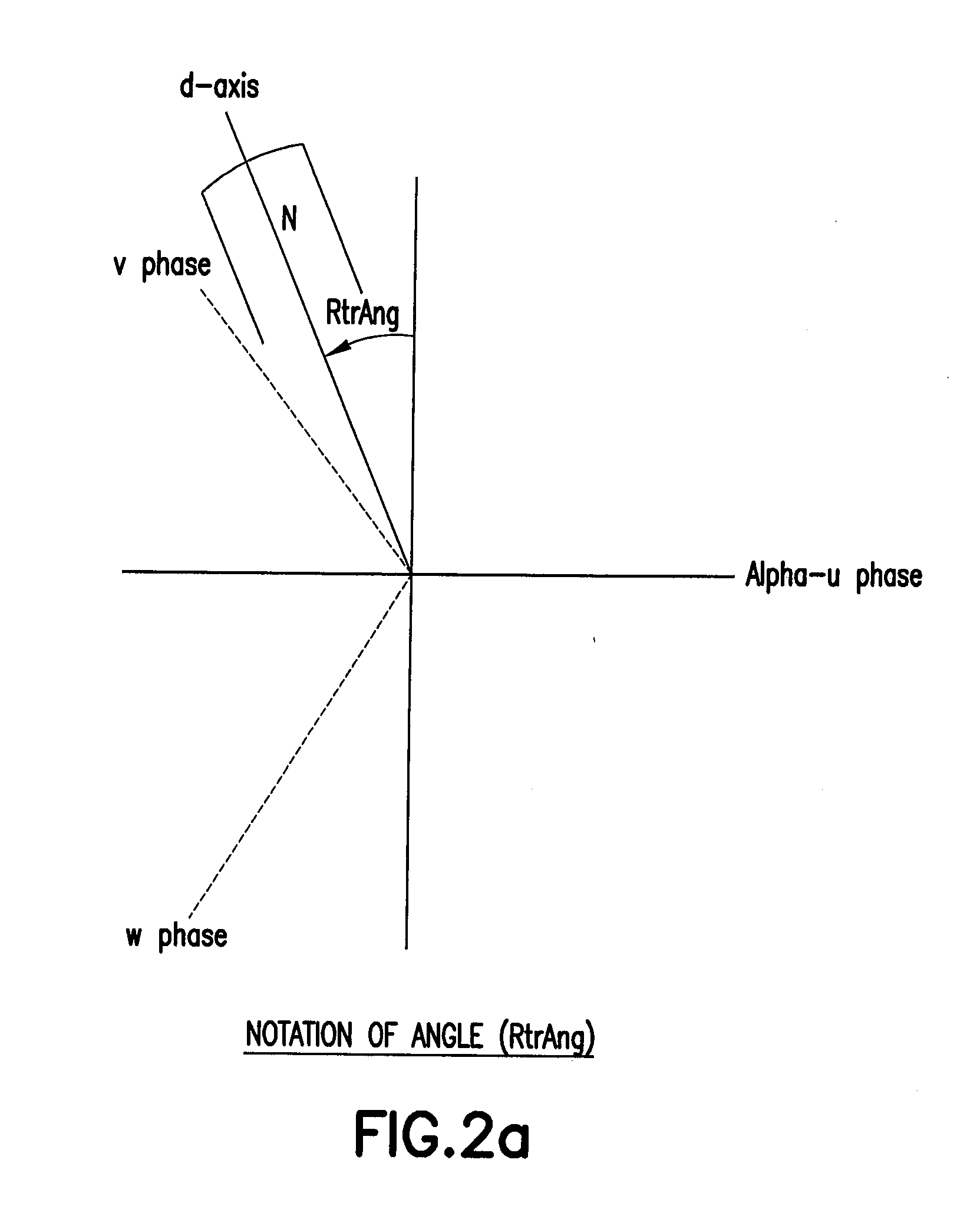
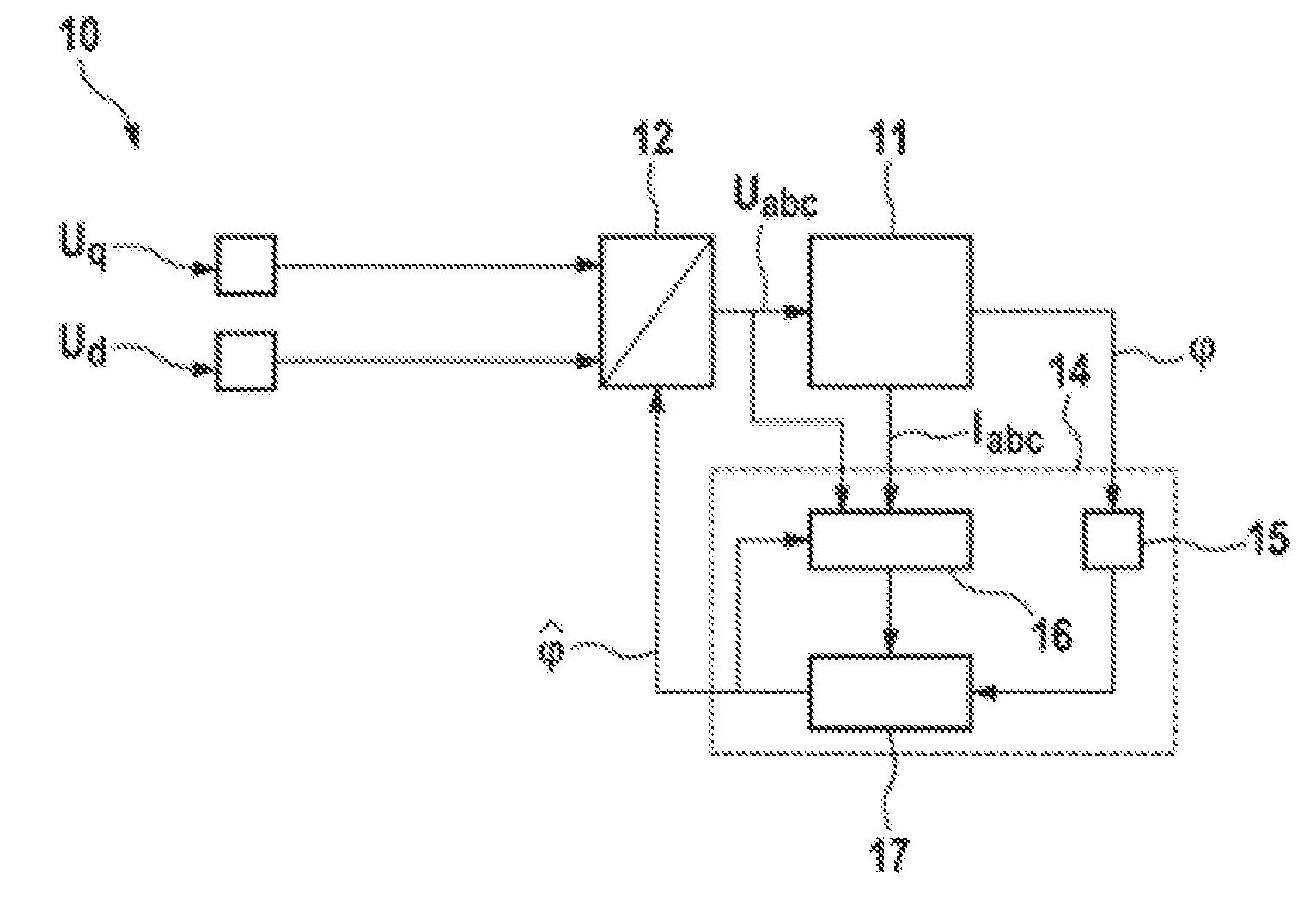
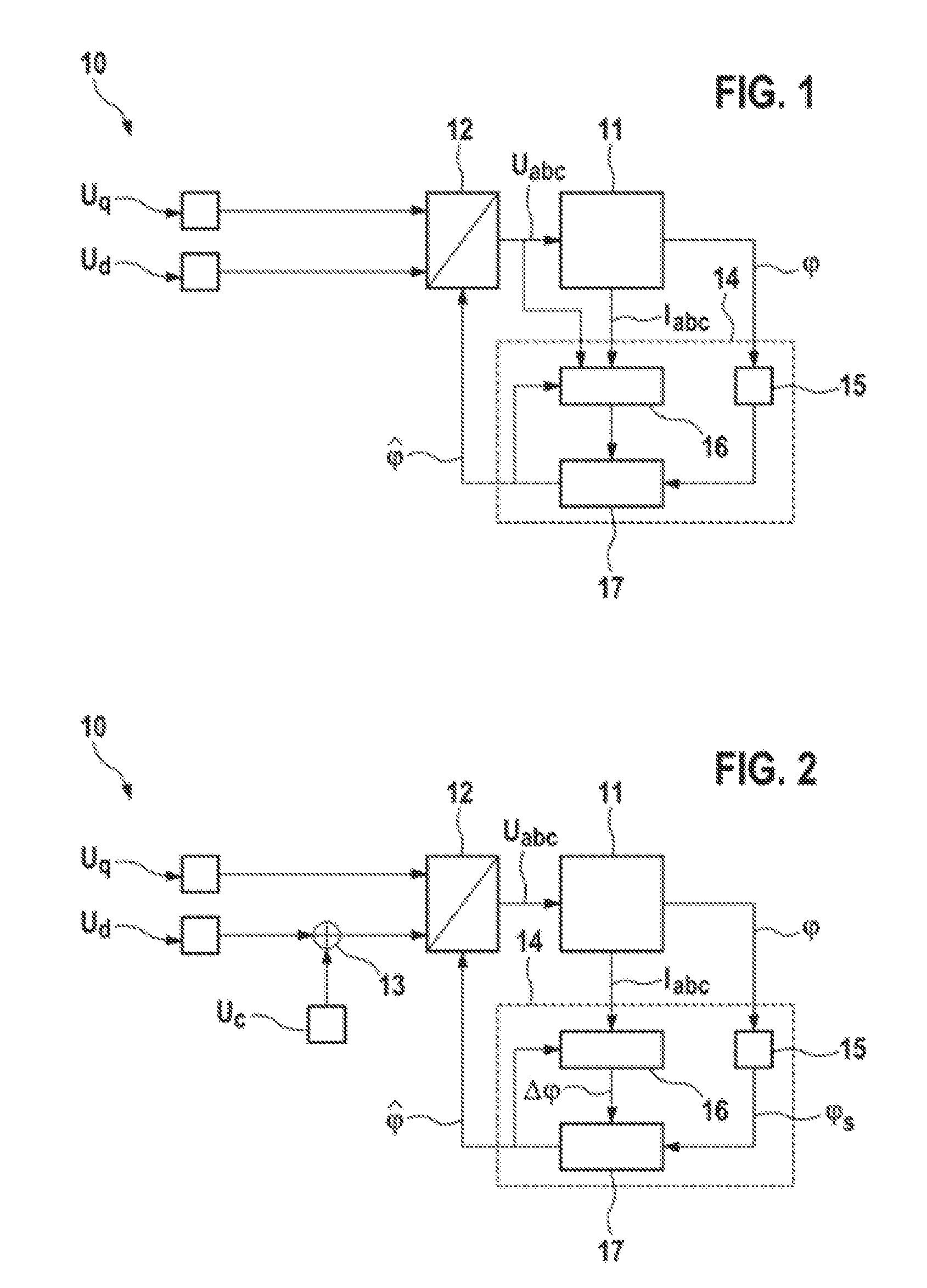
ActiveUS9225274B2Guaranteed uptimeImprove bindingVector control systemsStarter detailsCircumflexRotor angle
The invention relates to an apparatus for estimating angles in a synchronous machine (11), having an angle sensor device (15) which is designed to determine event-discrete measured values for a rotor angle (φ) of a rotor of the synchronous machine (11) and to output a measurement signal dependent on the determined measured values, an estimation device (16) which is designed to record current and / or voltage signals from the synchronous machine (11), to calculate a deviation (Δφ) of the rotor angle (φ) of the rotor of the synchronous machine (11) from an expected rotor angle on the basis of the recorded current and / or voltage signals and to output a deviation signal dependent on the calculated deviation (Δφ), and a combining device (17) which is designed to receive the measurement signal and the deviation signal and to calculate an estimated value ({circumflex over (φ)}) for the rotor angle (φ) of the rotor of the synchronous machine (11) from a combination of the measurement signal and the deviation signal.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method for determining the position of a rotor of a polyphase motor
ActiveUS20150268283A1Accurate measurementReduce speedElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlRotor angleElectrical current
The present disclosure relates to a method for determining the position of a rotor of a polyphase motor, e.g., the rotor angle, particularly at standstill. The method can include: applying voltage to phases of the motor, measuring a current in the phases, and determining the rotor position based on the measured current. According to the present disclosure, determination of the rotor position can be based on current values measured during a period where zero voltage is applied to the respective phases.
