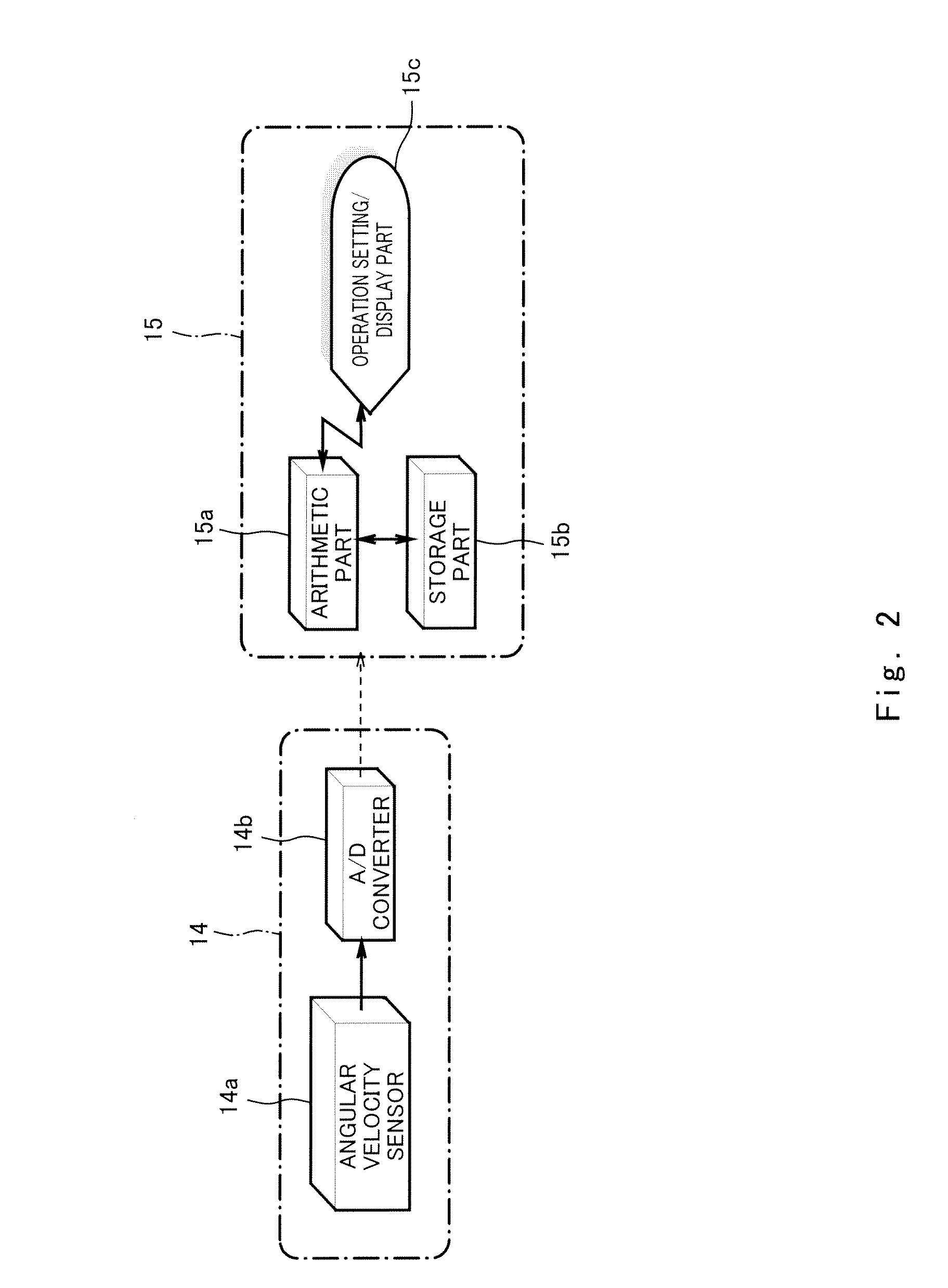
Patents
Literature
387 results about "Velocity estimation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Estimate Velocity. Velocity is a simple tool that measures the pace at which teams get work done. The sum of the estimates for your work items — user stories, backlog , defects—successfully completed in an iteration is your velocity.
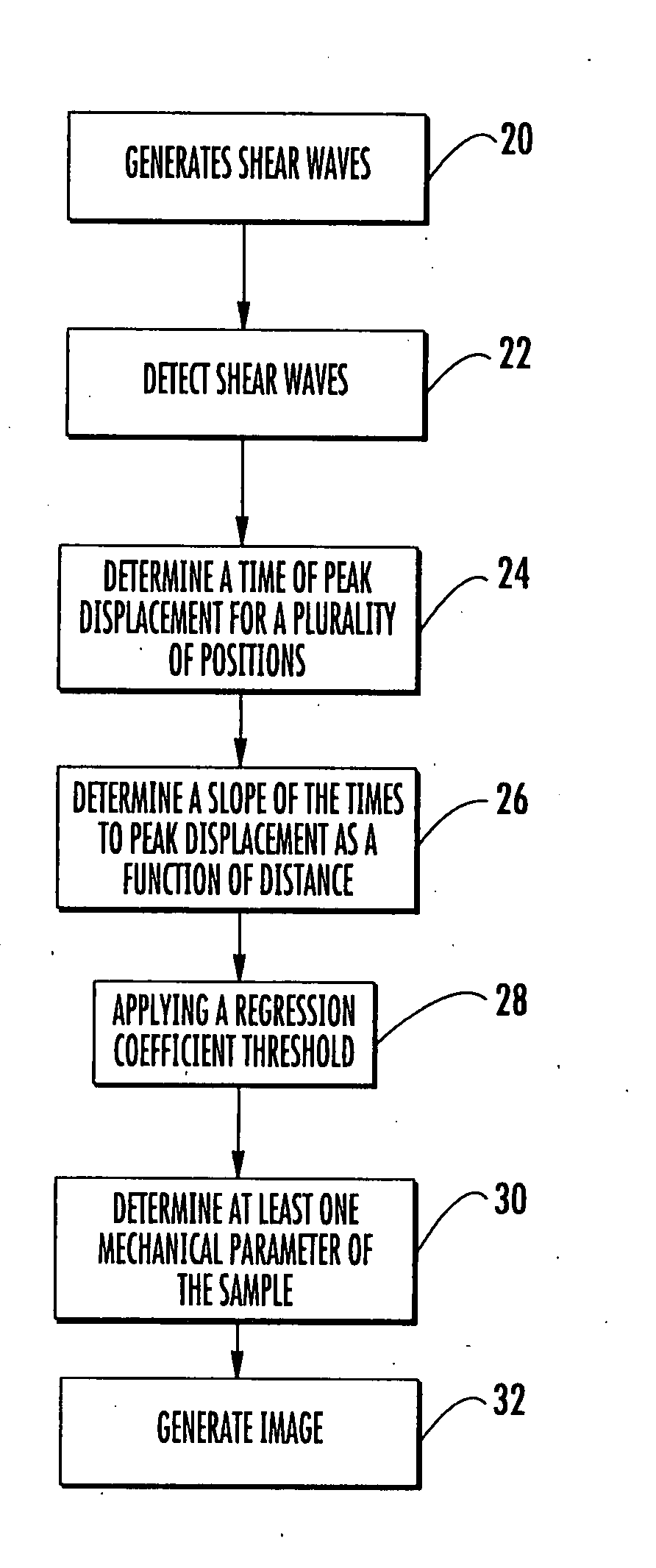
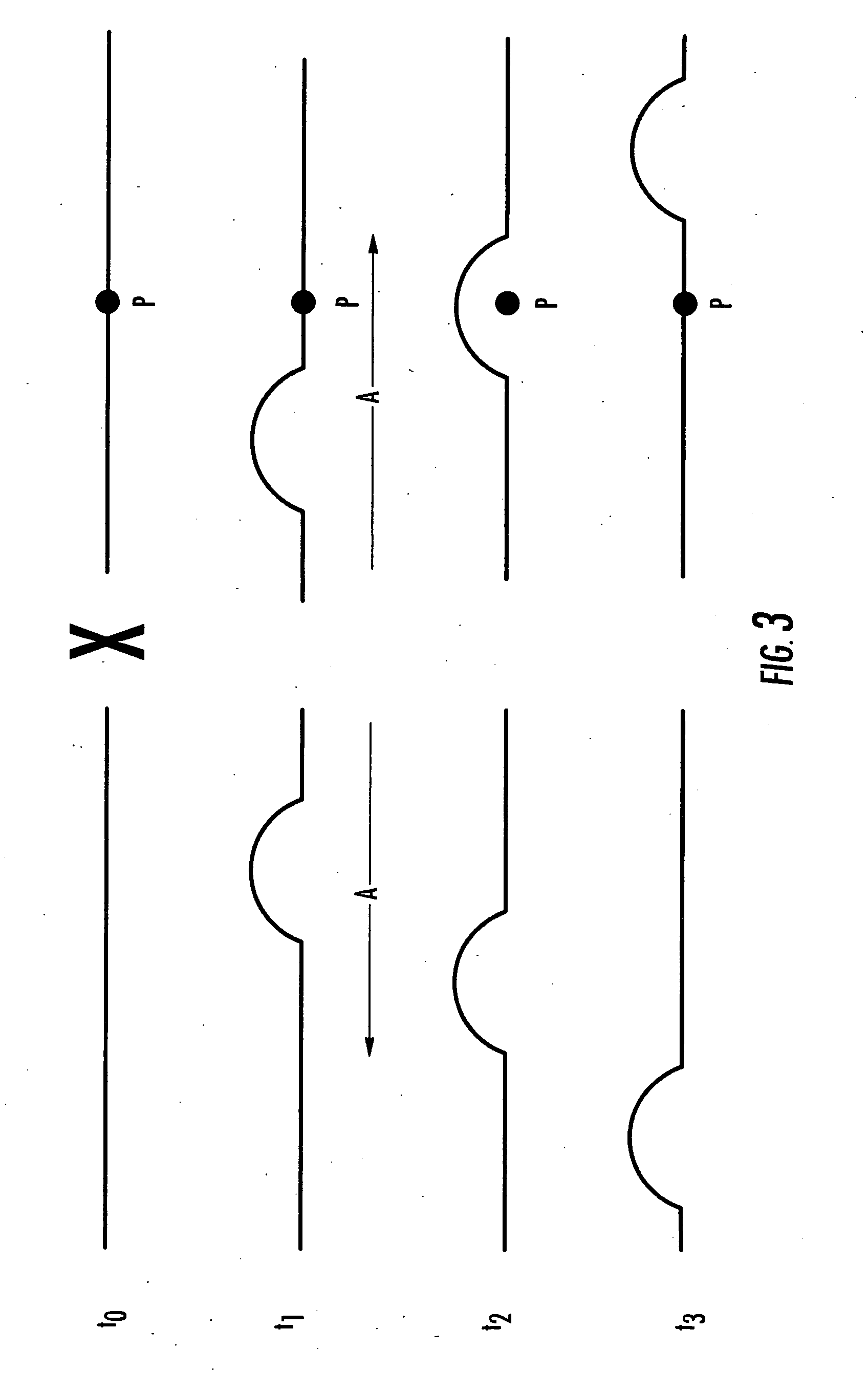
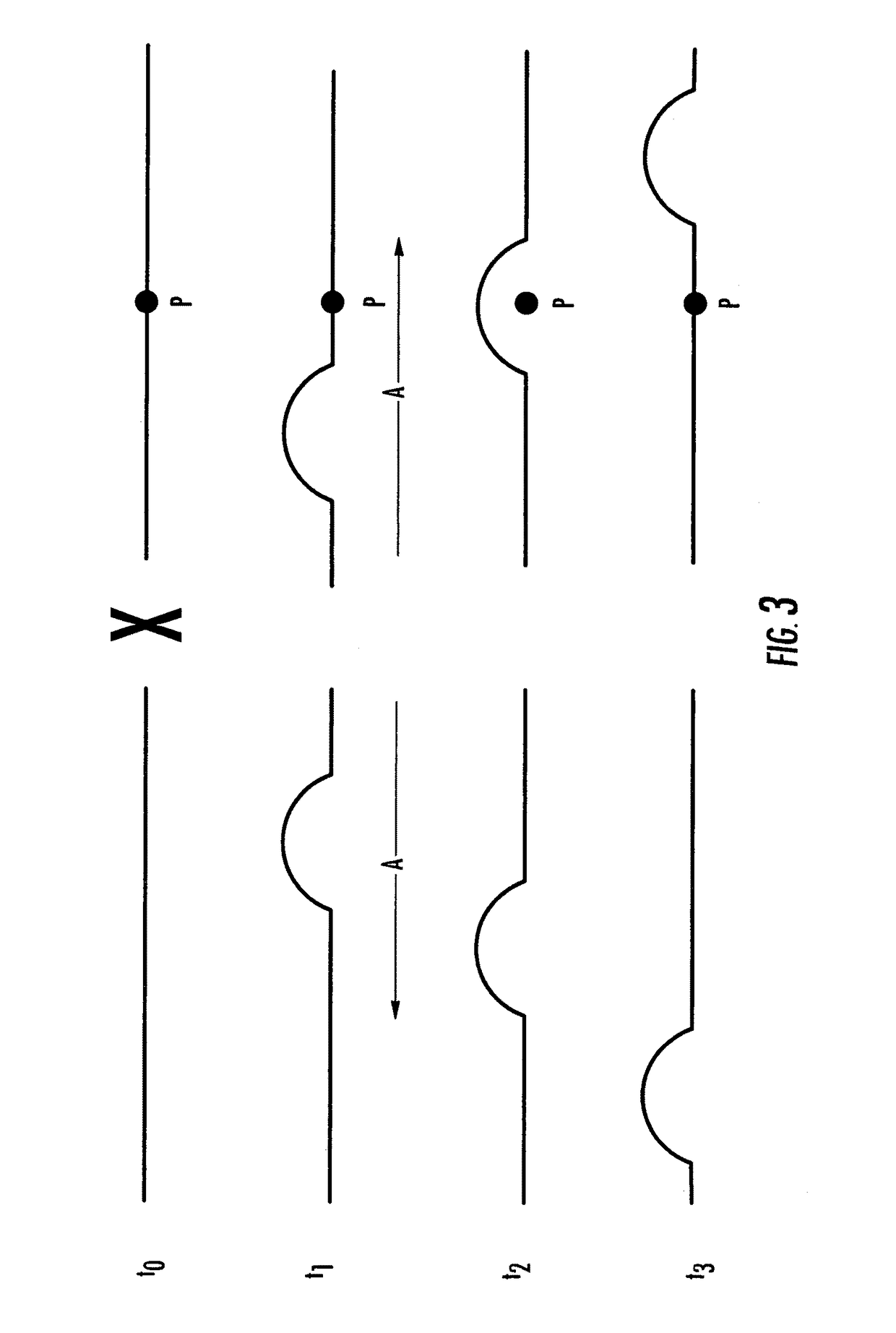
Methods, Systems and Computer Program Products for Ultrasound Shear Wave Velocity Estimation and Shear Modulus Reconstruction
ActiveUS20080249408A1Wave based measurement systemsOrgan movement/changes detectionShear modulusReconstruction method
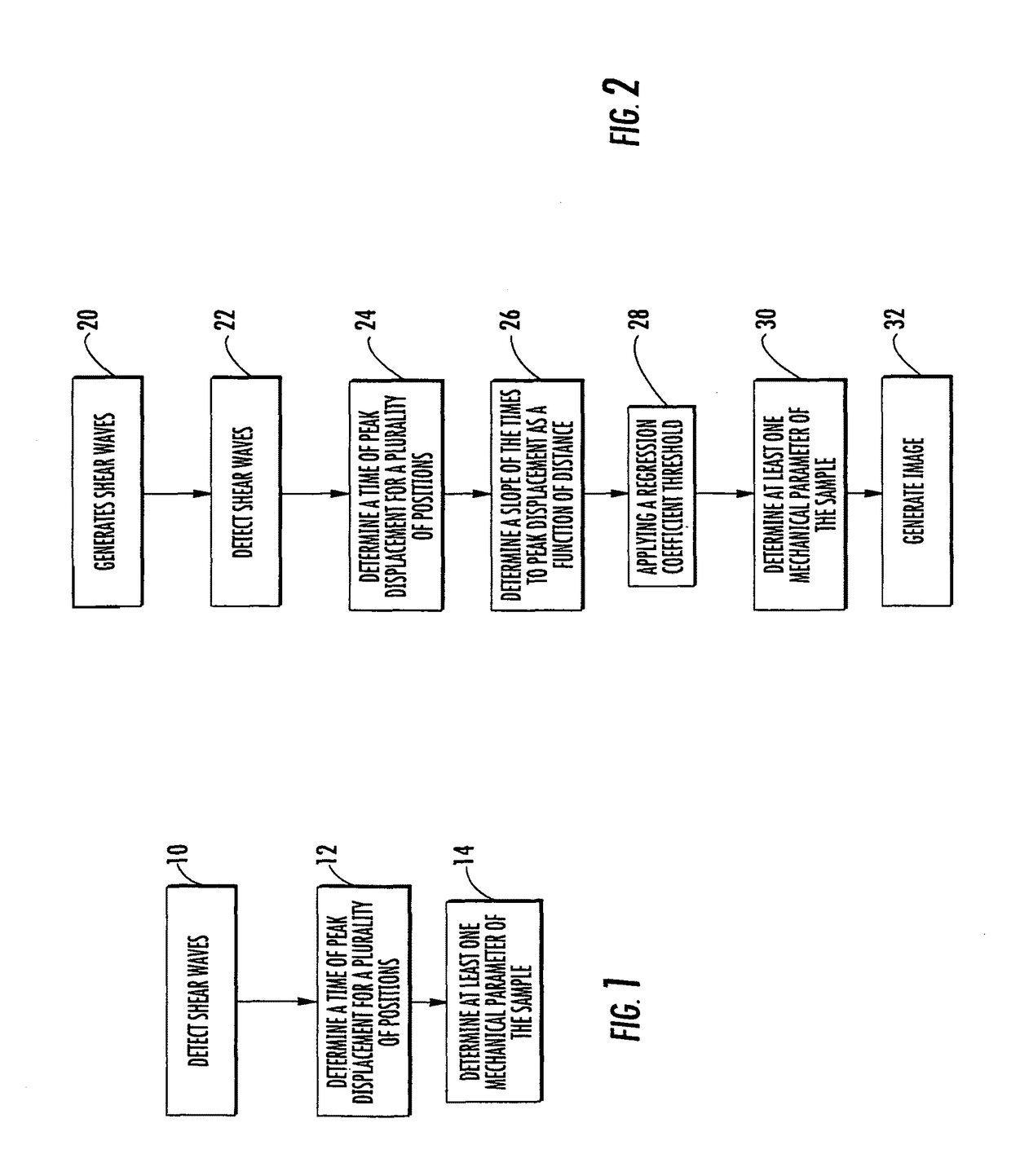
Methods for determining a mechanical parameter of a sample include detecting shear waves that have been generated in the sample by an applied shear wave source. A time of peak displacement of the shear waves for a plurality of sample positions is determined. At least one mechanical parameter of the sample based on the time of peak displacement for the plurality of sample positions is determined.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
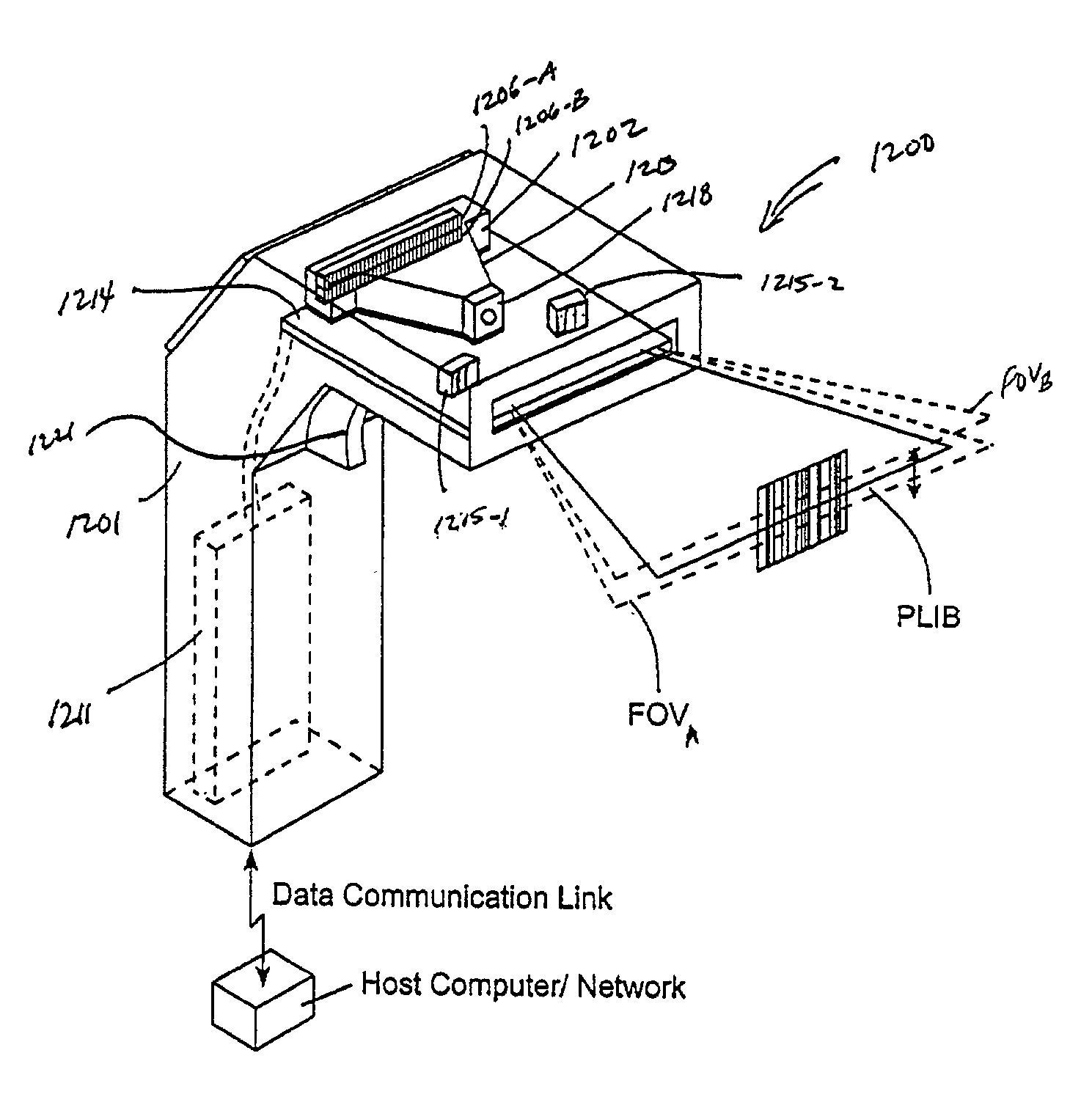
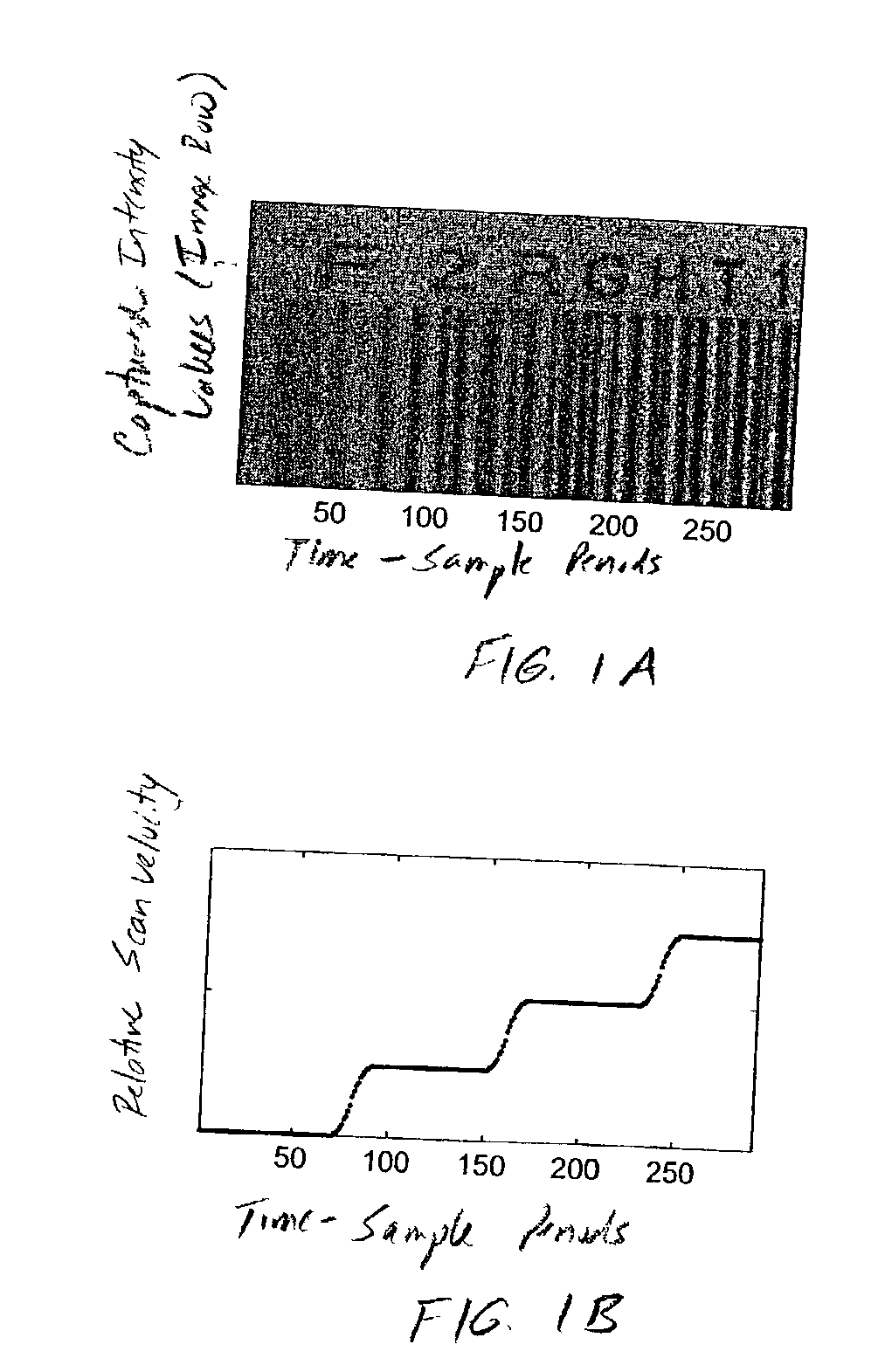
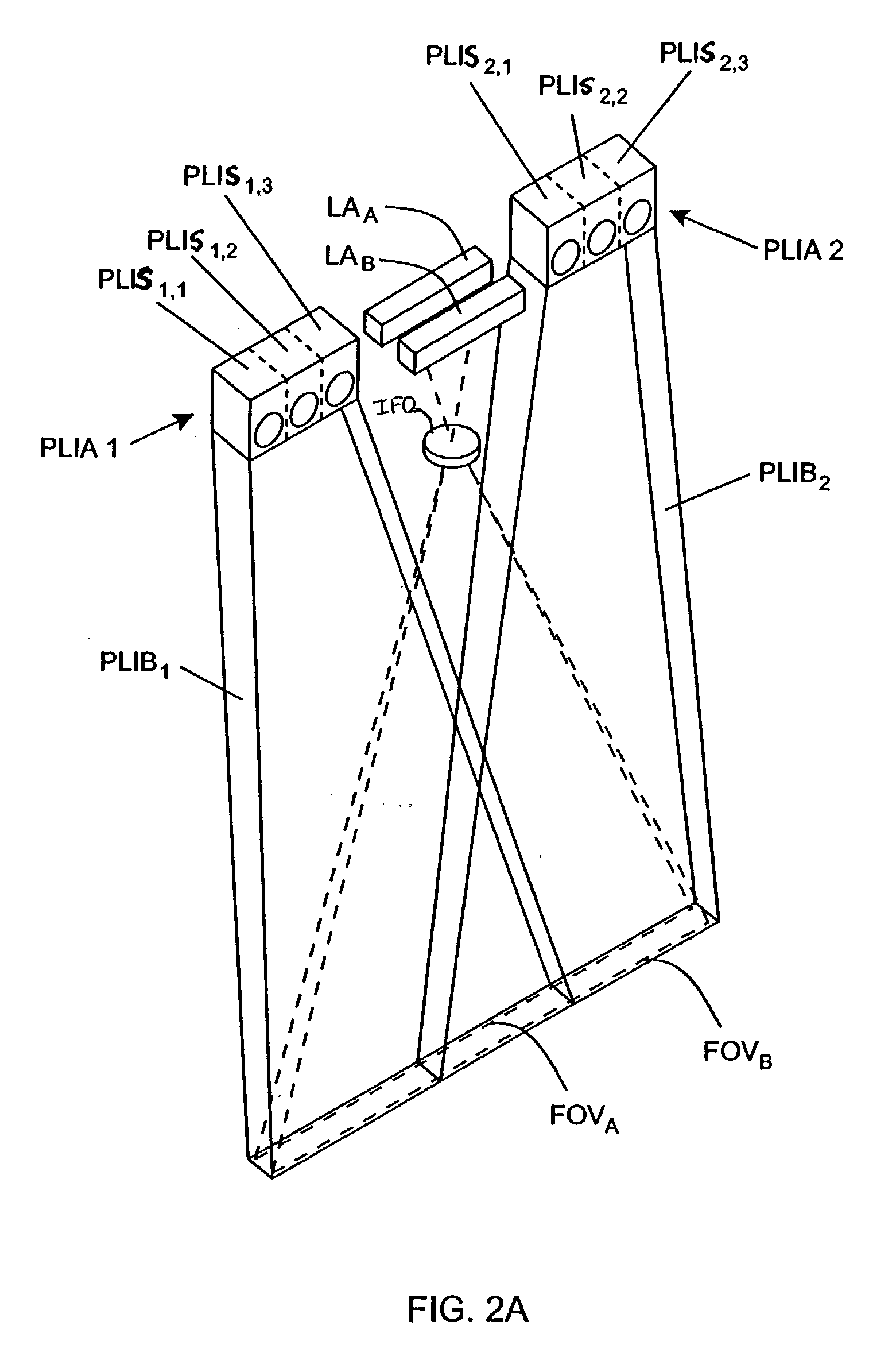
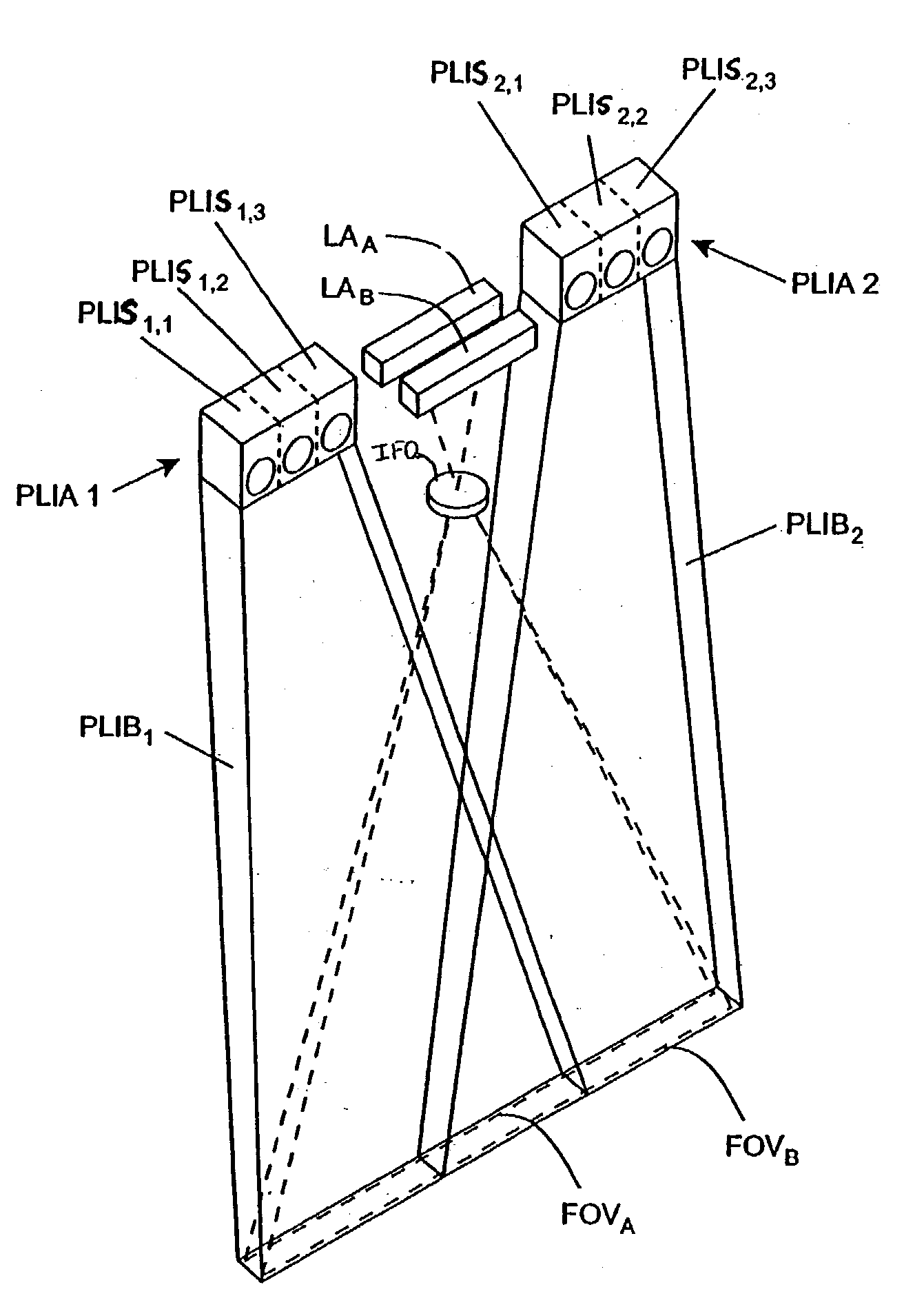
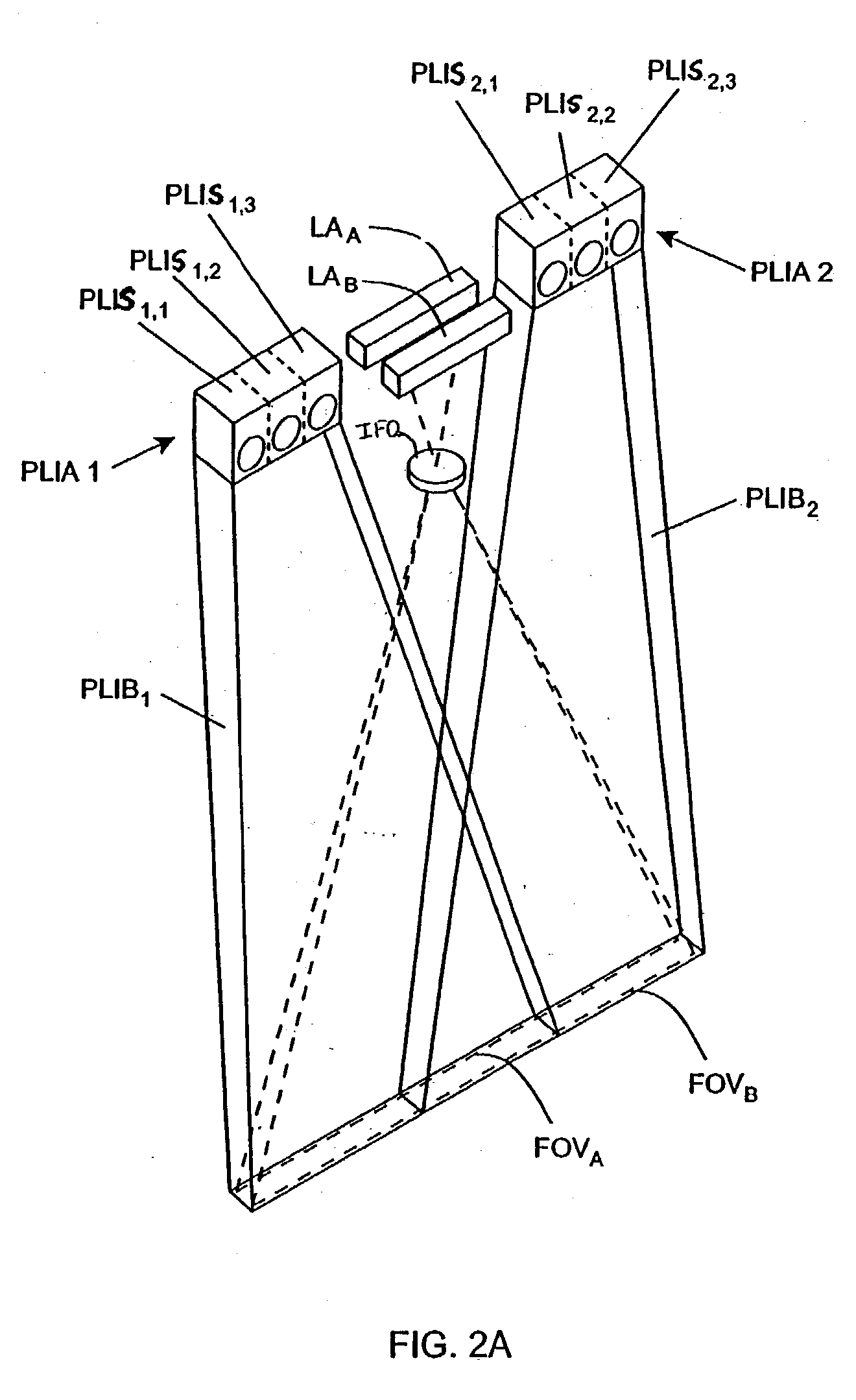
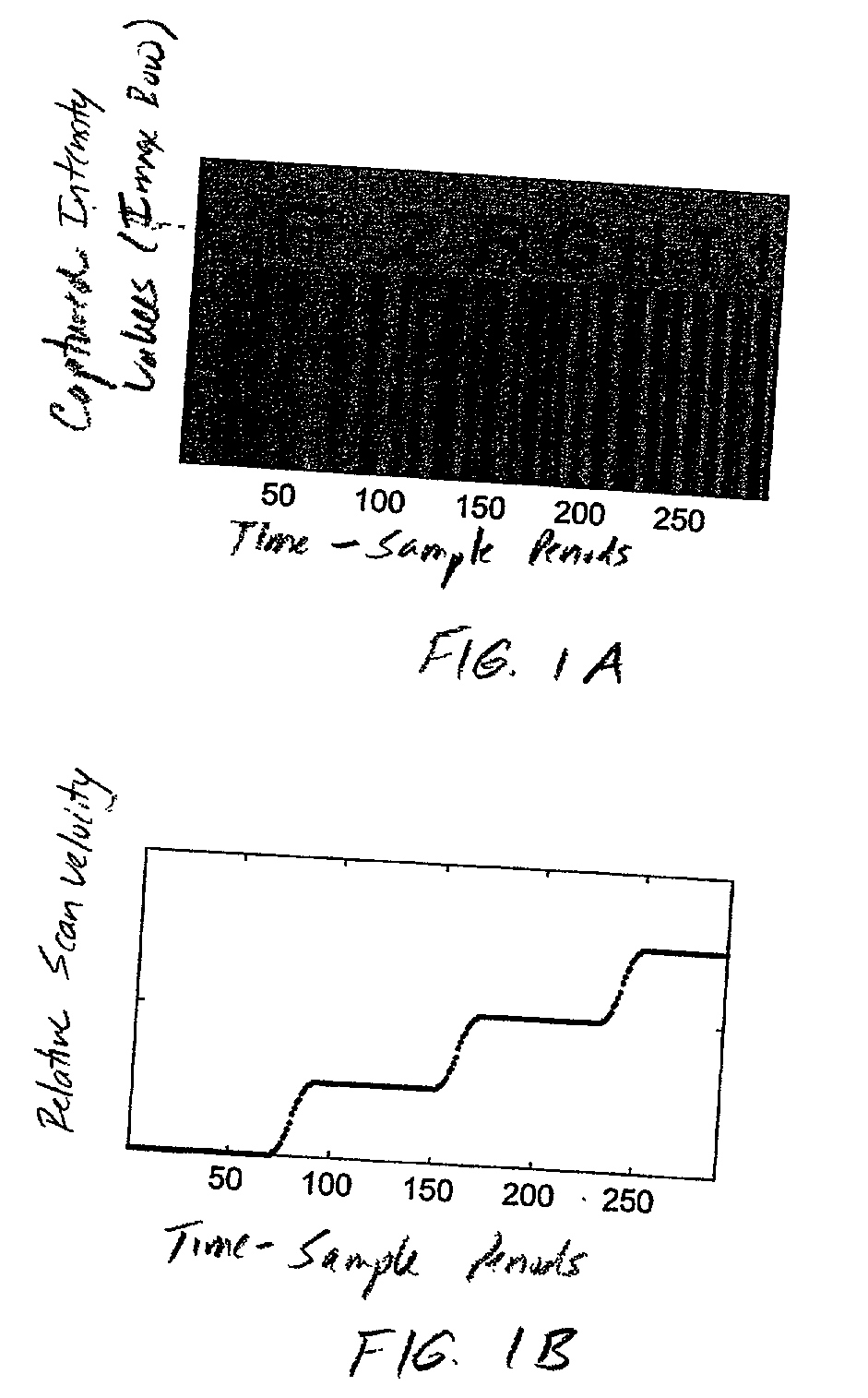
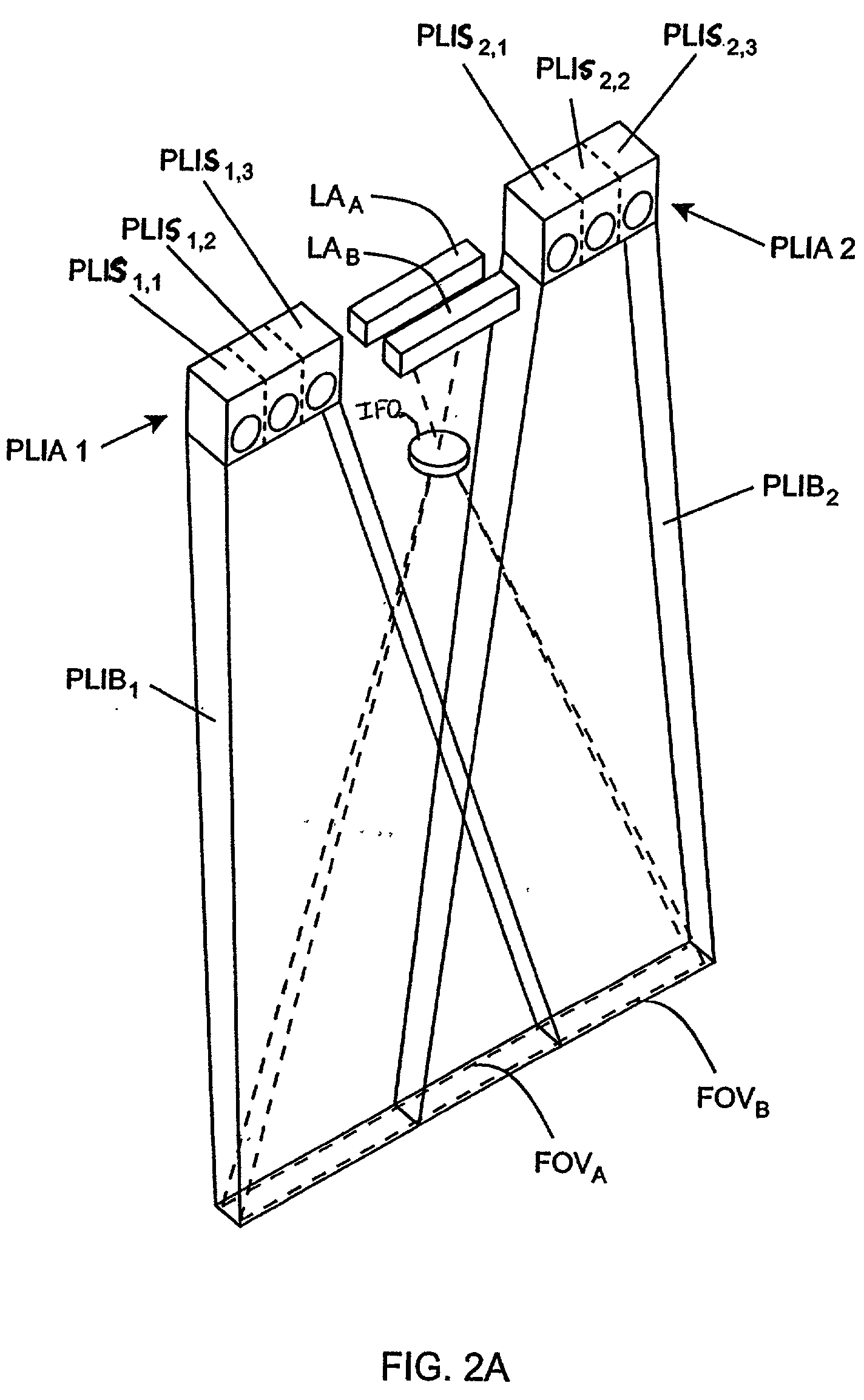
Handheld imaging device employing planar light illumination and linear imaging with image-based velocity detection and aspect ratio compensation
InactiveUS20030098352A1Low costReduce speckle noiseSensing by electromagnetic radiationCamera controlHand movements
A hand-held imaging device includes a plurality of linear imaging arrays, image formation optics, at least one illumination module and image processing circuitry that are embodied within a hand-holdable housing that is moved by hand movement past a target object to capture images of the target object. The plurality of linear imaging arrays and image formation optics provide field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear image arrays. The at least one illumination module produces planar light illumination that substantially overlaps the field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear imaging arrays. The image processing circuitry performs image-based velocity estimation operations, which analyzes pixel data values of a plurality of composite 2D images each derived from sequential image capture operations of a corresponding one linear imaging