Method for detecting rotor position in non position sensor switch magnetic resistance motor
A switched reluctance motor, rotor position technology, applied in devices using electric/magnetic methods, electronic commutation motor control, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as increasing motor output torque fluctuations and reducing motor system efficiency. , to achieve the effect of reducing manufacturing cost and process, convenient detection of rotor position, and increasing torque fluctuation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
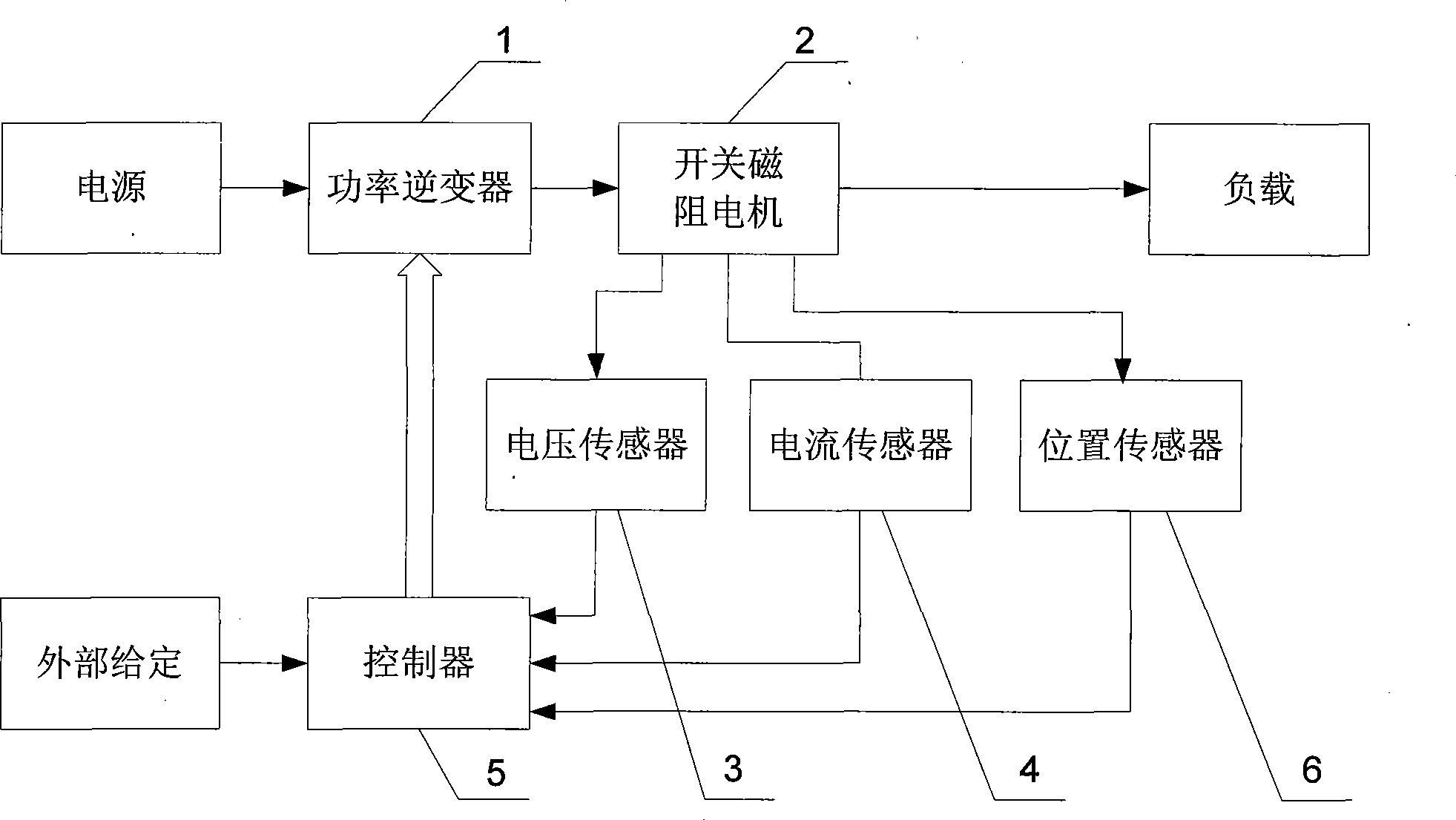
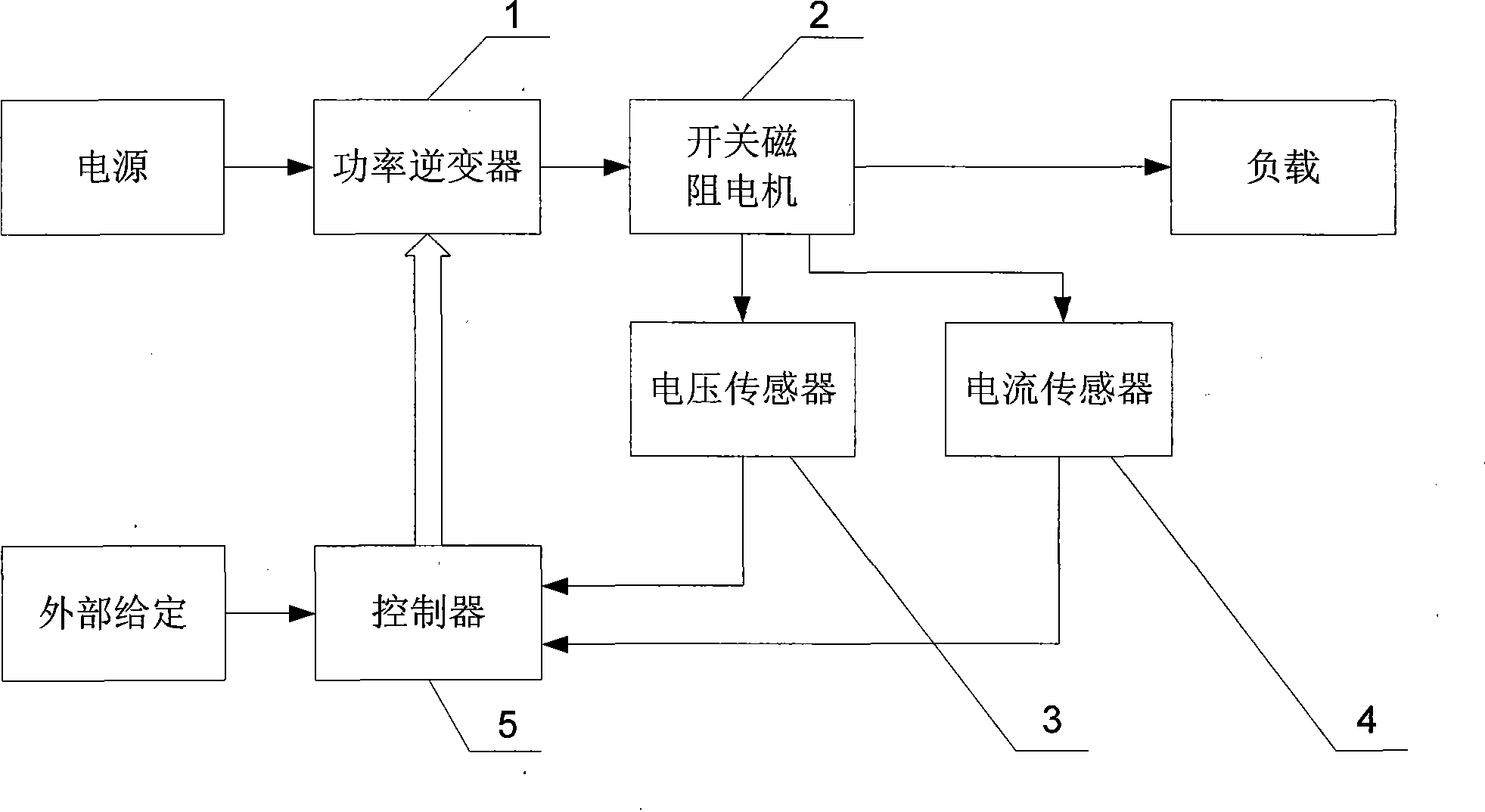
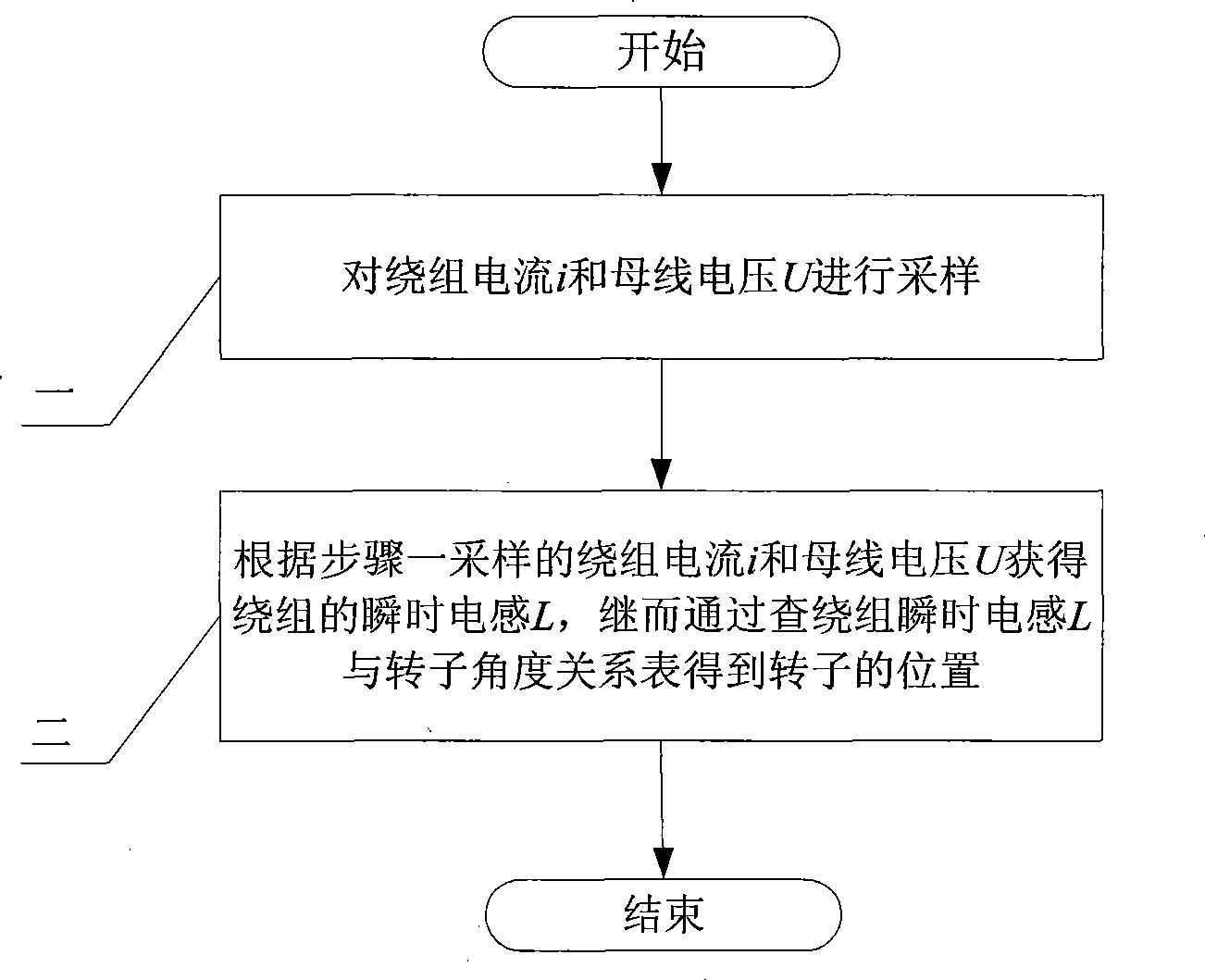
[0012] Specific implementation mode one, the following combination figure 2 , image 3 This embodiment is described. The device for implementing the method of this embodiment includes a power inverter 1, a switched reluctance motor 2, a voltage sensor 3, a current sensor 4, and a controller 5. The phase winding adopts chopper current closed-loop control. The method includes:
[0013] Step 1. Sampling the winding current i and the bus voltage U: the controller 5 samples the winding current i of the switched reluctance motor 2 measured by the current sensor 4 , and at the same time, the controller 5 samples the switched reluctance motor 2 measured by the voltage sensor 3 2 bus voltage U for sampling;
[0014] Step 2: Obtain the instantaneous inductance L of the winding according to the winding current i sampled in step 1 and the bus voltage U, and then obtain the position of the rotor by checking the relationship table between the instantaneous inductance L of the winding and ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0018] Specific implementation mode two, the following combination Figure 4 , Figure 5 Describe this embodiment. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the method for obtaining the instantaneous inductance L of the winding is:
[0019] The power tube of power inverter 1 is turned on, so that when the winding current i is in the rising phase, according to the formula
[0020] i ( t ) = U - U 1 R + ( i 0 - U - U 1 R ) e - R L t
[0021] Find the instantaneous i...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0039] Specific implementation mode three, the following combination Figure 6 Describe this embodiment. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the method for obtaining the relationship table between the instantaneous inductance L of the winding and the rotor angle is as follows: fix the motor rotor at a set angle, pass 50Hz alternating current into the winding, and measure Winding voltage U 2 and current I 2 , using the formula
[0040] 2 π × 50 × L = ( U 2 I 2 ) 2 - R 2
[0041] Calculate the instantaneous inductance L of the winding at the angular position of the rotor, where R is the eq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com