Owner:MAXON MOTOR AG
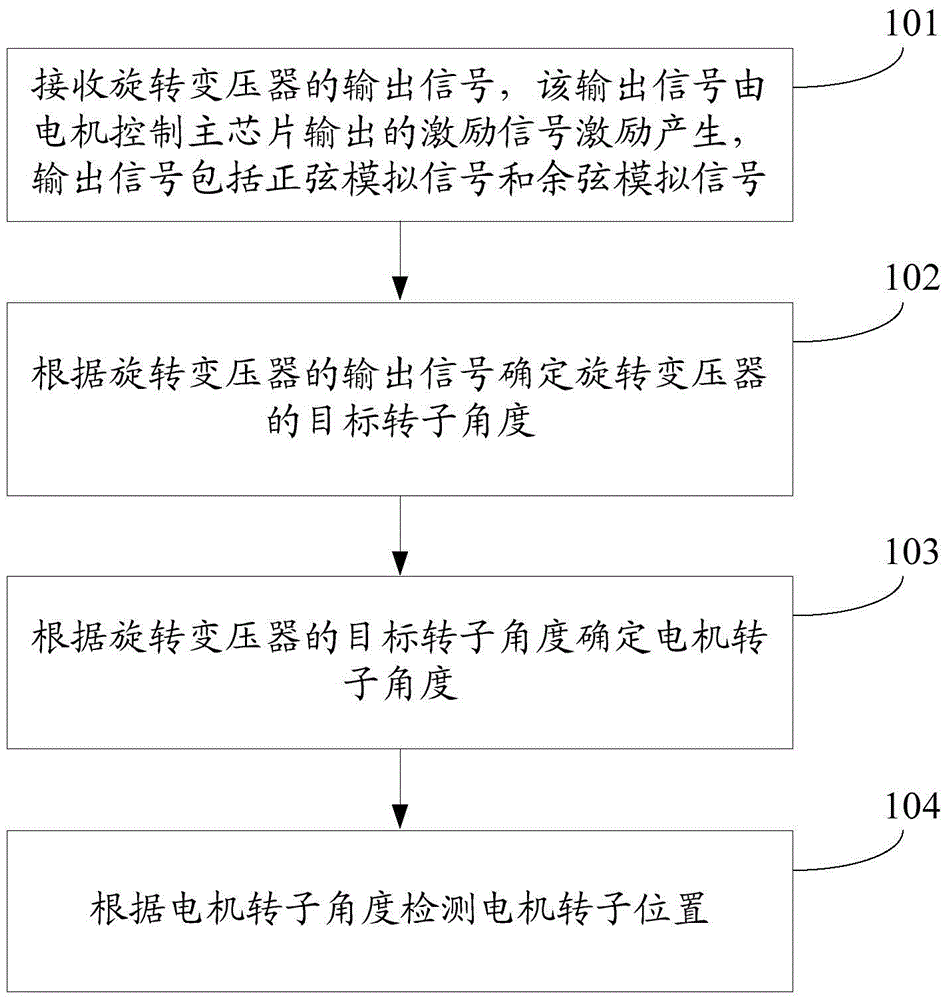
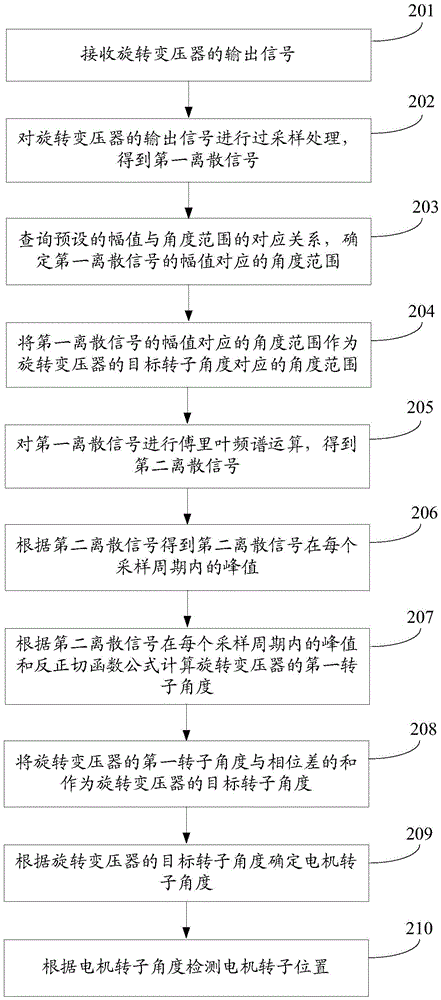
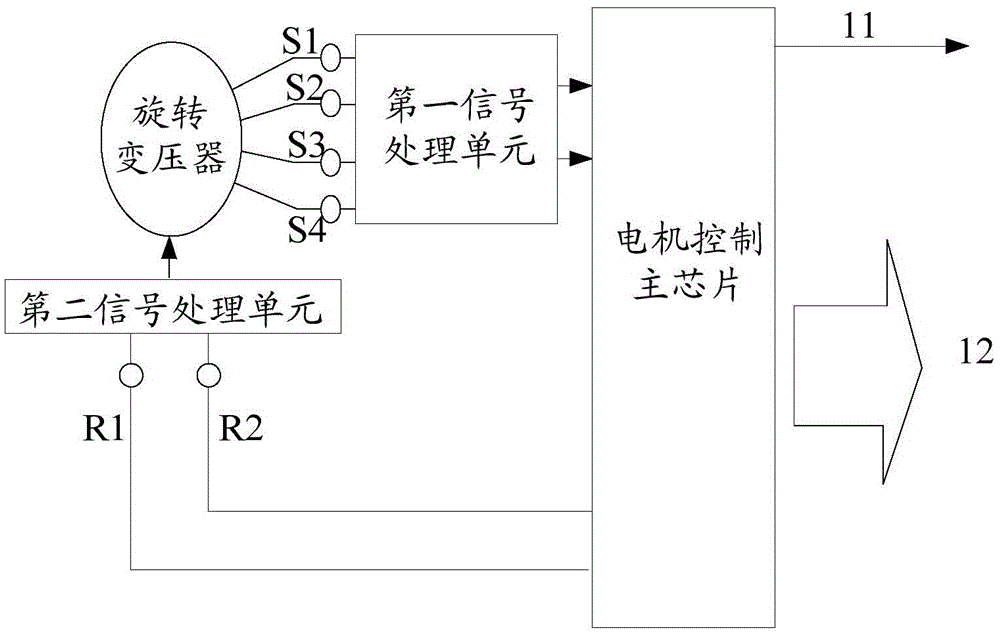
Motor rotor position detection method and device
The invention discloses a motor rotor position detection method and device and belongs to the technical field of driving control. The method is used for a motor control main chip and comprises the steps of: receiving output signals of a rotary transformer, wherein the output signals are excited by excitation signals