array to derive velocity data that represents an estimated velocity of the imaging device with respect to target object. The image processing circuitry produces a first image of portions of the target object, the first image having substantially constant aspect ratio, utilizing image transformation operations (or camera control operations) that are based upon the velocity data, to thereby compensate for aspect ratio distortions that would otherwise result from variations in velocity of the imaging device with respect to the target object(s). In addition, the image processing circuitry preferably carries out image-based horizontal jitter estimation and compensation operations, which estimate the horizontal jitter of the imaging device relative to the target object over the image capture operations from which the first image is derived, and transform the first image utilizing shift operations that are based upon such estimated horizontal jitter to produce a second image of portions of the target object which compensates for horizontal jitter distortion that would otherwise result therefrom. The first image, second image (or image derived from sharpening the first or second images) is preferably subject to image-based bar code detection operations and / or OCR operations carried out by the image processing circuitry, or output for display to a display device.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
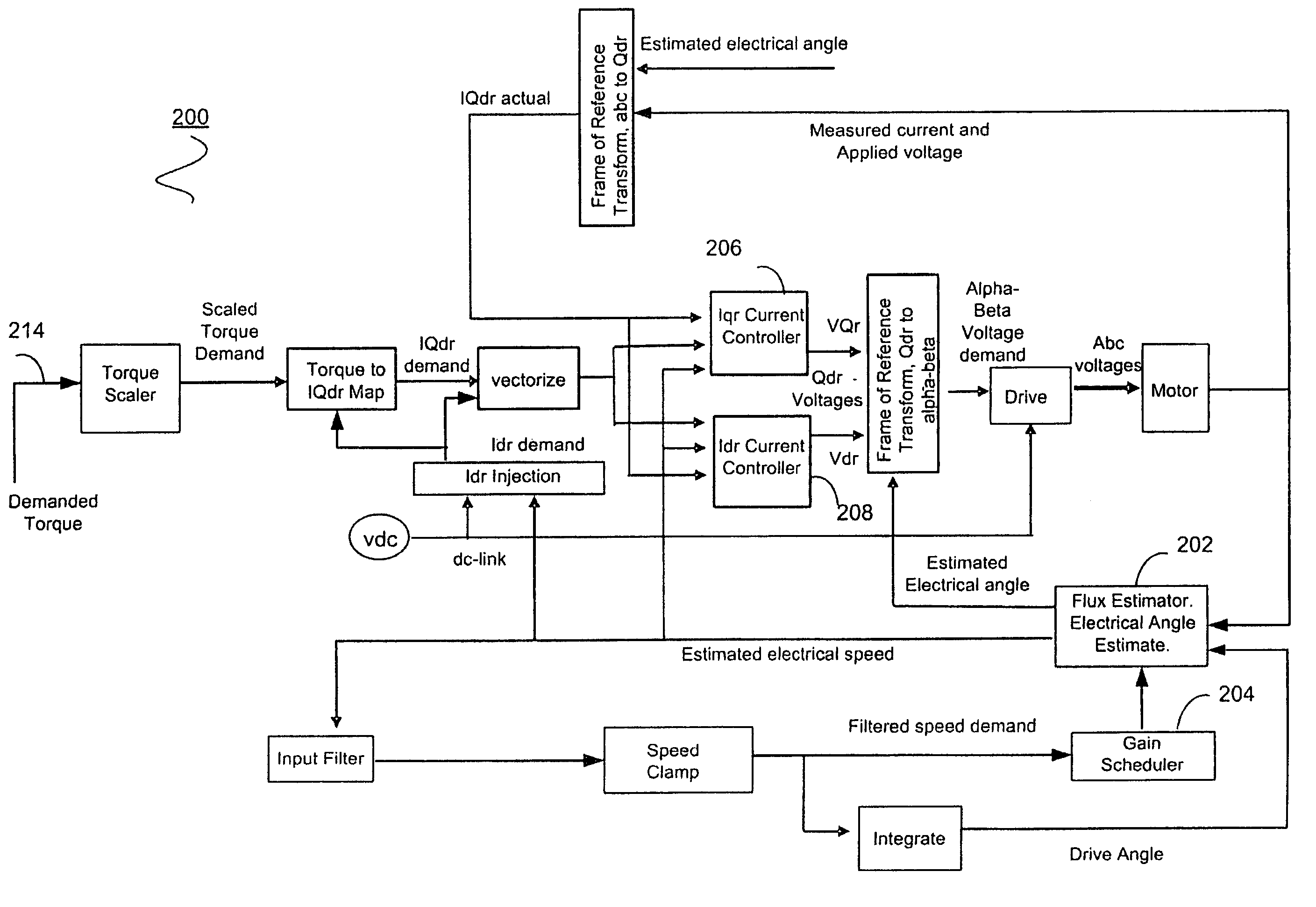
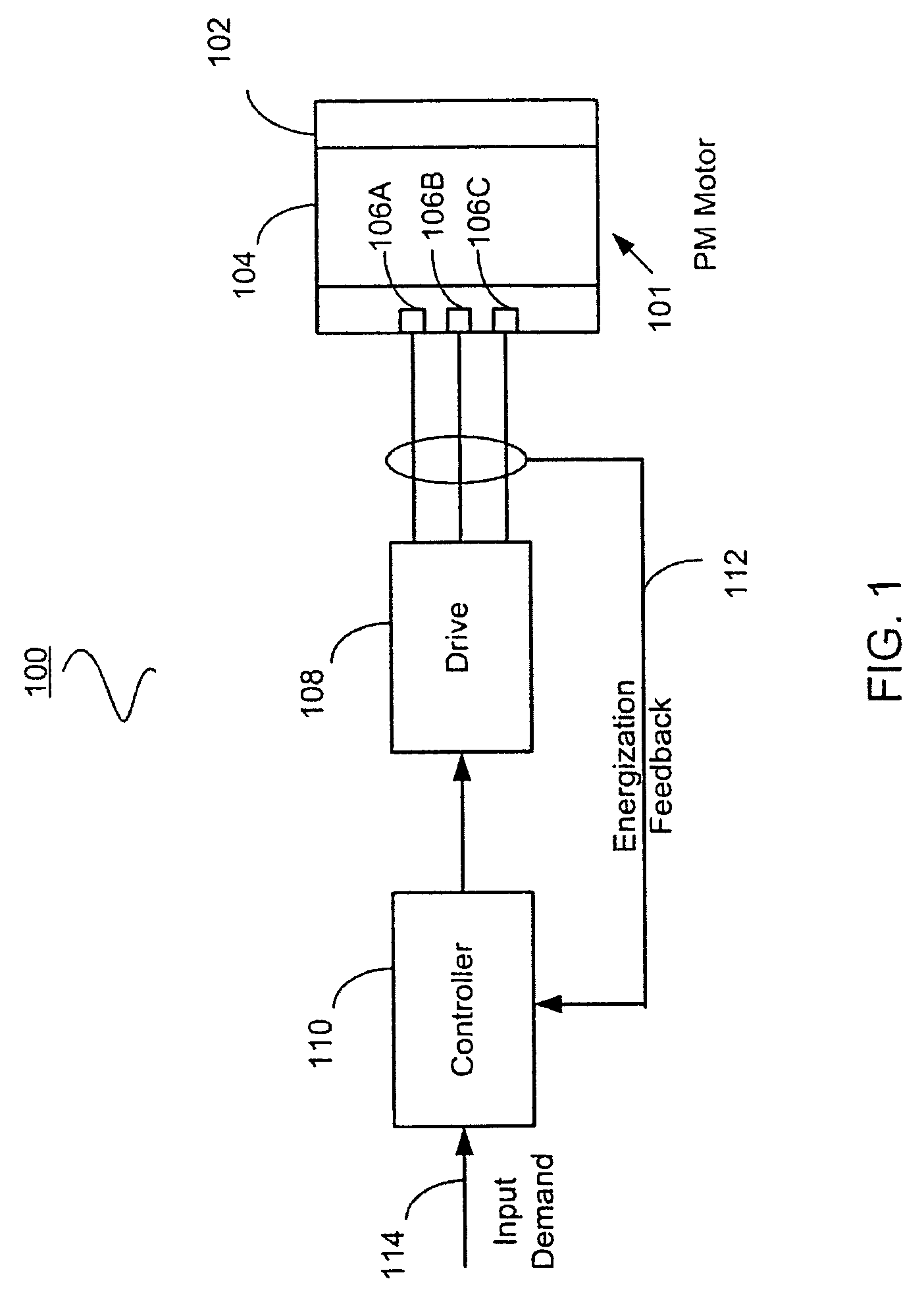
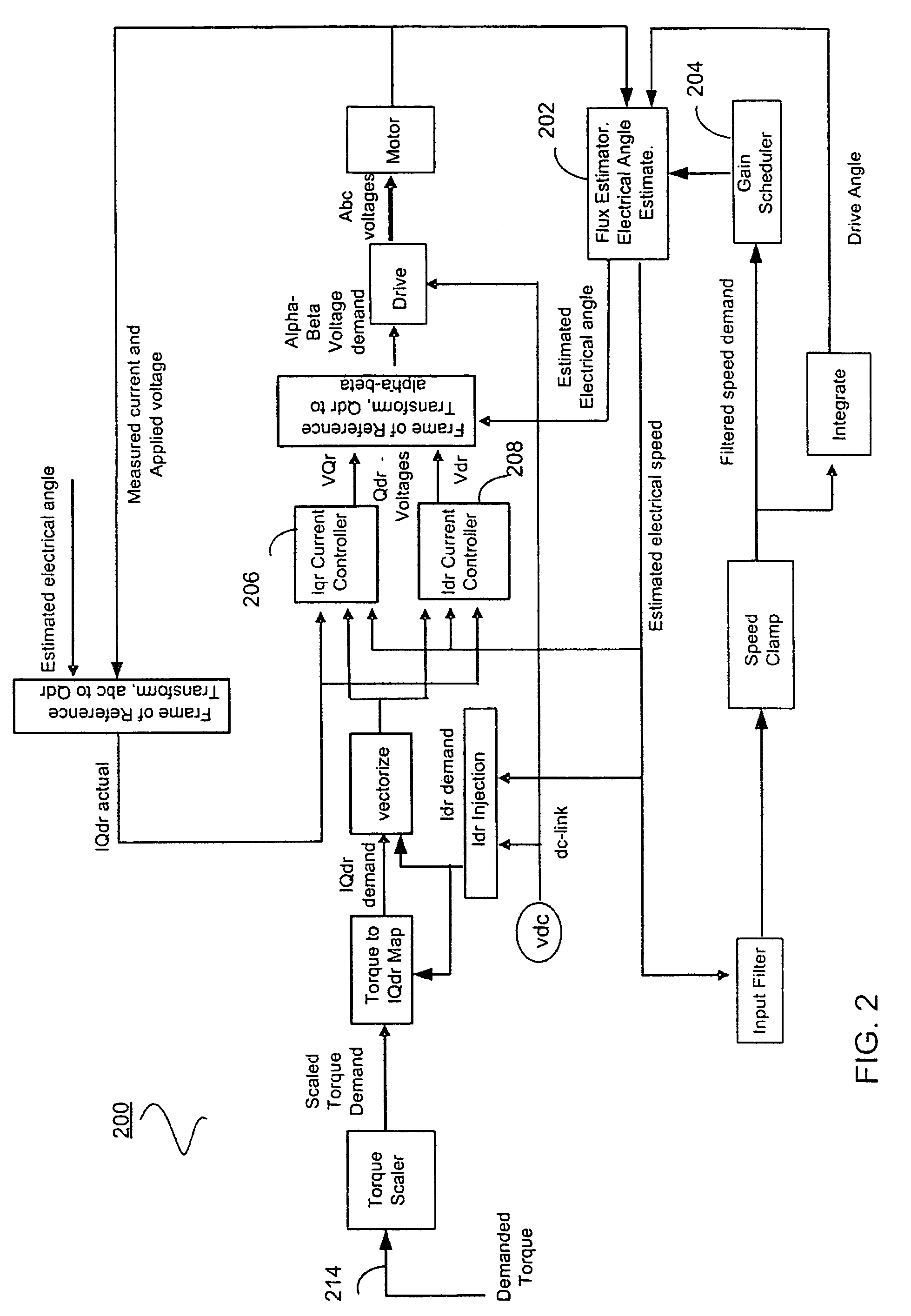
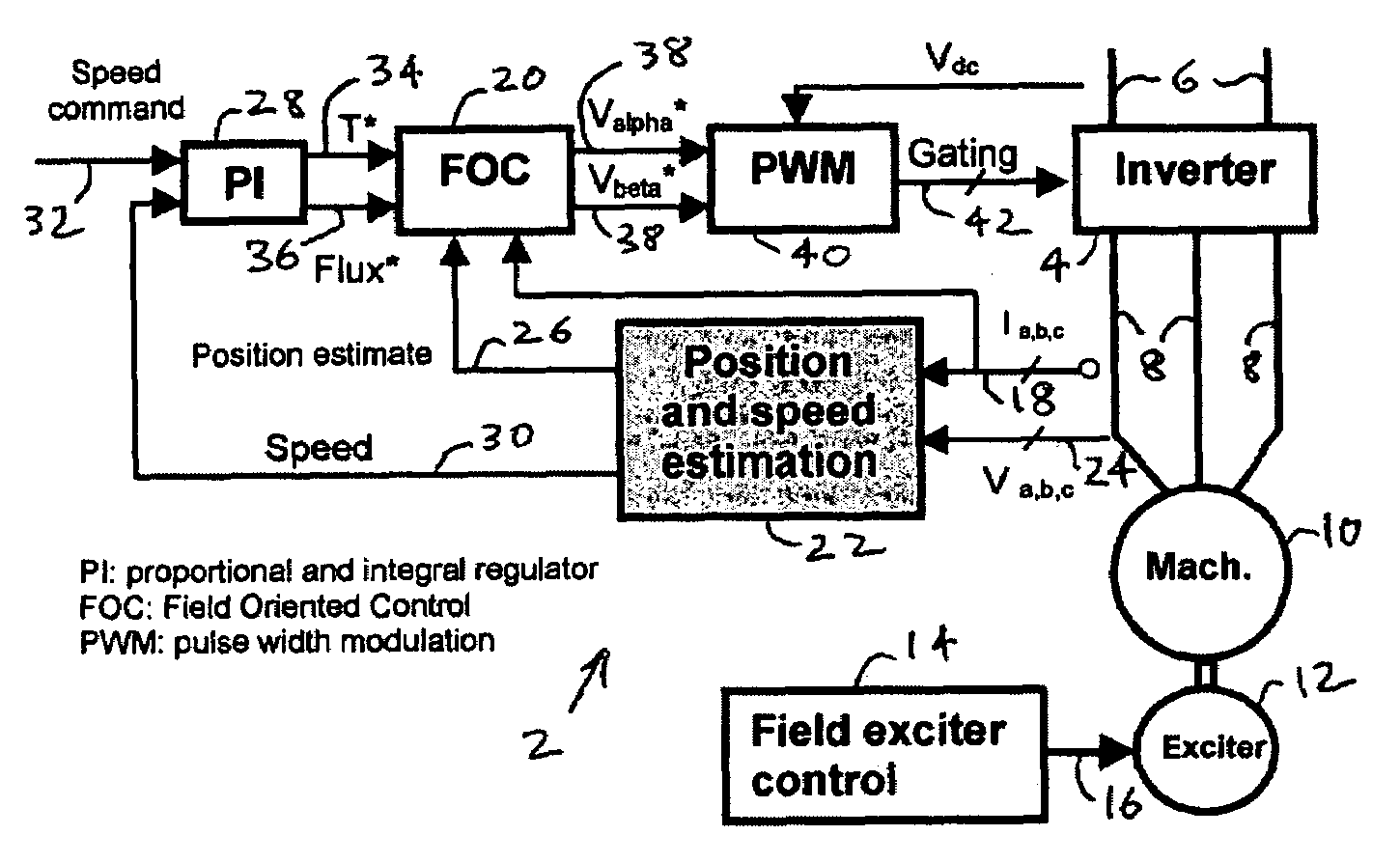
Sensorless control systems and methods for permanent magnet rotating machines
Systems and methods for controlling a rotating electromagnetic machine. The rotating machine, such as a permanent magnet motor or hybrid switched reluctance motor, includes a stator having a plurality of phase windings and a rotor that rotates relative to the stator. A drive is connected to the phase windings for energizing the windings. A controller outputs a control signal to the drive in response to an input demand such as a demanded speed or torque. Control methods (which can be implemented separately or in combination) include varying the gain of an estimator as a function of a demanded or estimated speed to position control system poles at desired locations, decoupling control system currents to achieve a constant torque with motor speed, compensating flux estimates of the estimator for saturation operation of the stator, estimating rotor position using averages of sample values of energization feedback, and calculating a trim adjusted speed error from a plurality of speed estimates.
Owner:COPELAND LP
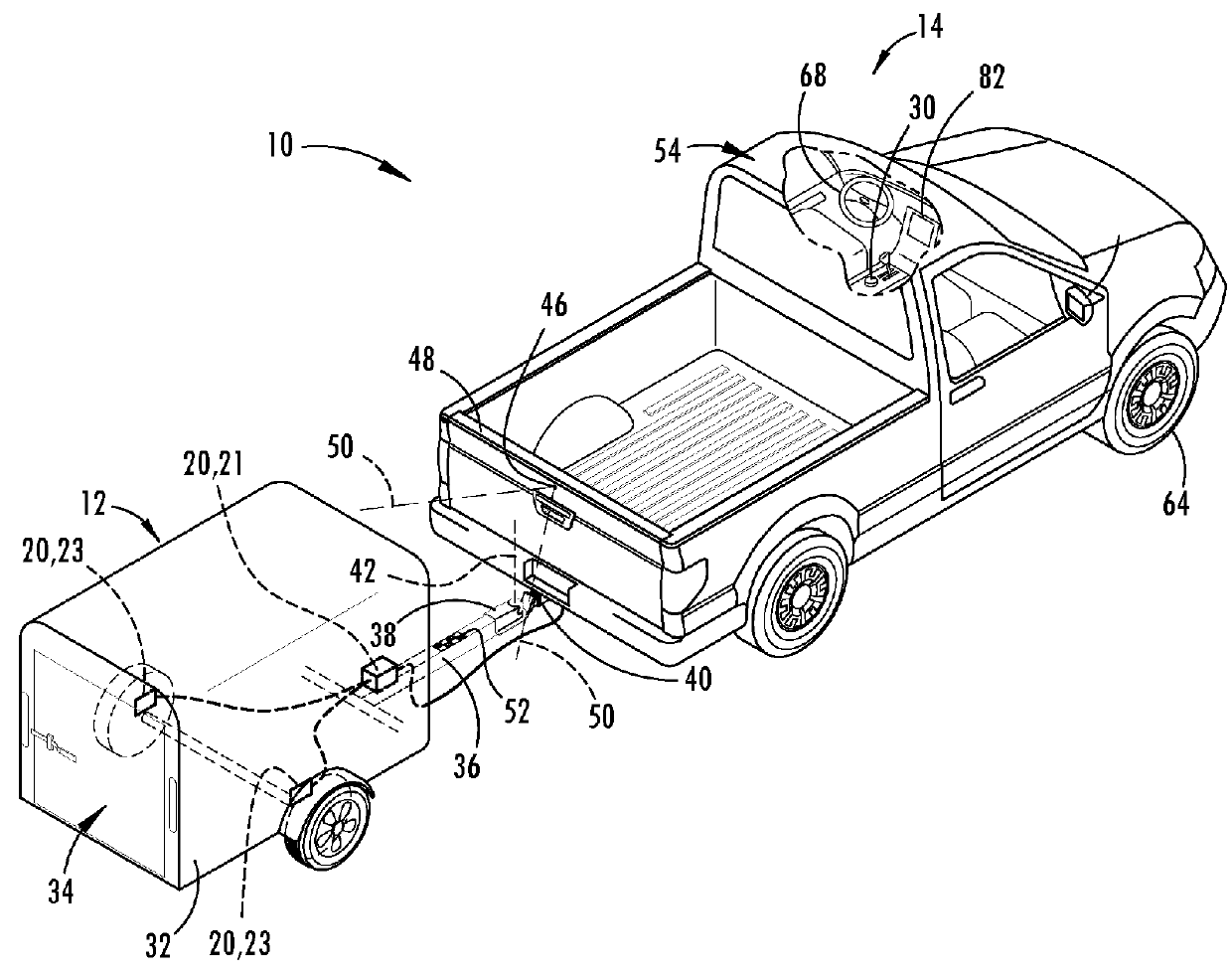
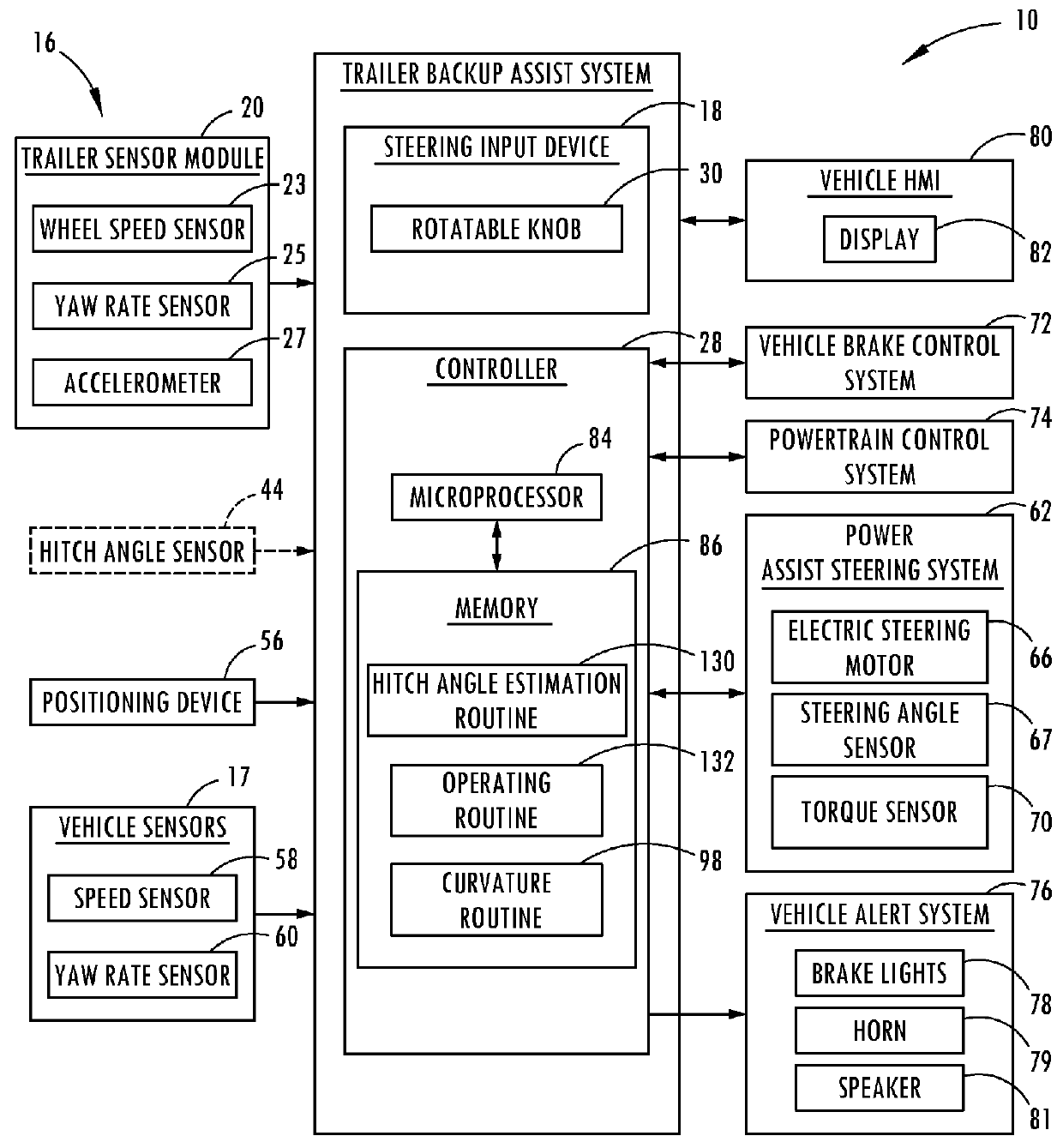
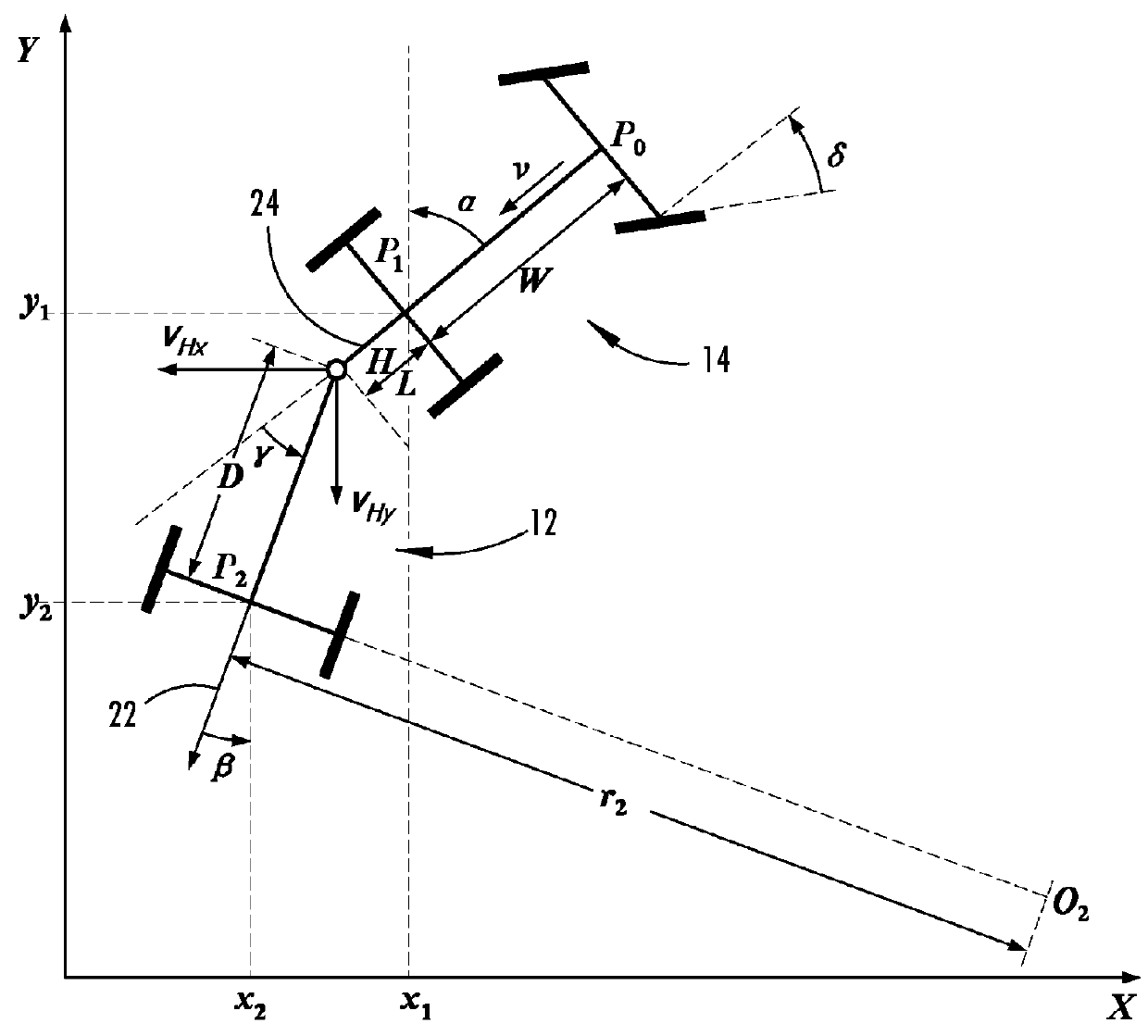
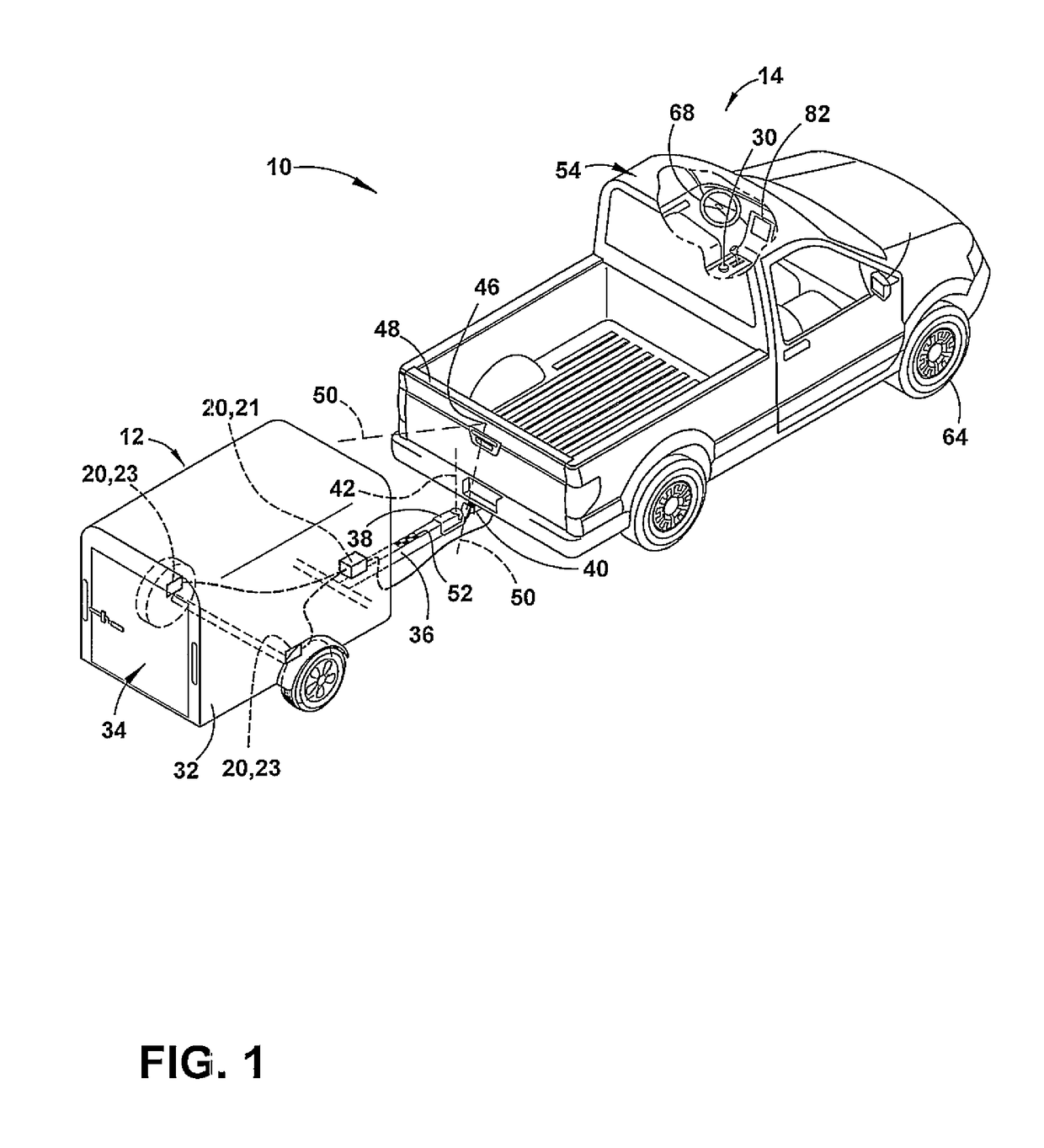
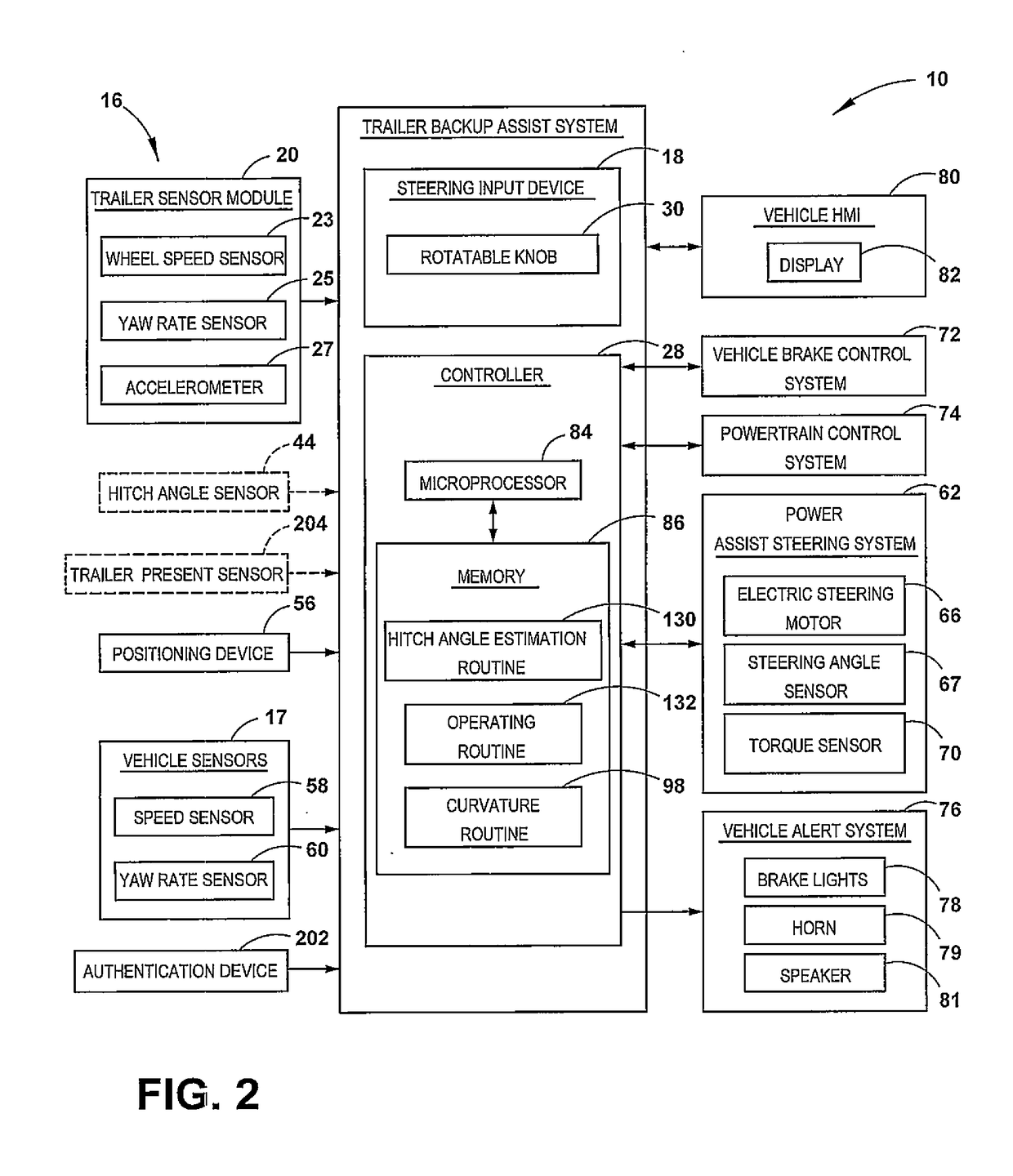
Trailer motion and parameter estimation system
ActiveUS9340228B2Linear/angular speed measurementVehicle steering/rolling behaviourSensor systemAuxiliary system
A trailer backup assist system for a vehicle reversing a trailer includes a sensor module adapted to attach to the trailer and generate a trailer yaw rate or a trailer speed. The trailer backup assist system also includes a vehicle sensor system that generates a vehicle yaw rate and a vehicle speed. Further, the trailer backup assist system includes a controller that estimates a hitch angle based on the trailer yaw rate or the trailer speed and the vehicle yaw rate and the vehicle speed in view of a kinematic relationship between the trailer and the vehicle.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Sensorless controller of AC motor and control method
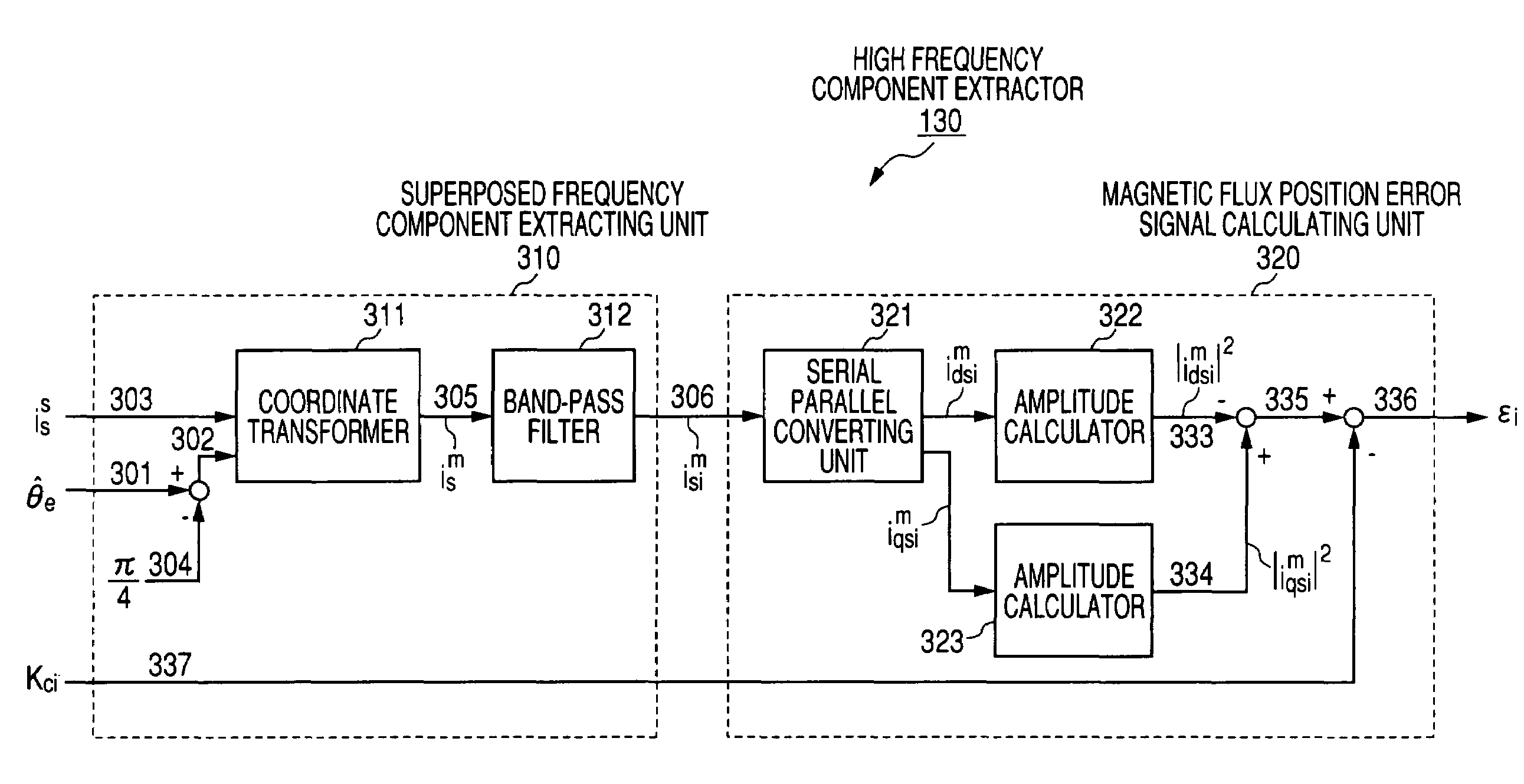
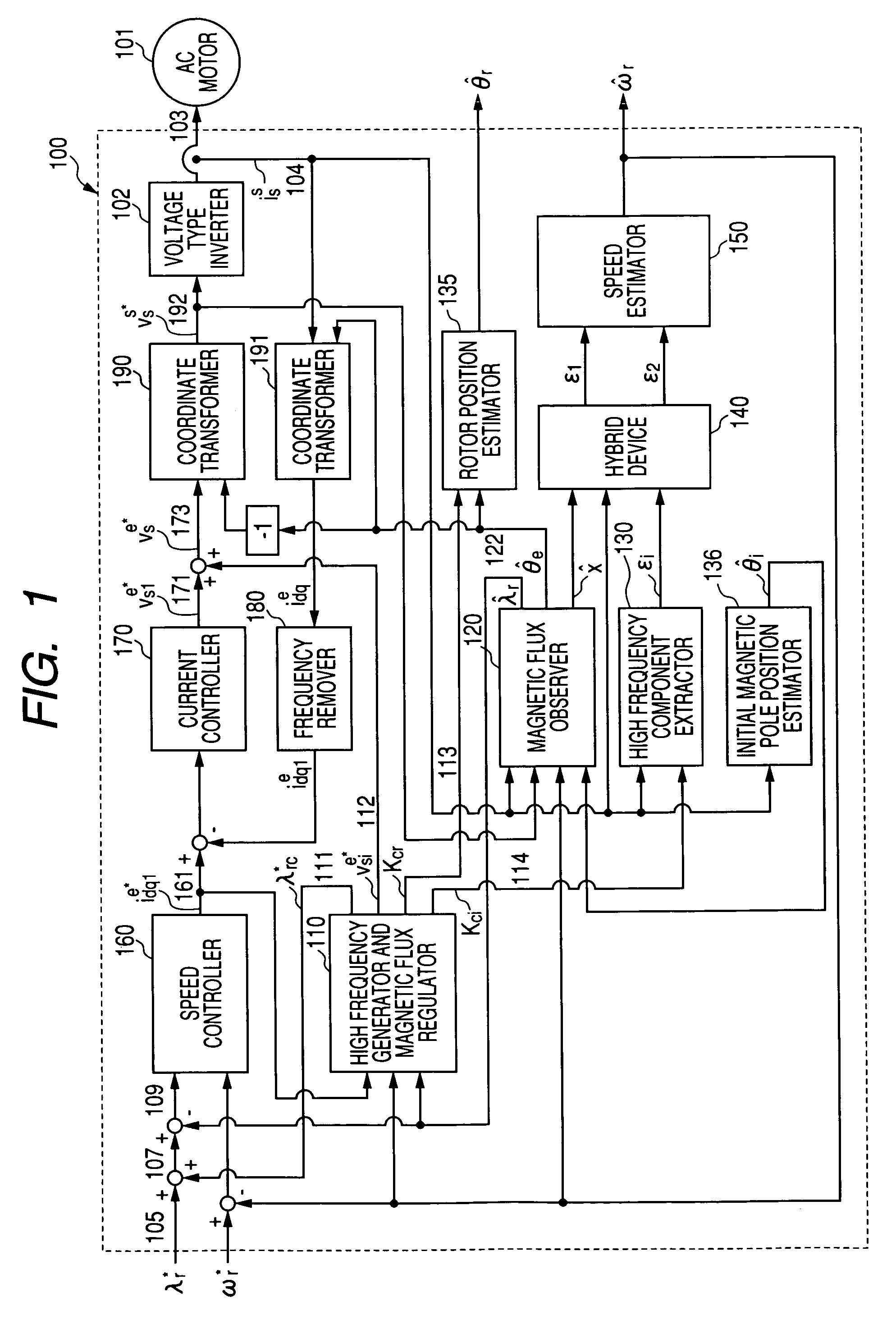
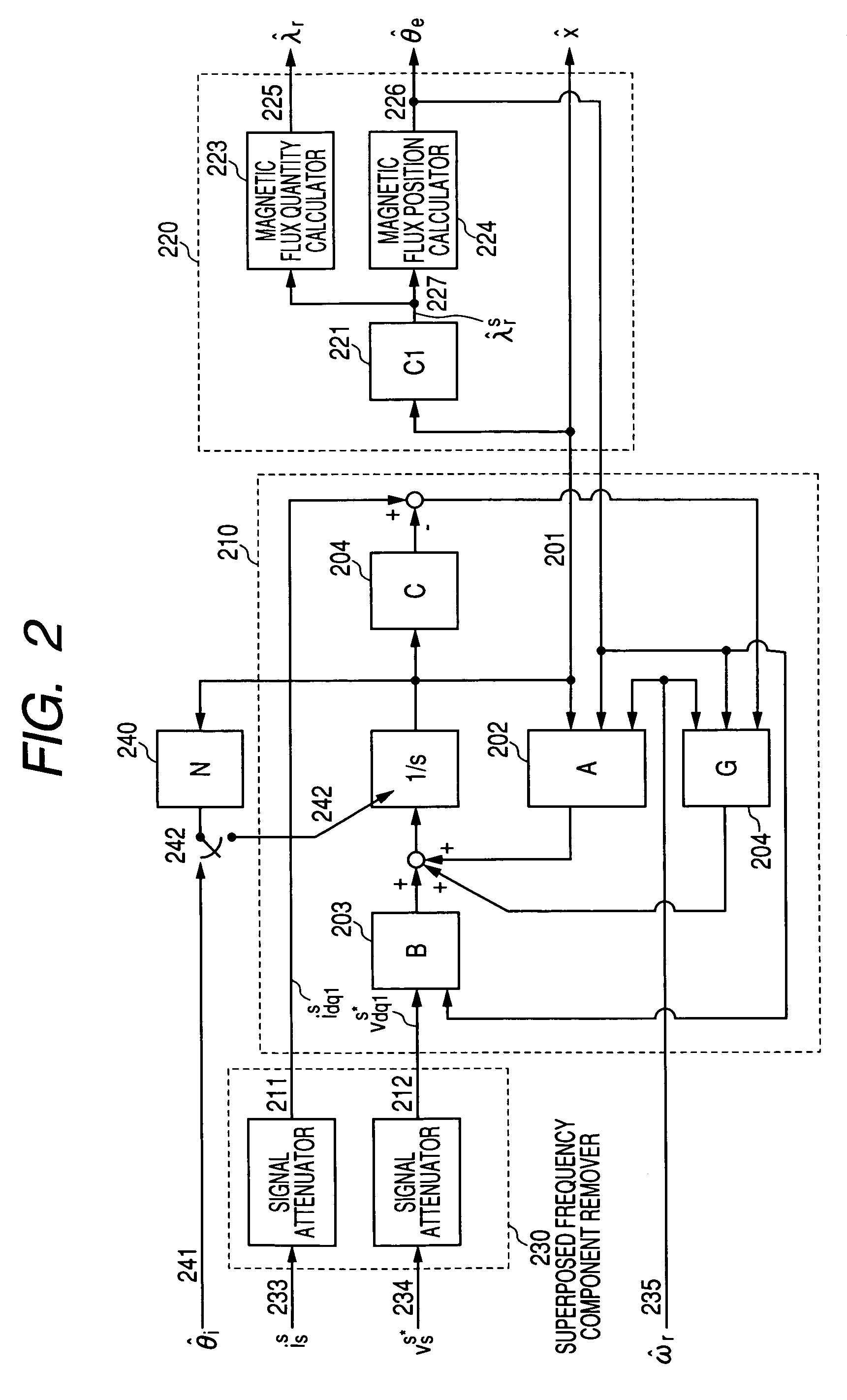
InactiveUS7045988B2Improve efficiencyMagnetic saliency at the high frequency is reducedVector control systemsSingle motor speed/torque controlLow speedSignal on
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
Methods, systems and computer program products for ultrasound shear wave velocity estimation and shear modulus reconstruction
ActiveUS8118744B2Wave based measurement systemsOrgan movement/changes detectionShear modulusReconstruction method
Owner:DUKE UNIV
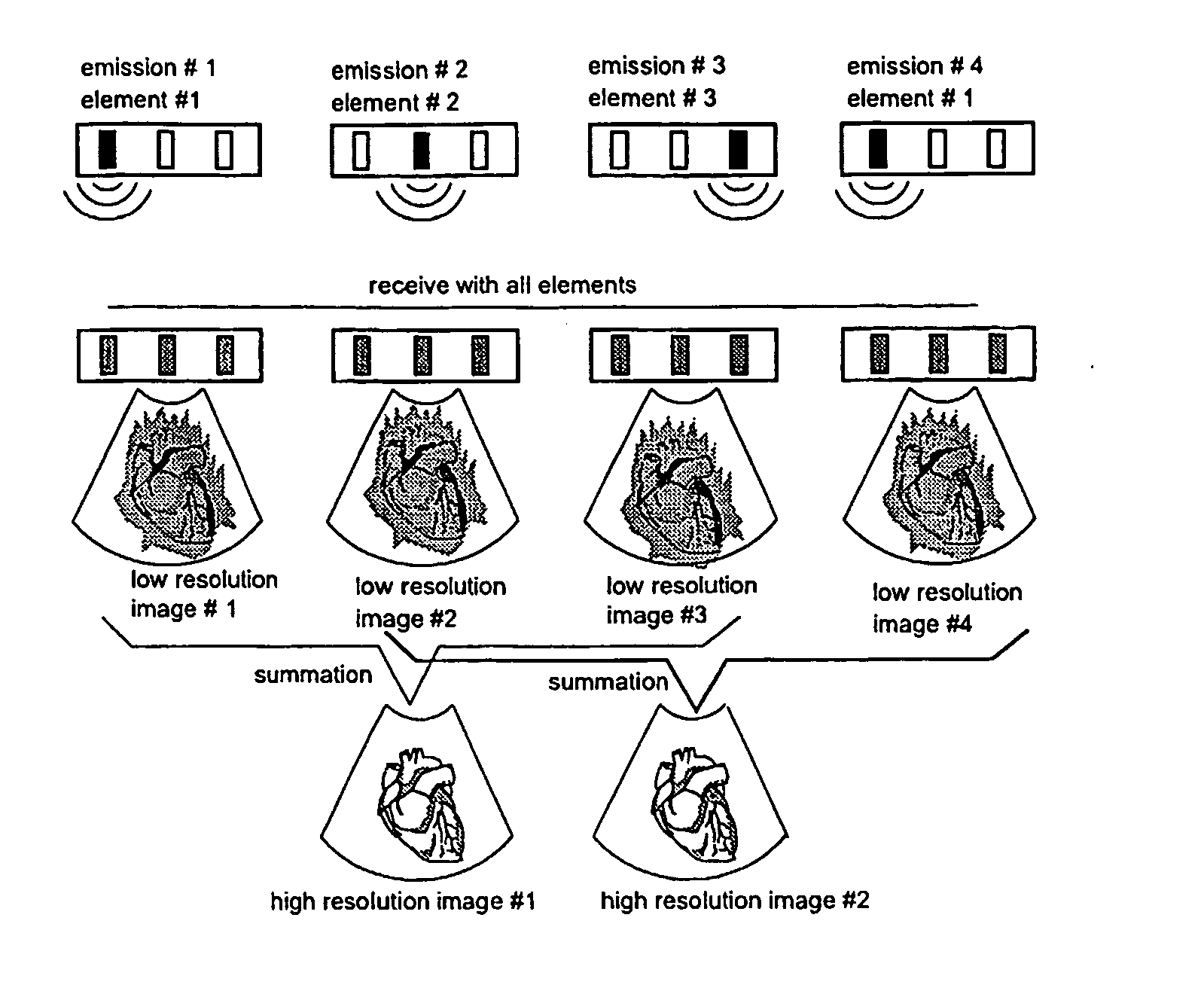
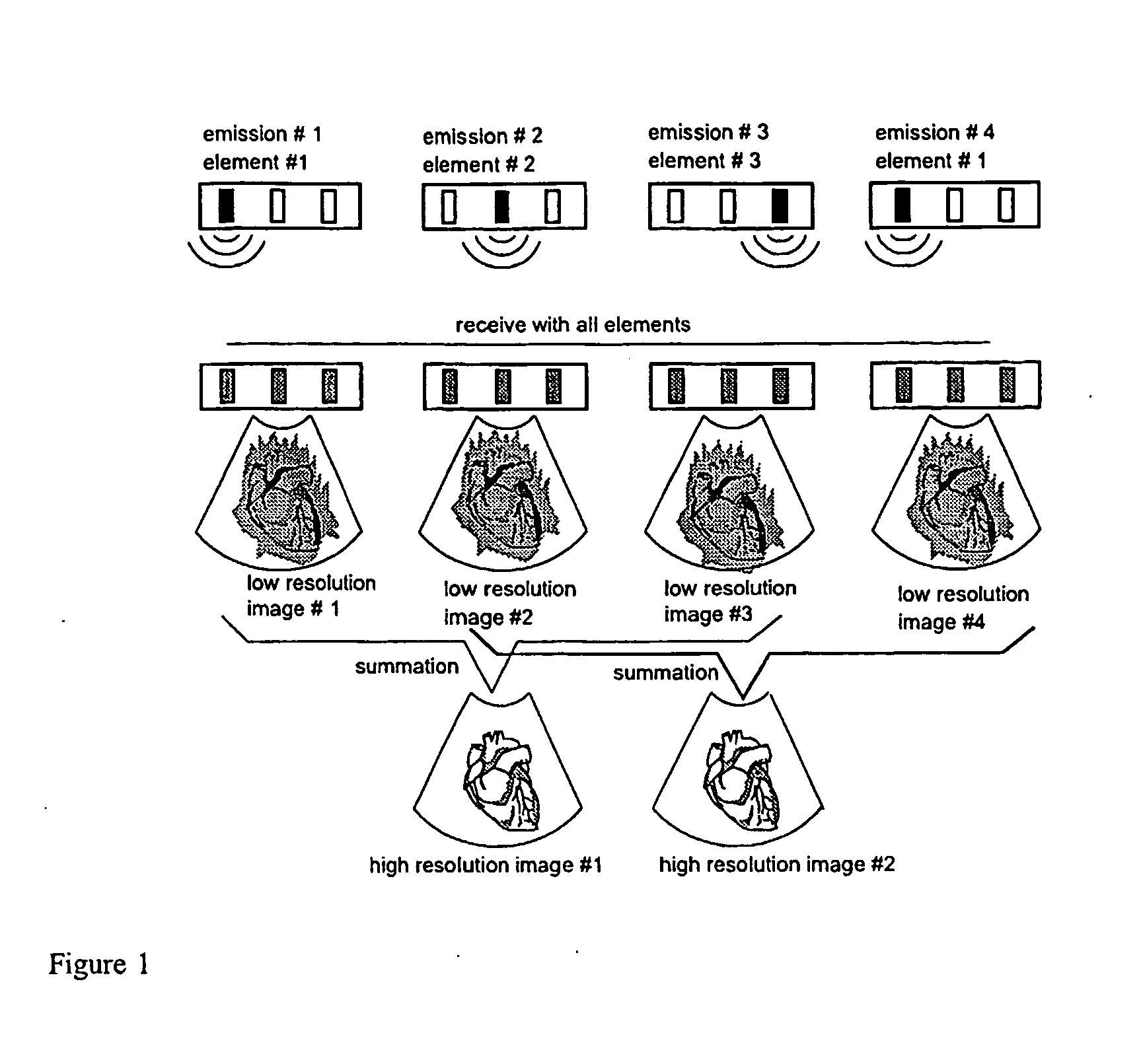
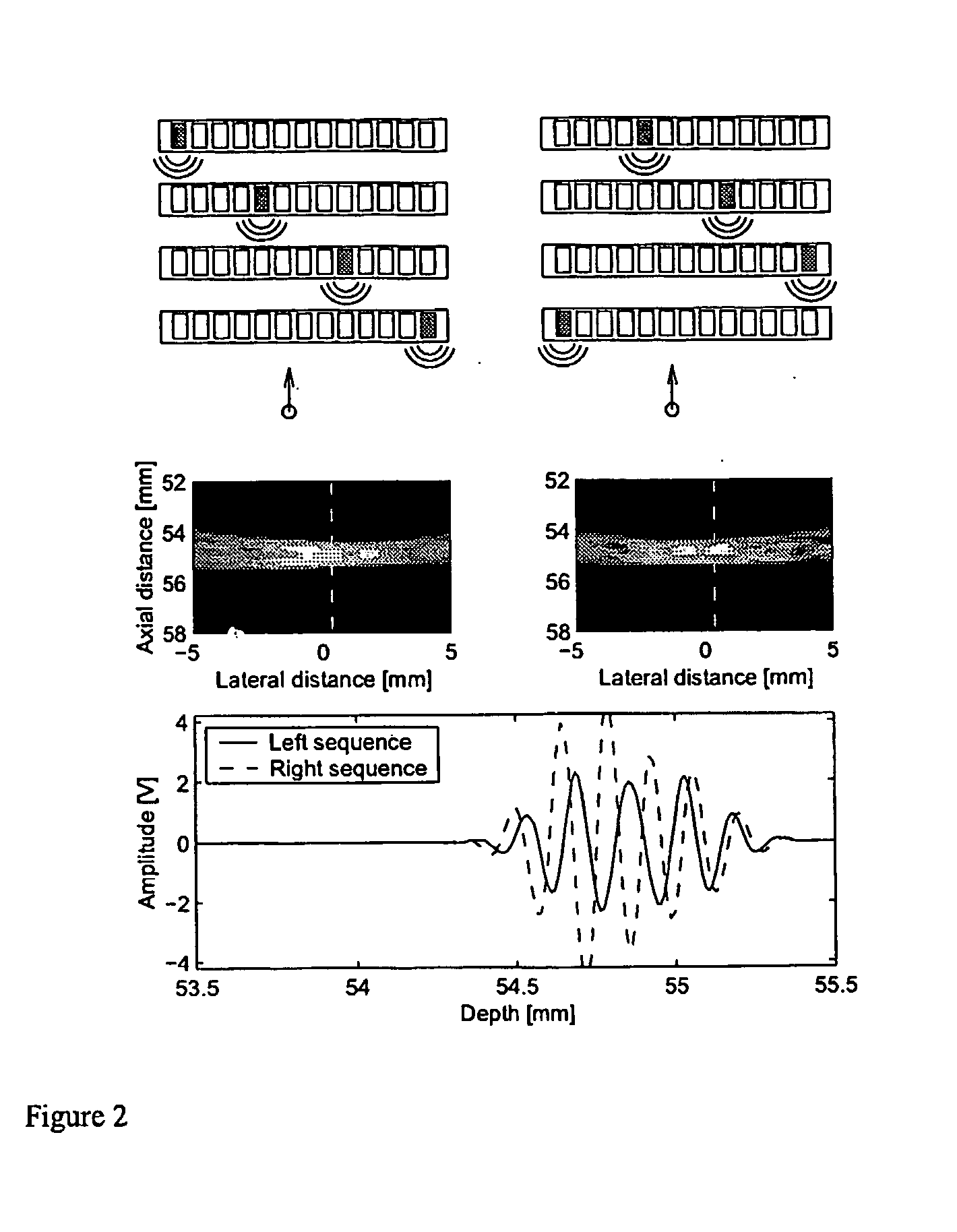
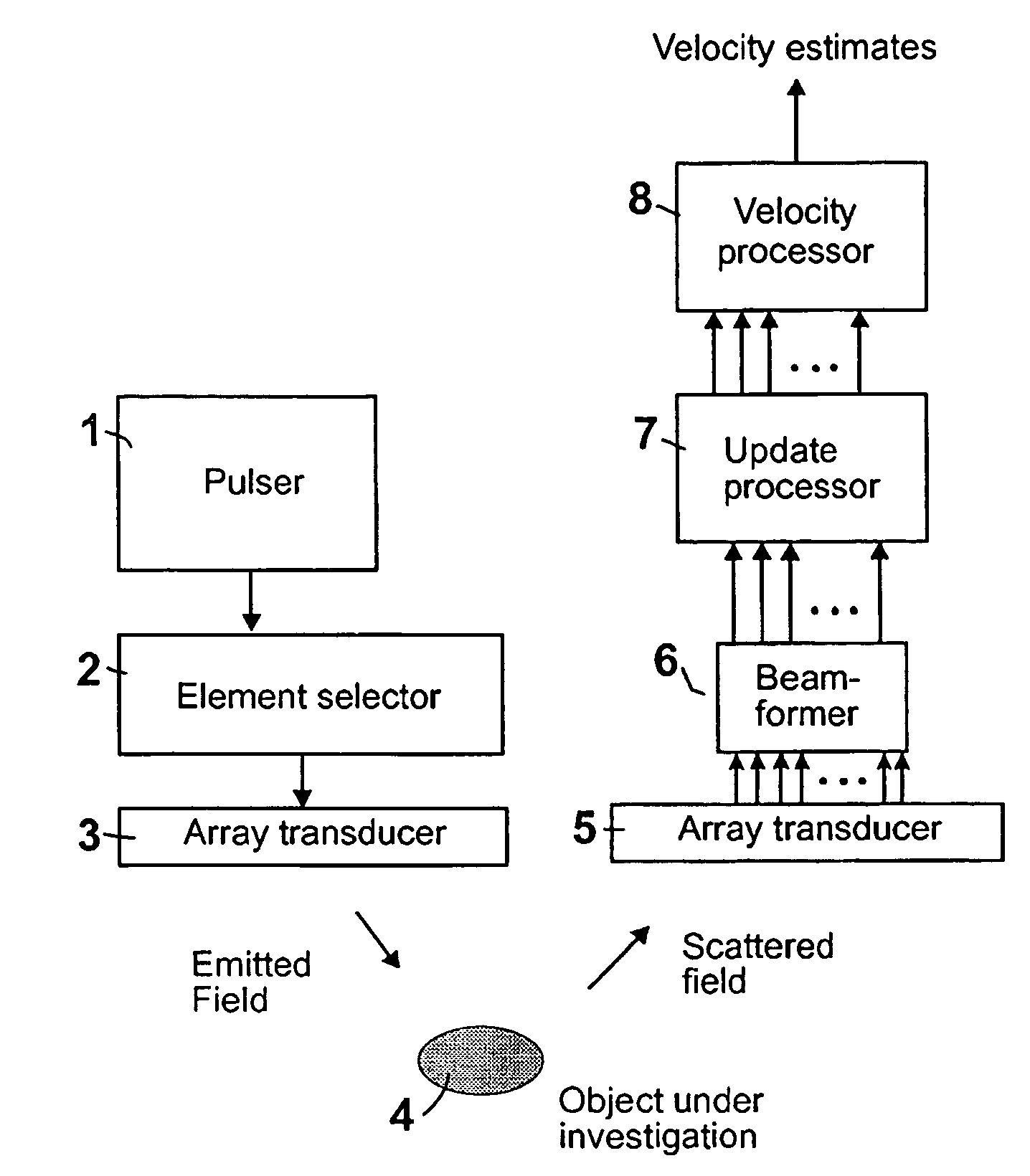
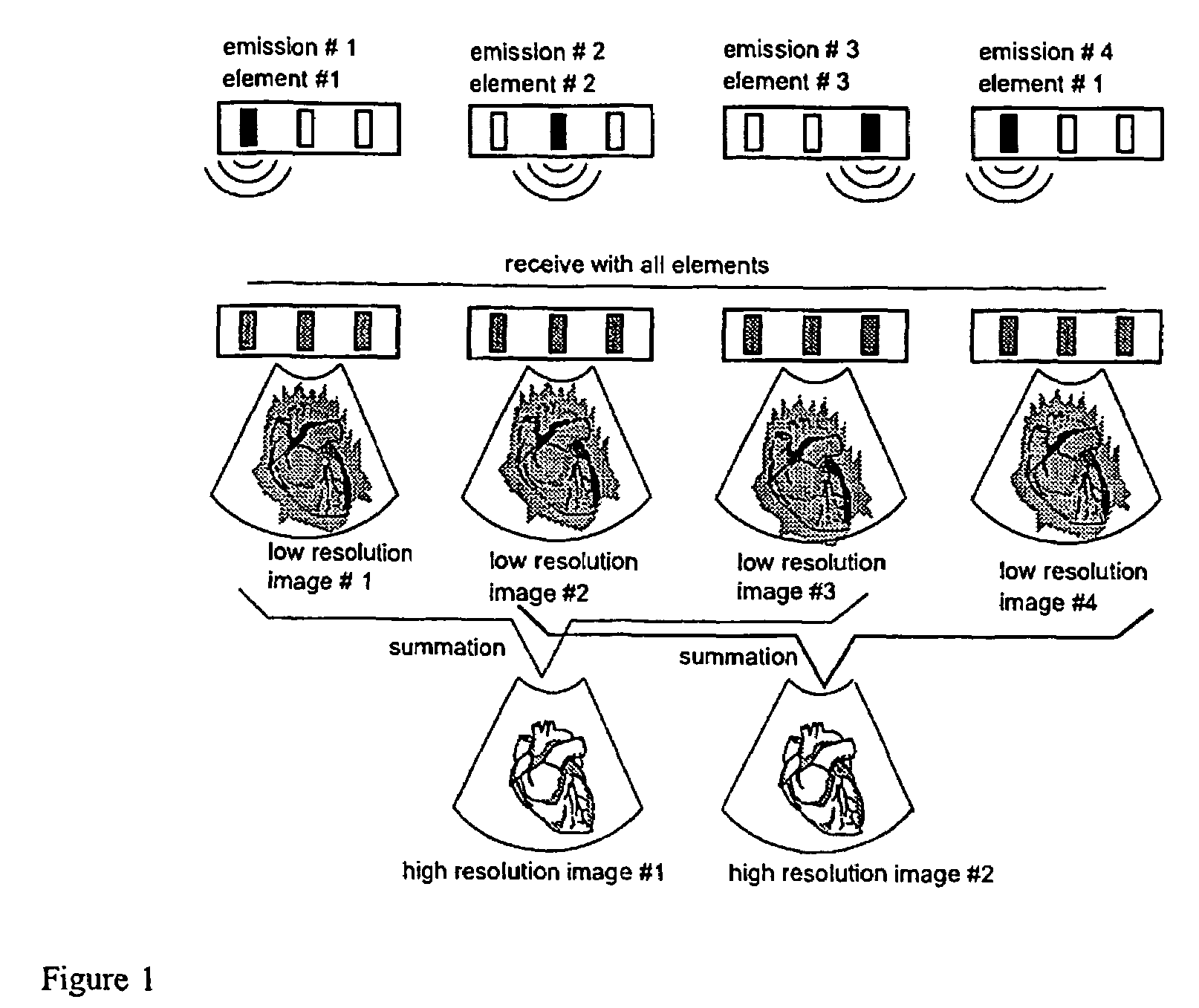
Apparatus and method for velocity estimation in synthetic aperture imaging
The invention relates to an apparatus for flow estimation using synthetic aperture imaging. The method uses a Synthetic Transmit Aperture, but unlike previous approaches a new frame is created after every pulse emission. In receive mode parallel beam forming is implemented. The beam formed RF data is added to the previously created RF lines obtained by the same transmit sequence. The apparatus comprises a pulser (1) to generate a pulsed voltage signal, that is fed to the emit beam former (2). The emit beam former (2) is connected to the emitting transducer array (3). The ultrasound is reflected by the object (4) and received by the elements of the transducer array (5). All of these signals are then combined in the beam processor (6) to focus all of the beams in the image in both transmit and receive mode and the simultaneously focused signals are used for updating the image in the processor (7). The estimation processor (8) to correlate the individual measurements to obtain the displacement between high-resolution images and thereby determine the velocity.