output by the motor control main chip and comprise sine analog signals and cosine analog signals; determining a target rotor angle of the rotary transformer according to the output signals of the rotary transformer; determining a motor rotor angle according to the target rotor angle of the rotary transformer; and detecting the position of the motor rotor according to the motor rotor angle. The motor rotor position detection method and device solve the problem in the prior art that the cost is relatively high when the rotary transformer is utilized to detect the position of the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor, the cost of permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor position detection is lowered, and the motor rotor position detection method and device can be used to detect the position of the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
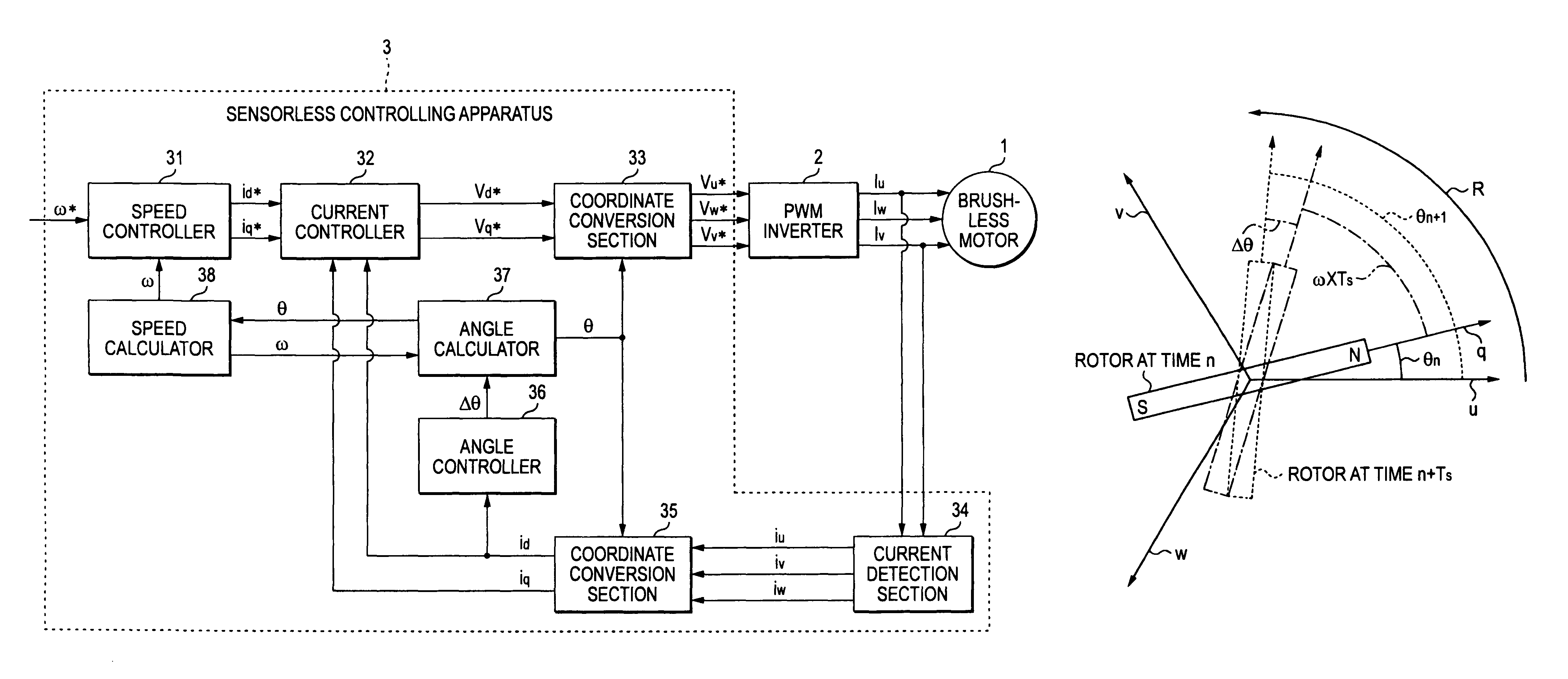
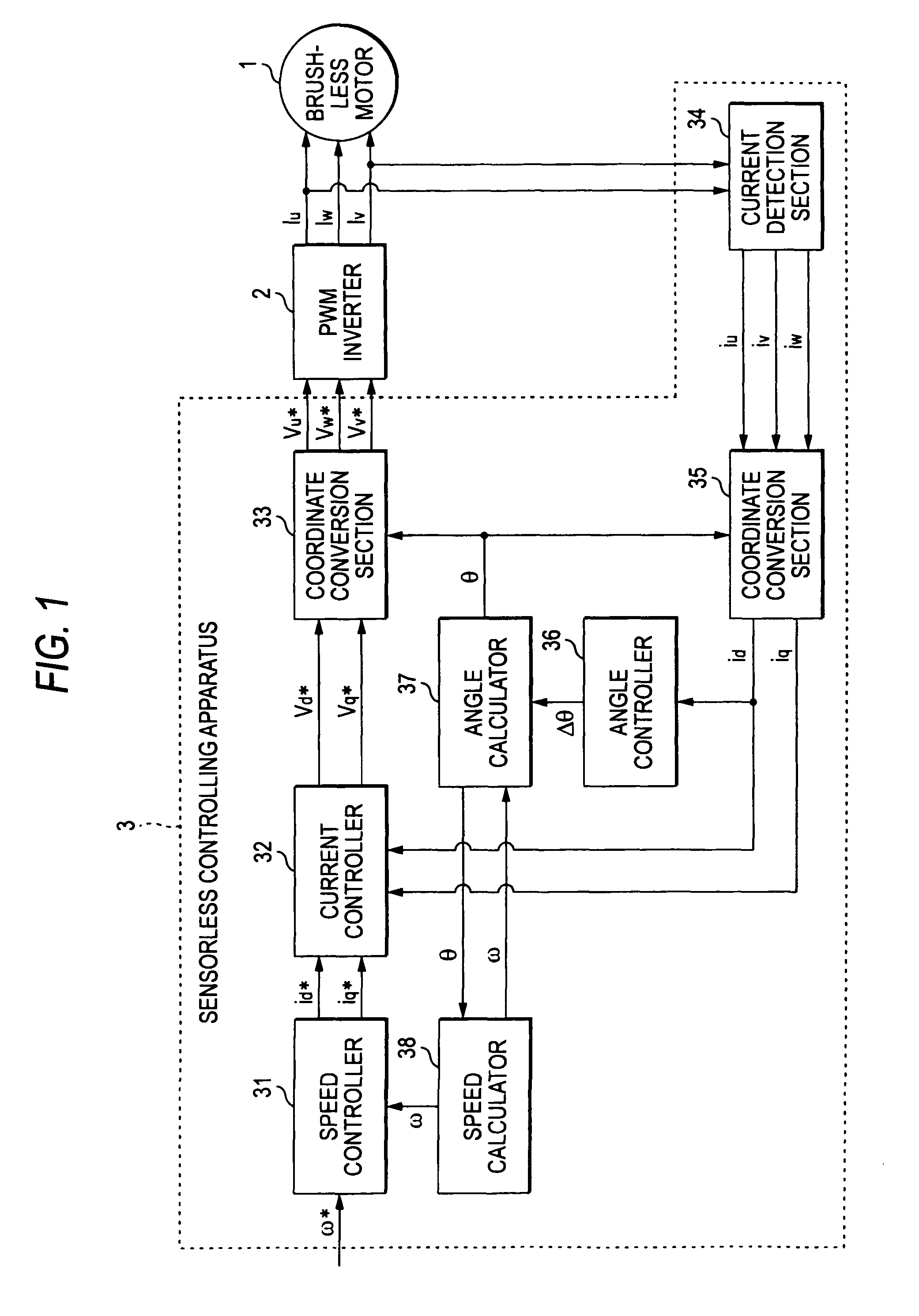
Sensorless controlling apparatus of brushless motor