Owner:B K MEDICAL
Fluid visualisation and characterisation system and method; a transducer
ActiveUS20130345994A1Reduce sensitivityCanceled outVolume meteringVolume flow measuring devicesSonificationTransducer
A fluid visualization and characterisation system includes a measuring section with a housing defining a fluid flow path for fluid flow. The measuring section includes one or more transducers to emit ultrasonic signals into the fluid flow, and at least one receiver to receive reflections of the ultrasonic signal from reflectors in the fluid flow. The system includes a memory for storing data and a processor operatively connected to the memory. The processor comprises several modules. A velocity estimating module is configured to apply one or more velocity estimation algorithms to received reflections of the ultrasonic signal, or data indicative thereof, to determine a velocity profile of the fluid flow. A deconvolution module is configured to apply a deconvolution algorithm at least to the determined velocity profile to determine a true velocity profile of the fluid flow. A fluid visualization and characterisation module is configured to determine characteristics of the fluid and / or fluid flow in by using the determined velocity profile and / or the true velocity profile.
Owner:SP TECHNICAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF SWEDEN +1
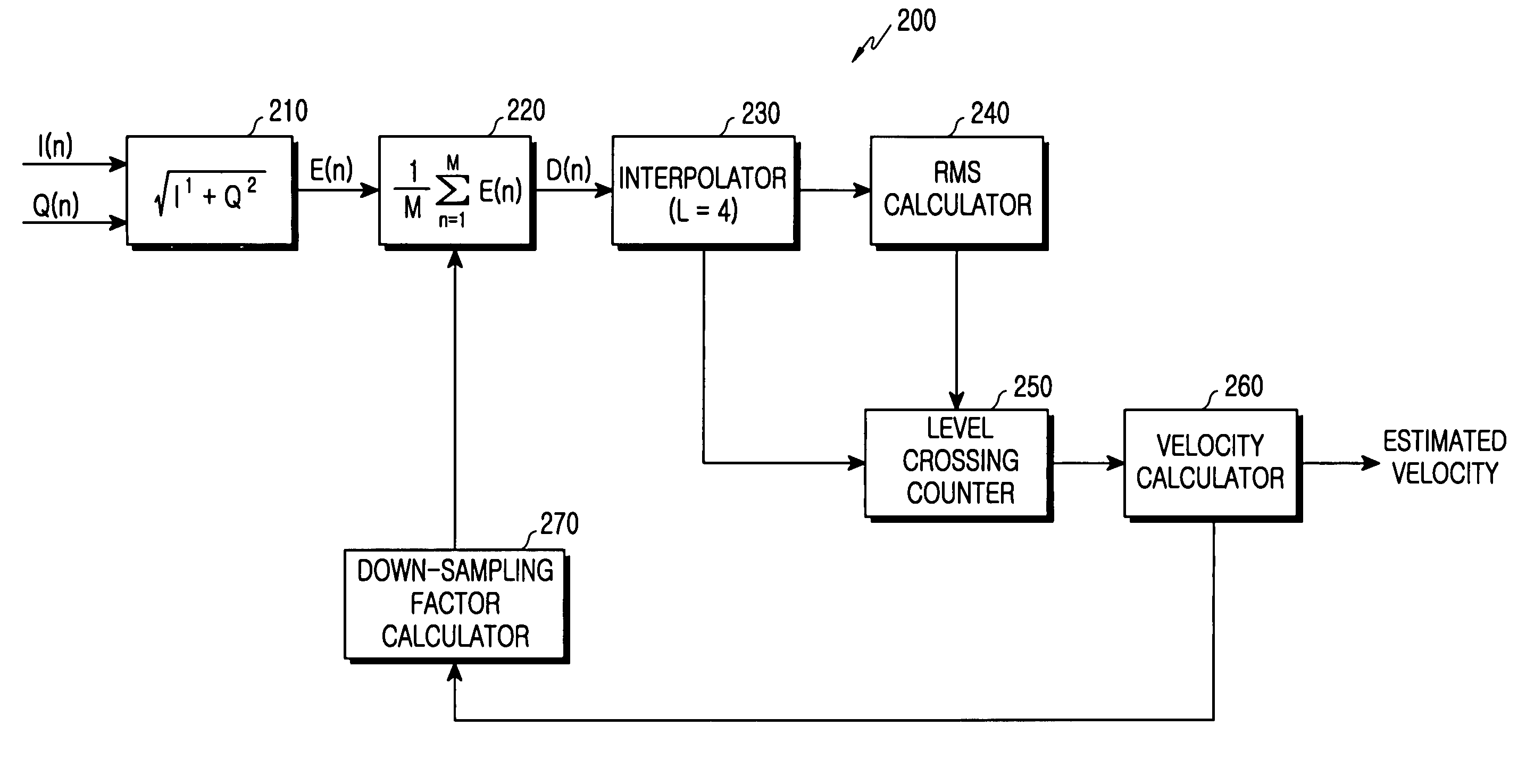
Velocity estimation apparatus and method using level crossing rate
ActiveUS7120440B2Improve accuracyMinimizing influence of noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSubstation equipmentLevel crossingCrossover frequency
Disclosed is a velocity estimator using a level crossing rate. The velocity estimator comprises a power calculator for calculating power values of a signal received from a mobile terminal; a mean power calculator for calculating mean power values for M power values according to a predetermined down-sampling factor M; an interpolator for interpolating the mean power values according to a predetermined interpolation ratio L; a root mean square calculator for calculating a root mean square value using an output of the interpolator; a level crossing counter for counting a level crossing frequency representing how many times the output of the interpolator crosses a level crossing threshold determined according to the root mean square value, for a predetermined time period; and a velocity calculator for calculating a velocity estimation value of the mobile terminal using the level crossing frequency.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Enhanced yaw rate trailer angle detection initialization
A trailer backup assist system for a vehicle reversing a trailer includes a sensor module adapted to attach to the trailer and generate a trailer yaw rate or a trailer speed. The trailer backup assist system also includes a vehicle sensor system that generates a vehicle yaw rate and a vehicle speed. Further, the trailer backup assist system includes a controller that estimates a hitch angle based on the trailer yaw rate or the trailer speed and the vehicle yaw rate and the vehicle speed in view of a kinematic relationship between the trailer and the vehicle.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
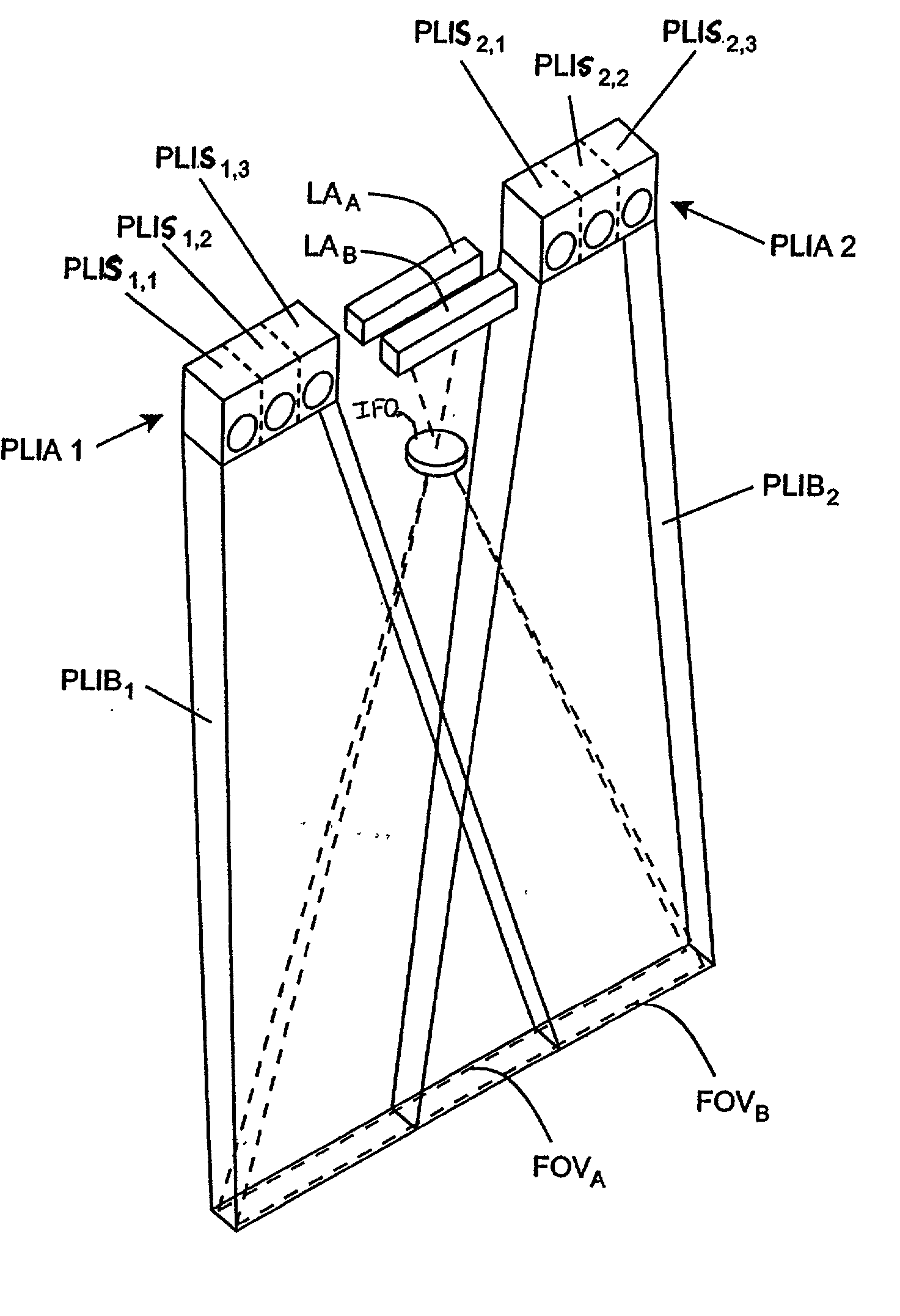
Planar light illumination and linear imaging (PLILIM) device with image-based velocity detection and aspect ratio compensation
InactiveUS20030156303A1Low costReduce speckle noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationCamera controlDisplay device
An imaging device comprising a plurality of linear imaging arrays and image formation optics that provide field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear image arrays. At least one illumination module produces planar light illumination that substantially overlaps the field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear imaging arrays. Image processing circuitry performs image-based velocity estimation operations, which analyzes pixel data values of a plurality of composite 2-D images each derived from sequential image capture operations of a corresponding one linear imaging array to derive velocity data that represents an estimated velocity of the imaging device with respect to at least one target object disposed in the fields of view. Preferably, the image processing circuitry also produces a first image of portions of the target object(s), the first image having substantially constant aspect ratio, utilizing image transformation operations (or camera control operations) that are based upon the velocity data, to thereby compensate for aspect ratio distortions that would otherwise result from variations in velocity of the imaging device with respect to the target object(s). In addition, the image processing circuitry preferably carries out image-based horizontal jitter estimation and compensation operations, which estimate the horizontal jitter of the imaging device relative to the target object(s) over the image capture operations from which the first image is derived and transform the first image utilizing shift operations that are based upon such estimated horizontal jitter to produce a second image of portions of the target object(s) which compensates for horizontal jitter distortion that would otherwise result therefrom. The first image or second image (or image derived from sharpening the first or second images) is preferably subject to image-based bar code detection operations and / or OCR operations, or output for display to a display device.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
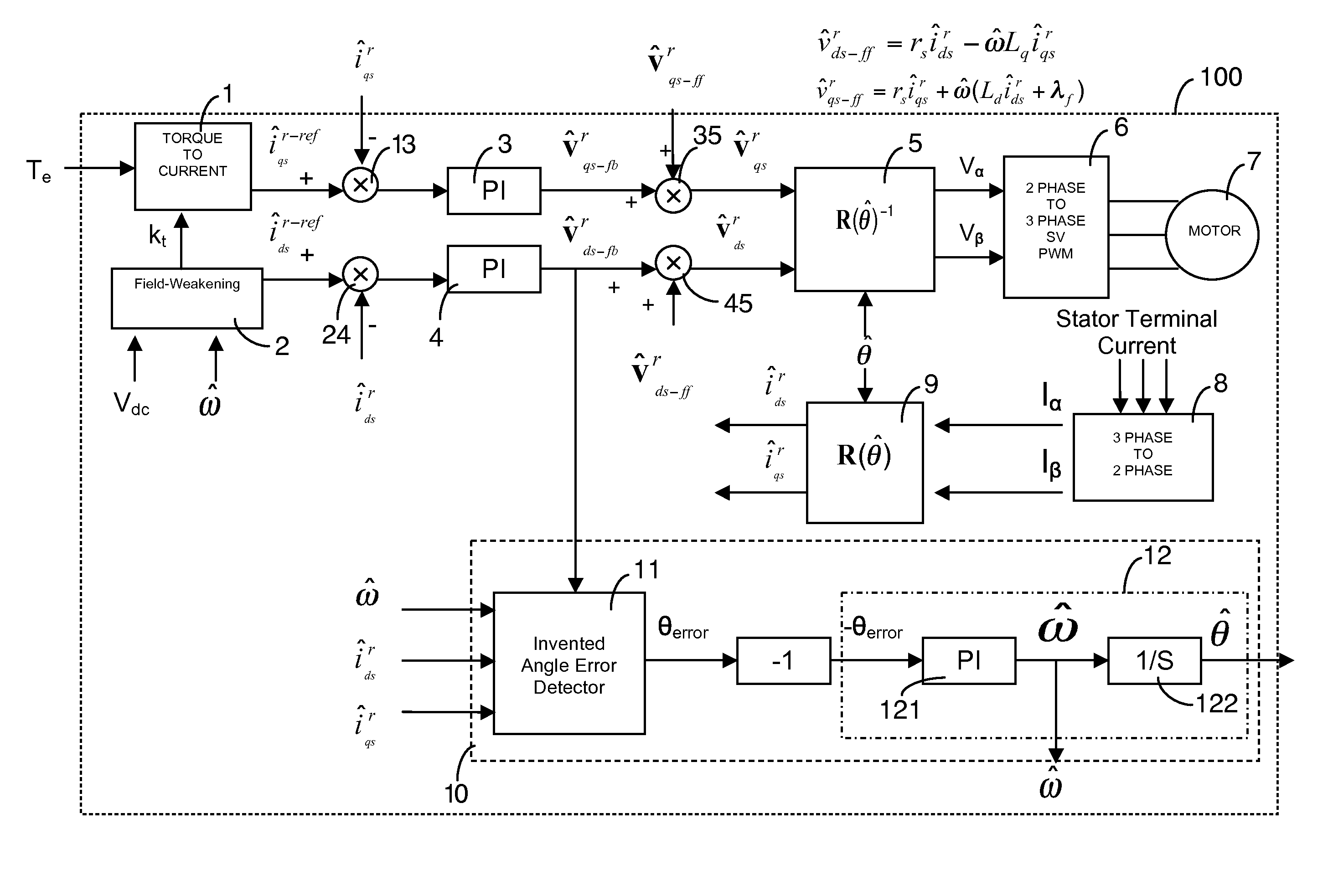
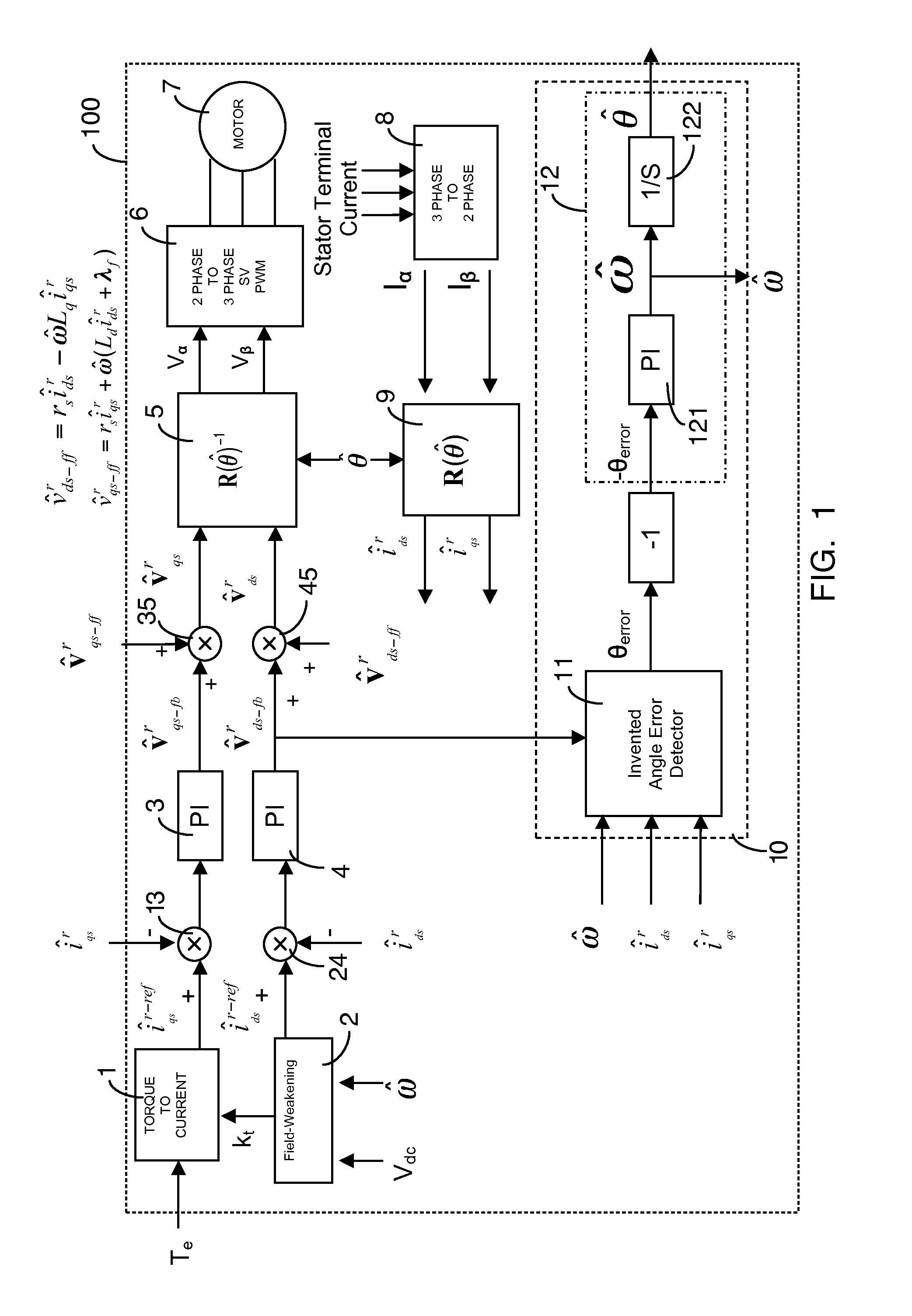
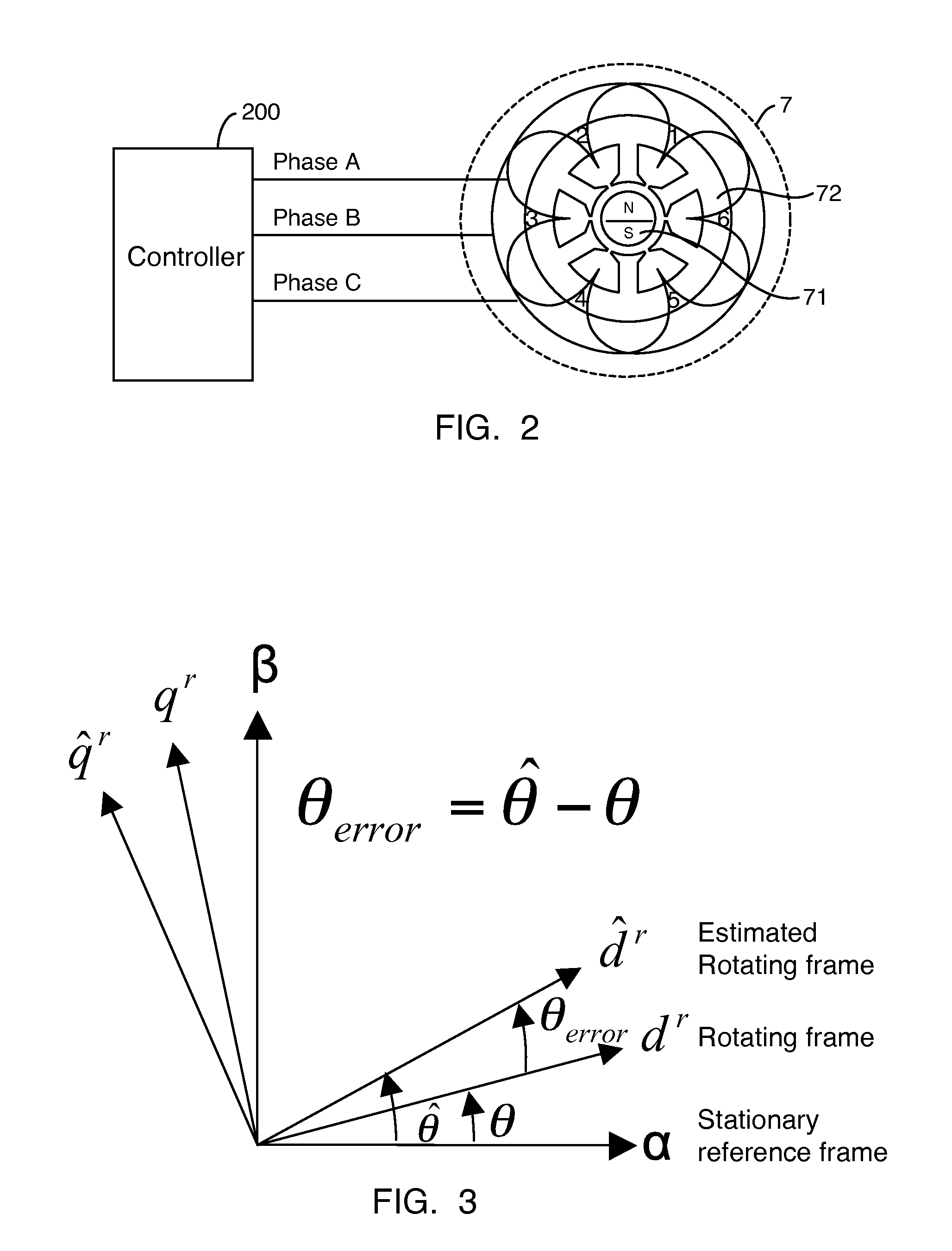
Position-sensorless control system and method of operation for a synchronous motor
InactiveUS20100109584A1Well formedMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlSynchronous motorControl system
This invention provides an advanced position and velocity estimation scheme used in a position-sensorless control system for synchronous operation of an electric motor. The system includes an electric motor having a stator and a rotor; an inverter for powering the electric motor; and a controller for controlling the inverter. The controller utilizes a control system comprising a rotor angle and angular velocity estimation block; an estimated angle error detector block; a field-weakening block; and a torque-to-current converter block, all of which operate to generate control commands for operation of the motor.
Owner:R & D DYNAMICS
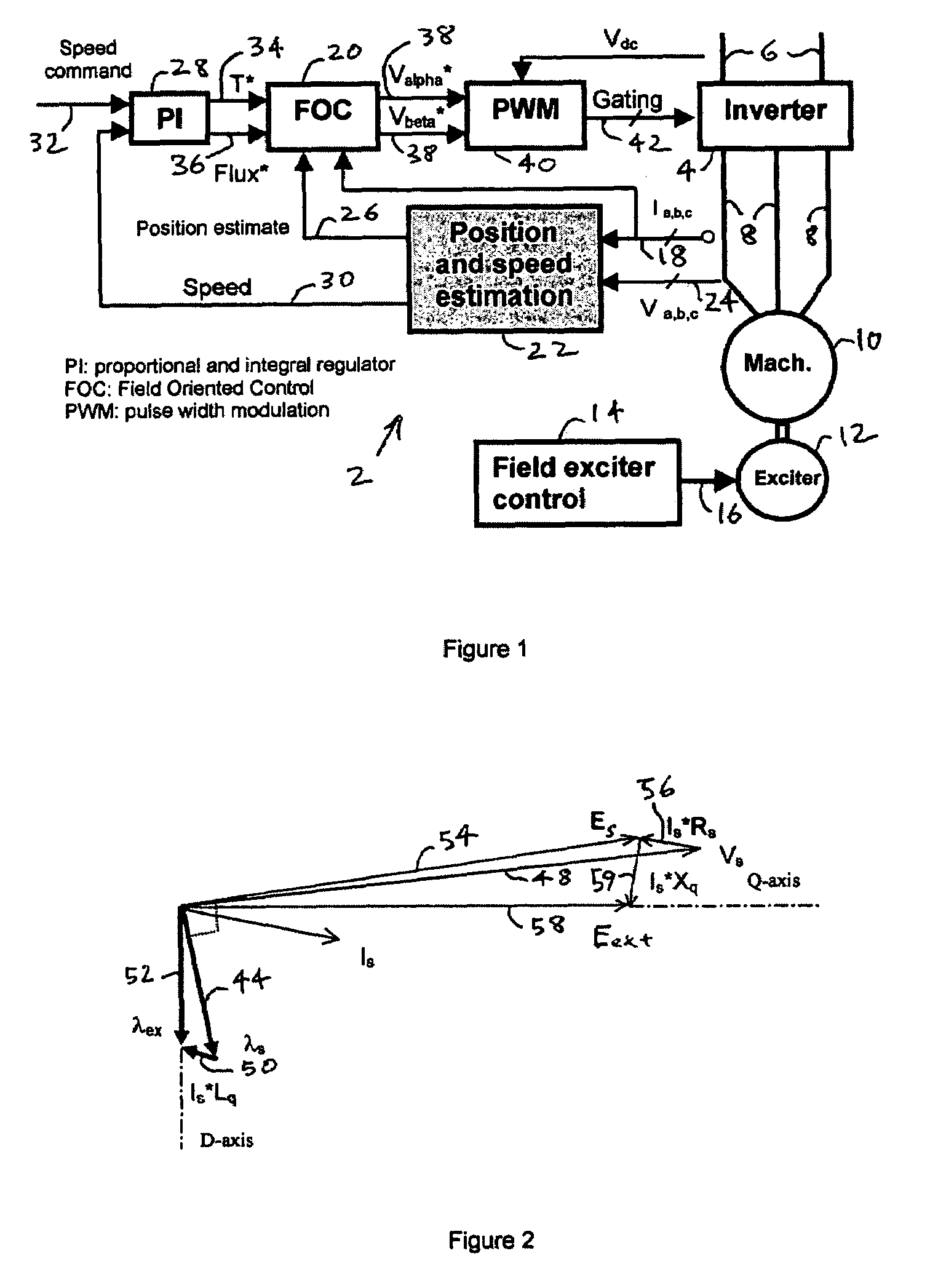
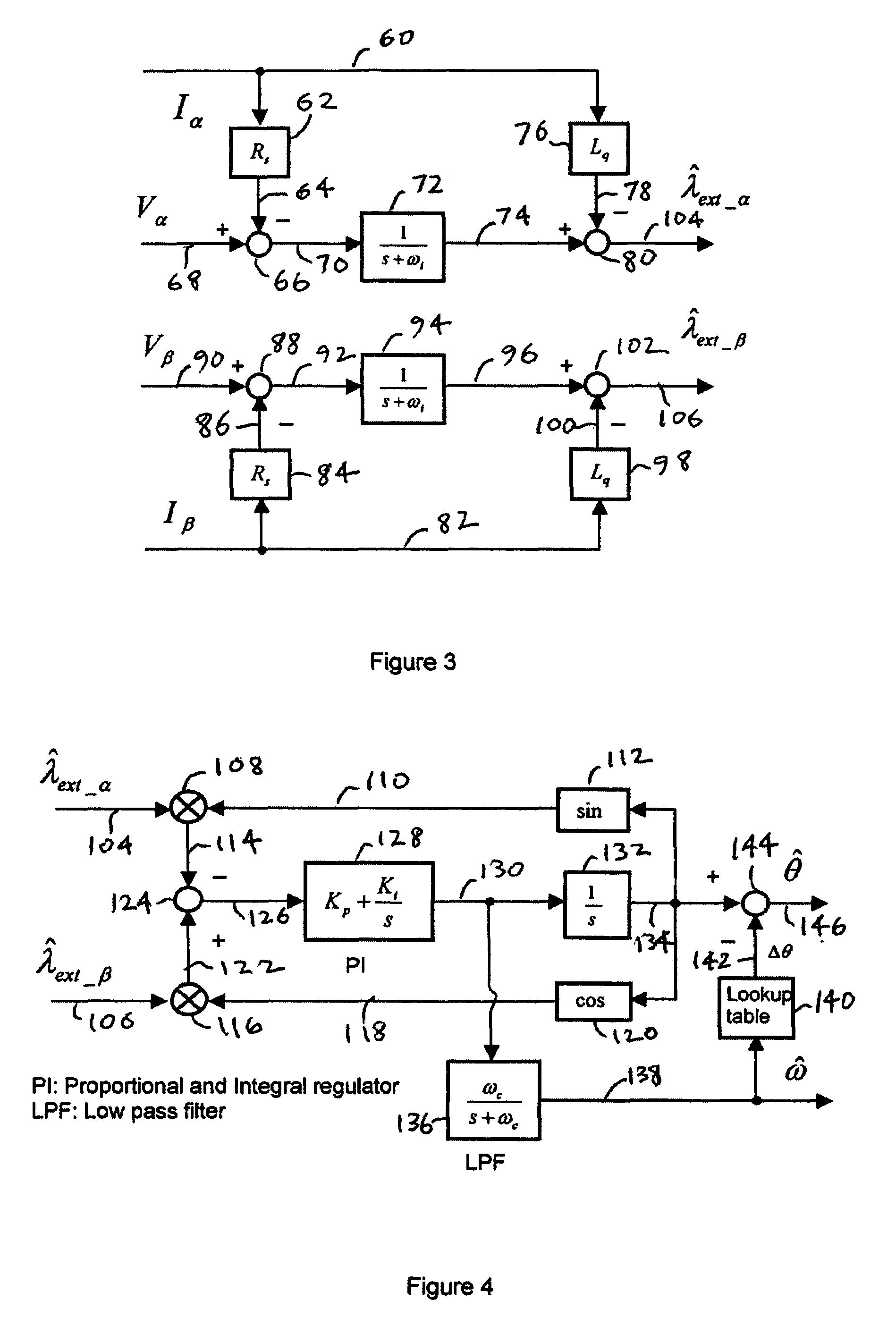
Shaft sensorless angular position and velocity estimation for a dynamoelectric machine based on extended rotor flux
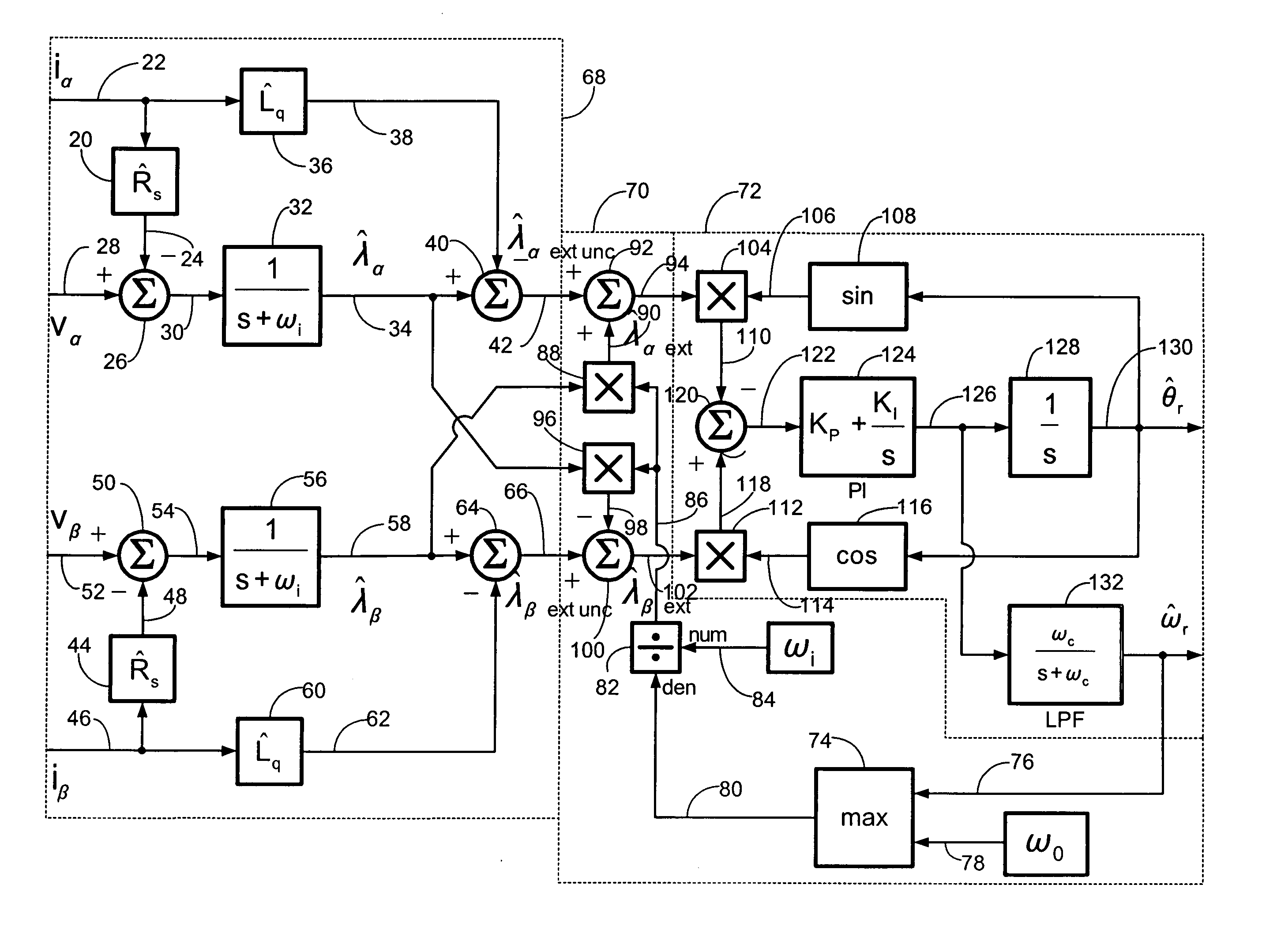
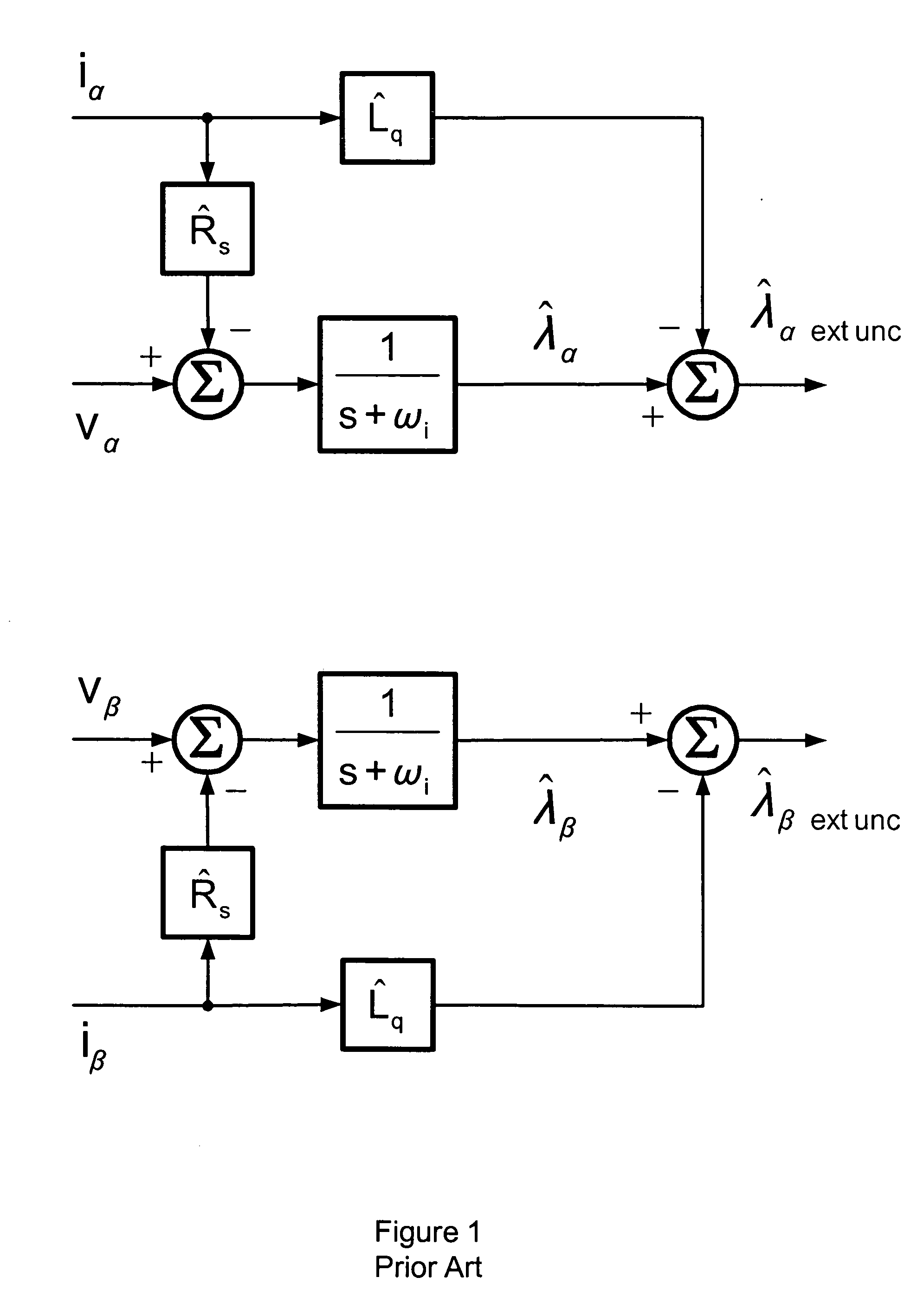
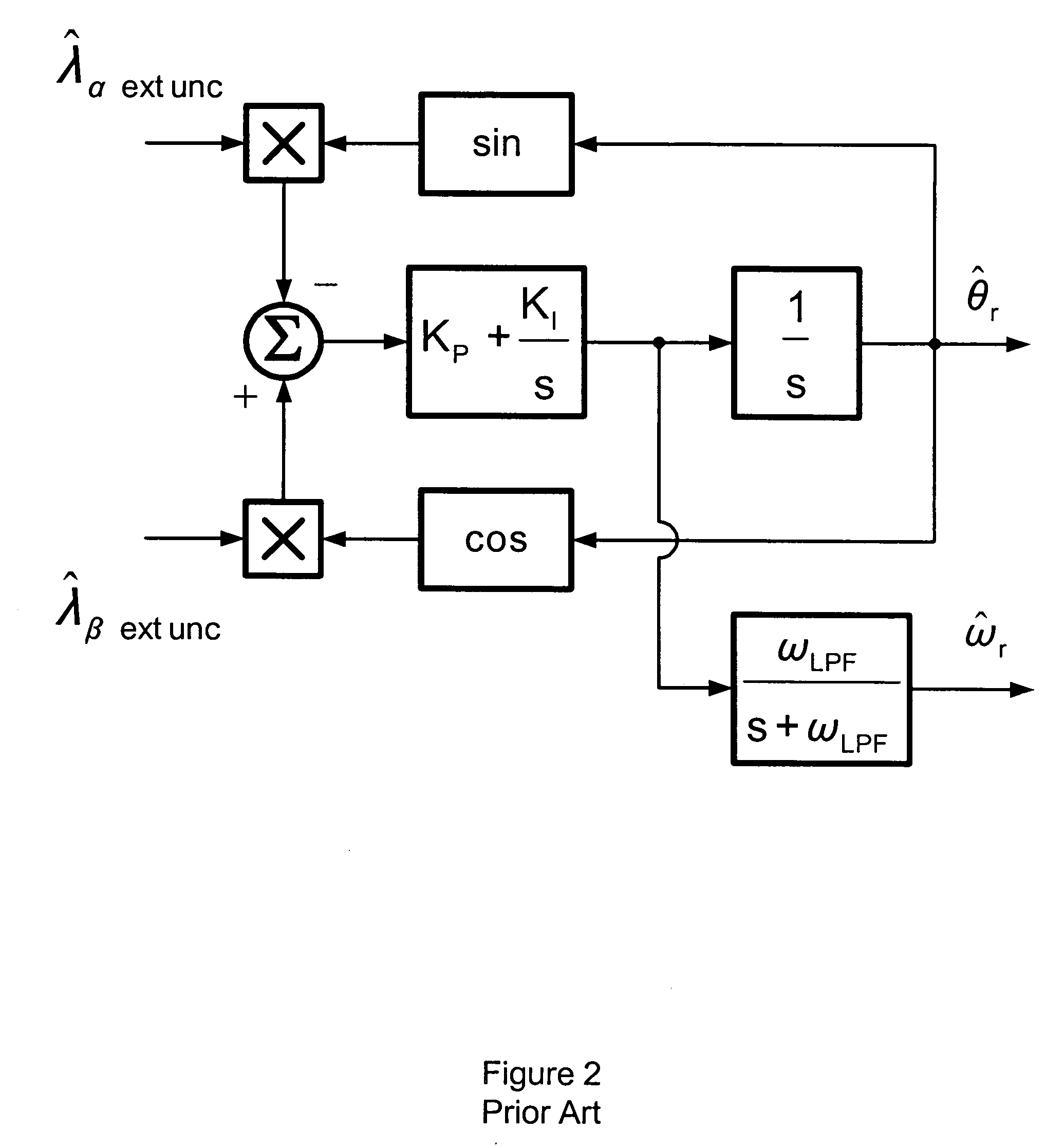
A shaft sensorless rotor angular position and velocity sensing system for a ynamoelectric machine that includes: a reference frame transformation function for transforming measured currents and potentials applied to a stator of the dynamoelectric machine to a two-phase α-β stationary frame to produce transformed currents Iα,Iβ and transformed potentials Vα,Vβ; first and second multipliers to produce signals Iα*RS,Iβ*RS; first and second summers to produce signals Vα,−Iα*RS,Vβ−Iβ*RS; first and second lag functions to produce signals1s+ωi(Vα-Iα*Rs),1s+ωi(Vβ-Iβ*Rs);third and fourth multipliers to produce signals Iα*Lq,Iβ*Lq; third and fourth summers to produce signals1s+ωi(Vα-Iα*Rs)-Iα*Lq,1s+ωi(Vβ-Iβ*Rs)-Iβ*Lqthat correspond to extended rotor flux values λext<sub2>—< / sub2>α,λext<sub2>—< / sub2>β; and a phase lock loop (PLL) to derive estimated rotor angular position and velocity values {circumflex over (θ)}, {circumflex over (ω)} for the dynamoelectric machine from the extended rotor flux values λext<sub2>—< / sub2>α,λext<sub2>—< / sub2>β.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
System of and method for using position, velocity, or direction of motion estimates to support handover decisions
InactiveUS7251491B2Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationUmbrella cellCommunications system
A method of and system for supporting a handover decision in a wireless communication system is described. An estimate of the position, velocity or direction of motion of a subscriber station is obtained. The estimate, or information derived there-from, is then used to support a handover decision. In one embodiment, an estimate of the velocity of the subscriber station is obtained if the handover rate experienced by the subscriber station exceeds a threshold while the subscriber station is within the coverage area of an umbrella cell. A decision is made to handover the subscriber station to the umbrella cell if the estimate of the velocity of the subscriber station exceeds a threshold. In a second embodiment, one or more estimates of the position, velocity, or direction of motion of the subscriber station are obtained responsive to the subscriber station experiencing a directed retry condition. A decision is made to handover the subscriber station from a serving cell to a target cell if the one or more estimates indicate that (1) the subscriber station is located closer to the target cell than the serving cell; or (2) the subscriber station is moving towards the target cell and away from the serving cell.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
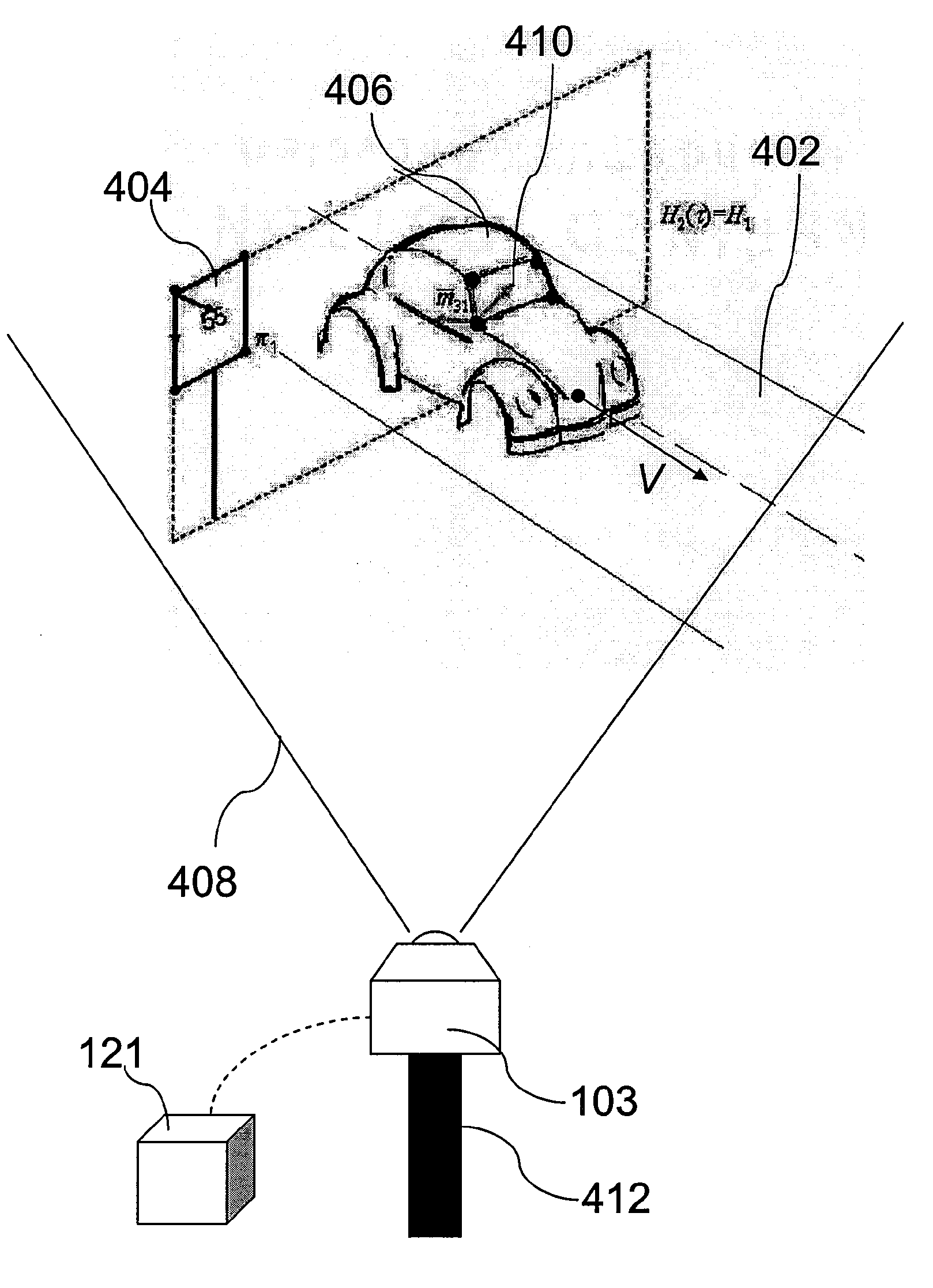
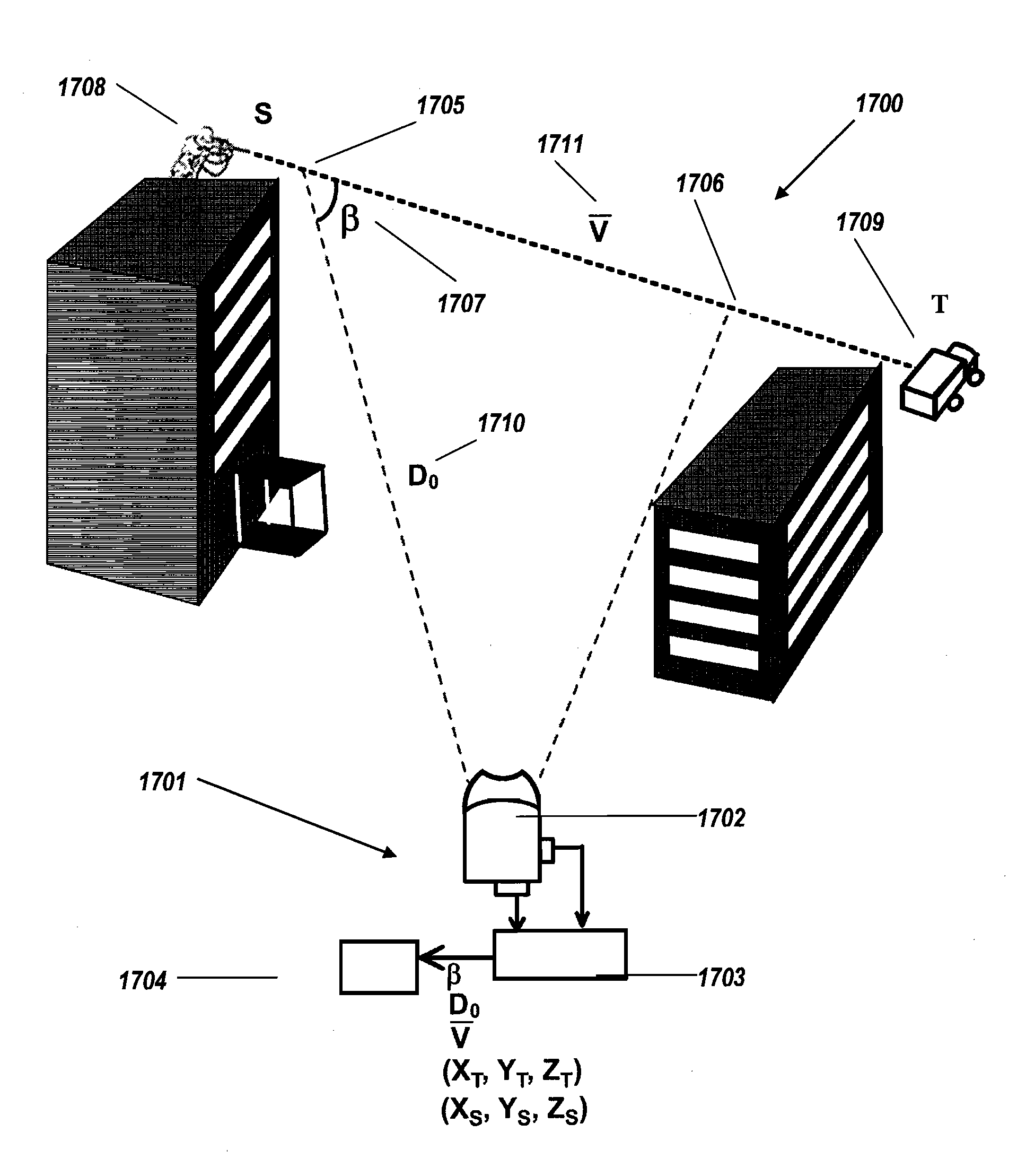
Passive single camera imaging system for determining motor vehicle speed
A system for passively determining a speed of moving vehicles includes a single imaging device (103) for acquiring a plurality of images at a first time and at least at one second later time, wherein each image includes a moving vehicle (406) on a vehicle pathway (402) and at least one fixed object (404) proximate to the vehicle, defining a first plane (π1) intersecting an adjacent portion of the vehicle pathway (402), wherein no geometric lengths of the vehicle (406) are known a priori. The system can also include a processor (121) operable to receive data associated with the images and determine a speed of the vehicle (406) in the images, wherein the processor (121) estimates at least one geometric length of the vehicle (406) by applying homography using the plurality of images, and where the processor (121) determines a speed of the vehicle (406) from the plurality of images and the estimated geometric length using a velocity estimation method.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
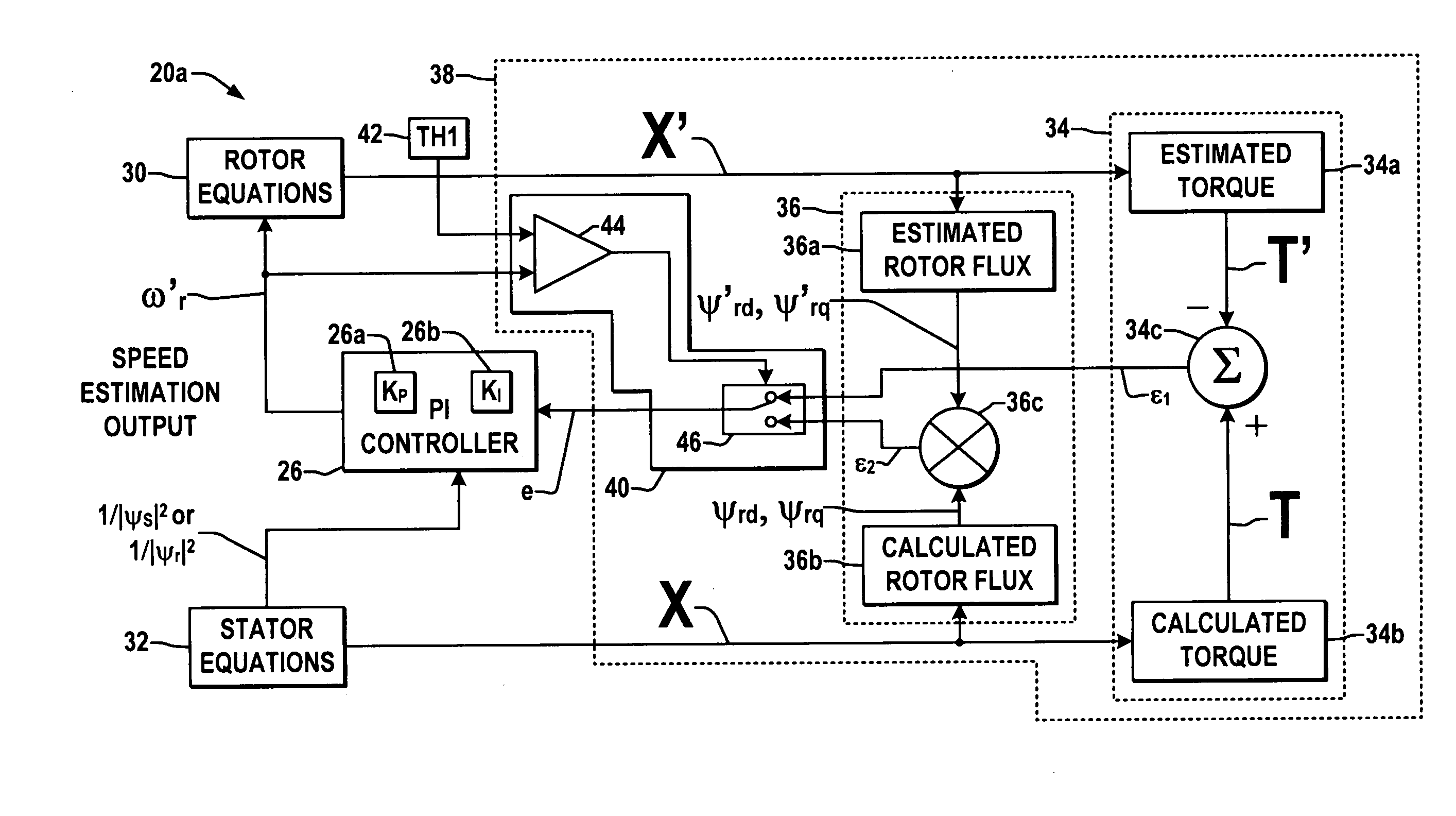
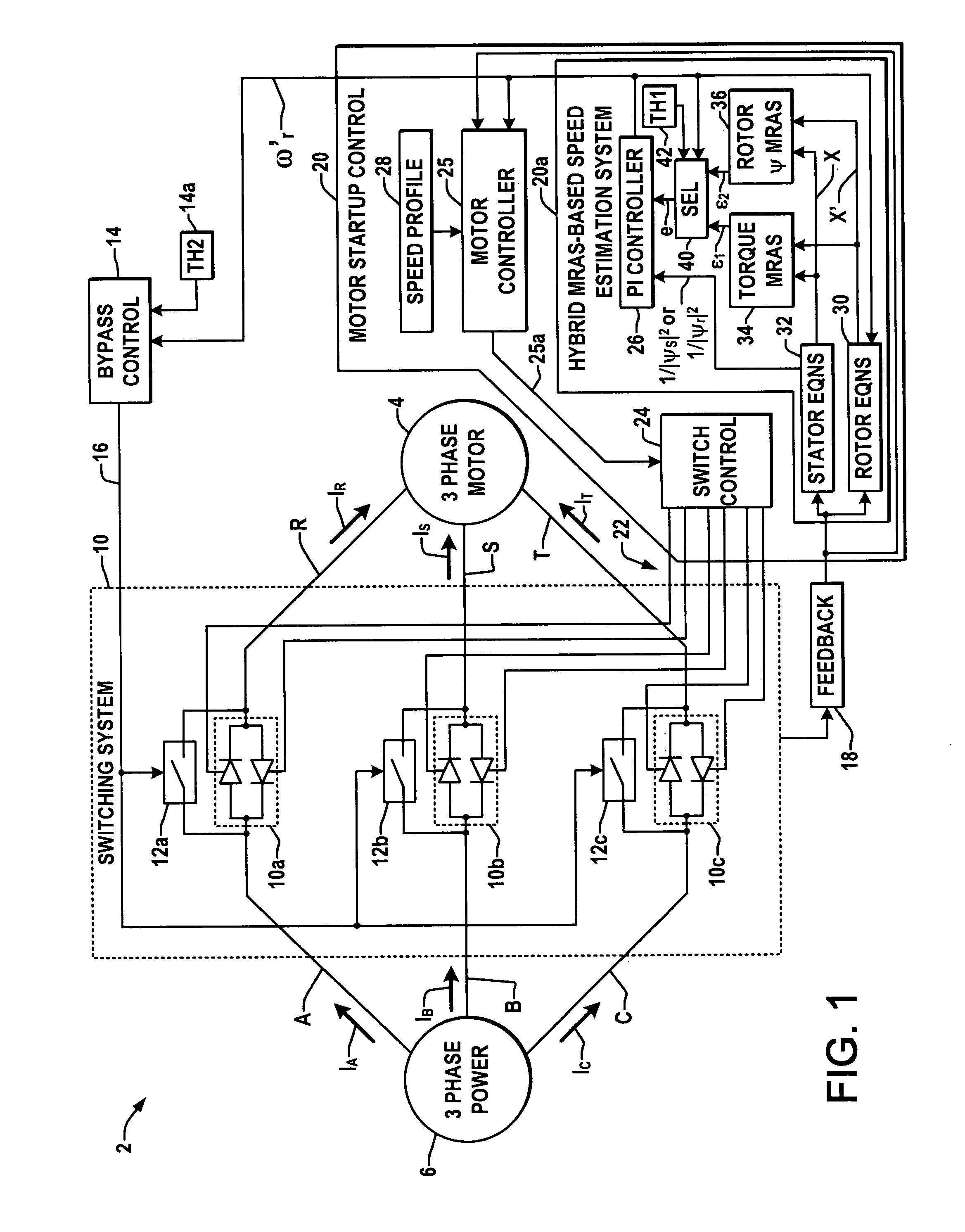
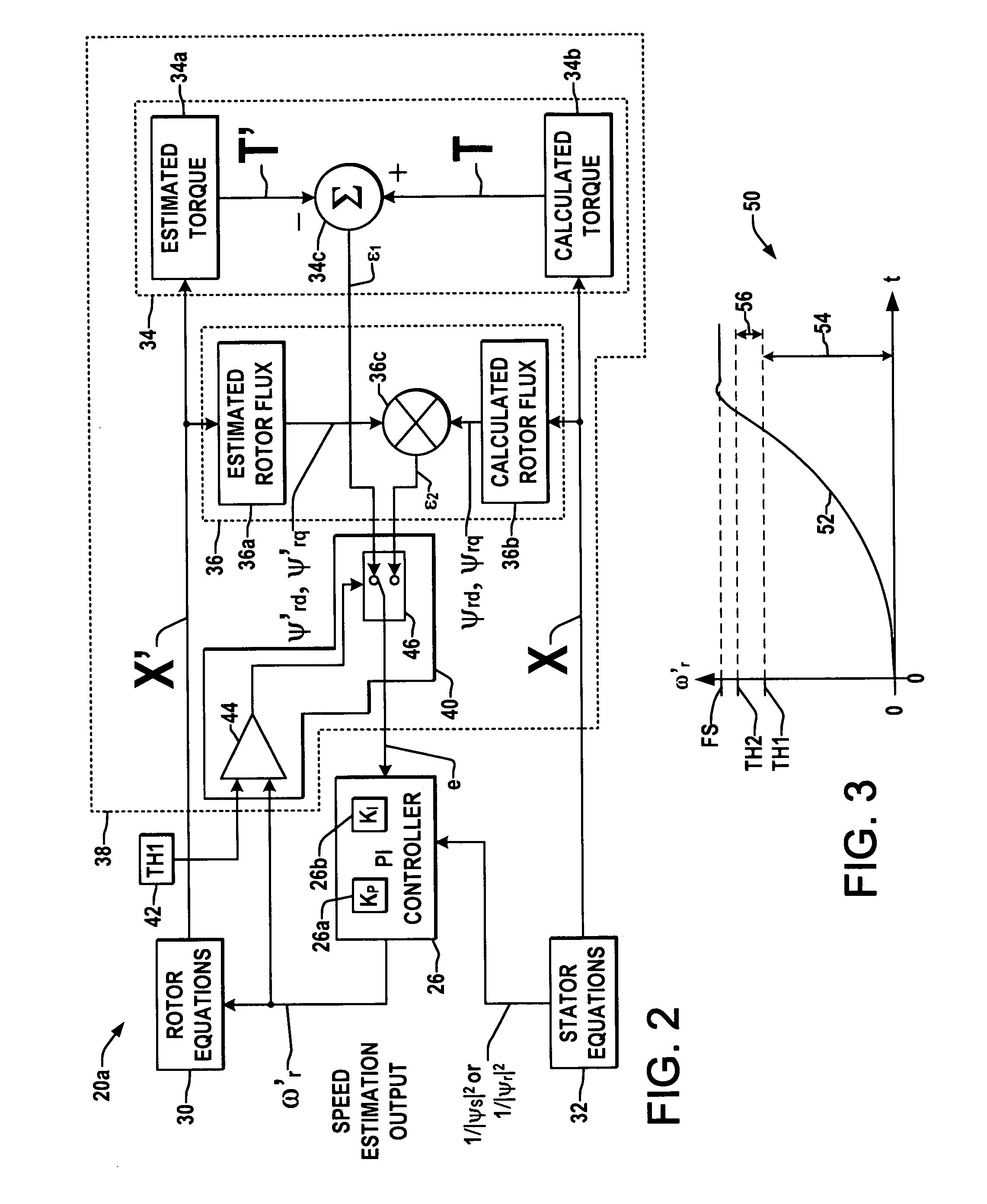
System and method for motor speed estimation using hybrid model reference adaptive system
ActiveUS7193387B1Less sensitiveEasy to understandAC motor controlElectric motor controlMotor speedMotor drive
Motor drives, motor speed controllers, motor speed estimation systems, and methods are presented for controlling motor startup speed and for estimating motor speed during startup, in which a speed estimate controller provides a rotor speed estimate based on a first error term from a torque-based MRAS component for a first range of motor speeds and based on a second error term from a rotor flux-based MRAS component for a second range of speeds.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
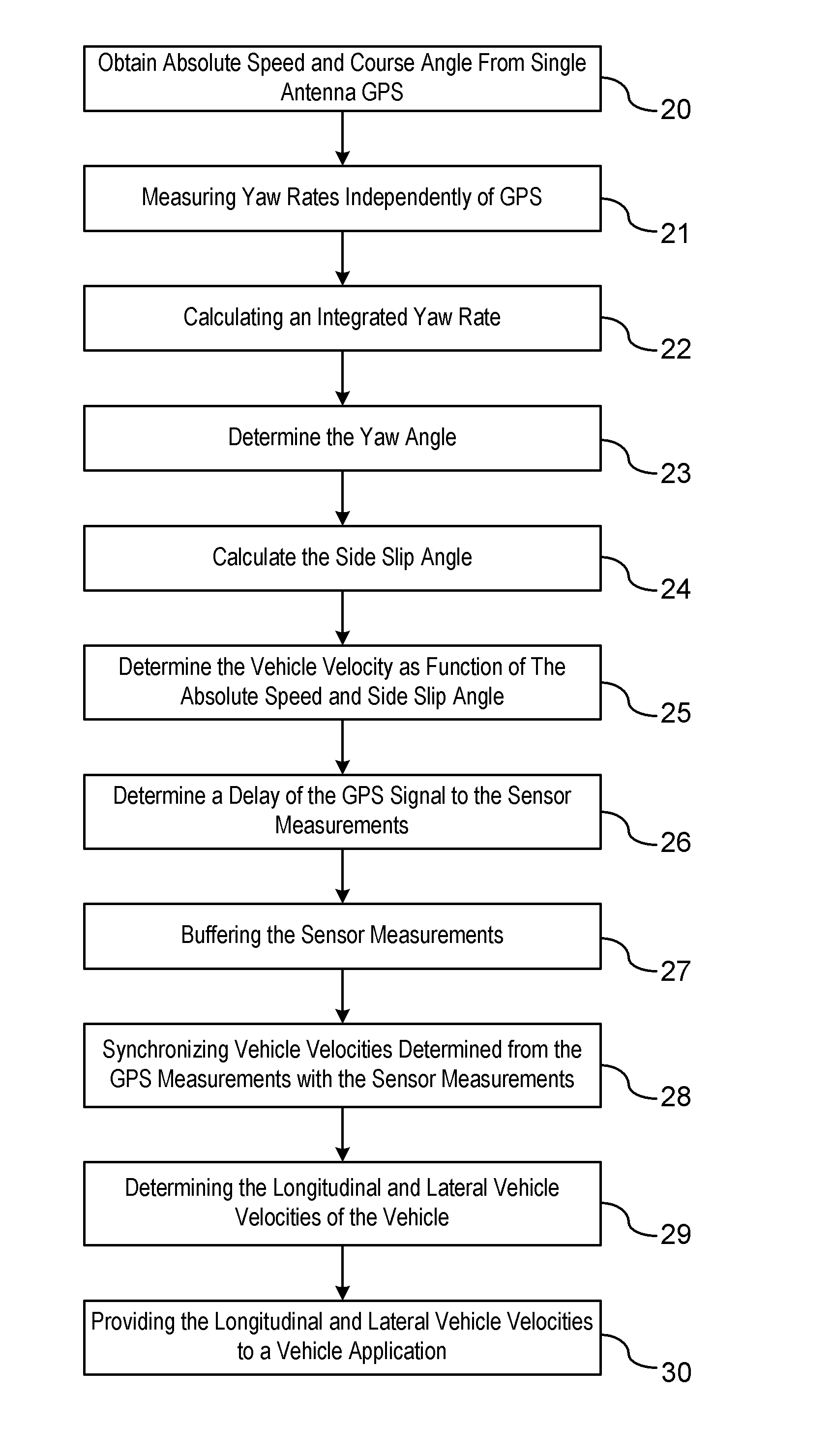
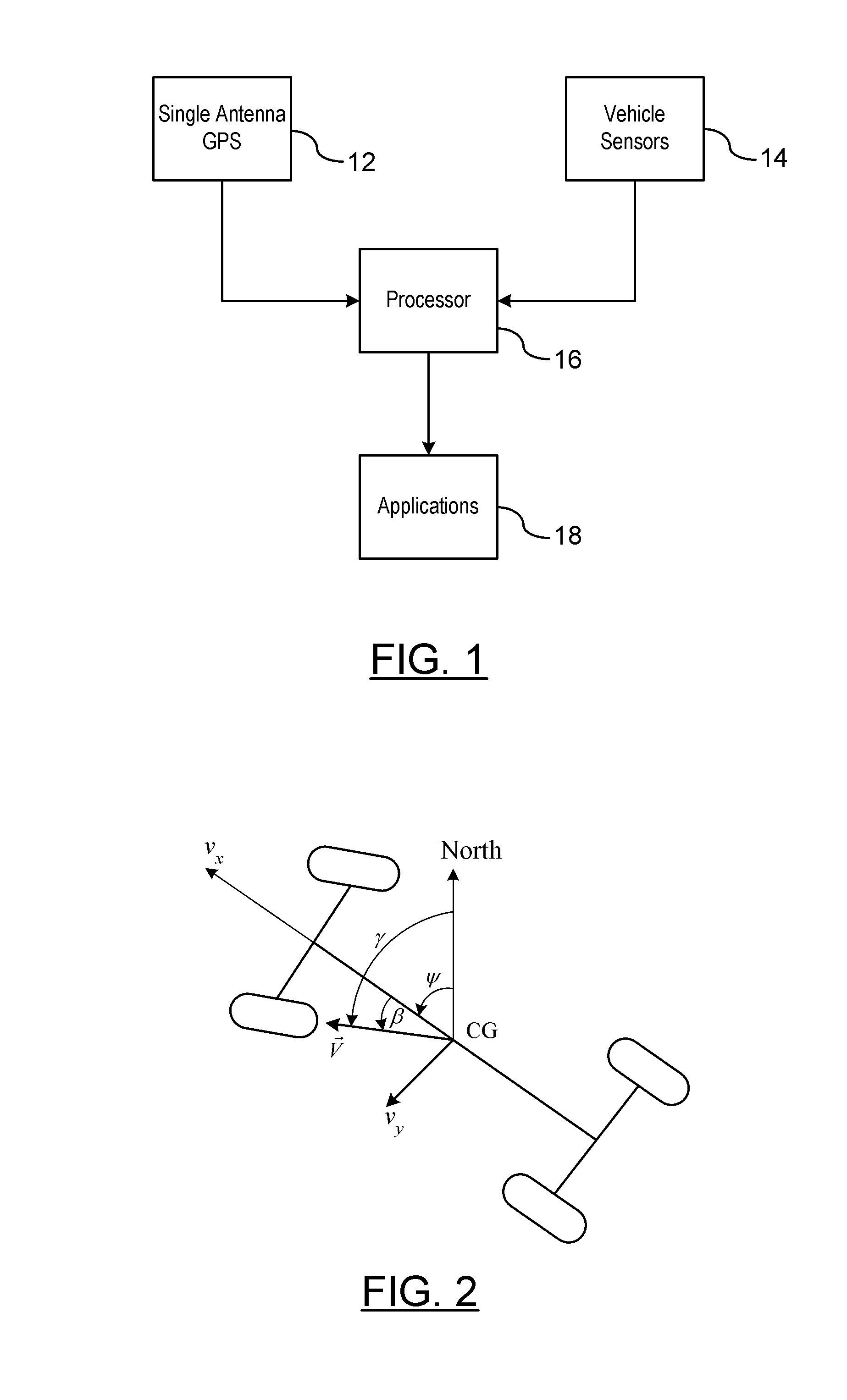
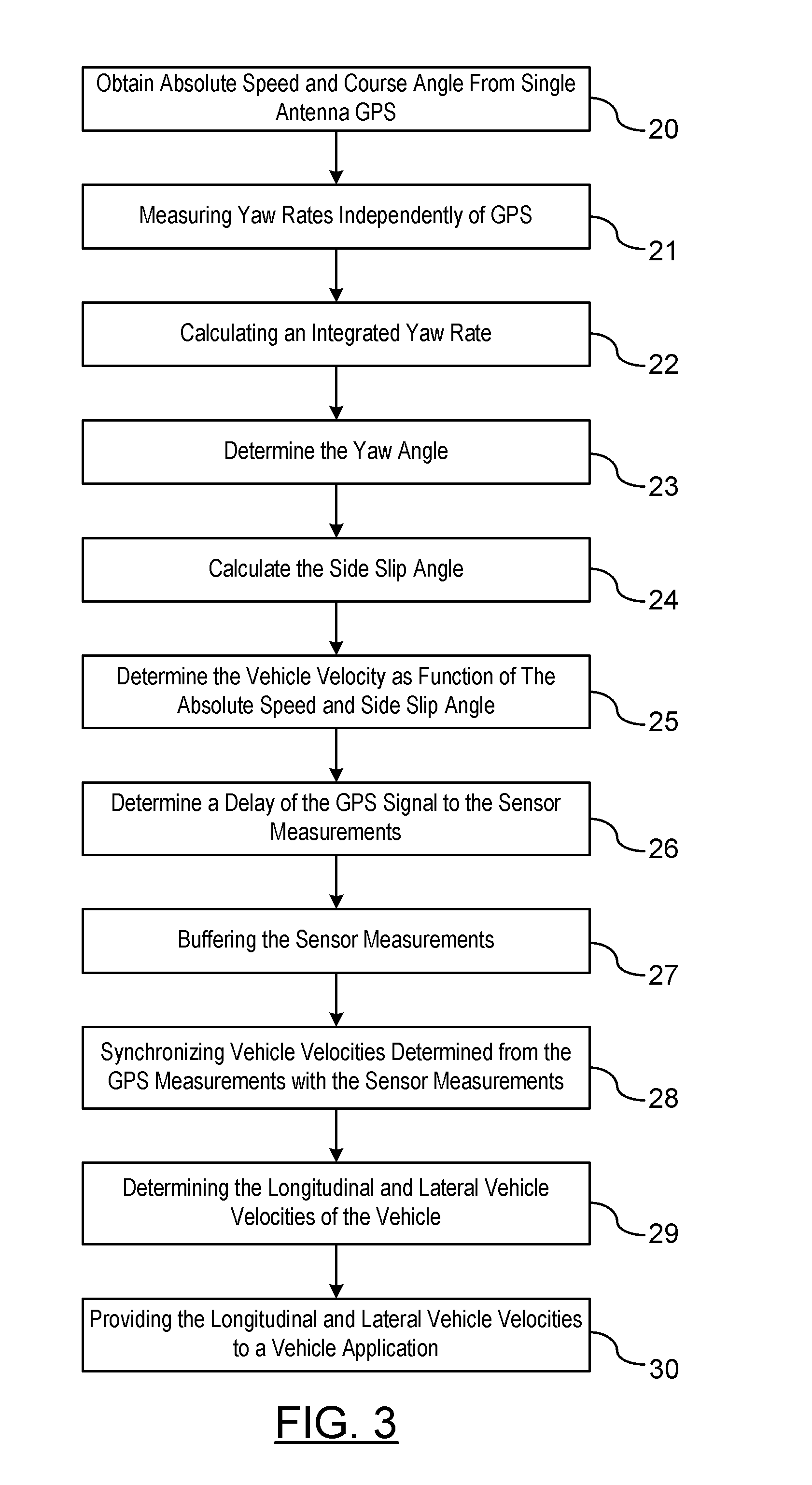
GPS-Enhanced Vehicle Velocity Estimation
ActiveUS20110112739A1Improve accuracyLow costAnalogue computers for trafficNavigation instrumentsGps measurementVehicle dynamics