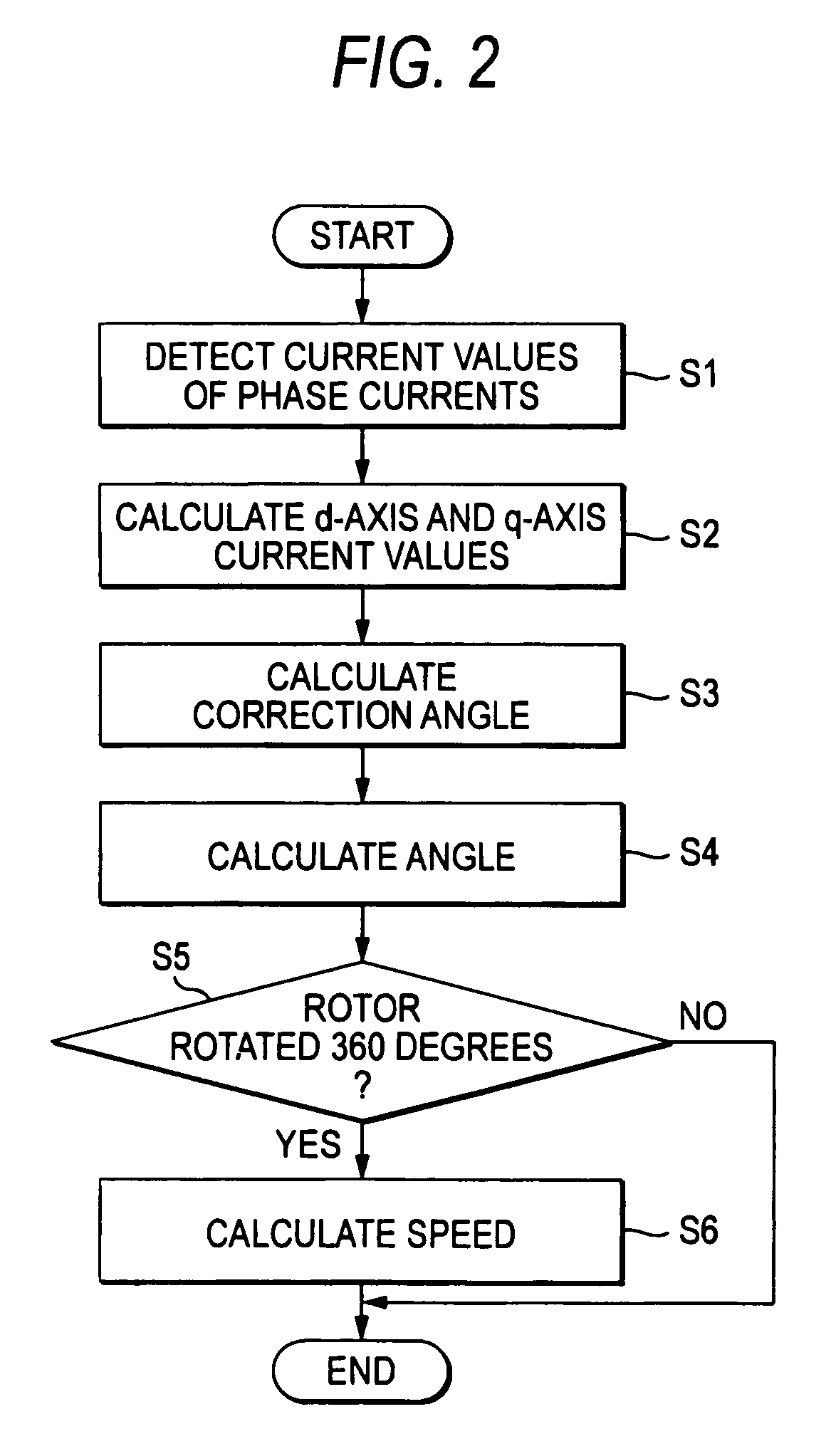
InactiveUS7944163B2Eliminate needHigh in general versatilitySynchronous motors startersVector control systemsBrushless motorsRotor angle
A sensorless controlling apparatus for controlling a brushless motor includes a speed calculator for calculating speed of a rotor ω, an angle calculator for calculating rotor angle θ at a predetermined time interval, and an angle controller for calculating correction angle Δθ based on the current value of a d-axis current (d-axis current value id), thereby controlling the rotor angle θ. The angle calculator uses the correction angle Δθ calculated by the angle controller, the speed ω calculated by the speed calculator, a predetermined time, and the rotor angle θ calculated by the angle calculator at a predetermined time to calculate the rotor angle at the predetermined time interval. Thus, the rotor angle θ calculated by the angle calculator is converged on the true angle of the rotor.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com