A method is provided for estimating vehicle velocity for a vehicle using a single-antenna global positioning system (GPS). An absolute speed and a course angle of the vehicle is measured using the single-antenna GPS. The yaw rates of the vehicle are measured independently of the GPS. An integrated yaw rate of the vehicle is calculated as a function of the measured yaw rates over a period of time. A yaw angle is determined as a function of a reference yaw angle and the integrated yaw rate. Aside slip angle is calculated as a function of the estimated yaw angle and the course angle provided by the GPS. The vehicle velocity is determined as a function of the absolute speed and the side slip angle. The vehicle velocity is provided to a vehicle dynamic control application.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Imaging engine employing planar light illumination and linear imaging
InactiveUS20030091244A1Low costReduce speckle noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesTime signalImage based
An imaging engine includes a plurality of linear imaging arrays, image formation optics, at least one illumination module and supporting circuitry that are embodied within a modular engine housing. The plurality of linear imaging arrays and image formation optics are mounted on an optical bench (which is integral to the engine housing) and provide field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear image arrays. The at least one illumination module produces planar light illumination that substantially overlaps the field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear imaging arrays. The supporting circuitry includes: timing signal generation circuitry that supplies timing signals to the linear imaging arrays in order to read out the row image data produced by such arrays (such row image data may be read out at a constant line rate or at a variable line rate); illumination control circuitry that supplies current to the illumination sources in the at least one illumination module; analog-to-digital conversion circuitry, which optionally filters row data image signal supplied thereto (to remove unwanted noise components) and converts the row image data supplied thereto into digital form; and data buffering circuitry, for storing the digital row image data generated by the analog-to-digital conversion circuitry and communicating the row image data stored therein over a data communication bus. One linear image array (e.g., linear imaging array C) may have a variable line rate that is controlled by the timing signals supplied thereto such that the image capture operations performed by the one linear imaging array (e.g. linear imaging array C) maintain a substantially constant aspect ratio, to thereby compensate for aspect ratio distortions that result from variations in velocity of engine with respect to target object(s). The variable line rate is based upon velocity estimates derived from processing of the pixel data values of other linear imaging arrays disposed therein. The supporting circuitry may optionally include a line rate adjustment module, preferably realized as part of a programmed controller, that is operably coupled to timing signal generation circuitry and adjusts the variable line rate of the one linear image device (e.g., linear imaging array C); output illumination control module, preferably realized as part of the programmed controller, that is operably coupled to the illumination control circuitry and adjusts the optical power level and / or illumination time period for the illumination that overlaps one or more of the FOVs of the linear imaging arrays of the engine for speckle reduction / constant white levels; and / or imaging processing circuitry, operably coupled to the data buffering circuitry over the data communication bus, that realizes portions of image-based mechanisms / techniques for image velocity estimation, aspect ratio compensation, jitter estimation and compensation, bar code detection, OCR, and image lift.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
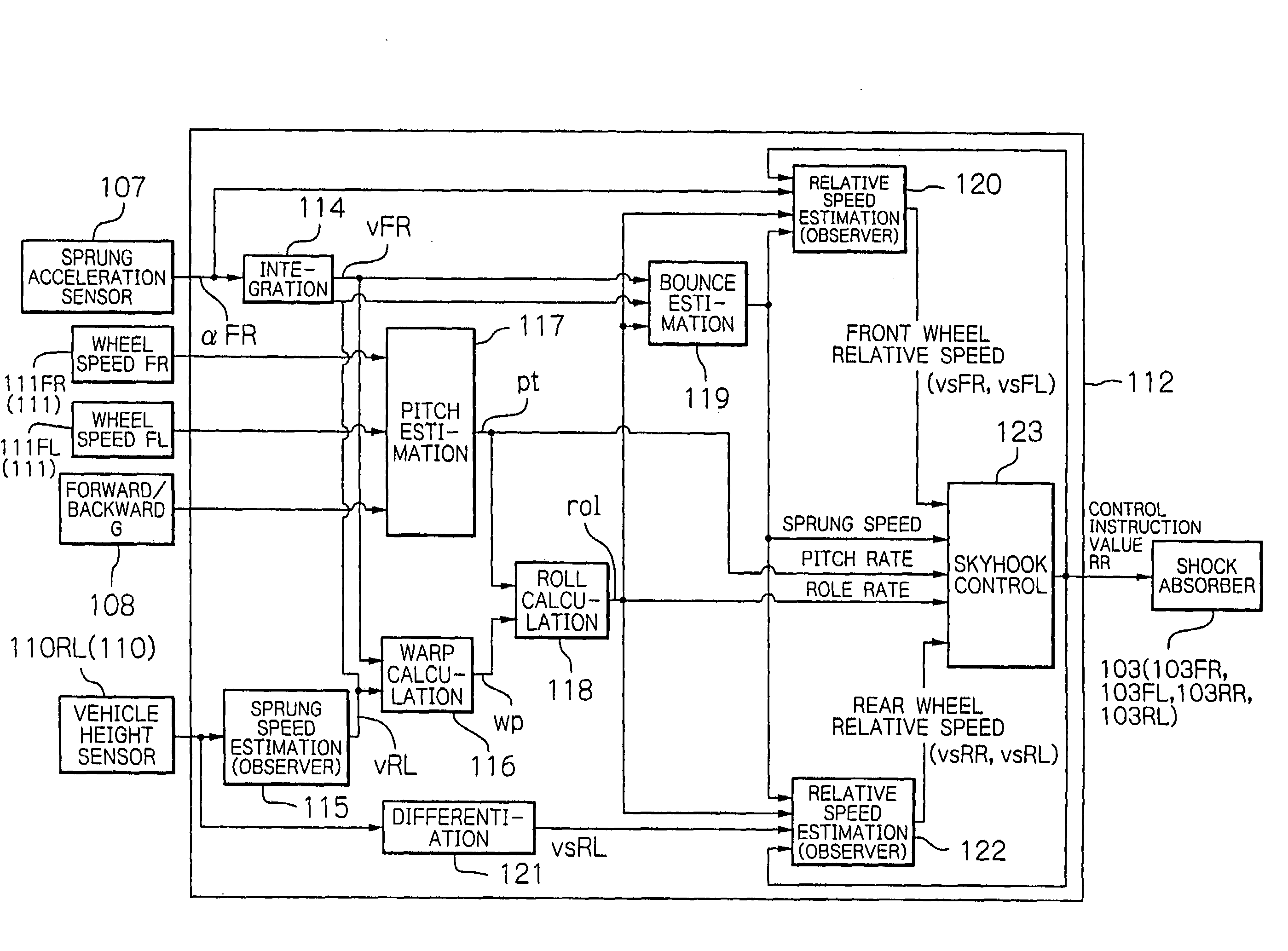
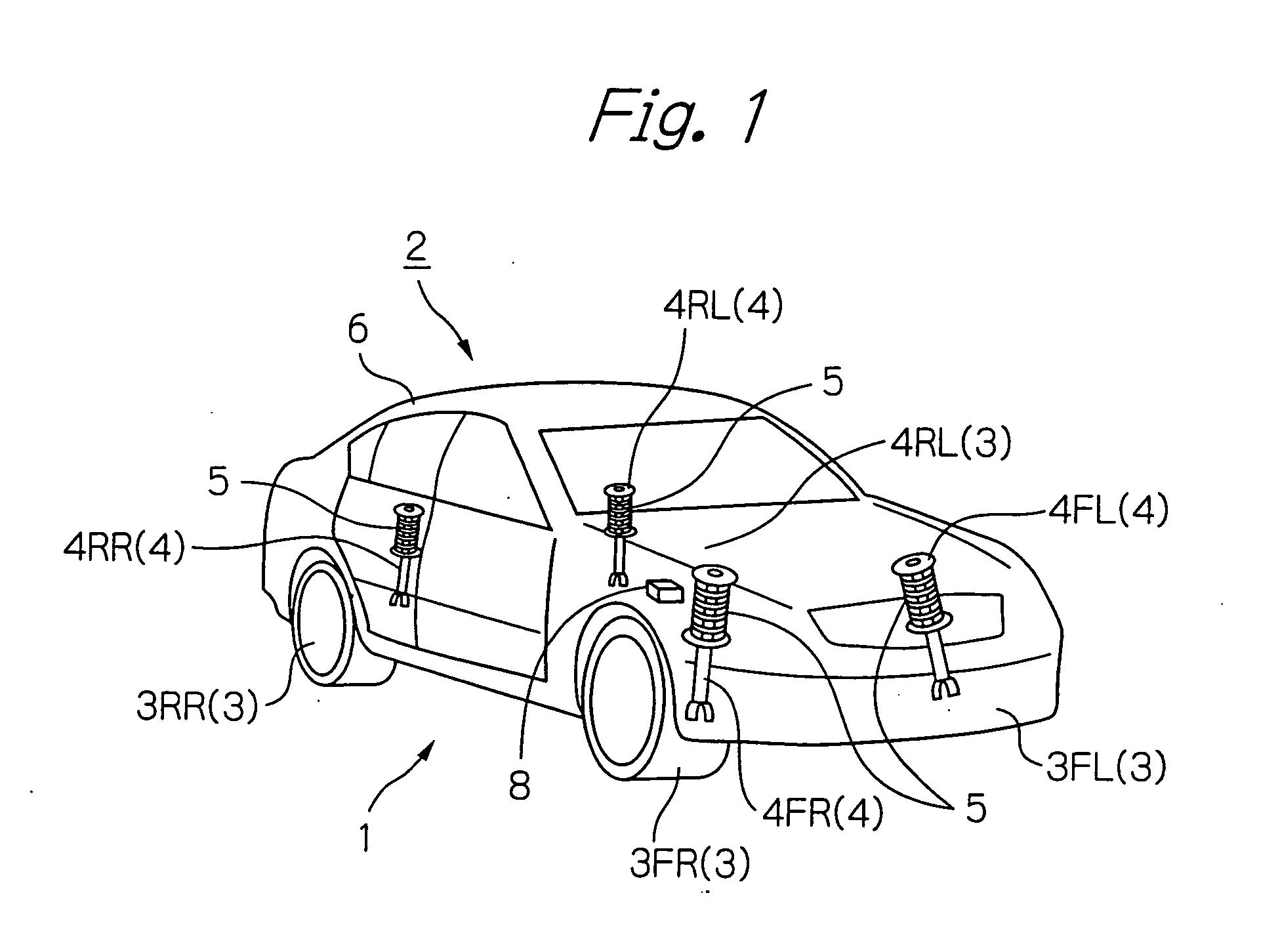
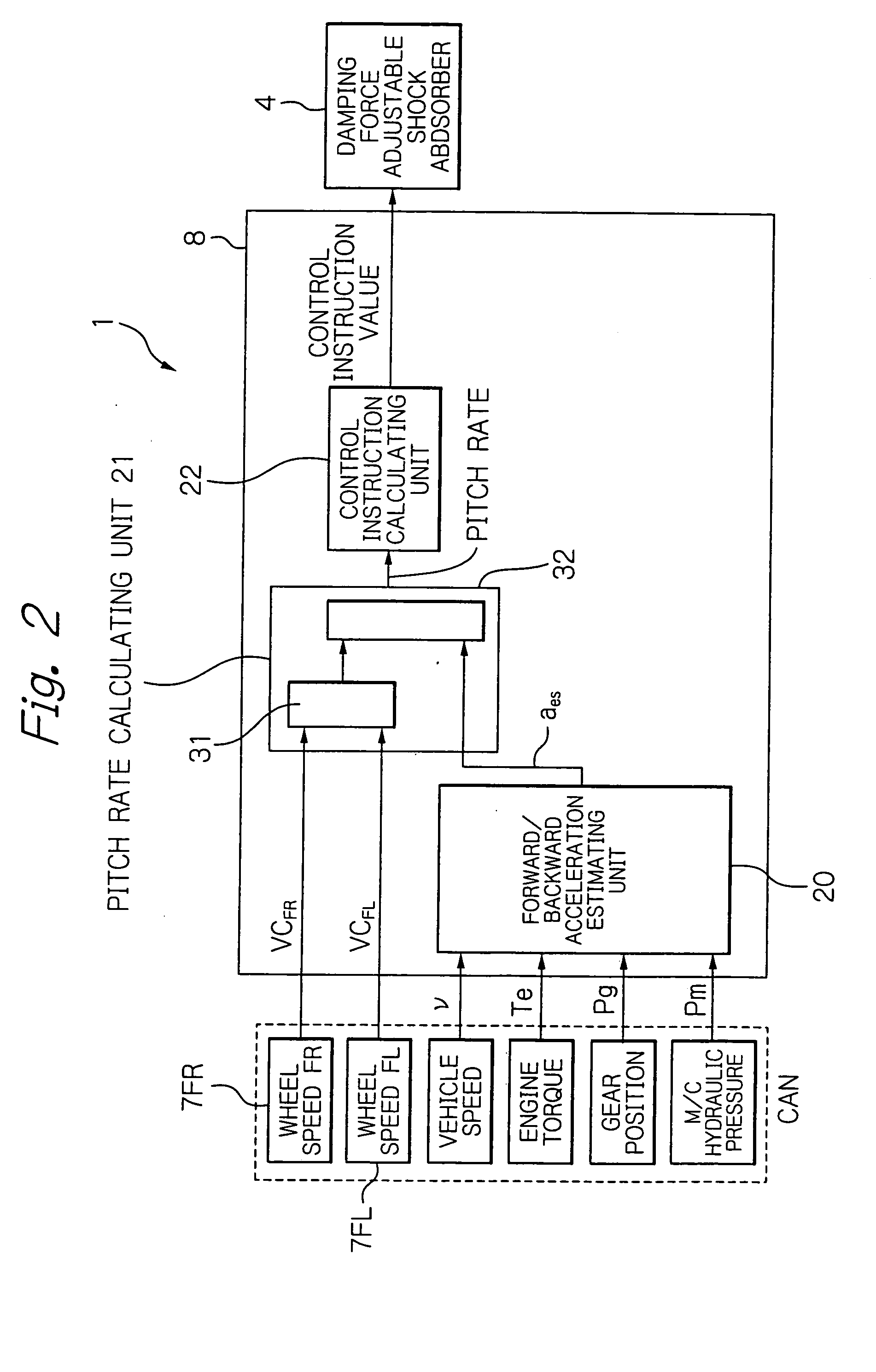
Suspension control apparatus
ActiveUS20090085309A1Reduce in quantitySpringsDigital data processing detailsWheel speed sensorEngineering
The present invention provides a suspension control apparatus requiring a reduced number of sensors. A pitch rate estimating unit 21 calculates a pitch rate used for creating a control instruction value, with use of a wheel-speed time-rate-of change obtained based on wheel speeds vcFL and vcFR detected by wheel speed sensors 7FL and 7FR, and an estimated forward / backward acceleration aes calculated by a forward / backward acceleration estimating unit 20.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
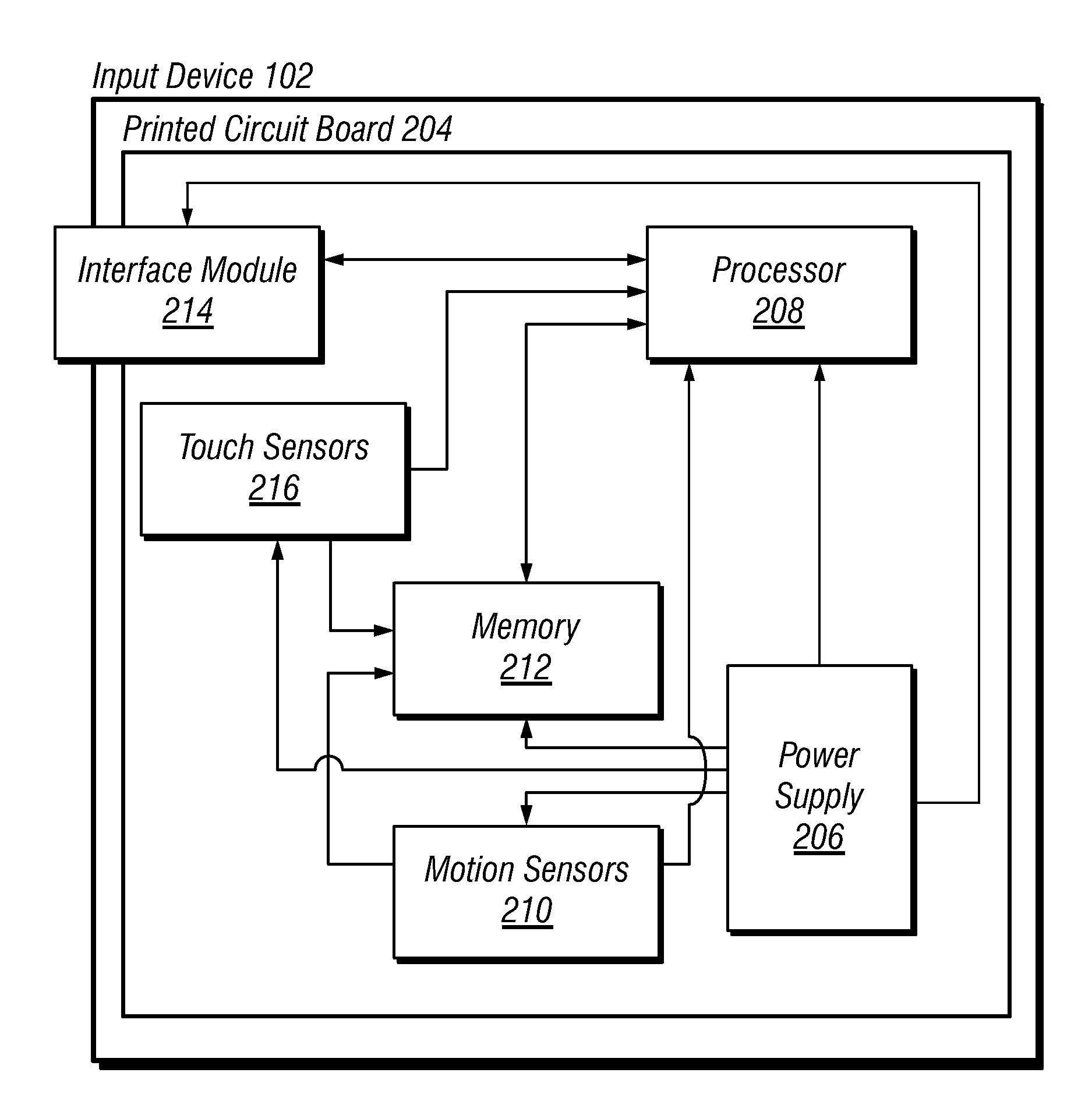
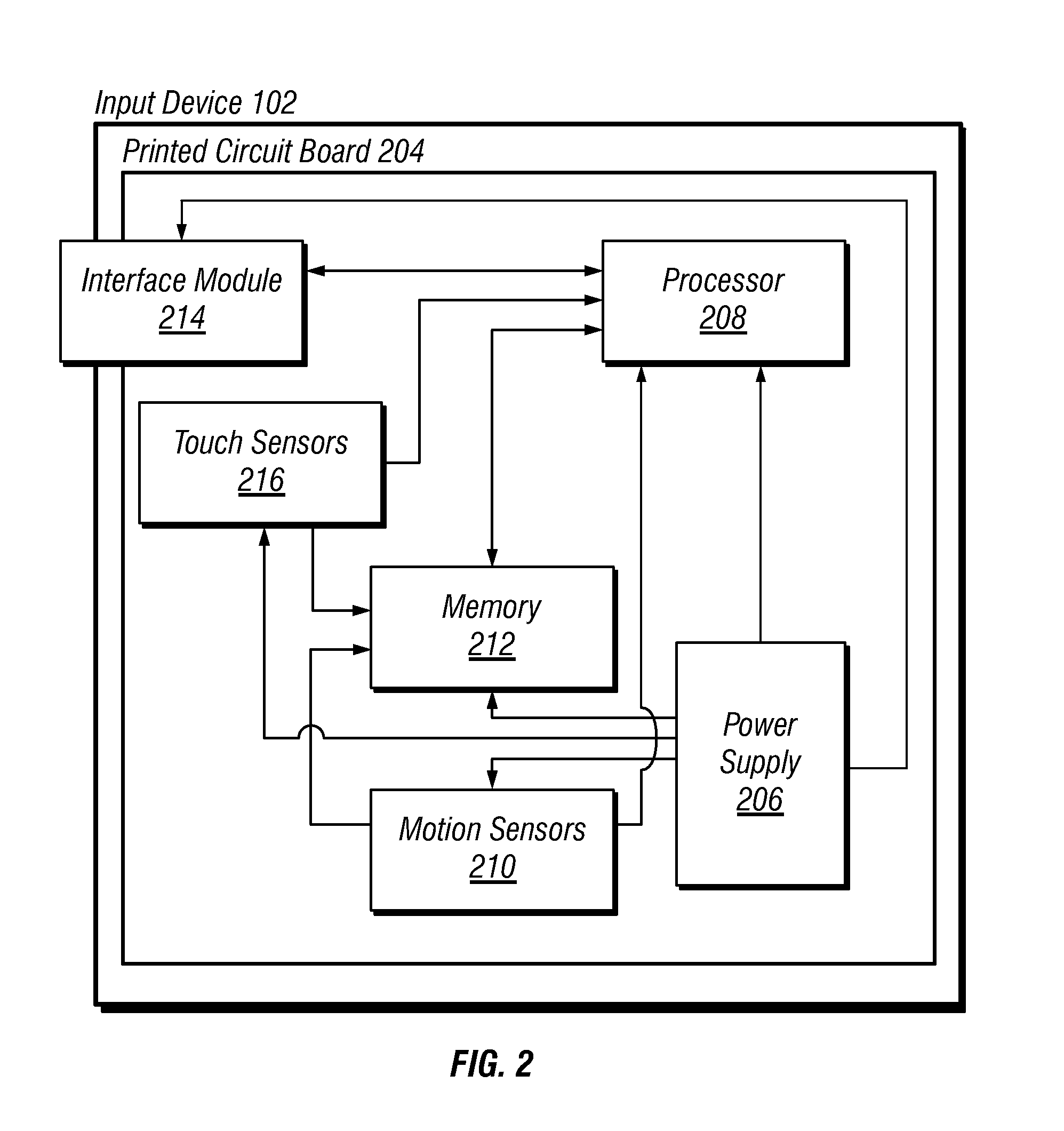
Hybrid inertial and touch sensing input device
ActiveUS20100039394A1Small range of motionWide rangeInput/output processes for data processingTouch SensesHuman–computer interaction
A method and apparatus for tracking coarse and fine motions associated with an electronic input device is disclosed. The electronic input device can have both an inertial sensor and a touch sensor. The method includes receiving inputs from an inertial sensor and a touch sensor, and dynamically adjusting a velocity estimate of the electronic input device based on weighting or predetermined thresholds of the inputs to maximize a tracking range of the input device.
Owner:APPLE INC
Passive Electro-Optical Tracker
InactiveUS20100278387A1High precisionShort enough reaction timeOptical radiation measurementImage enhancementTwo bandCcd camera
A passive electro-optical tracker uses a two-band IR intensity ratio to discriminate high-speed projectiles and obtain a speed estimate from their temperature, as well as determining the trajectory back to the source of fire. In an omnidirectional system a hemispheric imager with an MWIR spectrum splitter forms two CCD images of the environment. Three methods are given to determine the azimuth and range of a projectile, one for clear atmospheric conditions and two for nonhomogeneous atmospheric conditions. The first approach uses the relative intensity of the image of the projectile on the pixels of a CCD camera to determine the azimuthal angle of trajectory with respect to the ground, and its range. The second calculates this angle using a different algorithm. The third uses a least squares optimization over multiple frames based on a triangle representation of the smeared image to yield a real-time trajectory estimate.
Owner:LIGHT PRESCRIPTIONS INNOVATORS
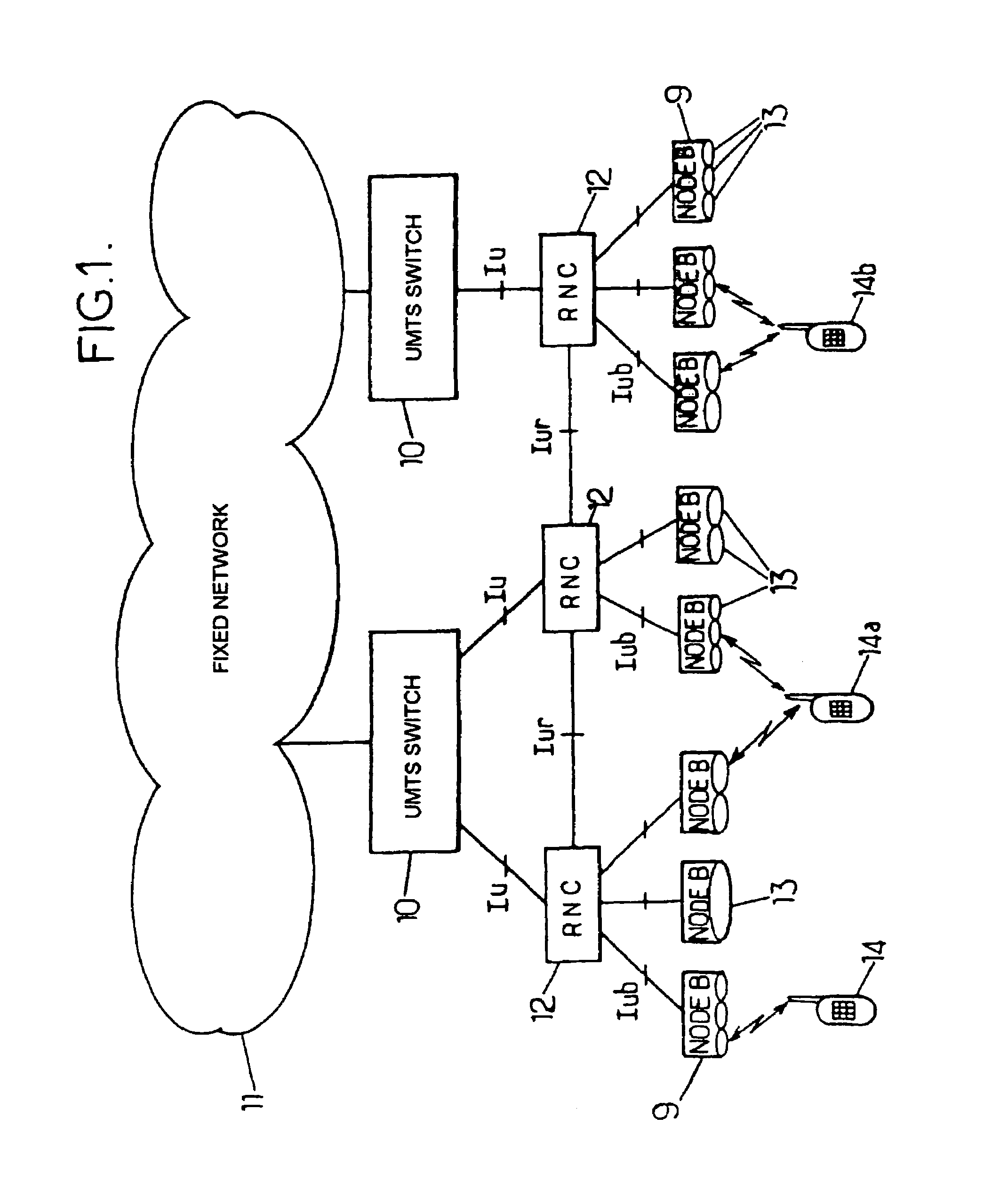
Method of controlling a mode of reporting of measurements on a radio interface and radio network controller for the implementation of the method
ActiveUS7418260B2Quick changeAvoids unnecessary uploadsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransceiverRadio networks
Parameters of radio propagation between a mobile terminal and at least one fixed transceiver are measured. Report messages indicating at least a part of the measured parameters, in accordance with a mode of reporting specified by the radio network controller are transmitted to the radio network controller. An estimate of speed of movement of the mobile terminal is obtained at the radio network controller. The report messages are processed at the radio network controller so as to determine, by taking account of the said estimate of speed, a mode of reporting to be specified for a part at least of the report messages.
Owner:RPX CORP
Apparatus and method for velocity estimation in synthetic aperture imaging
The invention relates to an apparatus for flow estimation using synthetic aperture imaging. The method uses a Synthetic Transmit Aperture, but unlike previous approaches a new frame is created after every pulse emission. In receive mode parallel beam forming is implemented. The beam formed RF data is added to the previously created RF lines obtained by the same transmit sequence. The apparatus comprises a pulser (1) to generate a pulsed voltage signal, that is fed to the emit beam former (2). The emit beam former (2) is connected to the emitting transducer array (3). The ultrasound is reflected by the object (4) and received by the elements of the transducer array (5). All of these signals are then combined in the beam processor (6) to focus all of the beams in the image in both transmit and receive mode and the simultaneously focused signals are used for updating the image in the processor (7). The estimation processor (8) to correlate the individual measurements to obtain the displacement between high-resolution images and thereby determine the velocity.
Owner:B K MEDICAL
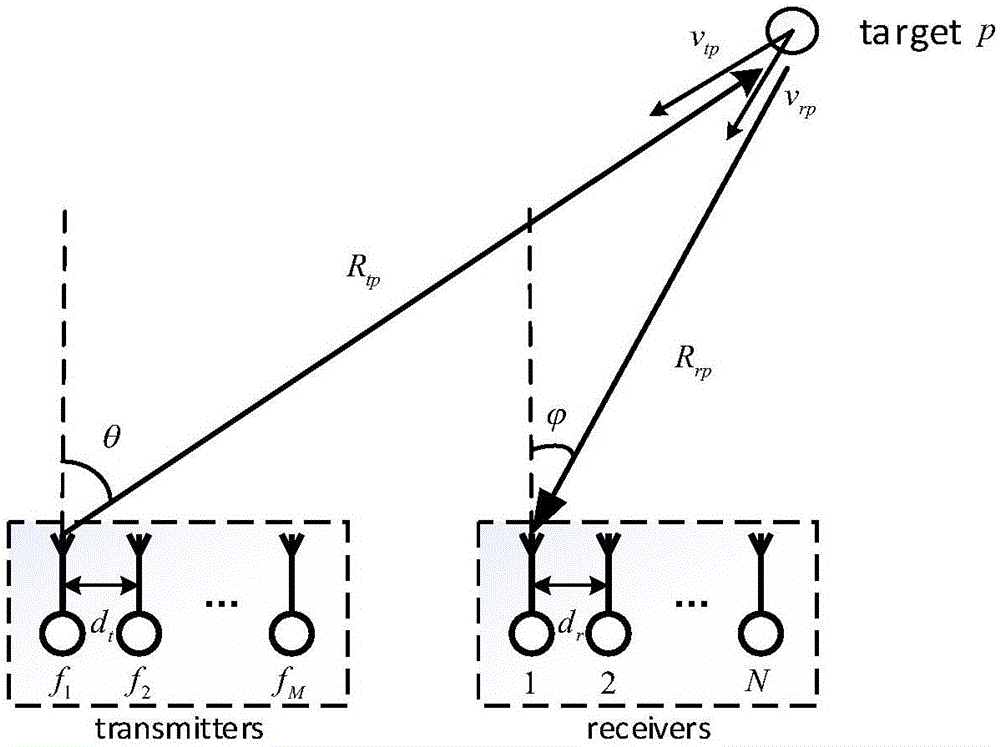
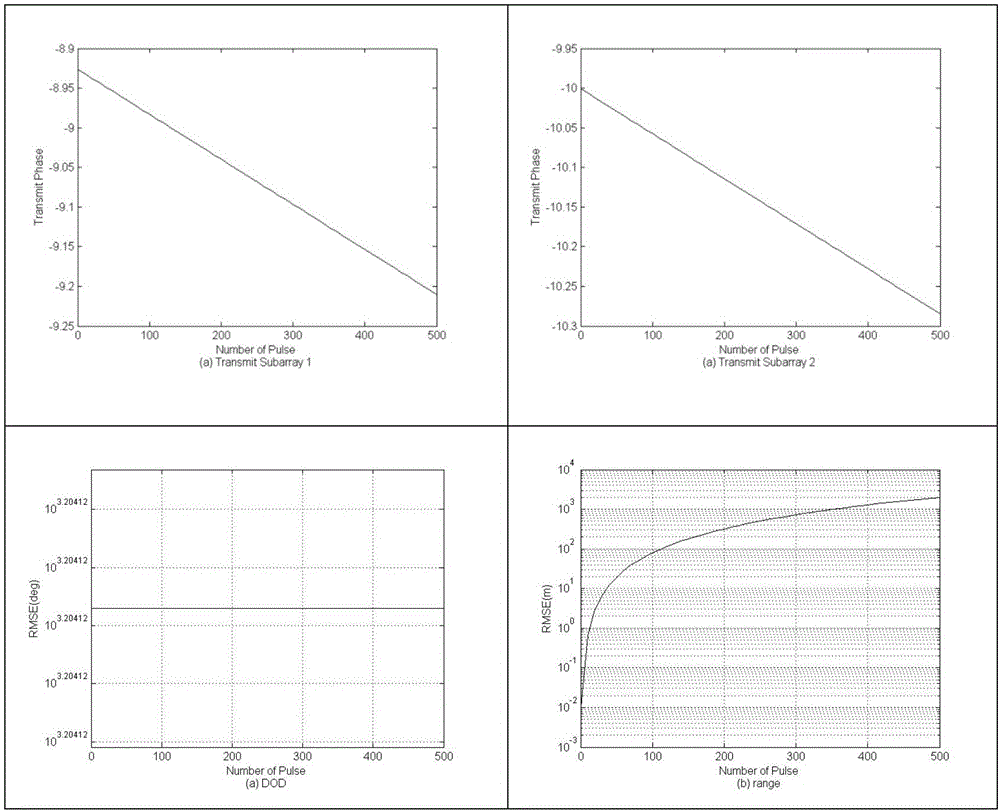
Multi-parameter combined estimation method based on bi-static FDA-MIMO radars
ActiveCN106353744AImprove estimation performanceSolve problems that are prone to ambiguityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEstimation methodsMultiple signal classification
The invention relates to a multi-parameter combined estimation method based on bi-static FDA-MIMO radars. The method comprises the following steps: firstly designing a transmitting signal by utilizing characteristics of FDA and MIMO radars; carrying out matched filtering, vectorization and spatial smooth processing on a receiving signal; then estimating a combined steering vector and estimating a DOA and a speed parameter by utilizing an ESPRIT algorithm, and carrying out decoupling and parameter estimation on the DOD and distance information by combining characteristics of a transmitting waveform; and carrying out ambiguity resolution on a distance result estimated by utilizing an ESPRIT algorithm and combining a distance estimated by virtue of a pulse delay estimation algorithm, and carrying out ambiguity resolution on a speed by virtue of an MUSIC algorithm by combining signal characteristics of a large number of pulses. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the problem that the distance and speed can not be accurately estimated under the condition of a single PRF can be effectively solved, and the estimation of the three-dimensional position and speed of a target can be realized; and a simulation result shows that the method provided by the invention has good estimation accuracy and stability.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
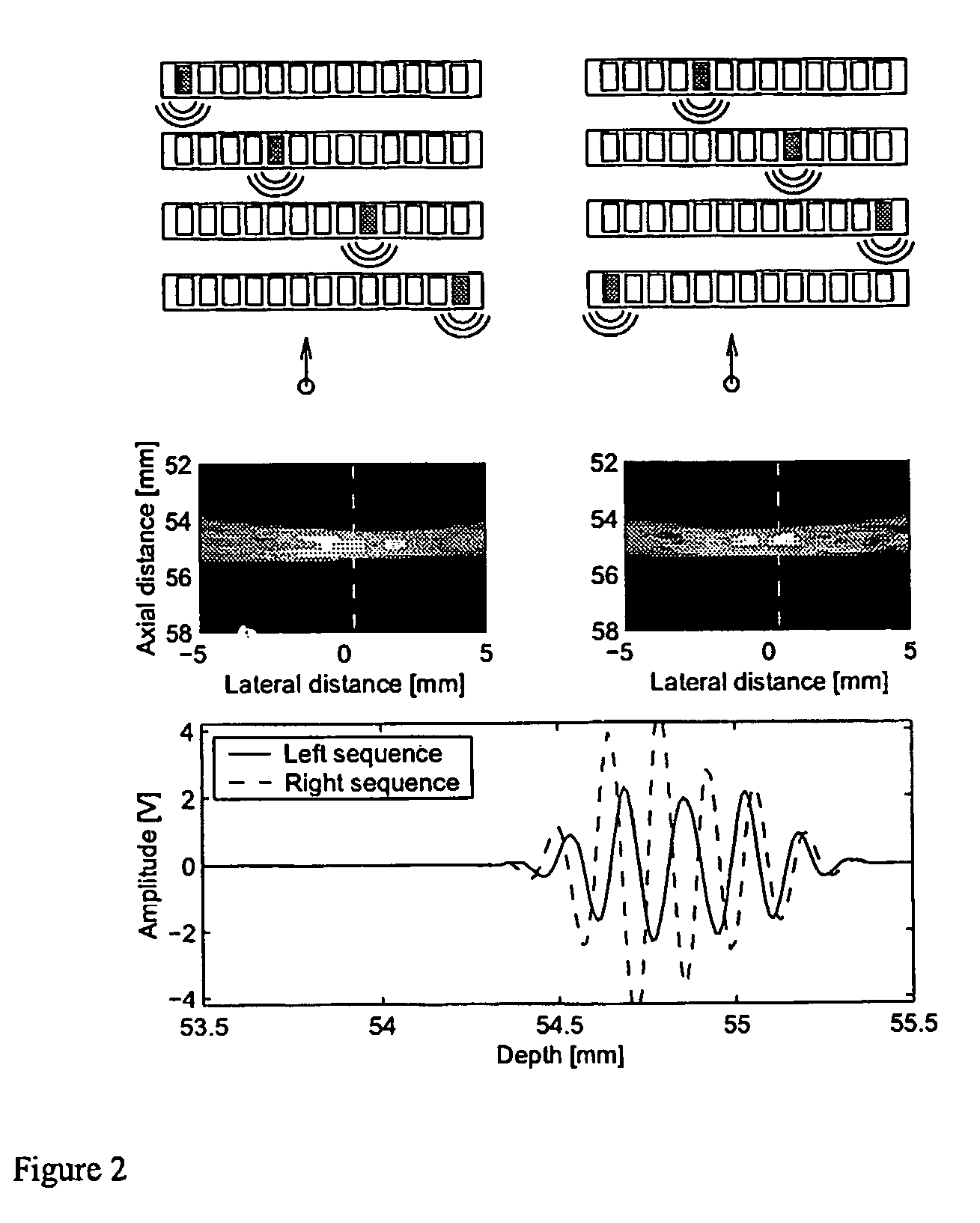
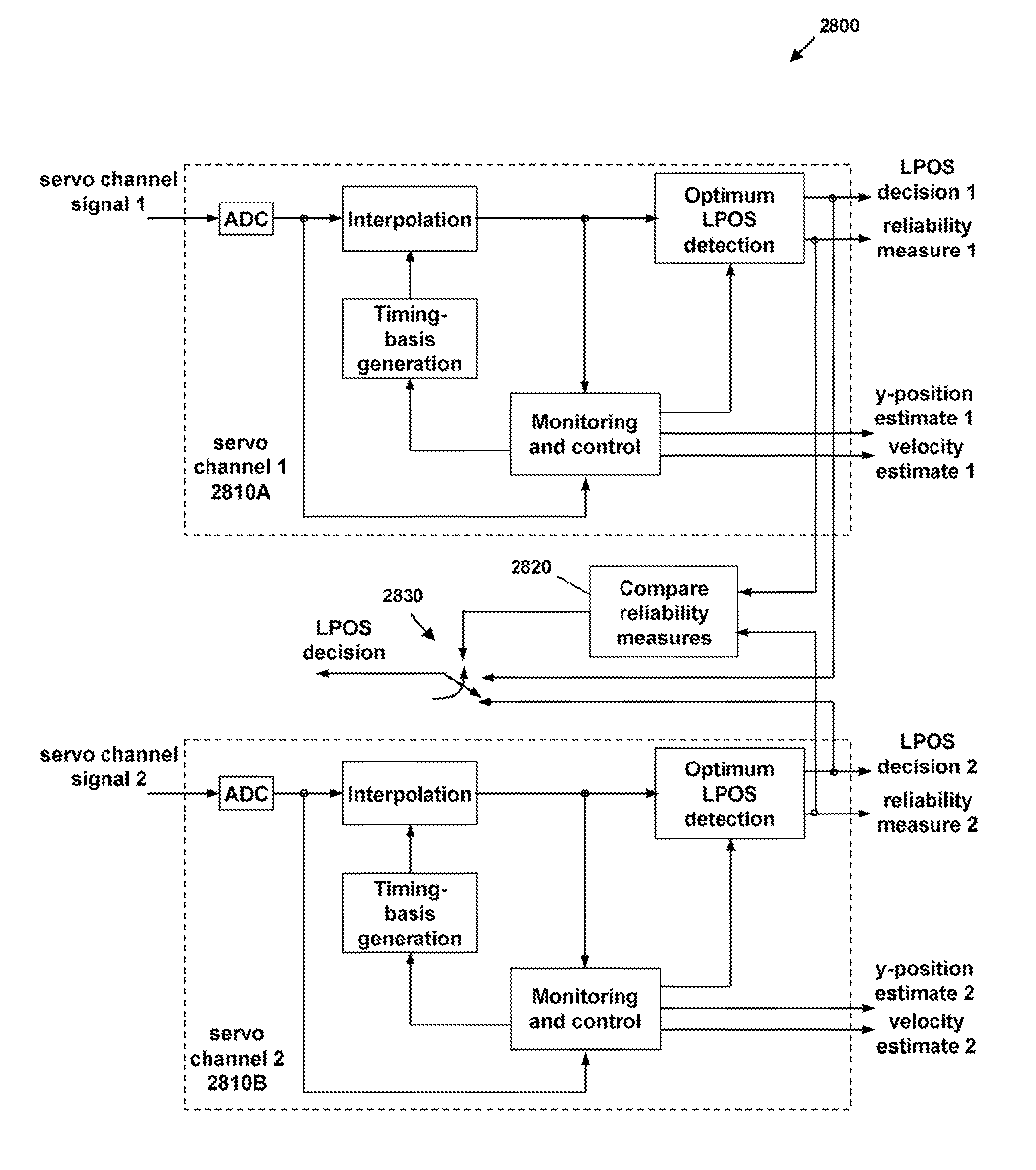
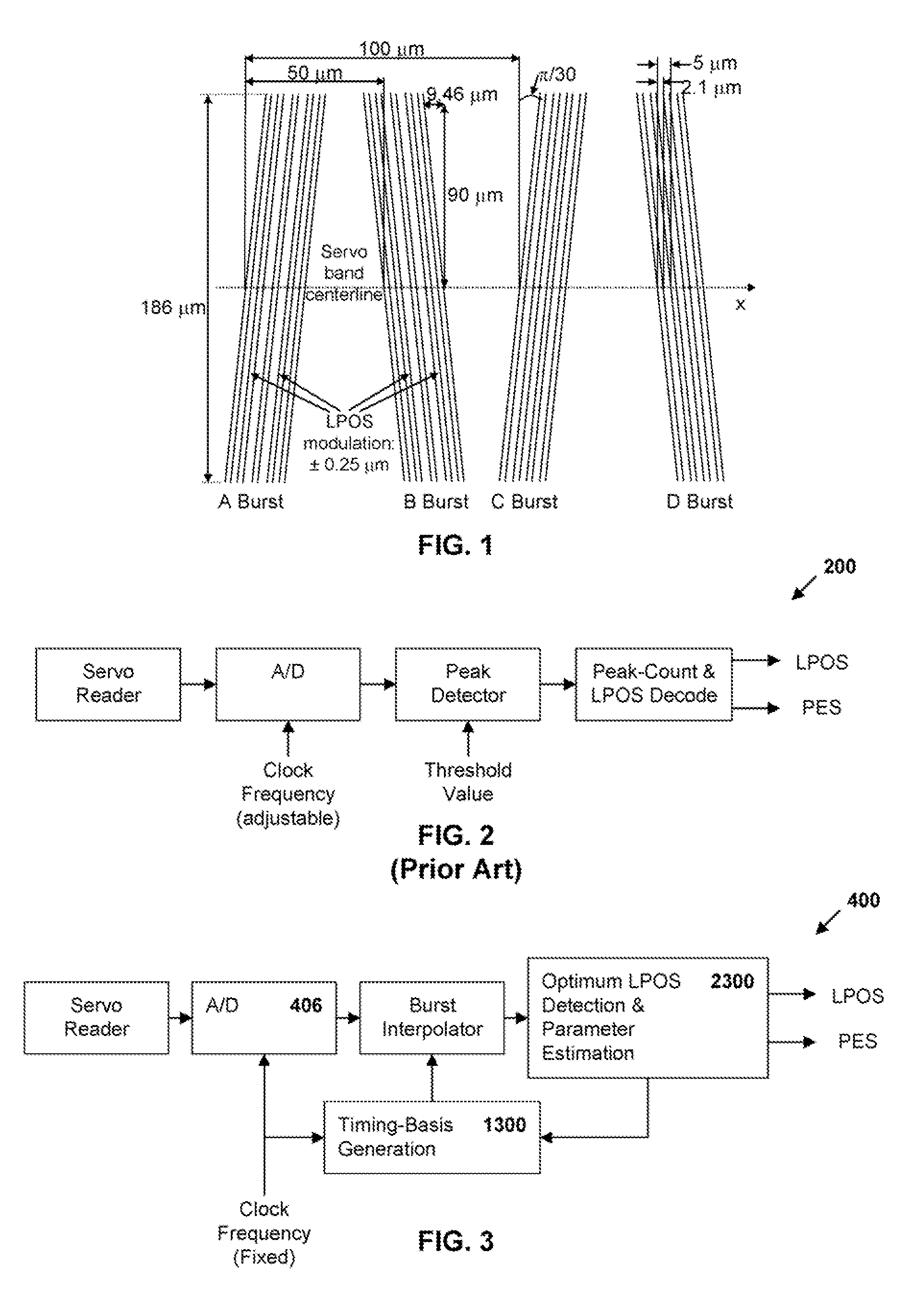
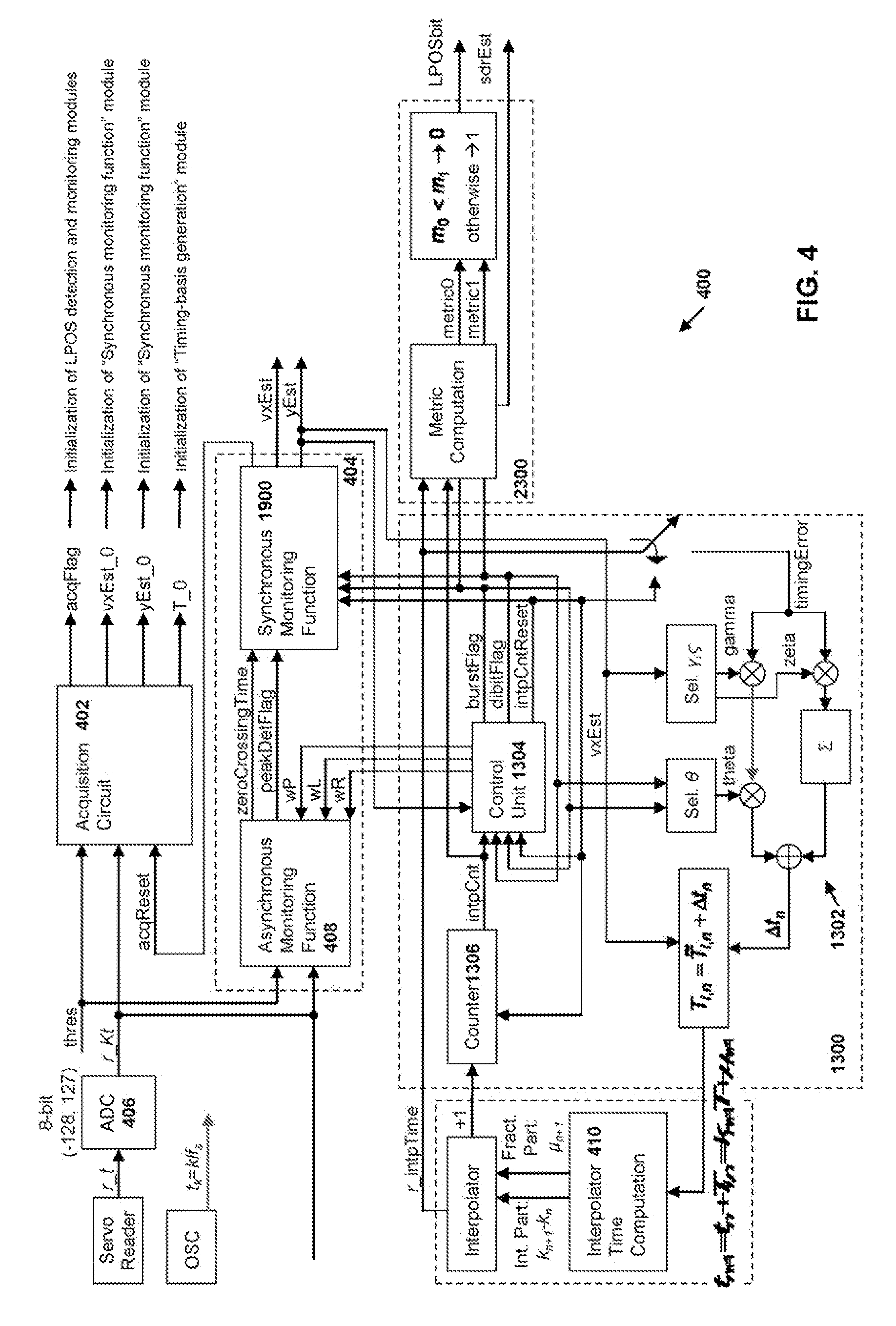
Synchronous servo channel for tape drive systems
InactiveUS7365929B2Avoid couplingFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageChannel parameterMagnetic tape
A fully synchronous servo channel for a data type drive is provided which includes the initial acquisition of synchronous servo channel parameters, generation of a timing basis for signal interpolation, generation of a tape velocity estimate and a y-position estimate and an optimum detection of longitudinal position (LPOS) symbols embedded in servo bursts.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
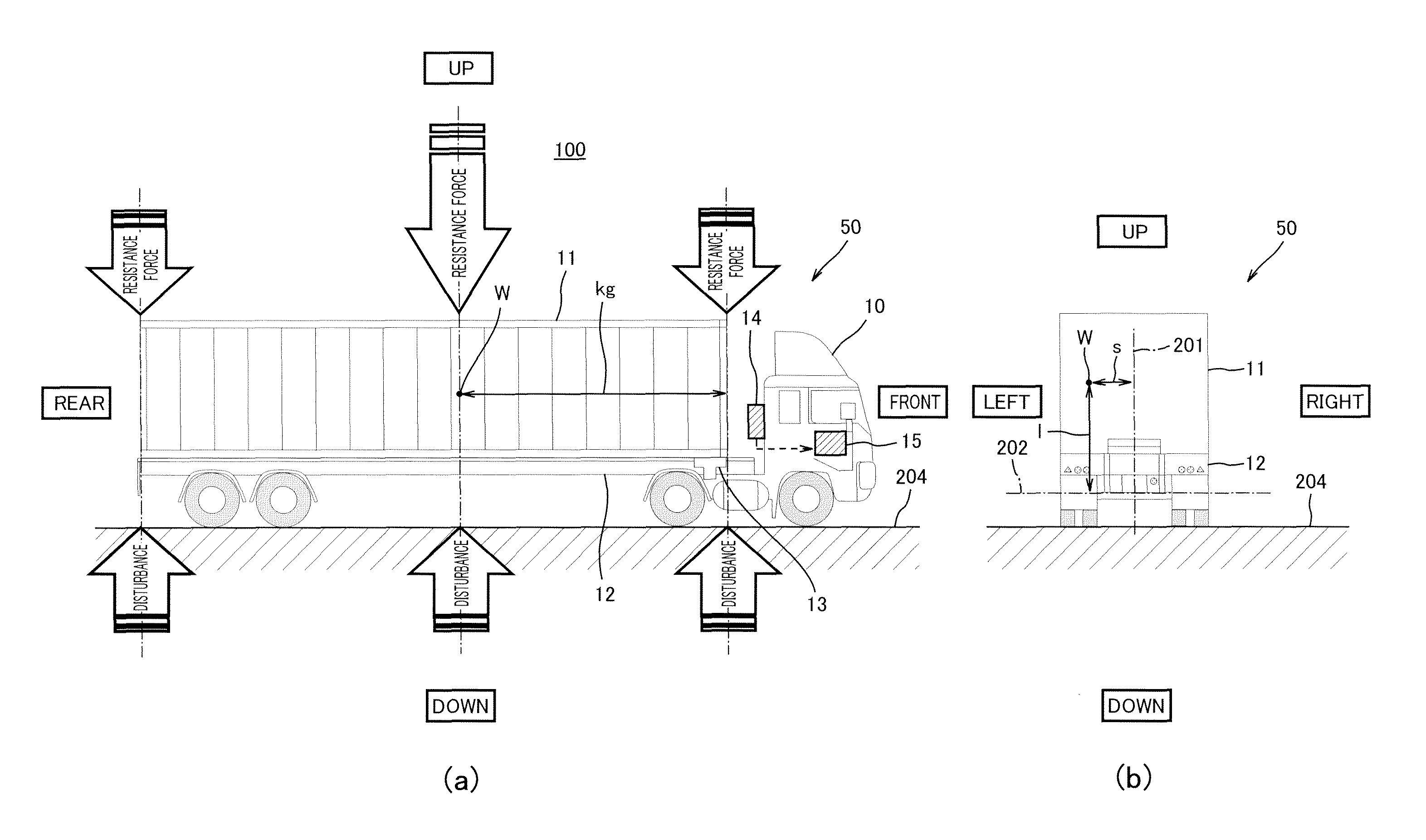
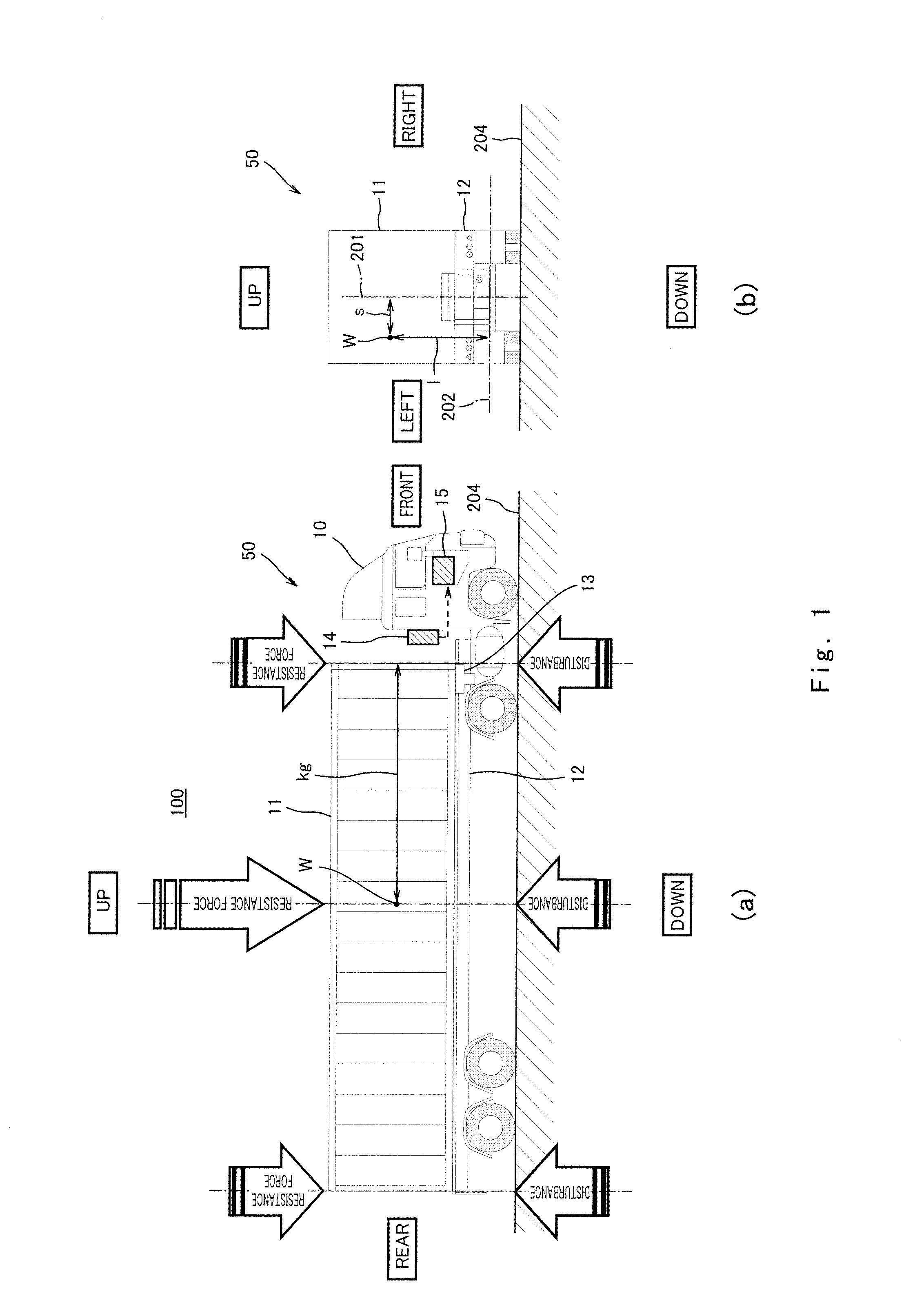
Center-of-Gravity Detection System, Lateral Rollover Limit Velocity Estimation System, and Cargo Weight Estimation System
ActiveUS20100198492A1Accurate locationAccurately derivedStatic/dynamic balance measurementBraking componentsRolloverThree-dimensional space
A center-of-gravity detection system includes a vehicle capable of carrying cargo and adapted to be towed by a towing vehicle, a shake detector configured to detect shakes in the directions of the self-weight and width of the towed vehicle during travel of the towed vehicle, and an arithmetic unit. The arithmetic unit is configured to derive, based upon physical quantities that correlate with the shakes, the location of the center of gravity, in three-dimensional space, of the towed vehicle.
Owner:TOKYO UNIV OF MANNE SCI & TECH
Angular position and velocity estimation for synchronous machines based on extended rotor flux
ActiveUS20070194742A1Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersCorrection algorithmIntegrator
A method of correcting the determination of extended rotor flux using a lag function and a correction algorithm that closely approximates a pure integrator function to correct for lag function errors that can extend the EFS control down to dynamoelectric machine speeds corresponding to as low as 10 Hz electrical frequency.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
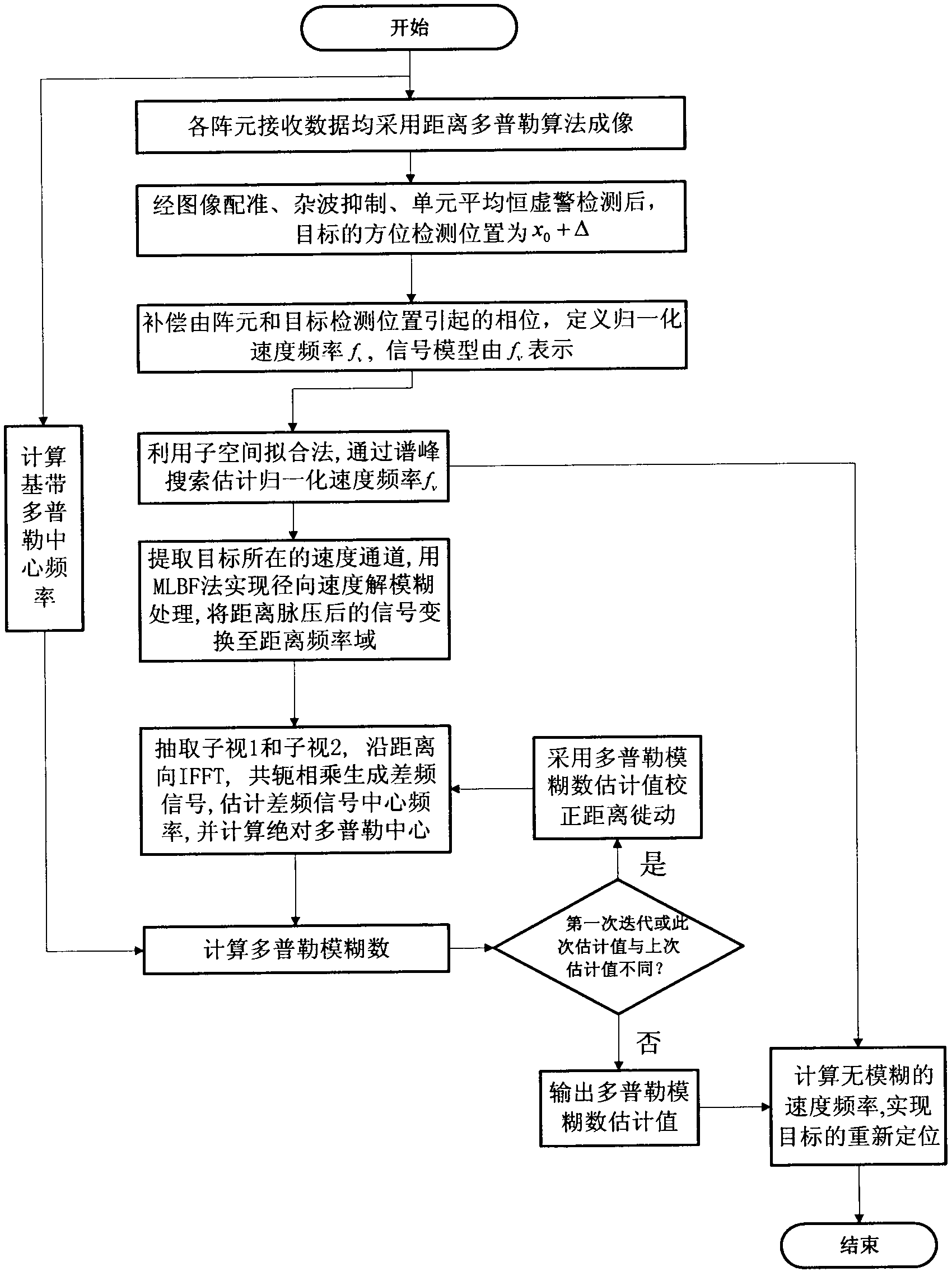
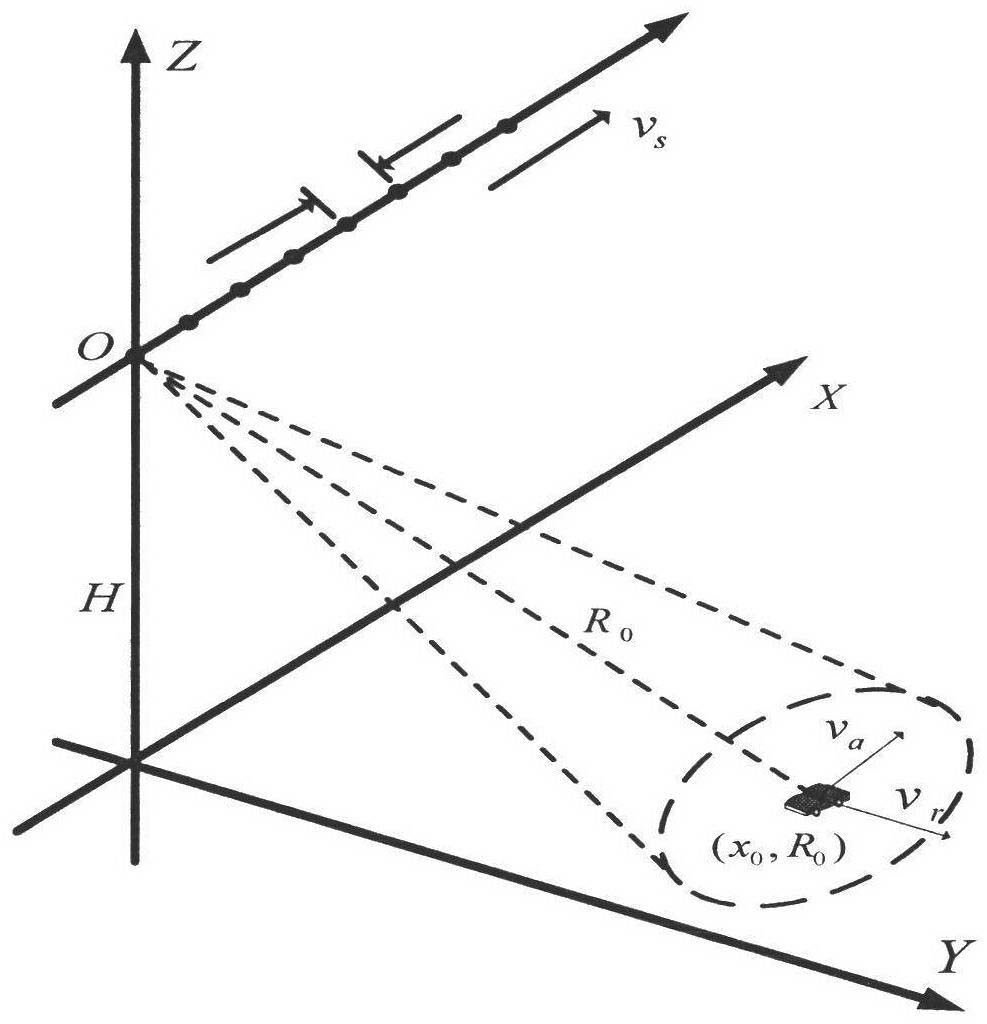
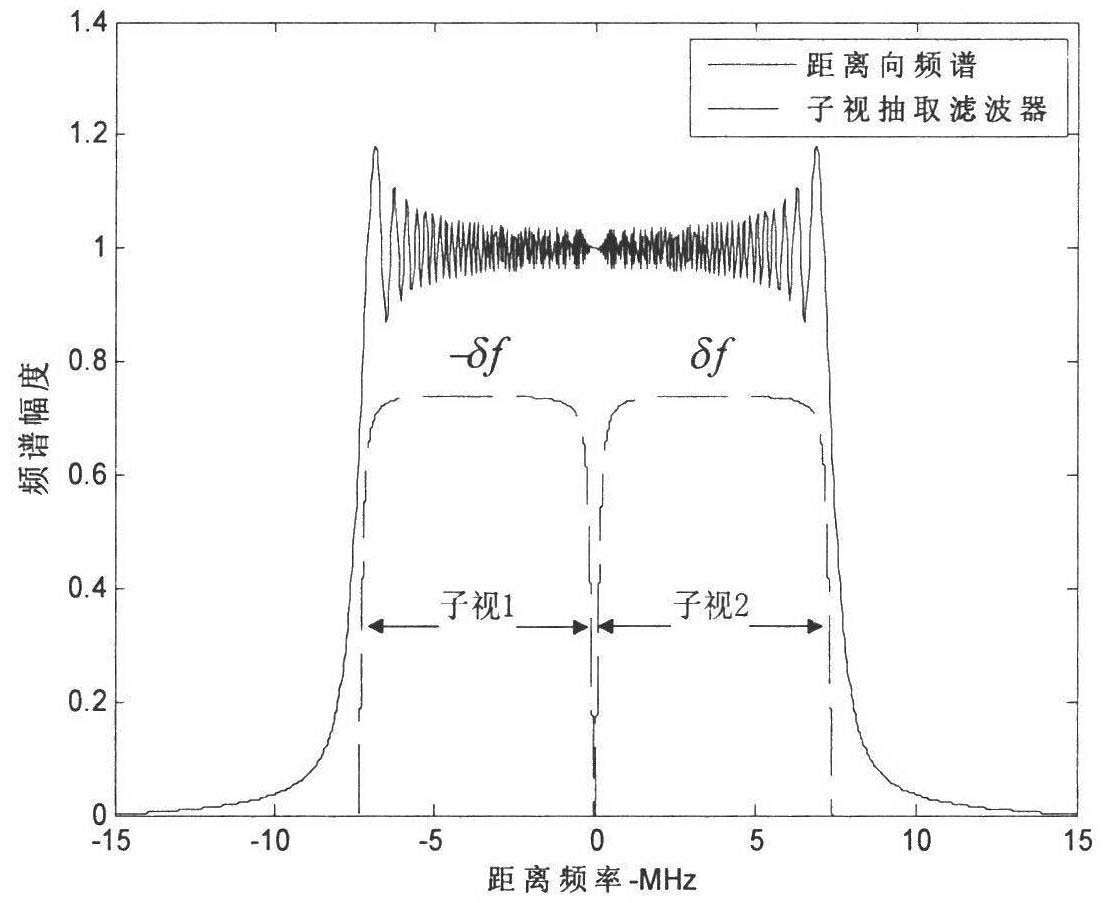
Method of moving-target relocation and velocity ambiguity resolution based on velocity synthetic aperture radar (VSAR) system
ActiveCN102565784AInaccurate speed estimationGood precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarInverse synthetic aperture radar
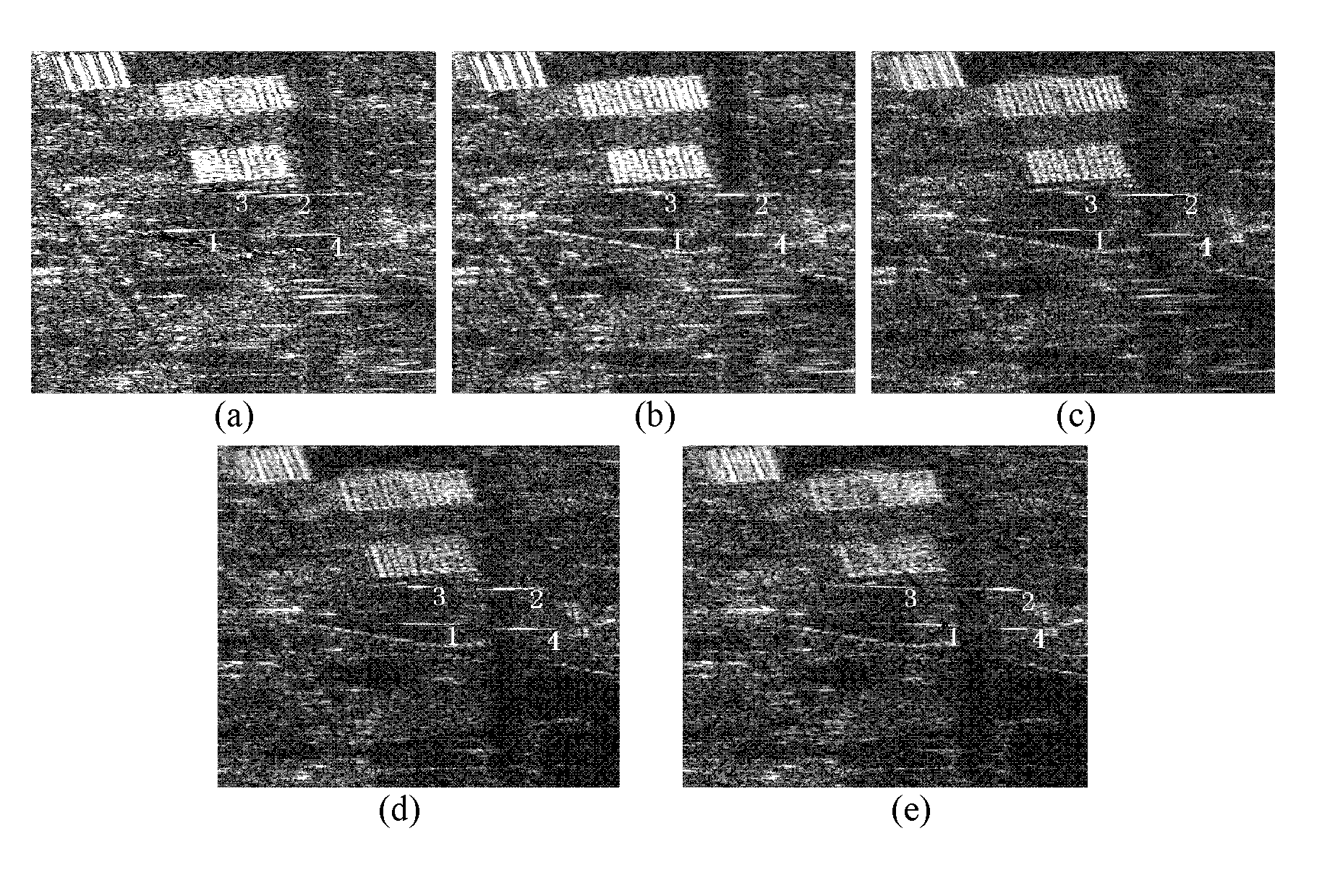
The invention discloses a method of moving-target relocation and velocity ambiguity resolution based on a velocity synthetic aperture radar (VSAR) system, which mainly solves the problems that the velocity estimation accuracy of a moving target is low and the velocity of a fast moving target is ambiguous in the radar detection system. According to the method of moving-target relocation and velocity ambiguity resolution based on the VSAR system, the process includes perform range-doppler algorithm imaging to received data of each of array elements of the VSAR system; detecting the moving target and recording the corresponding position of the moving target after image registration, clutter suppression and cell average constant false alarm detection processing; using subspace fitting algorithm to estimate normalized velocity frequency after phase compensation so that the velocity estimation accuracy is effectively improved; extracting speed channel of the target, using multi-look differential frequency method to estimate doppler ambiguity number; calculating radial velocity of non-ambiguity according to the ambiguity numbers and estimate value of the velocity frequency and achieving an accurate location of the target. According to the method of moving-target relocation and velocity ambiguity resolution based on the velocity synthetic aperture radar (VSAR) system, the estimation accuracy and the detection performance are improved. Due to the fact that the ambiguity resolution processing is merely required for 2-3 iterations, the calculation is reduced, the accurate probability of understanding doppler ambiguity is improved and the effectiveness of the method is proved in a simulation experiment.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
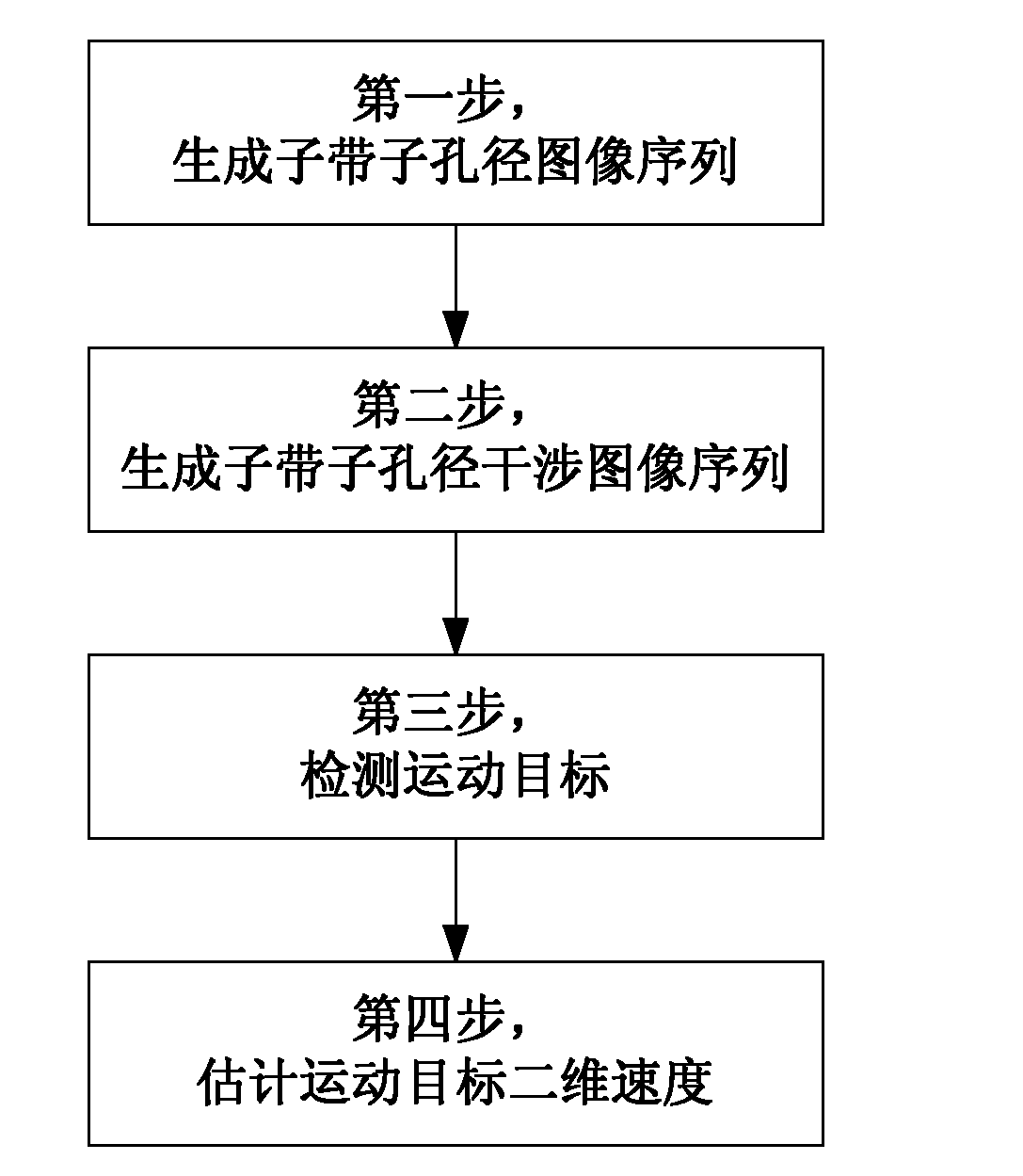
Ground moving target detection and parameter estimation method
InactiveCN102508244ABlind Speed EliminationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEstimation methodsSynthetic aperture radar
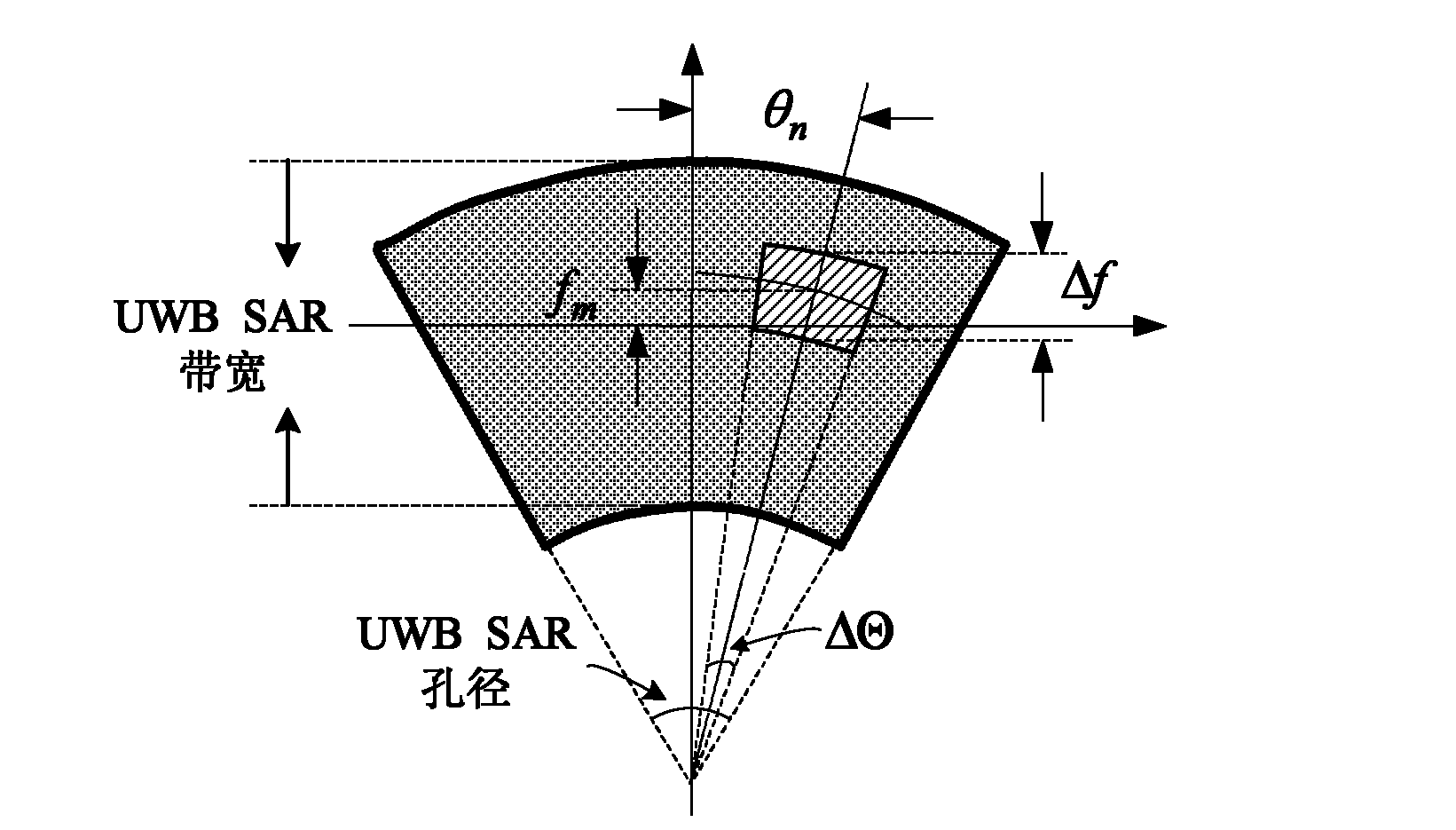
The invention provides a ground moving target detection and parameter estimation method. The technical scheme realizes the moving target detection and two-dimensional velocity estimation by combining with an interference image sequence with multiple sub-bands and sub-apertures on the basis of a three-way ultra-wide bandwidth (UWB) synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image. The specific steps of the method are as follows: 1, generating a sub-band sub-aperture image sequence; 2, generating a sub-band sub-aperture interference image sequence; 3, detecting the moving target; and 4, estimating the two-dimensional velocity of the moving target. By using the ground moving target indication and parameter estimation method provided by the invention, the moving target and a static target can be distinguished on an imaging position and a phase position; the radial velocity of the moving target can be estimated clearly; and the azimuth speed and distance speed can also be estimated.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
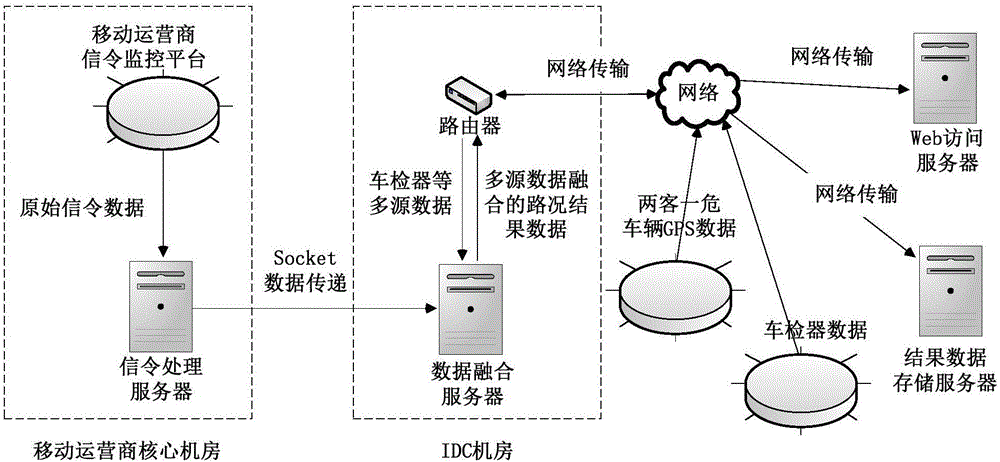
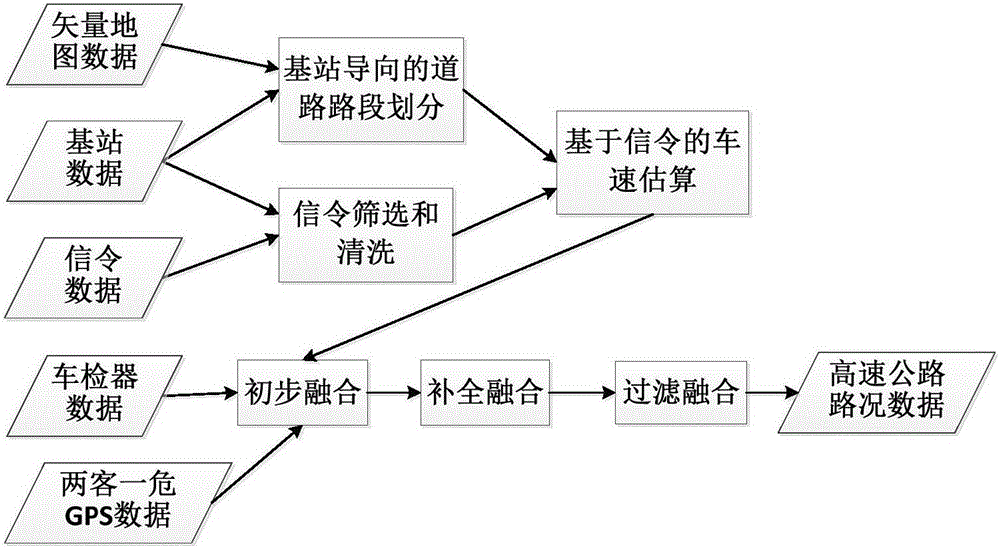
Real-time highway road condition information acquiring method based on data fusion
ActiveCN106205114AReal-time traffic collectionTraffic results are accurateRoad vehicles traffic controlEstimation methodsRoad networks
The invention discloses a real-time highway road condition information acquiring method based on data fusion, and belongs to the field of intelligent traffic. A vehicle velocity estimation method based on three kinds of data fusion is given by taking highway vehicle velocity based on mobile phone signaling estimation as basic data and combining data obtained from an induction coil type vehicle inspection device and GPS positioning data of floating vehicles (such as passenger vehicles, highway passenger vehicles and hazardous material transportation vehicles). According to the method, existing mobile communication facilities and vehicle inspection device resources are fully utilized, additional detection devices do not need to be installed, road condition estimation covering the whole road network can be obtained at low cost, and all-weather real-time road condition collection is achieved. The method is accurate in estimated road condition result, easy to popularize and suitable for highways.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com